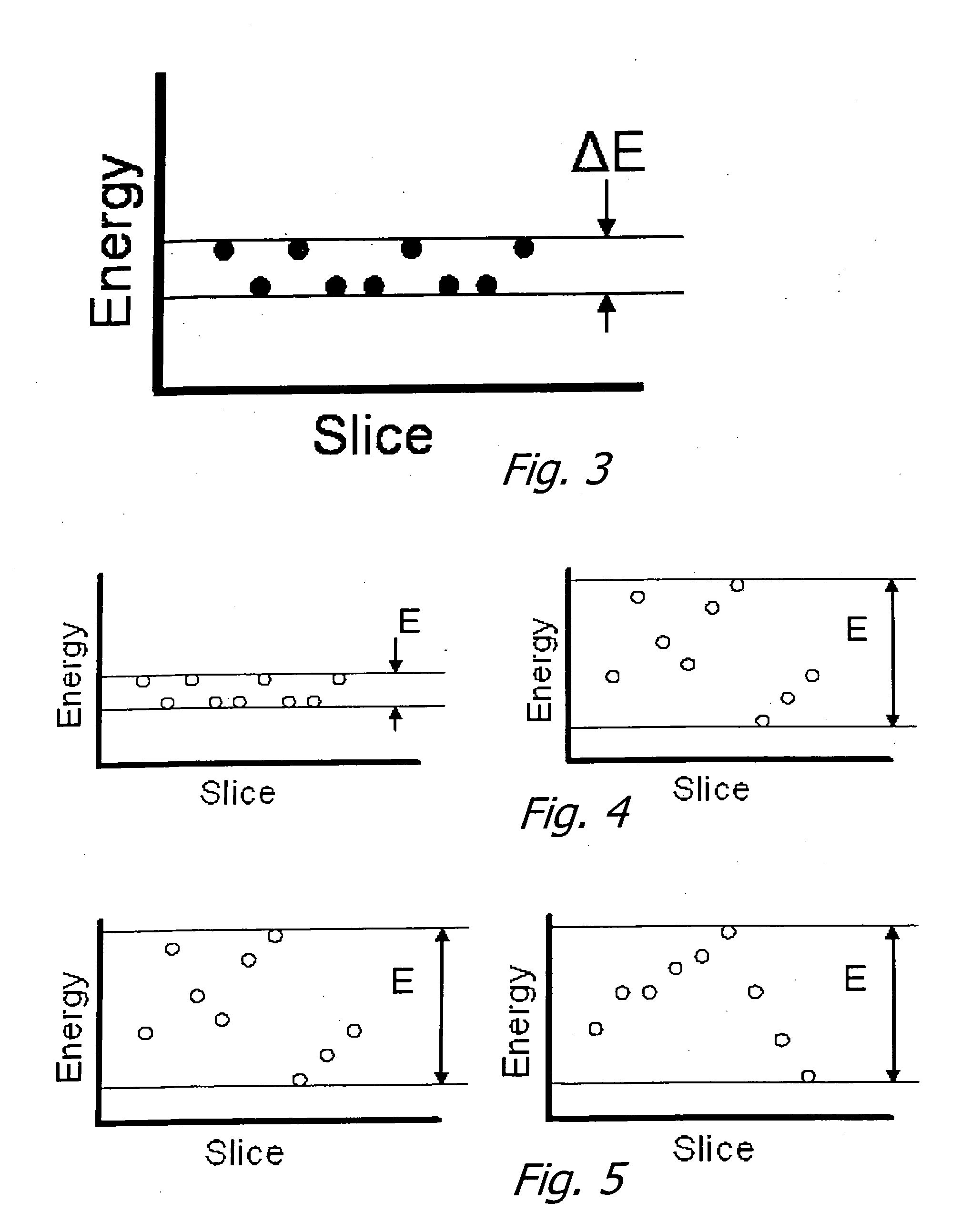
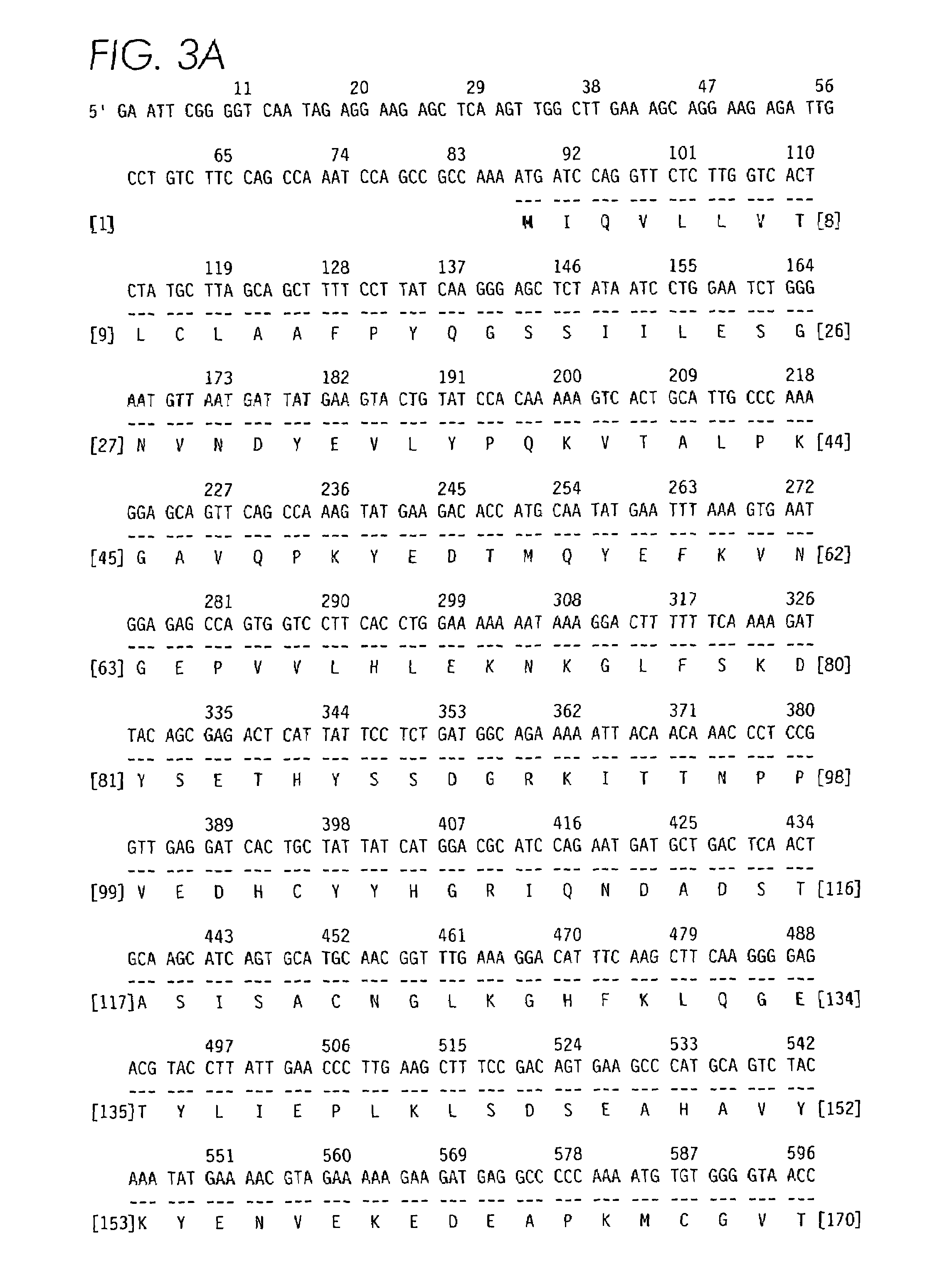Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
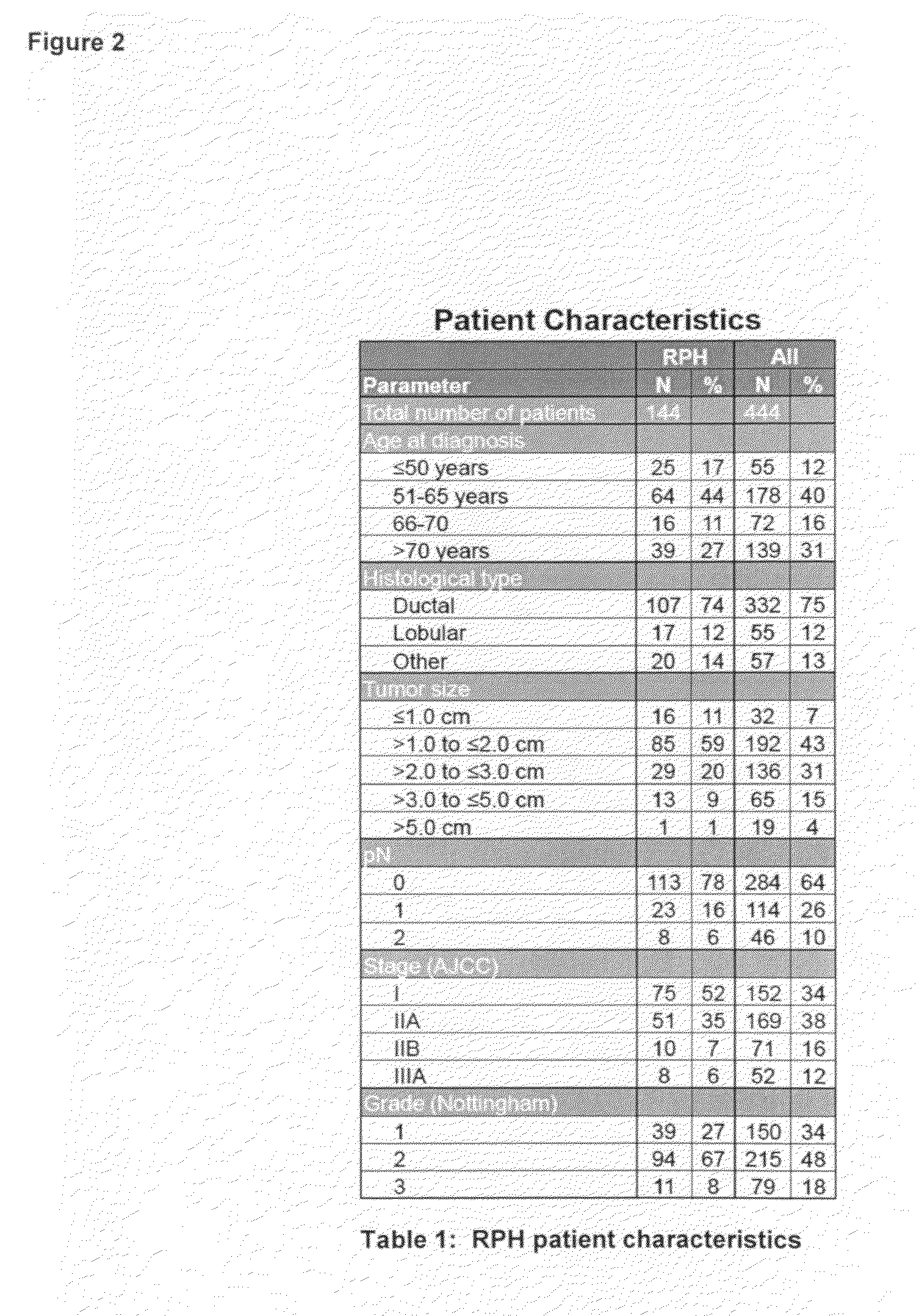
106 results about "Disease process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interactive psychophysiological profiler method and system
An efficient, objective, flexible and easily deployable system for conducting evaluations of mental and physiological state and recommending individualized treatment to improve said state is described. The method and system are based on commensurate measurement of mental functions, levels of stress and anxiety, and / or biologically active molecules such as neurotransmitters, immune markers including cytokines and hormones. The method and system are designed to assess an individual's cognitive function and the underlying physiology in order to delineate various disease processes, injuries, drug states, training stages, fatigue levels, stress levels, aging processes, predict susceptibility to stress and / or sleep deprivation, identify aptitude for training and / or characterize effects of any experimental conditions. The system and method may be used in recommending individualized treatment protocols, as well as to guide the treatment process by assessing the efficacy of such therapies in the clinical trials process.
Owner:ADVANCED BRAIN MONITORING
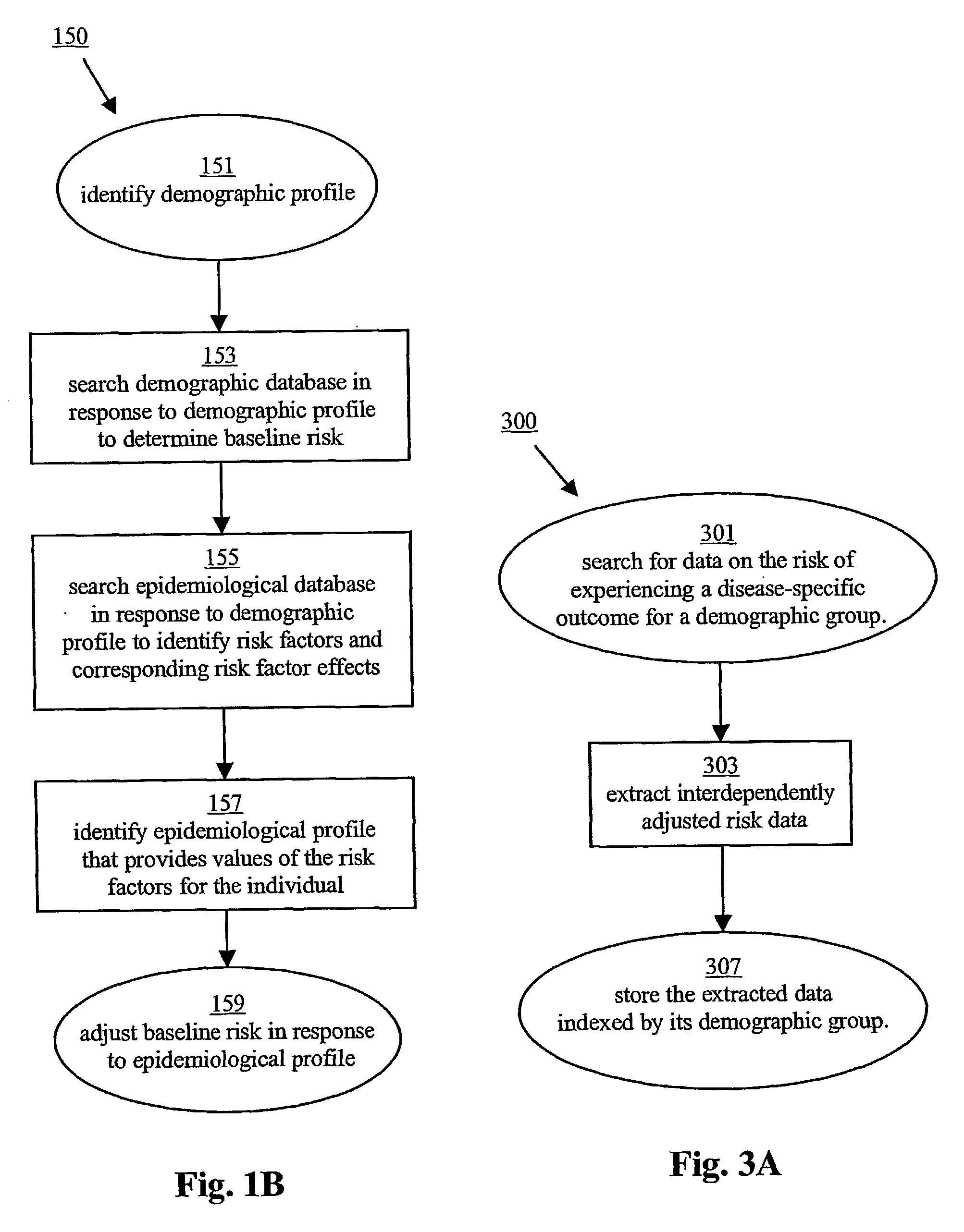
Medical risk assessment system and method
InactiveUS20030065241A1Computer-assisted medical data acquisitionComputer-assisted treatment prescription/deliveryDisease entityCrowds
A method of assessing risk for an individual to experience a specific outcome within a disease entity within a specified time frame is provided. Peer-reviewed scientific publications are analyzed to identify pertinent risk factors (212) for developing disease processes and their possible complications. Information that characterizes an individual (218) in relation to the identified risk factors is then received, preferably responsive to question (224) regarding any demographic values of an individual under test and questions regarding medical chracterisitics of the individual under test. An estimate of risk of the individual acquiring the outcome within a specified time frame is performed based on the identified plurality of risk factors (212). Assessment of medical risk and condition may include analyzing peer-reviewed scientific publications to identify populations affected by a medical outcome and for each population respective risk factors that affect risk of acquiring the medical outcome within a specified time-frame, associating an individual with one of the identified population, identifying information that characterizes the individual (218) in relation to the respective risk factors other associated population, and estimating risk of the individual having the medical outcome within the specified the time frame responsive to the identified information. Promotion of business on a site of a computer network is provided by supplying an on-line questionnaire (224) regarding characteristics of individual (218) under test, receiving information regarding characteristics of the individual under test, and responsive to the received information, providing an assessment of the individual under test having a medical outcome within a specified time frame.
