Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
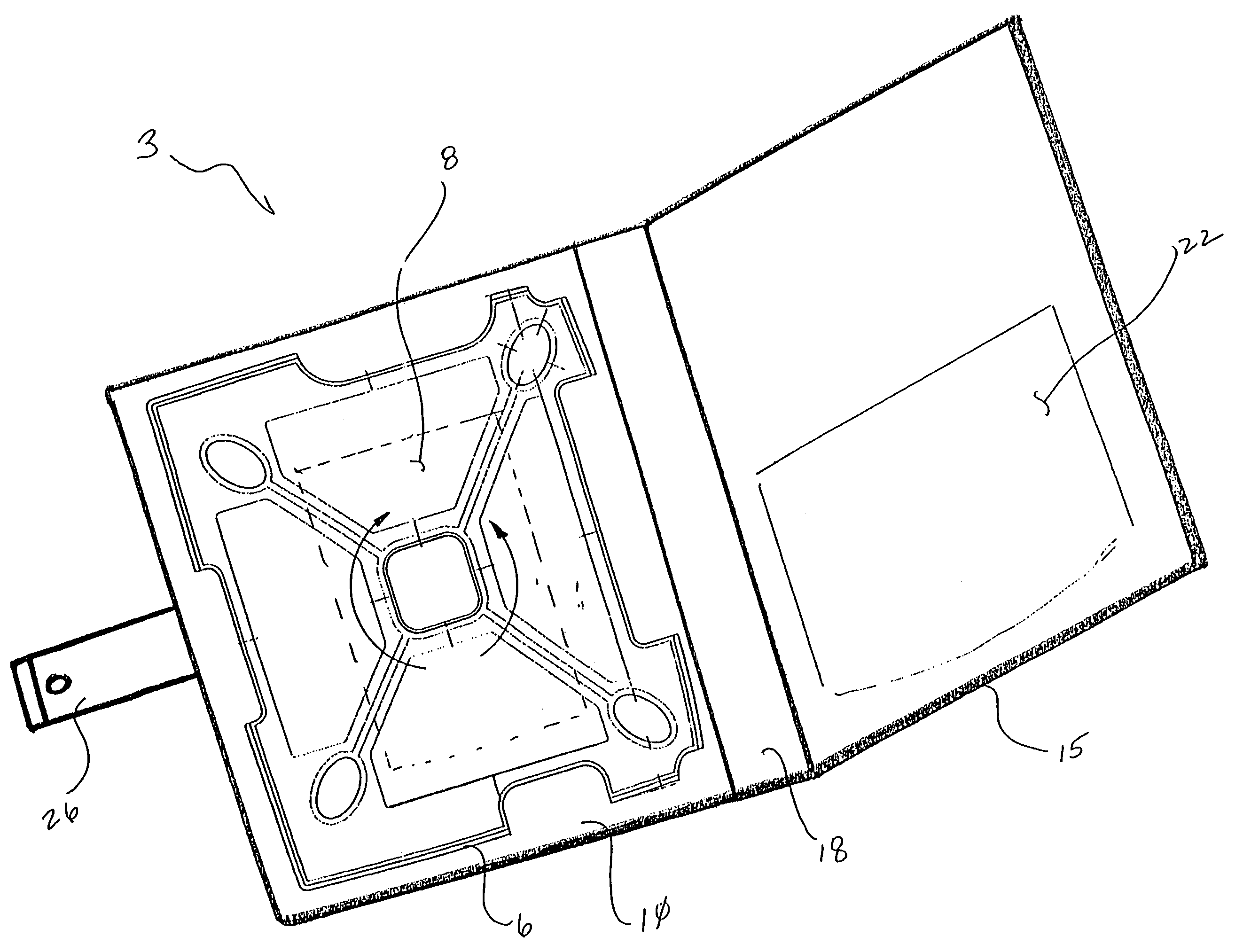
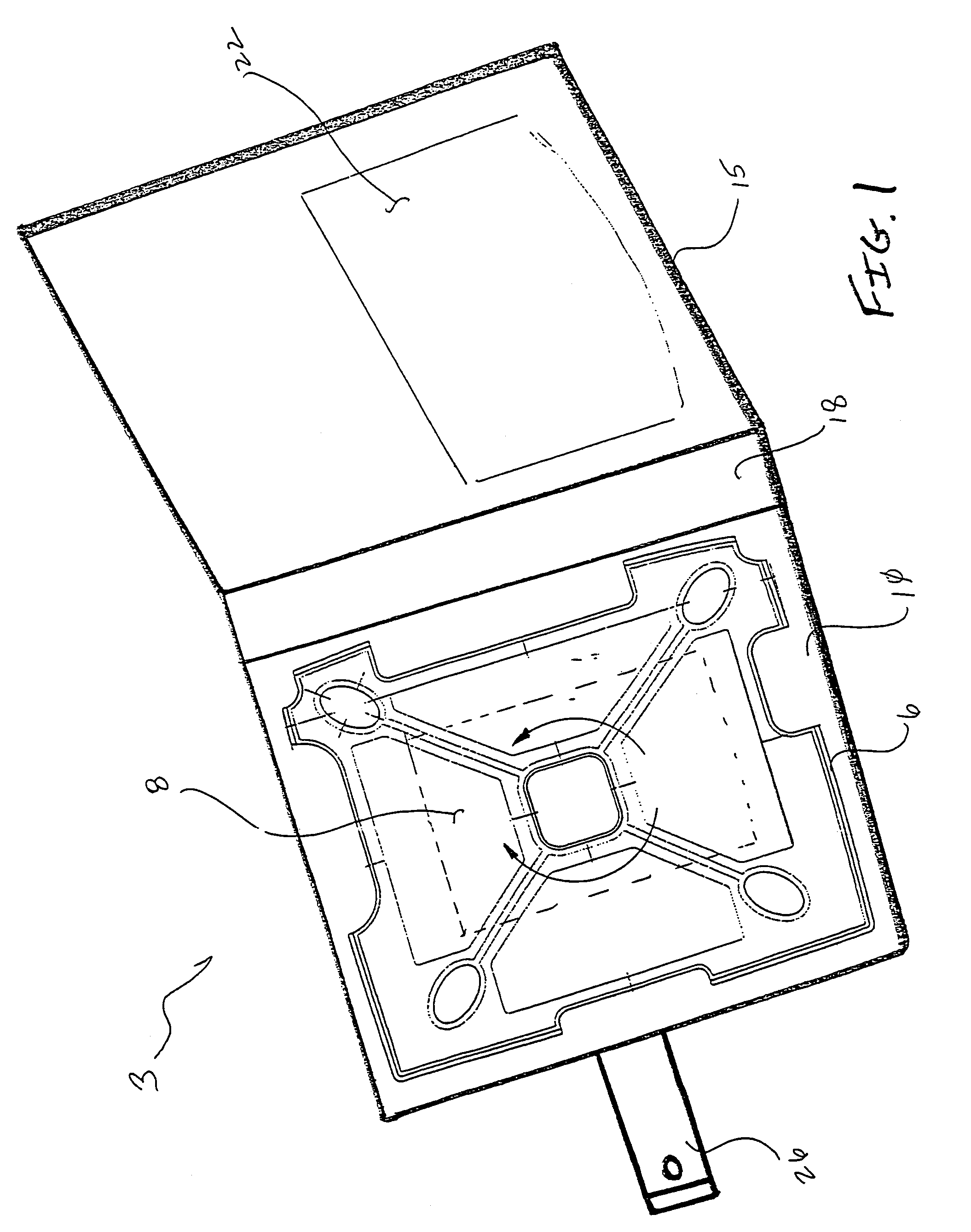
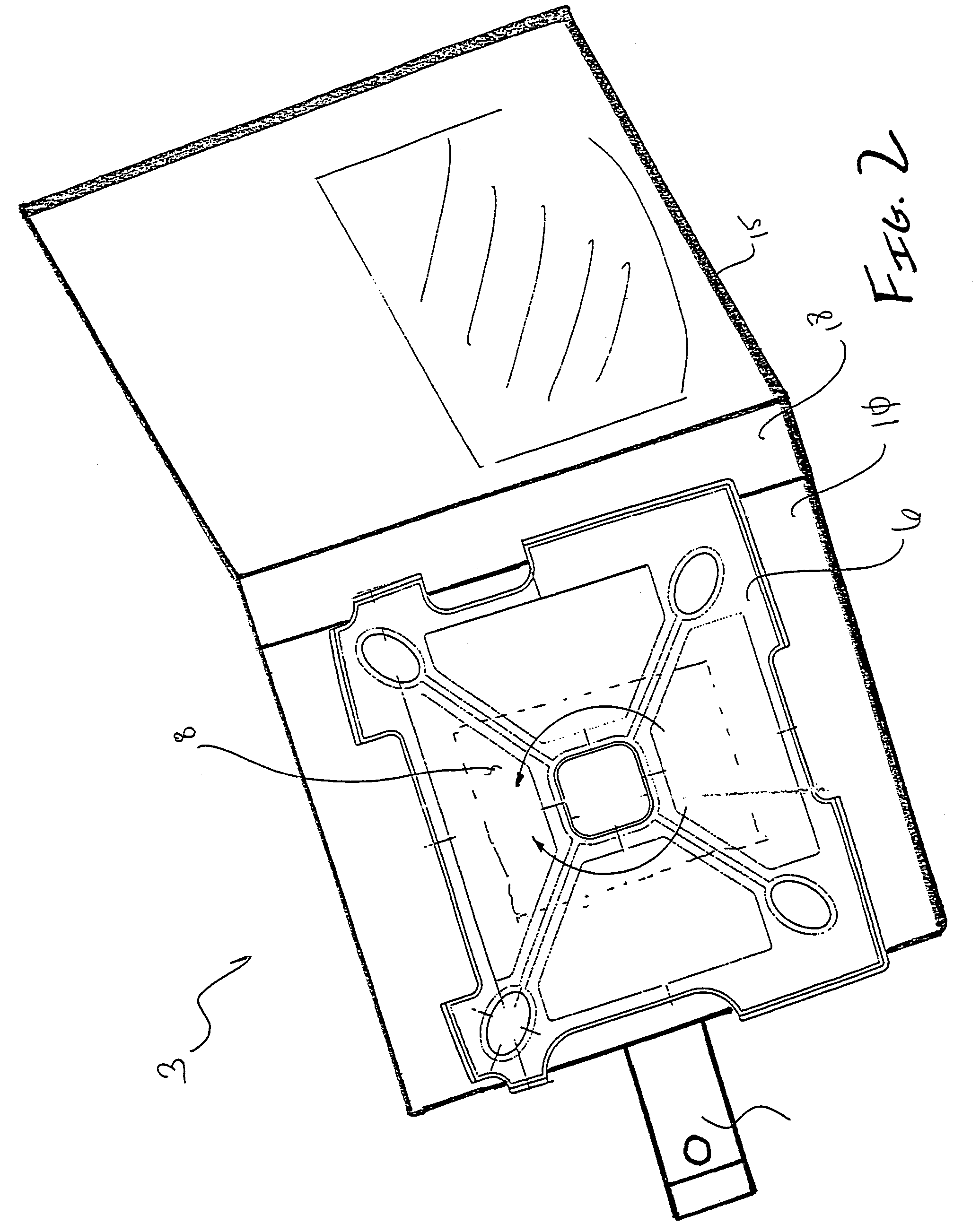
4790results about "Curtain suspension devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
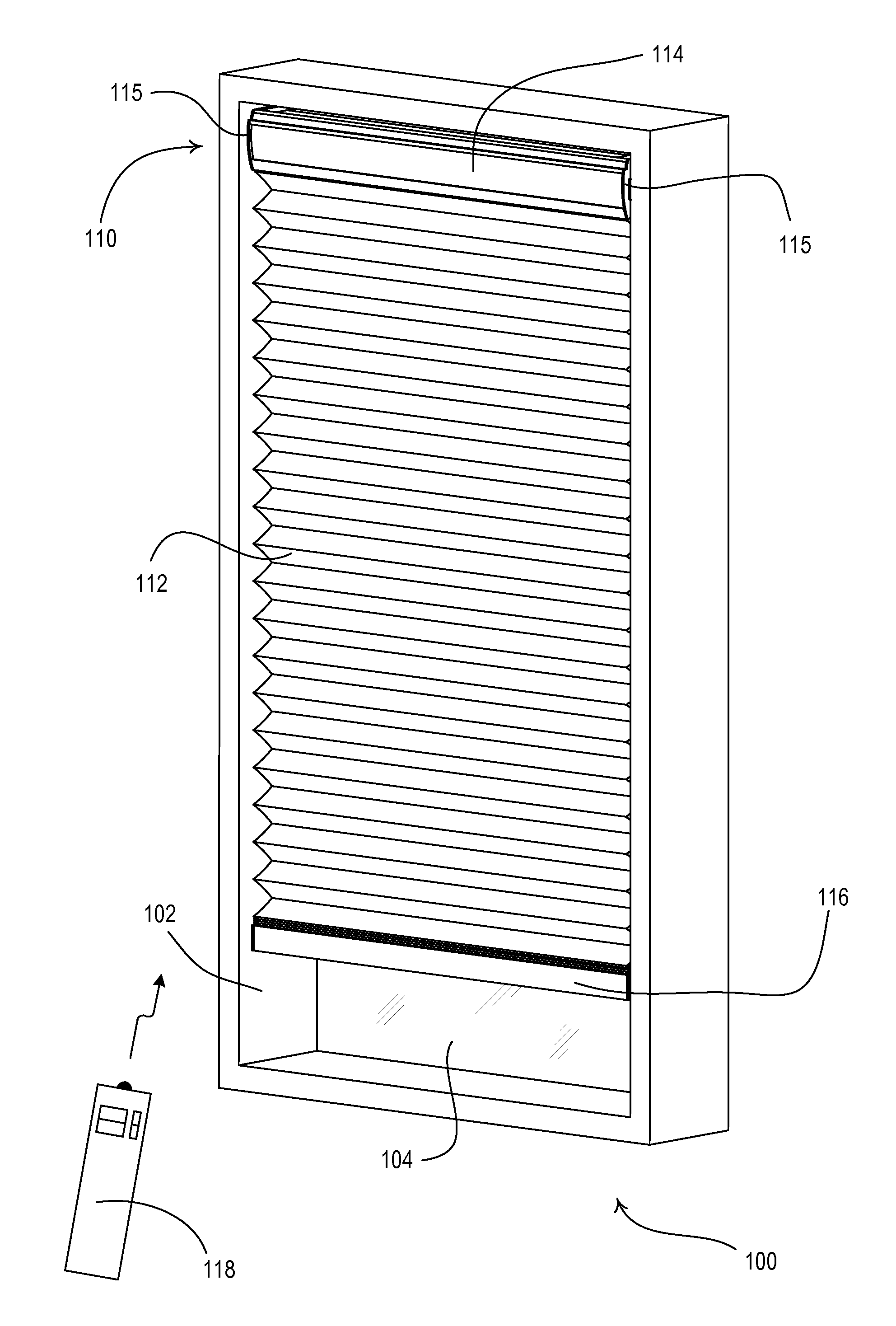
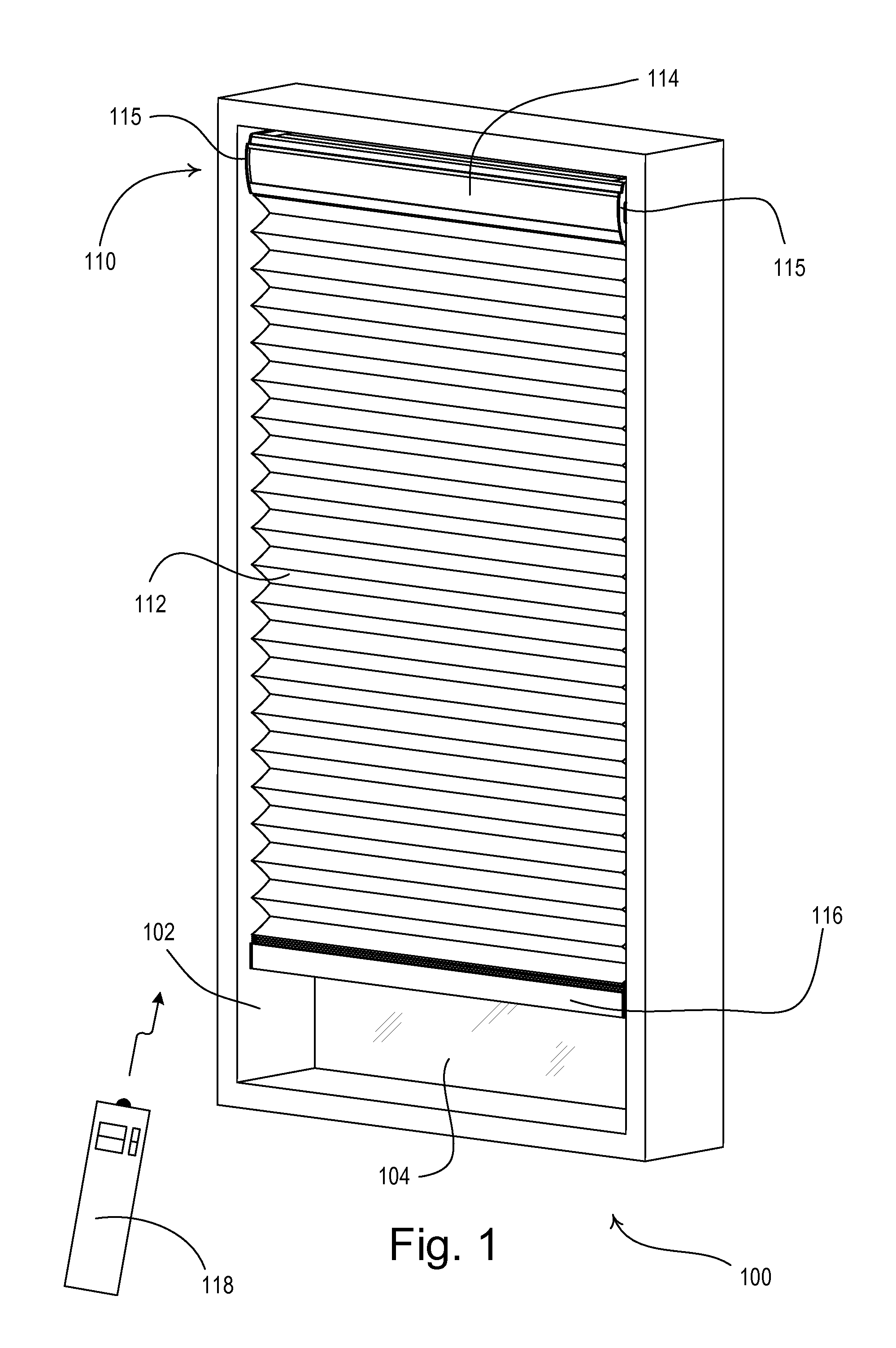
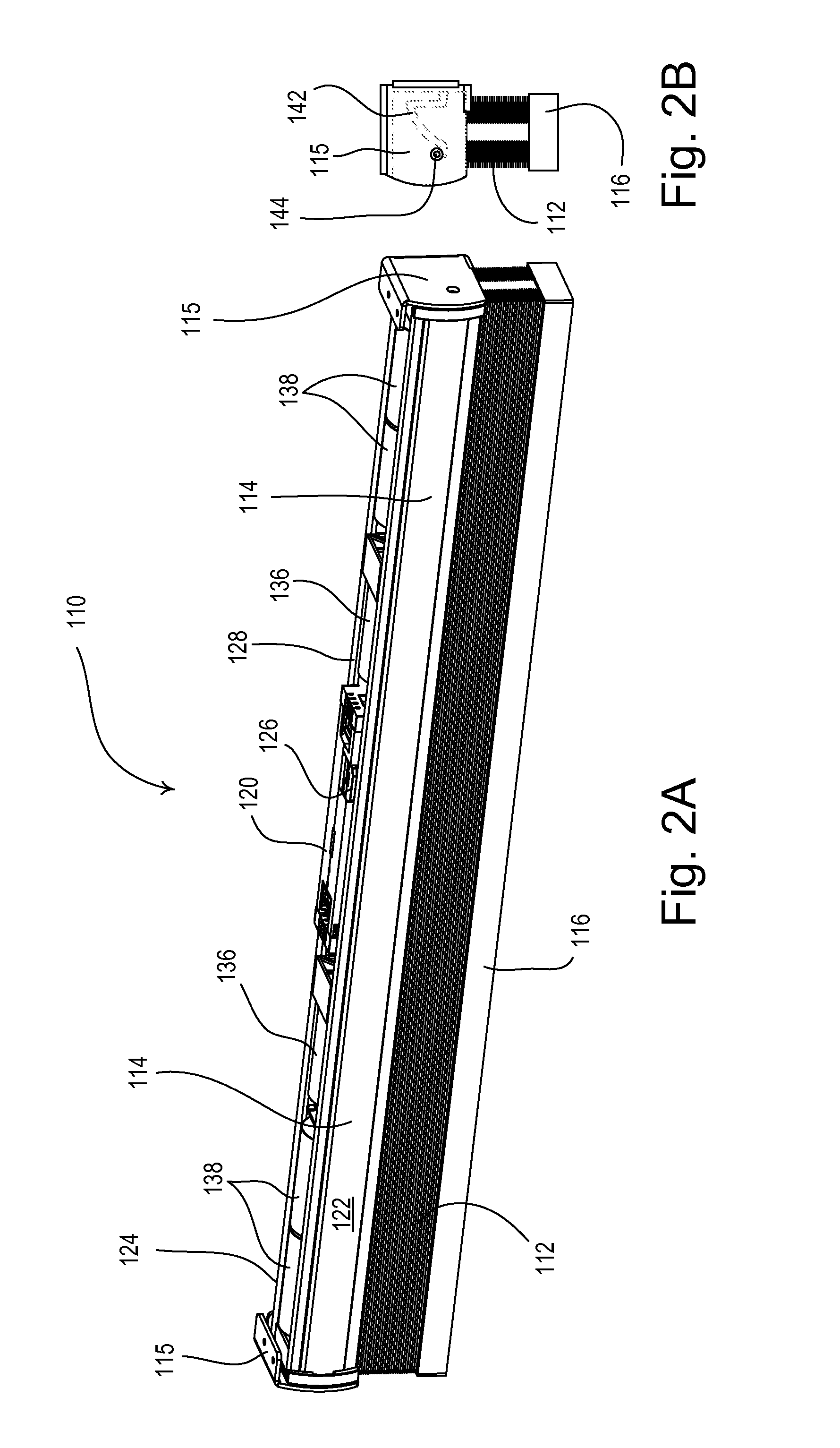
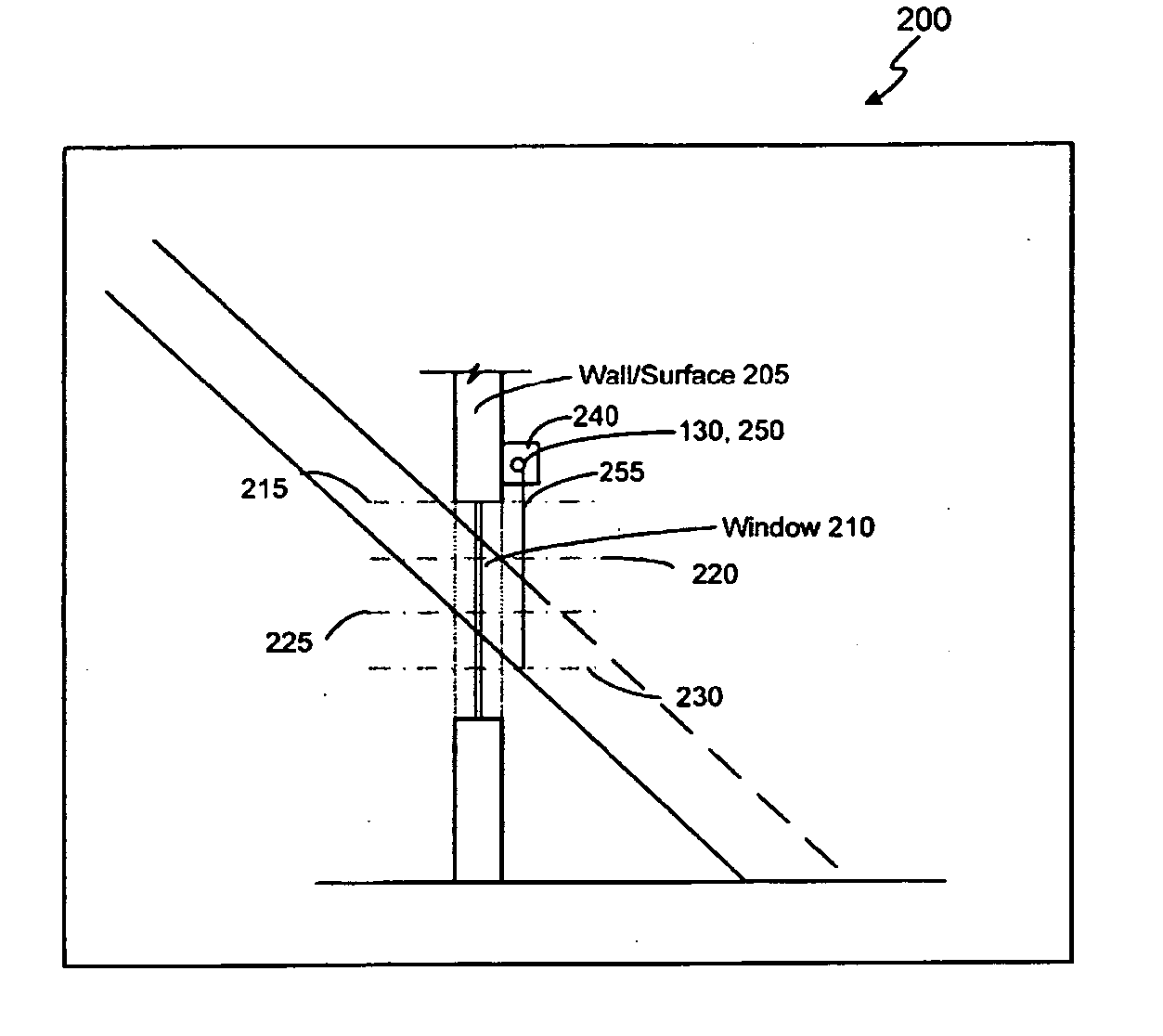
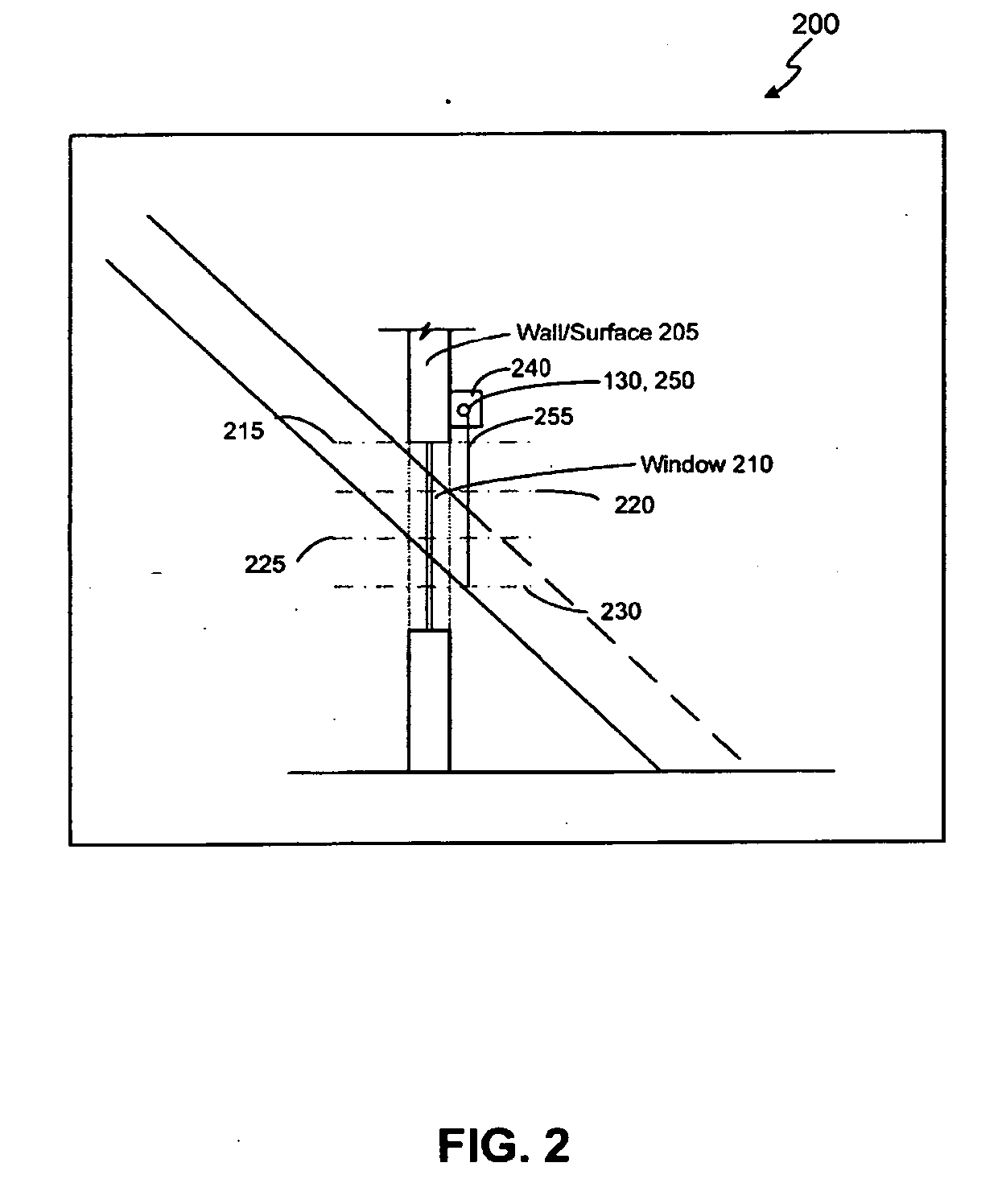
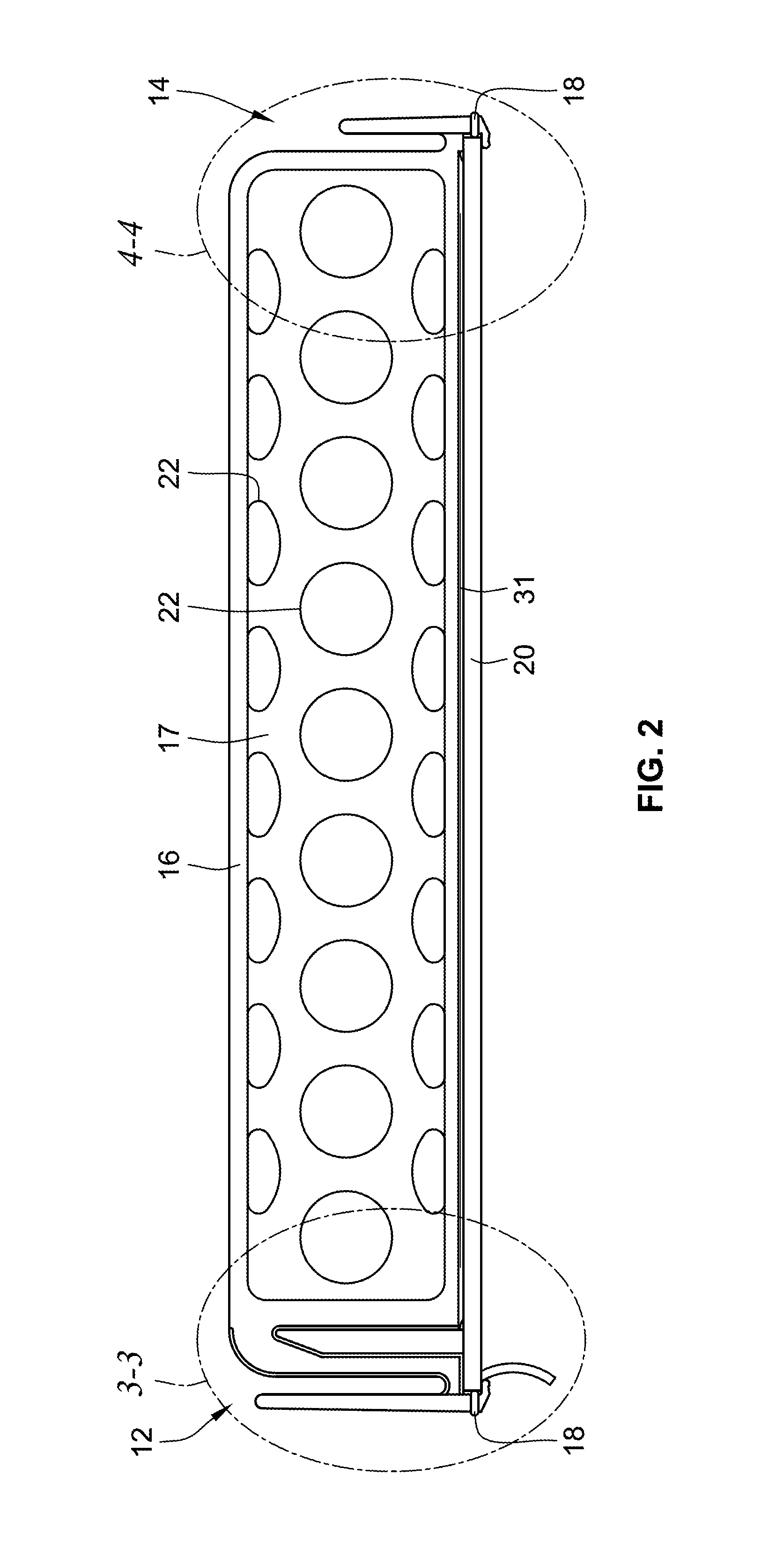
Motorized window treatment
ActiveUS20120261078A1Cheap replacementLong lastingEnergy efficient ICTLight dependant control systemsAutomatic controlRemote control
A motorized window treatment controls daylight entering a space through a window and includes a covering material, a drive shaft, lift cords received around the drive shaft and connected to the covering material, and a motor coupled to the drive shaft. It also includes a spring assist unit for the motor providing a torque that equals the torque provided by the weight on the lift cords at a position midway between fully-open and fully-closed positions, minimizing motor usage and conserving battery life. A photosensor for measuring the daylight outside the window and temperature sensors for measuring the temperatures inside and outside of the window may be provided. The position of the covering material is automatically controlled to save energy, or may also be controlled in response to an infrared or radio-frequency remote control.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
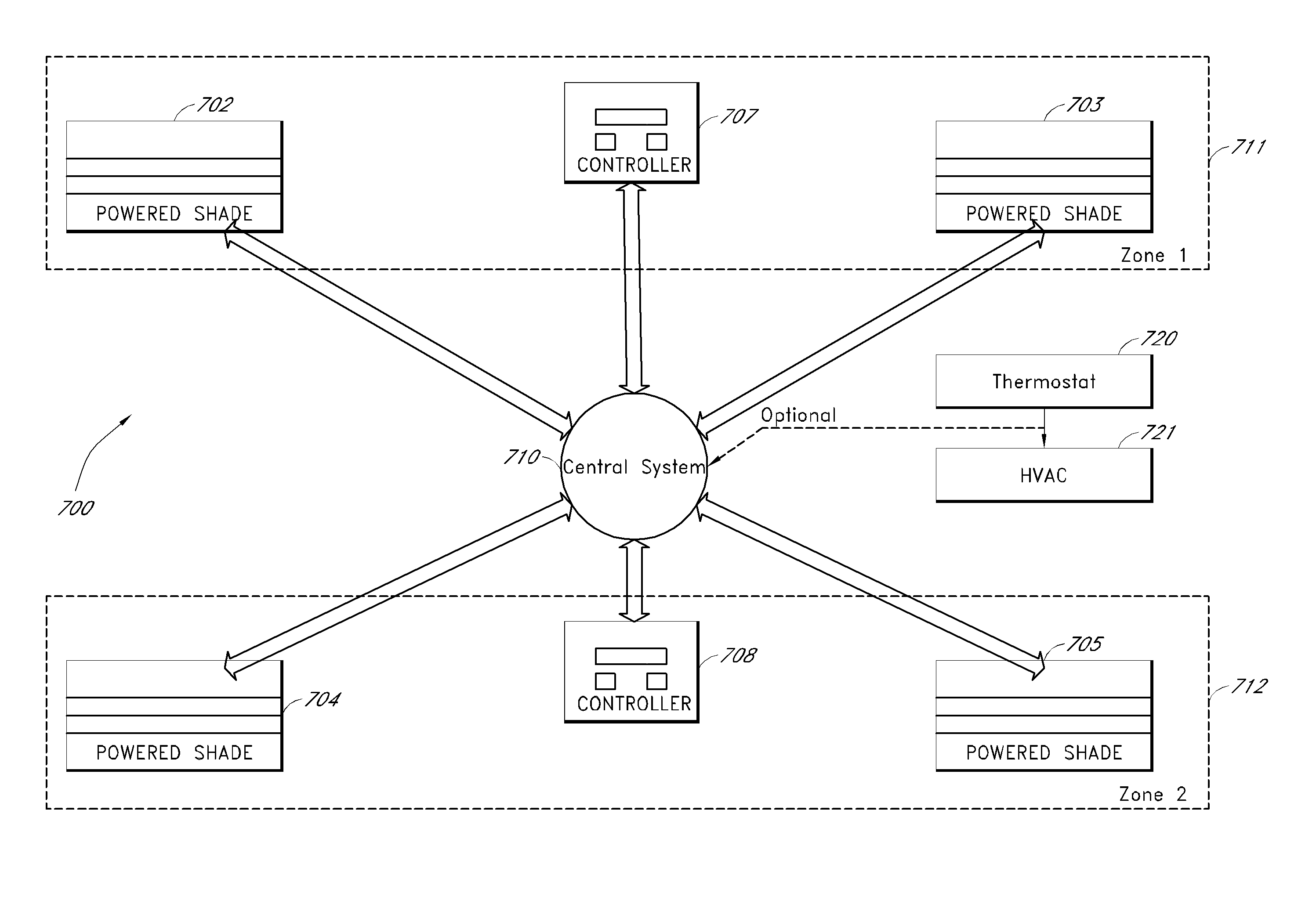
Motorized window shade system
InactiveUS7389806B2Raise and lower the window shadeReduce power consumptionScreensMechanical apparatusGroup controllerCommunications system
