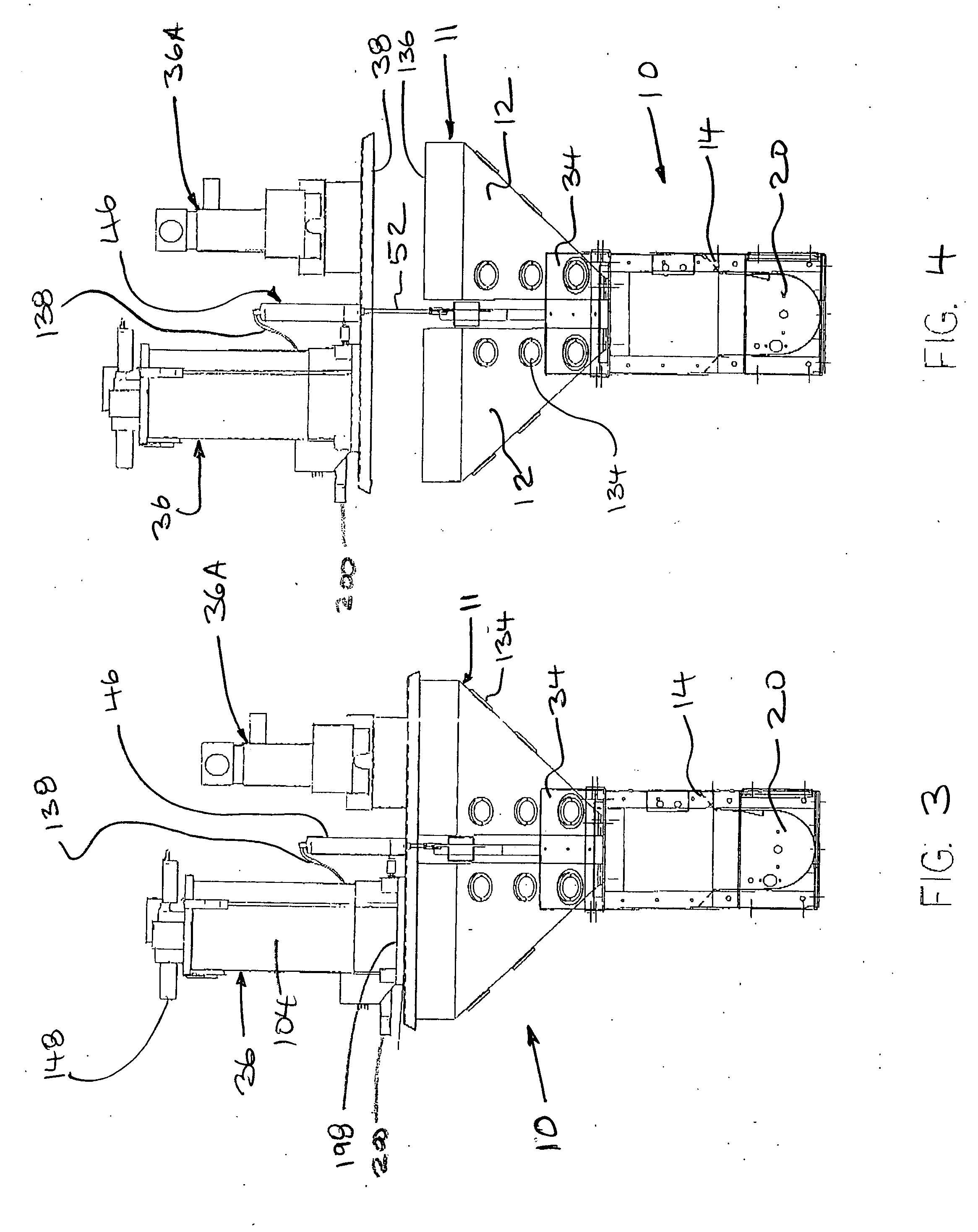
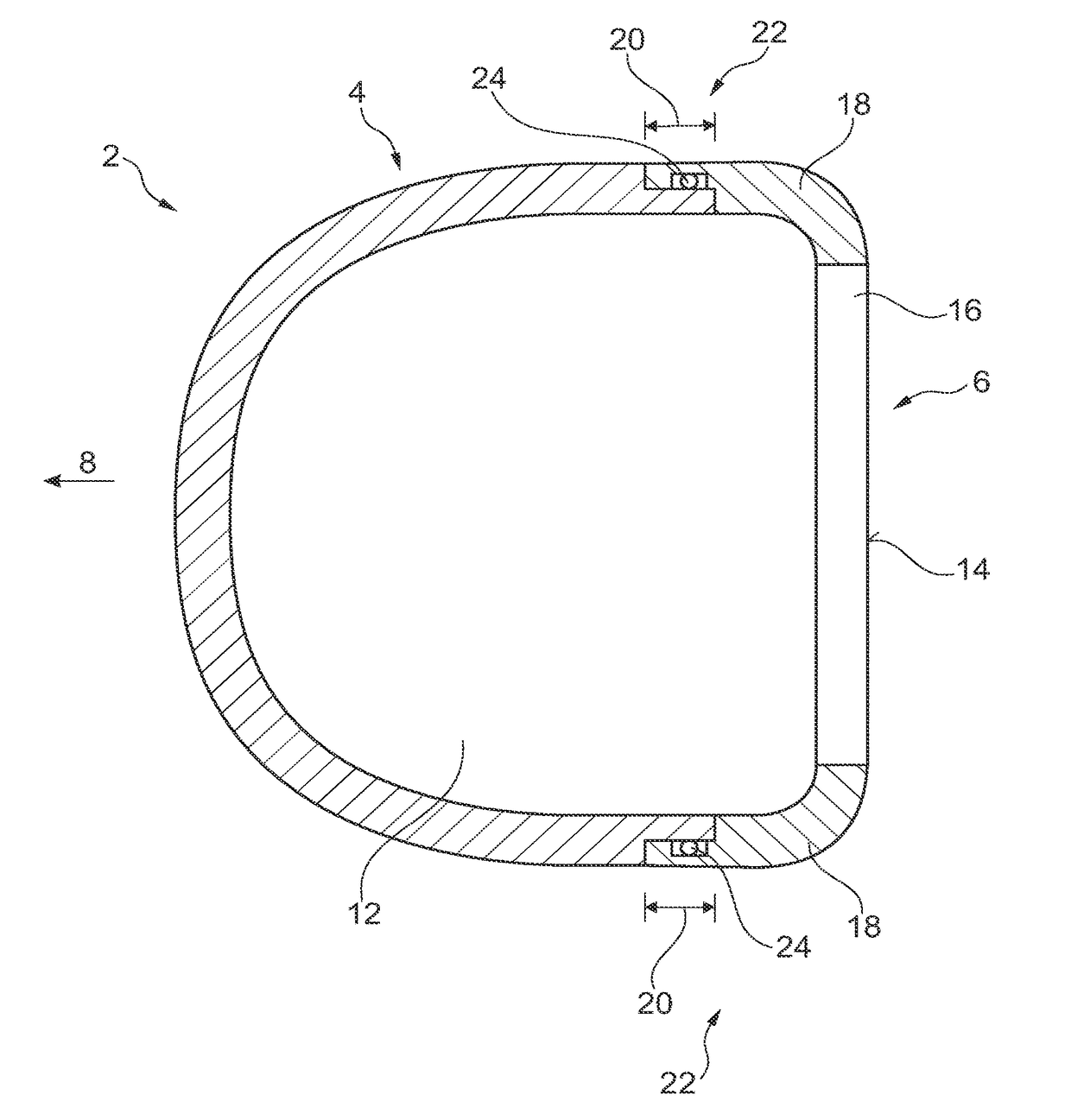
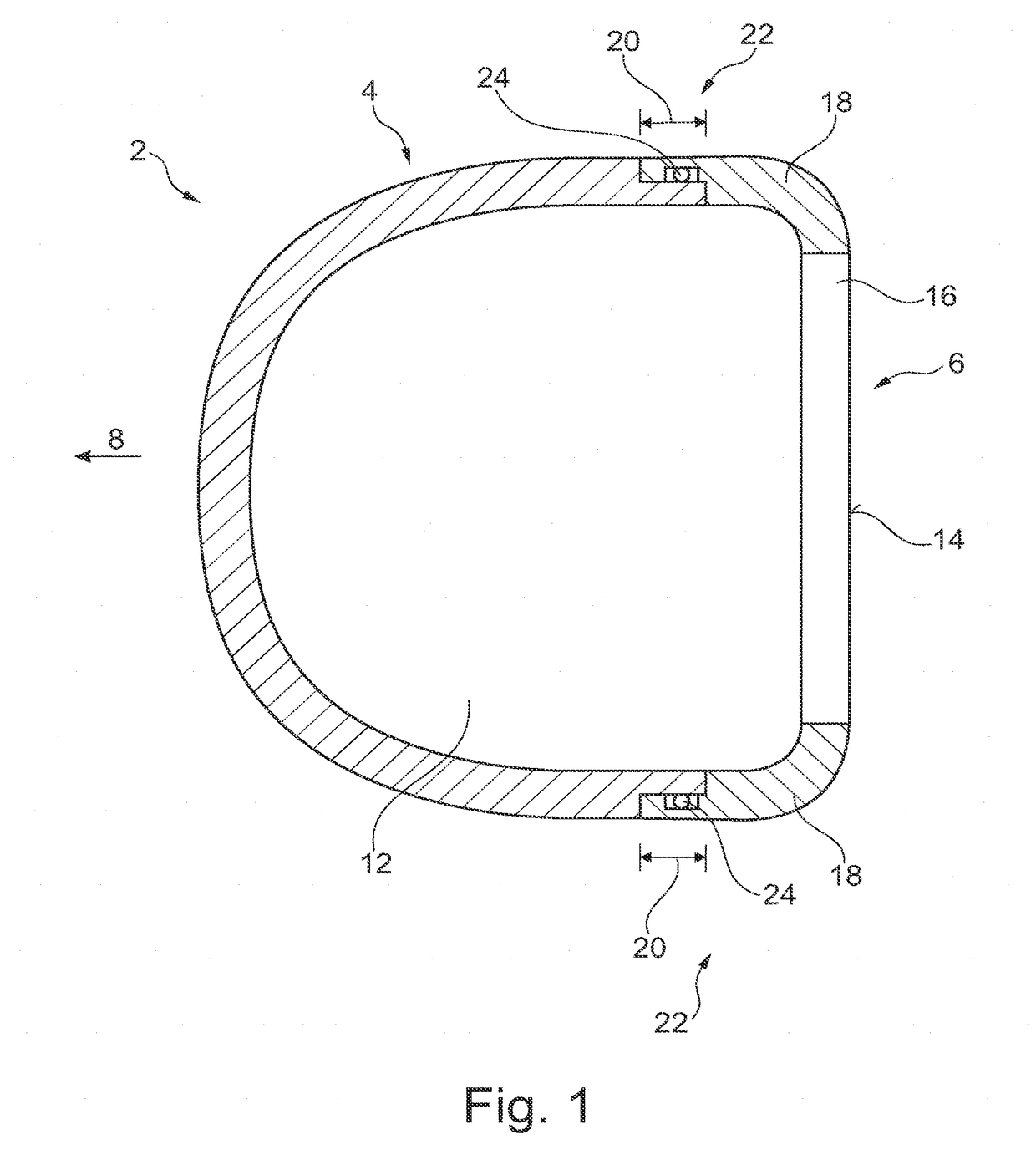
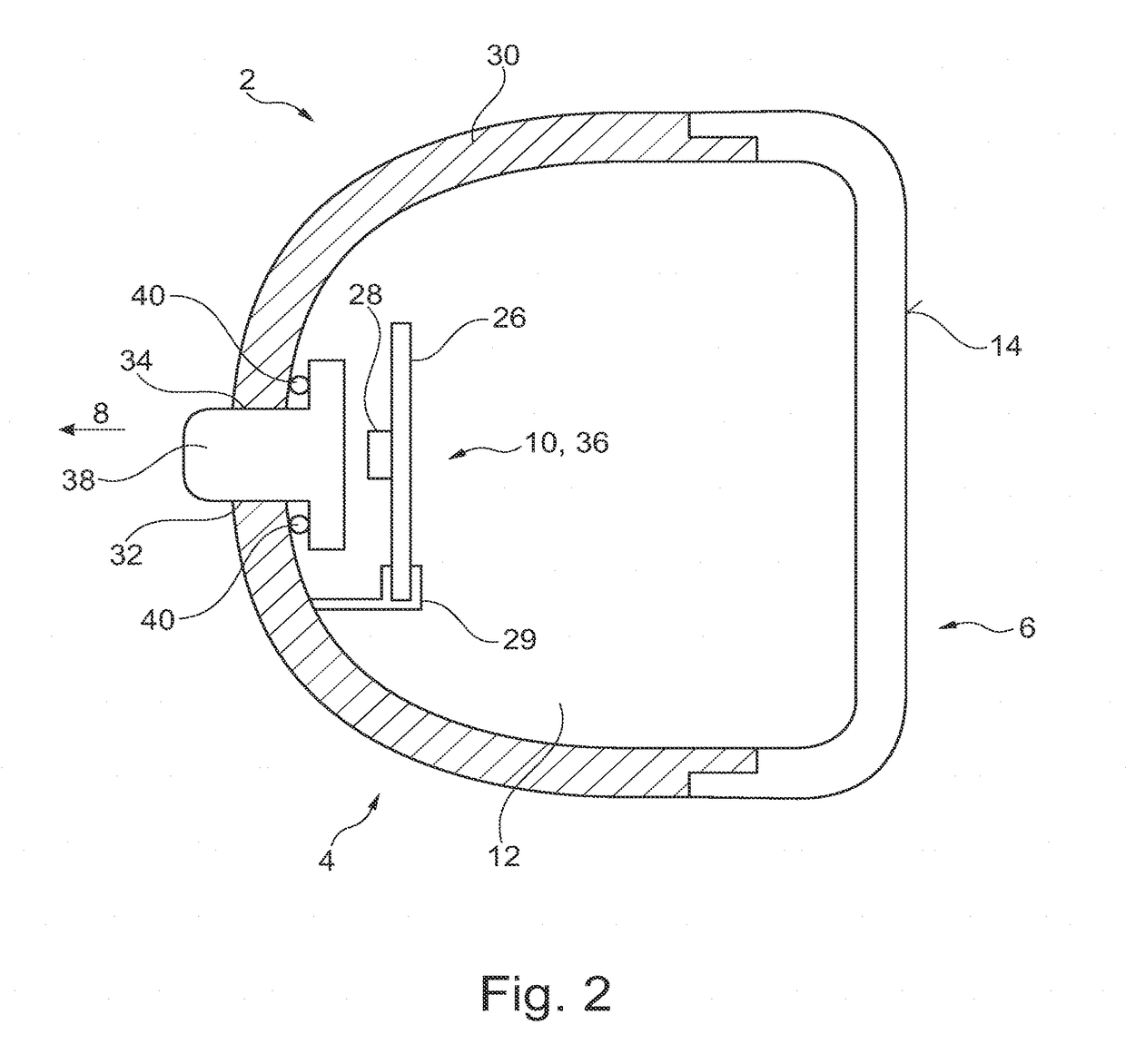
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
161results about How to "Ensure maintenance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
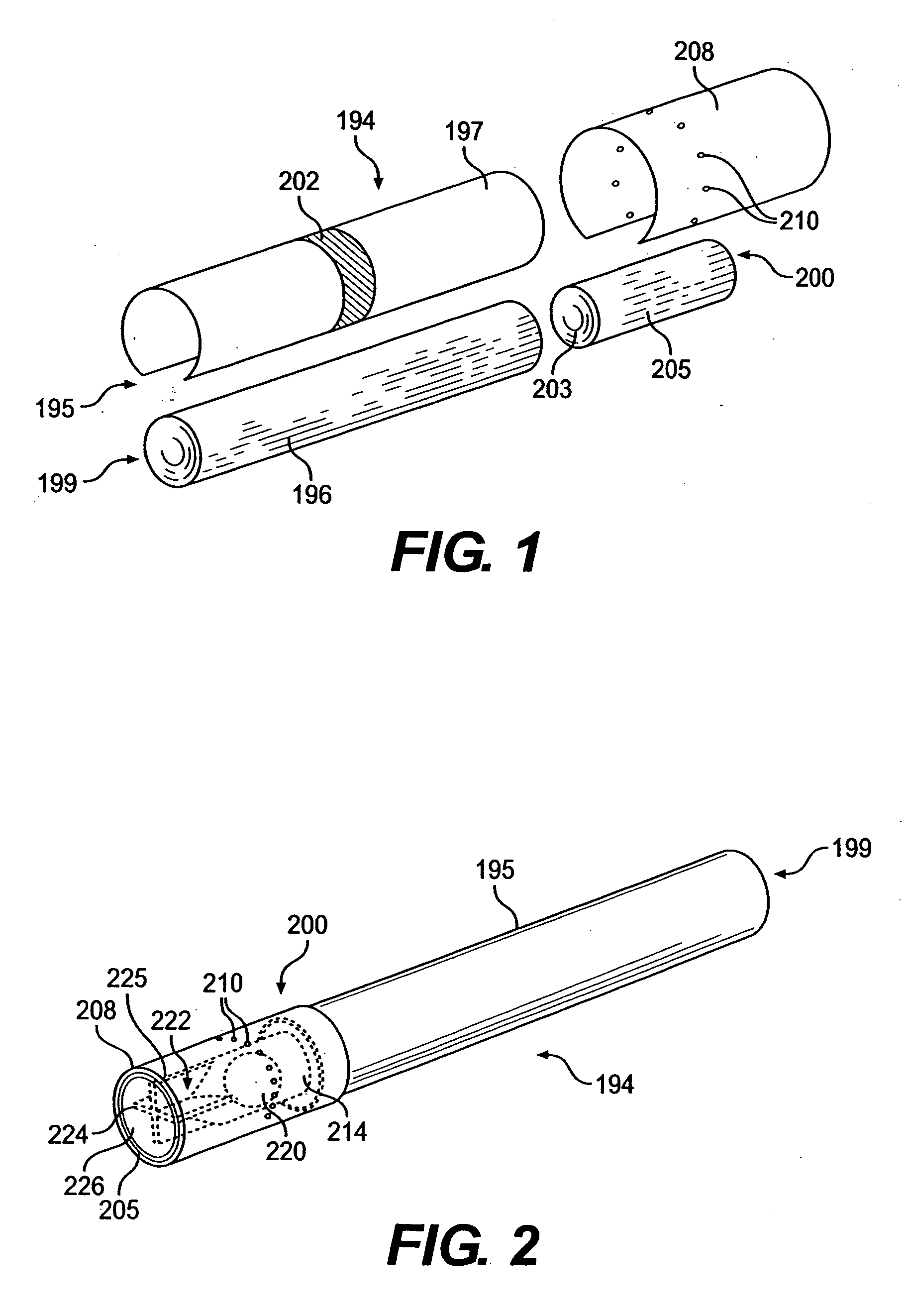
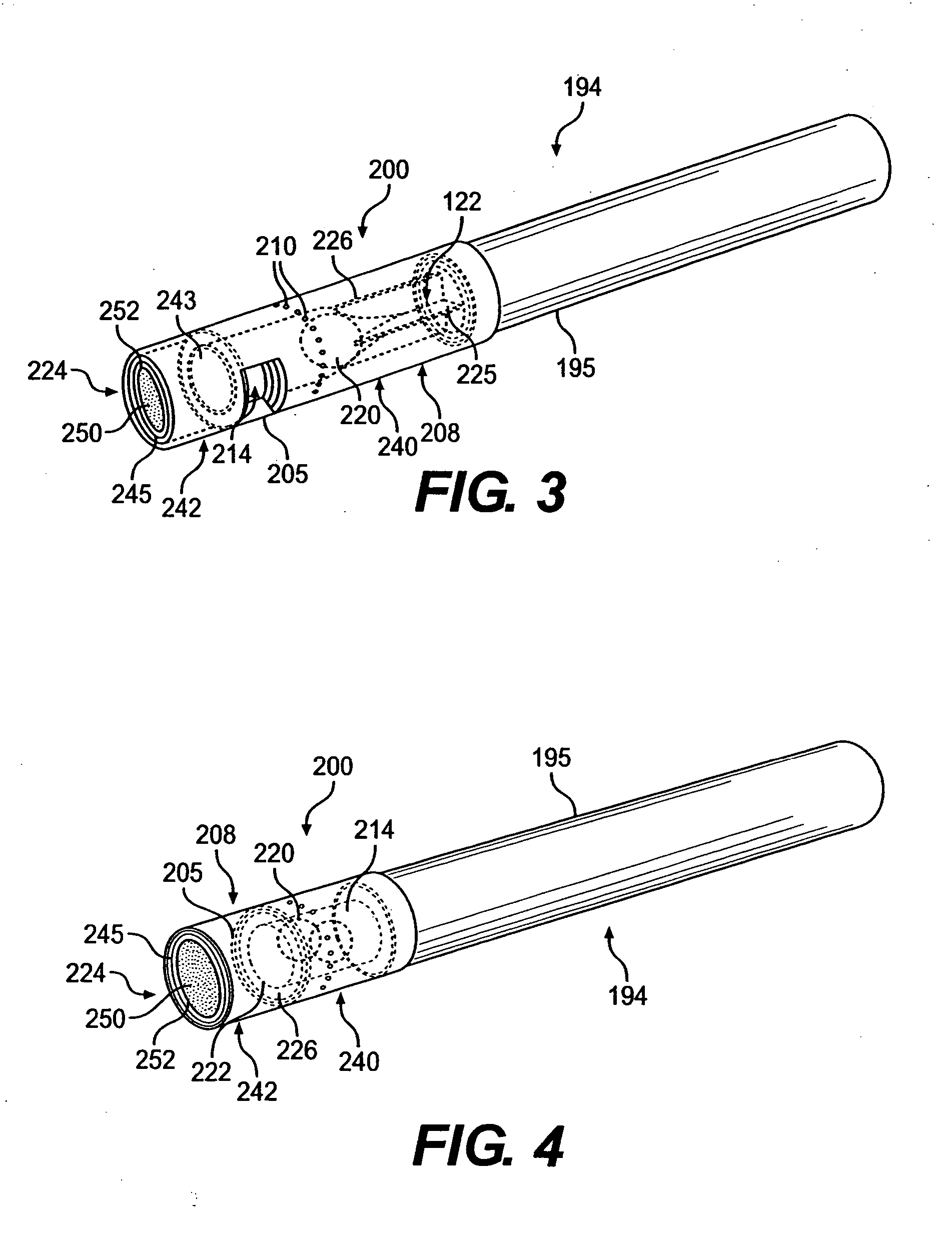
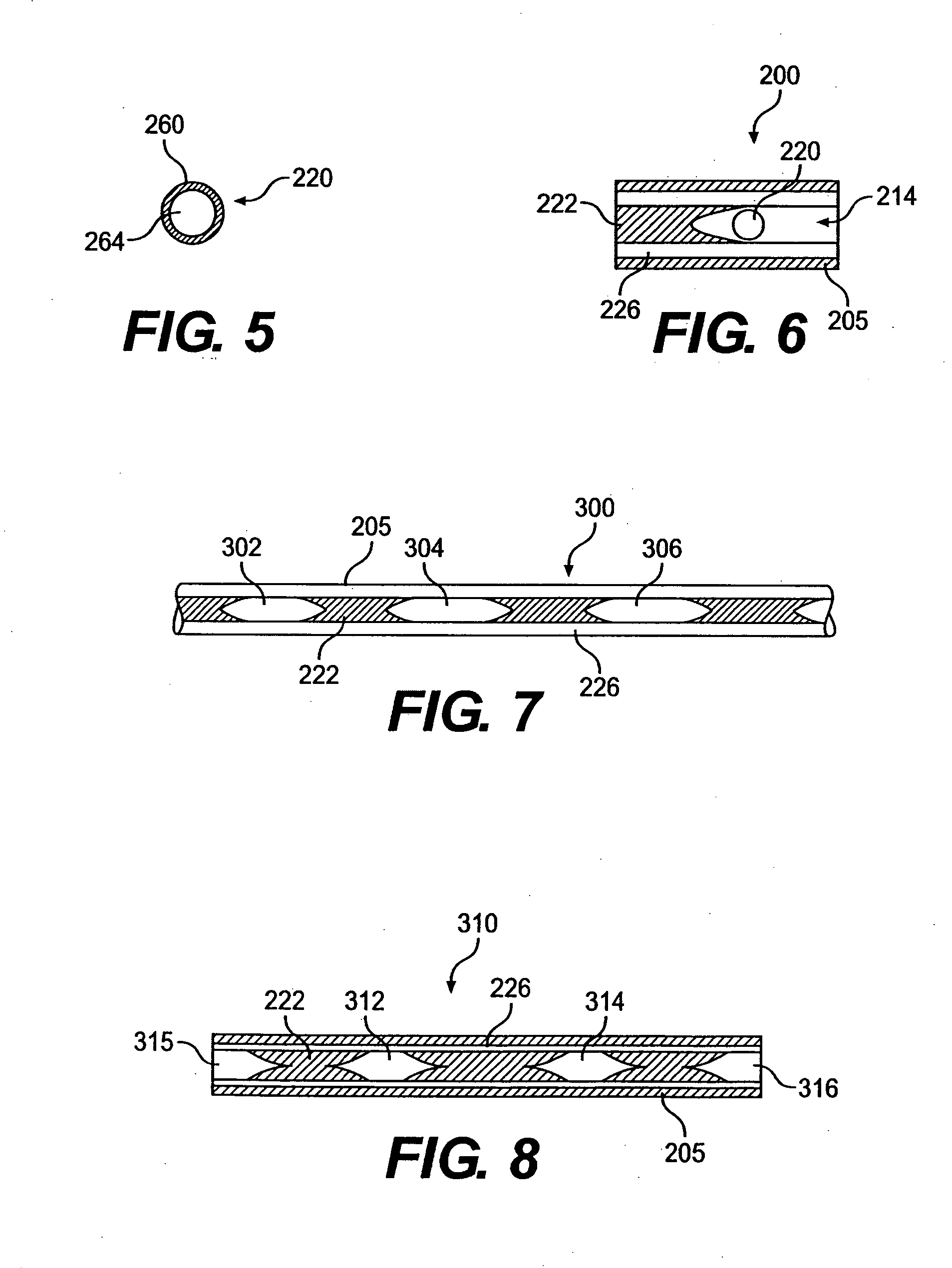
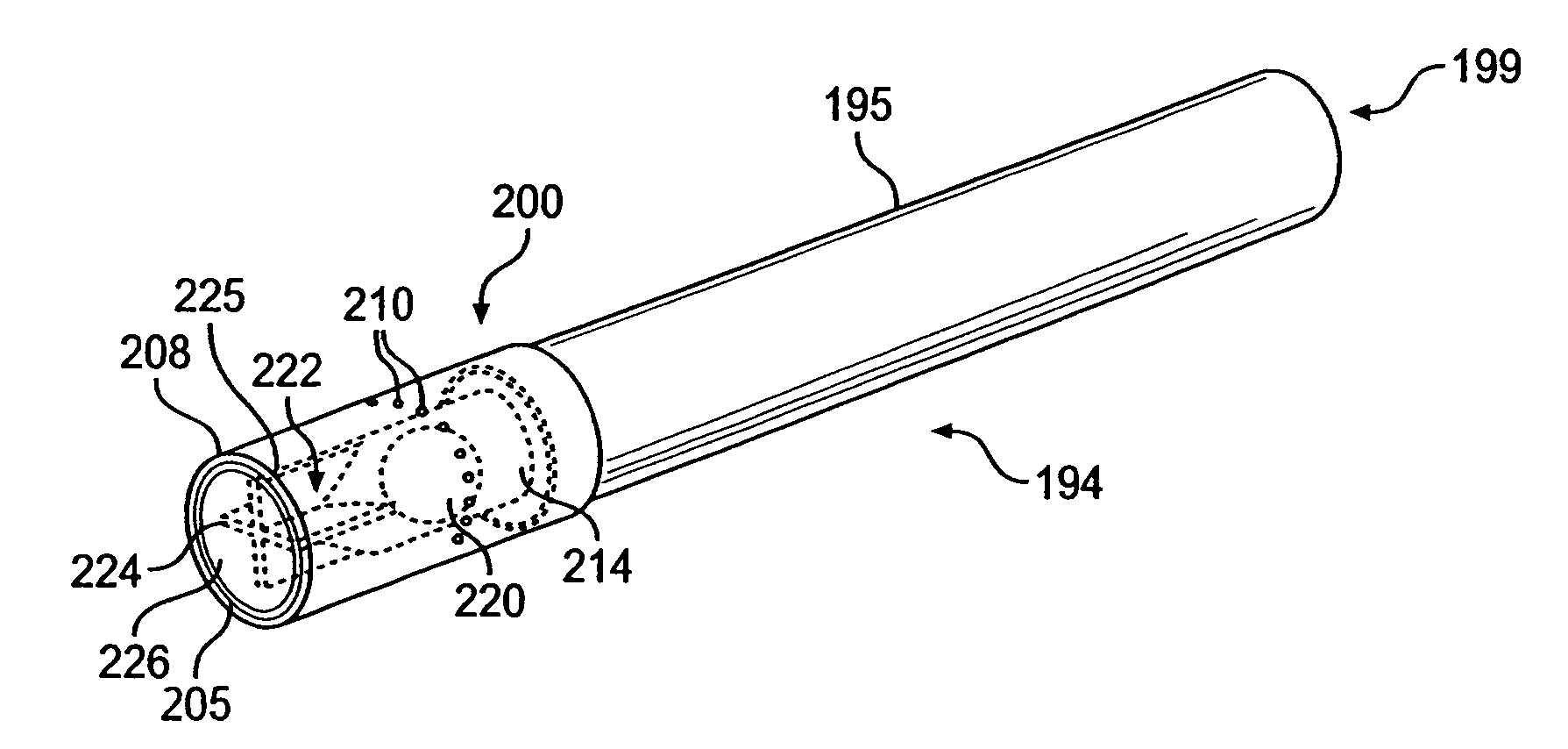
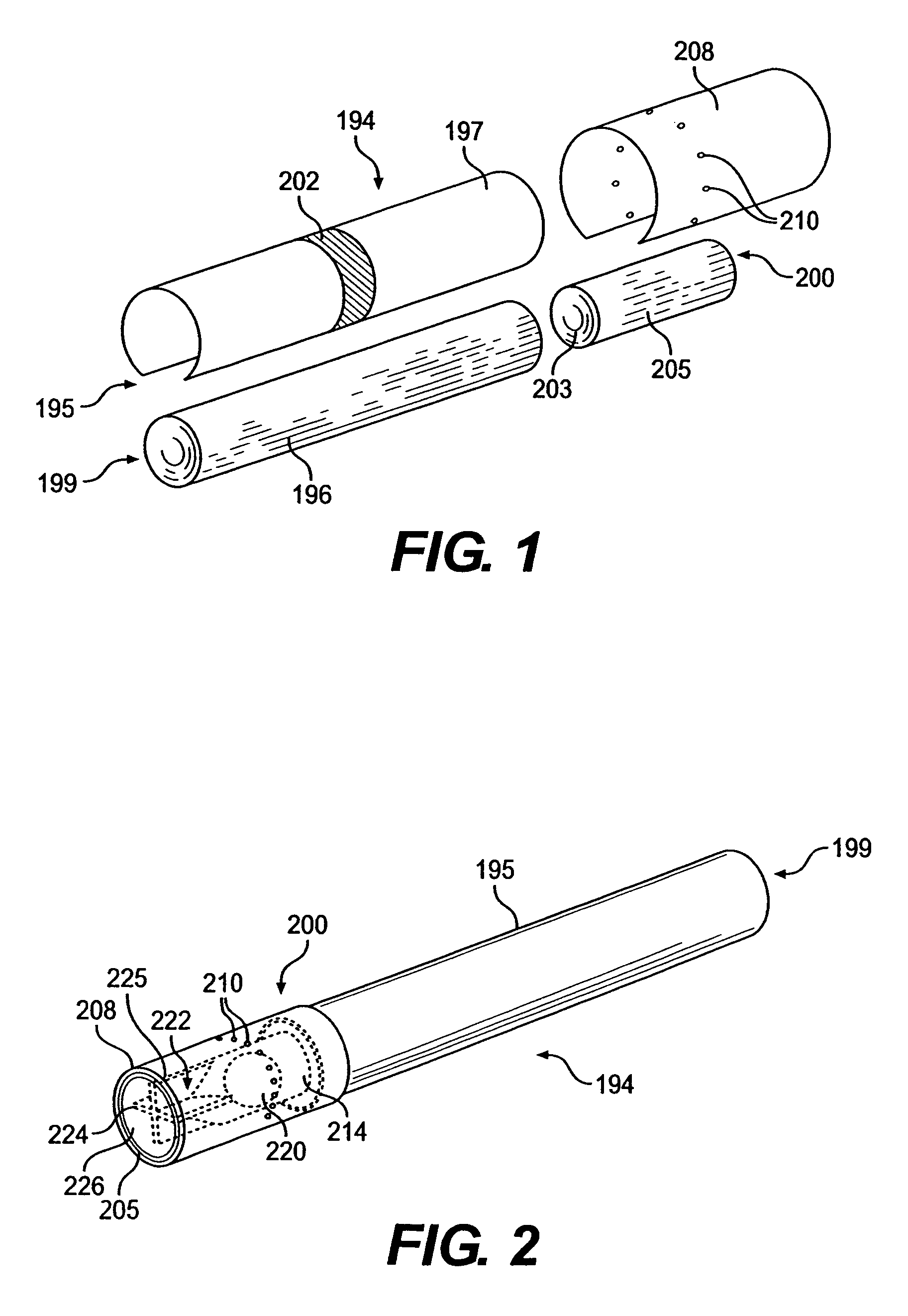
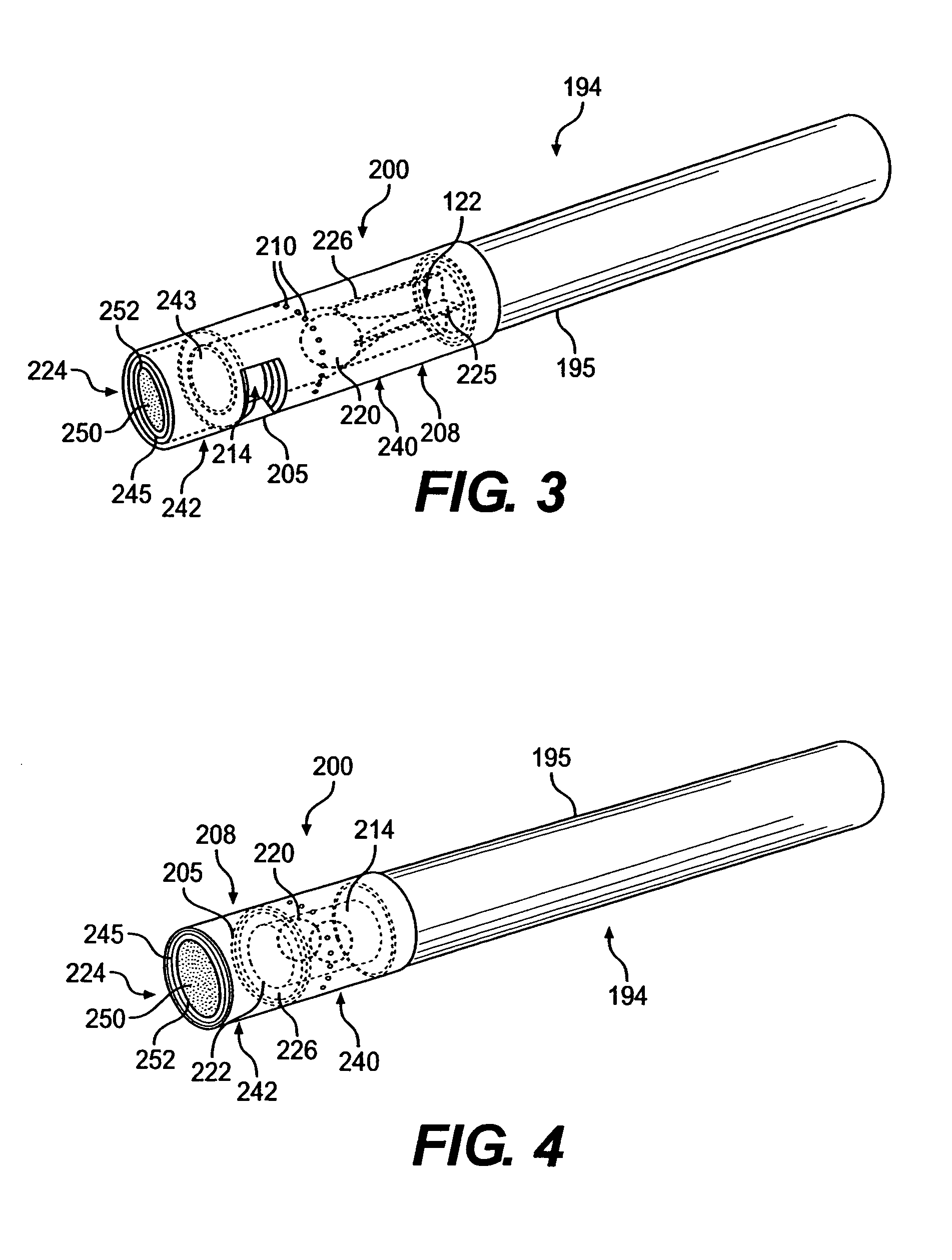
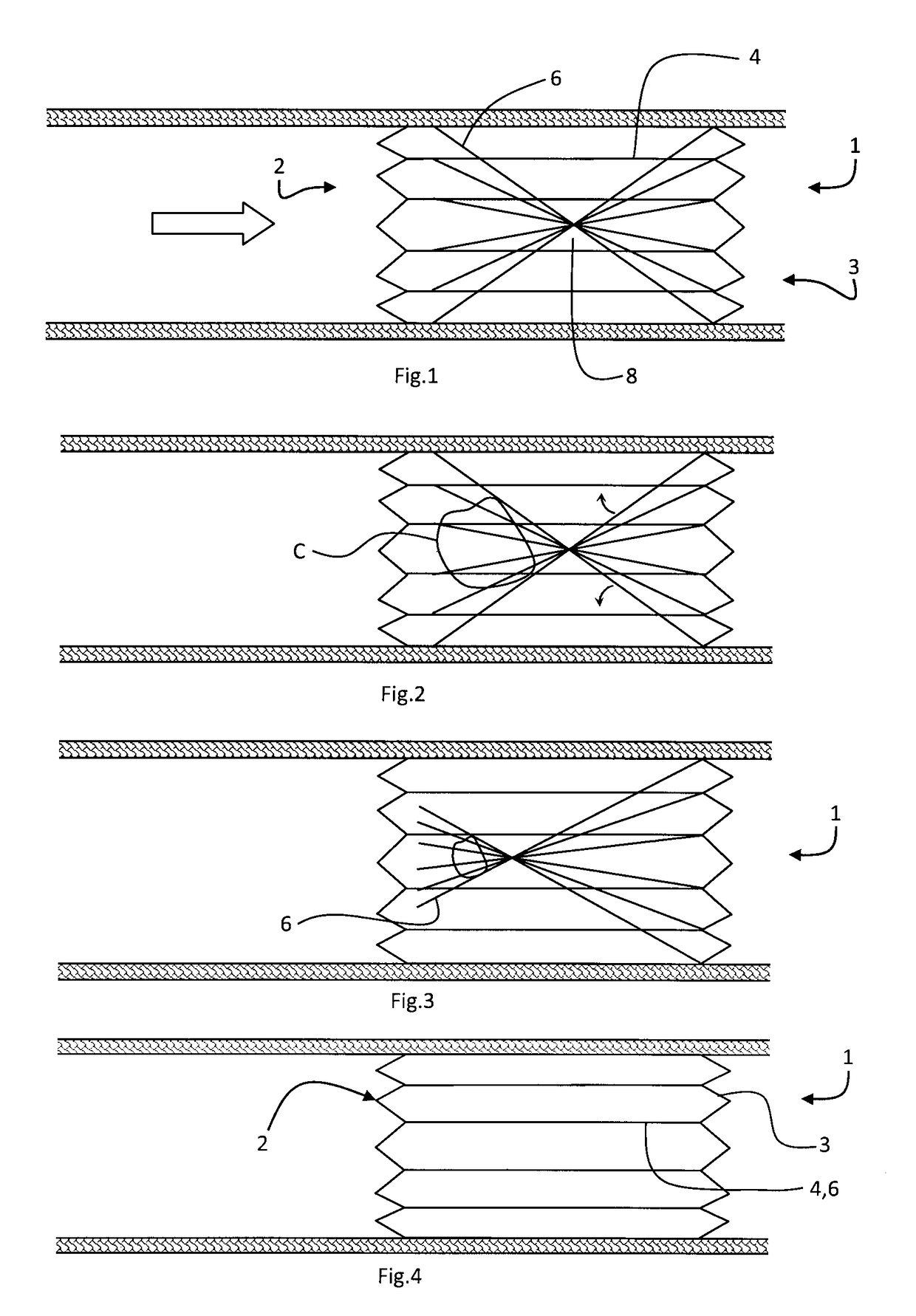
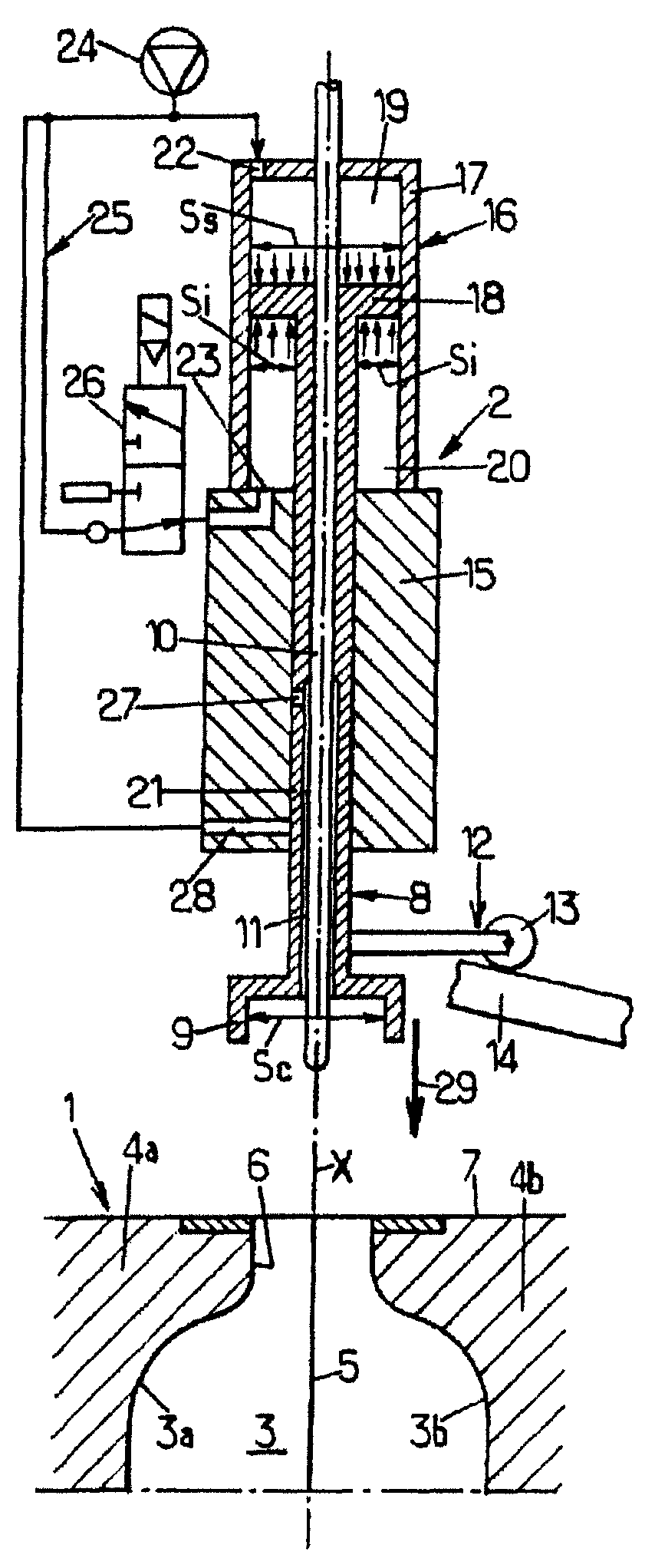
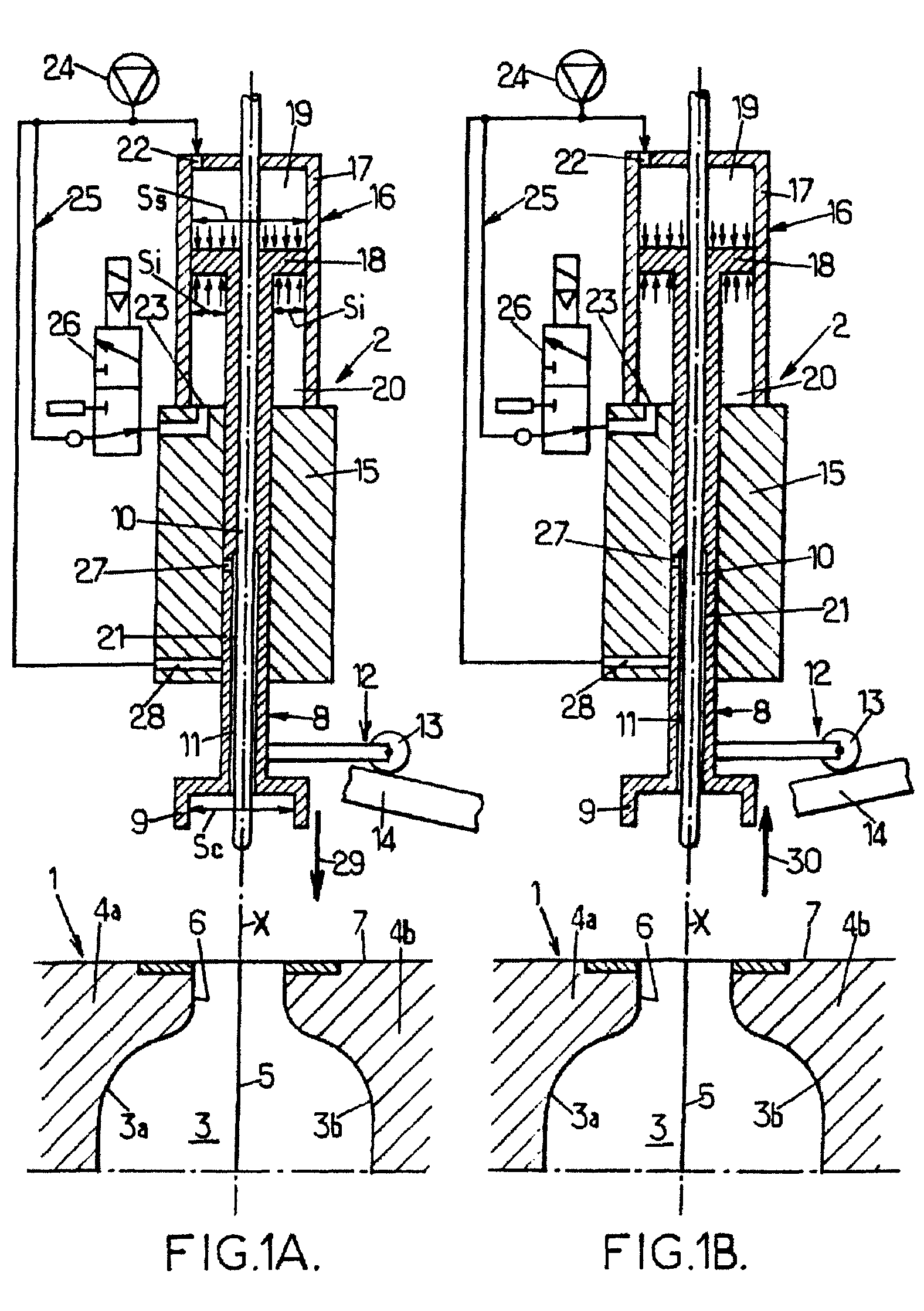
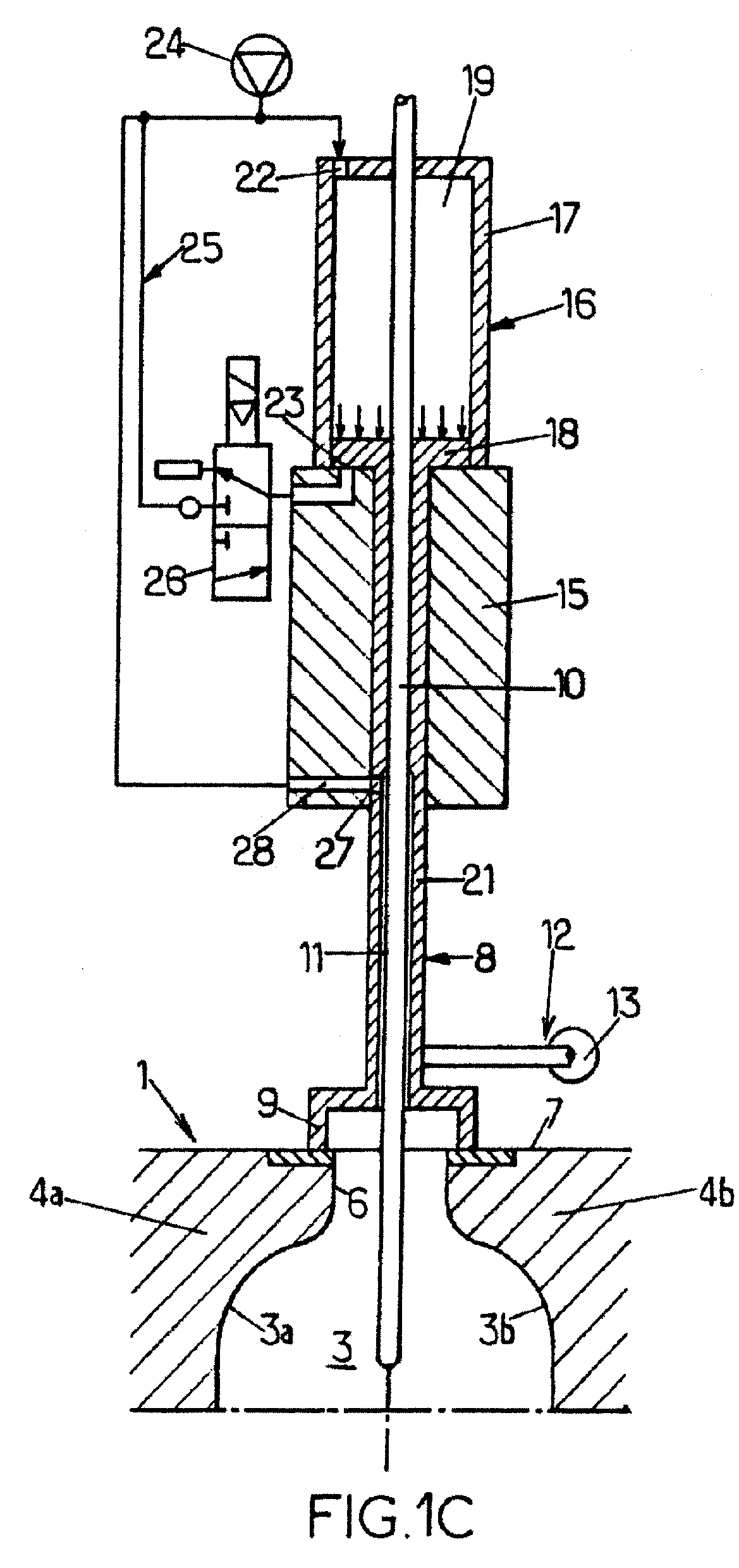
Filtered cigarette incorporating a breakable capsule
ActiveUS20060272663A1Ensure maintenanceTobacco treatmentPaper/cardboard wound articlesBiomedical engineeringFilter element
A filtered cigarette possesses at least one breakable capsule in its filter element. The filter element can possess a central cavity extending from the cigarette tobacco rod towards the middle of the filter element. The central cavity may be defined by an inner filter portion. The inner filter portion can be surrounded by an outer filter portion comprised of filter tow material that is generally permeable to the smoke generated by the cigarette. At least one breakable capsule is disposed in the central cavity of the filter element. The breakable capsules are spherical in shape, and are composed of a gelatin outer shell that encloses a payload of triglycerides and flavoring agents. The breakable capsules are adapted to rupture in response to pressure applied by the smoker to the outside region of the filter element.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
