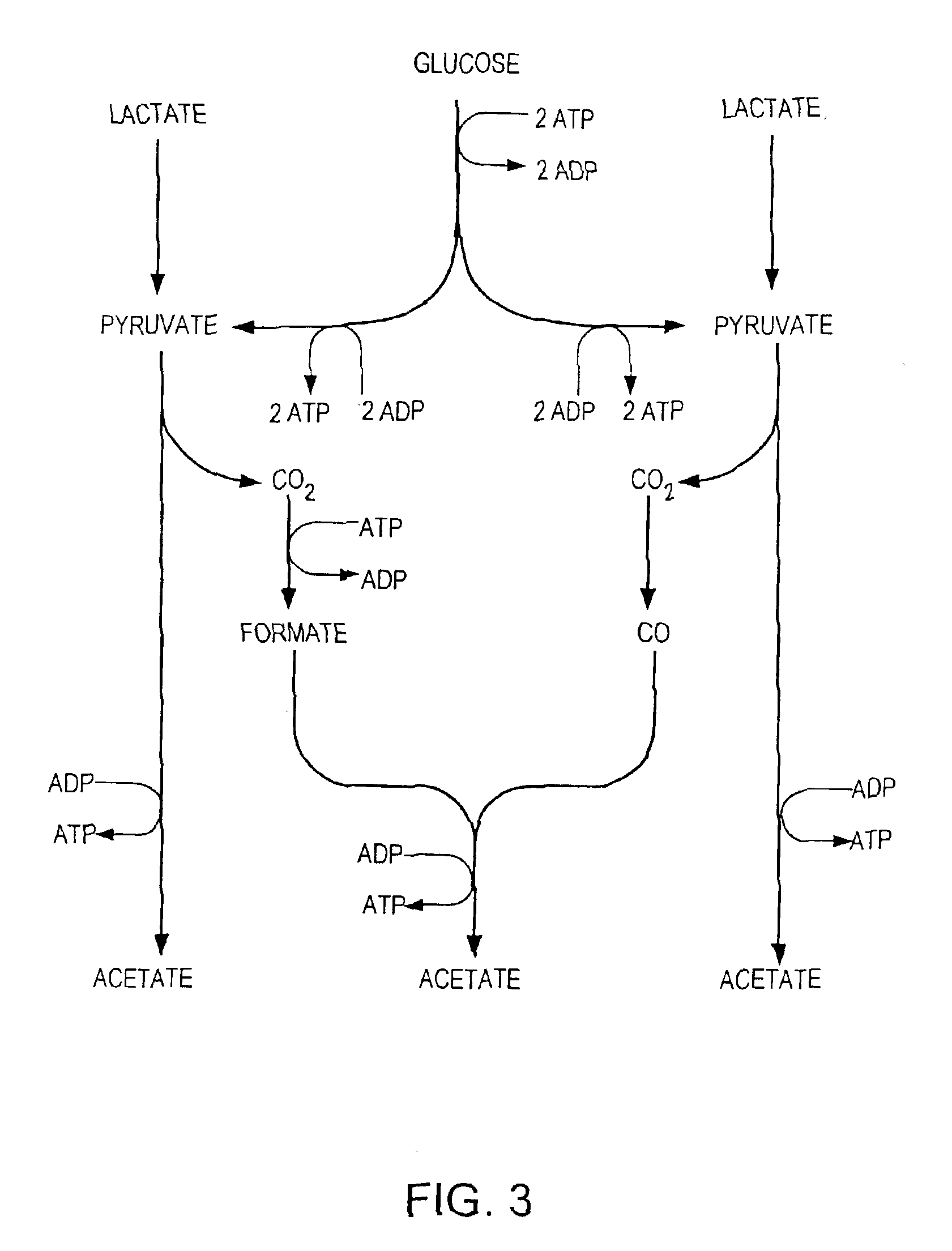
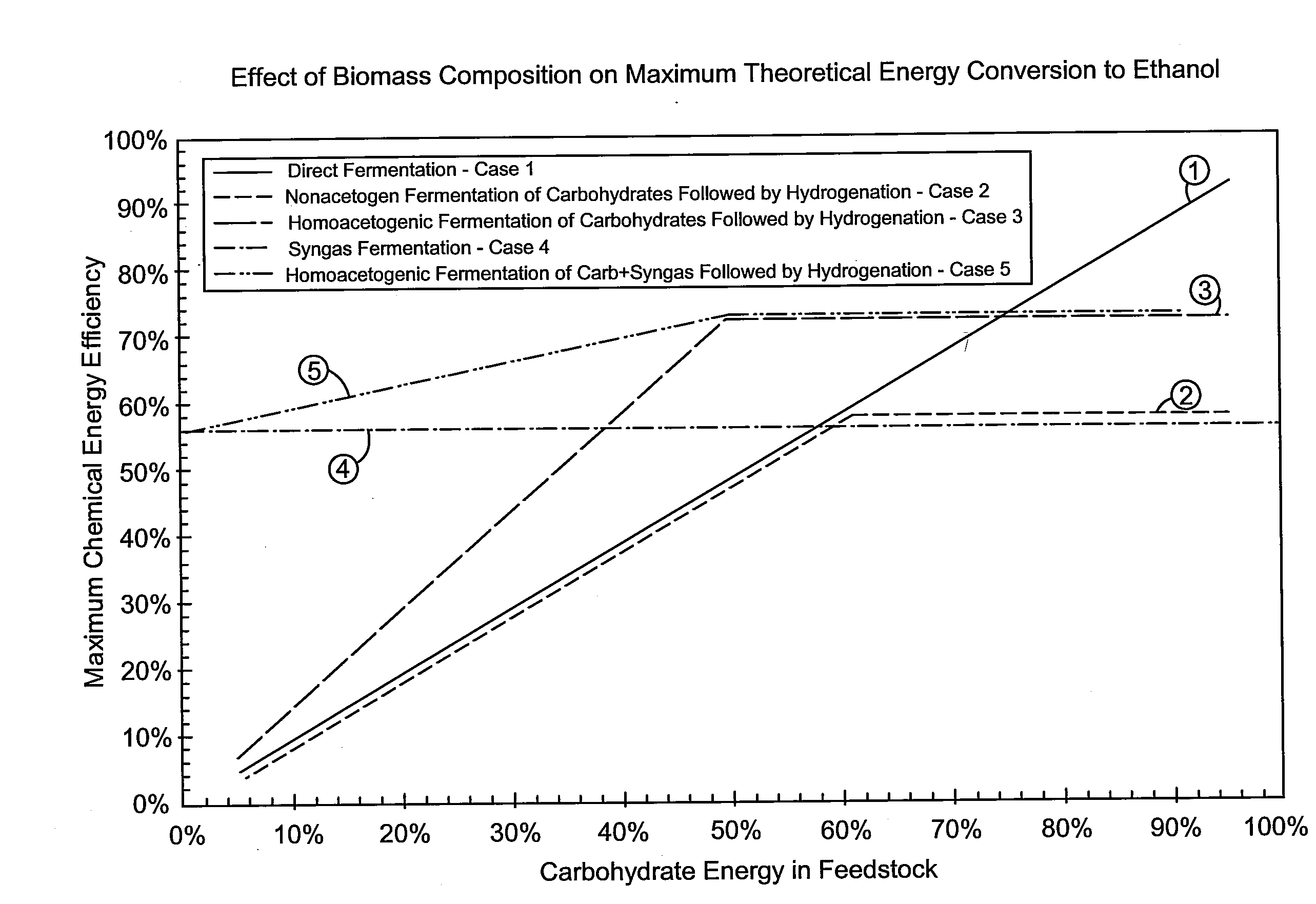
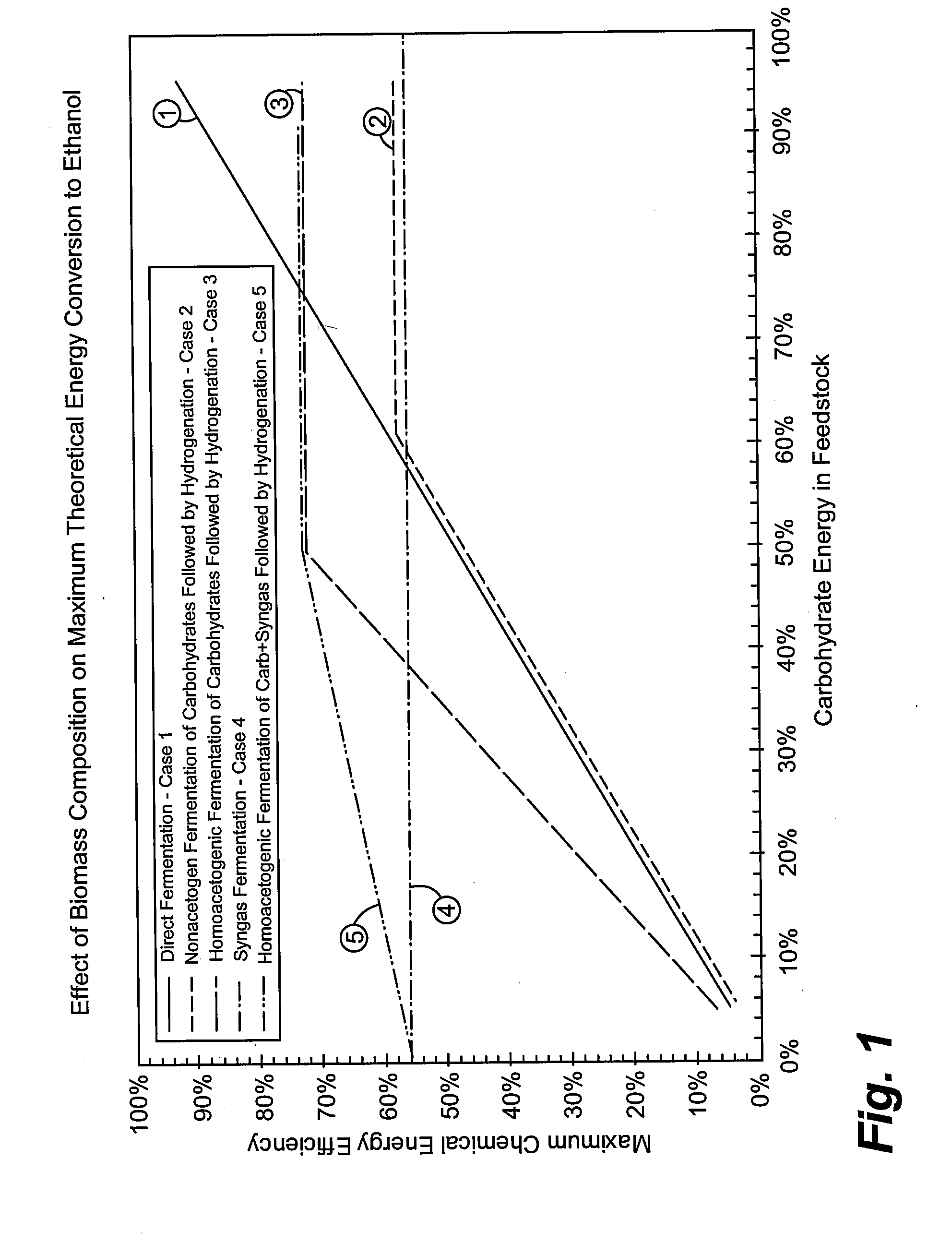
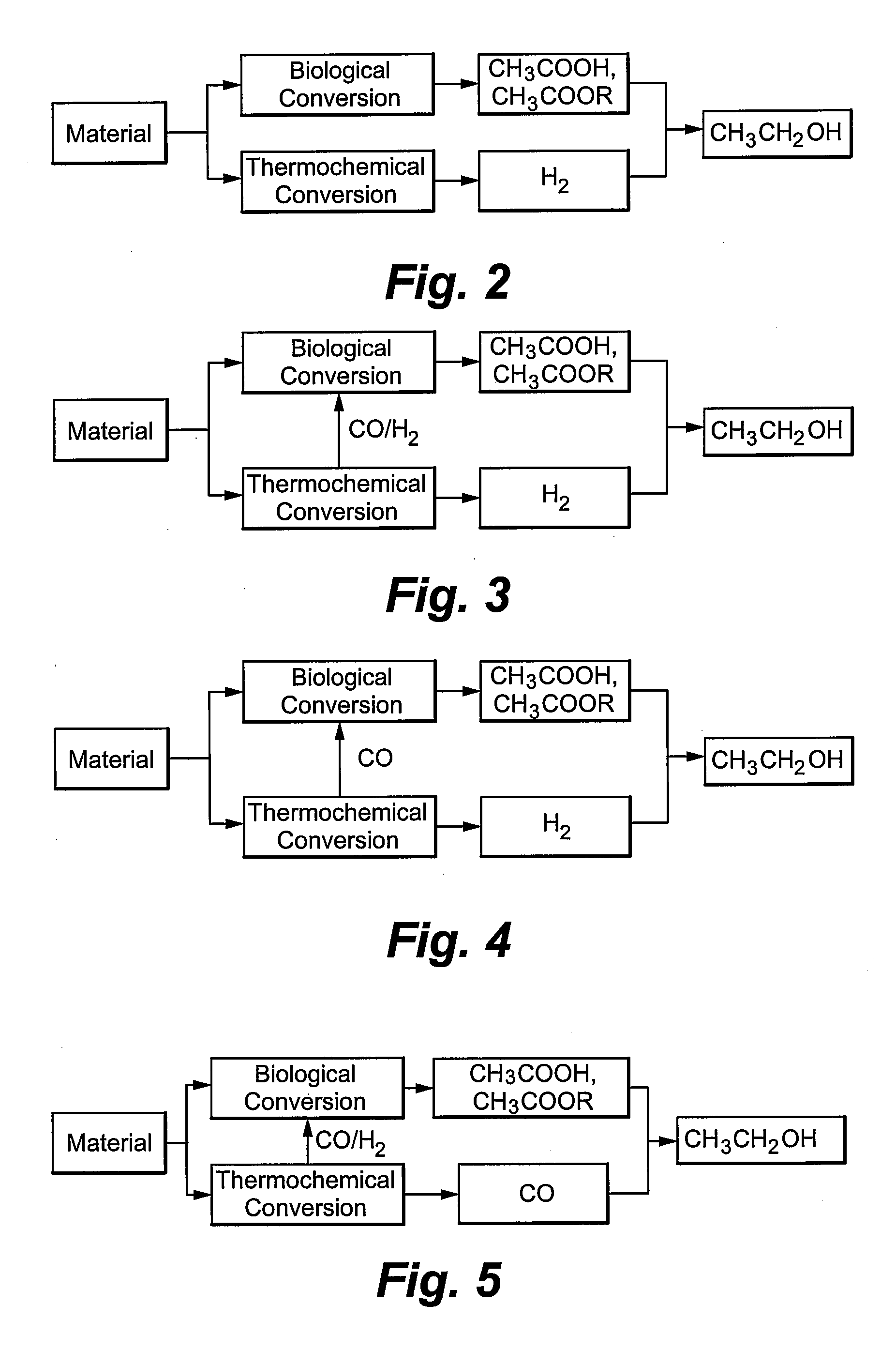
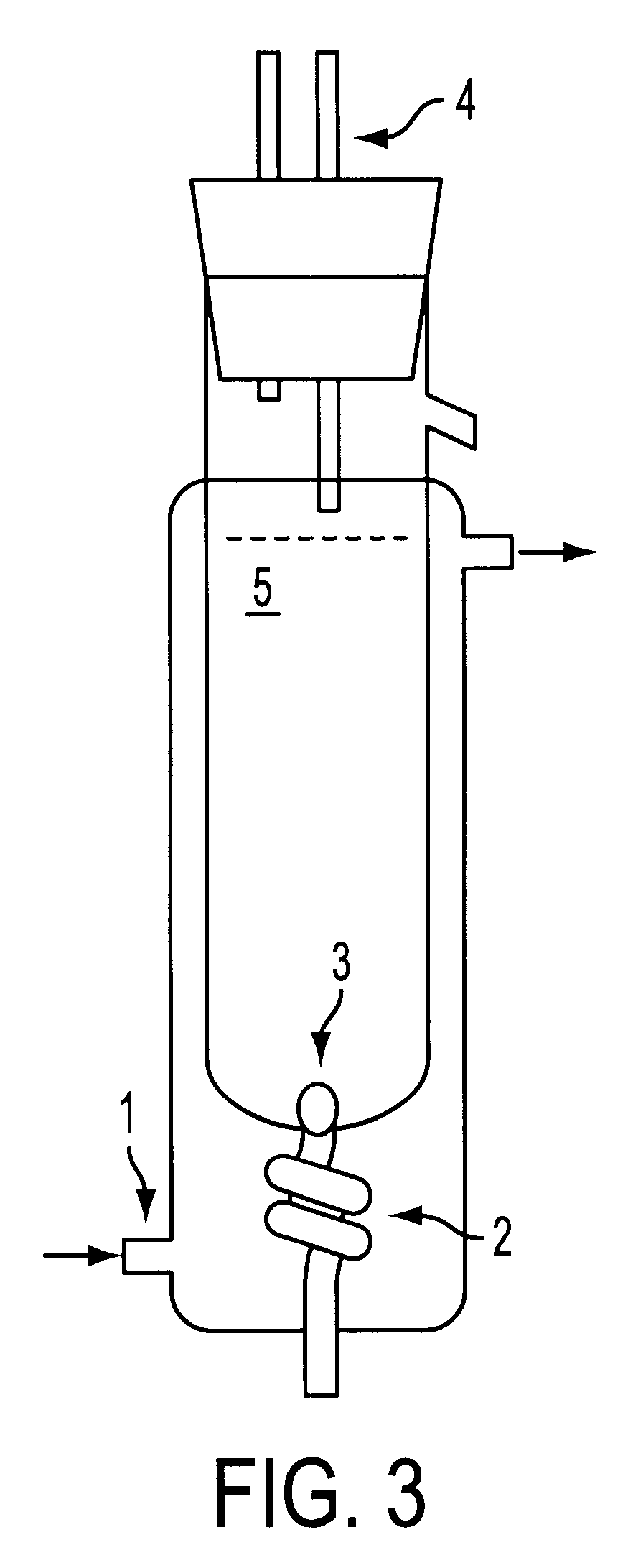
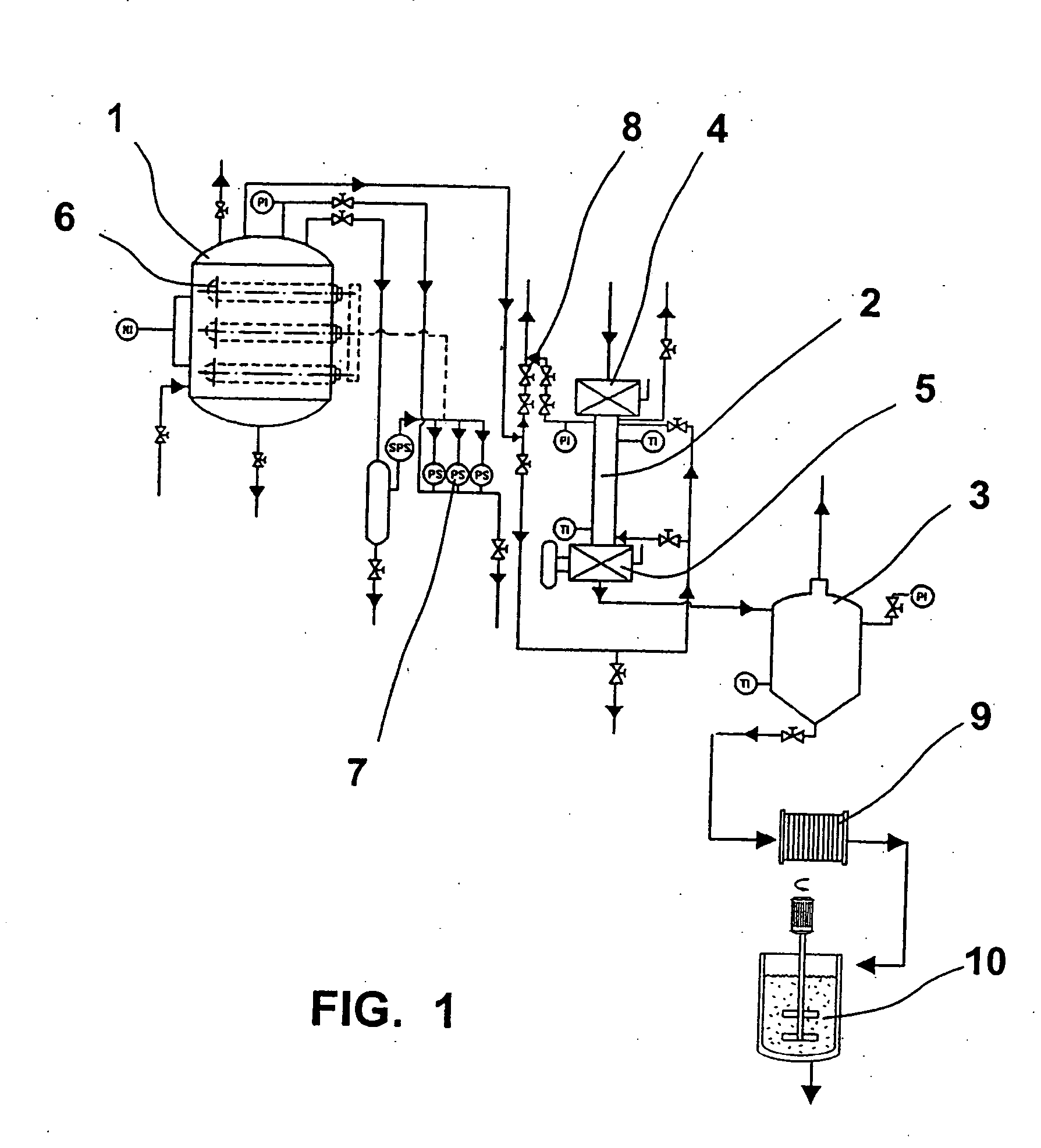
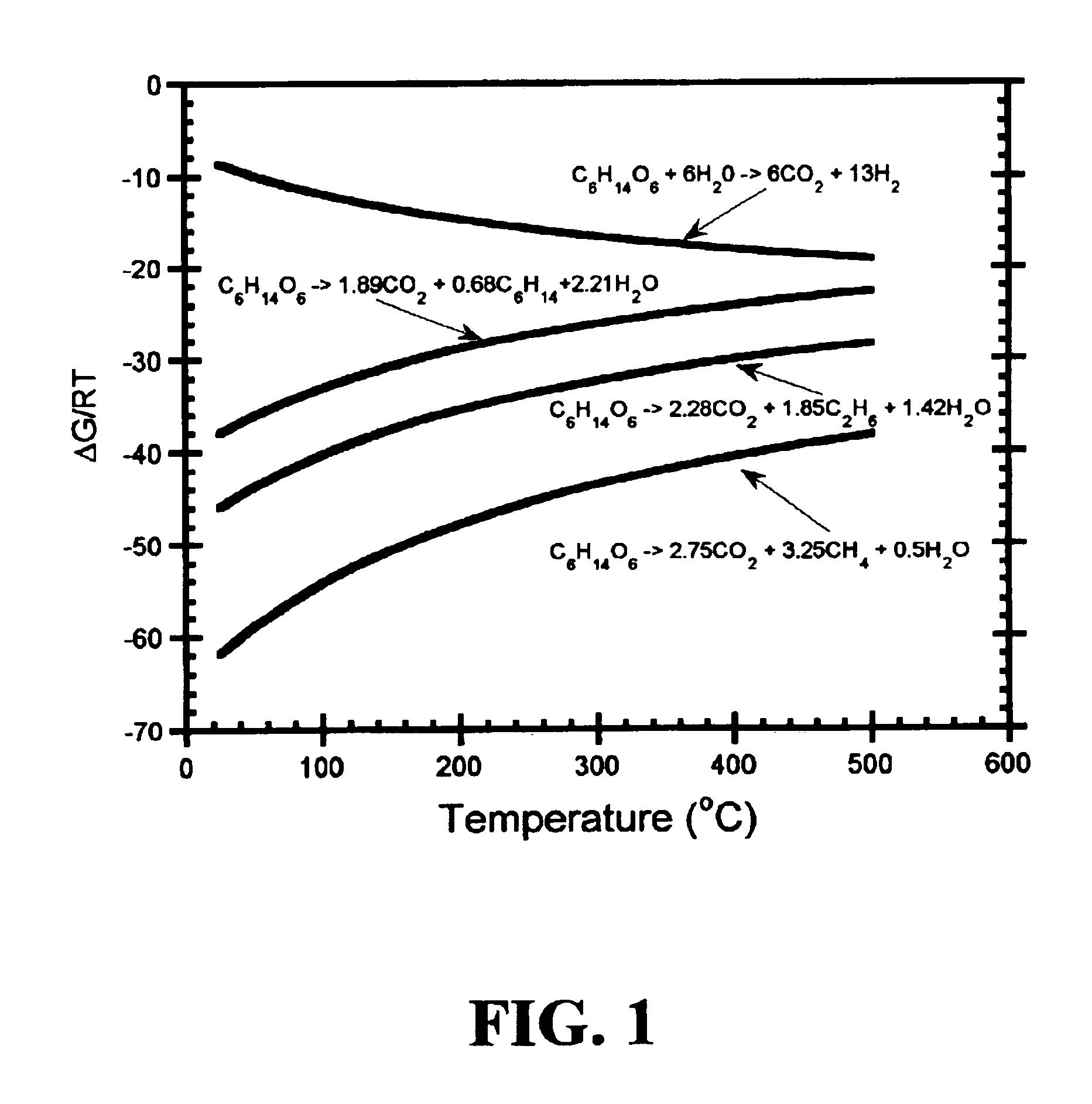
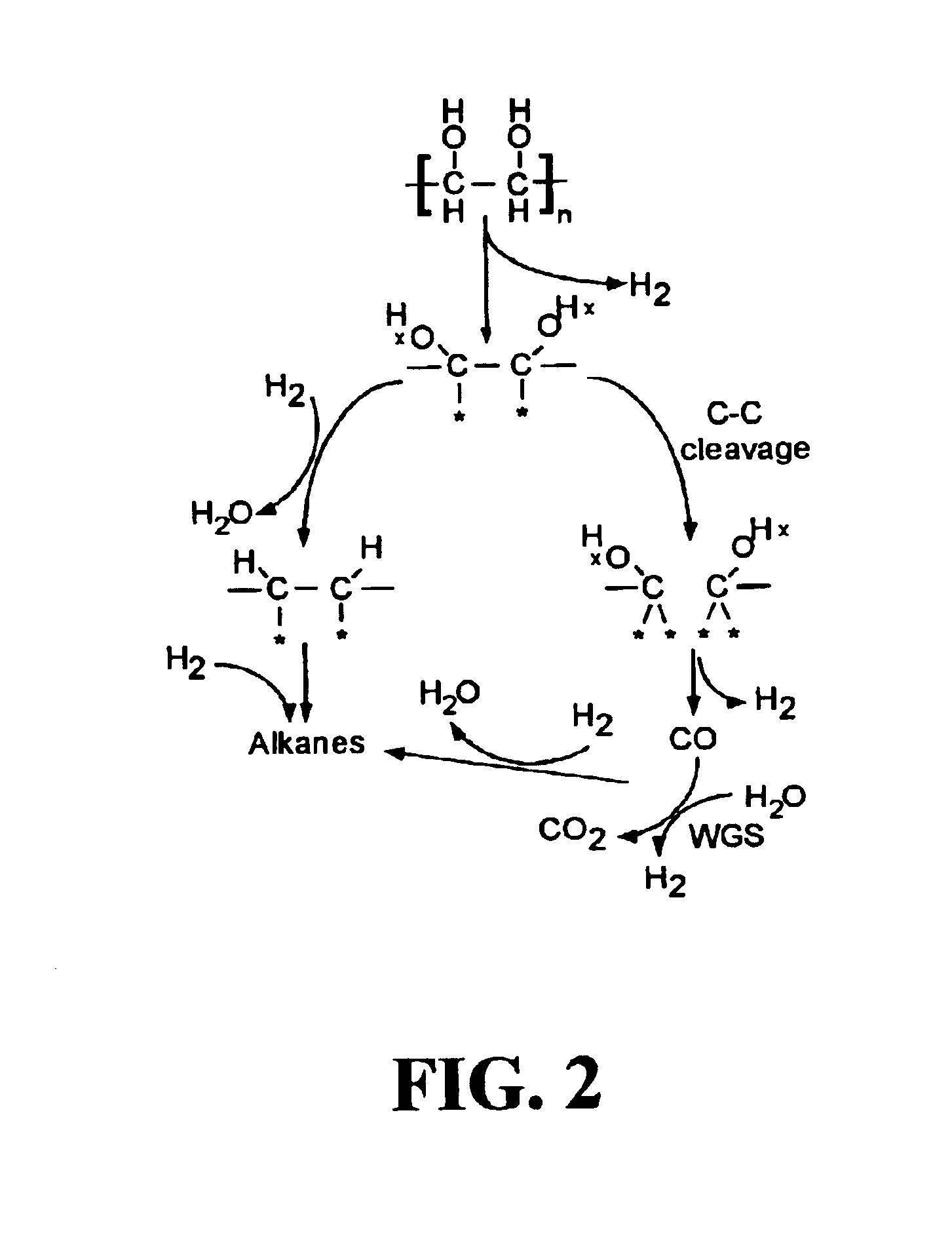
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
22796 results about "Biomass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biomass is plant or animal material used for energy production (electricity or heat), or in various industrial processes as raw material for a range of products. It can be purposely grown energy crops (e.g. miscanthus, switchgrass), wood or forest residues, waste from food crops (wheat straw, bagasse), horticulture (yard waste), food processing (corn cobs), animal farming (manure, rich in nitrogen and phosphorus), or human waste from sewage plants.
