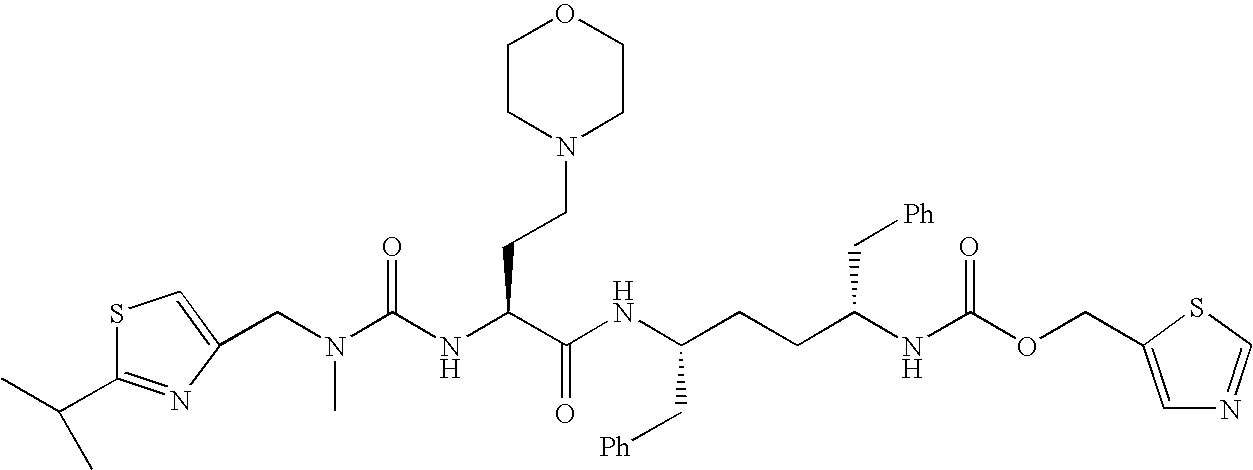
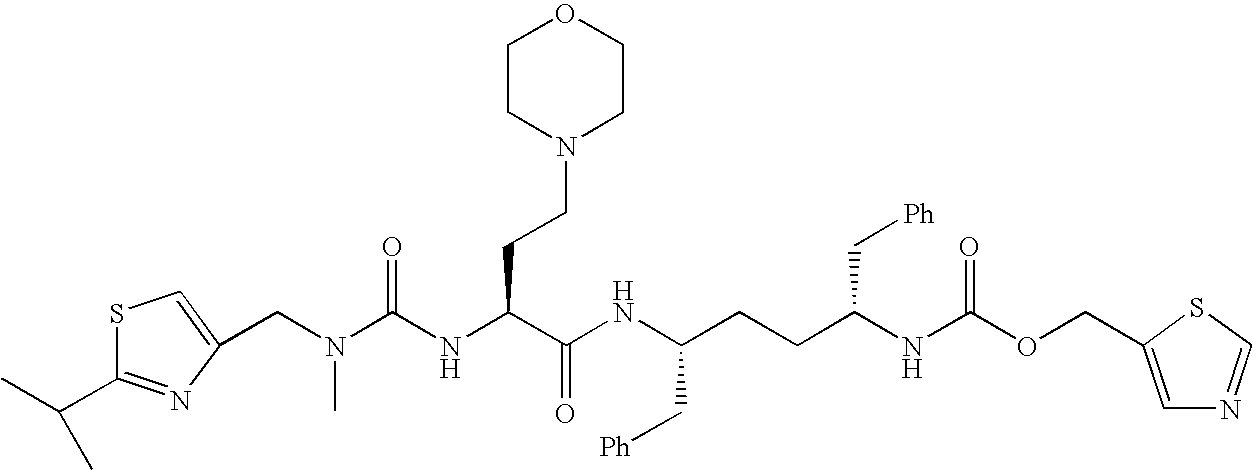
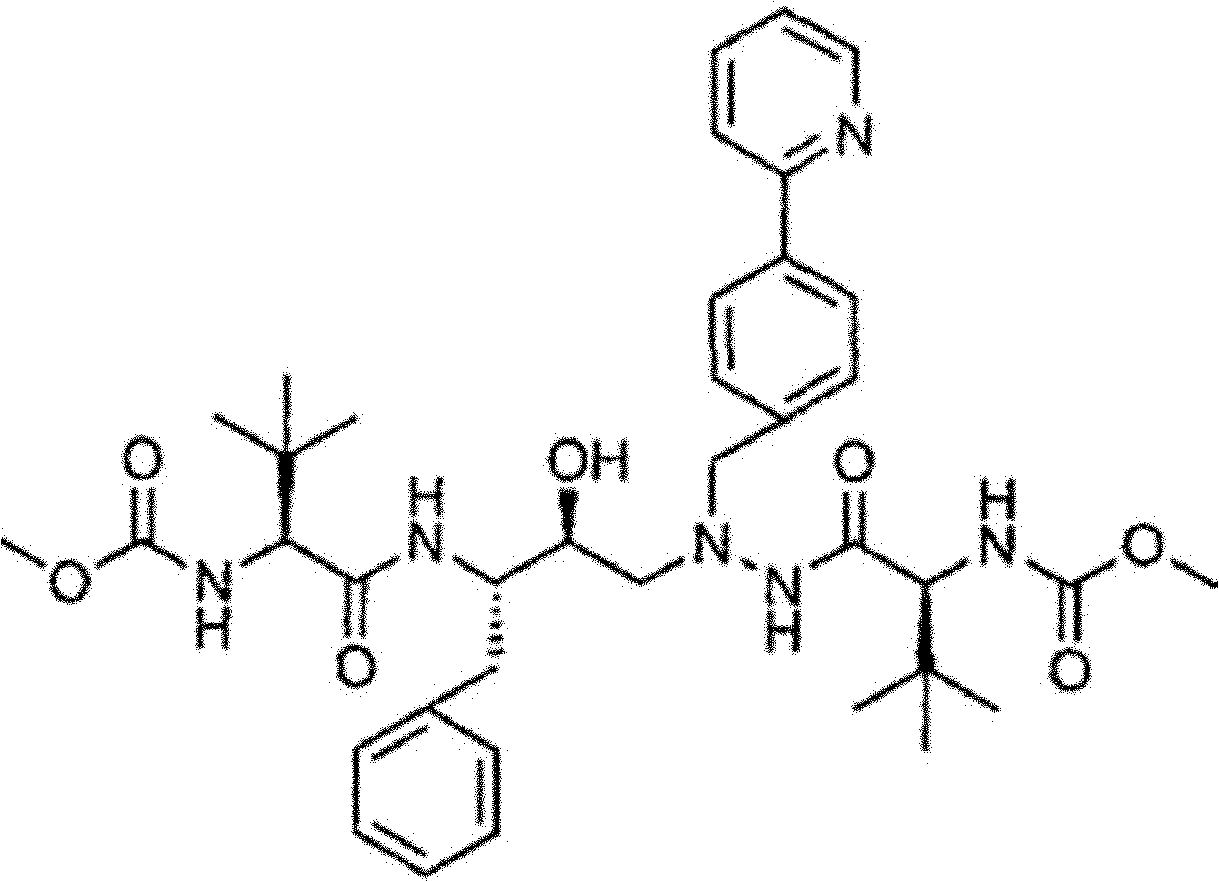
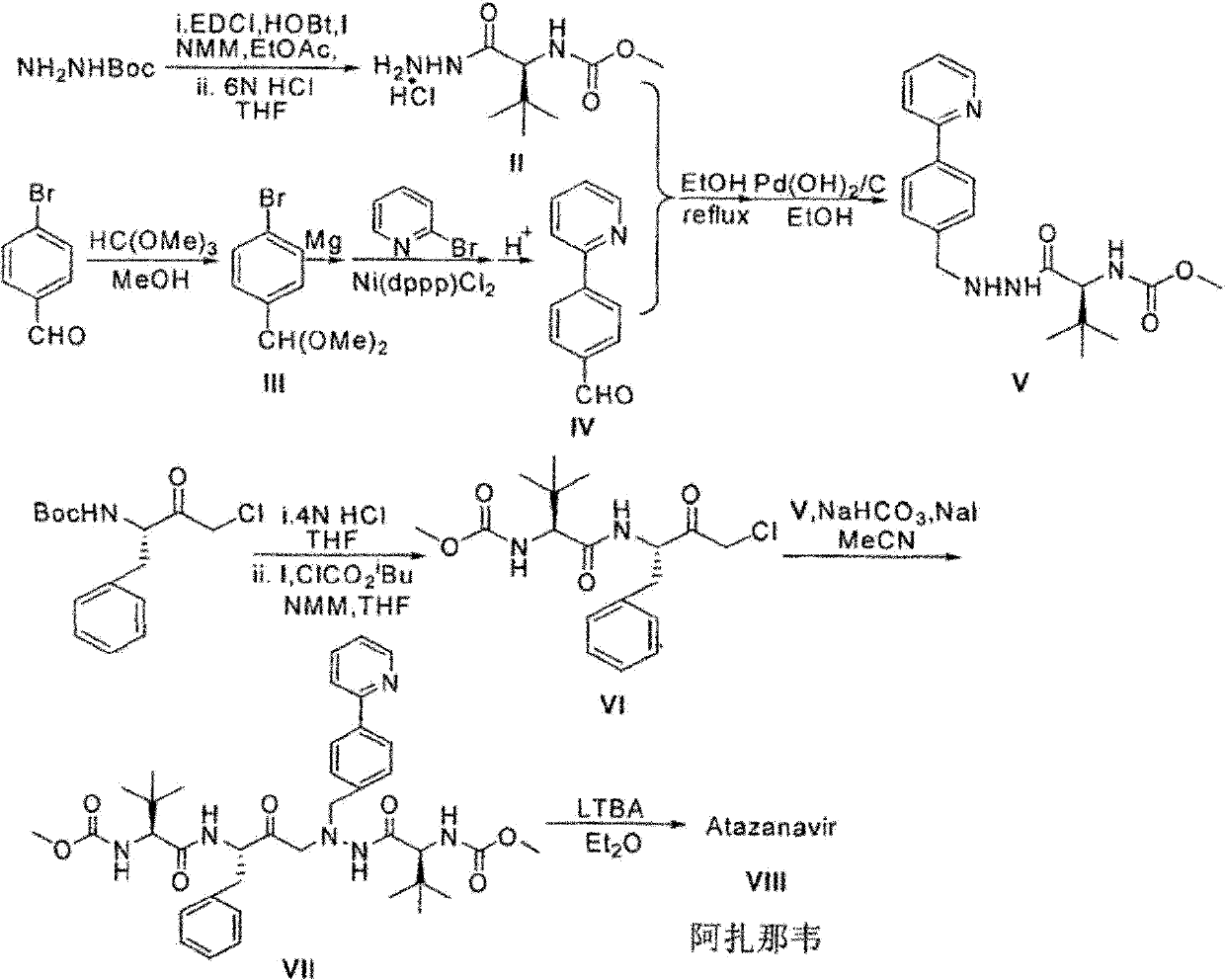
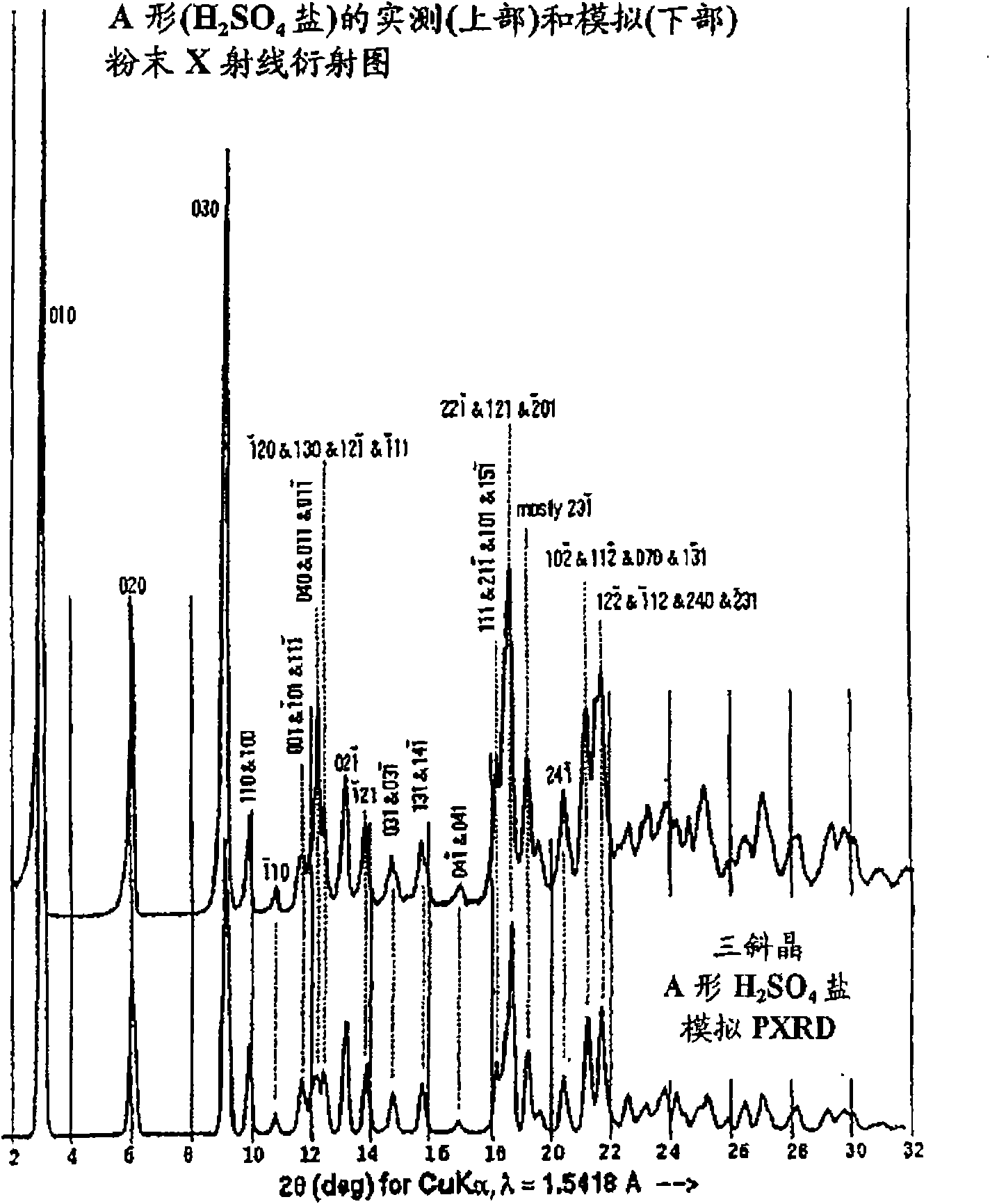
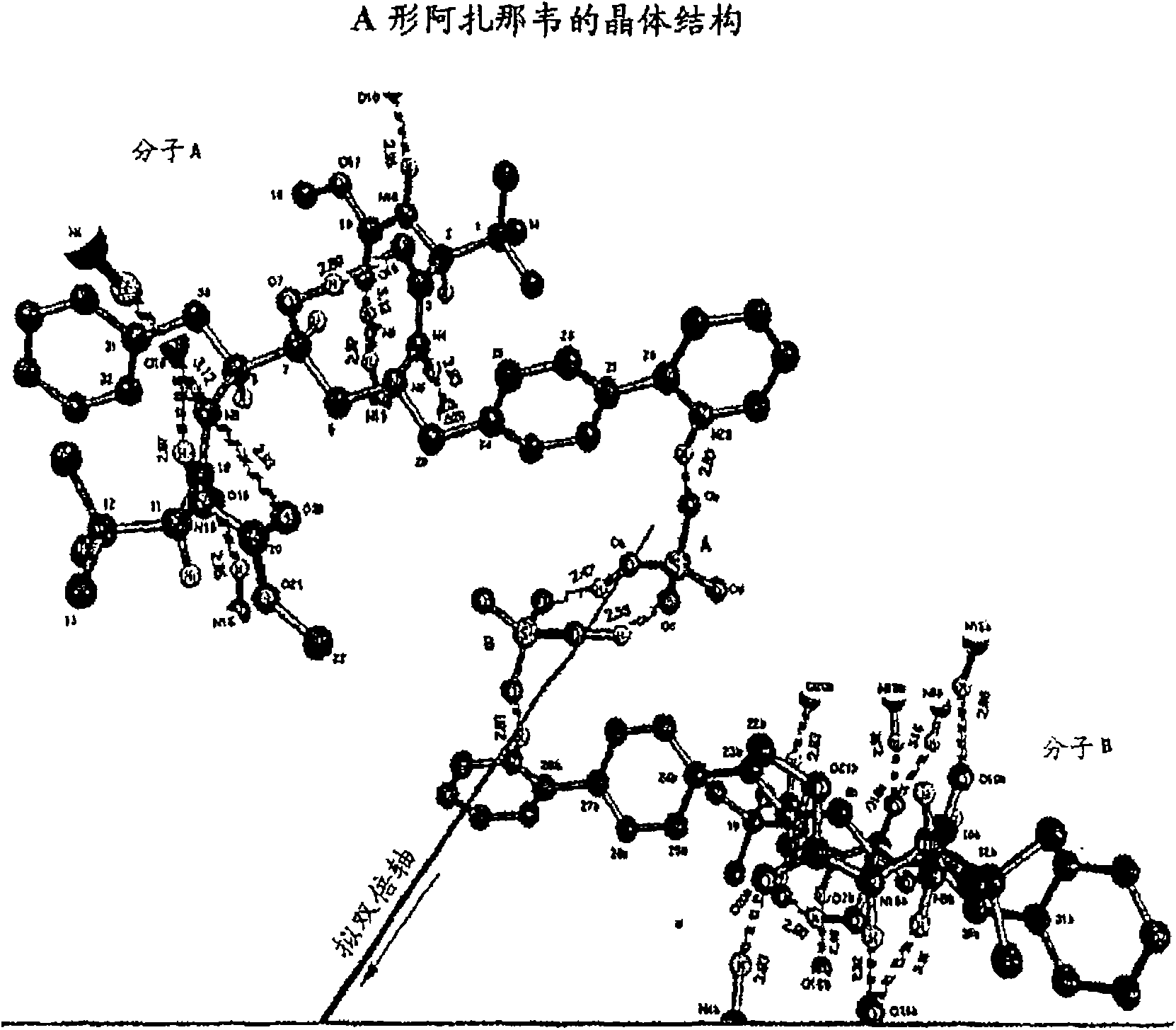
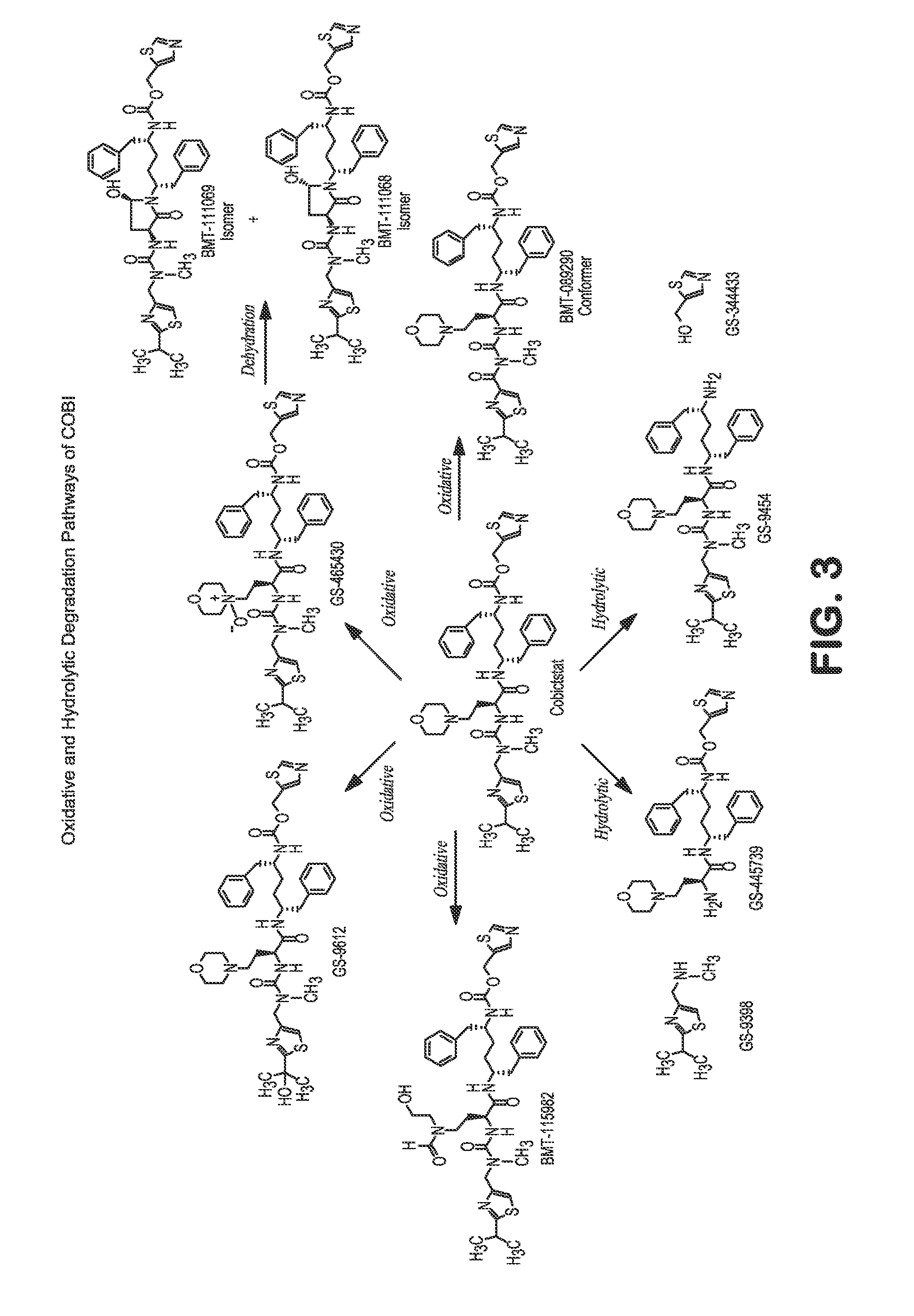
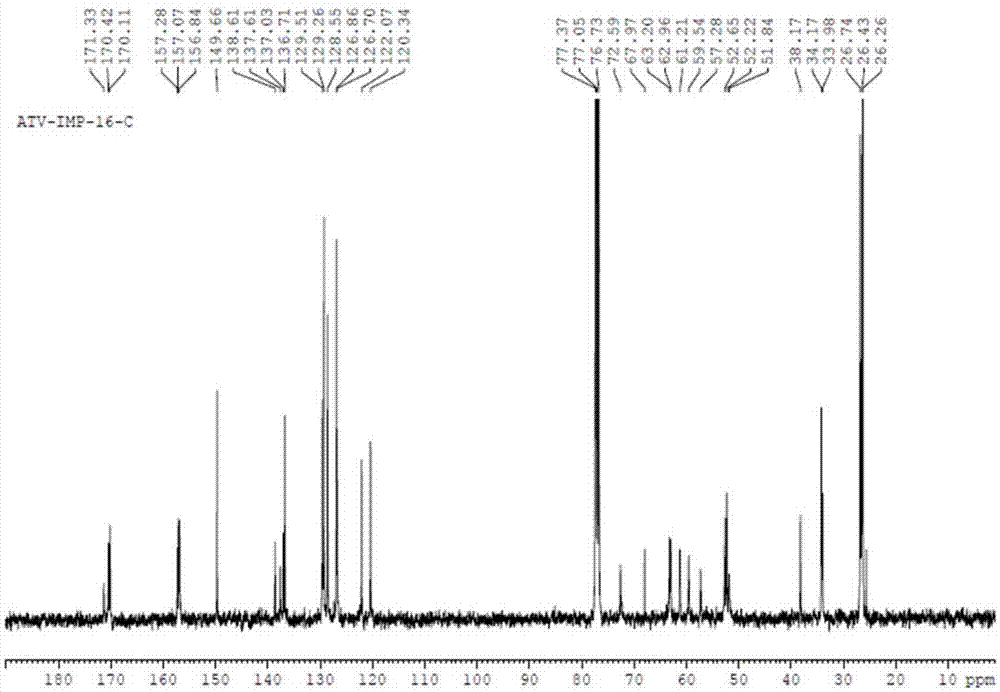
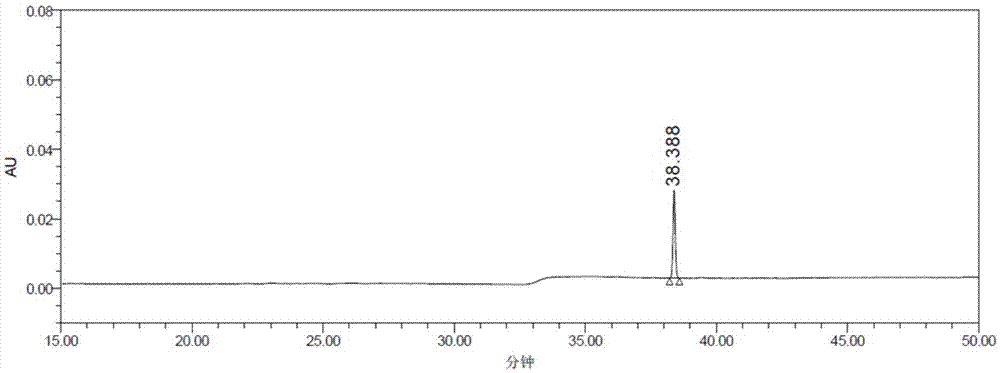
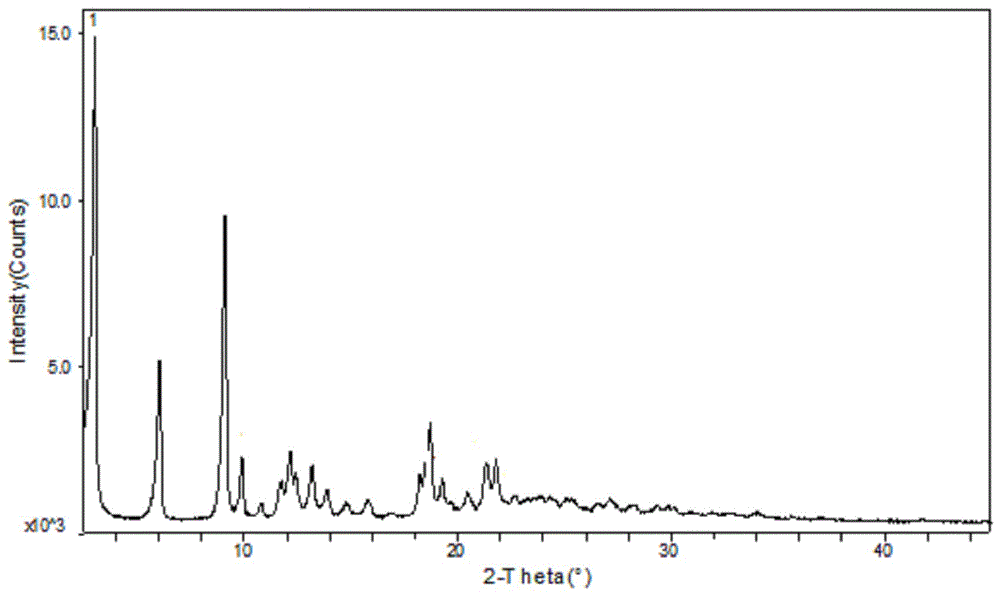
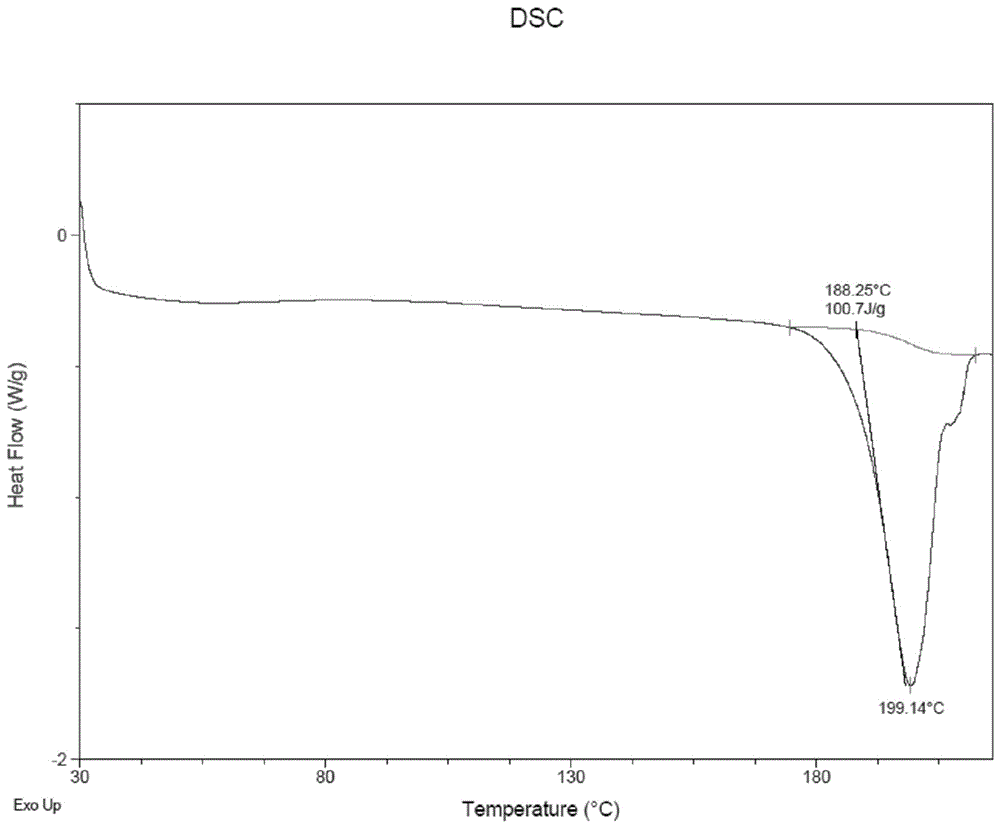
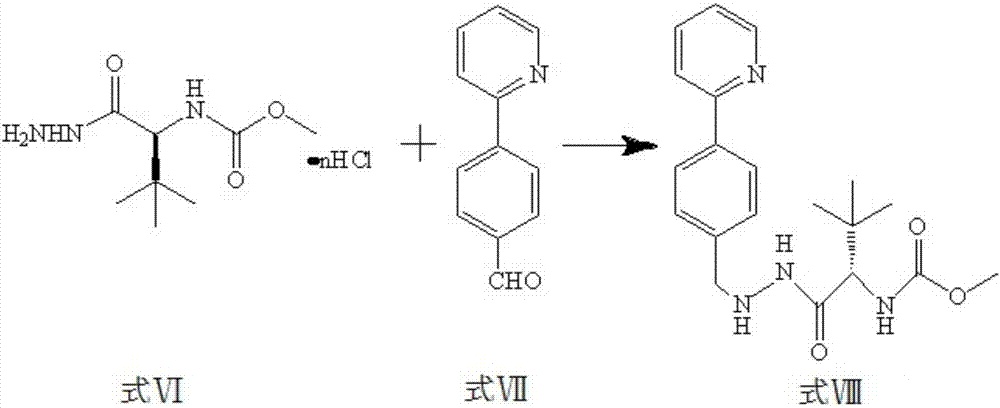
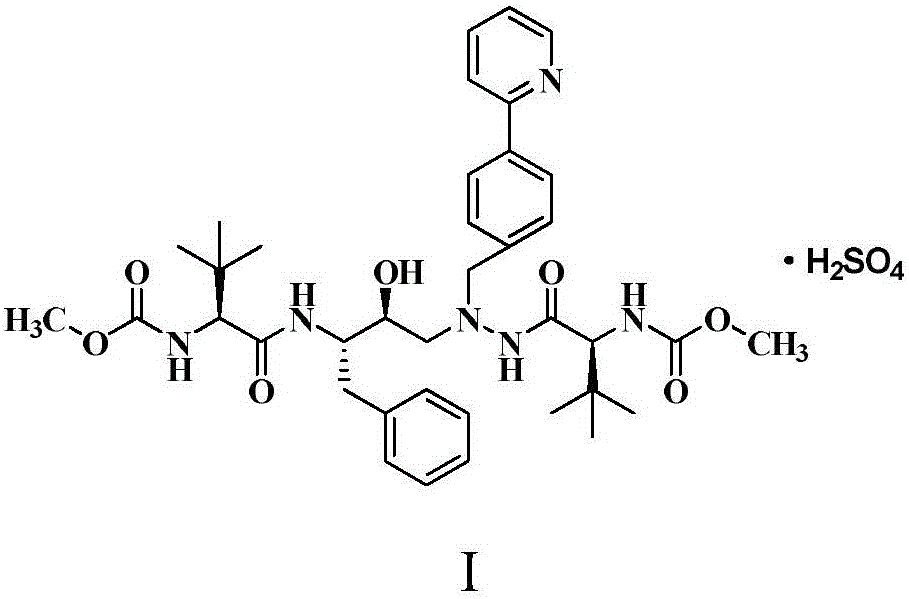
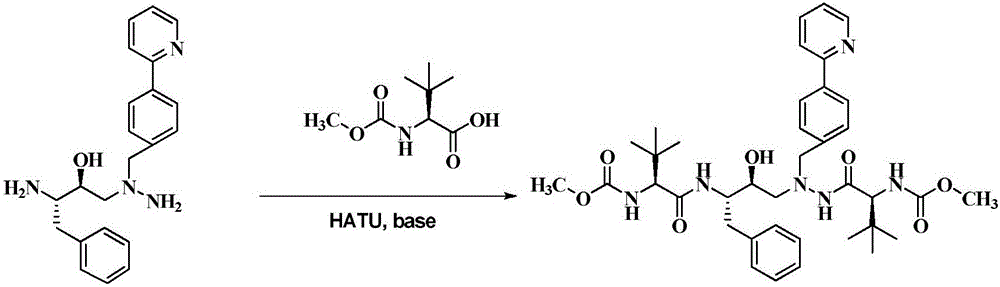
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
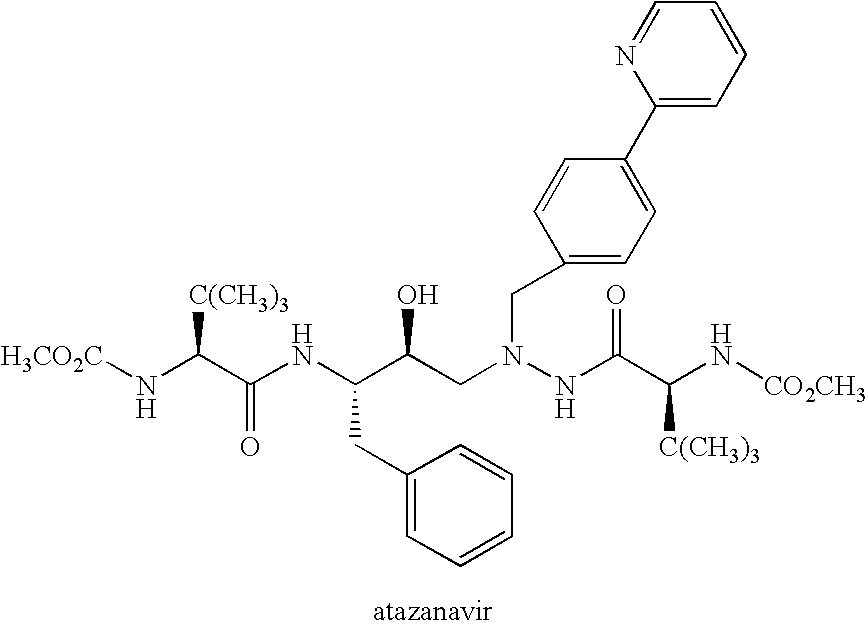
55 results about "Atazanavir" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
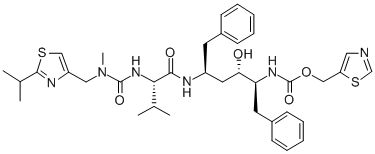
This drug is used with other HIV medications to help control HIV infection.
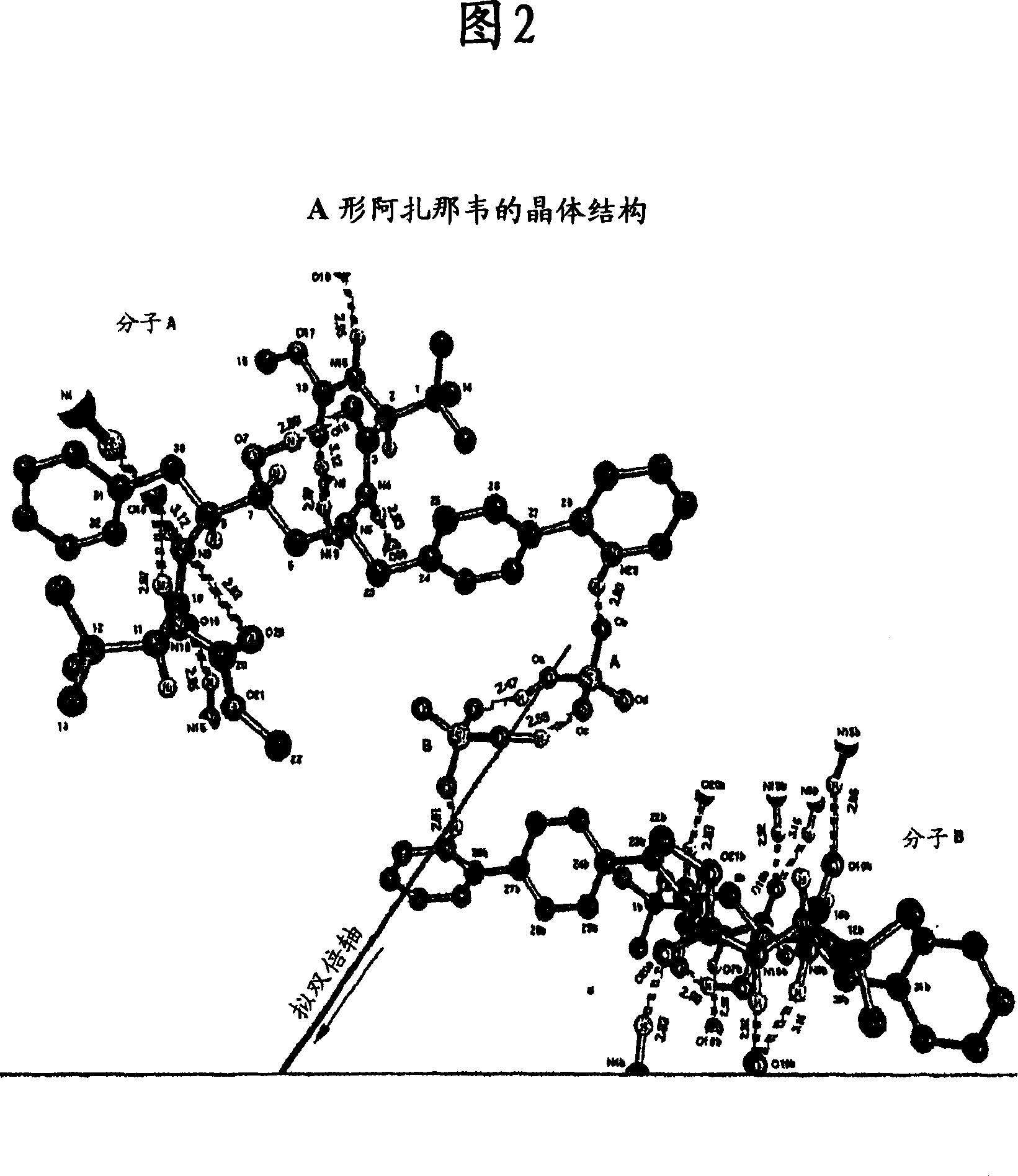
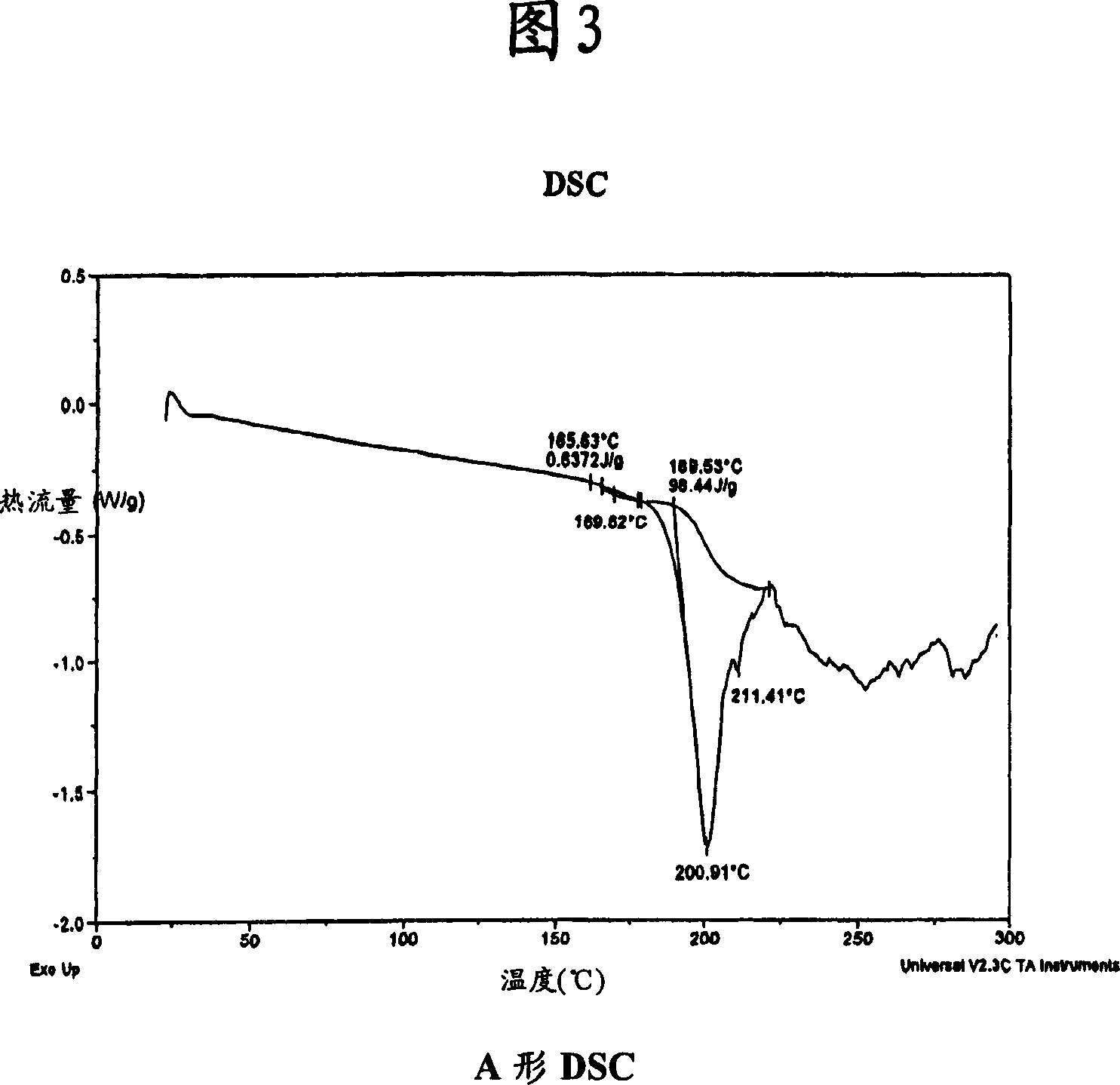
Process for preparing atazanavir bisulfate and novel forms
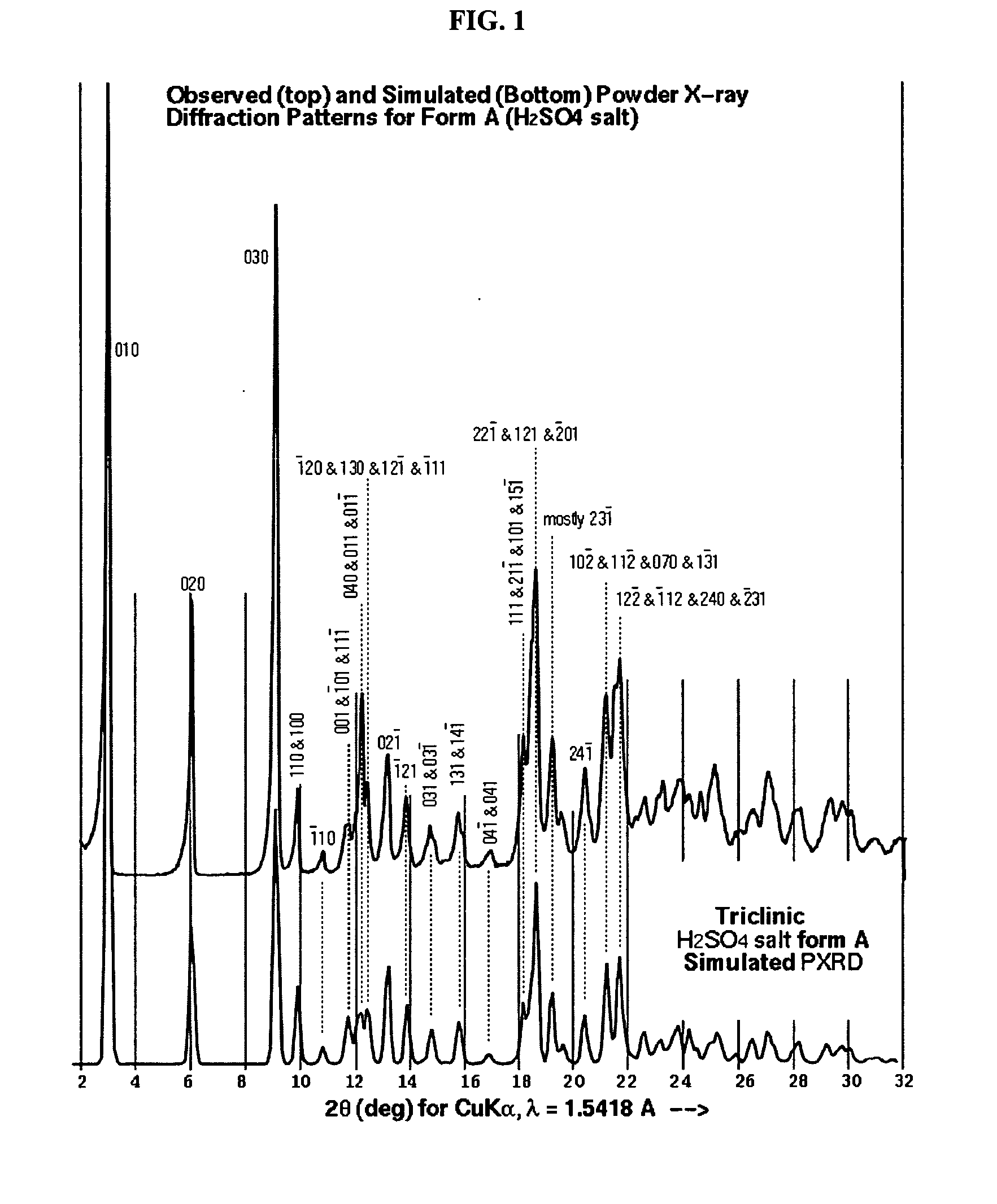
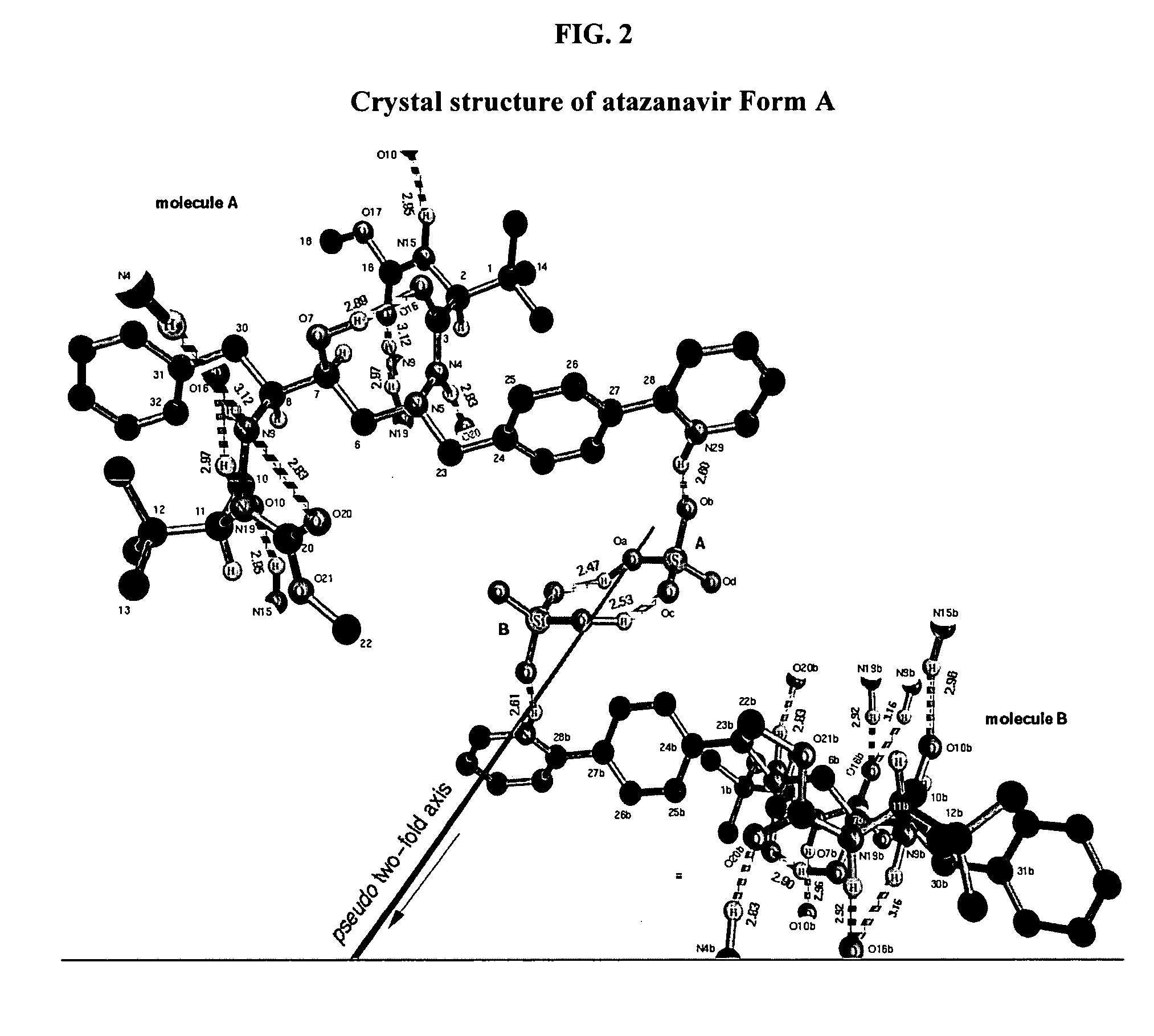
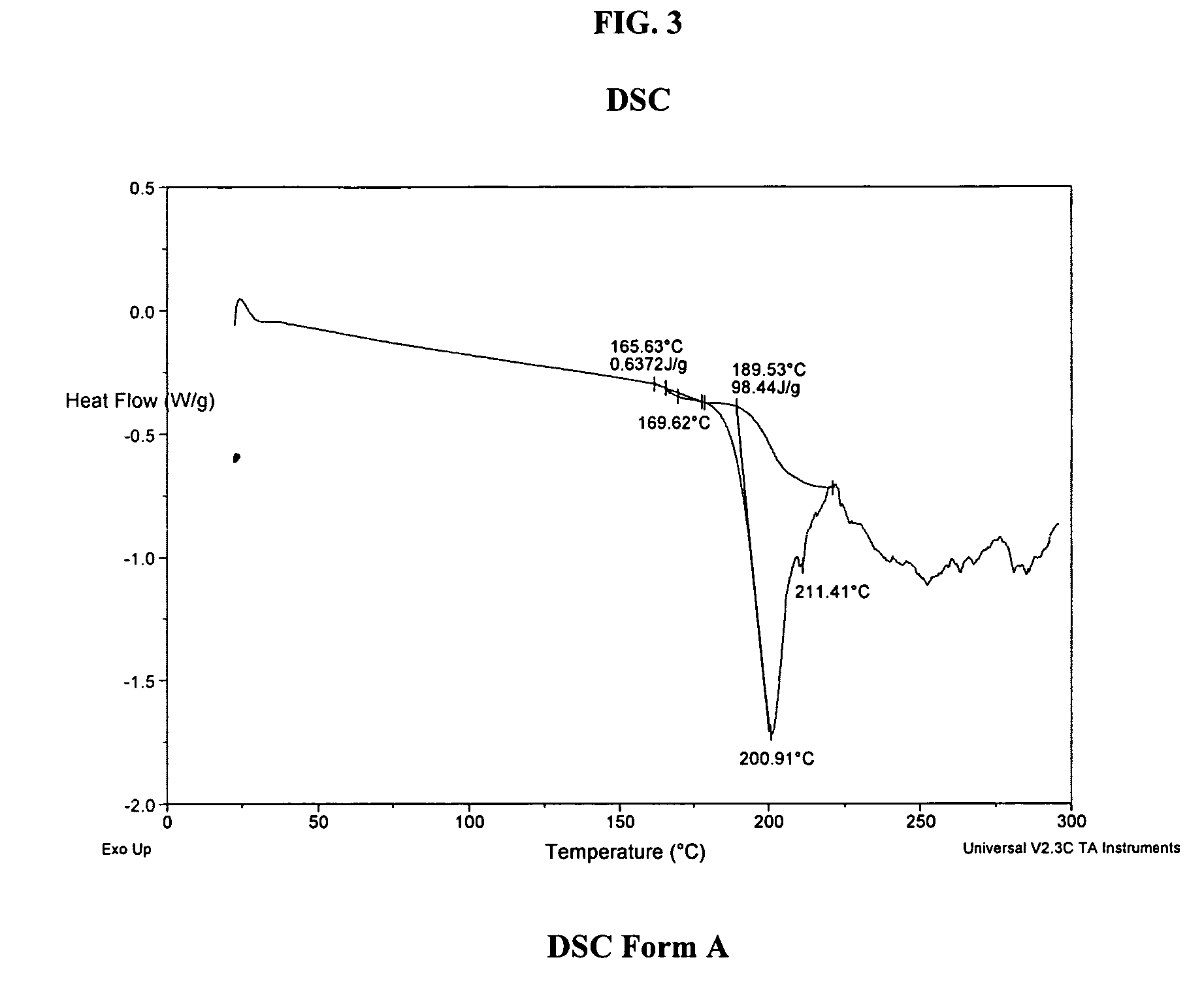
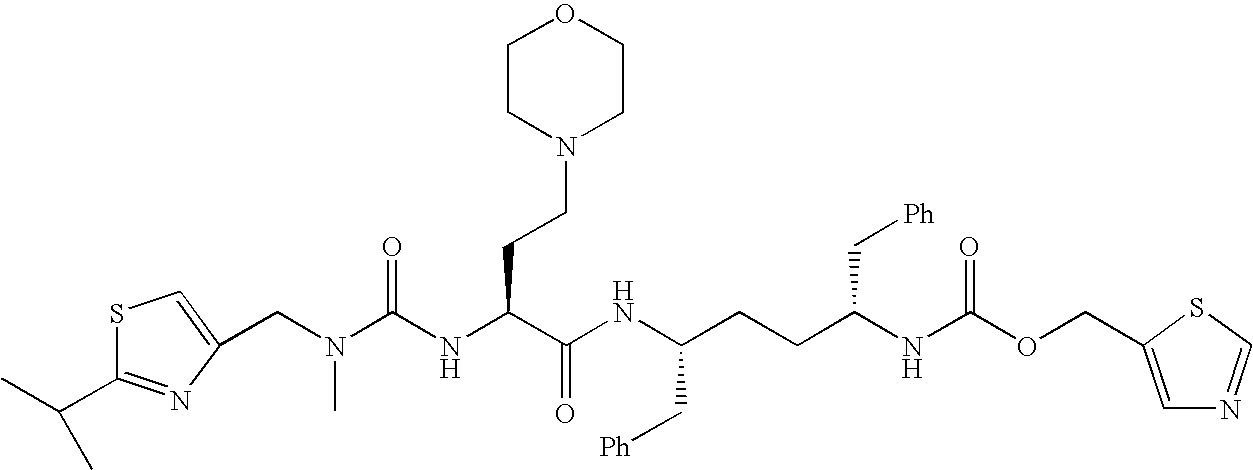
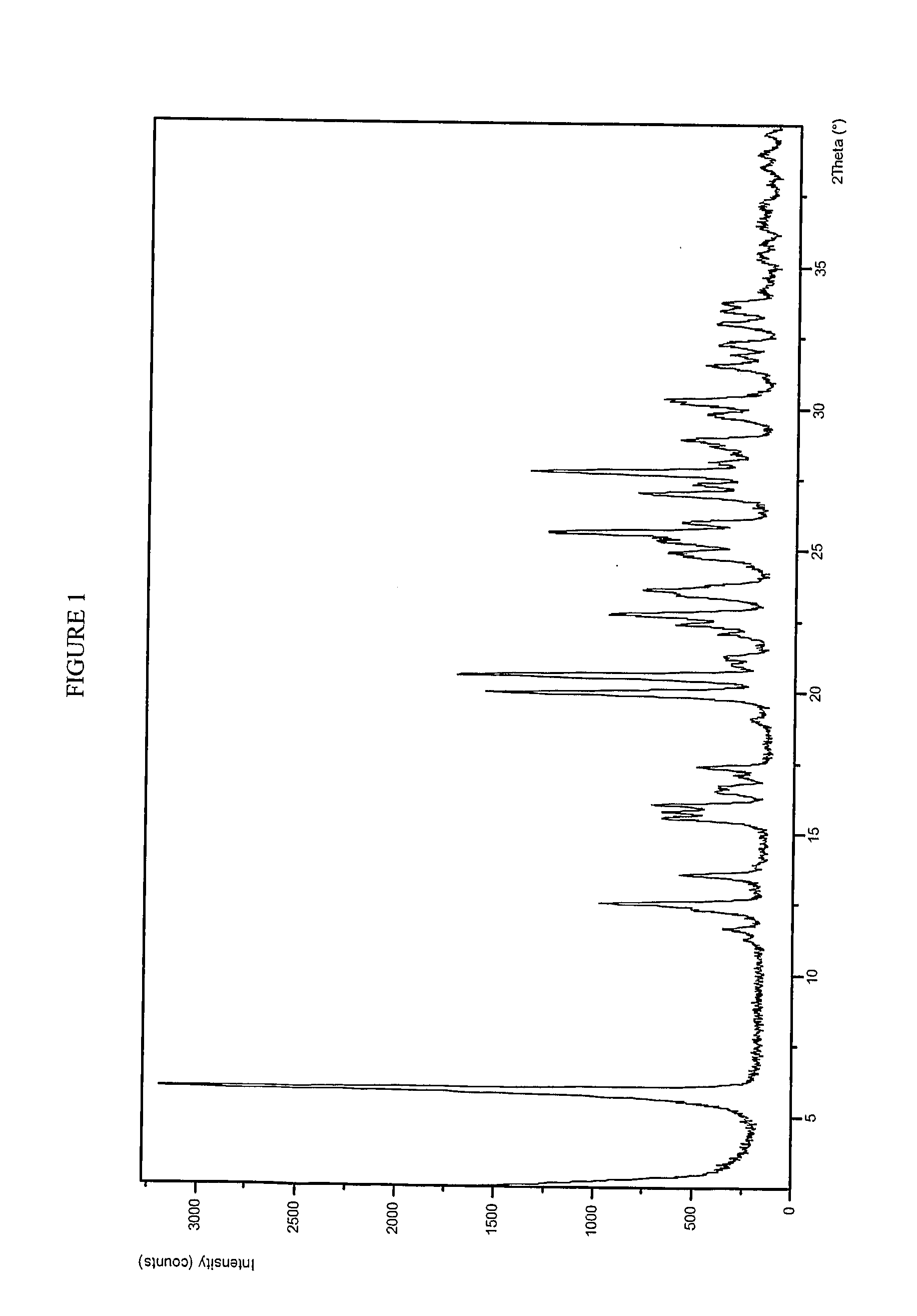
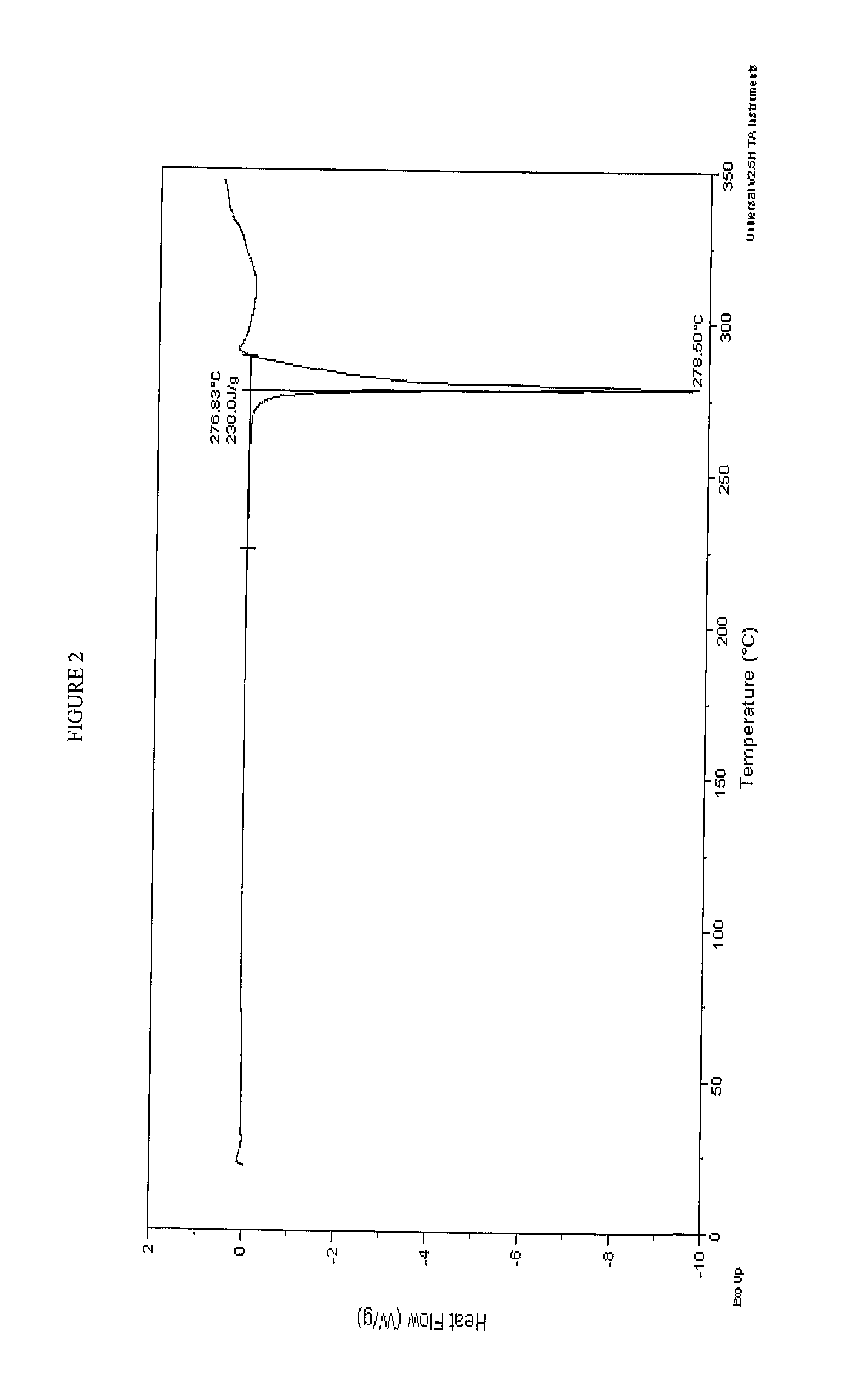
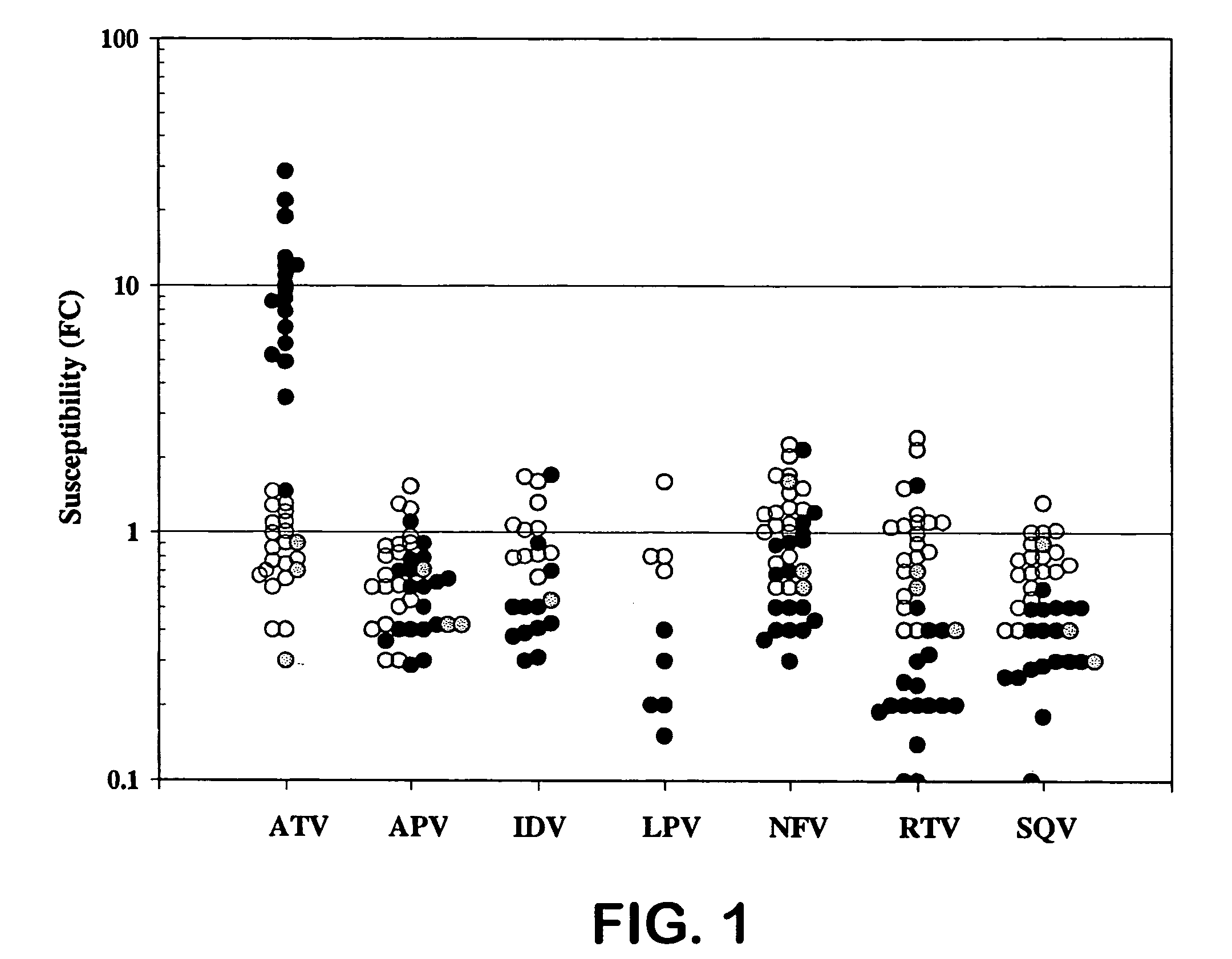
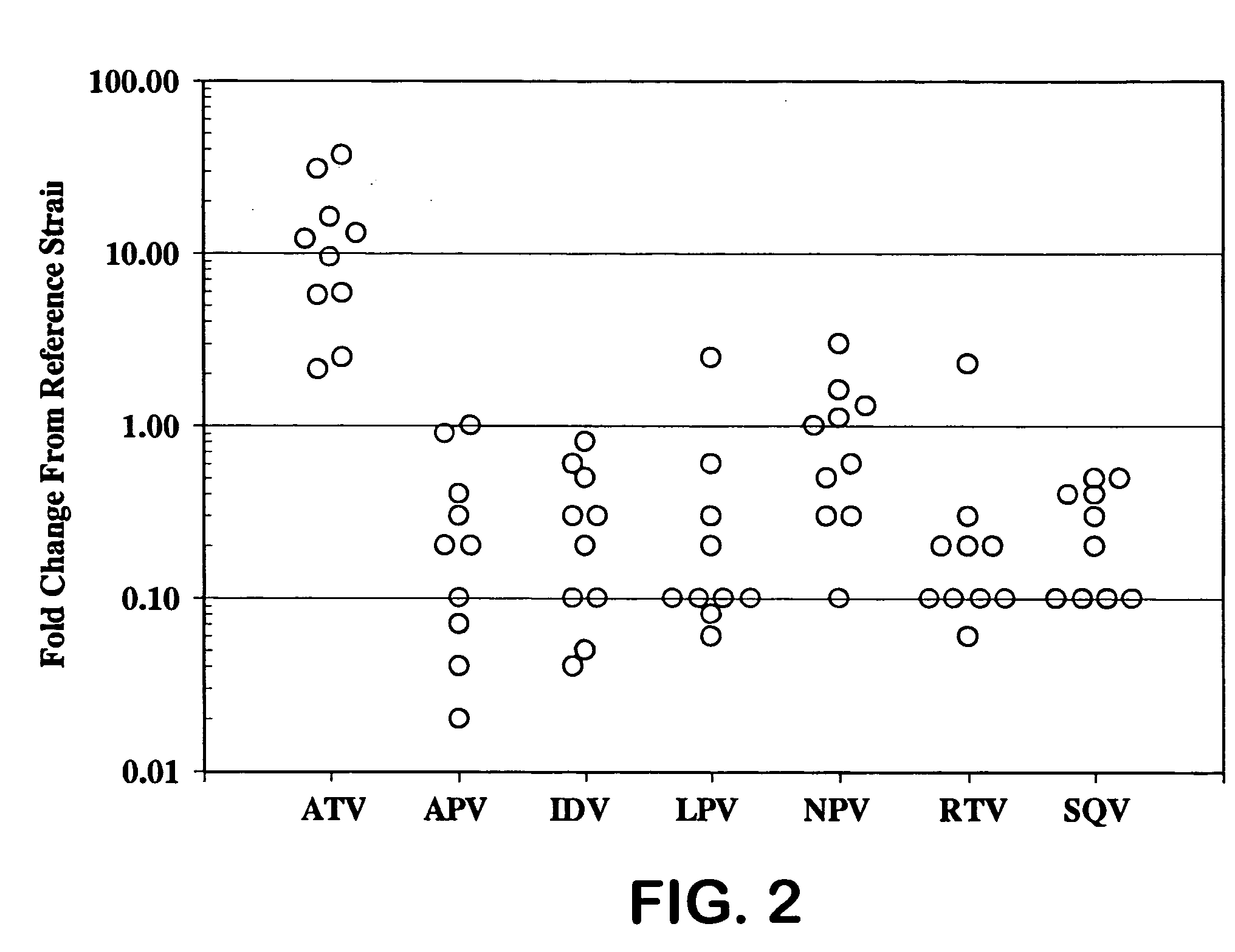
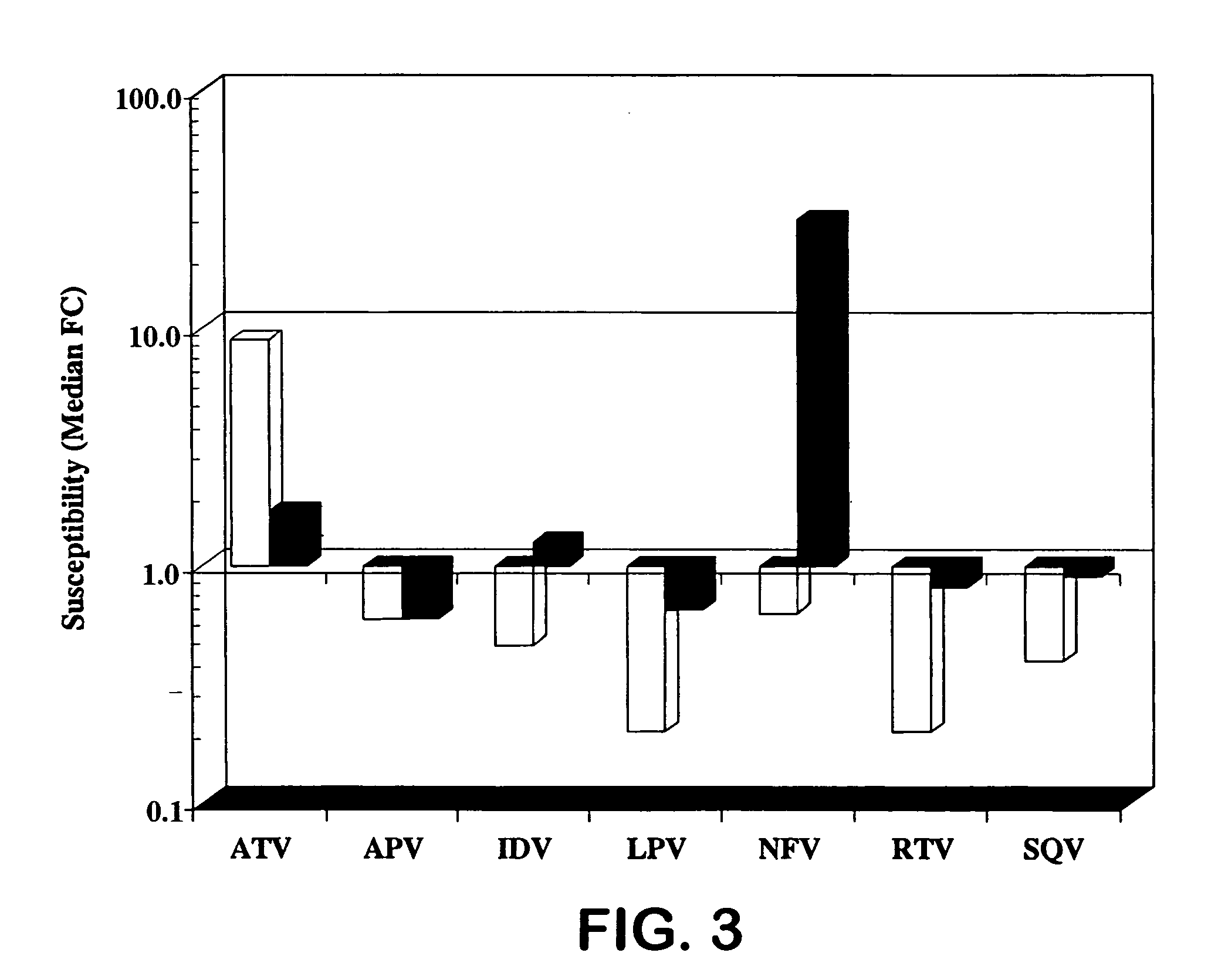
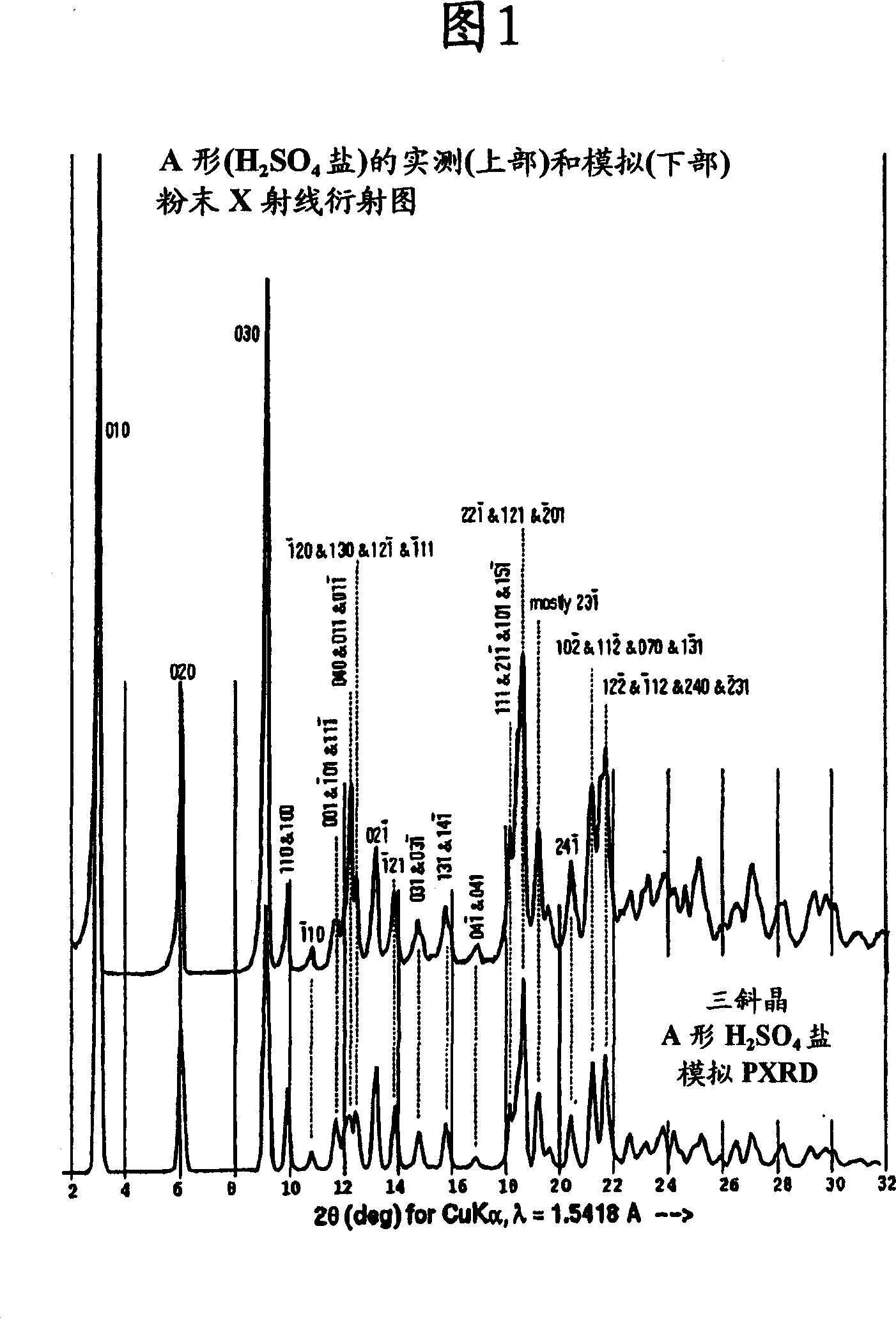
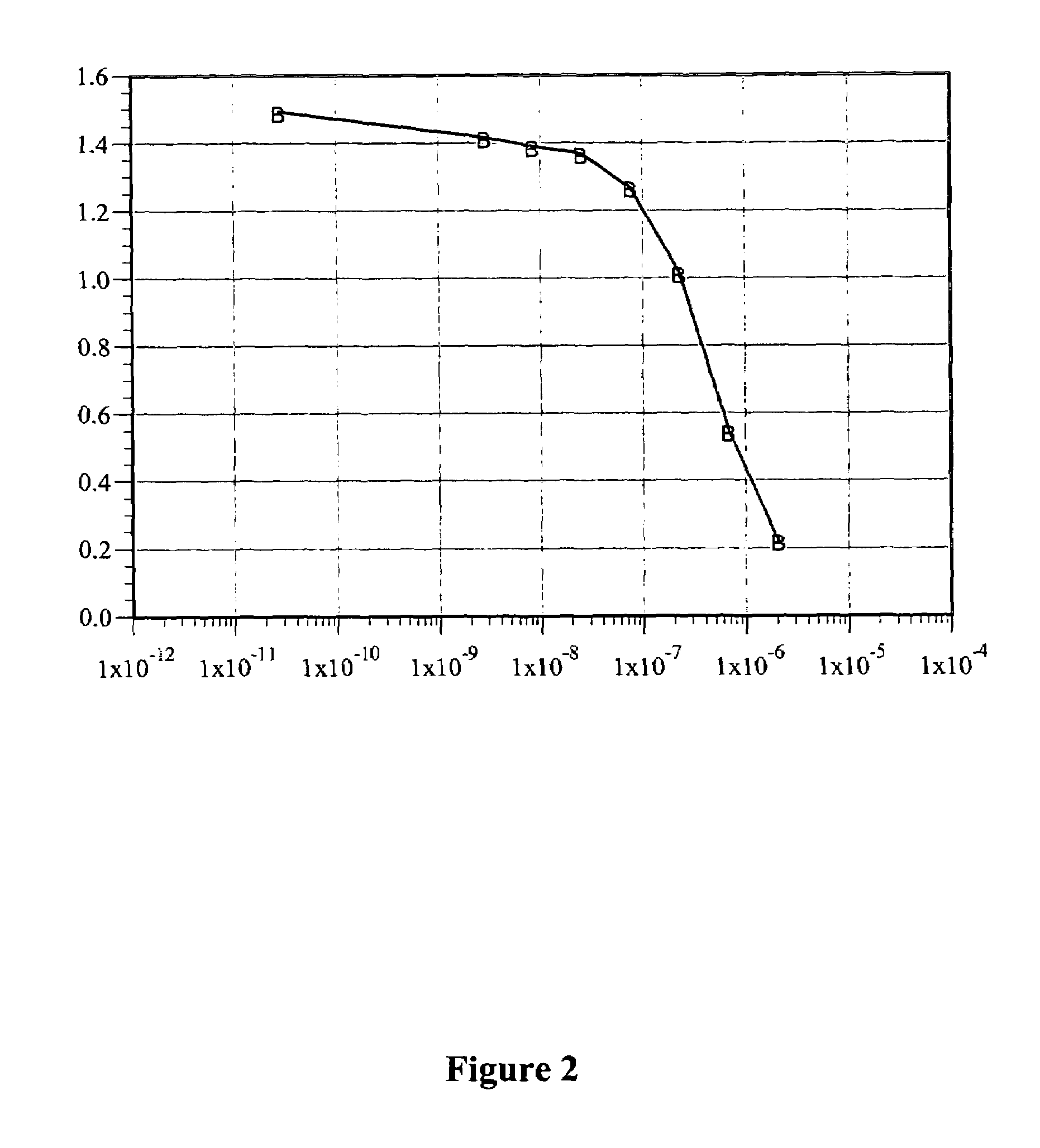
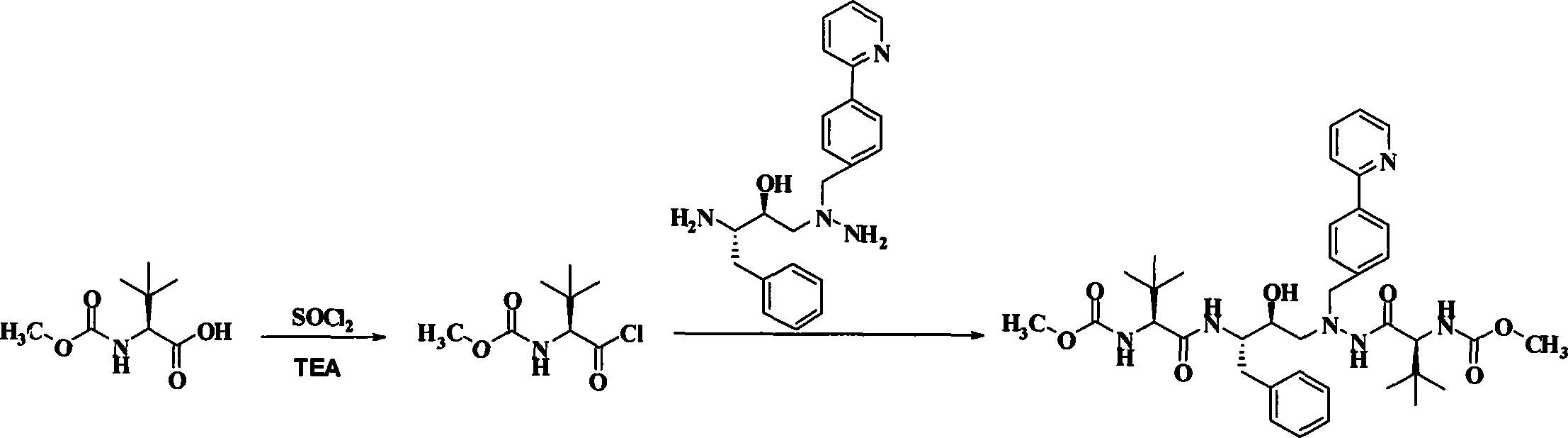
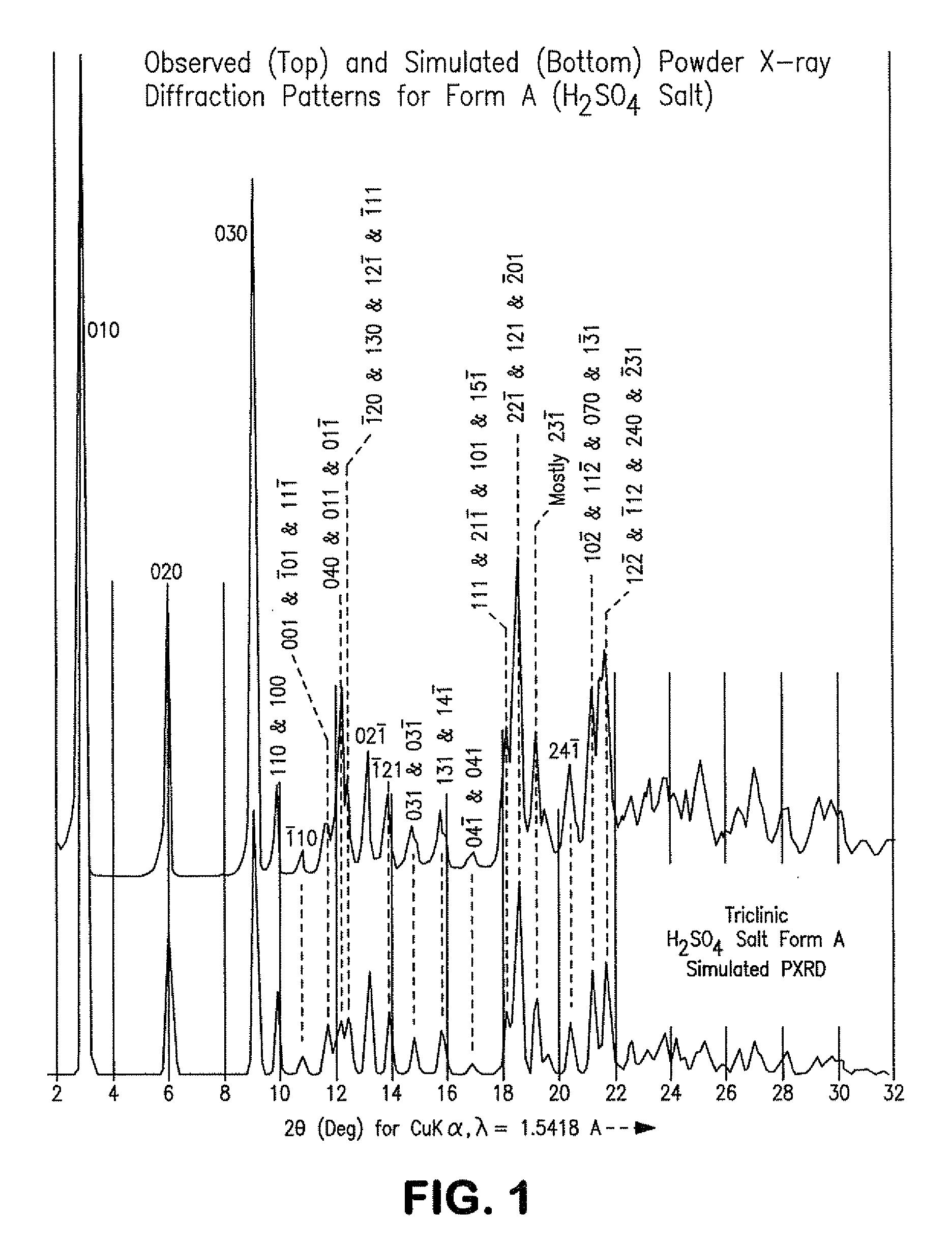
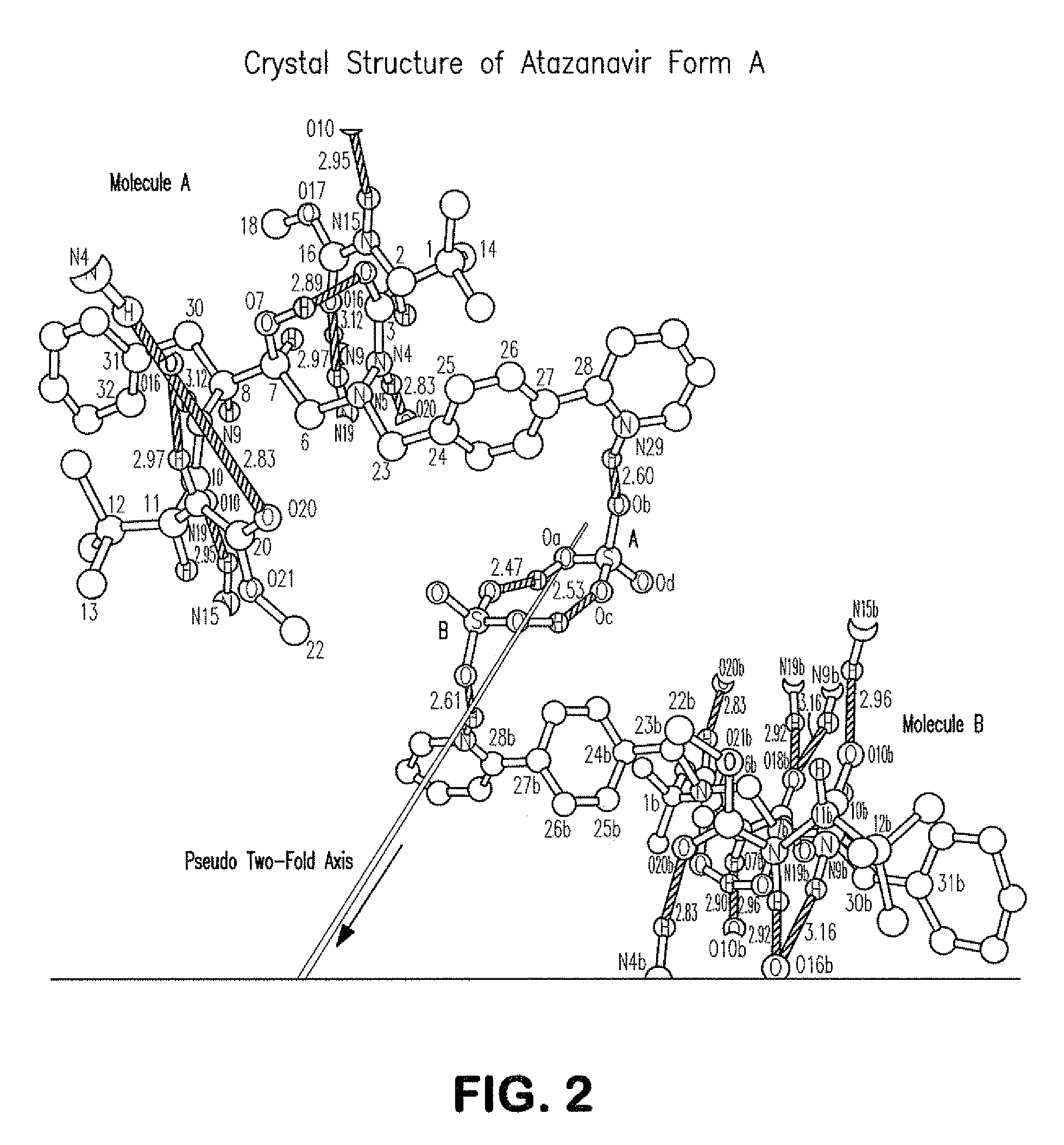
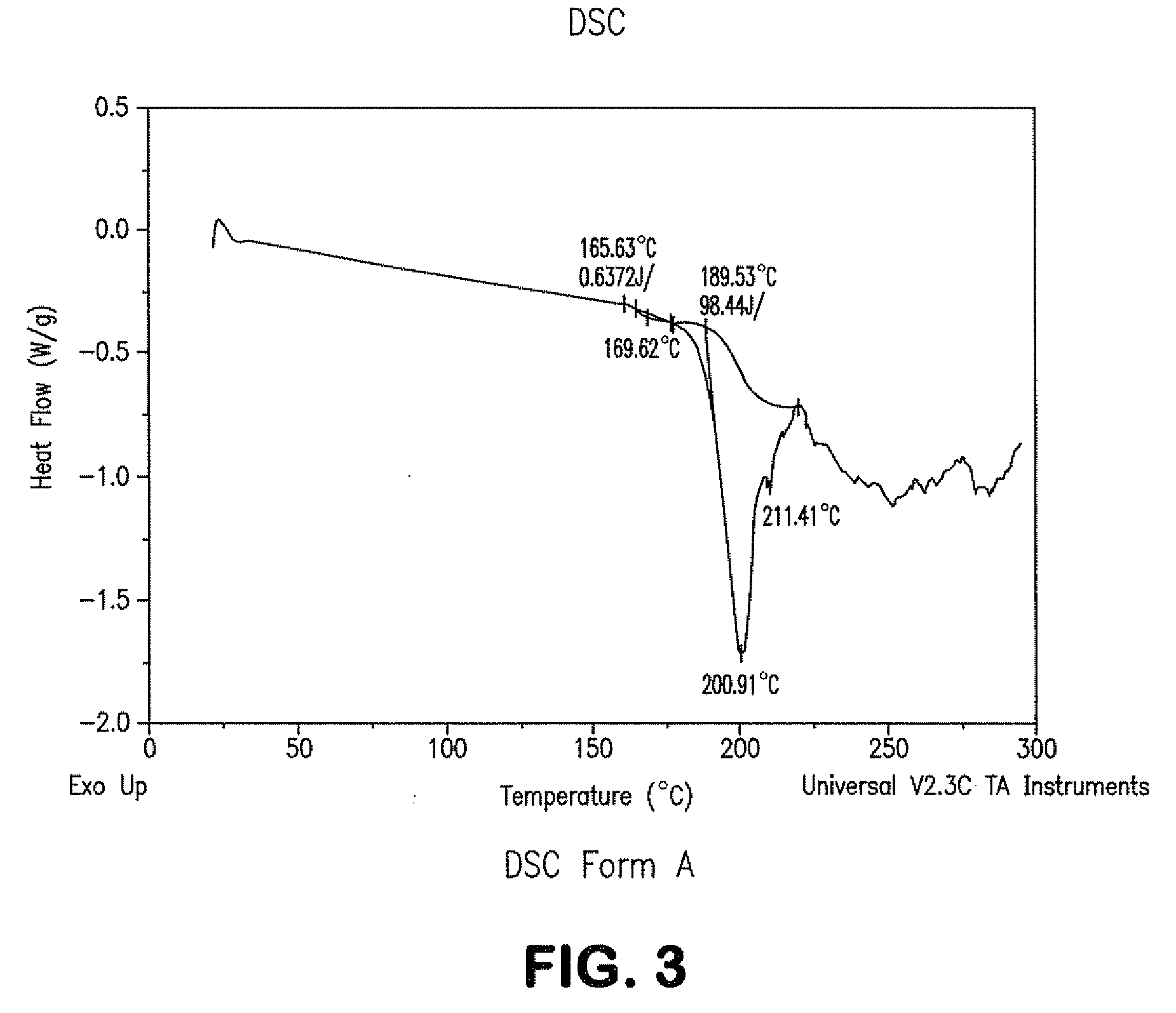
A process is provided for preparing the HIV protease inhibitor atazanavir bisulfate wherein a solution of atazanavir free base is reacted with concentrated sulfuric acid in an amount to react with less than about 15% by weight of the free base, seeds of Form A crystals of atazanavir bisulfate are added to the reaction mixture, and as crystals of the bisulfate form, additional concentrated sulfuric acid is added in multiple stages at increasing rates according to a cubic equation, to effect formation of Form A crystals of atazanavir bisulfate. A process is also provided for preparing atazanavir bisulfate as Pattern C material. A novel form of atazanavir bisulfate is also provided which is Form E3 which is a highly crystalline triethanolate solvate of the bisulfate salt from ethanol.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Therapeutic compositions and methods
InactiveUS20090093467A1Prolonged systemic exposureIncrease exposureBiocideAntiviralsCarboxylic acidViral infection
