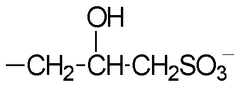
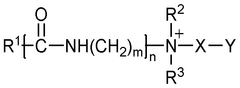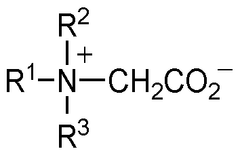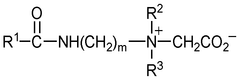Hydrochloric Acid in Industrial Cleaning: Leading Methods
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HCl Cleaning Evolution
The evolution of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in industrial cleaning has been marked by significant advancements in technology, safety measures, and application methods. Initially, HCl was primarily used in its raw form for heavy-duty cleaning tasks in industrial settings. However, as environmental and safety concerns grew, the industry began to develop more sophisticated and controlled approaches to HCl cleaning.
In the early stages, the use of HCl was characterized by manual application methods, often resulting in inconsistent cleaning results and potential hazards for workers. The 1970s and 1980s saw a shift towards automated cleaning systems, which allowed for more precise control of acid concentration and application. This period also witnessed the introduction of inhibited HCl formulations, designed to reduce corrosion on metal surfaces while maintaining cleaning efficacy.
The 1990s brought about a focus on environmental sustainability, leading to the development of closed-loop cleaning systems. These systems enabled the recycling and reuse of HCl solutions, significantly reducing waste and environmental impact. Simultaneously, advancements in material science led to the creation of acid-resistant equipment and containment systems, further enhancing safety and efficiency in industrial cleaning processes.
The turn of the millennium saw the integration of digital technologies into HCl cleaning methods. Computerized control systems and sensors allowed for real-time monitoring and adjustment of cleaning parameters, optimizing the use of HCl and improving overall cleaning performance. This era also marked the beginning of research into alternative cleaning agents and methods that could potentially replace or complement HCl in certain applications.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing "green" HCl cleaning solutions. These include the use of lower concentrations of HCl combined with surfactants and other additives to enhance cleaning power while reducing environmental impact. Additionally, there has been significant progress in the development of vapor phase HCl cleaning techniques, which offer improved penetration and reduced liquid waste.
The latest trend in HCl cleaning evolution involves the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms. These technologies are being used to optimize cleaning processes, predict maintenance needs, and further reduce the environmental footprint of industrial cleaning operations. As the industry continues to evolve, the focus remains on balancing effective cleaning performance with environmental responsibility and worker safety.
In the early stages, the use of HCl was characterized by manual application methods, often resulting in inconsistent cleaning results and potential hazards for workers. The 1970s and 1980s saw a shift towards automated cleaning systems, which allowed for more precise control of acid concentration and application. This period also witnessed the introduction of inhibited HCl formulations, designed to reduce corrosion on metal surfaces while maintaining cleaning efficacy.
The 1990s brought about a focus on environmental sustainability, leading to the development of closed-loop cleaning systems. These systems enabled the recycling and reuse of HCl solutions, significantly reducing waste and environmental impact. Simultaneously, advancements in material science led to the creation of acid-resistant equipment and containment systems, further enhancing safety and efficiency in industrial cleaning processes.
The turn of the millennium saw the integration of digital technologies into HCl cleaning methods. Computerized control systems and sensors allowed for real-time monitoring and adjustment of cleaning parameters, optimizing the use of HCl and improving overall cleaning performance. This era also marked the beginning of research into alternative cleaning agents and methods that could potentially replace or complement HCl in certain applications.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing "green" HCl cleaning solutions. These include the use of lower concentrations of HCl combined with surfactants and other additives to enhance cleaning power while reducing environmental impact. Additionally, there has been significant progress in the development of vapor phase HCl cleaning techniques, which offer improved penetration and reduced liquid waste.
The latest trend in HCl cleaning evolution involves the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms. These technologies are being used to optimize cleaning processes, predict maintenance needs, and further reduce the environmental footprint of industrial cleaning operations. As the industry continues to evolve, the focus remains on balancing effective cleaning performance with environmental responsibility and worker safety.
Industrial Demand
The industrial demand for hydrochloric acid in cleaning applications has been steadily growing due to its effectiveness and versatility. Across various sectors, including manufacturing, food processing, and healthcare, hydrochloric acid has become an essential component in cleaning solutions. Its ability to dissolve mineral deposits, remove rust, and sanitize surfaces makes it particularly valuable in industrial settings where tough cleaning challenges are common.
