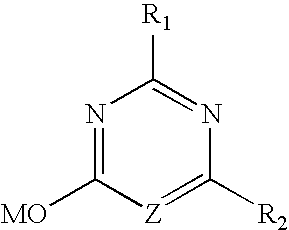
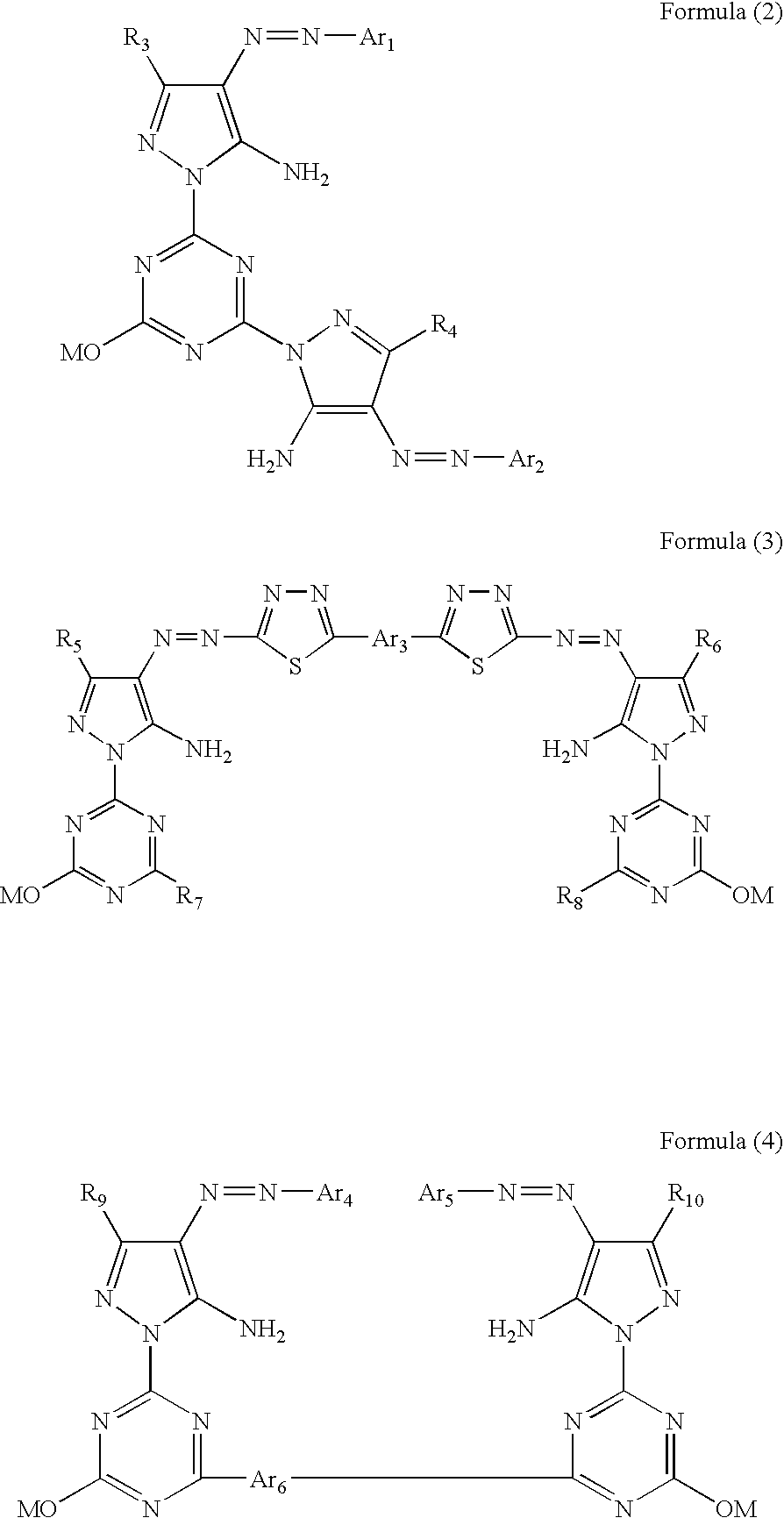
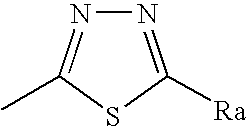
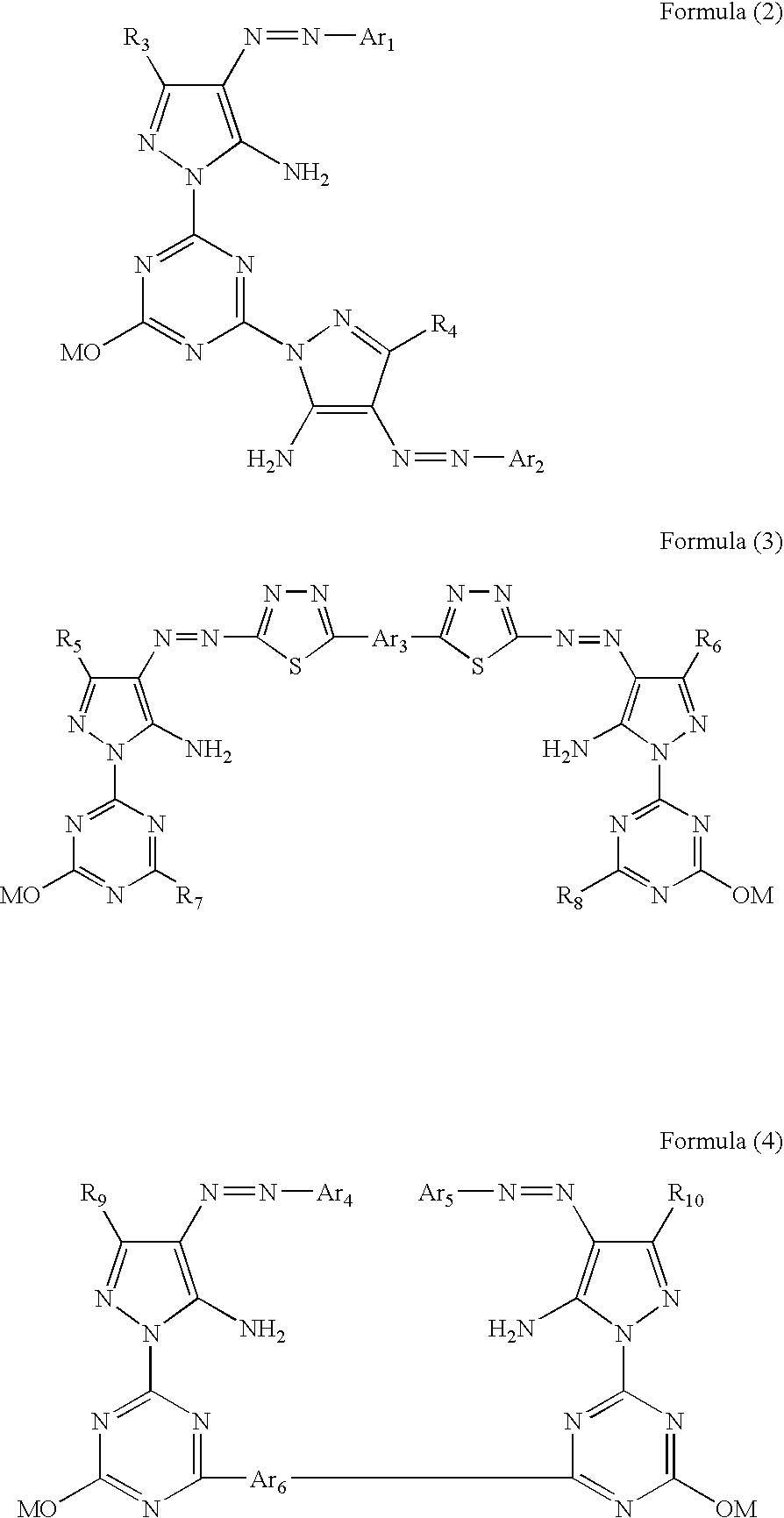
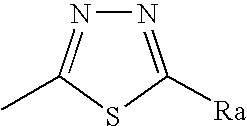
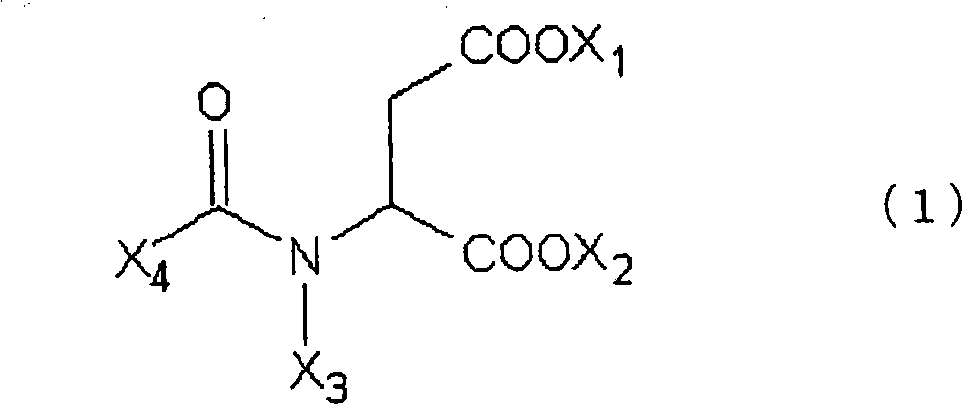
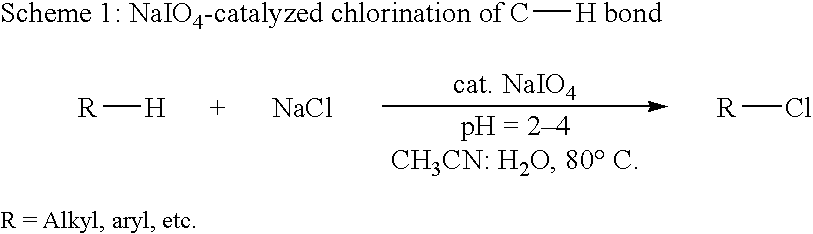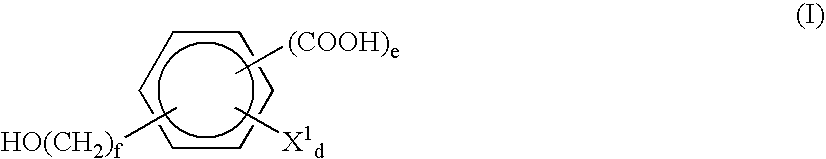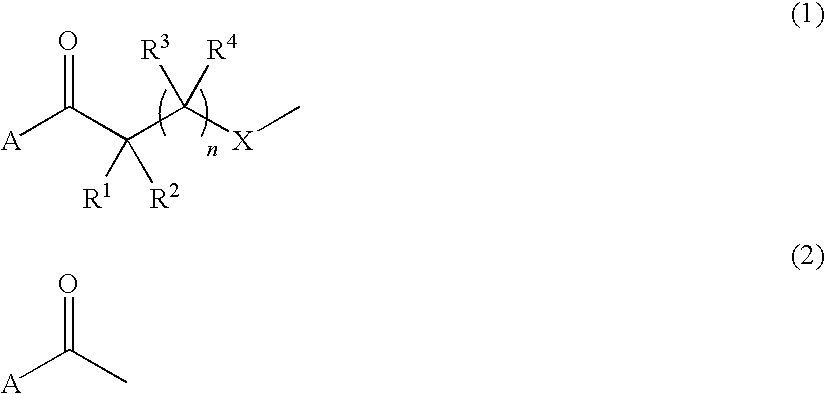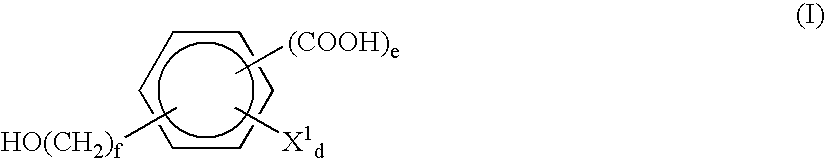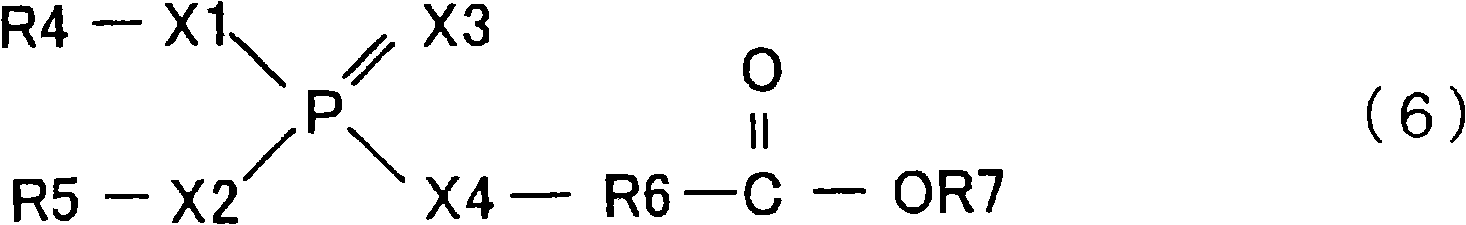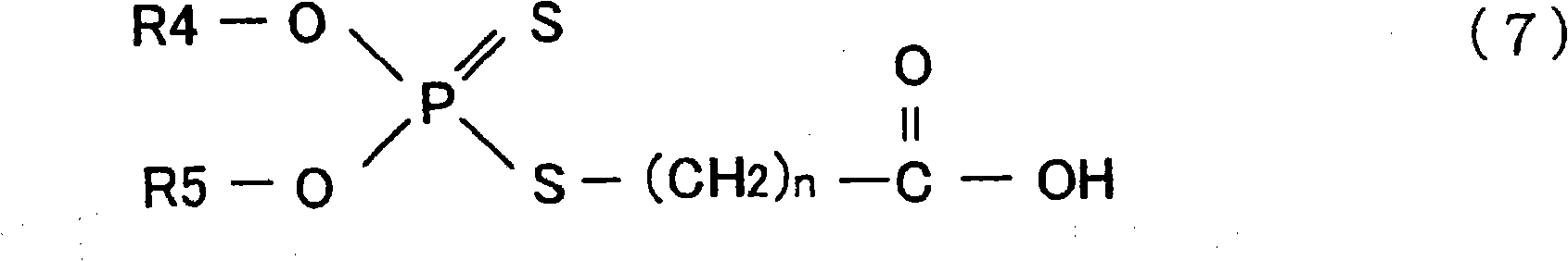Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
297 results about "Aliphatic compound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
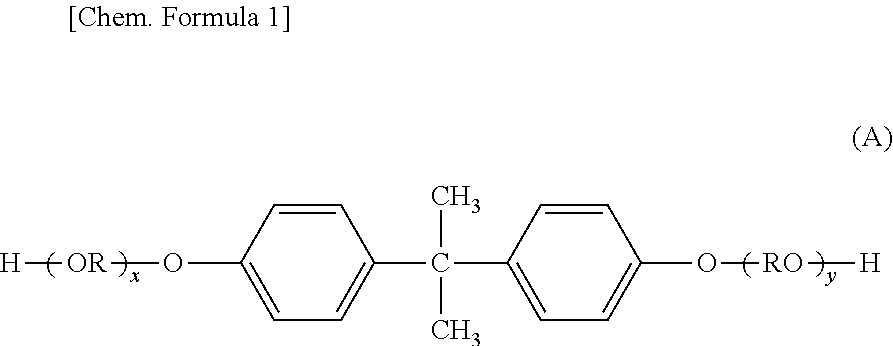
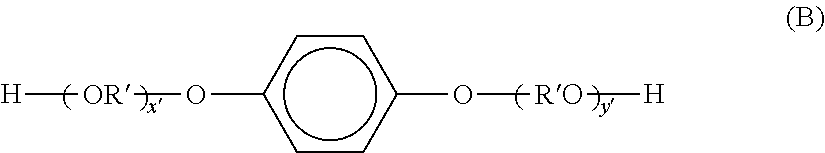
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons (compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (/ˌælɪˈfætɪk/; G. aleiphar, fat, oil), also known as non-aromatic compounds. Aliphatics can be cyclic, but if a unique type of especially stable cyclic bond exists in the molecule, called a benzene ring, then it is considered to be an aromatic compound. Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane, or unsaturated, like hexene and hexyne. Open-chain compounds (whether straight or branched) contain no rings of any type, and are thus aliphatic.
