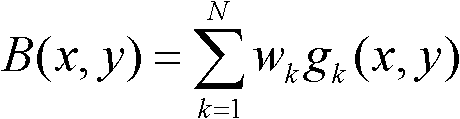Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116 results about "Cerebrospinal fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
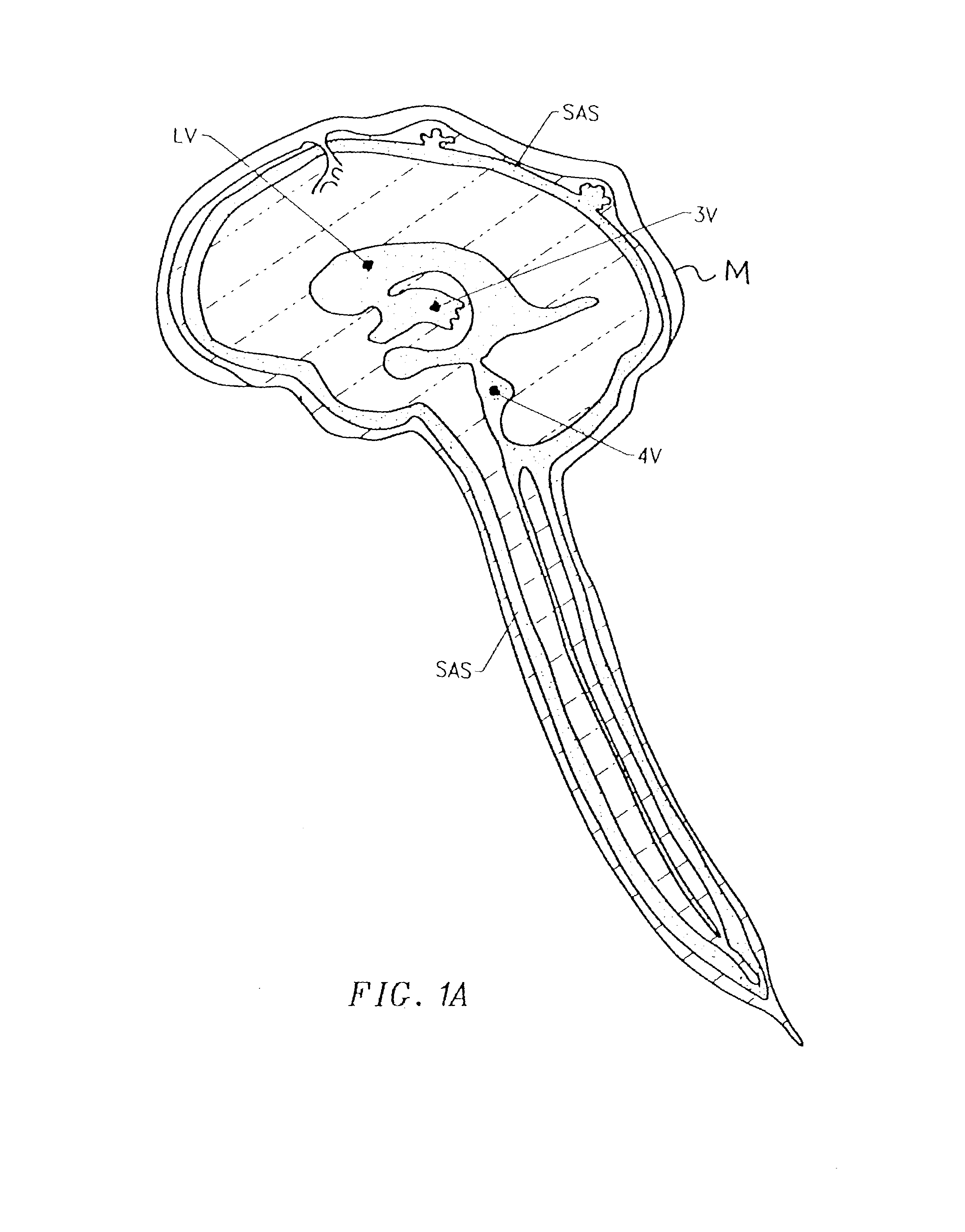
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found in the brain and spinal cord. It is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. There is about 125mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immunological protection to the brain inside the skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow.
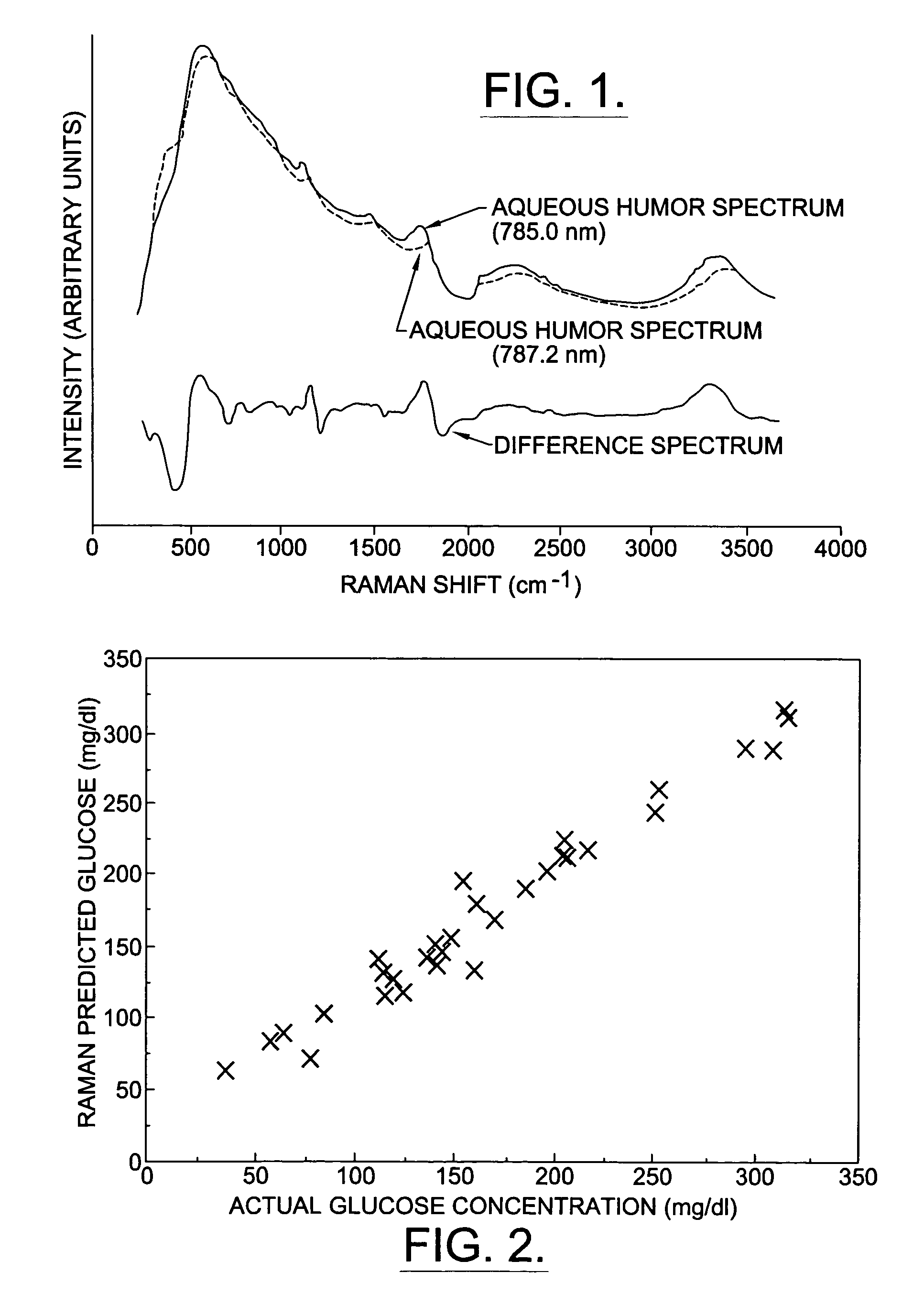
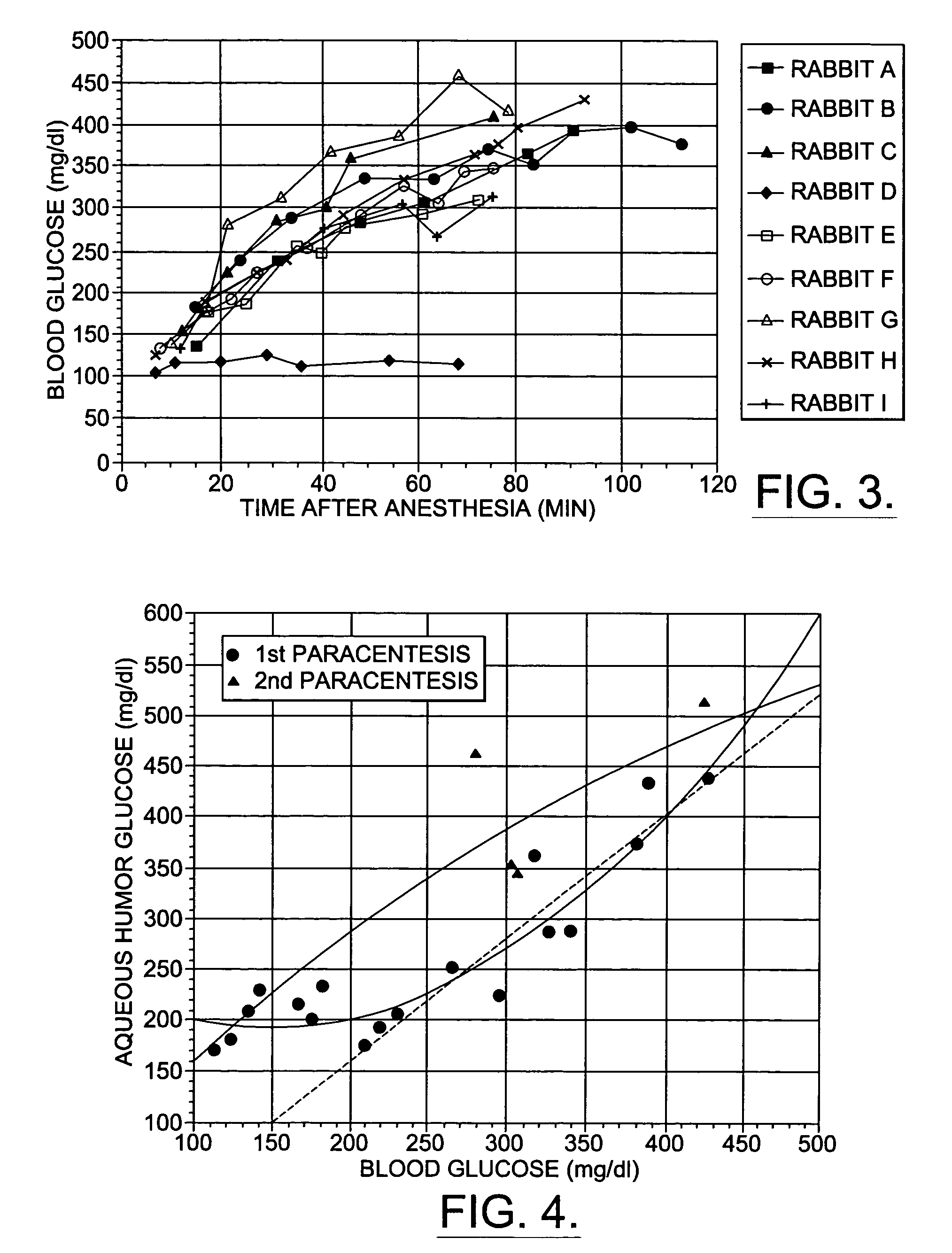
Assessing blood brain barrier dynamics or identifying or measuring selected substances or toxins in a subject by analyzing Raman spectrum signals of selected regions in the eye
InactiveUS6574501B2Reduced energy/density exposure ratingImproved margin of safetyRaman scatteringDiagnostic recording/measuringConjunctivaNon invasive
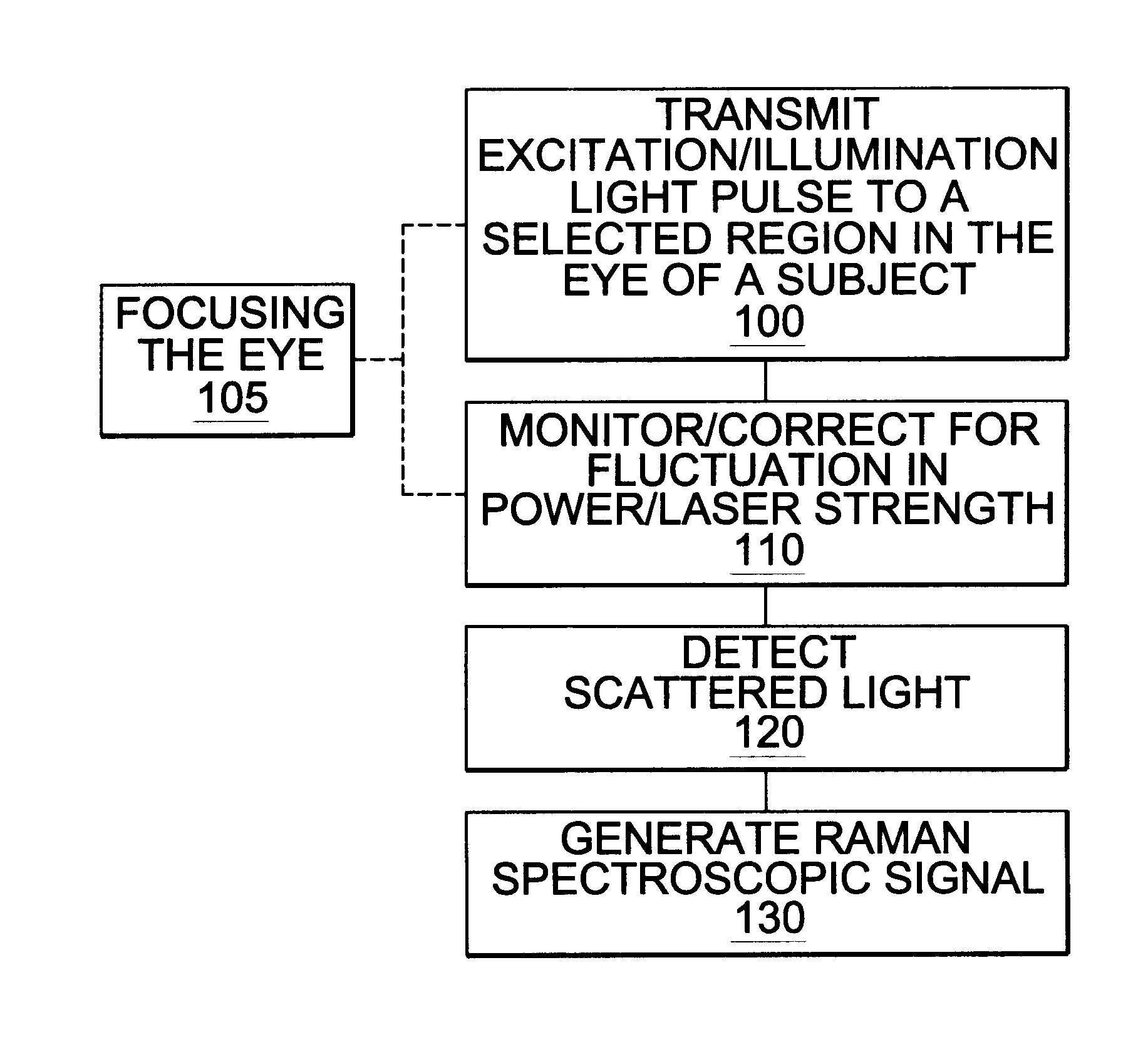
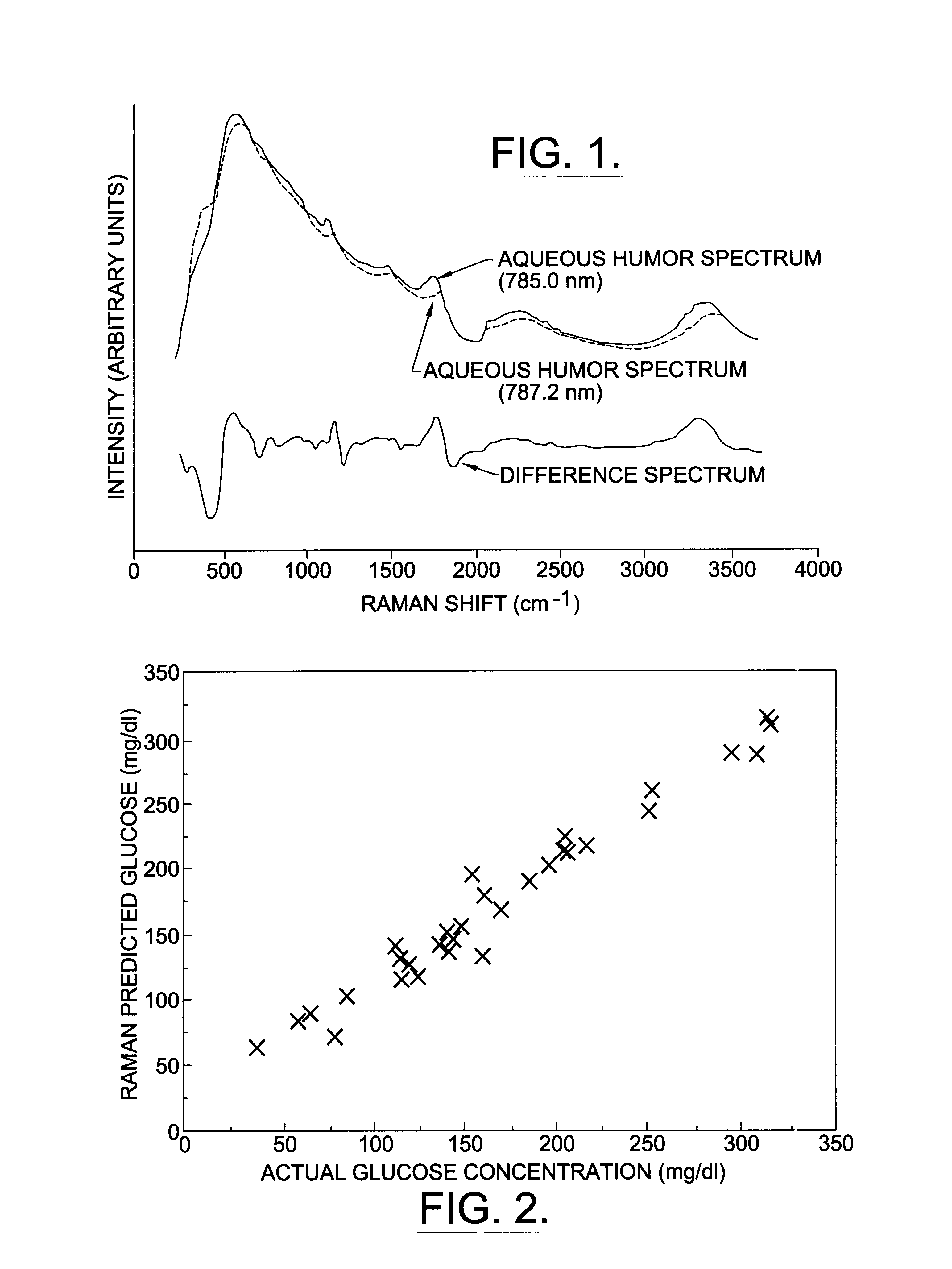
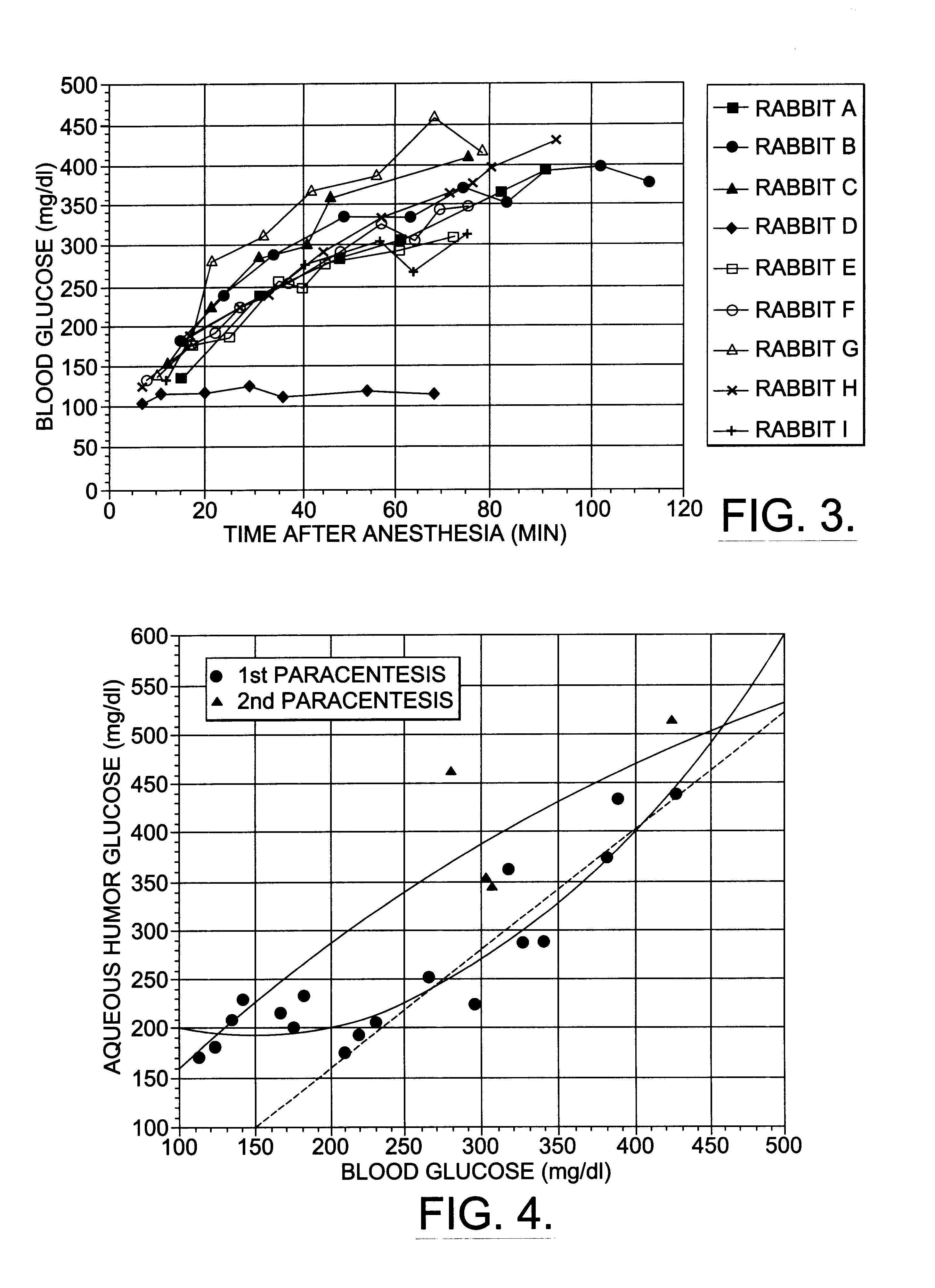
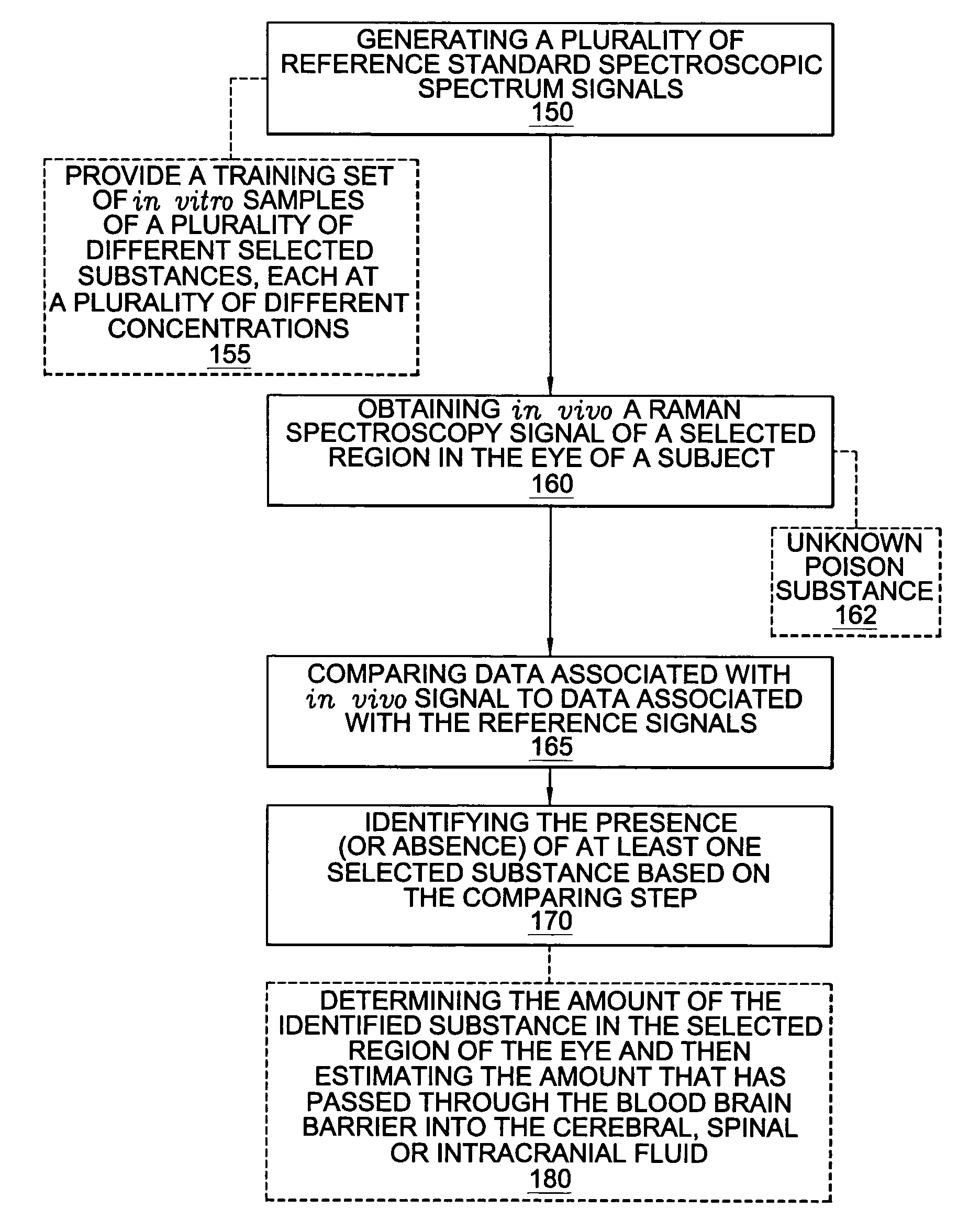
A non-invasive method for analyzing the blood-brain barrier includes obtaining a Raman spectrum of a selected portion of the eye and monitoring the Raman spectrum to ascertain a change to the dynamics of the blood brain barrier. Also, non-invasive methods for determining the brain or blood level of an analyte of interest, such as glucose, drugs, alcohol, poisons, and the like, comprises: generating an excitation laser beam (e.g., at a wavelength of 600 to 900 nanometers); focusing the excitation laser beam into the anterior chamber of an eye of the subject so that aqueous humor, vitreous humor, or one or more conjunctiva vessels in the eye is illuminated; detecting (preferably confocally detecting) a Raman spectrum from the illuminated portion of the eye; and then determining the blood level or brain level (intracranial or cerebral spinal fluid level) of an analyte of interest for the subject from the Raman spectrum. In certain embodiments, the detecting step may be followed by the step of subtracting a confounding fluorescence spectrum from the Raman spectrum to produce a difference spectrum; and determining the blood level and / or brain level of the analyte of interest for the subject from that difference spectrum, preferably using linear or nonlinear multivariate analysis such as partial least squares analysis. Apparatus for carrying out the foregoing methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES +1
Assessing blood brain barrier dynamics or identifying or measuring selected substances, including ethanol or toxins, in a subject by analyzing Raman spectrum signals
InactiveUS7398119B2Fast “ triage ” assessmentReliable and faster treatment decisionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationNon invasivePhysics
A non-invasive method for analyzing the blood-brain barrier includes obtaining a Raman spectrum of a selected portion of the eye and monitoring the Raman spectrum to ascertain a change to the dynamics of the blood brain barrier.Also, non-invasive methods for determining the brain or blood level of an analyte of interest, such as glucose, drugs, alcohol, poisons, and the like, comprises: generating an excitation laser beam at a selected wavelength (e.g., at a wavelength of about 400 to 900 nanometers); focusing the excitation laser beam into the anterior chamber of an eye of the subject so that aqueous humor, vitreous humor, or one or more conjunctiva vessels in the eye is illuminated; detecting (preferably confocally detecting) a Raman spectrum from the illuminated portion of the eye; and then determining the blood level or brain level (intracranial or cerebral spinal fluid level) of an analyte of interest for the subject from the Raman spectrum. In certain embodiments, the detecting step may be followed by the step of subtracting a confounding fluorescence spectrum from the Raman spectrum to produce a difference spectrum; and determining the blood level and / or brain level of the analyte of interest for the subject from that difference spectrum, preferably using linear or nonlinear multivariate analysis such as partial least squares analysis. Apparatus for carrying out the foregoing methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Methods, systems and devices for neuromodulating spinal anatomy
ActiveUS20100292769A1Minimizing complicationMinimize side effectsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSide effectSpinal anatomy
Devices, systems and methods for treating pain or other conditions while minimizing possible complications and side effects. Treatment typically includes electrical stimulation and / or delivery of pharmacological or other agents with the use of a lead or catheter. The devices, systems and methods provide improved anchoring which reduces migration of the lead yet allows for easy repositioning or removal of the lead if desired. The devices, systems and methods also provide for simultaneous treatment of multiple targeted anatomies. This shortens procedure time and allows for less access points, such as needle sticks to the epidural space, which in turn reduces complications, such as cerebral spinal fluid leaks, patient soreness and recovery time. Other possible complications related to the placement of multiple devices are also reduced.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Shunt
