VMware, Inc., headquartered in Palo Alto, California, is a global leader in virtualization and cloud infrastructure. Best known for its pioneering role in hypervisors and data center virtualization, VMware has expanded into hybrid cloud management, edge computing, and software-defined networking.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of VMware’s business segments, corporate structure, cloud strategy, product offerings, and technological innovation—highlighting how it stays competitive in the evolving enterprise IT landscape. You can explore similar insights through the PatSnap Eureka AI Agent, which uncovers emerging patent trends, product strategies, and digital transformation pathways.
Company Overview of VMware
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Company Name | VMware, Inc. |
| Founded | 1998 (spun out from EMC Corporation) |
| Headquarters | Palo Alto, California, USA |
| Founder(s) | Diane Greene, Mendel Rosenblum, Scott Devine, Edward Wang, Edouard Bugnion |
| CEO (2025) | Hock Tan (President and CEO, Broadcom Inc.) |
| Ownership | Fully acquired by Broadcom Inc. in November 2023 |
| Number of Employees | ~35,000 (as of 2024) |
| Core Mission | To enable digital transformation through multi-cloud services, virtualization, and modern application platforms |
| Target Customers | Global enterprises, financial institutions, telecoms, government agencies, cloud providers |
Corporate Structure
| Business Unit | Function |
|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure | Includes vSphere, vSAN, VMware Cloud Foundation for hybrid and private cloud |
| Modern Applications (Tanzu) | Kubernetes platform for container orchestration and microservices |
| Networking & Security | NSX for virtual networks, firewalls, SD-WAN |
| End-User Computing | Horizon (VDI), Workspace ONE (UEM) |
| Cross-Cloud Services | VMware Cloud on AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and multi-cloud automation |
| Broadcom Software Group | Now integrated under Broadcom’s infrastructure software portfolio |

Products and Services of VMware
VMware’s platform is built to provide digital infrastructure across data centers, edge, and public cloud, enabling unified operations and consistent security.
Core Solutions:
- vSphere
Industry-standard hypervisor for server virtualization and compute resource management. - VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF)
Full-stack private/hybrid cloud platform integrating vSphere, vSAN, NSX, and SDDC Manager. - Tanzu Platform
Container orchestration and Kubernetes-native development tools for modern applications. - NSX
Software-defined networking (SDN) with micro-segmentation, virtual routers, and firewalls. - vSAN
Hyperconverged storage that integrates with vSphere for simplified storage provisioning. - VMware Cloud
Multi-cloud services deployed across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Oracle, and IBM Cloud. - Workspace ONE & Horizon
Unified endpoint management (UEM) and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) for hybrid work.
Business Model
VMware operates a subscription-first, hybrid delivery business model combining software licenses, SaaS, and professional services.
| Revenue Stream | Description |
|---|---|
| License Sales | One-time software licenses for core infrastructure products |
| SaaS Subscriptions | Cloud-based services (VMware Cloud, Tanzu, Workspace ONE, Aria) |
| Support & Maintenance | Technical support, patching, software upgrades |
| Professional Services | IT transformation consulting, training, and solution architecture |
| OEM & Partner Revenue | Licensing through Dell, HPE, Lenovo, and cloud providers |
Market Position of VMware
VMware is widely recognized as the market leader in virtualization software and a top player in multi-cloud management.
| Segment | Position |
|---|---|
| Virtualization | #1 globally by market share (vSphere) |
| Hybrid Cloud | Competitive with Azure Stack, AWS Outposts (via VCF and VMware Cloud) |
| Kubernetes Platforms | Tanzu competes with Red Hat OpenShift and Google Anthos |
| SDN & SASE | NSX and VeloCloud recognized in Gartner Magic Quadrants |
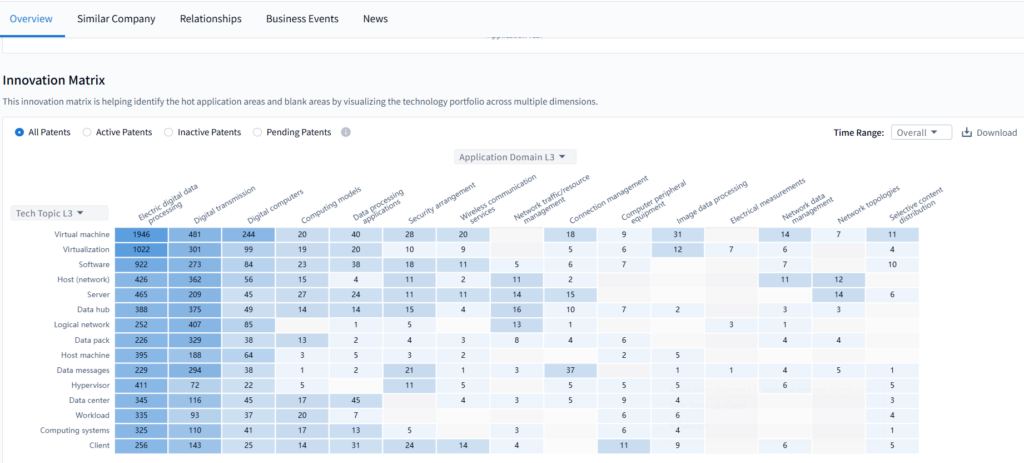
Innovation & Technology of VMware
VMware’s innovation engine is fueled by thousands of active patents spanning virtualization, container orchestration, telemetry, AI, and software-defined networking.
PatSnap Eureka reveals dense innovation clusters within VMware’s portfolio, especially between 2020–2024, with strong growth in container workloads, telemetry systems, and network traffic optimization.
