Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Ecological study" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ecological studies are studies of risk-modifying factors on health or other outcomes based on populations defined either geographically or temporally. Both risk-modifying factors and outcomes are averaged for the populations in each geographical or temporal unit and then compared using standard statistical methods.
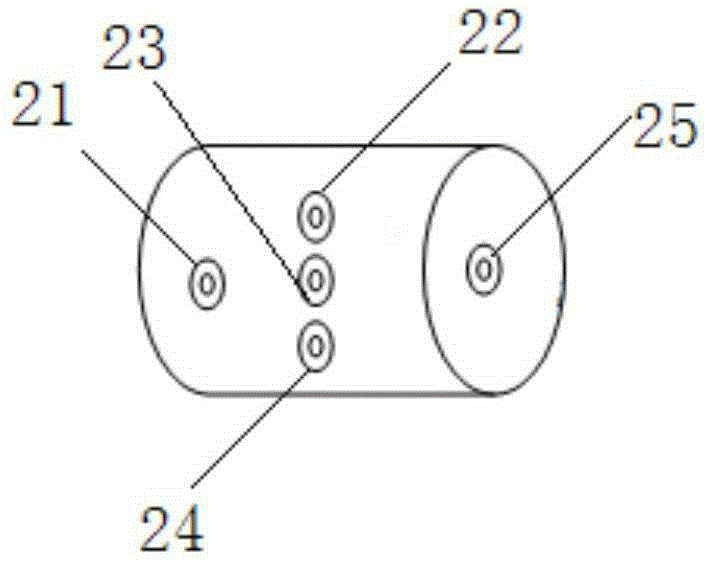
Quantification analysis method of fish habitat space characteristic influenced by gate dam regulation and control
ActiveCN107563610AReflect habitat statusWater resource protectionPisciculture and aquariaWater resource planningEcological study
The invention discloses a quantification analysis method of fish habitat space characteristics influenced by gate dam regulation and control; the method comprises the following steps: investigating fish