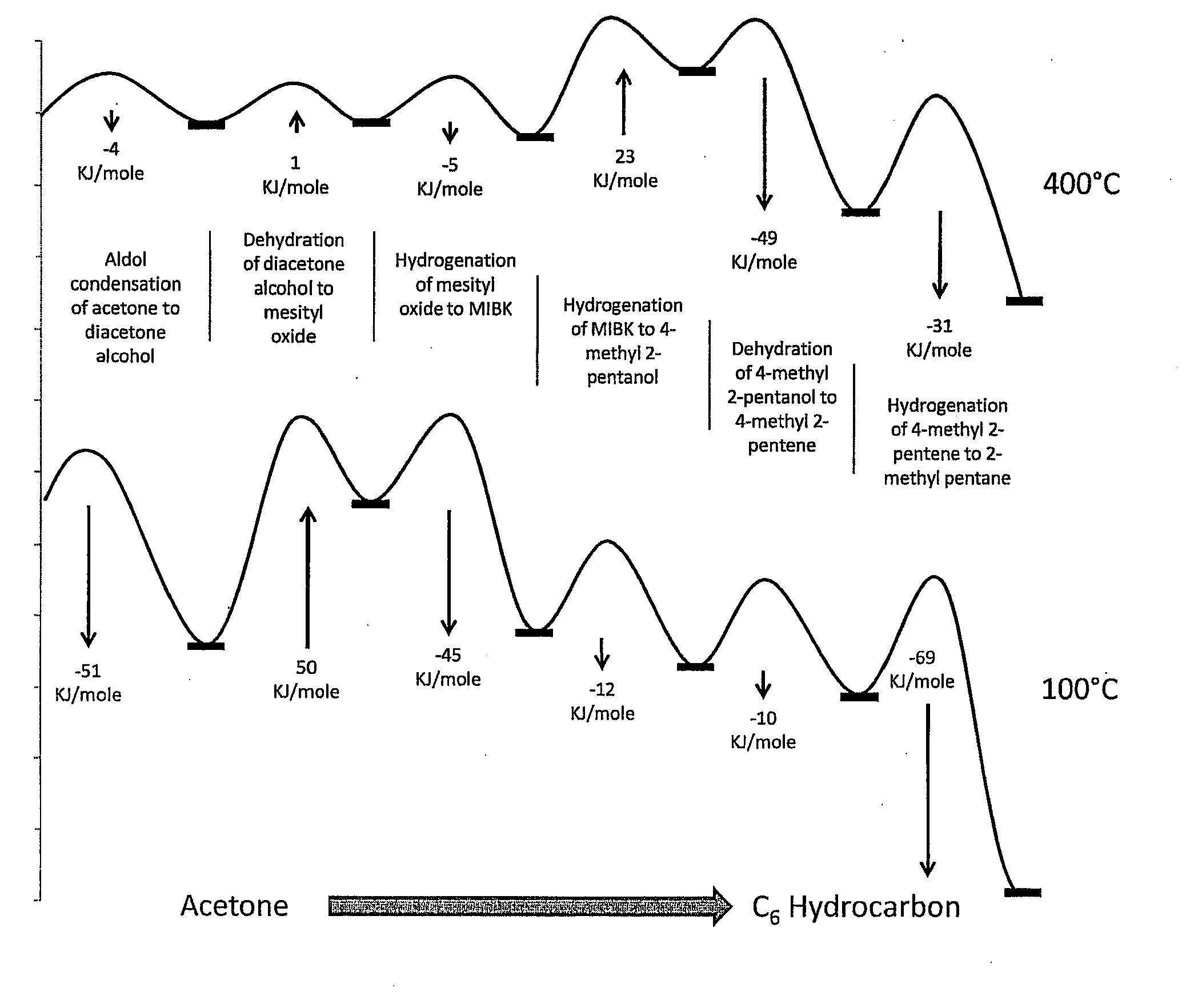
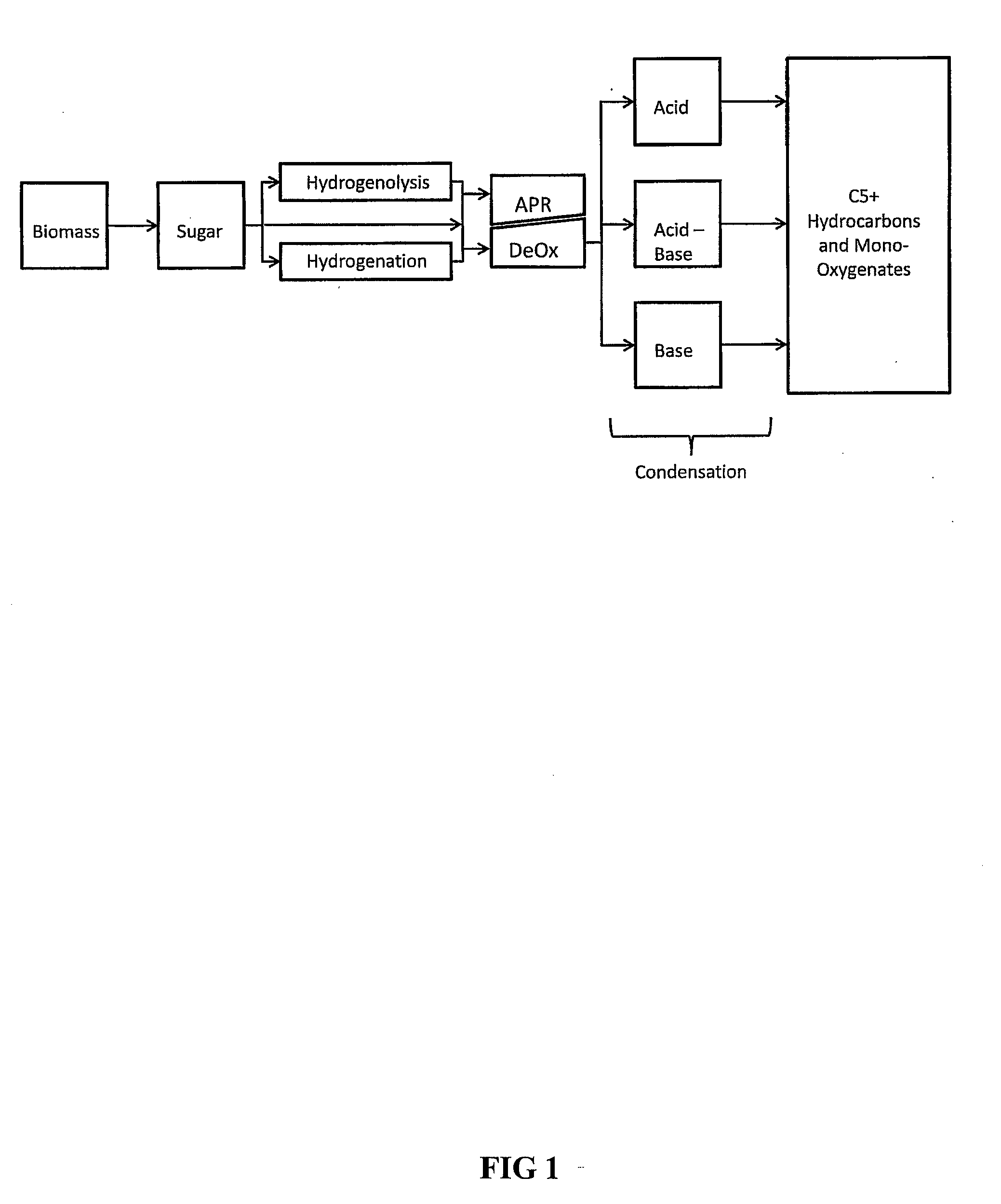
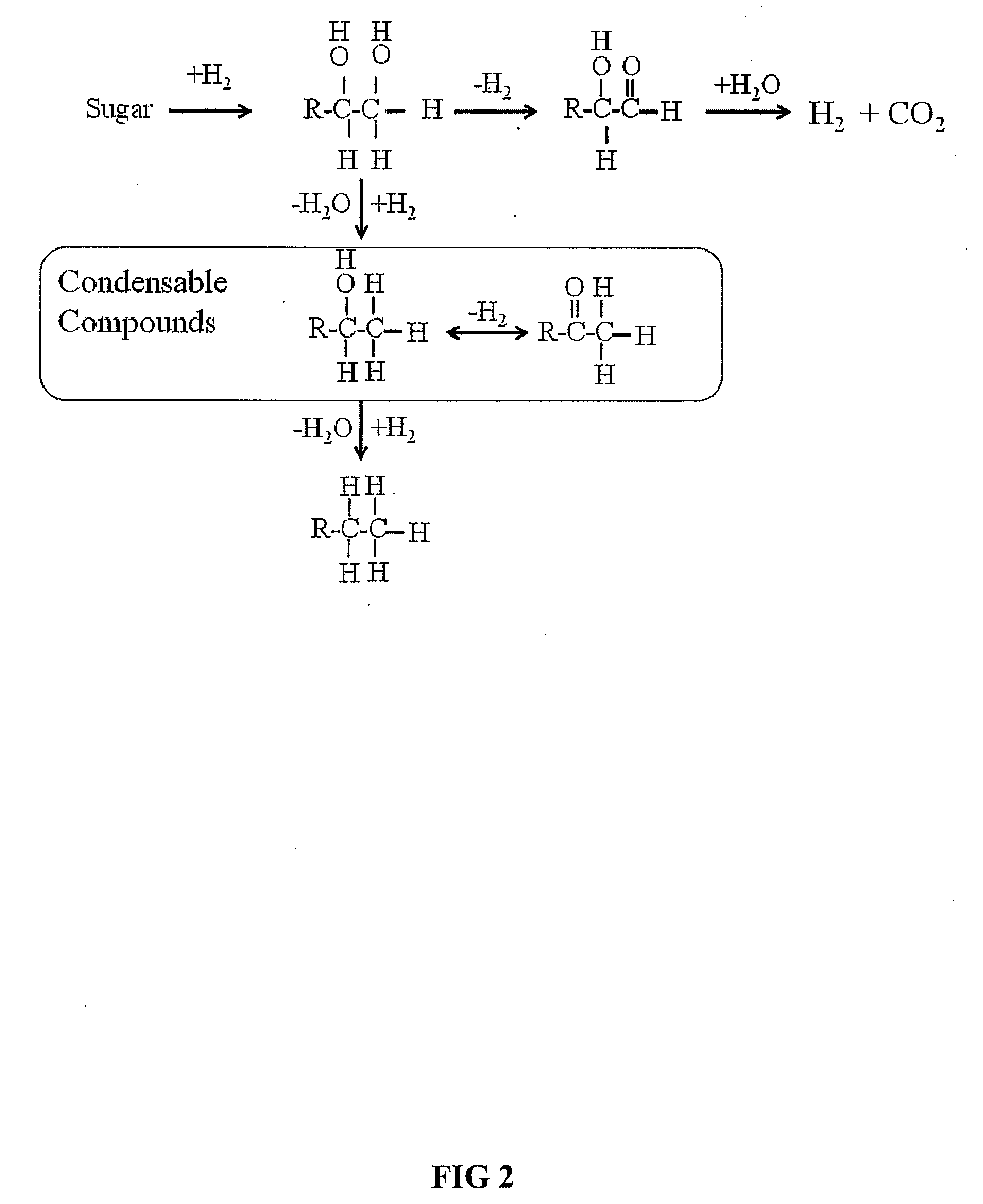
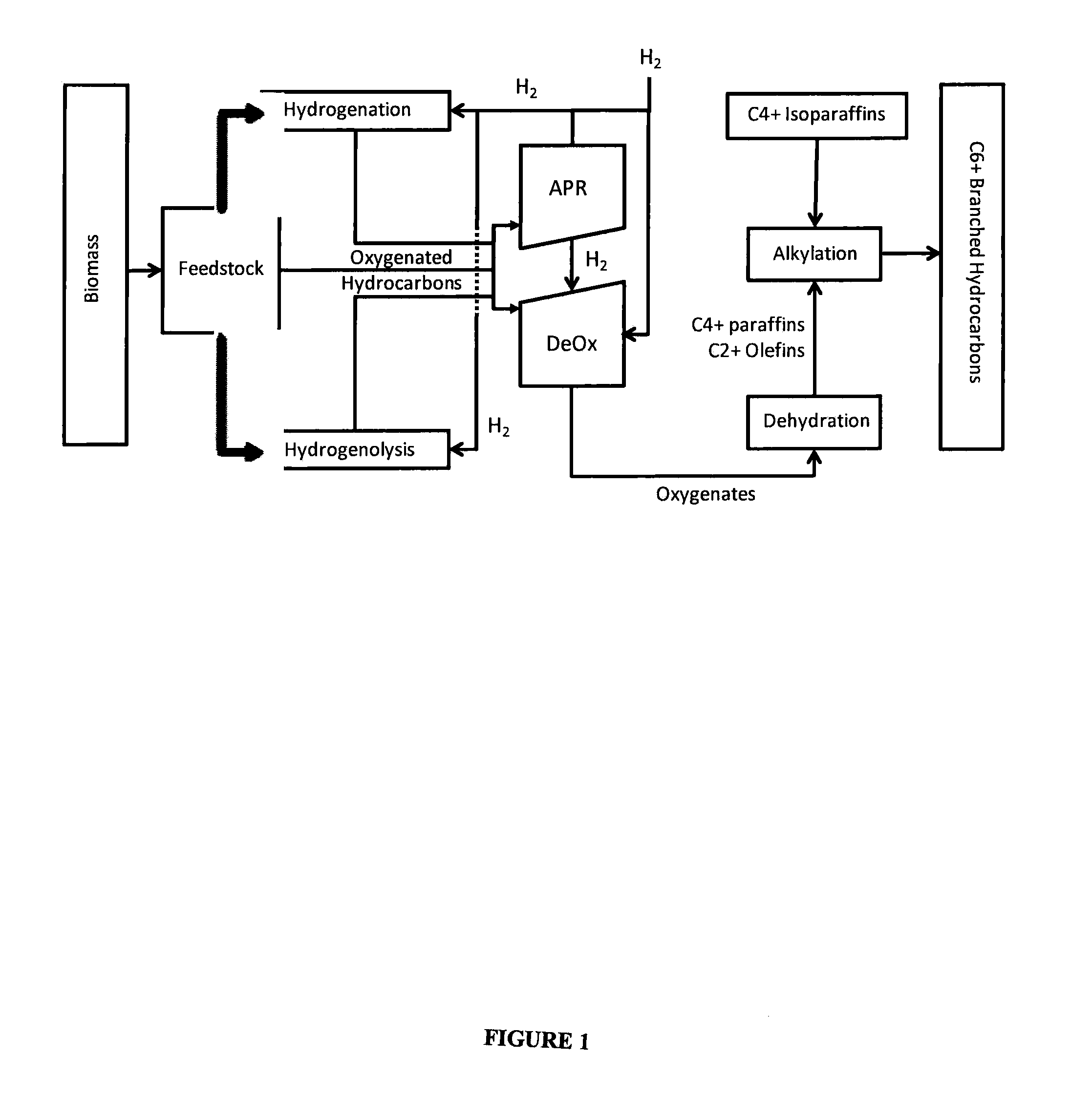
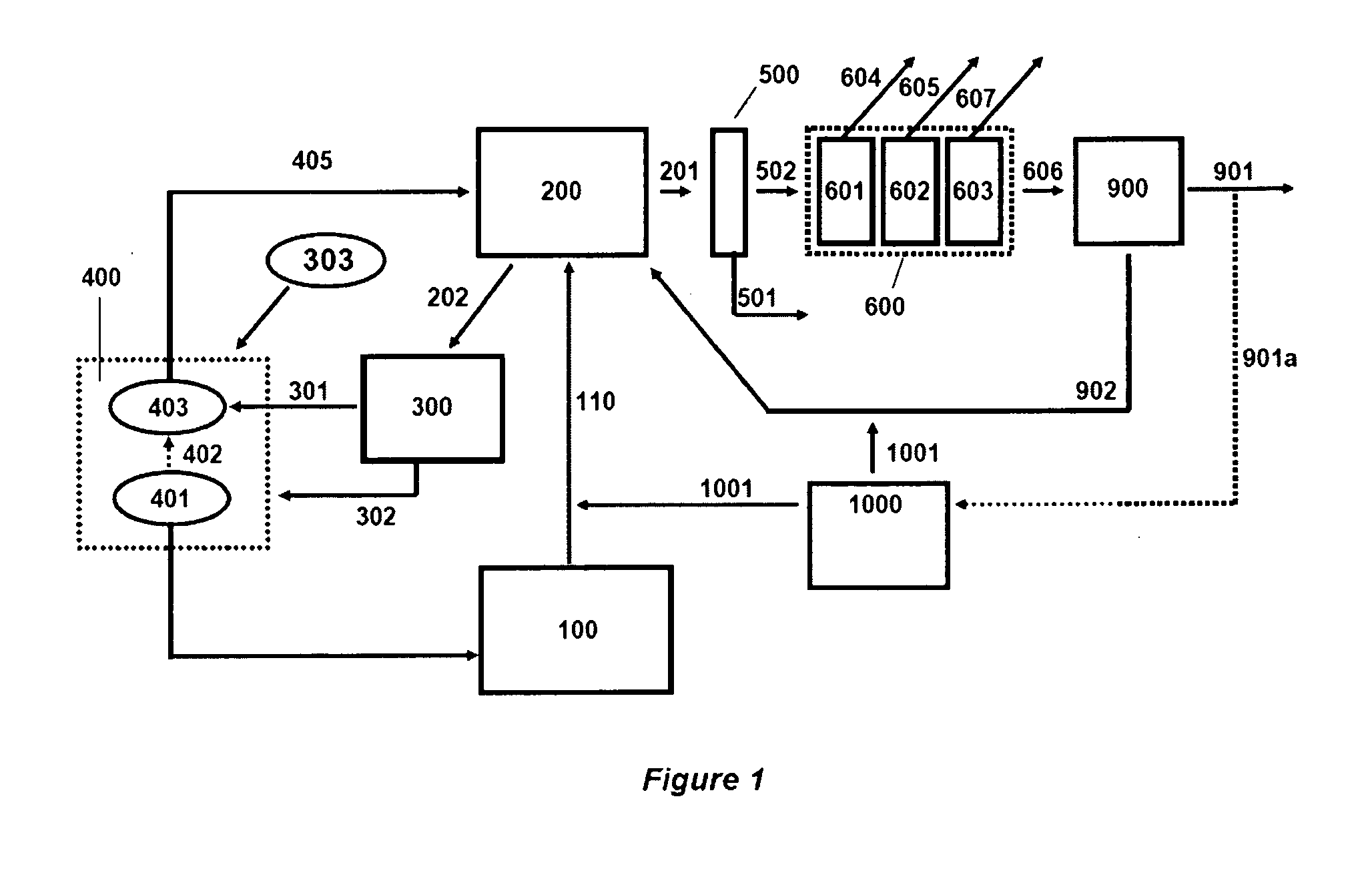
Synthesis of liquid fuels and chemicals from oxygenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080216391A1Organic compound preparationHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsFuranLiquid fuel
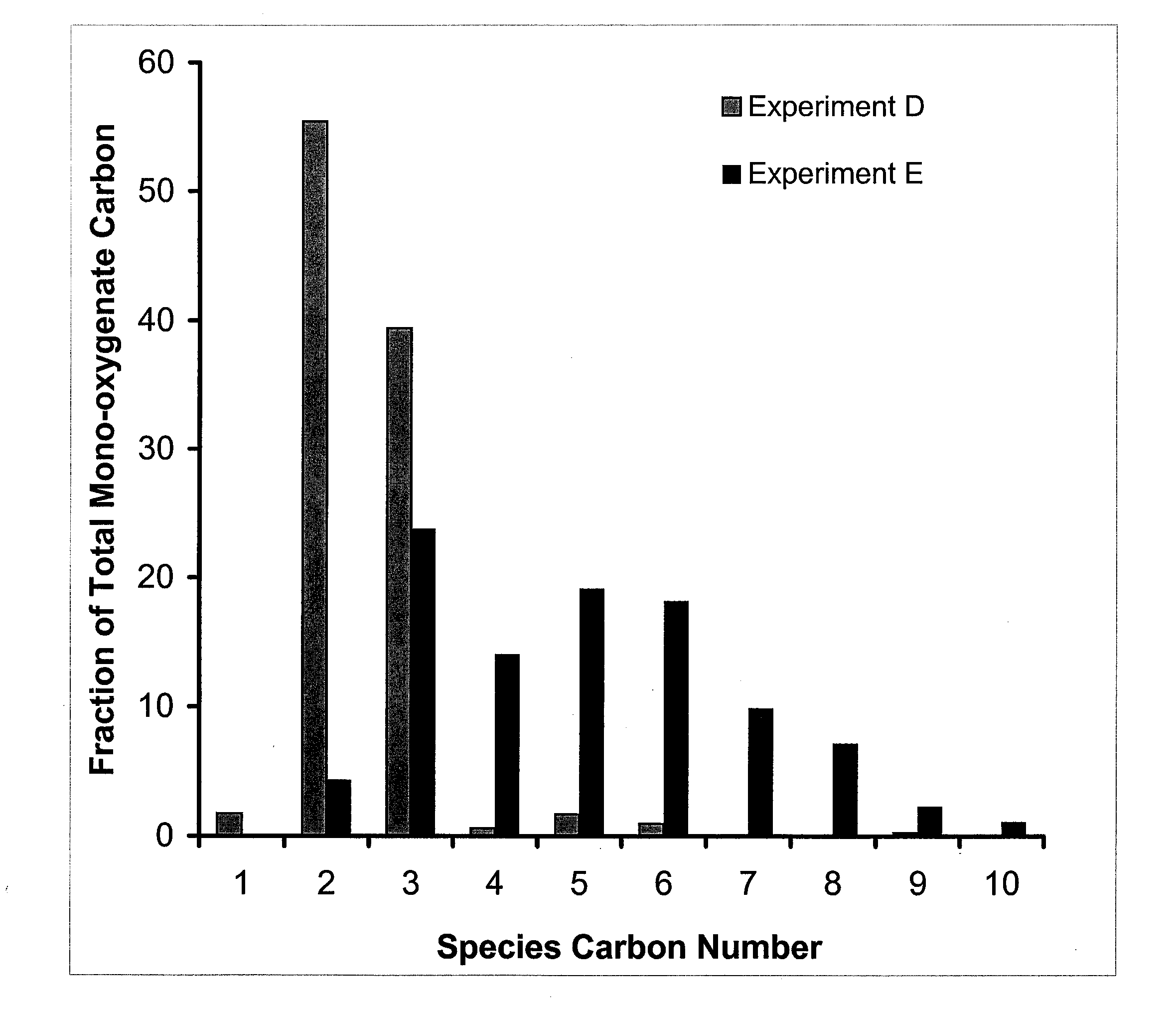
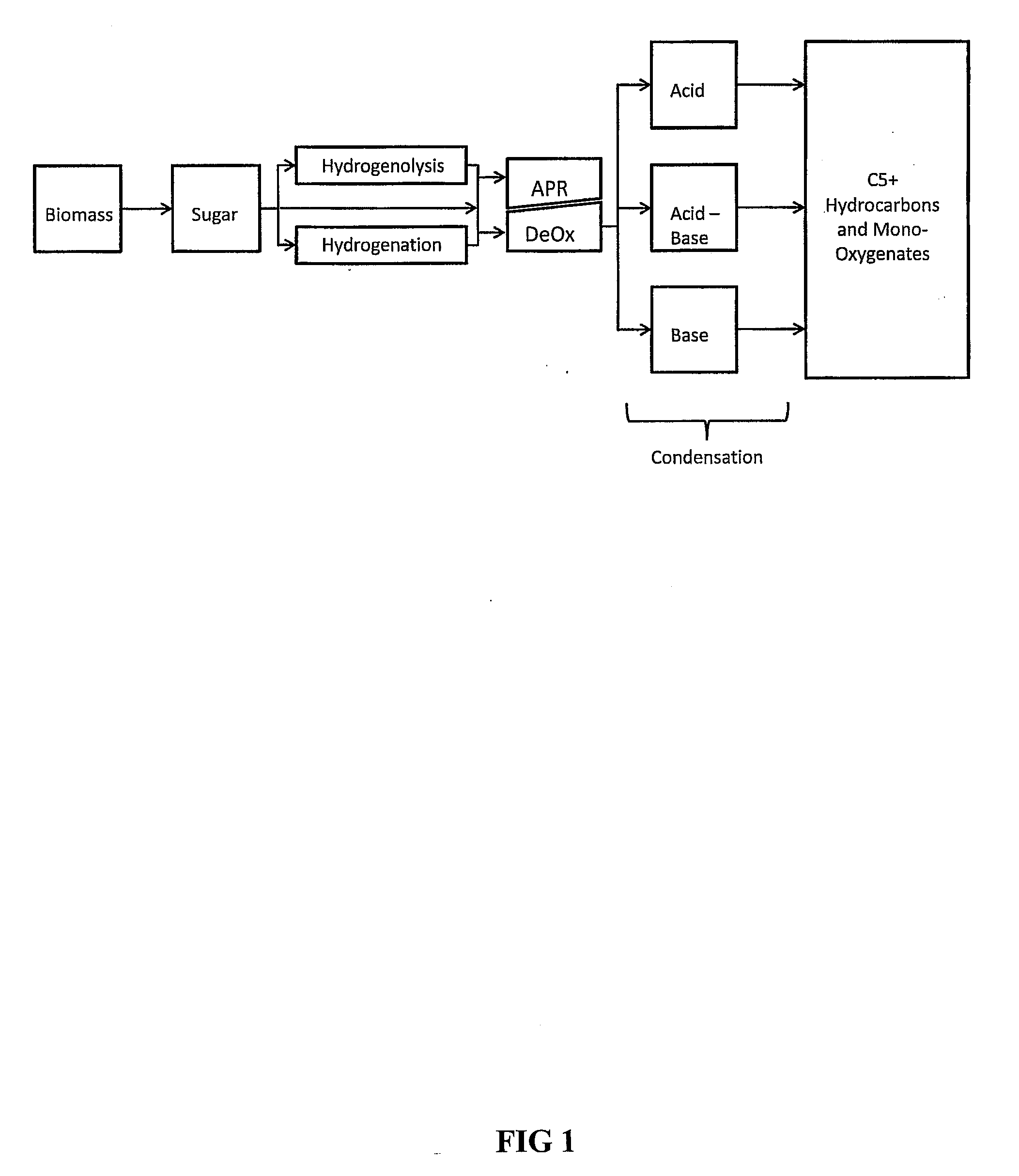
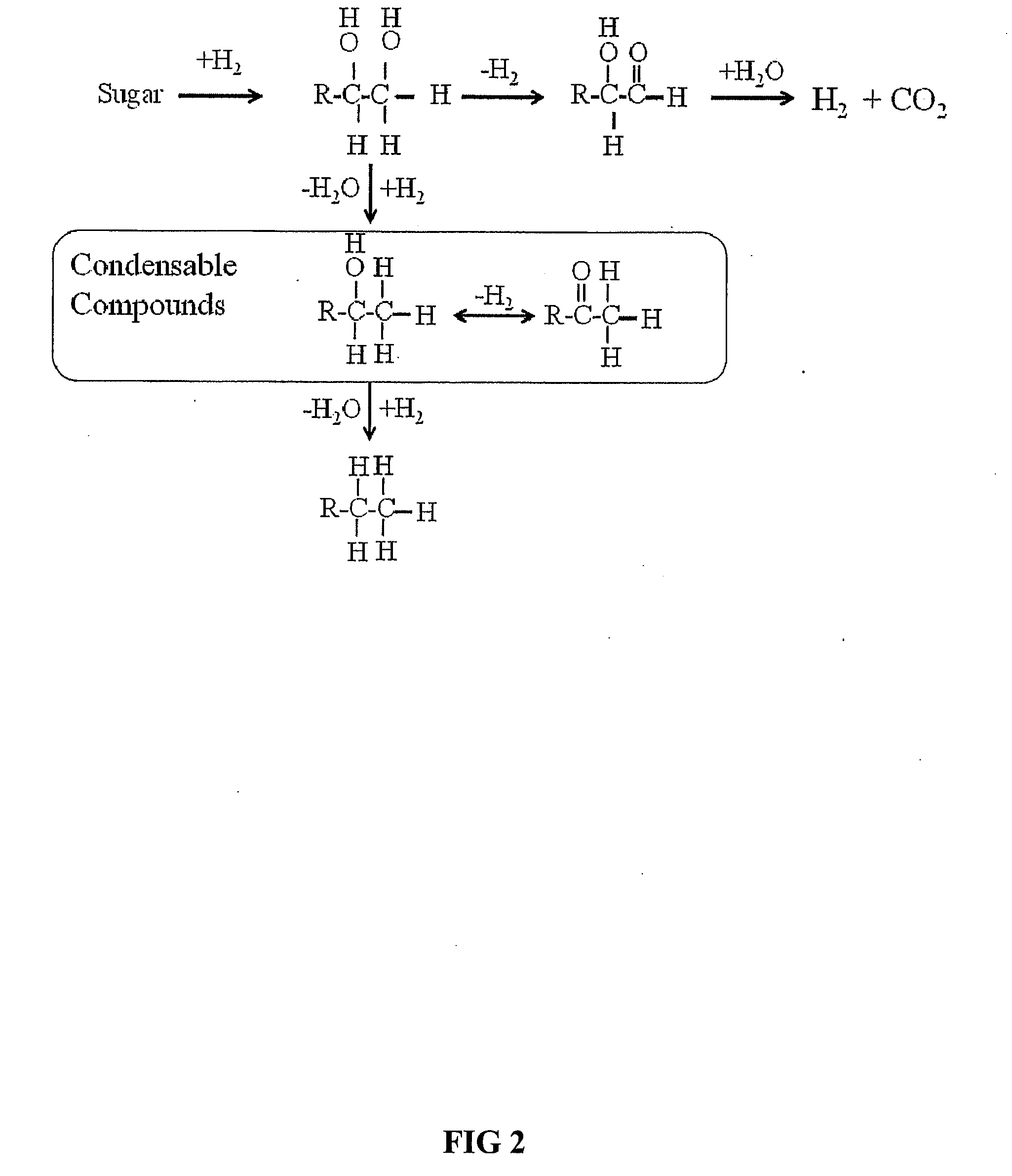
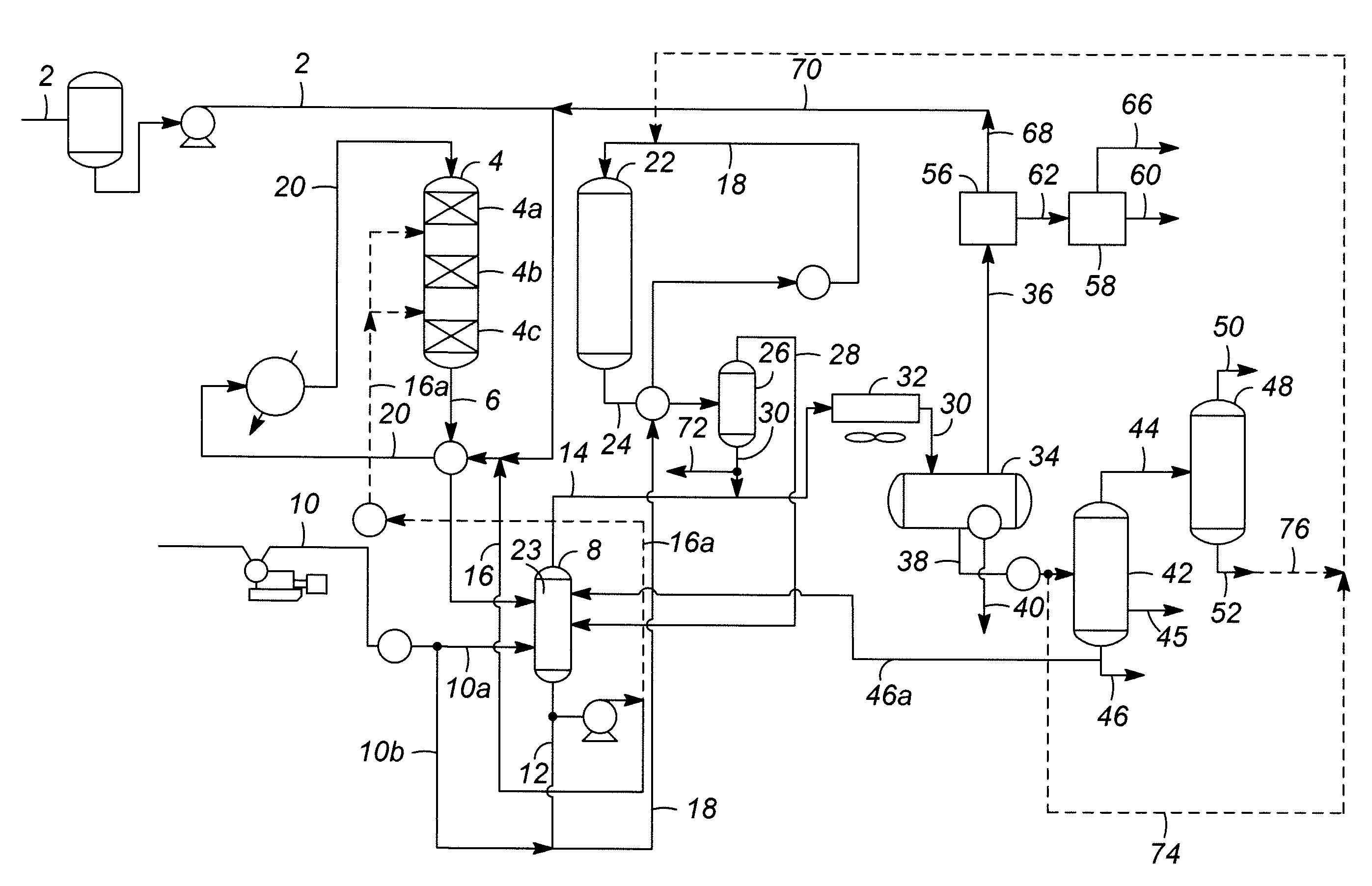
Processes and reactor systems are provided for the conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbons to hydrocarbons, ketones and alcohols useful as liquid fuels, such as gasoline, jet fuel or diesel fuel, and industrial chemicals. The process involves the conversion of mono-oxygenated hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, furans, carboxylic acids, diols, triols, and / or other polyols, to C4+ hydrocarbons, alcohols and / or ketones, by condensation. The oxygenated hydrocarbons may originate from any source, but are preferably derived from biomass.
