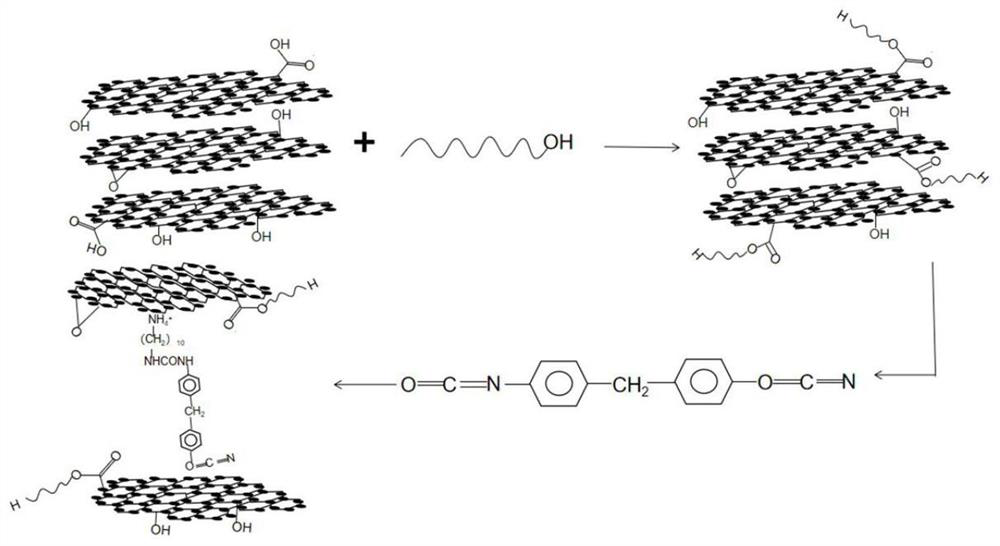
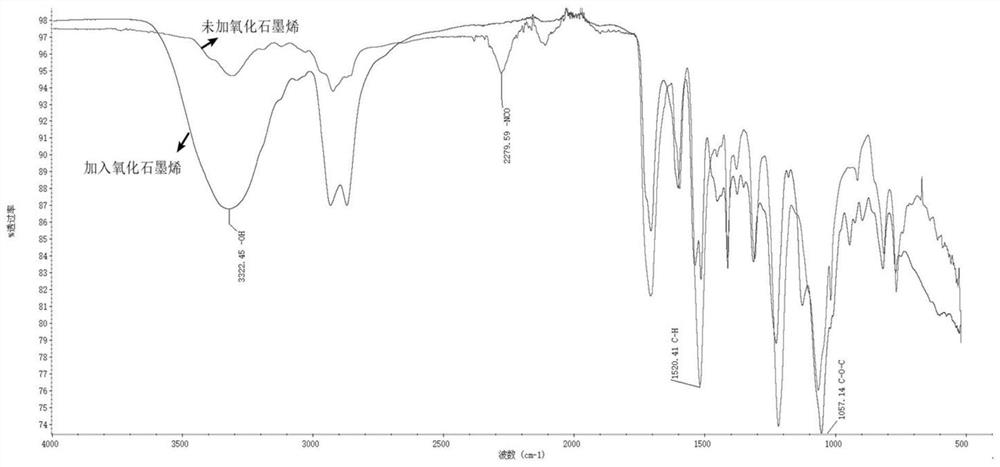
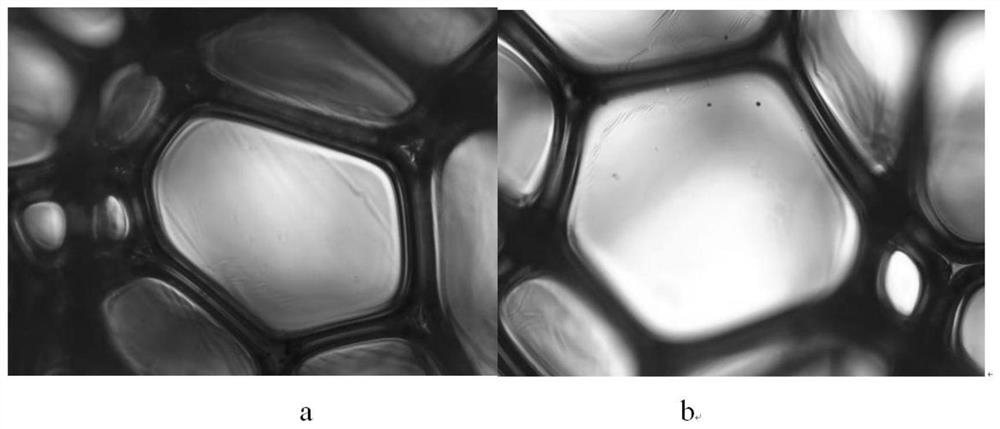
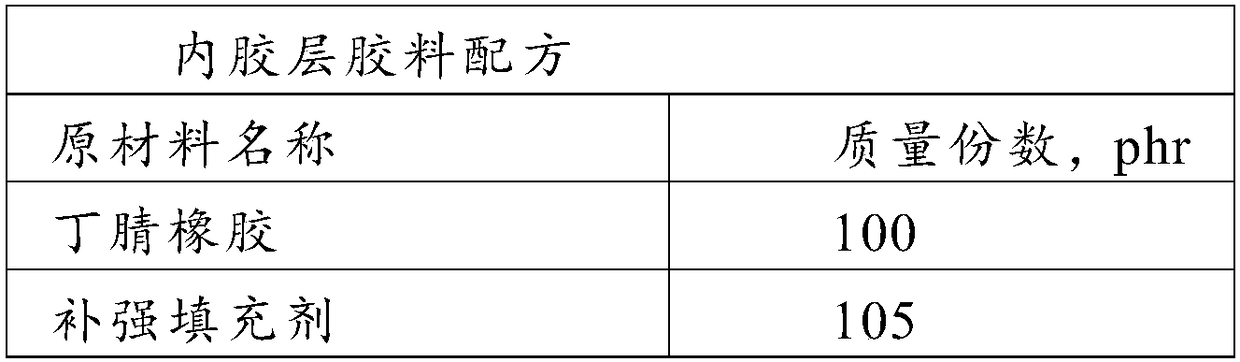
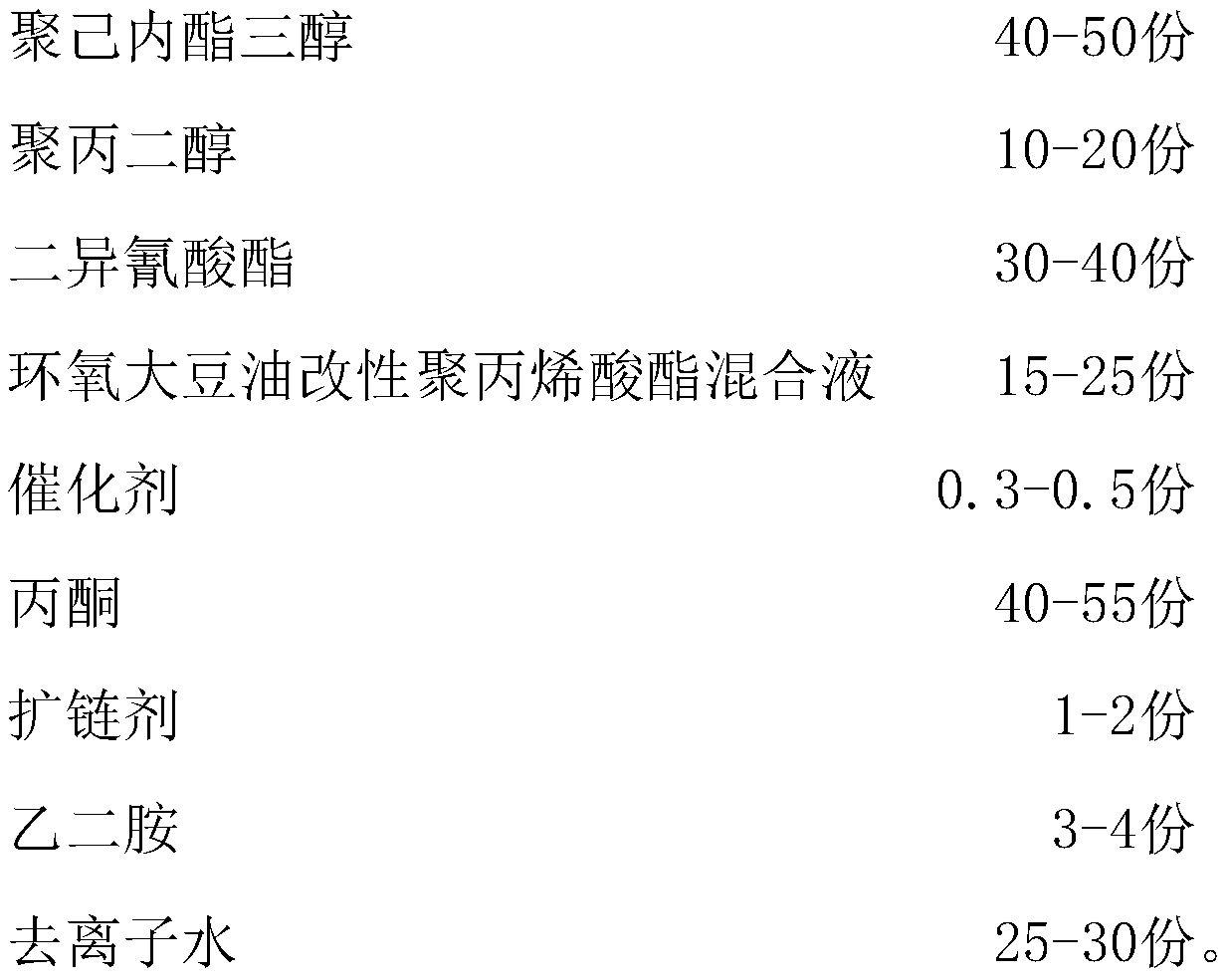
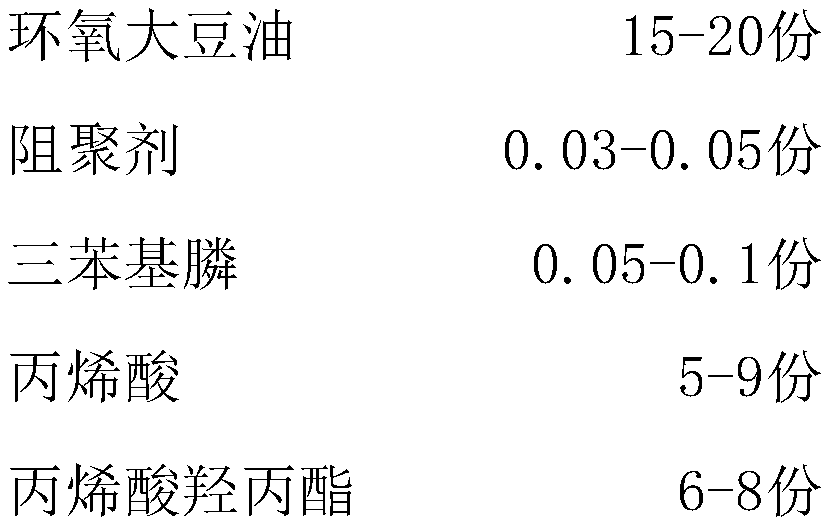
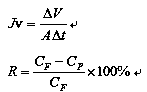Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35results about How to "Good degree of crosslinking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
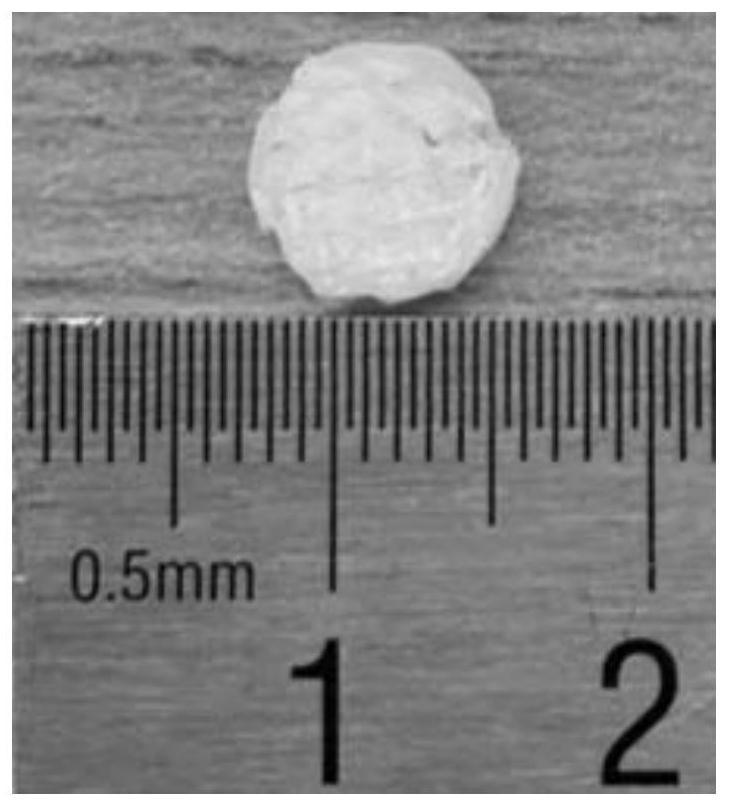
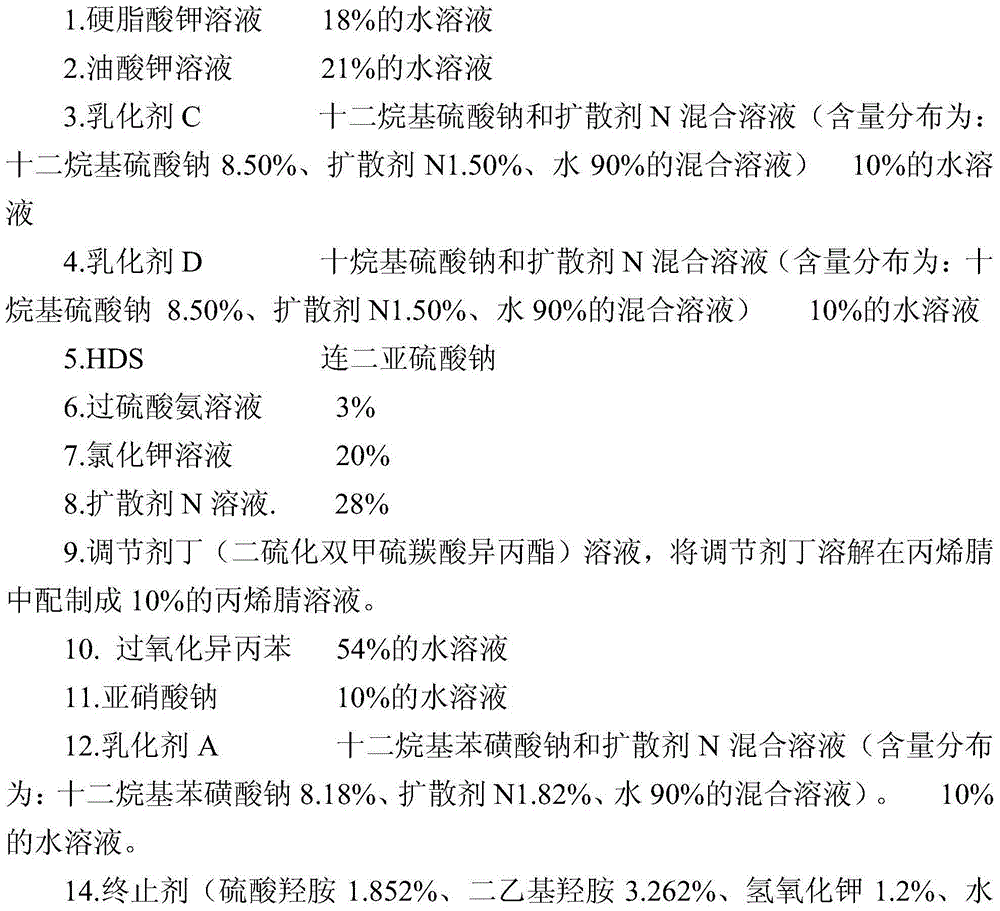
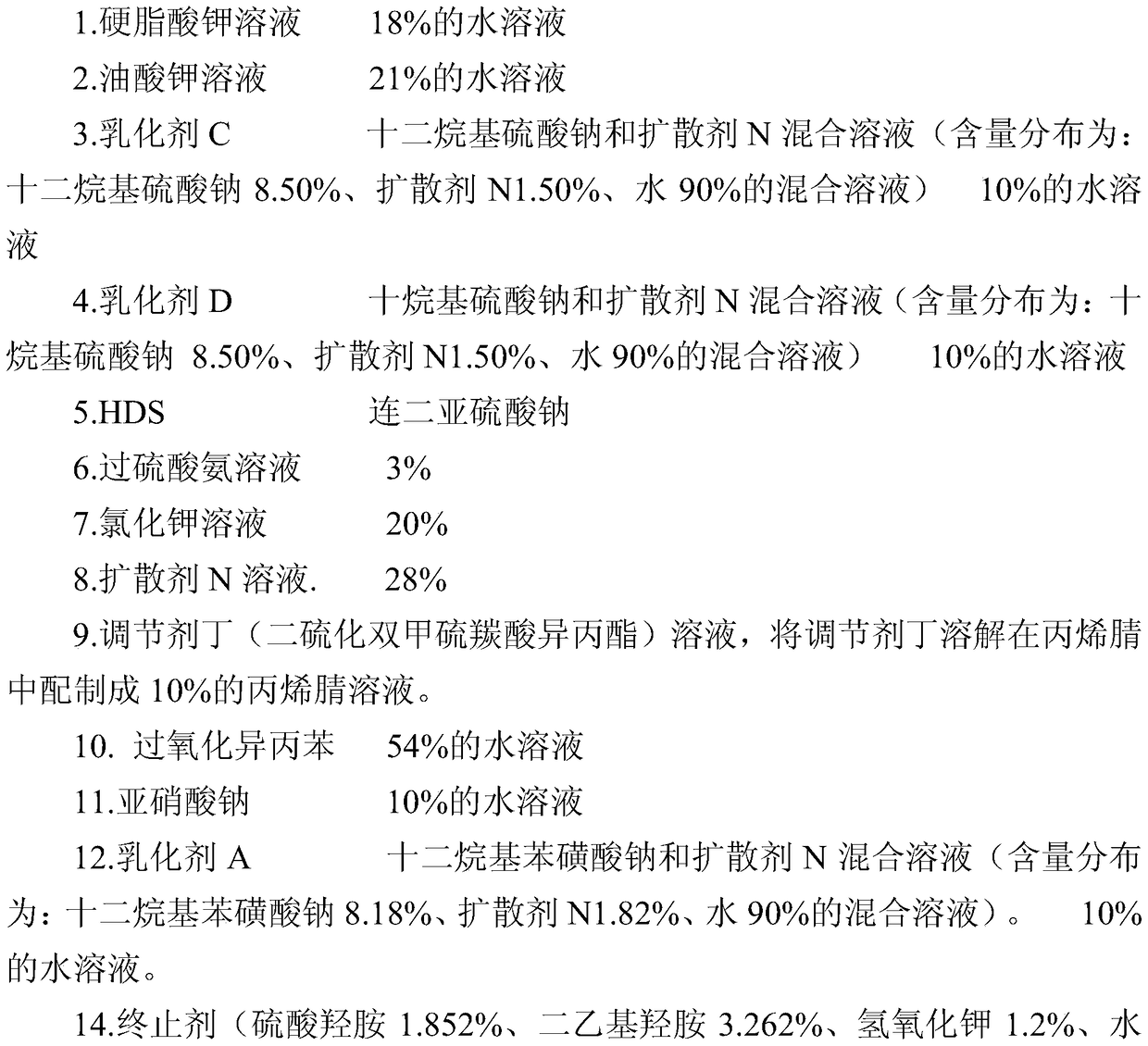
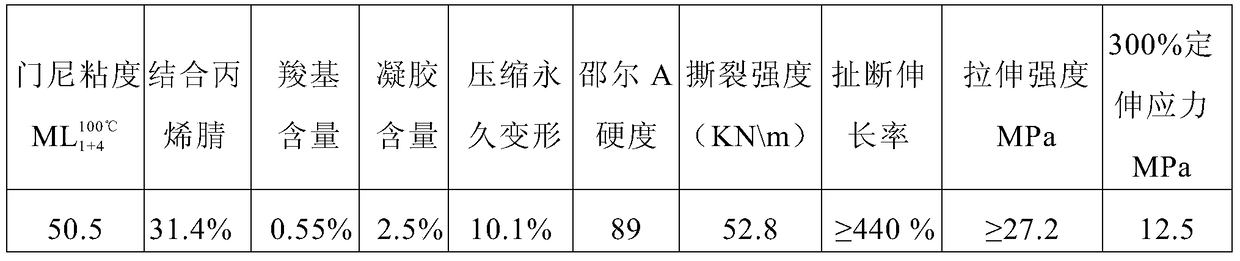
Preparation method of carboxyl nitrile rubber through emulsion polymerization
The invention relates to a preparation method of carboxyl nitrile rubber through emulsion polymerization. According to the preparation method, acrylonitrile, an emulsifier, an adjusting agent, and an initiator are added into a polymerization kettle, then butadiene is added, emulsion polymerization is carried out under stirring, and in the late phase of emulsion polymerization, unsaturated carboxylic acid and / or anhydride thereof is added into the polymerization kettle. The obtained carboxyl nitrile rubber has a low content of gel and a two-layer molecular structure, the index of conjugated acid is controllable; during the processing process, a three-dimensional network structure can be easily formed, thus the mechanical and physical properties of rubber products made of the carboxyl nitrile rubber are good; after processing, the Mooney viscosity is increased, the crosslinking degree of finished products is good, and especially, the elongation at break is prominently improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
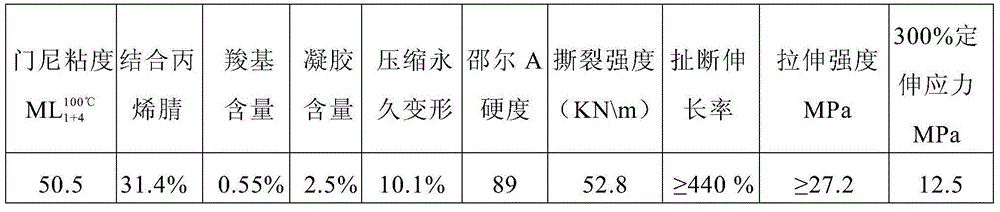
Method of preparing carboxyl styrene butadiene rubber through emulsion polymerization