The invention includes methods, compositions, and kits useful for treating a viral infection by administering 6-(3-chloro-2-fluorobenzyl)-1-[(2S)-1-hydroxy-3-methylbutan-2-yl]-7-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, with atazanavir or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and optionally with a compound that inhibits cytochrome P-450, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Method for catalytically synthesizing atazanavir intermediate
ActiveCN104911224AImprove recycling ratesImprove regeneration efficiencyChemical industryFermentationTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting groupButanone
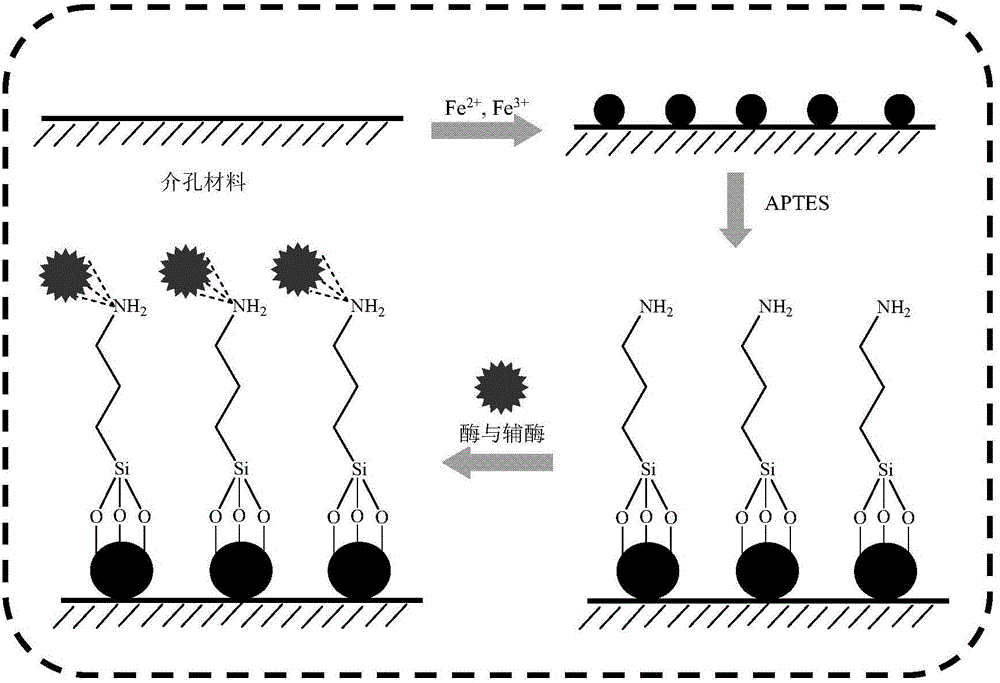
The invention discloses a method for catalytically synthesizing an atazanavir intermediate, which comprises the following steps: preparing a magnetic modified mesoporous material, co-immobilizing a carbonyl reduction enzyme and a coenzyme in the magnetic mesoporous material, and catalyzing (3S)-3-(tert-butyloxycarbonyl)amino-1-chloro-4-phenyl-(2R)-butanone by using the immobilized enzyme to generate the (3S)-3-(tert-butyloxycarbonyl)amino-1-chloro-4-phenyl-(2R)-butanol intermediate. The method has the advantages of high recovery rate of the carbonyl reduction enzyme and coenzyme, high regeneration efficiency of the coenzyme, low cost, wide market prospects and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Biological preparation method of intermediate of atazanavir
InactiveCN103468757AImprove reaction efficiencyGreen biotransformation processFermentationBenzeneSolvent
The invention relates to a biological preparation method of an intermediate of atazanavir. (S)-tertiary butyl (4-chloro-3-carbonyl-1-benzene butyl-2-yl) carbamic acid ester is taken as a substrate. The preparation method comprises the following steps of adding the substrate, a cosolvent and glucose into a reactor, stirring uniformly, weighing ketoreductase powder, glucose dehydrogenase and cofactor, dissolving in a water phase buffered solution with pH of 8-9, adding the obtained mixed solution into the reactor, stirring, controlling the temperature to be at 32DEG C-34 DEG C, and beginning reacting, wherein at the beginning of the reaction, the mass volume ratio concentration of the substrate is 0.05-0.2g / ml, and the mass ratio of the added ketoreductase to cofactor to glucose to the substrate is (0.02-0.03):(0.001-0.005):(0.8-1.2):1. Compared with the prior art, the biological preparation method realizes more environment-friendly and mild biological conversion process with high reaction efficiency, and has important application value.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
Method for preparing atazanavir
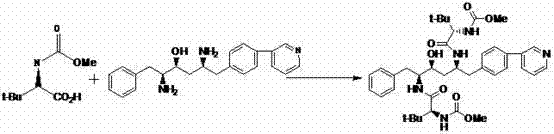