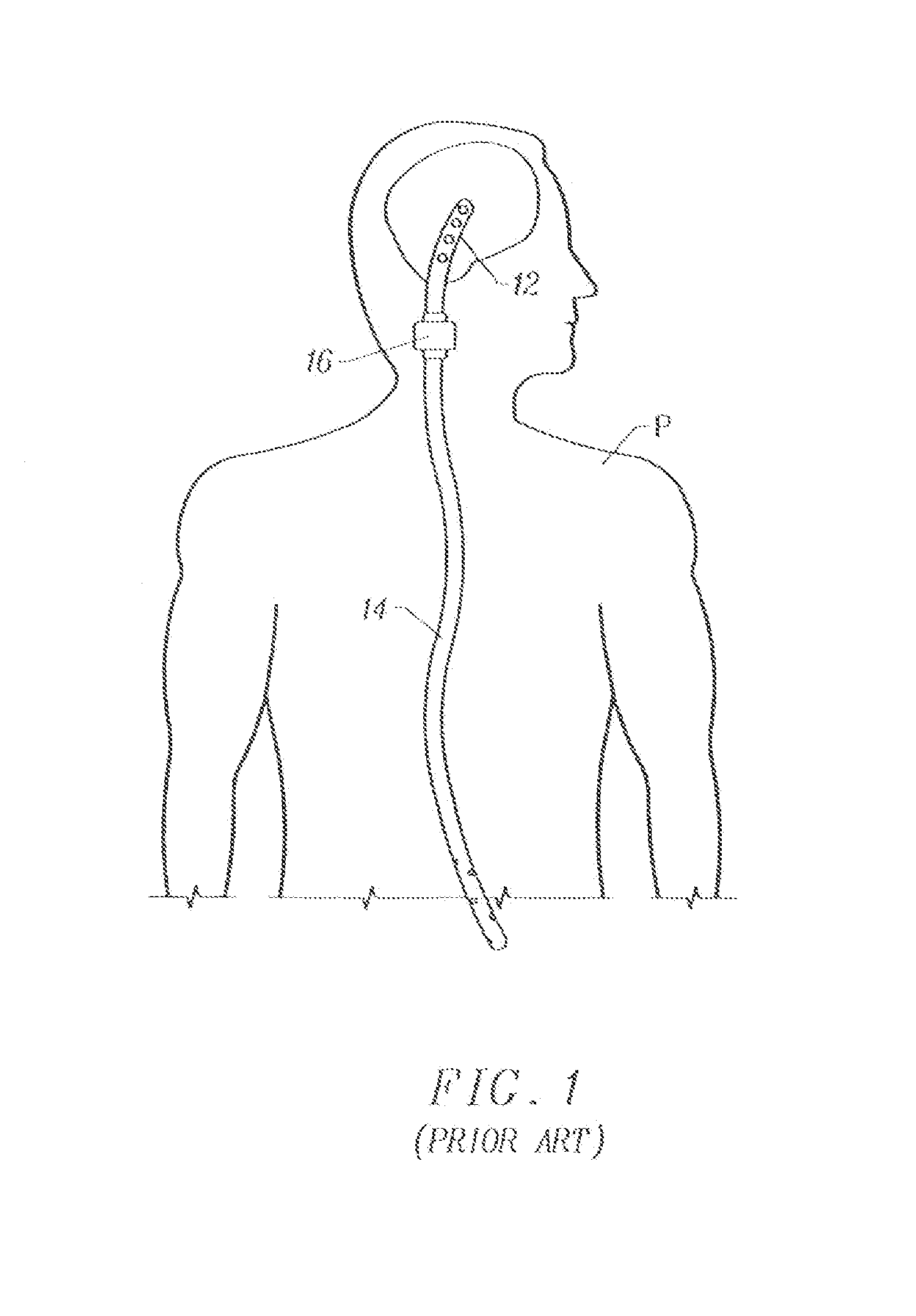
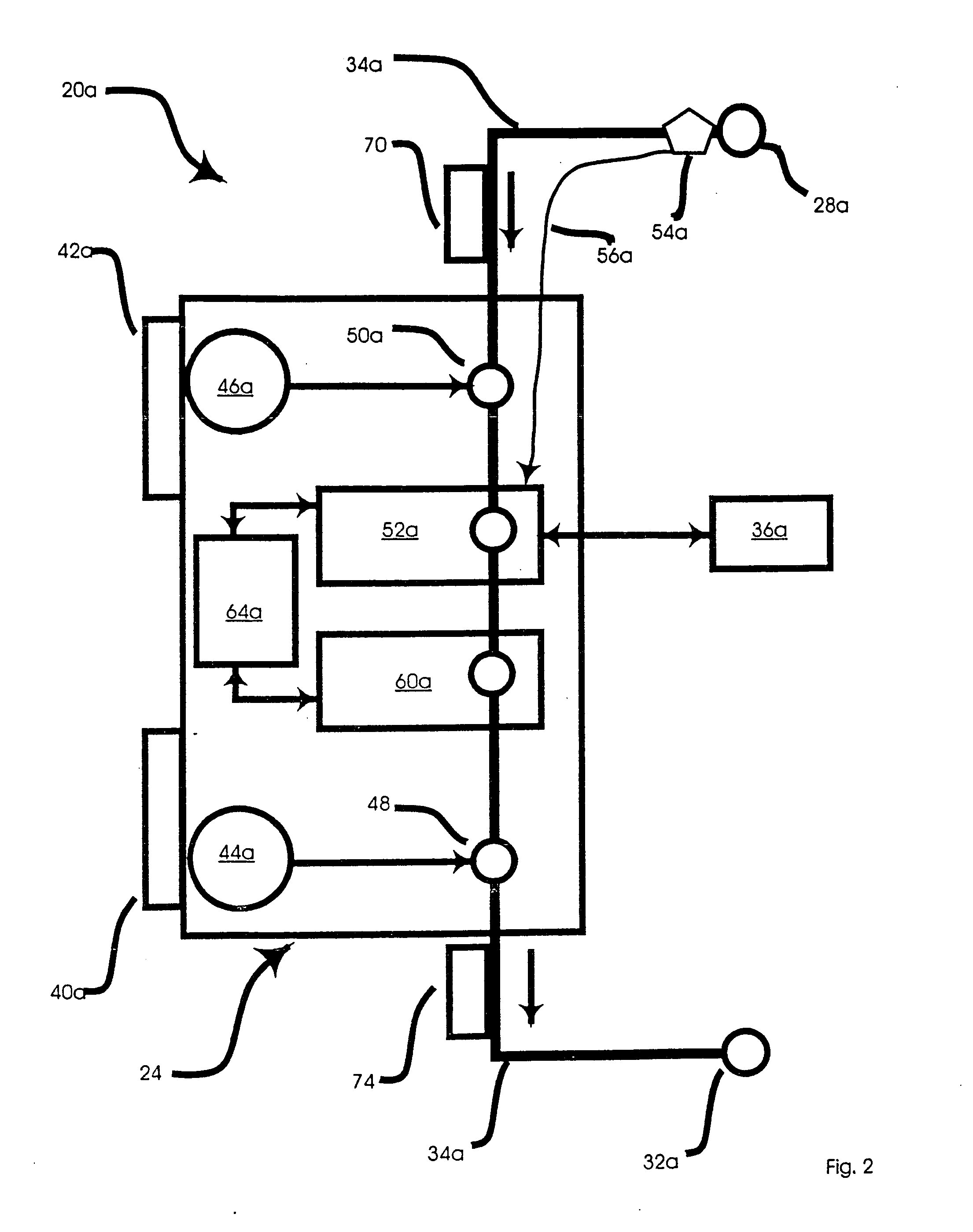
A shunt for draining cerebral spinal fluid from the brain is provided. In an embodiment, the shunt includes a master control unit that is located in the abdomen, which interconnects a ventricular catheter and a second catheter, typically located in the peritoneal cavity. In a specific embodiment, the master control unit includes a variety of ‘smart’ features including at least one access port to allow the injection of solutions for the prevention or removal of blockages in the catheter, and / or antibiotics. The access port can have other uses, such as allowing a point of access for physical navigation of a catheter or the like within the shunt, thereby providing another option for breaking-up blockages, and / or allowing an access point for repairing the shunt's components. Additionally, the master control unit includes a diagnostic unit that transmits, either wirelessly or through a wired connection via the access port, diagnostic information about the status of the patient and / or the shunt.
Owner:COWAN JOHN A +3
Fluid management flow implants of improved occlusion resistance
ActiveUS20060074388A1Reduce probabilityMaterial is expensiveWound drainsSurgeryDrugCerebrospinal fluid
This invention relates to achieving or improving uniform distribution of fluid flow in medical devices such as when combined with antibiotics impregnated in a catheter and / or with a drug-eluting catheter to further inhibit the catheter from becoming occluded by debris in the CSF or by bacterial biofilm formation or tissue proliferation in the catheter.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
Systems and methods for increasing cerebral spinal fluid flow
InactiveUS7185649B2Decreasing intracranial and intraocular pressureReduce pressureElectrocardiographyBreathing filtersVeinCerebrospinal fluid
In one embodiment, the invention provides a device for decreasing intracranial or intraocular pressures. The device comprises a housing having an inlet opening and an outlet opening that is adapted to be interfaced with a person's airway. The device further includes a valve system that is operable to regulate respiratory gas flows through the housing and into the person's lungs during spontaneous or artificial inspiration. The valve system assists in lowering intrathoracic pressures during each inspiration to repetitively lower pressures in the venous blood vessels that transport blood out of the head to thereby reduce intracranial or intraocular pressures.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Method and device for detecting analytes in fluids
InactiveUS6602719B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh concentrationBlood plasma
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Devices and Systems to Mitigate Traumatic Brain and Other Injuries Caused by Concussive or Blast Forces
ActiveUS20140343599A1Increase cerebral blood volumeDecrease intracranial complianceDevices for pressing relfex pointsTourniquetsSpinal columnInjury brain
A system for reducing the damaging effects of radiant energy, blast, or concussive events includes applying pressure to at least one jugular vein to reduce the egress of blood from the cranial cavity during or before the incidence of the imparting event. Reducing blood outflow from the cranial cavity increases intracranial volume and / or pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid to reduce the risk of traumatic brain injury and injuries to the spinal column. Reducing blood outflow further increases the intracranial pressure and volume, and thereby increases the pressure and volume of the cochlear fluid, the vitreous humor and the cerebrospinal fluid to thereby reduce the risk of injury to the inner ear, internal structure of the eye and of the spinal column. In addition, increasing intracranial pressure and volume reduces the likelihood of brain injury and any associated loss of olfactory function
Owner:TBI INNOVATIONS +1
Implantable subcutaneous valve for the treatment of hydrocephalus, and adjusting devices therefor
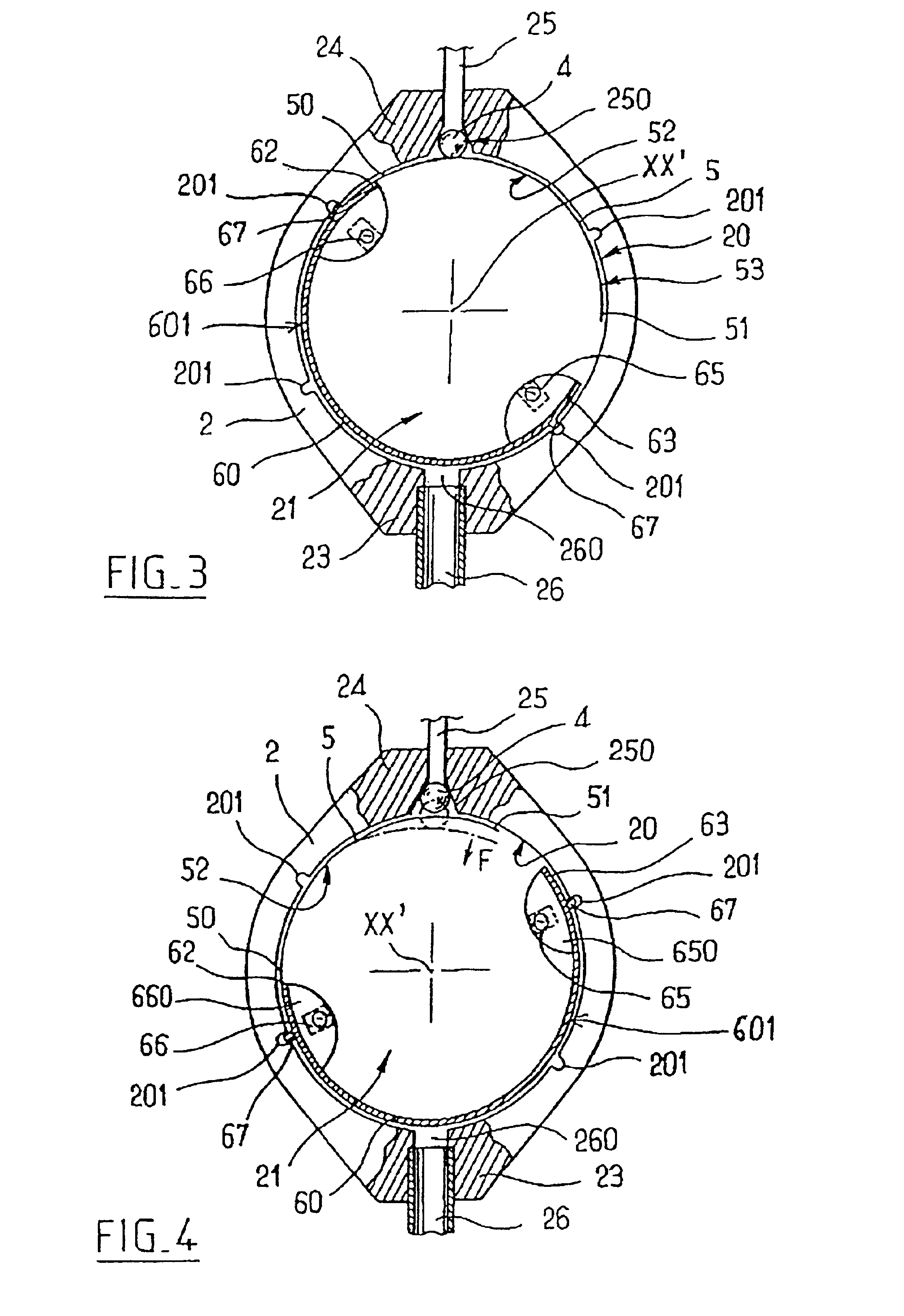
InactiveUS6840917B2Speed up the flowAvoid fixationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesWound drainsCerebrospinal fluidHydrocephalus
The invention relates to a subcutaneous valve having opening pressure that can be adjusted non-invasively from the outside, said valve comprising a body presenting a chamber with a cylindrical inside side wall, an inlet duct and an outlet duct for cerebospinal fluid both opening out in said side wall, a valve member such as a ball placed at the inside end of said inlet duct, a spring blade fitting closely to the side wall of said chamber and urging the valve member against its seat, and a moving member controlled from the outside and provided with means for locking it in a determined position, the length of the spring blade acting on the valve member being determined by the position of said moving member. The valve is remarkable in that said moving member is constituted by a resilient flexible arcuate blade fitting closely to the cylindrical inside wall of said chamber. The valve is applicable to the treatment of hydrocephalus.