Owner:HOHNLOSER JOERG
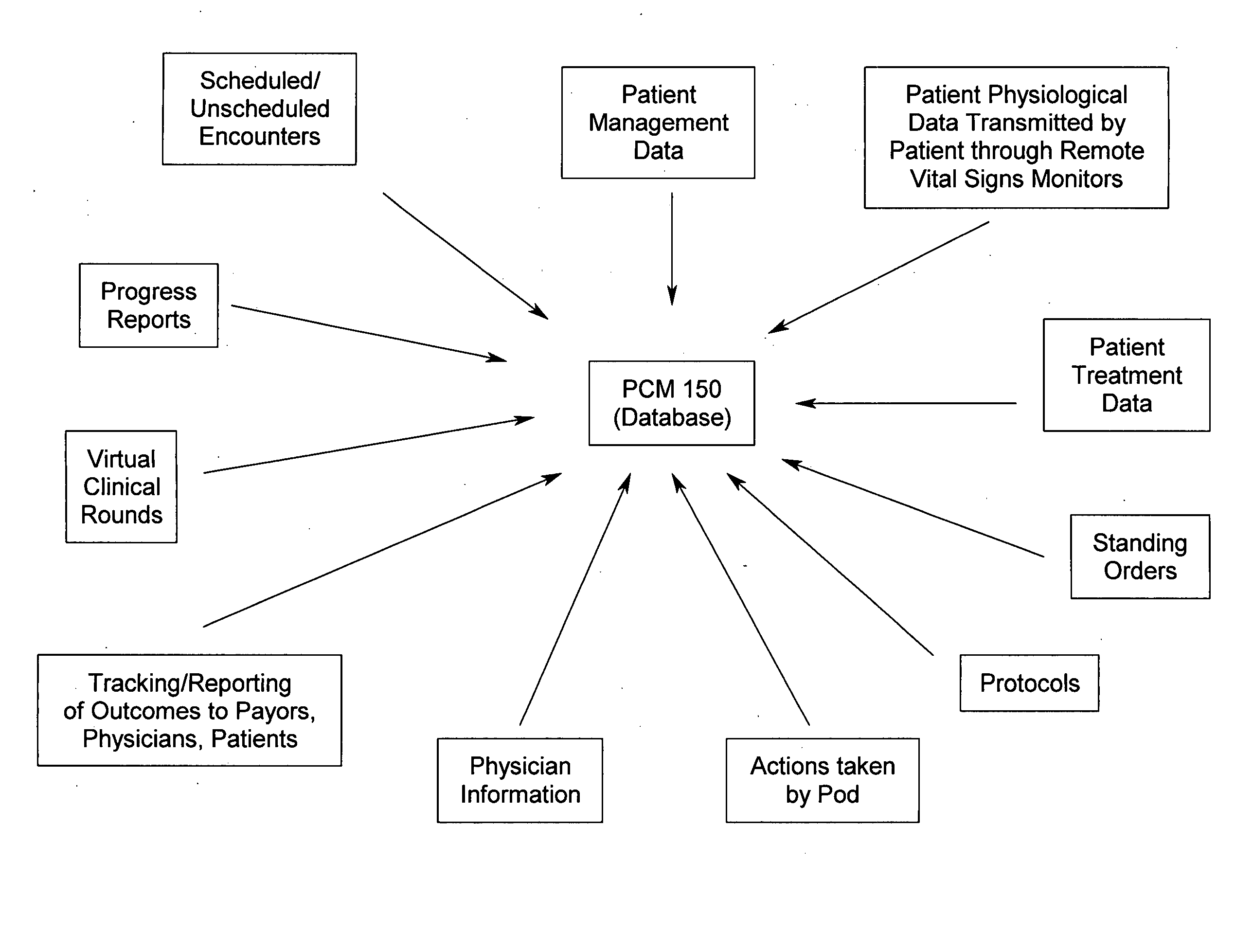
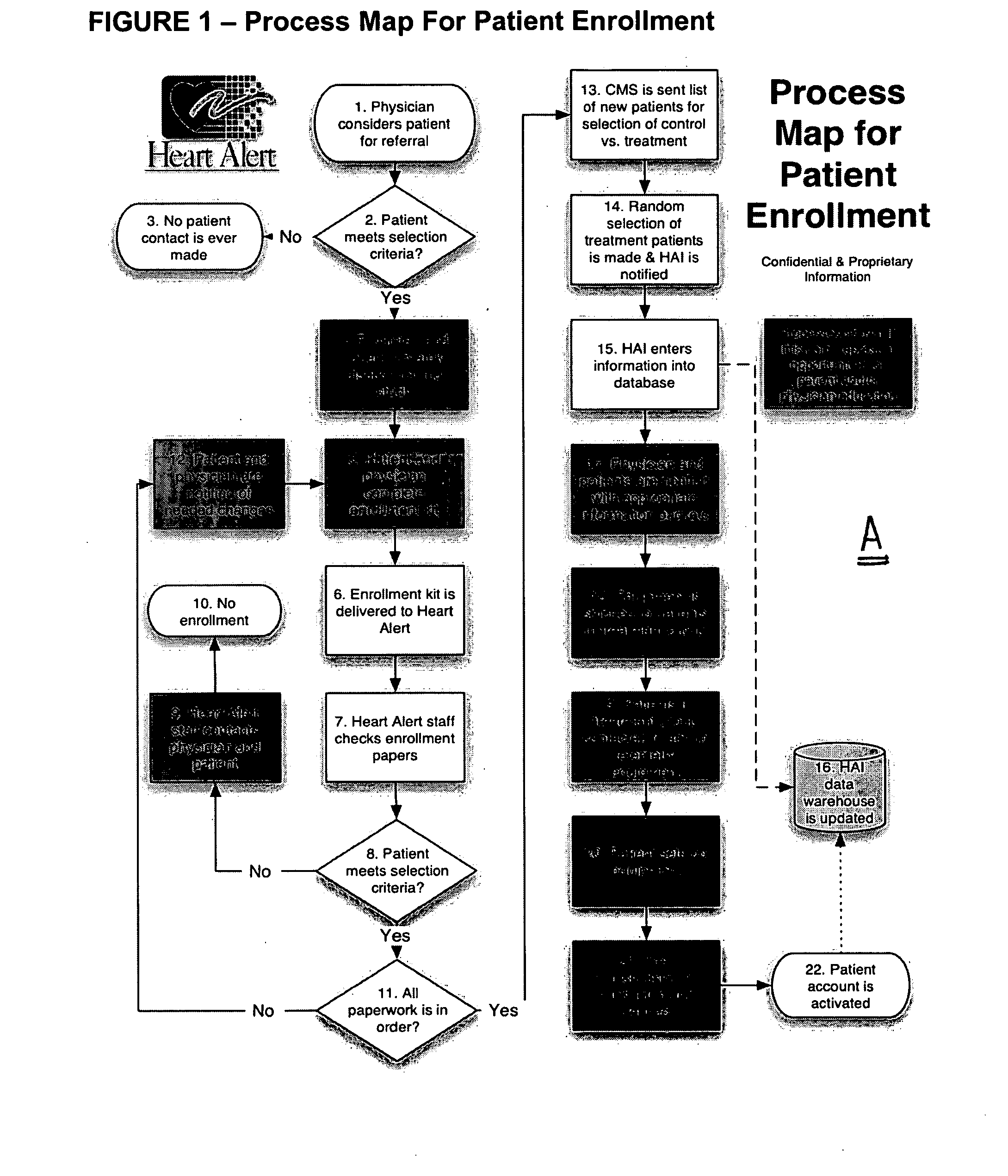
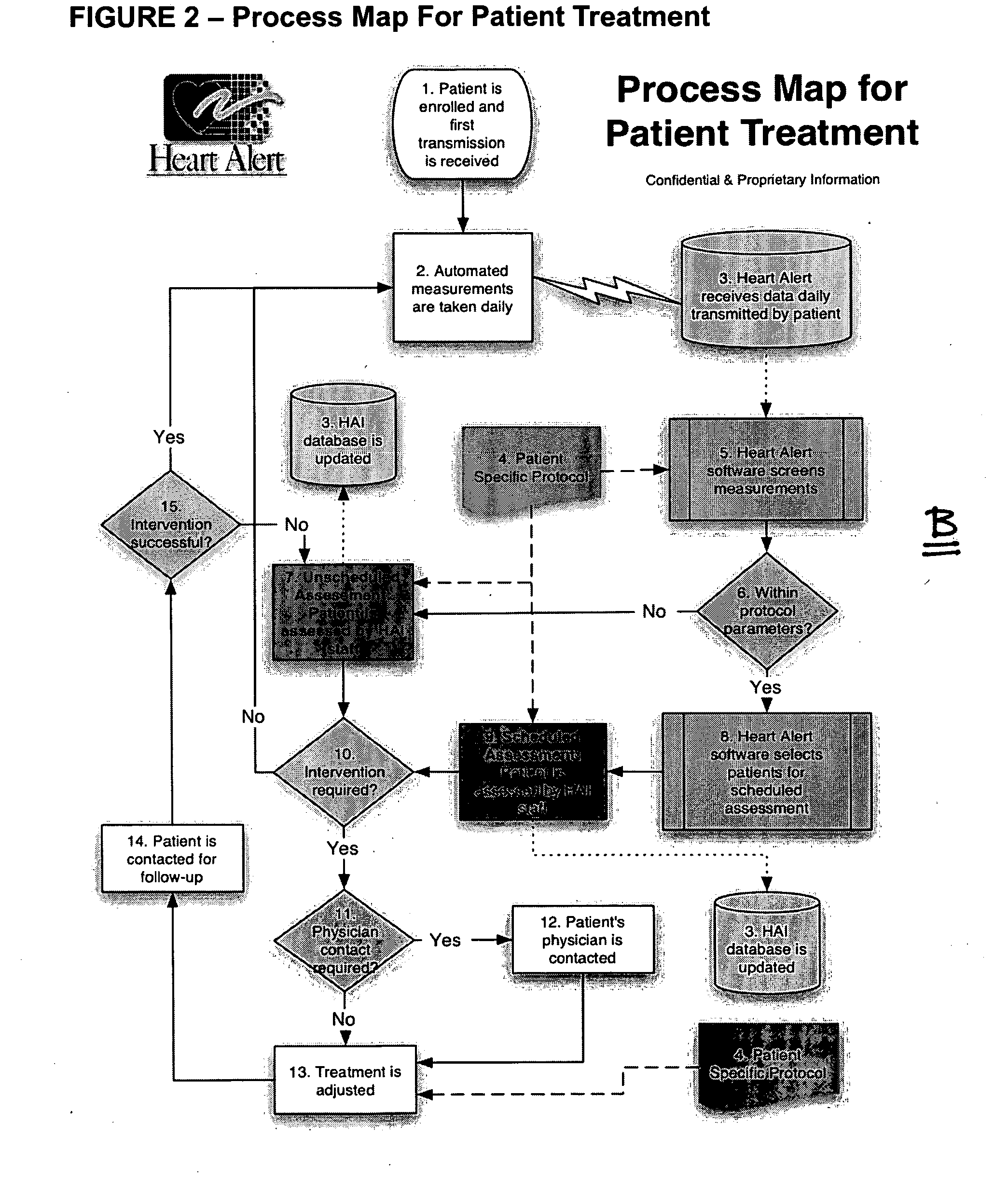
System and method for disease management
InactiveUS20050197545A1Increasing overall healthcare inefficiencies and financial lossImprove the quality of lifePhysical therapies and activitiesSurgeryIllness managementVital sign monitoring
A system and method for disease management that effectively eliminates unnecessary layers and / or intermediaries within the healthcare management system by enabling a disease management entity to operate as an extension of a physician's office, and thus, work closely with the patients and the patient's physicians to effectively empower patients towards self-care and a higher level of awareness and understanding of their disease process and treatment. The present system and method utilizes a team of highly trained healthcare professionals and technicians working together with patients and physicians, wherein remote vital sign monitoring equipment, software systems, and standing orders and treatment protocols, are utilized to effectively manage patients with chronic conditions. Additionally, as the disease management entity operates as an extension of a physician's office, the disease management entity is able to coordinate with a payor through the physician's office, and thus provide the payor with positive financial outcomes.
Owner:HOGGLE JOHN
Delivery systems for periadventitial delivery for treatment of restenosis and anastomotic intimal hyperplasia
InactiveUS6991804B2Preventing and reducing intimal hyperplasiaPrevent and reduce intimal hyperplasiaOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryIntimal proliferationPercent Diameter Stenosis
The invention provides methods for treating injuries to one or more internal structures of a subject by administering a drug delivery vehicle to an external surface of the injured structure. The drug delivery vehicle substantially adheres to the site of administration and provides for the release of a bioactive agent that reduces or prevents further injury to the internal structure by disease processes, such as hyperplasia.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Exhaled Breath Condensate Collection and Assay System and Method
InactiveUS20080214947A1Easy to determineDetermining the predictive ability of these testsRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsTime courseAssay
A method and system that provides for minute-to-minute EBC pH monitoring (or for other EBC characteristic monitoring) of a subject that greatly assists in determining the time-course of airway pH changes (or other characteristic changes) in evolving disease processes, and may assist in determining the predictive ability of these tests, as well as determining response to therapy.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA
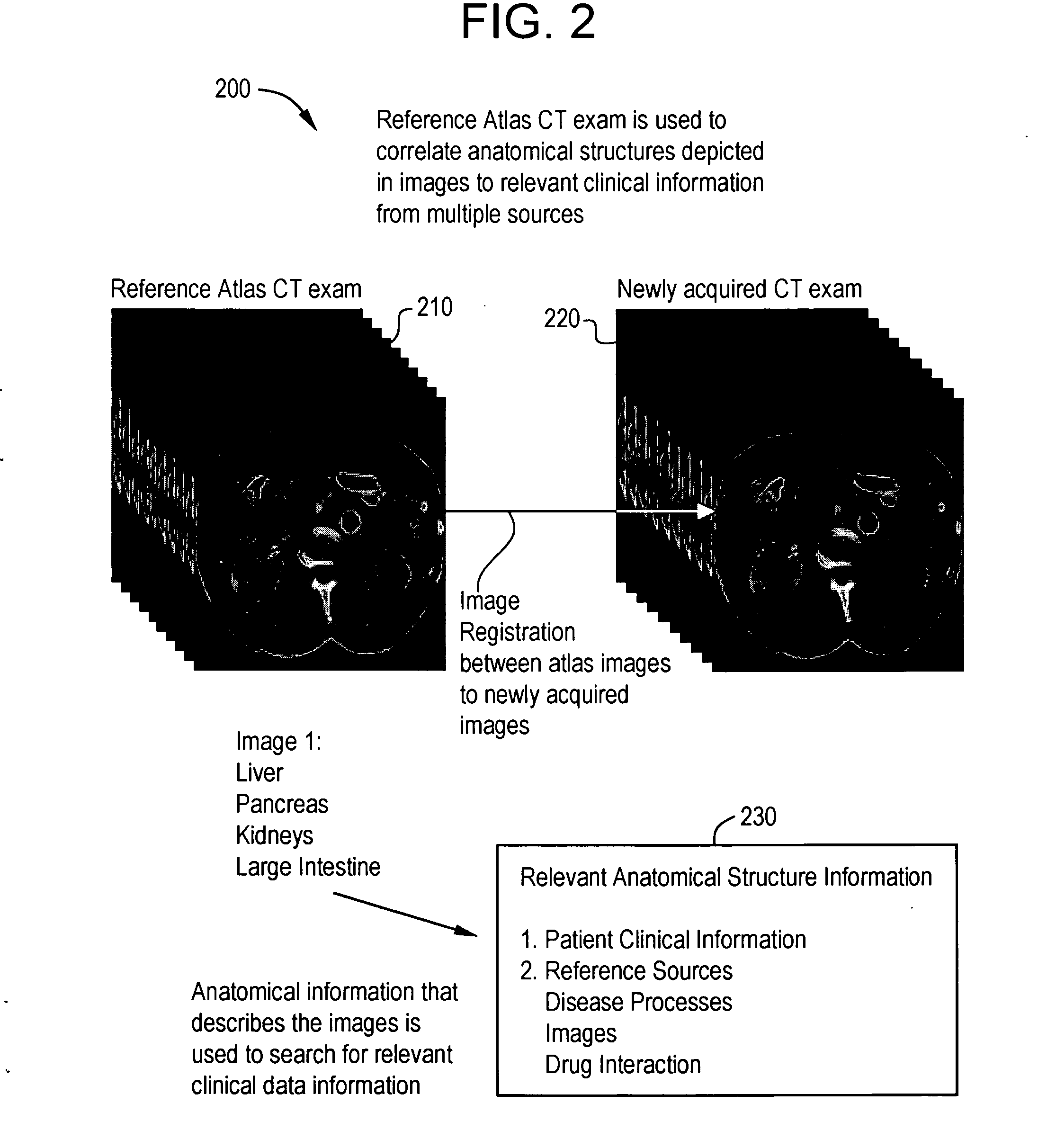
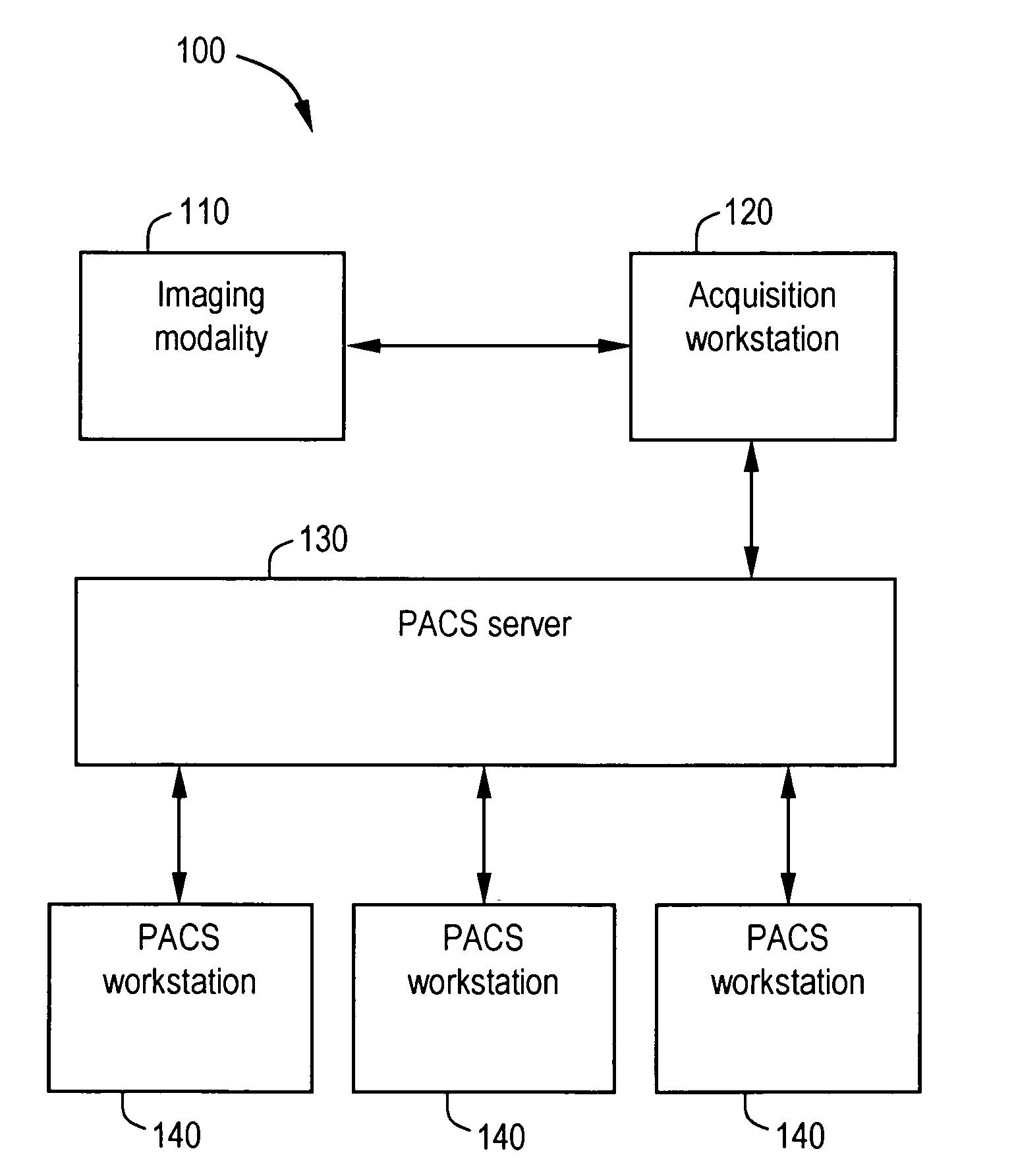
System and method for anatomy labeling on a PACS
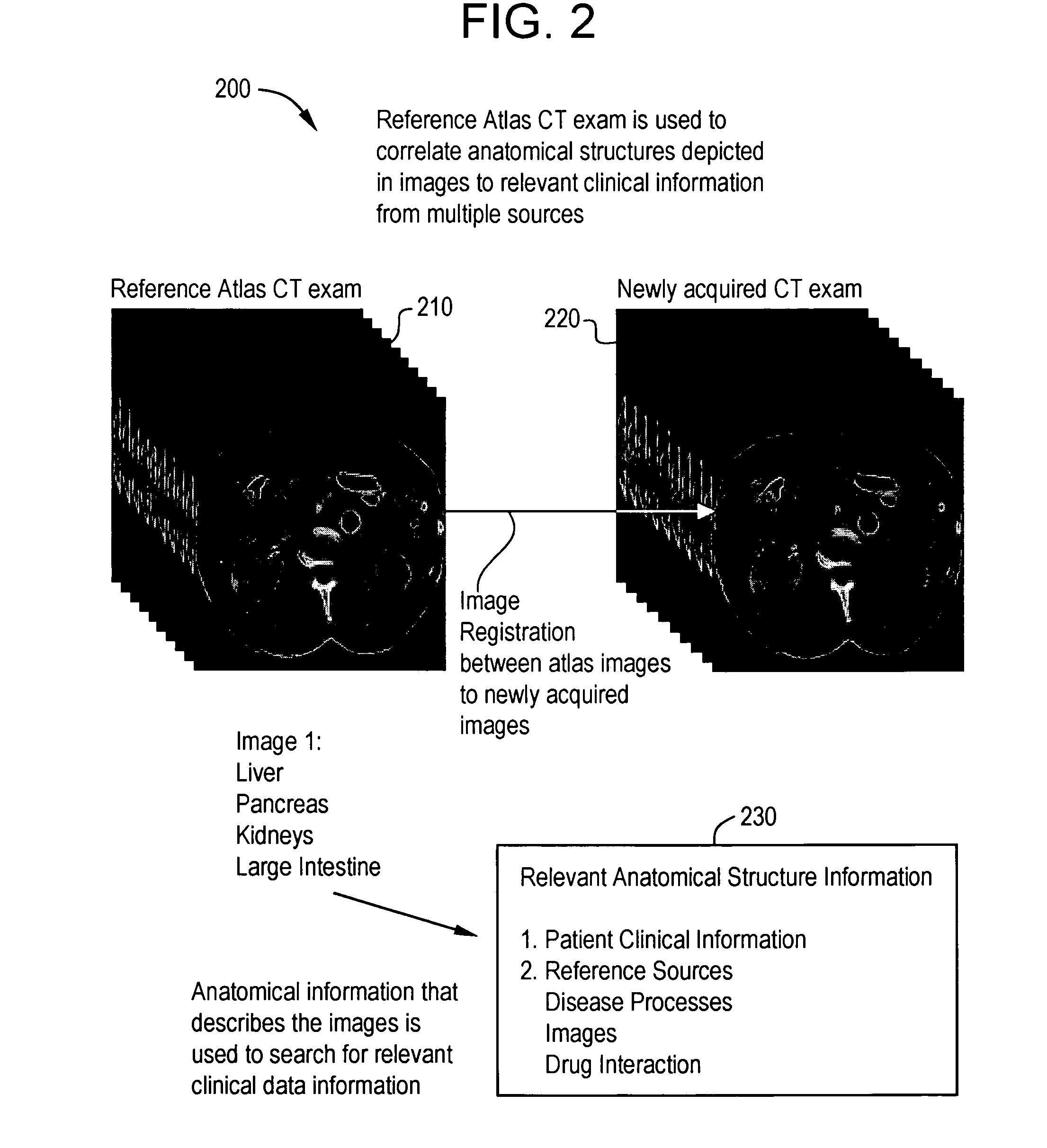
ActiveUS20070127790A1Narrow selectionImage enhancementImage analysisClinical informationDrug interaction
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide a system and method for image registration and display of relevant information. The method includes identifying one or more anatomical parts in an acquired image, mapping the acquired image to a reference image based on the one or more anatomical parts, storing anatomy information in relation to the acquired image, and displaying the acquired image based on the anatomy information. The method may also include controlling the displaying of the acquired image based on a voice command related to the anatomy information. Anatomy information may be displayed with the acquired image. Anatomy information may include clinical information, reference information, disease process information, a related image, and / or drug interaction information, for example. The acquired image may be displayed according to a display setting, such as a window level setting and / or other display setting, based on the anatomy information.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for the early detection of pancreatic cancer and other gastrointestinal disease conditions
InactiveUS20080248484A1Early diagnosisSpecific and focused early diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementOrgan systemNeoplasm
The present invention uses peripheral blood monocyte-lymphocyte for the early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, as well as other conditions of the pancreas and other organs. The peripheral blood lymphocytes recognize the new neoplasm in the pancreas, as well as disease processes in other organ systems. The evaluation of this specific recognition of the disease process by the peripheral blood monocyte-lymphocyte through gene microarray expression patterns constitute a successful method for the early detection of pancreatic cancer and other organ disease processes. This document describes the process used in this method of early diagnosis.
