Hydrochloric Acid in Pharmaceutical Preparations: Best Practices
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HCl in Pharma: Background and Objectives
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) has been a cornerstone in pharmaceutical preparations for decades, playing a crucial role in various aspects of drug development and manufacturing. This versatile compound has a rich history in the pharmaceutical industry, dating back to the early 20th century when its potential in drug formulation was first recognized.
The evolution of HCl usage in pharmaceuticals has been marked by significant milestones. Initially, it was primarily used as a simple pH adjuster. However, as our understanding of drug chemistry and bioavailability improved, HCl's applications expanded. It became an essential component in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), particularly in the production of salt forms of basic drugs to enhance their solubility and absorption.
In recent years, the pharmaceutical industry has witnessed a surge in the development of complex drug molecules, many of which require precise pH control during formulation. This trend has further emphasized the importance of HCl in pharmaceutical preparations. The acid's ability to create stable salt forms of drugs has become increasingly valuable, especially in the formulation of controlled-release medications and parenteral preparations.
The objectives of utilizing HCl in pharmaceutical preparations are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to improve the solubility and bioavailability of drug compounds, which is critical for achieving therapeutic efficacy. Additionally, HCl plays a vital role in ensuring the stability of drug formulations, protecting them from degradation and extending their shelf life. It also contributes to the enhancement of drug absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, particularly for weakly basic drugs.
Another key objective is the optimization of drug manufacturing processes. HCl's use in API synthesis and purification helps in achieving higher yields and purity levels, which is essential for meeting stringent regulatory standards. Furthermore, its role in pH adjustment during various stages of drug production contributes to process consistency and product quality.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the objectives for HCl usage are expanding to include more sophisticated applications. These include its use in novel drug delivery systems, nanotechnology-based formulations, and personalized medicine approaches. The ongoing research in these areas aims to leverage HCl's properties to develop more effective and targeted drug therapies.
Looking ahead, the pharmaceutical industry is focusing on developing best practices for HCl use that align with sustainable manufacturing principles and stringent safety standards. This includes exploring alternatives to traditional HCl sources, optimizing its use to minimize environmental impact, and developing advanced handling and safety protocols to protect workers and the environment.
The evolution of HCl usage in pharmaceuticals has been marked by significant milestones. Initially, it was primarily used as a simple pH adjuster. However, as our understanding of drug chemistry and bioavailability improved, HCl's applications expanded. It became an essential component in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), particularly in the production of salt forms of basic drugs to enhance their solubility and absorption.
In recent years, the pharmaceutical industry has witnessed a surge in the development of complex drug molecules, many of which require precise pH control during formulation. This trend has further emphasized the importance of HCl in pharmaceutical preparations. The acid's ability to create stable salt forms of drugs has become increasingly valuable, especially in the formulation of controlled-release medications and parenteral preparations.
The objectives of utilizing HCl in pharmaceutical preparations are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to improve the solubility and bioavailability of drug compounds, which is critical for achieving therapeutic efficacy. Additionally, HCl plays a vital role in ensuring the stability of drug formulations, protecting them from degradation and extending their shelf life. It also contributes to the enhancement of drug absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, particularly for weakly basic drugs.
Another key objective is the optimization of drug manufacturing processes. HCl's use in API synthesis and purification helps in achieving higher yields and purity levels, which is essential for meeting stringent regulatory standards. Furthermore, its role in pH adjustment during various stages of drug production contributes to process consistency and product quality.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the objectives for HCl usage are expanding to include more sophisticated applications. These include its use in novel drug delivery systems, nanotechnology-based formulations, and personalized medicine approaches. The ongoing research in these areas aims to leverage HCl's properties to develop more effective and targeted drug therapies.
Looking ahead, the pharmaceutical industry is focusing on developing best practices for HCl use that align with sustainable manufacturing principles and stringent safety standards. This includes exploring alternatives to traditional HCl sources, optimizing its use to minimize environmental impact, and developing advanced handling and safety protocols to protect workers and the environment.
Market Analysis for HCl-based Pharmaceuticals
The global market for hydrochloric acid (HCl) in pharmaceutical preparations has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for various medications and the expanding pharmaceutical industry. HCl plays a crucial role in the production of numerous drugs, including antihistamines, antacids, and certain antibiotics. The market size for HCl-based pharmaceuticals is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2021 to 2026.
