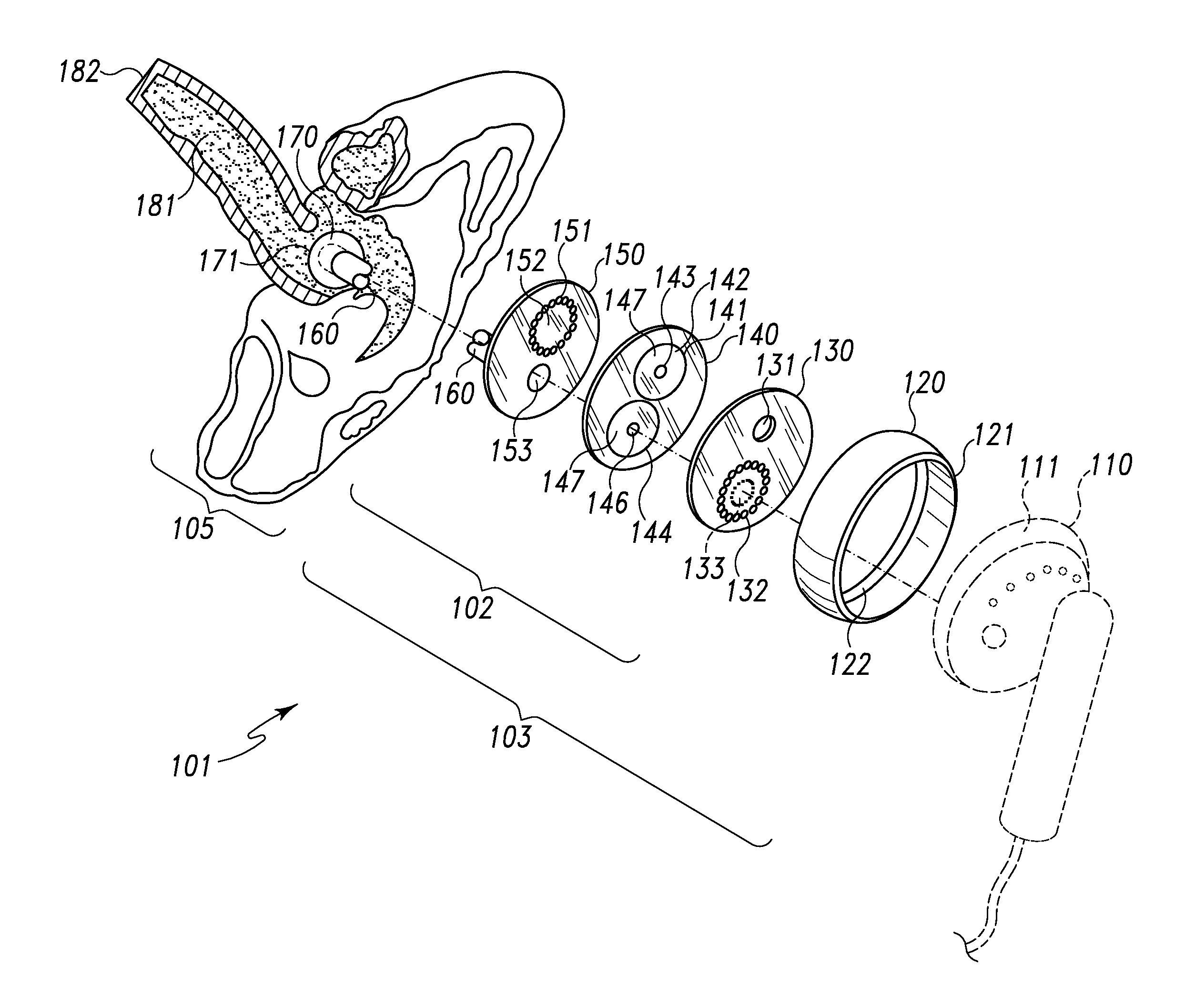
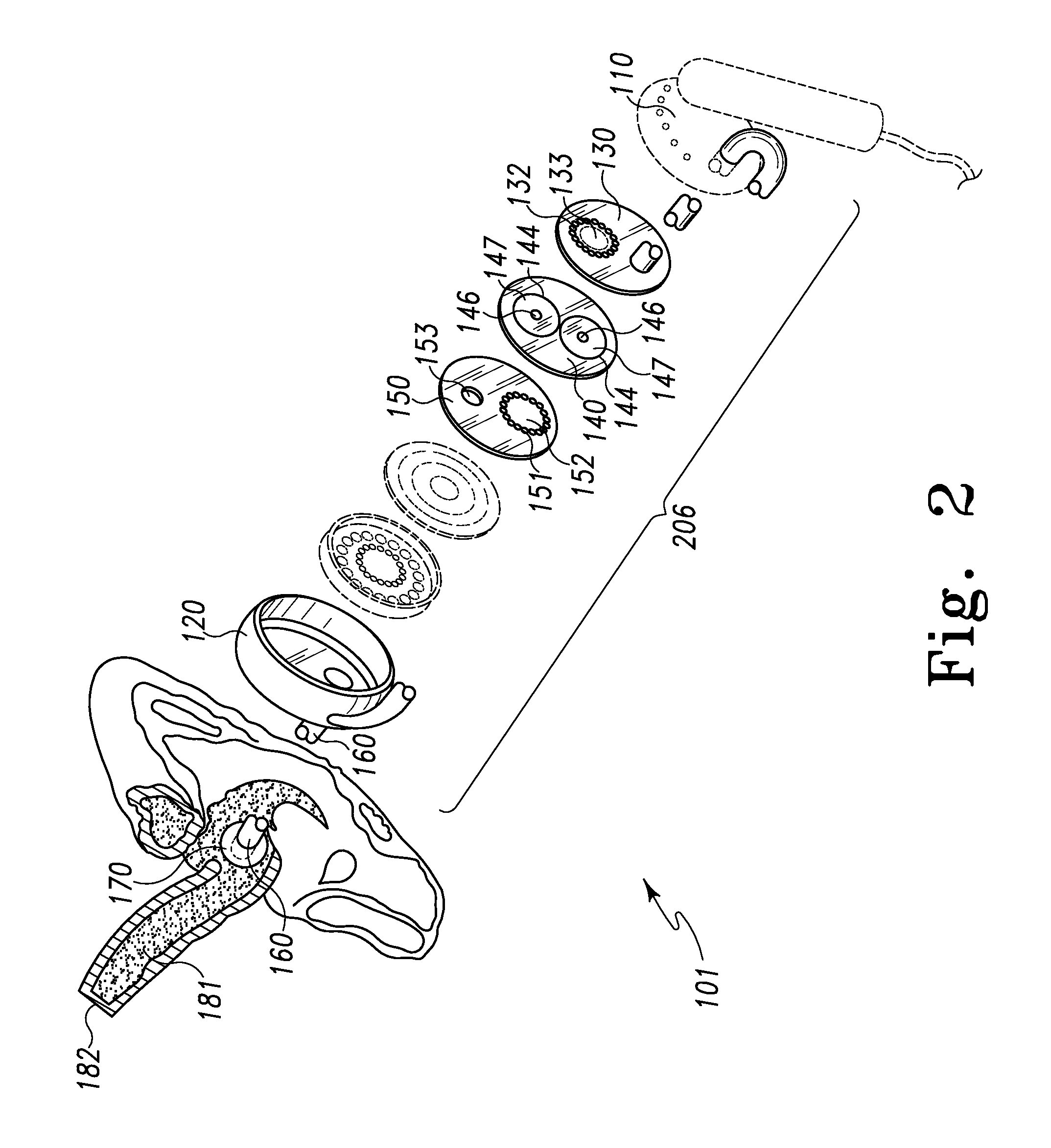
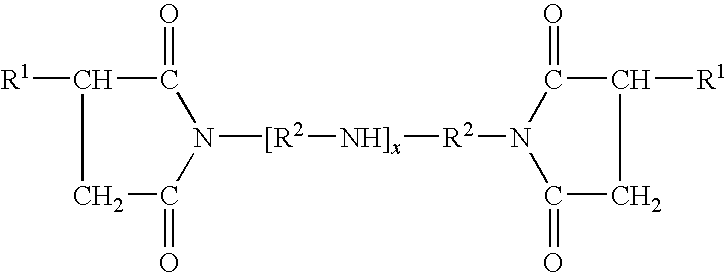Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5179 results about "Audiology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
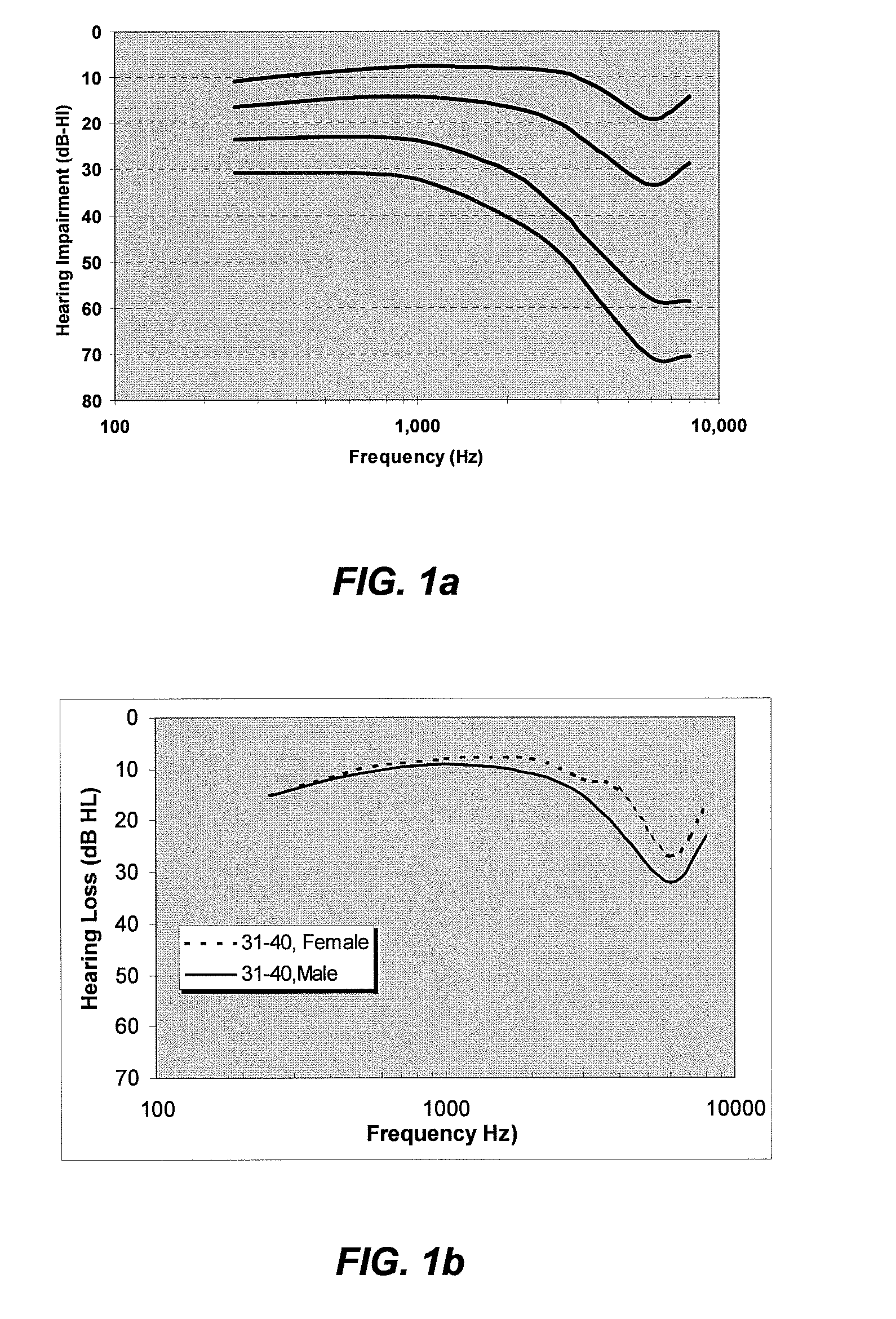
Audiology (from Latin audīre, "to hear"; and from Greek -λογία, -logia) is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies (e.g. behavioral hearing tests, otoacoustic emission measurements, and electrophysiologic tests), audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing (high, middle, or low frequencies) are affected, to what degree (severity of loss), and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found (outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, auditory nerve and/or central nervous system). If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present he or she will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation (e.g. hearing aids, cochlear implants, appropriate medical referrals).
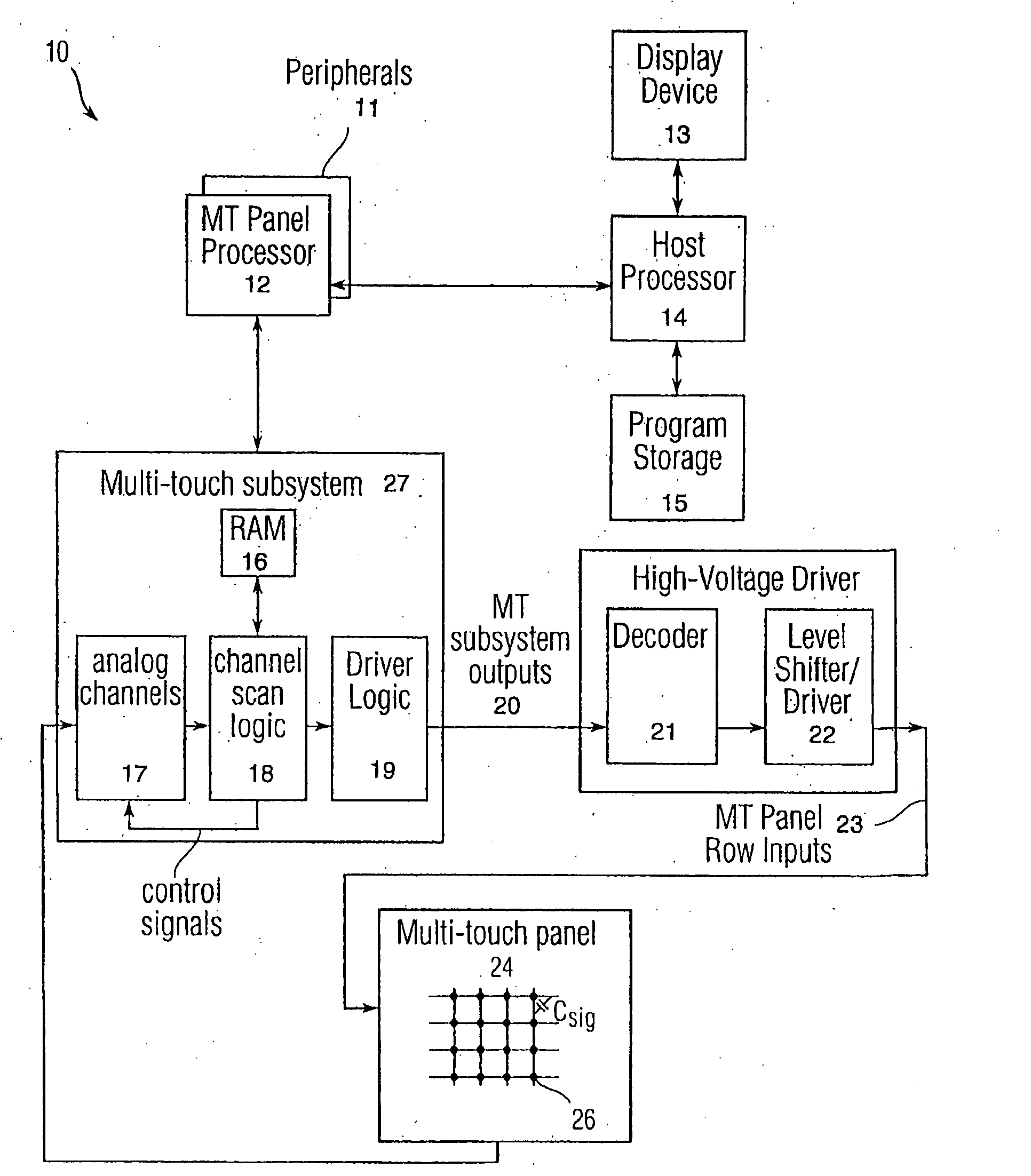
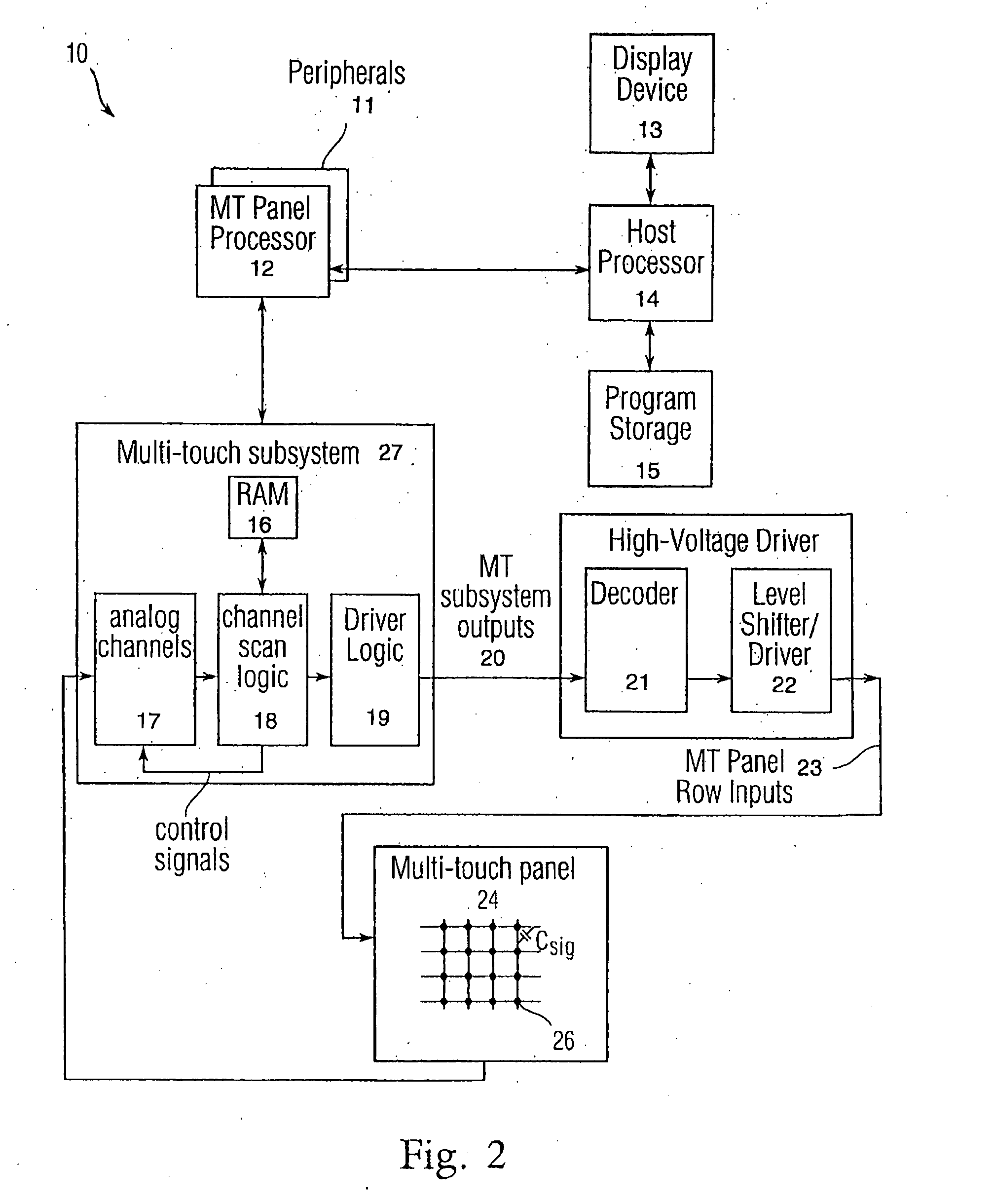
Detecting and interpreting real-world and security gestures on touch and hover sensitive devices
InactiveUS20080168403A1Digital output to display deviceComputer graphics (images)Application software
“Real-world” gestures such as hand or finger movements / orientations that are generally recognized to mean certain things (e.g., an “OK” hand signal generally indicates an affirmative response) can be interpreted by a touch or hover sensitive device to more efficiently and accurately effect intended operations. These gestures can include, but are not limited to, “OK gestures,”“grasp everything gestures,”“stamp of approval gestures,”“circle select gestures,”“X to delete gestures,”“knock to inquire gestures,”“hitchhiker directional gestures,” and “shape gestures.” In addition, gestures can be used to provide identification and allow or deny access to applications, files, and the like.