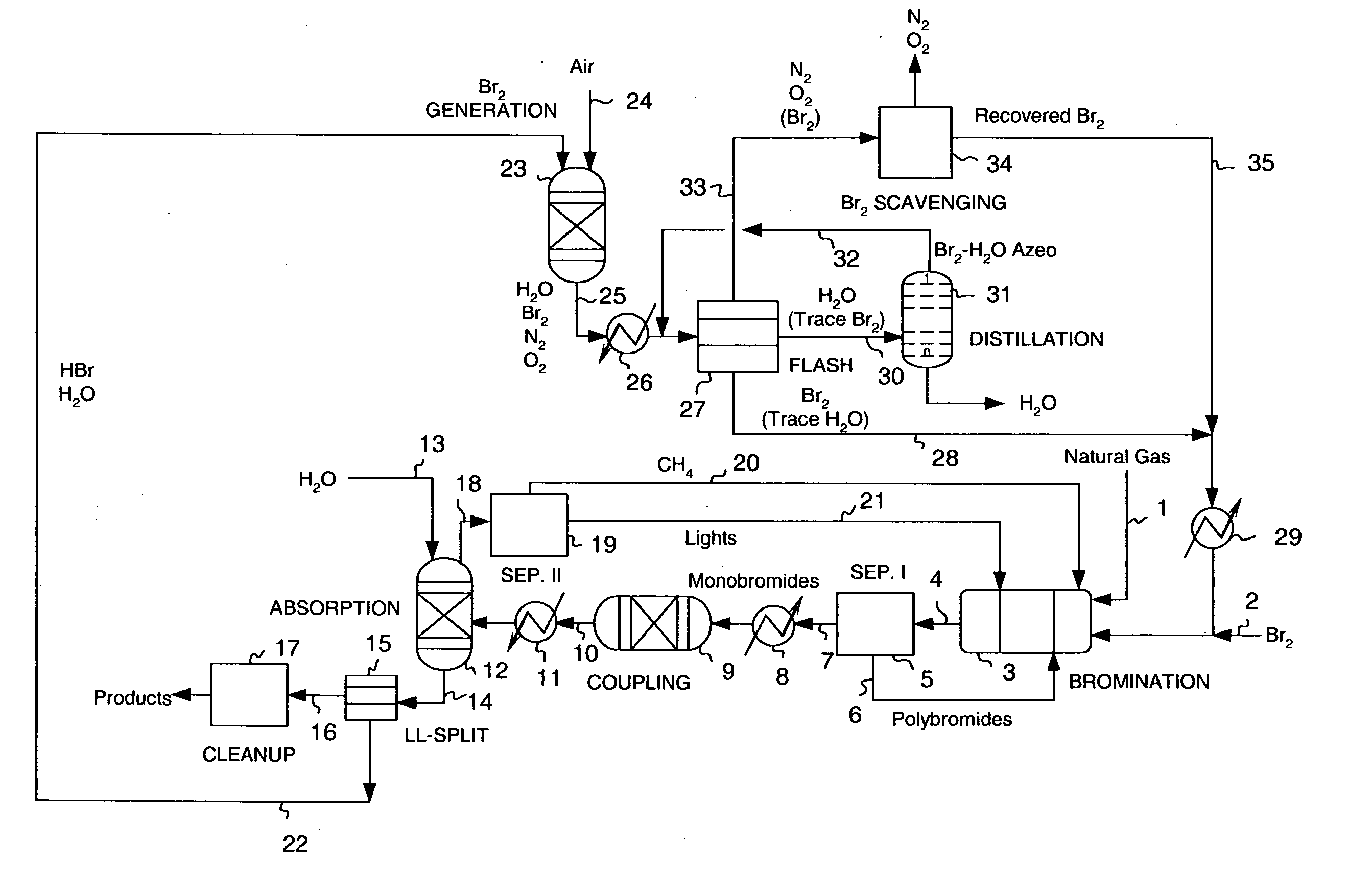
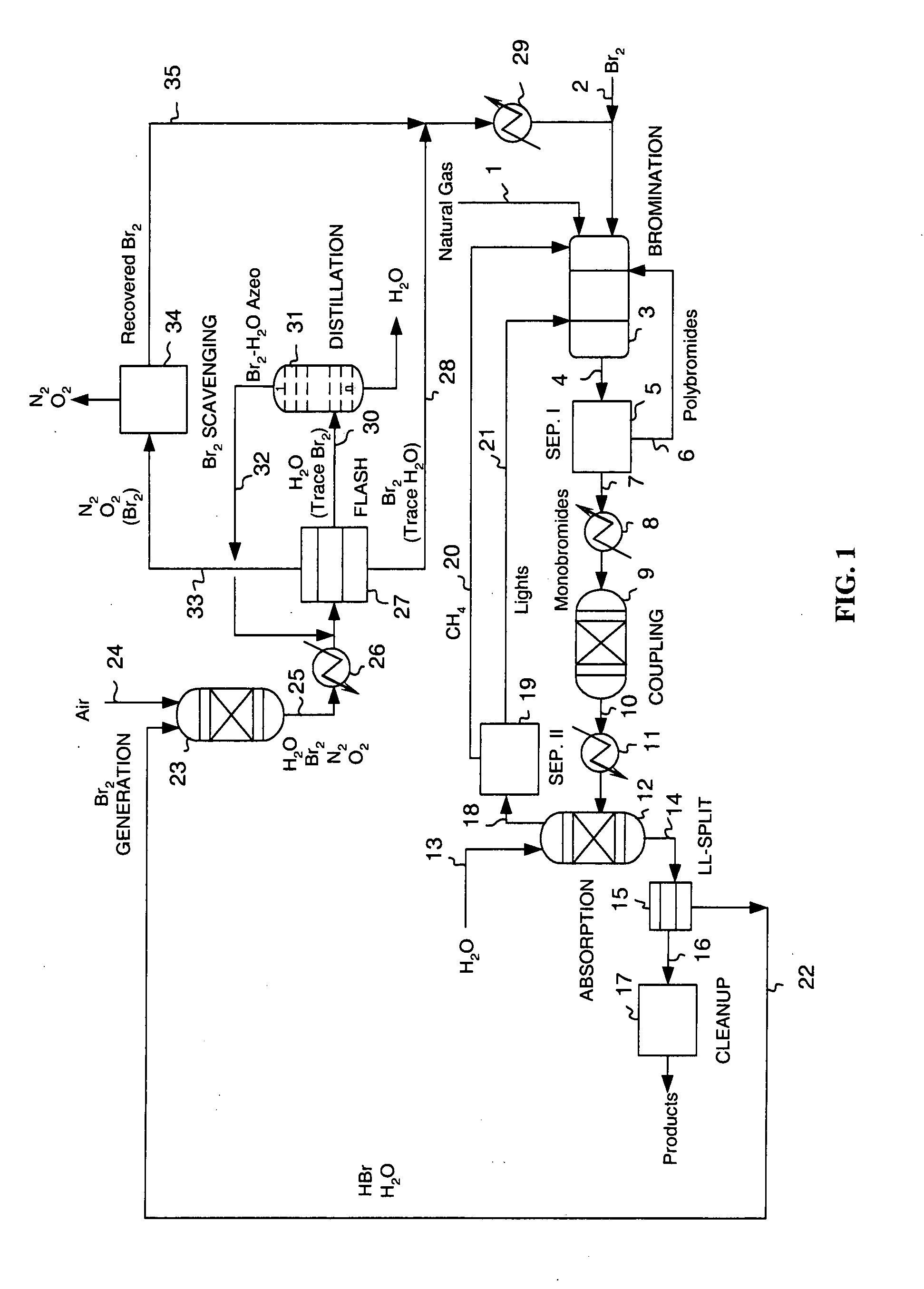
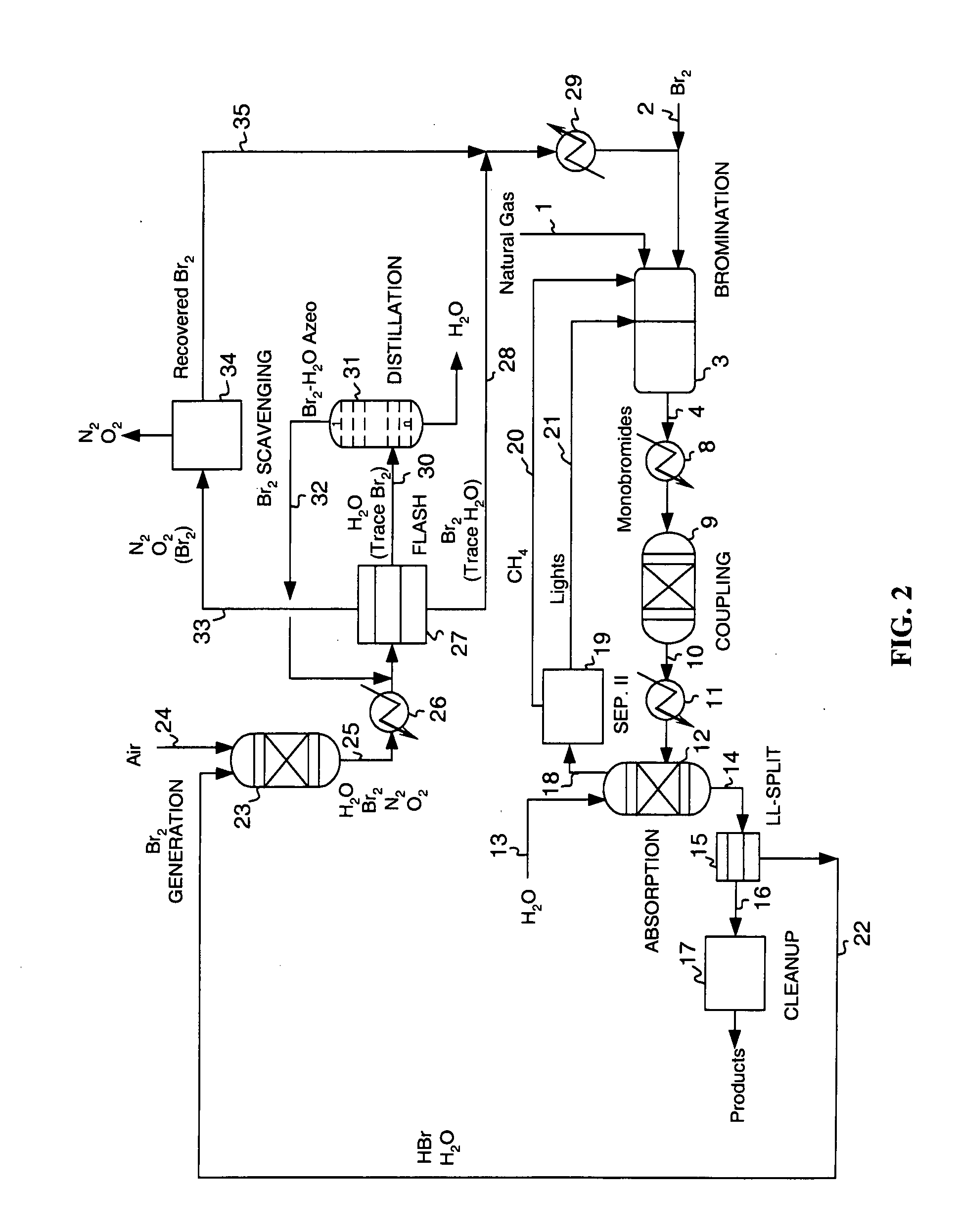
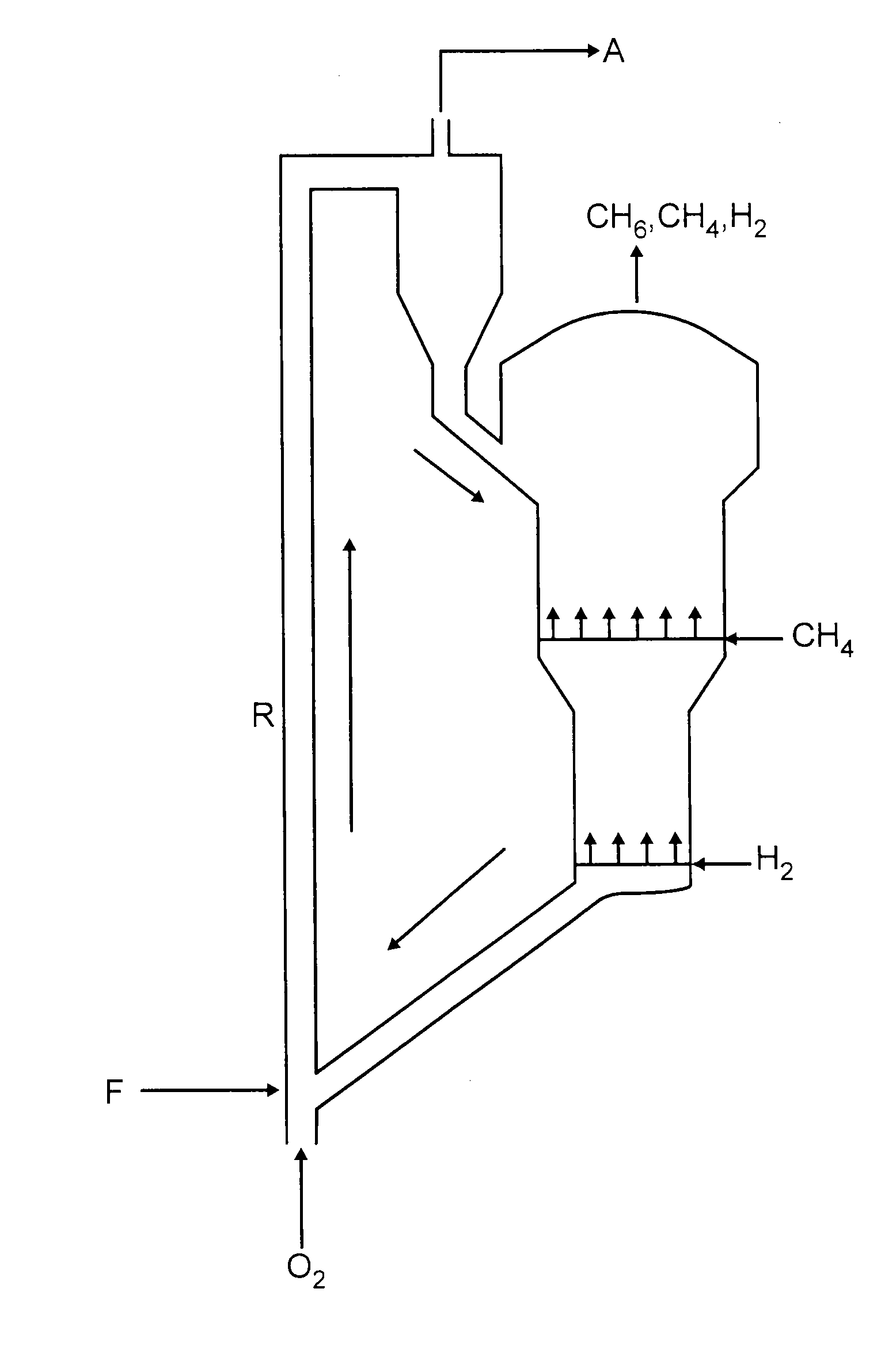
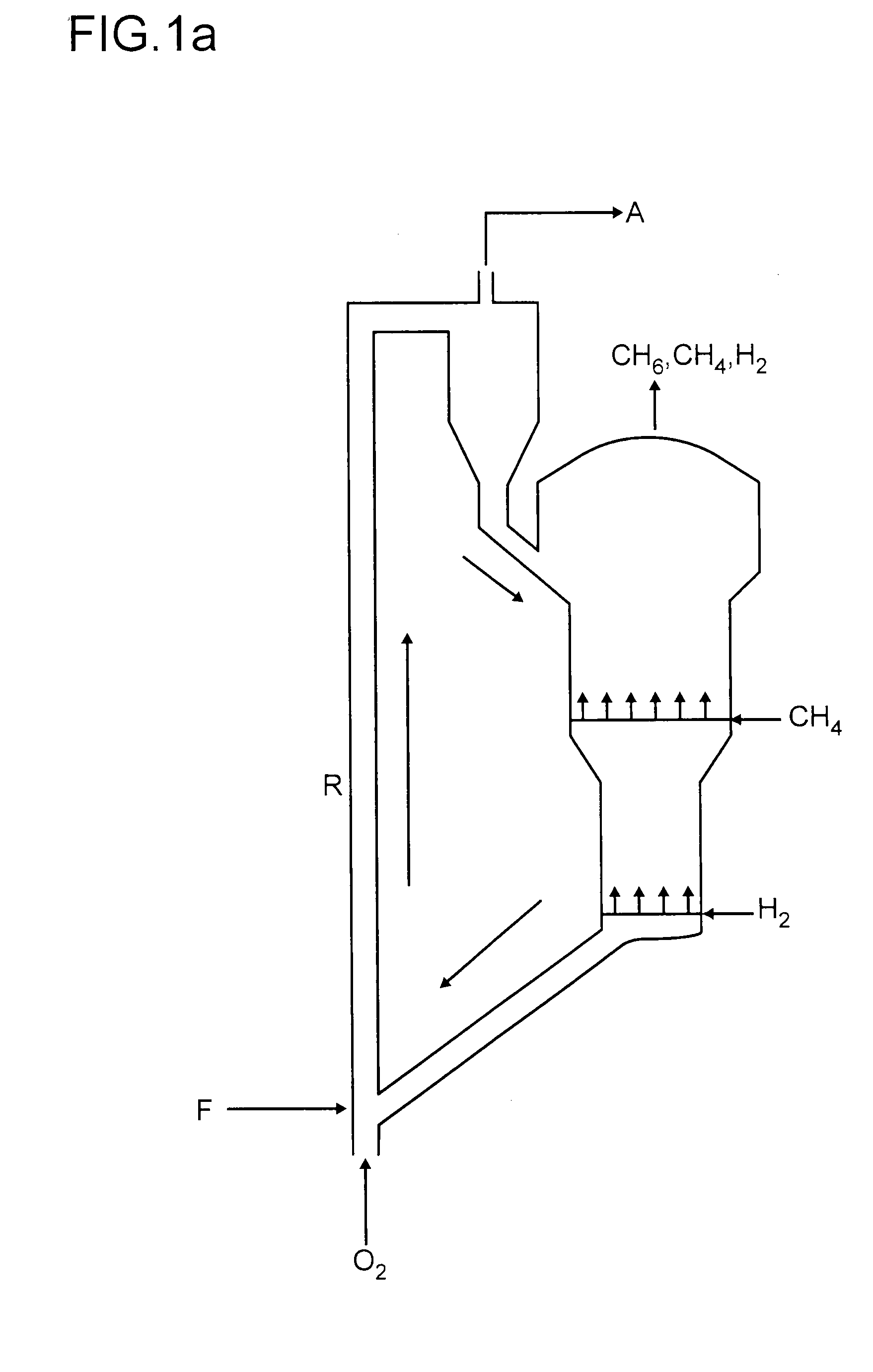
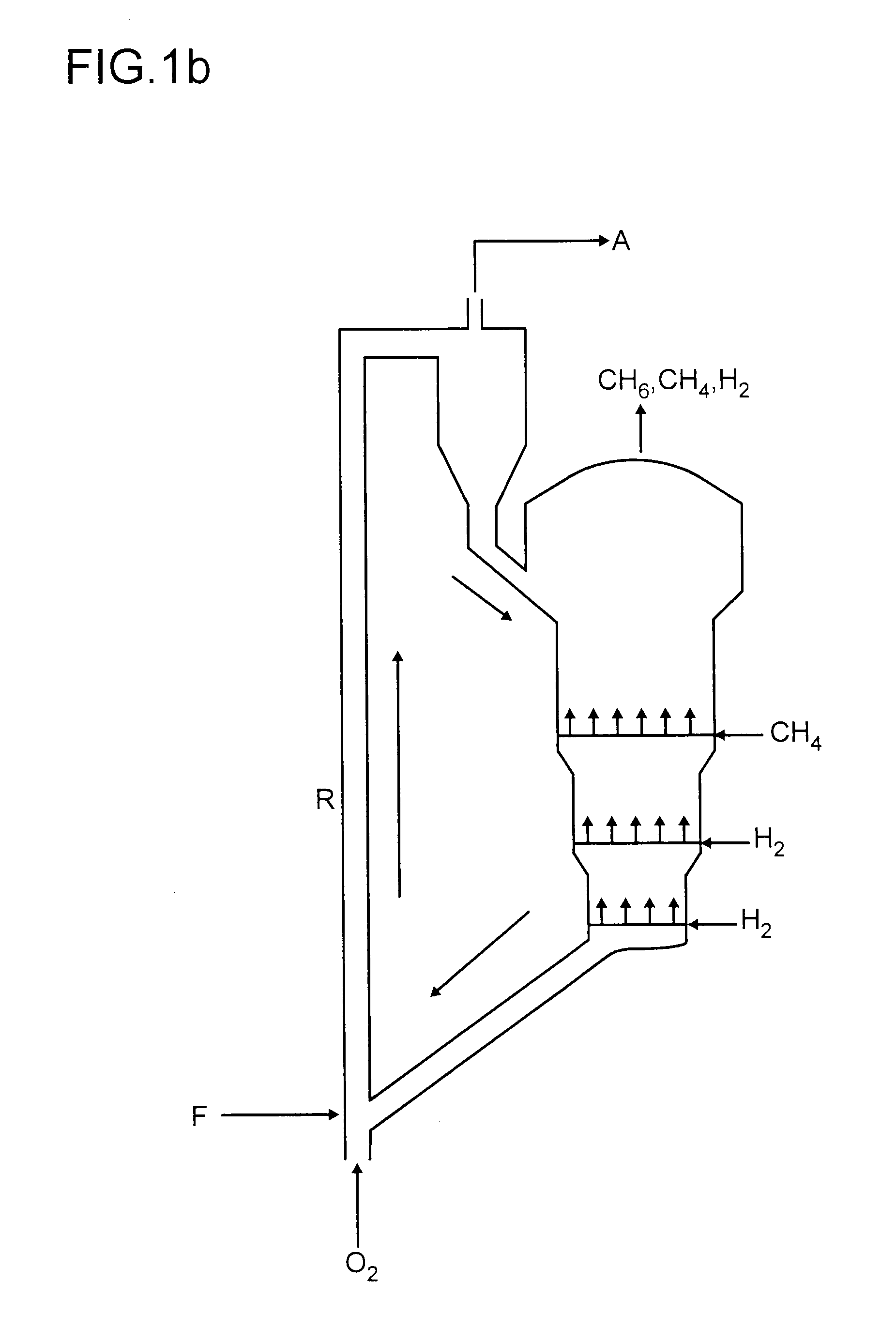
Continuous process for converting natural gas to liquid hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20070238909A1Easily toleratedContinuous regenerationMolecular sieve catalystLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryAlkaneOxygen
An improved continuous process for converting methane, natural gas, or other hydrocarbon feedstocks into one or more higher hydrocarbons or olefins by continuously cycling through the steps of alkane halogenation, product formation (carbon-carbon coupling), product separation, and regeneration of halogen is provided. Preferably, the halogen is continually recovered by reacting hydrobromic acid with air or oxygen. The invention provides an efficient route to aromatic compounds, aliphatic compounds, mixtures of aliphatic and aromatic compounds, olefins, gasoline grade materials, and other useful products.