The invention relates to a method of preparing carboxyl styrene butadiene rubber through emulsion polymerization. According to the method, styrene, an emulsifier, a conditioning agent, and an initiator are added into a polymerization kettle, then butadiene is added to carry out emulsion polymerization under stirring, and in the later period of reactions, unsaturated carboxylic acid and / or unsaturated carboxylic anhydride are added into the polymerization kettle. The prepared carboxyl styrene butadiene rubber has a low gel content, a controllable combined acid index, and a dual layer molecular structure; during the processing process, a three dimensional net-like structure can be formed easily; the mechanical and physical properties of rubber product are good, after processing, Mooney viscosity is increased, the crosslinking degree of finished product is good, and especially, the elongation at break is obviously improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Preparation method of high-strength wear-resistant polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel
ActiveCN111333865AHigh wear resistance and self-lubricationExcellent wear resistance and self-lubricationPolymer scienceCarbon Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-strength wear-resistant polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel. The preparation method is characterized in that the characteristics of high strength, excellentwear resistance, self-lubricating property and easiness in functional modification of a carbon nano material are utilized. The method comprises the steps of introducing a carboxyl group to the surface; compounding with polyvinyl alcohol to prepare polyvinyl alcohol / carbon nano material composite hydrogel; preliminarily forming a gel sample by adopting a freezing and unfreezing crosslinking method; then, the intermolecular hydrogen bonding effect and the crosslinking degree are enhanced through annealing treatment; further soaking the polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel in a saline solution to enable the polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel and metal ions to form a complexing bonding effect, so as to construct a multi-network structure, and effectively play an excellent reinforcing role of the carbon nanoparticles, thereby greatly improving the mechanical strength and the wear-resistant self-lubricating property of the polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel.