Owner:VIRENT
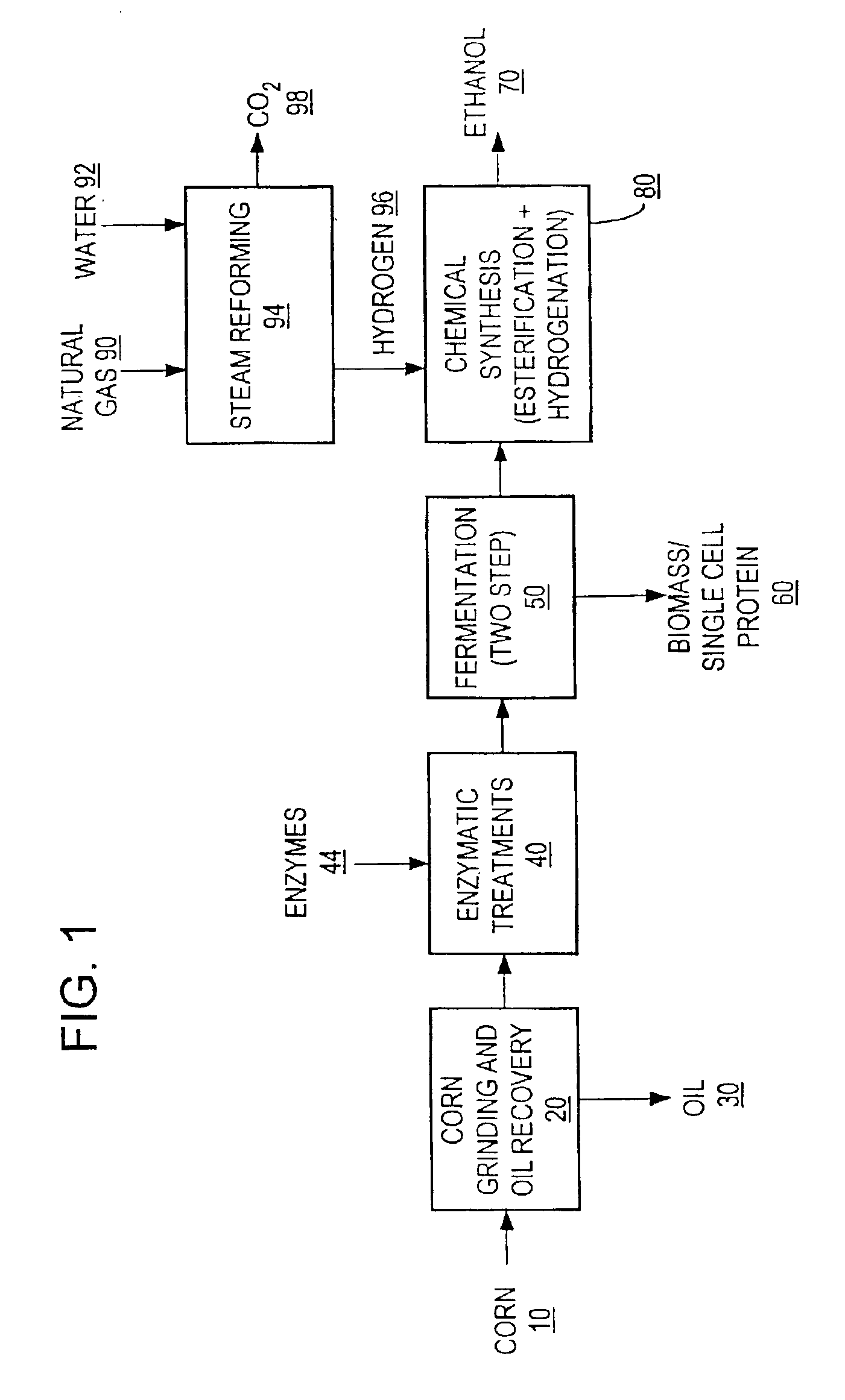
Process for producing ethanol
InactiveUS6927048B2High carbon yieldHigh protein concentrationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcetic acidHydrogenation reaction
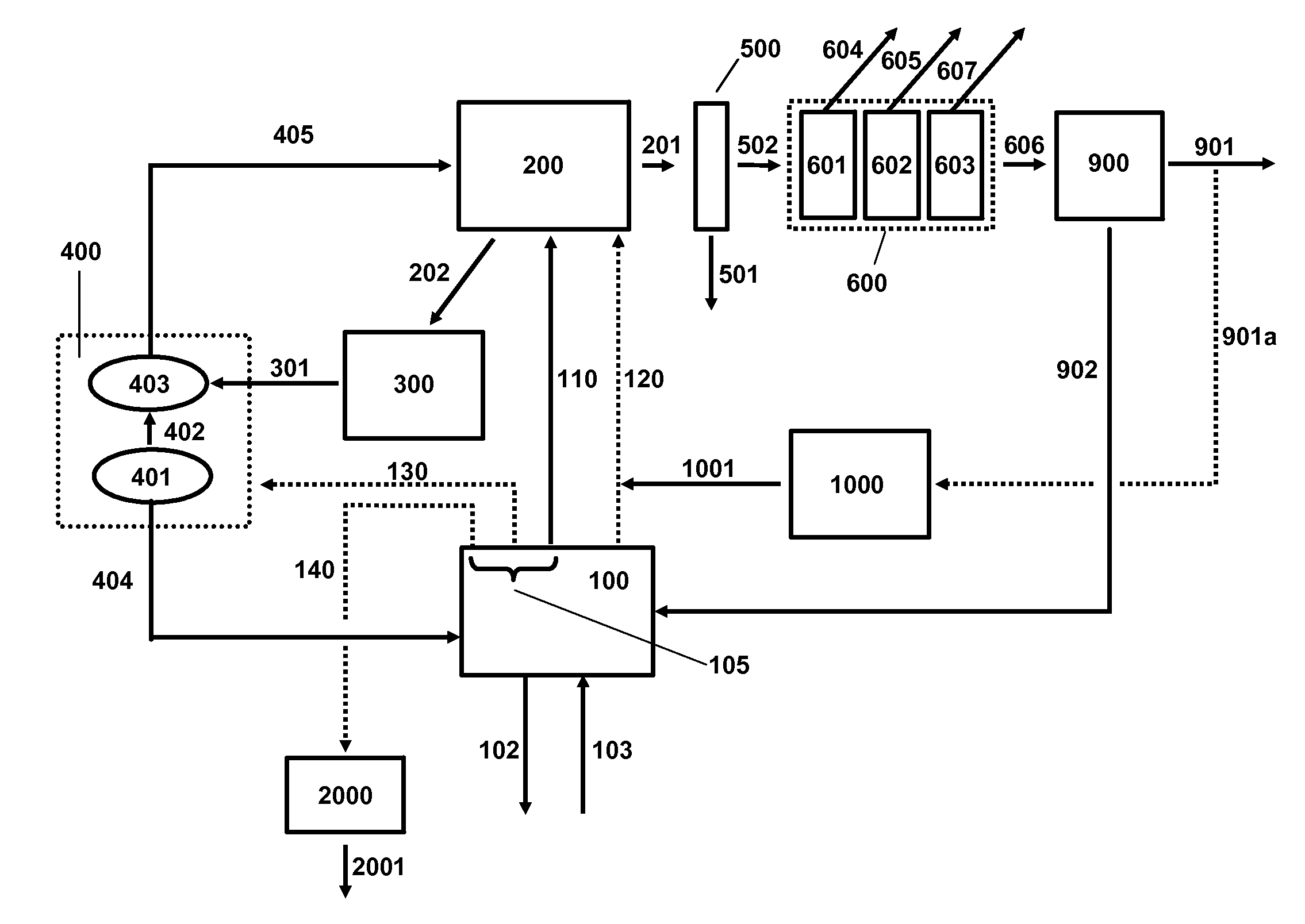
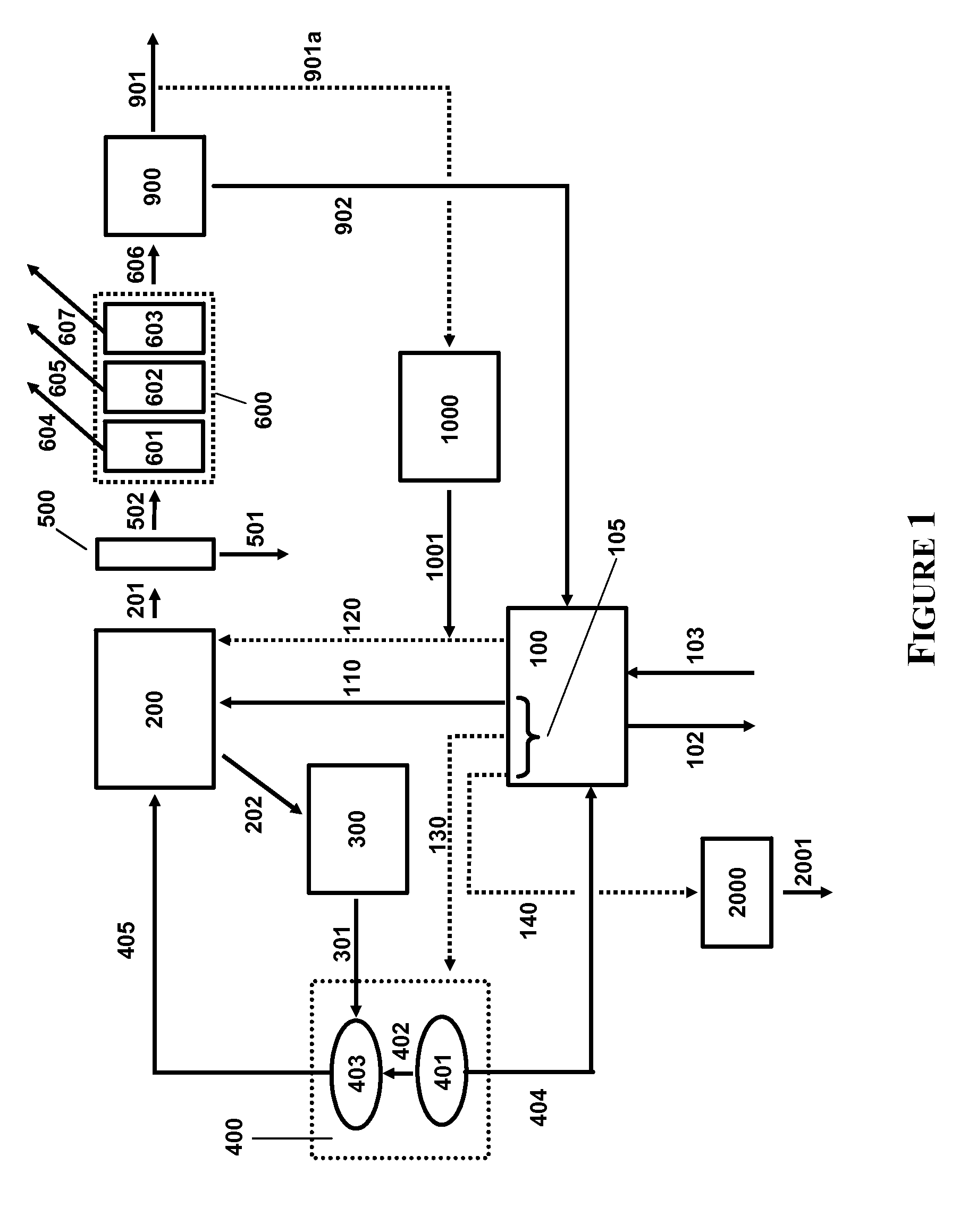
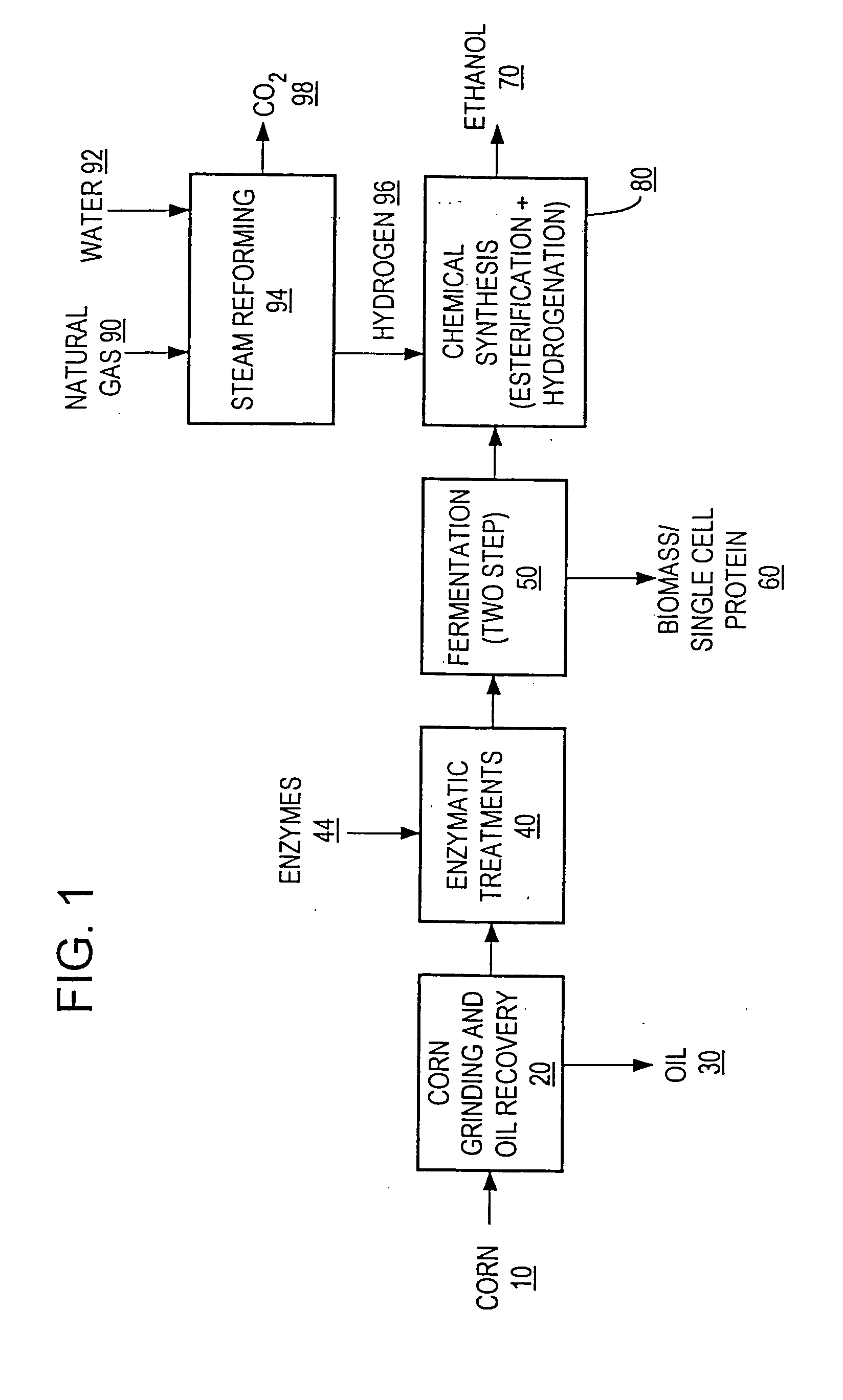
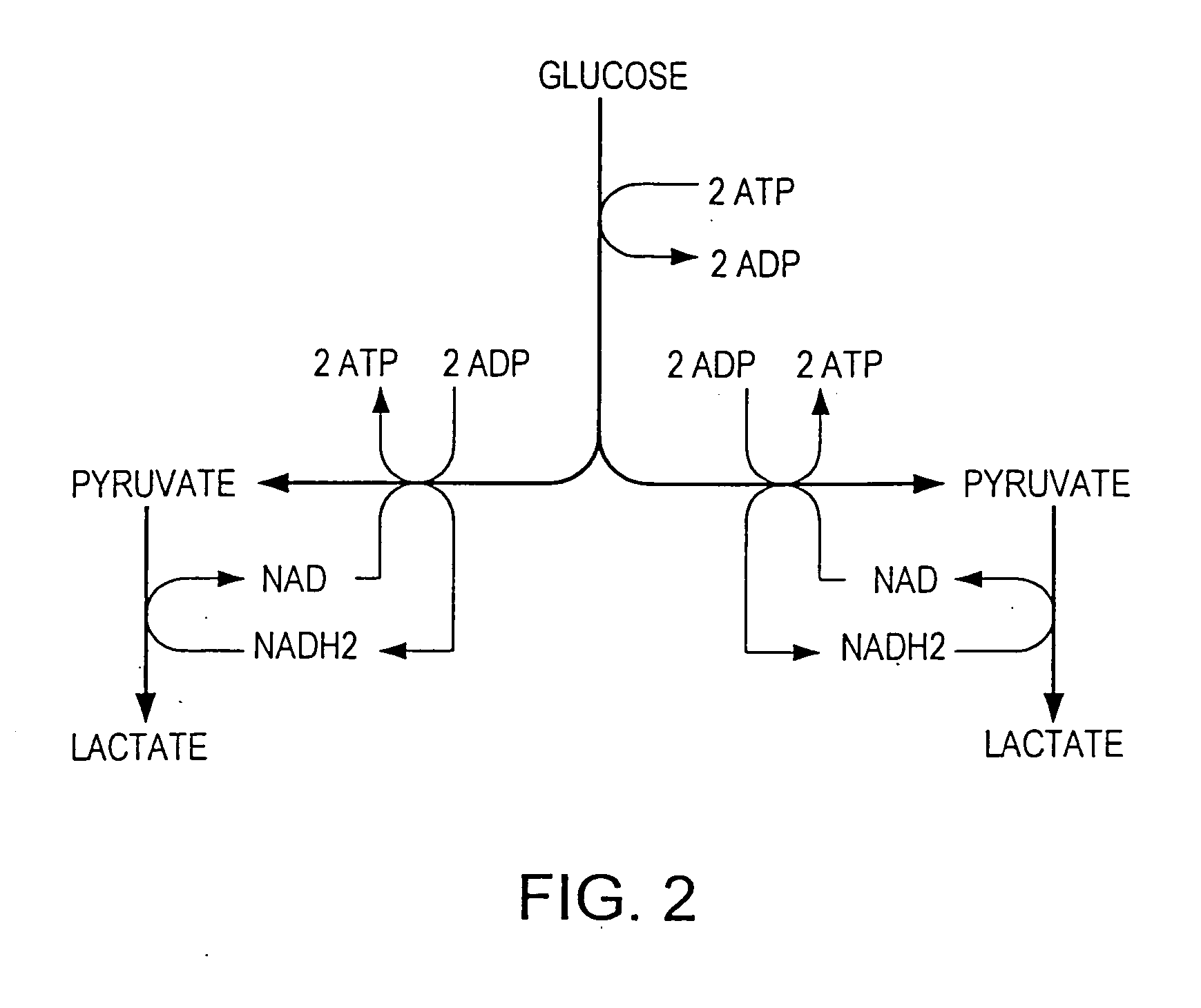
A process for producing ethanol including a combination of biochemical and synthetic conversions results in high yield ethanol production with concurrent production of high value coproducts. An acetic acid intermediate is produced from carbohydrates, such as corn, using enzymatic milling and fermentation steps, followed by conversion of the acetic acid into ethanol using esterification and hydrogenation reactions. Coproducts can include corn oil, and high protein animal feed containing the biomass produced in the fermentation.