Owner:REACTION 35 LLC
Catalytic process for regiospecific chlorination of alkanes, alkenes and arenes
InactiveUS6825383B1Save energyOrganic compound preparationPreparation by OH and halogen introductionMetal chlorideAlkene
The present invention provides a process for regiospecific chlorination of an aromatic or aliphatic compound with a chlorine source comprising a metal chloride and other than Cl2 and SO2Cl2 in presence of hypervalent iodine catalyst and in acidic medium.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Polishing fluid and polishing method
ActiveUS20050181609A1Increase chanceSuperior in dimensional accuracy and electric characteristicOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSlurry
A polishing slurry including an oxidant, a metal oxide dissolver, a metal inhibitor and water and having a pH from 2 to 5. The metal oxide dissolver contains one or more types selected from one or more acids (A-group) selected from acids of which the dissociation constant (pKa) of a first dissociable acid group is less than 3.7 and from which five acids of lactic acid, phthalic acid, fumaric acid, maleic acid and aminoacetic acid are excluded, ammonium salts of the A-group and esters of the A-group, and one or more types selected from one or more acids (B-group) selected from acids of which the dissociation constant (pKa) of a first dissociable acid group is 3.7 or more and the five acids, ammonium salts of the B-group and esters of the B-group. The metal inhibitor contains one or more types selected from the group consisting of aromatic compounds having a triazole skeleton and one or more types selected from the group consisting of aliphatic compounds having a triazole skeleton and compounds having any one of pyrimidine skeleton, imidazole skeleton, guanidine skeleton, thiazole skeleton and pyrazole skeleton. The polishing slurry having a high metal-polishing rate, reducing etching rate and polishing friction, results in the production, with high productivity, of semiconductor devices reduced in dishing and erosion in metal wiring.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Fungicide composition
ActiveCN101637157AGood synergyImprove the effect of disease preventionBiocideFungicidesThiocarbamateCarbamate
The invention provides a fungicide composition containing an active component A and an active component B, and application thereof in preventing and controlling various agricultural fungal diseases. The active component A in the composition is one of two methoxyl acrylic ester compounds; and as shown above, the active component B of the compound A1 and the compound A2 is one of the following fungicide varieties: thiocarbamate compounds or salt thereof, aliphatic compounds or salt thereof, carbamate compounds or salt thereof, oxazole compounds or salt thereof, thiazole compounds or salt thereof, amide compounds or salt thereof, organophosphorus compounds or salt thereof, imidazole compounds or salt thereof, antibiotic compounds or salt thereof, pyridine compounds or salt thereof and triazole compounds or salt thereof.
Owner:SHENYANG SINOCHEM AGROCHEMICALS R&D CO LTD
Stereolithographic resins with high temperature and high impact resistance
InactiveUS6989225B2High modulusHigh elongation at breakAdditive manufacturing apparatusImpression capsMeth-Cationic polymerization
A liquid radiation-curable composition that comprises(A) at least one polymerizing organic substance comprising a mixture of(1) at least one alicyclic epoxide having at least two epoxy groups; and(2) at least one difunctional or higher functional glycidylether of a polyhydric compound;(B) at least one free-radical polymerizing organic substance comprising a mixture of(1) optionally, at least one trifunctional or higher functional (meth)acrylate compound; and(2) at least one aromatic di(meth)acrylate compound;(C) at least one cationic polymerization initiator;(D) at least one free-radical polymerization initiator;(E) optionally, at least one hydroxyl-functional aliphatic compound; and(F) at least one hydroxyl-functional aromatic compound;wherein the concentration of hydroxyl groups in the radiation-curable composition is at least about 1.1 equivalent OH groups per kilogram;wherein the concentration of epoxy groups in the radiation-curable composition is at least about 5.5 equivalent epoxy groups per kilogram; andwherein the amount of trifunctional or higher functional (meth)acrylate compound (B)(1) is from 0% to about 3% of the composition and the amount of aromatic di(meth)acrylate compound (B)(2) is at least 10% of the composition.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Light-sensitive lithographic printing plate
InactiveUS20050214678A1High developing latitudeExcellent printing durabilityPhotosensitive materialsLithographySide chainTelomerization
A light-sensitive lithographic printing plate comprises a hydrophilic substrate provided thereon with an infrared light-sensitive layer which comprises (A) an acetal polymer having a specific structure; (B) a polymeric compound carrying, on the side chains, fluorinated aliphatic groups in which the fluorinated aliphatic groups are those derived from fluorinated aliphatic compounds prepared by the telomerization or oligomerization; and (C) a light-heat conversion substance. The light-sensitive lithographic printing plate is excellent in the both printing durability and the developing latitude.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Selective sorbents for purification of hydrocartons
InactiveUS7148389B2Organic compound preparationOther chemical processesPreferential adsorptionSorbent
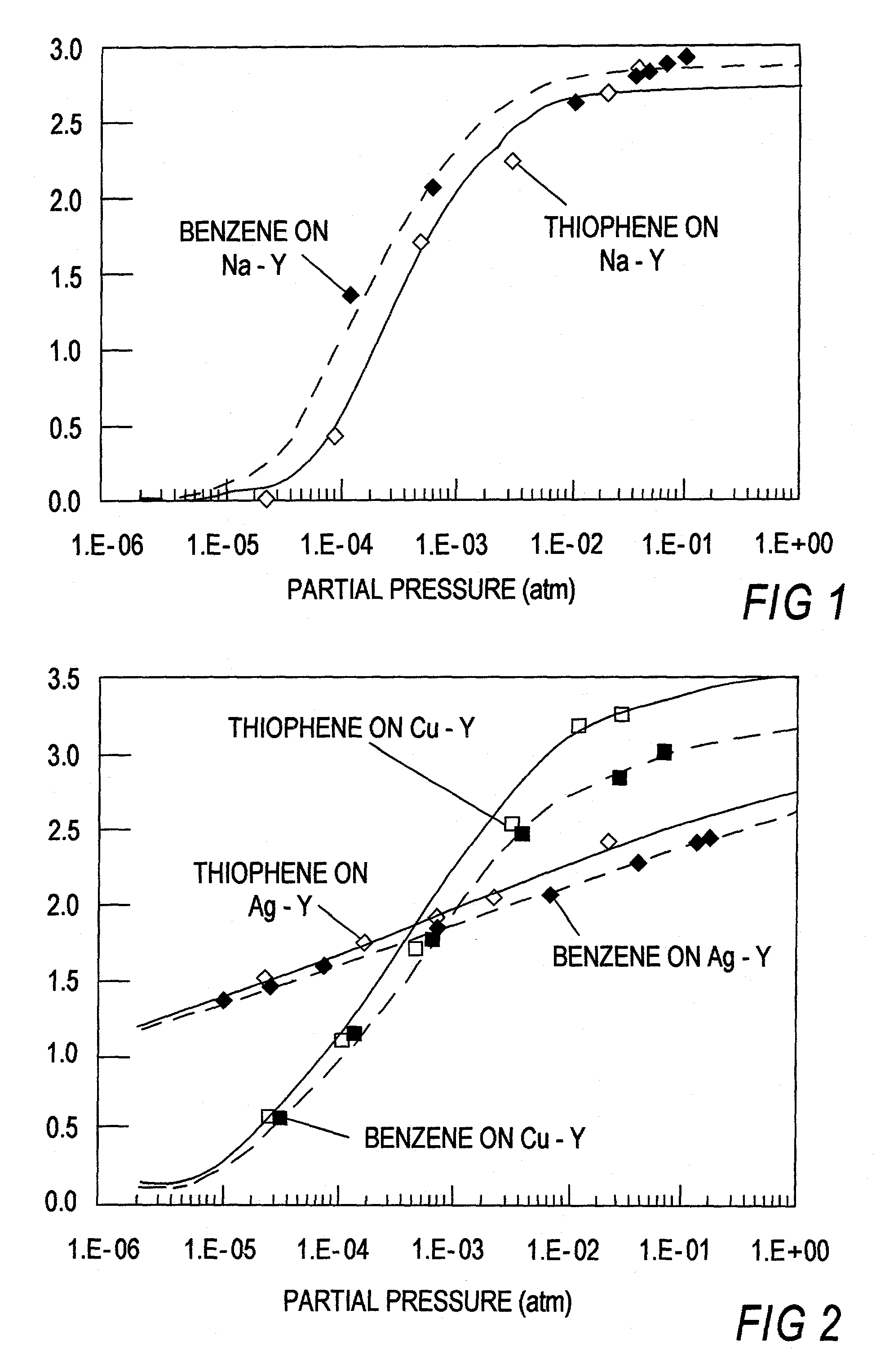
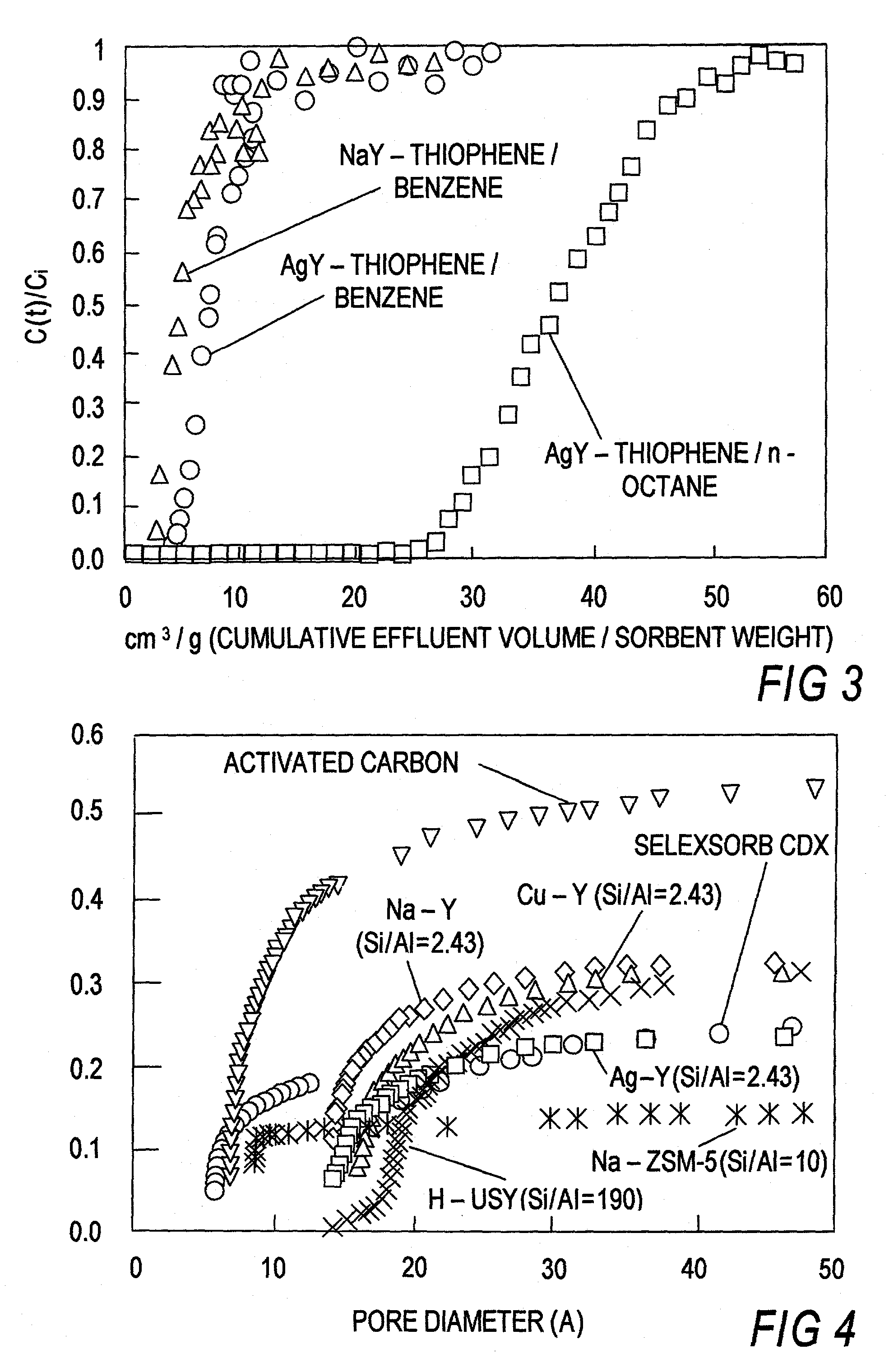
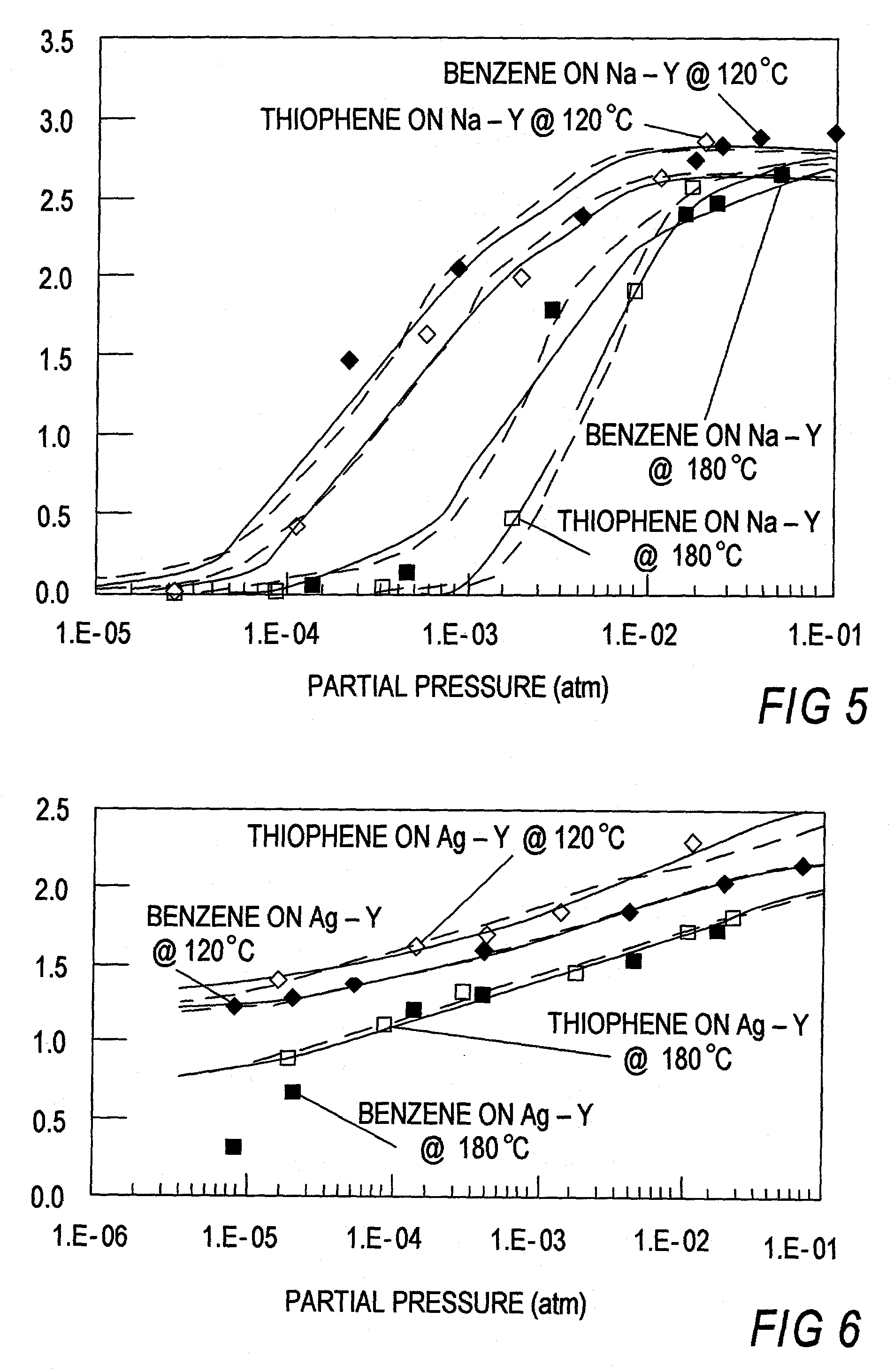
A method for removing thiophene and thiophene compounds from liquid fuel includes contacting the liquid fuel with an adsorbent which preferentially adsorbs the thiophene and thiophene compounds. The adsorption takes place at a selected temperature and pressure, thereby producing a non-adsorbed component and a thiophene / thiophene compound-rich adsorbed component. The adsorbent includes either a metal or a metal ion that is adapted to form π-complexation bonds with the thiophene and / or thiophene compounds, and the preferential adsorption occurs by π-complexation. A further method includes selective removal of aromatic compounds from a mixture of aromatic and aliphatic compounds.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Ink composition and inkjet recording method
ActiveUS20060016368A1Imparting lusterImparting water resistanceDisazo dyesMeasurement apparatus componentsYELLOW DYEPhosphoric acid
A novel ink composition, which has an absorption characteristic excellent in color reproducibility as a yellow color of one of the three primary colors, which has enough fastness against light, heat and humidity, and which does not cause bronze phenomenon, is provided. The ink composition contains water, a yellow dye having an oxidation potential nobler than 1.0 V, and an aromatic compound, aliphatic compound and / or a salt thereof having at least one of carboxyl group, sulfo group and phosphoric acid group.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Biodegradable Resin Composition
The present invention relates to a method of producing a biodegradable resin composition, which includes step (1) of mixing a biodegradable resin, a plasticizer and a crystal nucleating agent with one another at the melting point (Tm) of the biodegradable resin or more, wherein the crystal nucleating agent is an aliphatic compound having, in its molecule, two or more of at least one group selected from an ester group a hydroxyl group and an amide group, and step (2) of thermally treating the resulting biodegradable resin composition at a temperature of from the glass transition temperature (Tg) to less than Tm of the composition, as well as a biodegradable resin composition, which contains a biodegradable resin, a plasticizer, and the above crystal nucleating agent, and which satisfies the following conditions: the haze thereof with a thickness of 0.5 mm after thermal treatment at 60° C. for 36 or 60 hours is 20% or less; the storage elastic modulus (E′) at a temperature of 25° C. and a frequency of 50 Hz is 1×108 to 2×109 Pa; and the storage elastic modulus (E′) at a temperature of 60° C. and a frequency of 50 Hz is 1×107 to 1×109 Pa.