An electronically-controlled roll-up window shade that can easily be installed by a homeowner or general handyman is disclosed. The motorized shade includes an internal power source, a motor, and a communication system to allow for remote control of the motorized shade. One or more motorized shades can be controlled singly or as a group. In one embodiment, the motorized shades are used in connection with a zoned or non-zoned HVAC system to reduce energy usage. In one embodiment, the motorized shade is configured to have a size and form-factor that conforms to a standard manually-controlled motorized shade. In one embodiment, a group controller is configured to provide thermostat information to the motorized shade. In one embodiment, the group controller communicates with a central monitoring system that coordinates operation of one or more motorized shades. In one embodiment, the internal power source of the motorized shade is recharged by a solar cell.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Adjustable tilt mount
Owner:LEGRAND AV INC
Automated shade control method and system
ActiveUS20060207730A1Reduce brightnessKeep brightnessScreensLight dependant control systemsRadiometerSolar angle
This invention generally relates to automated shade systems that employ one or more algorithms to provide appropriate solar protection from direct solar penetration; reduce solar heat gain; reduce radiant surface temperatures; control penetration of the solar ray, optimize the interior natural daylighting of a structure and optimize the efficiency of interior lighting systems. The invention additionally comprises a motorized window covering, radiometers, and a central control system that uses algorithms to optimize the interior lighting of a structure. These algorithms include information such as: geodesic coordinates of a building; solar position; solar angle solar radiation; solar penetration angles; solar intensity; the measured brightness and veiling glare across a surface; time, solar altitude, solar azimuth, detected sky conditions, ASHRAE sky models, sunrise and sunset times, surface orientations of windows, incidence angles of the sun striking windows, window covering positions, minimum BTU load and solar heat gain.