In the manufacturing sector, hydrochloric acid is widely used for descaling and cleaning industrial equipment. The need for efficient maintenance of machinery and production lines drives the demand for hydrochloric acid-based cleaning solutions. As industries strive to maximize operational efficiency and extend the lifespan of their equipment, the use of hydrochloric acid in cleaning processes has become increasingly prevalent.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant market for hydrochloric acid in cleaning applications. Strict hygiene standards and the need for thorough sanitation of processing equipment have led to the adoption of hydrochloric acid-based cleaning methods. Its effectiveness in removing protein residues, mineral deposits, and other contaminants makes it an indispensable tool in maintaining food safety standards.
In the healthcare sector, hydrochloric acid plays a crucial role in disinfection and sterilization processes. Hospitals, laboratories, and pharmaceutical facilities rely on hydrochloric acid-based cleaning solutions to ensure a sterile environment and prevent the spread of infections. The ongoing global focus on healthcare and hygiene has further boosted the demand for effective cleaning agents, including those containing hydrochloric acid.
The construction industry also contributes to the demand for hydrochloric acid in cleaning applications. It is commonly used for cleaning concrete surfaces, removing efflorescence, and preparing surfaces for further treatment or coating. As urbanization continues and construction activities increase worldwide, the demand for hydrochloric acid in this sector is expected to grow.
Environmental regulations and sustainability concerns have influenced the industrial demand for hydrochloric acid in cleaning. While its effectiveness is undisputed, there is a growing emphasis on developing safer and more environmentally friendly formulations. This has led to innovations in hydrochloric acid-based cleaning products, focusing on reduced concentrations and improved safety profiles.
The global market for industrial cleaning chemicals, including hydrochloric acid-based solutions, has been expanding. Factors such as increasing industrialization, stringent hygiene standards, and the need for efficient cleaning processes in various sectors continue to drive this growth. As industries across the globe prioritize cleanliness and operational efficiency, the demand for effective cleaning solutions, including those utilizing hydrochloric acid, is expected to remain strong in the foreseeable future.
In the manufacturing sector, hydrochloric acid is widely used for descaling and cleaning industrial equipment. The need for efficient maintenance of machinery and production lines drives the demand for hydrochloric acid-based cleaning solutions. As industries strive to maximize operational efficiency and extend the lifespan of their equipment, the use of hydrochloric acid in cleaning processes has become increasingly prevalent.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant market for hydrochloric acid in cleaning applications. Strict hygiene standards and the need for thorough sanitation of processing equipment have led to the adoption of hydrochloric acid-based cleaning methods. Its effectiveness in removing protein residues, mineral deposits, and other contaminants makes it an indispensable tool in maintaining food safety standards.
In the healthcare sector, hydrochloric acid plays a crucial role in disinfection and sterilization processes. Hospitals, laboratories, and pharmaceutical facilities rely on hydrochloric acid-based cleaning solutions to ensure a sterile environment and prevent the spread of infections. The ongoing global focus on healthcare and hygiene has further boosted the demand for effective cleaning agents, including those containing hydrochloric acid.
The construction industry also contributes to the demand for hydrochloric acid in cleaning applications. It is commonly used for cleaning concrete surfaces, removing efflorescence, and preparing surfaces for further treatment or coating. As urbanization continues and construction activities increase worldwide, the demand for hydrochloric acid in this sector is expected to grow.
Environmental regulations and sustainability concerns have influenced the industrial demand for hydrochloric acid in cleaning. While its effectiveness is undisputed, there is a growing emphasis on developing safer and more environmentally friendly formulations. This has led to innovations in hydrochloric acid-based cleaning products, focusing on reduced concentrations and improved safety profiles.
The global market for industrial cleaning chemicals, including hydrochloric acid-based solutions, has been expanding. Factors such as increasing industrialization, stringent hygiene standards, and the need for efficient cleaning processes in various sectors continue to drive this growth. As industries across the globe prioritize cleanliness and operational efficiency, the demand for effective cleaning solutions, including those utilizing hydrochloric acid, is expected to remain strong in the foreseeable future.
