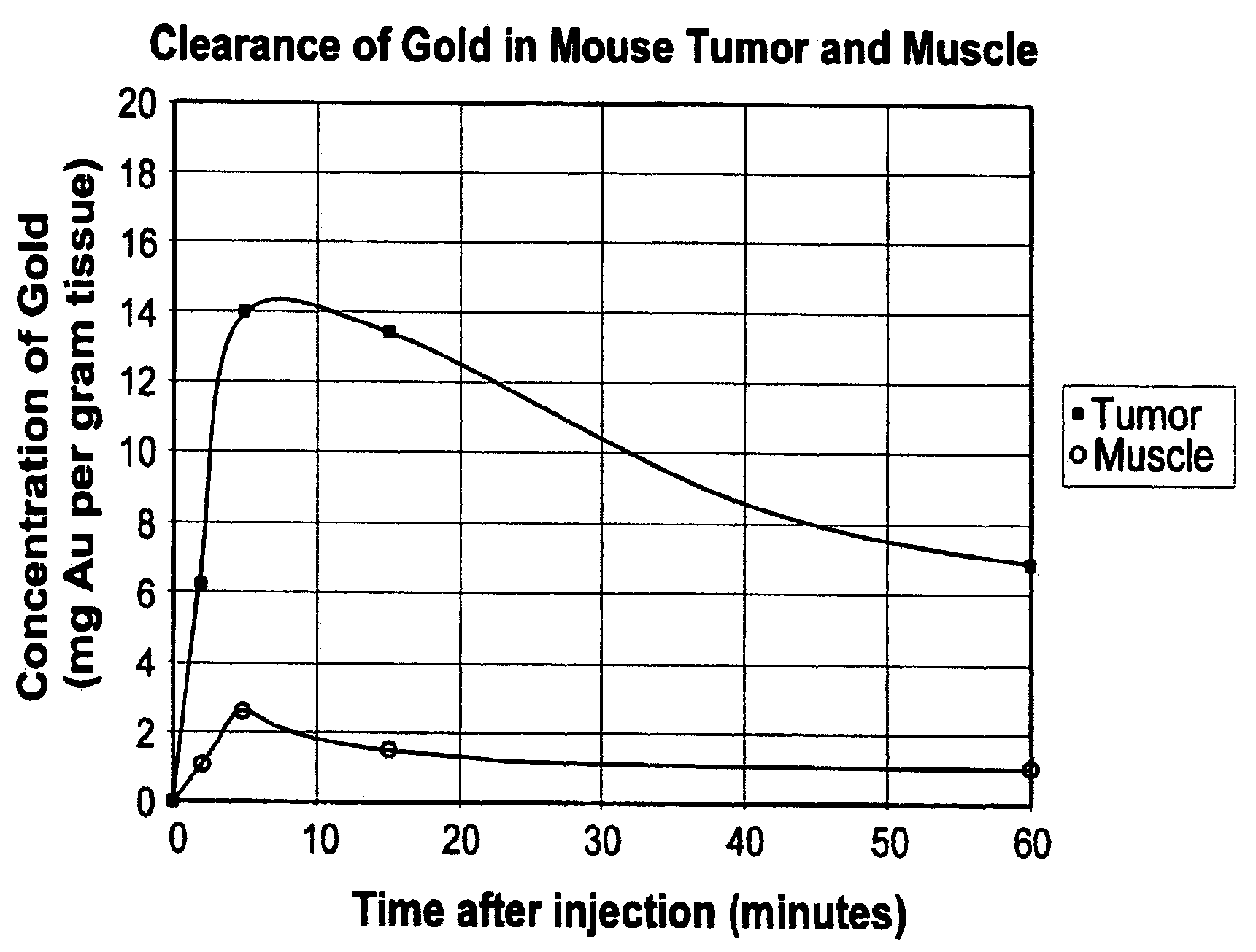
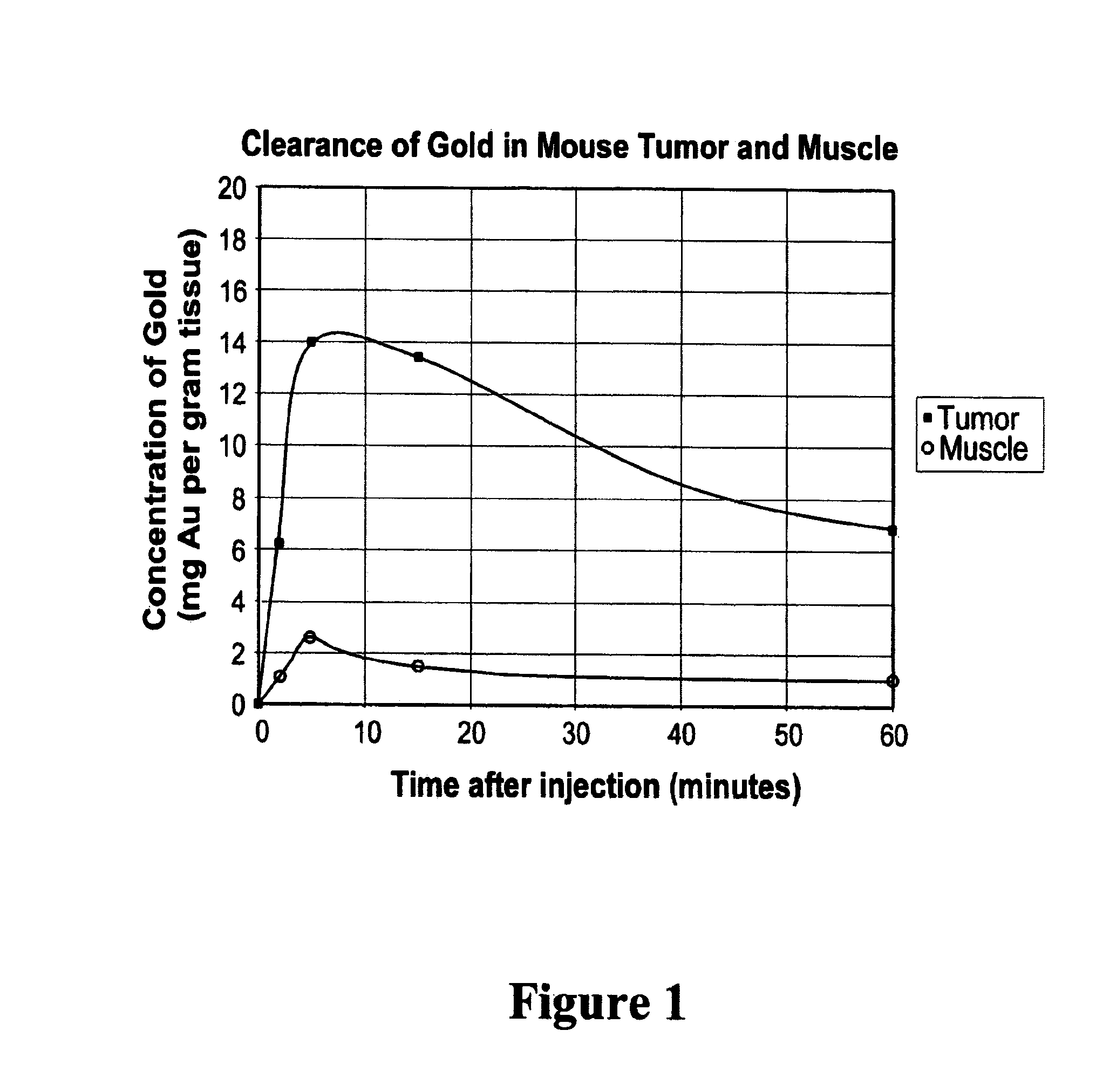
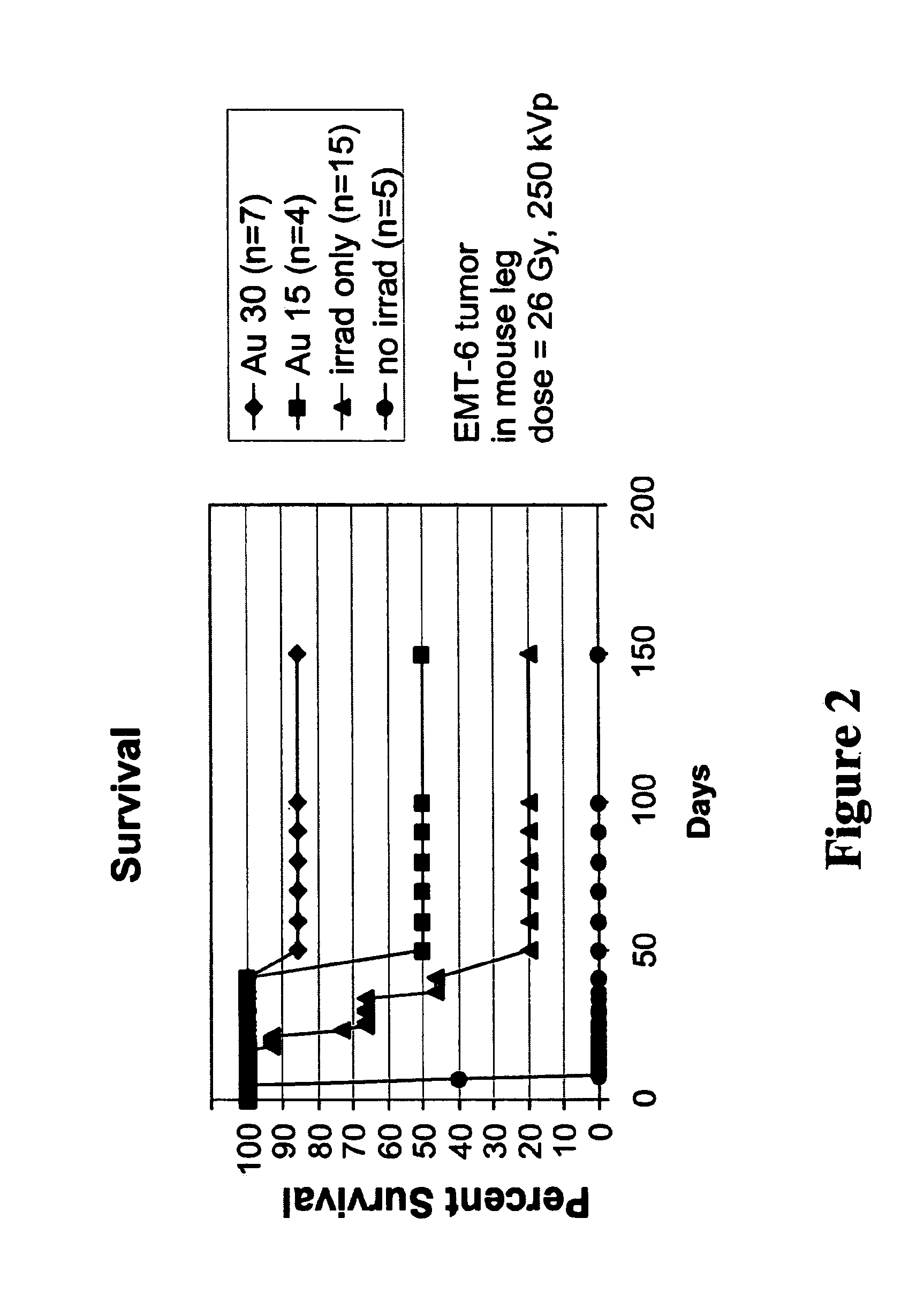
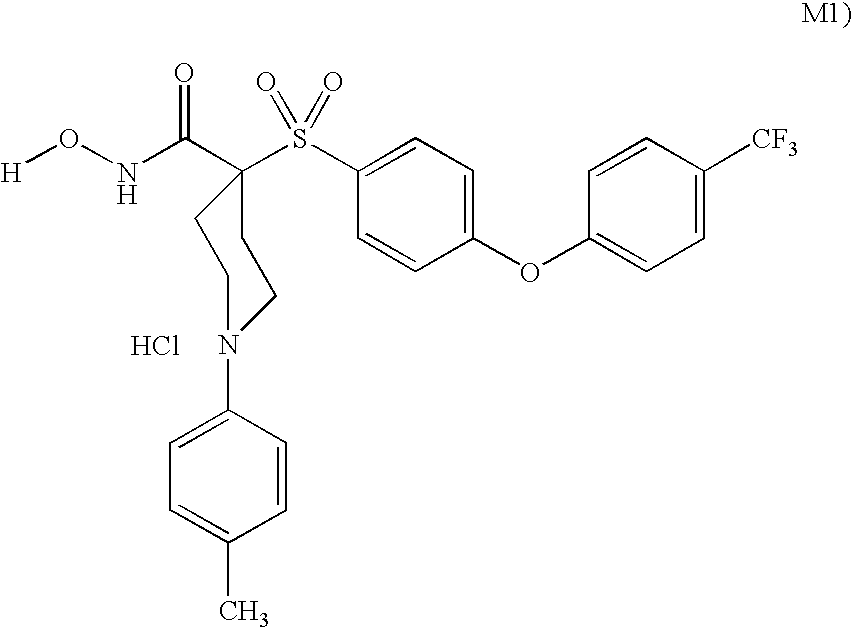
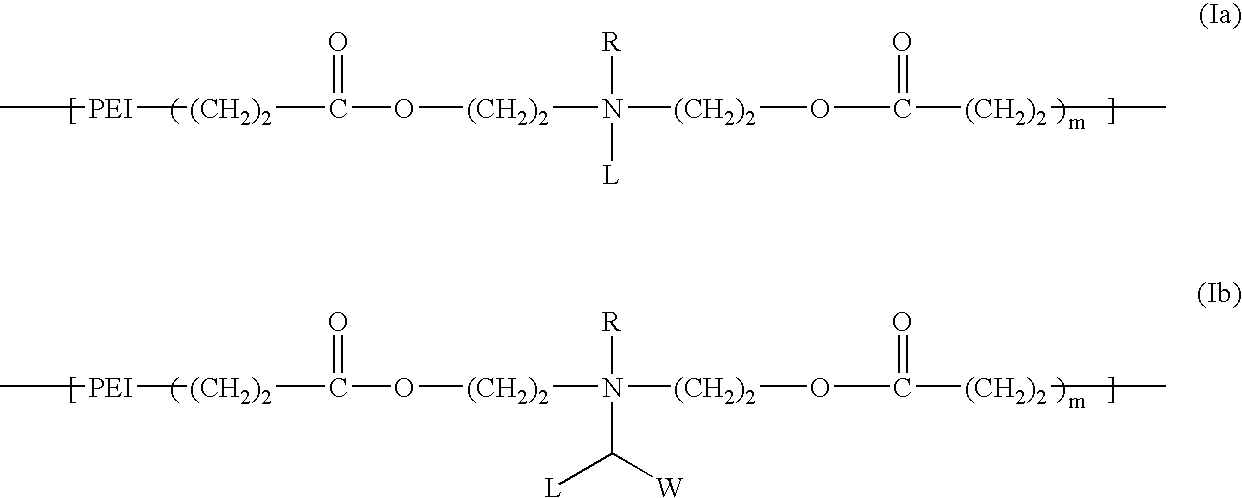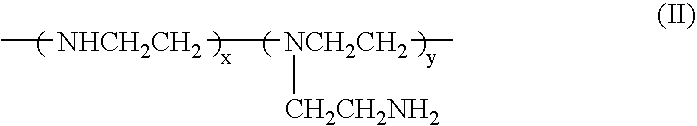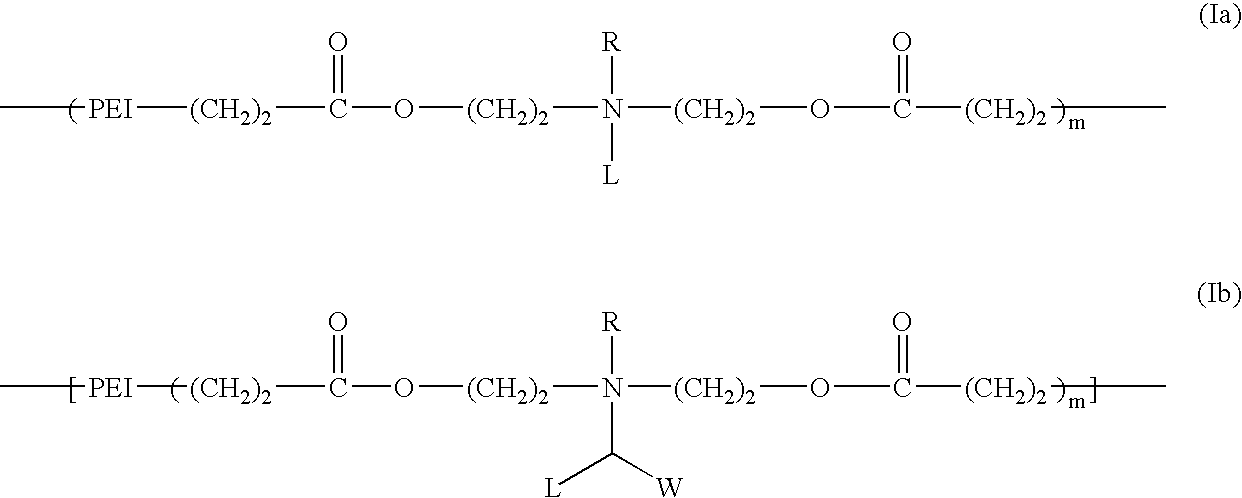Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
511results about "Radiosensitized materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of enhancing radiation effects with metal nanoparticles
Owner:NANOPROBES
Method of using a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor and one or more antineoplastic agents as a combination therapy in the treatment of neoplasia
InactiveUS6858598B1Reduce morbidityReduction in severity and frequencyHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDNA underwindingIrinotecan
A method of using an MMP inhibitor and optionally radiation therapy, and one or more antineoplastic agents of the topoisomerase class selected from the group consisting of irinotecan and topotecan, as a combination therapy for the treatment of neoplasia is disclosed.
