Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
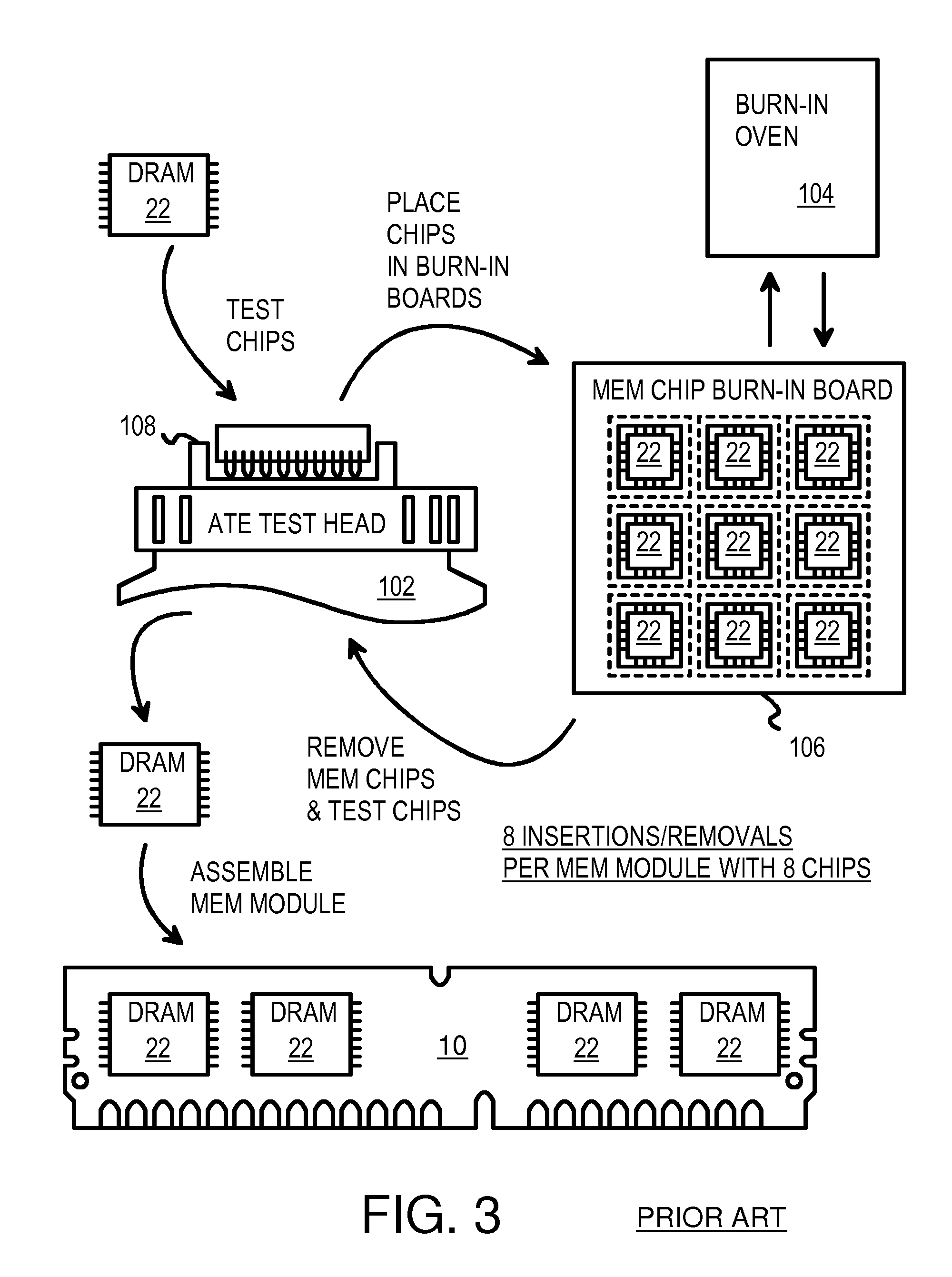
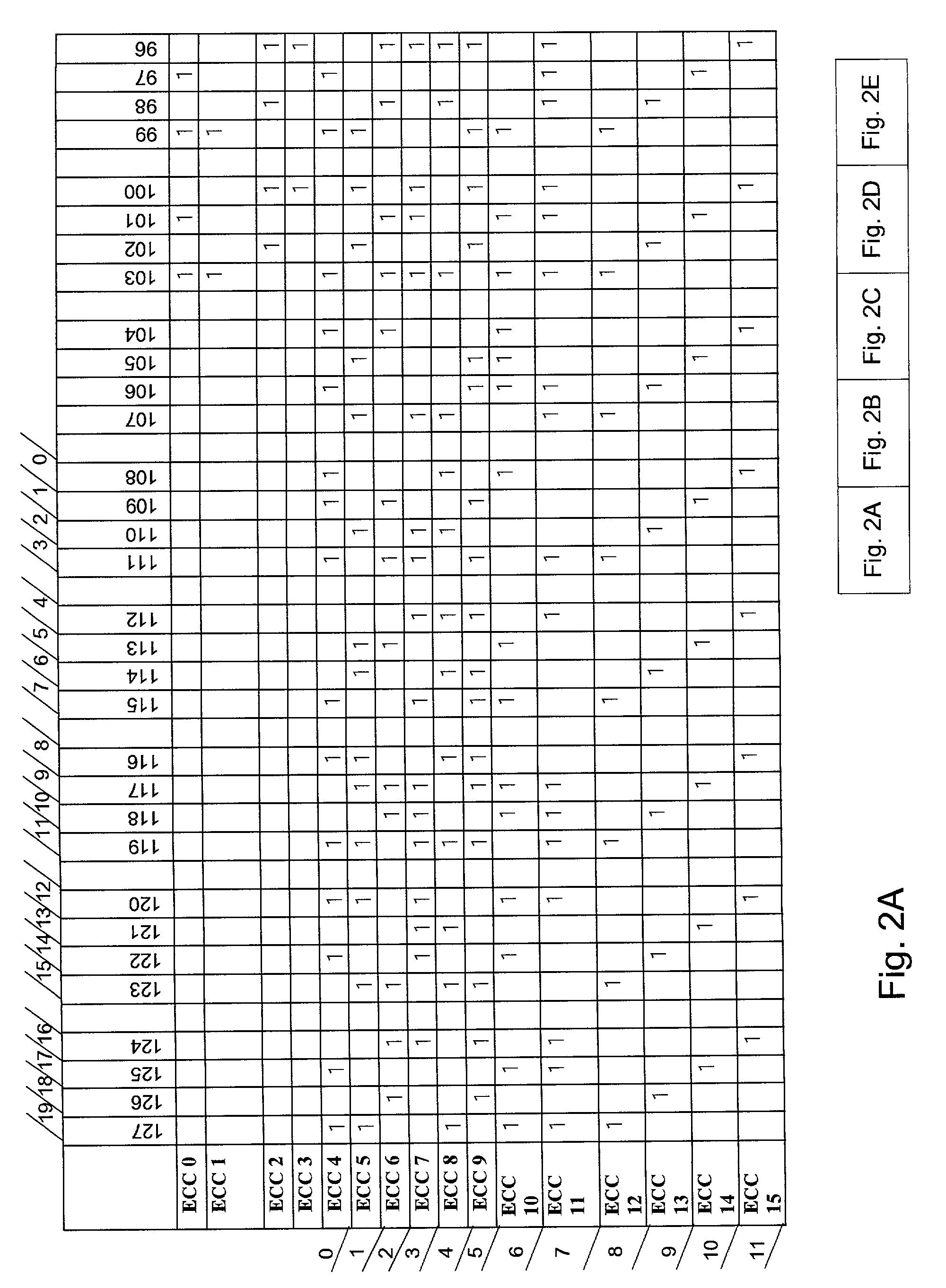
143 results about "Dram chip" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
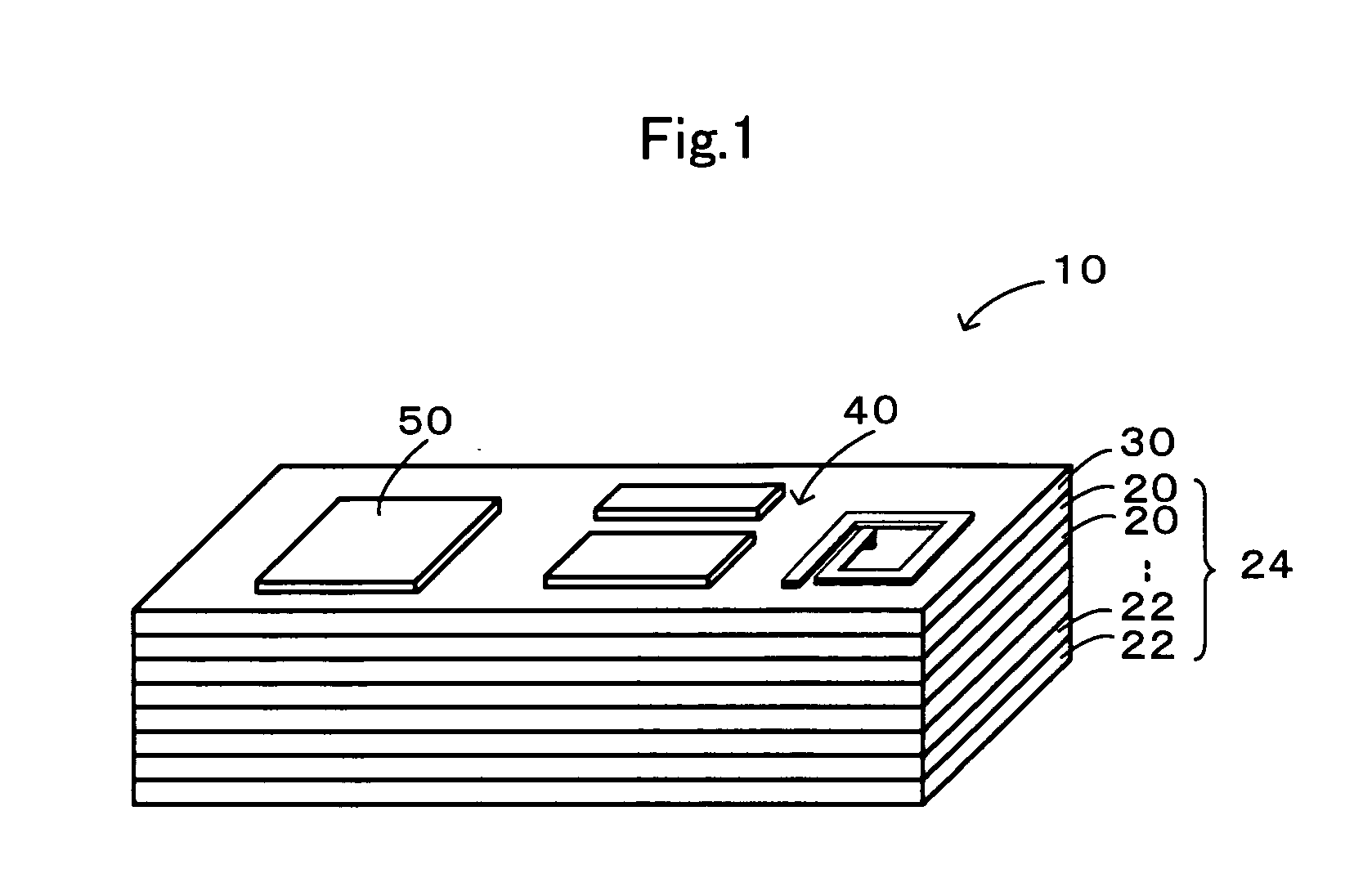
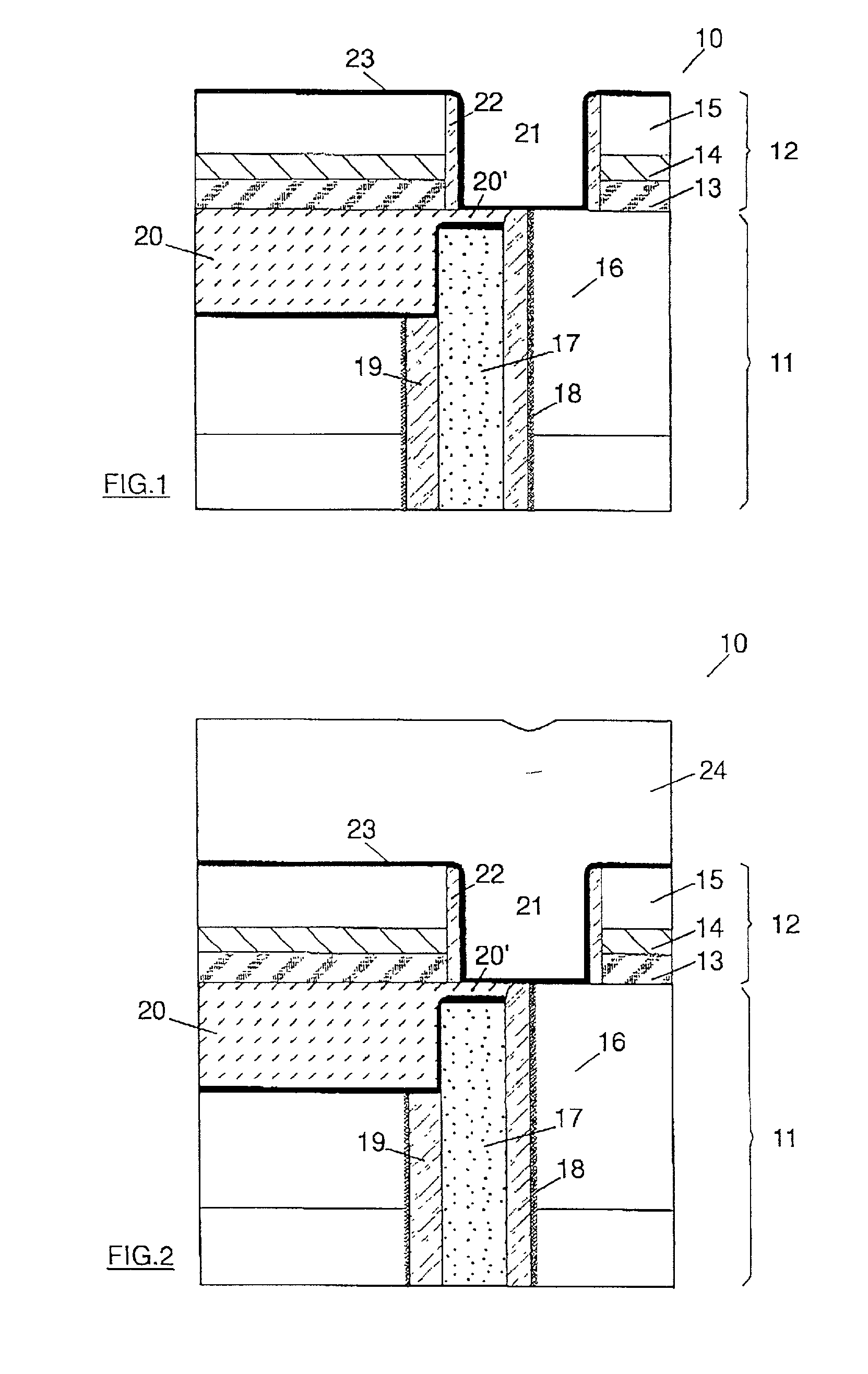
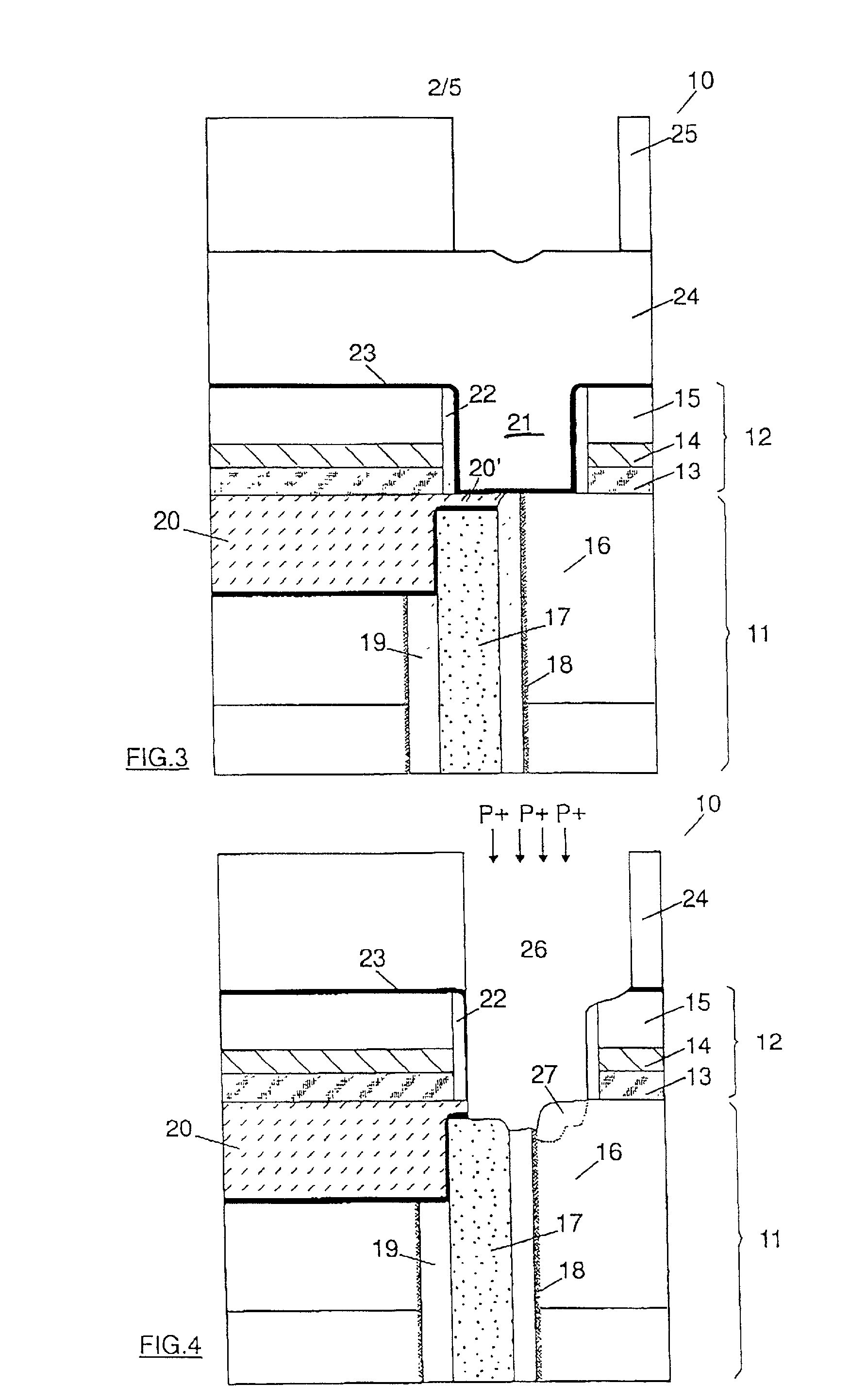
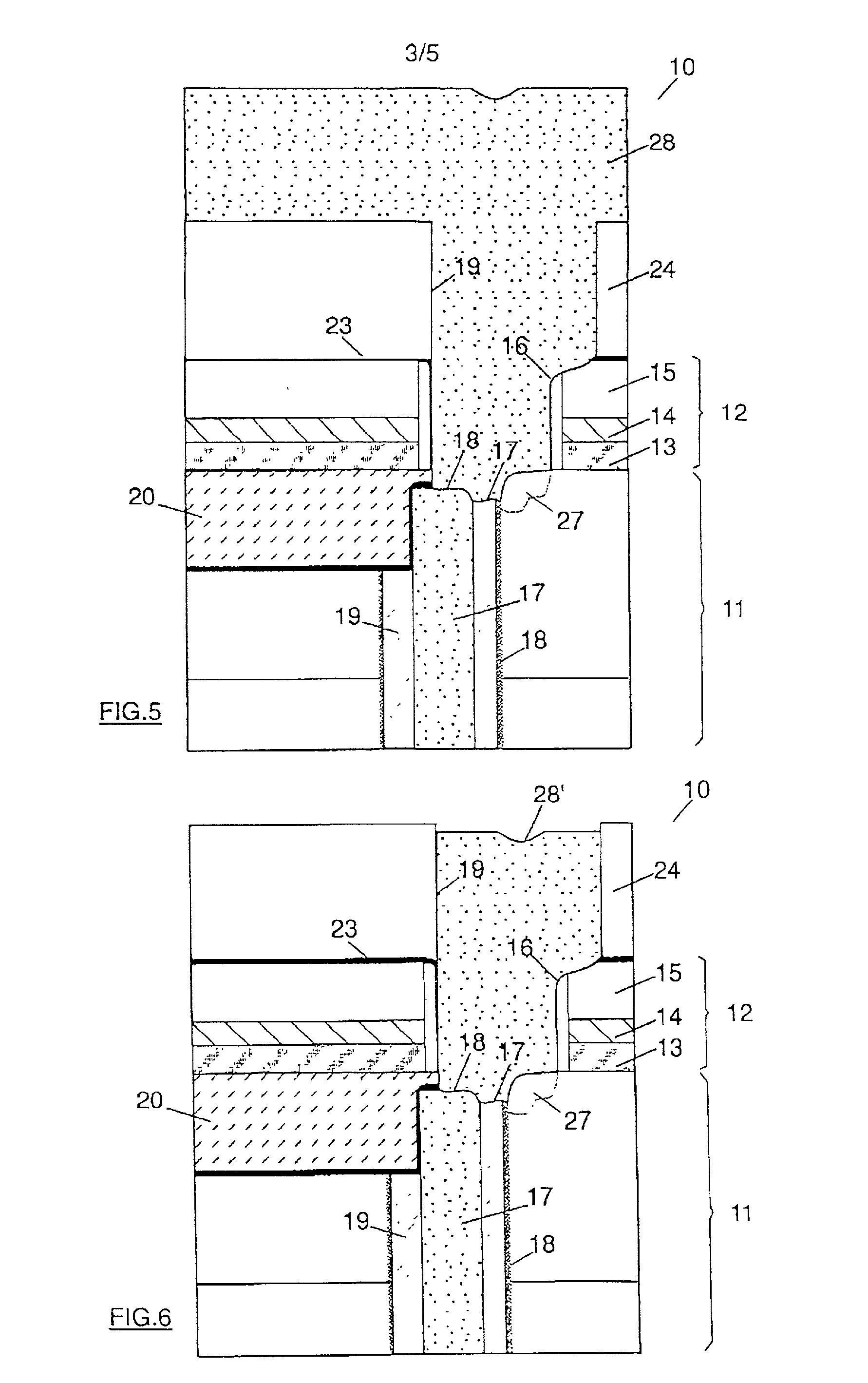
DRAM chip device well-communicated with flash memory chip and multi-chip package comprising such a device
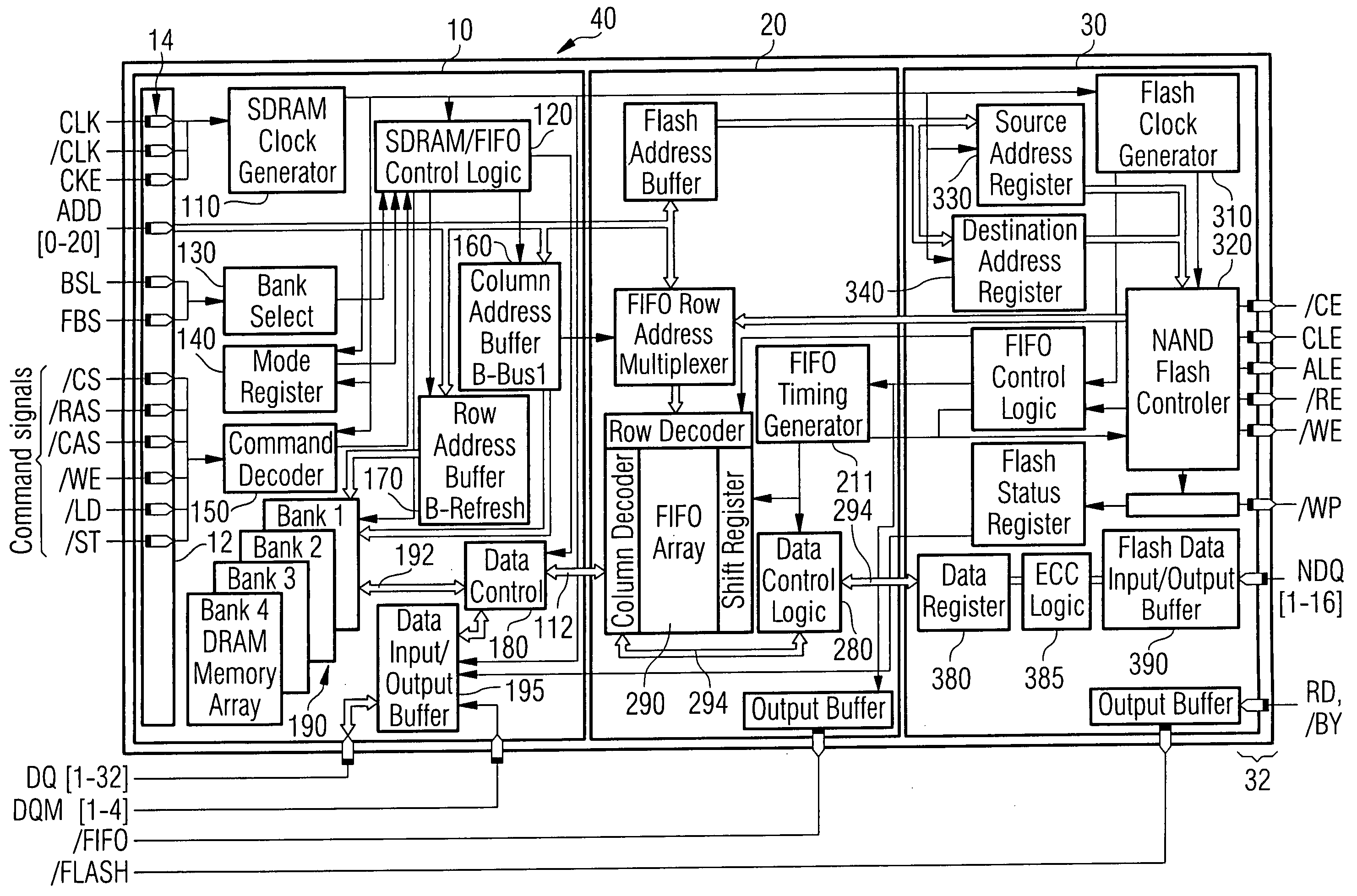
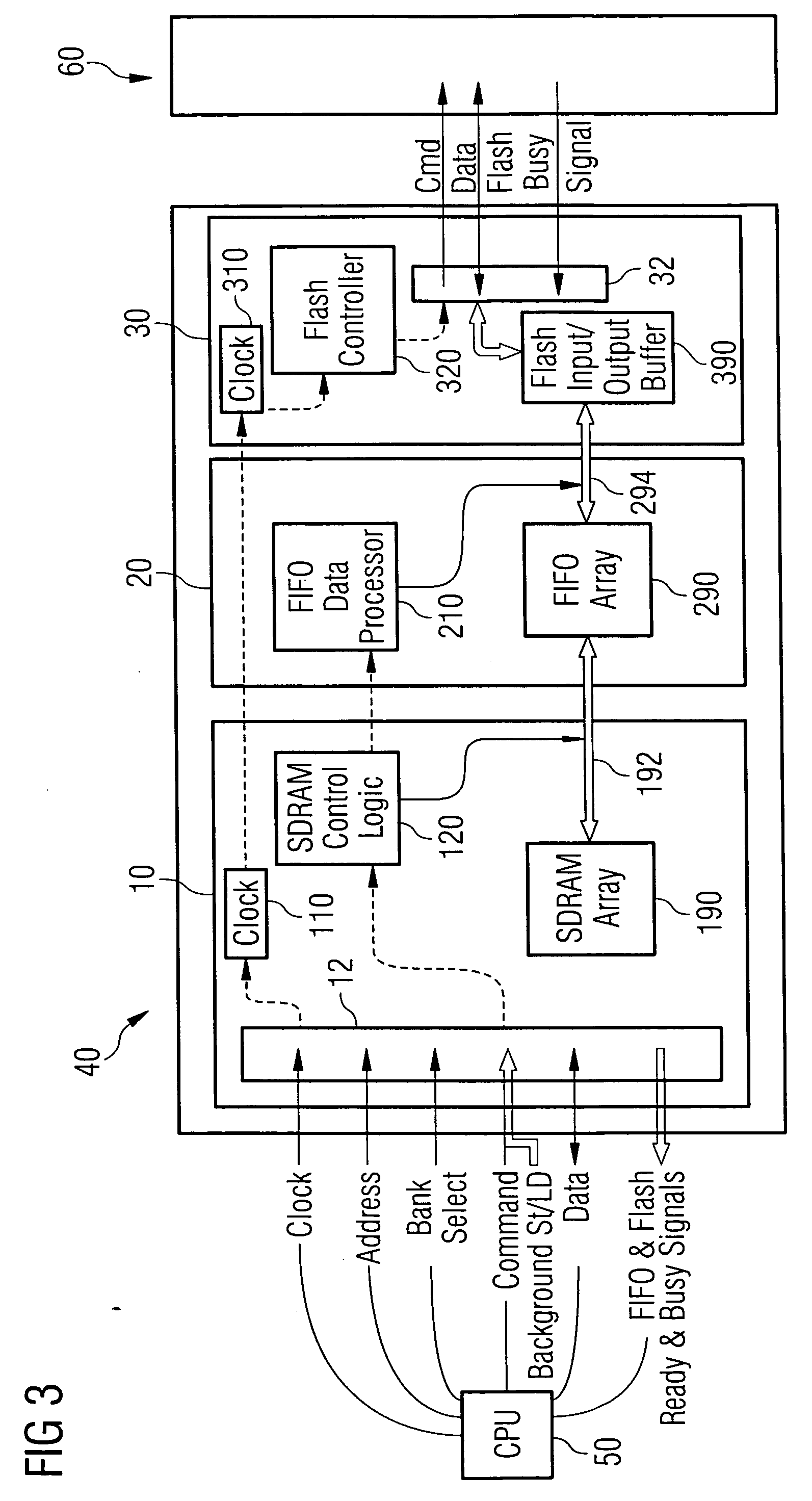
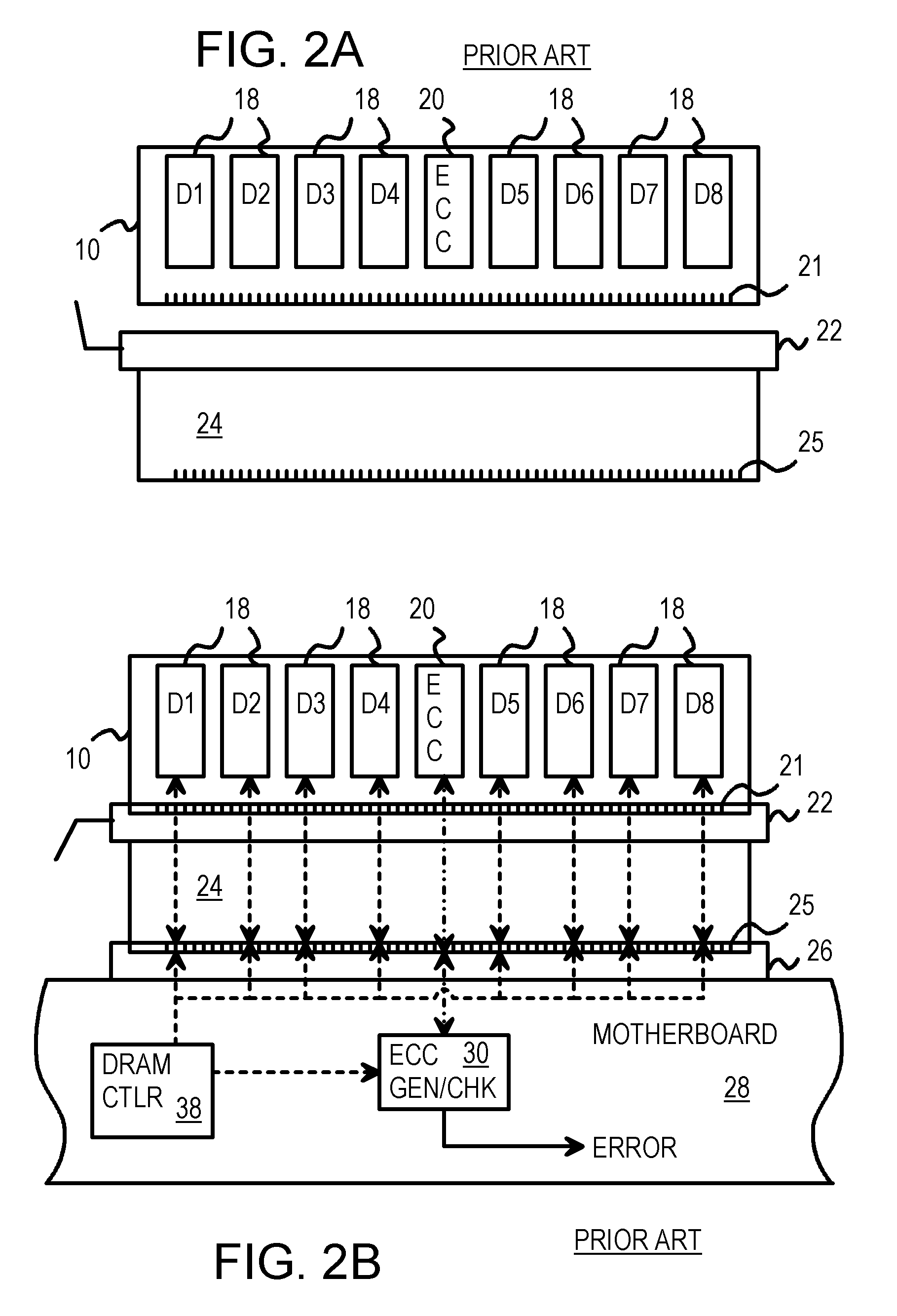
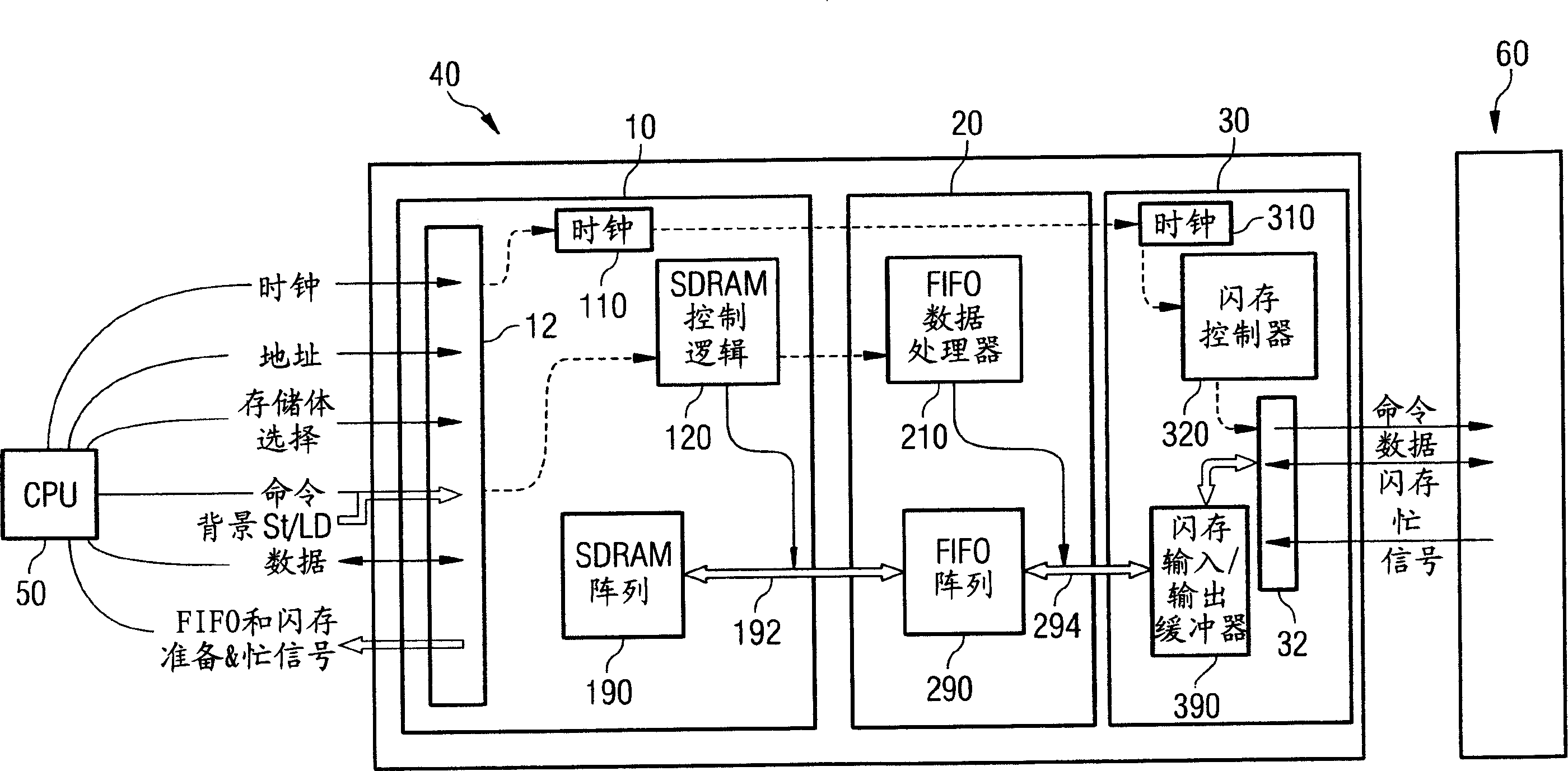
An SDRAM memory chip device comprises a non-volatile memory controller for operating a non-volatile memory, e.g., a NAND-flash, and a FIFO memory buffer. The FIFO memory buffer serves to operate background store and load operations between a FIFO buffer array and the non-volatile memory, while a host system such as a CPU exchanges data with the SDRAM work memory. The SDRAM memory chip device, therefore, has at least two additional pins as compared with conventional SDRAM standard for generating a set of additional commands. These commands are employed by the FIFO memory buffer to manage the data transfer between the FIFO buffer and each of the non-volatile memory and the volatile SDRAM memory. Two further pins reflecting the flash memory status provide appropriate issuance of load or store signals by the host system.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Memory module and memory system
ActiveUS7123497B2Increase chanceVarious problemDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusData signalComputer module
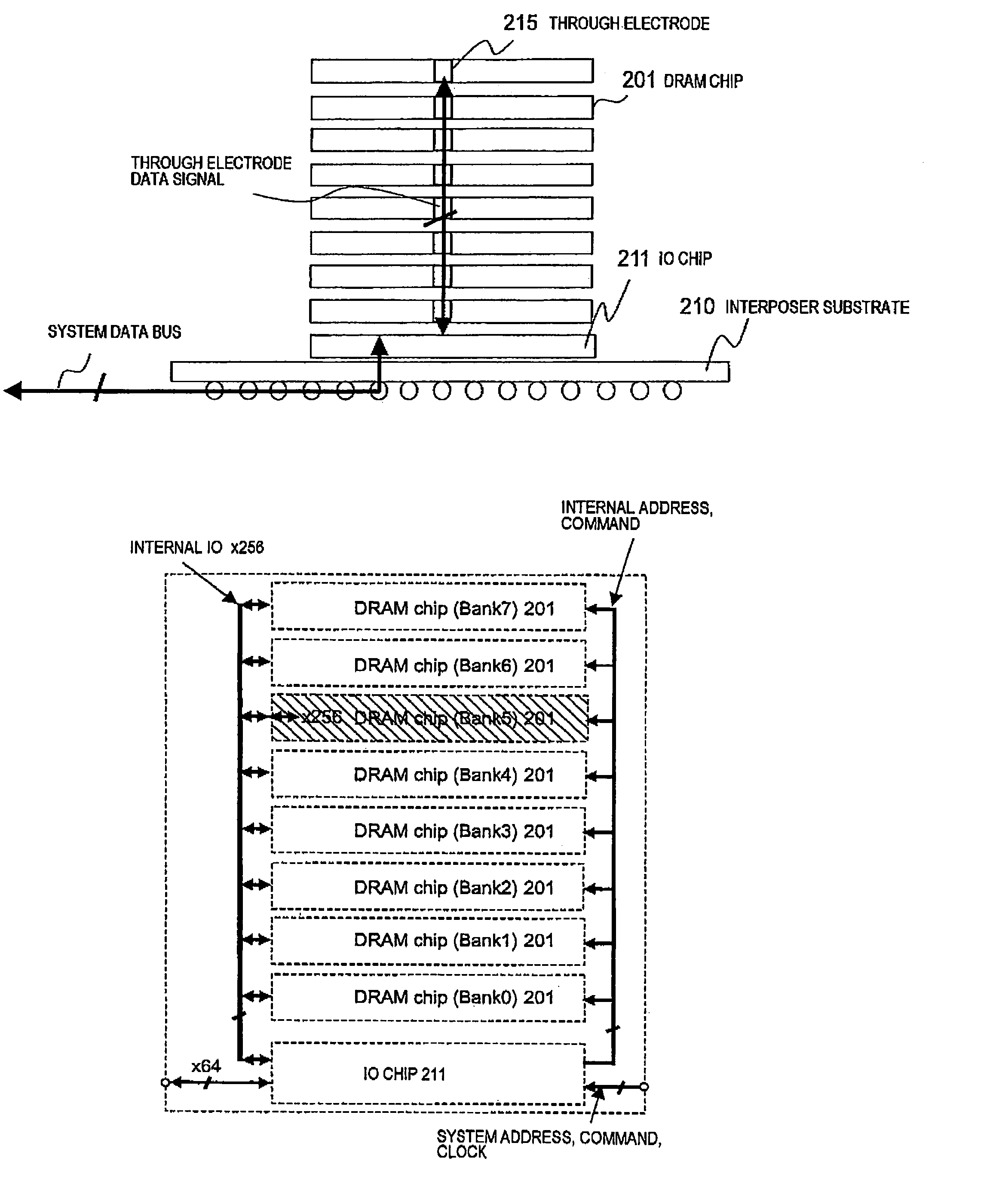
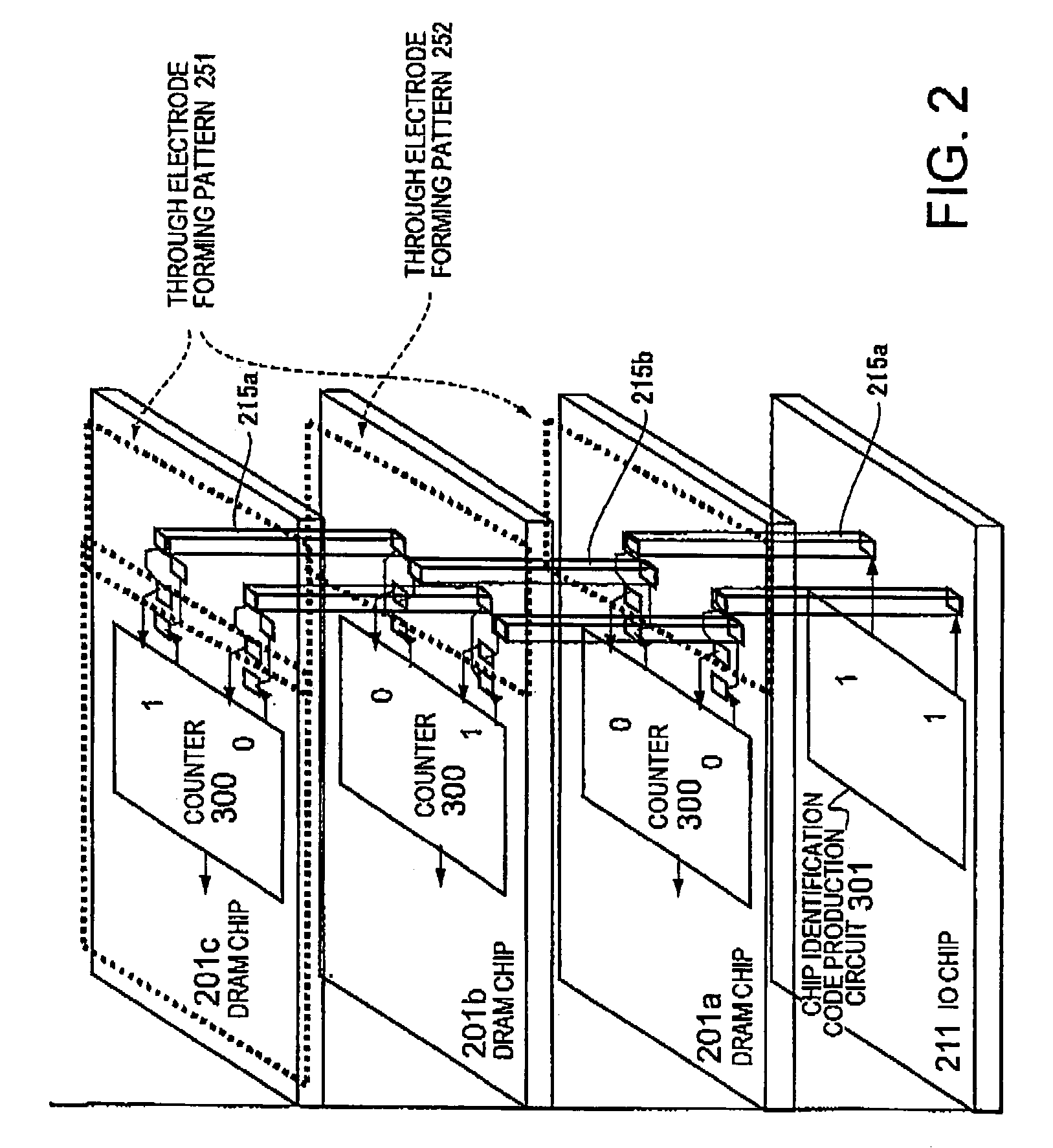
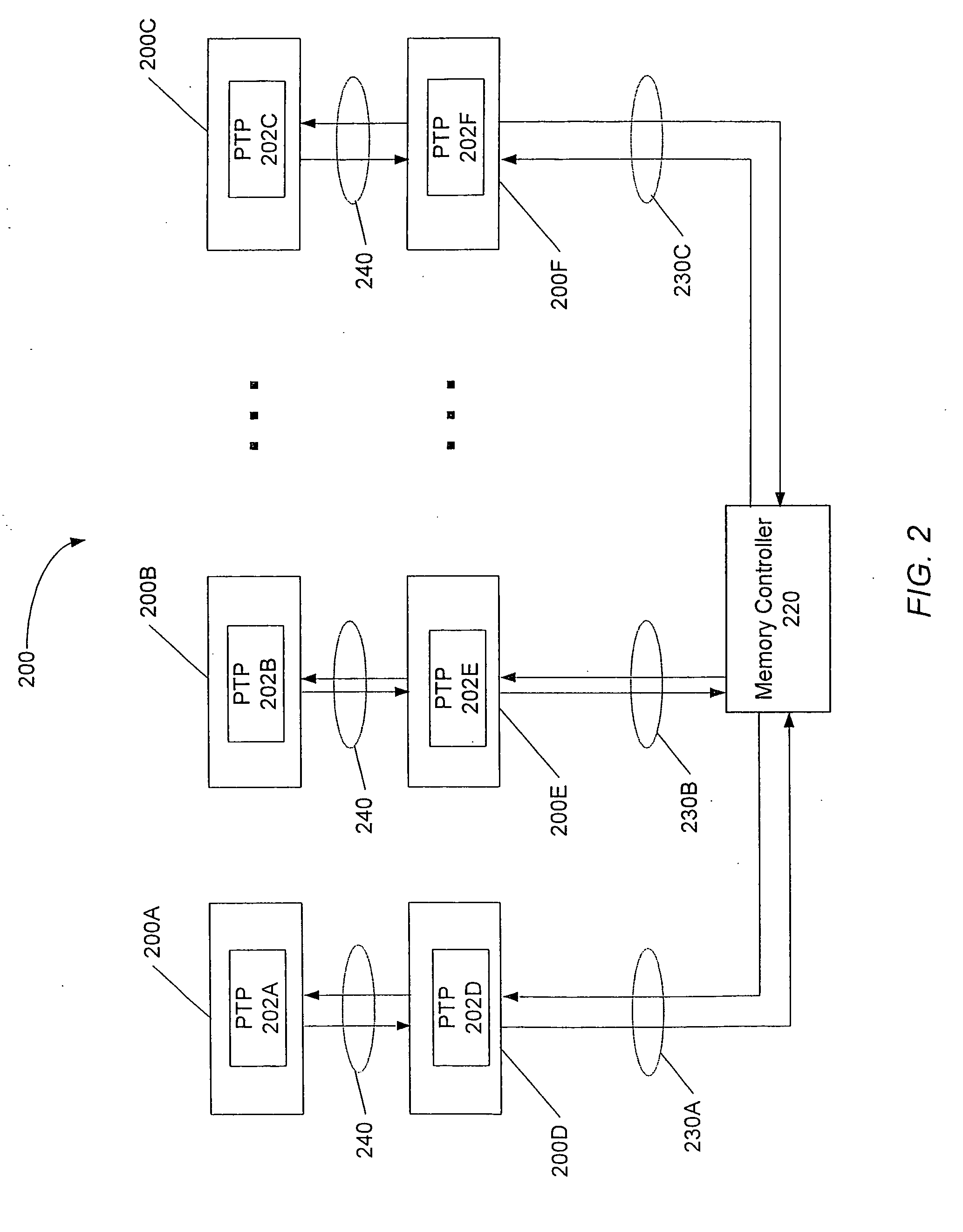
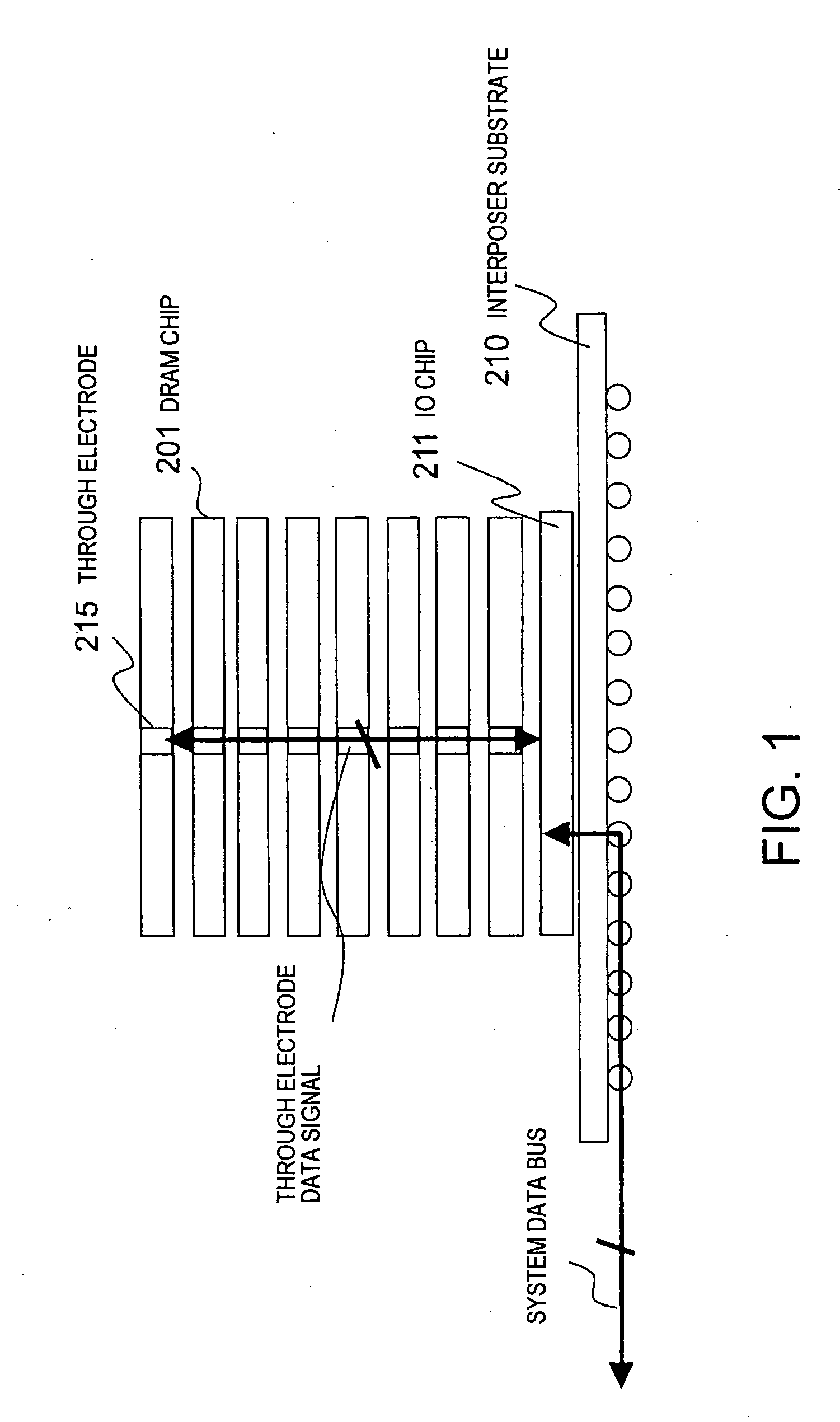
In a memory module including a plurality of DRAM chips which transmit / receive a system data signal with a predetermined data width and at a transfer rate and which transmit / receive an internal data signal having a larger data width and a lower transfer rate as compared with the system data signal, it has become clear that there is a restriction on the transfer rate of the system data signal and that speeding-up cannot be expected. A current consumption in a plurality of DRAMs constituting the memory module is large, and this is also a factor for hindering the speeding-up. There is obtained a memory module in which a plurality of DRAM chips are stacked on an IO chip and in which each DRAM chip is connected to the IO chip by a through electrode and which comprises a constitution for mutually converting the system data signal and the internal data signal in each DRAM chip by the IO chip. In this constitution, a wiring between the DRAM chips can be shortened, and DLL having a large current consumption may be disposed only on the IO chip.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20050139977A1Easy impedance matchingReduce signalingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterposerChipset
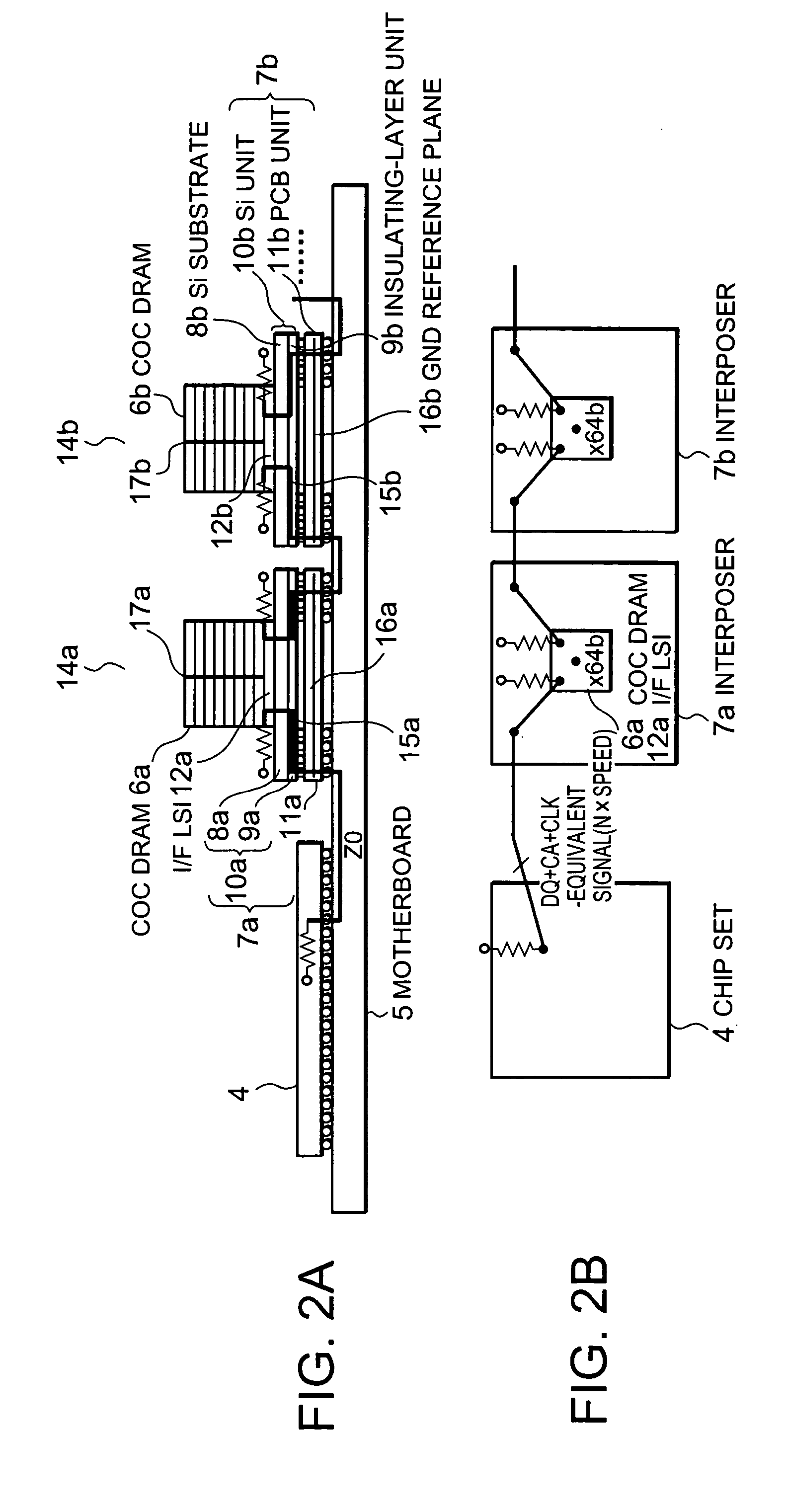
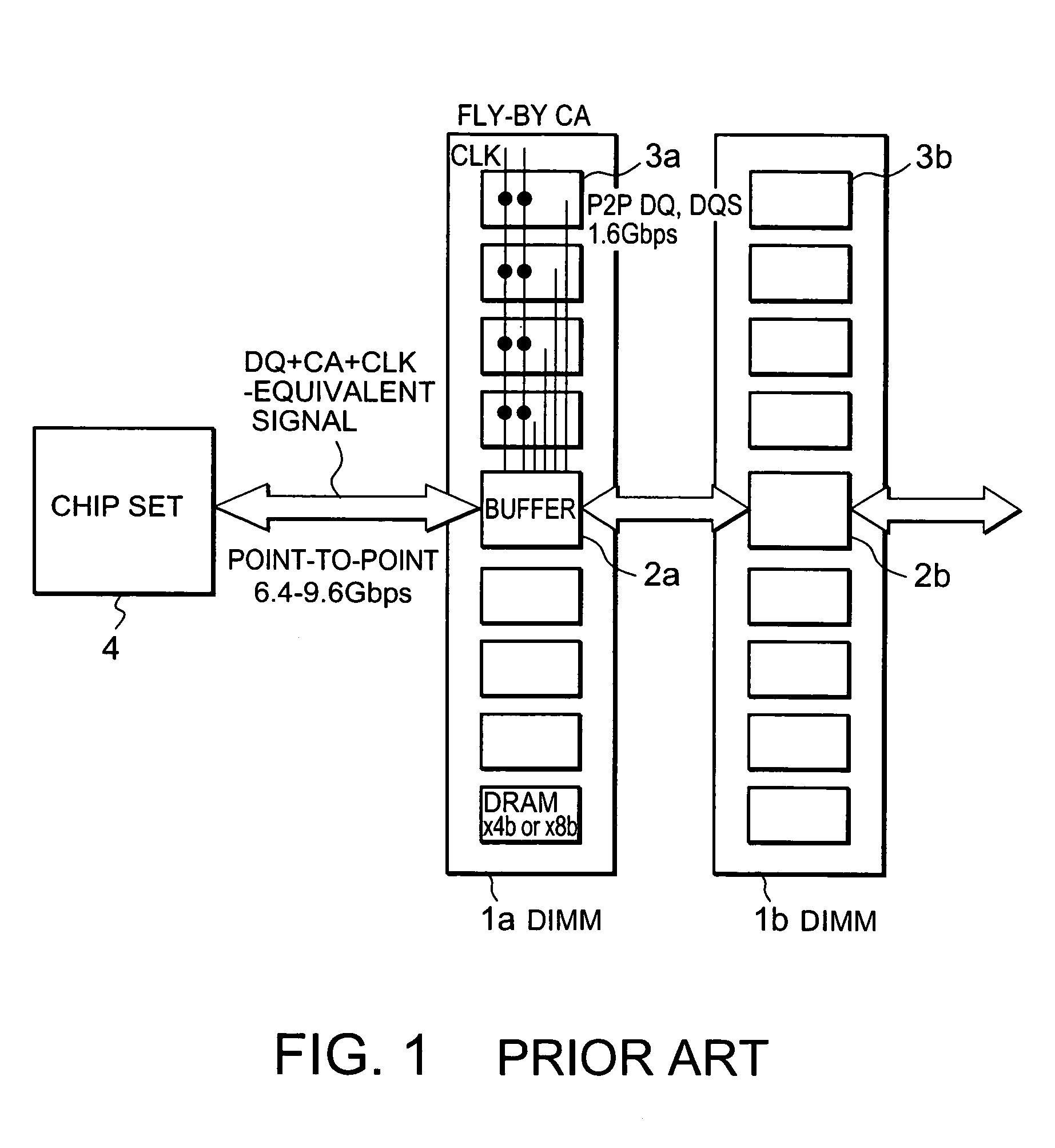
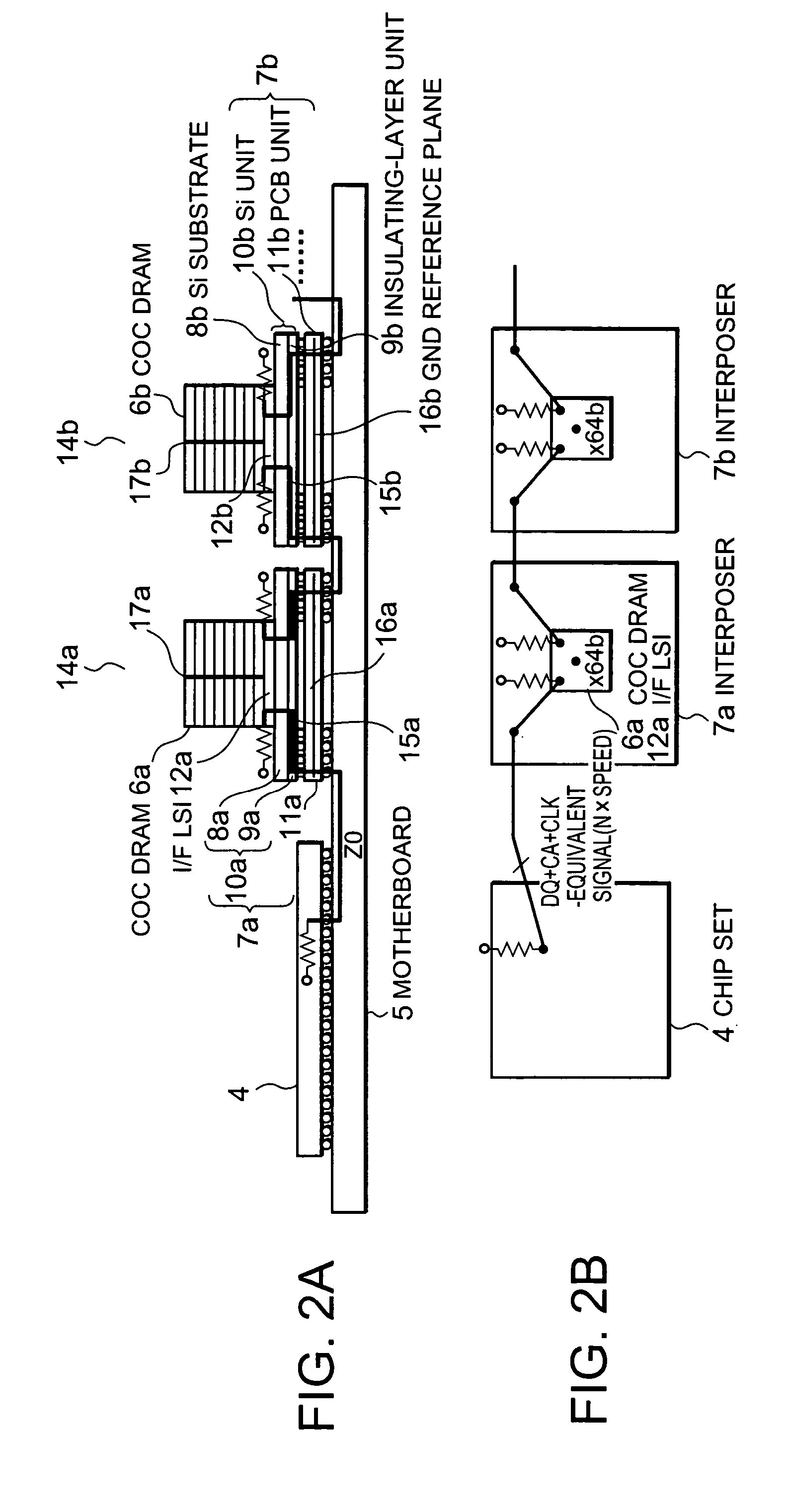
A COC DRAM including a plurality of stacked DRAM chips is mounted on a motherboard by using an interposer. The interposer includes a Si unit and a PCB. The Si unit includes a Si substrate and an insulating-layer unit in which wiring is installed. The PCB includes a reference plane for the wiring in the Si unit. The wiring topology between a chip set and the COC DRAM is the same for every signal. Accordingly, a memory system enabling a high-speed operation, low power consumption, and large capacity is provided.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
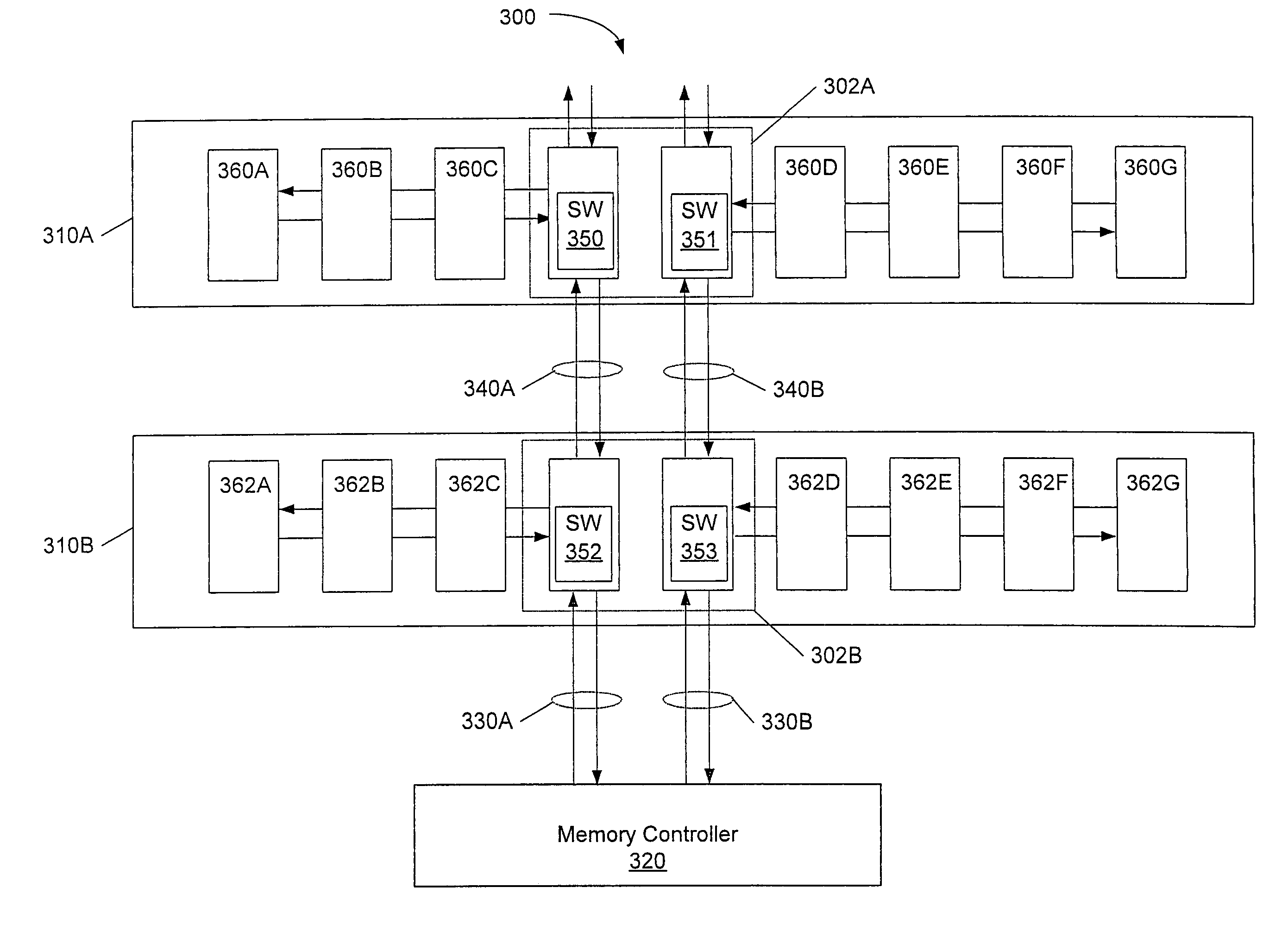
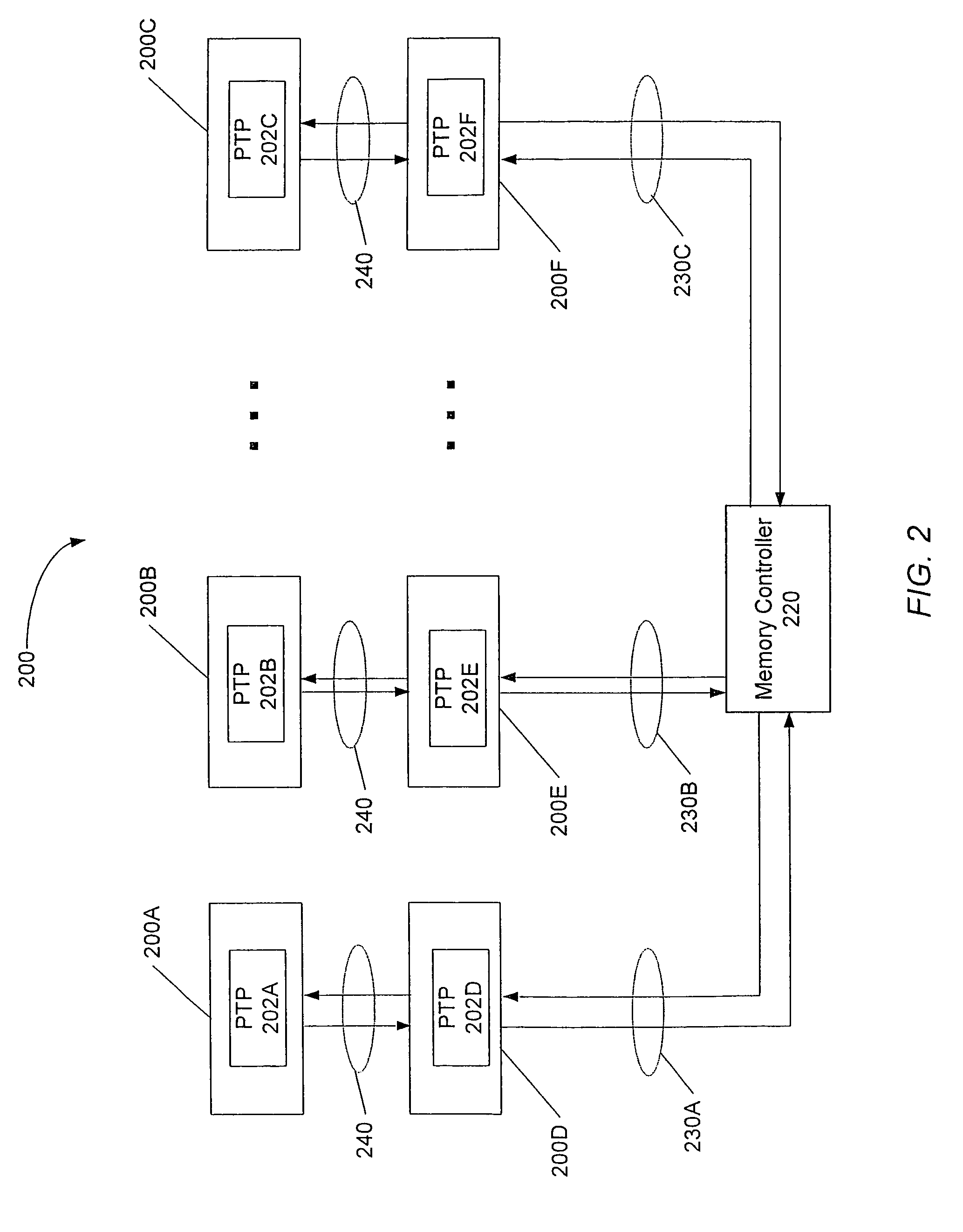
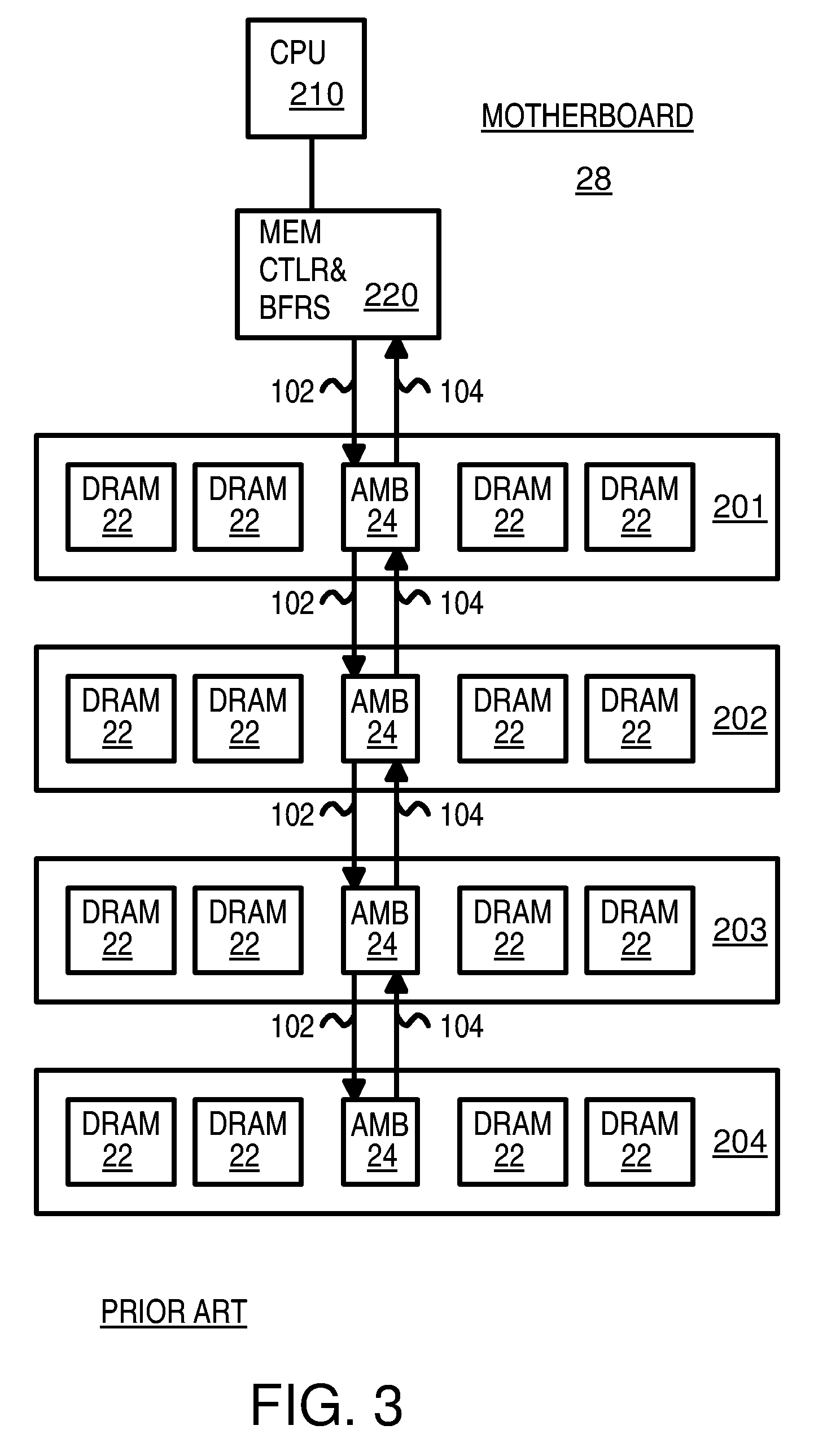
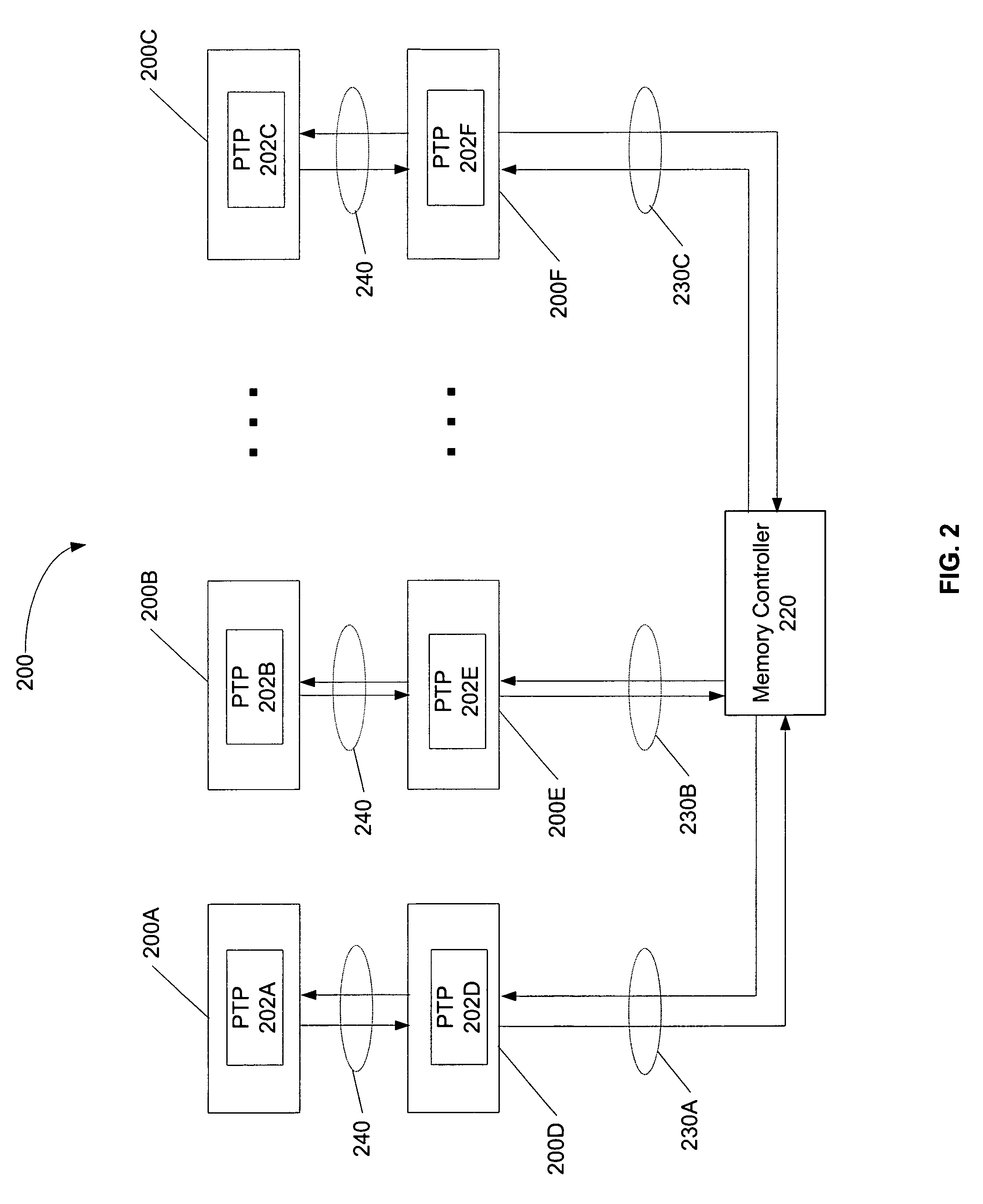
System memory board subsystem using dram with stacked dedicated high speed point to point links
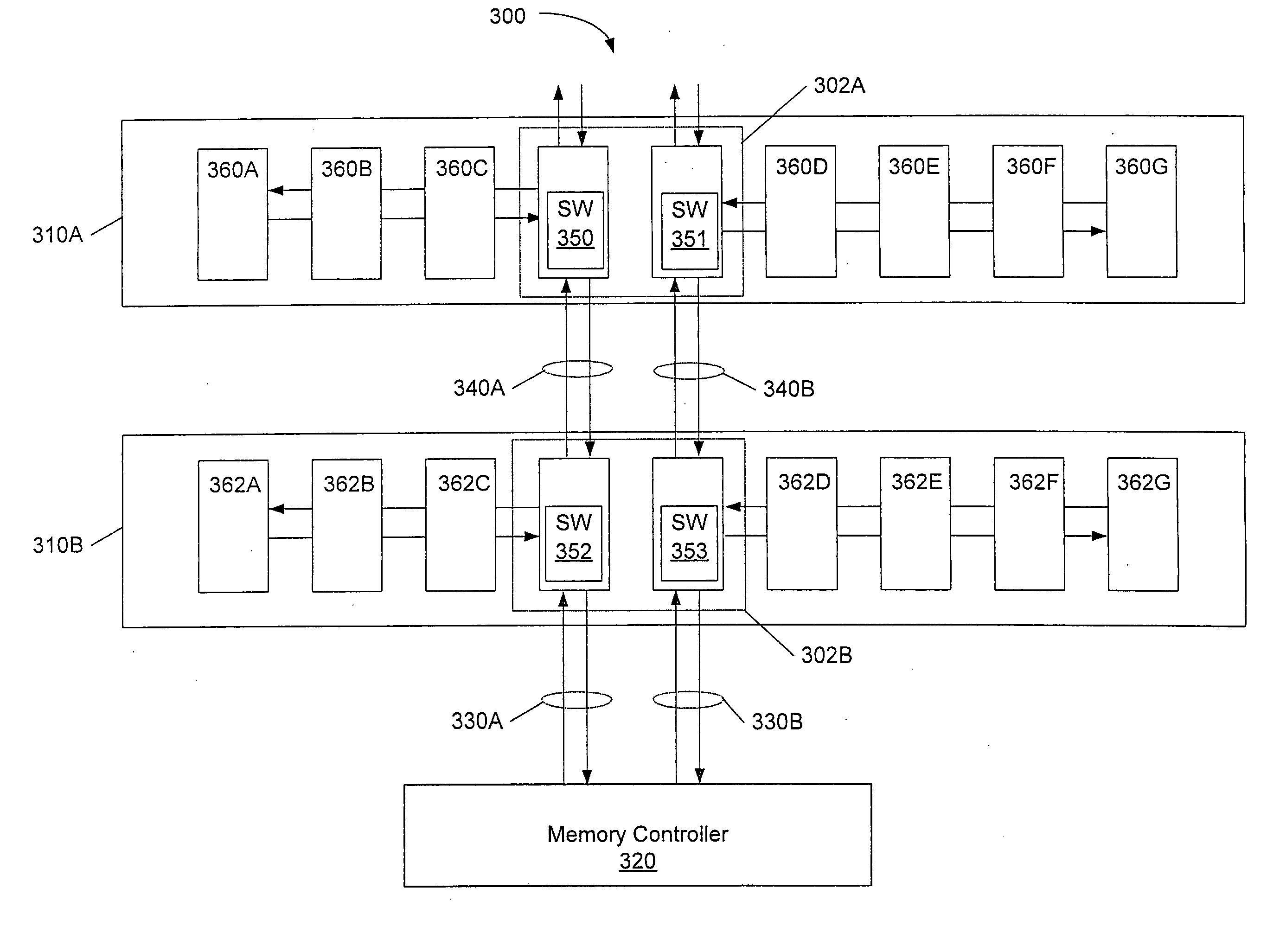
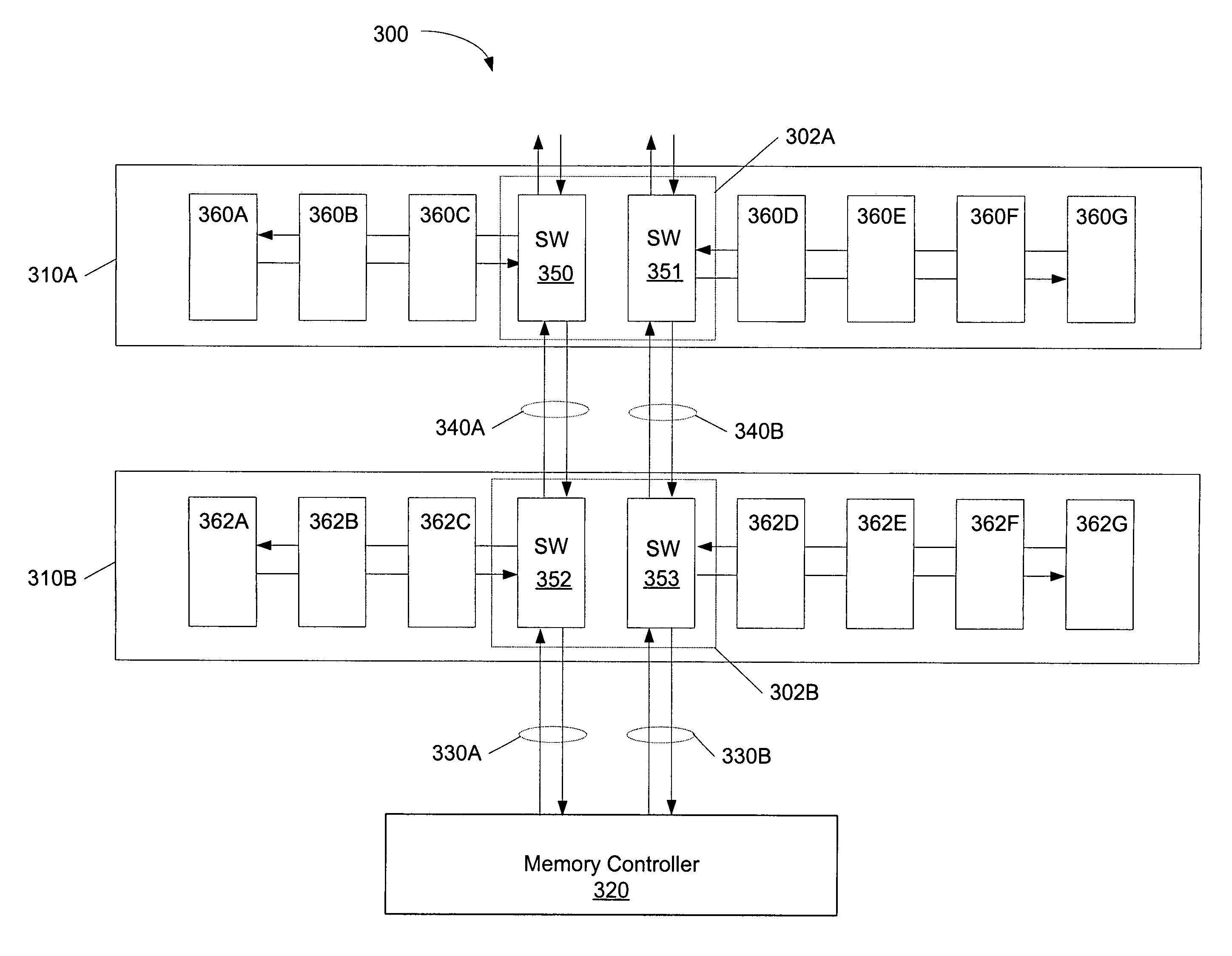
