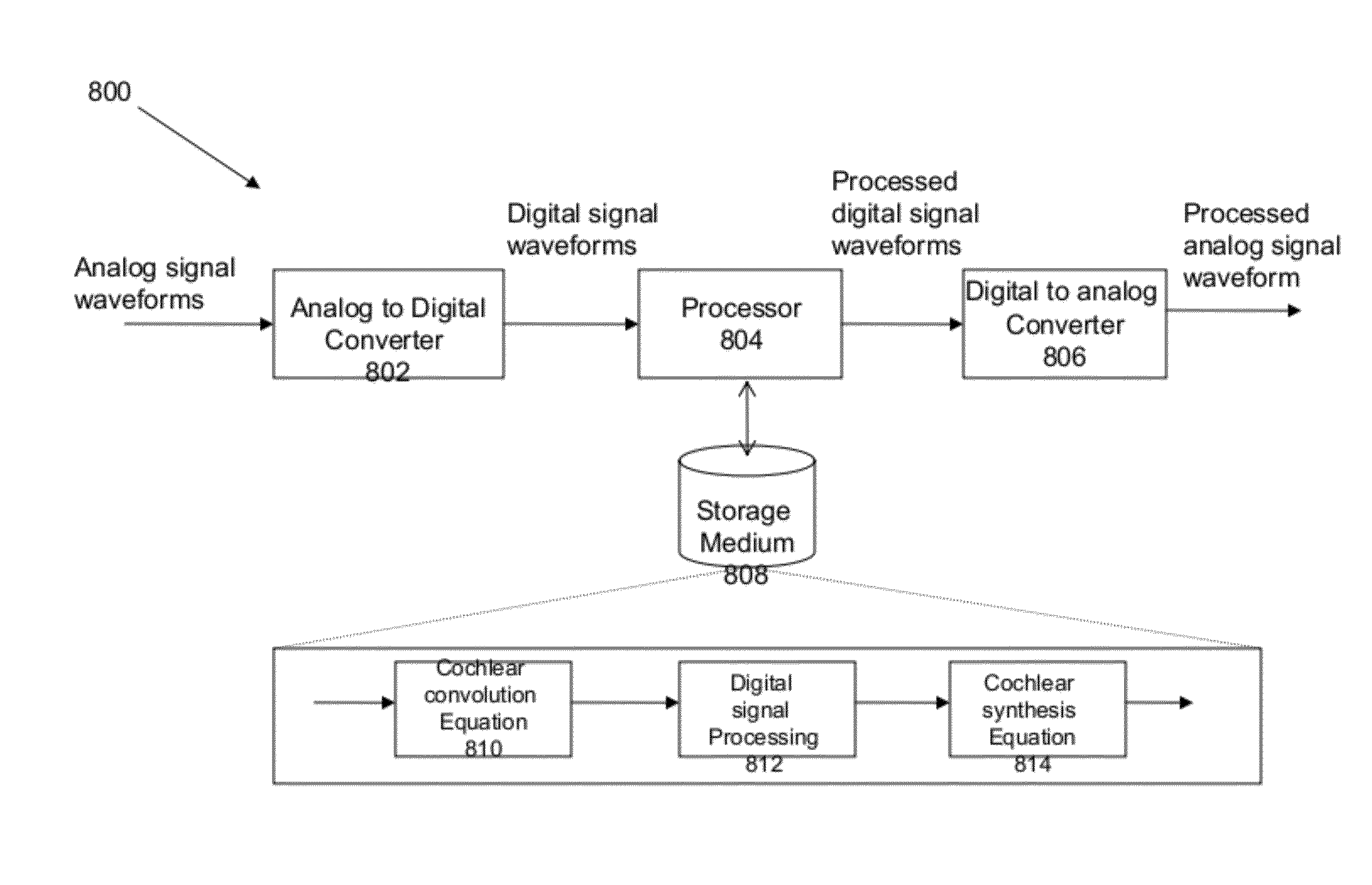
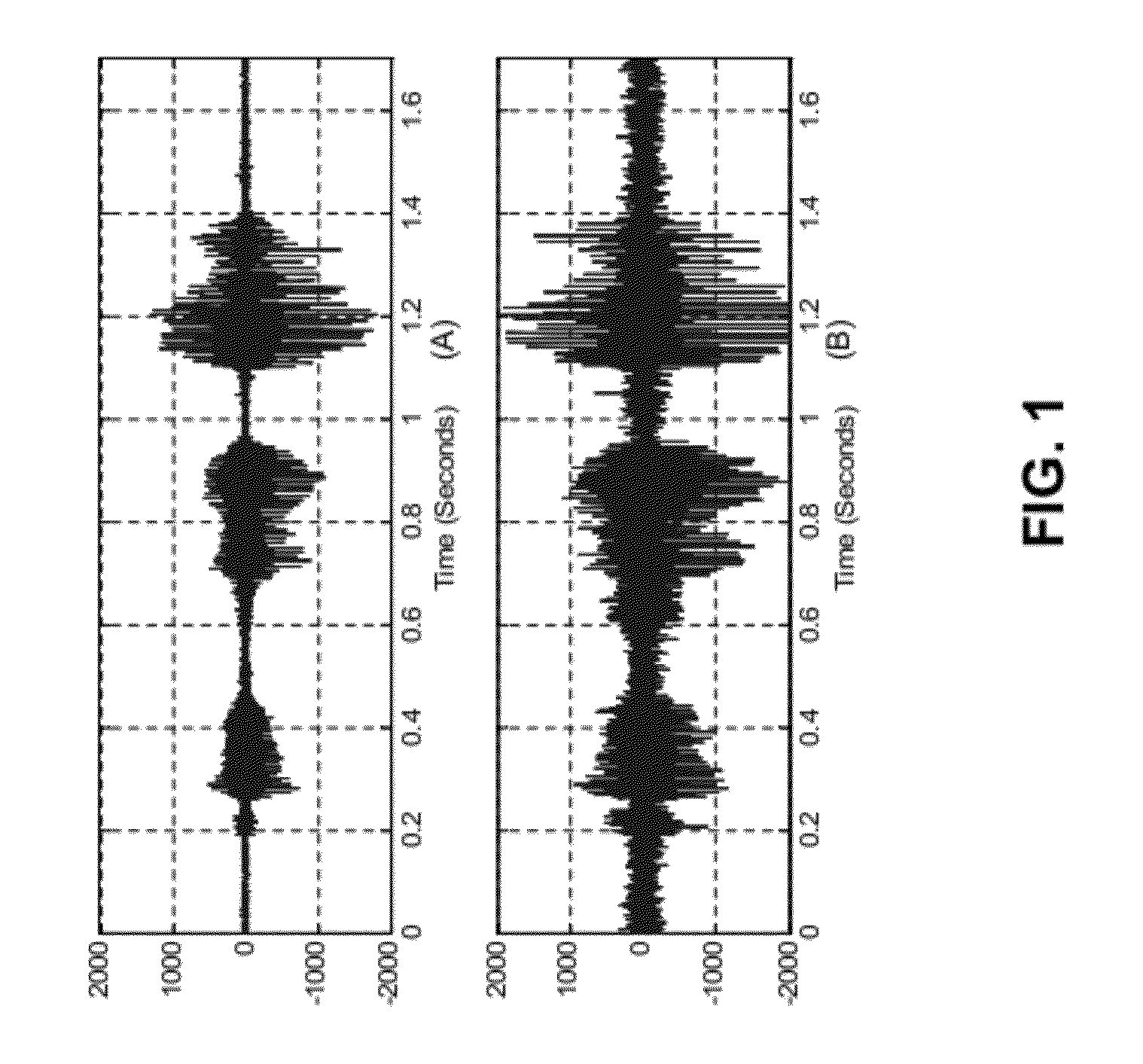
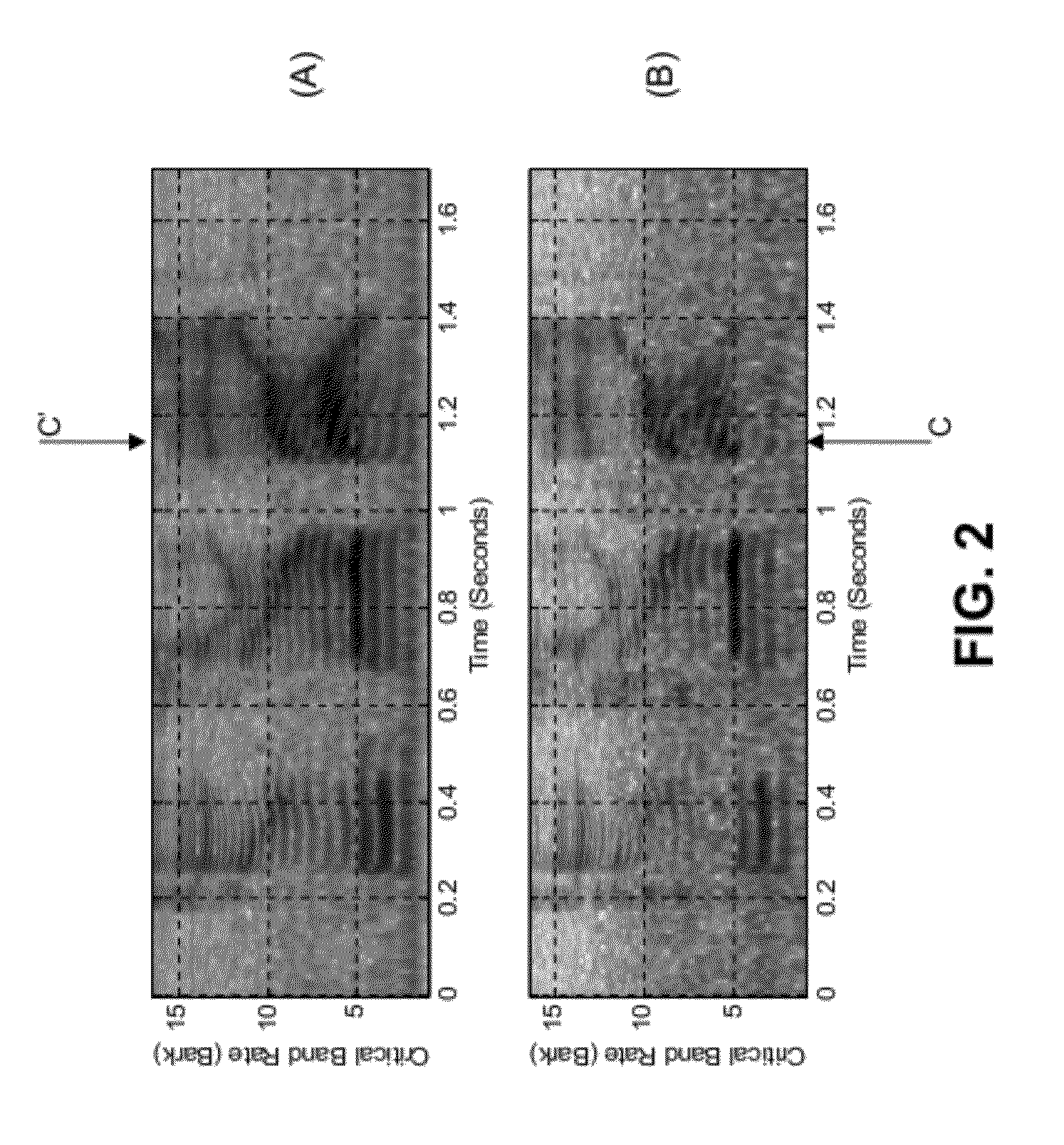
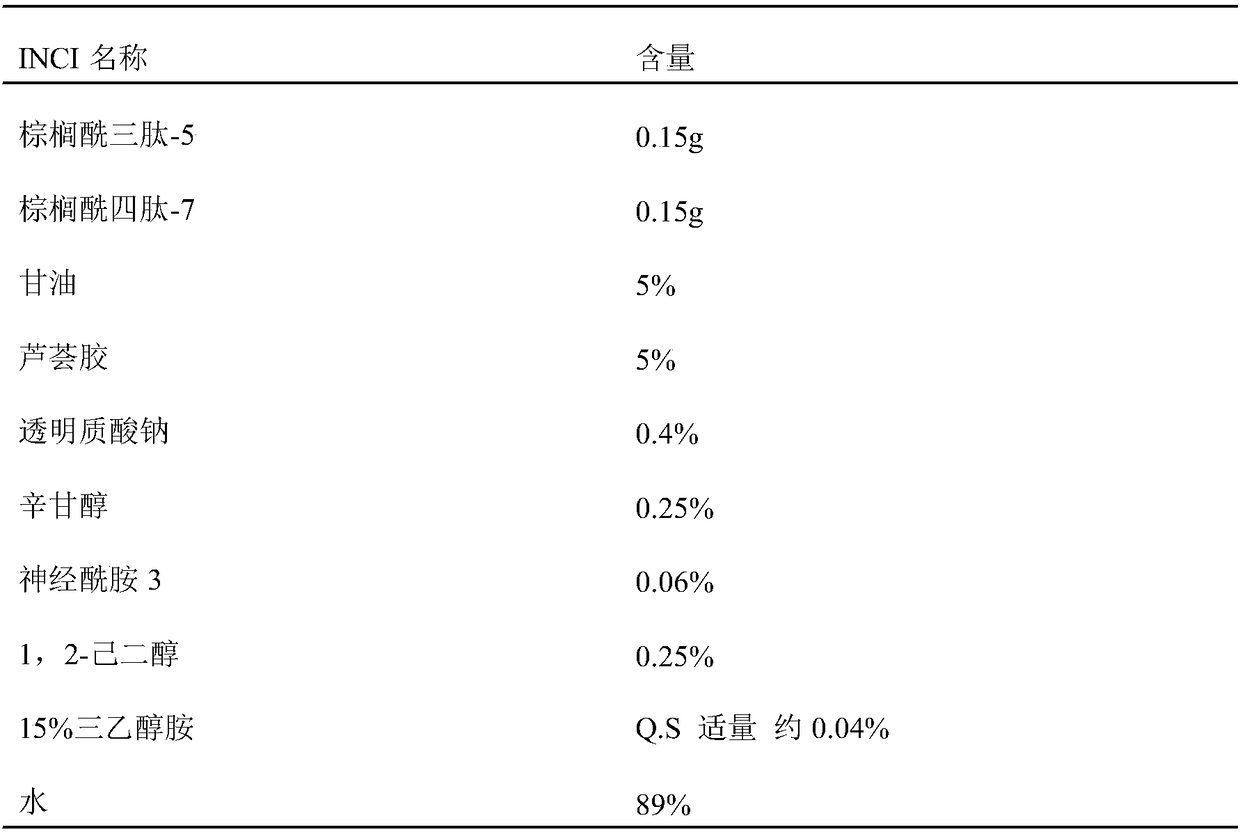
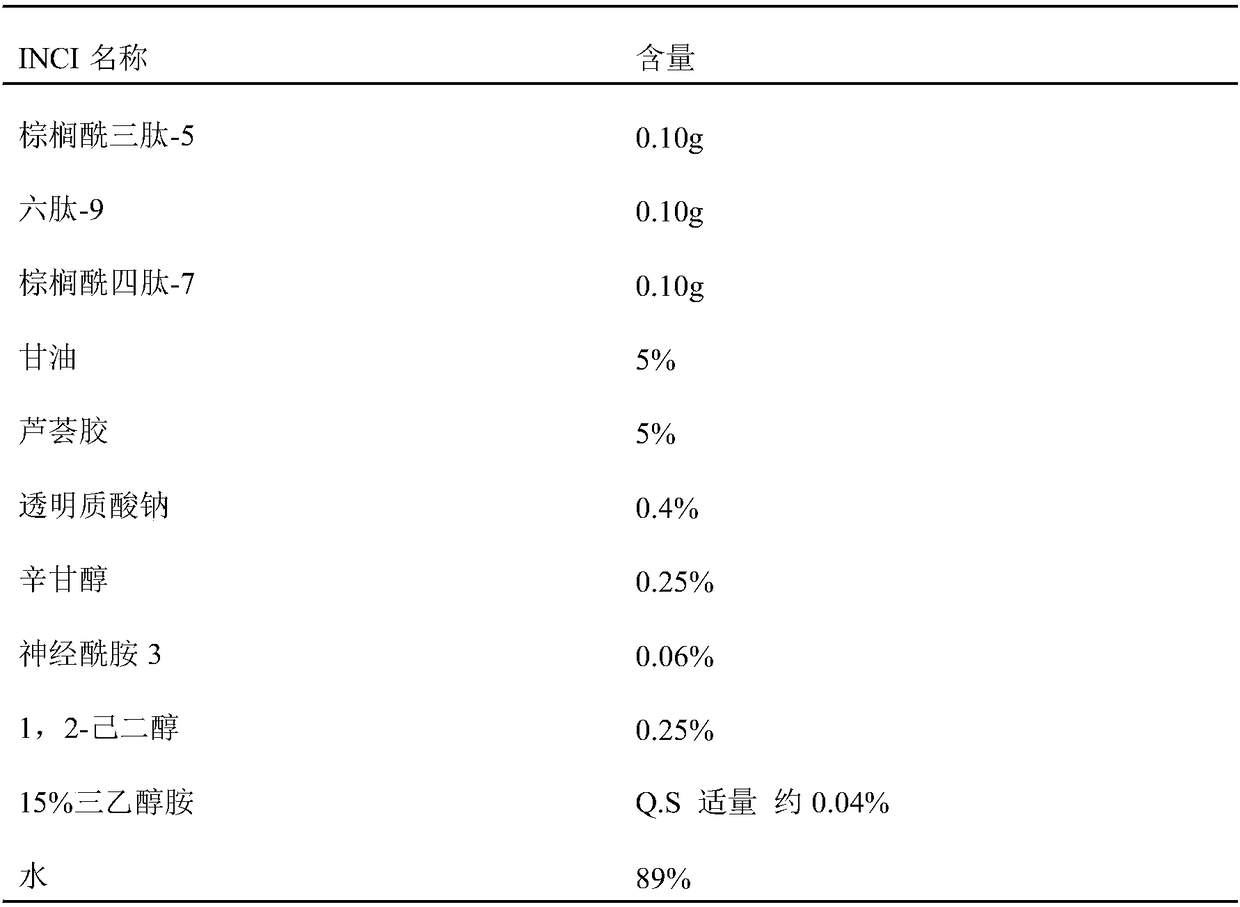
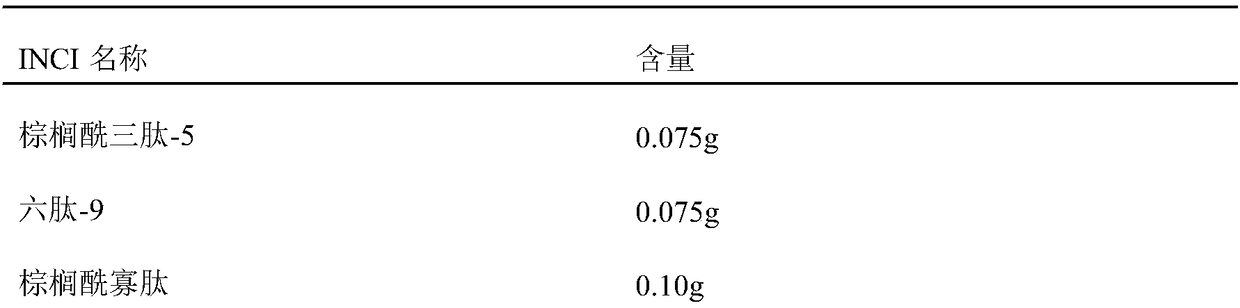
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
107 results about "Basilar membrane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
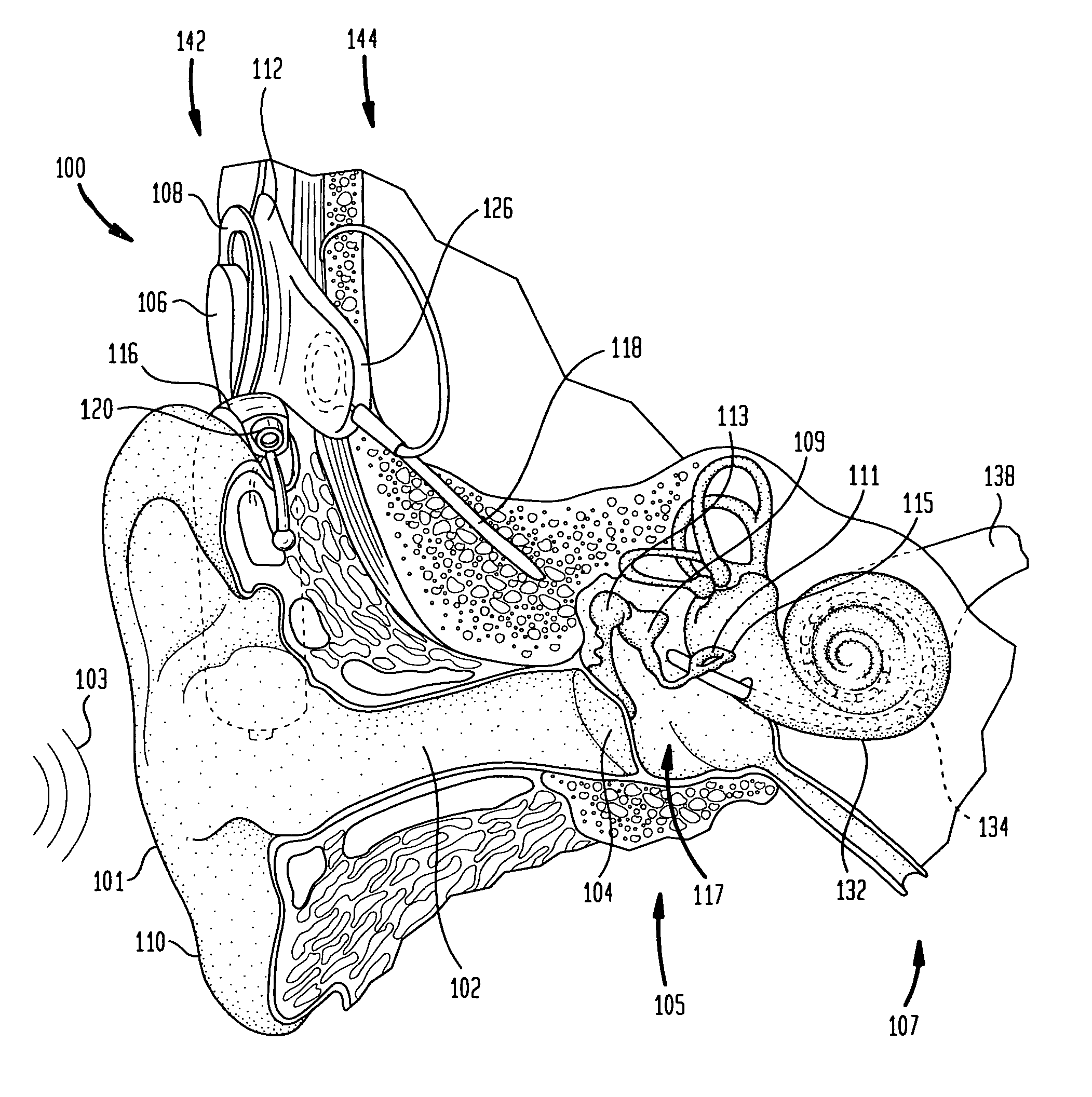
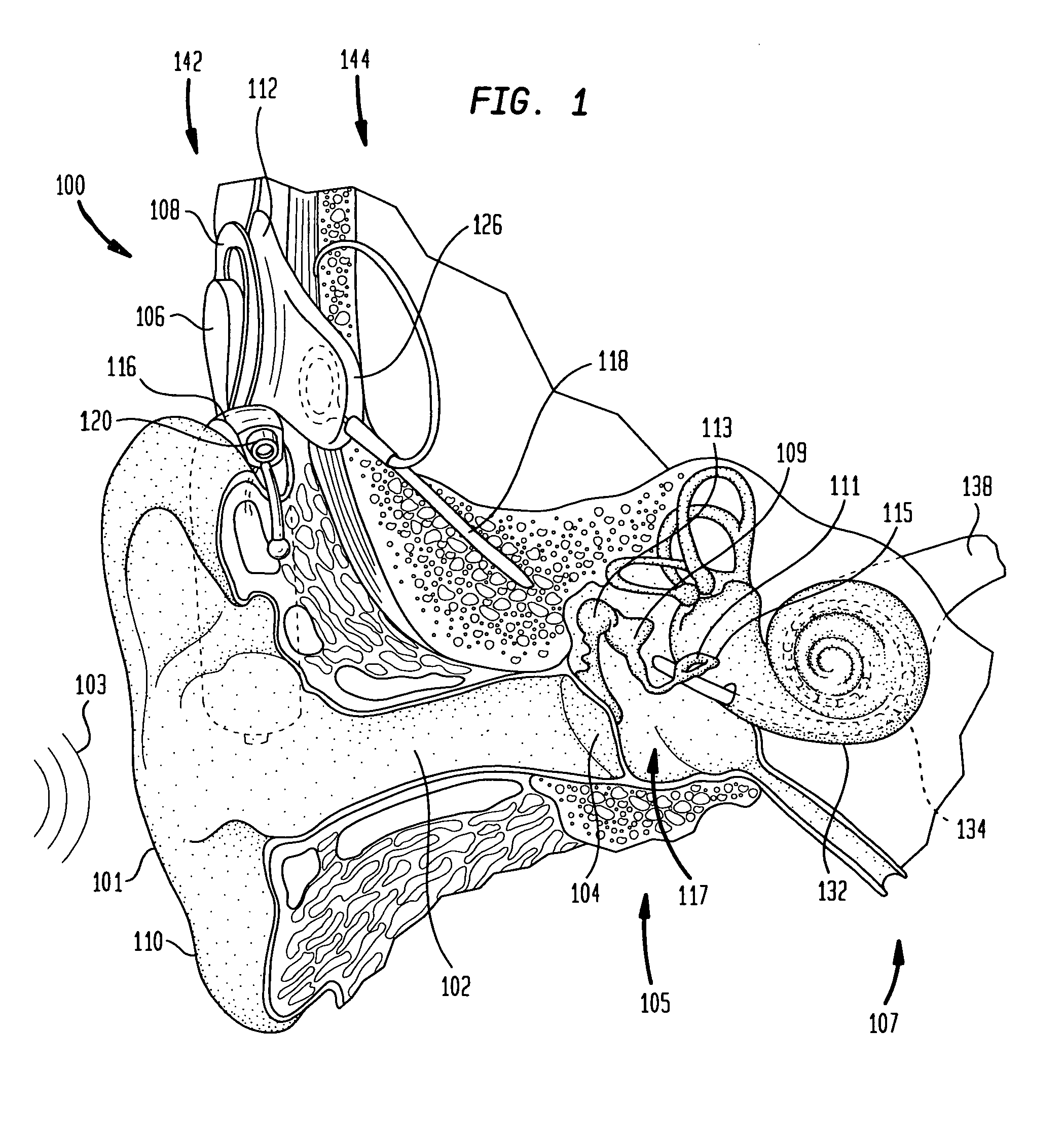
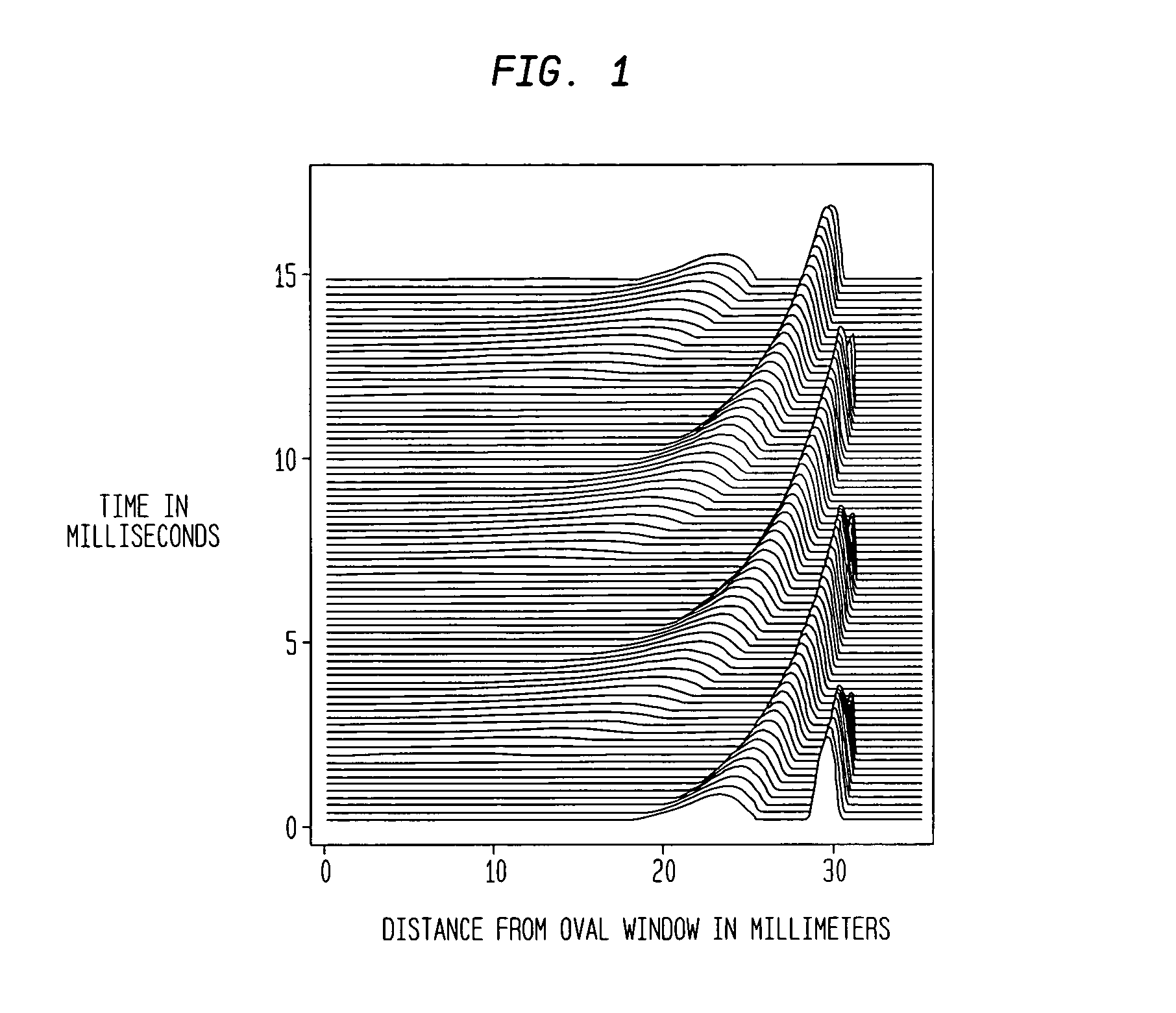
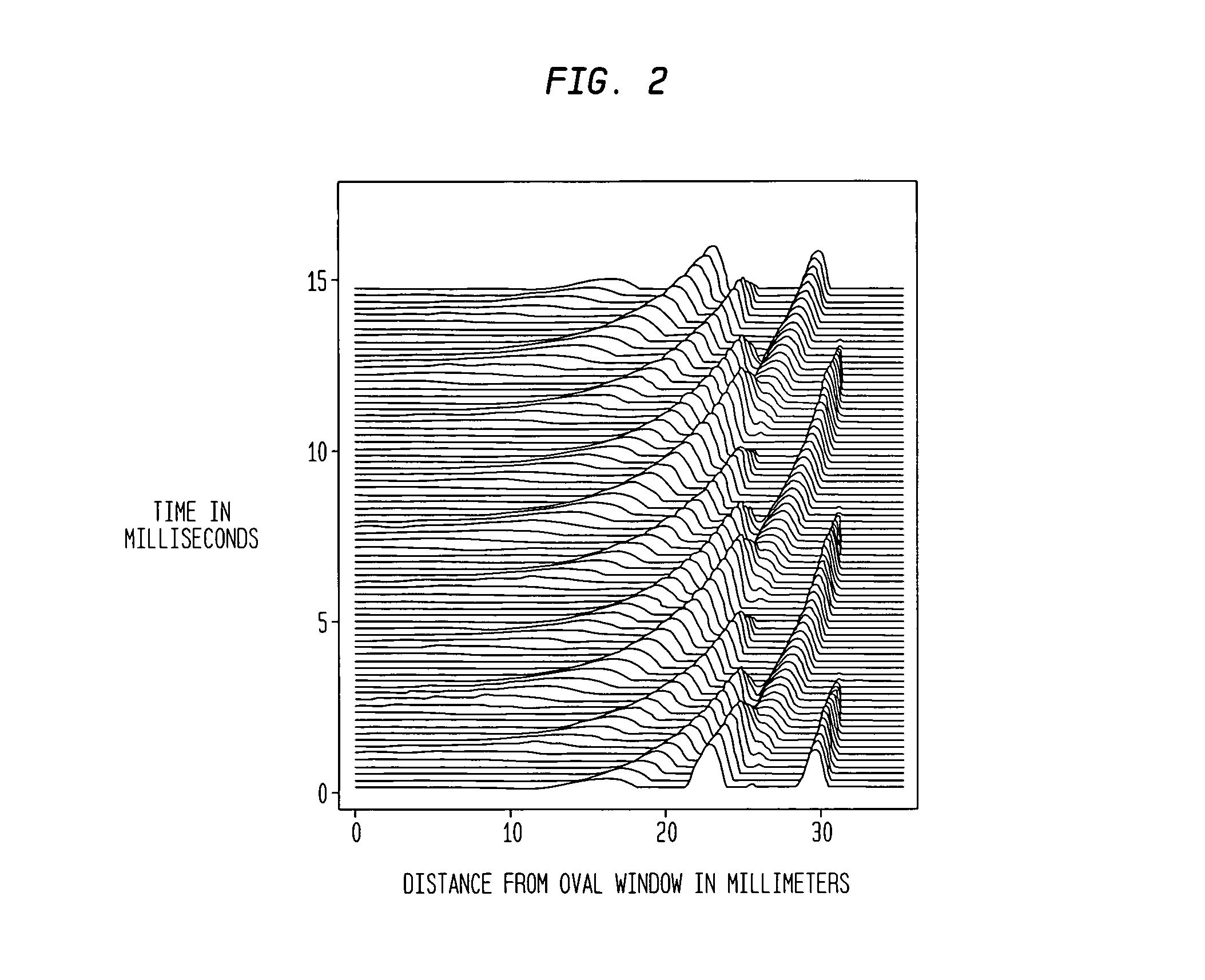
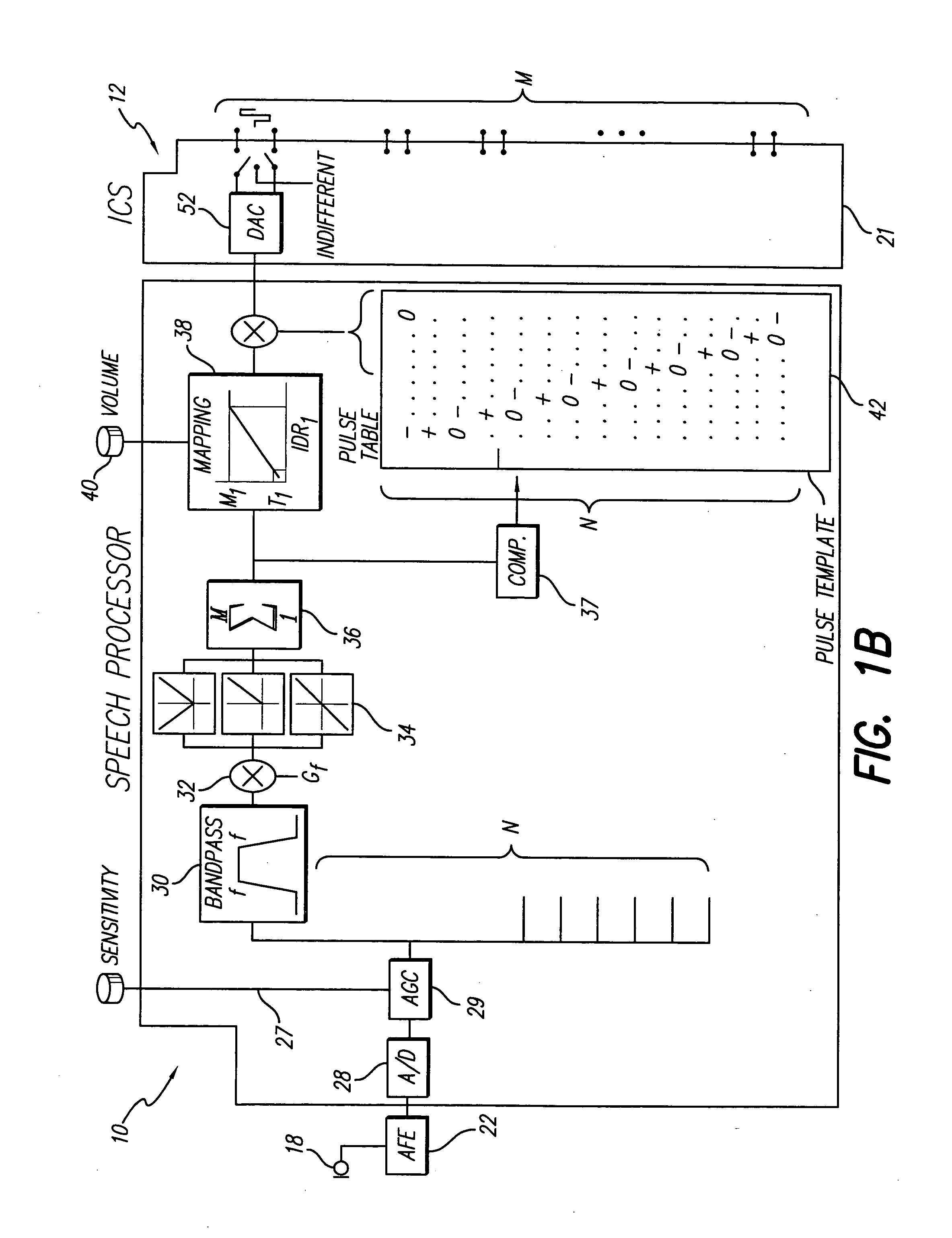
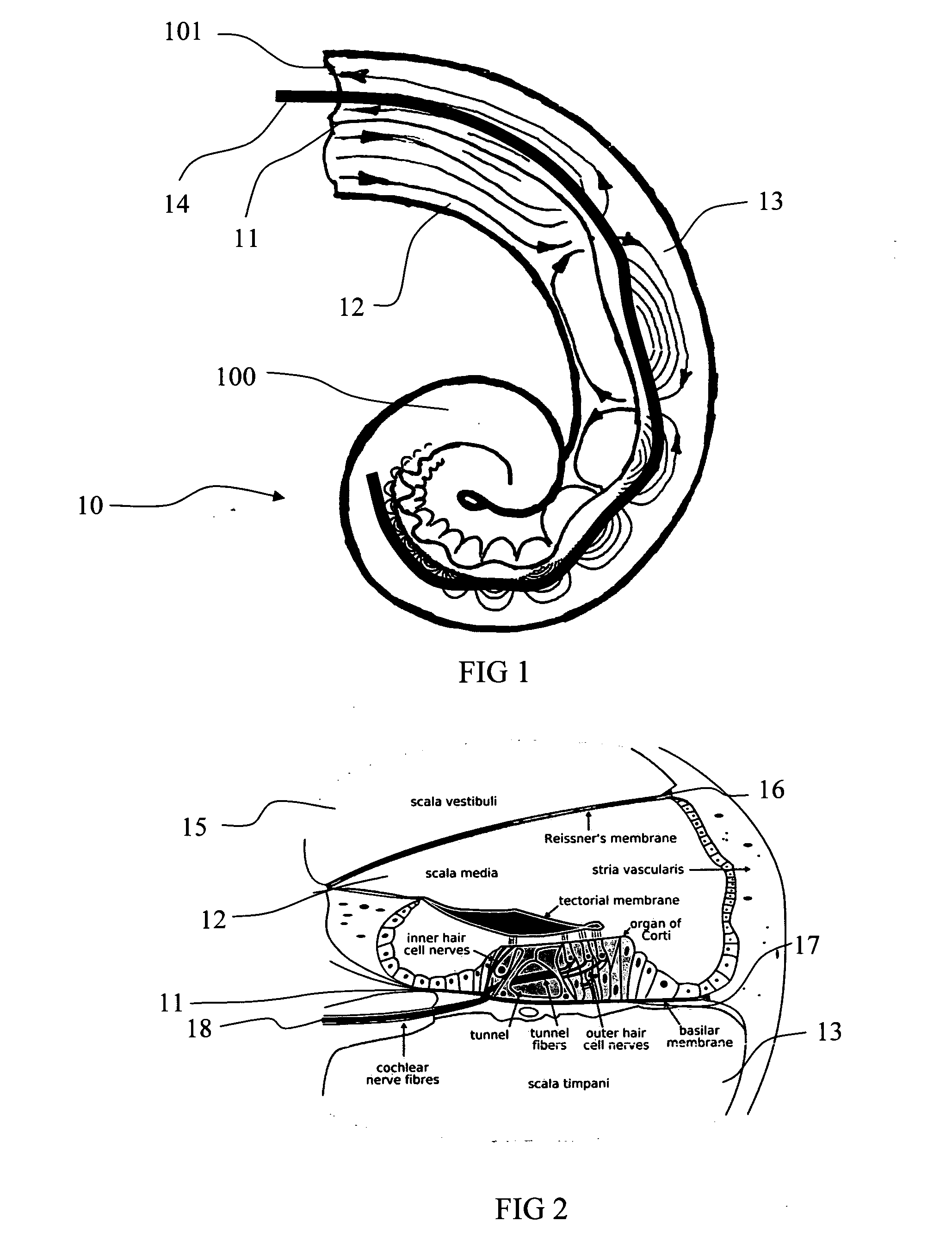
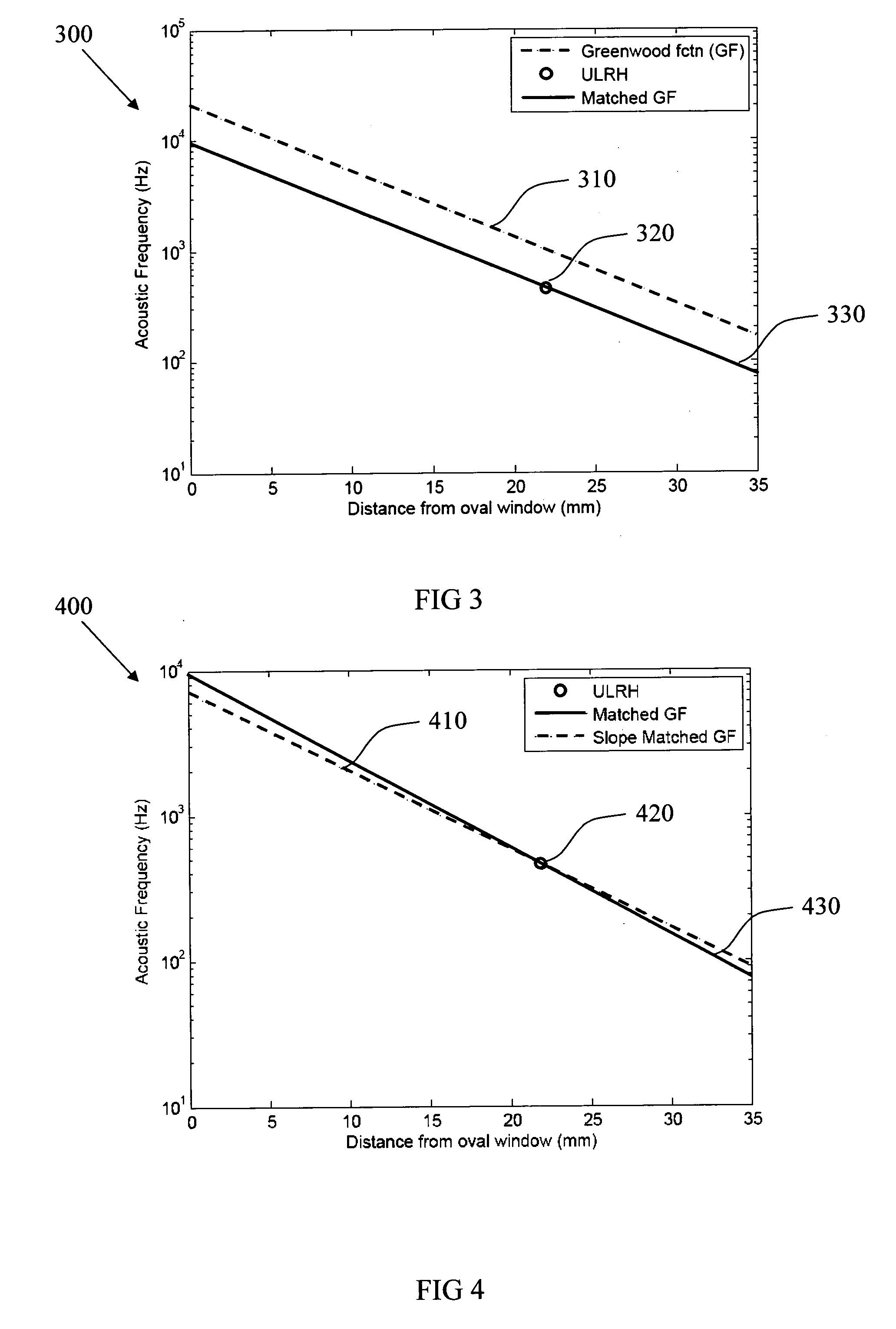
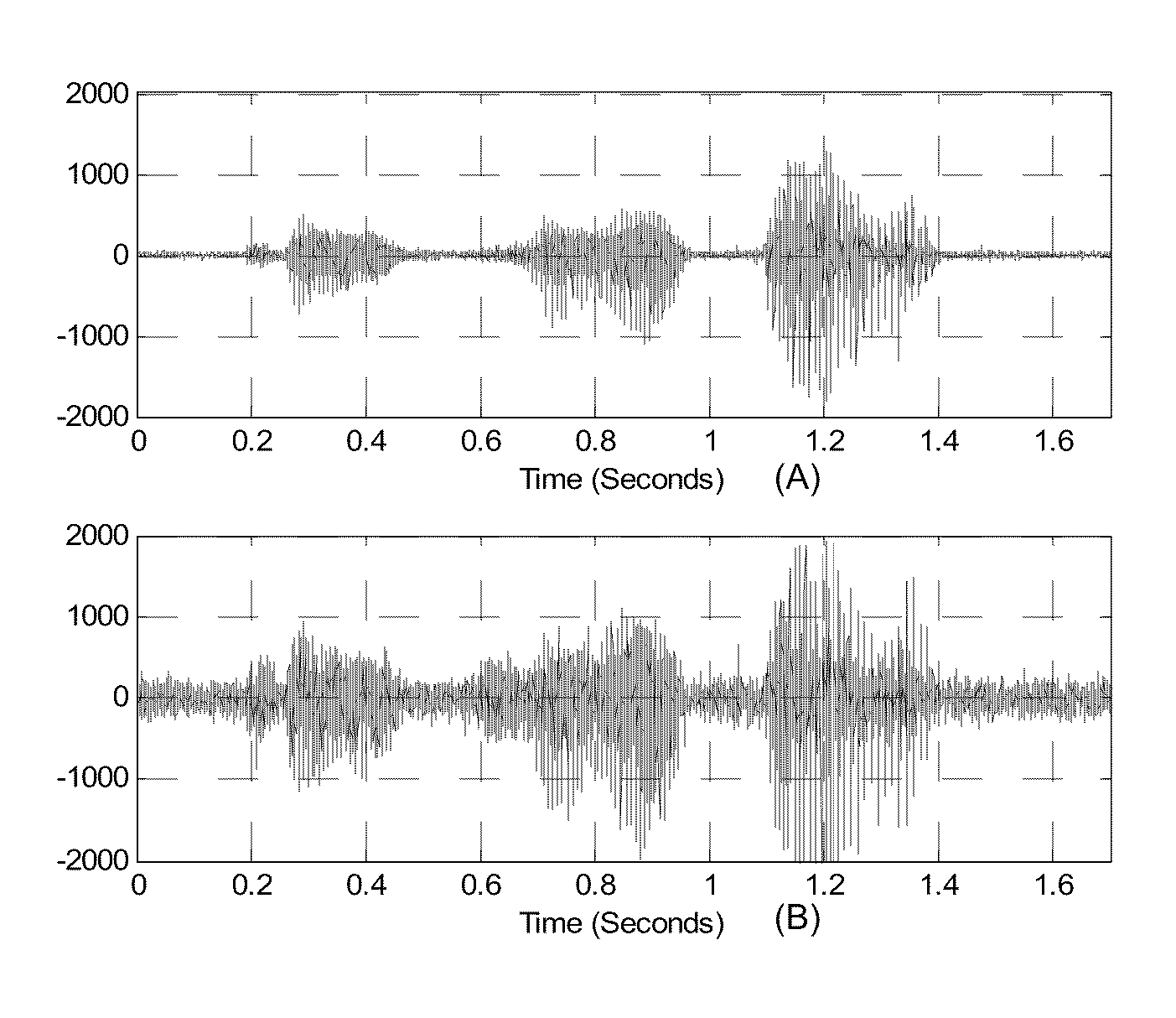
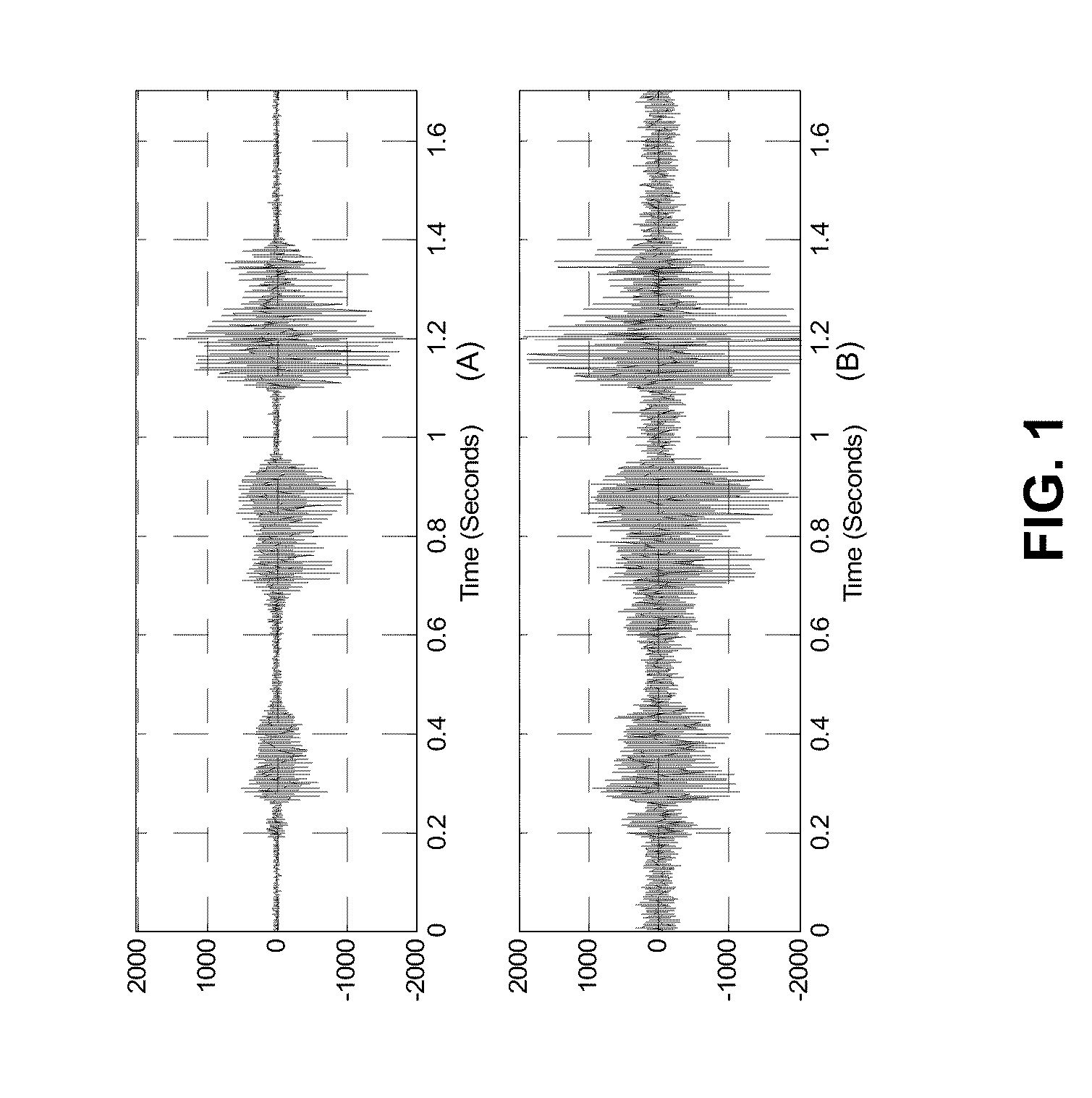
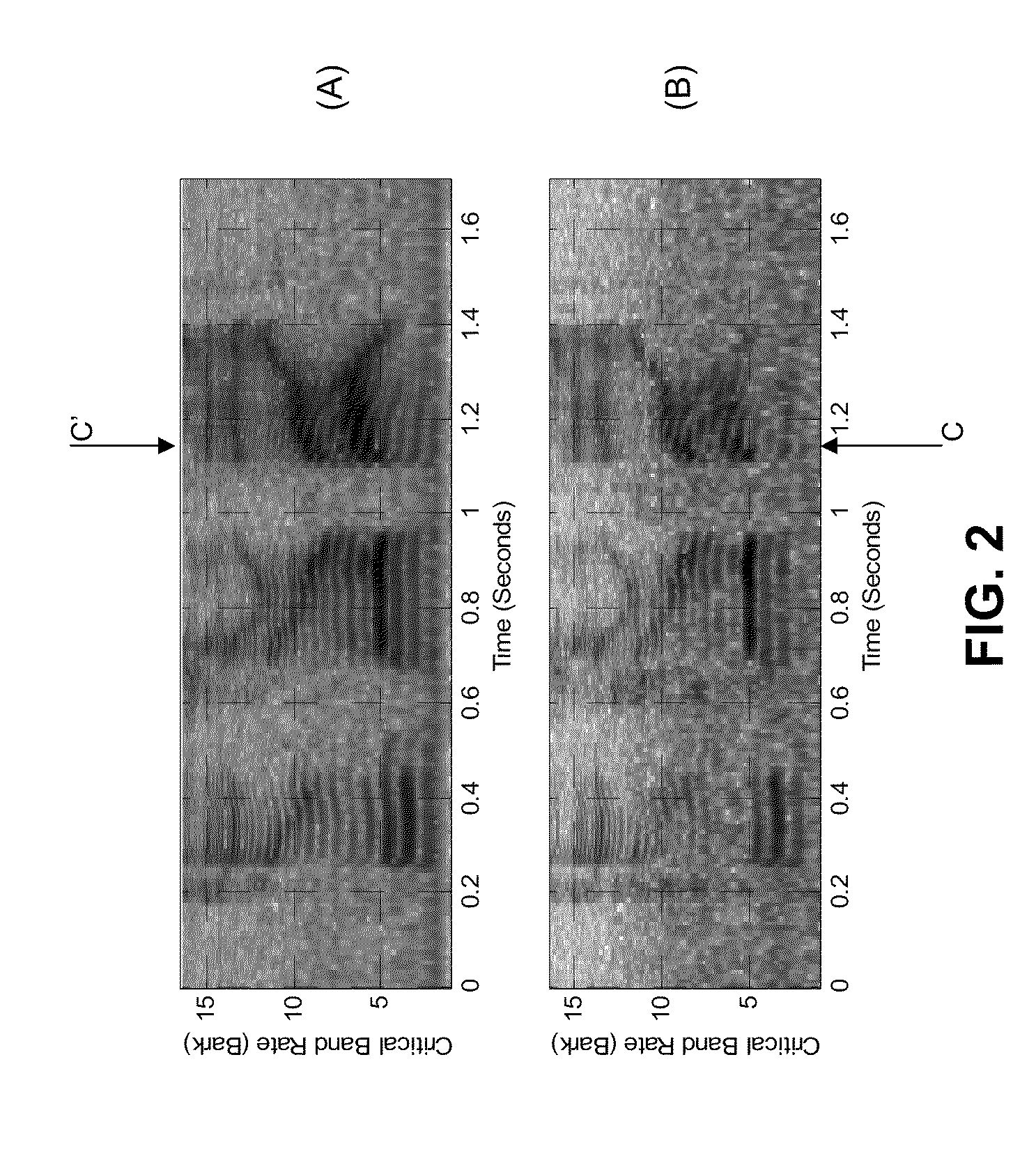
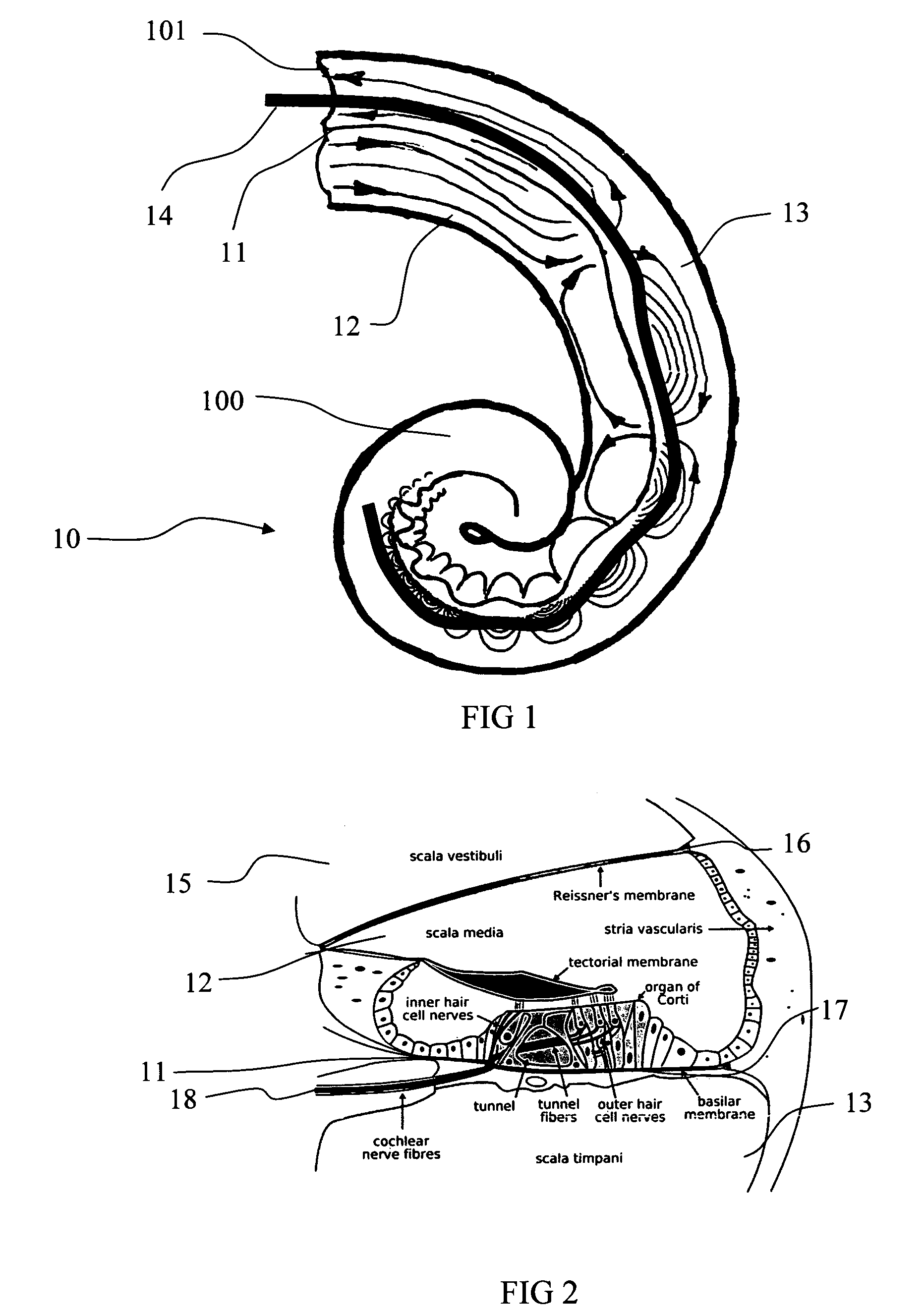
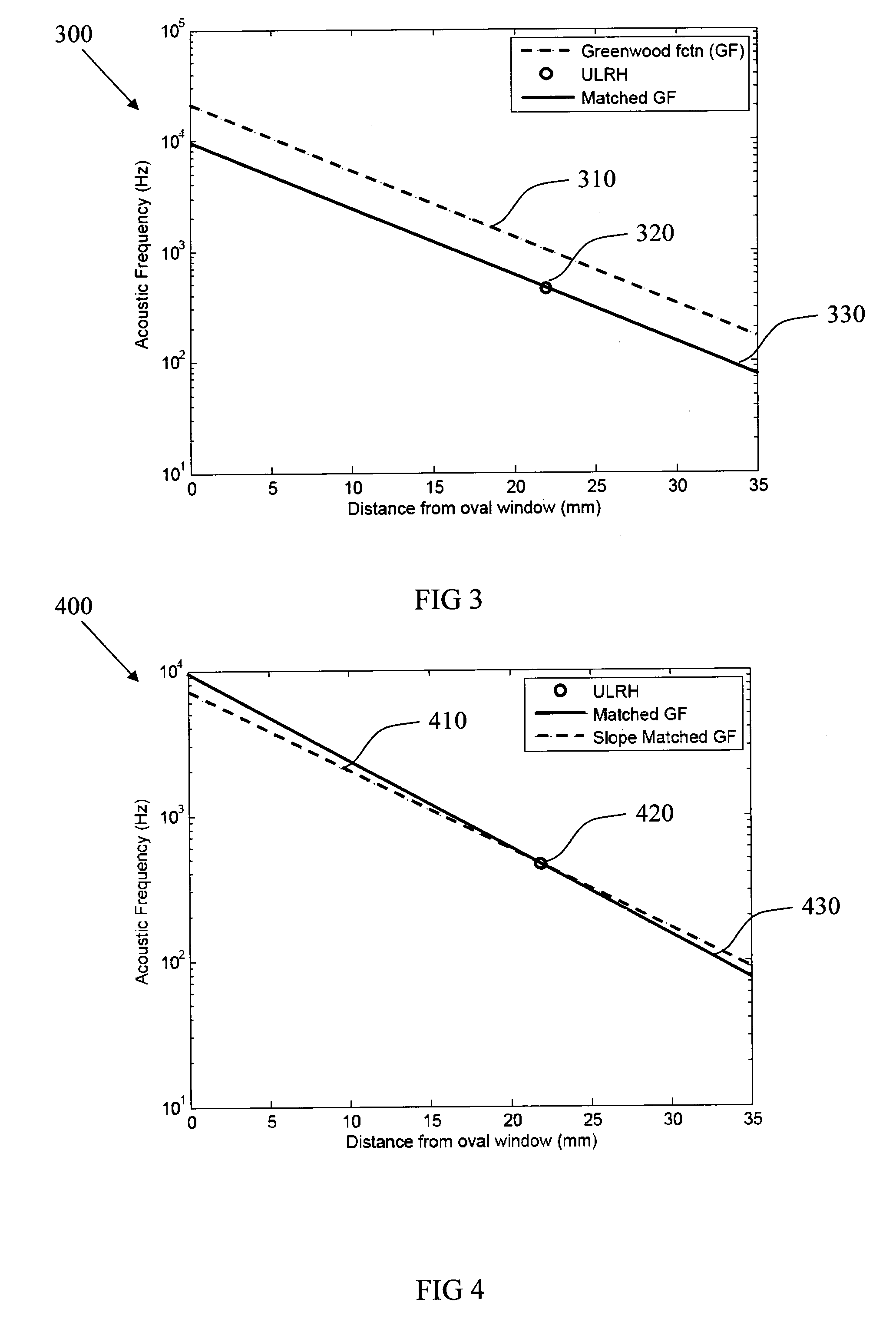
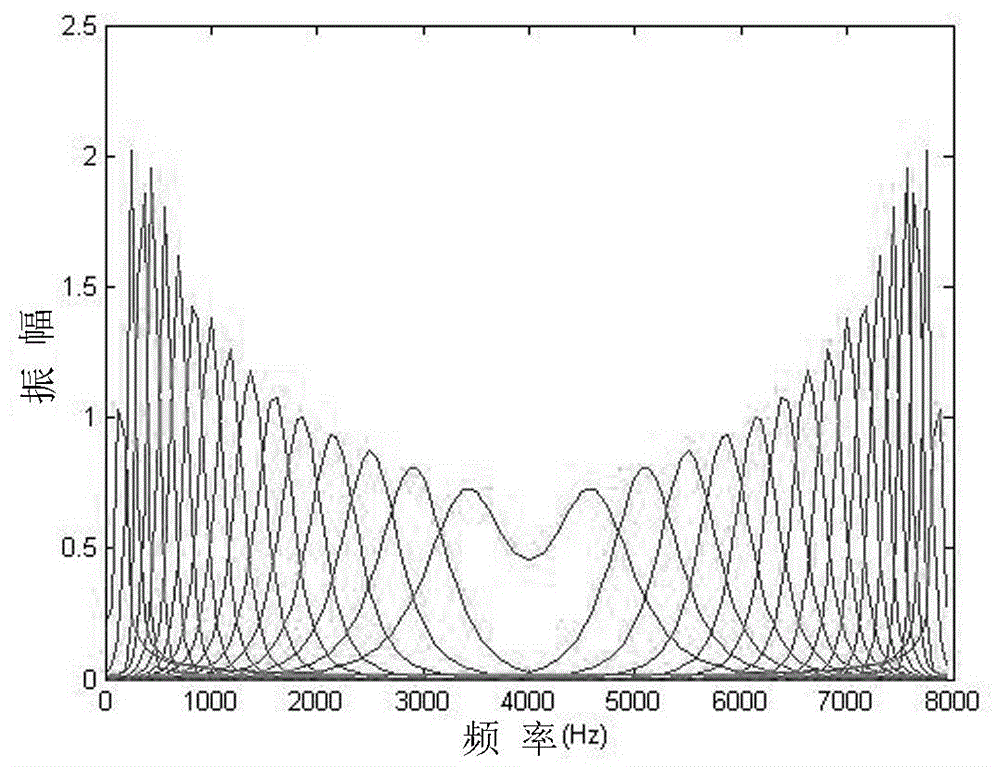
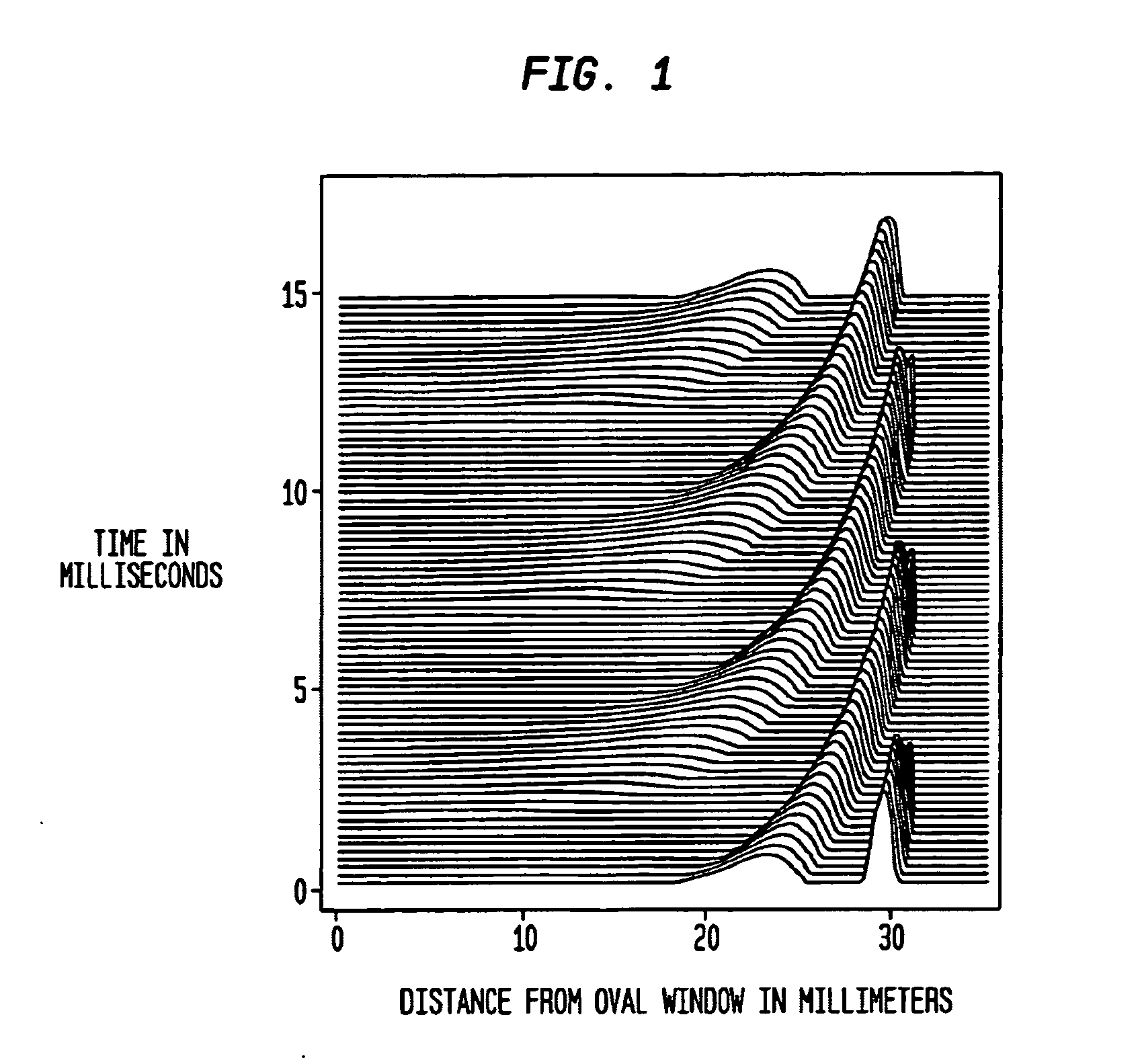
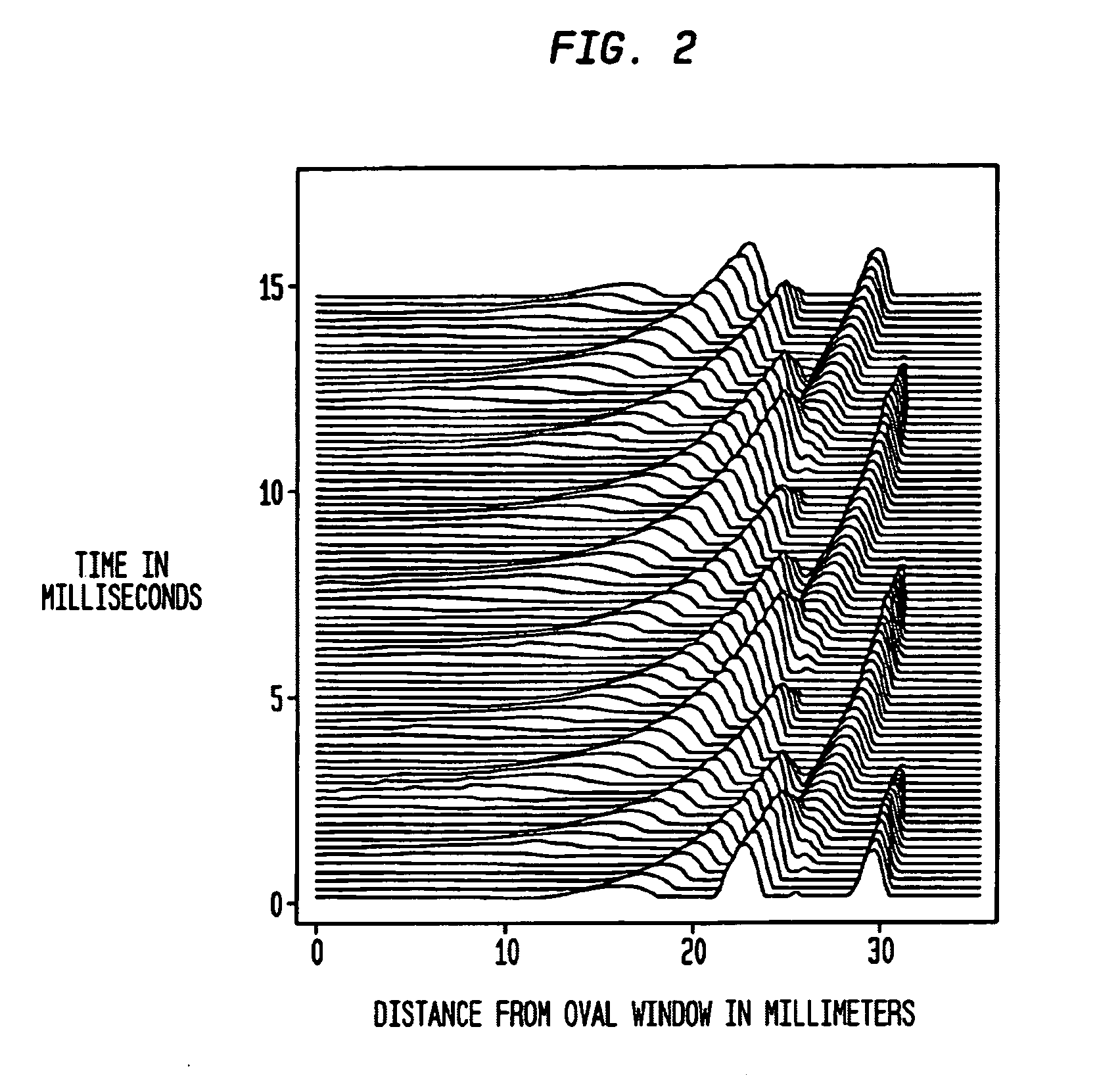
The basilar membrane within the cochlea of the inner ear is a stiff structural element that separates two liquid-filled tubes that run along the coil of the cochlea, the scala media and the scala tympani (see figure).
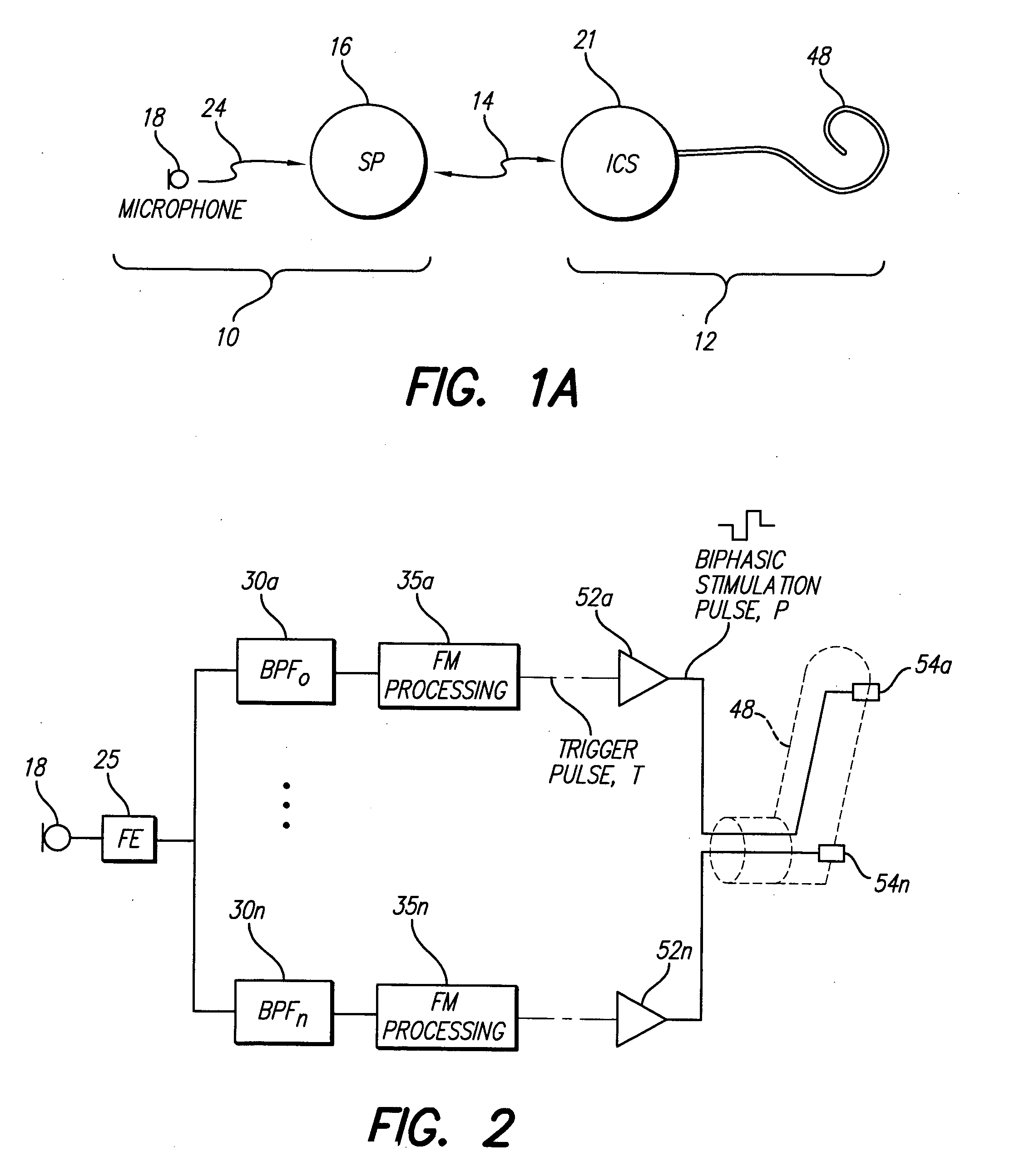
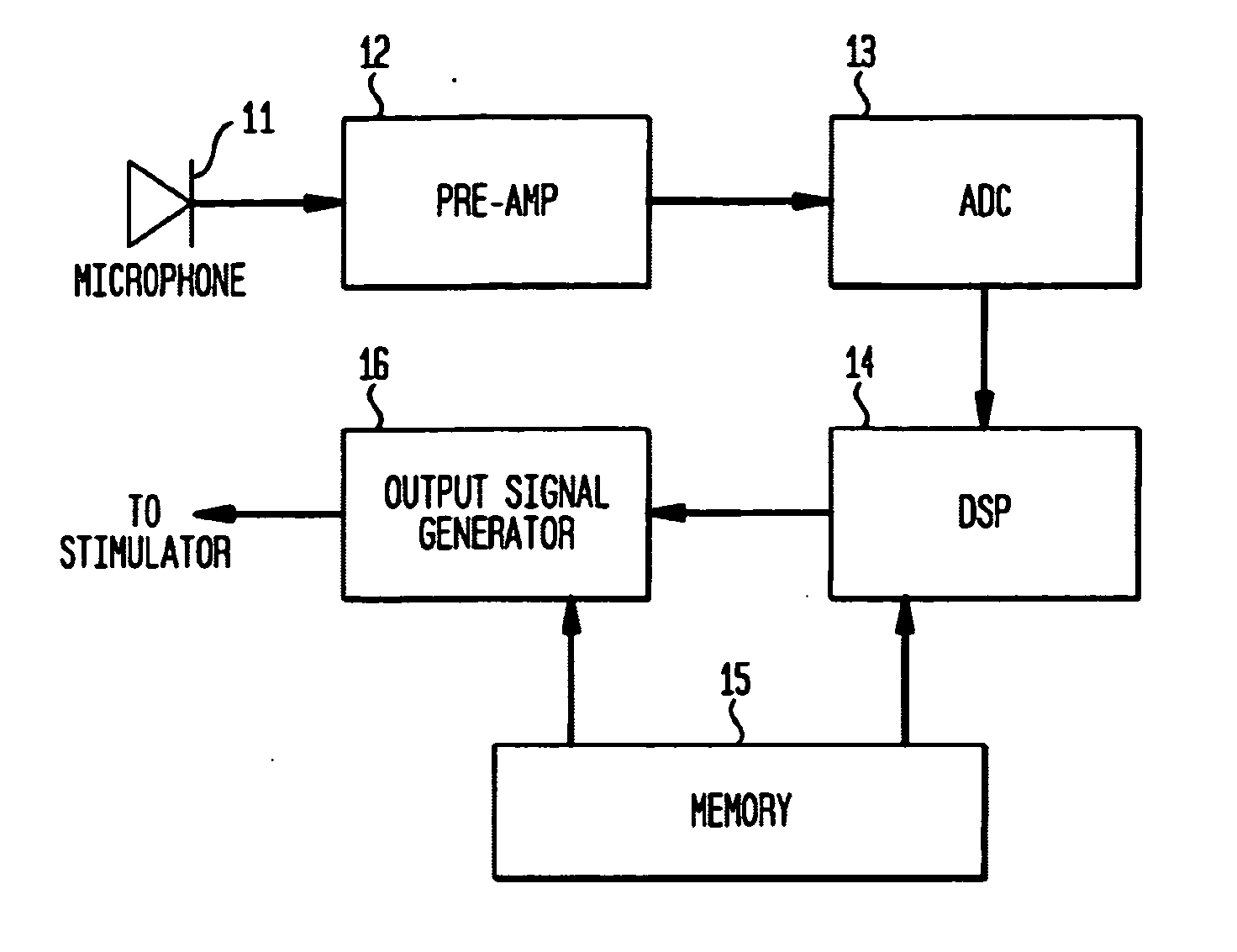
Independent and concurrent processing multiple audio input signals in a prosthetic hearing implant
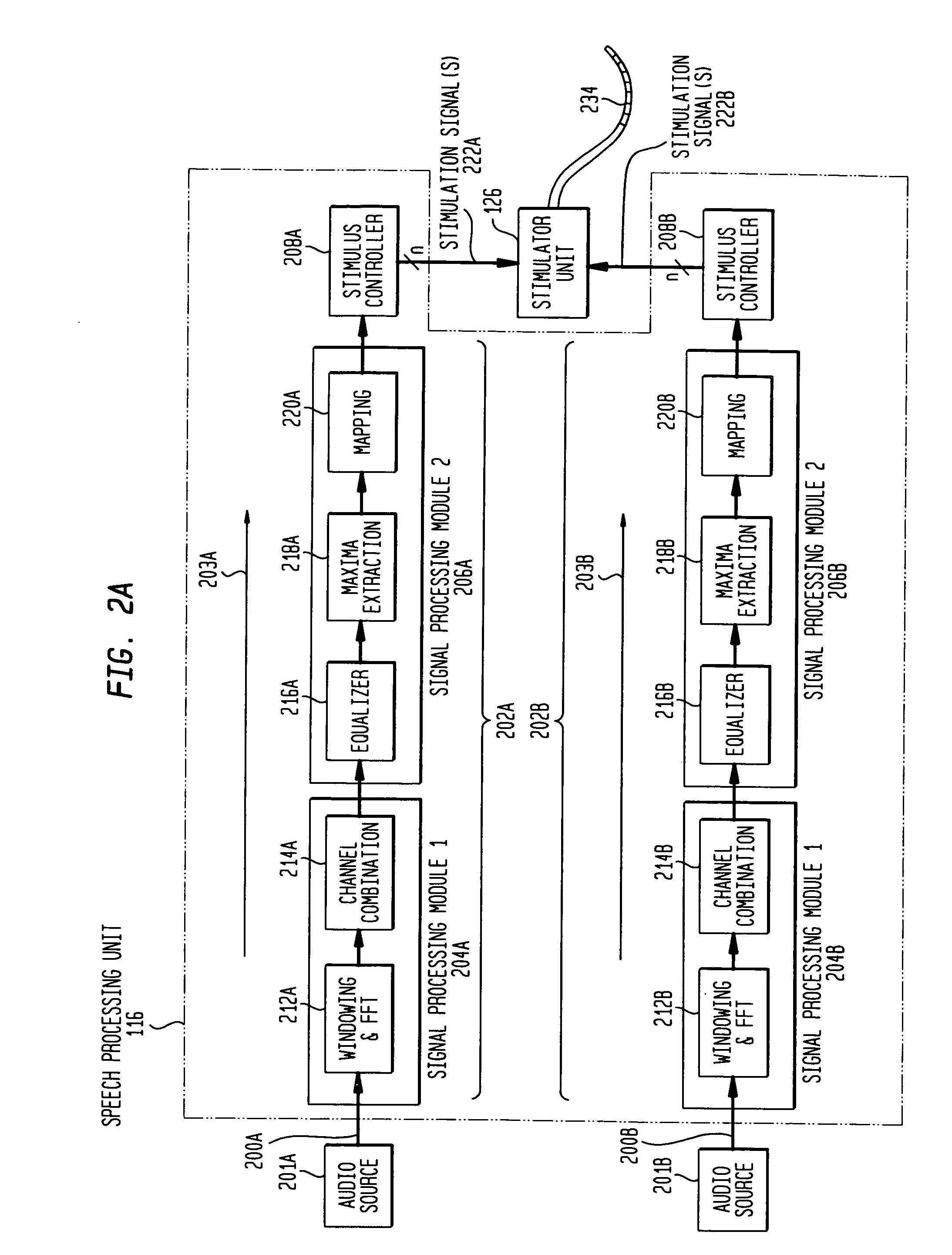
A prosthetic hearing implant capable of independently and concurrently processing multiple audio input signals such that each audio input signal is separately utilized to stimulate the basilar membrane of the implant recipient. A prosthetic hearing implant of the present invention