Owner:BAUER A ROBERT
Information processing method for disease stratification and assessment of disease progressing
InactiveUS20040243362A1Reducing time spent repetitivelyFailure can be accuratelyMedical simulationMedical data miningInformation processingOptimal treatment
A digital computer system stratifies in a set of patients, based on a set of observations. The observations can include physical, biochemical, histological, genetic, and gene-expression data, among other types of information. Adjustments can be made to account for the possibility that observations of several patients may begin at different points in the progression of their respective disease processes. Once these adjustments are made, the data are subjected to a statistical cluster analysis. Each cluster of patients potentially represents a different disease stratum, with its own underlying cause, optimum therapy, and prognosis. Once the strata are defined and patients are assigned to them, adjustments to the data can be refined. The cluster analysis then can be repeated, and so an iterative process of stratification and staging takes place.
Owner:PROSANOS CORP
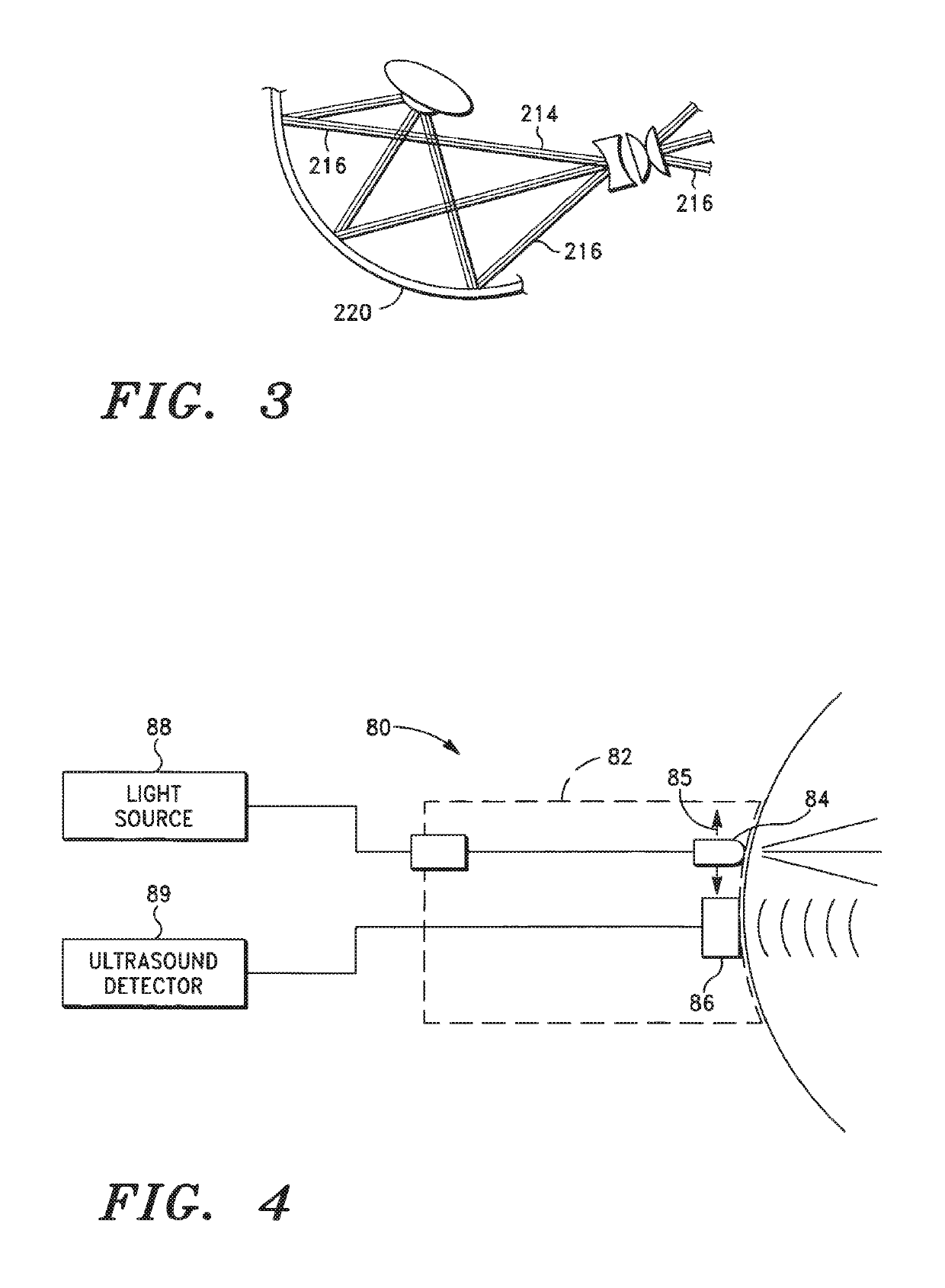
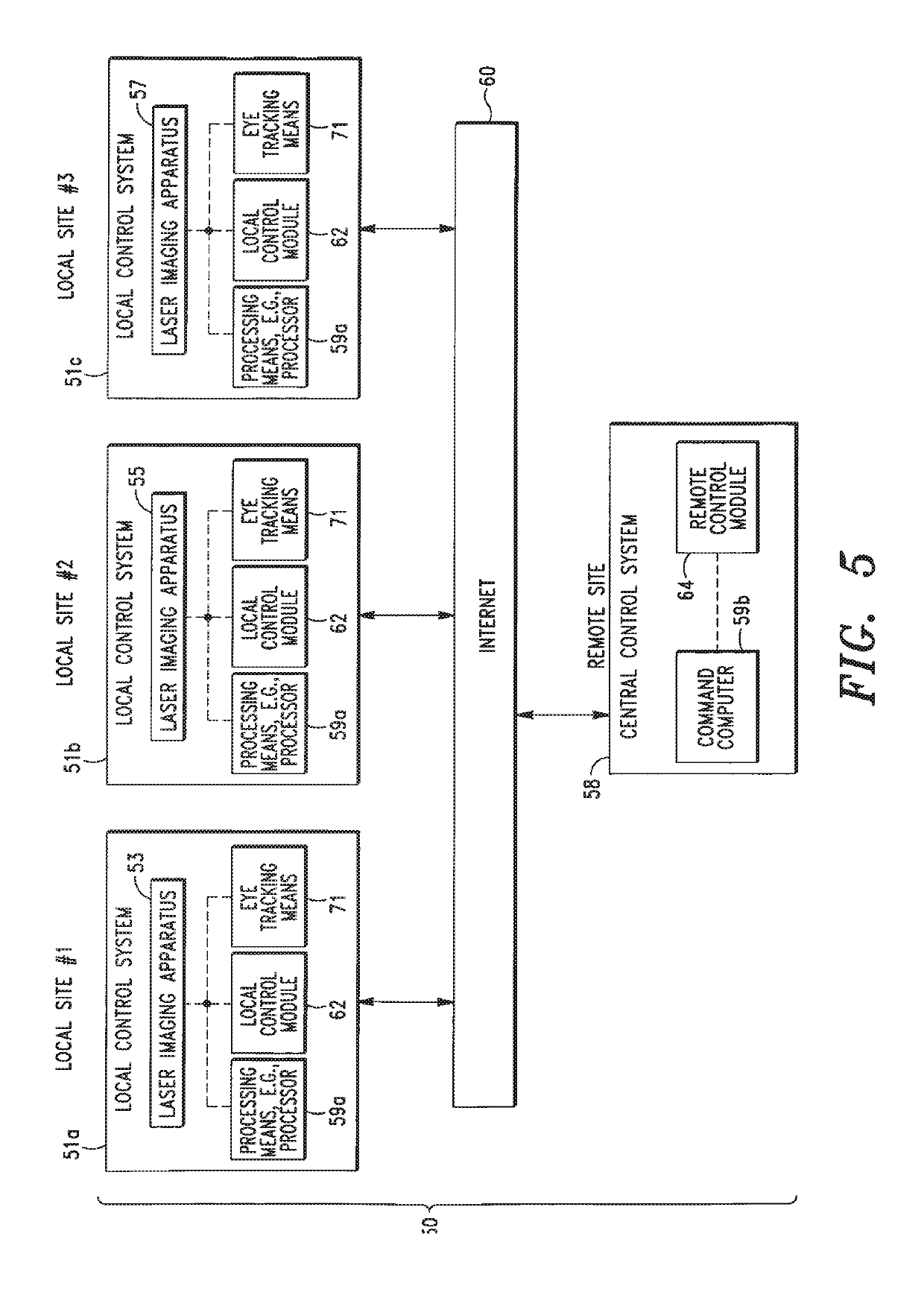
Remote Laser Treatment System With Dynamic Imaging
ActiveUS20180303667A1Eliminate needTrack displacementLaser surgeryAnti-theft devicesTherapeutic DevicesThe Internet
An integral laser imaging and treatment apparatus, and associated systems and methods that allow a physician (e.g., a surgeon) to perform laser surgical procedures on an eye structure or a body surface with an integral laser imaging and treatment apparatus disposed at a first (i.e. local) location from a control system disposed at a second (i.e. remote) location, e.g., a physician's office. In some embodiments, communication between the integral laser imaging and treatment apparatus and control system is achieved via the Internet®. Also, in some embodiments, the laser imaging and treatment apparatus includes a dynamic imaging system that verifies the identity of a patient, and is capable of being used for other important applications, such as tracking and analyzing trends in a disease process. Further, in some embodiments, the laser imaging and treatment apparatus determines the geographical location of the local laser generation unit of the system using GPS.
Owner:PEYMAN GHOLAM A
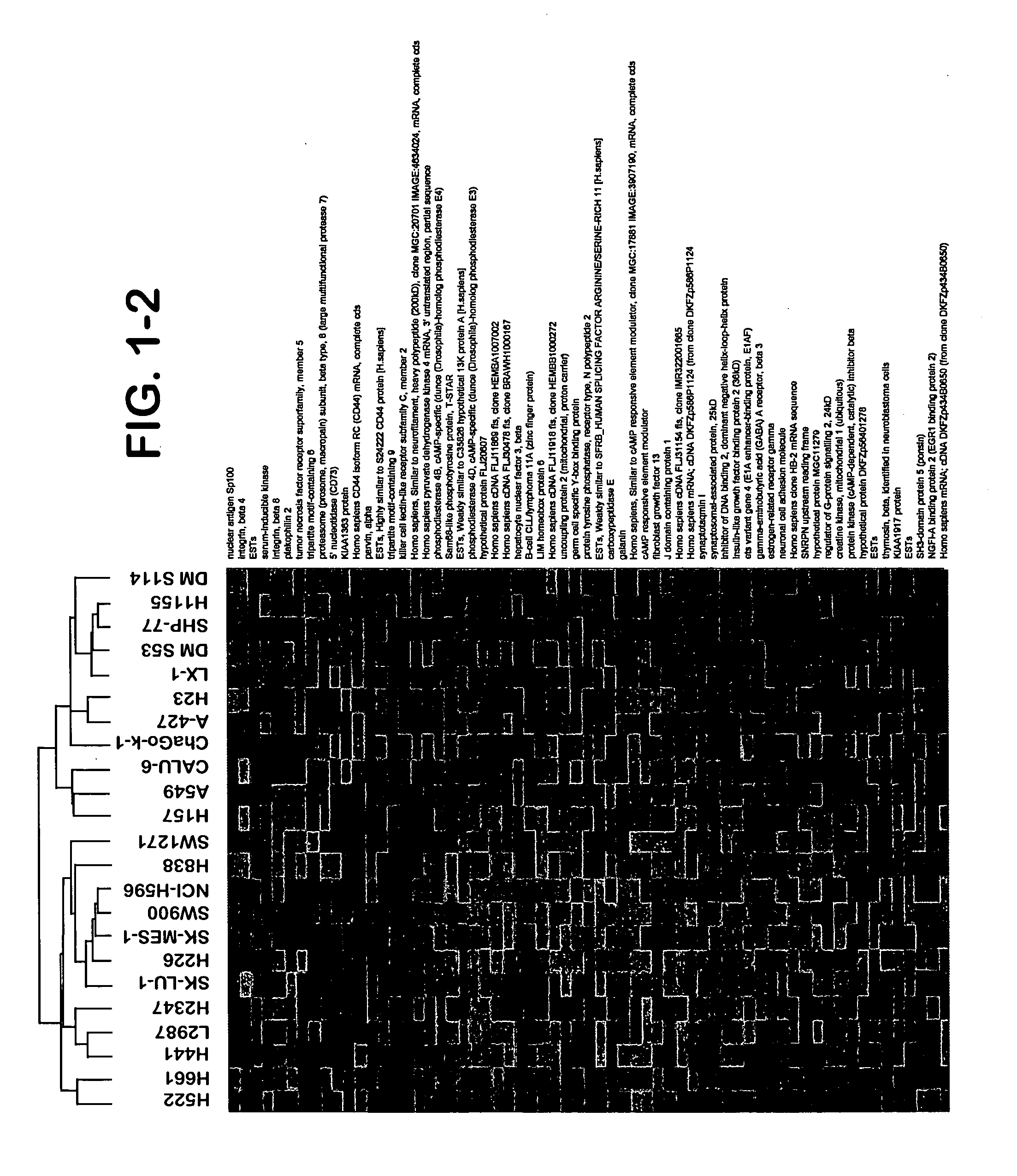
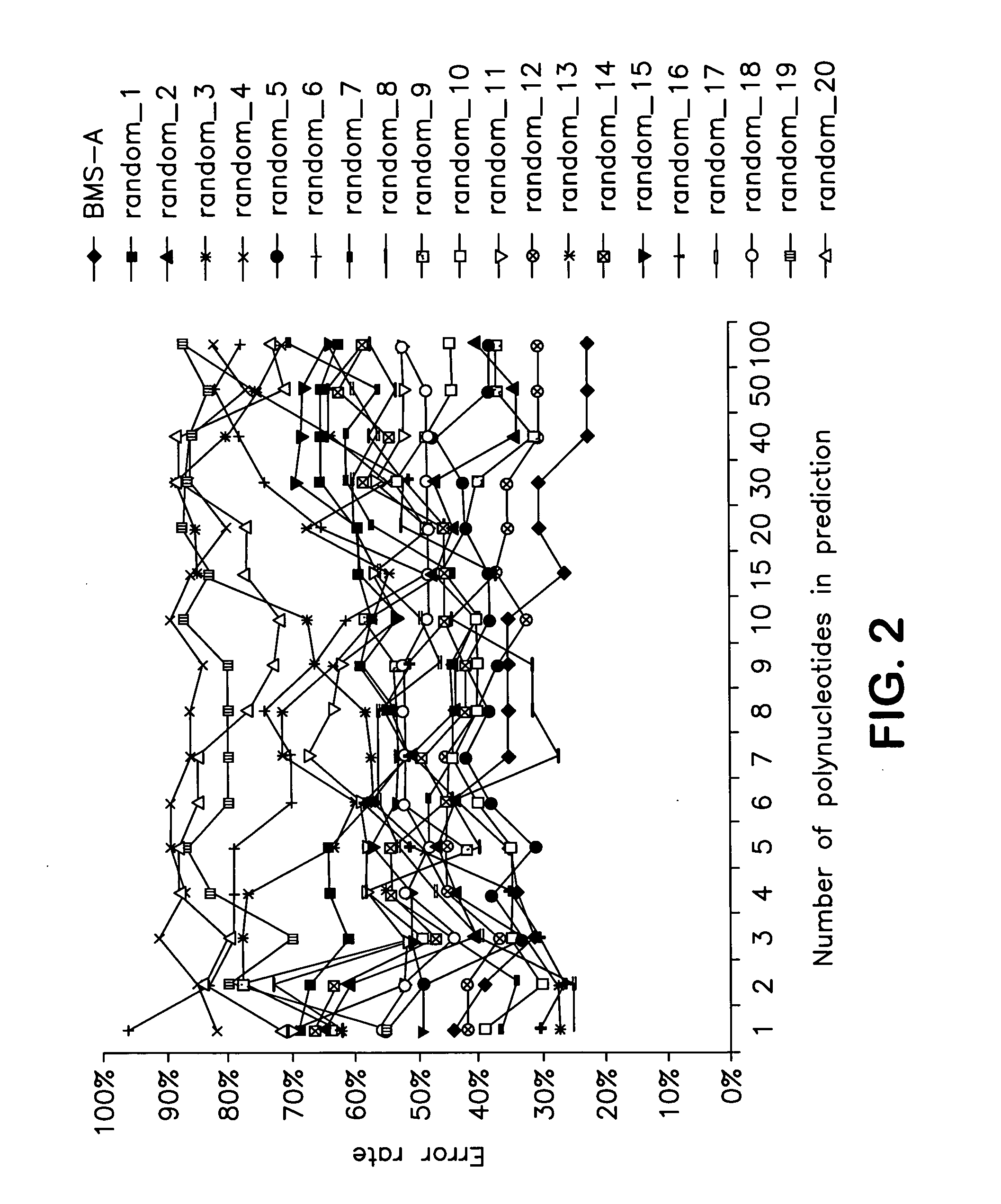
Identification of polynucleotides for predicting activity of compounds that interact with and/or modulate protein tyrosine kinases and/or protein tyrosine kinase pathways in lung cancer cells
InactiveUS20060019284A1Improved prognosisContinue treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsDisease areaProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The present invention describes polynucleotides that have been discovered to correlate to the relative intrinsic sensitivity or resistance of cells, e.g., lung cell lines, to treatment with compounds that interact with and modulate, e.g., inhibit, protein tyrosine kinases, such as, for example, members of the Src family of tyrosine kinases, e.g., Src, Fgr, Fyn, Yes, Blk, Hck, Lck and Lyn, as well as other protein tyrosine kinases, including, Bcr-abl, Jak, PDGFR, c-kit and Ephr. These polynucleotides have been shown, through a weighted voting cross validation program, to have utility in predicting the resistance and sensitivity of lung cell lines to the compounds. The expression level of some polynucleotides is regulated by treatment with a particular protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor compound, thus indicating that these polynucleotides are involved in the protein tyrosine kinase signal transduction pathway, e.g., Src tyrosine kinase. Such polynucleotides, whose expression levels correlate highly with drug sensitivity or resistance and which are modulated by treatment with the compounds, comprise polynucleotide predictor or marker sets useful in methods of predicting drug response, and as prognostic or diagnostic indicators in disease management, particularly in those disease areas, e.g., lung cancer, in which signaling through the protein tyrosine kinase pathway, such as the Src tyrosine kinase pathway, is involved with the disease process.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