Owner:GD SEARLE & CO
Trans carotenoids, their synthesis, formulation and uses
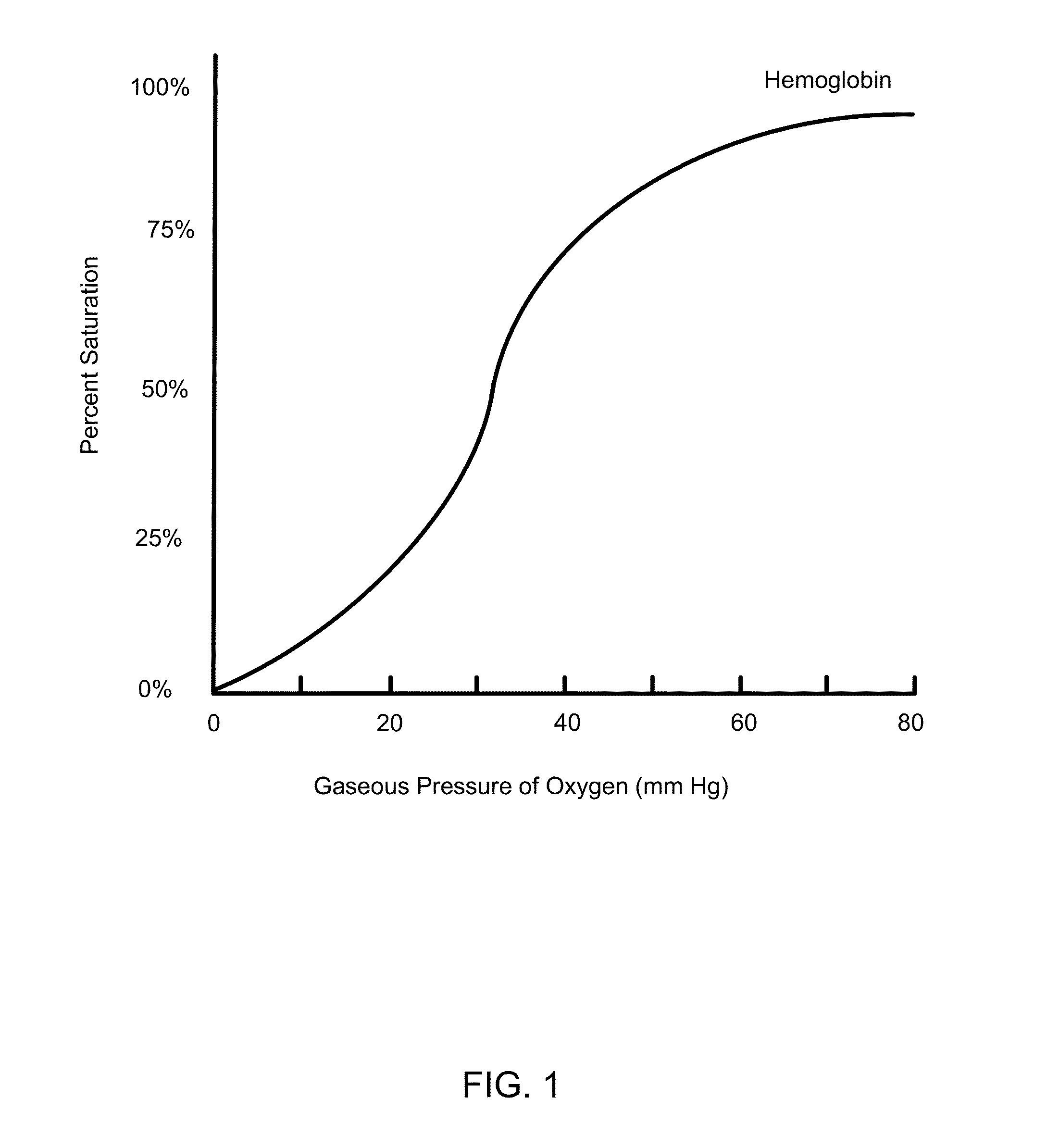
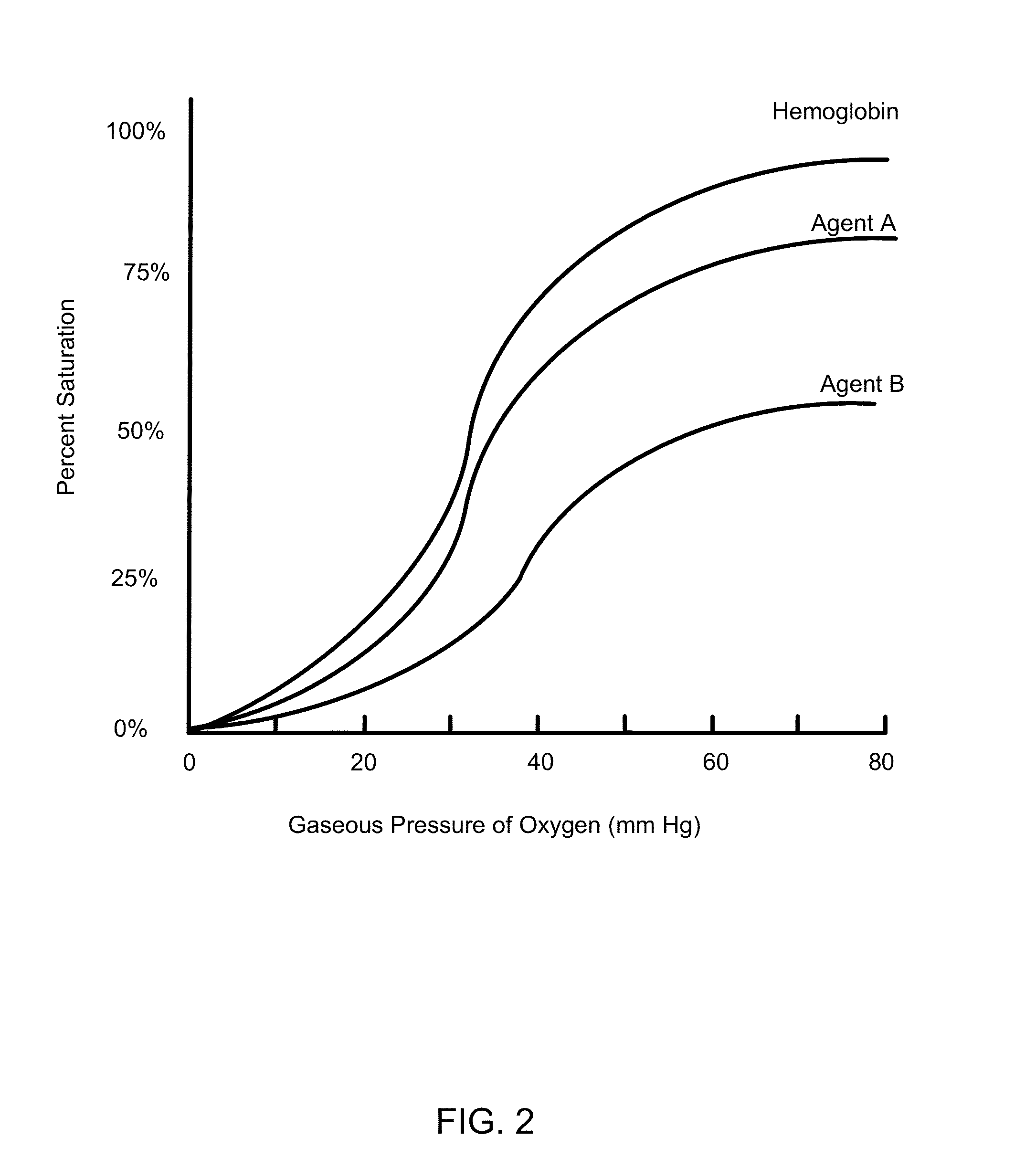
The invention relates to trans carotenoid compounds and salts thereof as well as compositions thereof, methods for making them, and uses thereof. These compounds are useful in improving diffusivity of oxygen between red blood cells and body tissues in mammals including humans.
Owner:DIFFUSION PHARMA LLC
Methods of enhancing radiation effects with metal nanoparticles
InactiveUS20050020869A1Good effectSignificant toxicityPowder deliveryElectrotherapyAbnormal tissue growthCompound (substance)
The present invention provides methods of using metal nanoparticles 0.5 to 400 nm in diameter to enhance the dose and effectiveness of x-rays or of other kinds of radiation in therapeutic regimes of ablating a target tissue, such as tumor. The metal nanoparticles can be administered intravenously, intra-arterially, or locally to achieve specific loading in and around the target tissue. The metal nanoparticles can also be linked to chemical and / or biochemical moieties which bind specifically to the target tissue. The enhanced radiation methods can also be applied to ablate unwanted tissues or cells ex vivo.