resource present situations in a research area, and screening a target fish; aiming at the screened target fish, and using indoor stress experiments and history data to build a quantification response relation curve of the target fish with respect to key habitat factors; gathering research area basic hydrology and landform data so as to build a water-power water environment model, and combiningthe quantification response relation curve of the target fish with respect to key habitat factor so as to build a habitat model facing fish habitats; introducing a landscape ecology theory and methodso as to evaluate the space characteristics of the habitat simulation result facing the fish habitat, and quantitatively analyzing the influences on the fish habitat space characteristics by the gatedam operations. The method can guide multi-gate dam river ecology restorations and protections, thus providing important theory and practice meanings for basin water resource planning and configurations.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
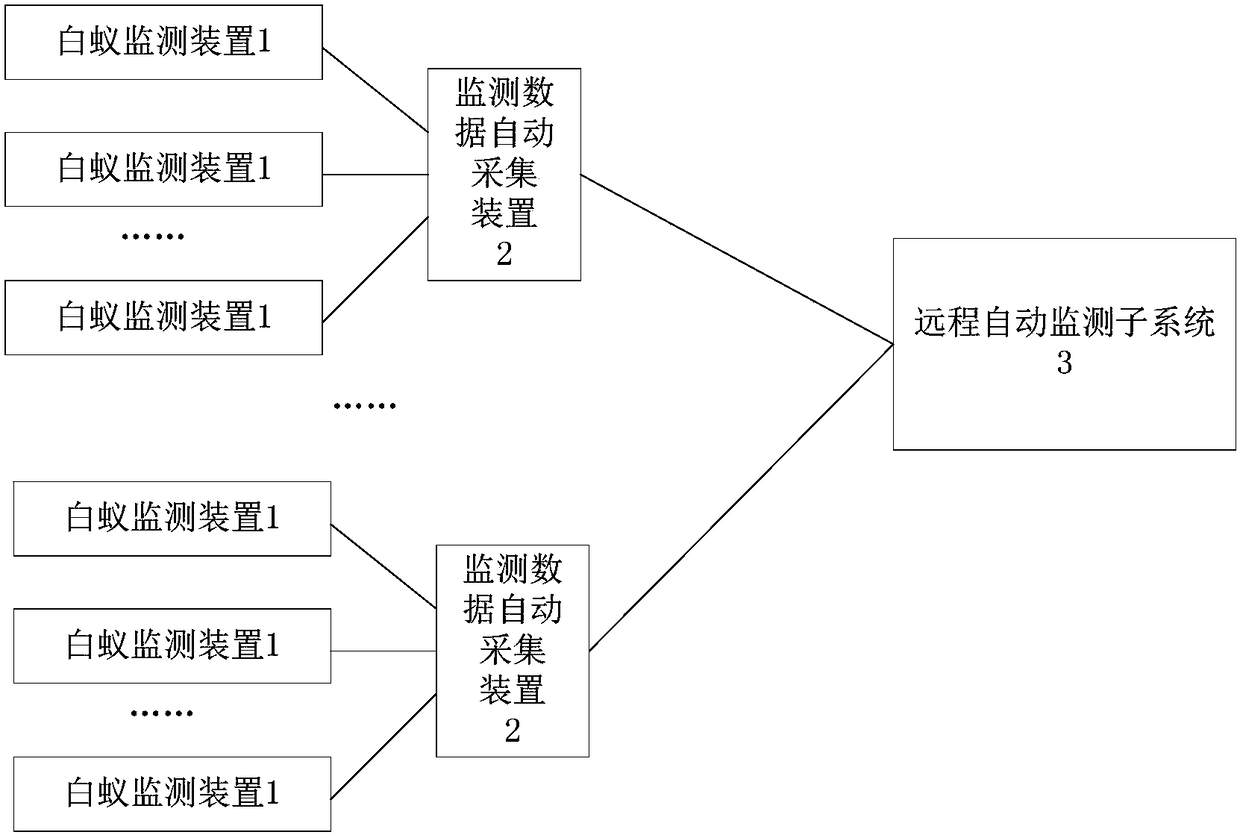
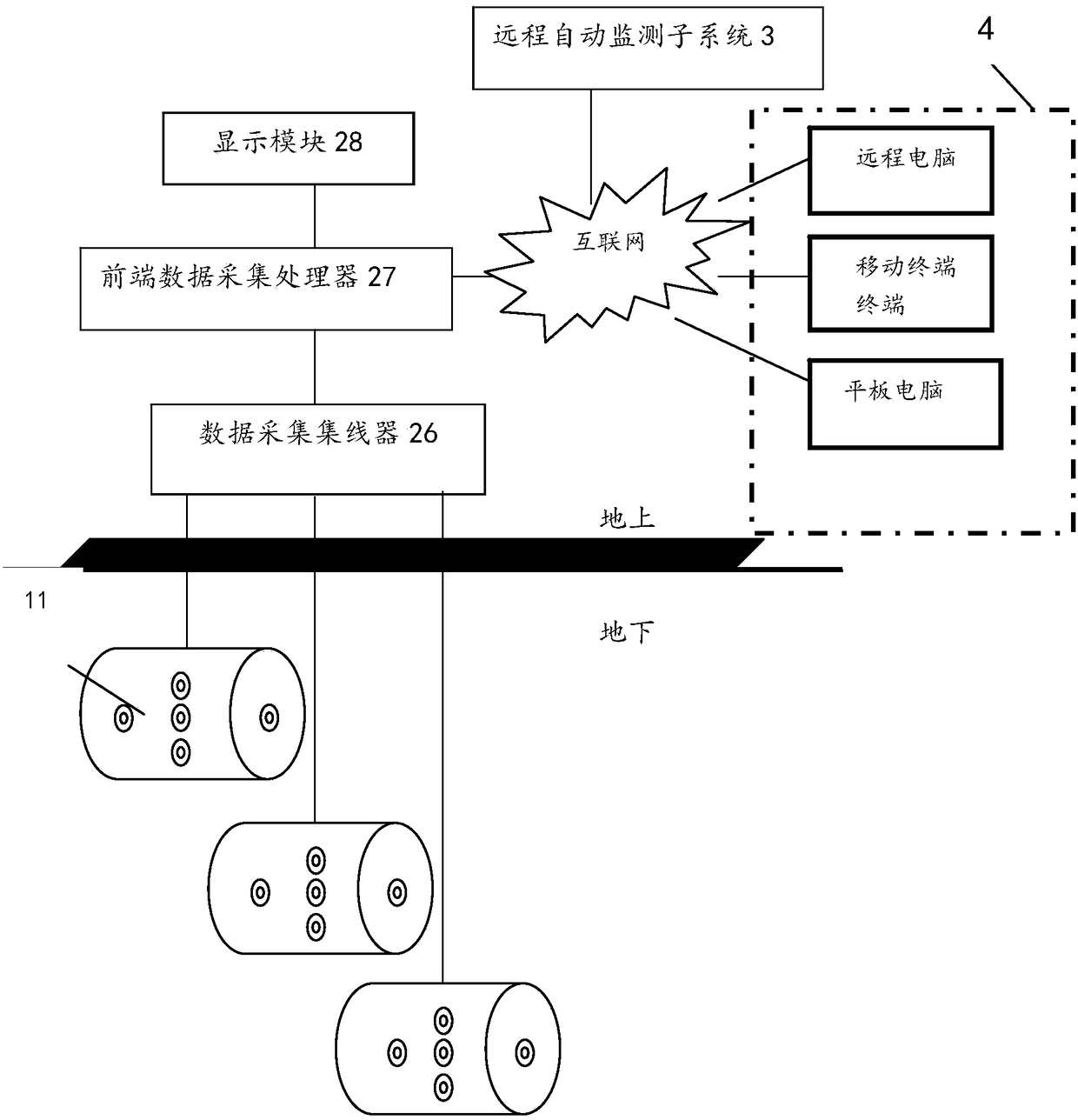
Automatic remote termite monitoring system based on internet of things
InactiveCN105230588AEffective prevention and control methodsImprove the effect of prevention and controlInsect catchers and killersEcologic studyEcological study
The invention provides an automatic remote termite monitoring system based on the internet of things. The automatic remote termite monitoring system comprises multiple termite monitoring devices, multiple automatic monitoring data collecting devices and an automatic remote monitoring subsystem; the termite monitoring devices are placed at different depths of the underground and used for storing baits to lure termites to be gathered, the automatic monitoring collecting devices are used for