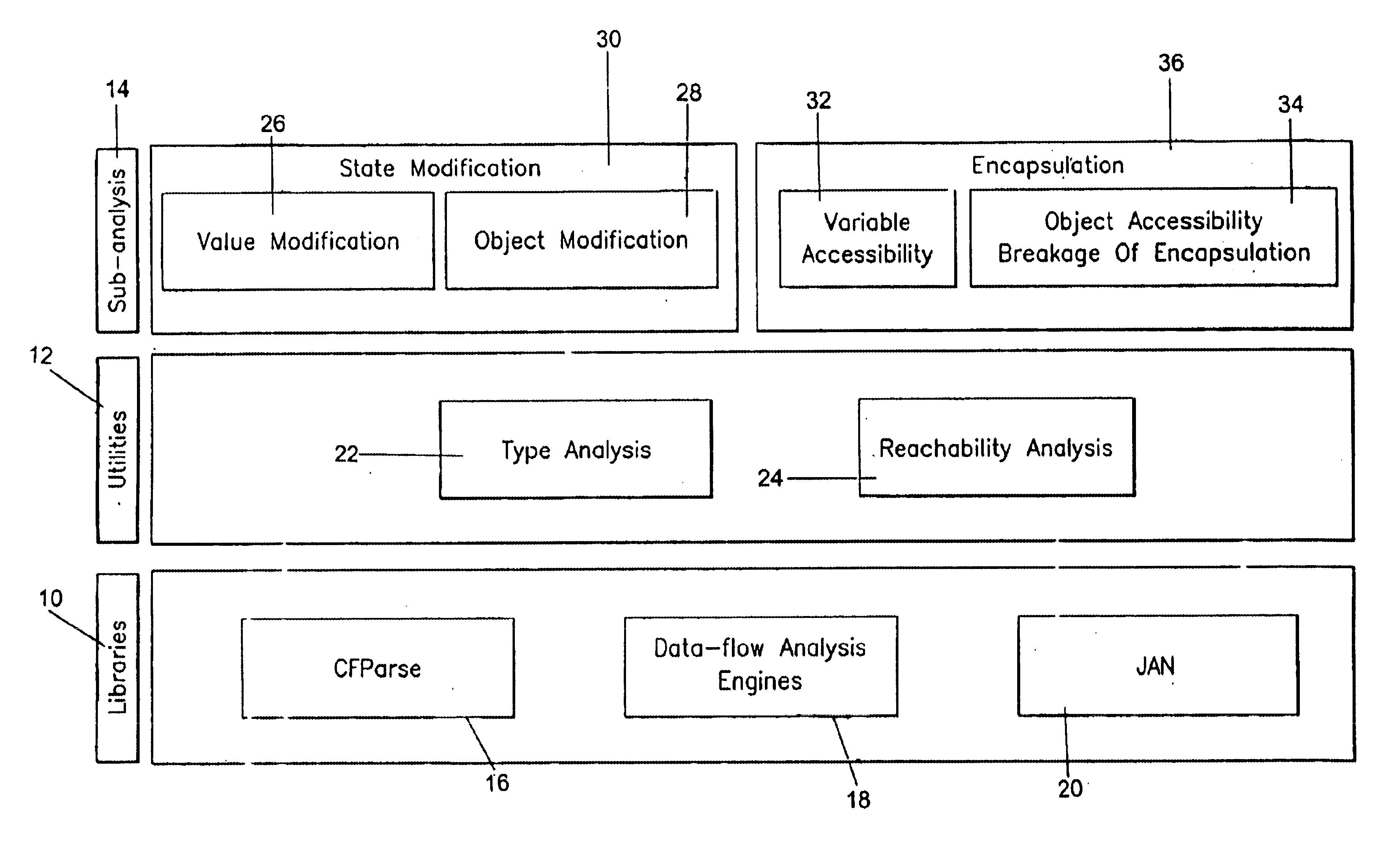
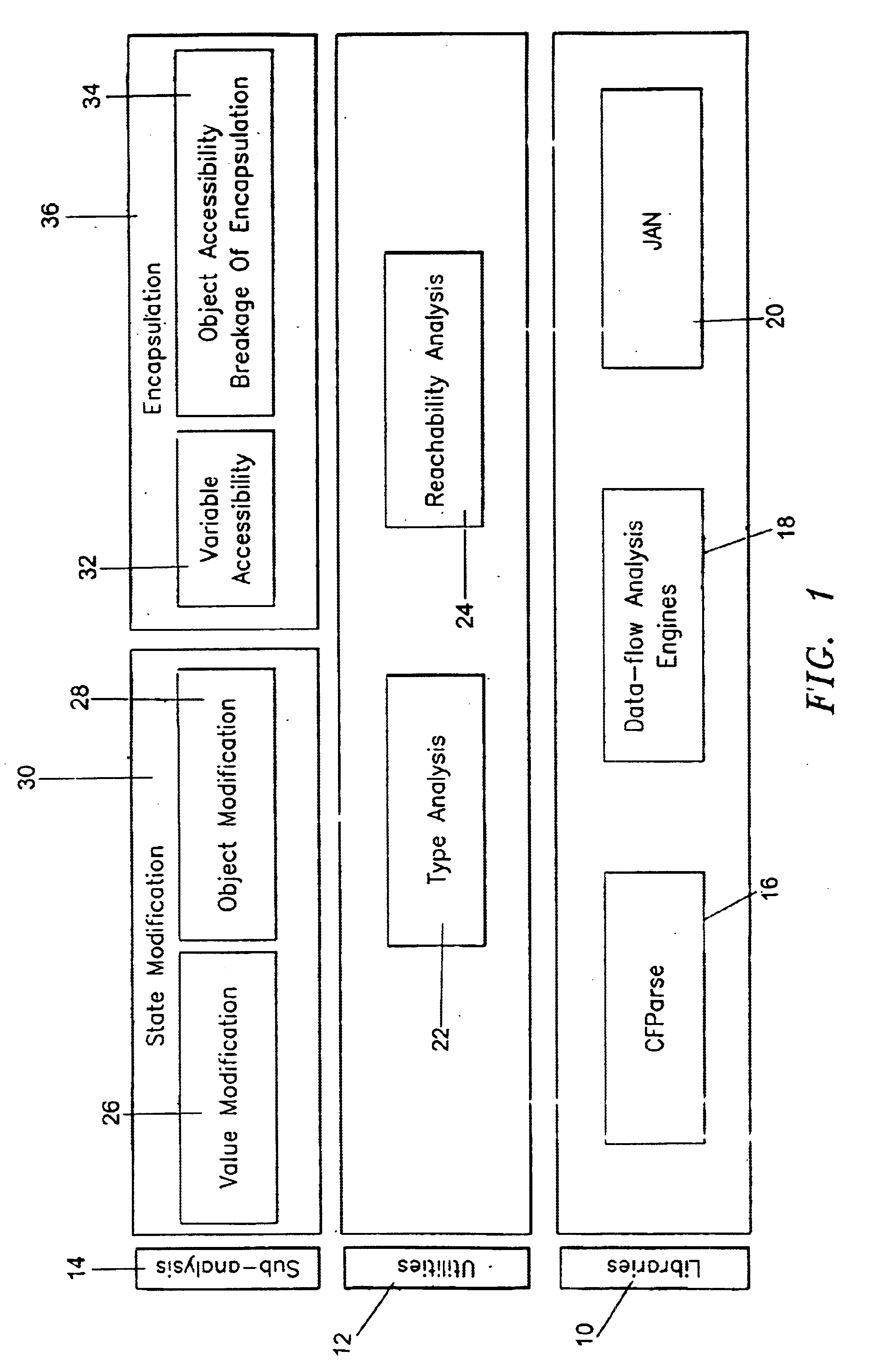
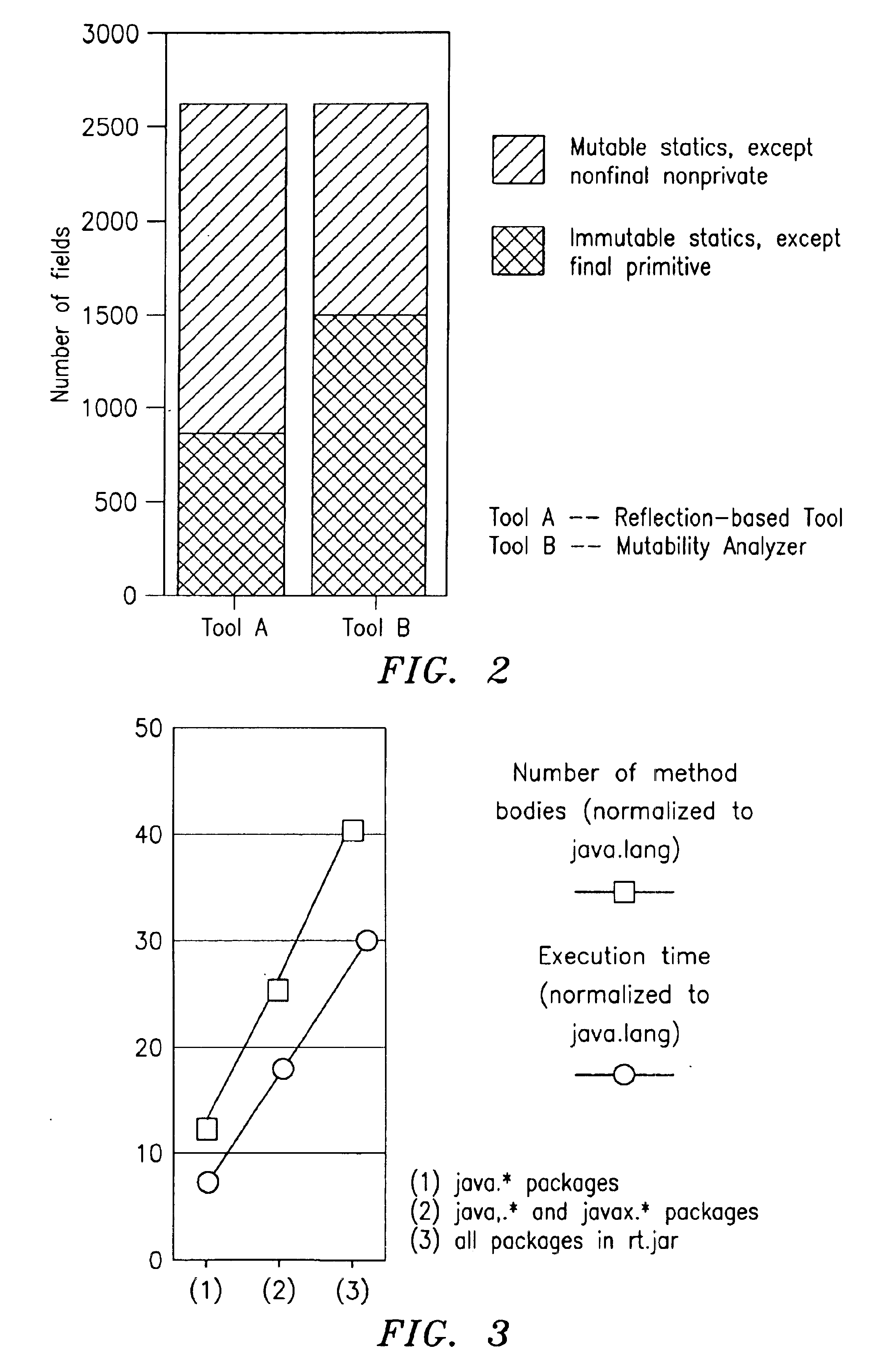
Mutability analysis in Java
InactiveUS6925638B1Reduce security risksEnsure maintenanceSoftware engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsExtensibilityHuman language
A system and method for detecting the mutability of fields and classes in an arbitrary program component written in an object oriented programming language is disclosed. A variable is considered to be mutable if a new value is stored into it, as well as if any of its reachable variables are mutable. The system and method uses a static analysis algorithm which can be applied to any software component rather than whole programs. The analysis classifies fields and classes as either mutable or immutable. In order to facilitate open-world analysis, the algorithm identifies situations that expose variables to potential modification by code outside the component, as well as situations where variables are modified by the analyzed code. An implementation of the analysis is presented which focuses on detecting mutability of class variables, so as to avoid isolation problems. The implementation incorporates intra- and inter-procedural data-flow analyses and is shown to be highly scalable. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the algorithms.