Owner:MECHOSHADE SYST LLC
Inventory system with mobile drive unit and inventory holder
ActiveUS7402018B2Disadvantages and reduced eliminatedInventory reduced eliminatedCurtain suspension devicesVehicle with removable loadingMechanical engineeringInventory system
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Microblinds and a method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS7684105B2Improve comfortLow costCurtain suspension devicesLight protection screensEngineeringElectric field
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Multi-positionable notebook computer case
ActiveUS7281698B2Easy to adaptEasy to viewDigital data processing detailsCurtain suspension devicesPersonal computerHuman–computer interaction
Owner:CASE LOGIC
Adjustable mounting assembly for standing seam panels
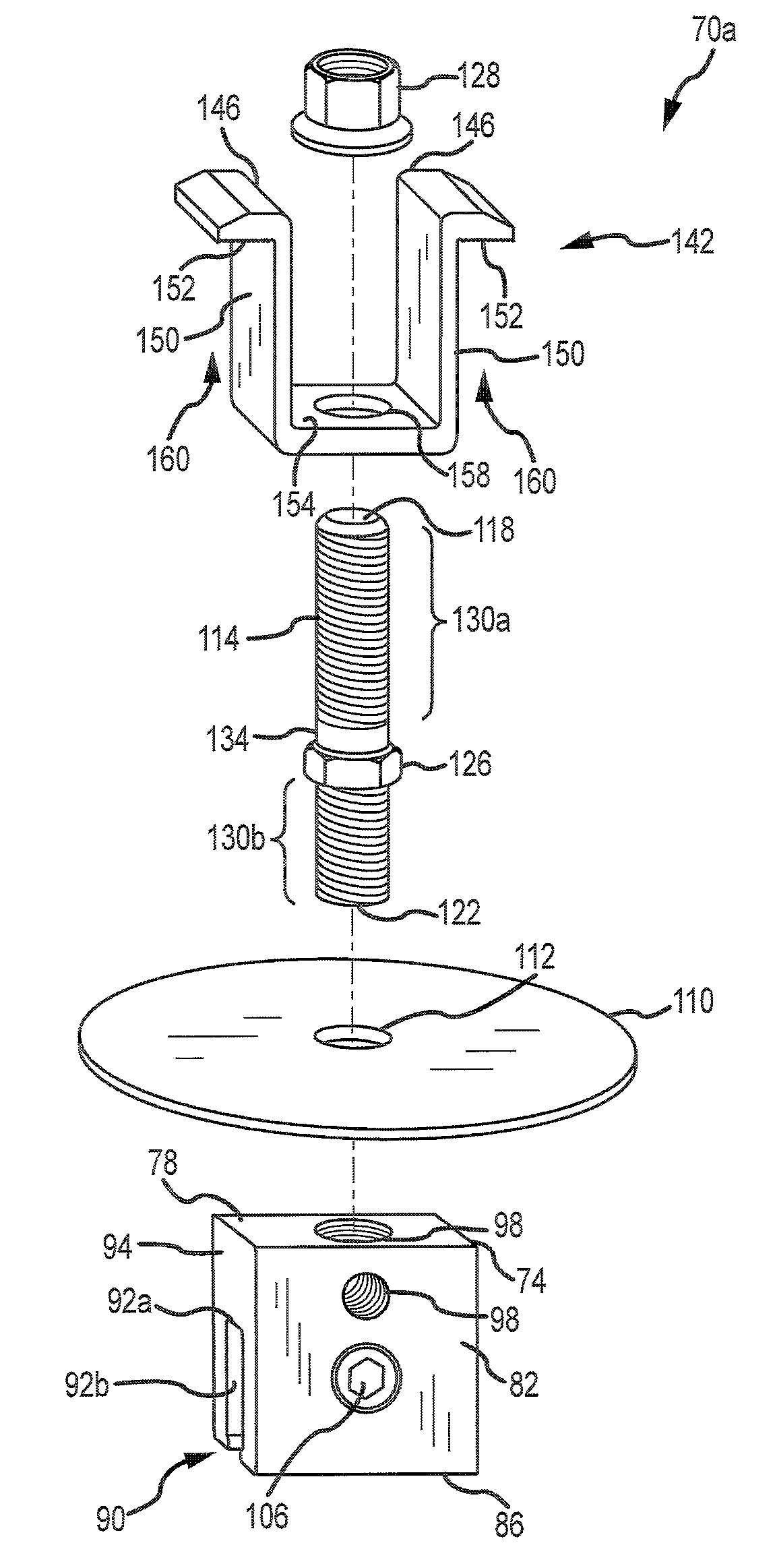
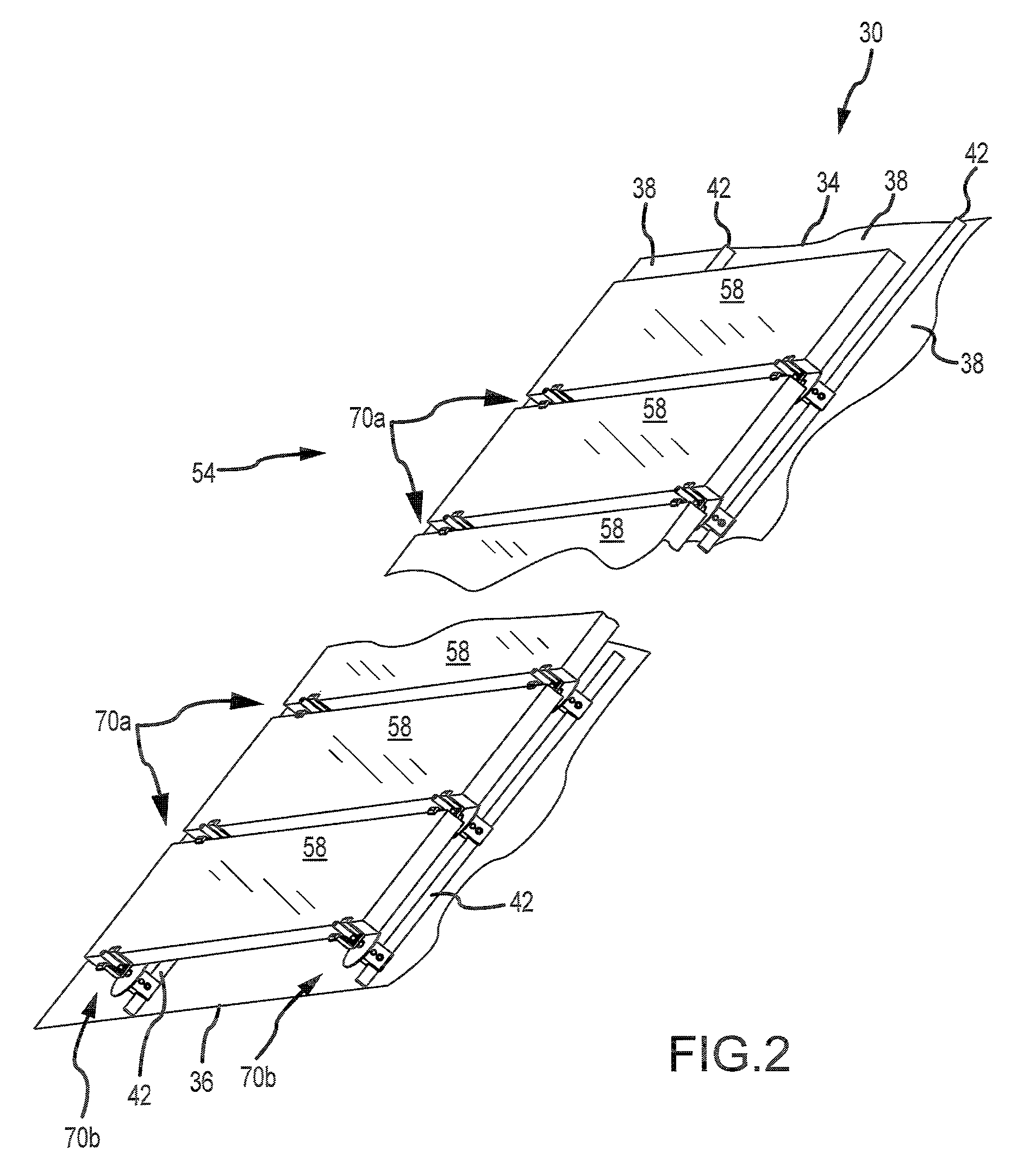
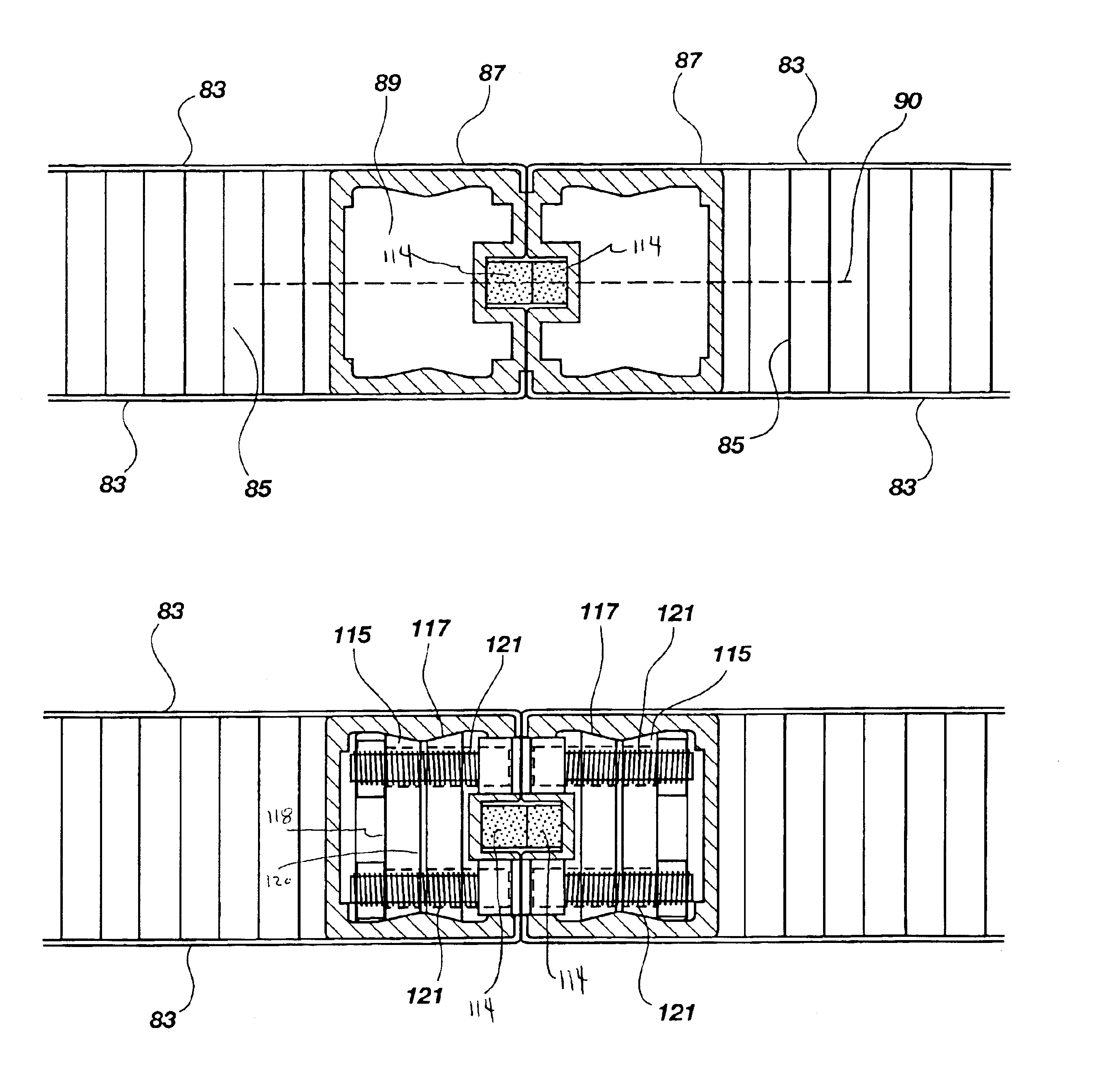
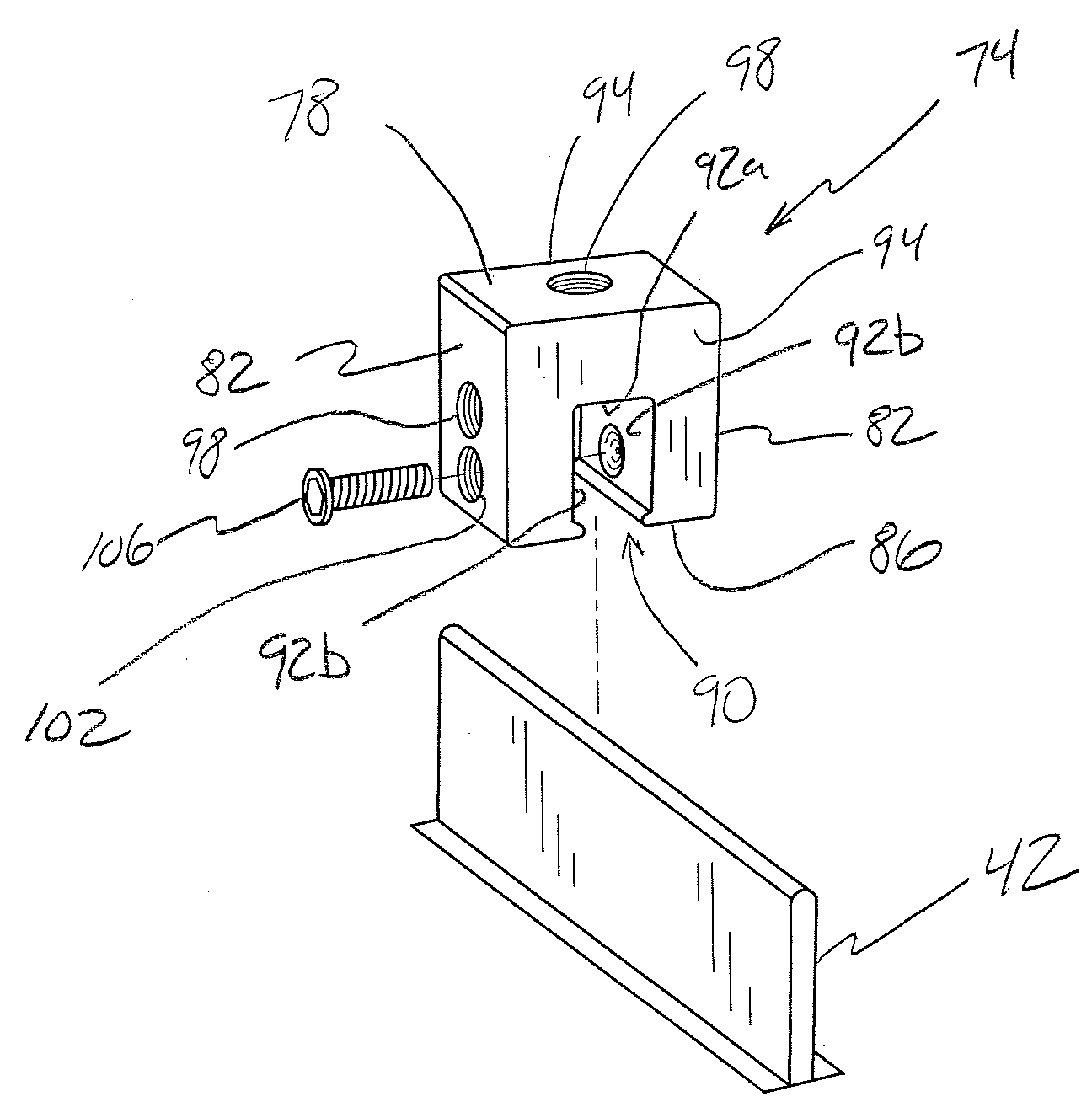
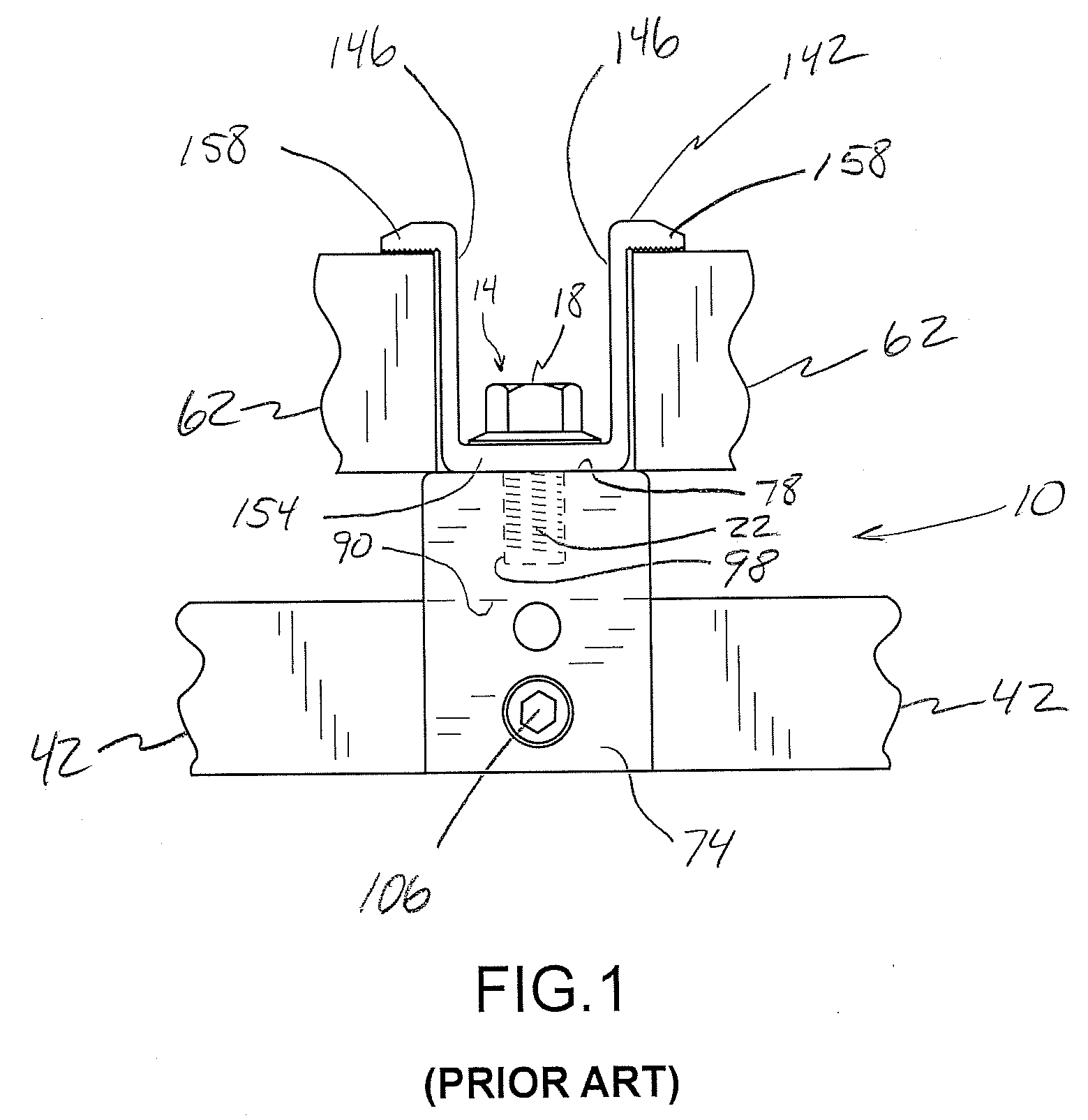
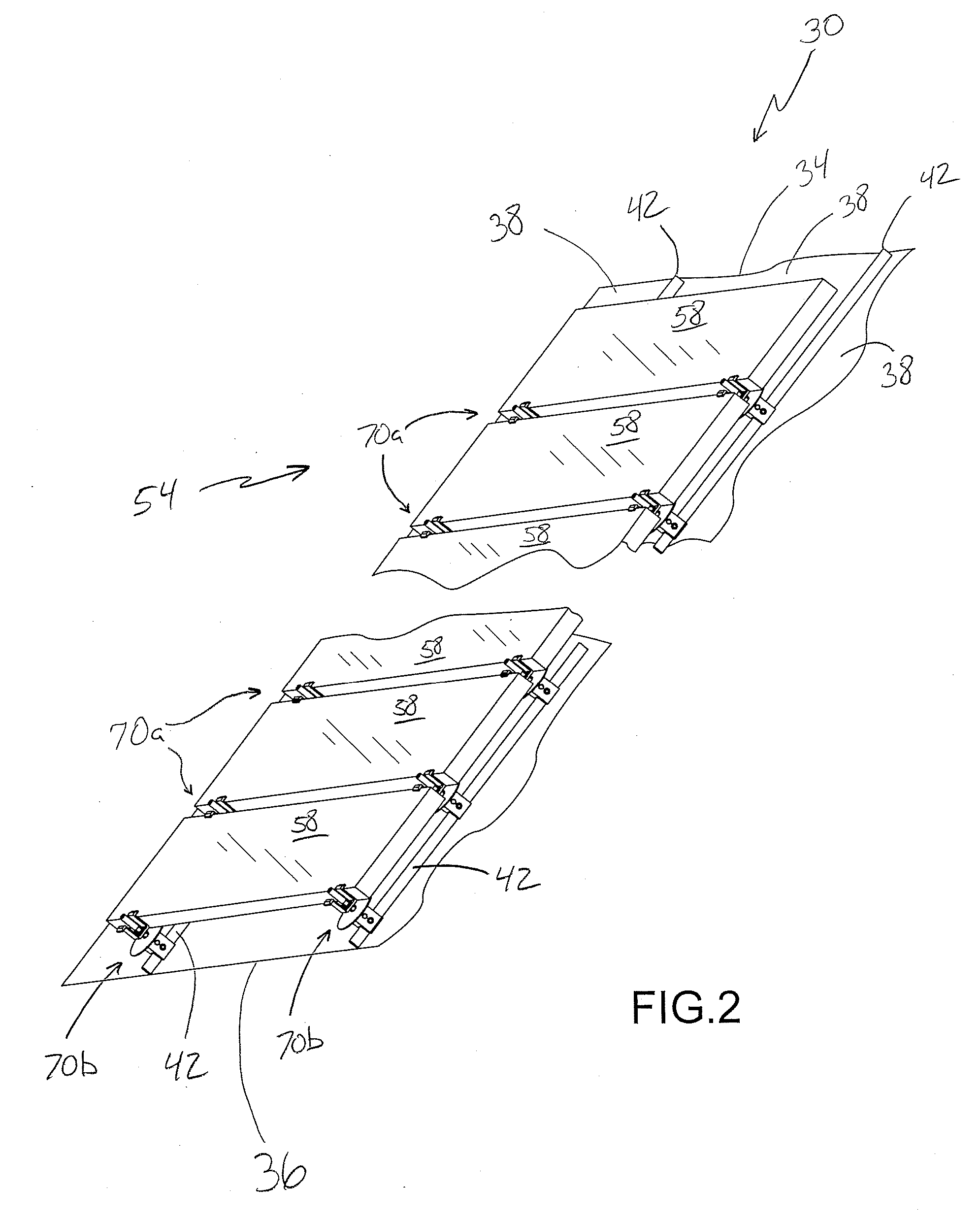
An adjustable mounting assembly (70a / 70b) for installing solar cell modules (58) on a building surface (34) is disclosed. The mounting assembly (70a / 70b) includes a mounting device (74), a stud (114) that may be threaded to the mounting device (74), a clamping member (142) that may be positioned on the stud (114), and a nut (128) that may be threaded onto the stud (114) to secure the clamping member (142) to the mounting device (74). A nut (126) is fixed to the stud (114) at an intermediate location along its length. This fixed nut (126) may be used to tighten the stud (114) to a mounting device (74), and furthermore may be positioned such that the stud (114) does not extend into a slot (90) of the mounting device (74).
