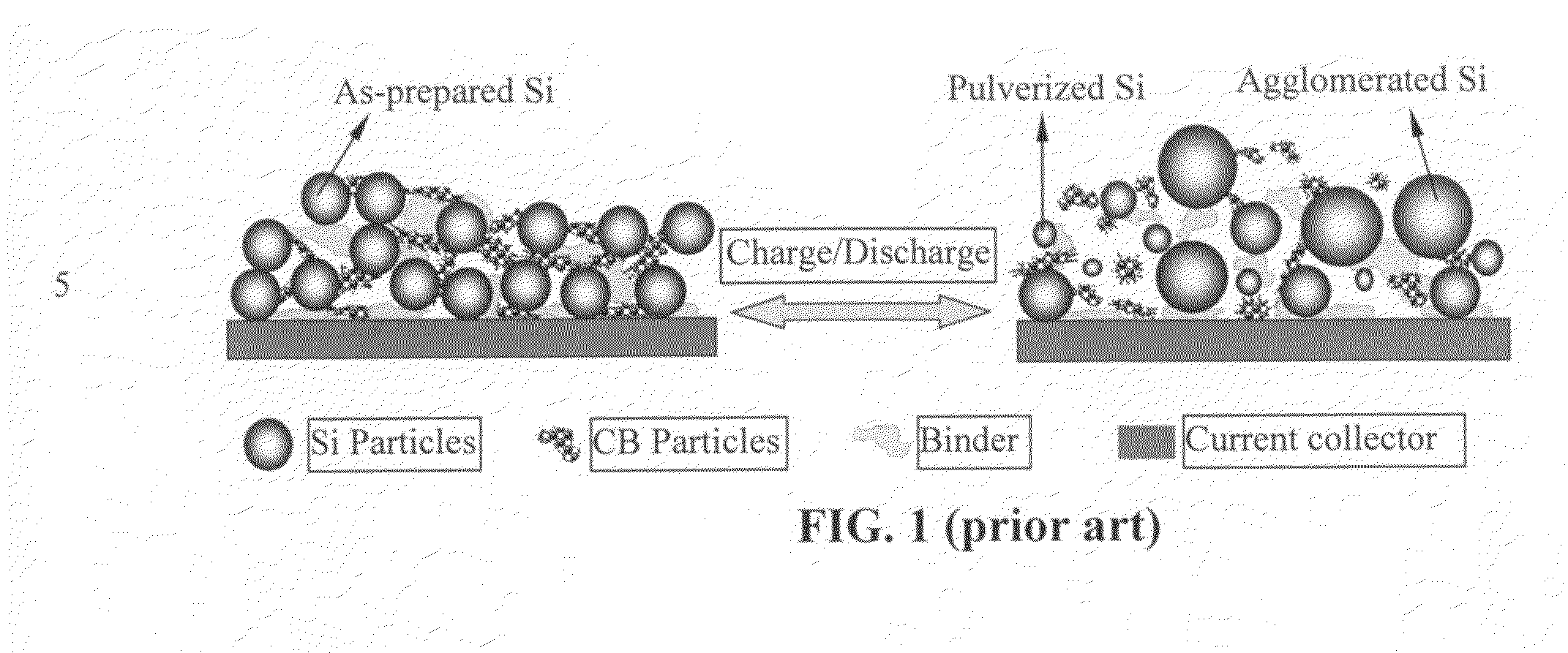
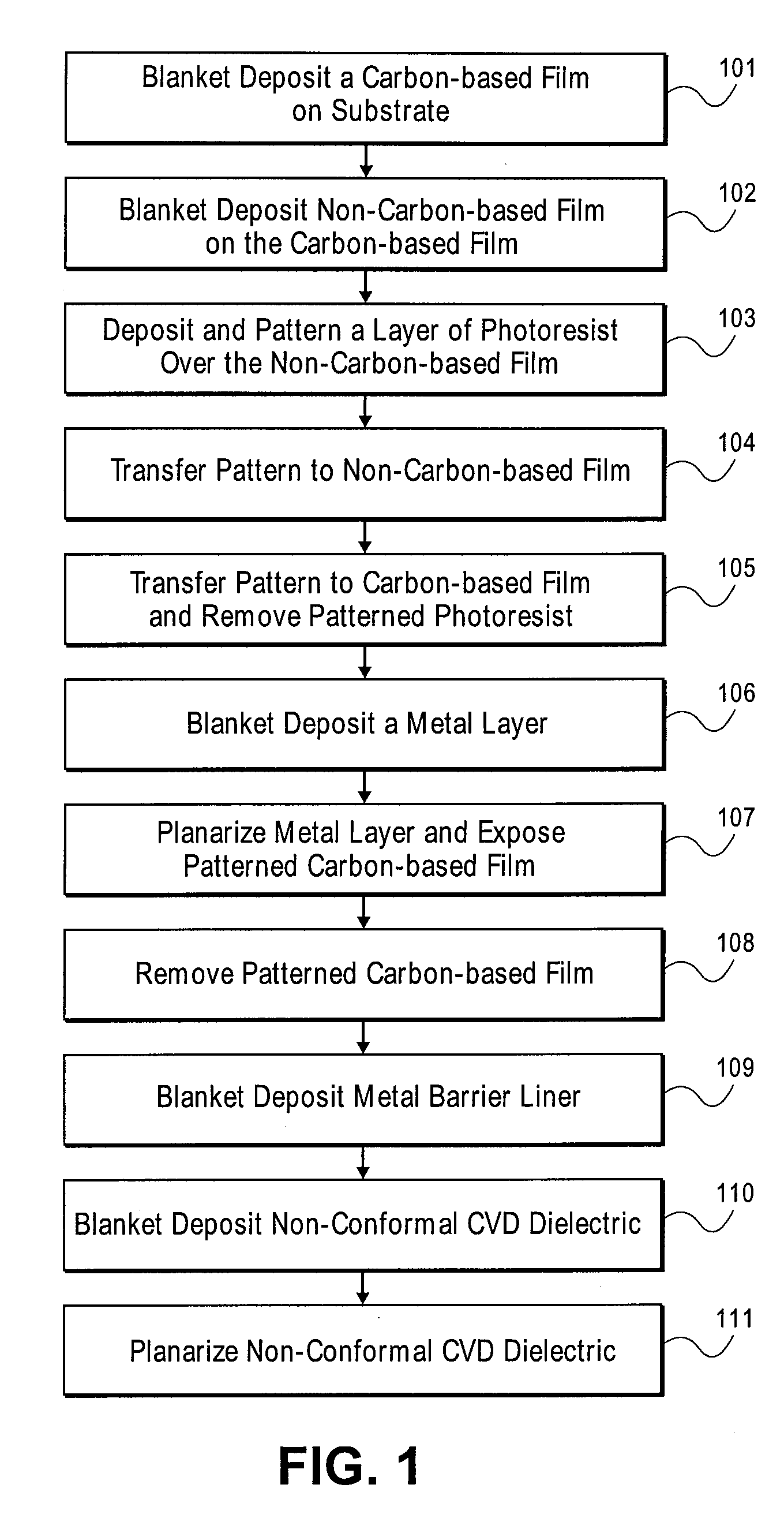
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3262 results about "Amorphous carbon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Amorphous carbon is free, reactive carbon that does not have any crystalline structure. Amorphous carbon materials may be stabilized by terminating dangling-π bonds with hydrogen. As with other amorphous solids, some short-range order can be observed. Amorphous carbon is often abbreviated to aC for general amorphous carbon, aC:H or HAC for hydrogenated amorphous carbon, or to ta-C for tetrahedral amorphous carbon (also called diamond-like carbon).
Liquid precursors for the CVD deposition of amorphous carbon films
ActiveUS20050287771A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDual frequencyHydrogen
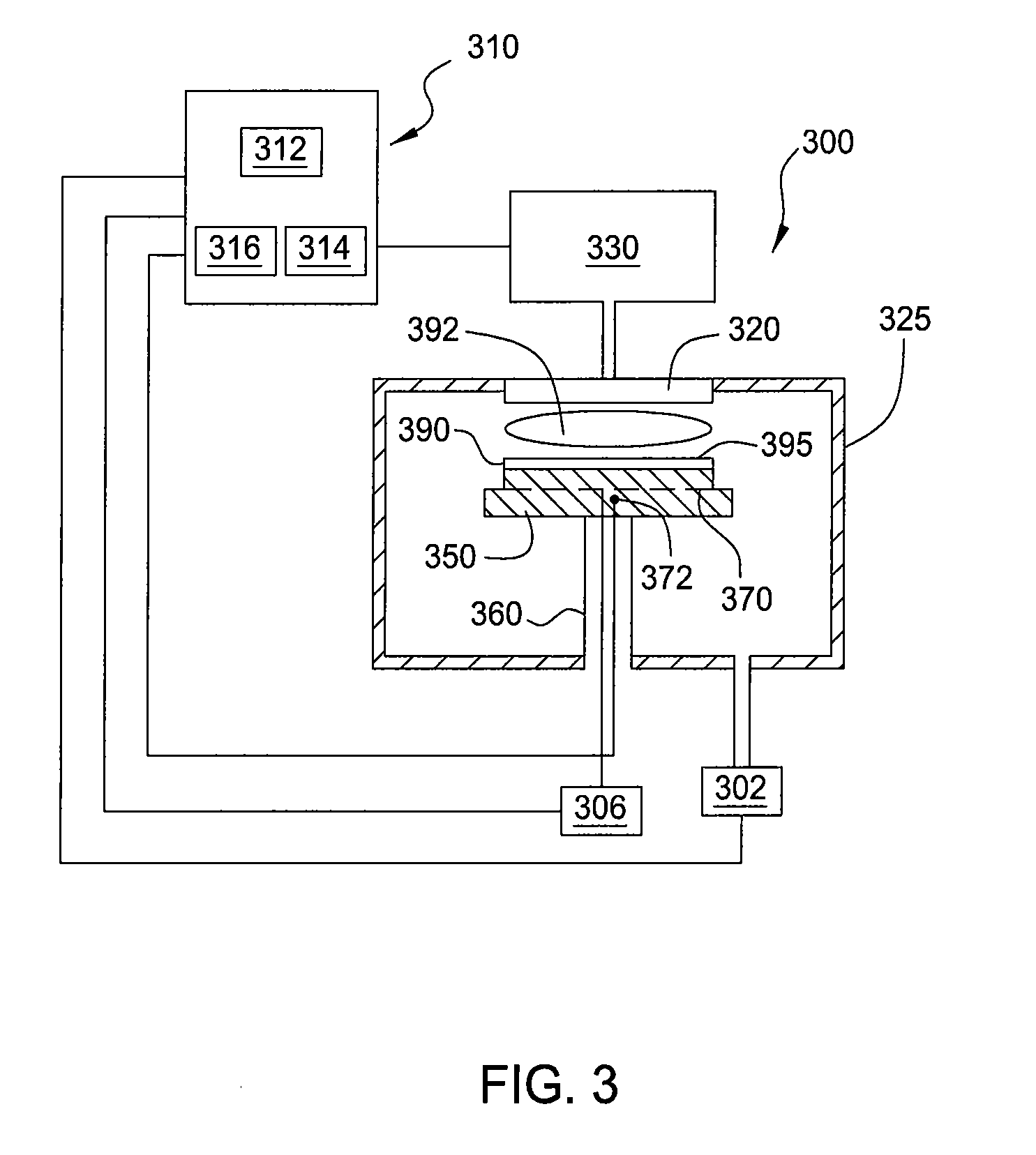
Methods are provided for depositing amorphous carbon materials. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for processing a substrate including positioning the substrate in a processing chamber, introducing a processing gas into the processing chamber, wherein the processing gas comprises a carrier gas, hydrogen, and one or more precursor compounds, generating a plasma of the processing gas by applying power from a dual-frequency RF source, and depositing an amorphous carbon layer on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
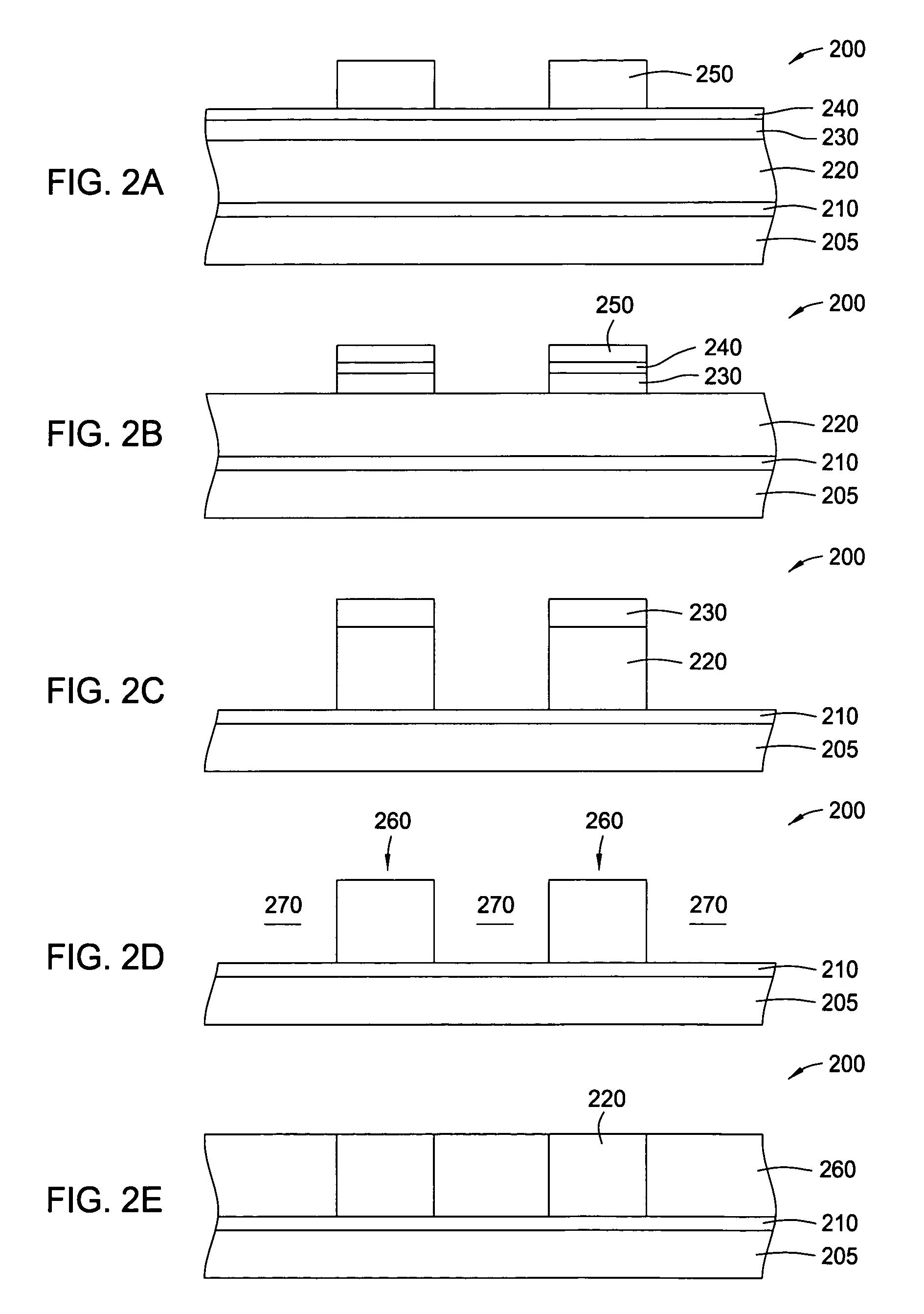
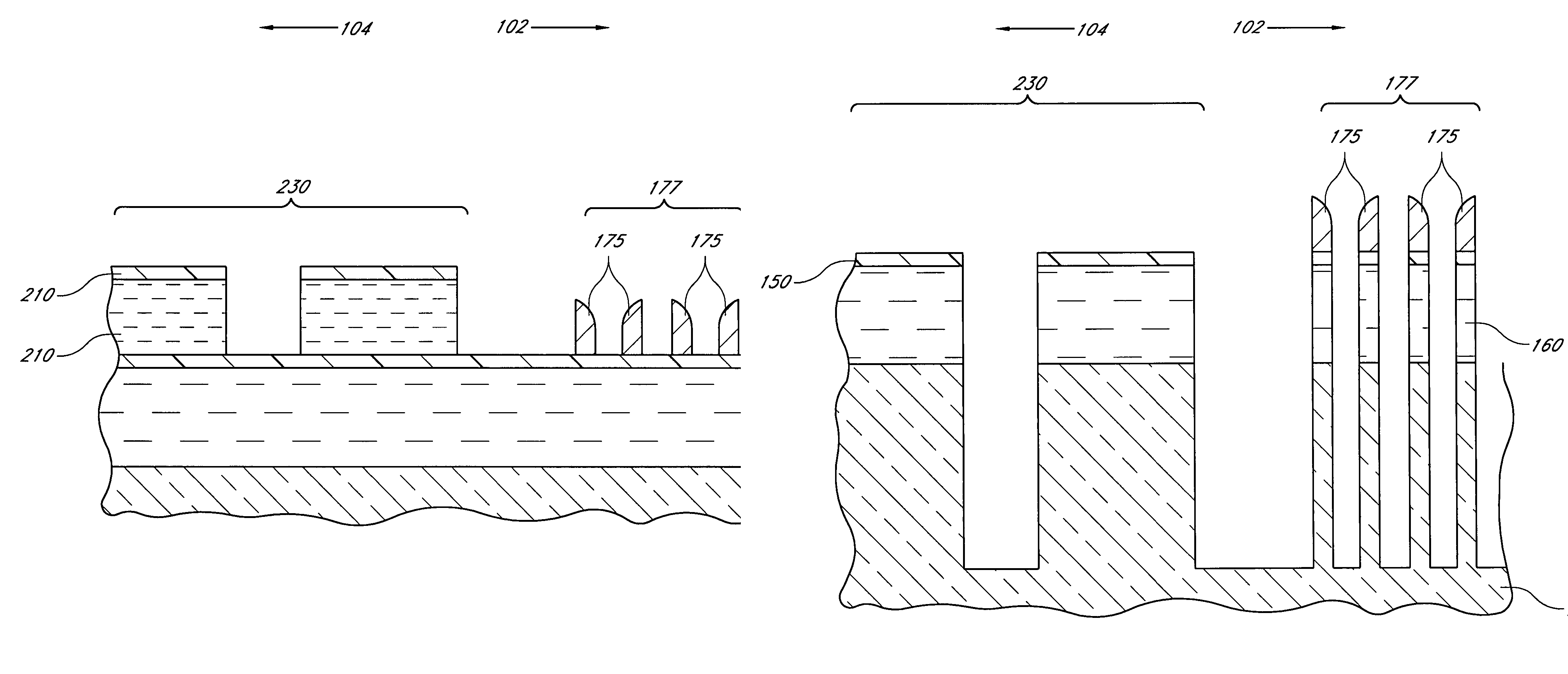
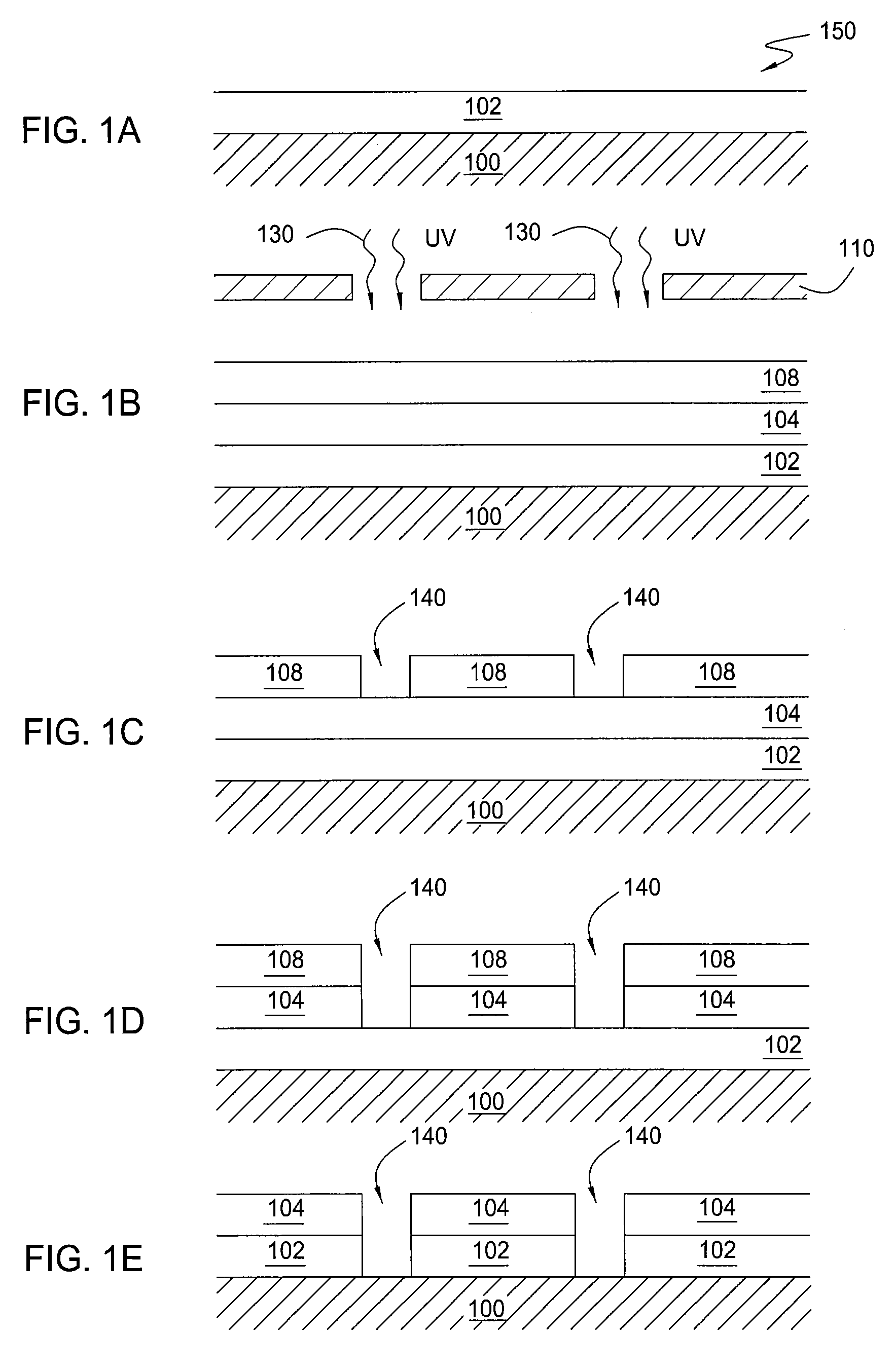
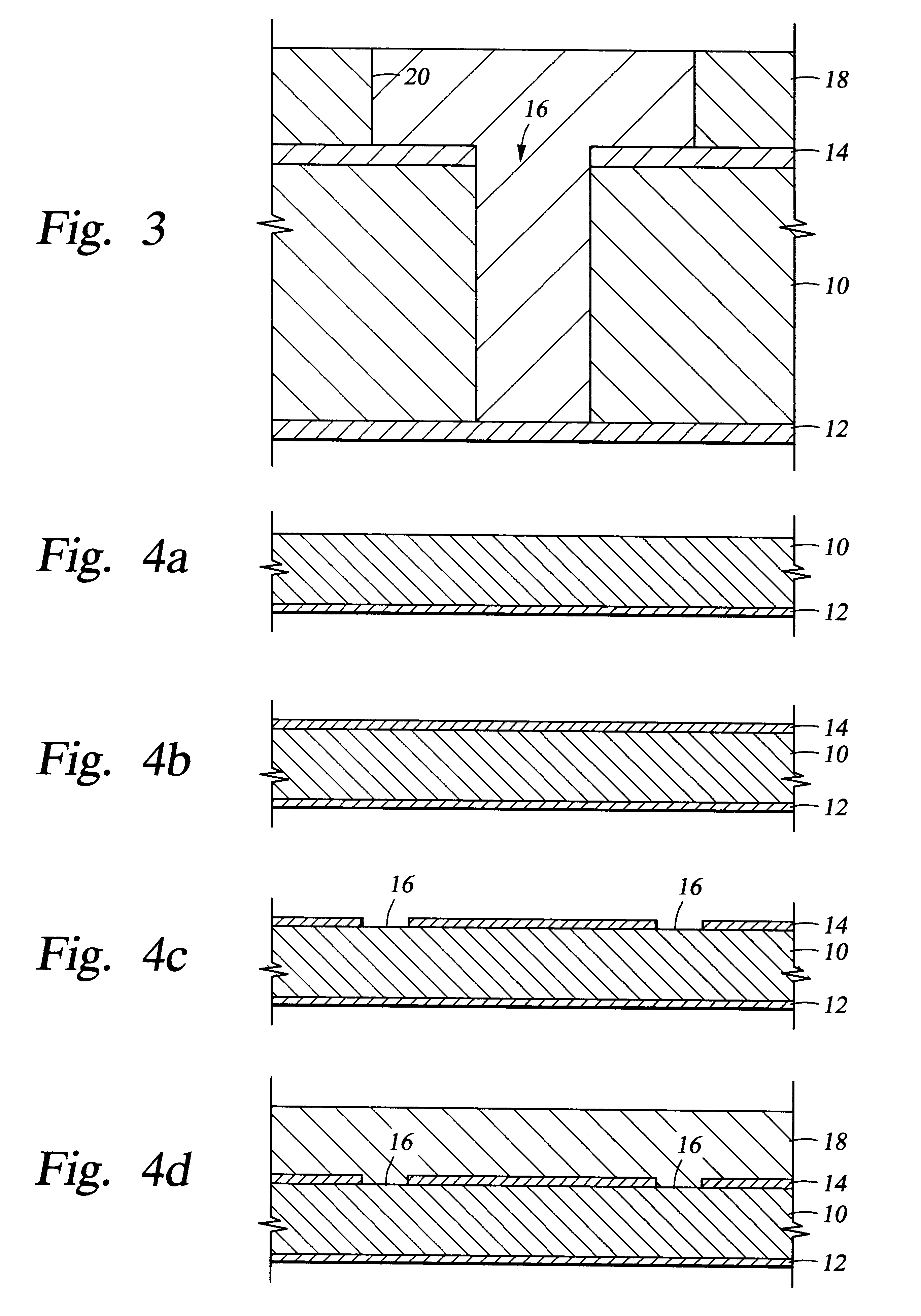
Method for integrated circuit fabrication using pitch multiplication
InactiveUS7115525B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistEngineering
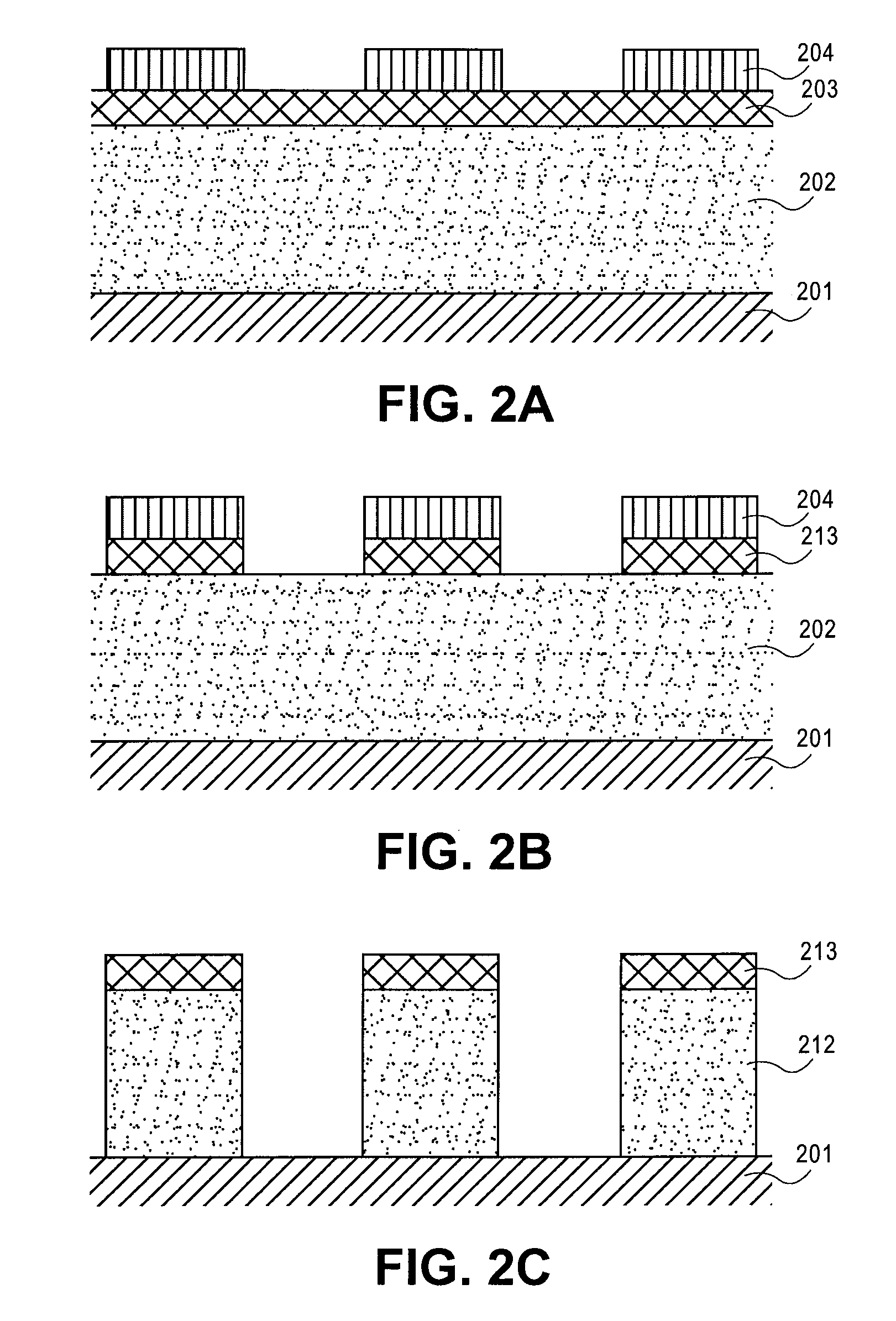
Different sized features in the array and in the periphery of an integrated circuit are patterned on a substrate in a single step. In particular, a mixed pattern, combining two separately formed patterns, is formed on a single mask layer and then transferred to the underlying substrate. The first of the separately formed patterns is formed by pitch multiplication and the second of the separately formed patterns is formed by conventional photolithography. The first of the separately formed patterns includes lines that are below the resolution of the photolithographic process used to form the second of the separately formed patterns. These lines are made by forming a pattern on photoresist and then etching that pattern into an amorphous carbon layer. Sidewall pacers having widths less than the widths of the un-etched parts of the amorphous carbon are formed on the sidewalls of the amorphous carbon. The amorphous carbon is then removed, leaving behind the sidewall spacers as a mask pattern. Thus, the spacers form a mask having feature sizes less than the resolution of the photolithography process used to form the pattern on the photoresist. A protective material is deposited around the spacers. The spacers are further protected using a hard mask and then photoresist is formed and patterned over the hard mask. The photoresist pattern is transferred through the hard mask to the protective material. The pattern made out by the spacers and the temporary material is then transferred to an underlying amorphous carbon hard mask layer. The pattern, having features of difference sizes, is then transferred to the underlying substrate.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
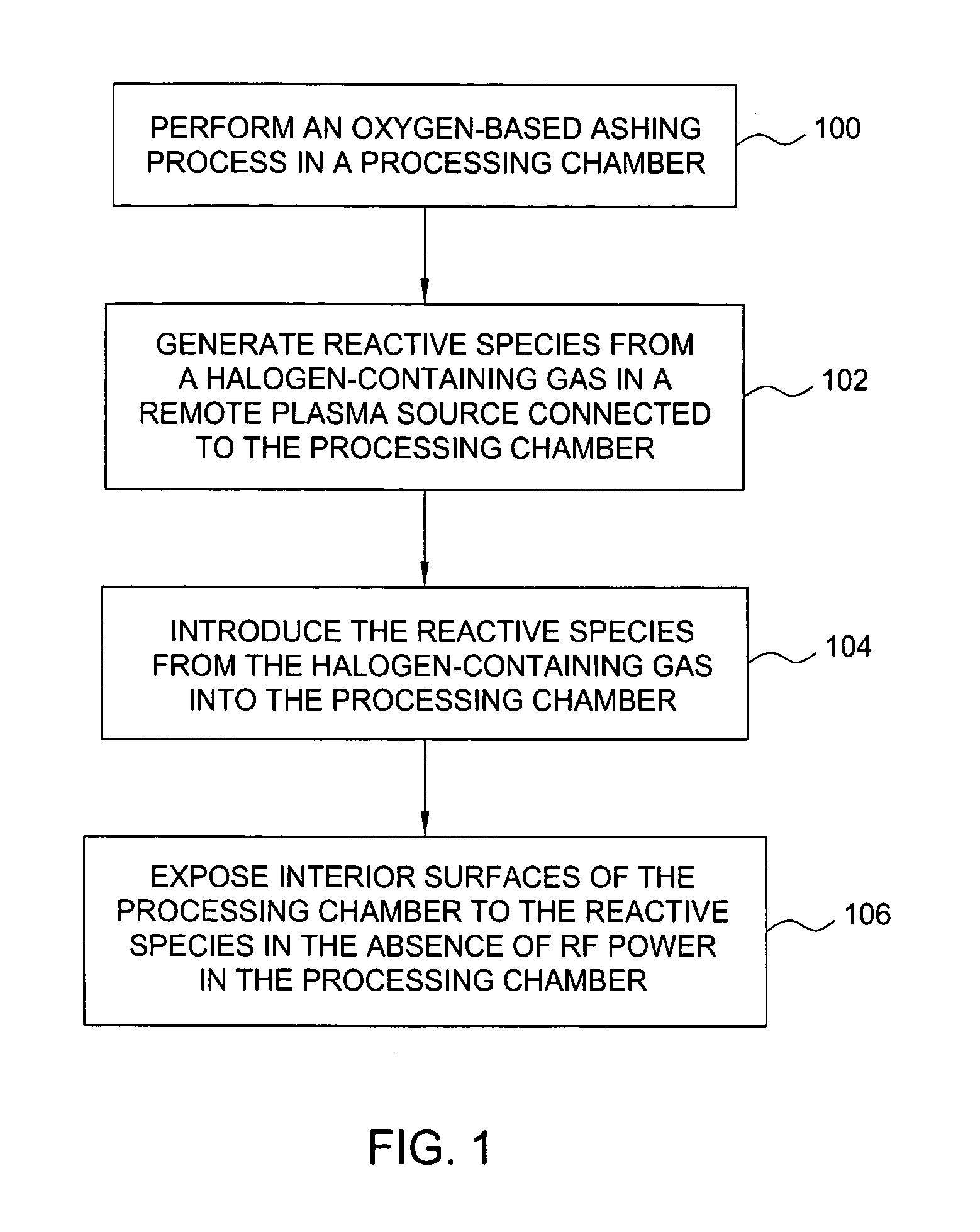
Enhancement of remote plasma source clean for dielectric films
Methods for cleaning semiconductor processing chambers used to process carbon-containing films, such as amorphous carbon films, barrier films comprising silicon and carbon, and low dielectric constant films including silicon, oxygen, and carbon are provided. The methods include using a remote plasma source to generate reactive species that clean interior surfaces of a processing chamber in the absence of RF power in the chamber. The reactive species are generated from an oxygen-containing gas, such as O2, and / or a halogen-containing gas, such as NF3. An oxygen-based ashing process may also be used to remove carbon deposits from the interior surfaces of the chamber before the chamber is exposed to the reactive species from the remote plasma source.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Substrate processing method, computer readable recording medium and substrate processing apparatus
