Triethanolamine (TEA) is a multifunctional organic chemical compound widely used in industrial and consumer products. It combines properties of both an amine and an alcohol, giving it unique versatility. TEA acts as a pH adjuster, emulsifier, corrosion inhibitor, and surfactant. These functions make it indispensable in industries such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, plastics, construction, and electronics. The demand for TEA continues to grow due to its ability to improve product stability, performance, and shelf life. However, evolving regulations and environmental concerns drive innovation in safer and greener alternatives. Therefore, understanding TEA’s composition, functional properties, and application scope is crucial for formulators and manufacturers.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of triethanolamine. We will explore its chemical structure, grades, performance characteristics, and major applications. Additionally, we will compare TEA to similar chemicals to highlight its advantages through PatSnap Eureka AI Agent.
What is Triethanolamine?
Triethanolamine is a viscous, colorless liquid with a mild ammonia-like odor. It acts as a tertiary amine and contains three hydroxyl groups, making it both a base and an alcohol.
- Chemical Formula: C₆H₁₅NO₃
- CAS Number: 102-71-6
- Appearance: Clear to pale yellow liquid
- Solubility: Miscible with water and alcohols
TEA’s unique structure provides alkaline properties and surface activity, crucial for its widespread use.

Composition & Properties/Performance
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 149.19 g/mol |
| Density | 1.124 g/cm³ (at 20°C) |
| Boiling Point | 335°C |
| Melting Point | 21°C |
| pH (10% solution) | 10.5–11.5 |
| Viscosity | 64 cP (at 25°C) |
| Flash Point | 179°C |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.01 mmHg (at 20°C) |
Key Functional Properties:
- Acts as a pH adjuster in cosmetic and industrial formulations
- Functions as an emulsifier, promoting mixture stability
- Serves as a corrosion inhibitor in metalworking fluids
- Provides surface-active properties improving wetting and spreading
- Exhibits buffering capacity to maintain formula stability
Material Grades & Designations
Common TEA grades include:
- Industrial Grade: General-purpose, high purity for industrial uses
- Cosmetic Grade: Meets USP/NF or equivalent pharmacopeia standards for skincare products
- Electronic Grade: Ultra-pure for electronics manufacturing
| Standard System | Grade Name/Designation | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM D1060 | Industrial TEA | Metal treatment, paints |
| USP/NF | Cosmetic Grade TEA | Personal care products |
| JIS K 2191 | Electronic Grade TEA | Semiconductor cleaning |
Application Landscape
TEA is critical in various sectors:
- Cosmetics & Personal Care: pH adjuster in lotions, shampoos, and creams
- Pharmaceuticals: Buffering agent and emulsifier in topical products
- Plastics & Rubber: Neutralizes acidic catalysts and acts as a curing agent
- Construction: Component in cement grinding aids and concrete additives
- Electronics: Used in photoresist formulations and cleaning agents
Example Use Cases:
- A leading skincare brand uses cosmetic-grade TEA for gentle pH balancing in moisturizers.
- Concrete producers incorporate TEA as a grinding aid to improve efficiency.
- Electronics manufacturers rely on ultra-pure TEA for semiconductor wafer cleaning.
Emerging Trends:
- Formulation of TEA-free alternatives due to regulatory scrutiny
- Use in bio-based surfactant systems to improve environmental profiles
- Innovations in low-odor, low-toxicity TEA derivatives
Triethanolamine vs Other Similar Materials
| Feature | Triethanolamine (TEA) | Monoethanolamine (MEA) | Diethanolamine (DEA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of OH Groups | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| pH Adjustment Ability | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Toxicity | Low to Moderate | Higher | Moderate |
| Typical Uses | Cosmetics, industrial | Gas treatment, scrubbing | Detergents, cosmetics |
Advantages of TEA:
- More hydrophilic due to three hydroxyl groups
- Better emulsification and pH buffering capacity
- Lower toxicity than DEA and MEA in cosmetic uses
- Versatile across personal care, construction, and electronics
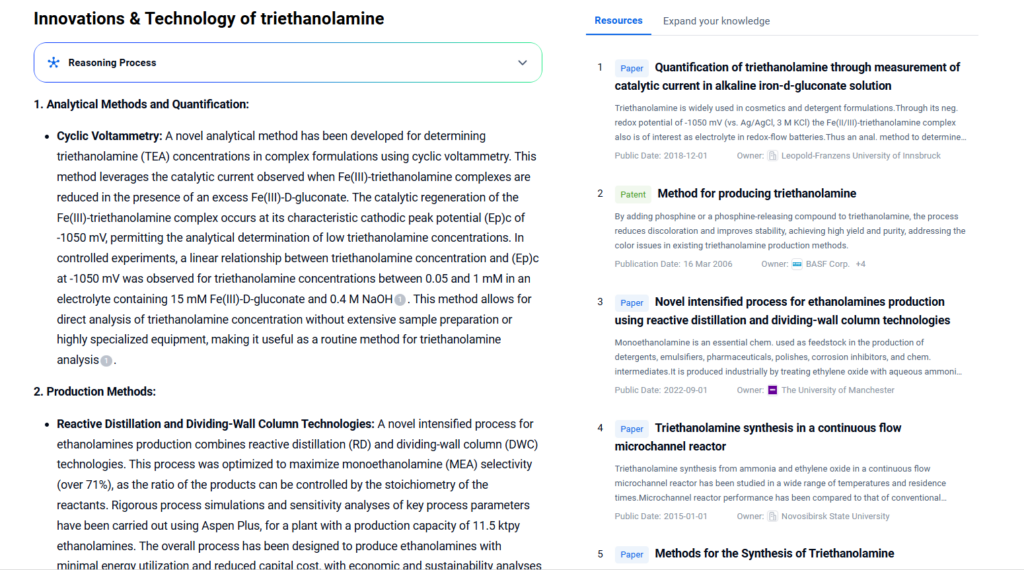
Innovations & Technology
Triethanolamine (TEA) continues to evolve through innovative research and technological advancements. These innovations aim to improve its performance, safety, and environmental footprint. Below are key areas where breakthroughs are taking place:
1. Modified Triethanolamine Derivatives
- Researchers develop low-odor and reduced-toxicity TEA derivatives to meet stricter regulations and consumer demand for milder products.