Owner:MARION BERNARD
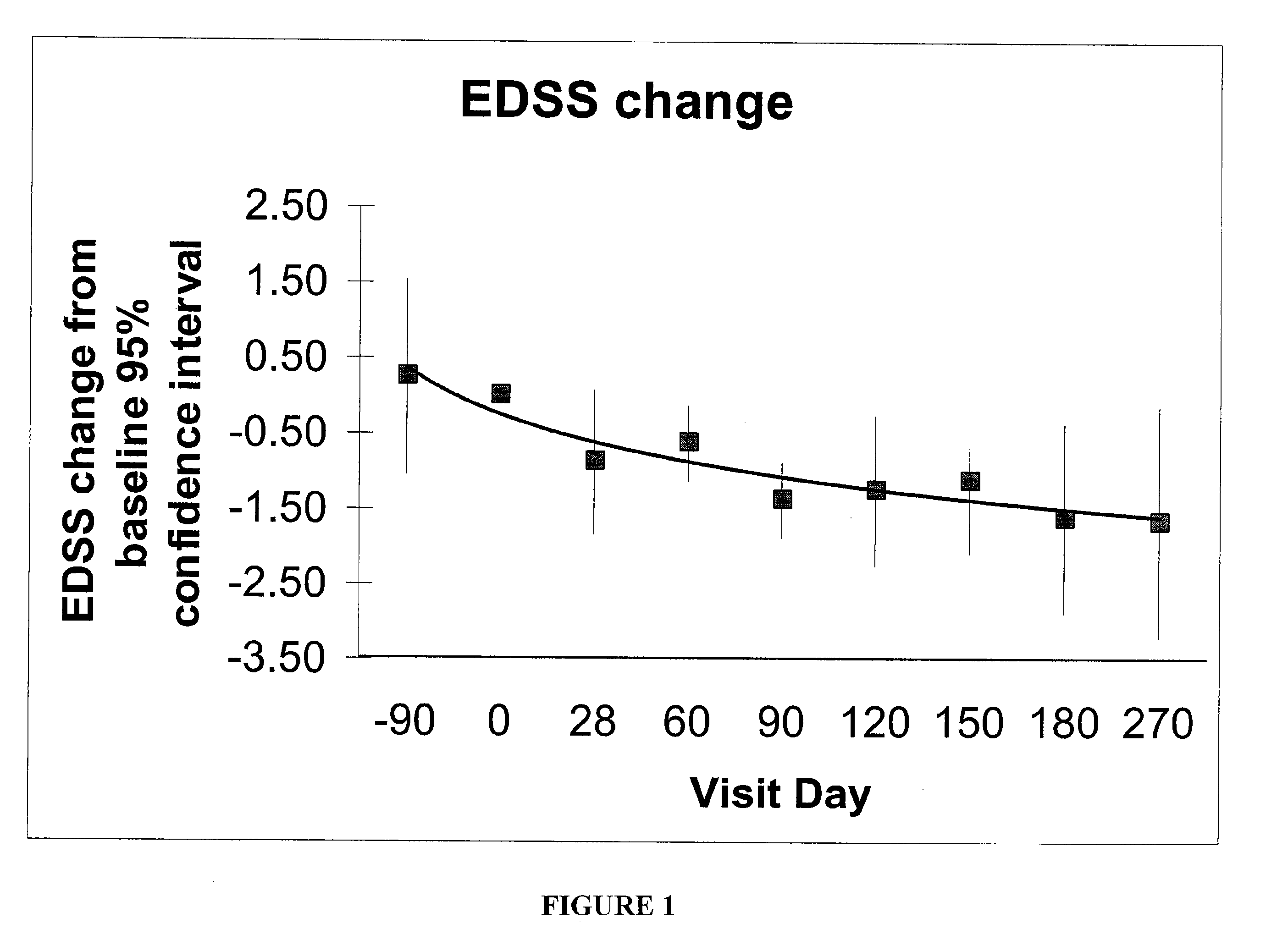
Methods for the treatment of a normal pressure hydrocephalus
InactiveUS7189221B2Reduces and eliminates symptomDecrease increaseWound drainsMedical devicesCerebrospinal fluidHydrocephalus
Normal pressure hydrocephalus is treated by removing cerebralspinal fluid (CSF) from a CSF space of a patient. In particular, CSF is drained while pressure within the CSF space remains within an expected normal range for the patient.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI
Skull patch and its prepn process
InactiveCN101019785AMeet aesthetic requirementsShorten operation timeBone implantSurgeryCerebrospinal fluidTitanium
The skull patch making process includes the following steps: computerized tomographic imaging to acquire the information of the skull defect part of the patient and the peripheral soft tissue, image designing to reconstruct the 3D head prototype of the patient, designing the dummy for the defect part, leading the designed dummy camber into fast laser forming machine for making patch mold, and final jointing, comparing and cutting titanium web plate to form the ultimate skull patch. The present invention has high precision, low cost, short making period and excellent post-operational restoring.
Owner:赵亚群
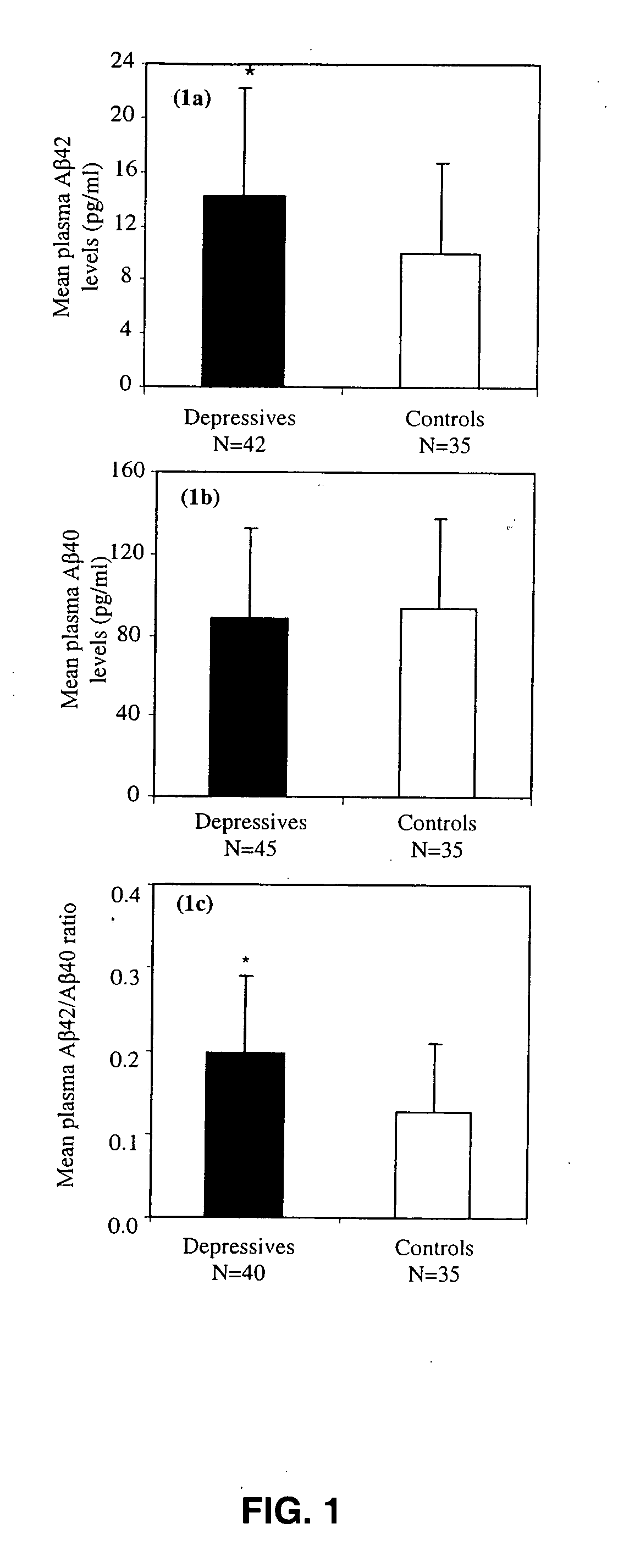
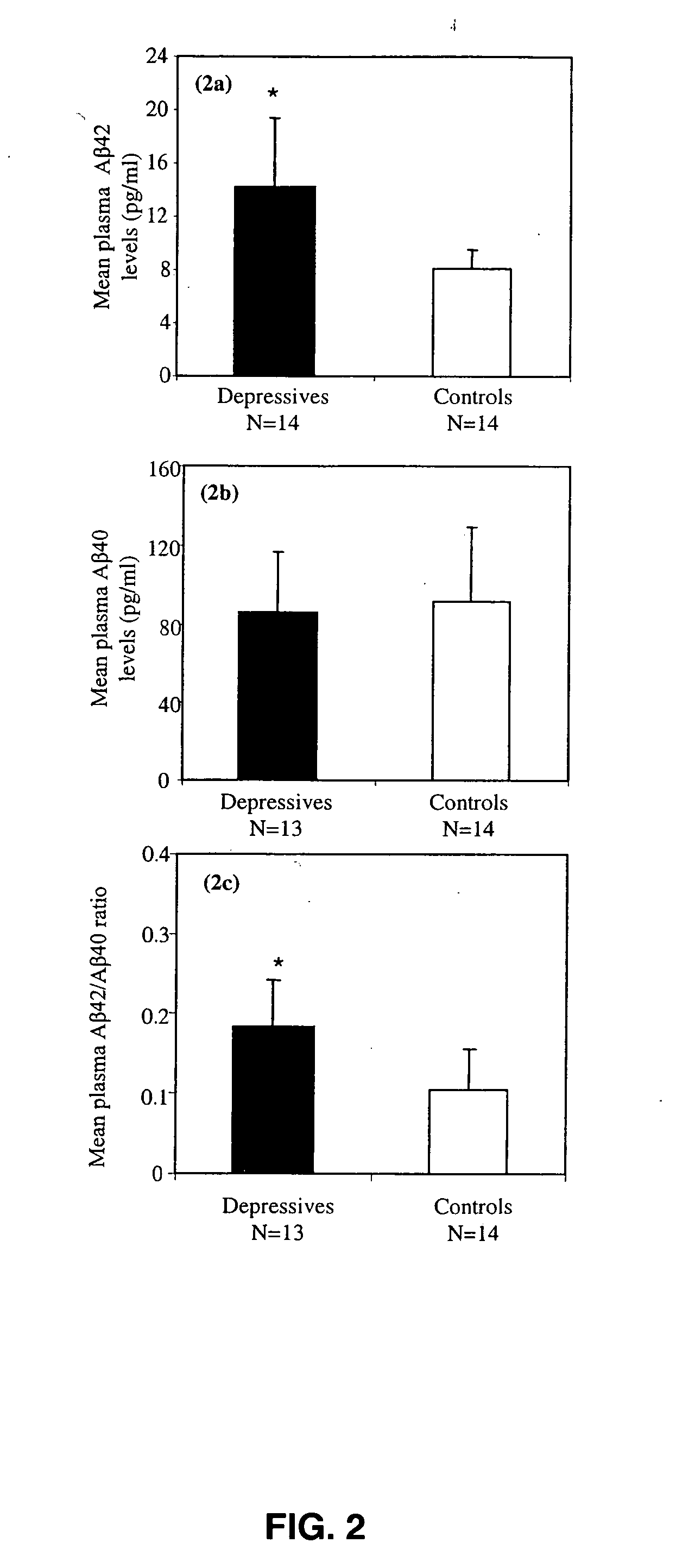
Methods and compositions for treatment and prevention of major depressive disorder
InactiveUS20060105394A1Rapid and sensitive screeningLower Level RequirementsNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansFibrilMild depression
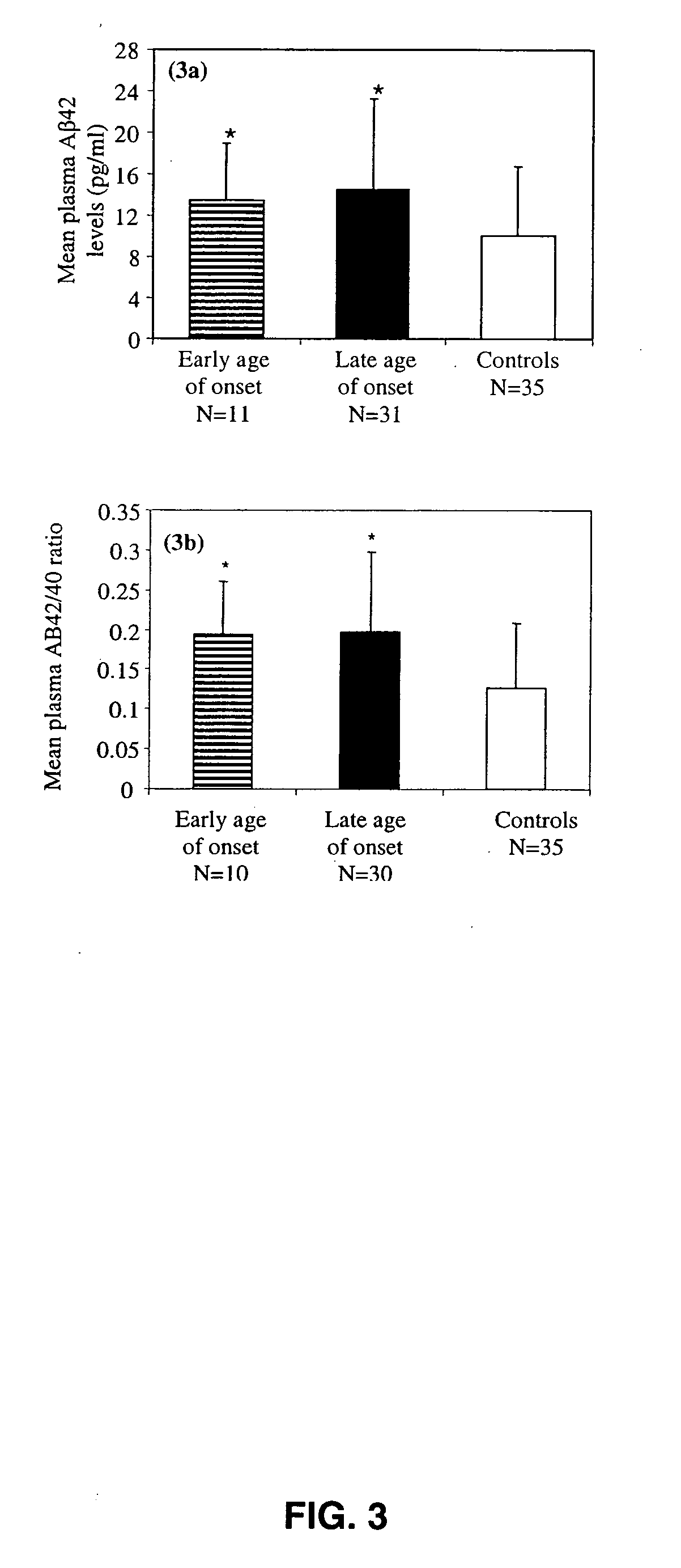
The present invention relates to methods of diagnosing, prognosing or treating diseases or disorders in which elevated levels of Abeta protein, including abeta1-42 are prevalent. In particular, the present invention relates to methods of diagnosing, prognosing or treating a major or minor depressive episode / disorder attributed to elevated levels of Abeta protein, including abeta1-42, found particularly in body fluids including whole blood, blood cells, serum, plasma, urine and CSF. The invention also relates to the treatment of these disorders by administering an agent that either prevents production of Abeta, prevents aggregation of Abeta fibrils, or that increases the degradation or clearance of Abeta. In addition, the invention provides a method of treating or preventing a major or minor depressive disorder comprising administering an agent that prevents or interferes with Abeta-induced neurotoxicity. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such agents and methods of screening for novel agents.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Diagnosing intrapulmonary infection and analyzing nasal sample
InactiveUS6461306B1Quick checkWithdrawing sample devicesMedical automated diagnosisCerebrospinal fluidNasal passages
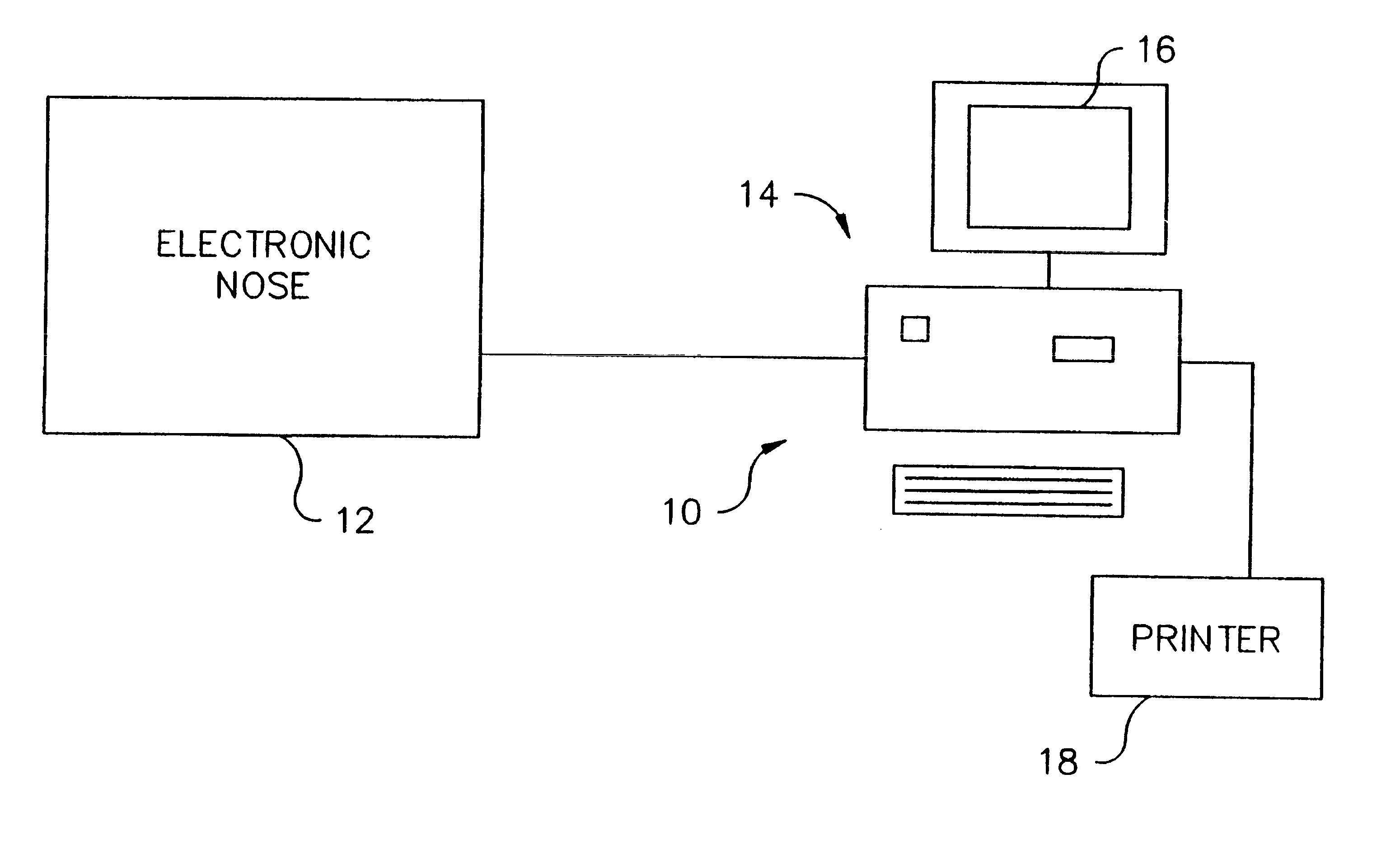
The presence of a pathologic process in a lung of a mammal is detected by applying exhaled gas of a mammal to an electronic nose (12). Data derived from the electronic nose (12) is used to determine whether a pathologic process is present in the lung of the mammal. The pathologic process may also be a lung infection such as pneumonia. Also, a mammalian fluid sample obtained from the sinus or nose is applied to an electronic nose (12) to determine if the fluid sample contains significant amounts of cebrospinal fluid.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Computerised cortex boundary extraction from MR images