Owner:KAO CORP
Layer configuration with improved stability to sunlight exposure
ActiveUS7820078B2Improve stabilityReduce surface resistanceHybrid capacitor electrodesConductive materialLight-emitting diodeHydrocarbons.aliphatic
Disclosed are a light-emitting diode, a photovoltaic device, a transistor, and an electroluminescent device, each comprising a layer disposed on a support, the layer comprising a [A] composition exclusive of hydroquinone comprising at least one polymer comprising (3,4-dialkoxythiophene) monomer units, a polyanion, at least one polyhydroxy group-containing aromatic compound exclusive of sulfo groups, at least one amino-compound or heterocyclic compound with at least one ring nitrogen atom, and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of polyhydroxy- and / or carboxy group or amide or lactam group containing aliphatic compounds and aprotic compounds with a dielectric constant ≧15.
Owner:AGFA GEVAERT AG
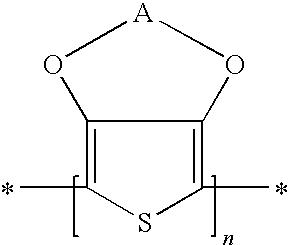
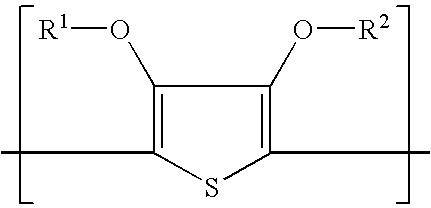
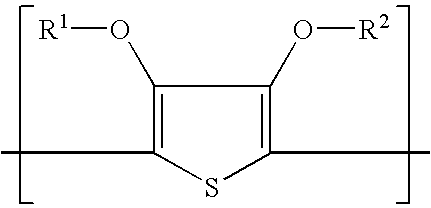
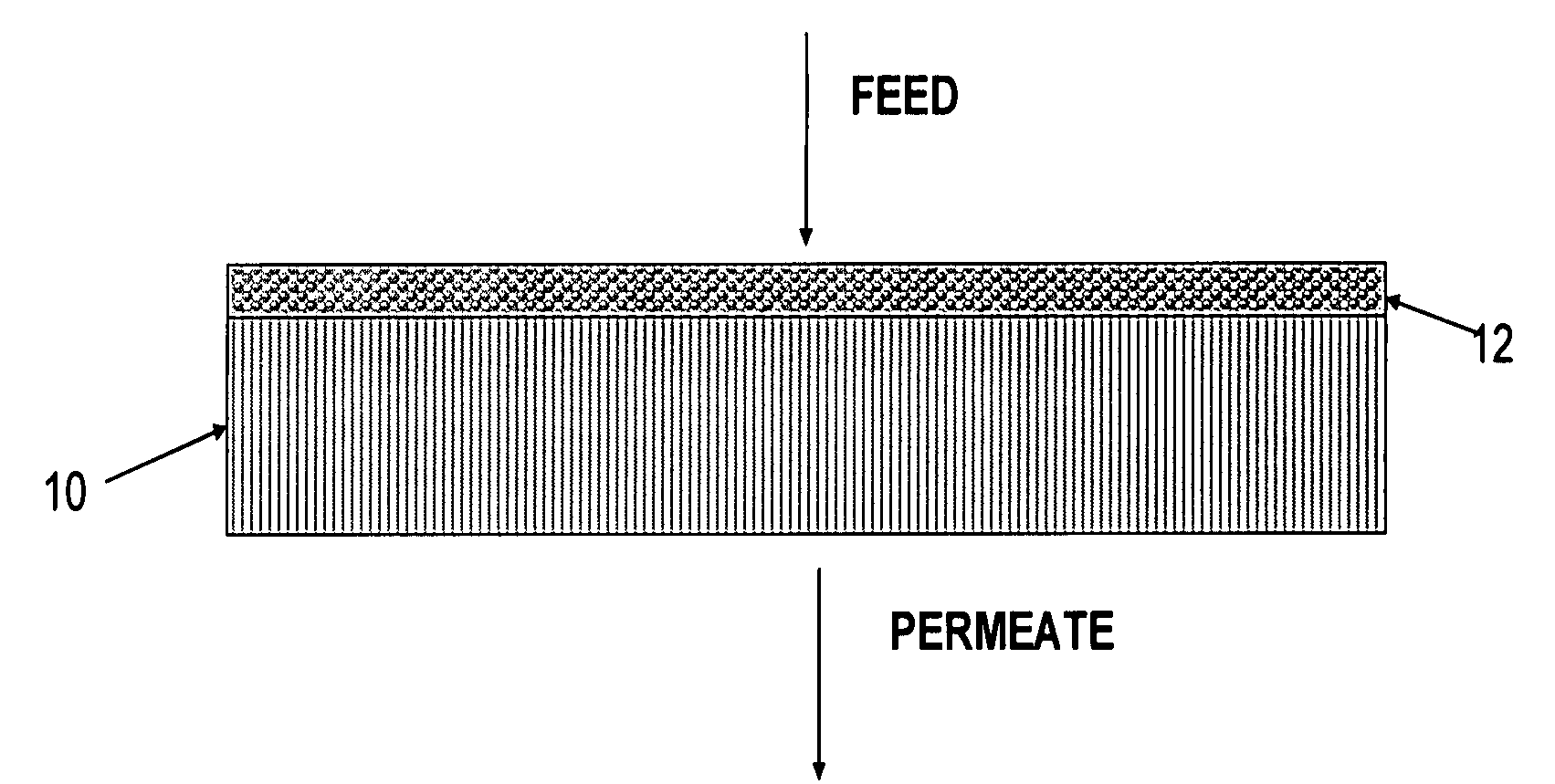
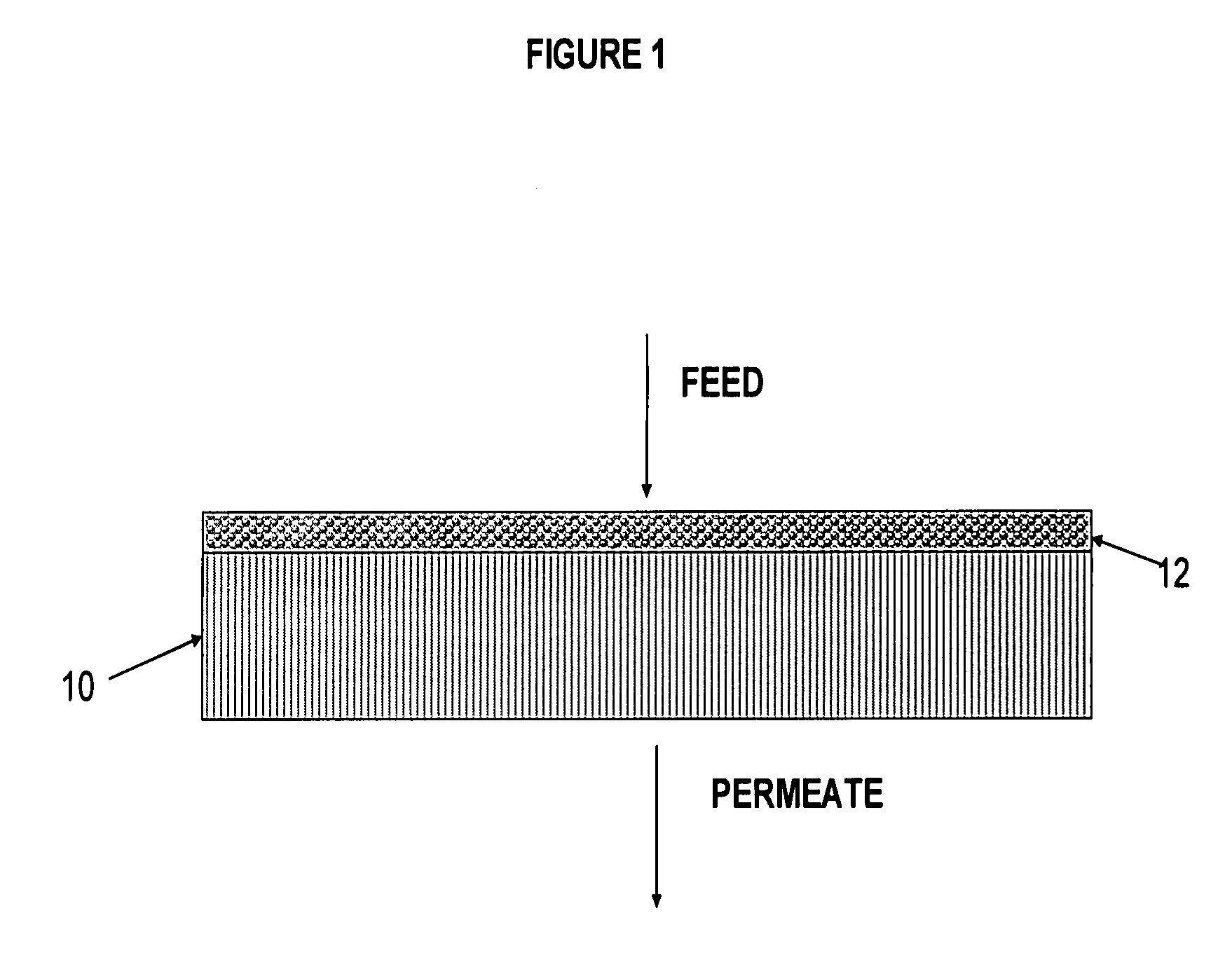
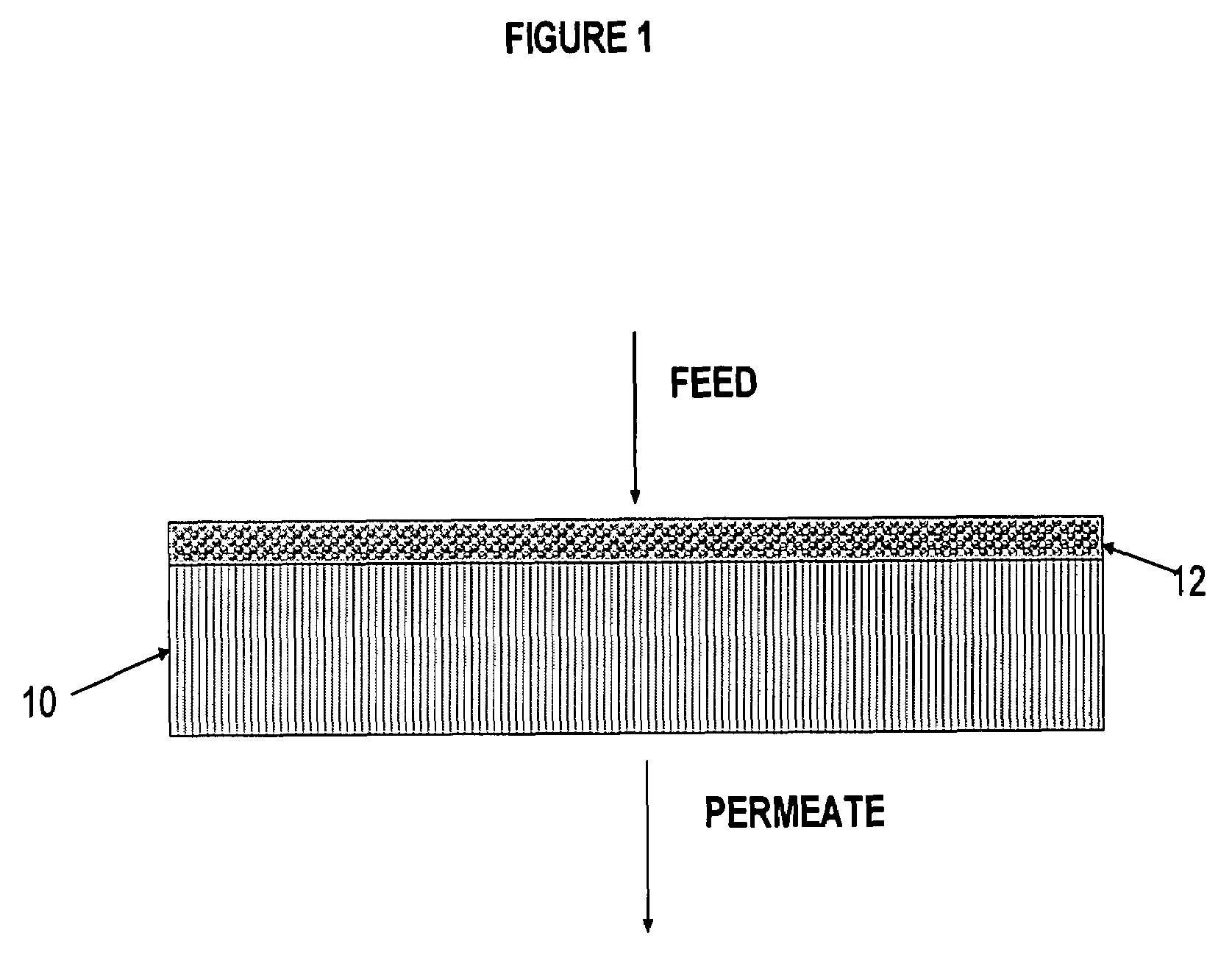
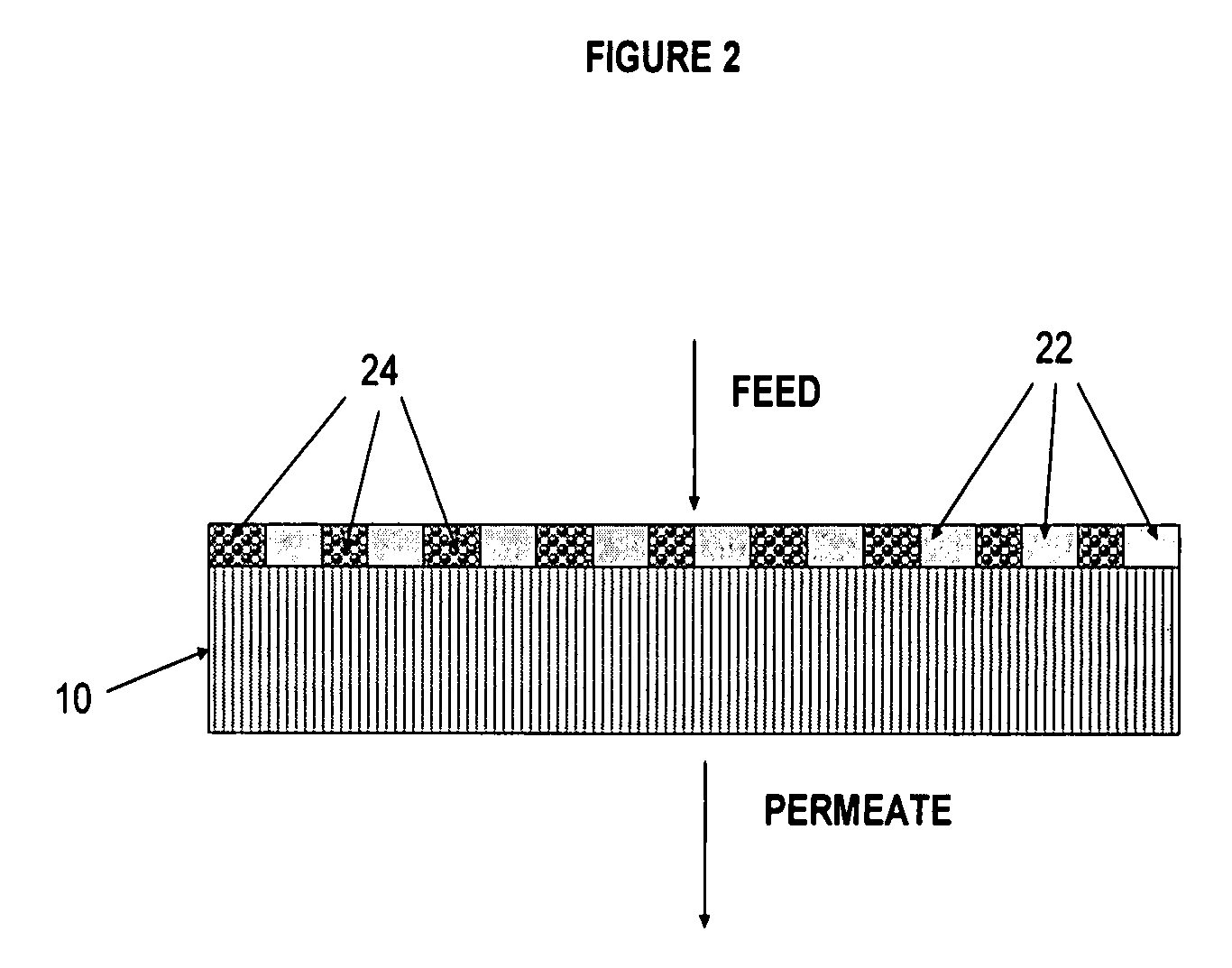
Polymer-coated inorganic membrane for separating aromatic and aliphatic compounds
InactiveUS20080035557A1Promotes uniform depositionMaximizing permeationMembranesDialysisSilicon dioxideMembrane composition
A membrane composition comprising an inorganic substrate which has a coating of an associating polymer. The membrane composition includes an inorganic substrate selected from the group consisting of a porous silica hollow tube, an alumina hollow tube and a ceramic monolith.