Owner:NANOPROBES
Combining Radioimmunotherapy and Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Improved Cancer Therapy
InactiveUS20110070156A1Organic active ingredientsHybrid immunoglobulinsParanasal Sinus CarcinomaAntiendomysial antibodies
Described herein are compositions and methods of use of radionuclide-antibody conjugates (for RAIT) and drug-antibody conjugates (ADC). The combination of RAIT and ADC was more efficacious than either RAIT alone, ADC alone, or the sum of effects of RAIT and ADC. The unexpected synergy resulted in decreased tumor growth rate and increased survival, with a high incidence of tumor-free survival in Capan-1 human pancreatic cancer xenografts in nude mice.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Antimicrobial conjugates
InactiveUS20080050448A1Influence antimicrobial activityHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideChemistryMetal nanoparticles
The present invention presents a metallic nanoparticle-ligand-photosensitiser conjugate, a method of making such conjugate, and a method of using such mixture for killing or preventing the growth of microbes.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
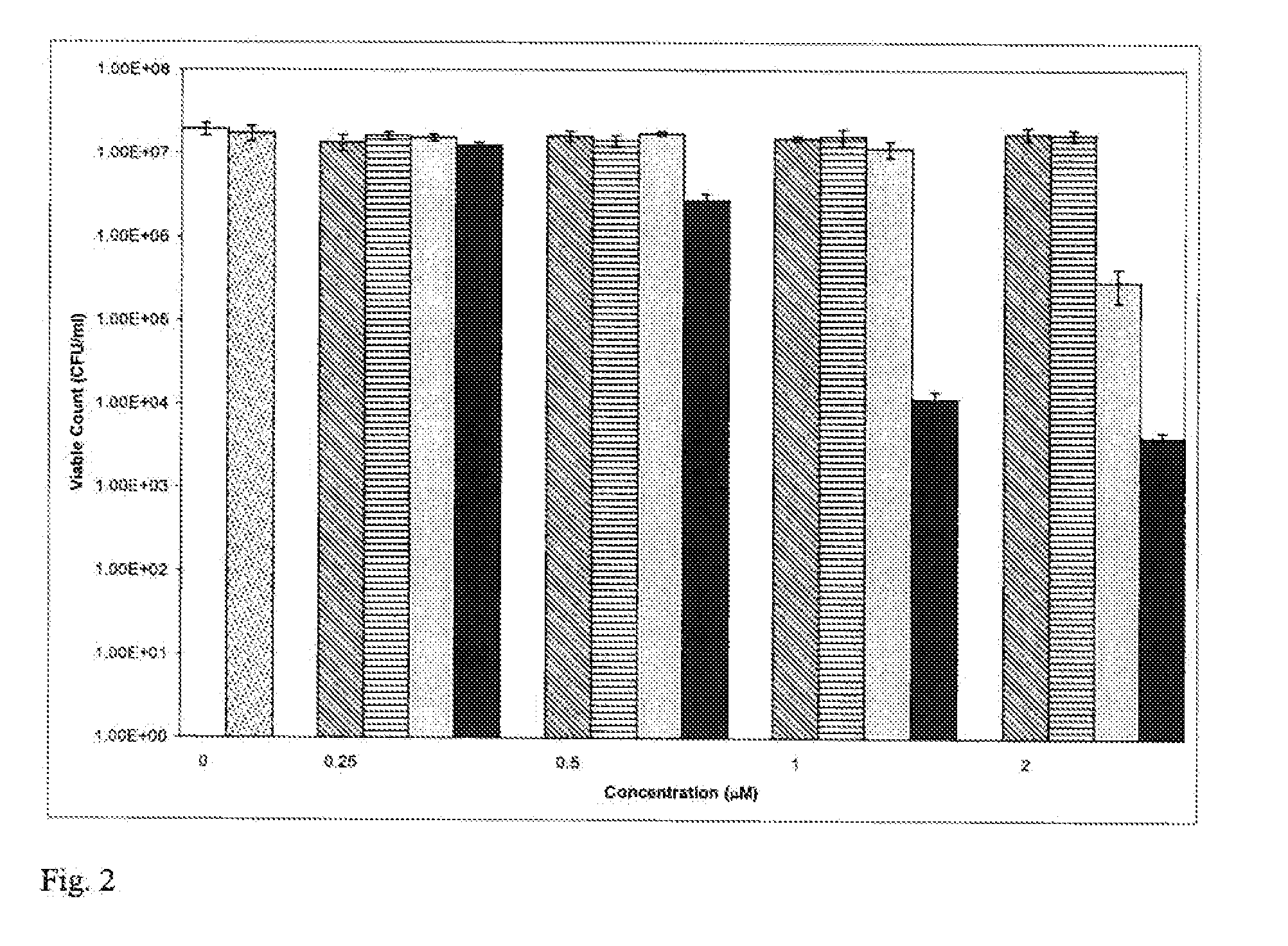
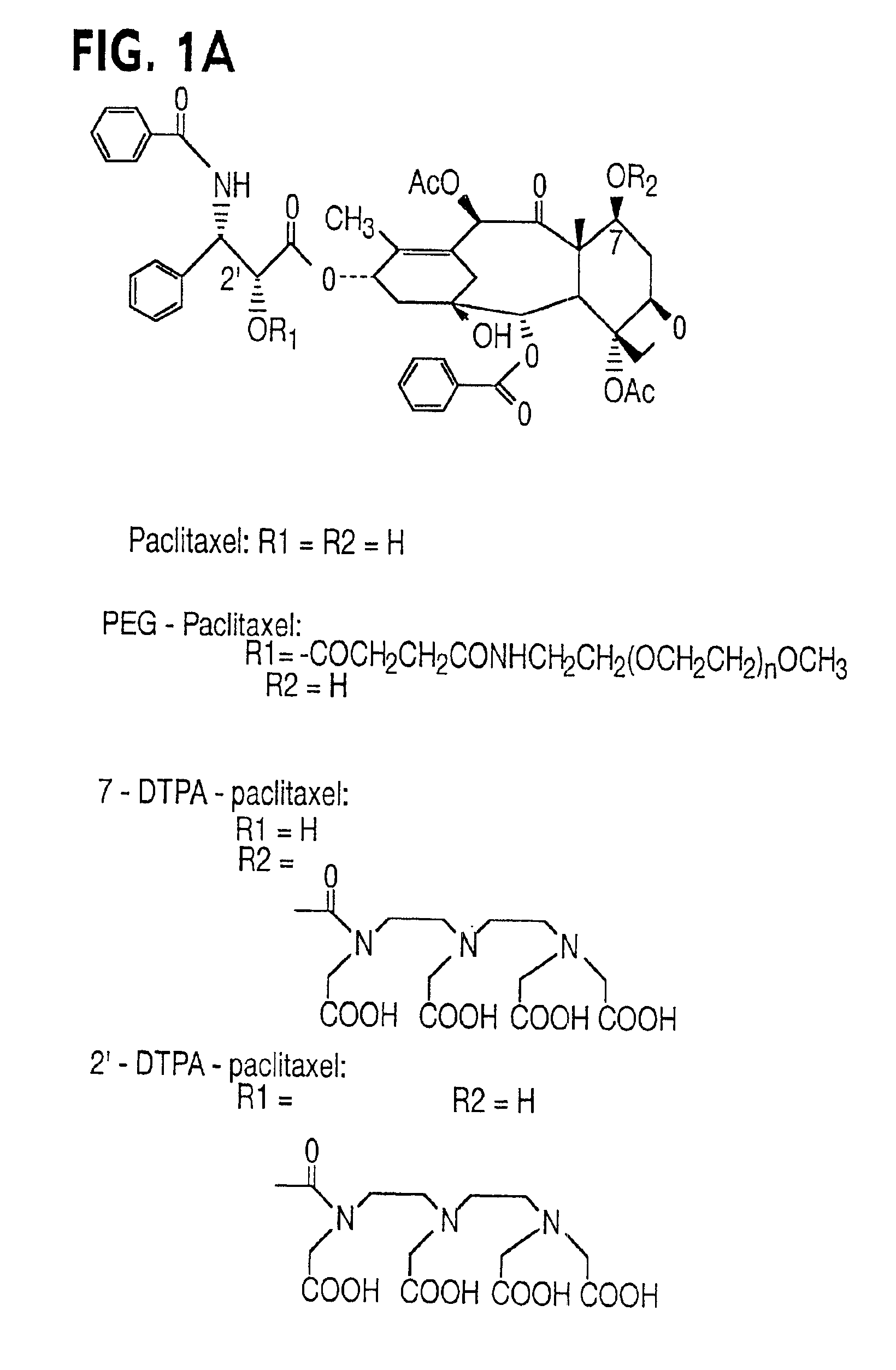
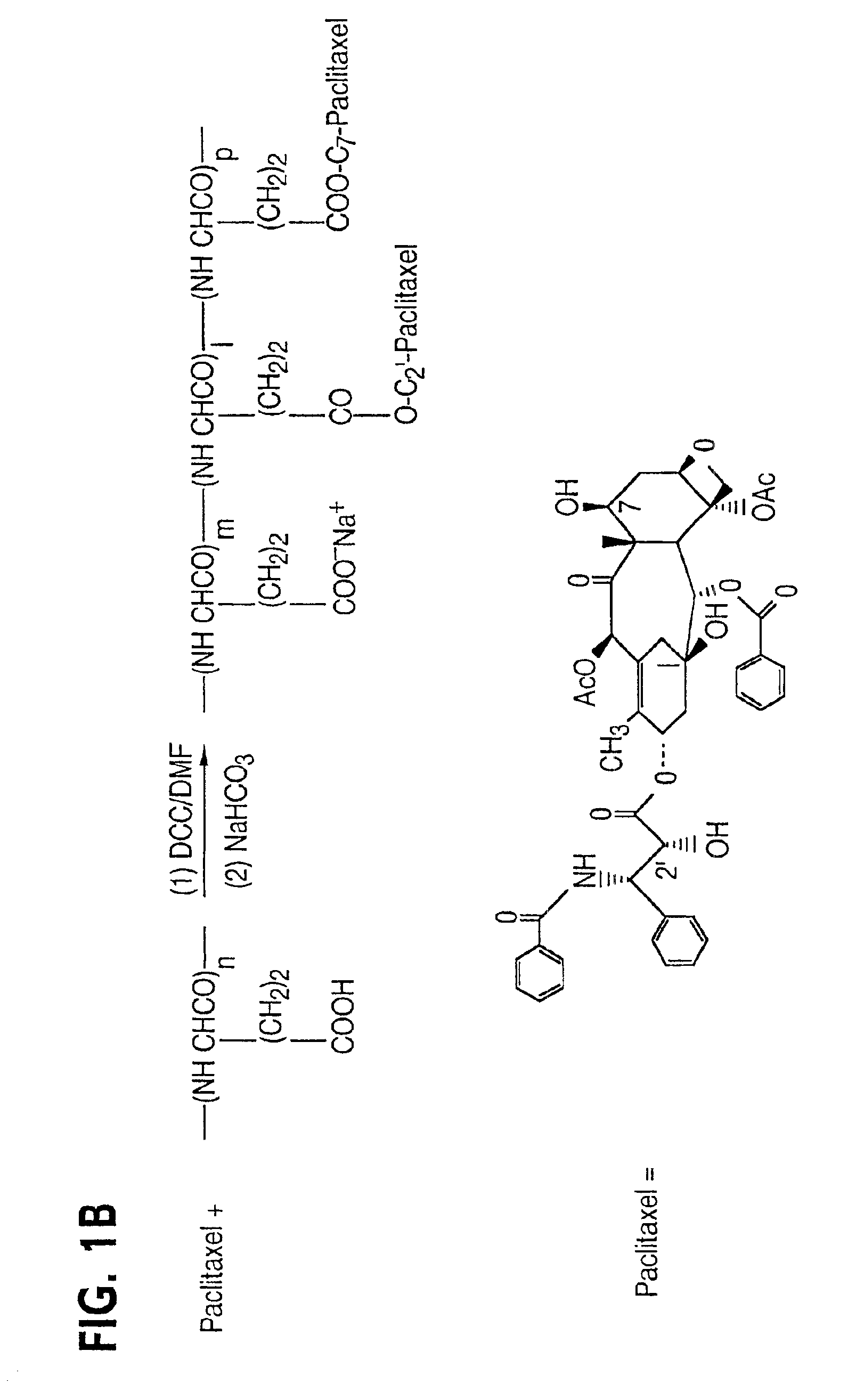
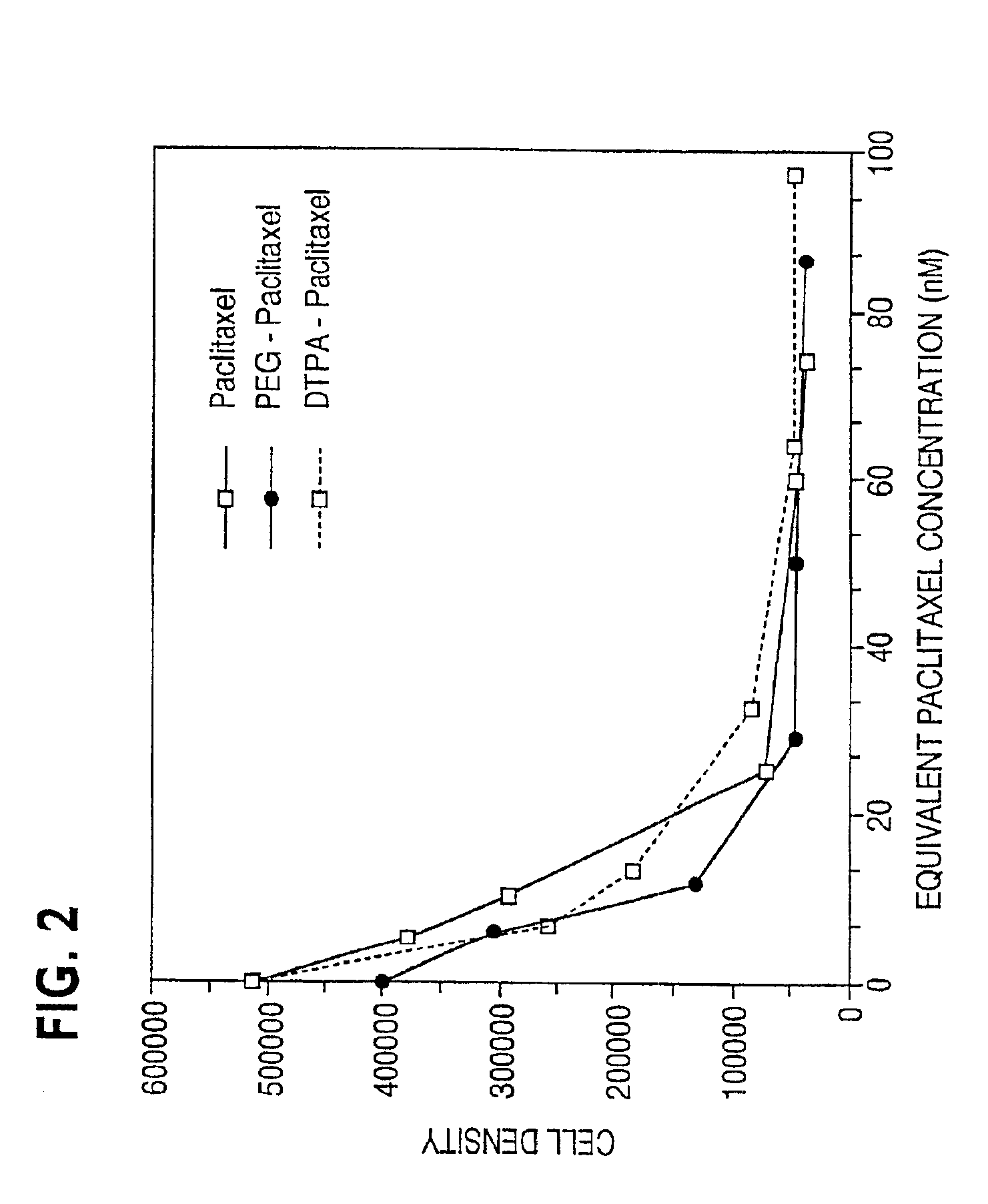
Water soluble paclitaxel derivatives
InactiveUS6884817B2Surprising antitumor activityImprove efficacyHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDocetaxel-PNPDocetaxel
Disclosed are water soluble compositions of paclitaxel and docetaxel formed by conjugating the paclitaxel or docetaxel to a water soluble polymer such as poly-glutamic acid, poly-aspartic acid or poly-lysine. Also disclosed are methods of using the compositions for treatment of tumors, auto-immune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. Other embodiments include the coating of implantable stents for prevention of restenosis.
Owner:PG TXL COMPANY
Upconversion of Light for Use in Optogenetic Methods
ActiveUS20140148880A1Easy to useReduce absorptionPeptide/protein ingredientsPhotodynamic therapyOptogeneticsNanoparticle
Provided herein are compositions comprising lanthanide-doped nanoparticles which upconvert electromagnetic radiation from infrared or near infrared wavelengths into the visible light spectrum. Also provided herein are methods activating light-responsive opsin proteins expressed on plasma membranes of neurons and selectively altering the membrane polarization state of the neurons using the light delivered by the lanthanide-doped nanoparticles.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Combination therapy including a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent
InactiveUS6916800B2Reduce morbidityReduction in severity and frequencyBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsCombination therapyMatrix metalloproteinase inhibitor
The present invention provides methods to treat or prevent neoplasia disorders in a mammal using a combination of a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent.
