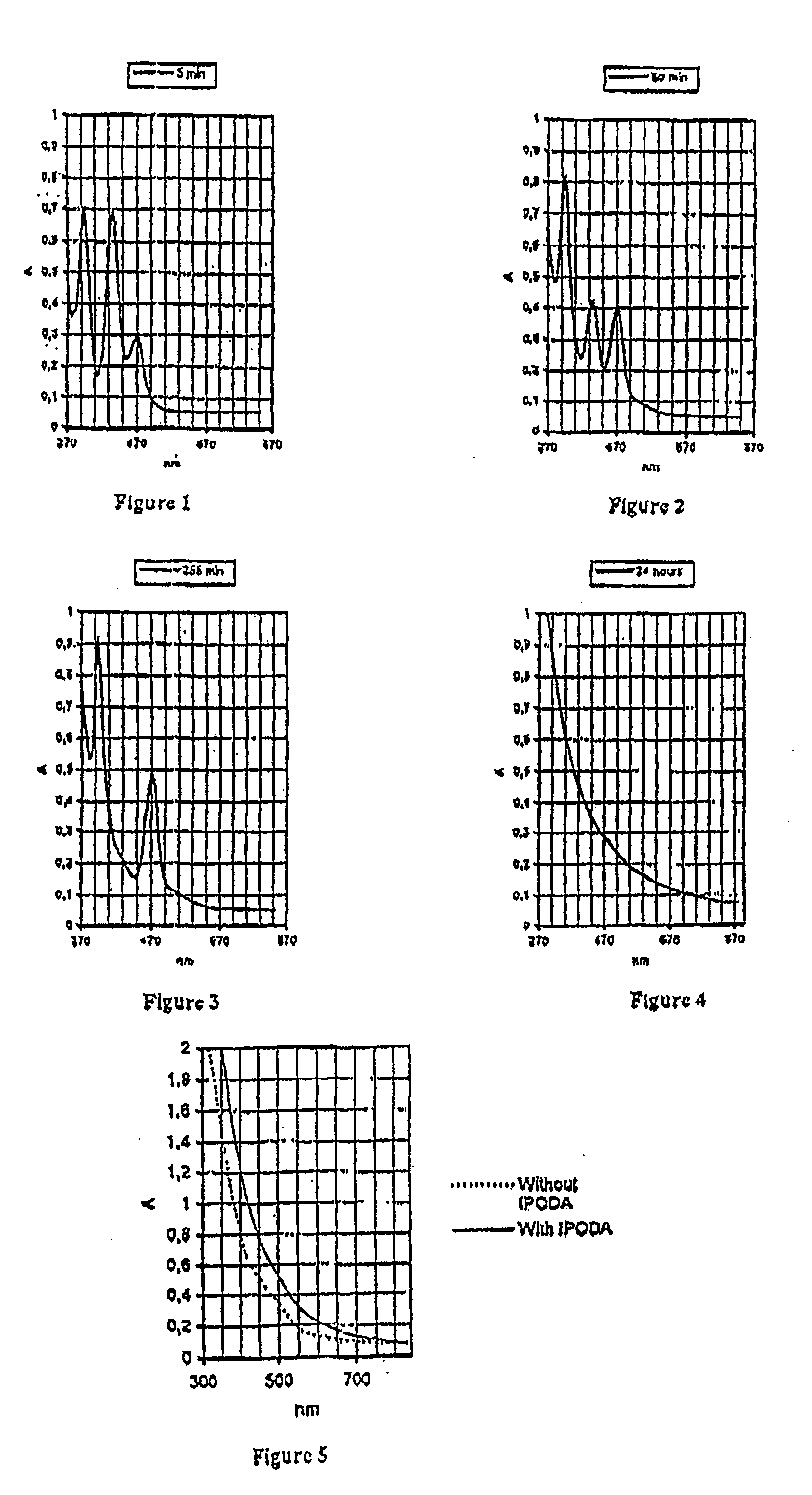
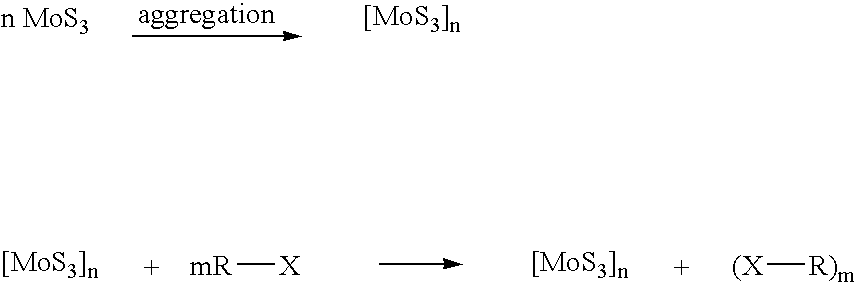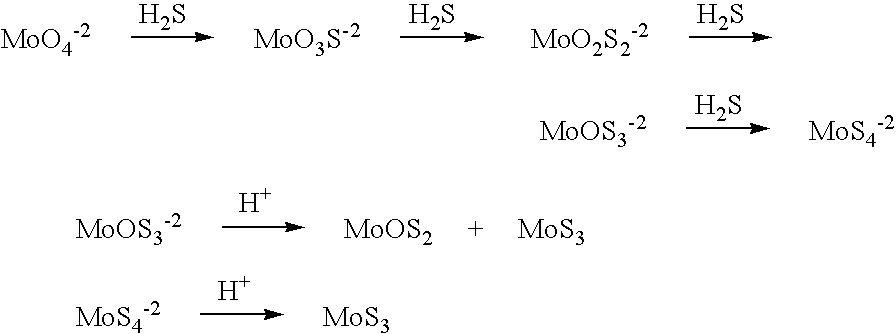Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
193 results about "Chemical interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chemical Interaction. Chemical interactions are interactions that are compelled by electrostatic forces which can occur both in vitro and in vivo.
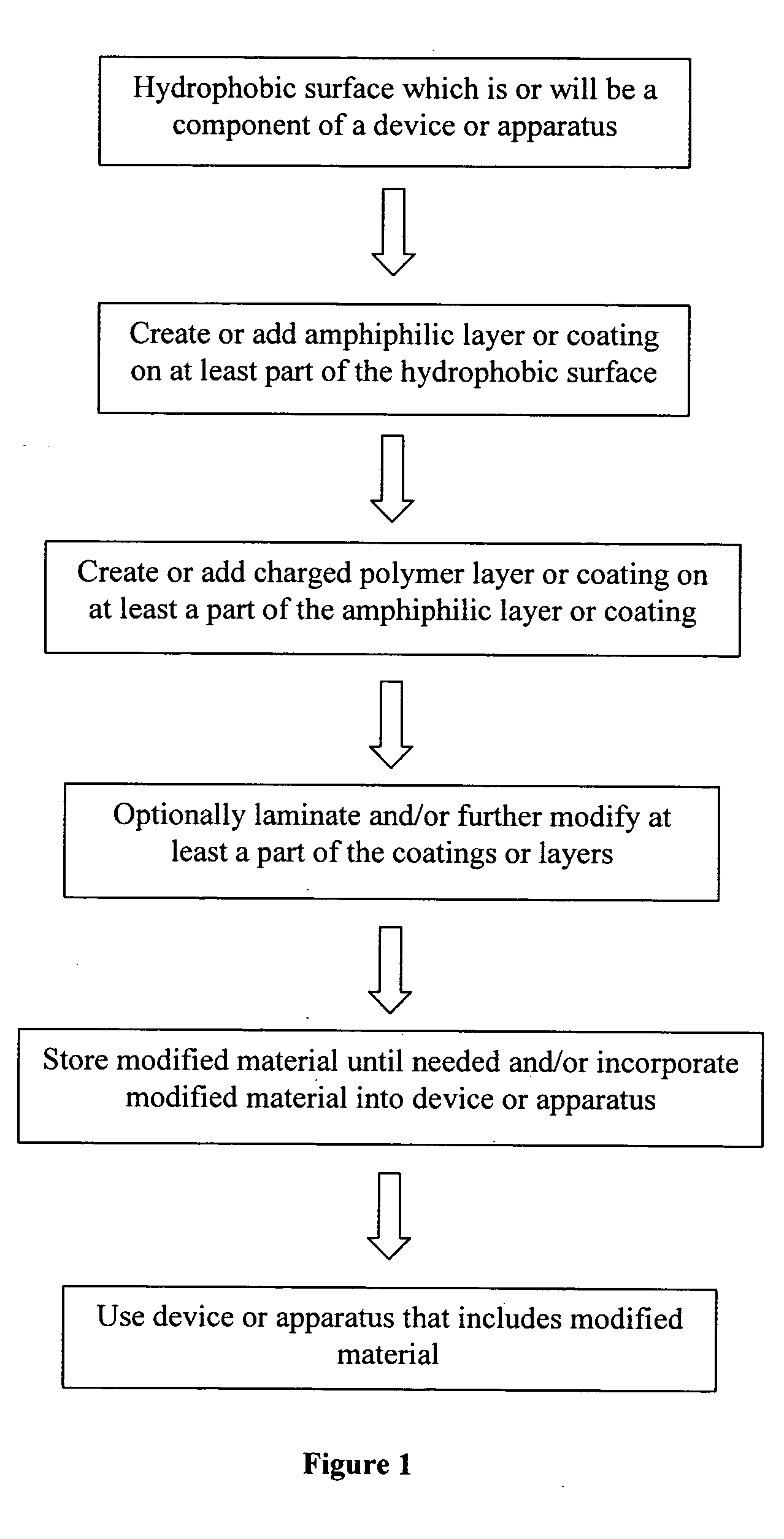
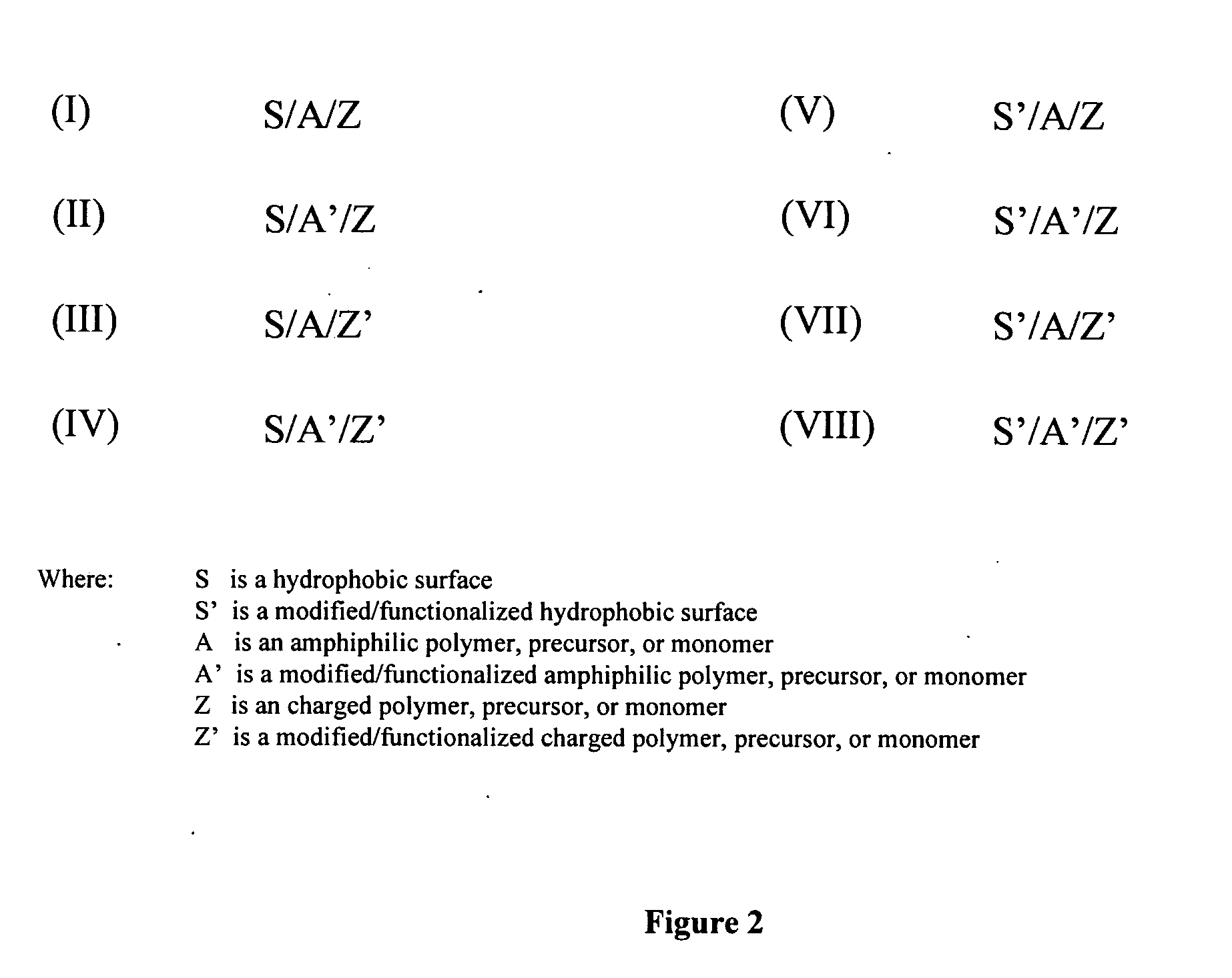
Methods, compositions and devices, including microfluidic devices, comprising coated hydrophobic surfaces
Methods are disclosed for coating at least a portion of a hydrophobic surface, including the surfaces of plastics or other polymers. Such methods include the use of a first coating layer and / or region that interacts with the hydrophobic surface, although the formation of a chemical bond between the first coating layer and the hydrophobic surface is not required. Subsequent layers may then interact chemically or non-chemically with at least a portion of the first coating layer and / or region. Such coated surfaces may be part of a device or apparatus, including microfluidic devices.