A memory system comprising memory modules including memory chips stacked with switching circuits. A memory controller coupled to the memory modules is configured to initiate memory accesses. When a stacked switching circuit detects the memory access, the switching circuit routes the access to another memory module if the access is not directed to a memory chip of the receiving memory module, or processes the access locally if the access is directed to a memory chip of the receiving memory module. The memory controller and memory modules are coupled via bi-directional serial links. Each memory module may include multiple stacked switching circuits, each of which may be coupled to fewer than all of the memory chips within the memory module. Switching circuits further include circuitry configured to de-serialize data prior to conveyance to a memory chip, and serialize data received from a DRAM chip prior to transmitting the received data. Switching circuits may be coupled to a stacked memory chip via a flexible interconnect, and may also be manufactured side by side with a corresponding memory chip on a flexible circuit board.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Memory module and memory system
ActiveUS20060262587A1Increase chanceTotal current dropDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusData signalTerm memory
In a memory module including a plurality of DRAM chips which transmit / receive a system data signal with a predetermined data width and at a transfer rate and which transmit / receive an internal data signal having a larger data width and a lower transfer rate as compared with the system data signal, the transfer rate of the system data signal is restricted. Current consumption in DRAMs constituting the memory module is large, hindering speed increases. For this memory module, a plurality of DRAM chips are stacked on an IO chip. Each DRAM chip is connected to the IO chip by a through electrode, and includes a constitution for mutually converting the system data signal and the internal data signal in each DRAM chip by the IO chip. Therefore, wiring between the DRAM chips can be shortened, and DLL having a large current consumption may be disposed only on the IO chip.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
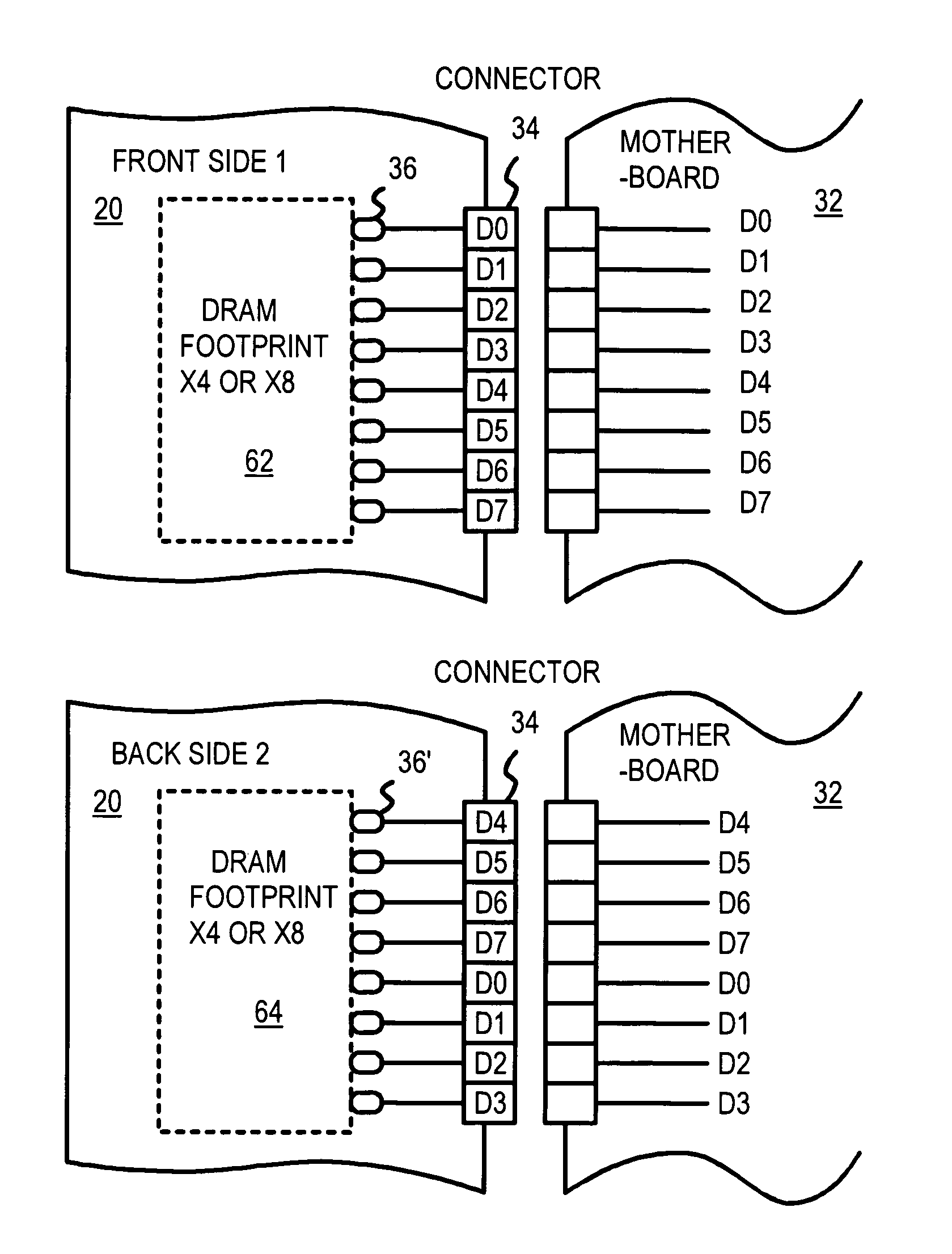
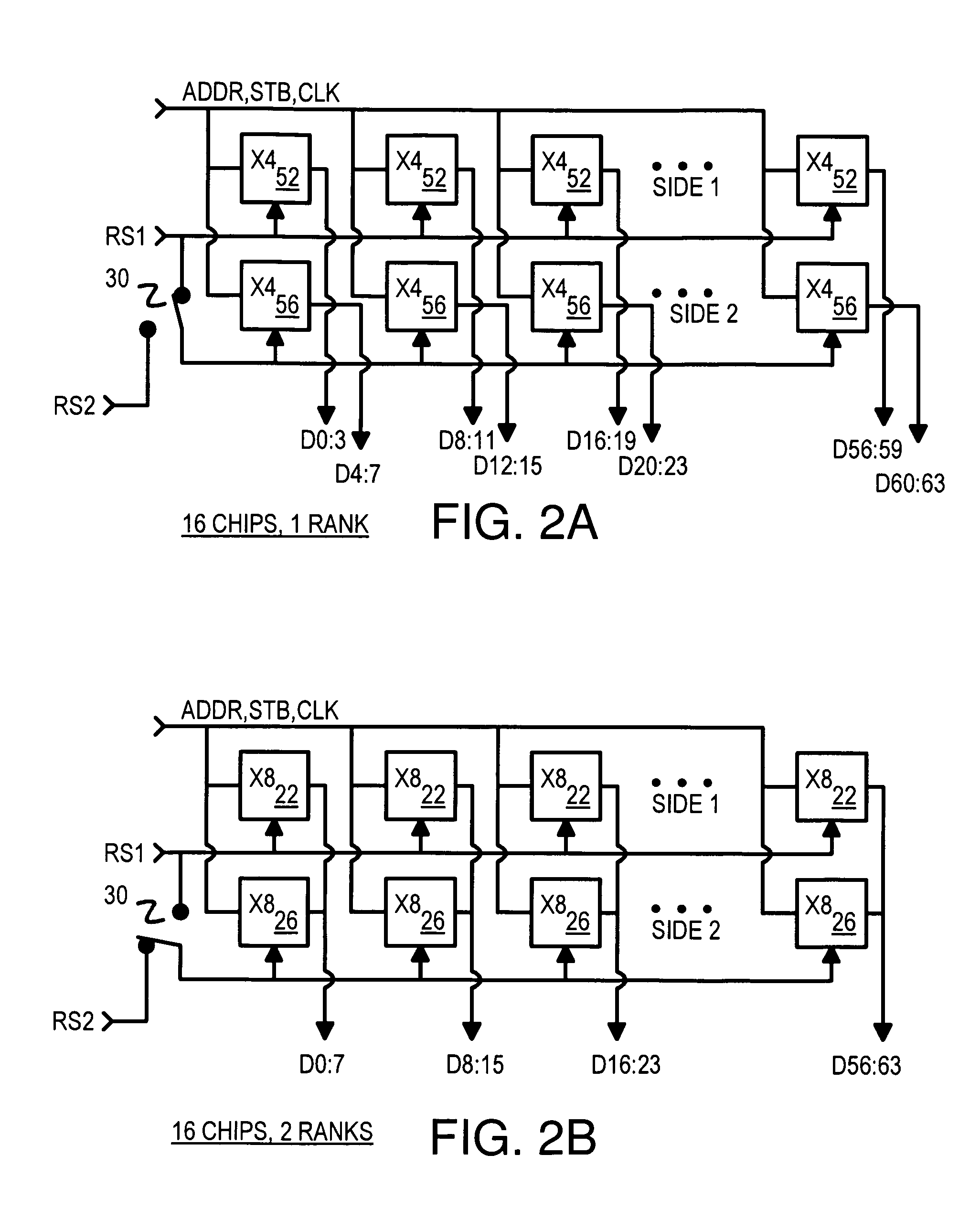
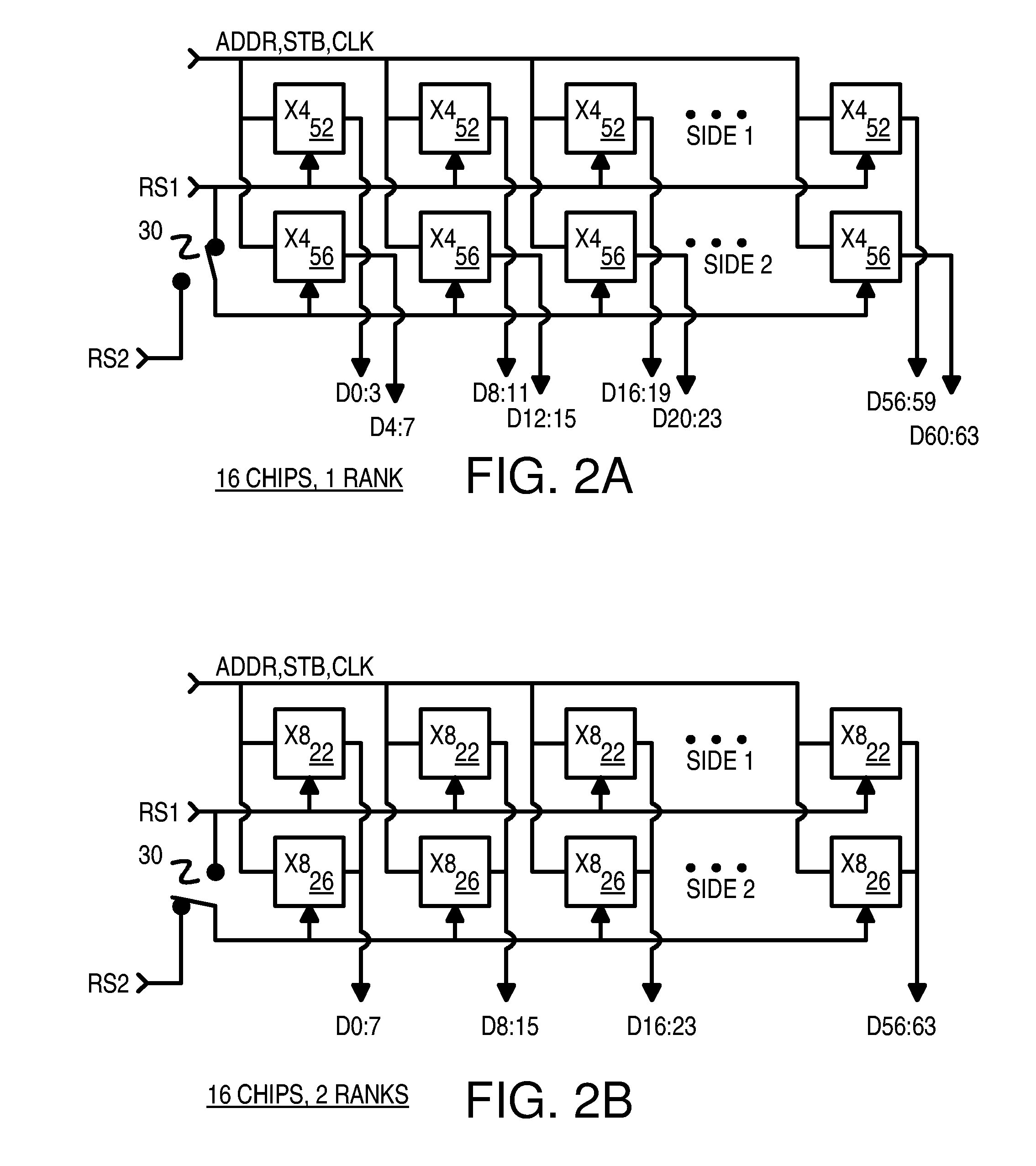
Memory-module board layout for use with memory chips of different data widths
A memory module substrate printed-circuit board (PCB) has multi-type footprints and an edge connector for mating with a memory module socket on a motherboard. Two or more kinds of dynamic-random-access memory (DRAM) chips with different data I / O widths can be soldered to solder pads around the multi-type footprints. When ×4 DRAM chips with 4 data I / O pins are soldered over the multi-type footprints, the memory module has a rank-select signal that drives chip-select inputs to all DRAM chips. When ×8 DRAM chips with 8 data I / O pins are soldered over the multi-type footprints, the memory module has two rank-select signals. One rank-select drives chip-select inputs to front-side DRAM chips while the second rank-select drives chip-select inputs to back-side DRAM chips. Wiring traces on the PCB cross-over data nibbles between the solder pads and the connector to allow two ×4 chips to drive a byte driven by only one ×8 chip.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
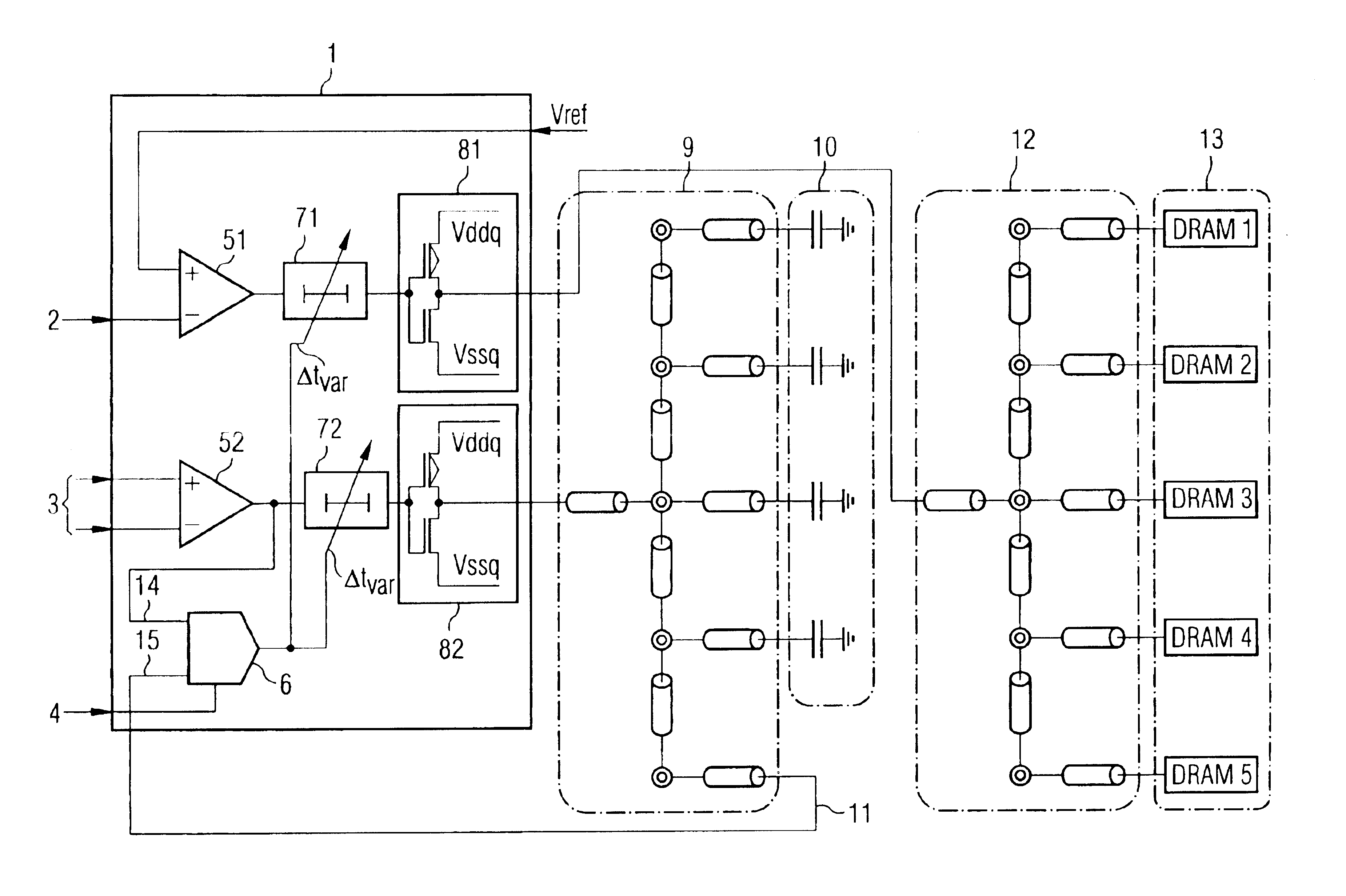
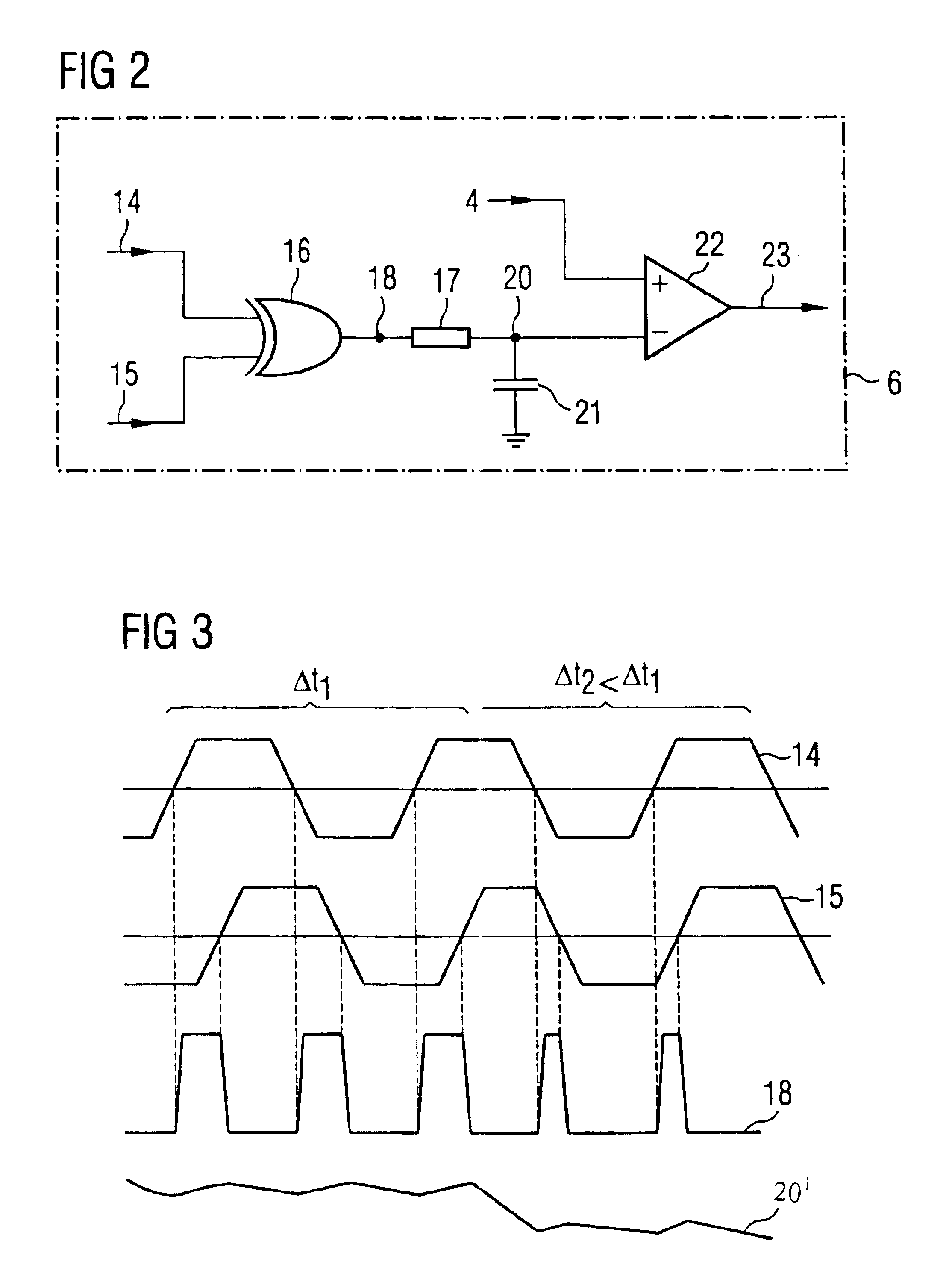
Buffer amplifier architecture for semiconductor memory circuits
A buffer amplifier architecture for buffering signals which are supplied in parallel to identical chips, particularly DRAM chips, on a semiconductor memory module, is disclosed. The architecture has adjustable delay circuits in each signal line and a delay detector circuit which receives a clock signal from the buffer amplifier architecture at the input and at the output of the buffer amplifier architecture, and takes the phase difference between the two signals to produce a control signal for setting the variable delay time of the delay circuits. To ensure that the delay time set by the delay detector circuit is independent of variations in parameters of the DRAM memory chips, the feedback path routed to the input of the delay detector circuit has a reference line network of the same structure and having the same electrical properties as capacitance elements which terminate the line network routed to the DRAM memory chips and the reference line network, and which have the same capacitances as the signal inputs on the DRAM memory chips.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Memory-Module Board Layout for Use With Memory Chips of Different Data Widths