Owner:重庆石墨烯研究院有限公司 +1
High wear-resistant high-tenacity rubber sealing element
The invention discloses a high wear-resistant high-tenacity rubber sealing element which comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-50 parts of epichlorohydrin rubber, 12-20 parts of methyl vinyl silicone rubber, 20-30 parts of nitrile rubber, 6-12 parts of kieselguhr, 4-8 parts of calcium carbonate, 2-4 parts of magnesium oxide, 12-16 parts of bismuth oxide, 10-20 parts of barium metaborate, 8-16 parts of a glass bead, 4-8 parts of modified aupoz fiber, 2-4 parts of a dimethyl silicone polymer, 3-6 parts of methylphenyldiethoxysilane, 4-8 parts of an epoxidized fatty acid methyl ester, 1-3 parts of magnesium stearate, 2-4 parts of diisononyl phthalate, 0.4-1 part of triallylisocyanurate, 2-4 parts of zinc diacrylate and 1.5-3 parts of dicumyl peroxide. The high wear-resistant high-tenacity rubber sealing element not only has excellent wear resistance and tenacity, but also has very good high temperature resistance, and meanwhile, the sealing element is difficult to age and long in service life.
Owner:安徽亚兰密封件股份有限公司
Electrical polyvinyl chloride casing
The invention discloses a polyvinyl chloride bushing for electrician. The raw materials include 50-60 parts of polyvinyl chloride, 5-10 parts of zeolite powder, 10-20 parts of talc powder and 10-20 parts of wollastonite powder in parts by weight. , 10-18 parts of fly ash, 8-16 parts of bentonite, 20-30 parts of expanded perlite, 4-8 parts of plasticizer, 1-2 parts of silane coupling agent, 1-2 parts of titanate coupling agent , 5-9 parts of cross-linking agent. The polyvinyl chloride bushing for electrician provided by the invention has good toughness, high pressure resistance, high flexural strength and excellent thermal stability.
Owner:ANHUI LANTONG TECH CO LTD
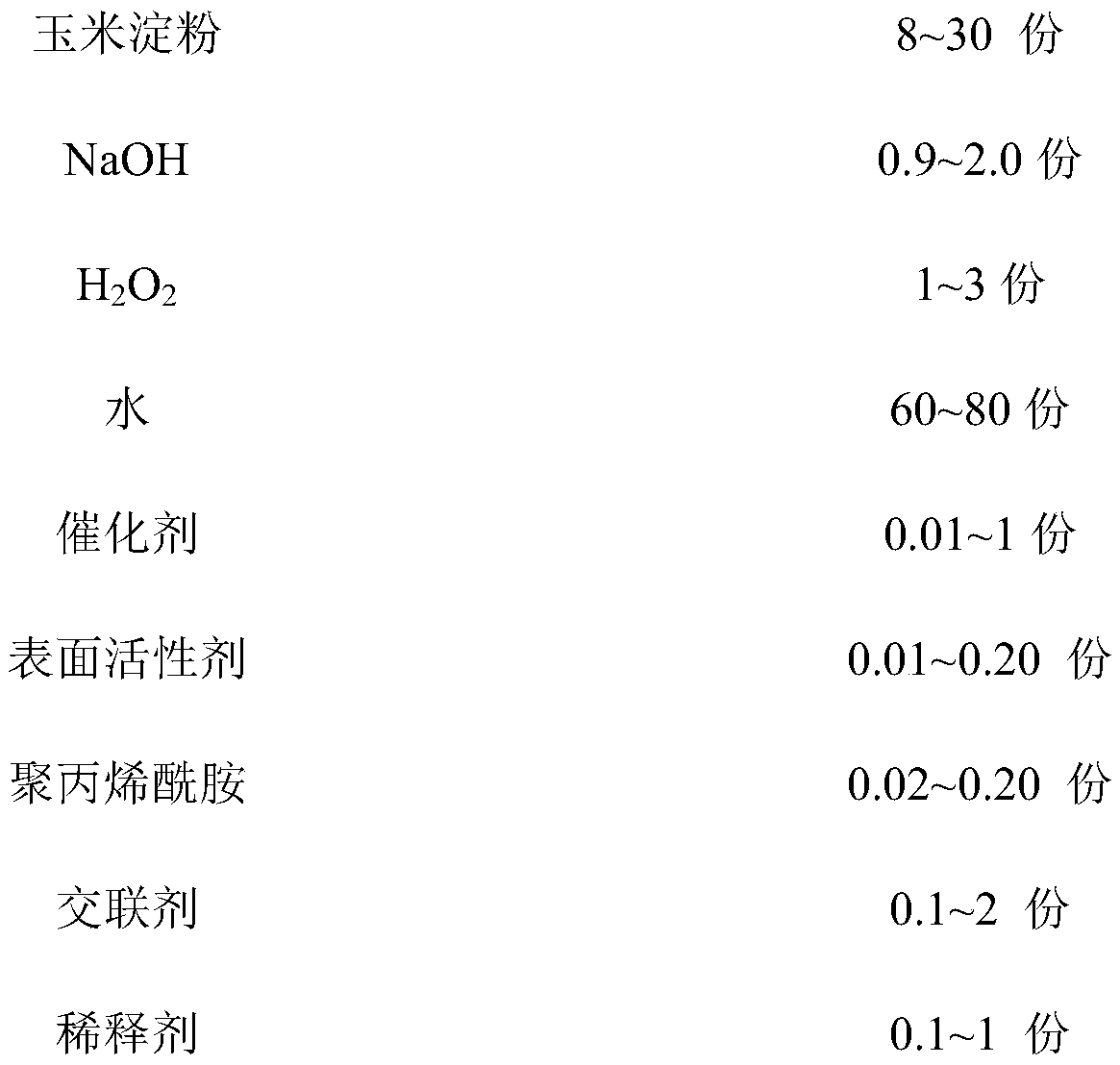
Oxidized corn starch adhesive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110804405AImprove initial tackExcellent adhesionNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesStarch derivtive adhesivesPtru catalystAdhesive
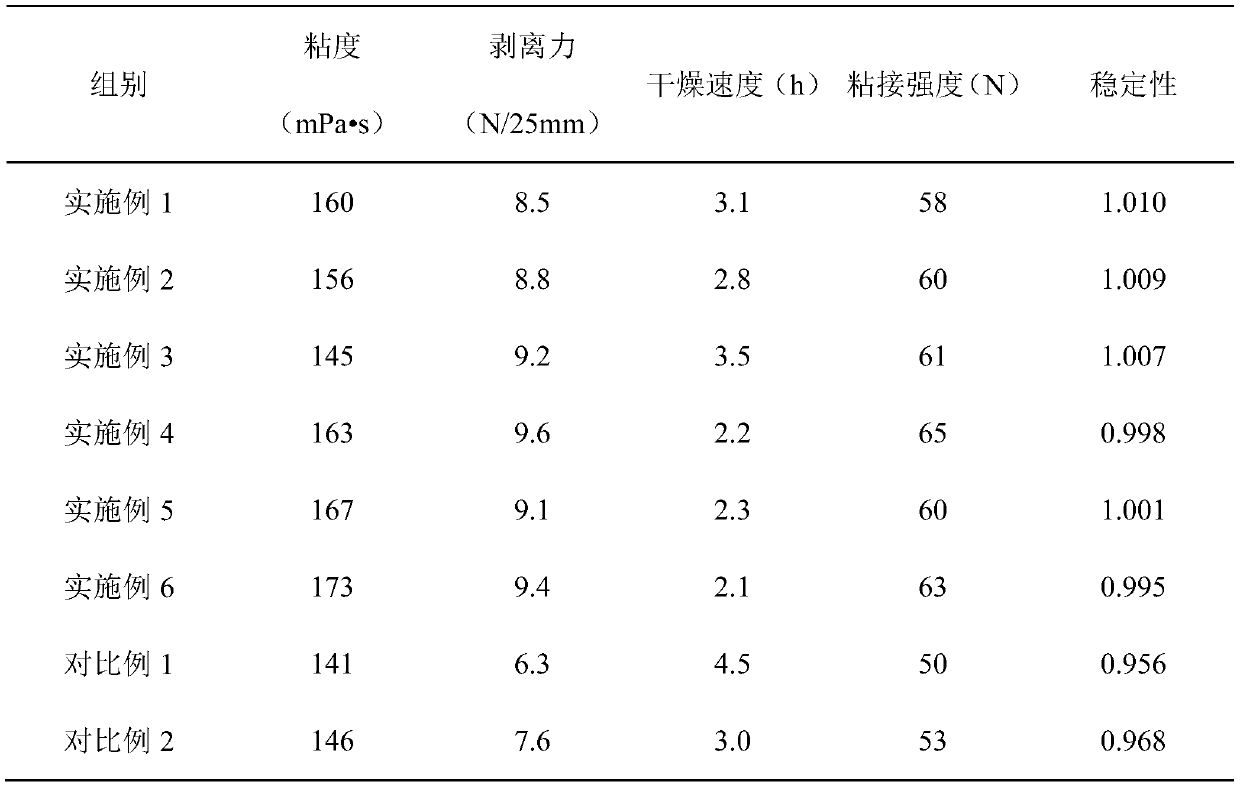
The invention discloses an oxidized corn starch adhesive and a preparation method thereof. The oxidized corn starch adhesive is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 8-30 partsof corn starch, 0.9-2.0 parts of NaOH, 1-3 parts of H2O2, 60-80 parts of water, 0.01-0.12 part of a catalyst, 0.01-0.20 part of a surfactant, 0.02-0.20 part of polyacrylamide, 0.1-2 parts of a cross-linking agent, 0.1-1 part of a diluent, 0.01-0.1 part of a defoaming agent, 0.1-5 parts of a drier and 0.01-0.5 part of a preservative. The preparation method comprises the following steps: pre-gelatinizing, oxidizing, gelatinizing, crosslinking and modifying the corn starch to obtain the oxidized corn starch adhesive; and the prepared oxidized corn starch adhesive is good in mechanical property,large in initial adhesion, high in adhesive force, high in drying speed and good in film-forming property and stability.