Owner:RMH TECH LLC
Motorized window shade system
InactiveUS20060185799A1Raise and lower the window shadeReduce power consumptionScreensMechanical apparatusGroup controllerCommunications system
An electronically-controlled roll-up window shade that can easily be installed by a homeowner or general handyman is disclosed. The motorized shade includes an internal power source, a motor, and a communication system to allow for remote control of the motorized shade. One or more motorized shades can be controlled singly or as a group. In one embodiment, the motorized shades are used in connection with a zoned or non-zoned HVAC system to reduce energy usage. In one embodiment, the motorized shade is configured to have a size and form-factor that conforms to a standard manually-controlled motorized shade. In one embodiment, a group controller is configured to provide thermostat information to the motorized shade. In one embodiment, the group controller communicates with a central monitoring system that coordinates operation of one or more motorized shades. In one embodiment, the internal power source of the motorized shade is recharged by a solar cell.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Mounting bracket
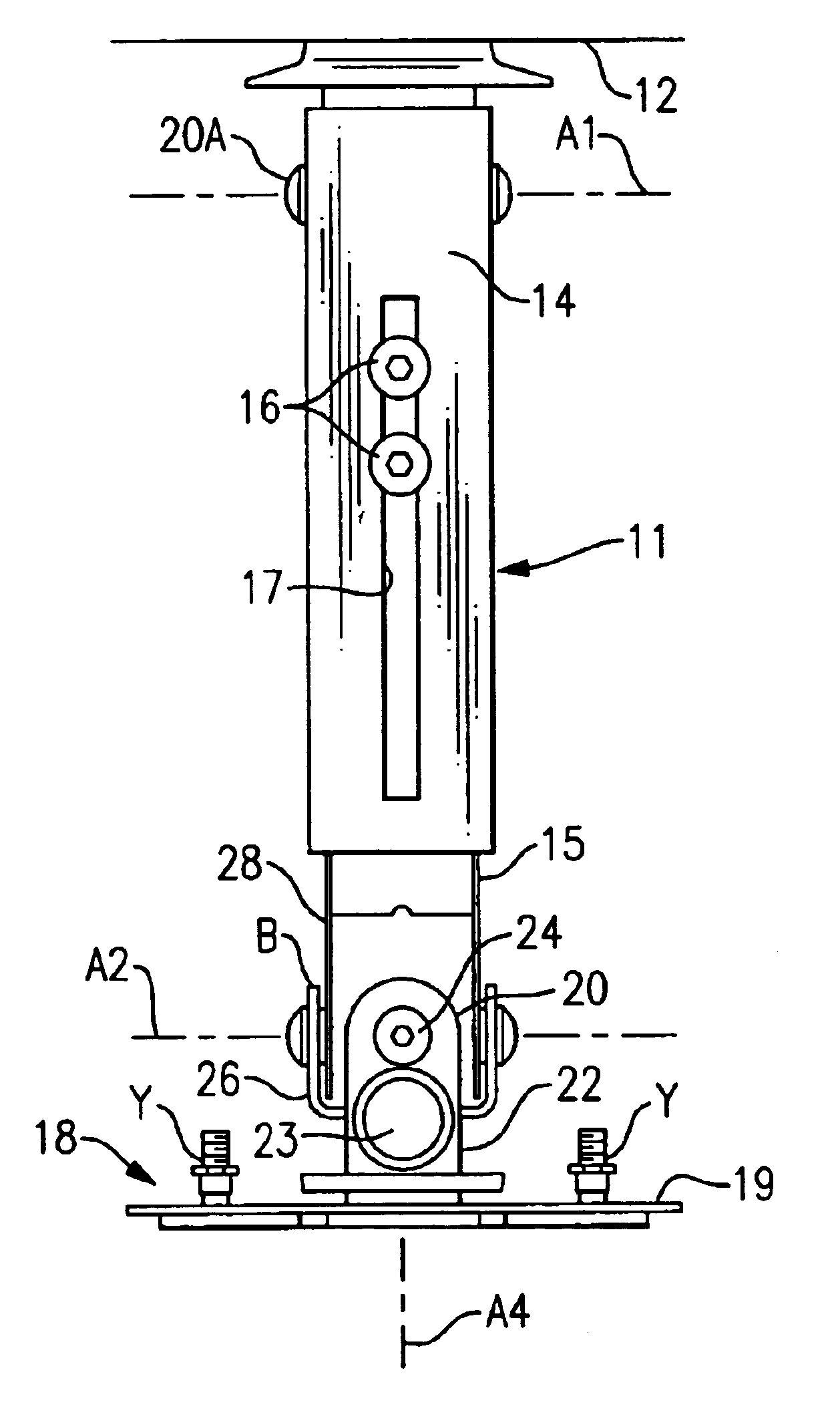
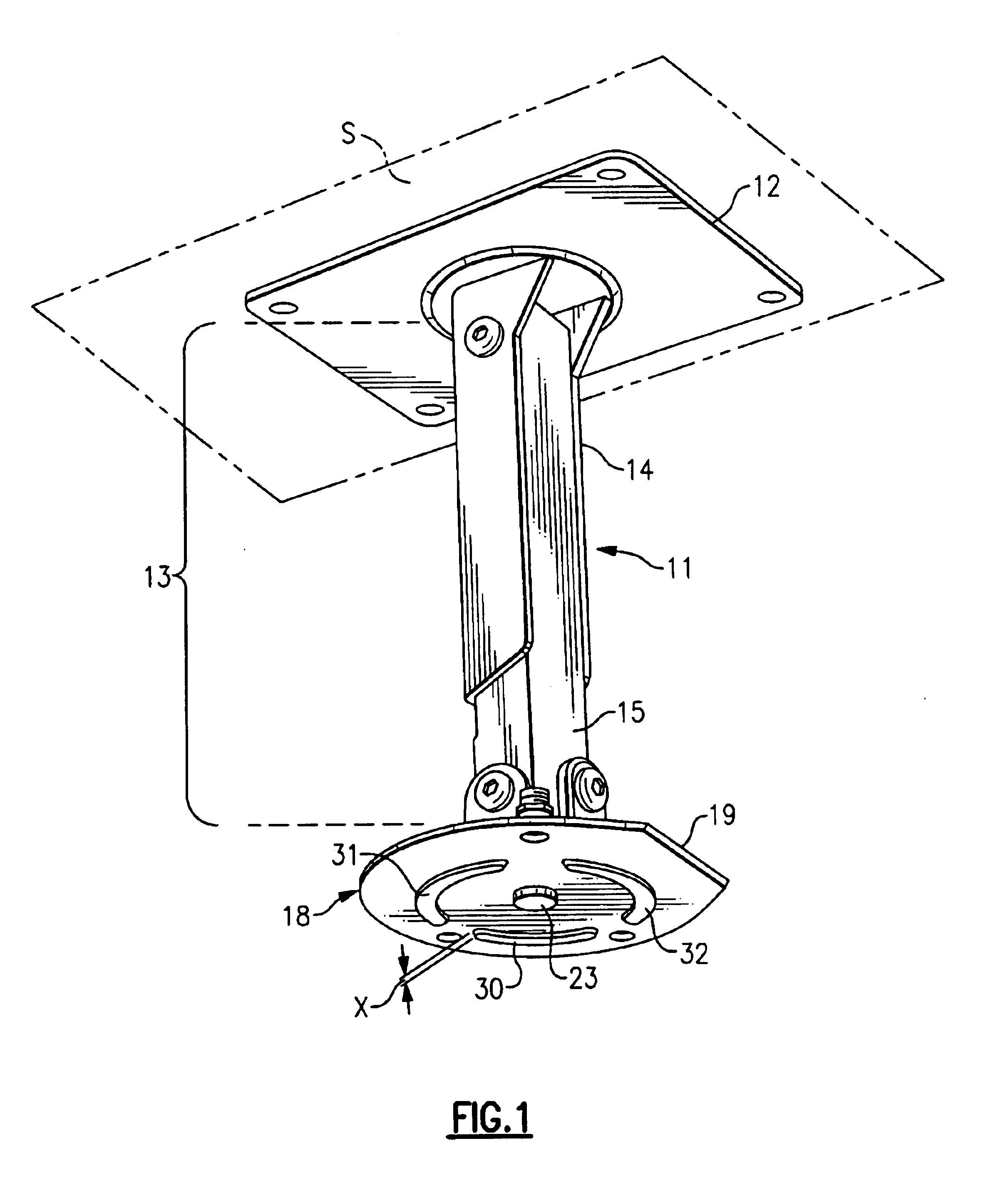
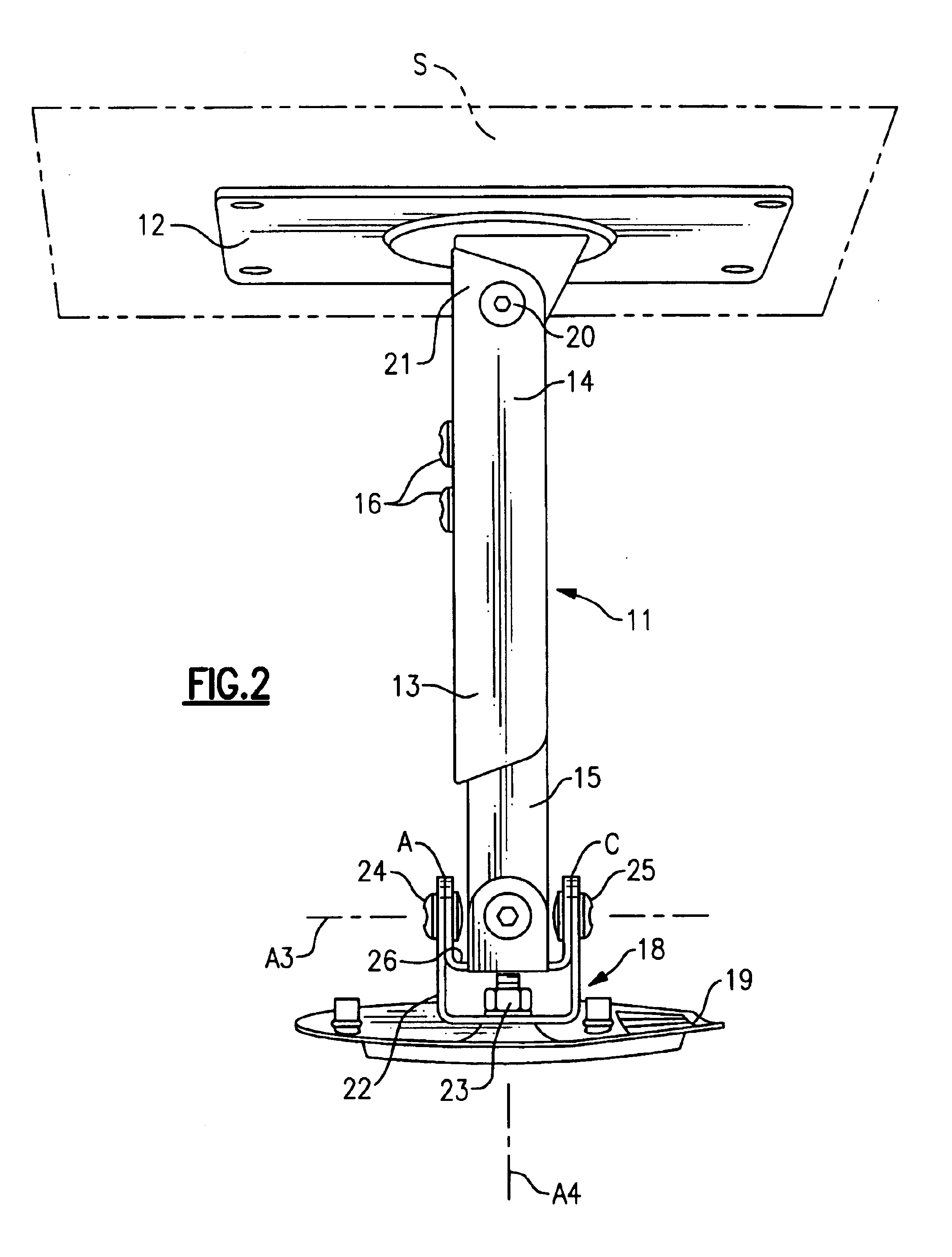
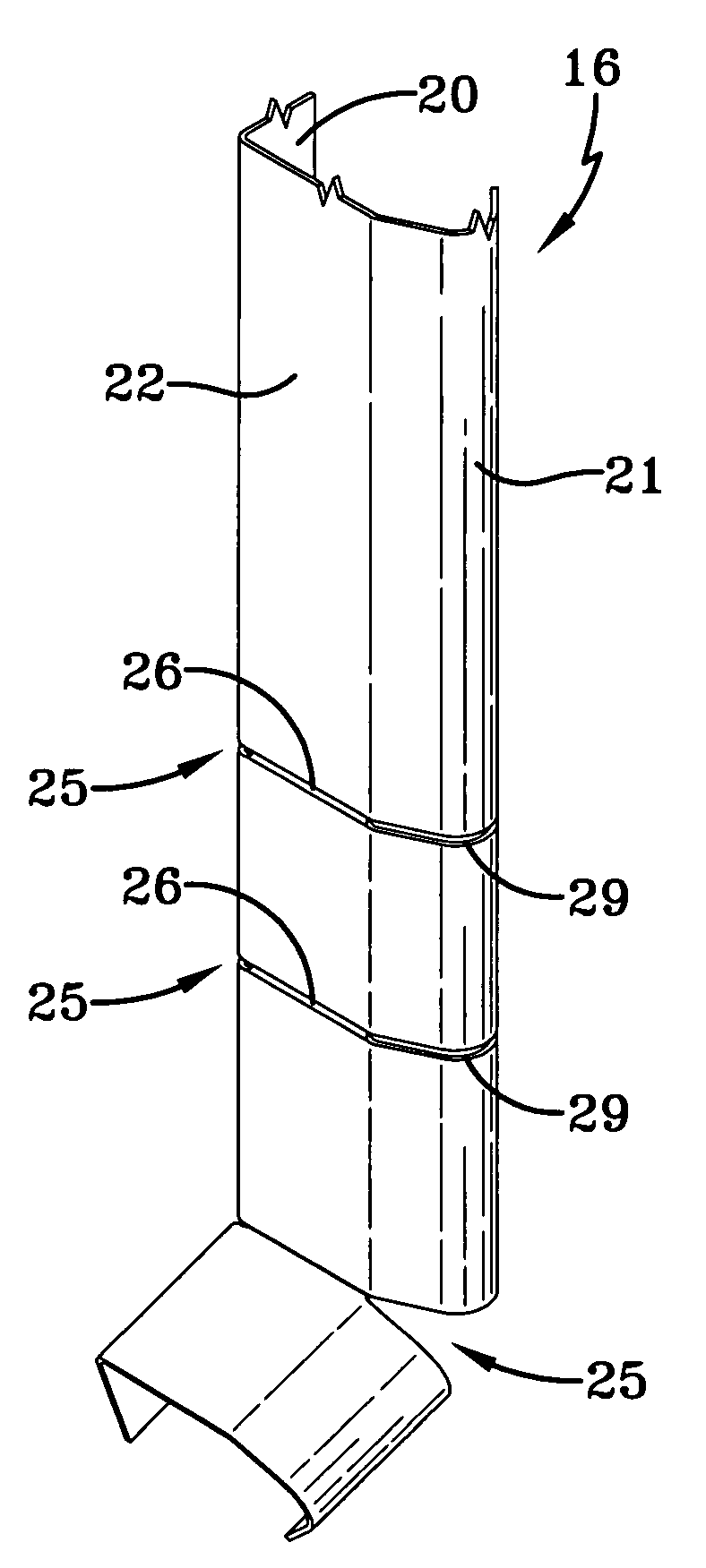
A mounting unit (11) for a attaching a working unit such as a video projector to a mounting surface which can be horizontal or vertical or at some angle intermediate the horizontal and the vertical comprising: an anchorage (12) whereby the unit can be attached to the mounting surface; a beam (13); a carrier (18) comprising in combination a holding plate (19) and a mounting plate; the carrier being adapted to provide for the attachment of a working unit to the mounting plate; a first pivot (20a) whereby a first end of the beam is pivotably attached to the anchorage to enable the beam to pivot about a first axis (a1); a second pivot whereby the other end of the beam to the first end is pivotably attached to the holding plate to enable the holding plate to pivot about a second axis (a2) parallel to the first axis; a third pivot (24) whereby the holding plate can pivot about a third axis perpendicular to the second axis; a fourth pivot (23) whereby the holding plate can pivot about a fourth axis (a4) perpendicular to the second and third axes; the carrier including mechanism whereby the mounting plate can be rotated about an fifth axis parallel to the holding plate.
Owner:LIGERTWOOD PETER
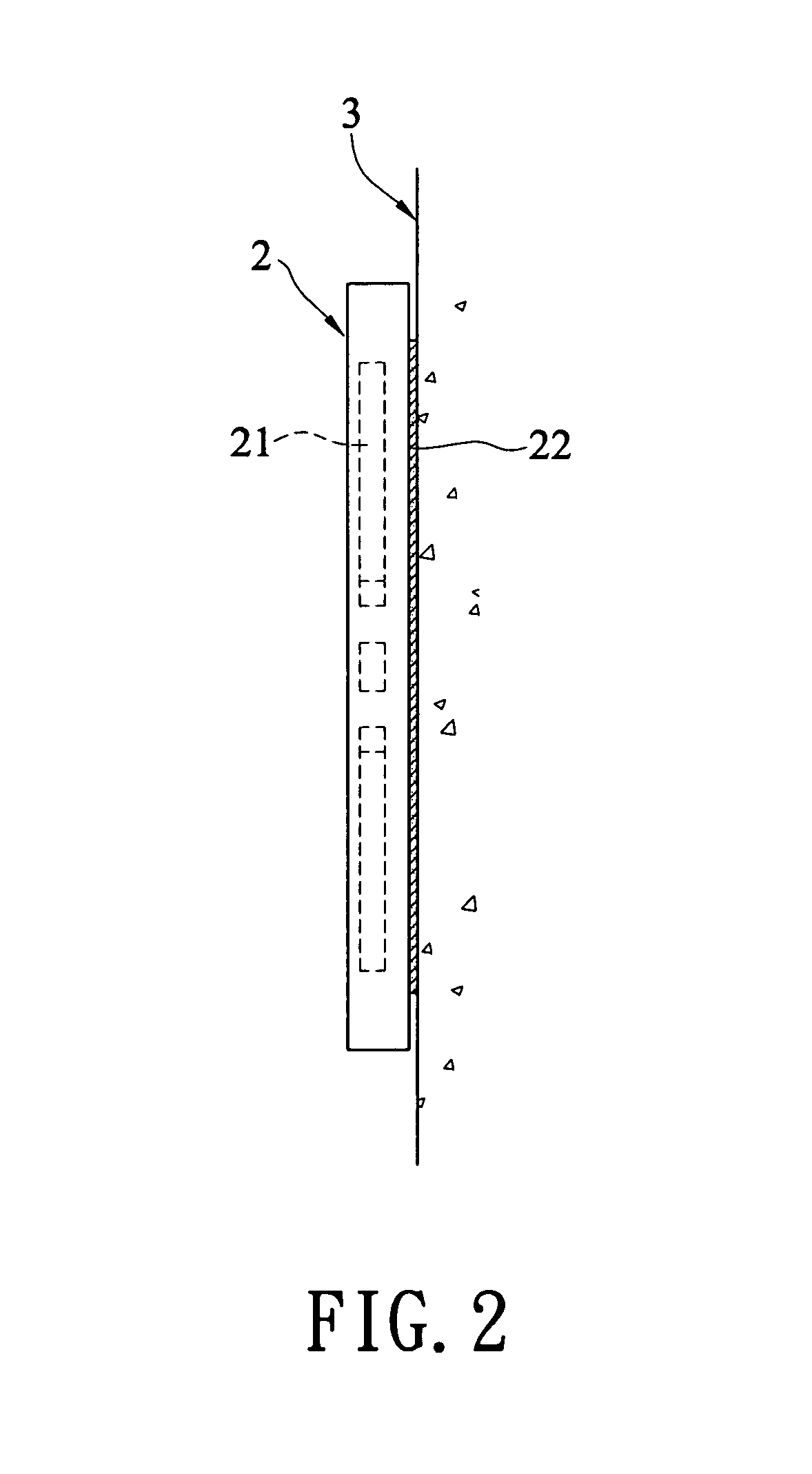
Breakaway track system for an overhead door
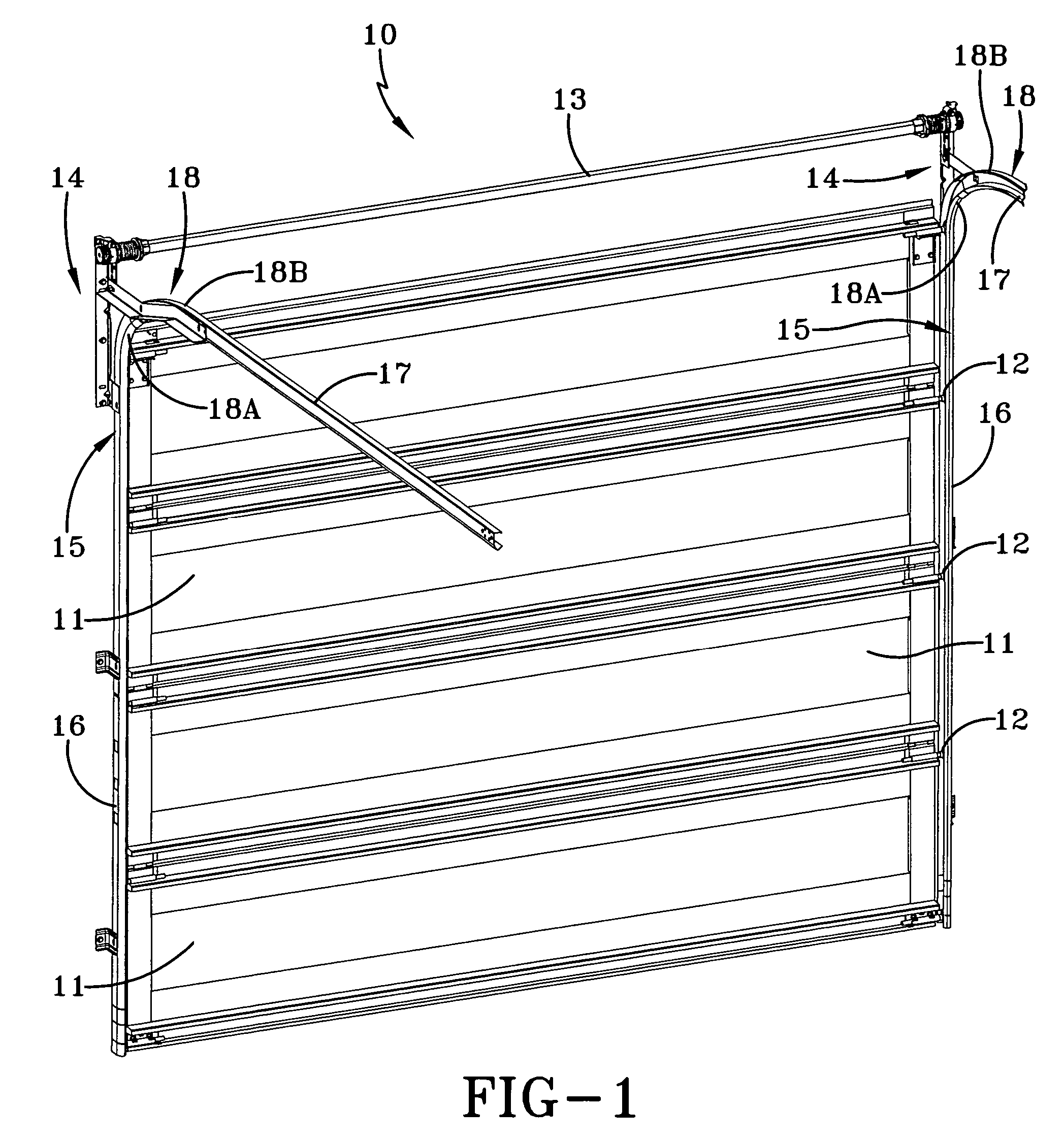
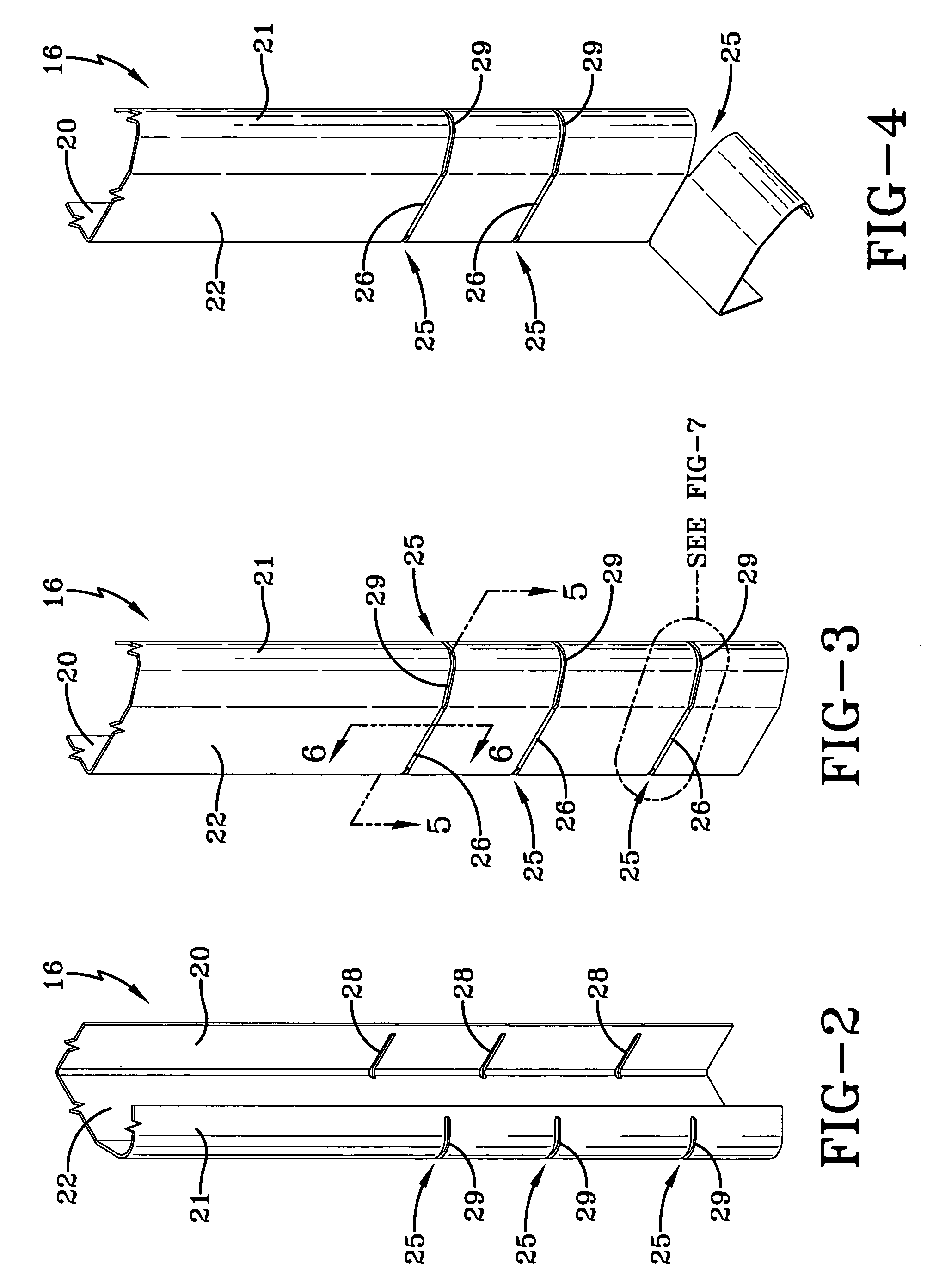
ActiveUS7219392B2Reduce necessityMinimize timeCurtain suspension devicesDoor arrangementMechanical engineeringEngineering
An overhead garage door (10) includes a plurality of panels (11) each carrying rollers (12) which ride in a track assembly (15). The track assembly (15) includes a generally vertically positionable component (16), a generally horizontally positionable component (17), and an arcuate transitional component (18) positioned between the vertical component (16) and the horizontal component (17). The vertical component (16) is generally U-shaped in end profile having a base portion (22) with branches (20, 21) extending from the edges thereof. The vertical component (16) is provided with a plurality of spaced separating systems (25), each of which includes a web (26) extending across the base portion (22) and the slots (28, 29) in the branches (20, 21). A selected portion of the length of the vertical component (16) may be removed by inserting a tool in the slots (28, 29) of one of the separating systems (25) and twisting it to break the webs (30, 31) adjacent to the slots (28, 29). Then by bending that portion on the web (26), it will breakaway to provide a vertical component (16) of the desired length.