The invention belongs to the field of chemical medicine, and particularly relates to a method for preparing atazanavir. A reaction formula is shown below. The method comprises the following steps: DEPBT is used as a condensing agent, and 1-[4-(pyridine-2-group)-phenyl group]-4 (S)-hydroxy-5 (S)-2, 5-diamido-6-phenyl group-2-aza-hexane and N-methoxycarbonyl group-L-tertiary leucine are reacted in an organic solvent to obtain an atazanavir monomer. In the existing literature, the condensing agent in the reaction often combines TPTU and carbodiimide and triazole compounds or uses carbodiimide compounds alone, but the compounds are dear and poisonous and have more pollution. The method uses DEPBT which is cheap, safe and environmental-friendly as the condensing agent. The method for preparing atazanavir is economically feasible, safe and environmental-friendly and has high yield, and products are easily separated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIUZHOU PHARM CO LTD
Use of Atazanavir for Improving the Pharmacokinetics of Drugs Metabolized by Ugt1a1
InactiveUS20070259894A1Improve pharmacokineticsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAtazanavirOral administration
A method for improving the pharmacokinetics of an orally administered drug that is directly metabolized by UGT1A1 comprises orally administering to a mammal in need of treatment with the drug a combination of the drug or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and atazanavir or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Novel method for synthesizing Atazanavir
InactiveCN102485713AMild reaction conditionsImprove securityOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionCarbamateTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting group
The invention discloses a novel method for synthesizing Atazanavir. The method comprises steps of: carrying out a nucleophilic substitution reaction on a compound shown as a formula I N-1-(t-butoxycarbony)-N-2-[4-(2-pyridyl) benzylidene]-hydrazine and a compound shown as a formula II (S)-4-chlorine-3-carbonyl-1-phenyl butane-2-tert-butyl carbamate to obtain an intermediate shown as a formula III; removing protective groups of the intermediate shown as a formula III and carrying out condensation reaction with N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine to obtain an intermediate shown as a formula IV; carrying out a reduction reaction on the intermediate shown as the formula IV; and a reaction formula is shown as below. The synthetic method has advantages of mild reaction conditions, high security, simple operation, simple purification treatment on end product, high purity, stable quality, easily available raw material, low price and high overall yield, so as to substantially reduce cost and apply to demand of large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACEBRIGHT PHARMA GRP +1