simultaneously receives discrete audio signals from each of one or more audio sources, generates a separate set of one or more stimulations signals for each audio signal, and concurrently applies the stimulation signals to the cochlear. Different channels of stimulation may be allocated to each audio input signal. Alternatively, different modes of stimulation may be used for each input signal. Or, in yet another example, the audio input signals may be time-multiplexed such that the input signals are applied in alternating timeslots. Or, in yet other examples, the input signals may be applied using a combination of stimulation channels, modes of stimulation, and alternating time slots. The stimulation signals may be delivered to the same or different electrodes depending on the quantity and frequency component of the received audio input signals, the quantity of available stimulation channels, and other factors.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
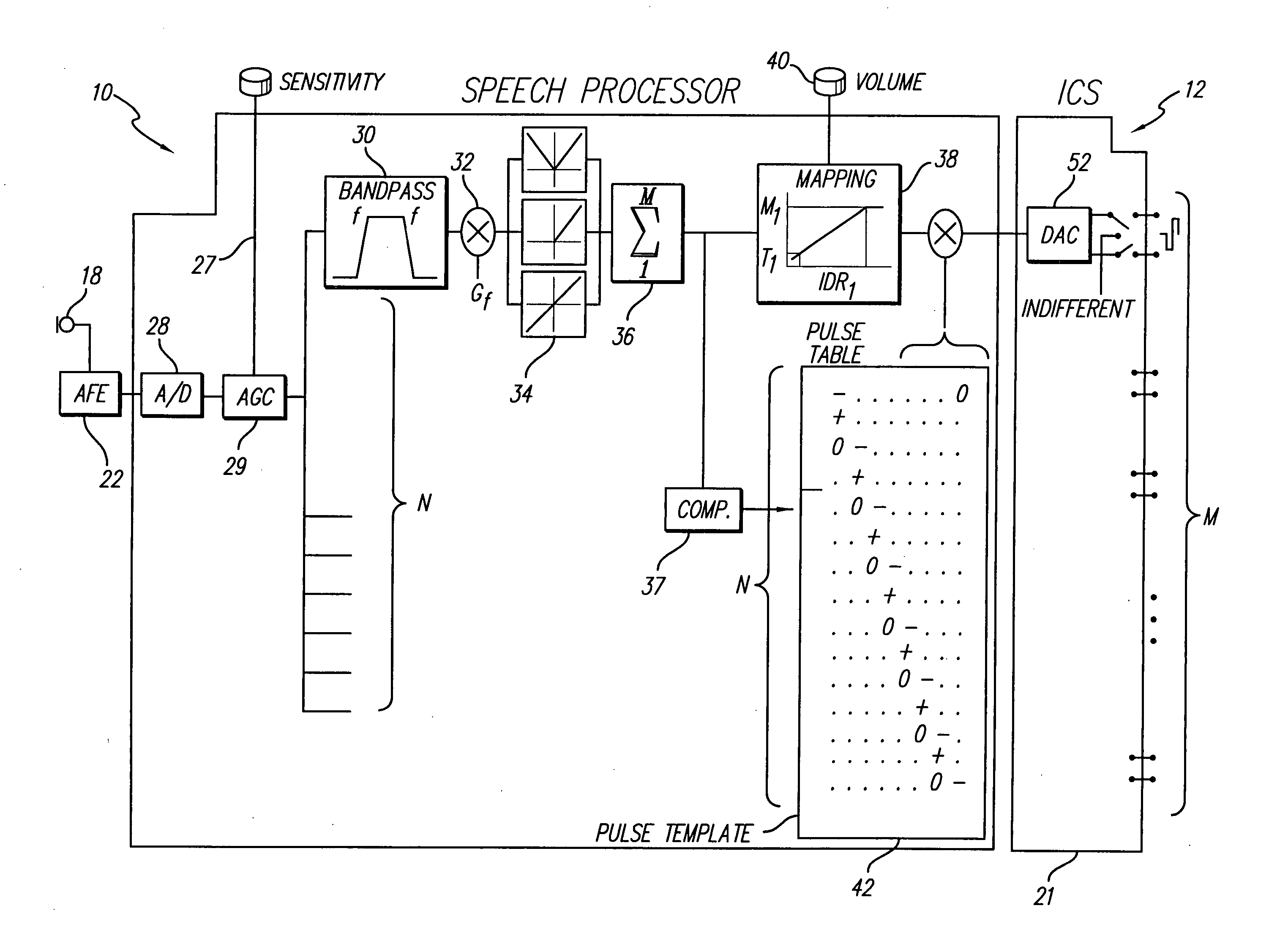
Sound processor for a cochlear implant
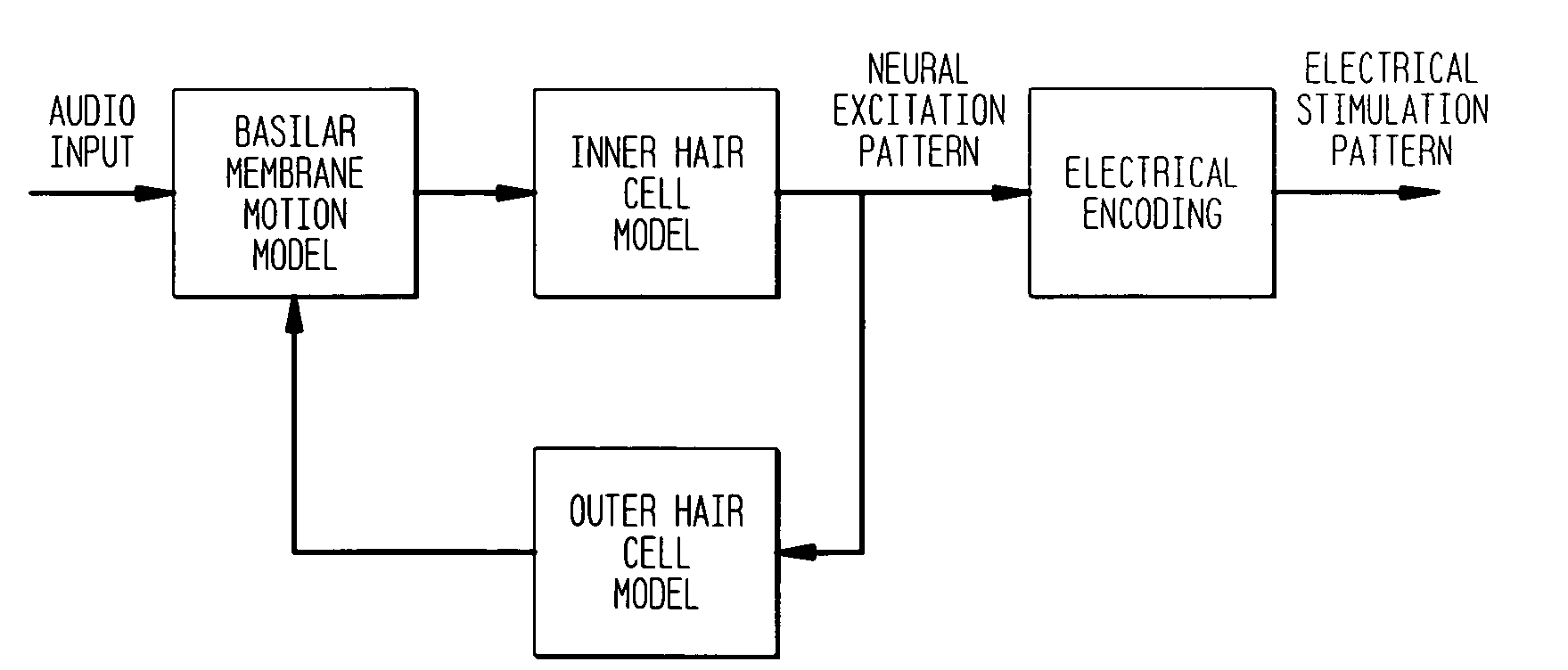
The sound processor and method uses a model of basilar membrane motion to select stimuli, based upon the predicted motion which the acoustic signal presented would produce in an acoustically excited normally hearing cochlea. The filter; used, in contrast to single channel per electrode approaches, cover multiple channels and overlap with each other. Consequently the stimuli presented produce a neural excitation pattern which approximates the spatio-temporal travelling wave observed on the basilar membrane in an acoustically excited normally hearing cochlea. Preferably, the predicted electrode stimuli are based upon the instantaneous predicted amplitude of the electrode location.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Frequency modulated stimulation strategy for cochlear implant system