InactiveUS20070062453A1Low dielectric constantImprove heat resistanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMicrowaveEngineering
In the present invention, Ar gas for plasma generation is supplied to a plasma generation region and butyne gas having a multiple bond is supplied to a film formation region at a substrate side as source gas, inside of a process vessel in an insulating film forming apparatus. A microwave is supplied inside of the process vessel from a radial line slot antenna under a state in which a bias voltage is not applied to a substrate W. A plasma is thereby generated in the plasma generation region, the butyne gas in the film formation region is activated by the plasma, and an insulating film of amorphous carbon is formed on the substrate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for integrated circuit fabrication using pitch multiplication
InactiveUS20060046484A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImage resolutionDifferences size
Different sized features in the array and in the periphery of an integrated circuit are patterned on a substrate in a single step. In particular, a mixed pattern, combining two separately formed patterns, is formed on a single mask layer and then transferred to the underlying substrate. The first of the separately formed patterns is formed by pitch multiplication and the second of the separately formed patterns is formed by conventional photolithography. The first of the separately formed patterns includes lines that are below the resolution of the photolithographic process used to form the second of the separately formed patterns. These lines are made by forming a pattern on photoresist and then etching that pattern into an amorphous carbon layer. Sidewall pacers having widths less than the widths of the un-etched parts of the amorphous carbon are formed on the sidewalls of the amorphous carbon. The amorphous carbon is then removed, leaving behind the sidewall spacers as a mask pattern. Thus, the spacers form a mask having feature sizes less than the resolution of the photolithography process used to form the pattern on the photoresist. A protective material is deposited around the spacers. The spacers are further protected using a hard mask and then photoresist is formed and patterned over the hard mask. The photoresist pattern is transferred through the hard mask to the protective material. The pattern made out by the spacers and the temporary material is then transferred to an underlying amorphous carbon hard mask layer. The pattern, having features of difference sizes, is then transferred to the underlying substrate.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
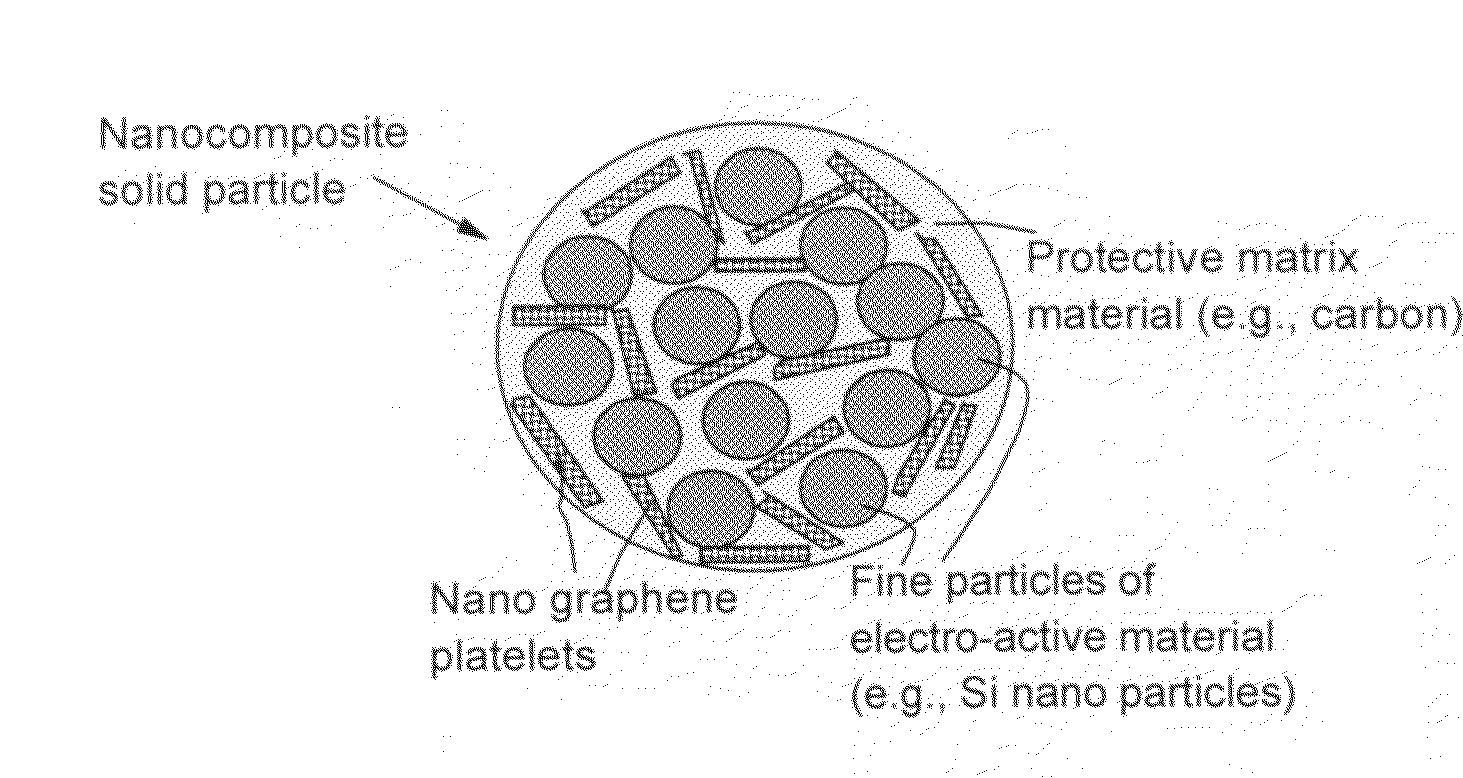
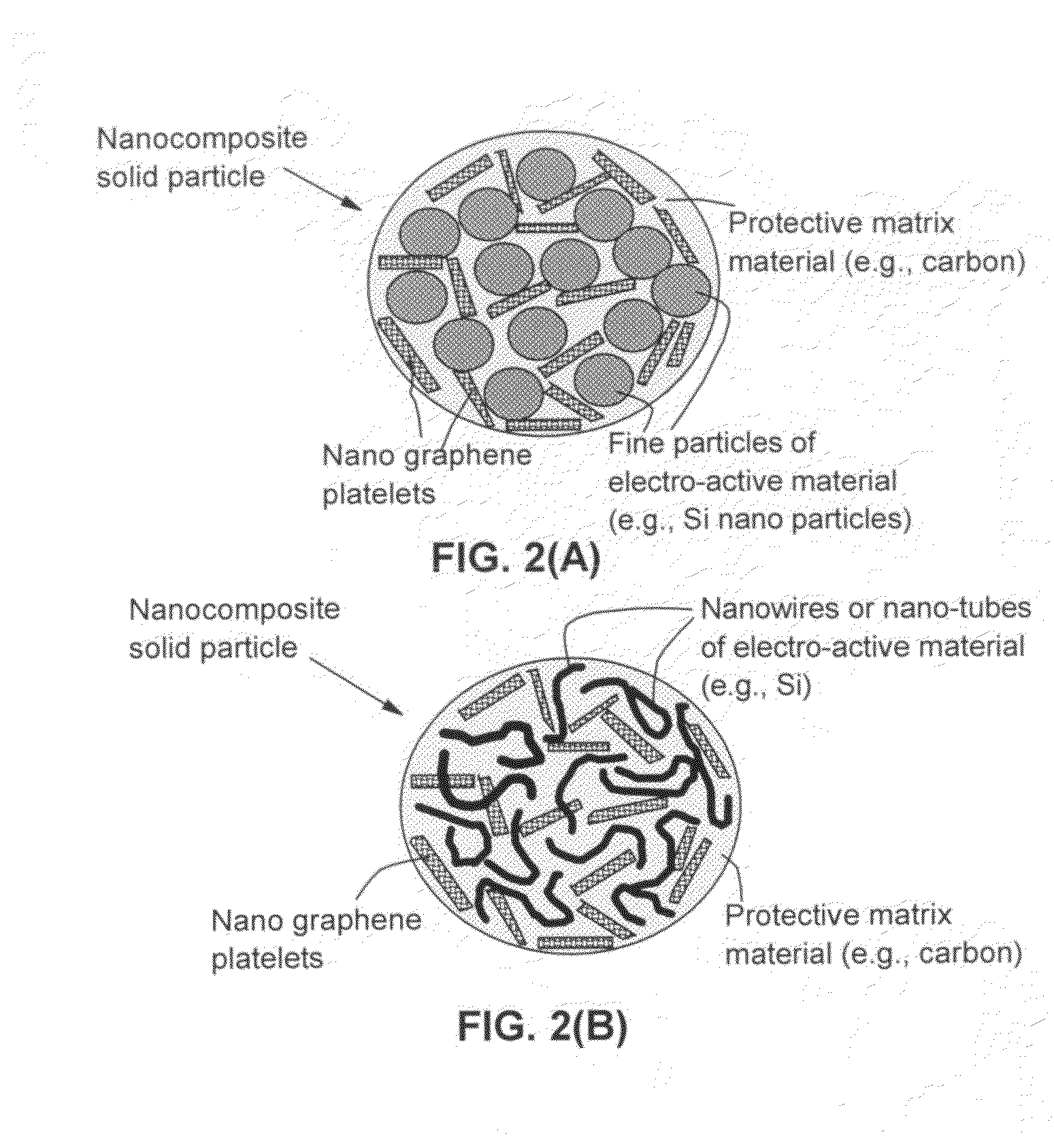
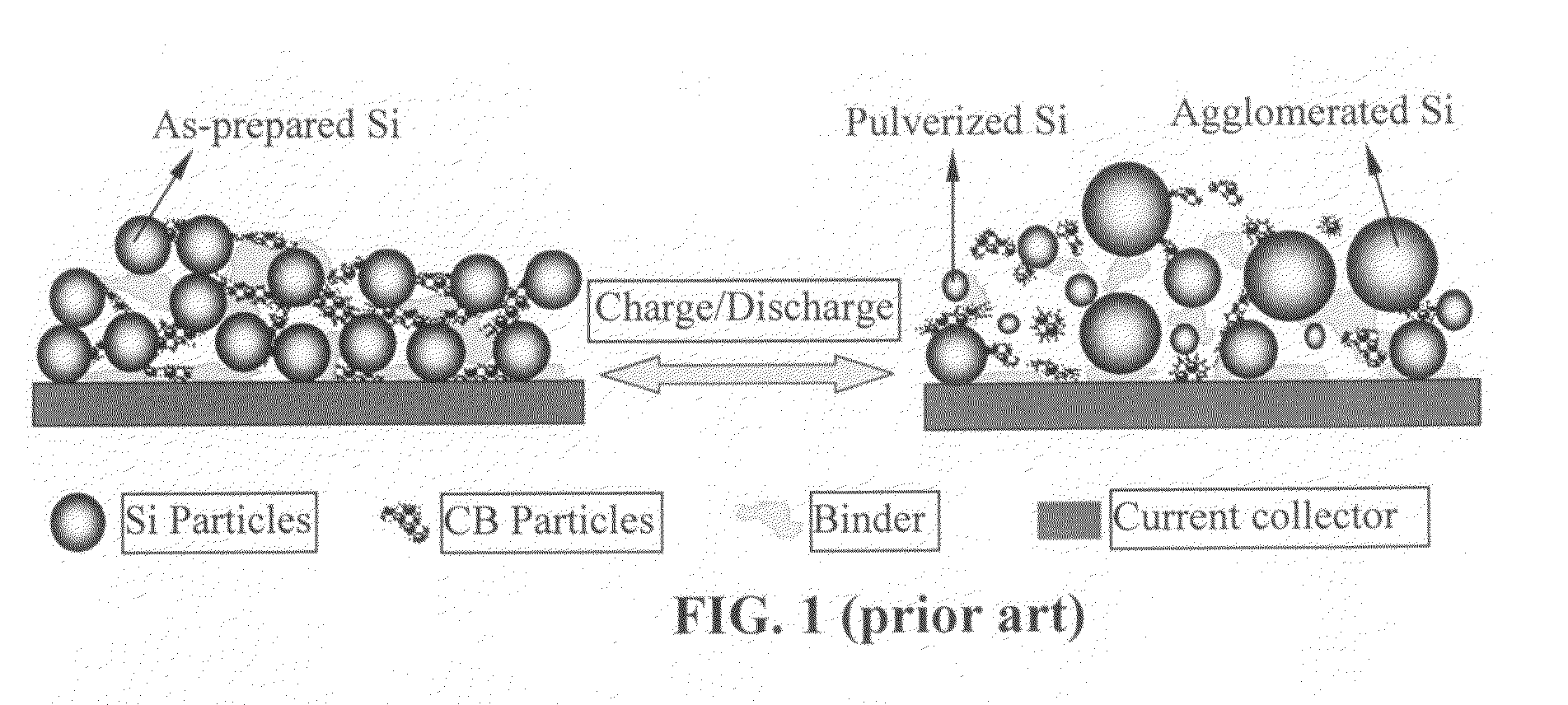
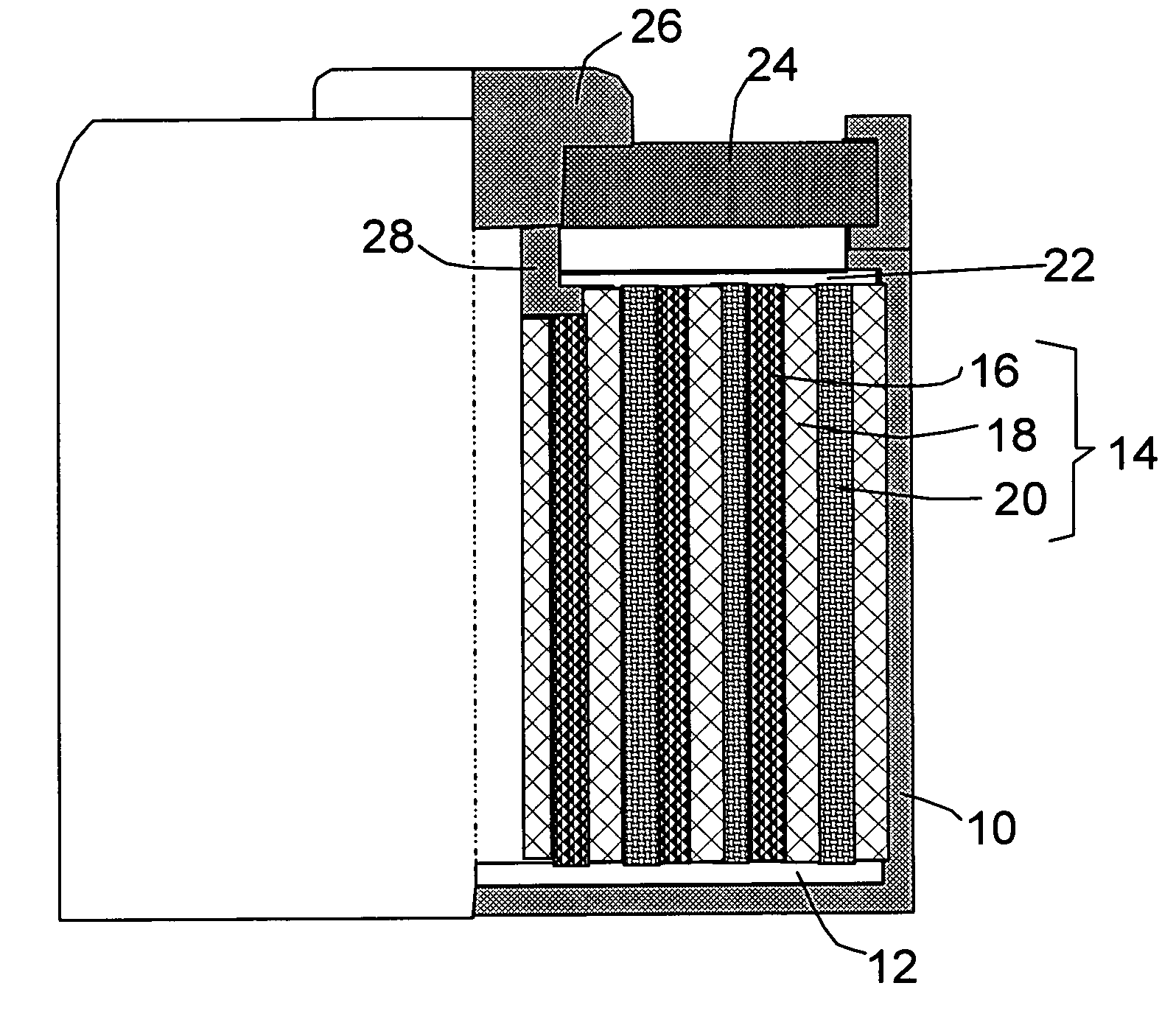
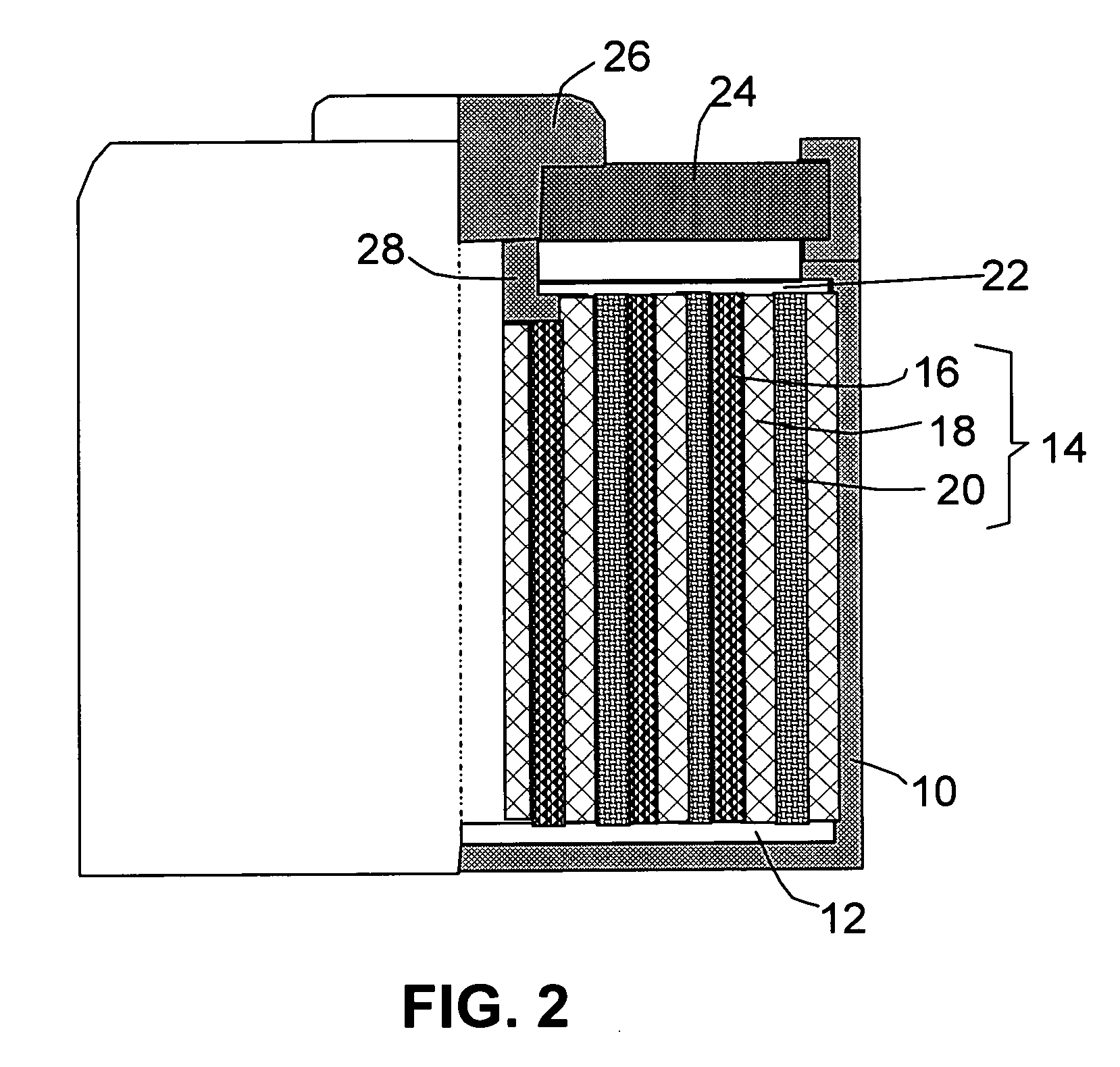
Nano graphene reinforced nanocomposite particles for lithium battery electrodes
ActiveUS20100143798A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthActive material electrodesSecondary cellsLithium metalNanocomposite
A solid nanocomposite particle composition for lithium metal or lithium ion battery electrode applications. The composition comprises: (A) an electrode active material in a form of fine particles, rods, wires, fibers, or tubes with a dimension smaller than 1 μm; (B) nano graphene platelets (NGPs); and (C) a protective matrix material reinforced by the NGPs; wherein the graphene platelets and the electrode active material are dispersed in the matrix material and the NGPs occupy a weight fraction wg of 1% to 90% of the total nanocomposite weight, the electrode active material occupies a weight fraction wa of 1% to 90% of the total nanocomposite weight, and the matrix material occupies a weight fraction wm of at least 2% of the total nanocomposite weight with wg+wa+wm=1. For a lithium ion battery anode application, the matrix material is preferably amorphous carbon, polymeric carbon, or meso-phase carbon. Such a solid nanocomposite composition provides a high anode capacity and good cycling stability. For a cathode application, the resulting lithium metal or lithium ion battery exhibits an exceptionally high cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for Depositing Conformal Amorphous Carbon Film by Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD)
