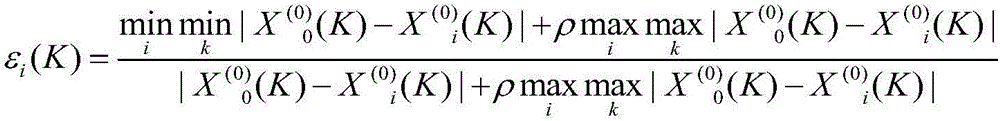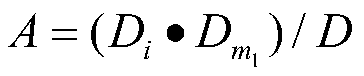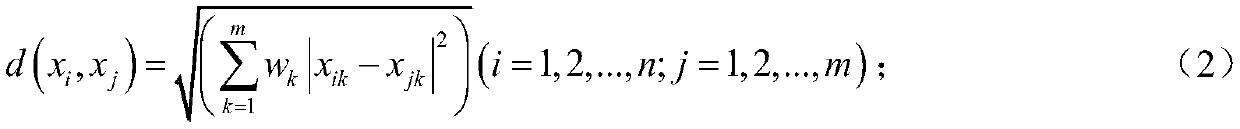Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56results about How to "Improve clustering quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
LDA fusion model and multilayer clustering-based news topic detection method
InactiveCN107423337AGood impetusImprove clustering qualitySemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsData dredgingTime complexity
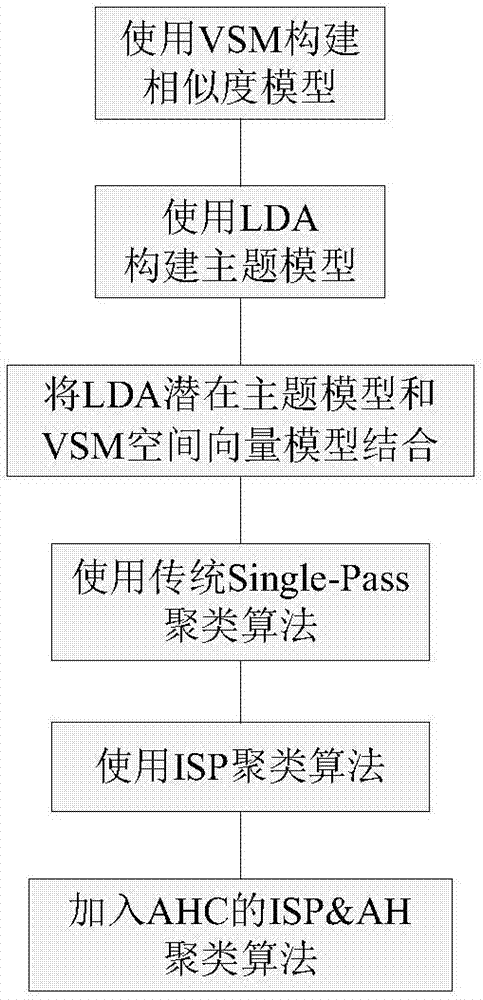
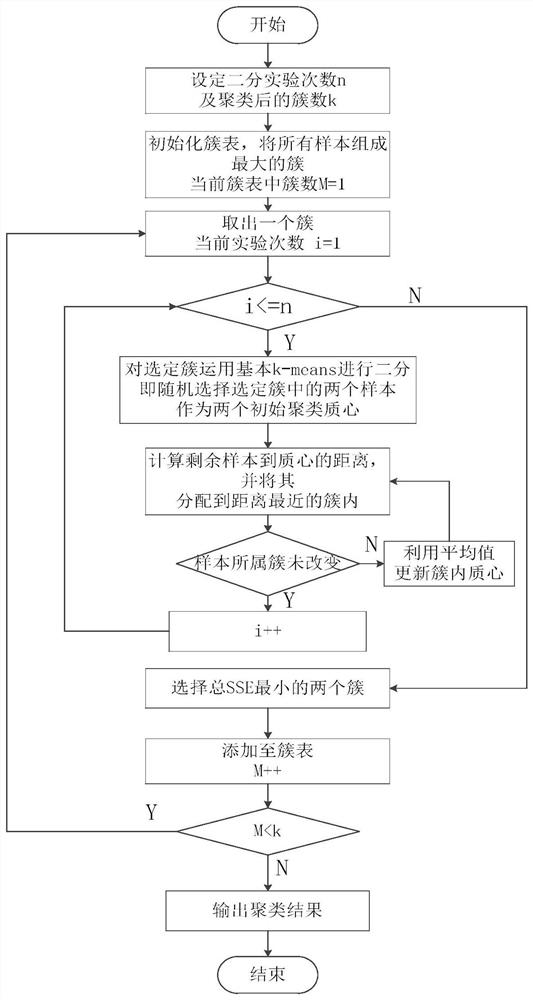
The invention belongs to the field of data mining, natural language processing and information retrieval, and provides a news topic detection method. For the defect of a TF-IDF-based vector space algorithm in semantics and the defects of time complexity and accuracy of textual level clustering, feature extraction, representation modeling, similarity calculation and quick and accurate text clustering methods for a large amount of news texts are improved. The LDA fusion model and multilayer clustering-based news topic detection method comprises the following steps of 1: building a similarity model by using a vector space model (VSM); 2: finally obtaining accurate parameter settings; 3: organically fusing two text models; 4: judging whether a topic is a new topic or not; 5: calculating the similarity until all documents are clustered; and 6: adding an ISP&AH clustering algorithm of AHC based on the step 5. The method is mainly applied to the design and manufacturing occasions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Wave band selection method for hyperspectral remote-sensing image
InactiveCN102521605ANarrow searchReduce the number of bandsImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionCluster algorithmSpectral clustering algorithm
The invention discloses a wave band selection method for a hyperspectral remote-sensing image. The wave band selection method improves the traditional wave band selection method for the hyperspectral remote-sensing image, which is analyzed on the basis of the important point of a time sequence. The wave band selection method for the hyperspectral remote-sensing image comprises the following steps: firstly, on the basis of visual clustering tendency evaluation, clustering by a spectral clustering algorithm to reduce a clustering number search range and improve the clustering quality; then, when an important redundant wave band is finally reduced, removing parts of a high-redundancy wave band according to the condition mutual information among wave bands; and searching an optimal wave band combination with a branch and bound method to improve the classification precision and reduce a final wave band number. Compared with the prior art, the wave band selection method for the hyperspectral remote-sensing image, which is disclosed by the invention, has a bigger advantage on the aspects of finally-selected wave band numbers and the corresponding classification correction rate, and the required calculation time is far lower than calculation time required with most traditional methods.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Driver fixation point clustering method based on density clustering method and morphology clustering method
InactiveCN103903276AReduce outliersOvercome clustering deficienciesImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionDriver/operatorDensity based
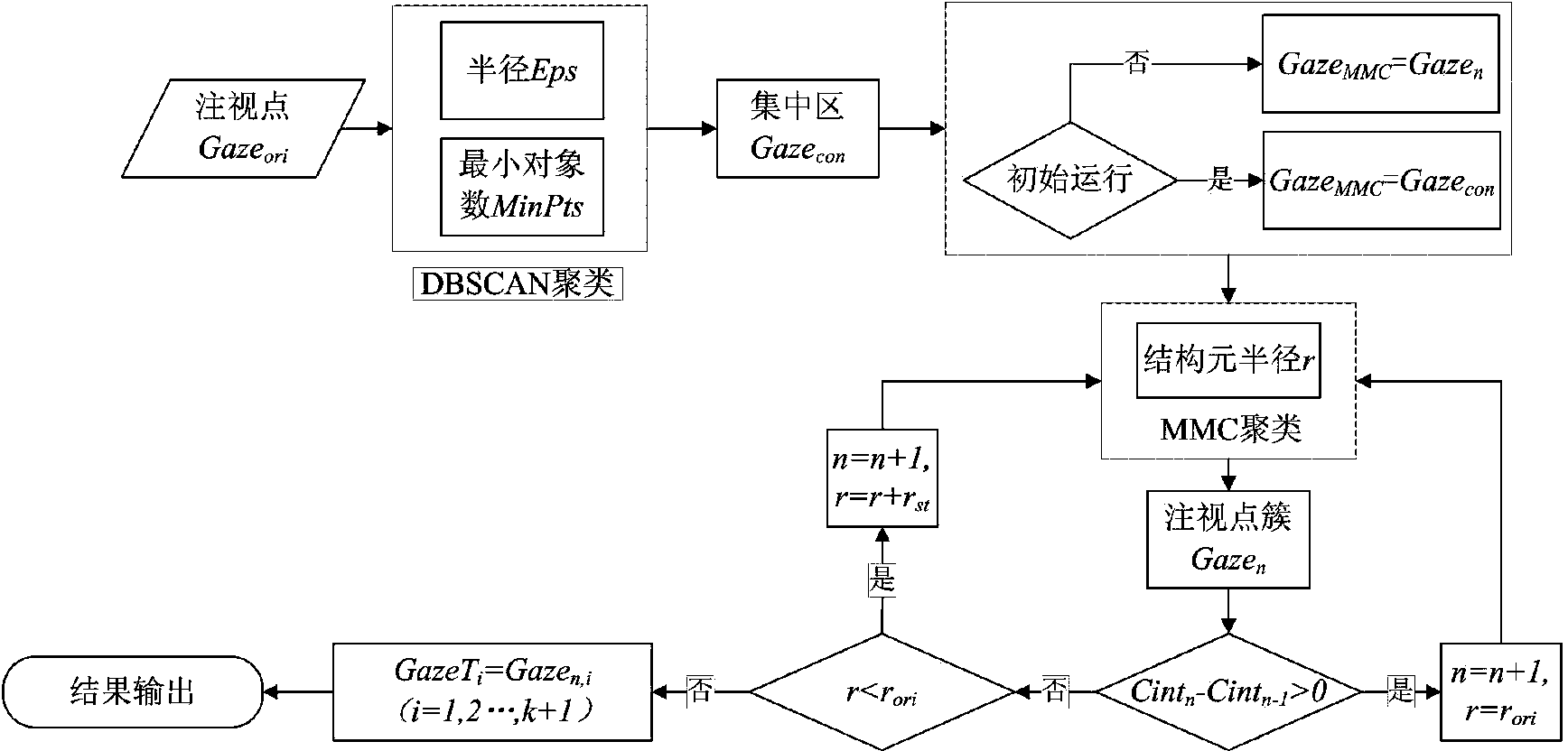
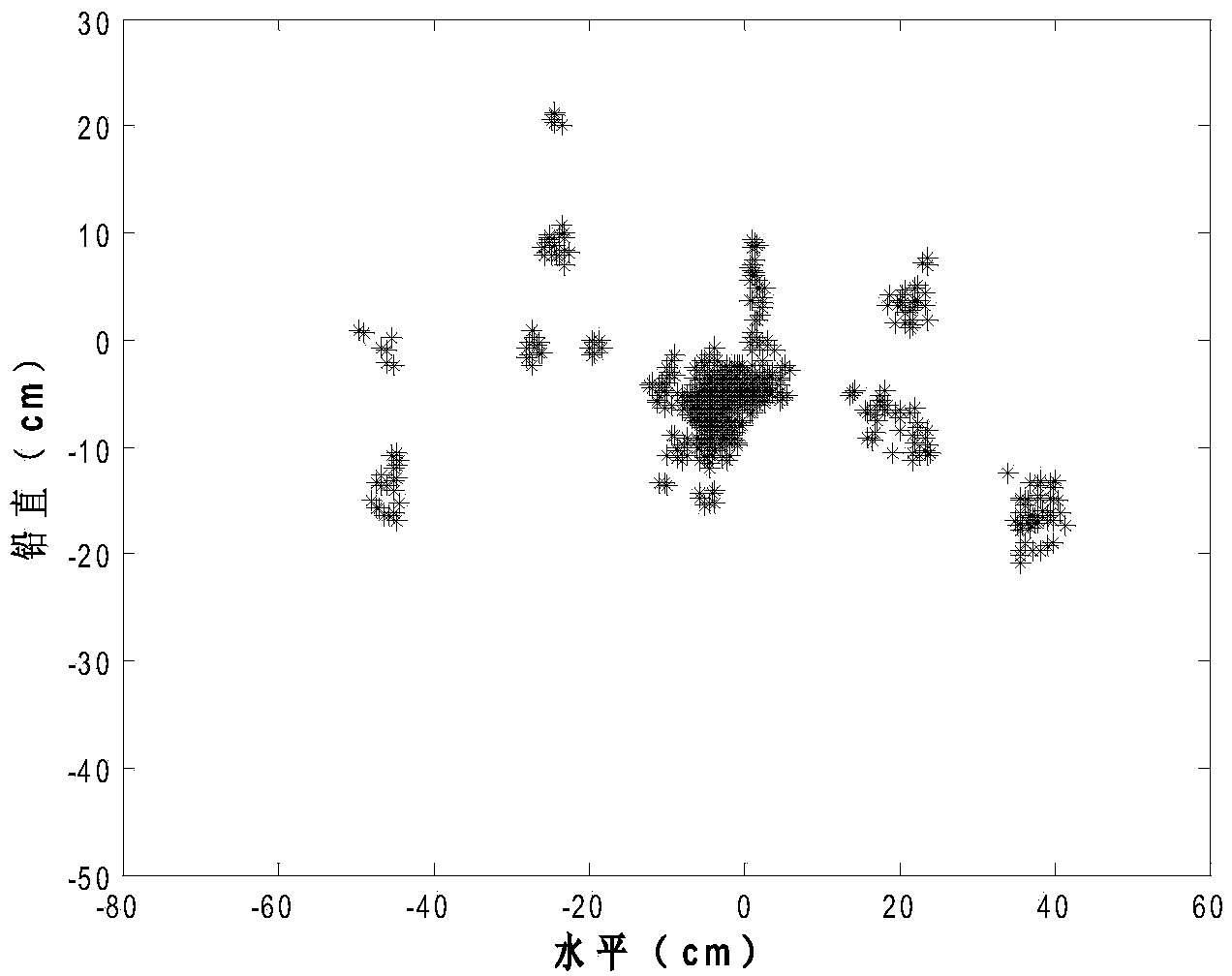
The invention provides a driver fixation point clustering method based on a density clustering method and a morphology clustering method, and belongs to the field of typical density clustering methods and mathematic morphology clustering methods. The driver fixation point clustering method includes the steps of putting forward a density method and mathematic morphology method combined self-adaption DBSCAN-MMC method, applying the method to driver fixation point clustering, setting the value of the Eps through fixation point structure parameters, obtaining an initial point set of MMC clusters through the DBSCAN, determining the number of the clusters, reducing outliers produced through DBSCAN clusters through the self-adaption MMC clusters, and completing clustering oriented to driver fixation areas. According to the method, the advantages of irregular shape clustering of the DBSCAN and the MMC are fully used, the defects of the two clustering methods are overcome, the clustering effect is superior to the clustering effect of the conventional DBSCAN clustering method and the conventional MMC clustering method when the driver fixation areas are divided, and the driver fixation clustering quality is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Zinc floatation condition state dividing method based on isomerism textural features
ActiveCN106257498ASmall scaleEliminate the effects ofCharacter and pattern recognitionCURE data clustering algorithmFeature vector