Technical Challenges
The use of hydrochloric acid in industrial cleaning presents several significant technical challenges that require careful consideration and innovative solutions. One of the primary issues is the highly corrosive nature of hydrochloric acid, which can cause severe damage to equipment, surfaces, and infrastructure if not properly managed. This corrosiveness necessitates the development of specialized handling and application techniques, as well as the use of resistant materials in cleaning equipment and storage containers.
Another major challenge is ensuring worker safety during the cleaning process. Hydrochloric acid poses serious health risks, including respiratory irritation, skin burns, and eye damage. Implementing robust safety protocols, providing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and designing effective ventilation systems are crucial to mitigate these risks. Additionally, the potential for harmful fumes and vapors requires advanced air quality monitoring and control measures.
The disposal of hydrochloric acid waste after cleaning operations presents environmental concerns and regulatory compliance challenges. Proper neutralization and treatment of acid waste are essential to prevent environmental contamination and comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This necessitates the development of efficient waste treatment processes and the implementation of closed-loop systems to minimize acid discharge.
Maintaining the effectiveness of hydrochloric acid in various cleaning applications is another technical hurdle. Factors such as concentration, temperature, and contact time significantly affect cleaning efficiency. Optimizing these parameters for different substrates and contaminants requires extensive research and testing. Furthermore, the potential for unwanted chemical reactions between the acid and certain materials or contaminants must be carefully evaluated to prevent secondary issues or reduced cleaning efficacy.
The scalability of hydrochloric acid cleaning methods from laboratory to industrial scale poses additional challenges. Ensuring consistent performance and maintaining safety standards when scaling up operations require sophisticated process control systems and automation technologies. This includes the development of precise dosing mechanisms, real-time monitoring systems, and adaptive cleaning protocols to accommodate varying industrial environments and cleaning requirements.
Lastly, the search for more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives to hydrochloric acid in industrial cleaning is an ongoing challenge. While hydrochloric acid is effective, its environmental impact and safety concerns drive the need for greener solutions. Developing cleaning agents that match or exceed the performance of hydrochloric acid while reducing environmental and safety risks is a complex task that demands continuous innovation in chemical formulations and application technologies.
Another major challenge is ensuring worker safety during the cleaning process. Hydrochloric acid poses serious health risks, including respiratory irritation, skin burns, and eye damage. Implementing robust safety protocols, providing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and designing effective ventilation systems are crucial to mitigate these risks. Additionally, the potential for harmful fumes and vapors requires advanced air quality monitoring and control measures.
The disposal of hydrochloric acid waste after cleaning operations presents environmental concerns and regulatory compliance challenges. Proper neutralization and treatment of acid waste are essential to prevent environmental contamination and comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This necessitates the development of efficient waste treatment processes and the implementation of closed-loop systems to minimize acid discharge.
Maintaining the effectiveness of hydrochloric acid in various cleaning applications is another technical hurdle. Factors such as concentration, temperature, and contact time significantly affect cleaning efficiency. Optimizing these parameters for different substrates and contaminants requires extensive research and testing. Furthermore, the potential for unwanted chemical reactions between the acid and certain materials or contaminants must be carefully evaluated to prevent secondary issues or reduced cleaning efficacy.
The scalability of hydrochloric acid cleaning methods from laboratory to industrial scale poses additional challenges. Ensuring consistent performance and maintaining safety standards when scaling up operations require sophisticated process control systems and automation technologies. This includes the development of precise dosing mechanisms, real-time monitoring systems, and adaptive cleaning protocols to accommodate varying industrial environments and cleaning requirements.
Lastly, the search for more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives to hydrochloric acid in industrial cleaning is an ongoing challenge. While hydrochloric acid is effective, its environmental impact and safety concerns drive the need for greener solutions. Developing cleaning agents that match or exceed the performance of hydrochloric acid while reducing environmental and safety risks is a complex task that demands continuous innovation in chemical formulations and application technologies.
Current HCl Methods
01 Production methods of hydrochloric acid
Various methods are employed for the production of hydrochloric acid, including chemical reactions and industrial processes. These methods may involve the use of specific catalysts, reactants, or equipment to efficiently produce hydrochloric acid at different concentrations and purities.- Production methods of hydrochloric acid: Various methods are employed to produce hydrochloric acid, including direct synthesis from hydrogen and chlorine, as a byproduct in chlorination processes, and through the reaction of sulfuric acid with sodium chloride. These production methods are optimized for efficiency and purity in industrial settings.