Owner:APPLE INC
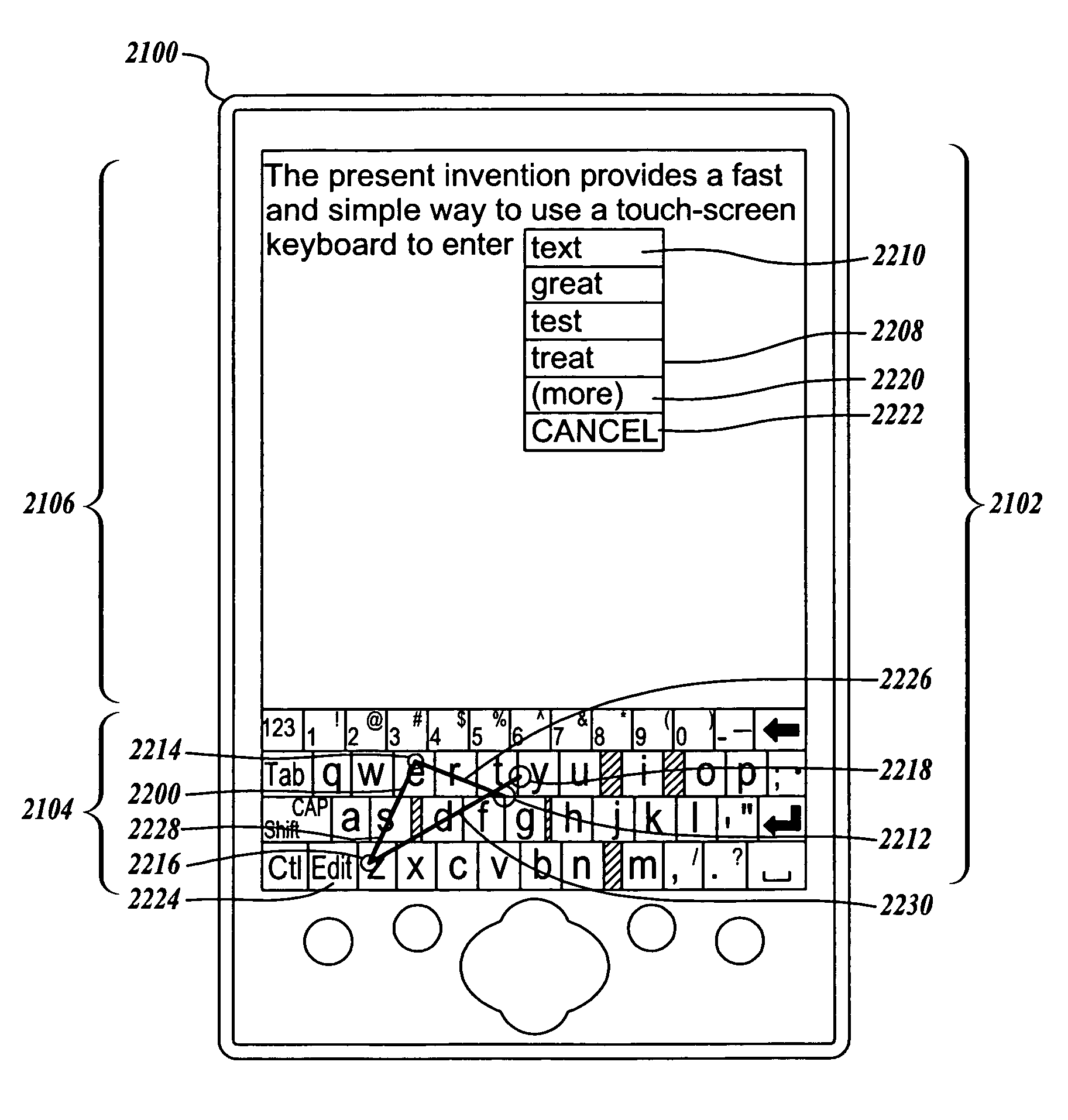
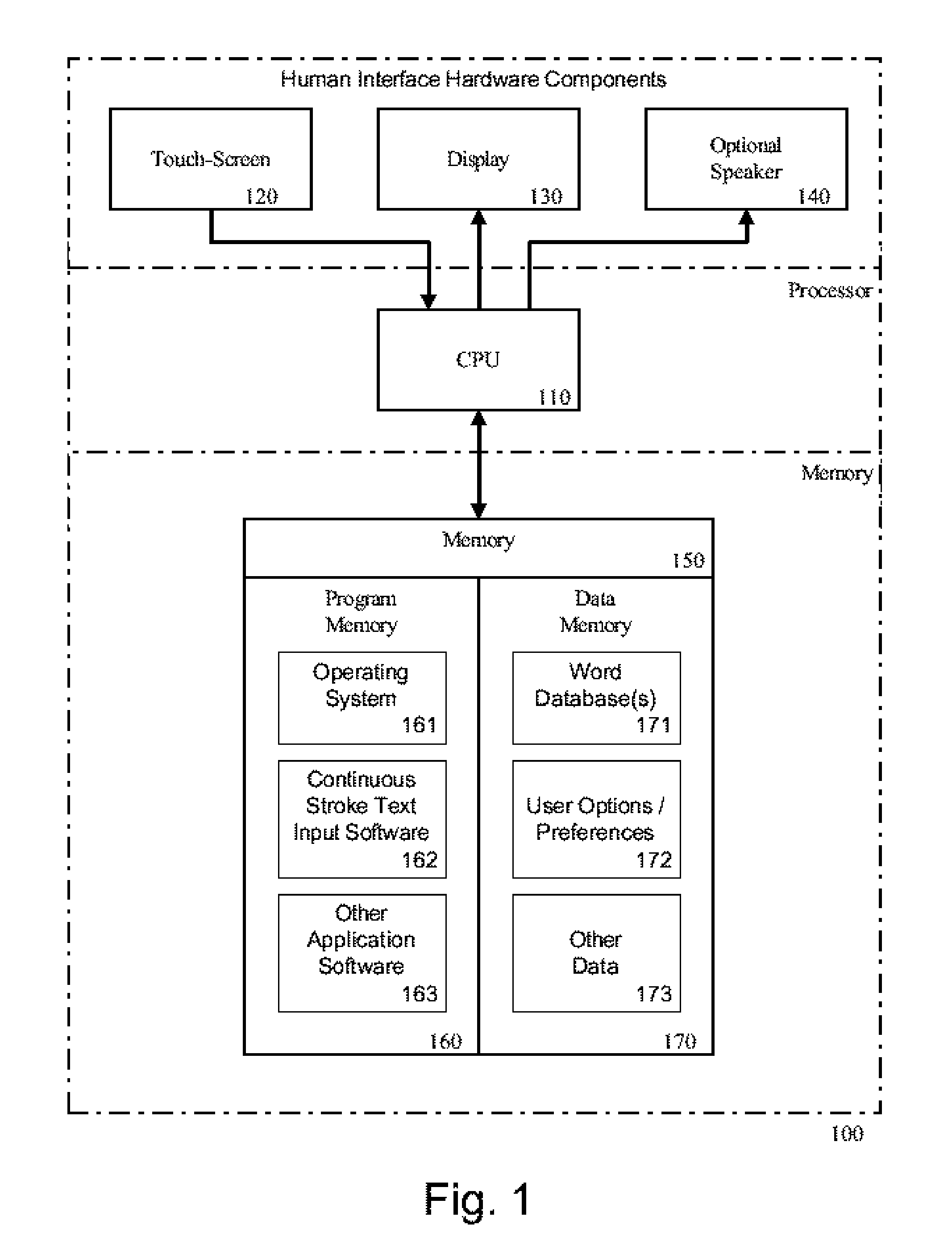
System and method for continuous stroke word-based text input
InactiveUS7453439B1Reduce in quantityIncrease text entry speedInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDistractionText entry
The disclosed System enables a small virtual keyboard on a touch-screen to be used to enter a word by contacting the keyboard on or near the key of the first letter, tracing through or near the key of each letter in sequence, and lifting the stylus from the keyboard in the vicinity of the key of the last letter. The input pattern is matched by scoring it against words in a database which includes an indication of relative frequency. A correctly spelled word is matched even when the input pattern corresponds to an incorrect spelling of a word. Words are ranked according to a score calculated from the weighted distances from each associated key to determined input path points, further weighted by the frequency of use and by other characteristics of the input path. Alternate word choices are presented to the user in a manner to minimize distraction.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
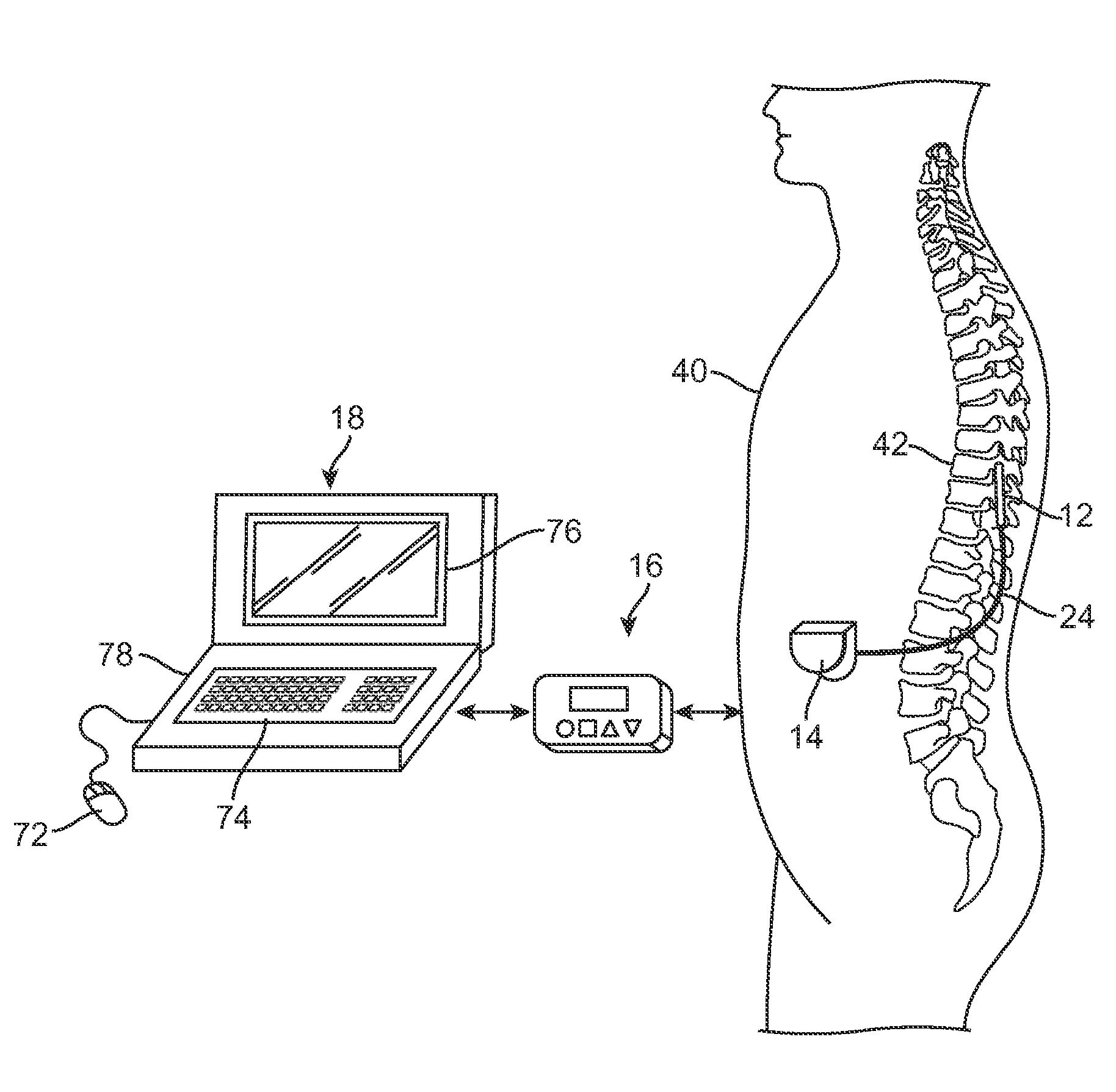
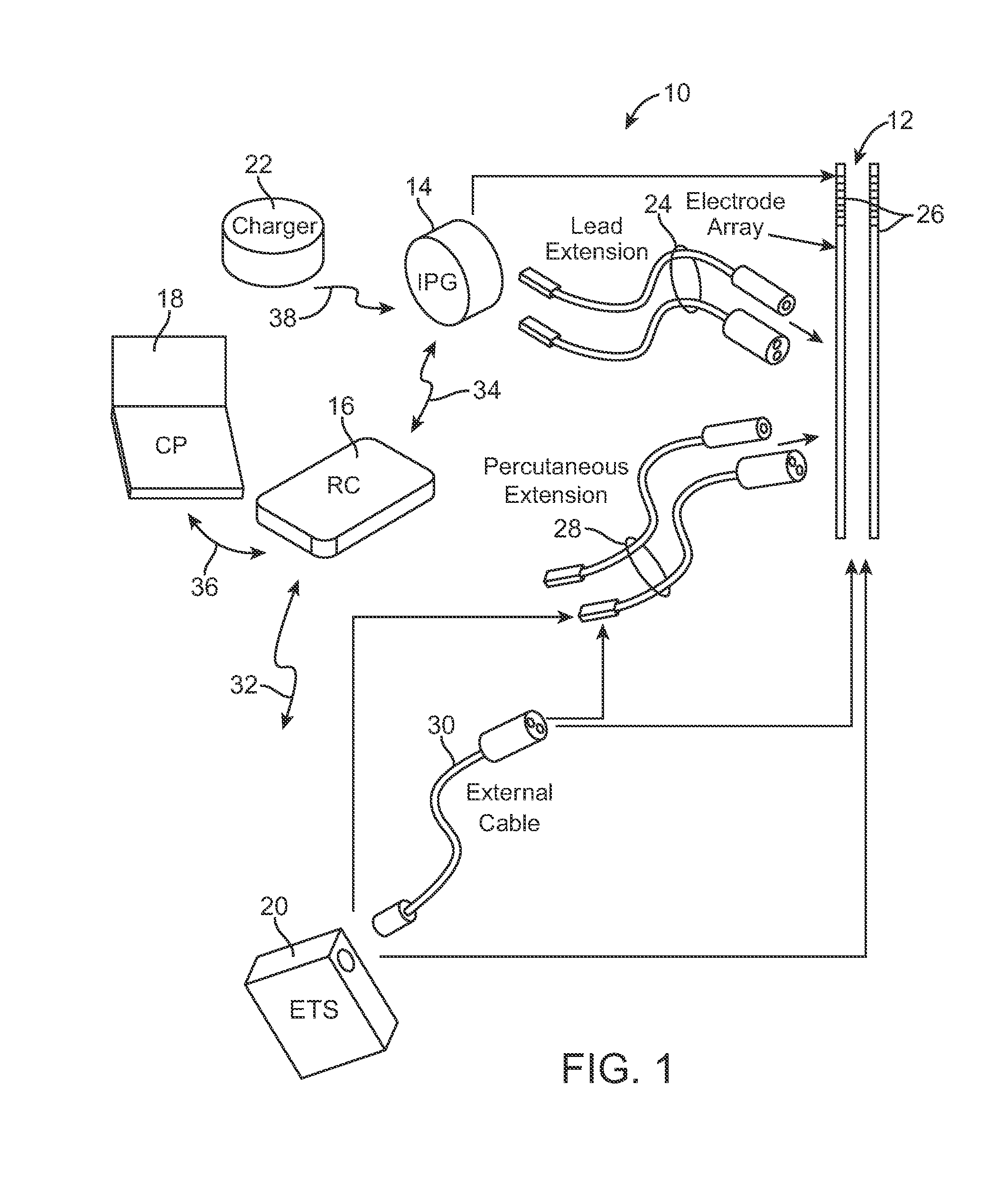
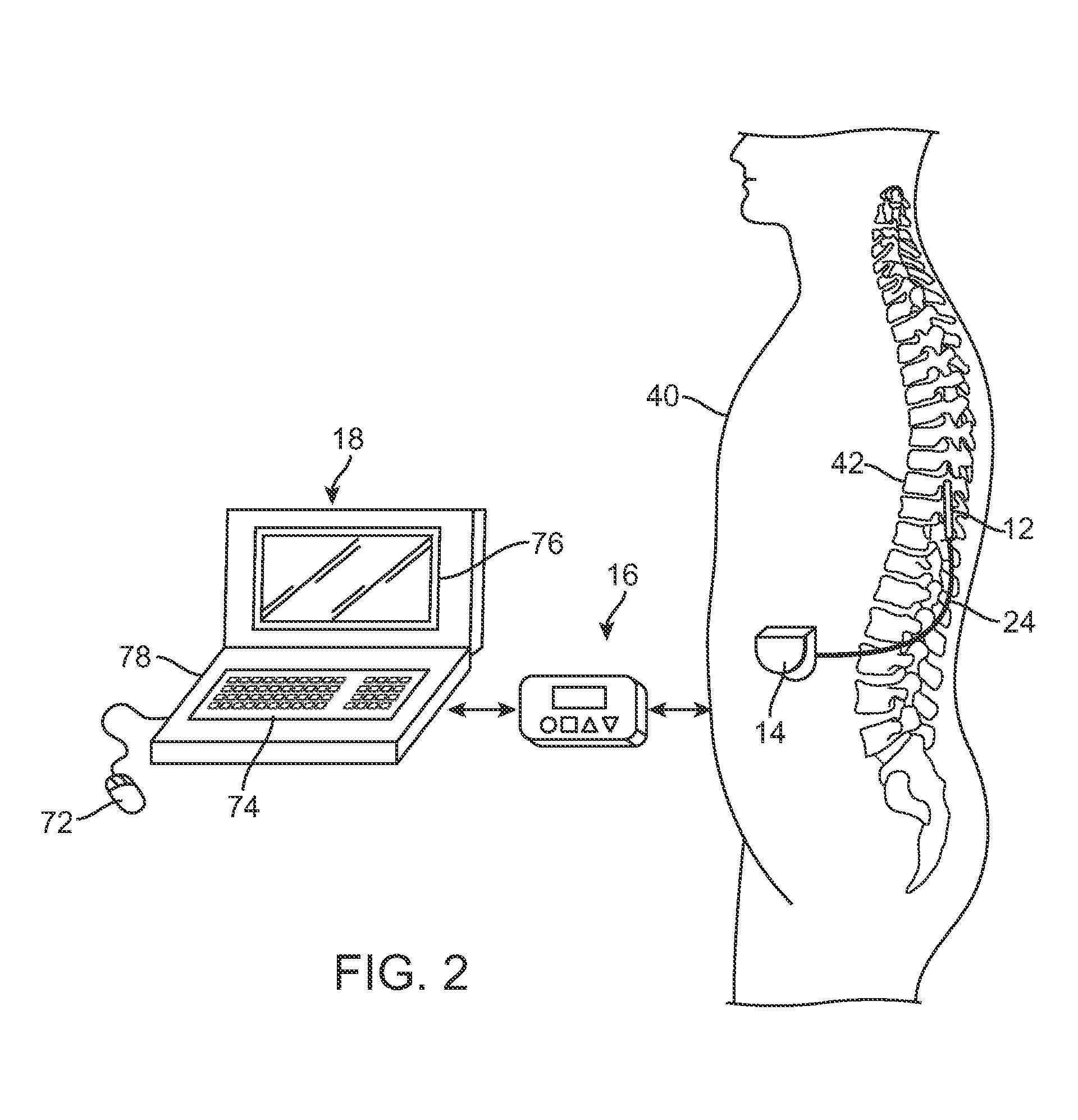
System and method for converting tissue stimulation programs in a format usable by an electrical current steering navigator
A method, computer medium, and system for programming a controller is provided. The controller controls electrical stimulation energy output to electrodes, and stores a set of programmed stimulation parameters associated with the electrodes. The programmed stimulation parameter set is compared with sets of reference stimulation parameters, each of the reference sets of stimulation parameters being associated with the electrodes. If an identical match is determined between the programmed stimulation parameter set and any one of the reference stimulation parameter sets exists based on the comparison, the identically matched stimulation parameter set is selected as an initial stimulation parameter set. If an identical match does not exist, a best between the programmed stimulation parameter set and the reference stimulation parameter sets is determined and selected as the initial stimulation parameter set. The controller is then programmed with a new set of programmable stimulation parameters based on the initial stimulation parameter set.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
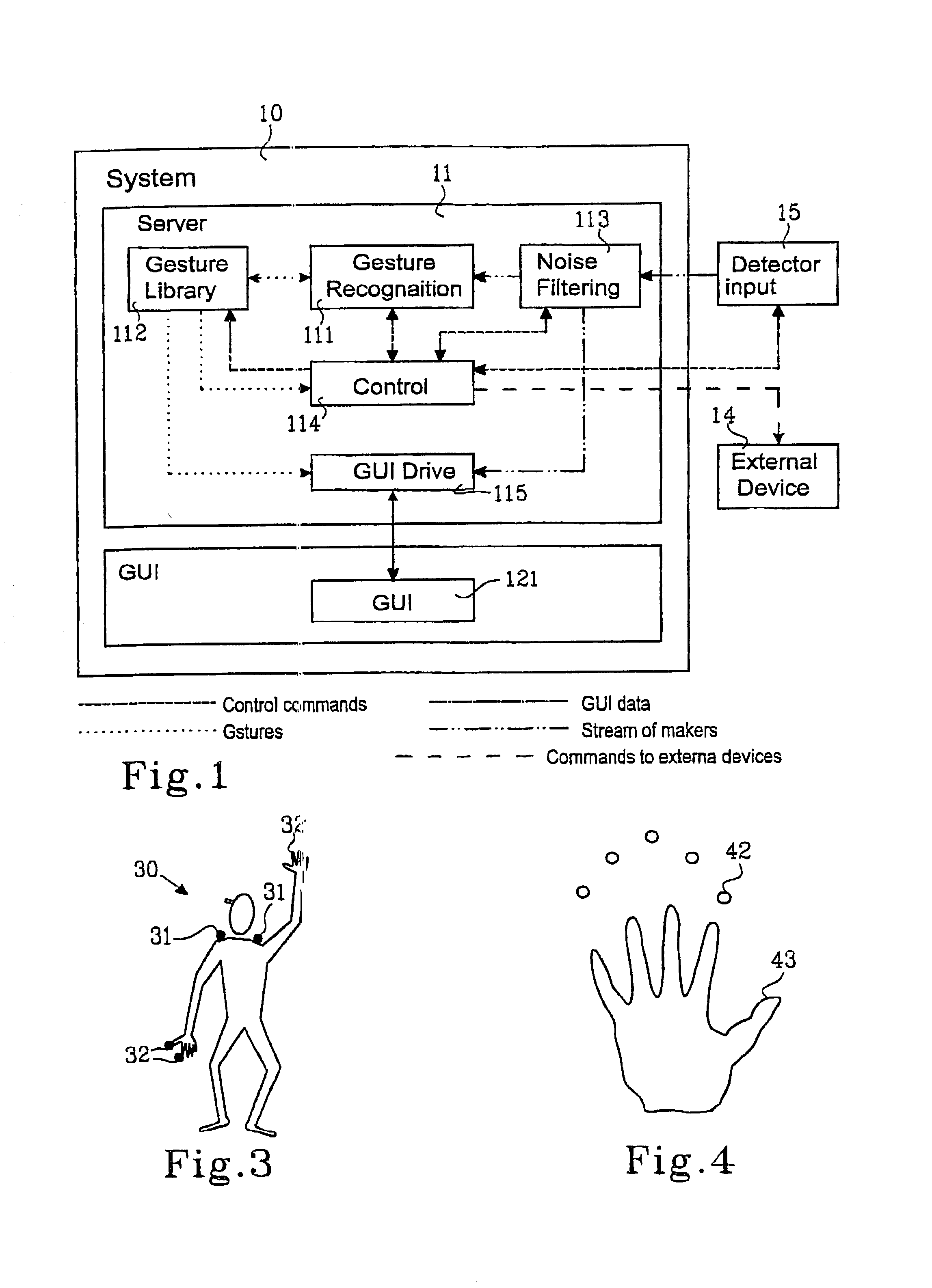
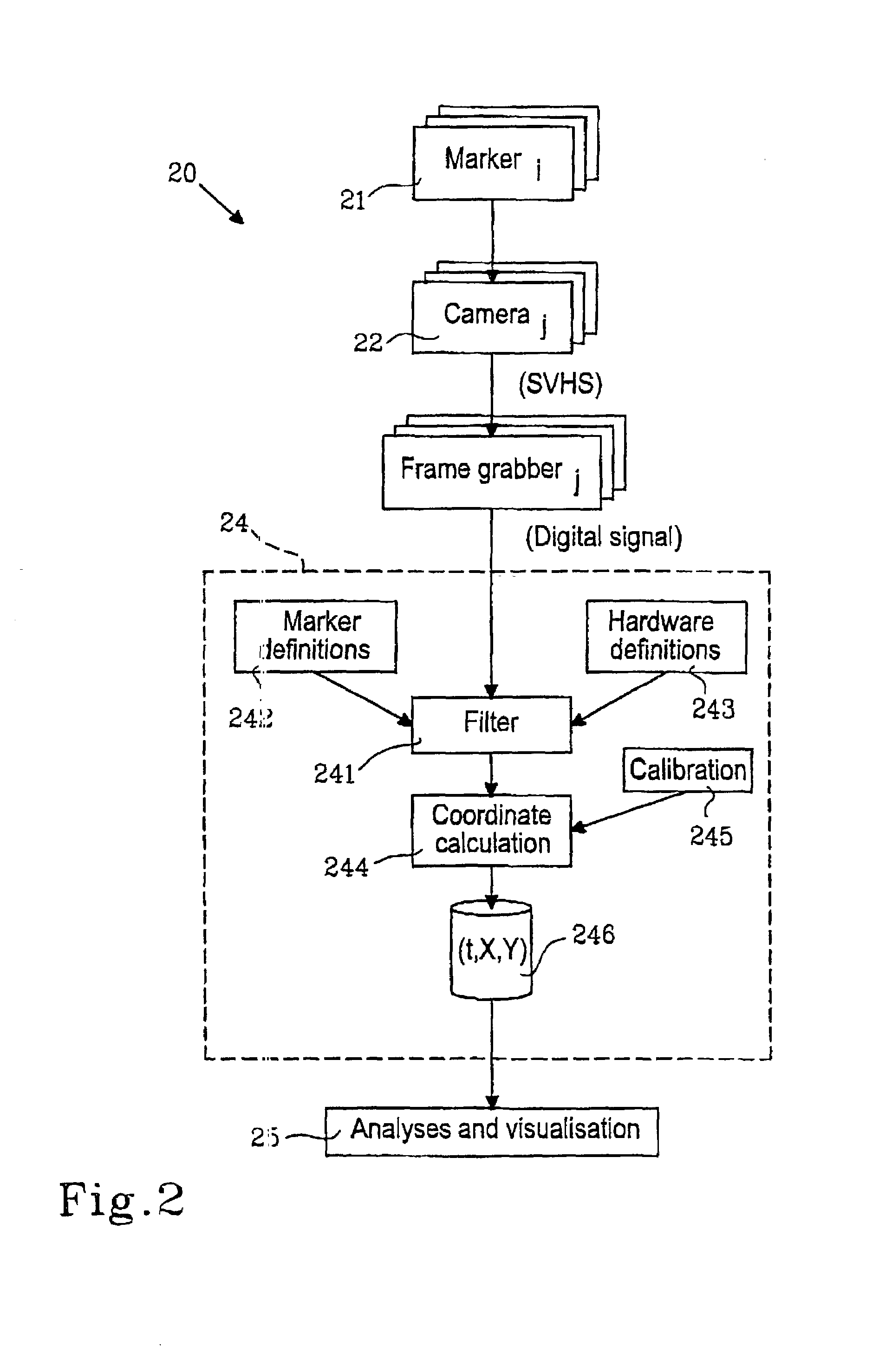
Gesture recognition system
A gesture recognition system includes: elements for detecting and generating a signal corresponding a number of markers arranged on an object, elements for processing the signal from the detecting elements, members for detecting position of the markers in the signal. The markers are divided into first and second set of markers, the first set of markers constituting a reference position and the system comprises elements for detecting movement of the second set of markers and generating a signal as a valid movement with respect to the reference position.
Owner:CREDOBLE
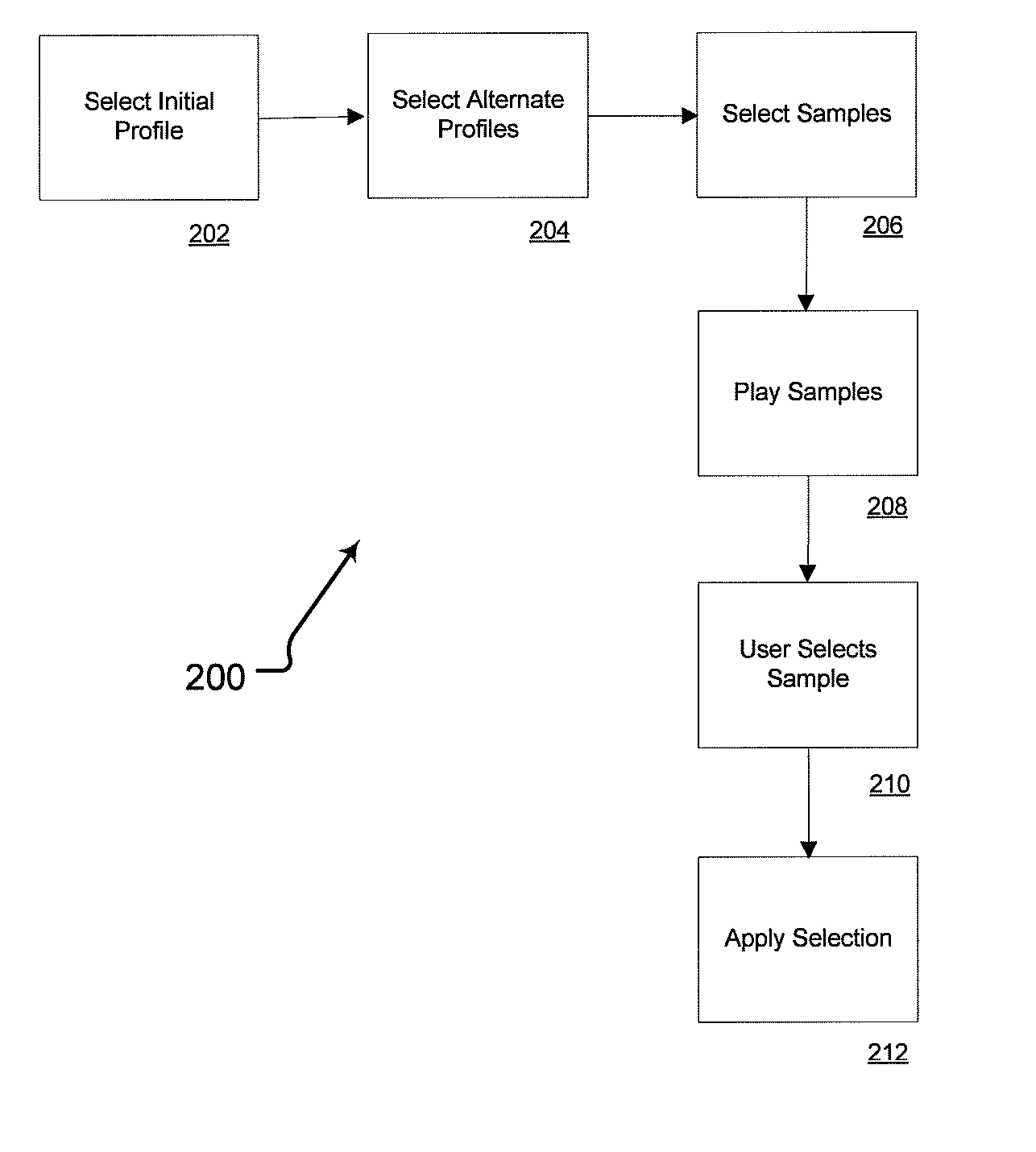
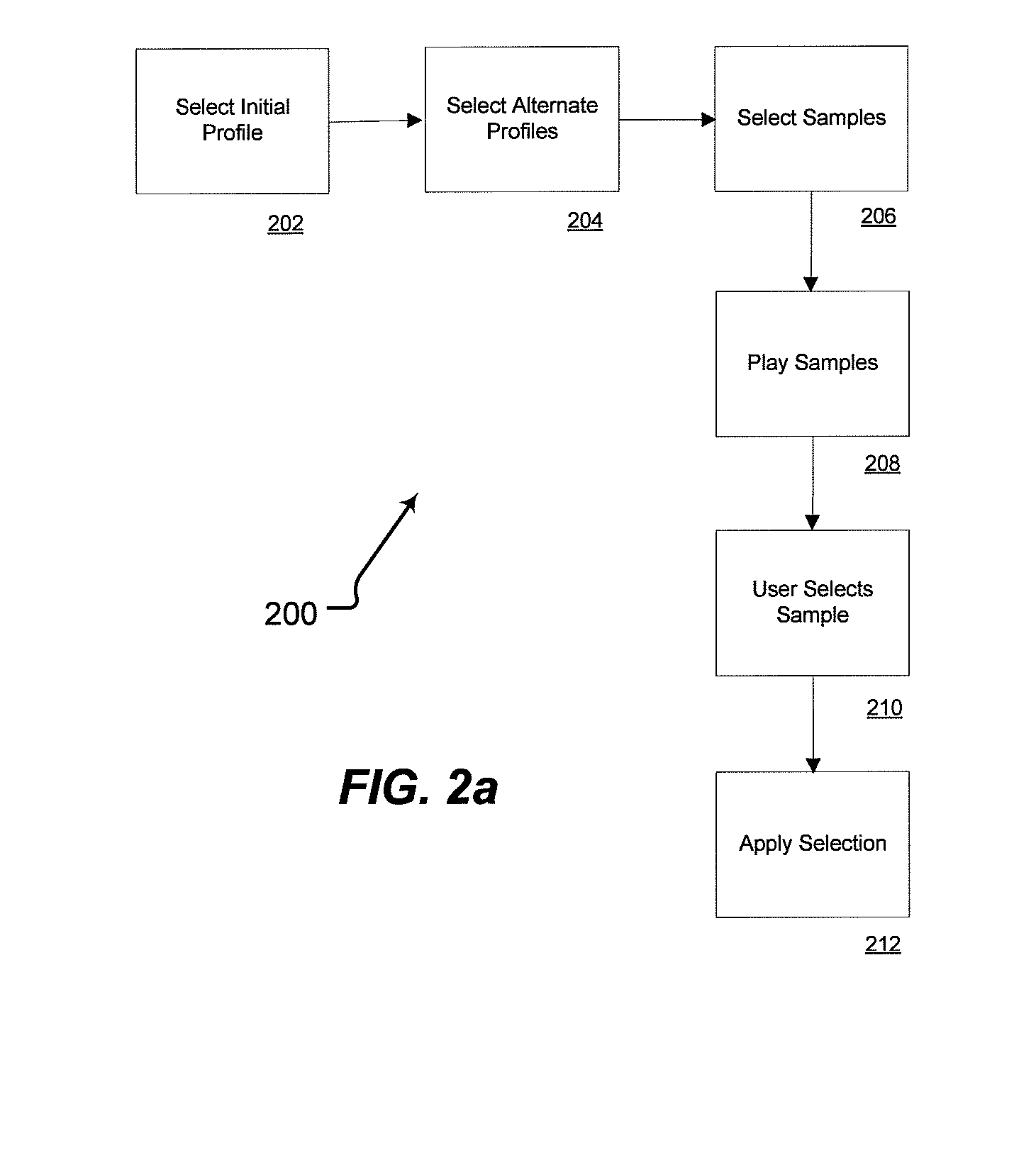
Personalized sound system hearing profile selection process
ActiveUS20080165980A1High sensitivityReduce sensitivityStereophonic circuit arrangementsDigital/coded signal combination controlPersonalizationUser input
A method of generating a personalized sound system hearing profile for a user. The method begins by selecting an initial profile, based on selected factors of user input. In an embodiment, the initial profile is selected based on demographic factors. Then the system identifies one or more alternate profiles, each having a selected relationship with the initial profile. The relationship between alternate profiles and the initial profile can be based on gain as a function of frequency, one alternate profile having a higher sensitivity at given frequencies and the other a lower sensitivity. The next step links at least one audio sample with the initial and alternate profiles and then plays the selected samples for the user. The system then receives identification of the preferred sample from the user; and selects a final profile based on the user's preference. An embodiment offers multiple sound samples in different modes, resulting in the selection of multiple final profiles for the different modes. Finally, the system may apply the final profile to the sound system.
