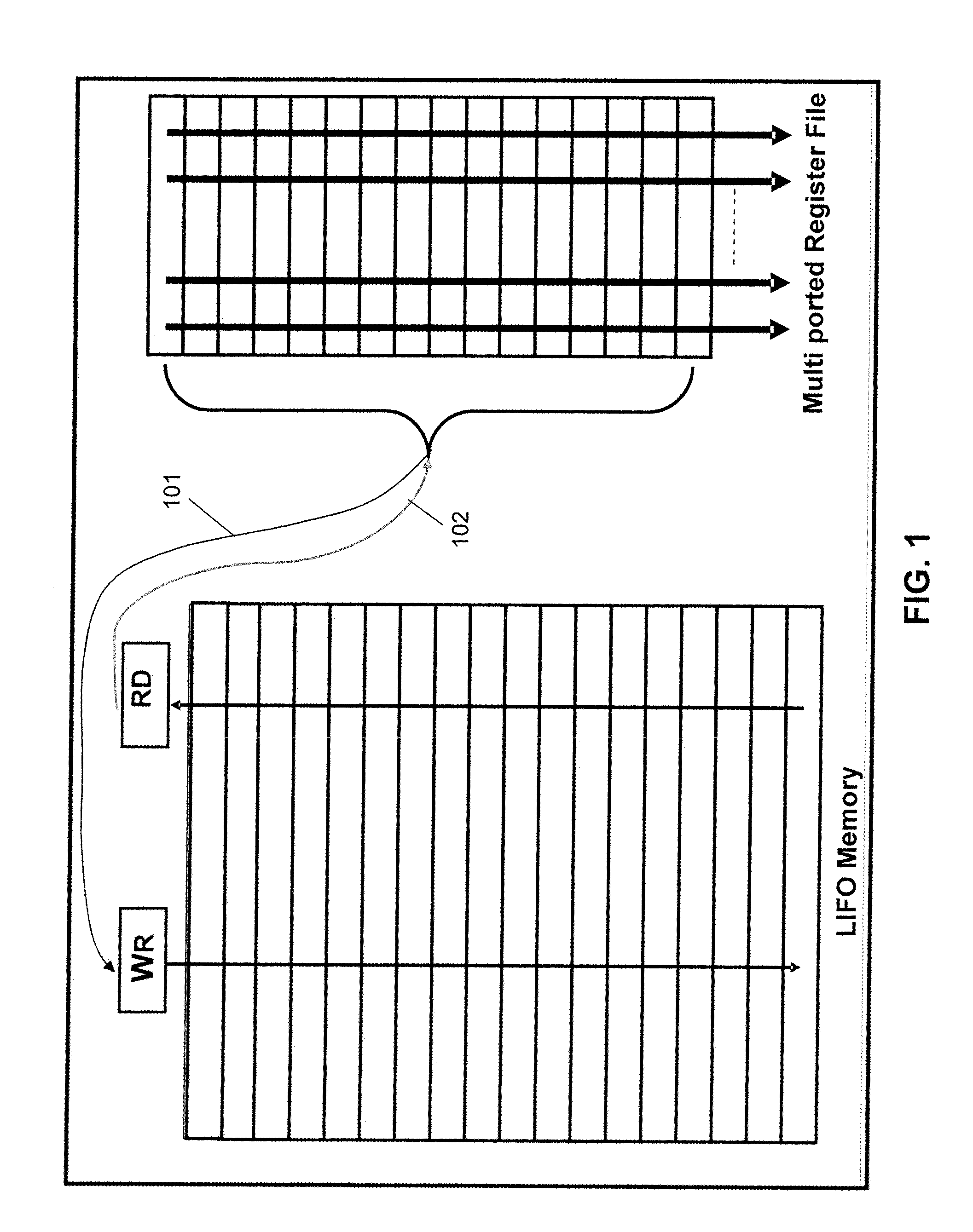
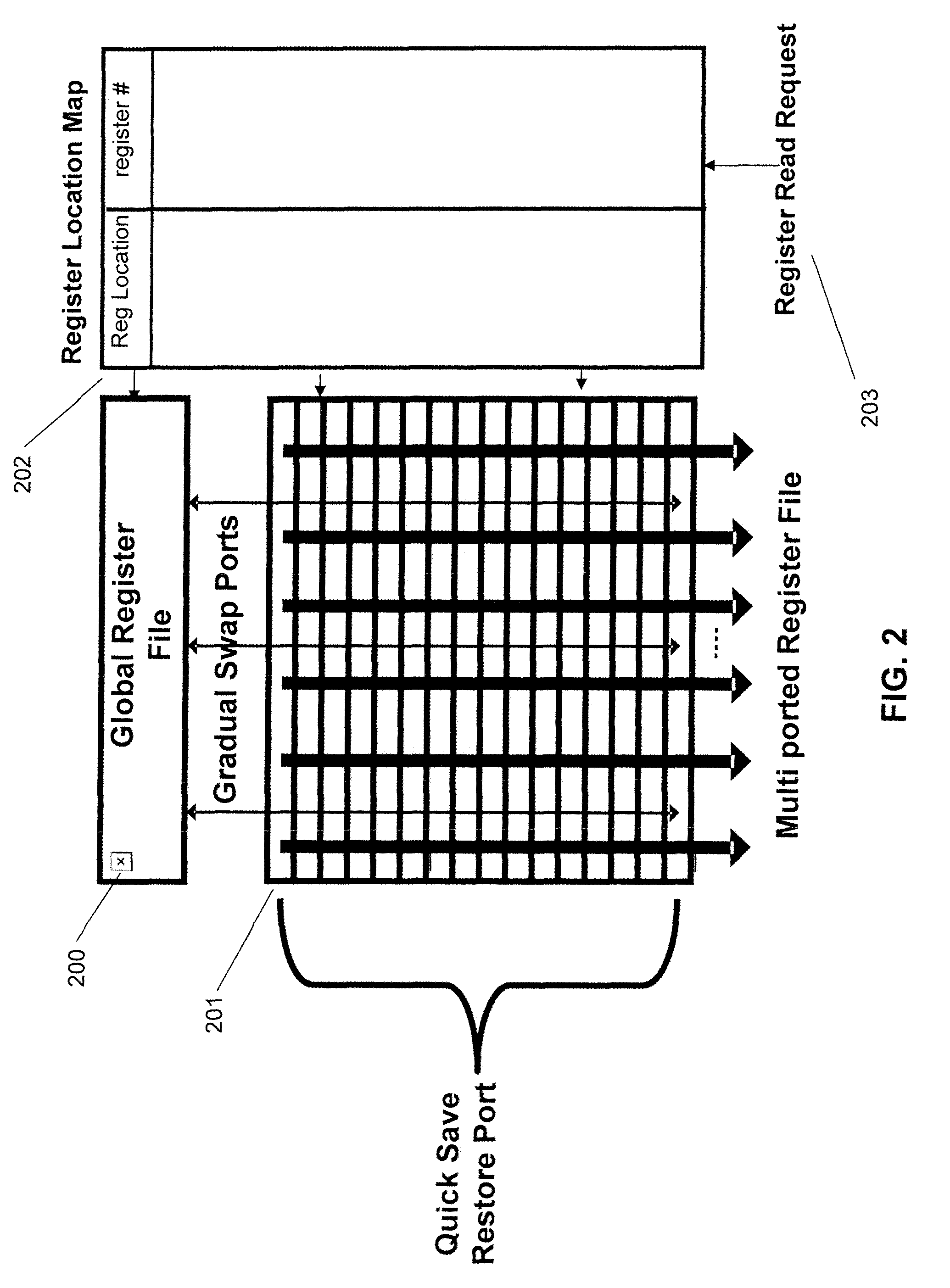
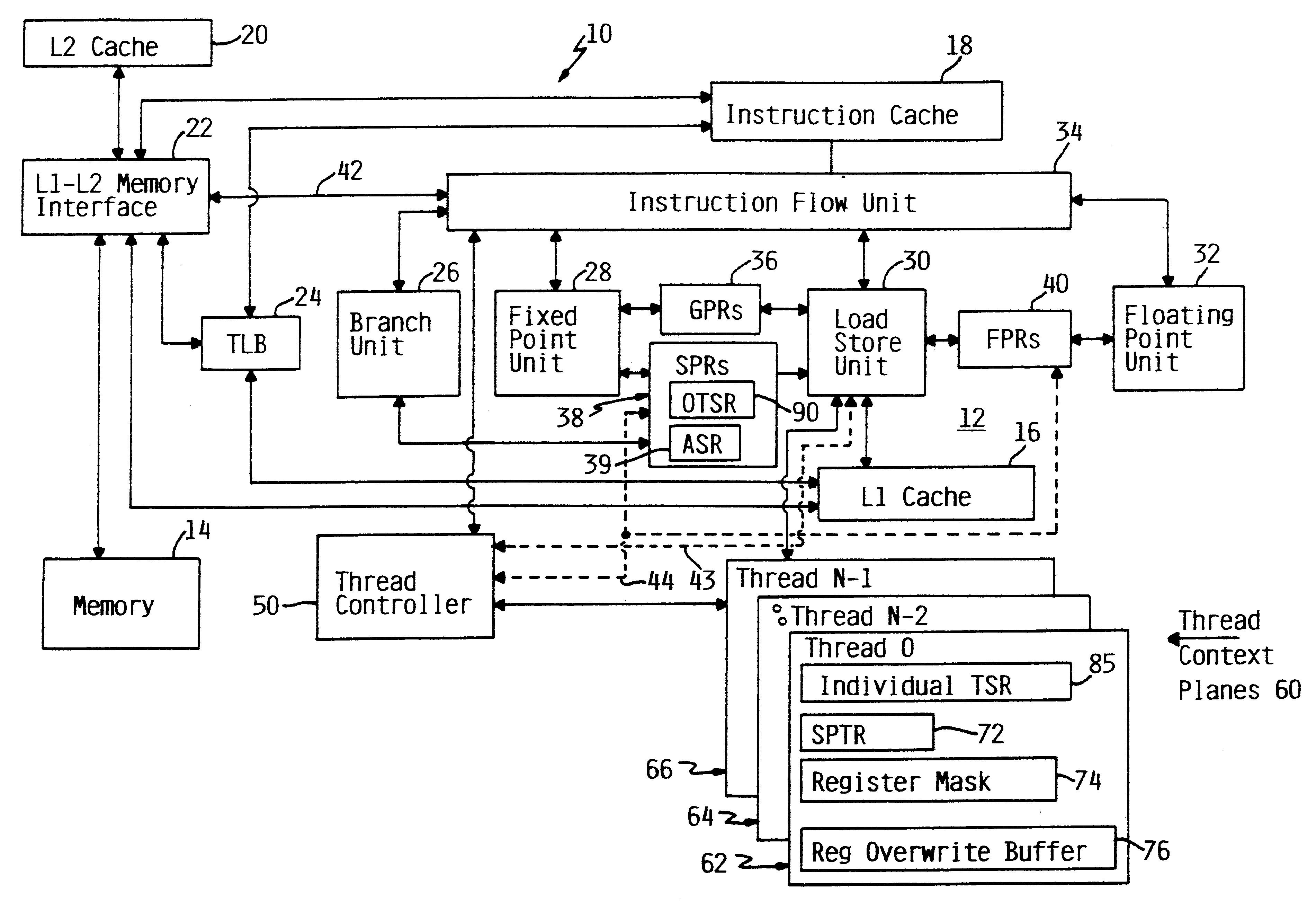
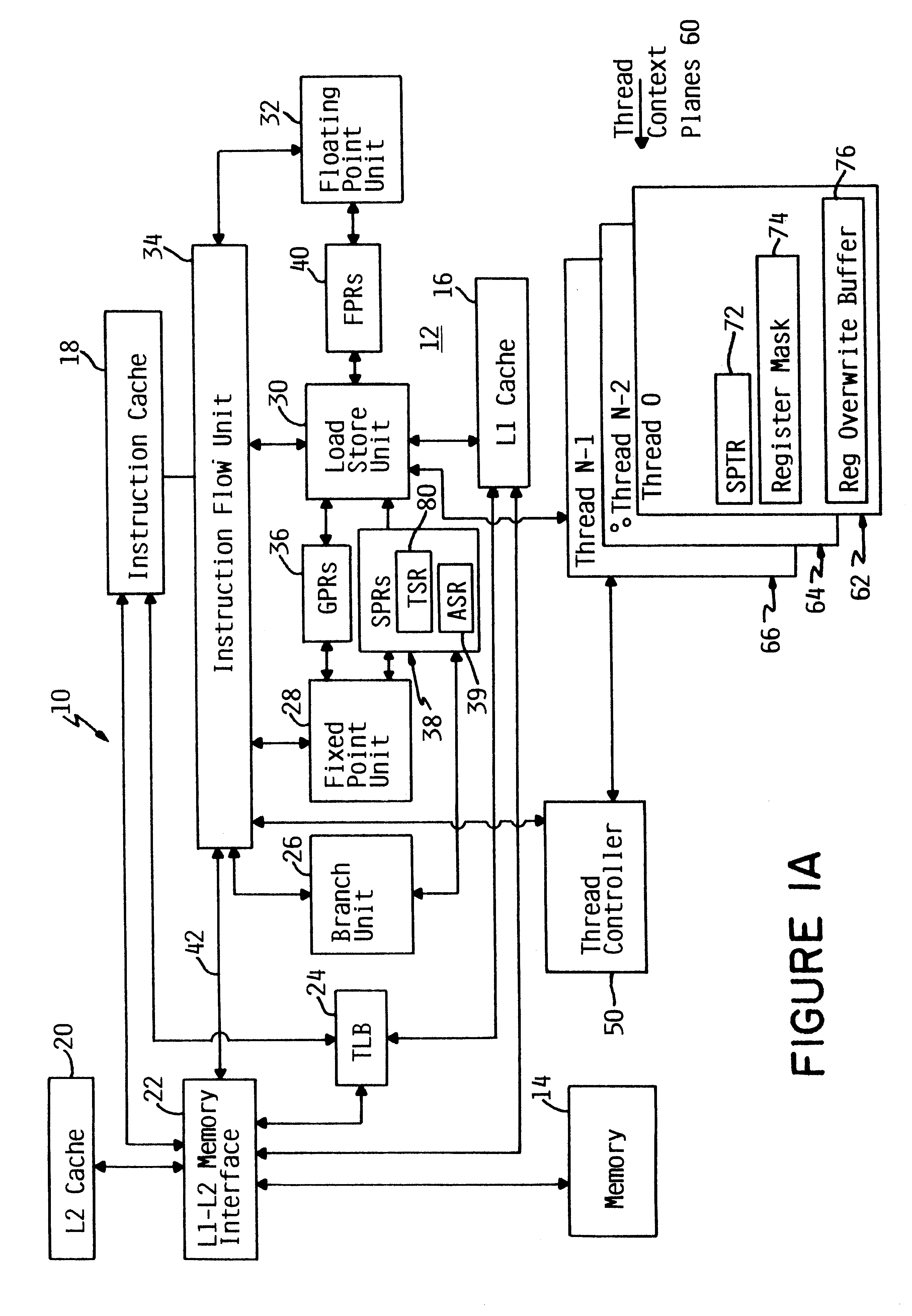
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
943results about "Program saving/restoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
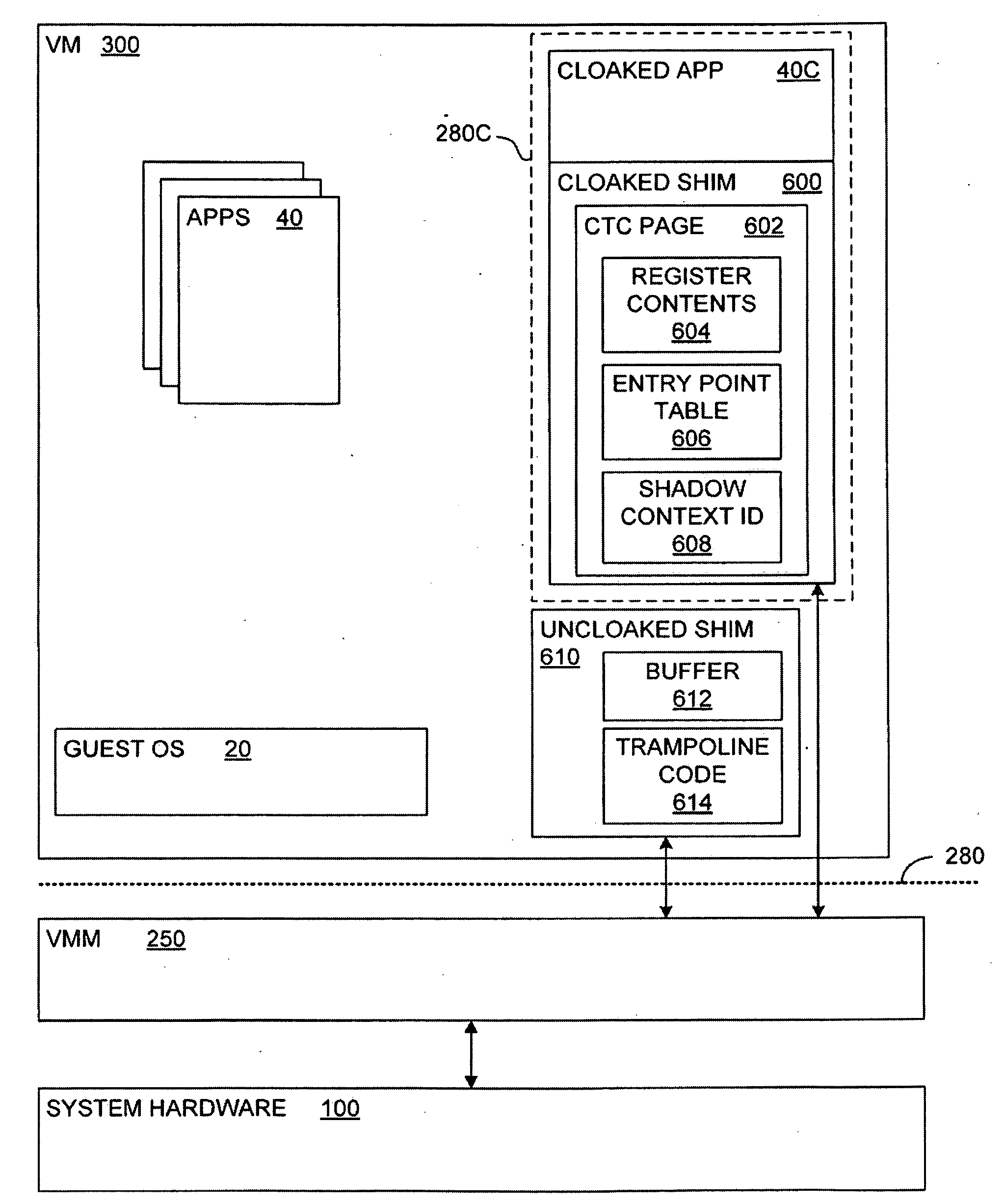
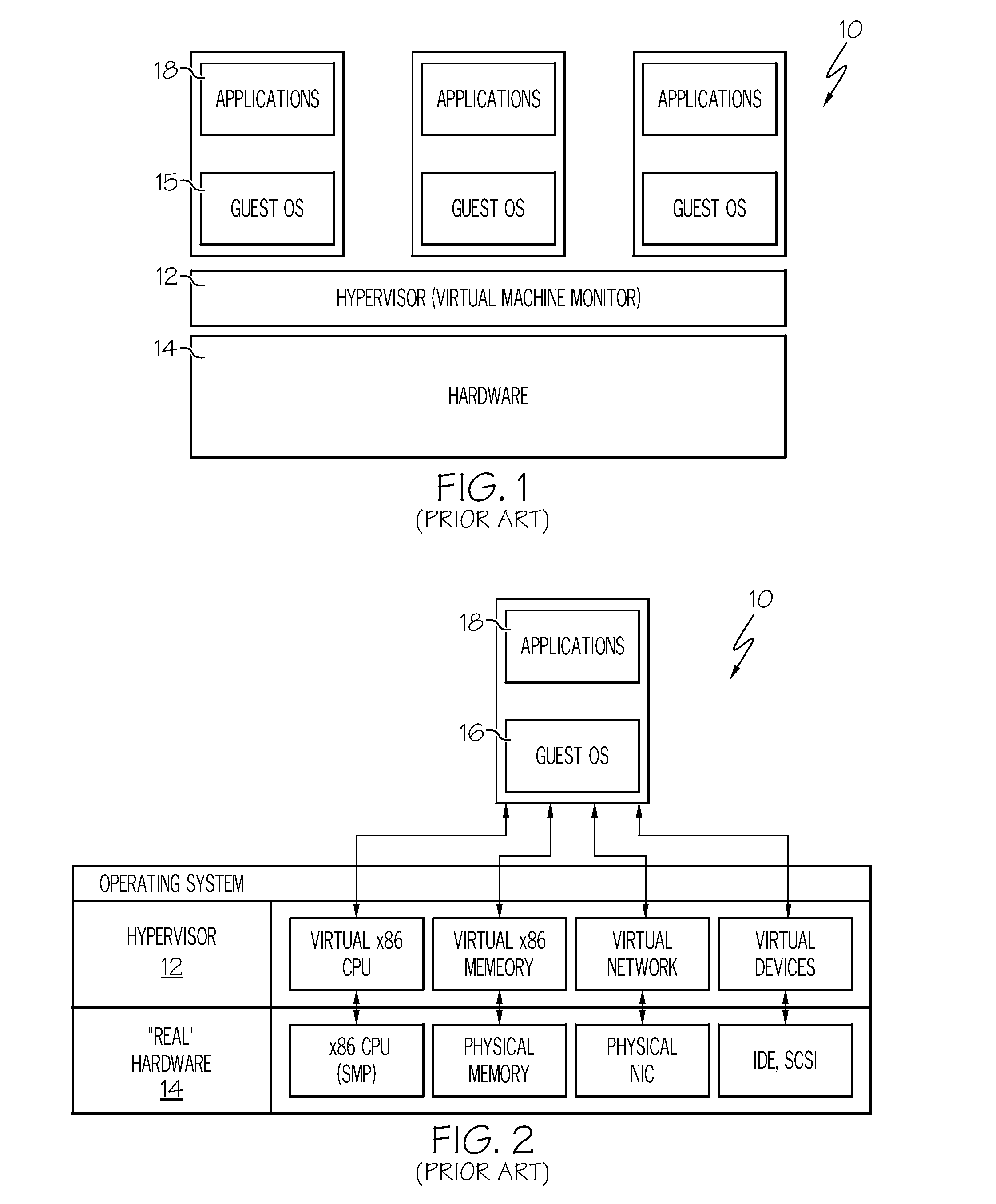
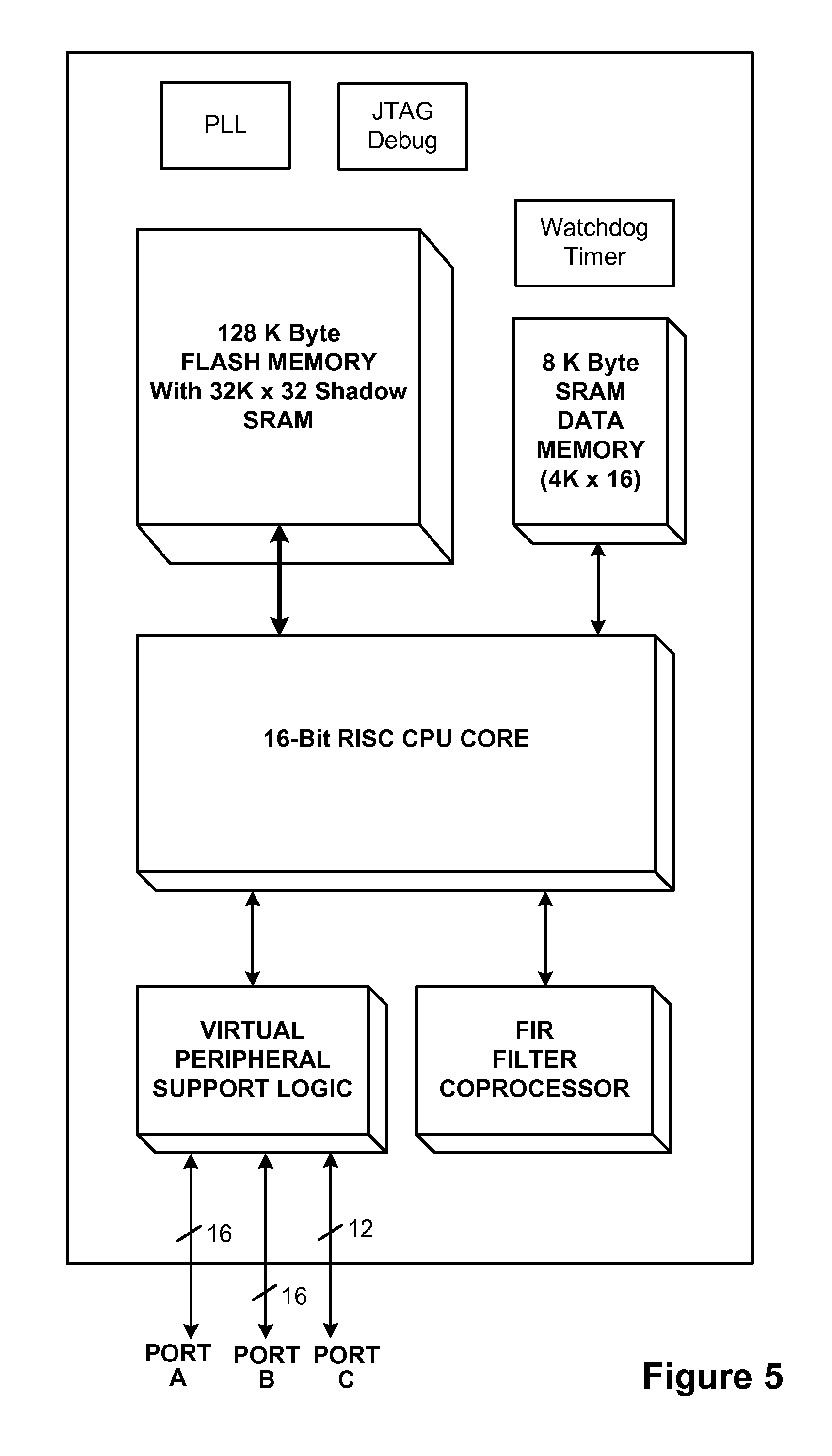
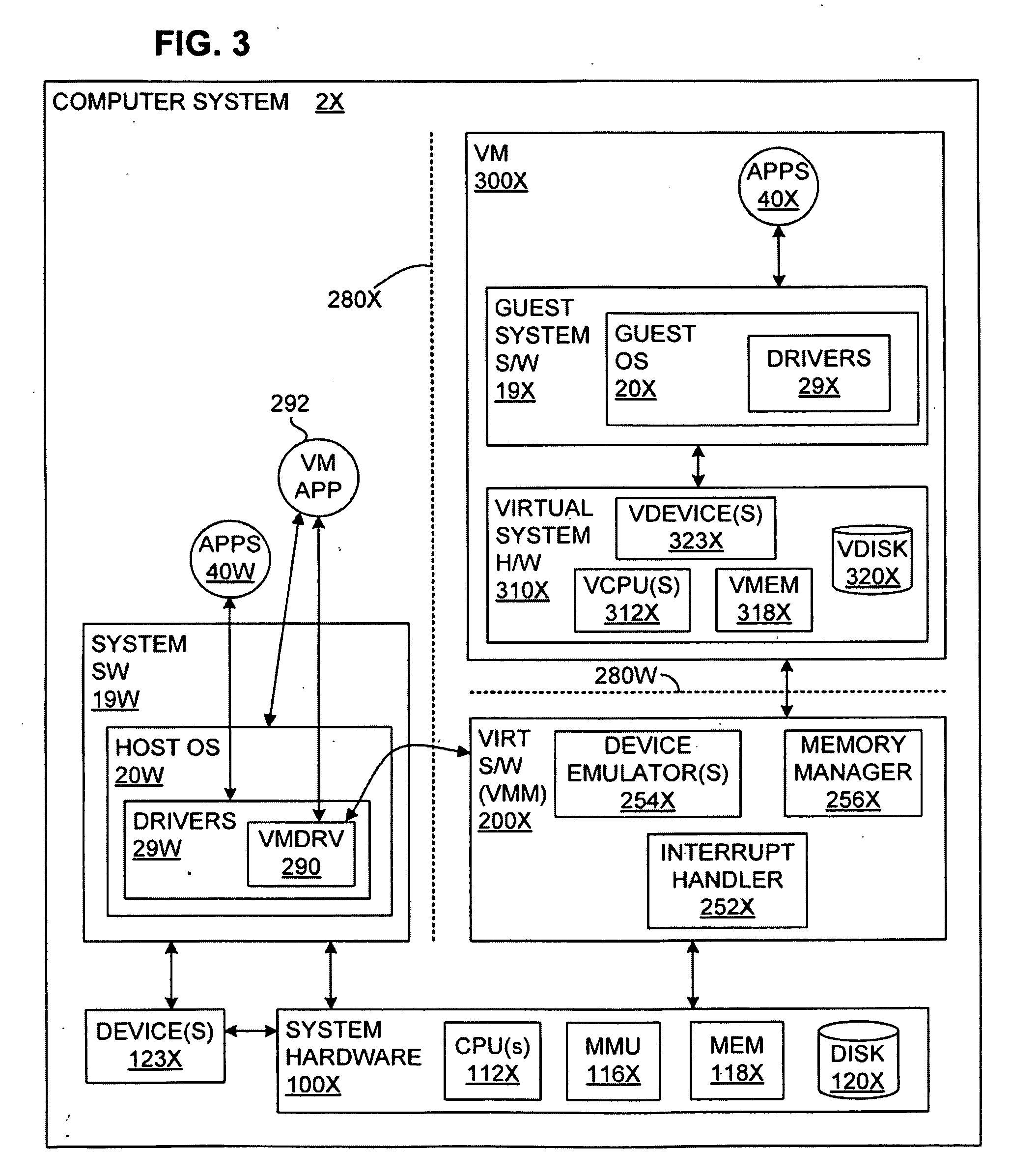
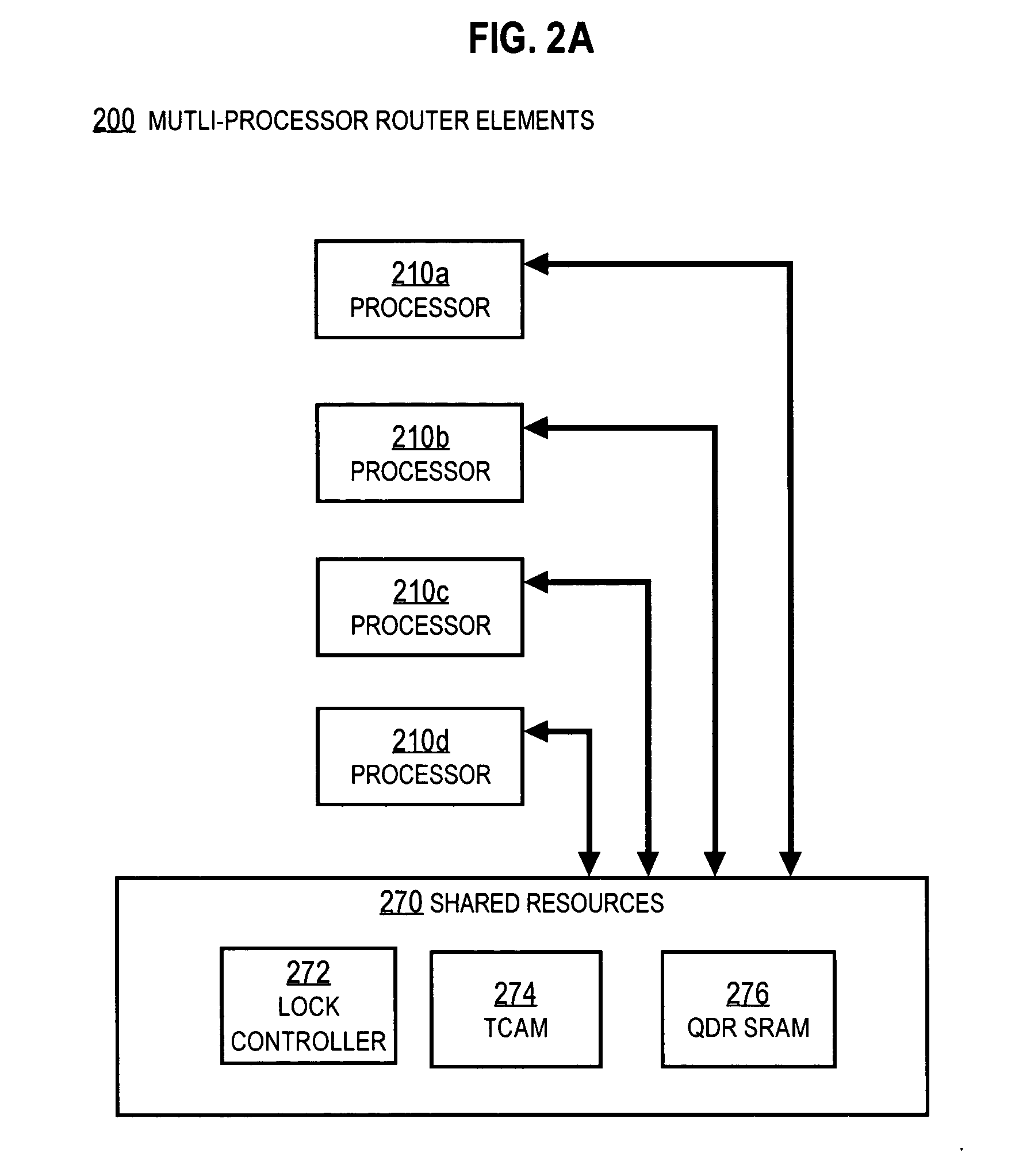
Transparent Memory-Mapped Emulation of I/O Calls
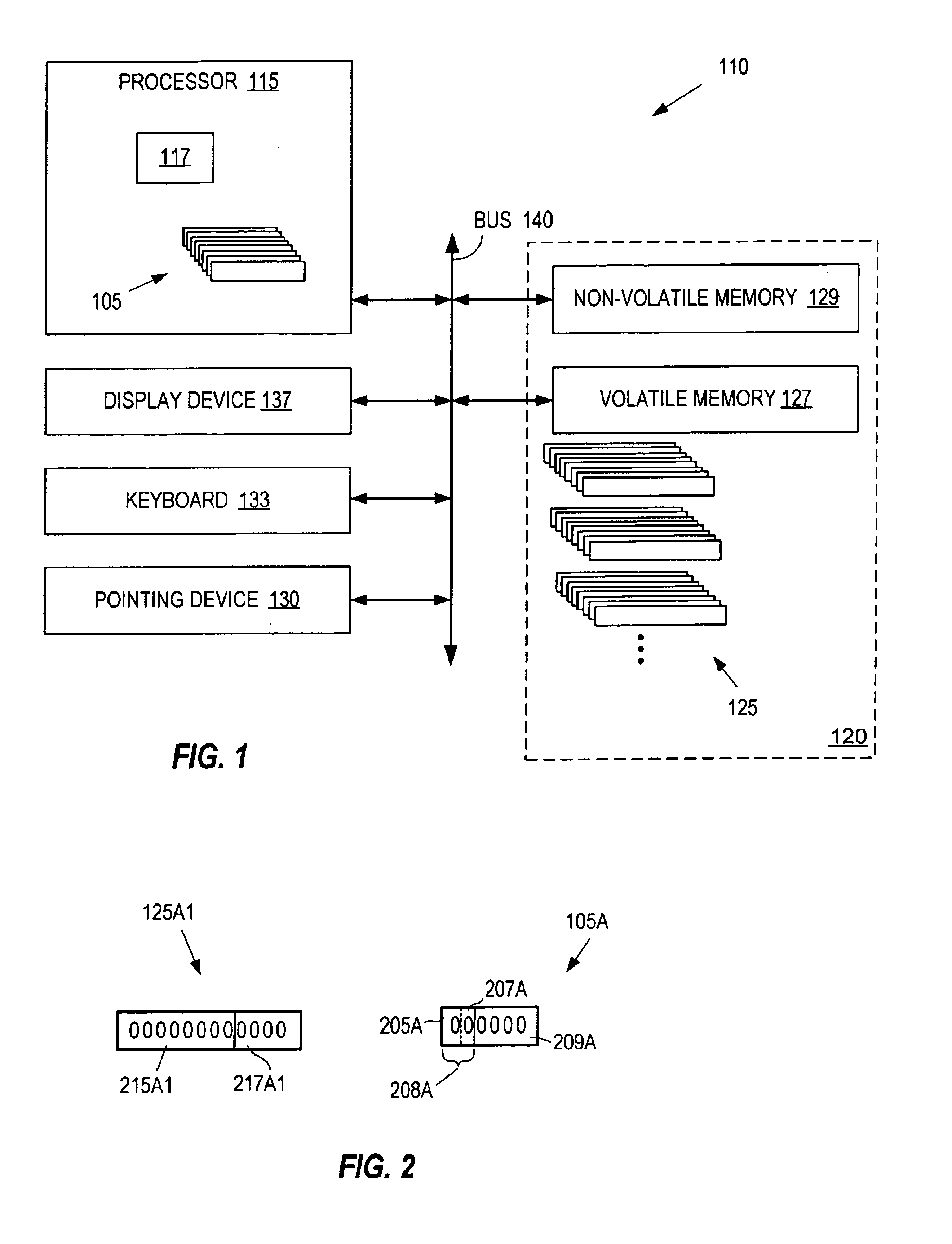
ActiveUS20090113425A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionSemanticsMemory map
A virtual-machine-based system provides a mechanism to implement application file I / O operations of protected data by implementing the I / O operations semantics in a shim layer with memory-mapped regions. The semantics of these I / O operations are emulated in a shim layer with memory-mapped regions by using a mapping between a process' address space and a file or shared memory object. Data that is protected from viewing by a guest OS running in a virtual machine may nonetheless be accessed by the process.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Providing VMM Access to Guest Virtual Memory
ActiveUS20090113110A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionVirtual memoryVirtual storage
A virtual-machine-based system provides a mechanism for a virtual machine monitor (VMM) to process a hypercall received from an application running in the virtual machine (VM). A hypercall interface causes the virtual memory pages, needed by the VMM to process the hypercall, to be available to the VMM. In one embodiment, when virtual memory pages needed by the VMM to process the hypercall are not available to the VMM, the application is caused to access the needed pages, in response to which the required virtual memory becomes available to the VMM.