Owner:PARTRIDGE RANDALL D +3
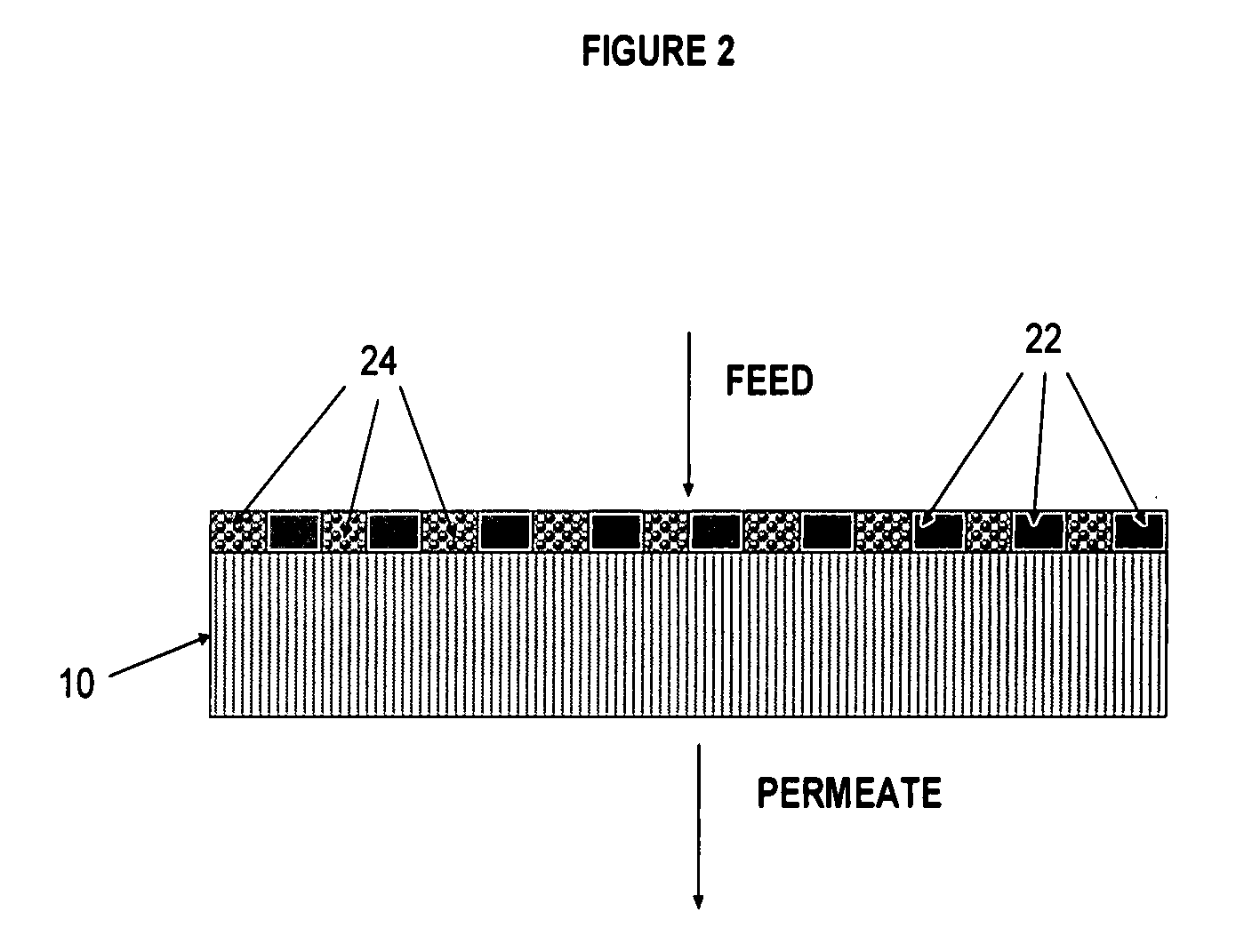
Polymer membrane for separating aromatic and aliphatic compounds
InactiveUS20080035575A1Improved physical integrityEasy to separateSemi-permeable membranesMembranesPorous substratePolymer science
This invention relates to a polymeric membrane composition comprising an associating polymer. The polymer coating is characterized as having hard and soft segments where the hard segment comprises TMPA, combined with HDPA. The membrane may utilize a porous substrate.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
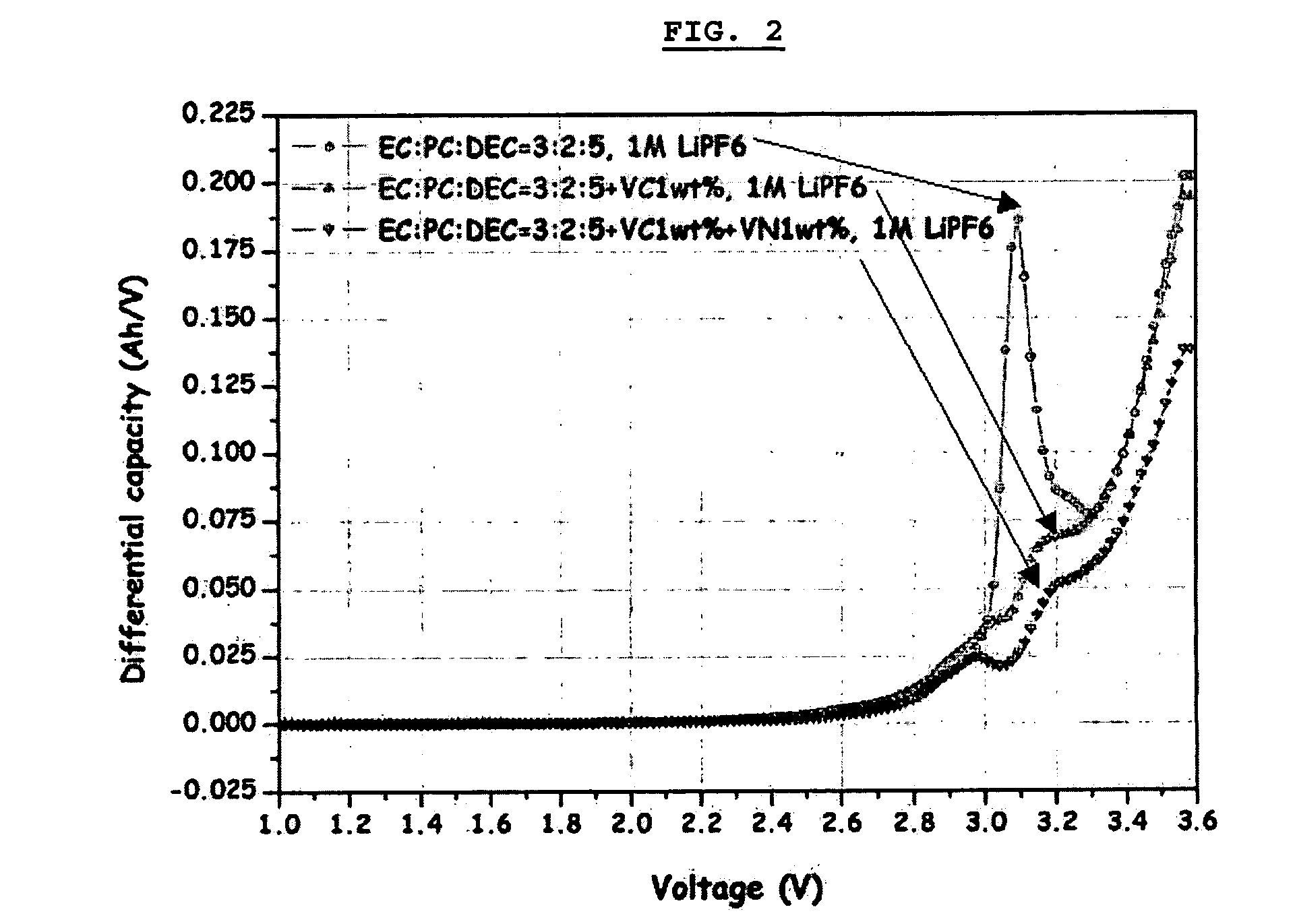
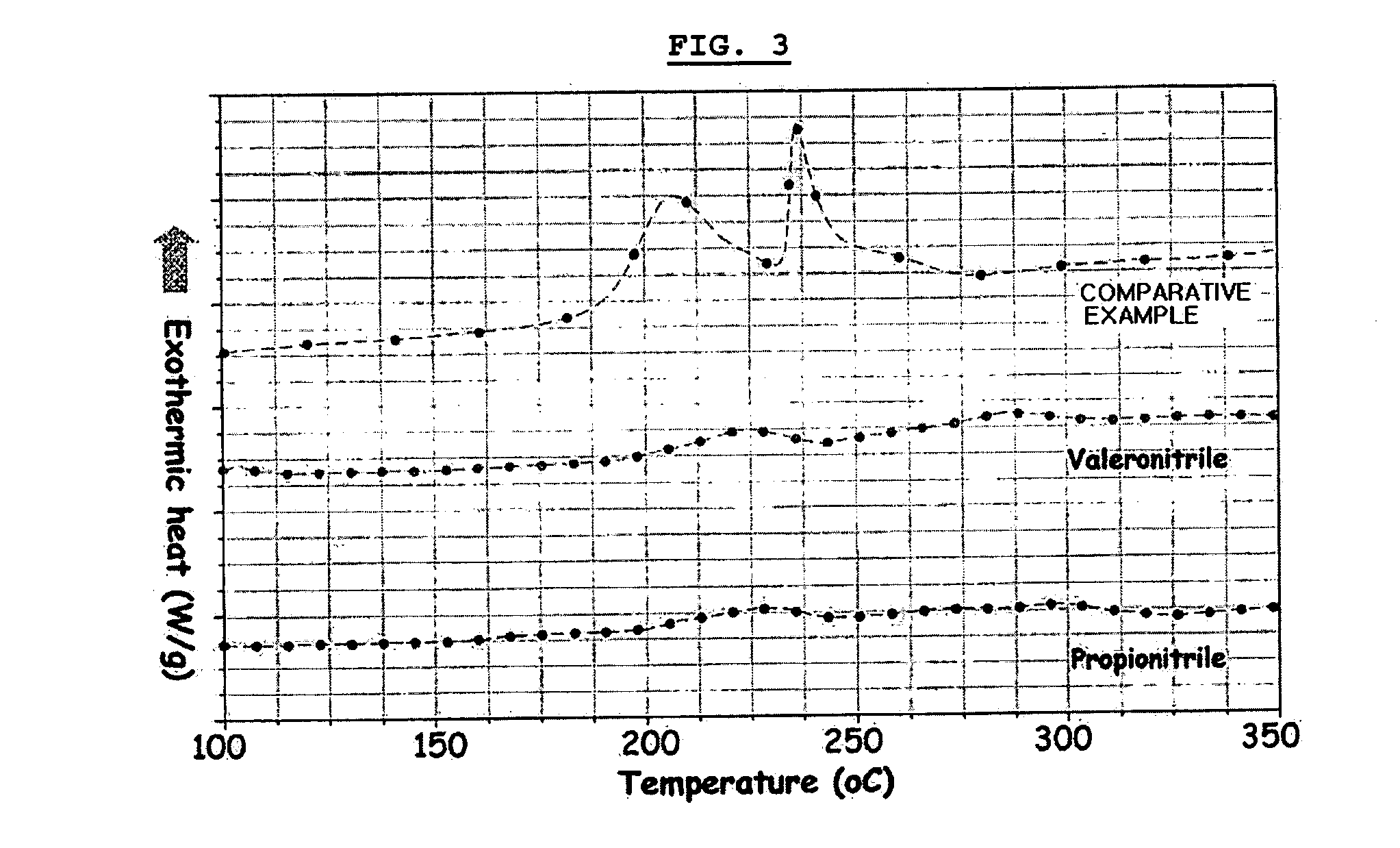
Electrochemical device comprising aliphatic mono-nitrile compound
ActiveUS20060204834A1Low viscosityImprove ionic conductivitySolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureSolventElectrochemical cell
Disclosed is a cathode comprising a complex formed between the surface of a cathode active material and an aliphatic mono-nitrile compound, and an electrochemical device comprising the cathode. A non-aqueous electrolyte containing a lithium salt, a solvent and an aliphatic mono-nitrile compound, and an electrochemical device comprising the electrolyte are also disclosed. The electrochemical device shows excellent low-temperature characteristics, high-temperature life characteristics and safety.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Cellulose Acylate Film, Method for Producing Cellulose Acylate Film, Polarizing Plate and Liquid Crystal Display Device
InactiveUS20090021671A1Stable in retardationDimensional stabilityLiquid crystal compositionsCellulosic plastic layered productsVitrificationCellulose
A method for producing a cellulose acylate film containing an additive comprising an aliphatic compound, the method contains a process of thermal shrinkage treatment at an atmospheric temperature higher than the glass transition temperature (Tg) in the state where at least one of the transverse direction and the machine direction of the film is free, and a cellulose acylate film obtained by the above method.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
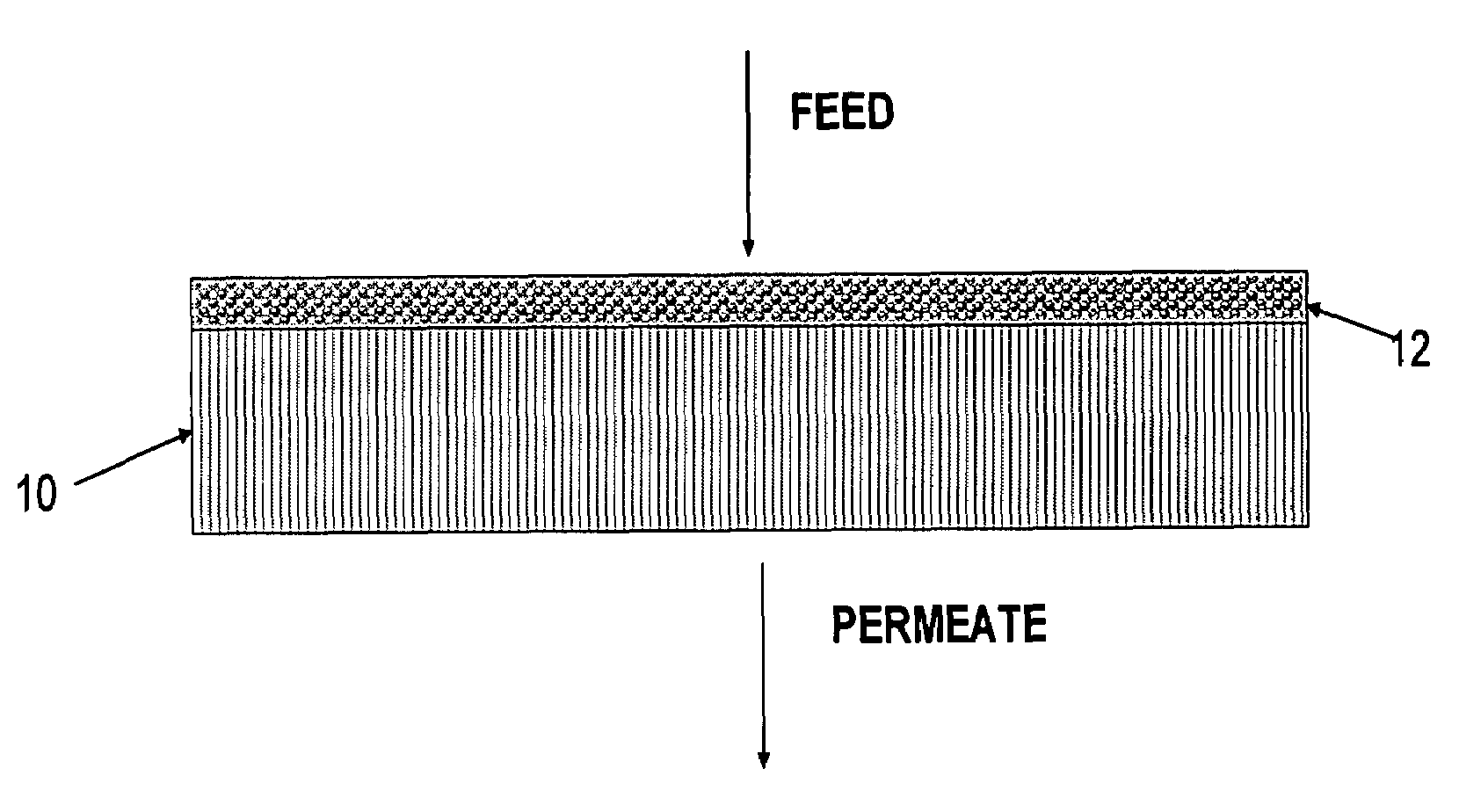
Composite Semipermeable Membranes, Methods for Production Thereof and Uses Thereof
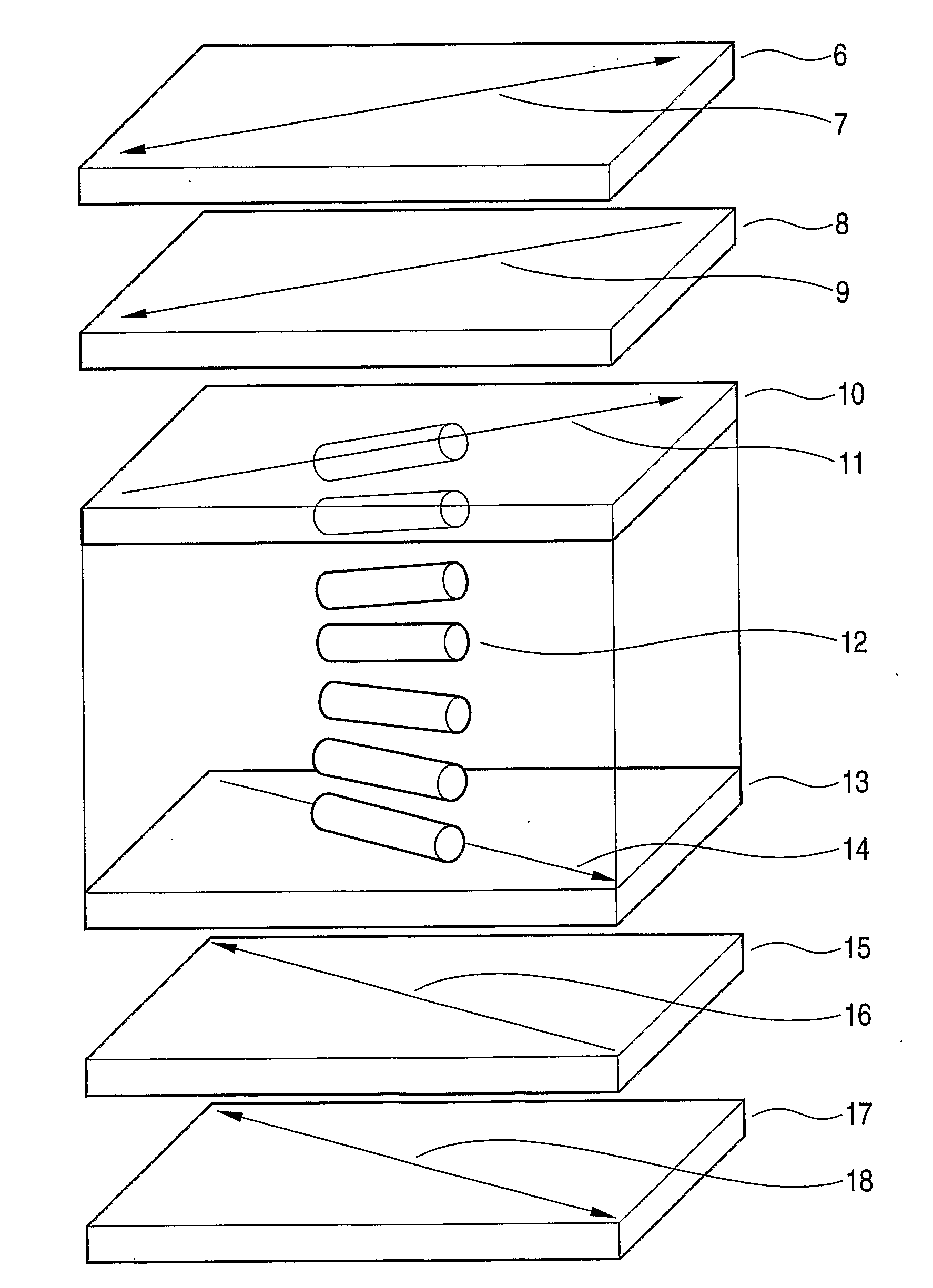
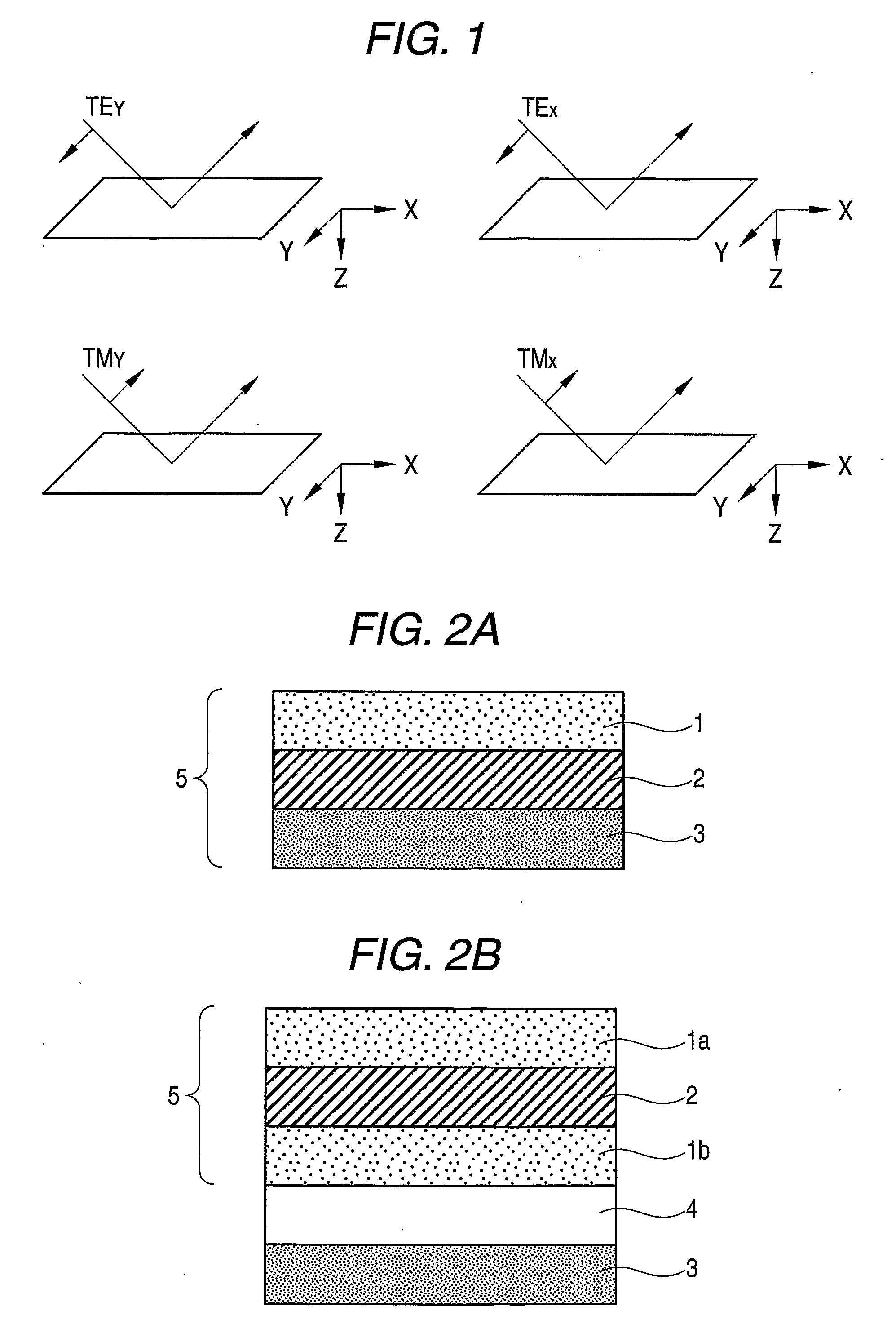
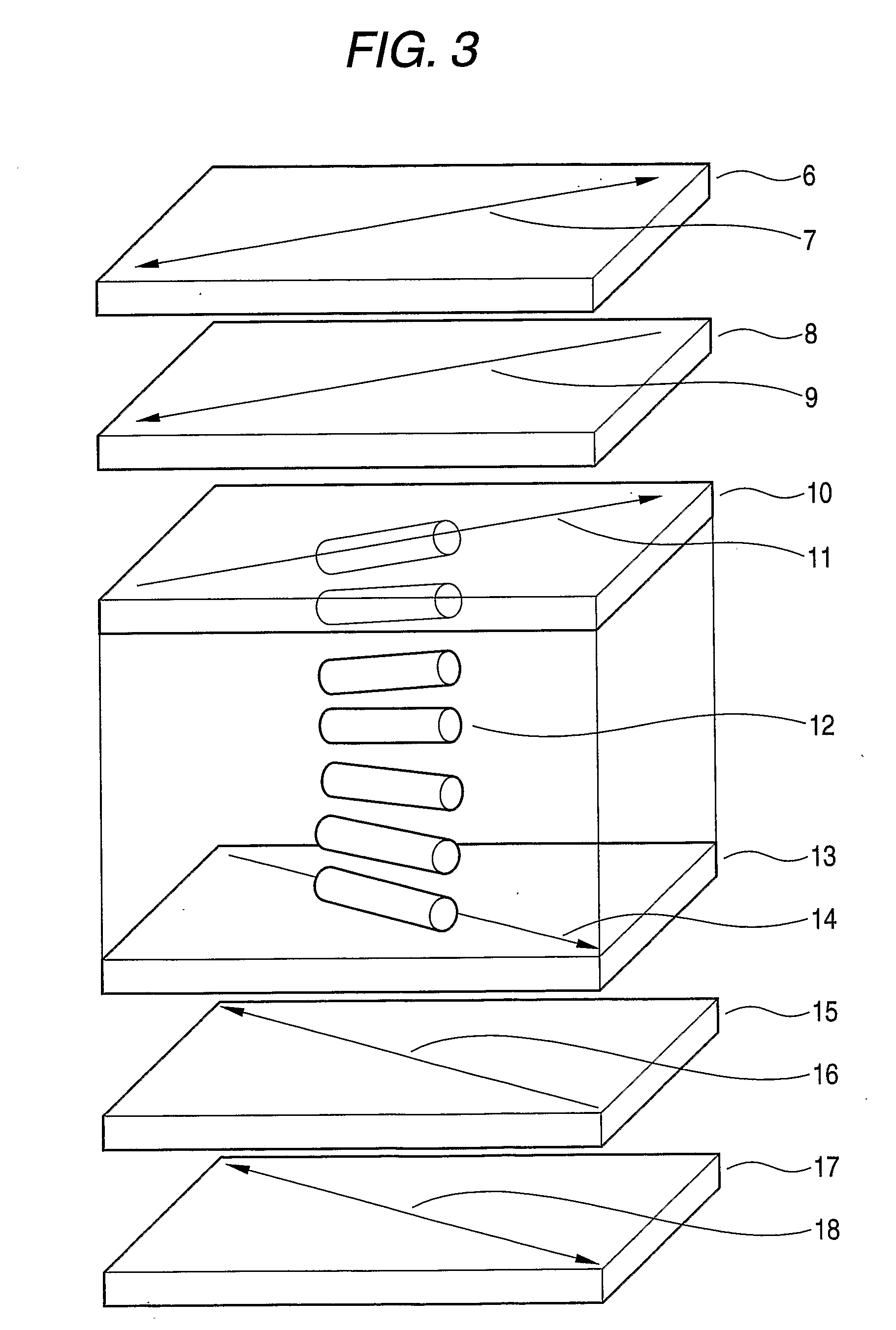
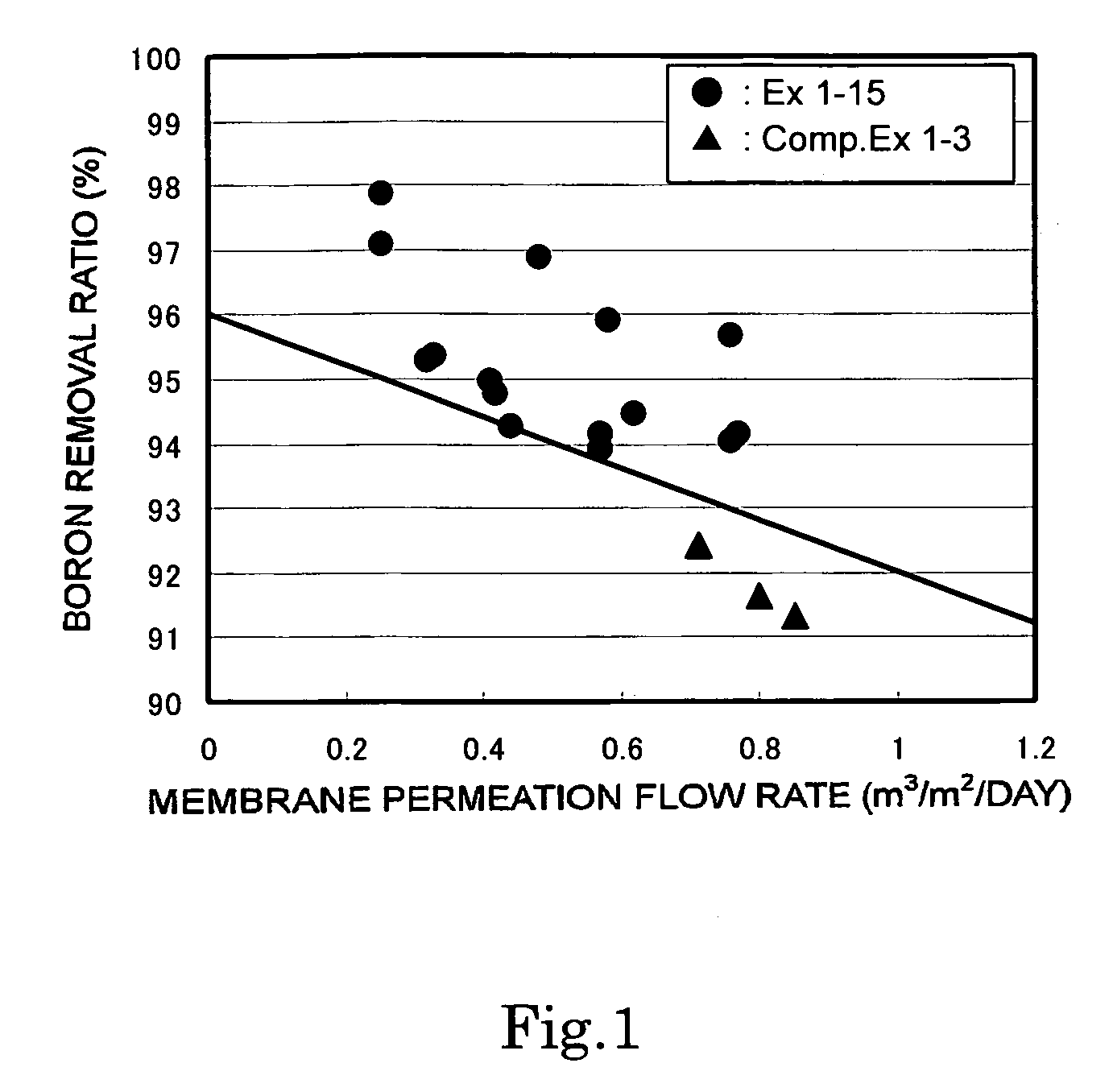
InactiveUS20090071903A1Improve desalination performanceHigh removal rateGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentPorous substratePolymer science
There is provided a composite semipermeable membrane that shows a high salt removal ratio and high performance in rejecting boron that is not dissociated in the neutral region. The composite semipermeable membrane is produced by a process that includes forming a separating functional polyamide layer on a porous substrate film, while using an organic solvent solution containing a specific cyclic aliphatic compound or a specific aromatic compound such that a polyamide molecule that forms the separating functional polyamide layer has a partial structure composed of “a cyclic aliphatic group or an aromatic group having at least two specific substituents, at least one of which contains a heteroatom bond and a carbonyl group at the β or γ position”.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Magnetic nanoparticles
ActiveUS20070166232A1Synthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsMagnetite NanoparticlesBiological materials
Magnetic nanoparticles are applicable in imaging, diagnosis, therapy, and biomaterial separation. The magnetic nanoparticles comprise a core represented as FexMavZy and a shell of an inner-transition element Mb or the compound thereof, wherein Ma is an inner-transition element, Z is an element of the group Vla, x is greater or equal to 0, and v, y are positive numbers. The surface of the shell is optionally modified by liposome, polymer, aliphatic compound, aromatic compound or combinations thereof.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for synthesizing acetylene alcohol polyoxyethylene ether
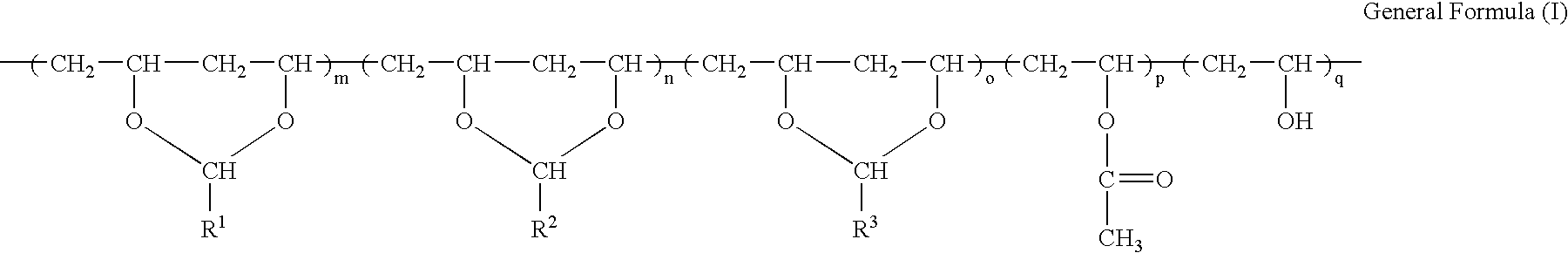
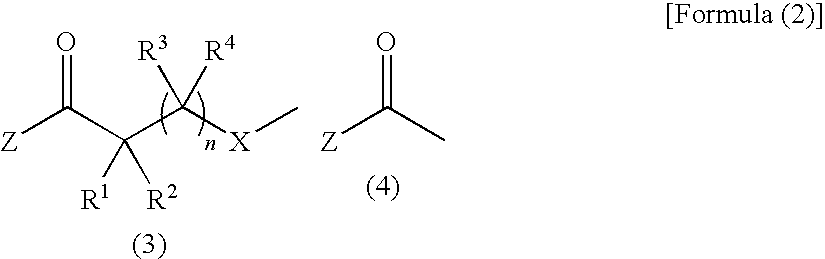
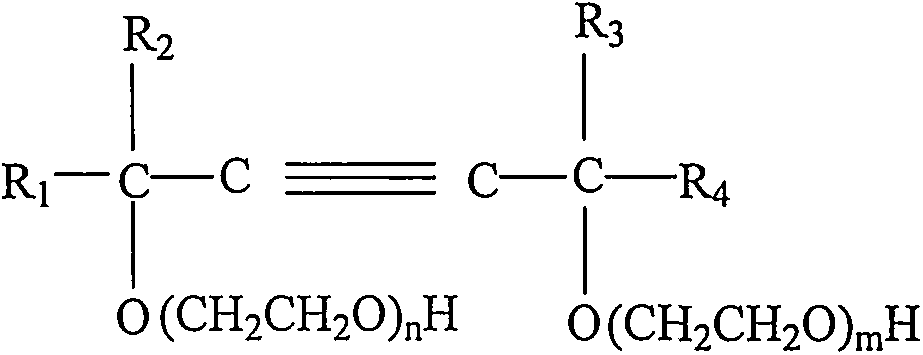