Owner:NORVIEL VERN
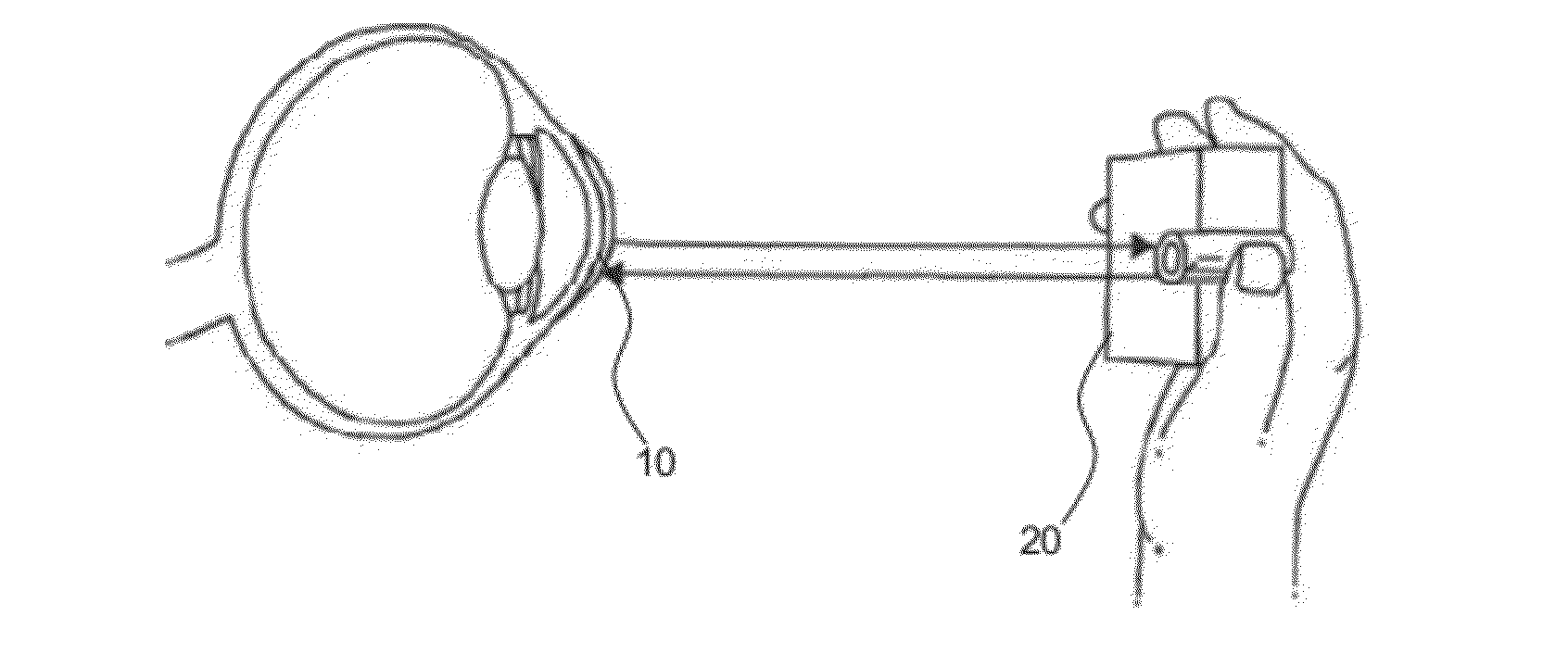
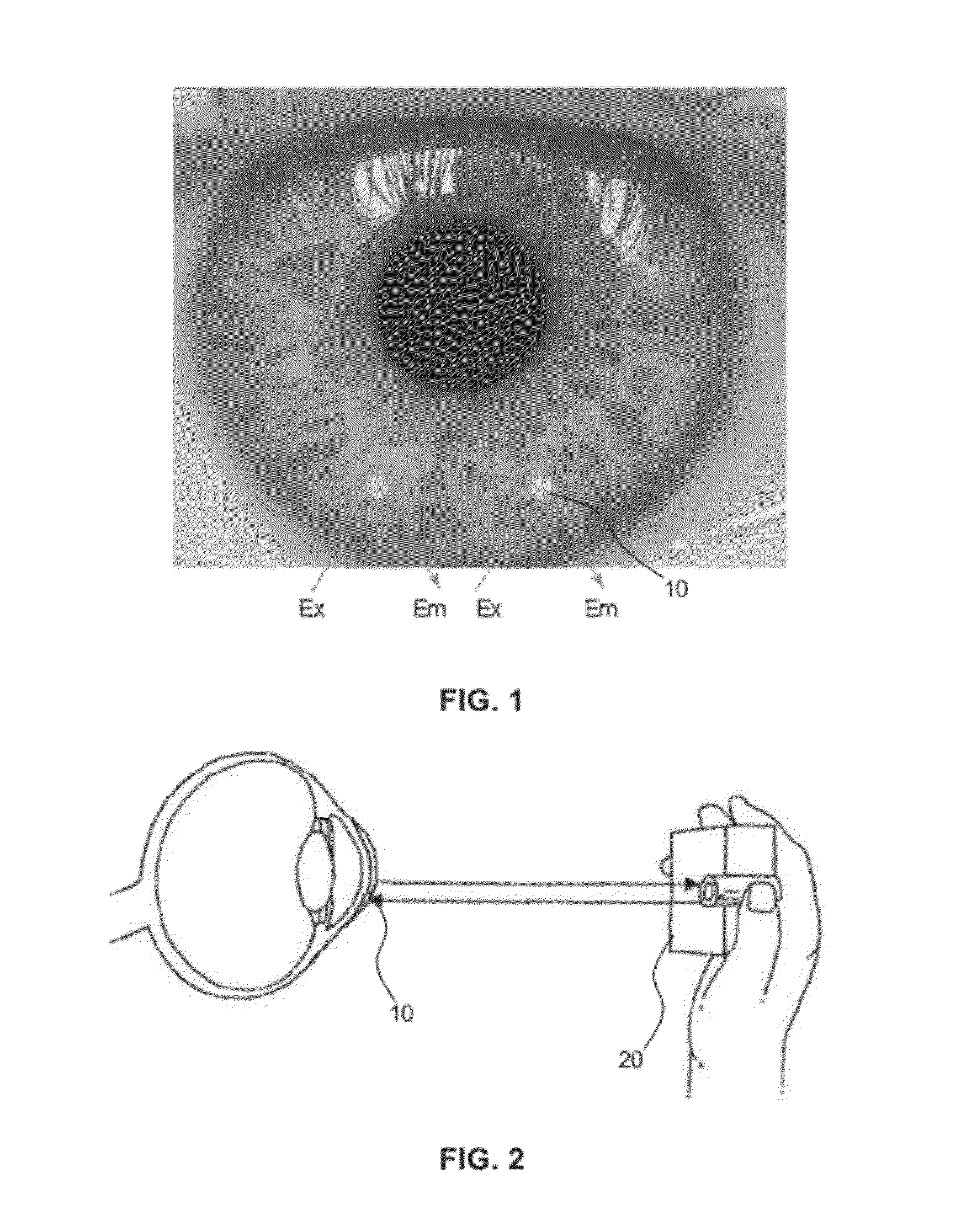
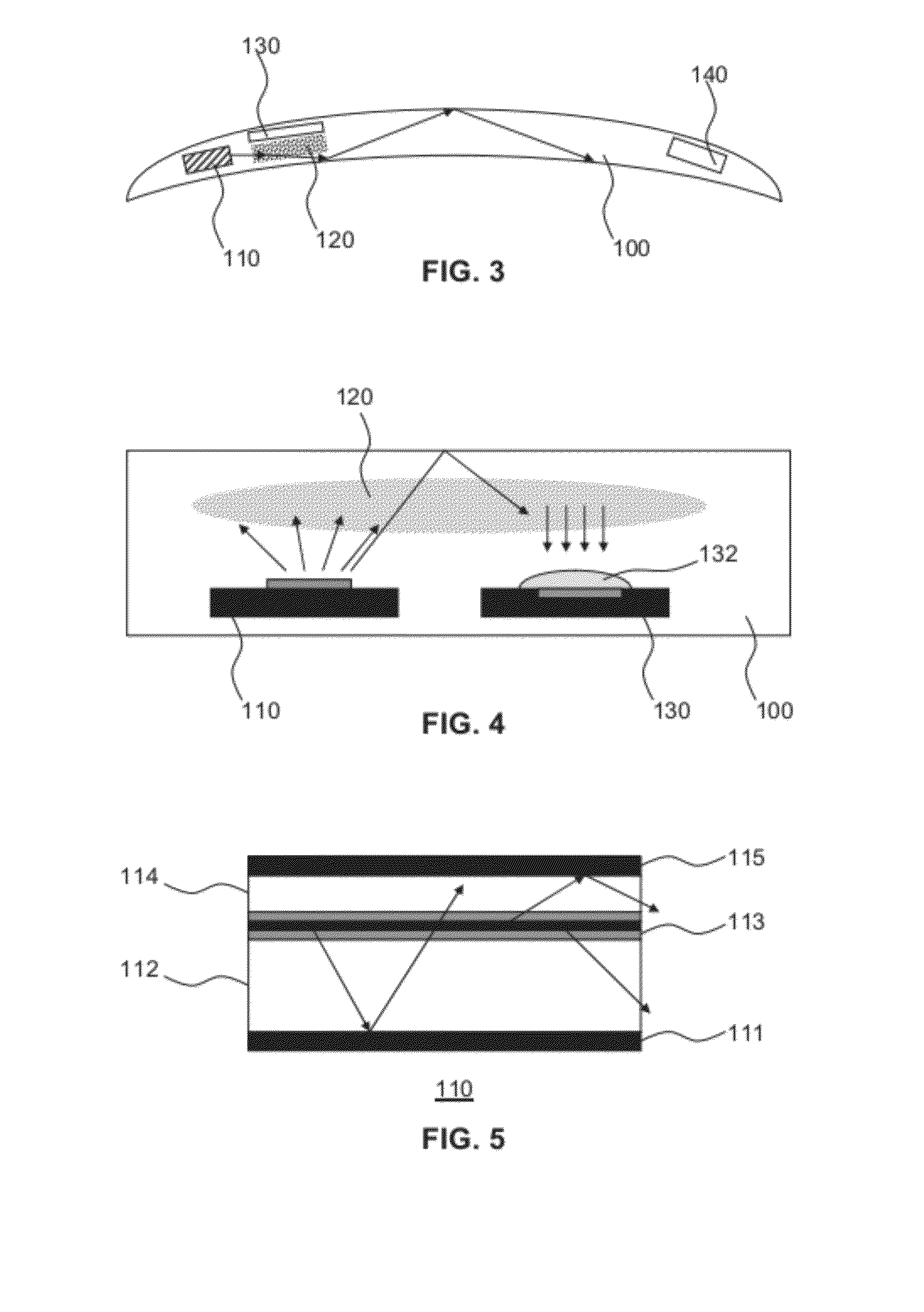
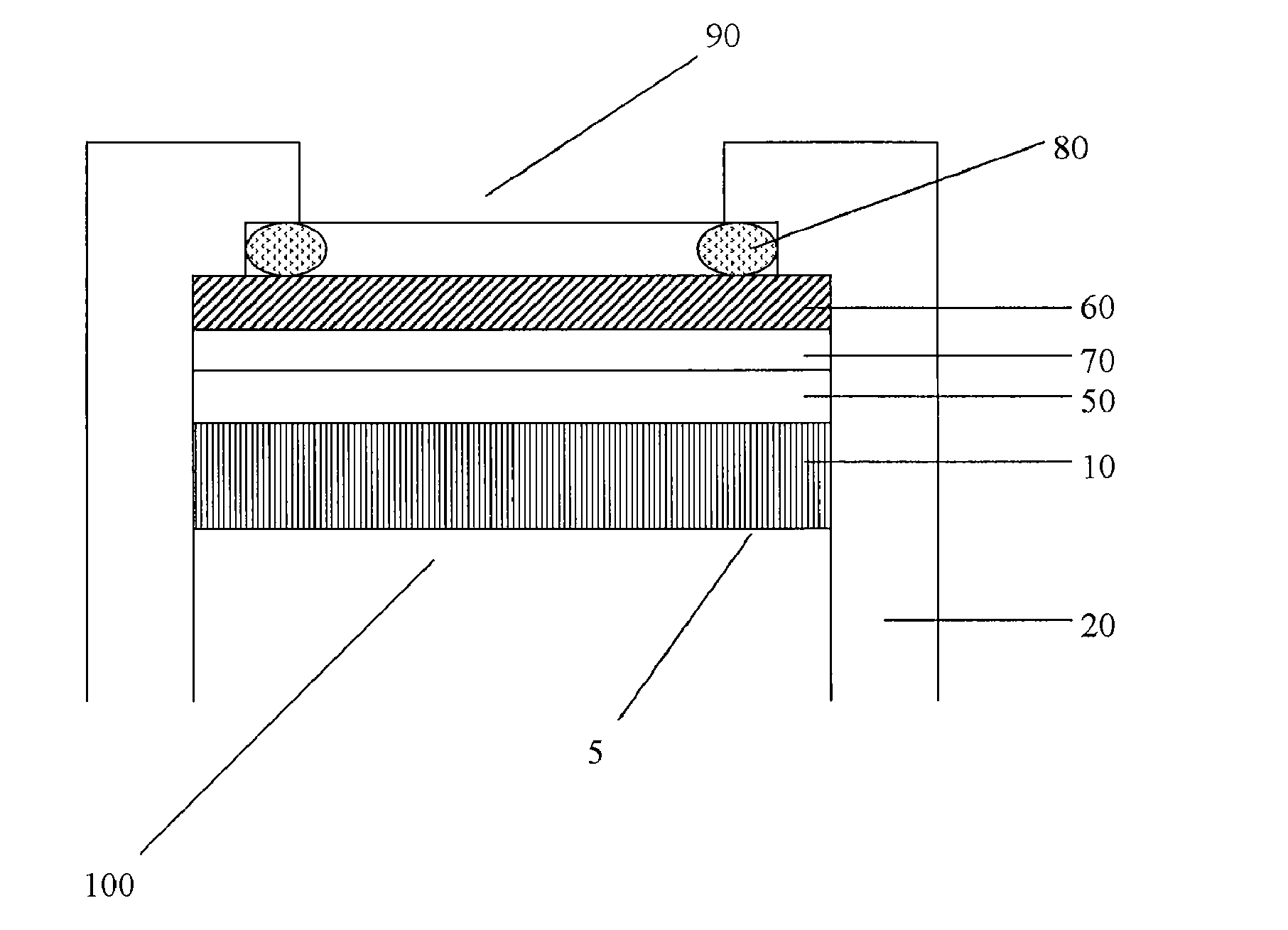
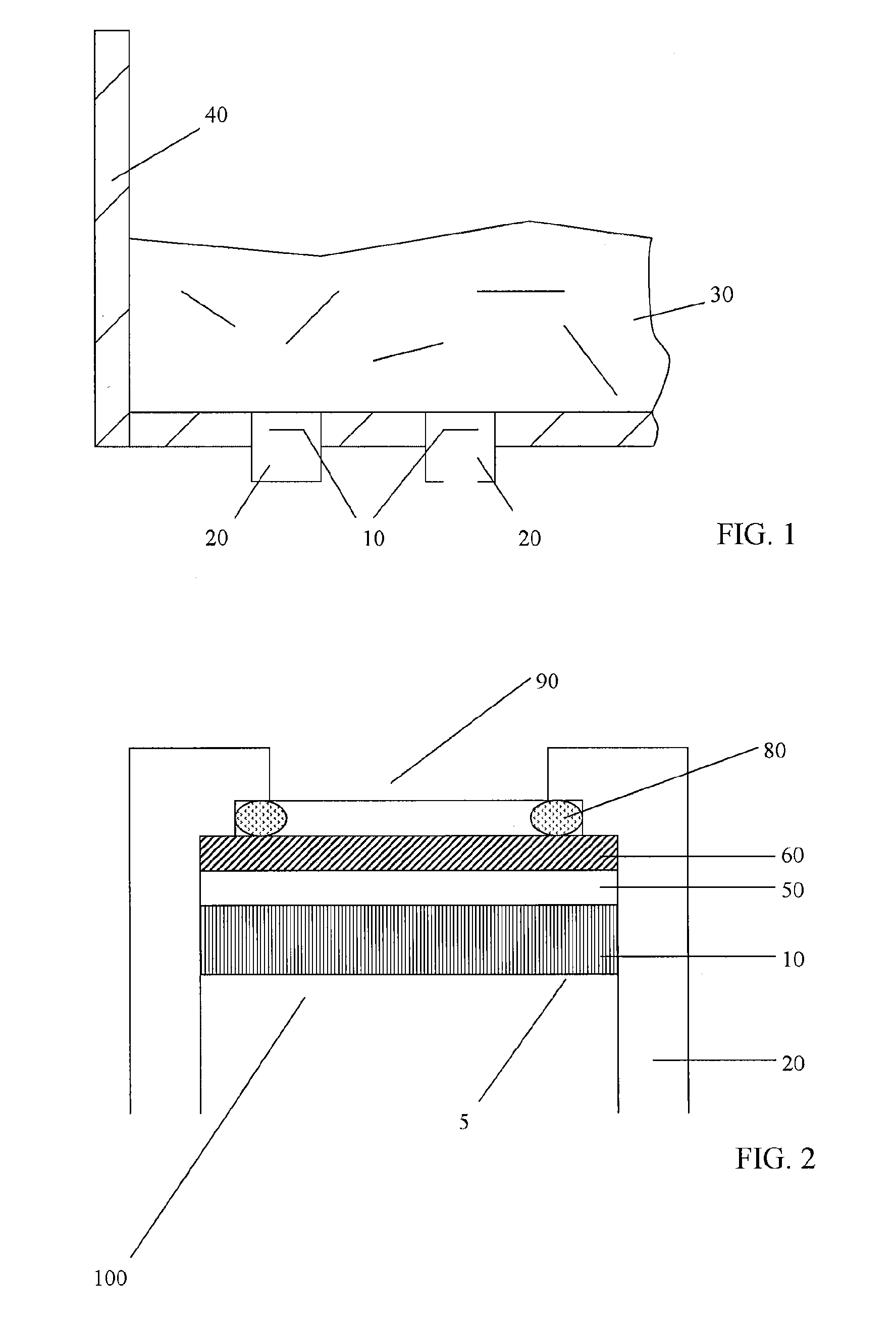
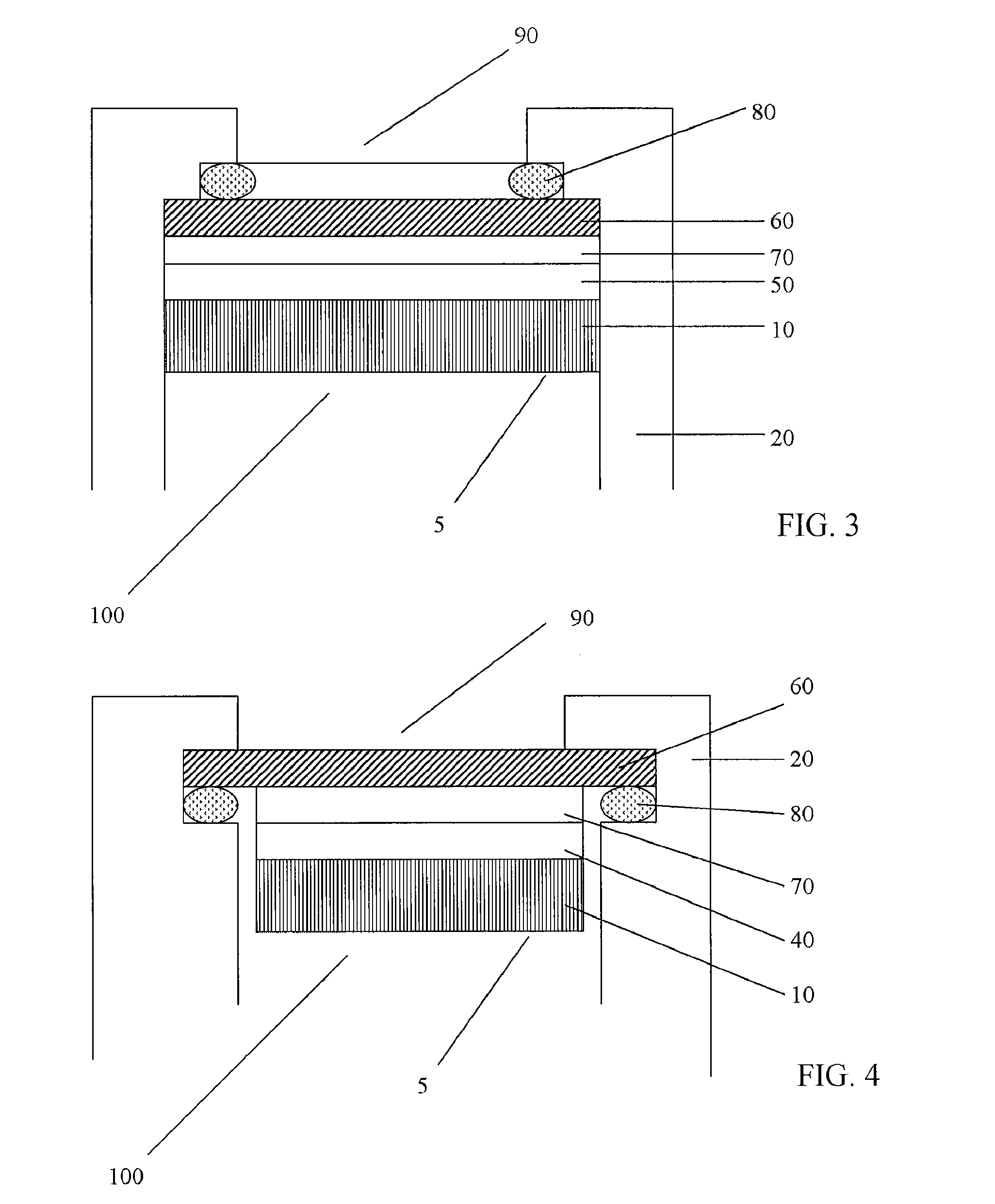
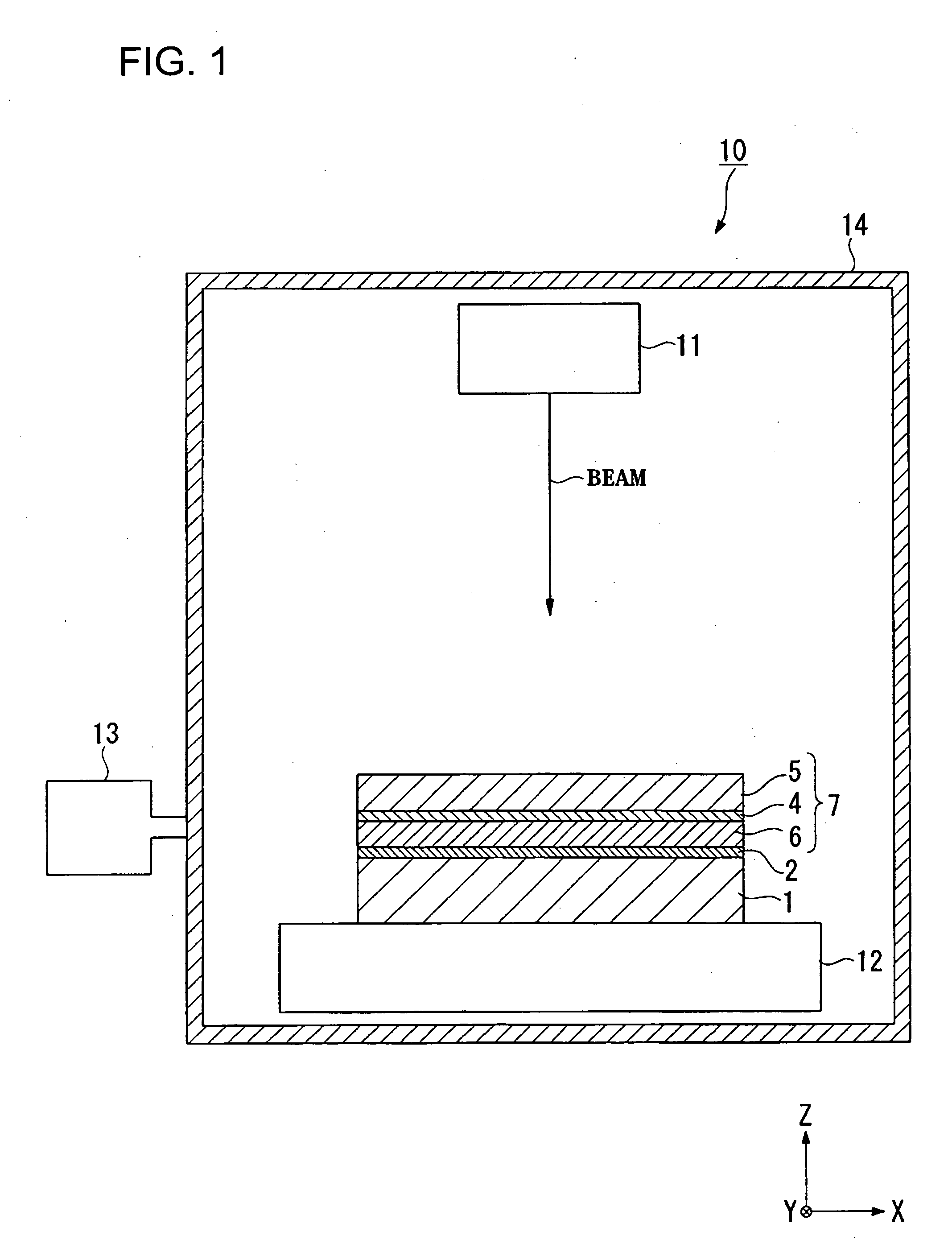
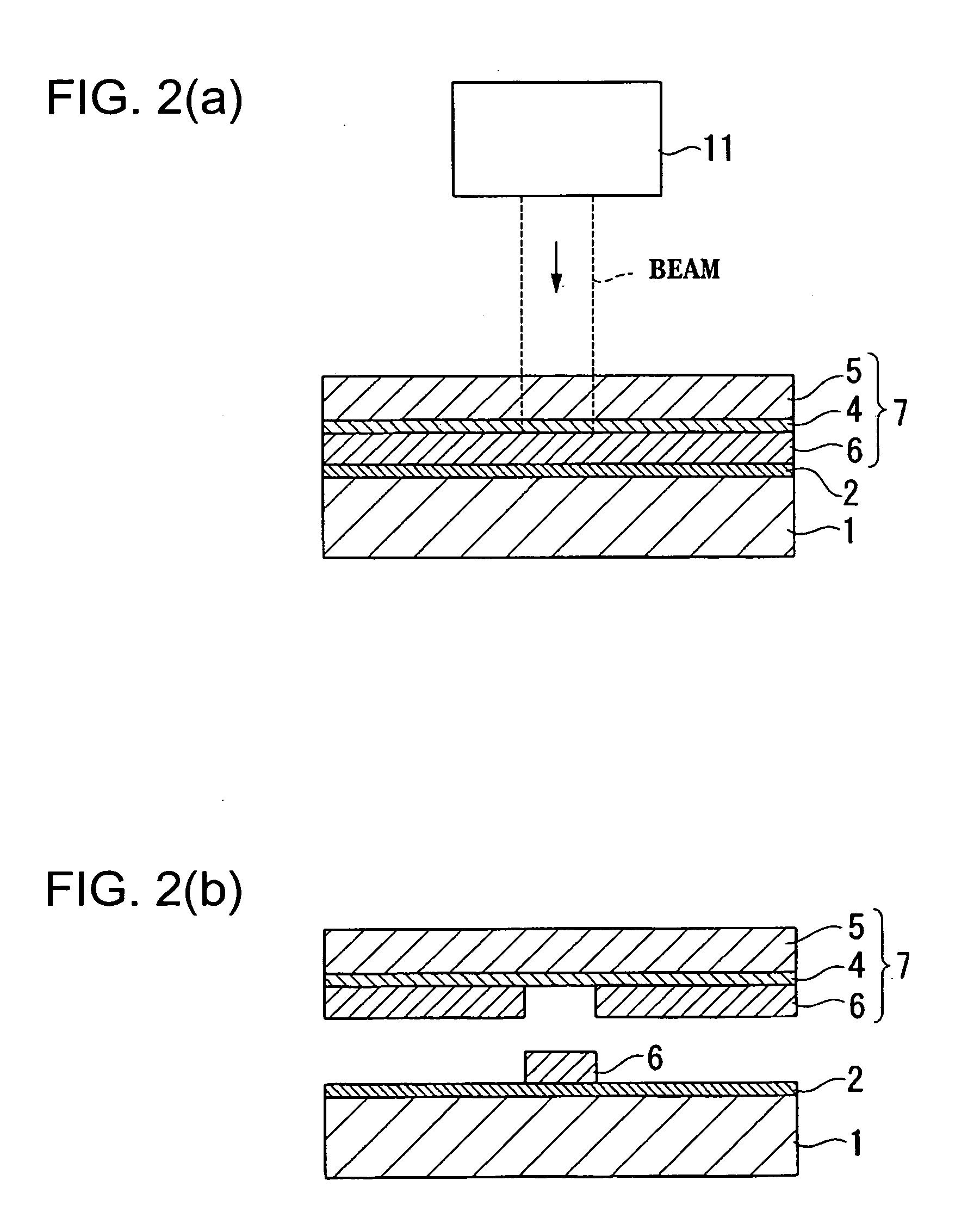
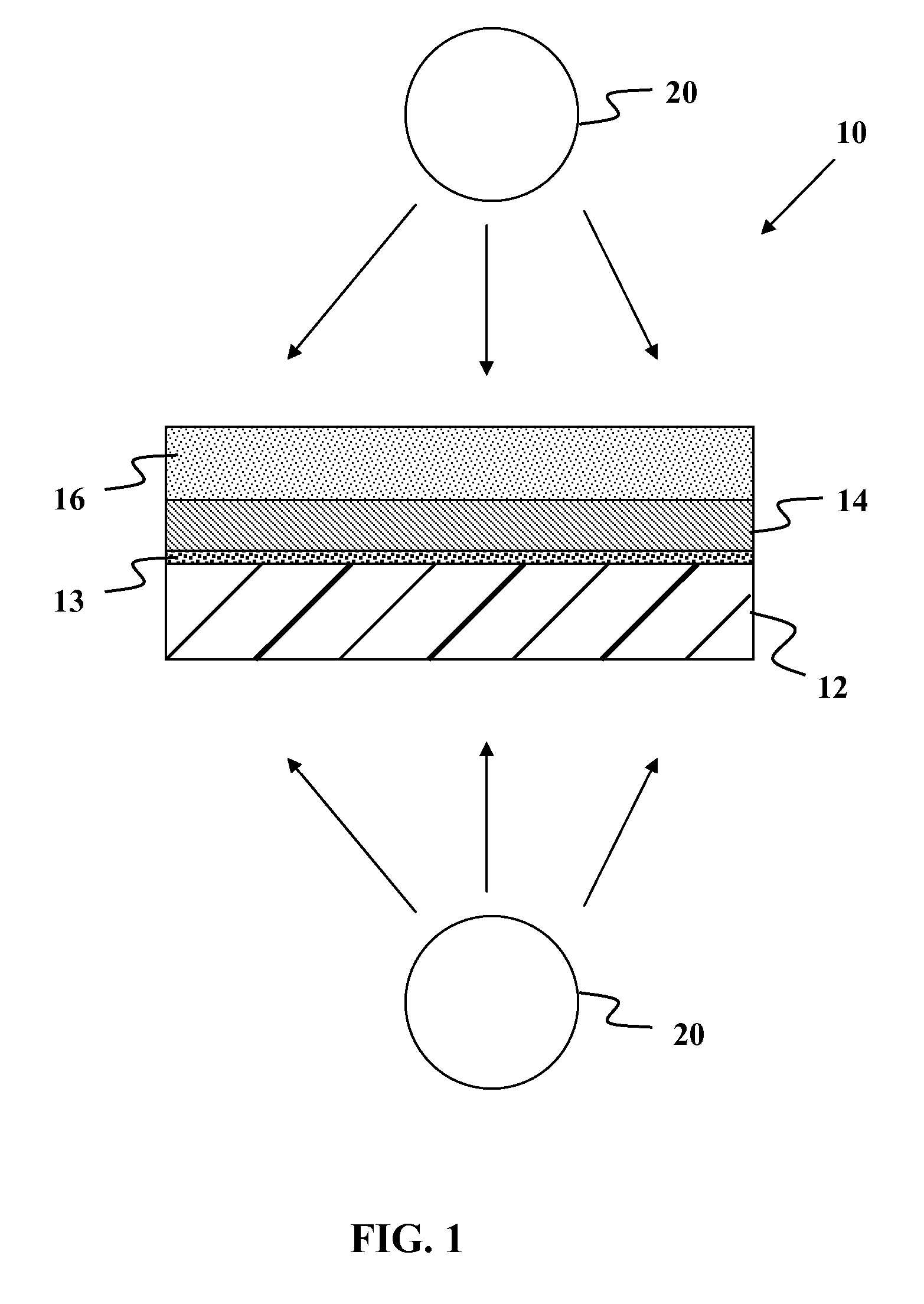
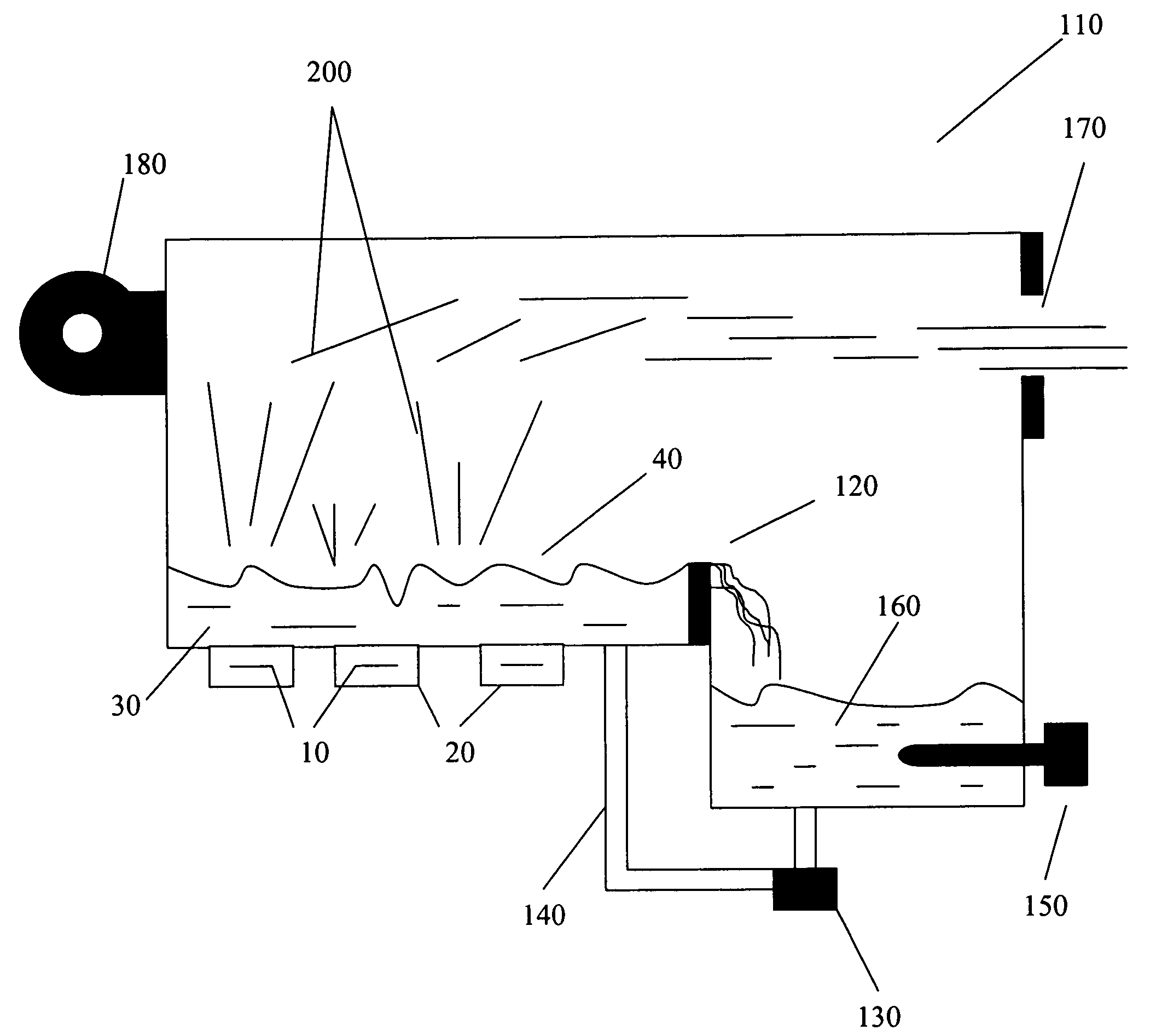
Flexible Eye Insert and Glucose Measuring System
ActiveUS20120259188A1Improve accuracyReduce exposureSolid-state devicesEye treatmentPhotodetectorStimulated emission
Disclosed is a flexible insert (100) for placement on the human eye, comprising a light source (110) in said insert such that light emitted from the light source is shielded from the human eye upon correct placement of the insert on the human eye, a light-responsive material (120) placed in the light path of the light source, said light-responsive material emitting light upon stimulation by the light from said light source, the intensity of said stimulated emission being sensitive to a chemical interaction of the light-sensitive material with an analyte of interest, a photodetector (130) for detecting the light emitted by the light-responsive material; and a transmitter (140) coupled to the photodetector for transmitting a photodetector reading. The insert may be used in conjunction with a reader for automated monitoring of an analyte of interest such as glucose in the tear fluid of its wearer.
Owner:NXP BV
Formation of solar cells with conductive barrier layers and foil substrates