The invention discloses a zinc floatation state dividing method based on isomerism textural features. Zinc floatation image textural features are extracted by combining a gray-level co-occurrence matrix algorithm which has a good effect on high-frequency band textural features and a Gauss Markov random field algorithm which has a good modeling effect on low-and-medium-frequency texture images, and the zinc floatation image textural features are subjected to Gauss normalization to serve as a textural feature vector. In an integrated clustering algorithm, partitional clustering with high efficiency is conducted firstly to eliminate the influences of noise points and outliers, then a hierarchical clustering algorithm with high clustering quality and high stability is adopted to combine clustering centers output through partitional clustering, and then a final clustering result is obtained. Experiments prove that the extracted textural feature quantity has high mode separability, and foam in different states can be distinguished with the integrated clustering algorithm; furthermore, the method can be directly realized on a computer and is low in cost, high in efficiency and easy to implement.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
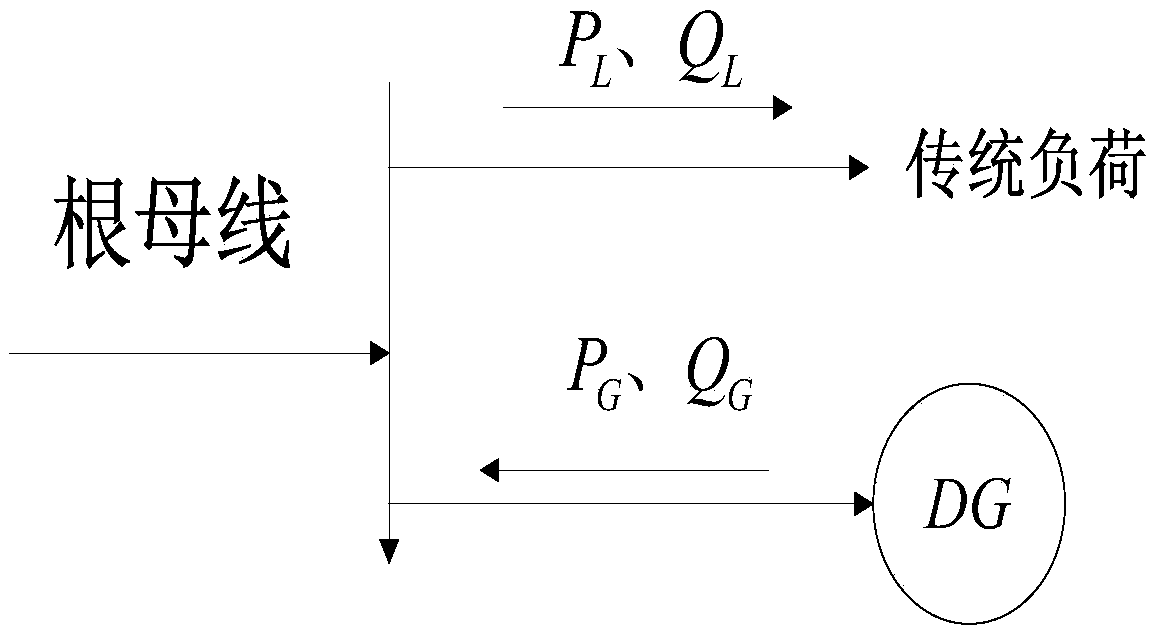
Transverse time axis clustering method in generalized load modeling on basis of time periods
ActiveCN104200032AImprove clustering effectImprove clustering qualitySpecial data processing applicationsSimulationTransverse plane
The invention discloses a transverse time axis clustering method in generalized load modeling on the basis of time periods. According to the method, root bus data formed by wind power and loads of the whole year are obtained; the data are processed, all the processed data are connected end to end, the data in rows form the transverse continuous data which are divided into M sections according to transverse time units THN, and all the data are transversely clustered; based on the transverse cluster result, a sample data source to be analyzed is divided into q transverse classes, and each class is represented by the respective clustering center; feature vectors are intersected and matched. The classes to which samples belong are judged through intersecting and matching of the feature vectors, generalized load modeling is utilized for setting up an accurate model and testing the effectiveness of the clustering strategy, and the simulation result shows that generalized load modeling carried out after clustering analysis makes the model practical on the basis of meeting the requirement for accuracy, and is beneficial for improving the simulation accuracy and the simulation effectiveness of an electrical power system.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Privacy protection clustering method for big data analysis and computer storage medium
InactiveCN110334757AHigh cluster availabilityGood clustering qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital data protectionCluster resultPrivacy protection
The invention discloses a privacy protection clustering method for big data analysis and a computer storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: normalizing data and selecting a central point; calculating a minimum privacy budget and distributing a privacy budget sequence, dividing a sample point to a nearest center point, generating Laplace noise, adding noise to parameters in the process of updating the center point, and performing continuously iterating until the difference of error quadratic sums of two adjacent iterations is smaller than a threshold value or the maximum iteration frequency is reached. According to the method, the sensitive information in the data set is protected by adding the noise obeying the Laplace distribution to the intermediate parameter in the clustering algorithm execution process; the problem that sensitive information of a data set is leaked in the execution process of the clustering algorithm is solved, the privacy budget allocation mode of the differential privacy protection clustering algorithm is improved, the availability of clustering results is improved under the same privacy protection degree, and the privacy leakage problem inbig data clustering mining is solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Cluster classification method for wind power plant
InactiveCN103955521AOptimized Value Modeling MethodReduce sensitivityForecastingEnergy efficient computingOperating pointClassification methods
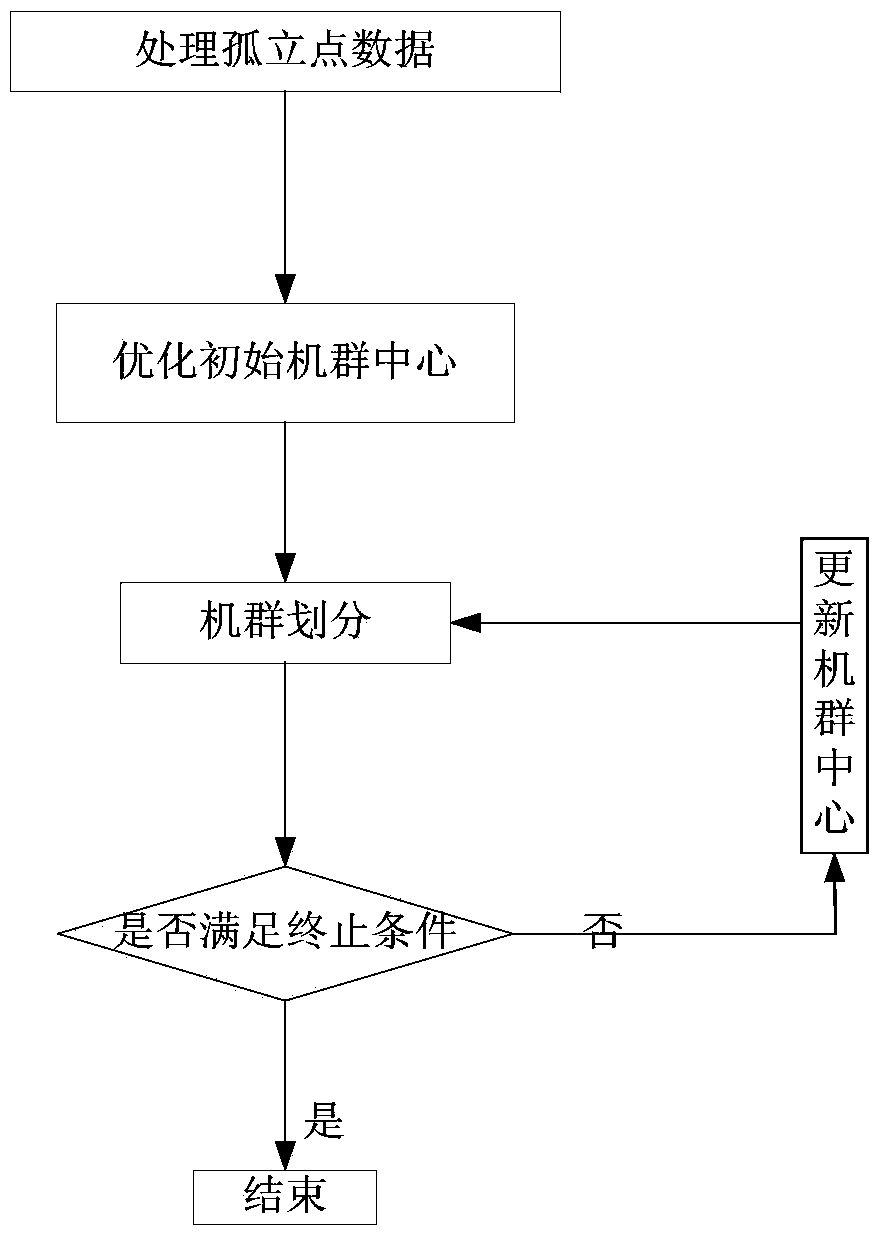
The invention belongs to the field of simulation of electric power systems, and particularly relates to a cluster classification for a wind power plant. Clusters are classified in a unit of the wind power plant according to the actually measured operating data of the wind power plant. In the process of acquiring the data, the actually measured data probably contain noise data because of the factors like the defect or the execution error of a measurement system. In order to reduce the interference of the noise data, the isolated point data in the actually measured operating data of the wind power plant are firstly processed according to the potential value of a sample point. When the central initial positions of the two clusters are nearer during the cluster classification, more redundant information is contained, and the classification result easily becomes the locally best. Aiming at the problem, a sample group with the smallest Euclidean distance moves towards the mean value point, the mean value of the moved sample group replaces the original sample group, so that the method acquires the central position of the diversified initial clusters, and the global searching ability is improved. By the adoption of the cluster classification for the wind power plant, provided by the invention, wind turbine generators having the near operating points are classified in the same cluster, and the equivalent modeling approach for the wind power plant is optimized.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