One of the primary factors contributing to this growth is the rising prevalence of gastrointestinal disorders worldwide. HCl is a key component in the production of antacids and proton pump inhibitors, which are widely used to treat conditions such as acid reflux and peptic ulcers. The aging global population and changing dietary habits have led to an increased incidence of these disorders, thereby boosting the demand for HCl-based medications.
Another significant driver of market growth is the expanding use of HCl in the production of various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). As the pharmaceutical industry continues to innovate and develop new drugs, the demand for high-purity HCl in API synthesis is expected to rise. This trend is particularly evident in the production of complex molecules and specialty pharmaceuticals.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for HCl-based pharmaceuticals, owing to their well-established healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by factors such as increasing healthcare awareness, rising disposable incomes, and government initiatives to improve healthcare access.
The market landscape for HCl-based pharmaceuticals is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major pharmaceutical companies and specialty chemical manufacturers. These companies are focusing on research and development activities to enhance the purity and quality of HCl used in pharmaceutical preparations, as well as to develop innovative drug formulations that leverage the properties of HCl.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces certain challenges. Stringent regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical-grade HCl and concerns about the environmental impact of HCl production processes are factors that may potentially hinder market growth. Additionally, the volatility in raw material prices and the availability of alternative materials in some applications pose challenges to market players.
In conclusion, the market for HCl-based pharmaceuticals presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve and address global health challenges, the demand for high-quality HCl in drug manufacturing is expected to remain strong. Companies that can navigate regulatory hurdles, invest in sustainable production methods, and develop novel applications for HCl in pharmaceuticals are likely to succeed in this dynamic market landscape.
One of the primary factors contributing to this growth is the rising prevalence of gastrointestinal disorders worldwide. HCl is a key component in the production of antacids and proton pump inhibitors, which are widely used to treat conditions such as acid reflux and peptic ulcers. The aging global population and changing dietary habits have led to an increased incidence of these disorders, thereby boosting the demand for HCl-based medications.
Another significant driver of market growth is the expanding use of HCl in the production of various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). As the pharmaceutical industry continues to innovate and develop new drugs, the demand for high-purity HCl in API synthesis is expected to rise. This trend is particularly evident in the production of complex molecules and specialty pharmaceuticals.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for HCl-based pharmaceuticals, owing to their well-established healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by factors such as increasing healthcare awareness, rising disposable incomes, and government initiatives to improve healthcare access.
The market landscape for HCl-based pharmaceuticals is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major pharmaceutical companies and specialty chemical manufacturers. These companies are focusing on research and development activities to enhance the purity and quality of HCl used in pharmaceutical preparations, as well as to develop innovative drug formulations that leverage the properties of HCl.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces certain challenges. Stringent regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical-grade HCl and concerns about the environmental impact of HCl production processes are factors that may potentially hinder market growth. Additionally, the volatility in raw material prices and the availability of alternative materials in some applications pose challenges to market players.
In conclusion, the market for HCl-based pharmaceuticals presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve and address global health challenges, the demand for high-quality HCl in drug manufacturing is expected to remain strong. Companies that can navigate regulatory hurdles, invest in sustainable production methods, and develop novel applications for HCl in pharmaceuticals are likely to succeed in this dynamic market landscape.
Current Challenges in HCl Pharmaceutical Use
The use of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in pharmaceutical preparations faces several significant challenges that impact its efficacy, safety, and overall application. One of the primary concerns is the corrosive nature of HCl, which can lead to degradation of equipment and packaging materials. This necessitates the use of specialized, acid-resistant materials throughout the manufacturing and storage processes, increasing production costs and complexity.
Another challenge lies in maintaining the stability of HCl-containing formulations over time. The acid's reactivity can lead to unwanted interactions with other ingredients, potentially altering the efficacy or safety profile of the final product. This is particularly problematic in multi-component pharmaceutical preparations, where the acid may catalyze degradation reactions or form undesired by-products.
Dosage accuracy presents a further challenge, as the concentration of HCl in pharmaceutical preparations must be precisely controlled. Even small variations can significantly affect the pH of the formulation, potentially altering its bioavailability, stability, or therapeutic effect. This requires highly accurate measurement and mixing techniques, as well as robust quality control processes.