Owner:PFIZER INC
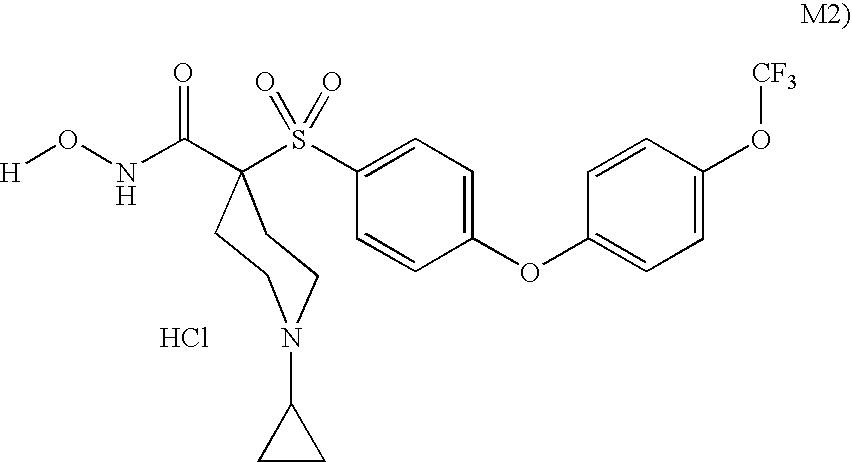
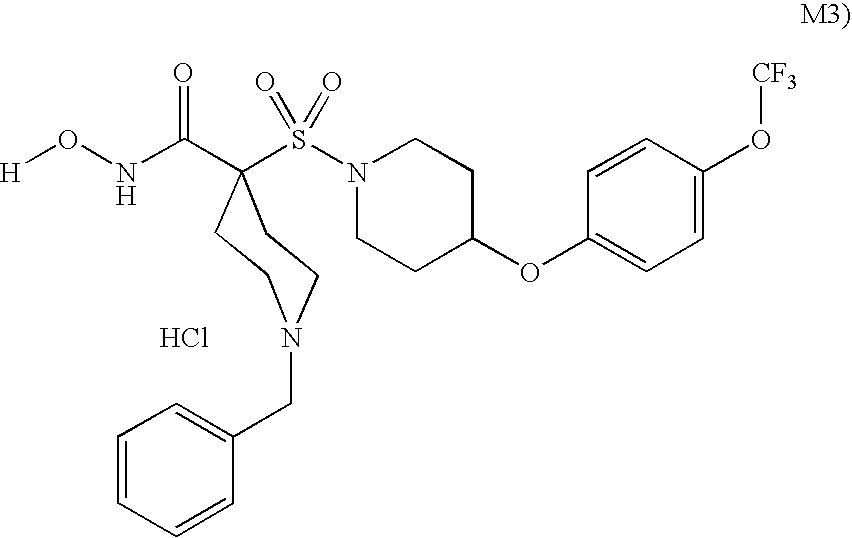
TRPM-2 antisense therapy using an oligonucleotide having 2′-O-(2-methoxy)ethyl modifications
InactiveUS6900187B2Improve in vivo stabilityImproved in vitroPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsIn vivoOligonucleotide
A compound consisting of an oligonucleotide of sequence CAGCAGCAGAGTCTTCATCAT, where the oligonucleotide has a phosphorothioate backbone throughout, the sugar moieties of nucleotides 1-4 and 18-21 bear 2′-O-methoxyethyl modifications, and the remaining nucleotides (nucleotides 5-17) are 2′-deoxynucleotides, and where the cytosines of nucleotides 1, 4 and 19 are 5-methylcytosines. The compound has increased stability in vivo and improved in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Methods and compositions for the treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20090232849A1Organic active ingredientsBacterial antigen ingredientsToxinCytotoxic Therapy
Compositions and a method for sensitizing a cancer for treatment by cytotoxic therapy is disclosed. The method includes the step of administering to the cancerous tissue or cells a pharmaceutical composition containing a Botulinum toxin, BT.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Nanoparticle radiosensitizers
InactiveUS20080003183A1Strong specificityPromote absorptionBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsSolubilityCell membrane
Herein is described Nanostructure Enhanced X-ray Therapy (NEXT), which uses nanomaterials as radiosensitizers to enhance electromagnetic radiation absorption in specific cells or tissues. The nanomaterial radiosensitizers emit Auger electrons and generate radicals in response to electromagnetic radiation, which can cause localized damage to DNA or other cellular structures such as membranes. The nanomaterial radiosensitizers contain moieties for specific targeting to molecules or structures in a cell or tissue, and can be functionalized for increased stability and solubility. The nanomaterial radiosensitizers can also be used as detection agents to help in early diagnosis of disease. Together with known techniques such as Computed Tomography or Computerized Axial Tomography (CT or CAT scan), these nanomaterial radiosensitizers could allow early diagnosis and treatment of diseases such as cancer and HIV.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
PARP inhibitors
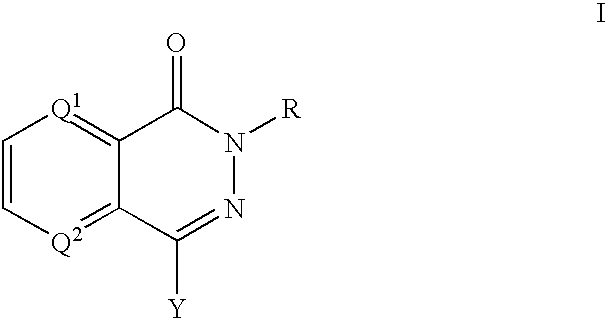
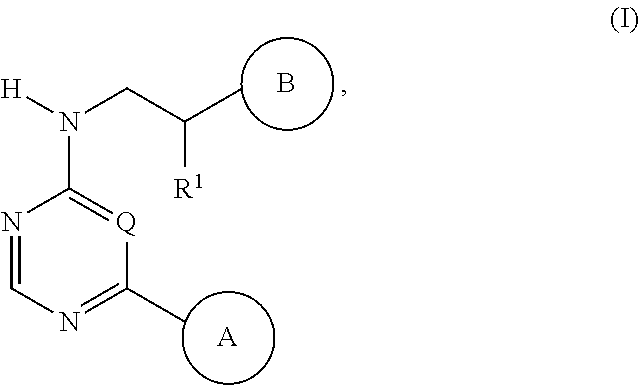
InactiveUS6924284B2None be use clinicallyReducing, arresting or ameliorating nervous insultBiocideNervous disorderArylPARP inhibitor
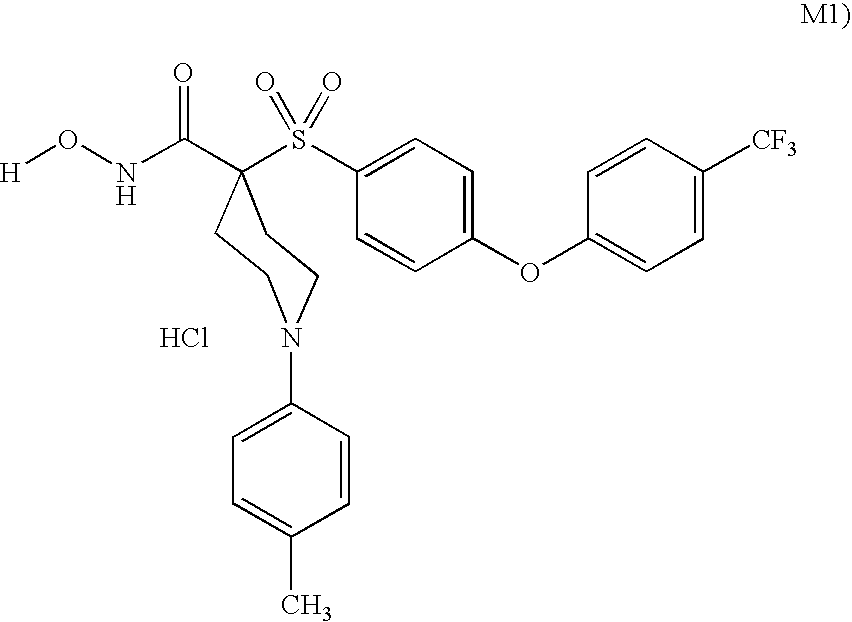
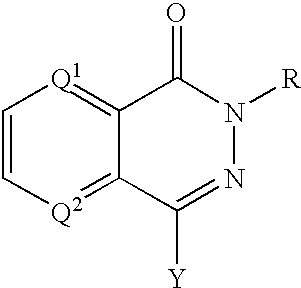
The present invention provides compounds comprising a bicyclic aryl moiety, such as 2H-phthalazin-1-one or derivatives thereof, compositions comprising the same, and methods for producing and using the same. In particular, the present invention provides compounds of the formula: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a hydrate, a solvate, or a prodrug thereof; where Q1, Q2 and Y are those defined herein.
Owner:ICOS CORP
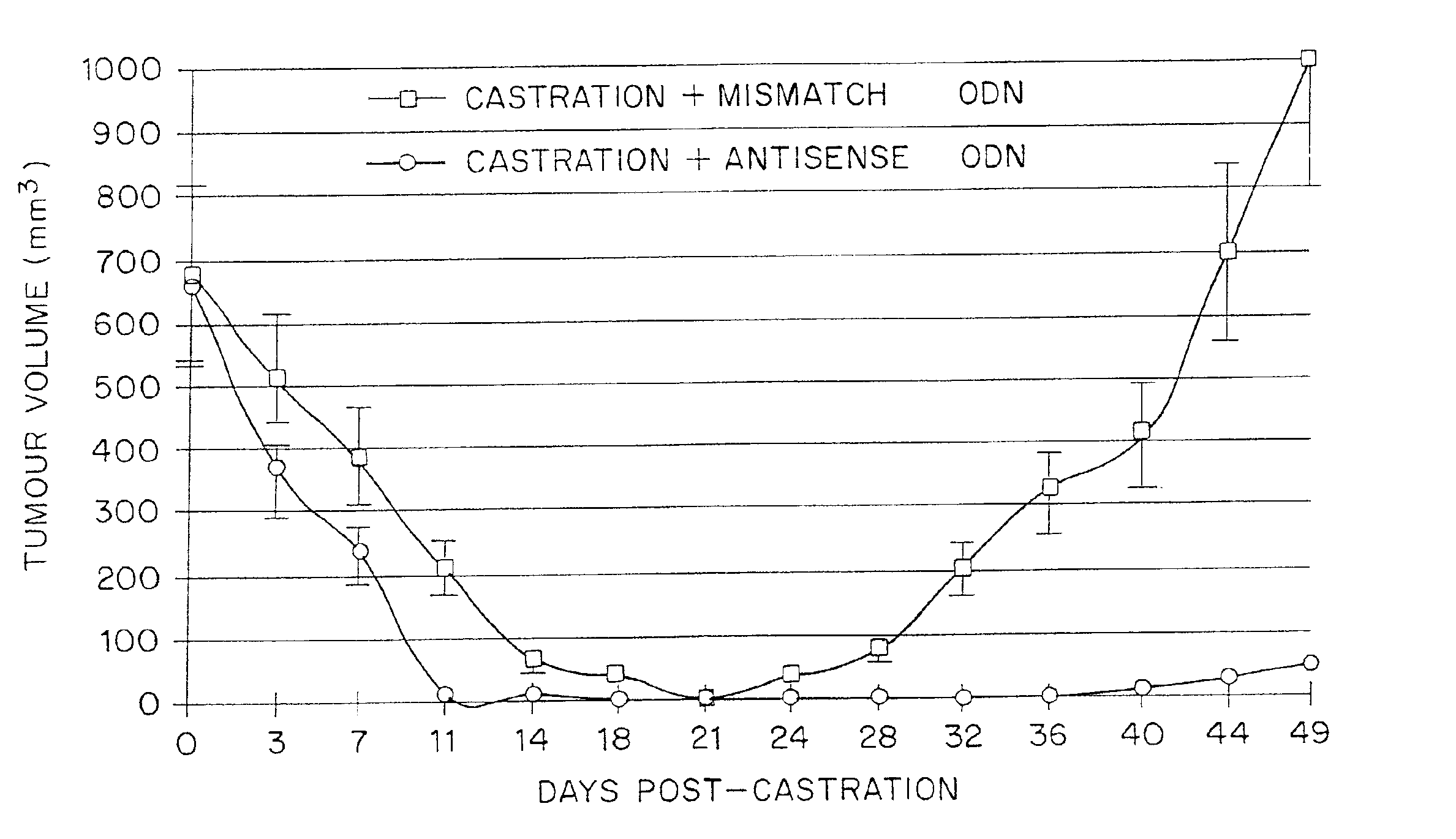
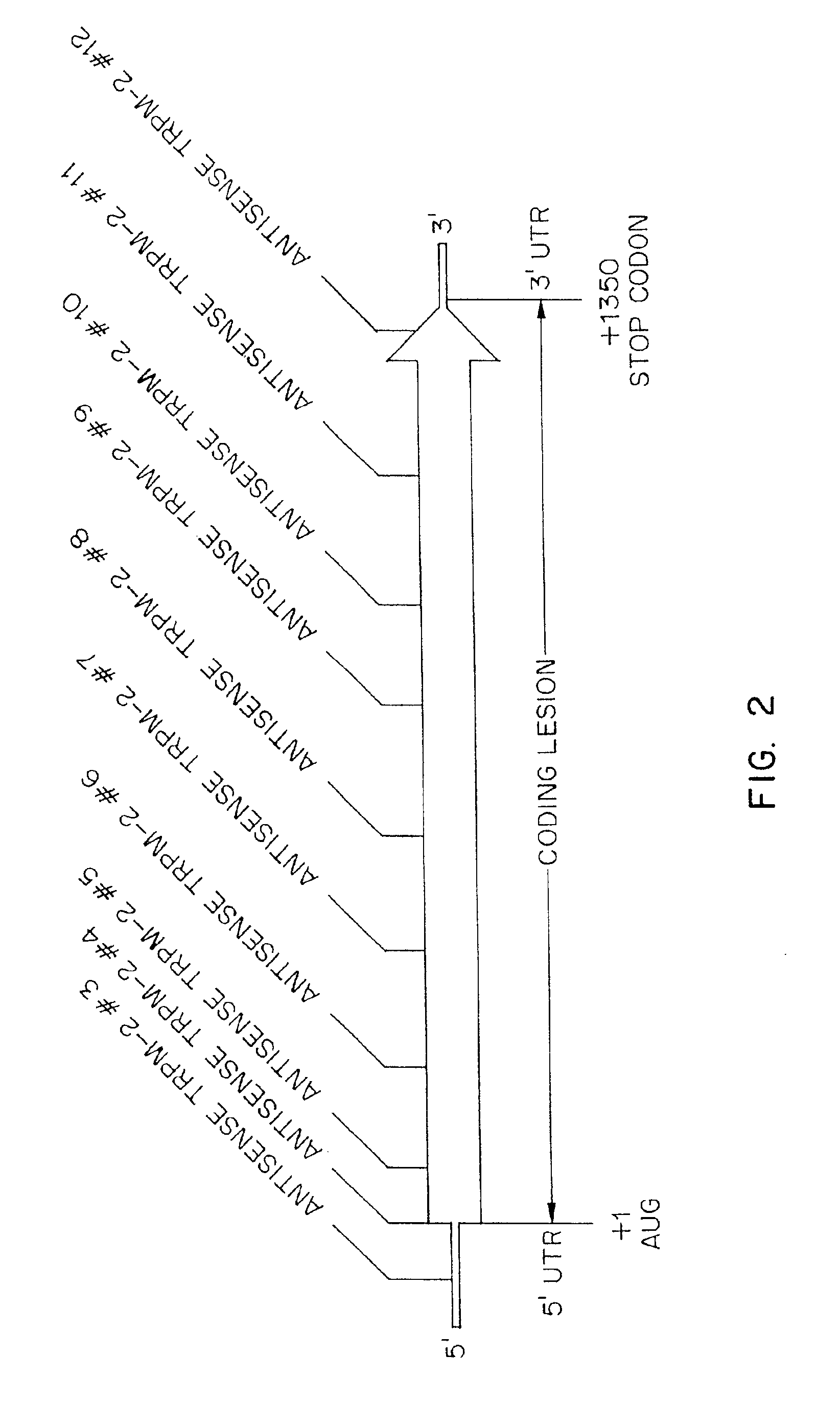
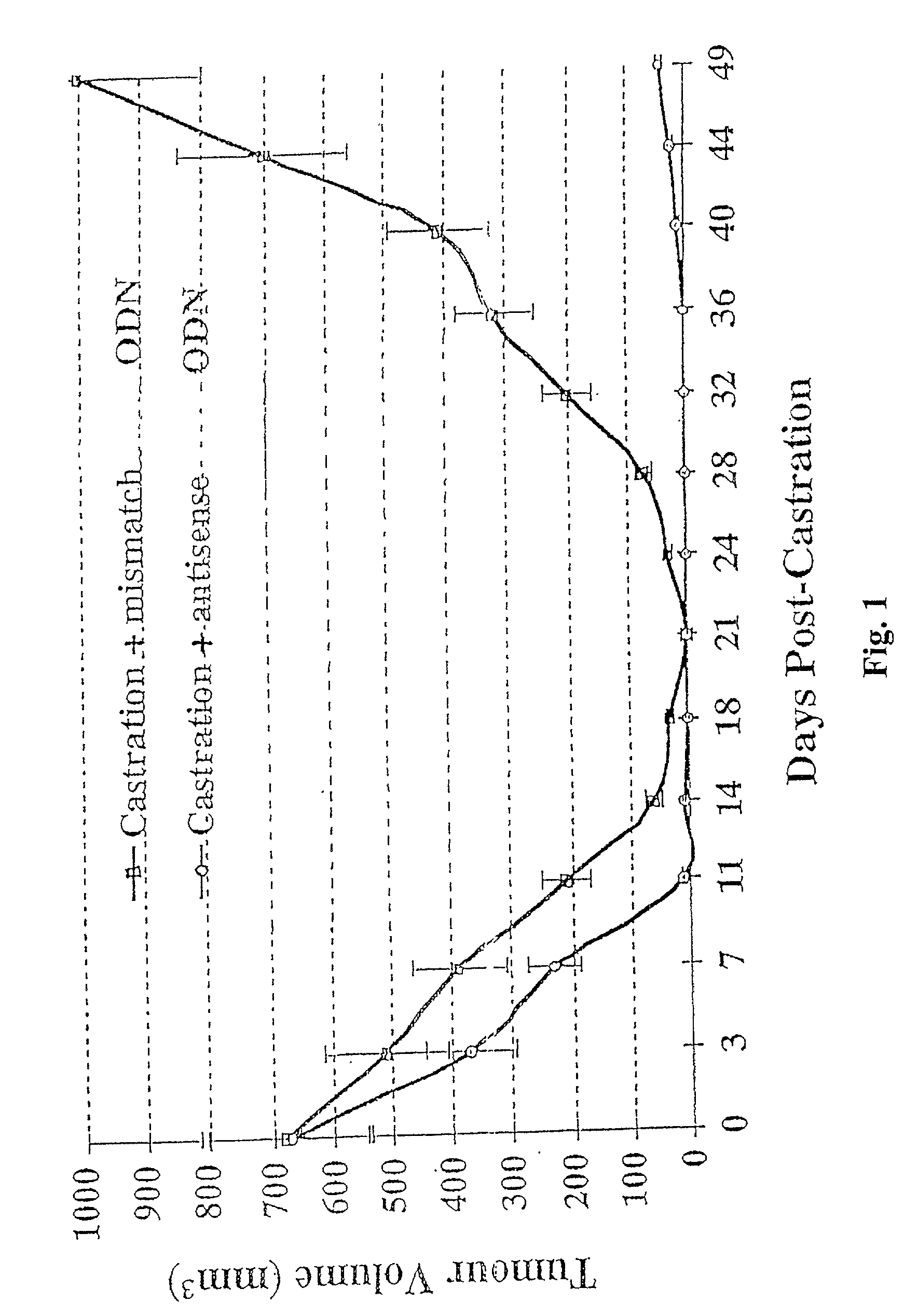
