Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
231results about "Gas cathode details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
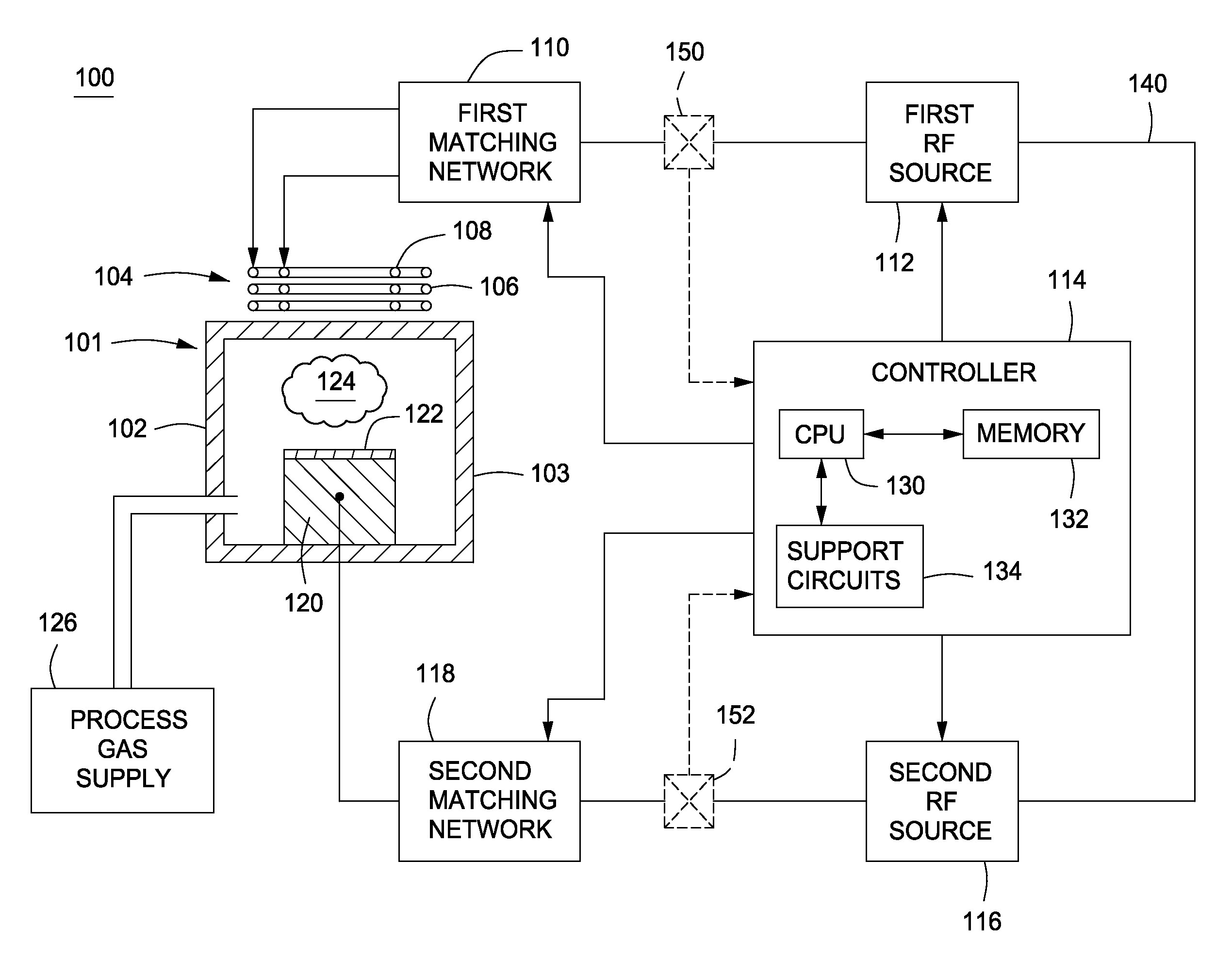
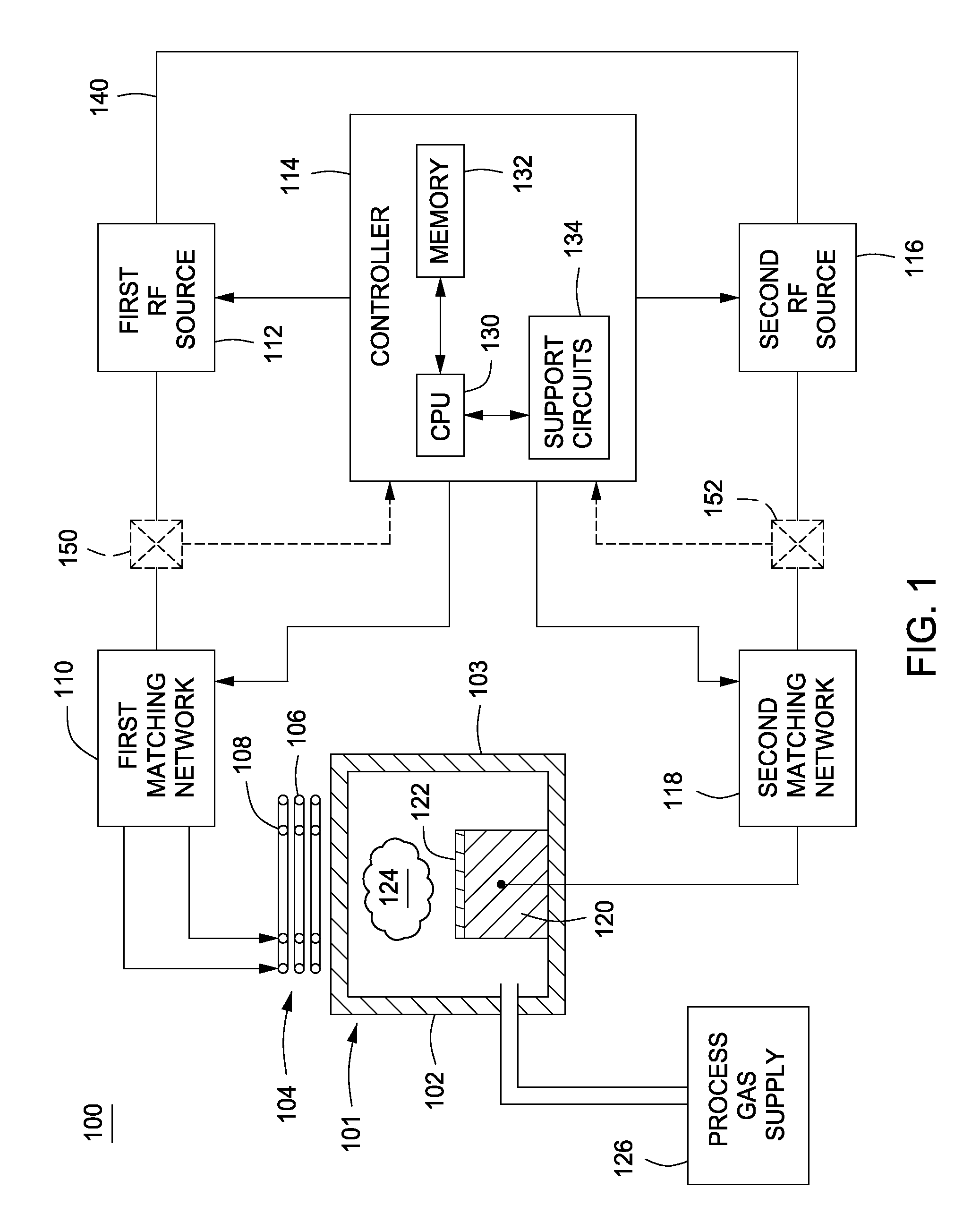
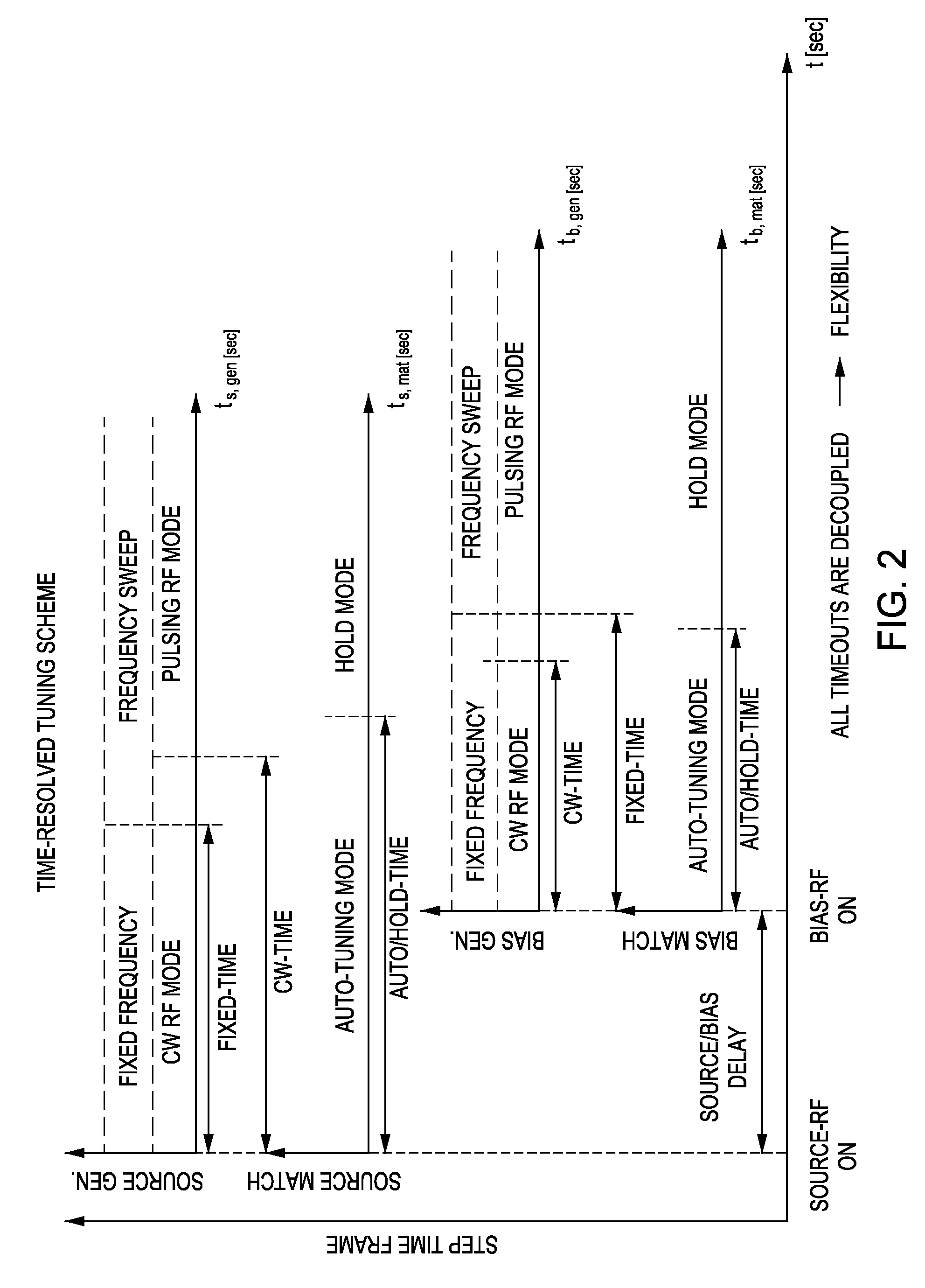
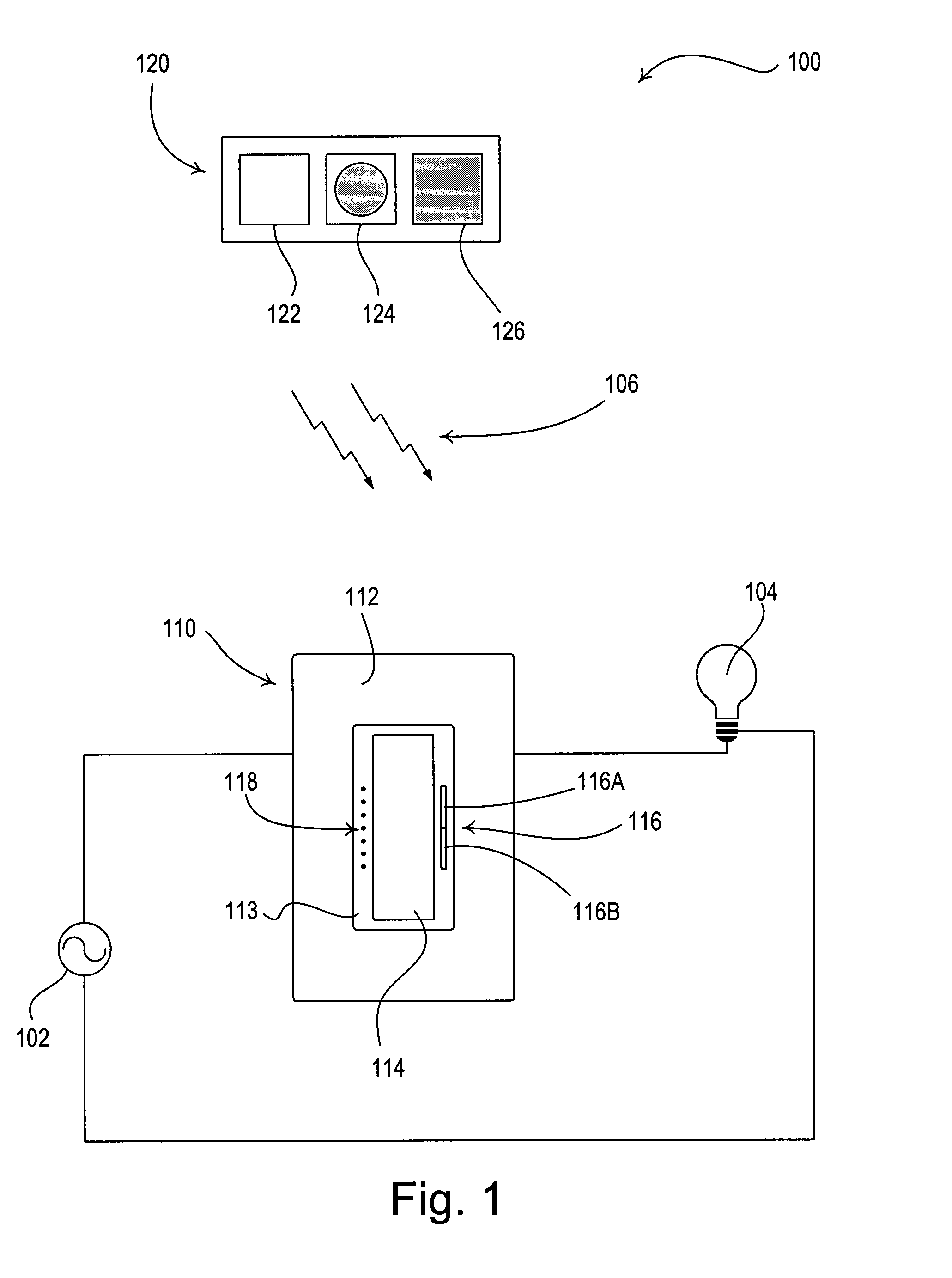
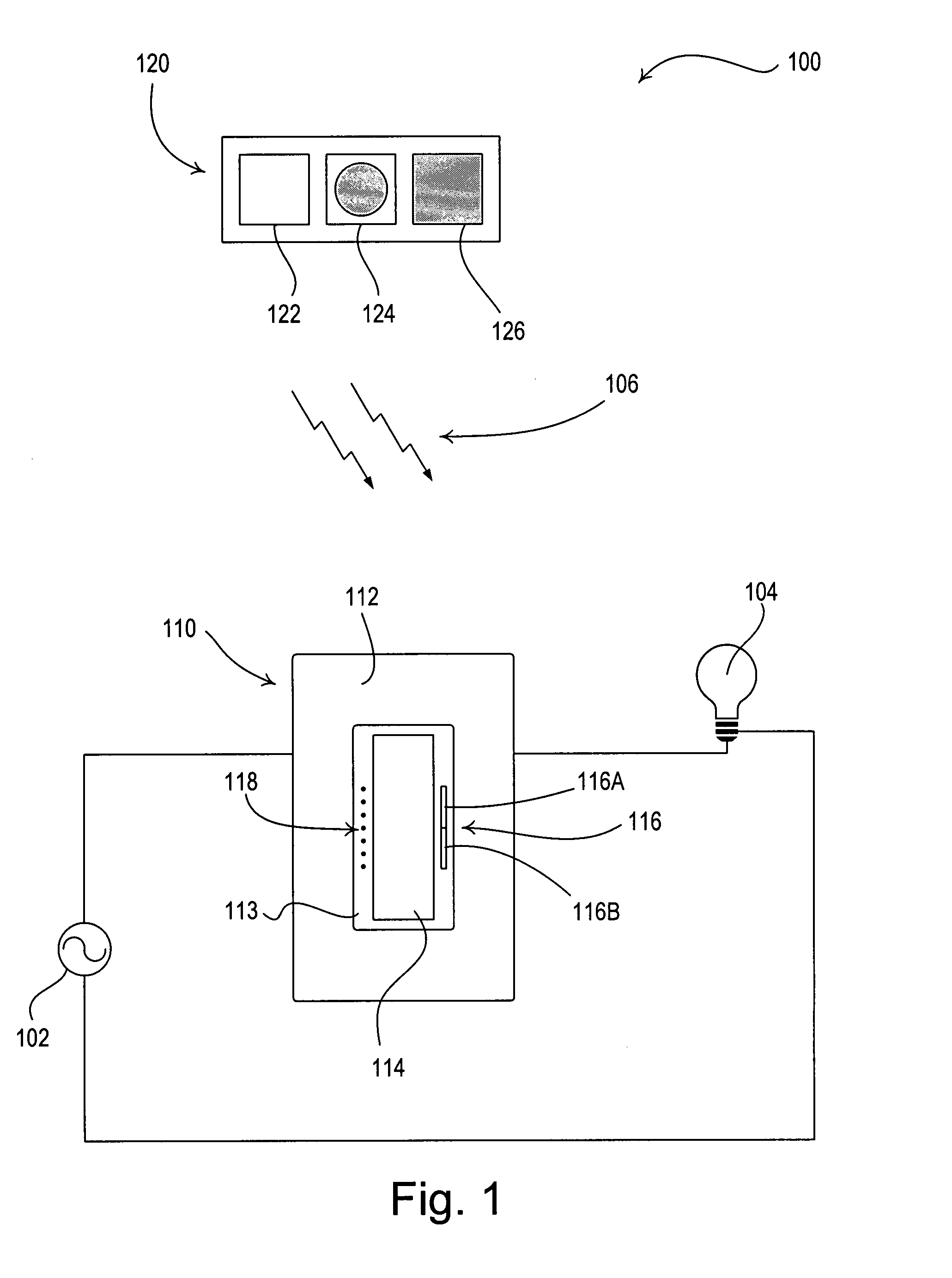
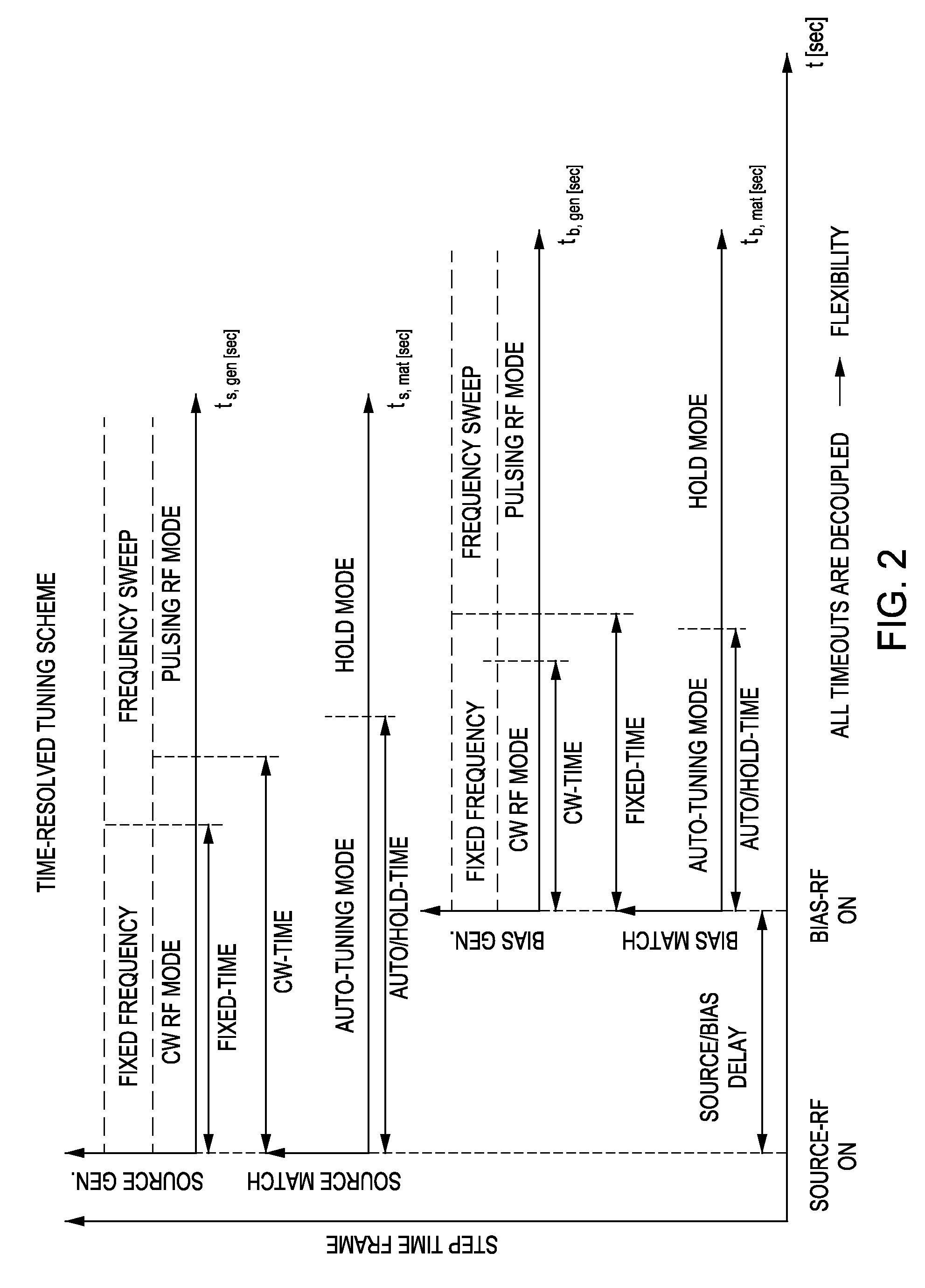
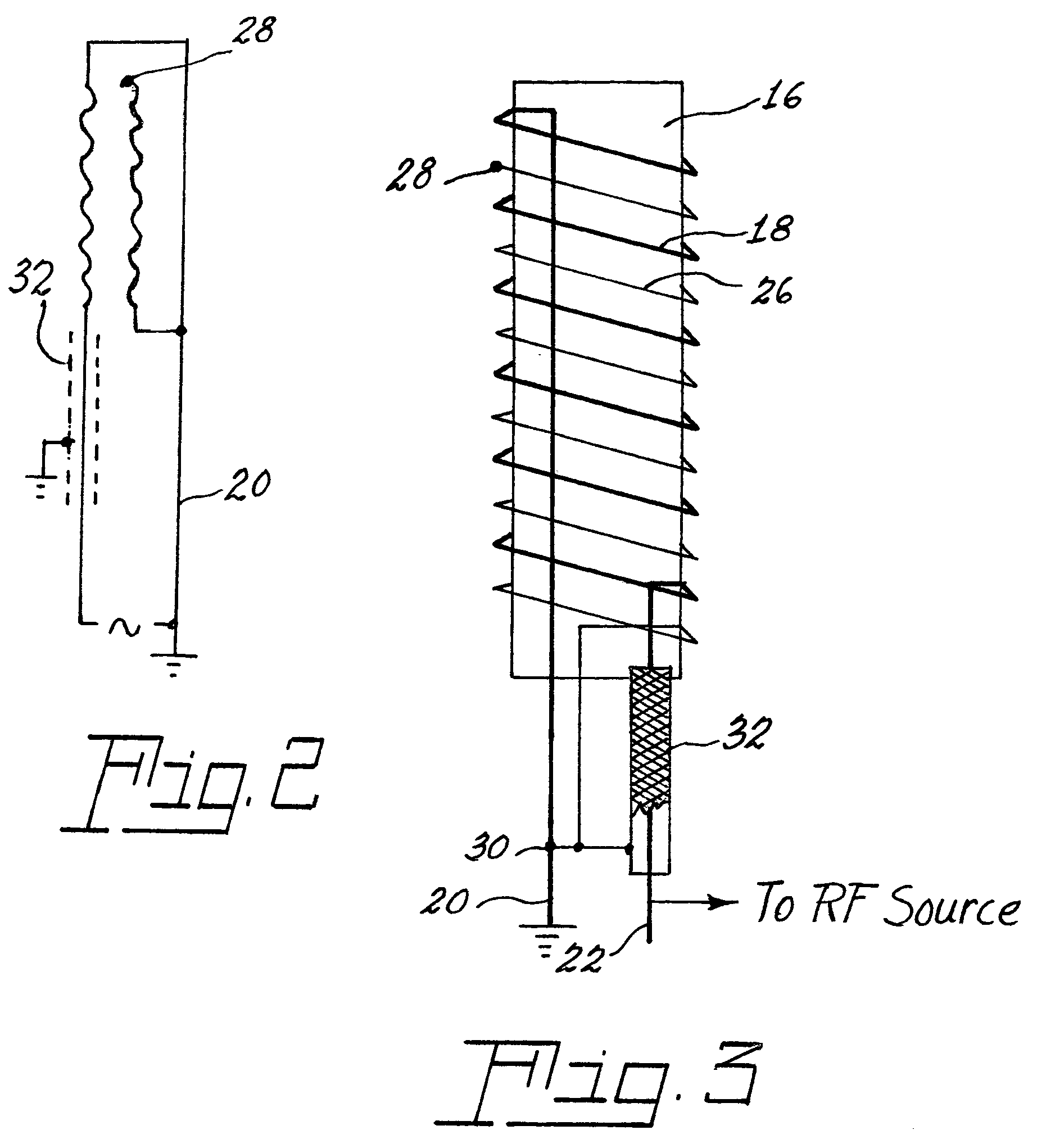
Method and apparatus for pulsed plasma processing using a time resolved tuning scheme for RF power delivery
ActiveUS20090284156A1Alternating current plasma display panelsElectric arc lampsProcess windowPlasma processing
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide methods and apparatus for pulsed plasma processing over a wide process window. In some embodiments, an apparatus may include an RF power supply having frequency tuning and a matching network coupled to the RF power supply that share a common sensor for reading reflected RF power reflected back to the RF power supply. In some embodiments, an apparatus may include an RF power supply having frequency tuning and a matching network coupled to the RF power supply that share a common sensor for reading reflected RF power reflected back to the RF power supply and a common controller for tuning each of the RF power supply and the matching network.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
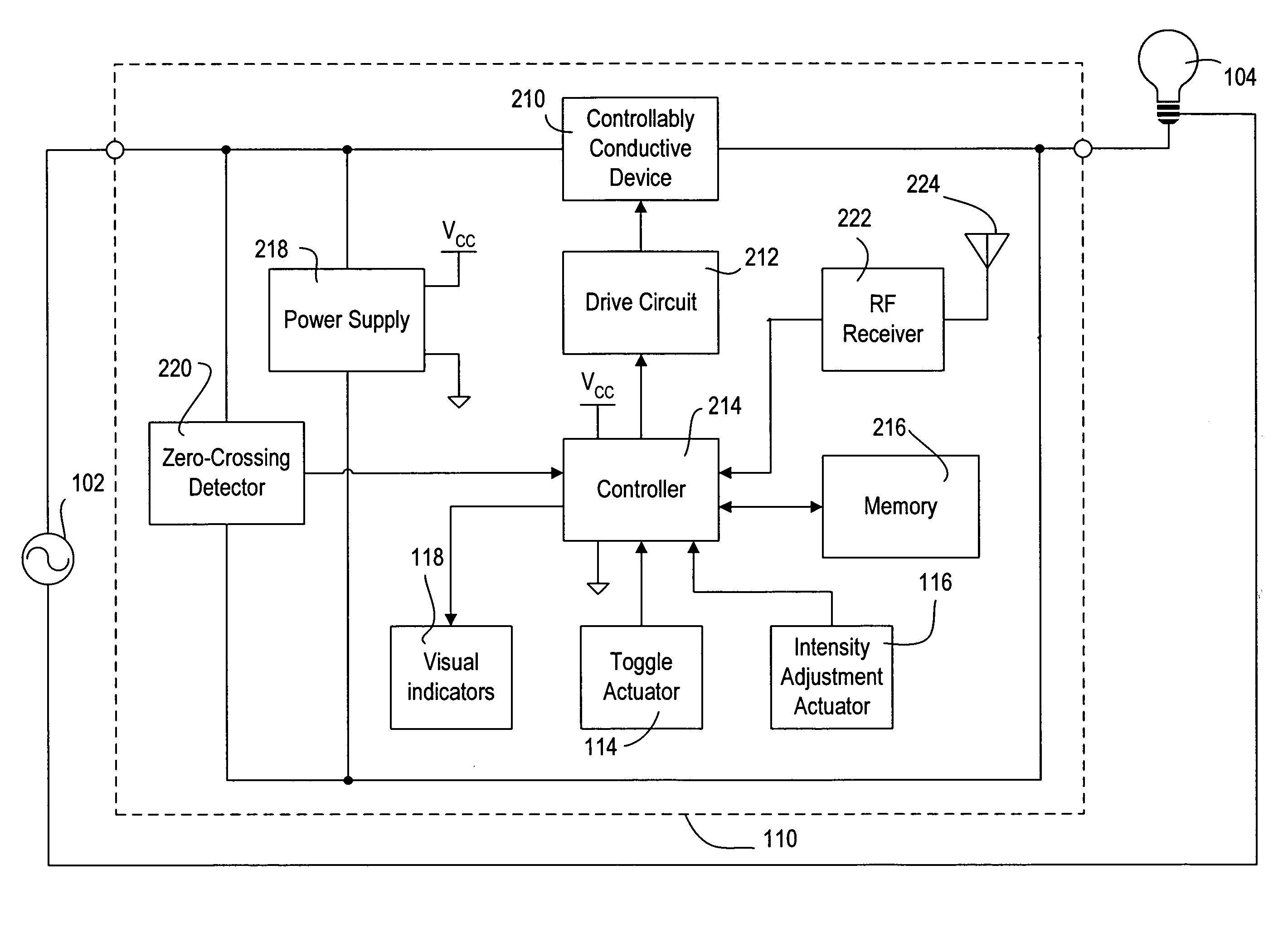
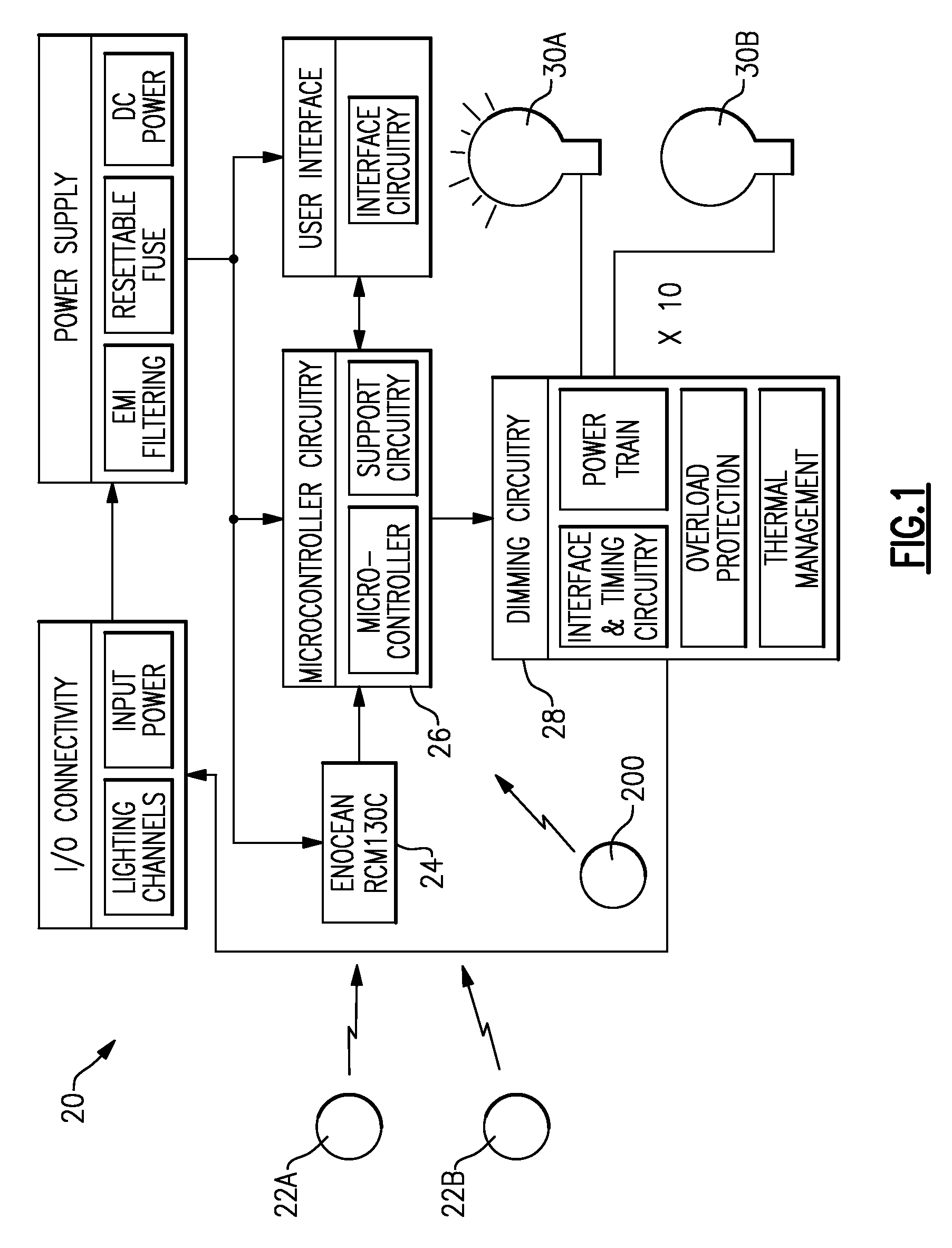
Method of programming a lighting preset from a radio-frequency remote control
ActiveUS7573208B2Alternating current plasma display panelsElectric light circuit arrangementWireless transmissionRemote control
The present invention provides a method of programming a preset intensity of a dimmer switch from a radio-frequency (RF) remote control. A user is able to adjust the intensity of the lighting load to a new intensity and subsequently press and hold a preset button on the remote control to program the new intensity as the preset intensity. The remote control transmits a wireless transmission to the dimmer switch, which immediately responds to the actuation of the preset button by controlling the intensity of the lighting load to an old preset intensity. The dimmer switch then blinks a light-emitting diode representative of the new intensity to provide feedback that the dimmer switch is in the process of programming the preset intensity to the new intensity. Eventually, the dimmer switch stores the new intensity as the preset intensity and stops blinking the light-emitting diode.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Method of programming a lighting preset from a radio-frequency remote control
ActiveUS20080218099A1Alternating current plasma display panelsElectric light circuit arrangementWireless transmissionRemote control