Owner:IBM CORP
Filtered cigarette incorporating a breakable capsule
ActiveUS7793665B2Ensure maintenanceTobacco treatmentPaper/cardboard wound articlesBiomedical engineeringFilter element
A filtered cigarette possesses at least one breakable capsule in its filter element. The filter element can possess a central cavity extending from the cigarette tobacco rod towards the middle of the filter element. The central cavity may be defined by an inner filter portion. The inner filter portion can be surrounded by an outer filter portion comprised of filter tow material that is generally permeable to the smoke generated by the cigarette. At least one breakable capsule is disposed in the central cavity of the filter element. The breakable capsules are spherical in shape, and are composed of a gelatin outer shell that encloses a payload of triglycerides and flavoring agents. The breakable capsules are adapted to rupture in response to pressure applied by the smoker to the outside region of the filter element.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
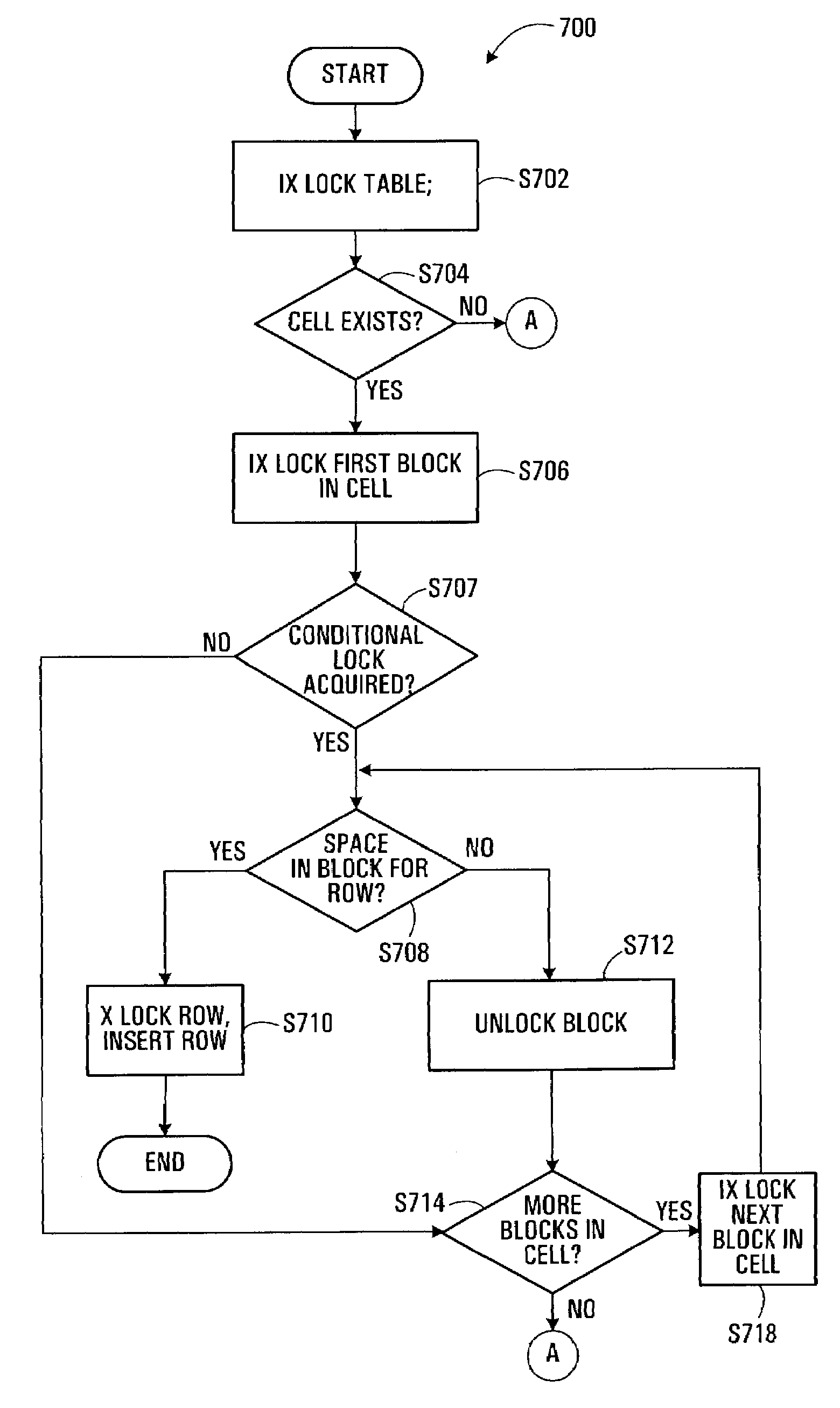
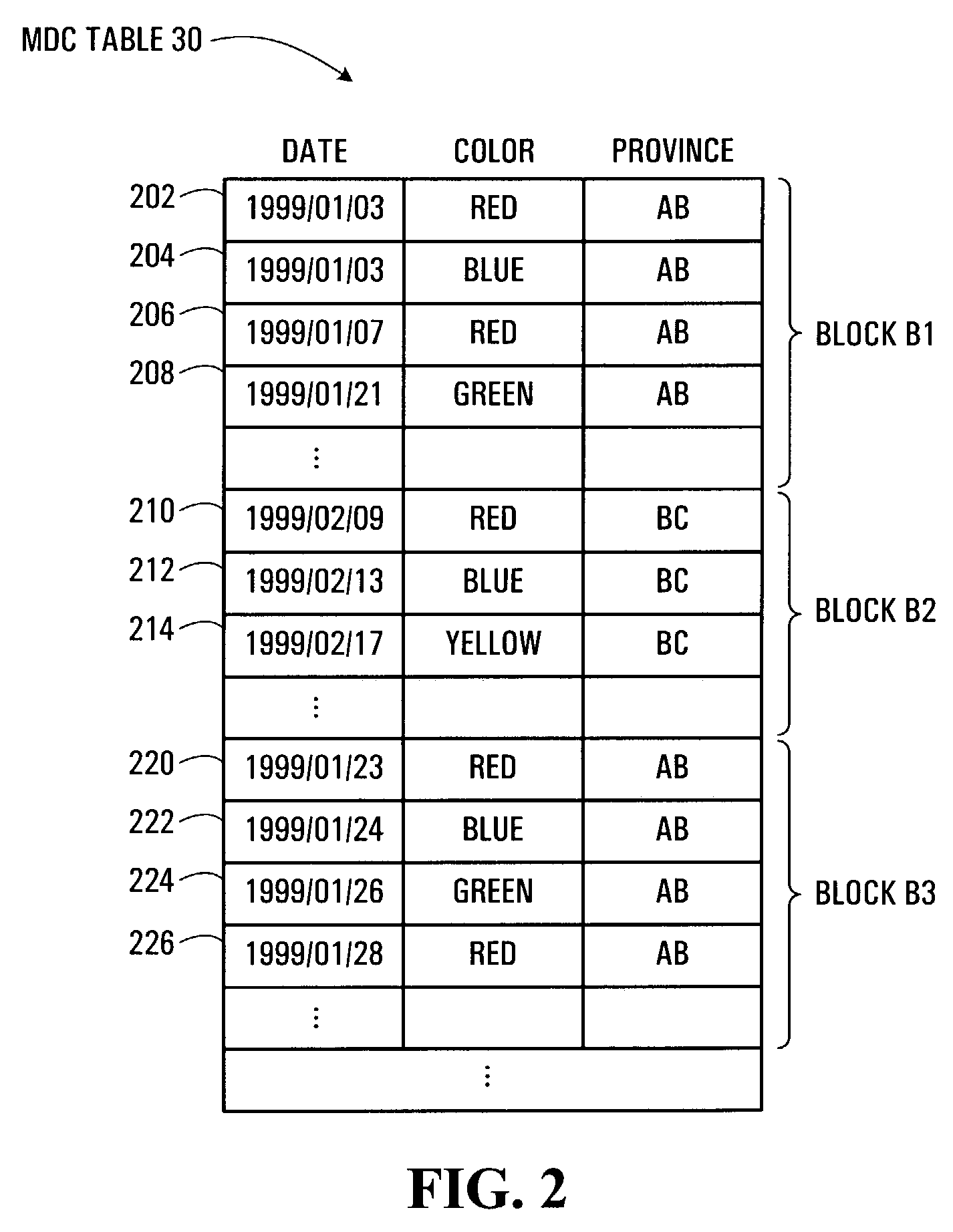
System and method for a multi-level locking hierarchy in a database with multi-dimensional clustering
InactiveUS7236974B2Avoiding undue locking overheadAvoid overheadData processing applicationsMulti-dimensional databasesGranularityRelational database
A multi-level locking hierarchy for a relational database includes a locking level applied to a multi-dimensionally clustering table, a locking level applied to blocks within the table, and a locking level applied to rows within the blocks. The hierarchy leverages the multi-dimensional clustering of the table data for efficiency and to reduce lock overhead. Data is normally locked in order of coarser to finer granularity to limit deadlock. When data of finer granularity is locked, data of coarser granularity containing the finer granularity data is also locked. Block lock durations may be employed to ensure that a block remains locked if any contained row remains locked. Block level lock attributes may facilitate detection of at least one of a concurrent scan and a row deletion within a block. Detection of the emptying of a block during a scan of the block may bar scan completion in that block.
Owner:IBM CORP
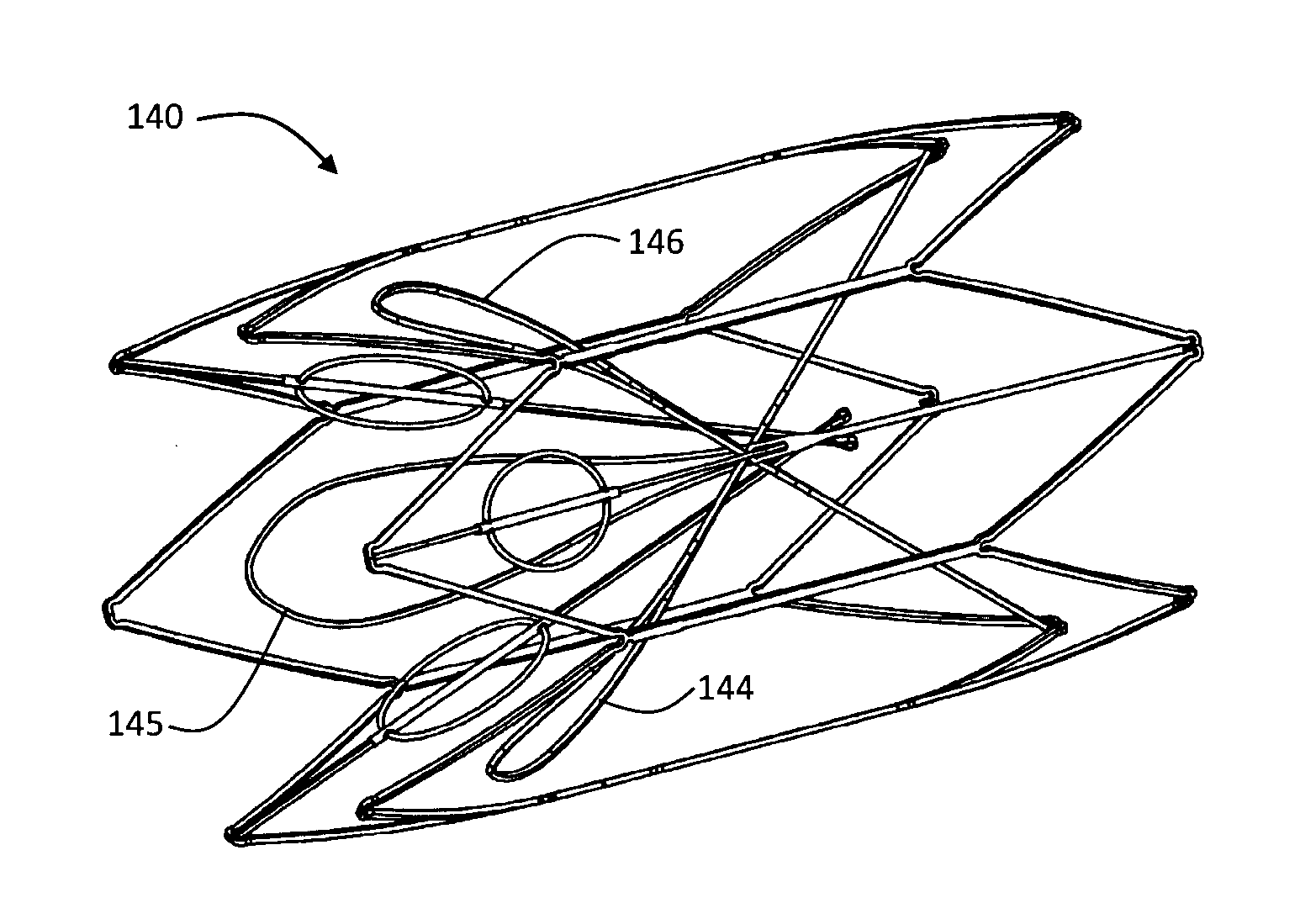
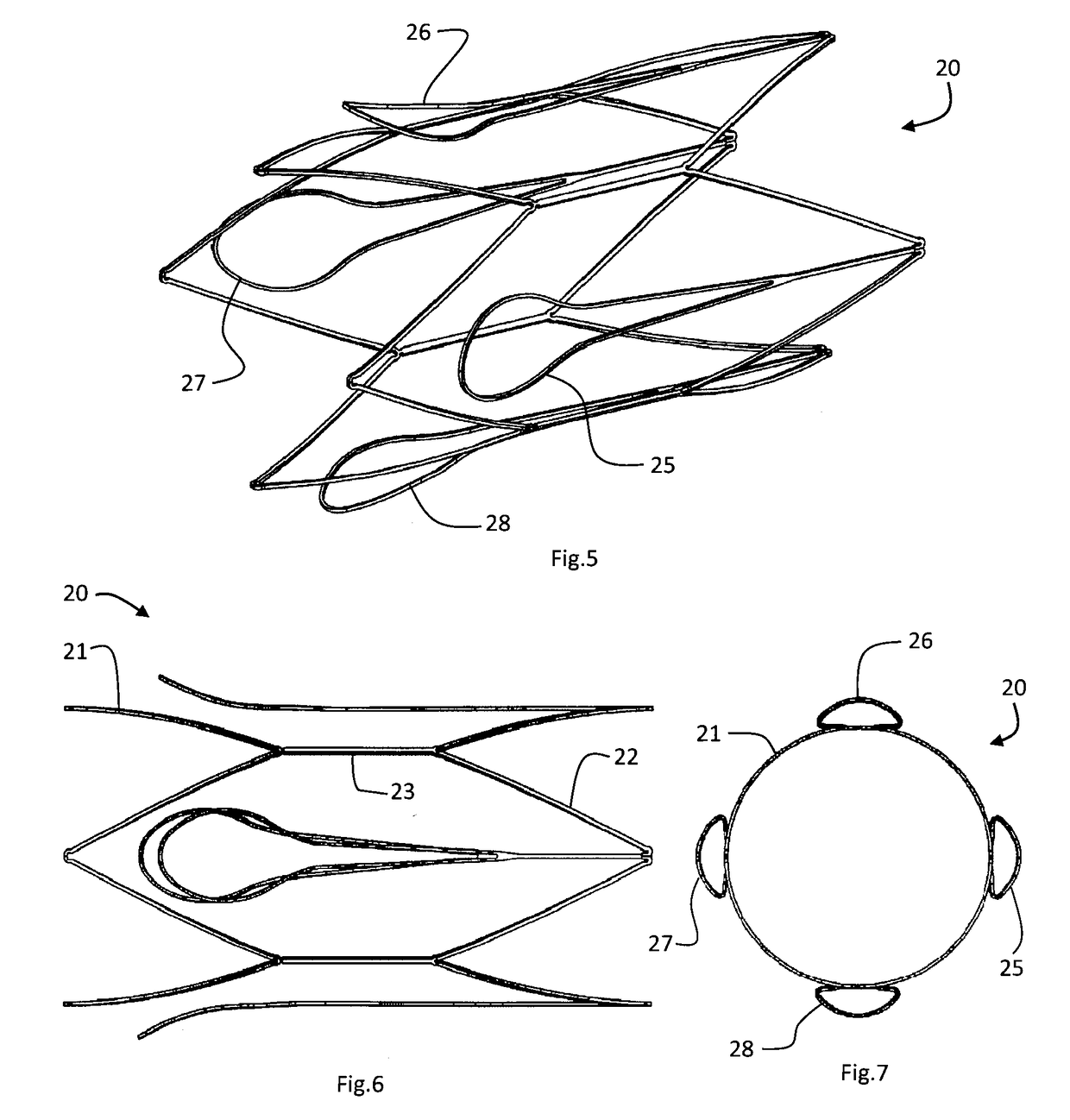
Vascular filter device
A vascular filter device comprises a support; and a filter comprising one or more filter elements configured to capture thrombus passing through a blood vessel. A holder holds the filter in a closed filtering state and releases to convert the filter to an open state after a period of time. The filter is adapted to retain thrombus after said conversion. In one case the filter elements are arranged to remain in a closed state after release by the holder, because they are blocked by a retained clot from opening fully, and the filter elements are biased to the open state with a bias level which is counter balanced by force exerted by a retained clot under action of blood flow.
Owner:COVIDIEN GROUP +1
Electrically isolated vertical light emitting diode structure
ActiveUS20100201280A1Improve thermalImprove conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIsolation layerProjection system
A light emitting device is provided having high luminous output while maintaining high wall plug efficiency, wherein the high thermal and electrical conductivity paths of the device are separated during the semiconductor wafer and die level manufacturing step. The device includes an electrical conducting mirror layer, which reflects at least 60% of generated light incident on it, and an isolation layer having electrical insulating properties and thermal conducting properties. A first electrode, which is not in contact with the main semiconductor layers of the device, is located on the mirror layer. A light emitting module, system and projection system incorporating the light emitting device are also described, as is a method of manufacture of the device.
Owner:LUMILEDS HLDG BV
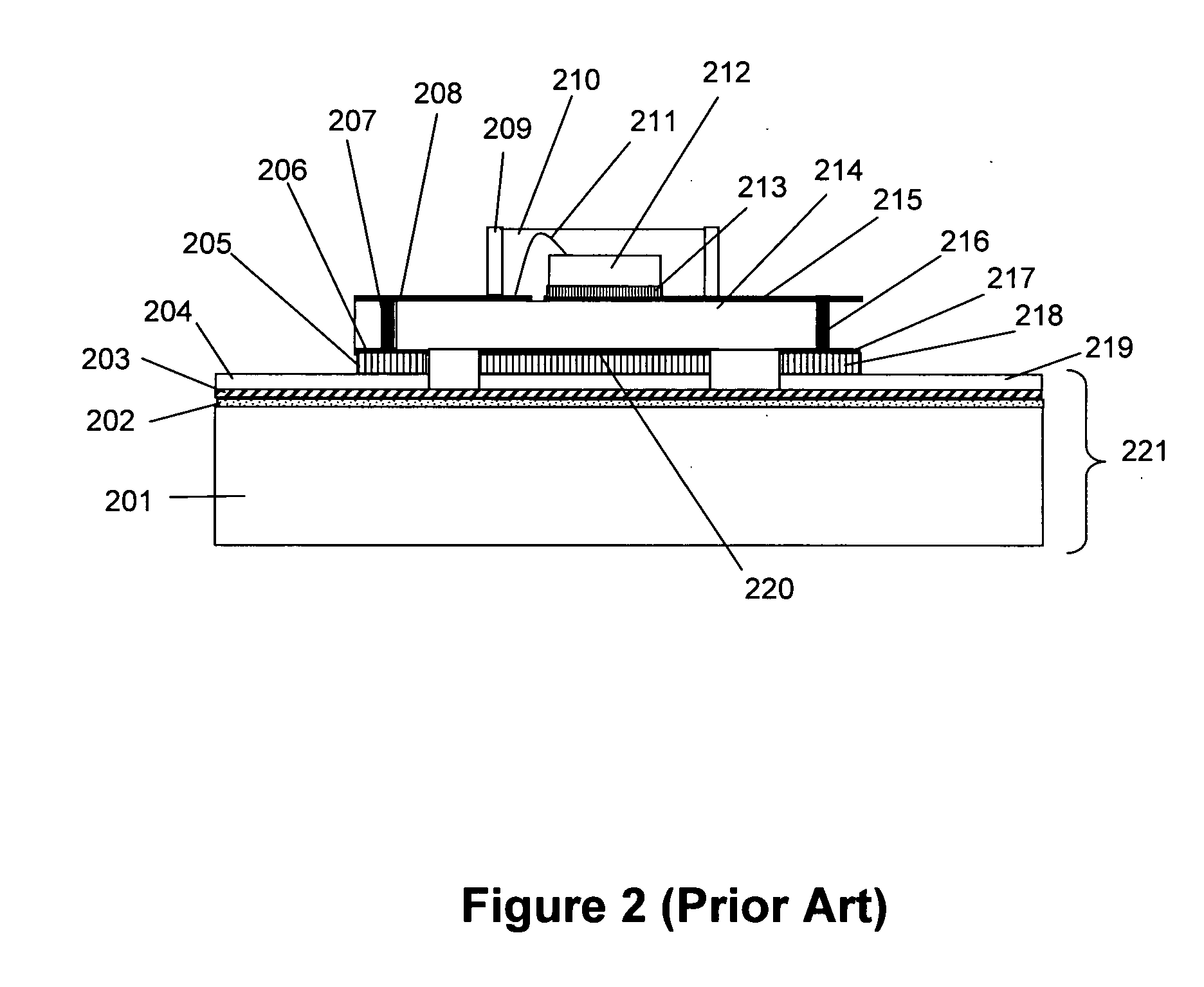
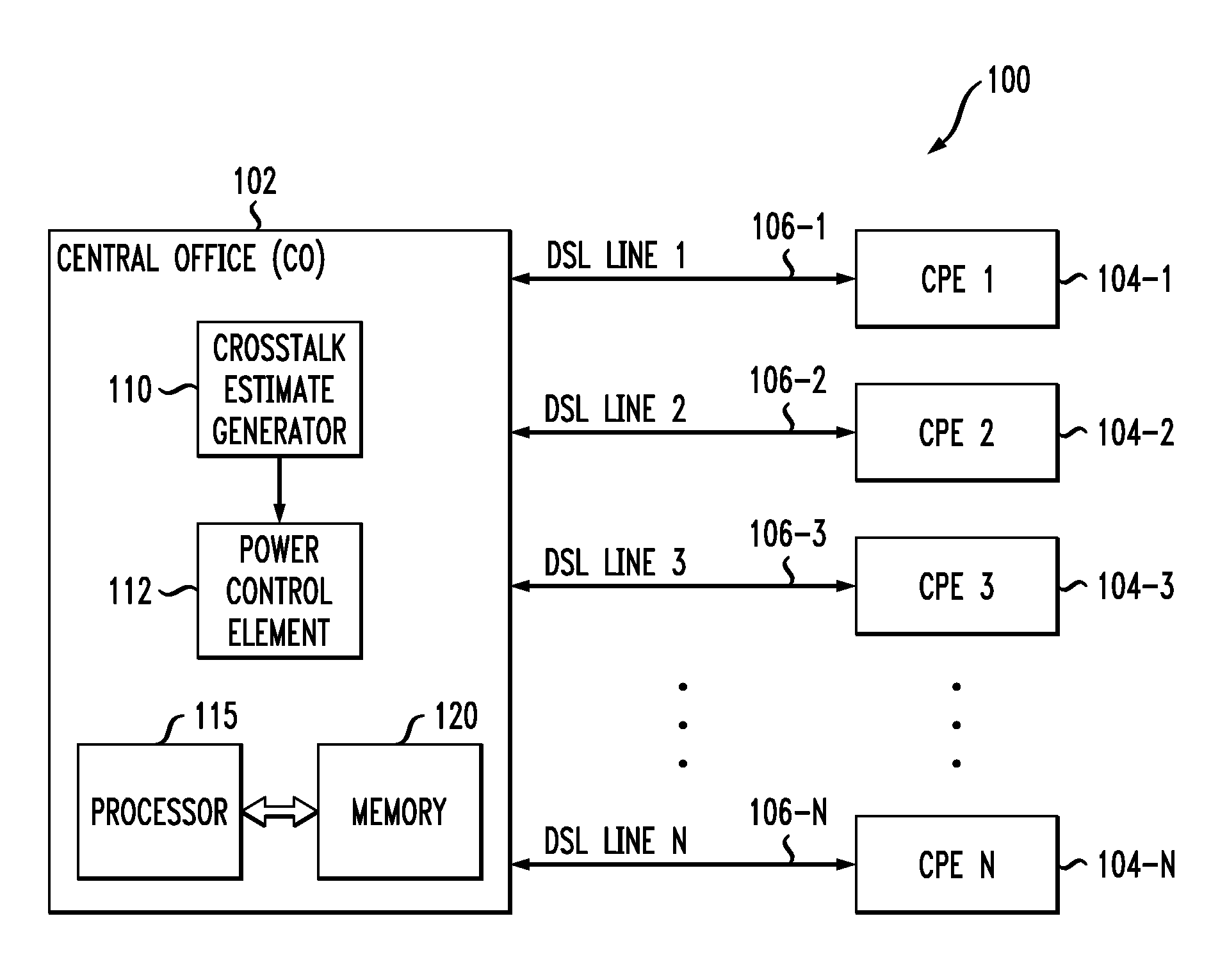
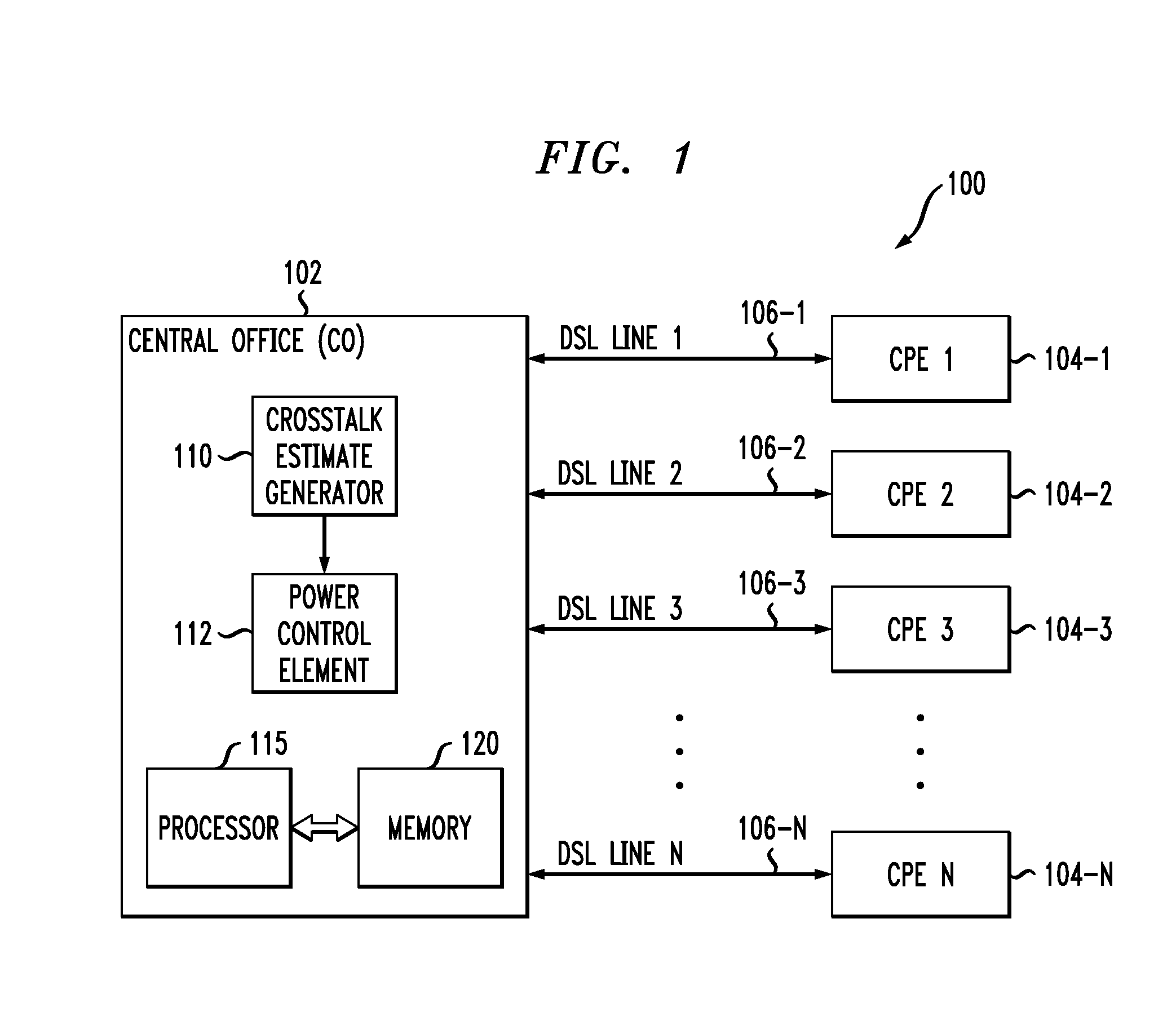
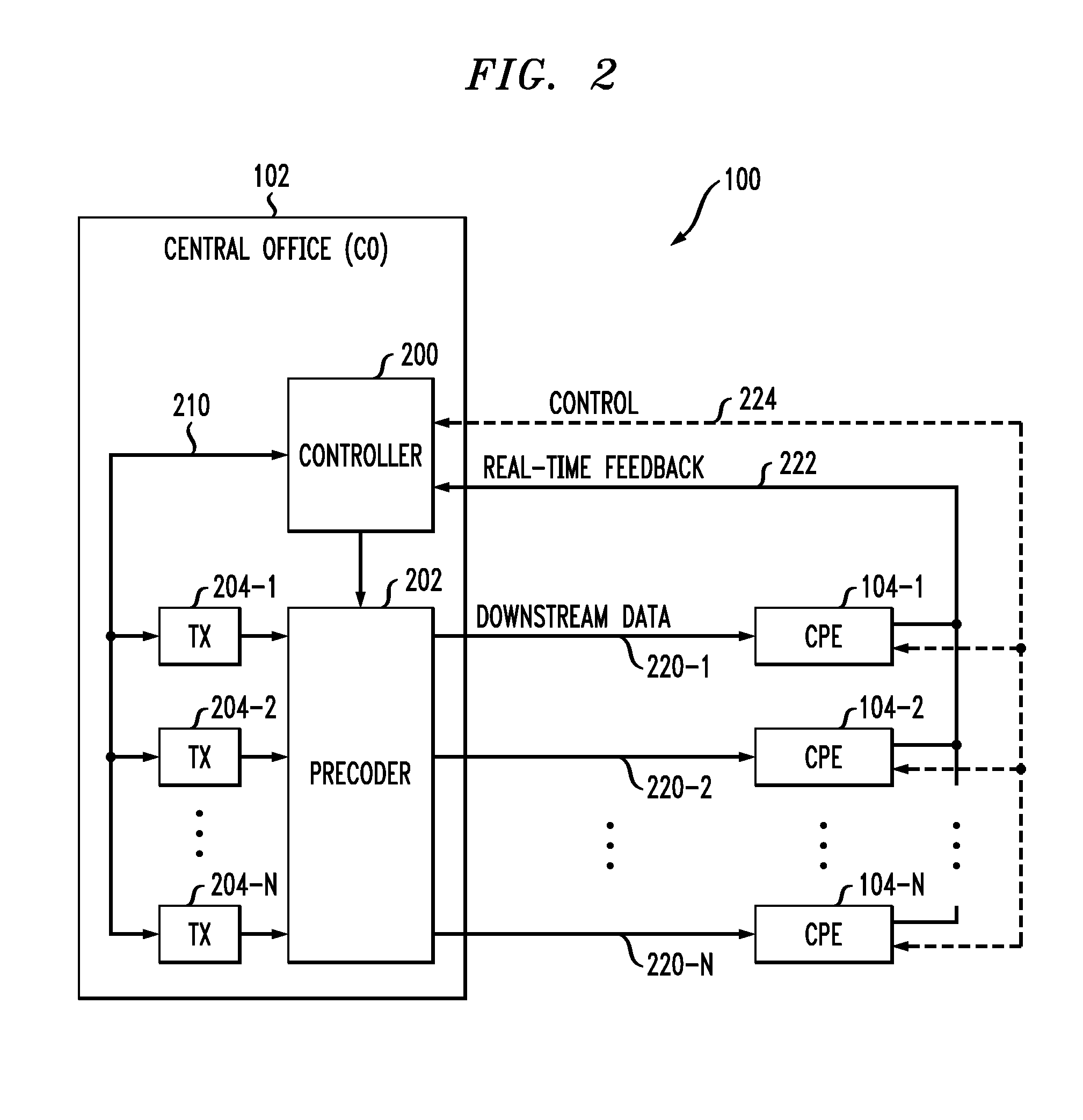
Crosstalk Estimation and Power Setting Based on Interpolation in a Multi-Channel Communication System
ActiveUS20100329444A1High speedMinimal impactTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstations coupling interface circuitsCommunications systemCrosstalk
An access node of a communication system comprises a plurality of transmitters adapted for communication with at least one receiver over a plurality of channels. The access node is operative to obtain estimated crosstalk coefficients between a joining channel and an active channel, and to set a power level of at least one signal transmitted over the joining channel based on the estimated crosstalk coefficients. The access node obtains the estimated crosstalk coefficients by first obtaining a subset of the estimated crosstalk coefficients and subsequently determining additional ones of the estimated crosstalk coefficients by applying an interpolation process to the estimated crosstalk coefficients in the subset. The access node sets the power level of the signal transmitted over the joining channel in a manner that ensures maintenance of a desired performance characteristic for the active channel.