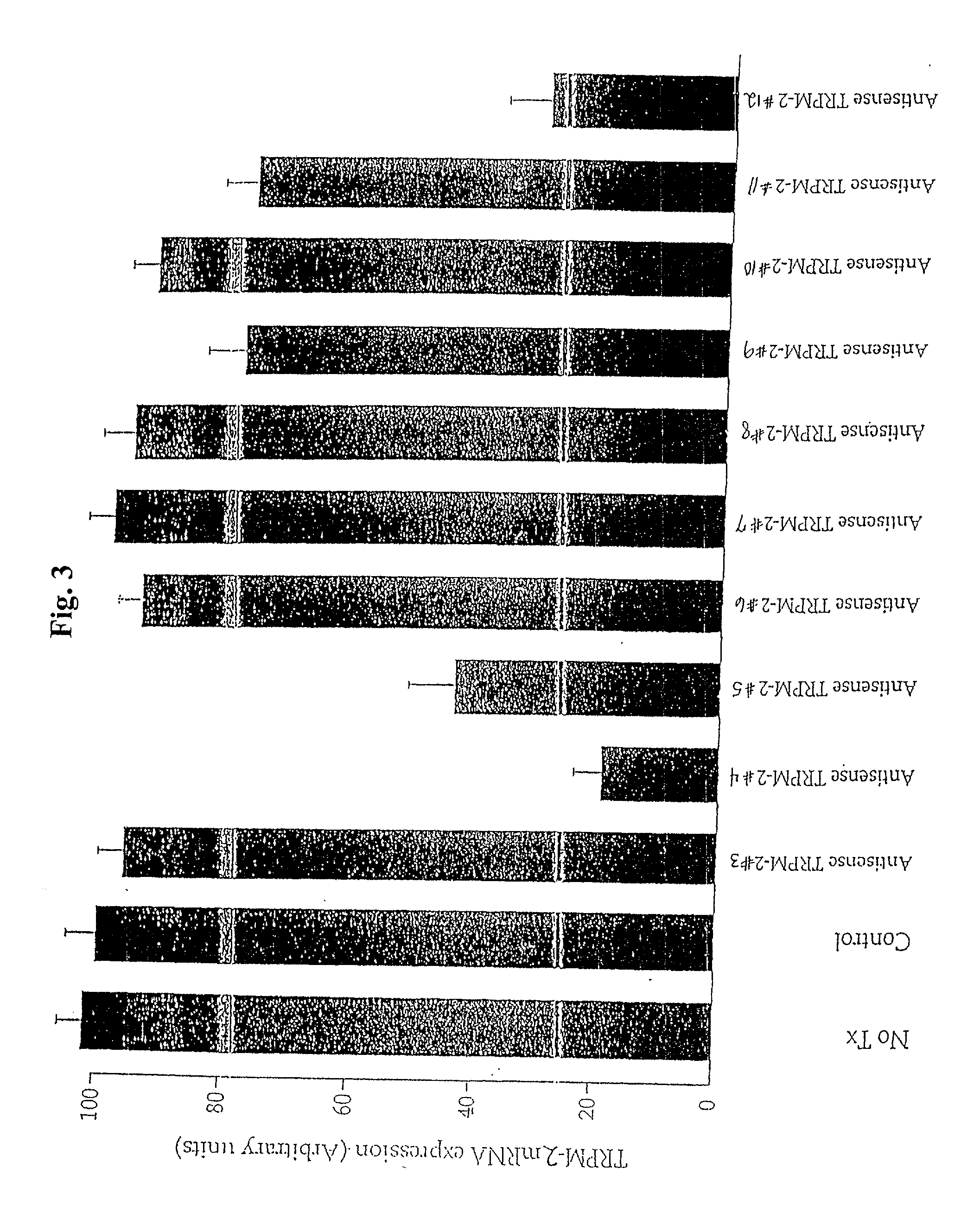
TRPM-2 antisense therapy
InactiveUS20020128220A1Increased chemosensitivityInhibit expressionApolipeptidesSugar derivativesDiseaseCancer type
It has now been determined that antisense therapy which reduces the expression of TRPM-2 provides therapeutic benefits in the treatment of cancer. In particular, such antisense therapy can be applied in treatment of prostate cancer and renal cell cancer. Addition of antisense TRPM-2 ODN to prostatic tumor cells in vivo is effective for delaying the onset of androgen independence. Thus, prostate cancer can be treated in an individual suffering from prostate cancer by initiating androgen-withdrawal to induce apoptotic cell death of prostatic tumor cells in the individual, and administering to the individual a composition effective to inhibit expression of TRPM-2 by the tumor cells, thereby delaying the progression of prostatic tumor cells to an androgen-independent state in an individual Combined use of antisense TRPM-2 and taxanes synergistically enhances cytotoxic chemosensitivity of androgen-independent prostate cancer. In addition, it has also been found that antisense TRPM-2 has beneficial effect for other cancer types. Specifically, antisense TRPM-2 ODN enhances chemosensitivity in human Renal cell cancer, a normally chemoresistant disease with no active chemotherapeutic agent having an objective response rate higher than 10%. Radiation sensitivity is also enhanced when cells expressing TRPM-2 are treated with antisense TRPM-2 ODN. Thus, the antisense TRPM-2 ODNs can be used to enhance hormone sensitivity, chemosensitivity and radiation sensitivity of a variety of cancer types in which expression of TRPM-2 has been observed.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Biodegradable cationic polymers
InactiveUS20060258751A1Reduce deliveryImprove degradation rateBiocideNanotechActive agentPolymer chemistry
Polymers comprising a polyethylenimine, a biodegradable group, and a relatively hydrophobic group are useful for the delivery of bioactive agents to cells.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
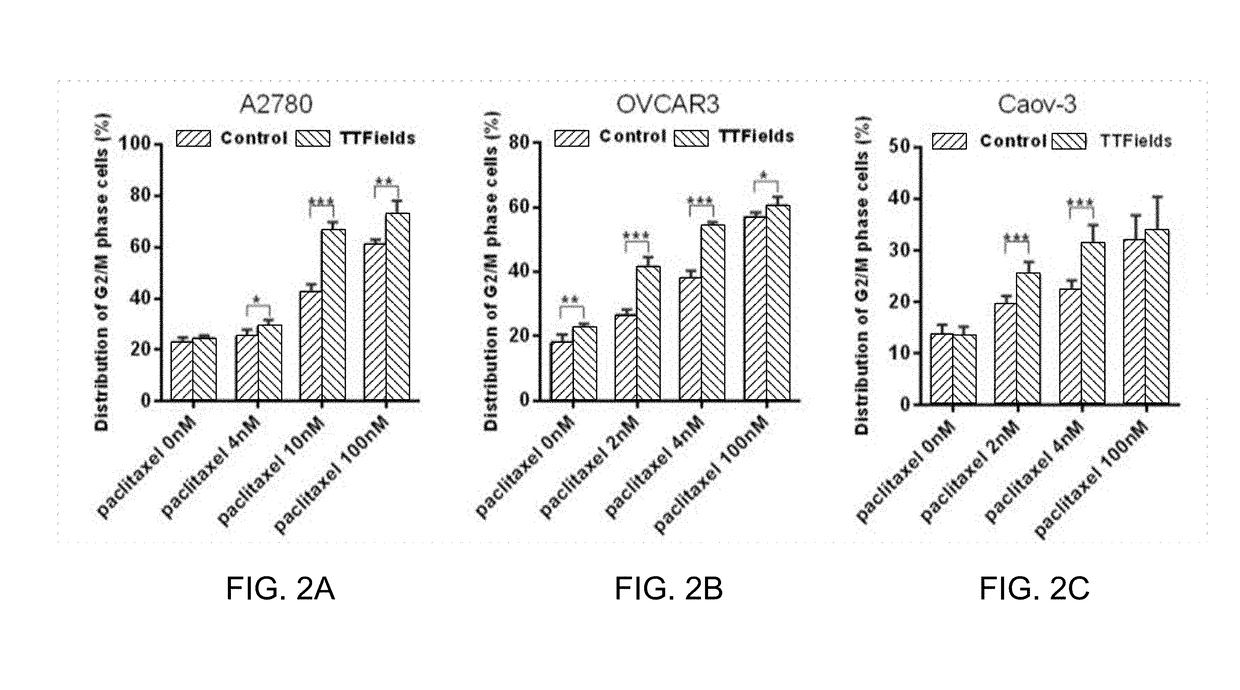
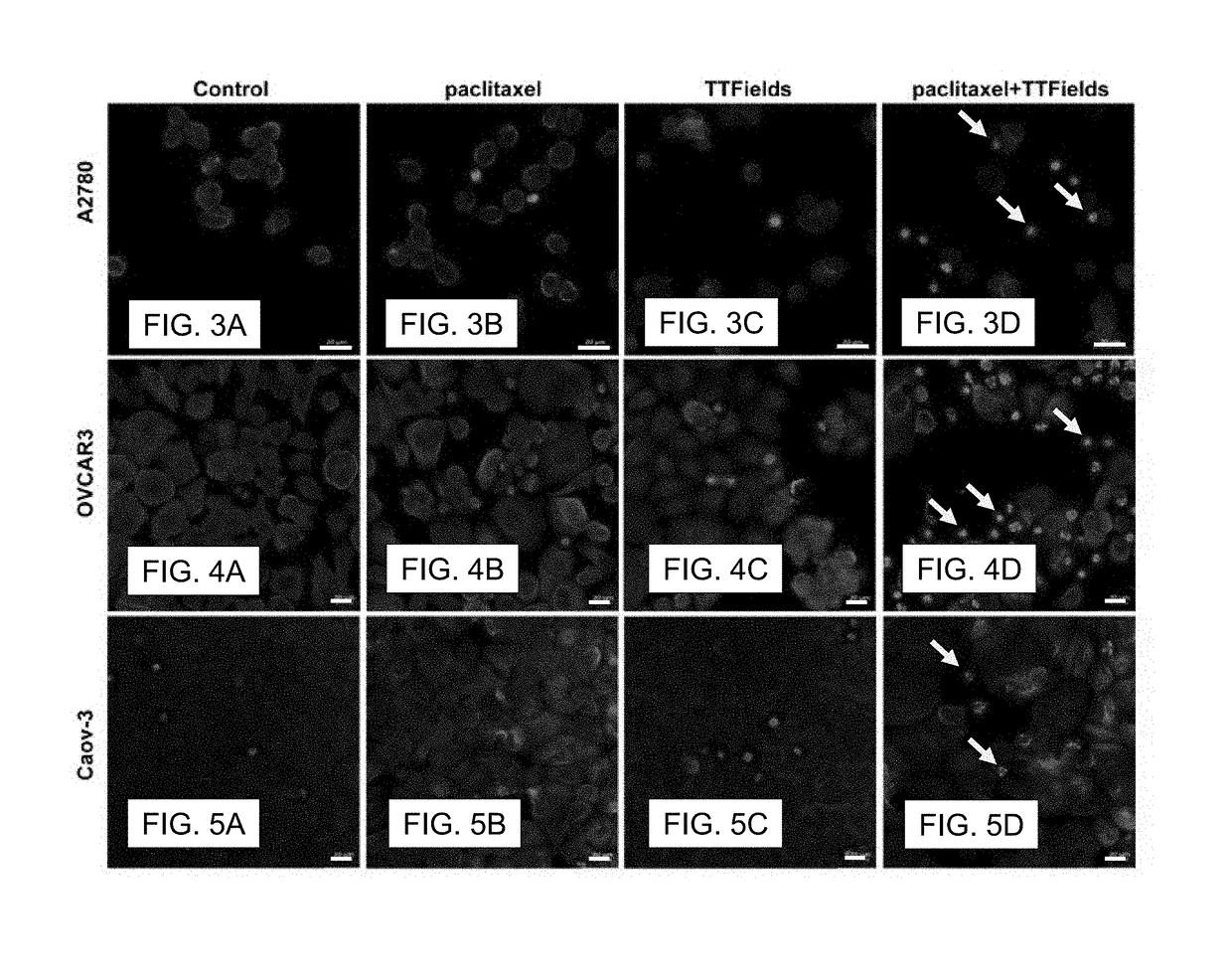
Synchronizing Tumor Cells to the G2/M Phase Using TTFields Combined with Taxane or Other Anti-Microtubule Agents
InactiveUS20180008708A1Raise the ratioOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyCancer cellRadiation therapy
Cancer cells can be synchronized to the G2 / M phase by delivering an anti-microtubule agent (e.g., paclitaxel or another taxane) to the cancer cells, and applying an alternating electric field with a frequency between 100 and 500 kHz to the cancer cells, wherein at least a portion of the applying step is performed simultaneously with at least a portion of the delivering step. This synchronization can be taken advantage of by treating the cancer cells with radiation therapy after the combined action of the delivering step and the applying step has increased a proportion of cancer cells that are in the G2 / M phase. The optimal frequency and field strength will depend on the particular type of cancer cell being treated. For certain cancers, this frequency will be between 125 and 250 kHz (e.g., 200 kHz) and the field strength will be at least 1 V / cm.