ActiveUS20060267172A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMemory chipNibble
A memory module substrate printed-circuit board (PCB) has multi-type footprints and an edge connector for mating with a memory module socket on a motherboard. Two or more kinds of dynamic-random-access memory (DRAM) chips with different data I / O widths can be soldered to solder pads around the multi-type footprints. When ×4 DRAM chips with 4 data I / O pins are soldered over the multi-type footprints, the memory module has a rank-select signal that drives chip-select inputs to all DRAM chips. When ×8 DRAM chips with 8 data I / O pins are soldered over the multi-type footprints, the memory module has two rank-select signals. One rank-select drives chip-select inputs to front-side DRAM chips while the second rank-select drives chip-select inputs to back-side DRAM chips. Wiring traces on the PCB cross-over data nibbles between the solder pads and the connector to allow two ×4 chips to drive a byte driven by only one ×8 chip.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
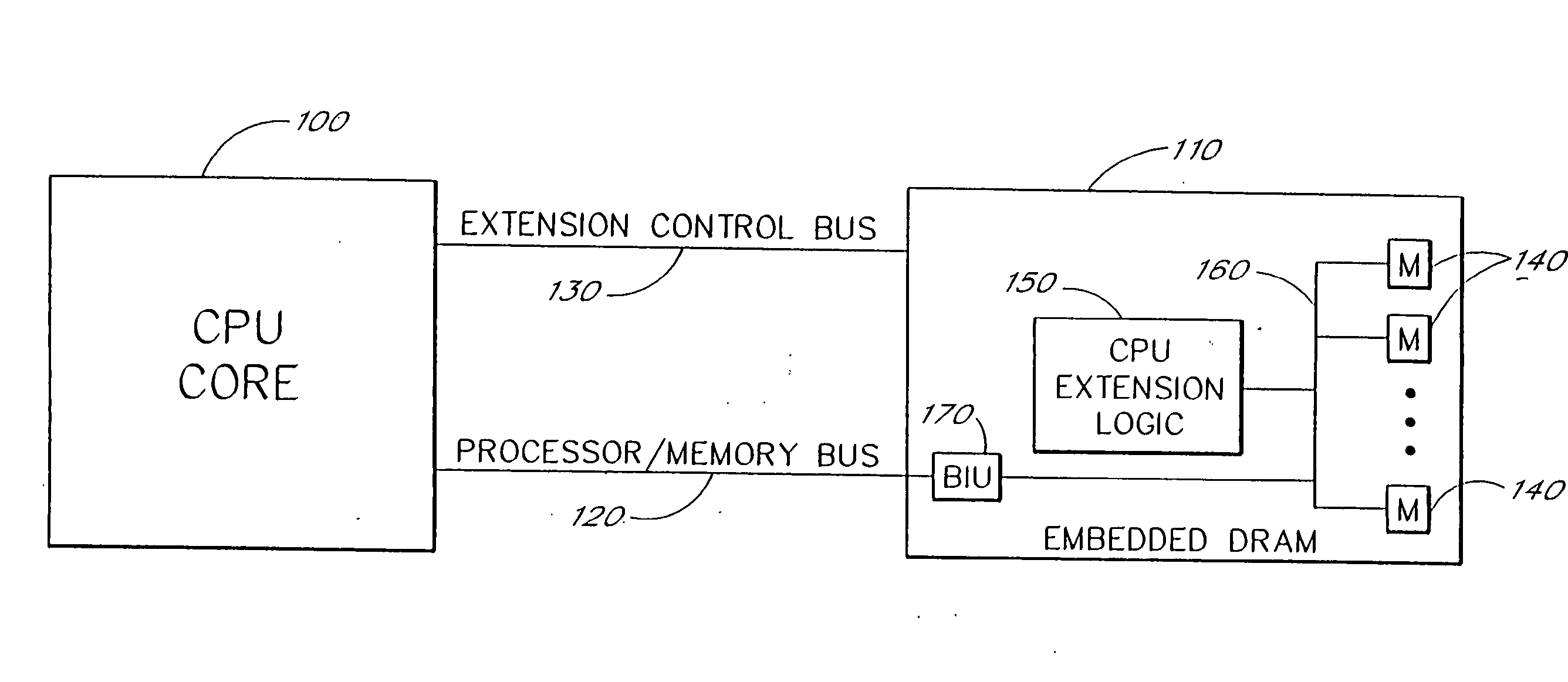
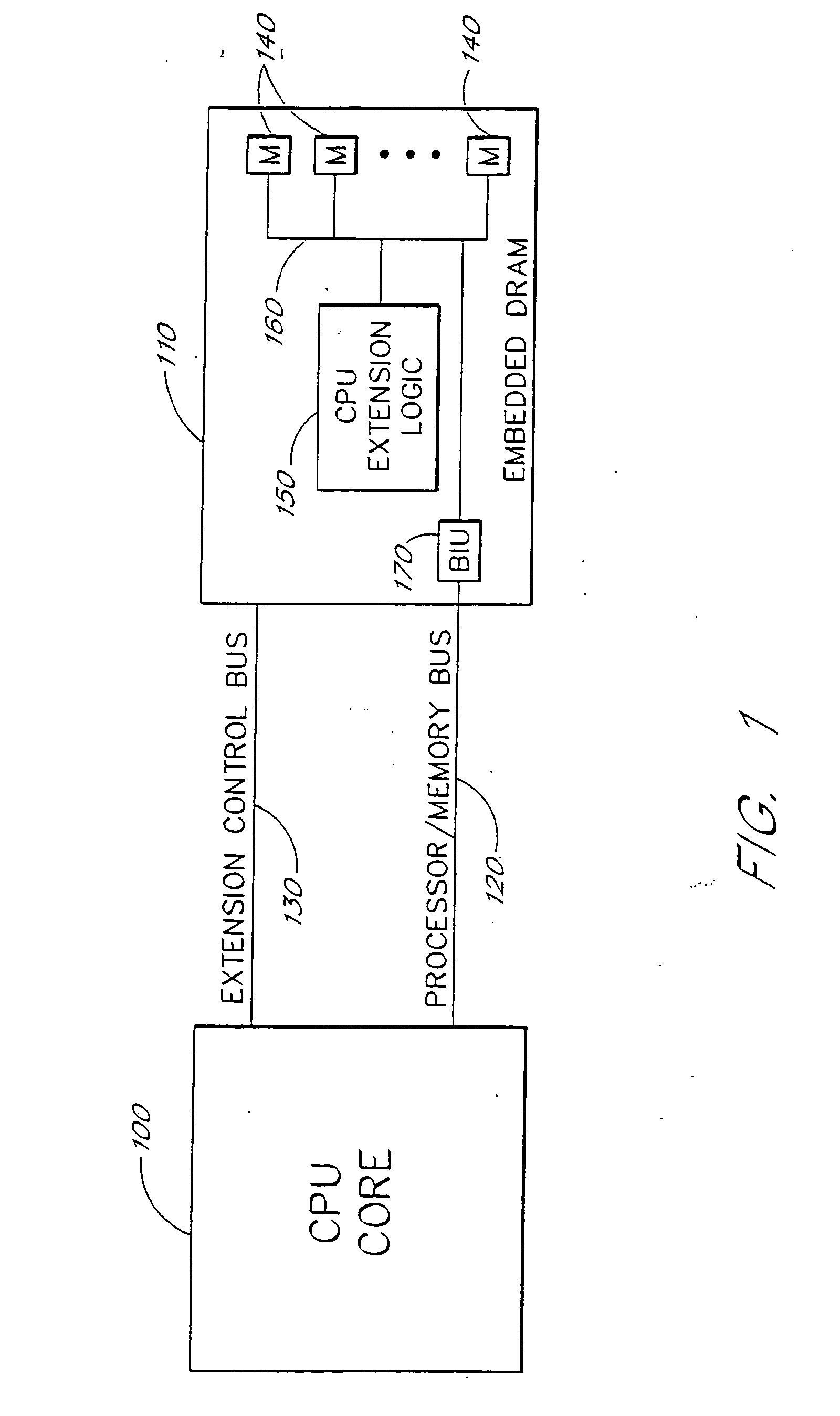
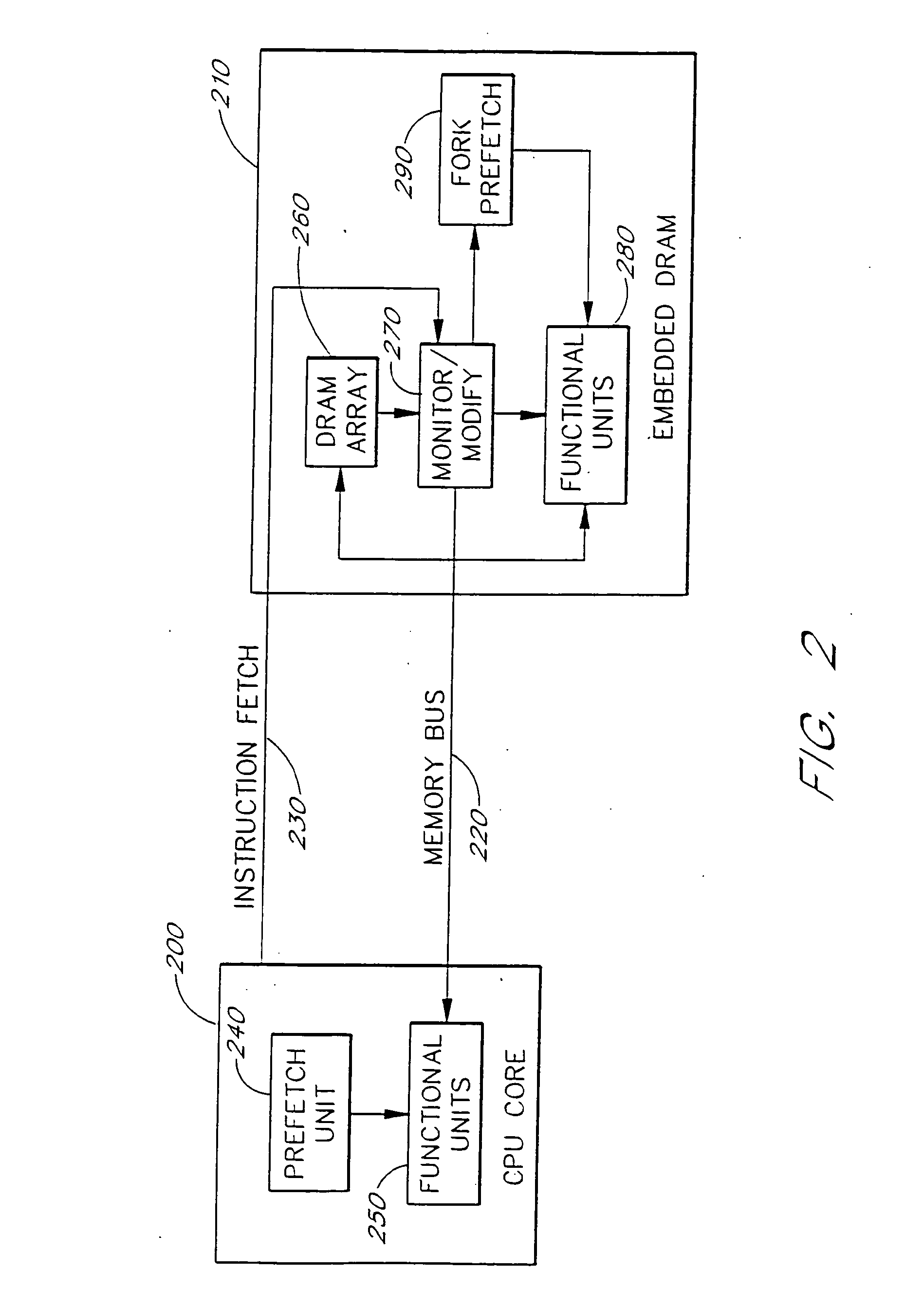
Split Embedded DRAM Processor
InactiveUS20080180450A1Effective cachingTraffic minimizationMultiple digital computer combinationsConcurrent instruction executionTraffic capacityGraphics
A processing architecture includes a first CPU core portion coupled to a second embedded dynamic random access memory (DRAM) portion. These architectural components jointly implement a single processor and instruction set. Advantageously, the embedded logic on the DRAM chip implements the memory intensive processing tasks, thus reducing the amount of traffic that needs to be bussed back and forth between the CPU core and the embedded DRAM chips. The embedded DRAM logic monitors and manipulates the instruction stream into the CPU core. The architecture of the instruction set, data paths, addressing, control, caching, and interfaces are developed to allow the system to operate using a standard programming model. Specialized video and graphics processing systems are developed. Also, an extended very long instruction word (VLIW) architecture implemented as a primary VLIW processor coupled to an embedded DRAM VLIW extension processor efficiently deals with memory intensive tasks. In different embodiments, standard software can be accelerated either with or without the express knowledge of the processor.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
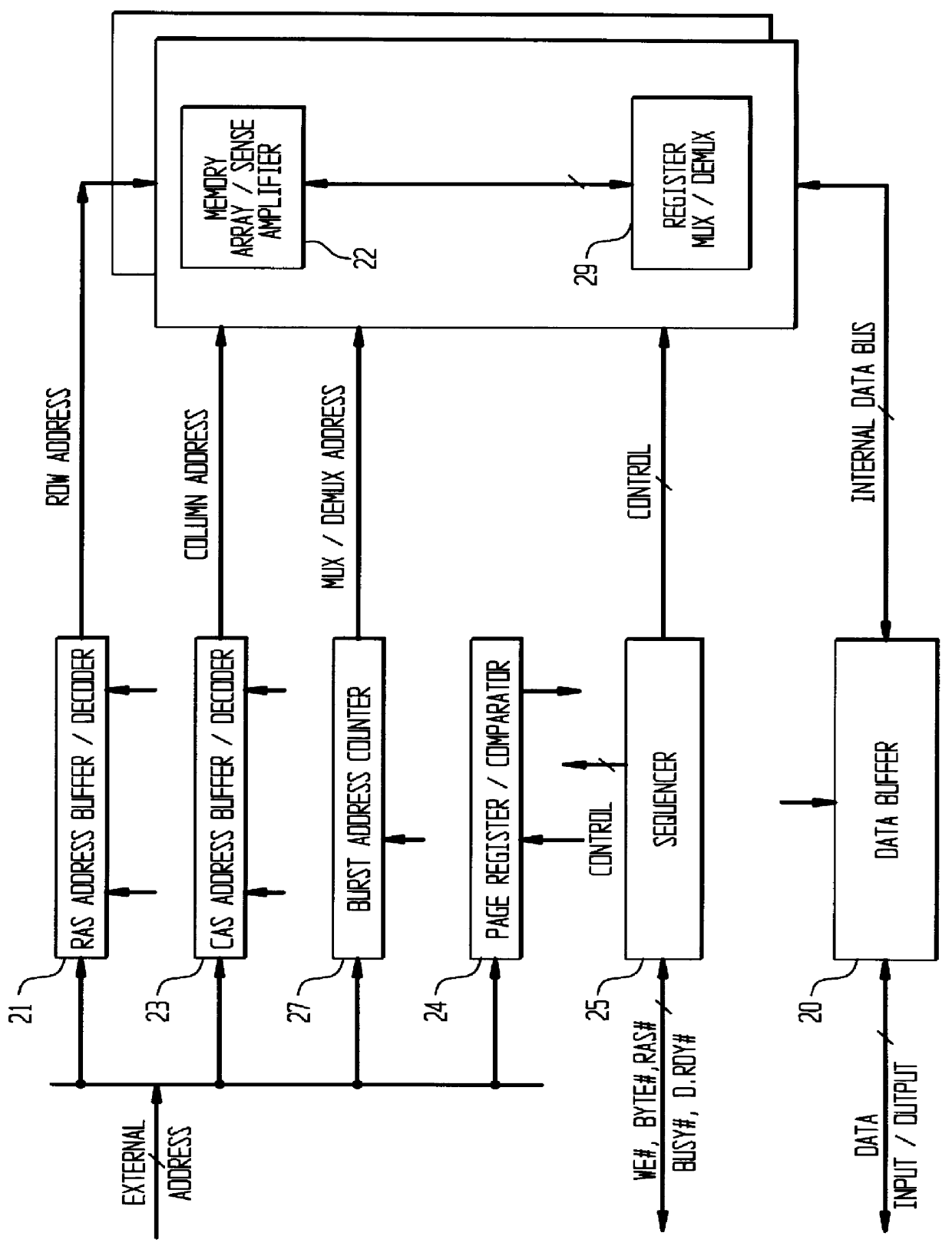
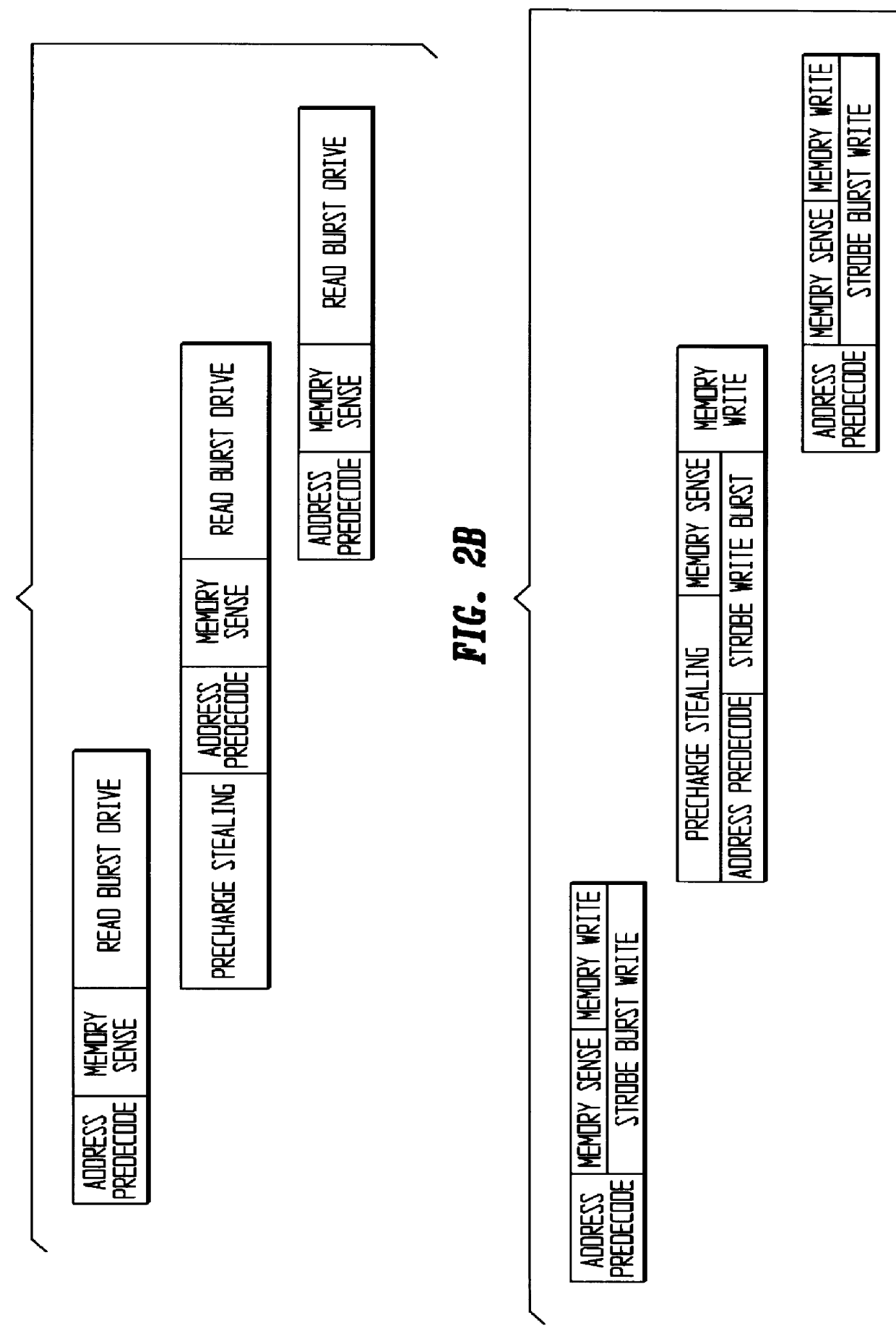
Hidden precharge pseudo cache DRAM
A new DRAM architecture, HPPC DRAM, is provided to support a high performance and low cost memory system. The HPPC DRAM has integrated the following concepts into a single DRAM chip. First, superset pin definitions backward-compatible to the traditional fast-page-mode DRAM SIMM. This allows one memory controller to support a memory system having both a traditional fast-page-mode DRAM and HPPC DRAM of this invention. Secondly, combining a memory array, a register of 4:1 Mux / Demux function, a RAS buffer / decoder, a CAS buffer / decoder, a burst address counter, a page register / comparator, a sequencer and a data buffer into a single DRAM IC chip. Using these intelligent peripheral circuits, the HPPC DRAM execute a pipeline cycle request and precharge cycle stealing. Thirdly, a precharge cycle stealing pipeline is implemented to the timing chain of read operation to eliminate the precharge cycle time which is achieved by executing read drive concurrently to the precharge cycle. This read timing chain shows that a zero wait state is sustained if there is a page-hit. Fourthly, a precharge cycle stealing pipeline is implemented to the timing chain of write operation to eliminate the precharge cycle time which is achieved by executing precharge cycle concurrently to address predecoding and data strobing.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