Owner:SHAANXI YUTENG IND
Composite gel made from modified rose dreg dietary fibers
ActiveCN108719958ALoose spatial network structureEasy dischargeFood ingredient functionsHardnessUltimate tensile strength
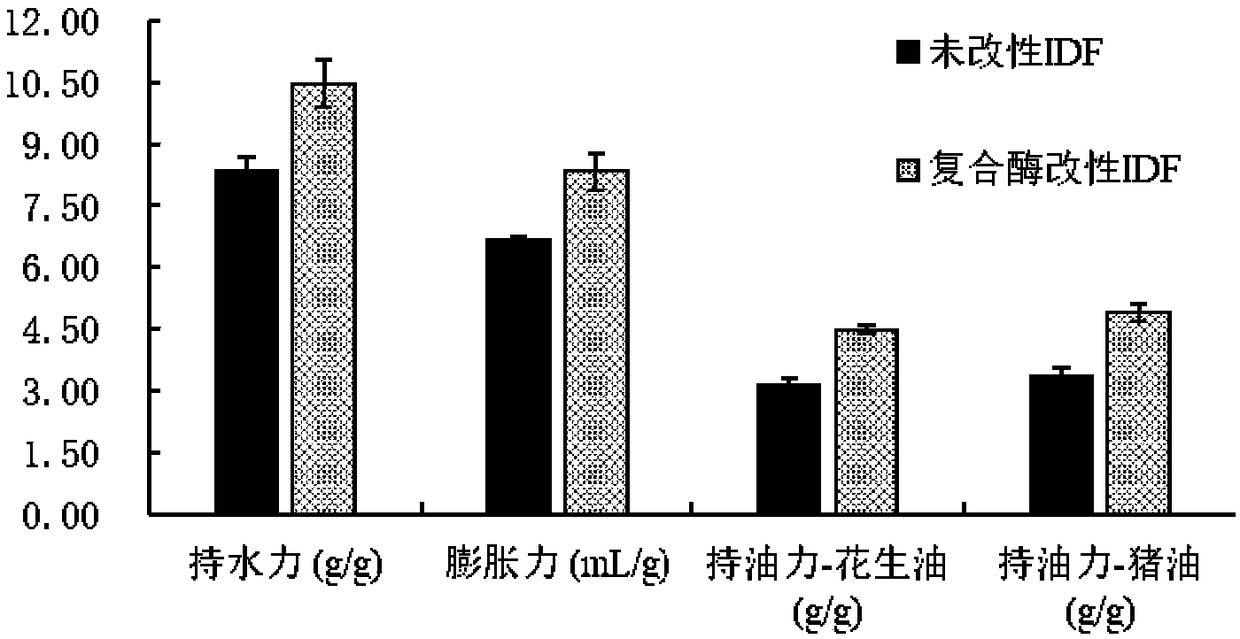
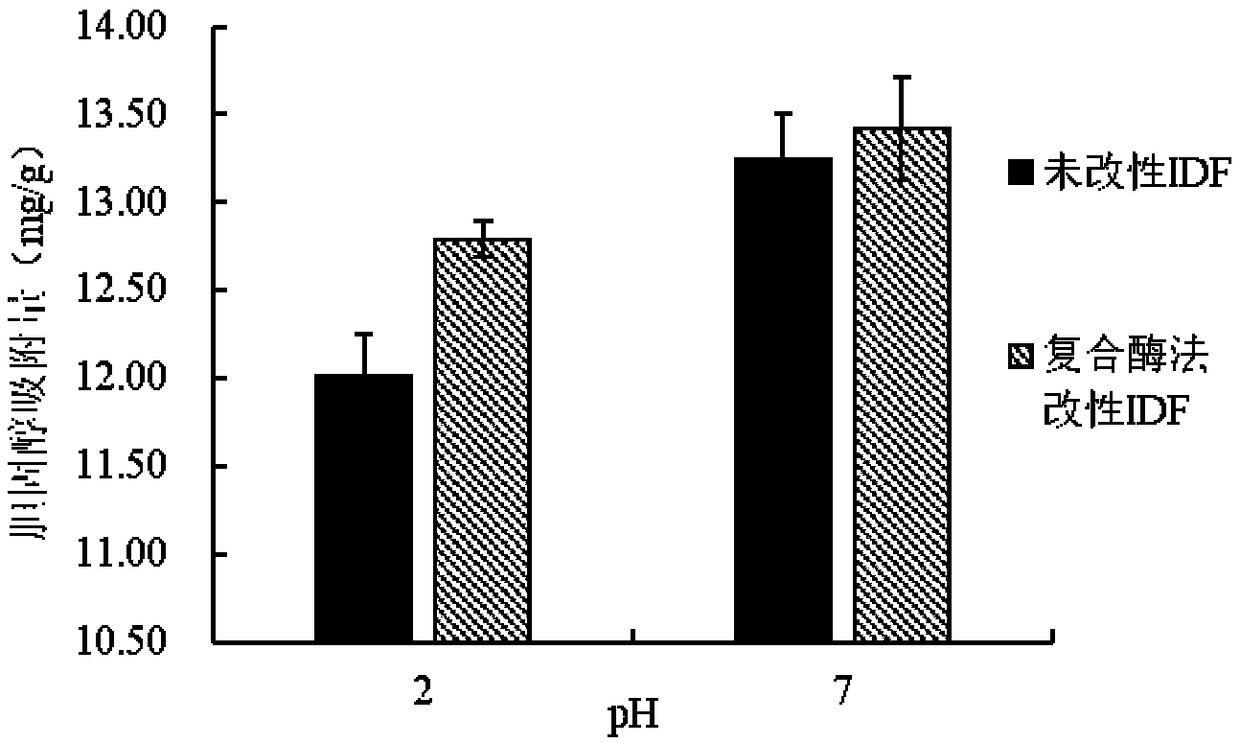
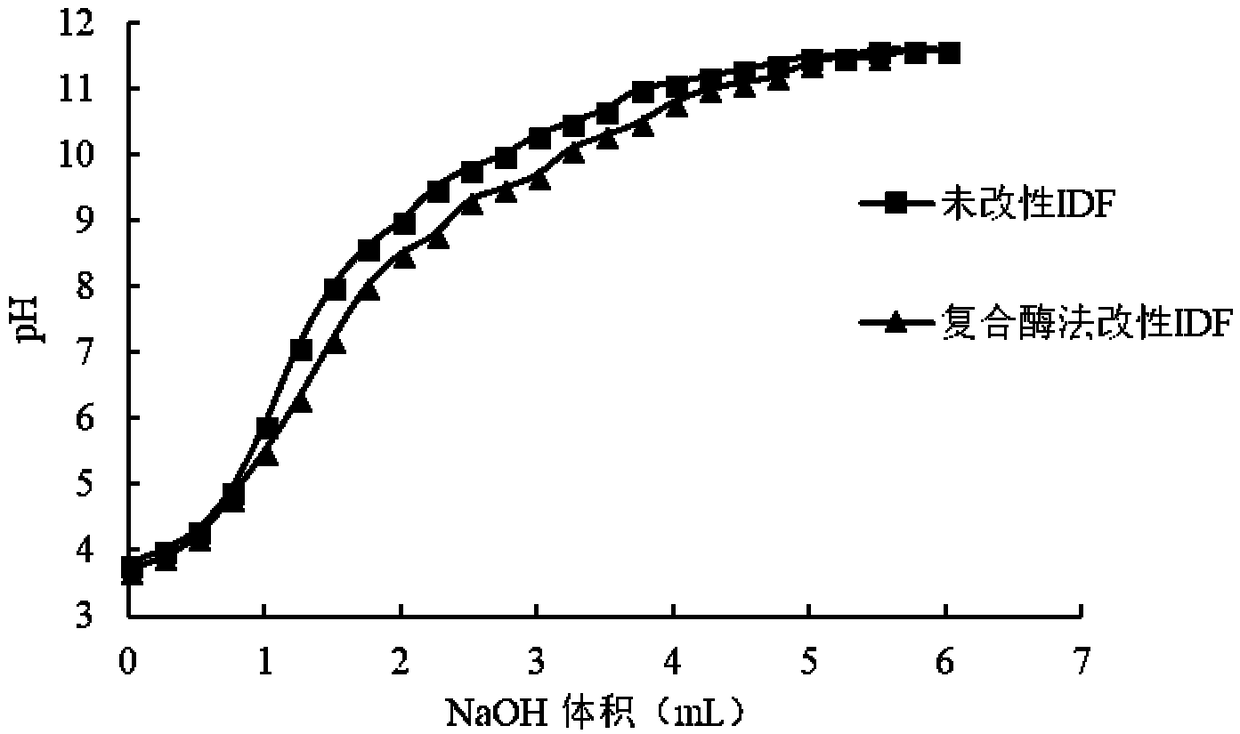
The invention belongs to the technical field of food processing and safety, and particularly relates to composite gel made from modified rose dreg dietary fibers and a preparation method of the composite gel. The composite gel comprises modified rose dreg dietary fibers and gelatin, wherein the content of the modified rose dreg dietary fibers is 0.1-2%, and the content of the gelatin is 5-10%. Themethod creatively uses rose dregs as the source of dietary fibers, and the dietary fibers can be used for preparing the composite gel after being modified. The composite gel has appropriate hardness,elasticity and taste, and can be used as a raw material or an auxiliary material of foods with certain processing intensity.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of graphene/waste polyurethane composite material
The invention belongs to the technical field of waste polyurethane recovery and reutilization, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a graphene / waste polyurethane composite material. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the waste polyurethane rigid foam subjected to crushing and a polyol, graphene oxide and additive blending system meeting different functional requirements are degraded and recycled according to a certain proportion for reutilization, and the graphene oxide / waste polyurethane composite material with excellent performance is prepared by utilizing a degradation product. The material has good thermal stability, thermal insulation performance and the like, and the apparent density, the compression strength, the water absorption rate and the like are all higher than national standards. In the recovery process, three wastes are not discharged, the method is green and environment-friendly, the recovery utilization rate of the waste polyurethane is close to 100%, and the degradation product can be directly utilized without subsequent treatment, so that the cost of the polyurethane rigid foam product is greatly reduced.