Owner:NOVOCURE GMBH
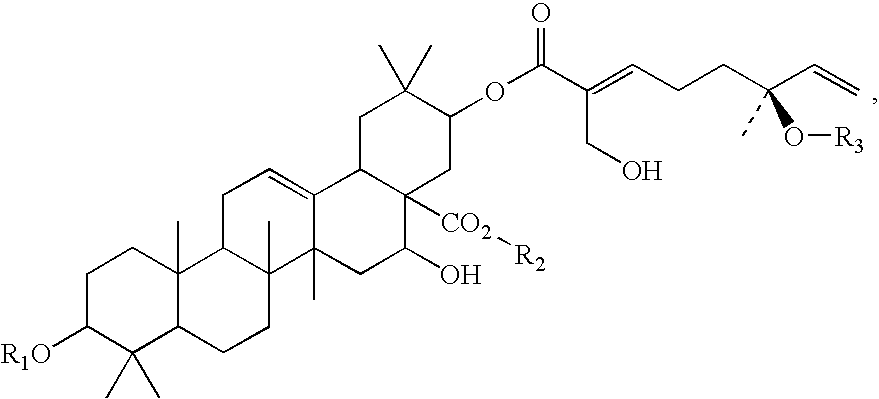
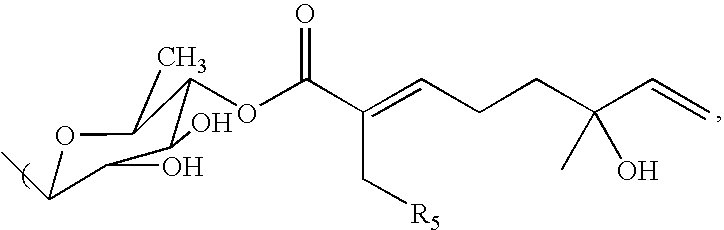
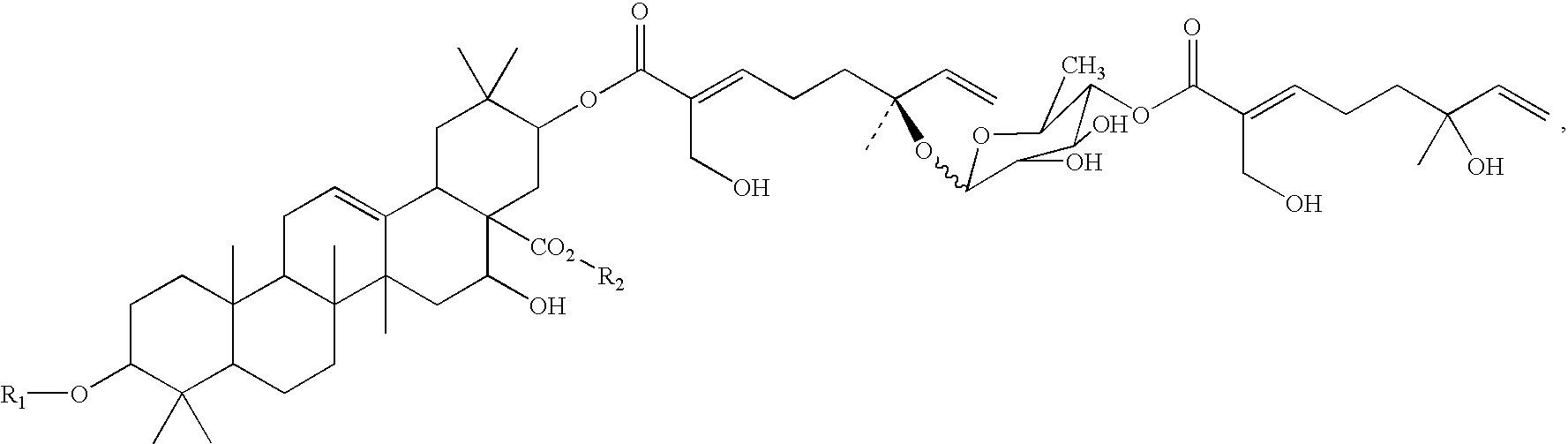
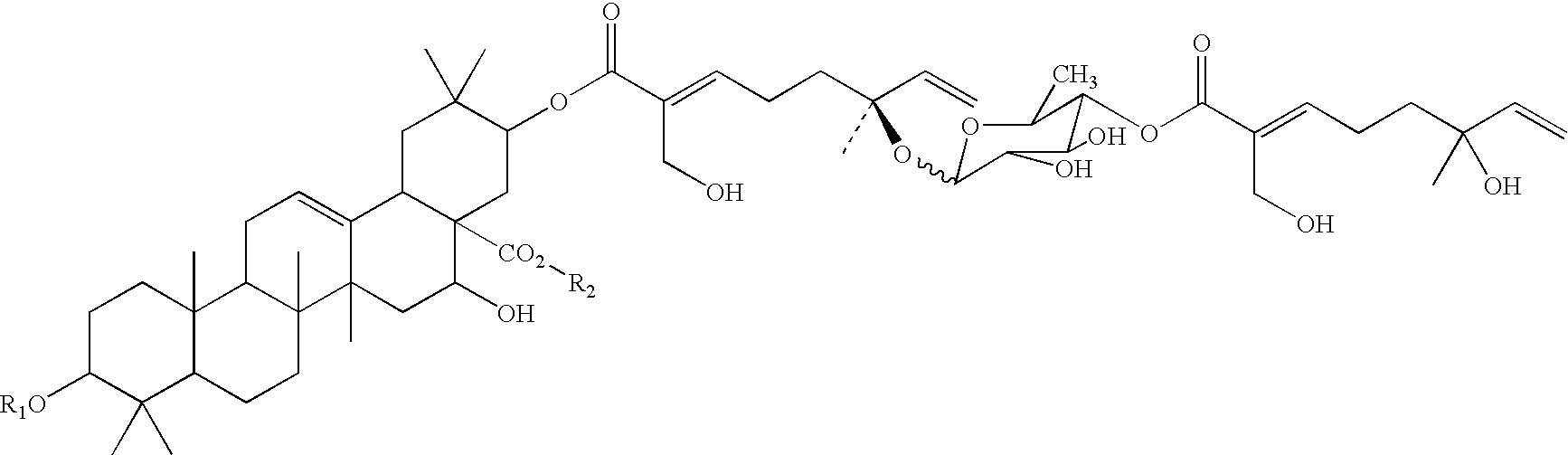
Triterpene compositions and methods for use thereof
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
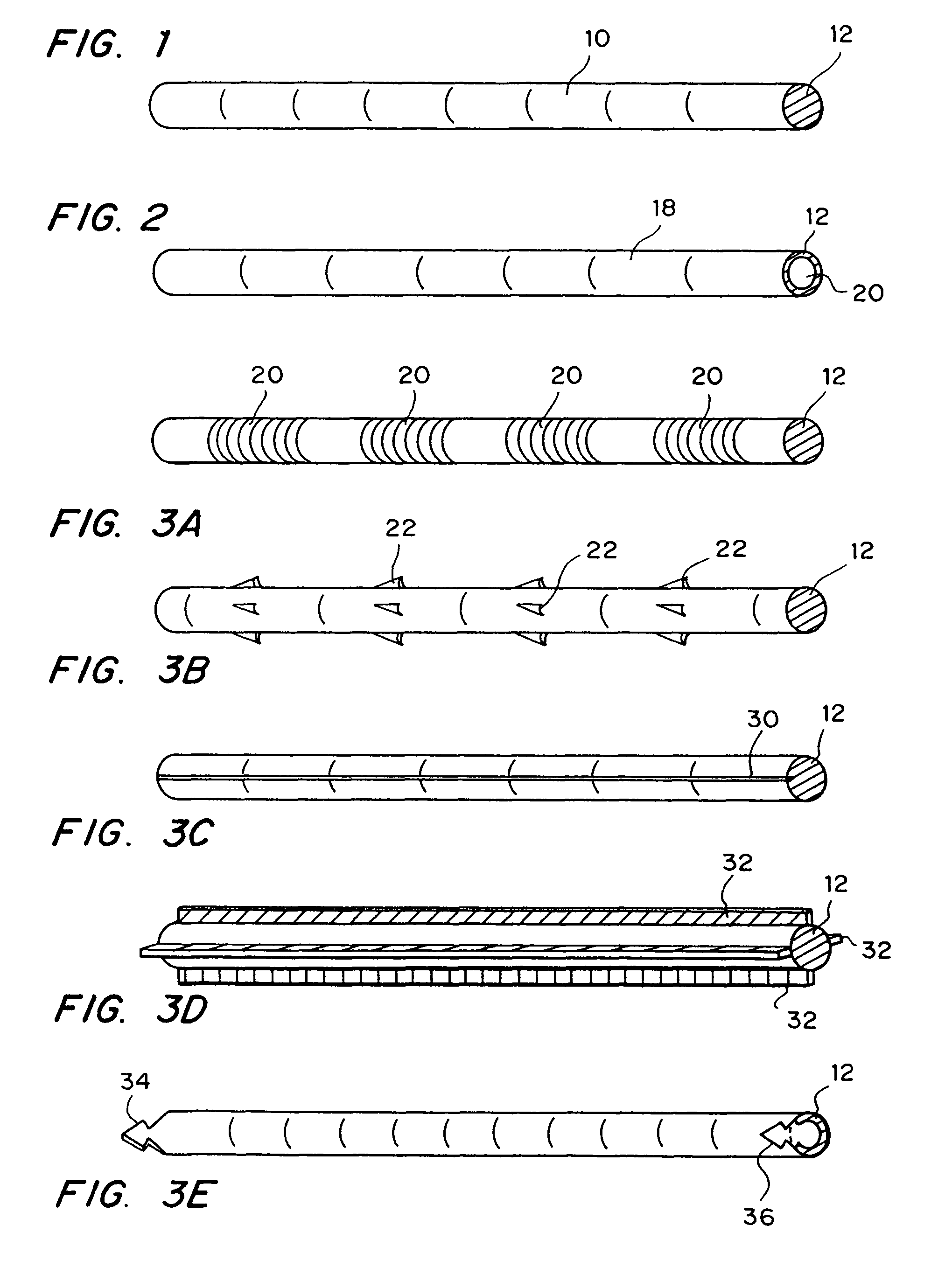
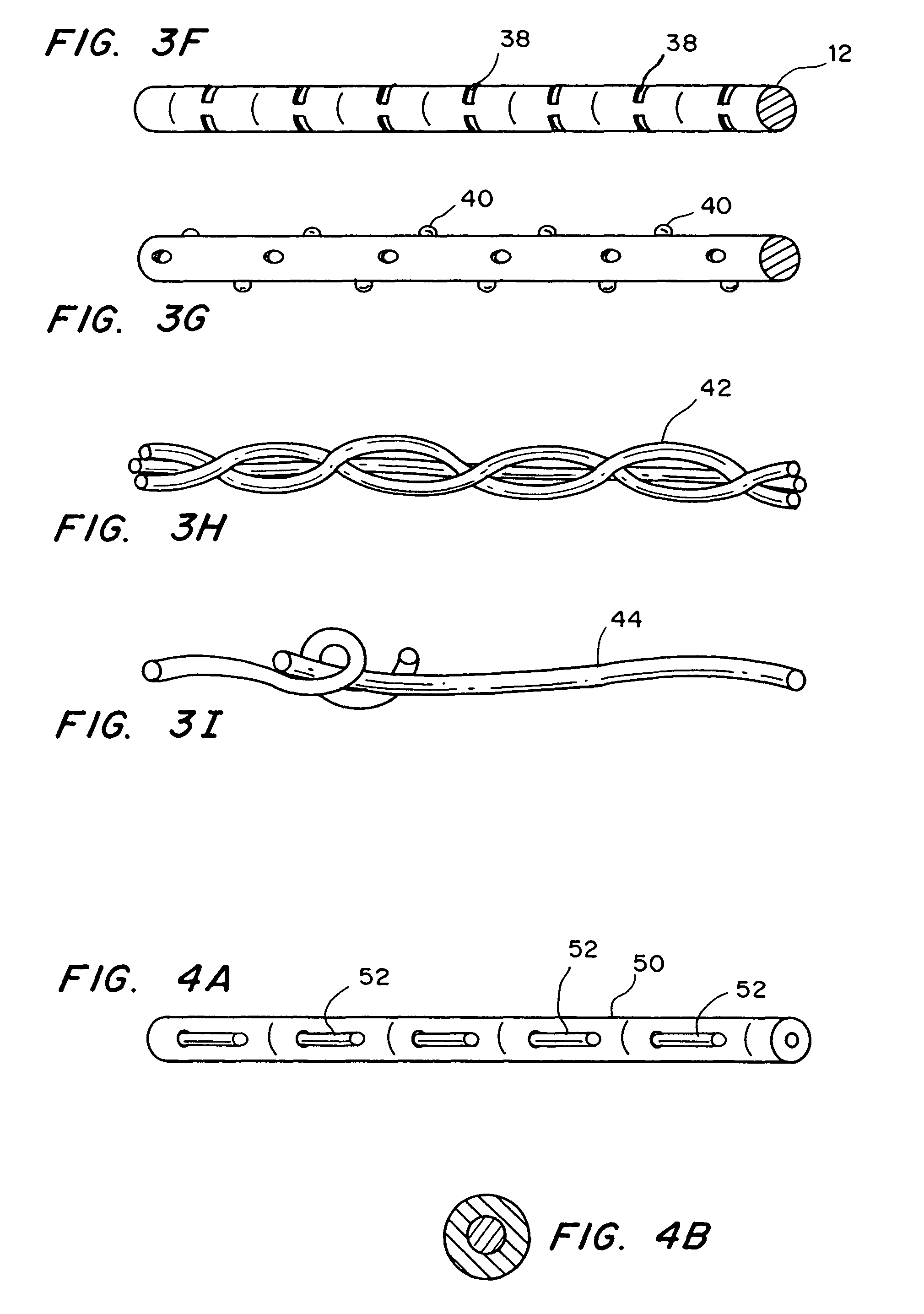
Flexible and/or elastic brachytherapy seed or strand
InactiveUS7776310B2Implanted accuratelyFocusSurgeryX-ray constrast preparationsBrachytherapyAdemetionine
A flexible or elastic brachytherapy strand that includes an imaging marker and / or a therapeutic, diagnostic or prophylactic agent such as a drug in a biocompatible carrier that can be delivered to a subject upon implantation into the subject through the bore of a brachytherapy implantation needle has been developed. Strands can be formed as chains or continuous arrays of seeds up to 50 centimeters or more, with or without spacer material, flaccid, rigid, or flexible.