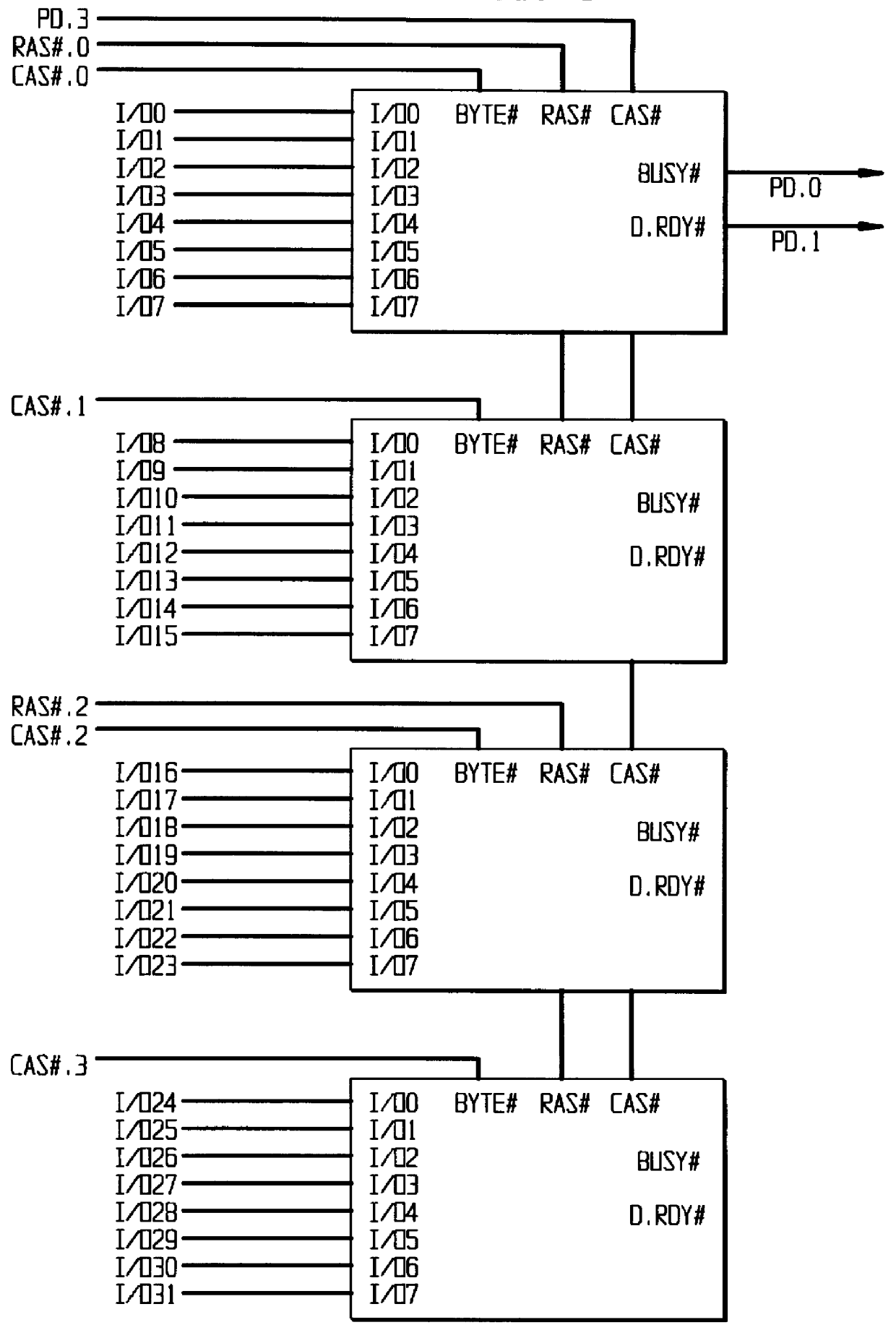
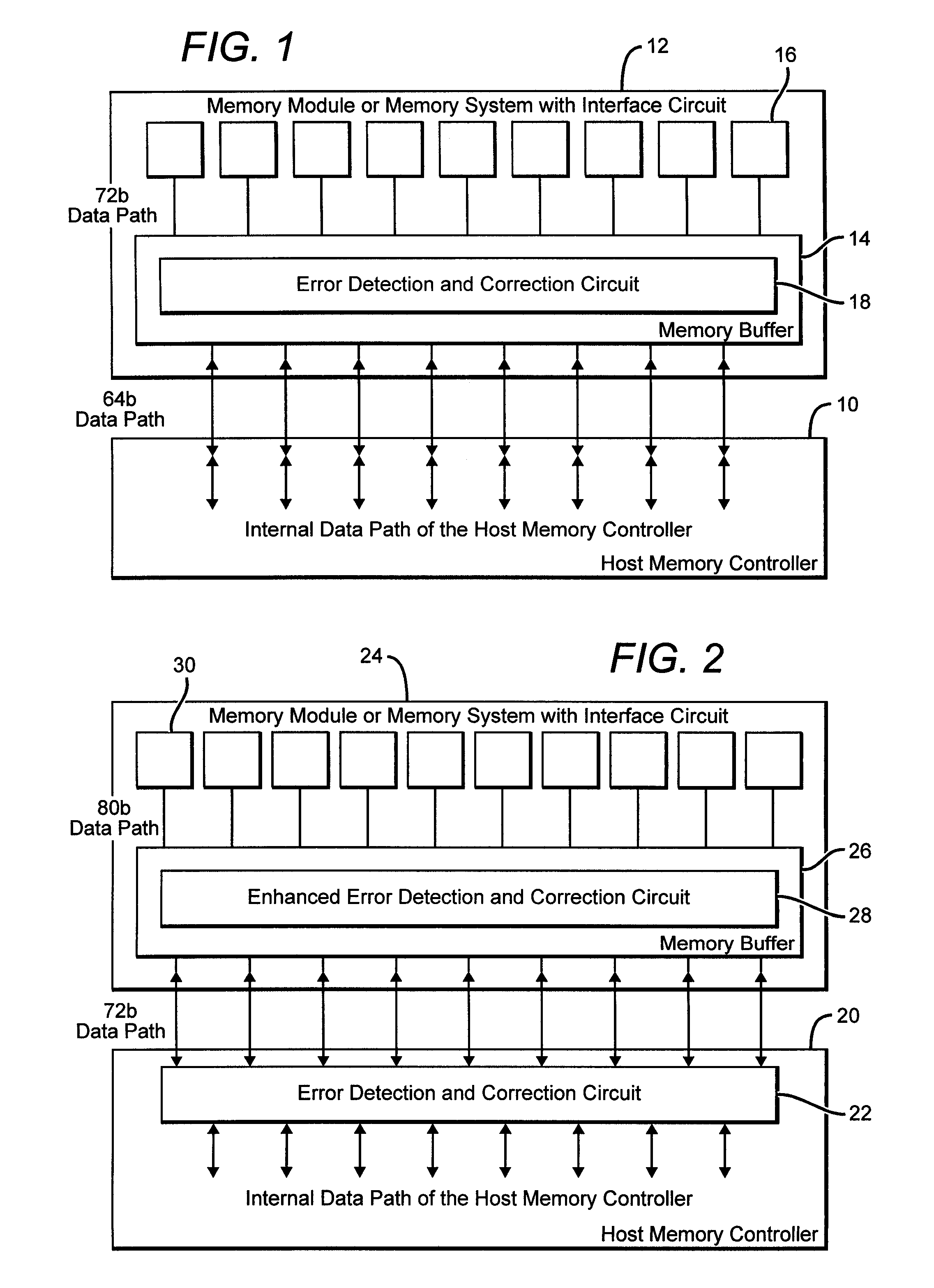
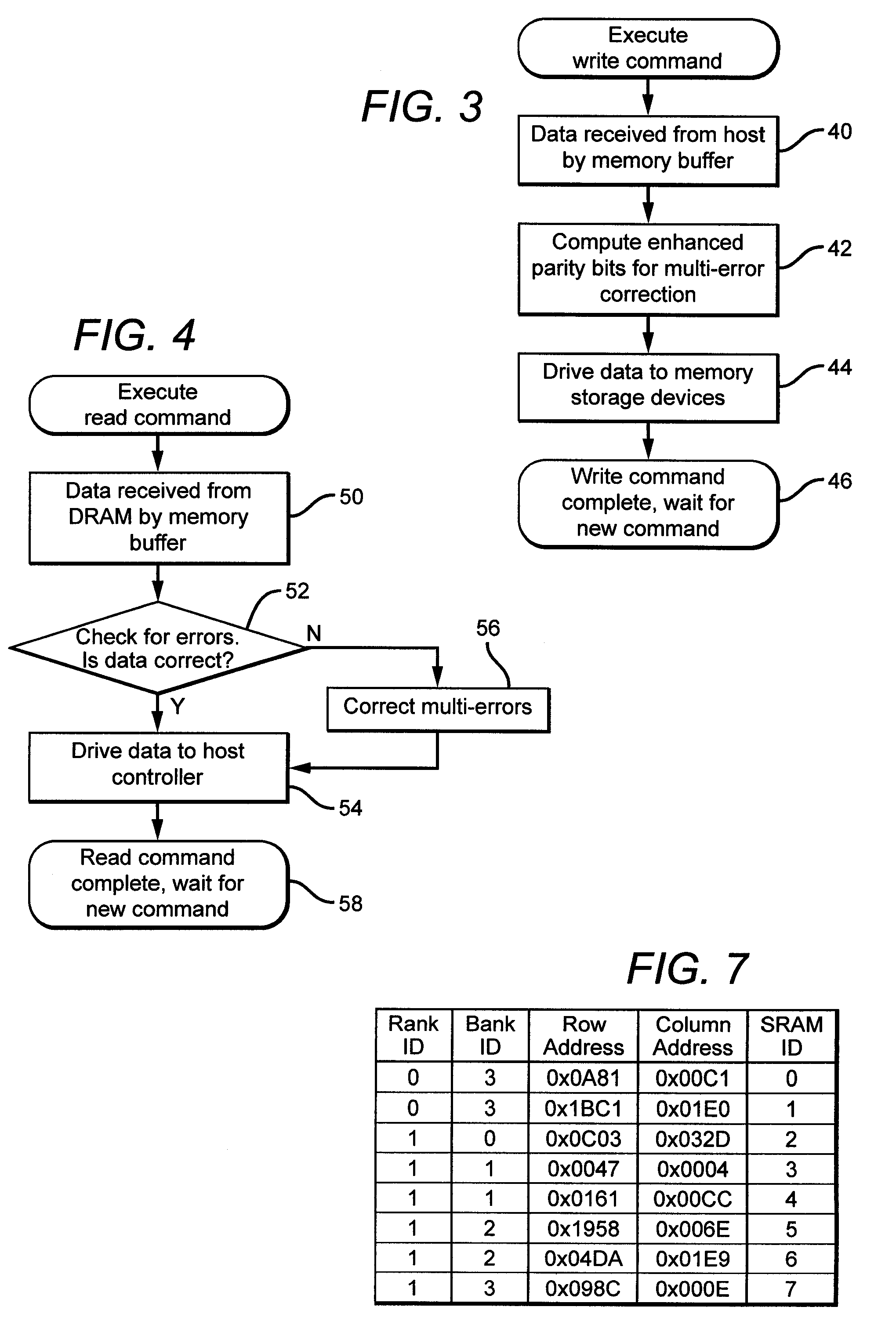
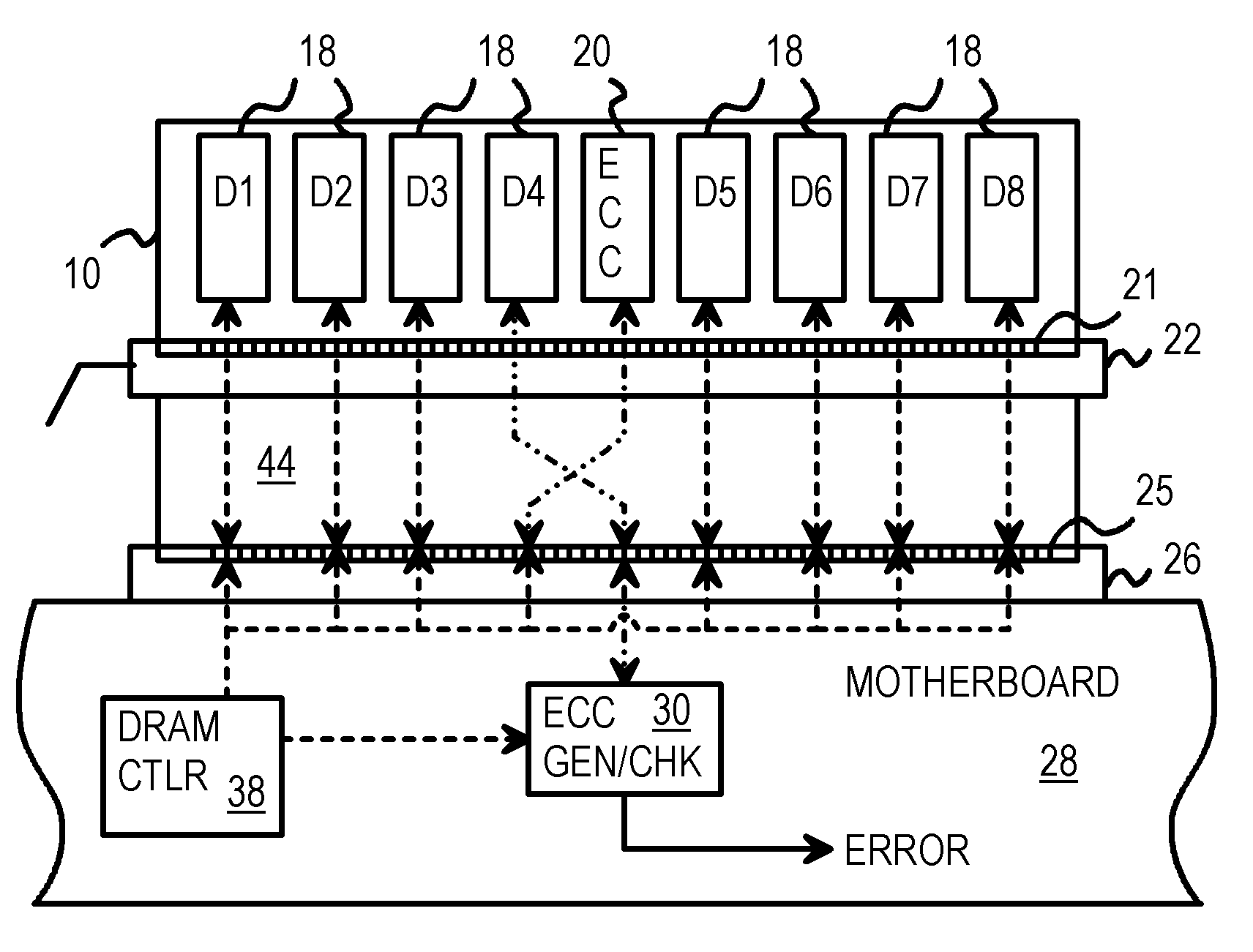
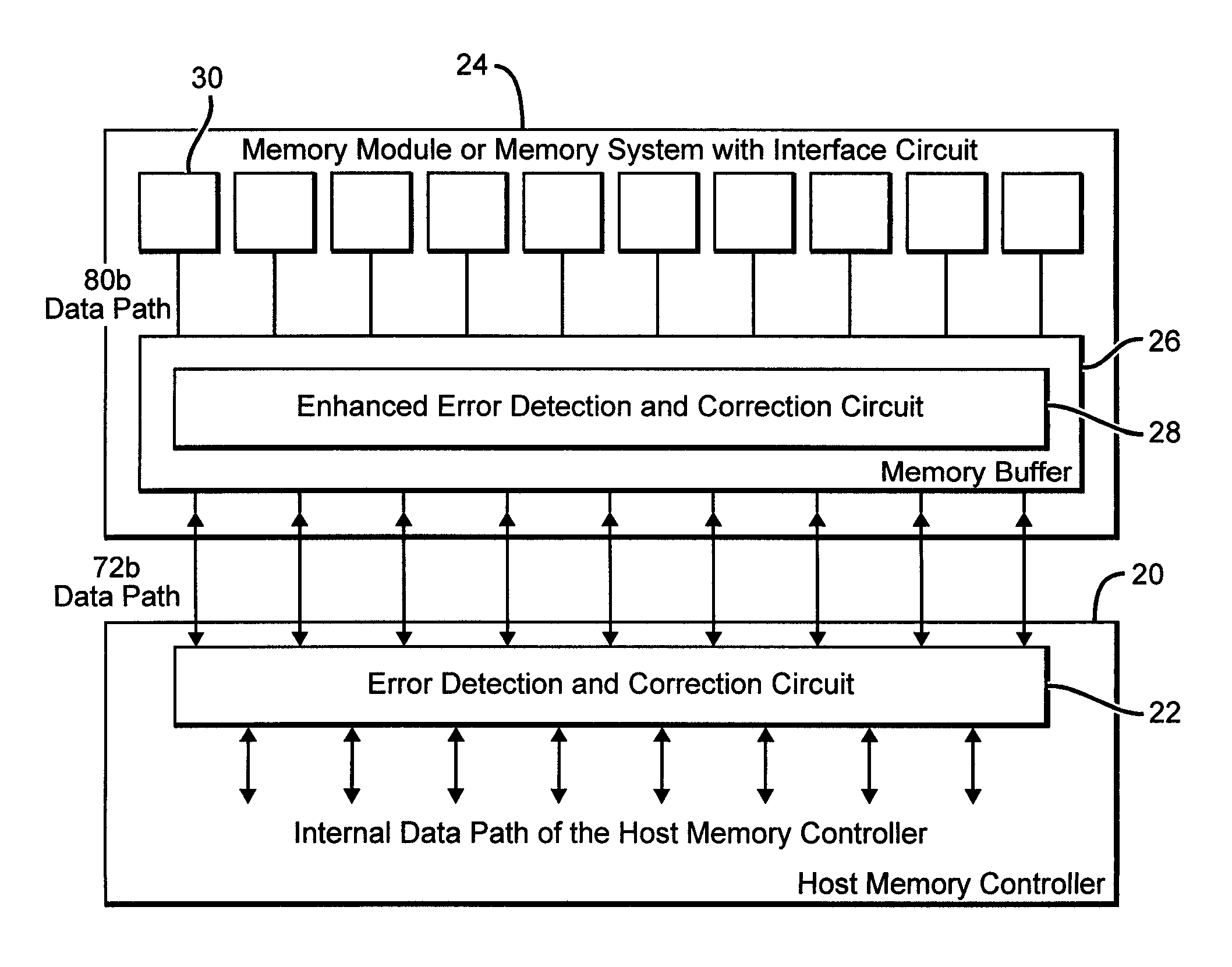
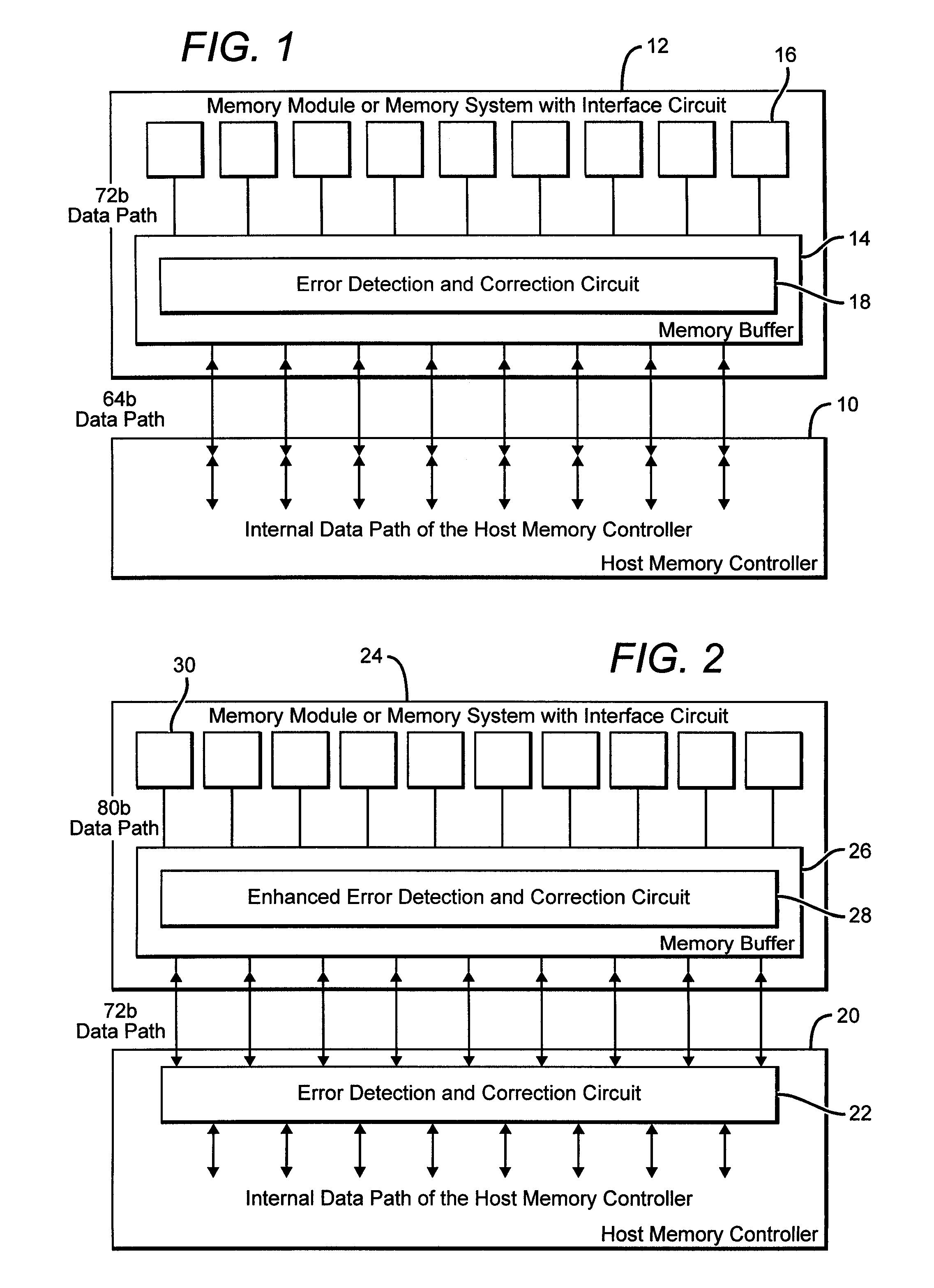
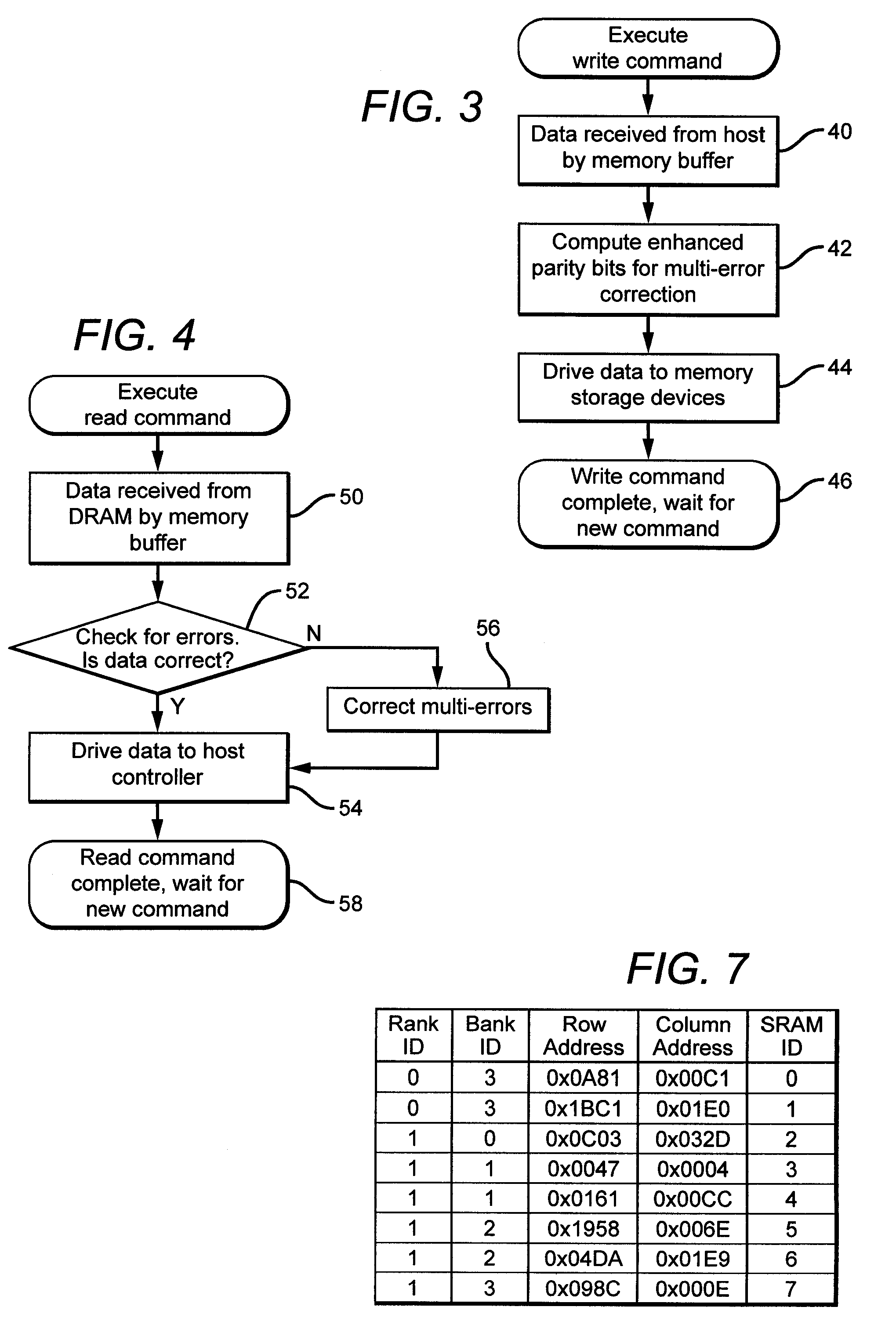
Systems and methods for error detection and correction in a memory module which includes a memory buffer
ActiveUS20120266041A1Without compromising integrity requirementError preventionTransmission systemsMultiplexingMultiplexer
The present systems include a memory module containing a plurality of RAM chips, typically DRAM, and a memory buffer arranged to buffer data between the DRAM and a host controller. The memory buffer includes an error detection and correction circuit arranged to ensure the integrity of the stored data words. One way in which this may be accomplished is by computing parity bits for each data word and storing them in parallel with each data word. The error detection and correction circuit can be arranged to detect and correct single errors, or multi-errors if the host controller includes its own error detection and correction circuit. Alternatively, the locations of faulty storage cells can be determined and stored in an address match table, which is then used to control multiplexers that direct data around the faulty cells, to redundant DRAM chips in one embodiment or to embedded SRAM in another.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
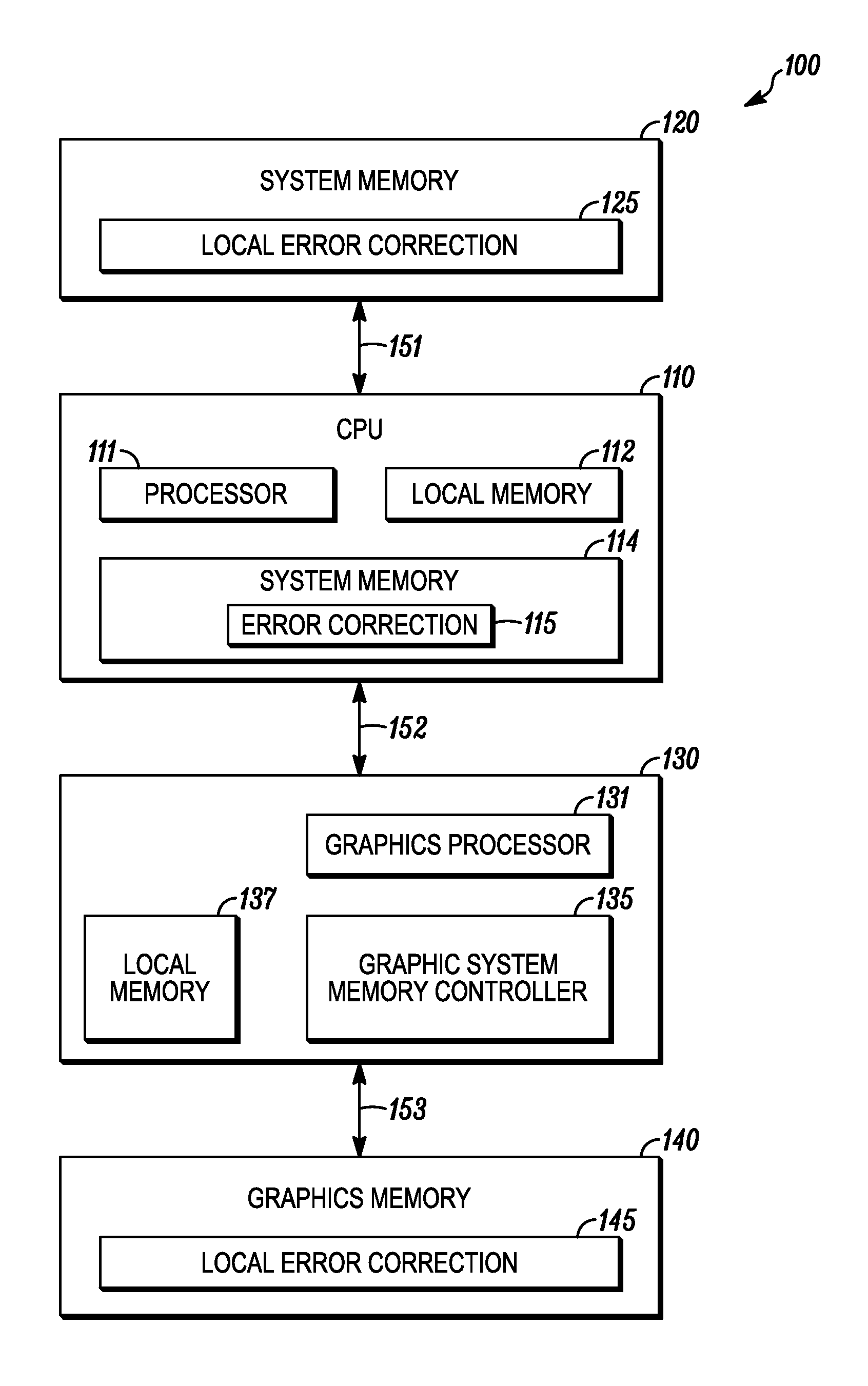
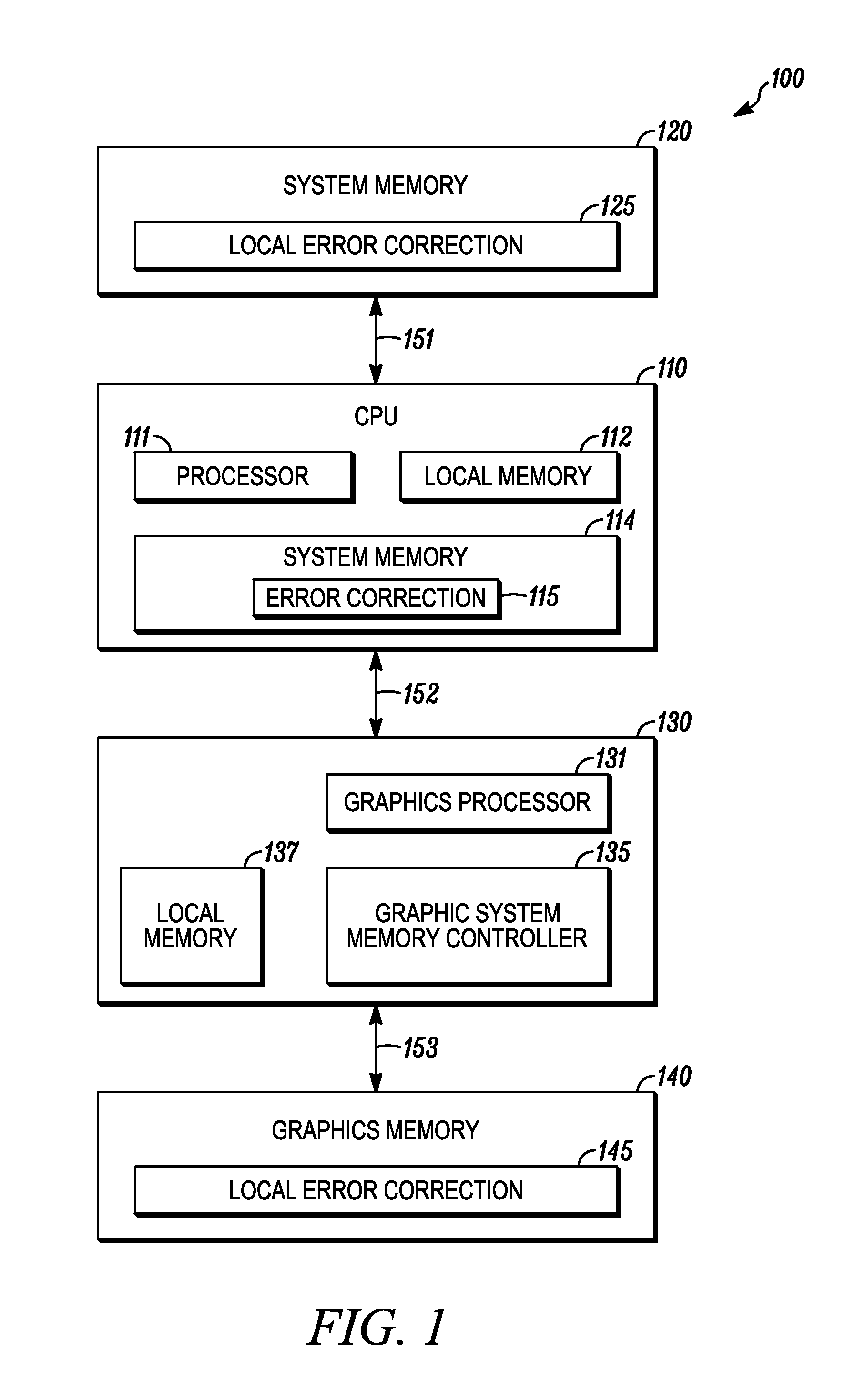
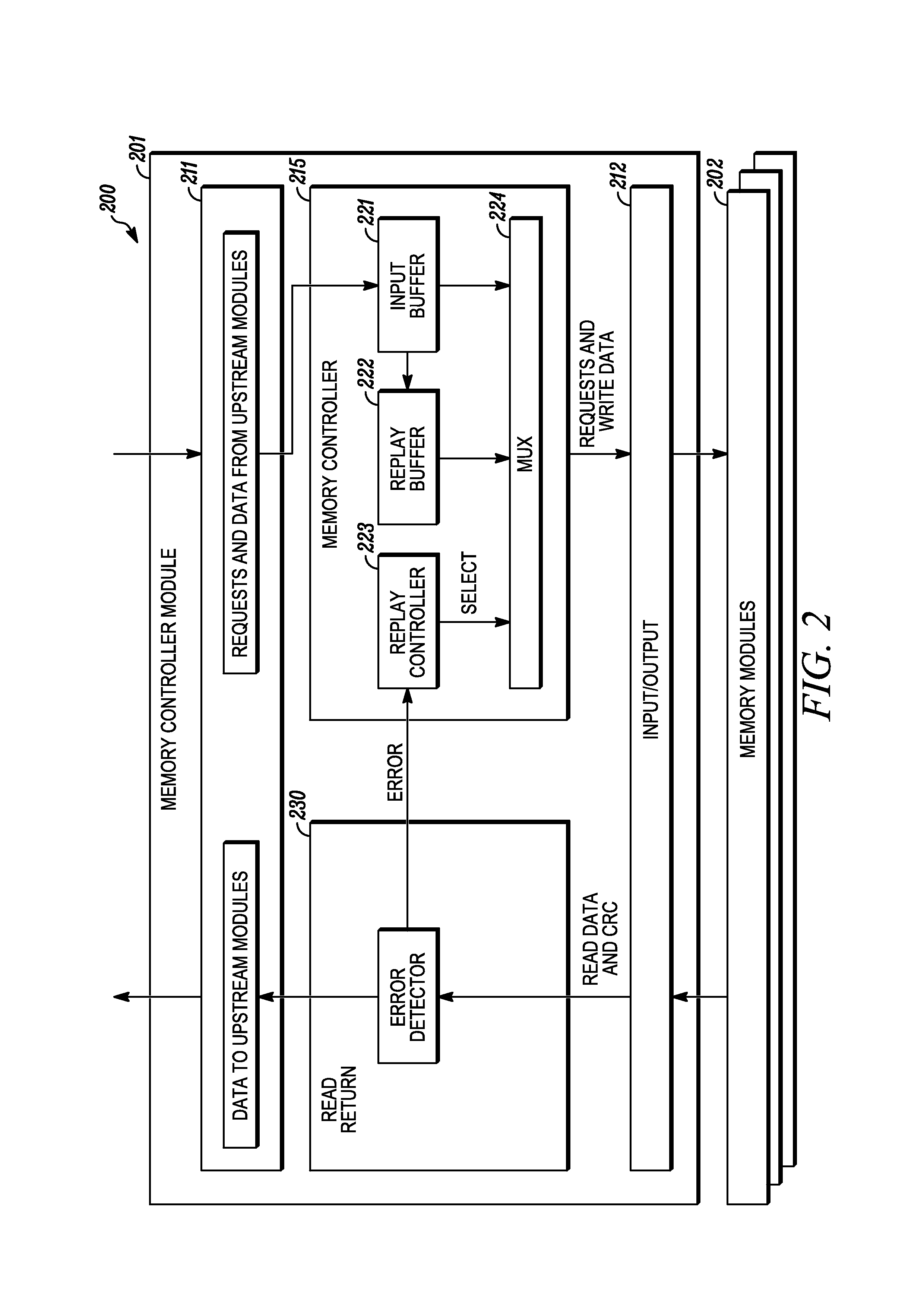
Memory-based error recovery
The present disclosure provides memory level error correction methods and apparatus. A memory controller is intermediate the memory devices, such as DRAM chips or memory modules, and a processor, such a graphics processor or a main processor. The memory controller can provide error correction. In an example, the memory controller includes a buffer to store instructions and data for execution by the controller and a replay buffer to store the instructions such that operations can be replayed to prior state before the error. An error detector receives data read from the memory devices and if no error is detected outputs the data. If an error is detected, the error detector signals the memory controller to replay the instructions stored in the replay buffer.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
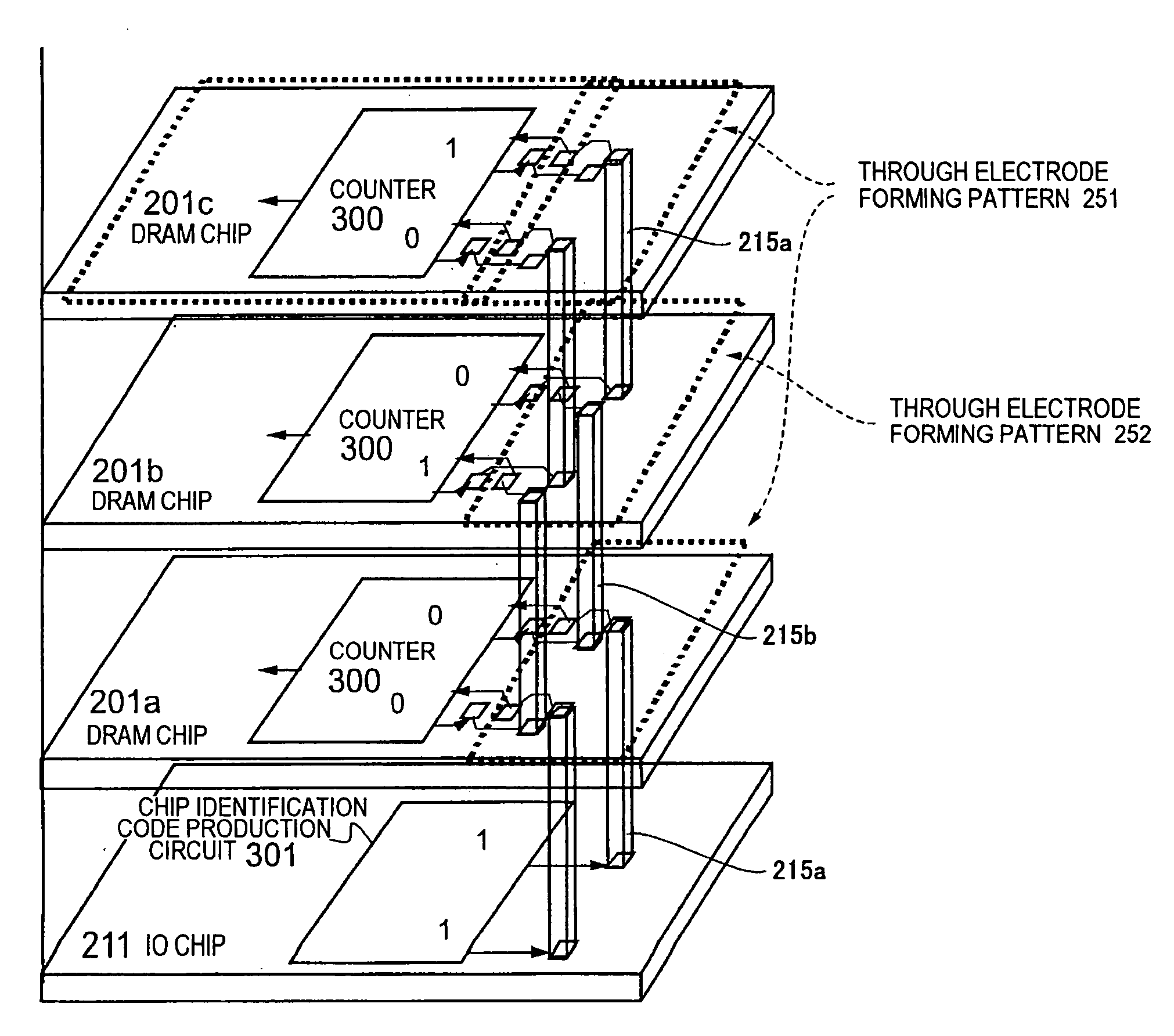
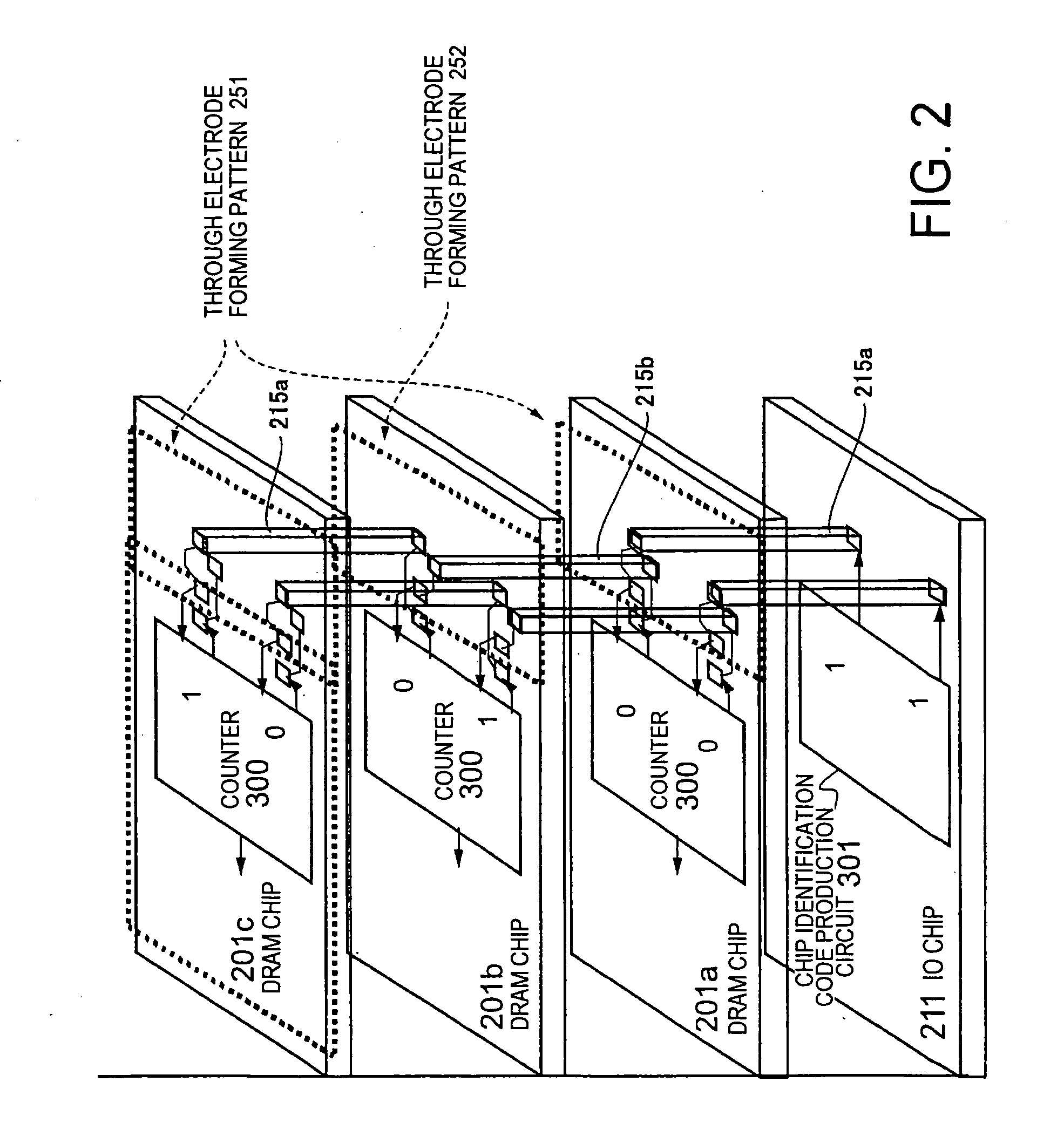
Manufacturing Method for Partially-Good Memory Modules with Defect Table in EEPROM
ActiveUS20090137070A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesSerial presence detectDram chip
A manufacturing method makes memory modules from partially-good DRAM chips soldered to its substrate. The partially-good DRAM chips have a number of defective memory cells that is below a test threshold, such as 10%. Packaged DRAM chips are optionally pre-screened and considered to pass when the number of defects found is less than the test threshold. A defect table is created during testing and written to a serial-presence-detect electrically-erasable read-only memory (SPD-EEPROM) on the memory module. The memory module is finally tested on a target-system tester that reads the defect table during booting, and redirects memory access to defective memory locations identified by the defect table. The memory modules may be burned in or tested at various temperatures and voltages to increase reliability.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
System memory board subsystem using DRAM with stacked dedicated high speed point to point links