ActiveUS20100093187A1Good shape retentionHighly conformalSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerNitrogen gas
Methods and apparatus for depositing an amorphous carbon layer on a substrate are provided. In one embodiment, a deposition process includes positioning a substrate in a substrate processing chamber, introducing a hydrocarbon source having a carbon to hydrogen atom ratio of greater than 1:2 into the processing chamber, introducing a plasma initiating gas selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, helium, argon, nitrogen, and combinations thereof into the processing chamber, with the hydrocarbon source having a volumetric flow rate to plasma initiating gas volumetric flow rate ratio of 1:2 or greater, generating a plasma in the processing chamber, and forming a conformal amorphous carbon layer on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
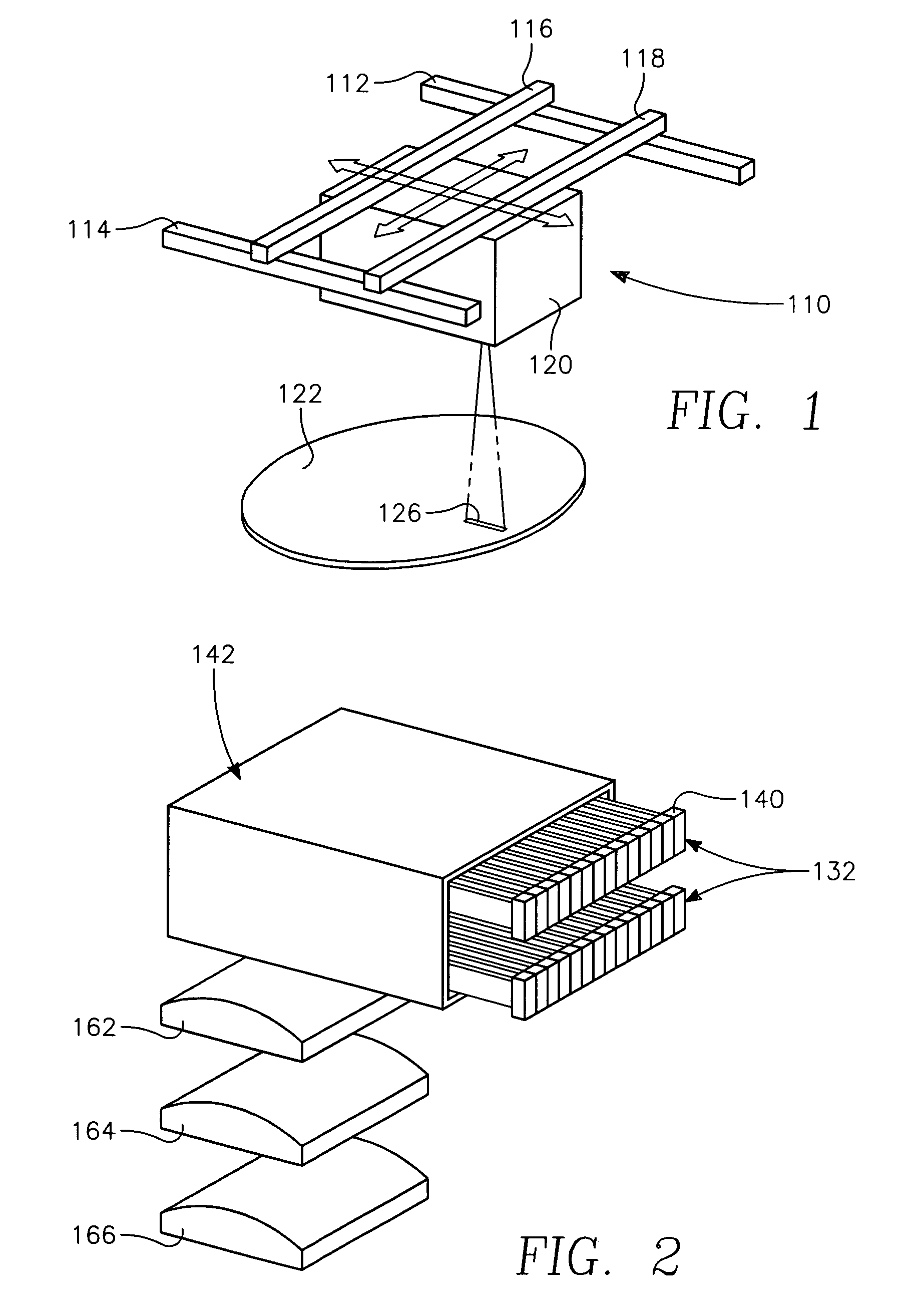
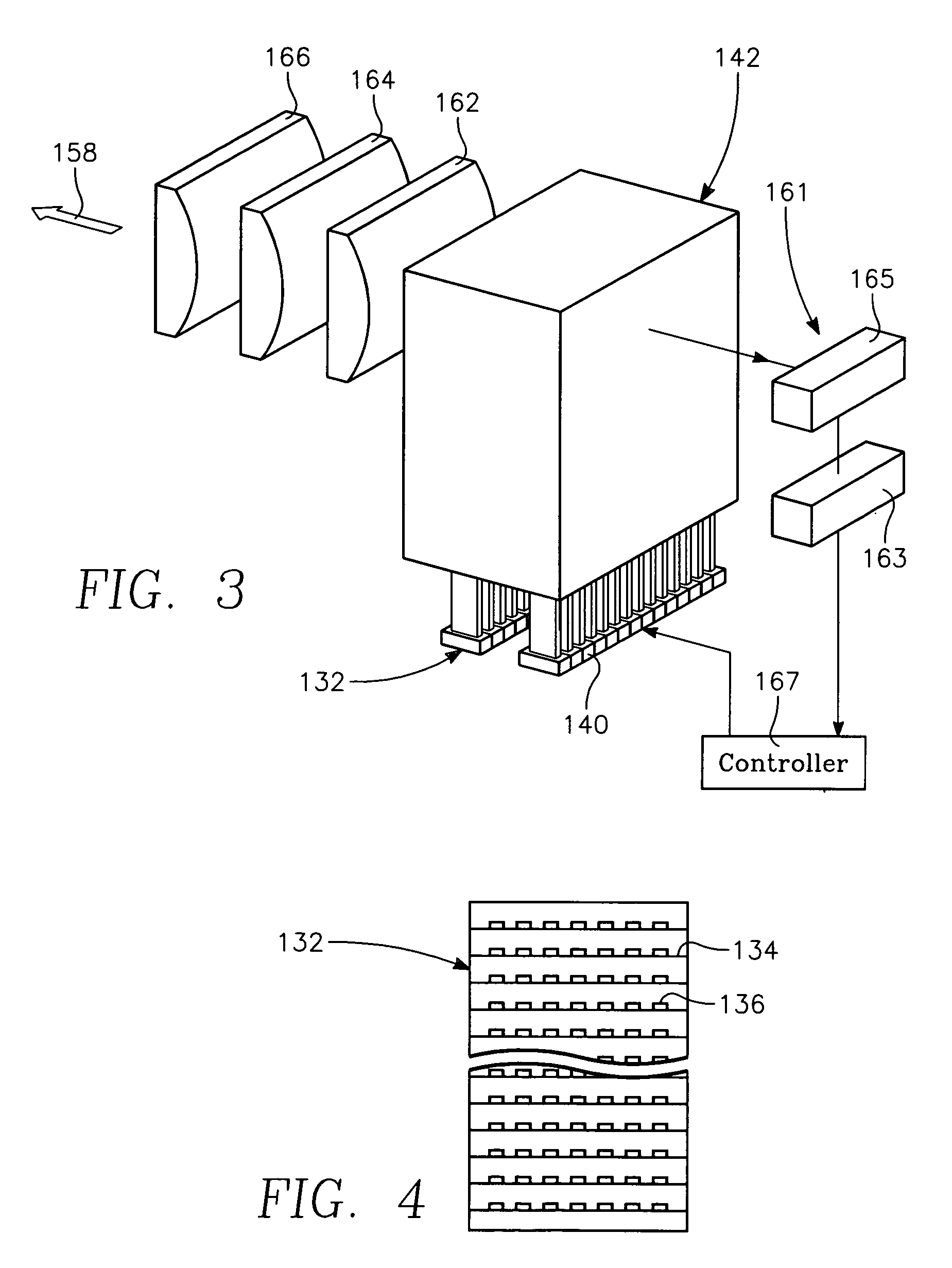
Copper conductor annealing process employing high speed optical annealing with a low temperature-deposited optical absorber layer
InactiveUS7335611B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCopper conductorLow temperature deposition
A method of forming a conductor in a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate includes forming high aspect ratio openings in a base layer having vertical side walls, depositing a dielectric barrier layer comprising a dielectric compound of a barrier metal on the surfaces of the high aspect ratio openings including the vertical side walls, depositing a metal barrier layer comprising the barrier metal on the first barrier layer, depositing a main conductor species seed layer on the metal barrier layer and depositing a main conductor layer. The method further includes annealing the main conductor layer by (a) directing light from an array of continuous wave lasers into a line of light extending at least partially across the thin film structure, and (b) translating the line of light relative to the thin film structure in a direction transverse to the line of light. The method of Claim 1 further comprising, prior to the annealing step, depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer on the main conductor layer. The step of depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer includes introducing a carbon-containing process gas into a reactor chamber containing the substrate in a process zone of the reactor, applying RF source power to an external reentrant conduit of the reactor to generate a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current passing through the process zone and applying a bias voltage to the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method For Depositing an Amorphous Carbon Film with Improved Density and Step Coverage
ActiveUS20080003824A1High densityLower thermal budgetPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbon layerKrypton
A method for depositing an amorphous carbon layer on a substrate includes the steps of positioning a substrate in a chamber, introducing a hydrocarbon source into the processing chamber, introducing a heavy noble gas into the processing chamber, and generating a plasma in the processing chamber. The heavy noble gas is selected from the group consisting of argon, krypton, xenon, and combinations thereof and the molar flow rate of the noble gas is greater than the molar flow rate of the hydrocarbon source. A post-deposition termination step may be included, wherein the flow of the hydrocarbon source and the noble gas is stopped and a plasma is maintained in the chamber for a period of time to remove particles therefrom.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of forming metal oxide hardmask
ActiveUS8901016B2Promote degradationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentAtomic layer depositionMetal
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Methods for the reduction and elimination of particulate contamination with CVD of amorphous carbon
InactiveUS20060014397A1Minimal defect formationReduce particle pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesVariable thicknessMicroparticle
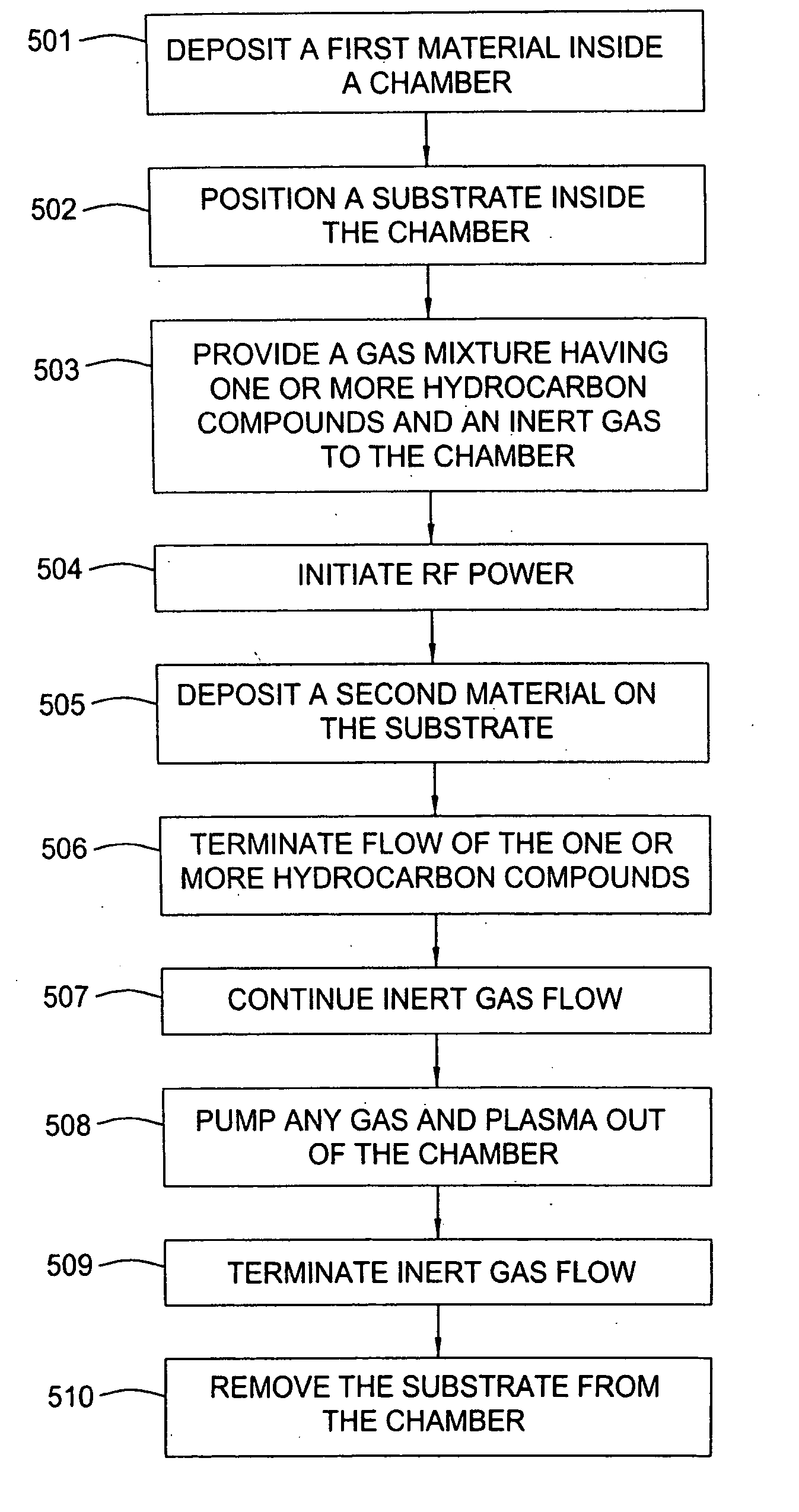
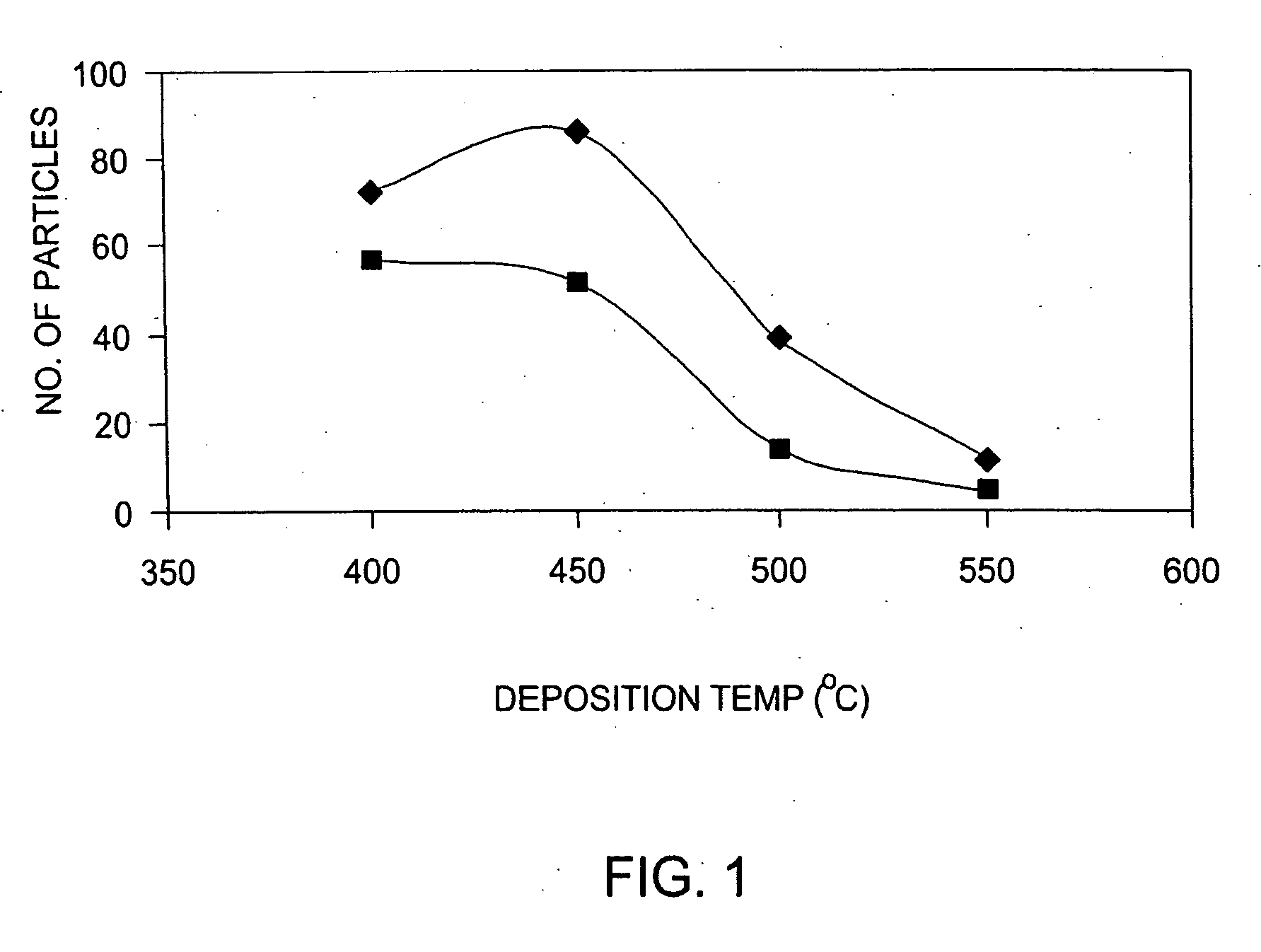