Owner:VMWARE INC
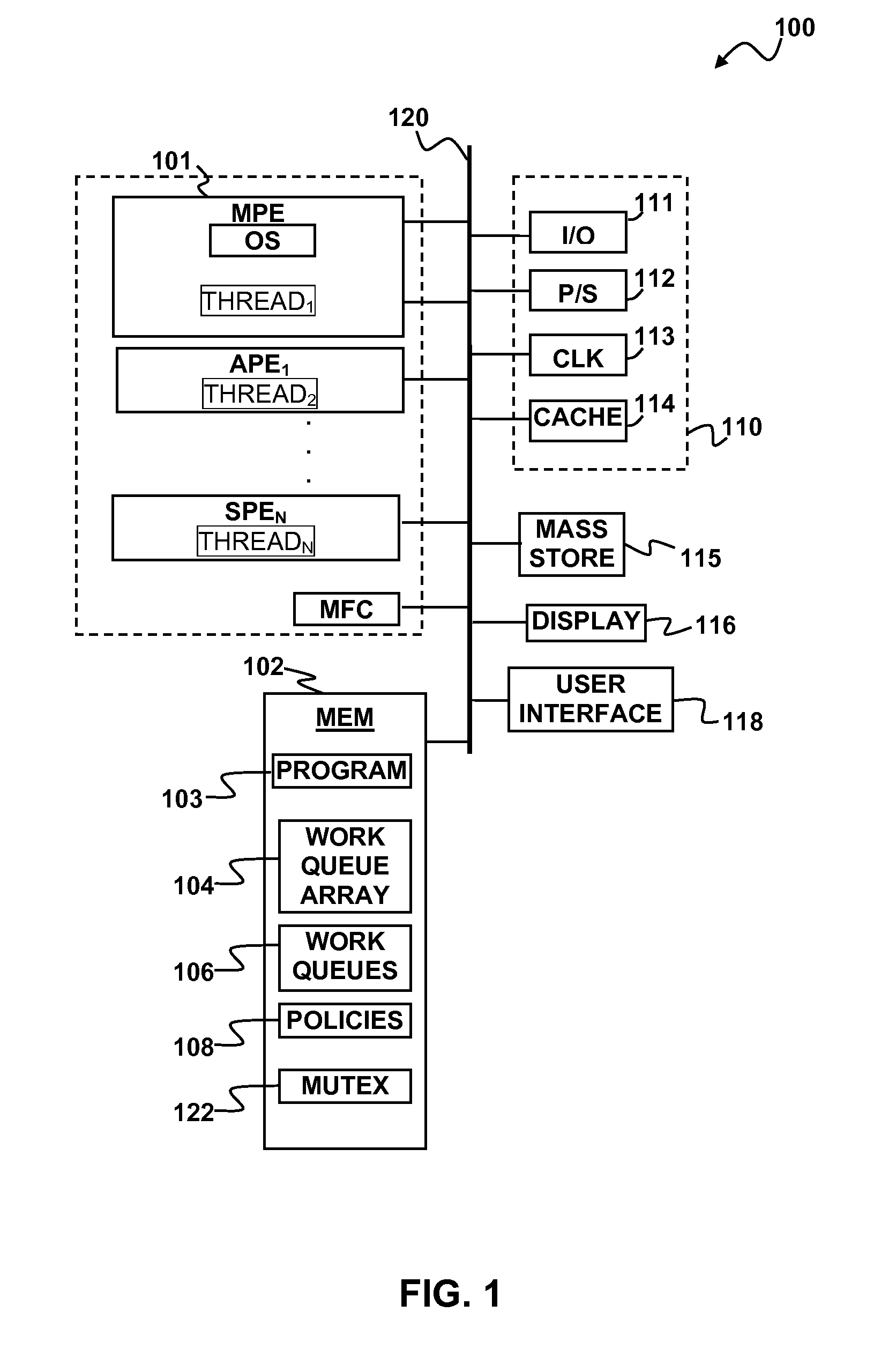
Hardware multithreading systems and methods
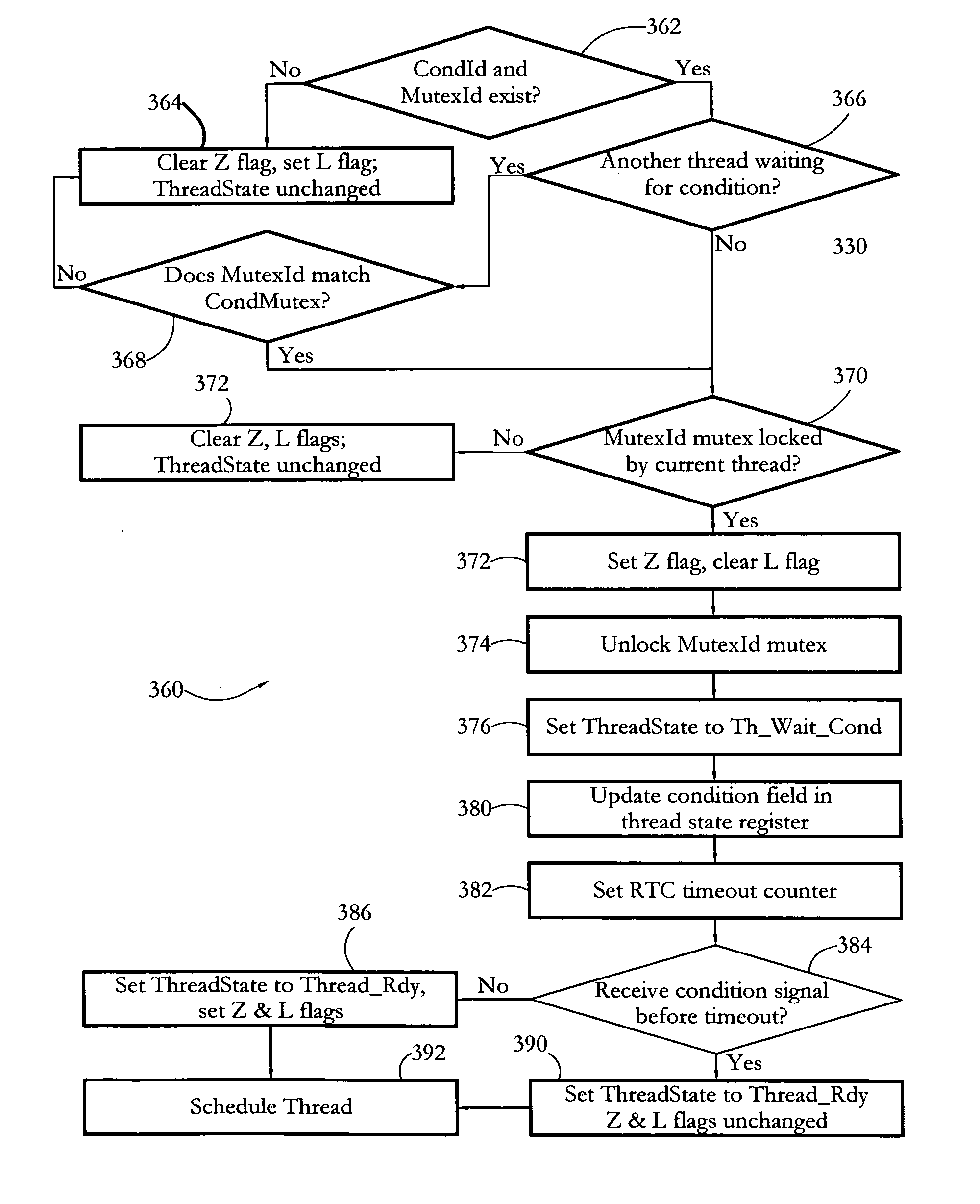
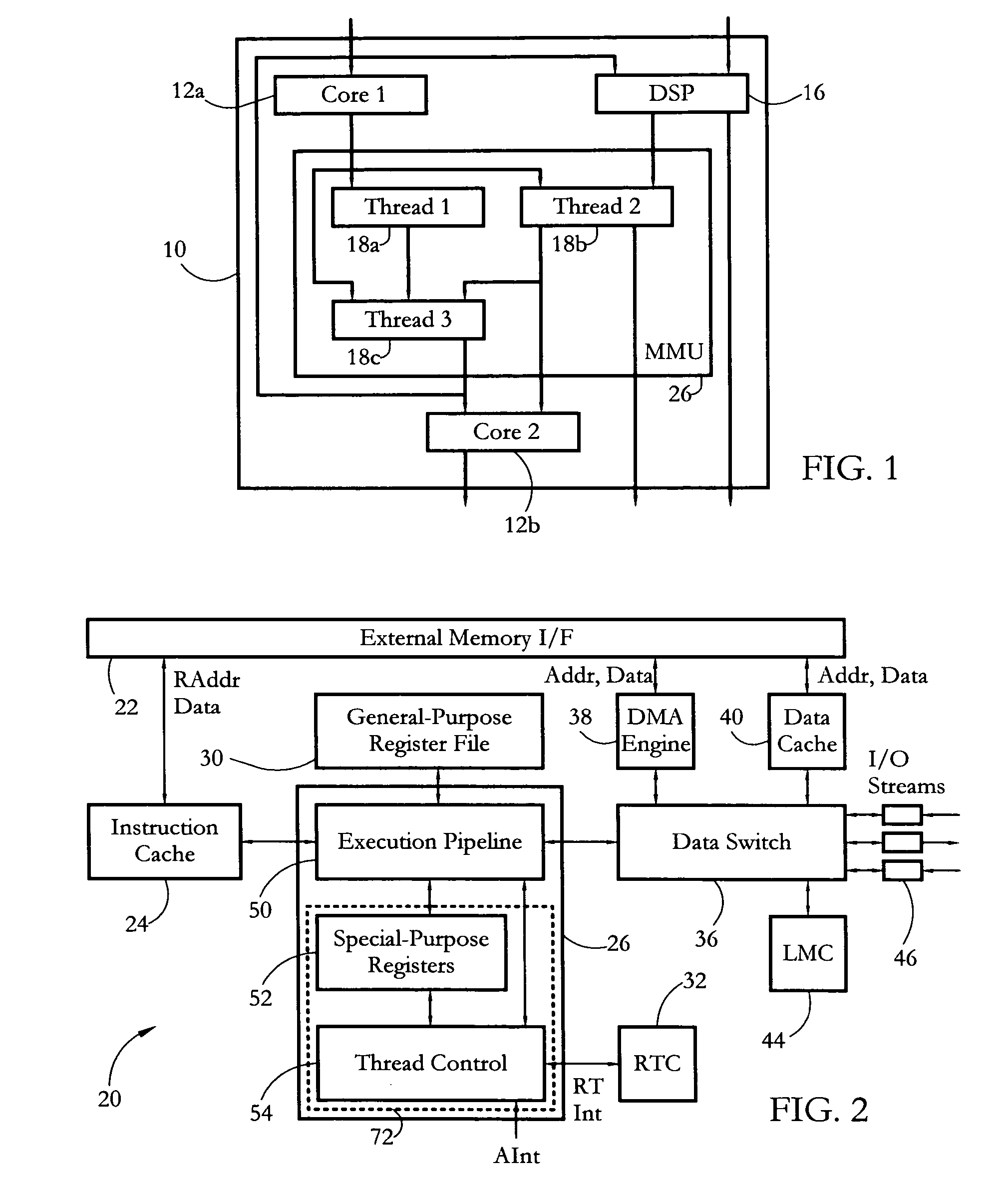
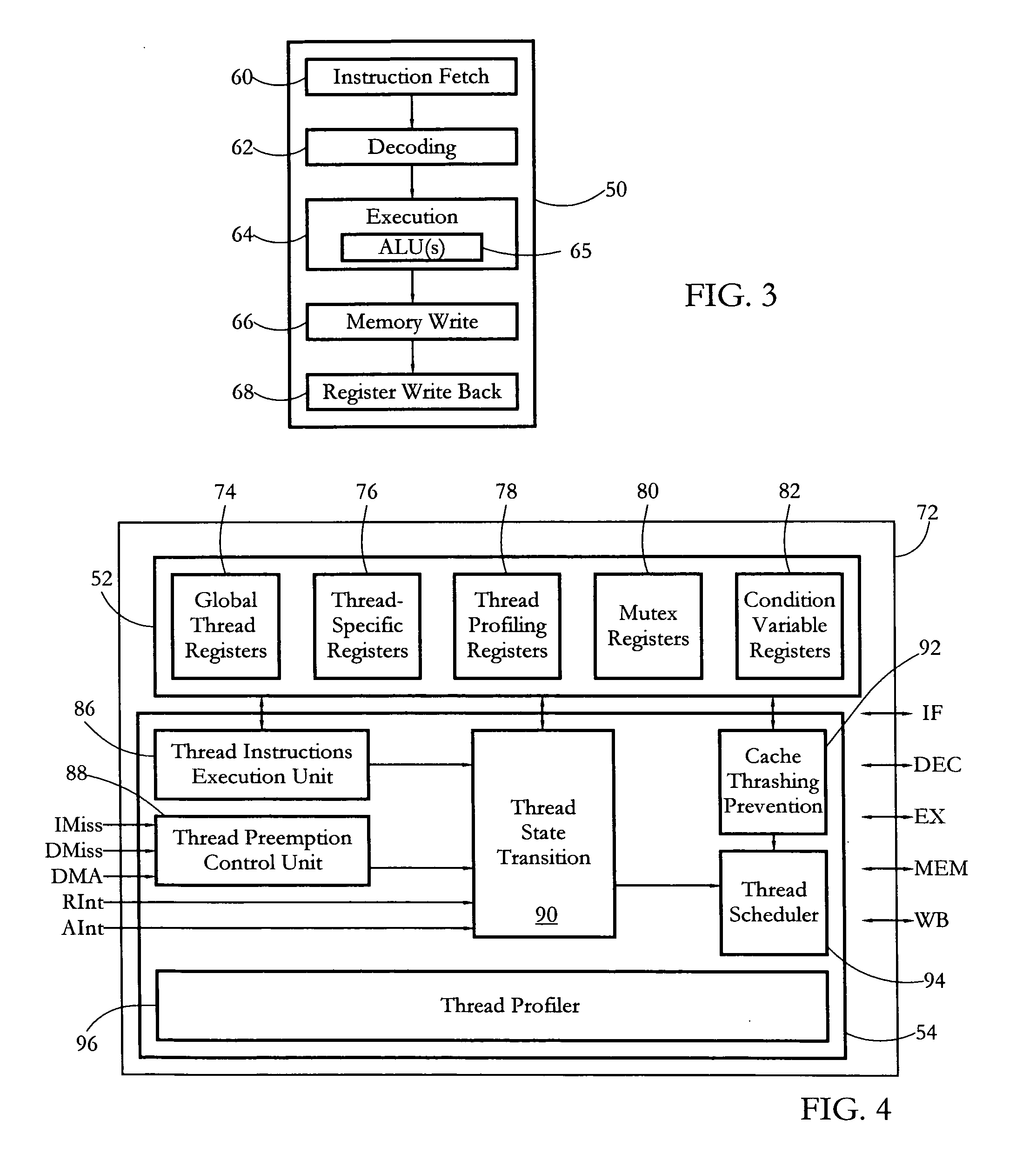
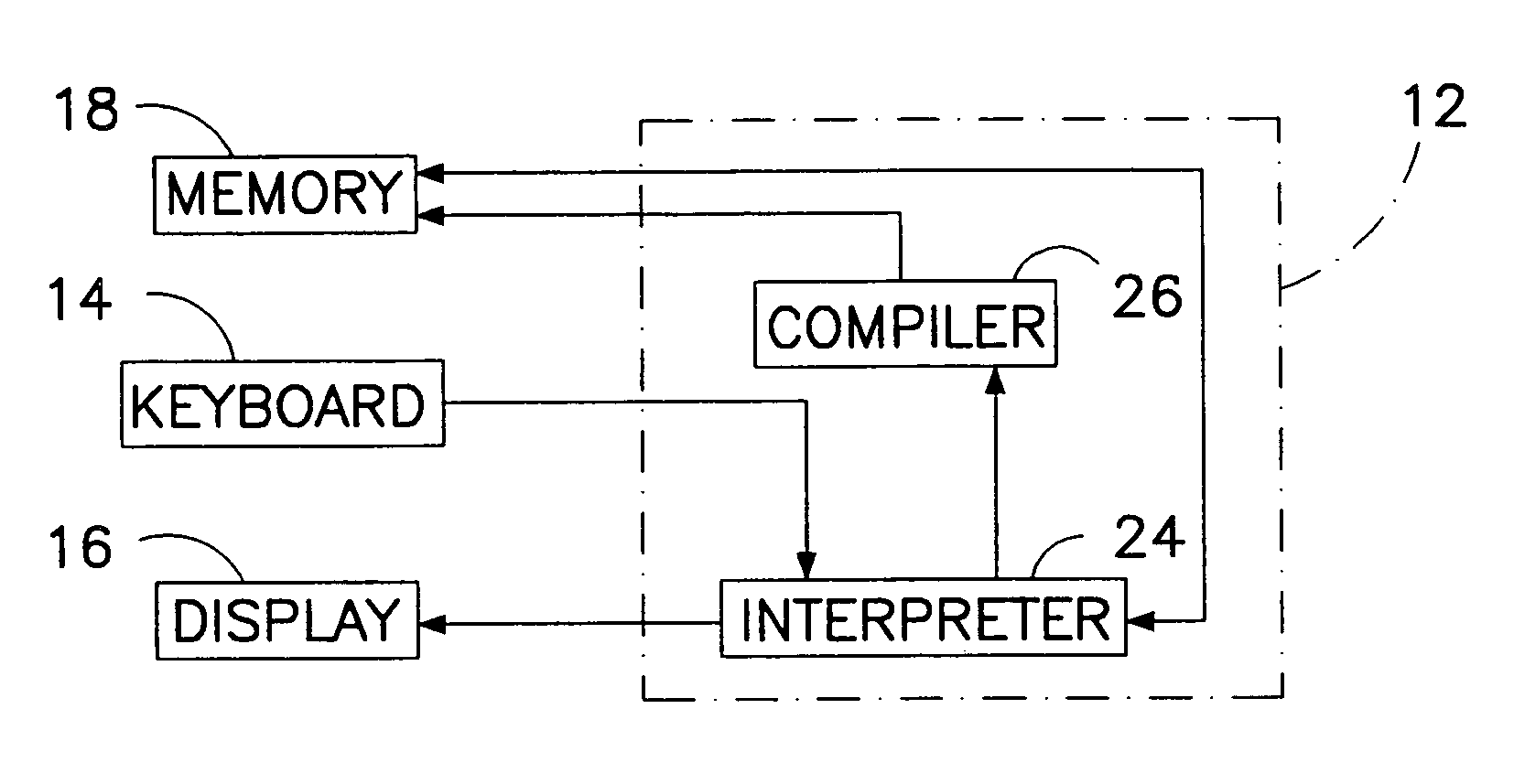
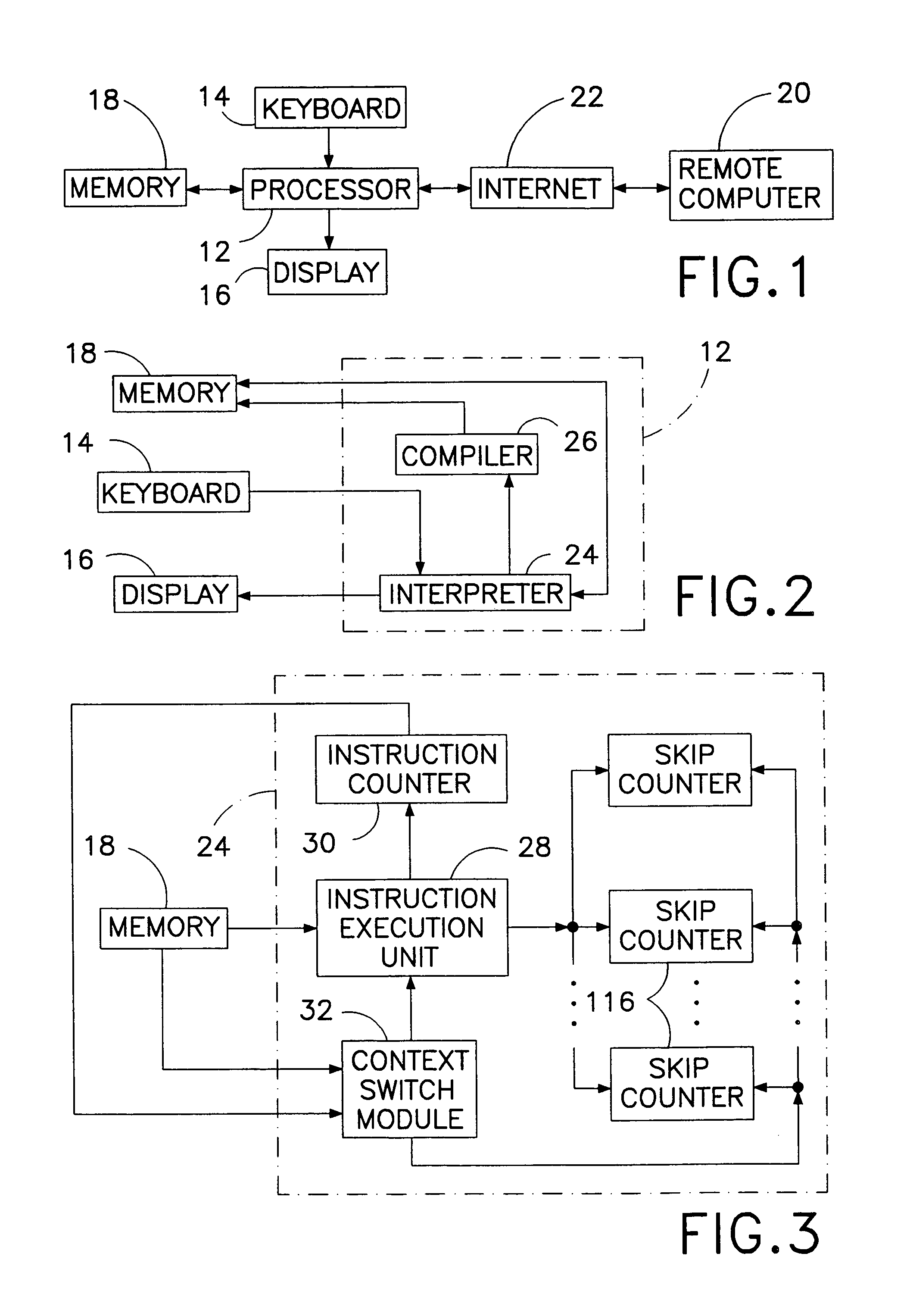
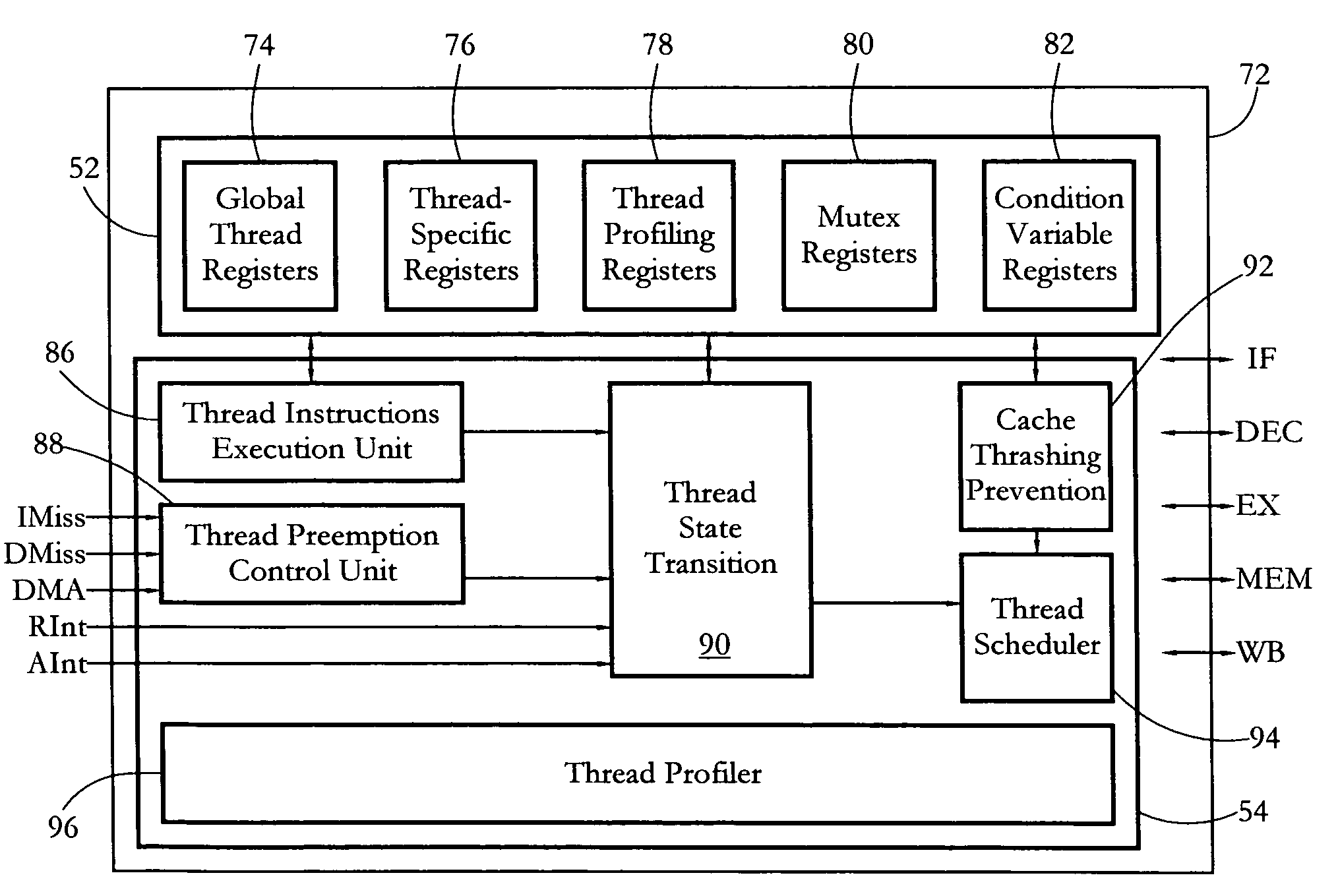
According to some embodiments, a multithreaded microcontroller includes a thread control unit comprising thread control hardware (logic) configured to perform a number of multithreading system calls essentially in real time, e.g. in one or a few clock cycles. System calls can include mutex lock, wait condition, and signal instructions. The thread controller includes a number of thread state, mutex, and condition variable registers used for executing the multithreading system calls. Threads can transition between several states including free, run, ready and wait. The wait state includes interrupt, condition, mutex, I-cache, and memory substates. A thread state transition controller controls thread states, while a thread instructions execution unit executes multithreading system calls and manages thread priorities to avoid priority inversion. A thread scheduler schedules threads according to their priorities. A hardware thread profiler including global, run and wait profiler registers is used to monitor thread performance to facilitate software development.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Apparatus and Method for Processing Complex Instruction Formats in a Multi-Threaded Architecture Supporting Various Context Switch Modes and Virtualization Schemes