Process for preparing atazanavir bisulfate and novel forms
A process is provided for preparing the HIV protease inhibitor atazanavir bisulfate wherein a solution of atazanavir free base is reacted with concentrated sulfuric acid in an amount to react with less than about 15% by weight of the free base, seeds of Form A crystals of atazanavir bisulfate are added to the reaction mixture, and as crystals of the bisulfate form, additional concentrated sulfuric acid is added in multiple stages at increasing rates according to a cubic equation, to effect formation of Form A crystals of atazanavir bisulfate. A process is also provided for preparing atazanavir bisulfate as Pattern C material. A novel form of atazanavir bisulfate is also provided which is Form E3 which is a highly crystalline triethanolate solvate of the bisulfate salt from ethanol.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB HLDG IRELAND UNLTD
Method of treating HIV infection in atazanavir-resistant patients using a combination of atazanavir and another protease inhibitor
A method of treating HIV infection in a human patient wherein the infecting HIV strain has become resistant to atazanavir, the method comprising administration of a therapeutically effective amount of a combination of atazanavir or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and at least one other HIV protease inhibitor. A method for enhancing the effectiveness of a second HIV protease inhibitor in treating HIV infection in a human patient whose HIV strain has become resistant to atazanavir or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, comprising administering to said human patient an amount of atazanavir or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof effective in maintaining the resistant strain, in combination with the second HIV protease inhibitor. The resistance to atazanavir in the human is manifested by the existence of the signature mutation consisting of I50L mutation in the HIV protease.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Process for preparing atazanavir bisulfate and novel forms
ActiveCN1980666AOrganic chemistryHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsHIV Protease InhibitorSolvent