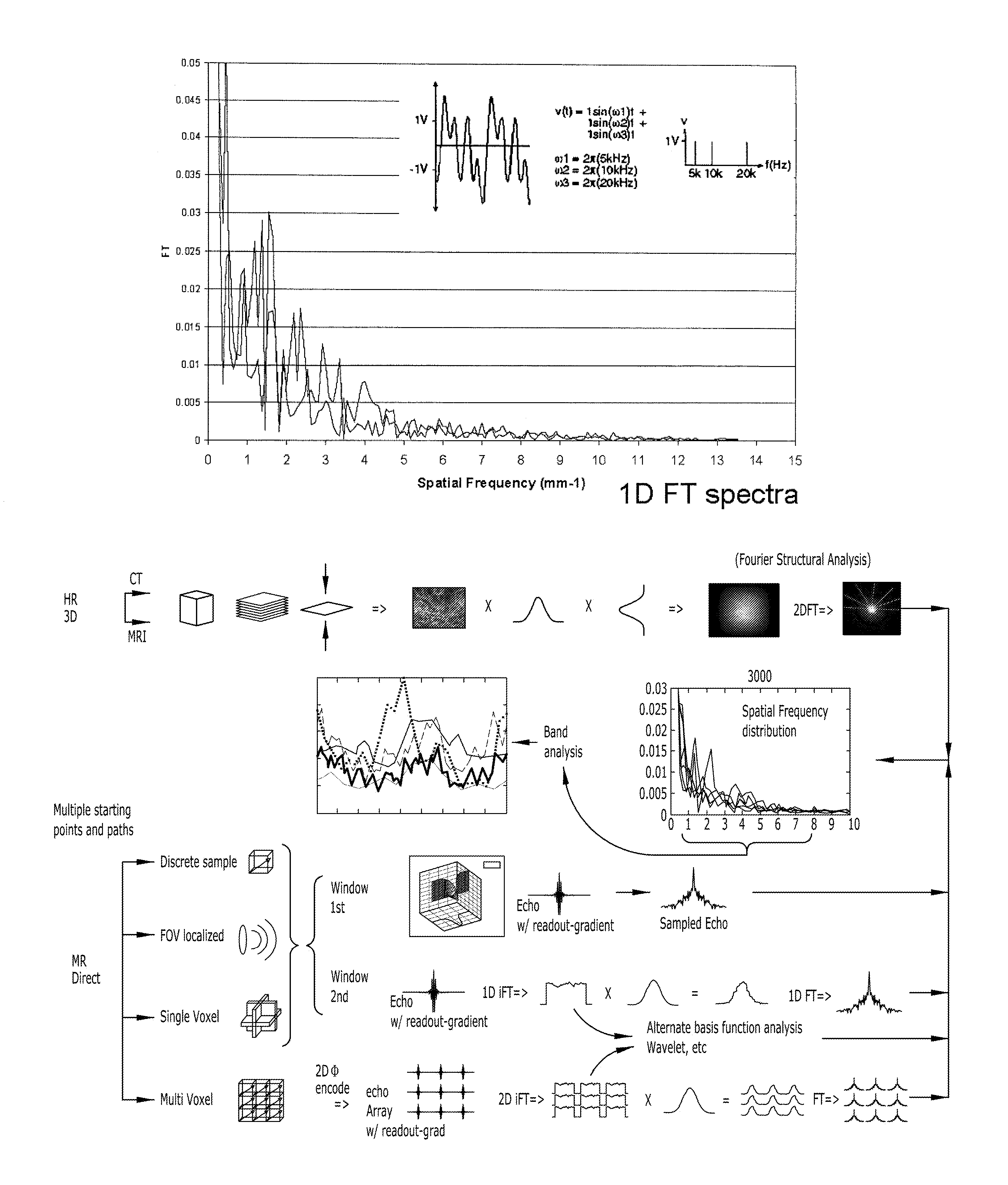
Structure assessment using spatial-frequency analysis
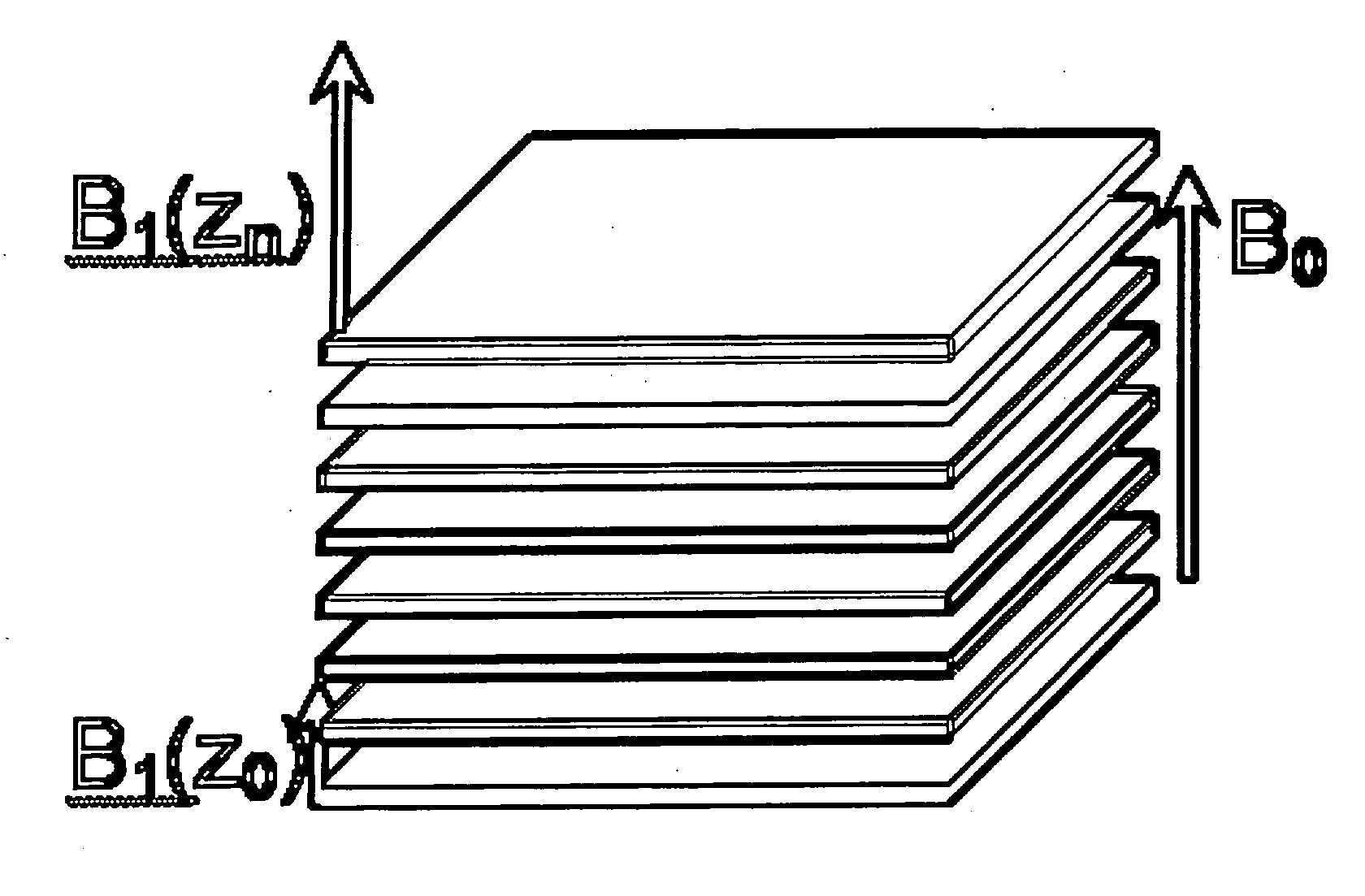
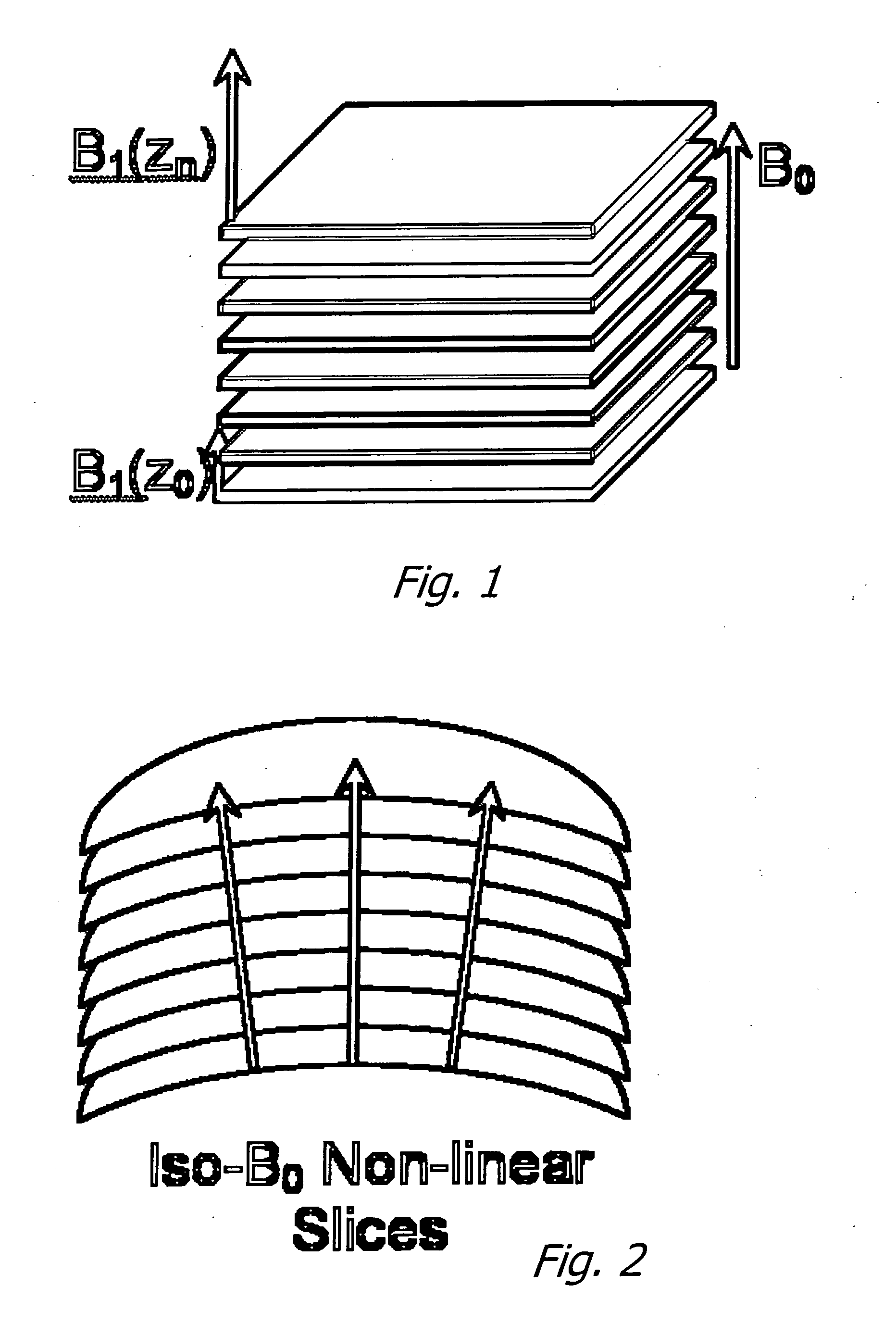
InactiveUS20070167717A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumSpectroscopy
The disclosed innovation is a method for acquiring spatial frequency spectra from specific locations in a 3D sample using modifications of the current MRI techniques for localized NMR spectroscopy. The innovation in its simplest abstraction is to add the use of a read out gradient to the current NMR spectroscopy pulse sequences and record the resultant echo. These techniques generate spectra from a selected region or generate an image of the results over a region of the sample. These methods can be applied to analyzing the structure of trabecular bone as well as for analyzing or diagnosing disease in cases where there is a difference in the spatial frequency power spectrum due to physiologic or disease processes. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:OSTEOTRONIX MEDICAL PTE LTD
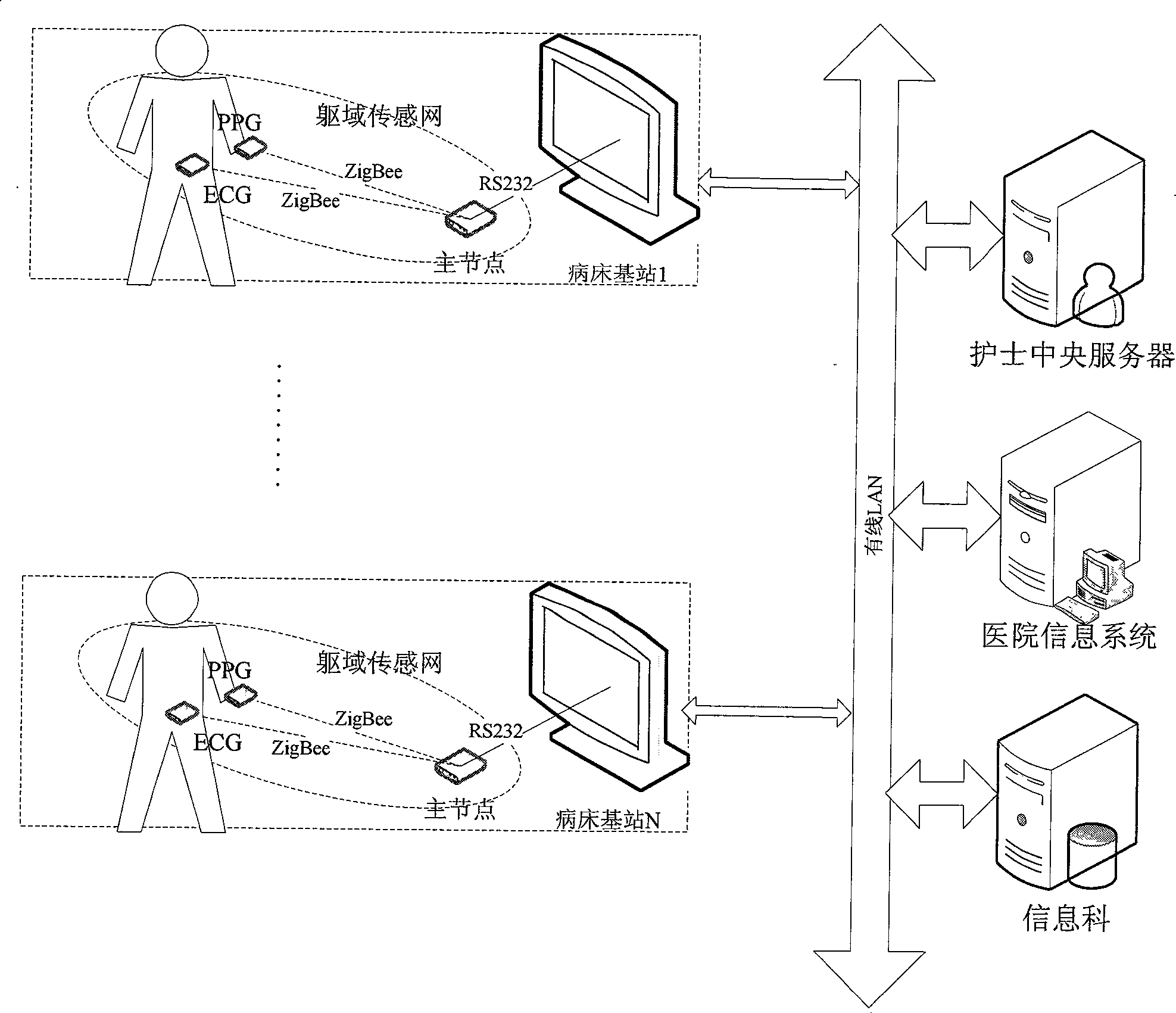
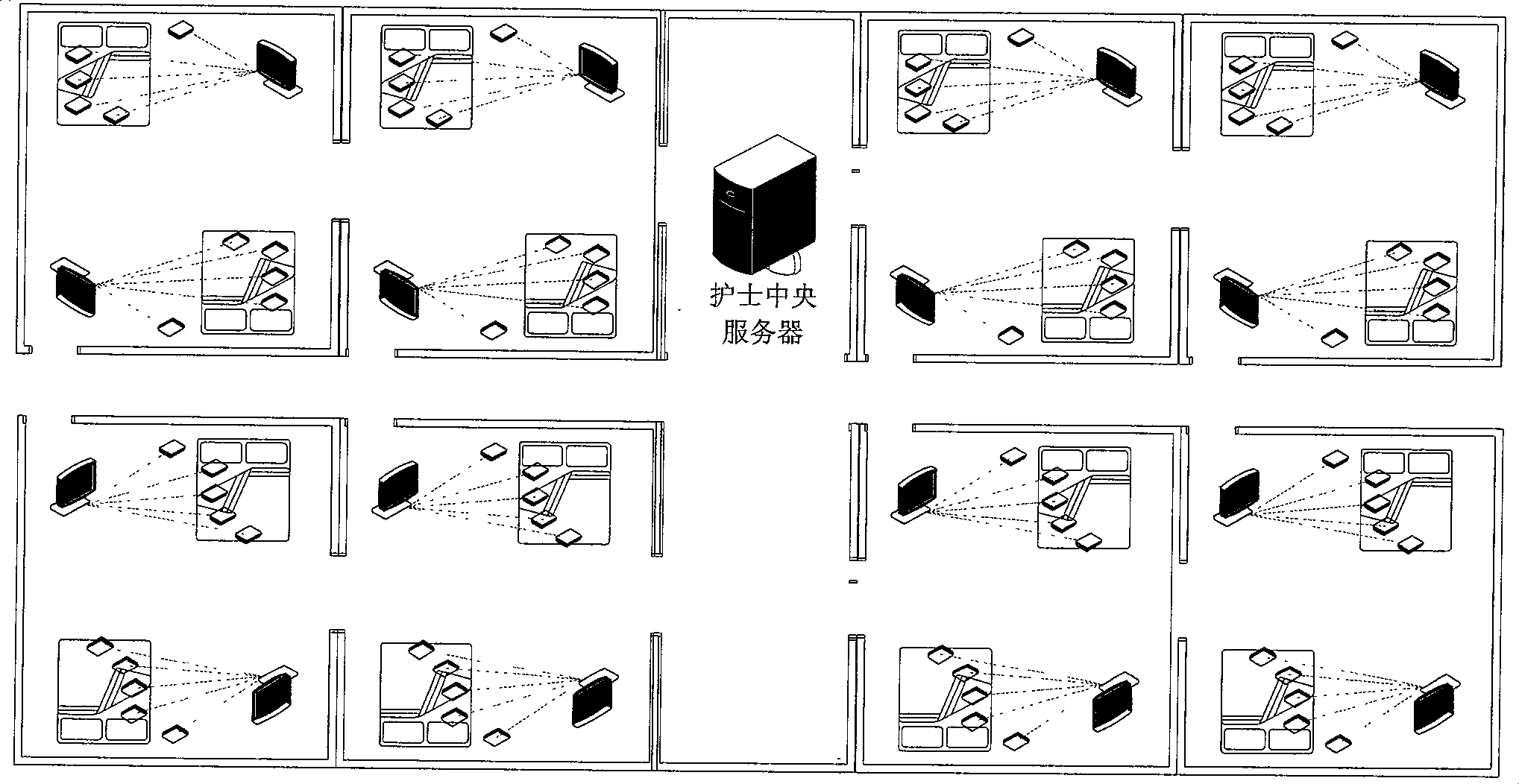
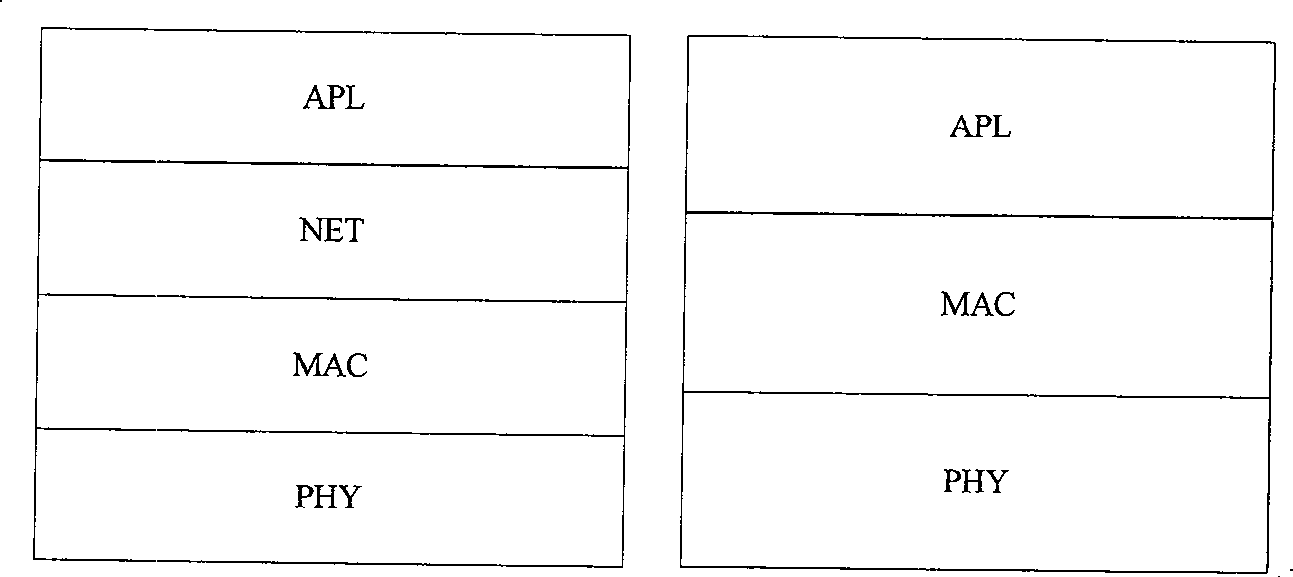
Sickroom wireless monitoring system based on ZigBee
InactiveCN101371801ARealize supervision and alarmRealize information storageNear-field transmissionTransmission systemsEcg signalPatient's room
The invention discloses a ward wireless monitoring system based on ZigBee and consists of a plurality of wireless physiological parameter miniaturization modules, a monitoring base station and a nurse central server. The invention also discloses the application of the ward wireless monitoring system based on ZigBee to ward centralized wireless monitoring and patient random movement monitoring. The ward wireless monitoring system can collect a variety of physiological parameters such as electrocardiosignals, heart rate, heart sound, oxygen saturation of blood, body temperature, and the like, and adopt ZigBee technology for wireless transmission of data so as to realize ward centralized wireless monitoring and patient random movement monitoring and facilitate the medical staff monitoring the disease process of patients and taking protection measures. The system of the invention has the advantages of low power consumption, miniaturization, low cost, convenient network formation, capability of detecting a variety of parameters, good extending and interactive ability and high reliability; the system can reflect the physiological status of the body more veritably and can greatly reduce the electric cable connection on critical patients, thus facilitating the wearing of patients as well as the diagnosis and treatment operation of doctors and nurses.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
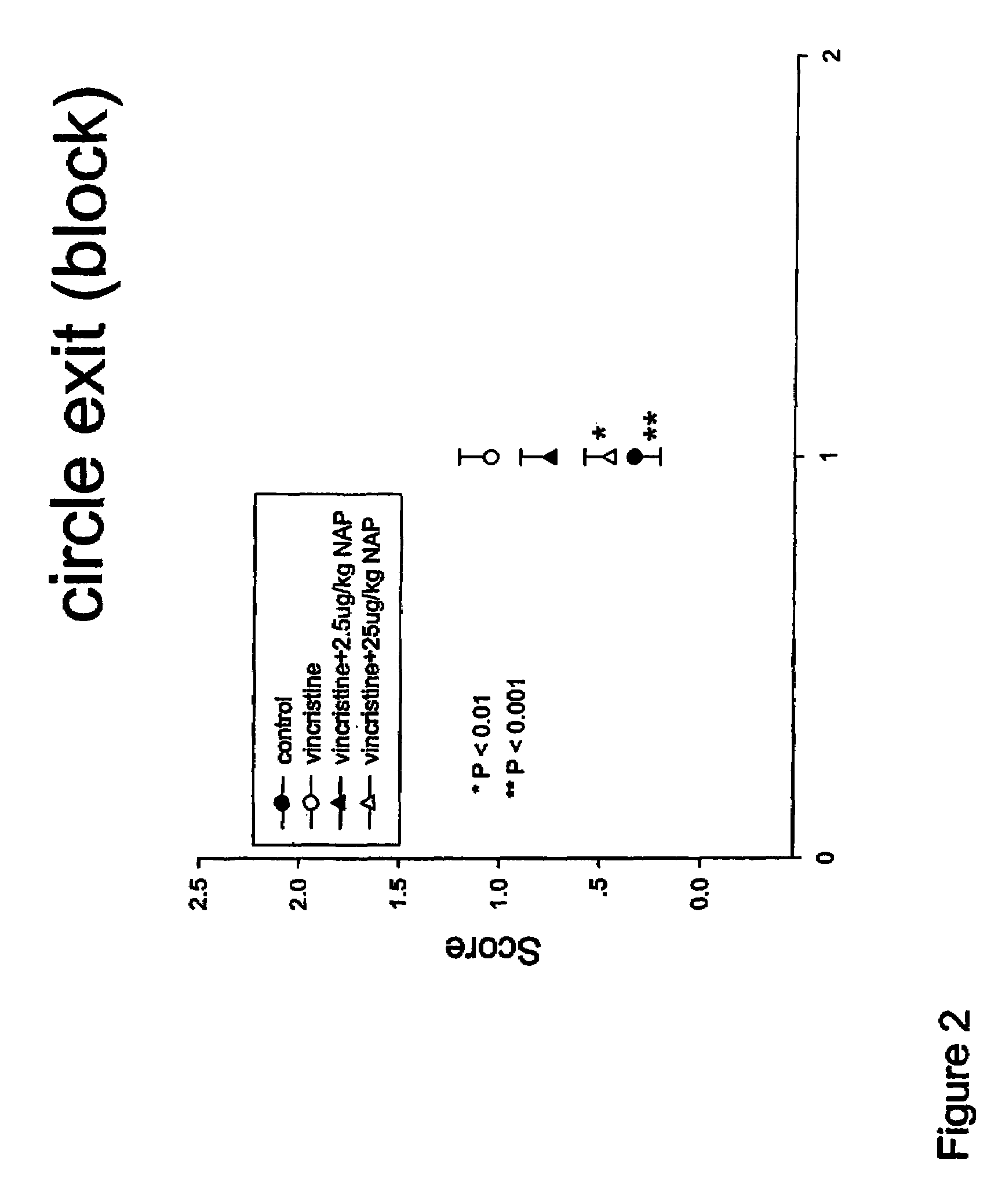
Method of Risk Management for Patients Undergoing Natalizumab Treatment
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) has been identified in patients taking natalizumab (NMAB) for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). This patent application provides a novel method of patient screening and monitoring intended to decrease the risk of PML and other opportunistic central nervous system (CNS) diseases in patients undergoing MS therapy with NMAB, and proposes a novel method of screening and monitoring intended to decrease the risk of opportunistic disease processes of the CNS during the treatment of other medical disorders with NMAB.