Owner:ZEACHEM
Energy Efficient Methods to Produce Products
InactiveUS20080193989A1Improve energy efficiencyEnergy efficiencyBiofuelsWaste based fuelBiomassChemistry
The invention relates to processes that efficiently convert carbon-containing materials, such as biomass, into products in such a manner that the energy, carbon, and mass content of the materials are efficiently transferred into such products. Such methods include converting the materials into at least one intermediate by a biological conversion process and at least one intermediate by a thermochemical conversion process and reacting the intermediates to form the product. Such methods have a chemical energy efficiency to produce the product that is greater than the chemical energy efficiency of a solely biological conversion process to produce the product and that is greater than the chemical energy efficiency of a process in which all of the material is initially subjected to a thermochemical conversion step as part of the process to produce the product.
Owner:ZEACHEM
Methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from synthesis gas
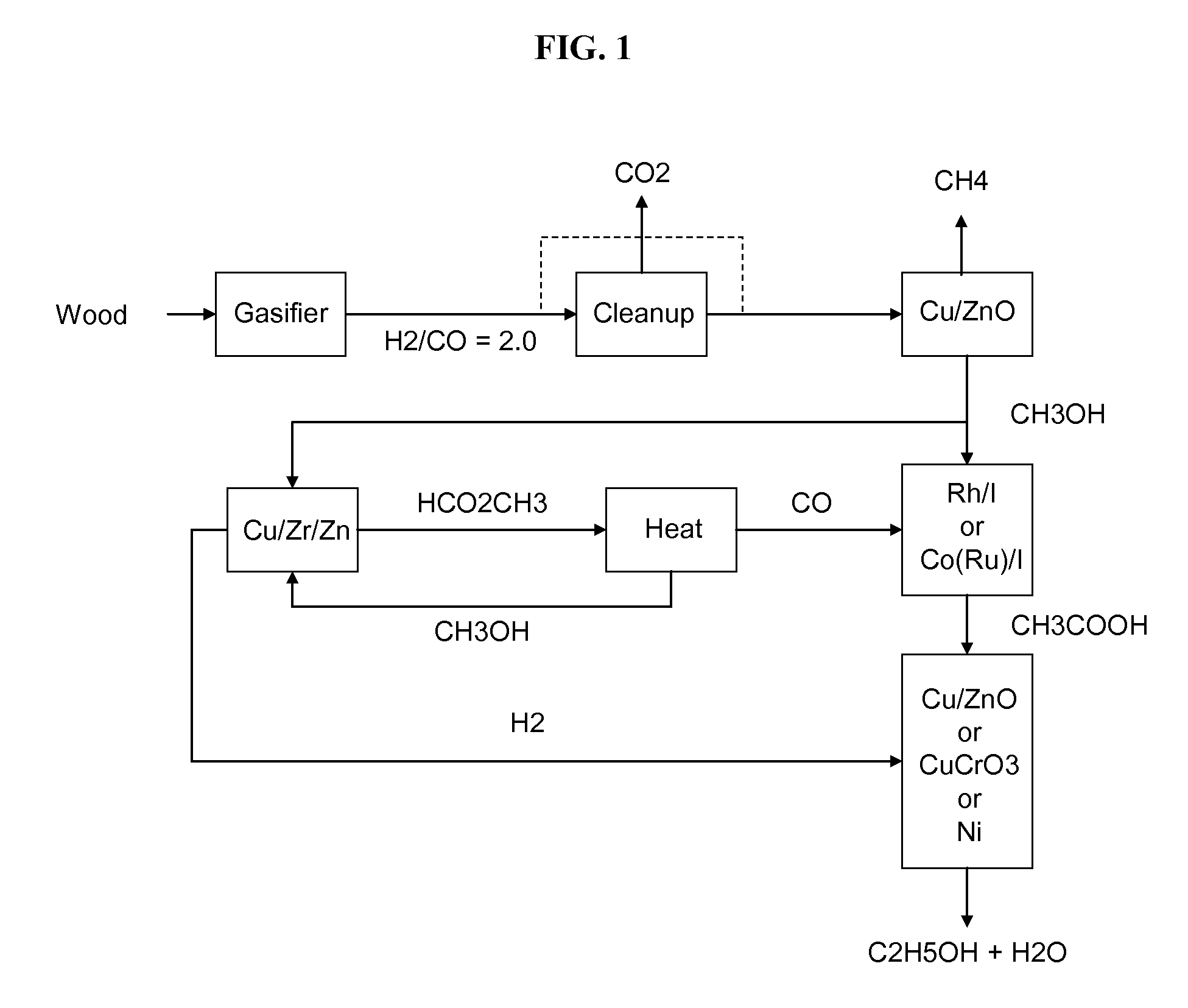
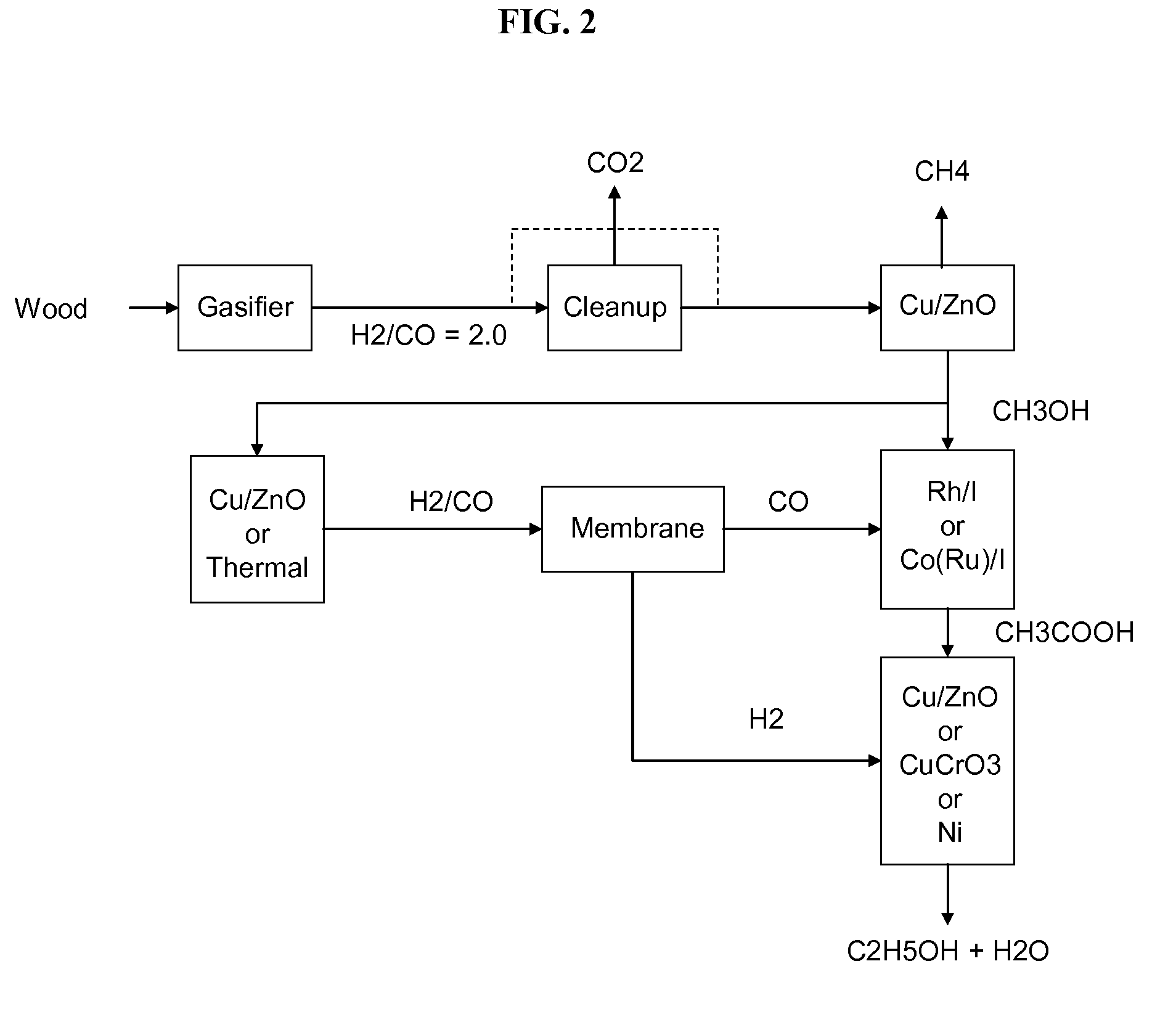
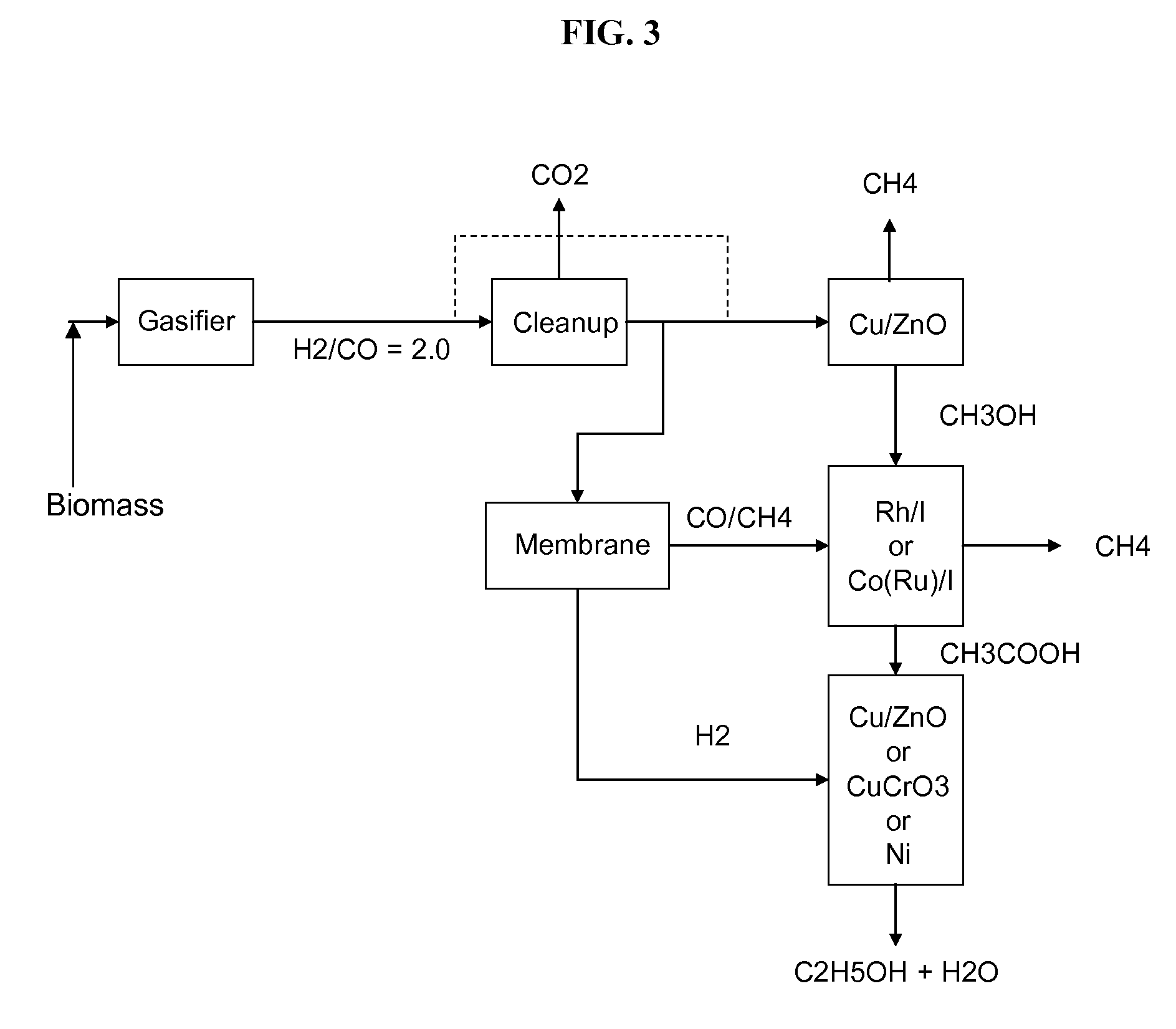
The invention provides methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from syngas. As disclosed herein, syngas derived from cellulosic biomass (or other sources) can be catalytically converted into methanol, which in turn can be catalytically converted into acetic acid or acetates. Finally, the acetic acid or acetates can be reduced to ethanol according to several variations. In some embodiments, yields of ethanol from biomass can exceed 100 gallons per dry ton of biomass.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Synthesis of liquid fuels and chemicals from oxygenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080300435A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionFuranLiquid fuel
Processes and reactor systems are provided for the conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbons to hydrocarbons, ketones and alcohols useful as liquid fuels, such as gasoline, jet fuel or diesel fuel, and industrial chemicals. The process involves the conversion of mono-oxygenated hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, furans, carboxylic acids, diols, triols, and / or other polyols, to C4+ hydrocarbons, alcohols and / or ketones, by condensation. The oxygenated hydrocarbons may originate from any source, but are preferably derived from biomass.
Owner:VIRENT
Method for processing lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS6555350B2High degreeReduce water consumptionSludge treatment by oxidationBiofuelsCelluloseWater flow
A method wherein lignocellulosic biomass materials are converted into combustible fuel products. In particular, the method is a continuous process, involving wet oxidation or steam explosion, for fermentatively converting such biomass materials into ethanol using a process design that permits all or part of the process water from the ethanol fermentation process to be recycled to reduce the consumption of process water. The effluent from the ethanol fermentation step may be subjected to an anaerobic fermentation step generating methane and a water effluent in which the amount of potentially inhibitory substances is at a sub-inhibitory level, which in turn permits all or part of the effluent water from the anaerobic fermentation step to be recycled into the process.
Owner:POET RES INC
Process for preparing materials for extraction
InactiveUS20060122410A1Improve extraction efficiencyQuality improvementFungiUnicellular algaeArachidonic acid supplementationFermentation
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a biomass, such as from a microbial fermentation, for an extraction process to separate desired chemicals, nutritional products, bioactive components, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, from the biomass. Particularly preferred substances to extract include docosahexaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid, and arachidonic acid. The present invention also includes extracting the prepared biomass. Biomasses to be treated in accordance with the methods of the invention include plant, animal, and microbial biomass, particularly a microorganism such as Crypthecodinium cohnii and a fungus such as Mortierella alpina.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Procedure for the production of ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass using a new heat-tolerant yeast
InactiveUS20050069998A1Low conversion rateReduce yieldFungiBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationSolid fraction
It includes the stages of grinding the lignocellulosic biomass to a size of 15-30 mm, subjecting the product obtained to steam explosion pre-treatment at a temperature of 190-230° C. for between 1 and 10 minutes in a reactor (2), collecting the pre-treated material in a cyclone (3) and separating the liquid and solid fractions by filtration in a filter press (9), introducing the solid fraction in a fermentation deposit (10), adding a cellulase at a concentration of 15 UFP per gram of cellulose and 12.6 International Units of β-glucosidase enzyme dissolved in citrate buffer pH 4.8, inoculating the fermentation deposit (10) with a culture of the heat-tolerant bacteria Kluyveromyces marxianus CECT 10875, obtained by chemical mutagenesis from strain DER-26 of Kluyveromyces marxianus and shaking the mixture for 72 hours at 42° C.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACIONES ENERGETICAS MEDIO AMBIENTALLES Y TECNOLOGICAS (C I E M A T)
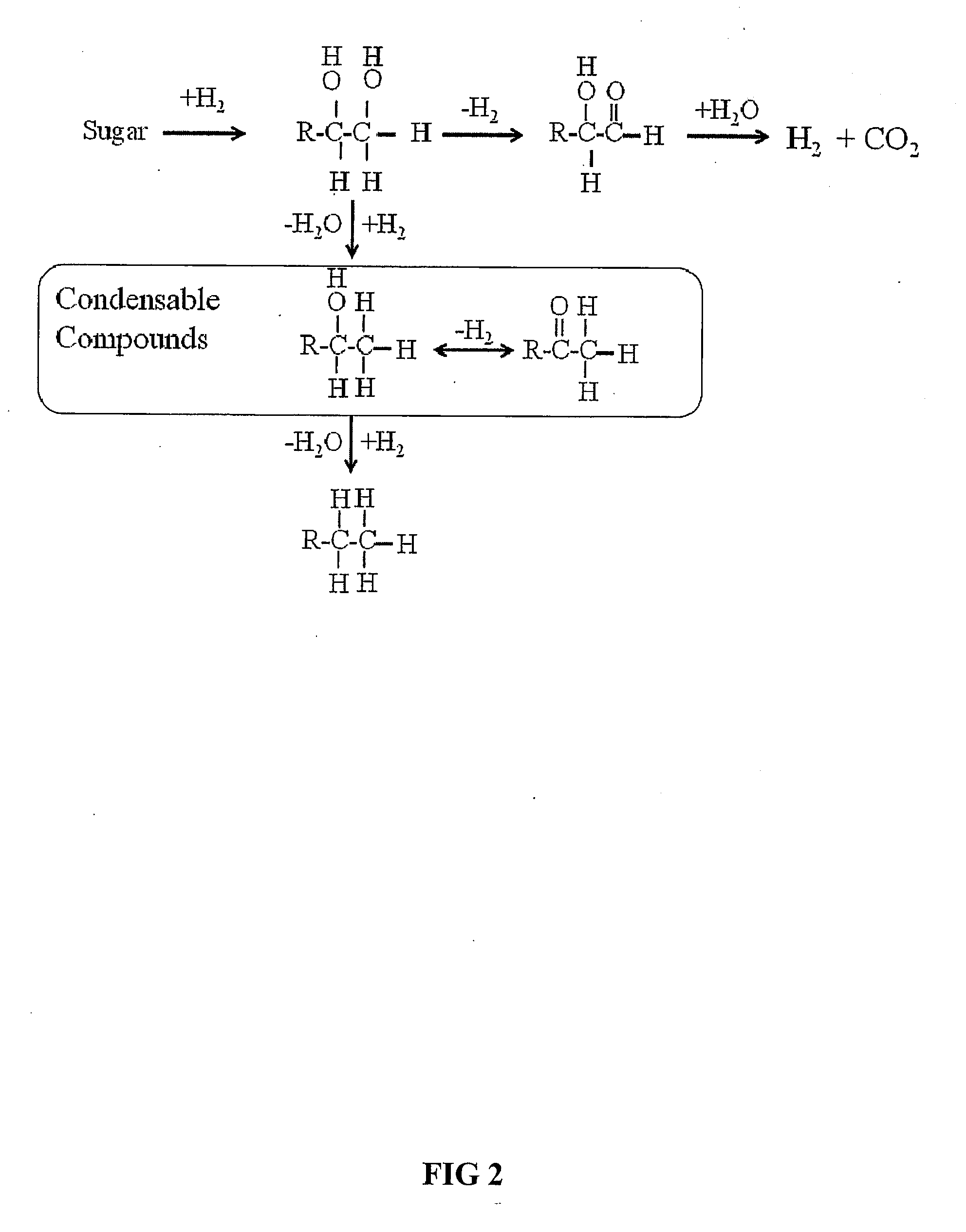
Low-temperature hydrocarbon production from oxygenated hydrocarbons
Disclosed is a method of producing hydrocarbons from oxygenated hydrocarbon reactants, such as glycerol, glucose, or sorbitol. The method can take place in the vapor phase or in the condensed liquid phase (preferably in the condensed liquid phase). The method includes the steps of reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon having at least two carbon atoms, in the presence of a metal-containing catalyst. The catalyst contains a metal selected from the group consisting of Group VIIIB transitional metals, alloys thereof, and mixtures thereof. These metals are supported on supports that exhibit acidity or the reaction is conducted under liquid-phase conditions at acidic pHs. The disclosed method allows the production of hydrocarbon by the liquid-phase reaction of water with biomass-derived oxygenated compounds.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Illumination systems, devices, and methods for biomass production
InactiveUS20090148931A1Sufficient amountMore energySolar heating energyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsLight energyLighting system
Illumination systems, devices, and methods for cultivating biomasses. A bioreactor system is operable for growing photosynthetic organisms. The bioreactor system includes a bioreactor and an illumination system. The illumination system includes one more optical waveguides configured to light at least some of a plurality of photosynthetic organisms retained in the bioreactor. In some embodiments, the one or more optical waveguides include a plurality of structures configured to direct light energy from a solar energy collector, and a plurality of artificial light sources, along the interior of the waveguide. In some embodiments, the one more optical waveguides include a plurality of light-diffusing structures configured to guide at least a portion of the light from the solar energy collector and a plurality of artificial light sources directed along the interior of the waveguide, to the exterior of the waveguide.