A memory system comprising memory modules including memory chips stacked with switching circuits. A memory controller coupled to the memory modules is configured to initiate memory accesses. When a stacked switching circuit detects the memory access, the switching circuit routes the access to another memory module if the access is not directed to a memory chip of the receiving memory module, or processes the access locally if the access is directed to a memory chip of the receiving memory module. The memory controller and memory modules are coupled via bi-directional serial links. Each memory module may include multiple stacked switching circuits, each of which may be coupled to fewer than all of the memory chips within the memory module. Switching circuits further include circuitry configured to de-serialize data prior to conveyance to a memory chip, and serialize data received from a DRAM chip prior to transmitting the received data. Switching circuits may be coupled to a stacked memory chip via a flexible interconnect, and may also be manufactured side by side with a corresponding memory chip on a flexible circuit board.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20110260781A1Efficient driveEffective expansionSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCapacitanceInductor
The interposer is disposed on an upper surface of the stacked structure formed by stacking a plurality of a DRAM chip and a plurality of a flash memory chip. Thus down-size of an entire device is accomplished. A boost converter having an inductor is used as a voltage boost circuit. Thus down-size of the entire device is accomplished in comparison to a voltage boost circuit using a charge pump connected in parallel with a plurality of a capacitance.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
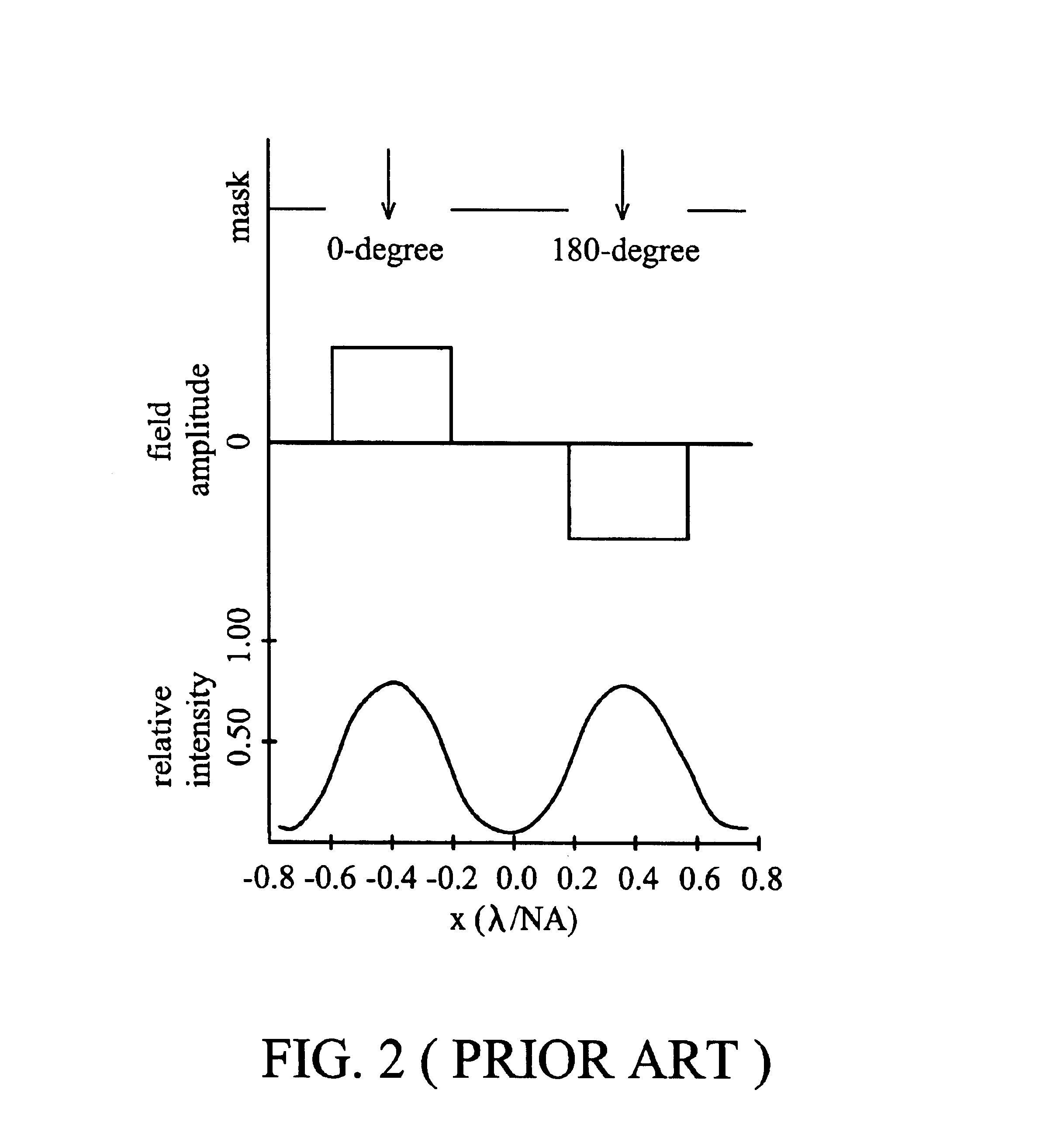
Method for fabricating semiconductor device with loop line pattern structure
InactiveUS6818515B1Eliminate needSimple processTransistorSolid-state devicesPhase differenceDram chip
An alternating phase shift mask with dark loops thereon, a memory array fabricated with the alternating phase shift mask, and a method of fabricating the memory. The dark loops in the mask always separate first regions with 180° phase difference from second regions with 0° phase difference to define active areas or gate-lines in a DRAM chip.
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS7385281B2Run at high speedReduce power consumptionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterposerEngineering
A COC DRAM including a plurality of stacked DRAM chips is mounted on a motherboard by using an interposer. The interposer includes a Si unit and a PCB. The Si unit includes a Si substrate and an insulating-layer unit in which wiring is installed. The PCB includes a reference plane for the wiring in the Si unit. The wiring topology between a chip set and the COC DRAM is the same for every signal. Accordingly, a memory system enabling a high-speed operation, low power consumption, and large capacity is provided.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
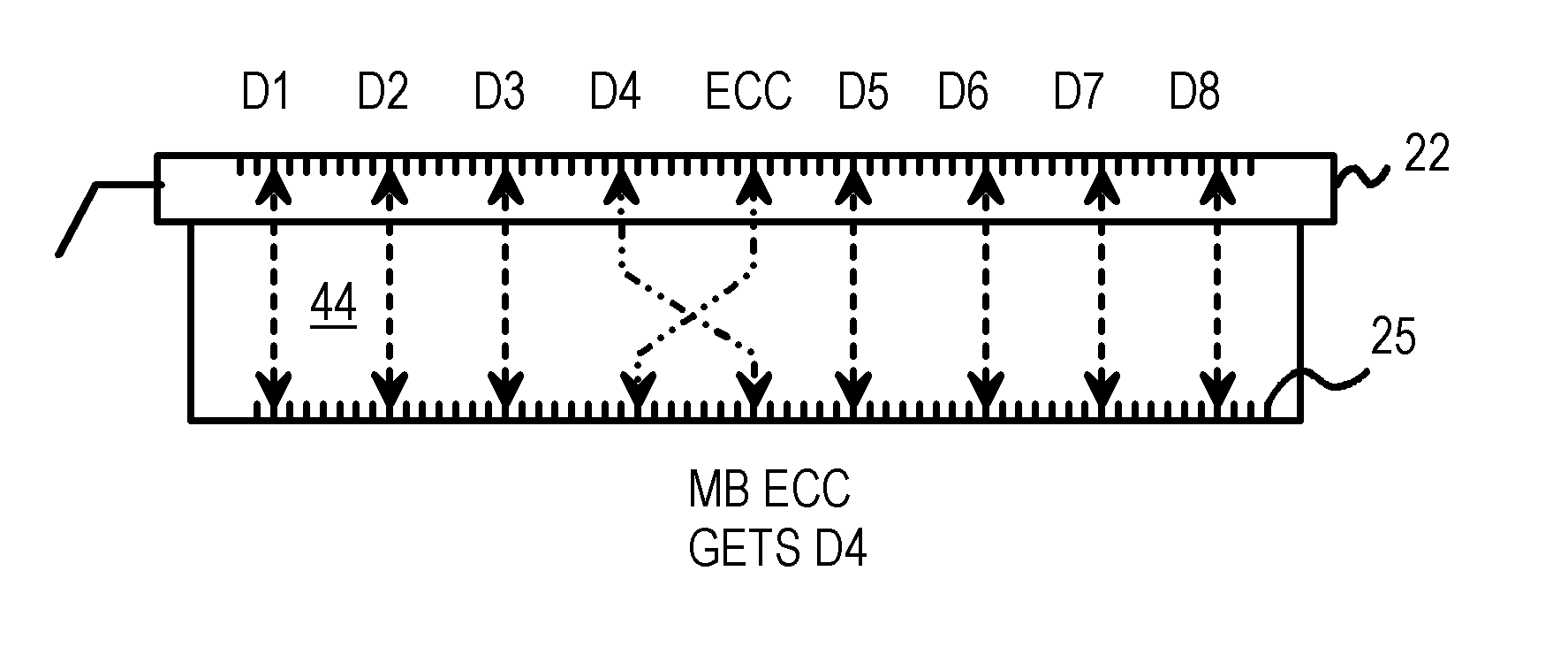
Extender card for testing error-correction-code (ECC) storage area on memory modules
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
DRAM chip device and multi-chip package comprising such a device
An SDRAM memory chip device comprises a non-volatile memory controller for operating a non-volatile memory, e.g., a NAND-flash, and a FIFO memory buffer. The FIFO memory buffer serves to operate background store and load operations between a FIFO buffer array and the non-volatile memory, while a host system such as a CPU exchanges data with the SDRAM work memory. The SDRAM memory chip device, therefore, has at least two additional pins as compared with conventional SDRAM standard for generating a set of additional commands. These commands are employed by the FIFO memory buffer to manage the data transfer between the FIFO buffer and each of the non-volatile memory and the volatile SDRAM memory. Two further pins reflecting the flash memory status provide appropriate issuance of load or store signals by the host system.
Owner:秦蒙达股份公司
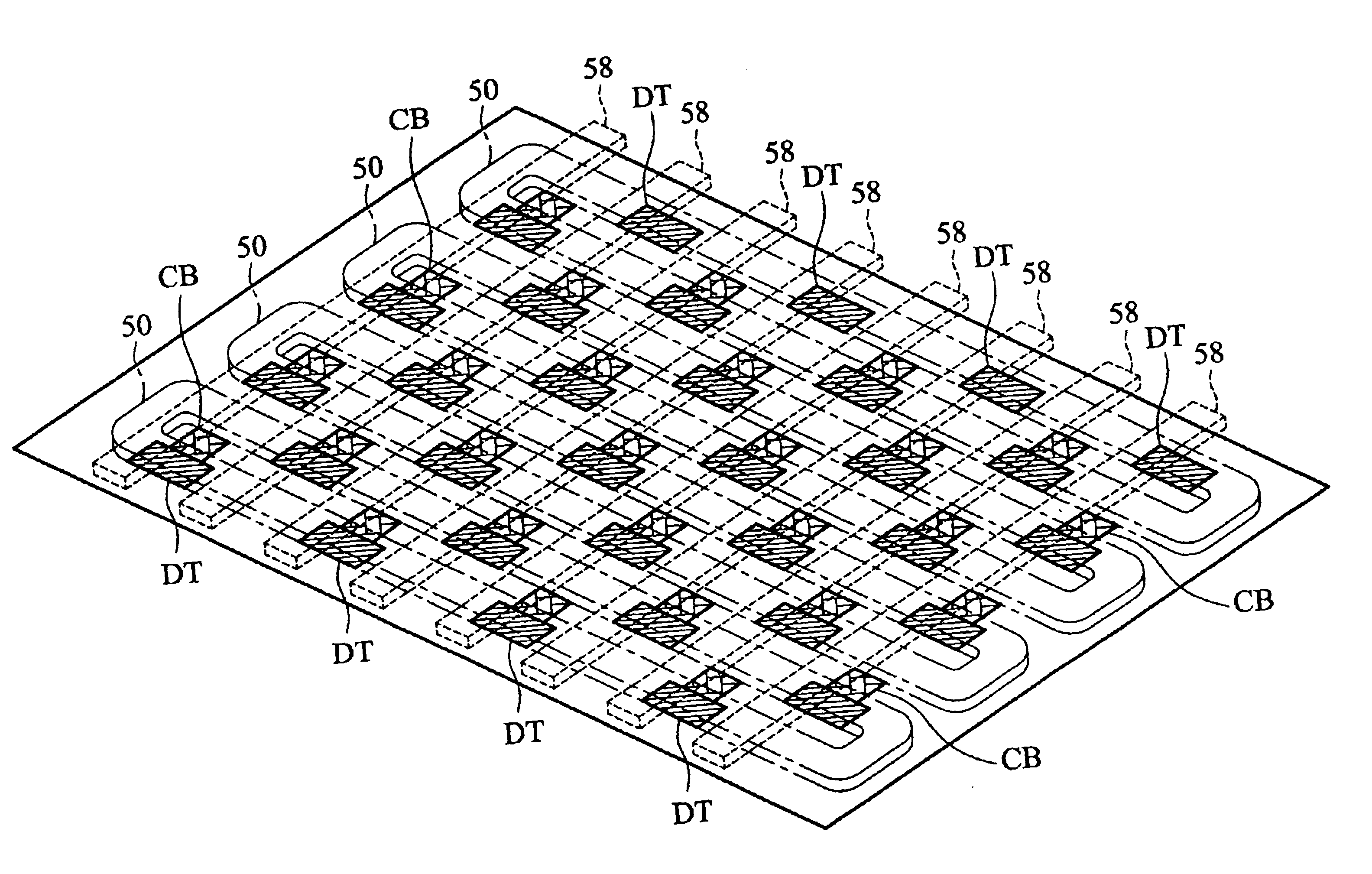
Memory module with a defective memory chip having defective blocks disabled by non-multiplexed address lines to the defective chip