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing an acetylene alcohol polyoxyethylene ether. The technical problem of unsaturation loss of the acetylene alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, caused by the existing synthesis method, is mainly solved. According to the method for synthesizing the acetylene alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, butynediol reacts with ethylene oxide in the presence of a catalyst to obtain the acetylene alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, wherein the catalyst comprises at least one of calcium hydroxide, a tertiary amine aliphatic compound and a protonic acid; the butynediol has a structure shown in a formula (I); R1 and R4 are independently selected from C3-C10 alkyl; R2 and R3 are independently methyl or ethyl. The technical problem is better solved, and the method can be applied to industrial production of the acetylene alcohol polyoxyethylene ether. The expression is as shown in the specification.
Owner:SHANGHAI DUOLUN CHEM
Solvent assisted oil recovery
InactiveUS20110152136A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce precipitationFlushingDrilling compositionEtherDiluent
The recovery of oil from a reservoir is assisted by injecting a diluent into the reservoir formation to reduce the viscosity of the crude oil. This diluent is a mixture of a material which is an asphaltene precipitant, especially supercritical carbon dioxide, and a more polar material which comprises at least one aliphatic compound which includes at least one of a cycloaliphatic ring, an olefinic unsaturation, an ester or ether group. The inclusion of such an aliphatic compound which is more polar than the asphaltene precipitant reduces asphaltene precipitation and can enhance the efficiency of oil recovery when the precipitant is by supercritical carbon dioxide.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Toner
The present invention provides a toner that excels in low-temperature fixability and also maintains charging performance, storability, and anti-hot offset property even in long-term image output. The toner comprising a toner particle containing an amorphous polyester resin, a crystalline polyester resin, wax, and a colorant, wherein a weight-average molecular weight (Mw) of the crystalline polyester resin is 5000 to 14,000, and the crystalline polyester resin includes 0.5 mass % to 15.0 mass % of a segment derived from one or more aliphatic compounds selected from the group consisting of aliphatic monocarboxylic acids with a carbon number of 8 to 20 and aliphatic monohydric alcohols with a carbon number of 8 to 20.
Owner:CANON KK
Ink composition and inkjet recording method
A novel ink composition, which has an absorption characteristic excellent in color reproducibility as a yellow color of one of the three primary colors, which has enough fastness against light, heat and humidity, and which does not cause bronze phenomenon, is provided. The ink composition contains water, a yellow dye having an oxidation potential nobler than 1.0 V, and an aromatic compound, aliphatic compound and / or a salt thereof having at least one of carboxyl group, sulfo group and phosphoric acid group.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Biodegradable resin composition
The present invention relates to a method of producing a biodegradable resin composition, which includes step (1) of mixing a biodegradable resin, a plasticizer, and a crystal nucleating agent with one another at the melting point (Tm) of the biodegradable resin or more, wherein the crystal nucleating agent is an aliphatic compound having, in its molecule, two or more of at least one group selected from an ester group, a hydroxyl group and an amide group, and step (2) of thermally treating the resulting biodegradable resin composition at a temperature of from the glass transition temperature (Tg) to less than Tm of the composition, as well as a biodegradable resin composition, which contains a biodegradable resin, a plasticizer, and the above crystal nucleating agent, and which satisfies the following conditions: the haze thereof with a thickness of 0.5 mm after thermal treatment at 60° C. for 36 or 60 hours is 20% or less; the storage elastic modulus (E′) at a temperature of 25° C. and a frequency of 50 Hz is 1×108 to 2×109 Pa; and the storage elastic modulus (E′) at a temperature of 60° C. and a frequency of 50 Hz is 1×107 to 1×109 Pa.
Owner:KAO CORP
Droplet-resistant flame-retardant polyester, nanometer compound material thereof and method for preparing same