InactiveUS20070000537A1Streamlined fabricationReduce the amount requiredPhotovoltaic supportsFinal product manufactureAmorphous siliconSolar cell
Methods and devices are provided for absorber layers formed on foil substrate. In one embodiment, a method of manufacturing photovoltaic devices may be comprised of providing a substrate comprising of at least one electrically conductive aluminum foil substrate, at least one electrically conductive diffusion barrier layer, and at least one electrically conductive electrode layer above the diffusion barrier layer. The diffusion barrier layer may prevent chemical interaction between the aluminum foil substrate and the electrode layer. An absorber layer may be formed on the substrate. In one embodiment, the absorber layer may be a non-silicon absorber layer. In another embodiment, the absorber layer may be an amorphous silicon (doped or undoped) absorber layer. Optionally, the absorber layer may be based on organic and / or inorganic materials.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
RF surfaces and RF ion guides
ActiveUS7365317B2Promote sportsFreedom of movementStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersPotential wellRf field
Apparatus and methods are provided for trapping, manipulation and transferring ions along RF and DC potential surfaces and through RF ion guides. Potential wells are formed near RF-field generating surfaces due to the overlap of the radio-frequency (RF) fields and electrostatic fields created by static potentials applied to surrounding electrodes. Ions can be constrained and accumulated over time in such wells. During