A method is provided for forming an amorphous carbon layer, deposited on a dielectric material such as oxide, nitride, silicon carbide, carbon doped oxide, etc., or a metal layer such as tungsten, aluminum or poly-silicon. The method includes the use of chamber seasoning, variable thickness of seasoning film, wider spacing, variable process gas flows, post-deposition purge with inert gas, and post-deposition plasma purge, among others, to make the deposition of an amorphous carbon film at low deposition temperatures possible without any defects or particle contamination.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
Use of amorphous carbon film as a hardmask in the fabrication of optical waveguides
Methods are provided for forming optical devices, such as waveguides, with minimal defect formation. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for forming a waveguide structure on a substrate surface including forming a cladding layer on the substrate surface, forming a core layer on the cladding layer, depositing an amorphous carbon hardmask on the core layer, forming a patterned photoresist layer on the amorphous carbon hardmask, etching the amorphous carbon hardmask, and etching the core material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of forming highly conformal amorphous carbon layer
ActiveUS7842622B1Easily ionizedReduce riskSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerSemiconductor
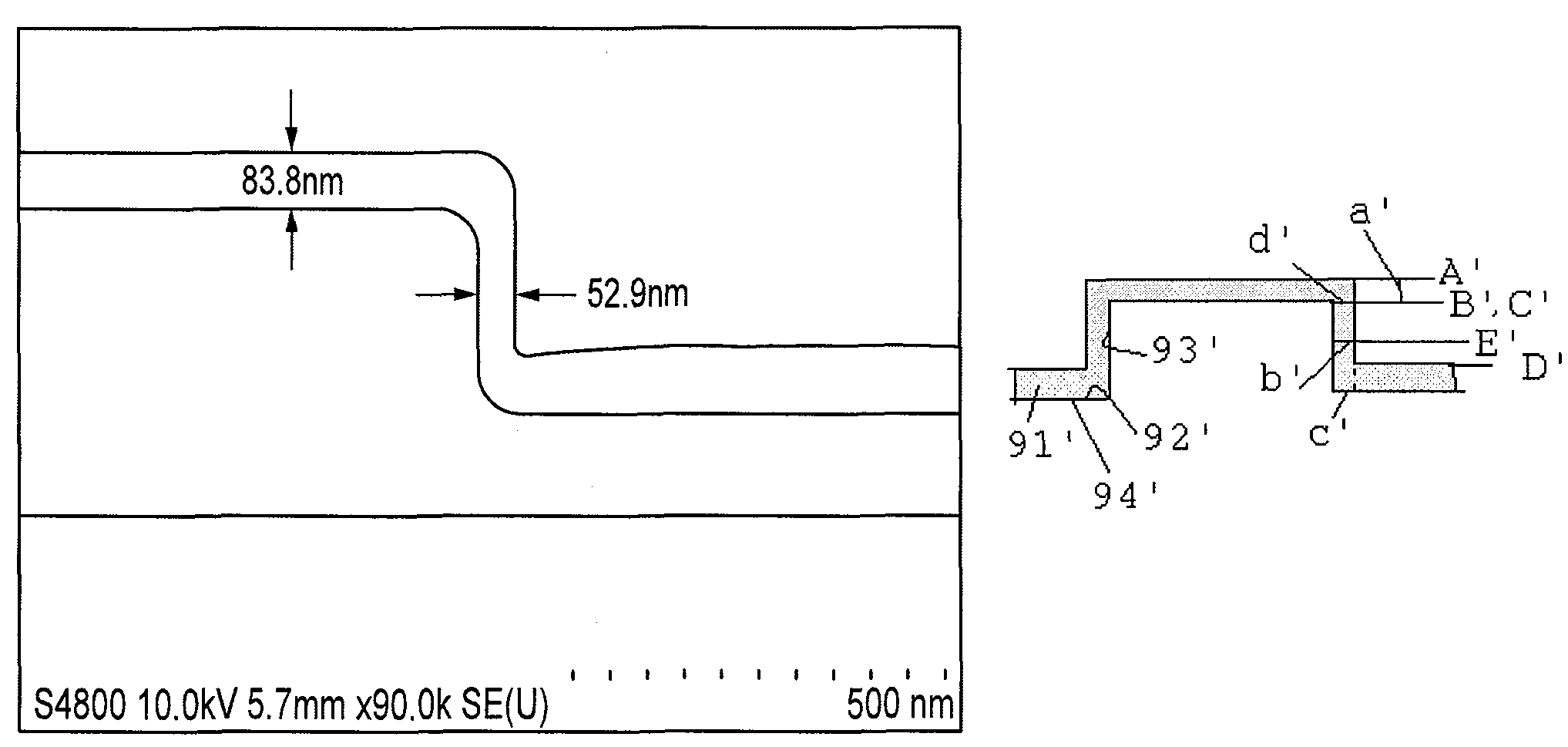
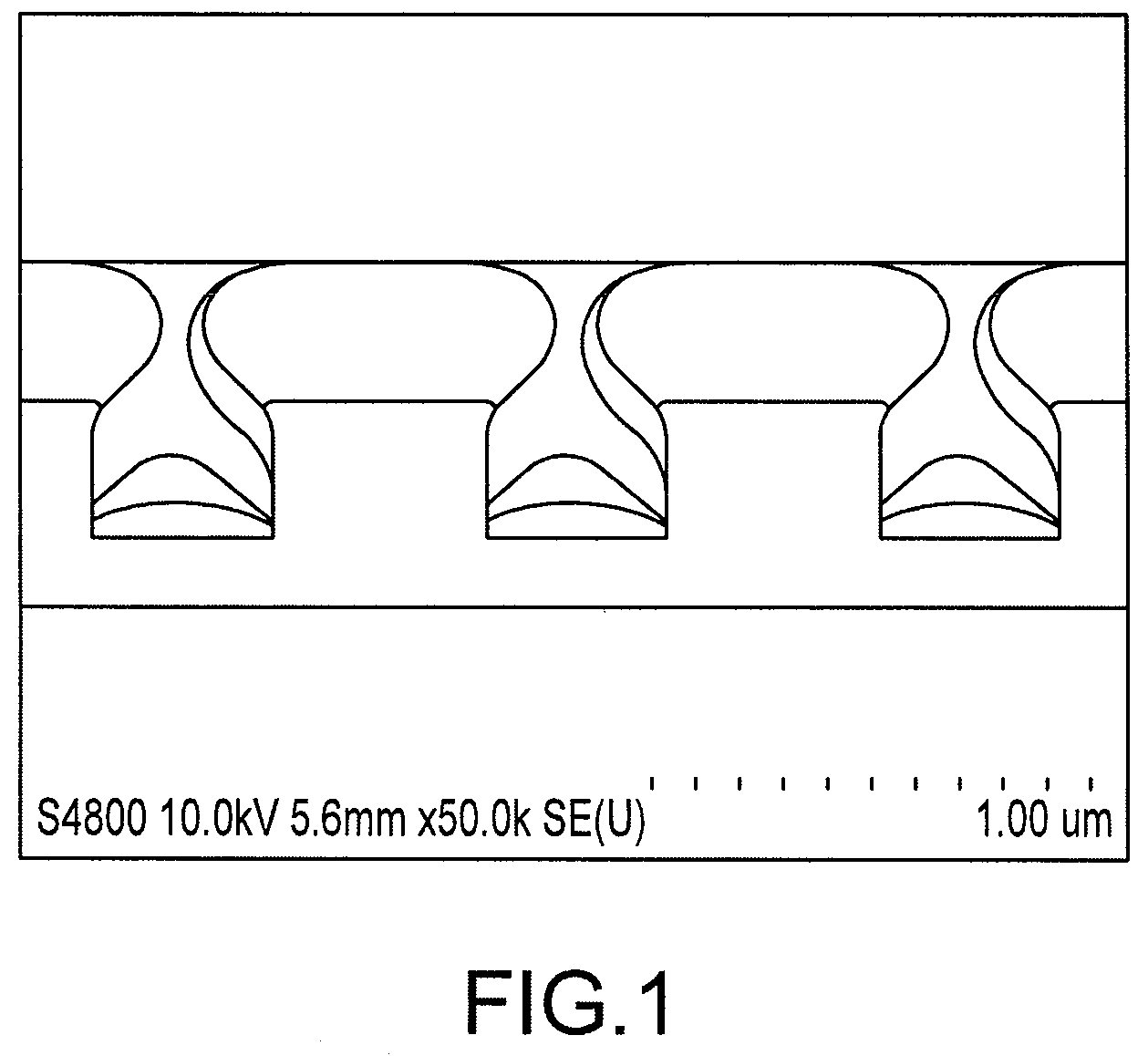
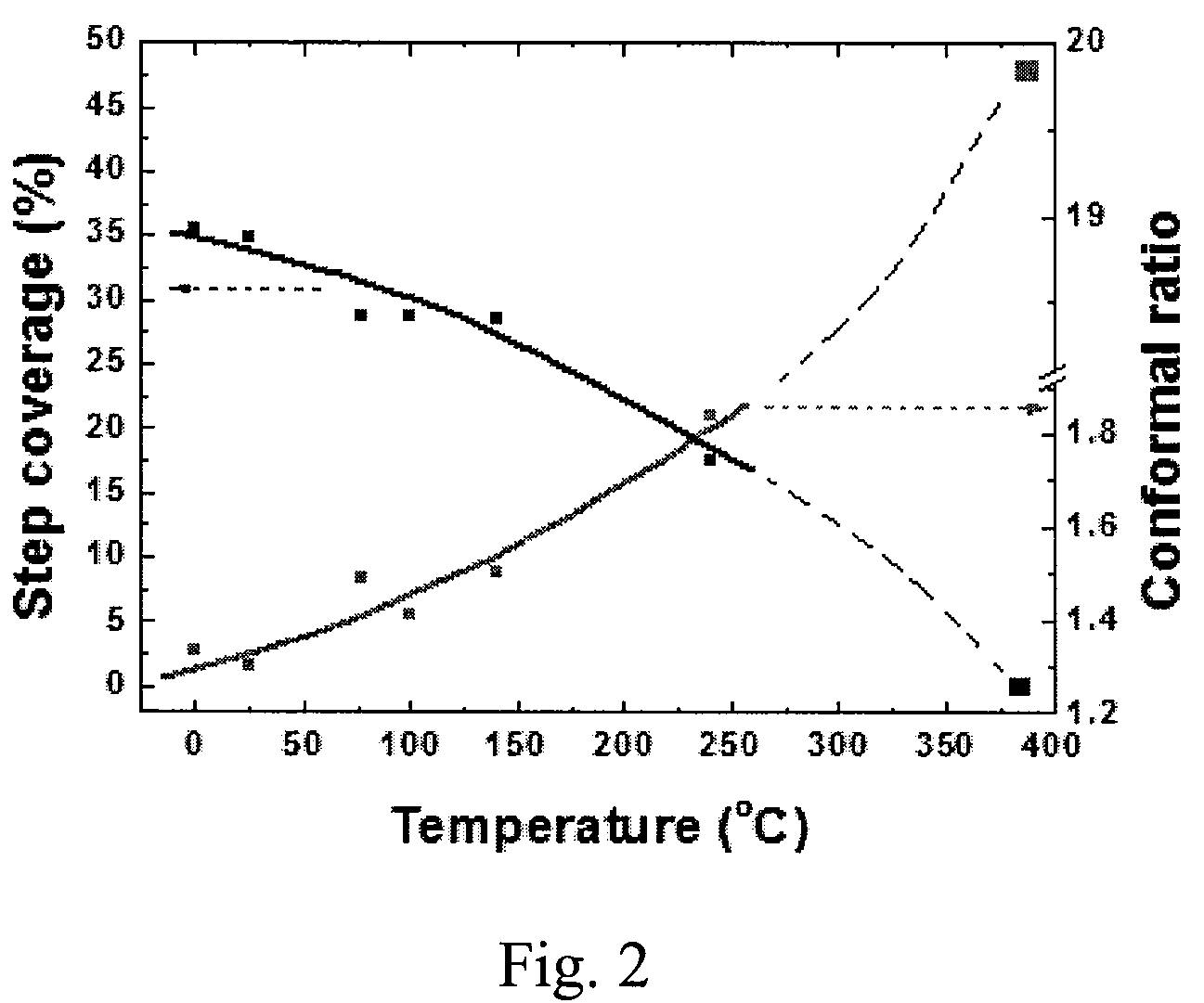
A method of forming a conformal amorphous hydrogenated carbon layer on an irregular surface of a semiconductor substrate includes: vaporizing a hydrocarbon-containing precursor; introducing the vaporized precursor and an argon gas into a CVD reaction chamber inside which the semiconductor substrate is placed; depositing a conformal amorphous hydrogenated carbon layer on the irregular surface of the semiconductor substrate by plasma CVD; and controlling the deposition of the conformal ratio of the depositing conformal amorphous hydrogenated carbon layer. The controlling includes (a) adjusting a step coverage of the conformal amorphous hydrogenated carbon layer to about 30% or higher as a function of substrate temperature, and (b) adjusting a conformal ratio of the conformal amorphous hydrogenated carbon layer to about 0.9 to about 1.1 as a function of RF power and / or argon gas flow rate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Multiple deposition for integration of spacers in pitch multiplication process
InactiveUS20070049040A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical reactionGas phase
Pitch multiplication is performed using a two step process to deposit spacer material on mandrels. The precursors of the first step react minimally with the mandrels, forming a barrier layer against chemical reactions for the deposition process of the second step, which uses precursors more reactive with the mandrels. Where the mandrels are formed of amorphous carbon and the spacer material is silicon oxide, the silicon oxide is first deposited by a plasma enhanced deposition process and then by a thermal chemical vapor deposition process. Oxygen gas and plasma-enhanced tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) are used as reactants in the plasma enhanced process, while ozone and TEOS are used as reactants in the thermal chemical vapor deposition process. The oxygen gas is less reactive with the amorphous carbon than ozone, thereby minimizing deformation of the mandrels caused by oxidation of the amorphous carbon.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Method of Forming Metal Oxide Hardmask
ActiveUS20120164846A1Promote degradationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentAtomic layer depositionMetal
A method of forming a metal oxide hardmask on a template includes: providing a template constituted by a photoresist or amorphous carbon formed on a substrate; and depositing by atomic layer deposition (ALD) a metal oxide hardmask on the template constituted by a material having a formula SixM(1-x)Oy wherein M represents at least one metal element, x is less than one including zero, and y is approximately two or a stoichiometrically-determined number.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
An etch stop layer for dual damascene process