Owner:SEEDLINGS LIFE SCI VENTURES
Magnetic field gradient structure characteristic assessment using one dimensional (1D) spatial-frequency distribution analysis
InactiveUS7932720B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientFrequency spectrum
The disclosed innovation is a method for acquiring spatial frequency spectra from specific locations in a 3D sample using modifications of the current MRI techniques for localized NMR spectroscopy. The innovation in its simplest abstraction is to add the use of a read out gradient to the current NMR spectroscopy pulse sequences and record the resultant echo. These techniques generate spectra from a selected region or generate an image of the results over a region of the sample. These methods can be applied to analyzing the structure of trabecular bone as well as for analyzing or diagnosing disease in cases where there is a difference in the spatial frequency power spectrum due to physiologic or disease processes. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:OSTEOTRONIX MEDICAL PTE LTD
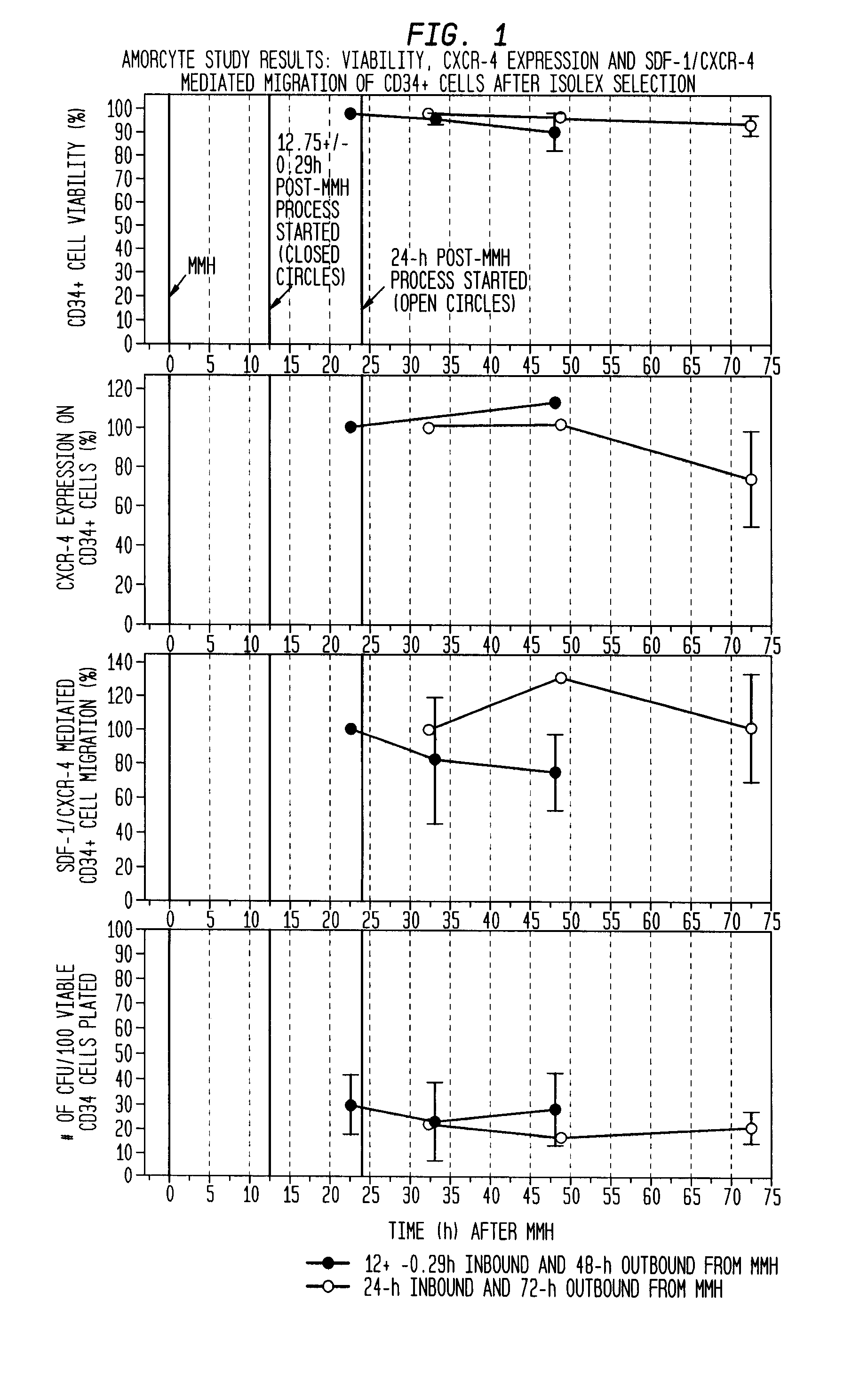
Infarct area perfusion-improving compositions and methods of vascular injury repair
ActiveUS20100143317A1Increase perfusionDecline in muscle functionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBlood vessel injuryPerfusion
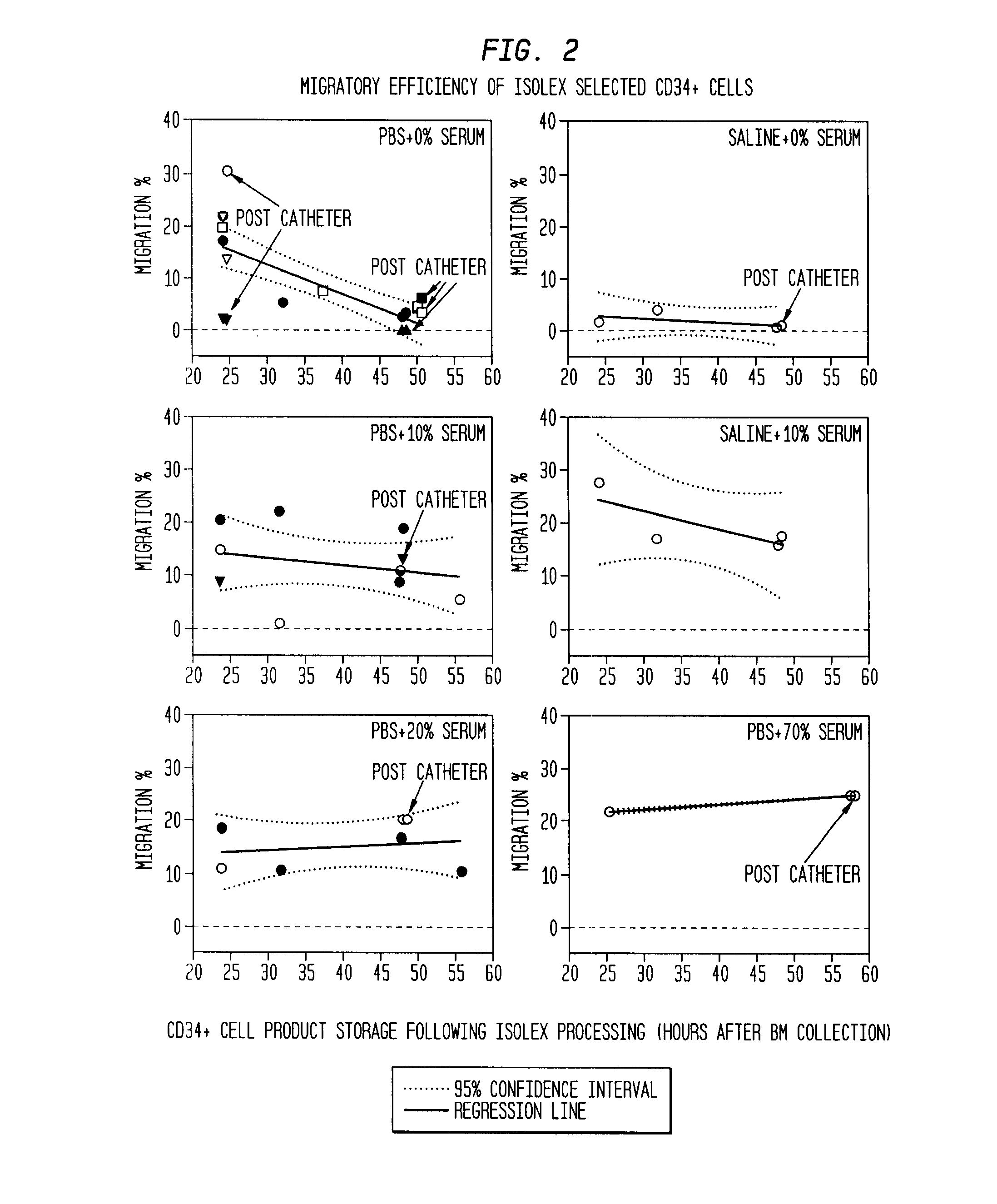
The described invention provides pharmaceutical compositions for treating an infarct area injury and methods of treating or repairing the infarct area injury in a revascularized subject in the aftermath of an acute myocardial infarction resulting from a natural disease process by administering to the subject parenterally through a catheter a sterile pharmaceutical composition containing a therapeutically effective amount of a nonexpanded sterile isolated chemotactic hematopoietic stem cell product as a first therapeutic agent and optionally a therapeutically effective amount of at least one compatible second therapeutic agent. The infarct area-improving amount of the sterile isolated chemotactic hematopoietic stem cell product comprises an enriched population of isolated autologous CD34+ cells containing a subpopulation of potent cells expressing CXCR-4 and having CXCR-4-mediated chemotactic activity such that the enriched population of isolated autologous CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells provides at least 0.5×106 potent CD34+ cells expressing CXCR-4 and having CXCR-4 mediated chemotactic activity.
Owner:CALADRIUS BIOSCI
Use of ADNF polypeptides for treating peripheral neurotoxicity
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
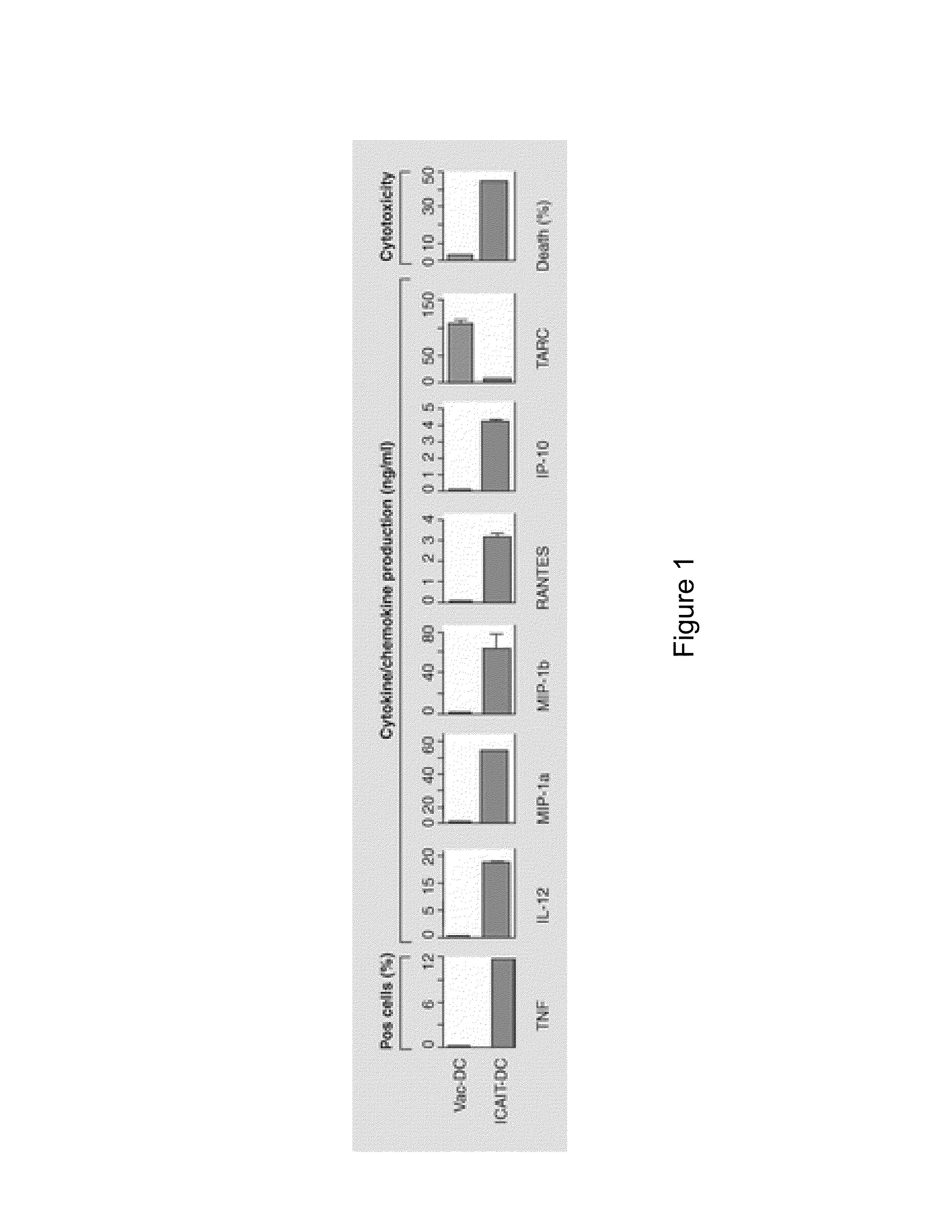
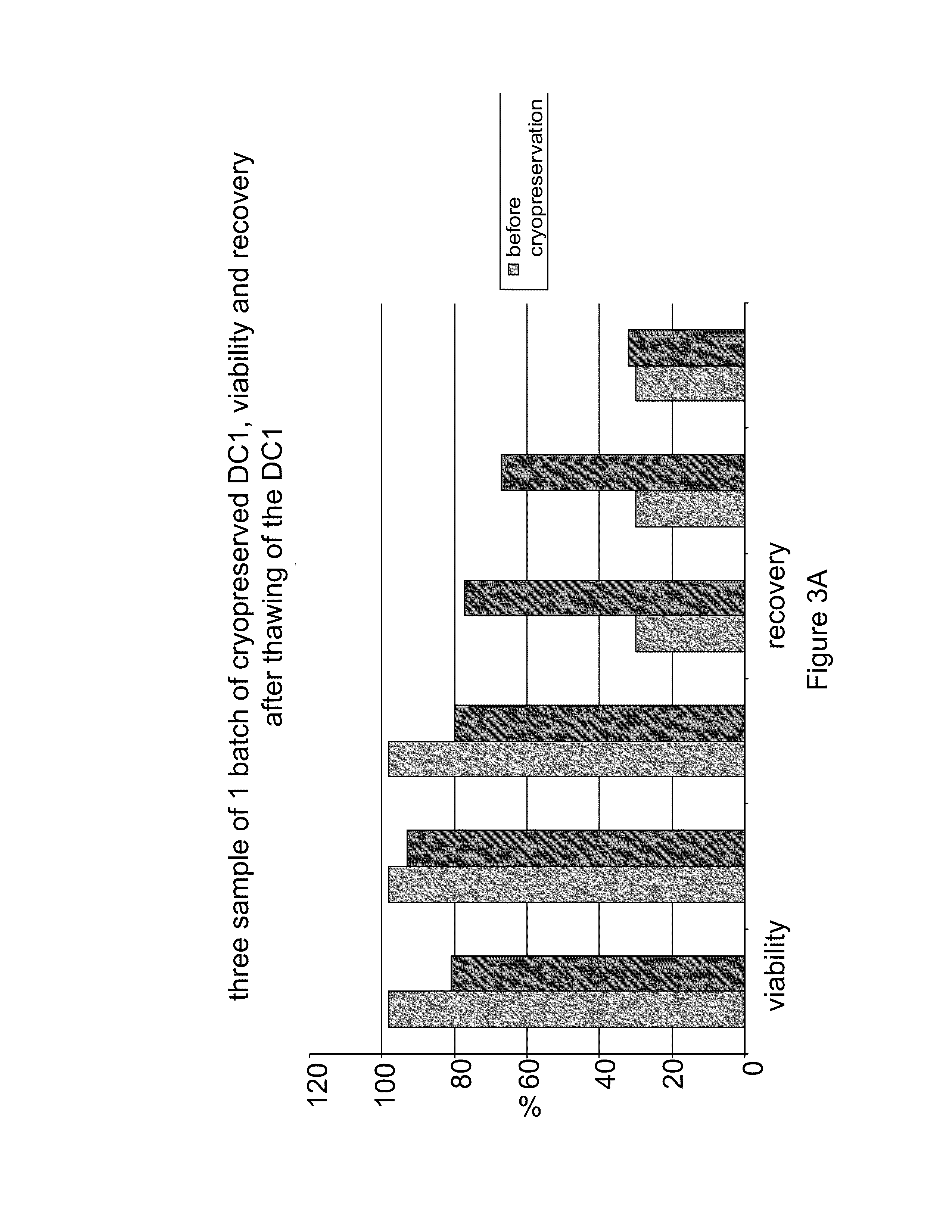
System and Method of Preparing and Storing Activated Mature Dendritic Cells
InactiveUS20130183343A1Promote recoveryImprove viabilityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDendritic cellVaccine Production
The present invention provides compositions and methods for generating and cryopreserving dendritic cells with superior functionality in producing stronger signals to T cells, resulting in a more potent DC-based anti-tumor vaccine. The present invention includes mature, antigen loaded DCs activated by Toll-like receptor agonists that induce clinically effective immune responses, preferably when used earlier in the disease process. The DCs of the present invention produce desirable levels of cytokines and chemokines, and further have the capacity to induce apoptosis of tumor cells. The cells can be cryopreserved and thawed for later use, thereby reducing the need for repeated pheresis and elutriation processes during vaccine production. These methods can also be utilized to directly target molecules involved in carcinogenetic signaling pathways and cancer stem cells.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Chinese medicine for treating chronic renal failure
InactiveCN101502619APromote absorptionAvoid absorptionMammal material medical ingredientsUrinary disorderLife qualityPinellia
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine for treating chronic renal failure and aims at solving the problems that the prior art supports the life by dialysis so as to result in short life cycle of patients and high cost and the like. The traditional Chinese medicine comprises the following raw materials: 30g of raidx astragali, 10g of white ginseng, 20g of rhizoma atractylodis macrocephalae, 20g of honey-fried licorice root, 20g of poria, 10g of Chinese angelica, 20g of rehmannia glutinosa, 20g of white paeony root, 10g of wrinkled gianthyssop herb, 15g of pinellia tuber and the like. The prescription is used for treating chronic uremia, can invigorate vigour, strengthening the spleen, replenishing blood, nourishing the blood, excreting water, expel toxin, strengthening the kidney and expel toxin, can reduce dialysis gradually by combining the modern medical method, finally separate the dialysis and transfusion, relieve economic burden of the patients, improve disease process fundamentally, improve life quality and courage and prolong life cycle.