ActiveUS20100161948A1Efficient context switchingEfficient switchingInstruction analysisDigital computer detailsVirtualizationProcessor register
A unified architecture for dynamic generation, execution, synchronization and parallelization of complex instructions formats includes a virtual register file, register cache and register file hierarchy. A self-generating and synchronizing dynamic and static threading architecture provides efficient context switching.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and method for retrofitting multi-threaded operations on a computer by partitioning and overlapping registers
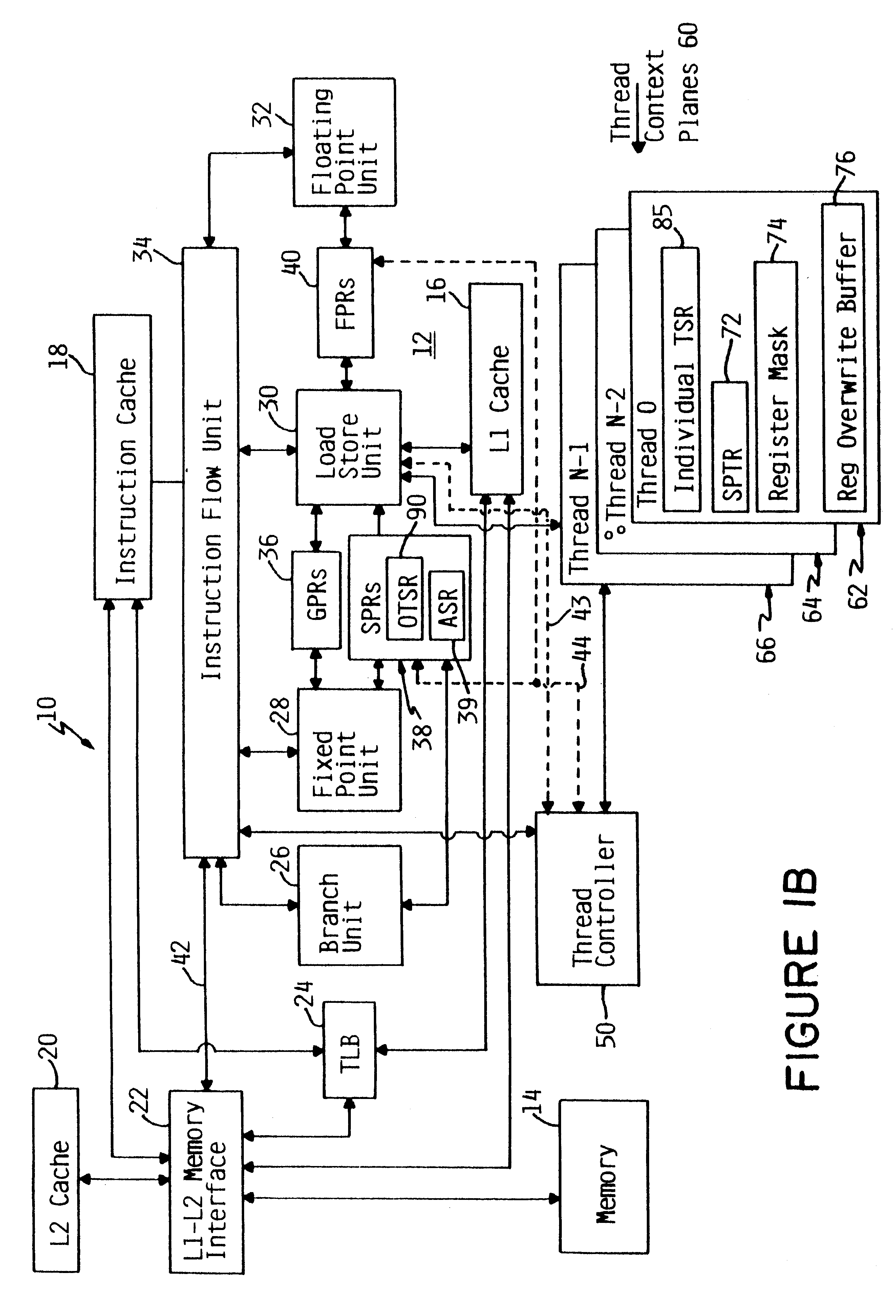
InactiveUS6233599B1Improve multithreading performance of processorImprove performanceResource allocationDigital computer detailsGeneral purposeProcessor register
An apparatus and method for performing multithreaded operations includes partitioning the general purpose and / or floating point processor registers into register subsets, including overlapping register subsets, allocating the register subsets to the threads, and managing the register subsets during thread switching. Register overwrite buffers preserve thread resources in overlapping registers during the thread switching process. Thread resources are loaded into the corresponding register subsets or, when overlapping register subsets are employed, into either the corresponding register subset or the corresponding register overwrite buffer. A thread status register is utilized by a thread controller to keep track of READY / NOT-READY threads, the active thread, and whether single-thread or multithread operations are permitted. Furthermore, the registers in the register subsets include a thread identifier field to identify the corresponding thread. Register masks may also be used to identify which registers belong to the various register subsets.