Owner:山东东特环保科技有限公司
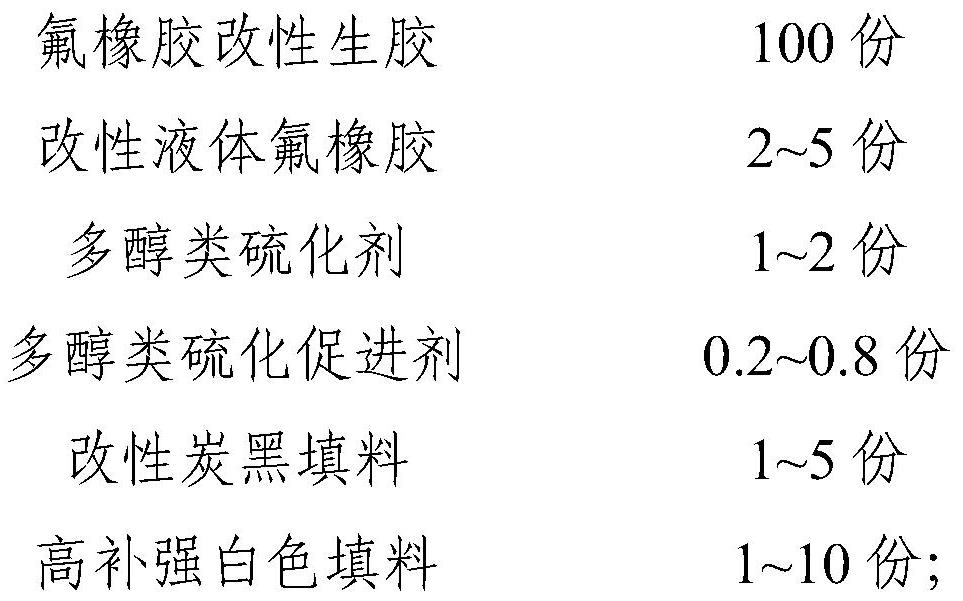
Fluororubber compound, preparation method and application thereof
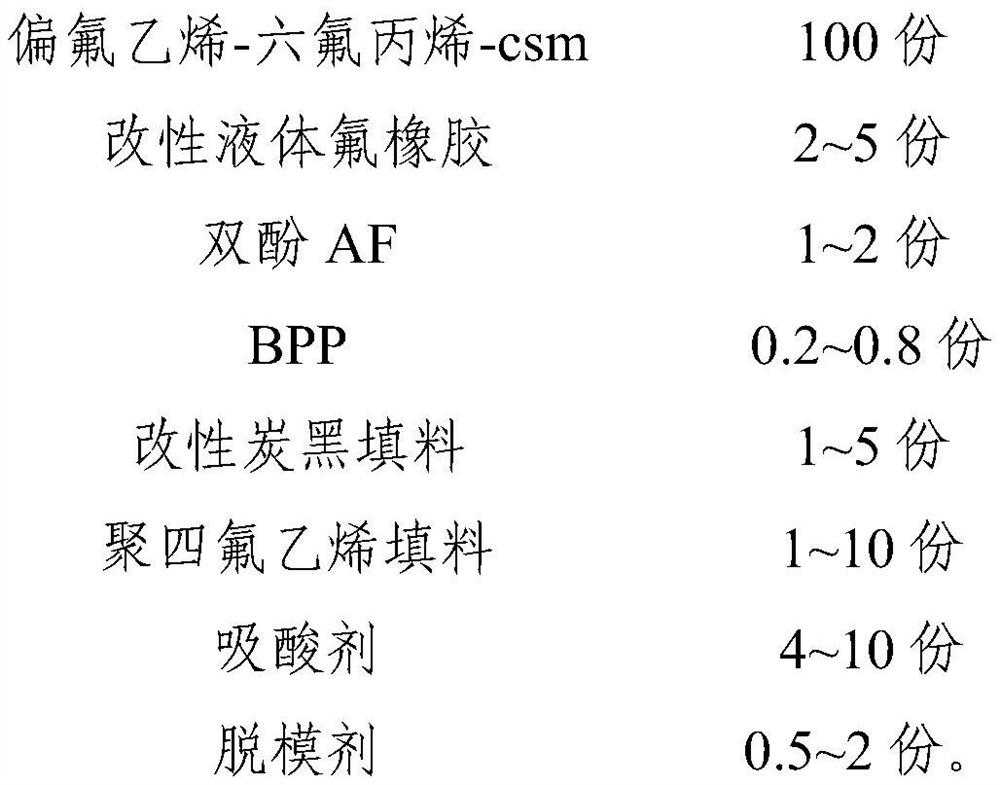
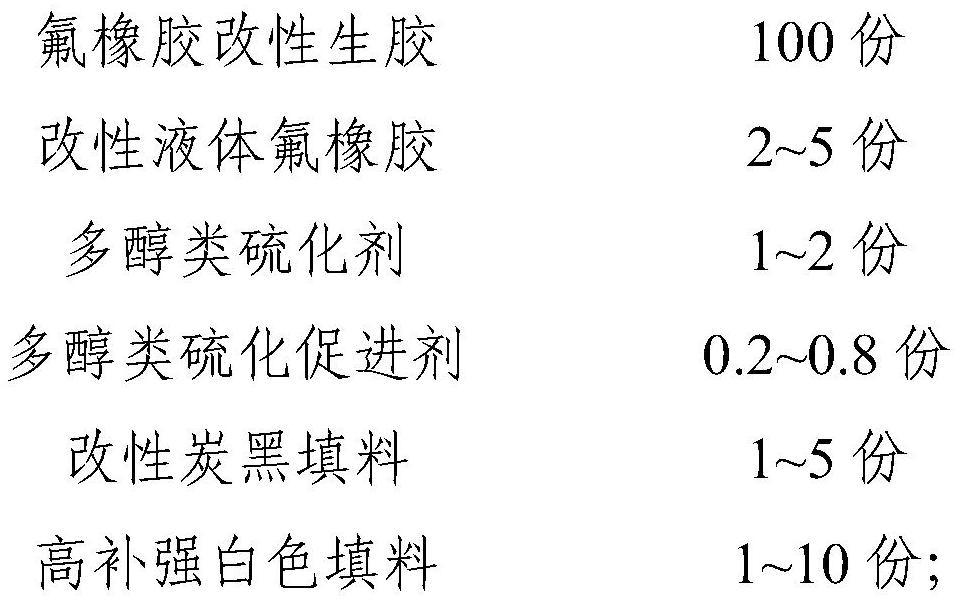
The invention relates to the technical field of rubber, in particular to a fluororubber compound, a preparation method and application thereof. The fluororubber compound is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 100 parts of fluororubber modified raw rubber, 2-5 parts of modified liquid fluororubber, 1.2-2.8 parts of a polyol vulcanizing aid, 1-5 parts of a modified carbon black filler and 1-10 parts of a high-reinforcement white filler. The preparation method of the fluororubber compound comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing the polyol vulcanizing aid, the high-reinforcement white filler, an acid acceptor and a release agent; (2) shearing and mixing the fluororubber modified raw rubber and the modified liquid fluororubber in an open mixing state, and then carrying out internal mixing; (3) adding the mixed additive obtained in the step (1) and modified carbon black filler into the mixed raw rubber, and performing refining; and (4) conducting remilling and thinning in an open mill in the form of a triangular packet. The fluororubber compound disclosed by the invention has high elasticity and low pressure change performance under the condition of extremely low hardness, and can be applied to the fields of automobiles, spaceflight and the like.
Owner:ZHONGHAO CHENGUANG RES INST OF CHEMICALINDUSTRY CO LTD
Preparation method of low-resistance high-transparency conductive film
ActiveCN113096885AGood dispersionGive full play to the conductivityConductive layers on insulating-supportsFinal product manufactureConductive materialsLow resistance
The invention relates to a conductive material technology, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a low-resistance high-transparency conductive film. The method comprises the following steps: performing carboxymethylation on hemicellulose through an etherification reaction, preparing an alkaline urine solution of hemicellulose, adding graphene to prepare gel, and performing hot press molding to obtain the conductive film. The conductive film prepared from carboxymethyl hemicellulose and graphene has excellent toughness, conductivity and visible light transmittance, high density and excellent mechanical properties, the conductivity of the conductive film is not obviously attenuated after the conductive film is bent for multiple times, the conductive film can be repeatedly utilized, and the cost is remarkably reduced.
Owner:佳雅威海新材料科技有限公司
A method for preparing carboxylated styrene-butadiene rubber by emulsion polymerization
ActiveCN105778002BGood physical and mechanical propertiesGood degree of crosslinkingPolymer scienceEmulsion polymerization
The invention relates to a method for preparing carboxylated styrene-butadiene rubber by emulsion polymerization. Styrene, an emulsifier, a regulator, and an initiator are added to a polymerization kettle, and after adding butadiene, emulsion polymerization is carried out under stirring. In the late stage of the reaction, Add unsaturated carboxylic acid and / or its anhydride of unsaturated carboxylic acid into the polymerization tank. The carboxylated styrene-butadiene rubber prepared by the method of the present invention has low gel content, controllable binding acid index, has a double-layer molecular structure, and is easy to form a three-dimensional network shape structure during processing, and has good physical and mechanical properties of rubber products, and is easy to process. After the Mooney viscosity increases, the degree of crosslinking of the finished product is good, especially the elongation at break is significantly improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
A composite scaffold of 3D printed degradable polymer scaffold and photocrosslinked hydrogel
ActiveCN111166933BIncrease the degree of cross-linkingImprove mechanical propertiesTissue regenerationProsthesis3d printPolymer science
The invention relates to a 3D-printed degradable macromolecular scaffold and photo-crosslinked hydrogel composite scaffold. The 3D-printed degradable macromolecular scaffold and photo-crosslinked hydrogel composite scaffold comprises a 3D-printed degradable macromolecular scaffold, wherein the interior of the 3D-printed degradable macromolecular scaffold comprises photo-crosslinked hydrogel with high substitution degree and photo-crosslinked hydrogel with low substitution degree, the photo-crosslinked hydrogel with high substitution degree is crosslinked with the photo-crosslinked hydrogel with low substitution degree, and preferably, a polycaprolactone (PCL) scaffold and methacrylic anhydride gelatin (GelMA) with different substitution degrees are crosslinked and compounded. In the composite scaffold, the 3D-printed degradable macromolecular scaffold has good mechanical properties; the photo-crosslinked hydrogel with high substitution degree has high crosslinking degree, can form a fiber network and micropores, and well supports cells; and the photo-crosslinked hydrogel with low substitution degree has multiple active sites, is beneficial to cell adhesion growth, and can adsorb alarge amount of nutrient solution. Through cooperation of the 3D-printed degradable macromolecular scaffold, the photo-crosslinked hydrogel with high substitution degree and the photo-crosslinked hydrogel with low substitution degree, the composite scaffold is suitable for cell growth and vascularization from an inner layer to an outer layer, and when the composite scaffold is used for medical human body repair, scaffold integration is realized to promote regeneration of new tissues.