The present invention provides a method of programming a preset intensity of a dimmer switch from a radio-frequency (RF) remote control. A user is able to adjust the intensity of the lighting load to a new intensity and subsequently press and hold a preset button on the remote control to program the new intensity as the preset intensity. The remote control transmits a wireless transmission to the dimmer switch, which immediately responds to the actuation of the preset button by controlling the intensity of the lighting load to an initial preset intensity. The dimmer switch then blinks a light-emitting diode representative of the new intensity to provide feedback that the dimmer switch is in the process of programming the preset intensity to the new intensity. Eventually, the dimmer switch stores the new intensity as the preset intensity and stops blinking the light-emitting diode.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Method and apparatus for pulsed plasma processing using a time resolved tuning scheme for RF power delivery
ActiveUS8264154B2Alternating current plasma display panelsElectric arc lampsProcess windowPlasma processing
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide methods and apparatus for pulsed plasma processing over a wide process window. In some embodiments, an apparatus may include an RF power supply having frequency tuning and a matching network coupled to the RF power supply that share a common sensor for reading reflected RF power reflected back to the RF power supply. In some embodiments, an apparatus may include an RF power supply having frequency tuning and a matching network coupled to the RF power supply that share a common sensor for reading reflected RF power reflected back to the RF power supply and a common controller for tuning each of the RF power supply and the matching network.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
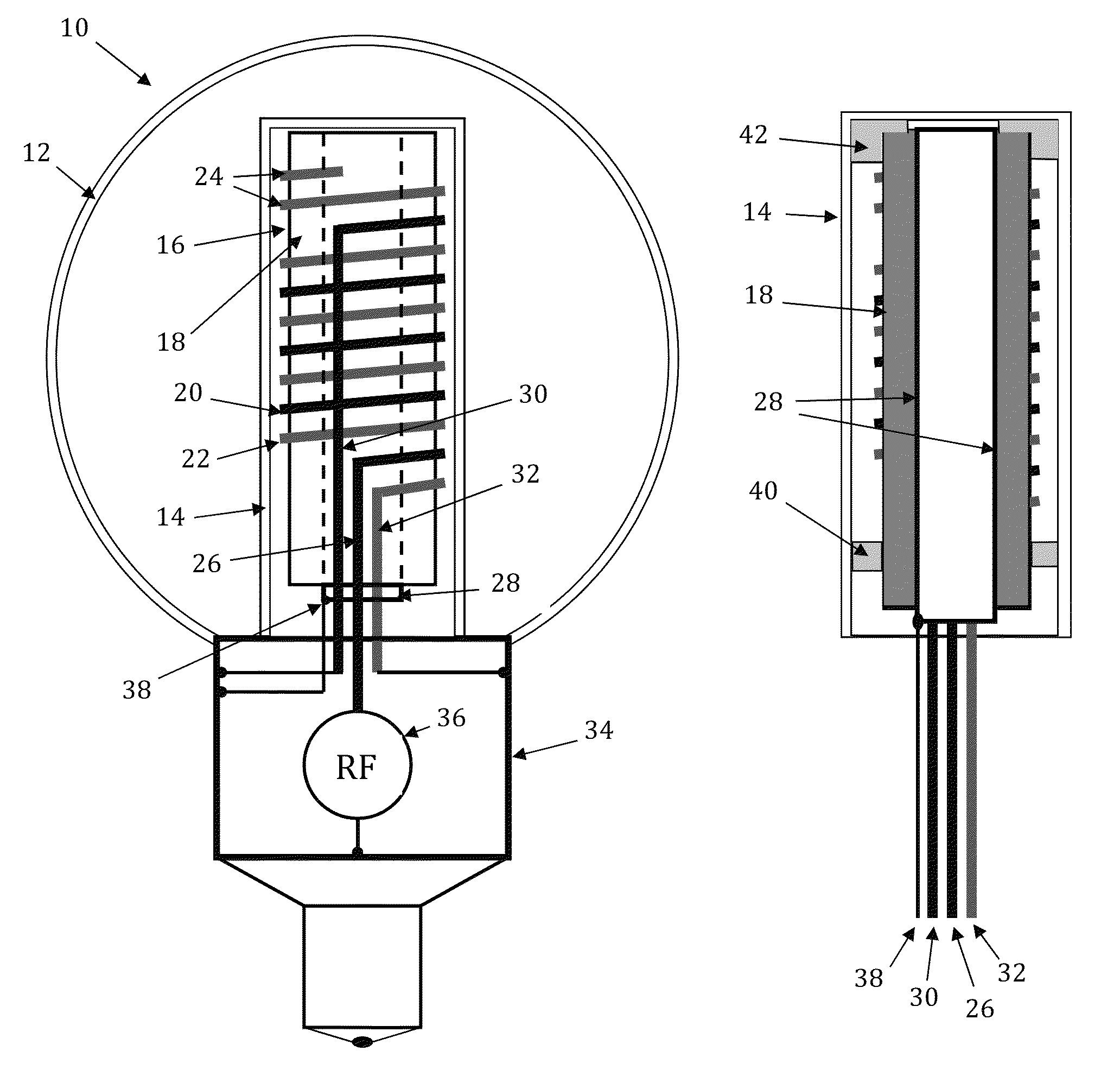
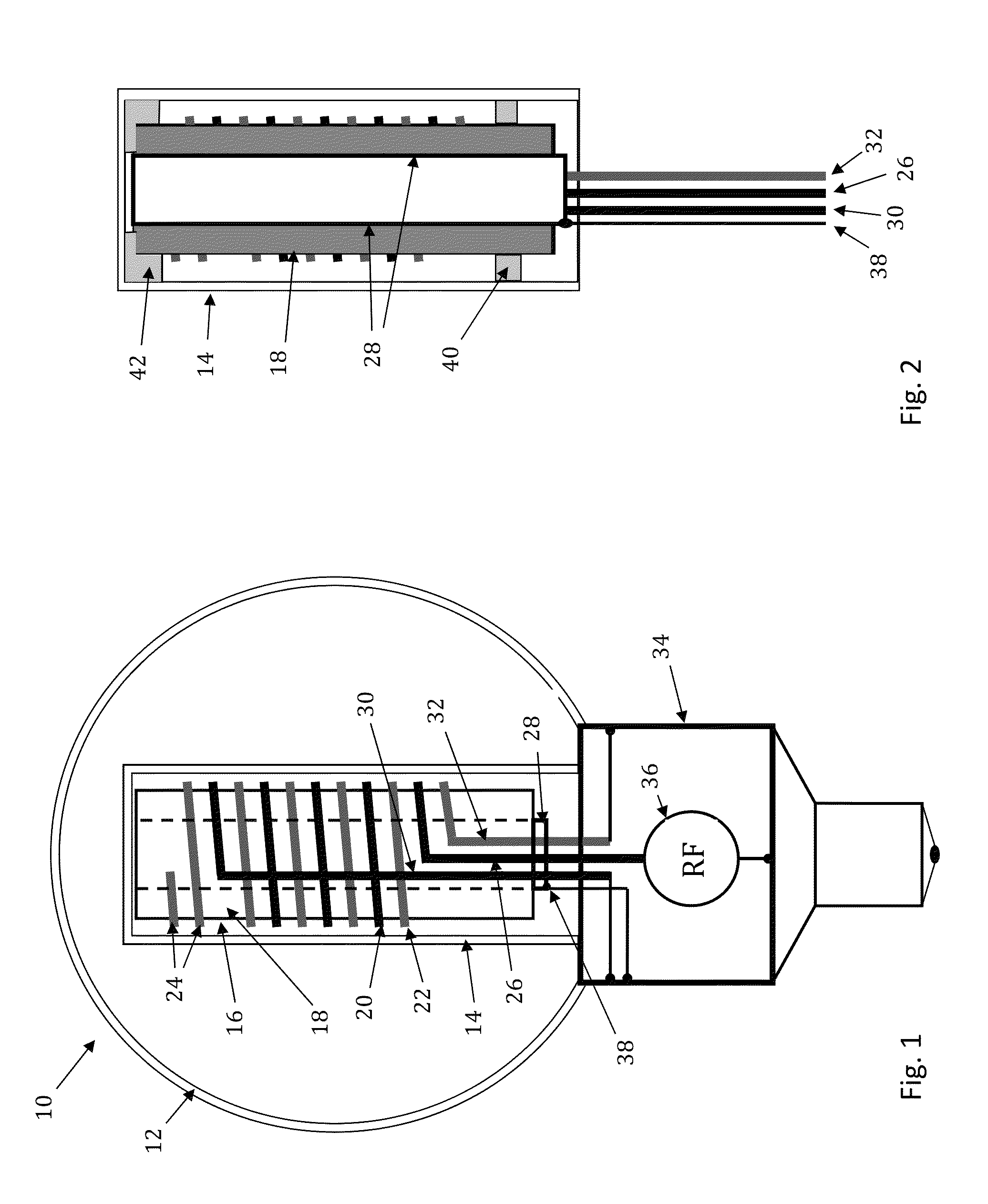
External resonator/cavity electrode-less plasma lamp and method of exciting with radio-frequency energy
ActiveUS7291985B2Increase rangeReduce the cost of the whole lampMagnetronsAlternating current plasma display panelsCapacitanceRadio frequency energy
Described is a plasma electrode-less lamp. The device comprises an electromagnetic resonator and an electromagnetic radiation source conductively connected with the electromagnetic resonator. The device further comprises a pair of field probes, the field probes conductively connected with the electromagnetic resonator. A gas-fill vessel is formed from a closed, transparent body, forming a cavity. The gas-fill vessel is not contiguous with (detached from) the electromagnetic resonator and is capacitively coupled with the field probes. The gas-fill vessel further contains a gas within the cavity, whereby the gas is induced to emit light when electromagnetic radiation from the electromagnetic radiation source resonates inside the electromagnetic resonator, the electromagnetic resonator capacitively coupling the electromagnetic radiation to the gas, which becomes a plasma and emits light.