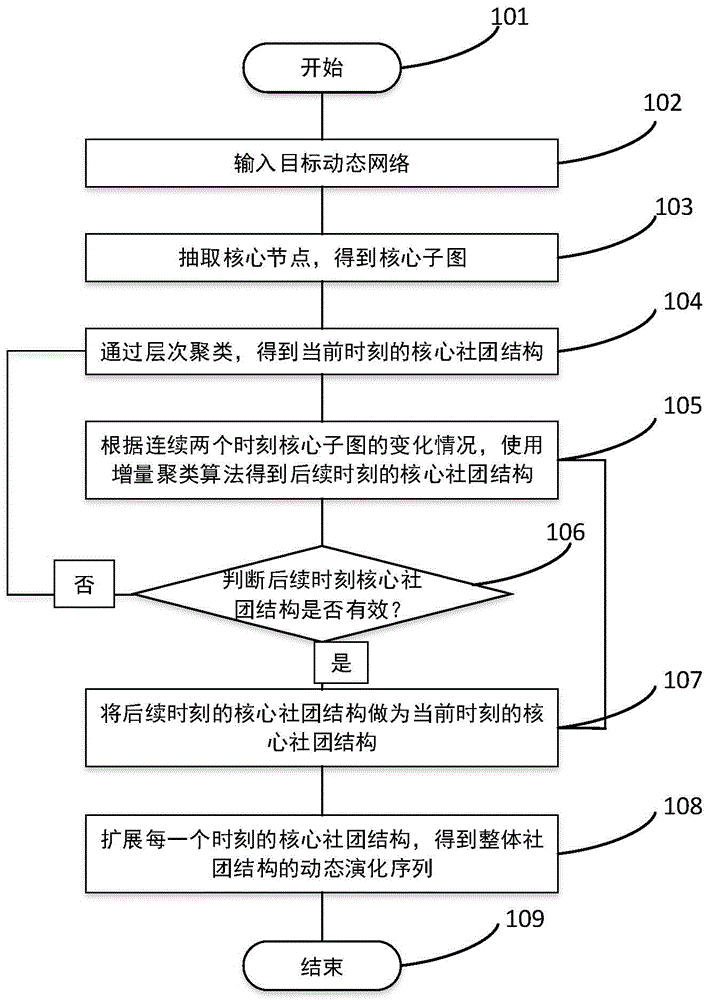
Dynamic social network community structure evolution method based on incremental clustering
InactiveCN105469315AFast community divisionQuick divisionData processing applicationsCluster algorithmHierarchical cluster algorithm
The present invention discloses a dynamic social network community structure evolution method based on incremental clustering to solve the problems of community structure detection and communication evolution tracking in a large scale network. The method comprises a step of extracting the core node of a whole network to form a core sub graph, a step of running a hierarchical clustering algorithm on the core sub graph at a time t=0 to obtain the initial structure of a core community, and using an extended algorithm on the above basis to obtain the community structure of the whole network, and a step of using an incremental clustering algorithm to obtain the core community structure of the whole network at present time according to the dynamic evolution condition of an adjacent time network at a time t which is larger than 0 and extending the core community structure to obtain a whole community structure. Through introducing the core sub graph, the incremental calculation in the whole network is avoided, the processing speed is accelerated, and thus the method is suitable for the community discovery in the large scale network. In addition, through introducing the concept of a community structure shift, the large error of the community structure after long time evolution is avoided, and the accuracy of community evolution tracking is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Clustering method, system and medium for automatically confirming cluster number based on coefficient of variation
ActiveCN109063769AEffective cluster analysisImprove clustering qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a clustering method, a system and a medium for automatically confirming the number of clusters based on a coefficient of variation, wherein, the density value of each data point in a data set is calculated, the density index is calculated according to the density value, and the data point with the largest density index is selected as a first clustering center; Calculating the shortest distance between each data point and the existing clustering center, calculating the probability that each data point is selected as the clustering center according to the shortest distance, and preselecting the clustering center according to the roulette disc method; Until the set cluster centers are selected, the initial cluster centers selected are used for k-means clustering to generate a corresponding number of clusters; Calculate the average intra-cluster coefficient of variation and the minimum inter-cluster coefficient of variation, then calculate the difference between theaverage intra-cluster coefficient of variation and the minimum inter-cluster coefficient of variation, compare the difference with the set value, and if the difference is less than the set value, merge the two clusters with the minimum inter-cluster coefficient of variation; Until the difference is greater than or equal to the set value, the clustering result is output.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Wind power plant modeling method based on actually-measured operating data
ActiveCN103942391AQuality improvementHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsOperating pointNoisy data
The invention relates to a wind power plant modeling method based on actually-measured operating data. According to the method, with the actually-measured operating data of a wind power plant as the criterion, group classification is carried out on units in the wind power plant, units with adjacent operating points are classified into the same group, equivalence is carried out on each group through a wind generation set, and then a multi-unit representation model of the wind power plant is established. In the group classification process, outlier data processing is carried out on noisy data in the actually-measured operating data of the wind power plant based on the definition and properties of entropy in the information theory so as to reduce interference of the noisy data. Furthermore, in the group classification process, the cluster center initialization process is optimized, the group clustering quality is improved, and the accuracy of the wind power plant model established through the method is greatly improved.