Owner:NOVAPRINT THERAPEUTICS SUZHOU CO LTD
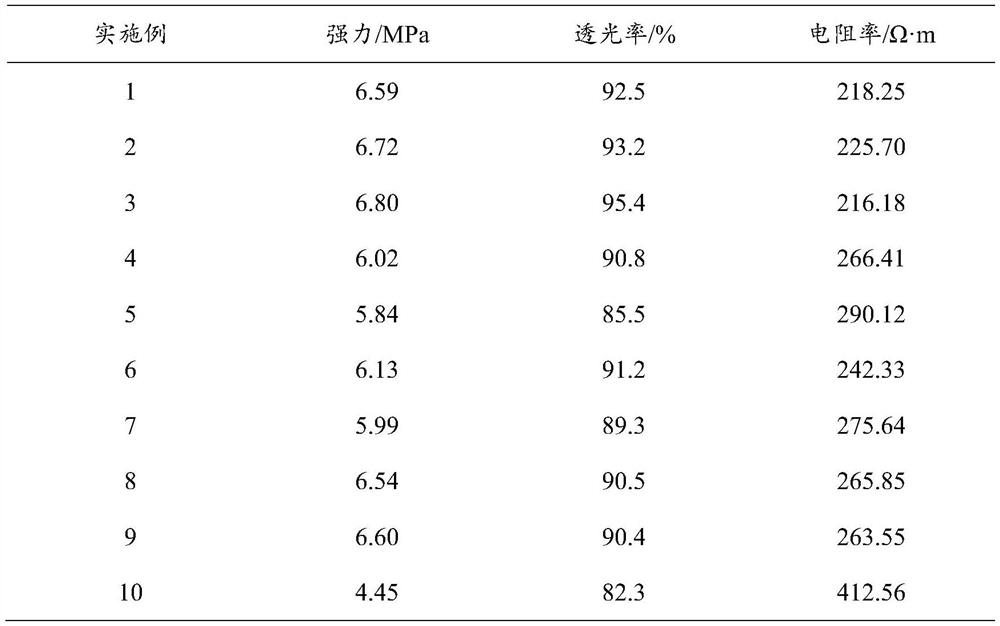
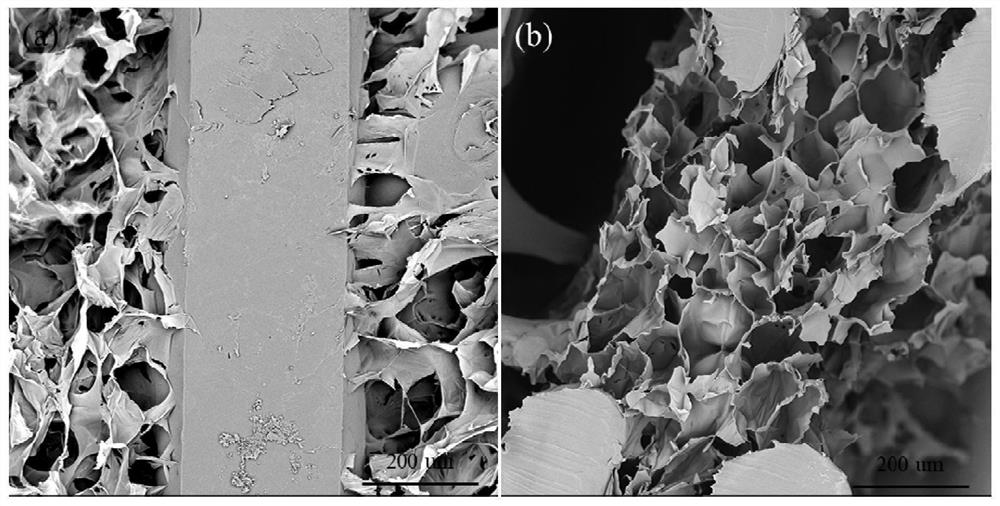
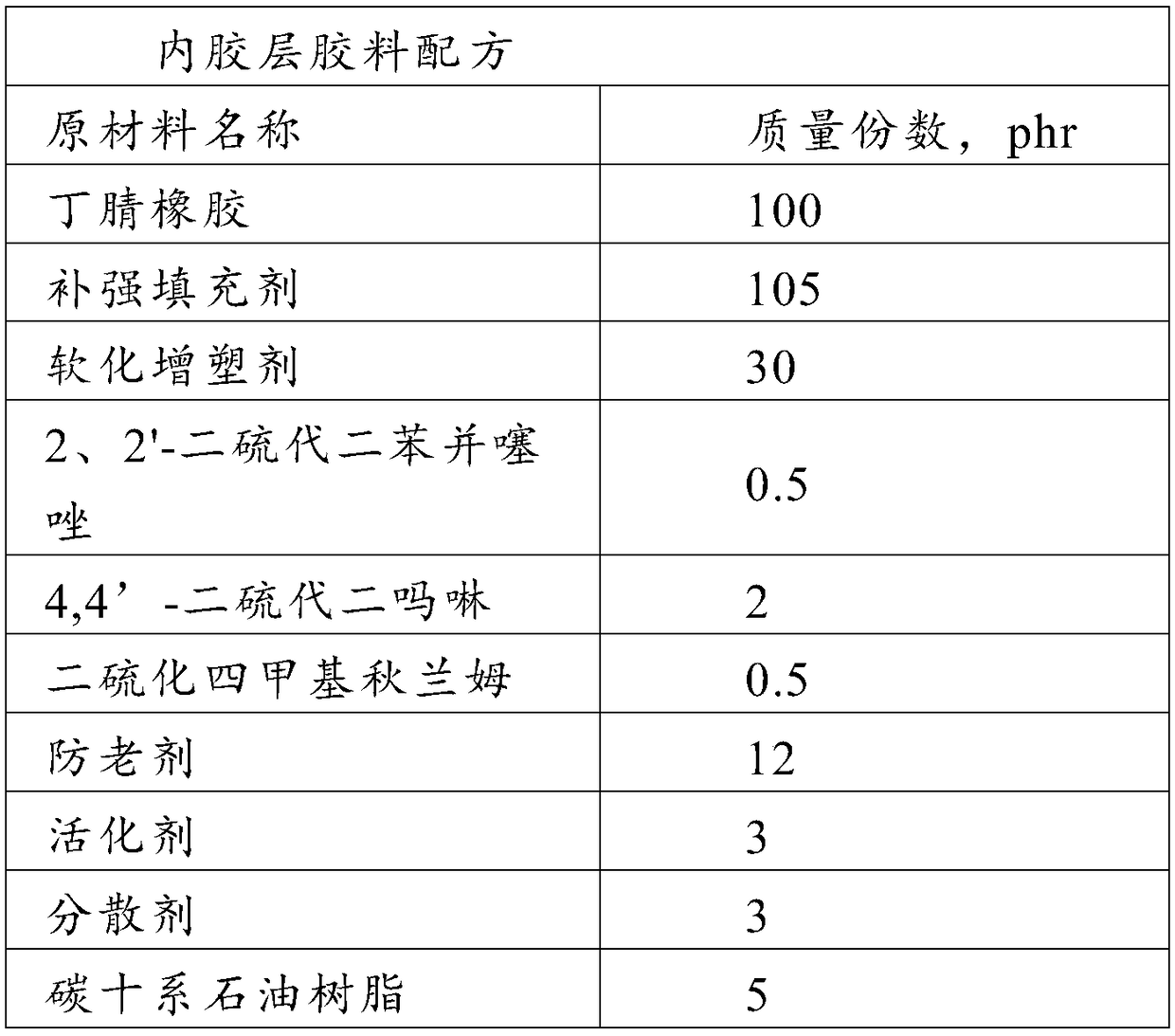
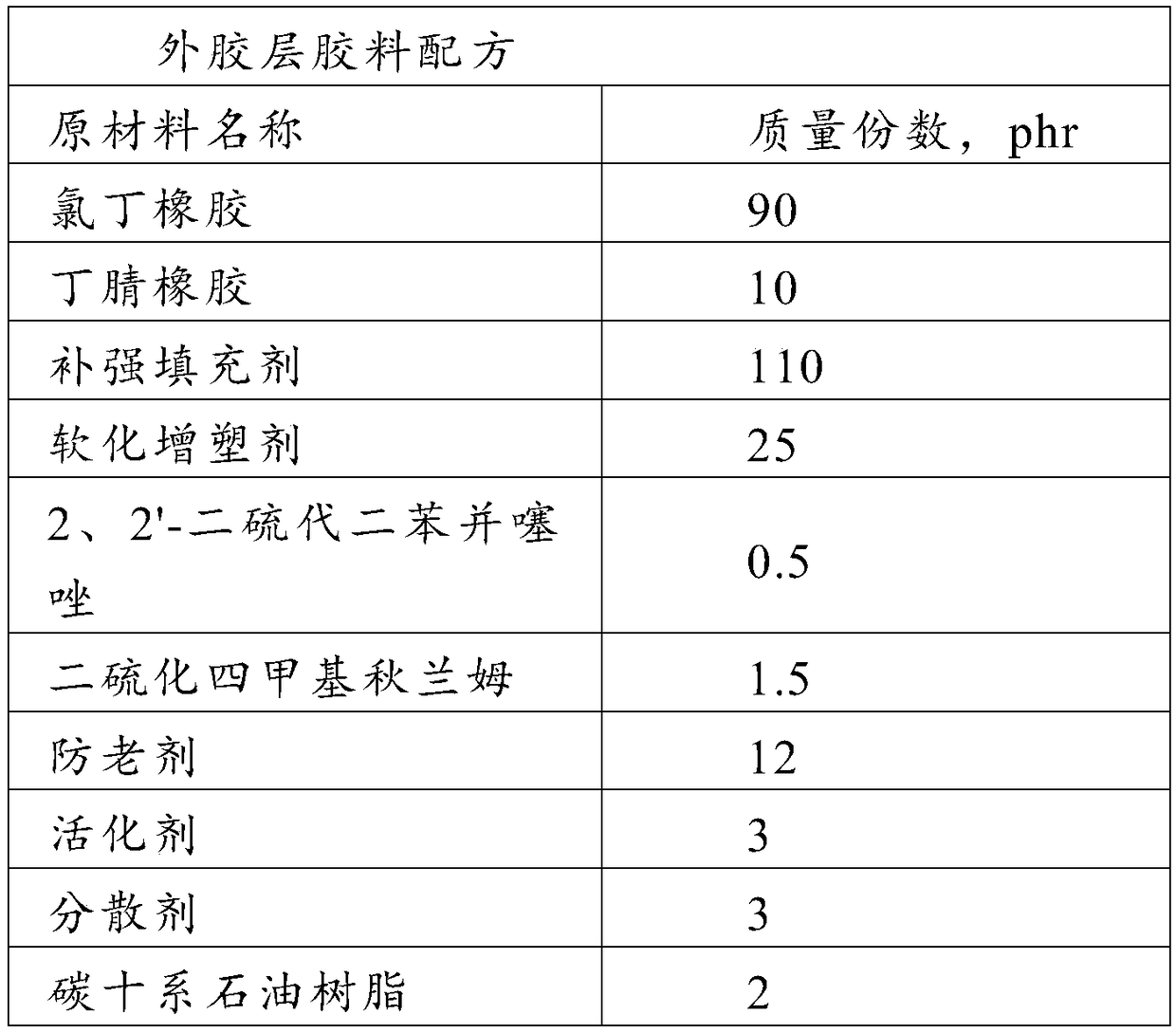
Rubber tube for car and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN108912423AGood degree of crosslinkingHigh bonding strengthFlexible pipesPetroleum resinPlasticizer
The invention discloses a rubber tube for a car and a manufacturing method thereof, belongs to the technical field of rubber products, and solves the problem that the rubber product is relatively poorin bonding strength as a result of a polar relationship between acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber and chloroprene rubber. The rubber tube comprises an inner rubber layer and an outer rubber layer, wherein the inner rubber layer comprises the following raw materials: acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber, a reinforcing filler, a softening plasticizer, 2, 2'- dithiobisbenzothiazole, 4 , 4'- dithiodimorpholine, tetramethyl thiuram disulfide, auxiliaries and C10-series petroleum resin; and the outer rubber layer comprises the following raw materials: chloroprene rubber, acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber, a reinforcing filler, a softening plasticizer, 2, 2'- dithiobisbenzothiazole, tetramethyl thiuram disulfide, auxiliaries and C10-series petroleum resin. The rubber tube provides a rubber product for the car.
Owner:瑞源橡塑制品有限公司
High-toughness polyvinyl chloride tubular product
The invention discloses a high-toughness polyvinyl chloride pipe, the raw materials of which include by weight: 35-42 parts of polyvinyl chloride, 10-18 parts of polyurethane rubber, 20-30 parts of butyl rubber, and 20-30 parts of filling and reinforcing agent 1-2 parts of epoxidized soybean oil, 1-2 parts of magnesium stearate, 1-2 parts of triphenyl phosphate, 1.5-3 parts of compatibilizer, and 2-4 parts of crosslinking agent. The high-toughness polyvinyl chloride pipe provided by the invention has good toughness, high pressure resistance, high flexural strength, and excellent high-temperature stability.