confinement, ions may be subjected to various processes, such as accumulation, fragmentation, collisional cooling, focusing, mass-to-charge filtering, spatial separation ion mobility and chemical interactions, leading to improved performance in subsequent processing and analysis steps, such as mass analysis. Alternatively, the motion of ions may be better manipulated during confinement to improve the efficiency of their transport to specific locations, such as an entrance aperture into vacuum from atmospheric pressure or into a subsequent vacuum stage.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
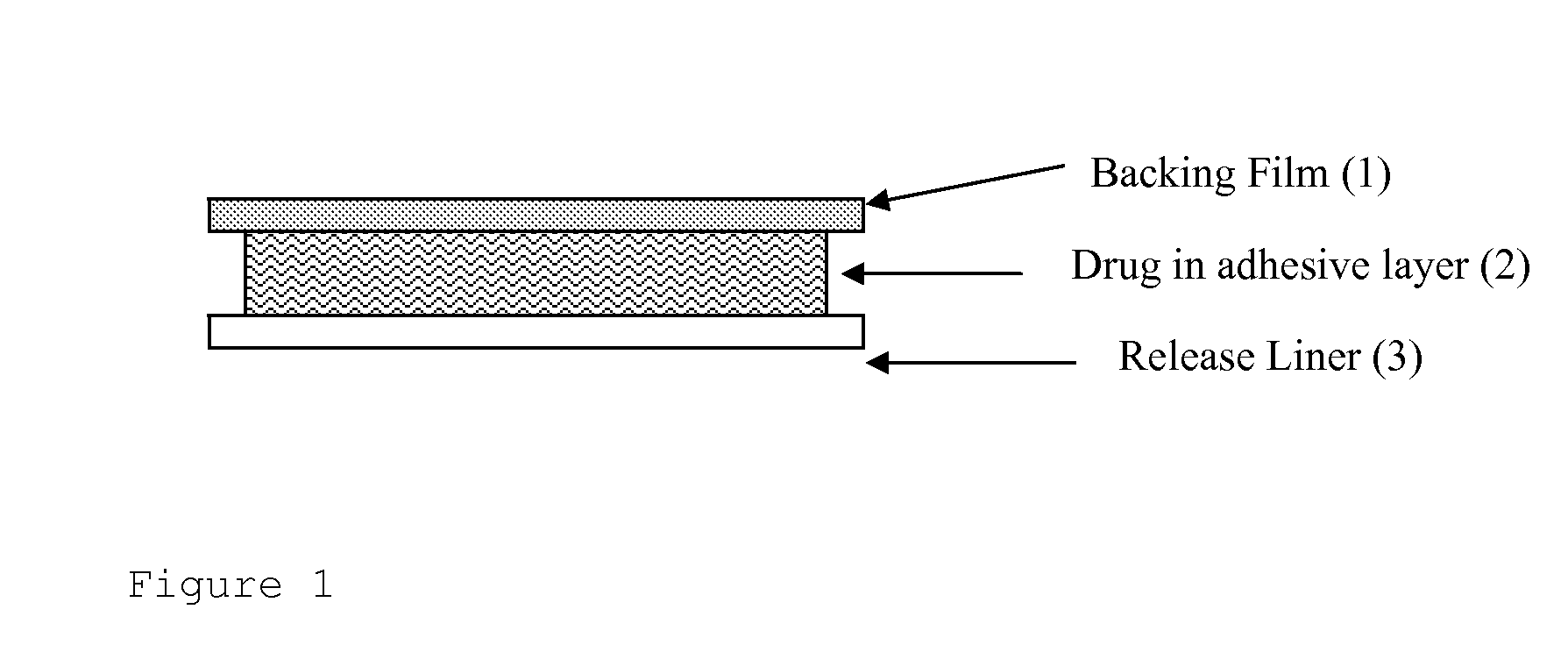
Transdermal drug delivery system for liquid active ingredient
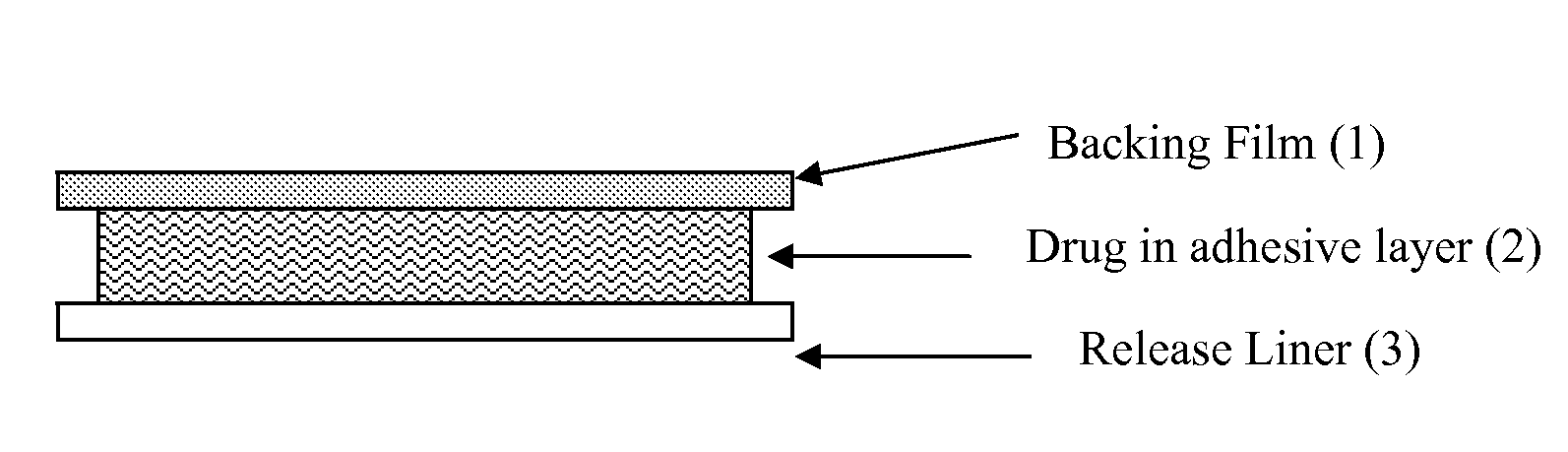
InactiveUS20100087768A1Reduce lossesModerate shearPowder deliveryBiocideAdditive ingredientCross linker
A monolithic device for transdermal administration of an active pharmaceutical ingredient which is selected from propargylamines and rivastigmine and is liquid at 25° C., has an adhesive matrix layer which includes the active ingredient in an acrylic polymer pressure sensitive adhesive without cross-linker agent containing a metal atom, the adhesive having a shear value of between 1.5 and 15 hours, and further includes a non-volatile coadjuvant selected from squalene and triethylcitrate present in the layer in an amount of 1 to 15 wt %. The combination provides good release of the drug in use, reduces loss of the drug during a drying step in manufacture, reduces chemical interaction of the layer with the drug and achieves low level of skin irritation.