Owner:TOPANGA USA
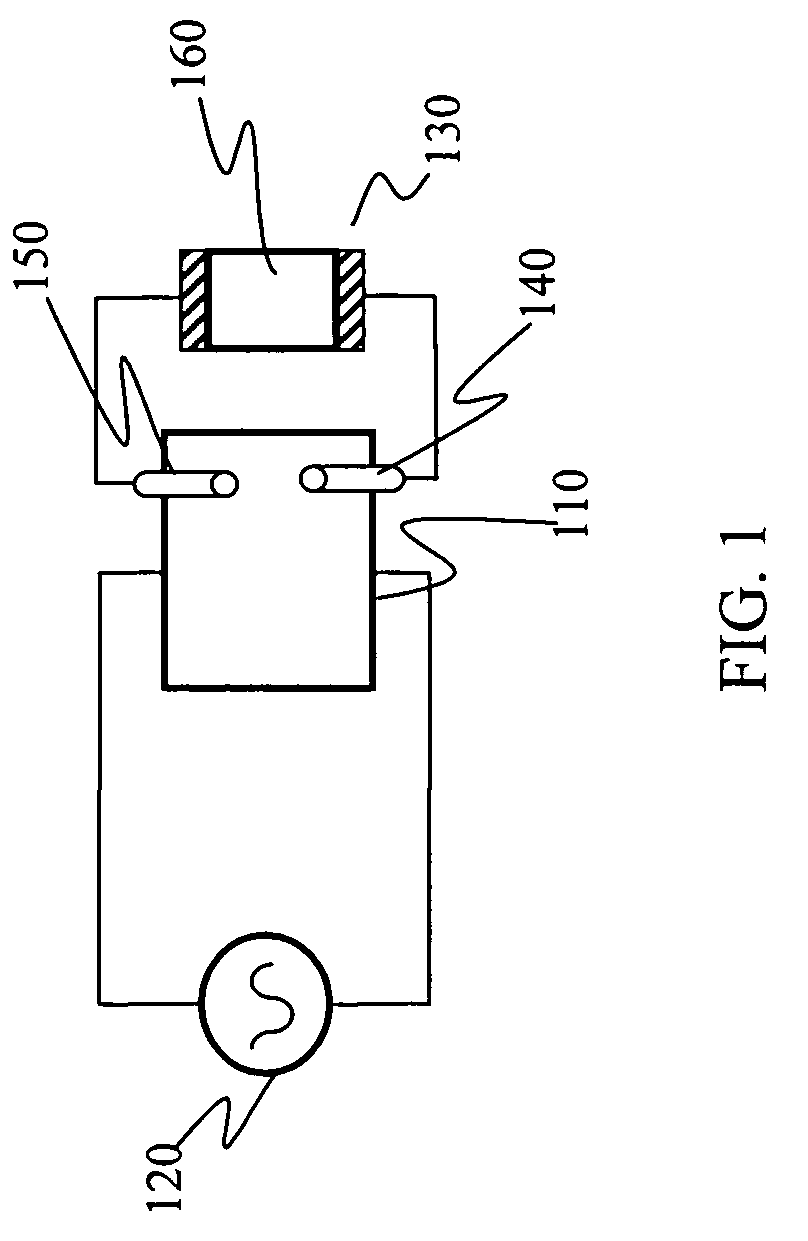
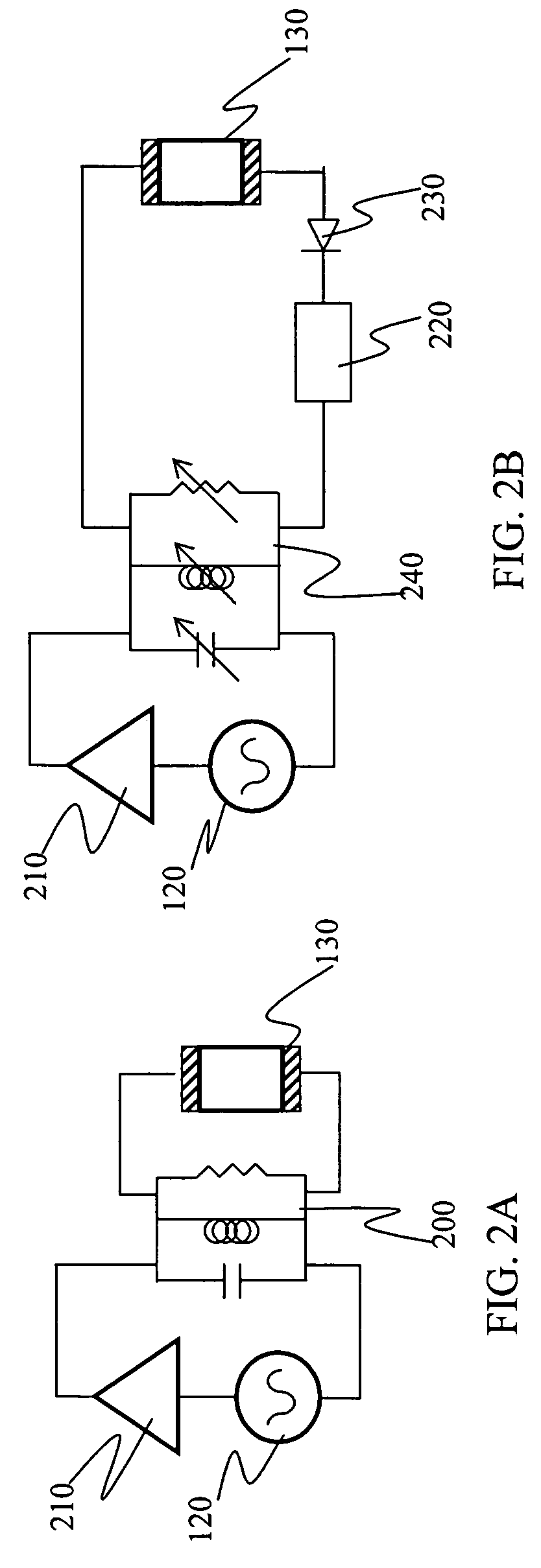
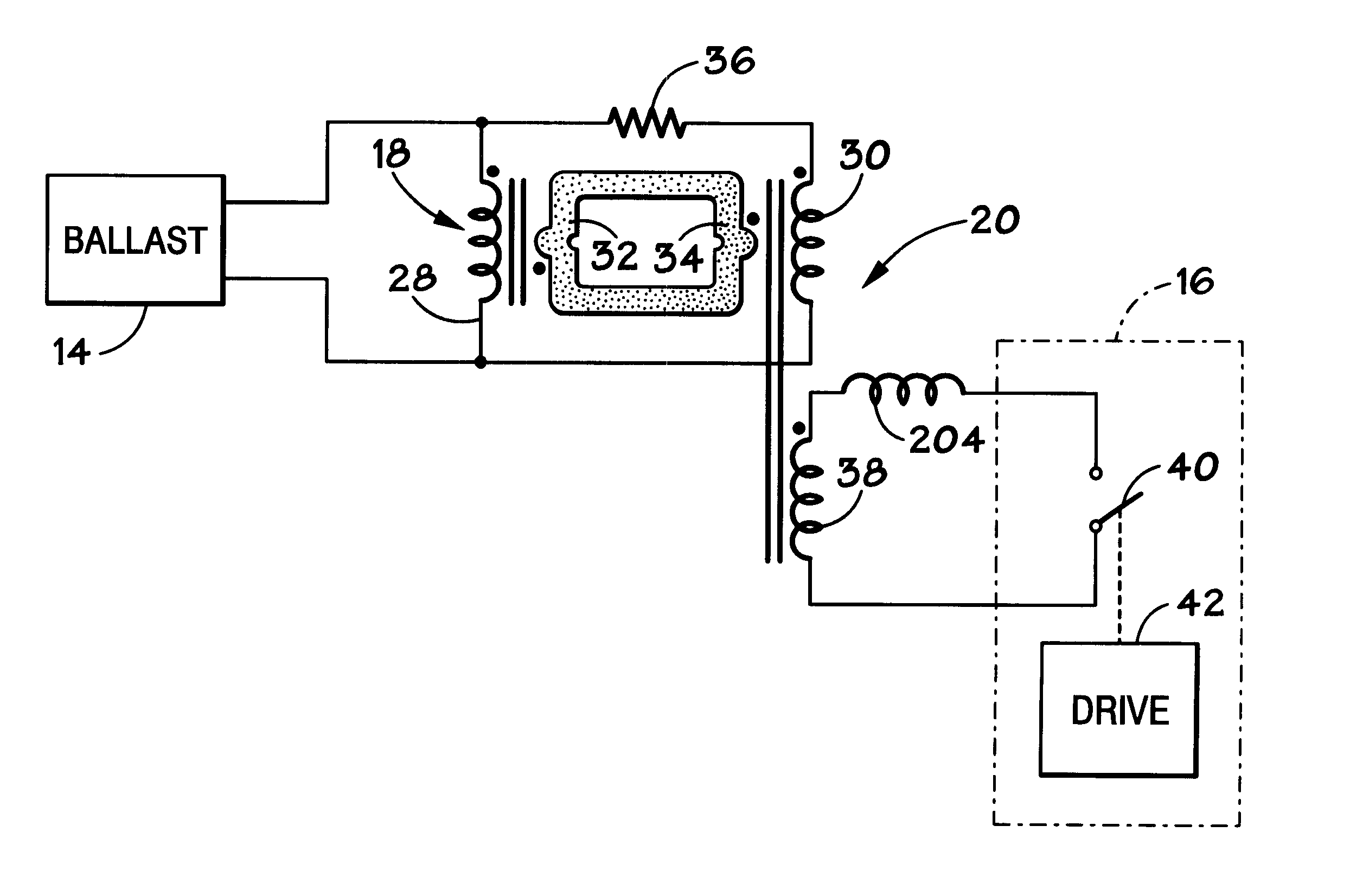
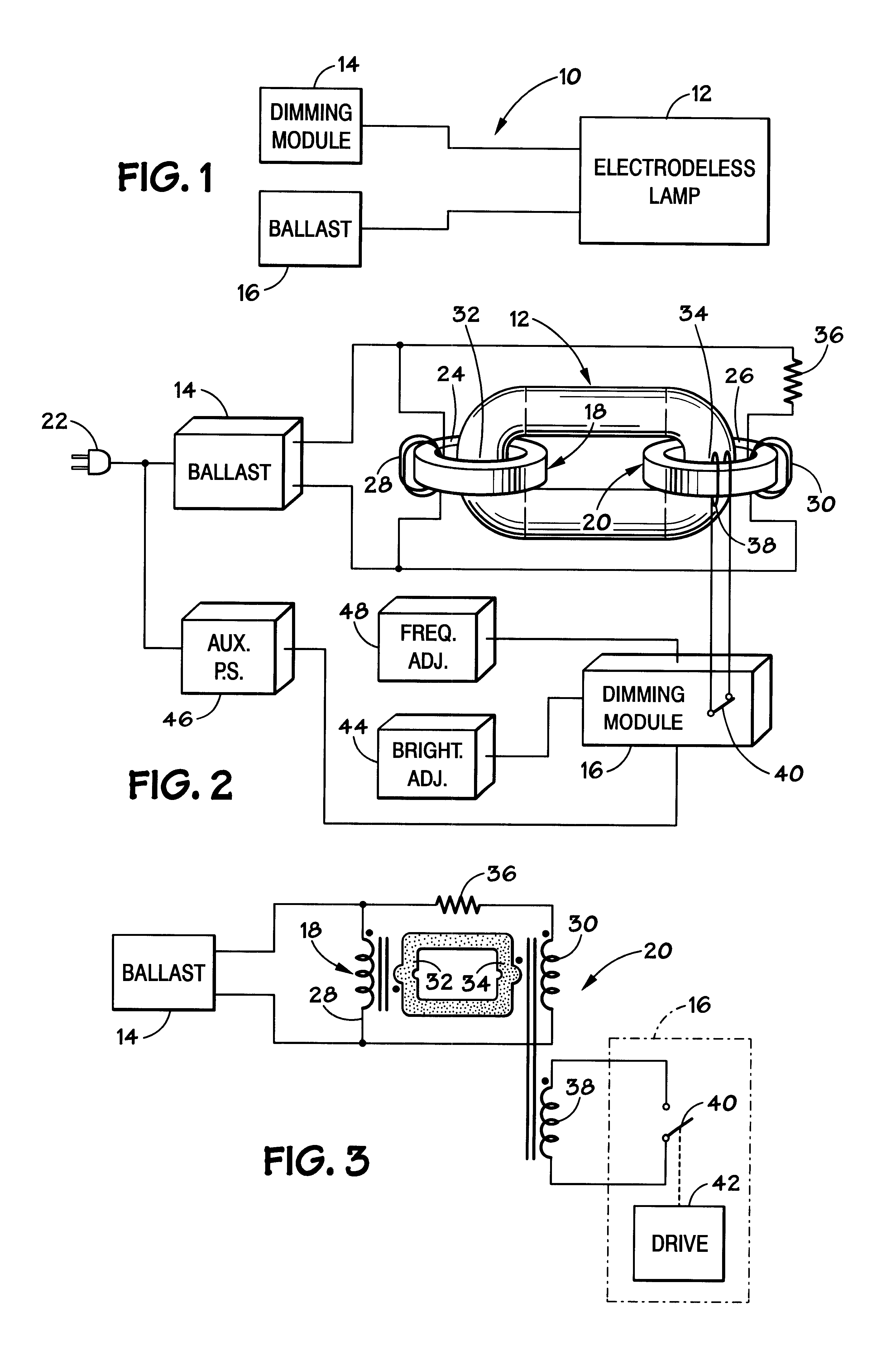
Magnetically shielded electrodeless light source
InactiveUS6433492B1Alternating current plasma display panelsElectric light circuit arrangementDisplay deviceConductor Coil
A dimmable electrodeless light source includes an electrodeless lamp, an electronic ballast and a dimming module. The light source further includes coupling transformers coupled to the electrodeless lamp for inductively coupling power to the lamp to generate light. An auxiliary winding electromagnetically coupled to the primary winding of at least one of the coupling transformers is driven by switching circuitry in the dimming module. The switching circuitry is pulse width modulated to control the average brightness of the light generated by the electrodeless lamp. An exemplary application for the dimmable electrodeless light source is as a backlight for a video display device, such as a liquid crystal display unit. The dimmable electrodeless light source further includes a magnetic shield device that is operably positioned with respect to the electrodeless lamp. The magnetic shield device produces a magnetic field that substantially opposes, and cancels, the magnetic field that is produced by the electrodeless lamp when energized. In an alternative embodiment, the magnetic shield device produces a magnetic field which, when combined with the lamp magnetic field, results in a total magnetic field that is substantially constant regardless of the energization level of the lamp (e.g., totally energized or dimmed). The magnetic shield thus reduces visual artifacts that might otherwise appear on a video display unit due to a variation of the magnetic field produced by the lamp.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Fast recovery electron multiplier
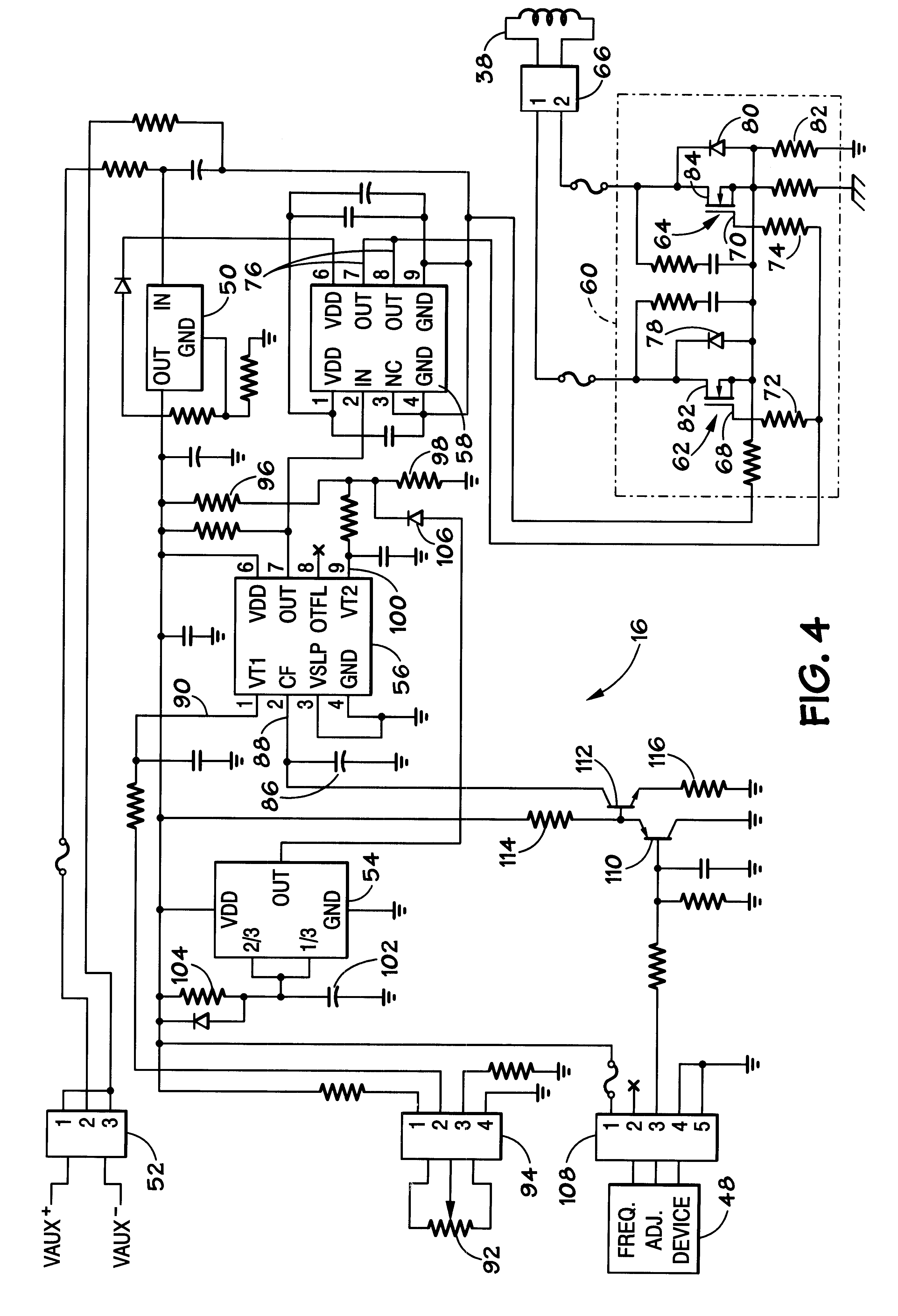
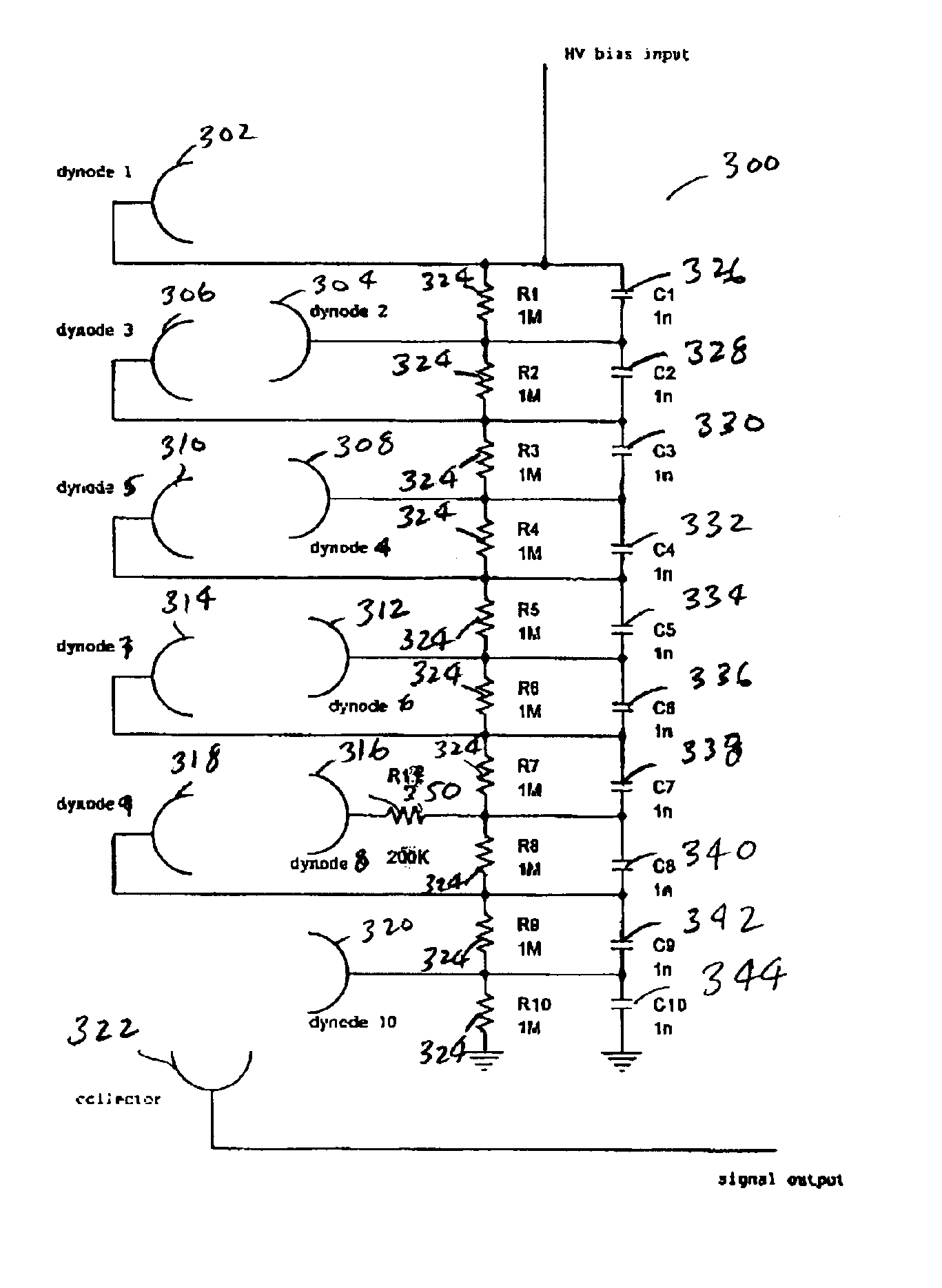
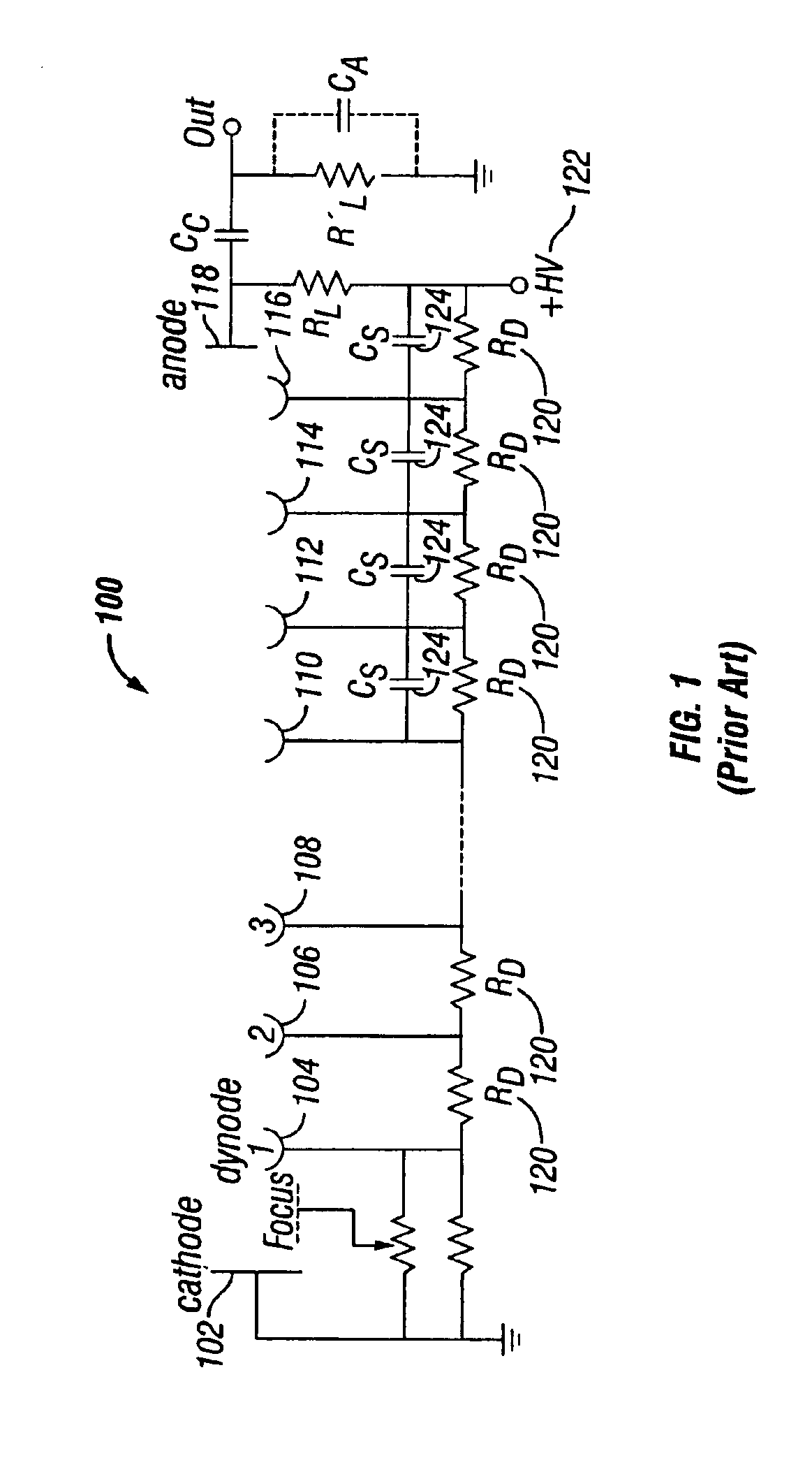
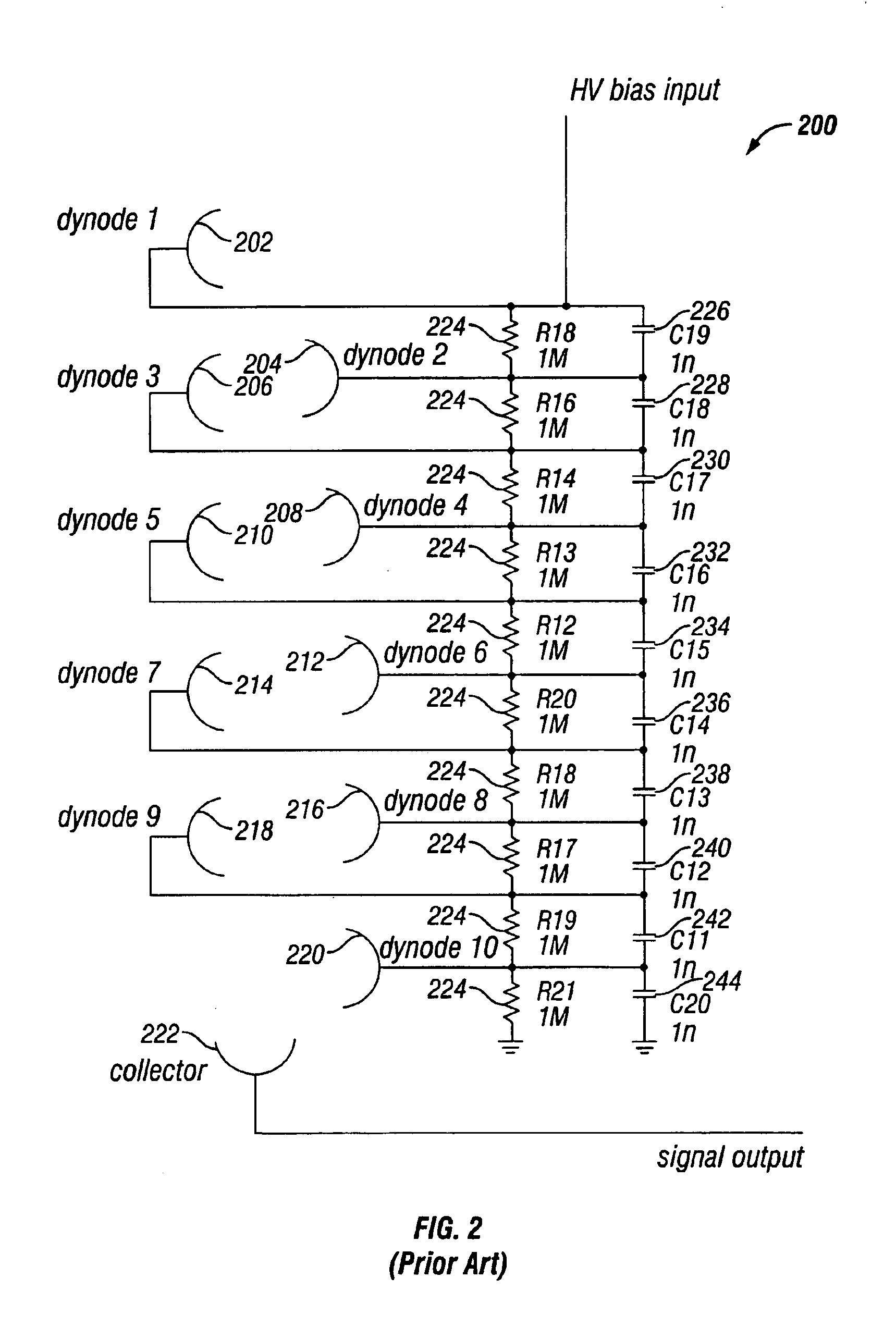
InactiveUS6841936B2Short timeControls are responsiveElectrode and associated part arrangementsAlternating current plasma display panelsElectron multiplierDynode