InactiveUS20070239227A1Provide temporal informationReduce power consumptionElectrotherapyTectorial membraneBand-pass filter
A new speech processing strategy, termed Frequency Modulated Stimulation (FMS), is provided for use with a cochlear prosthetic. The FMS strategy advantageously mimics the neural firing patterns of the healthy cochlea by controlling when and where stimulation pulses are presented in the cochlea. The benefits of this approach are its simplicity and its ability to provide temporal information at relatively low power consumption. The stimulation that results has high temporal precision and a low pulse presentation rate. The power efficiency of the FMS strategy is three to six times greater than that of a CIS strategy with comparable thresholds. The FMS strategy depends on the probability that at any point along the basilar membrane the ganglion cells are most likely to respond during the upward motion of the basilar membrane, when the hair cells are pushed toward the tectorial membrane. At low frequencies, this probability accounts for phase locking of the neurons to each peak of the motion. At high frequency locations, phase locking occurs at integer multiples of the vibration cycles because the vibration of the membrane is faster than the refractory period of the neurons. The FMS strategy provided by the invention takes advantage of the natural behavior of the ganglion cells by outputting a biphasic pulse at the preset integer multiples of the vibration cycles. Integer multiples are determined by counting the positive-to-negative zero crossings, or equivalent frequency counting, at the output of the band pass filters that decompose the incoming audio signal(s).