A downgraded memory module has downgraded DRAM chips soldered to its substrate. The downgraded DRAM chips have a defective memory cell in a logical quadrant of the memory. A physical MSB is a row address present on a non-downgraded DRAM of size S but not used on a downgraded DRAM size S / 2. The physical MSB and a second address pin are non-multiplexed address pins that do not carry column addresses. The physical MSB and the second address pin logically divided the DRAM into quadrants. Two good quadrants without defects are selected, and jumpers on the memory module drive the physical MSB and the second address pin with signals that select only these two quadrants and disable access to quadrants containing defects. DRAM chips can be marked or sorted into bins for combinations of good quadrants. Downgraded memory modules have all DRAM chips from the same bin that share jumper settings.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
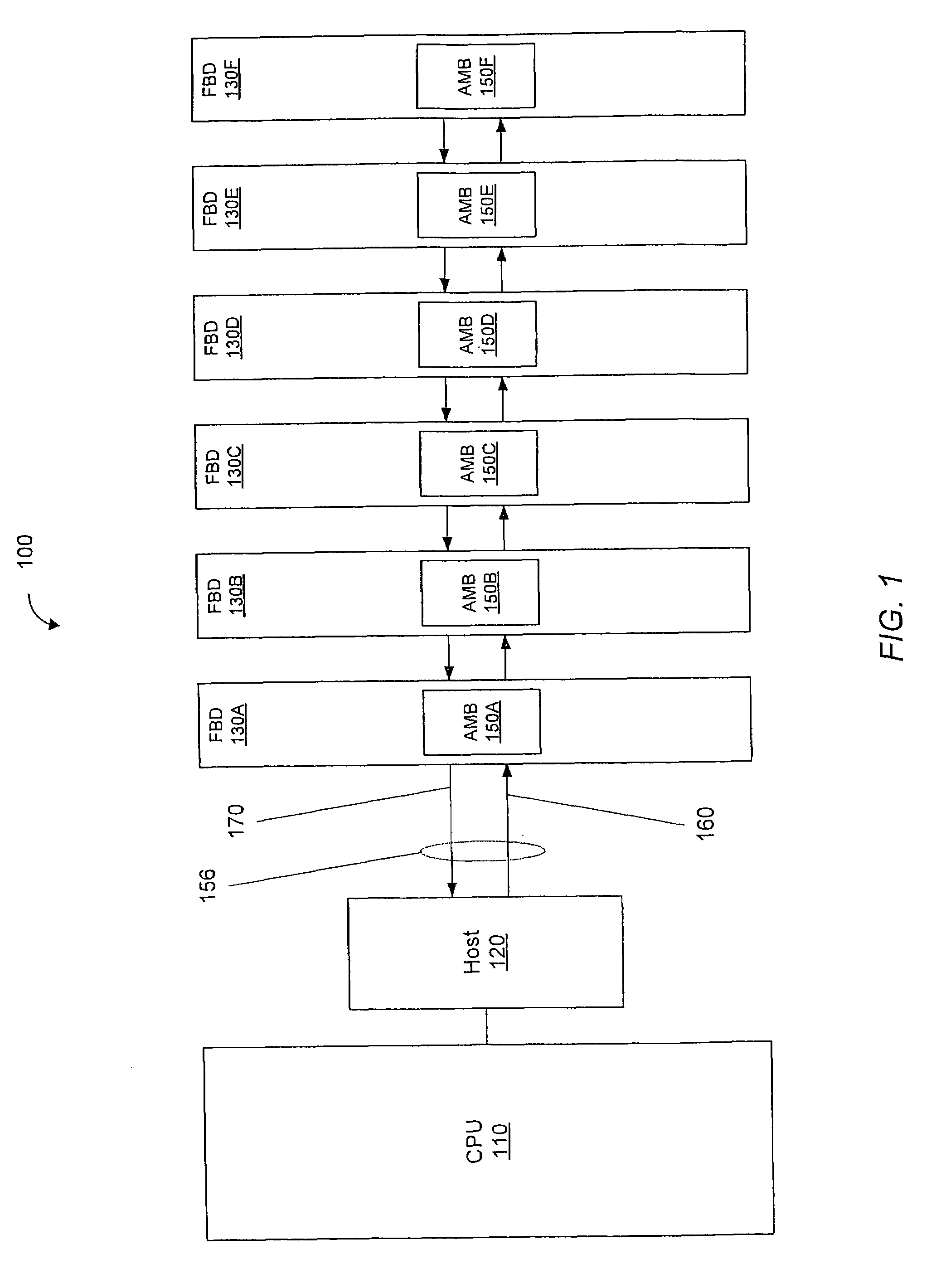
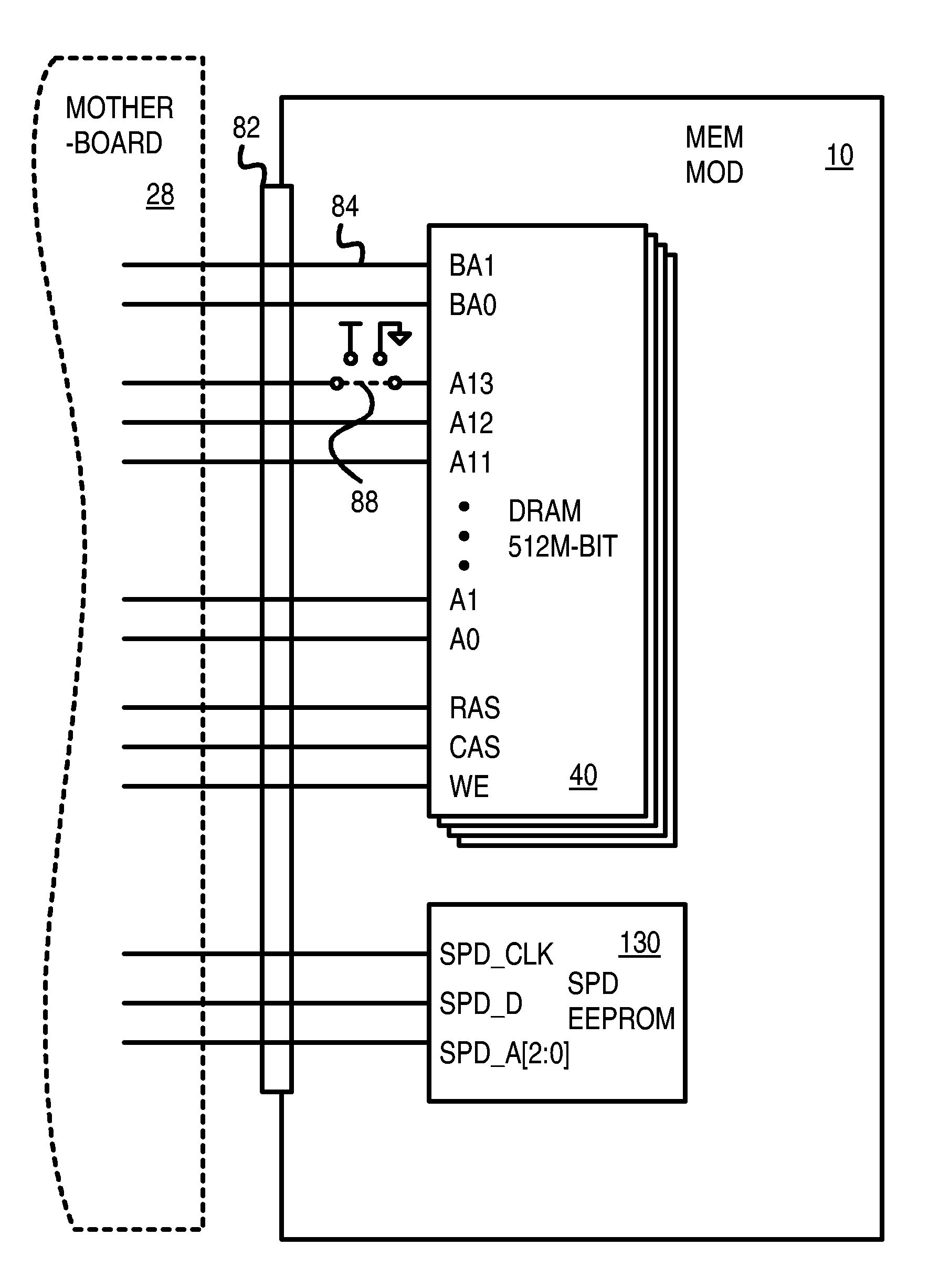
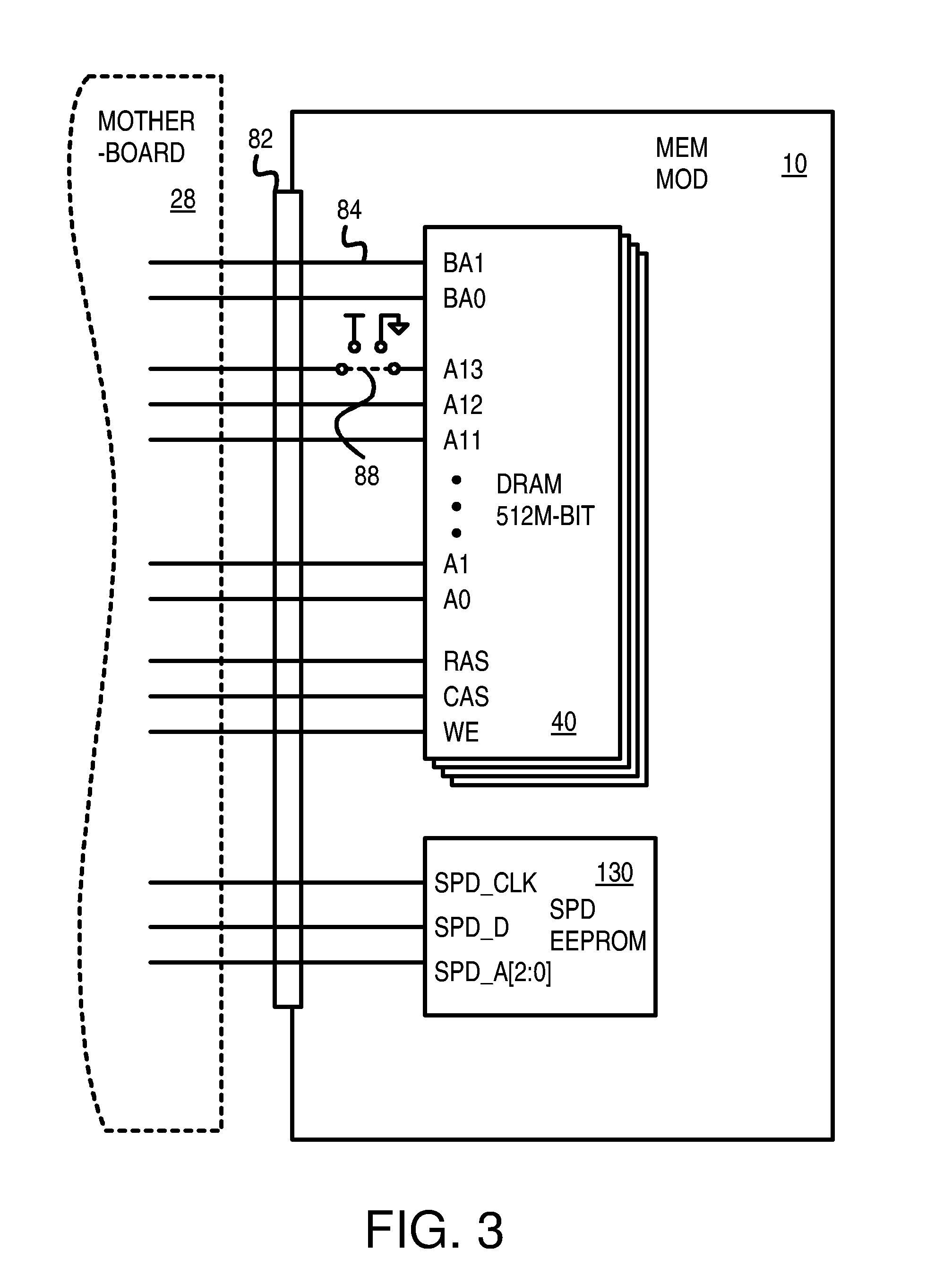
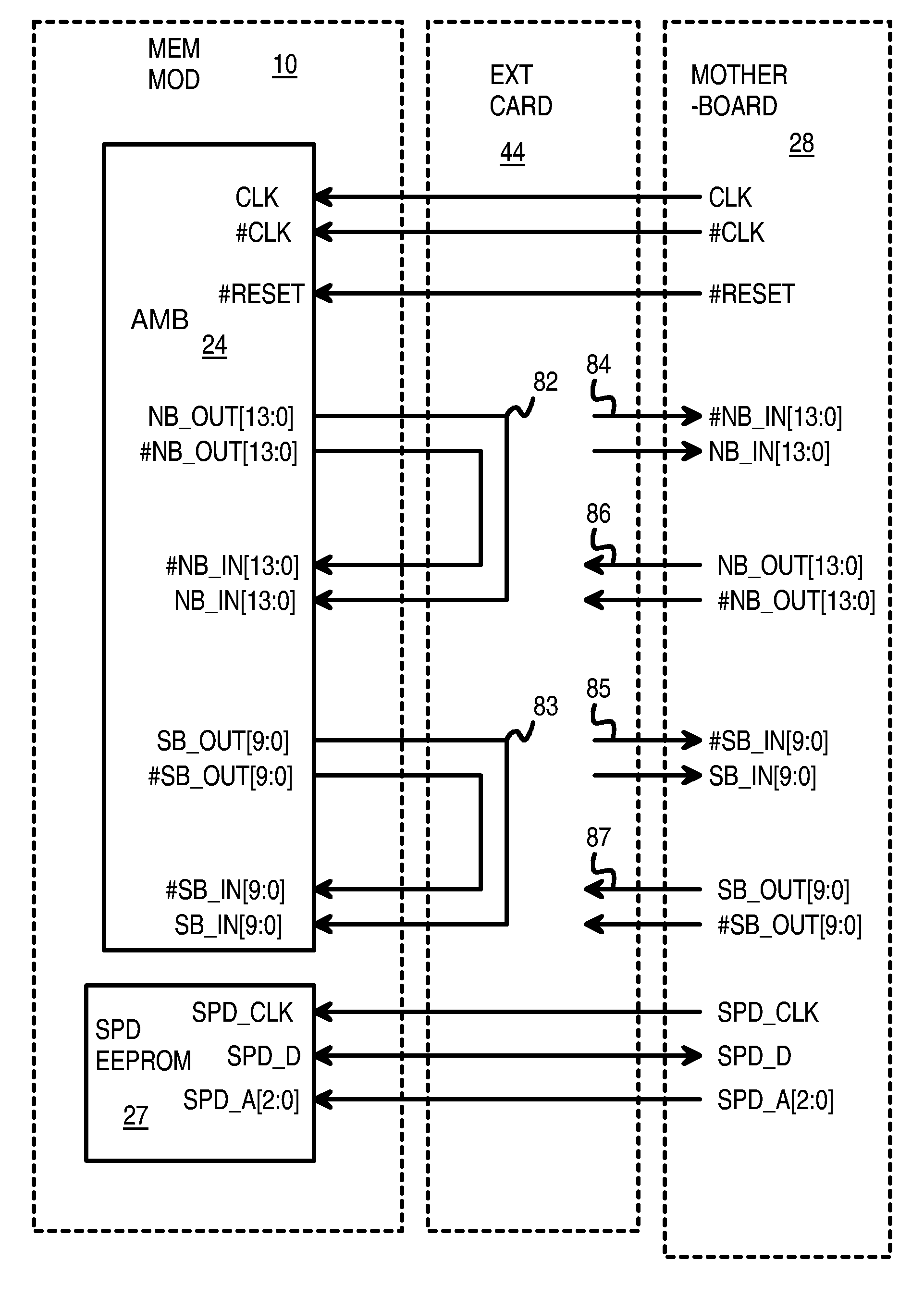
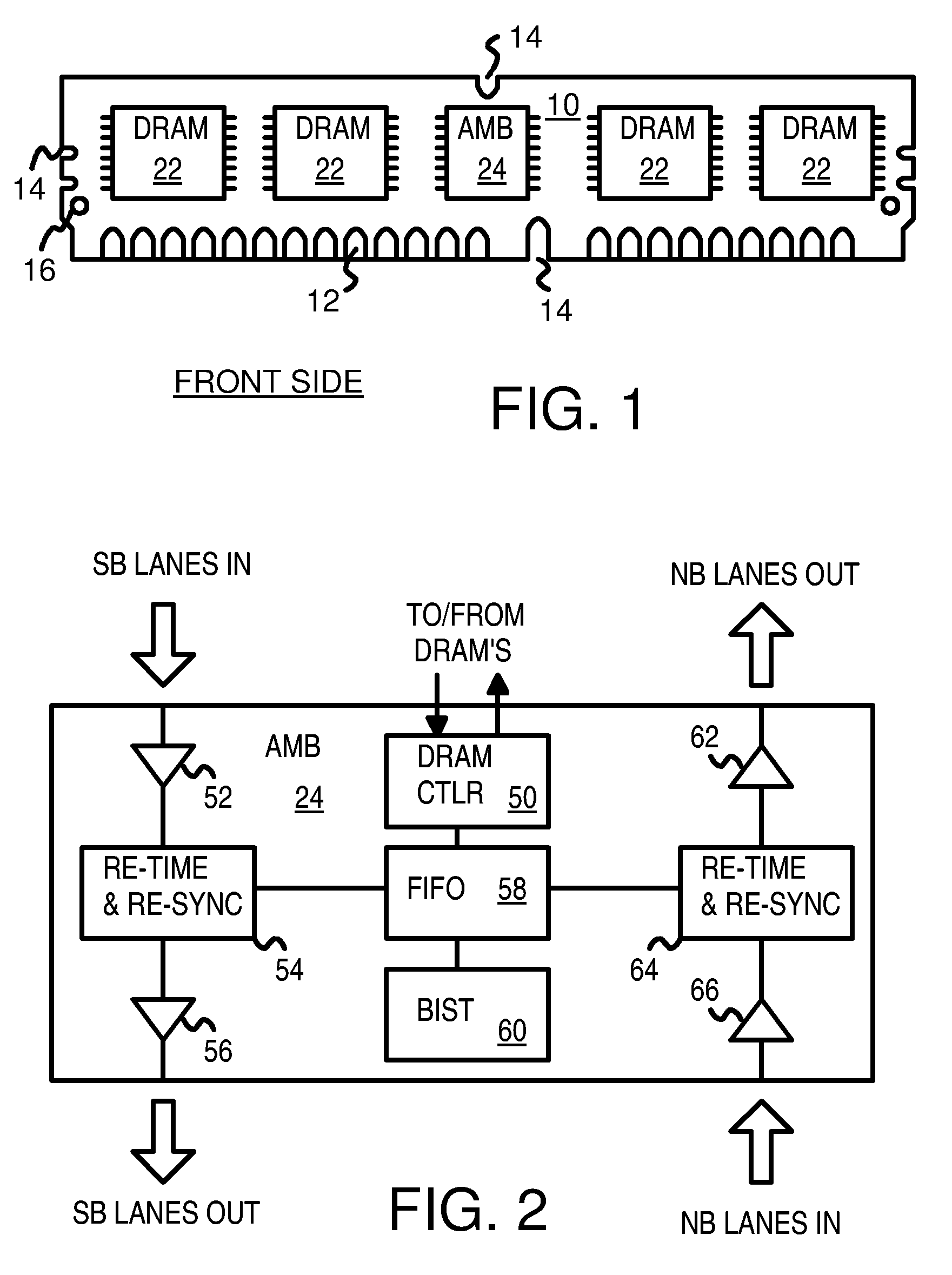
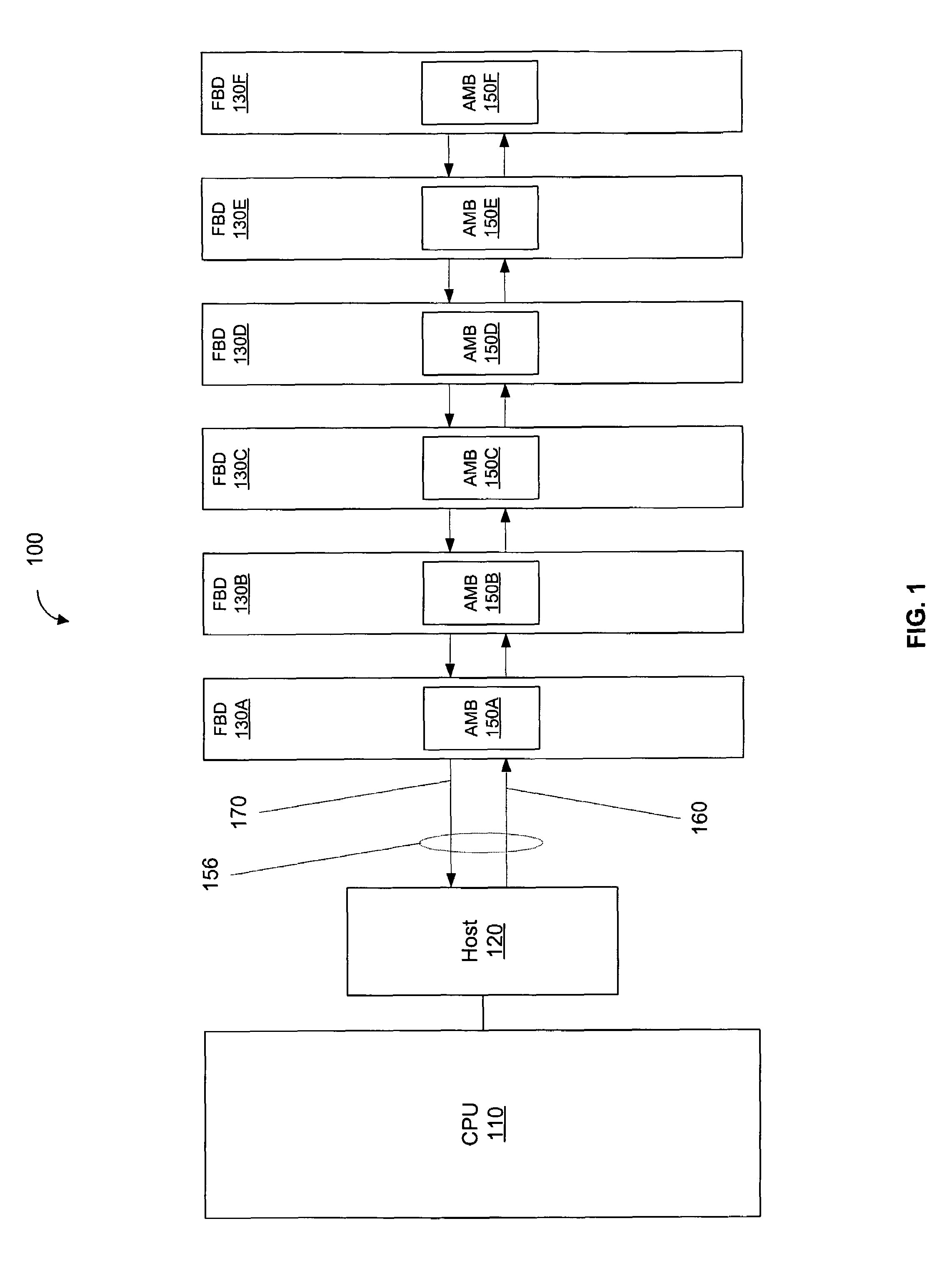
Loop-Back Memory-Module Extender Card for Self-Testing Fully-Buffered Memory Modules
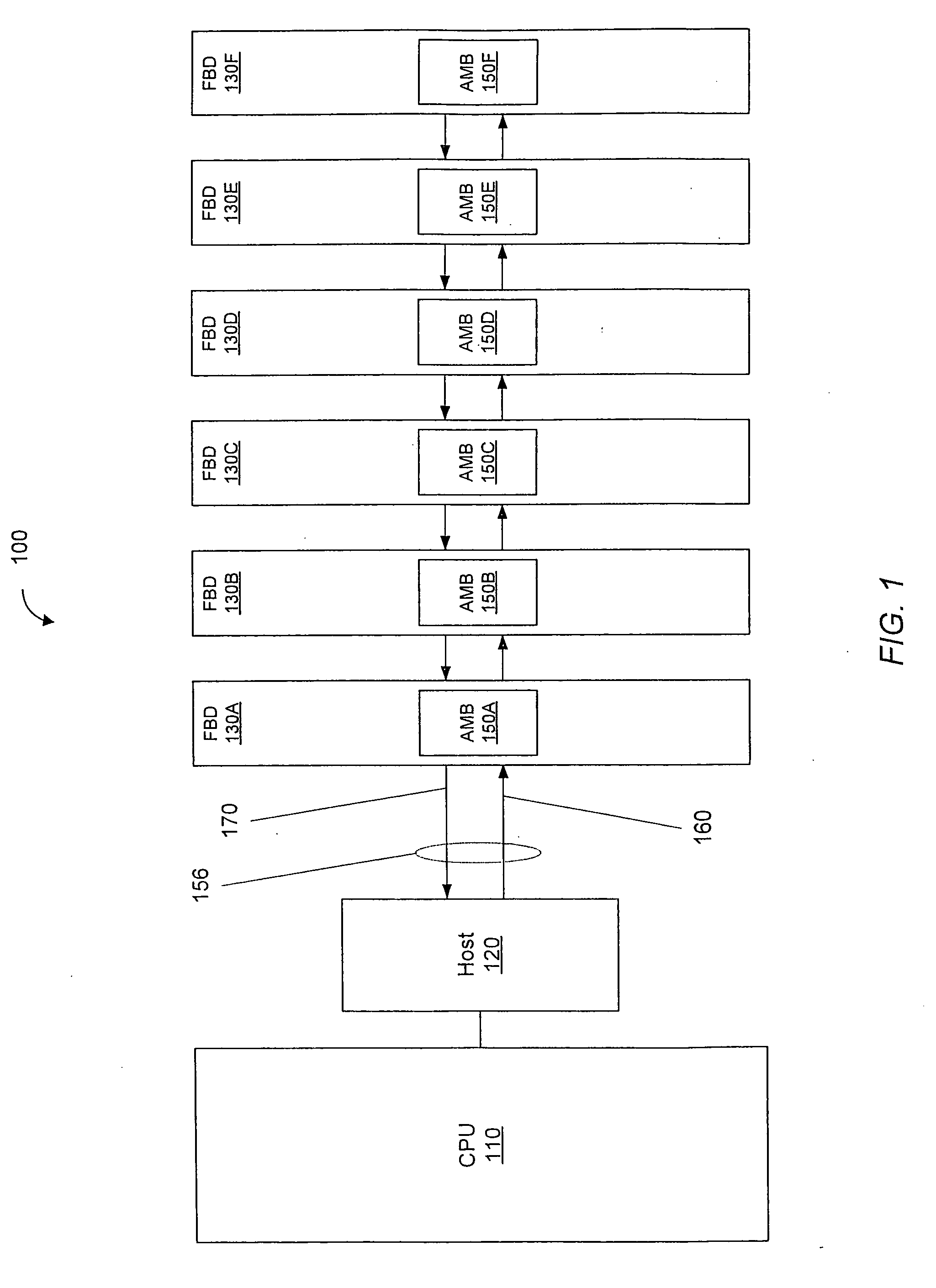
ActiveUS7197676B2Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionComputer modulePersonal computer
A loop-back extender card is plugged into a memory module socket on a personal computer (PC) motherboard. The extender card has a test socket that receives a memory module under test. An Advanced Memory Buffer (AMB) on the memory module fully buffers DRAM chips on the memory module. The AMB inputs from and outputs to the test socket differential northbound lanes (toward a processor) and southbound lanes (away from the processor). The extender card has northbound loopback traces that connect northbound lane outputs from the memory module back to northbound-lane inputs to the memory module. Southbound loopback traces connect southbound lane outputs from the memory module back to southbound-lane inputs to the memory module. The loop-back extender card allows the AMB to perform loopback testing without modifying the PC motherboard. Series / shunt resistors can be placed on the loopback traces, or serpentine traces can be used to increase loopback delays.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
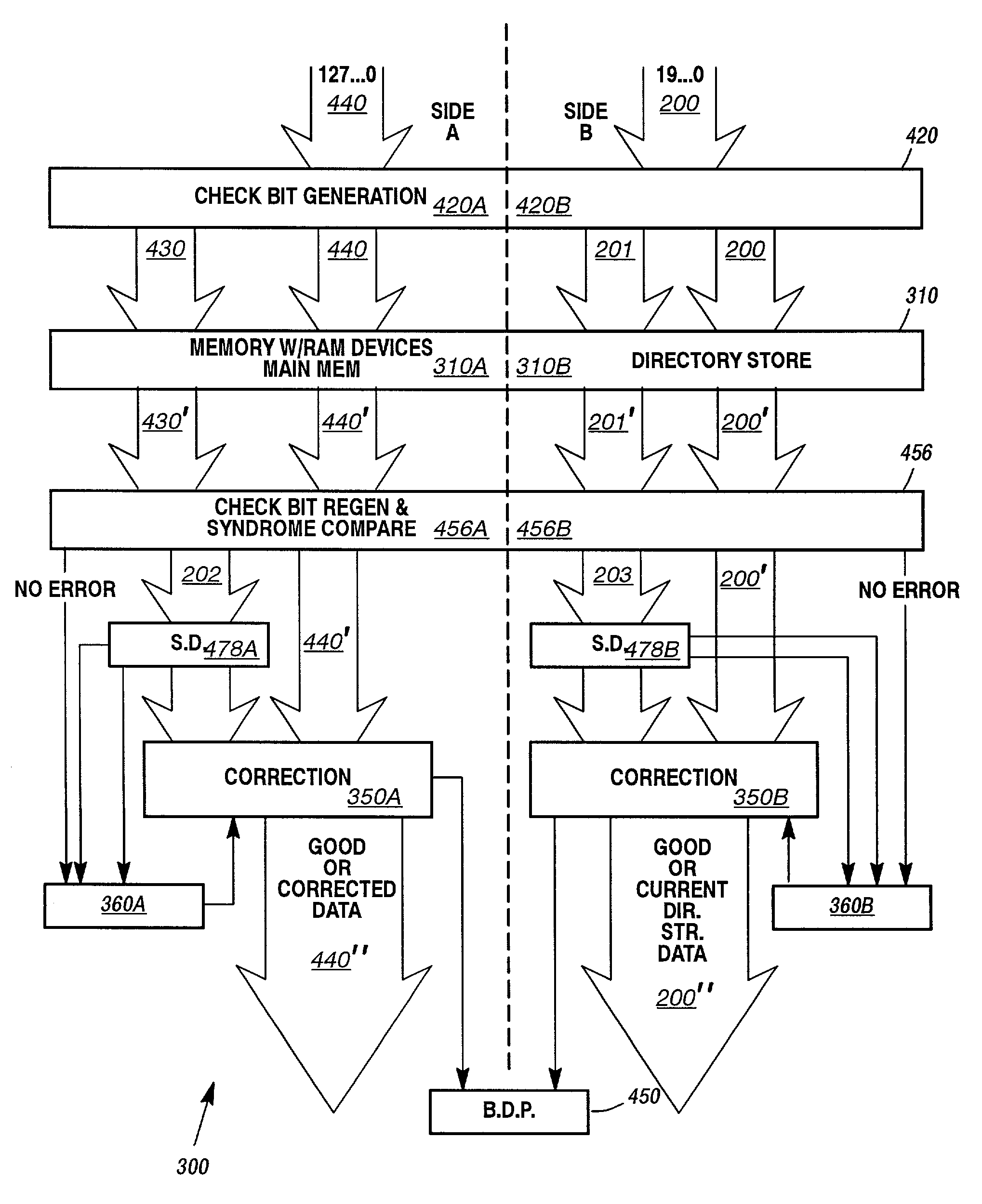
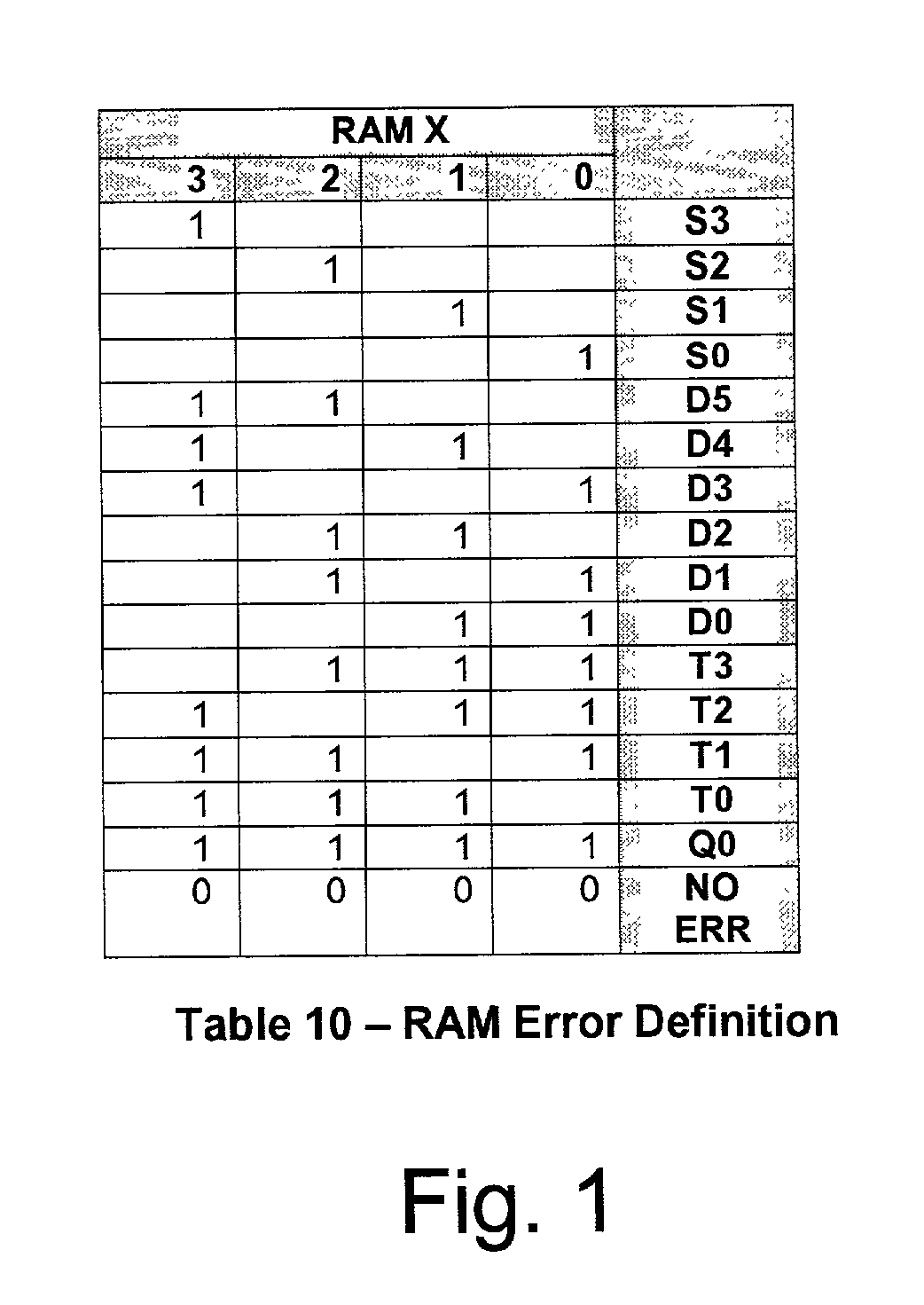
Familial correction with non-familial double bit error detection for directory storage
Error correction and error detection related to DRAM chip failures, particularly adapted server memory subsystems. The application of a code for 128 bit memories is applied to a 20 bit directory store to improve reliability of the directory store memory of the computer system. The code uses ×4 bit DRAM devices organized in a code word of 20 data bit words and 12 check bits. These 12 check bits provide a code capable of 4 bit adjacent error correction within a family (i.e., in a ×4 DRAM) and double bit non-adjacent error detection across the entire 20 bit word, with single bit correction across the word as well. Each device can be though of as a separate family of bits, errors occurring in more than one family are not correctable, but may be detected if only one bit in each of two families is in error. Syndrome generation and regeneration are used together with a specific large code word. Decoding the syndrome and checking it against the regenerated syndrome yield data sufficient for providing the features described.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
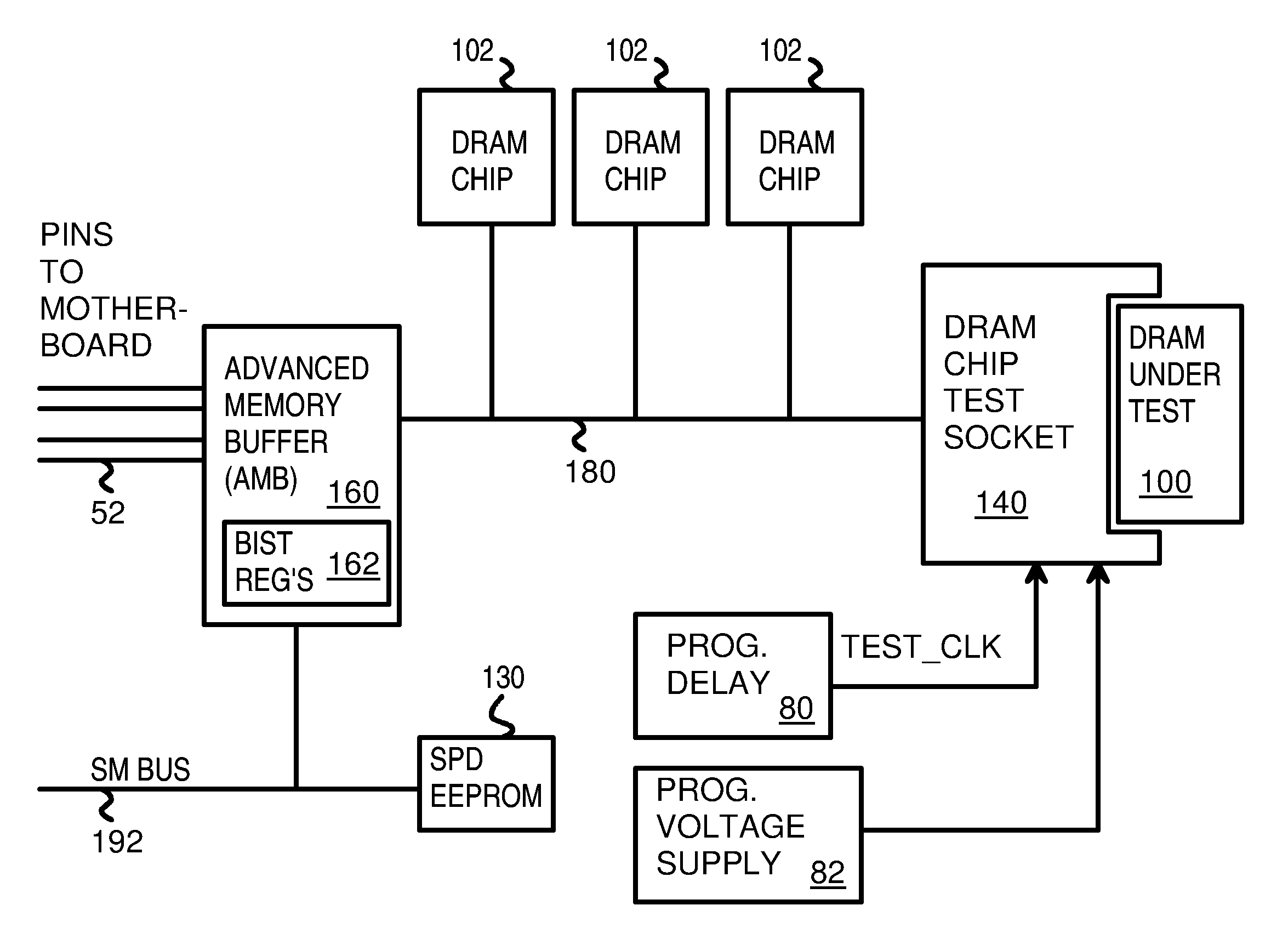
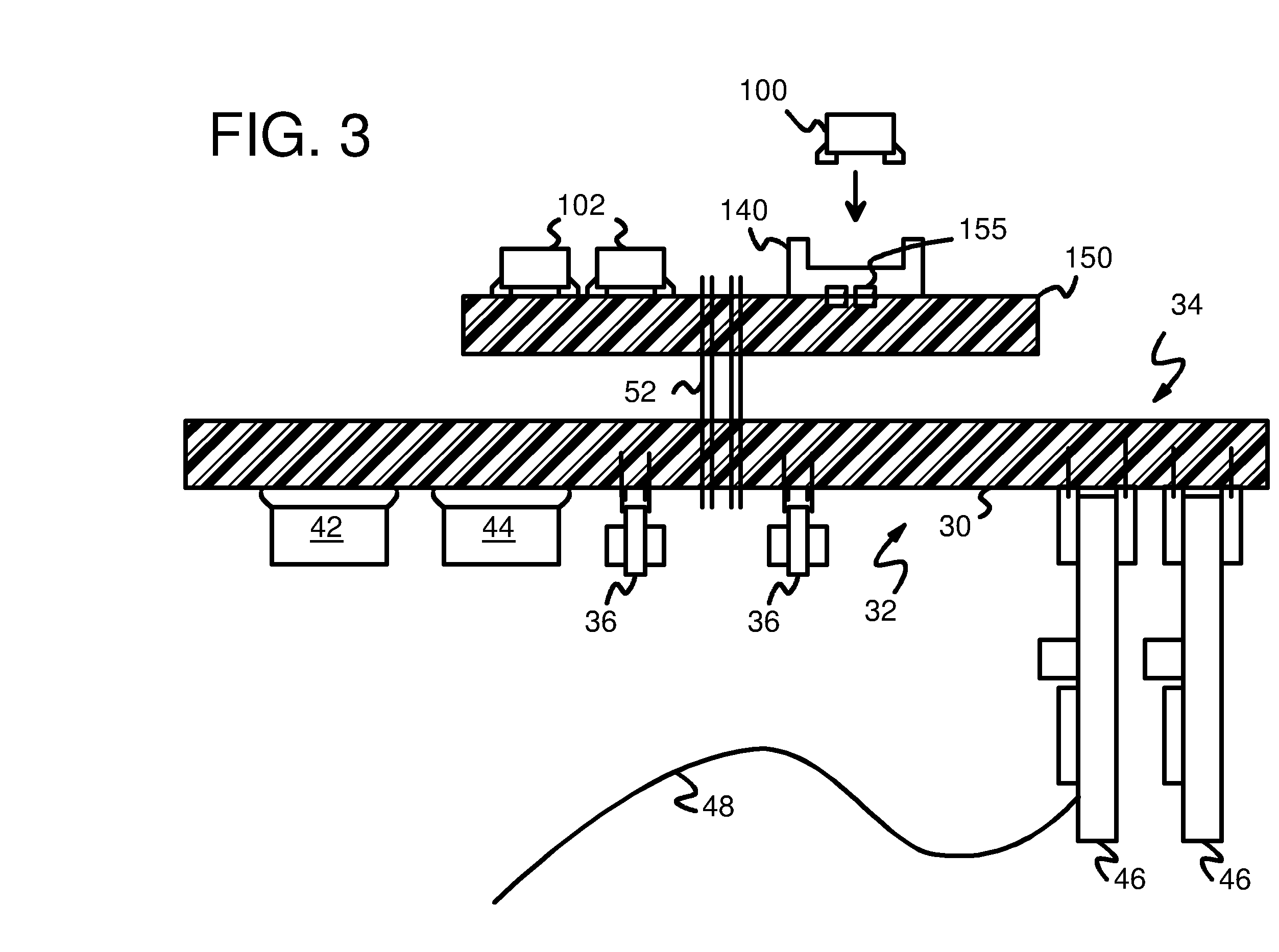
Testing DRAM Chips with a PC Motherboard Attached to a Chip Handler by a Solder-Side Adaptor Board with an Advanced-Memory Buffer (AMB)
Memory chips are tested by insertion into a chip test socket on a test adapter board that is mounted to the reverse or solder-side of a personal computer motherboard. A memory module socket is removed from the motherboard, and adapter pins are inserted into holes for the removed memory module socket, but from the reverse (solder) side of the motherboard. The adapter pins connect to the test adapter board either directly, through a connector plug, or through an intervening adapter board. The test adapter board has soldered onto it additional memory chips and buffer chips on a memory module, such as an Advanced Memory Buffer (AMB) for a fully-buffered memory module. The built-in-self-test (BIST) feature of the AMB may be used to test the memory chip under test in the chip test socket, or the processor on the motherboard may write and read the memory chip.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