A process is provided for preparing the HIV protease inhibitor atazanavir bisulfate wherein a solution of atazanavir free base is reacted with concentrated sulfuric acid in an amount to react with less than about 15% by weight of the free base, seeds of Form A crystals of atazanavir bisulfate are added to the reaction mixture, and as crystals of the bisulfate form, additional concentrated sulfuric acid is added in multiple stages at increasing rates according to a cubic equation, to effect formation of Form A crystals of atazanavir bisulfate. A process is also provided for preparing atazanavir bisulfate as Pattern C material. A novel form of atazanavir bisulfate is also provided which is Form E3 which is a highly crystalline triethanolate solvate of the bisulfate salt from ethanol.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB HLDG IRELAND
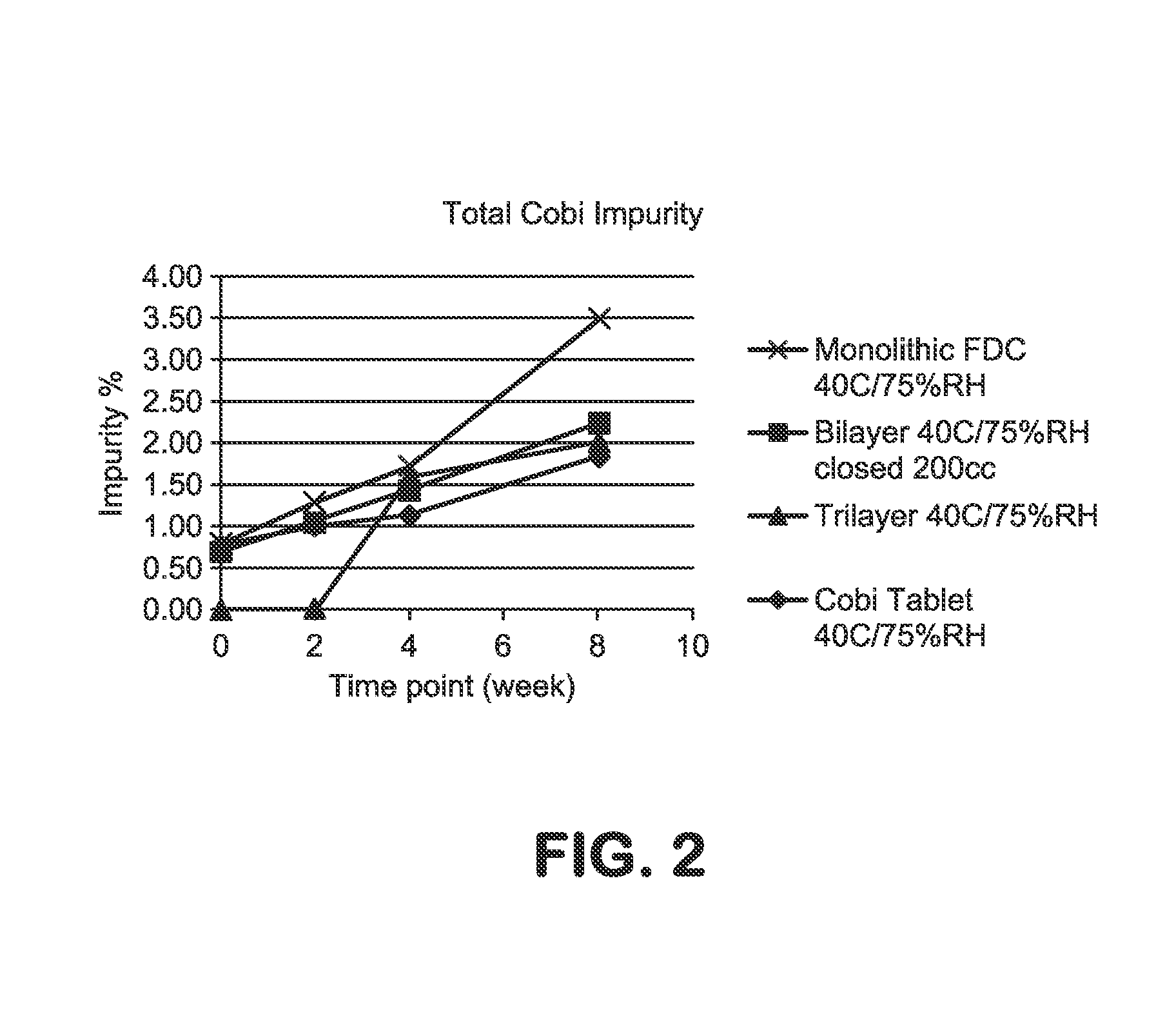
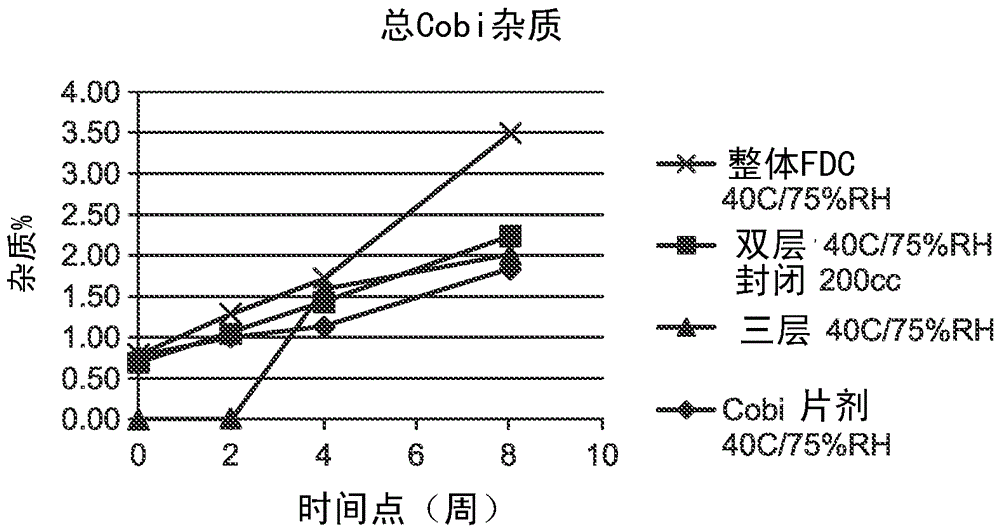
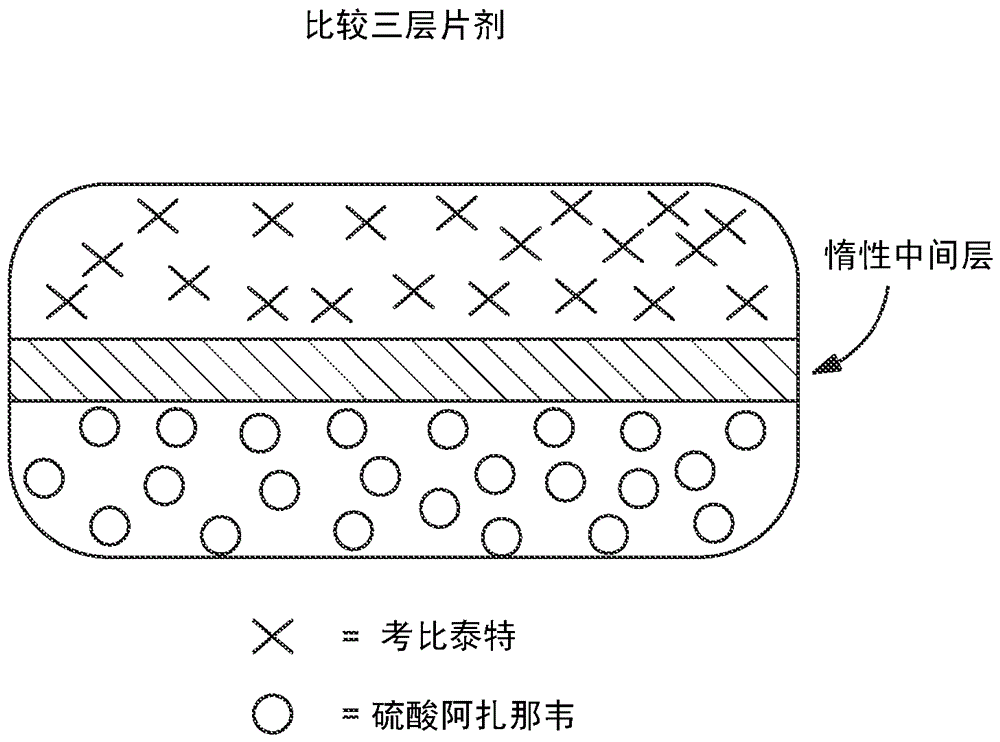
HIV treatment formulation of atazanavir and cobicistat
InactiveUS20160038502A1Reduced pill burdenPatient compliance is goodOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsCobicistatAtazanavir
Formulations of the HIV compounds atazanavir and cobicistat, and methods of treatment utilizing these formulations, are set forth.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
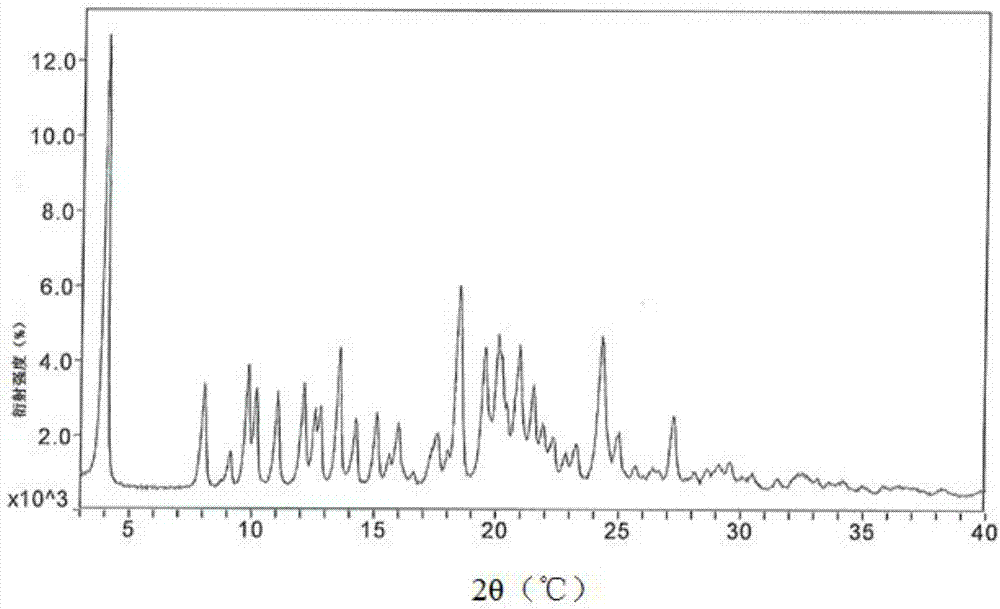
Method for preparing A type atazanavir sulfate
A disclosed method for preparing A type atazanavir sulfate comprises the following steps: step a) adding atazanavir free alkali into an organic solvent to prepare a transparent solution at a controlled temperature of 10-65 DEG C, wherein the organic solvent is at least one selected from dimethyl sulfoxide, ester solvents and ether solvents; step b) dropwise adding concentrated sulfuric acid into the transparent solution prepared in the step a); step c) after adding is finished, stirring for 0.5-10 h under the condition of thermal insulation; and step d) cooling, filtering, washing and drying. By selecting the specific solvent, the high-purity A type atazanavir sulfate is prepared at a high yield through simplest operations. The preparation period is short, the cost is low, no special equipment and no harsh conditions and operations are needed, and the method is extremely suitable for large-scale production and has practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI DESANO CHEM PHARMA
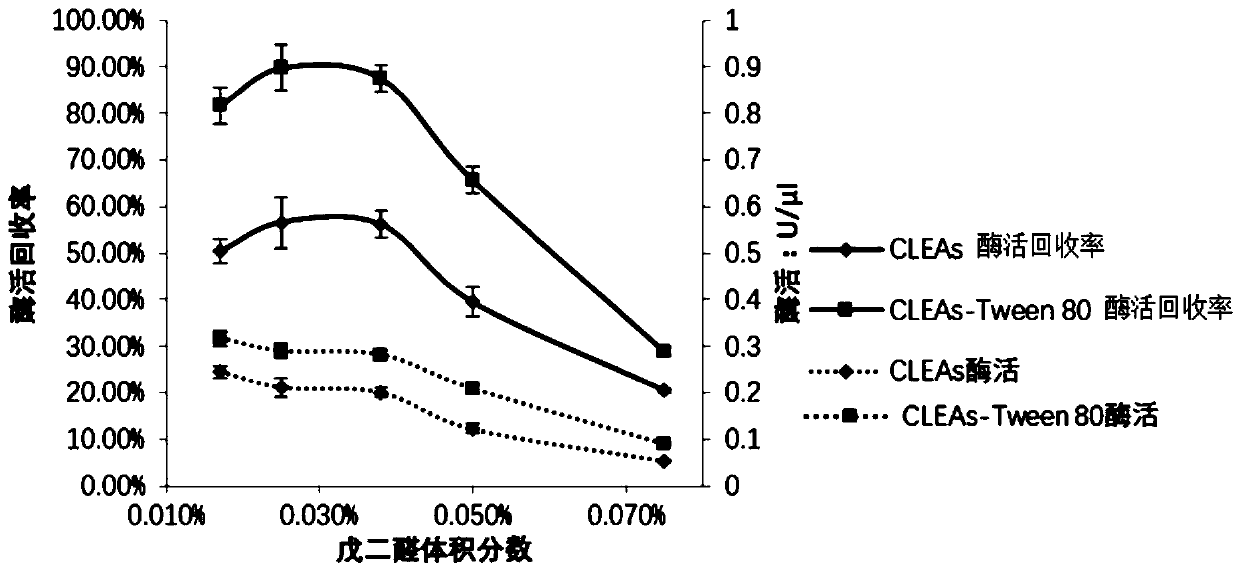
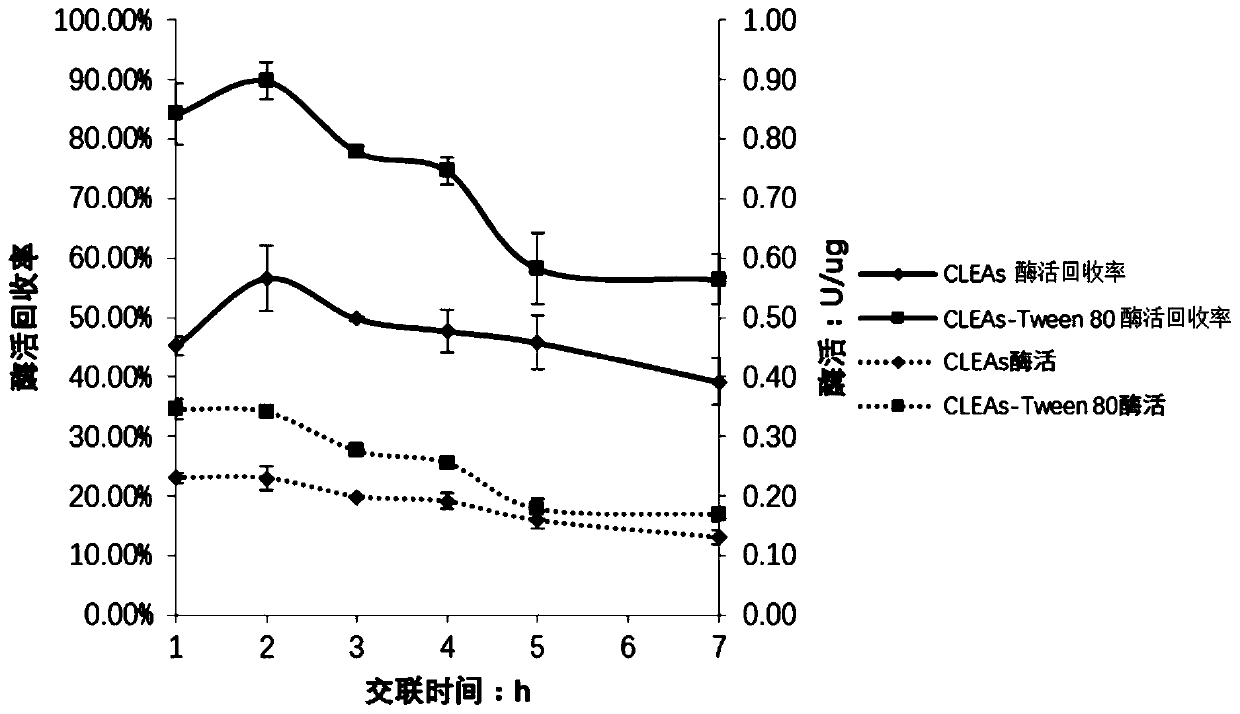
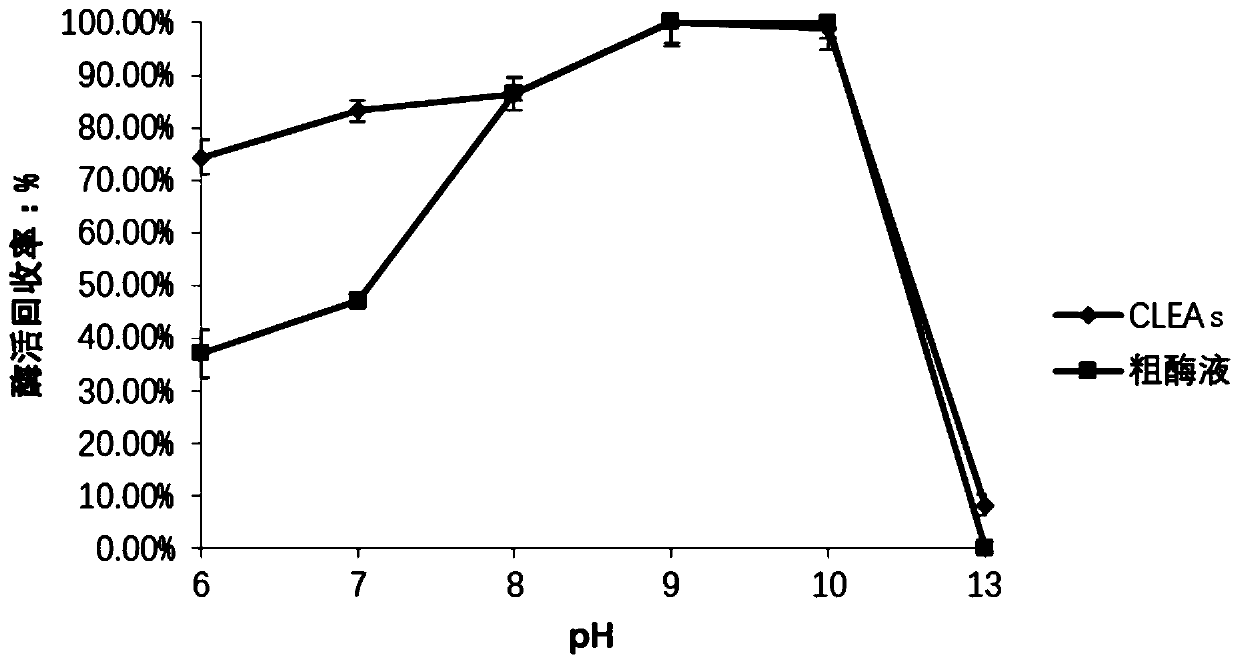
Method for catalyzing synthesis of atazanavir intermediate by carbonyl reductase CLEAs
InactiveCN109988789ASimple reaction systemEasy to purifyOrganic chemistryOxidoreductasesCarbamateReaction temperature