Owner:HIMPP
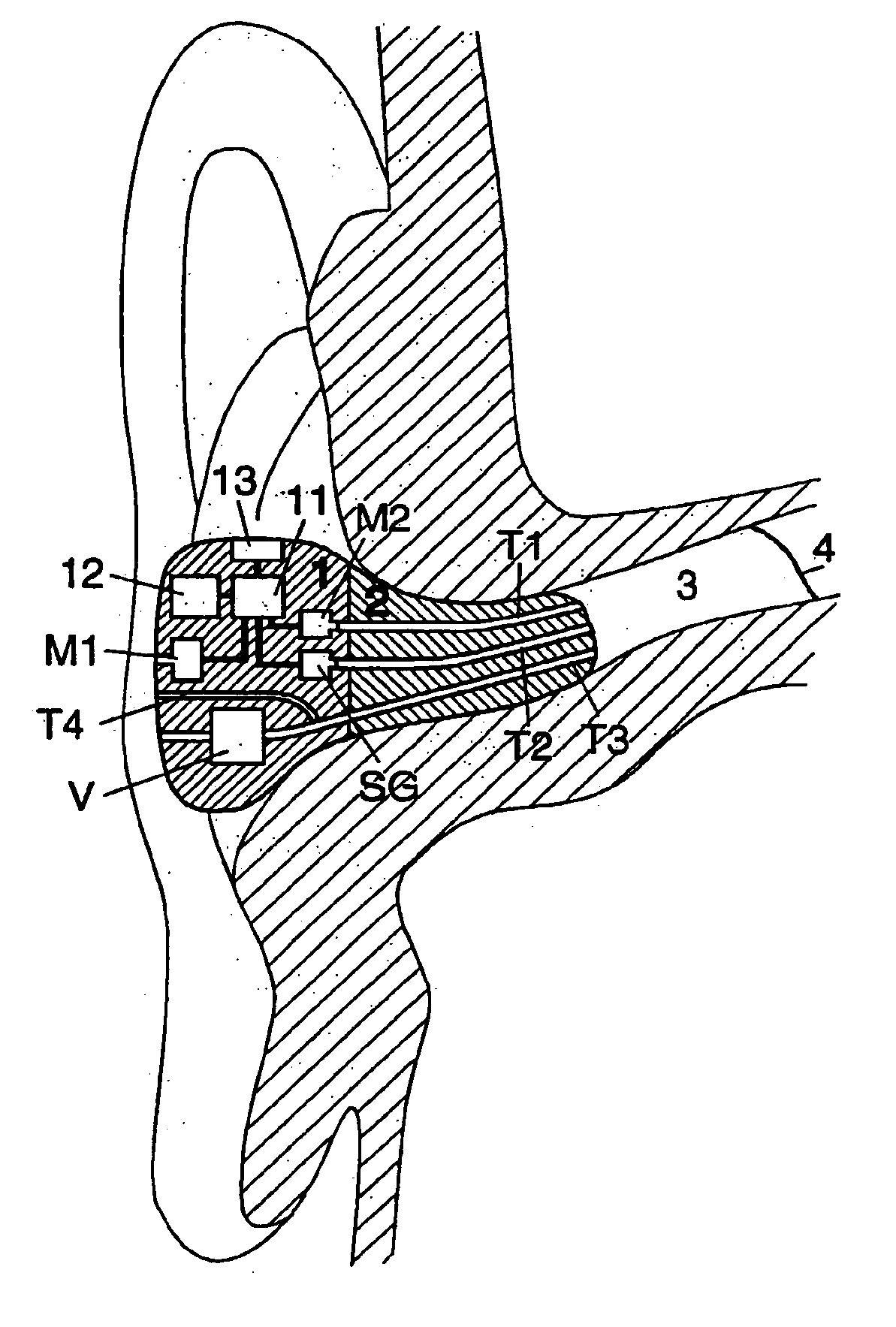
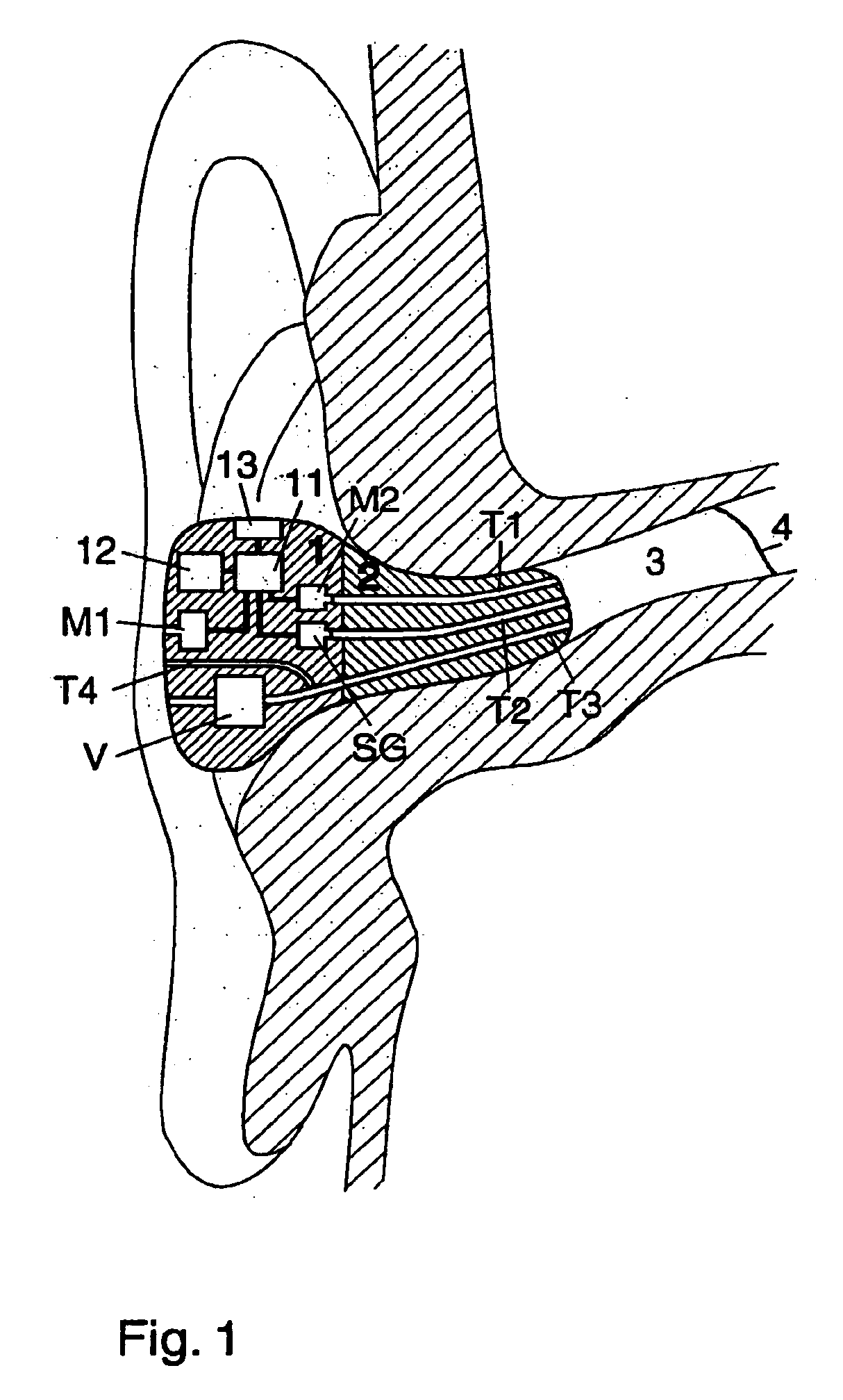
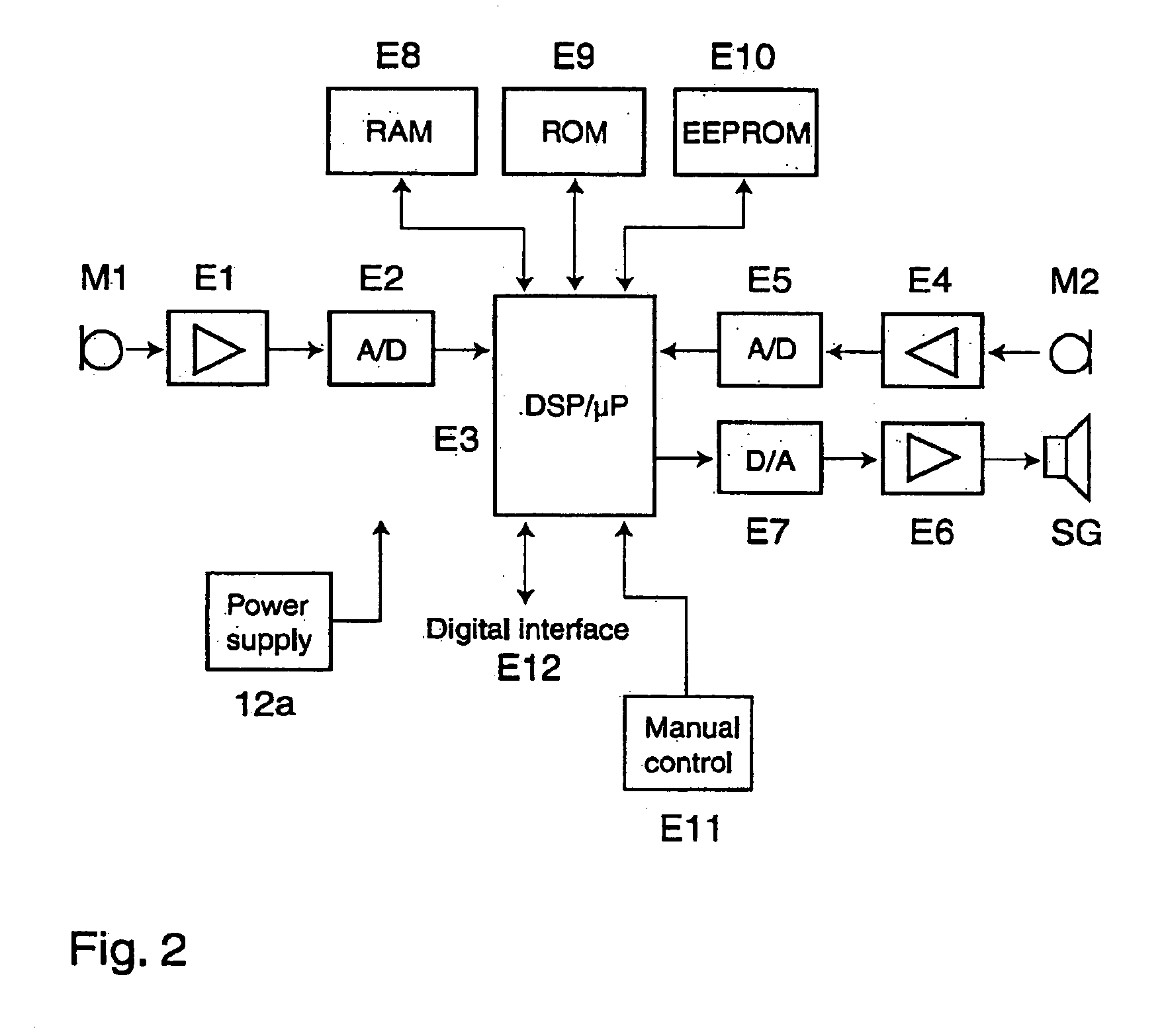
Ear terminal with microphone for voice pickup
InactiveUS6754359B1Hearing protectionQuality improvementSignal processingHearing aids signal processingEngineeringHeadphones
An ear terminal includes a sealing section arranged for use in the ear meatus of a human, with an inner microphone having a sound inlet for being directed into the meatus and an electronic unit including filtering elements coupled to the inner microphone for filtering the signal from the inner microphone, the filtering elements being programmable to transform the signals based on the sounds received in the ear by the inner microphone into sounds having essentially the characteristics of spoken sounds of the wearer of the ear terminal.
Owner:HONEYWELL HEARING TECH
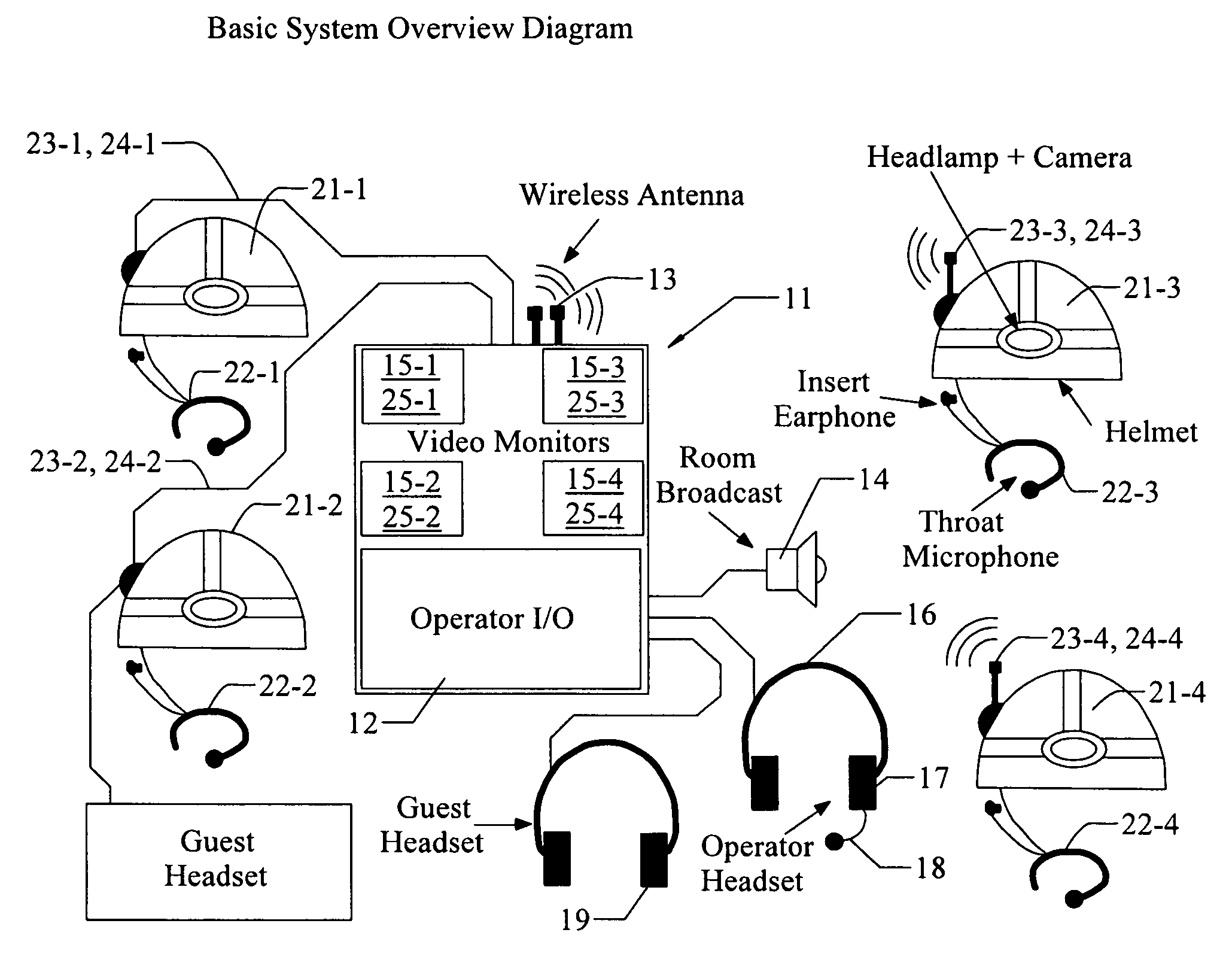
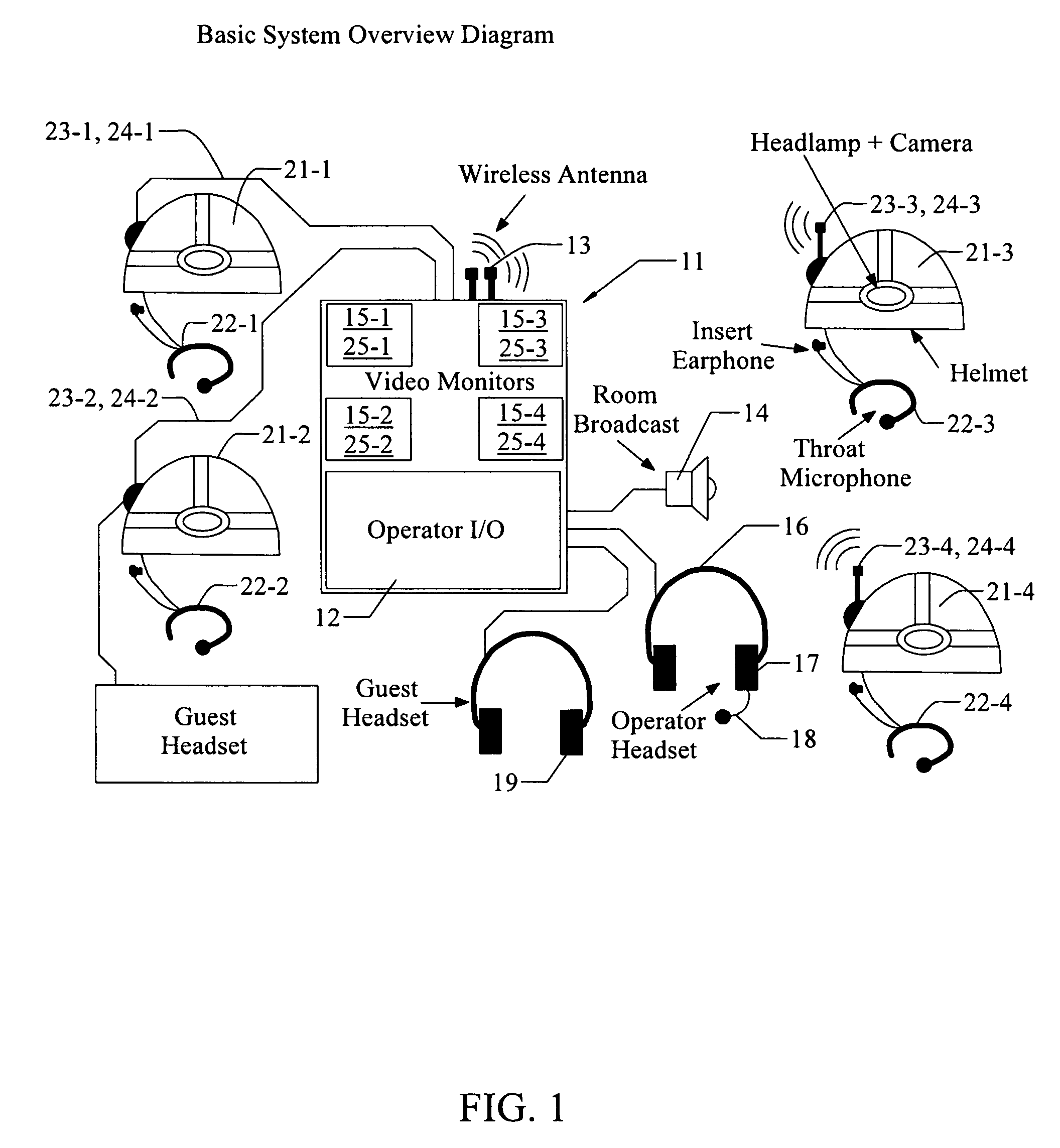
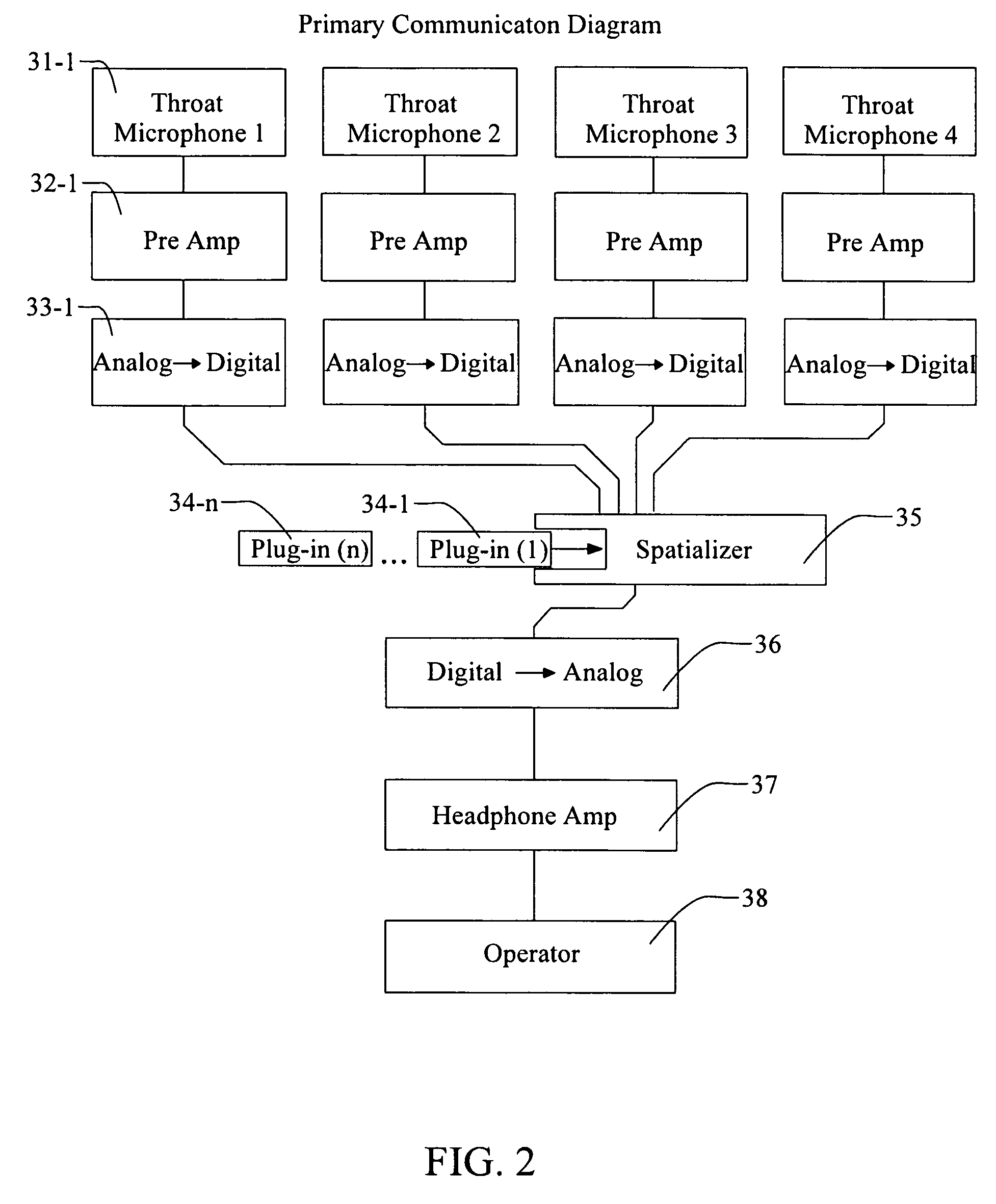
Reconfigurable auditory-visual display
InactiveUS7378963B1Easy to monitorEnhanced speech intelligibility and ease of monitoringCharacter and pattern recognitionAlarmsAuditory visualTransceiver
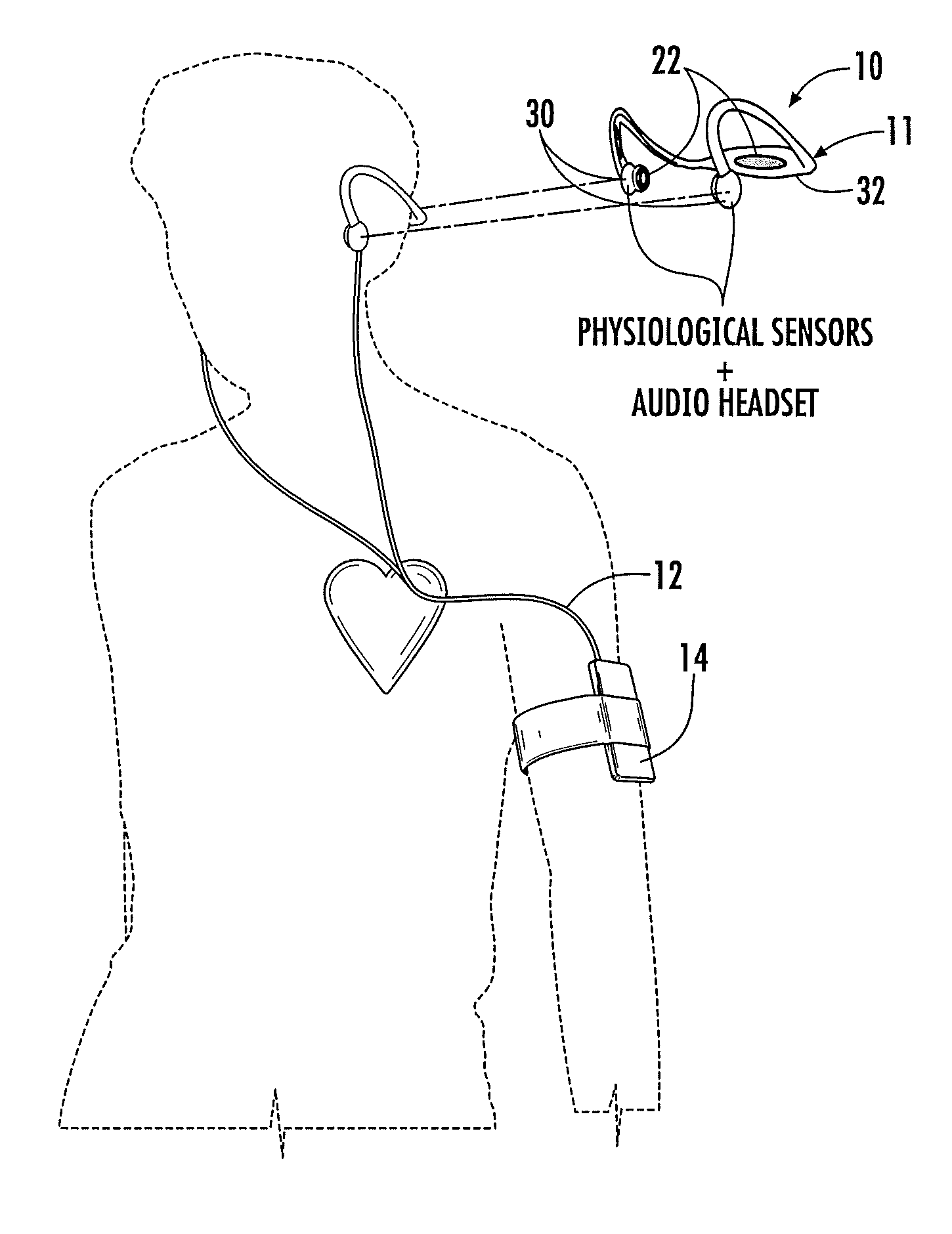
System and method for visual and audible communication between a central operator and N mobile communicators (N≧2), including an operator transceiver and interface, configured to receive and display, for the operator, visually perceptible and audibly perceptible signals from each of the mobile communicators. The interface (1) presents an audible signal from each communicator as if the audible signal is received from a different location relative to the operator and (2) allows the operator to select, to assign priority to, and to display, the visual signals and the audible signals received from a specified communicator. Each communicator has an associated signal transmitter that is configured to transmit at least one of the visual signal and the audio signal associated with the communicator, where at least one of the signal transmitters includes at least one sensor that senses and transmits a sensor value representing a selected environmental or physiological parameter associated with the communicator.
Owner:NASA
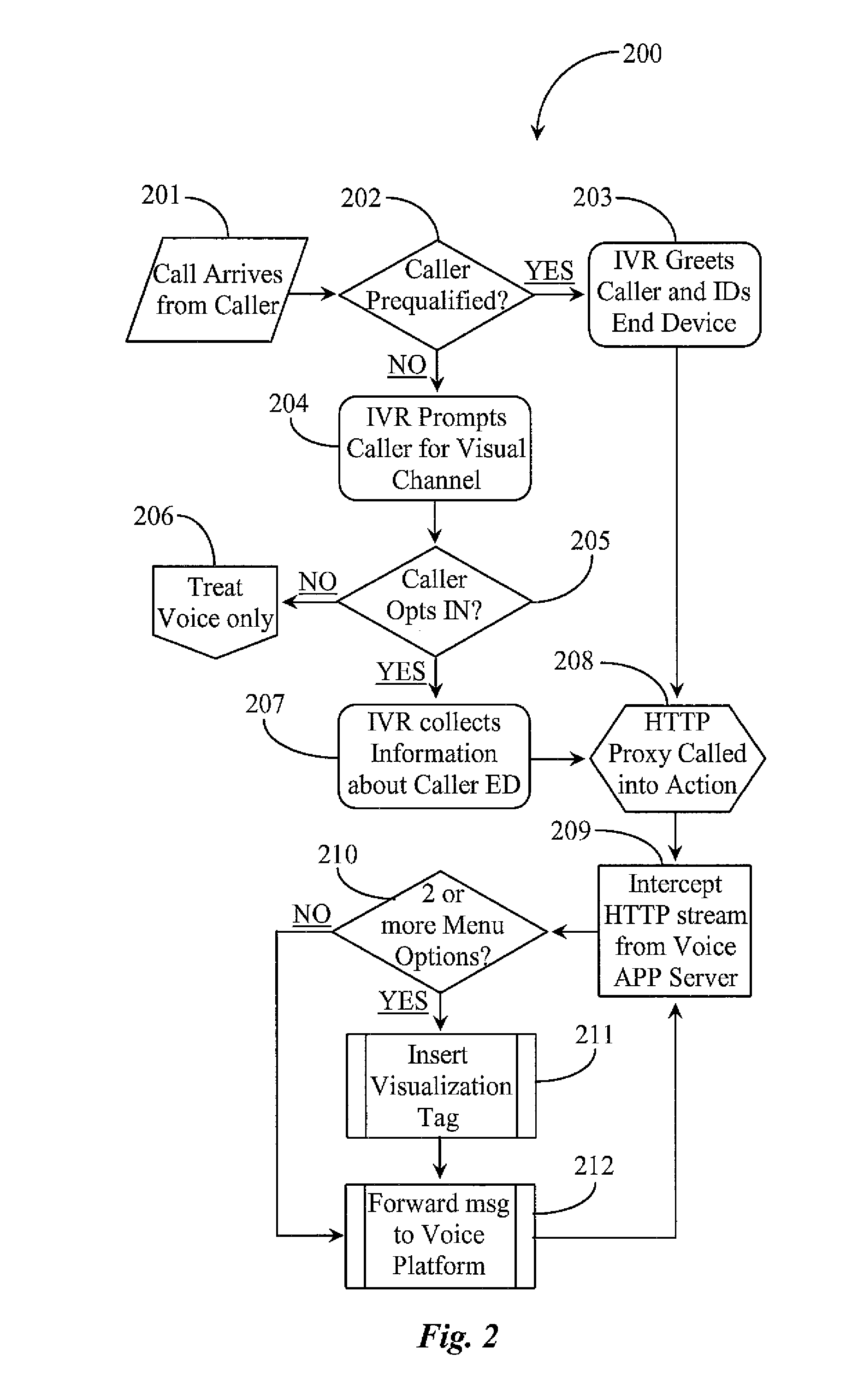
Voice Response Processing
InactiveUS20110211679A1Increase delayMost efficientSpecial service for subscribersMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsSpeech soundCommunication device
A method for transmitting choices to a caller has steps of (a) interacting by voice with a caller using a communication device; (b) encountering a point in the interaction that a choice between two or more options is to be provided to the caller; (c) determining if the caller's communication device is capable of receiving a text message; (d) selecting a compatible text message comprising the options; (e) associating with the text message a text message destination address to the caller's device; and (f) transmitting the text message to the caller's device. The interaction may be by IVR or by a live agent.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS +1
Processing methods and apparatus for monitoring physiological parameters using physiological characteristics present within an auditory canal
Methods and apparatus for monitoring at least one physiological parameter of an animal from one or more physiological characteristics present within an auditory canal of the animal. Physiological parameters are measured by sensing at least one physiological characteristic present within the auditory canal of the animal, the at least one physiological characteristic associated with a physiological parameter, and processing the at least one sensed physiological characteristic at a device positioned remotely from the auditory canal to determine the physiological parameter.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP
Video and audio conferencing system with spatial audio
ActiveUS20060104458A1Good directional beamEasy to separateMicrophonesSignal processingSide informationDisplay device
In some embodiments, spatially realistic audio may be provided for a conference call. Voices from participants on the left side of a display, in a conference call, may be directed through audio on the left side of the display at the other conferencing system in the conference call (similarly for voices from the center and right side of the display). In some embodiments, two speakers may be used in the system to create synthesized stereo sound at a location specified by directional information received as side information along with the existing audio channel. The location may be determined by using beamforming with integrated microphones on a camera or speakerphone. In some embodiments, the audio signal and directional information may be sent in the form of a left audio channel and a right audio channel.