Owner:刘云
System and method for anatomy labeling on a PACS
ActiveUS7590440B2Narrow selectionImage enhancementImage analysisDrug interactionRelevant information
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Protein microarrays on mirrored surfaces for performing proteomic analyses
InactiveUS7148058B2Enhanced signalFacilitating drug discoveryCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyAntigenStructure analysis
Provided are protein microarrays, their manufacture, use, and application. Protein microarrays in accordance with the present invention are useful in a variety preoteomic analyses. Various protein arrays in accordance with the present invention may immobilize large arrays of proteins that may be useful for studying protein-protein interactions to improve understanding of disease processes, facilitating drug discovery, or for identifying potential antigens for vaccine development. The protein array elements of the invention are native or modified proteins (e.g., antibodies or fusion proteins). The protein array elements may be attached directly to a organic functionalized mirrored substrate by a binding reaction between functional groups on the substrate (e.g., amine) and protein (e.g., activated carboxylic acid). Techniques for chemical blocking of the arrays are also provided. The invention contemplates spotting of array elements onto solid planar substrates, labeling of complex protein mixtures, and the analysis of protein binding to the array. The invention also enables the enrichment or purification, and subsequent sequencing or structural analysis of proteins that are identified as differential by the array screen. Kits including protein-binding microarrays for proteomic analysis in accordance with the present invention are also provided.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
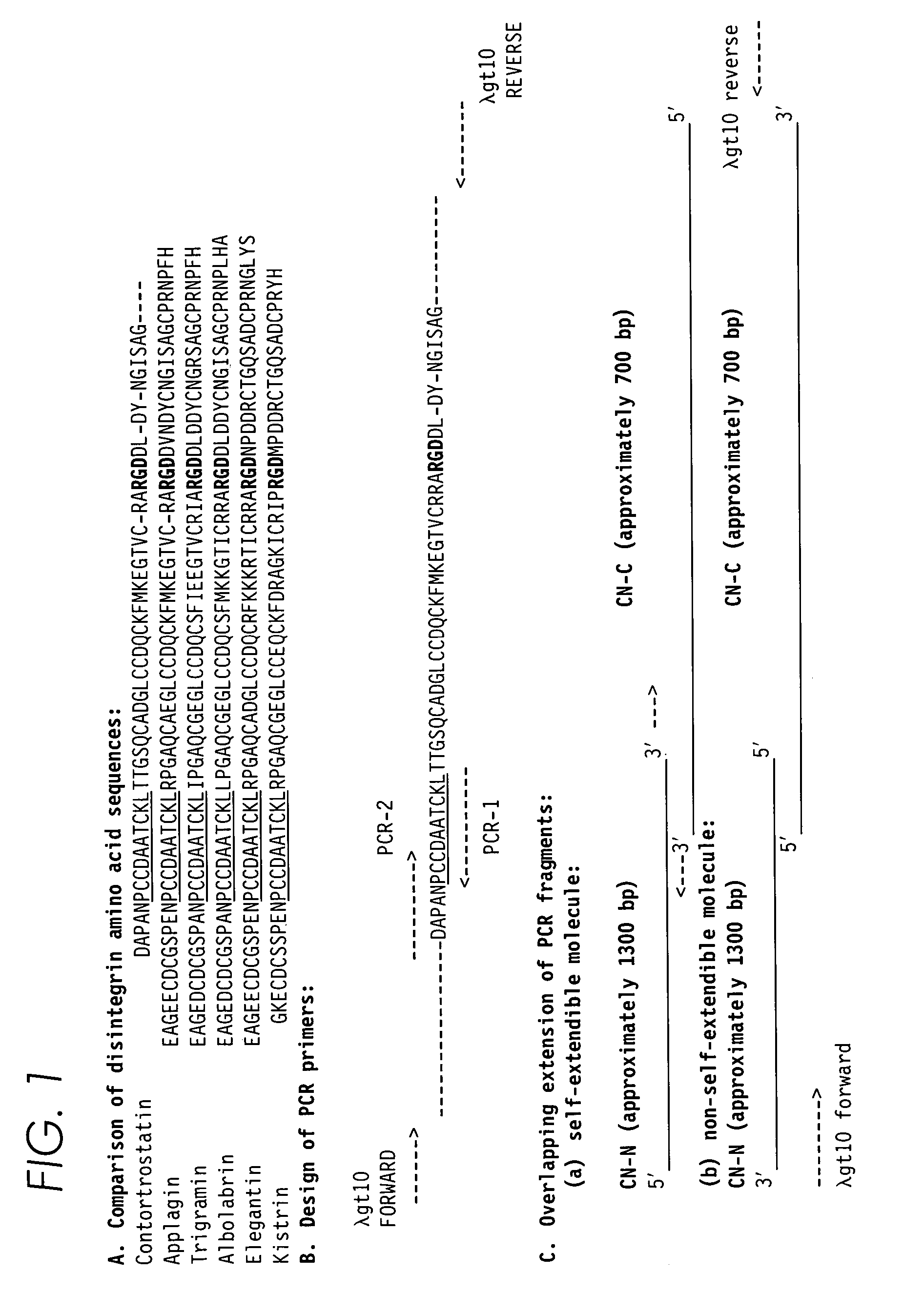
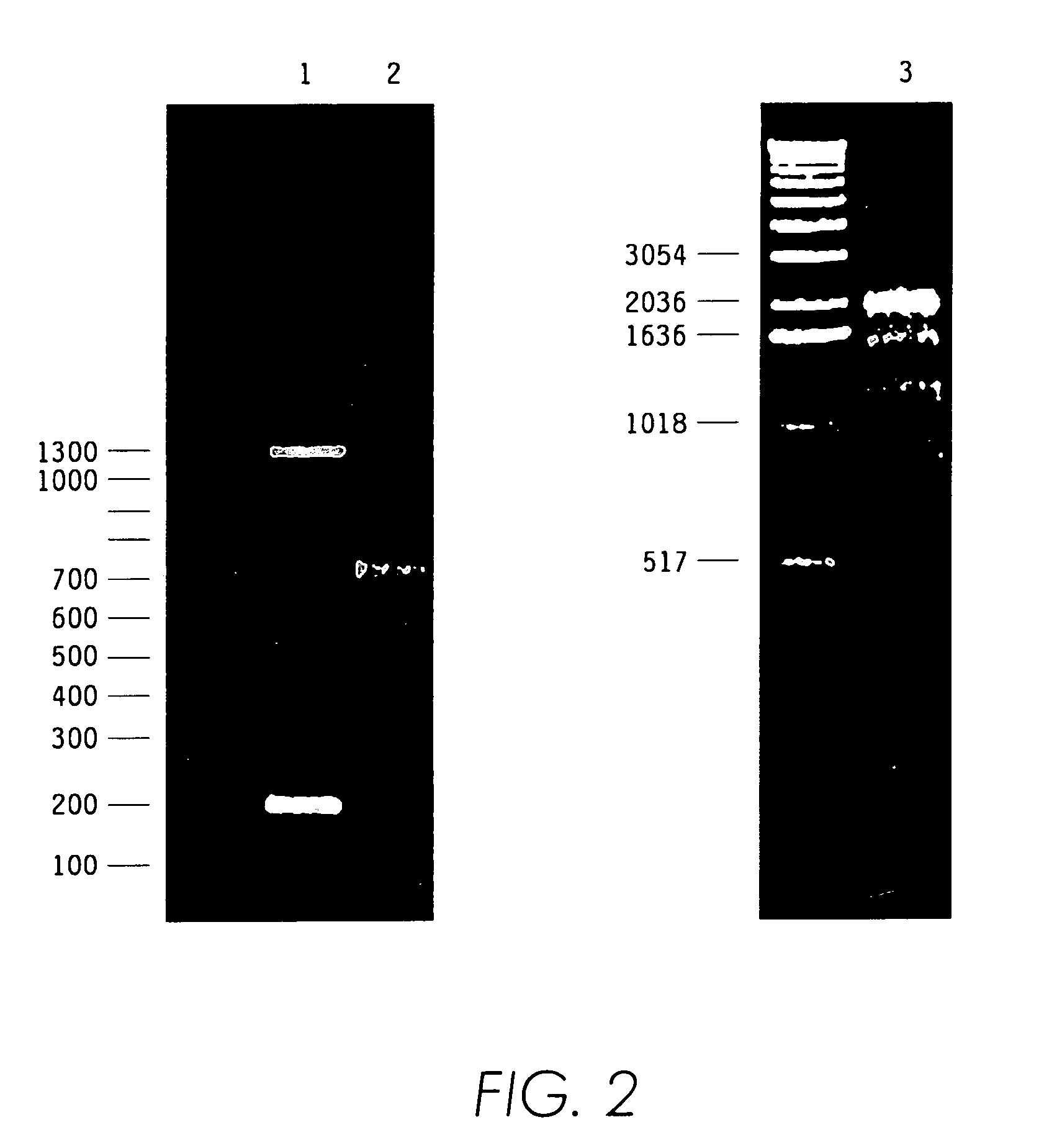
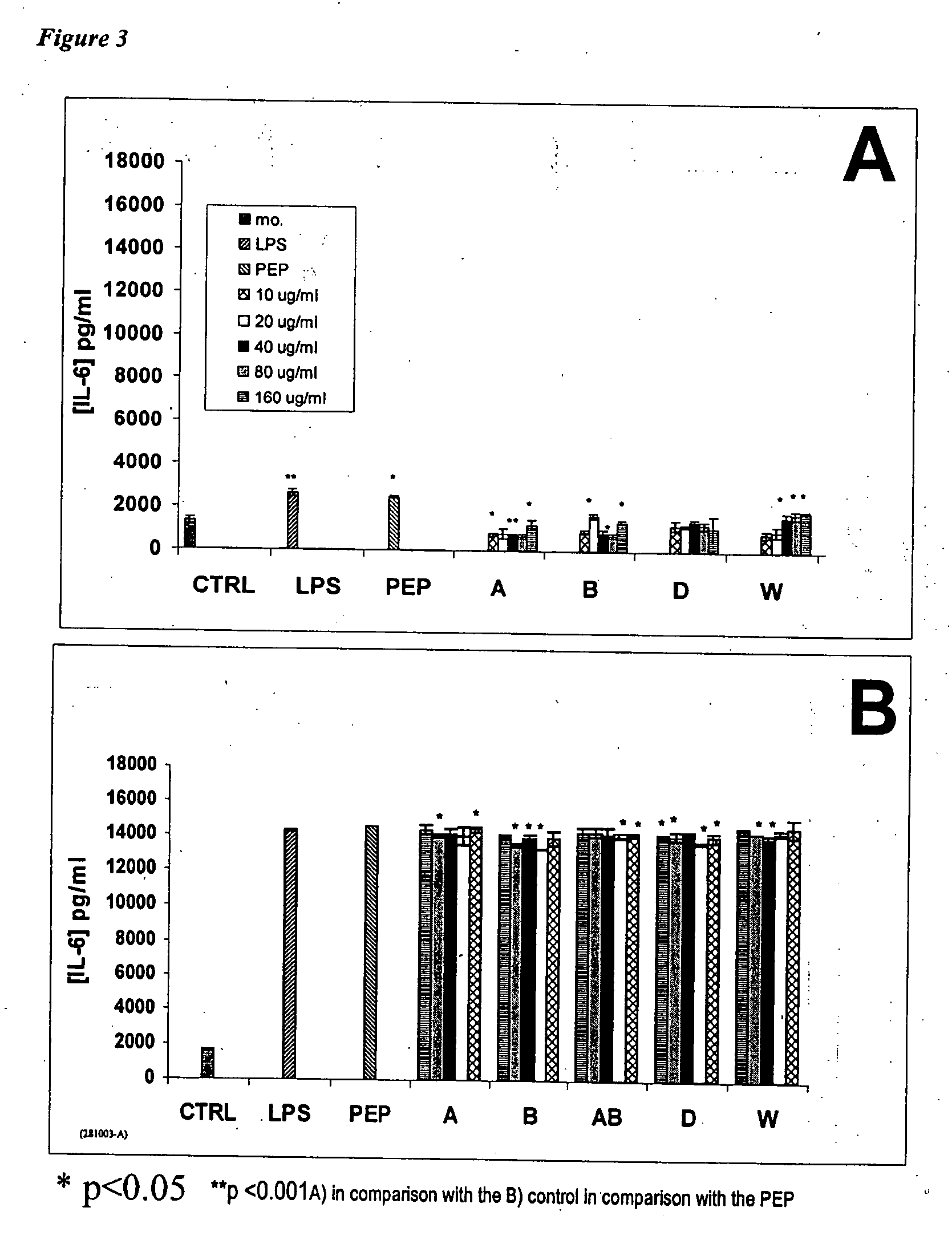
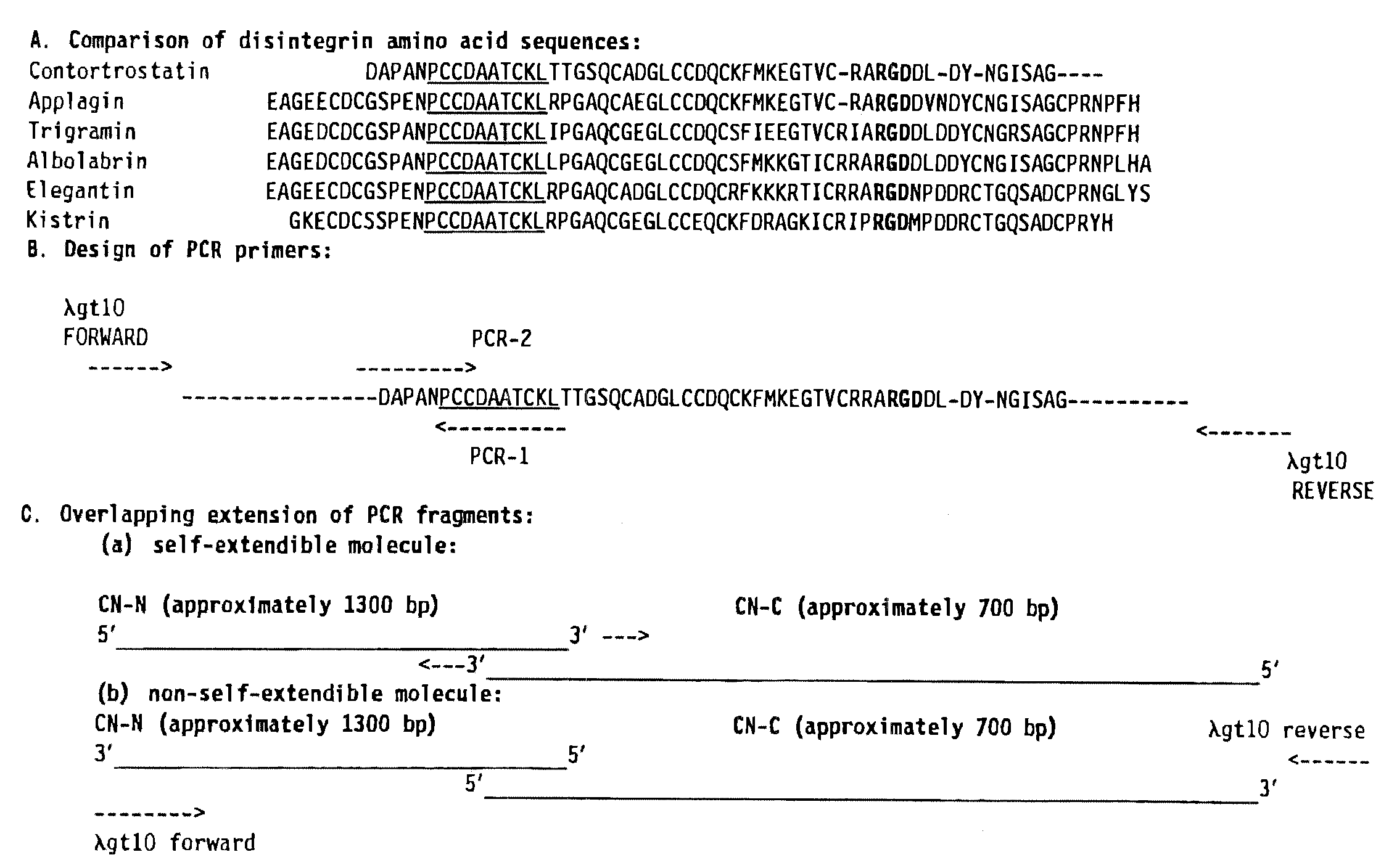
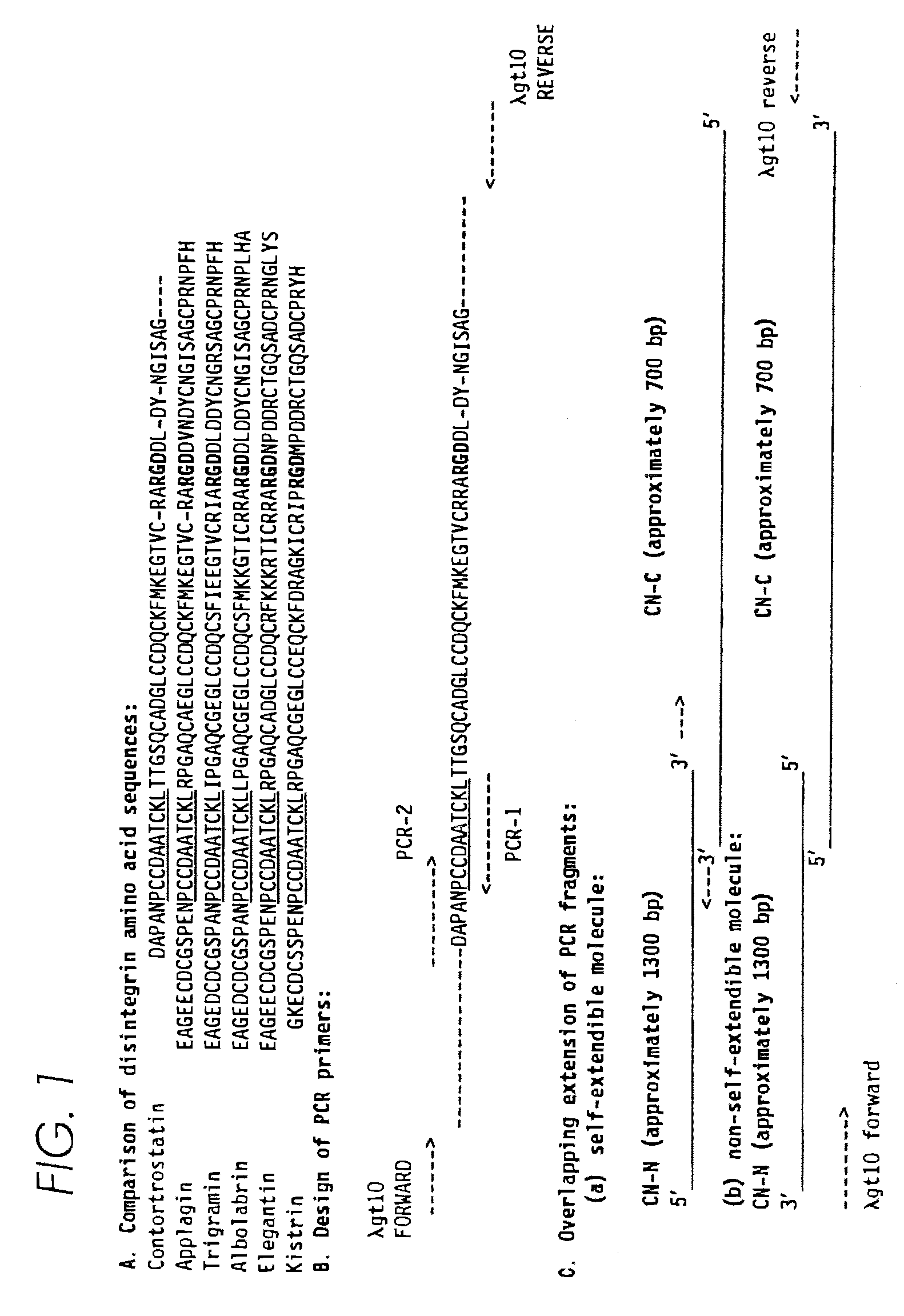
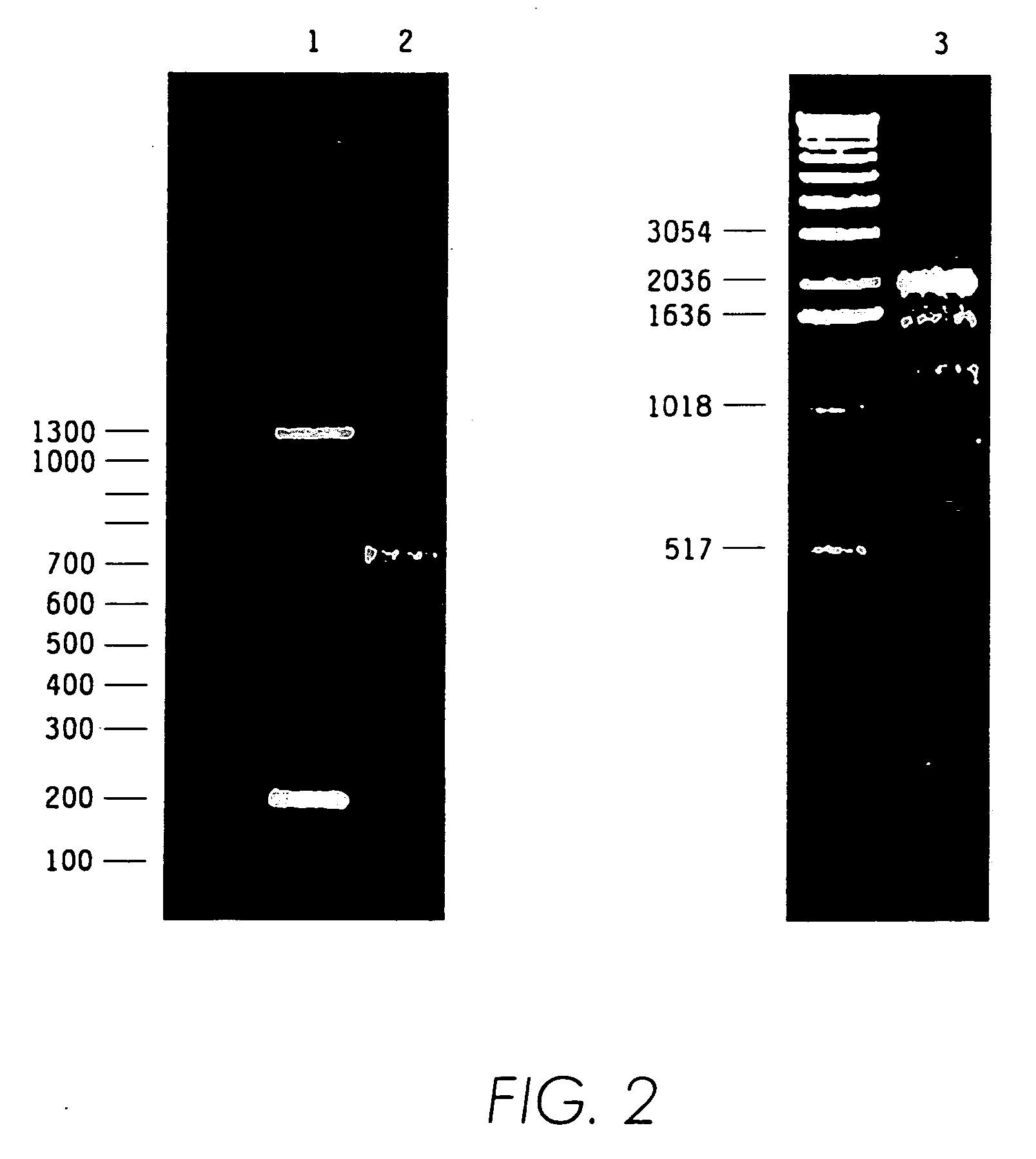
Contortrostatin CN and methods for its use in preventing metastasis and other conditions
InactiveUS7220724B2Minimal effectPrevent movementCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsLymphatic SpreadMotility
Contortrostatin, a homodimeric disintegrin, modulates the adhesion, motility, and invasiveness of integrin expressing tumor cells. When formulated as a pharmaceutically acceptable composition, the proteins can be used to treat patients by inhibiting or disrupting disease processes associated with an integrin binding to an αvβ3 or αvβ5 integrin.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
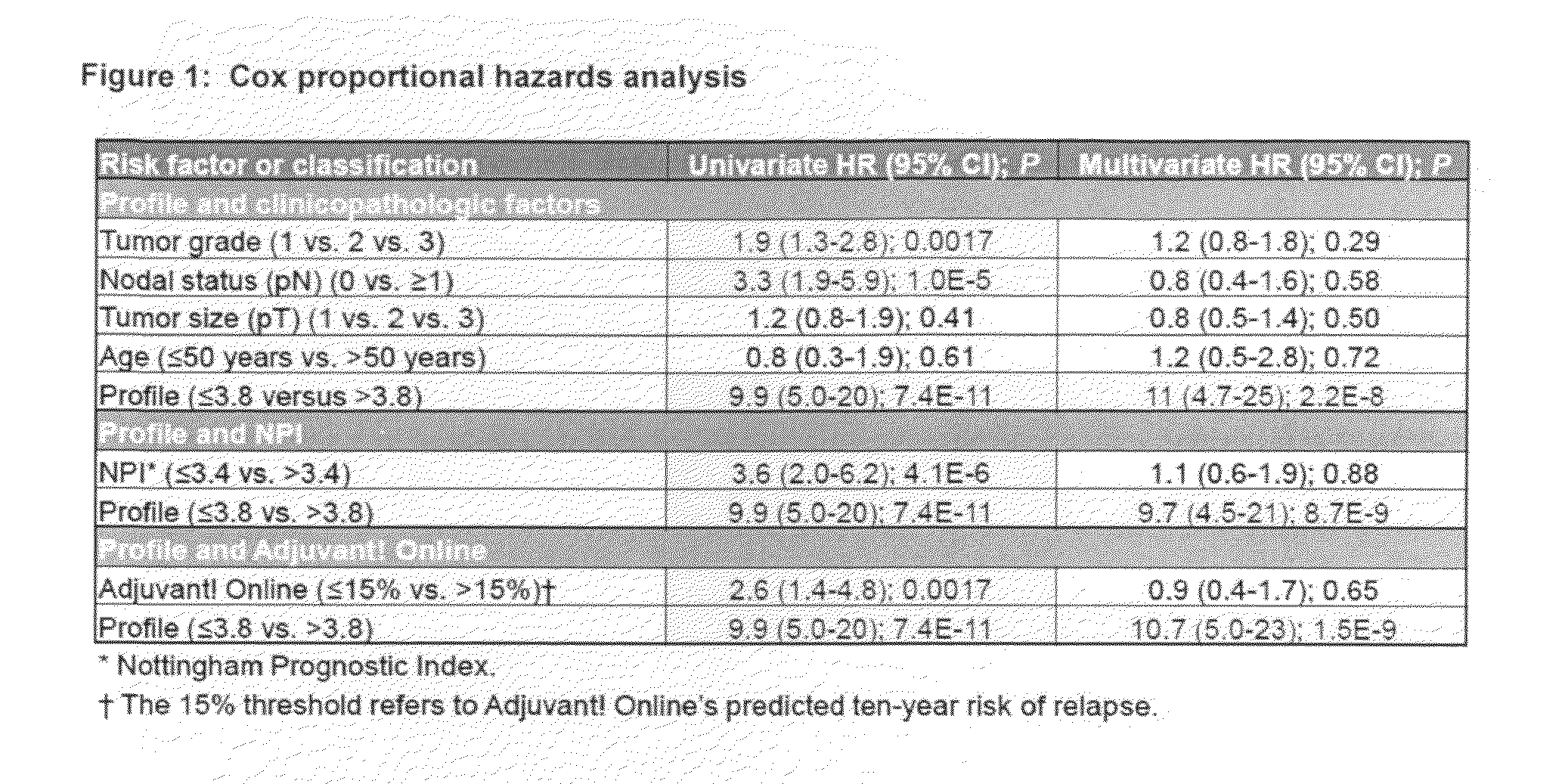
Molecular markers predicting response to adjuvant therapy, or disease progression, in breast cancer
Predicting response to adjuvant therapy or predicting disease progression in breast cancer is realized by (1) first obtaining a breast cancer test sample from a subject; (2) second obtaining clinicopathological data from said breast cancer test sample; (3) analyzing the obtained breast cancer test sample for presence or amount of (a) one or more molecular markers of hormone receptor status, one or more growth factor receptor markers, (b) one or more tumor suppression / apoptosis molecular markers; and (c) one or more additional molecular markers both proteomic and non-proteomic that are indicative of breast cancer disease processes; and then (4) correlating (a) the presence or amount of said molecular markers and, with (b) clinicopathological data from said tissue sample other than the molecular markers of breast cancer disease processes. A kit of (1) a panel of antibodies; (2) one or more gene amplification assays; (3) first reagents to assist said antibodies with binding to tumor samples; (4) second reagents to assist in determining gene amplification; permits, when applied to a breast cancer patient's tumor tissue sample, (A) permits observation, and determination, of a numerical level of expression of each individual antibody, and gene amplification; whereupon (B) a computer algorithm, residing on a computer can calculate a prediction of treatment outcome for a specific treatment for breast cancer, or future risk of breast cancer progression.