InactiveUS8031919B2Accurate modelingImproved and robust and accurateImage enhancementImage analysisData setVector field
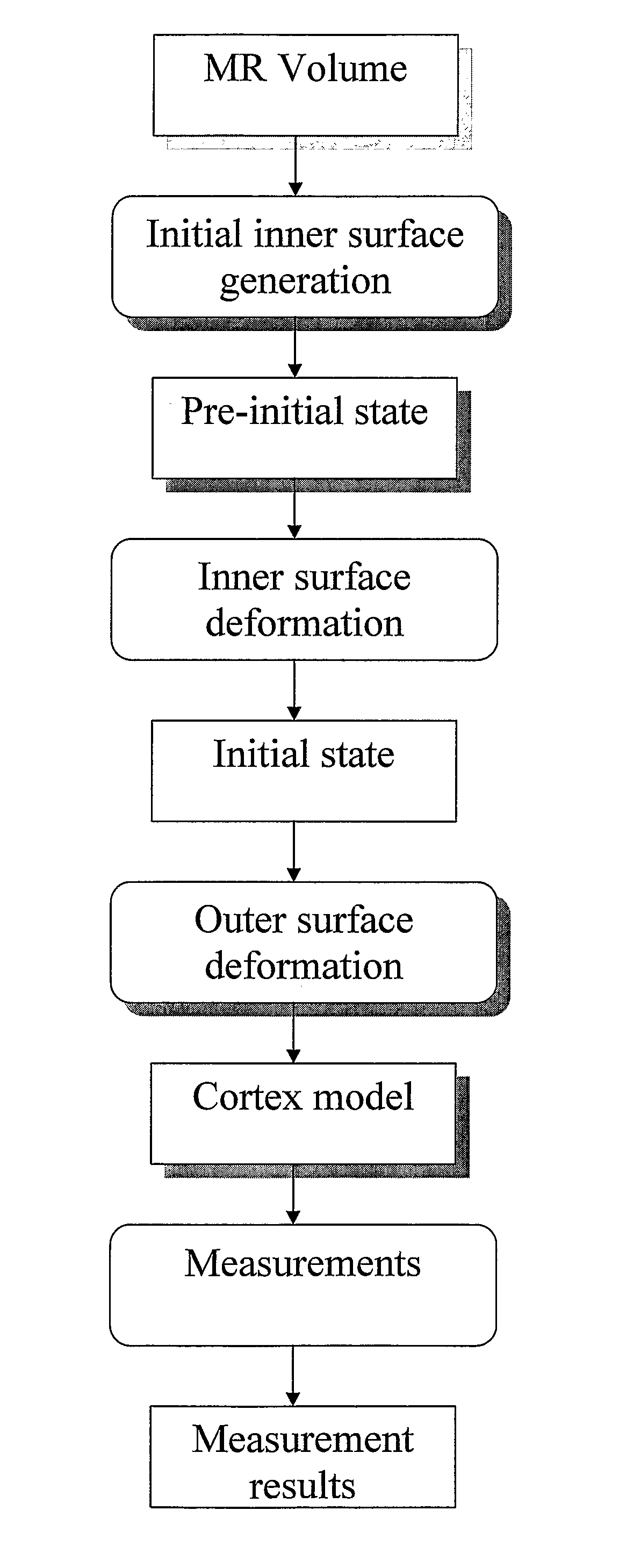
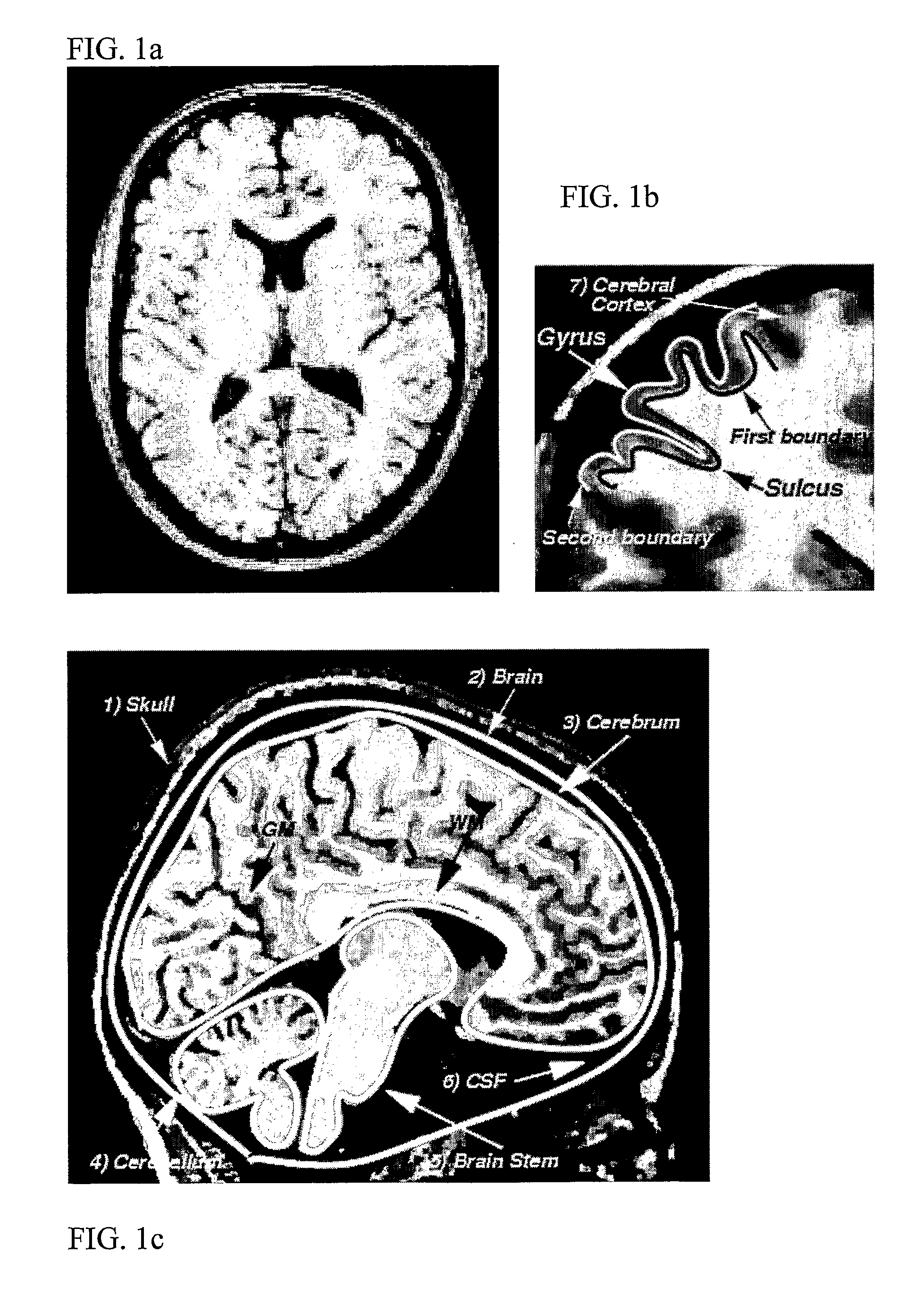
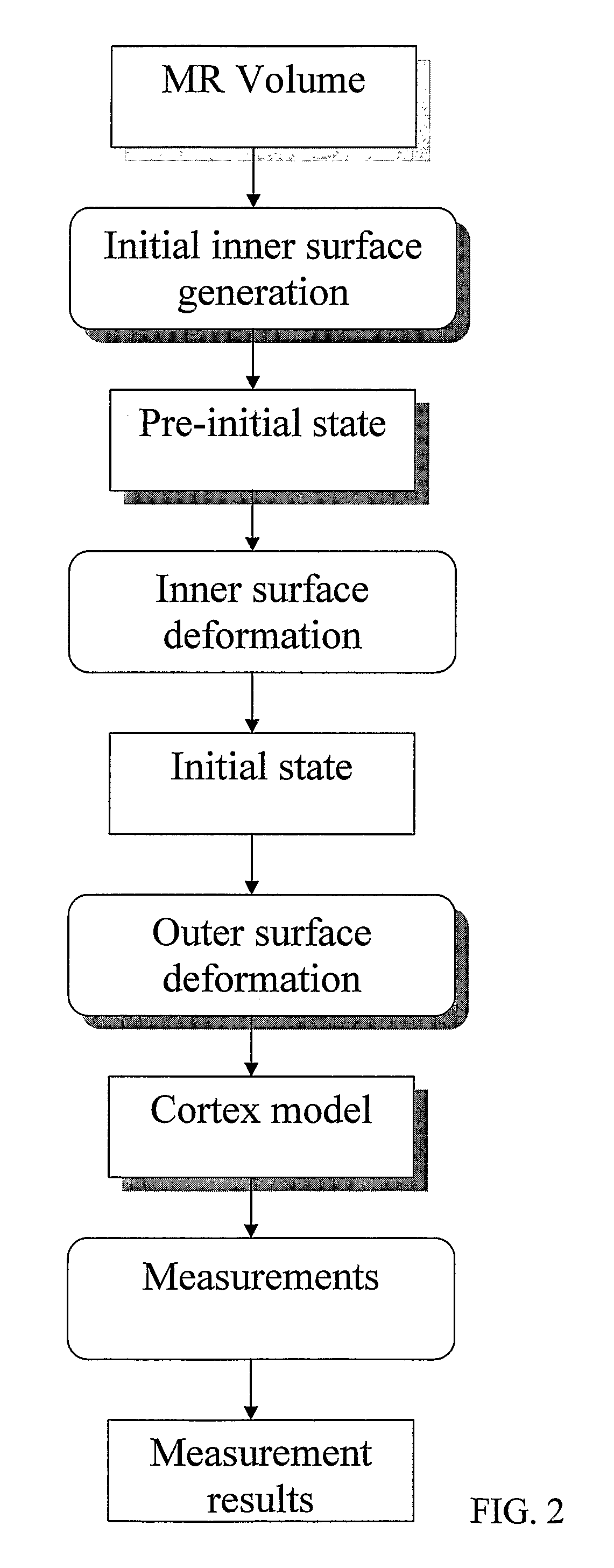
Method for processing digital images, such as magnetic resonance images of a brain. The images contain a first object, for example the cerebrum white matter, a second object, for example the cerebral cortex, and a third object, for example the cerebrospinal fluid. The method involves providing a digital dataset representing a deformable curve or surface that in an initial state approximates the boundary between the first object and the second object. Further, a vector force field is provided that for each point on the deformable curve or surface defines a direction from the point approximately towards the second boundary between the second and the third object, and this vector force field is applied for iteratively deforming the deformable curve or surface convergently towards the second boundary. In order to reconstruct a folded structure of the second object, for example the cortex, the vector force field also involves a normal vector field with a vector normal or approximately normal to the deformable curve or surface for each point on the deformable curve or surface.
Owner:AALBORG UNIV
Continuous carbon fiber reinforced composite material for bone repair
The continuous carbon fiber reinforced composite material for bone repair is prepared with continuous carbon fiber, continuous carbon fiber felt or continuous carbon fiber, cloth through soaking in methyl methacrylate monomer or pre-polymer and subsequent extruding or bulk molding. The composite material of the present invention includes methyl methacrylate and carbon fiber, and the carbon fiber content is 20-80 wt%. The composite material may be used as the external fracture fixing material, internal fracture fixing material and bone repairing material. The composite material has the features of light weight, no interference on NMR examination and excellent biocompatibility. It may be implanted inside life body without negative effect on tissue, blood, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENIUS ADVANCED MATERIAL (GRP) CO LTD
Measurement of a CNS protein in cerebrospinal or amniotic fluid
SNAP-25 (synaptosomal associated protein) is purified from cerebrospinal or amniotic fluid for immunoassay and quantitation. Quantitation of these proteins is useful in the diagnosis and monitoring of brain disorders and diseases such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer's.
Owner:STC UNM
Implantable subcutaneous value for the treatment of hydrocephalus, and adjusting devices therefor
InactiveUS20020058901A1Improves CSF flowSpeed up the flowOperating means/releasing devices for valvesWound drainsCerebrospinal fluidHydrocephalus
The invention relates to a subcutaneous valve having opening pressure that can be adjusted non-invasively from the outside, said valve comprising a body presenting a chamber with a cylindrical inside side wall, an inlet duct and an outlet duct for cerebospinal fluid both opening out in said side wall, a valve member such as a ball placed at the inside end of said inlet duct, a spring blade fitting closely to the side wall of said chamber and urging the valve member against its seat, and a moving member controlled from the outside and provided with means for locking it in a determined position, the length of the spring blade acting on the valve member being determined by the position of said moving member. The valve is remarkable in that said moving member is constituted by a resilient flexible arcuate blade fitting closely to the cylindrical inside wall of said chamber. The valve is applicable to the treatment of hydrocephalus.