- Purification and concentration techniques: Hydrochloric acid purification and concentration techniques involve distillation, membrane separation, and adsorption processes. These methods aim to remove impurities and adjust the acid concentration for specific industrial applications, ensuring high-quality product output.
- Applications in chemical processing: Hydrochloric acid is widely used in various chemical processes, including metal treatment, pH regulation, and as a reagent in organic synthesis. Its versatility makes it a crucial component in industries such as metallurgy, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
- Safety and handling considerations: Proper safety measures and handling procedures are essential when working with hydrochloric acid due to its corrosive nature. This includes using appropriate personal protective equipment, implementing spill containment strategies, and following strict storage and transportation guidelines to minimize risks.
- Environmental impact and waste management: Managing the environmental impact of hydrochloric acid production and use involves implementing waste treatment processes, recycling techniques, and emission control measures. These practices aim to minimize the acid's ecological footprint and comply with environmental regulations.
02 Applications in chemical processing
Hydrochloric acid is widely used in various chemical processing applications. It serves as a key reagent in industrial processes, such as metal treatment, pH adjustment, and as a catalyst in organic synthesis reactions. Its versatility makes it an essential component in many manufacturing processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Purification and treatment of hydrochloric acid
Techniques for purifying and treating hydrochloric acid are crucial for obtaining high-quality acid suitable for specific applications. These methods may include distillation, membrane separation, or chemical treatments to remove impurities and achieve desired concentrations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Storage and handling systems
Specialized storage and handling systems are designed for the safe management of hydrochloric acid. These systems may include corrosion-resistant materials, safety features, and specific designs to prevent leaks and ensure proper containment of the acid during storage and transportation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Environmental and safety aspects are crucial when dealing with hydrochloric acid. This includes methods for neutralization, proper disposal techniques, and safety measures to protect workers and the environment from potential hazards associated with the acid's corrosive nature and fumes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The industrial cleaning sector utilizing hydrochloric acid is in a mature stage, with a stable market size driven by consistent demand across various industries. The technology is well-established, with ongoing innovations focused on improving efficiency and environmental impact. Key players like Fluid Energy Group Ltd., Ecolab USA, Inc., and DuPont de Nemours, Inc. are at the forefront of developing advanced cleaning solutions. These companies, along with others such as LG Chem Ltd. and Wacker Chemie AG, are investing in research and development to enhance the effectiveness of hydrochloric acid-based cleaning methods while addressing safety and sustainability concerns. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical manufacturers and specialized cleaning solution providers, each striving to differentiate through product innovation and service quality.
Fluid Energy Group Ltd.
Technical Solution: Fluid Energy Group Ltd. has developed innovative hydrochloric acid-based cleaning solutions for industrial applications. Their proprietary formulations incorporate advanced surfactants and corrosion inhibitors to enhance cleaning efficacy while minimizing equipment damage[1]. The company's products are designed to be environmentally friendly, with reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to traditional cleaning agents[2]. Fluid Energy Group's technology allows for lower acid concentrations to be used effectively, typically ranging from 5-15% HCl, which improves safety and reduces environmental impact[3].
Strengths: Environmentally friendly formulations, enhanced safety profile, effective at lower acid concentrations. Weaknesses: May require specialized handling and application procedures, potentially higher initial cost compared to conventional HCl cleaners.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab has developed a range of hydrochloric acid-based cleaning solutions optimized for various industrial applications. Their technology focuses on controlled-release formulations that gradually dispense the active ingredients, providing sustained cleaning action while minimizing corrosion risks[4]. Ecolab's products often incorporate proprietary inhibitors and surfactants that allow for effective cleaning at lower acid concentrations, typically in the range of 10-20% HCl[5]. The company has also introduced smart dosing systems that automatically adjust acid concentration based on real-time monitoring of water quality and system conditions, improving efficiency and reducing chemical waste[6].
Strengths: Controlled-release technology, smart dosing systems, wide range of industry-specific formulations. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for optimal performance, potentially higher upfront costs for integrated systems.
Innovative HCl Tech
Synthetic acid compositions and uses thereof
PatentActiveCA2925142A1
Innovation
- A synthetic acid composition comprising urea and hydrogen chloride in a specific molar ratio, combined with metal iodides, alcohols, and phosphonic acids, which reduces corrosion rates, is non-fuming, non-toxic, and biodegradable, offering improved safety and environmental compatibility.