Owner:LIFESIZE INC
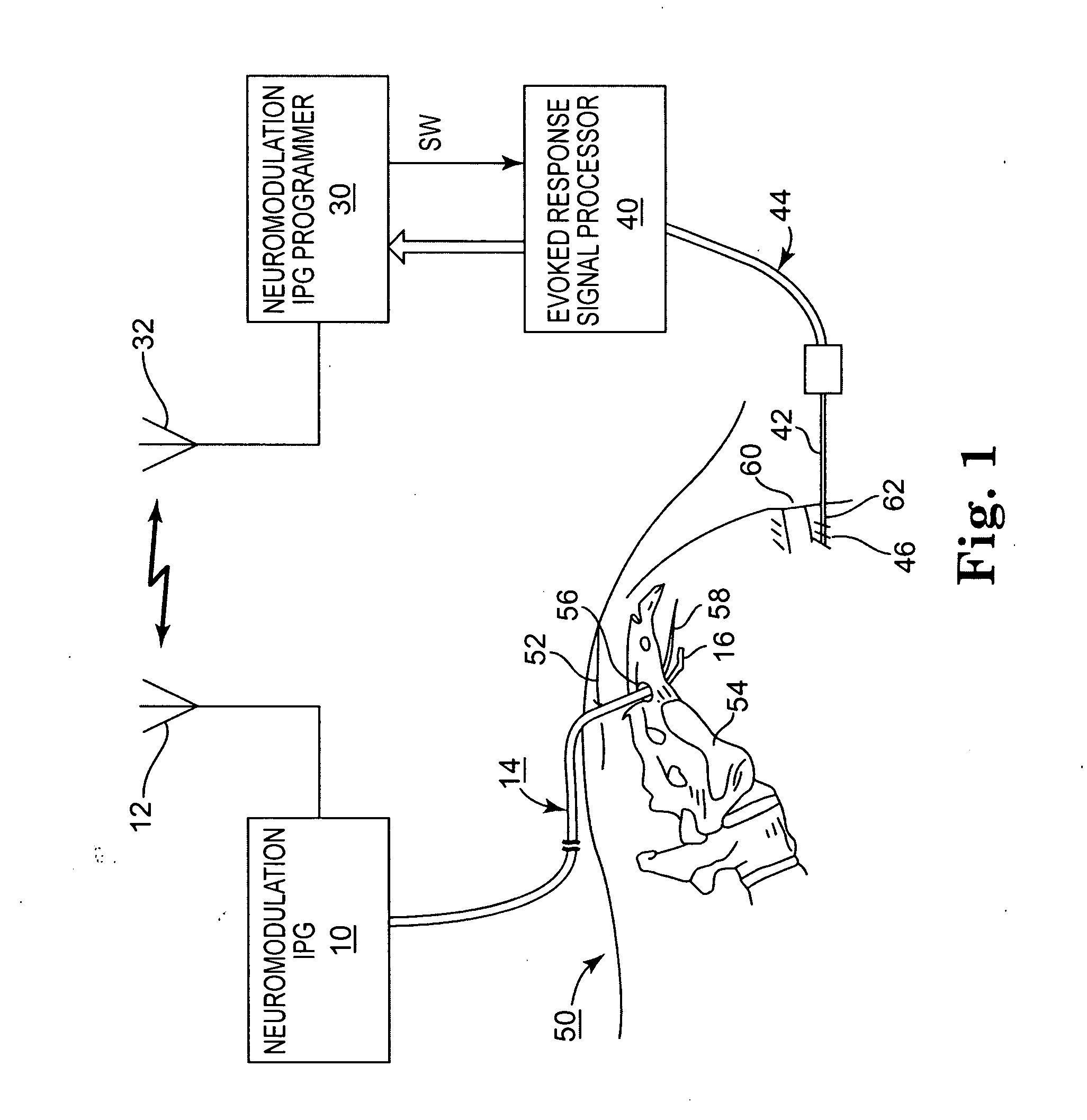
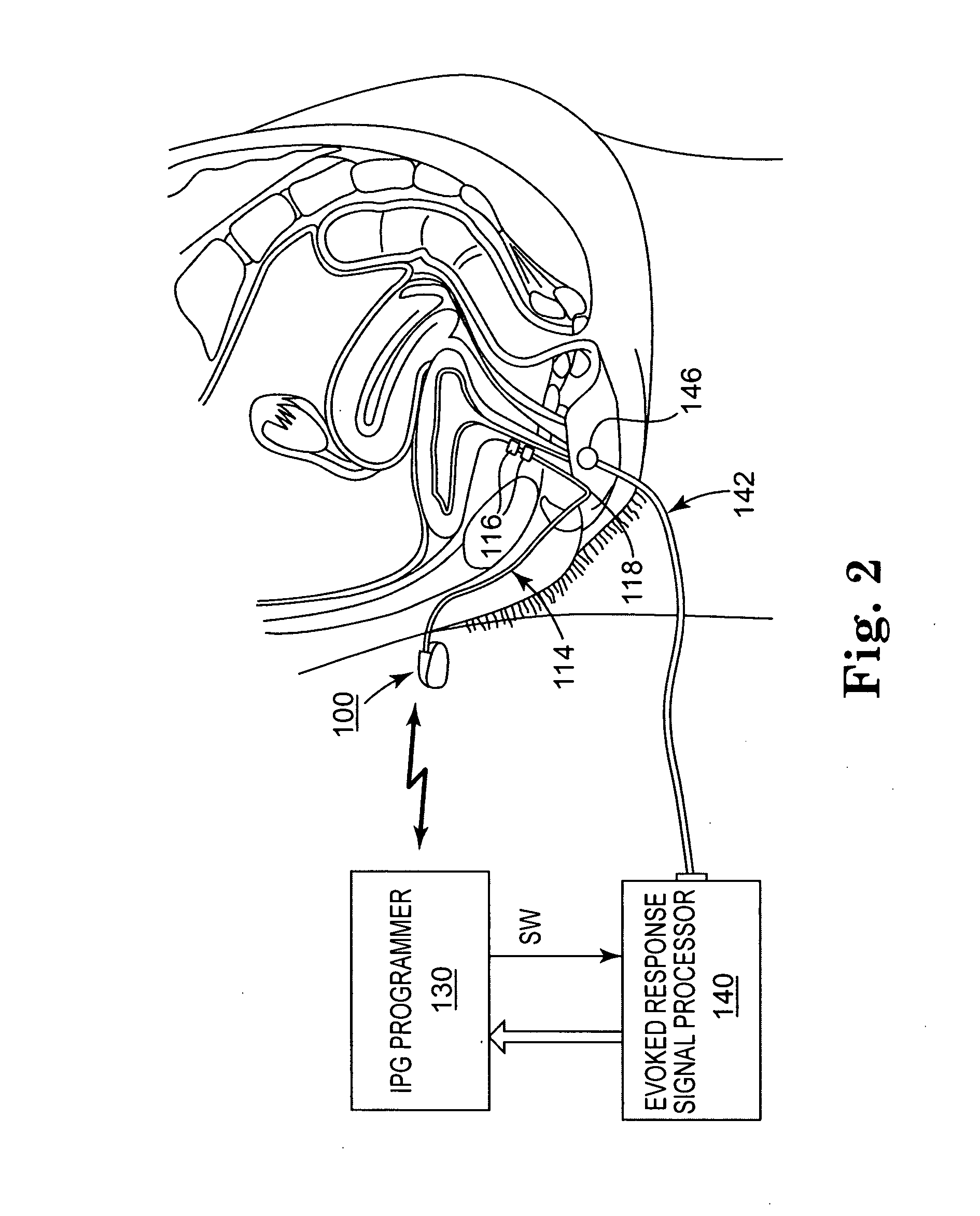
Testing Efficacy of Therapeutic Mechanical or Electrical Nerve or Muscle Stimulation
InactiveUS20070265675A1Rule out the possibilityReduce complicationsElectrotherapyMuscle tissuePelvic nerve
Methods and apparatus for testing of the efficacy of therapeutic stimulation of pelvic nerves or musculature to alleviate one of incontinence or sexual dysfunction are disclosed. A therapy delivery device is operable in a therapy delivery mode and a test mode and an evoked response detector is employed in the test mode to detect the evoked response to applied test stimuli. The test stimuli parameters of the test stimulation regimen are adjusted prior to delivery of each test stimulation regimen, and the evoked responses to the applied test stimulation regimens are compared to ascertain an optimal test stimulation regimen. The therapy stimulation regimen parameters are selected as a function of the test electrical stimulation parameters causing the optimal evoked response.
Owner:AMS RES CORP
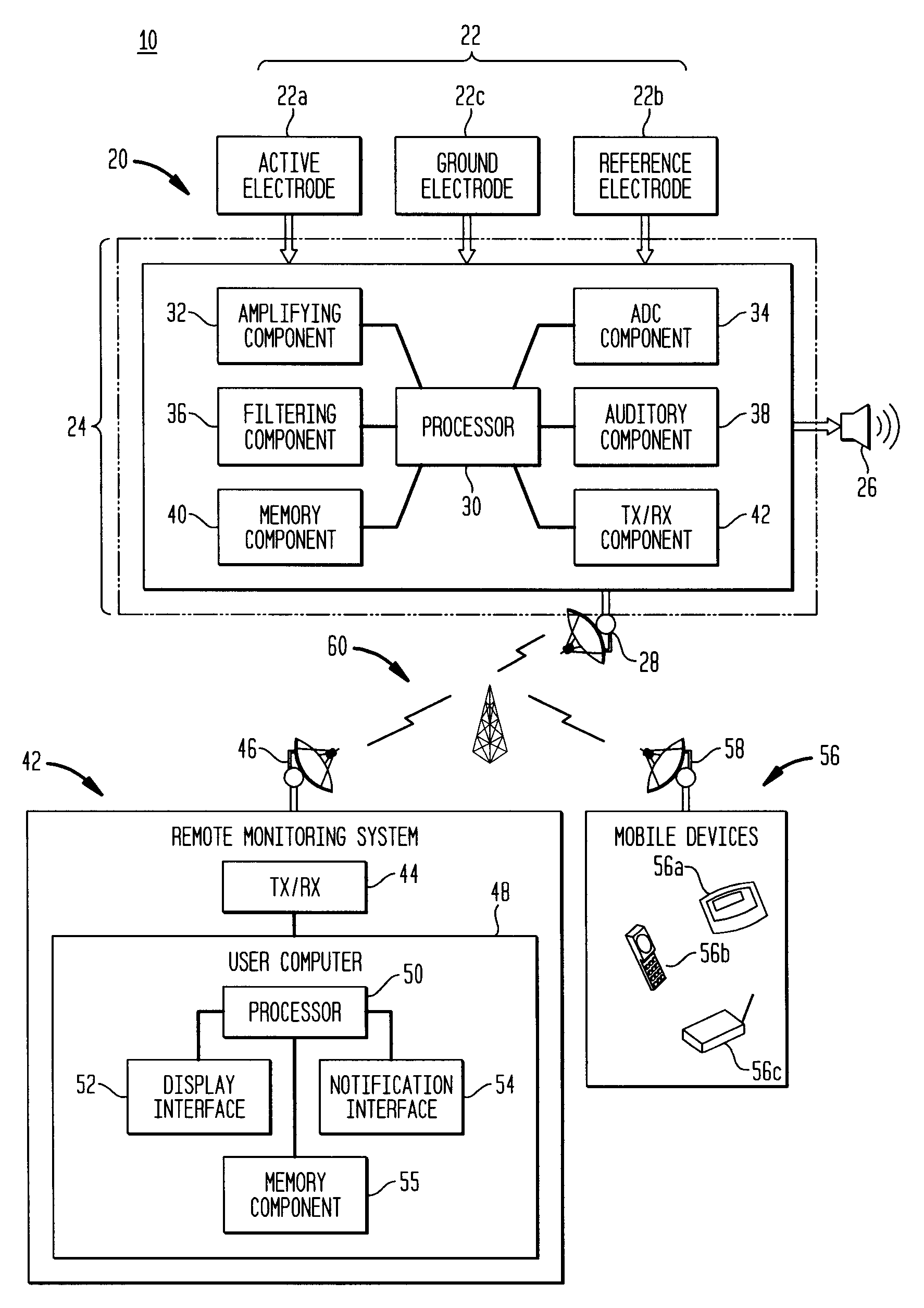
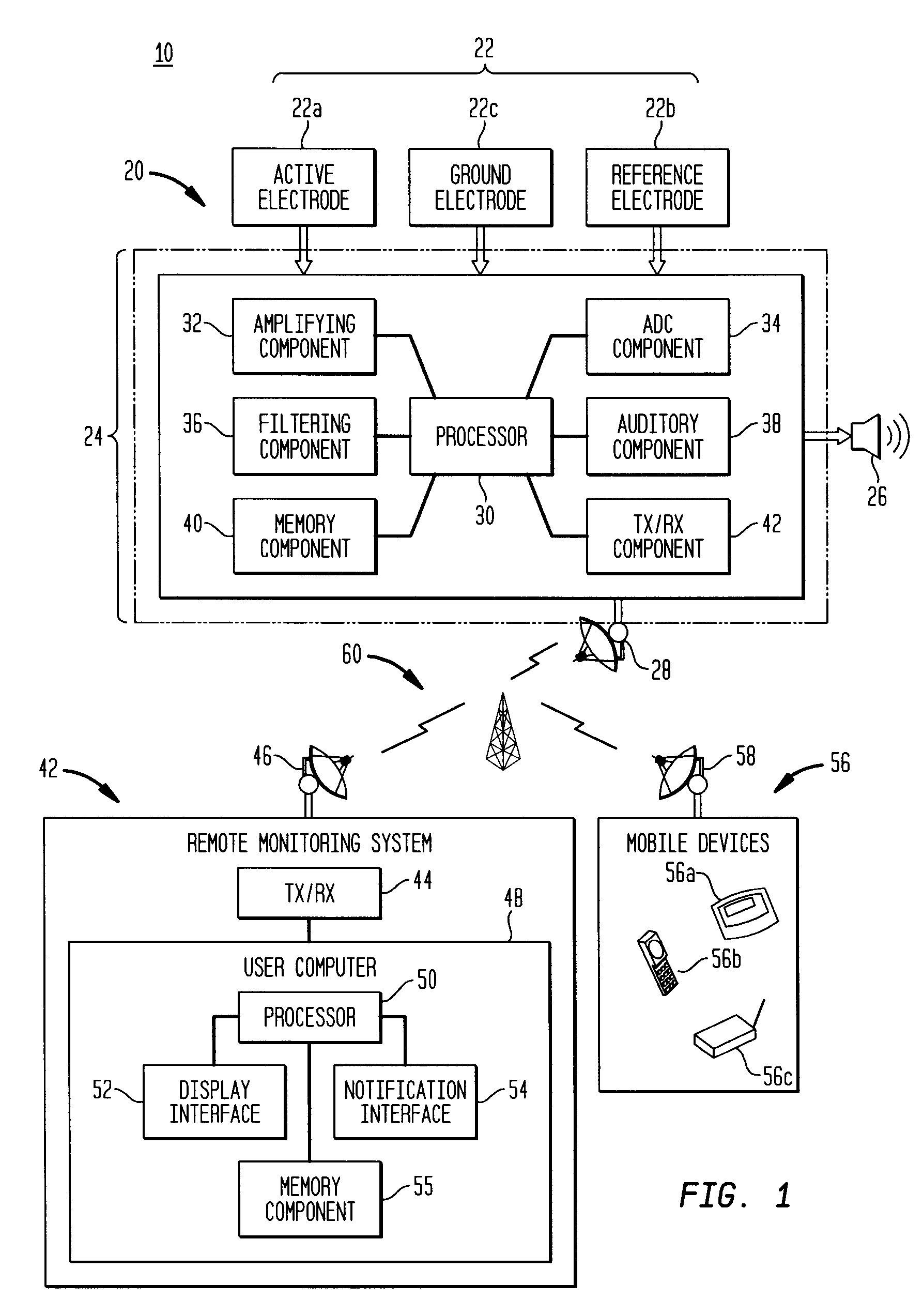
Apparatus and method for the measurement and monitoring of bioelectric signal patterns
InactiveUS20070112277A1Less cumbersomeMinimally invasiveElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyAuditory stimuliMeasurement device
A wireless apparatus and method for the measurement and monitoring of bioelectric signal patterns associated with EEG, EOG and EMG readings is provided. The apparatus is comprised of at least one measurement device employing the use of three bioelectric sensing electrodes, wherein at least one of the electrodes is configured for secure placement within the ear canal of an individual under medical surveillance. Acoustic stimulation may be provided directly into the ear canal of the individual via an auditory stimulus emitted from the measurement device for evoking brain activity and the subsequent measurement of bioelectric signal patterns associated with the evoked activity.
Owner:FISCHER RUSSELL J +3
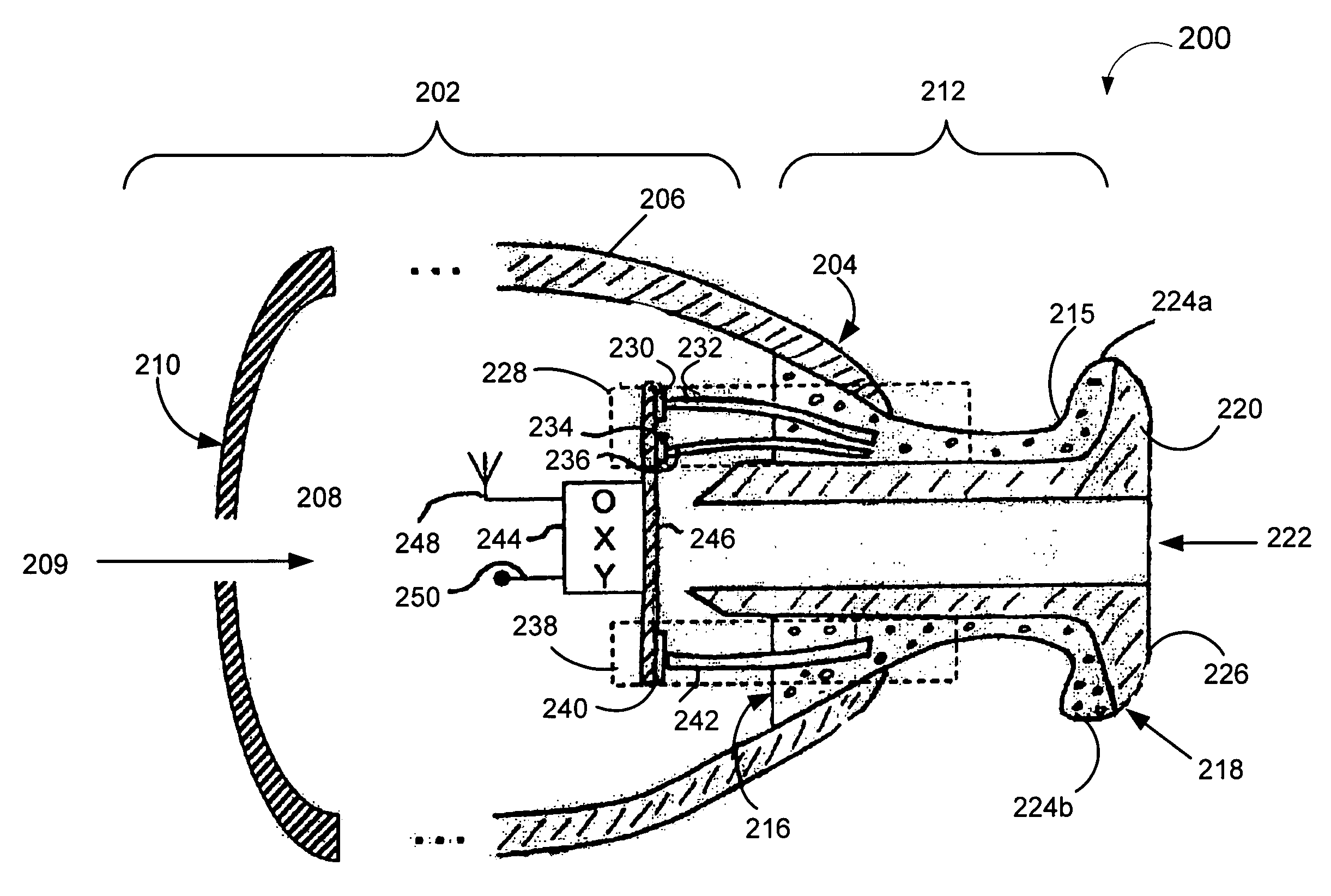
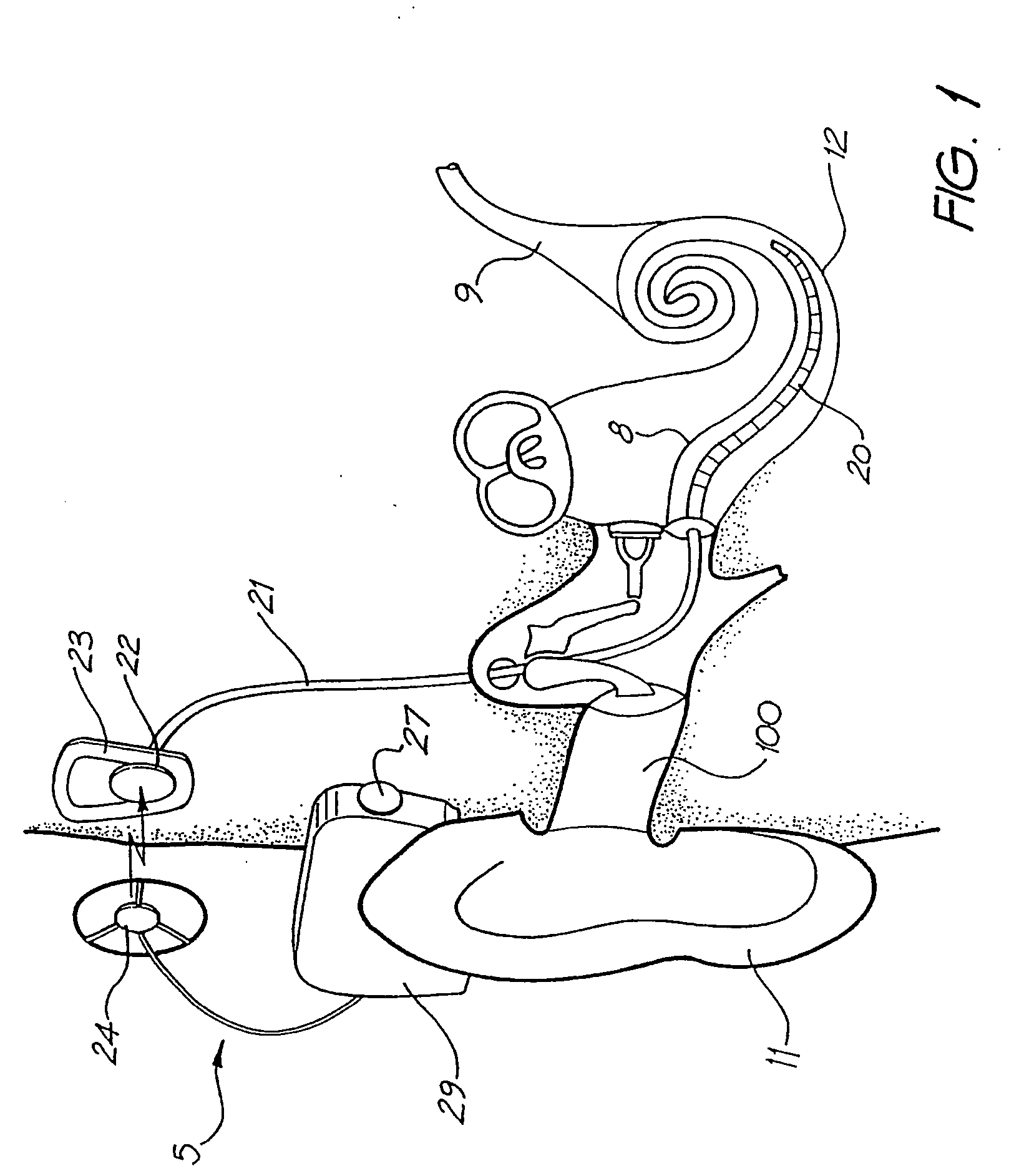
Pulse oximetry methods and apparatus for use within an auditory canal
Methods and apparatus for detecting oxygen saturation levels in blood from within an auditory canal of a living being proximal to a tympanic membrane are disclosed. The auditory canal is lined with tissue and includes a proximal bend and a distal bend located between the proximal bend and the tympanic membrane. Oxygen levels are detected by emitting one or more wavelengths of light into a first position on the tissue of the auditory canal in a first region defined by the distal bend and the tympanic membrane. The wavelengths of light are then sensed at a second position on the tissue of the auditory canal in the first region. A blood oxygen saturation level and / or pulse rate is then calculated responsive to intensity information corresponding to the wavelengths of light detected at the second position.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP
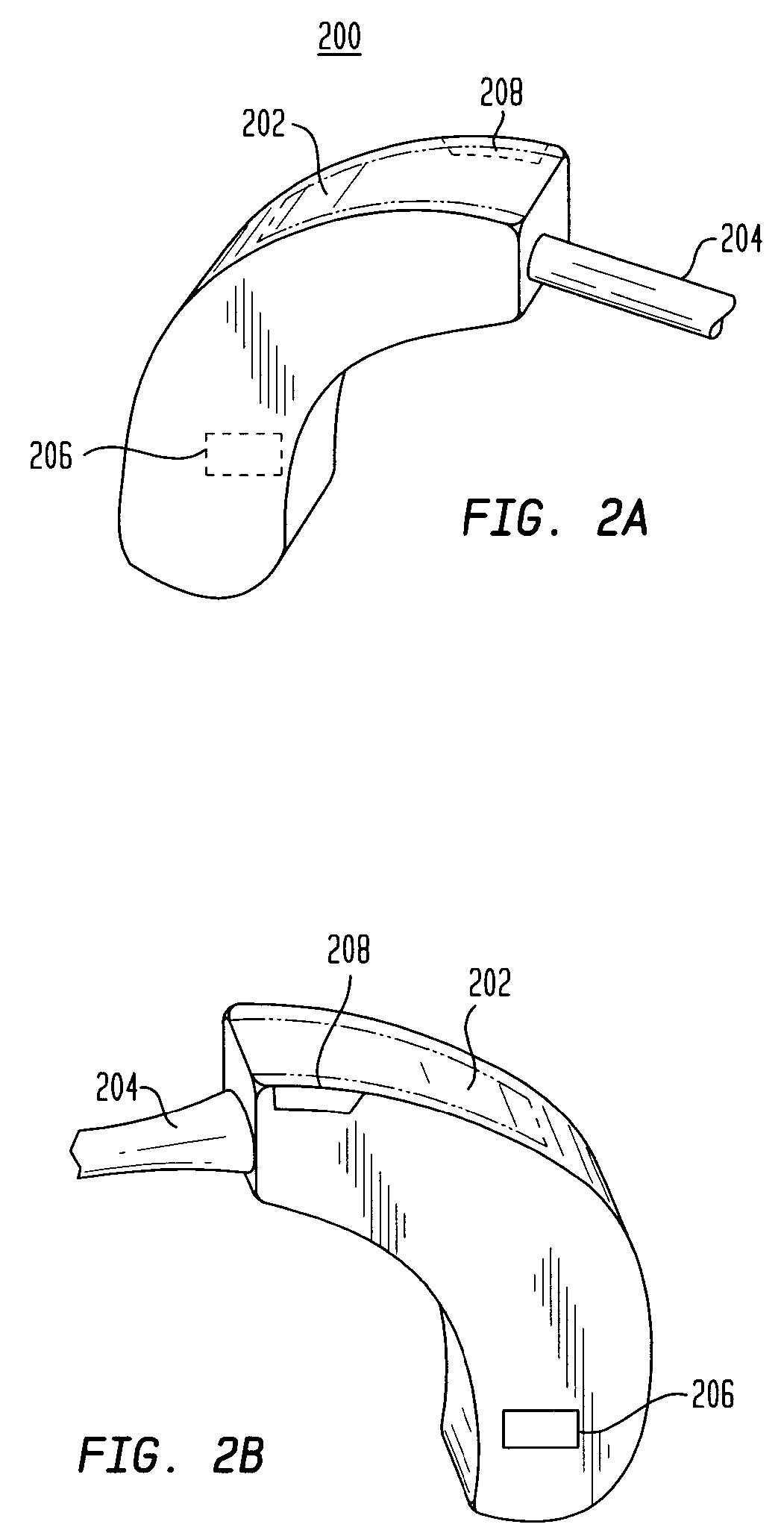
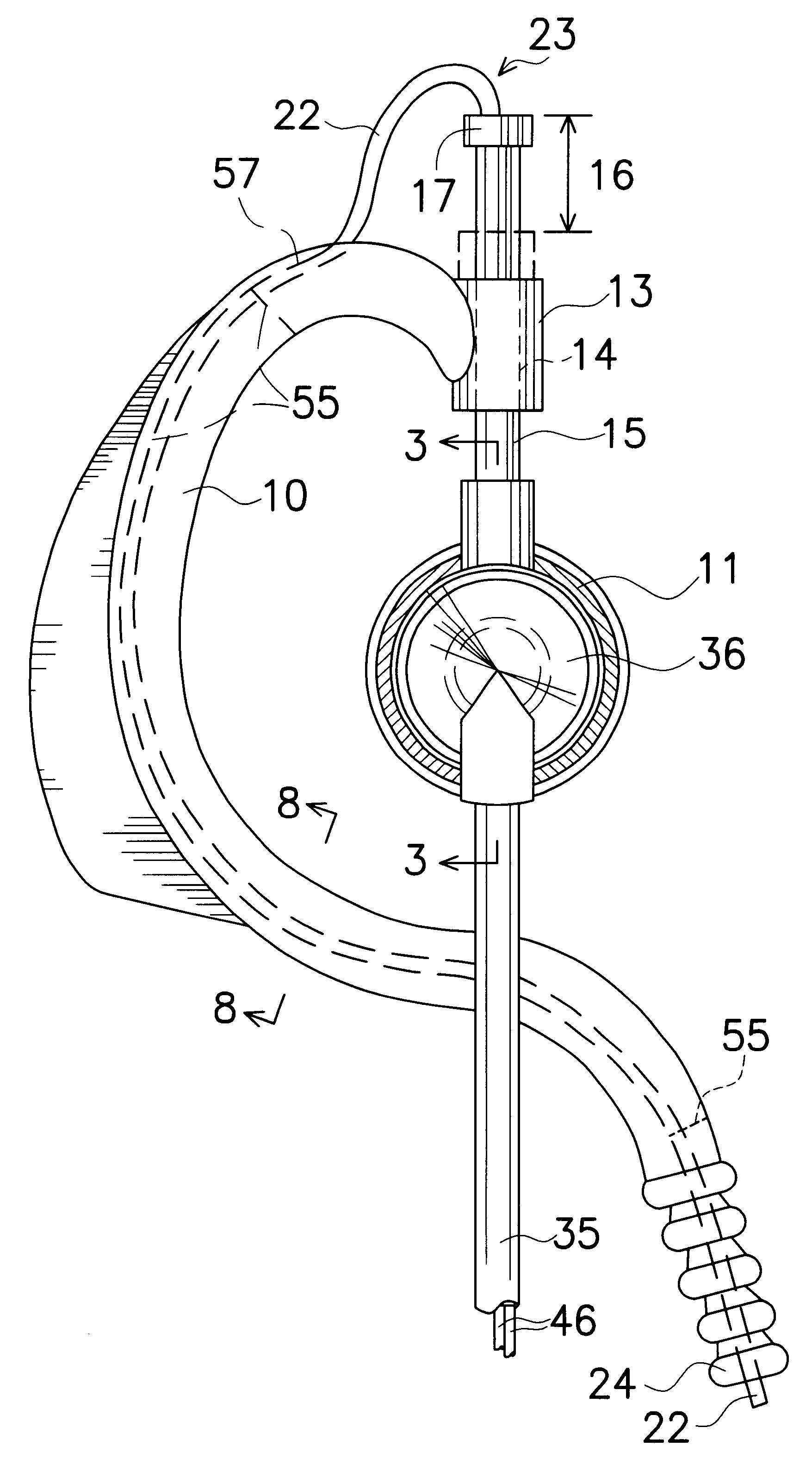
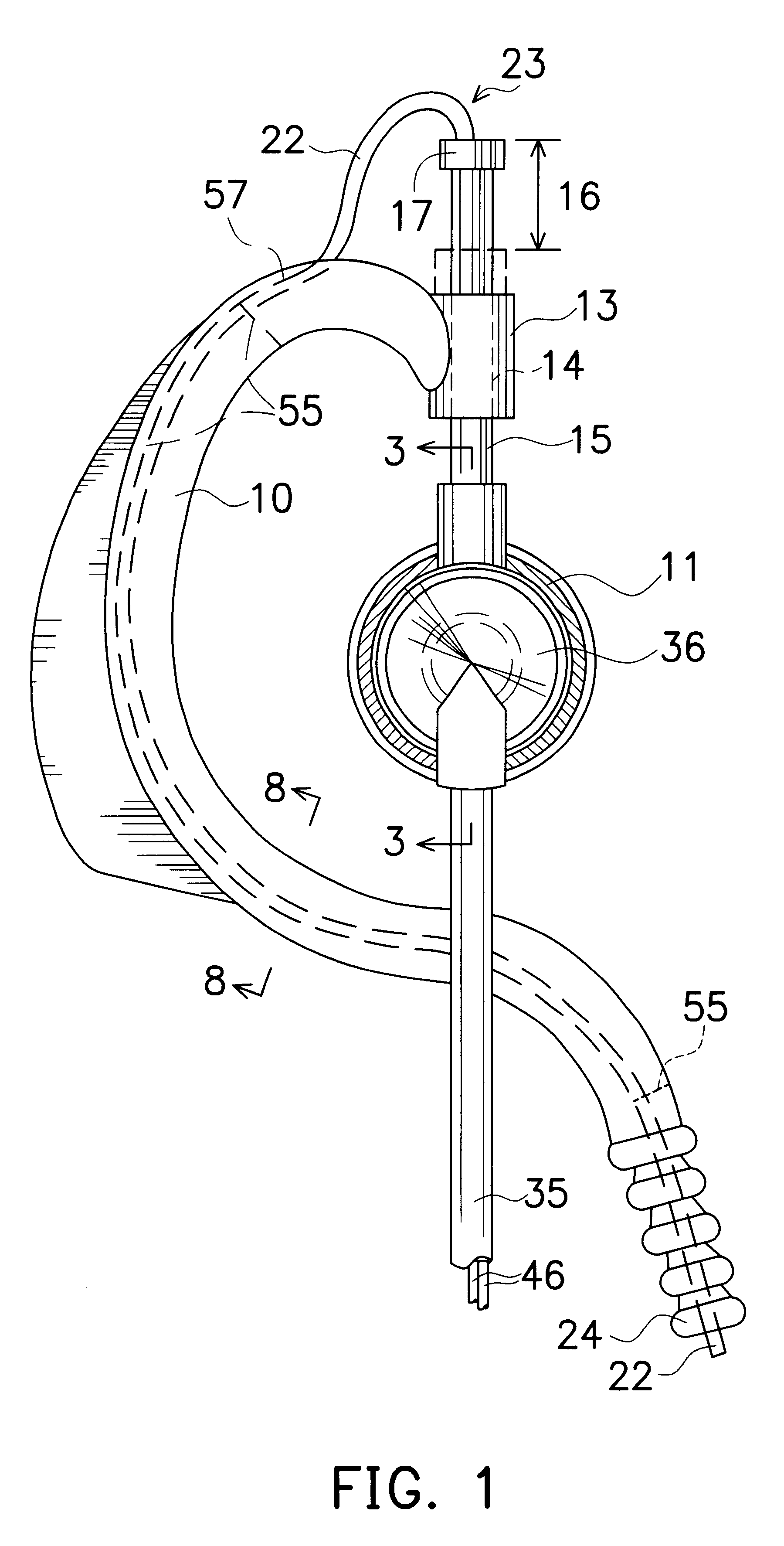
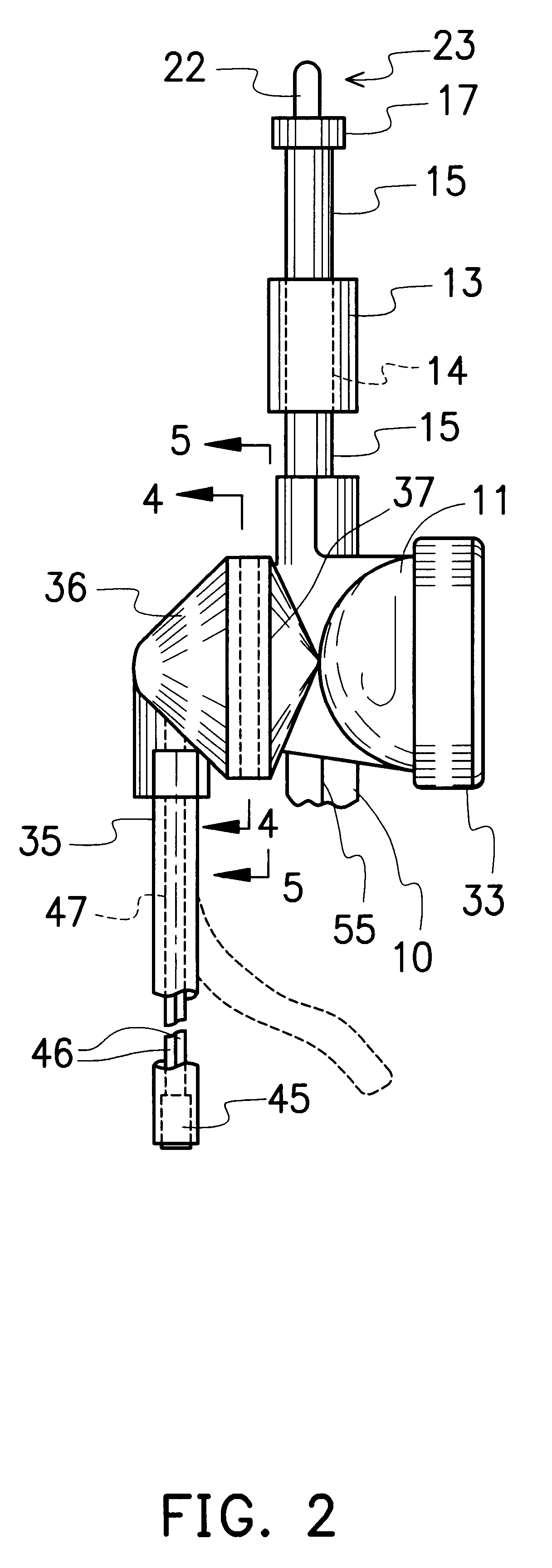
System and Method for the Simultaneous Bilateral Placement of Pressure Equalization Tubes
ActiveUS20080262508A1Facilitate visualFacilitate optical monitoringElectrotherapyEar treatmentEqualizationTarget tissue
Systems and methods for bilateral treatment of a patient having a head with a first ear and a second ear function by aligning a first device with a target tissue of the first ear; aligning a second device with a target tissue of the second ear; and therapeutically remodeling, with synchronization, the target tissues of the first and second ear with the first and second aligned devices, respectively.
Owner:TUSKER MEDICAL
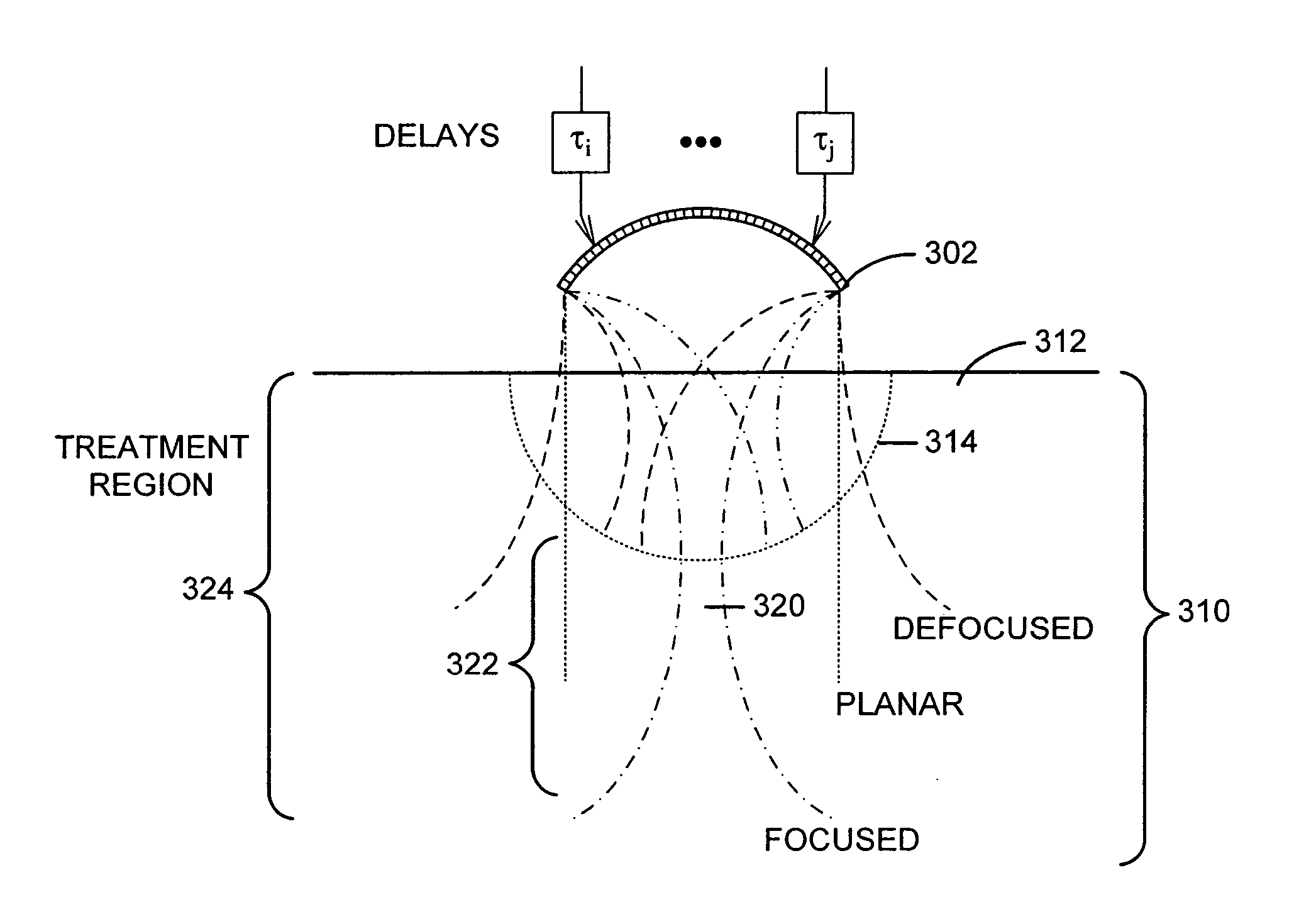
Method and system for combined ultrasound treatment
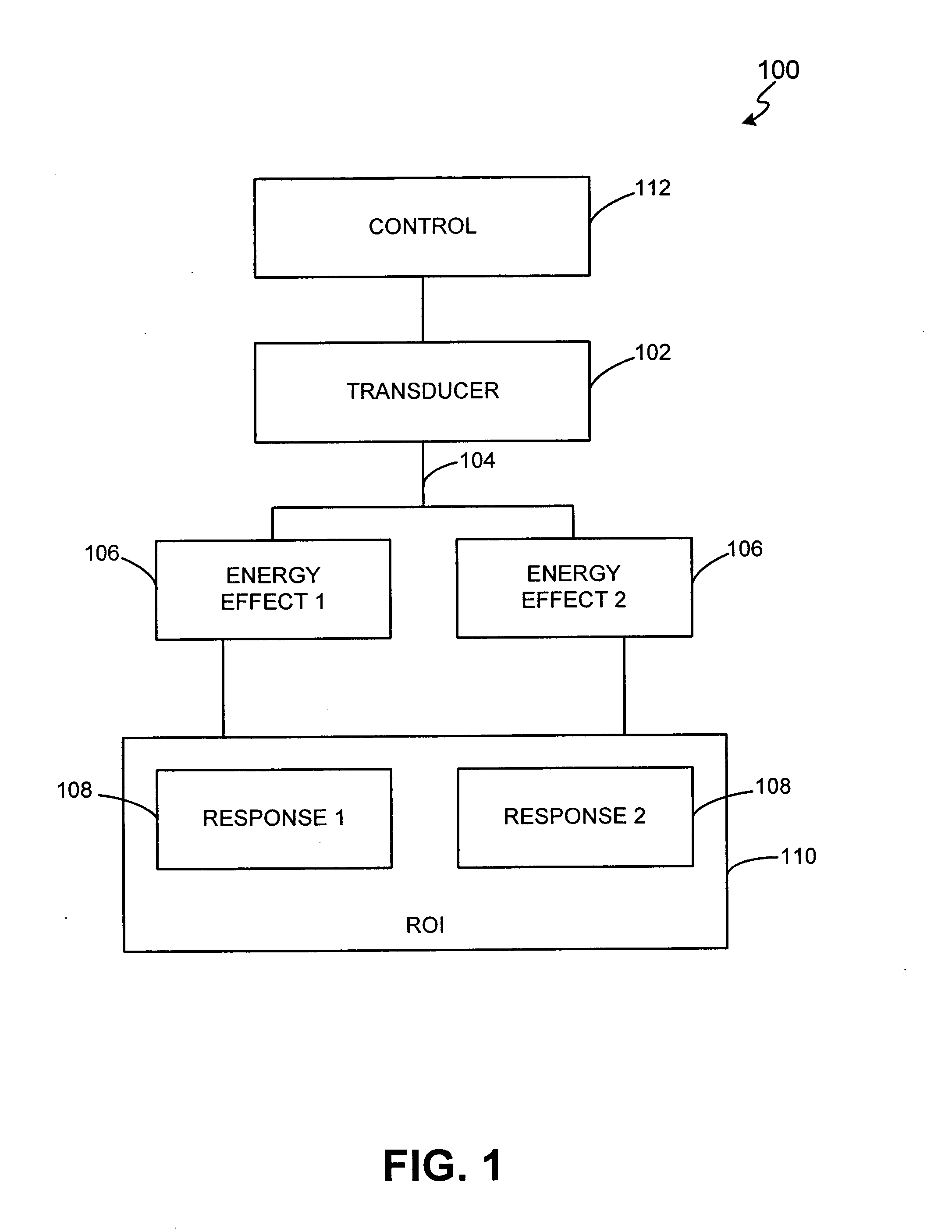
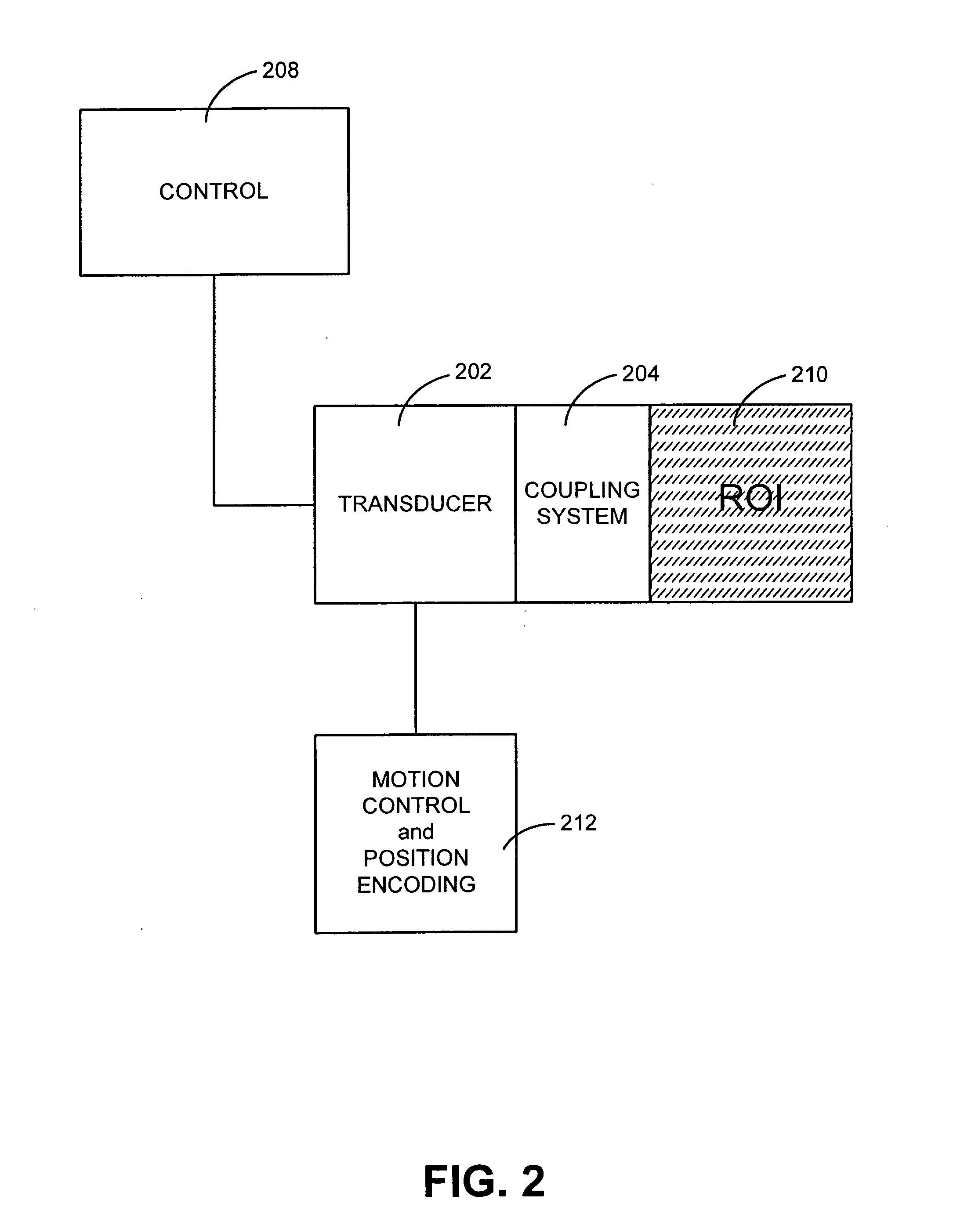
ActiveUS20060074355A1Facilitate initiationImprove responseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyTransducerNon invasive
A non-invasive method and system for combined ultrasound treatment are provided. An exemplary combined ultrasound treatment system comprises a transducer configured to deliver ultrasound energy to provide two or more energy effects to a region of interest. The energy effects facilitate the initiation of one or more responses in the region of interest. In accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a transducer is configured to deliver energy over varying temporal and / or spatial distributions in order to provide energy effects and initiate responses in a region of interest.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
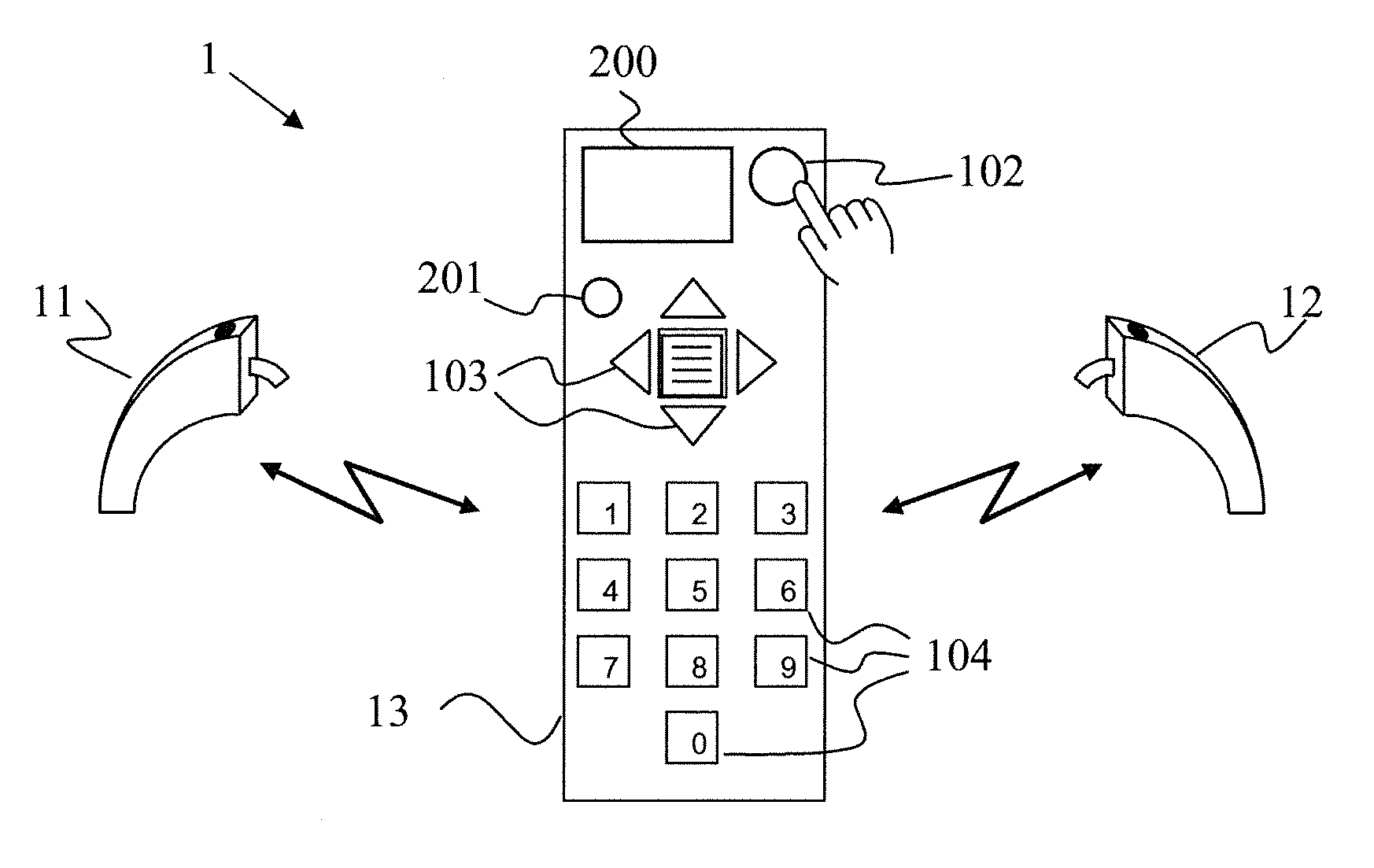
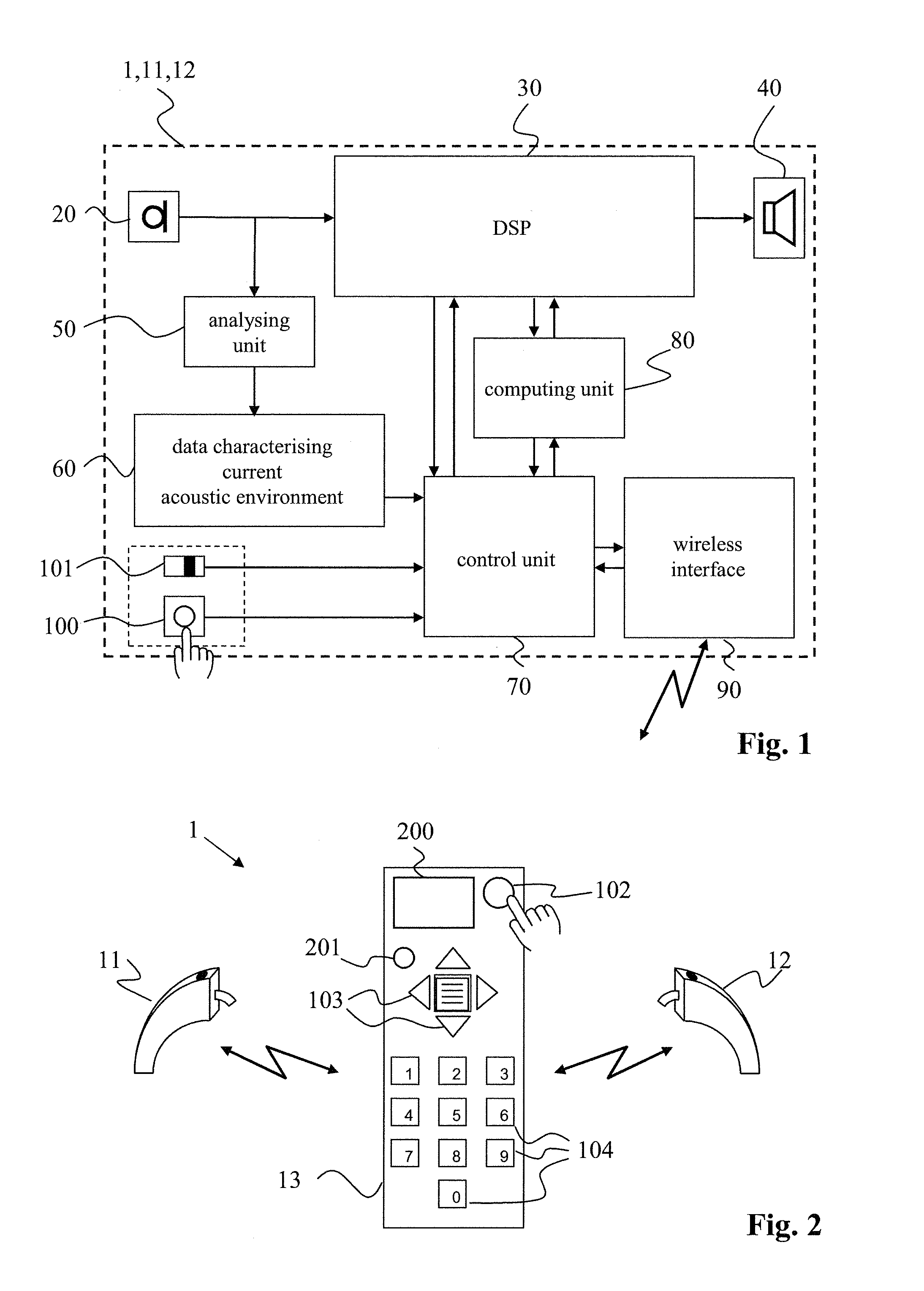
Hearing system and method for operating a hearing system
ActiveUS20130142345A1Satisfactory performanceSatisfactory hearing performanceHearing aids signal processingSets with customised acoustic characteristicsTransducerAuditory system
A hearing system (1) capable of assisting a user of the hearing system (1) to find a location where satisfactory hearing performance is achievable is described. The hearing system (1) comprises at least one hearing device (11, 12) with an input transducer (20), an output transducer (40), and a processing unit (30) operatively connected to the input transducer (20) as well as to the output transducer (40). The hearing system (1) further comprises a first means (50) for determining from a signal of the input transducer (20) at least one parameter (60) representative of a current acoustic environment at a current location, and a second means (40, 200, 201) for indicating to a user of the hearing system (1) a degree of suitability of the current location to achieve satisfactory hearing performance based on the at least one parameter (60).