The invention discloses droplet-resistant flame-retardant polyester. The flame-retardant polyester is prepared by random copolymerization of a branched monomer, terephthalic acid or dimethyl terephthalate, ethylene glycol and flame-retardant monomer, wherein the branched monomer is an aliphatic compound or aromatic compound having three or more functional groups; and the flame-retardant monomers adopts any of the following structures. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the droplet-resistant flame-retardant polyester, a nanometer compound material containing the droplet-resistant flame-retardant polyester and a method for preparing the nanometer compound material. Because the droplet-resistant flame-retardant polyester provided by the invention simultaneously contains the branched monomer and the fire retardant having the droplet-resistant effect, the melt viscosity of the droplet-resistant flame-retardant polyester at the high temperature is greatly improved, the sensitivity of the droplet-resistant flame-retardant polyester to temperature is lowered, and the droplet-resistant effect is good; because of the nanometer effect and the blocking effect, the nanometer compound material shows better droplet-resistant effect; and the polyester and the nanometer compound material can be directly used as raw materials for preparing fibers, engineering plastics, films and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Process for preparing aromatics from methane
InactiveUS20120022310A1Extended service lifeShort transport distanceCatalystsHydrocarbon preparation catalystsPtru catalystNon oxidative
The present invention relates to a process for carrying out endothermic, heterogeneously catalyzed reactions in which the reaction of the starting materials is carried out in the presence of a mixture of inert heat transfer particles and catalyst particles, where the catalyst particles are regenerated in a nonoxidative atmosphere at regular intervals and the heat of reaction required is introduced by separating off the inert heat transfer particles, heating the heat transfer particles in a heating zone and recirculating the heated heat transfer particles to the reaction zone. The process of the invention is particularly suitable for the nonoxidative dehydroaromatization of C1-C4-aliphatics in the presence of zeolite-comprising catalysts.
Owner:BASF AG
Polyolefin resin foam and process for production thereof
ActiveUS20100016458A1Improve compatibilityExcellent formabilityOther chemical processesFoundry mouldsCushioningPolyolefin
The present invention relates to a polyolefin resin foam which includes a polyolefin resin composition includes: (A) a rubber and / or a thermoplastic elastomer; (B) a polyolefin resin; and (C) at least one aliphatic compound selected from an aliphatic acid, an aliphatic acid amide and an aliphatic acid metallic soap, the compound having a polar functional group and having a melting point of 50 to 150° C., in which a content of the aliphatic compound is 1 to 5 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of the total amount of the rubber and / or thermoplastic elastomer and the polyolefin resin. The polyolefin resin foam of the invention is excellent in flexibility and cushioning properties, and has good processability, especially excellent cutting processability.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP +1
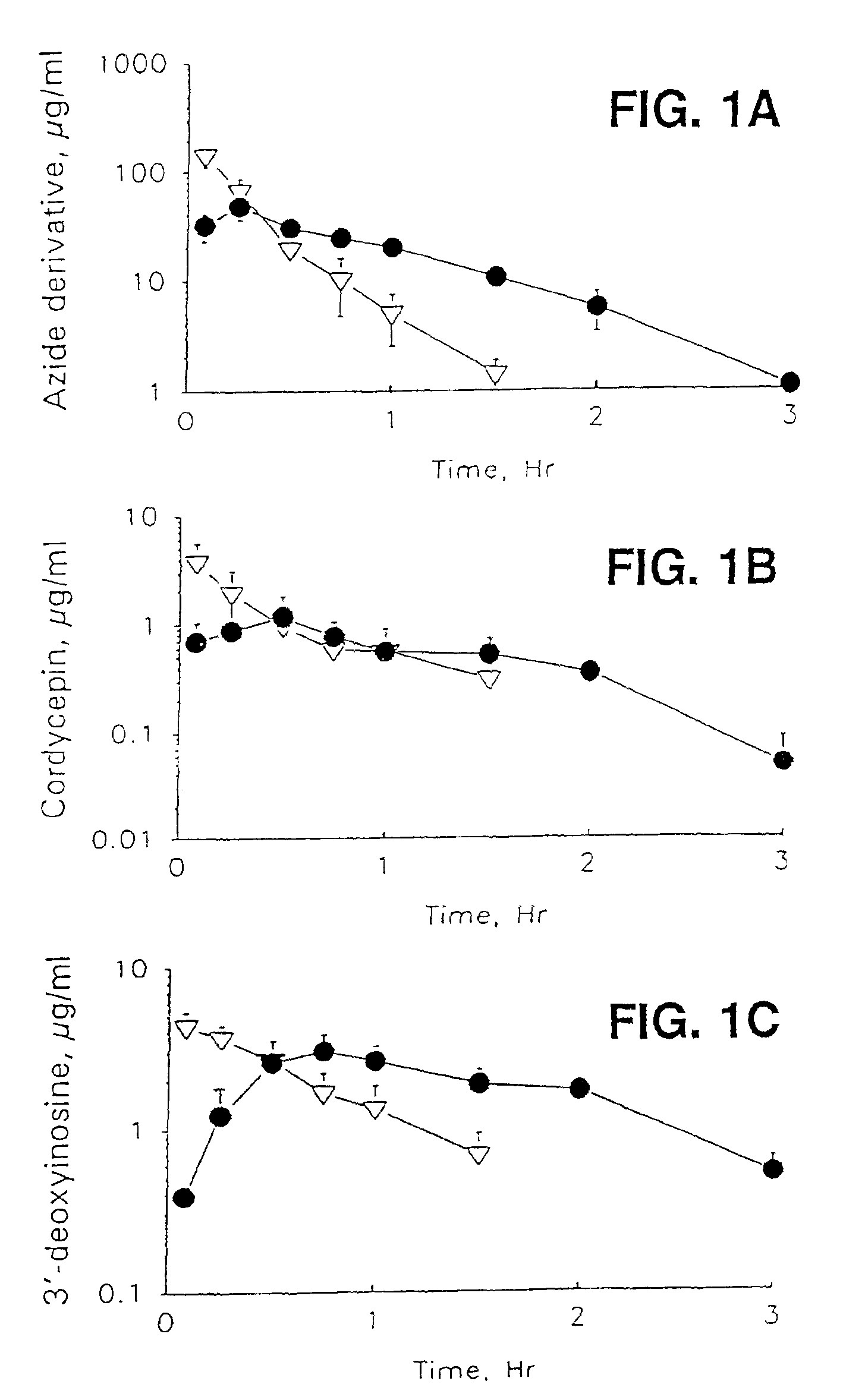
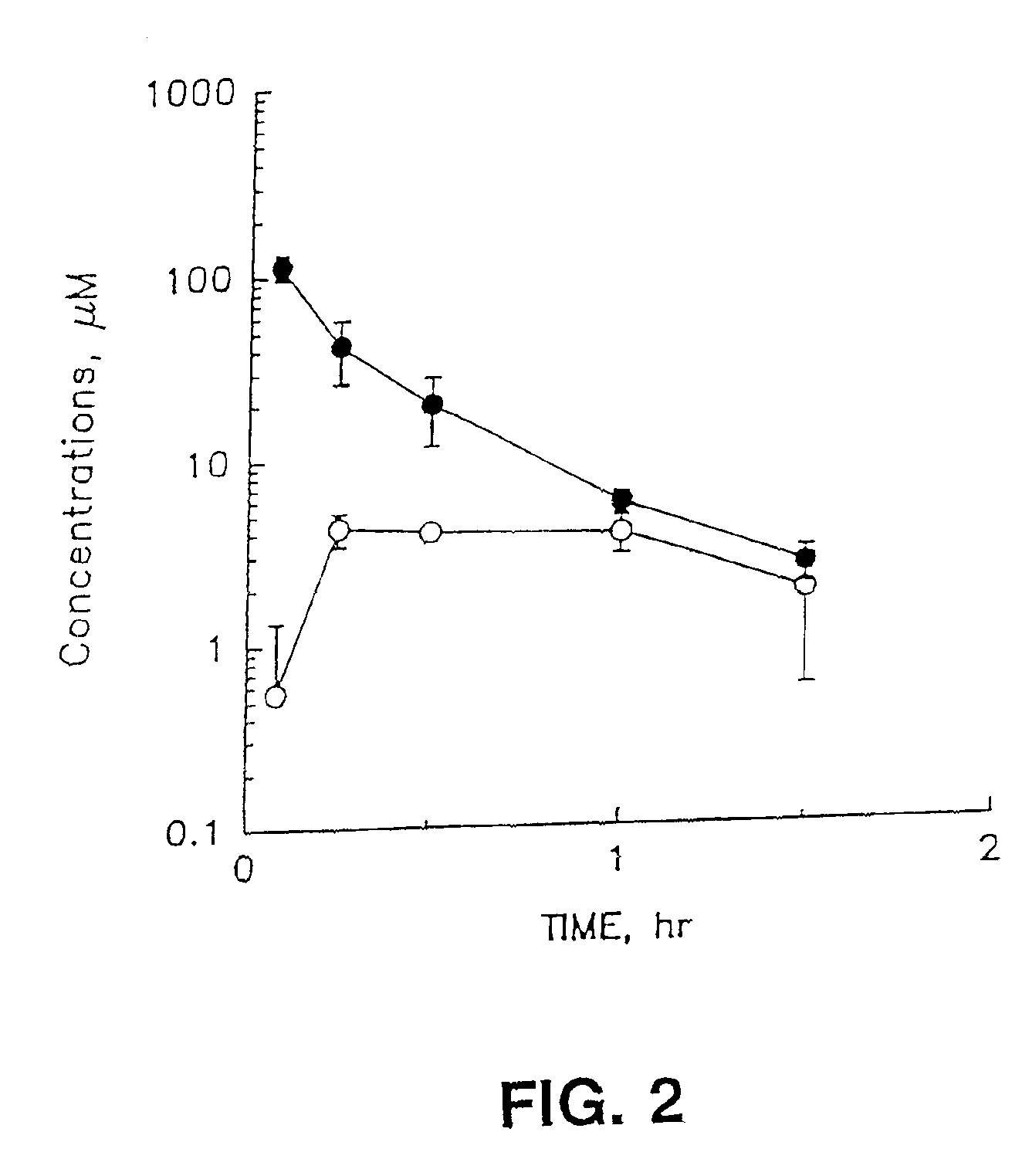
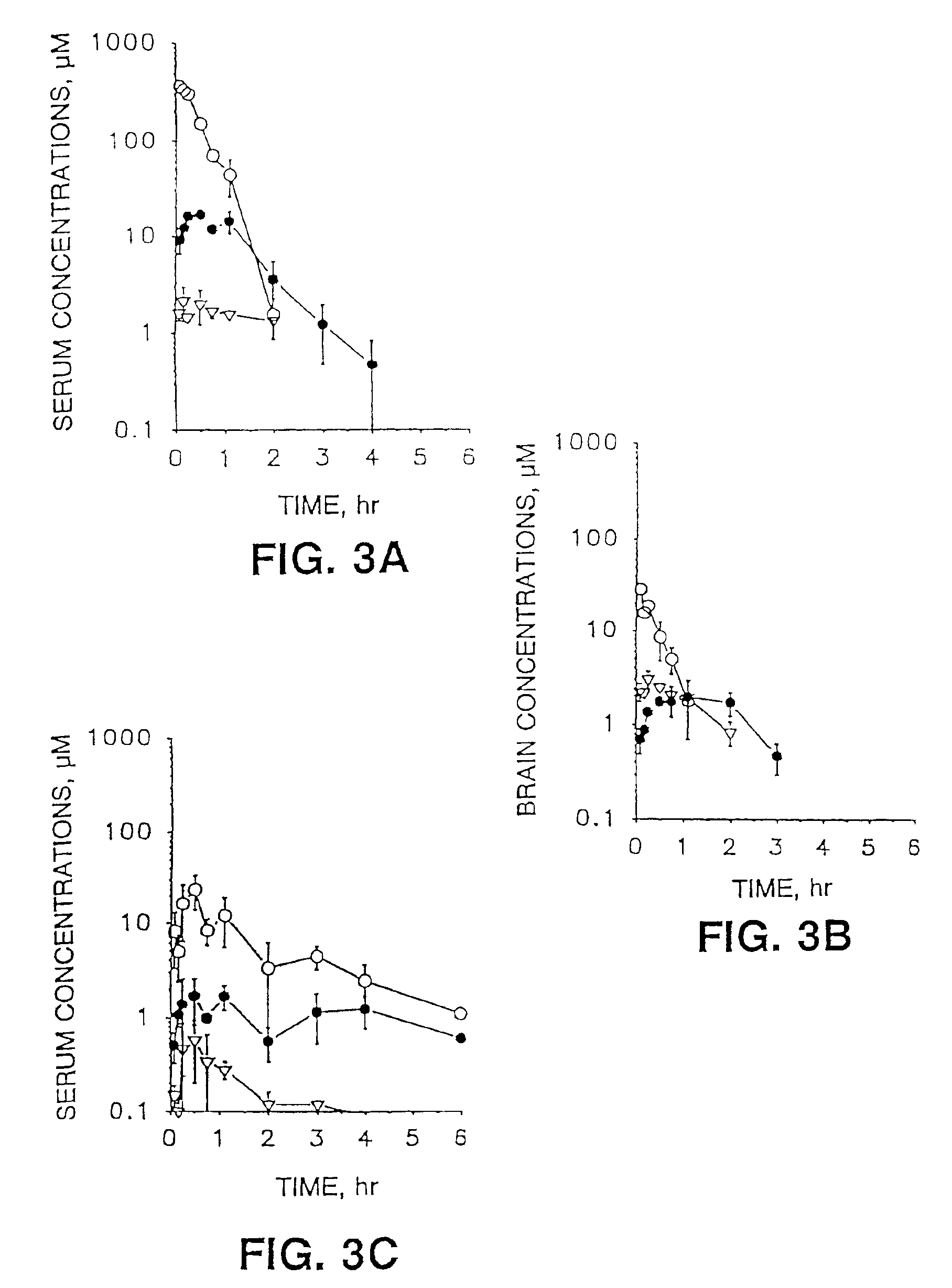
Therapeutic azide compounds
InactiveUS6949521B2Extended half-lifeDestroy effectivenessBiocideSugar derivativesHalf-lifeSide chain
Pharmaceutical prodrug compositions are provided comprising azide derivatives of drugs which are capable of being converted to the drug in vivo. Azide derivatives of drugs having amine, ketone and hydroxy substituents are converted in vivo to the corresponding drugs, increasing the half-life of the drugs. In addition azide prodrugs are often better able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier than the corresponding drugs. Especially useful are azide derivatives of cordycepin, 2′-F-ara-ddI, AraA, acyclovir, penciclovir and related drugs. Useful azide prodrugs are azide derivatives of therapeutic alicyclic amines, ketones, and hydroxy-substituted compounds, including aralkyl, heterocyclic aralkyl, and cyclic aliphatic compounds, where the amine or oxygen moiety is on the ring, or where the amine or oxygen moiety is on an aliphatic side chain, as well as therapeutic purines and pyrimidines, nucleoside analogs and phosphorylated nucleoside analogs.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC +1
Layer configuration with improved stability to sunlight exposure
InactiveUS20080290324A1Improve conductivityStability of layerHybrid capacitor electrodesConductive materialArylAlkoxy group