Owner:MICROSPHERIX
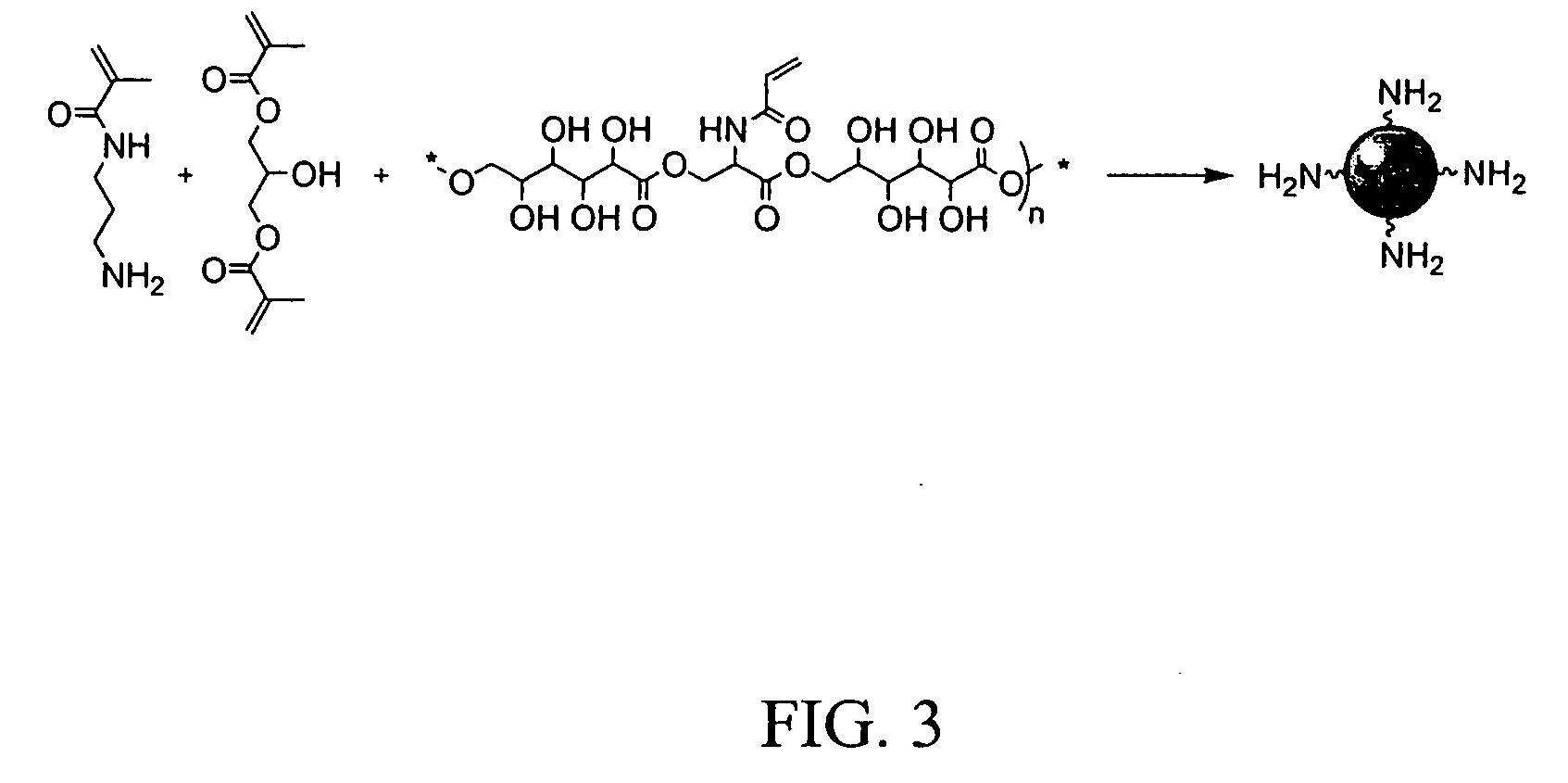
Biodegradable nanoparticles
The present invention relates to polymeric nanoparticles useful in drug and agent delivery, as well as for imaging, diagnosis and targeting. The polymeric nanoparticles of the present invention comprise polymers and cross-linkers that, when degraded, leave simple nontoxic biocompatible molecules that can be metabolized, excreted, or absorbed by the body. The present invention also relates to processes for producing the polymeric nanoparticles of the present invention, and methods of using them in drug and agent delivery, as well as imaging, diagnosis and targeting.
Owner:NEXT GENERATION THERAPEUTICS
Biocompatible Microbubbles to Deliver Radioactive Compounds to Tumors, Atherosclerotic Plaques, Joints and Other Targeted Sites
A composition and method for targeted use of radionuclide therapy for the treatment of cancer and cancerous tumors, atherosclerotic plaques, joints and other targeted sites. Microparticles, microbubbles, or nanoparticles deliver therapeutic doses of radiation, included radiation from alpha emitting radionuclides, to sites in a patient. The delivery may be targeted by targeting agents linked to the microparticles, microbubbles, or nanoparticles or by the external application of energy, or both.
Owner:CROWLEY ROSEMARY C
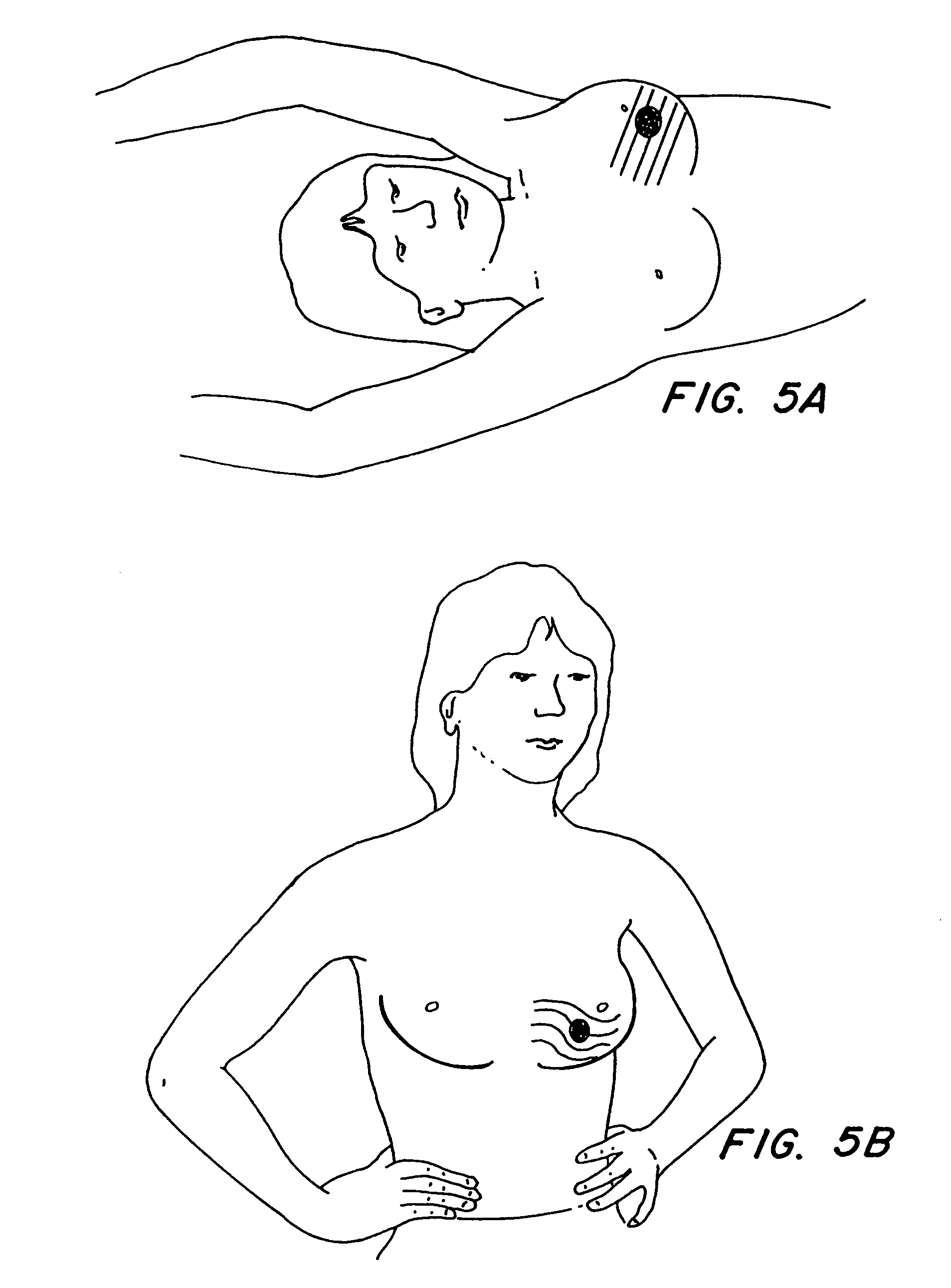
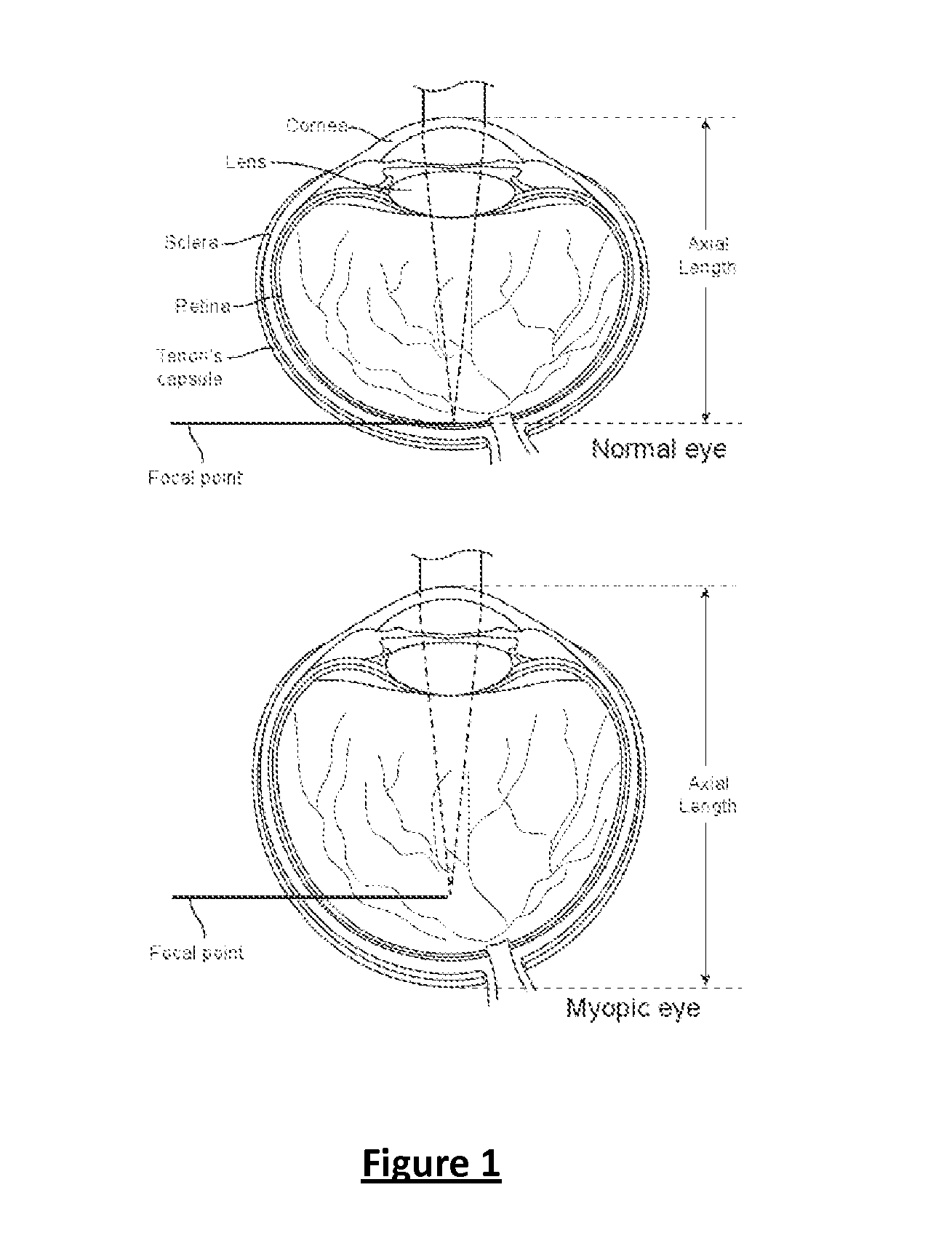
Method and apparatus for the delivery of photochemical (cross-linking) treatment to scleral tissue
ActiveUS20120209051A1Equally distributedOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCross-linkUva irradiation
Delivery systems and methods for delivering riboflavin (R / F) and UVA irradiation to the sclera are disclosed. The R / F is delivered and then activated with UVA irradiation through the use of LEDs or optical fibers, thereby causing cross-linking of the collagen tissue. Delivery systems include implantable structures which provide surfaces that conform to the sclera. The delivery systems include various types of structures for delivery of R / F onto the sclera surface. Additionally, the delivery systems include UVA sources which provide irradiation of R / F in sclera collagen tissue.