Owner:BIONAVITAS
Method and apparatus for producing synthesis gas from carbonaceous materials
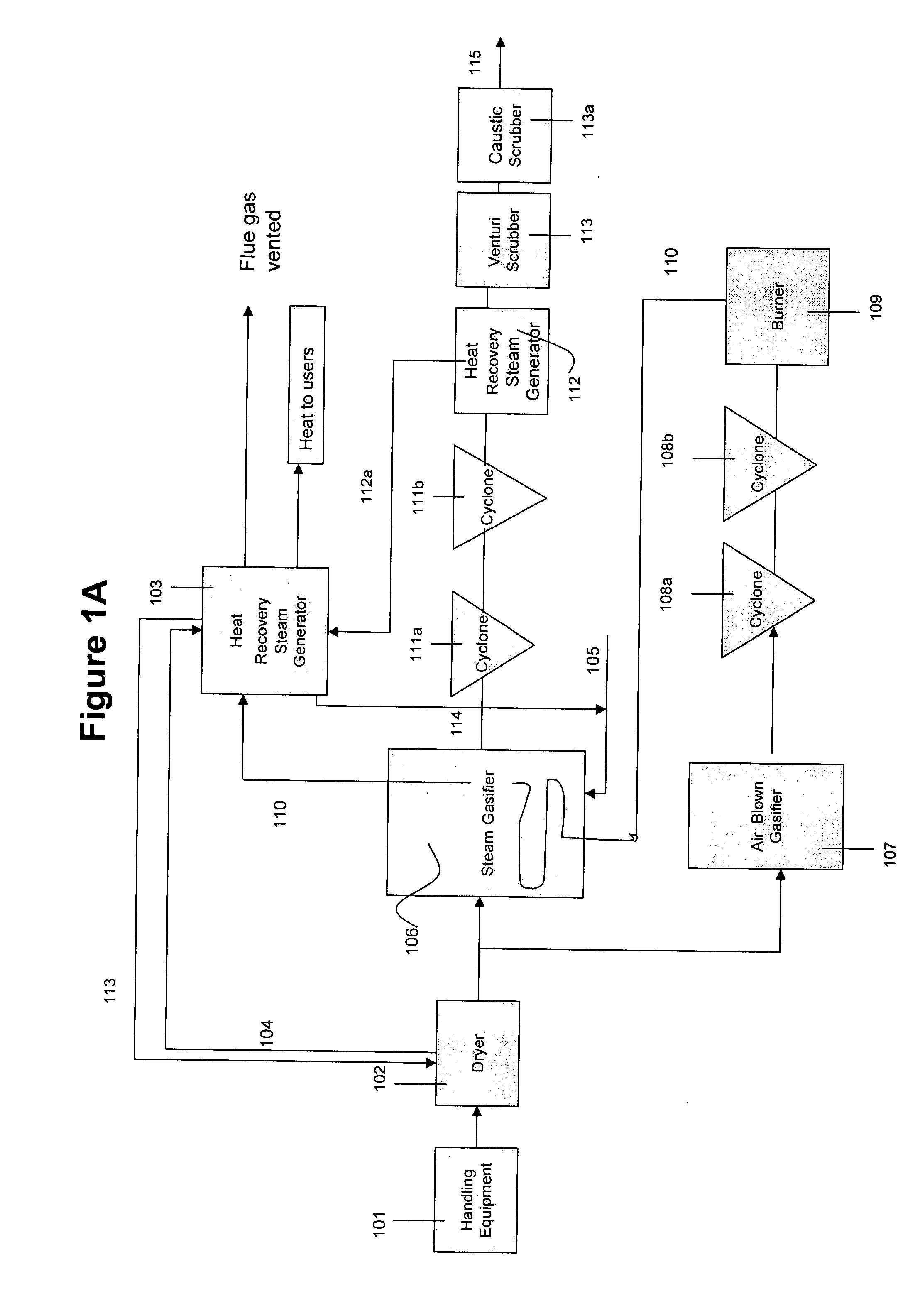
A method of producing syn gas from biomass or other carbonaceous material utilizes a controlled devolatilization reaction in which the temperature of the feed material is maintained at less than 450° F. until most available oxygen is consumed. This minimizes pyrolysis of the feed material. The method and apparatus utilizes the formed synthesis gas to provide the energy for the necessary gasification. This provides for a high purity syn gas and avoids production of slag.
Owner:JBK EXTRACTIONS
System and method for converting biomass to ethanol via syngas
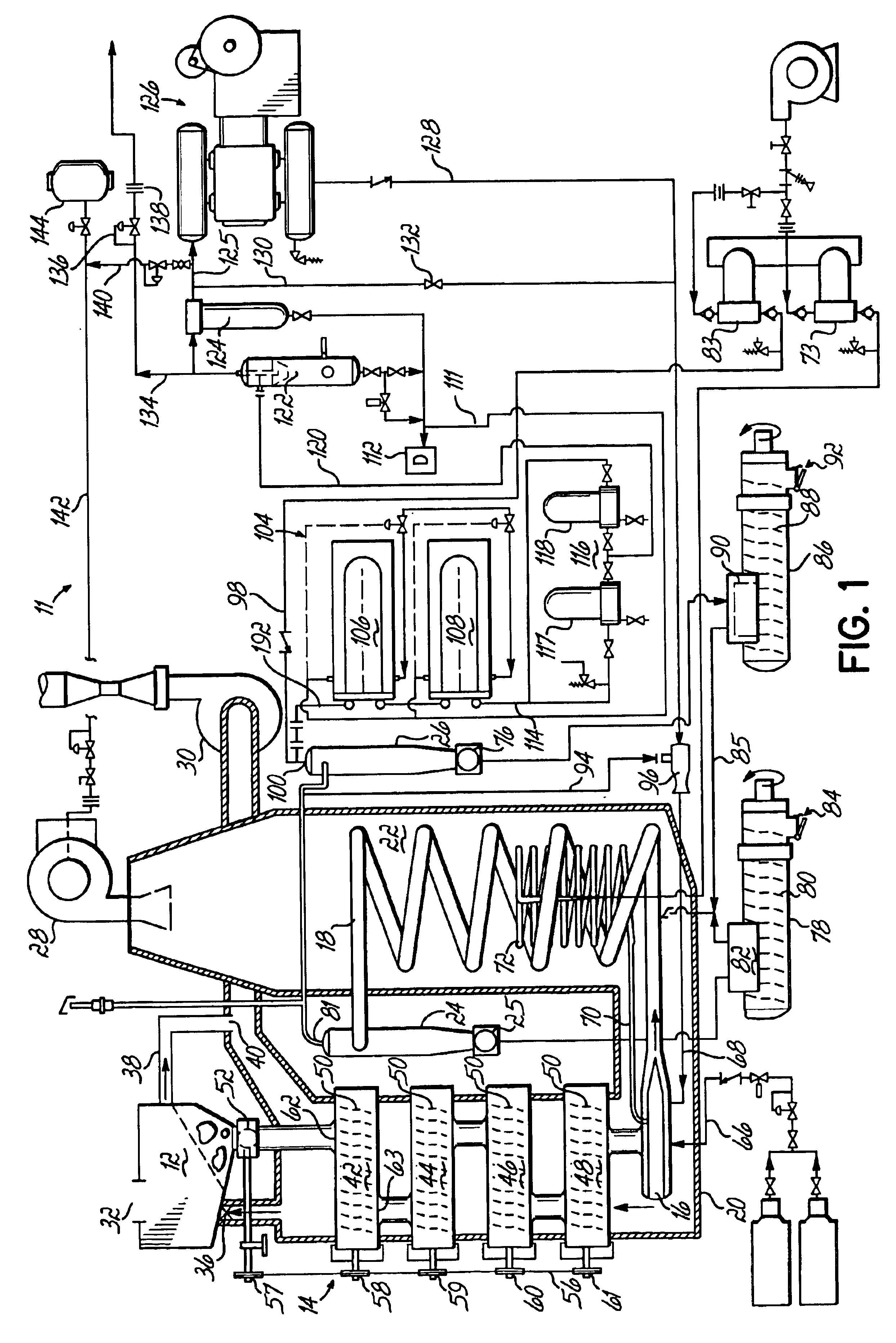
A method and apparatus for synthesizing ethanol using synthetic routes via synthesis gas are disclosed. A method and apparatus for gasifying biomass, such as biomass, in a steam gasifier that employs a fluidized bed and heating using hot flue gases from the combustion of synthesis gas is described. Methods and apparatus for converting synthesis gas into ethanol are also disclosed, using stepwise catalytic reactions to convert the carbon monoxide and hydrogen into ethanol using catalysts including iridium acetate.
Owner:WOODLAND BIOFUELS
Food Compositions of Microalgal Biomass
InactiveUS20100239712A1Cheaply and efficiently scaleReduce the amount requiredMilk preparationDough treatmentDry weightAdditive ingredient
The invention provides algal biomass, algal oil, food compositions comprising microalgal biomass, whole microalgal cells, and / or microalgal oil in combination with one or more other edible ingredients, and methods of making such compositions by combining algal biomass or algal oil with other edible ingredients. In preferred embodiments, the microalgal components are derived from microalgal cultures grown and propagated heterotrophically in which the algal cells comprise at least 10% algal oil by dry weight.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
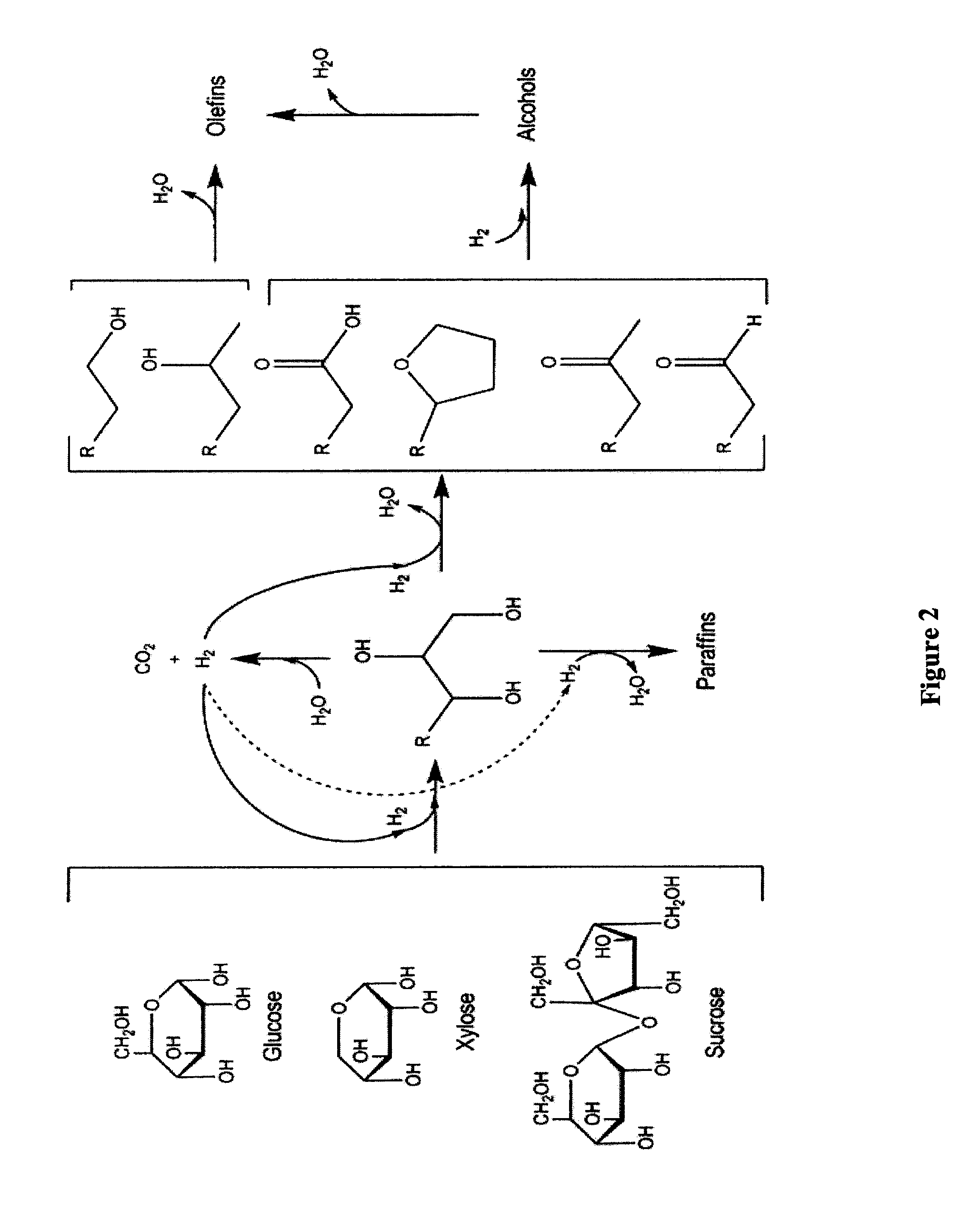
Synthesis of liquid fuels from biomass
ActiveUS20100076233A1Hydrocarbon by metathesis reactionLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionFuranAlkane
Processes and reactor systems are provided for the conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbons to paraffins useful as liquid fuels. The process involves the conversion of water soluble oxygenated hydrocarbons to oxygenates, such as alcohols, furans, ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, diols, triols, and / or other polyols, followed by the subsequent conversion of the oxygenates to paraffins by dehydration and alkylation. The oxygenated hydrocarbons may originate from any source, but are preferably derived from biomass.
Owner:VIRENT
Steam Generation Processes Utilizing Biomass Feedstocks
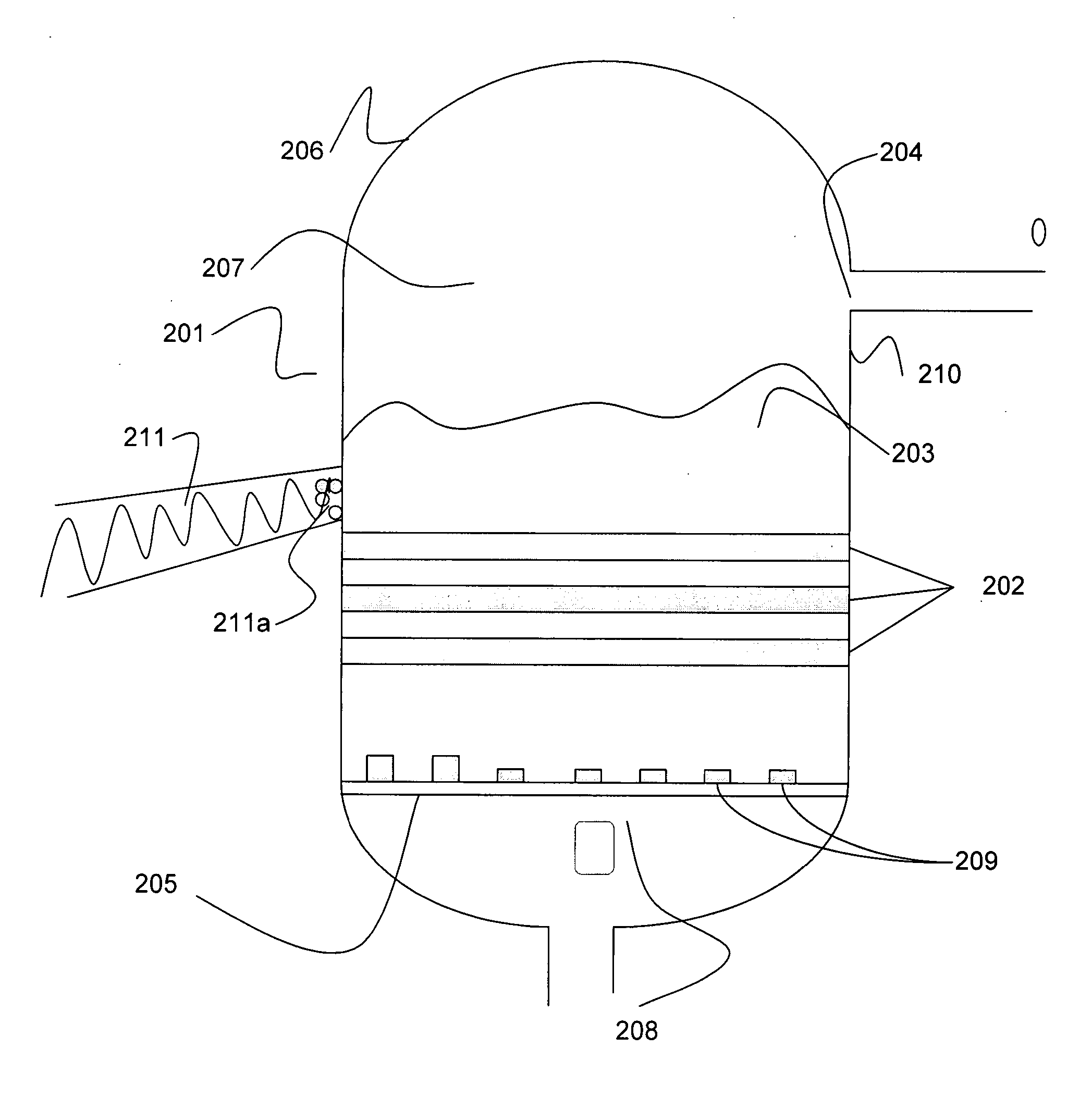
Integrated catalytic gasification processes are provided involving generating steam for converting carbonaceous materials to combustible gases, such as methane. Generally, steam generated from the combustion of a biomass is provided to a catalytic gasifier, wherein under appropriate temperature and pressure conditions, a carbonaceous feedstock is converted into a plurality of product gases, including, but not limited to, methane, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Process for producing ethanol
InactiveUS20060019360A1High carbon yieldHigh protein concentrationOrganic compound preparationChemical industryAcetic acidHydrogenation reaction
A process for producing ethanol including a combination of biochemical and synthetic conversions results in high yield ethanol production with concurrent production of high value coproducts. An acetic acid intermediate is produced from carbohydrates, such as corn, using enzymatic milling and fermentation steps, followed by conversion of the acetic acid into ethanol using esterification and hydrogenation reactions. Coproducts can include corn oil, and high protein animal feed containing the biomass produced in the fermentation.
Owner:ZEACHEM
Hydroprocessing Microalgal Oils
InactiveUS20100170144A1Improve efficiencyLow costHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon purification/separationChemical treatmentAlkaline hydrolysis
Fuels and other valuable compositions and compounds can be made from oil extracted from microbial biomass and from oil-bearing microbial biomass via hydroprocessing and / or other chemical treatments, including the alkaline hydrolysis of glycerolipids and fatty acid esters to fatty acid salts.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Synthesis of liqiud fuels and chemicals from oxygenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20080300434A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationHydrocarbon purification/separationFuranCarboxylic acid
Processes and reactor systems are provided for the conversion of oxygenated hydrocarbons to hydrocarbons, ketones and alcohols useful as liquid fuels, such as gasoline, jet fuel or diesel fuel, and industrial chemicals. The process involves the conversion of mono-oxygenated hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, furans, carboxylic acids, diols, triols, and / or other polyols, to C4+ hydrocarbons, alcohols and / or ketones, by condensation. The oxygenated hydrocarbons may originate from any source, but are preferably derived from biomass.
Owner:VIRENT
Method for preparing loading functional oxide porous carbon
InactiveCN101780952AThe shape is fine and differentFine and varied structureOther chemical processesBy adsorptionPorous carbonMaterials science
The invention relates to a method for preparing a loading functional oxide porous carbon, which belongs to the technical field of carbon material. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting biomass material, and carbonizing at the temperature of 400-1000 DEG C in vacuum or on inert condition; preparing porous carbon by a physical activating or chemical activating process according to the requirement on the pore structure by the carbonized porous carbon; immersing the porous carbon into a precursor solution of an element M, cleaning many times with distilled water, and drying; roasting on the porous carbon at the temperature of 300-1000 DEG C in vacuum or on inert atmosphere, and then the active carbon of the loading functional oxide MxOy is prepared. The active carbon of the loading functional oxide MxOy prepared by the invention has the special pore structure of the biomass, also has the functions performed by the oxides, and has important application value in water treatment, hydrogen storage, photocatalysis, fuel cells and relevant fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
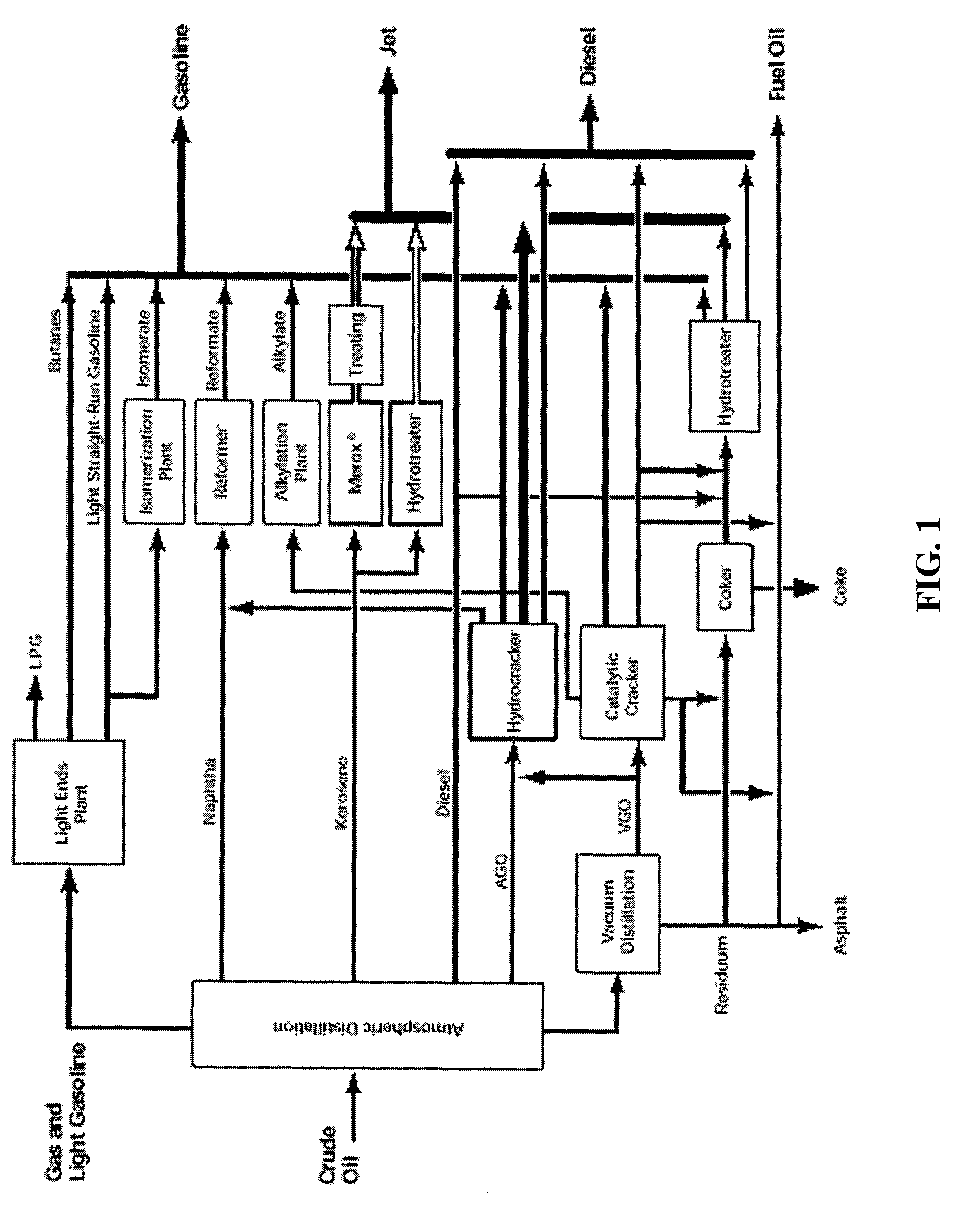
Production of Blended Fuel from Renewable Feedstocks
A process for producing a blended fuel from a paraffin rich component and a cyclic rich component, where each of the components are generated from a renewable feedstock, is presented. The paraffin rich component is generated from a first renewable feedstock comprising at least one component selected from the group consisting of glycerides, free fatty acids, biomass, lignocellulose, free sugars, and combinations thereof. The cyclic rich component is generated from a second renewable feedstock comprising at least one component selected from the group consisting of glycerides, free fatty acids, free fatty alkyl esters, biomass, lignocellulose, free sugars, and combinations thereof. The blended fuel may a gasoline boiling point range blended fuel, a diesel boiling point range blended fuel, an aviation boiling point range blended fuel, any combination thereof, or any mixture thereof.