Owner:OVERHEAD DOOR
Remotely attachable and separable coupling
InactiveUS7287738B2Easy to disengageSecure supportSubstation/switching arrangement detailsPicture framesSmoke detectorsCoupling
An article for mounting from or against the ceiling is removably coupled to a base fixedly secured to the ceiling, by a person standing on the floor, supporting the article on an elongated rod, and thrusting the article against the base to couple the article and the secured base. The article is removed by inserting the rod into the article, exerting a force on the rod to uncouple the article from the base, and supporting the article on the rod as the article is lowered. The article is thus positioned on or hung from the ceiling, without being manually contacted by the person. The article may be used to mount other devices, such as a sign, smoke detector, etc. or may include such device as a part of the mount.
Owner:ACCESSMOUNT LLC
Inventory system with mobile drive unit and inventory holder
ActiveUS20060210382A1Disadvantages and reduced eliminatedInventory reduced eliminatedCurtain suspension devicesVehicle with removable loadingMechanical engineeringInventory system
A system for transporting inventory includes an inventory holder and a mobile drive unit. The inventory holder includes a frame capable of storing inventory items and a docking plate capable of receiving a docking head from underneath. The mobile drive unit, includes a docking head capable of coupling to the docking plate and a drive module capable of propelling the mobile drive unit. The mobile drive unit is further capable to move the inventory holder when the docking head is coupled to the inventory holder.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
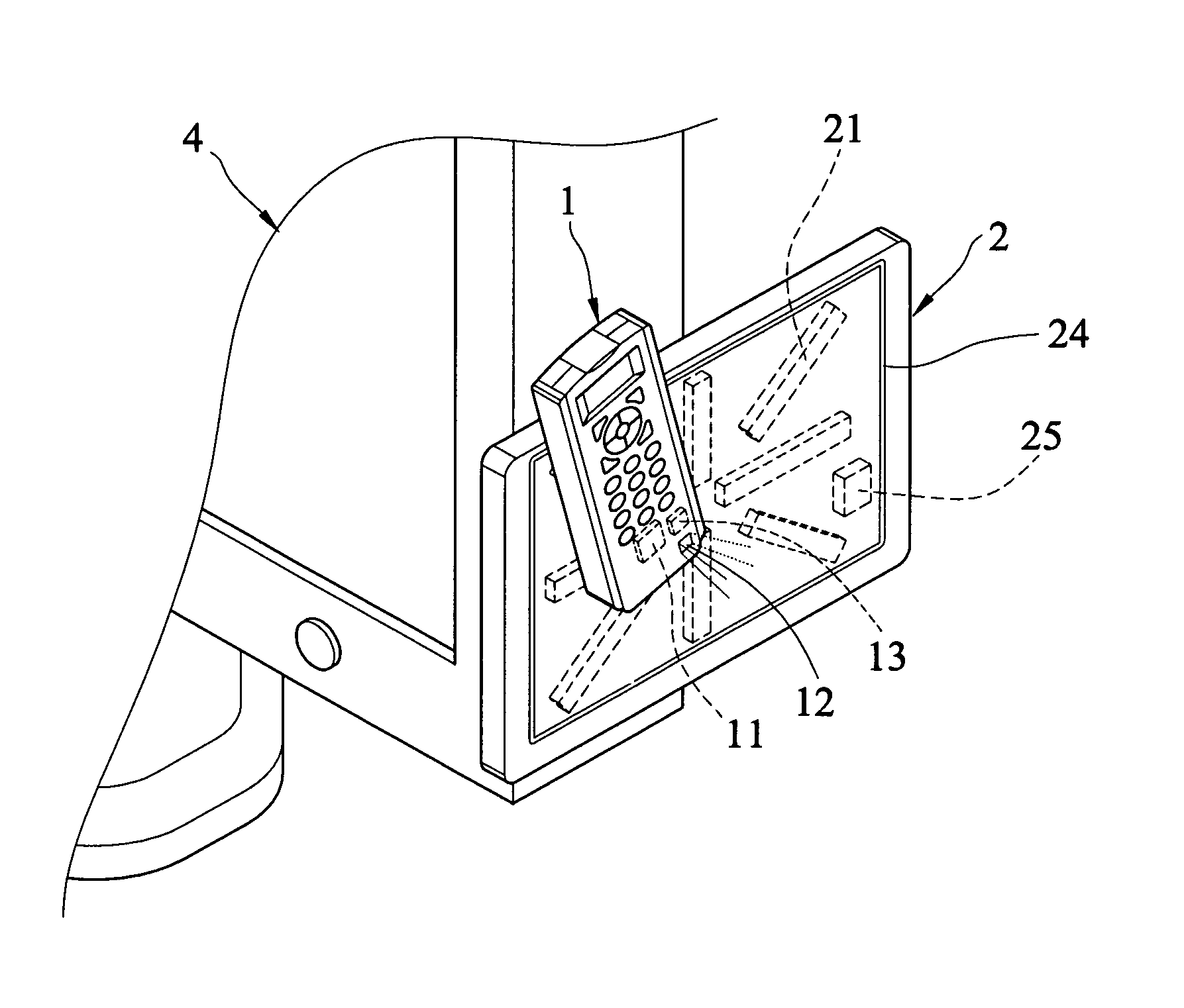
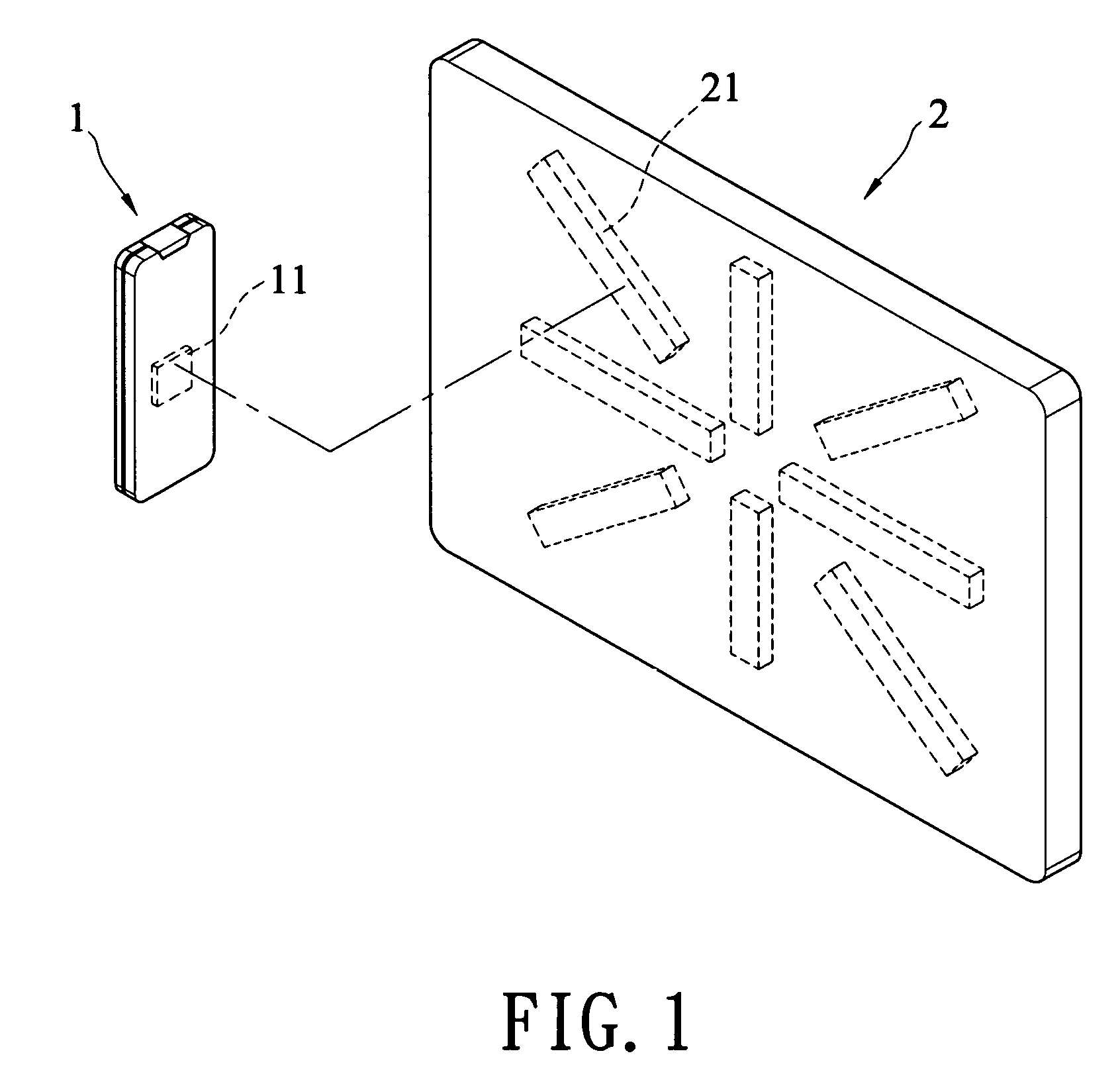
Portable electronic device and magnetic fixation board therefor
InactiveUS8016255B2Convenient ArrangementEasy to usePicture framesCurtain suspension devicesElectric equipmentElectron
Owner:LIN PI FEN
Wall panel assembly and method of assembly
A wall assembly includes at least two panel elements which are configured for contiguous placement adjacent to one another. Each of the panel elements defines a hollow internal passageway. The panels are configured to permit a contiguous placement whereby the respective passageways of the panels are brought into registration with one another. A connection element is positioned within one of the passageways. The connection element is accessible through a slot defined within the sidewall of the panel wherein the connection element resides. The connection element is slidable whereby it may be displaced partially into the second panel element. The connection element is thereafter actuatable whereby its lateral dimension is decreased to form a pressure fit union with the interior sidewalls of the two passageways. In its spatially decreased configuration, the connection element provides a means of interconnecting the two panel elements together.
Owner:AIRTEX MFG LLLP
Light control panel
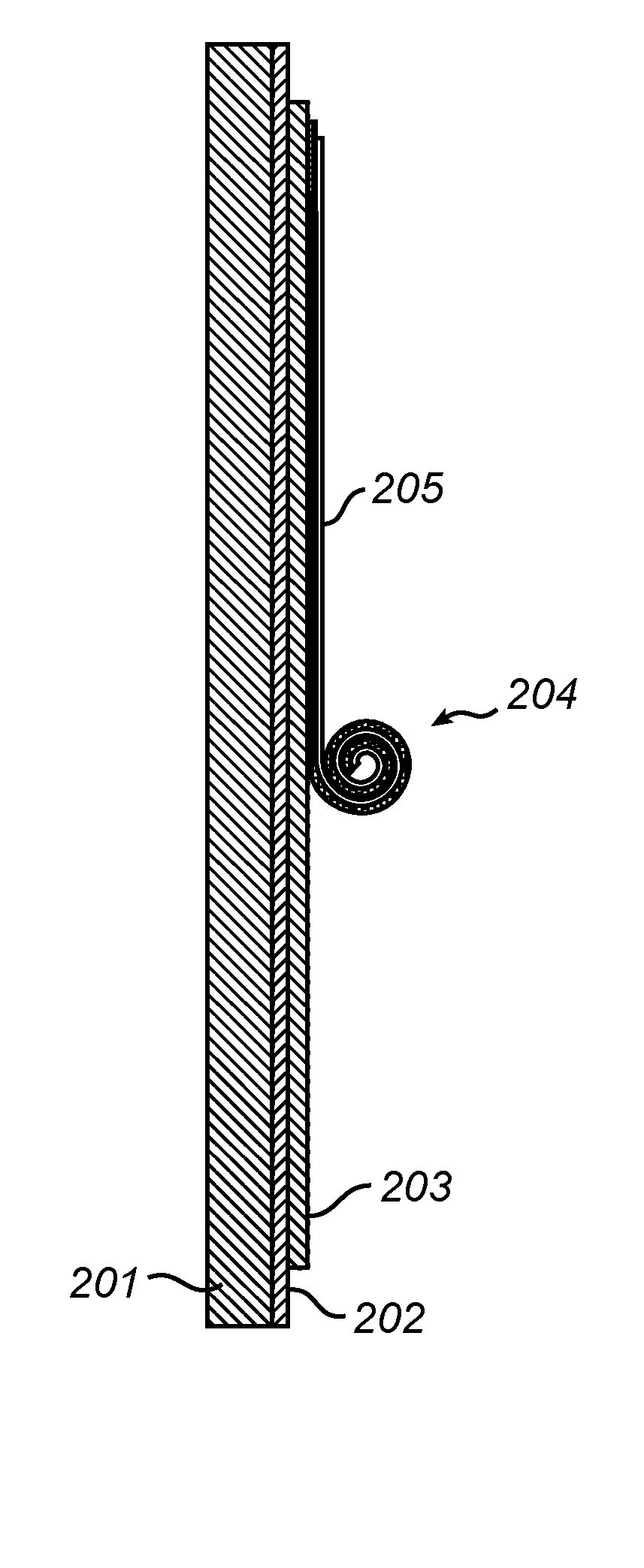
Alight control panel is provided, comprising: a transmissive substrate; a transmissive electrically conductive layer arranged on a surface of said substrate; a transmissive dielectric layer arranged on said electrically conductive layer; a flexible roll-up blind attached to said dielectric layer, said flexible roll-up blind layer comprising a flexible electrically conductive layer and a flexible optically functional layer, said flexible layer having naturally a rolled configuration and being capable of unrolling in response to electrostatic force; and an optoelectronic device. The panel may be useful in various energy saving applications including smart windows for buildings or vehicles, e.g. providing an energy efficient light source or utilizing solar radiation for energy conversion.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Adjustable mounting assembly for standing seam panels
ActiveUS20080302928A1Not to damagePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energySolar cellMechanical engineering
An adjustable mounting assembly (70a / 70b) for installing solar cell modules (58) on a building surface (34) is disclosed. The mounting assembly (70a / 70b) includes a mounting device (74), a stud (114) that may be threaded to the mounting device (74), a clamping member (142) that may be positioned on the stud (114), and a nut (128) that may be threaded onto the stud (114) to secure the clamping member (142) to the mounting device (74). A nut (126) is fixed to the stud (114) at an intermediate location along its length. This fixed nut (126) may be used to tighten the stud (114) to a mounting device (74), and furthermore may be positioned such that the stud (114) does not extend into a slot (90) of the mounting device (74).
Owner:RMH TECH LLC
Portable electronic device and magnetic fixation board therefor
InactiveUS20100102182A1Convenient ArrangementEasy to usePicture framesCurtain suspension devicesEngineeringElectric equipment
Owner:LIN PI FEN
Motorized window shade system and mount
InactiveUS20090308543A1Reduce gap sizeRaise and lower the window shadeScreensCurtain suspension devicesGroup controllerCommunications system
An electronically-controlled roll-up window shade that can easily be installed by a homeowner or general handyman is disclosed. The motorized shade includes an internal power source, a motor, and a communication system to allow for remote control of the motorized shade. One or more motorized shades can be controlled singly or as a group. In one embodiment, the motorized shades are used in connection with a zoned or non-zoned HVAC system to reduce energy usage. In one embodiment, the motorized shade is configured to have a size and form-factor that conforms to a standard manually-controlled motorized shade. In one embodiment, a group controller is configured to provide thermostat information to the motorized shade. In one embodiment, the group controller communicates with a central monitoring system that coordinates operation of one or more motorized shades. In one embodiment, the internal power source of the motorized shade is recharged by a solar cell.