Owner:MARION BERNARD
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) sorting algorithm based method for correcting and segmenting grayscale nonuniformity of MR (Magnetic Resonance) image
InactiveCN102135606AAccurate divisionVolume effect suppressionMagnetic measurementsSorting algorithmNear neighbor
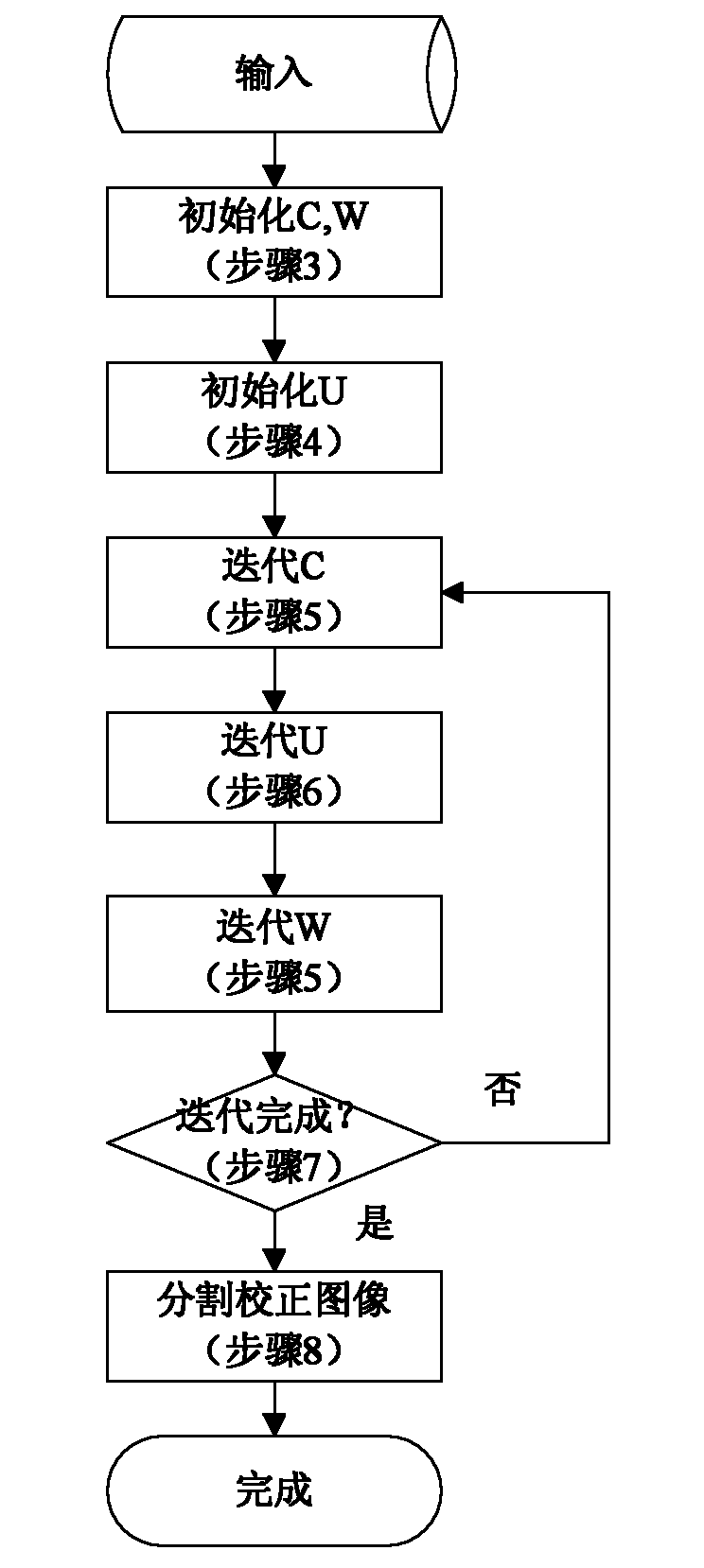
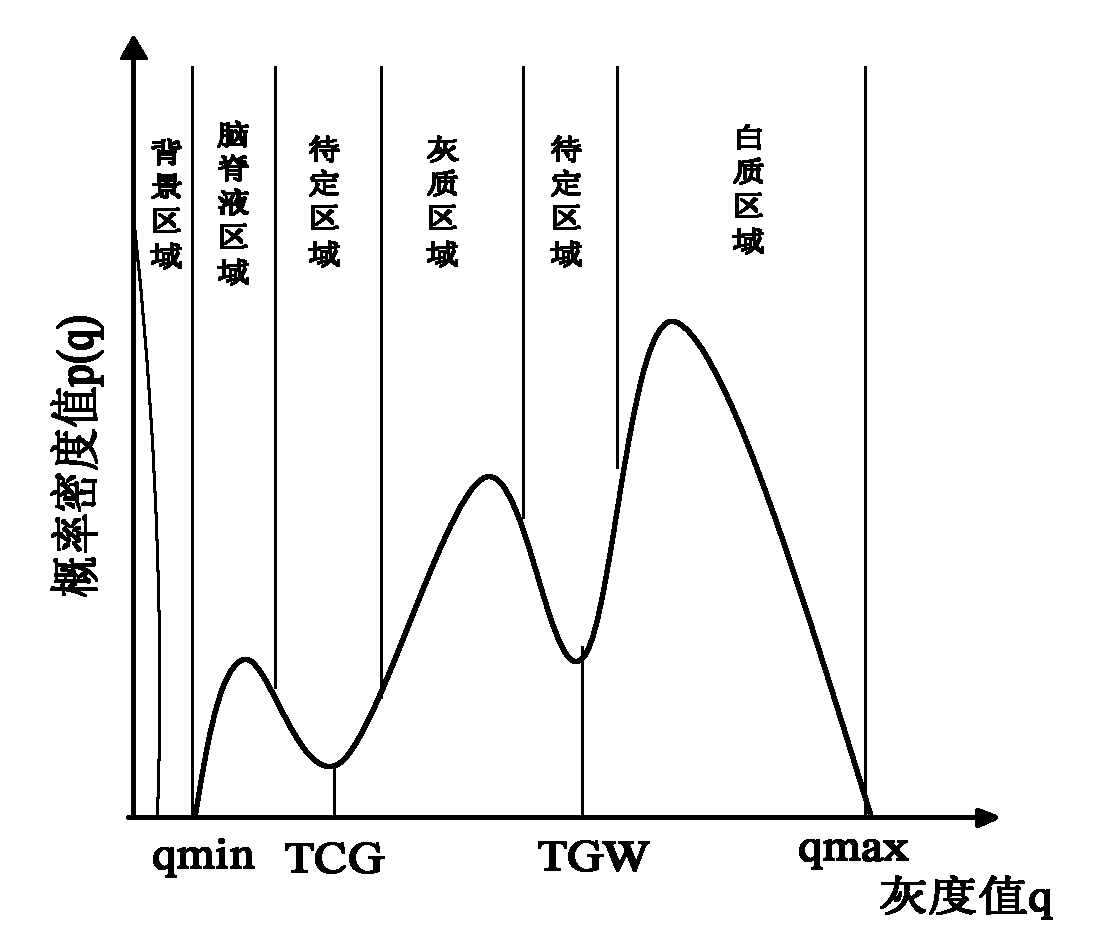
The invention relates to a KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) sorting algorithm based method for correcting and segmenting the grayscale nonuniformity of an MR (Magnetic Resonance) image, belonging to the field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly constructing a grayscale nonuniform field model by utilizing surface fitting knowledge and using a group of orthonormalization basis functions, and establishing energy functions; and then solving model parameters according to an energy function minimization principle to realize grayscale nonuniformity correction and image segmentation, wherein subordinate functions are solved by adopting an iterative algorithm and the KNN algorithm in the model parameter solving process, therefore a partial volume effect is greatly reduced while a grayscale nonuniform field is eliminated, and the influence of noises on the correction and the segmentation of the grayscale nonuniformity of the MR image is reduced. The subordinate functions are solved with KNN through the following steps of: firstly acquiring an accurate smooth normalization histogram by using a kernel estimation algorithm; then respectively solving a threshold value TCG between cerebrospinal fluids and gray matters and a threshold value TGW between the gray matters and white matters by using a maximum between-cluster variance method; carrying out rough sorting on the KNN sorting algorithm by utilizing the two threshold values; and finally accurately sorting points to be fixed by adopting the traditional KNN sorting algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
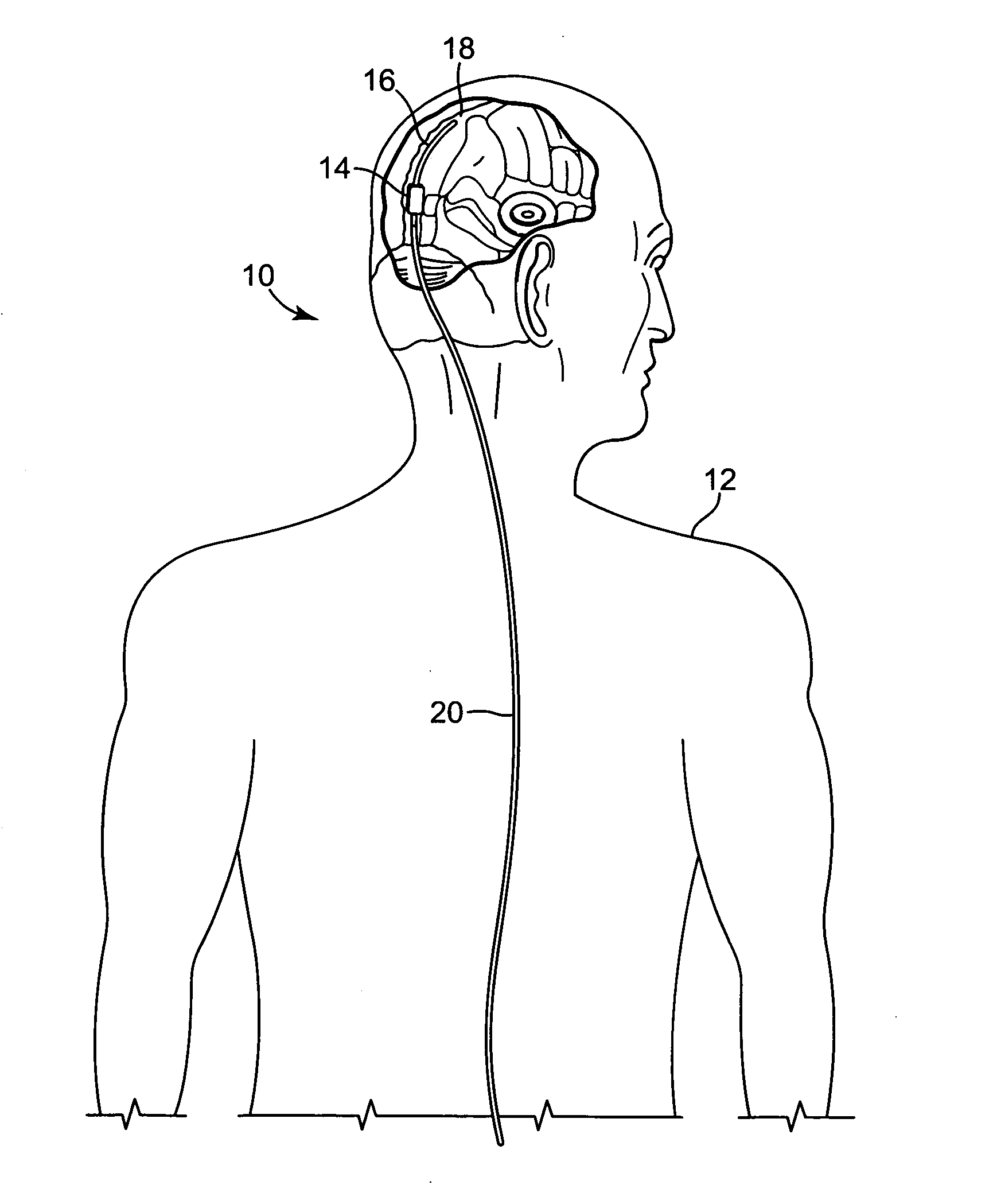
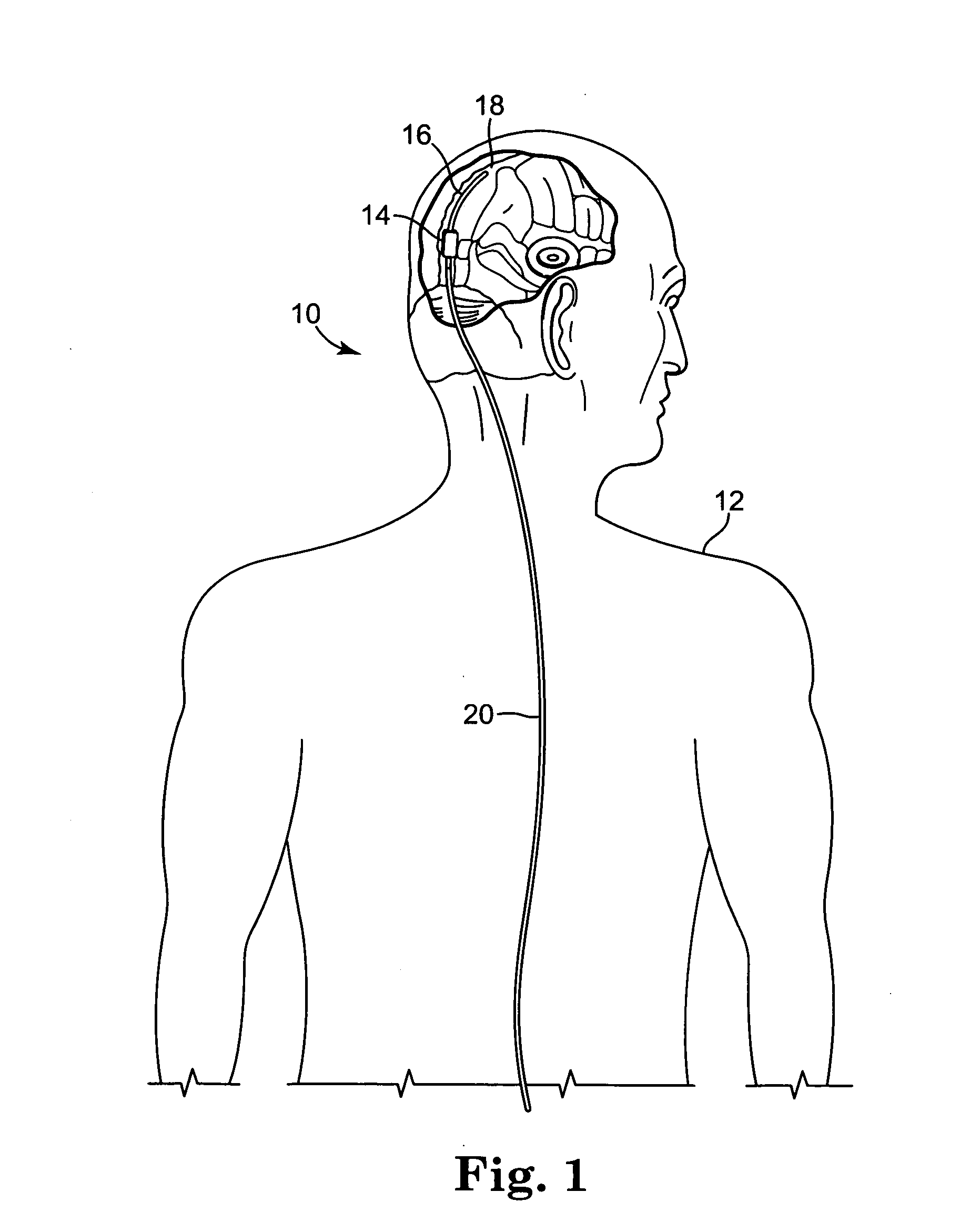
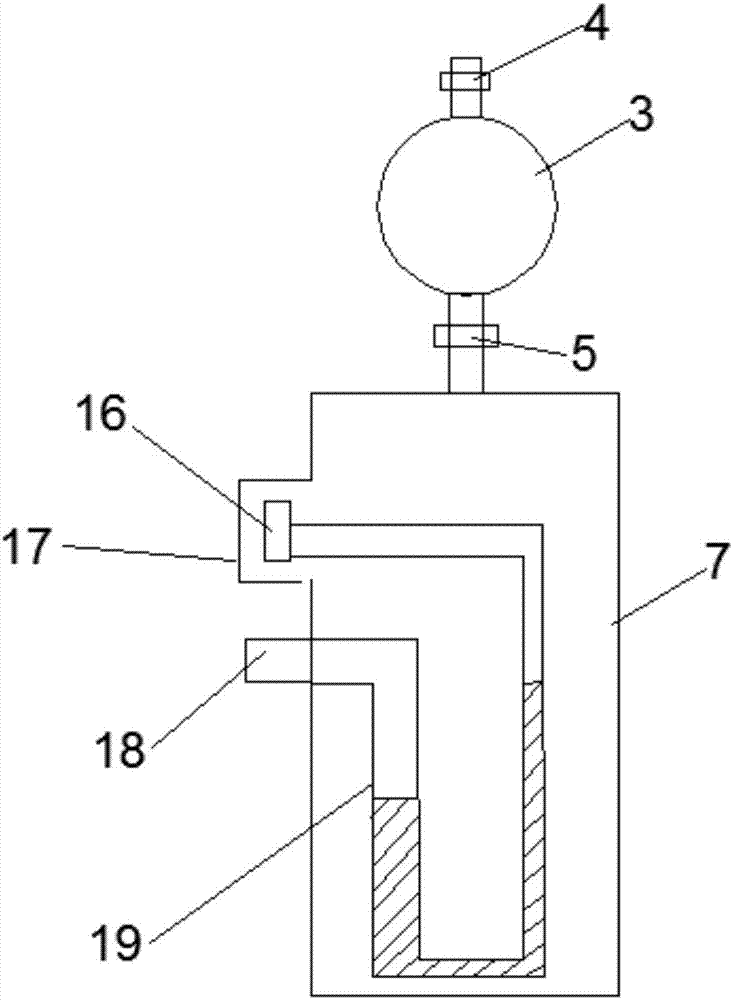
Intracranial pressure monitor and drainage catheter assembly
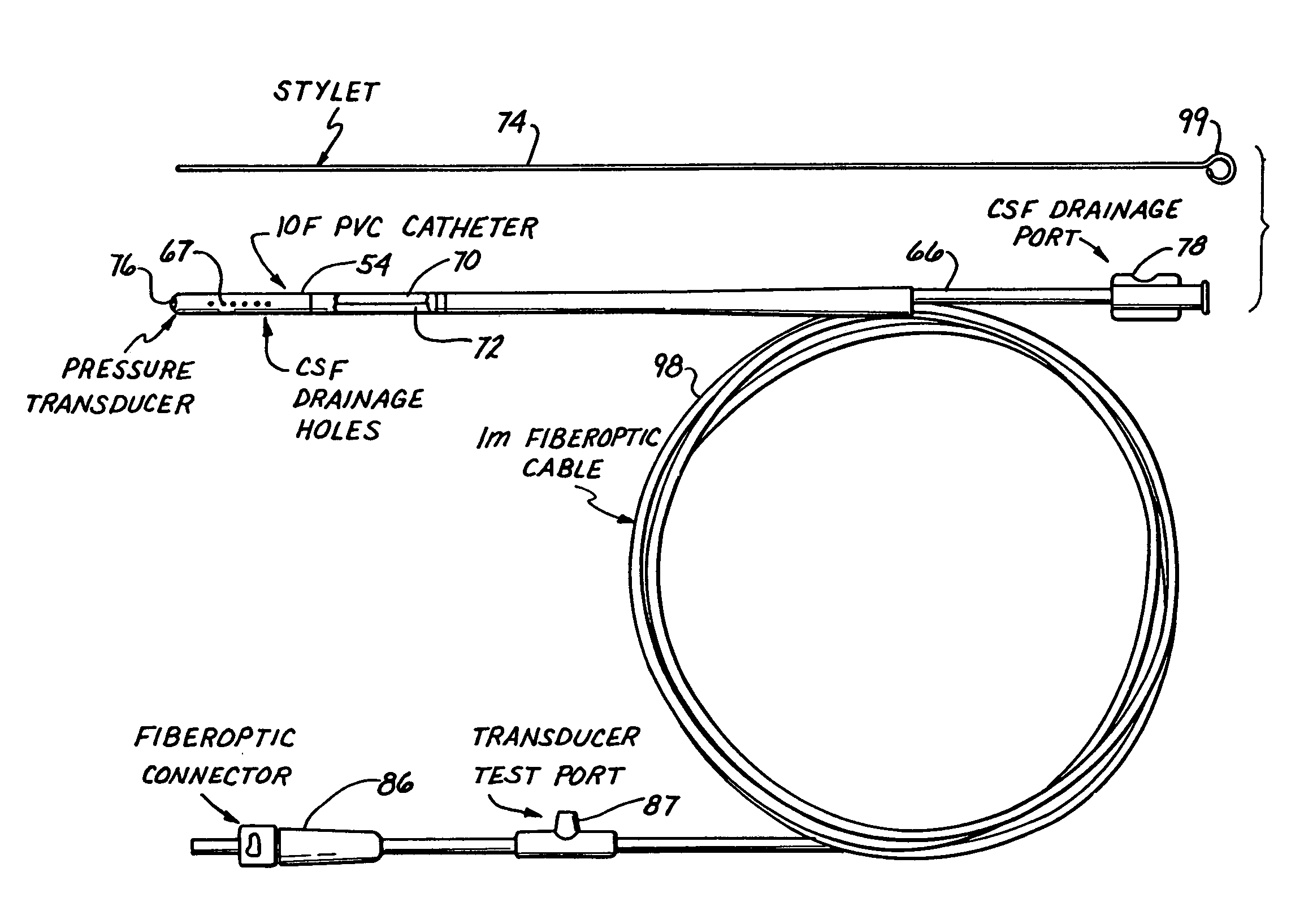
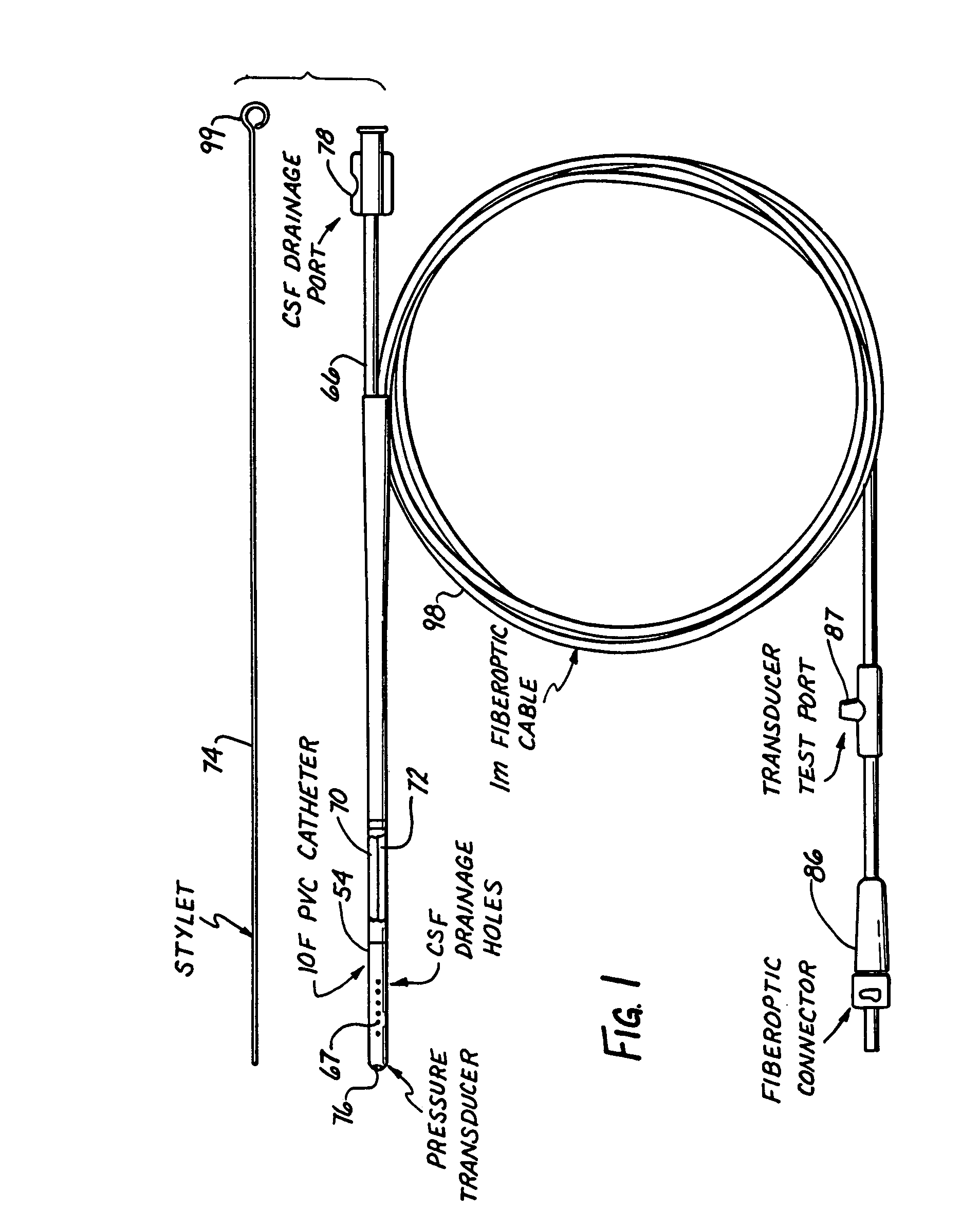
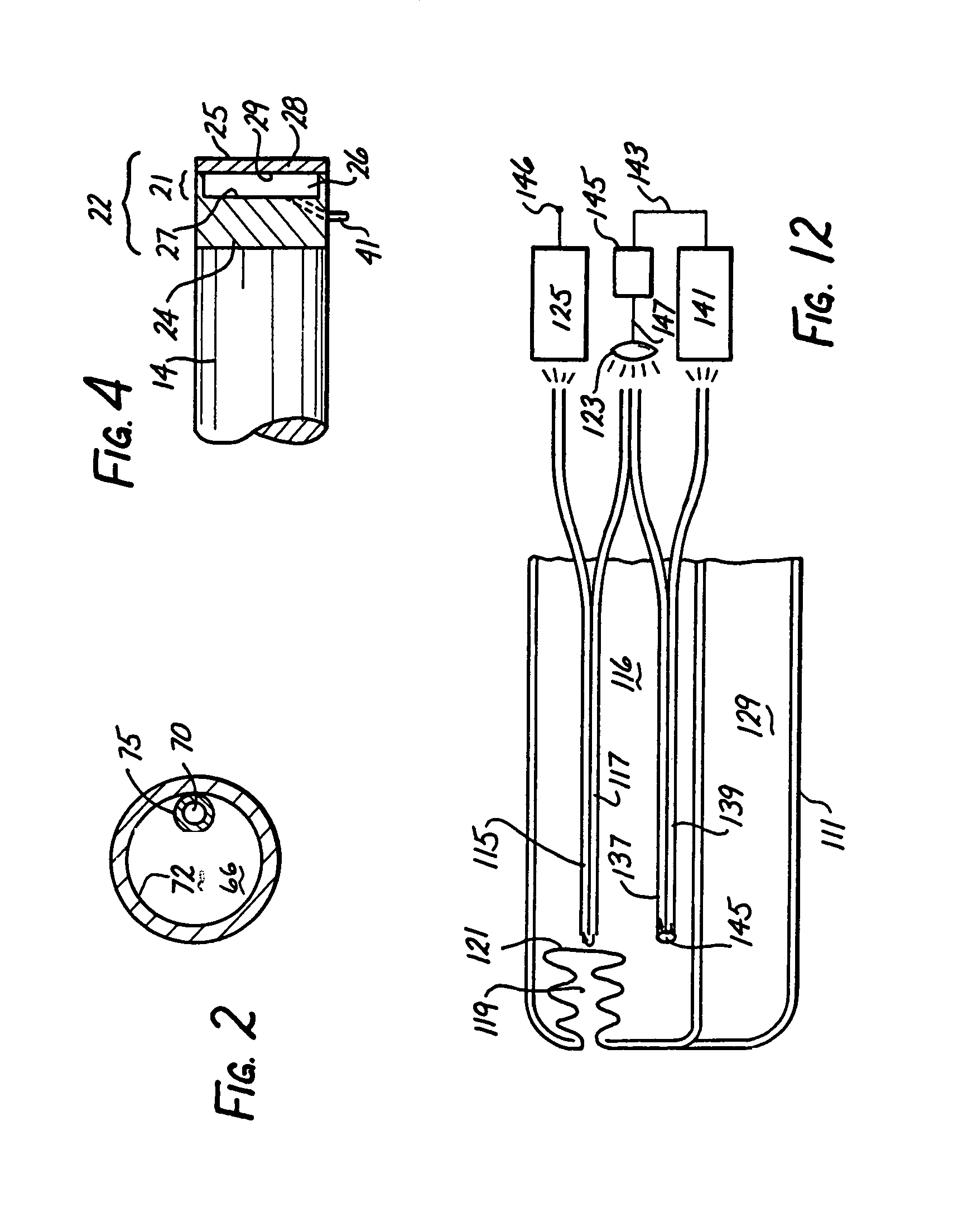
A monitor-driven intracranial catheter assembly including dual lumen catheter for monitoring intracranial pressure via a pressure sensor located in one lumen while simultaneously draining cerebrospinal fluid through another lumen. A third lumen can also be provided with a side port for receiving a stylet. The stylet is used as a stiffening agent to aid in advancing the catheter into the patient's brain. The pressure sensor is preferably a spectral modulation sensor that communicates with a photodetector apparatus by means of a single optical fiber, thus minimizing the diameter of the catheter. The photodetector is self-correcting for signal errors caused by temperature change, changes in intensity of the input light, and transmission losses within the optical apparatus. Moreover, the photodetector operates off the output voltage of the standard hospital monitor by “scaling” the signal from the monitor to provide a pressure measurement signal that emulates the output of a piezoresistive strain gauge sensor or Wheatstone bridge. Therefore, the entire catheter assembly is designed to be used with any of the common types of hospital monitors. The pressure monitoring catheter assembly can be used in any situation requiring very sensitive pressure measurements and can be zeroed and calibrated in situ.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Shunt and access port