Owner:UOP LLC
Slurry dewatering and conversion of biosolids to a renewable fuel
ActiveUS20060096163A1Readily removed mechanicallyLow oxygenBio-organic fraction processingBiofuelsEmission standardSlurry
In the processes for treating municipal sewage and storm water containing biosolids to discharge standards, biosolids, even after dewatering, contain typically about 80% water bound in the dead cells of the biosolids, which gives biosolids a negative heating value. It can be incinerated only at the expense of purchased fuel. Biosolids are heated to a temperature at which their cell structure is destroyed and, preferably, at which carbon dioxide is split off to lower the oxygen content of the biosolids. The resulting char is not hydrophilic, and it can be efficiently dewatered and / or dried and is a viable renewable fuel. This renewable fuel can be supplemented by also charging conventional biomass (yard and crop waste, etc.) in the same or in parallel facilities. Similarly, non-renewable hydrophilic fuels can be so processed in conjunction with the processing of biosolids to further augment the energy supply.
Owner:SGC ADVISORS
Process and system for converting carbonaceous feedstocks into energy without greenhouse gas emissions
ActiveUS20070099038A1High hydrogen contentFuel cells groupingHydrogen separation using solid contactPetroleum cokePetroleum
The process of the invention converts carbonaceous feedstock such as coal, hydrocarbon oil, natural gas, petroleum coke, oil shale, carbonaceous-containing waste oil, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing military waste, carbonaceous-containing industrial waste, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing sewage sludge and municipal solid waste, carbonaceous-containing agricultural waste, carbonaceous-containing biomass, biological and biochemical waste, and mixtures thereof into electrical energy without the production of unwanted greenhouse emissions. The process uses a steam / CO2 reformer operating in the exit range of at least 700° to about 1600° C. (1300-2900°0 F.) to convert the carbonaceous feedstock and a greenhouse gas stream into a synthesis gas comprising mostly carbon monoxide and hydrogen that contains poisons and the compounds that poison fuel cells. The syngas is sent to an interface zone to remove these poisons and other fouling compounds that are electrochemically oxidized in an electricity-producing fuel cell into an exit gas comprising carbon dioxide and water.
Owner:RAVEN SR INC
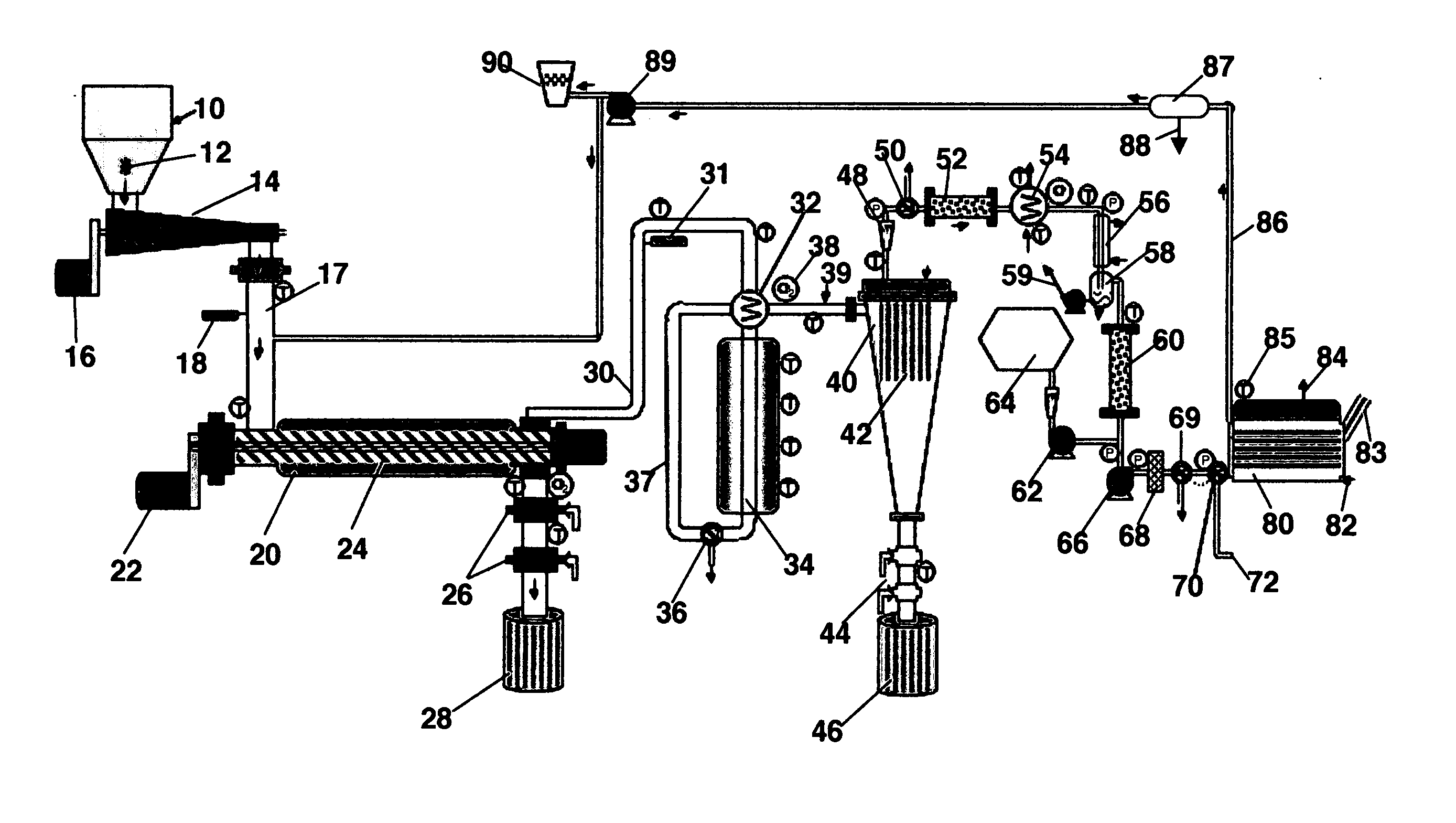
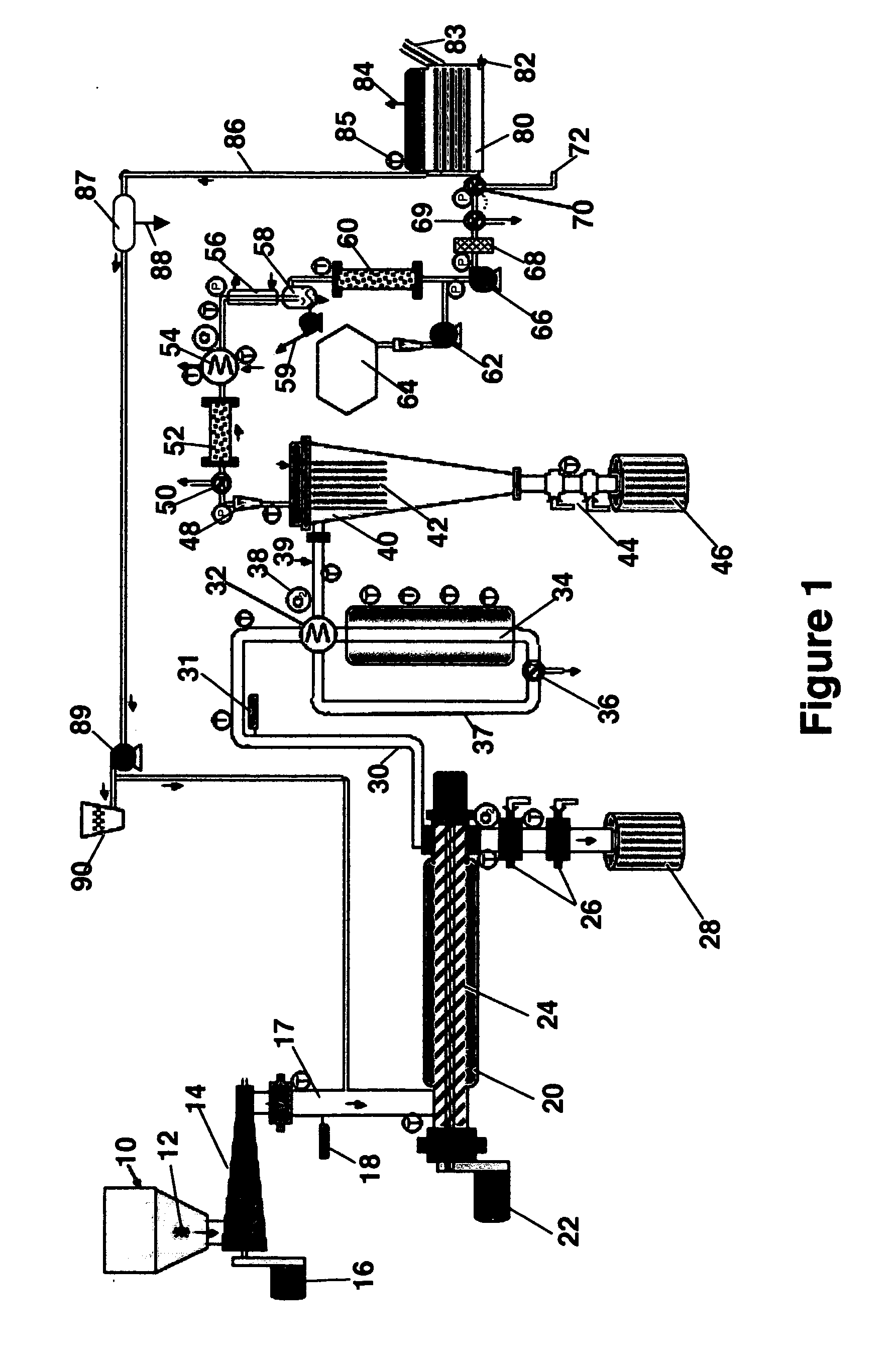
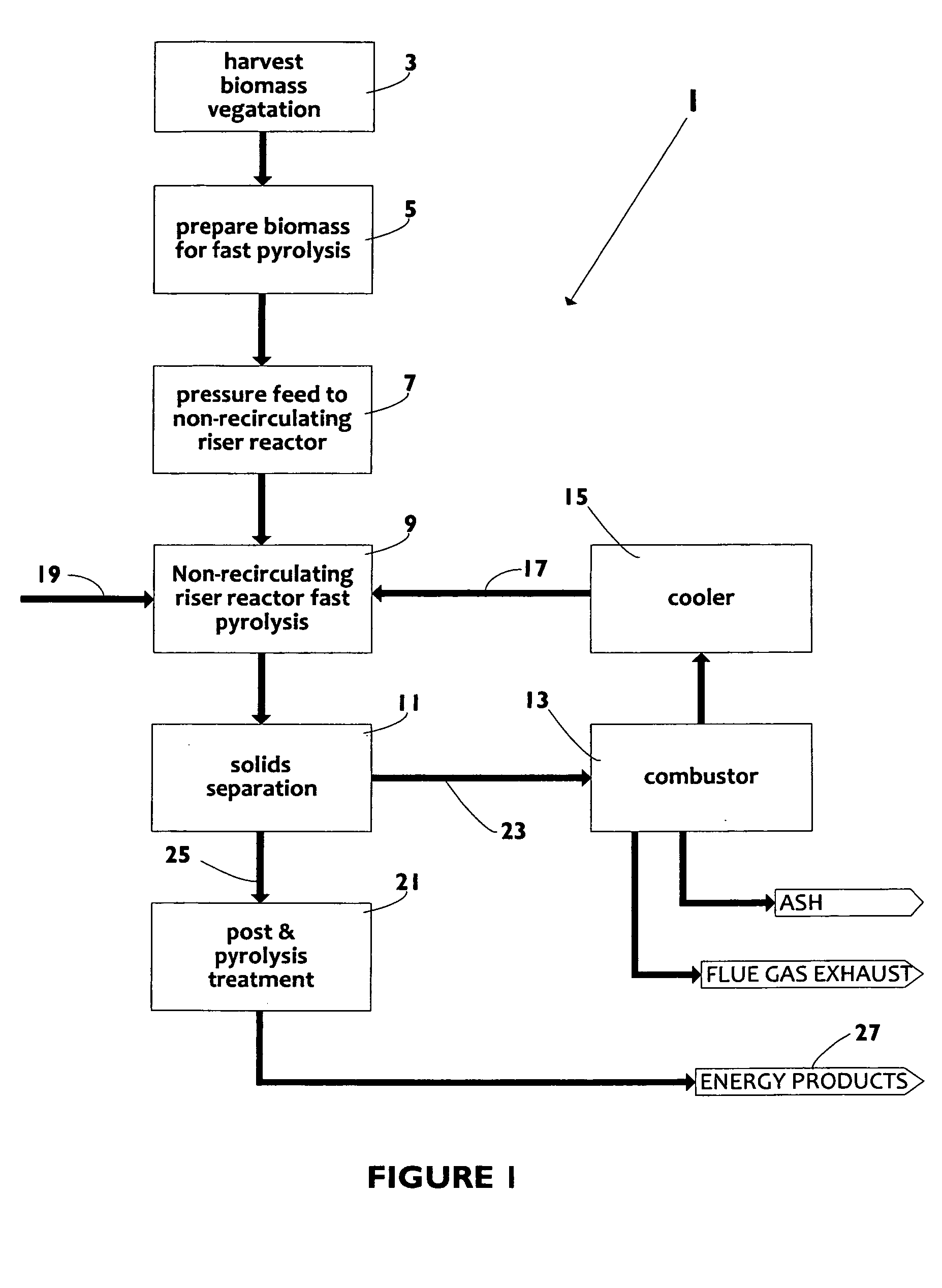
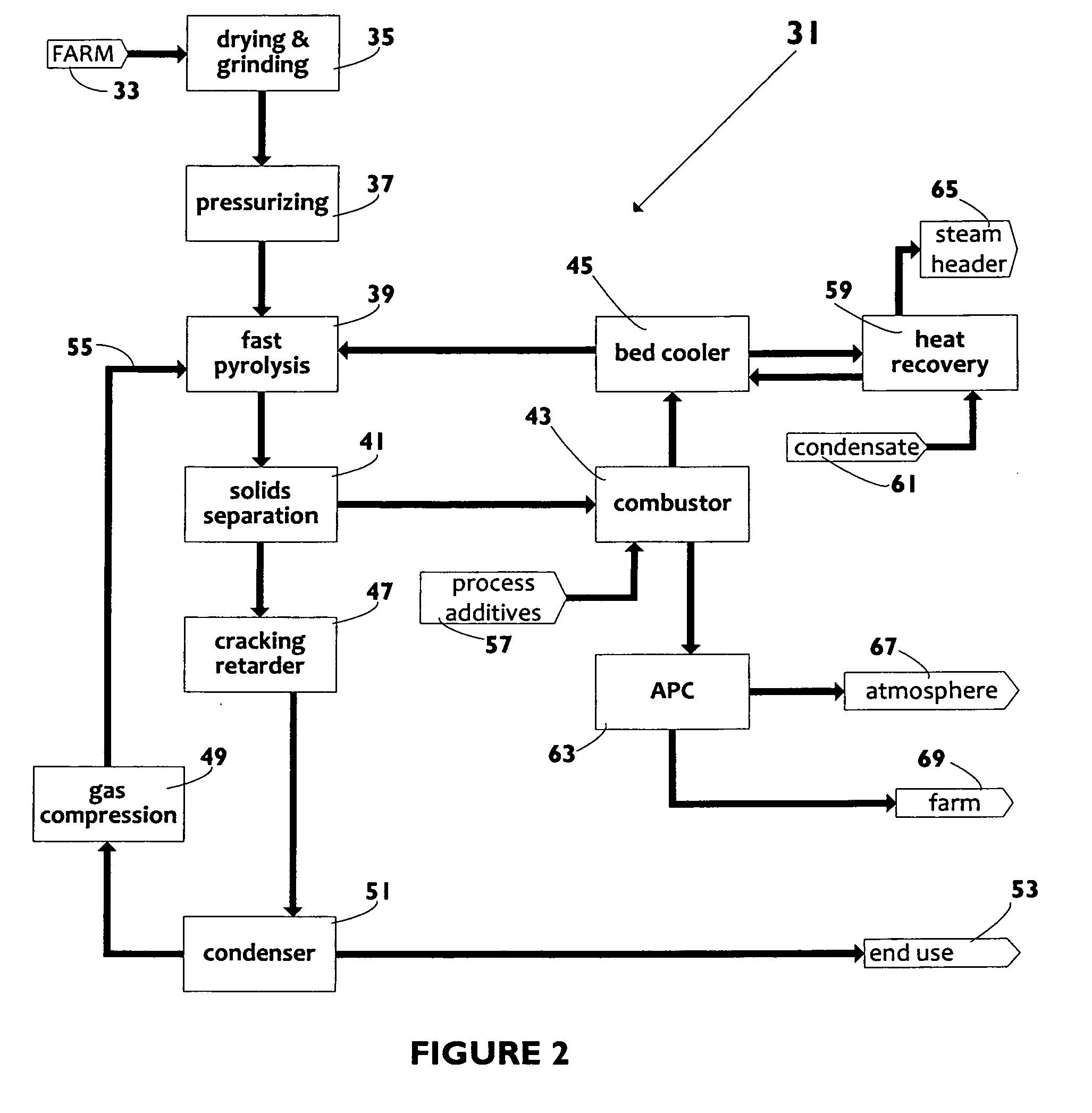
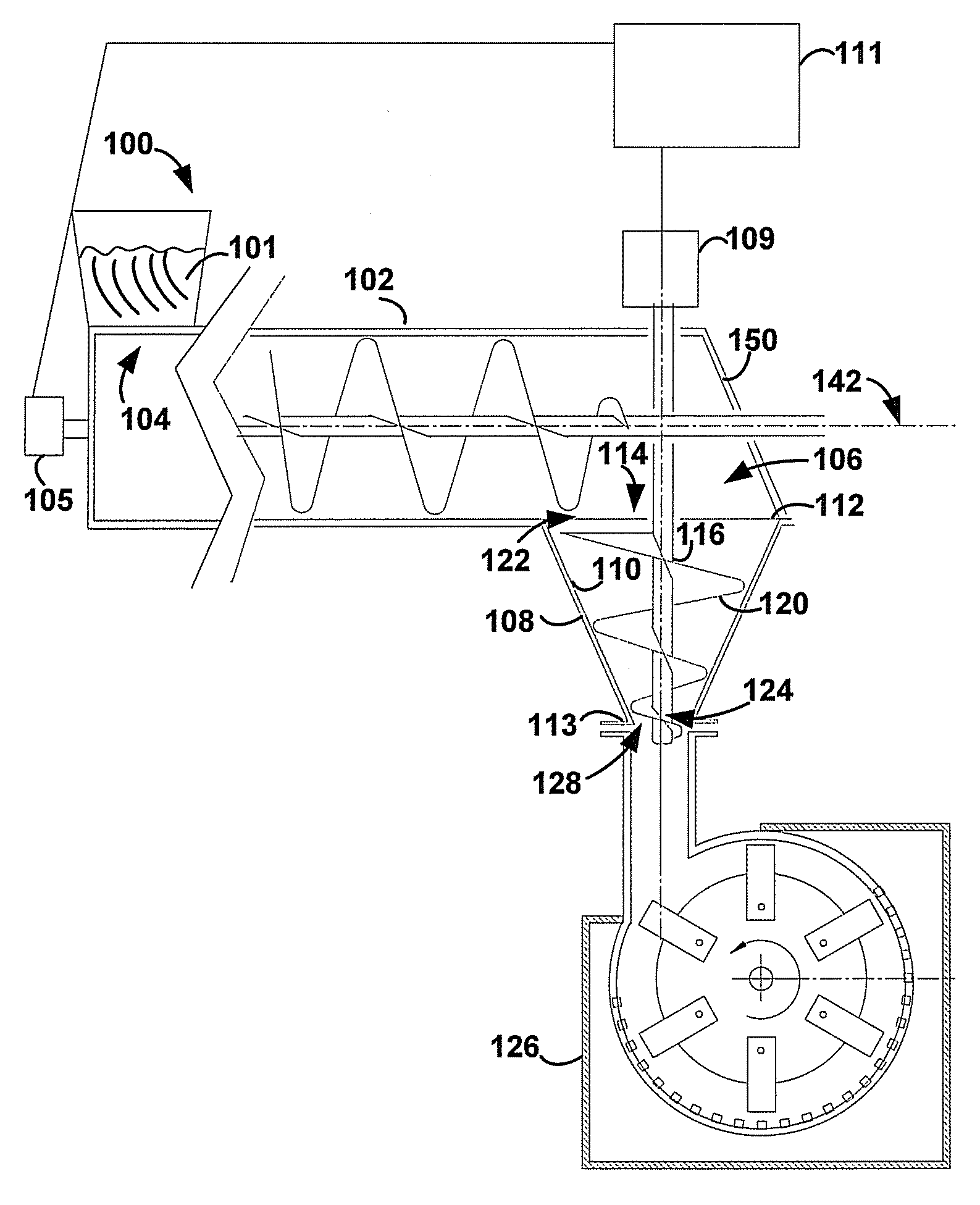
Biomass fast pyrolysis system utilizing non-circulating riser reactor
A biomass fast pyrolysis system for conversion of biomass vegetation to synthetic gas and liquid fuels includes: a) a non-circulating riser reactor for pyrolysis of biomass vegetation feedstock utilizing a heat carrier, the non-circulating riser reactor being physically structured and adapted to have a rate of reaction of at least 8,000 biomass vegetation feedstock lbs / hr / ft2, utilizing a ratio of heat carrier to biomass vegetation feedstock of about 7:1 to about 11.5:1, the riser reactor having a base input region at its bottom, a central reaction region and an output region at its top, the riser reactor including a cyclone disengager at its output region for separation of pyrolysis resulting char and heat carrier from the pyrolysis product gases, the cyclone disengager having an output downcomer and an output upcomer, the cyclone disengager output downcomer being connected to and feeding into a side combustor unit, the riser reactor being a non-circulating riser reactor in that the heat carrier is not returned directly to the riser reactor from the cyclone disengager and travels first down the cyclone disengager output downcomer to the side combustor unit; and, b) the side combustor unit for combusting pyrolysis resultant char and reheating the heat carrier the side combustor having a heat carrier downcomer connected to the base input region of the riser reactor.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENERGY GLOBAL
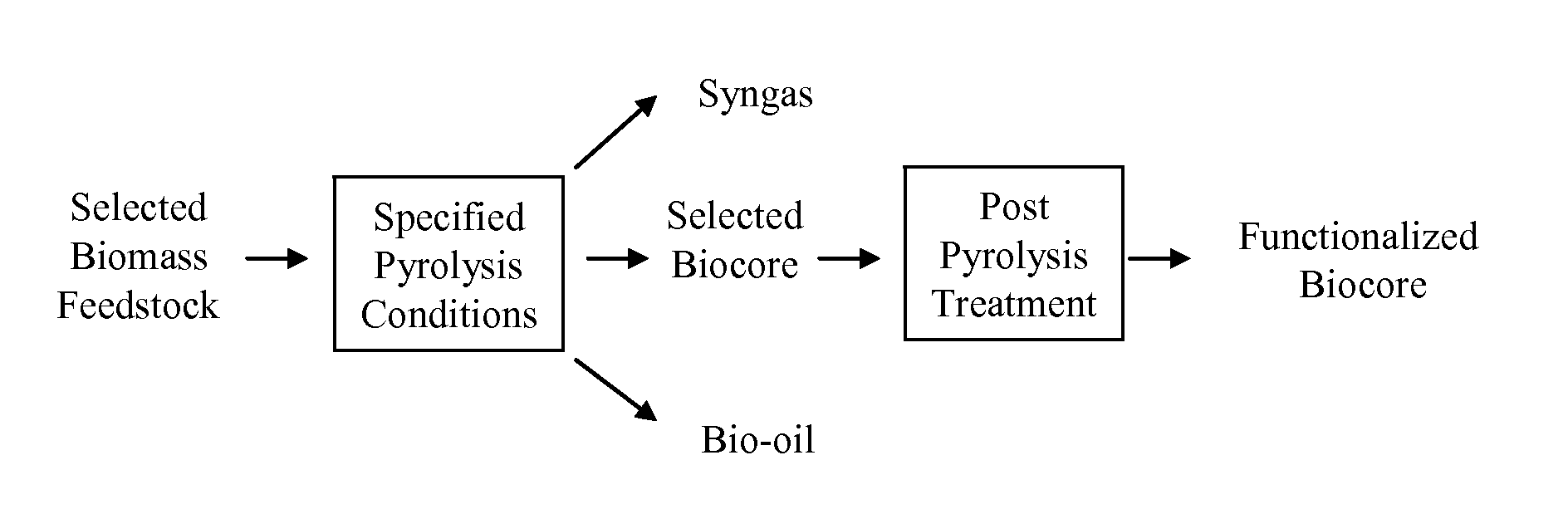
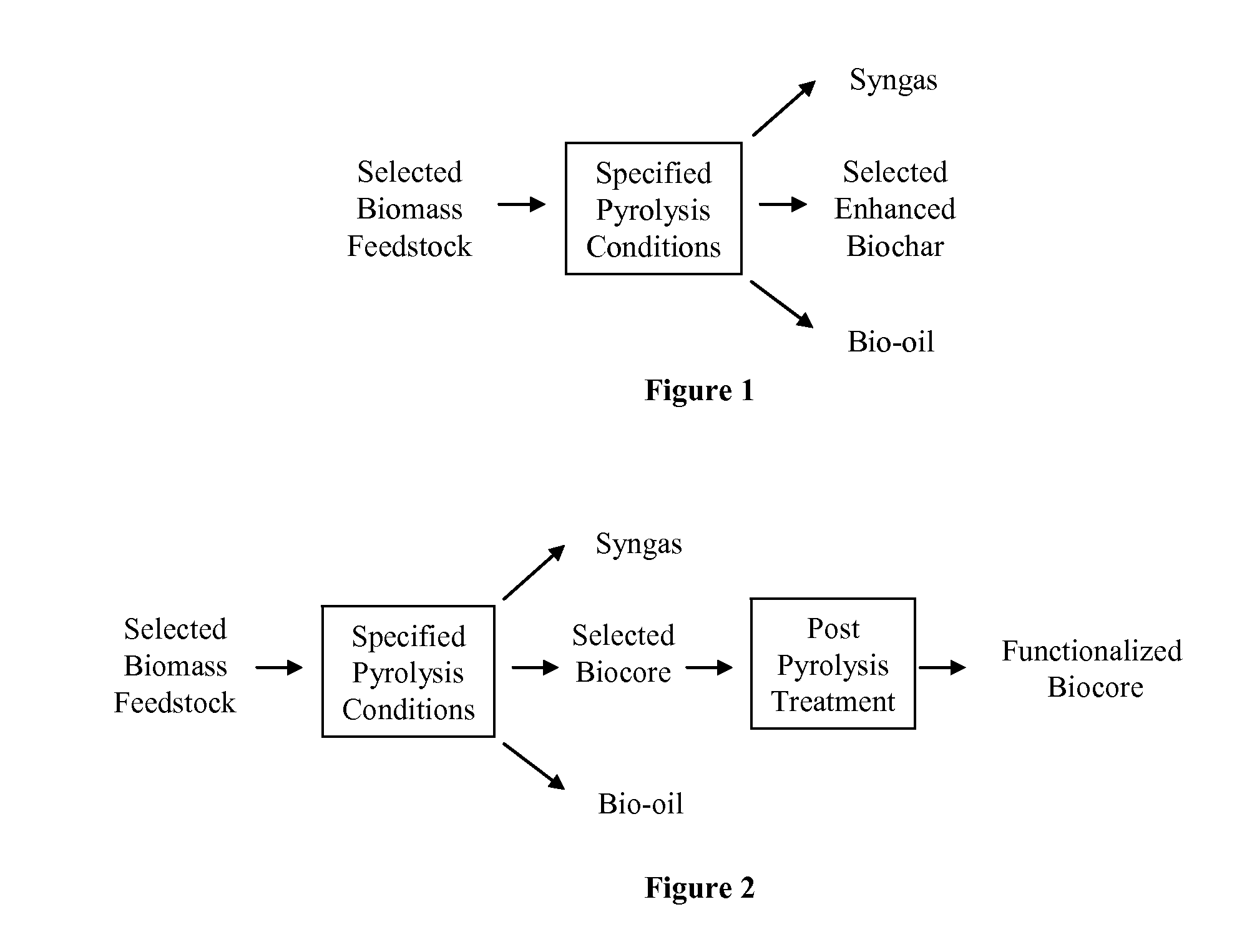
Biochar
ActiveUS8361186B1Enhanced and functionalizedCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersForming gasBiological activation
The invention provides for methods, devices, and systems for pyrolyzing biomass. A pyrolysis unit can be used for the pyrolysis of biomass to form gas, liquid, and solid products. The biomass materials can be selected such that an enhanced biochar is formed after pyrolysis. The biomass can be pyrolyzed under specified conditions such that a selected biochar core is formed. The pyrolysis process can form a stable biochar core that is inert and / or resistant to degradation. The biochar or biochar core can be functionalized to form a functionalized biochar or functionalized biochar core. Functionalization can include post-pyrolysis treatments such as supplementation with microbes or physical transformations including annealing and / or activation.