Owner:RPX CORP
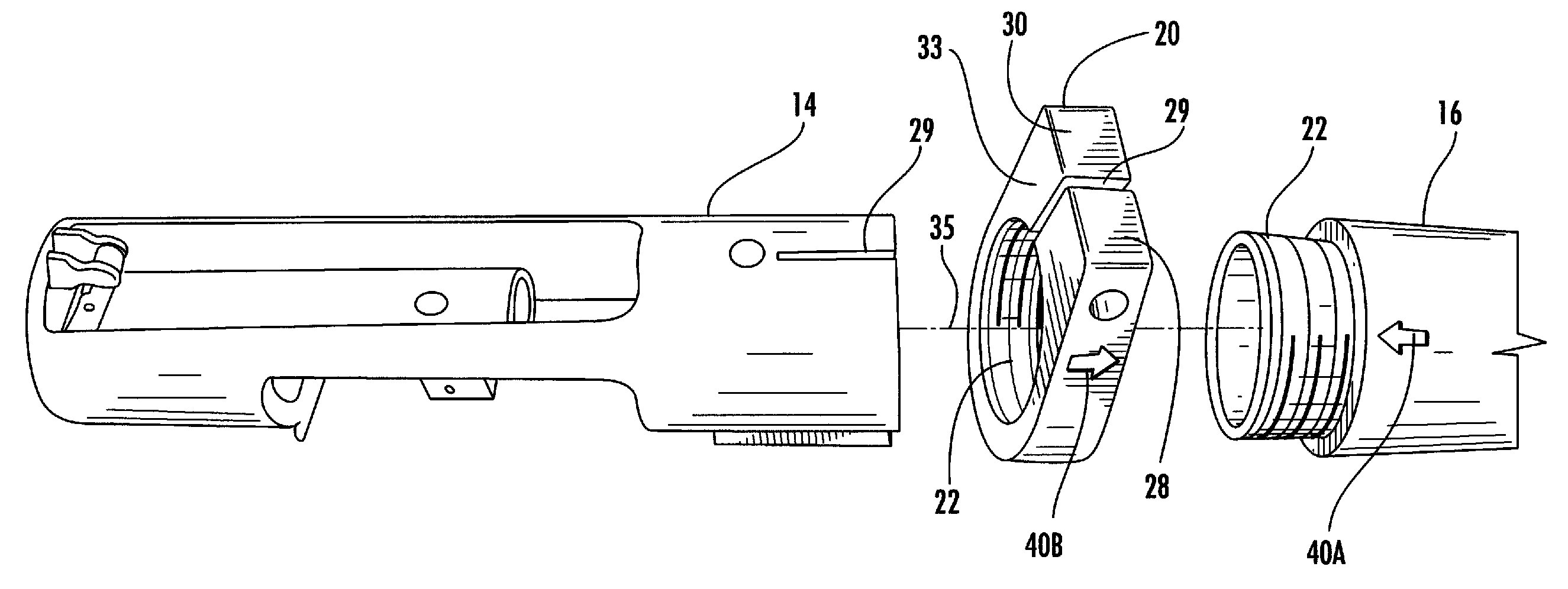
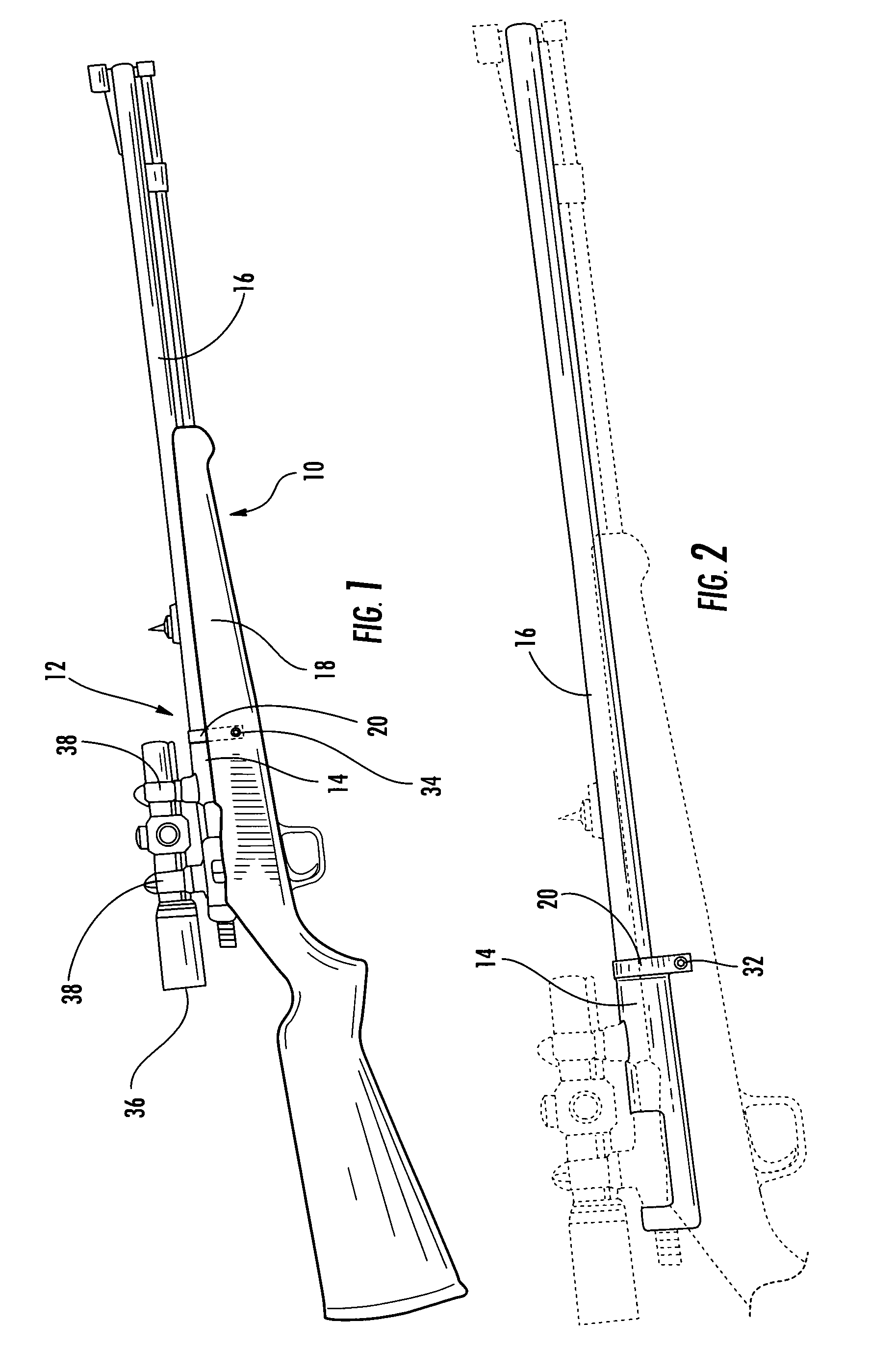
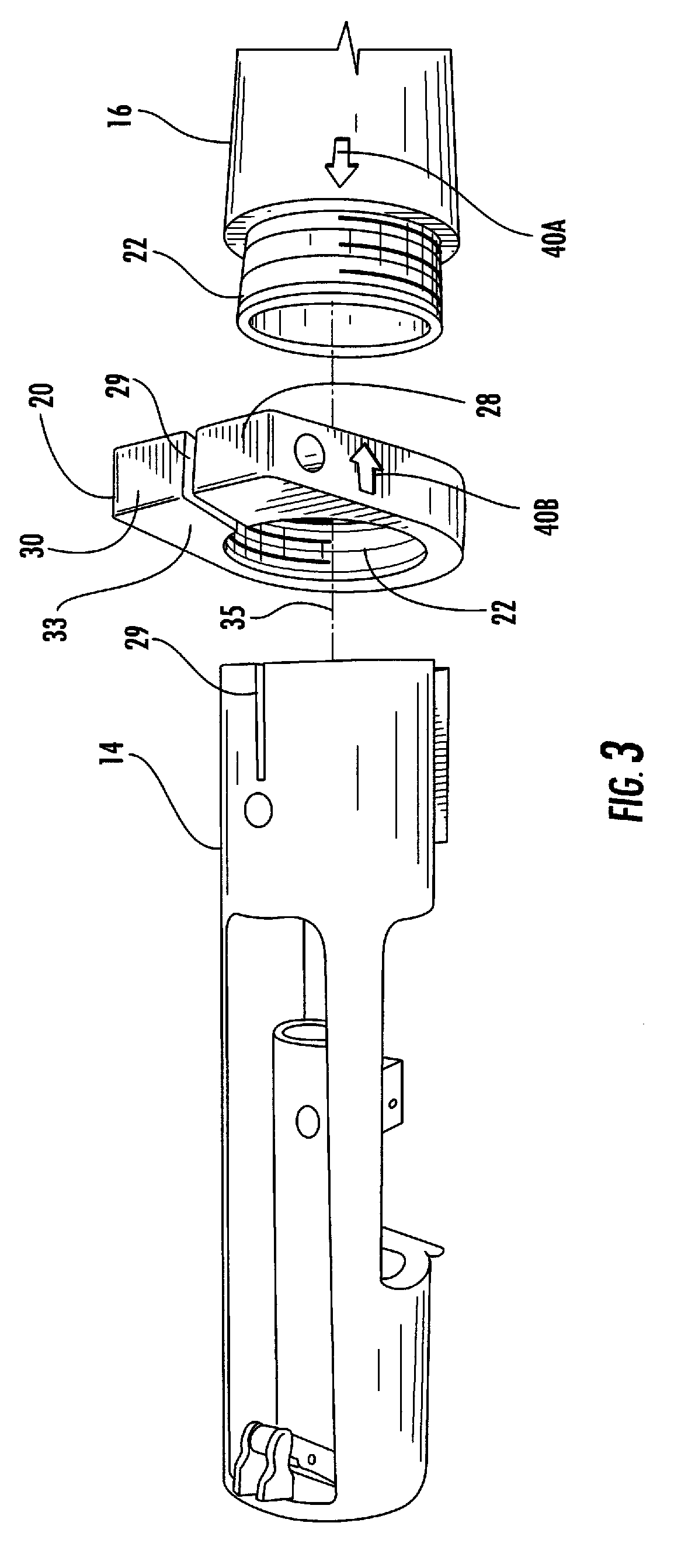
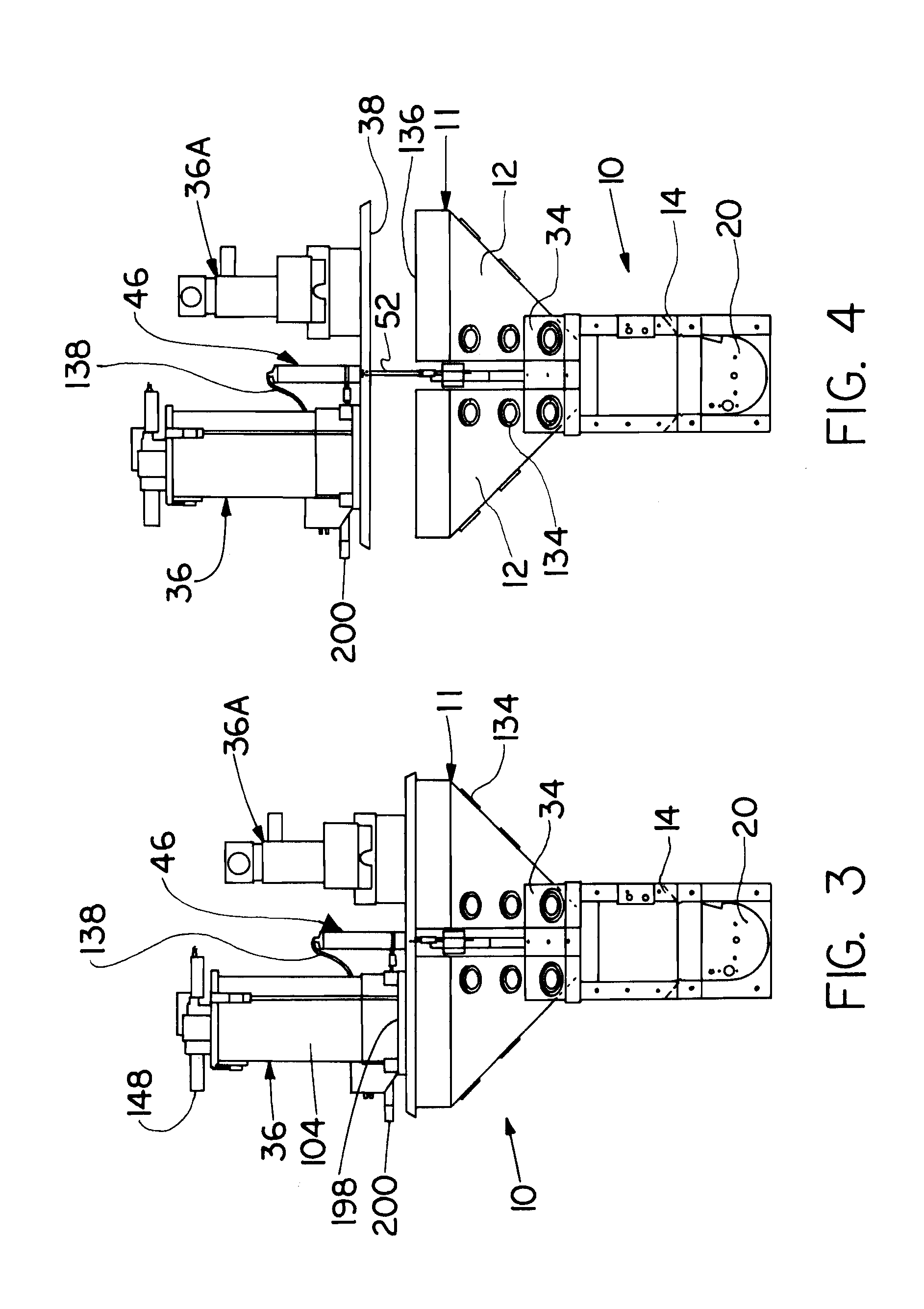
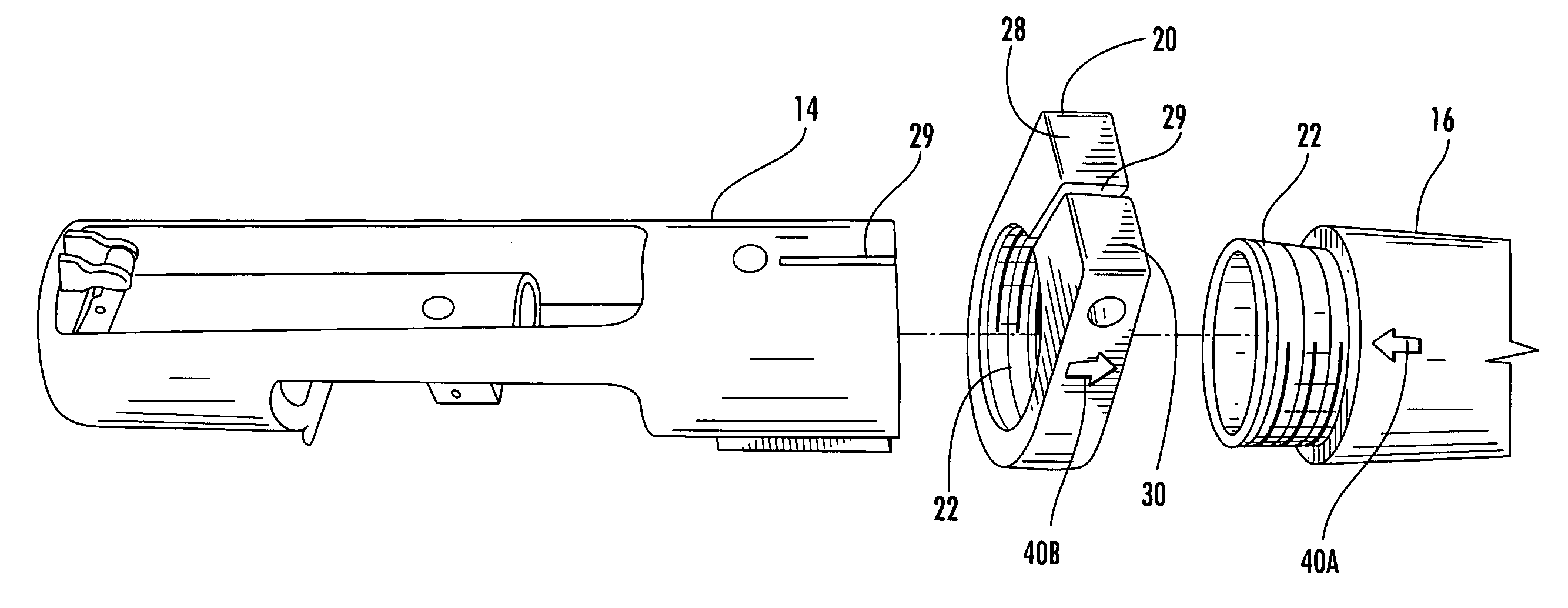
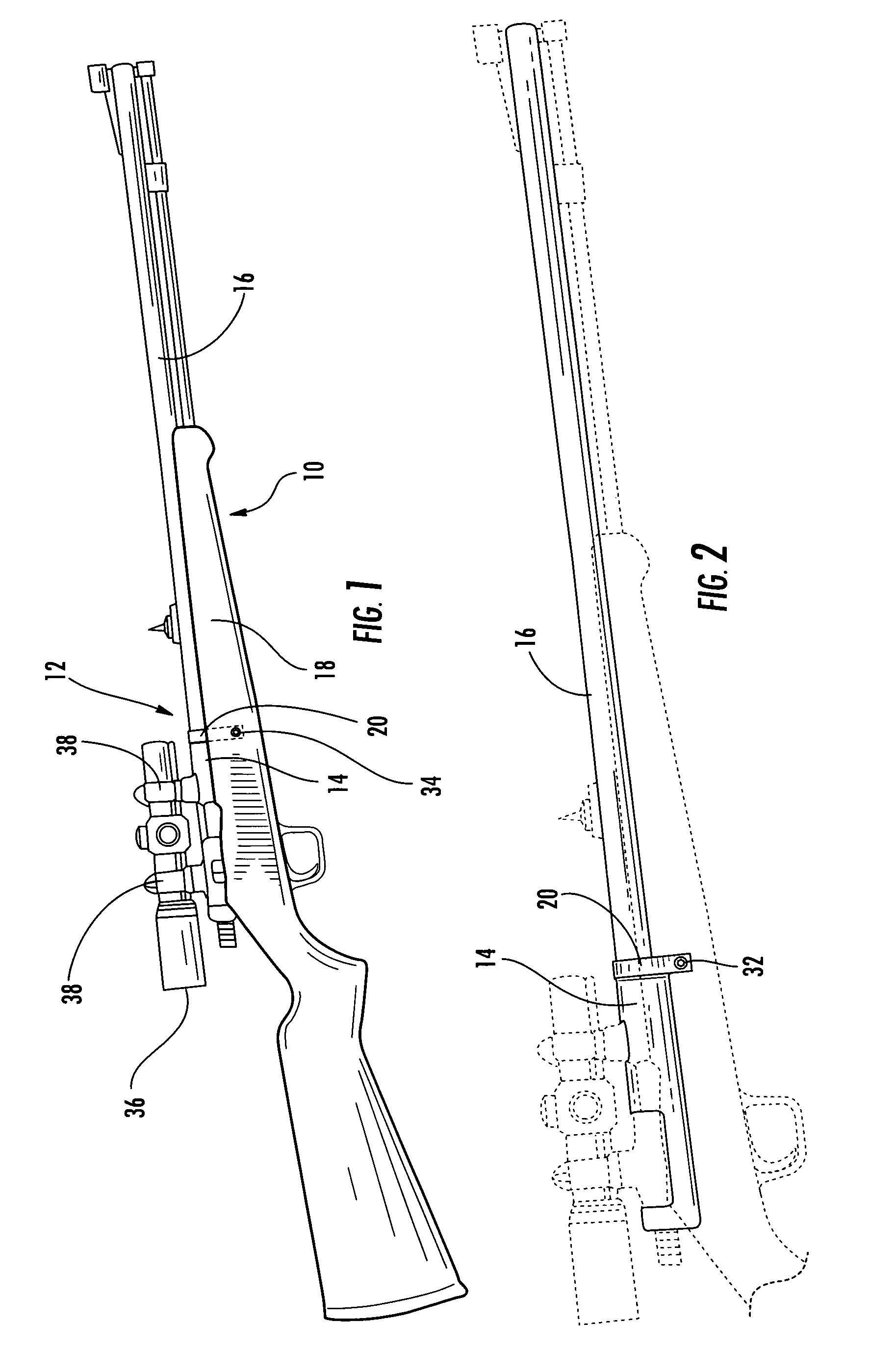
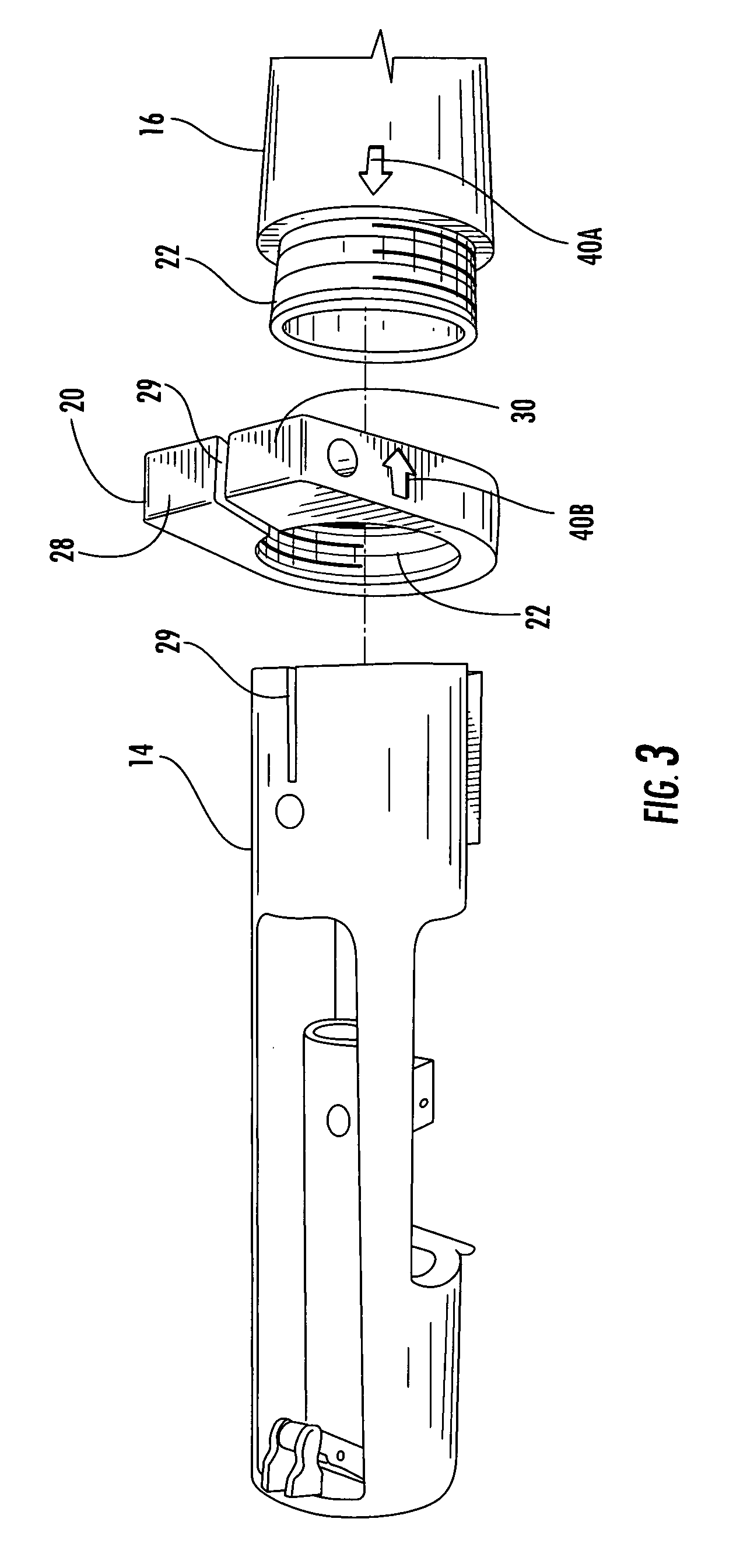
Interchangeable barrel system for rifles
InactiveUS7451564B2Maintaining repeatable accuracyEasy to replaceBarrel mountingField conditionsTelecommunications
A system for use with firearms which permits the ready exchange of barrels on a single action and stock assembly. The barrels may be quickly and easily exchanged under field conditions using a single simple tool and without removing the action and receiver from the firearm stock. Barrels of different calibers may be used on a single firearm leading to greater versatility. The system relies on a pinch lug or clamp attached to the receiver which will draw all barrels onto the receiver and into invariable coaxial alignment with the receiver and action thus insuring the bullet will always have the same trajectory.
Owner:FULL NELSON
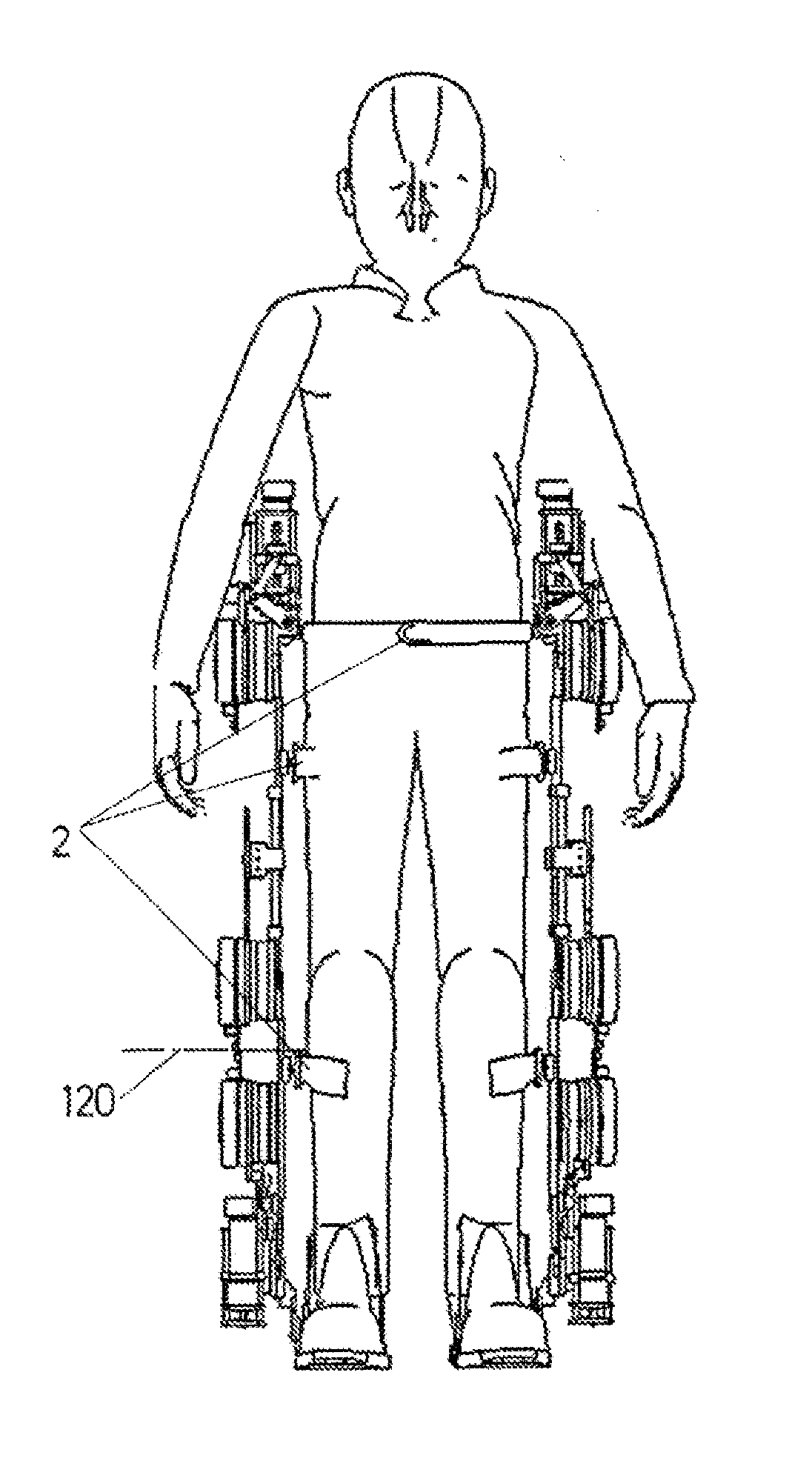
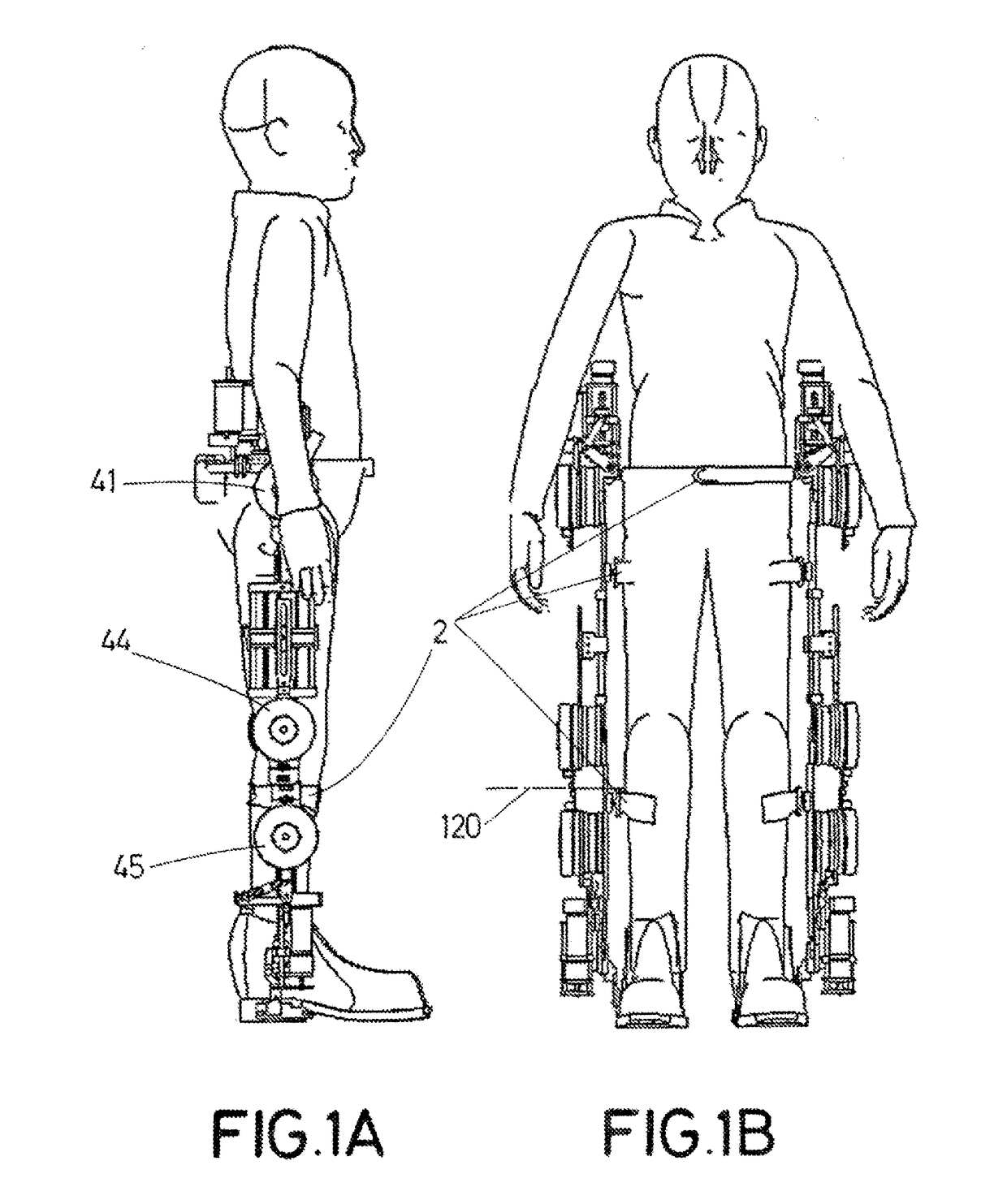
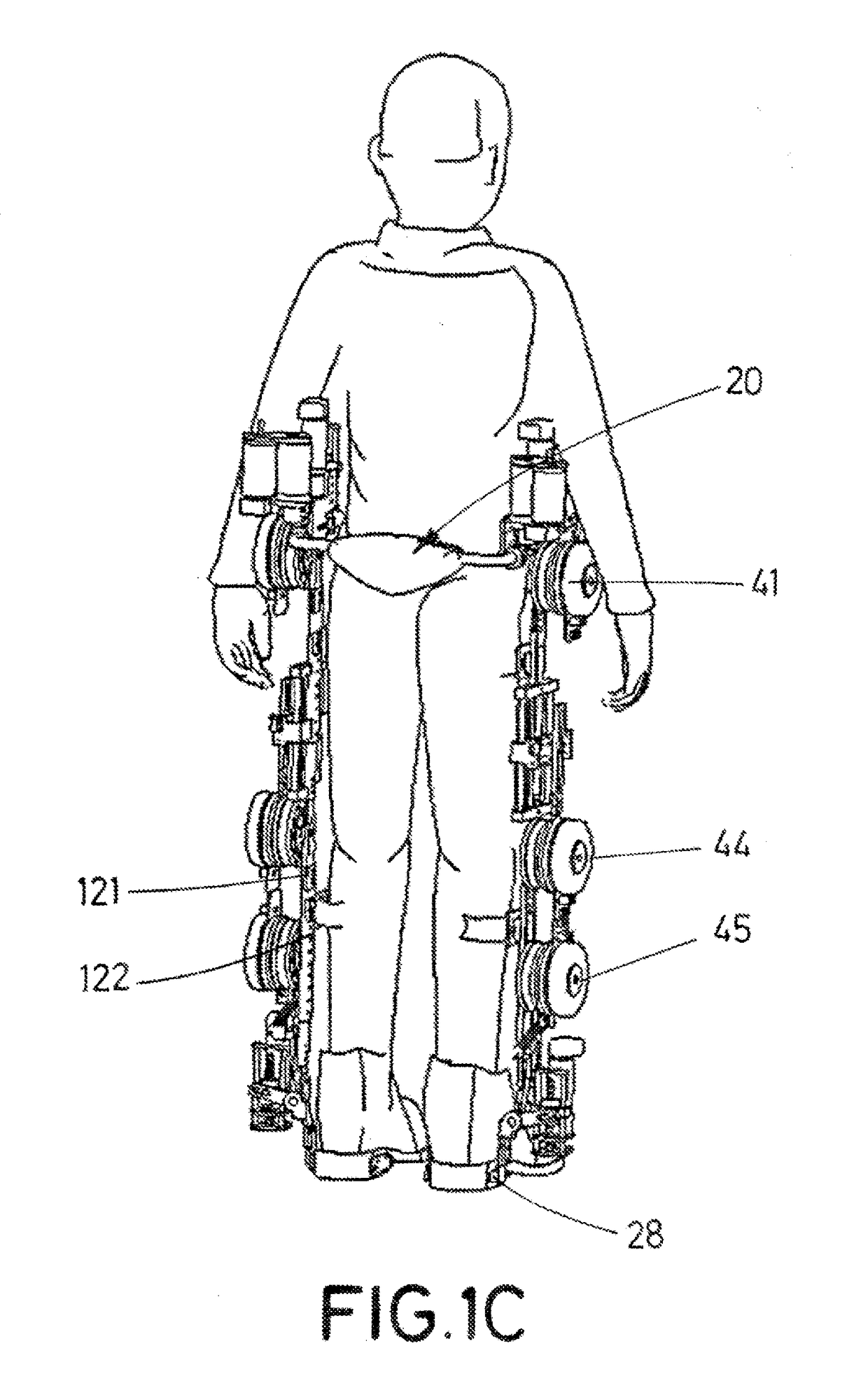
Exoskeleton for assisting human movement
ActiveUS20170340504A1Ensure maintenanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsSagittal planePhysiological movement
The invention relates to an exoskeleton for assisting human movement, which can be fitted to the user in terms of dimensions, tension and ranges of joint motion, either manually or automatically. Said exoskeleton can be fitted to the user in the anteroposterior direction in the sagittal plane, with the user in a horizontal or sitting position, without requiring a functional transfer. The exoskeleton has a modular design which is compatible with human biomechanics and reproduces a natural and physiological movement in the user, with up to 7 actuated and controlled degrees of movement per limb, ensuring that the user maintains equilibrium during locomotion.