The potential for adverse effects on patients is another critical concern. While HCl plays crucial roles in many pharmaceutical formulations, its improper use or excessive concentrations can lead to irritation or damage to mucous membranes, particularly in oral or topical preparations. Balancing the acid's beneficial properties with its potential for harm requires careful formulation and extensive safety testing.
Environmental considerations also pose challenges in HCl pharmaceutical use. The production, handling, and disposal of HCl and HCl-containing products must adhere to strict environmental regulations to prevent pollution and protect ecosystems. This necessitates the implementation of sophisticated waste management systems and may limit the scale or location of manufacturing operations.
Regulatory compliance represents an ongoing challenge, with authorities worldwide imposing stringent requirements on the use of HCl in pharmaceuticals. Manufacturers must navigate complex regulatory landscapes, ensuring that their processes and products meet evolving standards for safety, efficacy, and quality. This often requires substantial investments in research, documentation, and quality assurance systems.
Lastly, the pharmaceutical industry faces challenges in sourcing high-purity HCl suitable for medicinal use. Ensuring a consistent supply of pharmaceutical-grade HCl, free from contaminants and meeting strict quality standards, can be difficult and costly. This supply chain challenge can impact production schedules and ultimately affect the availability of critical medications.
Another challenge lies in maintaining the stability of HCl-containing formulations over time. The acid's reactivity can lead to unwanted interactions with other ingredients, potentially altering the efficacy or safety profile of the final product. This is particularly problematic in multi-component pharmaceutical preparations, where the acid may catalyze degradation reactions or form undesired by-products.
Dosage accuracy presents a further challenge, as the concentration of HCl in pharmaceutical preparations must be precisely controlled. Even small variations can significantly affect the pH of the formulation, potentially altering its bioavailability, stability, or therapeutic effect. This requires highly accurate measurement and mixing techniques, as well as robust quality control processes.
The potential for adverse effects on patients is another critical concern. While HCl plays crucial roles in many pharmaceutical formulations, its improper use or excessive concentrations can lead to irritation or damage to mucous membranes, particularly in oral or topical preparations. Balancing the acid's beneficial properties with its potential for harm requires careful formulation and extensive safety testing.
Environmental considerations also pose challenges in HCl pharmaceutical use. The production, handling, and disposal of HCl and HCl-containing products must adhere to strict environmental regulations to prevent pollution and protect ecosystems. This necessitates the implementation of sophisticated waste management systems and may limit the scale or location of manufacturing operations.
Regulatory compliance represents an ongoing challenge, with authorities worldwide imposing stringent requirements on the use of HCl in pharmaceuticals. Manufacturers must navigate complex regulatory landscapes, ensuring that their processes and products meet evolving standards for safety, efficacy, and quality. This often requires substantial investments in research, documentation, and quality assurance systems.
Lastly, the pharmaceutical industry faces challenges in sourcing high-purity HCl suitable for medicinal use. Ensuring a consistent supply of pharmaceutical-grade HCl, free from contaminants and meeting strict quality standards, can be difficult and costly. This supply chain challenge can impact production schedules and ultimately affect the availability of critical medications.
Best Practices for HCl in Drug Formulations
01 Production methods of hydrochloric acid
Various methods are employed to produce hydrochloric acid, including the reaction of chlorine with hydrogen, the chlorination of hydrocarbons, and as a byproduct in chemical processes. These production methods aim to optimize yield, purity, and efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.- Production methods of hydrochloric acid: Various methods are employed for the production of hydrochloric acid, including direct synthesis from hydrogen and chlorine, as a byproduct in chlorination processes, and through the reaction of sulfuric acid with sodium chloride. These methods are optimized for efficiency and purity in industrial settings.
- Purification and concentration techniques: Techniques for purifying and concentrating hydrochloric acid involve distillation, membrane separation, and adsorption processes. These methods aim to remove impurities and achieve desired concentration levels for various industrial applications.
- Applications in chemical processing: Hydrochloric acid is widely used in chemical processing, including metal treatment, pH regulation, and as a reagent in various chemical reactions. Its versatility makes it essential in industries such as metallurgy, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
- Safety and handling considerations: Proper safety measures and handling procedures are crucial when working with hydrochloric acid due to its corrosive nature. This includes the use of specialized storage containers, protective equipment, and neutralization techniques for spills or disposal.