Owner:IBM CORP
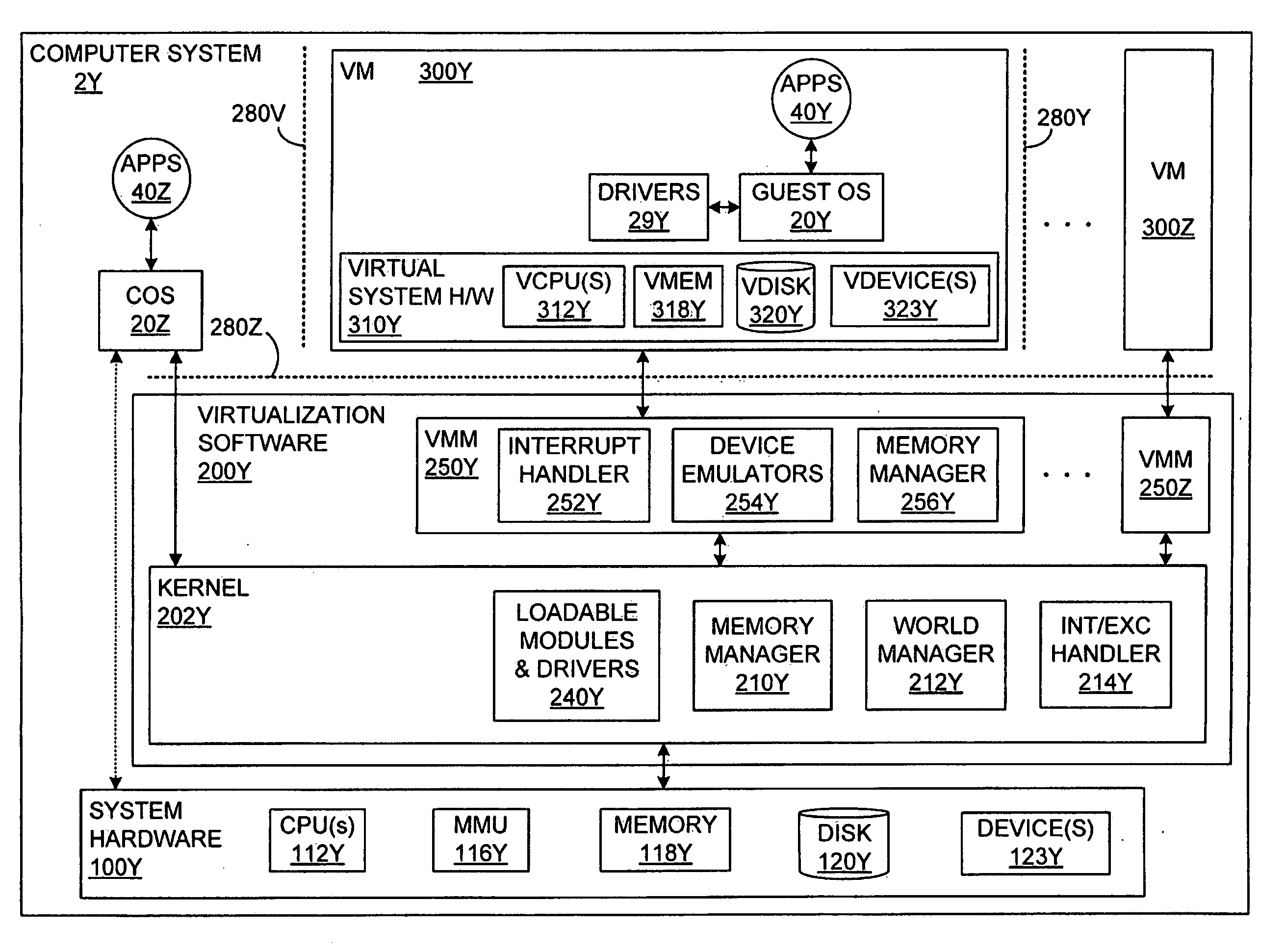
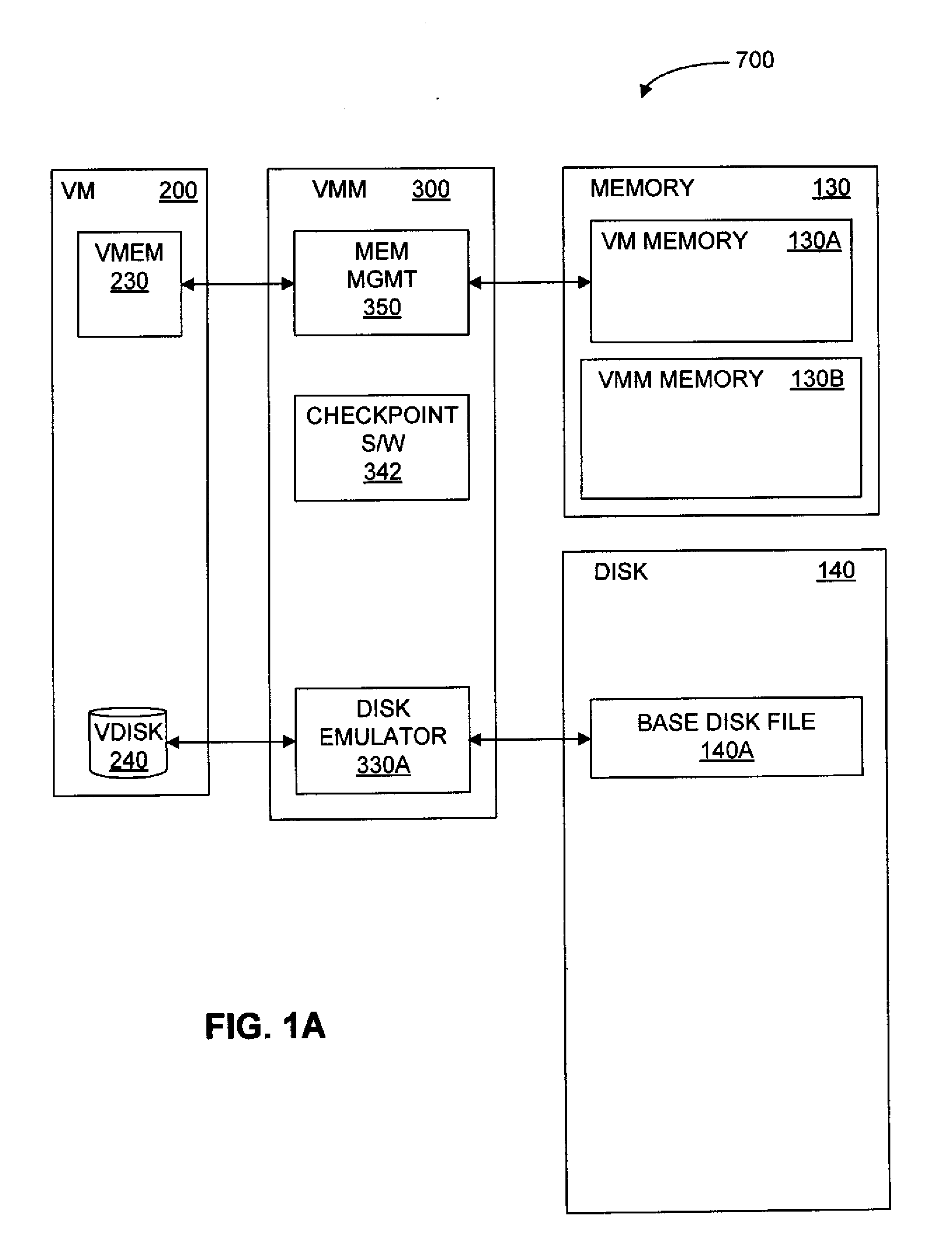
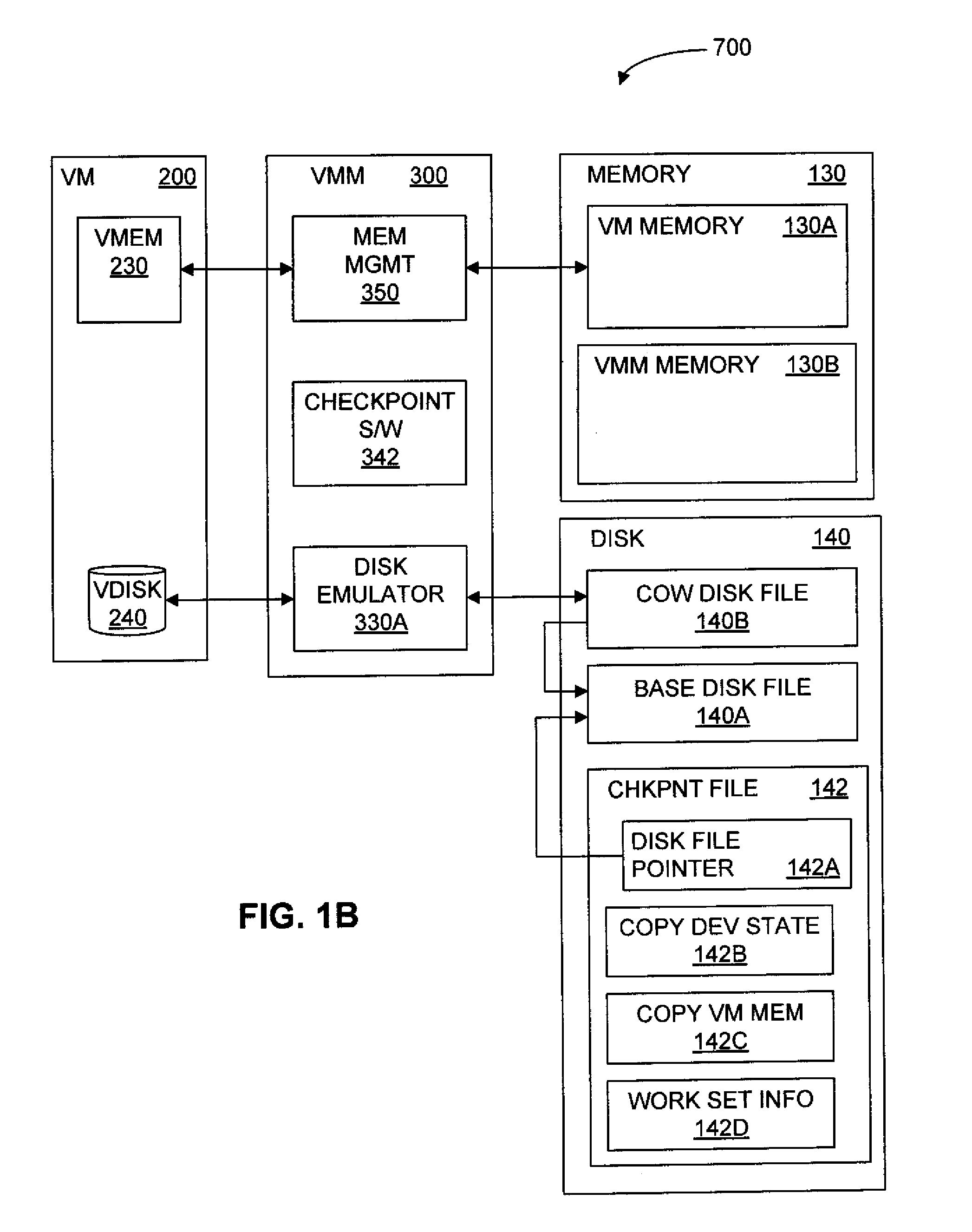
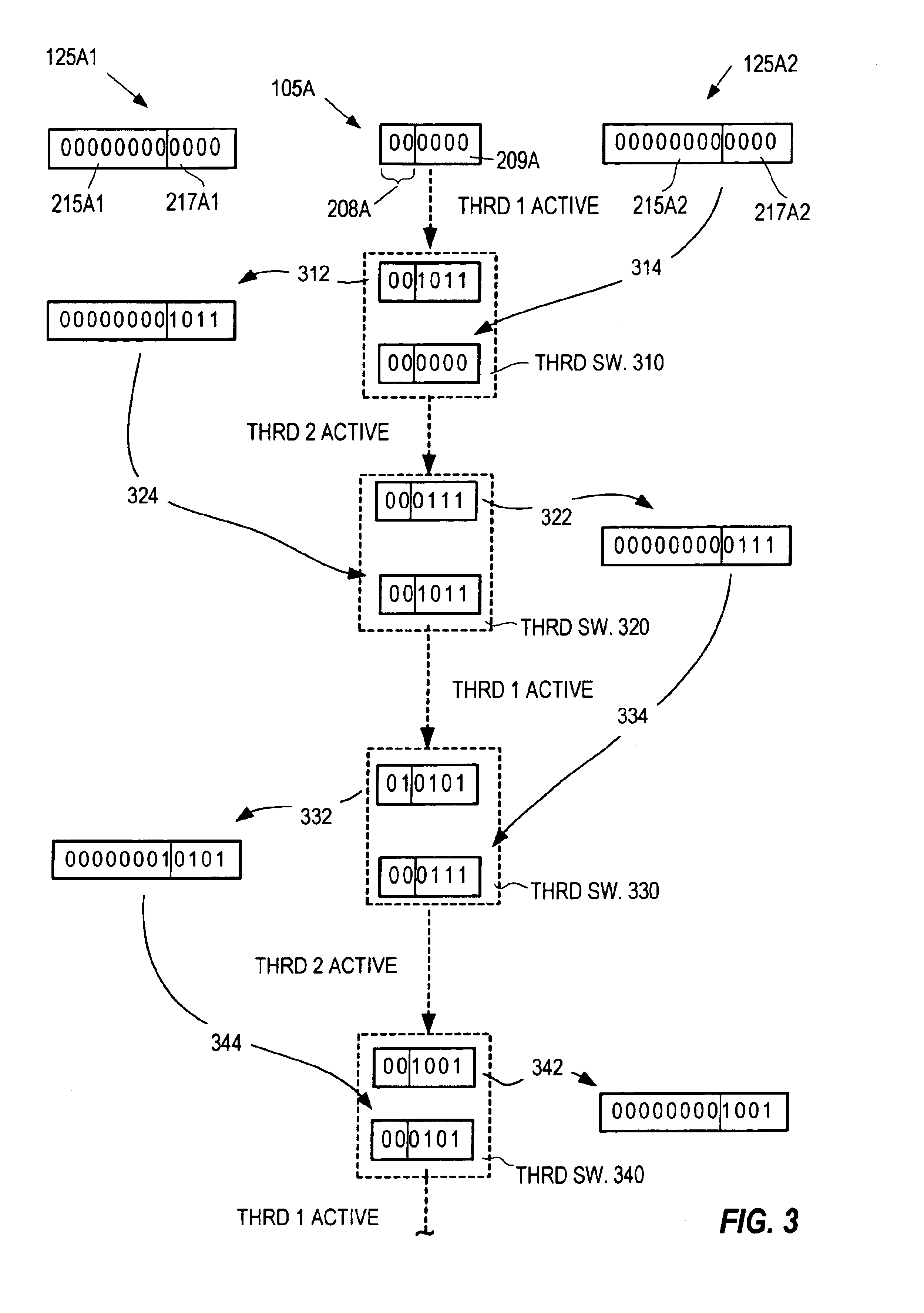
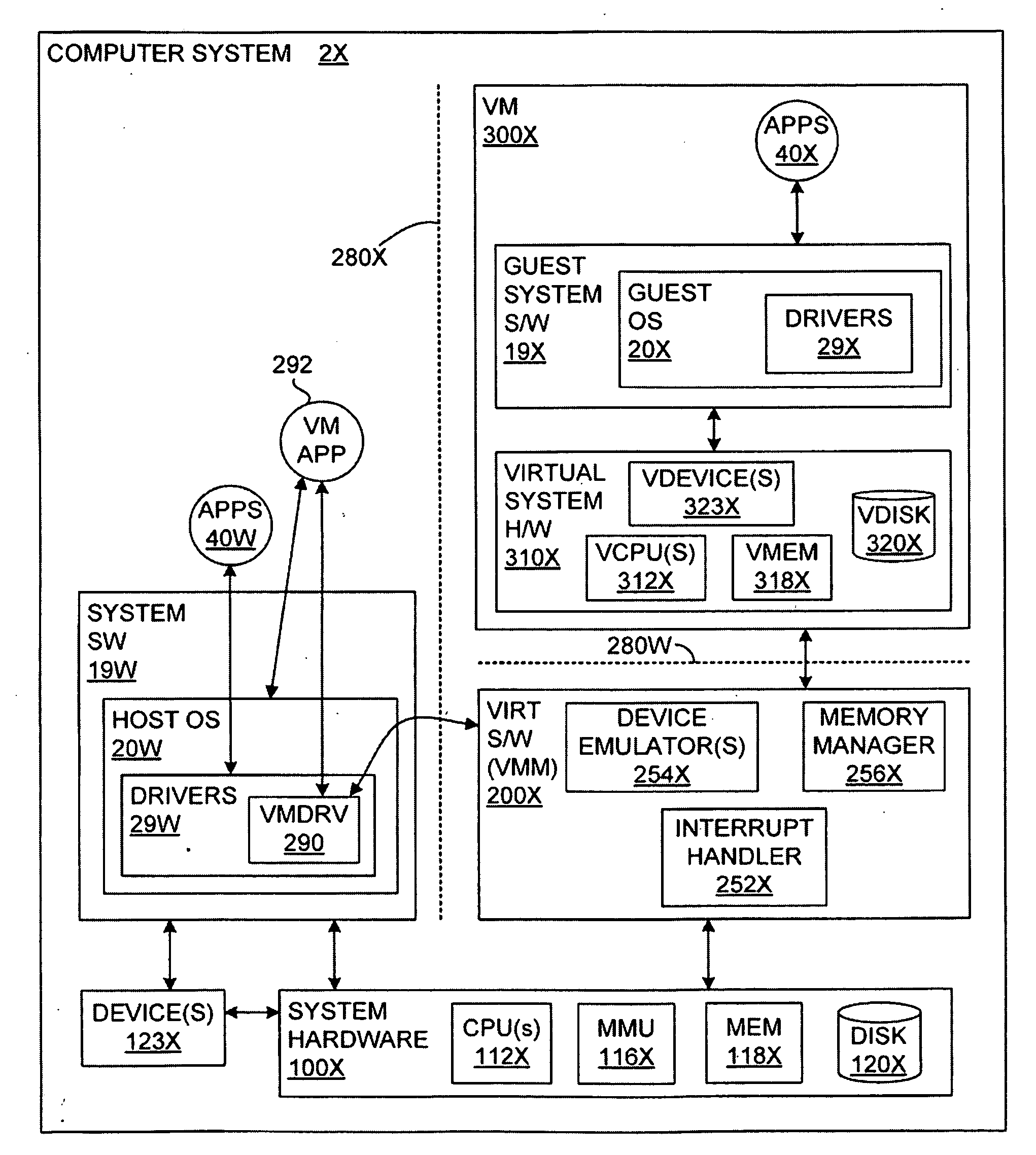
Saving and Restoring State Information for Virtualized Computer Systems
InactiveUS20100070678A1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputerized systemActive memory
Prior to or while the state of a virtual machine (“VM”) is being saved, such as in connection with the suspension or checkpointing of a VM, a set of one or more “active” memory pages is identified, this set of active memory pages comprising memory pages that are in use within the VM before operation of the VM is suspended. This set of active memory pages may constitute a “working set” of memory pages. To restore the state of the VM and resume operation, in some embodiments, (a) access to persistent storage is restored to the VM, device state for the VM is restored, and one or more of the set of active memory pages are loaded into physical memory; (b) operation of the VM is resumed; and (c) additional memory pages from the saved state of the VM are loaded into memory after operation of the VM has resumed.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Method, apparatus and computer program product for efficient per thread performance information
InactiveUS6925424B2Solve excessive overheadAvoid interactionDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringProcessor registerComputer science
A value in a counter on a processor is incremented for occurrences of a monitored event, providing a measured value for the event. The value of the counter register for a first thread is saved responsive to a switch from the first thread to a second thread. The value is saved in an accumulator in system memory. Then, responsive to a switch back to the first thread, the value for the first thread is restored from the accumulator. In this way, a counter may be read, and its value, for the first thread, for example, remains consistent despite any intervening thread switches. Since the counter register may be read directly, in the user state, this provides a faster and more consistent way to update performance counts.
Owner:IBM CORP
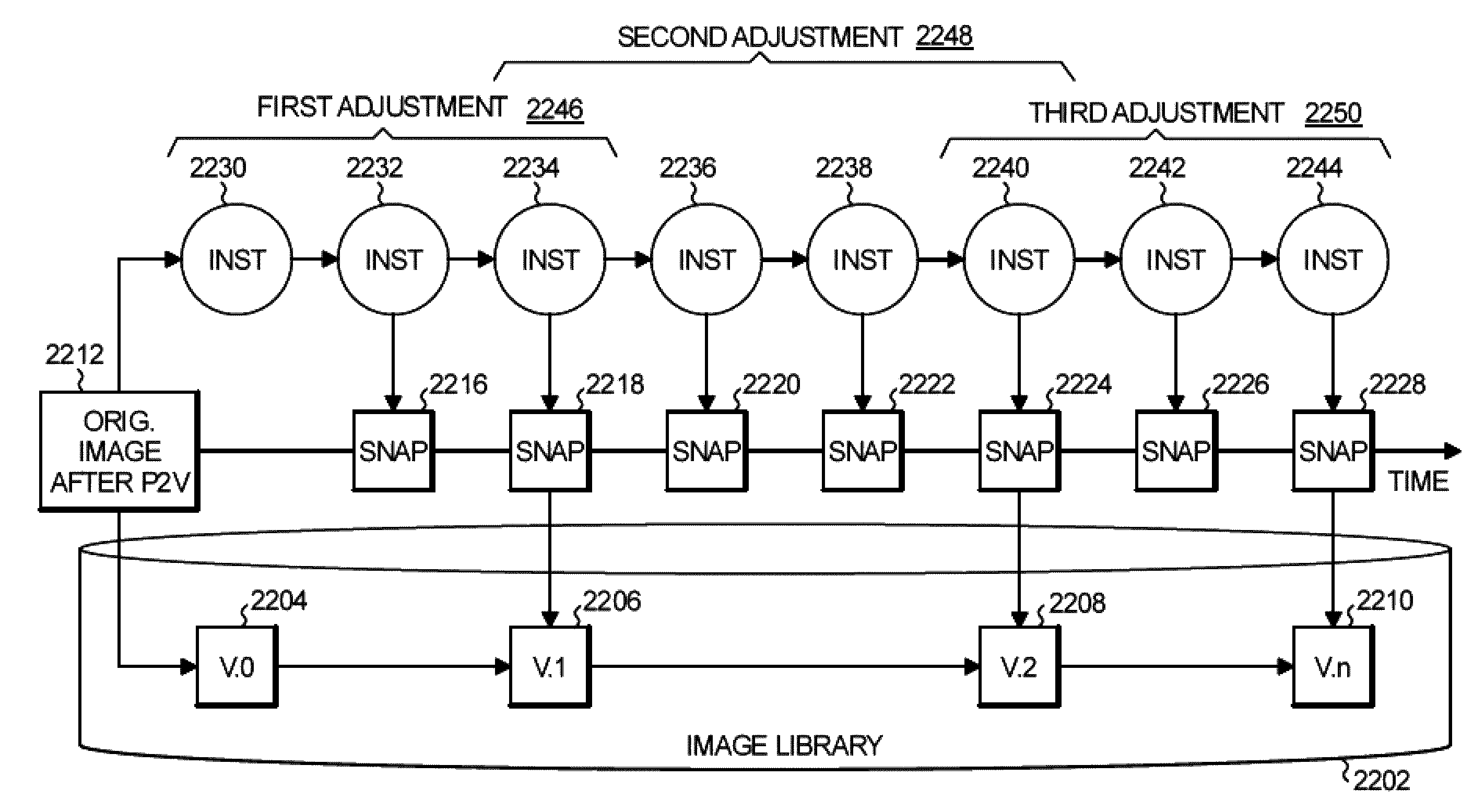
Use of snapshots to reduce risk in migration to a standard virtualized environment
ActiveUS9092837B2Reduce risk of migrationResource allocationImage acquisitionShort termsSource system
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Use of snapshots to reduce risk in migration to a standard virtualized environment
ActiveUS20140146055A1Reduce riskReduce risk of migrationError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsSoftware engineeringSource system
During a process of migrating a source system into a standardized virtual environment, virtual machine instances of the source system executing in a hypervisor are snapshotted as virtual machine images in an operational repository of the hypervisor. The virtual machine images in the operational repository are short-term snapshots. From time to time during the migration process, long-term snapshots of the source system are created by checking given ones of the virtual machine images from the hypervisor operational repository into an image library as image objects.
