Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5069results about "Conversion constructional details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
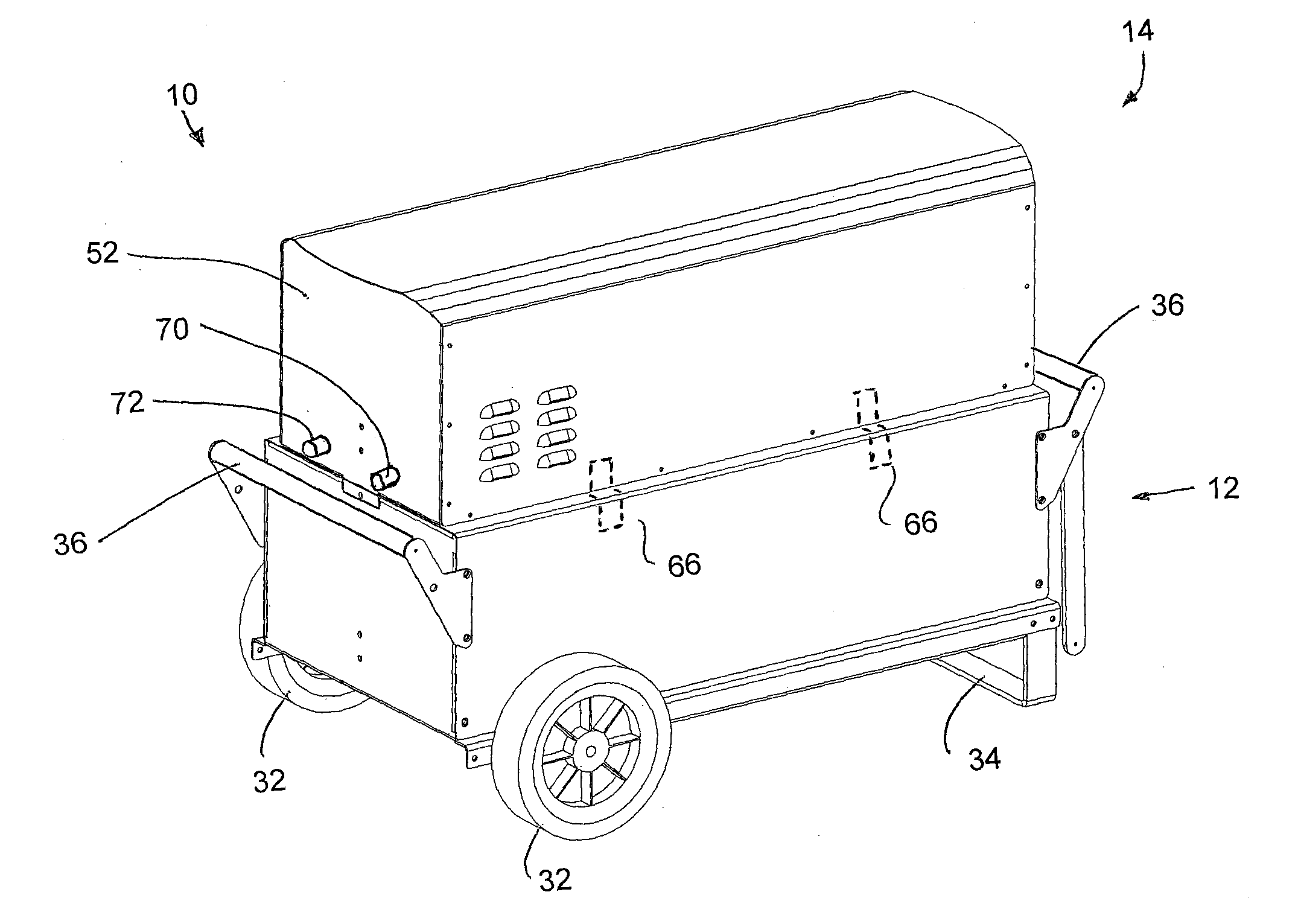
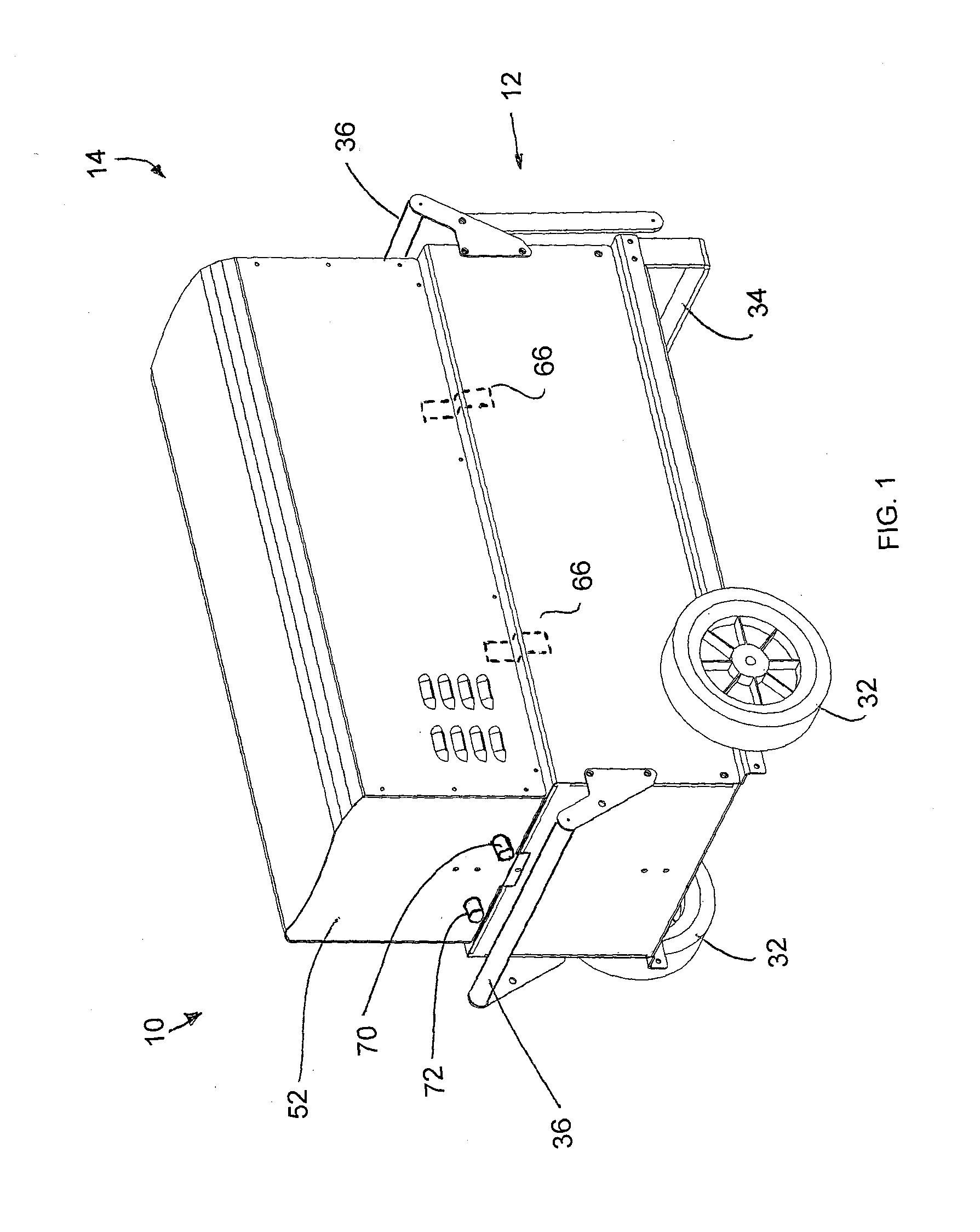
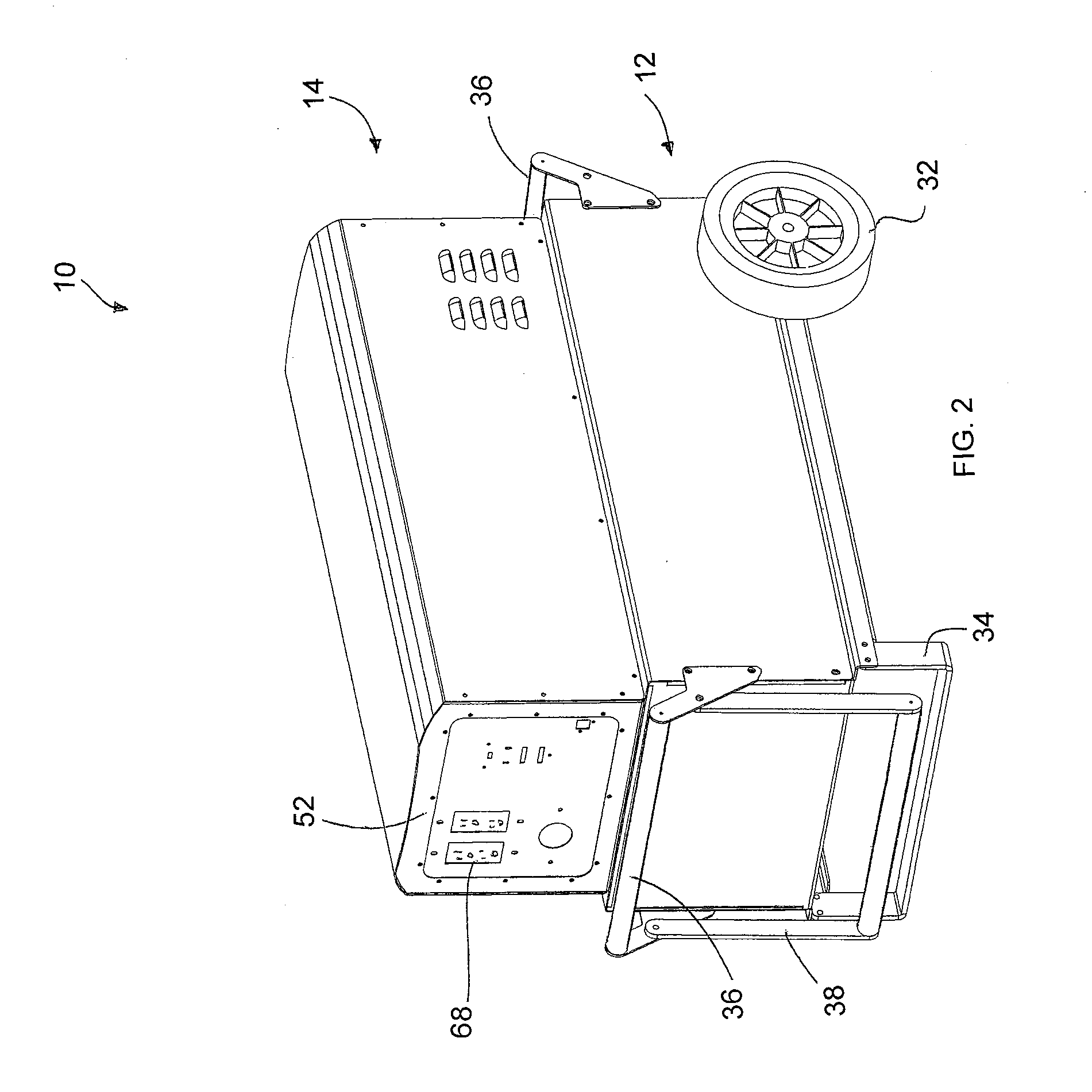
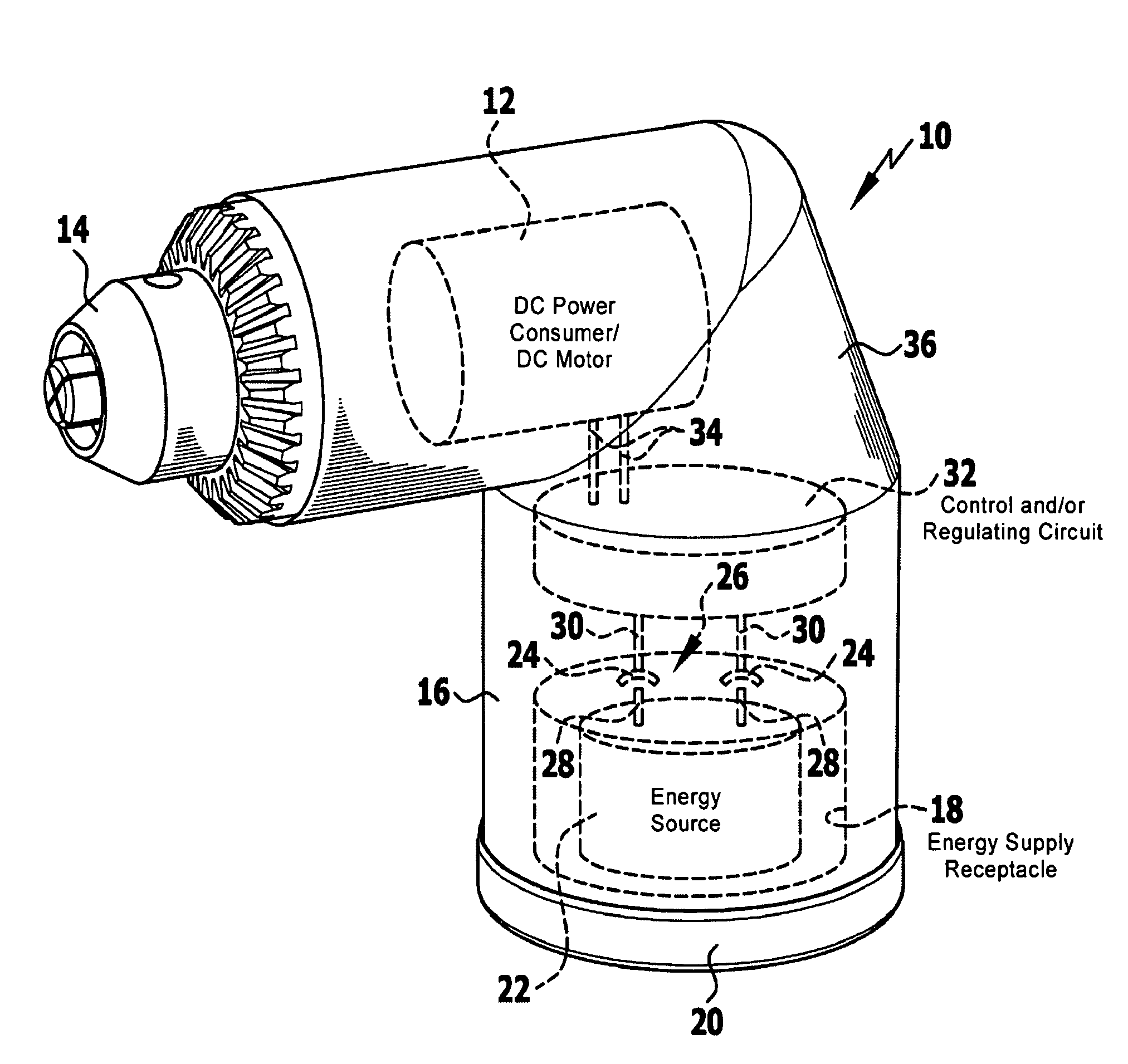
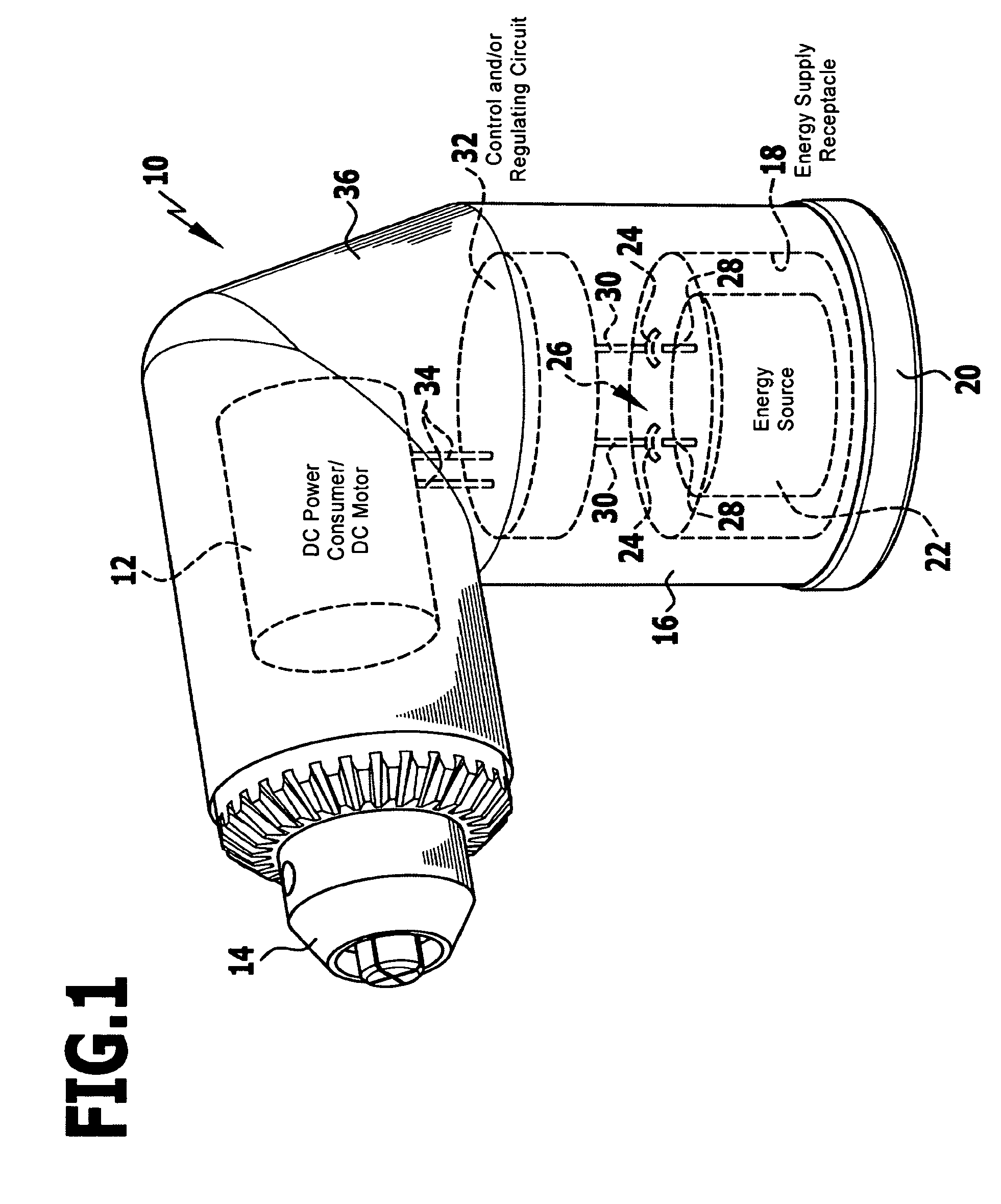
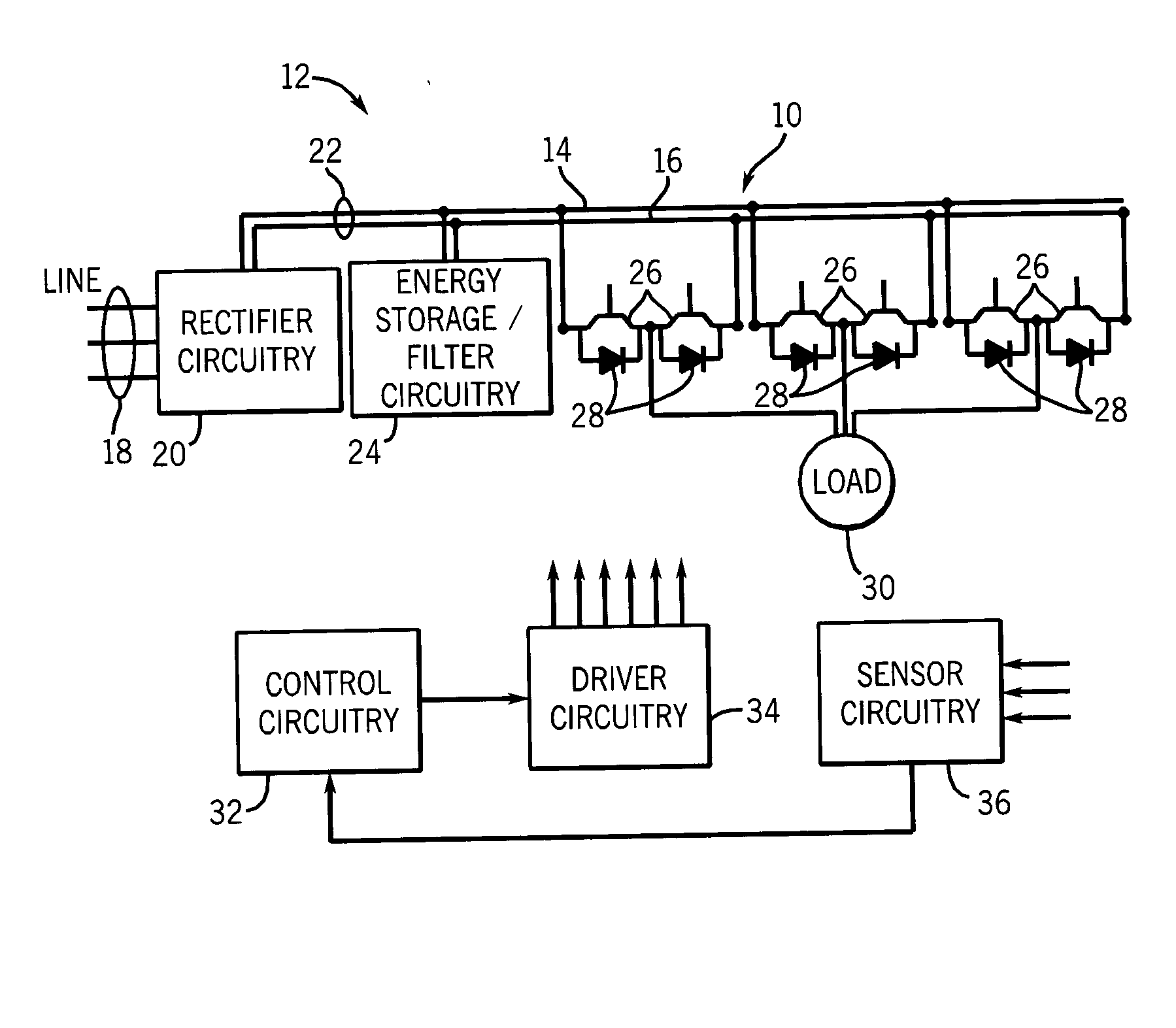
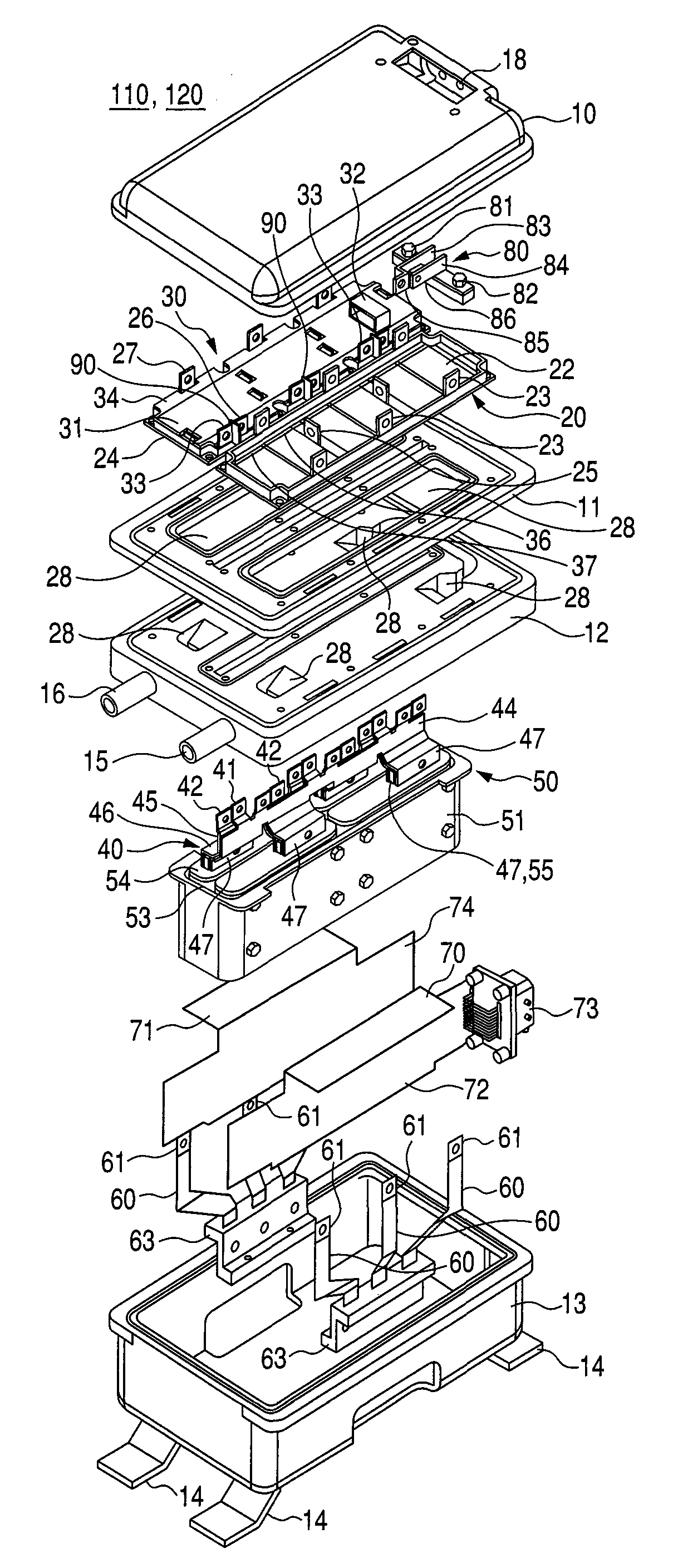
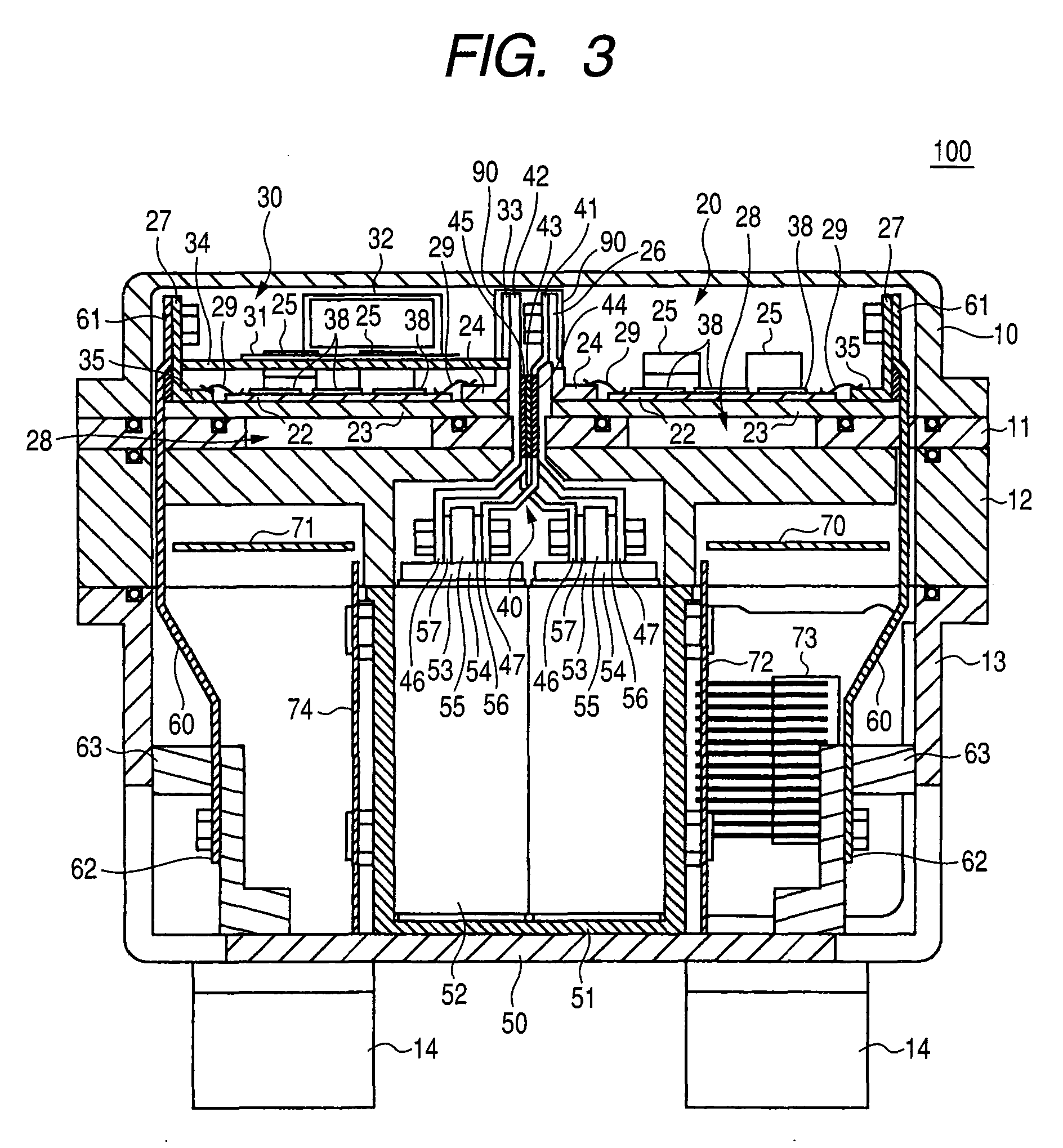
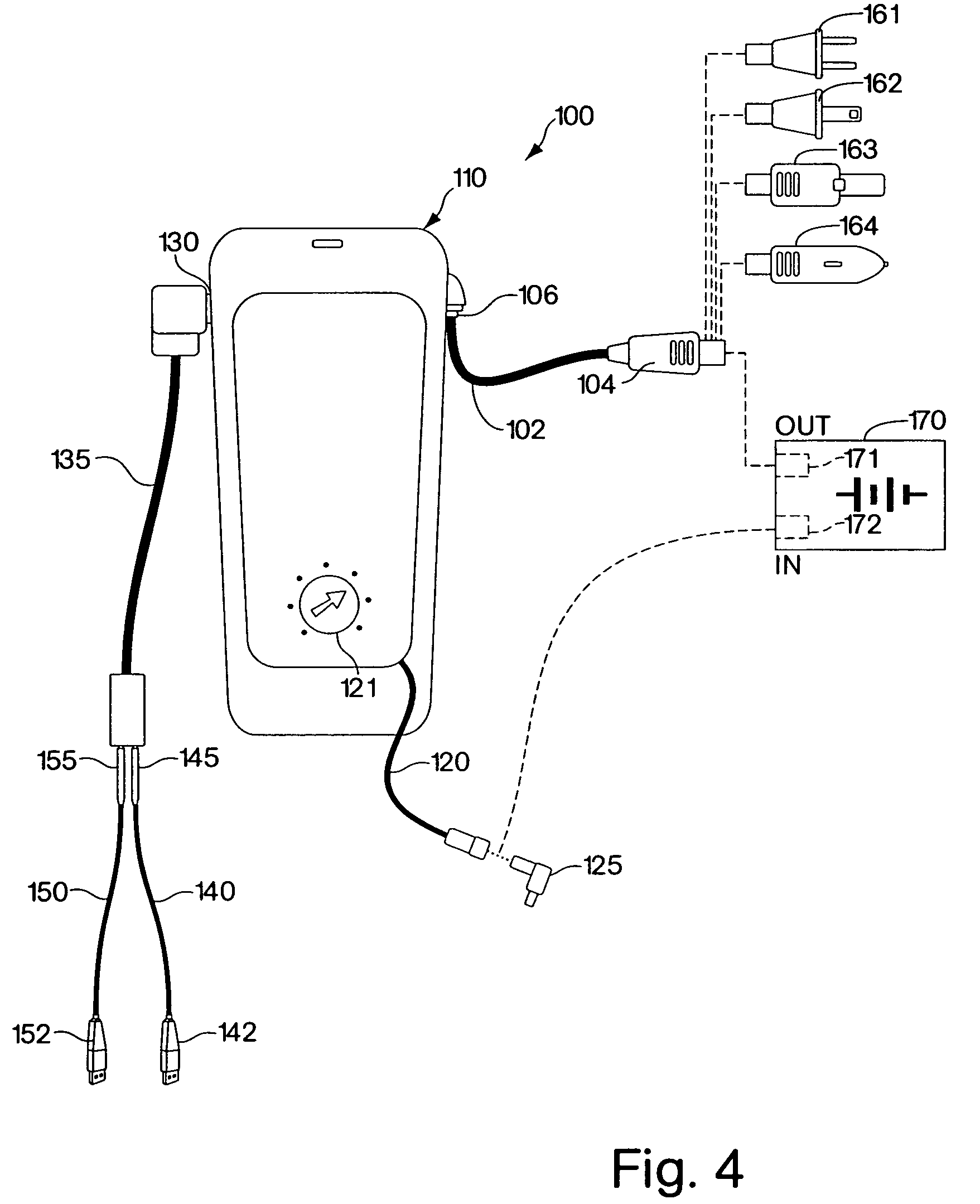
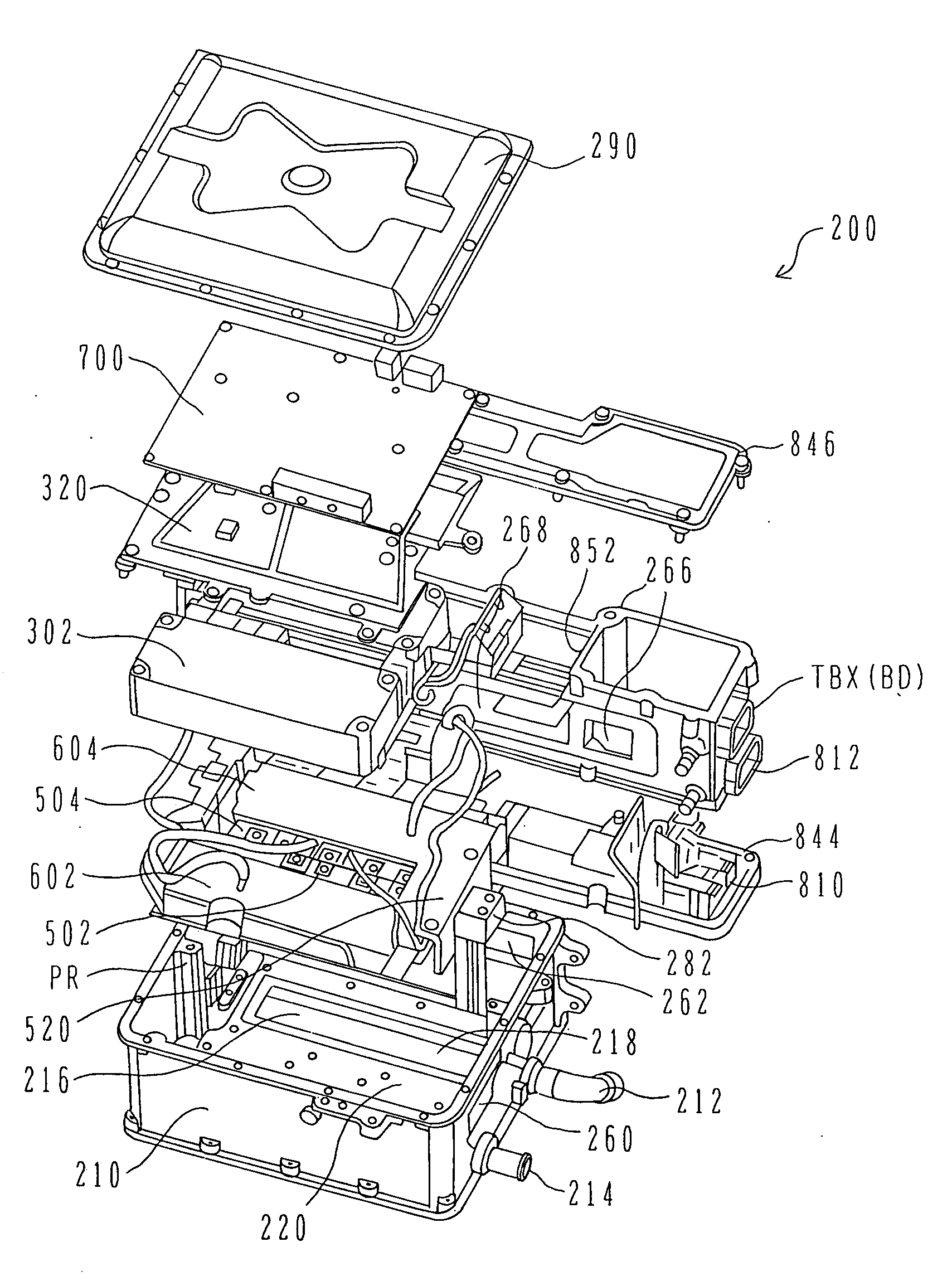
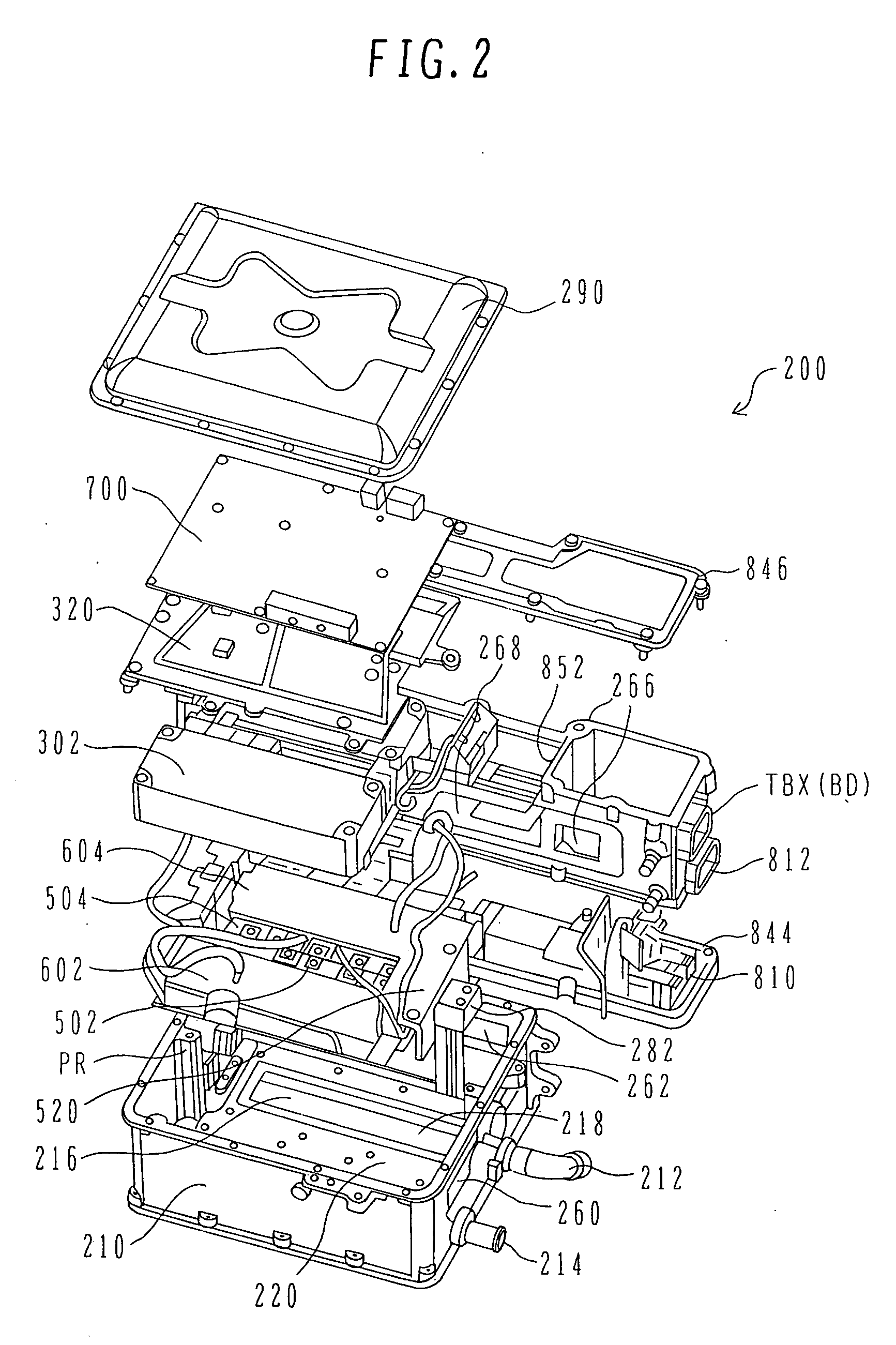
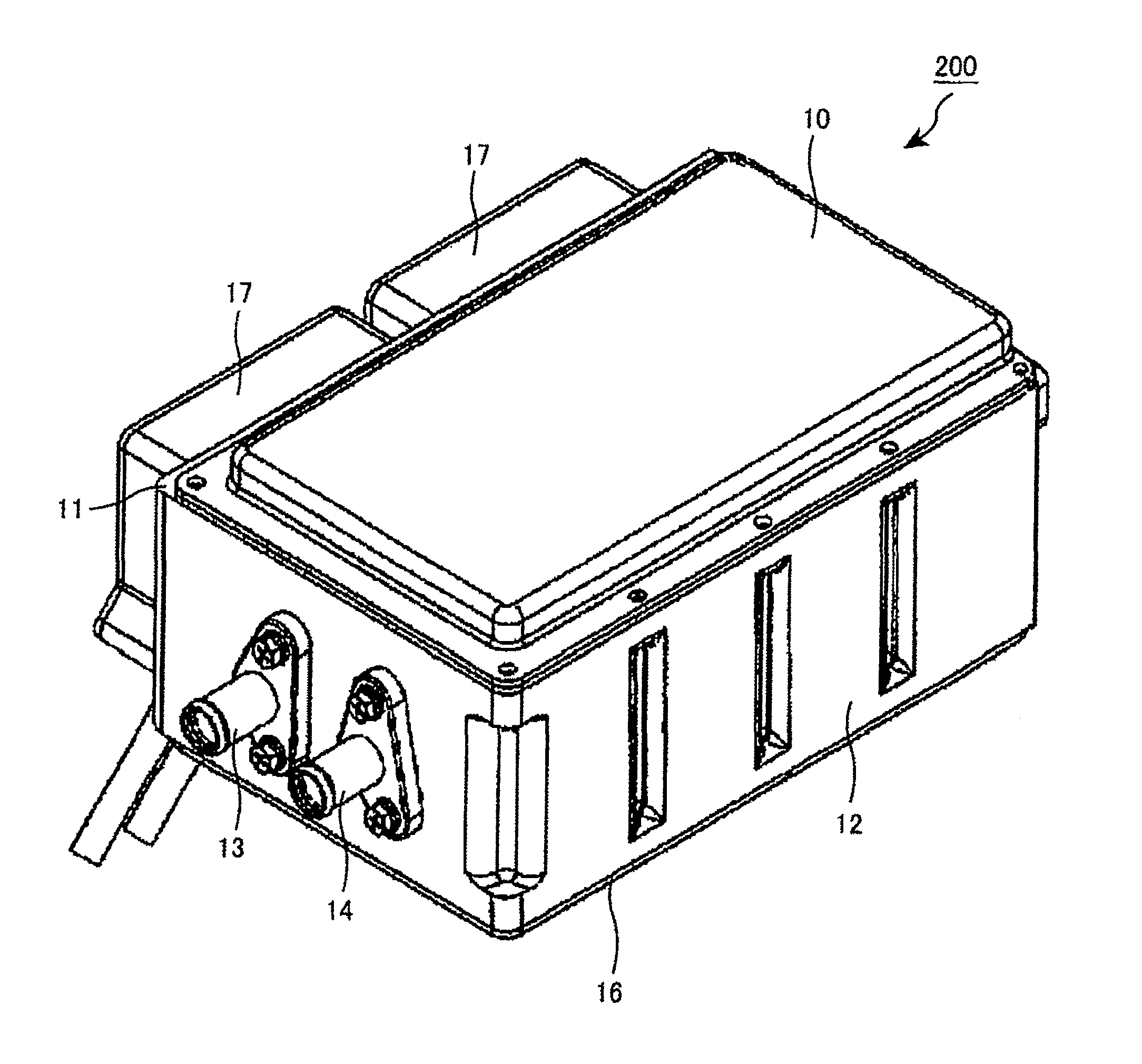
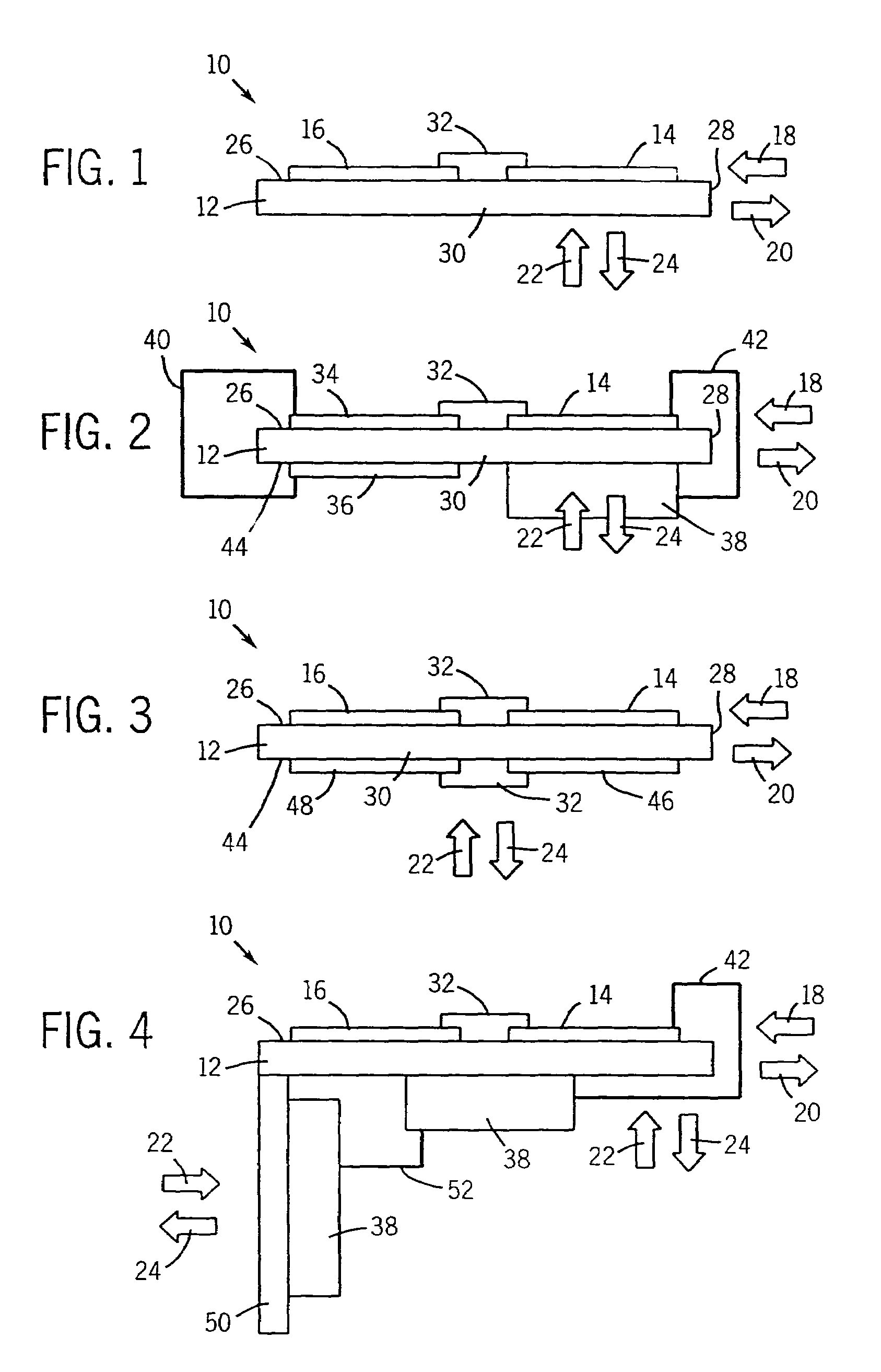
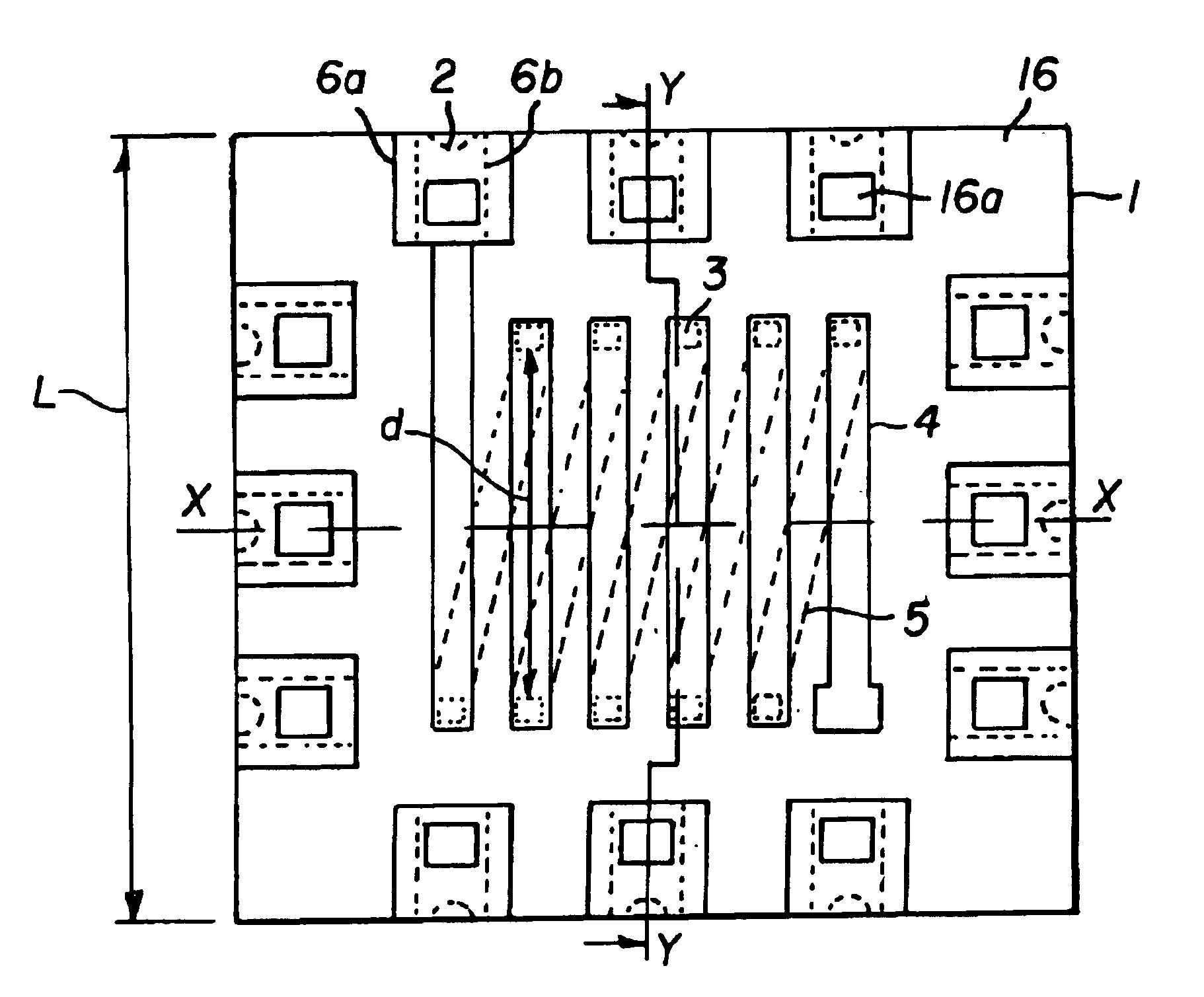
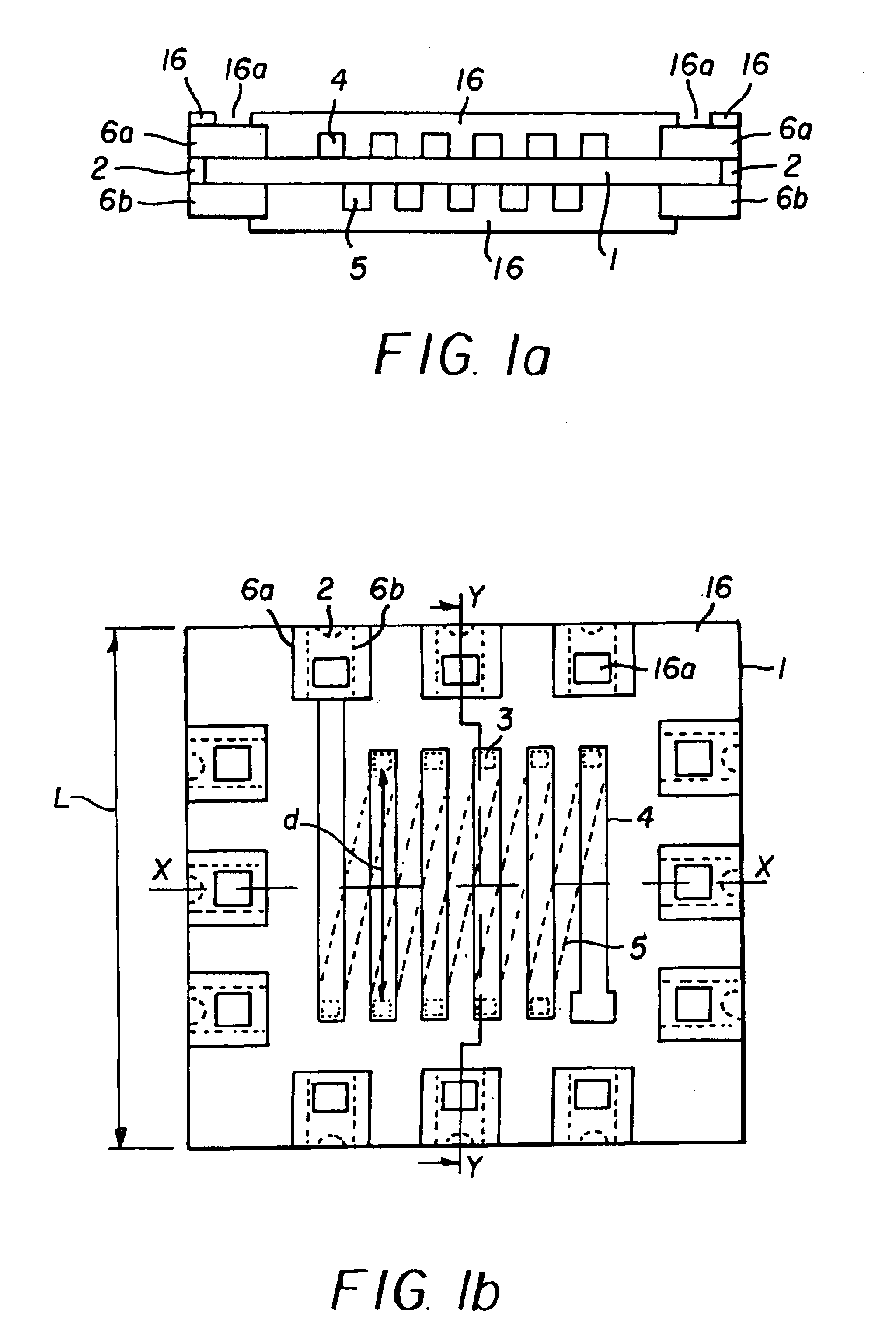
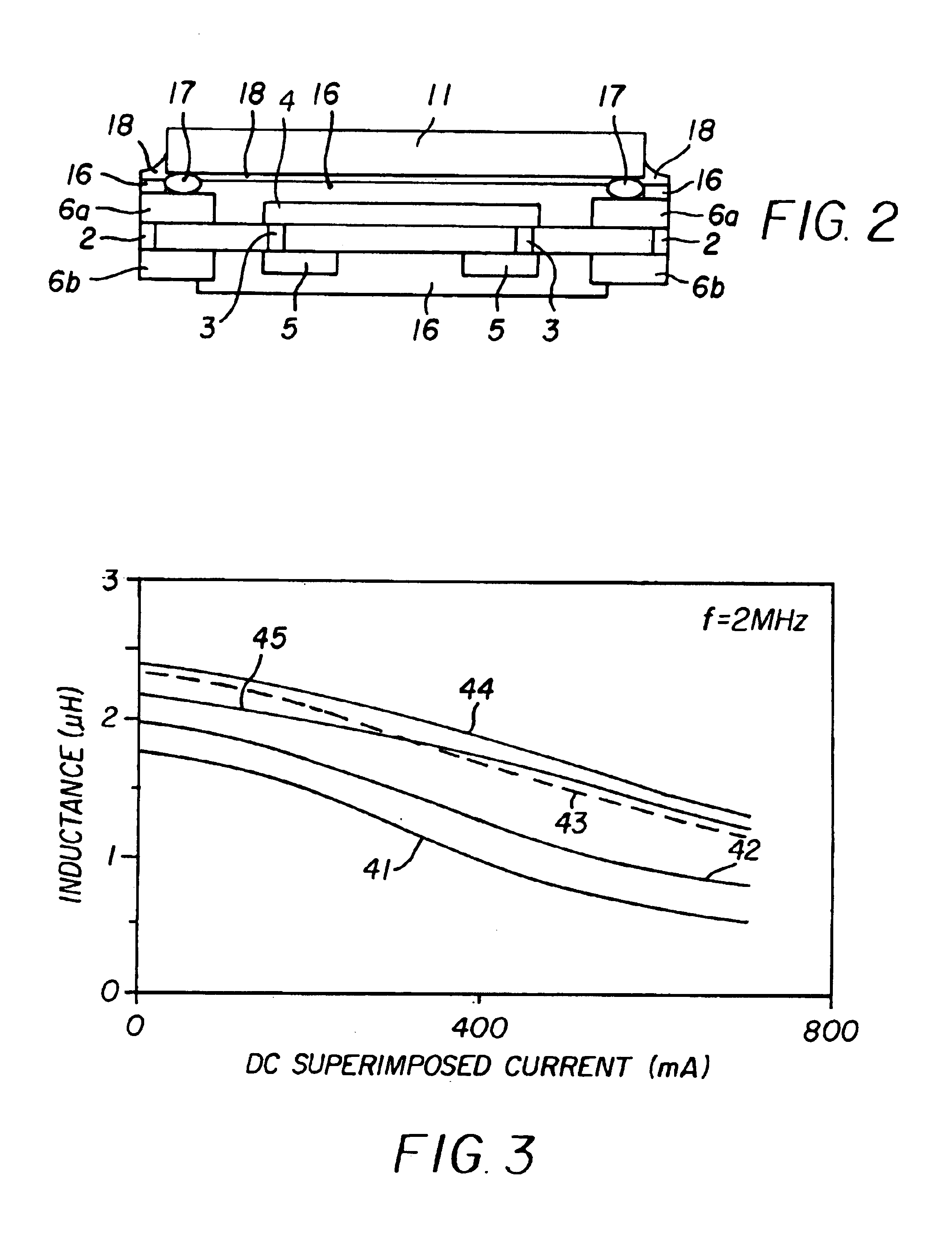
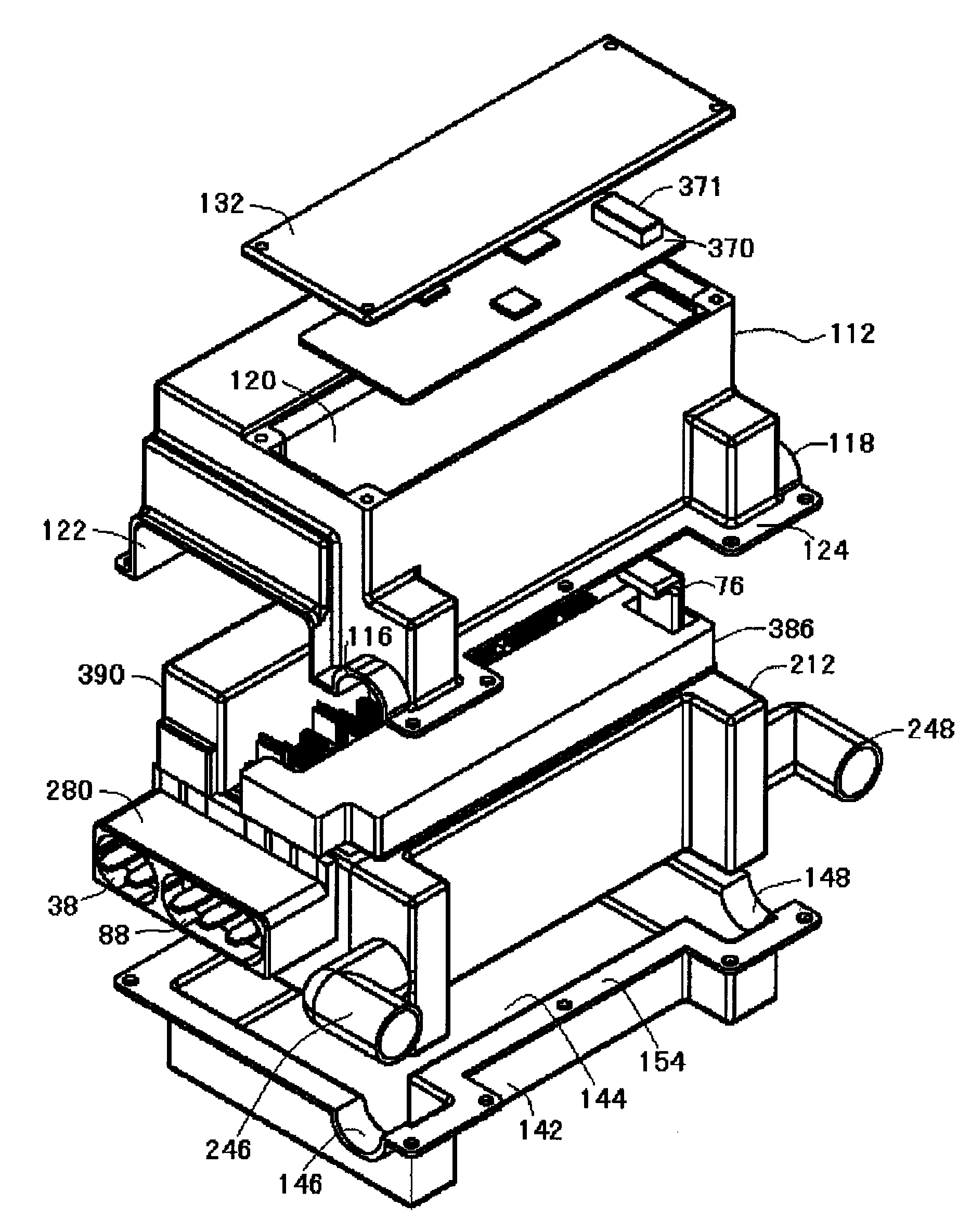
Portable Power Supply Device
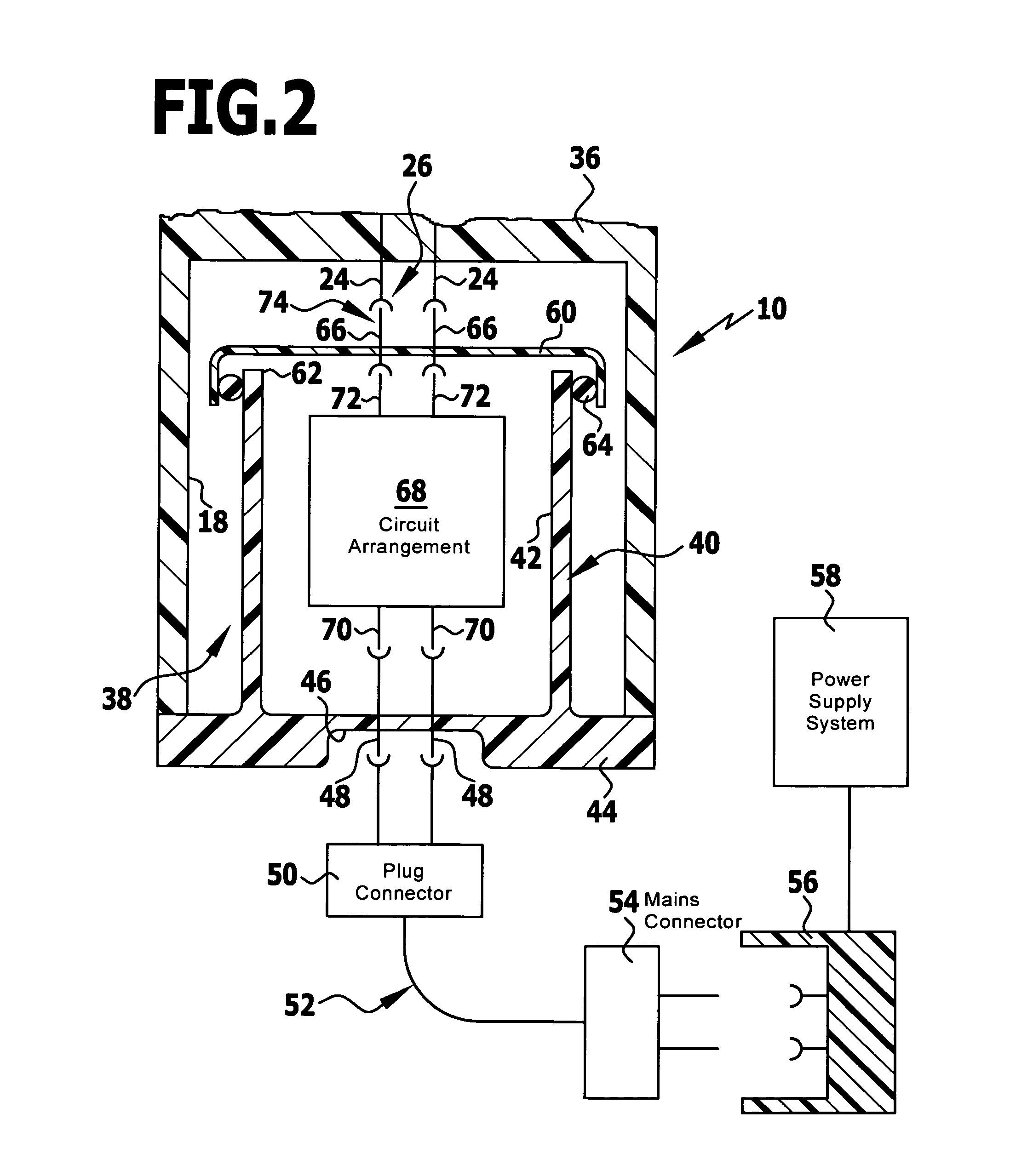
InactiveUS20110101794A1Keep it portableLarge electric powerBatteries circuit arrangementsConversion constructional detailsElectricityElectrical battery
A portable power supply device comprises a stackable battery housing locating a plurality of batteries therein and an inverter housing locating an inverter therein which is arranged to convert the direct current from the batteries to an alternating current. The inverter housing is readily separable from the battery housing such that one or more battery housings can be readily interchangeable to provide a constant supply of power and to allow a variety of charging configurations of the batteries. First electrical connectors on the battery housing and second electrical connectors on the inverter housing automatically connect the inverter to the batteries upon stacking of the inverter housing on the battery housing. Furthermore charging terminals are mounted externally on the inverter housing for ready access to connect to a charging device in a convenient manner without requiring the housings to be opened or separated form one another.
Owner:SCHROEDER KIRK +1
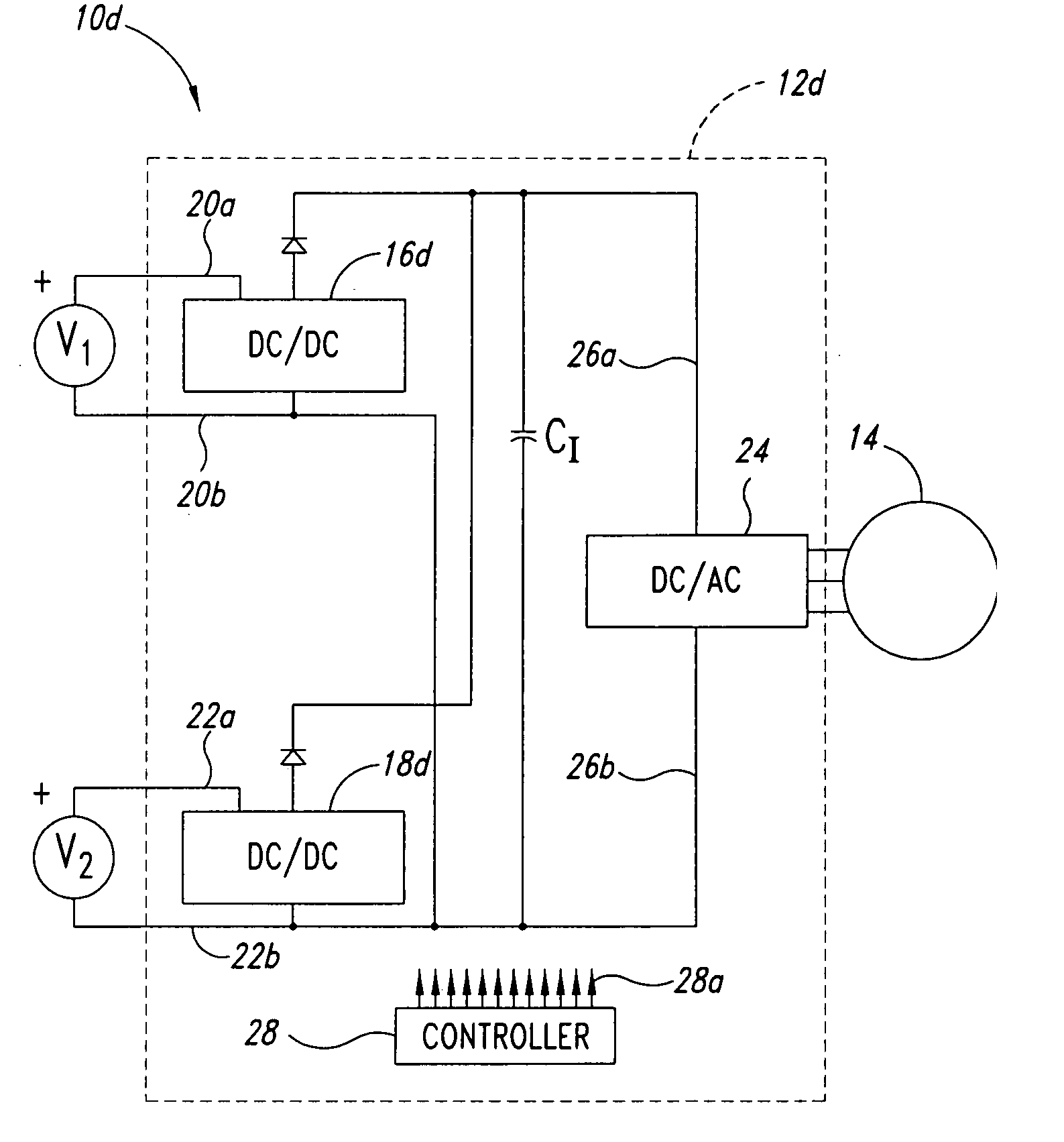
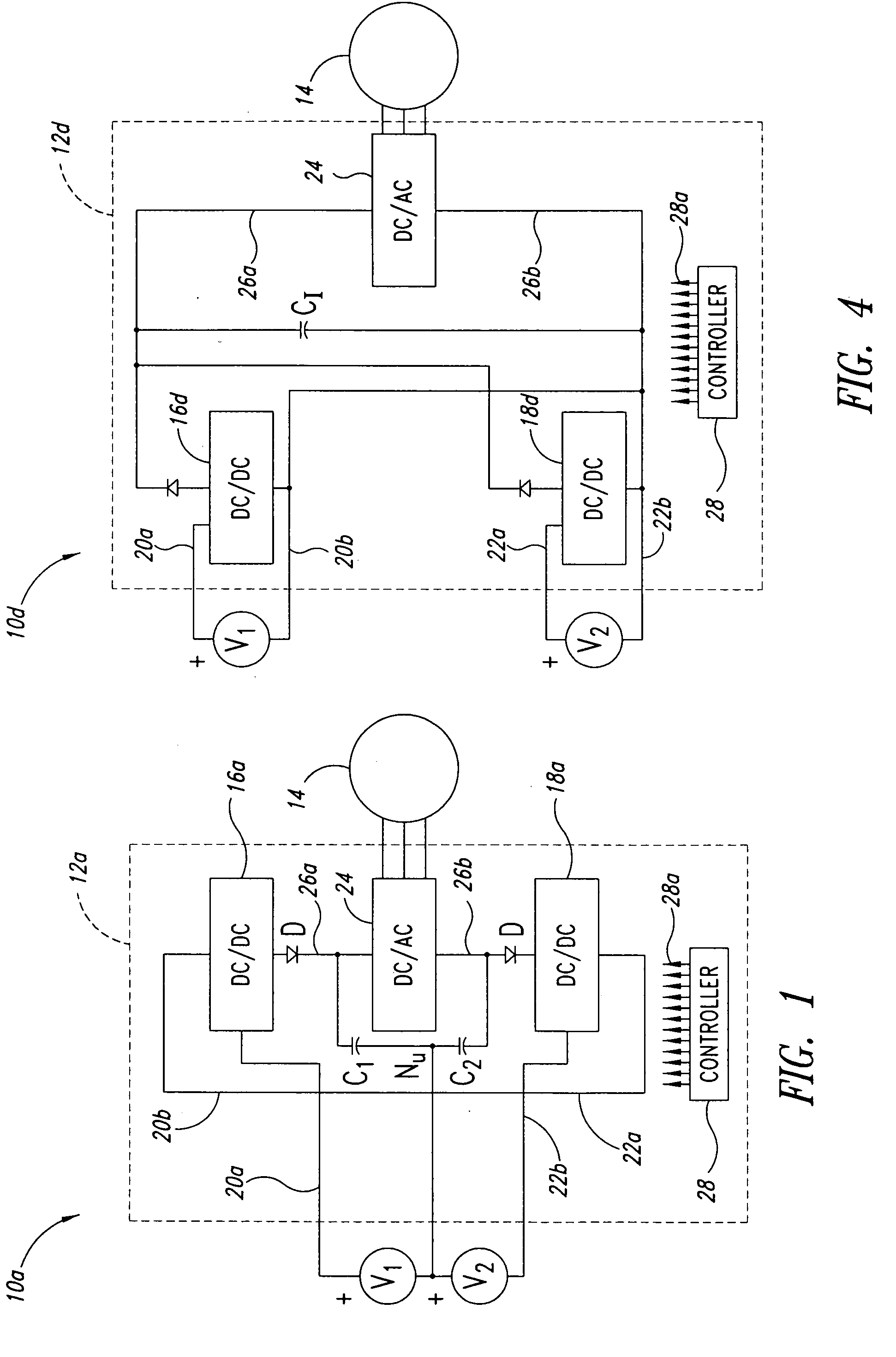
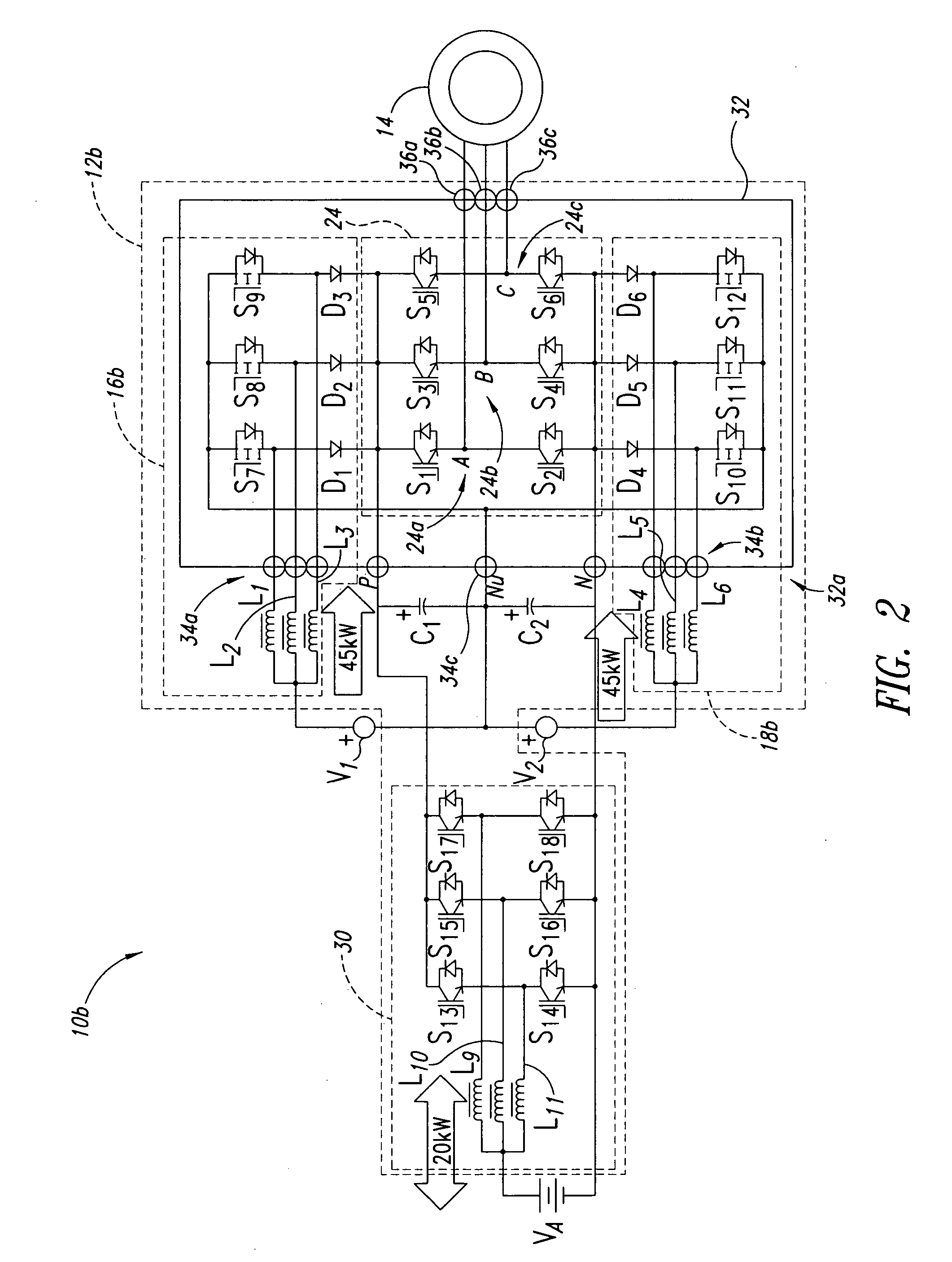
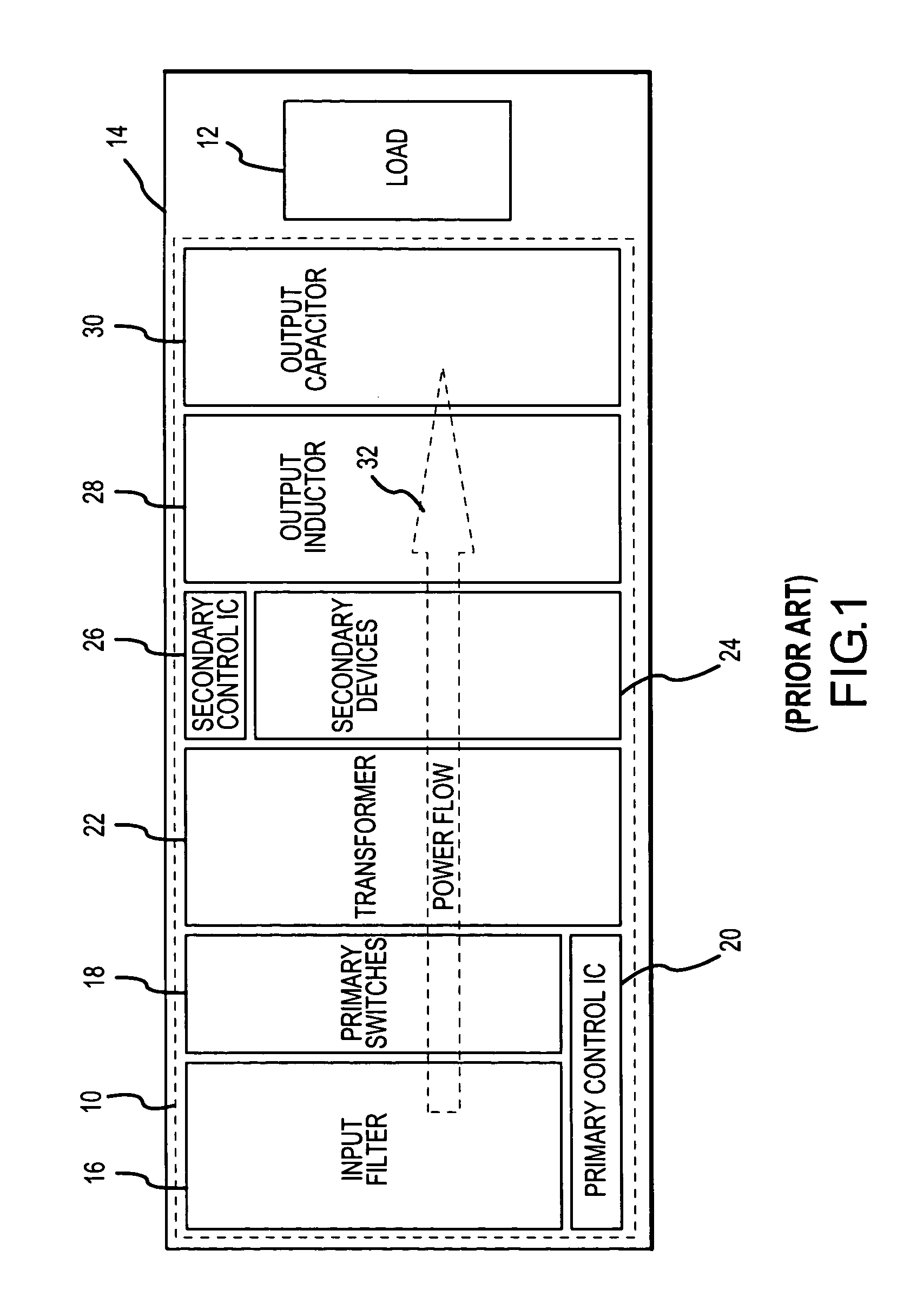
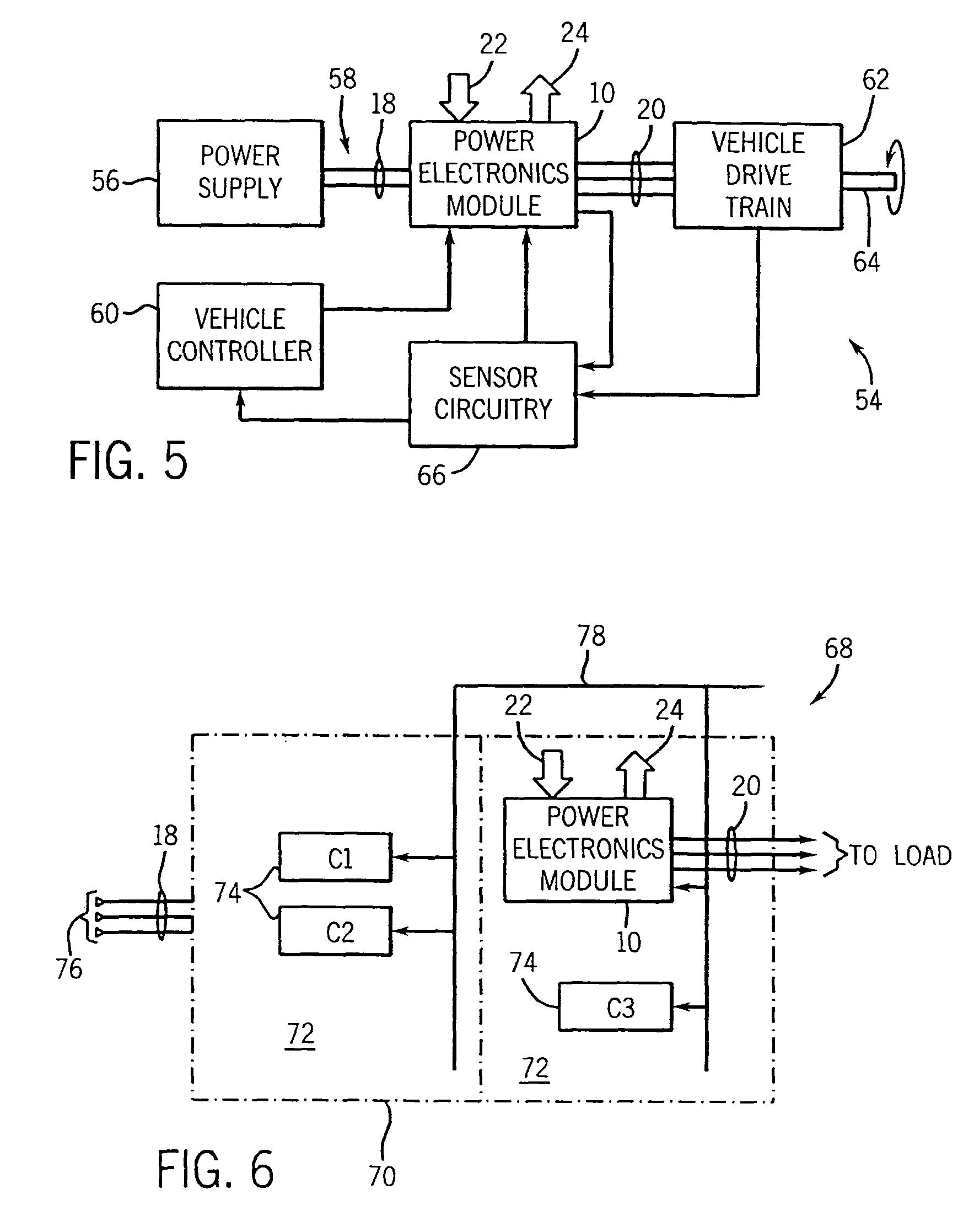
Power system method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060152085A1Protect the loadDc network circuit arrangementsConversion constructional detailsElectric power systemEngineering
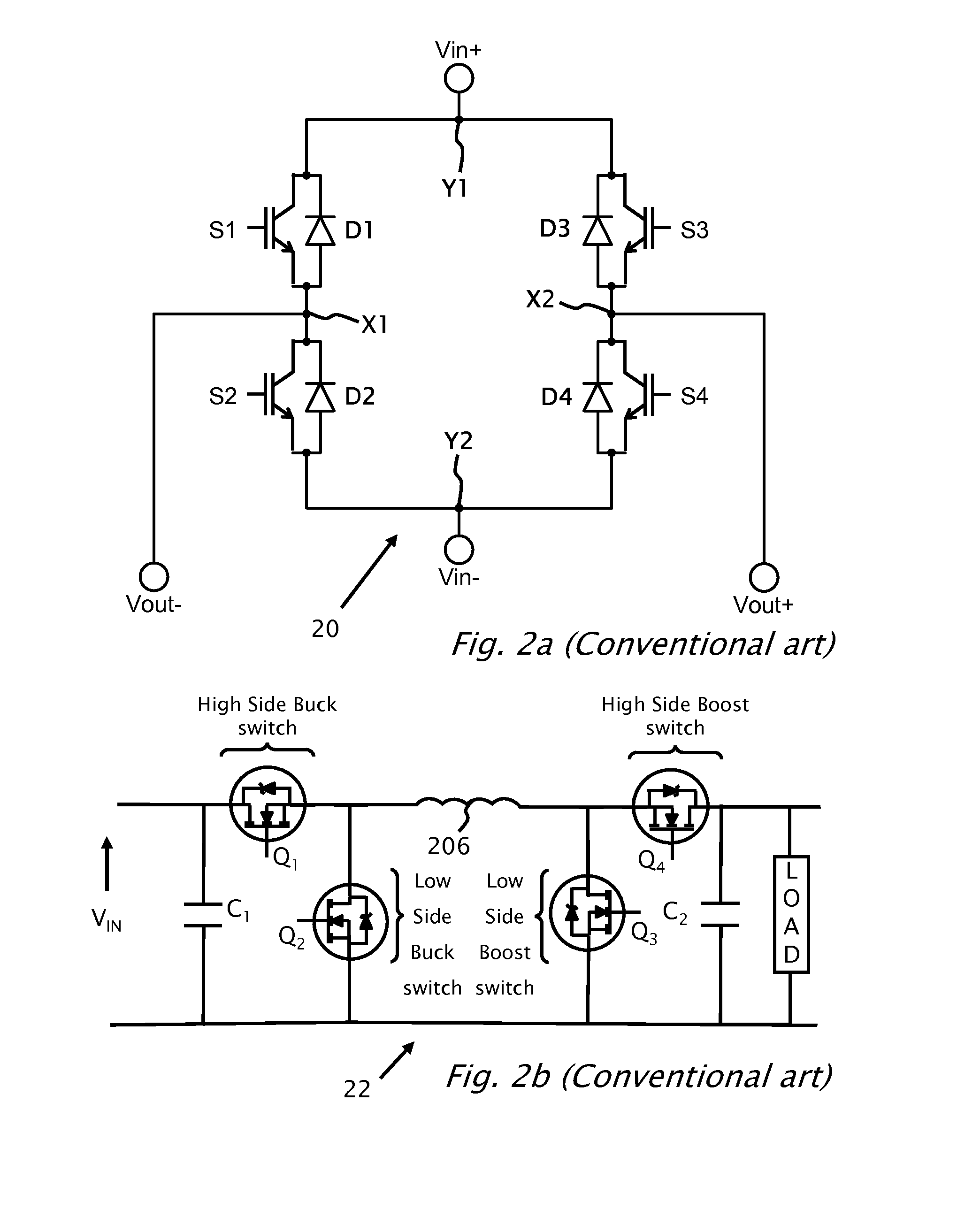
Power converter system topologies comprise a first DC / DC converter to pull a positive rail of a high voltage bus up, while a second DC / DC converter pushes a negative rail of the high voltage bus down. One or both the DC / DC converters may be bi-directional. Such topologies are suitable for use with separate primary power sources, and / or auxiliary power sources. Such topologies may include a DC / AC converter, which may be bi-directional. Such topologies may include one or more auxiliary DC / DC converters, which may be bi-directional. Multiple substrates, including at least one stacked above another may enhance packaging.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE CORP
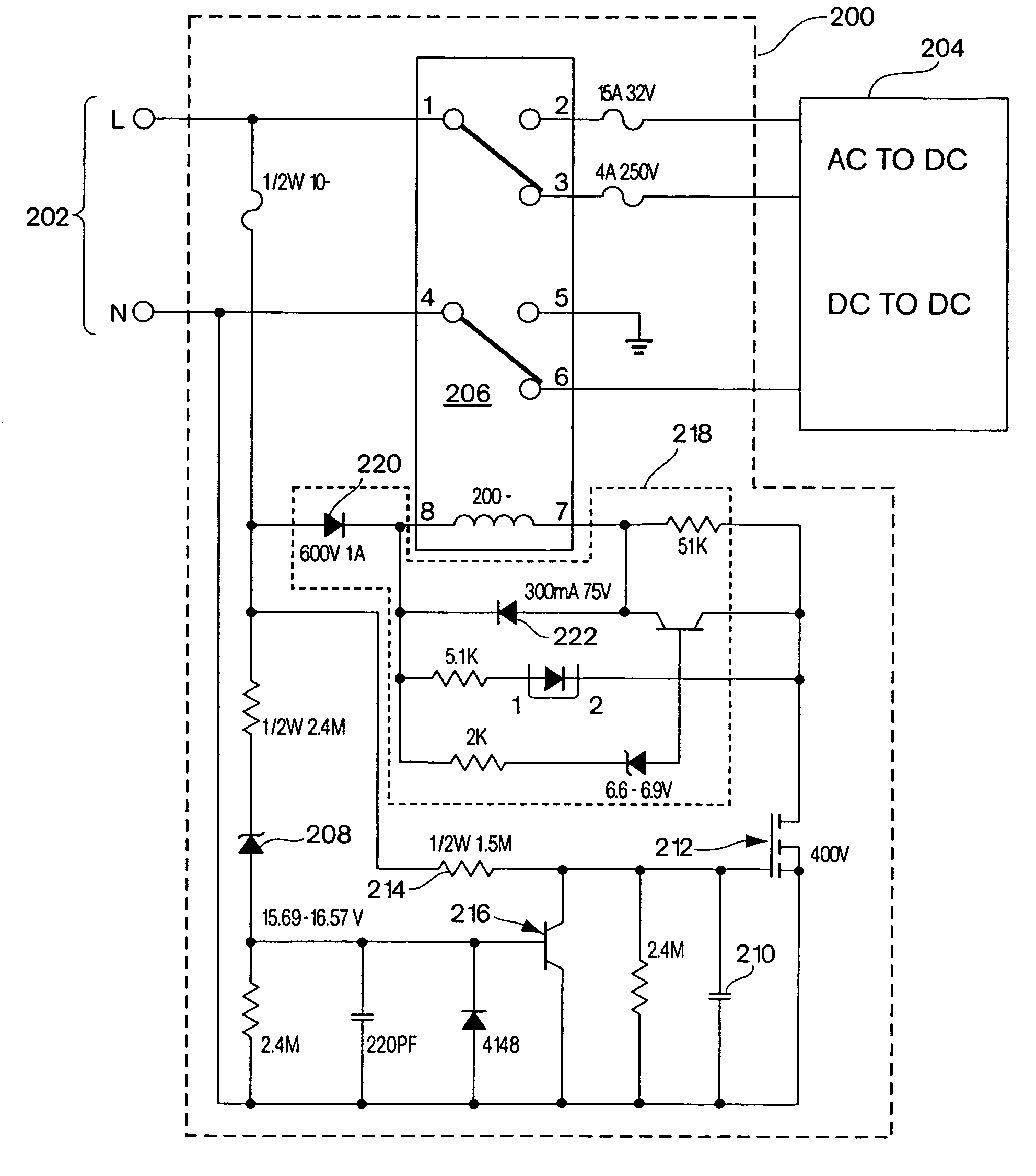
Surgical switch mode power supply and surgical DC power tool
ActiveUS8241235B2Conversion constructional detailsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPower toolDc voltage
Owner:AESCULAP AG
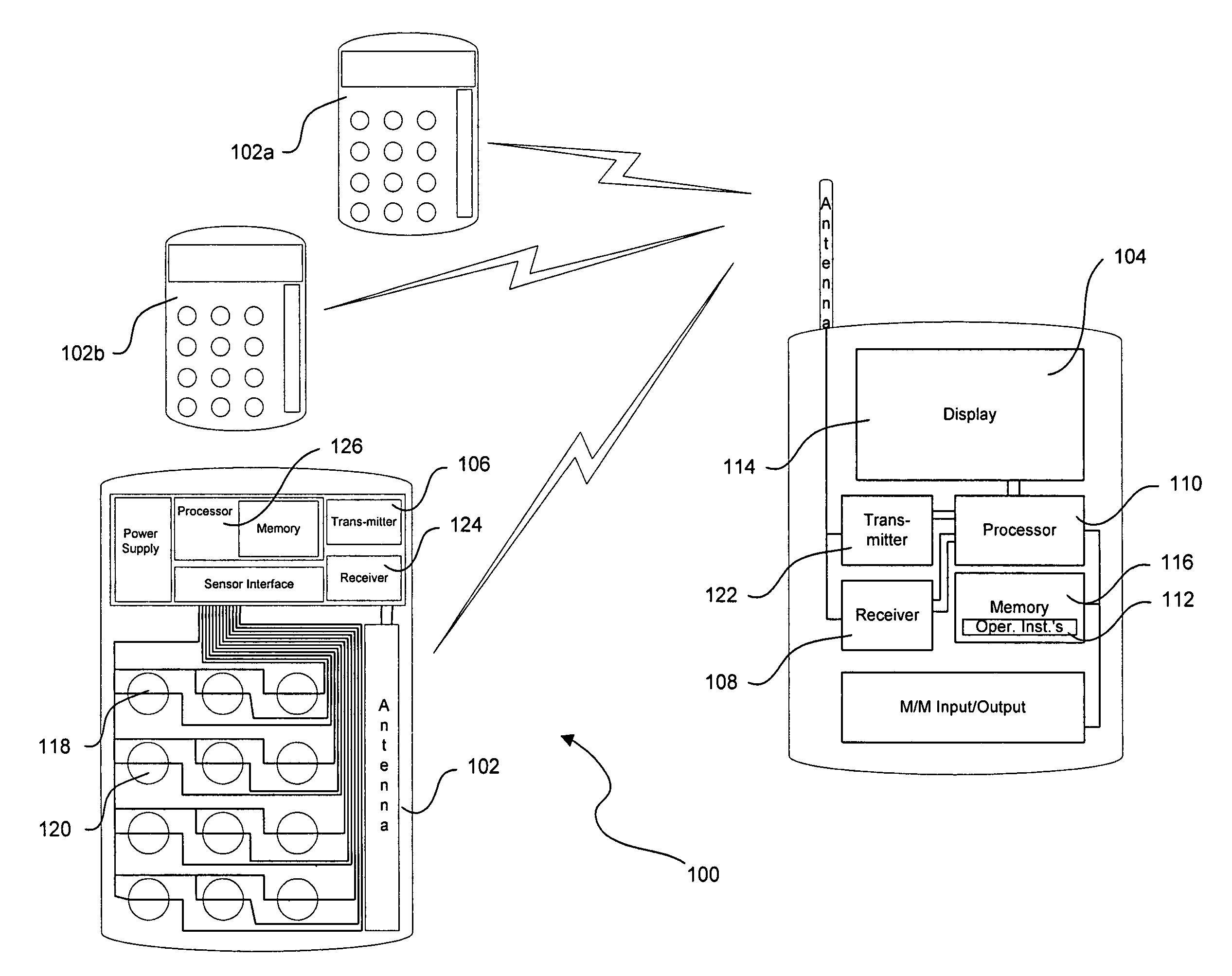
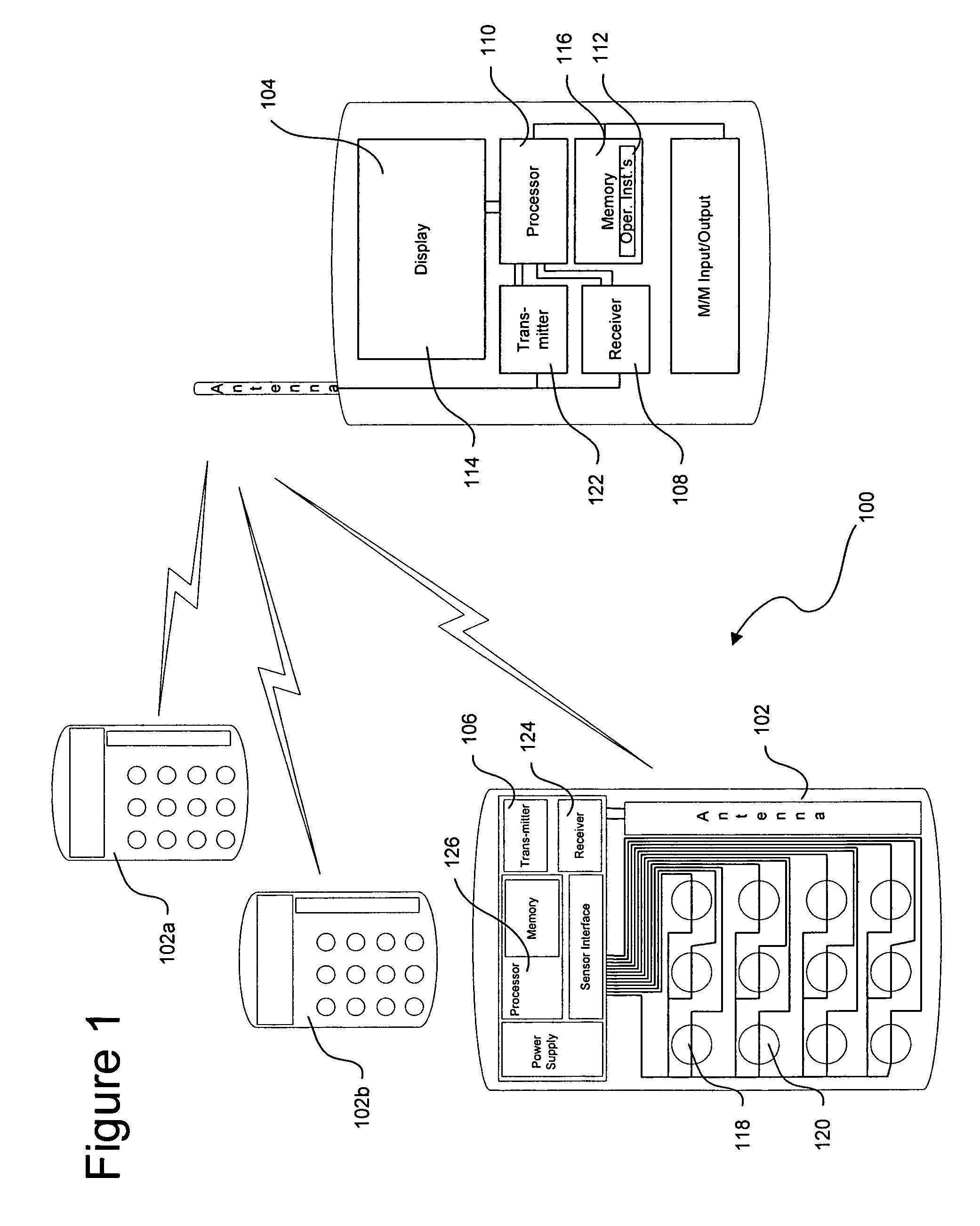
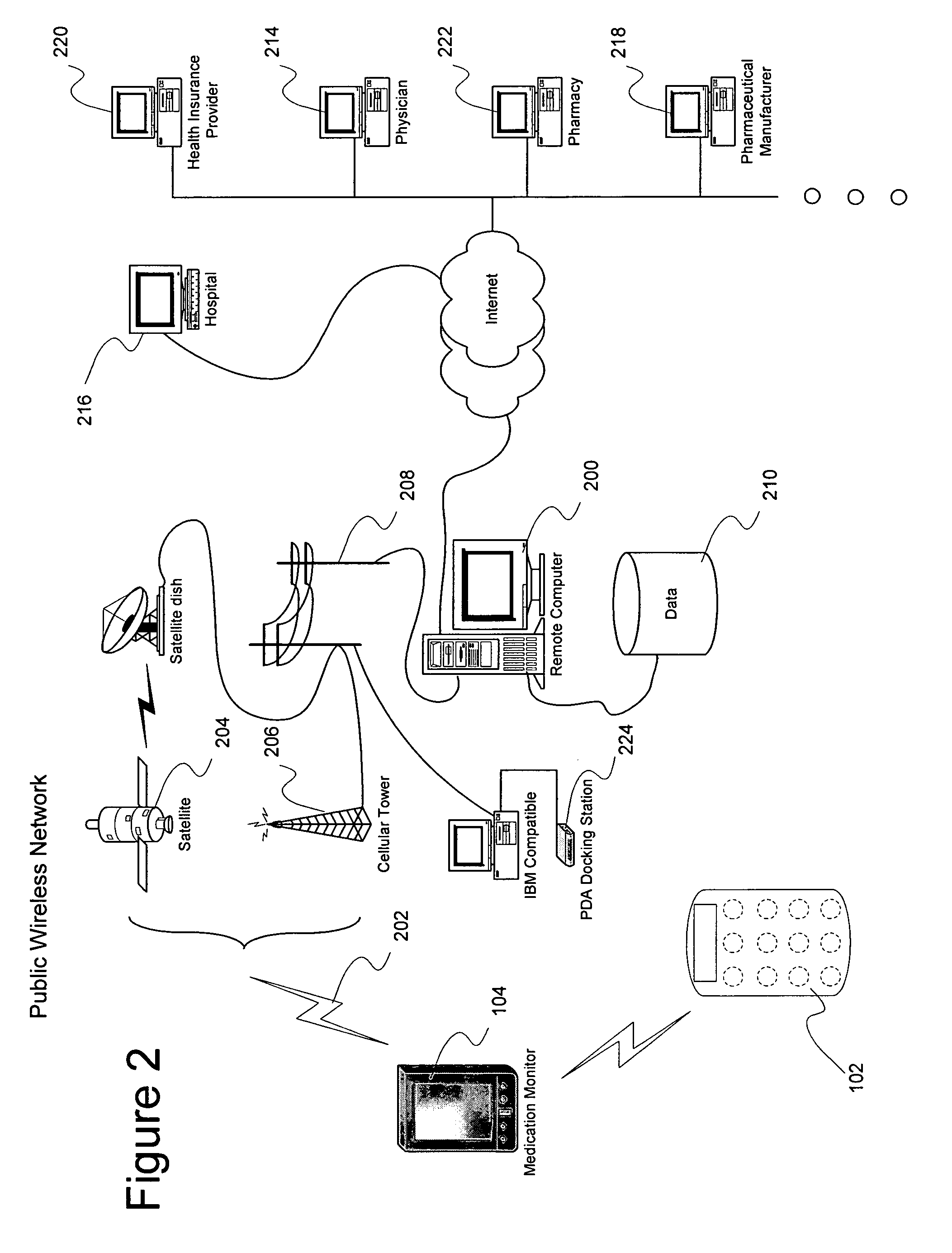