Owner:SONOVA AG
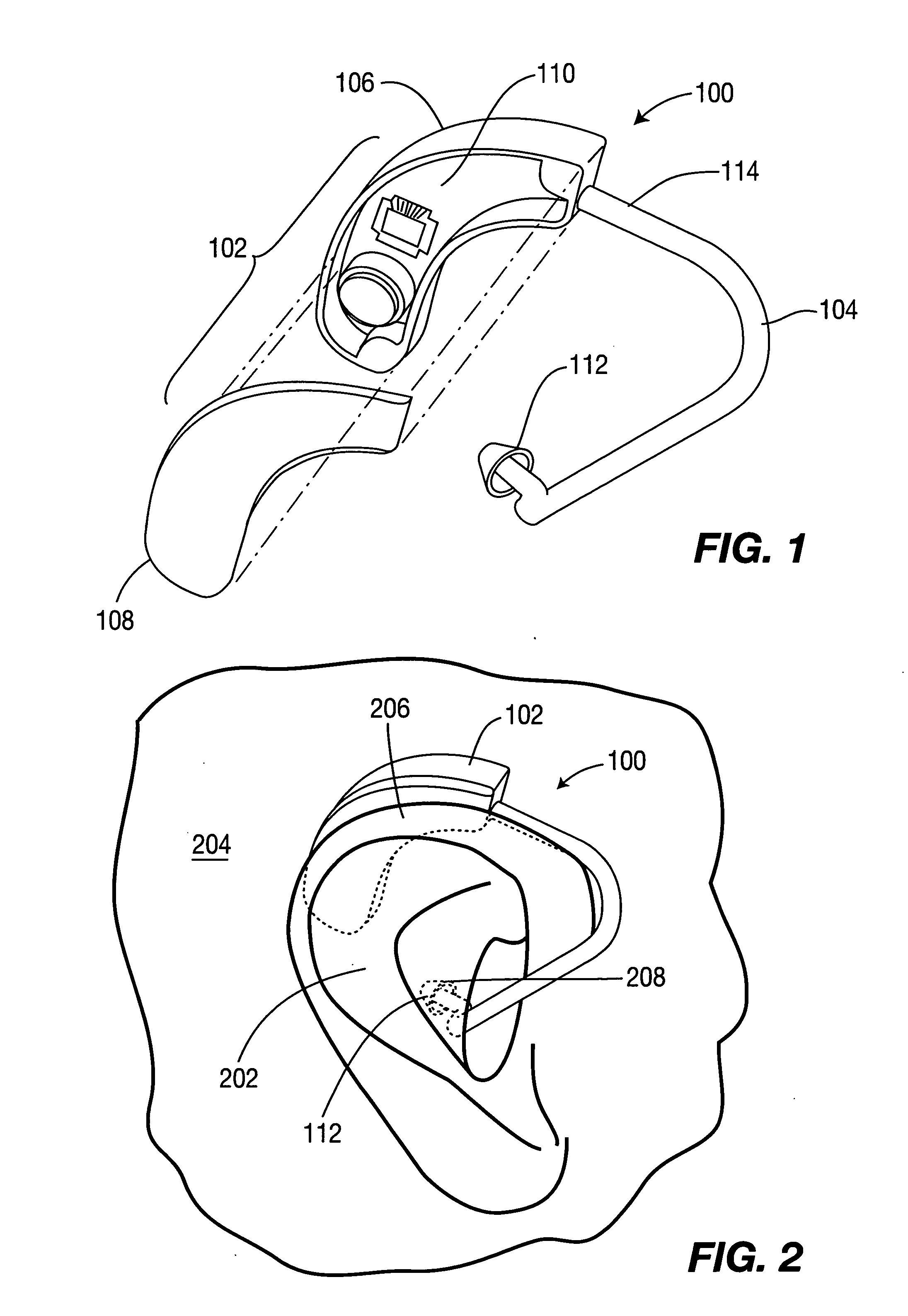
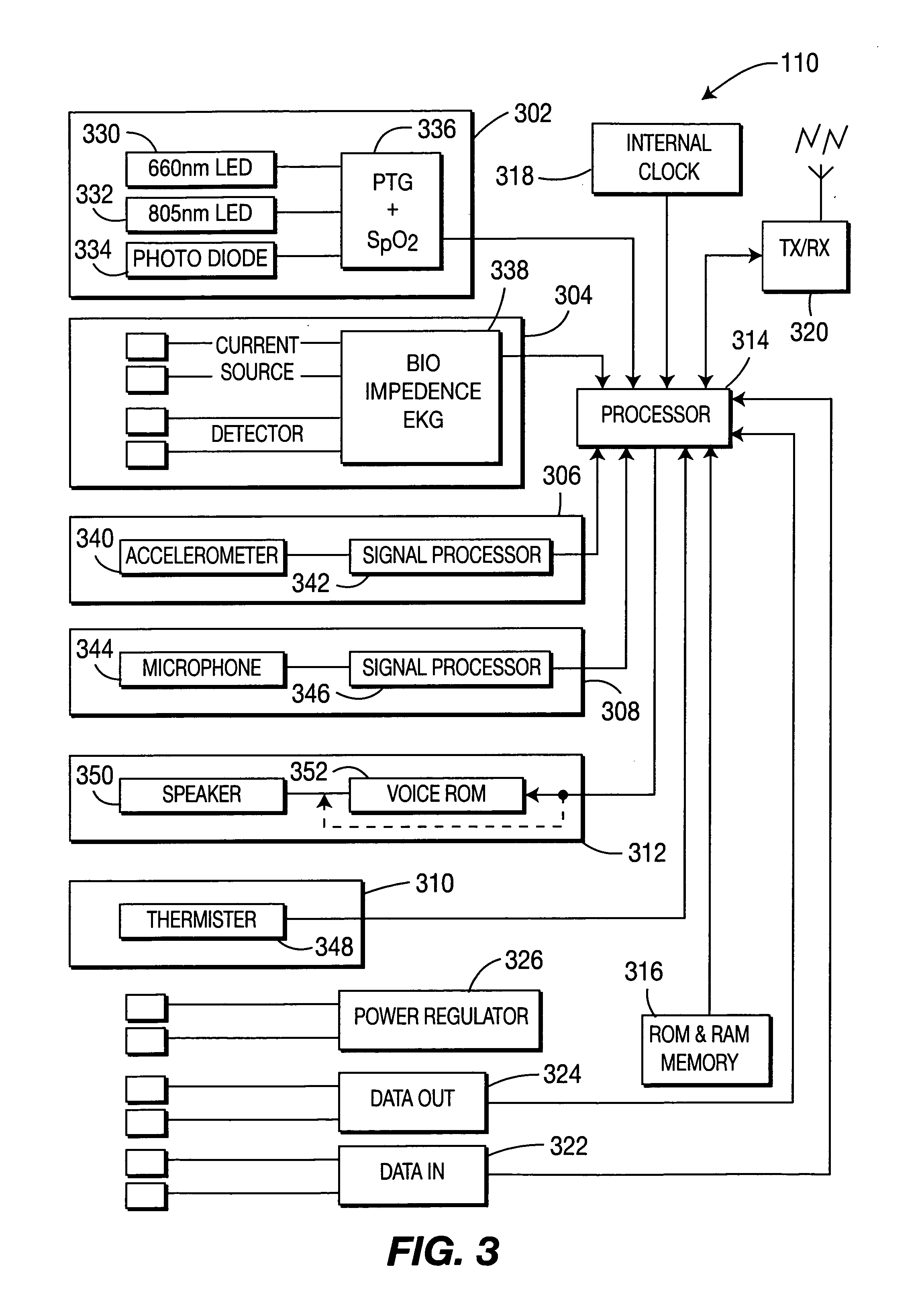
Methods and Apparatus for Measuring Physiological Conditions
InactiveUS20100217100A1Convenient and unobtrusiveElectroencephalographyDiagnostics using lightAudiologyCardiopulmonary function
A monitoring apparatus includes a housing configured to be attached to an ear of a subject, and a plurality of electrodes supported by the housing. The electrodes are configured to at least partially contact a portion of the body of the subject when the housing is attached to the ear of the subject, and are configured to detect and / or measure at least one neurological and / or cardiopulmonary function of the subject. The housing may include one or more physiological sensors configured to detect and / or measure physiological information from the subject and / or one or more environmental sensors configured to detect and / or measure environmental conditions in a vicinity of the subject.
Owner:VALENCELL INC
Programmable auditory prosthesis with trainable automatic adaptation to acoustic conditions
An auditory prosthesis (30) comprising a microphone (27) for receiving the sound and producing a microphone signal responding to the received sound, an output device for providing audio signals in a form receivable by a user of the prosthesis (30), a sound processing unit (33) operable to receive the microphone signal and carry out a processing operation on the microphone signal to produce an output signal in a form suitable to operate the output device, wherein the sound processing unit (33) is operable in a first mode in which the processing operation comprises at least one variable processing factor which is adjustable by a user to a setting which causes the output signal of the sound processing unit (33) to be adjusted according to the preference of the user for the characteristics of the current acoustic environment.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
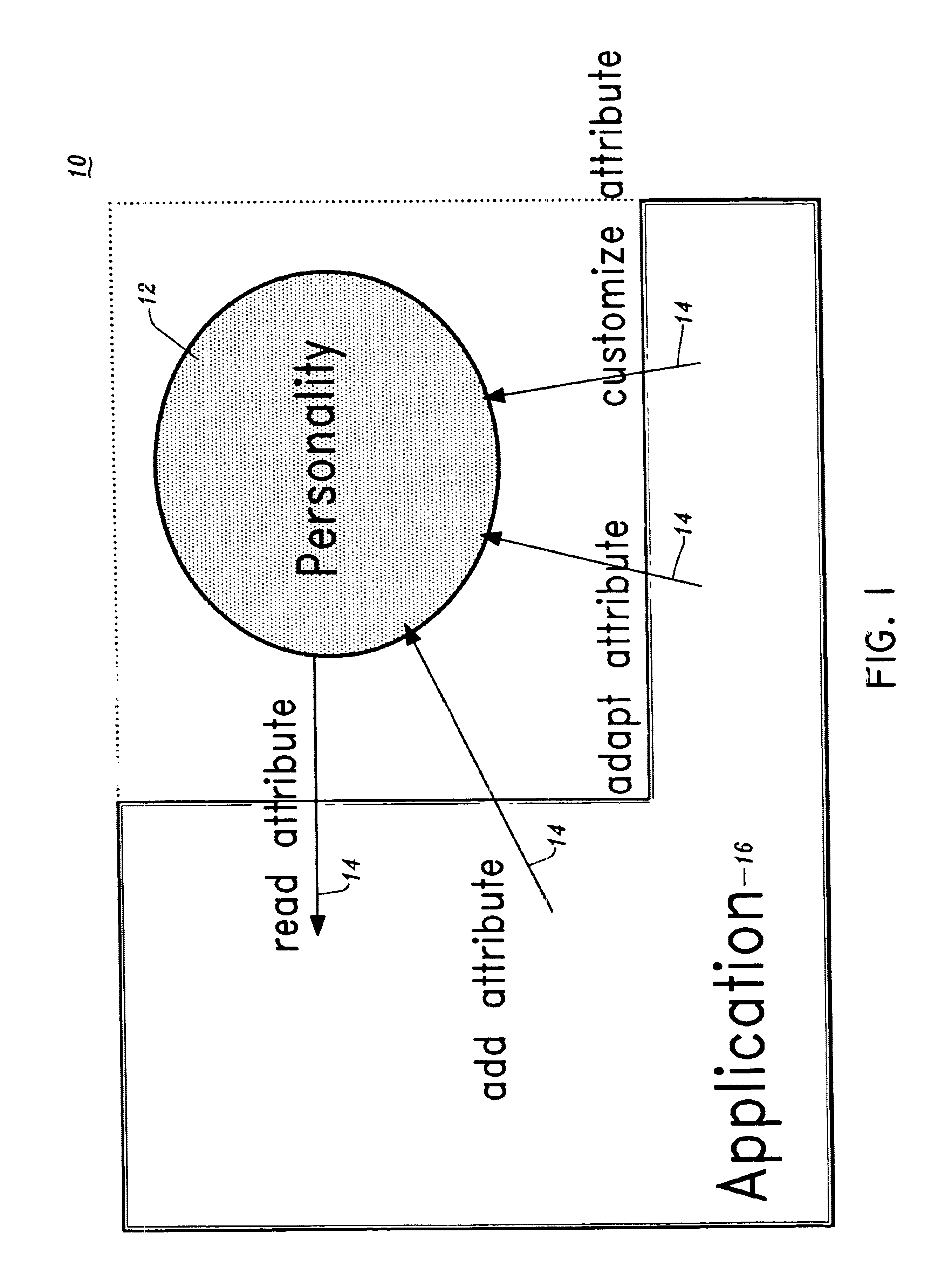
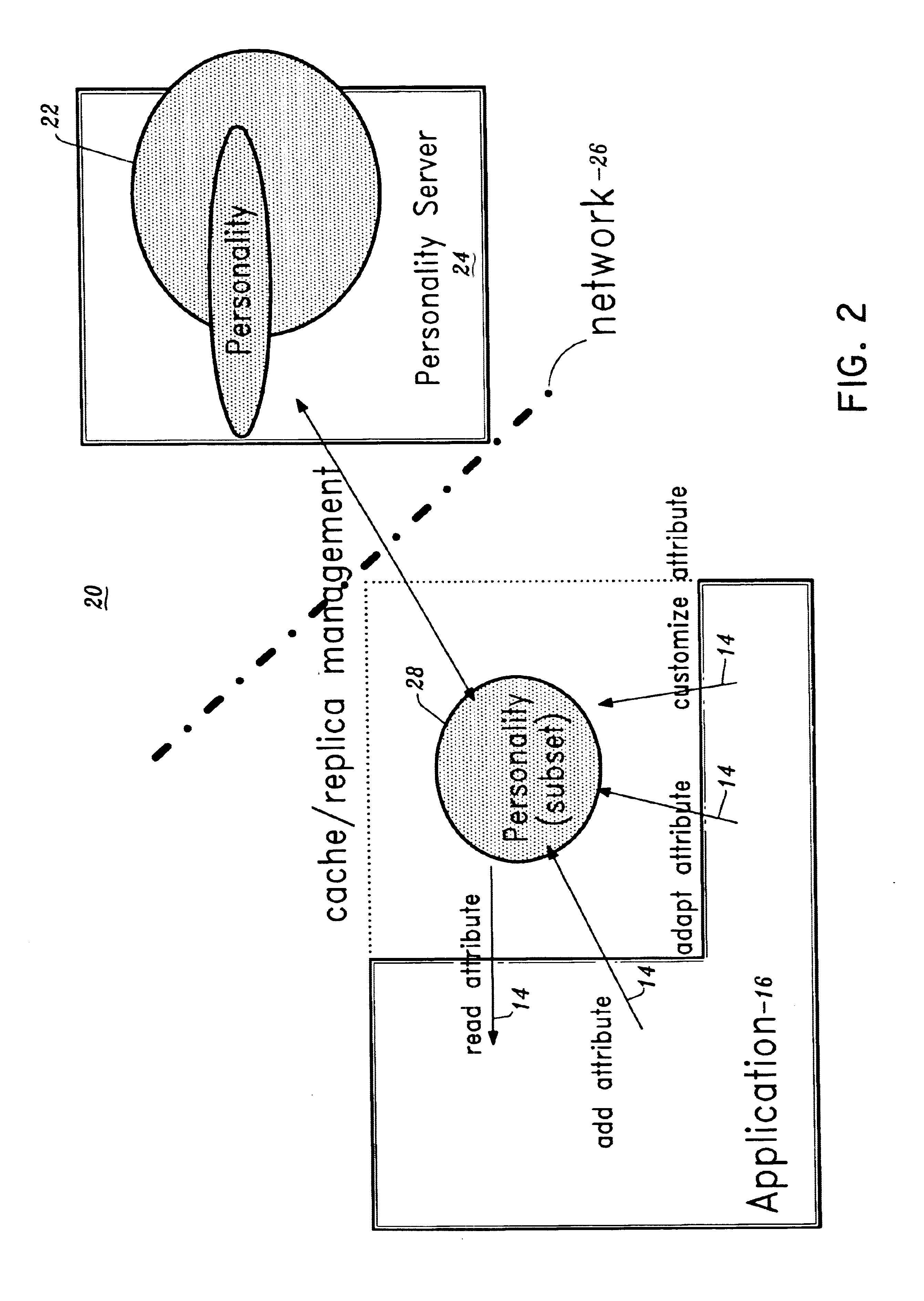
Personality generator for conversational systems
A method for providing a personality for a conversational system includes providing a plurality of attributes for determining a behavior of the conversational system. When a command is presented to the conversational system for execution, the command is responded to by employing the plurality of attributes such that the user experiences an interface with human characteristics.
Owner:PENDRAGON NETWORKS +1
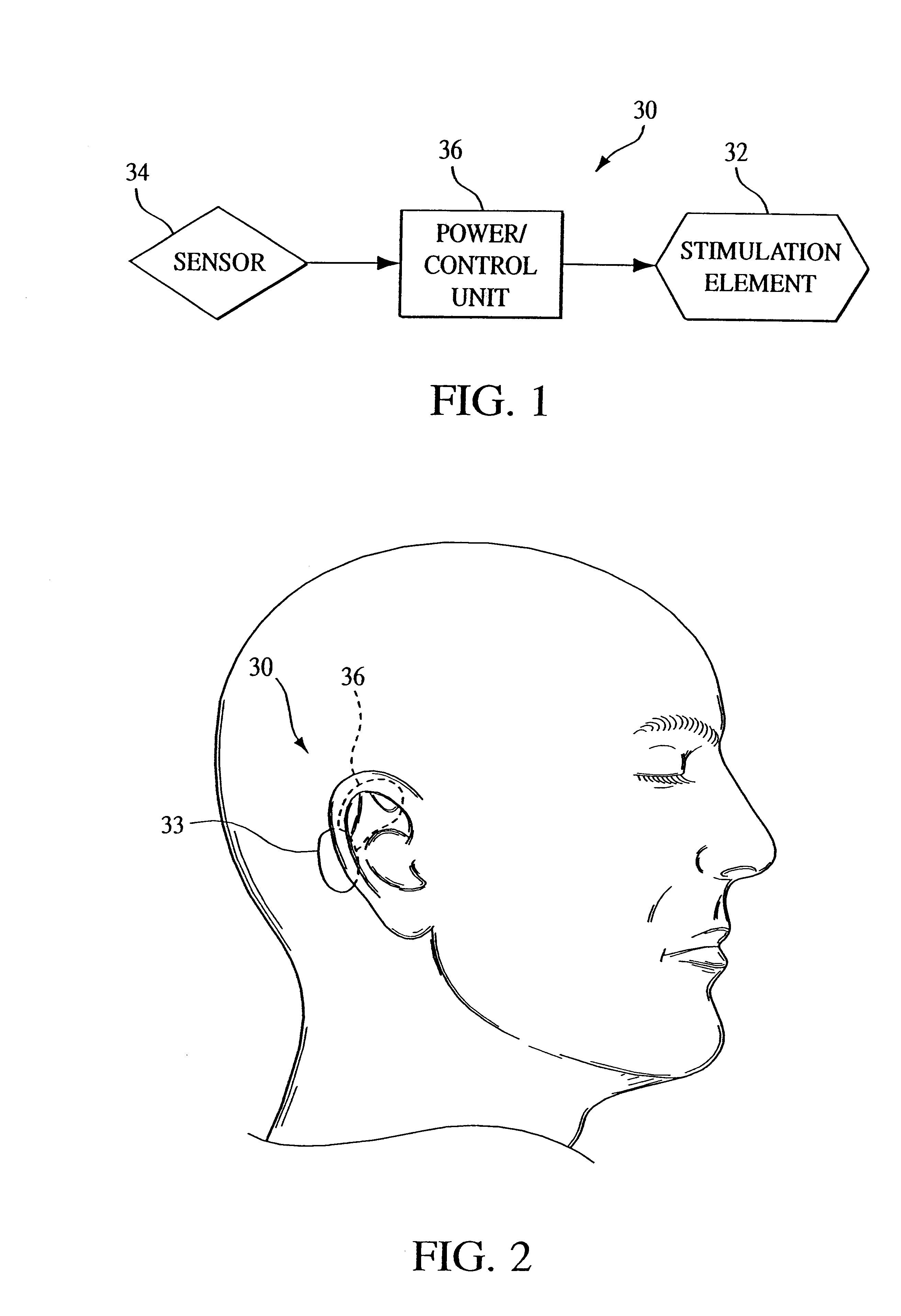
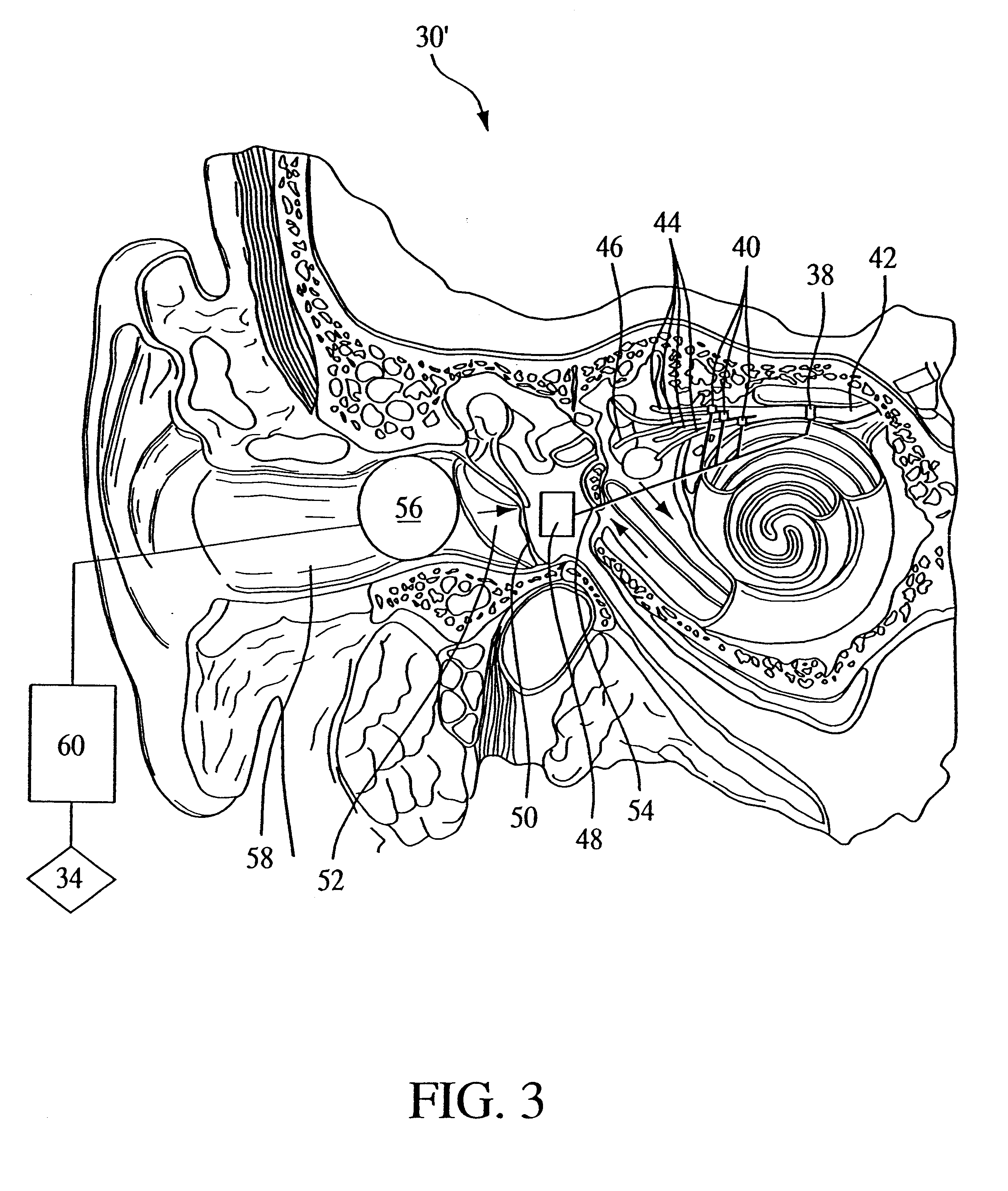
Vestibular stimulation system and method
InactiveUS6748275B2Augmenting or controlling a patient's natural respiratory functionImprovement effortsInternal electrodesExternal electrodesSleep inductionControl unit
An apparatus and method in which the portions of the labyrinth associated with the labyrinthine sense and / or the nerves associated therewith are stimulated to perform at least one of the following functions: augment or control a patient's respiratory function, open the patient's airway, induce sleep, and / or counteract vertigo. In one embodiment, the vestibular stimulating system of the present invention includes 1) a stimulation element that performs the actual stimulation of the tissue, 2) a sensor to detect a physiological condition of the patient, and 3) a power / control unit that receives the signals provided by the sensor and causes stimulation energy to be provided to the stimulation element at an appropriate timing, level, pattern, and / or frequency to achieve the desired function. However, the present invention also contemplates eliminating the sensor in favor of applying a predetermined pattern of stimulation to the patient.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
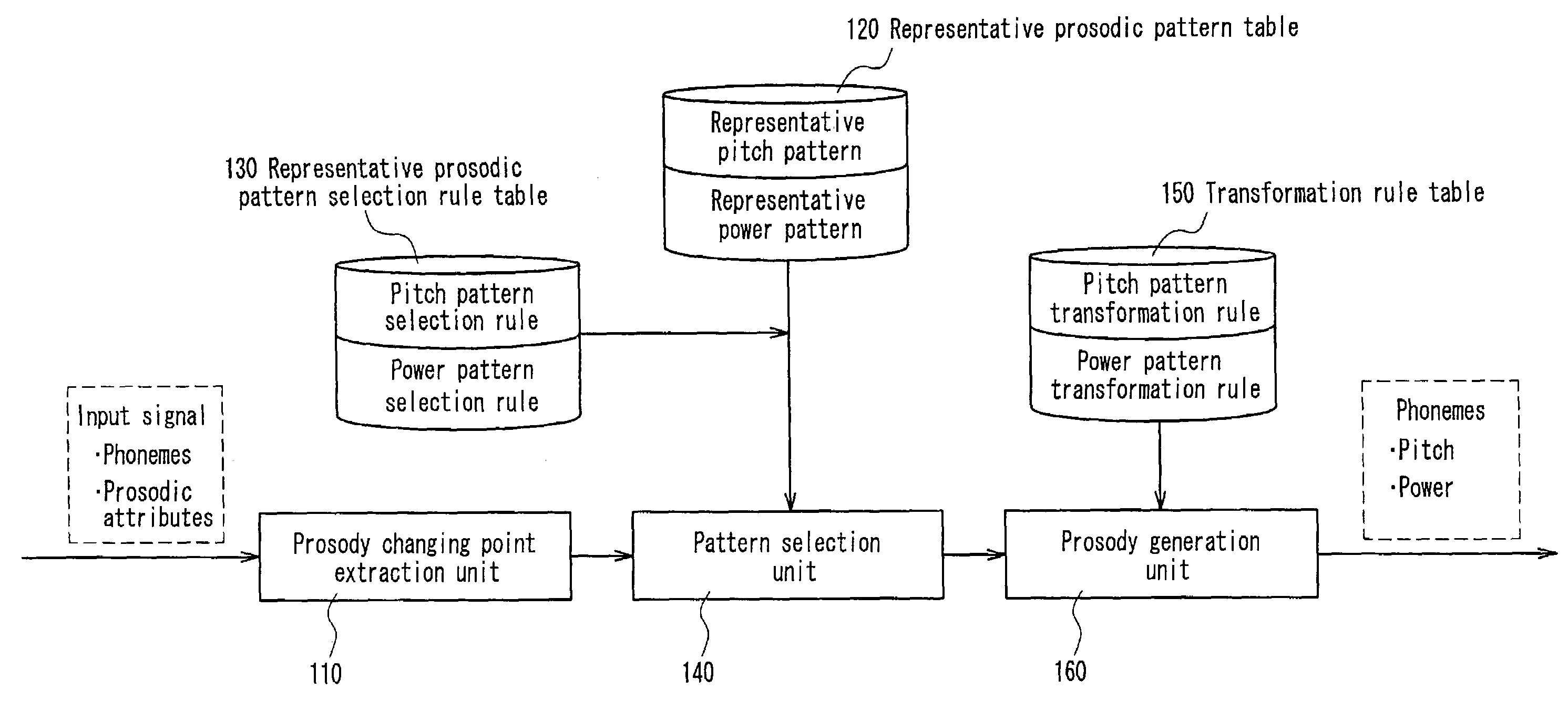
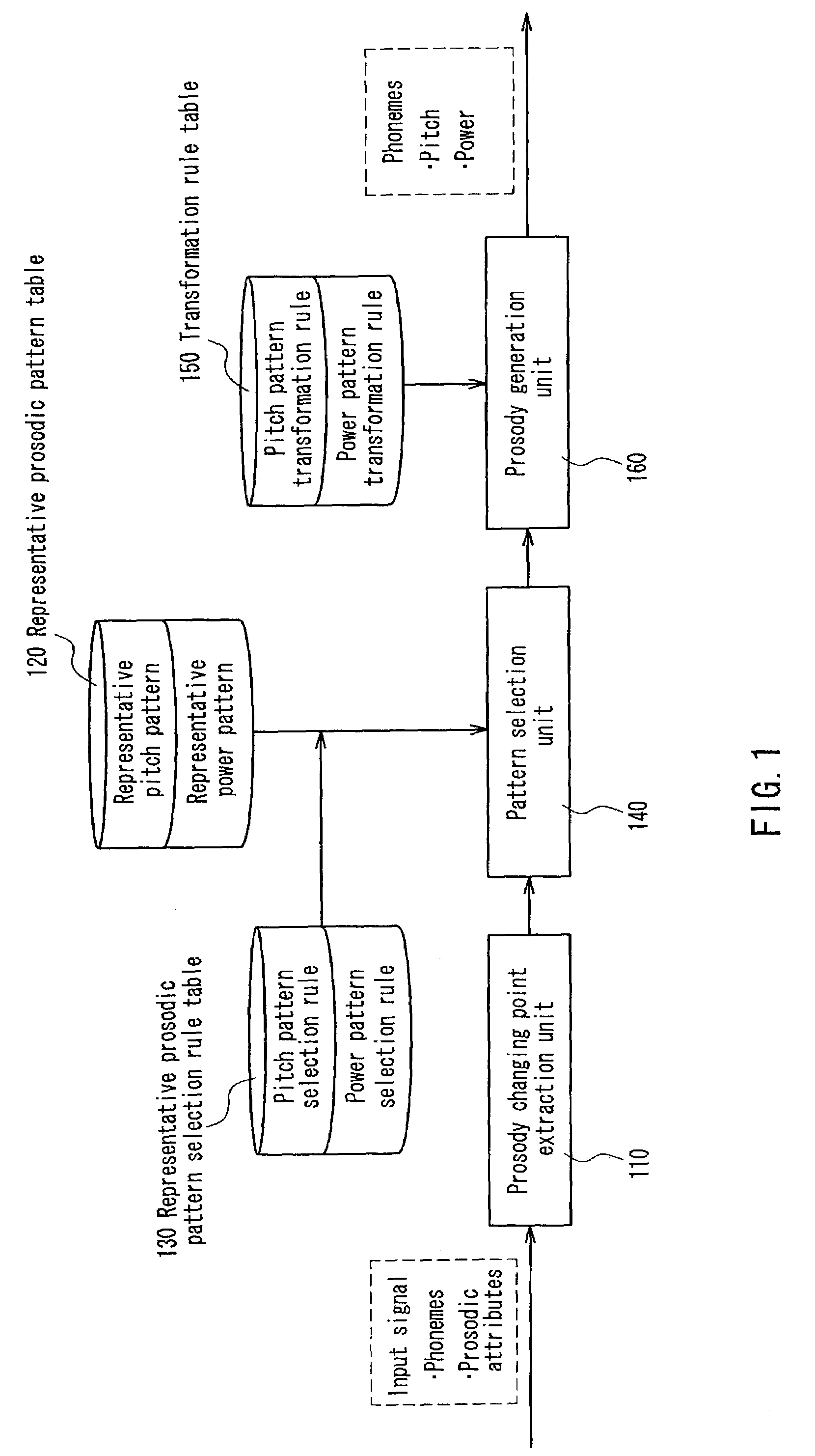
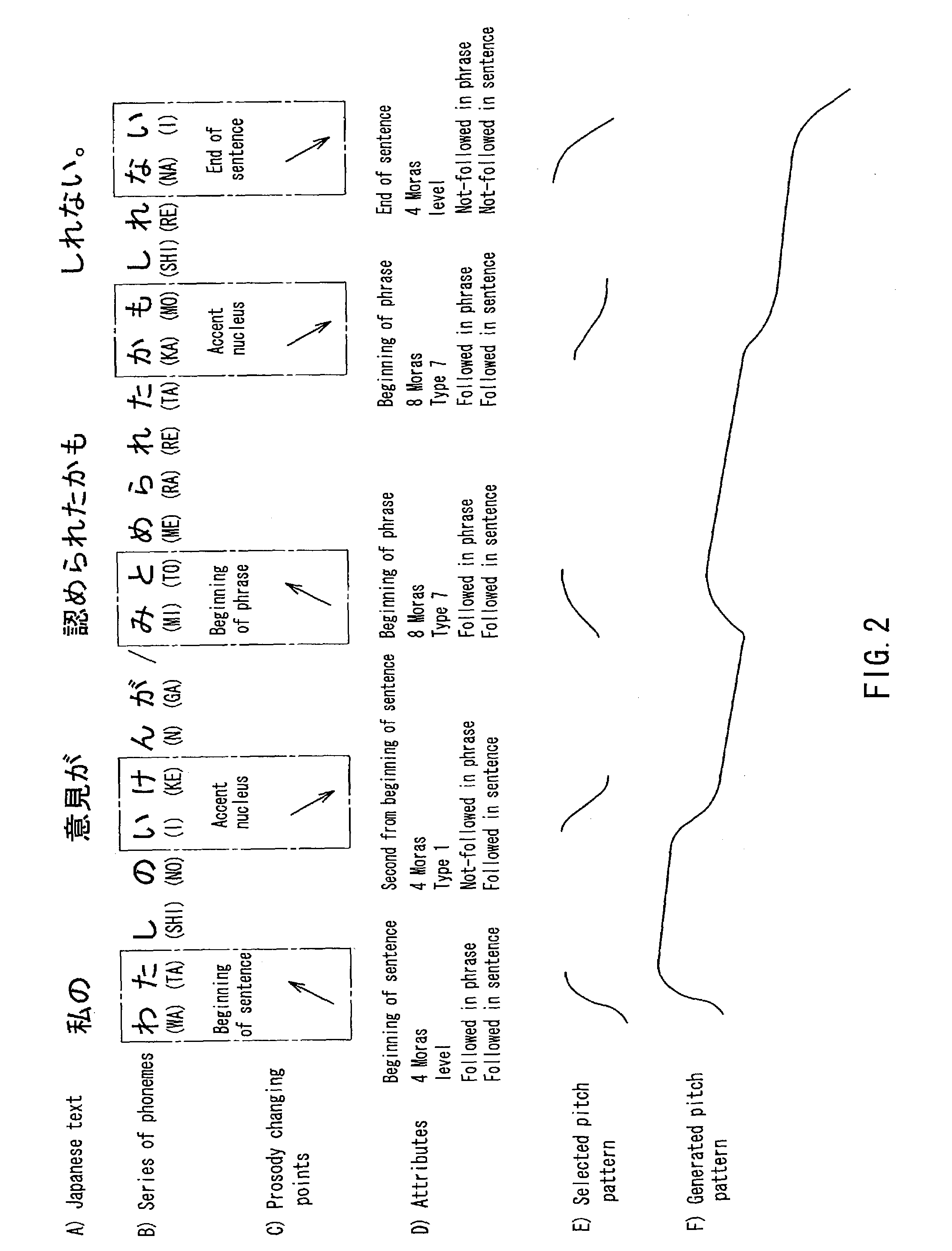
Prosody generating device, prosody generating method, and program
ActiveUS7200558B2Suppression of distortionSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsStatistical learningPattern selection
A prosody generation apparatus capable of suppressing distortion that occurs when generating prosodic patterns and therefore generating a natural prosody is provided. A prosody changing point extraction unit in this apparatus extracts a prosody changing point located at the beginning and the ending of a sentence, the beginning and the ending of a breath group, an accent position and the like. A selection rule and a transformation rule of a prosodic pattern including the prosody changing point is generated by means of a statistical or learning technique and the thus generate rules are stored in a representative prosodic pattern selection rule table and a transformation rule table beforehand. A pattern selection unit selects a representative prosodic pattern from the representative prosodic pattern selection rule table according to the selection rule. A prosody generation unit transforms the selected pattern according to the transformation rule and carries out interpolation with respect to portions other than the prosody changing points so as to generate prosody as a whole.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