Method of cleaning
PatentWO2025104445A1
Innovation
- The use of one or more biosurfactants to provide cleaning for industrial equipment, either alone or in combination with non-biological anionic surfactants, succinic acid derived dispersants, and terpenes, to effectively remove undesirable substances.
Environmental Impact
The use of hydrochloric acid in industrial cleaning processes has significant environmental implications that require careful consideration and management. The primary environmental concerns associated with hydrochloric acid usage include air pollution, water contamination, and soil degradation.
Air pollution is a major issue, as hydrochloric acid can release harmful vapors and fumes during cleaning operations. These emissions can contribute to the formation of acid rain, which has far-reaching effects on ecosystems, buildings, and human health. To mitigate this impact, industrial facilities often implement advanced air scrubbing systems and vapor recovery technologies to capture and neutralize acid emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
Water contamination is another critical environmental concern. Improper disposal or accidental spills of hydrochloric acid can lead to the acidification of water bodies, severely impacting aquatic life and water quality. Industrial facilities must adhere to strict wastewater treatment protocols to neutralize acid-containing effluents before discharge. Additionally, the implementation of closed-loop cleaning systems and water recycling technologies can significantly reduce the volume of contaminated wastewater generated.
Soil degradation can occur when hydrochloric acid comes into contact with the ground, altering soil pH and potentially rendering it unsuitable for plant growth. This risk necessitates proper handling, storage, and containment measures to prevent spills and leaks. In cases where soil contamination does occur, remediation techniques such as soil washing, chemical neutralization, and bioremediation may be employed to restore soil quality.
The environmental impact of hydrochloric acid use extends beyond immediate pollution concerns. The production and transportation of hydrochloric acid also contribute to the overall environmental footprint of industrial cleaning processes. As such, many industries are exploring alternative cleaning methods and greener substitutes to reduce their reliance on hydrochloric acid.
To address these environmental challenges, regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented stringent guidelines for the use, handling, and disposal of hydrochloric acid in industrial settings. These regulations often mandate the use of best available technologies (BAT) for pollution control, regular environmental monitoring, and comprehensive emergency response plans.
Furthermore, the industrial sector is increasingly adopting cleaner production principles and circular economy approaches to minimize the environmental impact of hydrochloric acid use. This includes optimizing cleaning processes to reduce acid consumption, implementing more efficient application methods, and exploring opportunities for acid recovery and reuse within industrial operations.
As environmental concerns continue to shape industrial practices, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on developing more environmentally friendly cleaning alternatives and improving the sustainability of hydrochloric acid-based cleaning methods. These efforts aim to balance the need for effective industrial cleaning with the imperative of environmental protection, driving innovation in the field of industrial cleaning technologies.
Air pollution is a major issue, as hydrochloric acid can release harmful vapors and fumes during cleaning operations. These emissions can contribute to the formation of acid rain, which has far-reaching effects on ecosystems, buildings, and human health. To mitigate this impact, industrial facilities often implement advanced air scrubbing systems and vapor recovery technologies to capture and neutralize acid emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
Water contamination is another critical environmental concern. Improper disposal or accidental spills of hydrochloric acid can lead to the acidification of water bodies, severely impacting aquatic life and water quality. Industrial facilities must adhere to strict wastewater treatment protocols to neutralize acid-containing effluents before discharge. Additionally, the implementation of closed-loop cleaning systems and water recycling technologies can significantly reduce the volume of contaminated wastewater generated.
Soil degradation can occur when hydrochloric acid comes into contact with the ground, altering soil pH and potentially rendering it unsuitable for plant growth. This risk necessitates proper handling, storage, and containment measures to prevent spills and leaks. In cases where soil contamination does occur, remediation techniques such as soil washing, chemical neutralization, and bioremediation may be employed to restore soil quality.
The environmental impact of hydrochloric acid use extends beyond immediate pollution concerns. The production and transportation of hydrochloric acid also contribute to the overall environmental footprint of industrial cleaning processes. As such, many industries are exploring alternative cleaning methods and greener substitutes to reduce their reliance on hydrochloric acid.