Owner:MURPHY KIERAN P +2
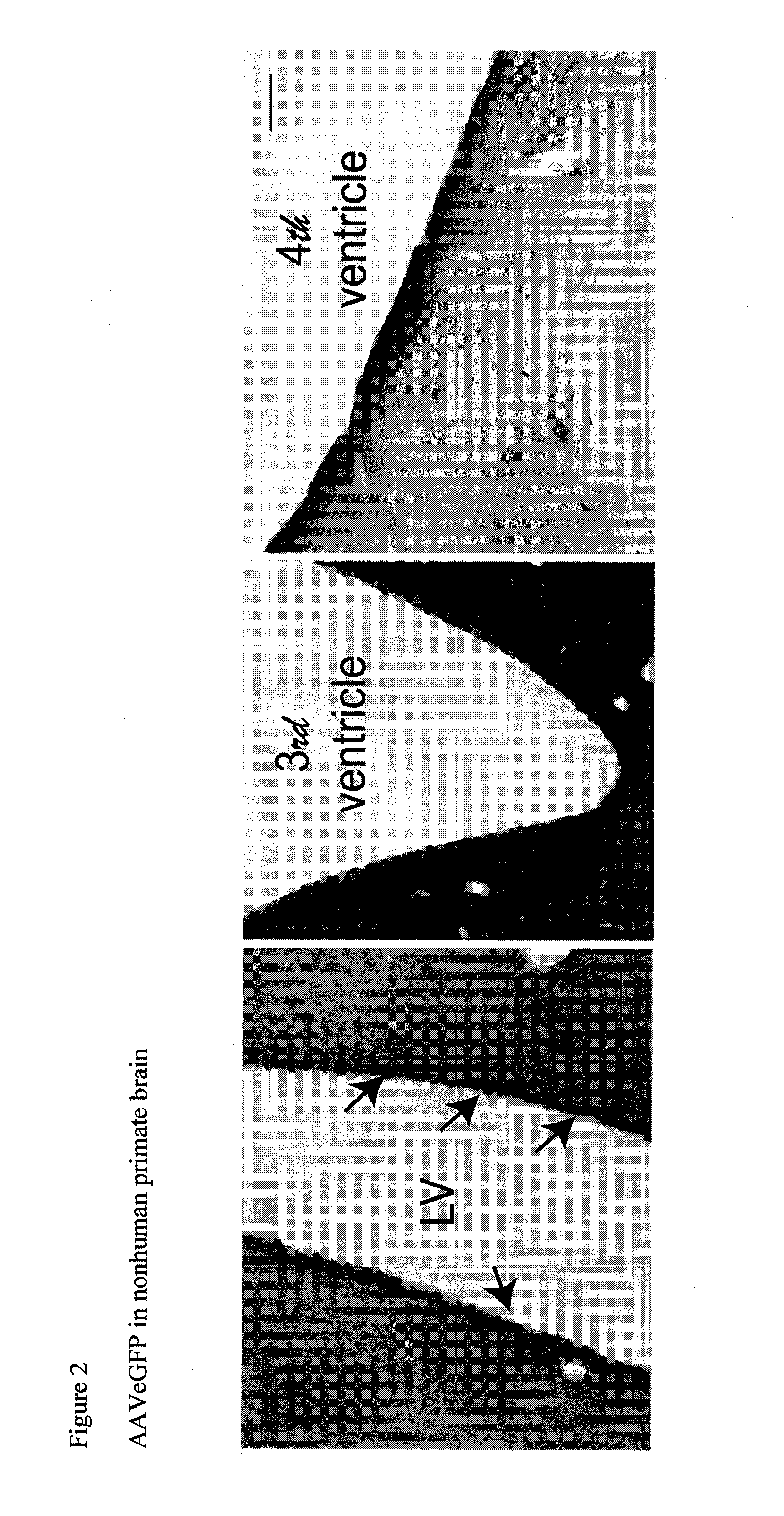
Methods and compositions for treating brain diseases
The present disclosure provides methods of treating a disease in a non-rodent mammal comprising administering to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the non-rodent mammal an rAAV2 particle containing a vector comprising a nucleic acid encoding a therapeutic protein inserted between a pair of AAV inverted terminal repeats in a manner effective to infect an ependymal cell in the non-rodent mammal, wherein the ependymal cell secretes the therapeutic protein so as to treat the disease.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
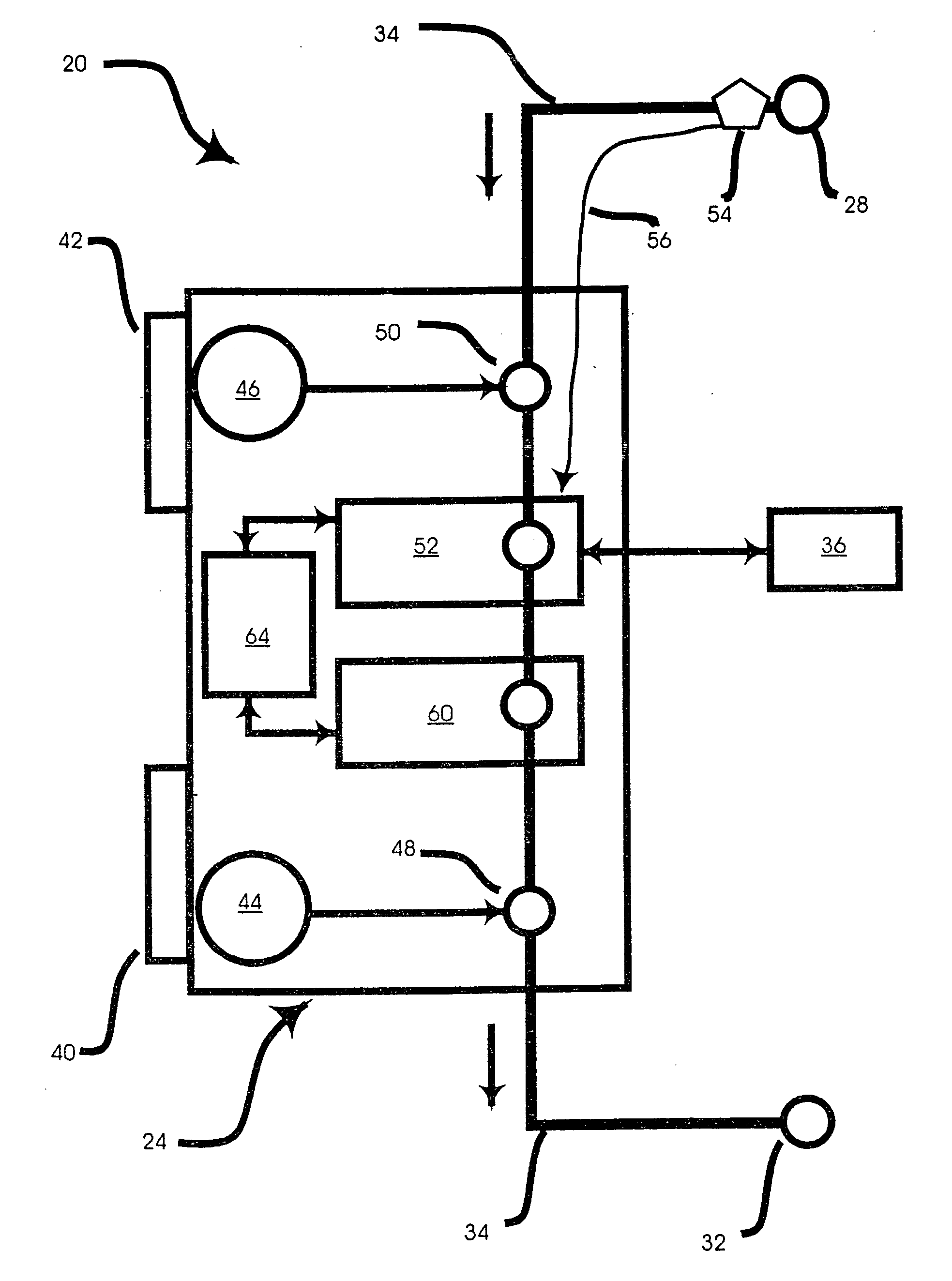
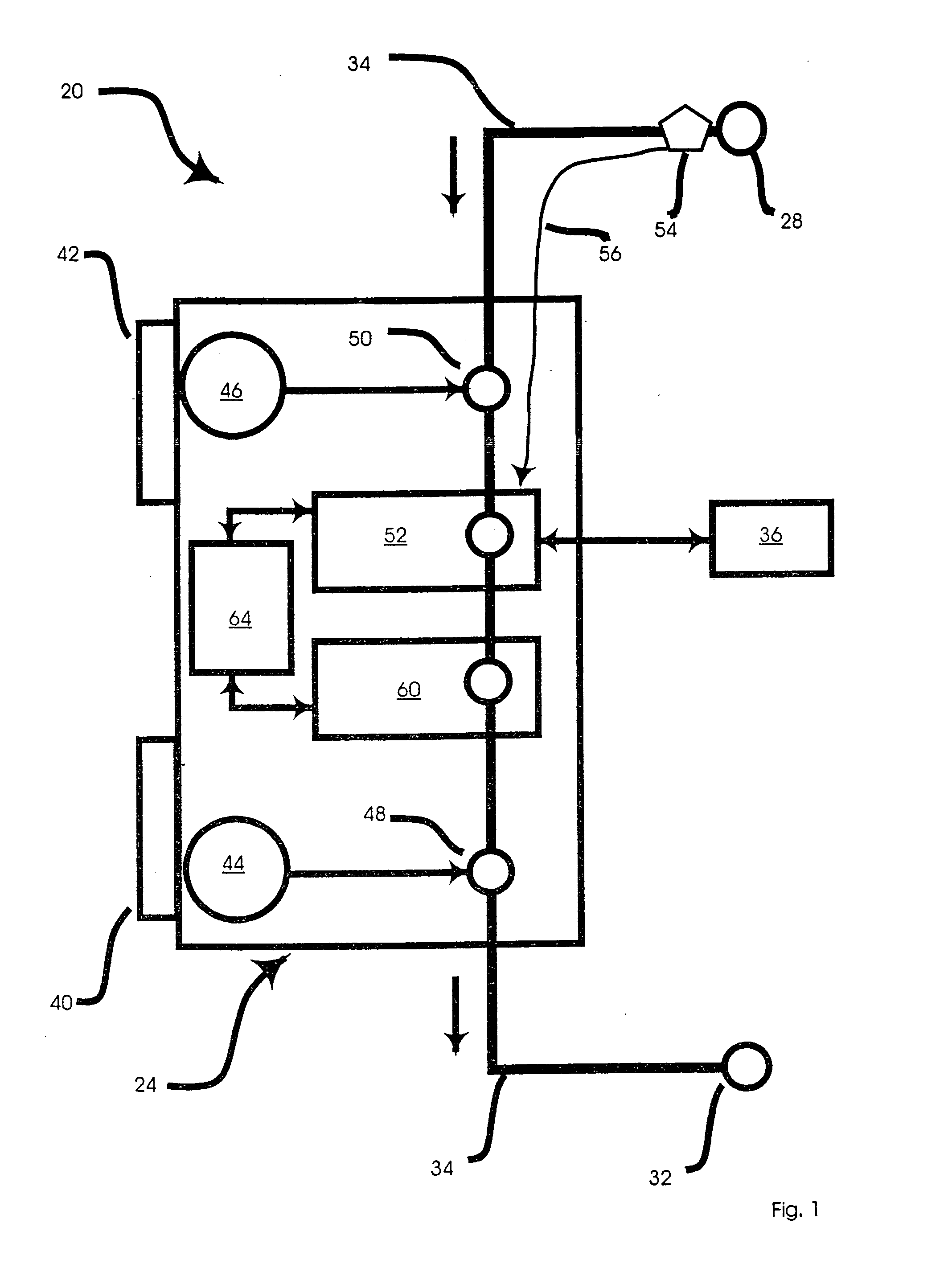
Implantable cerebral spinal fluid flow device and method of controlling flow of cerebral spinal fluid
InactiveUS20060247569A1Reduce decreaseReduce usageWound drainsIntravenous devicesBiomedical engineeringCerebrospinal fluid flow
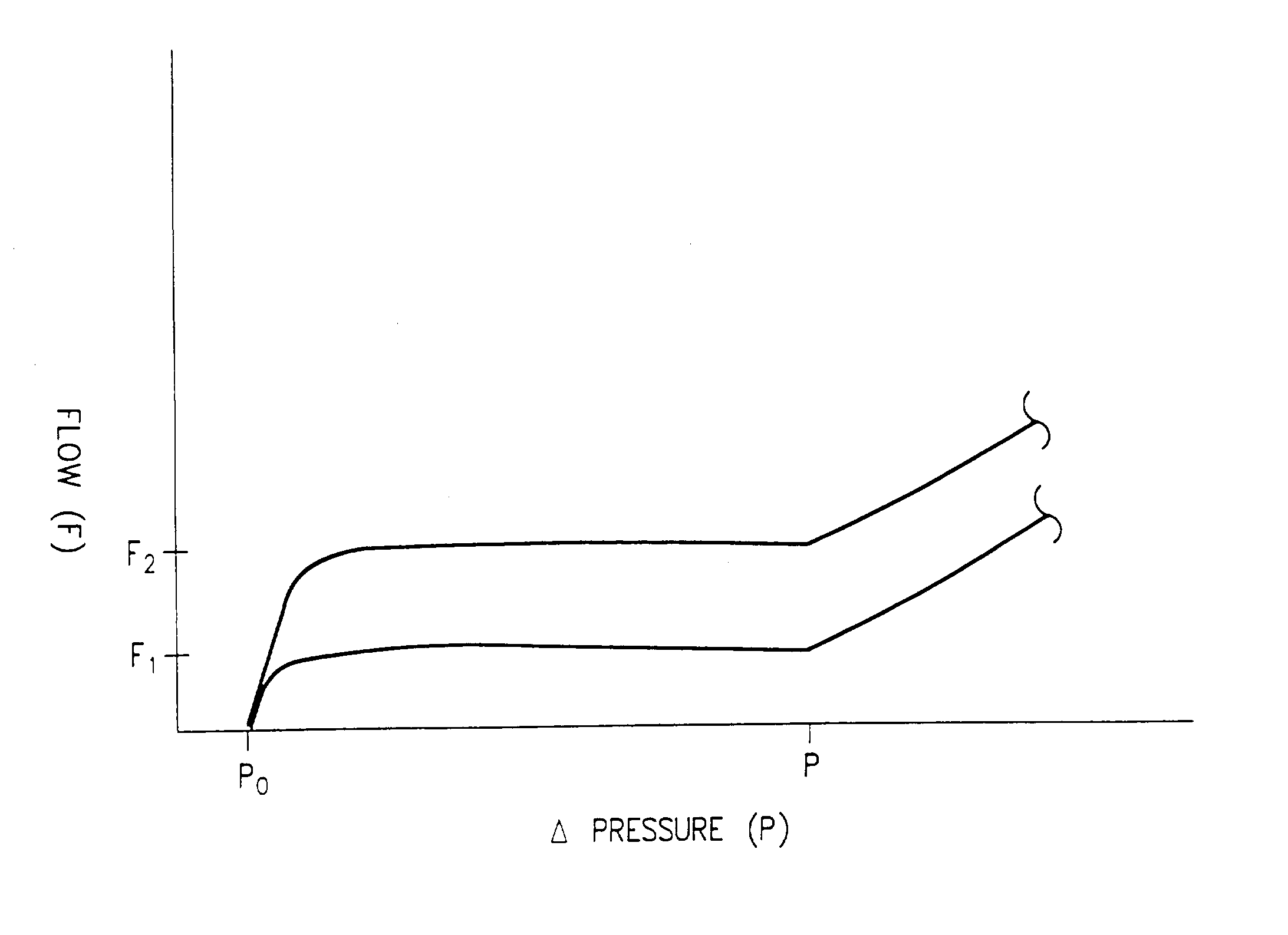
An implantable cerebral spinal fluid flow device and method. A body has an inlet for the cerebral spinal fluid, an outlet for the cerebral spinal fluid and a first interior cavity fluidly coupled with the inlet and the outlet. A first rotational element is mounted in the first interior cavity in a pathway between the inlet and the outlet. The first rotational element provides resistance to flow of the cerebral spinal fluid from the inlet to the outlet. In the method, the cerebral spinal fluid flow device is implanted. Resistance to rotation of the first rotational element to flow of the cerebral spinal fluid from the inlet to the outlet is provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
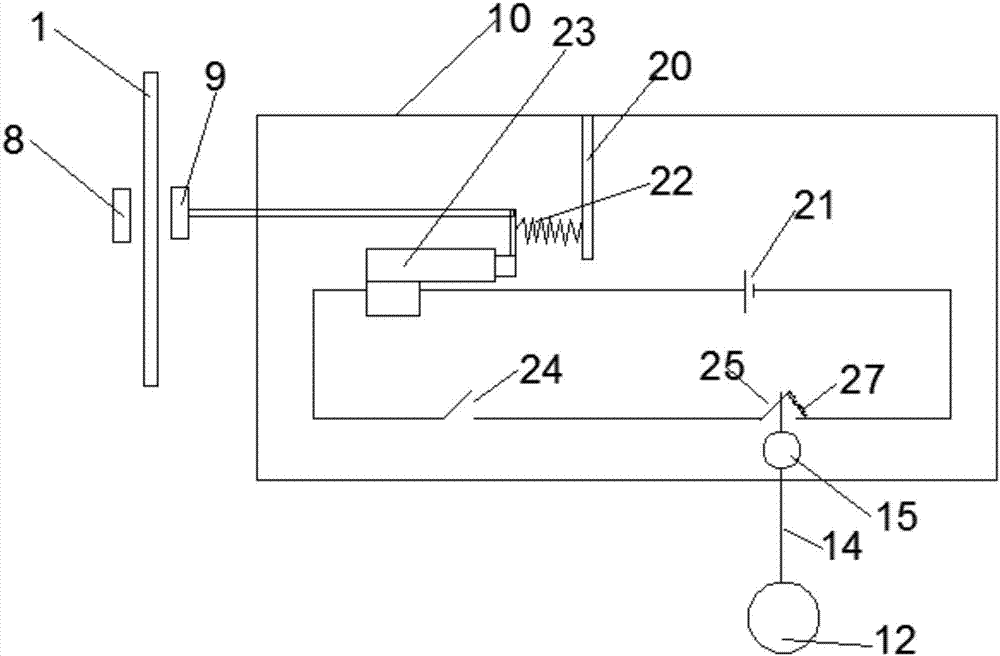
Wireless motion capture test head system
ActiveUS8700354B1Easy to decoupleEasily disconnected and decoupled and connected and disconnectedDigital computer detailsAcceleration measurementMicrocontrollerCerebrospinal fluid
A wireless motion capture test head system including at least one motion capture element, an isolator, mount and an external computer. The motion capture element(s) may include a memory, a wireless motion capture sensor, a radio and a microcontroller. The microcontroller may collect sensor values data from the wireless motion capture sensor, store the data in the memory, analyze the data, recognize an event within the data to determine event data, and transmit the event data associated with the event via the radio. The isolator may surround the at least one motion capture element to simulate physical acceleration dampening of cerebrospinal fluid around a human brain, in order to minimize translation of linear acceleration and rotational acceleration of the event data to obtain an observed linear acceleration and an observed rotational acceleration of the at least one motion capture element coupled in an inner portion of a headform.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
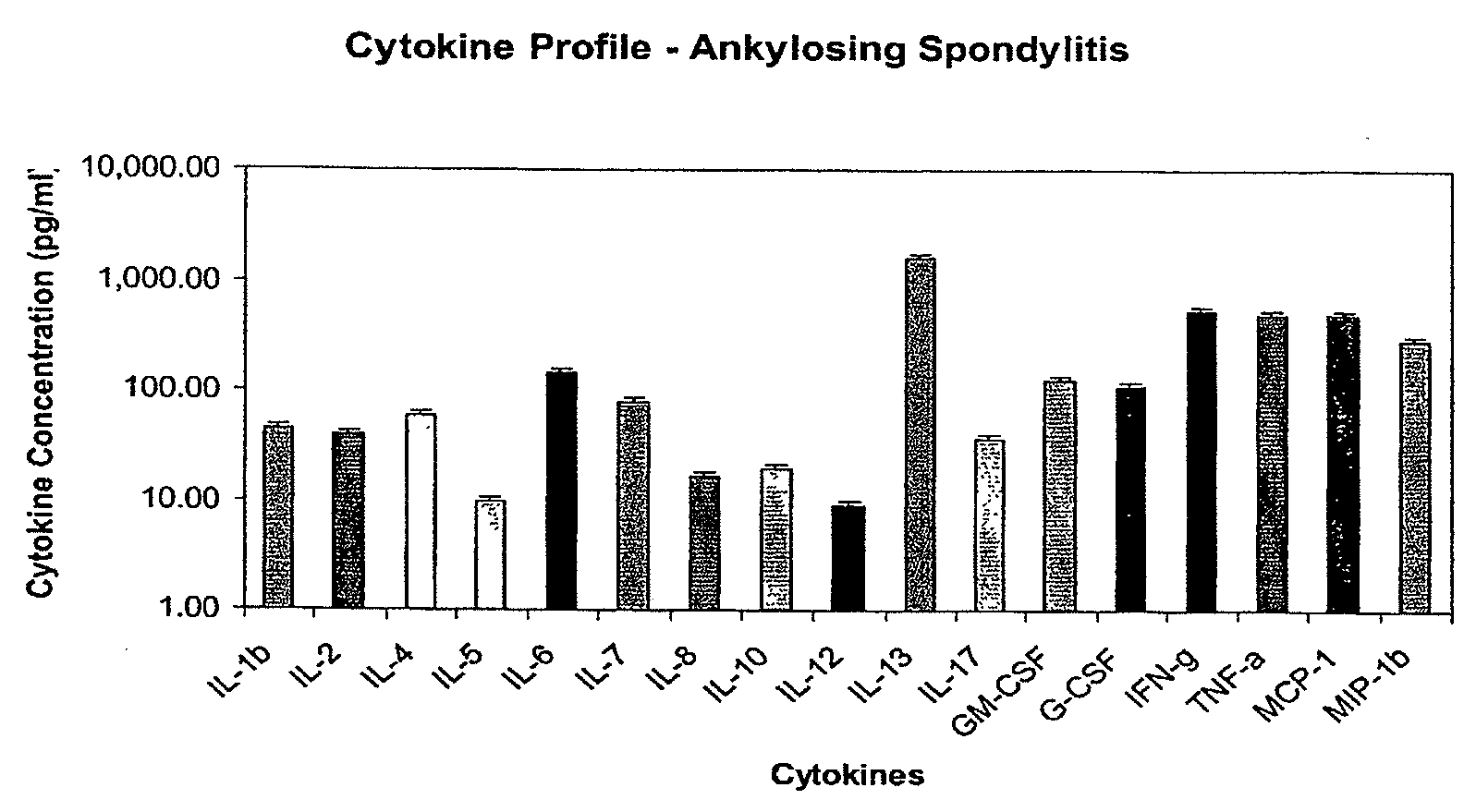
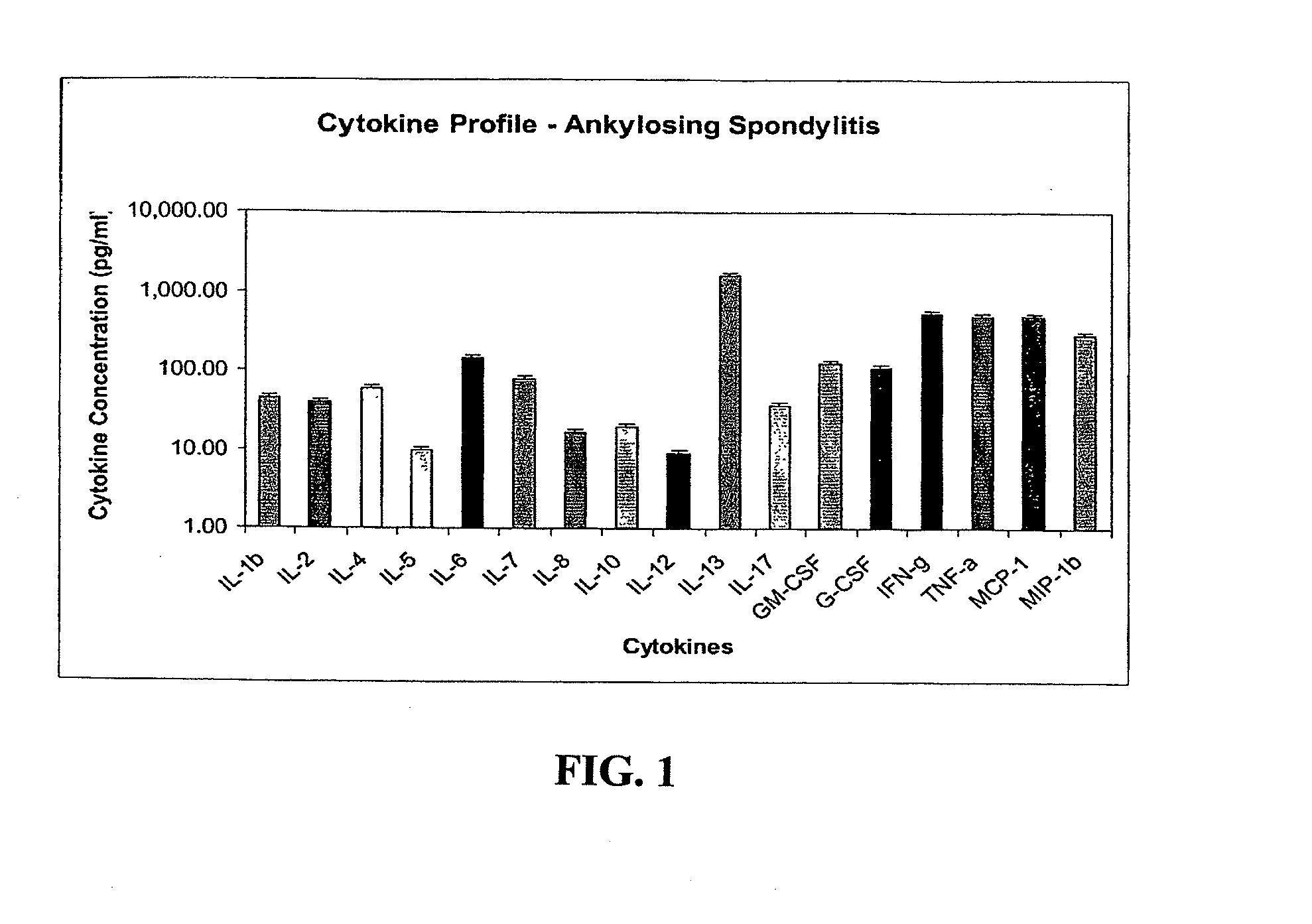