Owner:IBM CORP
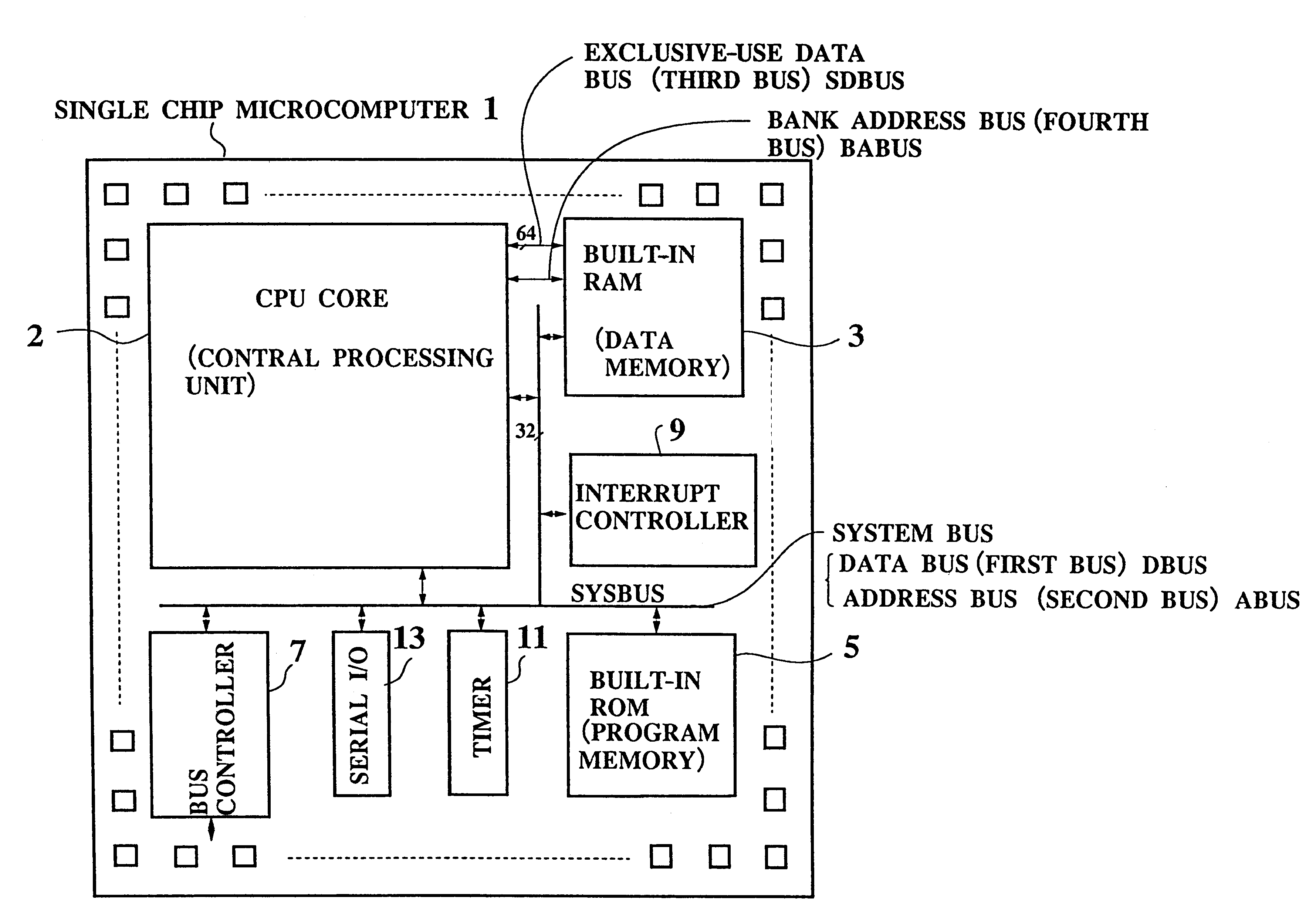
Single chip microcomputer having a dedicated address bus and dedicated data bus for transferring register bank data to and from an on-line RAM
InactiveUS6223279B1Efficiently chip spaceData transferArchitecture with single central processing unitSpecial data processing applicationsGeneral purposeProcessor register
A single chip microcomputer comprises a central processing unit (CPU) 2, a on-chip RAM 3, a on-chip ROM 5, a first bus DBUS for connecting the CPU, RAM, and ROM with one another and transferring data between them, a second bus ABUS for passing address data corresponding to the data passed through the first bus, a third bus SDBUS for connecting the CPU 2 with the RAM 3 and transferring data between them, the number of bits of the third bus SDBUS being larger than that of the first bus DBUS, and a fourth bus BABUS for connecting the CPU 2 with the RAM 3 and passing address data corresponding to the data passed through the third bus SDBUS. The CPU 2 has a data memory RF serving as general purpose registers for providing internal data to the third bus SDBUS, and a bank specifying register BP for holding positional data of a mapping region in the RAM 3 where the contents of the data memory RF are mapped and providing the positional data to the fourth bus BABUS. The RAM 3 has a memory cell array 31, a bank address control circuit 35 connected to the fourth bus BABUS, for generating a real address according to the contents of the bank specifying register BP (BP0, BP1), and a selection circuit 37 for selecting the real address generated by the bank address control circuit 35, or the address provided through the second bus ABUS.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
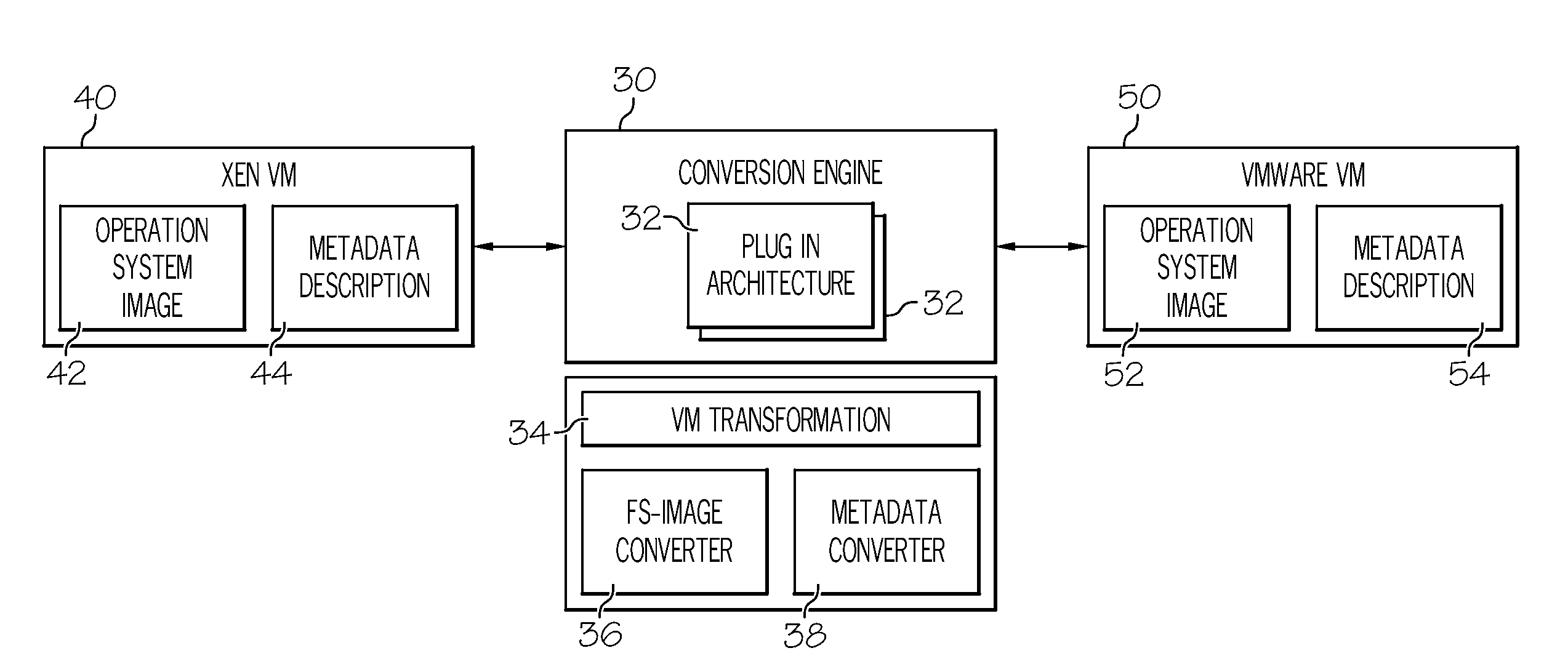
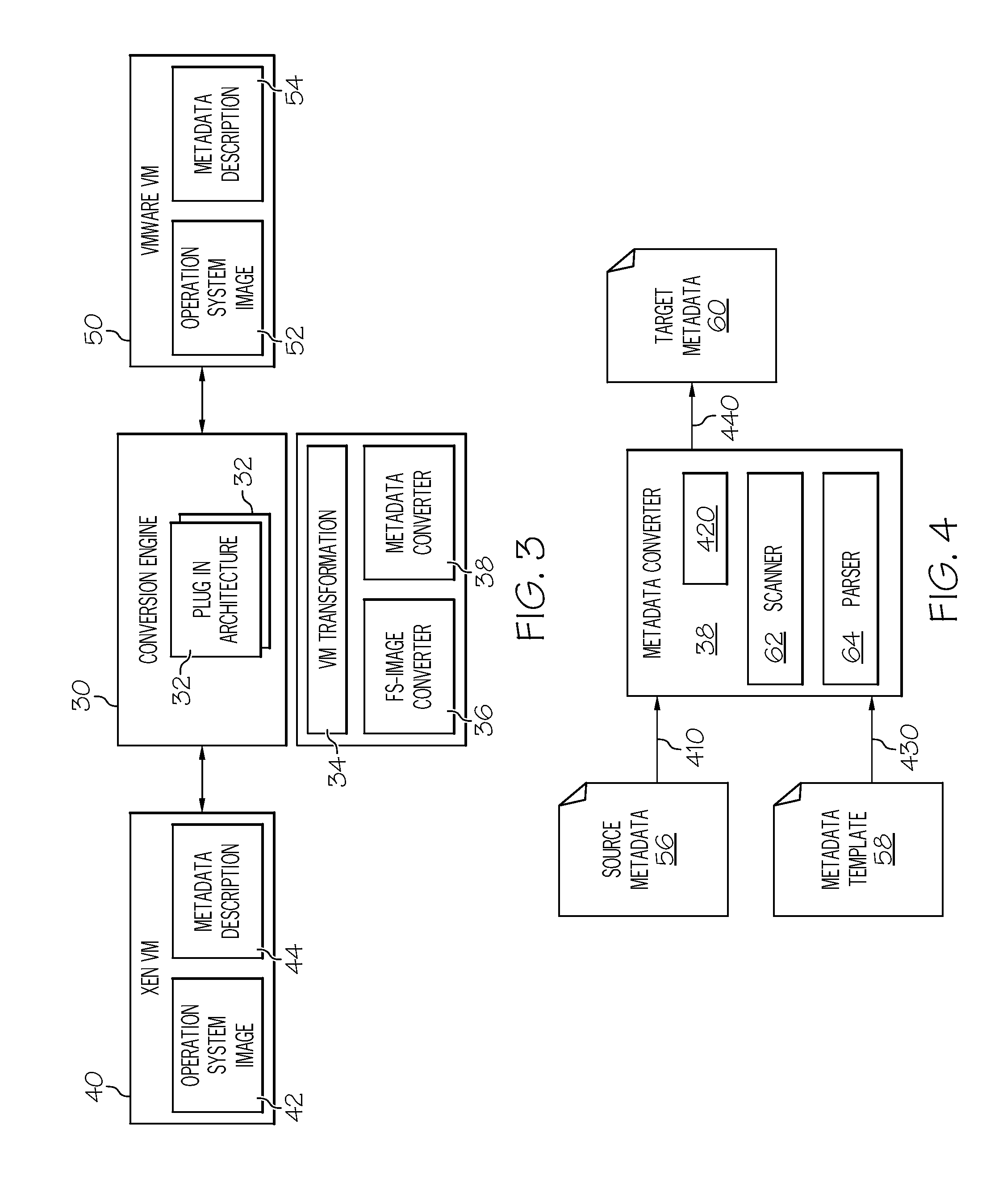
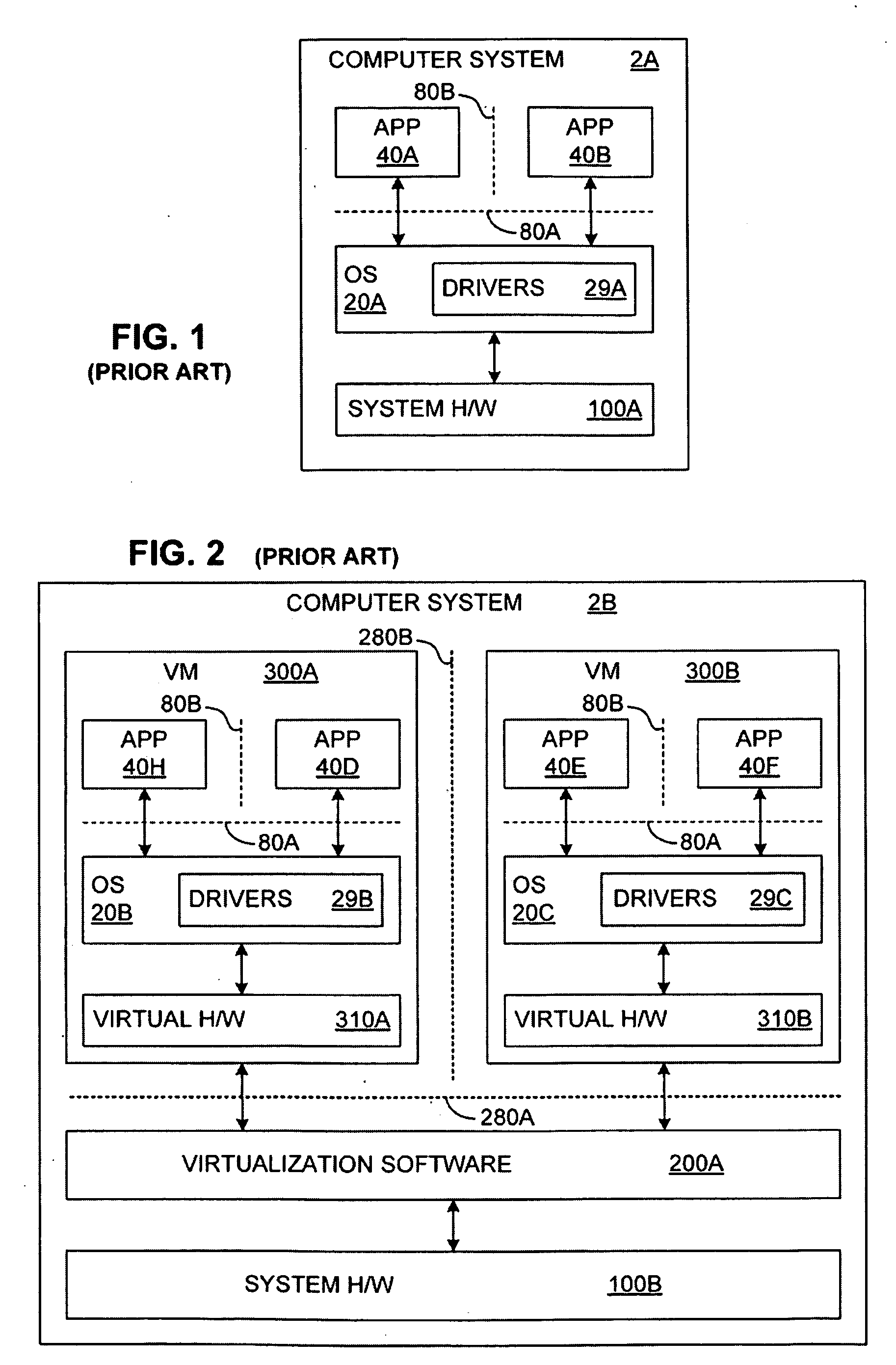
Method and System for Migrating Virtual Machines Between Hypervisors
ActiveUS20080263258A1Computer security arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationFile systemData storing
A method for migrating virtual machines between hypervisors is disclosed. Initially, metadata describing a virtual machine are automatically scanned and parsed. The structure of the metadata of a source virtual machine are automatically analyzed. Elements of this structure are mapped to corresponding entries of a target virtual machine. A target metadata descriptor to be used as part of the target virtual machine is generated. A predefined layout description of the data stored in a file system image of the source virtual machine read. A predefined layout description of the data to be stored in a file system image to be used at the target virtual machine is also read. The data are extracted from the source virtual machine. A template of a file system image for the target virtual system is generated. Storage space corresponding to the target virtual machine is allocated, and the extracted data are inserted into the allocated storage space.
Owner:IBM CORP
System with high power and low power processors and thread transfer
A processing system comprises a first processor that has active and inactive states and that processes at least one thread during the active state. A second processor has active and inactive states. The second processor consumes less power when operating in the active state than the first processor operating in the active state. A control module communicates with the first and second processors and selectively transfers the at least one thread from the first processor to the second processor and selects the inactive state of the first processor. The second processor processes the at least one thread.
Owner:SUTARDJA SEHAT
Computer multi-tasking via virtual threading using an interpreter
InactiveUS7234139B1Eliminate dependenciesDifferent operationalProgram initiation/switchingInterprogram communicationLocal variablePseudocode
In the operation of a computer, a plurality of bytecode or pseudocode instructions, at least some of the pseudocode instructions comprising a plurality of machine code instructions, are stored in a computer memory. For each of a plurality of tasks or jobs to be performed by the computer, a respective virtual thread of execution context data is automatically created. The virtual threads each include (a) a memory location of a next one of the pseudocode instructions to be executed in carrying out the respective task or job and (b) the values of any local variables required for carrying out the respective task or job. At least some of the tasks or jobs each entails execution of a respective one of the pseudocode instructions comprising a plurality of machine language instructions. Each of the tasks or jobs are processed in a respective series of time slices or processing slots under the control of the respective virtual thread, and, in every context switch between different virtual threads, such context switch is undertaken only after completed execution of a currently executing one of the pseudocode instructions.
Owner:CERINET USA
Hardware multithreading systems with state registers having thread profiling data
According to some embodiments, a multithreaded microcontroller includes a thread control unit comprising thread control hardware (logic) configured to perform a number of multithreading system calls essentially in real time, e.g. in one or a few clock cycles. System calls can include mutex lock, wait condition, and signal instructions. The thread controller includes a number of thread state, mutex, and condition variable registers used for executing the multithreading system calls. Threads can transition between several states including free, run, ready and wait. The wait state includes interrupt, condition, mutex, I-cache, and memory substates. A thread state transition controller controls thread states, while a thread instructions execution unit executes multithreading system calls and manages thread priorities to avoid priority inversion. A thread scheduler schedules threads according to their priorities. A hardware thread profiler including global, run and wait profiler registers is used to monitor thread performance to facilitate software development.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Methods and systems for scheduling processes in a multi-core processor environment
InactiveUS20070204268A1Energy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingOperational systemMulti-core processor
Embodiments of the present invention provide efficient scheduling in a multi-core processor environment. In some embodiments, each core is assigned, at most, one execution context. Each execution context may then asynchronously run on its assigned core. If execution context is blocked, then its dedicated core may be suspended or powered down until the execution context resumes operation. The processor core may remain dedicated to a particular thread, and thus, avoid the costly operations of a process or context switch, such as clearing register contents. In other embodiments, execution contexts are partitioned into two groups. The execution contexts may be partitioned based on various factors, such as their relative priority. One group of the execution contexts may be assigned their own dedicated core and allowed to run asynchronously. The other group of execution contexts, such as those with a lower priority, are co-scheduled among the remaining cores by the scheduler of the operating system.
Owner:RED HAT
System and method for instruction level multithreading scheduling in a embedded processor
A system and method for enabling multithreading in a embedded processor, invoking zero-time context switching in a multithreading environment, scheduling multiple threads to permit numerous hard-real time and non-real time priority levels, fetching data and instructions from multiple memory blocks in a multithreading environment, and enabling a particular thread to modify the multiple states of the multiple threads in the processor core.
Owner:MAYFIELD XI +9
Adaptive spin-then-block mutual exclusion in multi-threaded processing
ActiveUS20090328053A1Avoid excessive delayMiss migrationMemory systemsProgram saving/restoringSpinsEngineering
Adaptive modifications of spinning and blocking behavior in spin-then-block mutual exclusion include limiting spinning time to no more than the duration of a context switch. Also, the frequency of spinning versus blocking is limited to a desired amount based on the success rate of recent spin attempts. As an alternative, spinning is bypassed if spinning is unlikely to be successful because the owner is not progressing toward releasing the shared resource, as might occur if the owner is blocked or spinning itself. In another aspect, the duration of spinning is generally limited, but longer spinning is permitted if no other threads are ready to utilize the processor. In another aspect, if the owner of a shared resource is ready to be executed, a thread attempting to acquire ownership performs a “directed yield” of the remainder of its processing quantum to the other thread, and execution of the acquiring thread is suspended.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Instruction-level multithreading according to a predetermined fixed schedule in an embedded processor using zero-time context switching
A system and method for enabling multithreading in a embedded processor, invoking zero-time context switching in a multithreading environment, scheduling multiple threads to permit numerous hard-real time and non-real time priority levels, fetching data and instructions from multiple memory blocks in a multithreading environment, and enabling a particular thread to modify the multiple states of the multiple threads in the processor core.