The present invention provides a carbon based etch stop, such as a diamond like amorphous carbon, having a low dielectric constant and a method of forming a dual damascene structure. The low k etch stop is preferably deposited between two dielectric layers and patterned to define the underlying interlevel contacts / vias. The second or upper dielectric layer is formed over the etch stop and patterned to define the intralevel interconnects. The entire dual damascene structure is then etched in a single selective etch process which first etches the patterned interconnects, then etches the contact / vias past the patterned etch stop. The etch stop has a low dielectric constant relative to a conventional SiN etch stop, which minimizes the capacitive coupling between adjacent interconnect lines. The dual damascene structure is then filled with a suitable conductive material such as aluminum or copper and planarized using chemical mechanical polishing.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Process for producing nano graphene reinforced composite particles for lithium battery electrodes
ActiveUS20100176337A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsFiberLithium metal
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Plasma etching method
ActiveUS20140377960A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallurgyResidence time
In a plasma etching method of performing a plasma etching on an amorphous carbon layer of a substrate to be processed by using an inorganic film as a mask, the substrate being mounted in a processing chamber, the plasma etching on the amorphous carbon layer is performed by using O2 gas as a processing gas and the O2 gas to flow in the processing chamber such that a residence time of the O2 gas becomes 0.37 msec or less. The amorphous carbon layer is used as an etching mask of an etching target film formed on the substrate. The plasma etching is performed by using the O2 gas only.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
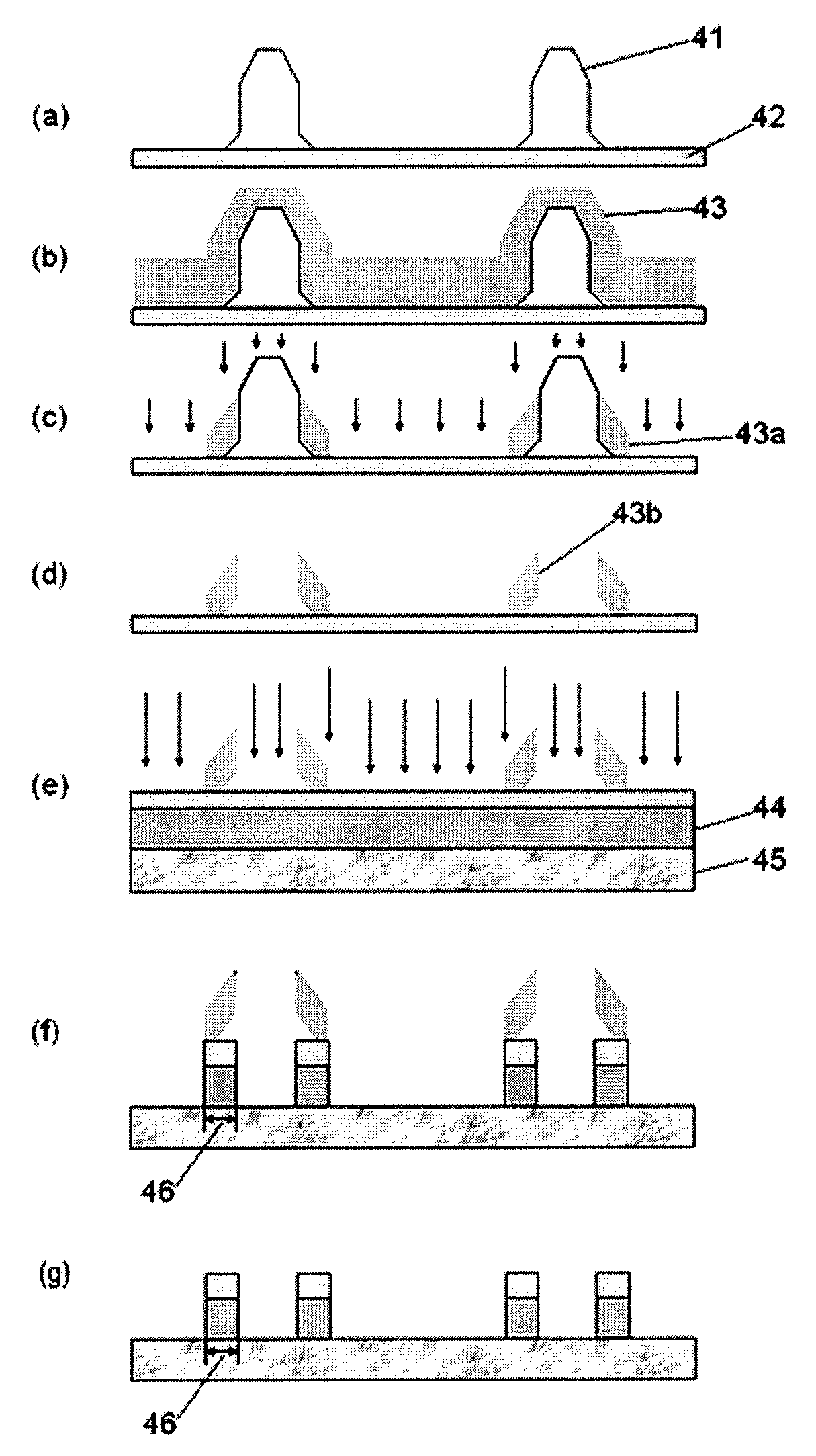
Planarizing etch hardmask to increase pattern density and aspect ratio
InactiveUS20110291243A1Easy to disassembleAdd depthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAnti-reflective coatingEngineering
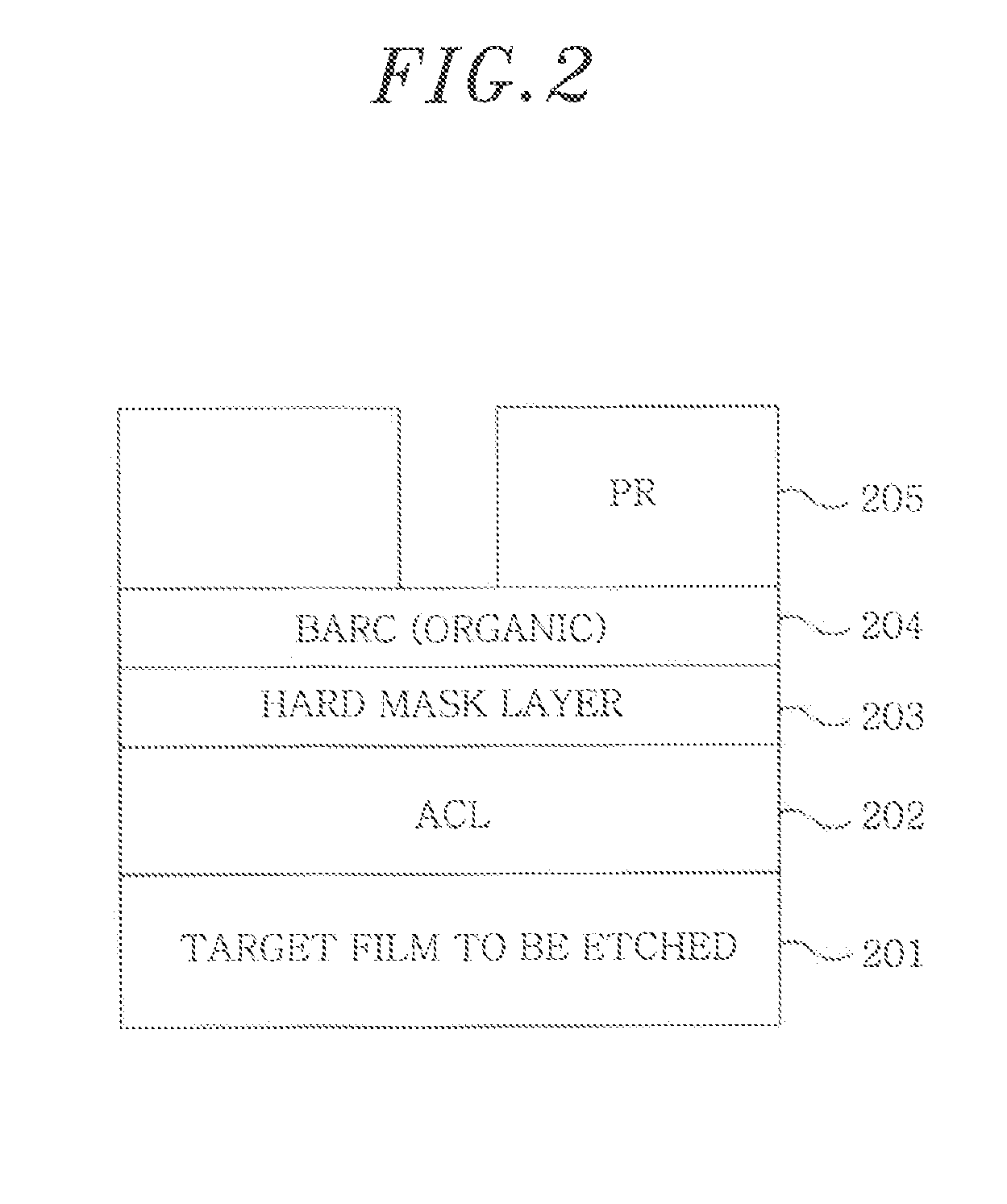
Methods for manufacturing a semiconductor device in a processing chamber are provided. In one embodiment, a method includes depositing over a substrate a first base material having a first set of interconnect features, filling an upper portion of the first set of interconnect features with an ashable material to an extent capable of protecting the first set of interconnect features from subsequent processes while being easily removable when desired, planarizing an upper surface of the first base material such that an upper surface of the ashable material filled in the first set of interconnect features is at the same level with the upper surface of the first base material, providing a substantial planar outer surface of the first base material, depositing a first film stack comprising a second base material on the substantial planar outer surface of the first base material, forming a second set of interconnect features in the second base material, wherein the second set of interconnect features are aligned with the first set of interconnect features, and removing the ashable material from the first base material, thereby extending a feature depth of the semiconductor device by connecting the second set of interconnect features to the first set of interconnect features. In another embodiment, a method includes providing a base material having a first film stack deposited thereon, wherein the base material is formed over the substrate and having a first set of interconnect features filled with an amorphous carbon material, the first film stack comprising a first amorphous carbon layer deposited on a surface of the base material, a first anti-reflective coating layer deposited on the first amorphous carbon layer, and a first photoresist layer deposited on the first anti-reflective coating layer, and patterning a portion of the first photoresist layer by shifting laterally a projection of a mask on the first photoresist layer relative to the substrate a desired distance, thereby introducing into the first photoresist layer a first feature pattern to be transferred to the underlying base material, wherein the first feature pattern is not aligned with the first set of interconnect features.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Multiple deposition for integration of spacers in pitch multiplication process