Owner:KATES LAWRENCE
Adjustable mounting bracket for flat panel display
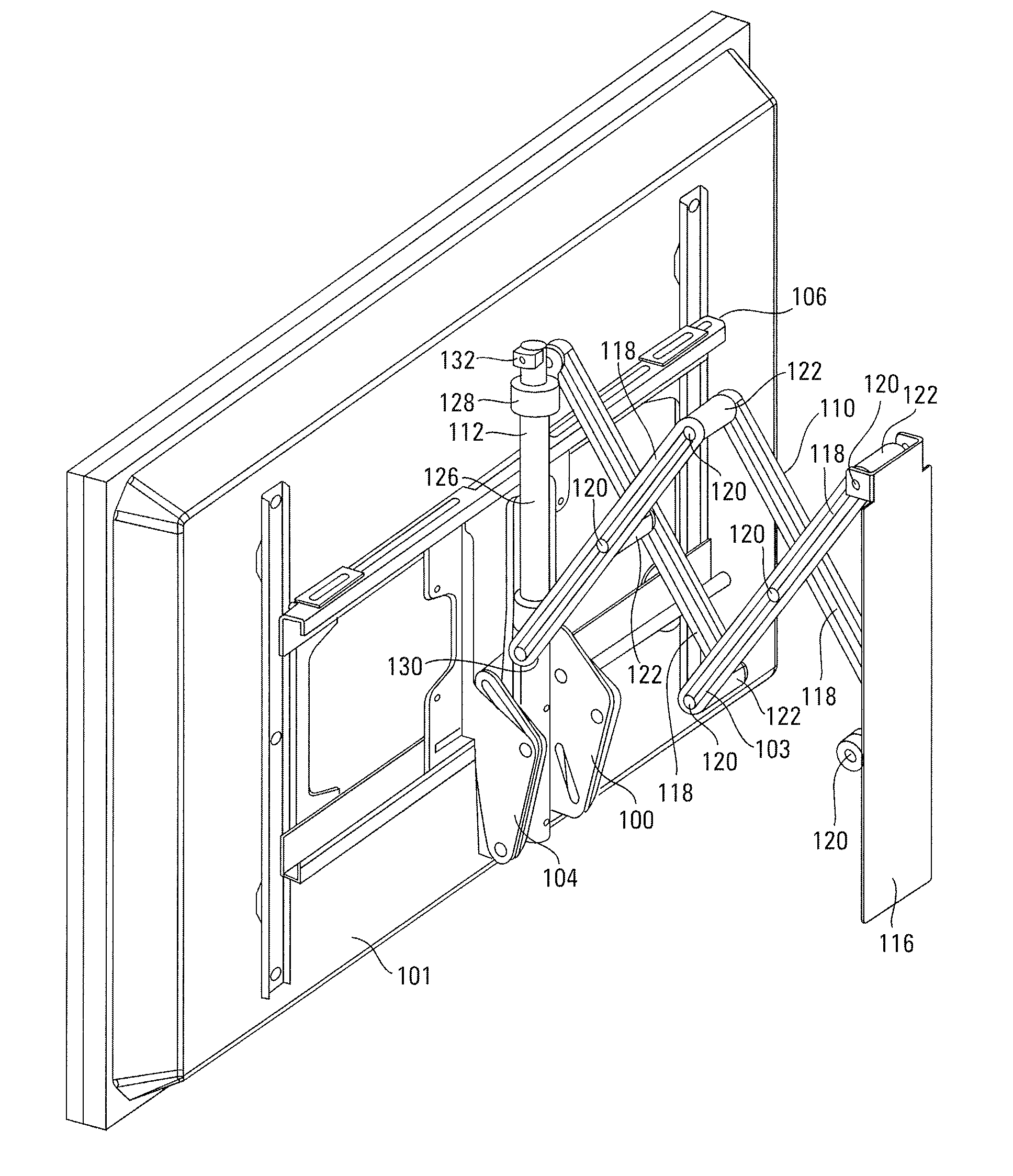
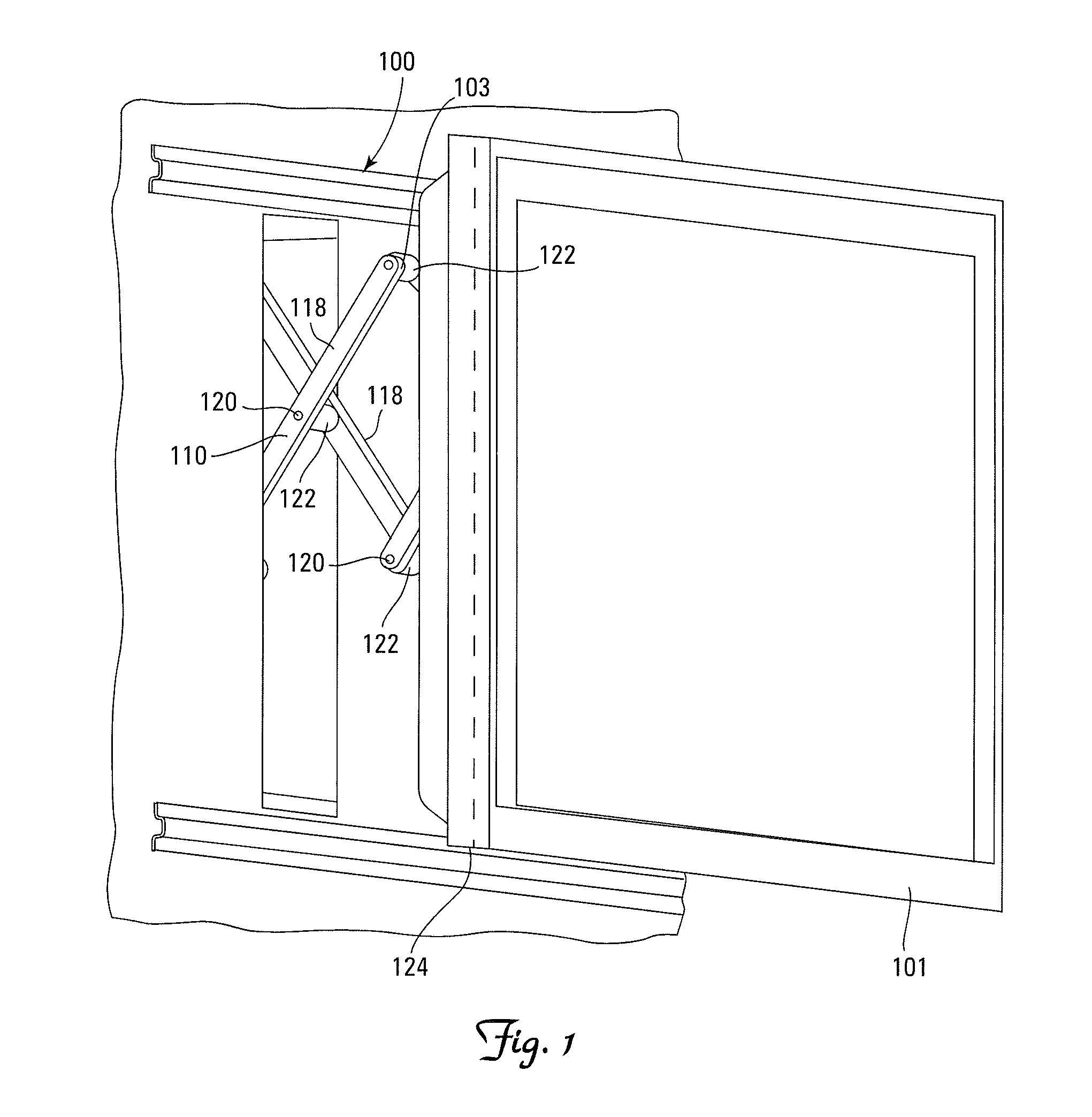
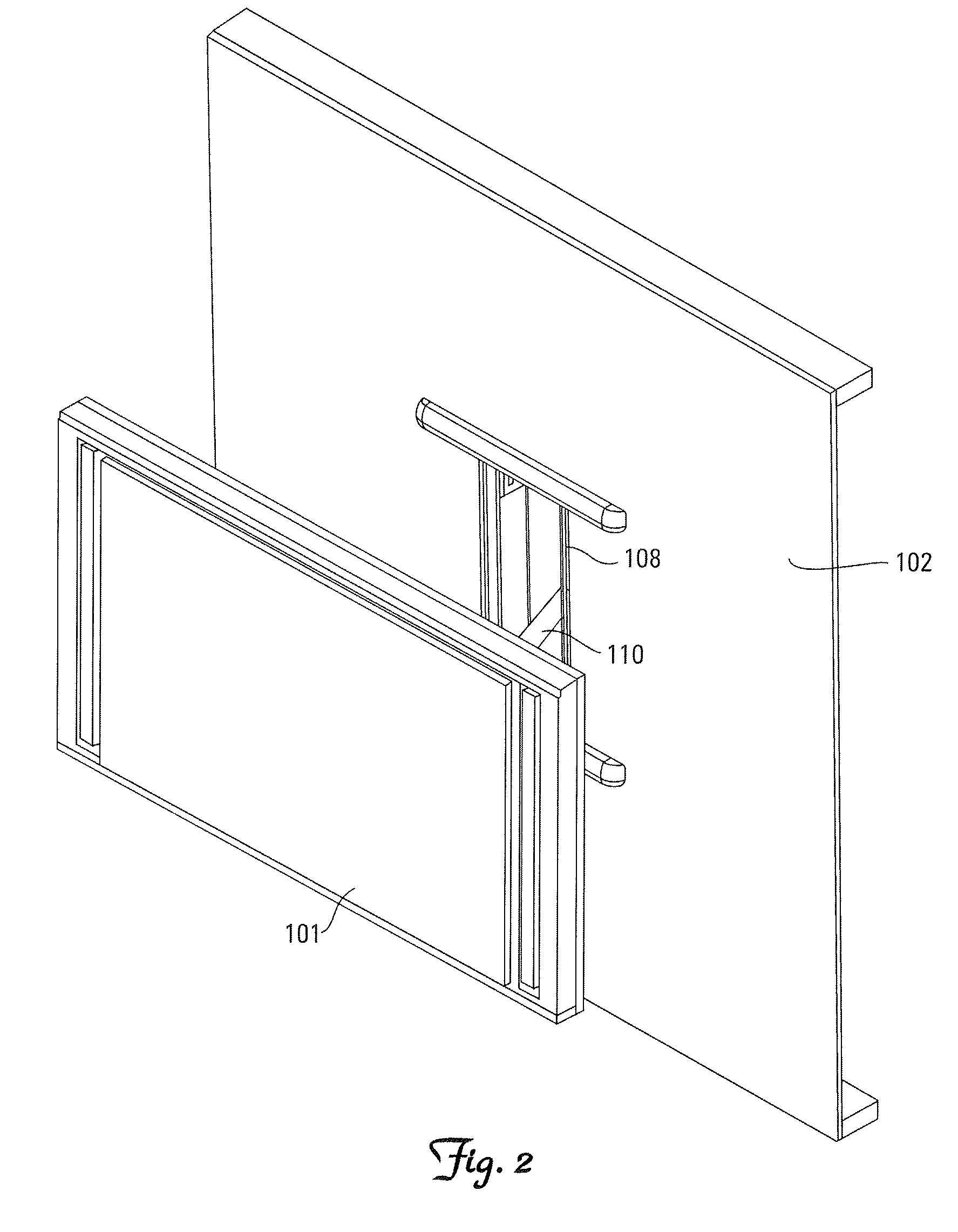
ActiveUS7316379B1Flexible couplingPrevent disengagementPicture framesCurtain suspension devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
A mounting bracket apparatus for adjustably supporting a flat panel display from a wall. The mounting bracket includes a wall bracket, a display bracket and two traversing mounts. The traversing mounts are supportively disposed between the wall bracket and the display bracket, and driven along a pair of substantially parallel linear axes by a pair of actuators enabling vertical adjustment of the display bracket. The traversing mounts are flexibly coupled between the wall bracket and the display bracket, thereby enabling misalignment of the positions to adjust the skew of the display bracket relative to the wall bracket.
Owner:LEGRAND AV INC
Manual roller shade having clutch mechanism, chain guide and universal mounting
A manual roller shade includes a clutch mechanism having a gear train transferring rotation of an input sprocket to rotation of an output member engaging a roller tube. The gear train includes a sun gear, planet gears supported by a carrier and engaging the sun gear, and a ring gear engaging the planet gears. According to one embodiment, the carrier does not rotate. The ratio between the diameters of the input sprocket and the roller tube is selected to offset mechanical advantage of the gear train to provide an effective gear train ratio of approximately 2:1. A drive chain guide system includes spaced guide wheels controlling where a drive chain is suspended from the manual shade. A roller shade mounting system includes a bracket receiving either an input assembly of the manual roller shade or a motor of a motorized roller shade to facilitate conversion.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Flexible display apparatus
InactiveUS20120204453A1Easily rolled and unrolledScreensShutters/ movable grillesEngineeringFlexible display
Provided is a flexible display apparatus that includes: a flexible display apparatus including: a flexible display panel; a housing including an opening through which the flexible display panel enters and exits the housing; a cylinder disposed within the housing to coil and uncoil the flexible display panel; and a stretcher that selectively extends from the opening to support the flexible display panel, such that the flexible display panel is substantially planar when the flexible display panel is extended outside of the housing.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