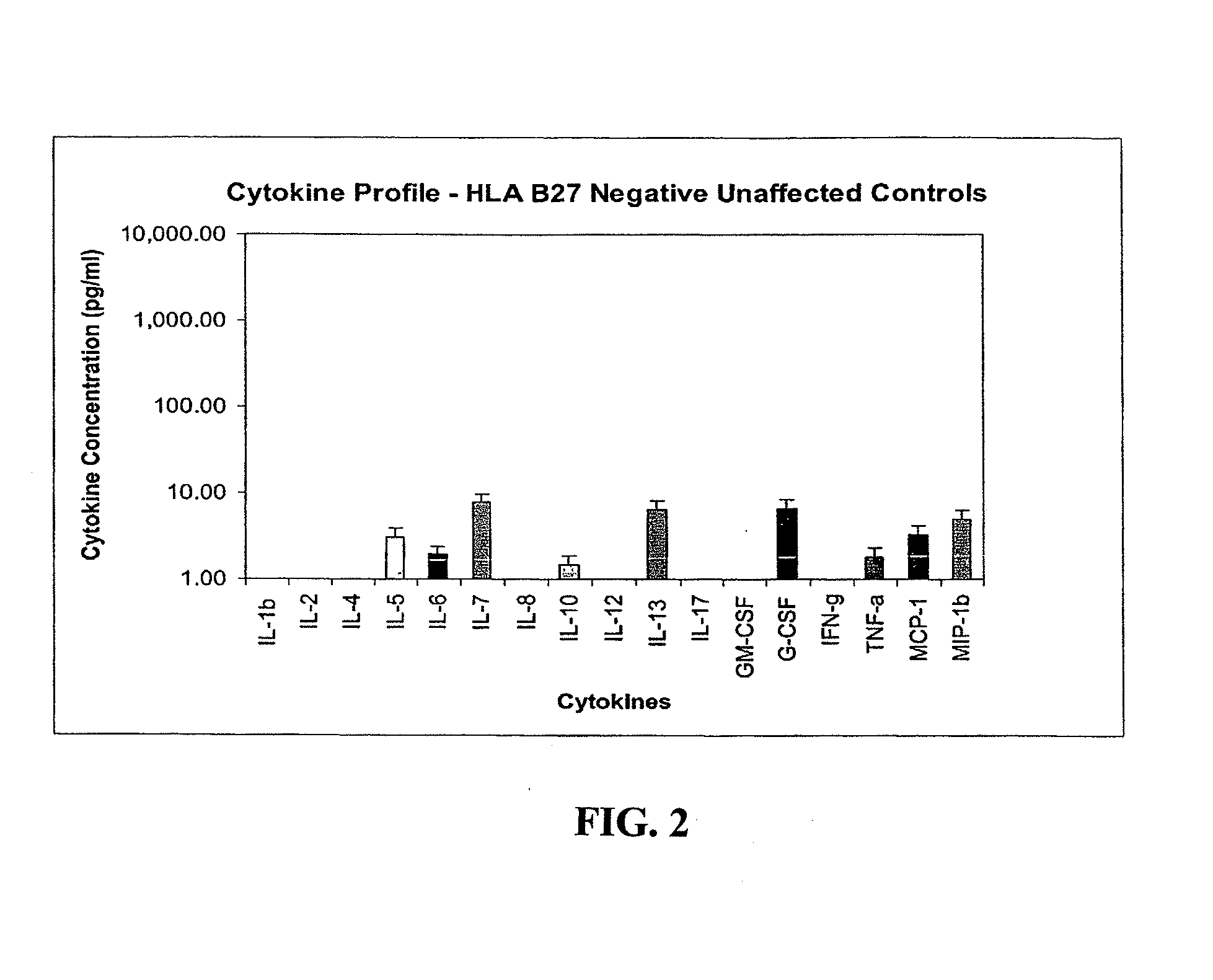
Method of using cytokine assay to diagnose, treat, and evaluate inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS20090325167A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCerebrospinal fluidFactor ii
The invention provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or evaluating inflammatory and autoimmune diseases by sampling peripheral blood, serum, plasma, tissue, cerebrospinal fluit, or other bodily fluids from a human subject having a suspected diagnosis. The sample is analyzed for the presence and amount of certain cytokines, which provides the diagnosis, prognosis or evaluation of therapeutic response.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA +1
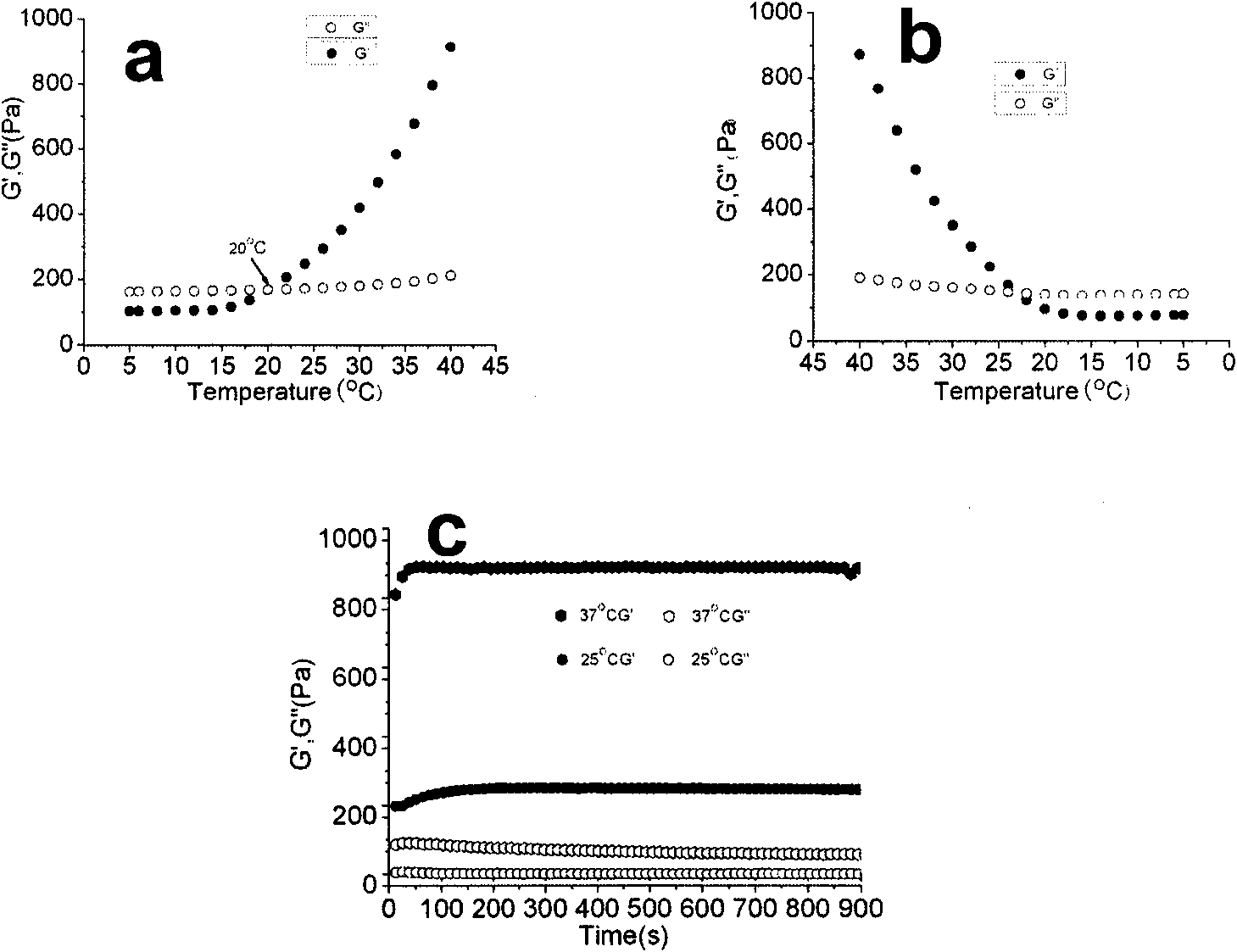
Temperature sensitive chitosan preparation and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101579353ALong in vivo residence timeHigh molecular weightOrganic active ingredientsSurgical drugsBiocompatibility TestingBiological materials
The invention relates to medical biomaterial technical field. The currently popular post operation tissue blocking preventing agent has the disadvantages that internal degradation time is fast, operation steps are cockamamie, and the agent is not applicable to minimally invasive surgery. The invention aims at providing an antiblocking material with favorable temperature responsivity, biocompatibility and biodegradability, namely a temperature sensitive chitosan preparation as well as the preparation method and application thereof. The invention, by carrying out hydroxyl butylation reaction on chitosan, controls reaction condition, attaches the chitosan with unique temperature responsivity and maintains other inherent biological characteristics of the chitosan. The temperature sensitive chitosan preparation of the invention has favorable temperature sensitive property and favorable gelatin recoverability, and is easy to operate in operation application; the favorable biocompatibility ensures the safety of the application of the temperature sensitive chitosan; the gelation time and internal residence time are controllable, thus meeting different application requirements; and animal experiments of the post operation tissue blocking and the cerebrospinal leakage prove that the invention has good clinical application prospect.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
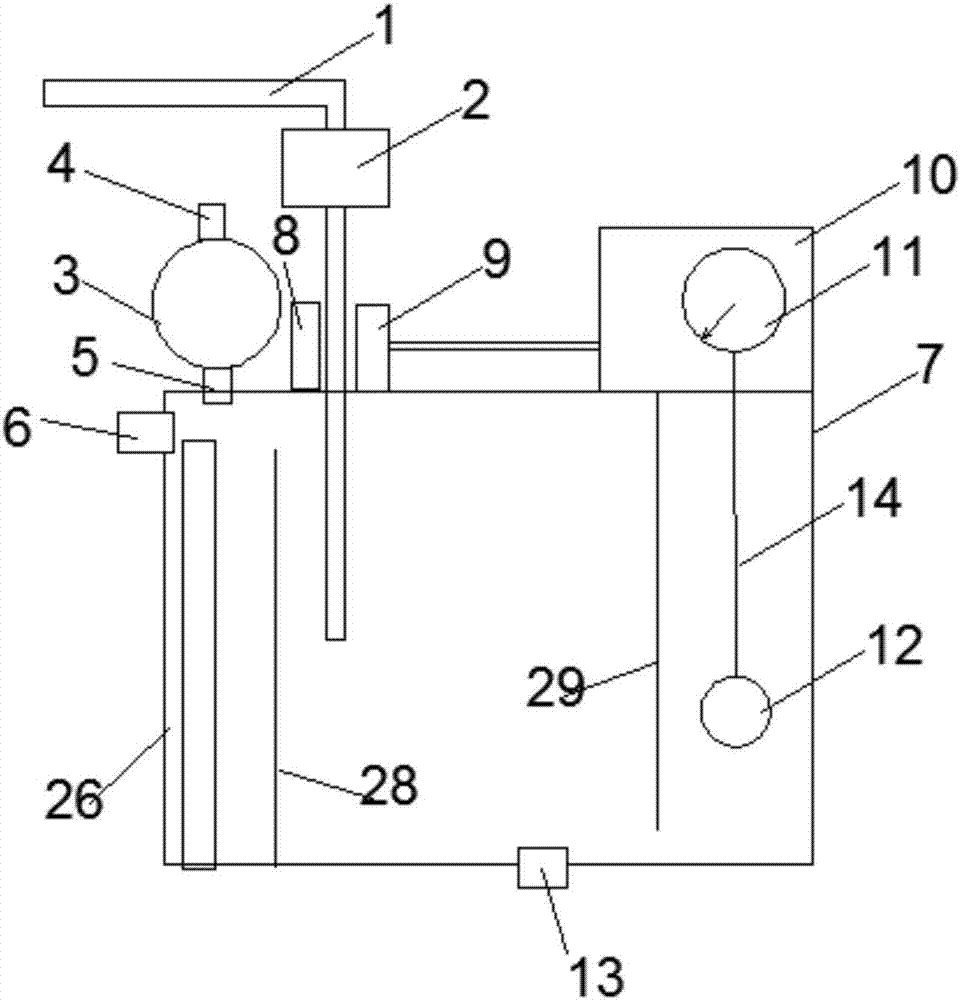
Device capable of automatically controlling drainage volume
PendingCN106963998ARelieve stressReduce work stressMedical devicesIntravenous devicesCerebrospinal fluidAutomatic control
The invention provides a device capable of automatically controlling drainage volume which can be connected to wound or body cavity effusion drainage tubes such as urinary vessels, abdominal dropsy drainage tubes, closed thoracic drainage tubes, pericardial catheter drainage tubes, ventricular drainage tubes, T drainage tubes, and fistula drainage tubes to realize draining and flushing and especially for the condition that there may be leakage of cerebrospinal of spinal postoperation incision. By means of the automatic drainage volume control device, the drainage tubes can be automatically clipped and closed after the preset drainage volume is reached; at the same time, the negative pressure of the drainage device can be regulated and monitored to realize accurate drainage to avoid complications due to excessive or insufficient drainage and be helpful for the healing of wounds.