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Improvements for cochlear implants
InactiveUS20110238176A1Accurate perceptionImprove binaural hearingHead electrodesProsthesisCochlear implantationHearing perception
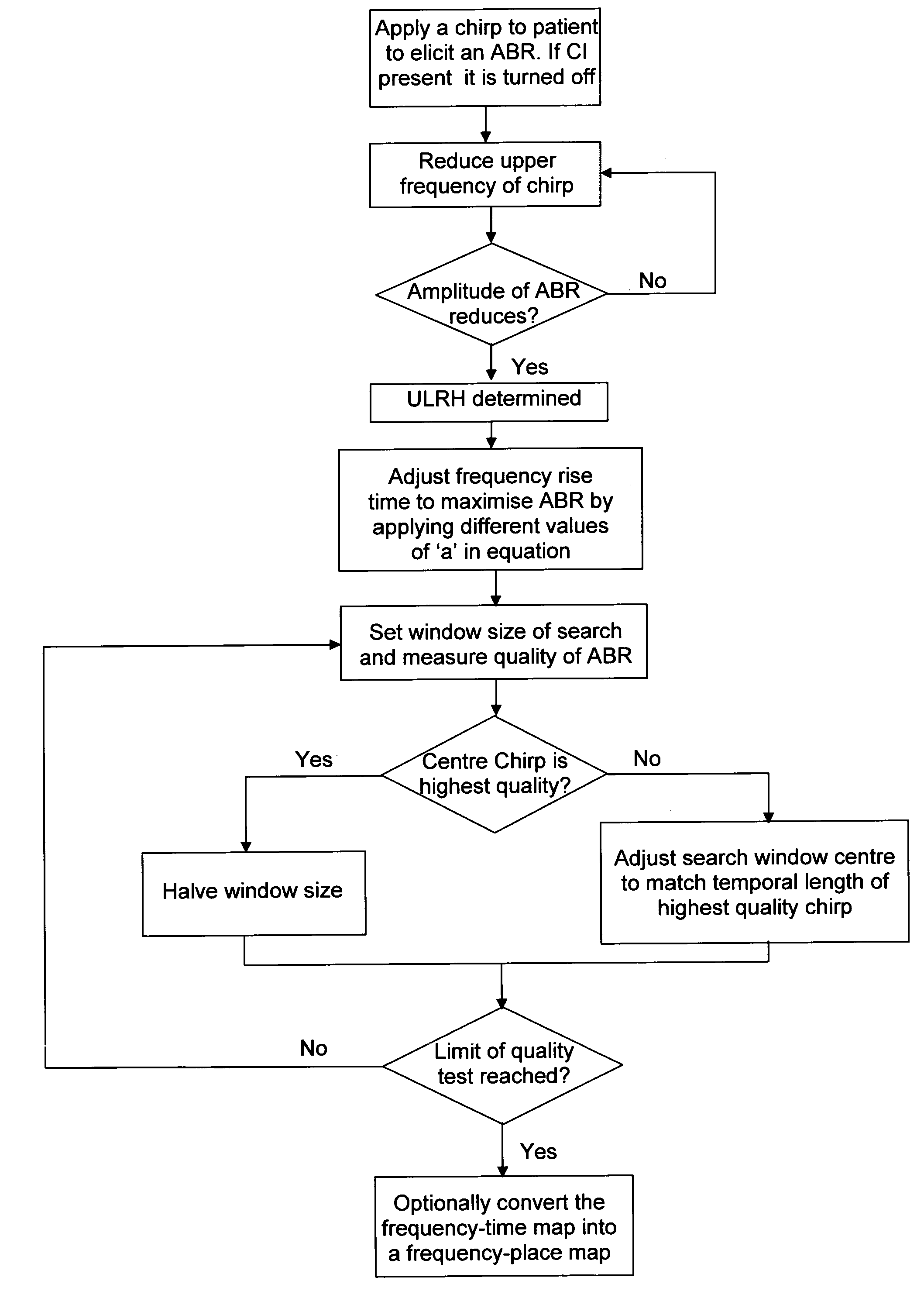
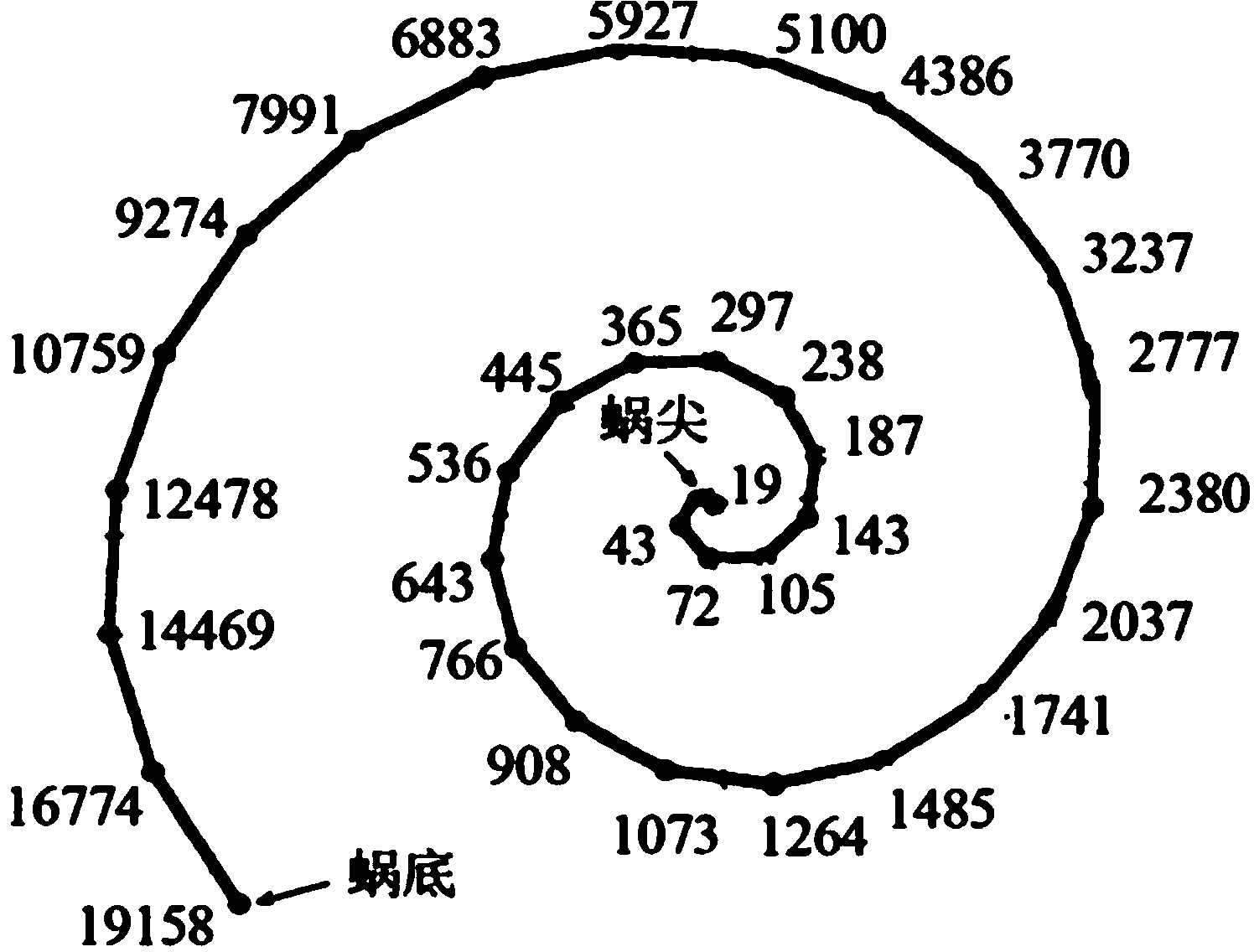
The invention relates to a method of generating a place-frequency map for accurate positioning of a cochlear implant whereby the place-frequency map is used to relate a physical position of the cochlear implant to a tonotopic map of the basilar membrane / spiral ganglion. The invention also relates to a method of electrically positioning of an already inserted cochlear implant within the cochlea to provide stimuli to only the parts of the cochlea that have reduced or no residual hearing.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIV OF THE
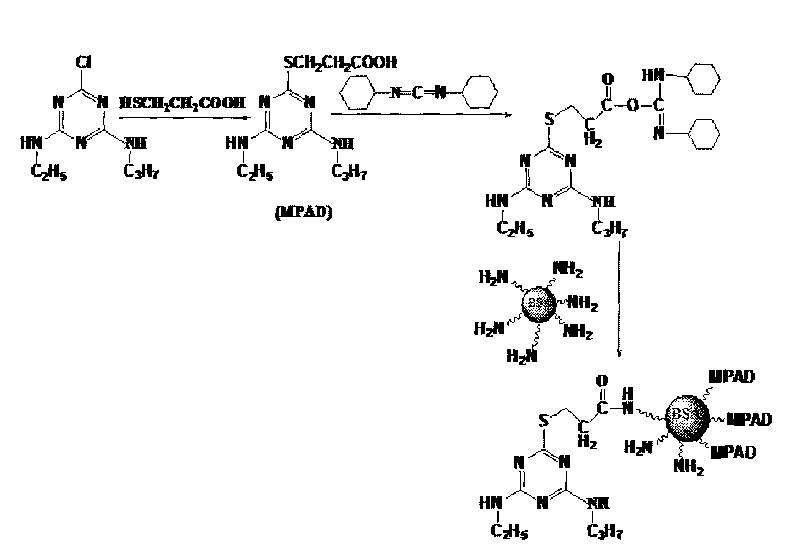
Method for preparing nanofiltration membrane by adopting layer-by-layer self-assembly method
ActiveCN105169962APore Size ControlImprove interception effectSemi-permeable membranesPolymer scienceFruit juice
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nanofiltration membrane by adopting a layer-by-layer self-assembly method, and relates to a preparation method of a nanofiltration membrane, aiming at solving the problems that a nanofiltration membrane prepared by adopting an existing method cannot have both good interception performance and high water flux. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a polyacrylonitrile solution, preparing a polyacrylonitrile basilar membrane, preparing a treated polyacrylonitrile basilar membrane, assembling a layer of polyethlenimine, assembling a layer of graphene oxide, and reassembling polyethlenimine and graphene oxide, thus obtaining the nanofiltration membrane. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a layer-by-layer self-assembly method is adopted, polyethlenimine and graphene oxide are adopted for modifying a PAN membrane, so that the hydrophilia and the pore size of the surface of the membrane are effectively adjusted; because the membrane is relatively thin, relatively large flux can be obtained, and the obtained nanofiltration membrane has good interception performance. The method can be applied to the fields of antibiotics separating, fruit juice concentrating and seawater desalting.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Metal circuit board of aluminum baseplate magnetic-controlled sputtering-jetted and LED illuminating device
InactiveCN101076223AReduce thermal resistanceEvenly distributedPrinted circuit detailsSolid-state devicesOxide coatingElectron
The preparation method comprises: making insulation oxidation treatment for the surface of aluminium substrate to form a oxide coating having electrical insulation property on the aluminium substrate surface; using masking or photo etch approach to form circuit pattern on the oxide coating; using magnetron sputtering method to alternatively deposit basilar membrane, conduction membrane and soldering membrane so as to form the metalized circuit layer with heat conductivity and solderability; encapsulating electronic component or LED chip on it. The invention can be used the encapsulation substrate of the thick film circuit and LED chip.