The invention relates to the field of medicine, in particular to a method for catalyzing synthesis of an atazanavir intermediate by a carbonyl reductase CLEAs. The method uses (S)-tert-butyl (4-chloro-3-carbonyl-1-phenylbutyl-2-yl) carbamate as a substrate and a carbonyl reductase NaSDR crosslinked aggregate as a catalyst, and the catalyzing synthesis of tert-butyl ((2S, 3R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutyl-2-yl)) carbamate is carried out in a system in which a co-substrate, a co-solvent and a buffer solution are present. By the adoption of the method for the catalyzing synthesis of the atazanavir intermediate by the carbonyl reductase CLEAs, a reaction system is simpler, additional expensive coenzymes are not necessary, and glucose is not required to participate in a coenzyme cycle; in addition, the reaction temperature is closer to room temperature; the carbonyl reductase NaSDR crosslinked aggregate as a biocatalyst has better temperature stability and pH stability and can be reusedin 6 batches, so that the method is more energy-saving and environmentally friendly, and cost is further reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF MEDICINE & HEALTH SCI
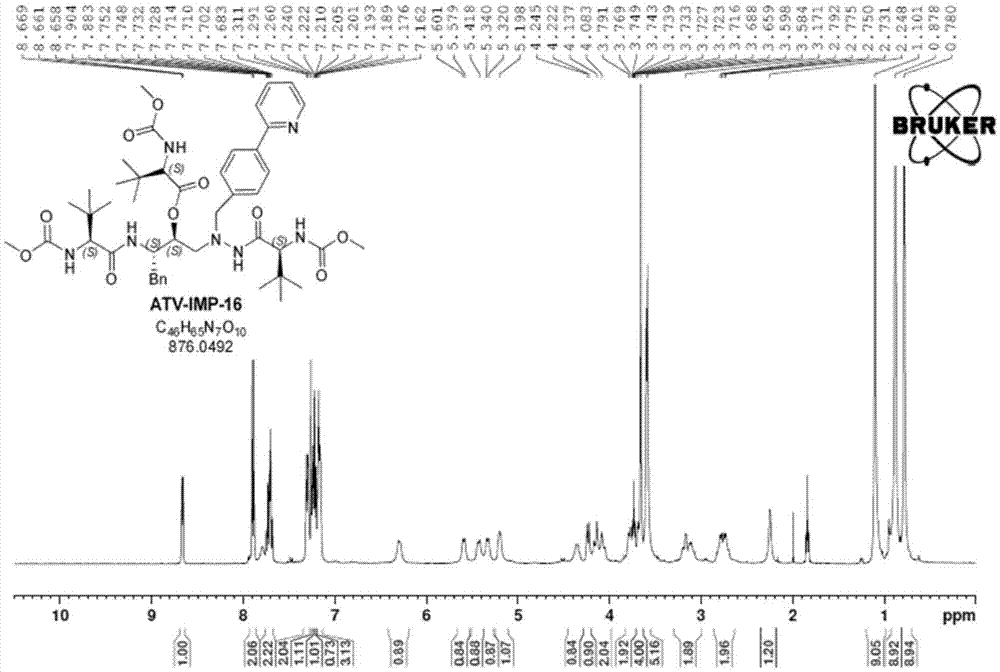
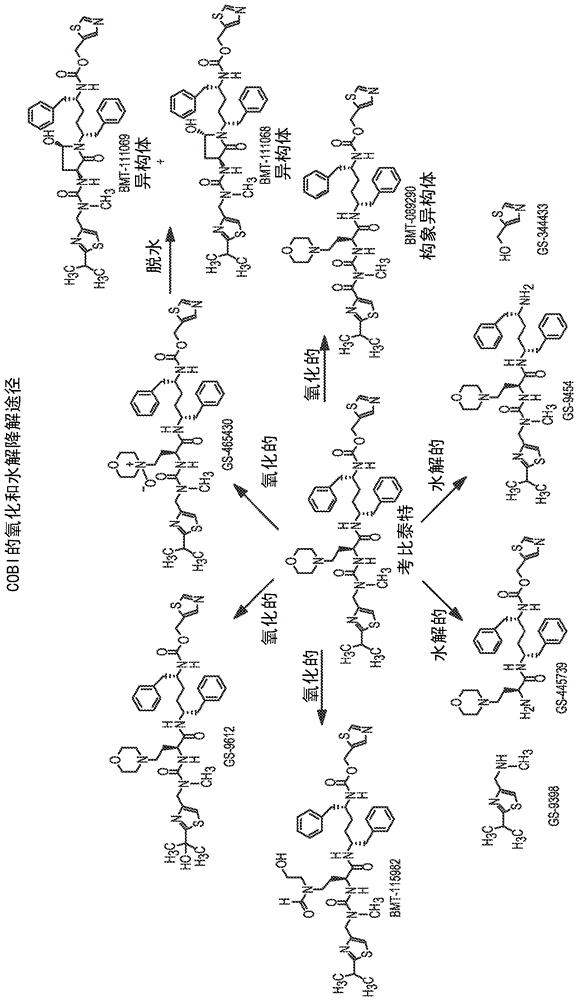
Atazanavir bulk drug impurity or salt thereof, preparation method and applications thereof
PendingCN107021919AValid identificationQuality improvementOrganic chemistryComponent separationChemical compoundQuality control
The present invention discloses an atazanavir bulk drug impurity or a salt thereof, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of the atazanavir bulk drug impurity represented by a formula (I) comprises: in a solvent, under the catalysis of a condensation agent, carrying out a condensation reaction defined in the specification on a compound represented by a formula (II) or a hydrochloride thereof and a compound represented by a formula (III) to prepare the atazanavir bulk drug impurity represented by the formula (I). The invention further discloses applications of the atazanavir bulk drug impurity represented by the formula (I) or the salt thereof as an impurity reference substance in atazanavir quality control. According to the present invention, the atazanavir bulk drug impurity or the salt thereof is the essential substance for the quality control of the atazanavir or the salt thereof, and can effectively identify the impurity in the atazanavir or the salt product thereof so as to control the quality of the atazanavir or the salt thereof; and the operation of the preparation method is simple. The condensation reaction process is defined in the specification.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +2
Novel Antiretroviral Combination
The invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing a combination of atazanavir and ritonavir, to methods of making them, and their use in medicine.