Owner:LINKE STEVEN +2
Immunoglobulin Cleavage Fragments as Disease Indicators and Compositions for Detecting and Binding Such
InactiveUS20090155280A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansSkeletal disorderProteinase activityImmunoglobulin IgE
The invention relates to antibody compositions and use of the composition to detect disease processes associated with elaboration of proteases. The reagents are directed to assessing an IgG breakdown product that is the result of such proteolytic cleavage. The invention further relates to the use of a therapeutic immunospecific for IgG breakdown products retaining antigen binding but having lost effector functions.
Owner:CENTOCOR ORTHO BIOTECH
Remote laser treatment system with dynamic imaging
ActiveUS10456209B2Eliminate needTrack displacementLaser surgeryAnti-theft devicesTherapeutic DevicesThe Internet
An integral laser imaging and treatment apparatus, and associated systems and methods that allow a physician (e.g., a surgeon) to perform laser surgical procedures on an eye structure or a body surface with an integral laser imaging and treatment apparatus disposed at a first (i.e. local) location from a control system disposed at a second (i.e. remote) location, e.g., a physician's office. In some embodiments, communication between the integral laser imaging and treatment apparatus and control system is achieved via the Internet®. Also, in some embodiments, the laser imaging and treatment apparatus includes a dynamic imaging system that verifies the identity of a patient, and is capable of being used for other important applications, such as tracking and analyzing trends in a disease process. Further, in some embodiments, the laser imaging and treatment apparatus determines the geographical location of the local laser generation unit of the system using GPS.
Owner:PEYMAN GHOLAM A
Chitosan oligosaccharides and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070167400A1Reduce inflammationMinimization reductionBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDietary supplementMedicine
The present invention is directed towards compositions and methods for reducing or controlling inflammation and for treating inflammatory disease processes and other pathological conditions. The present invention relates to mixtures comprising at least one oligosaccharide of chitosan or a component thereof as novel pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements or cosmetic compositions containing such mixtures, and to the use of such mixtures for preparing a medicament or a dietary supplement for the suppression of hypersensitivity reaction and / or inflammation in human and animals.
Owner:DNP CANADA
Nano-element traditional Chinese medicinal fabric antibacterial underwear for preventing and treating psoriasis
InactiveCN102078029AAmphibian material medical ingredientsElectrotherapyHigh morbidityHumoral immune reaction
The invention discloses nano-element traditional Chinese medicinal fabric antibacterial underwear for preventing and treating psoriasis, which belongs to the technical field of functional healthy fabric underwear production. Psoriasis is a skin disease which has high morbidity and stubborn disease process, is easy to relapse, is difficult to cure and does serious harm to the physical and psychological health of people. Far infrared heat effect takes effect in deep subcutaneous tissues through medical stone, tourmaline and a nano silver (Ag) antimicrobial agent, so the underwear expands blood vessels, quickens blood flow, increases cell activity and blood oxygen content, makes human bodies absorb more negative ions and trace elements, promotes body metabolism, enhances cellular immunity and humoral immunity of the human bodies, promotes the balance of elements in the human bodies, strengths the regeneration activity of cells and resists bacteria, cancers and inflammation. The underwear prevents and treats psoriasis when a user wears the underwear.