Implementing decoupling devices inside a TSV DRAM stack
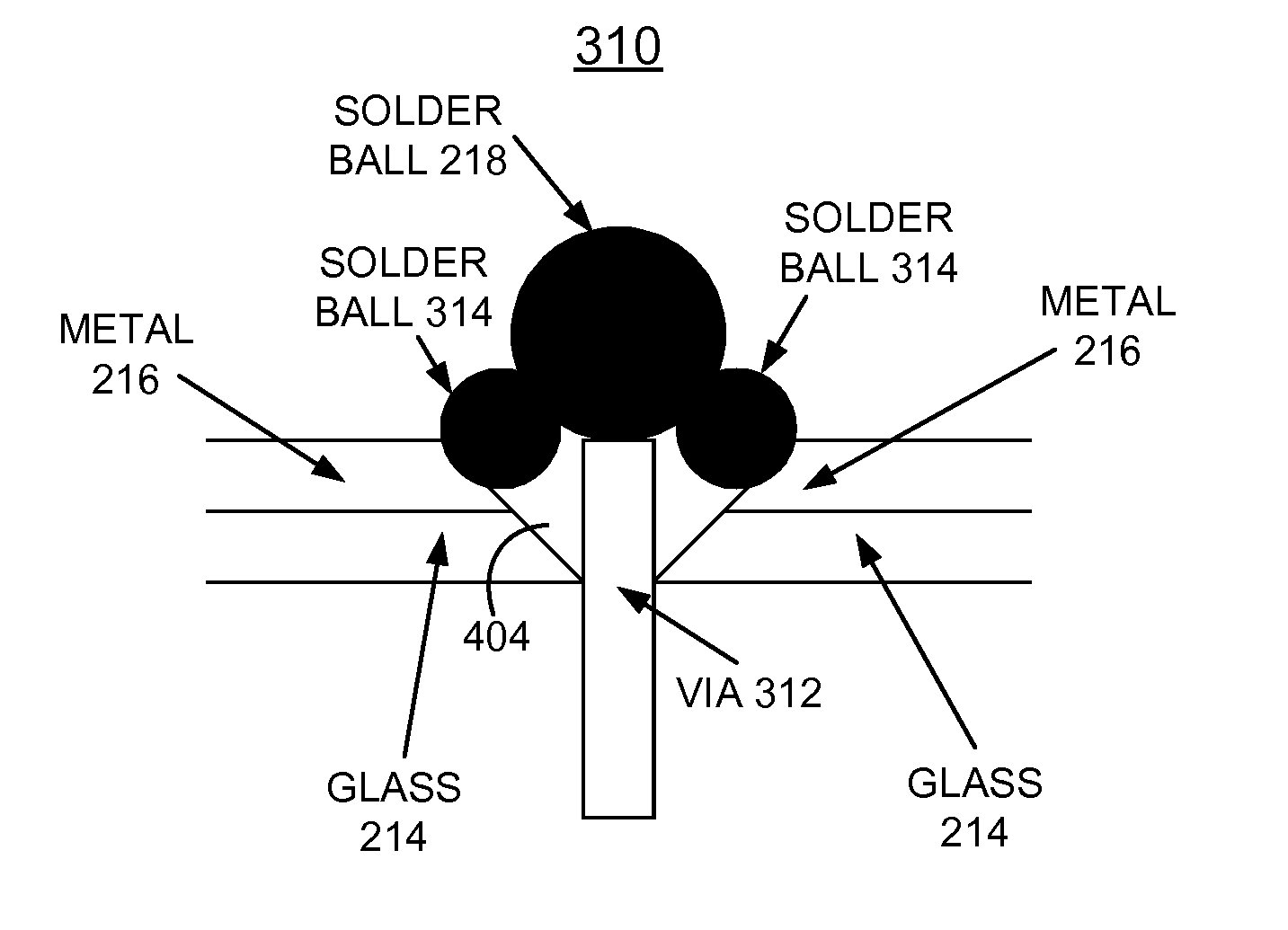
InactiveUS8697567B2Overcome disadvantagesMinimize impactSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricElectrical conductor
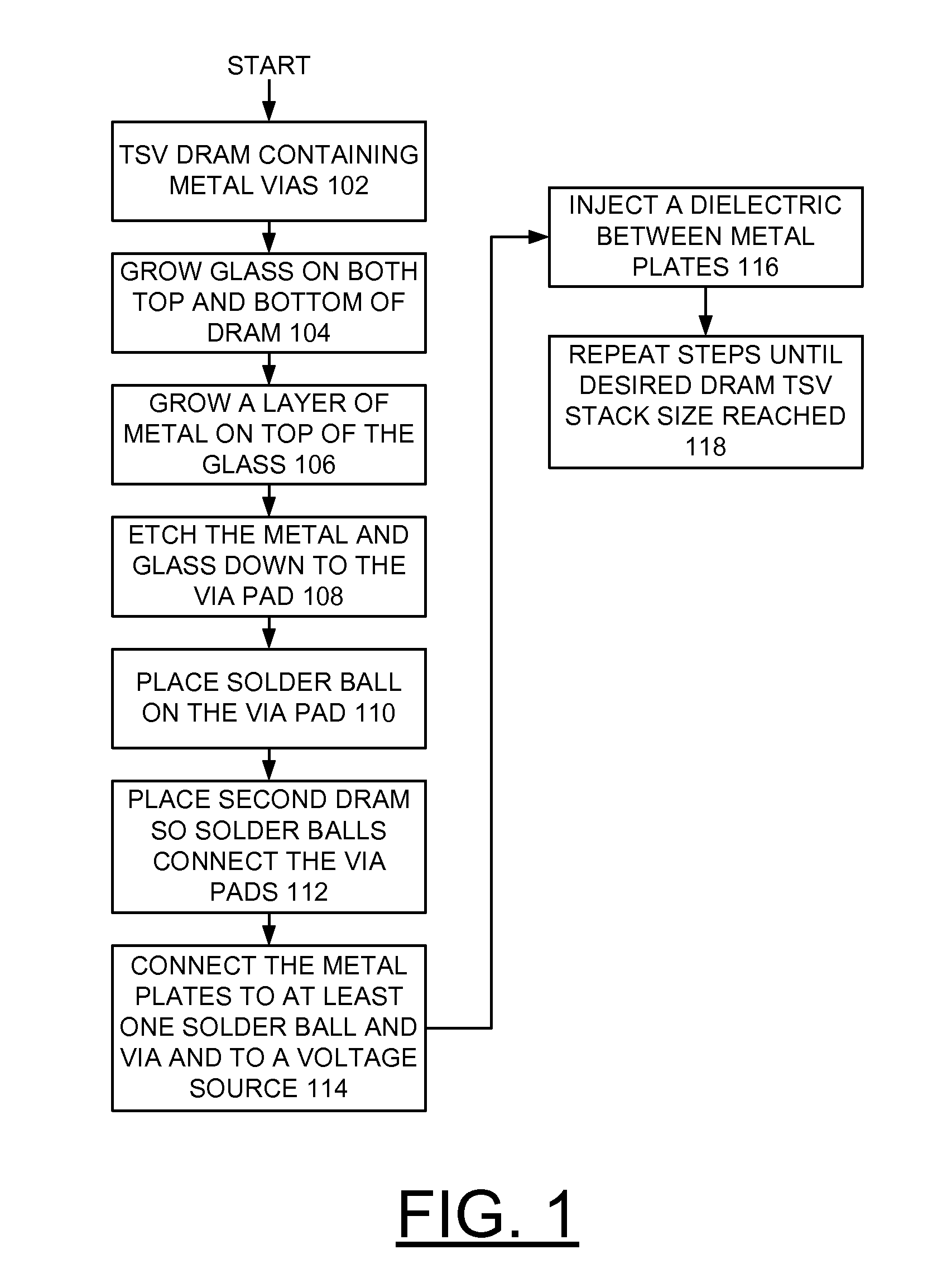
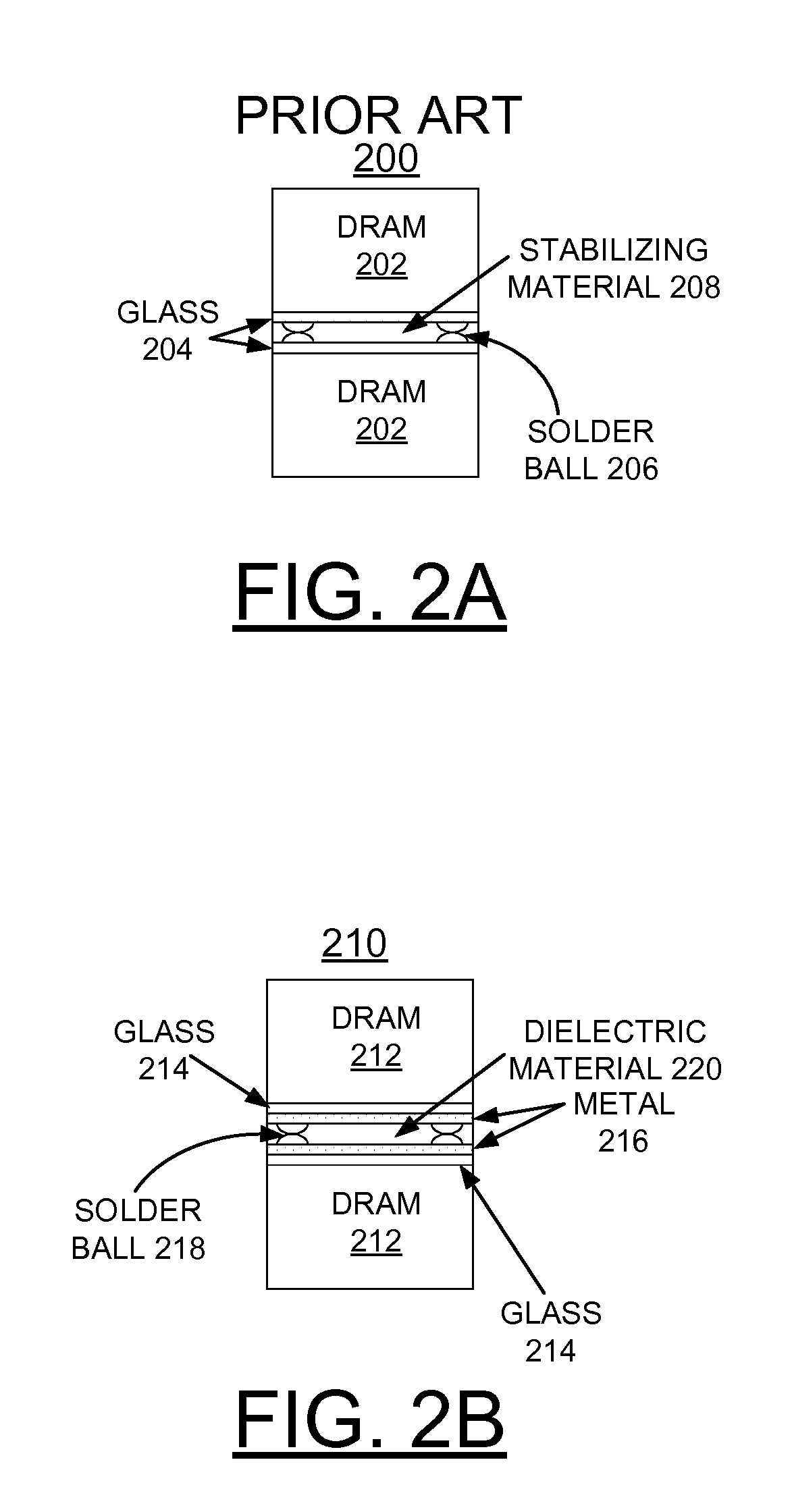
A method and structures are provided for implementing decoupling capacitors within a DRAM TSV stack. A DRAM is formed with a plurality of TSVs extending completely through the substrate and filled with a conducting material. A layer of glass is grown on both the top and bottom of the DRAM providing an insulator. A layer of metal is grown on each glass layer providing a conductor. The metal and glass layers are etched through to TSVs with a gap provided around the perimeter of via pads. A respective solder ball is formed on the TSVs to connect to another DRAM chip in the DRAM TSV stack. The metal layers are connected to at least one TSV by one respective solder ball and are connected to a voltage source and a dielectric is inserted between the metal layers in the DRAM TSV stack to complete the decoupling capacitor.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for error detection and correction in a memory module which includes a memory buffer
ActiveUS8694857B2Without compromising integrity requirementError preventionTransmission systemsMultiplexerParallel computing
The present systems include a memory module containing a plurality of RAM chips, typically DRAM, and a memory buffer arranged to buffer data between the DRAM and a host controller. The memory buffer includes an error detection and correction circuit arranged to ensure the integrity of the stored data words. One way in which this may be accomplished is by computing parity bits for each data word and storing them in parallel with each data word. The error detection and correction circuit can be arranged to detect and correct single errors, or multi-errors if the host controller includes its own error detection and correction circuit. Alternatively, the locations of faulty storage cells can be determined and stored in an address match table, which is then used to control multiplexers that direct data around the faulty cells, to redundant DRAM chips in one embodiment or to embedded SRAM in another.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
System memory board subsystem using DRAM with integrated high speed point to point links
ActiveUS7533212B1Digital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory chipMemory controller
A memory system comprising memory modules including memory chips including integrated switching circuits. A memory controller coupled to the memory modules is configured to initiate memory accesses. When a switching circuit within a memory chip detects the memory access, the switching circuit routes the access to another memory module if the access is not directed to a memory chip of the receiving memory module, or processes the access locally if the access is directed to a memory chip of the receiving memory module. The memory controller and memory modules are coupled via bi-directional serial links. Each memory module may include multiple switching circuits, each of which may be coupled to fewer than all of the memory chips within the memory module. Switching circuits further include circuitry configured to de-serialize data prior to conveyance to a memory chip, and serialize data received from a DRAM chip prior to transmitting the received data.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
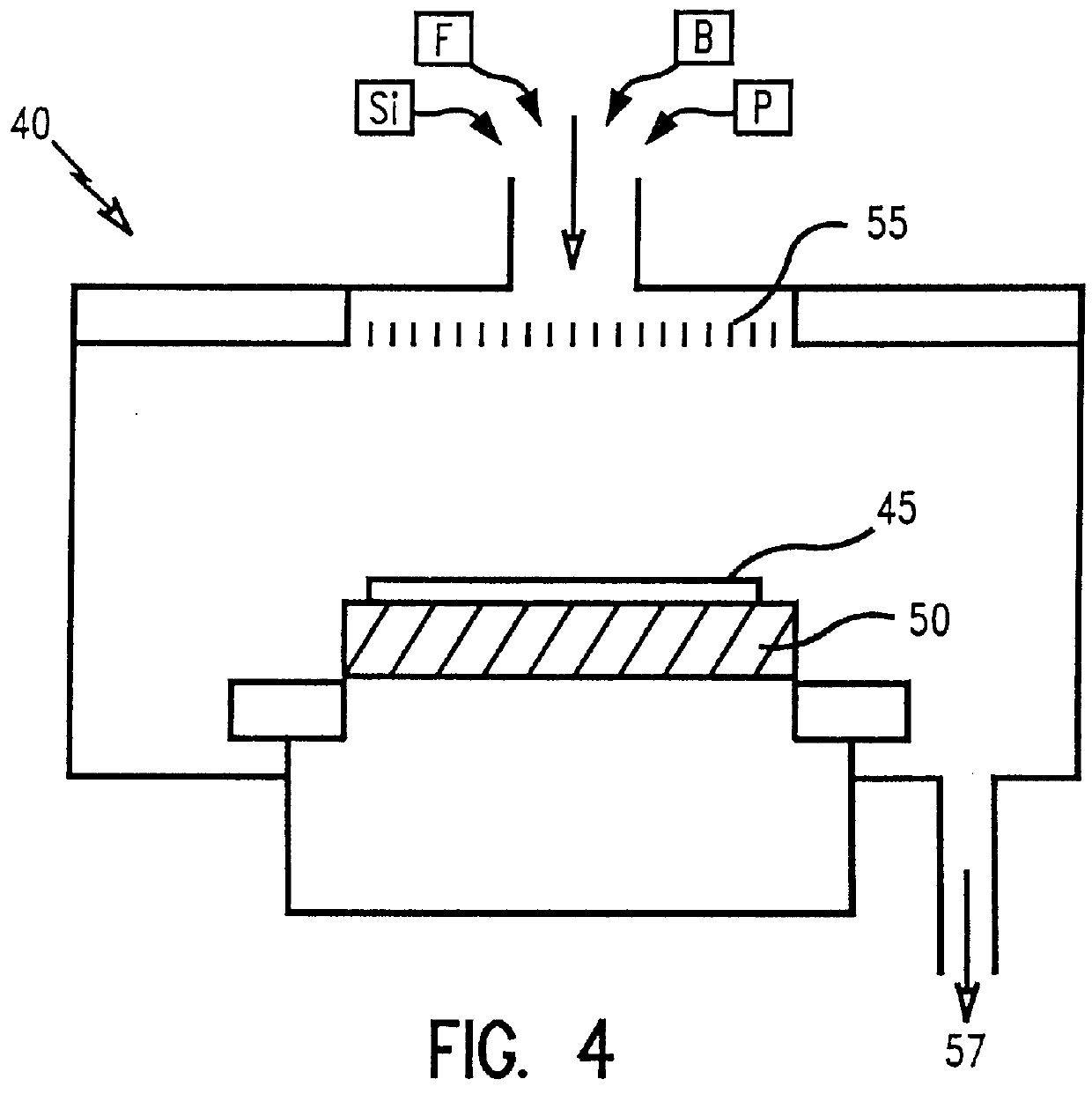
Borophosphosilicate glass incorporated with fluorine for low thermal budget gap fill
InactiveUS6159870AStrong Gap Filling CapabilityHigh aspect ratio gapsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBorophosphosilicate glassChemistry