Owner:MARSI BIONICS +2
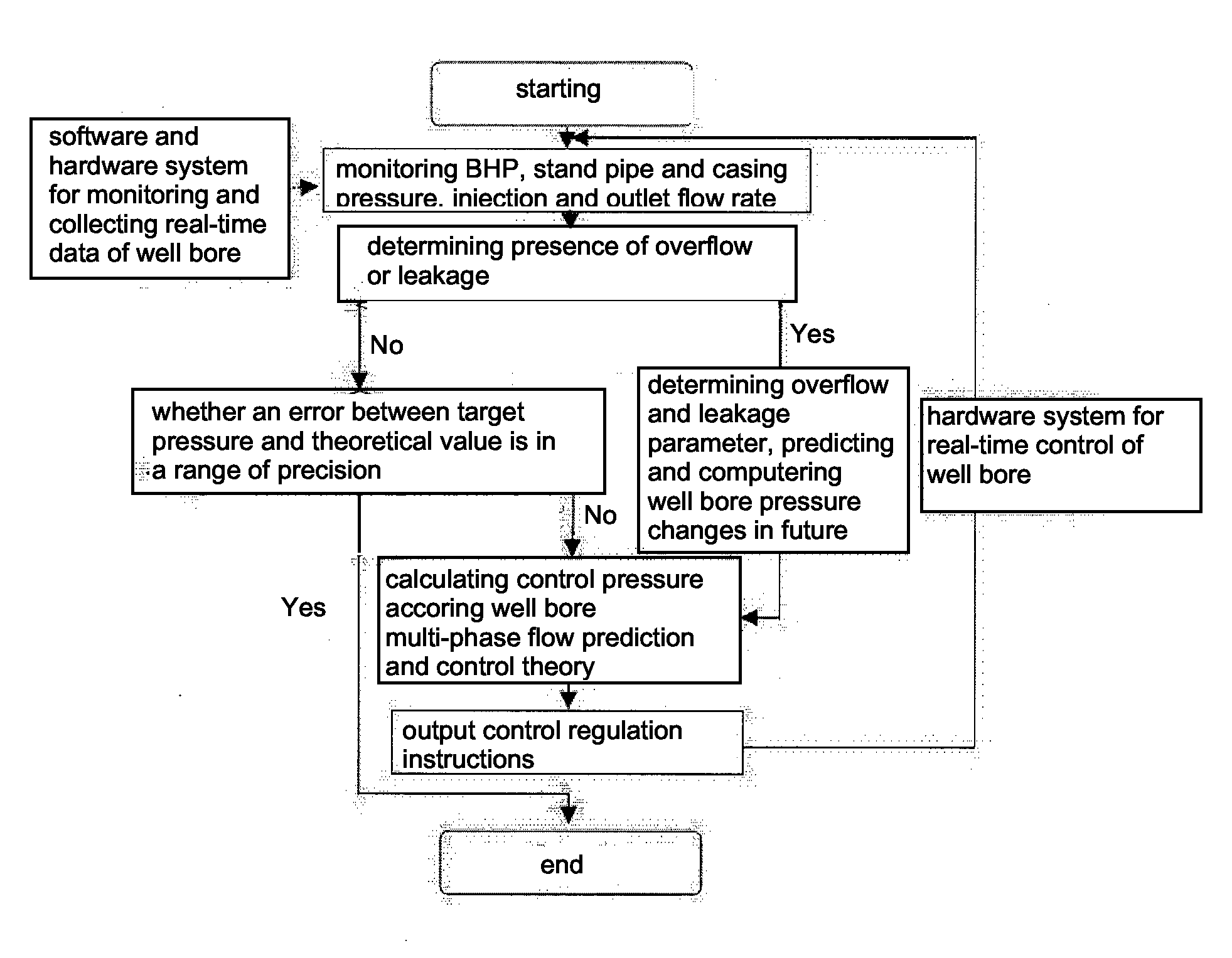
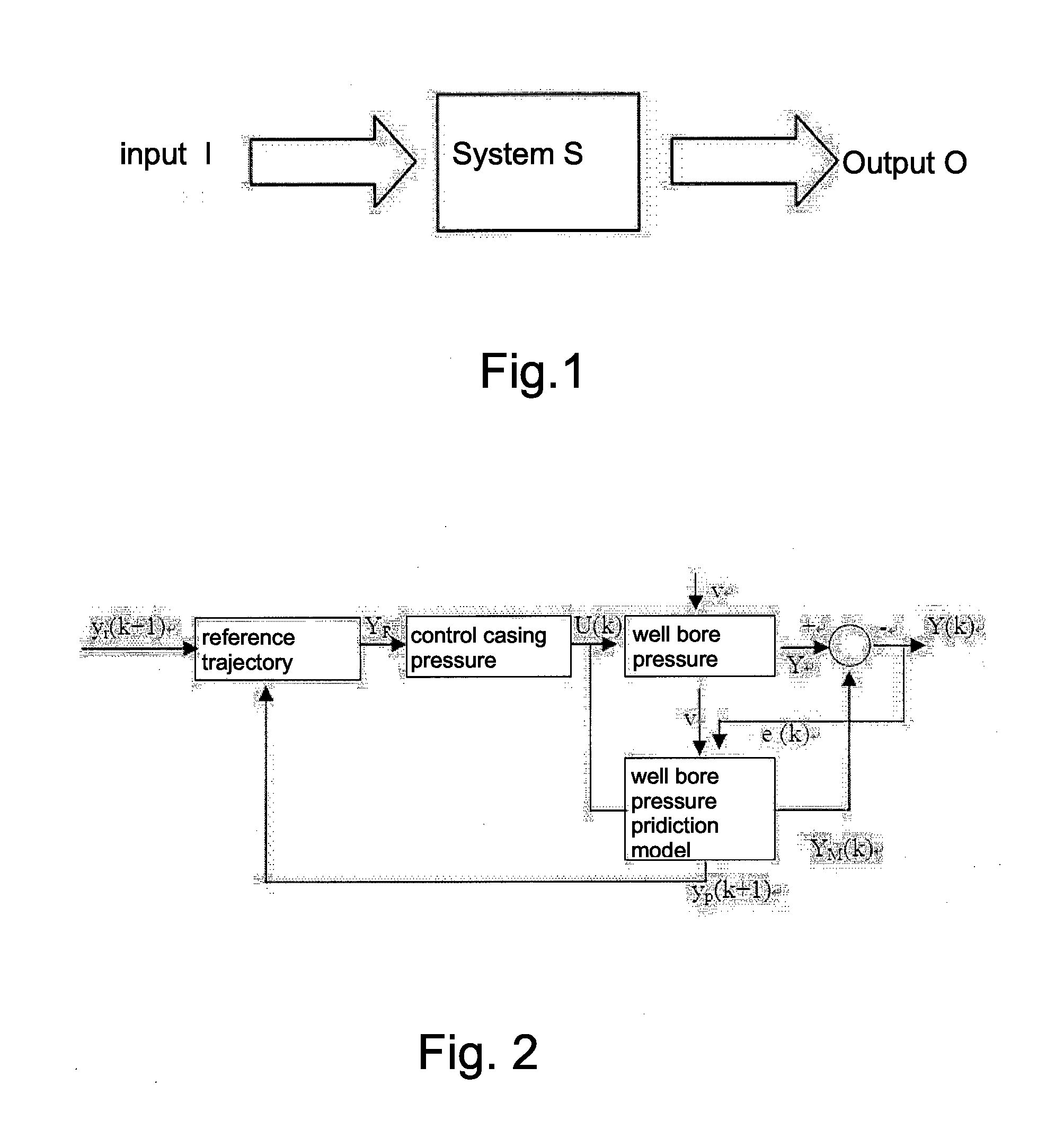
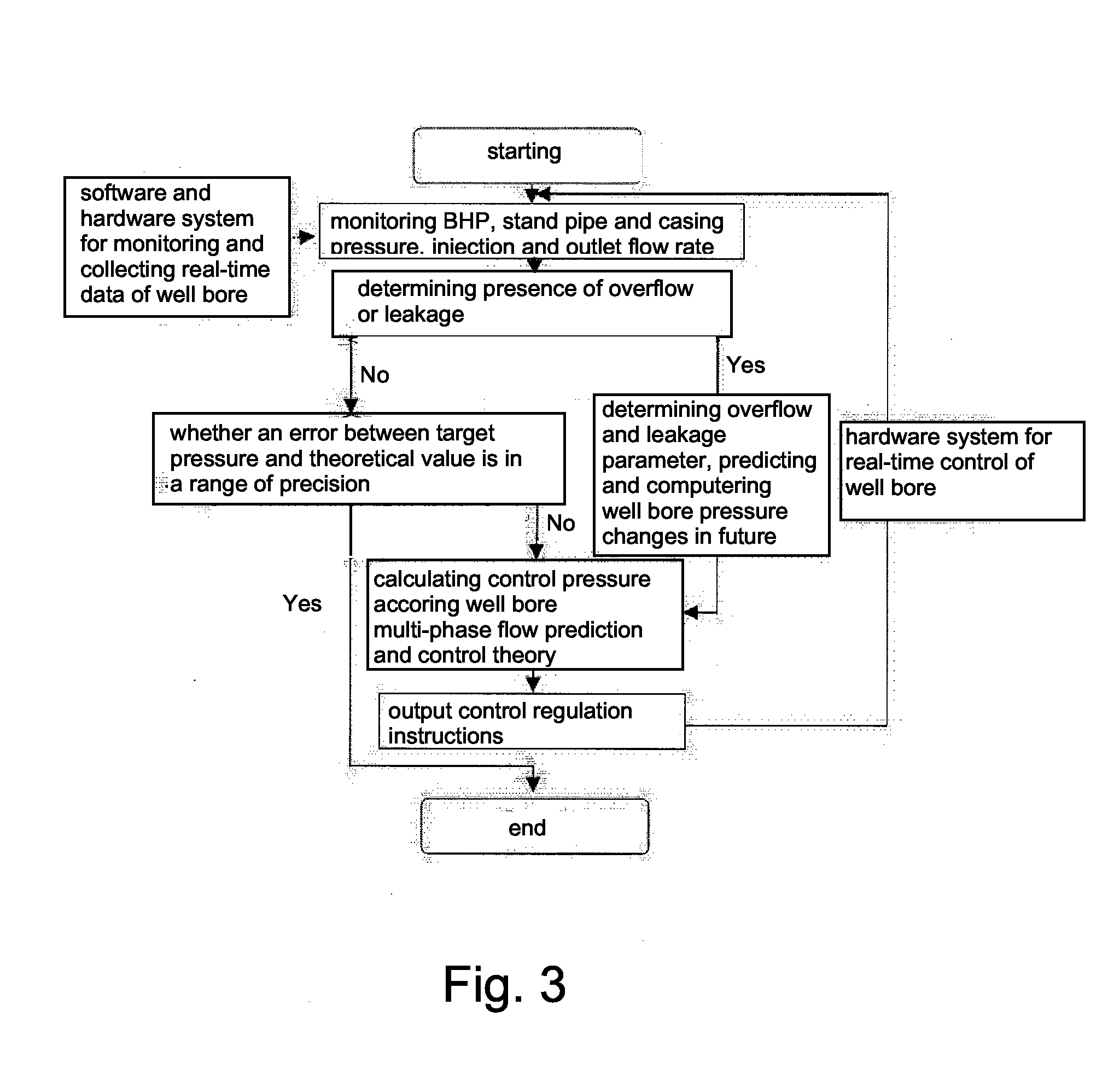
Method for controlling well bore pressure based on model prediction control theory and systems theory
ActiveUS20140262246A1Easy to controlReducing underground complex accidentsSurveyConstructionsPresent methodStart time
A method for controlling well bore pressure based on model prediction control theory and systems theory, which belongs to the field of well bore pressure control technique, includes: detecting a well bottom pressure, a stand pipe pressure, a casing pressure, an injection flow rate and an outlet flow rate during construction process, and determining the presence of overflow or leakage; if there is no overflow or leakage, then fine-adjusting the wellhead casing pressure according to the slight fluctuations of the well bottom pressure, the stand pipe pressure or the casing pressure, ensuring that the well bottom pressure, the stand pipe pressure or the casing pressure are at a set value; if there is overflow or leakage, then using a well bore multi-phase flow dynamic model to simulate and calculate the overflow or leakage position and starting time of the overflow or leakage, predicting the variation over a future time period of the well bore pressure in the well drilling process, and utilizing an optimization algorithm to calculate the control parameter under a minimum of an actual well bottom pressure difference during the future period; and repeating the optimization process for the next time period after a first control parameter is selected and set. The present method enables the well bore pressure to be controlled within the allowable fluctuation range of a project, thus achieving precise pressure control.
Owner:CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP CHUANQING DRILLING ENG CO LTD
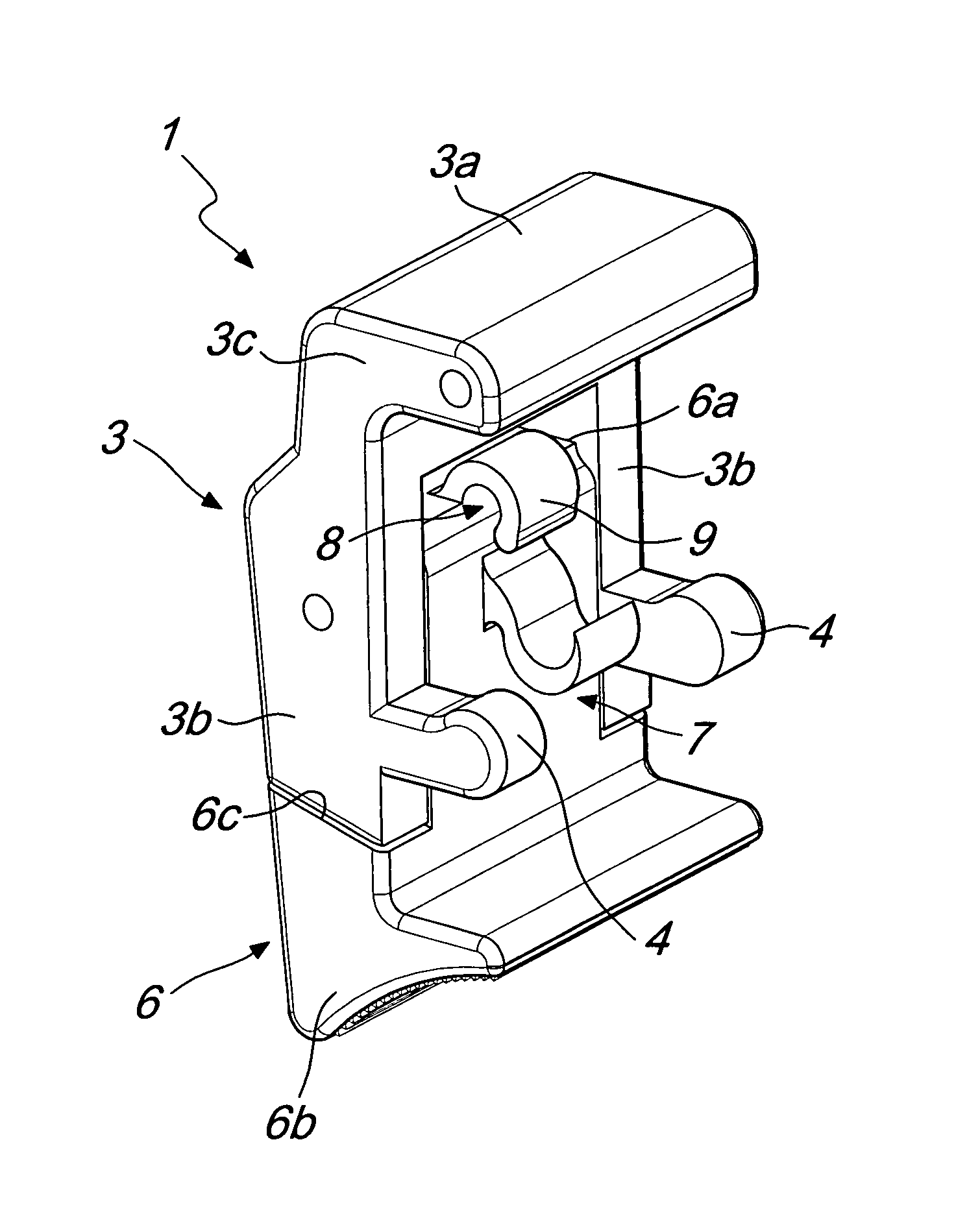
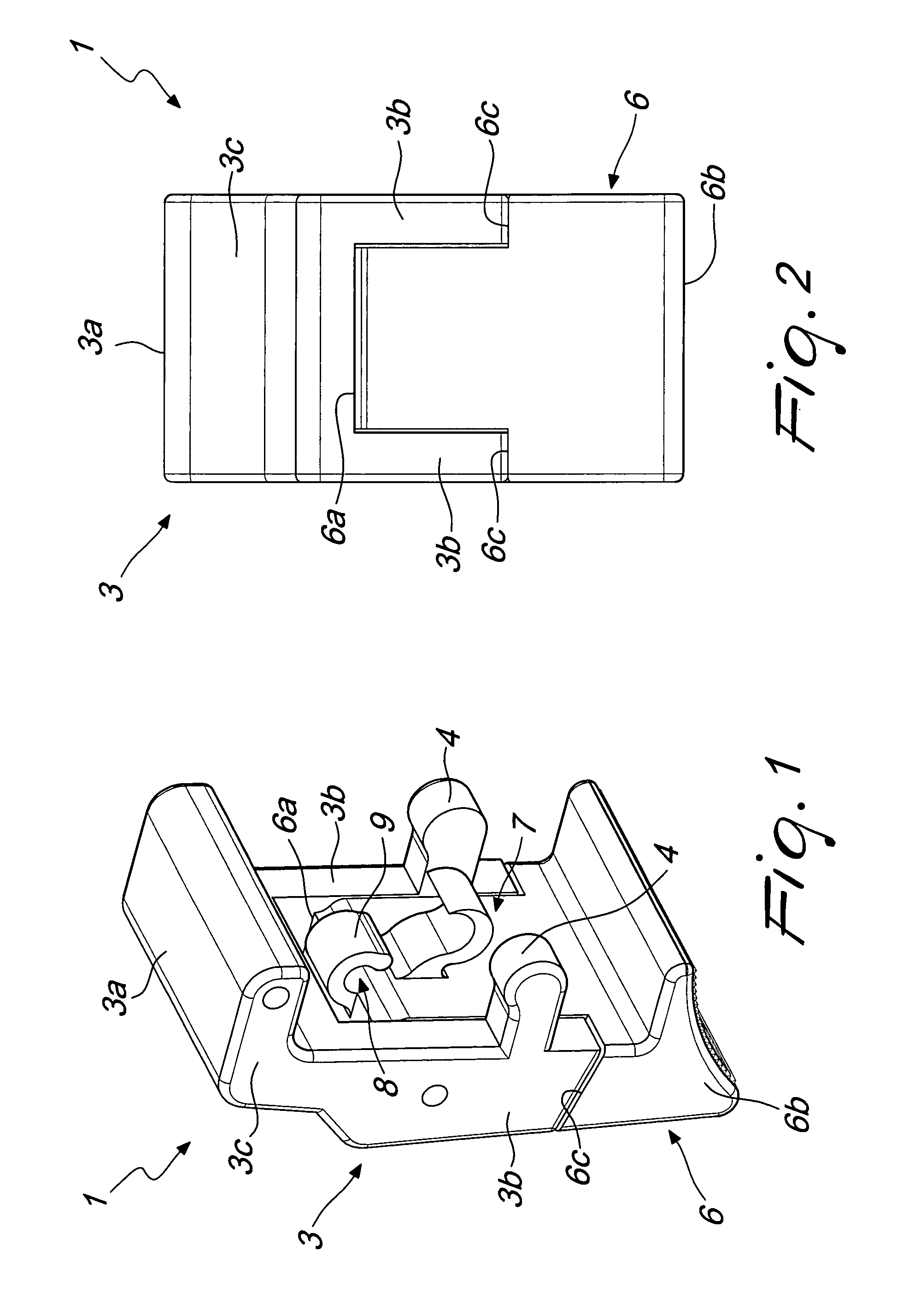
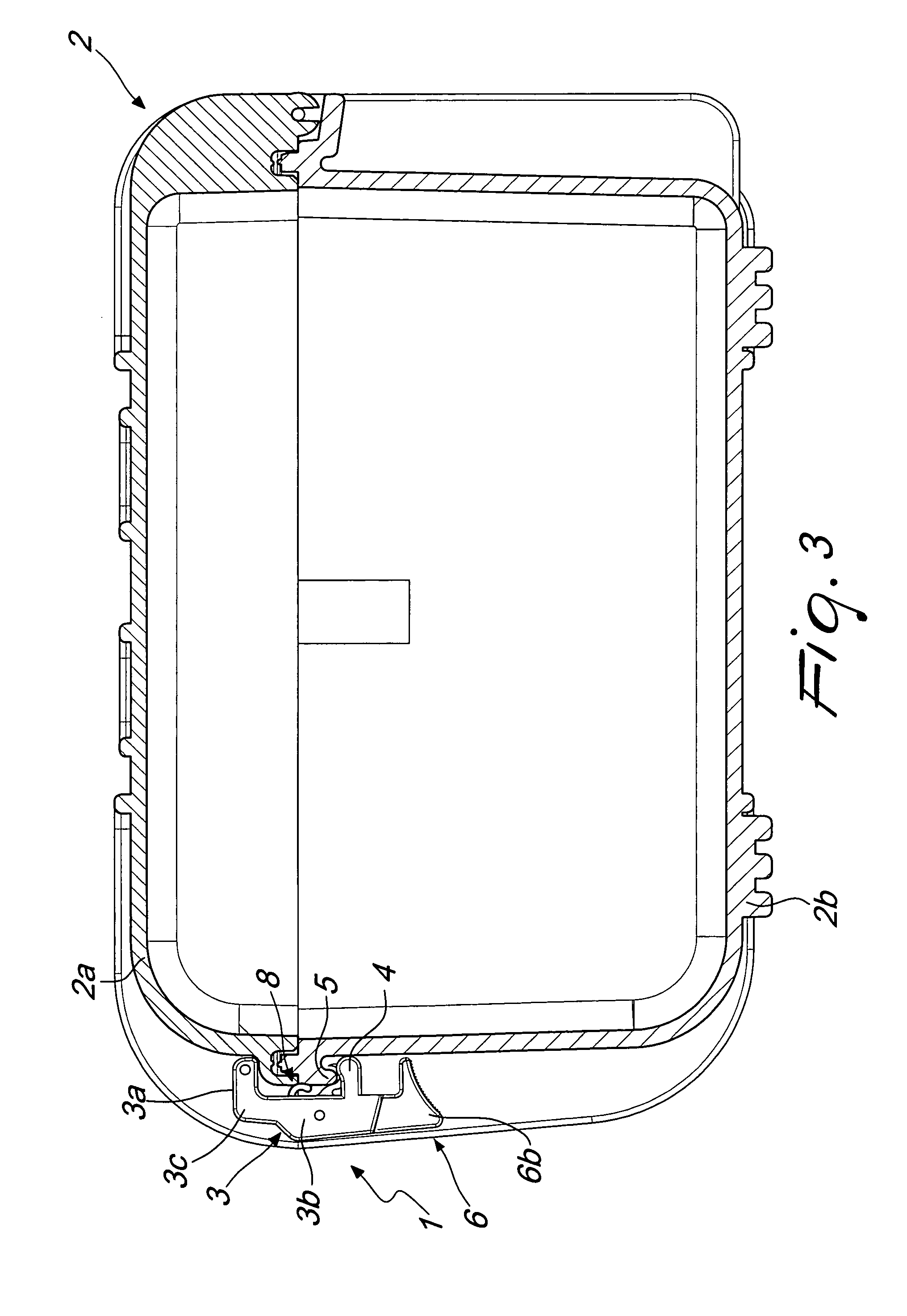
Lock, particularly for suitcases, trunks and the like
InactiveUS8328247B2Easy to solveEnsure maintenanceBuilding locksWing fastenersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A lock for carrying cases comprises at least one block hinged at a first end to a first half-shell. The block is rotatable about a pivoting axis from a closed configuration, in which at least one tab that protrudes on the opposite side with respect to the pivoting axis engages elastically and detachably a perimetric ridge that protrudes from a second half-shell, to couple the first half-shell to the second half-shell, to an opening configuration, in which the tab is disengaged from the ridge, and vice versa. The lock comprises a lever, which is hinged to the block at a first end portion thereof and can be gripped at a second end portion thereof, which is opposite to the first one, for the rotation of the block and the disengagement of the tab from the ridge.
Owner:G T LINE
Separator
ActiveUS20140165977A1Improve efficiencyReduce sealCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentFilter mediaEngineering
A separator has a first inlet arranged to receive a fluid stream, and first and second separation stages coupled together in series; A pump coupled to the second separation stage generates an area of reduced pressure to draw the fluid stream through the first and second separation stages. One of the stages includes a variable impactor separator comprising a first chamber arranged to receive the fluid stream, and a second chamber coupled to the first chamber through an aperture to accelerate the first fluid stream. The stream is incident upon an impaction surface to separate contaminants from the fluid stream. An actuator adjusts the open area of the aperture according to a pressure differential between fluid pressure in the first chamber and a reference fluid pressure in a third chamber. The other of the separation stages is a second variable impactor separator or a filter media.