Owner:CIPLA LTD
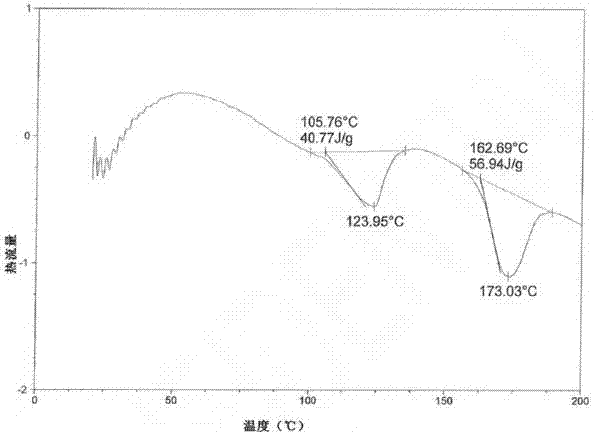
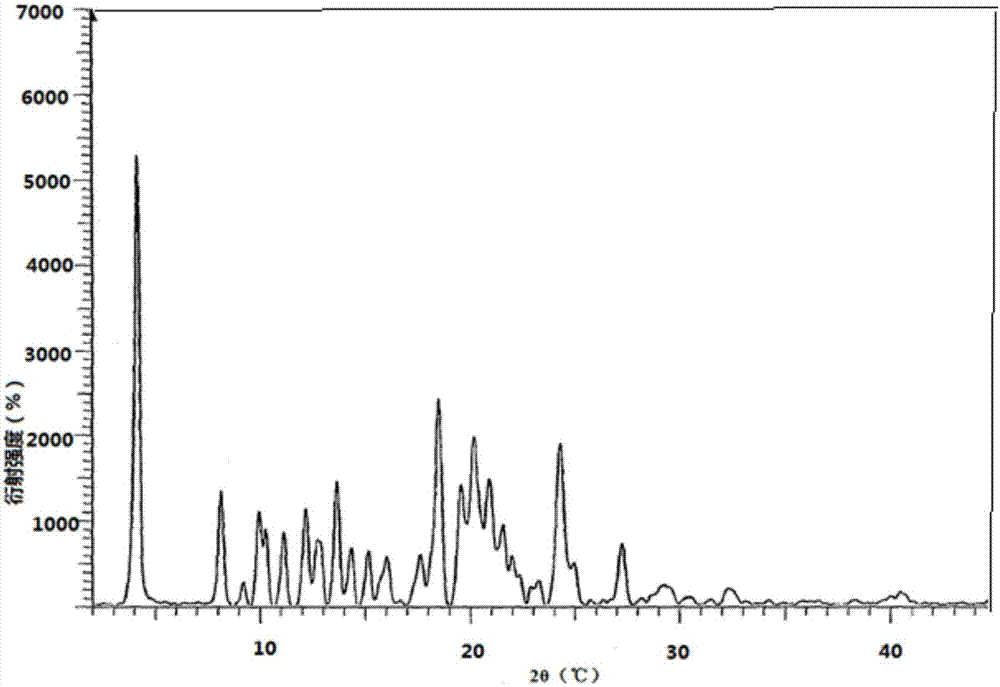
Method for preparing A-type crystal of Atazanavir disulfate
The invention discloses a method for preparing an A-type crystal of Atazanavir disulfate. The method comprises the following steps that a, Atazanavir free alkali is placed in ethyl alcohol, the mixture is stirred at room temperature, then concentrated sulfuric acid is added dropwise, the reaction liquid is heated and stirred, then an inert solvent is added, cooling and crystallization are carried out, drying is carried out after filtering, and an Atazanavir ethyl alcohol compound E-type crystal is obtained, wherein the molar concentration of concentrated sulfuric acid is preferably 15 mol / L to 18.4 mol / L; b, the Atazanavir ethyl alcohol compound E-type crystal obtained in the step a is placed in acetone, heating, refluxing and stirring are carried out, drying is carried out after cooling and filtering, and the A-type crystal of Atazanavir disulfate is obtained. According to the crystal transformation preparation method, the operability of the process is improved, the external properties of the product are improved, and the quality and purity of the product are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHYNDEC PHARMA HAIMEN CO LTD +2
Compound tablet containing atazanavir and ritonavir and preparation method of compound tablet
InactiveCN111939137AProcess parameter control is simpleSuitable for industrial mass productionOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsUse medicationPatient compliance
The invention relates to the field of pharmaceutical preparations, in particular to a compound tablet containing atazanavir and ritonavir and a preparation method of the compound tablet. According tothe method, the problems of poor thermal stability and poor water solubility of ritonavir in the compound tablets are solved by utilizing a hot melt extrusion technology, and the atazanavir and ritonavir compound tablet which is simpler in process difficulty, equipment conditions and process description control and better in bioavailability is researched and designed and is bioequivalent to singleatazonavir and ritonavir; and therefore, the medication mode is simplified, the patient compliance is improved, and the drug resistance risk is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI DESANO PHARMA INVESTMENT
Methods of inhibiting transmission of a costimulatory signal of lymphocytes
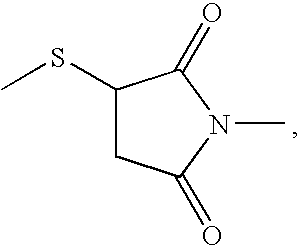
Activated haptens useful for generating immunogens to the HIV protease inhibitor atazanavir, immunogens useful for producing antibodies to atazanavir, and antibodies and labeled conjugates useful in immunoassays for determination of atazanavir. The haptens feature an activated functionality at the central, non-terminal hydroxyl group.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Alcohol dehydrogenase for producing Atazanavir intermediate
ActiveCN109943542AMild reaction conditionsLow equipment requirementsBiofuelsOxidoreductasesWild typeSolvent
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase for producing an Atazanavir intermediate and belongs to the technical field of medical biology. The alcohol dehydrogenase shows stronger catalytic activity than a wild alcohol dehydrogenase shown as SEQ ID NO.8 and can be obtained by means of in-vitro recombination, polynucleotide mutagenesis, DNA shuffling, error-prone PCR, directional evolution methods and the like. The alcohol dehydrogenase has one or more mutations of following characteristics including T37A, D38E, P41K, D44N, V45K. The alcohol dehydrogenase has the advantages that, the reaction conditions are mild, the requirement for equipment is low, high temperature or cooling in a production process is not required, and the energy consumption is low; since enzyme catalysis has highefficiency and exclusive selectivity, no by-products are generated when a method is utilized to produce key intermediates of Atazanavir, and purification is convenient. In addition, a reaction solventmainly consists of water, the discharge amount of three wastes is small, and the alcohol dehydrogenase is environmentally friendly.
Owner:NANJING NUOYUN BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of atazanavir hydrosulfate crystal form H1
ActiveCN107382833AGood repeatabilitySimple and fast operationOrganic chemistry methodsAcetic acidPotential market
The invention discloses a preparation method of an atazanavir hydrosulfate crystal form H1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing atazanavir hydrosulfate with a solvent, and stirring to obtain the atazanavir hydrosulfate crystal form H1, wherein the solvent is a mixed solvent of methanol, butanone and ethyl acetate. The preparation method of an atazanavir hydrosulfate crystal form H1 disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high repeatability, easiness in operation and high yield; the methanol content in the product meets the requirements for medicinal use, and the chromatographic purity is high; thus, the product is more applicable to medicament and suitable for industrial production and has a potential market value.
Owner:SHANGHAI VIWIT PHARMA CO LTD
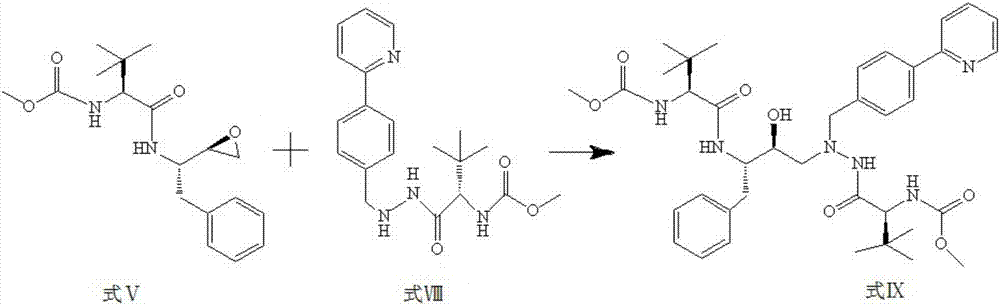
Method for synthesis of atazanavir
ActiveCN107540603AWide variety of sourcesLow priceOrganic chemistryOrganic solventCombinatorial chemistry
The invention discloses a method for synthesis of atazanavir. The method comprises that a compound methyl (S)-1-((S)-2-ethoxyethyl-1-phenylethane-2-yl-amino)-3, 3-dimethyl-1-carbonylbutane-2-yl-carbamate shown in the formula V and a compound N-1-[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tertiary leucine]-N-2-[4-(2-pyridyl)-benzyl]hydrazine shown in the formula VIII undergo a nucleophilic substitution reaction in anorganic solvent to produce a compound 1-[4-(2-pyridyl)phenyl]-5(S)-2, 5-bis{[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tertiary leucine]amino}-4(S)-hydroxy-6-phenyl-2-azahexane VIII shown in the formula IX, wherein the compound shown in the formula IX is atazanavir. The method utilizes raw materials having a wide raw material source, the product is easy to purify, a cost is low, the synthesis processes are simple, the operation is simple, the process is simple, special requirement on equipment is avoided and large-scale production feasibility is realized.
Owner:湖州优研知识产权服务有限公司
Method for preparing anti-AIDS drug-Atazanavir monomer
The invention discloses a method which is used for preparing an Atazanavir monomer and applied in the technical field of drug synthesis. The method comprises the steps that N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tertiary leucine and 1-[4-(pyridine-2-yl)-phenyl]-4(S)-hydroxyl-5(S)-2,5-diamido-6-phenyl-2-aza-hexane are subjected to an amidation reaction by taking HATU as a condensing agent under the condition of organic alkali and an organic solvent, certain aftertreatment is conducted, and then the Atazanavir monomer is obtained. According to the method, the synthetic yield of Atazanavir is increased, the purity is high, and the cost of raw materials is effectively reduced; meanwhile, the reaction time is short, material putting is easy, nitrogen protection is not needed, the material putting temperature can be properly controlled, by-products of HATU can be washed off more easily, the preparation time is greatly shortened, the working efficiency is improved, and therefore the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NORTHEAST PHARMA GRP
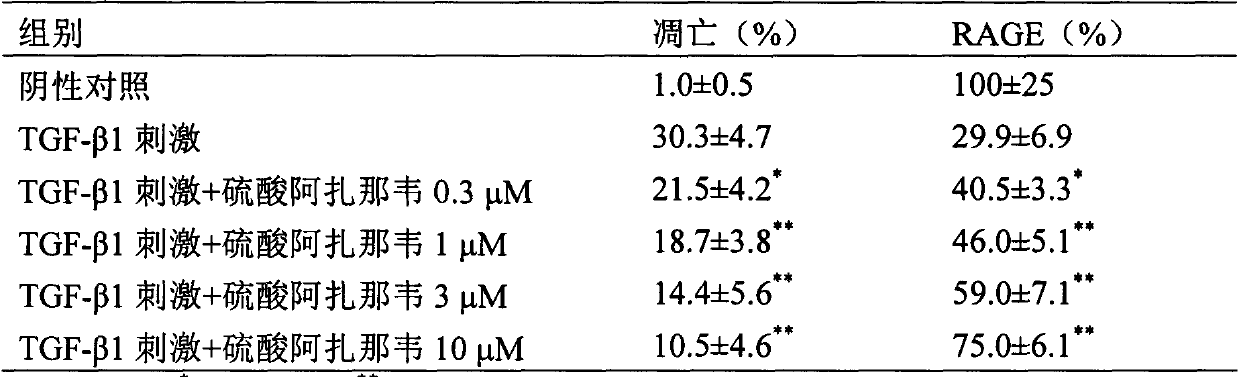
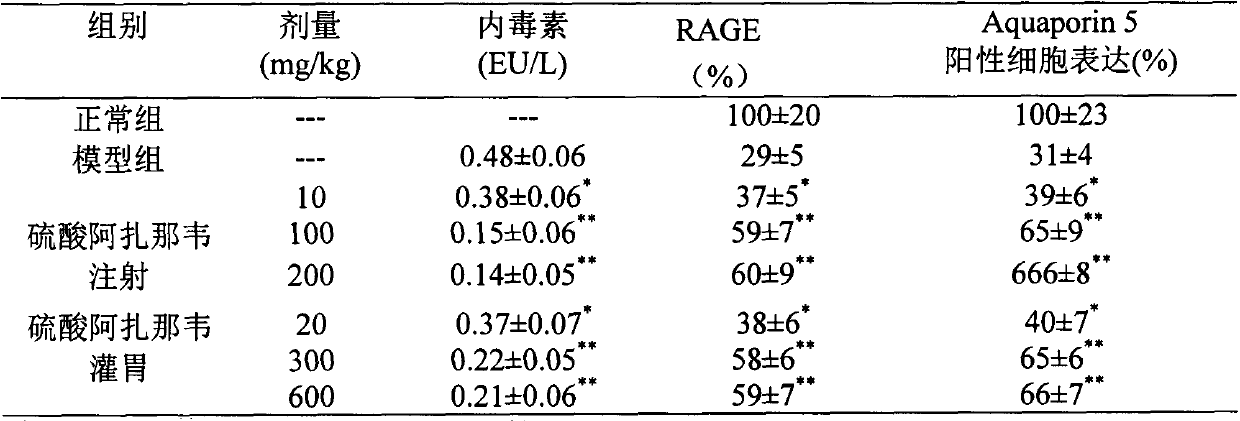
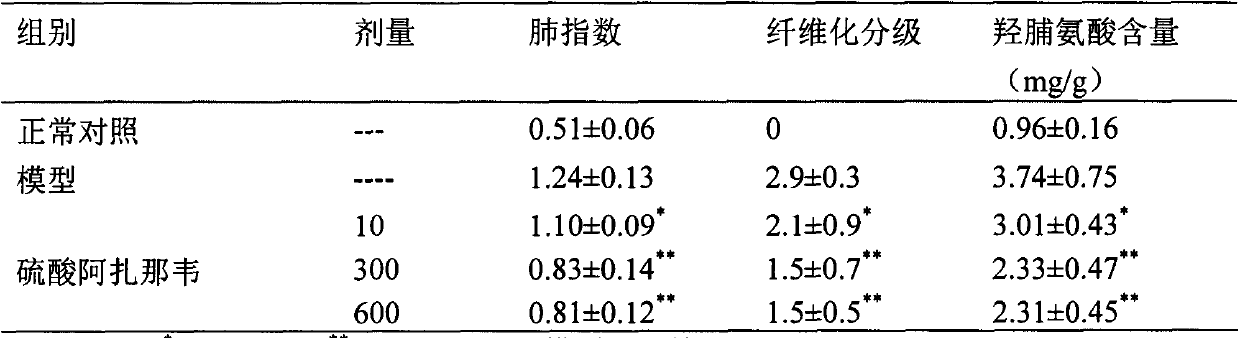
Application of atazanavir in preparation of medicine for preventing or treating acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome and pulmonary fibrosis
InactiveCN103989679AOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderApoptosisARDs - Acute respiratory distress syndrome