Owner:AMARIN TECH
Method and apparatus for detection of molecules using nanopores
InactiveUS20070178507A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle electronMolecular analysis
A molecular analysis device comprises a molecule sensor and a nanopore that passes through, partially through, or substantially near the molecule sensor. The molecule sensor may comprise a single electron transistor including a first terminal, a second terminal, and a nanogap or at least one quantum dot positioned between the first terminal and the second terminal. The molecular sensor may also comprise a nanowire that operably couples a first and a second terminal. A nitrogenous material that may be disposed on at least part of the molecule sensor is configured for a chemical interaction with an identifiable configuration of a molecule. The molecule sensor develops an electronic effect responsive to a molecule or responsive to a chemical interaction.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Methods and devices for using Raman-active probe constructs to assay biological samples
InactiveUS20050148100A1Radiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseProtein profiling
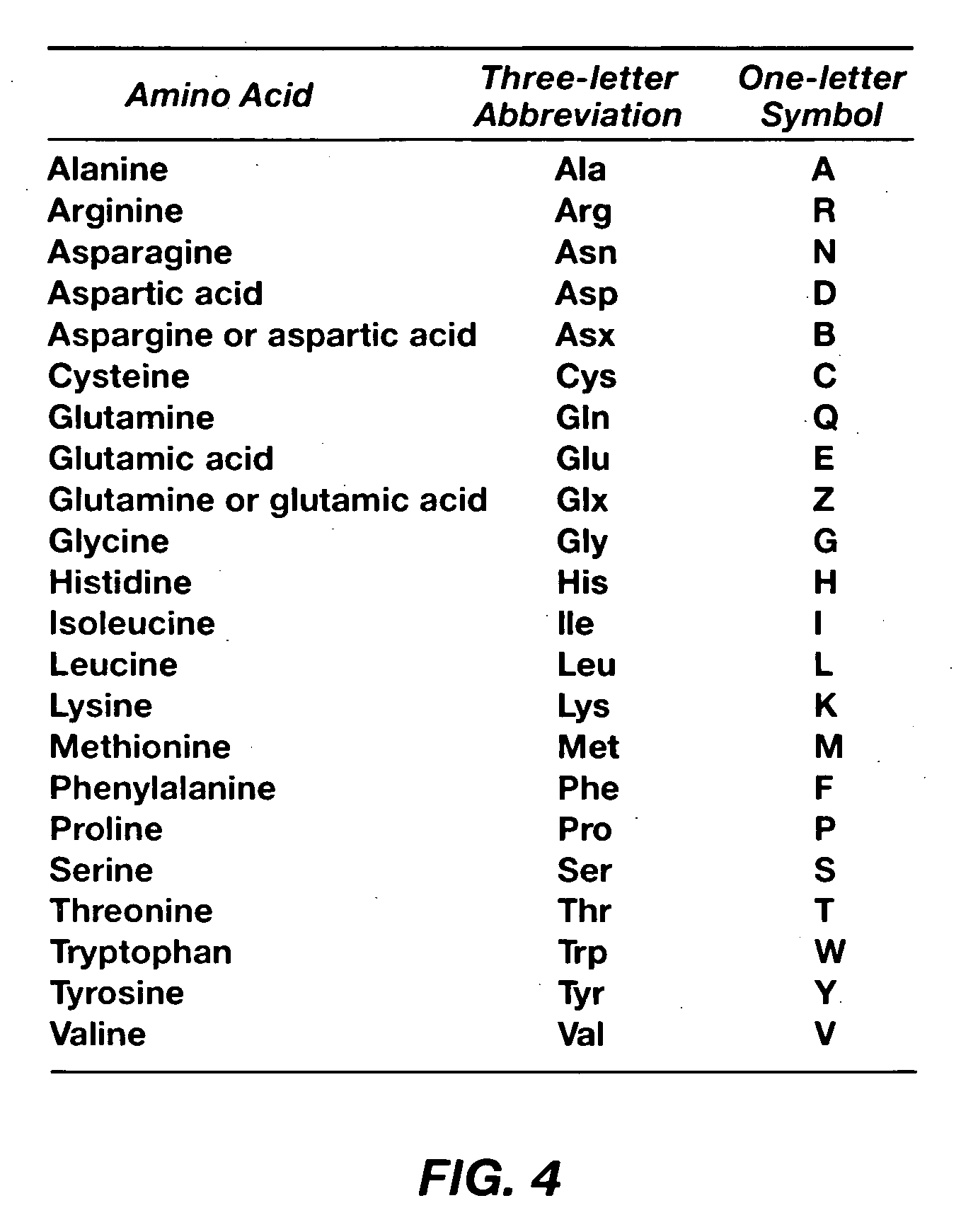
Various methods of using Raman-active or SERS-active probe constructs to detect analytes in biological samples, such as the protein-containing analytes in a body fluid are provided. The probe moieties in the Raman-active constructs are selected to bind to and identify specific known analytes in the biological sample or the probe moieties are designed to chemically interact with functional groups commonly found in certain amino acids so that the invention methods provide information about the amino acid composition of protein-containing analytes or fragments in the samples. In some cases, the Raman-active or SERS-active probe constructs, when used in the invention methods, can identify particular protein-containing analytes or types of such analytes so that a protein profile of a patient sample can be made. When compared to a data base of Raman or SERS spectra of normal samples, a disease state of a patient can be identified using the methods disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and Apparatus for an Improved Aerosol Generator and Associated Uses and Equipment
ActiveUS20110114744A1Reduce probabilityLow temperature of insideMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesChemical reactionTransducer
The invention is an apparatus and methods for optimizing the performance and protecting one or more aerosol generating transducers from deterioration while operating in a chemically reactive aqueous solution by utilizing one or more protective barrier techniques to eliminate chemical interaction between the aqueous solution and the transducers, among other features of the generator including these transducers. The method of the present invention produces an aerosol producing transducer with the transducer housing and assembly to be constructed in such a way as to assure its efficient and effective long-term and problem free operation in an aqueous solution that is chemically reactive.
Owner:ALTAPURE
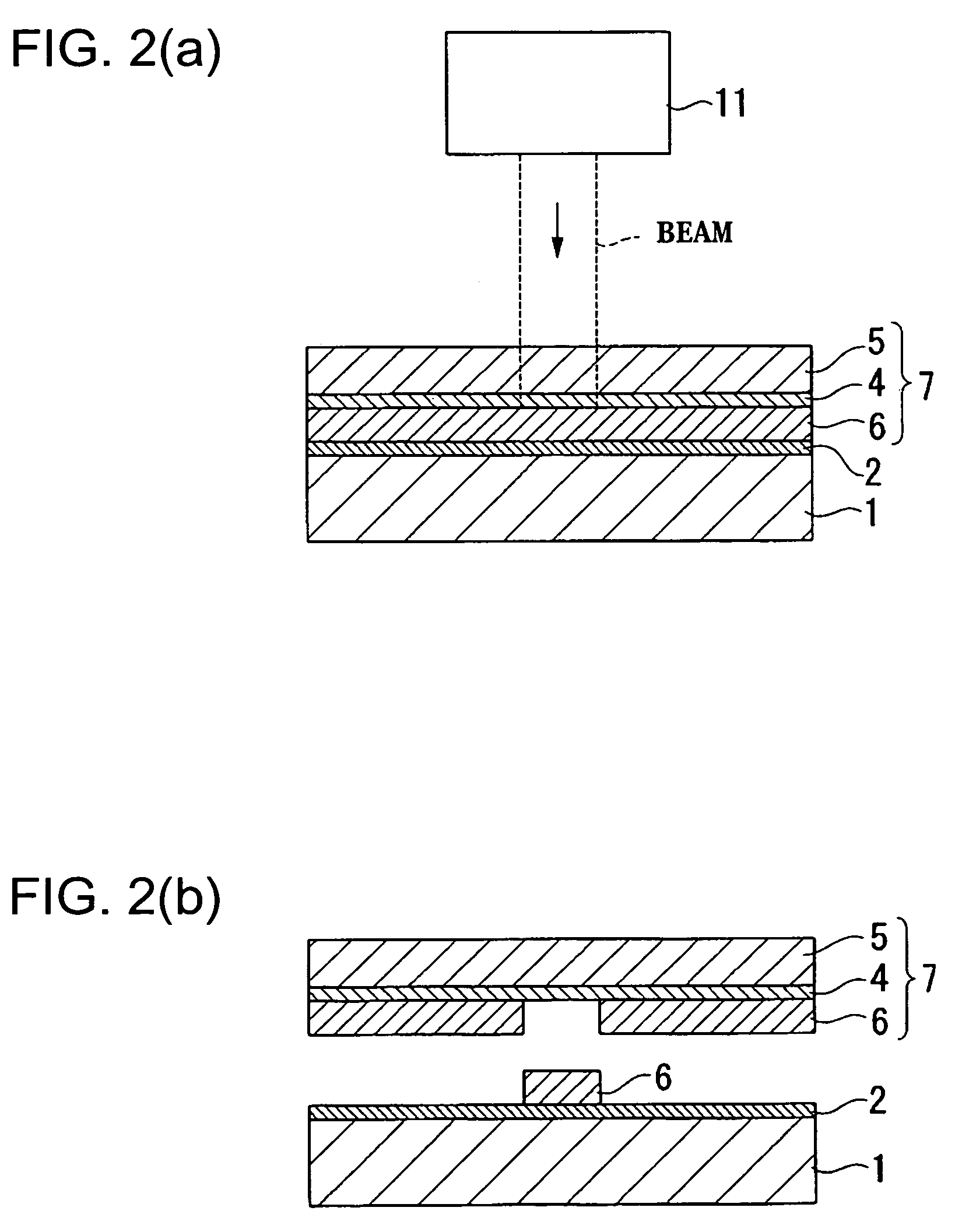
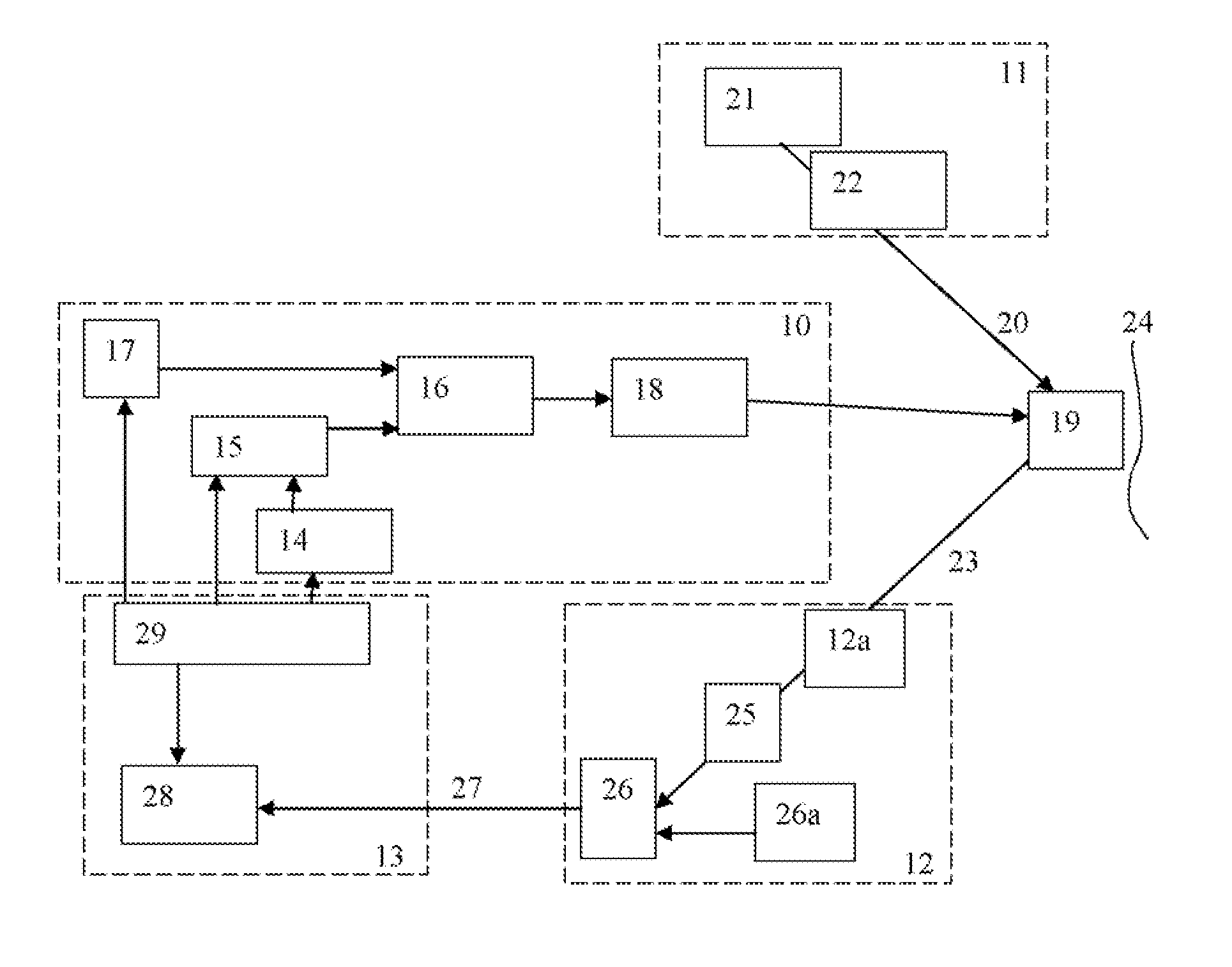
Method for forming film, method for forming wiring pattern, method for manufacturing semiconductor device, electro-optical device, and electronic device
ActiveUS20050087289A1Efficiently converted into thermal energySmall diameterElectric lighting sourcesSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
Exemplary embodiments of the invention to provide an efficient and productive method to form a reliable film. A method to form a film according to exemplary embodiments of the present invention, in which a transferring layer formed on a substrate is transferred to a workpiece to form a predetermined film on the workpiece, includes treating a surface of the workpiece to enhance or improve the adhesion between the transferring layer and the workpiece by chemical interaction.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL KEYSTONE TECH LLC
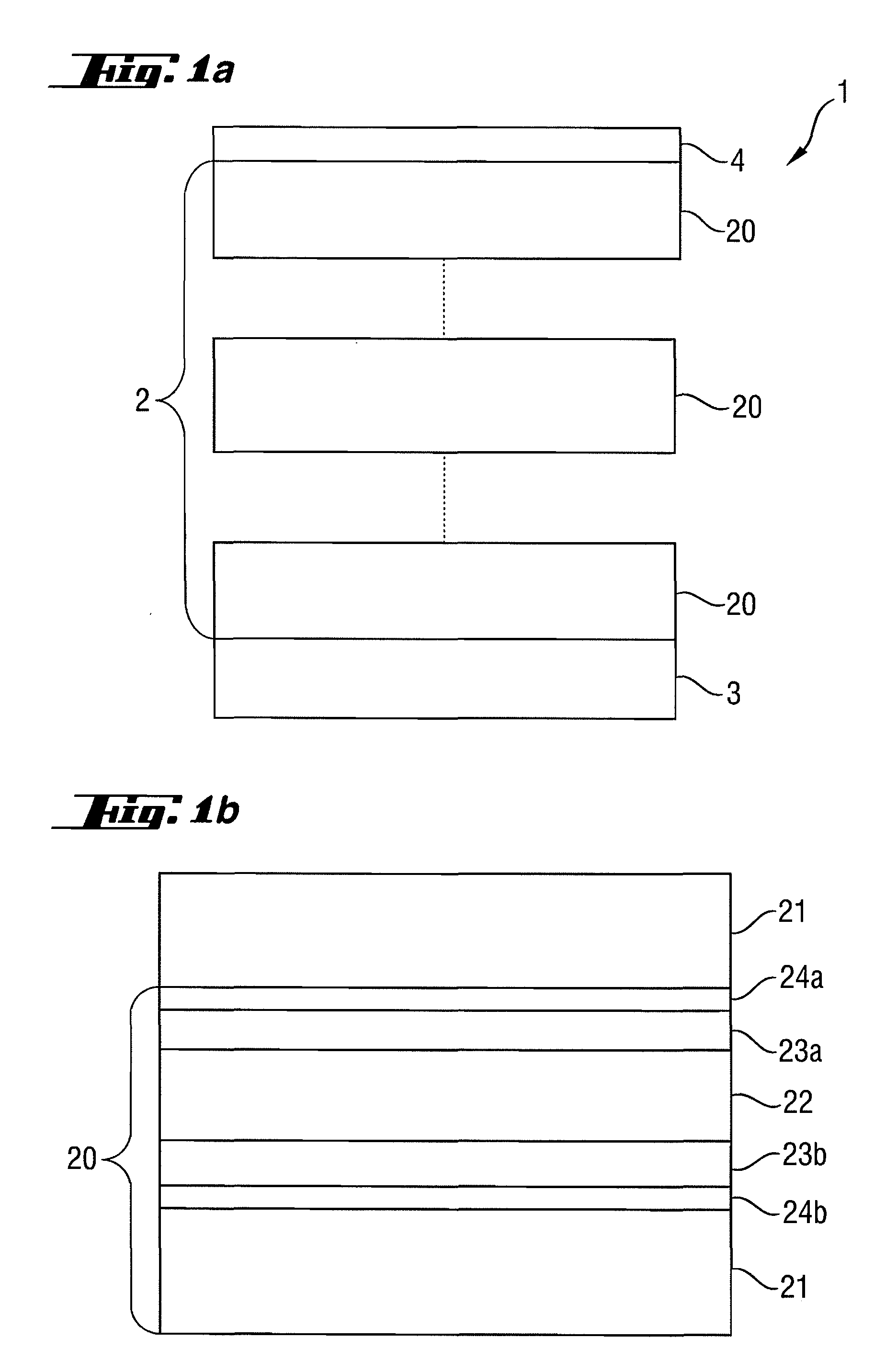
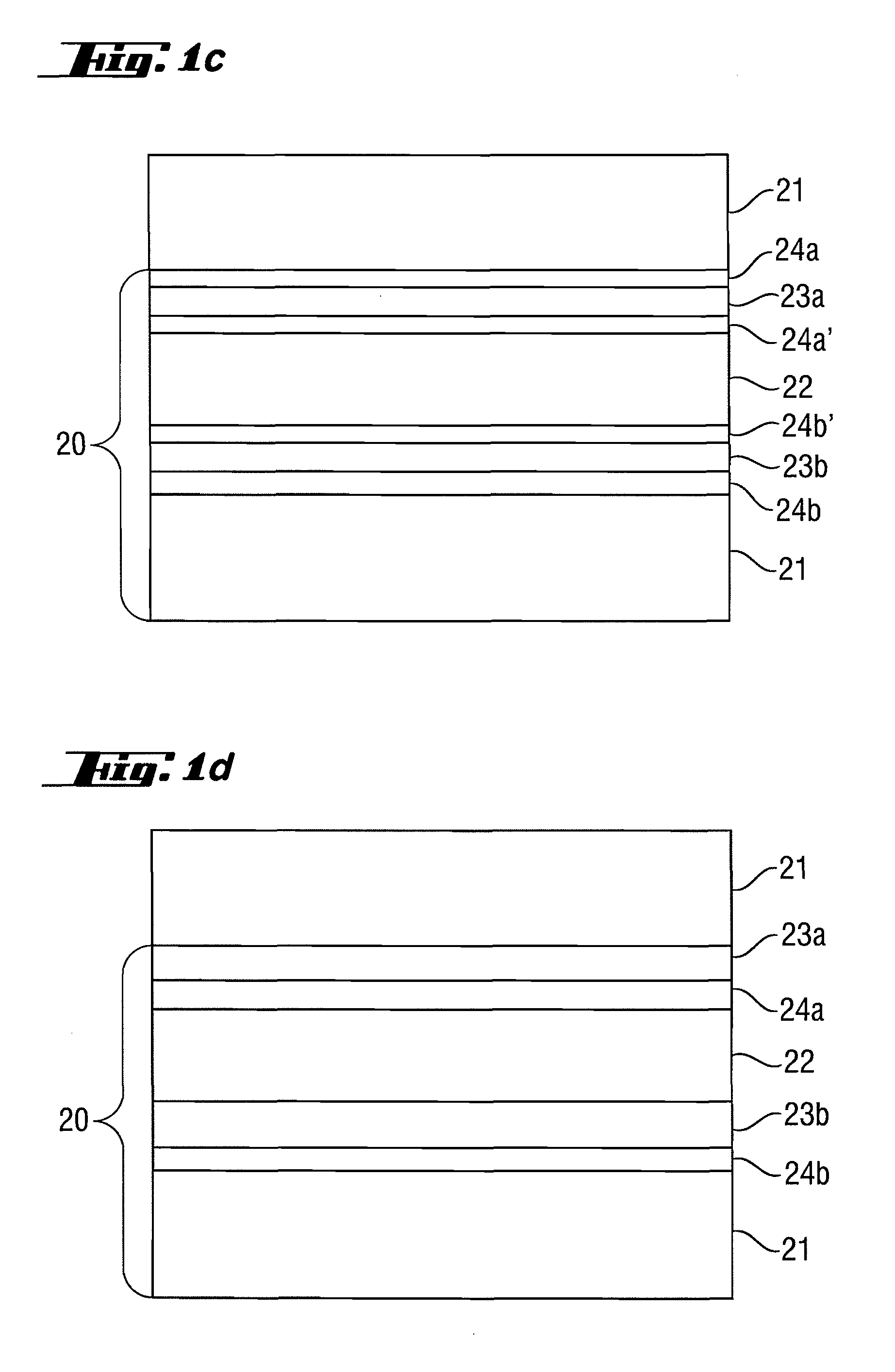
Reflective optical element for EUV lithography device
ActiveUS20100027107A1Improve reflectivityIncrease of maximum reflectivityMirrorsNanoinformaticsCatoptricsComputational physics
A reflective optical element exhibits an increase in the maximum reflectivity at operating wavelengths in the extreme ultraviolet or soft x-ray wavelength range. A first additional intermediate layer (23a, 23b) and a second additional intermediate layer (24a, 24b) are provided between the absorber layer (22) and the spacer layer (21), wherein the first additional intermediate layer increases the reflectivity and the second additional intermediate layer (24a,b) prevents chemical interaction between the first additional intermediate layer (23a,b) and the adjoining spacer layer (21) and / or the absorber layer (22).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Storage container for inkjet cartridges having removable capping means and a method for storing inkjet cartridges