A method of depositing a fluorinated borophosphosilicate glass (FBPSG) on a semiconductor device as either a final or interlayer dielectric film. Gaps having aspect ratios greater than 6:1 are filled with a substantially void-free FBPSG film at a temperature of about 480 DEG C. at sub-atmospheric pressures of about 200 Torr. Preferably, gaseous reactants used in the method comprise TEOS, FTES, TEPO and TEB with an ozone / oxygen mixture. Dopant concentrations of boron and phosphorus are sufficiently low such that surface crystallite defects and hygroscopicity are avoided. The as-deposited films at lower aspect ratio gaps are substantially void-free such that subsequent anneal of the film is not required. Films deposited into higher aspect ratio gaps are annealed at or below about 750 DEG C., well within the thermal budget for most DRAM, logic and merged logic-DRAM chips. The resultant FBPSG layer contains less than or equal to about 5.0 wt % boron, less than about 4.0 wt % phosphorus, and about 0.1 to 2.0 wt % fluorine.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of plasma etching doped polysilicon layers with uniform etch rates
InactiveUS20010001729A1Improve the level ofEtching process is accuratelySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingSilicate glass
In wafer semiconductor manufacture, a method of etching an arsenic doped polysilicon layer down to a patterned boro-phospho-silicate-glass (BPSG) layer provided with a plurality of openings with an uniform etch rate is disclosed. The method relies on a combination of both system and process improvements. The system improvement consists to hold the wafer in the reactor during the etch process with an electrostatic chuck device to have a perfect plasma environment around and above the wafer. On the other hand, the process improvement consists in the use of a non dopant sensitive and not selective chemistry. A NF3 / CHF3 / N2 gas mixture with a 11 / 8.6 / 80.4 ratio in percent is adequate in that respect. The etch time duration is very accurately controlled by an optical etch endpoint detection system adapted to detect the intensity signal transition of a CO line at the BPSG layer exposure. The process is continued by a slight overetching. When the above method is applied to the doped polysilicon strap formation in DRAM chips, excessive or insufficient etching of the polysilicon layer is avoided, so that the doped polysilicon strap thickness is thus much more uniform, opening to opening, within a wafer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Extender Card for Testing Error-Correction-Code (ECC) Storage Area on Memory Modules
Memory modules with an extra dynamic-random-access memory (DRAM) chip for storing error-correction code (ECC) are tested on a personal computer (PC) motherboard tester using a cross-over extender card inserted into a memory module socket on the motherboard. ECC code generated on the motherboard is normally stored in the extra ECC DRAM chip, preventing test patterns such as checkerboards and walking-ones to be written directly to the ECC DRAM chip. During testing, the cross-over extender card routes signals from the motherboard for one of the data DRAM chips to the ECC DRAM chip, while the ECC code is routed to one of the data DRAM chips. The checkerboard or other test pattern is thus written and read from the ECC DRAM chip that normally stores the ECC code. The cross-over extender card can be hardwired, or can have a switch to allow normal operation or testing of the ECC DRAM chip.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
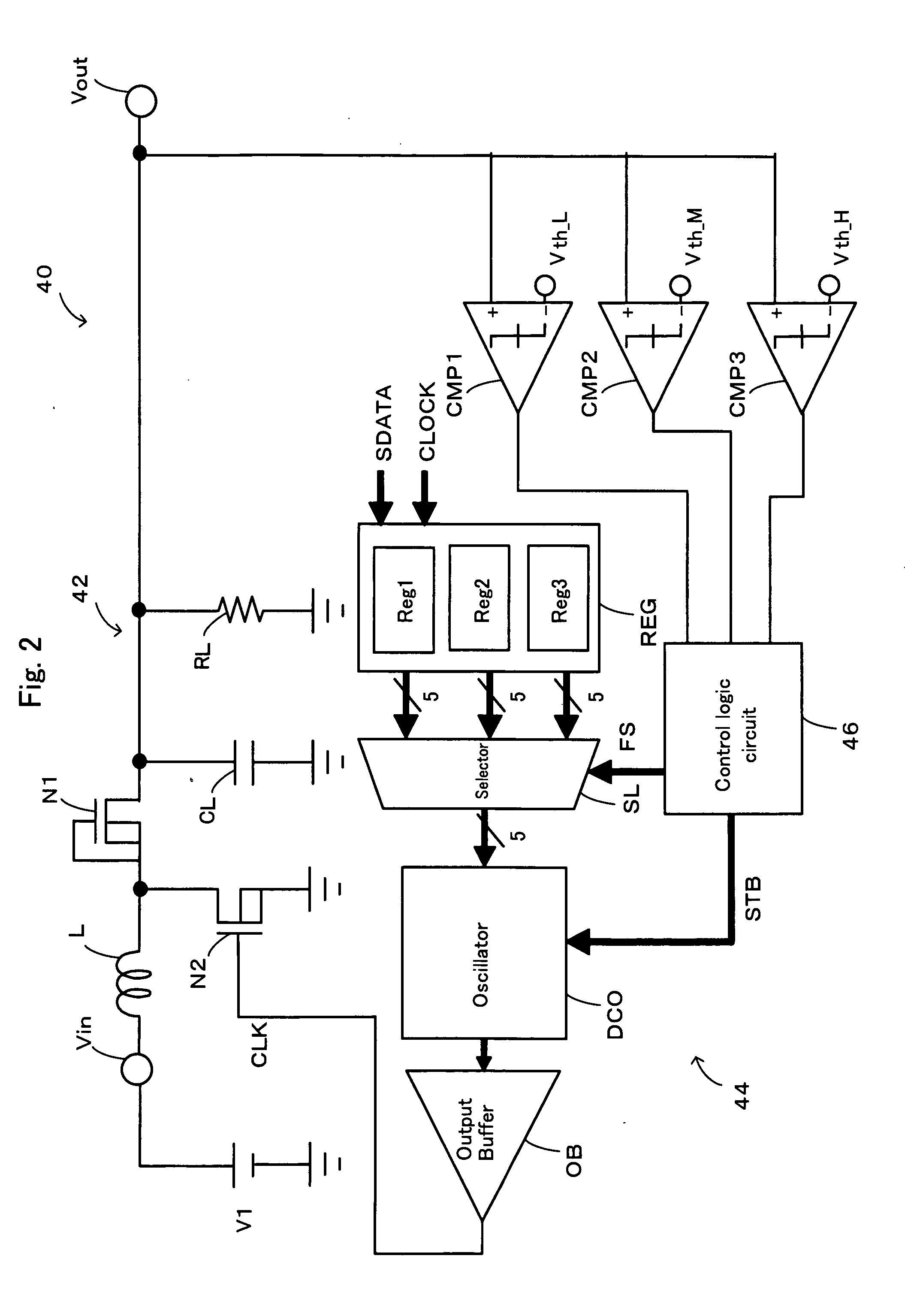
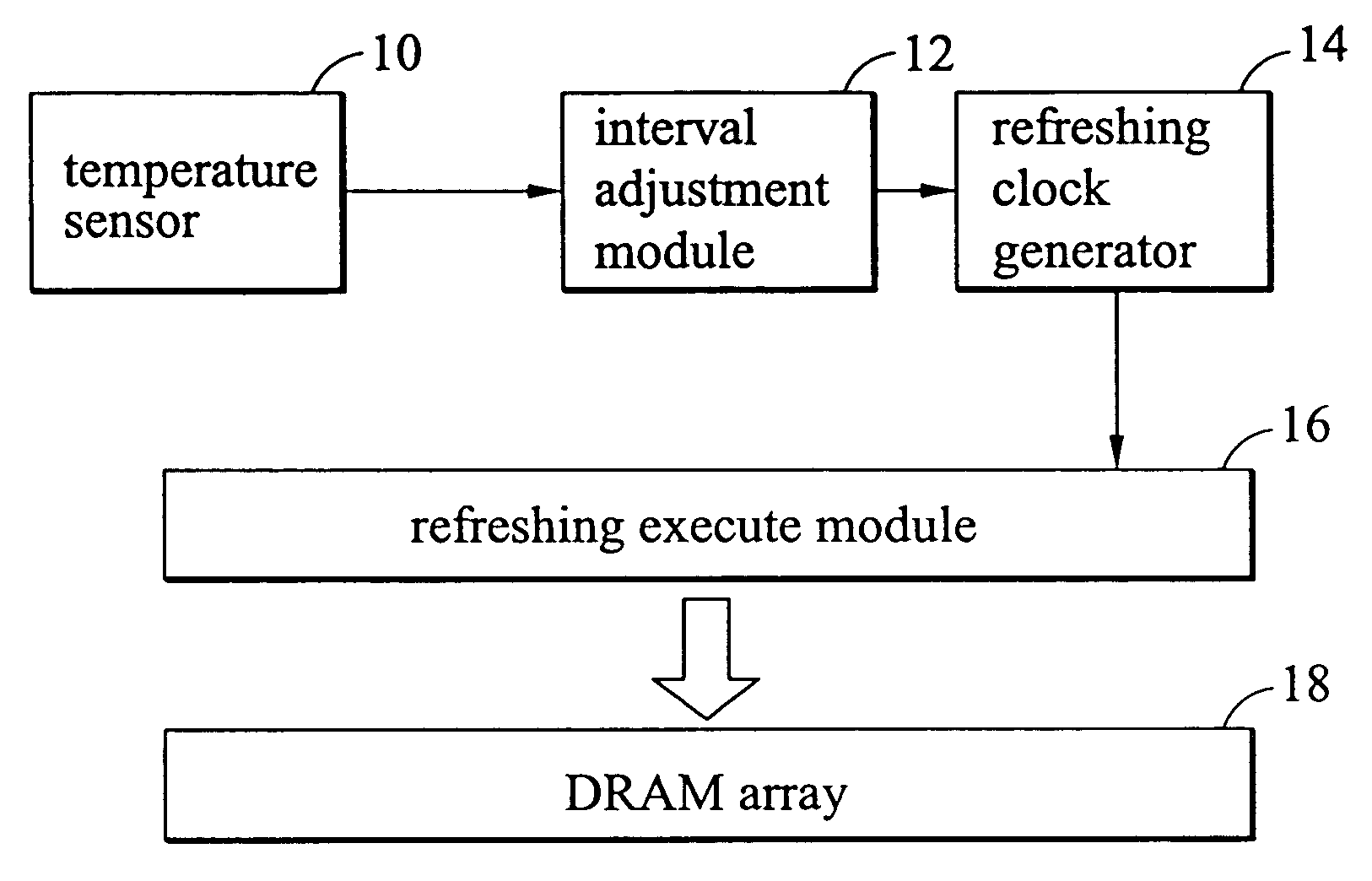
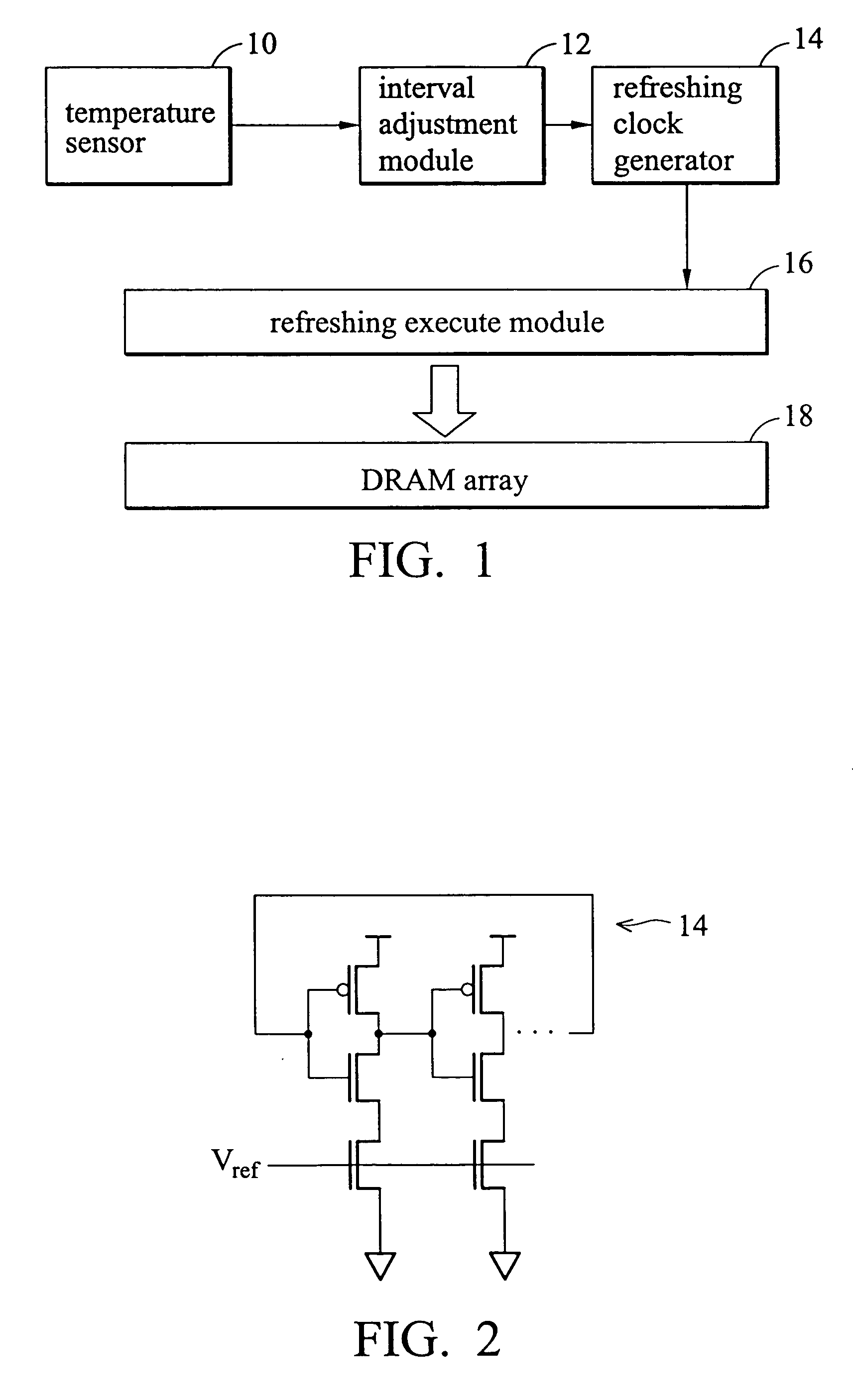
Method and system of adjusting DRAM refresh interval
A method of refreshing a DRAM chip. A working temperature is detected for the DRAM, and a corresponding refresh interval is decided accordingly. A refresh timing clock is generated with the corresponding refresh interval, and the DRAM is refreshed. The refresh interval decreases with increased working temperature, and increased with working temperature decrease.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com