The invention provides novel application of atazanavir medicines, and in particular relates to application of atazanavir in inhibiting generation and development of acute lung injury / acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI / ARDS) and pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting apoptosis of I type alveolar epithelial cells and promoting expression of receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) of I type alveolar epithelial cells, so as to prevent or treat ALI / ARDS and pulmonary fibrosis. According to the application, the injected dose of atazanavir ranges from 100 to 2000mg, preferably 100 to 1000mg; the oral dose of atazanavir ranges from 200 to 6000mg, preferably 200 to 3000mg.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Novel method for preparing atazanavir monomer
The invention discloses a method for preparing an atazanavir monomer. The method is applied to the technical field of medicines and comprises steps as follows: at the proper temperature, weak base is used as an acid-binding agent, under a certain organic solvent condition, N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine firstly reacts with thionyl chloride to produce N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine acyl chloride, then the N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine acyl chloride and 1-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)-phenyl]-4(S)-hydroxyl-5(S)-2,5-diamino-6-phenyl-2-azahexane have an amide formation reaction at the room temperature, and the atazanavir monomer is obtained. The method has the advantages as follows: (1), the thionyl chloride is cheap, so that the costs of raw materials are effectively reduced, and the method is suitable for industrialization; (2), the produced pollution is less and is converted into soluble effluent brine after after-treatment, so that the method is relatively environment-friendly; (3), the operation is simple, the product yield is high, separation and purification are easy, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NORTHEAST PHARMA GRP
Process for preparing atazanavir bisulfate and novel forms
ActiveUS20090203630A1Dipeptide ingredientsOrganic compound preparationHIV Protease InhibitorMedicinal chemistry
A process is provided for preparing the HIV protease inhibitor atazanavir bisulfate wherein a solution of atazanavir free base is reacted with concentrated sulfuric acid in an amount to react with less than about 15% by weight of the free base, seeds of Form A crystals of atazanavir bisulfate are added to the reaction mixture, and as crystals of the bisulfate form, additional concentrated sulfuric acid is added in multiple stages at increasing rates according to a cubic equation, to effect formation of Form A crystals of atazanavir bisulfate.A process is also provided for preparing atazanavir bisulfate as Pattern C material. A novel form of atazanavir bisulfate is also provided which is Form E3 which is a highly crystalline triethanolate solvate of the bisulfate salt from ethanol.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Novel synthetic method of HIV-1 protease inhibitor atazanavir
InactiveCN101391978BLow priceEasy recrystallization purificationOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionMethyl carbamateMethyl carbazate
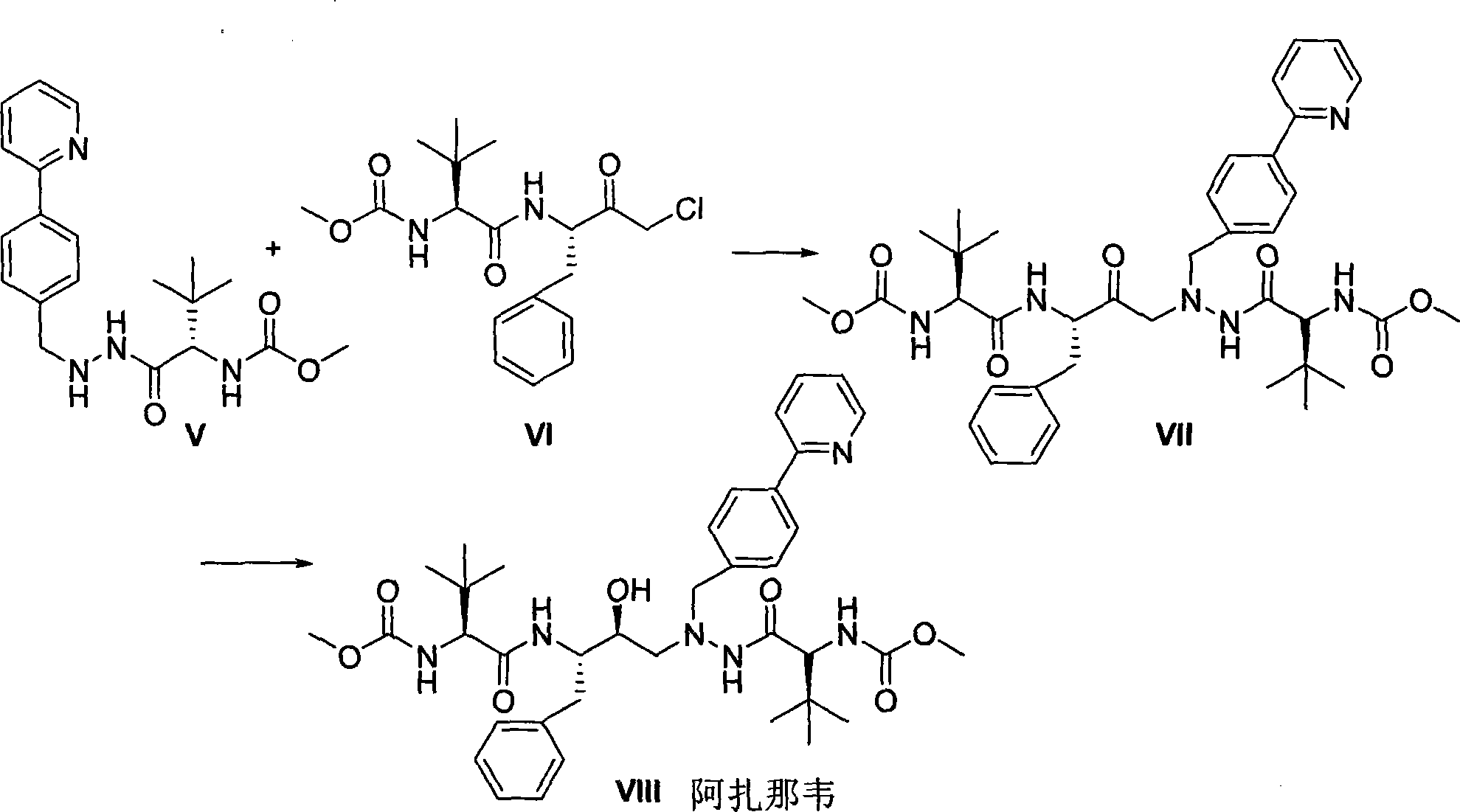
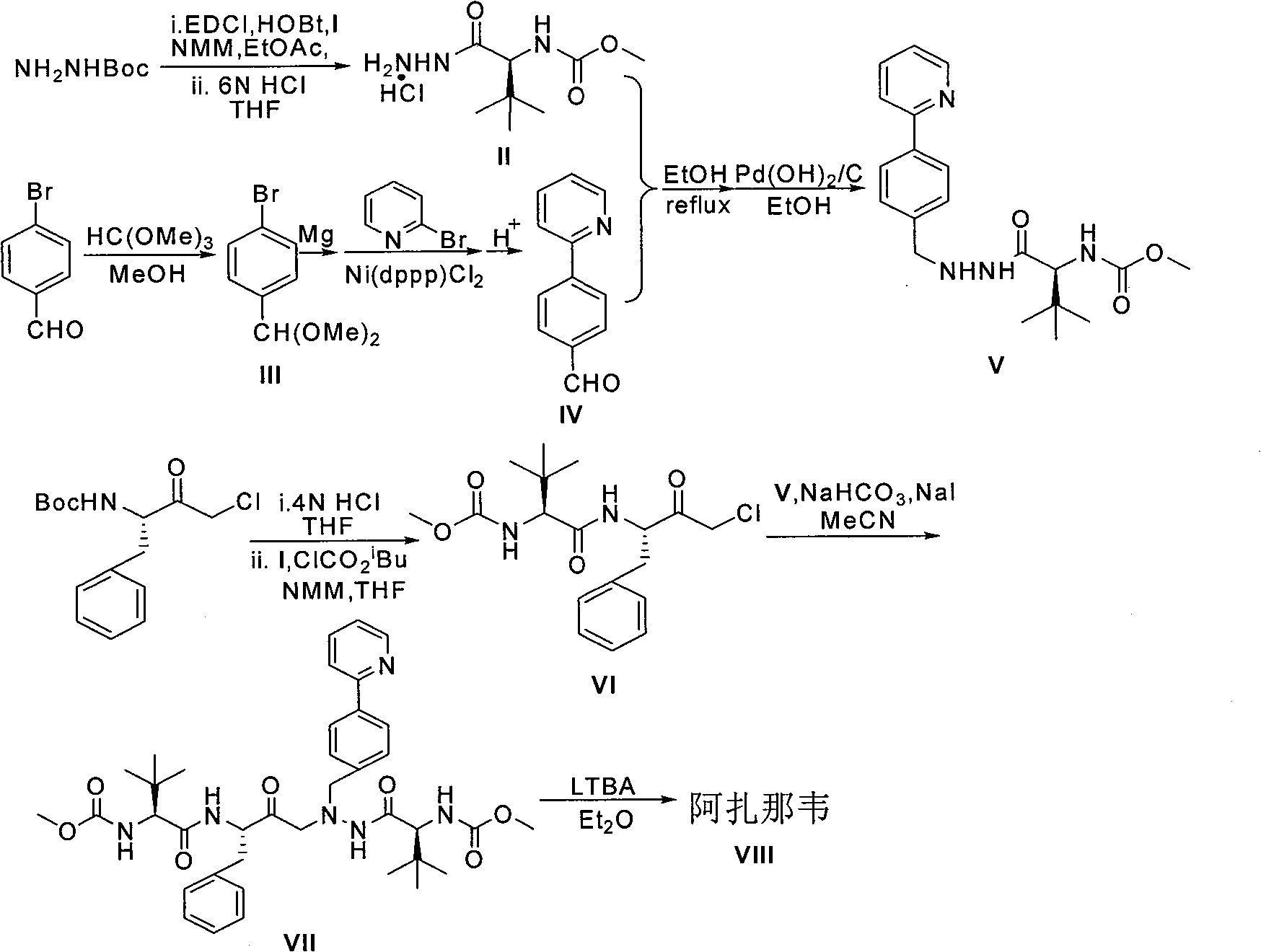
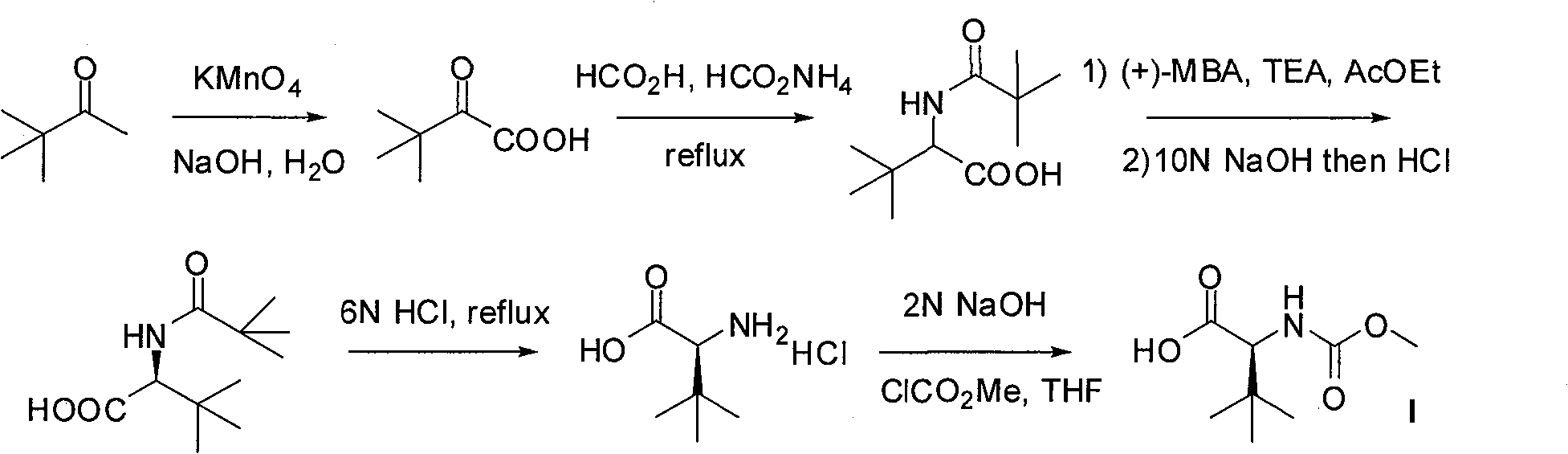
The invention relates to a new synthetic method of an HIV-1 protease inhibitor, Atazanavir, which adopts a convergent-typed synthetic strategy, introduces a construction unit, methoxycarbonyl-tert-lencyl, as an N atom protecting group in the whole early synthetic stage, and takes the diastereomeric selective reduction of aminoketone as the key and final reaction step of the new process. The method comprises the steps that: the compound of formula V, namely, N-1-[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tert-leucine]-N-2-[4-(2-pyridyl)-phenmethyl]hydrazine, and the compound of formula VI, namely, (S)-1-((S)-4-chlorine-3-carbonyl-1-phenyl butane-2-yl-2-amino)-3, 3-dimethyl-1-carbonyl butane-2-yl-methyl carbamate, are treated with nucleophilic substitution reaction to generate the compound of formula VII, namely, 1-[4-(2-pyridyl)phenyl]-5(S)-2, 5-bis{[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tert-leucineyl] amino}-4-carbonyl-6-phenyl-2-azahexane; and the compound of formula VII is treated with reduction reaction to generate the Atazanavir. The invention has the advantages of less process route steps, easily-controlled reaction conditions, simple and convenient operation, low-price and easily-obtained raw material, high product yield, low cost and being suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
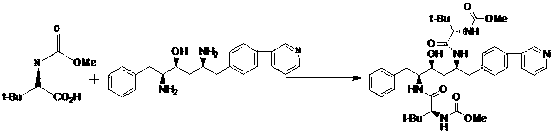
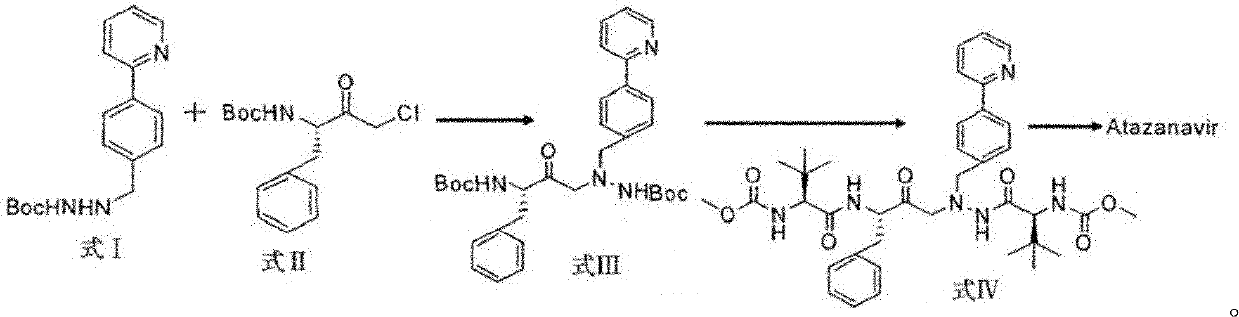
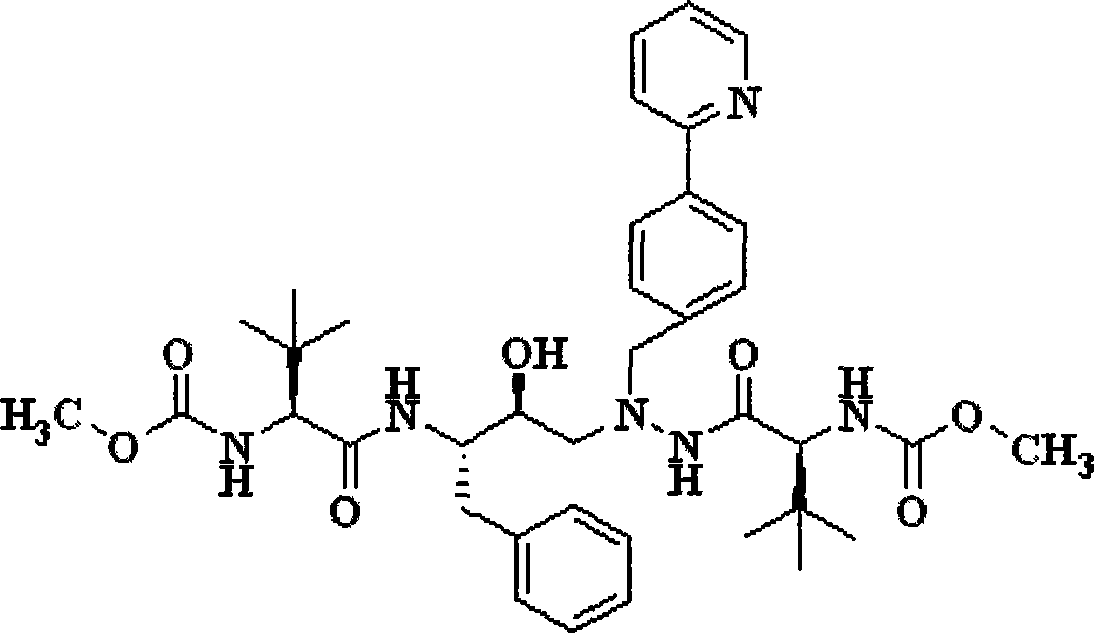
A kind of preparation method of atazanavir
The present invention relates to the field of chemical medicaments. Disclosed is an Atazanavir preparation method, with a reaction formula as represented in figure (I). The present invention uses DEPBT as a condensing agent; 1-[4-(pyridine-2-yl)-phenyl]-4(S)-hydroxy-5(S)-2, 5-diamino-6- phenyl-2-azahexane is reacted with N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tertiary leucine in an organic solvent to give the Atazanavir. The condensing agent normally used in the reaction in existing literatures is TPTU, a combination of carbon diimine compounds and benzotriazole compounds, or only the carbon diimine compounds. However, the compounds are expensive, toxic and heavily pollutive. The present invention uses inexpensive, safe and environment-friendly DEPBT as the condensing agent, and provides an economically feasible, safe and environment-friendly Atazanavir preparation method with high yield and easy product separation.
Owner:瑞博(杭州)医药科技有限公司
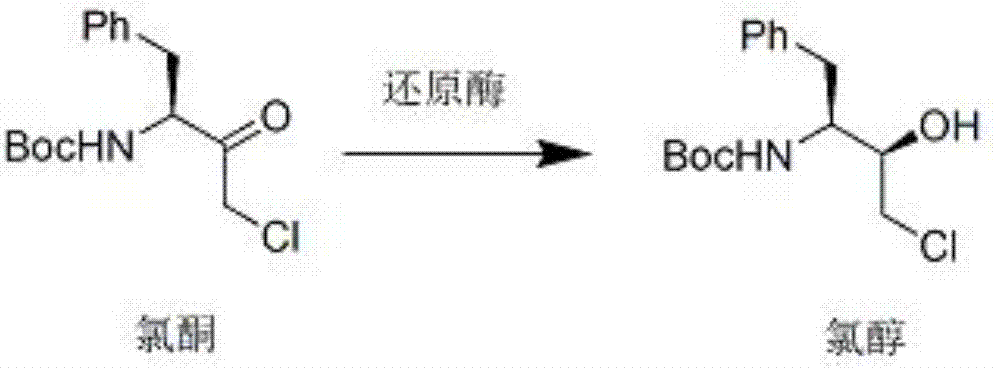
Method used for synthesis of atazanavir intermediate chlorhydrin via bio-enzyme catalysis
The invention provides a method used for synthesis of atazanavir intermediate chlorhydrin via bio-enzyme catalysis. The method comprises following steps: 1, methyl tert-butyl ether, purified water, and a reductase are delivered into a reaction bottle, the temperature is maintained to be 25 to 30 DEG C for 30min, the temperature is reduced to 10 to 15 DEG C, chlorone is added in batches in about 1.5h while the temperature is maintained to be 10 to 15 DEG C, and then the temperature is maintained to be 10 to 15 DEG C for 24h of reaction; and 2, post-treatment is carried out. According to the method, reduction of chlorone is ensured via green environment-friendly enzyme technology, so that problems in the prior art such as low selectivity, complex fermentation technology, and applications of reducing agents, such as sodium borohydride and aluminum hydrogen, which are dangerous and are difficult to treat in an environment-friendly manner are solved.
Owner:四川奇格曼药业有限公司
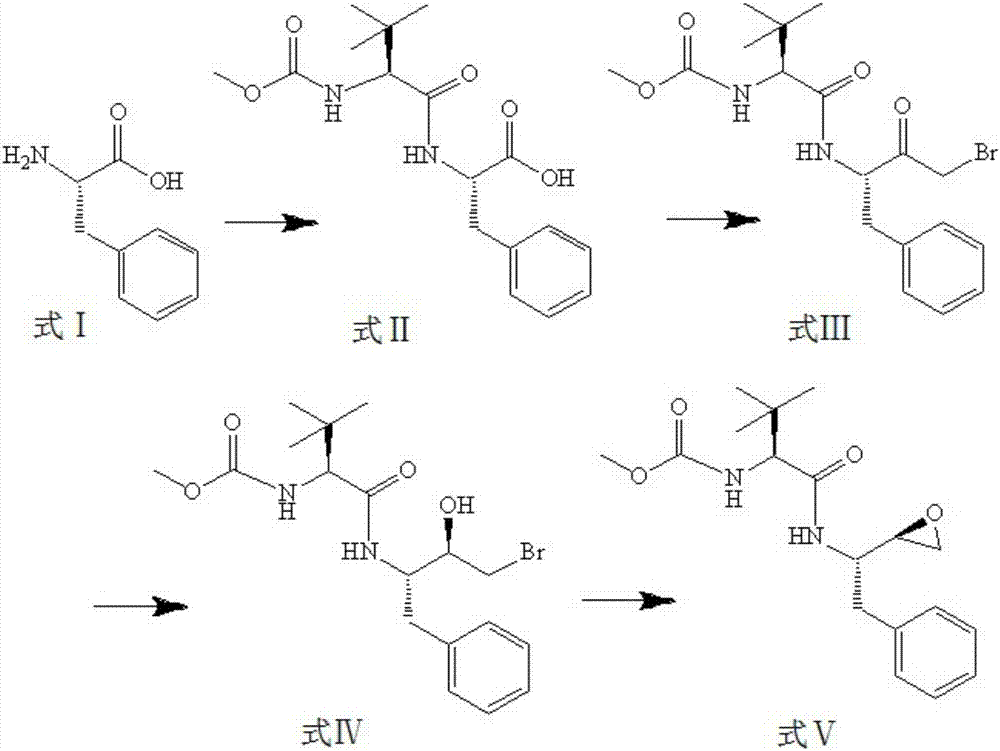
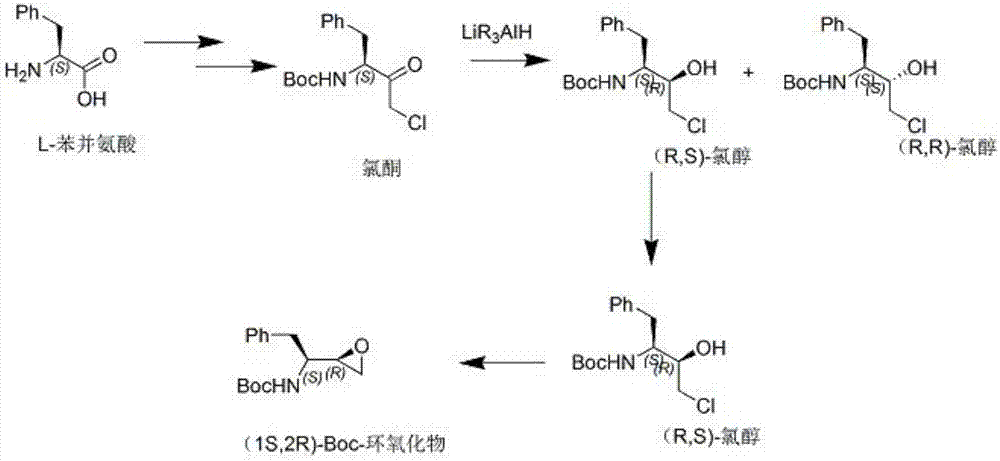
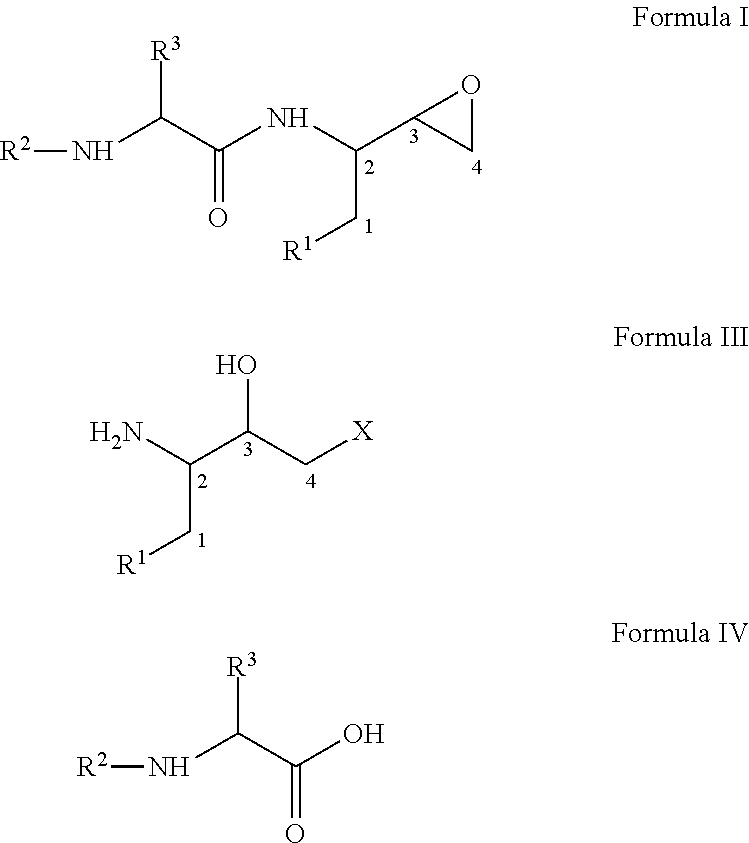
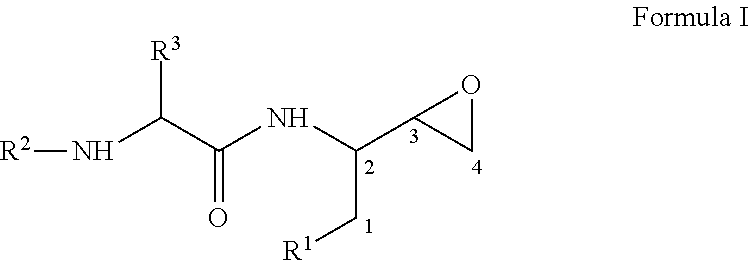
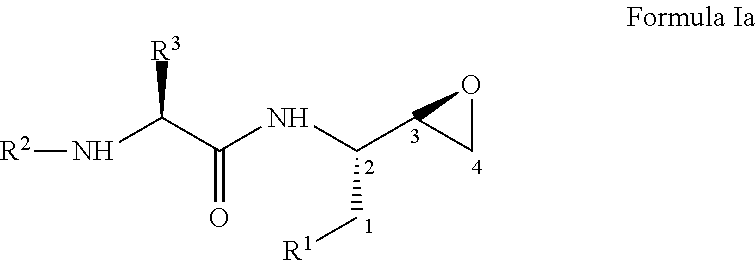
Process for the preparation of 3,4-epoxy-2-amino-1-substituted butane derivatives and intermediate compounds thereof
InactiveUS20110178305A1Efficient processingEasy to operateCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationEpoxyButane
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of threo-3,4-epoxy-2-amino-1-substituted butane derivatives represented by general Formula I which comprises reacting compound of Formula III or salt thereof with an active ester of acid of Formula IV and treating the product thereof with base. The carbon atom bonded to the radical R3 in Formula I and IV is in the (R)-, (S)- or (R,S)-configuration. The compounds of Formula I and III, particularly in their (2S,3R) configuration are useful intermediates for the preparation of atazanavir bisulfate.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Hiv treatment formulation of atazanavir and cobicistat
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB HLDG IRELAND UNLTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com