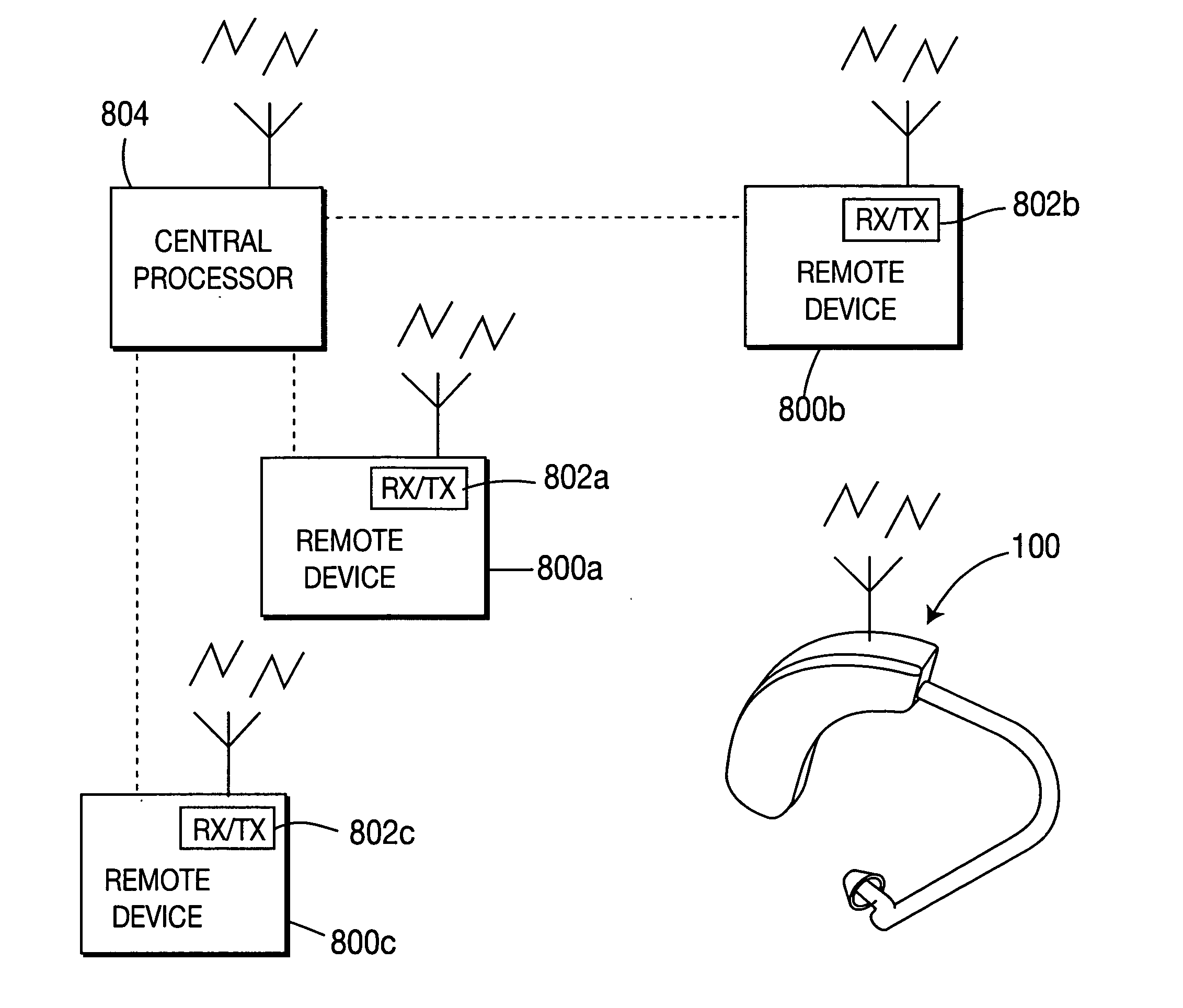
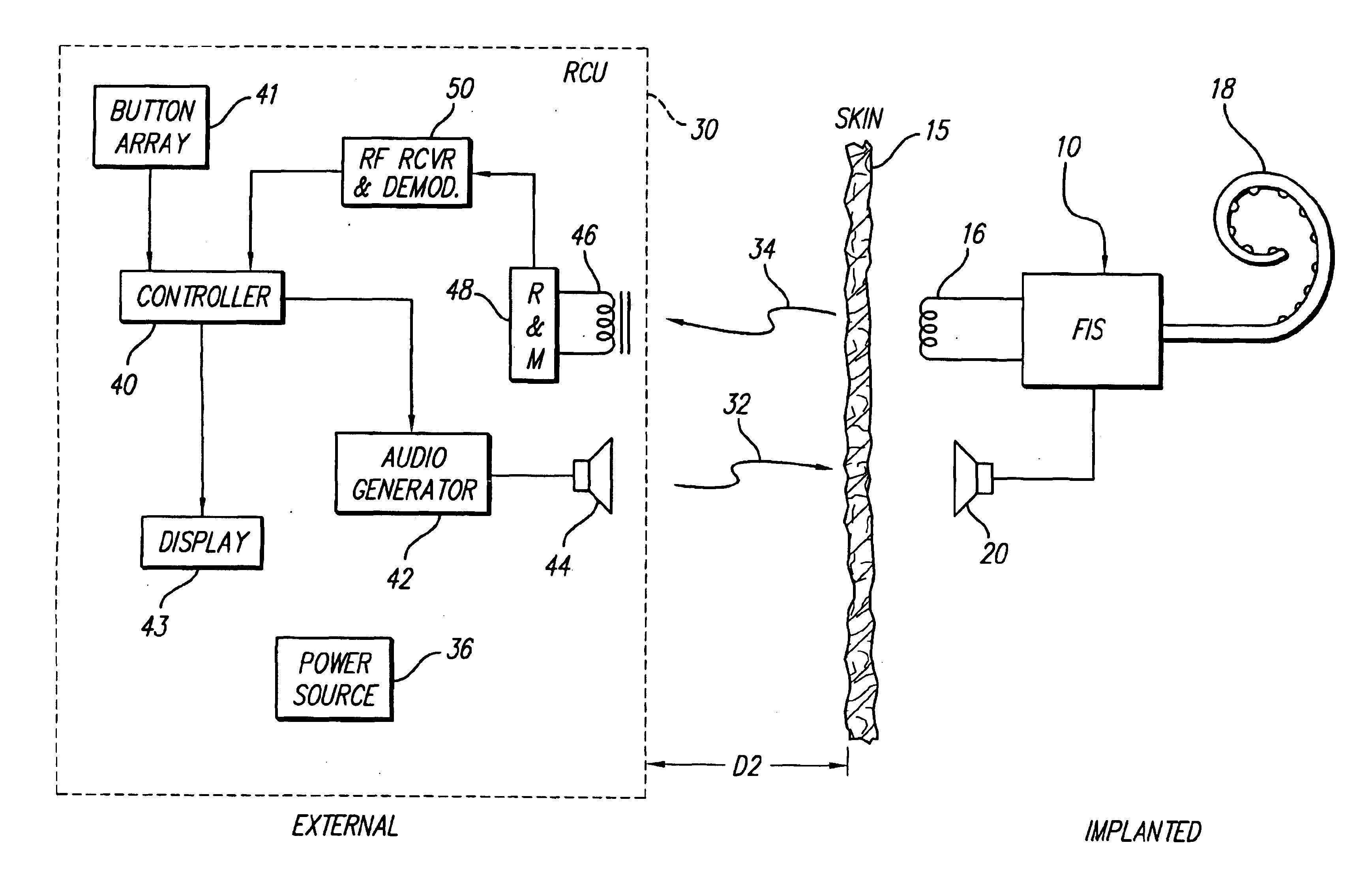
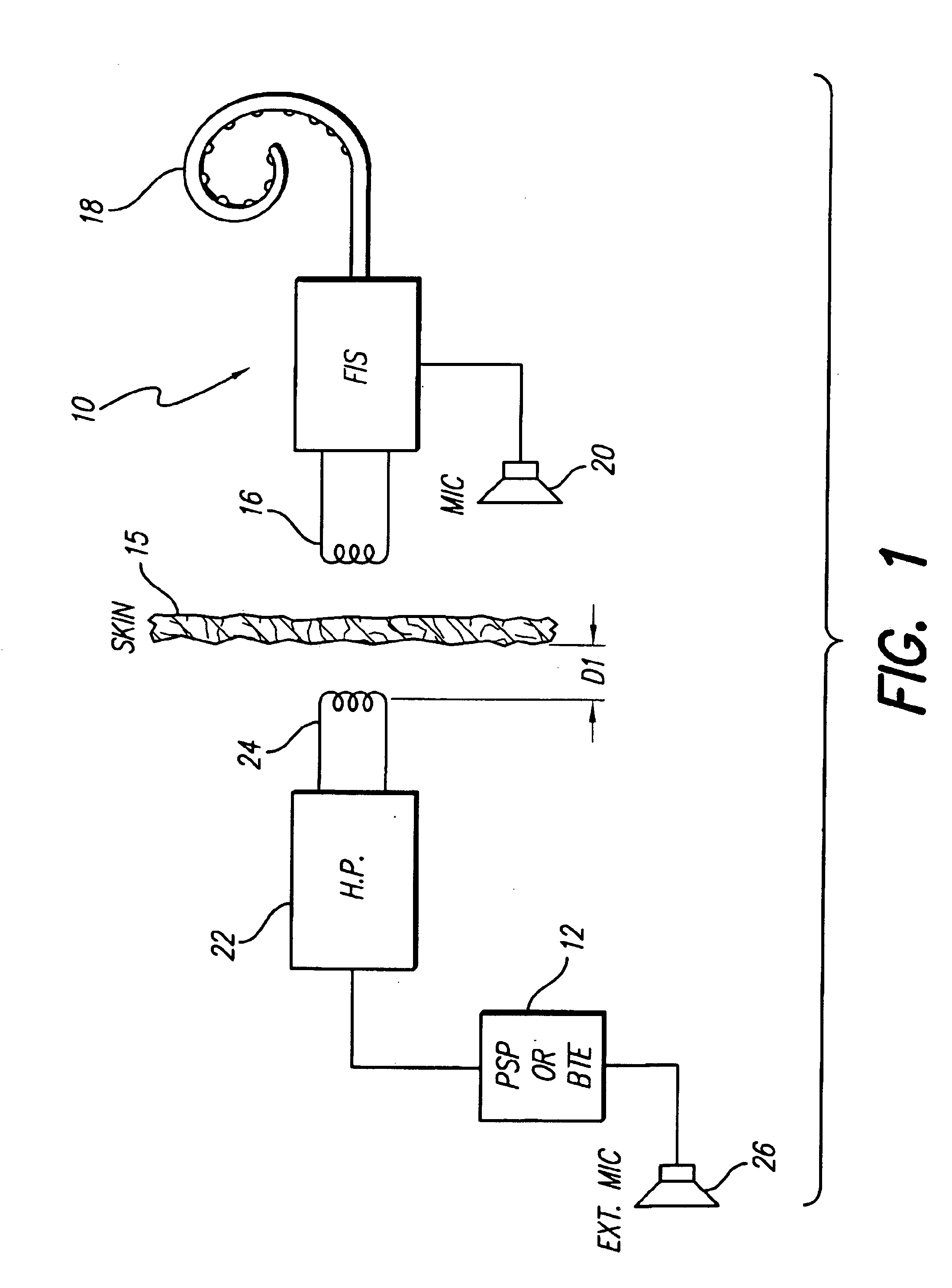
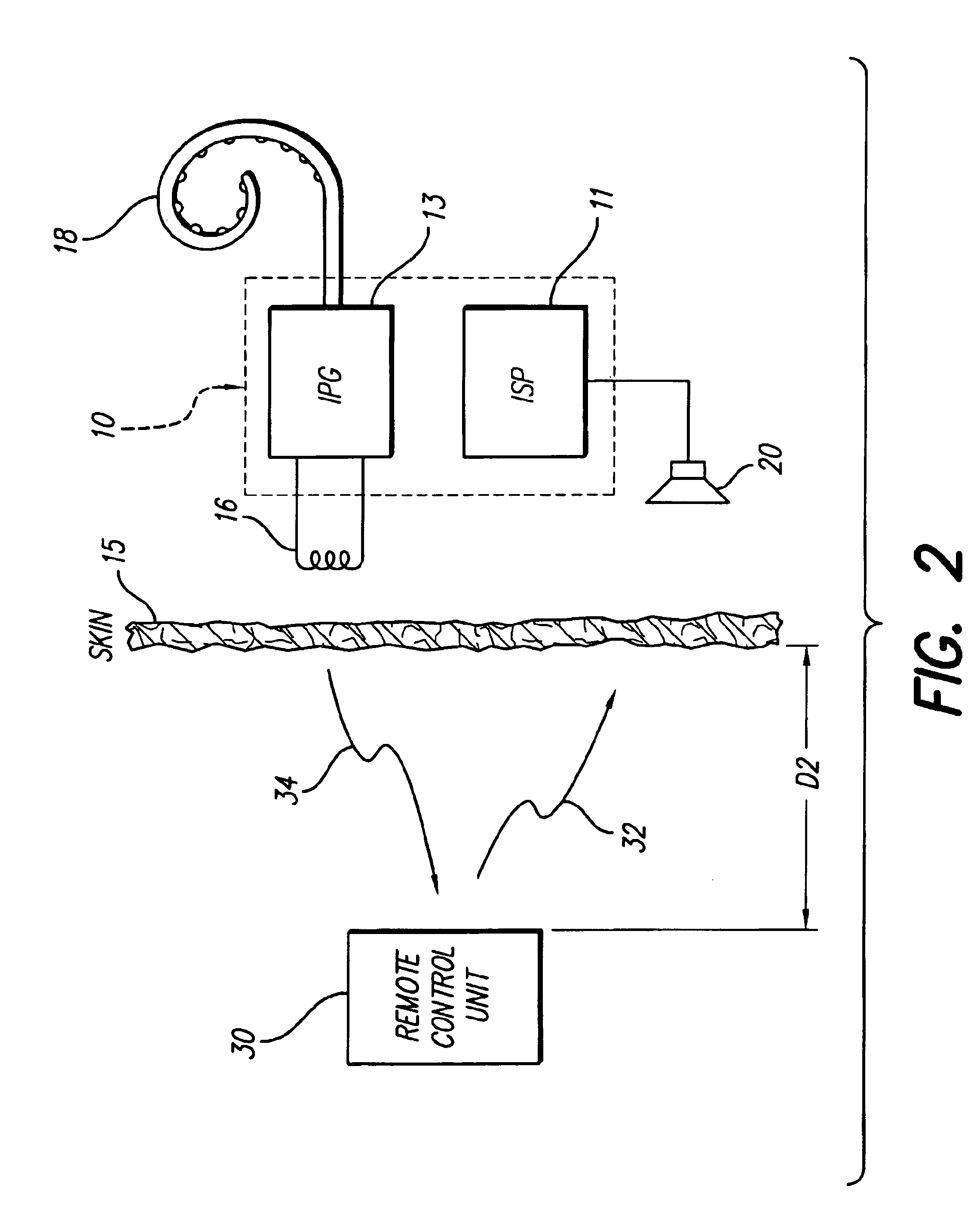
Implantable neural stimulator system including remote control unit for use therewith
InactiveUS6842647B1Reliable transmissionElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsControl signalRemote control
An implantable neural stimulation system, such as an auditory Fully Implantable System (FIS), includes: (1) an implanted device capable of providing desired tissue or nerve stimulation; and (2) a remote control unit that provides a mechanism for readily controlling the implant device, i.e., for selectively adjusting certain stimulation parameters associated with the tissue stimulation of the implanted device. The remote control unit uses a first signal path to send signals to the implant device, and a second signal path to receive signals from the implant device. The combination of these two signal paths provides a full-duplex channel between the remote control unit and the implant device through which air appropriate control and status signals may be sent and received. In one embodiment, the first signal path comprises an audio signal path through which audio control signals, e.g., a tone sequence or a 32-bit word FSK modulated between 300 and 1200 Hz, are sent; and the second signal path comprises a RF signal path through which a BPSK, QPSK or FM modulated RF signal is received. The full-duplex channel allows operation of the remote control unit, i.e., allows signals to be successfully sent to and received from the implant device, from as far away as 45-60 cm from the implant device.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
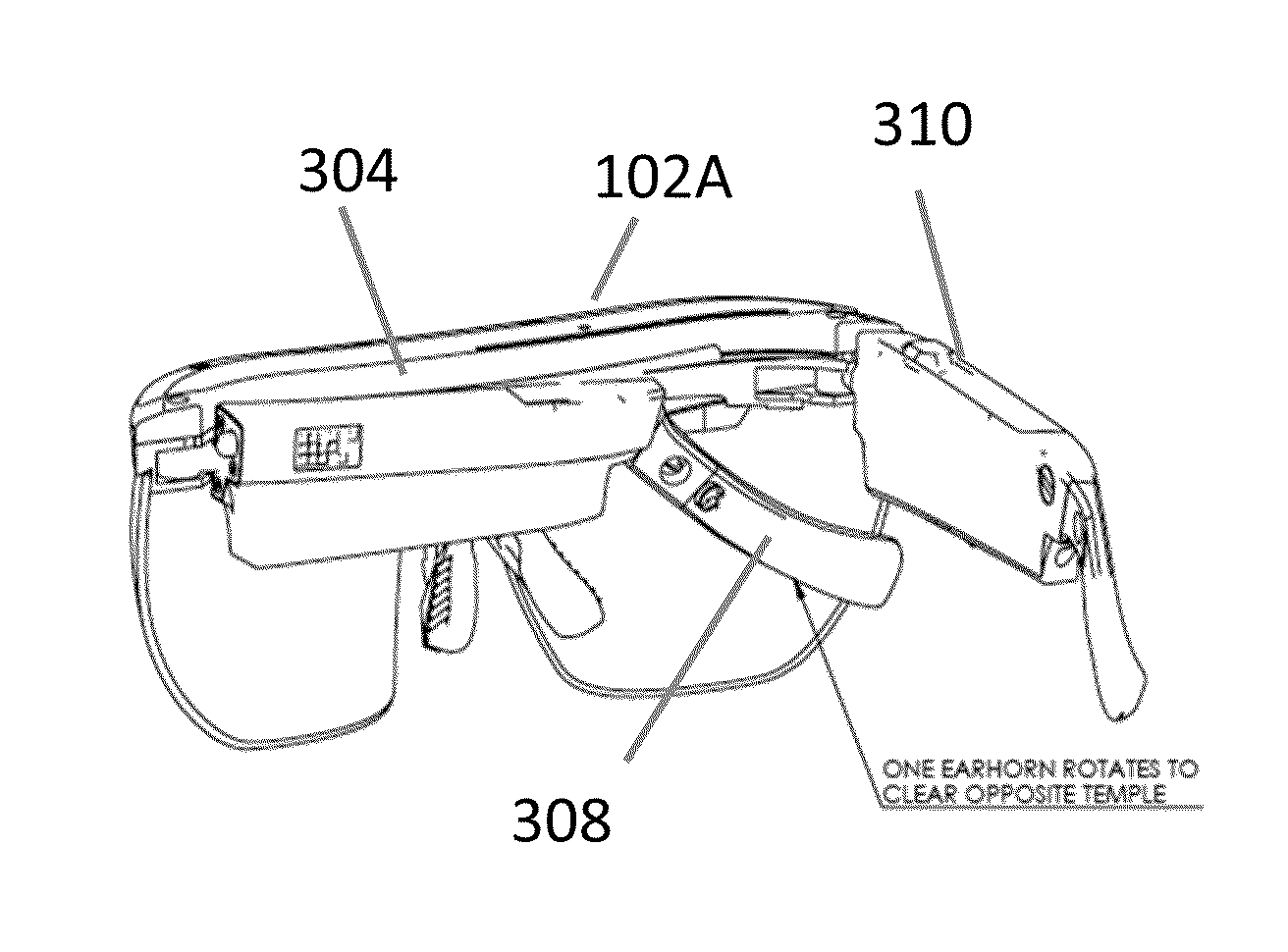
Temple and ear horn assembly for headworn computer
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
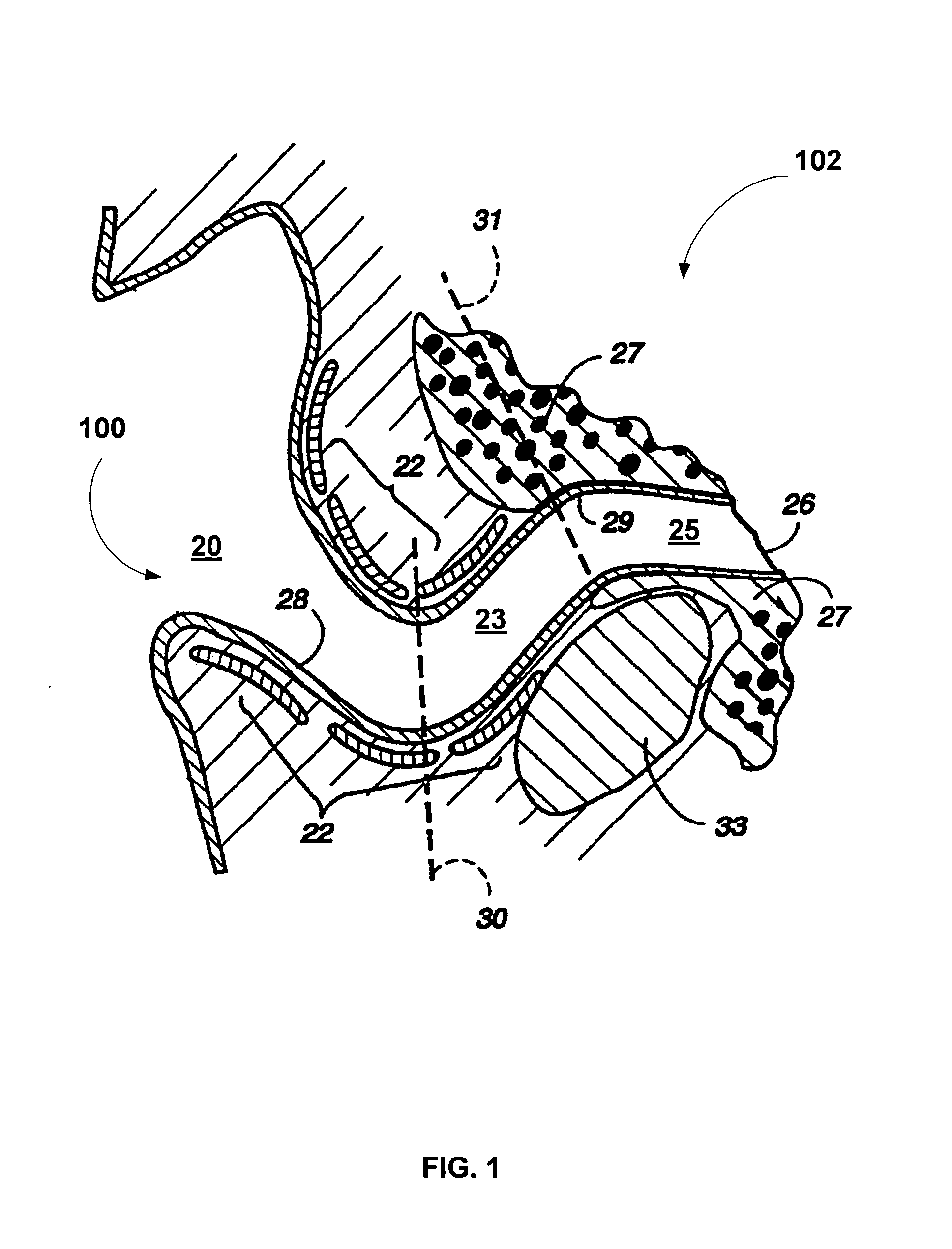
Apparatus and methods for directly displacing the partition between the middle ear and inner ear at an infrasonic frequency
ActiveUS7179238B2Alleviate vertigo, tinnitus, fullness of the ear and/or hearing lossUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyMiddle ear functionInner Ear Diseases
An apparatus for displacing a partition between a middle ear and an inner ear to treat the symptoms of Meniere's disease or endolymphatic hydrops comprises a treatment member for being disposed in the middle ear adjacent the partition and a driver for driving the treatment member to move against the partition to thereby displace the partition at an infrasonic frequency to influence fluid distribution in the inner ear. A method for treating an ear comprises the steps of disposing a treatment device within the middle ear and moving at least a portion of the treatment device against the partition at an infrasonic frequency to displace the partition to influence fluid in the inner ear.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Adjustable earphones for personal audio and communication systems
InactiveUS6427018B1Prevent rusting and other corrosionAvoid partialMicrophonesLoudspeakersCommunications systemEngineering
An ear mounted earphone includes a speaker housing for positioning a speaker at the entrance to the auditory canal of an ear of a user. An elongate boom extends from the speaker housing and through a sleeve at one end of an earpiece so that the boom may be moved longitudinally and rotationally within the sleeve for adjustment purposes and will be frictionally held in adjusted position by the sleeve during use. A microphone arm with microphone may be rotatably mounted on the speaker housing to provide a microphone when the earphones are used with a communication system. The rotatability of the microphone arm allowing the same earphone and microphone arm to be adjusted for use with either the right or left ear of a user. An earpiece may be conveniently integrally molded as a single piece with a slit formed therein intermediate its length so the wire to the speaker and microphone can be positioned within the earpiece. The speaker may be waterproofed by a thin waterproof material such as mylar.