Drug delivery management system
The present invention relates to assisting patients in the taking of medication, and to assisting third parties in accumulating information regarding patient medication intake. The invention may be embodied a system including a portable medication monitor used in association with an instrumented medication package to provide intake data acquisition and patient support functions. The system may further be connected to a computer or computer network allowing information distribution between the medication monitor and third parties, such as physicians or pharmacists.
Owner:DDMS HLDG
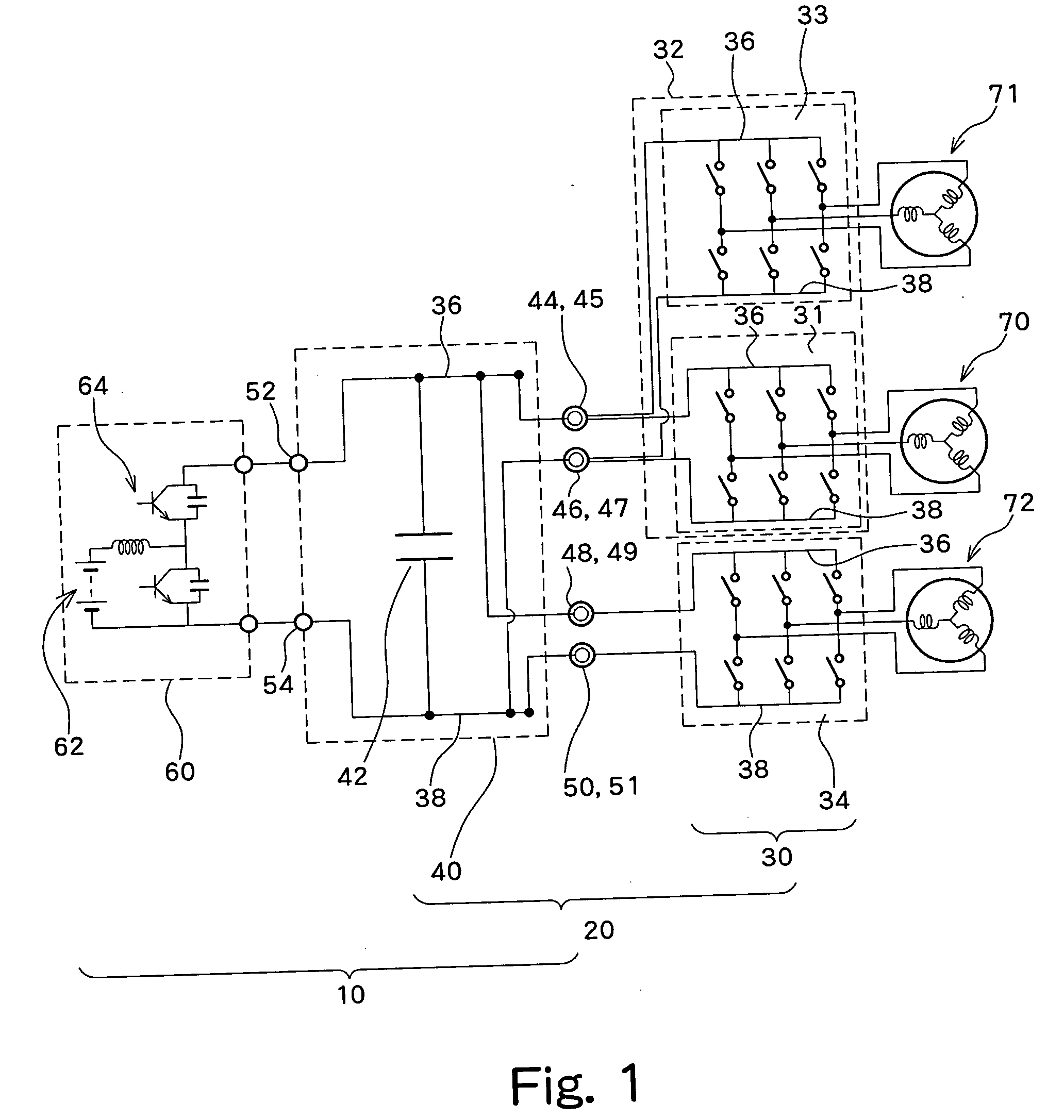
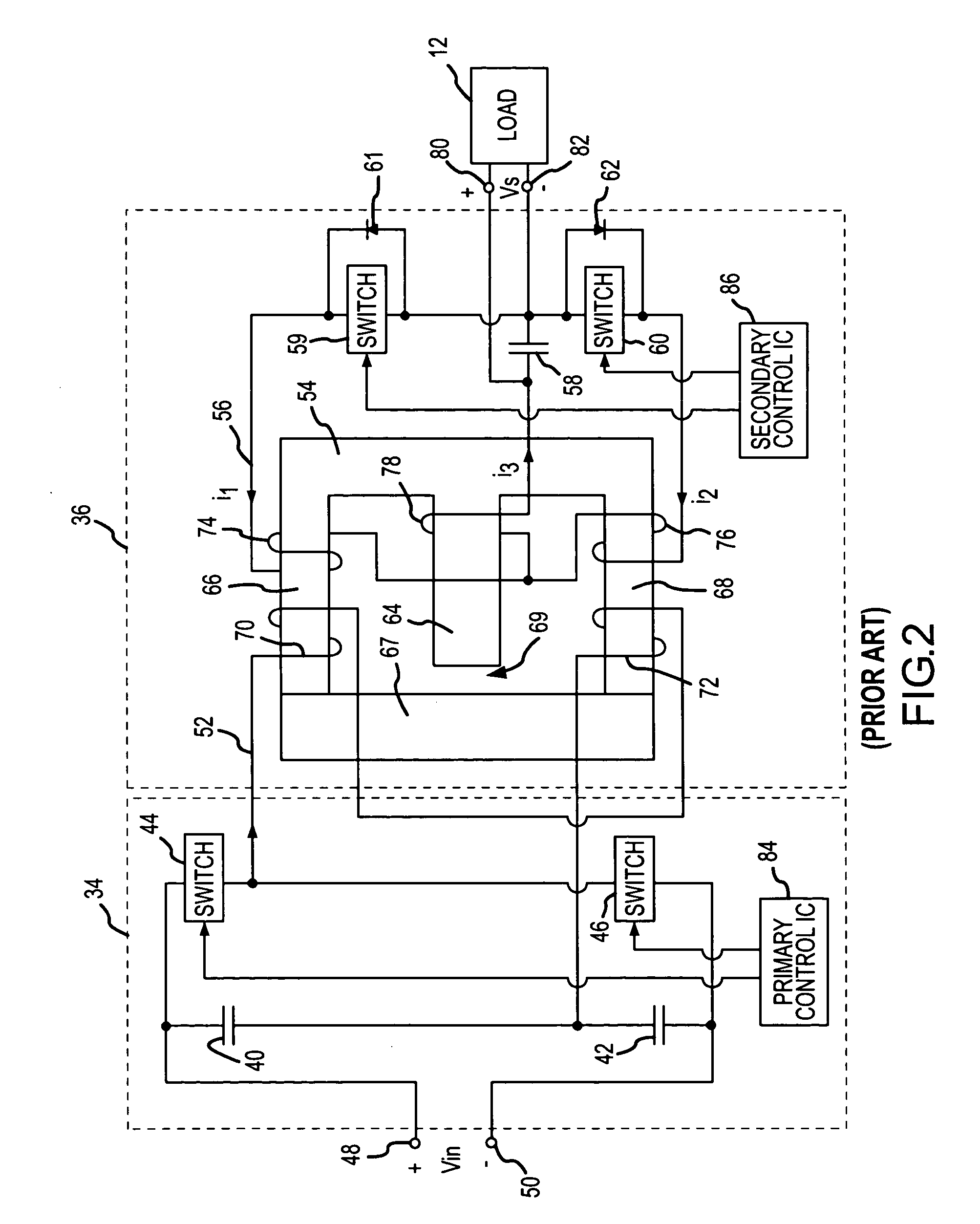
Bus structure for power switching circuits
ActiveUS20050068820A1Easy to optimizeReduction in parasitic conductanceBus-bar/wiring layoutsConversion constructional detailsElectricityPower switching
A bus system is disclosed for use with switching devices, such as power electronic devices. The system includes generally parallel bus elements that define electrical reference planes, such as for a dc bus. The bus elements are separated from one another by insulative layers, with additional insulative layers being available for separating the system from other circuit components. Portions of the bus elements are extended or exposed to permit connection to the circuit elements, including packaged switching circuits and energy storage or filtering circuits. The bus system may be conformed to a variety of geometric configurations, and substantially reduces parasitic inductance and total loop inductance in the resulting circuitry.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH +1
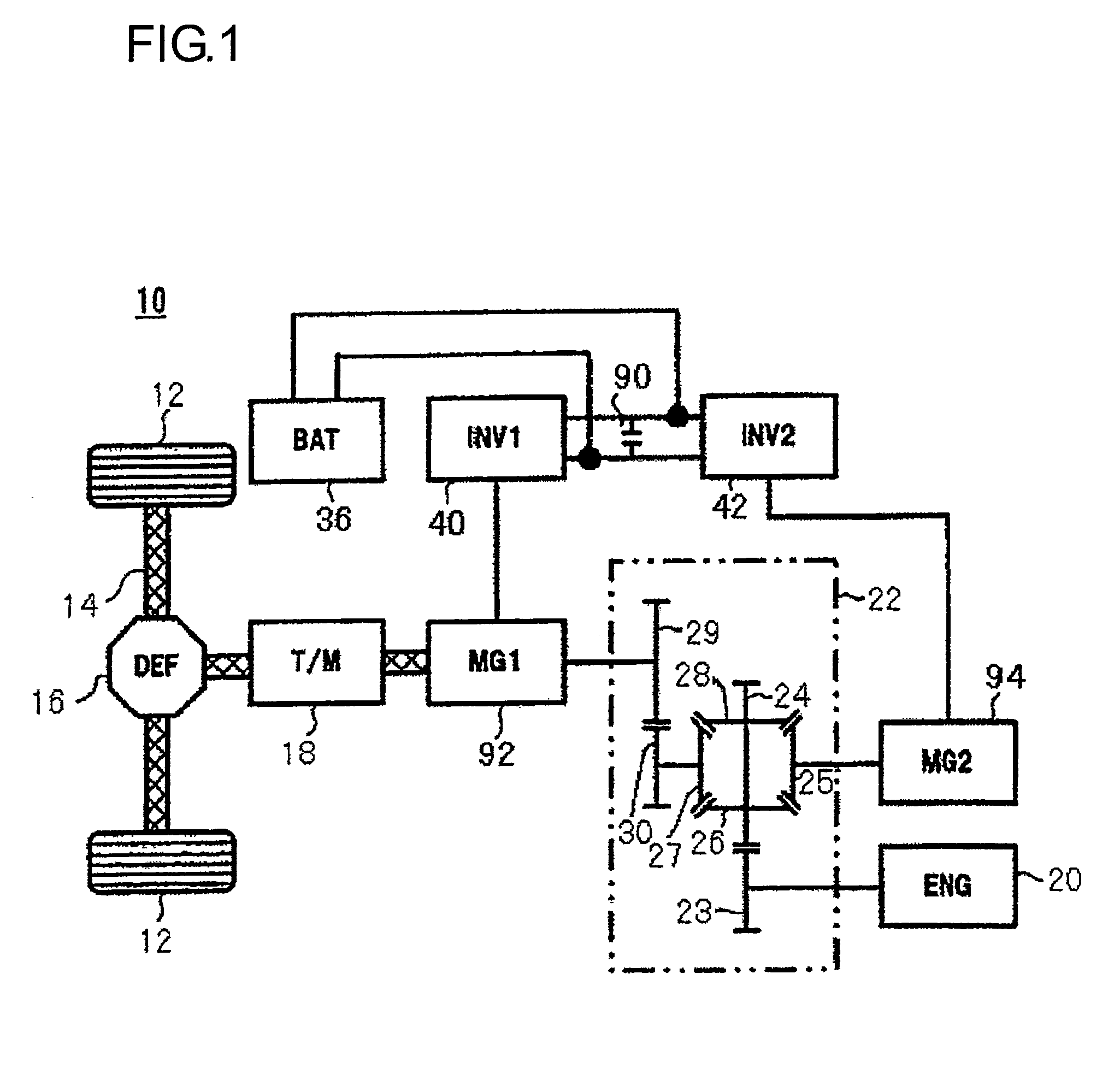
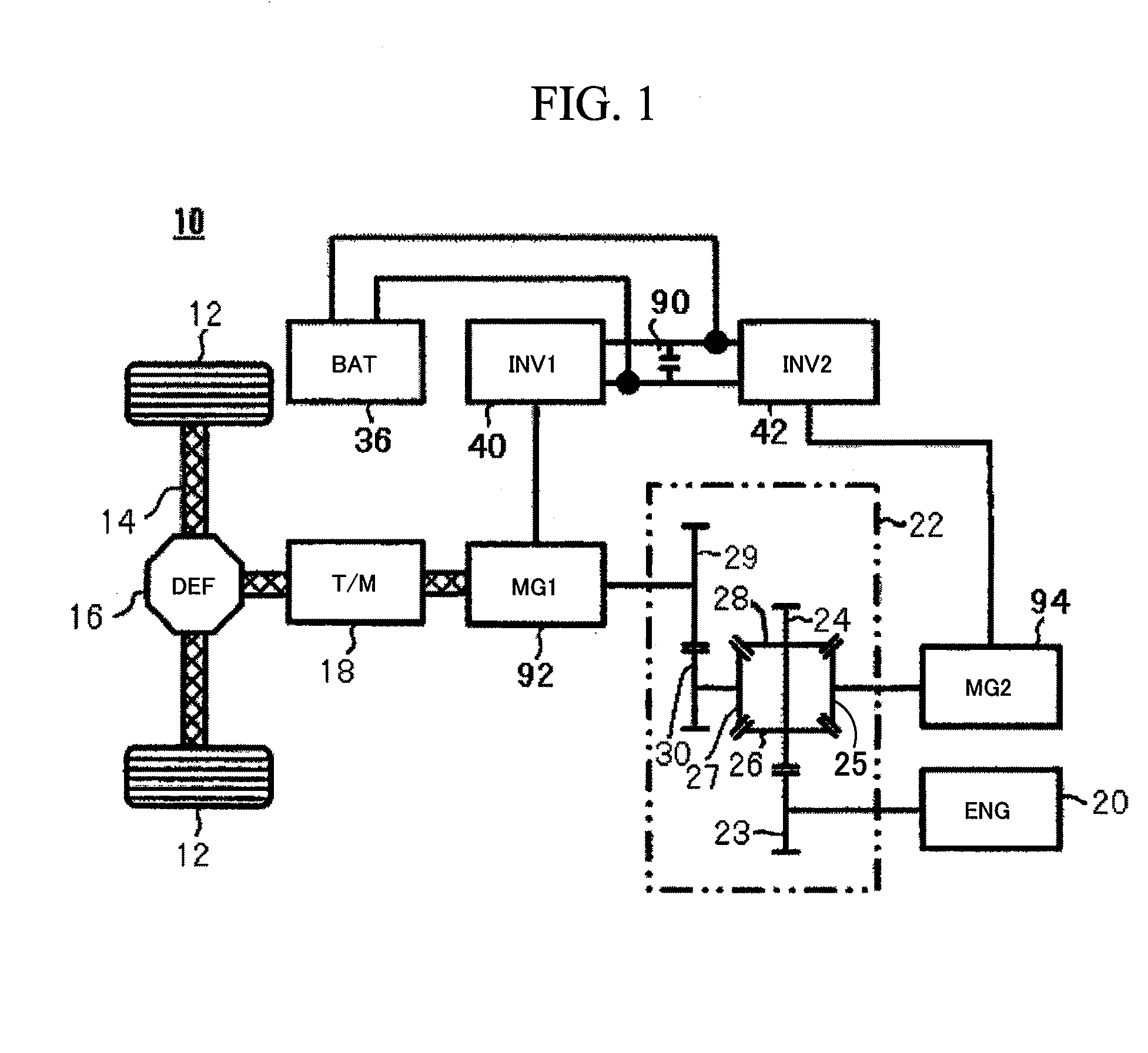
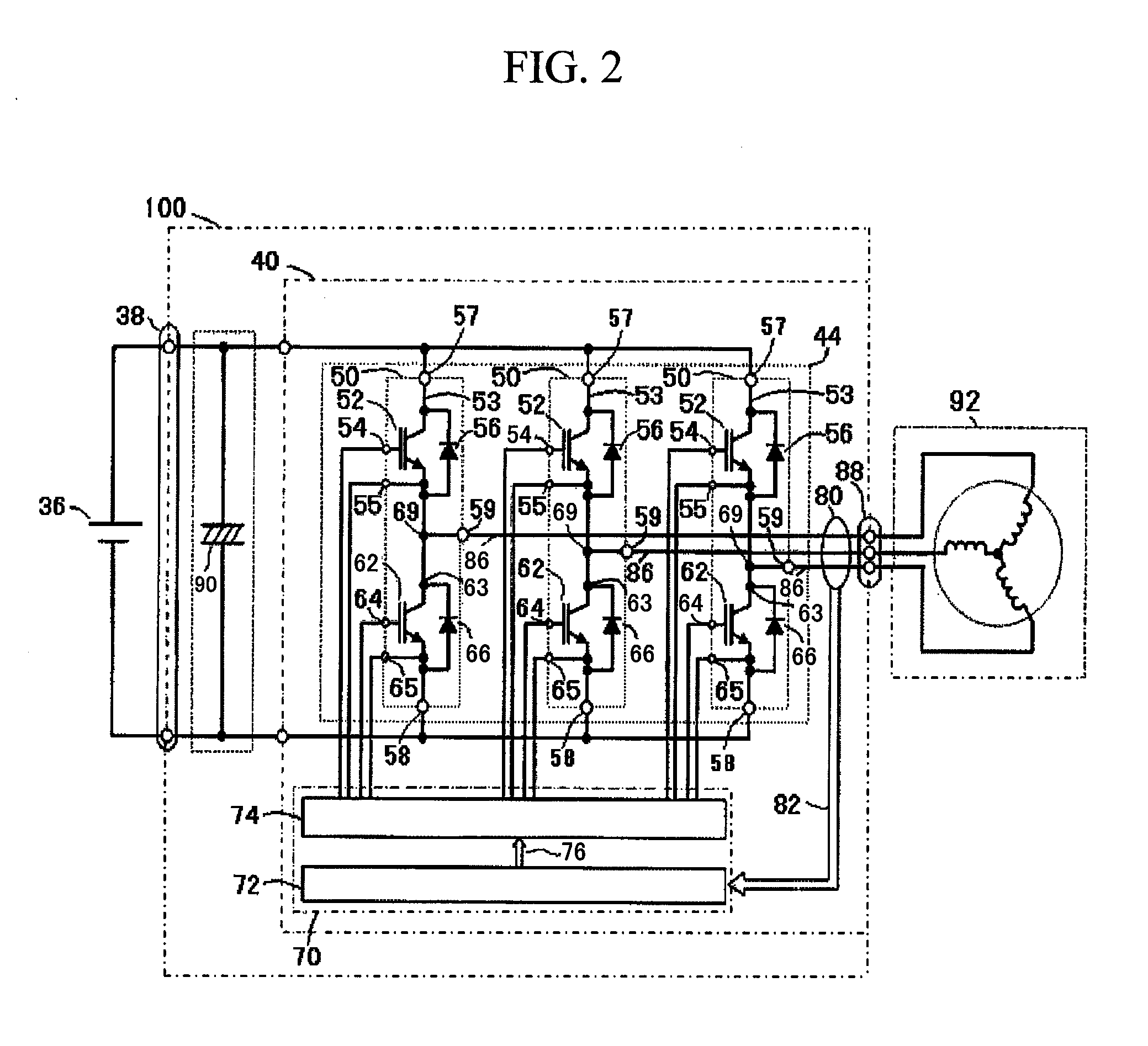
Inverter unit for vehicle
InactiveUS20060208660A1Efficient arrangementEfficient use ofConversion constructional detailsElectric machinesCapacitorElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
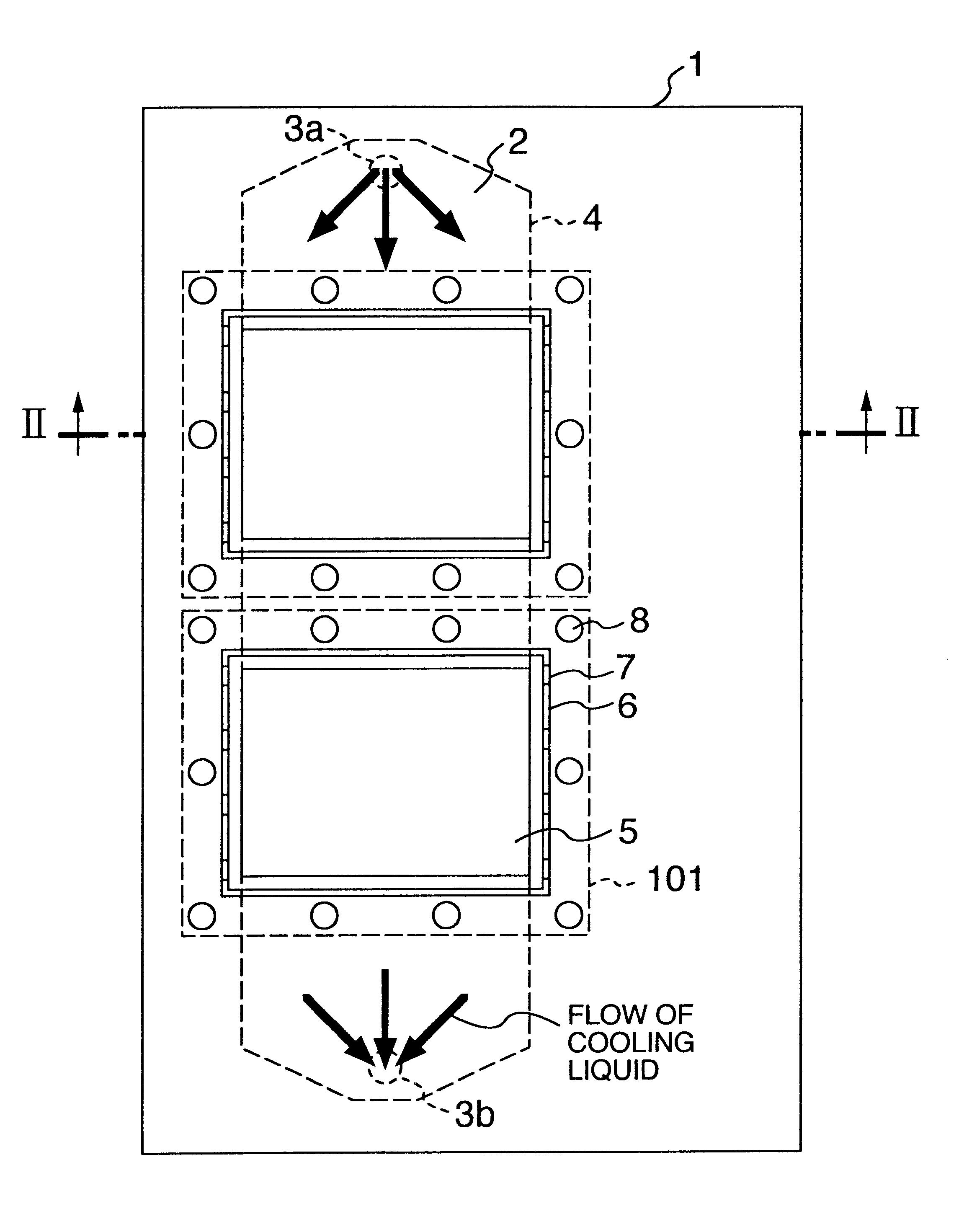
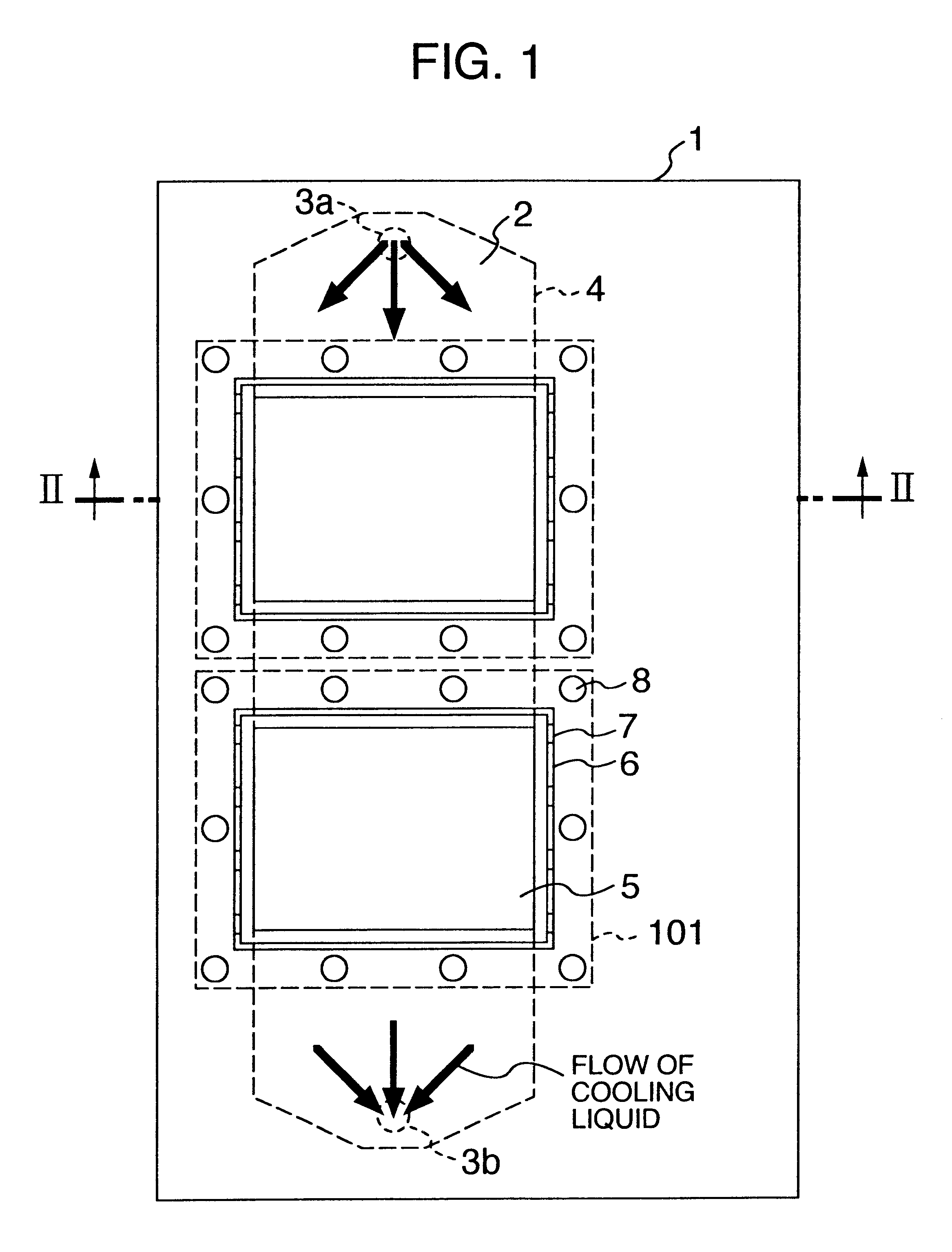
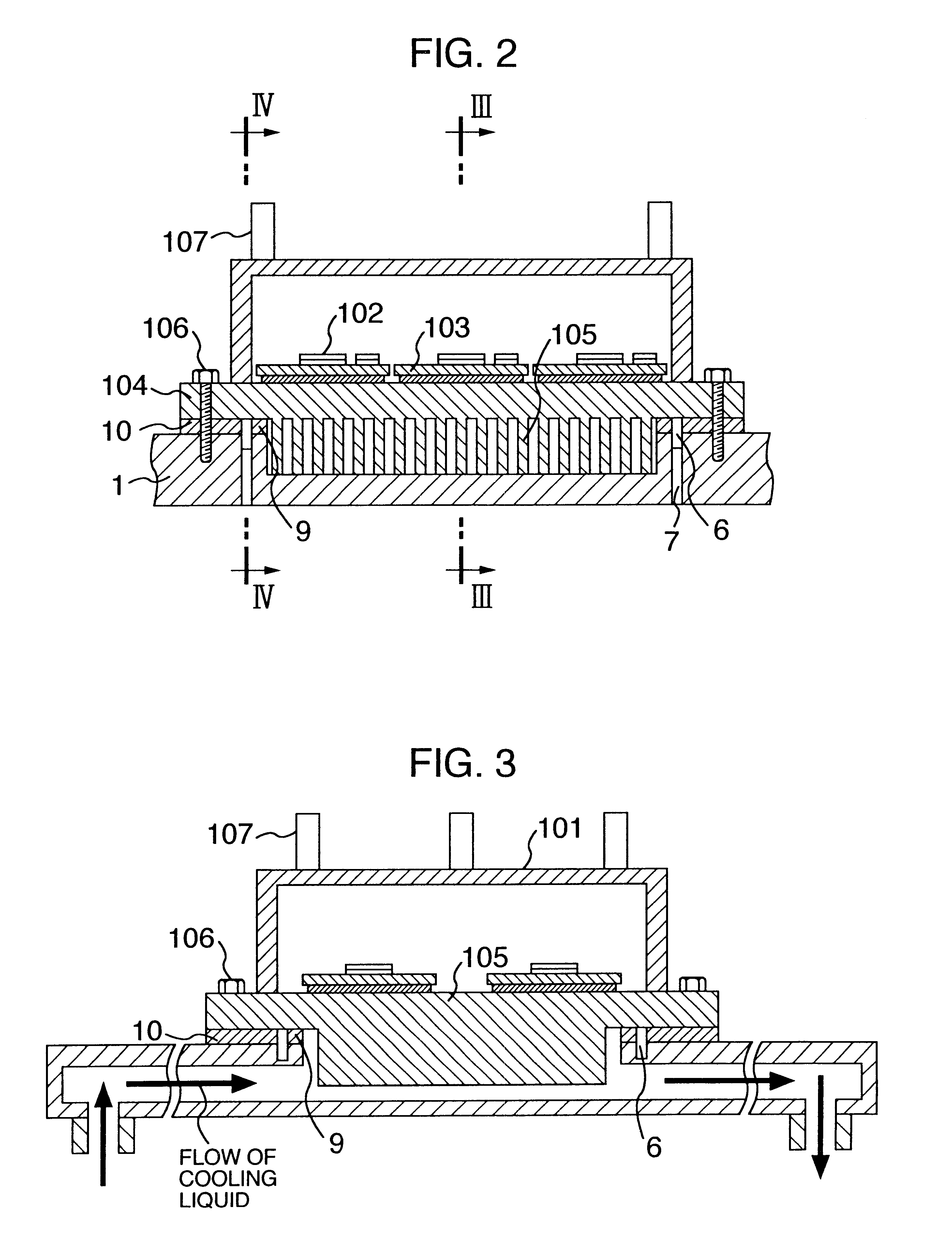
Power inverter
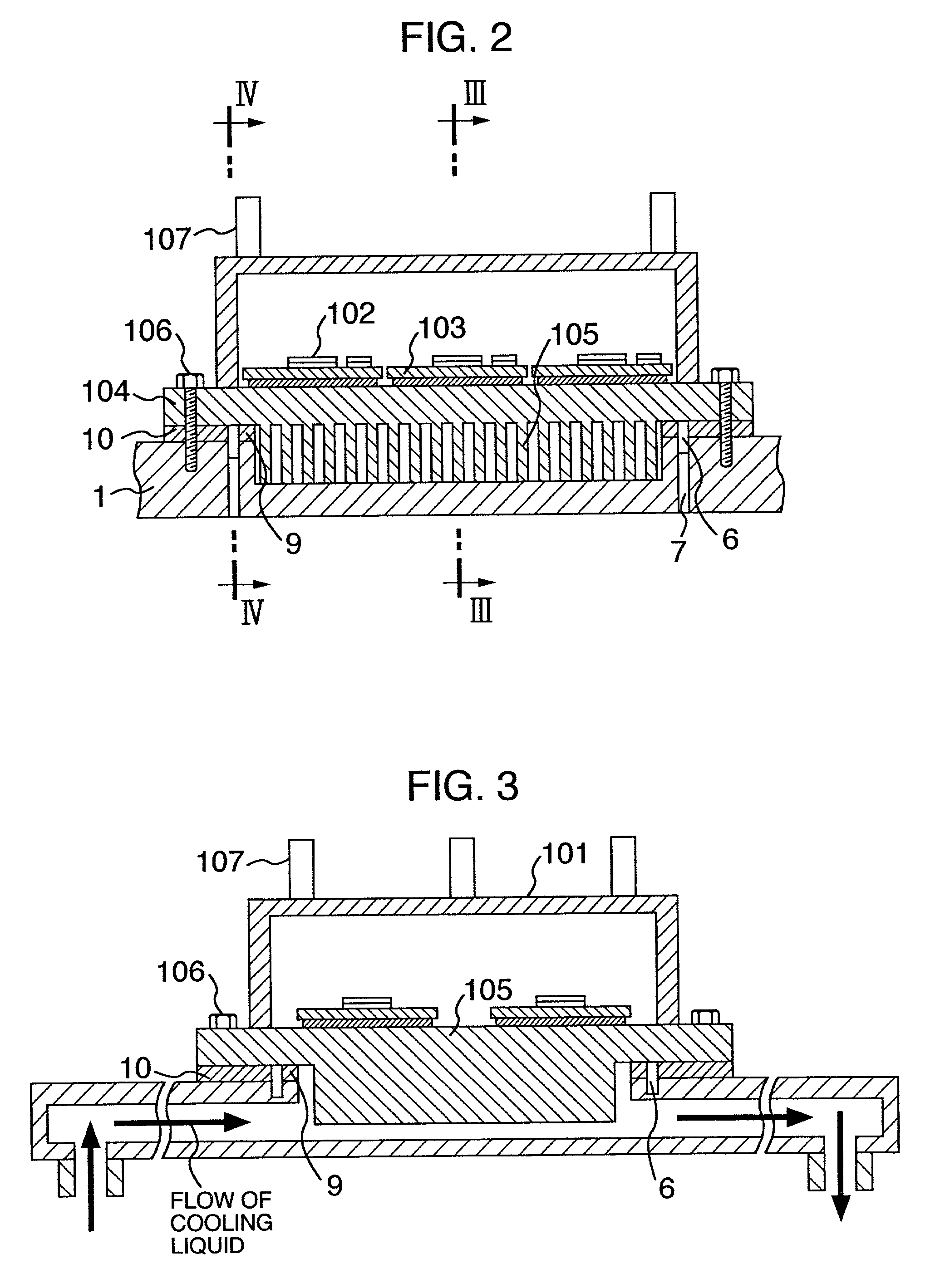
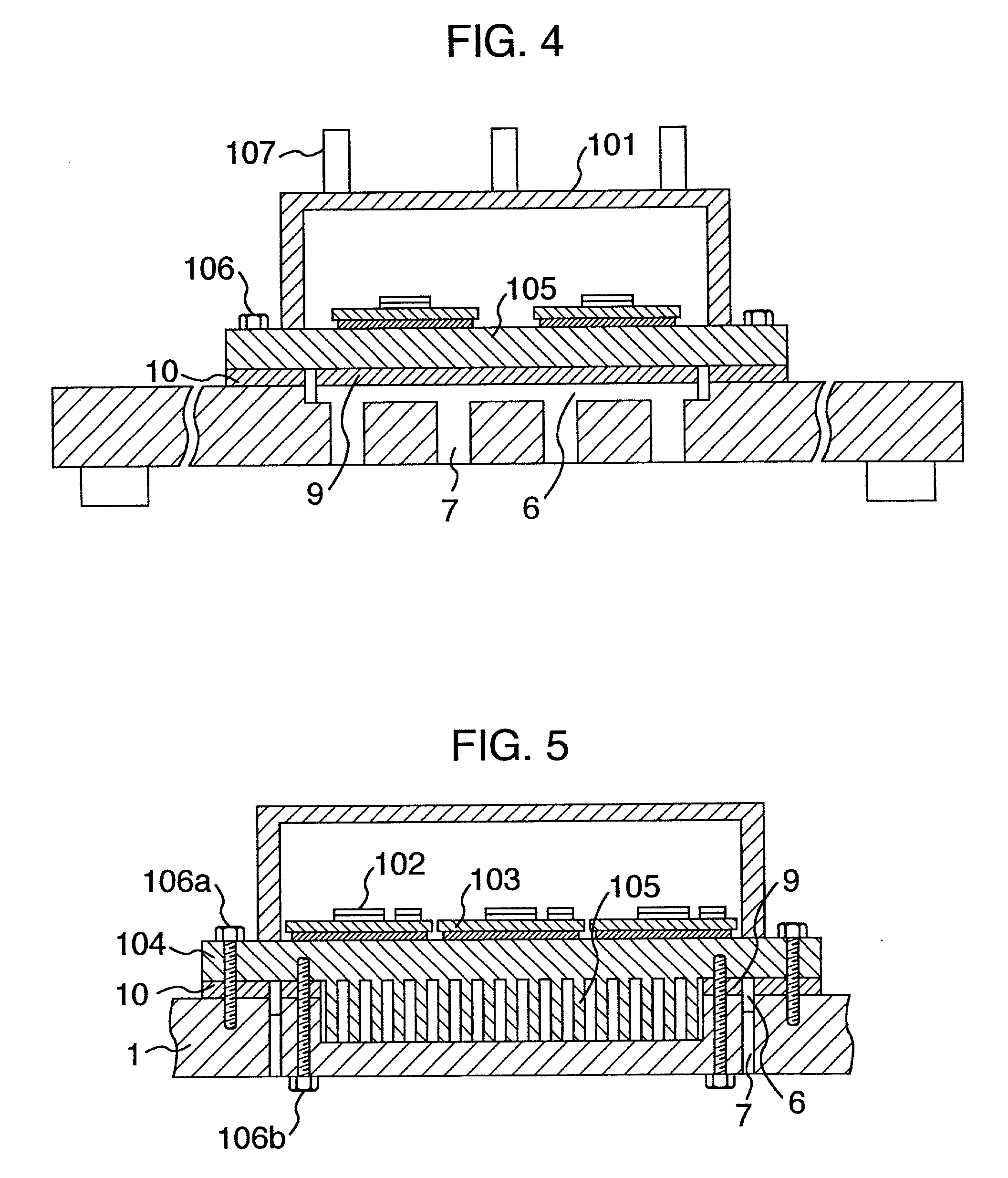
InactiveUS20010014029A1Improve cooling effectPrevent leakageConversion constructional detailsSolid-state devicesPower inverterEngineering
A heat sink or cooling case has a cooling channel and at least one opening formed to face part of the channel. A first seal is provided outside the at least one opening. A cooling case has a groove located outside the first seal. Holes are discretely formed in the groove and leads from the groove to an exterior of the cooling case. A second seal is provided outside the groove. A radiating plate constituting a circuit case is mounted on the heat sink by using a clamping device inn or outside the second seal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
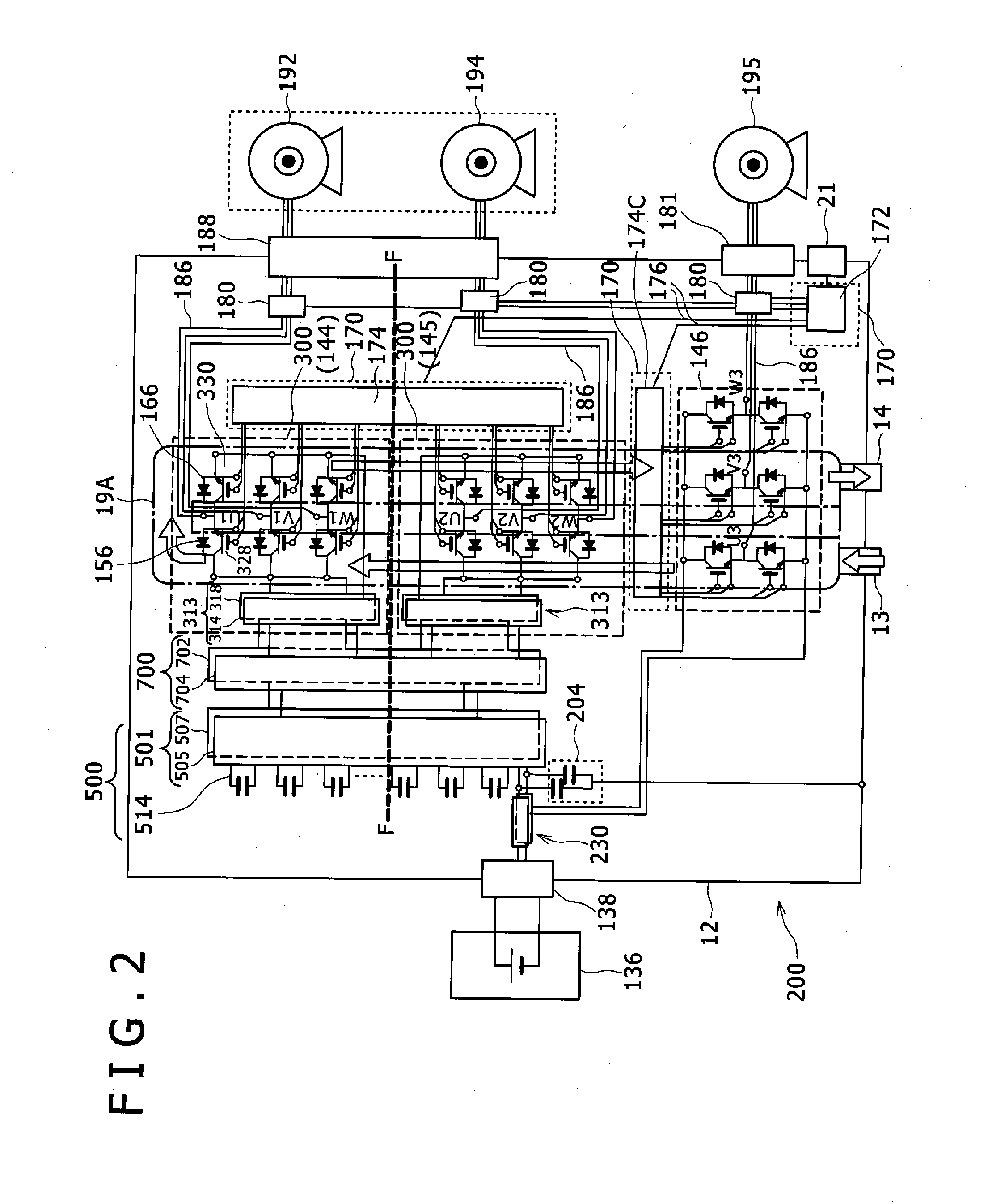
Power Conversion Apparatus and Electric Vehicle
ActiveUS20100025126A1Reduce inductanceImprove cooling effectCasings with connectors and PCBConversion constructional detailsDriver circuitComputer module