Owner:FULL CIRCLE BIOCHAR
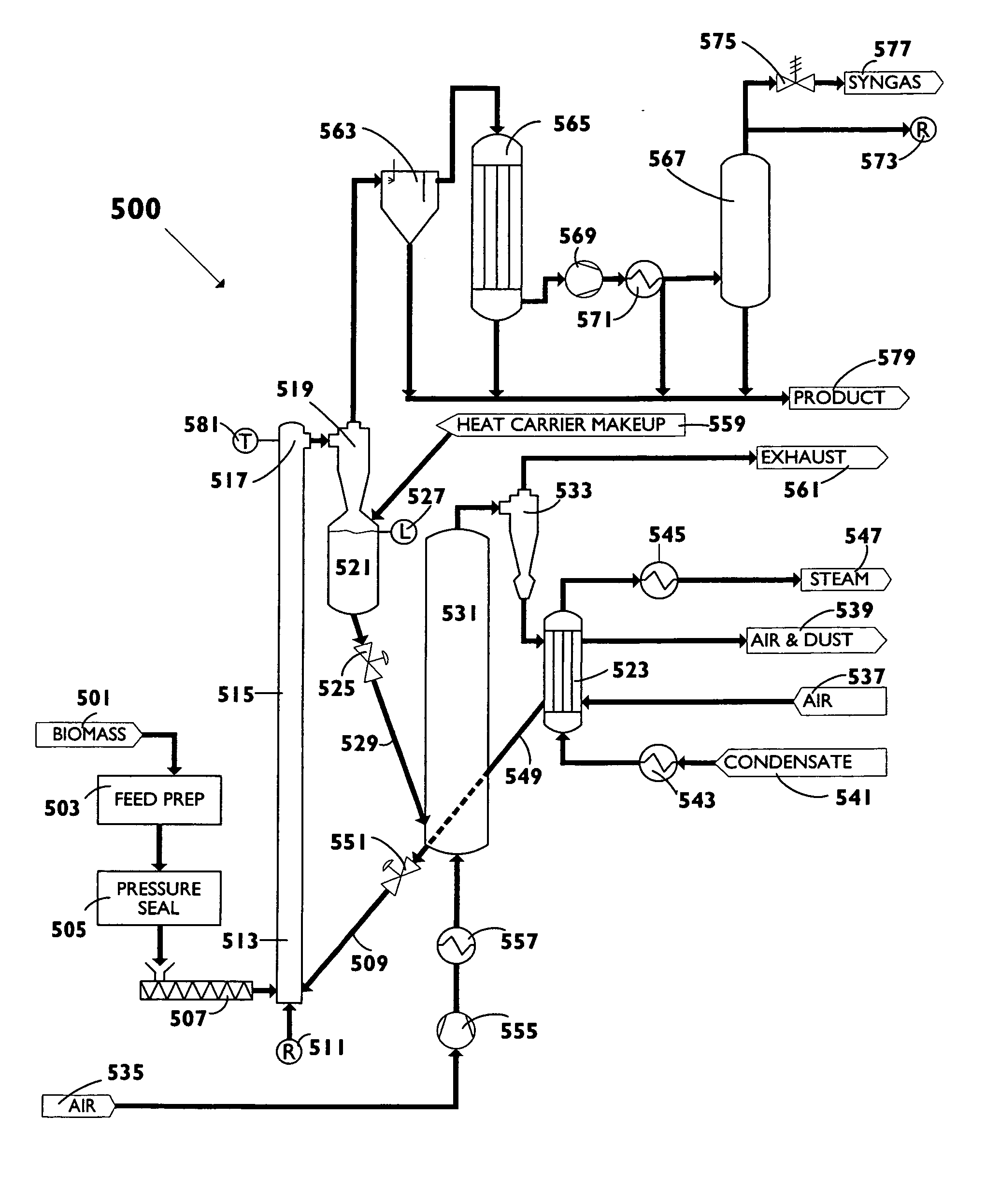
Co-Feed of Biomass as Source of Makeup Catalysts for Catalytic Coal Gasification
Continuous processes are provided for converting a carbonaceous feedstock comprising biomass containing alkali metal, non-biomass components, and at least one gasification catalyst including an alkali metal recovered from solid char, into a plurality of gaseous products including methane and at least one or more of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other higher hydrocarbons.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
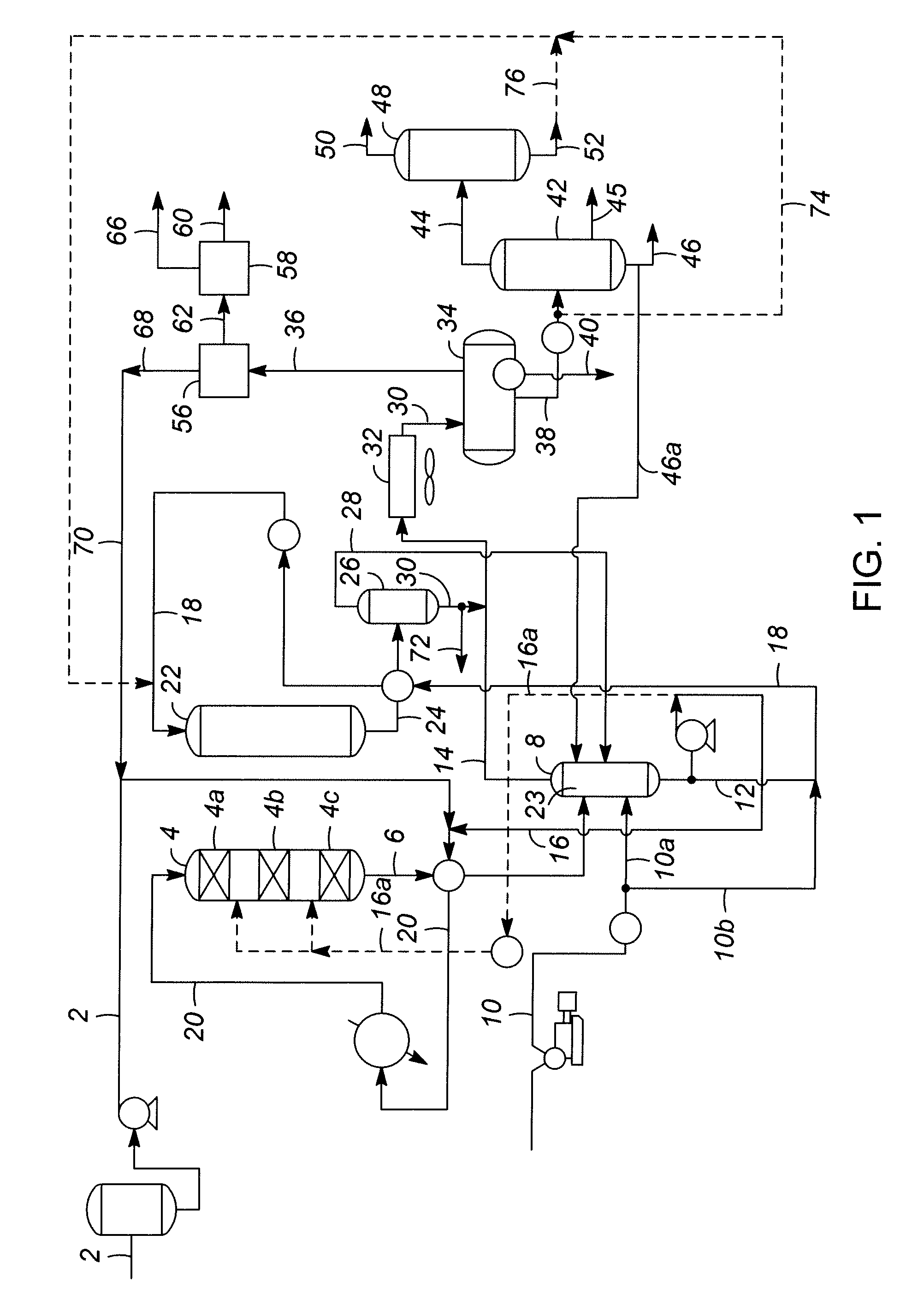
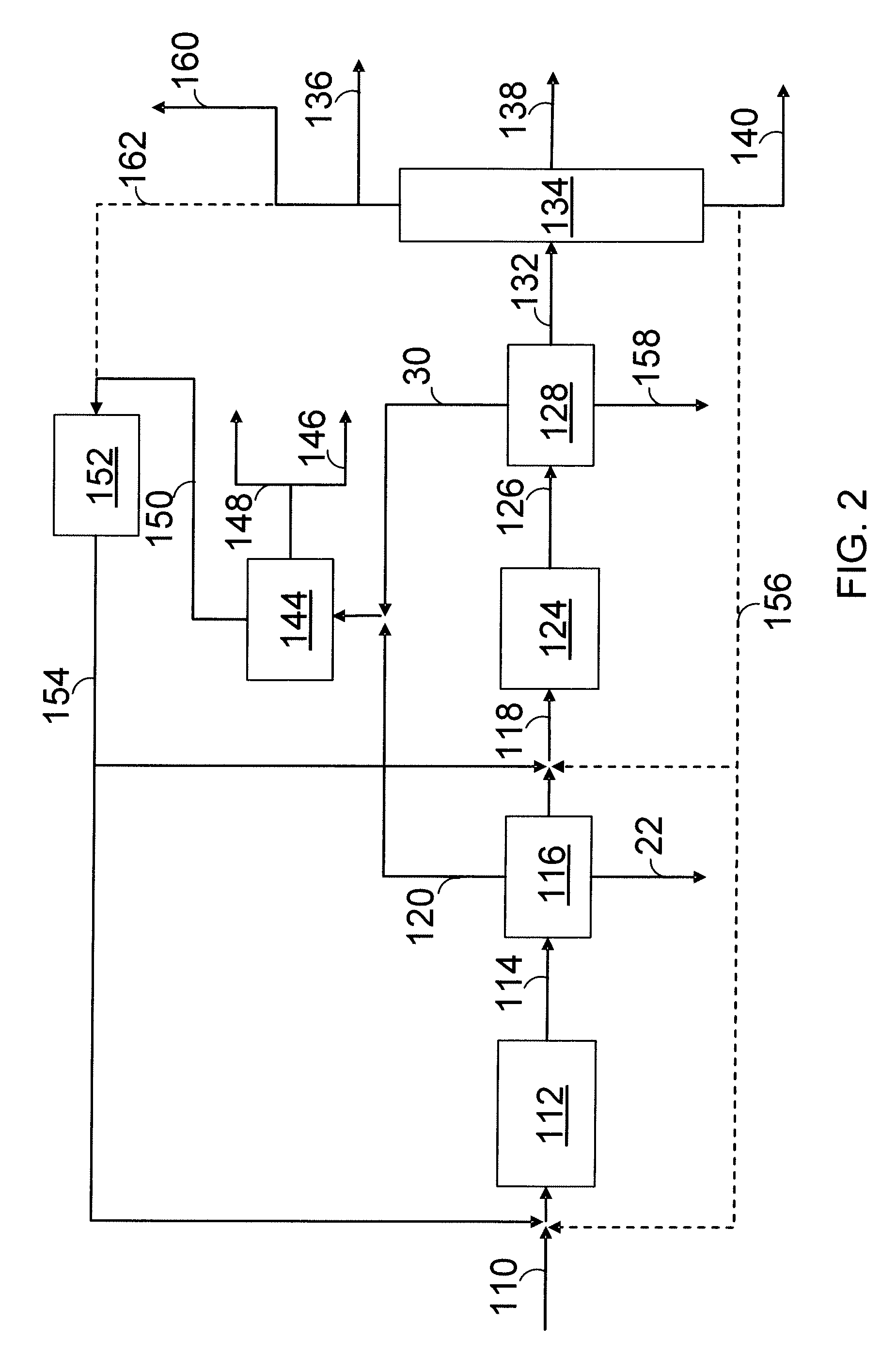
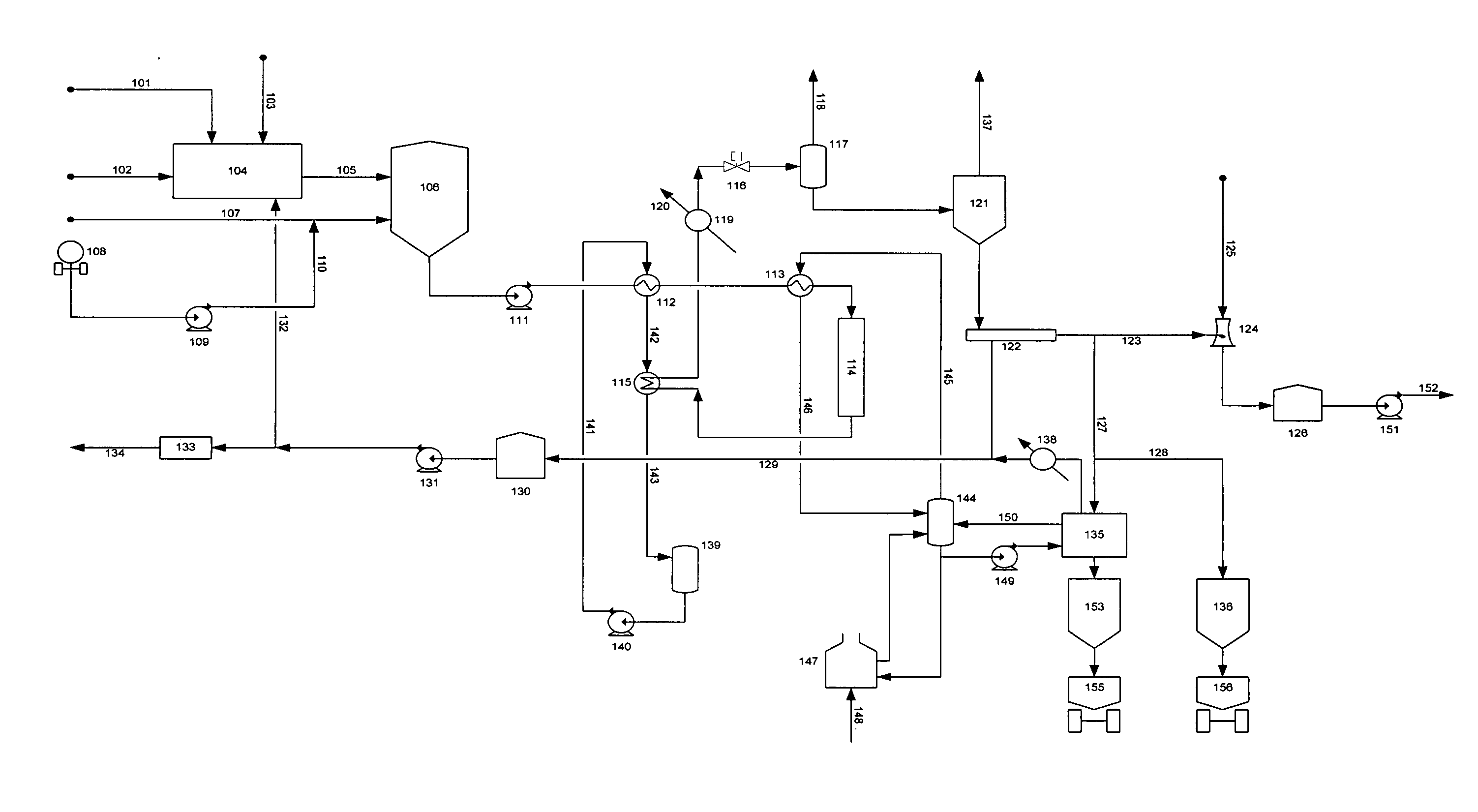
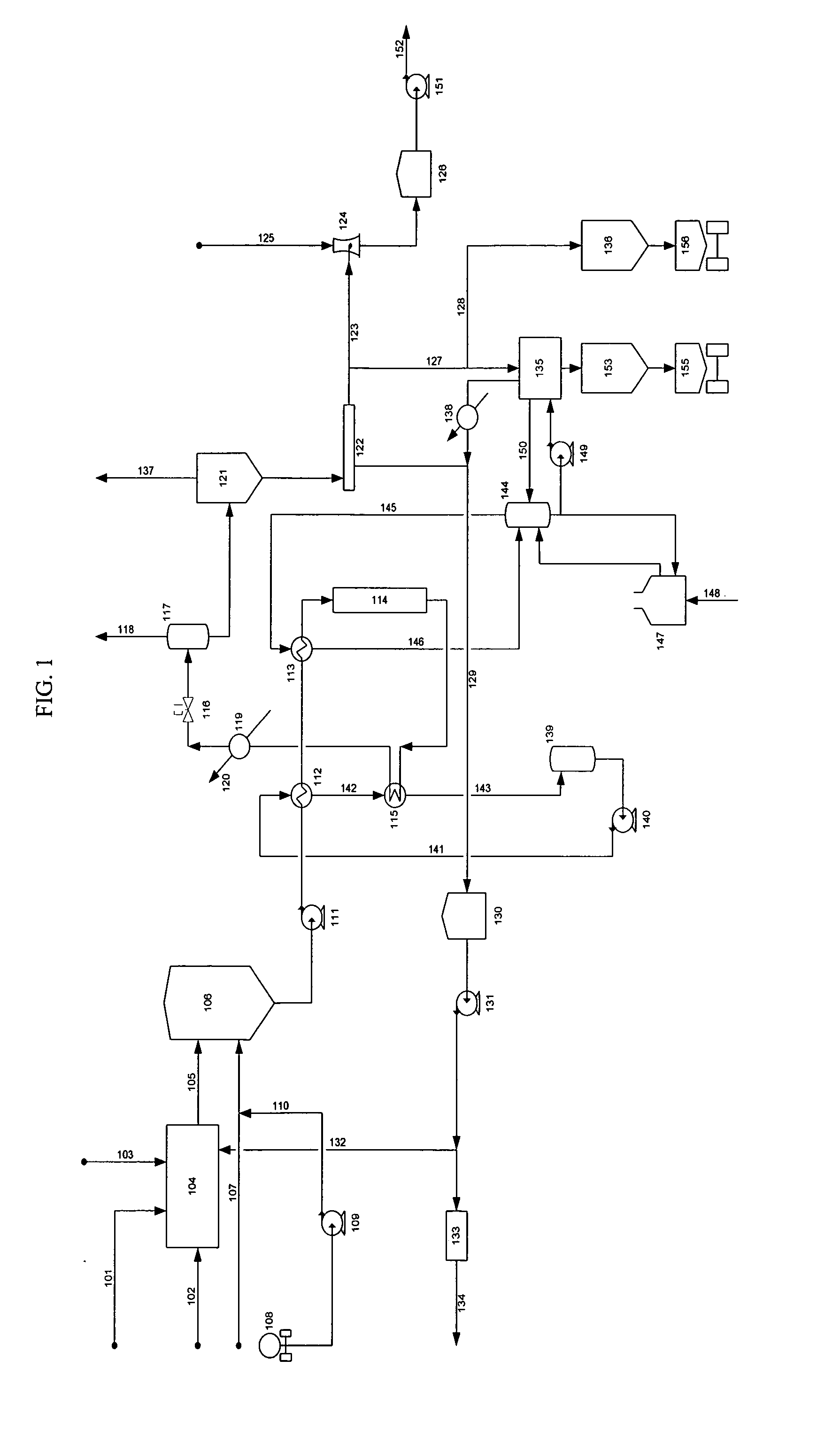
Process for conversion of biomass to fuel
ActiveUS7816570B2Meet growth needsEasy to processFatty acid esterificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAlkaneChain length
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Process for preparing materials for extraction
InactiveUS7678931B2Improve extraction efficiencyQuality improvementFungiUnicellular algaeArachidonic acid supplementationFermentation
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a biomass, such as from a microbial fermentation, for an extraction process to separate desired chemicals, nutritional products, bioactive components, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, from the biomass. Particularly preferred substances to extract include docosahexaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid, and arachidonic acid. The present invention also includes extracting the prepared biomass. Biomasses to be treated in accordance with the methods of the invention include plant, animal, and microbial biomass, particularly a microorganism such as Crypthecodinium cohnii and a fungus such as Mortierella alpina.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Compactor Feeder
A compactor feeder and methods for feeding relatively low-density biomass materials into a grinding device (such as a hammer mill) is described. The compactor feeder increases the density of the relatively low-density biomass materials in order to fill the grinding device with the biomass materials at a rate that is sufficient to substantially equal the design capacity of the grinding device.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Extracts from plant and non-plant biomass and uses thereof
Novel oil extracts from Angiosperm and Gymnosperm plants and other-plant biomass from human, veterinary, birds, aquatic species, microbial and mycological sources useful in human, veterinary and agricultural, mycological and microbiological applications are described. Methods of preparation of these extracts in oil and methods of application and administration are also described.