An improved electron multiplier bias network that limits the response of the multiplier when the multiplier is faced with very large input signals, but then permits the multiplier to recover quickly following the large input signal. In one aspect, this invention provides an electron multiplier, having a cathode that emits electrons in response to receiving a particle, wherein the particle is one of a charged particle, a neutral particle, or a photon; an ordered chain of dynodes wherein each dynode receives electrons from a preceding dynode and emits a larger number of electrons to be received by the next dynode in the chain, wherein the first dynode of the ordered chain of dynodes receives electrons emitted by the cathode; an anode that collects the electrons emitted by the last dynode of the ordered chain of dynodes; a biasing system that biases each dynode of the ordered chain of dynodes to a specific potential; a set of charge reservoirs, wherein each charge reservoir of the set of charge reservoirs is connected with one of the dynodes of the ordered chain of dynodes; and an isolating element placed between one of the dynodes and its corresponding charge reservoir, where the isolating element is configured to control the response of the electron multiplier when the multiplier receives a large input signal, so as to permit the multiplier to enter into and exit from saturation in a controlled and rapid manner.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
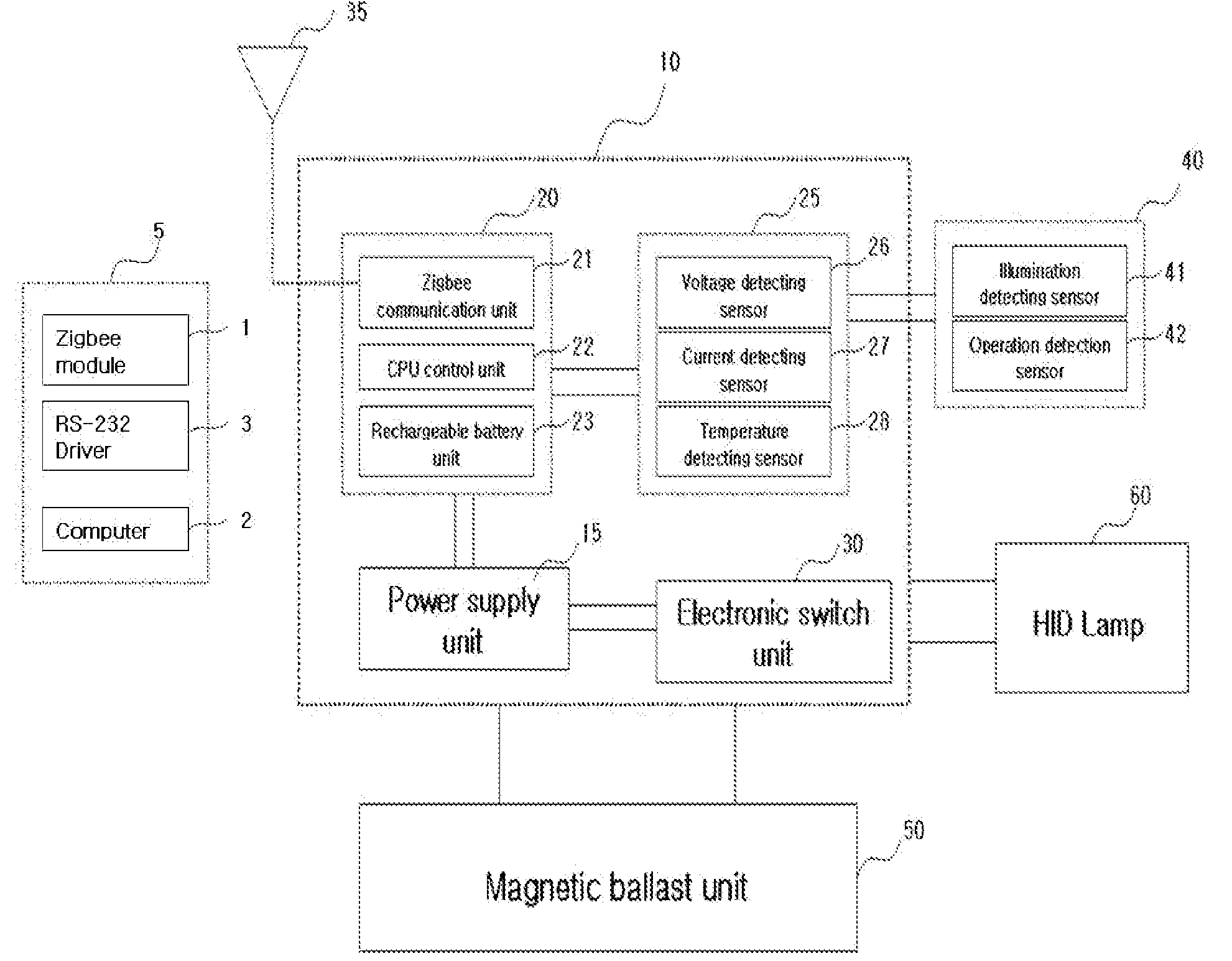
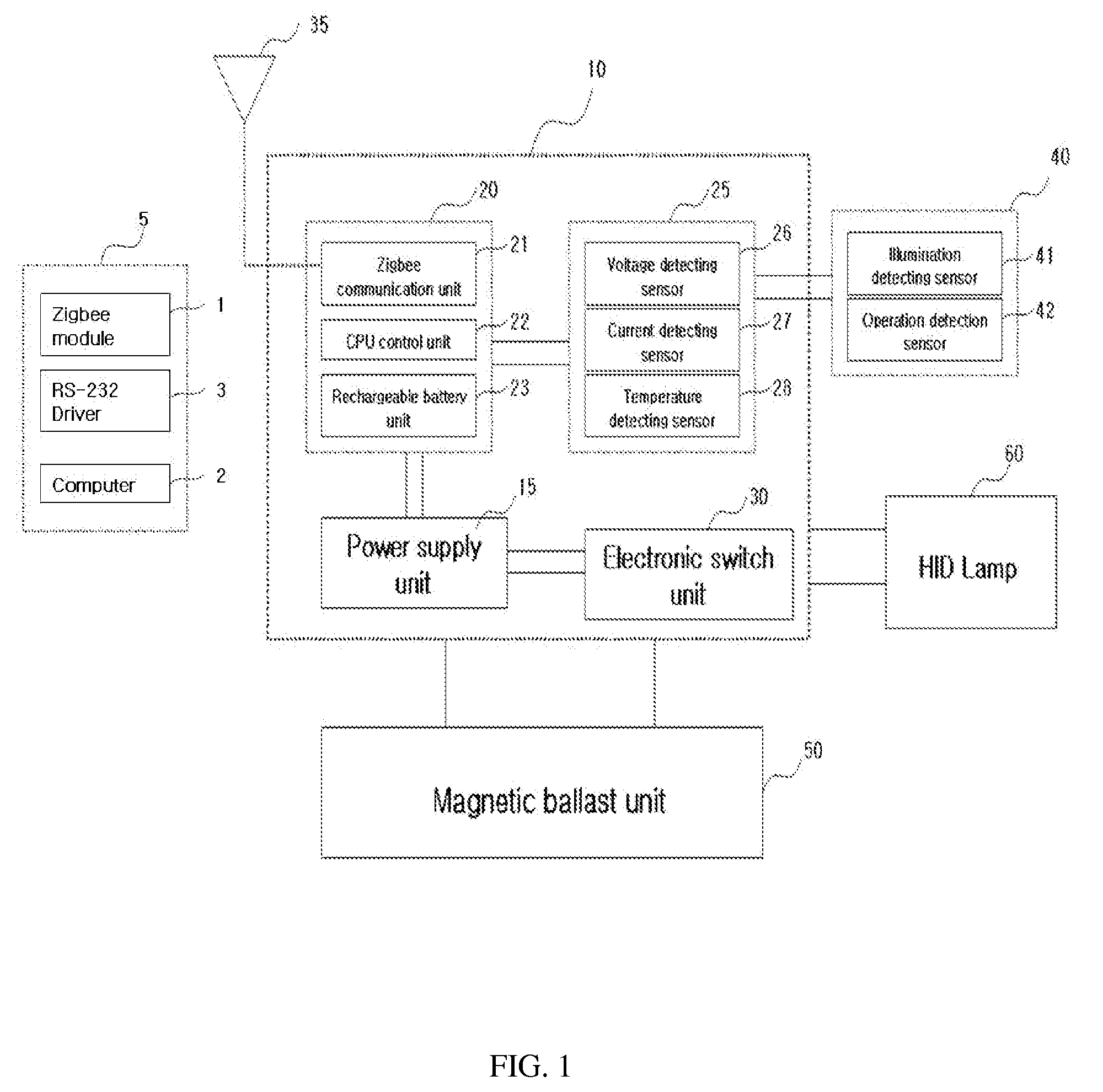
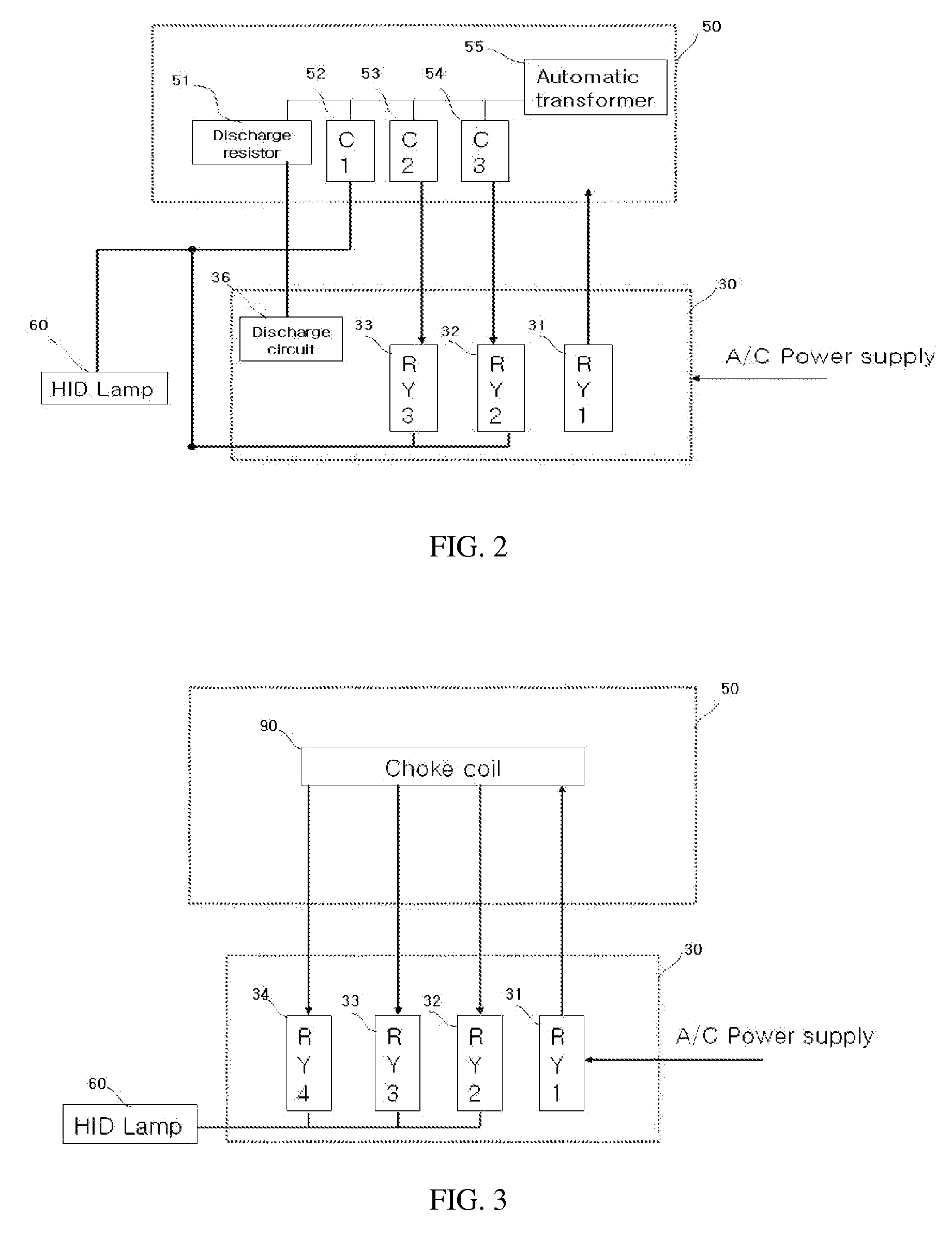
Ballast control system for hid lamp using zigbee
InactiveUS20080218317A1Easy to replaceEnergy efficient ICTLighting elementsControl systemElectronic switch
A control system for an HID lamp, which in one implementation includes a magnetic ballast control system for an HID lamp using Zigbee. A plurality of condensers or choke coils of different capacities is mounted on a magnetic ballast for the lamp, and an electronic switch unit controls illumination according to change of such capacities. RF transmitting / receiving means using a Zigbee-based frequency are employed to turn the HID on and off, and to control illumination through wireless remote communications, thereby achieving considerable energy savings. Operational states of the HID lamp and ballast can be bi-directionally controlled through the communication module, with failures of the HID lamp and ballast automatically detected and notified to users, thereby eliminating inconvenient confirmation processes. The magnetic ballast control system is useful in street lamps, tunnel lamps, factory lamps, warehouse lamps, landscape illuminations, and the like.