The metallic case of a power conversion apparatus includes a casing having a side wall, as well as an upper case and a lower case, a first area being formed between a cooling jacket provided at the inner periphery of the side wall and the lower case, the metal base plate dividing the first area between the cooling jacket and the upper case into a lower side second area and an upper side third area, first and second power modules being fastened to a top surface and a capacitor module being provided in the first area, driving circuits that drive inverter circuits of the power modules respectively being provided in the second area, and a control circuit that controls the driver circuits being provided in the third area.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Power inverter
InactiveUS6414867B2Improve cooling effectAllows sizeConversion constructional detailsSolid-state devicesPower inverterEngineering
A heat sink or cooling case has a cooling channel and at least one opening formed to face part of the channel. A first seal is provided outside the at least one opening. A cooling case has a groove located outside the first seal. Holes are discretely formed in the groove and lead from the groove to an exterior of the cooling case. A second seal is provided outside the groove. A radiating plate constituting a circuit case is mounted on the heat sink by using a clamping device inside or outside the second seal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Power Converter
ActiveUS20080130223A1Avoid excessive volumeIncrease productionConversion constructional detailsSolid-state devicesIntermediate stageSemiconductor
First and second bases and composing a coolant path structure are arranged at the middle stage of the power converter, and semiconductor modules and a capacitor are arranged on both surfaces of the coolant path structure. Furthermore, through-holes are formed in the first and second bases, and cables of DC and AC circuits are laid via the through-holes.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
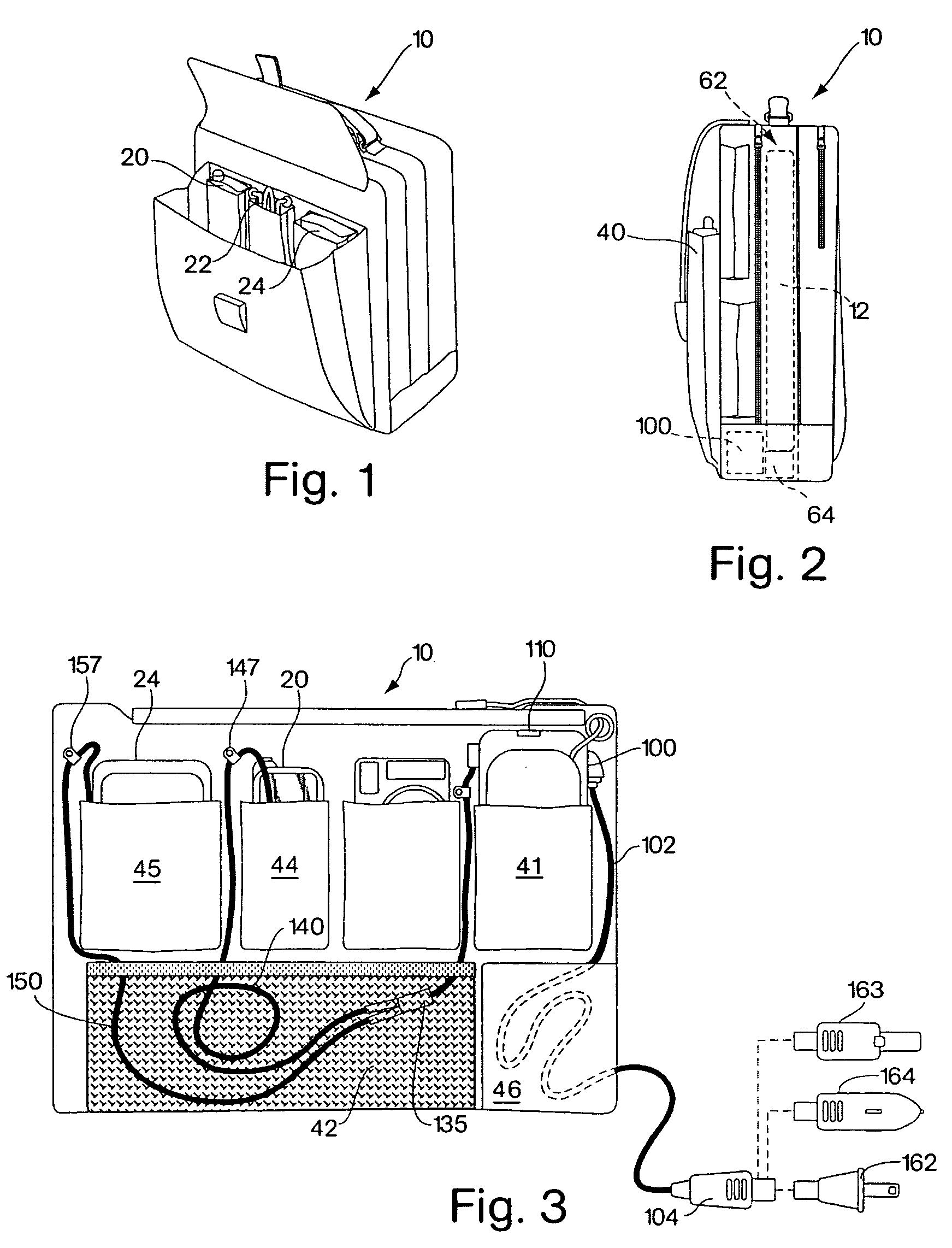
Universal multiple device power adapter and carry case
InactiveUS7224086B2Easy to chargeEasy accessCoupling device connectionsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power systemElectrical battery
The present invention is directed to a carrying case with an integrated power supply system for providing power to multiple electronic devices from a single power source. In addition to allowing quick access and storage of various electronic devices, the carrying case also allows the individual electronic devices to be easily connected to the power source and eliminates the need to carry multiple charging cords. In certain embodiments, the power supply system further includes an additional battery or other power source, which increases the runtime of connected electronic devices and reduces the need to carry additional individual batteries for the individual devices. With different connectors on the input to the power system, different AC or DC power sources may be utilized. Different connectors can also be used to provide power to different electronic devices.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
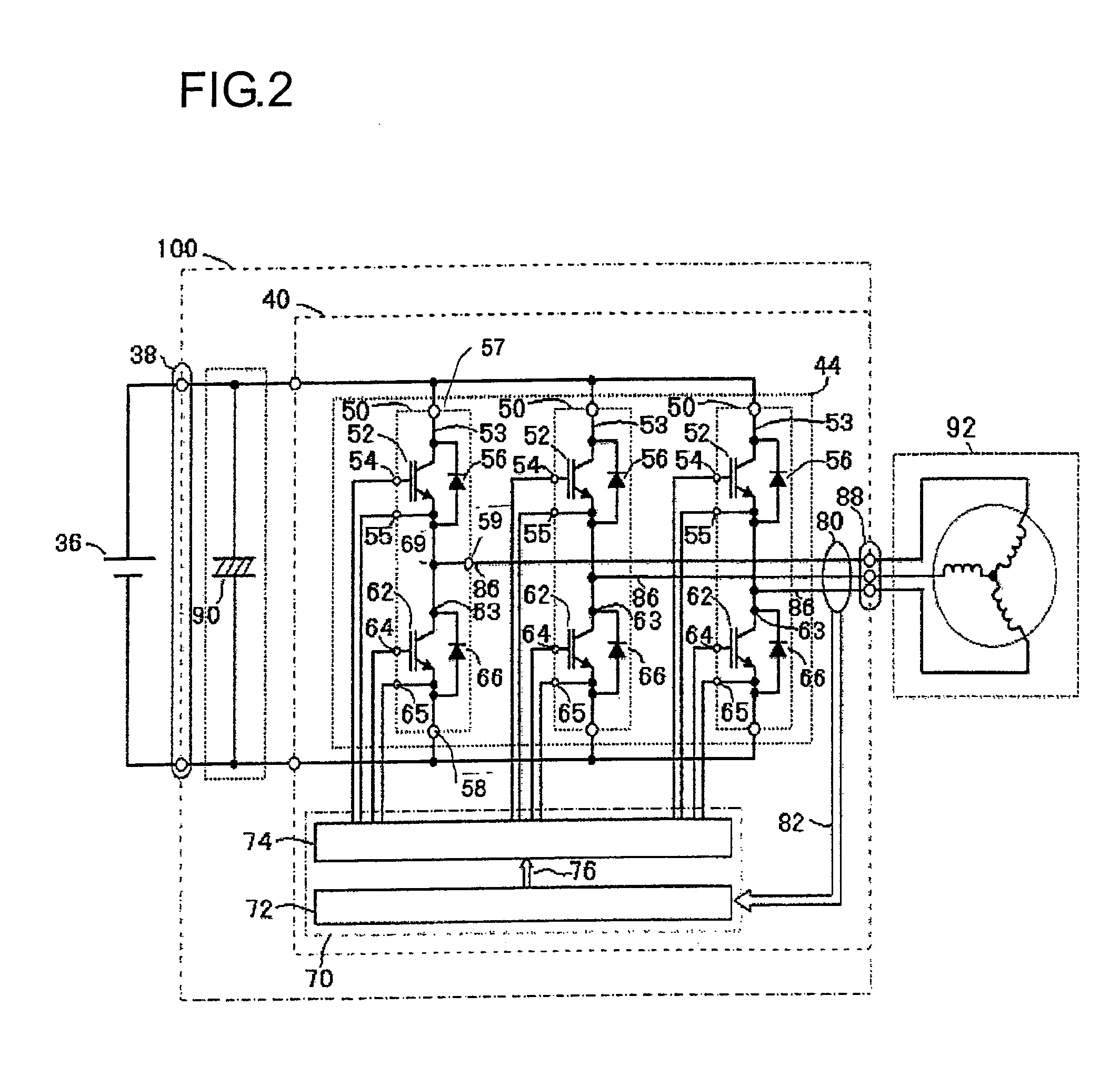
Electric Power Conversion Apparatus
ActiveUS20090231811A1Reduce the burden onImprove cooling effectHybrid vehiclesAC motor controlWater channelEngineering