Owner:ANHUI LANTONG TECH CO LTD
Vacuum plastic uptake adhesive with high peel strength and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111454422APromote environmental protectionGood compatibilityPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolymer scienceAdhesive
The invention relates to the technical field of plastic uptake materials, in particular to a high-peel-strength vacuum plastic uptake material and a preparation method thereof, wherein the high-peel-strength vacuum plastic uptake material comprises the following raw materials: polycaprolactone triol, polypropylene glycol, diisocyanate, epoxidized soybean oil / modified polyacrylate mixed solution, acatalyst, acetone, a chain extender, ethylenediamine and deionized water. The vacuum plastic uptake adhesive has higher solid content and lower thermal activation temperature, so that the curing speed is higher, and the film forming time is shorter.
Owner:东莞市冠力胶业有限公司
Reactive polyurethane hot melt adhesive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112694860AReduce generationAvoid foamingPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesPolymer sciencePolyol
The invention relates to a reactive polyurethane hot melt adhesive and a preparation method thereof. The reactive polyurethane hot melt adhesive comprises a component A and a component B, wherein the component A is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 25-50 parts of polyamine of which the functionality is not less than 2, 30-60 parts of polyol with the functionality being not less than 2, 0-30 parts of thermoplastic resin, and 0.01-0.1 part of a catalyst, and the component B is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 90-100 parts of a polyurethane prepolymer with the functionality of not less than 2. The reactive polyurethane hot melt adhesive provided by the invention does not depend on external moisture, does not easily generate gas, and can quickly improve the crosslinking degree and bonding degree in a short time.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIYUN CHEM IND
Self-temperature-control photothermal effect microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN113332499APrecise control of local temperaturePrecise temperature controlEnergy modified materialsInorganic non-active ingredientsVanadium dioxideMicrosphere
The invention relates to the field of medical materials, in particular to a self-temperature-control photothermal effect microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The self-temperature-control photothermal effect microsphere comprises a core layer and a shell layer from inside to outside, the shell layer adopts a tungsten-doped vanadium dioxide / hydrogel intermediate and coats a core body structure of nano-particles with a photothermal effect, the self-control thermal therapy microsphere is obtained by utilizing the influence of W doping on the phase change temperature of the vanadium dioxide nano-particles, and the local temperature of a focus can be accurately controlled through photothermal conversion. According to the self-temperature-control photothermal effect microsphere, the W doped vanadium dioxide nanoparticles are added into the shell layer, the temperature of the microspheres is regulated and controlled through the phase change temperature, and when the doping amount of tungsten is 1.5%-1.85%, the temperature can be controlled at 40-55 DEG C. By controlling the dosage and the type of the hydrogel intermediate, the anionic cross-linking agent and the nanoparticles or the tungsten-doped vanadium dioxide nanoparticles in the core layer and the shell layer, the obtained microspheres have good elasticity and drug loading property.
Owner:上海玮沐医疗科技有限公司
Electrophoretic paint
InactiveCN103952058AGood degree of crosslinkingGuaranteed smoothPaints for electrolytic applicationsEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyElectrophoresis
The invention provides an electrophoretic paint which comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 60-65% of epoxy resin, 5-10% of auxiliaries and 30-40% of a curing agent, wherein 5-10% of the assistant and 25-35% of the curing agent are added into the 60-65% of epoxy resin. Kaolin can enable the grinded product to suspend and be not easy to precipitate. The viscosity is 40-50Pa.s, the thickness of the prepared film is greater than 40 microns, and the crosslinking degree of resin is improved, so that the surface smoothness of the film is ensured while the thickness of the film is adjusted, and thus the demand of the product is met.
Owner:GUANGDE ZHONGYIN CHEM
High-mechanical-strength resin adhesive
InactiveCN106367002AGood compatibilityGood degree of crosslinkingNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesOil/fat/wax adhesivesButadiene-styrene rubberHydroxyethyl cellulose
The invention discloses a high-mechanical-strength resin adhesive which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 120 parts of 191 unsaturated polyester resin, 3-7 parts of benzoperoxide, 10-20 parts of hydroxyethyl cellulose, 4-8 parts of carbon fiber, 8-16 parts of corundum, 6-12 parts of glass powder, 4-10 parts of mica powder, 8-14 parts of graphite powder, 3-7 parts of aluminum oxide powder, 8-12 parts of kaolin, 3-7 parts of calcined argil, 2-4 parts of ground calcium carbonate, 6-12 parts of vapor-phase silicon dioxide, 15-25 parts of epoxy soybean oil, 15-35 parts of modified styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer, 1.5-2.5 parts of dispersing agent and 100-160 parts of water. The high-mechanical-strength resin adhesive disclosed by the invention has the advantages of excellent high-temperature resistance, high polymerization density and high mechanical strength.
Owner:ANHUI SKY EYE INTELLIGENT TECH
A kind of rose dregs modified dietary fiber composite gel
ActiveCN108719958BLoose spatial network structureEasy dischargeFood ingredient functionsBiotechnologyGelatin
The invention belongs to the technical field of food processing and safety, and in particular relates to a rose residue modified dietary fiber composite gel and a preparation method thereof. The composite gel contains rose dregs modified dietary fiber and gelatin, the content of the rose dregs modified dietary fiber is 0.1-2%, and the content of the gelatin is 5-10%. The invention creatively uses rose dregs as a source of dietary fiber, and after modification, it is used to prepare a composite gel, which has suitable hardness, elasticity and taste, and can be used as a raw material for food with certain processing strength.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Rubber plug for puncture-type infusion connecting member heparin cap
The invention discloses a rubber plug for a puncture-type infusion connecting member heparin cap and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The rubber plug comprises, by weight, 100 parts of isoprene rubber, 3-5 parts of transparent zinc oxide, 1-3 parts of stearic acid, 1-1.3 parts of sulfur, 0.1-0.4 part of promoter TRA, 0.1-0.3 part of promoter TMTM and 5-8 parts of lightweight magnesium carbonate. The rubber plug has the advantages of stable physiochemical and biological performance, excellent compatibility with medicine, resistance to perforation, good closing performance after puncture and capability of meeting clinical using needs.
Owner:林洁
Pultrusion method of high-viscosity epoxy resin composition for carbon fibers
The invention provides a pultrusion method of a high-viscosity epoxy resin composition for carbon fibers.Bisphenol A type epoxy resin is taken as a main body resin component, pyridine epoxy resin with bipyridine and terpyridine rings is added, so that the high viscosity and low curing rate of the bisphenol A type epoxy resin are improved, the adhesion and curing speed of the bisphenol A type epoxy resin and carbon fibers are improved, and the interlayer peel strength and mechanical property of a product are improved; meanwhile, polysiloxane polyether glycol, nano filler and chopped fibers are added for toughening. On the other hand, according to the exothermic peak, curing speed and other parameters of the high-viscosity epoxy resin composition, a proper pultrusion process is screened out, the high-viscosity epoxy resin composition has high linear speed and curing speed and high demolding performance, and the obtained product has good surface quality and good mechanical properties.
Owner:广东华彩复合材料有限公司
Preparation method of cross-linked modified polyimide organic solvent-resistant composite membrane, prepared composite membrane and application of the membrane