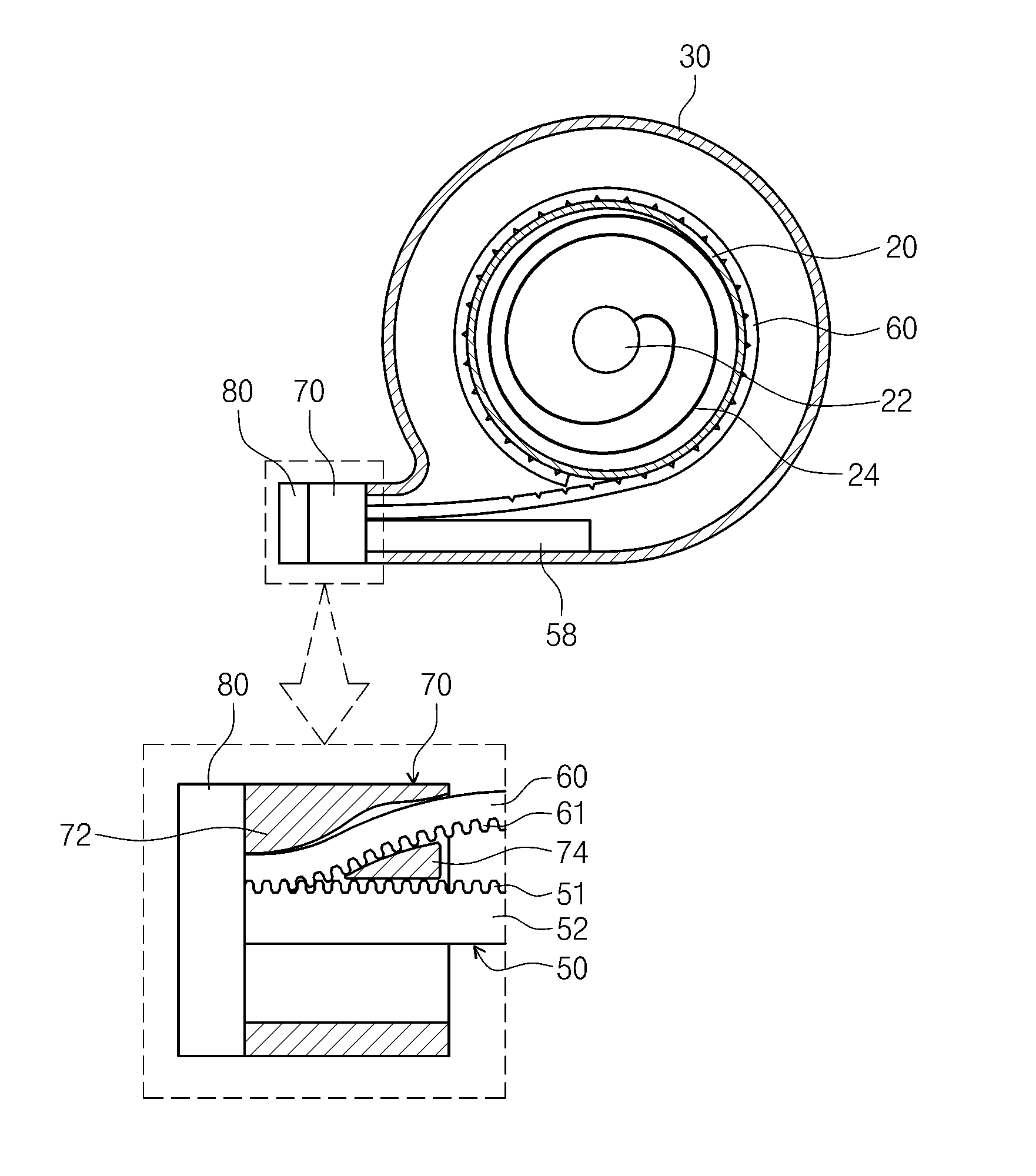
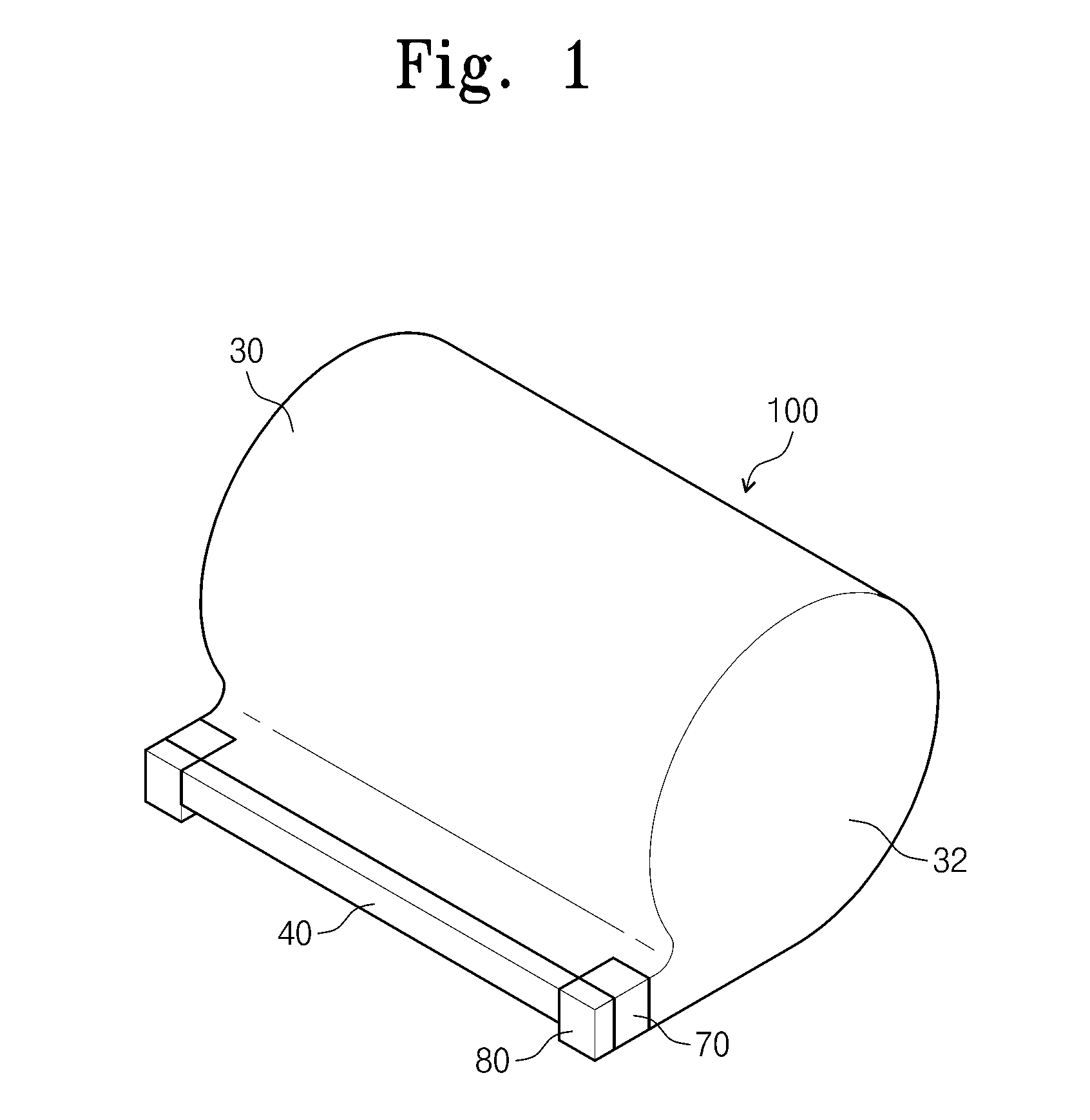
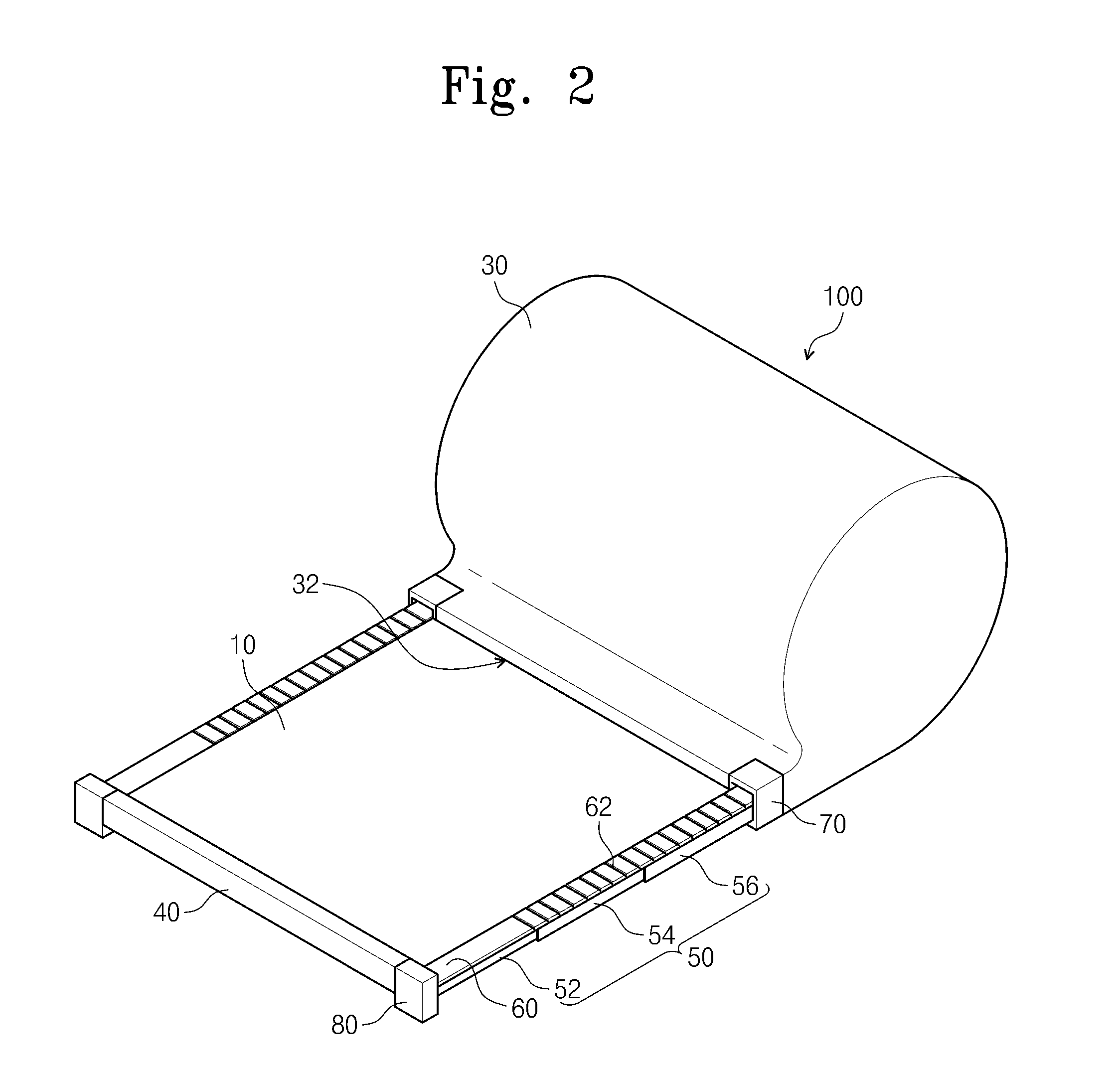
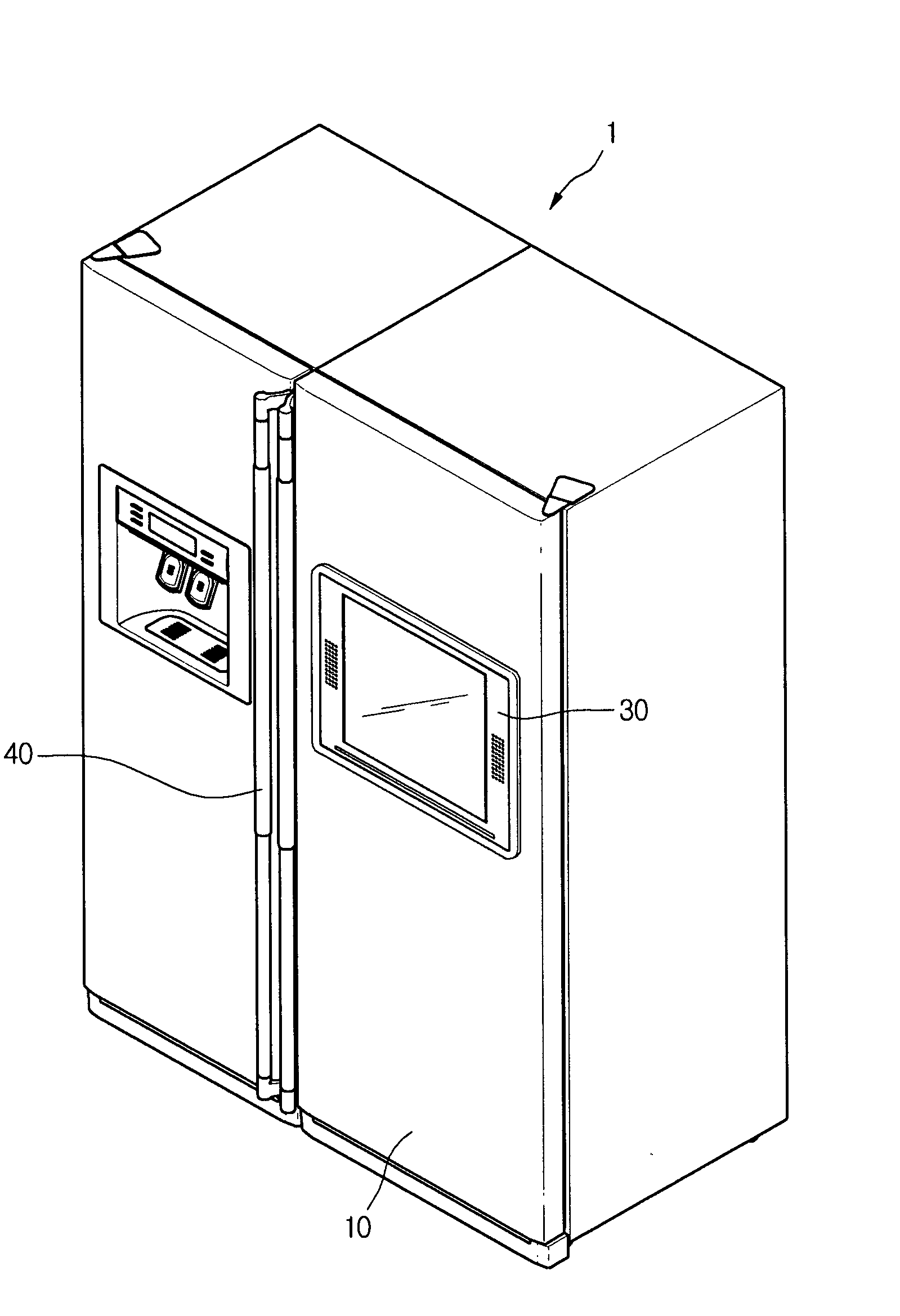
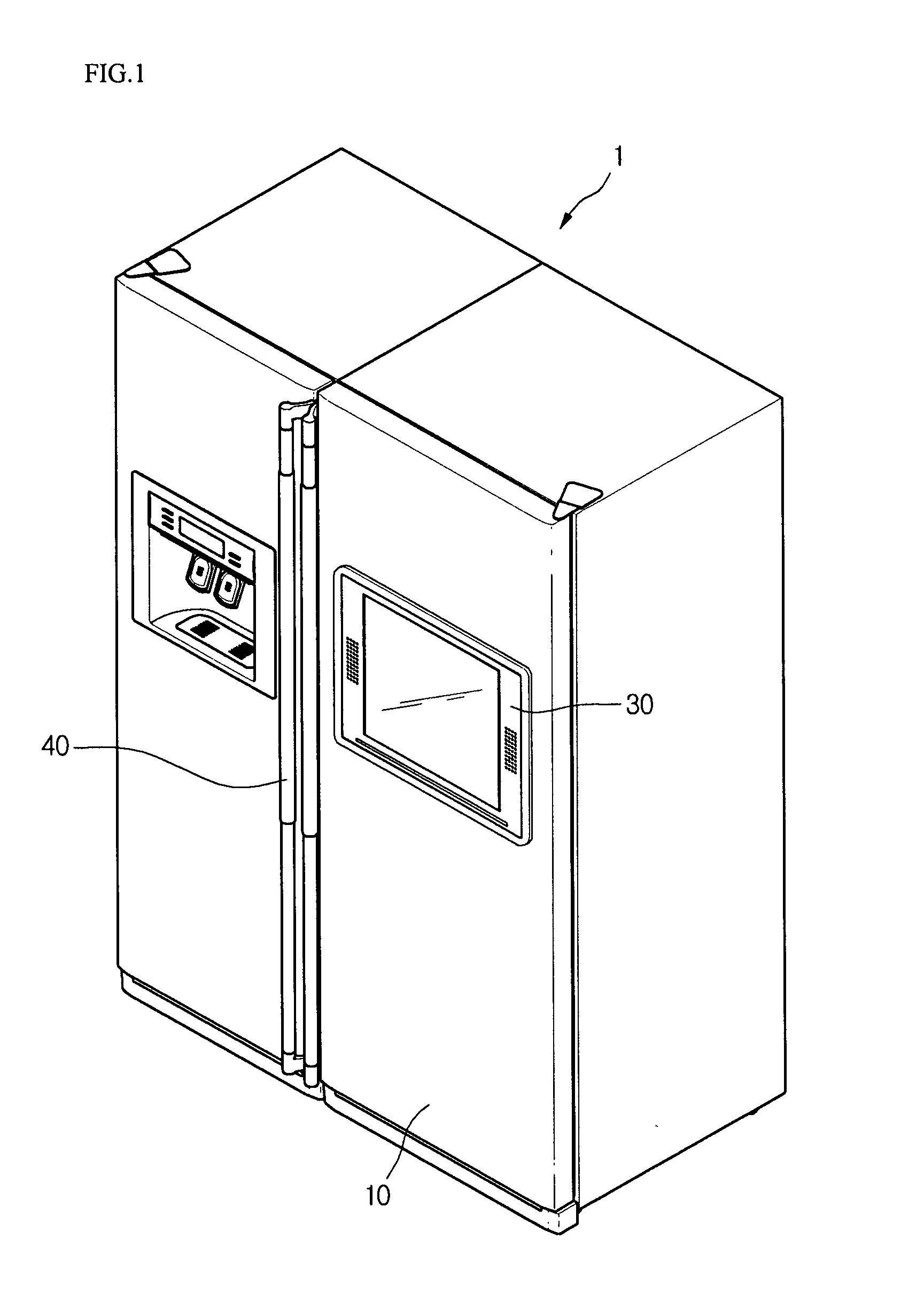
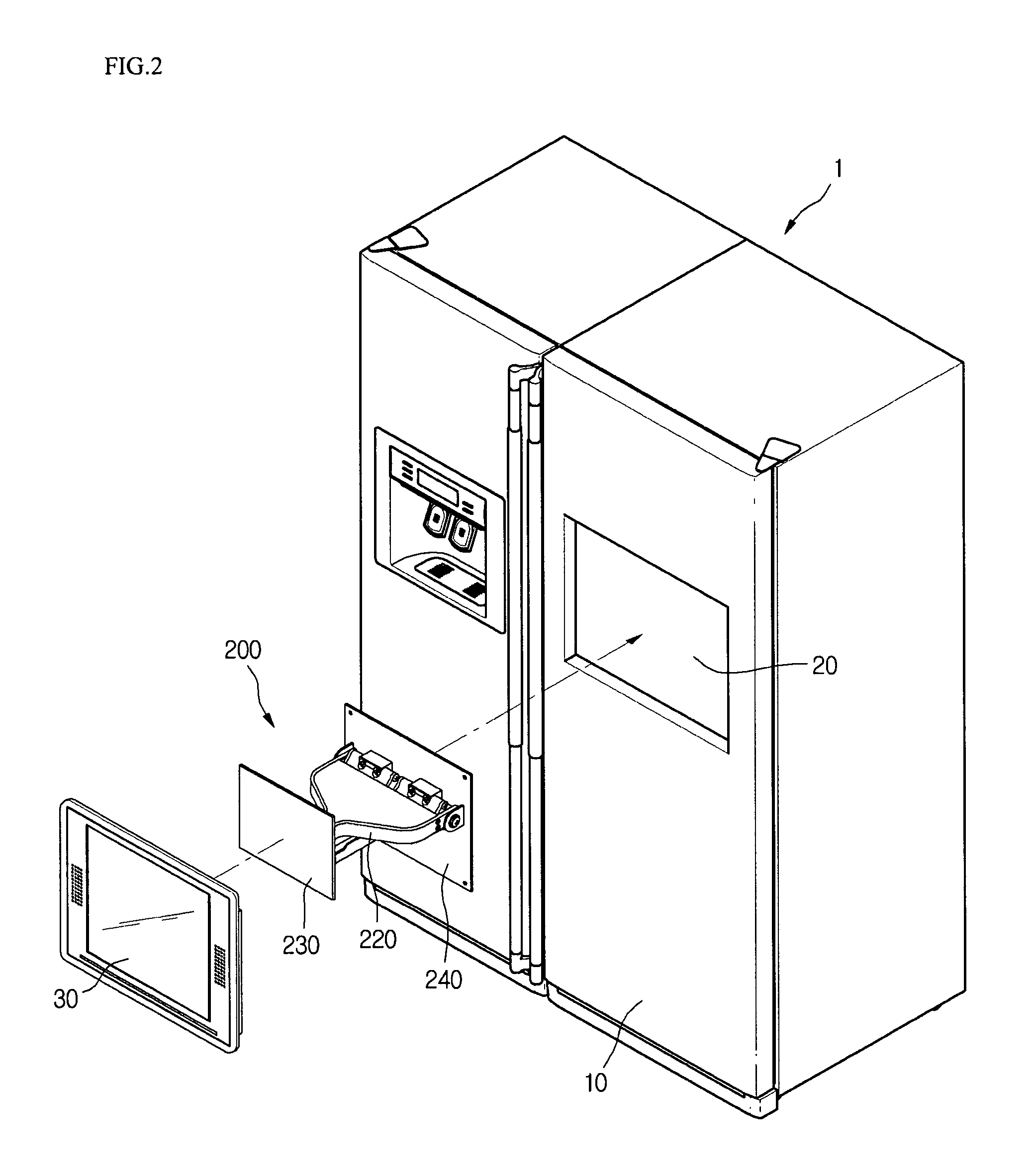
Refrigerator and display device guiding apparatus of the same
InactiveUS20060118694A1Depth is minimizedReduced insulation performancePicture framesDoors/windowsDisplay deviceEngineering
A display device guiding apparatus includes a receiving portion in which a display device can be received and a guide unit provided between the display device and the receiving portion. The guide unit includes a hinge assembly for pivoting the display at a predetermined angle, an arm assembly having first and second ends respectively connected to the hinge assembly and the receiving portion, and a pivot control unit providing a pivotal force of the arm assembly with respect to the receiving portion.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
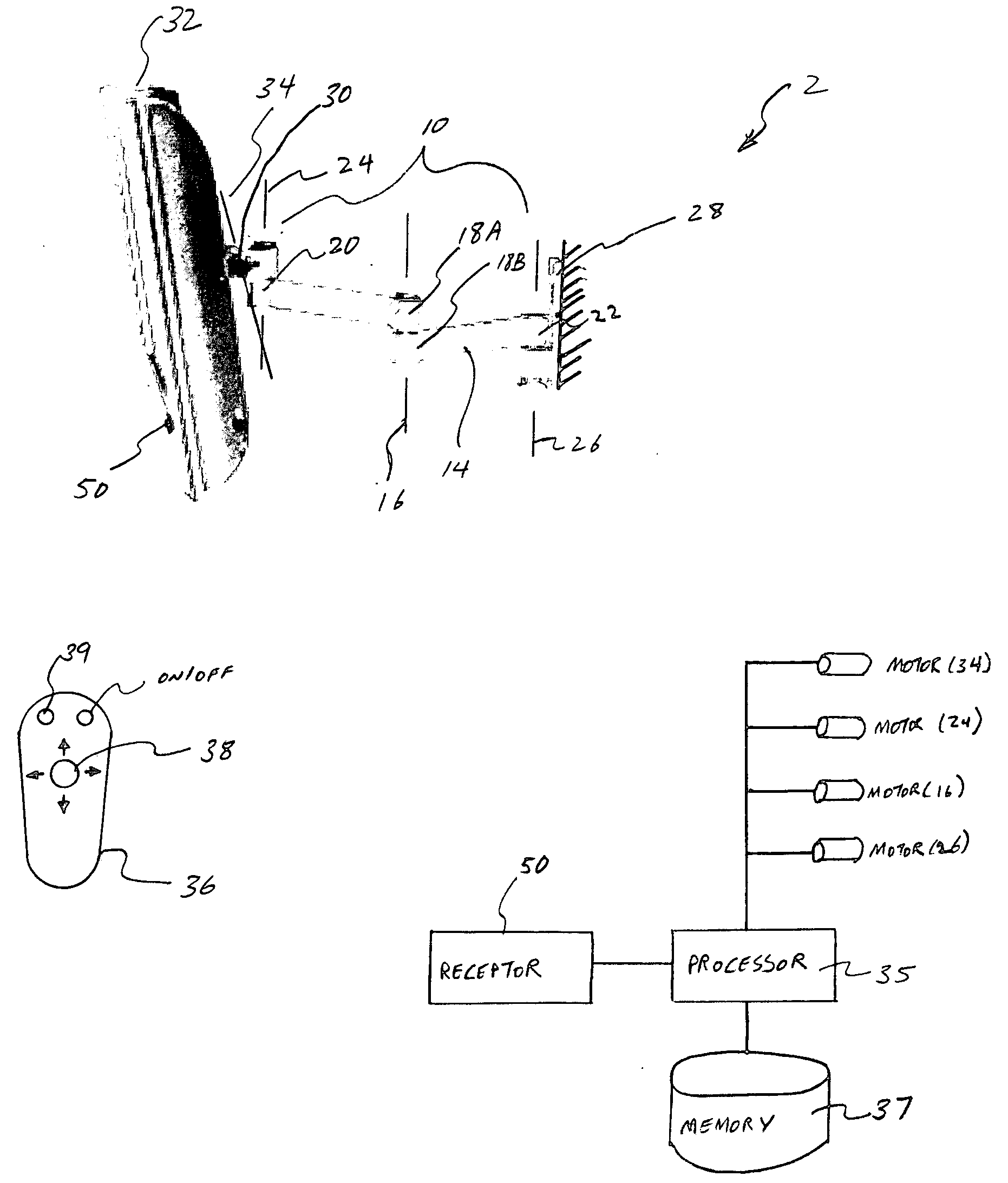
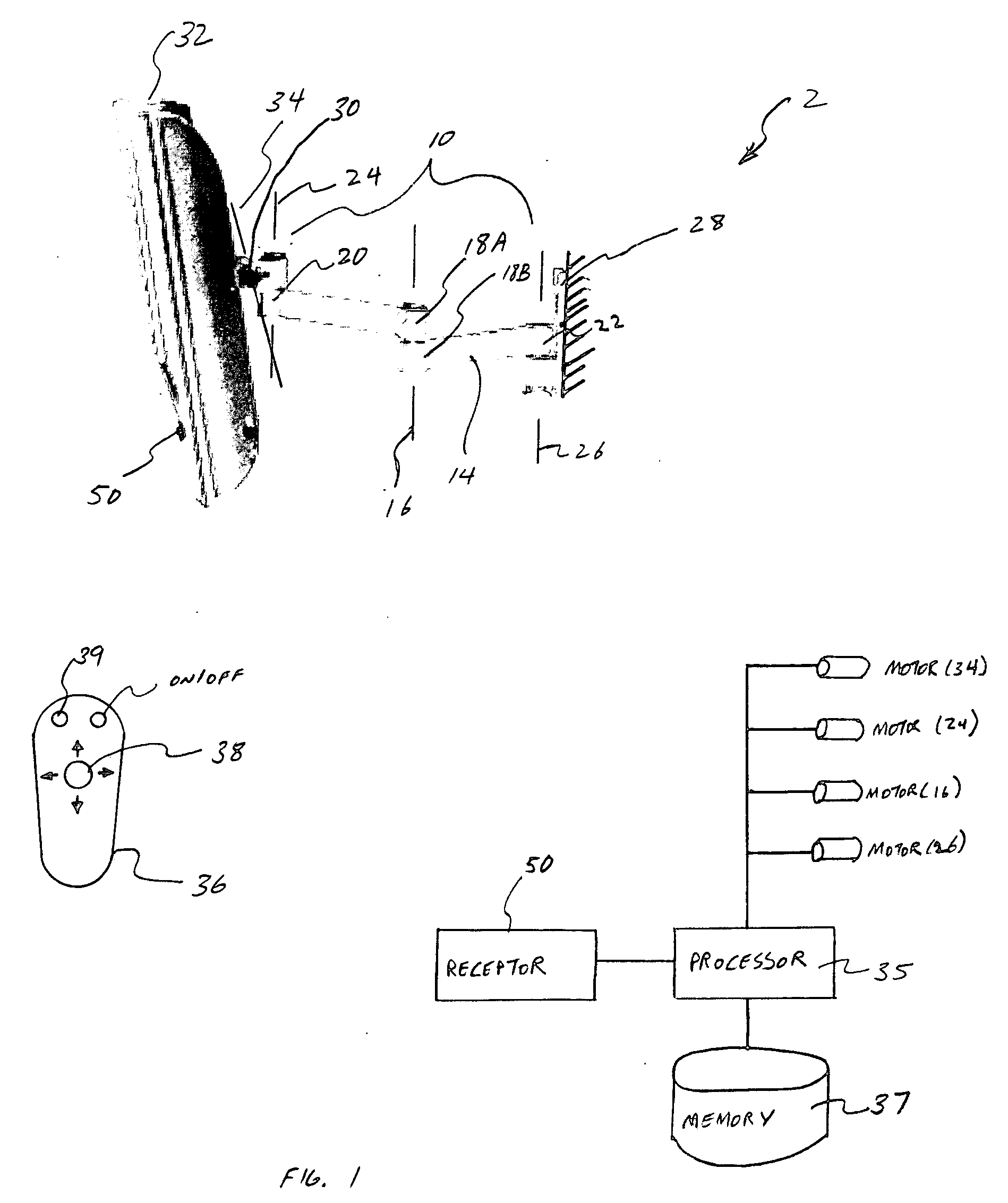
Viewing angle adjustment system for a monitor
InactiveUS20050179618A1Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsControl signalRemote control
This invention provides a support arm to couple a monitor to a surface such as a wall or ceiling to remotely adjust the viewing angle of the monitor. The support arm includes at least one motor along a pivot axis in the support arm. The motor may be activated by a processor based on the control signal provided by the remote control. The support arm may include a plurality of pivot axes with a motor in each of the pivot axis to adjust the viewing angle along the vertical and horizontal planes. The support arm may be also provided with a tracking device that follows the movement of the viewer to adjust the viewing angle of the monitor corresponding to the movement of the viewer. The support arm may also receive periodic signal from the remote control to determine the location of the remote control. Based on the periodic signal, the processor may adjust the viewing angle of the monitor towards the location of the remote control.