- Environmental impact and recycling: Efforts to minimize the environmental impact of hydrochloric acid production and use include developing recycling methods, implementing closed-loop systems, and exploring alternative production processes that reduce waste and emissions.
02 Purification and concentration of hydrochloric acid
Techniques for purifying and concentrating hydrochloric acid involve distillation, membrane separation, and adsorption processes. These methods aim to remove impurities and increase the acid concentration for various industrial applications, ensuring high-quality products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of hydrochloric acid in chemical processing
Hydrochloric acid is widely used in chemical processing, including metal treatment, pH regulation, and as a reagent in various reactions. Its versatility makes it essential in industries such as metallurgy, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety measures and handling of hydrochloric acid
Proper safety measures and handling procedures are crucial when working with hydrochloric acid due to its corrosive nature. This includes the use of appropriate personal protective equipment, storage containers, and neutralization techniques to mitigate risks associated with its use.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental considerations in hydrochloric acid use
Environmental considerations in the use of hydrochloric acid include proper disposal methods, emission control, and recycling techniques. These practices aim to minimize the environmental impact of hydrochloric acid production and usage while complying with regulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HCl Pharmaceutical Production
The hydrochloric acid in pharmaceutical preparations market is in a mature stage, with established players and well-defined applications. The global market size is substantial, driven by the widespread use of hydrochloric acid in drug formulation and manufacturing processes. Technologically, the field is well-developed, with companies like Sandoz AG, Janssen Products LP, and Merck Patent GmbH leading innovation. These firms, along with others such as Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. and Eli Lilly & Co., have extensive experience in pharmaceutical-grade hydrochloric acid production and application. The focus is on optimizing production methods, enhancing purity, and developing novel applications to maintain competitive edges in this established market.
Sandoz AG
Technical Solution: Sandoz, a division of Novartis, has implemented a comprehensive approach to using hydrochloric acid in generic drug manufacturing. They have developed a scalable platform for acid-base reactions that optimizes the use of hydrochloric acid across multiple product lines[8]. This platform incorporates in-line dilution systems and advanced process analytical technology (PAT) to ensure precise acid concentrations and pH control. Sandoz has also invested in green chemistry initiatives, implementing solvent recycling systems that recover and purify hydrochloric acid for reuse, significantly reducing waste and environmental impact[10]. Furthermore, the company has developed a risk-based approach to handling and storing hydrochloric acid, implementing advanced containment systems and safety protocols to minimize potential hazards[12].
Strengths: Scalable and efficient manufacturing platform, environmentally friendly practices, and advanced safety measures. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in adapting the platform for highly specialized or novel drug formulations.
Bayer Intellectual Property GmbH
Technical Solution: Bayer has developed a sophisticated approach to using hydrochloric acid in pharmaceutical preparations, focusing on both innovation and sustainability. They have implemented a novel continuous manufacturing process that precisely controls the addition of hydrochloric acid, allowing for more consistent product quality and reduced variability between batches[13]. This system incorporates real-time monitoring and feedback control, utilizing advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms to optimize acid usage. Bayer has also developed a proprietary acid-resistant coating technology for tablets and capsules, which provides enhanced stability for acid-sensitive drugs[15]. Additionally, the company has invested in green chemistry initiatives, implementing a closed-loop system for hydrochloric acid recovery and purification, significantly reducing waste and environmental impact in their manufacturing processes[17].
Strengths: Advanced continuous manufacturing, innovative coating technology, and sustainable practices. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs and potential complexity in regulatory approval for novel manufacturing processes.
Innovations in HCl Handling and Safety
A method for manufacturing pharmaceutical grade hypochlorous acid
PatentPendingUS20250129486A1
Innovation
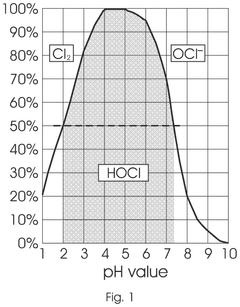
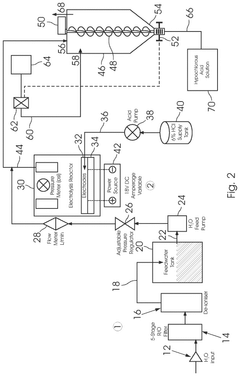
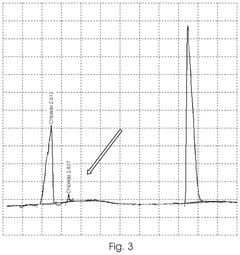
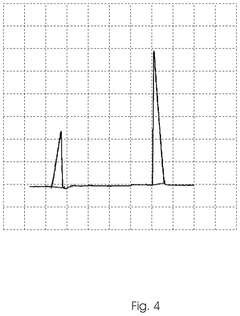
- A method involving the electrolysis of platinum grade hydrochloric acid in a single chamber reactor, using platinum grade disodium hydrogen orthophosphate as a real-time buffering agent to adjust the pH from 1.5 to 2.5 to between 4.0 and 5.8, thereby producing pharmaceutical grade HOCl that is free from toxic by-products.