InactiveUS20080149593A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical reactionGas phase
Pitch multiplication is performed using a two step process to deposit spacer material on mandrels. The precursors of the first step react minimally with the mandrels, forming a barrier layer against chemical reactions for the deposition process of the second step, which uses precursors more reactive with the mandrels. Where the mandrels are formed of amorphous carbon and the spacer material is silicon oxide, the silicon oxide is first deposited by a plasma enhanced deposition process and then by a thermal chemical vapor deposition process. Oxygen gas and plasma-enhanced tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) are used as reactants in the plasma enhanced process, while ozone and TEOS are used as reactants in the thermal chemical vapor deposition process. The oxygen gas is less reactive with the amorphous carbon than ozone, thereby minimizing deformation of the mandrels caused by oxidation of the amorphous carbon.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Air gap interconnects using carbon-based films
InactiveUS20100093168A1Improve electrical isolationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal interconnectPorous carbon
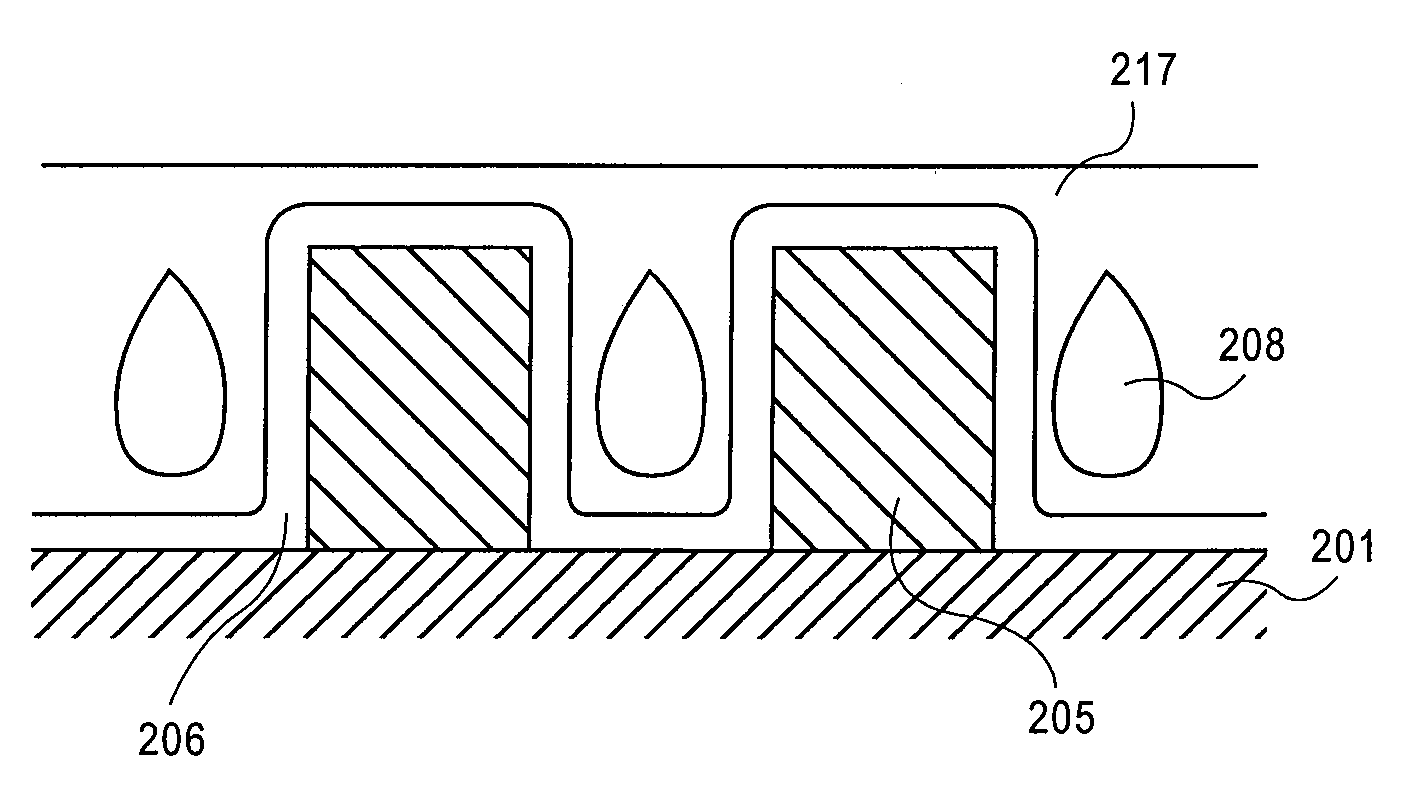
A method of forming an interconnect structure comprising: forming a sacrificial inter-metal dielectric (IMD) layer over a substrate, wherein the sacrificial IMD layer comprising a carbon-based film, such as amorphous carbon, advanced patterning films, porous carbon, or any combination thereof; forming a plurality of metal interconnect lines within the sacrificial IMD layer; removing the sacrificial IMD layer, with an oxygen based reactive process; and depositing a non-conformal dielectric layer to form air gaps between the plurality of metal interconnect lines. The metal interconnect lines may comprise copper, aluminum, tantalum, tungsten, titanium, tantalum nitride, titanium nitride, tungsten nitride, or any combination thereof. Carbon-based films and patterned photoresist layers may be simultaneously removed with the same reactive process. Highly reactive hydrogen radicals processes may be used to remove the carbon-based film and simultaneously pre-clean the metal interconnect lines prior to the deposition of a conformal metal barrier liner.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090081879A1Increased anisotropySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideSemiconductor
There is provided a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device including processing a substrate to be processed by using an amorphous carbon hard mask that includes processing an amorphous carbon film formed on the substrate to be processed to provide a hard mask, and forming a protective film comprising a silicon oxide film on a sidewall of the amorphous carbon film exposed during or after processing the amorphous carbon film; and the protective film preferably formed by sputtering an intermediate mask comprising at least a silicon oxide on the amorphous carbon film.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
Method for fabricating semiconductor device using amorphous carbon layer as sacrificial hard mask
ActiveUS20060024945A1Minimizing pattern deformationEtch selectivity of hardSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistDevice material
Disclosed is a method for fabricating a semiconductor device by using an amorphous carbon layer as a sacrificial hard mask. The method includes the steps of: forming an amorphous carbon layer on an etch target layer; forming a photoresist pattern on the amorphous carbon layer; etching the amorphous carbon layer by using the photoresist pattern to form a sacrificial hard mask; and etching the etch target layer by using the sacrificial hard mask to form a predetermined pattern.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Copper conductor annealing process employing high speed optical annealing with a low temperature-deposited optical absorber layer
InactiveUS20070032095A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCopper conductorEngineering