Owner:GRS CONSULTING
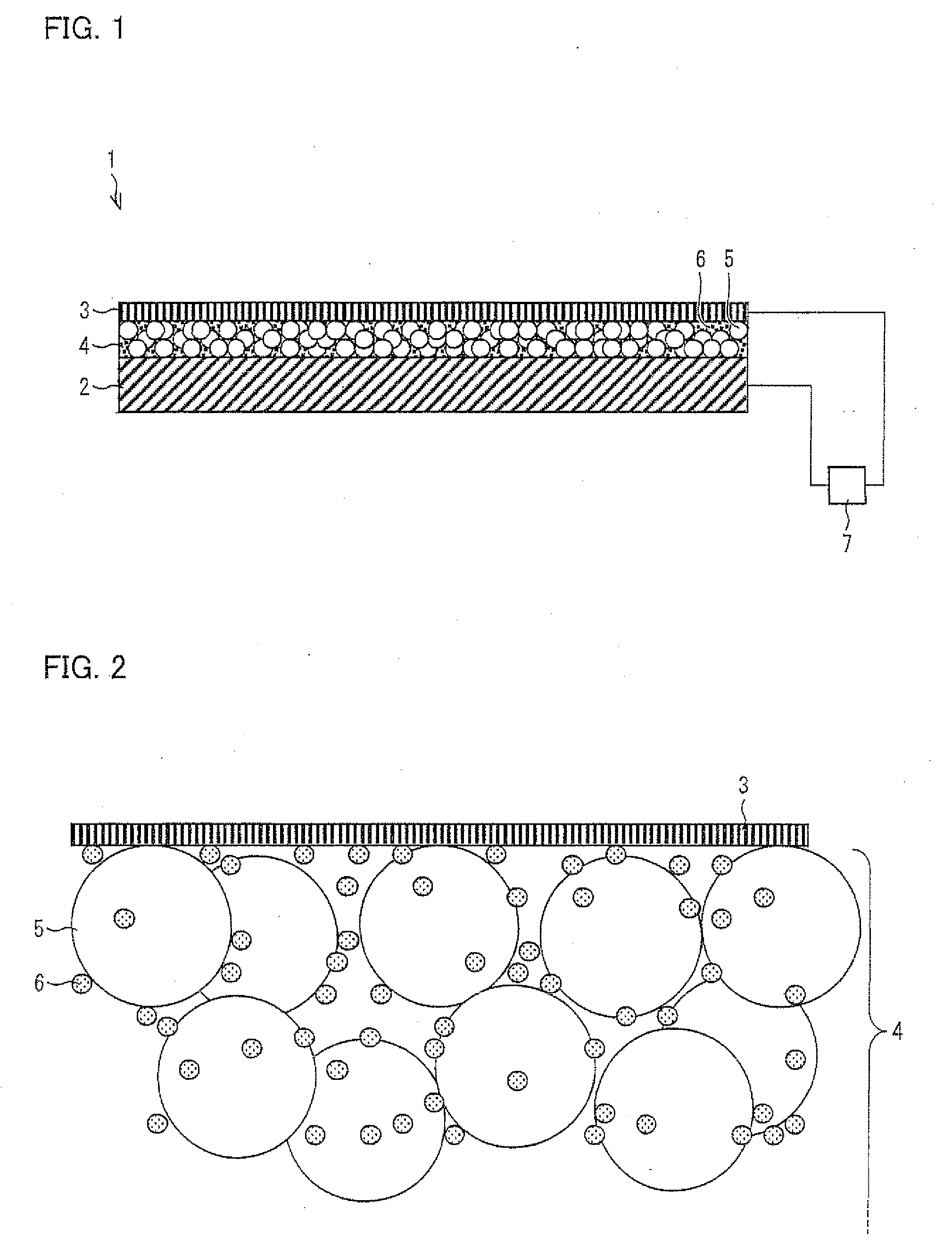
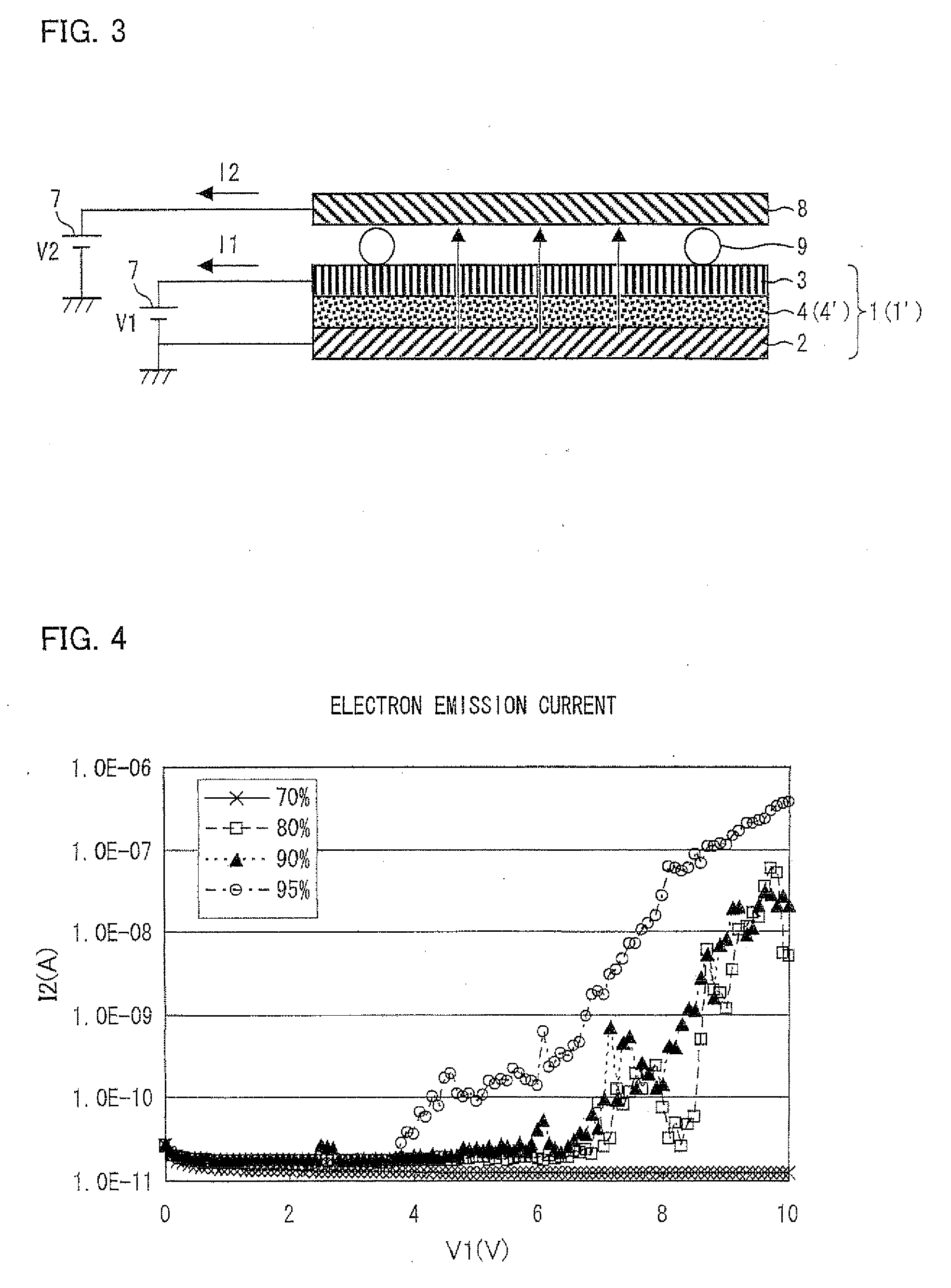
Electron emitting element, electron emitting device, light emitting device, image display device, air blowing device, cooling device, charging device, image forming apparatus, electron-beam curing device, and method for producing electron emitting element
ActiveUS20100278561A1Not easy to degradeEfficiently dissipatedNanoinformaticsAlternating current plasma display panelsHigh resistanceHazardous substance
An electron emitting element (1) includes a substrate (2), an upper electrode (3), and a fine particle layer (4) sandwiched between the substrate (2) and the upper electrode (3). The fine particle layer (4) includes metal fine particles (6) with high resistance to oxidation, and insulating fine particles (5) larger in size than the metal fine particles (6). The electron emitting element (1) can steadily emit electrons not only in vacuum but also in the atmosphere. Further, the electron emitting element (1) can work without electric discharge so that harmful substances such as ozone, NOx, or the like are scarcely generated. Accordingly, degradation of the electron emitting element (1) due to oxidation does not occur. Therefore, the electron emitting element (1) has a long life and can steadily work continuously for a long period of time even in the atmosphere.
Owner:SHARP KK
Solid-state lighting of a white light with tunable color temperatures
ActiveUS8358089B2Reduce dependenceImprove distributionLight source combinationsPoint-like light sourceSmart lightingPlanckian locus
Owner:ALEDDRA INC
External resonator/cavity electrode-less plasma lamp and method of exciting with radio-frequency energy
ActiveUS20070075652A1Reduce the cost of the whole lampIncrease rangeMagnetronsAlternating current plasma display panelsCapacitanceRadio frequency energy
Described is a plasma electrode-less lamp. The device comprises an electromagnetic resonator and an electromagnetic radiation source conductively connected with the electromagnetic resonator. The device further comprises a pair of field probes, the field probes conductively connected with the electromagnetic resonator. A gas-fill vessel is formed from a closed, transparent body, forming a cavity. The gas-fill vessel is not contiguous with (detached from) the electromagnetic resonator and is capacitively coupled with the field probes. The gas-fill vessel further contains a gas within the cavity, whereby the gas is induced to emit light when electromagnetic radiation from the electromagnetic radiation source resonates inside the electromagnetic resonator, the electromagnetic resonator capacitively coupling the electromagnetic radiation to the gas, which becomes a plasma and emits light.
Owner:TOPANGA USA
Solid-state lighting of a white light with tunable color temperatures
ActiveUS20110273107A1Alleviates thermal dependenceBroaden spectral power distributionLight source combinationsPoint-like light sourceSmart lightingPlanckian locus
A light-emitting diode (LED)-based solid-state device comprises a color mixing mechanism to dynamically change the correlated color temperature (CCT) of a white light. With different lumen proportions for white phosphor-coated LEDs and integrated red and green LEDs, the light mixtures can be located in any one of eight CCT quadrangles. In practice, CCTs of a white-light can be tuned in a continuous manner. Because all the possible light mixtures on the chromaticity diagram correspond to a line segment that overlays the Planckian locus within the eight CCT tolerance quadrangles, the effect of LED intensity fluctuations that may put the mixture out of white light region is reduced. Also, because the two additional LEDs that mix with the white phosphor-coated LEDs contribute to the overall spectral power distribution (SPD) that substantially matches the SPD of standard illuminants, a CRI of 80 can be reached.
Owner:ALEDDRA INC
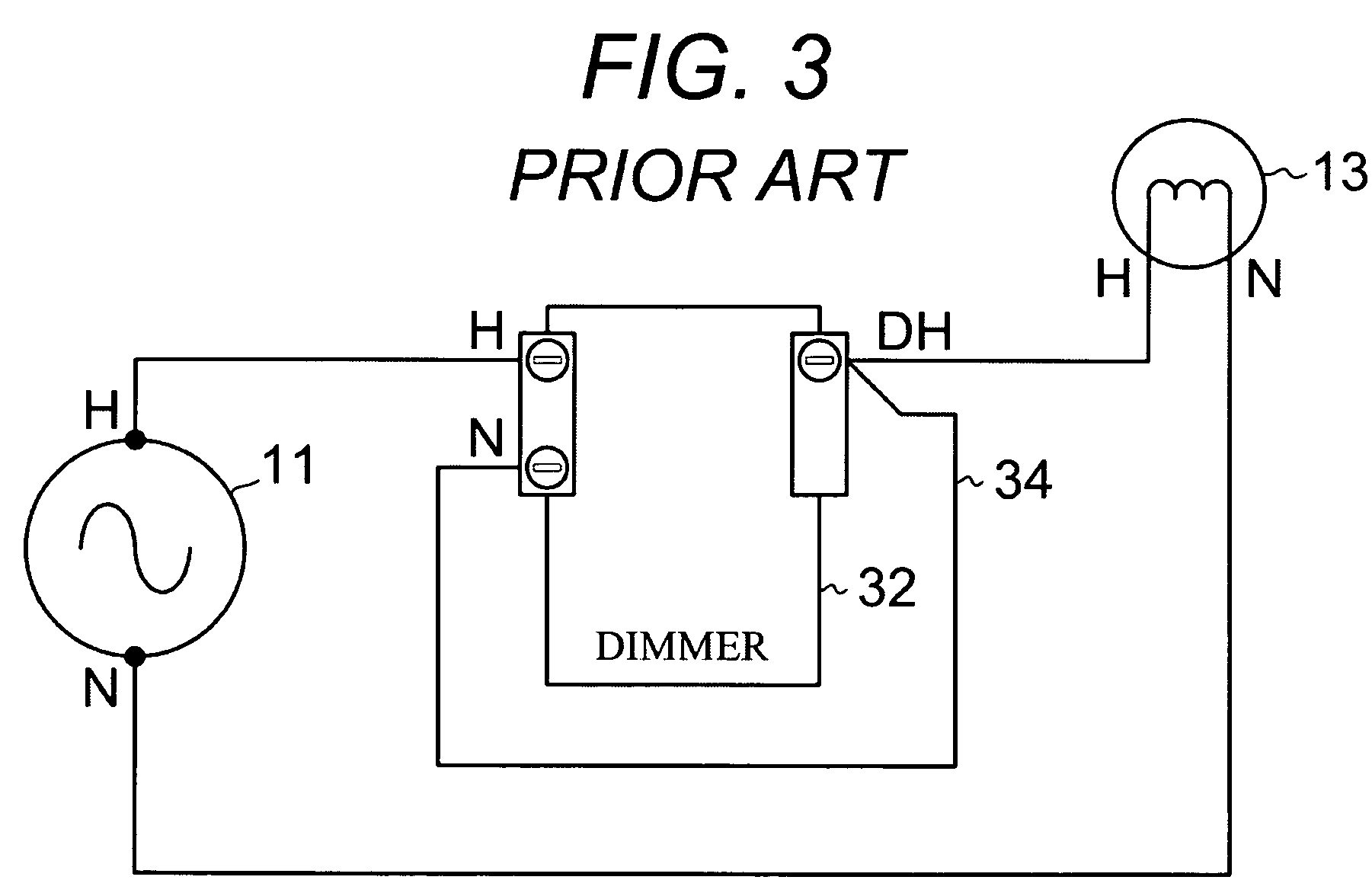
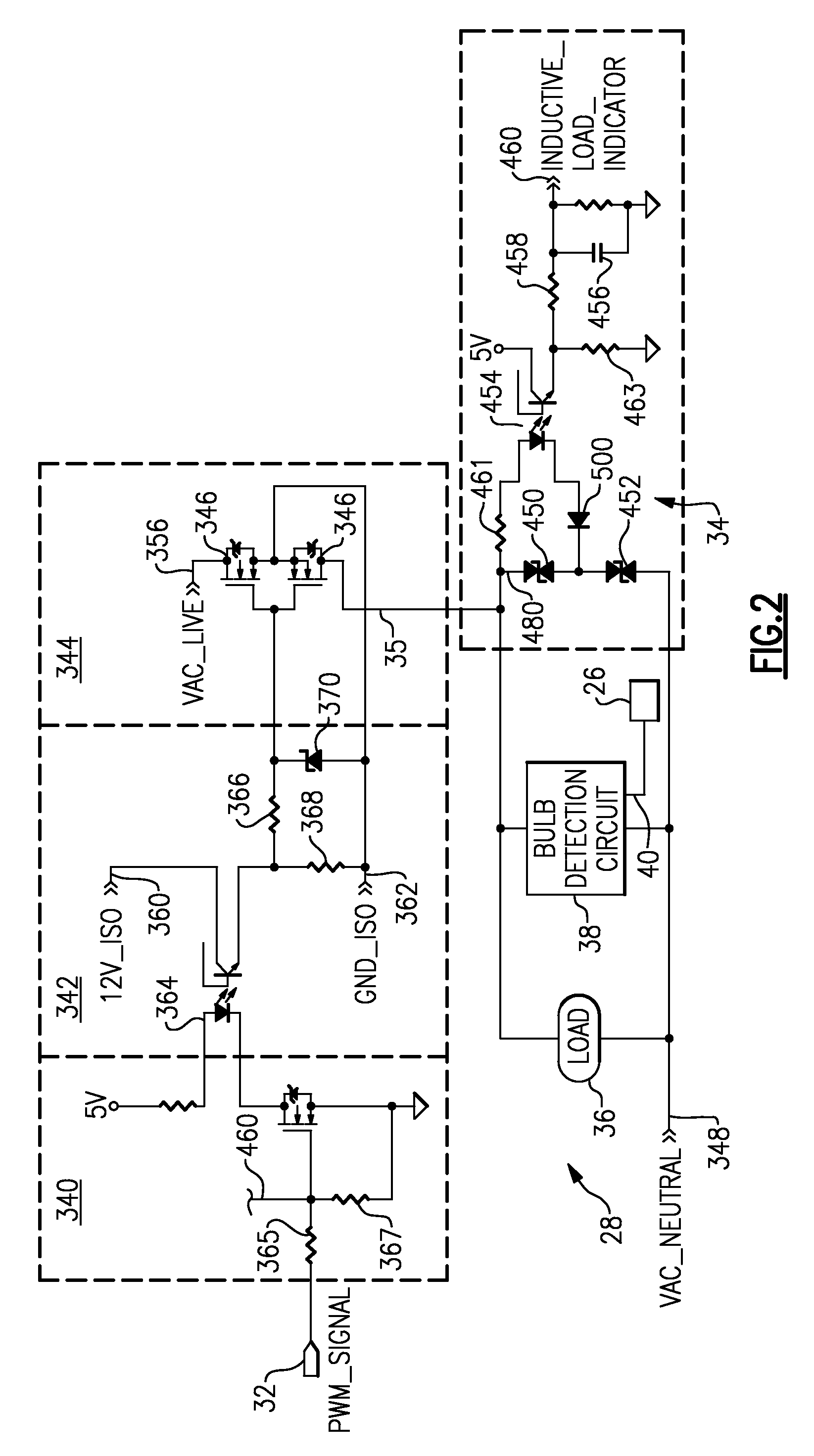
Lighting dimmer adaptable to four wiring configurations
ActiveUS7928663B1Avoid loadAlternating current plasma display panelsElectric light circuit arrangementDimmerElectrical and Electronics engineering
A lighting dimmer (52) adaptable to four wiring configurations is capable of use in serial or parallel lighting circuits and in place of two-way or three-way switches. The dimmer operates in series when one active input wire (H) is connected and in parallel when two active input wires (H, N) are connected. The dimmer is operated in place of a two-way switch by connecting one output wire (DH1) and in place of a three-way switch by connecting two output wires (DH1, DH2).