Owner:GRID POWER PLANNING & RES CENT OF GUANGDONG GRID POWER CO LTD
Satellite telemetry data clustering method based on time series special points
ActiveCN106709509AReduce data volumeAddressing the Limitations of Similarity MeasuresCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmSimilarity measure
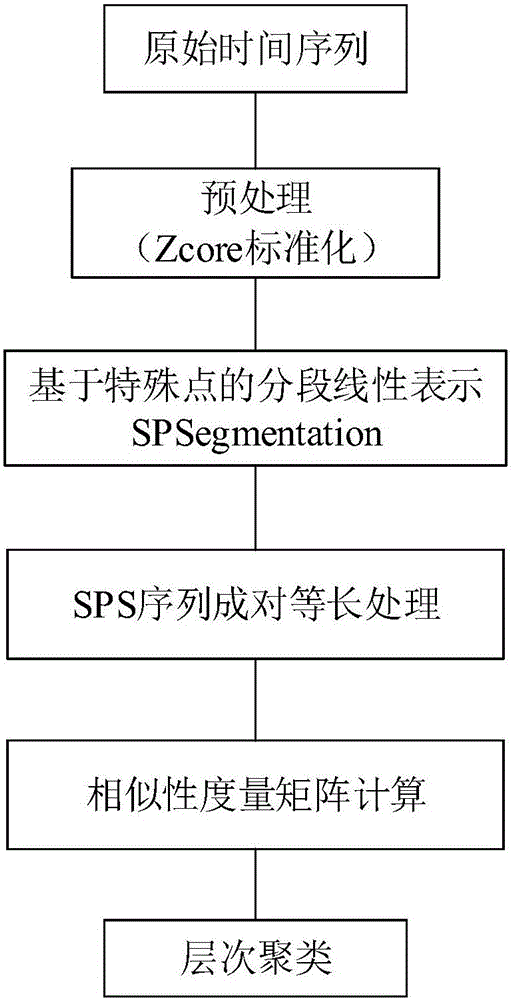
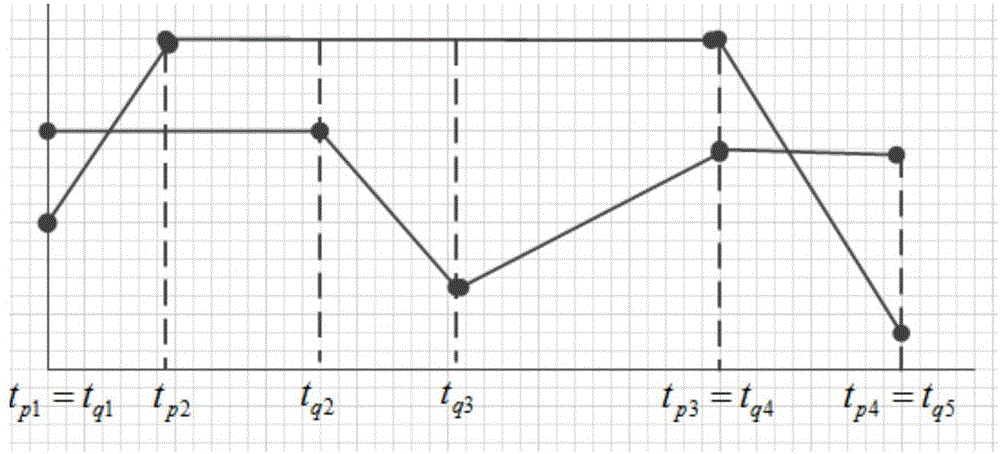
The invention provides a satellite telemetry data clustering method based on time series special point. The satellite telemetry data clustering method comprises steps that step1, a Zscore algorithm is used for preprocessing of an original time series set X=(x1, x2...Xl); step2, an SPSegmentation segmentation expression method is used to extract all of special points of every original time series Xi to form a special point series SPSi=(xi(tp1), xi(tp2).. .xi(tpk)), which is used to replace the original series to be used as clustering input; step3, the corresponding time position supplementing and aligning processing of any two special point series SPSi and SPSj is carried out, and then the time positions of the special points of the sequences corresponding to the various elements of the two SPS on an original time axis are aligned with each other; step 4, the similarity coefficient calculation of the aligned special point series is carried out, and because the sequence aligning is carried out, most of similarity measurement calculations are usable, and finally, a PSPS_Dist similarity matrix is acquired; step 5, an agglomerative hierarchical clustering algorithm is adopted to realize time series clustering.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Multi-partition clustering preprocessing method of stream data
ActiveCN106570104AReduce workloadImprove clustering efficiencyRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsStreaming dataPretreatment method
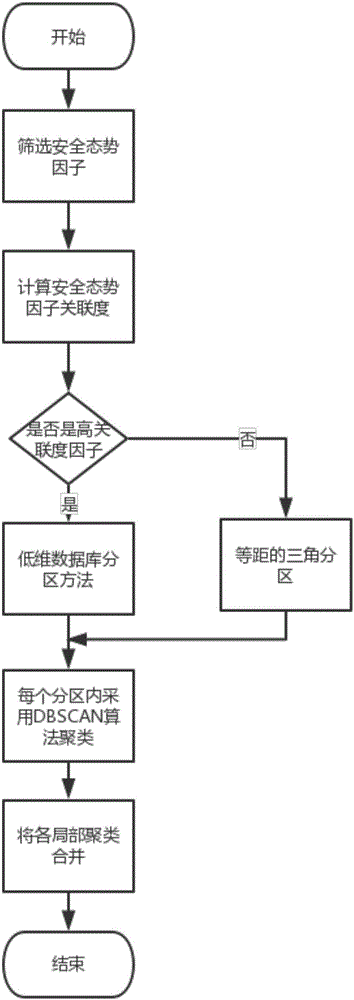
The invention relates to a multi-partition clustering preprocessing method of stream data. The method includes the following steps that: the trend factors of the stream data are screened, and a correlation degree is calculated; statistical analysis is performed on the stream data, a low-dimensional database partitioning method is adopted for high-correlation factors in a high-dimensional database, and isometric triangle partitioning is performed on low-correlation factors; a distribution-based partitioning method is adopted for a low-dimensional database; a DBSCAN (density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise) algorithm is adopted to perform clustering in each rule partition; and local clustering results are merged. According to the multi-partition clustering preprocessing method of the stream data of the invention, multi-partition improvement is made for the clustering preprocessing of the stream data, and therefore, data distribution is more uniform, clustering results are more accurate, and distributed parallel processing of the data is realized, and the pressure of low data preprocessing efficiency of a large number of data sequences which arrive sequentially, fast and continuously can be alleviated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Improved density peak clustering-based social network community discovery method
ActiveCN108647739ASolving clustering problemsRobustData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionCommunity structureVariable kernel density estimation
The invention discloses an improved density peak clustering-based social network community discovery method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly calculating two indexes for each userin a network, wherein the two indexes comprise local densities and relative distances, the local densities are calculated by adoption of Gaussian kernel density estimation, and the relative distancesrepresent a distances between users and points which are greater than the users in the aspect of density and which are close to the users; selecting a point which has a large local density and relatively large relative distance as a community center on the basis of Gaussian distribution, and distributing the residual non-center points to communities of points which are greater than the non-centerpoints in the aspect of density and which are closest to the non-center points; and finally, measuring distance between every two communities on the basis of combination factors, wherein the communities, the combination factors of which are greater than a given threshold value, are combined into one community. Compared with the prior art, the method is capable of discovering spherical and non-spherical community structures in social networks at the same time, so that fewer parameters are needed under the premise of obtaining relatively high correctness and then the problem of clustering communities with any shapes is solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-view clustering and mining oriented personal privacy protection method
ActiveCN107688752ARealize personalized privacy protection needsImprove clustering qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital data protectionOrder setPersonalization
The invention discloses a multi-view clustering and mining oriented personal privacy protection method, and belongs to the technical field of information safety. The multi-view clustering and mining oriented personal privacy protection method has the advantages that privacy partial-order topological classification algorithms (PT, privacy topology) are proposed, privacy relations are defined at first for representing sensitivity difference of different privacy data, privacy partial-order sets are constructed for representing the sensitivity difference of the different privacy data, topologicalclassification algorithms are accordingly designed for the privacy data, and privacy line order sets are solved; multi-view clustering is carried out on views of original data, privacy degrees, tuplesensitivity, the privacy line order sets and the like for multiple views of the privacy data; clustering oriented personal anonymity algorithms (PPOC, personal privacy oriented classtering) are proposed, personal protection operation can be carried out on different clusters by variable k-anonymity strategies by the aid of multi-view clustering oriented privacy protection algorithms which can meetpersonal requirements, and personal protection operation with different exertion degrees can be carried out on different tuples in the same clusters by the variable k- anonymity strategies by the aidof the multi-view clustering oriented privacy protection algorithms.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Target grouping method based on SA-PFCM + + algorithm
PendingCN111275132AReduce difficultyImprove clustering qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionData setClassi cation
The invention discloses a target grouping method based on an SA-PFCM + + algorithm. The method includes: firstly initializing parameters, solving a mean value of the data set; calculating a first weighted Euclidean distance between each sample point and the mean value; after sorting, D2 is used for sampling to select a first initial clustering center; calculating a second weighted Euclidean distance between each sample point and the clustering center; after sorting, D2 is used for sampling to select the next initial clustering center; until the number of the initial clustering centers reachesa set condition; then, corresponding parameters are iteratively updated according to the initial clustering center; and calculating a corresponding Xie-Beni-Sun (XBS for short) index until the iteration frequency value reaches a set threshold value or the clustering member does not change any more, then updating the initial parameter value until a set stop condition is reached, comparing the XBS indexes under different clustering numbers, and outputting the cluster number and the class cluster under the set XBS index. The difficulty of target grouping in situation assessment is effectively reduced, and the decision-making efficiency is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Mixing attribute data flow cluster method based on reinforcement cluster edge detection of grid
InactiveCN105184318AImprove clustering qualityStrong ability to handle edge networksCharacter and pattern recognitionNumeric ValueData space
The invention discloses a mixing attribute data flow cluster method based on reinforcement cluster edge detection of a grid, comprising steps of 1) a grid pre-processing process, 2) an online grid maintenance process, and 3) an off-line cluster process. The grid pre-processing process includes steps of dividing a d dimension data space where the data object is positioned, dividing each dimension of numeric data into P equally-divided sections according to the size of the grid granularity due to the fact that the mixing attribute comprises a numeric value attribute and the classification attribute, dividing classification data of each dimension according to the possible number of the value in the domain and dividing a data space into a plurality of measure polytopes which are not mutually intersected, wherein each rectangle grid unit expression is S1,J1*S2,j2*...*Sd,jd, wherein the attributes Si,(i<d) is an attribute on the data space S, and the subscript ji expresses the section obtained on the dimension of the Si. The invention provides a mixing attribute data flow cluster method based on reinforcement cluster edge detection of a grid which is high in cluster quality and strong in processing rim network.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Precision agriculture-oriented weighted spatial fuzzy clustering method and device
InactiveCN103678683AImprove clustering qualityData processing applicationsClimate change adaptationDynamic clusteringWeighting coefficient
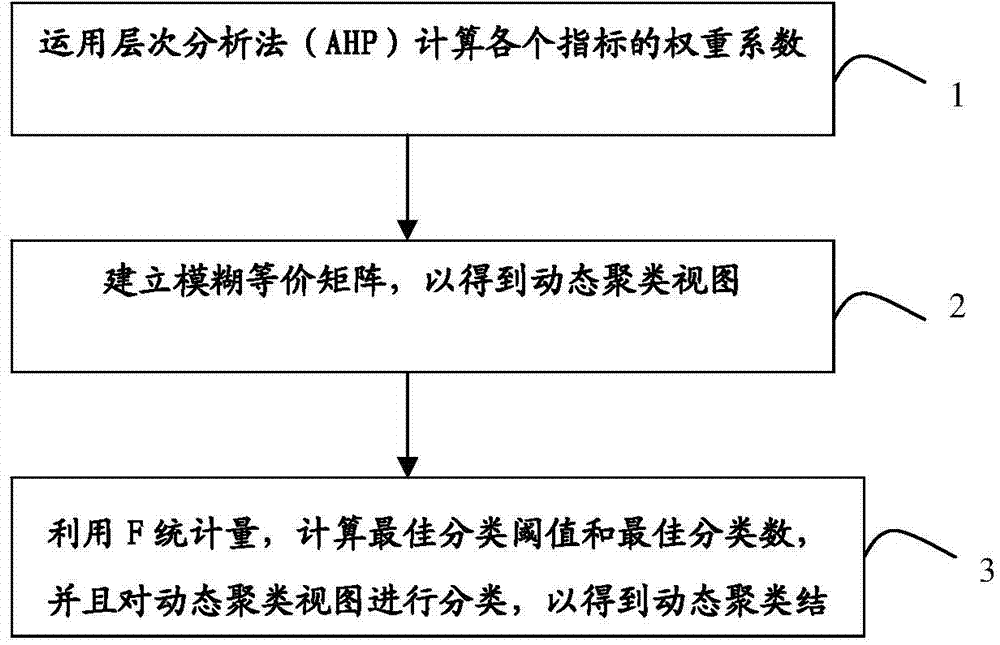
The invention discloses a precision agriculture-oriented weighted spatial fuzzy clustering method and device. The method comprises the following steps that 1) according to data of various input indexes, weight coefficients of all the indexes are calculated by using the analytic hierarchy process so as to obtain a general goal weight matrix; 2) according to an input original data matrix, the general goal weight matrix is used for building fuzzy equivalent matrixes, and according to different classification threshold values, the fuzzy equivalent matrixes are classified so as to obtain dynamic clustering views; 3) by means of F-statistics, the optimal classification threshold value and the optimal number of categories are calculated, and the dynamic clustering views are classified so as to obtain dynamic clustering results.