Owner:COTRON
Multifunctional Dispersants
The present invention provides a composition comprising the product prepared by hearing together: (a) a dispersant; and (b) a 1,3-dicarboxylic acid or 1,4-dicarboxylic acid of an aromatic compound, or a reactive equivalent thereof; and at least one of: (c) 2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole or a hydrocarbyl-substituted 2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole, or an oligomer thereof; (d) a borating agent; and (e) a phosphorus acid compound, or a reactive equivalent thereof, said heating being sufficient to provide a reaction product of (a), (b), and (c), (d), or (e), which is soluble in an oil of lubricating viscosity. The invention further provides a use for the composition.
Owner:THE LUBRIZOL CORP
High sensitivity noise immune stethoscope
ActiveUS20070165872A1Efficient couplingHigh elastic modulusTransducer detailsStethoscopeEngineeringActive systems
A physiological sensing stethoscope suitable for use in high-noise environments is disclosed. The stethoscope is designed to be substantially matched to the mechanical impedance of monitored physiological activity and substantially mismatched to the mechanical impedance of air-coupled acoustic activity. One embodiment of the stethoscope utilizes a passive acoustic system. Another embodiment utilizes an active Doppler system. The passive and active systems can be combined in one stethoscope enabling switching from a passive mode to an active mode suitable for use in very high-noise environments. The stethoscope is suitable for use in environments having an ambient background noise of 100 dBA and higher. The passive includes a head having a housing, a flexural disc mounted with the housing, and an electromechanical stack positioned between the housing and the flexural disc in contact with the skin of a patient. The active system detects Doppler shifts using a high-frequency transmitter and receiver.
Owner:ACTIVE SIGNAL TECH
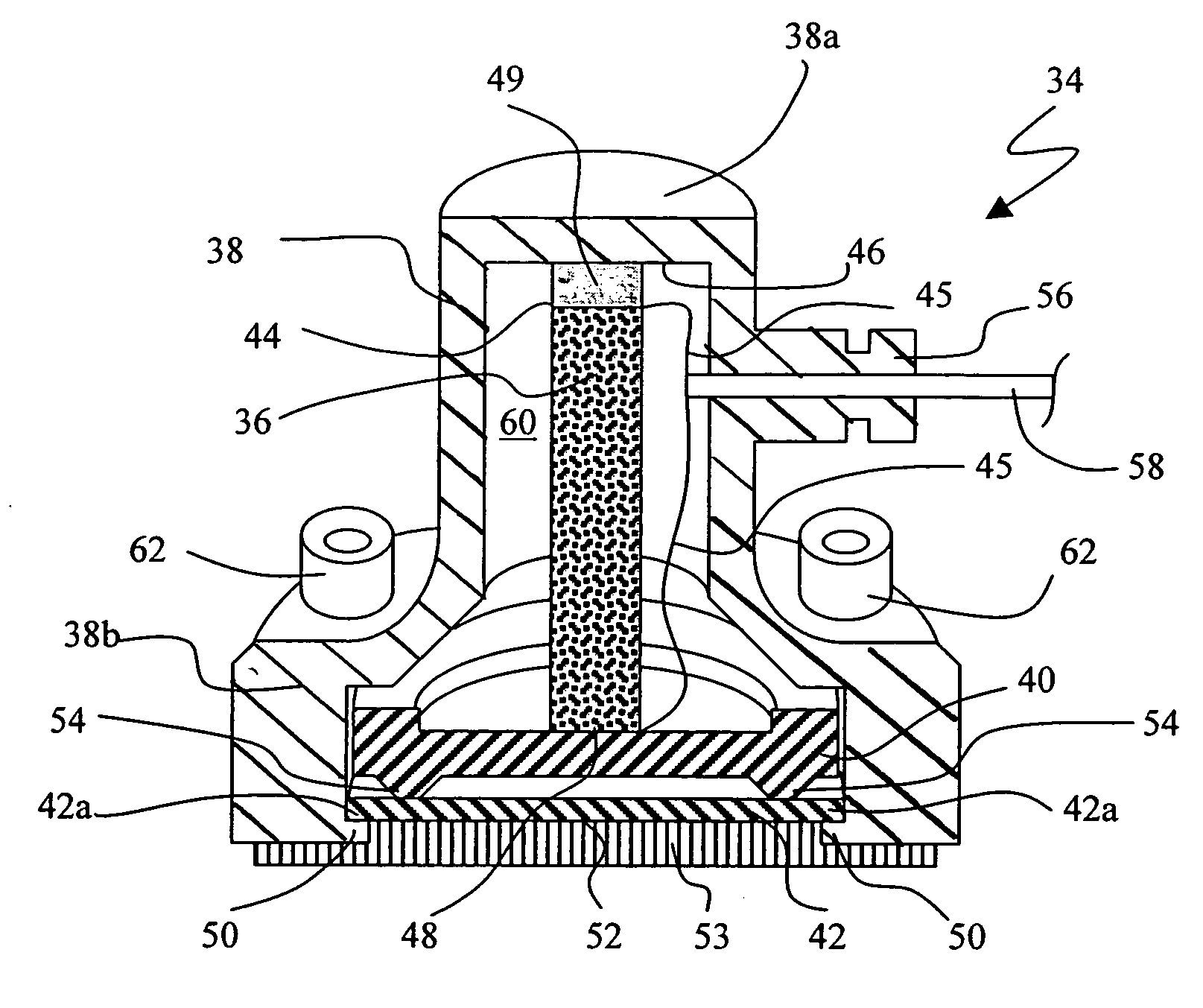
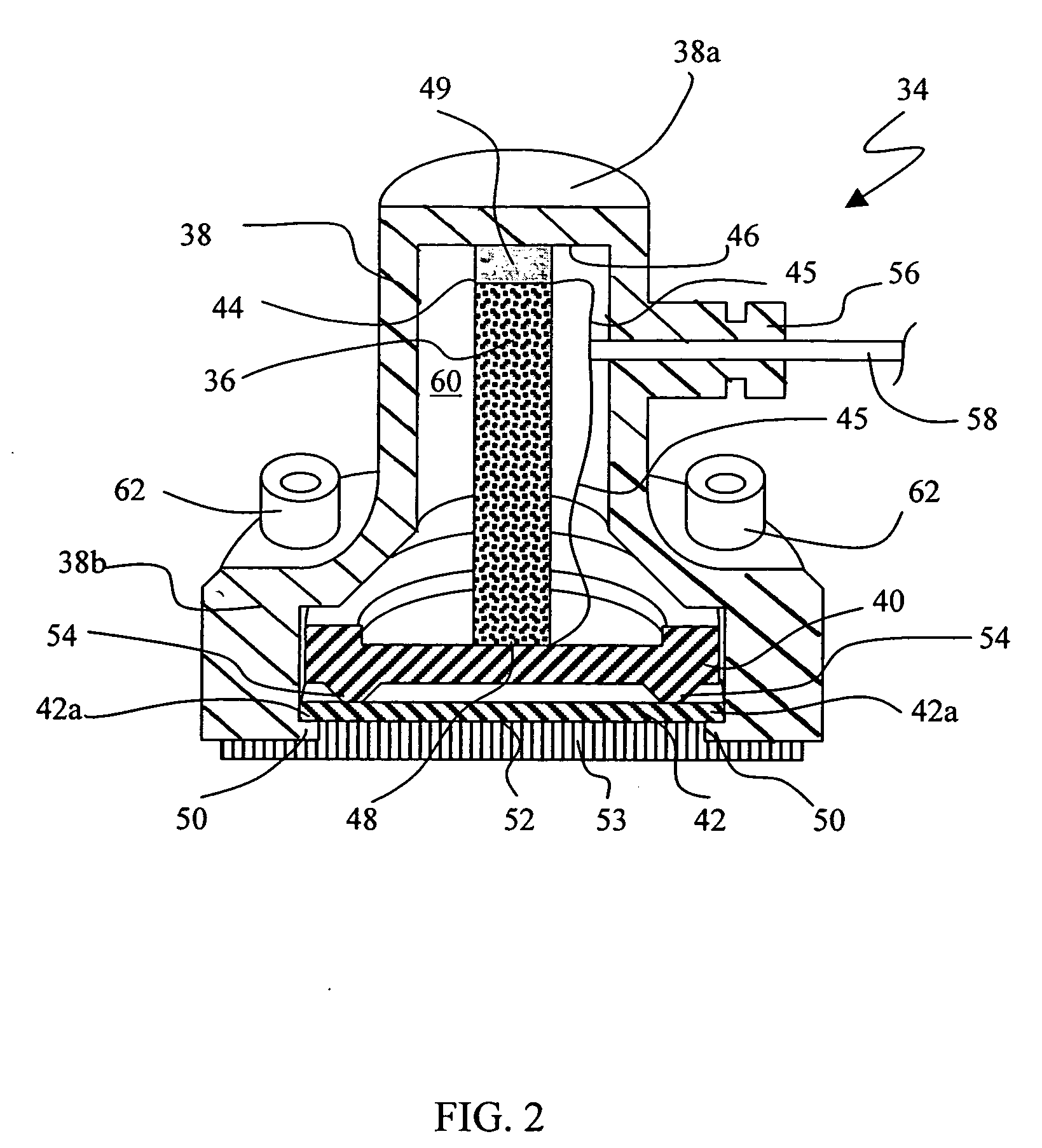
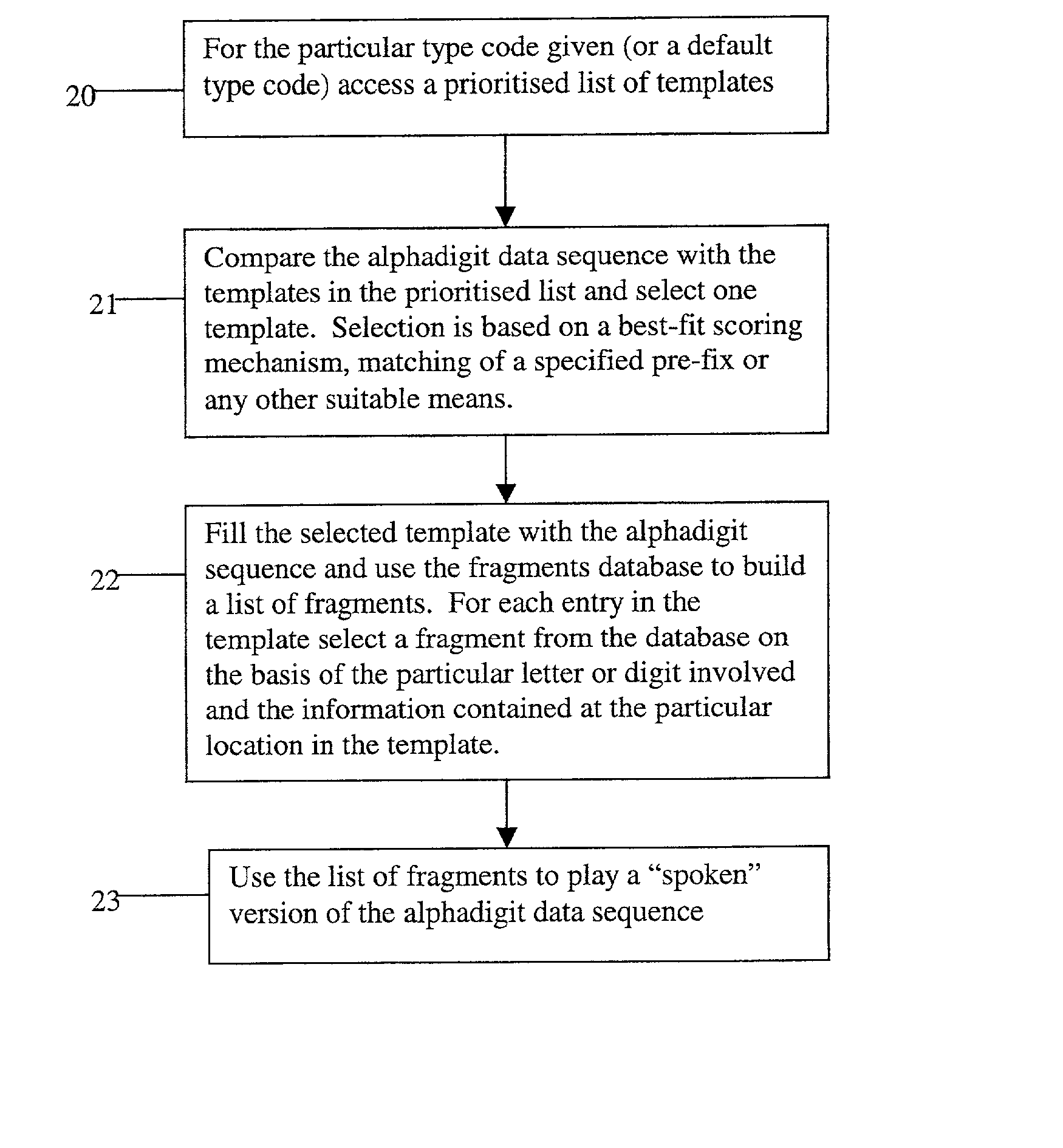
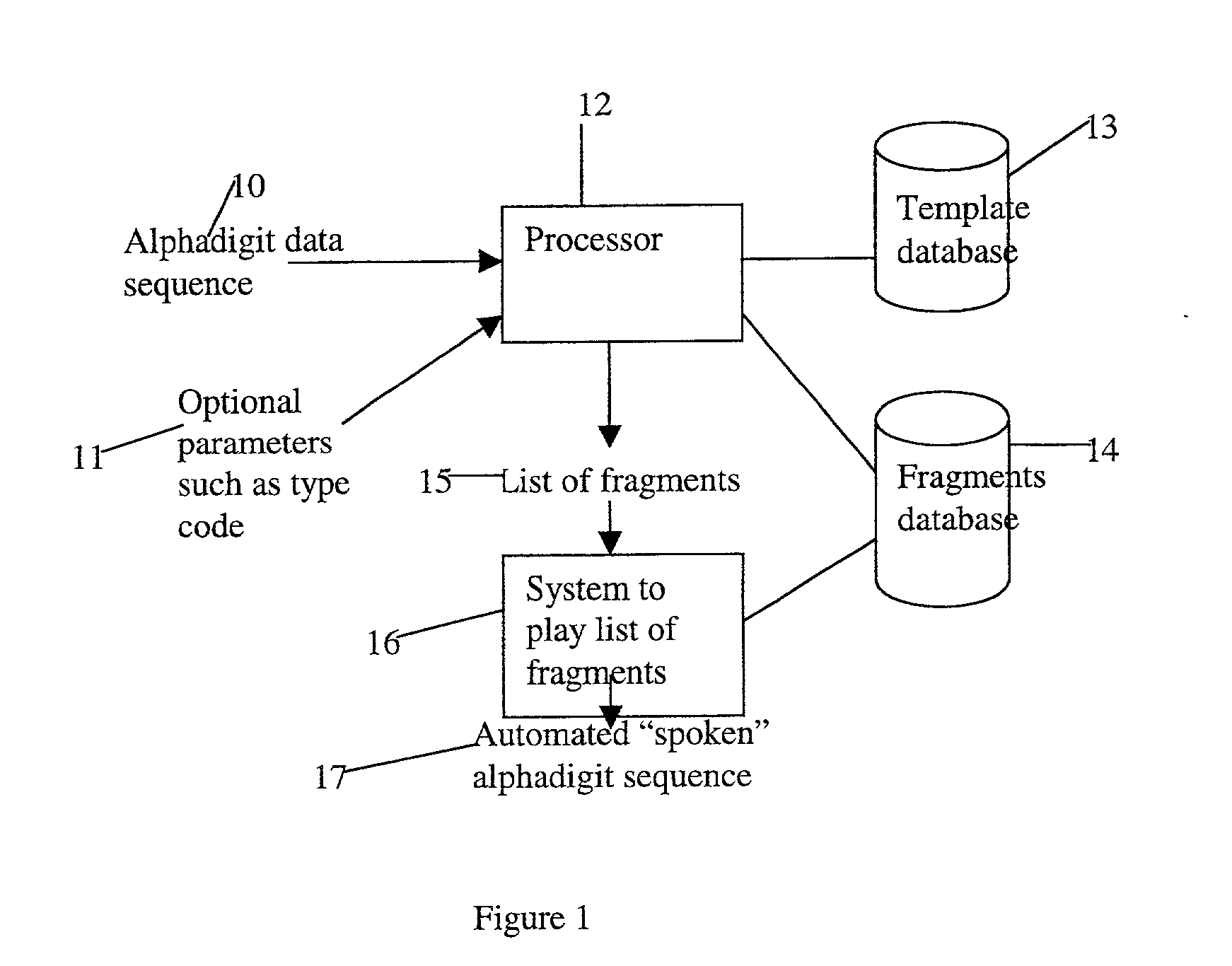
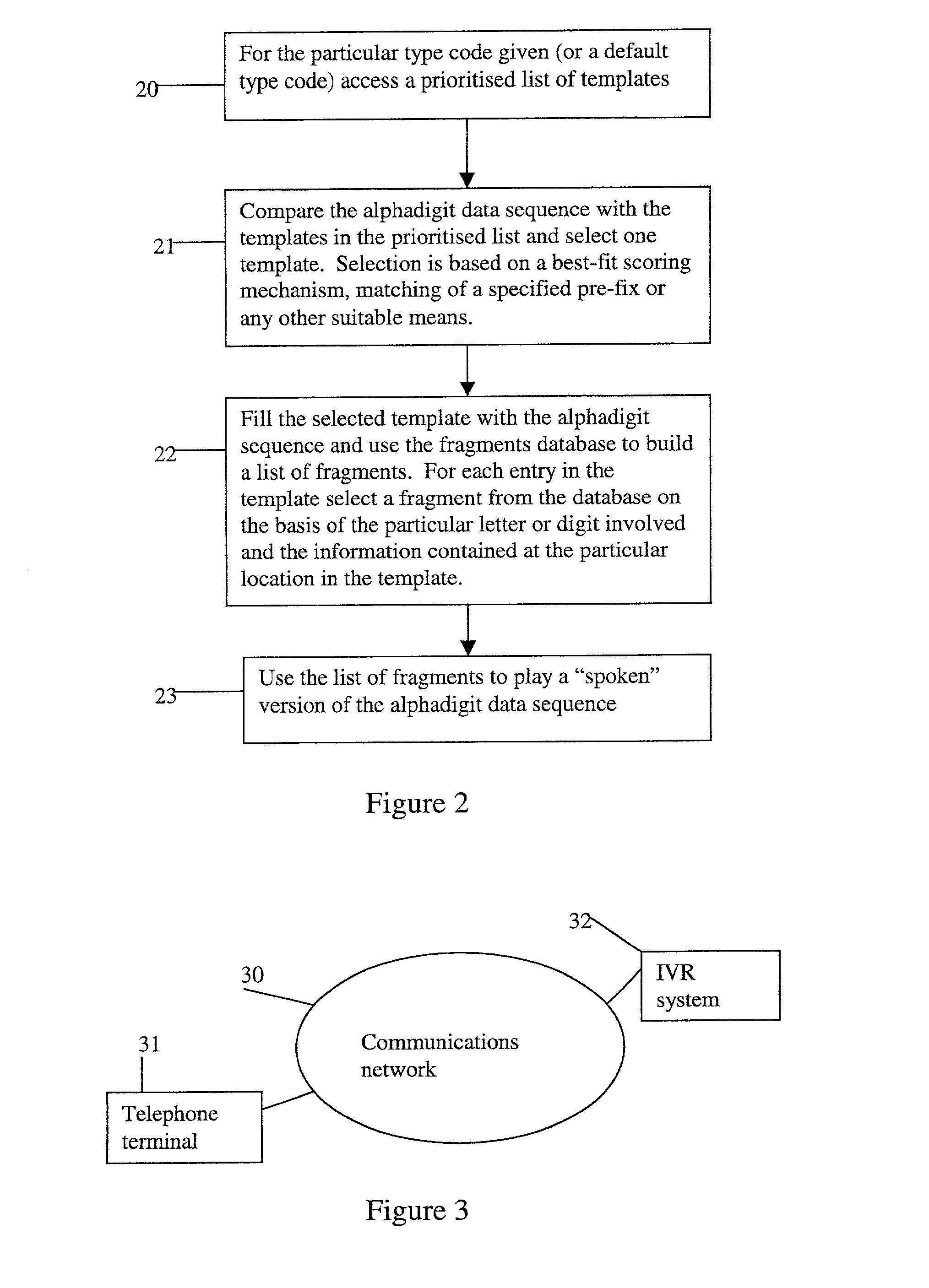
Method and apparatus for playing recordings of spoken alphanumeric characters
InactiveUS20030101045A1Simple configurationSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSpoken languageLettering
Automated systems for "speaking" telephone numbers, zip codes and the like typically produce unrealistic results that do not sound like an actual human speaking the telephone number or zip code. By using templates together with four or more types of fragment for each alphanumeric character this problem is addressed. A fragment is a recording of a spoken alphanumeric character as spoken at a particular location within an utterance. A template is a sequence of fields, each field representing part of a sequence of alphanumeric characters. Templates comprise information about the manner in which a sequence of alphanumeric characters is to be played, such as which fragments to use and when to use pauses. Using this method alphanumeric character sequences such as telephone numbers, zip codes and the like are played with human-like intonation in real time.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Method for assessing brain function and portable automatic brain function assessment apparatus
A method and apparatus for performing rapid brain assessment may provide emergency triage to head trauma patients by analyzing a combination of spontaneous and evoked brain potentials. The spontaneous and evoked potentials are analyzed, and the results classified, to present a real-time assessment of a patient's brain, diagnosing any potential abnormalities therein.
Owner:BS HLDG +2
Diaphonic acoustic transduction coupler and ear bud
ActiveUS20090028356A1Improve fidelityMinimizing listener fatigueEar treatmentIntra aural earpiecesTransducerImpedance matching
The disclosed methods and devices incorporate a novel expandable bubble portion which provides superior fidelity to a listener while minimizing listener fatigue. The expandable bubble portion may be expanded through the transmission of low frequency audio signals or the pumping of a gas to the expandable bubble portion. In addition, embodiments of the acoustic device may be adapted to consistently and comfortably fit to any ear, providing for a variable, impedance matching acoustic seal to both the tympanic membrane and the audio transducer, respectively, while isolating the sound-vibration chamber within the driven bubble. This reduces the effect of gross audio transducer vibration excursions on the tympanic membrane and transmits the audio content in a manner which allows the ear to utilize its full inherent capabilities.
Owner:ASIUS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com