A composition exclusive of hydroquinone comprising at least one polymer comprising (3,4-dialkoxythiophene) monomer units, in which the two alkoxy groups may be the same or different or together represent an optionally substituted oxy-alkylene-oxy bridge, a polyanion, at least one aromatic compound exclusive of sulfo groups and containing at least two hydroxy groups and at least one polyhydroxy- and / or carboxy group or amide or lactam group containing aliphatic compound and / or at least one aprotic compound with a dielectric constant ≧15; and a layer configuration on a support, said layer configuration comprising a layer exclusive of hydroquinone comprising at least one polymer comprising optionally substituted (3,4-dialkoxythiophene) monomer units, in which the two alkoxy groups may be the same or different or together represent an optionally substituted oxy-alkylene-oxy bridge, a polyanion, at least one aromatic compound exclusive of sulfo groups and containing at least two hydroxy groups and at least one polyhydroxy- and / or carboxy group or amide or lactam group containing aliphatic compound and / or at least one aprotic compound with a dielectric constant ≧15.
Owner:AGFA-GEVAERT NV
Toner
ActiveUS9158217B2Excellent low temperature fixabilityImprove stabilityDevelopersPolyesterPolymer science
Owner:CANON KK
Method for preparing graphene strip by adopting low-temperature chemical vapour deposition
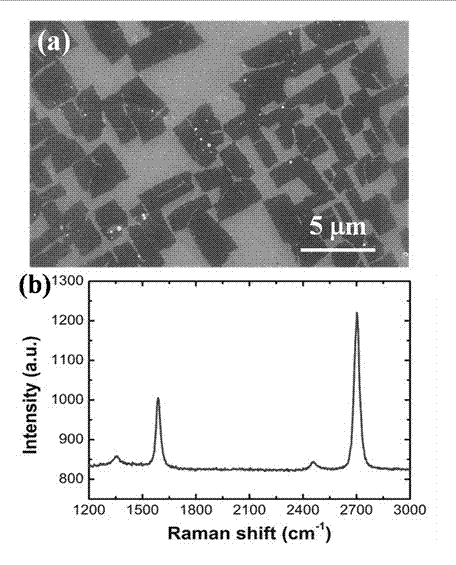
InactiveCN103086370ALow growth temperatureNo shape clipping requiredGrapheneNanotechnologySemiconductor materialsElectrolysis
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of semiconductor materials and in particular relates to a method for preparing a graphene strip by adopting low-temperature chemical vapour deposition. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: firstly carrying out electrolytic polishing on a copper foil, then placing the copper foil into a quartz tube reactor, annealing under the condition of hydrogen, and then adjusting flow velocity of the hydrogen to be 2.4-3.0sccm and introducing a liquid carbon source at the temperature of 500-580 DEG C, and growing a graphene strip on the copper foil while pressure is controlled to be 2.0-10.0Torr and growth time is controlled to be 10-50 minutes, so that the graphene strip growing on the copper foil is obtained. According to the method, the copper foil subjected to electrolytic polishing is adopted, so that chemical activity of the surface of the copper foil is higher; and the adopted carbon source is a carbon-containing organic solvent which has the characteristics of aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds and the characteristics between the characteristics of the aromatic compounds and the characteristics of the aliphatic compounds, and compared with a gas carbon source commonly used in the prior art such as methane, the carbon-containing organic solvent is more beneficial to low-temperature growth of the graphene strip.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
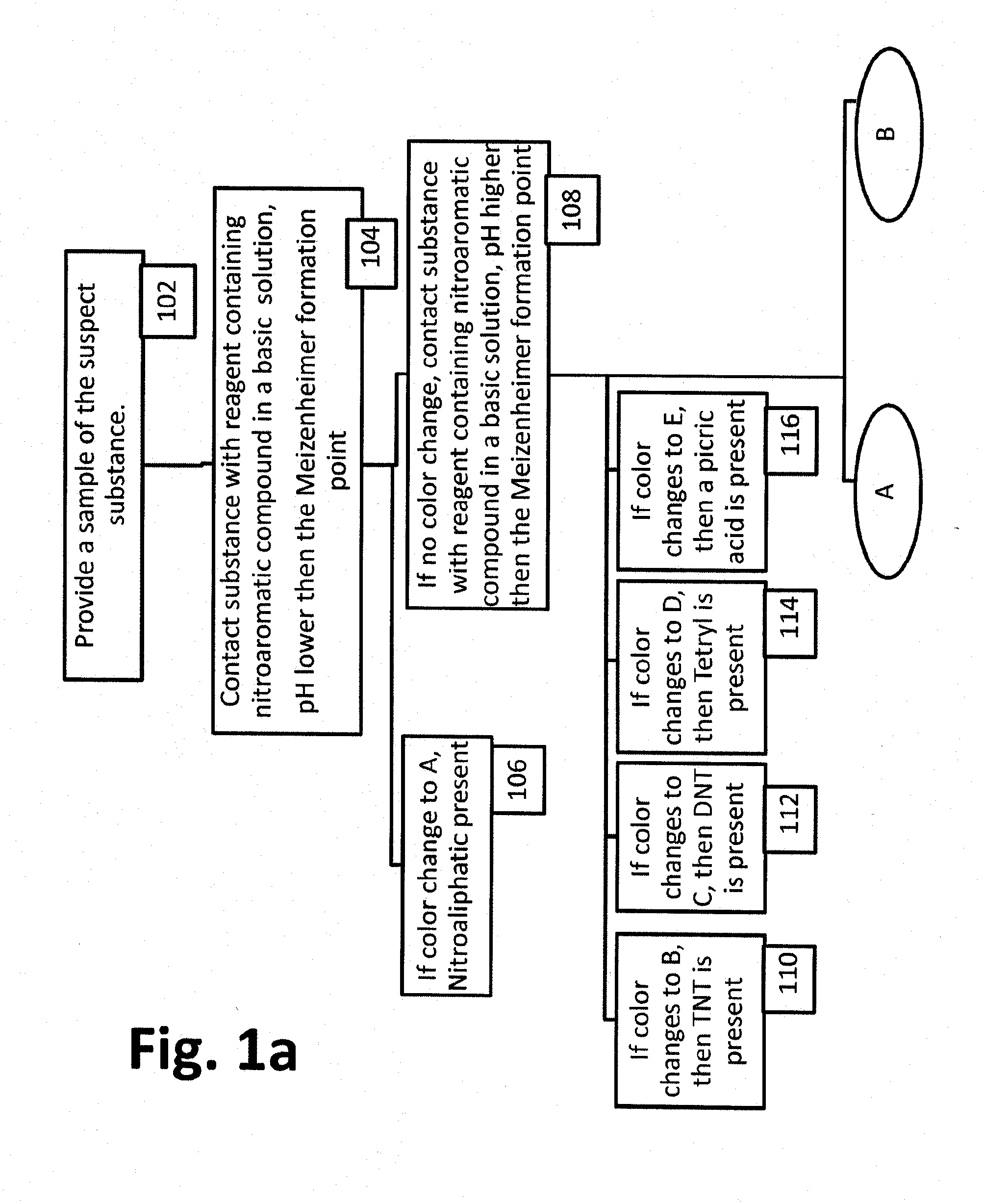
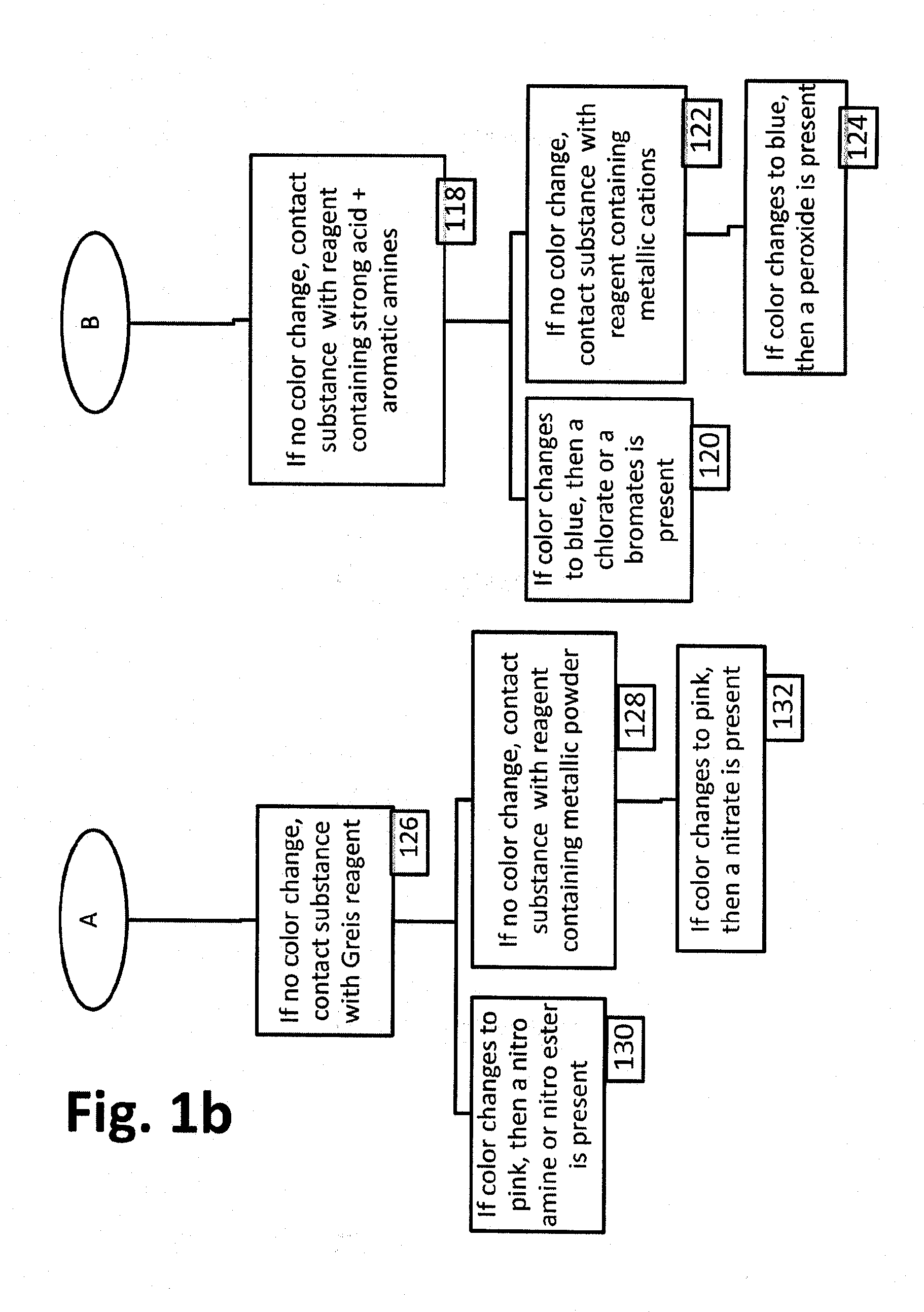
Reagent method and kit for the detection of nitro aliphatic compounds
A method for the detection of explosives using a single sample. The explosives include nitro aliphatic and nitro aromatic-based explosives. The method includes steps which require different pHs to discriminate between these types of explosives and at least in the detection step of the nitro aliphatic explosive requires the presence of a nitro aromatic compound. A kit for detecting explosives which includes a medium for collecting a sample, a base optionally impregnated on the medium; and a nitro aromatic solution for detecting a nitro aliphatic explosive by contacting the solution with the sample on the medium. A reagent including a nitro aromatic compound, having one or more additional electron withdrawing groups, in the presence of a basic compound usable for detecting nitro aliphatic explosives.
Owner:MISTRAL
Lubricating oil composition
InactiveCN101568626APrevent rustReduce coefficient of frictionAdditivesChemical compositionAliphatic amine
The present invention provides a lubricating oil composition comprising a base oil, an aspartic acid derivative and an aliphatic amine compound. The lubricating oil composition is ideal as an industrial lubricating oil such as for example for a hydraulic working oil in hydraulic equipment. Primary amine, secondary amine, diamine, and / or tertiary amines may be employed for the aliphatic amine compound.
Owner:SHOWA SHELL SEKIYU KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com