Owner:CRESTRON ELECTRONICS
Apparatus and Method for Regulating the Output of a Plasma Electron Beam Source
ActiveUS20110080093A1Turn easilyEasy to controlElectric arc lampsDischarge tube/lamp detailsPlasma electronBeam source
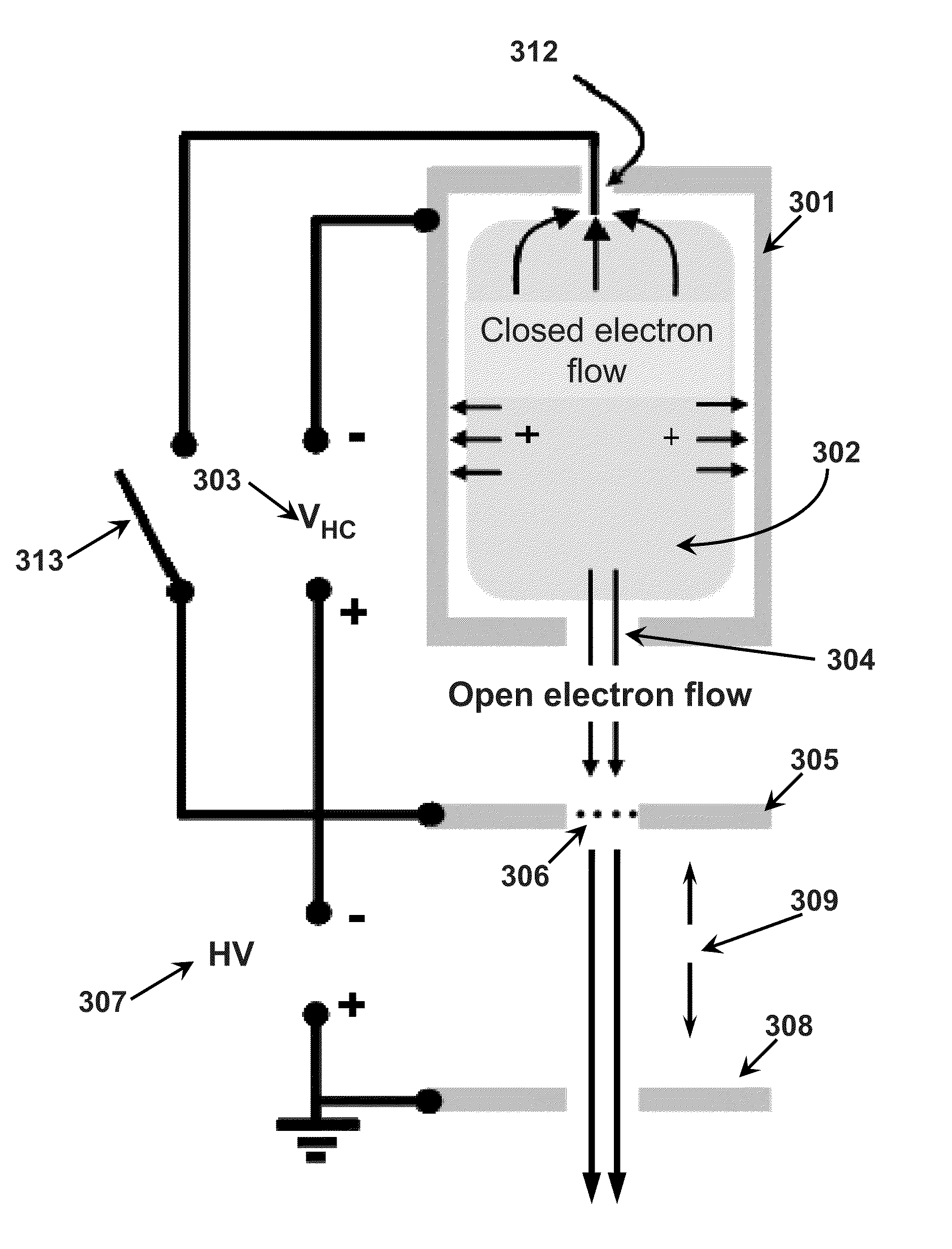
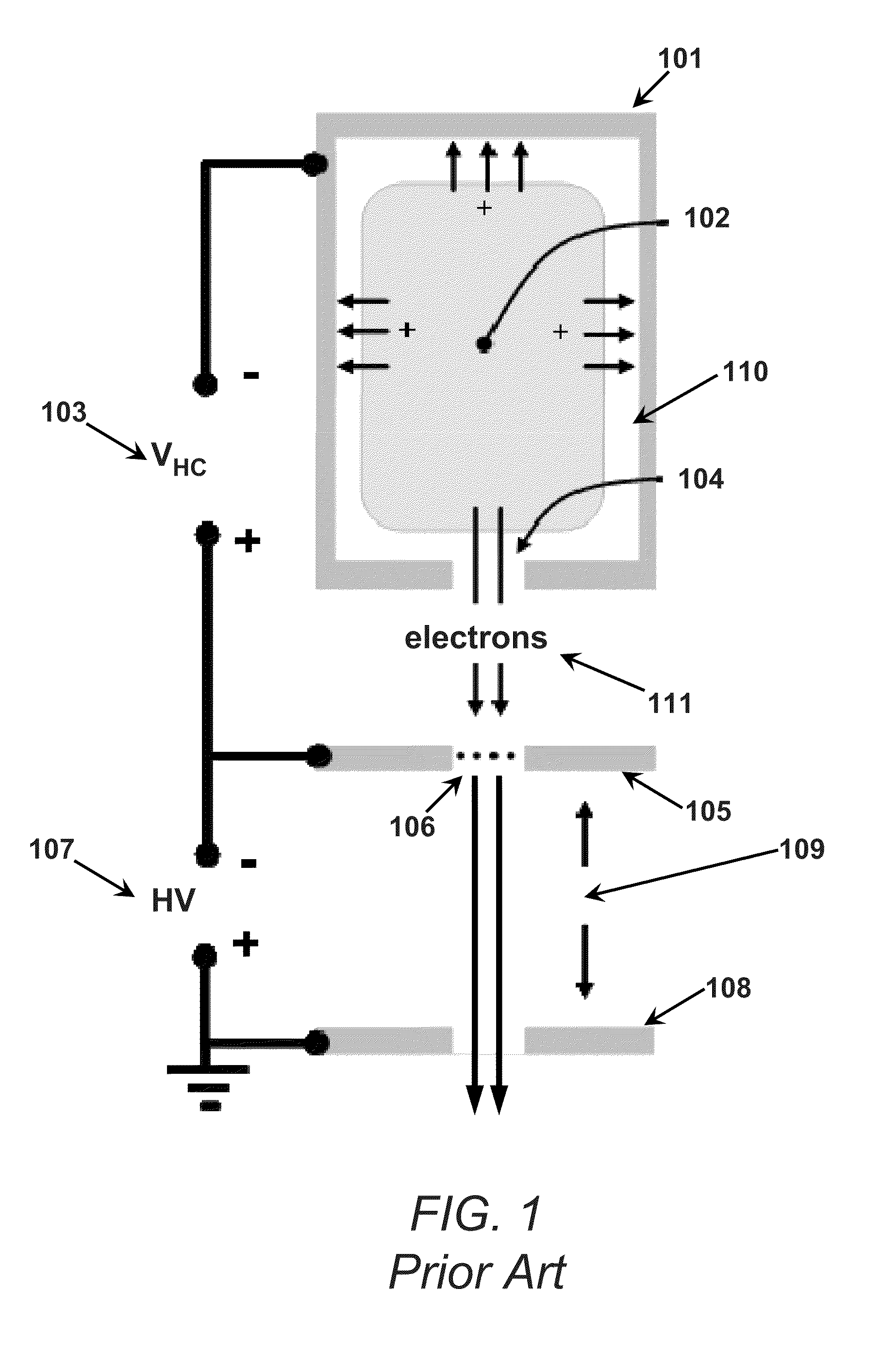
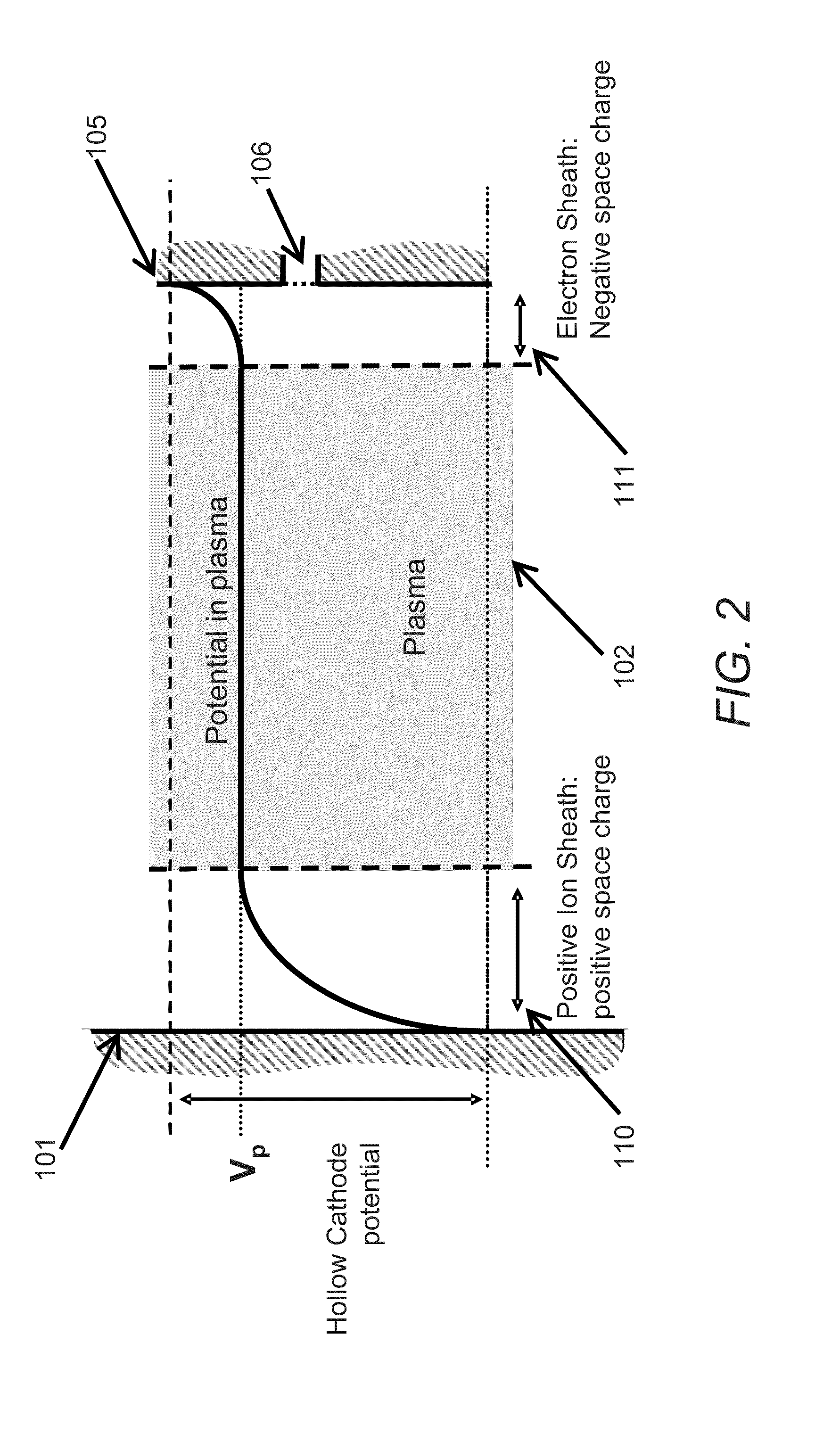
An apparatus and method for controlling electron flow within a plasma to produce a controlled electron beam is provided. A plasma is formed between a cathode and an acceleration anode. A control anode is connected to the plasma and to the acceleration anode via a switch. If the switch is open, the ions from the plasma flow to the cathode and plasma electrons flow to the acceleration anode. With the acceleration anode suitably transparent and negatively biased with a DC high voltage source, the electrons flowing from the plasma are accelerated to form an electron beam. If the switch is closed, the ions still flow to the cathode but the electrons flow to the control anode rather than the acceleration anode. Consequently, the electron beam is turned off, but the plasma is unaffected. By controlling the opening and closing of the switch, a controlled pulsed electron beam can be generated.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
RF induction lamp with reduced electromagnetic interference
InactiveUS7180230B2Improve efficiencyImproves electrostatic symmetryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsBeam/ray deflecting arrangementsElectromagnetic interferenceFluorescent lamp
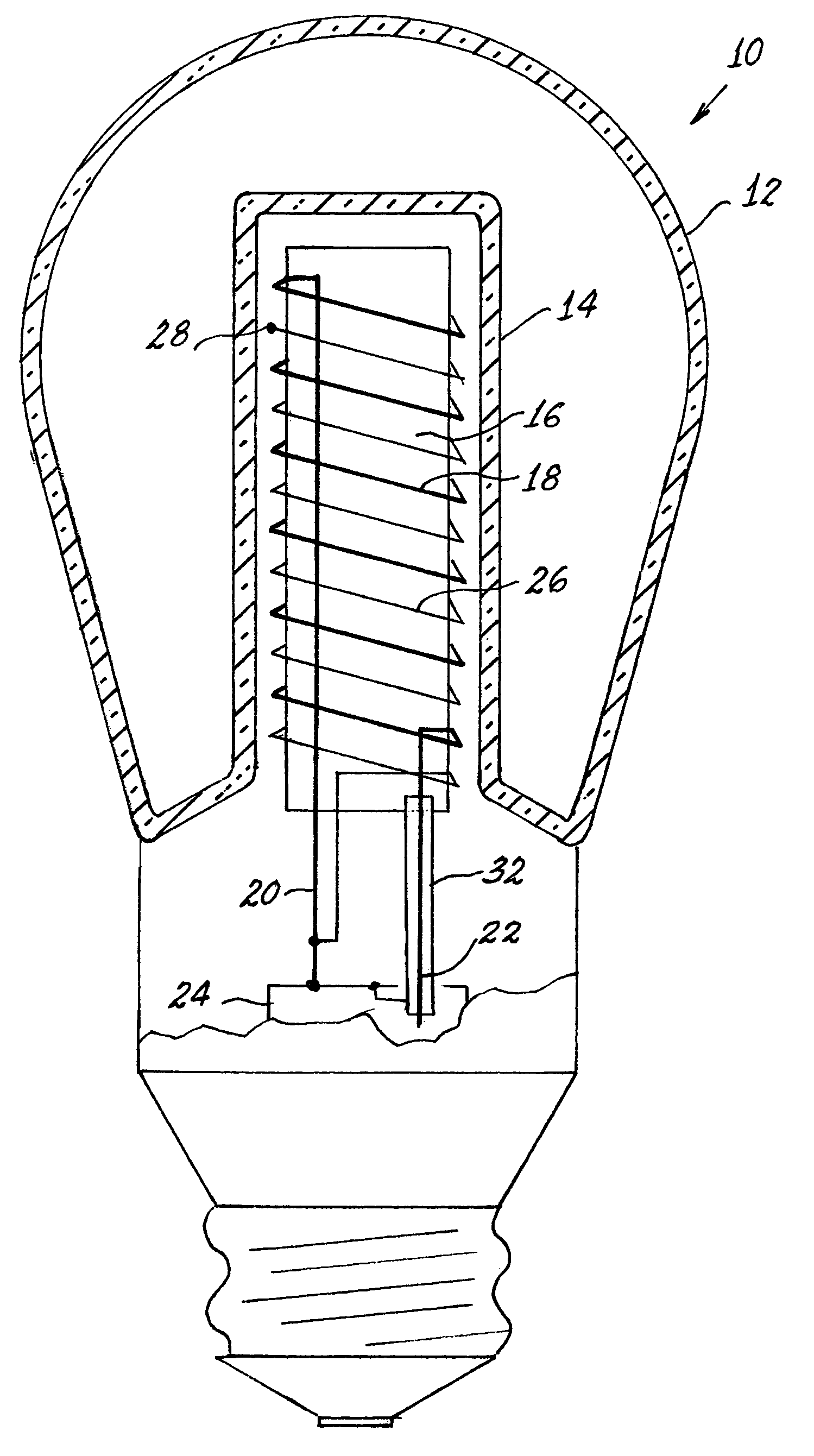
An electrodeless fluorescent lamp 10 has an envelope 12 that includes a chamber 14. A core 16 of magnetic material, preferably ferrite, is positioned in the chamber 14 and has a first winding 18 surrounding the core and having first and second lead-in wires 20, 22, attached to a high frequency voltage supply or ballast 24. A second winding 26 surrounds the core 16, respective turns of the second winding 26 being located adjacent turns of the first winding 18 and electrically insulated therefrom. The second winding 26 has a free end 28 and has another end 30 connected to one of the lead-in wires, for example 20. A braided sheath 32 surrounds the other of the lead-in wires 22. The first winding 18 is generally called the RF antenna. The braided sheath 32 is connected to the local ground. This inexpensive solution alone reduces the conductive EMI level sufficiently to pass all existing regulations on such interference with significant reserve.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
Dimmer adaptable to either two or three active wires
ActiveUS7609007B1Eliminate needAlternating current plasma display panelsElectric light circuit arrangementFull waveDimmer
A dimmer (42) adaptable to either two (H, DH) or three (H, N, DH) active wires includes a first full-wave rectifier (D1, D2, D3, D4) across an AC power hot (H) terminal and a dimmer hot (DH) terminal and a second full-wave rectifier (D1, D4, D5, D6) across the AC power hot (H) terminal and an AC power neutral (N) terminal. The dimmer (42) operates in a two-wire configuration by drawing power through a load (13) when a control circuit (422) is not conducting or in a three-wire configuration, when the AC power neutral (N) terminal is connected, by drawing power from AC power hot (H) and AC power neutral (N) terminals.
Owner:CRESTRON ELECTRONICS
RF induction lamp with reduced electromagnetic interference
InactiveUS8698413B1Low costEMI suppressionAlternating current plasma display panelsDischarge tube main electrodesPhosphorEnd-group
An induction RF fluorescent lamp configuration provides reduced EMI, including a lamp envelope with a re-entrant cavity both covered on the partial vacuum side with phosphor and filled with a working gas mixture, a tubular ferromagnetic core on the non-vacuum side said re-entrant cavity wound directly on the said core with two windings having different numbers of turns, a first active winding having one end connected to an RF ballast and the other end connected to local ground, and a second passive winding having one end grounded and the other end free.