Owner:CLO SYST
Motorized window shade system
InactiveUS20080236763A1Raise and lower the window shadeReduce power consumptionScreensMechanical apparatusCommunications systemGroup controller
An electronically-controlled roll-up window shade that can easily be installed by a homeowner or general handyman is disclosed. The motorized shade includes an internal power source, a motor, and a communication system to allow for remote control of the motorized shade. One or more motorized shades can be controlled singly or as a group. In one embodiment, the motorized shades are used in connection with a zoned or non-zoned HVAC system to reduce energy usage. In one embodiment, the motorized shade is configured to have a size and form-factor that conforms to a standard manually-controlled motorized shade. In one embodiment, a group controller is configured to provide thermostat information to the motorized shade. In one embodiment, the group controller communicates with a central monitoring system that coordinates operation of one or more motorized shades. In one embodiment, the internal power source of the motorized shade is recharged by a solar cell.
Owner:NEST LABS
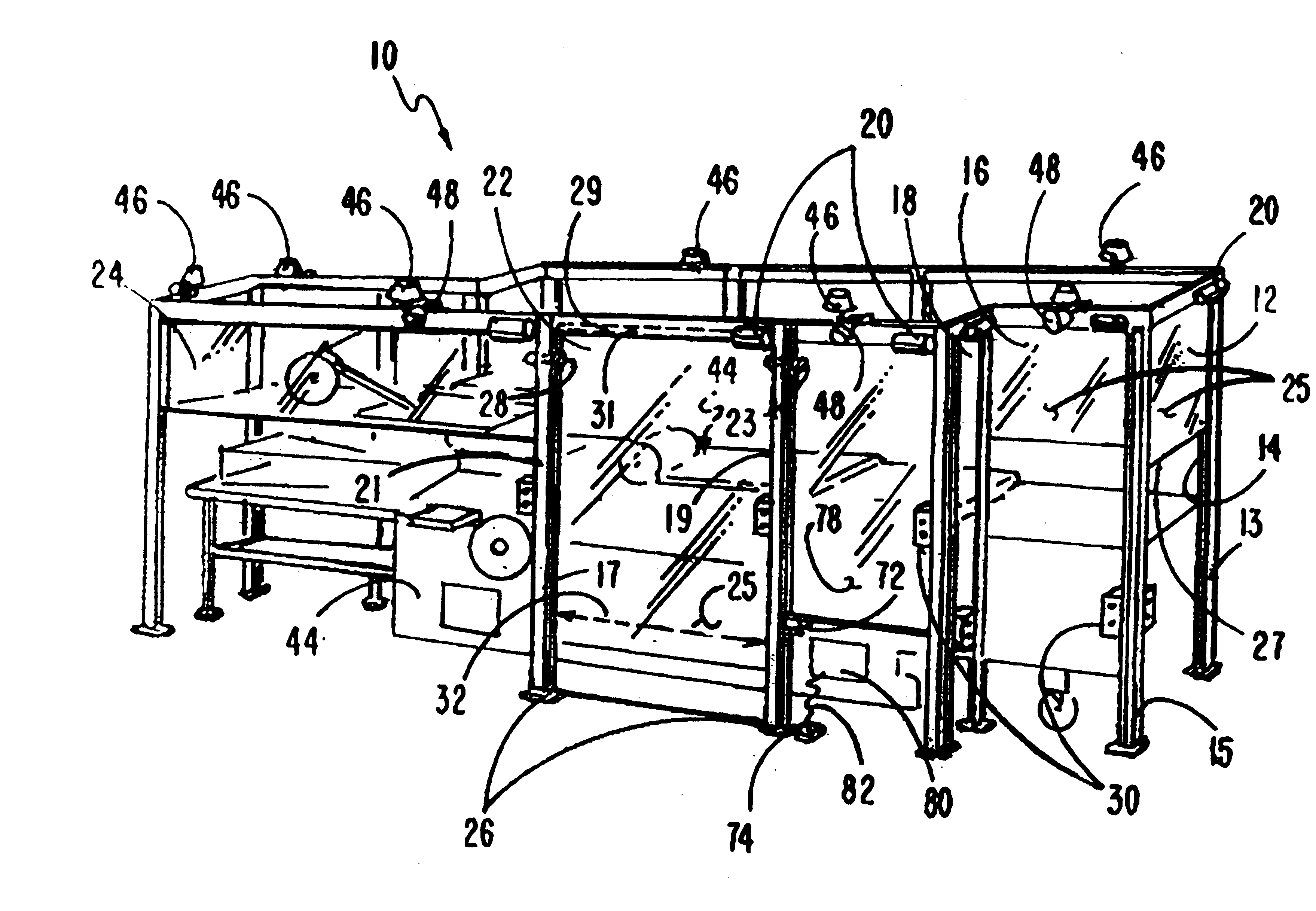
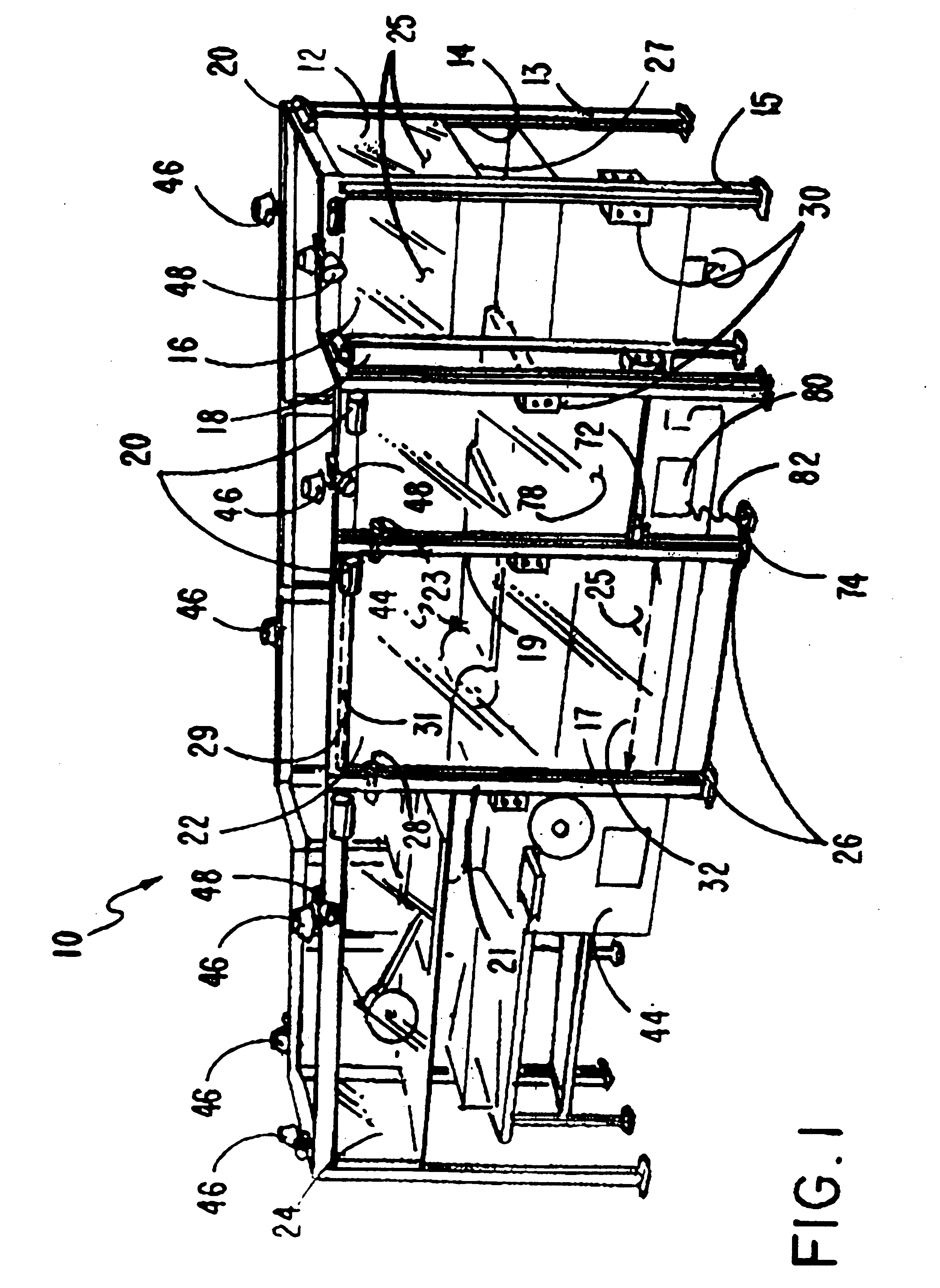
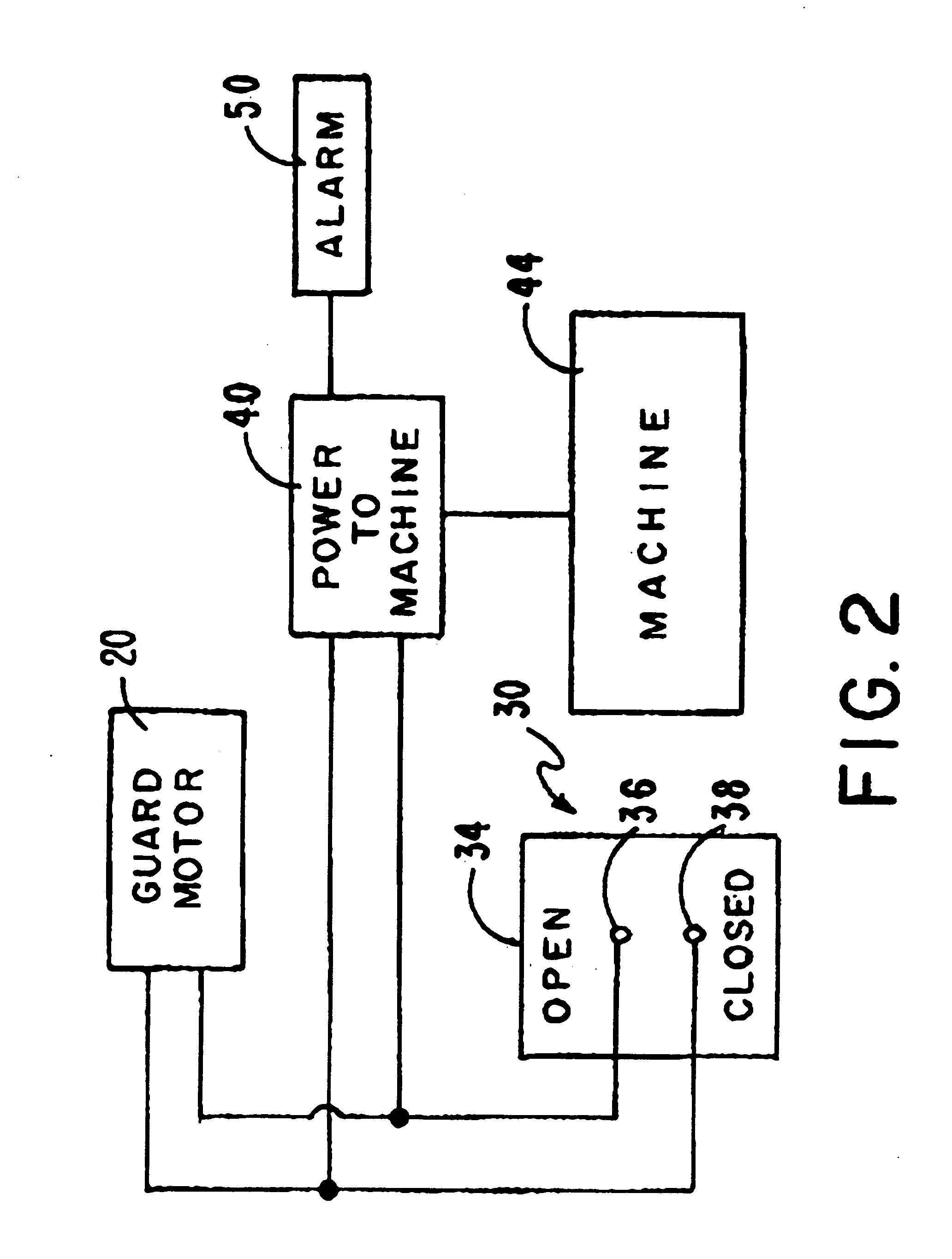
Machine safety guard
InactiveUS6325195B1Easy to operateProvide securityYielding couplingShutters/ movable grillesUnit systemEngineering
A machine safety guard unit system having a flexible panel moved upwards and downwards between track members with the system positioned between the operative parts of a machine and a machine operator, such panel when closed protecting the machine operator and when moved upwards into its open mode, allowing access to the machine and preventing the machine from operating. In some embodiments more than one of such units can be disposed around a machine with alarm means; and in yet other embodiments, with interengagement means connecting such units.
Owner:RITE HITE HLDG CORP
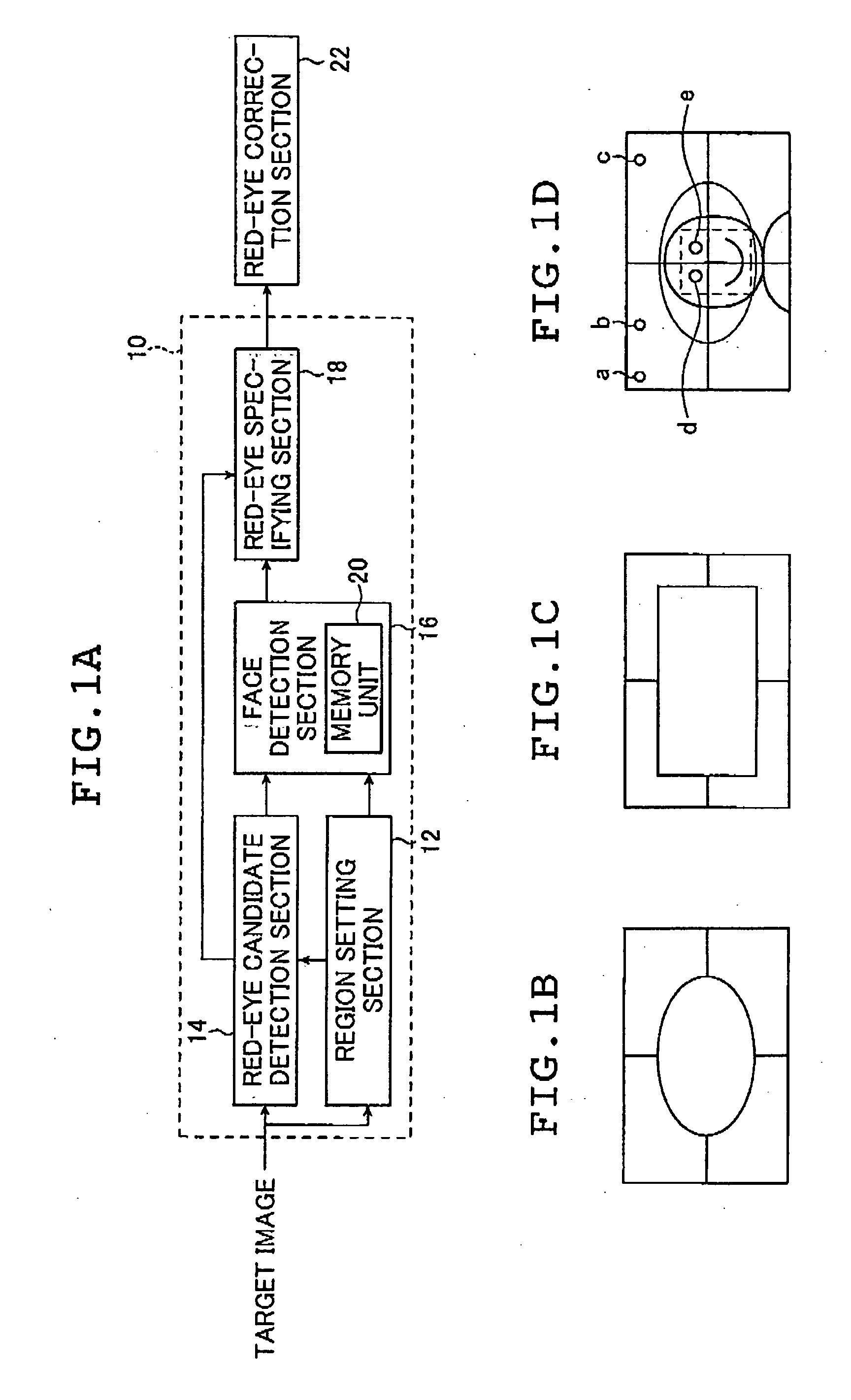
Particular-region detection method and apparatus, and program therefor
ActiveUS20050238217A1Reduce needIncrease speedShutters/ movable grillesCurtain suspension devicesFace detectionRegion detection
The particular region detecting method and apparatus detect particular region candidates in an image, then perform face detection in a region including one of the detected particular region candidates and specify as a particular region of a detection target the one candidate included in the region where a face can be detected. In the method and apparatus, detection conditions is changed for at least one of the candidate detection and the face detection between main and non-main portion regions of the image, face information regarding the face detected in the region is stored and the face detection corresponding to a particular region candidate to be next subjected to the face detection is performed using the thus stored face information. The program is caused a computer to execute the method.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
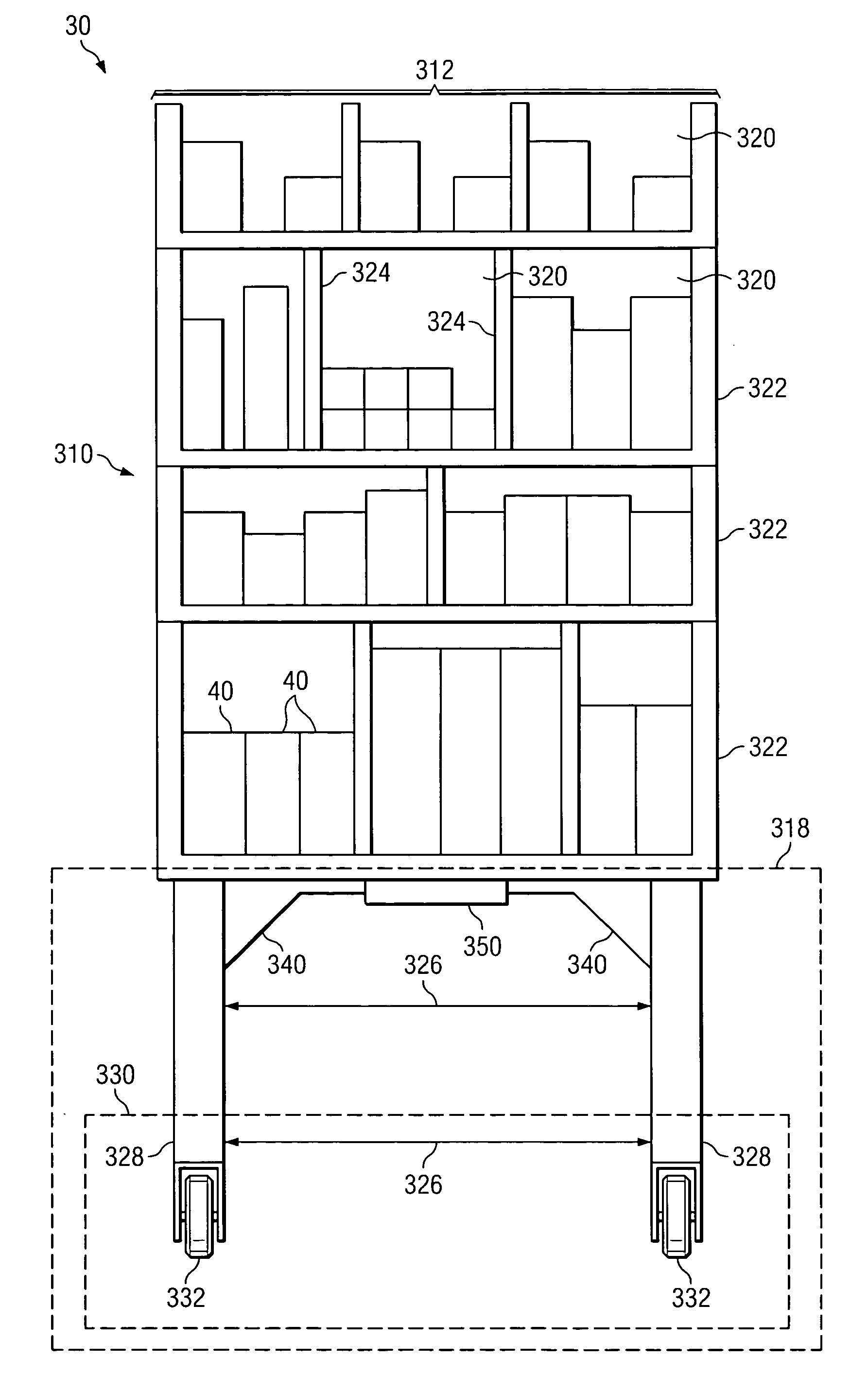
Stand alone divider for shelving
Owner:FASTENERS FOR RETAIL
In-wall mount
ActiveUS20090050763A1Eliminate needPrecise positioningCurtain suspension devicesFurniture partsDisplay deviceEngineering
An in-wall mount for supporting an electronic display from a wall. The in-wall mount includes a wall interface structure, a display interface structure, and an extensible arm assembly. The display interface structure is selectively outwardly shiftable relative to the wall interface structure between a first position wherein the display interface structure is proximate the wall interface structure and a second position wherein the display interface structure is spaced apart from the wall interface structure, the display interface structure rising vertically relative to the wall interface structure as the display interface structure is shifted from the first position to the second position.
Owner:LEGRAND AV INC
Mounting appratus for slide rail
Owner:FULIAN PRECISION ELECTRONICS (TIANJIN) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com