Crystallization of hydrohalides of pharmaceutical compounds
PatentInactiveEP2436381A1
Innovation
- A process involving the use of trialkylsilylhalogenides to generate hydrohalogenic acids in situ, allowing for the preparation of crystalline hydrohalides of organic amines in anhydrous conditions, using protic or aprotic solvents to control the formation of specific crystal structures, such as Moxifloxacin hydrochloride solvates and Linezolid hydrochloride forms.
Regulatory Framework for HCl in Pharmaceuticals
The regulatory framework for hydrochloric acid (HCl) in pharmaceutical preparations is a complex and evolving landscape that encompasses various national and international guidelines. At the forefront of these regulations is the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which has established stringent requirements for the use of HCl in drug formulations. The FDA's guidance documents outline specific quality standards, safety assessments, and manufacturing practices that must be adhered to when incorporating HCl into pharmaceutical products.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides comprehensive guidelines on the use of excipients, including HCl, in medicinal products. These guidelines emphasize the importance of risk assessment and quality control measures to ensure the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical preparations containing HCl. The EMA's regulations also address the need for proper labeling and documentation of HCl usage in drug products.
Internationally, the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) has developed harmonized guidelines that are widely adopted by regulatory agencies worldwide. These guidelines provide a framework for assessing the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical ingredients, including HCl, and promote consistency in regulatory approaches across different regions.
The World Health Organization (WHO) also plays a crucial role in shaping the global regulatory landscape for pharmaceutical excipients. The WHO's guidelines on Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for pharmaceutical excipients provide essential recommendations for the production and quality control of substances like HCl used in drug formulations.
Regulatory bodies in other major pharmaceutical markets, such as Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and Health Canada, have also established specific requirements for the use of HCl in pharmaceutical preparations. These regulations often align with international standards while addressing unique national considerations.
A key aspect of the regulatory framework is the emphasis on risk management and quality assurance throughout the pharmaceutical supply chain. Manufacturers are required to implement robust quality management systems, conduct thorough risk assessments, and maintain detailed documentation of their processes and controls related to HCl usage.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the environmental impact of HCl production and usage in pharmaceuticals. Environmental protection agencies in various countries have set guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of HCl to minimize potential ecological risks associated with its industrial use.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are regularly updated to address emerging challenges and incorporate new scientific knowledge. This dynamic nature of regulations necessitates ongoing vigilance and adaptation from pharmaceutical companies to ensure compliance and maintain the highest standards of safety and efficacy in their products containing HCl.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides comprehensive guidelines on the use of excipients, including HCl, in medicinal products. These guidelines emphasize the importance of risk assessment and quality control measures to ensure the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical preparations containing HCl. The EMA's regulations also address the need for proper labeling and documentation of HCl usage in drug products.
Internationally, the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) has developed harmonized guidelines that are widely adopted by regulatory agencies worldwide. These guidelines provide a framework for assessing the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical ingredients, including HCl, and promote consistency in regulatory approaches across different regions.
The World Health Organization (WHO) also plays a crucial role in shaping the global regulatory landscape for pharmaceutical excipients. The WHO's guidelines on Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for pharmaceutical excipients provide essential recommendations for the production and quality control of substances like HCl used in drug formulations.
Regulatory bodies in other major pharmaceutical markets, such as Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and Health Canada, have also established specific requirements for the use of HCl in pharmaceutical preparations. These regulations often align with international standards while addressing unique national considerations.