ActiveCN105944579BExcellent resistance to organic solventsPrevent disengagementMembranesSemi-permeable membranesCross-linkOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cross-linking modified polyimide organic-solvent-resistant composite membrane and the prepared composite membrane and application of the membrane, wherein the preparation method comprises an interfacial polymerization step, a chemical imidization treatment step, a replacement-solvent replacement treatment step and a cross-linking step. A solvent-resistant nanofiltration membrane prepared by the preparation method is greatly enhanced in solvent resistance; further, the separation property of the membrane is not basically changed; the membrane has quite good solvent permeability, further, is simple in preparation process, and has quite good application prospects at the aspects of the separation of an organic solvent system and the treatment of water containing organic solvents.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
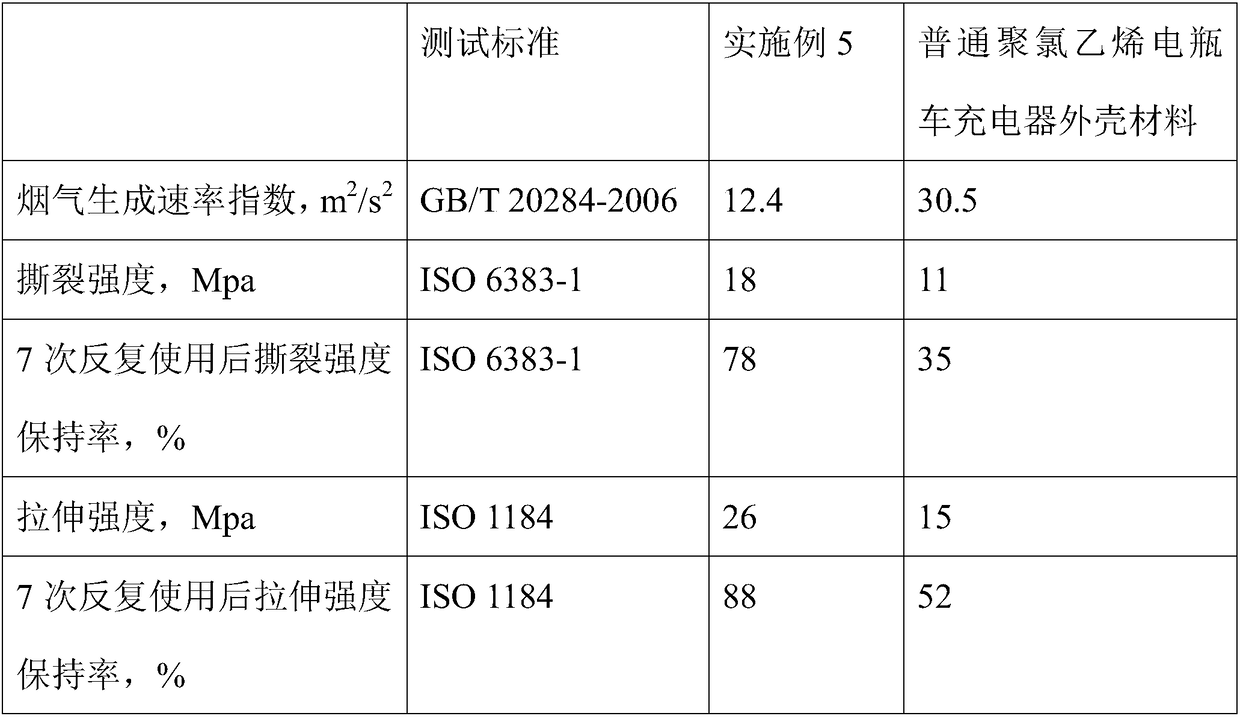
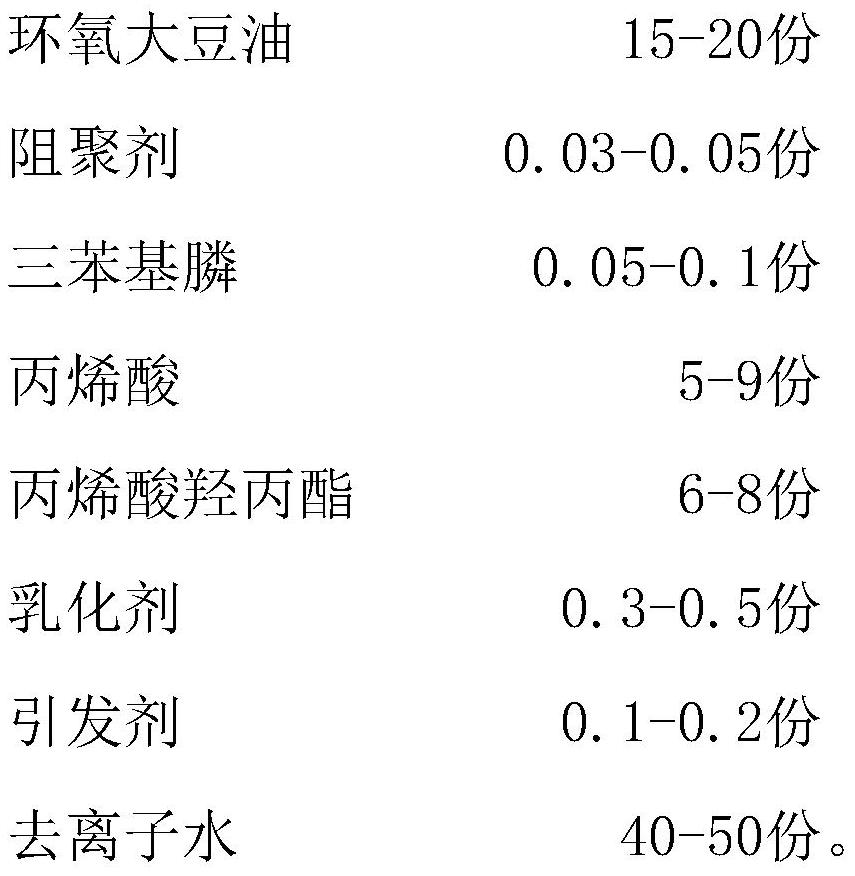
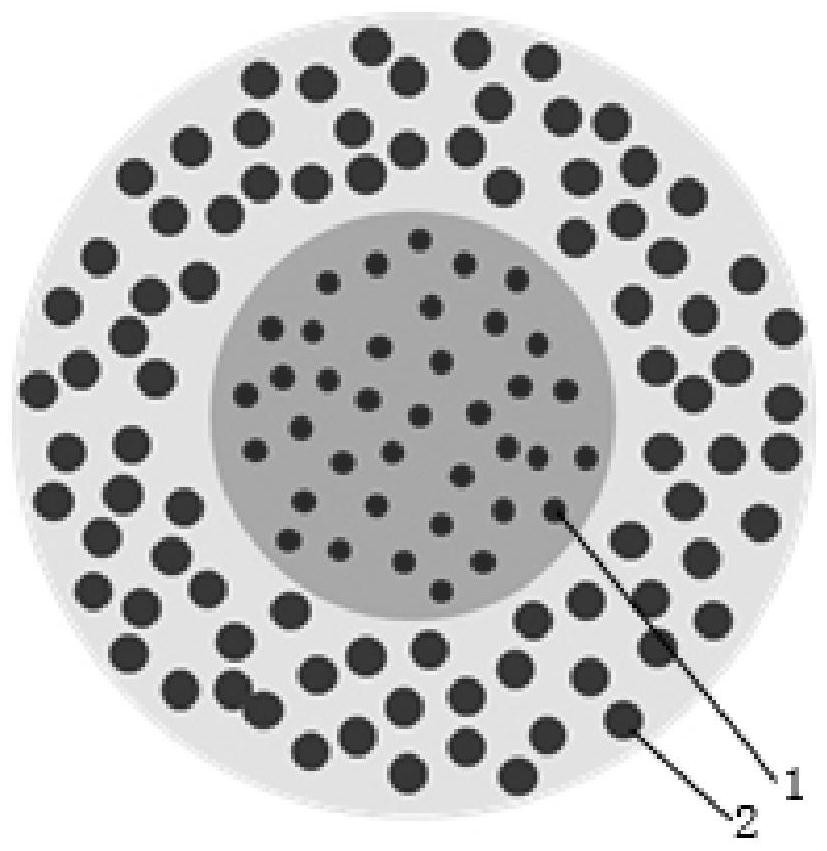
Flame-retardant shell material for battery car chargers
The invention discloses a flame-retardant shell material for battery car chargers. Raw materials of the flame-retardant shell material comprise, by weight, 125-130 parts of a base material, 2-10 partsof modified Sa-son seed gum, 0.3-1 part of disproportionated rosin, 1-2 parts of zinc stearate, 0.4-1 part of 2-ethylhexyl 9,10-epoxyoctadecanoate, 1.5-2.5 parts of a cross-linking agent, 20-30 partsof magnesium hydroxide, 4-12 parts of melamine formaldehyde resin, 8-12 parts of white carbon black, 10-16 parts of coal gangue, 2-8 parts of calcined kaolin, 10-16 parts of sepiolite powder and 0.1-0.6 part of a titanate coupling agent. The modified Sa-son seed gum is prepared by the following steps: stirring Sa-son seed gum, lactalbumin and water, adding the polyurethane fibers and glycerol triglycidyl ether, performing stirring, introducing nitrogen until saturation, adding potassium persulfate, heating and stirring the obtained mixture, filtering the mixture to obtain a precipitate, washing the precipitate, and drying the washed precipitate to obtain the modified Sa-son seed gum.
Owner:天长市优信电器设备有限公司
A kind of vacuum suction plastic with high peeling strength and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111454422BPromote environmental protectionGood compatibilityPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesEpoxyPolymer science
Owner:东莞市冠力胶业有限公司
Sealing part for automobile heat radiator
The invention discloses a sealing part for an automobile heat radiator. The sealing part is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 15-25 parts of fluorous rubber, 20-40 parts of epichloro-hydrin rubber, 8-16 parts of chloroprene rubber, 1-2 parts of dicumyl peroxide, 0.2-0.6 part of triallyl isocyanurate, 1-2 parts of zinc dimethacrylate, 1-4 parts of methylphenyldiethoxysilane, 1-2 parts of polydimethylsiloxane, 2-6 parts of modified bamboo fibers, 5-15 parts of aluminum borate whiskers, 10-14 parts of aluminum oxide, 2-6 parts of anthracite coal, 2-8 parts of apatite, 5-12 parts of attapulgite, 1-2 parts of magnesium oxide, 2-4 parts of chlorinated paraffin, 0.5-1.2 parts of magnesium stearate and 1-2 parts of dioctylterephthalate. The sealing part disclosed by the invention has excellent wear resistance and toughness and also has a very good high-temperature-resisting performance; and meanwhile, the sealing part is not easy to age and the service life is long.
Owner:安徽亚兰密封件股份有限公司
A self-controlling temperature photothermal effect microsphere and its preparation method
InactiveCN113332499BPrecise control of local temperaturePrecise temperature controlEnergy modified materialsInorganic non-active ingredientsVanadium dioxideMicrosphere
The invention relates to the field of medical materials, more specifically, the invention relates to a self-controlling temperature photothermal effect microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The microspheres include a core layer and a shell layer from the inside to the outside. The shell layer uses a tungsten-doped vanadium dioxide / hydrogel intermediate to cover the core structure of nanoparticles containing photothermal effects. Influenced by the phase transition temperature of vanadium oxide nanoparticles, self-controlling thermotherapy microspheres can be obtained, and the local temperature of the lesion can be precisely controlled through photothermal conversion. The invention adds W doping to the vanadium dioxide nanoparticles in the shell layer, and controls the temperature of the microspheres through the phase transition temperature, and when the doping amount of tungsten is 1.5-1.85%, the temperature can be controlled at 40-55°C. By controlling the dosage and types of hydrogel intermediates, anionic crosslinking agents and nanoparticles or tungsten-doped vanadium dioxide nanoparticles in the core layer and the shell layer, the obtained microspheres have good elasticity and drug-loading properties.
Owner:上海玮沐医疗科技有限公司
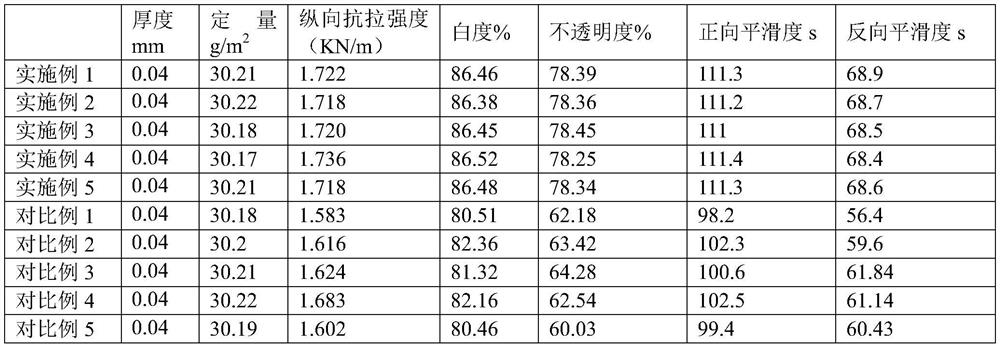
Preparation method of highly filled bible paper
InactiveCN112064399AImprove filler retentionHigh densityDefoamers additionMechanical paper treatmentPapermakingSizing
The invention relates to the technical field of papermaking, and provides a preparation method of highly-filled bible paper in order to solve the problem that the retention rate of filler in the biblepaper is low. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) pulping: mixing and pulping raw material pulp, modified filler and an auxiliary agent to prepare mixed pulp; (2) raw paper preparing: sequentially performing alkaline solution soaking, net part dehydration, squeezing and pre-drying on the mixed pulp to obtain raw paper; (3) sizing: entering a surface sizing treatment procedure, and performing surface sizing on the raw paper in the step (2) by adopting a high-pressure filling sizing agent to obtain a paper sheet subjected to surface sizing treatment; and (4) post-treatment: carrying out post-drying, calendaring and finishing on the paper sheet subjected to surface sizing treatment, and rolling to obtain a finished product. By modifying the surface of the filler, introducing the high-fluidity sizing emulsion and improving the paper preparation process, the bible paper which is good in integrity, uniform in filler dispersion, high in filler retention rate and highin opacity is finally prepared.
Owner:浙江哲丰新材料有限公司
A kind of method that emulsion polymerization prepares carboxylated nitrile butadiene rubber
The invention relates to a method for preparing carboxylated nitrile rubber by emulsion polymerization. Acrylonitrile, emulsifier, regulator and initiator are added to a polymerization kettle, and after adding butadiene, emulsion polymerization is carried out under stirring. In the later stage of the reaction, the The unsaturated carboxylic acid and / or its anhydride are added to the polymerization tank at the end of the reaction. The carboxyl nitrile butadiene rubber prepared by the method of the present invention has low gel content, controllable binding acid index, has a double-layer molecular structure, and is easy to form a three-dimensional network shape structure in the processing process, and has good physical and mechanical properties of the rubber product, and is easy to process. After the Mooney viscosity increases, the degree of crosslinking of the finished product is good, especially the elongation at break is significantly improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Production method of photovoltaic roof tiles
ActiveCN101974962BControl displacementImprove alignment accuracyRoof covering using slabs/sheetsRoof covering using tiles/slatesRoof tileRoom temperature
The invention relates to a production method of photovoltaic roof tiles, which comprises the following steps: laminating in twice, and simultaneously stacking in twice, wherein in the primary laminating, products are initially evacuated, silicon cell chips are initially positioned, and package sealing compounds are initially hot melted and crosslinked; and a second layer of package sealing compounds is laid after the temperature is reduced to room temperature, and the secondary laminating is carried out after a glass covering plate is placed on the package sealing compounds. The invention hastwo-time laminating technology so as to effectively control the offset of the silicon cell chips in the laminating process, extremely improve the arrangement accuracy of cell units, and extremely reduce fracture of tile type back pieces and the silicon cell chips; optimized technology parameters ensure the optimum crosslinking extent of the package sealing compounds, and ensure the ultraviolet and aging resistant performance of the products to the full extent; and simultaneously, the optimized technology parameters are greatly reduced so as to basically avoid bubbles remained in the products.
Owner:浙江贝盛绿能科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com