Owner:ZHENGJIANG PUBLIC INFORMATION
Clustering method and device
InactiveCN108875760AFast convergenceImprove clustering qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification resultCluster result
The invention provides a clustering method, and aims at carrying out category classification on points of a certain set. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining appointed result attributes of partial points in the set, wherein the appointed result attributes are used for limiting category classification results of the points; and operating a clustering algorithm by taking the appointed result attributes of the partial points in the set as constraint conditions, so as to obtain clustering results according with the appointed result attributes. Through the clustering method and device, analyzers can influence clustering results through setting appointed result attributes of points, so that the clustering results are guided to directions according with analysis demands, and theconvergence speed of clustering analysis in improved while the clustering quality is enhanced.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
Semi-supervised image clustering subspace learning algorithm based on local linear regression
InactiveCN102968639ATotal Forecast Error OptimizationImprove clustering effectCharacter and pattern recognitionData setInner class
The invention discloses a semi-supervised image clustering subspace learning algorithm based on local linear regression. Firstly, a local linear regression model is used for predicting a coordinate of a training sample in a clustering subspace, a local prediction error between a predicted value and a true value is obtained, and then a minimized objective function of a total predicted error is obtained; then according to two constrain conditions of inter-class dispersion maximization and inner-class dispersion minimization, and a marked sample and an unmarked sample are used for calculating an inter-class dispersion matrix and a total dispersion matrix; and finally, the inter-class dispersion matrix and the total dispersion matrix are blended in the minimized objective function of the total predicted error to obtain an objective function for solving clustering subspace, and function solving is performed through generalized characteristic root to obtain the optimal clustering subspace. The semi-supervised image clustering subspace learning algorithm based on the local linear regression makes full use of the marked sample, the unmarked sample and a local adjacent relation in a training data set to obtain good clustering results.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Intention recognition method and device based on multi-round K-means algorithm, and electronic equipment
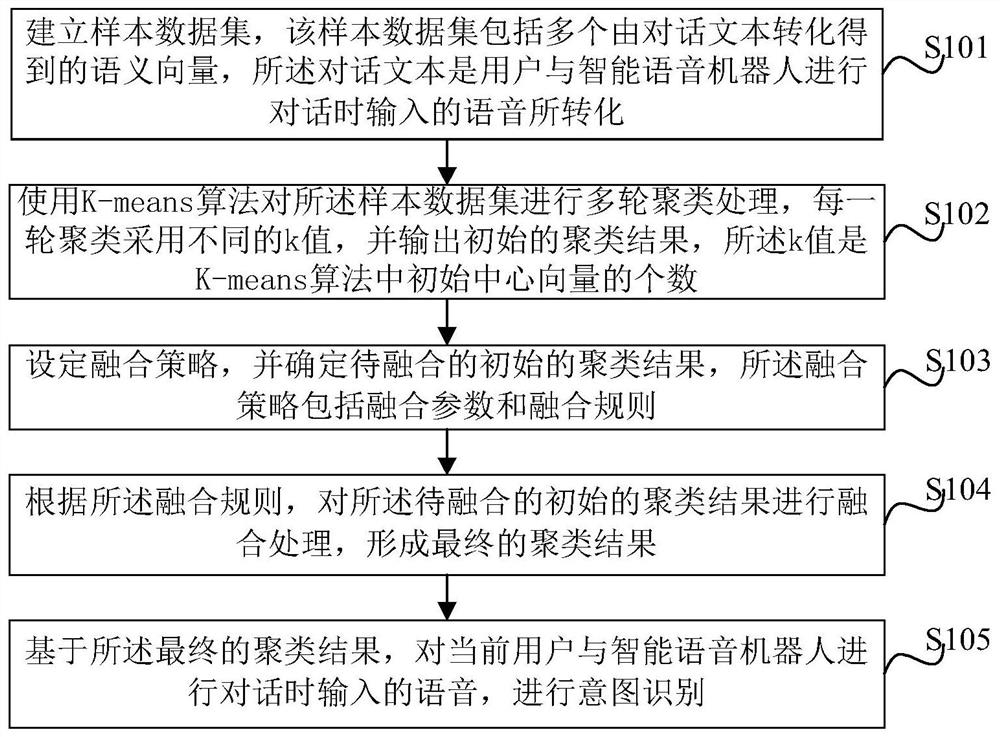
PendingCN111966798APrecise intent classification and identificationImproving intent clustering qualityNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionCluster resultEngineering
The invention provides an intention recognition method and device based on a multi-round K-means algorithm, and electronic equipment. The method comprises steps that a sample data set is established,the sample data set comprises a plurality of semantic vectors obtained through conversion of a dialogue text, and the dialogue text is converted from voice input when a user performs dialogue with anintelligent voice robot; multiple rounds of clustering processing are conducted on the sample data set by using a K-means algorithm, and an initial clustering result is outputted; fusion denoising isconducted on all the initial clustering results to form a final clustering result; and based on the final clustering result, intention recognition is conducted on the voice input when the current userperforms conversation with the intelligent voice robot. According to the method, an improved K-means algorithm is adopted to perform multiple rounds of clustering processing, and fusion denoising isperformed on clustering results of the multiple rounds of clustering so that more accurate intention classification and identification can be realized, the intention clustering quality can be enhanced, and the method can further be optimized.
Owner:北京奇保信安科技有限公司
Longitudinal time axis clustering method in generalized load modeling on basis of seasonality
ActiveCN104200106AImprove clustering effectImprove clustering qualitySpecial data processing applicationsElectricityEngineering
The invention discloses a longitudinal time axis clustering method in generalized load modeling on the basis of seasonality. According to the method, root bus data formed by wind power and loads of the whole year are obtained; transverse time axis pre-clustering is carried out, single day time re-clustering is carried out, longitudinal time unit clustering is carried out, longitudinal time axis clustering results of the whole year are output, a longitudinal time axis clustering method is utilized for analyzing the data of the whole year, and categorical data considering the seasonality are obtained for accurate modeling. An AP algorithm and a longitudinal time axis clustering strategy considering the seasonality are utilized, the large sample data actually measured can be partitioned reasonably, and the simulation result shows that compared with a traditional modeling method, generalized load modeling carried out after clustering analysis makes a model practical on the basis of meeting the requirement for accuracy, and is beneficial for improving the simulation accuracy and the simulation effectiveness of an electrical power system.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Clustering-classification-based FILTERSIM simulation method
InactiveCN107644233AHigh similarityLow similarityCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingSimulation
The invention, which relates to the technical field of image processing, provides a clustering-classification-based FILTERSIM simulation method, so that a technical problem of improving a simulation effect is solved. According to the method, K objects are selected randomly from a training image as initial mass centers of K clusters; all objects in the training image are distributed to clusters with the mass centers closest to objects; the mass centers of all clusters are calculated again and then all objects are distributed again, the above-mentioned operation is repeated continuously until the mass centers of all clusters do not change, and then the training image is divided into K training blocks, so that each training block has one cluster; and then all training blocks are simulated byusing a FILTERSIM simulation method. The method provided by the invention can be applied to fields of weather forecasting and resource exploration and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
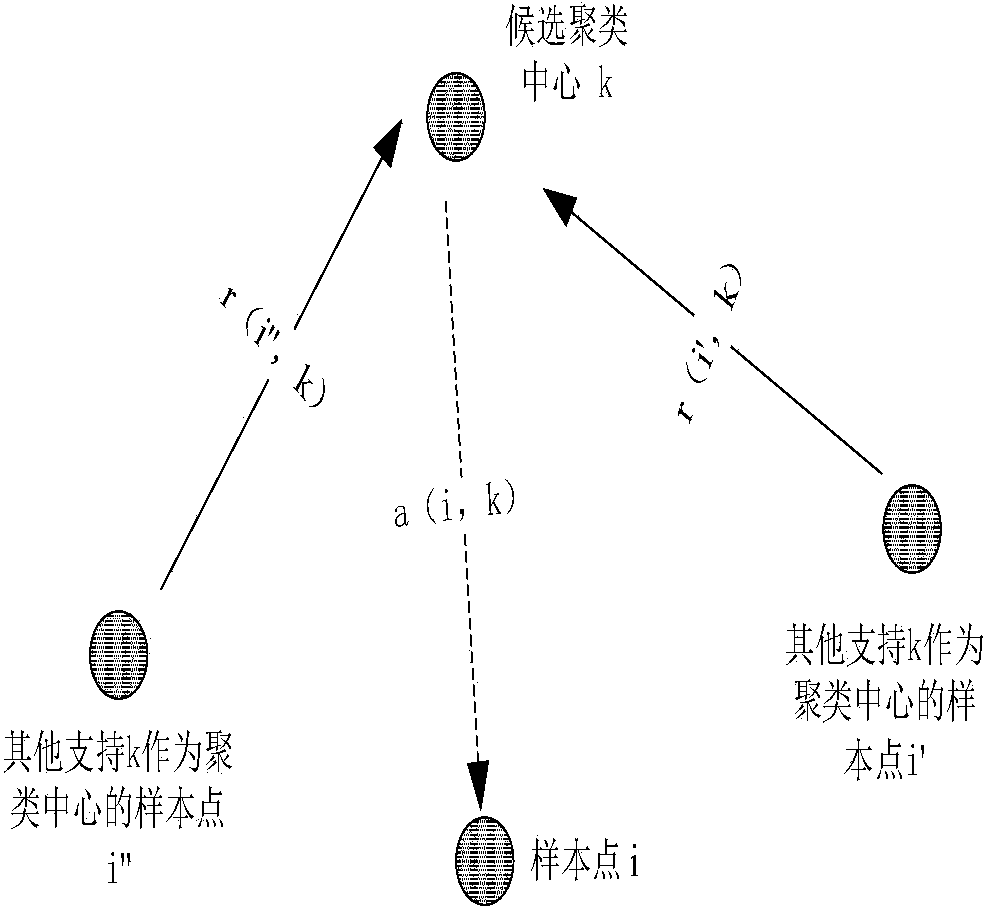
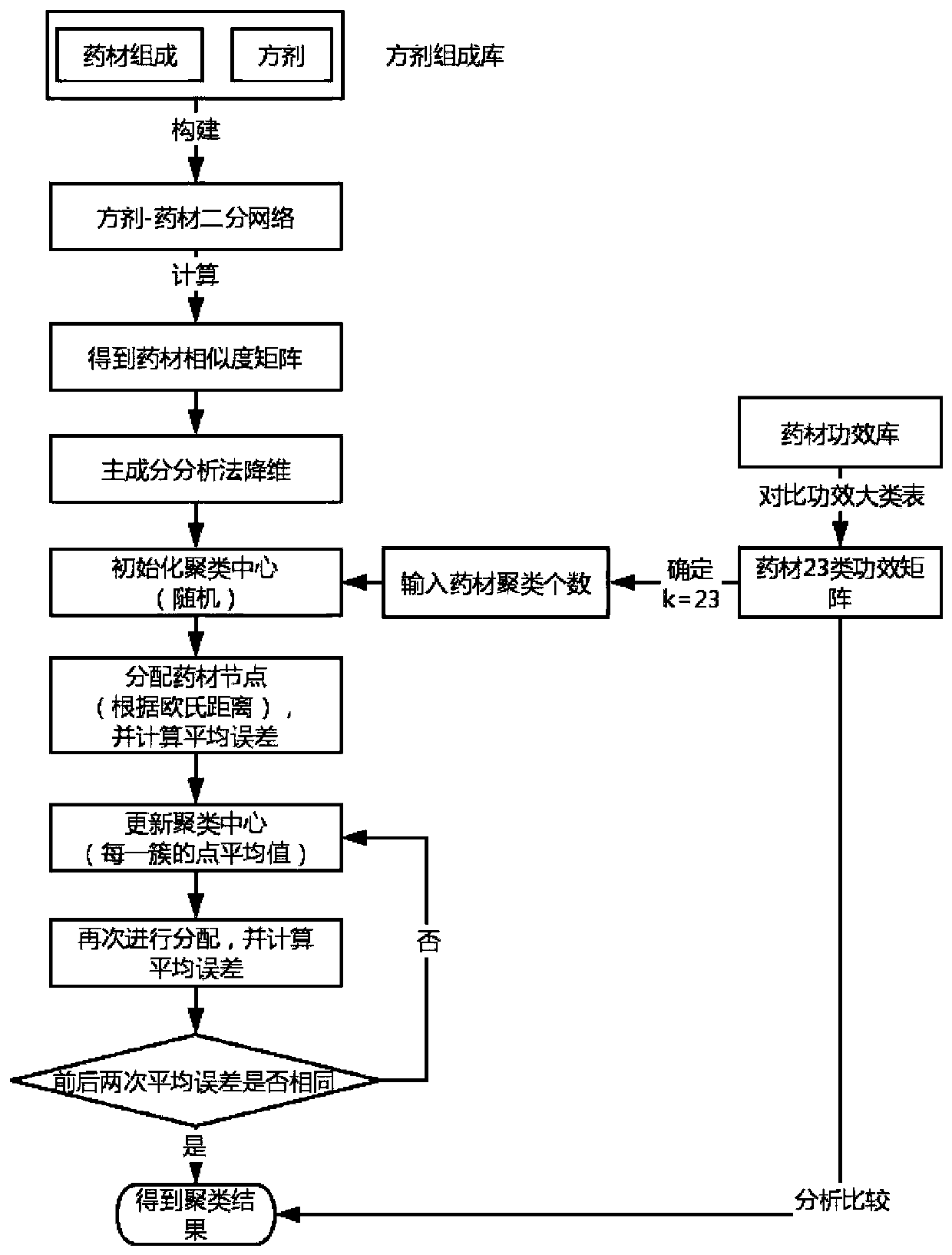
Kmeans clustering method for efficacy of traditional Chinese medicinal materials based on node similarity
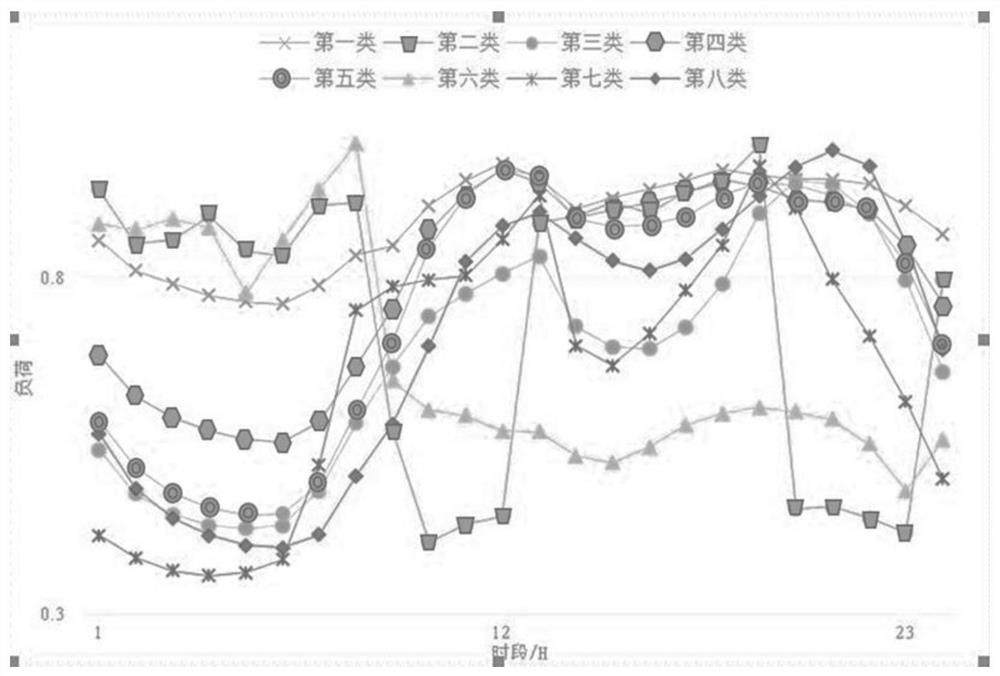
PendingCN111370140AImprove clustering qualityConducive to determining the outcomeMedical data miningCharacter and pattern recognitionMedicinal herbsEfficacy
The invention discloses a Kmeans clustering method for the efficacy of traditional Chinese medicinal materials based on node similarity. The method comprises the following steps: collecting related traditional Chinese medicine data, and processing the data to form a prescription composition library, a medicinal material efficacy library and a channel-tropism binary table of the nature and taste ofmedicinal materials; summarizing and classifying the efficacy of the traditional Chinese medicinal materials according to 23 efficacy tables, and constructing a medicinal material efficacy matrix; constructing a prescription-medicinal material bipartite network based on the prescription composition library; calculating expected values of medicinal material pairs based on degree distribution, andtaking the expected values of the medicinal material pairs as the similarity of the traditional Chinese medicinal materials; establishing a Kmeans clustering model based on the similarity of the traditional Chinese medicinal materials; and clustering the traditional Chinese medicinal materials based on the clustering model to obtain potential effects possibly possessed by the traditional Chinese medicinal materials. According to the method, the accuracy of Kmeans clustering via a medicinal material similarity matrix can reach 0.728. Meanwhile, Kmeans is used for clustering the nature-taste channel-tropism data of traditional medicinal materials, an obtained final result is 0.646, which is about 0.08 higher; and therefore, clustering result is allowed to be more accurate through the method.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Dynamic streaming data clustering method
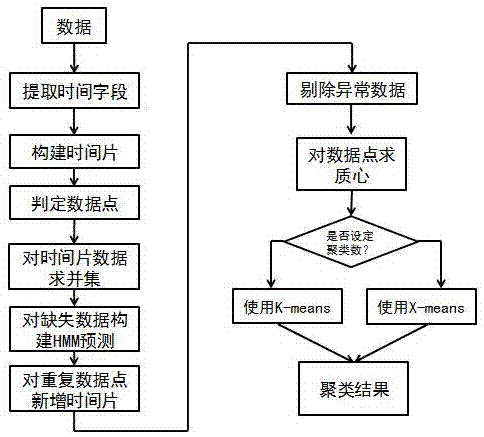
PendingCN107273930AGood clustering effectEfficient use ofCharacter and pattern recognitionStreaming dataMissing data
The invention discloses a dynamic streaming data clustering method, which comprises the steps of converting structured data into time field streaming data, sorting the time field streaming data according to time fields so as to acquire time slices, and solving a union set; building a training model, and building HMM prediction for the missing data; checking the data validity, and adding time slices for repeated data points; eliminating abnormal data, checking whether data with abnormal fluctuations exists or not according to all of the time slices; and performing mass center data clustering. According to the invention, special optimization is performed in allusion to characteristics of the data, an HMM is adopted to perform prediction in allusion to the missing data, and processing is performed in allusion to repeated data with the same identification in the same time slice, so that time-varying characteristics of the data can be reflected more accurately, abnormal data can be distinguished, the number of clustering categories is optimized automatically, and a high-quality clustering result is acquired.
Owner:CHENGDU SEFON SOFTWARE CO LTD
Mixed feature data clustering method and system based on tree base learner
PendingCN114004271AImprove clustering qualityAutomatically determine the number of clustersCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningData setFeature data
The invention belongs to the technical field of mixed feature data set clustering, and discloses a mixed feature data clustering method and system based on a tree base learner, and the method comprises the steps: S1, carrying out the random sub-sampling of a sample set, and generating N different sub-sample sets; s2, performing tree-based learning device training on each sub-sample set, and obtaining N trees after training and the number K of clusters; s3, counting a similarity matrix between any two samples based on the N trained trees, and normalizing all the similarity matrixes to obtain a plurality of normalized similarity matrixes; and S4, taking the number K of the clusters and the plurality of normalized similarity matrixes as input of a spectral clustering model to obtain a final clustering result of the sample set. The data clustering method under the conditions of high latitude and mixed features is designed, and the problem that clustering is difficult due to the fact that a similarity concept cannot be clearly defined under the conditions that the data set dimension is too high and continuous features and discrete features are mixed can be solved.