An electric power conversion apparatus includes: a channel case in which a cooling water channel is formed; a double side cooling semiconductor module that comprises an upper and lower arms series circuit of an inverter circuit; a capacitor module; a direct current connector; and an alternate current connector. The semiconductor module comprises a first and a second heat dissipation metals whose outer surfaces are heat dissipation surfaces, the upper and lower arms series circuit is disposed tightly between the first heat dissipation metal and the second heat dissipation metal, and the semiconductor module further comprises a direct current positive terminal, a direct current negative terminal, and an alternate current terminal which protrude to outside. The channel case is provided with the cooling water channel which extends from a cooling water inlet to a cooling water outlet, and a first opening which opens into the cooling water channel.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Switching Circuit Layout With Heatsink
ActiveUS20100124027A1Conversion constructional detailsCross-talk/noise/interference reductionEngineeringLine segment
A circuit board adapted for use in an switching converter for connecting a plurality of switches including a first switch, a second switch, a third switch and a fourth switch. The circuit board has a layout for connecting the switches. The layout is adapted for locating the switches substantially at or symmetrically with respect to the endpoints of a right-angle cross. The right-angle cross is formed from two line segments intersecting with a ninety degree angle. The circuit board may offsets the switches perpendicularly to the line segments at the endpoints of the line segments either in a clockwise or a counterclockwise direction.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
Photovoltaic module-mounted ac inverter
ActiveUS20080285317A1Total current dropIncrease the ripple frequencyConversion constructional detailsElectric power transfer ac networkEngineeringTransistor
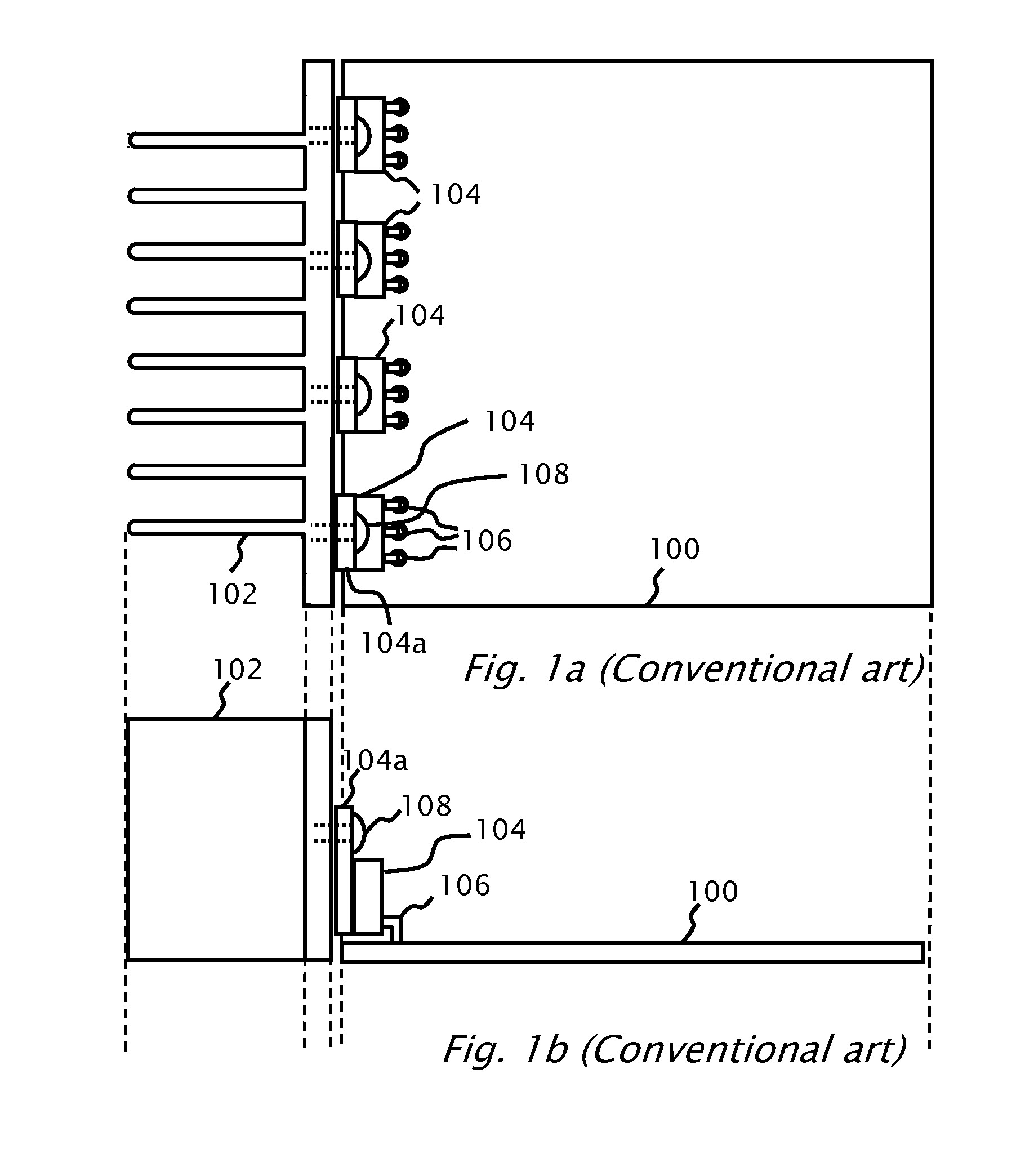
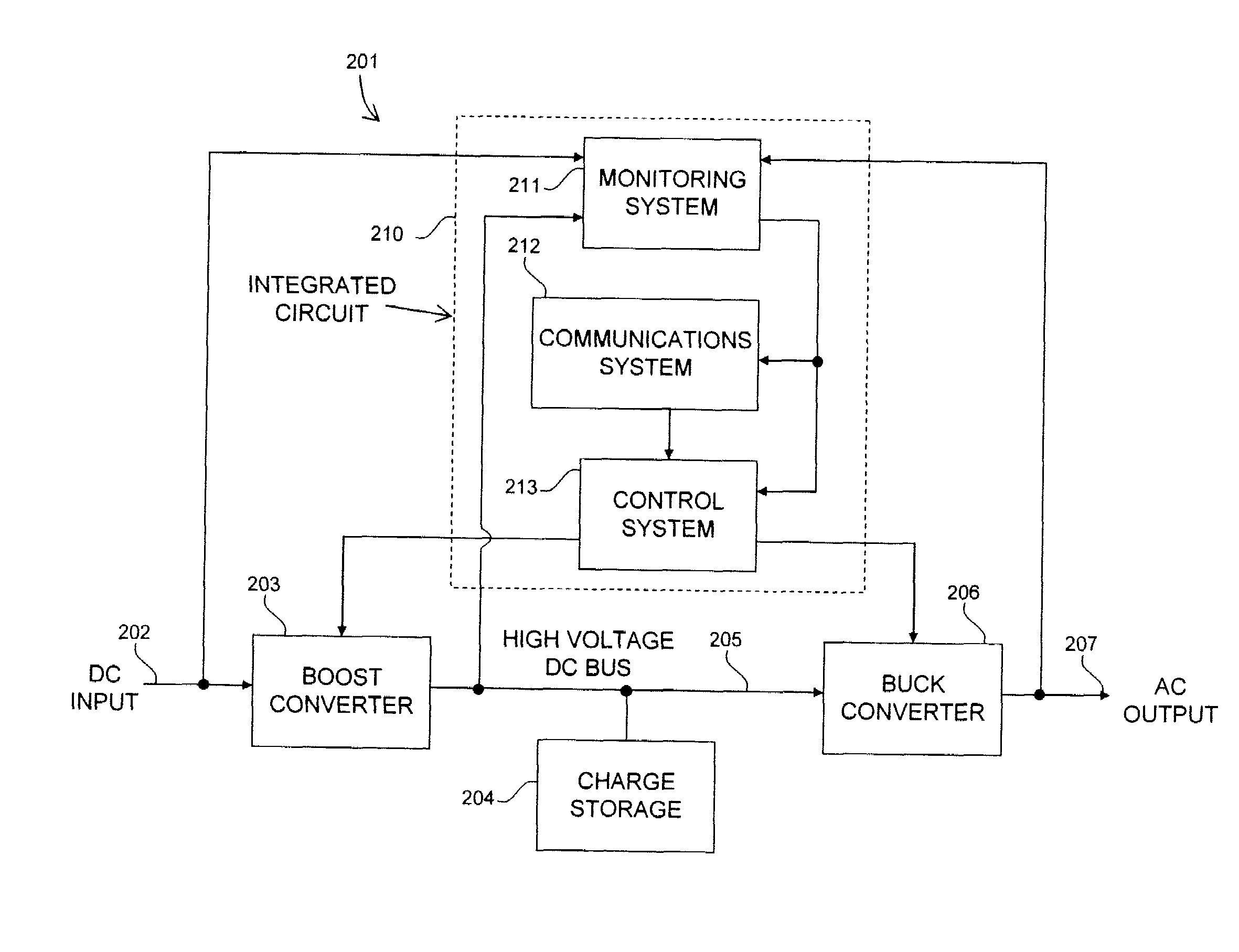
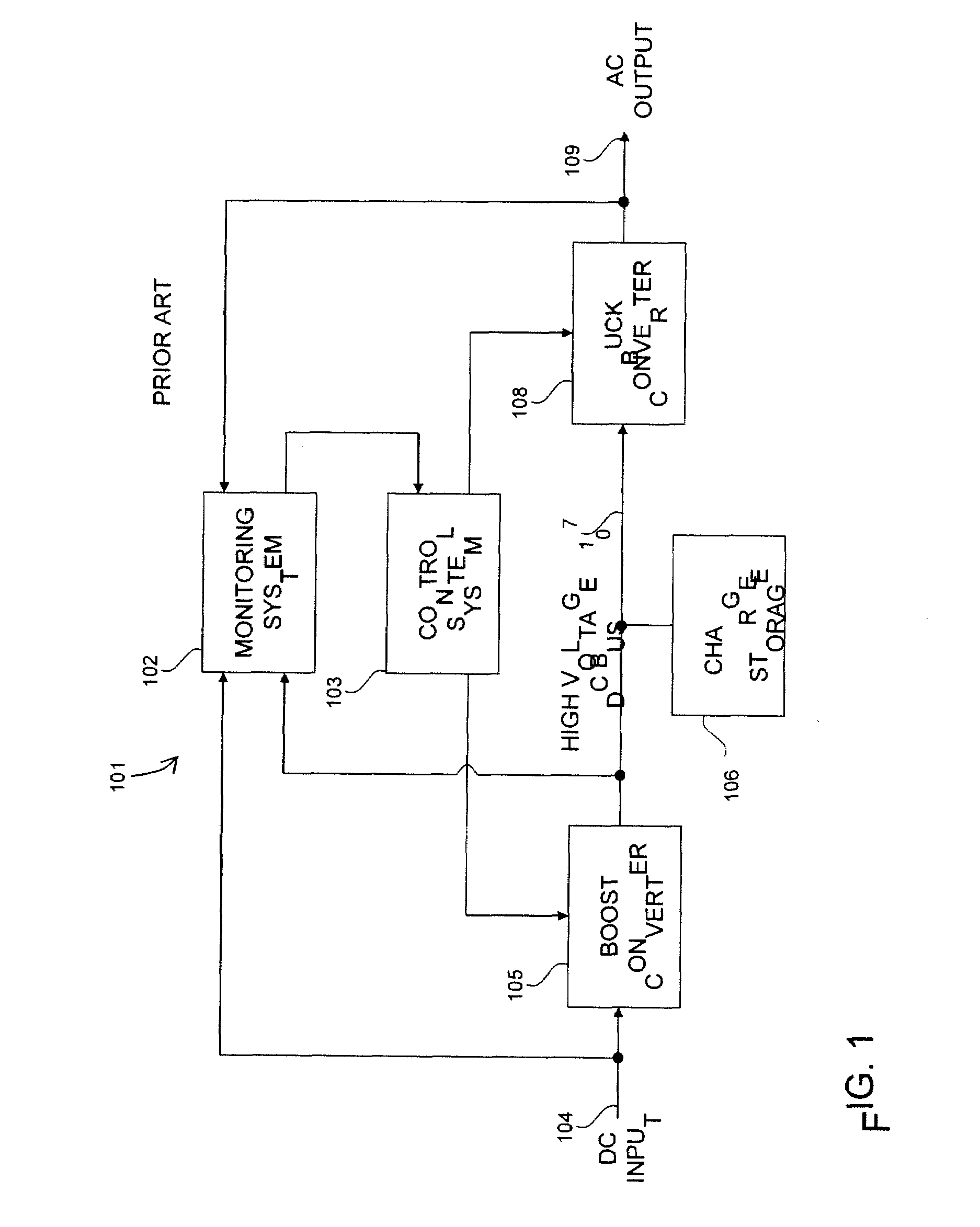
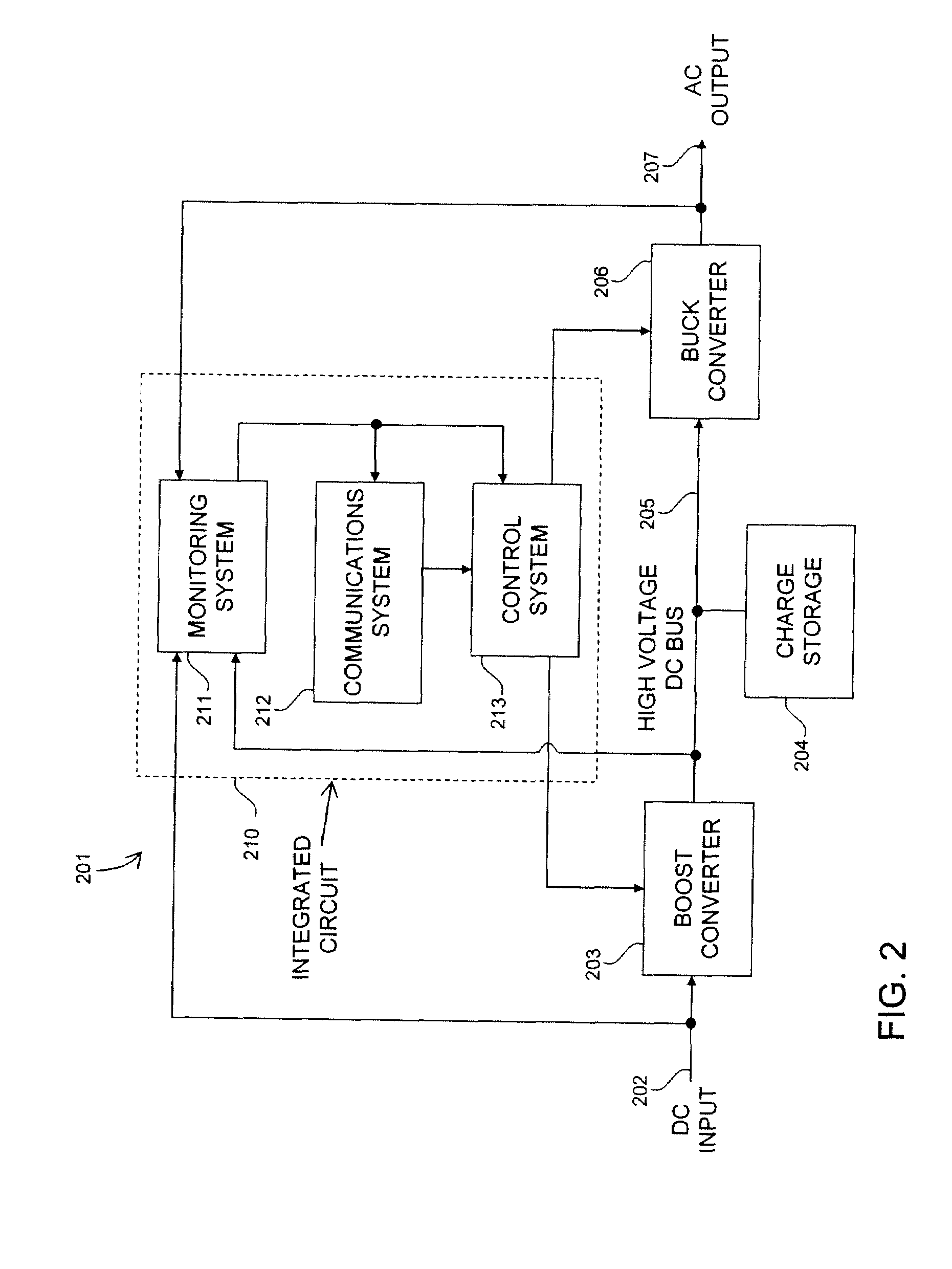
A photovoltaic module-mounted AC inverter circuit uses one or more integrated circuits, several power transistors configured as switches, several solid-dielectric capacitors for filtering and energy storage, several inductors for power conversion and ancillary components to support the above elements in operation. The integrated circuit includes all monitoring, control and communications circuitry needed to operate the inverter. The integrated circuit controls the activity of pulse-width modulated power handling transistors in both an input boost converter and a single-phase or multi-phase output buck converter. The integrated circuit also monitors all power processing voltages and currents of the inverter and can take appropriate action to limit power dissipation in the inverter, maximize the available power from the associated PV module and shut down the inverter output if the grid conditions so warrant. The integrated circuit implements power line communications by monitoring the AC wiring for signals and generating communications signals via the same pulse-width modulation system used to generate the AC power. Communications is used to report inverter and PV module status information, local identification code and to allow for remote control of inverter operation.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
Modular HVDC converter
ActiveUS20090295225A1Small sizeEasy to operateCoupling device connectionsDc network circuit arrangementsModularityHigh-voltage direct current
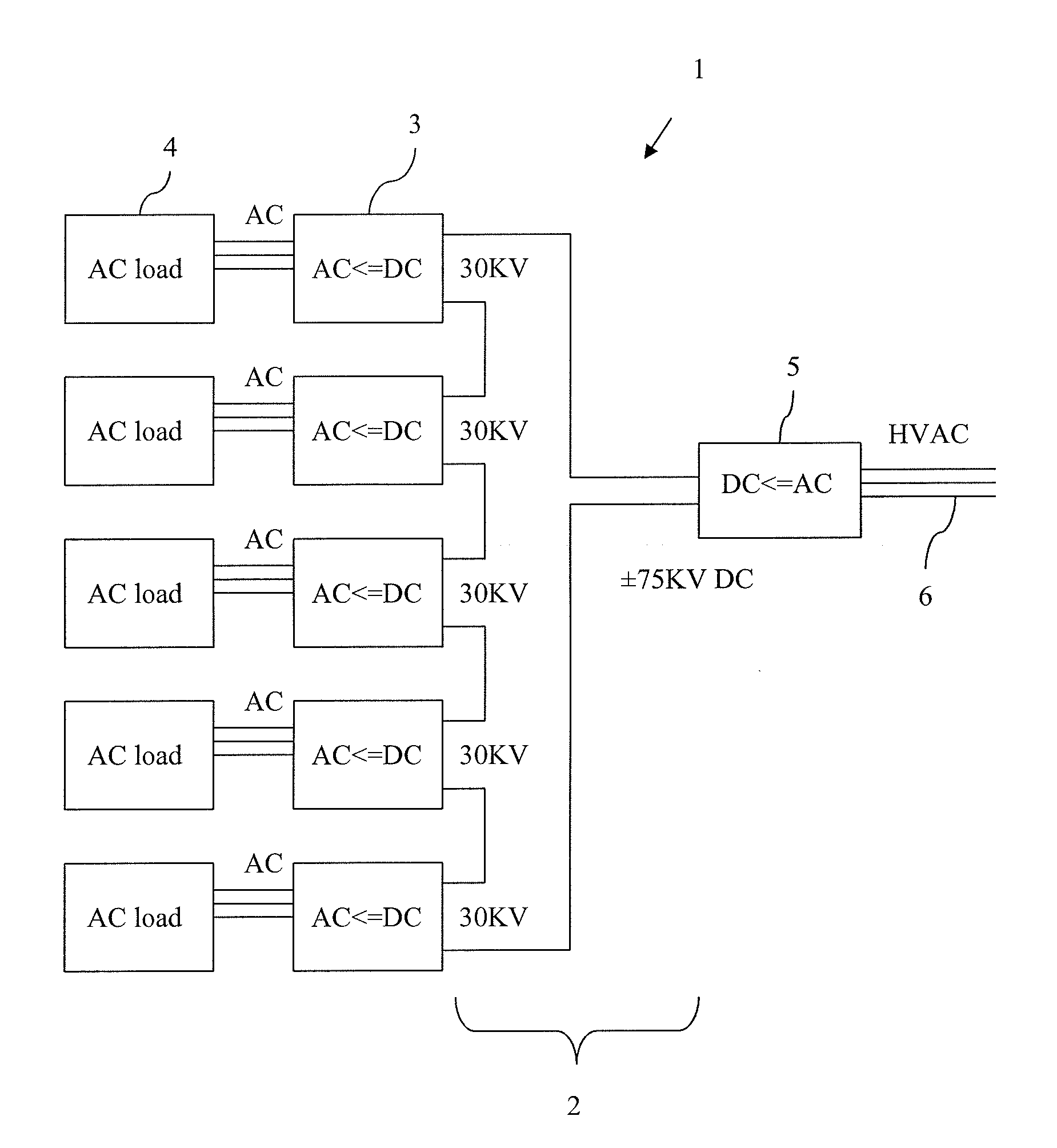
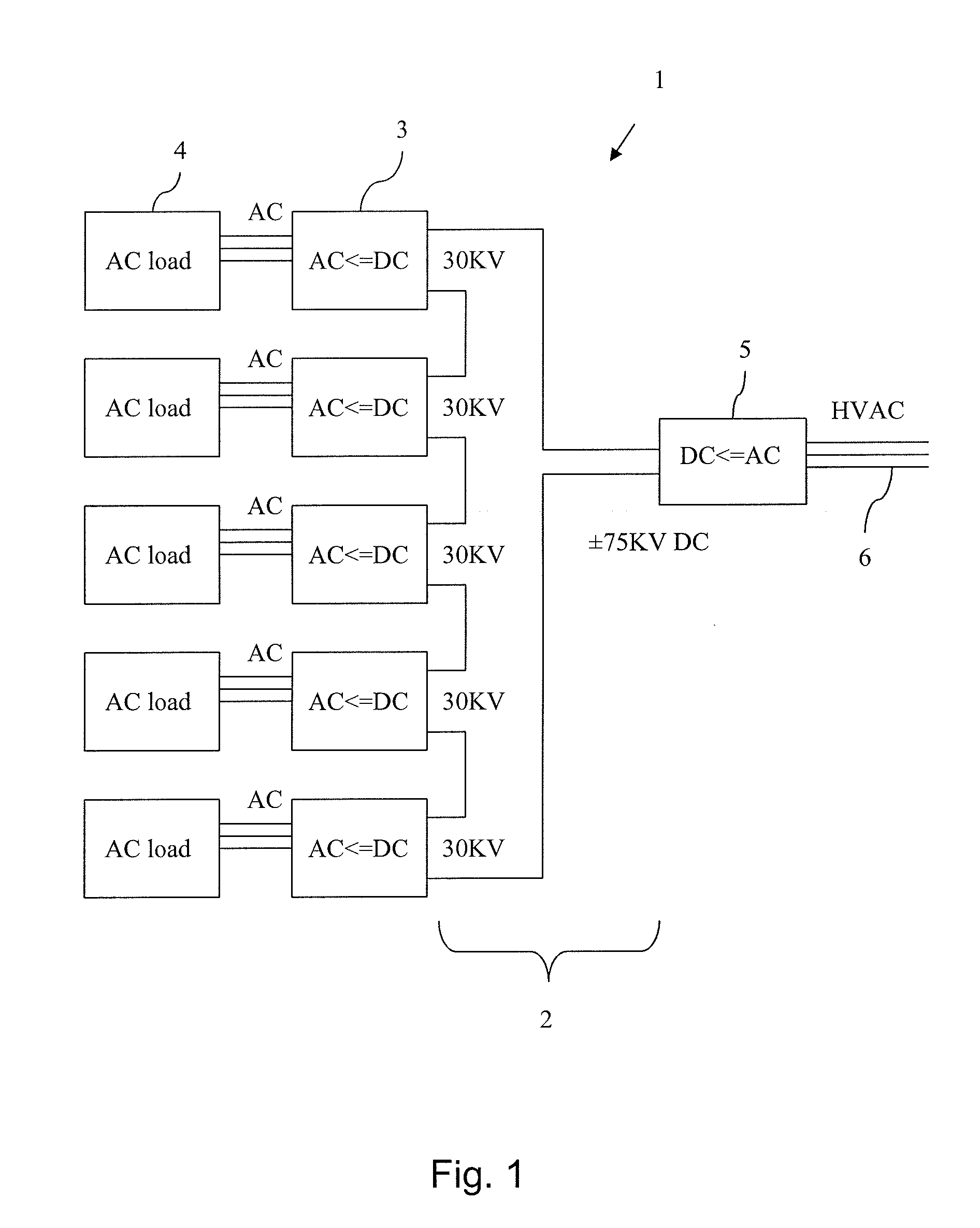
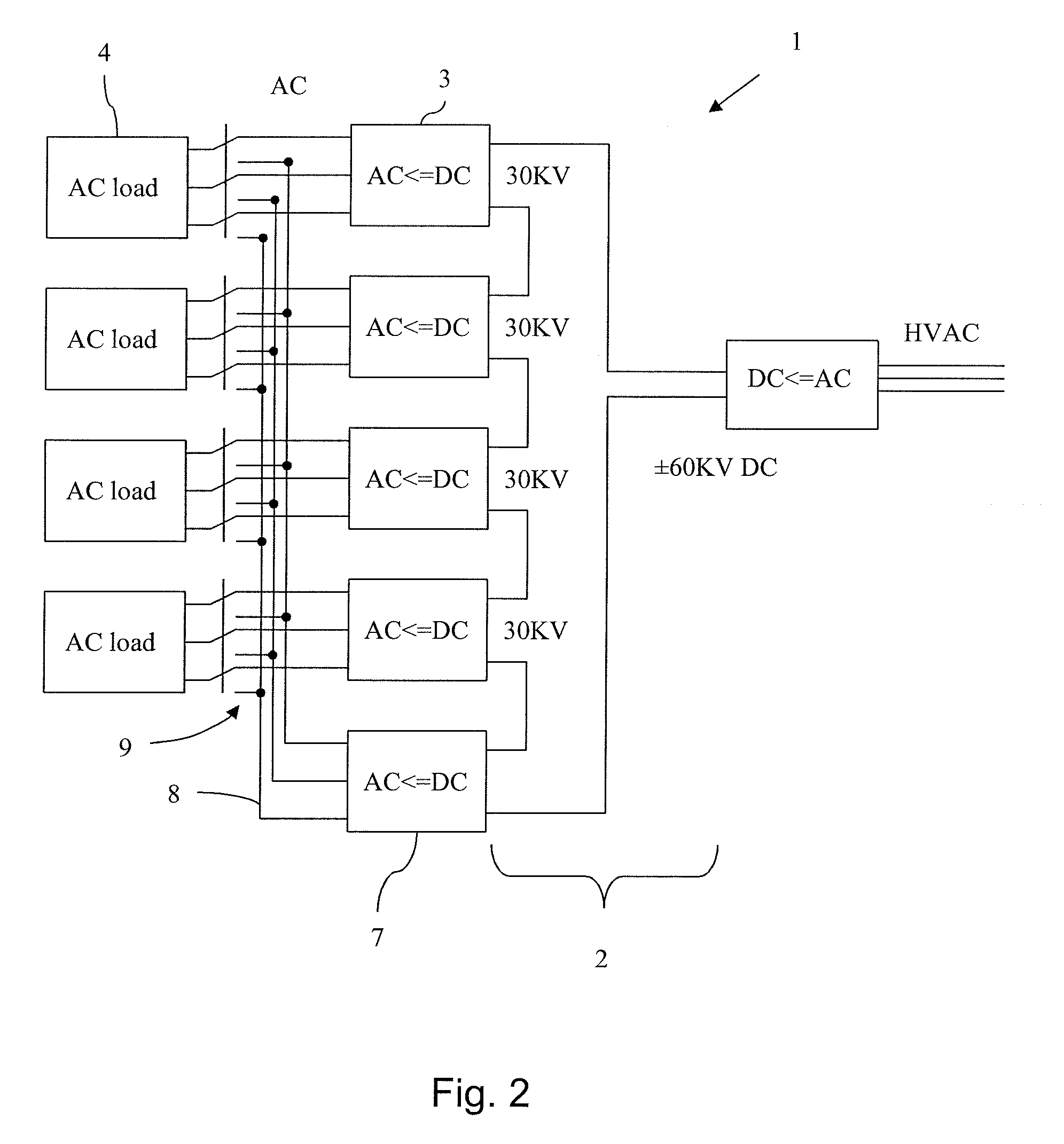
A modular HVDC converter system including a high voltage direct current network, and at least two DC / AC converters being connected in series to the HVDC network. Each of the DC / AC converters is arranged to provide AC to a separate AC load.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