Owner:PARKER HANNIFIN MFG LTD
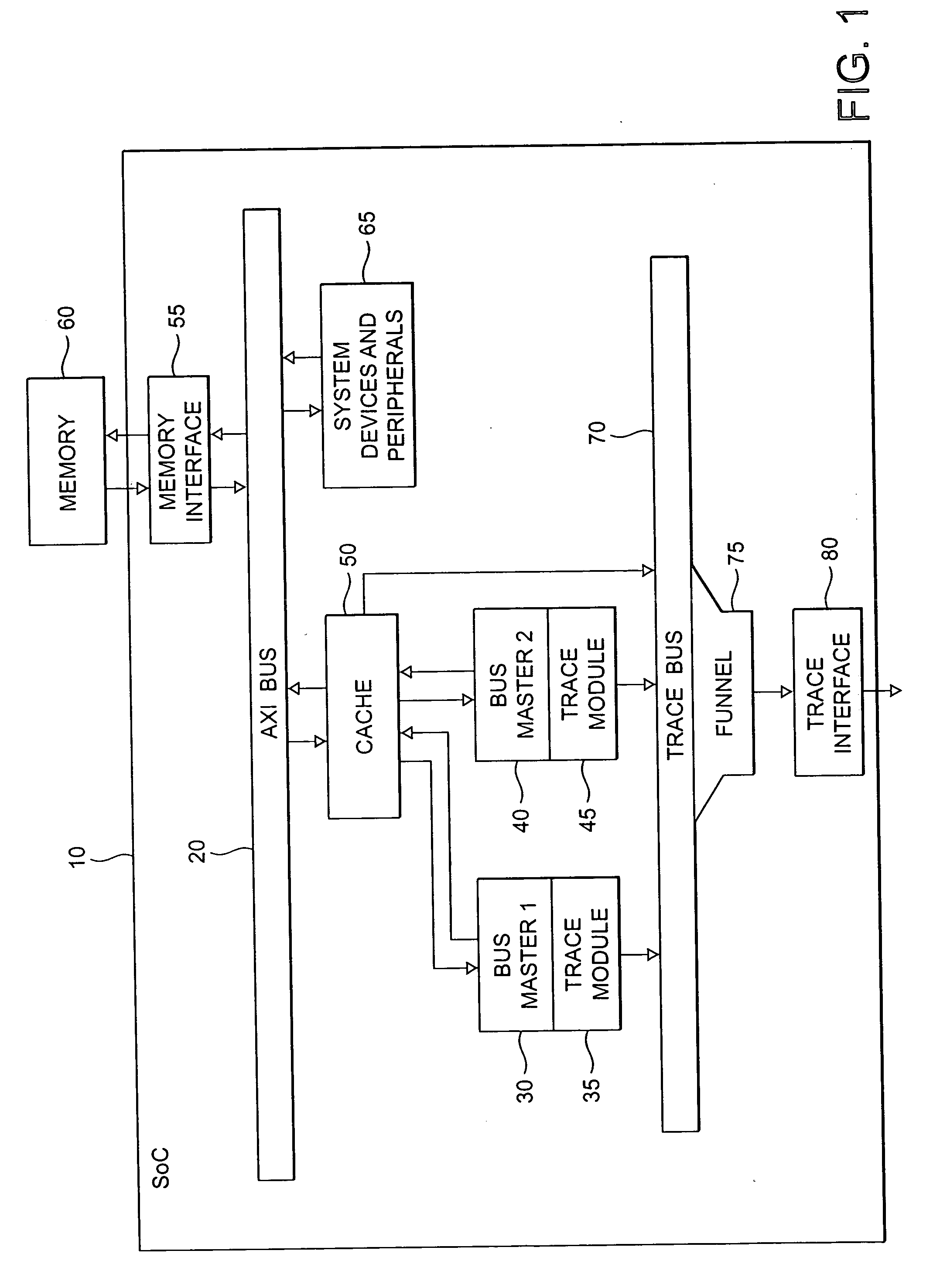
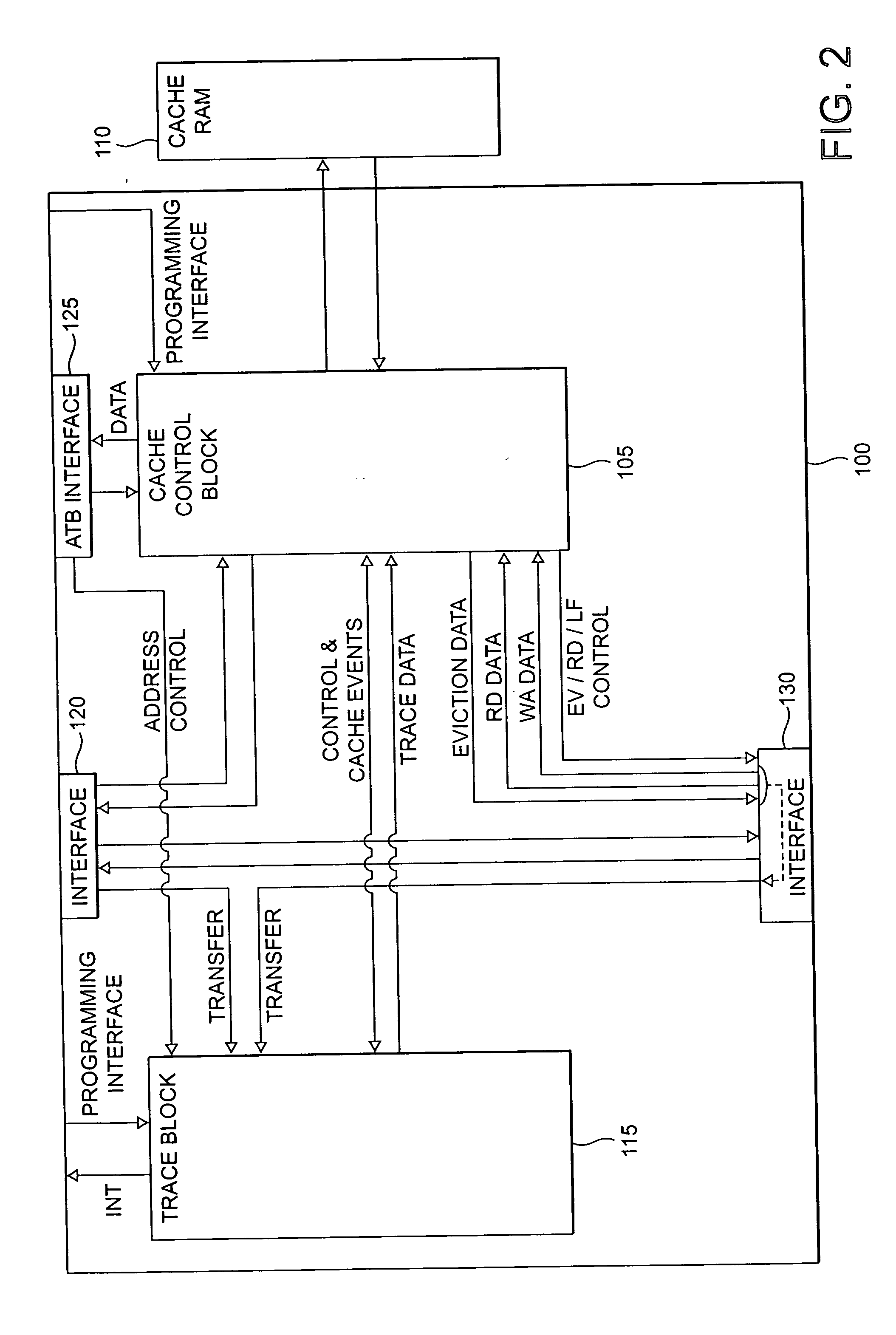
Storage of trace data within a data processing apparatus
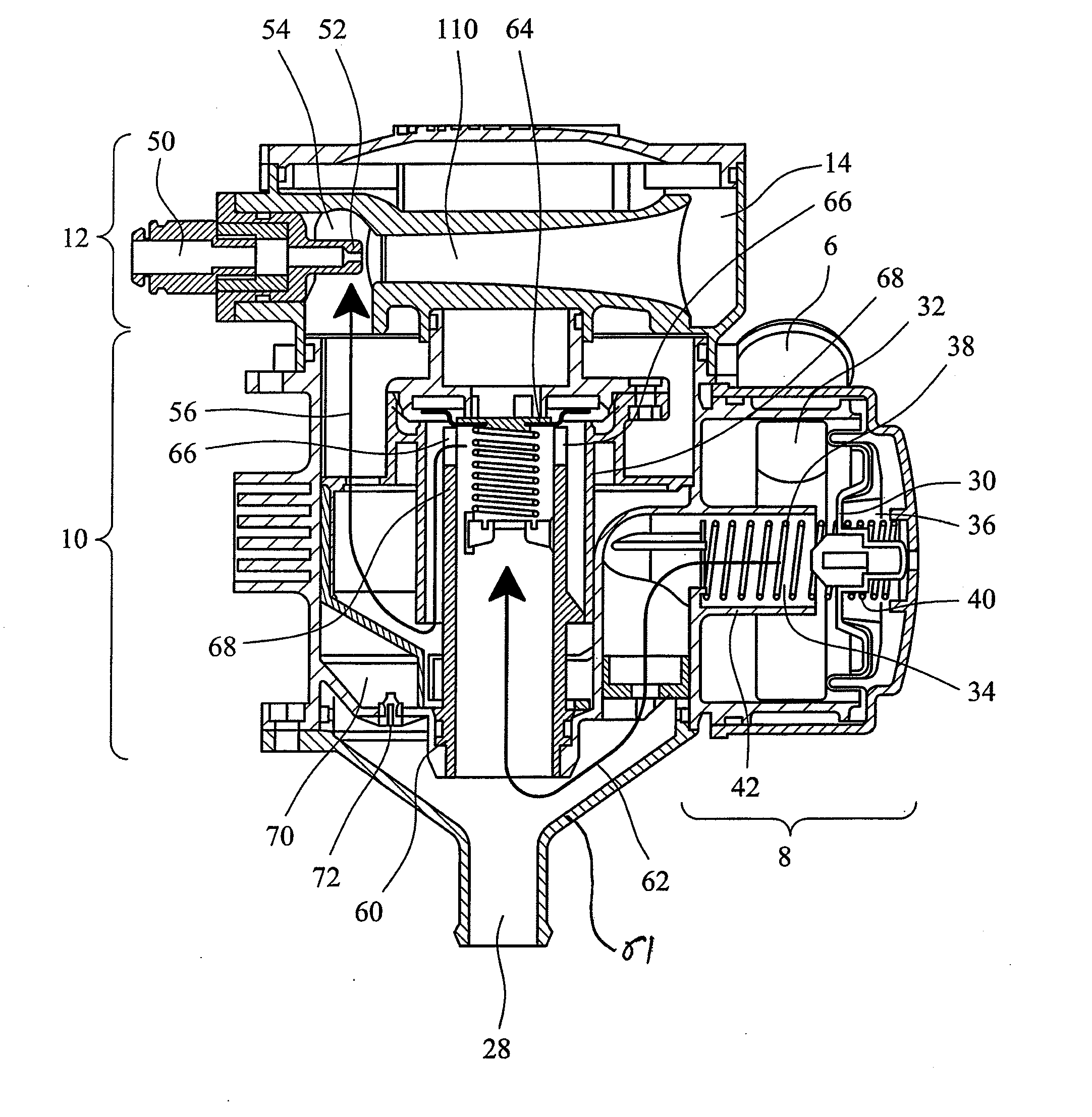
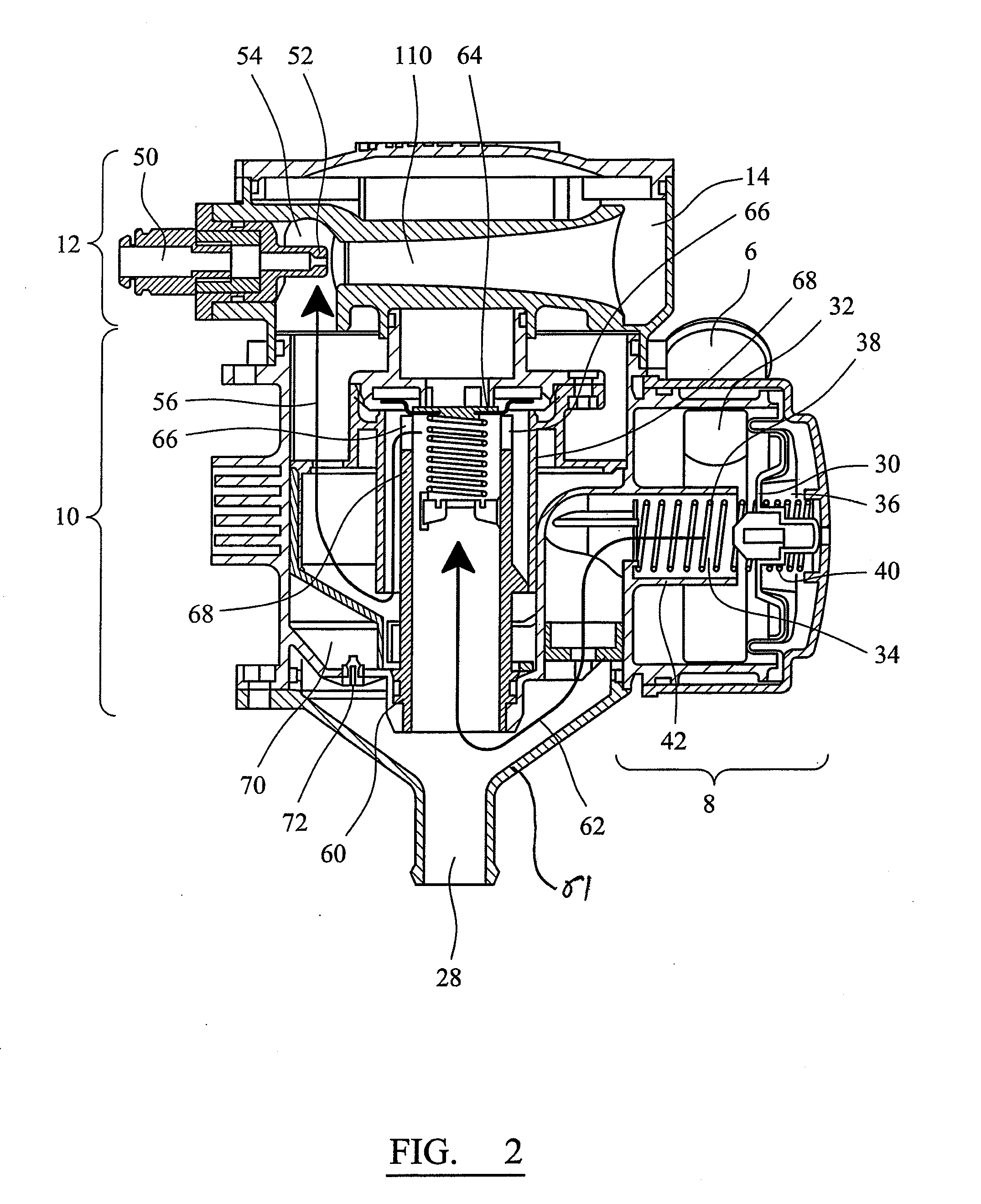
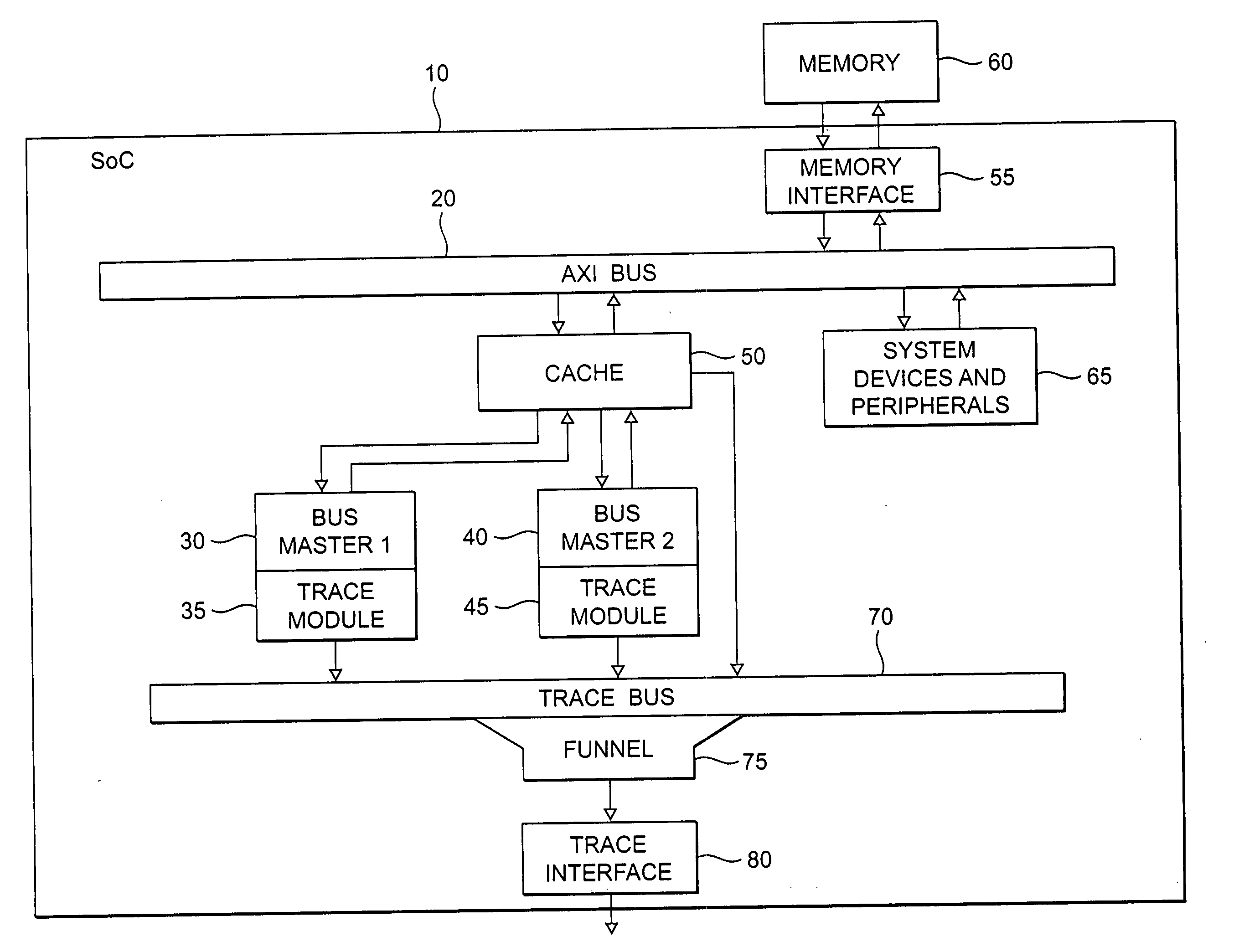
ActiveUS20060112310A1Ensure maintenanceEfficient implementationError detection/correctionControl memoryData value
The present invention provides a data processing apparatus and method for storing trace data. The data processing apparatus comprises a bus operable to interconnect a number of master devices and slave devices to enable transactions to be routed between the master and slave devices. Each master device is able to initiate a transaction, with the transaction specifying a transaction address. A cache is interposed between at least one of the master devices and the bus and is operable to receive the transaction issued by that master device. The cache has a cache memory and a cache controller operable to control access to the cache memory. The cache controller comprises caching logic operable to selectively cache a data value of the transaction at a location in the cache memory chosen dependent on the transaction address. Control storage is provided identifying a trace address range specifying a trace region. Further, trace logic is provided which is operable to selectively generate as trace data one or more attributes associated with the transaction and to provide in association with that trace data a trace address selected from the trace address range. The caching logic is then operable to store the trace data at a location in the cache memory chosen dependent on the trace address. In this way, the cache can be used in a flexible manner to not only act as a normal cache but also to selectively store within the cache trace data.
Owner:ARM LTD
Gravimetric blender with power hopper cover
InactiveUS8092070B2Low costEnsure maintenanceFlow mixersTransportation and packagingMaterial storage
A gravimetric blender has a frame, at least one material storage hopper at the top of the frame including a hopper cover, a weigh bin located within the frame, below the hopper, for receipt of material from the hopper to be weighed and being adapted for downward discharge of the material in the bio bin after the material received from the hopper has been weighed, at least one load cell connecting the weigh bin to the frame for sensing the weight of contents of the weigh bin, a mixer within the frame below the hopper, for mixing material weighed in the weigh bin after that material falls downwardly from the weigh bin to the mixer, and a guide adapted for vertical movement of the hopper cover therealong between positions which the cover contacts and thereby closes the hopper and at which the cover is spaced vertically above the hopper so that the hopper is open at the top.
Owner:MAGUIRE STEPHEN B
Interchangeable barrel system for rifles
InactiveUS20070186458A1Maintaining repeatable accuracyEasy to replaceBarrel mountingGun barrelIndustrial engineering
A system for use with firearms which permits the ready exchange of barrels on a single action and stock assembly. The barrels may be quickly and easily exchanged under field conditions using a single simple tool and without removing the action and receiver from the firearm stock. Barrels of different calibers may be used on a single firearm leading to greater versatility. The system relies on a pinch lug or clamp attached to the receiver which will draw all barrels onto the receiver and into invariable coaxial alignment with the receiver and action thus insuring the bullet will always have the same trajectory.
Owner:FULL NELSON
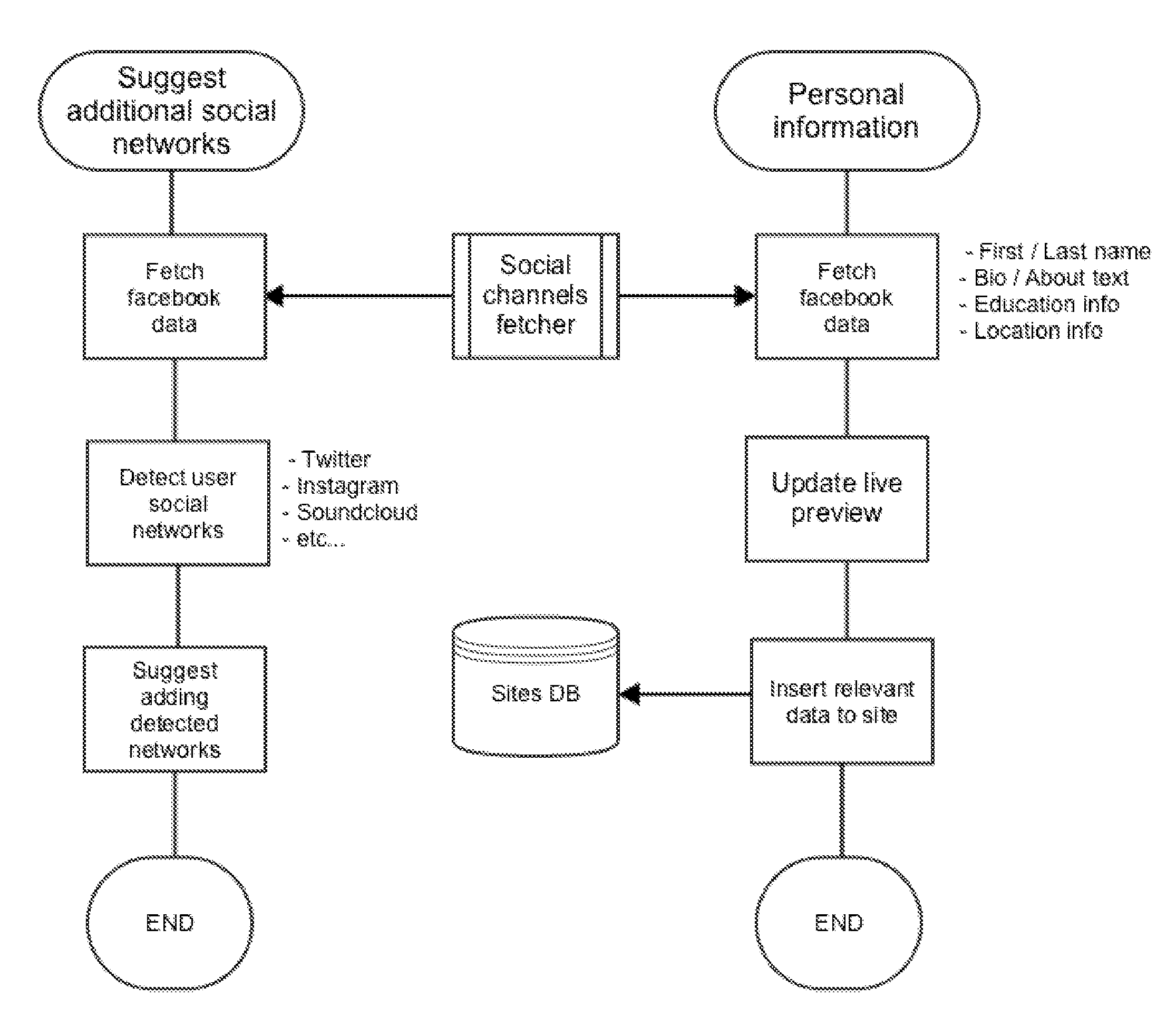
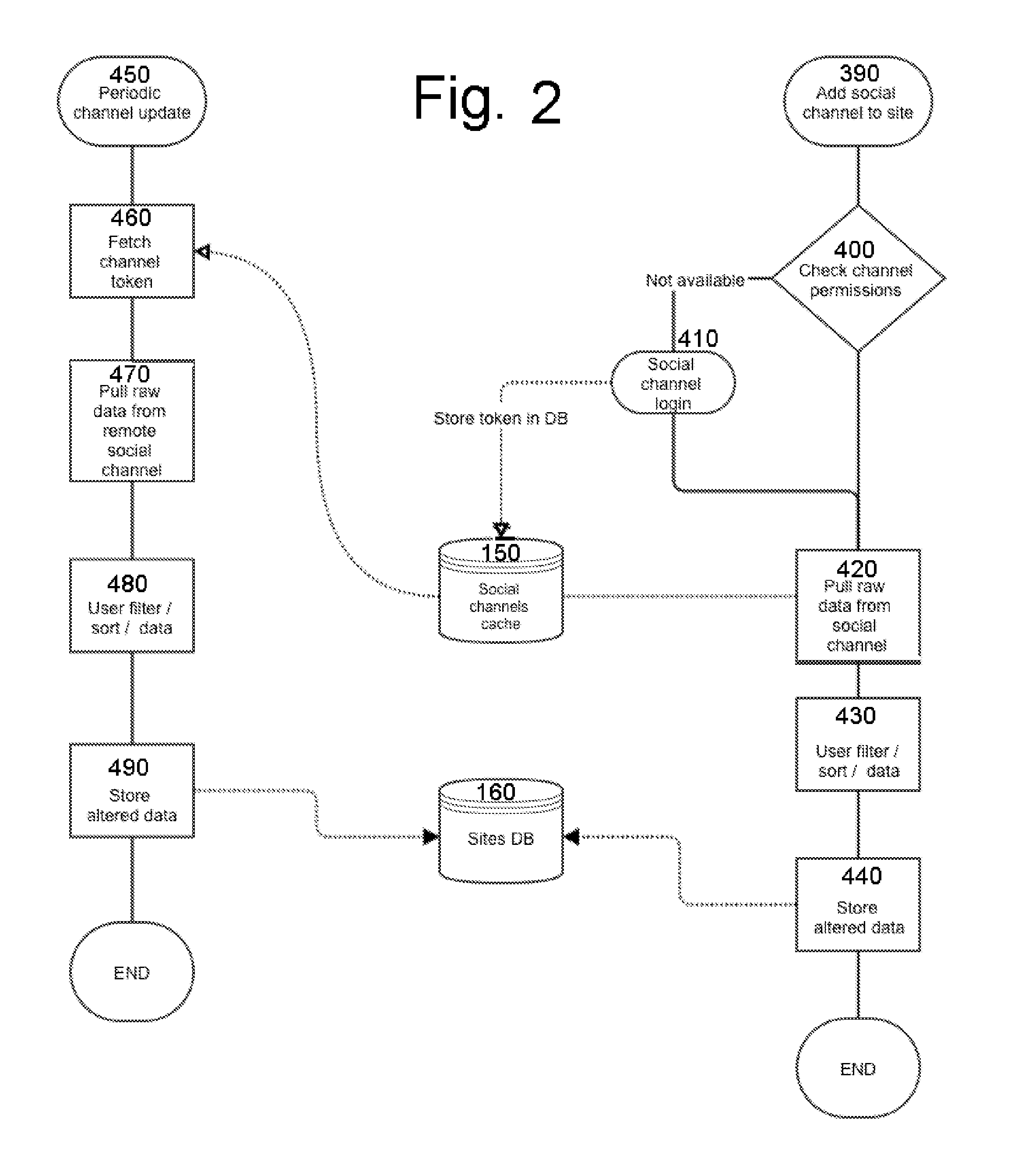
All-in-One Website Generator System and Method with a Content-Sensitive Domain Suggestion Generator
InactiveUS20160179769A1Easy to integrateQuickly populatedDatabase updatingWebsite content managementDomain nameName server
A dynamic, rapid website-generating system and method is detailed. The system is configured to expedite and simplify the website creation and hosting processes for the end user web-creator, while dynamically creating content based on the web-creator's online footprint via permitted, associated social networks. The system is configured to provide domain name suggestions to the web-creator based on data gathered from social networks, as well as based upon web-content crafted and / or uploaded to the website during construction. Domain is decided by user from a pool of available domains that have been suggested after the website is built, such that the domains suggested relate to the website content of the website that has been built. Domain setup and registration, hosting setup, name server / DNS setup, and uploading are all automated to streamline the process for the novice web-creator.
Owner:GERSHOM EFRAIM +4
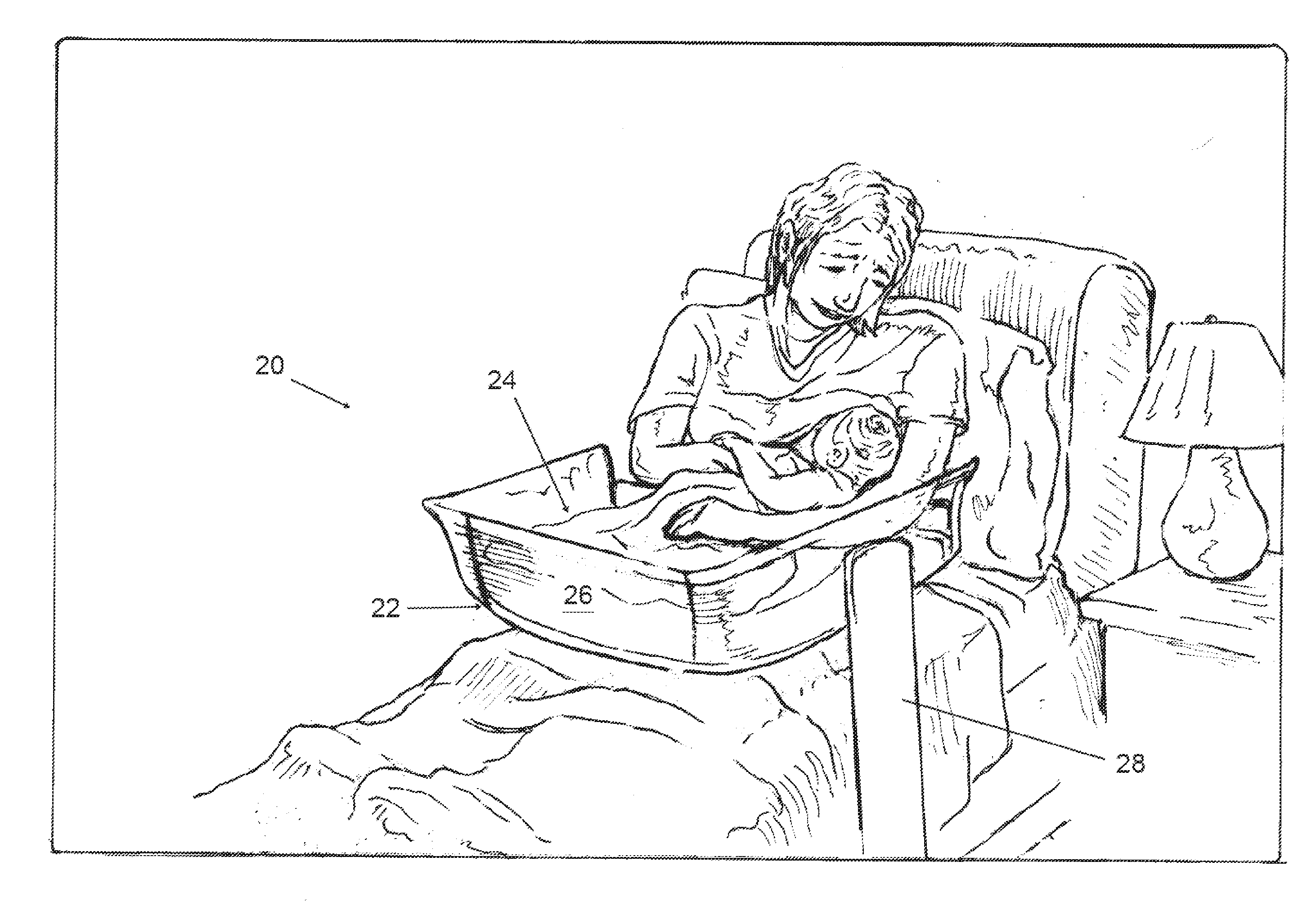
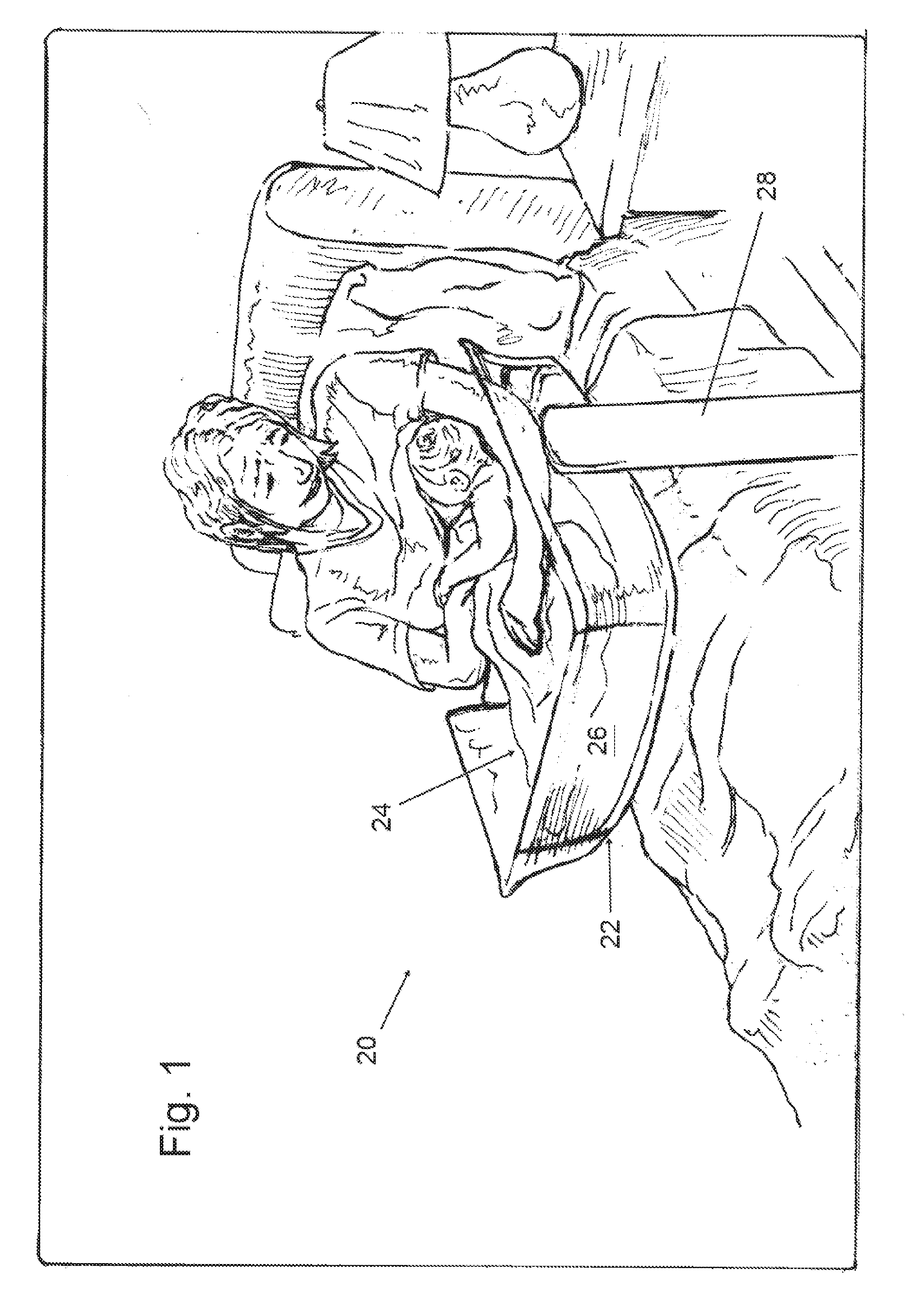
Easy-access safety bassinet
An easy-access over-the-bed bassinet especially useful in hospitals for new mothers that has a barrier to prevent the infant from rolling off a sleeping platform, wherein one wall may be lowered to permit a mother to reach in and cradle the infant. The convertible wall has a restoring mechanism to move it back to its original barrier position upon removal of the weight of the mother's arms. The convertible wall may translate vertically into a frame, or pivot about a bottom edge, or pivot or roll underneath the sleeping platform. The bassinet may include a strap that maintains contact of the mother against the bassinet while breast feeding the baby in the bassinet. The entire sleeping platform may tilt about a horizontal axis, and may rotate about a vertical axis for ease of positioning relative to the mother. The bassinets are mounted on sturdy frames that permit over-the-bed positioning.
Owner:LONG PATRICIA
Electrode systems and methods of using electrodes
ActiveUS20070262059A1Decrease impedanceLow voltageElectric discharge tubesArc welding apparatusEngineeringCarbon Dioxide / Helium
An electrode assembly comprises a coil of electrode material surrounded by a shield having one or more outlets and a supply of shielding gas directed along an axis X-X of said coil before exiting from said shield.