Owner:浙江浙石油综合能源销售有限公司 +1
Power load curve clustering method
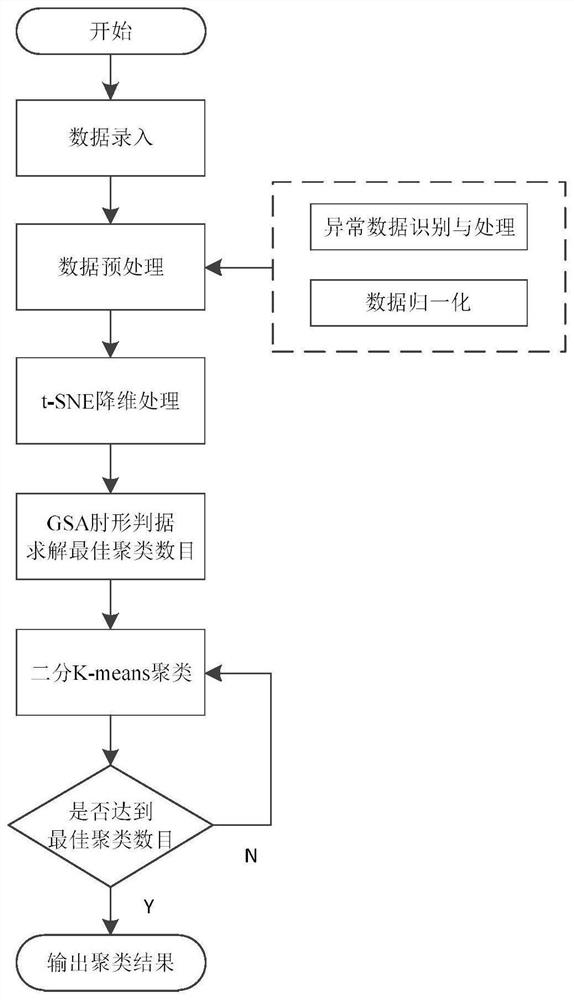
PendingCN112270338AImprove clustering qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesData setDimensionality reduction
The invention discloses a power load curve clustering method, which comprises the steps of preprocessing historical load data to obtain a load data set; performing dimension reduction processing on the load data set to obtain a low-dimensional load data set; calculating the low-dimensional load data set by adopting a GSA elbow criterion method to obtain an optimal clustering number K; and performing clustering analysis on the low-dimensional load data set according to the optimal clustering number K to obtain a clustering result. Load is processed through a t-SNE dimension reduction technology, clustering analysis is carried out on the load by combining a GSA elbow criterion and a binary K-means algorithm, and experiments prove that the improved algorithm has better clustering quality.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
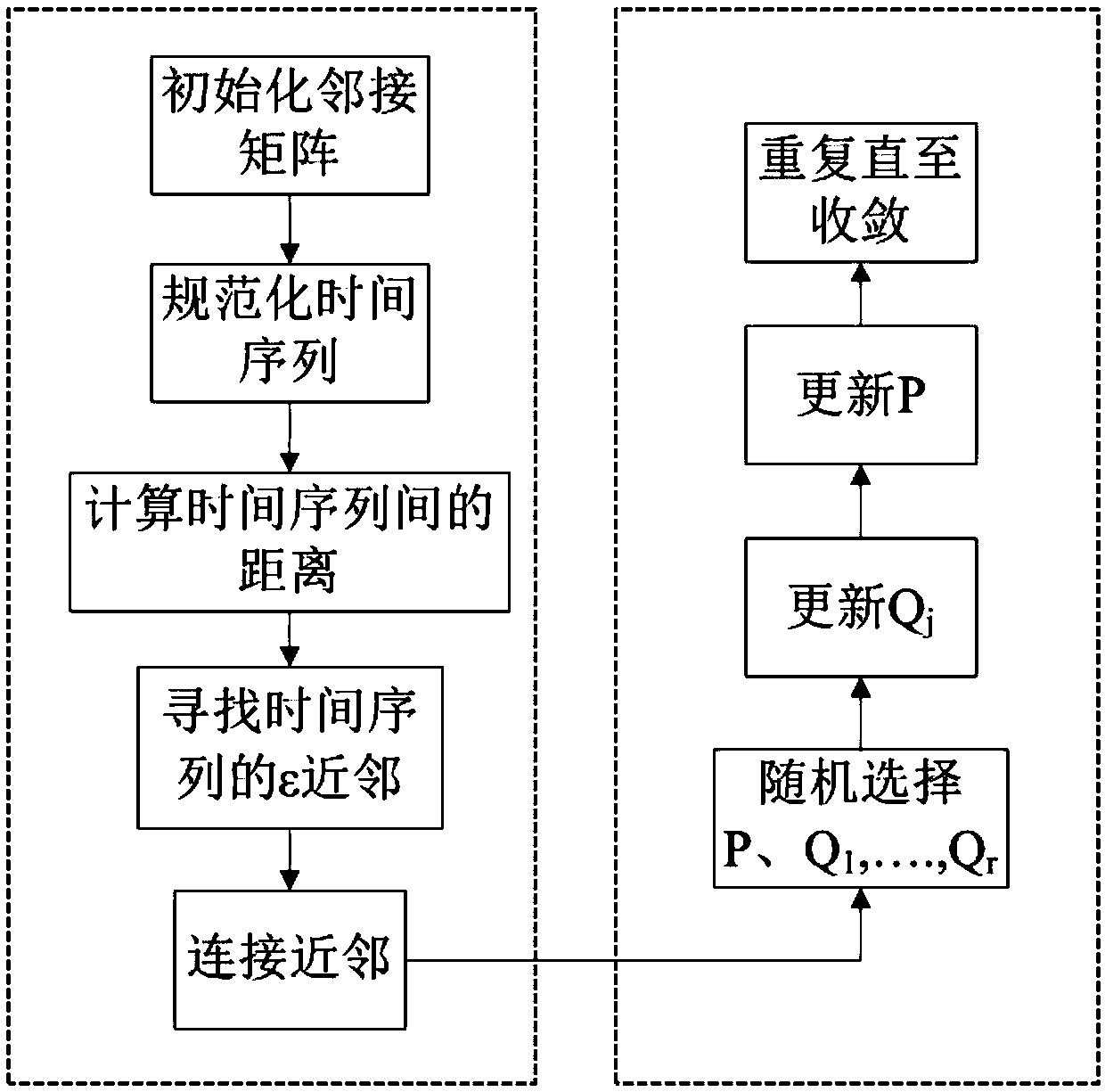
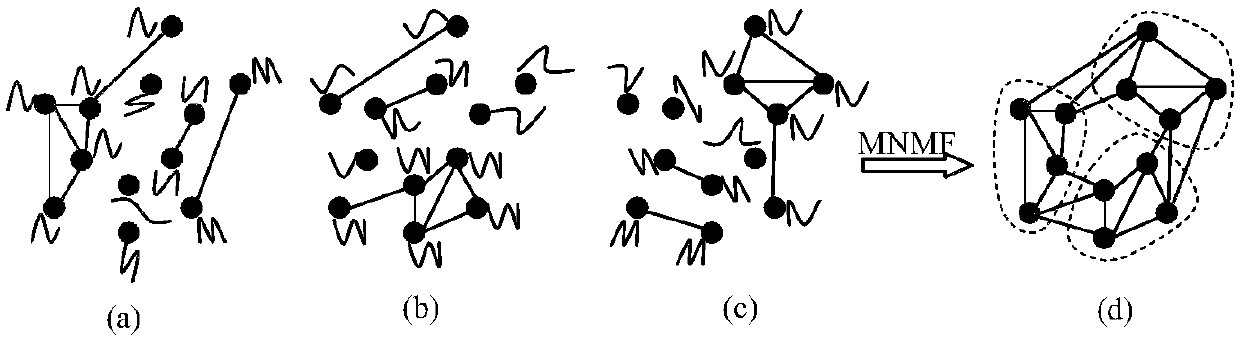
Multi-relation network-based MNMF clustering method of multi-variable time sequences
ActiveCN108830310ASimple structureRich semantic informationCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsData miningComputer science
The invention discloses a multi-relation network-based MNMF clustering method of multi-variable time sequences. The multi-variable time sequences are converted into a multi-relation network G; and themulti-relation network G is jointly decomposed through MNMF to obtain clustering results of the multi-variable time sequences. The method of the invention effectively fuses complex relations in and among variables into a clustering process, and improves clustering performance.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Data clustering method and device for constructing knowledge base
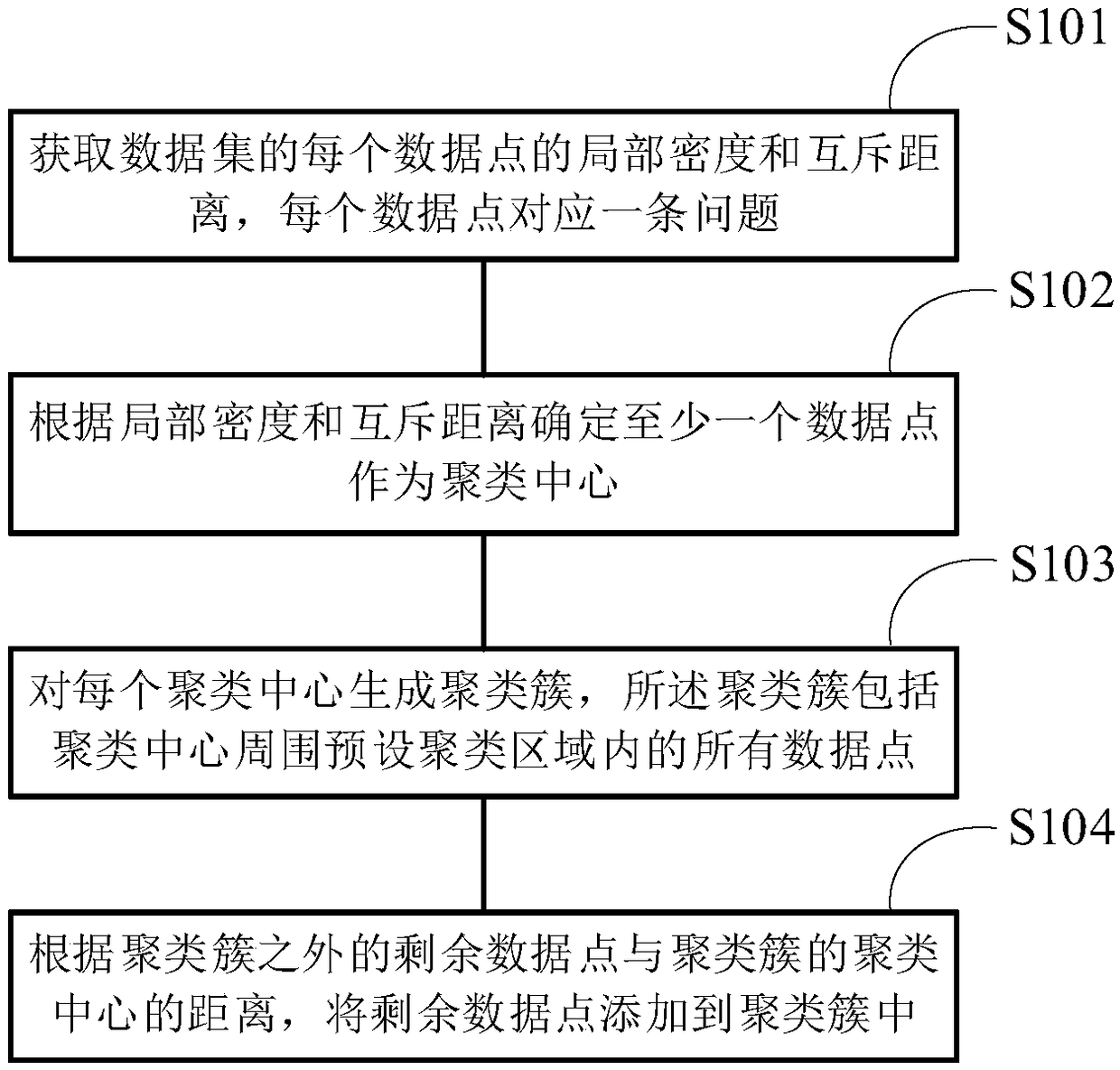
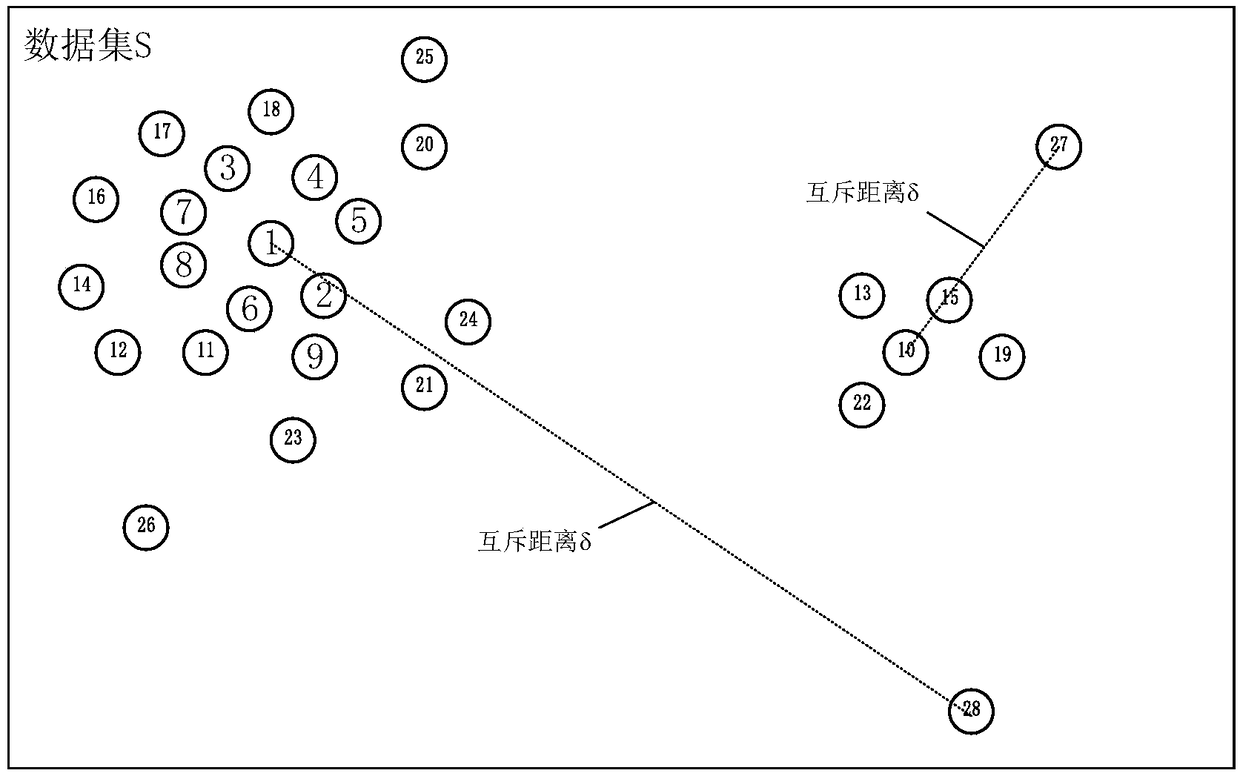
PendingCN109446520AImprove data clustering qualityImprove problem clustering qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingMachine learningData point
Embodiments of the present application provide a data clustering method and apparatus for constructing a knowledge base, wherein the method includes obtaining a local density and a mutually exclusivedistance of each data point of a data set, each data point corresponding to a problem; determining at least one data point as a clustering center according to the local density and the mutual exclusion distance; generating clusters for each clustering center, wherein the clusters comprise all data points in a preset clustering area around the clustering center; according to the distance between the remaining data points outside the cluster and the cluster center, adding the remaining data points to the cluster. The present application is based on the idea of clustering of local density maxima,when the method of the present application generates a knowledge base for an intelligent question answering system, the quality of the question clustering can be improved, so that the intelligent question answering system provides a more reliable intelligent question answering service for a user.