Owner:蔡勇
Pigment-containing artificial skin detection model and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a pigment-containing artificial skin detection model and a preparation method thereof. The artificial skin detection model is an epidermal layer structure with activity, which is constructed by compositely inoculating cutin formative cells and melanophores to the surface of a support membrane made from a biodegradable material through culture and comprises a stratum basale, a stratum spinosum, a stratum granulosum and a stratum corneum, and a basilar membrane structure is formed between the epidermal layer and the biodegradable material positioned below the epidermal layer. Compared with the conventional product, the invention can better simulate the pigment components of natural skin and more accurately reflect the whitening and sunscreen effect of cosmetics because of containing the melanophores, nourish the cutin formative cells by using the support membrane made from the biodegradable material as an enderonic layer, control the contraction of the epidermal layer with the strength and enhance the stability of the detection model and has low raw material cost, short manufacturing period and mass production; and in addition, the prepared artificial skin detection model can be directly used for the efficacy detection of the cosmetics and the skin irritation detection of textiles, the cosmetics and chemicals.
Owner:GUANGDONG BOXI BIO TECH CO LTD
Thinned high-barrier liquid packaging film and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101274690AImprove rigidityIncreasing the thicknessFlexible coversWrappersHigh densityMedium density
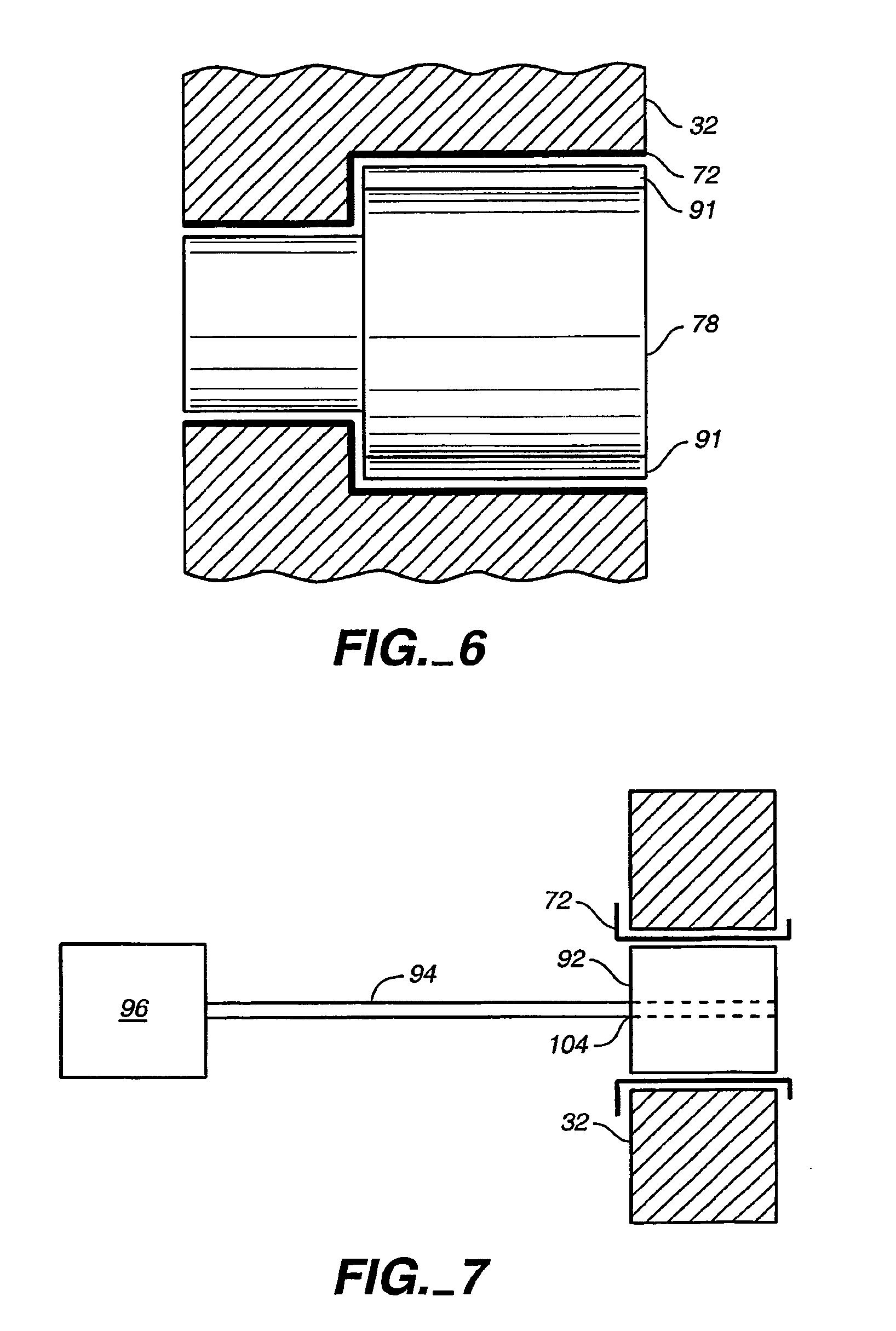
The invention relates to a thin-reducing and high impermeable liquid packaging membrane and a manufacturing method thereof. The product comprises a polyvinyl basilar membrane, a high impermeable polyvinyl alcohol layer, a composite adhesive layer and a protective polythene membrane layer, wherein, the polyvinyl basilar membrane comprises an outer layer, a middle layer and an inner layer and the outer layer and the middle layer comprise at least one of the two materials which are medium-density polythene or high-density polythene. The manufacturing method of the product comprises the steps of the preparation of the polyvinyl basilar membrane, the preparation of polyvinyl alcohol coating liquid and the preparation of the protective polythene membrane layer, coating and compounding, wherein, the polyvinyl alcohol coating liquid is diluted and the diluted polyvinyl alcohol coating liquid is coated on the outer layer of the polyvinyl basilar membrane to form the high impermeable polyvinyl alcohol layer and then the protective polythene member layer and the polyvinyl alcohol coating layer are compounded, cured and cut. The product of the invention has low thickness, good rigidness, high impermeable property, environmental protection, convenient use, low cost and simple technique.
Owner:马龙升
Tissue engineered skin with basilar membrane and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101954124ASimple methodEasy to get materialsArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsEpidermis structureManufacturing technology
The invention relates to the technical fields of tissue engineering and medical wound repair. At present, a living skin substitute constructed by using the materials of polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, collagen, hyaluronic acid, and the like as a dermic bracket has the defects that on one hand, host materials are difficult to extract, the living skin substitute has complicated manufacturing technology and is expensive in cost and difficult to widely popularize and apply clinically; and on the other hand, the living skin substitute does not have a skin basilar membrane structure so that healed skin does not resist pressure and wear, and the living skin has unfirm adhesion to the epidermis and is easy to shed and break or form water blisters so that the structural and morphological development of the normal epidermis is influenced; and allogeneic acellular dermis is taken from cadaver skin and is limited in sources and expensive in cost, and thus clinical application is limited. The invention aims at providing a skin substitute which uses surface-finished and modified amnion as the basilar membrane and blood plasma as stroma, which has the advantages of wide material sources, low cost and simple preparation method. An animal experiment proves that the complete basilar membrane and hemidesmosomes can be retained in in-vivo transplantation, and the formation of an epidermal structural form is accelerated and promoted.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
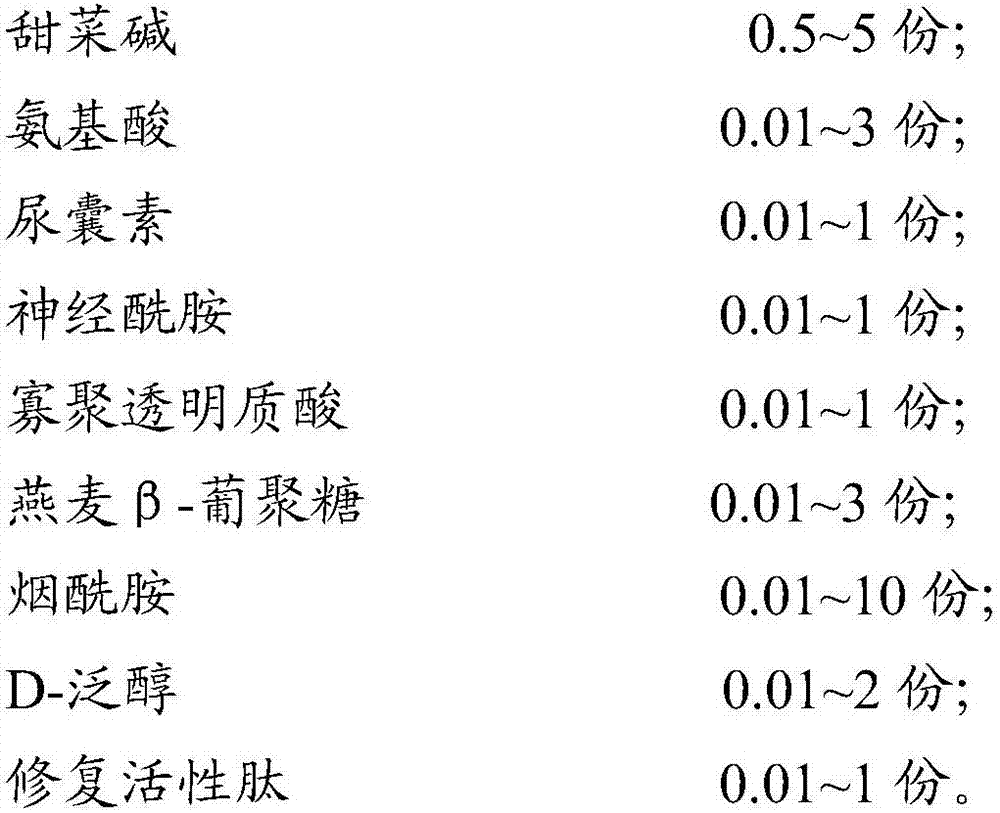
Skin repairing and moisturizing composition and application of same in preparation of cosmetics
ActiveCN106963660AAvoid degradationEasy to synthesizeCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBetaineCutin
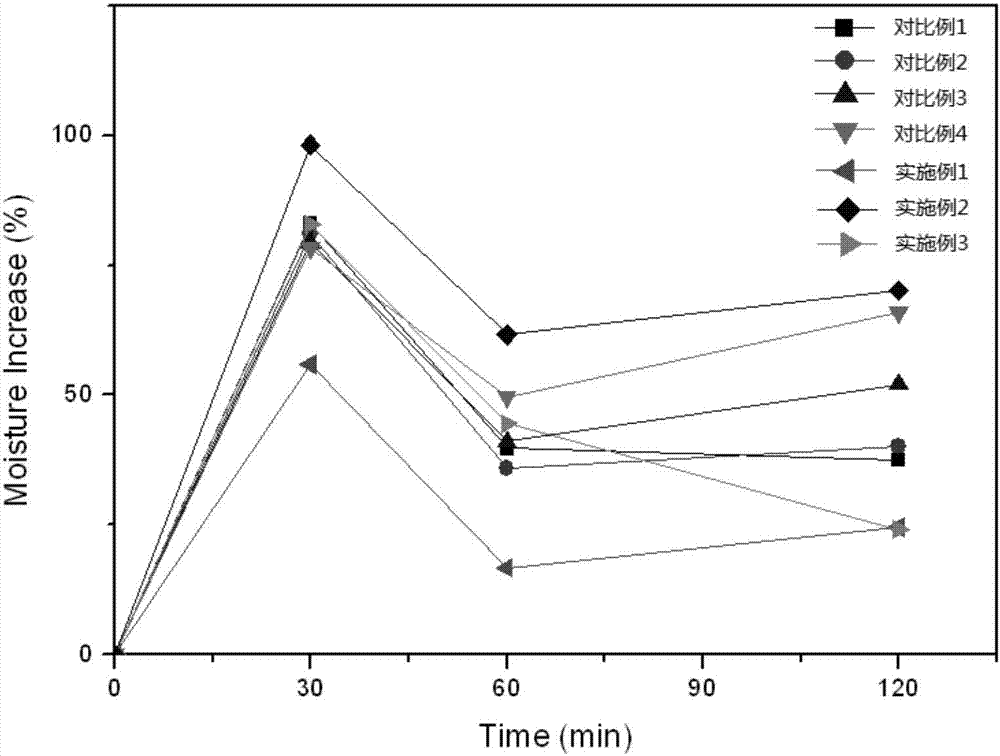
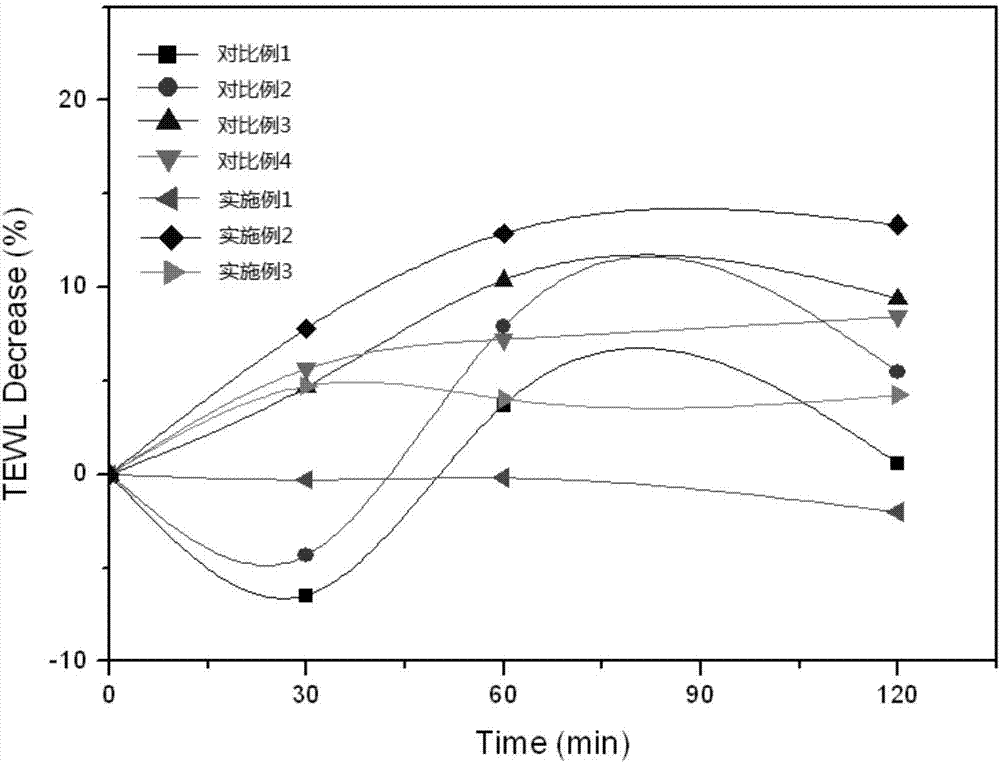
The invention relates to the technical field of cosmetics, in particular to a moisturizing composition and application of the same in preparation of the cosmetics. According to the composition, betaine, amino acid, allantoin, oat beta-glucan, oligomerized hyaluronic acid, nicotinamide, ceramide, repairing bioactive peptide and D-panthenol are compounded reasonably. Through triple barrier repairing of skin corium layers, basilar membranes and skin cuticulae, the composition can have good effect of increasing skin moisture content and reducing skin moisture loss. The effect is improved remarkably as compared with the effect of the individually-used components or conventional moisturizing compositions. In a proper ratio, the synergistic effect is achieved through compounding of the components, and accordingly, the moisturizing effect is improved. Experiments show that the moisturizing composition can increase the skin moisture content to 98.19% within 30 minutes, and the skin moisture content can be kept increased by above 70% after two hours.