Owner:KANE SHANTARAM GOVIND
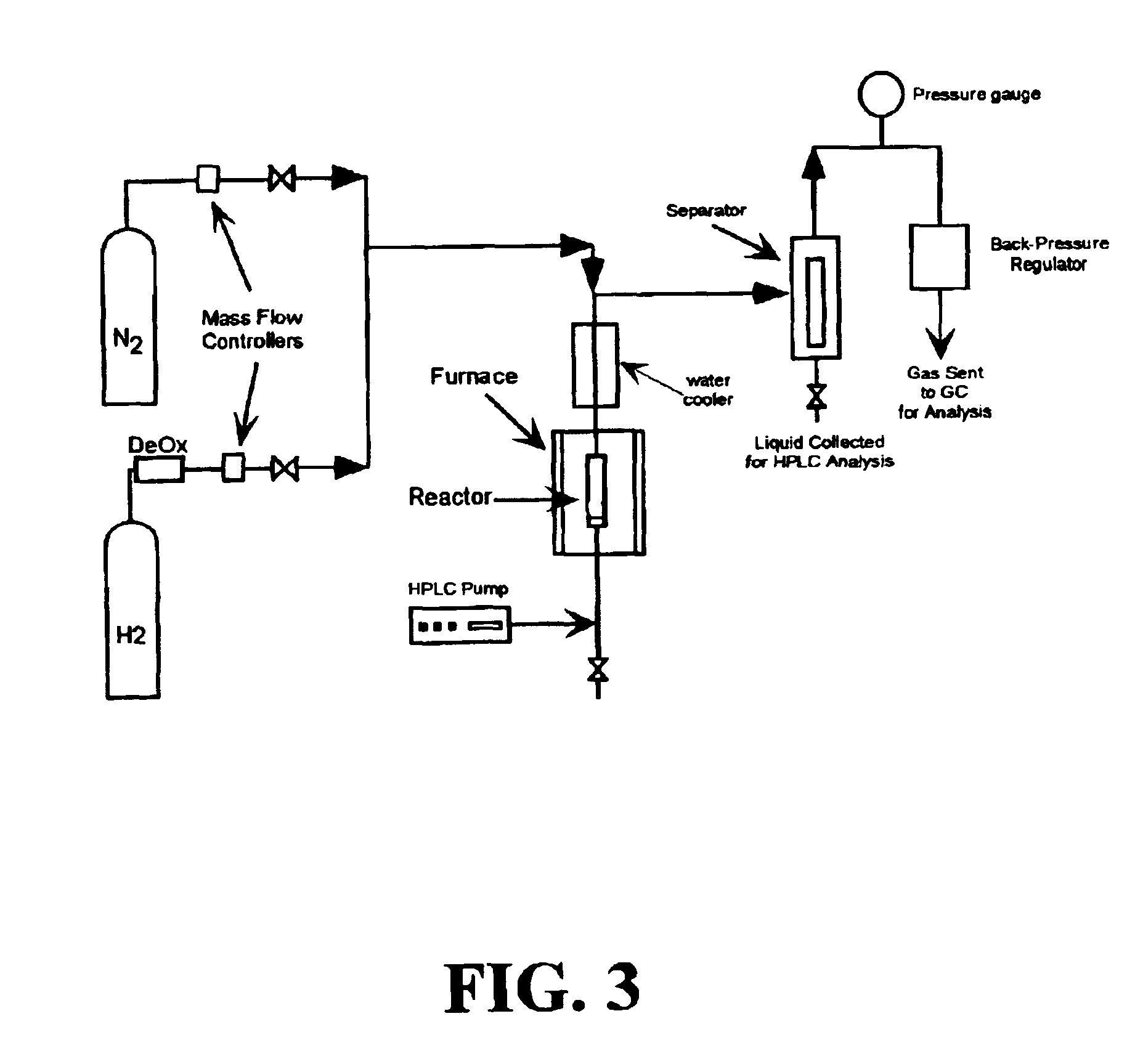
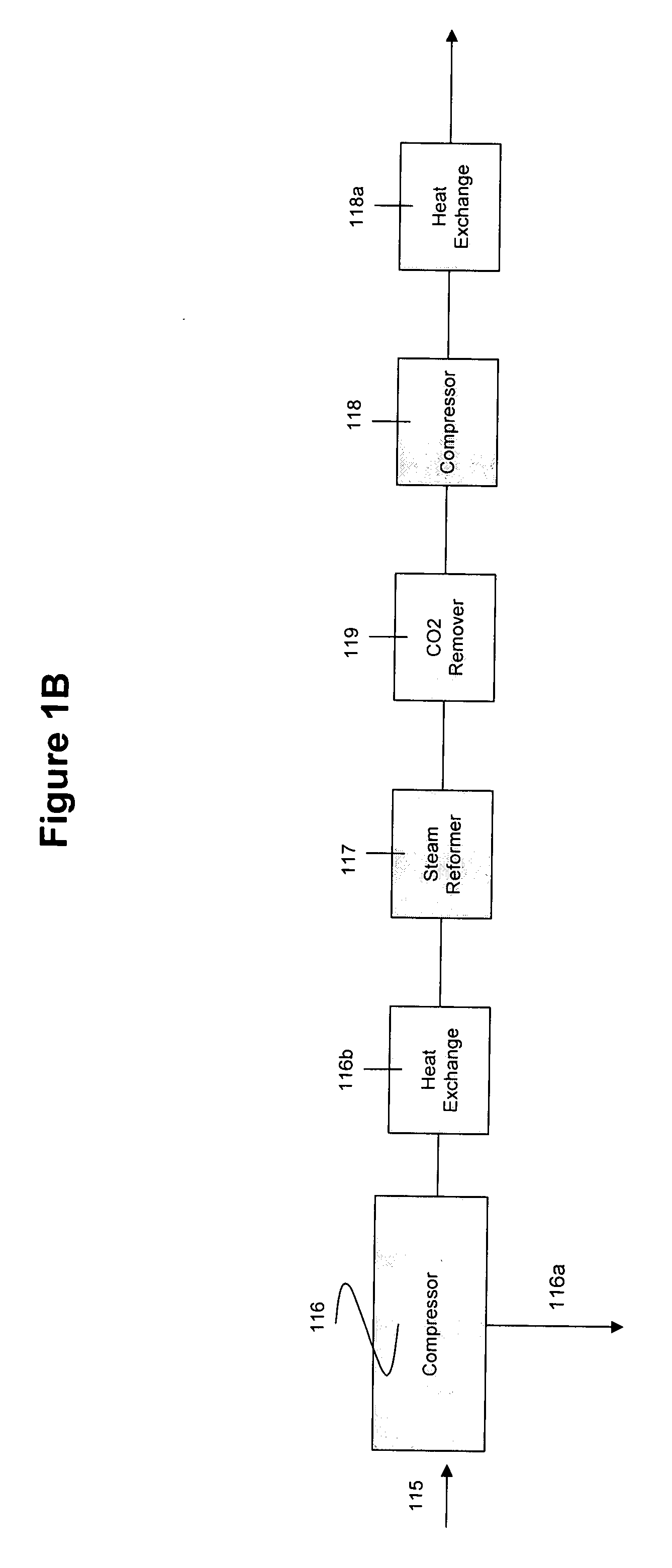
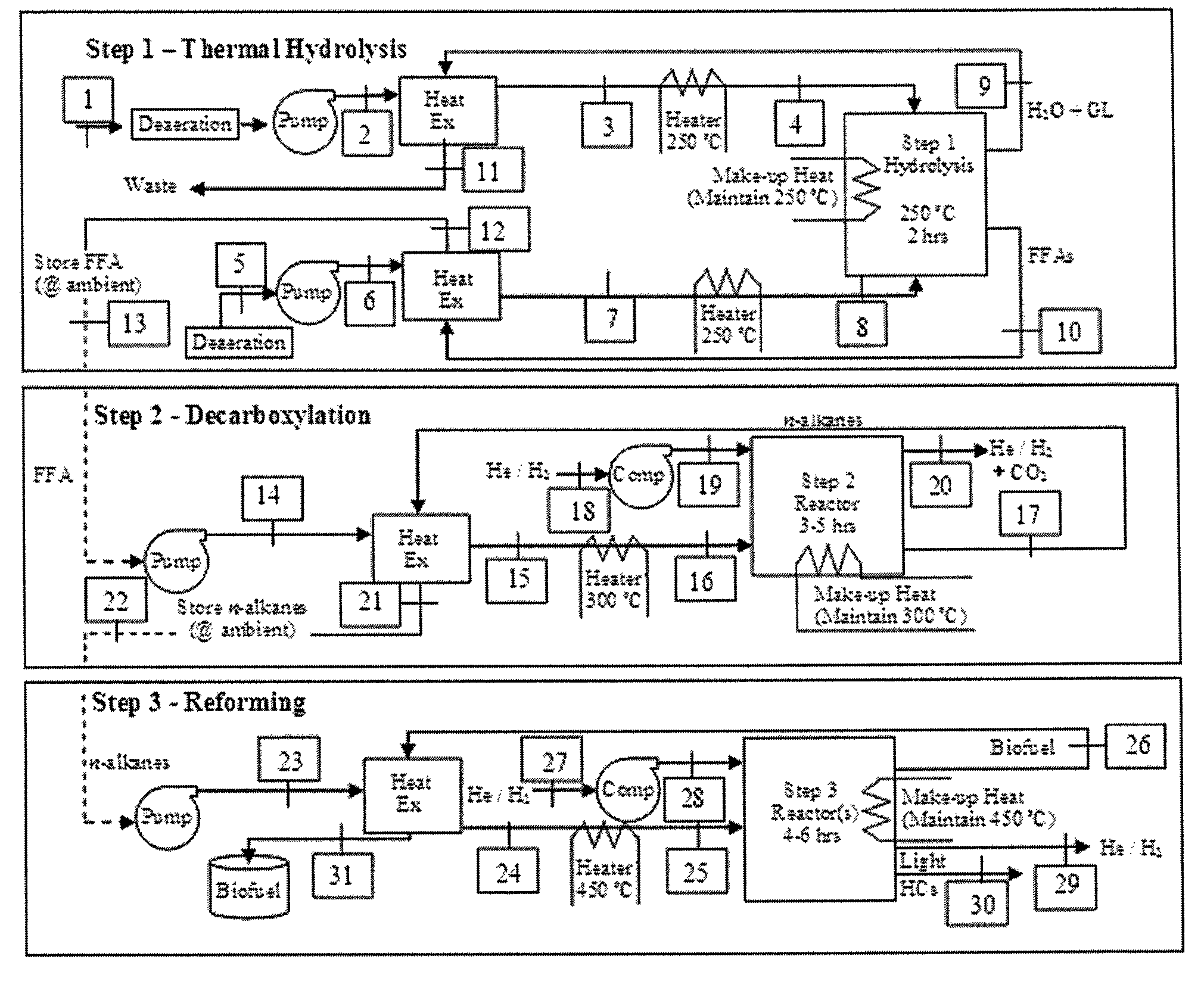
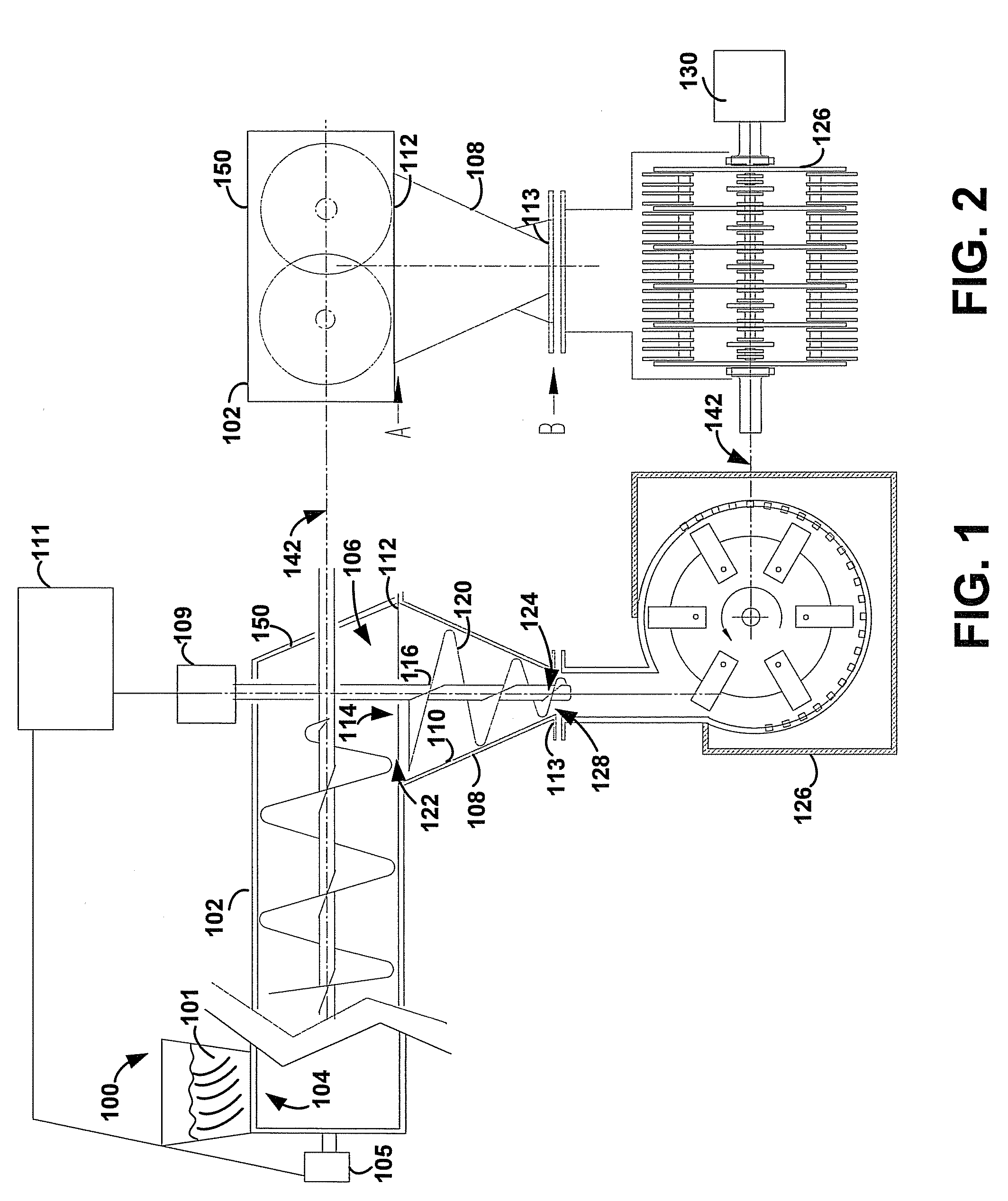
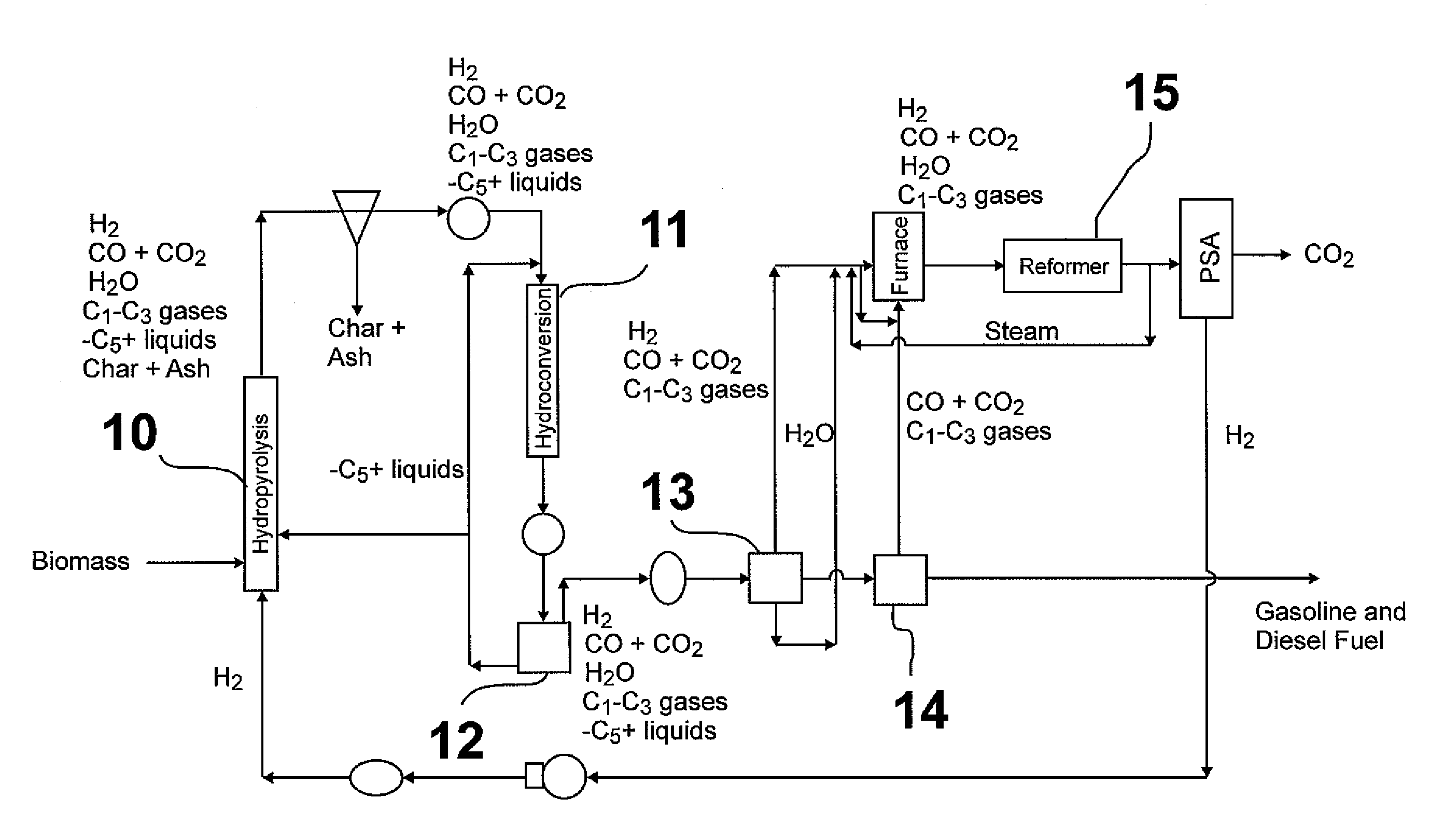
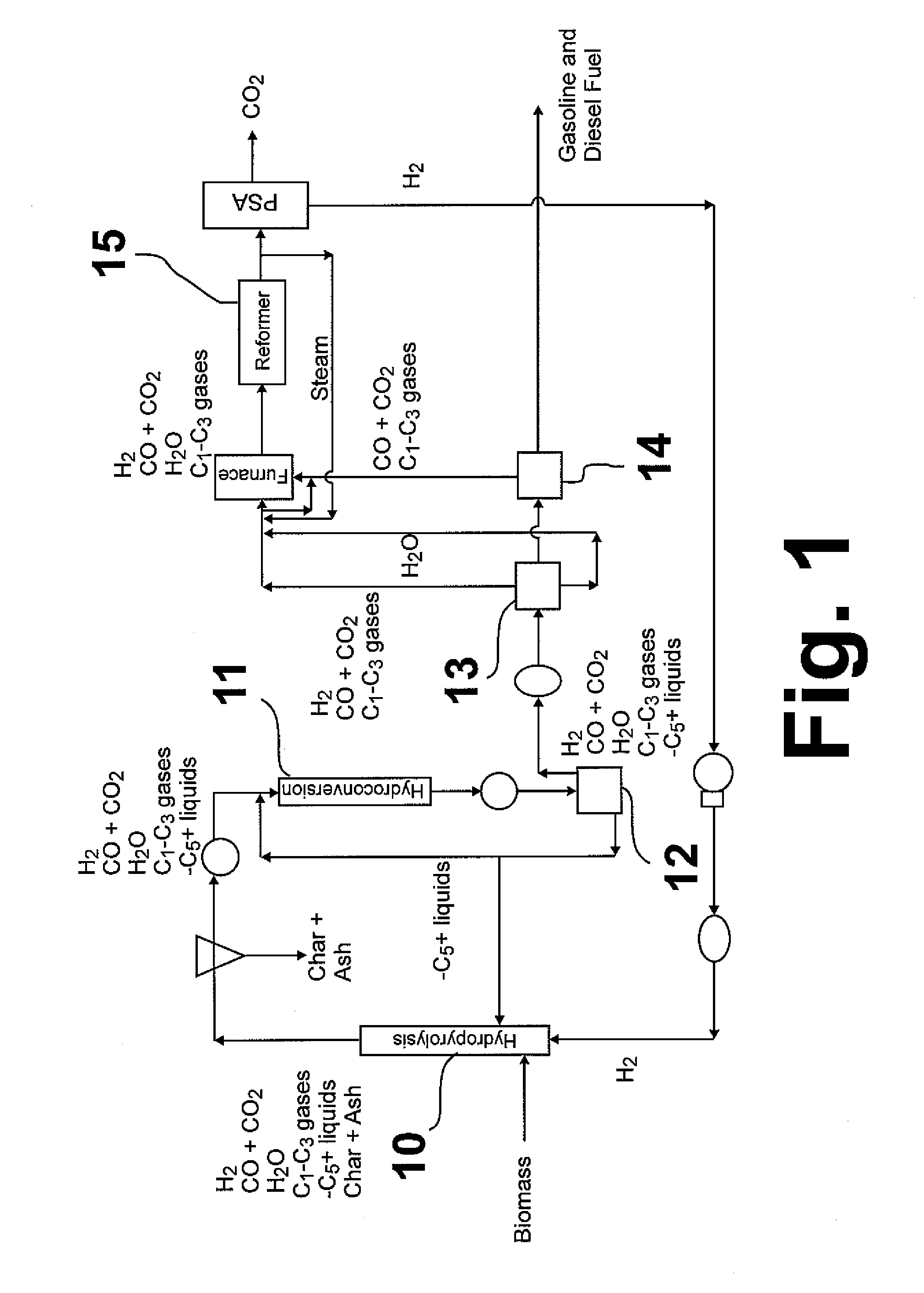
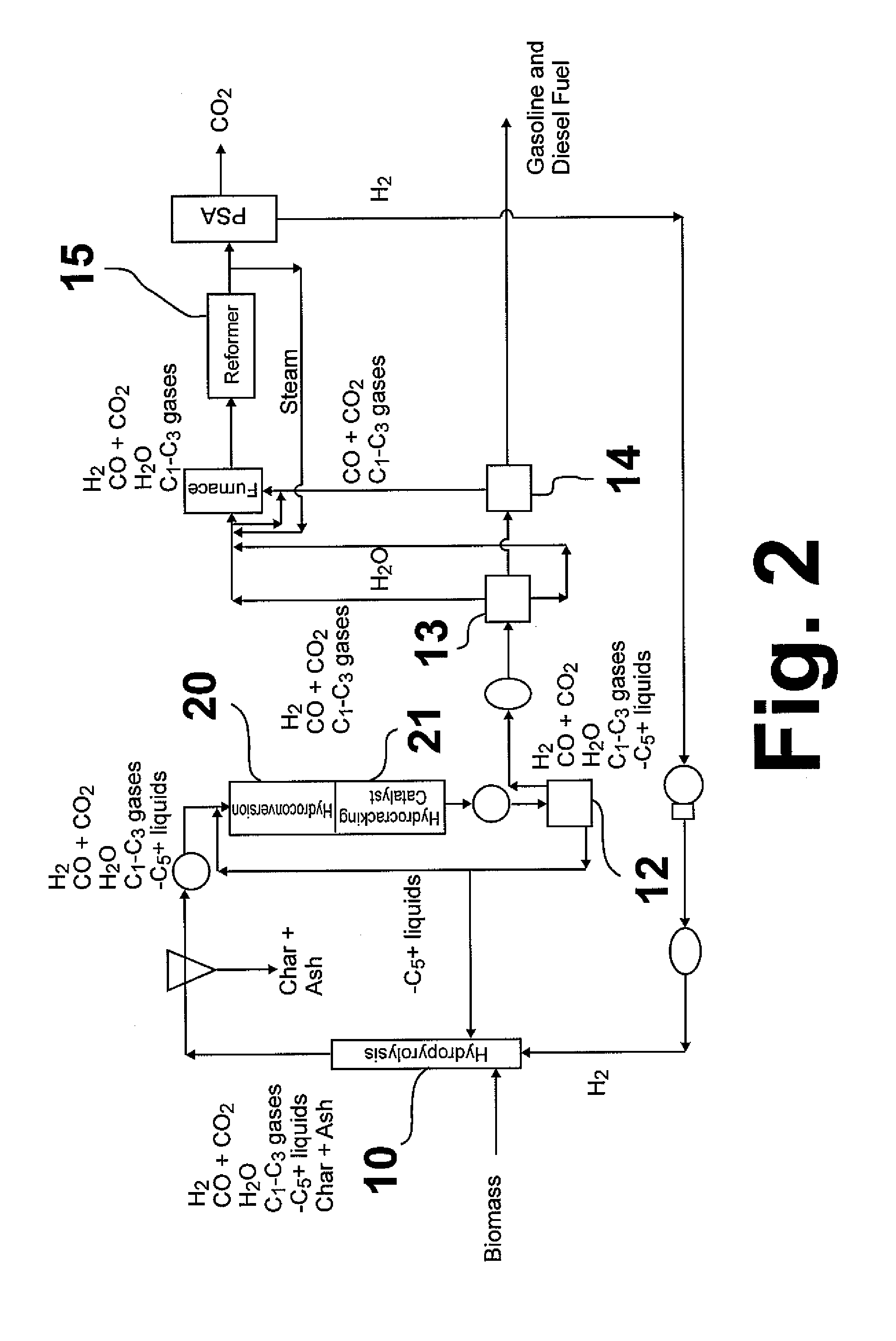
Hydropyrolysis of biomass for producing high quality liquid fuels
A self-sustaining process for producing high quality liquid fuels from biomass in which the biomass is hydropyrolyzed in a reactor vessel containing molecular hydrogen and a deoxygenating catalyst, producing a partially deoxygenated hydropyrolysis liquid, which is hydrogenated using a hydroconversion catalyst, producing a substantially fully deoxygenated hydrocarbon liquid and a gaseous mixture comprising CO and light hydrocarbon gases (C1-C3). The gaseous mixture is reformed in a steam reformer, producing reformed molecular hydrogen, which is then introduced into the reactor vessel for hydropyrolizing the biomass. The deoxygenated hydrocarbon liquid product is further separated to produce diesel fuel, gasoline, or blending components for gasoline and diesel fuel.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com