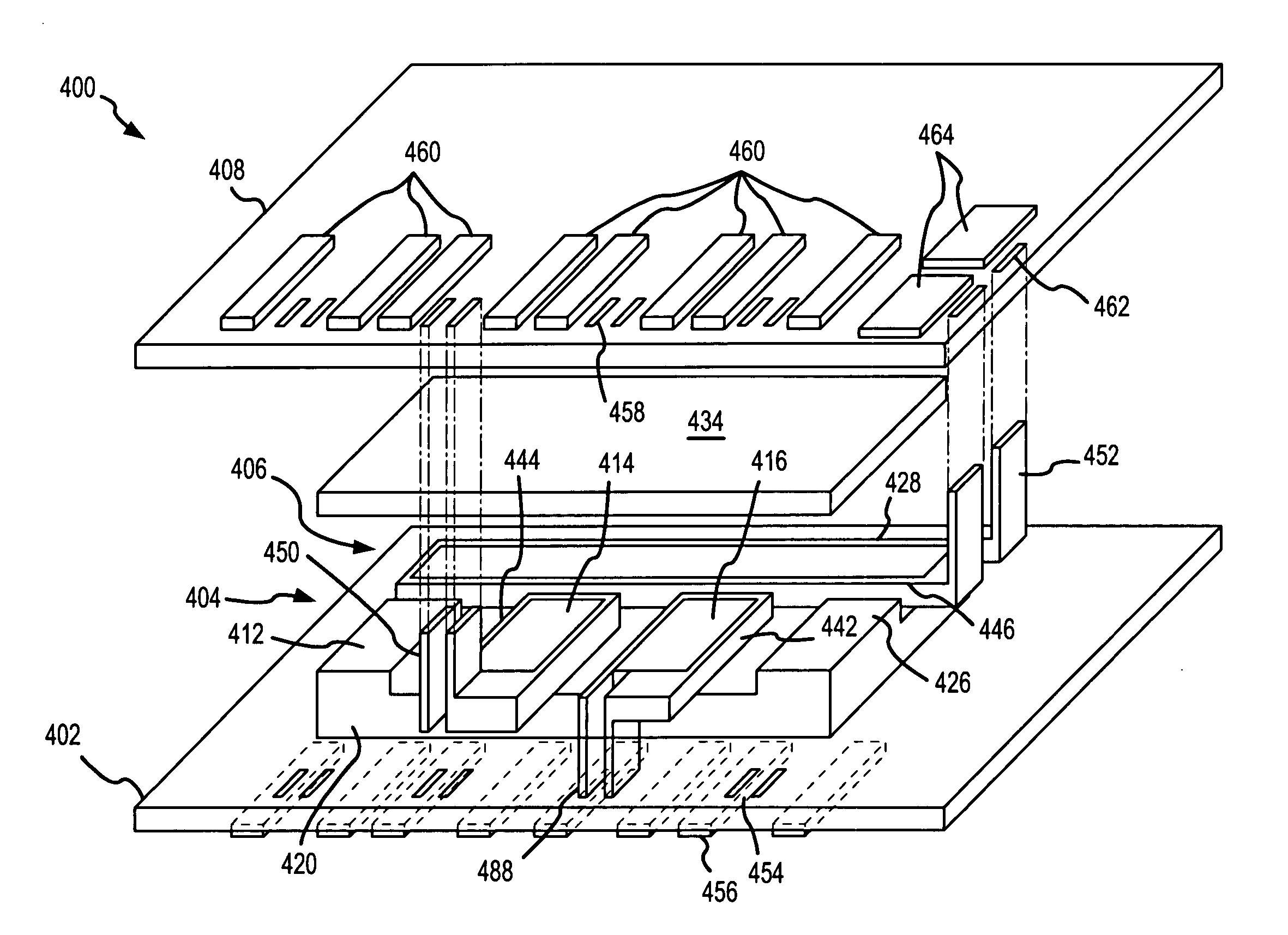
Vertically packaged switched-mode power converter
ActiveUS7012414B1Tight regulationFast transient responseTransformersConversion constructional detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceCellular architecture
A vertically packaged cellular power converter solves the problems associated with conventional designs and paves the way for a cellular circuit architecture with ultra-low interconnect resistance and inductance. The vertical packaging results in a power flow in the vertical direction (from the bottom to the top) with very short internal interconnects, thereby minimizing the associated conduction losses and permitting high conversion efficiency at high currents. The cellular architecture is ideally suited for generating multiple supply voltages.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
Universal serial bus voltage transformer
InactiveUS7212420B2Reduce financial burdenEasy to useTwo pole connectionsConversion constructional detailsElectricityTransformer
The present invention provides a universal serial bus (USB) voltage transformer, which comprises a main body, a transformer circuit unit, and several connectors. The transformer circuit unit is disposed in or at the inside of the main body. The connectors are electrically connected to the transformer circuit unit directly or via a connection cable. A USB voltage transformer having travel charging function is thus formed. The USB voltage transformer of the present invention can simultaneously charge several portable electronic devices like mobile phones, personal digital assistants, electronic translators, and small cameras.
Owner:LIAO SHENG HSIN
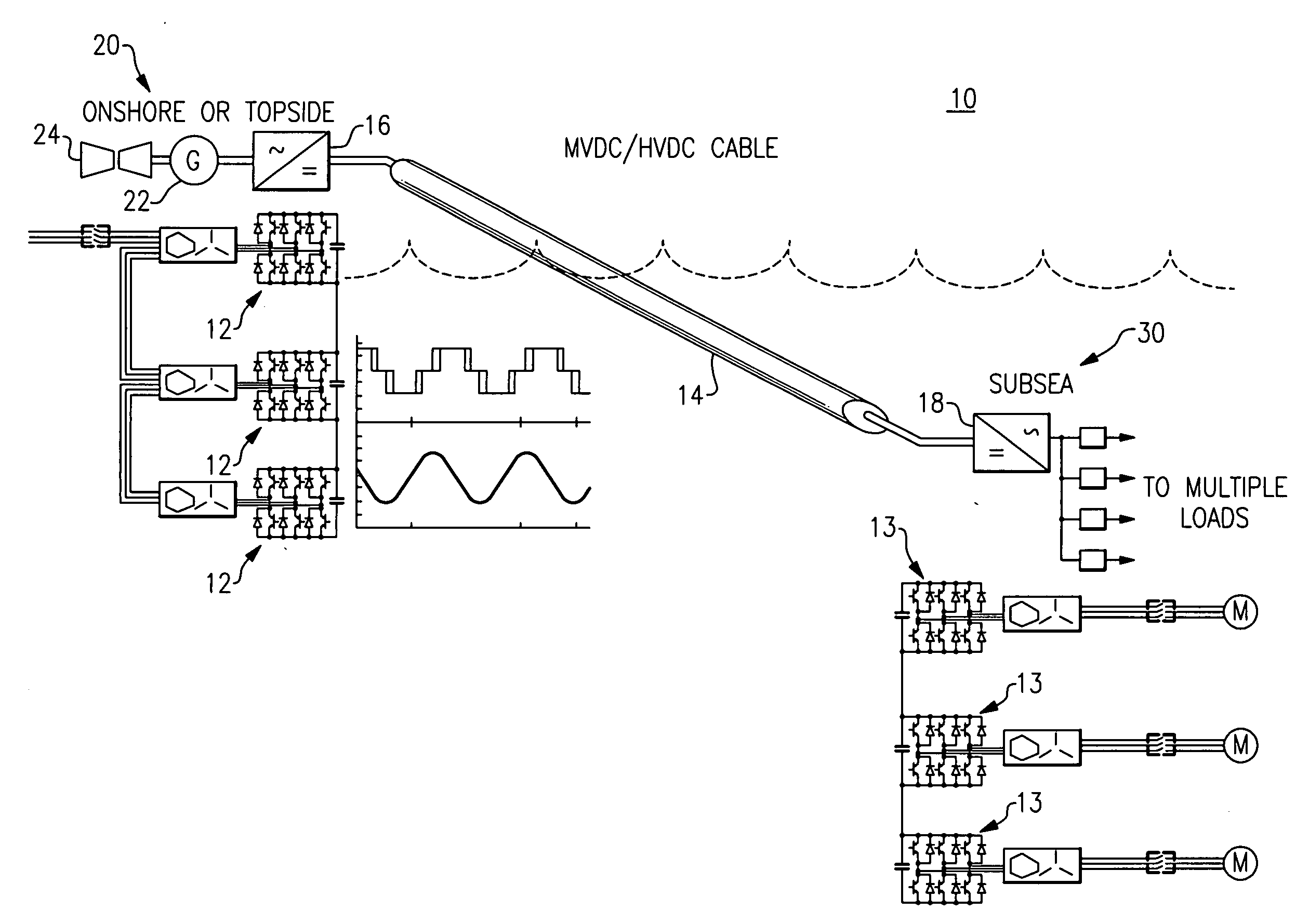
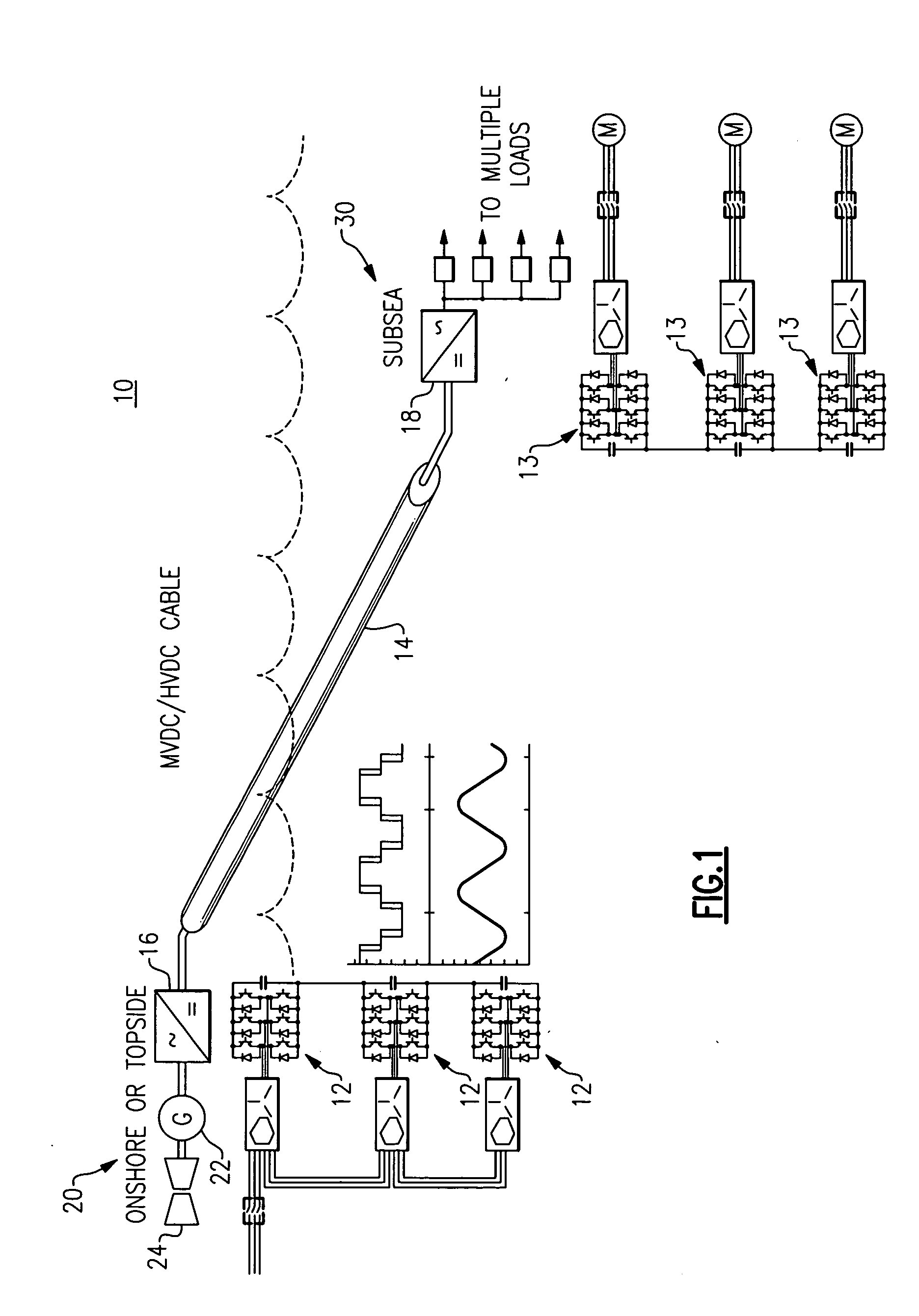
Modular stacked subsea power system architectures
InactiveUS20100133901A1Dc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalModularityShore
A sub-sea power delivery system includes a plurality of modular power converter building blocks on each of the power source side and the sub-sea load side that are stacked and interconnected to meet site expansion requirements and electrical load topologies. The power delivery system comprises a system DC transmission link / bus, wherein the system DC link is configured to carry HVDC or MVDC power from an onshore utility or topside power source to multiple sub-sea load modules. The stacked modular power converter topology on the sub-sea side of the sub-sea power delivery system is symmetrical with the stacked modular power converter topology on the on-shore / top-side of the sub-sea power delivery system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Power electronics device for controlling an electric machine
InactiveUS6326761B1Small space requirementCompact designElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectric machineEngineering
A power electronics device for controlling an electric machine including a power section arranged within a housing which can be closed via a cover element. The power section has a plurality of capacitors and a plurality of power semiconductors which are connected to a power bus bar. In addition, a control device is provided for controlling the power electronics device. The capacitors, power semiconductors, and control device are cooled via a cooling device which is formed as a profile having an essentially U-shaped cross section. The cooling device has two lateral limbs and a base region through which cooling ducts are arranged. A suitable cooling medium flows through the cooling ducts and the ends of the cooling ducts opposite the housing cover are closed by a covering element. The capacitors, the power semiconductors and the control device are connected to the cooling device such that thermal exchange occurs between these components and the cooling device.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