Owner:AGM CONTAINER CONTROLS
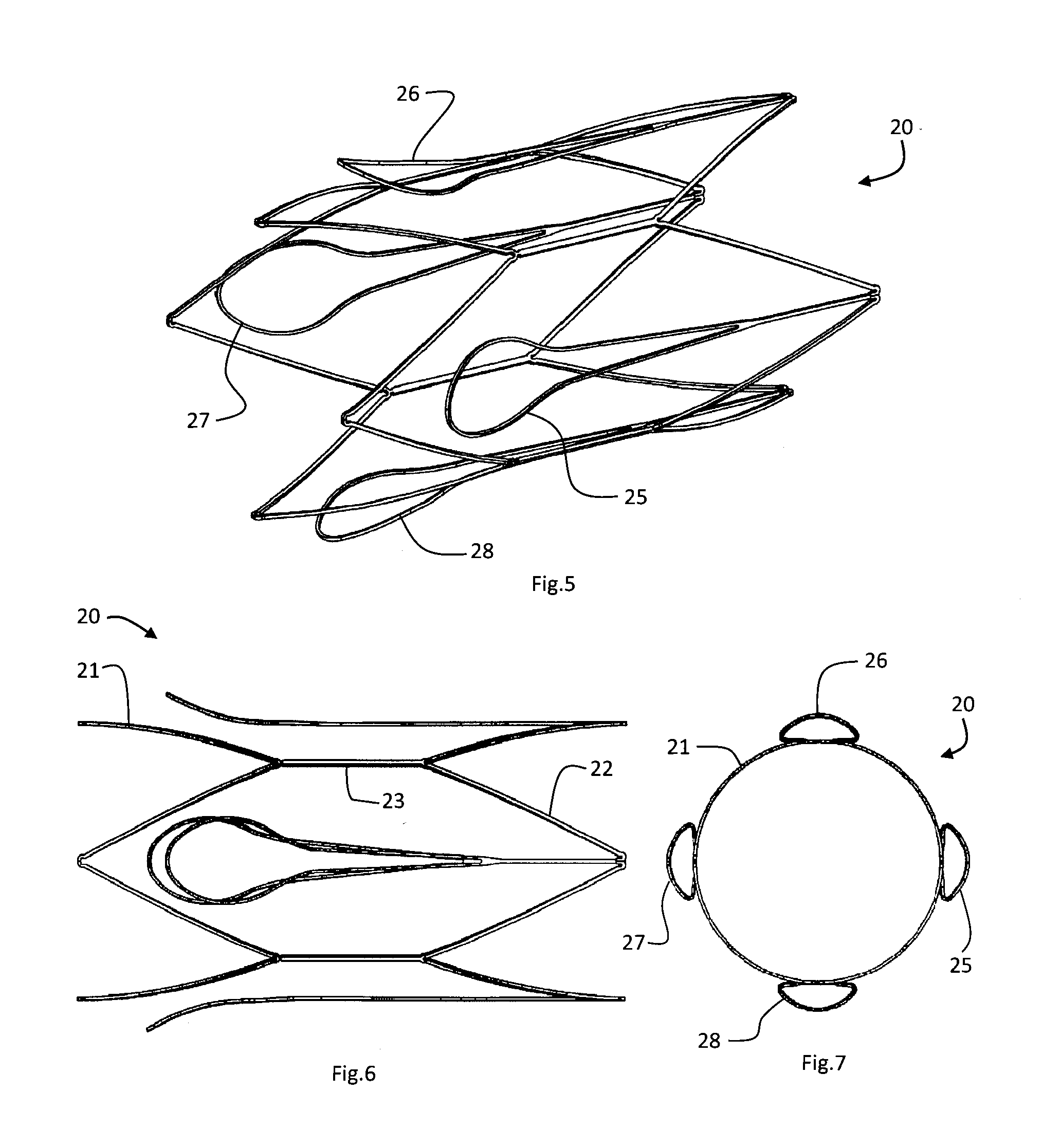
Vascular filter device
A vascular filter device comprises a support; and a filter comprising one or more filter elements configured to capture thrombus passing through a blood vessel. A holder holds the filter in a closed filtering state and releases to convert the filter to an open state after a period of time. The filter is adapted to retain thrombus after said conversion. In one case the filter elements are arranged to remain in a closed state after release by the holder, because they are blocked by a retained clot from opening fully, and the filter elements are biased to the open state with a bias level which is counter balanced by force exerted by a retained clot under action of blood flow.
Owner:COVIDIEN GROUP +1
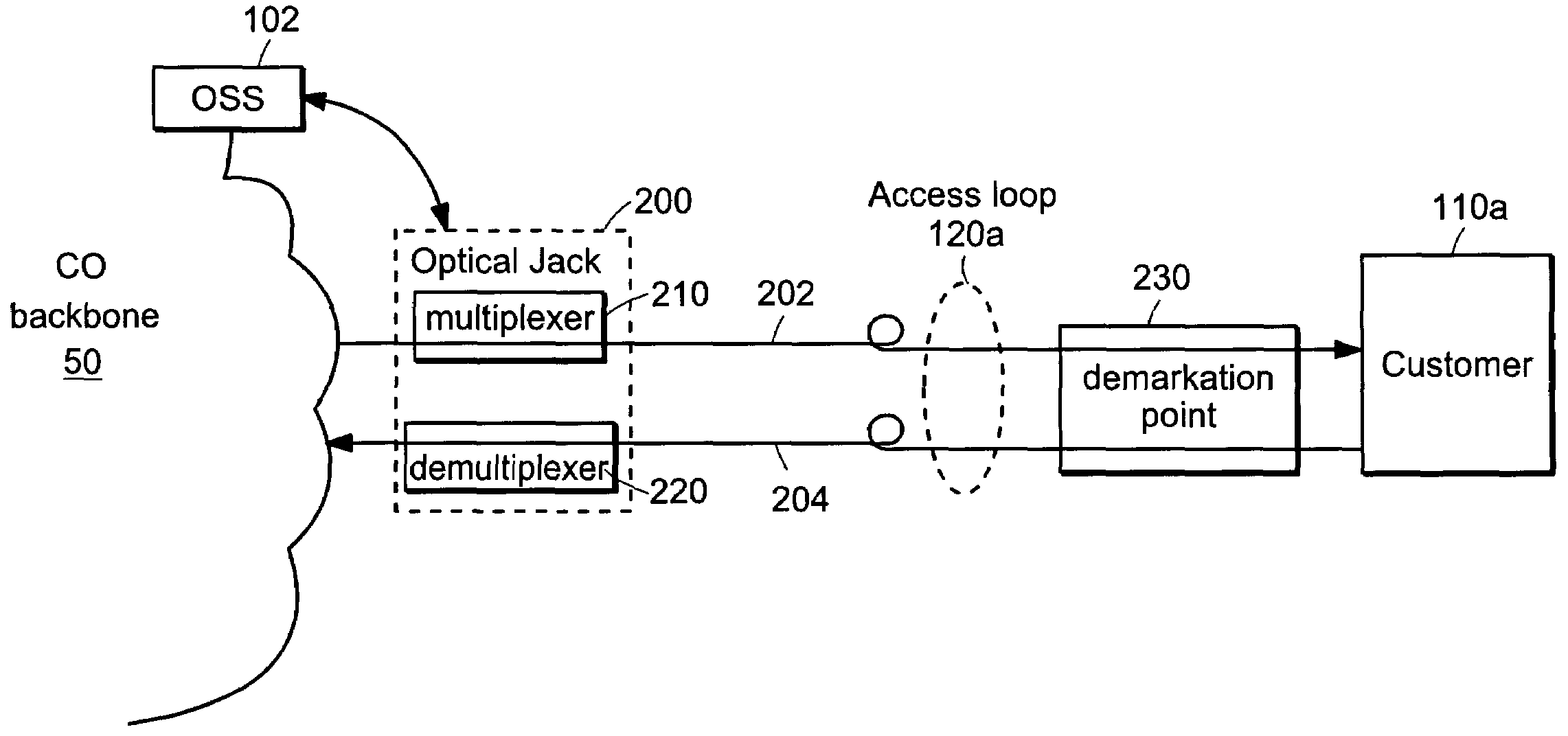
Optical communication management systems
InactiveUS7394981B2High sensitivityLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingMultiplexer
An optical medium, whether inside or outside an internet / telecommunications backbone, is managed using a management signal at a wavelength which is distinct from wavelengths of service signals. A multiplexer multiplexes the management signal onto the optical medium, after which a demultiplexer demultiplexes the management signal for analysis. Performance of customer channels may be inferred from performance of the management signal.
Owner:MANIFOLD ROBERT H
Procedure and configuration in order to transmit data
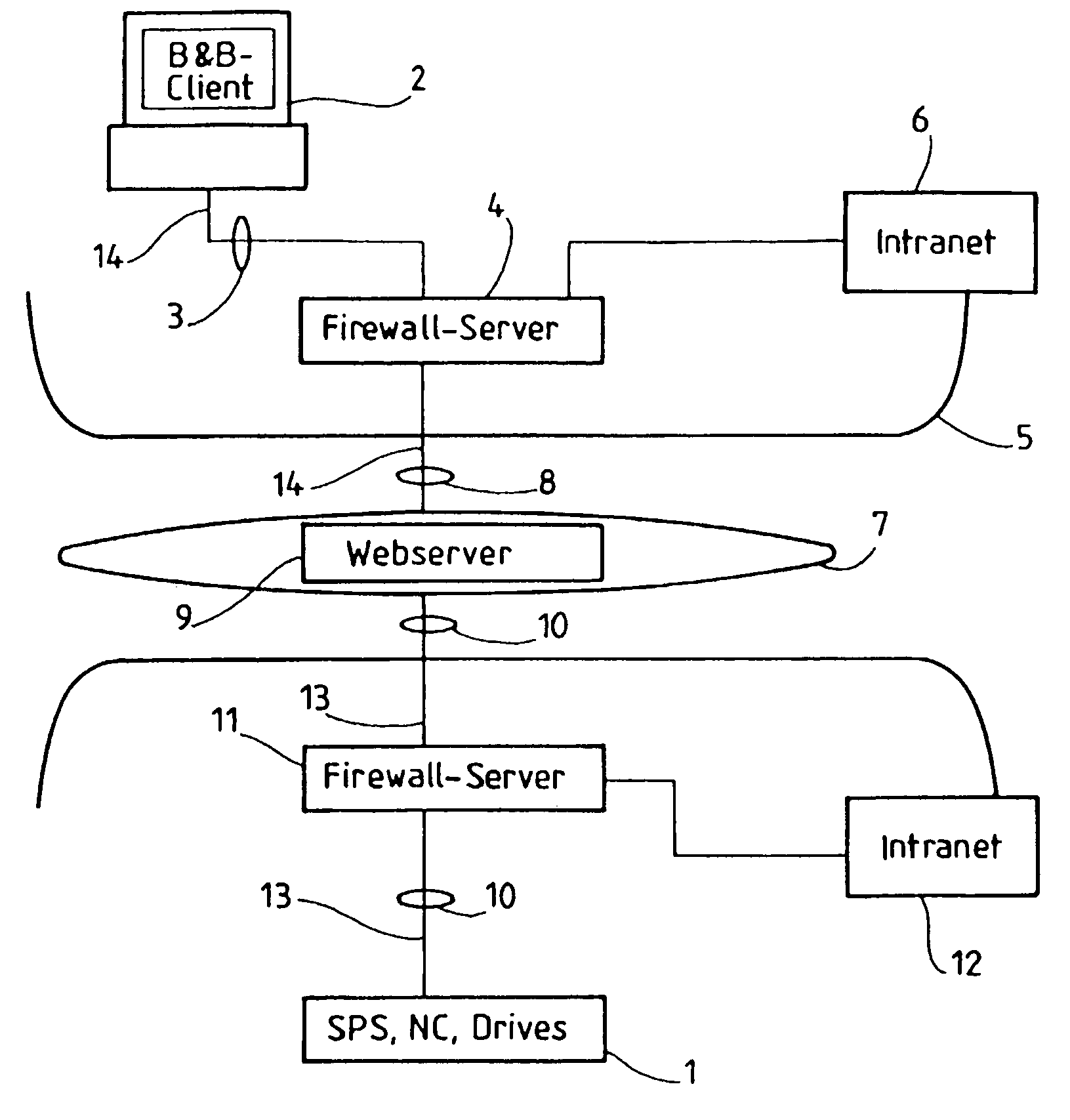
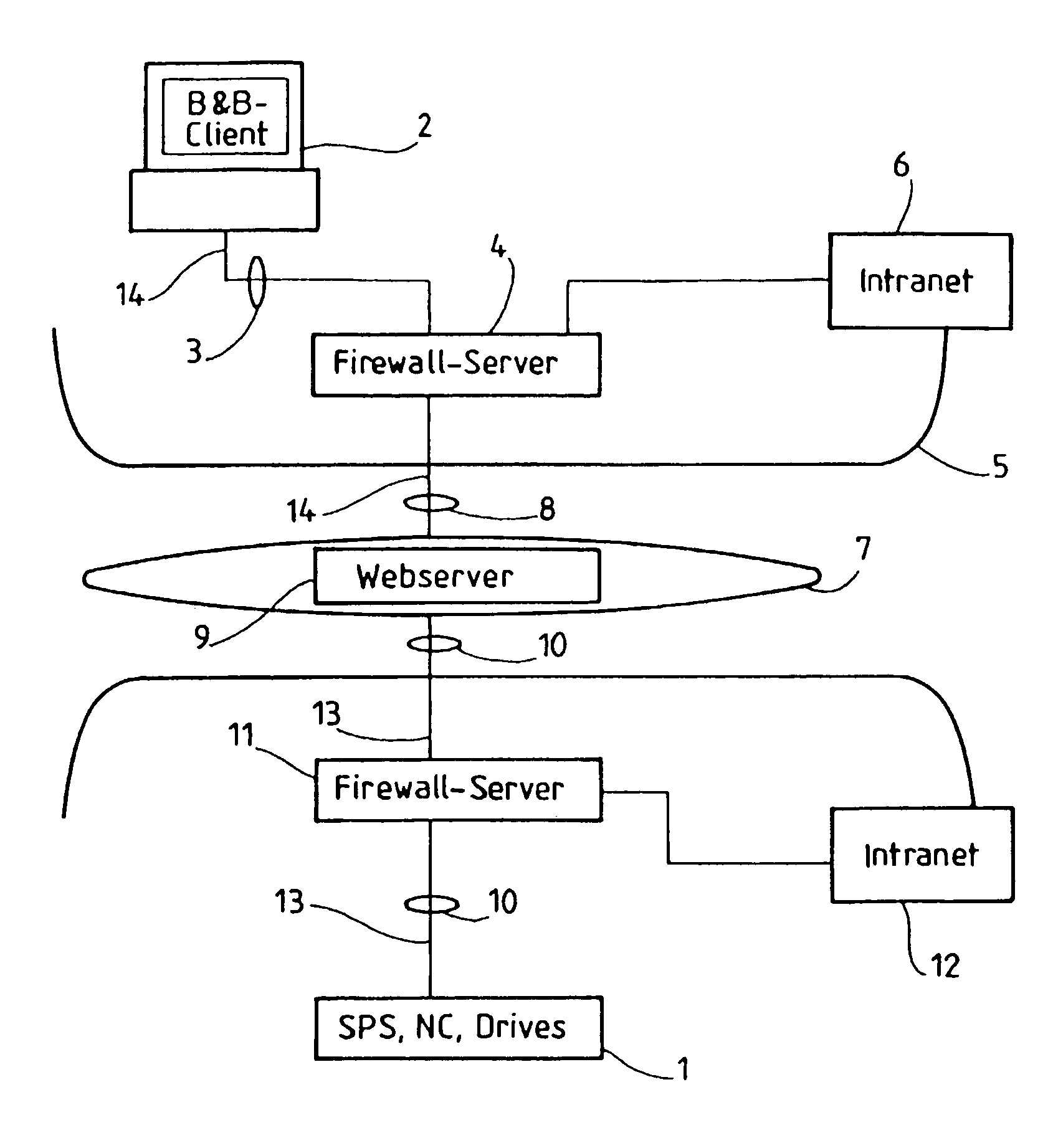
ActiveUS7200660B2Easy to solveEnsure maintenanceMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsWeb serviceClient-side
Procedure to transmit data, especially data used to operate and observe a system in which a request to build up a transfer channel to a web server is sent from a web client, comprising the following properties:a message that demands a connection to build up a first transfer channel is sent to a web server from the system that needs to be watched or operated;this request stays open and thus creates a tunnel for data transfer between system and web server;at least one additional channel of transfer is generated while the web client requests connection between client and web server;the client establishes contact with the system via the data transfer tunnel in order to send and receive reference data bi-directionally.
Owner:ININET IP
Gravimetric blender with power hopper cover
InactiveUS20070291578A1Low costEnsure maintenanceFlow mixersTransportation and packagingEngineeringMaterial storage
A gravimetric blender has a frame, at least one material storage hopper at the top of the frame including a hopper cover, a weigh bin located within the frame, below the hopper, for receipt of material from the hopper to be weighed and being adapted for downward discharge of the material in the bio bin after the material received from the hopper has been weighed, at least one load cell connecting the weigh bin to the frame for sensing the weight of contents of the weigh bin, a mixer within the frame below the hopper, for mixing material weighed in the weigh bin after that material falls downwardly from the weigh bin to the mixer, and a guide adapted for vertical movement of the hopper cover therealong between positions which the cover contacts and thereby closes the hopper and at which the cover is spaced vertically above the hopper so that the hopper is open at the top.
Owner:MAGUIRE STEPHEN B
Rearview device with moveable head assembly
InactiveUS20180126910A1Ensure maintenanceSmall mirror sizeOptical viewingMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
A rear view device for a motor vehicle includes a base assembly for arrangement on the motor vehicle, a moveable head assembly attached to the base assembly, and an actuation mechanism, the actuation mechanism including a fixed part attached to the base assembly and a moveable part attached to the head assembly, where the actuation mechanism allows movement of the moveable part with respect to the fixed part in one or more axes.
Owner:SMR PATENTS S A R L
Aircraft side fairing
ActiveUS8490365B2Improve insulation performanceAvoid disadvantagesLayered productsWingsAirplaneWaste management
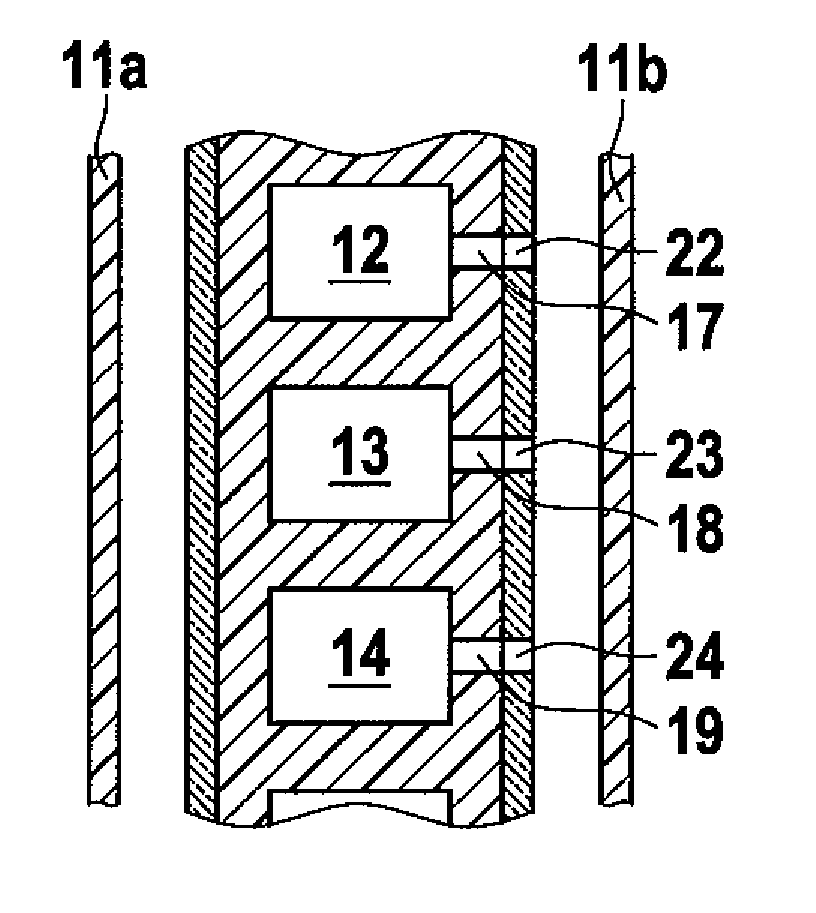
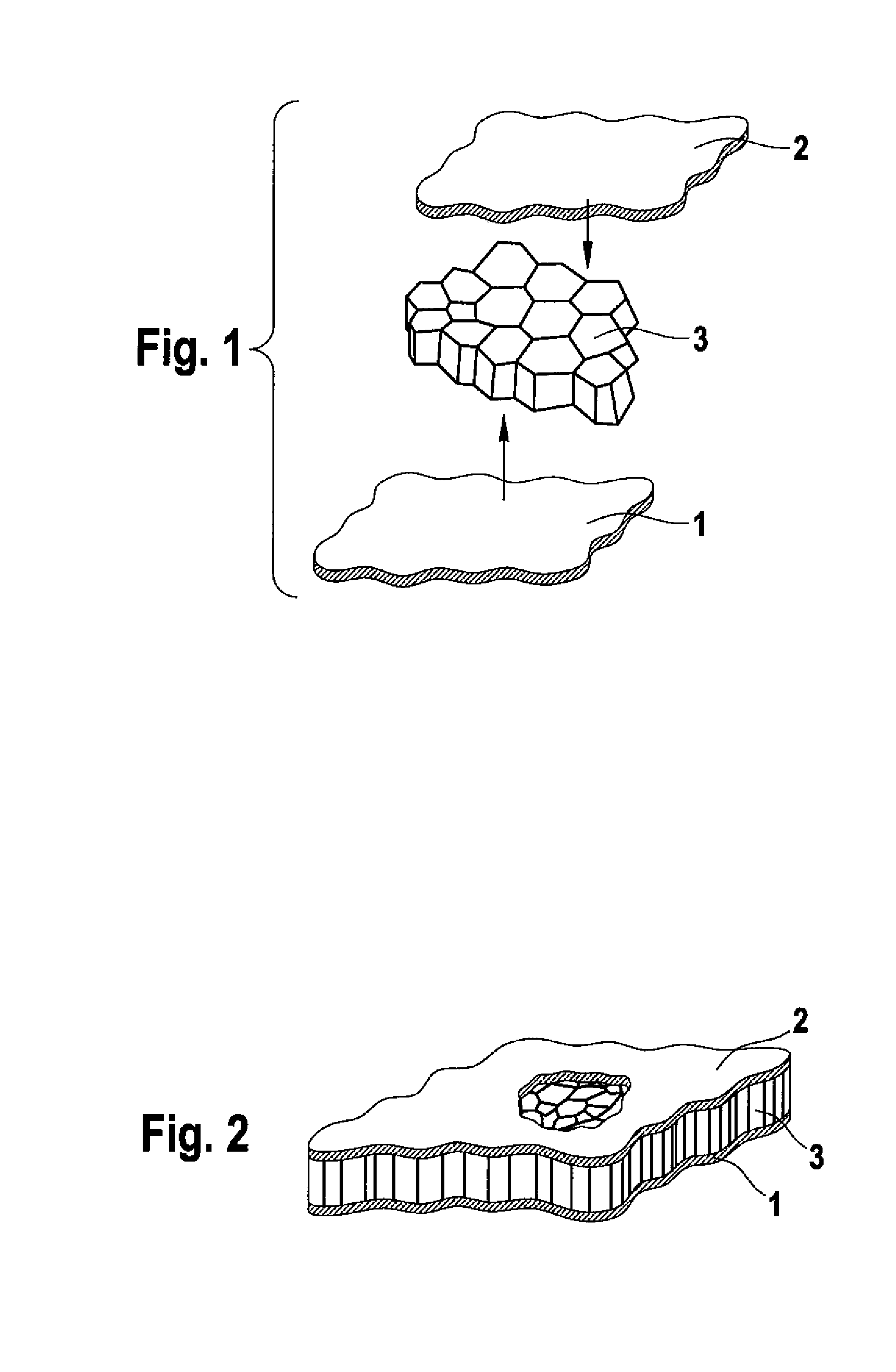
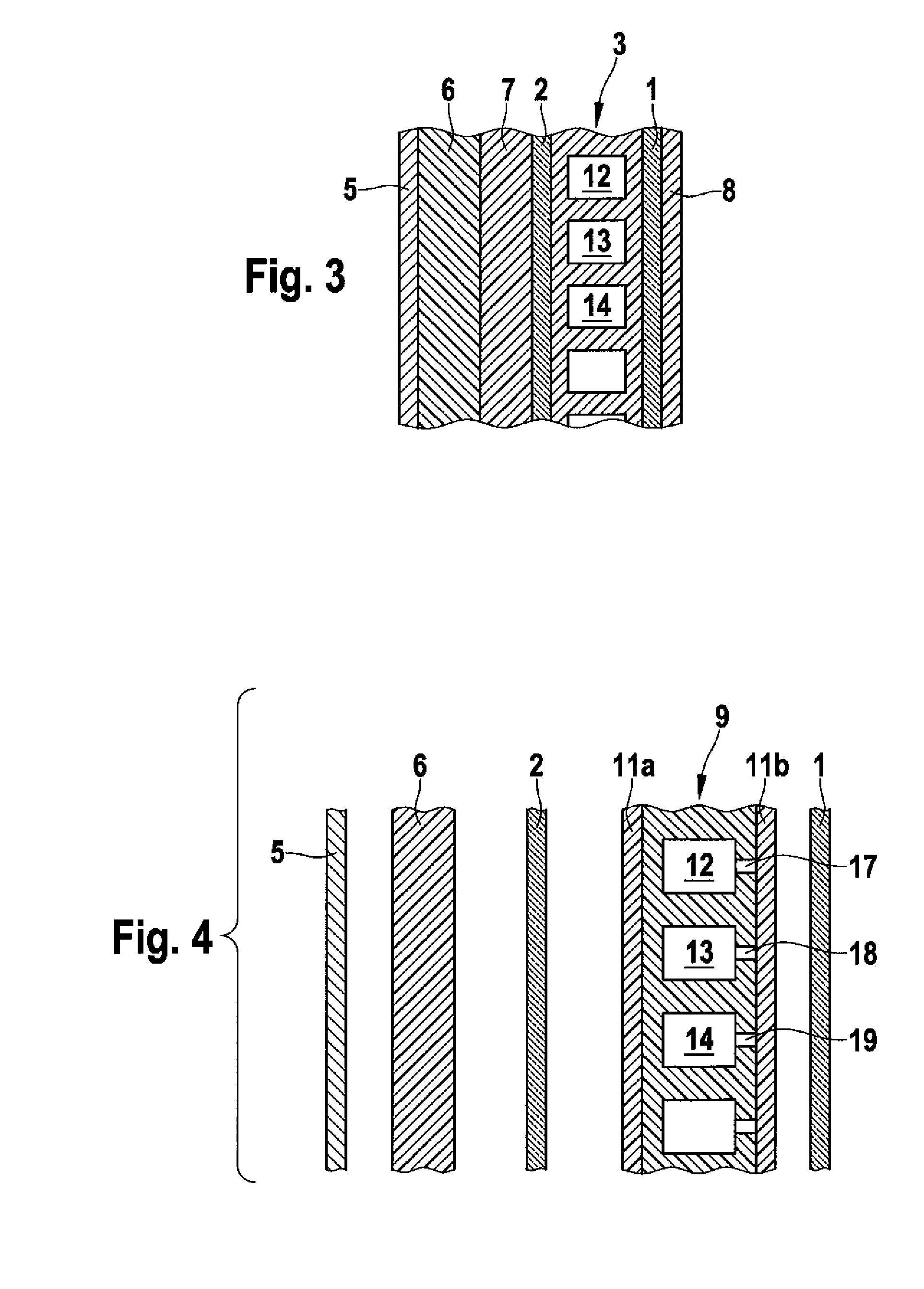
The invention relates to an aircraft side fairing, with a component (9) in the form of individual hollow chambers (12, 13, 14) which are arranged essentially in a preferably curved plane and are arranged between two cover layers (1, 2), wherein a gastight film which completely encases the component (9) with the hollow chambers (12, 13, 14) is provided and, after application of a vacuum to evacuate the hollow chambers (12, 13, 14), surrounds the component (9) with the hollow chambers in a gastight manner.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
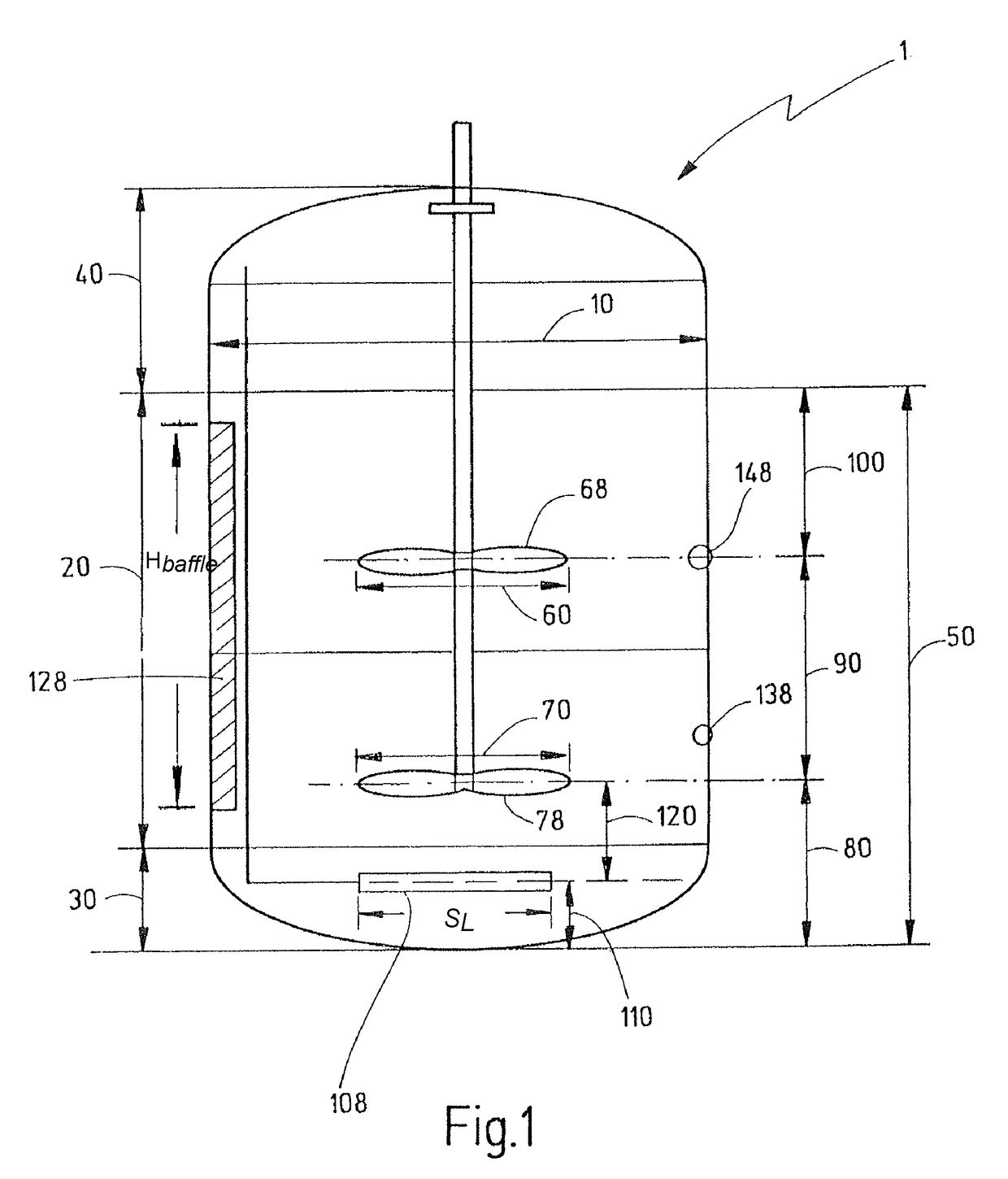
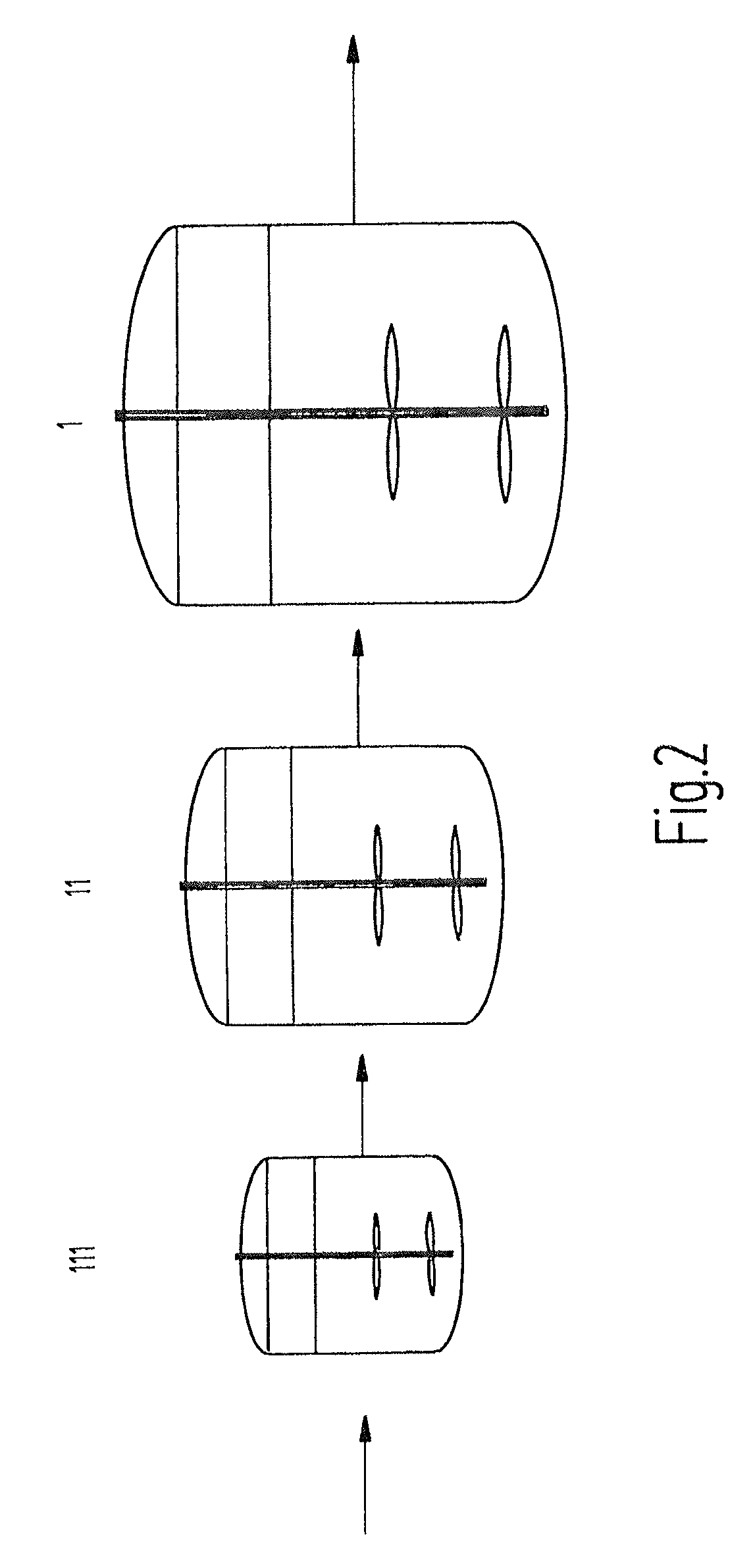
Bioreactor for the cultivation of mammalian cells
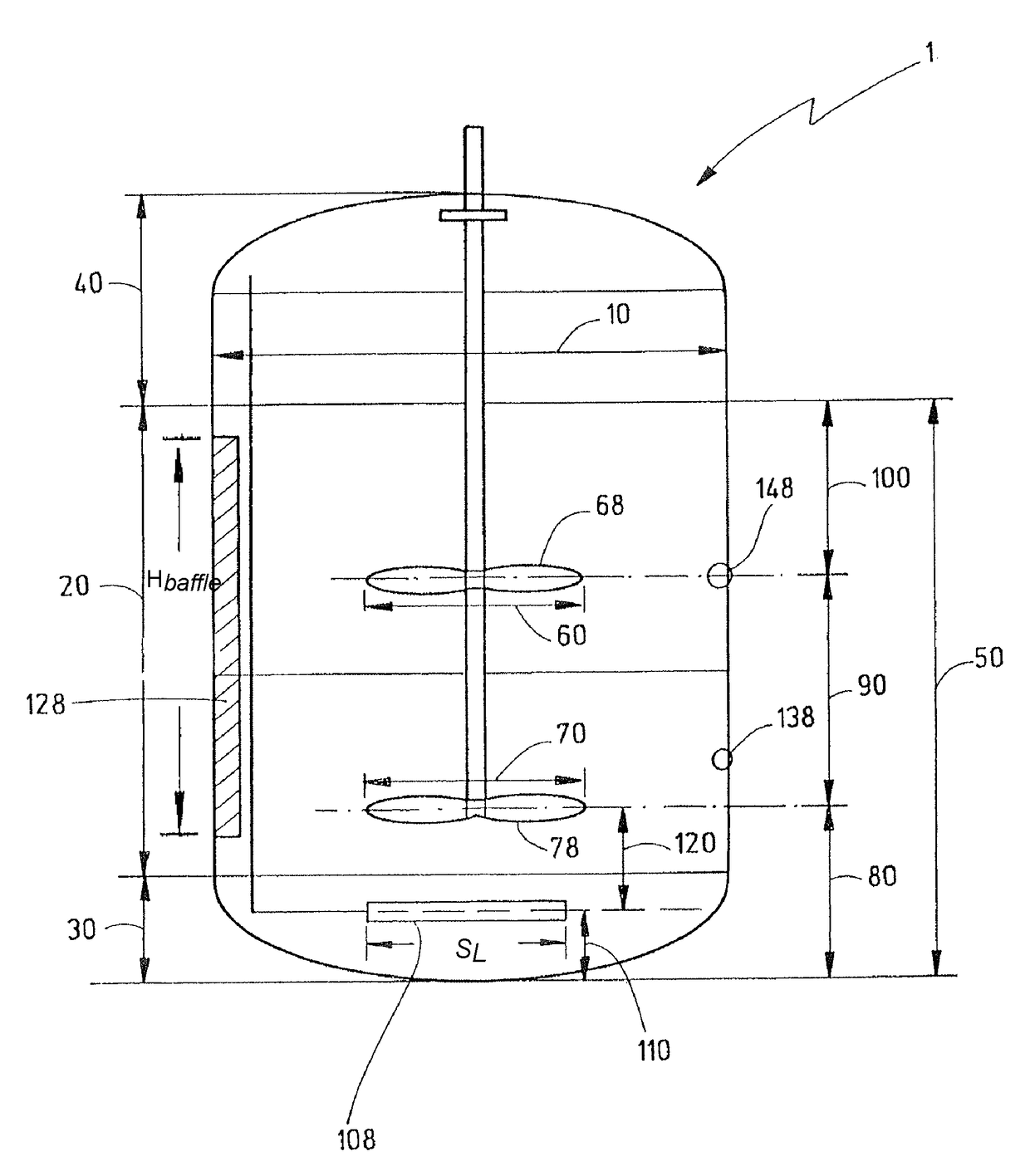
ActiveUS9670446B2MaintenanceEnsure maintenanceAnimal cellsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImpellerMammal
The present invention relates to large-scale bioreactors having at least two impellers, large-scale bioreactor systems and methods for the large scale cultivation and propagation of mammalian cells using these bioreactors.