Owner:HUNAN YUJIA COSMETICS MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for processing audio and speech signals
ActiveUS20100250242A1Reduce distortionReduce noiseHearing aids signal processingSpeech recognitionTime domainNoise reduction
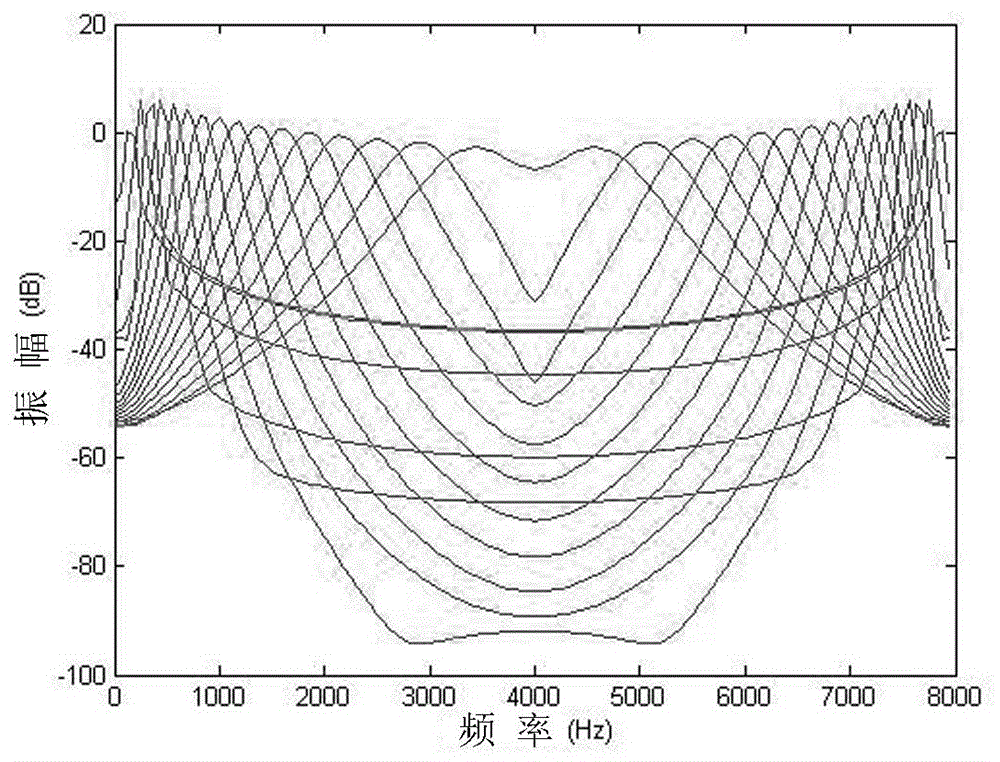
A method and device for processing signals representing speech or audio via a plurality of filters that approximate behaviors of the basilar membrane of human cochlea. Each of the plurality of filters is formed from a mother filter via the dilation and a shift in time and has the similar impulse response of the basilar membrane to the frequency band for which the filter represents. Any process can be conducted and any feature can be extracted in the domain of the filters' outputs for applications, such as noise reduction, speech synthesis, coding, and speech and speaker recognition. Processed signals can be synthesized back to the time domain via an inverse cochlear transform
Owner:LI CREATIVE TECH
NGF (nerve growth factor) chitosan microsphere and high-bionic stent slow releasing system and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102600506AGood sustained release effectPromote recoveryMicroballoon preparationProsthesisDefect repairChitosan microspheres
The invention discloses an NGF (nerve growth factor) chitosan microsphere and high-bionic stent slow releasing system, which is a cylindrical collagen and chitosan nerve stent. Chitosan microspheres buried with nerve growth factors are uniformly loaded in the stent. A preparation method of the stent includes firstly, preparing the chitosan microspheres buried with the nerve growth factors by an emulsification chemical-crosslink method; secondly, preparing the collagen and chitosan nerve stent with mutually parallel axial microtubules sample structures; and finally, compounding the chitosan microspheres onto the collagen and chitosan nerve stent via after-compounding technology and preparing the NGF chitosan microsphere and high-bionic stent slow releasing system. The stent structure is similar to a normal nerve basilar membrane structure, and the stent realizes an effect of physically guiding regeneration nerves to the greatest extent. Besides, the stent can slowly release the nerve growth factors with bioactivity for 12 weeks, can lead the nerve growth factors to be effectively released to a nerve injury portion for a long time, and accordingly achieves the purpose of promoting long nerve defect repair better and faster.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for processing audio and speech signals
ActiveUS8359195B2Reduce distortionReduce noiseHearing aids signal processingSpeech recognitionTime domainNoise reduction
A method and device for processing signals representing speech or audio via a plurality of filters that approximate behaviors of the basilar membrane of human cochlea. Each of the plurality of filters is formed from a mother filter via the dilation and a shift in time and has the similar impulse response of the basilar membrane to the frequency band for which the filter represents. Any process can be conducted and any feature can be extracted in the domain of the filters' outputs for applications, such as noise reduction, speech synthesis, coding, and speech and speaker recognition. Processed signals can be synthesized back to the time domain via an inverse cochlear transform.
Owner:LI CREATIVE TECH
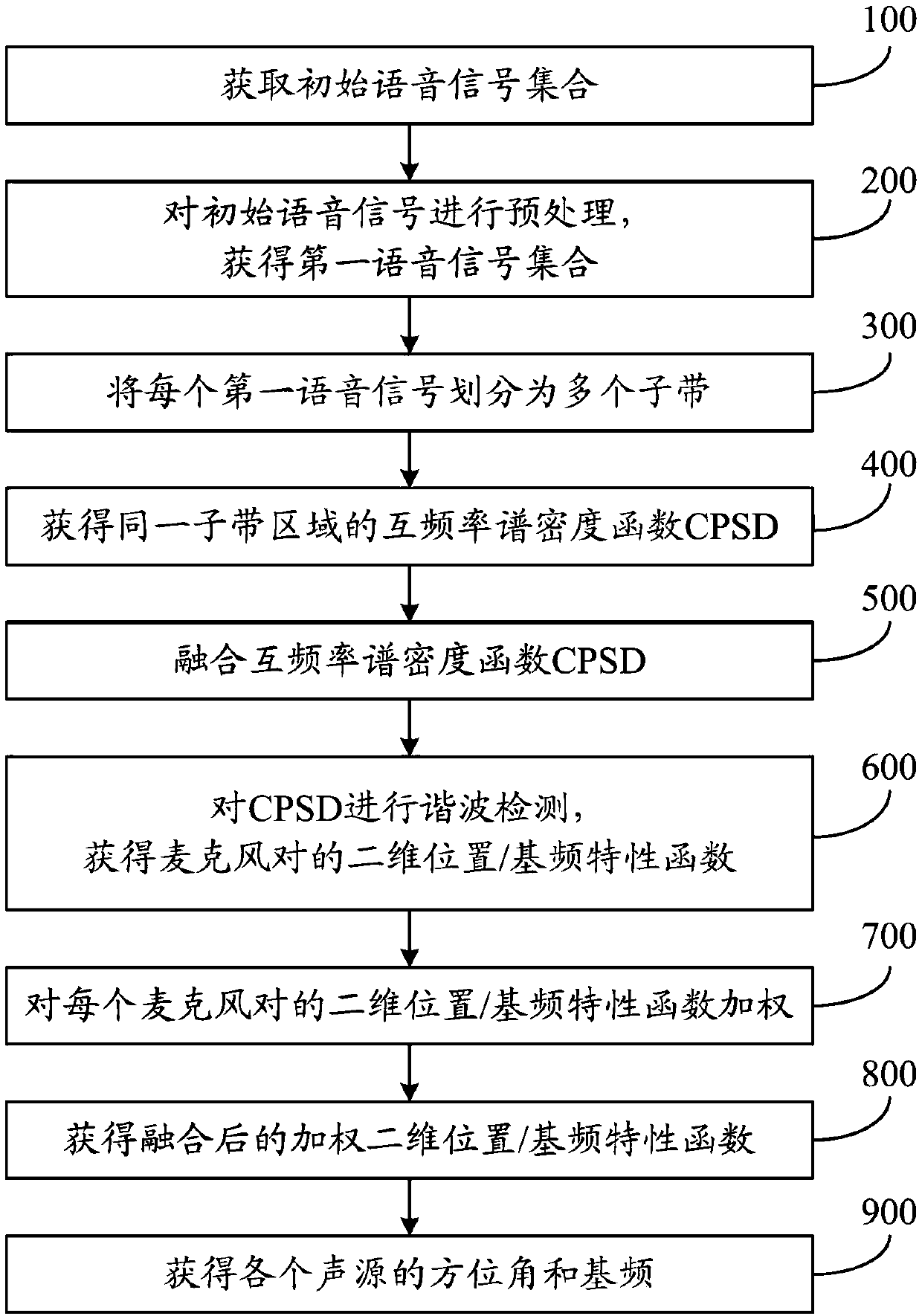
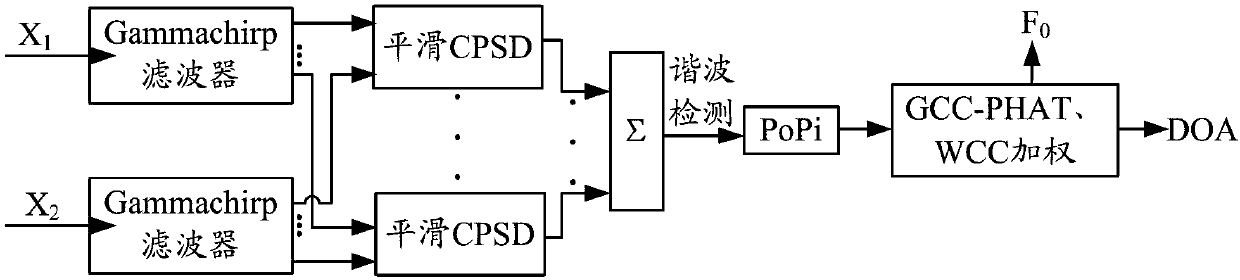
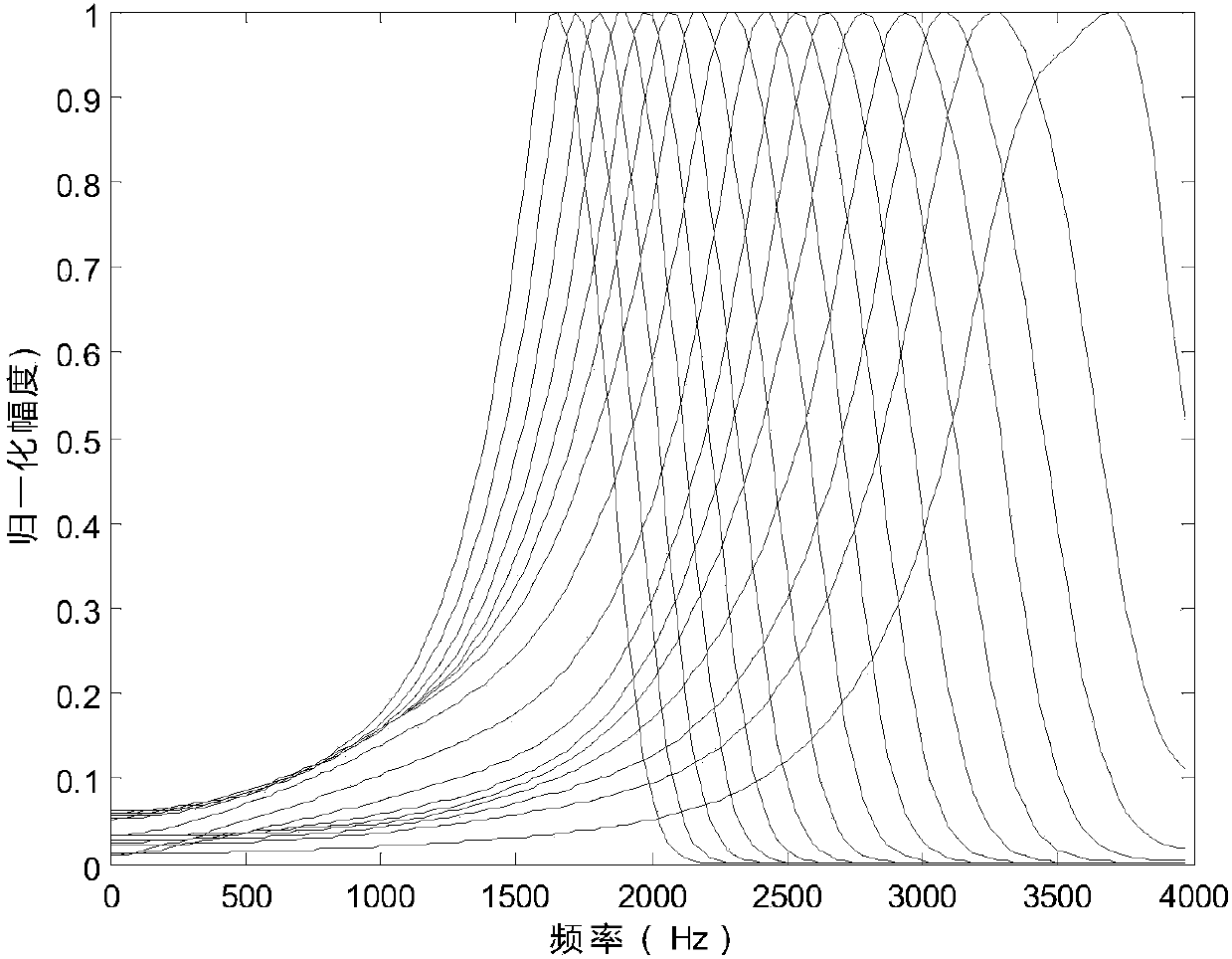
Method and system for multi-sound localization
ActiveCN108198568AAvoid mutual interferenceAvoid interferenceSpeech analysisPosition fixationSound sourcesBase frequency
The invention discloses a method and a system for multi-sound localization. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an initial voice signal set; pre-processing each initial voice signal; dividing the pre-processed signals into a plurality of sub-bands via a basilar membrane filter; acquiring a cross-power spectral density functions of a same sub-band; fusing the cross-power spectral density functions of all sub-bands; acquiring a two-dimensional position / base frequency characteristic function of a microphone pair corresponding to each first voice signal; acquiring the two-dimensional position / base frequency characteristic function of each microphone pair; acquiring a fused weighted two-dimensional position / base frequency characteristic function; and confirming azimuth angles and base frequencies of various sound sources within a preset threshold range in accordance with a function value of the fused weighted two-dimensional position / base frequency characteristic function. According to the method and the system provided by the invention, mutual interference between sound signals is avoided and localization accuracy is improved. Moreover, the method and the system are relatively high in reverberation resistance, and locations of the various sound sources can be accurately estimated under a circumstance of strong reverberation.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Composite electret fiber filtering material
ActiveCN101125266AImprove stabilityImprove filtration efficiencyConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiltration separationFiberFilter material
The present invention relates to a composite electrets fiber filtering material. The present invention is made by the method as follows:(1) compound the polyfluortetraethylene membrane and the basilar membrane to form a composite material; (2) electret the composite material to form composite electrets membrane; (3) composite electrets membrane forms fiber by extending, and then the product is gained by making the fiber into net. The composite electrets fiber filtering material has the advantages of extremely high electrets electric charge stability, prominent filtering efficiency, low pressure loss, long service life, wide appliance and board service scale.
Owner:TONGXIANG JIANMIN FILTER MATERIALS
Tissue engineering nerval stent and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a tissue engineering nerval stent and a preparation method and an application thereof. The chemical extraction method is adopted for removing main antigens, namely cells, axons and myelin sheaths, which can cause the rejection, and chondroitinase ABC is further adopted for removing chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan in xenogeneic nerves, thereby getting acellular xenogenic nerves with a complete vessel of a basilar membrane of an extracellular matrix and can be used as the tissue engineering nerval stent. The tissue engineering nerval stent is applicable to restoring peripheral nerve defect of rats, rabbits, dogs, human beings and the like, plays a very obvious role in promoting the regeneration of the axons and can further increase the length of restoring the peripheral nerve defect, thereby being a great nerve transplantation medical material.