Owner:LUCIDITY LIGHTS
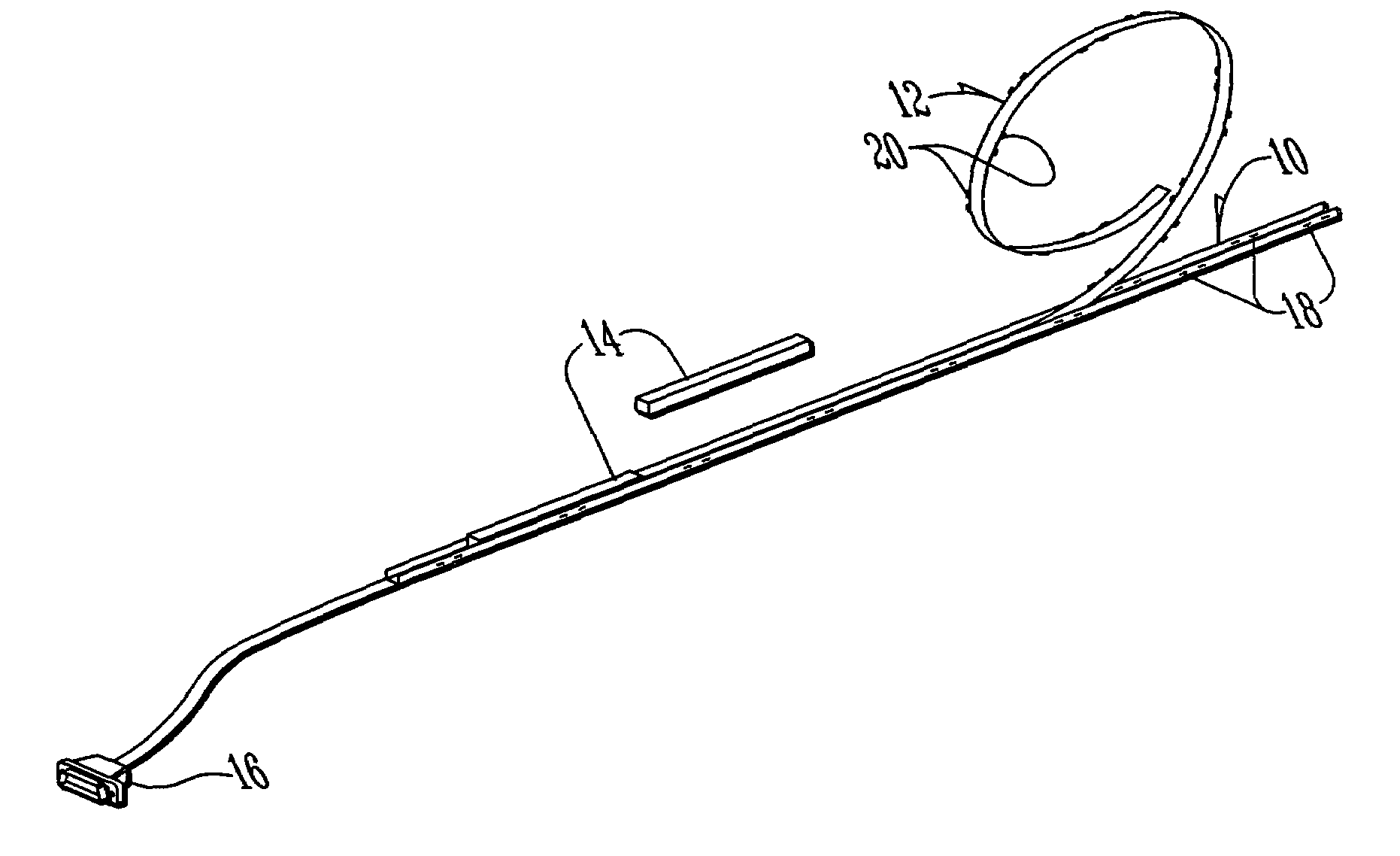
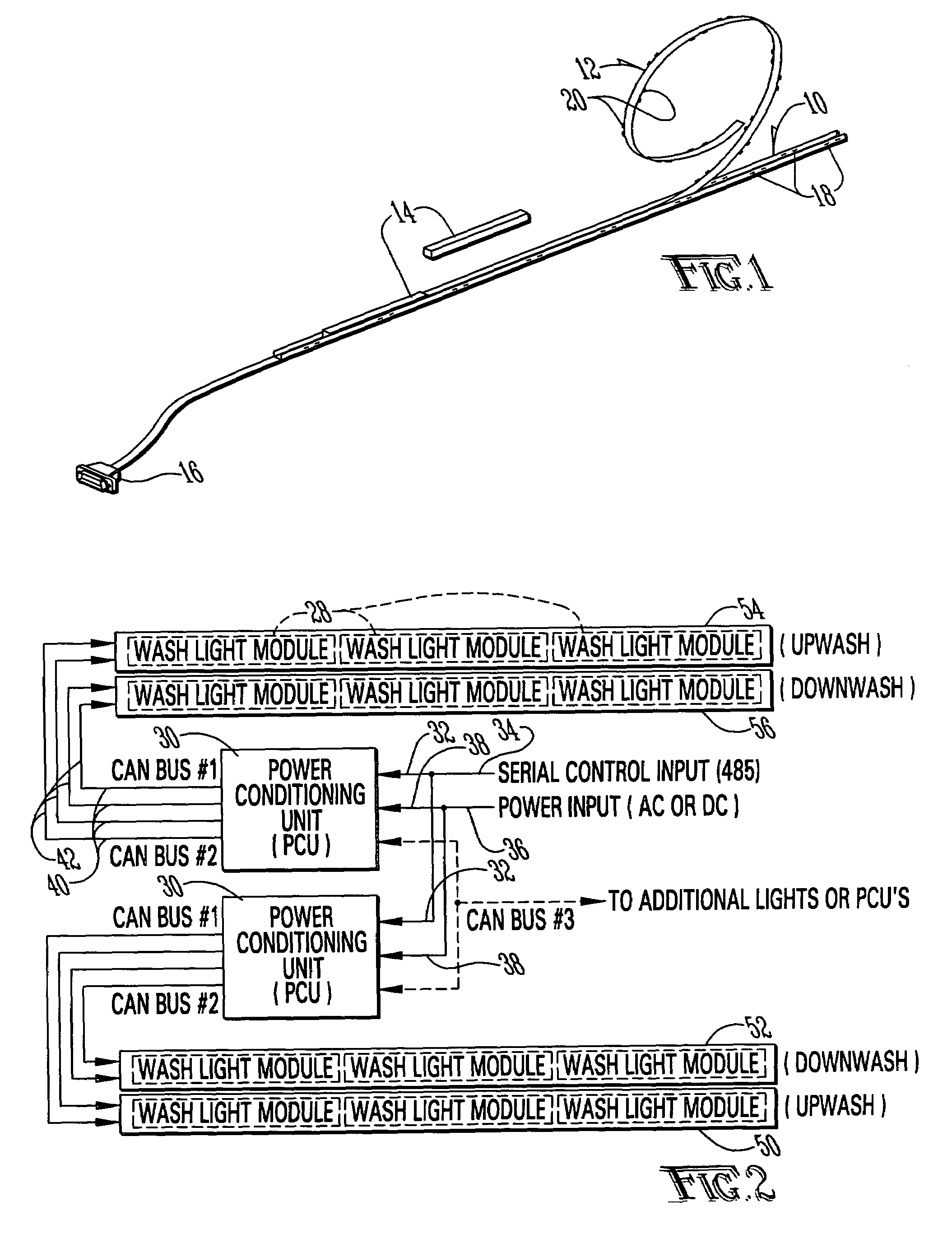
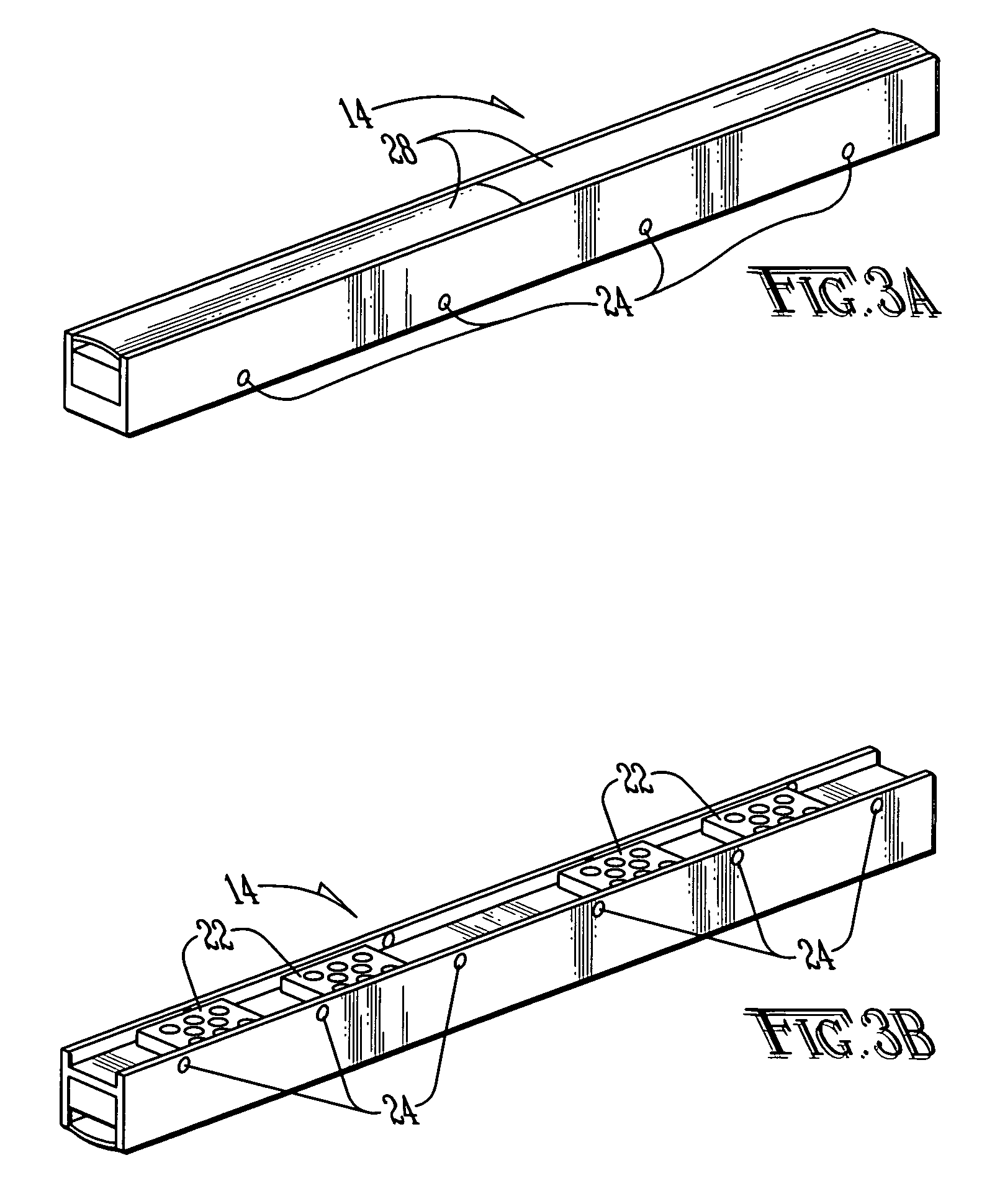
Lighting assembly
InactiveUS7114827B2Equally distributedClean light outputLighting support devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesEffect lightModularity
A lighting assembly that is modular and highly configurable is disclosed. The assembly consists of one or more light fixtures that are fitted into a mounting rail. A flat, flexible cable lies within the rail and makes contact with the light fixtures through spring-loaded connectors. A power conditioning unit supplies power to the lighting assembly. The lighting assembly may be assembled and maintained with a minimum of tools, and is adaptable to a wide variety of environments and lighting design options.
Owner:IDD AEROSPACE +1
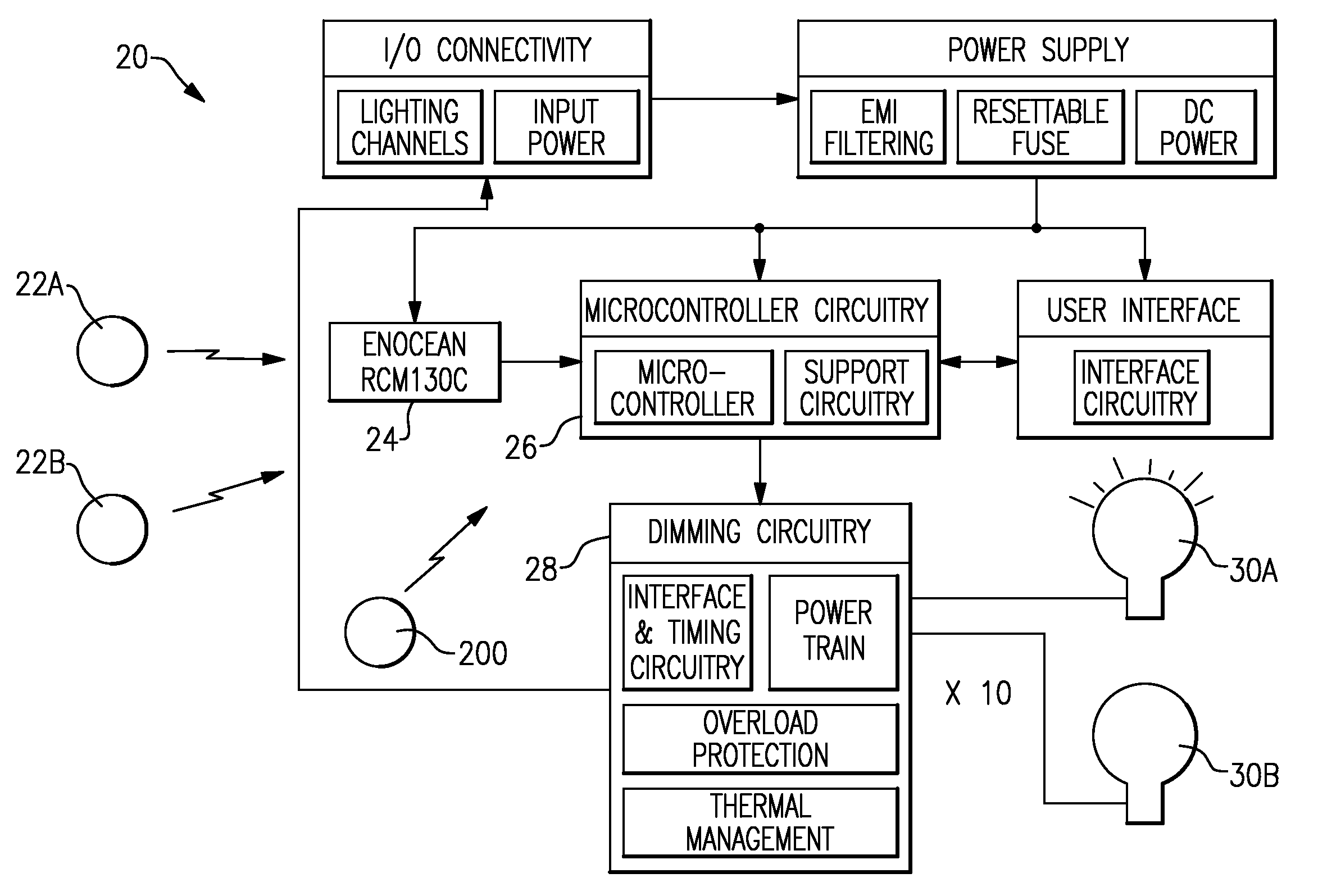
Dimming algorithms based upon light bulb type
ActiveUS20080315787A1Easy to controlAlternating current plasma display panelsElectric light circuit arrangementEffect lightEngineering
A lighting control circuit for dimming a light is provided with different algorithms that are utilized to dim fluorescent and incandescent lights. Some method of identifying the type of light which is to be dimmed, reports to a control for the lighting control circuit, and the appropriate algorithm is then selected and utilized.
Owner:ENOCEAN
RF induction lamp with reduced electromagnetic interference
InactiveUS20050280344A1Improves electrostatic symmetryImprove efficiencyBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsBeam/ray deflecting arrangementsElectromagnetic interferenceEngineering
An electrodeless fluorescent lamp 10 has an envelope 12 that includes a chamber 14. A core 16 of magnetic material, preferably ferrite, is positioned in the chamber 14 and has a first winding 18 surrounding the core and having first and second lead-in wires 20, 22, attached to a high frequency voltage supply or ballast 24. A second winding 26 surrounds the core 16, respective turns of the second winding 26 being located adjacent turns of the first winding 18 and electrically insulated therefrom. The second winding 26 has a free end 28 and has another end 30 connected to one of the lead-in wires, for example 20. A braided sheath 32 surrounds the other of the lead-in wires 22. The first winding 18 is generally called the RF antenna. The braided sheath 32 is connected to the local ground. This inexpensive solution alone reduces the conductive EMI level sufficiently to pass all existing regulations on such interference with significant reserve.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
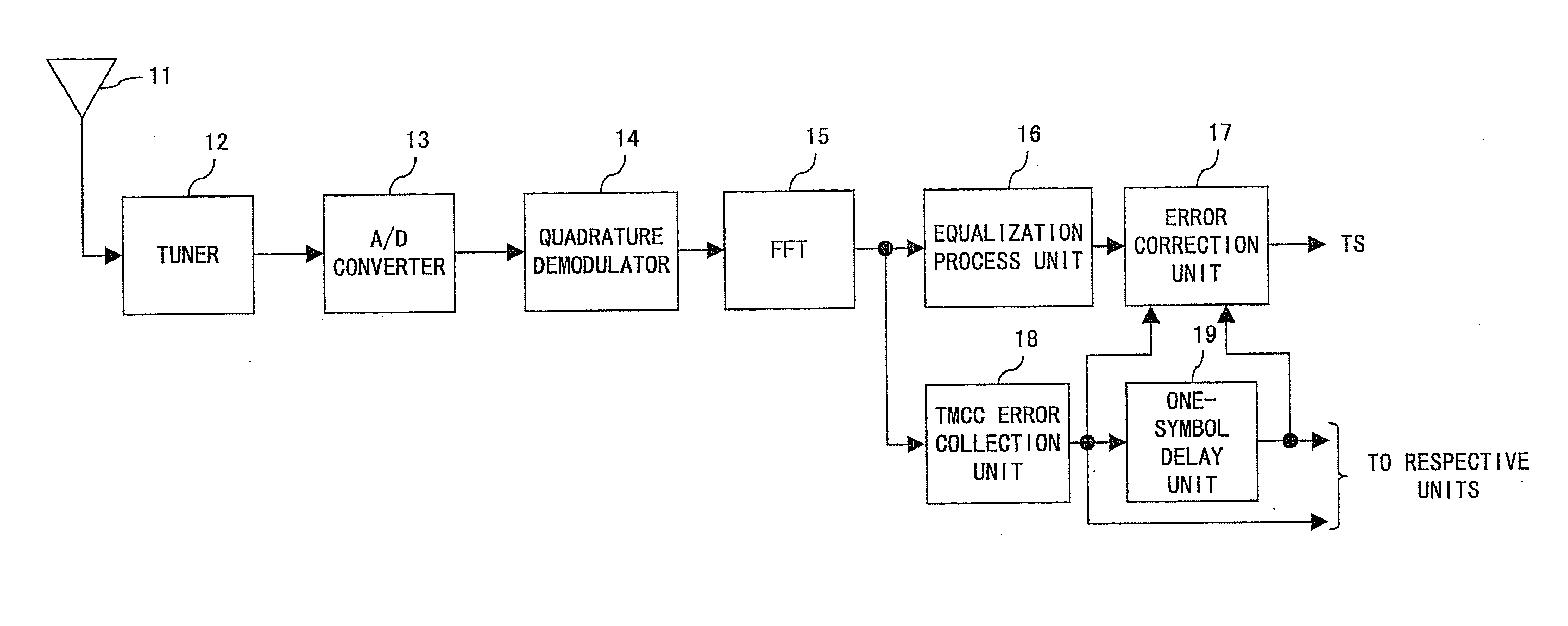
Device and method for receiving digital signal transmitted using OFDM method
InactiveUS20070288832A1Reduce memory capacityData representation error detection/correctionAlternating current plasma display panelsEngineeringDemodulation
A receiver that receives a digital signal transmitted on the basis of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) method. This receiver comprises a demodulation unit for demodulating the digital signal, a demapping unit for demapping demodulated data output from the demodulation unit, a frequency deinterleave unit for executing a frequency deinterleaving process on data output from the demapping unit, a delay unit for delaying control information superposed on the digital signal by a prescribed time period, and a time deinterleave unit for executing, on the basis of the interleave length specified by the control information delayed by the delay unit, a time deinterleaving process on data on which the frequency deinterleaving process has been executed.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
LED bulb
InactiveUS20110163675A1Reduce weightLow production costPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsElectricityEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of illumination lamps, in particular to an LED bulb. The invention comprises a lamp cap, a lampshade, LEDS and a circuit board, wherein the bottom end of the lampshade is mounted and fixed at the top end of the lamp cap; the circuit board is mounted and fixed in the lampshade and also electrically connected with the lamp cap; and the lampshade is filled with a mixed gas which transfers heat produced by the LEDS outside the bulb. The invention transfers heat produced by the LEDS by a mixed gas; the LED bulb has such advantages to as small weight, small volume and low production cost; besides, by using the mixed gas as heat transfer medium, the invention can radiate heat produced by the LEDS outside the bulb rapidly so as to effectively solve the heat radiation issue of the LEDS and prolong the service life of the LEDS.