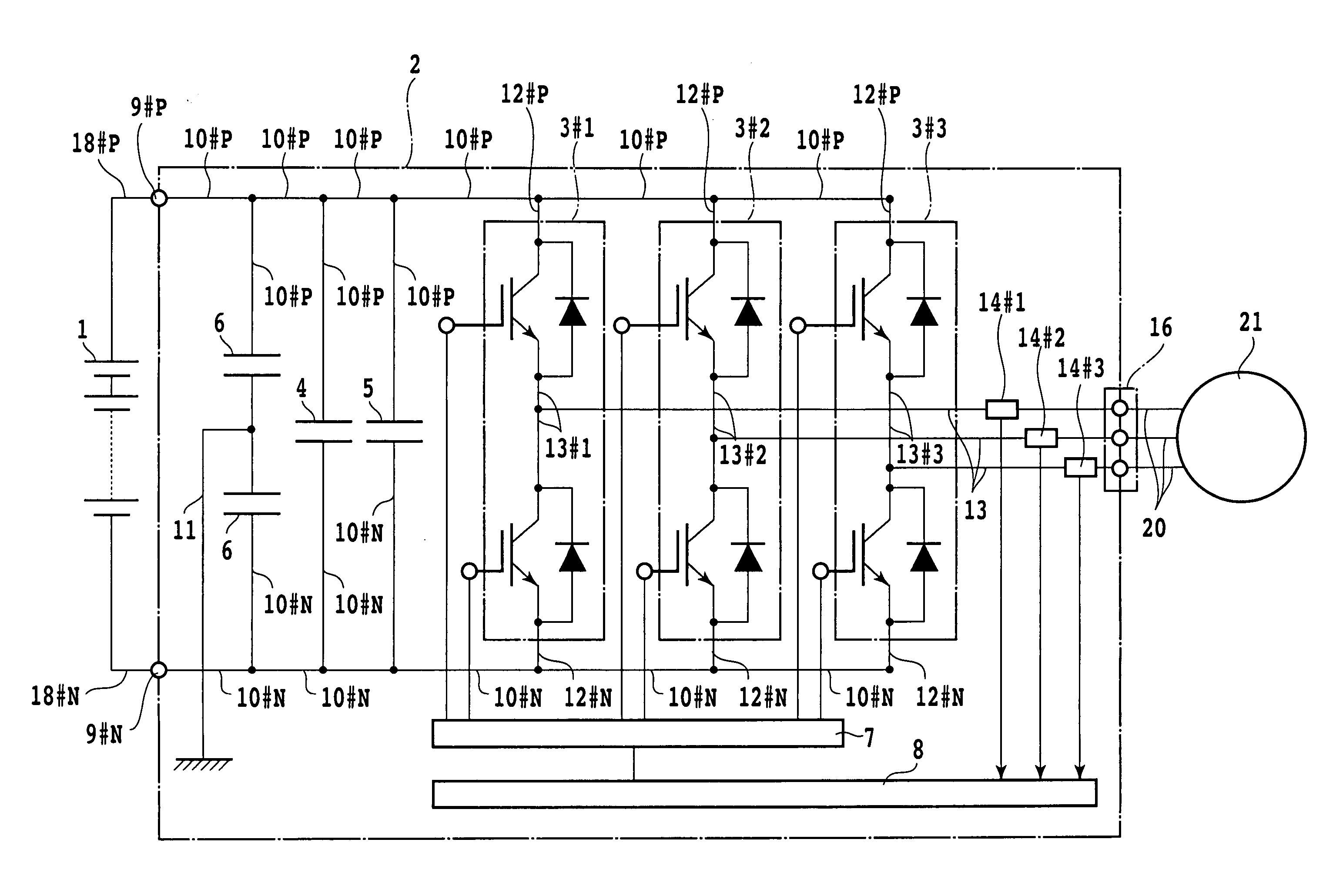
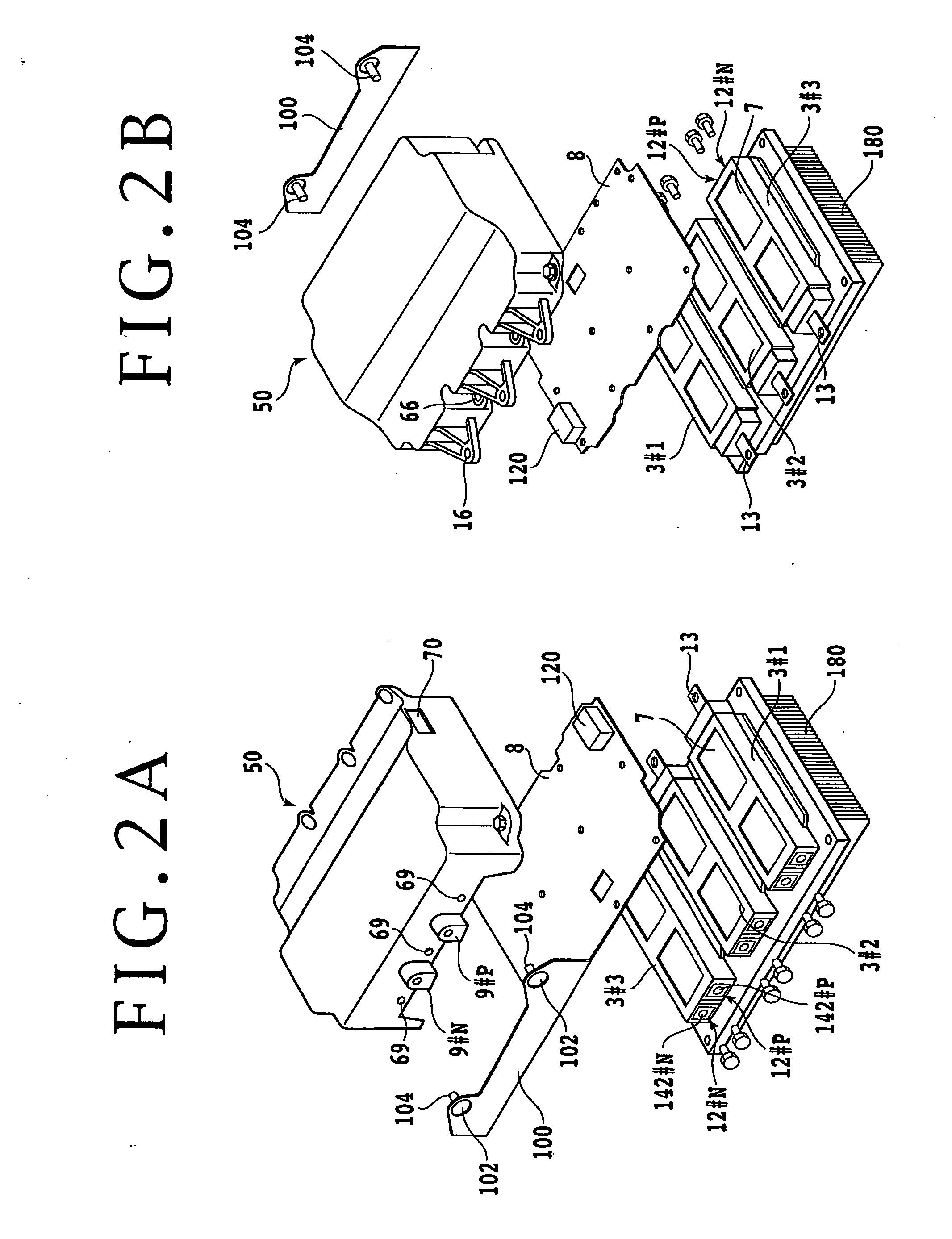
Electric Power Converter
InactiveUS20080049476A1Reduce inductanceReduce heatConversion constructional detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
The present invention provides a highly reliable electric power converter reduced in parasitic inductance.An electric power converter that includes a capacitor module which has a DC terminal, an inverter which coverts a direct current into an alternating current, and heat release fins which cool the inverter, is constructed so that: the inverter has a power module including a plurality of power semiconductor elements; the power module further has a metallic base, a dielectric substrate provided on one face of the metallic base, a power semiconductor element fixed to the dielectric substrate, and a DC terminal; the metallic base has the heat release fins on the other face; the DC terminal in the power module and the DC terminal in the capacitor module are each formed by stacking flat plate conductors via an insulator; the two positive and negative DC terminals have respective front ends bent in opposite directions; a plane including the bent sections is used as a surface for connecting the power module and the capacitor module; and the insulators overlap each other at the connection surface.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Vertically packaged switched-mode power converter
ActiveUS20060038549A1Tight regulationFast transient responseTransformersConversion constructional detailsCellular architectureElectrical resistance and conductance
A vertically packaged cellular power converter solves the problems associated with conventional designs and paves the way for a cellular circuit architecture with ultra-low interconnect resistance and inductance. The vertical packaging results in a power flow in the vertical direction (from the bottom to the top) with very short internal interconnects, thereby minimizing the associated conduction losses and permitting high conversion efficiency at high currents. The cellular architecture is ideally suited for generating multiple supply voltages.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
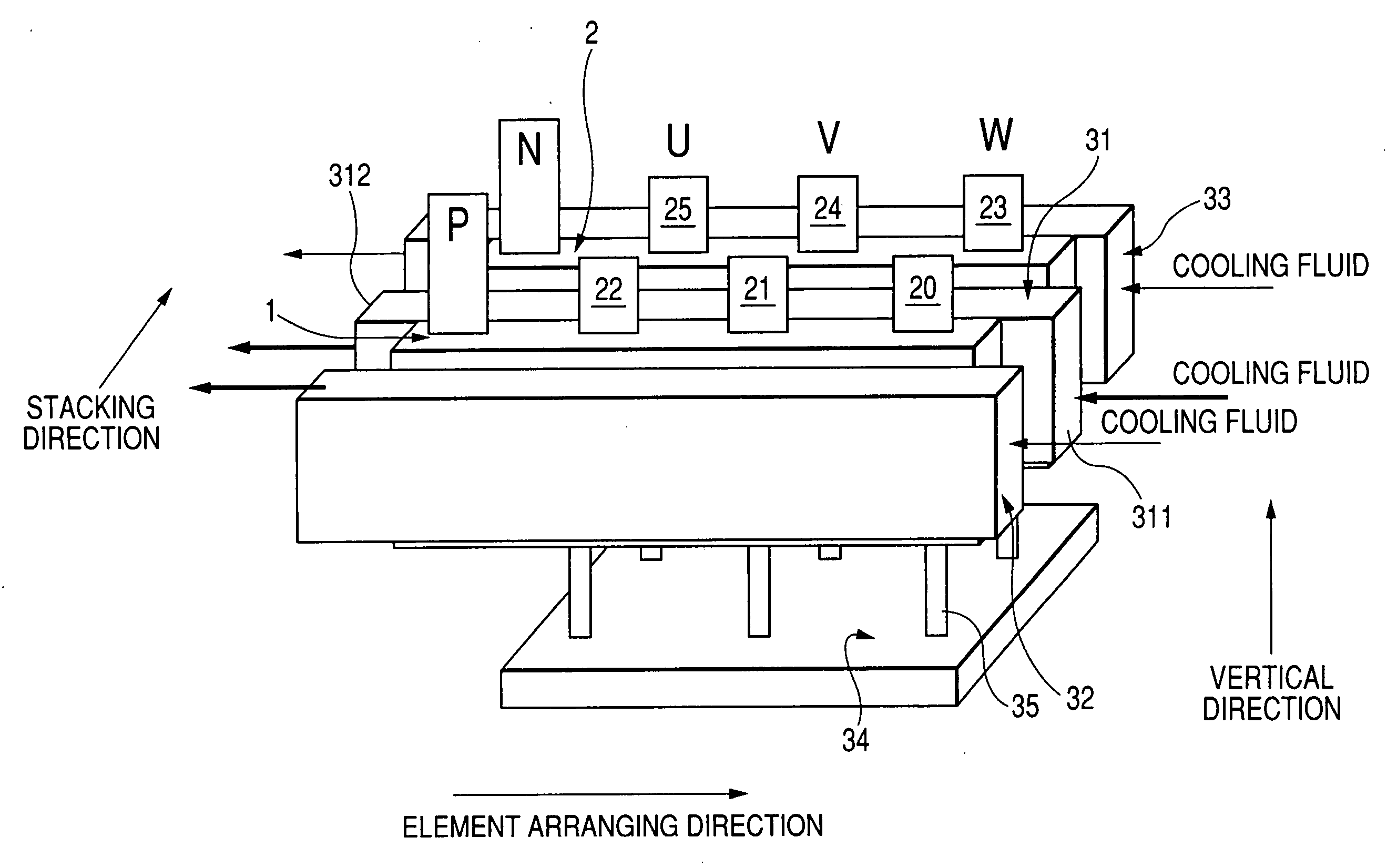
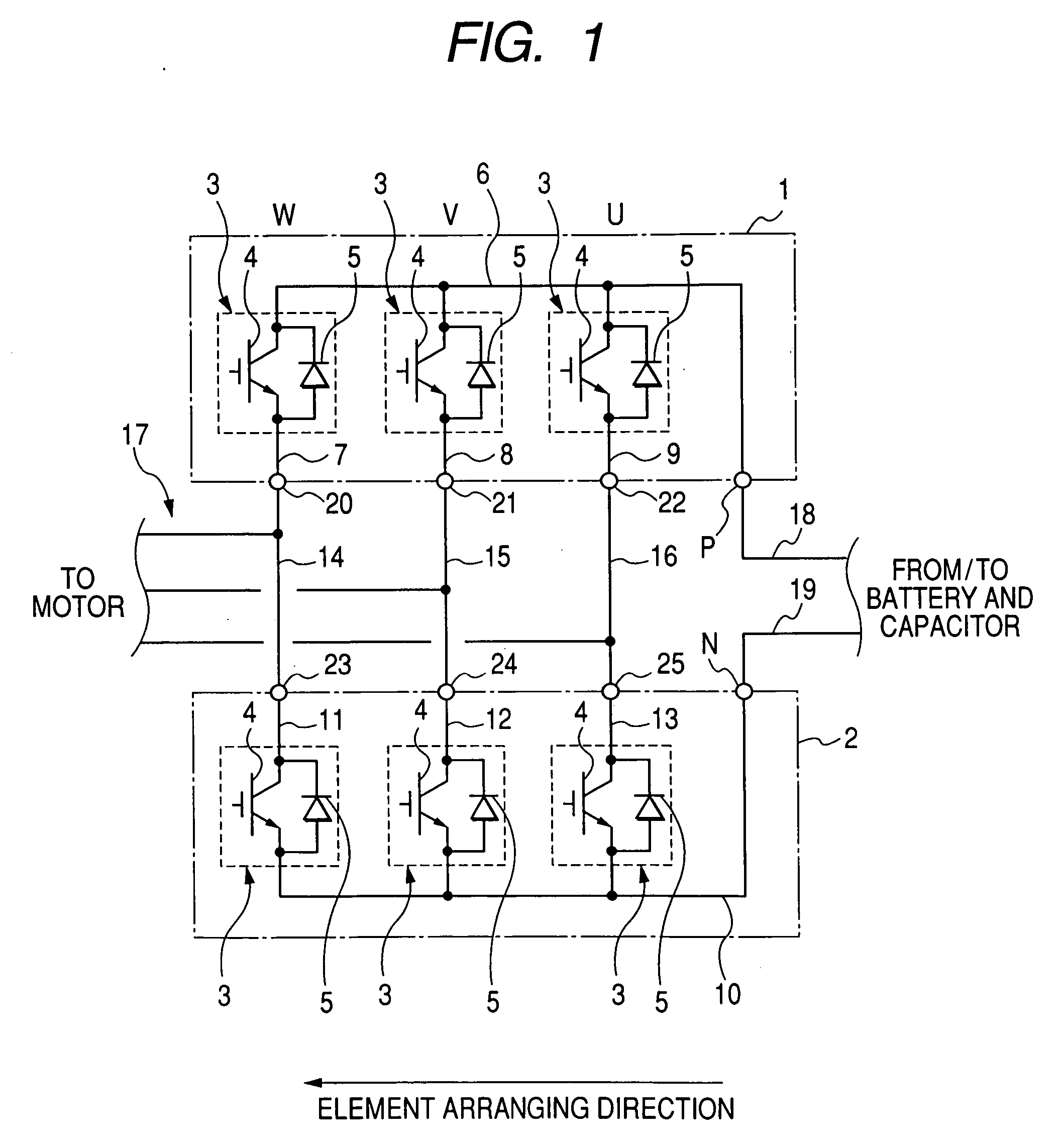
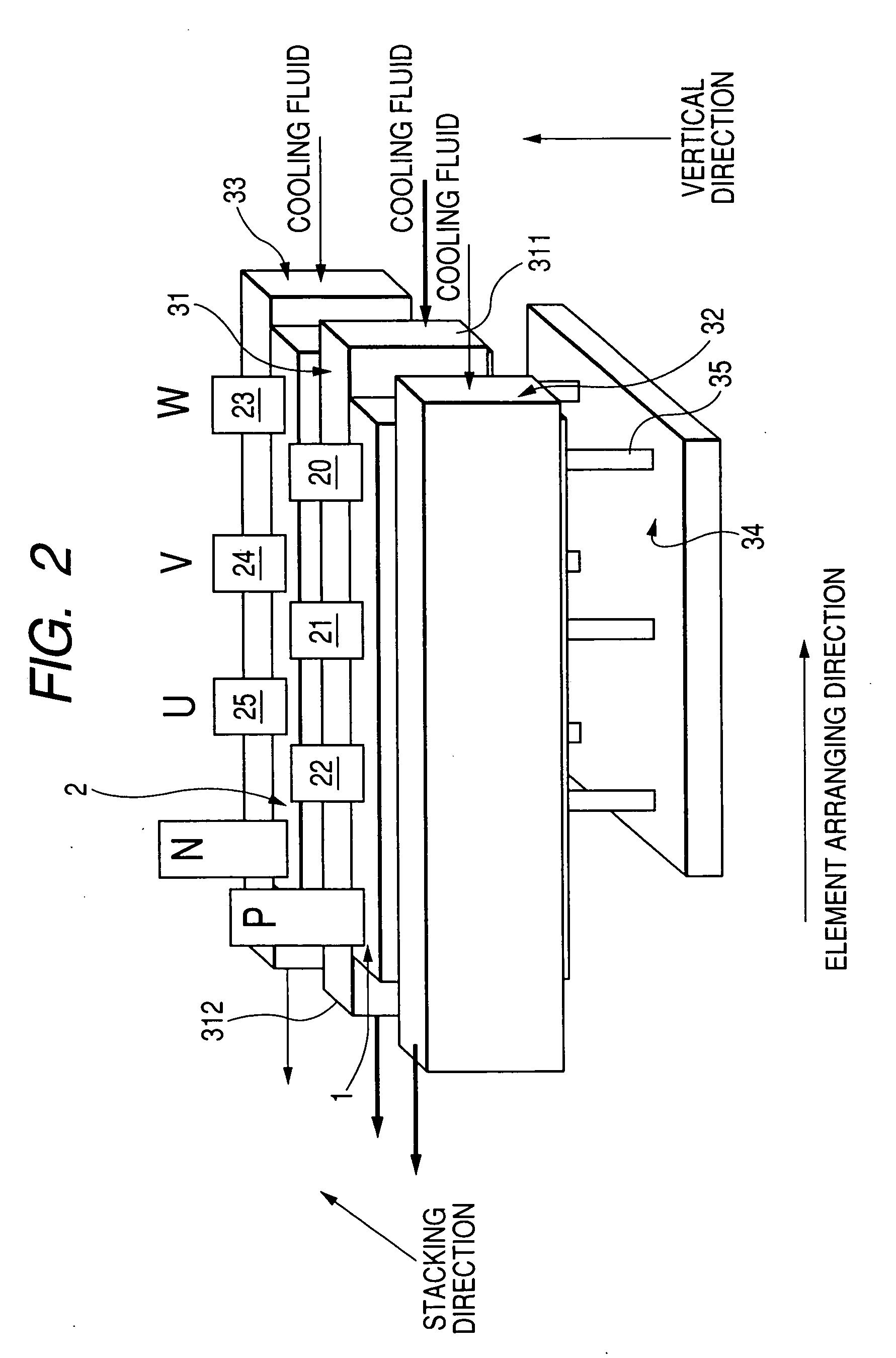
Module type multiphase inverter
ActiveUS20070076355A1Easy to manufactureEasy wiringConversion constructional detailsSubstation/switching arrangement cooling/ventilationEngineeringAlternating current
A multiphase inverter has two card shaped arm modules facing each other along a stacking direction. Each module has semiconductor switching elements disposed along an element arranging direction substantially perpendicular to the stacking direction, a common heat sink plate connecting direct current electrodes of the elements with one of terminals of the power source, and phase heat sink plates connecting respective alternating current electrodes of the elements with respective multiphase terminals of a motor. The elements of each module correspond to all phases of an alternating current. Each common heat sink plate forms a principal surface of the corresponding module, and the phase heat sink plates of each module forms another principal surface. The principal surfaces of each module face each other along the stacking direction.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electric circuit module as well as power converter and vehicle-mounted electric system that include the module