A storage container for storing inkjet cartridges, when removed from the carriage of a printer, having a capping housing for holding one or more caps, associated with each cartridge, for capping the printhead of the cartridge, wherein the caps are easily removable from the storage container by a user. The provision of manually removable cap allows the cap of a storage container to be matched to a particular cartridge having a specific printhead, ink formulation and lifetime. This ensures the efficacy of the cartridge is maintained during storage and prevents contamination of one cartridge by ink residue that may be left on a cap by another cartridge, which can damage the printhead due to chemical interaction between the different ink formulations.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Photovoltaic Devices With Conductive Barrier Layers and Foil Substrates
InactiveUS20080308148A1Reduce the amount requiredCost-effectivelyPhotovoltaic supportsFinal product manufactureAmorphous siliconDiffusion barrier
Methods and devices are provided for absorber layers formed on foil substrate. In one embodiment, a method of manufacturing photovoltaic devices may be comprised of providing a substrate comprising of at least one electrically conductive aluminum foil substrate, at least one electrically conductive diffusion barrier layer, and at least one electrically conductive electrode layer above the diffusion barrier layer. The diffusion barrier layer may prevent chemical interaction between the aluminum foil substrate and the electrode layer. An absorber layer may be formed on the substrate. In one embodiment, the absorber layer may be a non-silicon absorber layer. In another embodiment, the absorber layer may be an amorphous silicon (doped or undoped) absorber layer. Optionally, the absorber layer may be based on organic and / or inorganic materials.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Novel resin curing agents
A curable resin comprising a curing agent, wherein the curing agent comprises an adjustable structural unit having a stable chain-like arrangement which is adjustable to a stable ring-like arrangement, wherein the ring-like arrangement comprises the constituents of the chain-like arrangement with two terminal constituents exhibiting an attractive chemical interaction, and is adjustable back from the ring-like arrangement to the chain-like arrangement by separation of the two terminal constituents.
Owner:HEXCEL COMPOSITES SAS
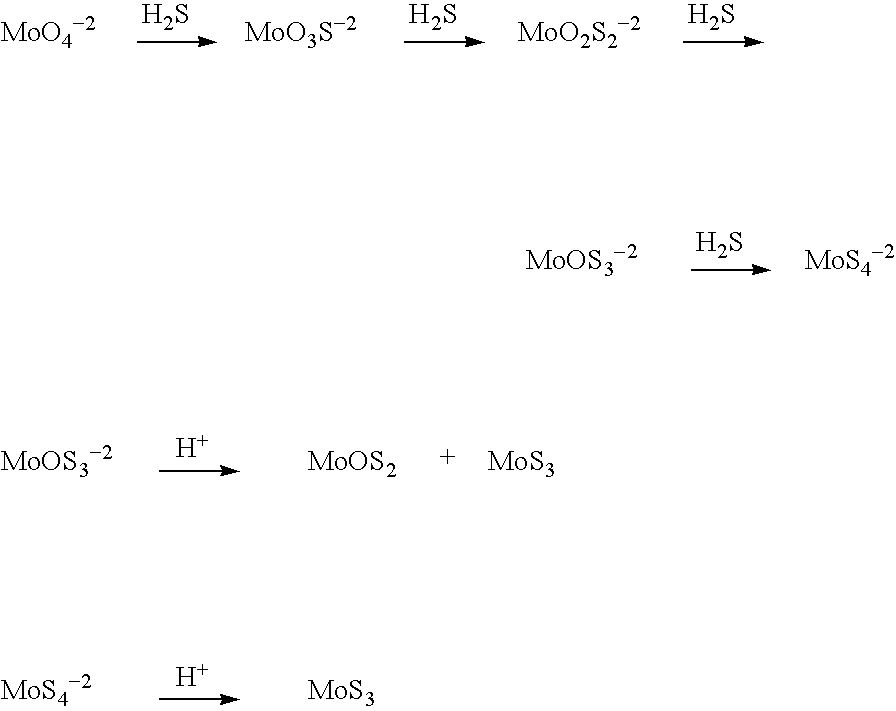
Nanosized particles of molybdenum sulfide and derivatives,method for its preparation and uses thereof as lubricant additive
InactiveUS20050065044A1Prevent coagulationProvide solubilityGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsAdditivesMolybdenum compoundsSulfidation
A lubricant composition is disclosed that comprises: (a) a lubricant and (b) at least one molybdenum-containing compound in the form of surface-capped nanosized particles of the general formula: (Z)n(X—R)m wherein Z is an inorganic moiety comprising molybdenum and sulfur in the form of particles having dimensions in the range of from about 1 to about 100 nm; (X—R) is a surface-capping reagent wherein R is a C4 to C20 straight or branched-chain alkyl or alkylated cycloalkyl radical or radicals and X is a functional group capable of specific sorption and / or chemical interaction with molybdenum / sulfur moiety; n is the number of molecules of Z in the particles; m is an integer representing the amount of surface-capping reagents relative to a single particle; and the ratio of m to n is in the range of from about 1:1 to about 10:1.
Owner:CROMPTON CORP
Flexible eye insert and glucose measuring system
Disclosed is a flexible insert (100) for placement on the human eye, comprising a light source (110) in said insert such that light emitted from the light source is shielded from the human eye upon correct placement of the insert on the human eye, a light-responsive material (120) placed in the light path of the light source, said light-responsive material emitting light upon stimulation by the light from said light source, the intensity of said stimulated emission being sensitive to a chemical interaction of the light-sensitive material with an analyte of interest, a photodetector (130) for detecting the light emitted by the light-responsive material; and a transmitter (140) coupled to the photodetector for transmitting a photodetector reading. The insert may be used in conjunction with a reader for automated monitoring of an analyte of interest such as glucose in the tear fluid of its wearer.