- Chemical modification techniques such as alkylation and esterification enhance TEA’s compatibility in sensitive formulations, especially in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
- These derivatives retain core functionalities like pH adjustment while minimizing skin irritation potential.
2. Bio-Based and Sustainable TEA Production
- Innovation focuses on producing TEA from renewable biomass instead of petrochemical feedstocks.
- Processes using fermentation or green chemical synthesis reduce carbon footprint and reliance on fossil resources.
- These bio-based TEA variants help companies meet sustainability goals and regulatory pressures such as REACH and FDA guidelines.
3. TEA-Enhanced Surfactants and Emulsifiers
- New formulations combine TEA with biosurfactants to create highly effective and eco-friendly emulsifiers.
- Such combinations improve foam stability, surface wetting, and cleaning efficiency in personal care and industrial cleaners.
- AI-driven screening tools, like PatSnap Eureka, assist in identifying optimal blends quickly.

4. Smart Formulations for Controlled Release
- Advanced TEA-based materials serve as carriers for controlled release of active ingredients in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
- Nano-encapsulation technologies integrate TEA to improve delivery efficiency and reduce dosage frequency.
- These systems boost product efficacy and user compliance.
5. AI and Data-Driven Material Innovation
- PatSnap Eureka AI Agent enables rapid patent landscape analysis to spot emerging TEA-related technologies.
- Companies use this data to design novel molecules, avoid IP conflicts, and accelerate go-to-market strategies.
- AI tools also support predictive modeling for TEA blends, optimizing formulation performance before physical testing.
6. Green Manufacturing and Waste Reduction
- Process innovations reduce hazardous waste and energy use during TEA synthesis.
- Catalysts and solvents are being replaced with greener alternatives, enhancing process safety and compliance.
- Closed-loop manufacturing reduces emissions and recycles byproducts, aligning with circular economy principles.
Through these technological advances, triethanolamine remains relevant and competitive. The continuous innovation not only boosts its functional value but also supports sustainability and regulatory compliance across industries. PatSnap Eureka AI Agent tracks these innovations, revealing patent trends and technological clusters in real time.
Sustainability & Environmental Impact
- TEA is biodegradable under aerobic conditions but requires proper wastewater treatment.
- Production traditionally relies on petrochemical feedstocks, prompting research into bio-based alternatives.
- Regulatory bodies monitor TEA for potential toxicity and allergenicity, influencing formulation strategies.
- Compliance with REACH, RoHS, and FDA ensures safe use in regulated products.
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent Capabilities
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent supports TEA developers by:
- Monitoring global patents related to TEA chemistry and applications
- Mapping competitor innovations and product launches
- Analyzing regulatory changes impacting TEA use
- Identifying emerging substitutes and green alternatives
- Providing data-driven insights for R&D strategy and IP management
Conclusion
Triethanolamine remains a vital chemical across multiple industries due to its versatile chemistry and wide-ranging applications. Its ability to balance pH, stabilize emulsions, and inhibit corrosion underpins its ongoing demand. TEA’s compatibility with various formulations ensures it plays a key role in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, plastics, construction, and electronics.
At the same time, regulatory scrutiny and environmental concerns encourage innovation. The development of low-odor, bio-based, and less toxic TEA derivatives marks the industry’s response to these challenges. Meanwhile, companies must adapt formulations and sourcing strategies to meet evolving standards. In summary, triethanolamine’s importance is set to continue, driven by both its functional benefits and the innovation ecosystem supporting its sustainable future.
FAQs
When used in regulated concentrations, TEA is generally safe for topical applications.
Some individuals may develop sensitivity, but it is rare at cosmetic usage levels.
TEA has three hydroxyl groups, making it more hydrophilic and less toxic than MEA or DEA.
Yes, TEA biodegrades under aerobic conditions but should be managed in wastewater systems.
Key industries include cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, construction, plastics, and electronics.
For more scientific explanations of Triethanolamine , try PatSnap Eureka AI Agent.