InactiveUS20060232942A1Reduce the impactImprove fuel economyConversion constructional detailsPropulsion using ac induction motorsComputer moduleEngineering
A power module constructs a pressurizing tool by laminating an elastic member as well as a DC positive-side wiring member and DC negative-side wiring member in which currents flow in opposite directions. The pressurizing tool presses a first fixing tool, and then the first fixing tool presses semiconductor equipment. The semiconductor equipment is fixed to a heat dissipating member with its heat dissipating surface brought into surface contact with side wall surfaces of the heat dissipating member. The power module can enhance heat dissipation between a heat dissipating member and semiconductor equipment, and enables the semiconductor equipment to be fixed to the heat dissipating member without adding other components to the power module.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Selective potting for controlled failure and electronic devices employing the same
InactiveUS7187528B2Reduce the possibilityBatteries circuit arrangementsConversion constructional detailsDriver circuitElectrical Failure
A selectively protected electrical system includes or operates with a power source, a load, a power driver circuit for controllably transferring power from the power source to the load, the power driver circuit being encapsulated in a potting material, and a controller for enabling and disabling the power driver circuit, the controller being un-encapsulated by the potting material. If a contaminant induced electrical fault occurs in the selectively protected electrical system, the electrical fault is more likely to occur in the un-encapsulated controller, such that the selectively protected electrical system is disabled. The contaminant is inhibited from contacting and inducing an electrical fault in the power driver circuit, thus providing for a controlled failure of the selectively protected electrical system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Power Semiconductor Module
InactiveUS20080224303A1Improve cooling effectThermal resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConversion constructional detailsSemiconductor chipEngineering
A power semiconductor module with its thermal resistance and overall size reduced. Insulating substrates with electrode metal layers disposed thereon are joined to both the surfaces of a power semiconductor chip by using, for example, soldering. Metal layers are disposed also on the reverse surfaces of the insulating substrates and the metal layers are joined to the heat spreaders by using brazing. Heat radiating fins are provided on the heat radiating surface of at least one of the heat spreaders. The heat radiating side of each of the heat spreaders is covered by a casing to form a refrigerant chamber through which refrigerant flows to remove heat transmitted from the semiconductor chip to the heat spreader.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor Device, and Power Conversion Device Using Semiconductor Device