A key aspect of the regulatory framework is the emphasis on risk management and quality assurance throughout the pharmaceutical supply chain. Manufacturers are required to implement robust quality management systems, conduct thorough risk assessments, and maintain detailed documentation of their processes and controls related to HCl usage.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the environmental impact of HCl production and usage in pharmaceuticals. Environmental protection agencies in various countries have set guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of HCl to minimize potential ecological risks associated with its industrial use.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are regularly updated to address emerging challenges and incorporate new scientific knowledge. This dynamic nature of regulations necessitates ongoing vigilance and adaptation from pharmaceutical companies to ensure compliance and maintain the highest standards of safety and efficacy in their products containing HCl.
Environmental Impact of HCl in Drug Manufacturing
The environmental impact of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in drug manufacturing is a critical concern for the pharmaceutical industry. HCl is widely used in various stages of drug production, including synthesis, purification, and formulation. However, its corrosive nature and potential for environmental contamination necessitate careful management and stringent control measures.
One of the primary environmental risks associated with HCl in drug manufacturing is its potential to contribute to acid rain formation if released into the atmosphere. When HCl vapors combine with moisture in the air, they can form acidic precipitation, which can harm ecosystems, damage infrastructure, and affect human health. To mitigate this risk, pharmaceutical facilities must implement robust air pollution control systems, such as scrubbers and absorption towers, to neutralize and capture HCl emissions.
Water pollution is another significant concern. Improper disposal of HCl-containing wastewater can lead to the acidification of water bodies, causing detrimental effects on aquatic life and water quality. Advanced wastewater treatment systems, including neutralization and ion exchange processes, are essential for removing HCl and other acidic compounds before discharge.
The production and transportation of HCl also contribute to the industry's carbon footprint. Energy-intensive processes involved in HCl synthesis and purification, as well as the fuel consumption associated with its transportation, add to greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and optimizing supply chain logistics can help reduce these environmental impacts.
Soil contamination is a potential risk if HCl is accidentally spilled or leaked during handling or storage. Acidification of soil can alter its chemical properties, affecting plant growth and soil microorganisms. Proper containment measures, spill prevention protocols, and emergency response plans are crucial to minimize the risk of soil contamination.
To address these environmental concerns, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly adopting green chemistry principles and sustainable manufacturing practices. This includes exploring alternative reagents and processes that reduce or eliminate the use of HCl where possible. Additionally, closed-loop systems and recycling technologies are being implemented to minimize waste generation and maximize resource efficiency.
Regulatory compliance plays a vital role in managing the environmental impact of HCl in drug manufacturing. Stringent environmental regulations, such as those set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and similar bodies worldwide, require pharmaceutical companies to monitor and report their emissions, implement best available technologies for pollution control, and adhere to strict waste management practices.
One of the primary environmental risks associated with HCl in drug manufacturing is its potential to contribute to acid rain formation if released into the atmosphere. When HCl vapors combine with moisture in the air, they can form acidic precipitation, which can harm ecosystems, damage infrastructure, and affect human health. To mitigate this risk, pharmaceutical facilities must implement robust air pollution control systems, such as scrubbers and absorption towers, to neutralize and capture HCl emissions.
Water pollution is another significant concern. Improper disposal of HCl-containing wastewater can lead to the acidification of water bodies, causing detrimental effects on aquatic life and water quality. Advanced wastewater treatment systems, including neutralization and ion exchange processes, are essential for removing HCl and other acidic compounds before discharge.
The production and transportation of HCl also contribute to the industry's carbon footprint. Energy-intensive processes involved in HCl synthesis and purification, as well as the fuel consumption associated with its transportation, add to greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and optimizing supply chain logistics can help reduce these environmental impacts.
Soil contamination is a potential risk if HCl is accidentally spilled or leaked during handling or storage. Acidification of soil can alter its chemical properties, affecting plant growth and soil microorganisms. Proper containment measures, spill prevention protocols, and emergency response plans are crucial to minimize the risk of soil contamination.
To address these environmental concerns, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly adopting green chemistry principles and sustainable manufacturing practices. This includes exploring alternative reagents and processes that reduce or eliminate the use of HCl where possible. Additionally, closed-loop systems and recycling technologies are being implemented to minimize waste generation and maximize resource efficiency.
Regulatory compliance plays a vital role in managing the environmental impact of HCl in drug manufacturing. Stringent environmental regulations, such as those set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and similar bodies worldwide, require pharmaceutical companies to monitor and report their emissions, implement best available technologies for pollution control, and adhere to strict waste management practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!