Owner:ULTRAPOWER SOFTWARE
Method for improving data clustering quality by improving k-means based on deviation maximization method
InactiveCN110766087AAffect data classification resultsClearly distinguish the distanceCharacter and pattern recognitionData setAlgorithm
A method for improving data clustering quality by improving k-means based on a deviation maximization method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) performing deviation maximization weight calculation on read-in data: 2) calculating a weight wk of each attribute of a sample by using the deviation maximization method, and then constructing a weighting matrix; 3) weighting the attributes of the data set: 4) calling a k-means algorithm or a k-means + + algorithm, judging whether iteration is terminated or not by judging whether the result is converged to a specified threshold value or not, and finally obtaining a clustering result. Aiming at the defect that an algorithm in the prior art is used for carrying out indifference processing on all data sample attributes, the invention discloses a method for improving data clustering quality by improving k-means based on a deviation maximization method, and the method specifically comprises the steps: carrying out the weighting of attributes, obtaining the objective weight value of each attribute according to the specific information in a data set, increasing the difference of all data, and achieving a better data clusteringeffect.
Owner:山东正云信息科技有限公司
Intention recognition method and device based on multi-parameter K-means algorithm and electronic equipment
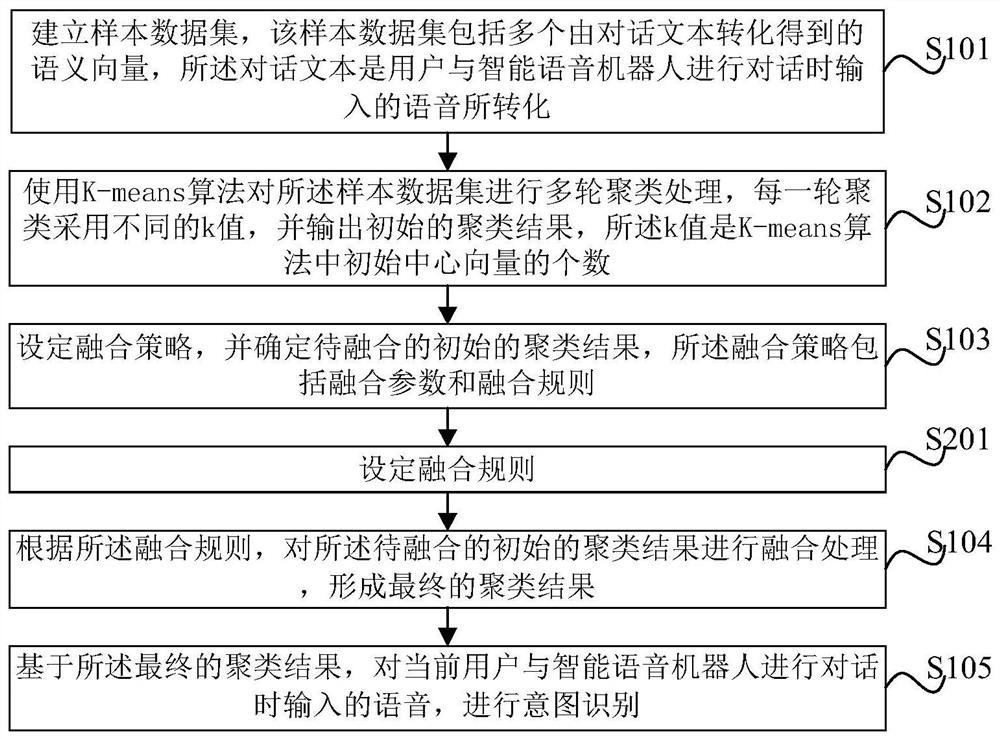
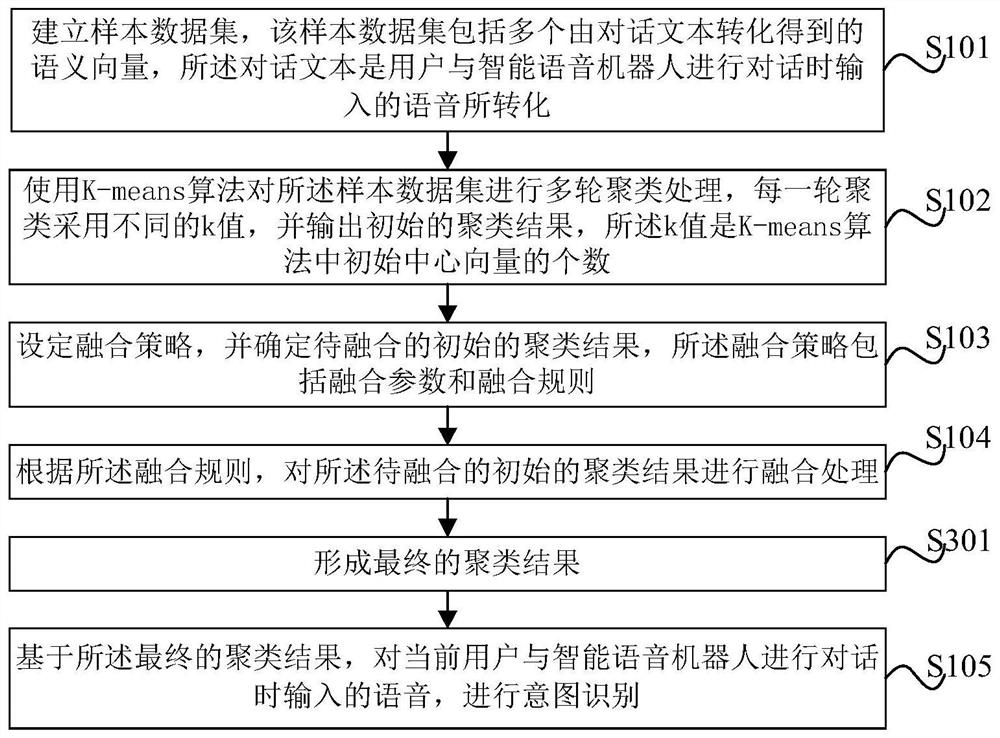
InactiveCN111950294AThe recognition effect is accurateImprove clustering qualitySemantic analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSemantic vectorData set
The invention provides an intention recognition method and device based on a multi-parameter K-means algorithm and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a sampledata set, wherein the sample data set comprises a plurality of semantic vectors obtained by conversion of dialogue texts; performing multiple rounds of clustering processing on the sample data set byusing the K-means algorithm, adopting different k values for each round of clustering, and outputting an initial clustering result; setting a fusion strategy, determining an initial clustering resultto be fused, wherein the fusion strategy comprises fusion parameters and fusion rules; according to the fusion rule, performing fusion processing on the initial clustering result to be fused to forma final clustering result; and based on the final clustering result, performing intention recognition on the voice input by the current user dialogue. According to the method, the improved K-means algorithm is adopted, more accurate intention classification and recognition are achieved, the intention clustering quality is improved, and the method is optimized.
Owner:北京奇保信安科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com