ActiveUS20110051371A1Reduce inductanceOverall small sizeHybrid vehiclesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceElectrical conductor
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Power converter connection configuration
InactiveUS7450388B2Small and light and efficient configurationImprove performanceMagnetic/electric field screeningDigital data processing detailsModular unitModularity
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Capacitor mounting type inverter unit
InactiveUS20070002594A1Low costReduce the numberConversion constructional detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitorElectrical and Electronics engineering
Disclosed herein is a capacitor mounting type inverter unit having a cooling block, an inverter including a plurality of phases of switching circuits provided on the cooling block, and a smoothing capacitor. The inverter unit includes a cover having a first recess for accommodating the inverter and a second recess for accommodating the smoothing capacitor. The second recess has a depth larger than that of the first recess. The second recess is filled with resin in the condition where the smoothing capacitor is accommodated in the second recess.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Microminiature power converter
ActiveUS6930584B2Multiple-port networksConversion constructional detailsElectrical conductorSemiconductor
A microminiature power converter includes a semiconductor substrate on which a semiconductor integrated circuit is formed, a thin film magnetic induction element, and a capacitor. The thin film magnetic induction element includes a magnetic insulating substrate, and a solenoid coil conductor in which a first conductor is formed on a first principal plane of the magnetic insulating substrate, a second conductor is formed on a second principal plane of the magnetic insulating substrate, and a connection conductor is formed in a through hole passing through the magnetic insulating substrate are connected. A relationship of a length L of the magnetic insulating substrate in a direction vertical to a magnetic field generated by the solenoid coil and a length d of the coil conductor is d≧L / 2.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
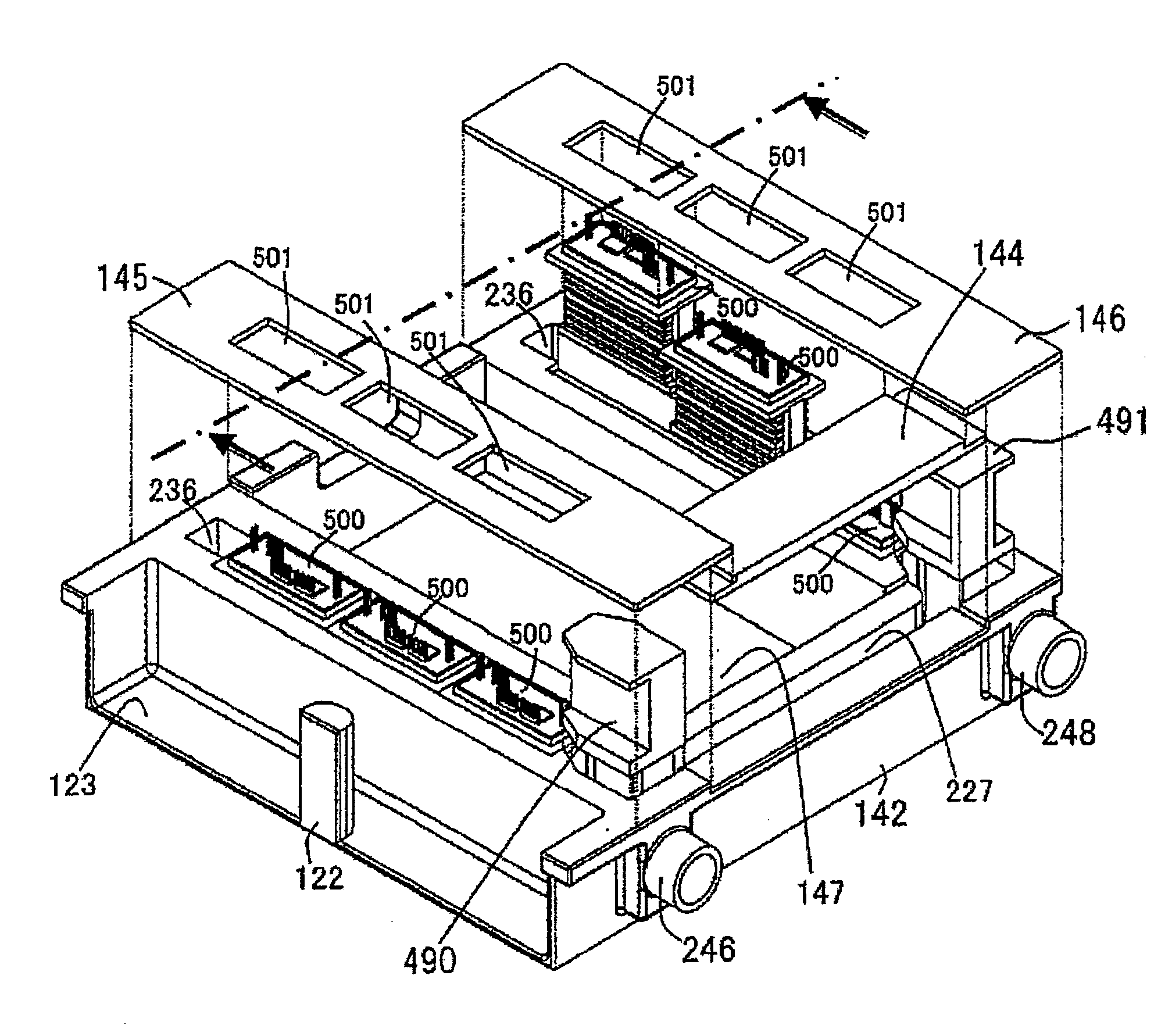
Power conversion apparatus
ActiveUS20080186751A1Improve cooling effectSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConversion constructional detailsElectricityProduction rate
Technology leading to a size reduction in a power conversion apparatus comprising a cooling function and technology relating to enhancing productivity and enhancing reliability necessary for commercial production are provided. Series circuits comprising an upper arm and lower arm of an inverter circuit are built in a single semiconductor module 500. The semiconductor module has cooling metal on two sides. An upper arm semiconductor chip and lower arm semiconductor chip are wedged between the cooling metals. The semiconductor module is inserted inside a channel case main unit 214. A DC positive electrode terminal 532, a DC negative electrode terminal 572, and an alternating current terminal 582 of a semiconductor chip are disposed in the semiconductor module. The DC terminals 532 and 572 are electrically connected with a terminal of a capacitor module. The alternating current terminal 582 is electrically connected with a motor generator via an AC connector.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com