A method of forming a conductor in a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate includes forming high aspect ratio openings in a base layer having vertical side walls, depositing a dielectric barrier layer comprising a dielectric compound of a barrier metal on the surfaces of the high aspect ratio openings including the vertical side walls, depositing a metal barrier layer comprising the barrier metal on the first barrier layer, depositing a main conductor species seed layer on the metal barrier layer and depositing a main conductor layer. The method further includes annealing the main conductor layer by (a) directing light from an array of continuous wave lasers into a line of light extending at least partially across the thin film structure, and (b) translating the line of light relative to the thin film structure in a direction transverse to the line of light. The method of Claim 1 further comprising, prior to the annealing step, depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer on the main conductor layer. The step of depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer includes introducing a carbon-containing process gas into a reactor chamber containing the substrate in a process zone of the reactor, applying RF source power to an external reentrant conduit of the reactor to generate a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current passing through the process zone and applying a bias voltage to the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
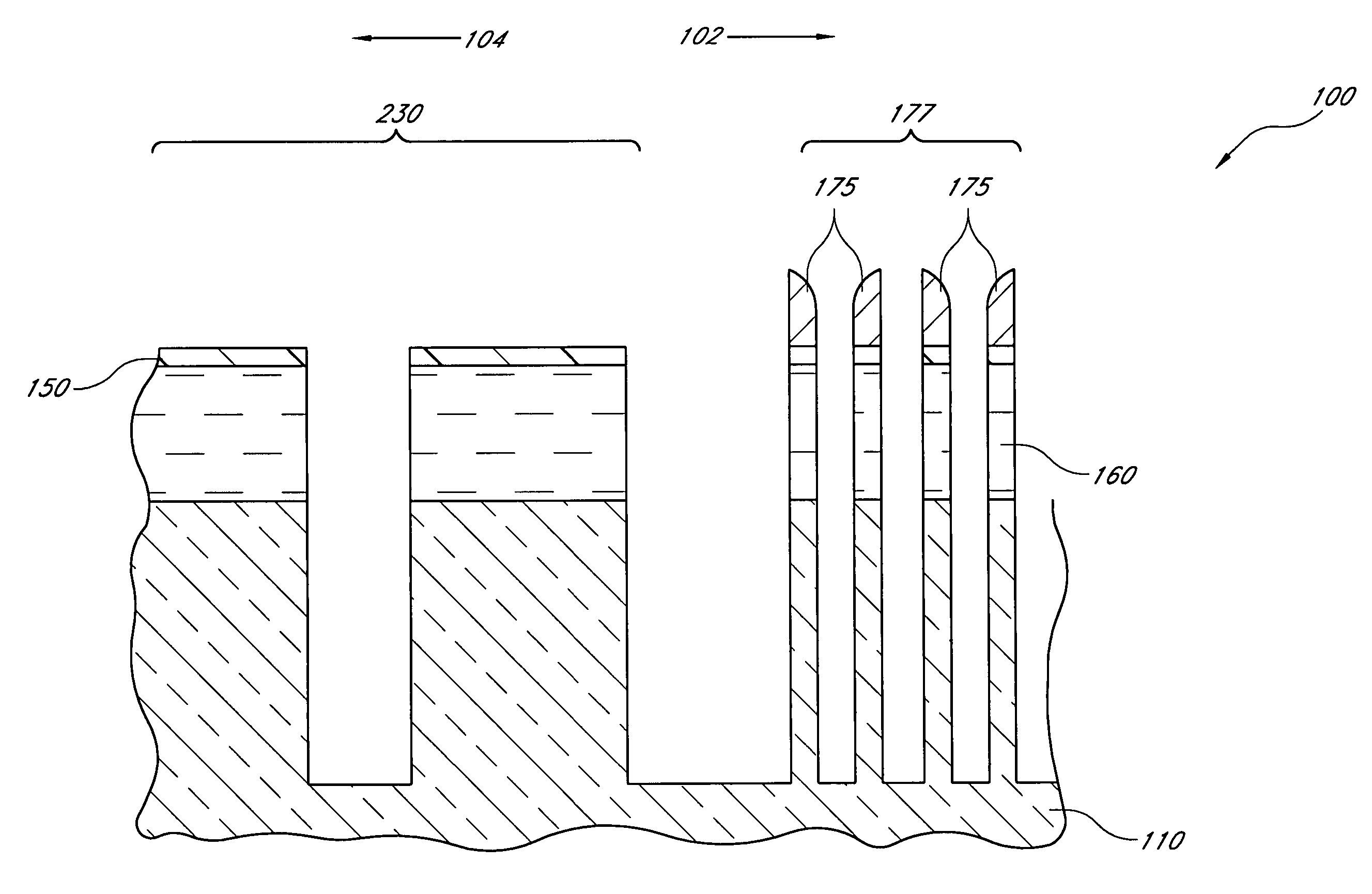
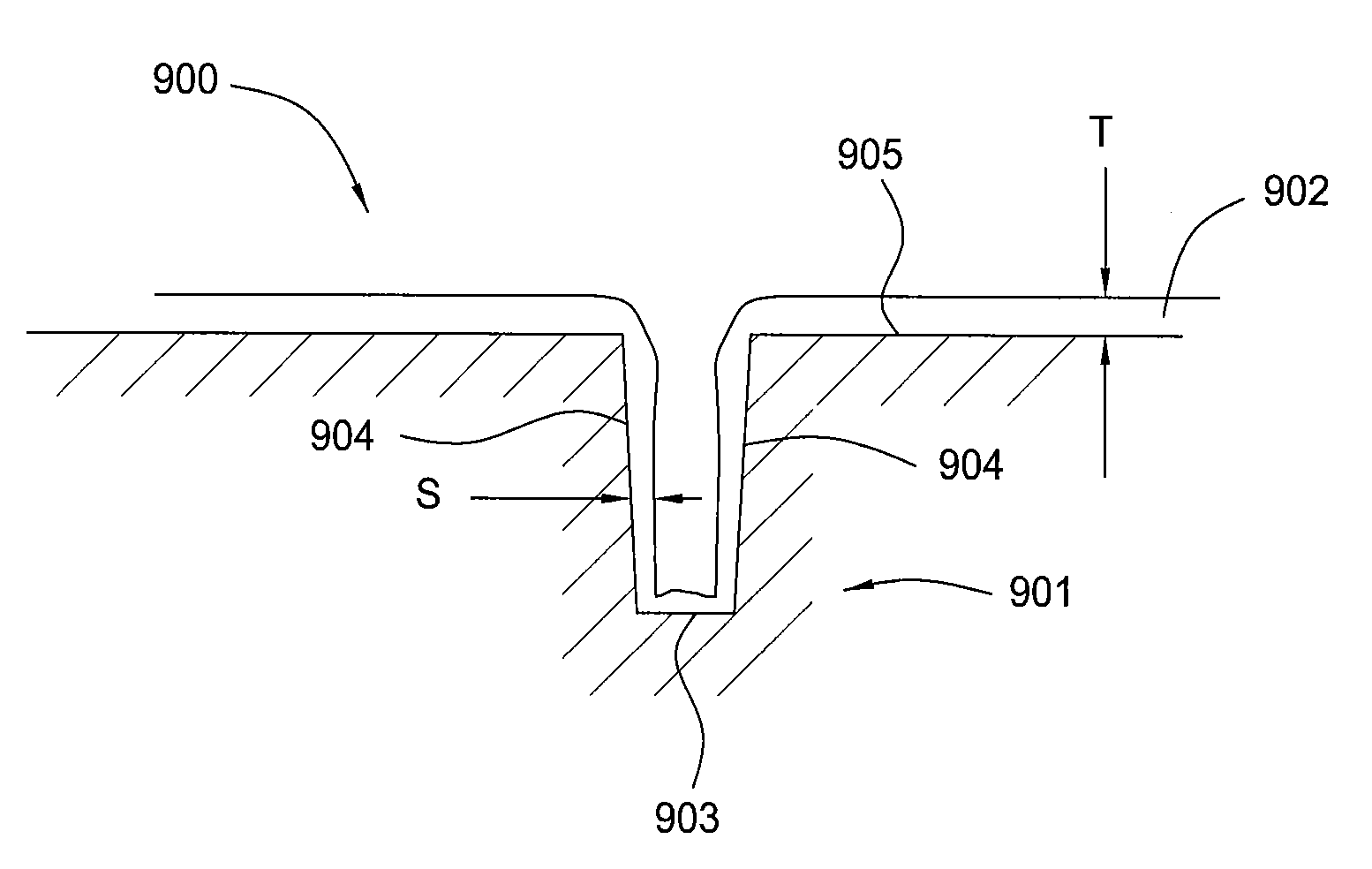
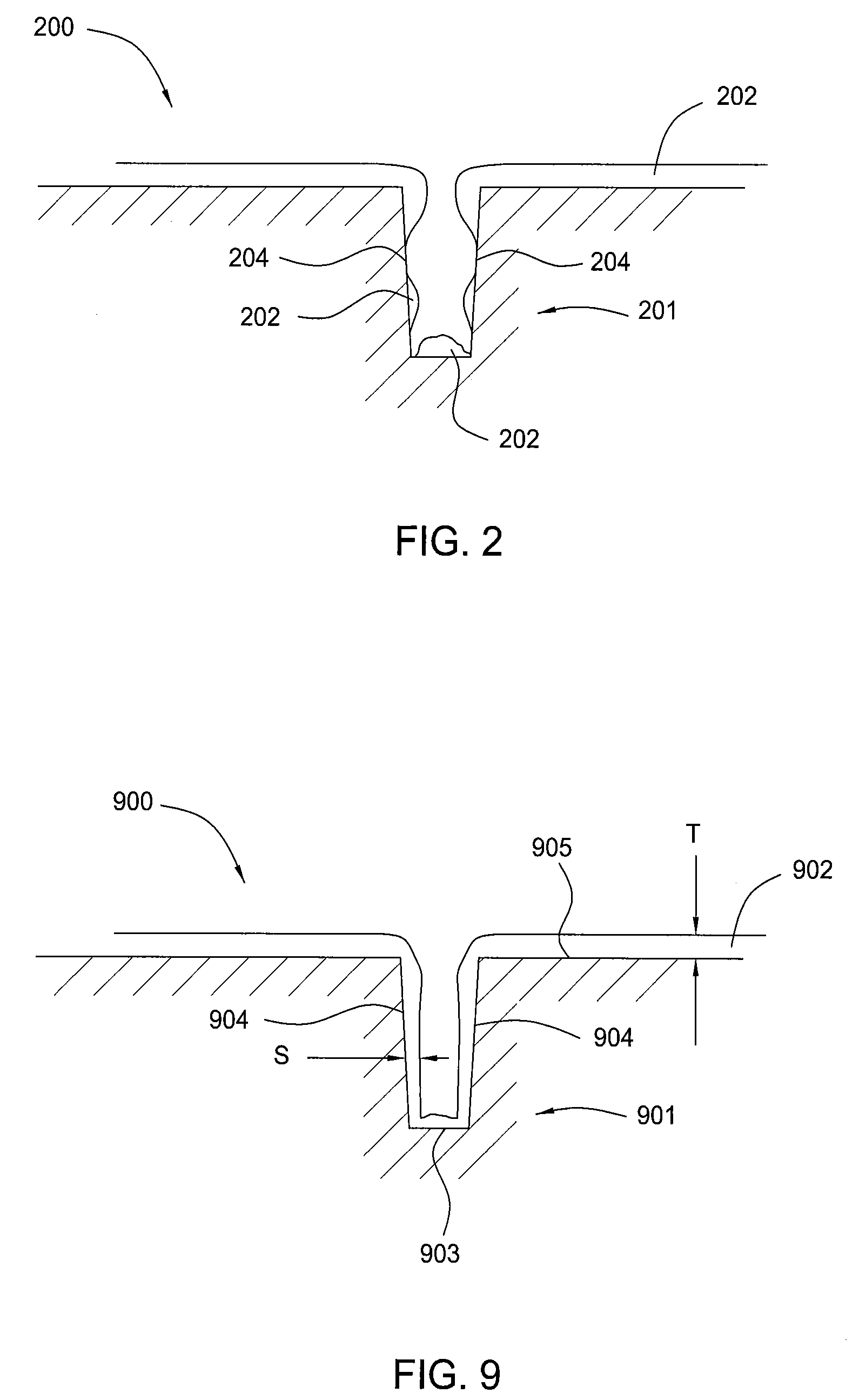
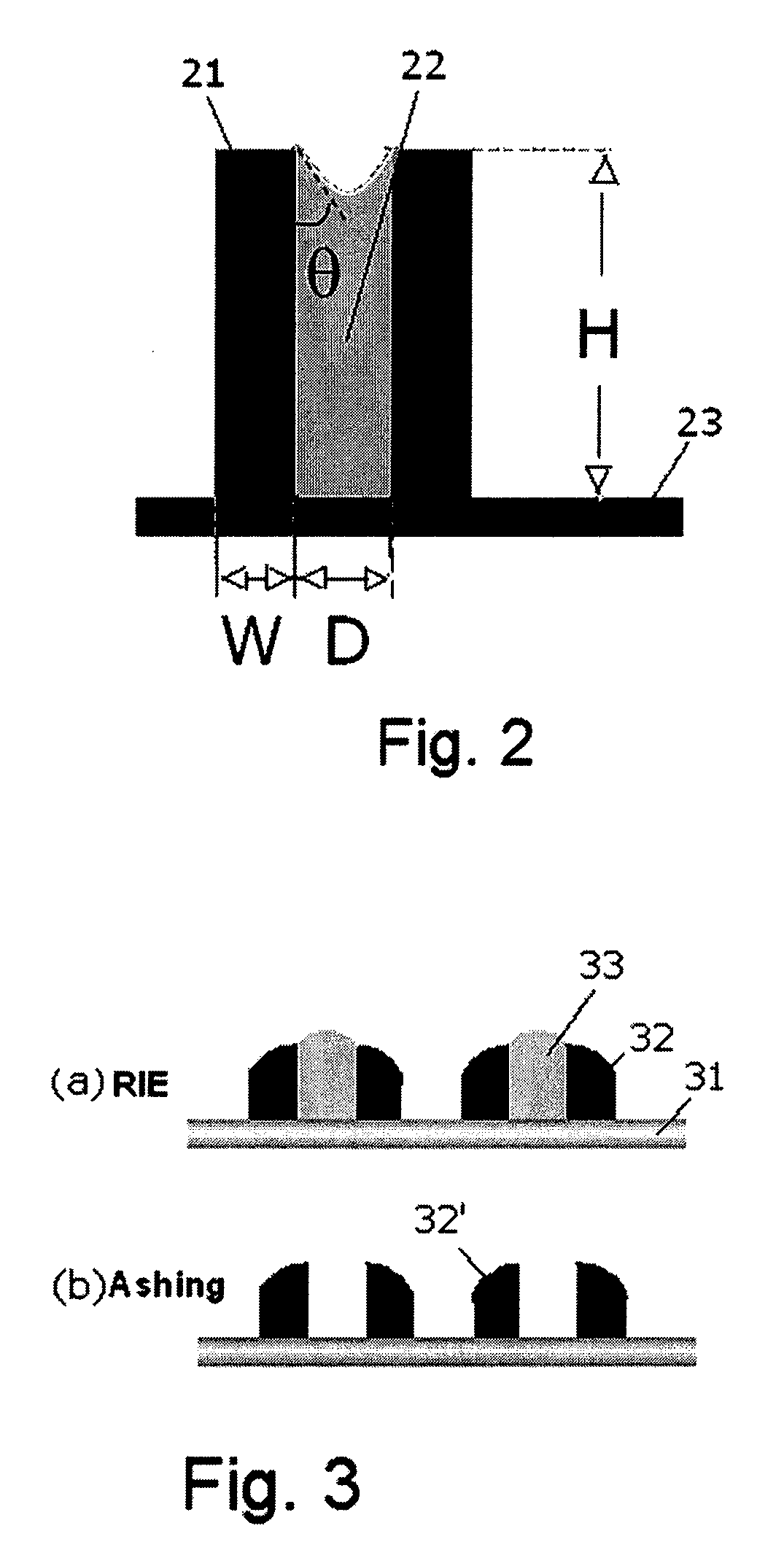
Method for forming sublithographic features during the manufacture of a semiconductor device and a resulting in-process apparatus
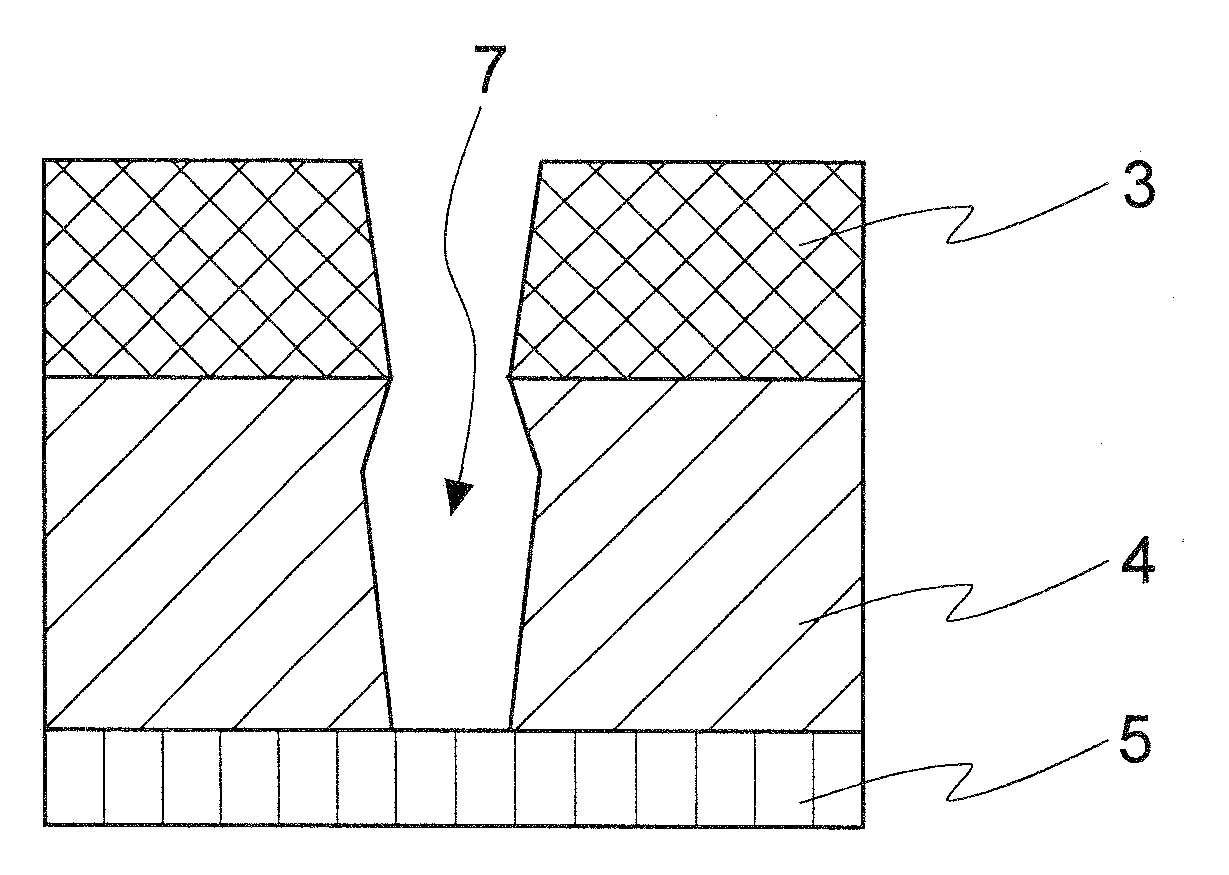
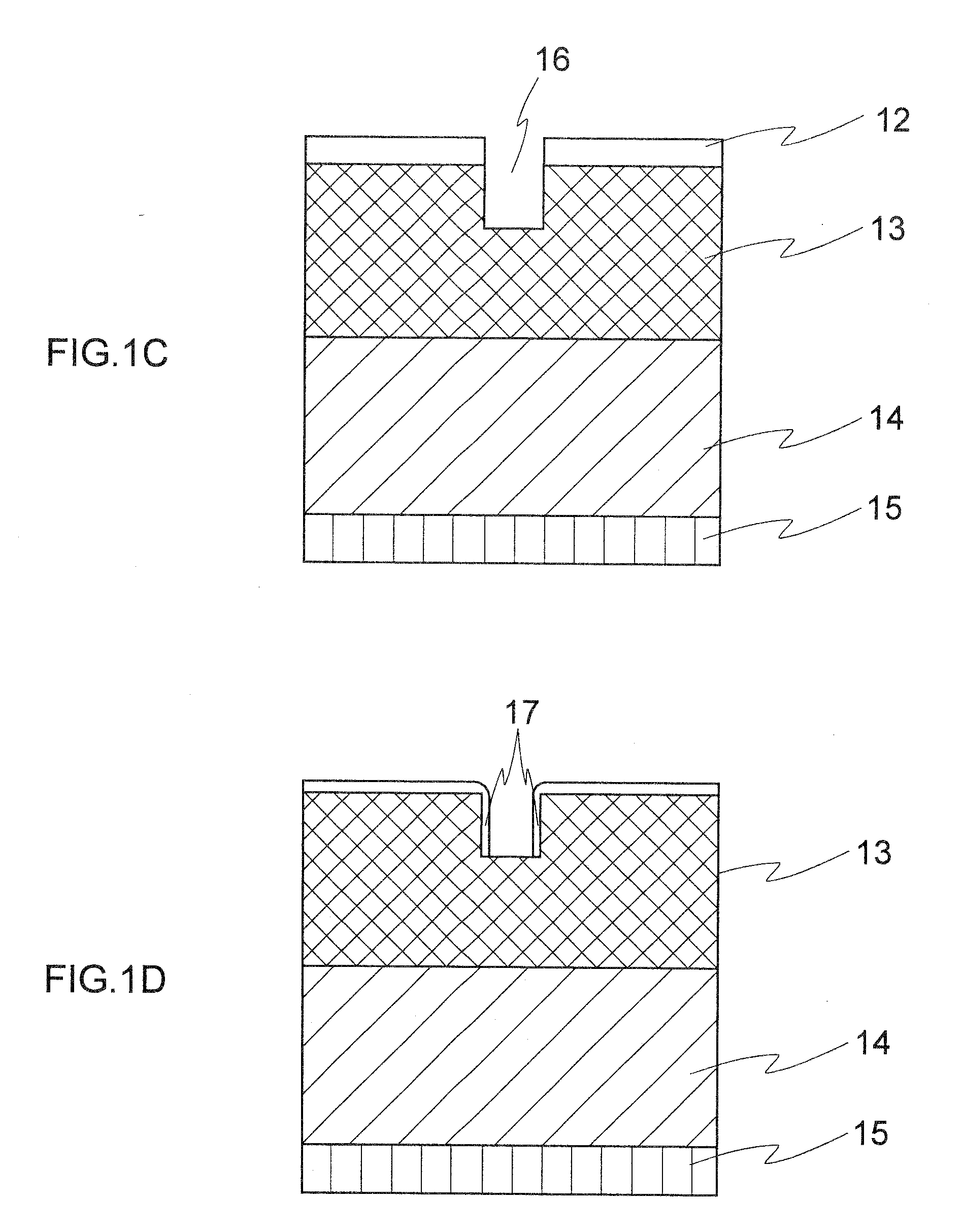
A method for forming a semiconductor device comprises forming a layer to be etched, then forming a hard mask layer over the layer to be etched. The hard mask is etched to form an opening defined by first and second cross-sectional sidewalls in the hard mask layer. In one embodiment, the opening in the hard mask layer is formed at the minimum limits allowable by optical lithography. A conformal spacer layer is formed over the hard mask layer and on the sidewalls of the hard mask, then spacer etched to form first and second cross-sectional spacers along the first and second sidewalls in the patterned hard mask layer. The hard mask and spacers are preferably formed from amorphous carbon. The layer to be etched is etched using the hard mask layer and the spacers as a pattern, then the hard mask layer and spacers are removed.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Reprogrammable metal-to-metal antifuse employing carbon-containing antifuse material
InactiveUS7459763B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHydrogenMetal interconnect
A reprogrammable metal-to-metal antifuse is disposed between two metal interconnect layers in an integrated circuit. A lower barrier layer is formed from Ti. A lower adhesion-promoting layer is disposed over the lower Ti barrier layer. An antifuse material layer selected from a group comprising at least one of amorphous carbon and amorphous carbon doped with at least one of hydrogen and fluorine is disposed over the lower adhesion-promoting layer. An upper adhesion-promoting layer is disposed over the antifuse material layer. An upper Ti barrier layer is disposed over the upper adhesion-promoting layer.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
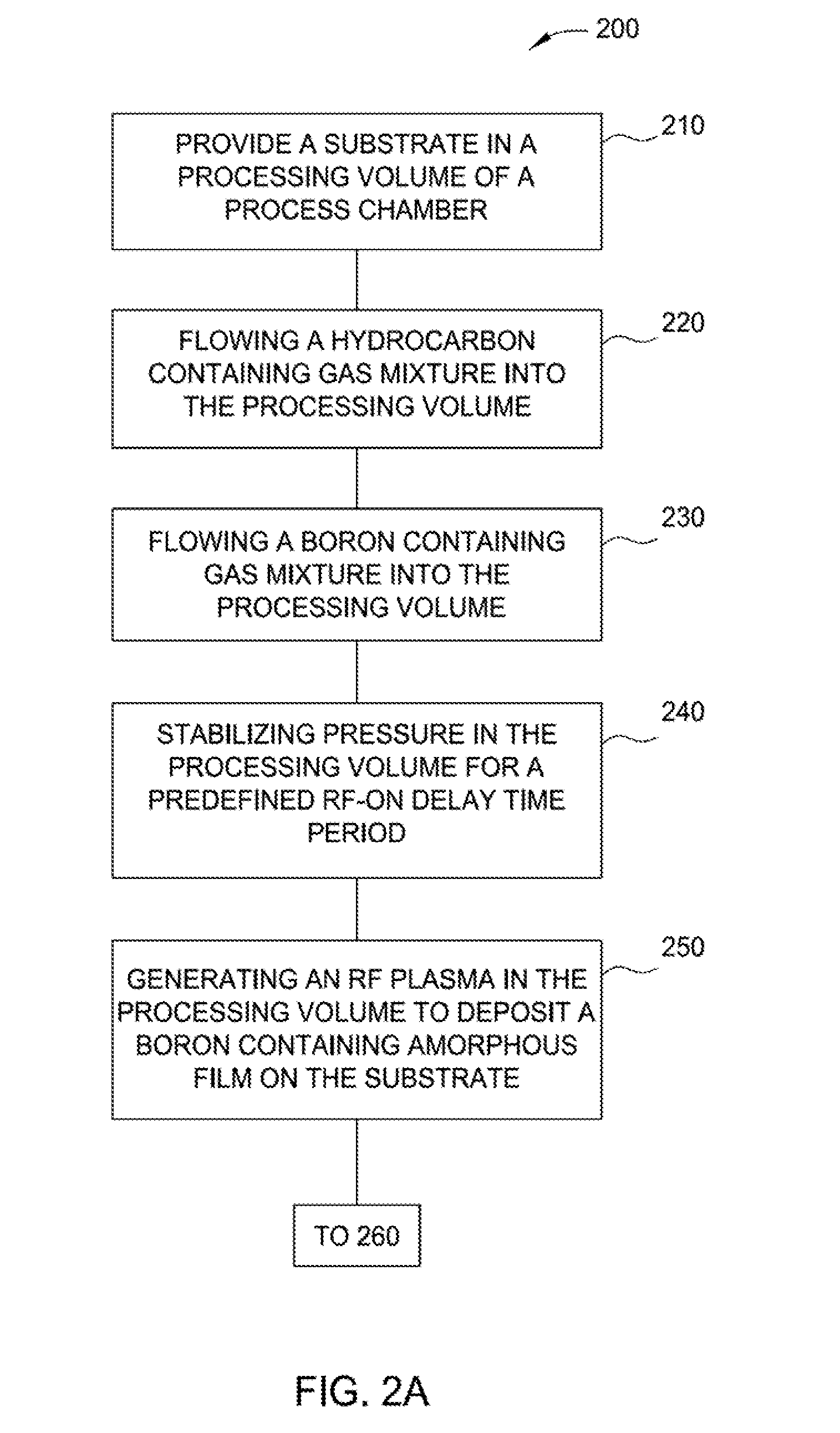
Methods to improve in-film particle performance of amorphous boron-carbon hardmask process in pecvd system
ActiveUS20170062218A1Reduce particle pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBoron containingDelayed time
Implementations of the present disclosure generally relate to the fabrication of integrated circuits. More particularly, the implementations described herein provide techniques for deposition of boron-containing amorphous carbon films on a substrate with reduced particle contamination. In one implementation, the method comprises flowing a hydrocarbon-containing gas mixture into a processing volume having a substrate positioned therein, flowing a boron-containing gas mixture into the processing volume, stabilizing the pressure in the processing volume for a predefined RF-on delay time period, generating an RF plasma in the processing volume after the predefined RF-on delay time period expires to deposit a boron-containing amorphous film on the substrate, exposing the processing volume of the process chamber to a dry cleaning process and depositing an amorphous boron season layer over at least one surface in the processing volume of the process chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