Owner:ALEYEGN TECH LLC
Targeted nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and treatment
InactiveUS20100034735A1Increase local concentrationGood choicePowder deliveryIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCancers diagnosis
The invention provides modified gold nanoparticles that enable a non-invasive, real time, targeted cancer imaging-therapeutic in one step. After reaching the cancer targets, the designed targeted gold nanoparticles significantly enhance conventional treatment modalities at the cellular level. In this aspect the gold nanoparticles of the invention are modified to be bound to a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) tracer.
Owner:ALBERTA HEALTH SERVICES +1
Nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy, x-ray induced photodynamic therapy, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and any combination thereof
ActiveCN107001031AExhibit nanorod morphologyPowder deliveryPhotodynamic therapyCo administrationImmunotherapeutic agent
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) comprising photosensitizers are described. The MOFs can also include moieties capable of absorbing X- rays and / or scintillation. Optionally, the photosensitizer or a derivative thereof can form a bridging ligand of the MOF. Further optionally, the MOF can comprise inorganic nanoparticles in the cavities or channels of the MOF or can be used in combination with an inorganic nanoparticle. Also described are methods of using MOFs and / or inorganic nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy or in X-ray induced photodynamic therapy, either with or without the co-administration of one or more immunotherapeutic agent and / or one or more chemotherapeutic agent.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
In vivo panning for ligands to radiation-induced molecules
InactiveUS20030130190A1Increase choiceReduced flexibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementIn vivoTargeting ligands
A method for identifying a molecule that binds an irradiated tumor in a subject and molecules identified thereby. The method includes the steps of: (a) exposing a tumor to ionizing radiation; (b) administering to a subject a library of diverse molecules; and (c) isolating from the tumor one or more molecules of the library of diverse molecules, whereby a molecule that binds an irradiated tumor is identified. Also provided are therapeutic and diagnostic methods using targeting ligands that bind an irradiated tumor.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
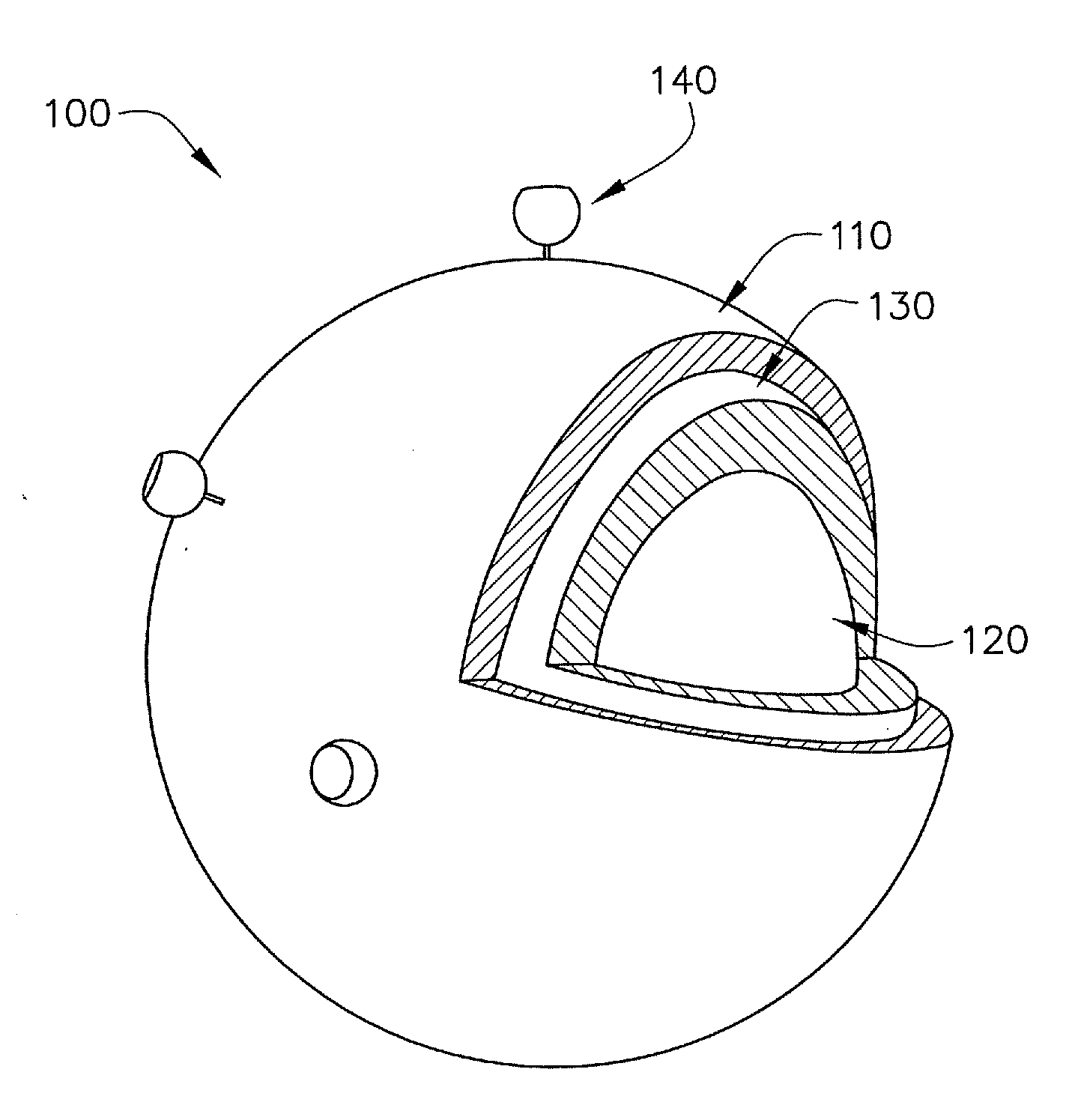
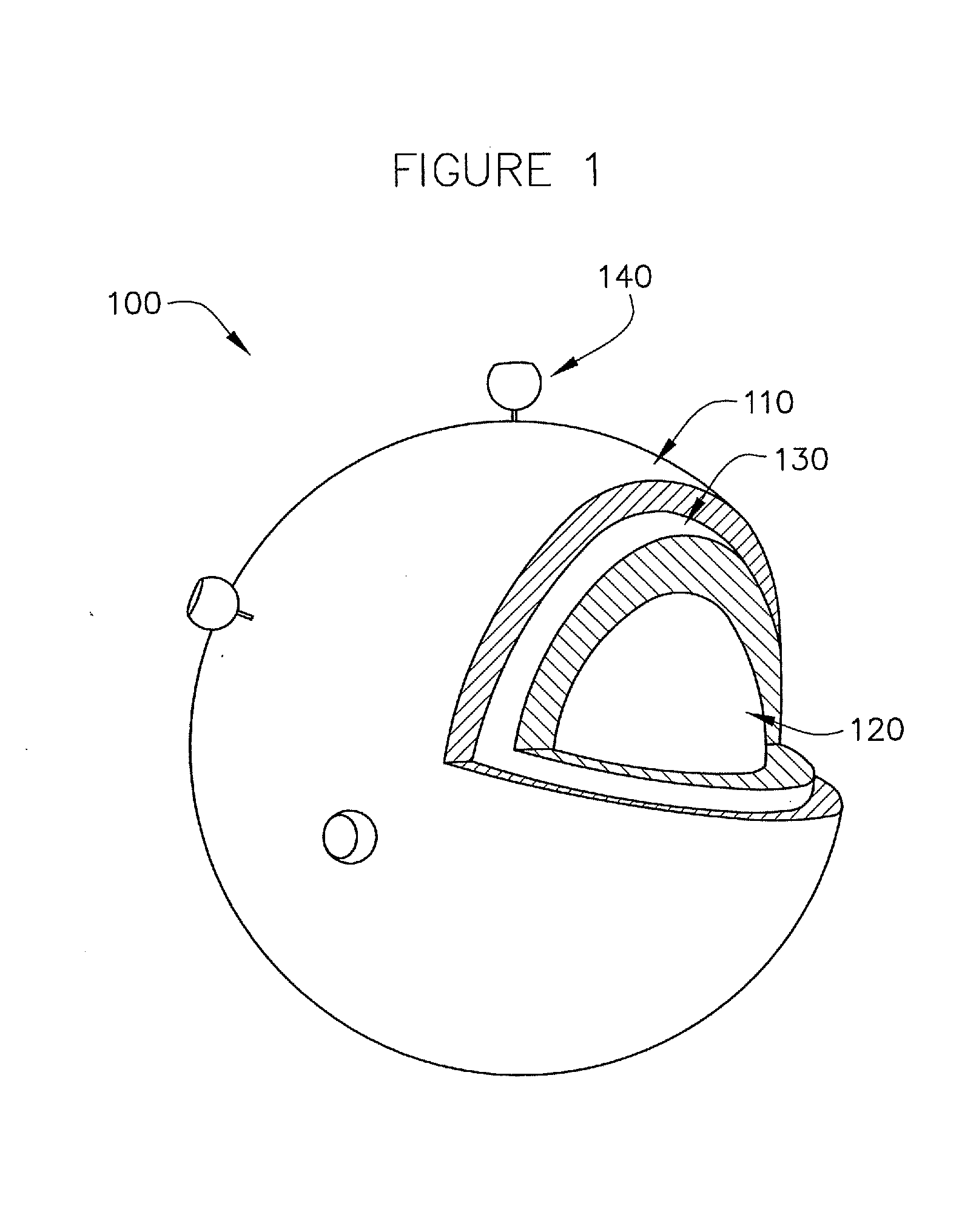
Inorganic Nanoparticles of High Density to Destroy Cells In-Vivo
ActiveUS20110213192A1Safely employedEfficient emissionsBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsHigh energy photonIsotope
The present application relates to novel excitable particles which can be used in the health sector. It more particularly relates to particles which can generate electrons and / or high energy photon when excited by ionizing radiations such as X- Rays, γ-Rays, radioactive isotope and / or electron beams, and to the uses thereof in health, in particular in human health. The inventive particles are made of an inorganic material comprising oxygen, in particular an oxide, said material having an adequate density, and can be activated in vitro, ex vivo, or in vivo, by controllable external excitation, in order to disturb, alter or destroy target cells, tissues or organs. The invention also relates to methods for the production of said particles, and to pharmaceutical or medical device compositions containing same.
Owner:NANOBIOTIX SA
Triterpene compositions and methods for use thereof
InactiveUS20060073222A1None of potential benefitsAntibacterial agentsBiocideApoptosisAcacia victoriae
The invention provides novel saponin mixtures and compounds which are isolated from the species Acacia victoriae and methods for their use. These compounds may contain a triterpene moiety, such as acacic or oleanolic acid, to which oligosaccharides and monoterpenoid moieties are attached. The mixtures and compounds have properties related to the regulation of apoptosis and cytotoxicity of cells and exhibit potent anti-tumor effects against a variety of tumor cells.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Compositions and Methods for Inducing Nanoparticle-mediated Microvascular Embolization of Tumors
InactiveUS20140363496A1Improve permeabilityImprove retentionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsNitric oxideWilms' tumor
Nanoparticle mediated microvascular embolization (NME) of tumor tissue may occur after systemic administration of PEM, leading to widespread shutdown of vascular flow, hemorrhage, and necrosis. PEM constructs are developed that incorporate large amounts of iron-containing protein, possess high oxygen affinities, and demonstrate delayed nitric oxide binding. Such properties induce selective NME of tumors after extravasation, and will likely enhance the effect of VEGFR TKIs and / or mTOR inhibitors.
Owner:POSEIDA THERAPEUTICS INC
Monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes as chemotherapeutic and radiation sensitizers and immunomodulators
A method of sensitizing tumor cells to radiation thereapy, chemotherapy and immunomodulatory thereapy, comprising the step of exposing the tumor cell to an effective amount of at least one monoterpene or sesquiterpene and treating the tumor cell is disclosed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com