To address these environmental challenges, regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented stringent guidelines for the use, handling, and disposal of hydrochloric acid in industrial settings. These regulations often mandate the use of best available technologies (BAT) for pollution control, regular environmental monitoring, and comprehensive emergency response plans.
Furthermore, the industrial sector is increasingly adopting cleaner production principles and circular economy approaches to minimize the environmental impact of hydrochloric acid use. This includes optimizing cleaning processes to reduce acid consumption, implementing more efficient application methods, and exploring opportunities for acid recovery and reuse within industrial operations.
As environmental concerns continue to shape industrial practices, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on developing more environmentally friendly cleaning alternatives and improving the sustainability of hydrochloric acid-based cleaning methods. These efforts aim to balance the need for effective industrial cleaning with the imperative of environmental protection, driving innovation in the field of industrial cleaning technologies.
Safety Regulations
The use of hydrochloric acid in industrial cleaning processes is subject to stringent safety regulations due to its corrosive nature and potential health hazards. These regulations are designed to protect workers, the environment, and the general public from the risks associated with handling and using this powerful chemical.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards in the United States mandate specific requirements for the use of hydrochloric acid in industrial settings. These include proper labeling of containers, provision of Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), and implementation of appropriate engineering controls such as ventilation systems to minimize exposure.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a crucial aspect of safety regulations. Workers handling hydrochloric acid must wear appropriate PPE, including chemical-resistant gloves, goggles or face shields, and protective clothing. Respiratory protection may also be required depending on the concentration and application method of the acid.
Storage and handling regulations are equally important. Hydrochloric acid must be stored in properly labeled, corrosion-resistant containers in well-ventilated areas. Secondary containment systems are often required to prevent spills from spreading. Transportation of hydrochloric acid is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT), which specifies packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements.
Emergency response procedures are a critical component of safety regulations. Facilities using hydrochloric acid must have clearly defined protocols for spill containment, neutralization, and disposal. Eye wash stations and safety showers must be readily accessible in areas where the acid is used or stored.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the use of hydrochloric acid for industrial cleaning. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the disposal of hydrochloric acid and its byproducts. Proper neutralization and treatment of acid waste are required before disposal, and facilities must comply with local, state, and federal regulations regarding wastewater discharge.
Training and education are fundamental aspects of safety regulations. Employers are required to provide comprehensive training to workers on the hazards of hydrochloric acid, proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the use of PPE. Regular refresher training is often mandated to ensure ongoing compliance and safety awareness.
Monitoring and record-keeping are essential components of regulatory compliance. Employers must maintain accurate records of acid usage, employee training, exposure monitoring, and any incidents or near-misses involving hydrochloric acid. Regular inspections and audits may be conducted by regulatory agencies to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards in the United States mandate specific requirements for the use of hydrochloric acid in industrial settings. These include proper labeling of containers, provision of Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), and implementation of appropriate engineering controls such as ventilation systems to minimize exposure.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a crucial aspect of safety regulations. Workers handling hydrochloric acid must wear appropriate PPE, including chemical-resistant gloves, goggles or face shields, and protective clothing. Respiratory protection may also be required depending on the concentration and application method of the acid.
Storage and handling regulations are equally important. Hydrochloric acid must be stored in properly labeled, corrosion-resistant containers in well-ventilated areas. Secondary containment systems are often required to prevent spills from spreading. Transportation of hydrochloric acid is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT), which specifies packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements.
Emergency response procedures are a critical component of safety regulations. Facilities using hydrochloric acid must have clearly defined protocols for spill containment, neutralization, and disposal. Eye wash stations and safety showers must be readily accessible in areas where the acid is used or stored.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the use of hydrochloric acid for industrial cleaning. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the disposal of hydrochloric acid and its byproducts. Proper neutralization and treatment of acid waste are required before disposal, and facilities must comply with local, state, and federal regulations regarding wastewater discharge.
Training and education are fundamental aspects of safety regulations. Employers are required to provide comprehensive training to workers on the hazards of hydrochloric acid, proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the use of PPE. Regular refresher training is often mandated to ensure ongoing compliance and safety awareness.
Monitoring and record-keeping are essential components of regulatory compliance. Employers must maintain accurate records of acid usage, employee training, exposure monitoring, and any incidents or near-misses involving hydrochloric acid. Regular inspections and audits may be conducted by regulatory agencies to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!