Owner:SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV
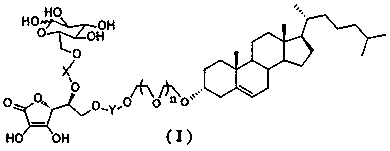
Novel dual brain-targeting lipid material and application thereof in drug delivery system
InactiveCN108517033AImprove targetingIncrease concentrationOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMedicinePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a novel lipid material which is used for prolonging the circulation time and increasing drug targets to be transmitted to the brain. According to the novel lipid material, polyethylene glycol is used for bridging, one side of polyethylene glycol is connected with cholesterol, and the other side of polyethylene glycol is connected with glucose and vitamin C, so that the defect of the targeting capability of lipidosomes modified by single glucose or vitamin C is made up for, transfer for crossing a blood-brain and blood-brain spinal fluid dual barrier is achieved, the brain targeting of drugs is improved, and the central concentration of the drugs is increased. The novel lipid material can be used for different dosage forms including liposomes, nanoparticles and micelles, and paclitaxel liposomes prepared from the material have an obvious brain targeting function and wide application prospects.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Chinese traditional medicine composition for treating hydrocephalus, cerebral edema and intracranial hypertension
InactiveCN1634385ASignificant diuretic effectEnhanced diuretic effectUnknown materialsDrug compositionsAdemetionineRhizome
The invention relates to a Chinese traditional medicine composition for treating hydrocephalus, cerebral edema and intracranial hypertension which comprises fish encephalolith, raw astragalus root, oriental water plantain rhizome, Poria cocos, plantain seeds, notoginseng, root of red rooted saliva, sweetgum fruit, grassleaved sweetflag rhizome, evodia rutaecarpa, and achyranthes and cyathula root.
Owner:谢静
Method for treatment of demyelinating central nervous system disease
ActiveUS20070048255A1Treating and diminishing symptomPrevent demyelinatingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCerebrospinal fluid
A method for treating demyelinating central nervous system diseases in a subject that comprises administering to the subject a composition comprising a therapeutically active amount of colony stimulating factor or CSF-like ligand. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the CSF is a GM-CSF. In a most preferred embodiment of the present invention, CSF is sargramostim.
Owner:HUNTER SAMUEL F
Method and kit for detection of Anti-beta amyloid antibodies
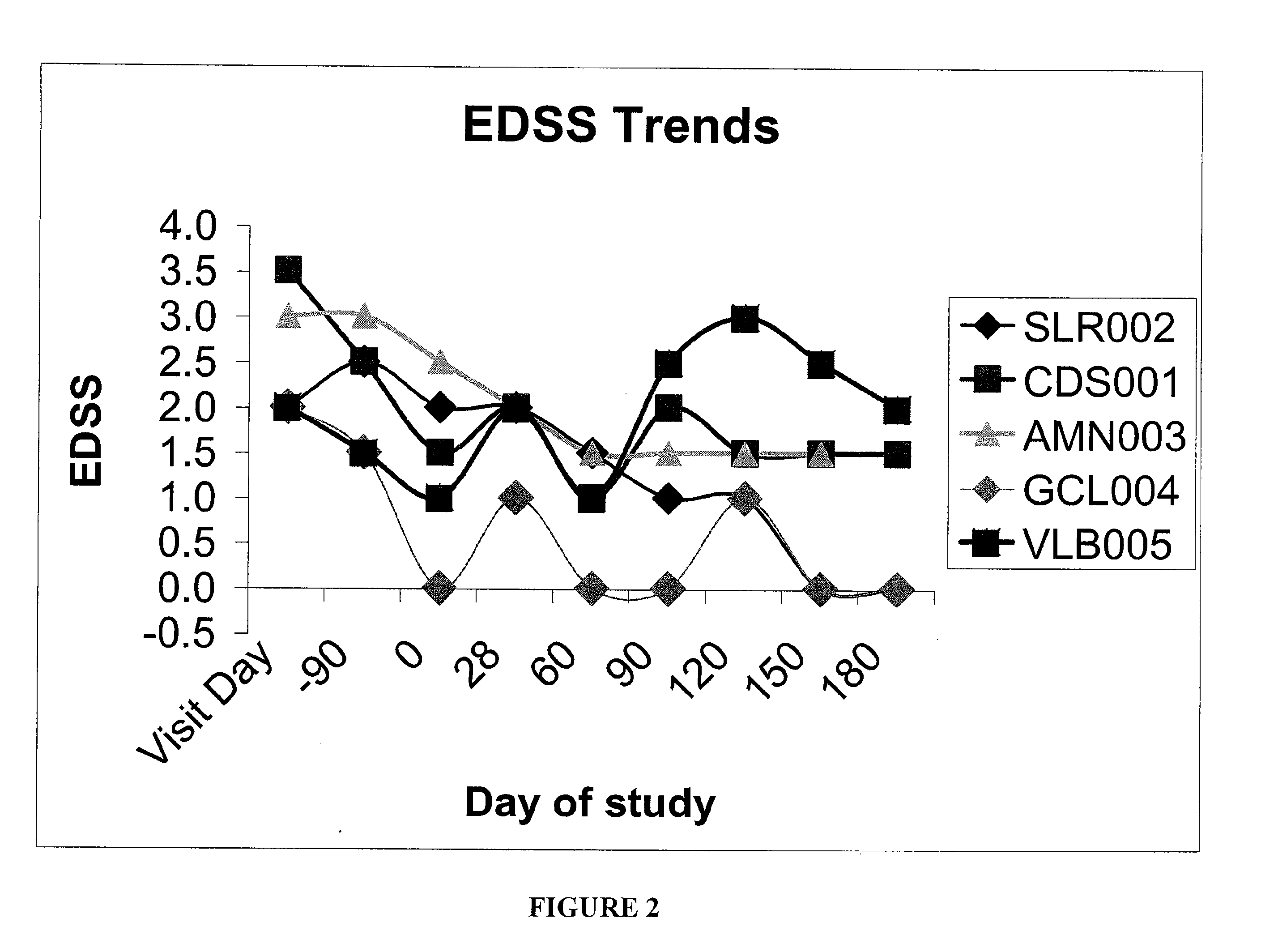
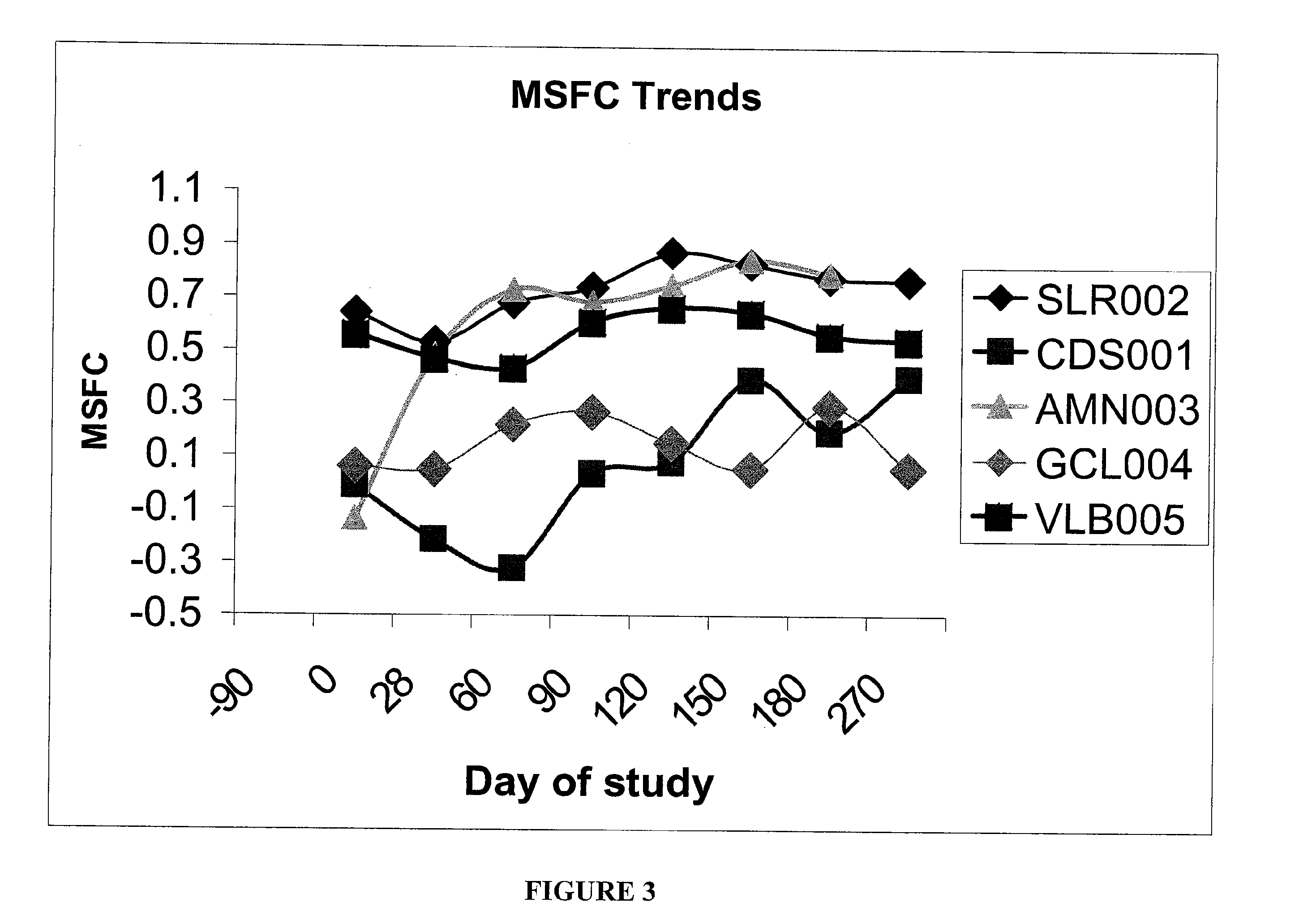
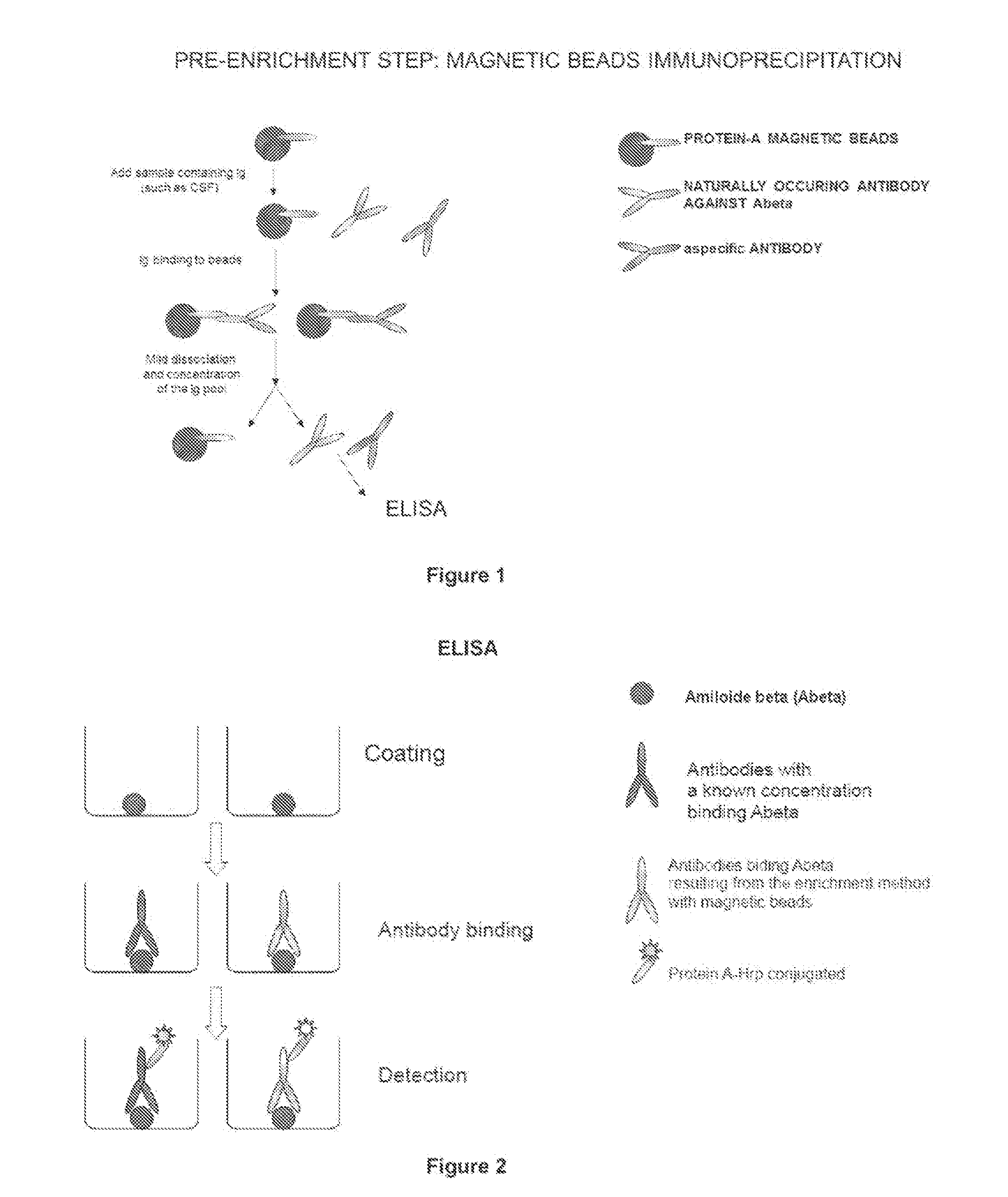
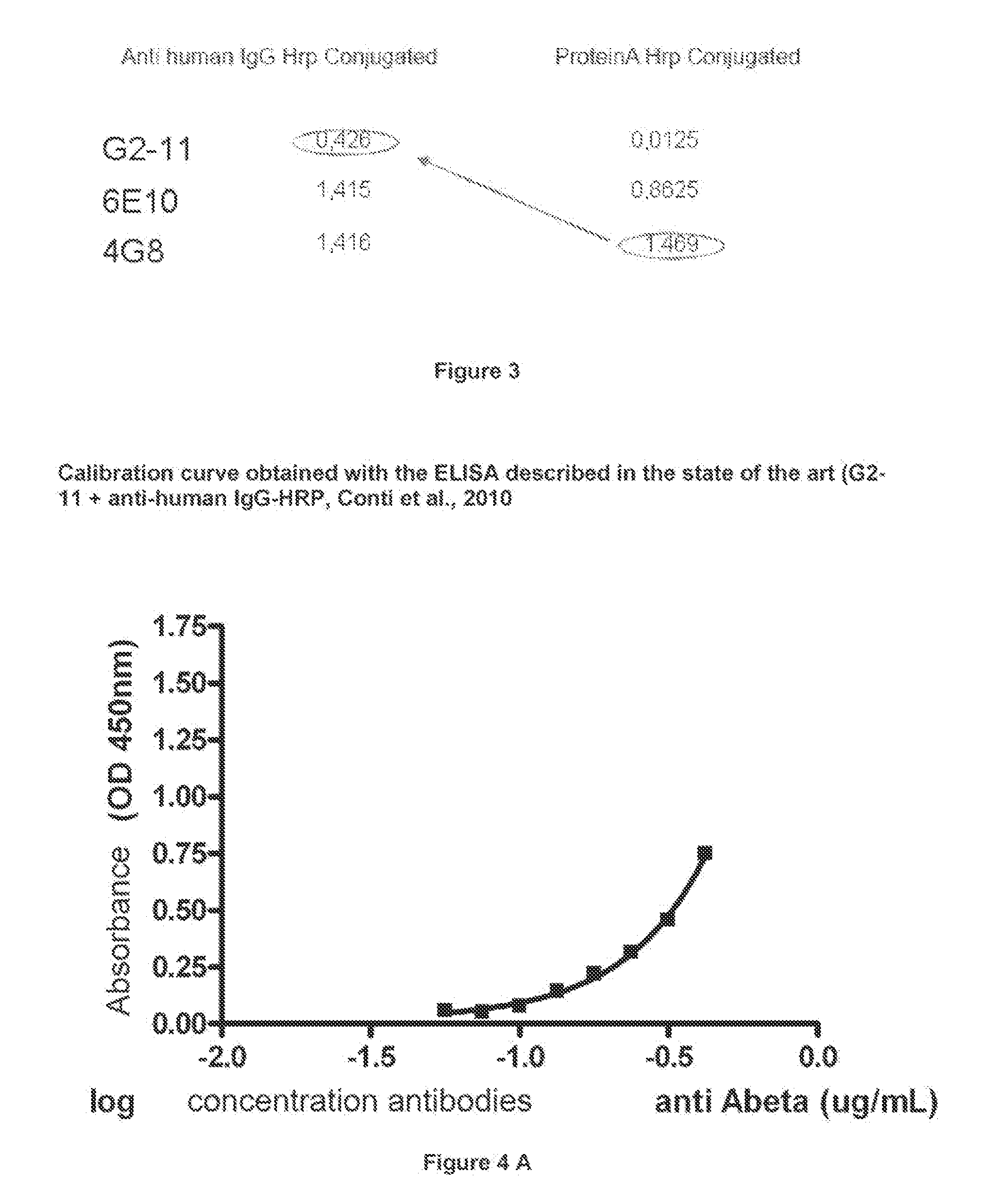
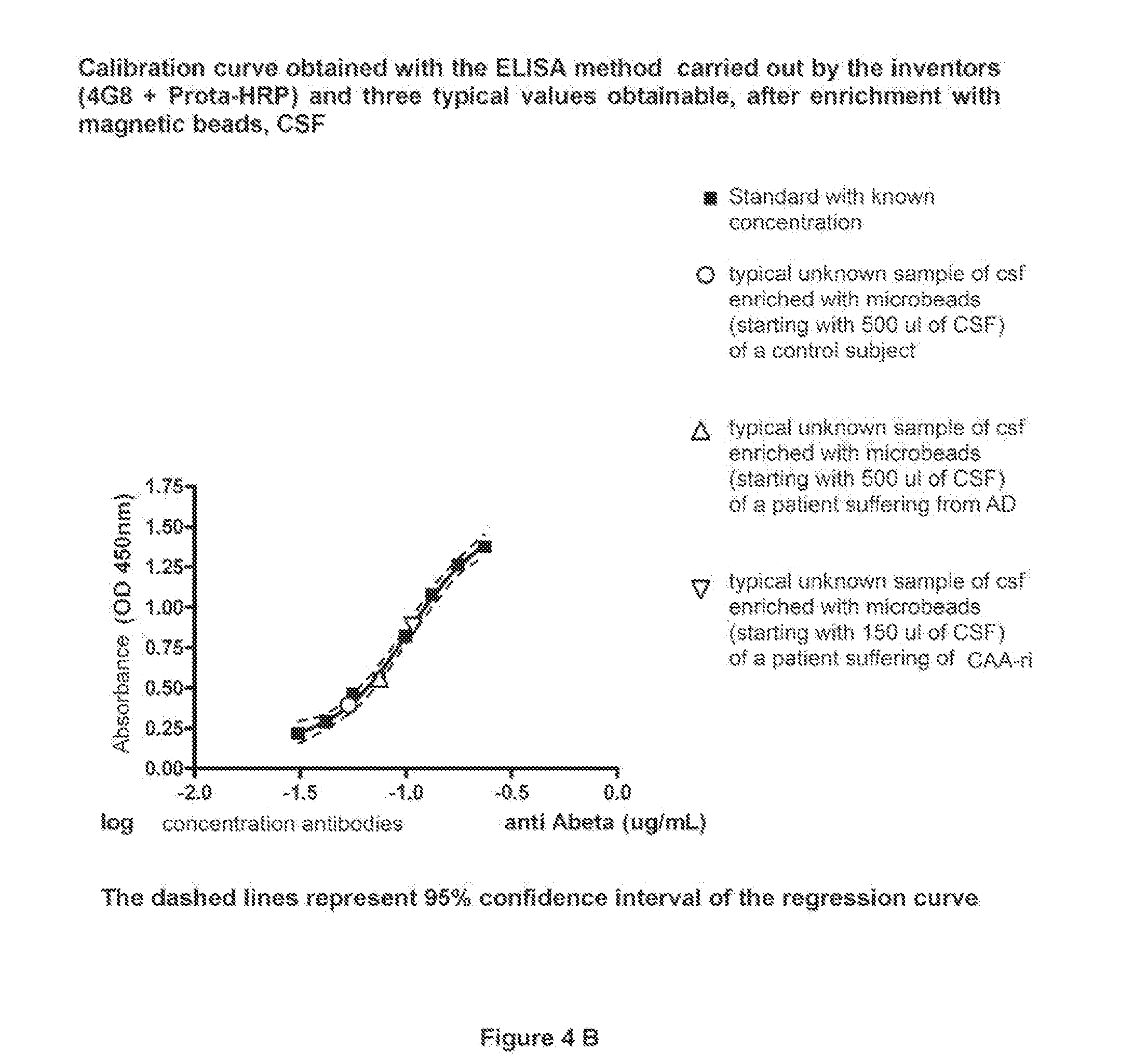
InactiveUS20150094218A1Easy to disassembleHigh sensitivityPeptide librariesLibrary screeningCrystallographyCerebrospinal fluid
An in vitro method and a kit for the quantification of antibodies anti-beta amyloid protein in a sample of cerebrospinal fluid comprising the following steps a) concentrating the quantity of said antibodies of said sample with magnetic micro beads coated with macromolecules capable of binding said antibodies b) analysing the concentrated sample obtained in step a) by immunoenzyme assay or by radioimmunoassay; c) analysing a sample comprising antibodies anti-beta amyloid protein having a known titre with the same assay used in step b) and elaborating the related calibration curve, wherein said antibody having a known titre is a murine antibody belonging to the IgG2a or IgG2b class or a human or humanized antibody belonging to the IgG2b or IgGi class.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI MILANO BICOCCA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com