Key Innovation Categories & Technologies
1. Virtualization Infrastructure
- vSphere & ESXi: Core hypervisor stack enabling resource abstraction, load balancing, HA (high availability), and vMotion live migration
- vCenter: Centralized management with API-driven automation and multi-node orchestration
- Virtual GPU (vGPU): Patents related to GPU virtualization for AI/ML and high-performance compute (HPC) workloads
2. Containerization & Kubernetes (Tanzu)
- VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid: Full-stack Kubernetes platform
- Patents involve:
- Container orchestration using overlay networks
- Cluster federation and resource auto-scaling
- Container image update pipeline security
- Pod isolation using virtual infrastructure extensions
3. Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Site Management
- VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) integrates compute, storage, network, and cloud management into a single stack
- Patents emphasize:
- Data synchronization between multiple cloud sites
- Stateful service orchestration across hybrid environments
- Dynamic load shifting based on telemetry input
4. Software-Defined Networking (NSX)
- NSX enables microsegmentation, firewall rule enforcement, service insertion, and distributed routing
- Innovations in:
- Smart NIC acceleration and zero-trust policy distribution
- Packet-level traffic classification and response
- Event-based flow rerouting in case of service degradation
5. Telemetry, Observability & AI-Driven Optimization
- VMware Aria Operations (formerly vRealize) incorporates AI/ML for telemetry analytics, forecasting, and anomaly detection
- Patents include:
- Telemetry agents embedded in containers/VMs
- Predictive modeling of compute load and storage I/O
- Graphical dashboard generation using real-time stream processing
Market Presence and Financials of VMware
| Metric | Value (2024) |
|---|---|
| Annual Revenue | ~$13 billion |
| Cloud/SaaS Revenue Share | >40% and growing year-over-year |
| Employees | ~35,000 |
| Top Customers | Fortune 500, governments, banks, telecoms |
| Cloud Partners | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Oracle, IBM |
Broadcom’s acquisition will further shift VMware toward infrastructure software monetization, with continued emphasis on mission-critical enterprise systems.
VMware Competitors Analysis in Cloud Computing and Virtualization
In the enterprise cloud computing and virtualization market, VMware competes with several major technology providers, each offering unique strengths.
- Microsoft Azure remains one of VMware’s most prominent competitors, known for its end-to-end cloud platform, seamless integration with Active Directory (AD), and the strong Microsoft 365 ecosystem. While Azure dominates in the public cloud segment, VMware maintains a competitive edge in private cloud infrastructure and data center virtualization, making it a preferred choice for enterprises prioritizing hybrid cloud deployments.
- Red Hat OpenShift, backed by IBM, is a leader in enterprise Kubernetes platforms. Its strength lies in container orchestration and hybrid cloud-native application management, with strong adoption across enterprises leveraging IBM’s enterprise services. VMware differentiates itself with a broader legacy virtualization install base and deeper integration with multi-cloud environments, allowing organizations to extend existing workloads without major refactoring.
- Nutanix competes in hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI), offering a simplified user interface and streamlined deployment for private and hybrid clouds. While Nutanix has made significant strides in infrastructure modernization, VMware offers deeper ecosystem integration, enhanced NSX network virtualization, and a wider range of partner solutions, making it more adaptable for complex enterprise workloads.
- Google Anthos focuses on Kubernetes-based hybrid cloud built on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), with strong capabilities in AI and machine learning infrastructure. While Anthos excels in modern app deployment across multi-cloud environments, VMware’s enterprise-grade Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) architecture provides a more mature, full-stack solution for large-scale enterprise IT modernization.
In summary, while Microsoft Azure, Red Hat OpenShift, Nutanix, and Google Anthos each bring distinct strengths to the cloud and virtualization market, VMware continues to lead in integrated hybrid cloud solutions, virtualization technologies, and enterprise-scale software-defined infrastructure—making it a key choice for organizations seeking flexible, secure, and high-performance IT platforms.
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent Capabilities
Using PatSnap Eureka’s Company Search AI Agent, enterprise leaders and analysts can:
- Map VMware’s IP strengths in container orchestration, SDN, edge compute, and cloud services
- Track filing activity in areas like hybrid networking, cloud security, and telemetry-based optimization
- Compare competitive filings and identify partnership/M&A trends in the virtualization ecosystem
- Explore emerging technologies like virtual GPU provisioning, policy-driven networking, and smart infrastructure layers
Eureka empowers decision-makers to uncover high-impact IP clusters, market convergence, and innovation strategies shaping VMware’s future.
Conclusion
VMware remains a cornerstone of enterprise IT transformation, evolving from virtual machines to multi-cloud automation, container platforms, and intelligent edge systems. Backed by Broadcom and a dense IP portfolio, it continues to define the modern digital infrastructure stack.
With the PatSnap Eureka’s Company Search AI Agent, analysts and strategists can unlock deep insights into VMware’s innovation path—making it easier to anticipate tech trends, align R&D efforts, or uncover white space opportunities in virtualization and cloud orchestration.
FAQ
VMware is a leading provider of virtualization and cloud computing software. Virtualization technology allows multiple operating systems and applications to run on a single physical server.
As of July 2024, VMware is a subsidiary of Broadcom Inc. Broadcom completed its acquisition of VMware in November 2023.
VMware is most known for pioneering server virtualization with its VMware vSphere product suite. It revolutionized data center operations by allowing multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, and it is also a major player in cloud computing and desktop virtualization.
No, VMware is owned by Broadcom.
Yes, NASA uses VMware technology. Like many large organizations, NASA leverages virtualization for server consolidation, efficient resource utilization, and to support its complex IT infrastructure and various missions.