Owner:MAYFIELD XI +8
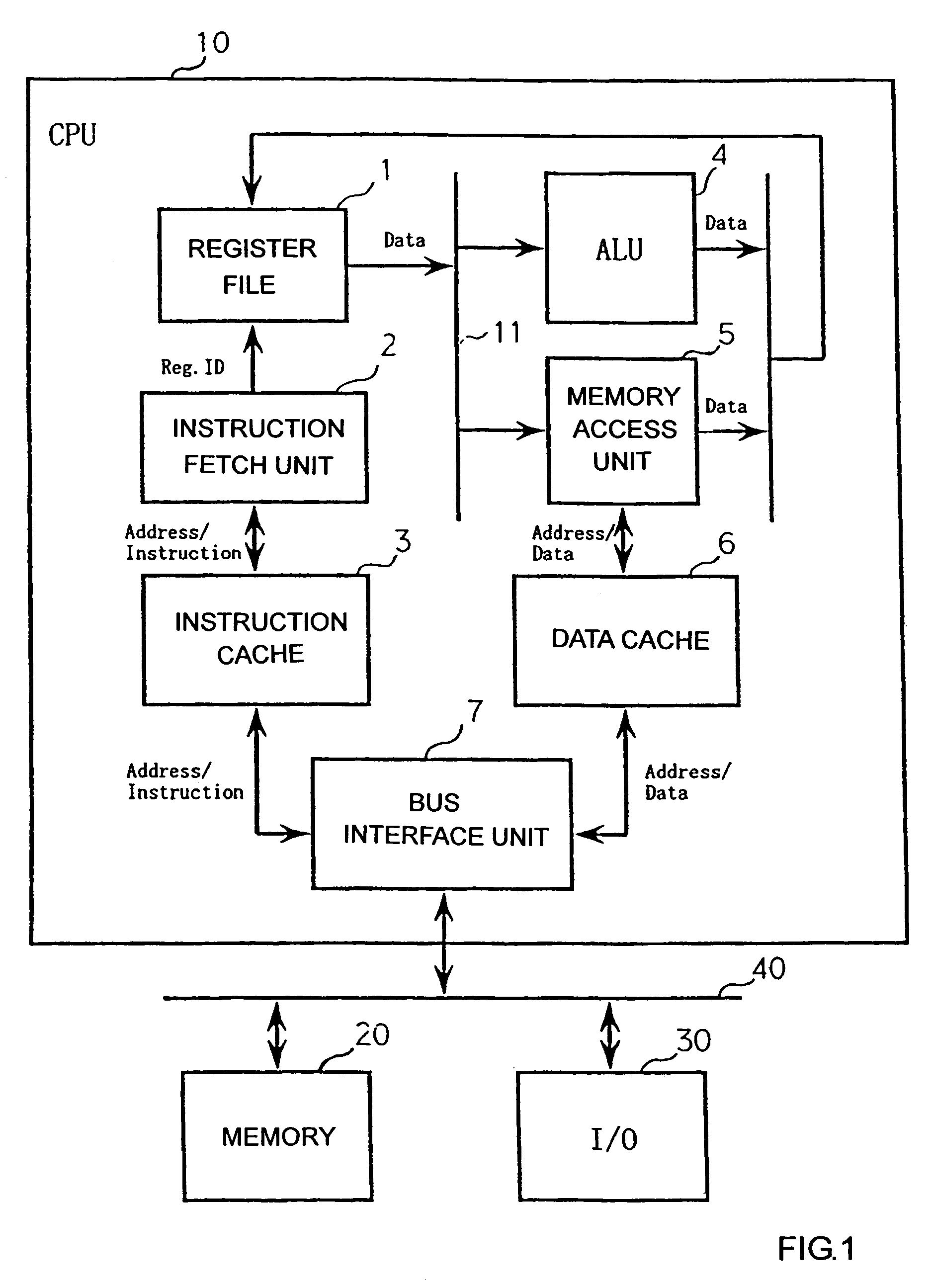
Context switching method, device, program, recording medium, and central processing unit
ActiveUS20070022428A1Reduce overheadMinimize time quantumProgram initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsOperational systemProcessor register
In an application in which context switching often occurs such as in a real time OS, it is possible to significantly reduce the overhead caused by the context switching. The OS issues a Swap instruction and a context switch starts. The Swap instruction is issued together with a thread (i.e., context) ID to be replaced, to a thread control unit (9). The thread ID is used to uniquely identify threads stored in a context cache (8). The thread control unit (9) saves data from a register file (1) to the context cache (8) via a context-dedicated bus (12) and transmits data of a new thread from the context cache (8) to the register file (1). According to the thread ID received, the thread control unit (9) automatically interchanges the necessary number of data in the register file (1) and the data in the context cache (8).
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
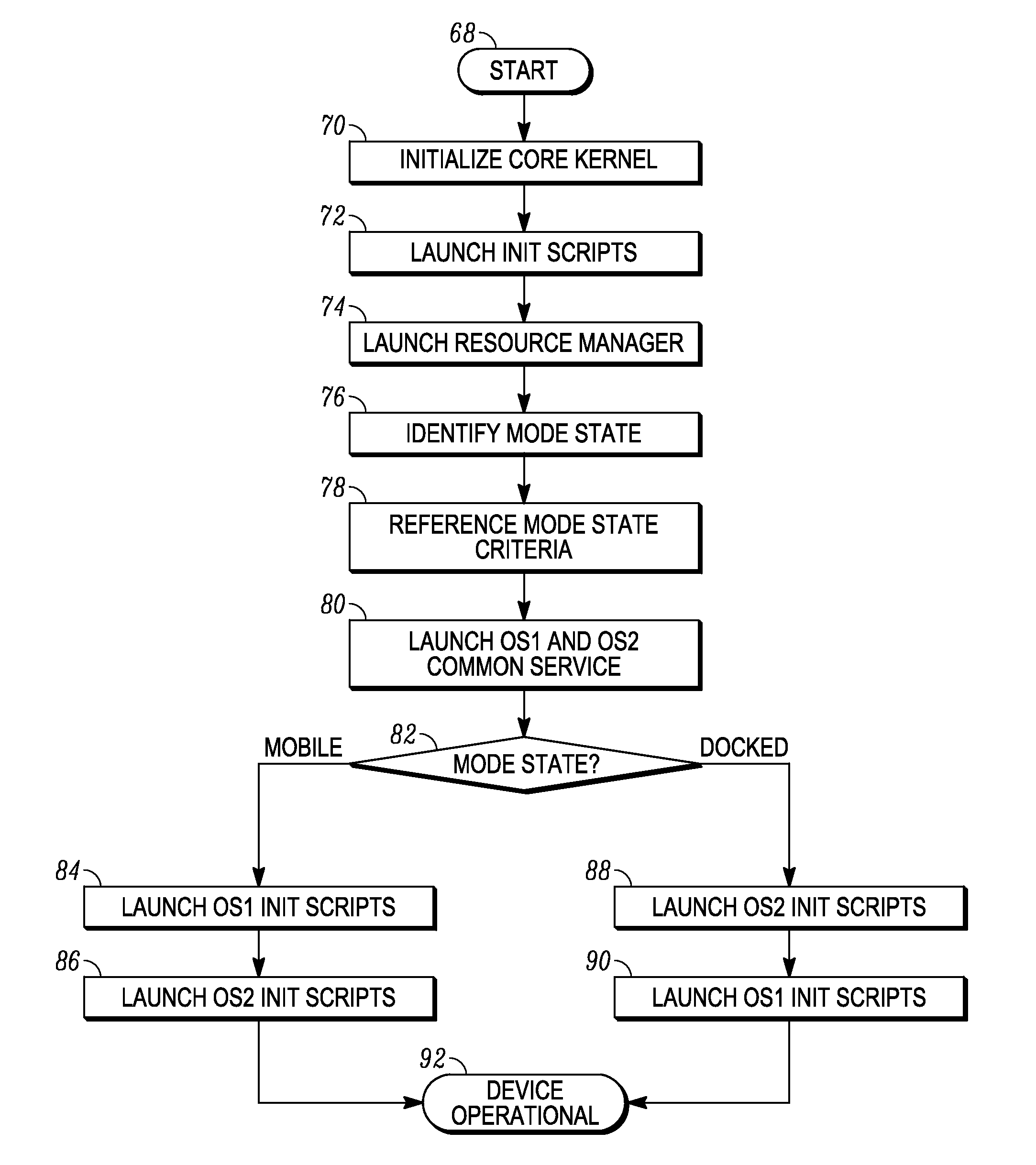
System and method for initiating a multi-environment operating system
Various embodiments of the present invention provide a mobile computing device that operates multiple, co-existing and independent operating system environments on a common kernel. A booting process for initiating a multiple operating system environment is also provided. Additionally, various embodiments of the present invention include processes for managing a switch between one operating system environment to a second operating system environment.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Transparent VMM-Assisted User-Mode Execution Control Transfer
ActiveUS20090113424A1Privacy protectionImprove integrityMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionOperational systemExecution control
A virtual-machine-based system provides a control-transfer mechanism to invoke a user-mode application handler from existing virtual hardware directly, without going through an operating system kernel running in the virtual machine. A virtual machine monitor calls directly to the guest user-mode handler and the handler transfers control back to the virtual machine monitor, without involving the guest operating system.
Owner:VMWARE INC
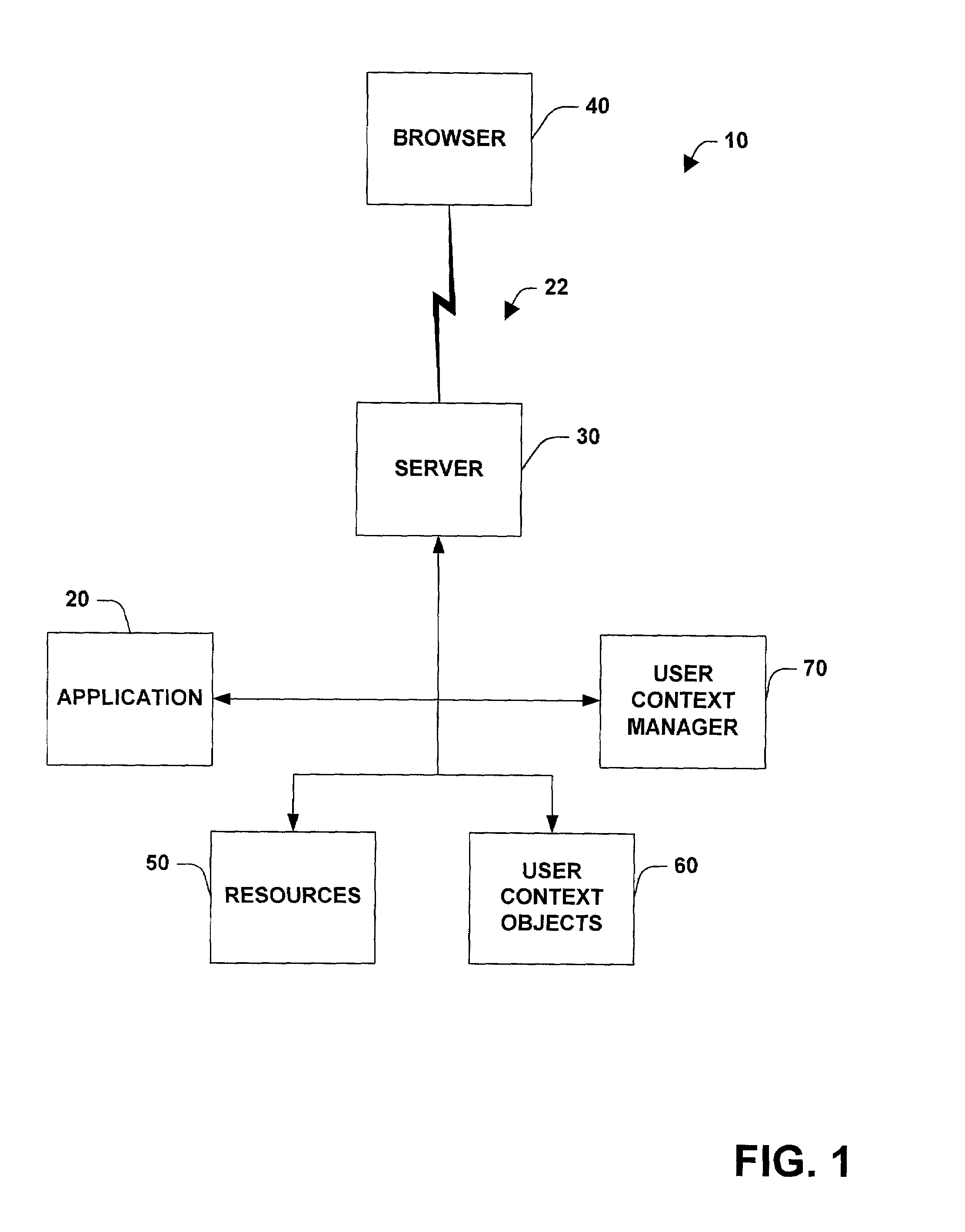
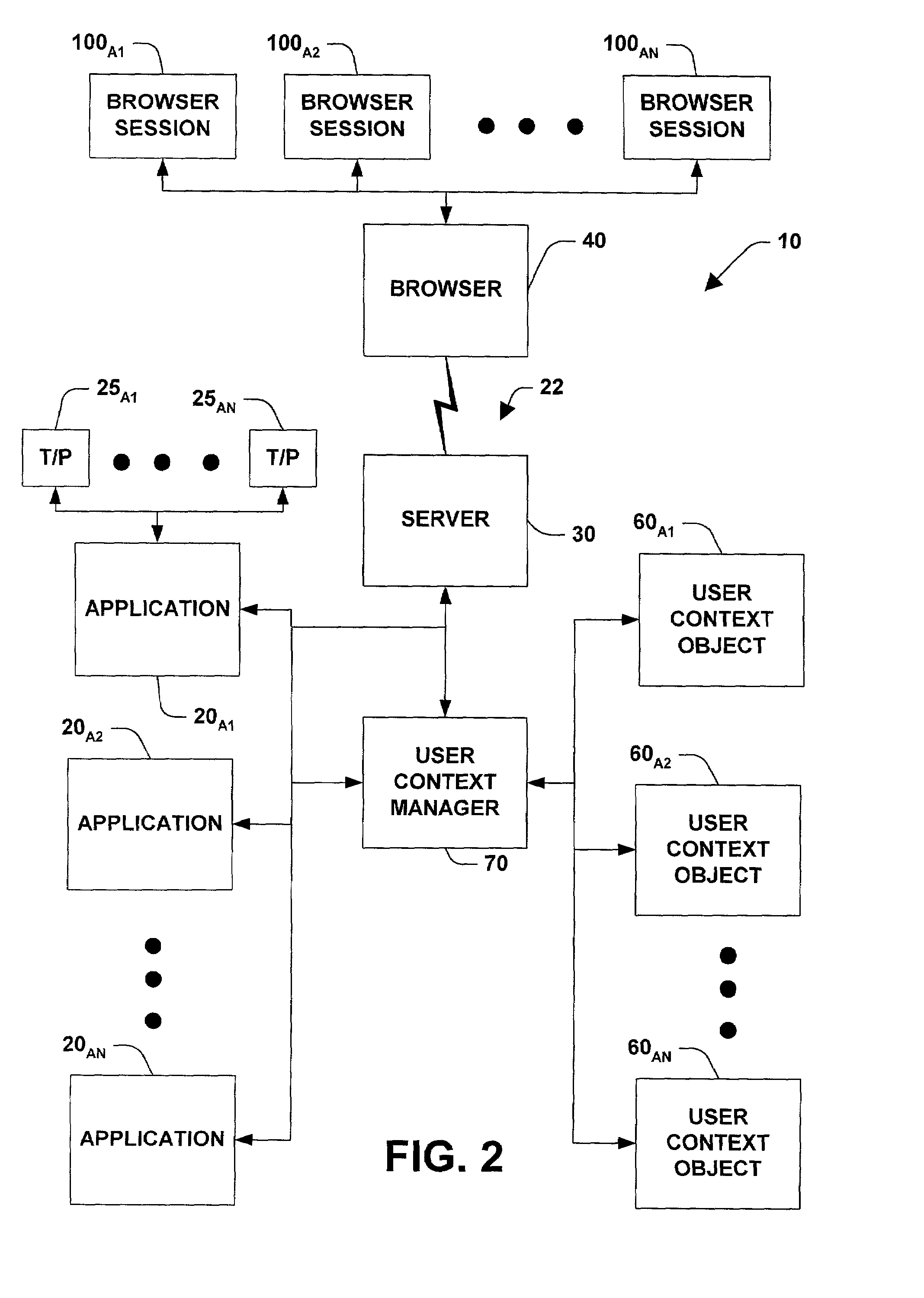
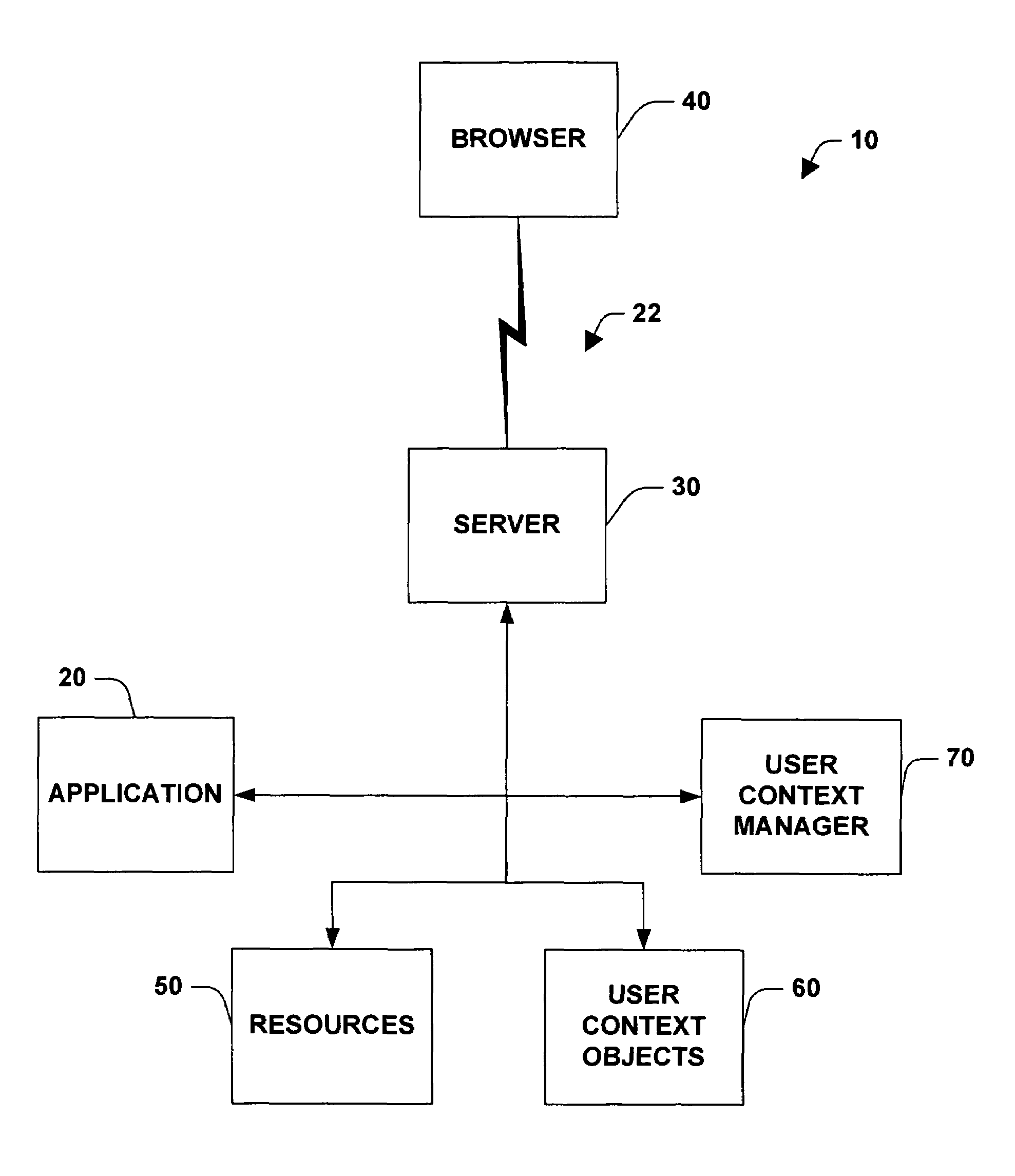
System and method for managing states and user context over stateless protocols
InactiveUS7065568B2Easy remote accessEasy maintenanceMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationStateless protocolThe Internet
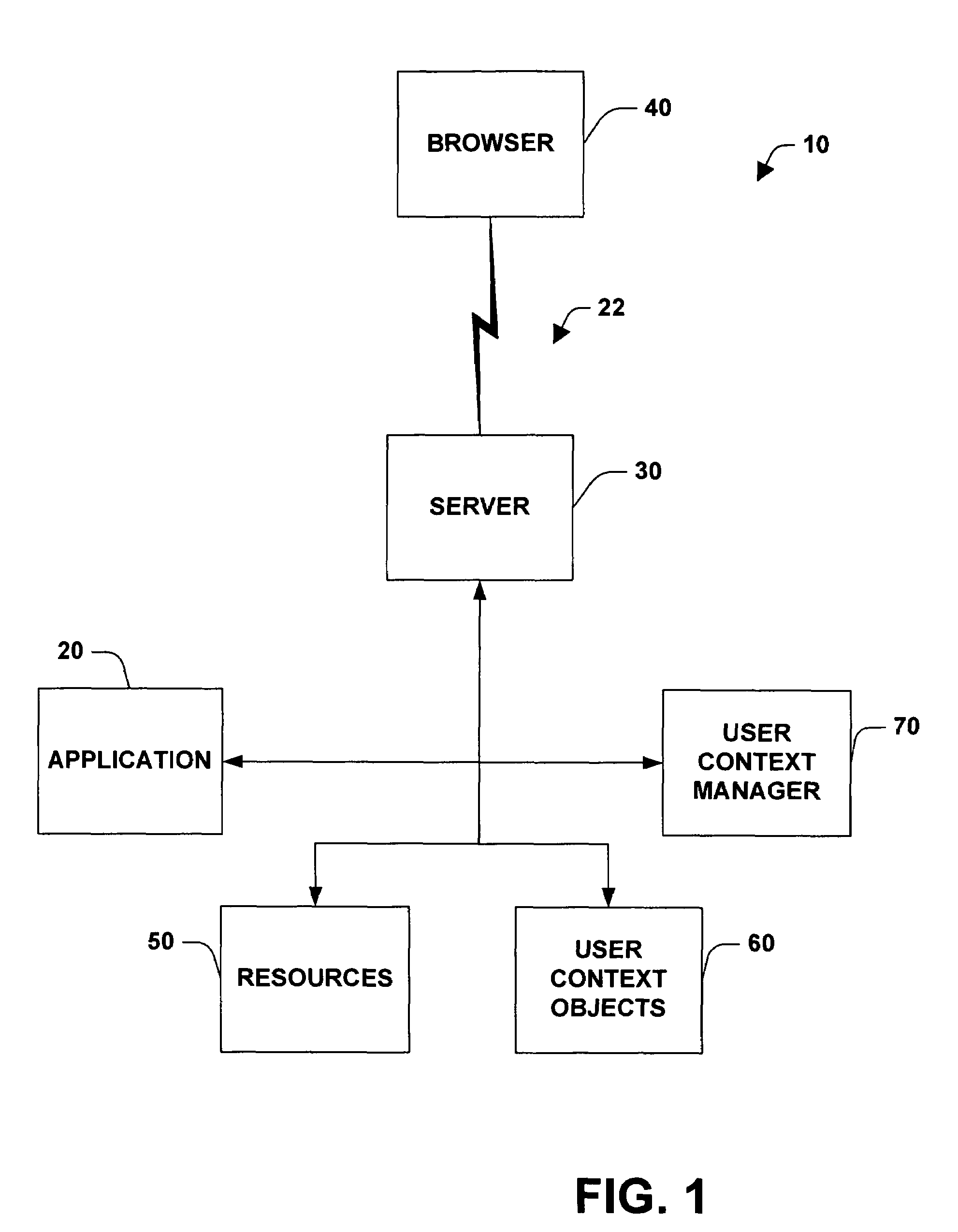
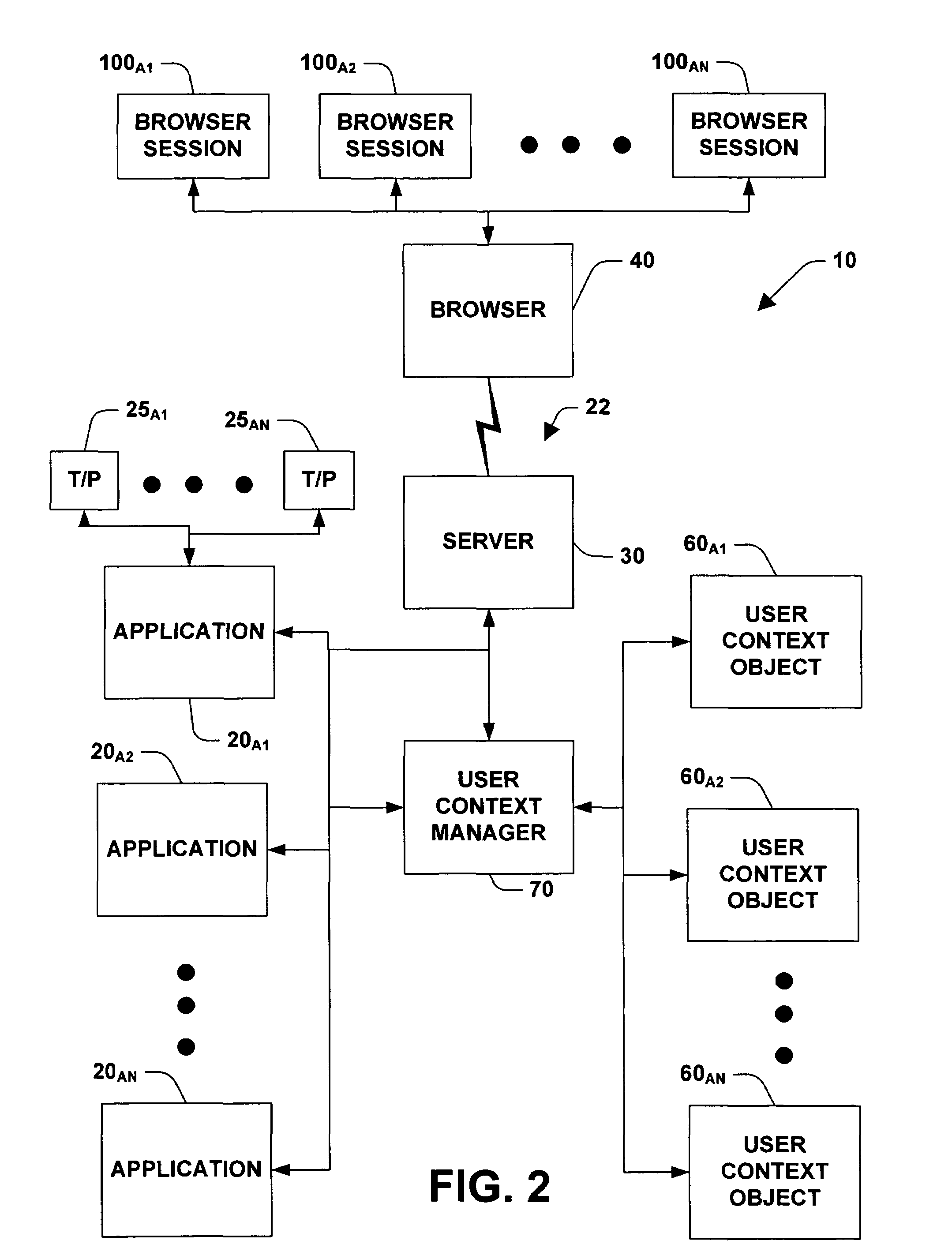