Owner:DONGGUAN KAIYU PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
Dial control with LED light ring
An illuminated control for a gas range or the like provides arcuate reflective chambers capped by diffusers to create a substantially continuous glowing circular sector indicating the status of a possibly low visibility gas flames. Line power may be used for direct drive of light emitting diodes illuminating the reflective chambers through the use of discrete series-connected voltage dropping resistors distributed to prevent heat concentration.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Discharge lamp lighting device, control method thereof, and projector
ActiveUS20090237009A1Drive stabilityAccurate settingAlternating current plasma display panelsElectric light circuit arrangementDc currentEffect light
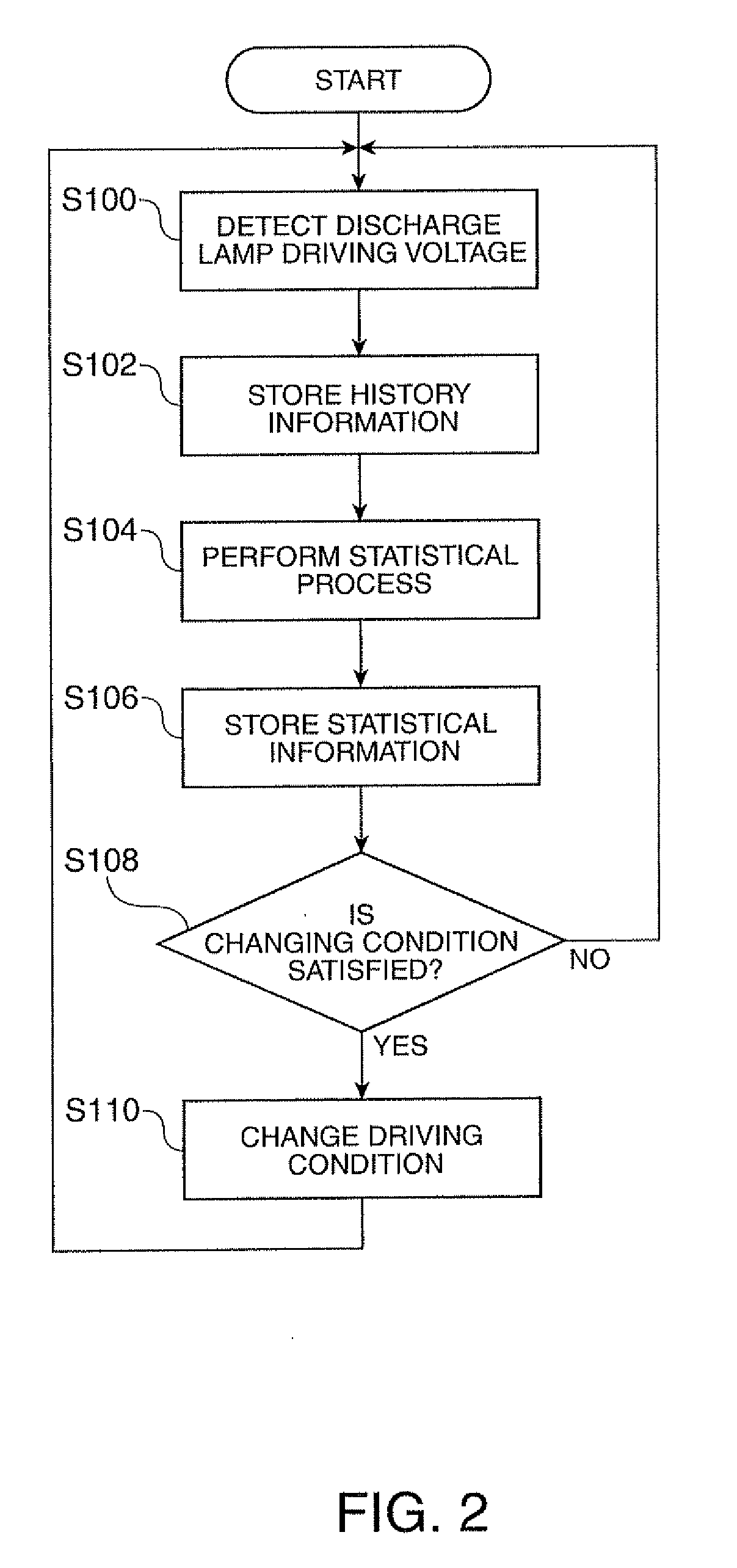
A discharge lamp lighting device includes: a power control circuit outputting DC current; an AC conversion circuit generating and outputting discharge lamp driving AC current by inverting the polarity of the DC current at a predetermined timing; a control circuit performing an AC conversion control process of controlling a polarity inversion timing of the discharge lamp driving AC current on the AC conversion circuit and performing an interval current control process of controlling a current value of the DC current every polarity inversion timing interval on the power control circuit; a detection unit detecting a discharge lamp driving voltage at the time of normal lighting; a history information storage periodically storing history information of the detected discharge lamp driving voltage, a statistics processing unit statistically processing the stored history information every predetermined period; and a statistical information storage storing information having been subjected to the statistical process as statistical information. Here, the control circuit sets and controls at least one of a frequency, a duty ratio, and a waveform of the discharge lamp driving AC current on the basis of a time-dependent tendency of the statistical information.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
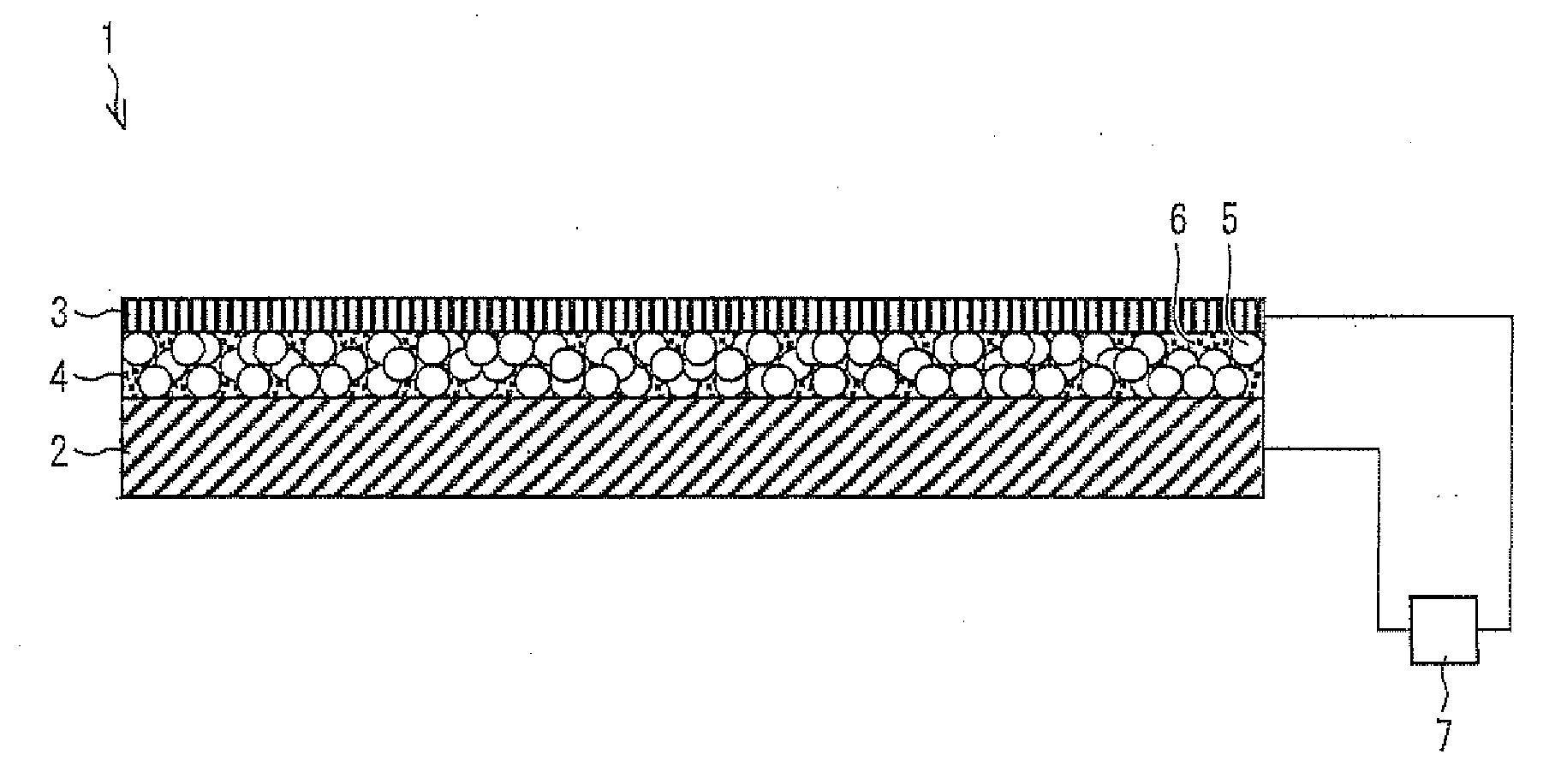
Electron emitting element, electron emitting device, light emitting device, image display device, air blowing device, cooling device, charging device, image forming apparatus, and electron-beam curing device
ActiveUS20100296845A1Improve energy efficiencyNanoinformaticsAlternating current plasma display panelsThin film electrodeDisplay device
The present invention provides an electron emitting element which has good energy efficiency and which is capable of controlling a value of current flowing in an electron acceleration layer and an amount of emitted electrons by adjusting a resistance value of the electron acceleration layer and an amount of generated ballistic electrons. An electron emitting element 1 includes an electron acceleration layer 4 including a fine particle layer containing insulating fine particles. In the electron emitting element 1, Ie=α·R−0.67 where Ie [A / cm2] is electron emission current per unit area during the voltage application and R is element resistance [Ω·cm2] per unit area, the element resistance being obtained by dividing (a) a voltage applied between the electrode substrate 2 and the thin-film electrode 3 during the voltage application by (b) current in element per unit area which current flows between the electrode substrate 2 and the thin-film electrode 3 during the voltage application, and where α is not less than 2.0×10−6, and the electron emission current Ie is not less than 1.0×10−9.
Owner:SHARP KK
Low ozone ratio, high-performance dielectric barrier discharge reactor
InactiveUS20110115415A1Inhibition formationPromotes rapid oxidationAlternating current plasma display panelsDischarge tube main electrodesPlatinumMetal catalyst
A dielectric barrier discharge reactor made in the form of a module formed of two electrode panels that are vertically arranged in a parallel manner each having a plurality of metal discharge needles and a meshed treatment unit set between the electrode panels in a parallel manner. The meshed treatment unit includes a substrate having a size equal to the electrode panels, and a metal catalyst prepared from gold, silver, platinum, nickel, manganese, chrome or their combination and coated on the substrate. The dielectric barrier discharge reactor is practical for home or public space application to purify air.
Owner:HONG KUN LIANG
Electron emitting element, electron emitting device, light emitting device, image display device, cooling device, and charging device
ActiveUS20100196050A1Reduce the amount requiredInadequate flowNanoinformaticsAlternating current plasma display panelsThin film electrodeDisplay device
An electron emitting element of the present invention includes an electron acceleration layer provided between an electrode substrate and a thin-film electrode, which electron acceleration layer includes (a) conductive fine particles and (b) insulating fine particles having an average particle diameter greater than that of the conductive fine particles. The electron emitting element satisfies the following relational expression: 0.3x+3.9≦y≦75, where x (nm) is an average particle diameter of the insulating fine particles, and y (nm) is a thickness of the thin-film electrode 3. Such a configuration allows modification of the thickness of the thin-film electrode with respect to the size of the insulating particles, thereby ensuring electrical conduction and allowing sufficient current to flow inside the element. As a result, stable emission of ballistic electrons from the thin-film electrode is possible.
Owner:SHARP KK
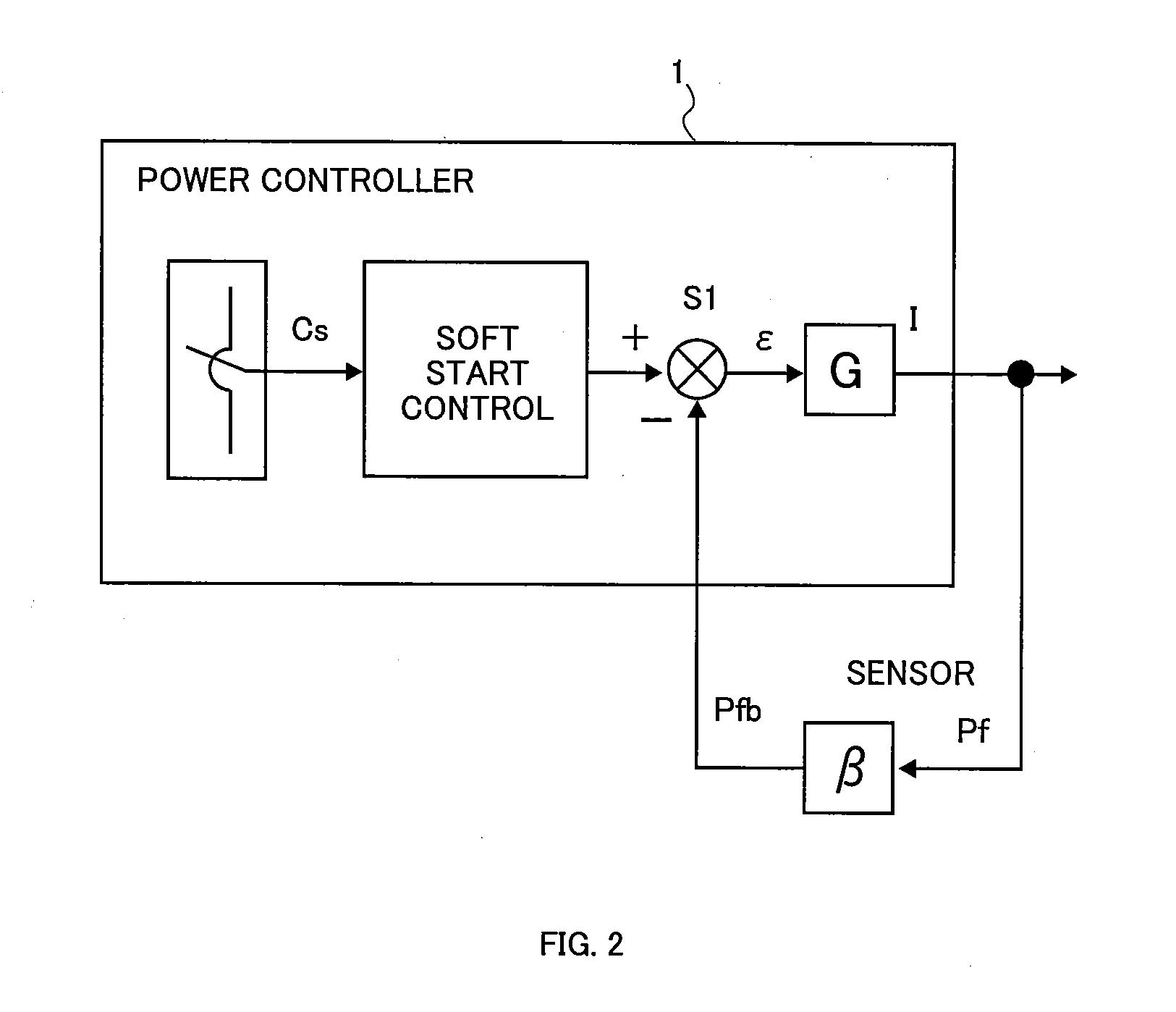
Abnormal discharge suppressing device for vacuum apparatus
ActiveUS20100187998A1Stable power supplyGrowth inhibitionVolume/mass flow measurementAlternating current plasma display panelsPower controllerTime range
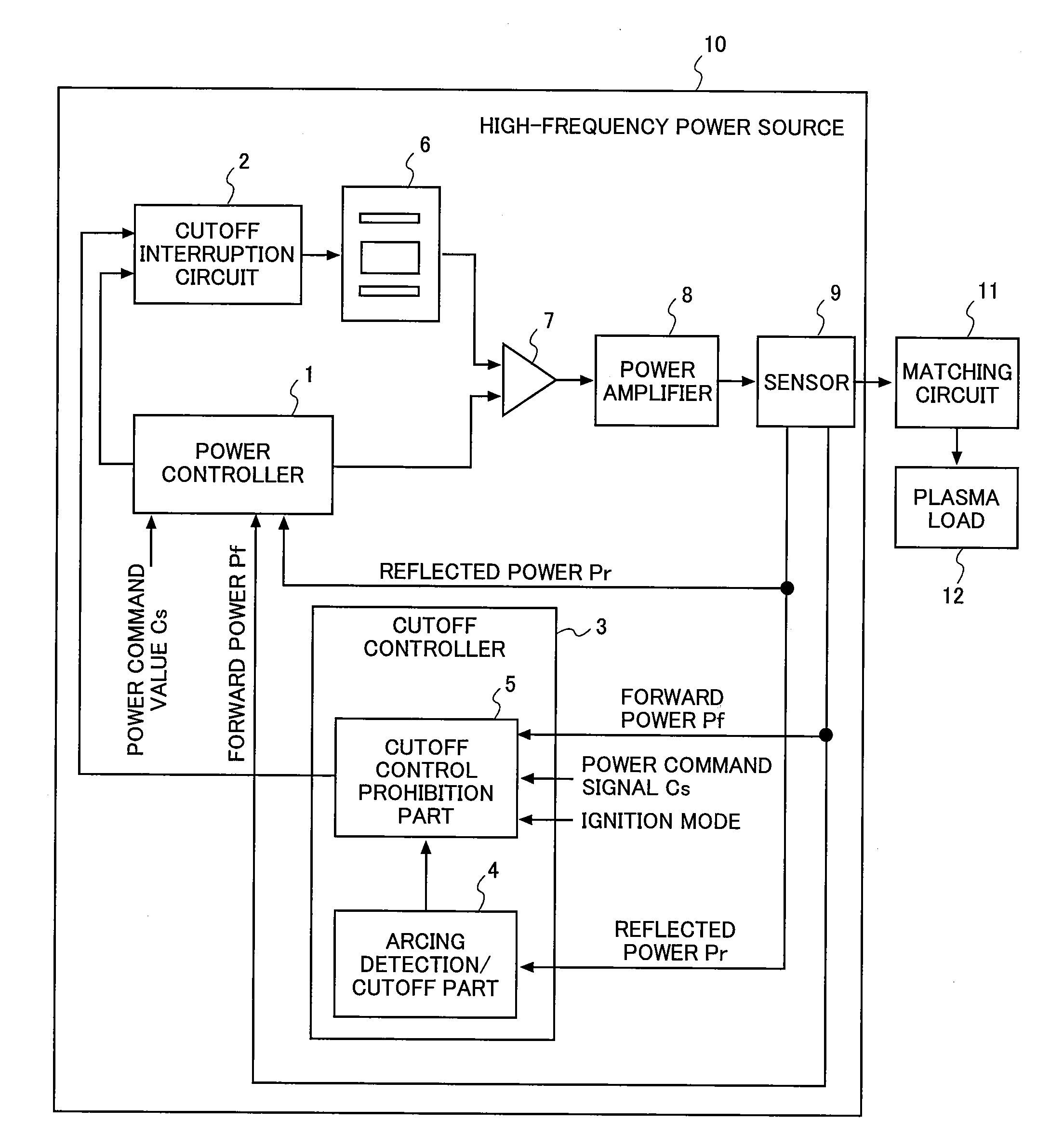
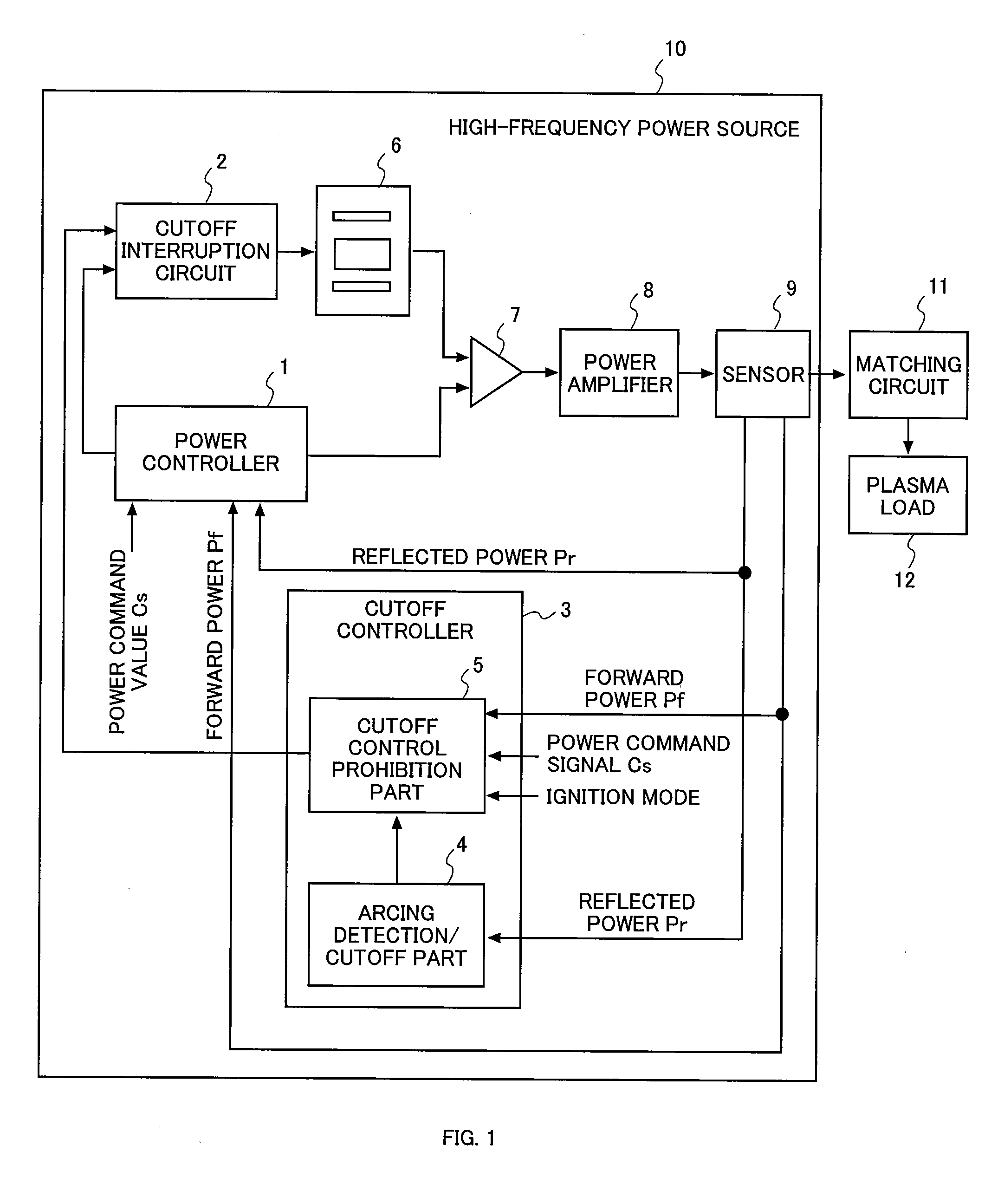
The present invention is directed to an apparatus for suppressing abnormal electrical discharge used for vacuum equipment which supplies power from a high-frequency power source to a plasma reaction chamber and executes a film formation process, provided with a power controller for controlling the high-frequency power source based on a deviation between a power command value and a power feedback value, and a cutoff controller for cutting off the power supply from the high-frequency power source to the plasma reaction chamber, based on a detection of the abnormal electrical discharge within the plasma reaction chamber. The cutoff controller exercises a first handling cutoff control and a second handling cutoff control, each having a different cutoff time. The first handling cutoff allows ions to remain in the plasma reaction chamber, and exercises the cutoff control over the high-frequency power source within a time duration which allows an arcing element to disappear. On the other hand, the second handling cutoff control exercises cutoff control over the high-frequency power source within a time range which allows abnormal arc ions to disappear. Accordingly, it is possible to supply power to plasma stably.
Owner:KYOSAN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device and method of reducing a discharge time of a liquid crystal capacitor thereof
ActiveUS20080143702A1Shorten discharge timeAlternating current plasma display panelsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A liquid crystal display device includes: a power supply unit which outputs a supply voltage at a first level when an outside power is supplied and outputs the supply voltage at a second level when the outside power is removed; a discharge unit which outputs a discharge signal when the supply voltage at the second level is input; and a liquid crystal panel including a gate discharge line, a plurality of gate lines connected to the gate discharge line, a plurality of thin film transistors connected to the plurality of gate lines, and a plurality of liquid crystal capacitors connected to the thin film transistors and which charges to a gradation display voltage. The thin film transistor is turned on to discharge the gradation display voltage charged in the plurality of liquid crystal capacitors when the discharge signal is provided to the gate discharge line.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Projector and driving method of light source for projector
InactiveUS20080297739A1Quality improvementWide contact areaProjectorsAlternating current plasma display panelsSurface layerElectrical polarity
A projector includes an discharge lamp which has a first electrode and a second electrode and emits light by generating discharge between the first and second electrodes, and a driving system which supplies power by alternating polarities of the first electrode and the second electrode. The driving system is operable in a restoration mode. The driving system melts surface layers of a tip and a surrounding area of the tip extending from a main body of one of the first and second electrodes, and expands a new tip on a tip area of the main body of the one electrode in the restoration mode.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com