Owner:NXP BV
Method for forming film, method for forming wiring pattern, method for manufacturing semiconductor device, electro-optical device, and electronic device
ActiveUS7217334B2Enhance and improve adhesionHigh quality transmissionElectric lighting sourcesSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Exemplary embodiments of the invention to provide an efficient and productive method to form a reliable film. A method to form a film according to exemplary embodiments of the present invention, in which a transferring layer formed on a substrate is transferred to a workpiece to form a predetermined film on the workpiece, includes treating a surface of the workpiece to enhance or improve the adhesion between the transferring layer and the workpiece by chemical interaction.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL KEYSTONE TECH LLC
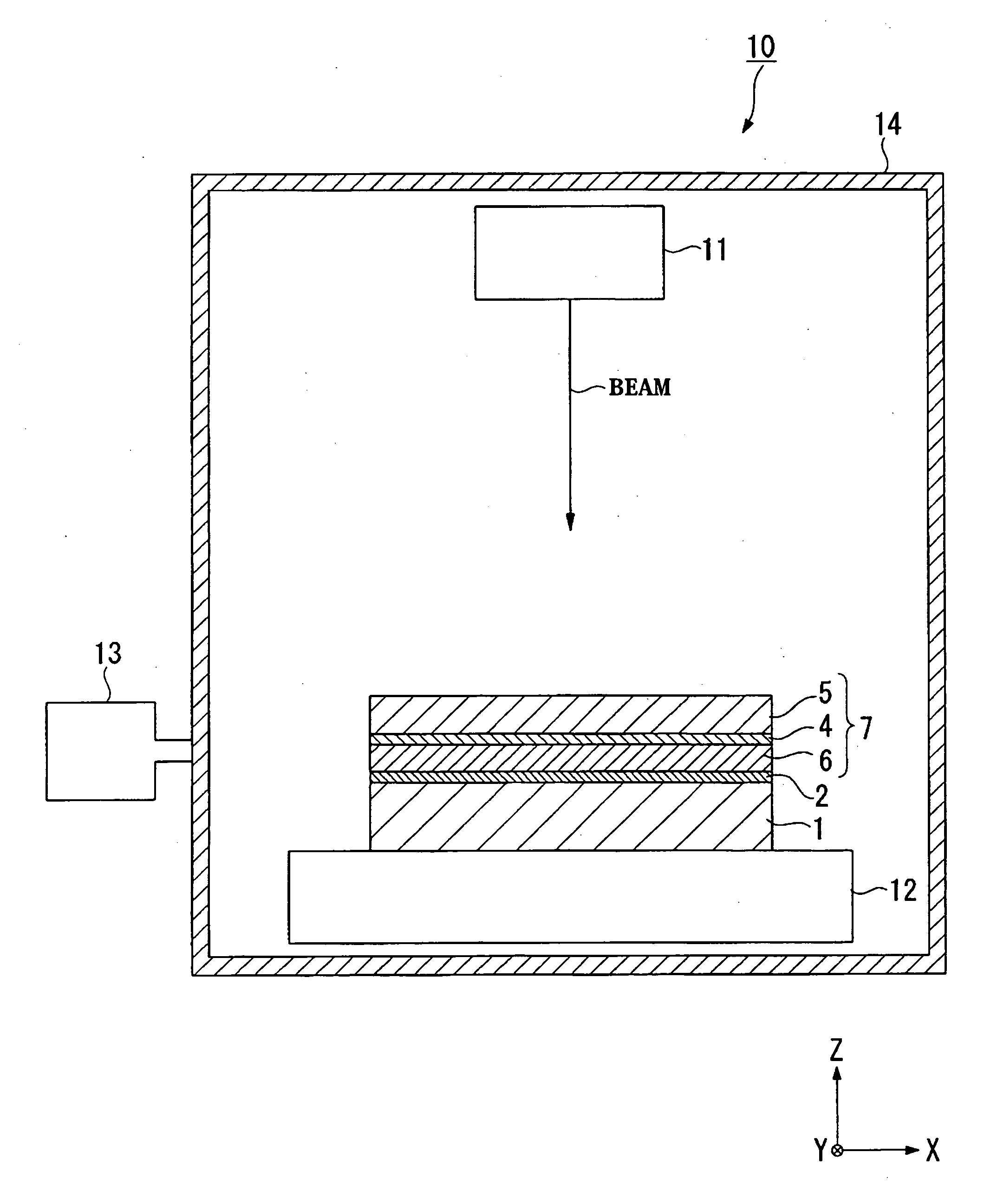
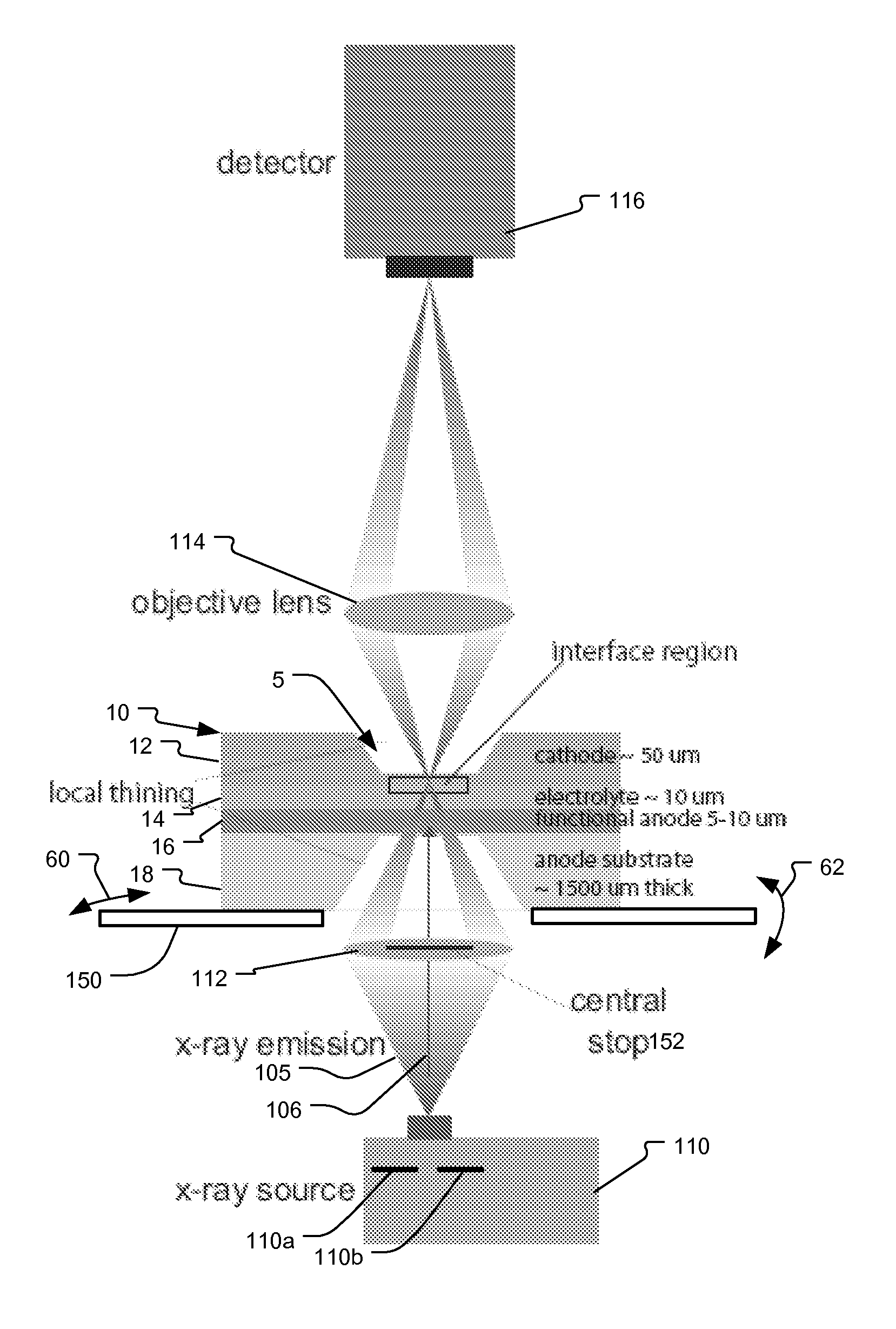
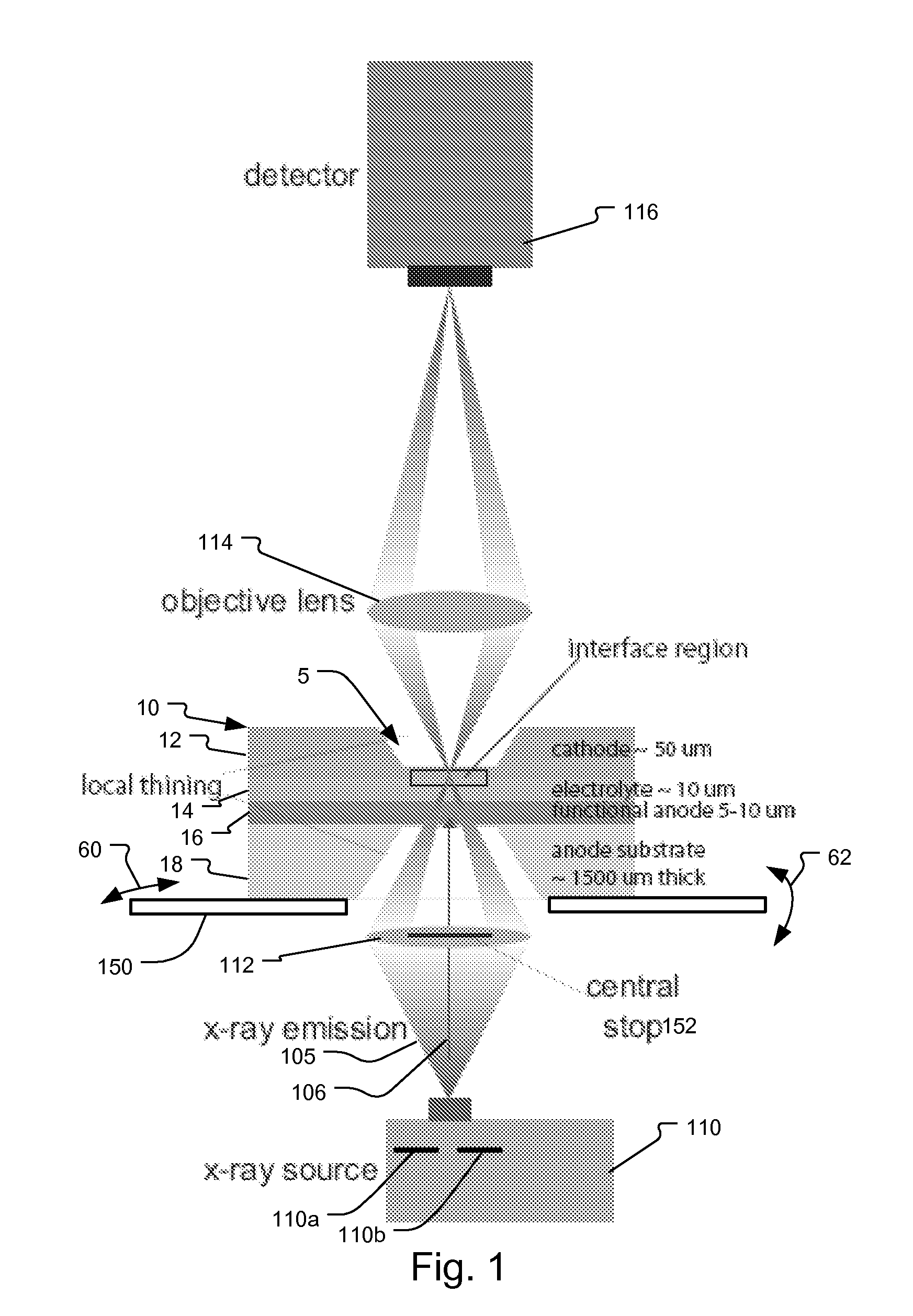
System and method for fuel cell material x-ray analysis
ActiveUS7499521B2Shorten development timeImprove reliabilityRadiation/particle handlingUsing wave/particle radiation meansHard X-raysMetrology
An imaging technology for fuel cells is based on x-ray microscopy. A metrology system images the electro-chemical interaction areas of solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFC) in-situ. This system takes advantage of both the penetrating power and elemental absorption contrast of hard x-ray radiation to image the internal interaction areas in a SOFC. The technology can further take advantage of the strong dependence of the x-ray absorption on material type and energy to distinguish the four major material types: cathode, electrolyte, air, and low-Z contaminants such as sulfur.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Investment casting pins
Owner:OROFLEX PIN DEV
Method And Apparatus For An Improved Aerosol Generator And Associated Uses And Equipment
InactiveUS20080233001A1Quickly and easily setQuickly and easily and operatedSelf-acting watering devicesMovable spraying apparatusChemical reactionTransducer
The invention is an apparatus and methods for optimizing the performance and protecting one or more aerosol generating transducers from deterioration while operating in a chemically reactive aqueous solution by utilizing one or more protective barrier techniques to eliminate chemical interaction between the aqueous solution and the transducers, among other features of the generator including these transducers. The method of the present invention produces an aerosol producing transducer with the transducer housing and assembly to be constructed in such a way as to assure its efficient and effective long-term and problem free operation in an aqueous solution that is chemically reactive.
Owner:ALTAPURE
Nanosized particles of molybdenum sulfide and derivatives, method for its preparation and uses thereof as lubricant additive
InactiveUS6878676B1Prevent coagulationProvide solubility and stabilityGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsAdditivesNano sizeSulfur
A lubricant composition is disclosed that comprises: (a) a lubricant and (b) at least one molybdenum-containing compound in the form of surface-capped nanosized particles of the general formula: (Z)n(X—R)m wherein Z is an inorganic moiety comprising molybdenum and sulfur in the form of particles having dimensions in the range of from about 1 to about 100 nm; (X—R) is a surface-capping reagent wherein R is a C4 to C20 straight or branched-chain alkyl or alkylated cycloalkyl radical or radicals and X is a functional group capable of specific sorption and / or chemical interaction with molybdenum / sulfur moiety; n is the number of molecules of Z in the particles; m is an integer representing the amount of surface-capping reagents relative to a single particle; and the ratio of m to n is in the range of from about 1:1 to about 10:1.