A system and method for facilitating remote access of an application available via a stateless protocol is provided. Such applications are typically accessed via the World Wide Web portion of the Internet (the “Web”) using a browser application and an HTTP protocol. The system can include one or more components for caching data associated with the remote access, the data comprising state and / or user specific information. The state and / or user specific information can be stored in a user context object (UCO). One or more user context objects can be managed by a user context manager that facilitates locating user context objects and reclaiming memory associated with user context objects that are no longer necessary to support remote access of the application accessed via a stateless protocol.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for managing states and user context over stateless protocols
InactiveUS7353266B2Easy remote accessEasy maintenanceMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationStateless protocolThe Internet
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
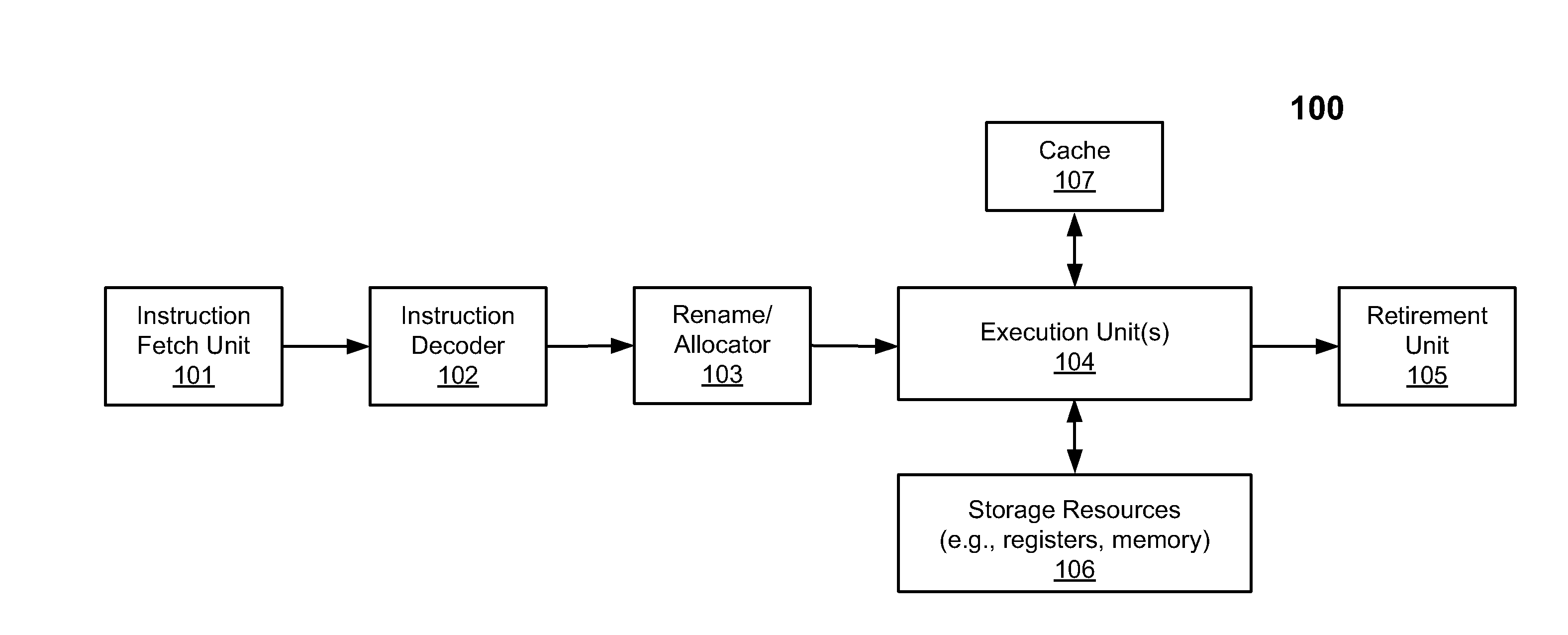
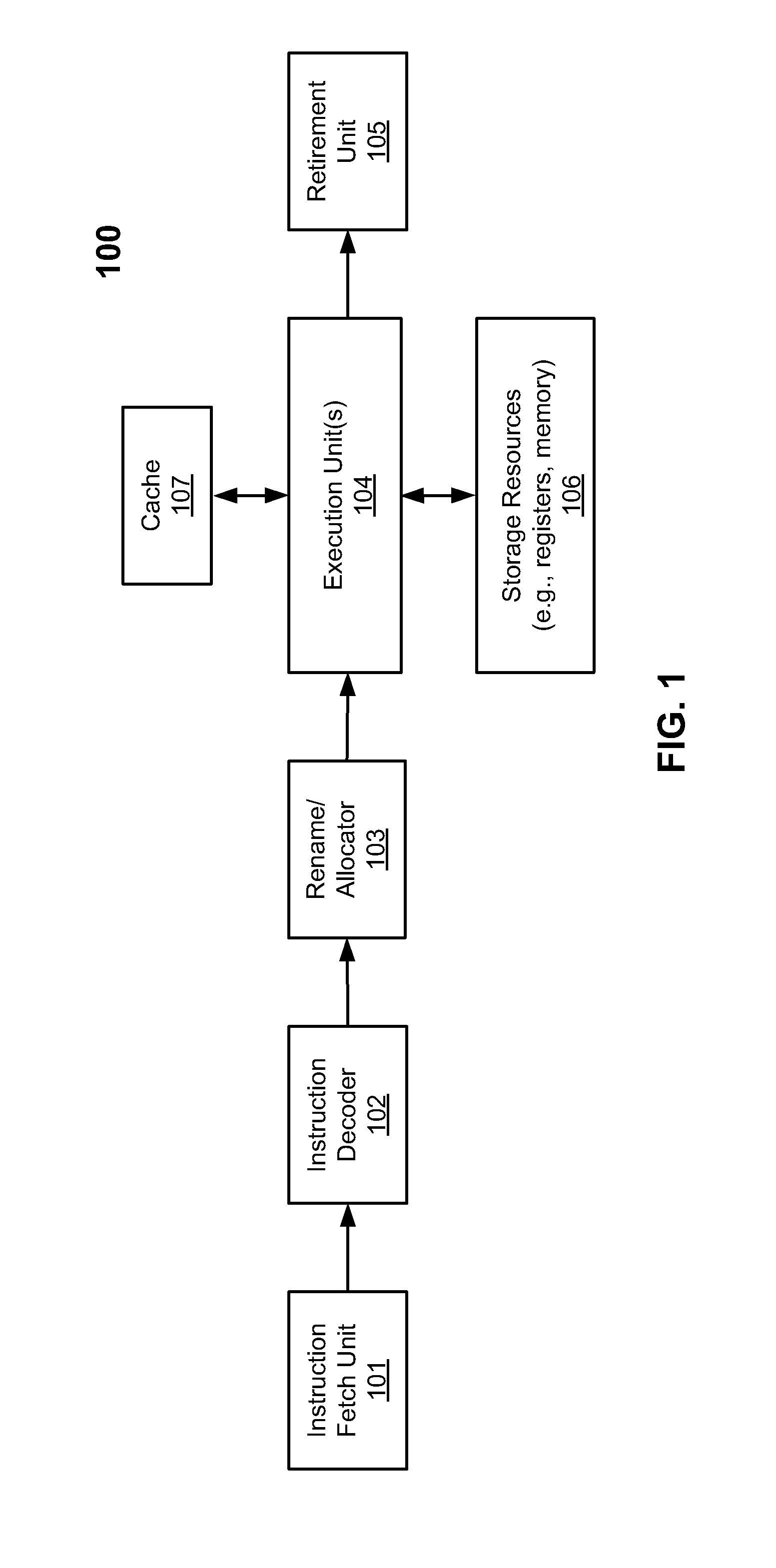
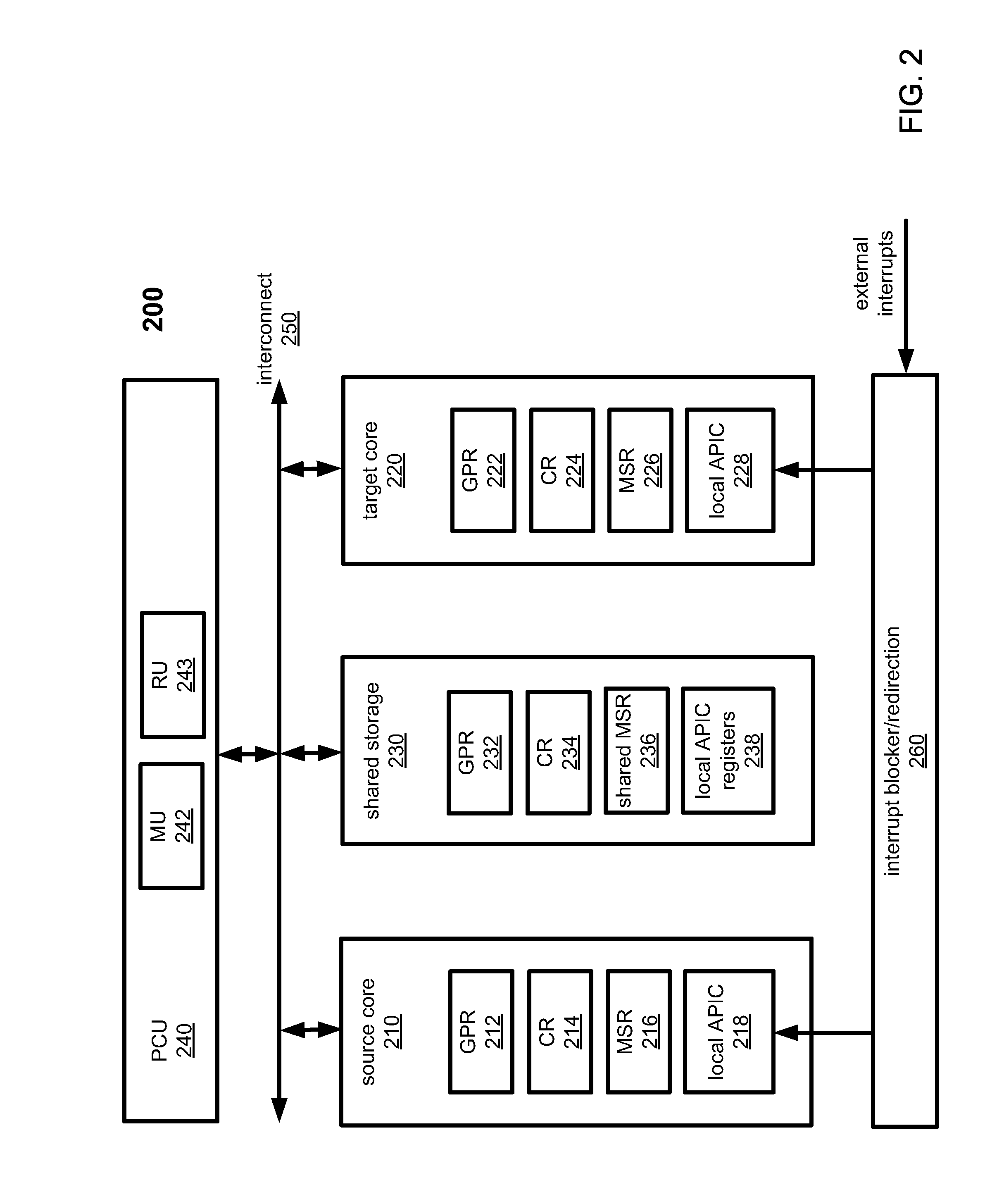
Thread migration support for architectually different cores
According to one embodiment, a processor includes a plurality of processor cores for executing a plurality of threads, a shared storage communicatively coupled to the plurality of processor cores, a power control unit (PCU) communicatively coupled to the plurality of processors to determine, without any software (SW) intervention, if a thread being performed by a first processor core should be migrated to a second processor core, and a migration unit, in response to receiving an instruction from the PCU to migrate the thread, to store at least a portion of architectural state of the first processor core in the shared storage and to migrate the thread to the second processor core, without any SW intervention, such that the second processor core can continue executing the thread based on the architectural state from the shared storage without knowledge of the SW.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Context switching system having context cache and a register file for the save and restore context operation
InactiveUS8020169B2Reduce overheadMinimize time quantumProgram initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsOperational systemContext switch
In an application in which context switching often occurs such as in a real time OS, it is possible to significantly reduce the overhead caused by the context switching. The OS issues a Swap instruction and a context switch starts. The Swap instruction is issued together with a thread (i.e., context) ID to be replaced, to a thread control unit (9). The thread ID is used to uniquely identify threads stored in a context cache (8). The thread control unit (9) saves data from a register file (1) to the context cache (8) via a context-dedicated bus (12) and transmits data of a new thread from the context cache (8) to the register file (1). According to the thread ID received, the thread control unit (9) automatically interchanges the necessary number of data in the register file (1) and the data in the context cache (8).