Owner:LONZA BIOLOGICS PLC
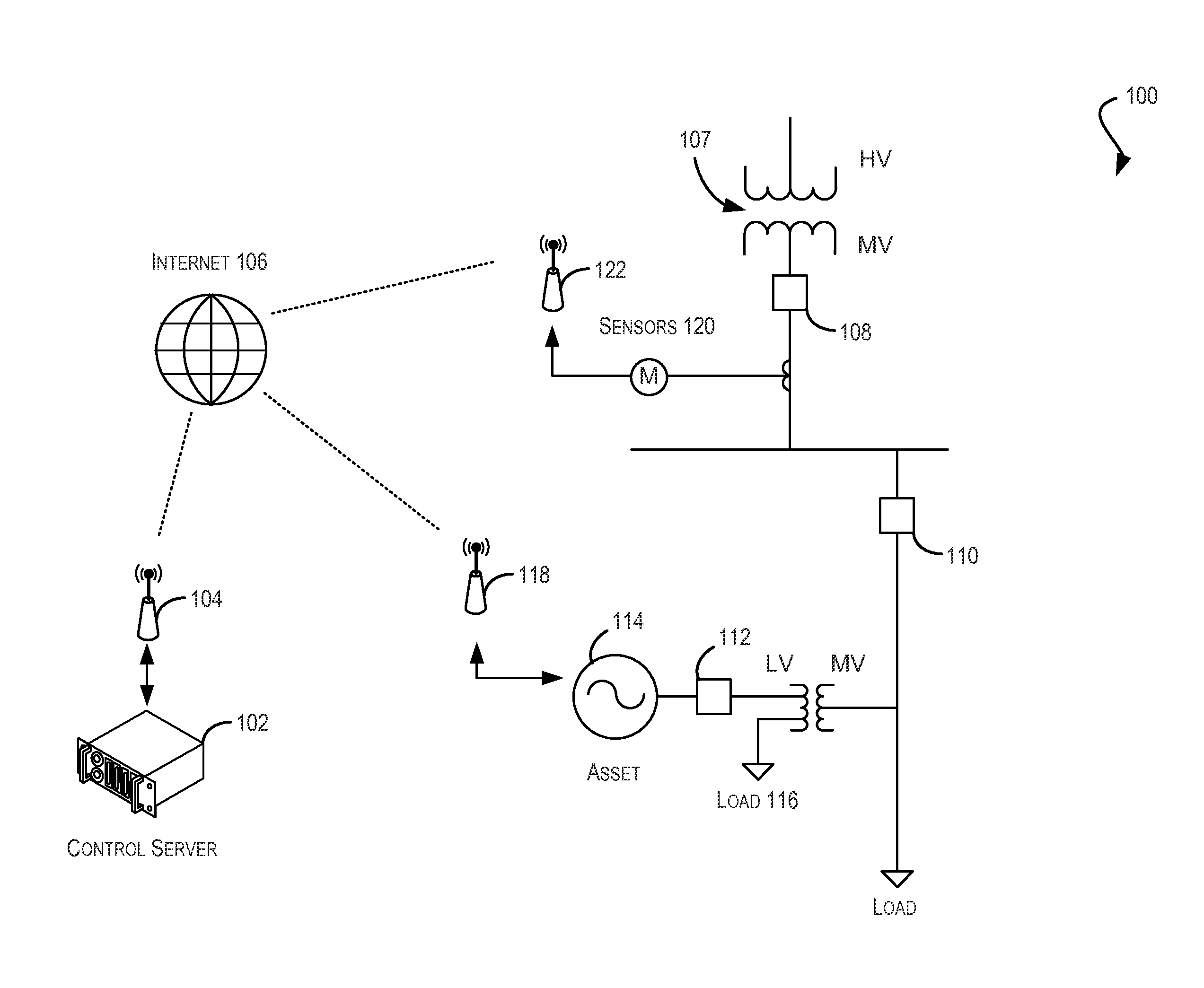
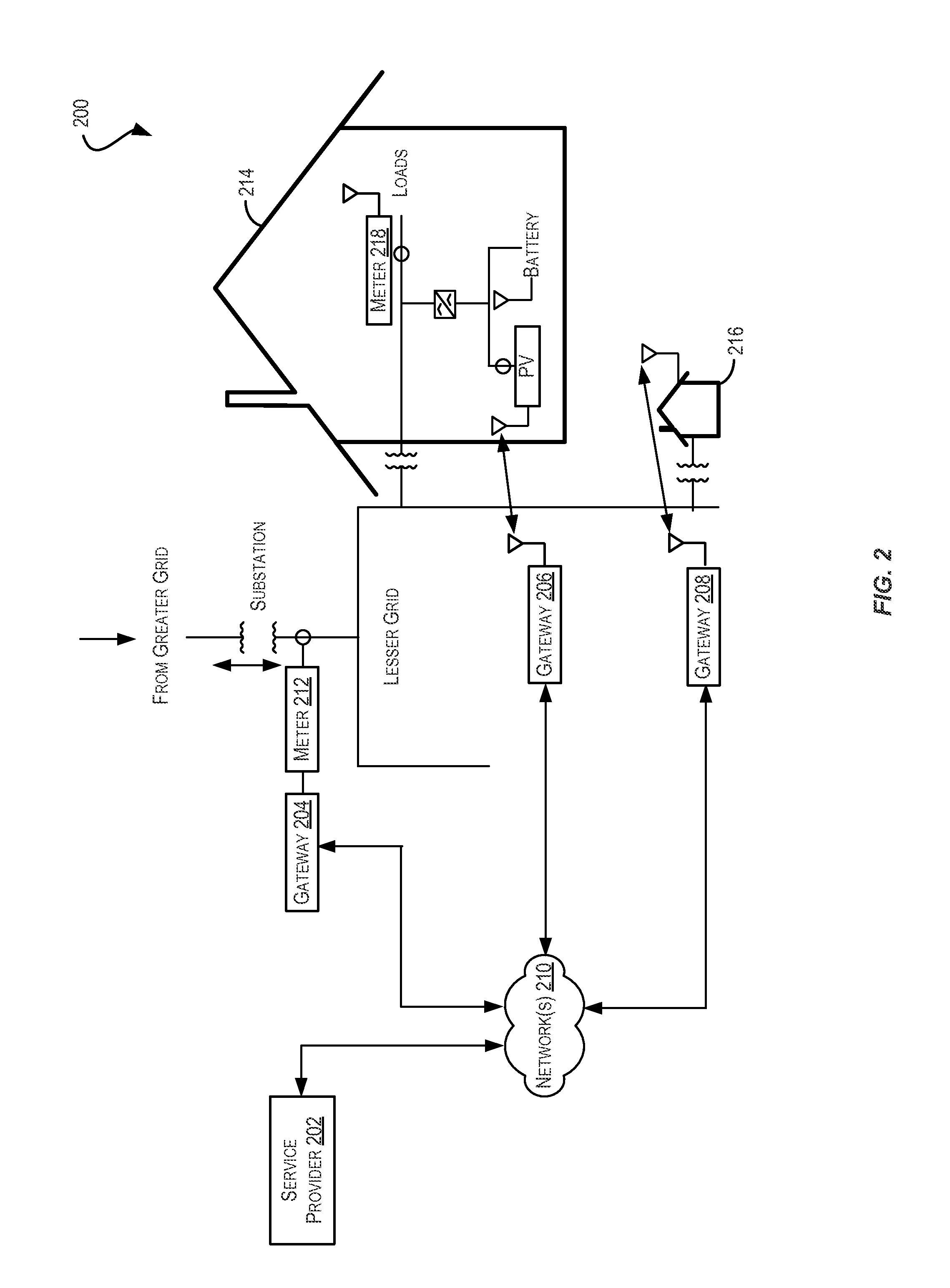
Controlling a distributed generation management system
ActiveUS20160344188A1Ensure maintenanceComputer controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAutomotive engineeringManagement system
Techniques for controlling a distributed generation management system may be provided. Real-time power generation information may be collected from sensors of energy generation systems that make up a grid of controlled systems. An aggregate real-time power generation requirement may be determined for the grid based on the real-time power generation information. Using the aggregate requirements, a power profile may be calculated for the grid that indicates a level of power generation for the grid. In some examples, a control signal to control power generation may be generated and provided to the controlled systems.
Owner:TESLA INC
Epoxide-based composition
An epoxide-based composition comprising a combination of an epoxide and a curing agent, wherein the epoxide is selected from a phenyl glycidyl ether-based polyepoxide and the curing agent is a salt compound composed of a N-alkanol piperidine and a carboxylic acid.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Device for moulding thermoplastic containers by blow-moulding or stretch blow-moulding
Device for moulding thermoplastic containers by blow-moulding hot preforms, comprising a mould (1) and blow-moulding means (2) comprising a bell nozzle (8) which is axially displaceable between a raised position and a blow-moulding position in abutment against the mould; the driving means comprising mechanical means (12) with a cam follower roller (13) / cam (14) and pneumatic means (16) with a piston (18) integral with the upper end of the nozzle and sliding in a fixed enclosure (17), defining therein an upper chamber (19) connected to a source (24) of control fluid and a lower chamber (20) connected to this source and to the upper chamber via a solenoid valve (26); the upper face of the piston has a surface area which is greater than that of its lower face and that of the bell (9) of the nozzle.
Owner:SIDEL PARTICIPATIONS SAS
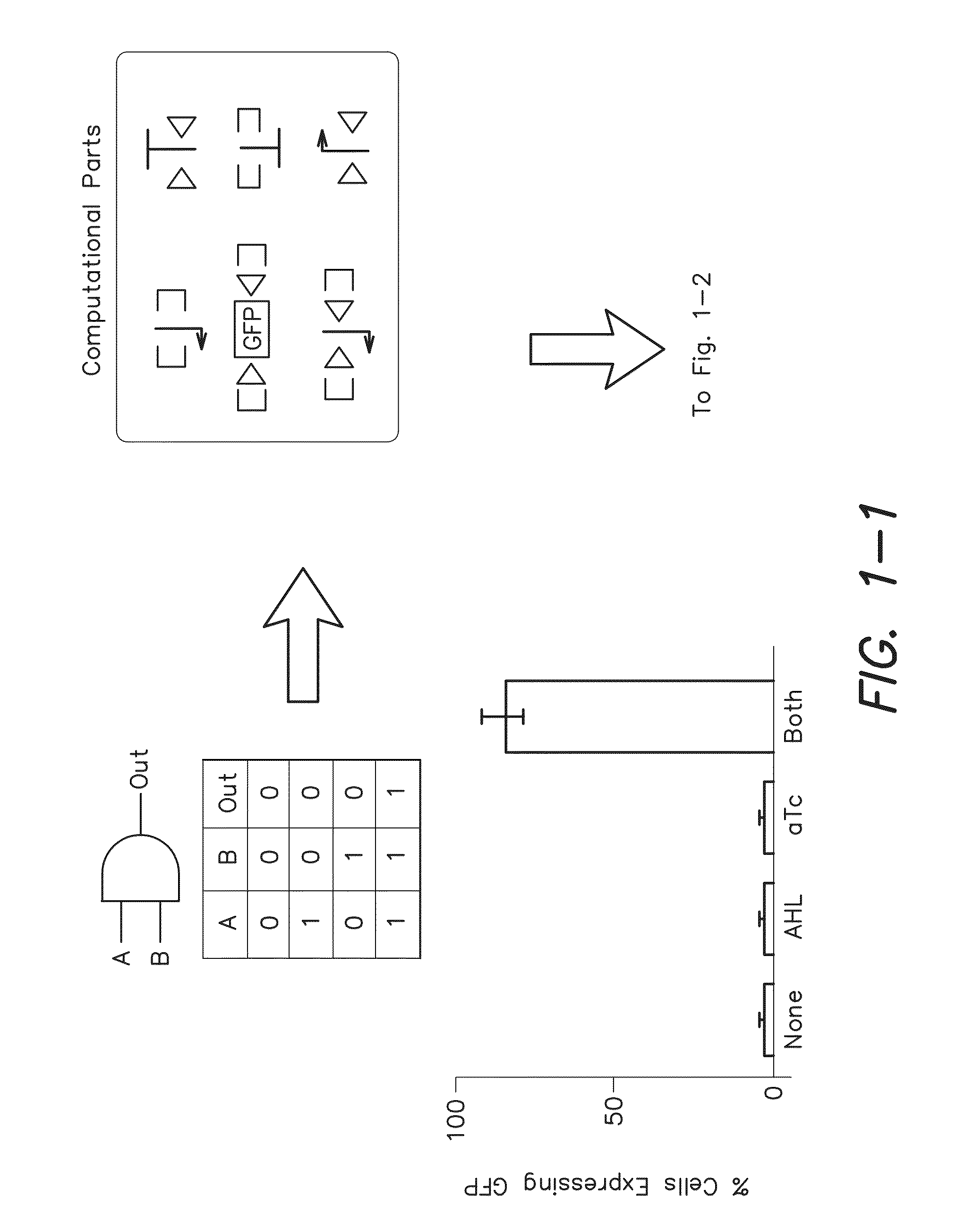
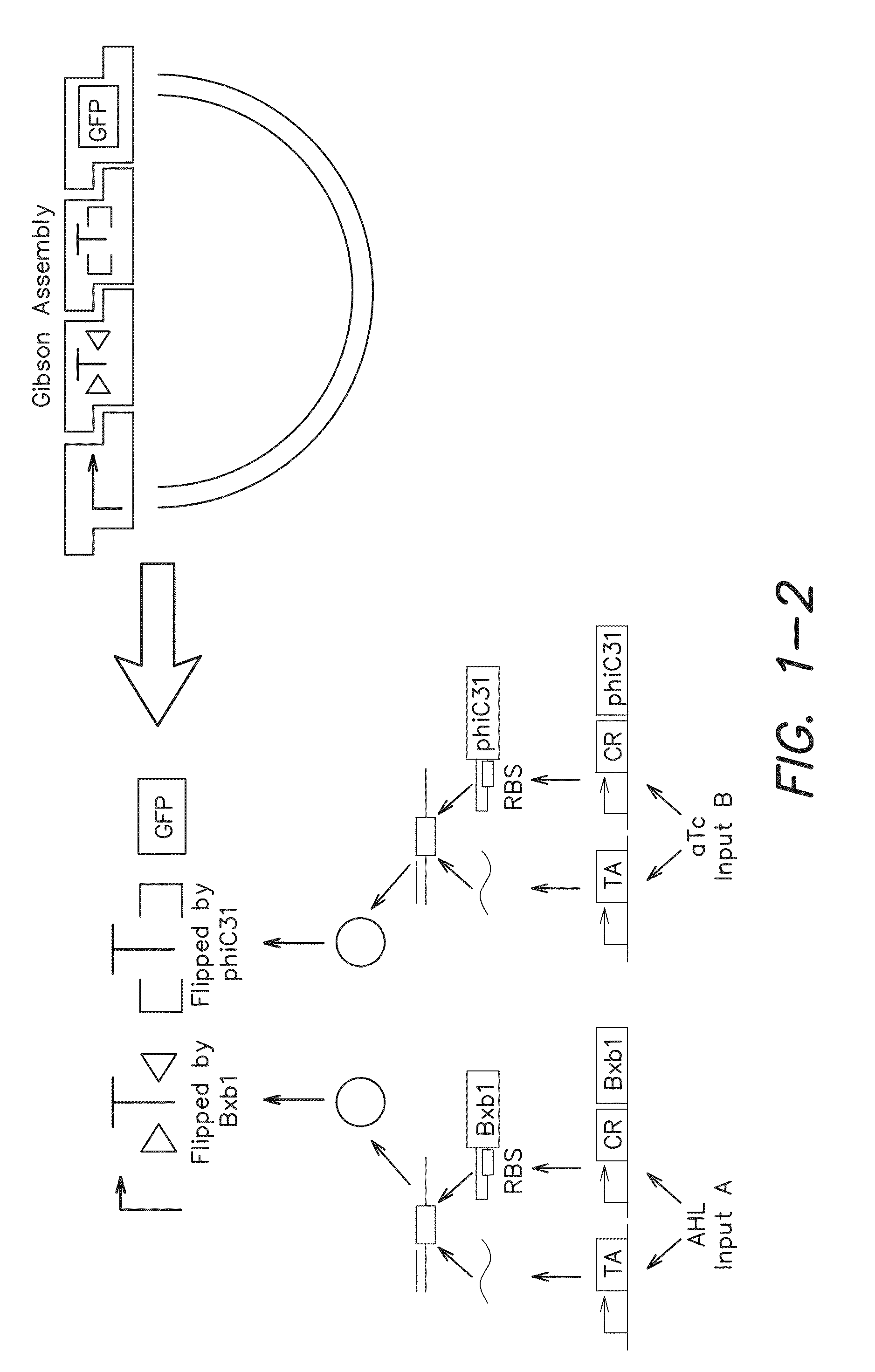
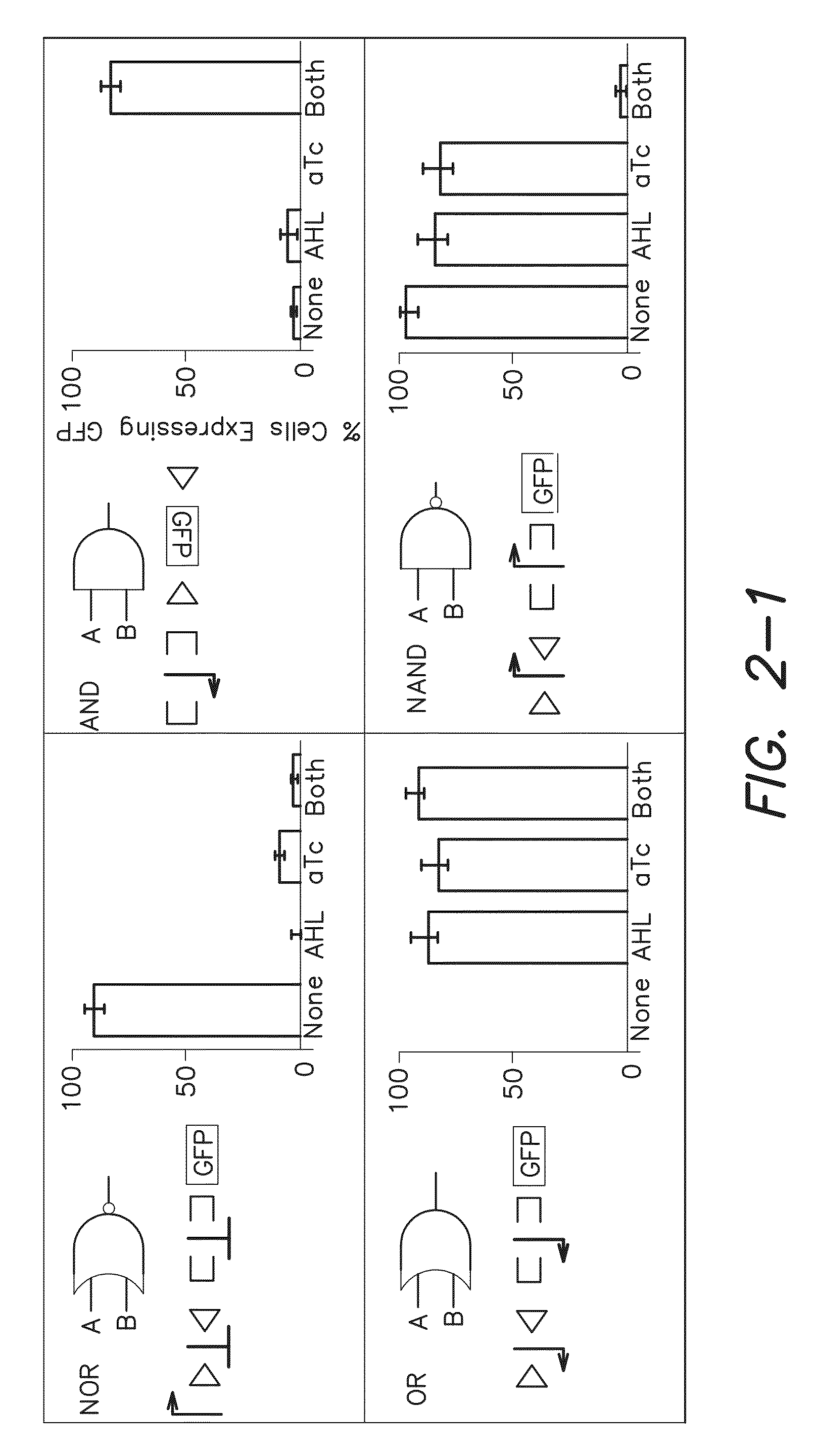
Recombinase-based logic and memory systems
The invention provides, inter alia, recombinase-based systems that provide for integrated logic and memory in living cells.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
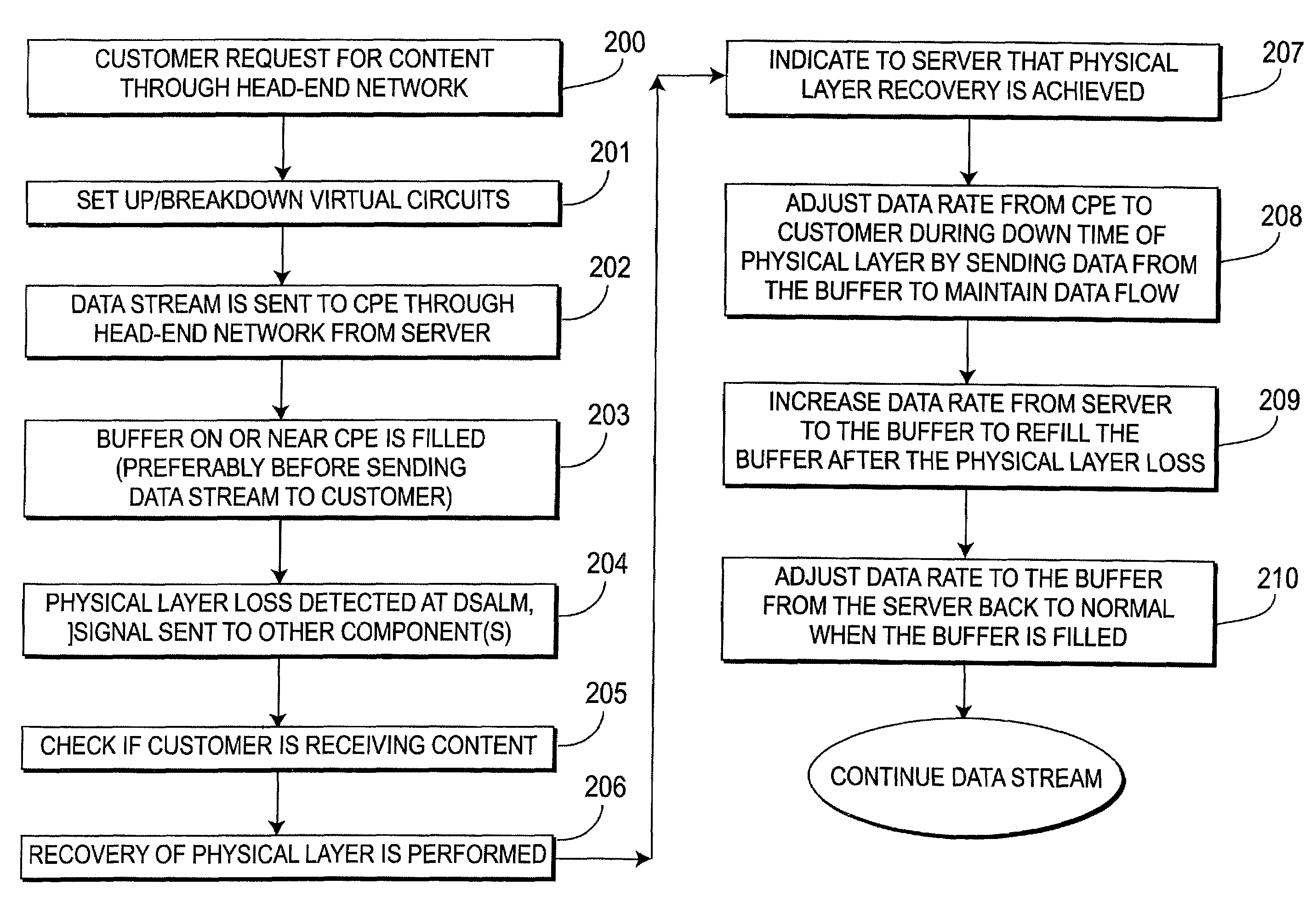
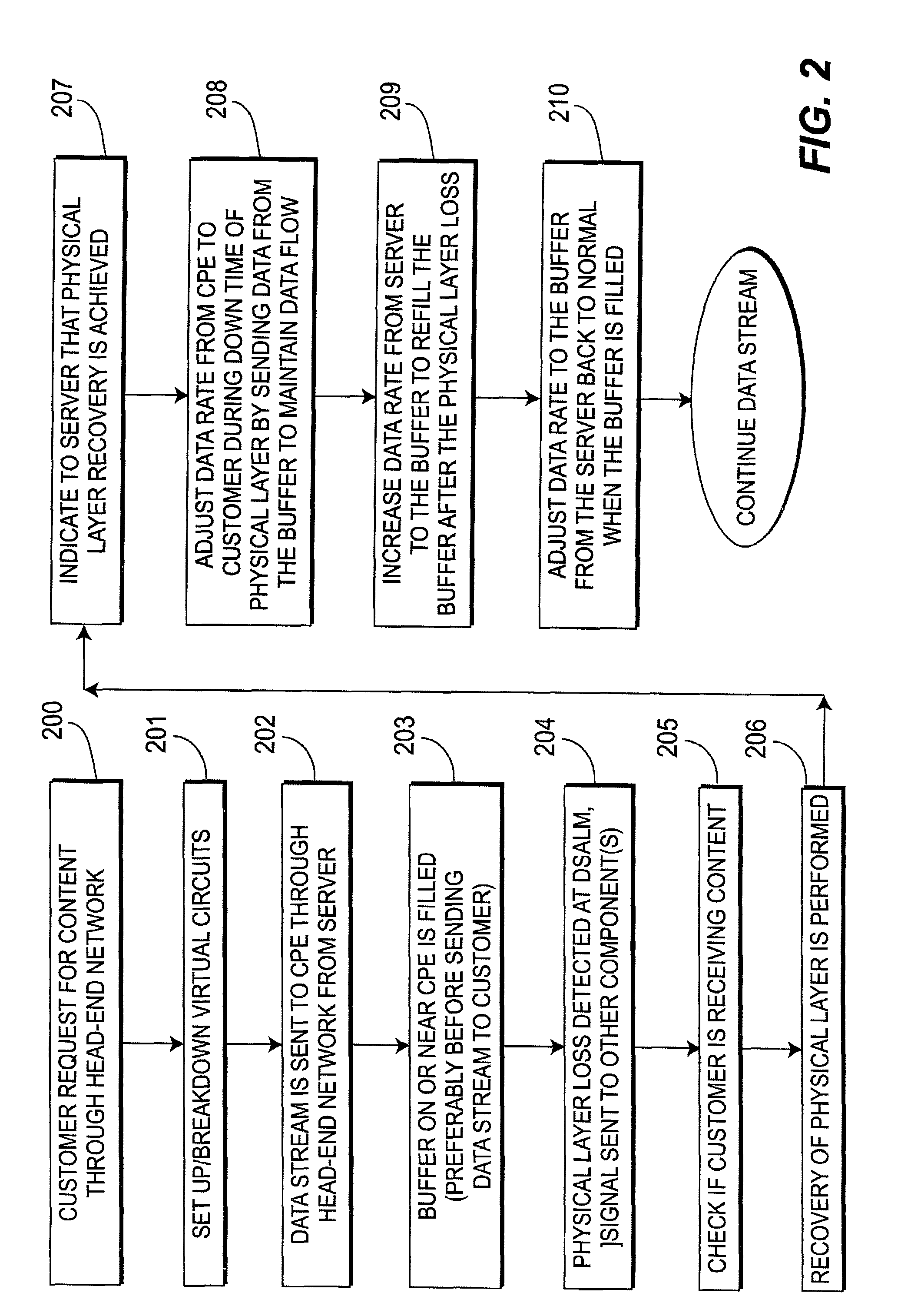
Physical layer recovery in a streaming data delivery system
InactiveUS7512650B2Ensure maintenanceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData streamData rate
An asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) digital document delivery system is provided. A customer premise unit is configured to permit a customer to order and receive a data stream. A buffer is coupled to the customer premise unit to store the data stream before transmitting the data stream to a customer. A server includes digital documents stored thereon for delivery to customers through a switched ATM network. A control mechanism is employed to control a data rate of the data stream between the server and the buffer to ensure maintenance of a steady data stream from the customer premise unit to a customer during a loss of a physical layer between the server and the customer premise unit.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com