Owner:CROMPTON CORP
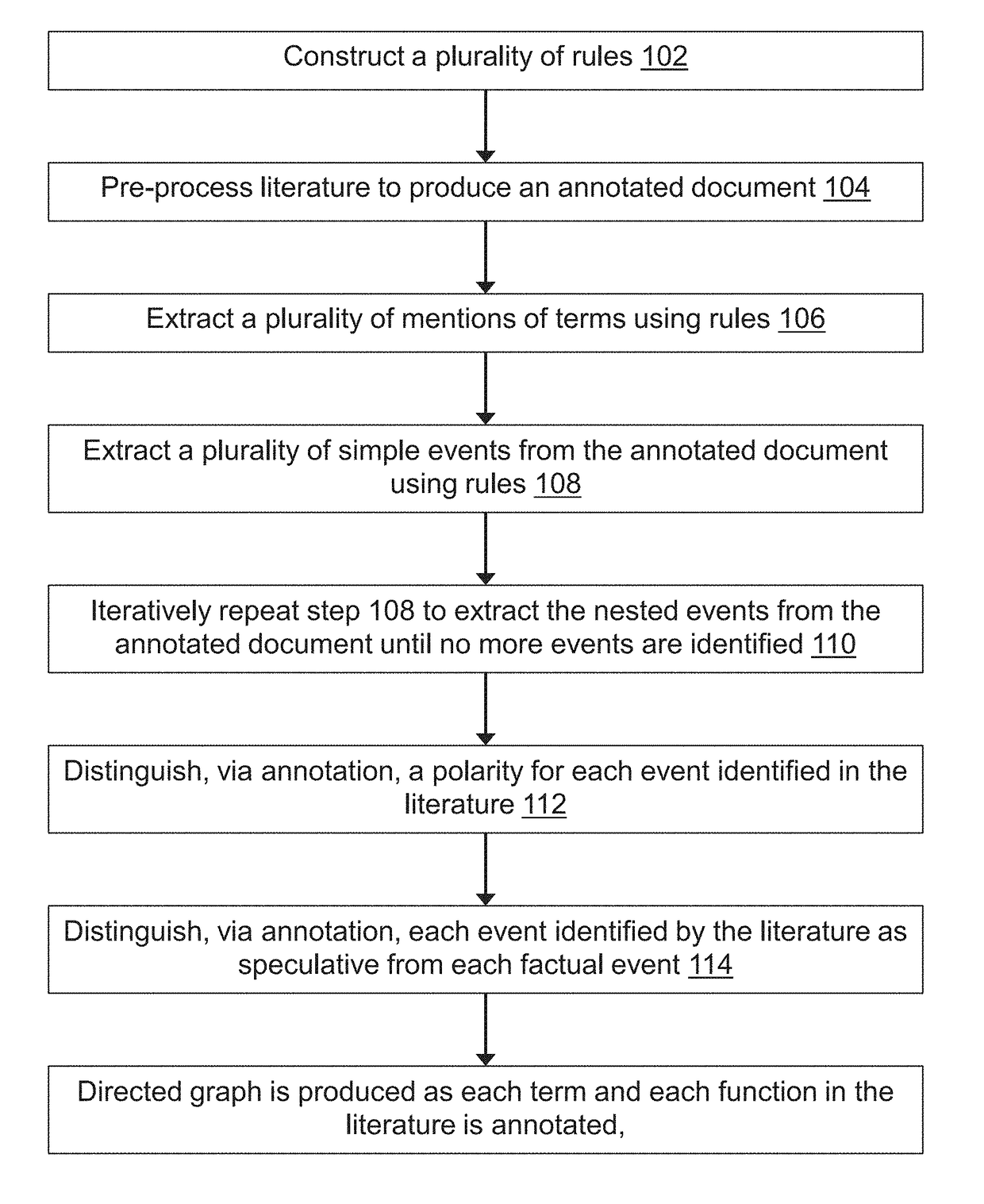
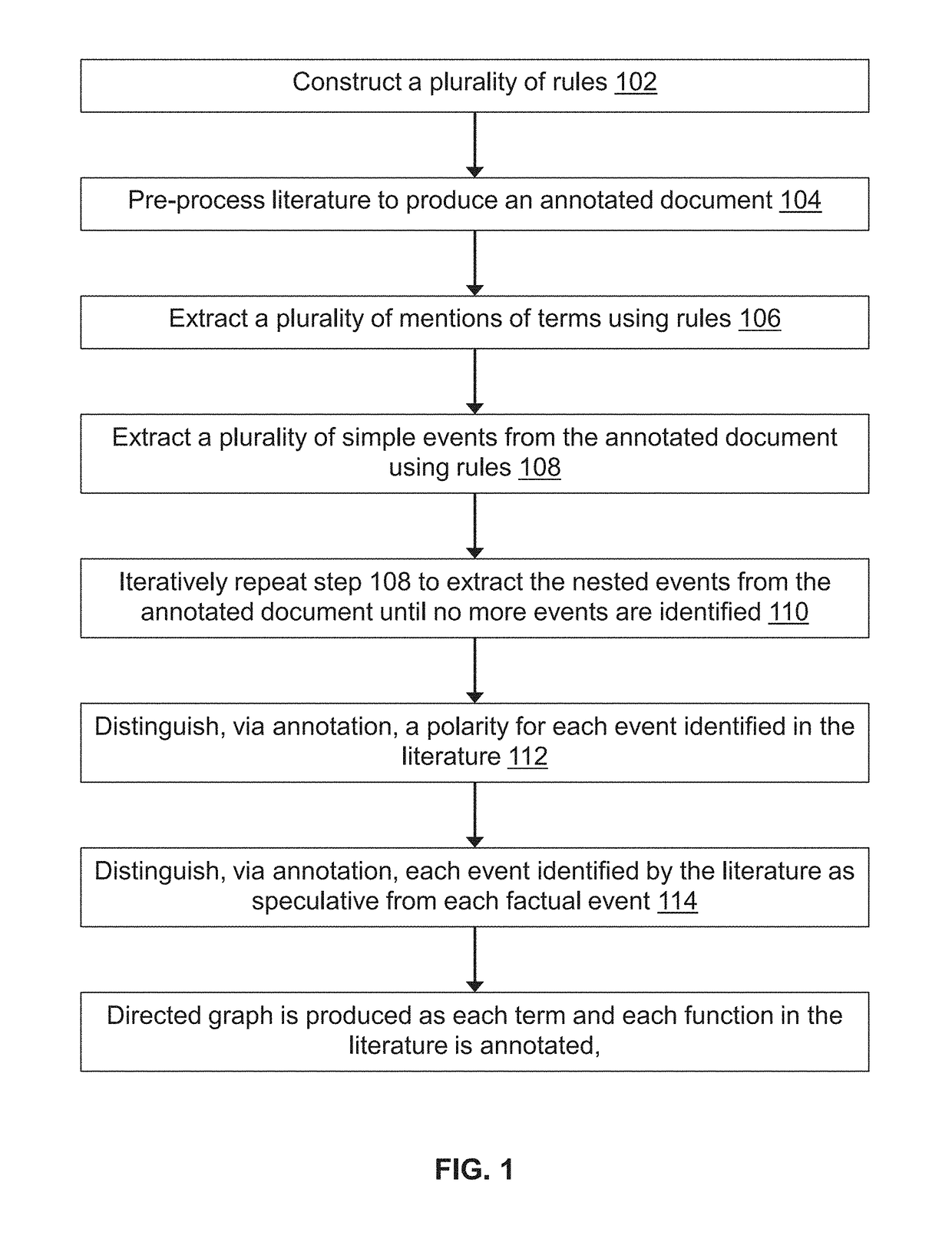
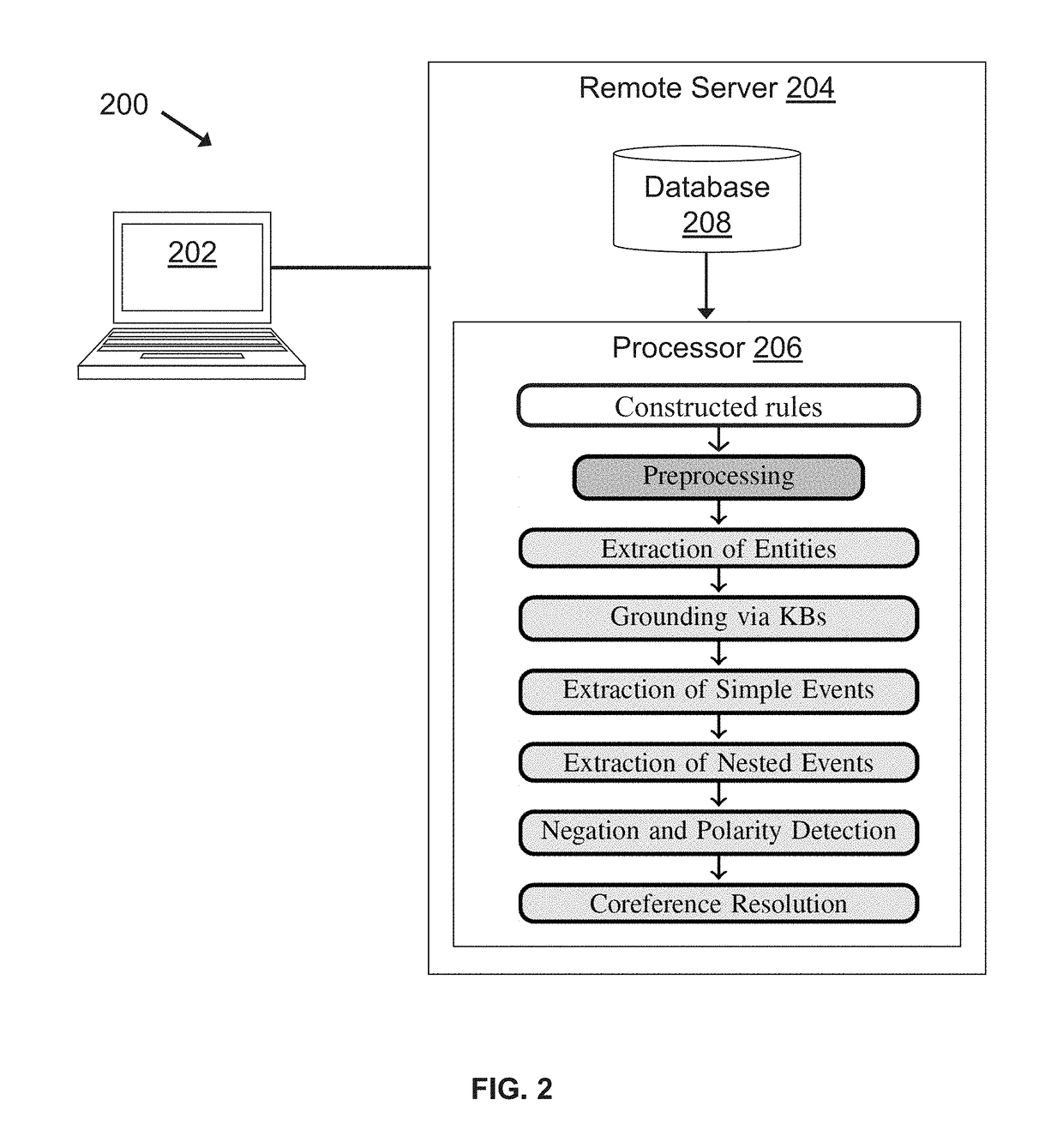
Methods for extracting and assessing information from literature documents
InactiveUS20180260474A1Complex structureWeb data indexingNatural language data processingSignalling pathwaysSemantics
A machine reading system is described herein that includes a framework in which grammar rules can be developed using a concise language that combines syntax and semantics. The resulting technology thus reduces the development time for new grammars in a new domain. An enormous amount of information appears in the form of natural language across millions of academic papers and other literature sources. For example, in the biological domain, there is a tremendous ongoing effort to extract individual chemical interactions from these texts, but these interactions are only isolated fragments of larger causal mechanisms such as protein signaling pathways. The proposed rule-based event extraction framework can model underlying syntactic representations of events in order to extract signaling pathway fragments. Though application to the biomedical domain is herein described, the framework is domain-independent and is expressive enough to capture most complex events annotated by domain experts.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Formation of solar cells with conductive barrier layers and foil substrates
InactiveUS7732229B2Reduce the amount requiredCost-effectivelyPhotovoltaic supportsFinal product manufactureAmorphous siliconSolar cell
Methods and devices are provided for absorber layers formed on foil substrate. In one embodiment, a method of manufacturing photovoltaic devices may be comprised of providing a substrate comprising of at least one electrically conductive aluminum foil substrate, at least one electrically conductive diffusion barrier layer, and at least one electrically conductive electrode layer above the diffusion barrier layer. The diffusion barrier layer may prevent chemical interaction between the aluminum foil substrate and the electrode layer. An absorber layer may be formed on the substrate. In one embodiment, the absorber layer may be a non-silicon absorber layer. In another embodiment, the absorber layer may be an amorphous silicon (doped or undoped) absorber layer. Optionally, the absorber layer may be based on organic and / or inorganic materials.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Manufacturing Method of Three-Dimensional Cross-Linked Foam for Uppers of Shoes
The present invention provides a manufacturing method of three-dimensional cross-linked foam for uppers of shoes, comprising: preparing a plurality of foaming materials in a planar or three-dimensional shape with a cross-linked foaming suppressed; forming at least one interfacing pattern on at least one foaming material to prevent physical and chemical interactions between the foaming materials, the interfacing pattern formed of at least one interfacing material; cross-linked foaming of the foaming material having the interfacing pattern thereon to obtain a cross-linked foam in a planar shape, the cross-linked foam having at least one inner cavity structure therein; and vacuum molding the planar cross-linked foam in a vacuum molding die to obtain a cross-linked foam having a shape corresponding to a last, the planar cross-linked foam disposed in a cavity of the vacuum molding die, the cavity having a shape corresponding to the last.
Owner:PARK LTD
High sensitivity coherent photothermal interferometric system and method for chemical detection
A photo-thermal interferometric spectroscopy system is disclosed that provides information about a chemical at a remote location. A first light source assembly is included that emits a first beam. The first beam has one or more wavelengths that interact with the chemical and change a refractive index of the chemical. A second laser produces a second beam. The second beam interacts with the chemical resulting in a third beam with a phase change that corresponds with the change of the refractive index of the chemical. A detector system is positioned remote from the chemical to receive at least a portion of the third beam. An adaptive optics system at least partially compensates the light beam degradation caused by atmospheric turbulence. A focusing system is used to bring together the light passed through the chemical; the focusing system includes a multimode fiber for the light collection, The detector system provides information on a phase change in the third beam relative to the second beam that is indicative of at least one of, absorption spectrum and concentration of the chemical.
Owner:CELIGHT
Manufacturing Method of Three-Dimensional Cross-Linked Foam for Uppers of Shoes
InactiveUS20080141469A1Dimension and shape stabilityFeel goodShoemaking devicesSolesCompression moldingCross-link
Owner:PARK LTD
Portable fire containment and extinguisher system for in flight aircraft/cabin fires caused by lithium ion battery fires of personal electronic devices in passenger aircraft
ActiveUS9339671B1Increase Thermal MassIncrease surface areaFire rescueJet aeroplaneFire extinguisher
A fire suppression system usable in an aircraft cabin comprising a portable flight case with a dual shell, linings, valves, indicators, agency / industry-approved fire extinguishers and such. The case is able to be retrieved from storage for easy hand carriage in an aircraft / cabin for rapid deployment to any location inside it wherein a fire caused by batteries such as a Lithium Ion battery used in Personal Electronic Devices (PED) has erupted and to be able to enclose the PED fire inside the unit, and discharge into the unit, the fire extinguisher through ports such that the infused extinguishing medium would rapidly envelop the PED on fire inside the flight case while simultaneously allowing the egress of the initial smoke into containing flexible bags and equalizing the displaced volume being replaced by the extinguishing medium thus maintaining a pressurized environment, to chemically interact with and suppress the fire.
Owner:RAJ ANTHONY ANAND +2
Pre-ignition fuel treatment system
InactiveUS7487764B2Improve responseHighly combustibleInternal combustion piston enginesThermal treatment of fuelNuclear engineeringFuel treatment
A method and apparatus for reforming a hydrocarbon fuel which increases the efficiency with which said fuel's energy content may be extracted resulting in improved combustibility and reduction of by-products produced. The hydrocarbon fuel is cracked and ionized in a reactor vessel by means of a feedback loop of electro-chemical interactions with a reactor rod comprised of materials which are both magnetic and catalytic.
Owner:LEE DENNIS
Method and apparatus for optimizing aerosol generation with ultrasonic transducers
ActiveUS20070053789A1Reduced effectivenessIncrease energy outputMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesChemical reactionUltrasonic sensor
The invention is an apparatus and methods for optimizing the performance and protecting one or more aerosol generating transducers from deterioration while operating in a chemically reactive aqueous solution by utilizing one or more protective barrier techniques to eliminate chemical interaction between the aqueous solution and the transducers. The method of the present invention produces an aerosol producing transducer with the transducer housing and assembly to be constructed in such a way as to assure its efficient and effective long-term and problem free operation in an aqueous solution that is chemically reactive.
Owner:ALTAPURE
Vapor deposition system
ActiveUS20110126762A1Liquid surface applicatorsChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseWater vapor
A system for depositing a thin film on a substrate using a vapor deposition process is described. The deposition system includes a process chamber having a vacuum pumping system configured to evacuate the process chamber, a substrate holder coupled to the process chamber and configured to support the substrate, a gas distribution system coupled to the process chamber and configured to introduce a film forming composition to a process space in the vicinity of a surface of the substrate, a non-ionizing heat source separate from the substrate holder that is configured to receive a flow of the film forming composition and to cause thermal fragmentation of one or more constituents of the film forming composition when heated, and one or more power sources coupled to the heating element array and configured to provide an electrical signal to the at least one heating element zone. The deposition system further includes a remote source coupled to the process chamber and configured to supply a reactive composition to the process chamber to chemically interact with the substrate, wherein the remote source comprises a remote plasma generator, a remote radical generator, a remote ozone generator, or a water vapor generator, or a combination of two or more thereof.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Ink for inkjet, ink set for inkjet, and inkjet recording method
InactiveUS20070120920A1Measurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsOrganic solventWater soluble
An ink for inkjet comprising: a dye; and water and / or a water-miscible organic solvent, wherein the dye comprises a dye compound having at least one heterocyclic structure, and the ink further comprises, as an additive, at least one compound capable of chemically interacting with the dye compound.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com