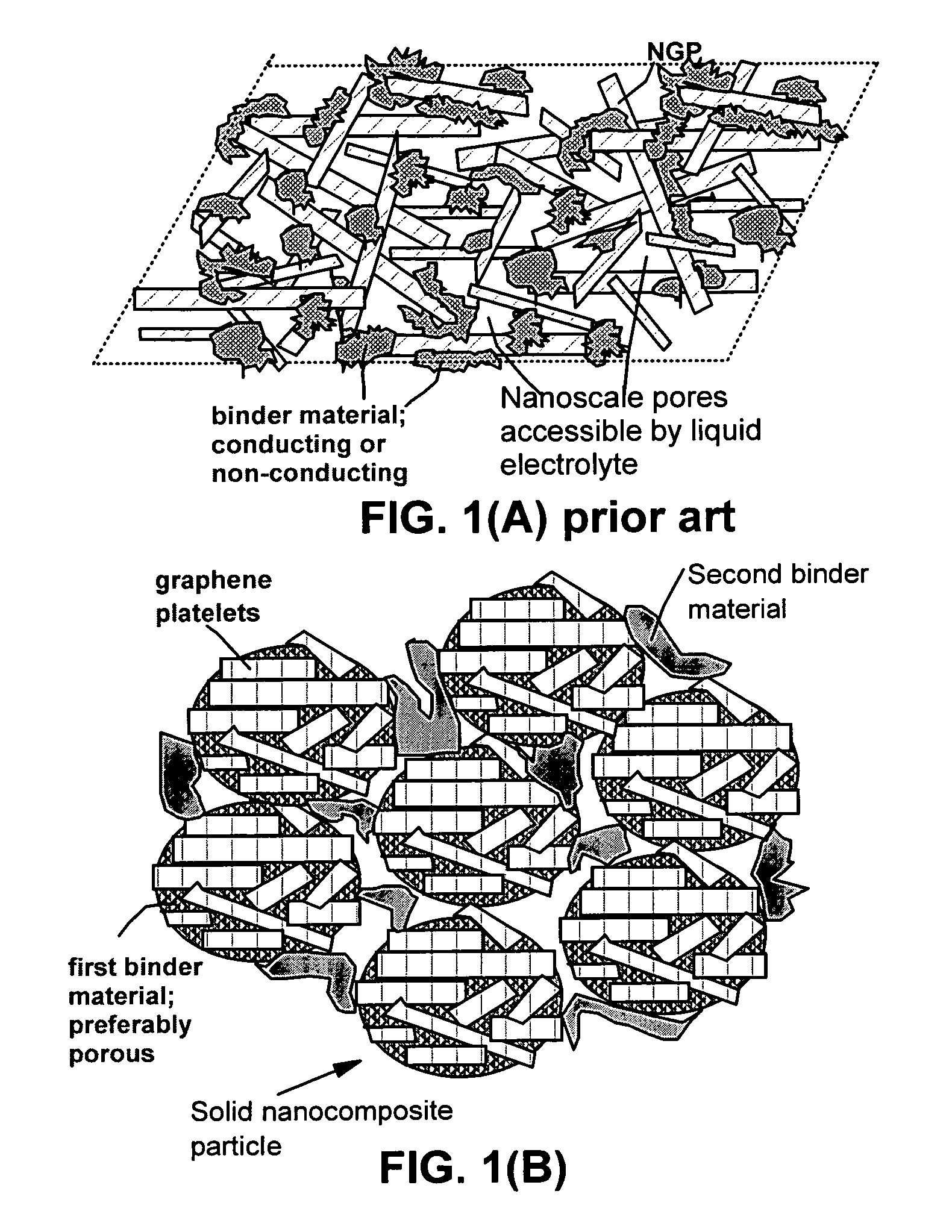
Graphene nanocomposites for electrochemical cell electrodes
ActiveUS20100021819A1High and reversible anode capacityTedious and energy-intensiveMicroscopic fiber electrodesHybrid capacitor electrodesGraphene nanocompositesSolid particle
A composite composition for electrochemical cell electrode applications, the composition comprising multiple solid particles, wherein (a) a solid particle is composed of graphene platelets dispersed in or bonded by a first matrix or binder material, wherein the graphene platelets are not obtained from graphitization of the first binder or matrix material; (b) the graphene platelets have a length or width in the range of 10 nm to 10 μm; (c) the multiple solid particles are bonded by a second binder material; and (d) the first or second binder material is selected from a polymer, polymeric carbon, amorphous carbon, metal, glass, ceramic, oxide, organic material, or a combination thereof. For a lithium ion battery anode application, the first binder or matrix material is preferably amorphous carbon or polymeric carbon. Such a composite composition provides a high anode capacity and good cycling response. For a supercapacitor electrode application, the solid particles preferably have meso-scale pores therein to accommodate electrolyte.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR GRP LLC
Plasma etching method and plasma etching apparatus
ActiveUS20140134847A1Reduce roughnessImproving cross-sectional shape of lineElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenSilicon oxide
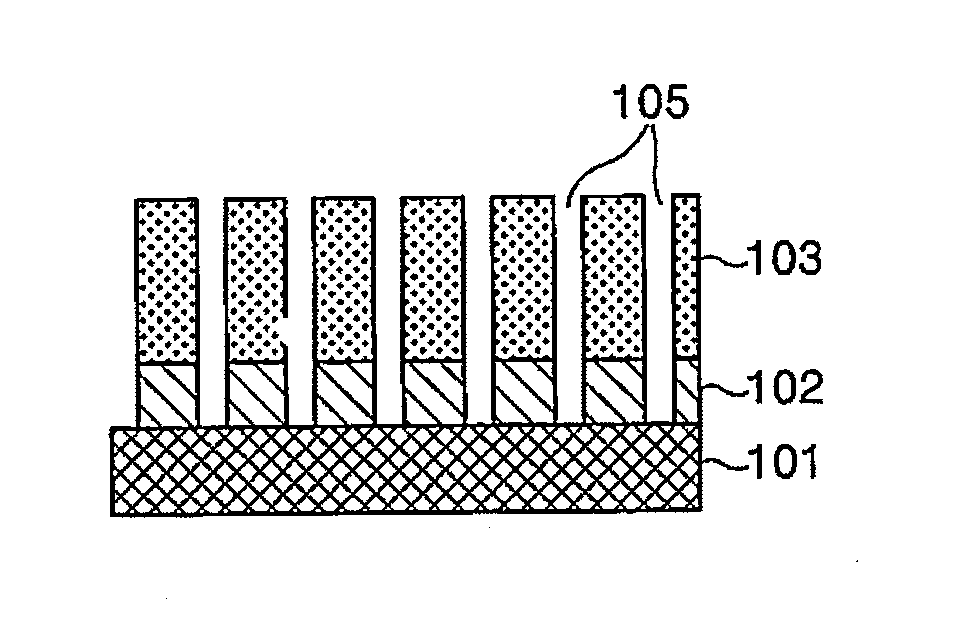
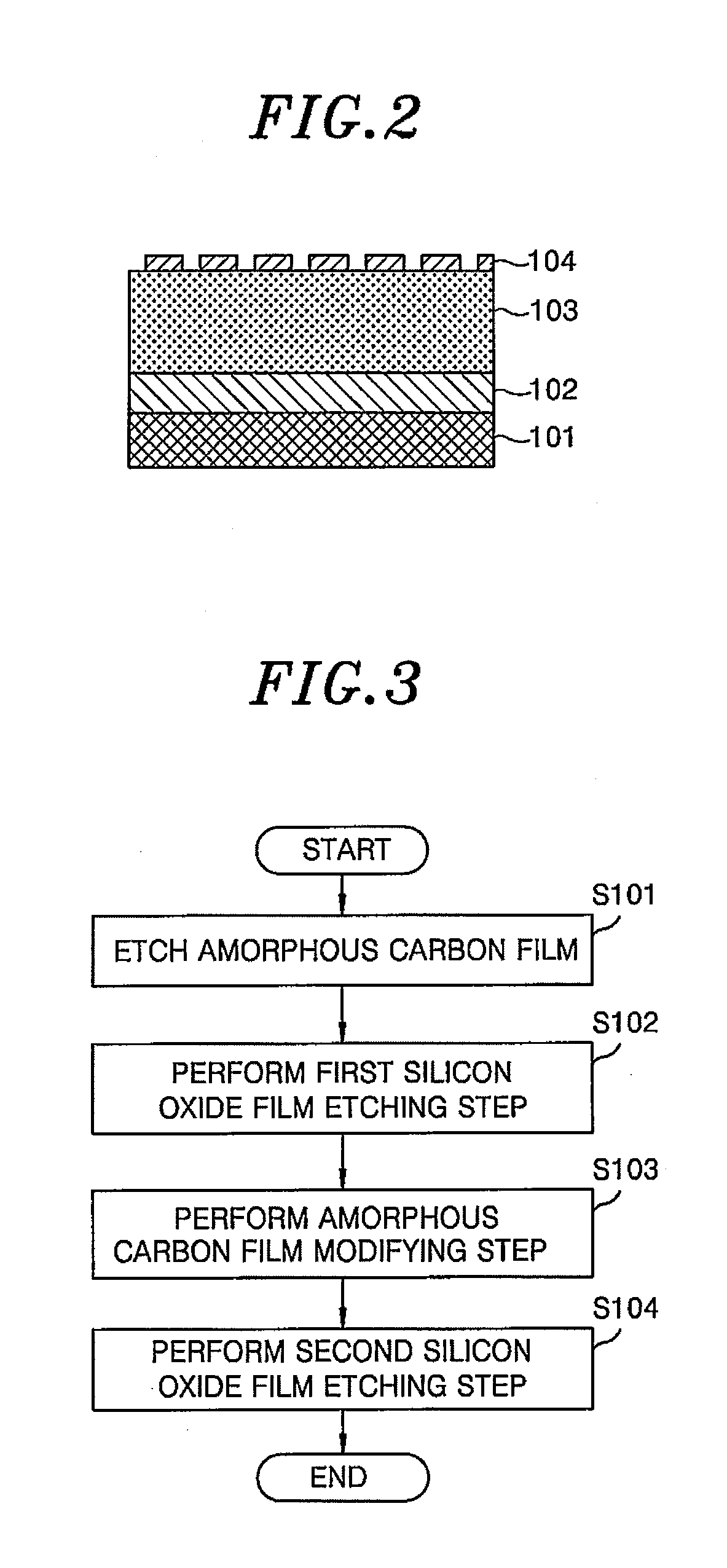
A plasma etching method includes etching an amorphous carbon film by a plasma of an oxygen-containing gas using, as a mask, an SiON film having a predetermined pattern formed on a target object, etching a silicon oxide film by a plasma of a processing gas using the amorphous carbon film as a mask while removing the SiON film remaining on the etched amorphous carbon film by the plasma of the processing gas. The plasma etching method further includes modifying the amorphous carbon film by a plasma of a sulfur-containing gas or a hydrogen-containing gas while applying a negative DC voltage to an upper electrode containing silicon after the SiON film is removed from the amorphous carbon film, and etching the silicon oxide film again by the plasma of the processing gas using the modified amorphous carbon film as a mask.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method of forming amorphous carbon film and method of manufacturing semiconductor device using the same
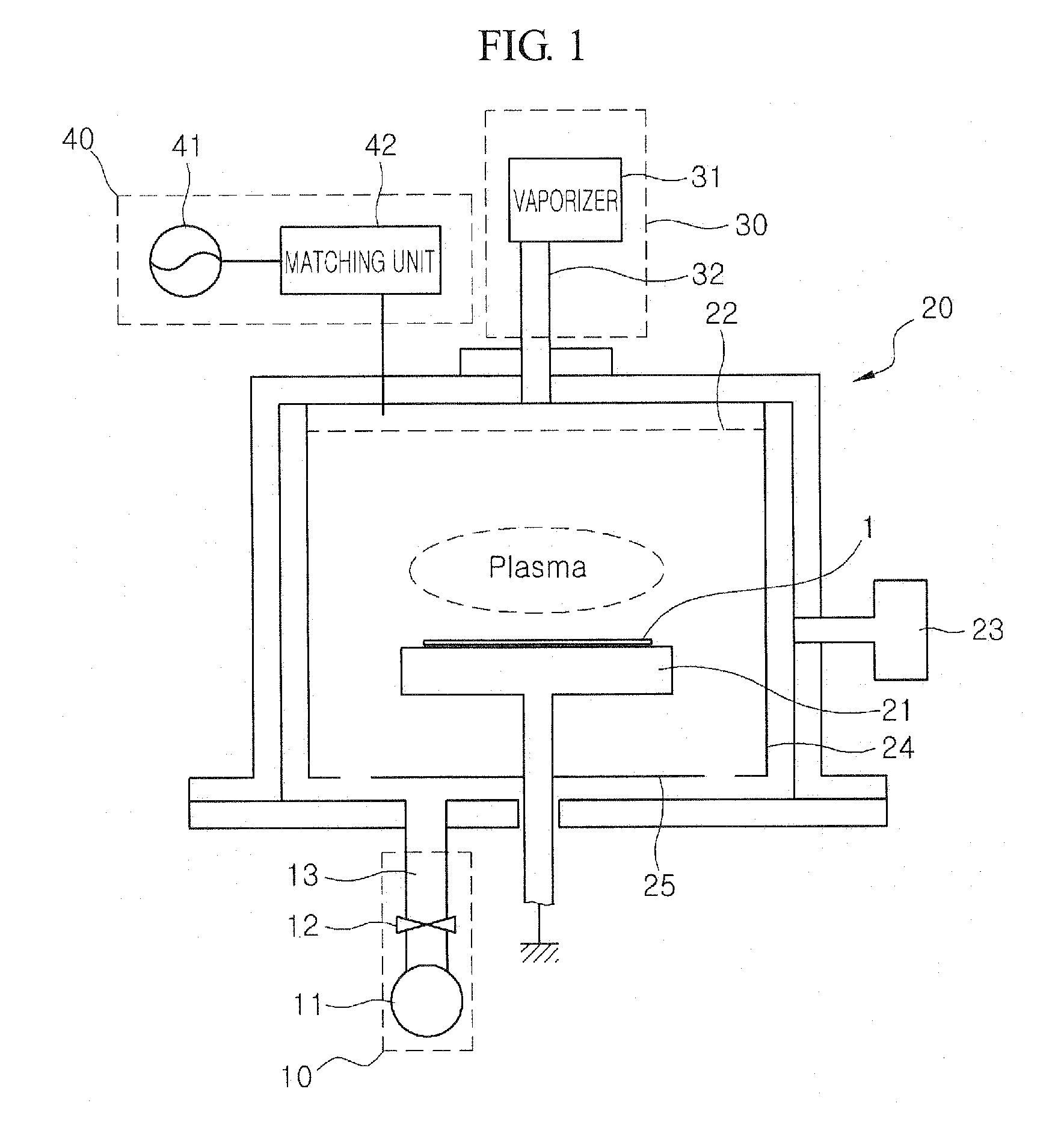
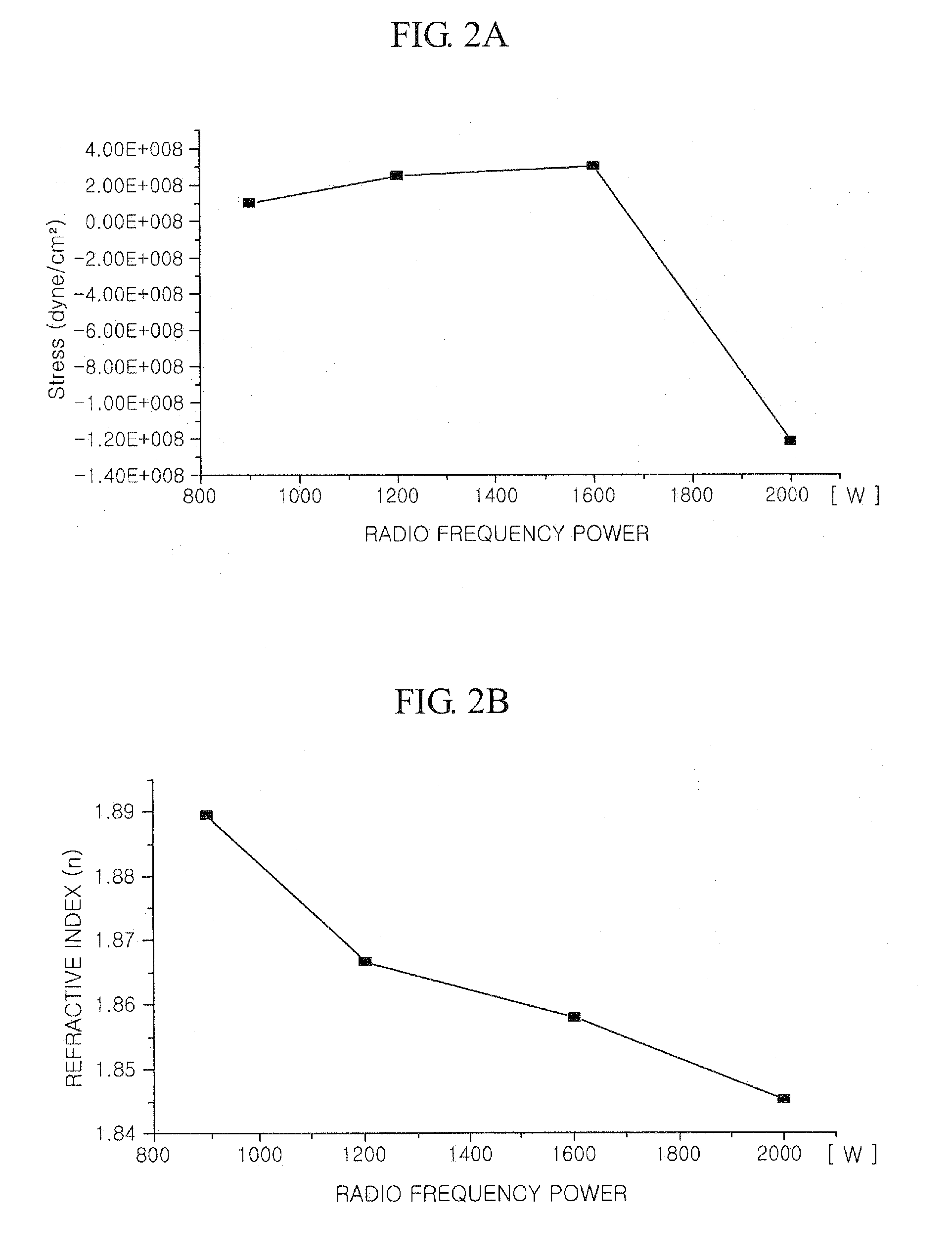
InactiveUS20080293248A1Better controllableLight absorption coefficient is lowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRefractive indexDiffuse reflection
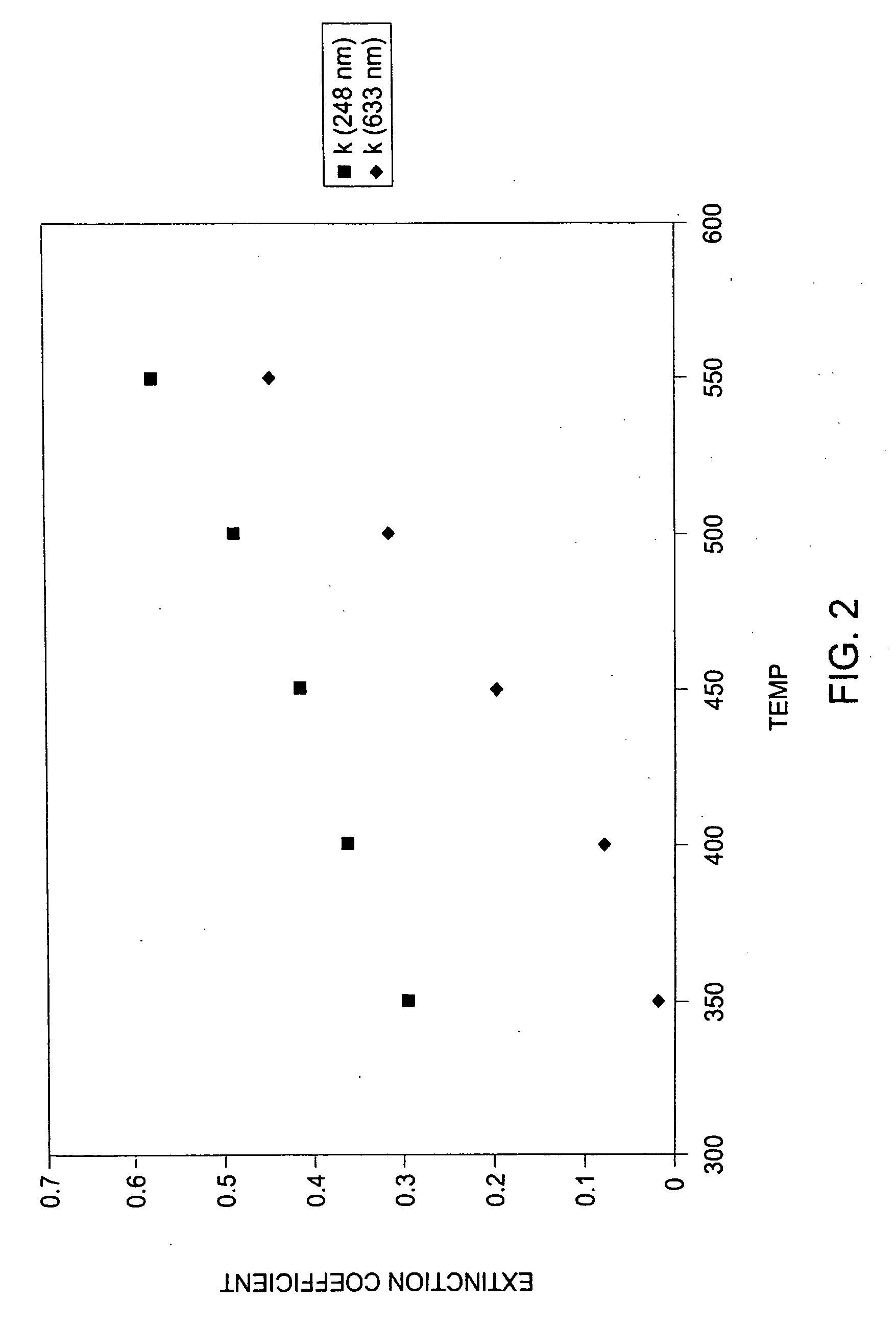
The present invention relates to a method of forming an amorphous carbon film and a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device using the method. An amorphous carbon film is formed on a substrate by vaporizing a liquid hydrocarbon compound, which has chain structure and one double bond, and supplying the compound to a chamber, and ionizing the compound. The amorphous carbon film is used as a hard mask film.It is possible to easily control characteristics of the amorphous carbon film, such as a deposition rate, an etching selectivity, a refractive index (n), a light absorption coefficient (k) and stress, so as to satisfy user's requirements. In particular, it is possible to lower the refractive index (n) and the light absorption coefficient (k). As a result, it is possible to perform a photolithography process without an antireflection film that prevents the diffuse reflection of a lower material layer.Further, a small amount of reaction by-product is generated during a deposition process, and it is possible to easily remove reaction by-products that are attached on the inner wall of a chamber. For this reason, it is possible to increase a cycle of a process for cleaning a chamber, and to increase parts changing cycles of a chamber. As a result, it is possible to save time and cost.
Owner:TES CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com