Owner:成进学
Contortrostatin (CN) and methods for its use in preventing metastasis and other conditions
InactiveUS20070123458A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsLymphatic SpreadMotility
Contortrostatin, a homodimeric disintegrin, modulates the adhesion, motility, and invasiveness of integrin expressing tumor cells. When formulated as a pharmaceutically acceptable composition, the proteins can be used to treat patients by inhibiting or disrupting disease processes associated with an integrin binding to an αvβ3 or αvβ5 integrin.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Use of ADNF polypeptides for treating peripheral neurotoxicity
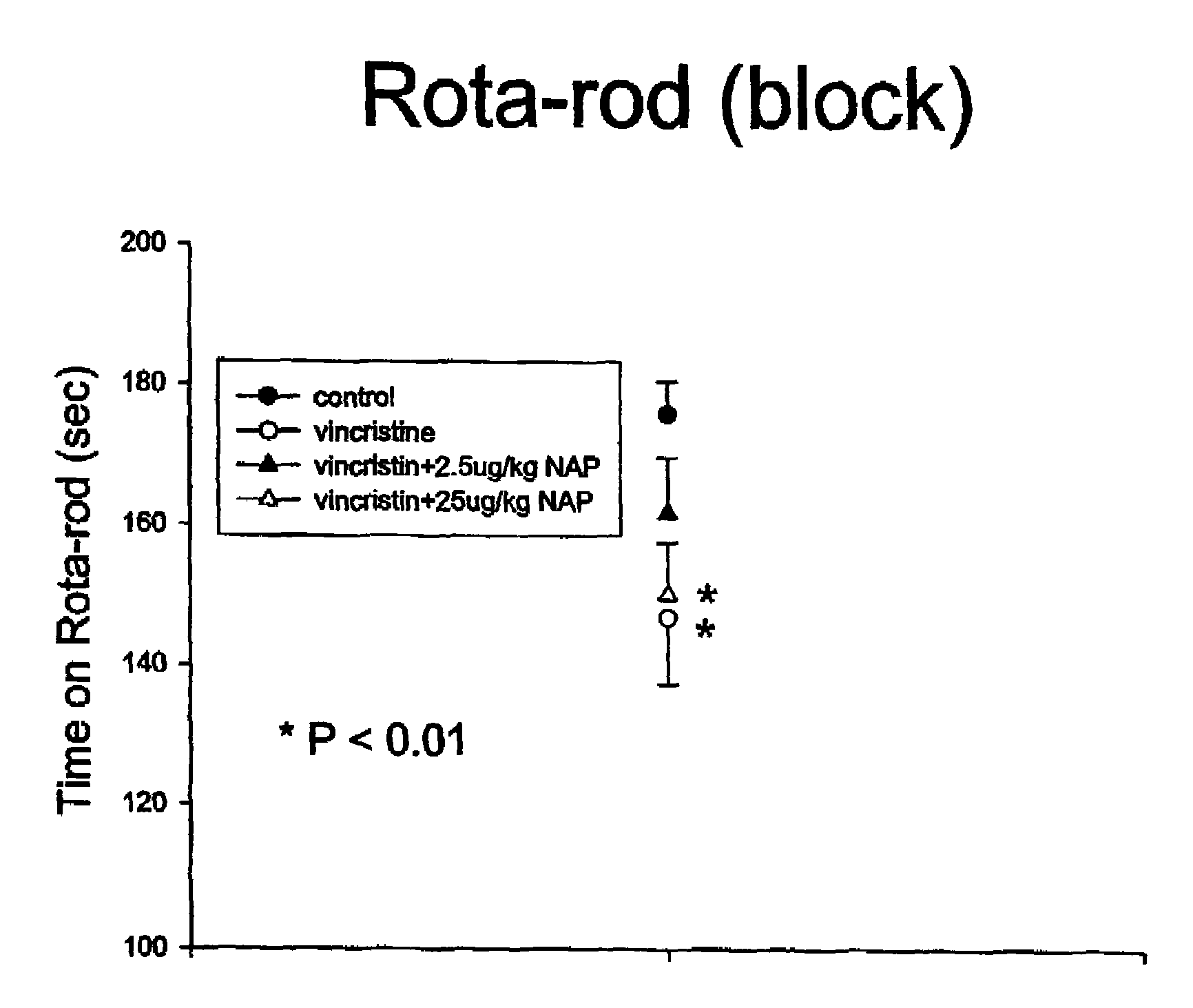
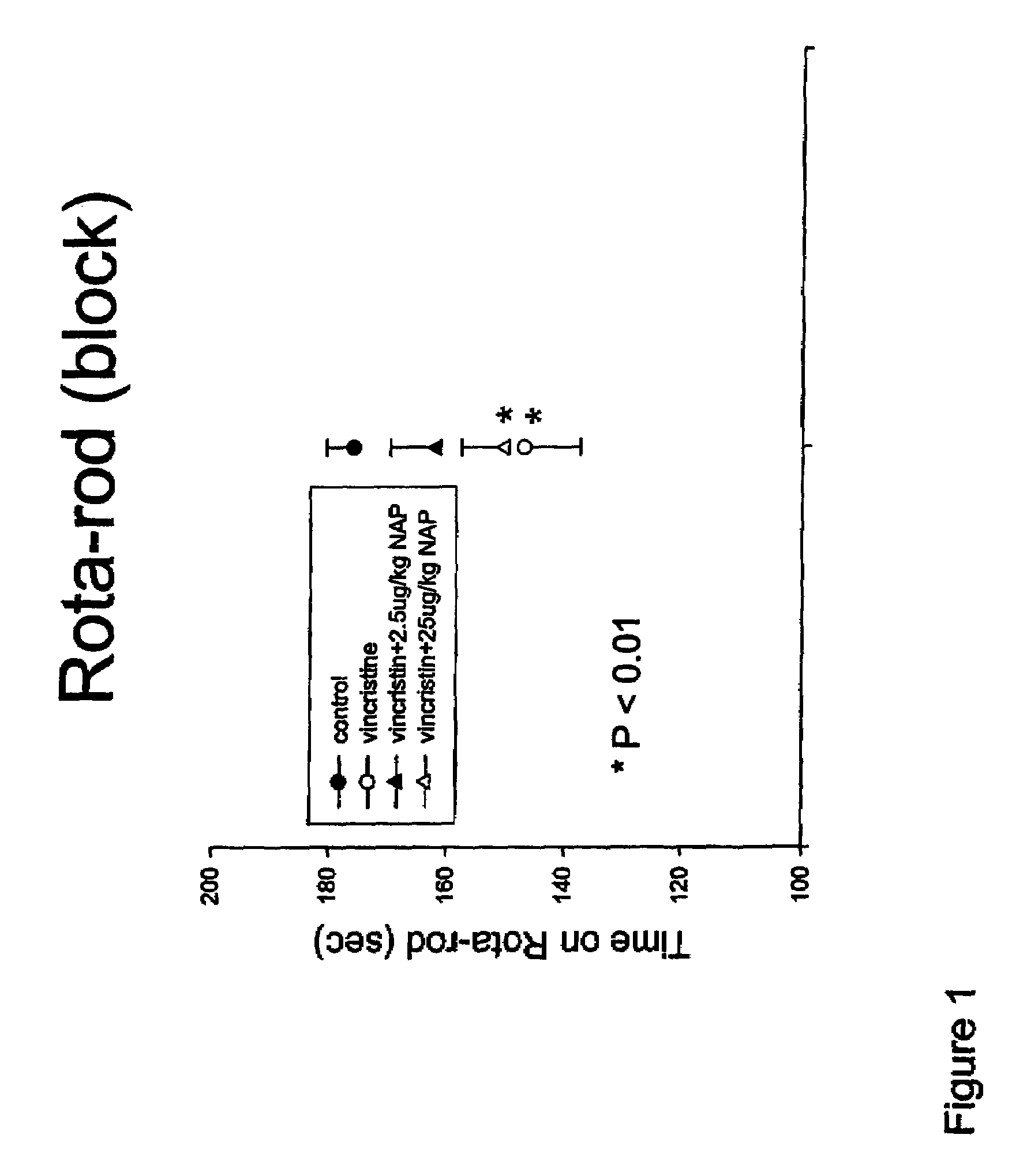
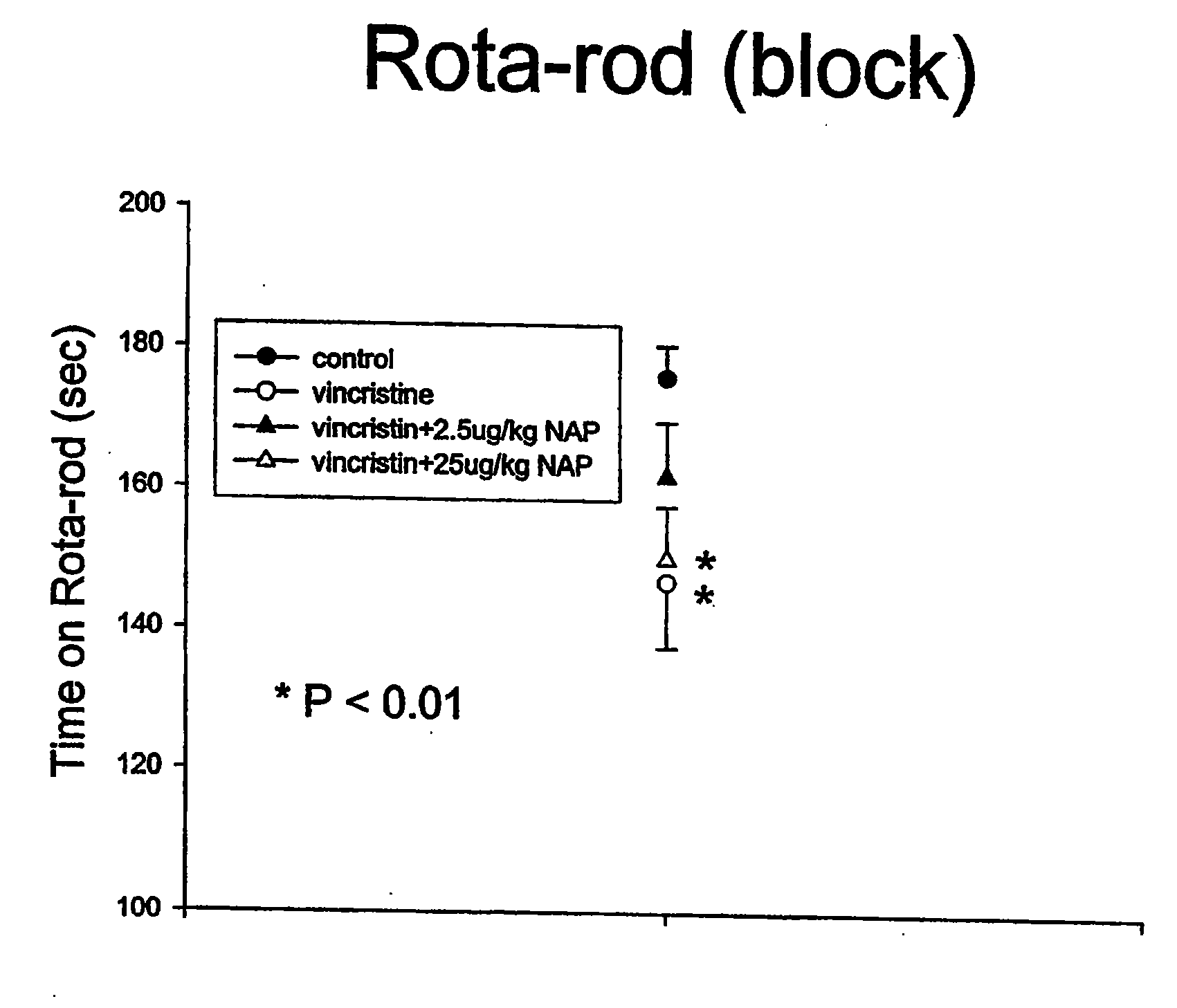
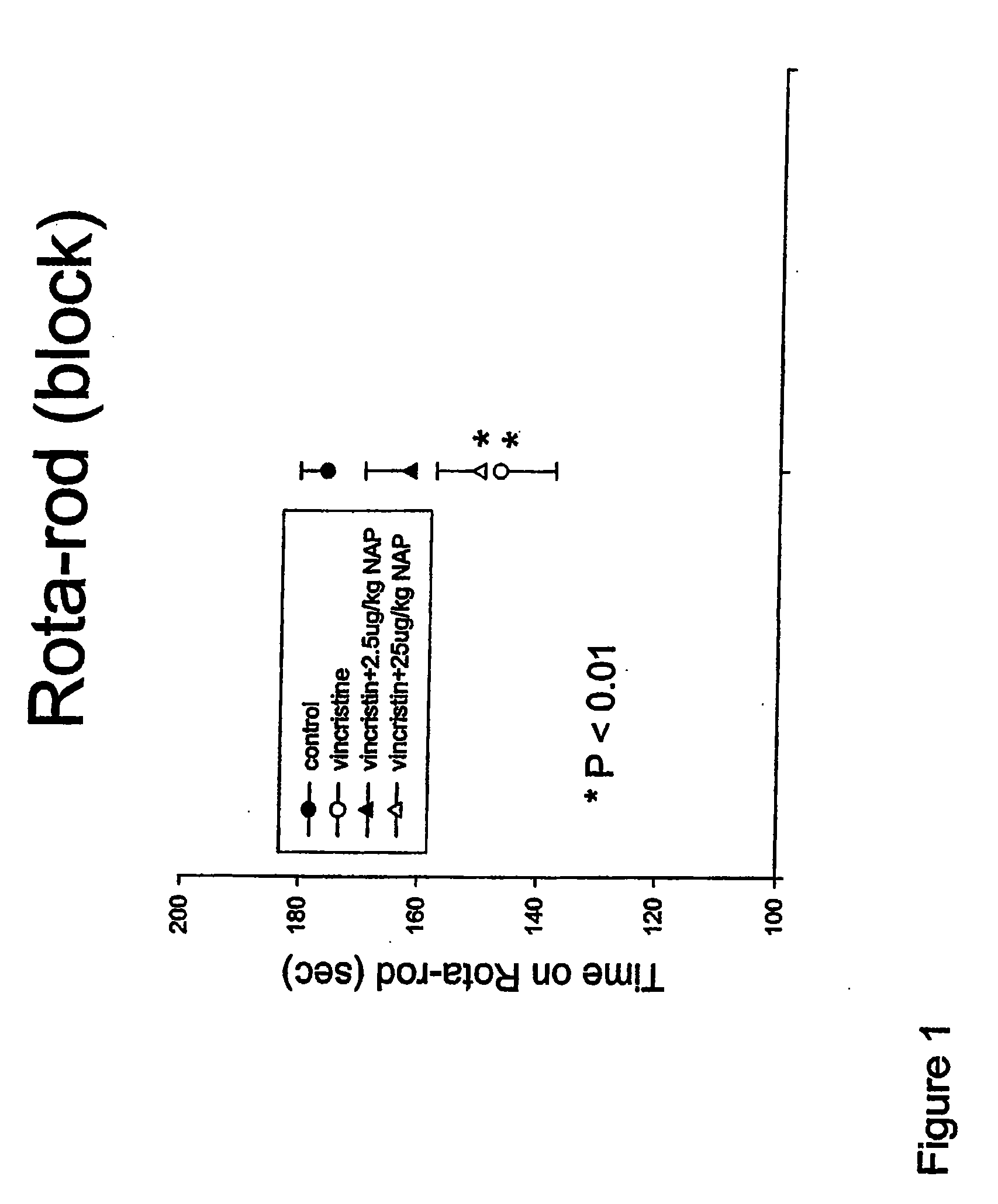
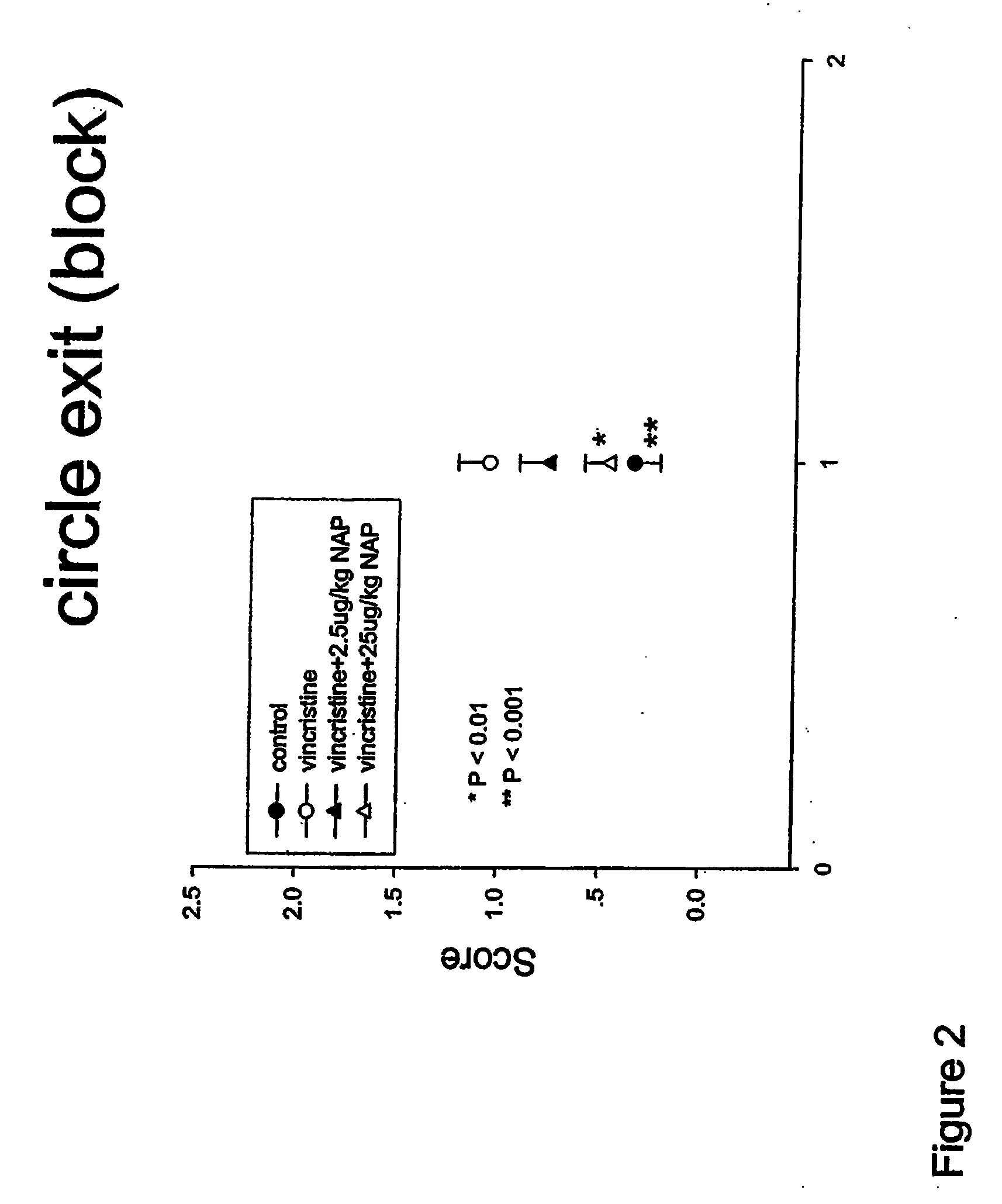
This invention relates to the use of ADNF polypeptides in the treatment of neurotoxicity induced by chemical agents or by disease processes. The ADNF polypeptides include ADNF I and ADNF III (also referred to as ADNP) polypeptides, analogs, subsequences such as NAP and SAL, and D-amino acid versions (either wholly D-amino acid peptides or mixed D- and L-amino acid peptides), and combinations thereof which contain their respective active core sites.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Method for the prediction of individual disease course in sepsis
InactiveUS20100086909A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingDisease courseProbability of survival
The invention relates to the use of gene expression profiles, obtained in vitro from a patient sample, for the generation of criteria for the prediction of an individual course of disease in sepsis. The invention is further of use for determining the probability of survival in sepsis, the assessment of the course of disease in sepsis during treatment and for the classification of sepsis patients.
Owner:SIRS LAB
Construction method and application of diet-induced insulin resistance model
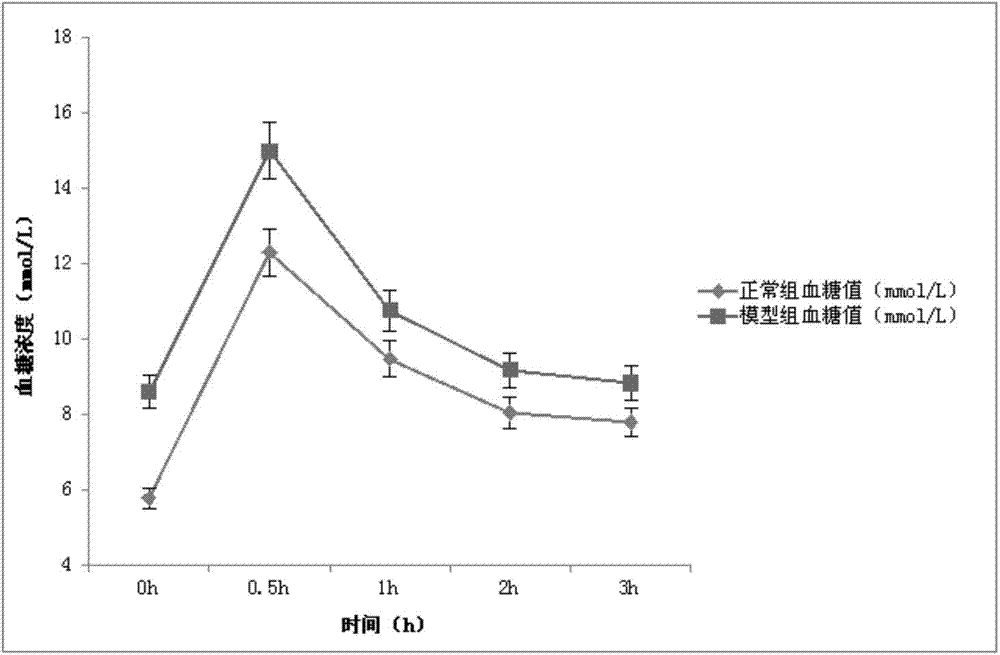
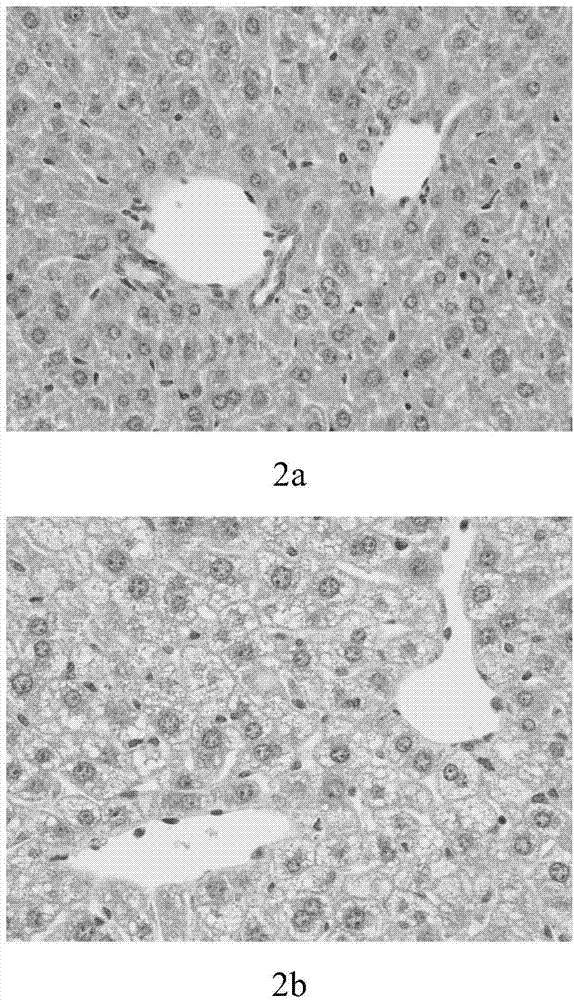
ActiveCN104705258AAvoid the problems of instability and low molding rateEliminate adverse reactionsAnimal husbandryHigh fatIn vivo
The invention discloses a construction method of a diet-induced insulin resistance model. Male Kunming mice are induced to generate insulin resistance by being fed with high fat and high glucose food and drinking fructose solutions of a certain concentration, and the insulin resistance model is obtained. The insulin resistance disease process of human beings is simulated in the method, a manufactured animal model has hyperinsulinemia, glucose and lipid metabolism disorders and other insulin resistance classical symptoms, and the method can be suitable for mechanism research of the disease and screening of relevant medicine. Model induction is carried out through the high fat and high glucose food and low-concentration fructose drinking water, the insulin resistance disease process of the human beings can be greatly simulated, result reliability is high, the bad reaction generated by chemical reagents is removed, and the problems that when the mice are only fed with food, the model is unstable, and the model construction success rate is low are solved. Energy intake is larger than consumption through feeding of the high fat and high glucose food, in-vivo energy disequilibrium is caused, and central obesity and fat accumulation are caused, and the aim of enabling an organism to generate insulin resistance is achieved.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com