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
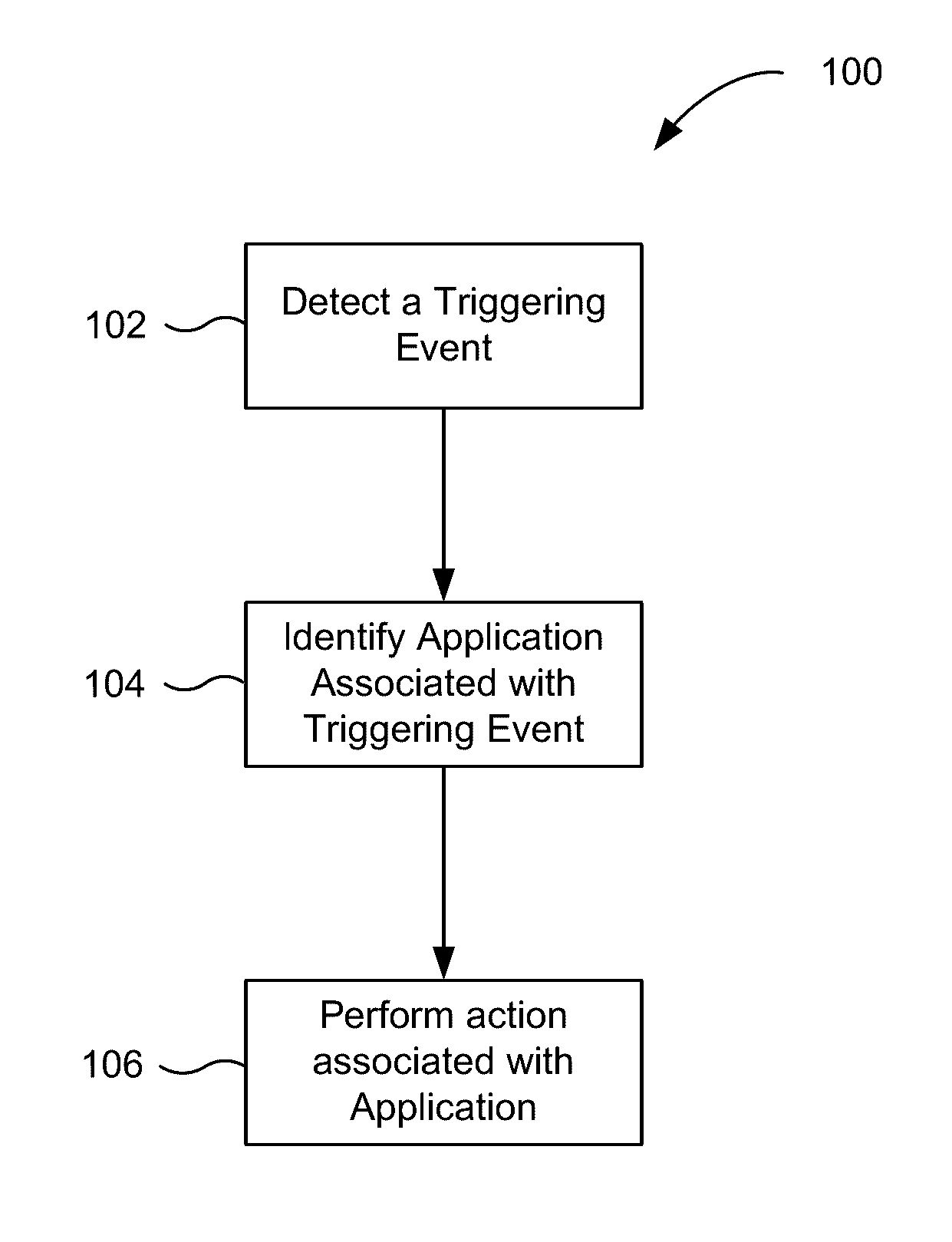
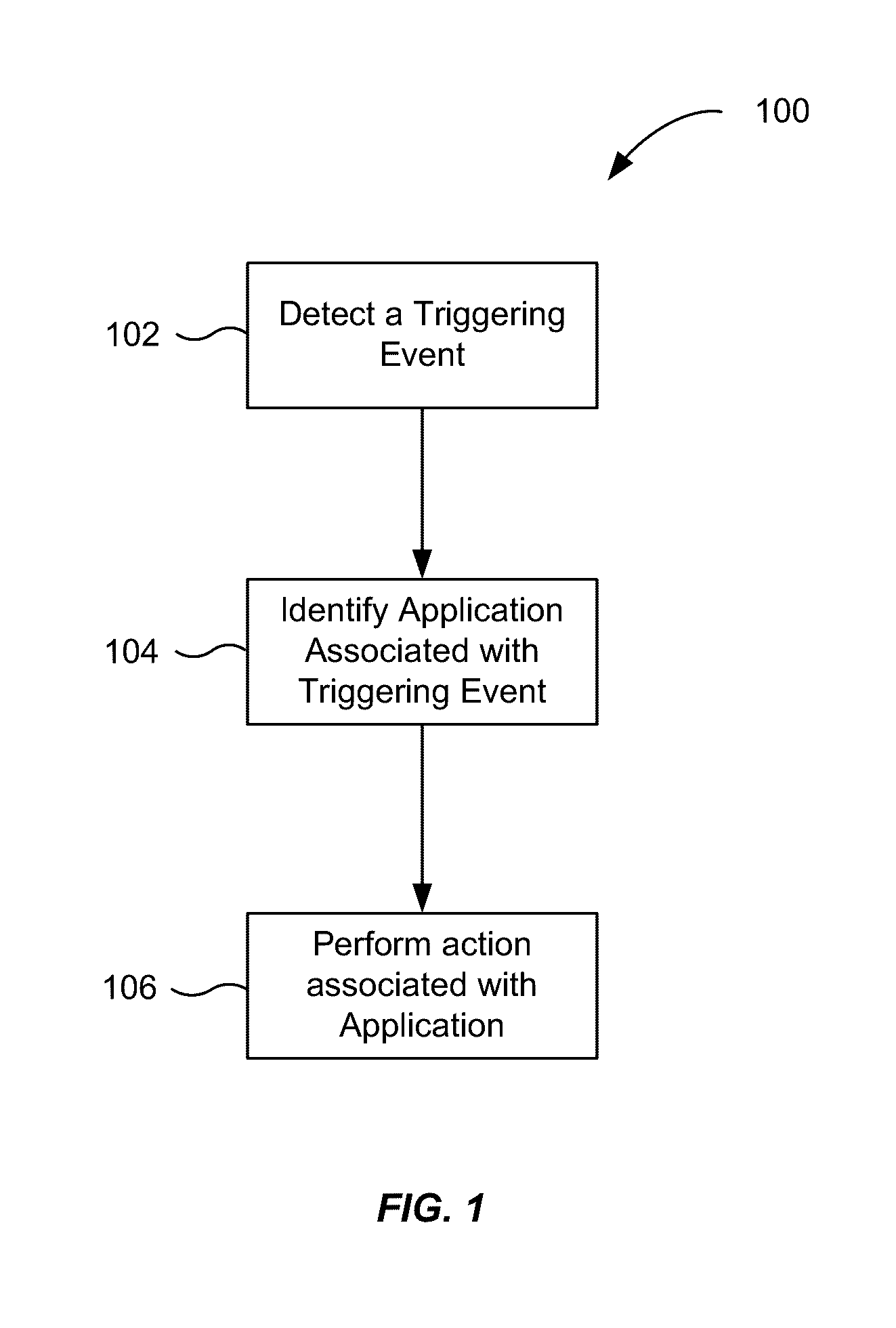
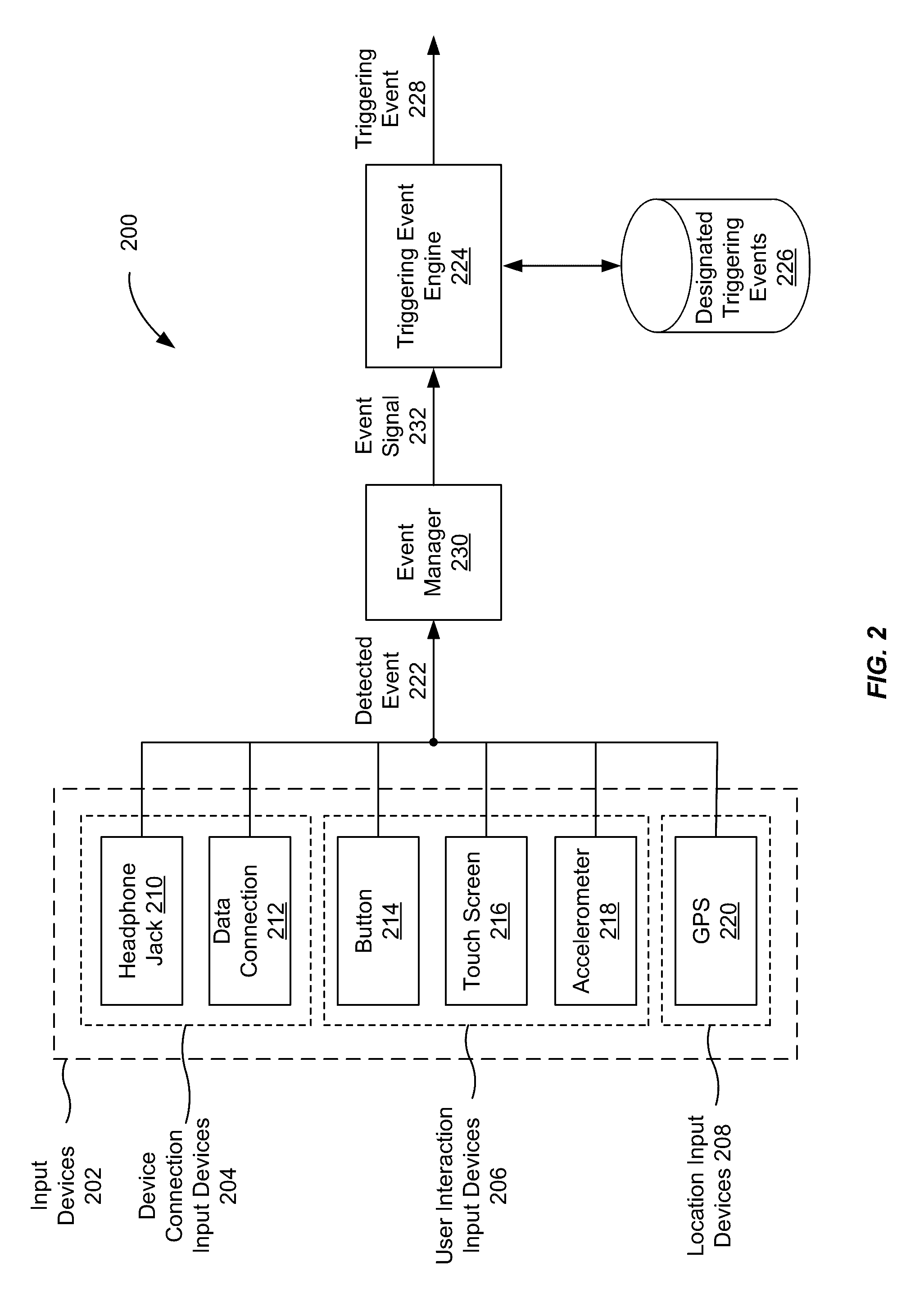
Application recommendation based on detected triggering events
ActiveUS20160357362A1Accurate recommendationEasy accessSubstation equipmentMachine learningComputer scienceThreshold probability
An event can be detected by an input device. The event may be determined to be a triggering event by comparing the event to a group of triggering events. A first prediction model corresponding to the event is then selected. Contextual information about the device specifying one or more properties of the computing device in a first context is then received, and a set of one or more applications is identified. The set of one or more applications may have at least a threshold probability of being accessed by the user when the event occurs in the first context. Thereafter, a user interface is provided to a user for interacting with the set of one or more applications.
Owner:APPLE INC
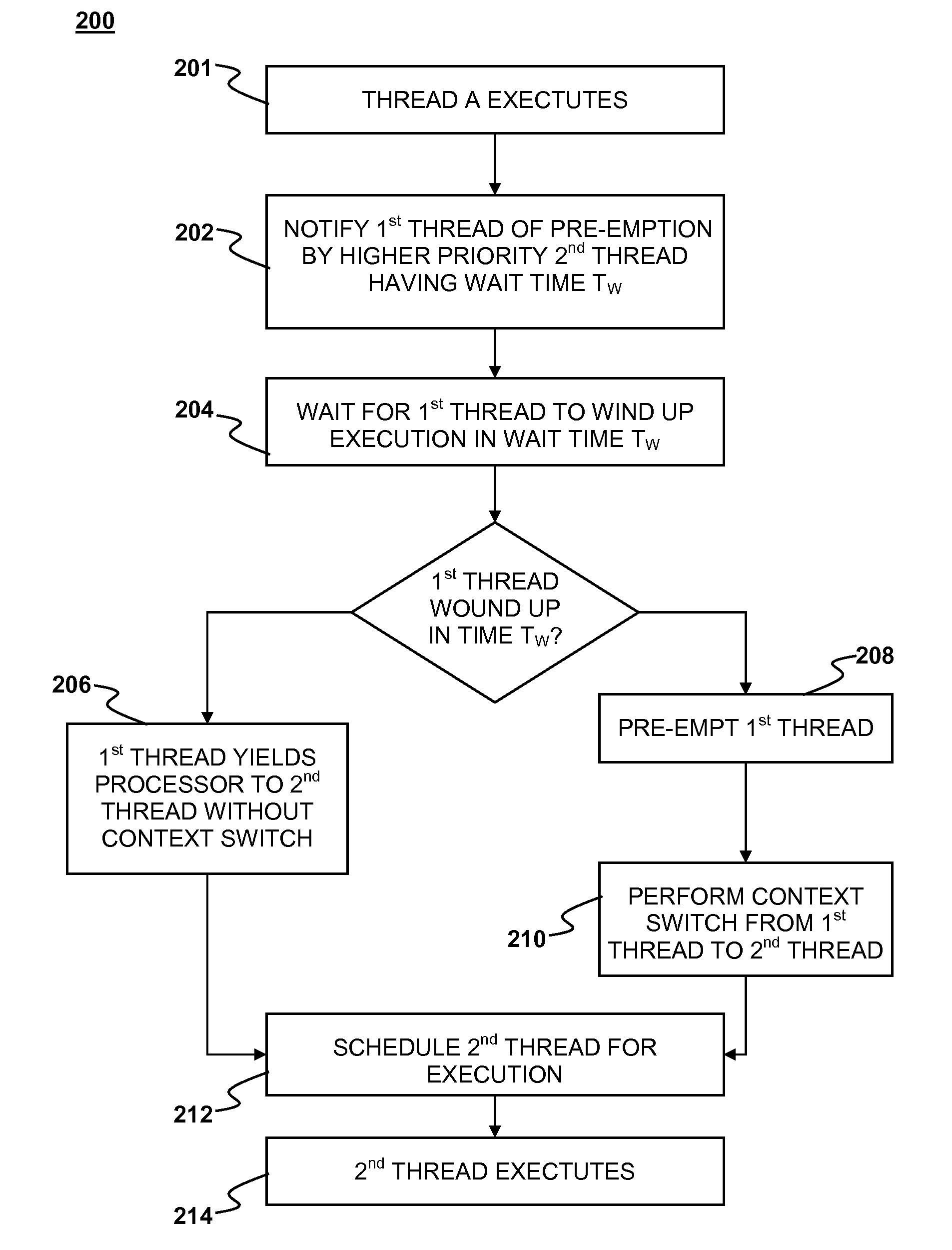
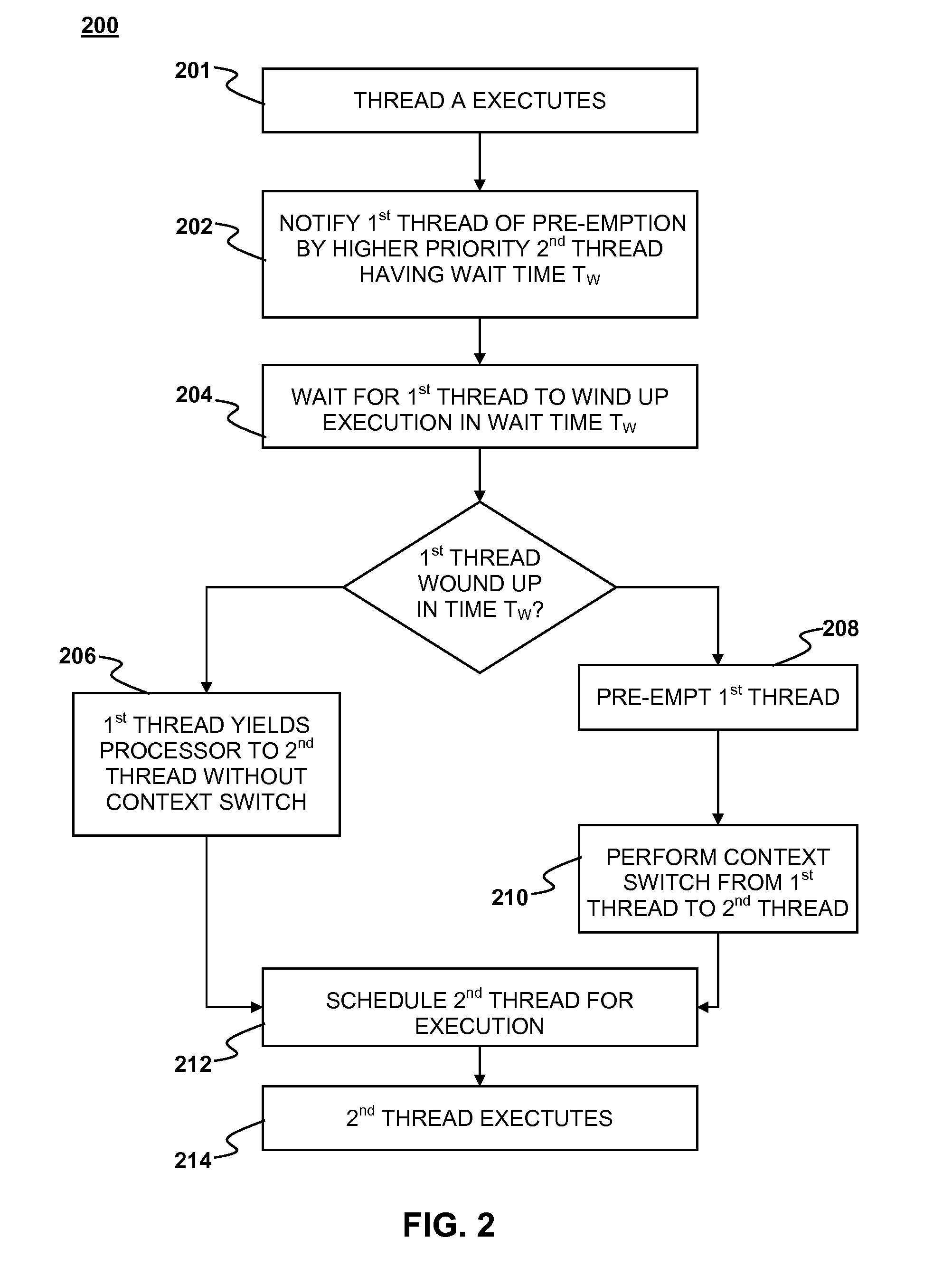
Multi-threaded processing with reduced context switching
Multi-threaded processing with reduced context switching is disclosed. Context switches may be avoided through the use of pre-emption notification, a pre-emption wait time attribute and a no-context-save yield.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
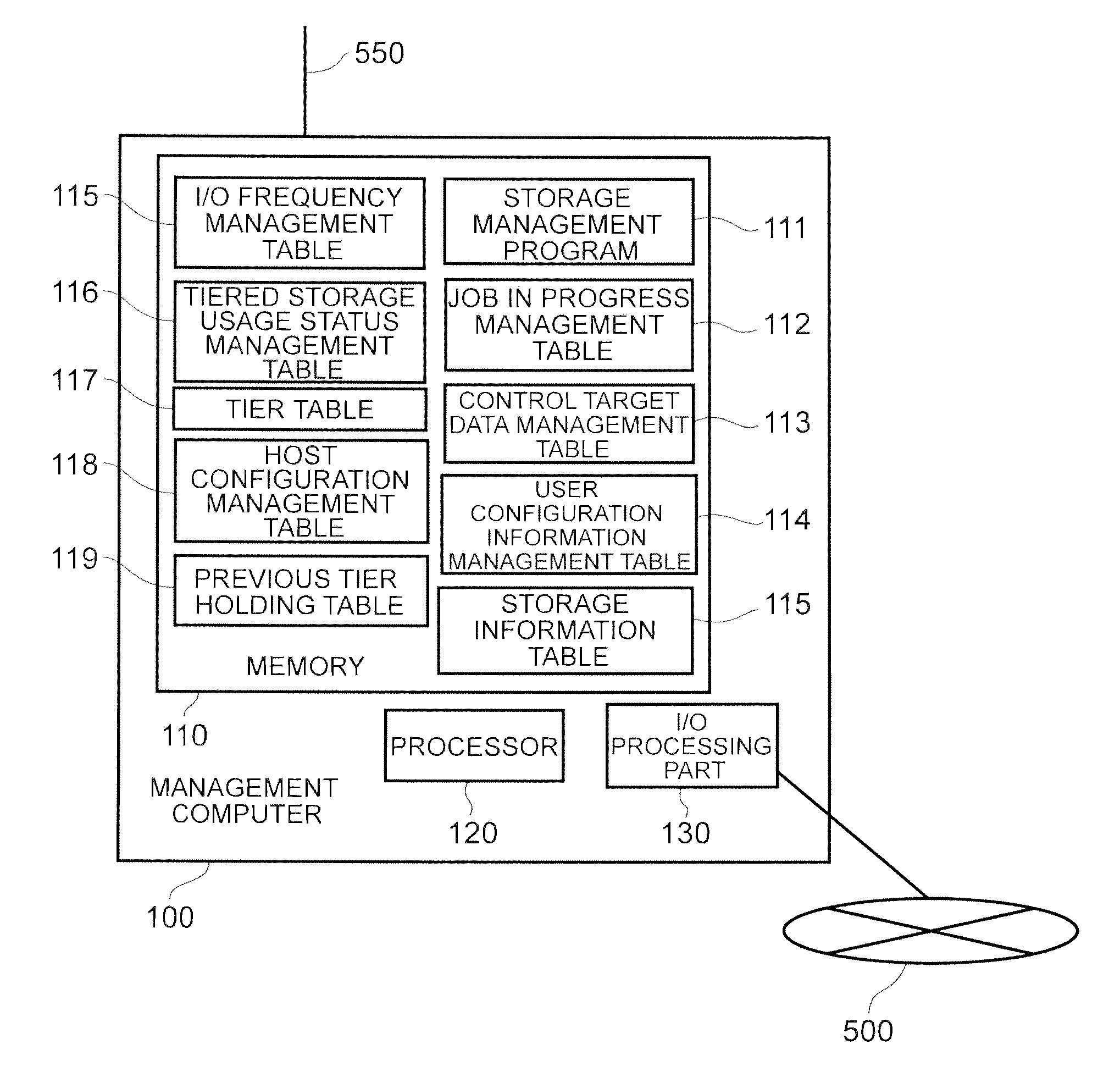
Computer system and storage management method
InactiveUS20130111129A1Easy to useDigital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData controlGranularity
Data is placed in tiered storage with a suitable granularity according to application characteristics. The storage apparatus comprises a controller for managing storage areas, provided by storage media of a plurality of types of varying performance, as pools, and for assigning the storage areas in page units to a virtual volume from any tiered storage among a plurality of types of tiered storage which the pool comprises in response to a data write request from the host computer, wherein, for specific data which is managed by the host computer, the controller specifies an area with a high referencing frequency among the specific data on the basis of organization information of the specific data, and moves this area to another of the tiered storage with a higher performance than an already assigned tiered storage.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
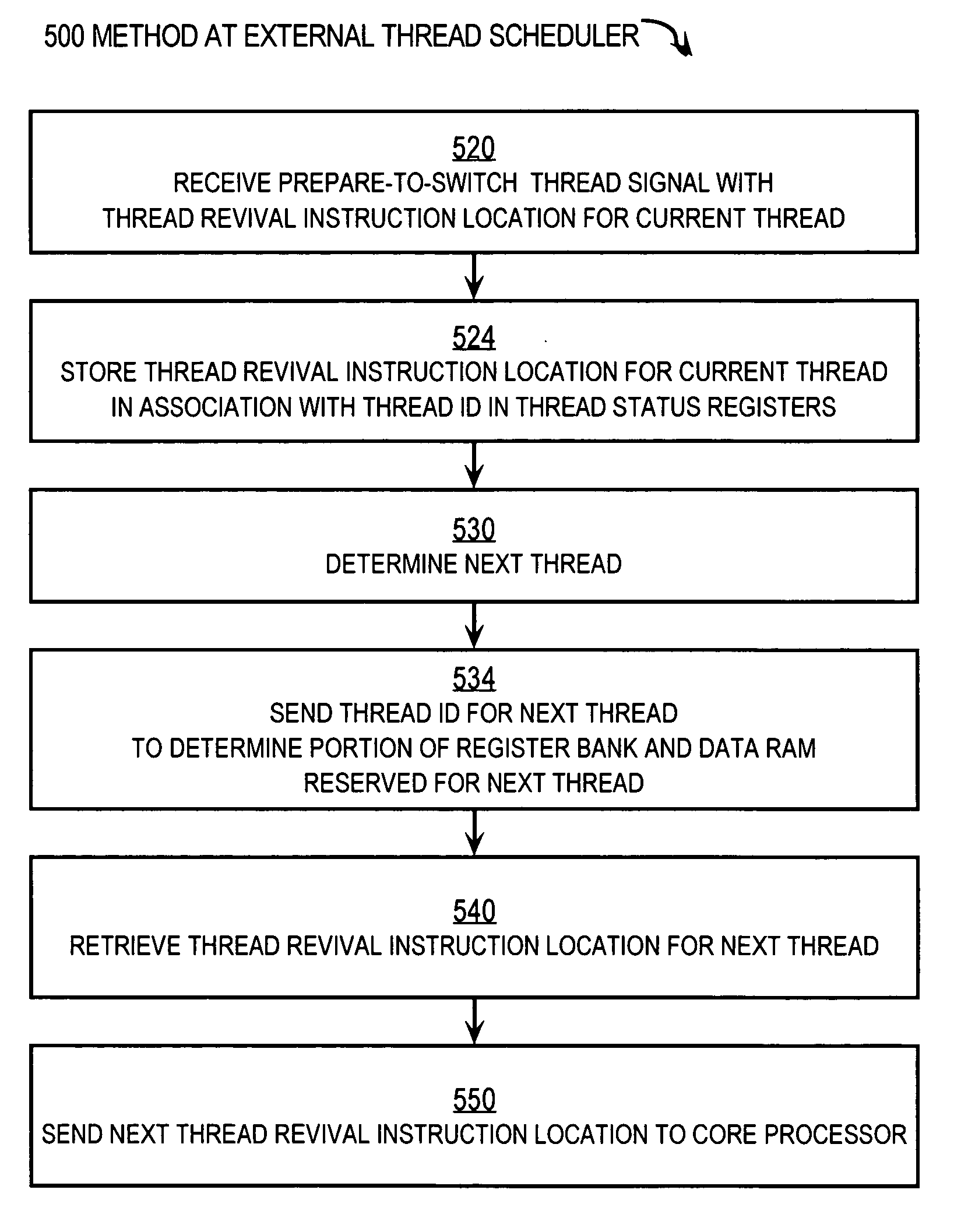
Techniques for hardware-assisted multi-threaded processing
ActiveUS20070294694A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsThread schedulingProcessor register
Techniques for processing each of multiple threads that share a core processor include receiving an intra-thread register address from the core processor. This address contains C bits for accessing each of 2c registers for each thread. A thread ID is received from a thread scheduler external to the core processor. The Thread ID contains T bits for indicating a particular thread for up to 2T threads. A particular register is accessed in a register bank that has 2(C+T) registers using an inter-thread address that includes both the intra-thread register address and the thread ID. The particular register holds contents for the intra-thread register address for a thread having the thread ID. Consequently, register contents of all registers of all threads reside in the register bank. Thread switching is accomplished rapidly by simply accessing different slices in the register bank, without swapping contents between a set of registers and memory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Deriving component statistics for a stream enabled application
ActiveUS20090119644A1Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsApplication softwareOperating system
A technique for generating component usage statistics involves associating components with blocks of a stream-enabled application. When the streaming application is executed, block requests may be logged by Block ID in a log. The frequency of component use may be estimated by analyzing the block request log with the block associations.
Owner:NUMECENT HLDG
Popular searches
Micro-instruction address formation Machine execution arrangements Computation using denominational number representation Concurrent instruction execution Hardware monitoring Data acquisition and logging Redundant operation error correction Software deployment Digital data processing details Microprogram loading
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com