Owner:卢世璧
Electrostatic resistant film and product including the same
InactiveCN101321426AImprove performanceStable peel forceFilm/foil adhesivesElectrostatic chargesProtection layerMembrane configuration
The invention relates to an antistatic membrane and articles containing the membrane. The membrane comprises: a basilar membrane; a conducting layer located on one surface of the basilar membrane; a protecting layer located on the surface of the conducting layer opposite to the basilar membrane to protect the conducting layer. The protecting layer contains particles restricting reduction of conductivity of the membrane surface and macromolecular film forming polymer. The grain diameter of at least part of particles is larger than the thickness of the protecting layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
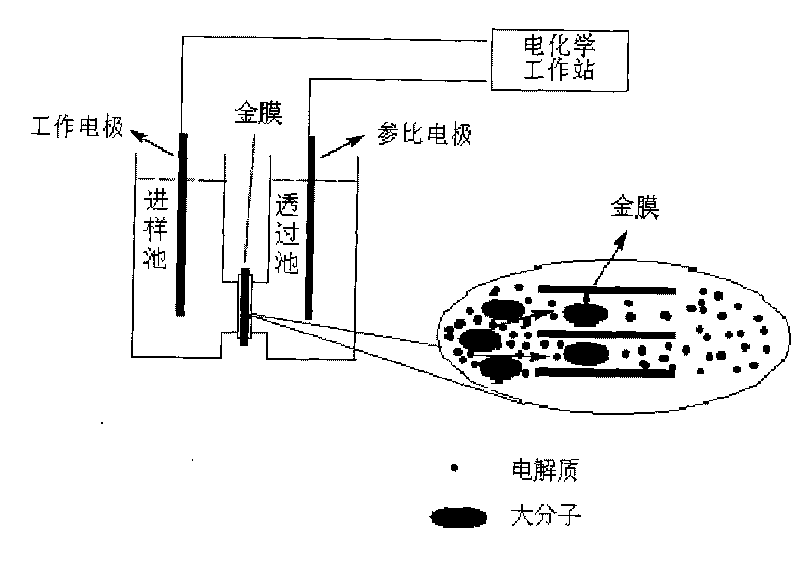
Gold nano-channel membrane for detecting atrazine and application thereof
InactiveCN101718742AImprove detection efficiencyStrong specificityMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemistryWorkstation
The invention provides a chloride modified gold nano-channel membrane for detecting atrazine and a method for detecting the atrazine by using the gold nano-channel membrane. In the invention, polycarbonate membrane is taken as basilar membrane, Au nano-channel membrane with the diameter of 20-50 nm is prepared by using a chemical precipitation method, and chloride ions self-assembles to the pore wall of the gold nano-channel through a gold-chloride covalent bond. The detection method comprises the following steps of: placing the chloride modified gold nano-channel membrane between a sample injection pool and a transmission pool; adding a buffer solution containing atrazine antibody into the sample injection pool; adding a buffer solution into the transmission pool; maintaining a parallel liquid level of the two pools; applying voltage on the two pools and measuring basement currents; adding a buffer solution containing a sample to be tested into the sample injection pool and carrying out a current signal test through a electrochemical workstation, wherein if current undershoot occurs, the sample to be tested contains the atrazine. The invention has the advantages of high detectionefficiency, strong specificity, capability of measuring the atrazine with the concentration lower limit of 1.7*10-10 M, and better application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Cochlear implants
InactiveUS8554330B2Accurate perceptionImprove binaural hearingHead electrodesProsthesisCochlear implant surgeryFrequency map
The invention relates to a method of generating a place-frequency map for accurate positioning of a cochlear implant whereby the place-frequency map is used to relate a physical position of the cochlear implant to a tonotopic map of the basilar membrane / spiral ganglion. The invention also relates to a method of electrically positioning of an already inserted cochlear implant within the cochlea to provide stimuli to only the parts of the cochlea that have reduced or no residual hearing.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIV OF THE
Artificial cochlea acoustic nerve conductive electrode array capable of sensing music melodies
ActiveCN104013480APrecise deliveryImproved music perceptionEar treatmentProsthesisHarmonicBase frequency
The invention discloses an artificial cochlea acoustic nerve conductive electrode array capable of sensing music melodies. According to the base frequency of music notes, at the frequency sensing position of a human ear basilar membrane, the area between the top of a cochlea and the bottom of the cochlea is divided into frequency areas with specific stimulation signals according to a frequency band corresponding to a note with a half pitch; a specific electrode for conducting signals of the frequency band is arranged in each audio frequency area, namely the electrode is arranged at the frequency band corresponding to a possible base frequency and harmonic frequency of the music notes. The number of the electrodes is 80, and the electrodes correspond to the music audio frequency range of 60-6000 Hz. The artificial cochlea electrodes are distributed according to the scheme, harmonic features of music notes of various musical instruments within the range of 60-6000 Hz can be accurately transmitted in a relative complete mode, and subharmonic elements of each note can be accurately expressed; meanwhile, according to the electrode distribution scheme, the electrodes are distributed more densely than existing electrodes capable of sensing voice information, and voice feature information can still be transmitted accurately.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
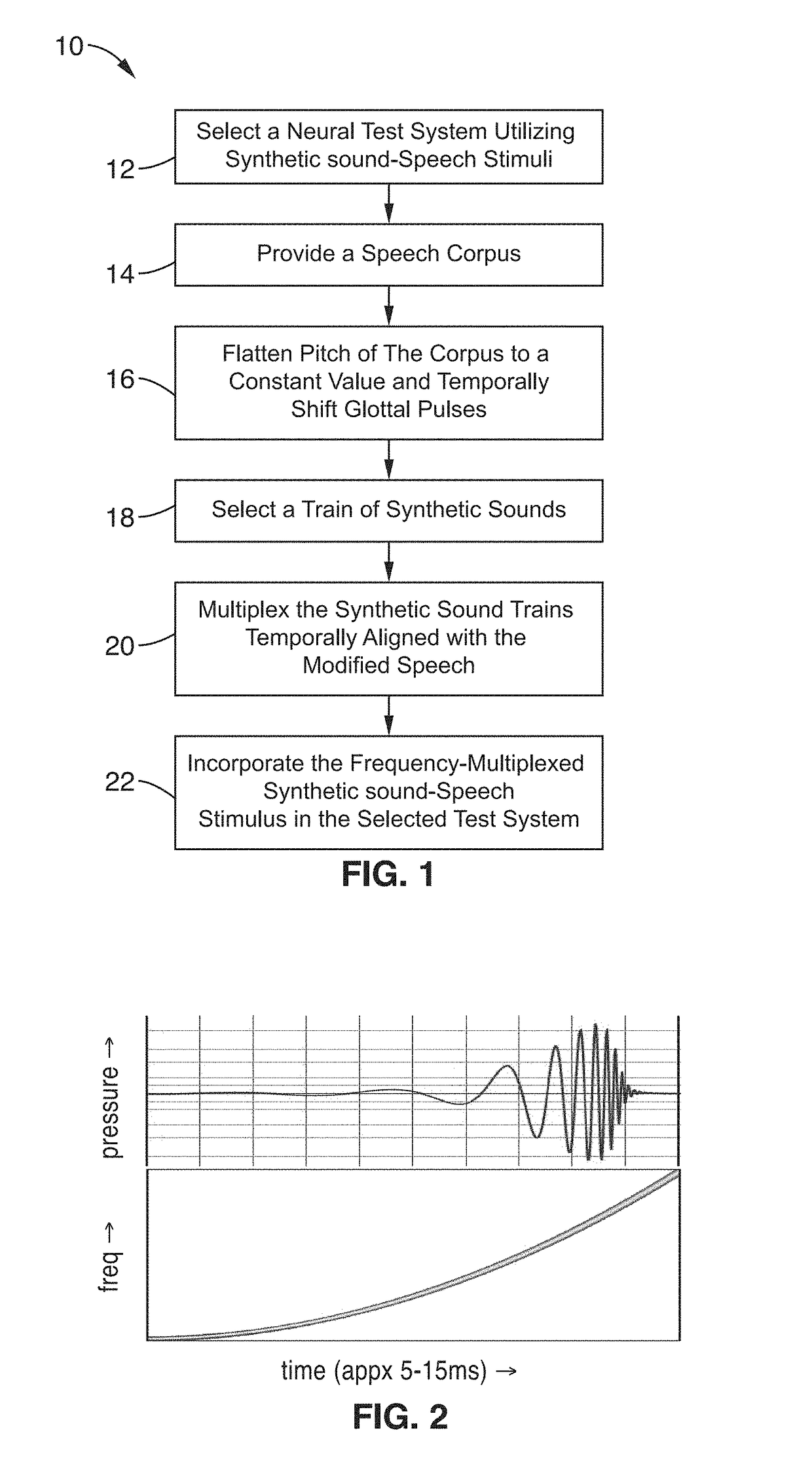
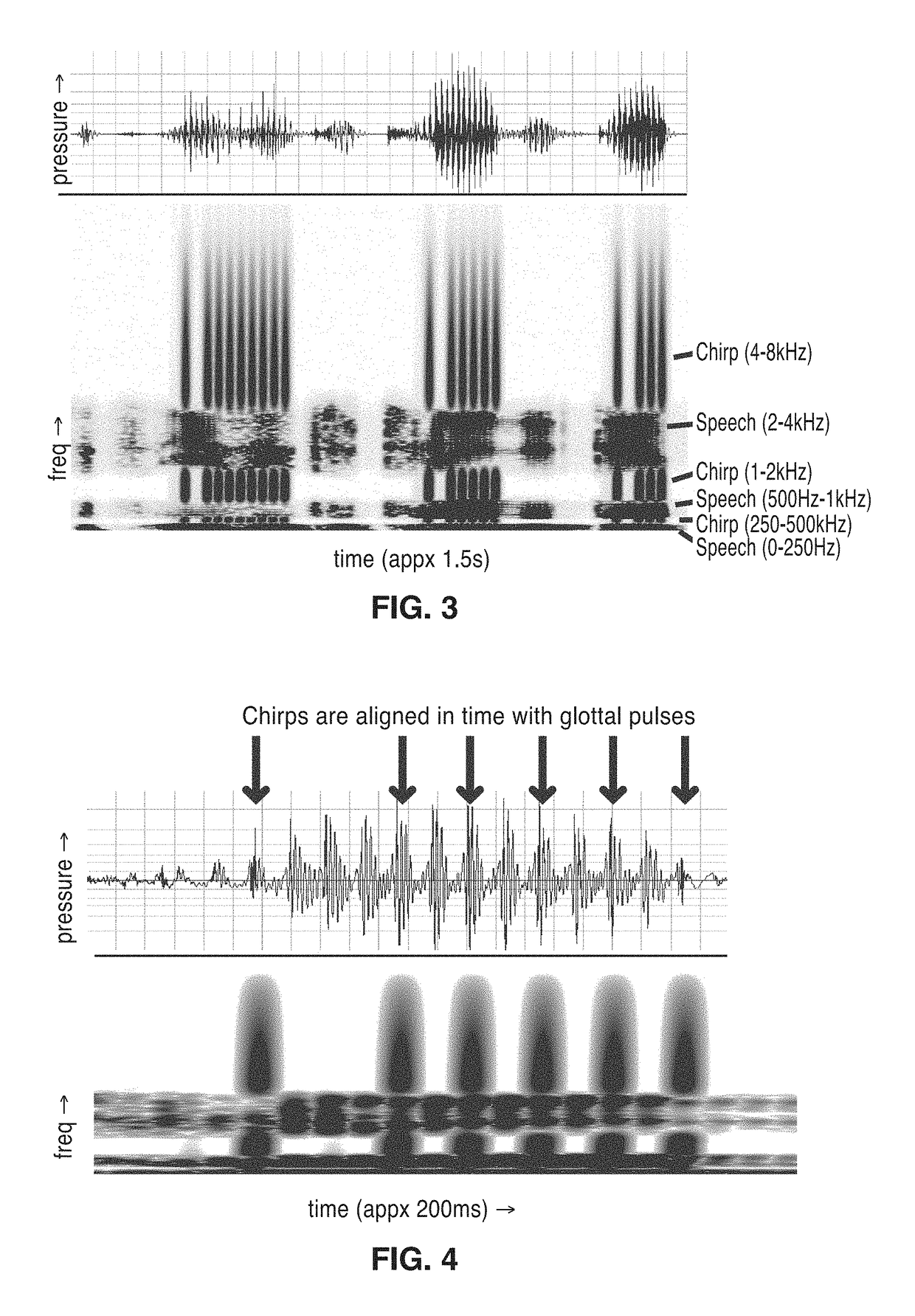
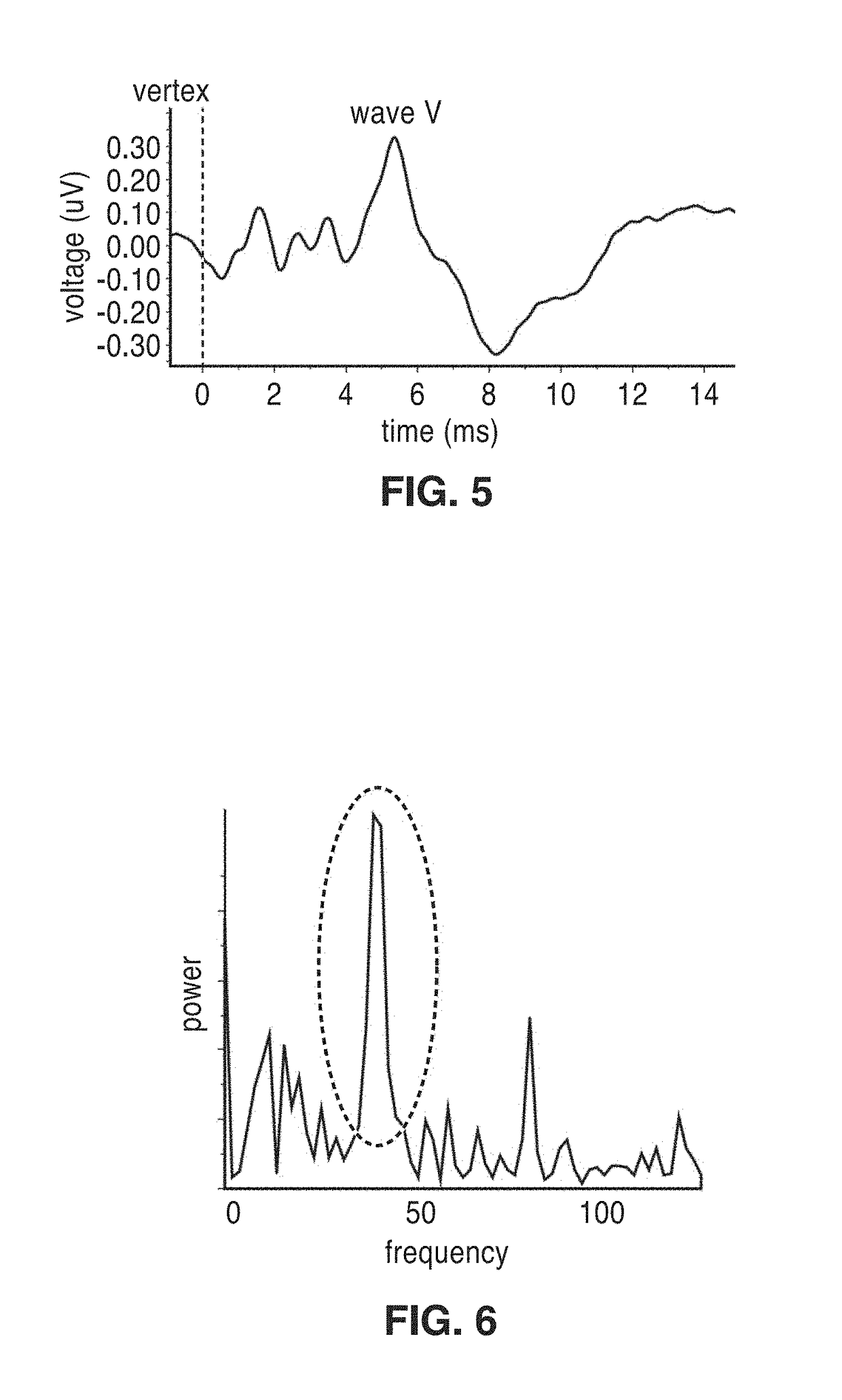
Frequency-multiplexed speech-sound stimuli for hierarchical neural characterization of speech processing
ActiveUS20170196519A1Accelerated programMaximize responseElectroencephalographySensorsMultiplexingAuditory system
A system and method for generating frequency-multiplexed synthetic sound-speech stimuli and for detecting and analyzing electrical brain activity of a subject in response to the stimuli. Frequency-multiplexing of speech copora and synthetic sounds helps the composite sound to blend into a single auditory object. The synthetic sounds are temporally aligned with the utterances of the speech corpus. Frequency multiplexing may include splitting the frequency axis into alternating bands of speech and synthetic sound to minimize the disruptive interaction between the speech and synthetic sounds along the basilar membrane and in their neural representations. The generated stimuli can be used with both traditional and advanced techniques to analyze electrical brain activity and provides a rapid, synoptic view into the functional health of the early auditory system, including how speech is processed at different levels and how these levels interact.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dry film, micro-lens and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101165592APhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusMembrane configurationMicrolens
The present invention relates to dry film, microlens and the preparing method thereof. Said dry film contains (I) the basilar membrane having a surface with the three-dimensional ten-point average roughness SRz below 2.2 mum and the three-dimensional maximum height SRmax the same as 4.0 mum and a thickness from 10 mum to 50 mum; (II) the radioactive ray sensibility resin composition layer with the thickness from 2mum to 200mum laminated on the surface of said basilar membrane (I); and (III) the cover membrane covering said radioactive ray sensibility resin composition layer (II).
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Preparation method of nerve defect repair material of vessel basilar membrane imitating structure
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nerve defect repair material of a vessel basilar membrane imitating structure, and belongs to the fields of a tissue engineering technology and a biological material. On the basis of the arrangement of peripheral nerve collagen fibers and the structural characteristics of a nerve fiber vessel basilar membrane, the peripheral nerve defect repair material of the vessel basilar membrane imitating structure is prepared mainly from a high polymer material and a natural material in accordance with an electro-spinning technology and a pore-forming technology. Different from other nerve conduits, the cross section of the material is represented as a porous micro-tubular structure and fiber arrangement on the tube wall is highly oriented in a direction consistent with the moving direction of microtubule. The specific surface area of the tube wall of the material is significantly improved, and the structure of the microtubule is similar to that of the nerve fiber vessel basilar membrane; a plurality of nerve growth promoting substances can be added; and the tissue engineering peripheral nerve defect repair material is good in biocompatibility and convenient for the nerve fibers to grow in the direction of principal axis of the repair material, and the repair material has an application prospect.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
Polypeptide composition for preventing and improving striae gravidarum
PendingCN108904320AAvoid decompositionMaintain densityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSide effectCuticle
The invention discloses a polypeptide composition for preventing and improving striae gravidarum. The composition contains one, two or three polypeptides of a polypeptide for promoting collagen synthesis and promoting epithelial regeneration, a polypeptide for supplementing fibronectin and a polypeptide for promoting elastin synthesis, and one or two polypeptides of a polypeptide for reducing inflammatory response and tightening the skin and a polypeptide for delaying skin aging and raising defensive power of the skin. The polypeptide composition of the invention is safe to human body, has noirritating or toxic or side effect, can repair epidermis, basilar membrane and dermis of the skin, diminish inflammation, promote growth of connective tissues and increase generation of collagen and elastin, and can be used for antenatal prevention and postnatal repair of striae gravidarum.
Owner:SHENZHEN WINKEY MEDICAL RES DEV
Speaker recognition feature extraction method based on PSNCC (perception spectrogram Norm cochlea-filter coefficient)
InactiveCN106653004AImprove robustnessImproved temporal robustnessSpeech recognitionPattern perceptionBoundary detection
The invention discloses a speaker recognition feature extraction method based on a PSNCC (perception spectrogram norm cochlea-filter coefficient). The speaker recognition feature extraction method comprises the following steps: first, constructing a cochlea filter group conforming to traveling wave impulse response and nolinear frequency distribution of a cochlear basilar membrane; then carrying out speech enhancement and two-dimensional enhancement based on auditory perception features on voice, and carrying out two-dimensional boundary detection on a pure voice spectrum structure in continuous distribution, thus obtaining a perception spectrogram structure norm parameter PSN; finally, further normalizing all cochlea-filter coefficients output by the cochlea filter group in the time domain through the perception spectrogram structure norm parameter PSN, and extracting the PSNCC feature parameter. According to the PSNCC feature parameter extracted by adopting the method, the robust performance of the feature parameter is improved from two aspects, namely, the time domain and the frequency domain, and further, the recognition rate of a speaker recognition system under the noise environment with low signal to noise ratio is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Cochlear fenestration burrs
InactiveUS20070260254A1Good adhesionEasy to disassembleHead electrodesSurgeryBony labyrinthRound window
Owner:LESINSKI S GEORGE
Seamless laser graphic transfer technology between basilar membranes
InactiveCN101844480ALow price and low usageLow price usageDecorative surface effectsPattern printingMembrane configurationBasilar membrane
The invention discloses a seamless laser graphic transfer technology between basilar membranes, which comprises the following steps: coating: coating laser transfer paint on one side of a basilar membrane A by a coating machine, and then heating, drying and curing the paint; mould pressing: carrying out double-roll mould pressing on the basilar membrane A by a printing roller and a compression roller on a mould pressing machine, and then transferring the laser graphics on the printing roller after mould pressing onto the transfer basilar membrane A so as to reach the seamless effect; membrane combining: arranging the transfer basilar membrane A on a die assembly machine which overlaps with the transfer basilar membrane A and the basilar membrane B which are provided with seamless laser graphics on the surface, and then mould pressing the membranes together via a membrane combining compression roller; and stripping: stripping the transfer basilar membrane A and the basilar membrane B after combination by a cutting machine, the seamless laser graphic information on the transfer basilar membrane A is transferred to the surface of the basilar membrane B at this time, the seamless laser graphic information on the transfer basilar membrane A still exists, and the membrane combination and stripping processes can be repeated for many times. The technology can greatly reduce the use amount of the transfer membranes.
Owner:江苏中印印务集团有限公司
Sound processor for a cochlear implant
The sound processor and method uses a model of basilar membrane motion to select stimuli, based upon the predicted motion which the acoustic signal presented would produce in an acoustically excited normally hearing cochlea. The filter; used, in contrast to single channel per electrode approaches, cover multiple channels and overlap with each other. Consequently the stimuli presented produce a neural excitation pattern which approximates the spatio-temporal travelling wave observed on the basilar membrane in an acoustically excited normally hearing cochlea. Preferably, the predicted electrode stimuli are based upon the instantaneous predicted amplitude of the electrode location.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Biological gel membrane for cell culture as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103087533AReduce lossesImprove efficiencyArtificial cell constructsEmbryonic cellsMatrigel3D cell culture
The invention discloses a biological gel membrane for cell culture as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The biological gel membrane contains biocompatible Matrigel, chitosan chloride and gelatin. The biological gel membrane can simulate structure, composition, physical properties and functions of an in-vivo cell basilar membrane, and can support proliferation of multiple cells. The biological gel membrane is liquid at room temperature, becomes a gel membrane when the temperature is more than 34 DEG C and is semi-liquid when the temperature is reduced, so cells can be recovered by changing the temperature, the consumption of enzyme is reduced, loss and functional change of the cells are reduced, and the amplification efficiency of the cells is improved. The invention also provides the method for preparing the biological gel membrane and the application in the cell culture.
Owner:黑龙江省重生生物科技有限公司
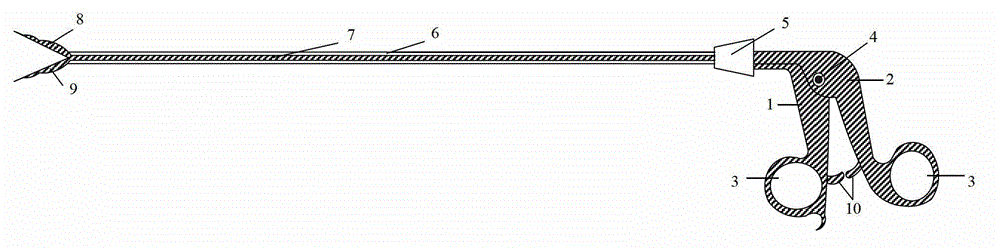
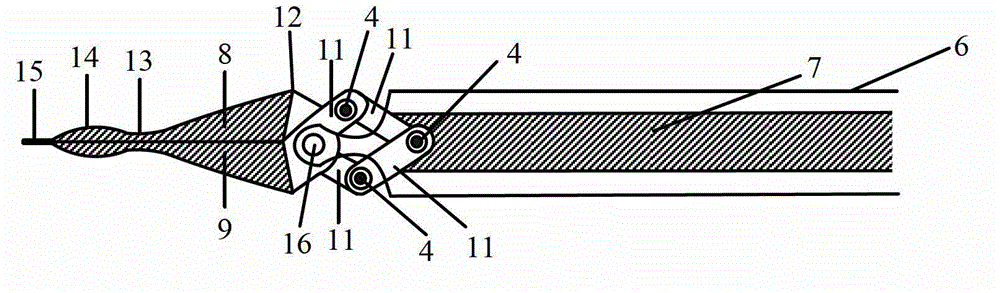
Lower opener for endoscope
InactiveCN102715925ASimple structural designEasy to operateSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisMedicineMetallic materials
The invention relates to the field of medical devices and discloses a lower opener for an endoscope. According to the lower opener, two opener heads are symmetrical to each other and are connected and matched with each other, and can be separated and drawn; when the two opener heads are drawn, a calabash shape with a circular blunt pointed end can be formed; during operation, the circular blunt pointed end punctures a basilar membrane, the edge of crevasse is fixed on the middle concave parts of the calabash-shaped opener heads, and the opener heads are separated to open and expand the crevasse to meet the operation requirements; and the puncturing and opening functions can be realized by using one machine; and the lower opener is simple in structural design and ensures that operation is easy and convenient to implement, and the operation effect is safe and effective. The inner sides of handheld handles are provided with tooth plates which are provided with multi-tooth lock catches matched with each other; and by fixing the positions of the handheld handles, the separating and drawing width of the opener heads can be controlled, the size of the opened mouth can be controlled conveniently, and the operation is convenient to implement. The lower opener is made of metal materials, so that the lower opener can be disinfected and sterilized at high temperature, cannot be damaged easily, can be used repeatedly, and reduces operation cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com