monitoring environmental data in shells and termite activity video data and sending an alarm signal when the fact that the environment data exceed the standard or the termite activities are abnormal is judged; the automatic remote monitoring subsystem is used for receiving the environmental data and the video data to form continuous termite monitoring history data and analyzing ecological feature information of termites by analyzing the influences of the environmental data on the termite activities according to the termite monitoring history data. According to the automatic remote termite monitoring system based on the internet of things, automatic acquiring and automatic analyzing of the related data needed by termite ecological study can be achieved, and the termite controlling effect and efficiency are significantly improved.
Owner:熊忠阳 +1
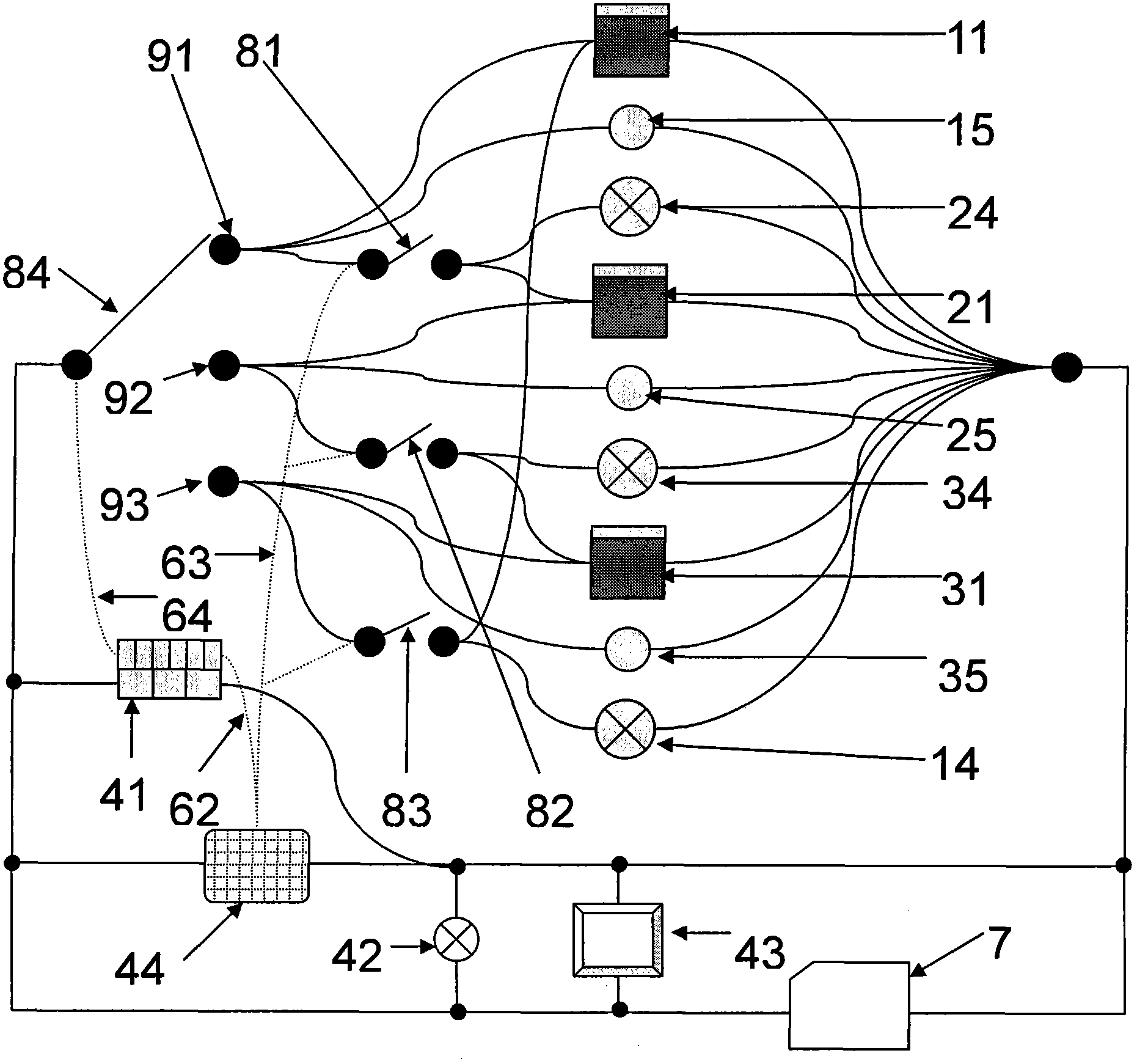
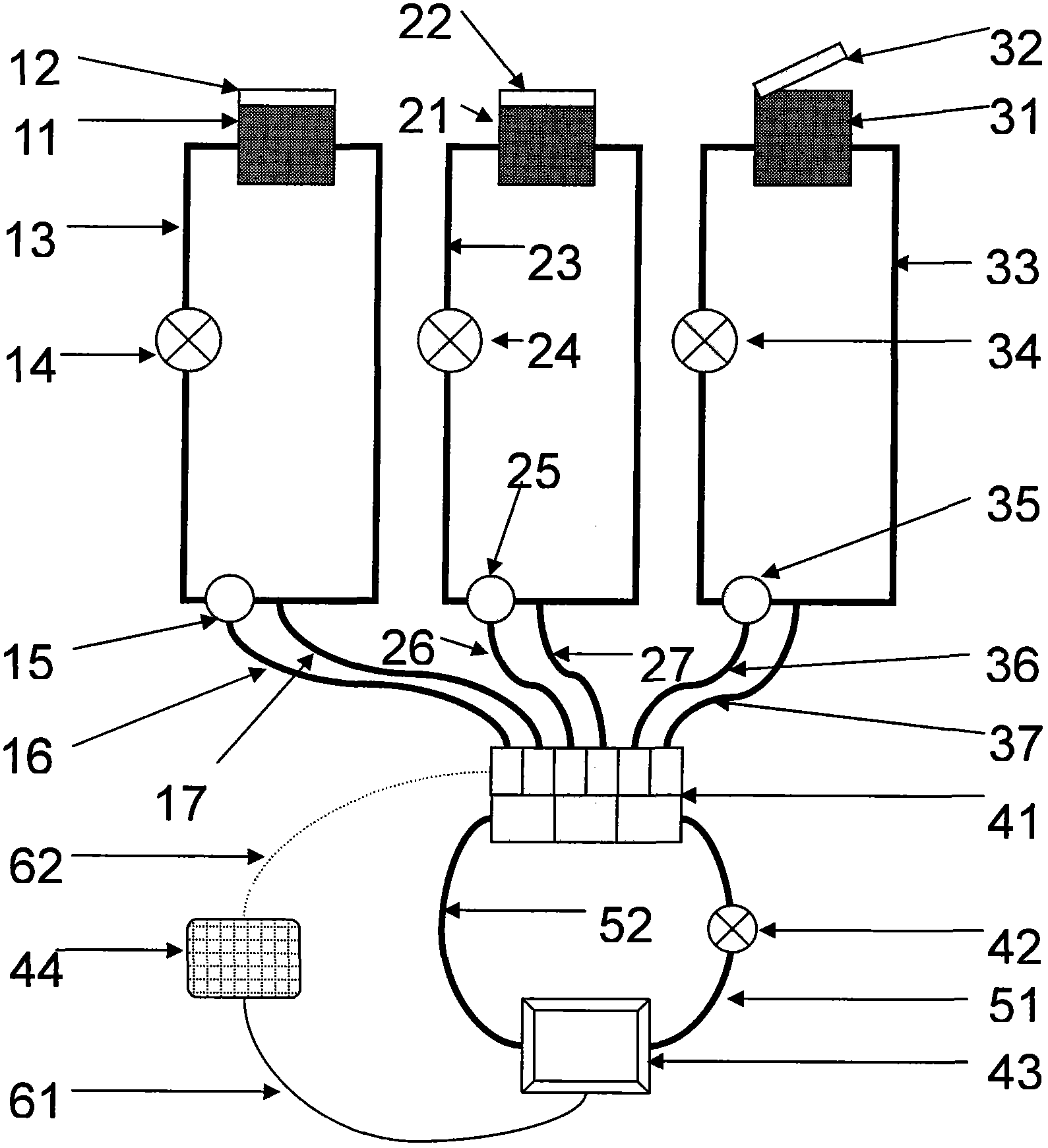
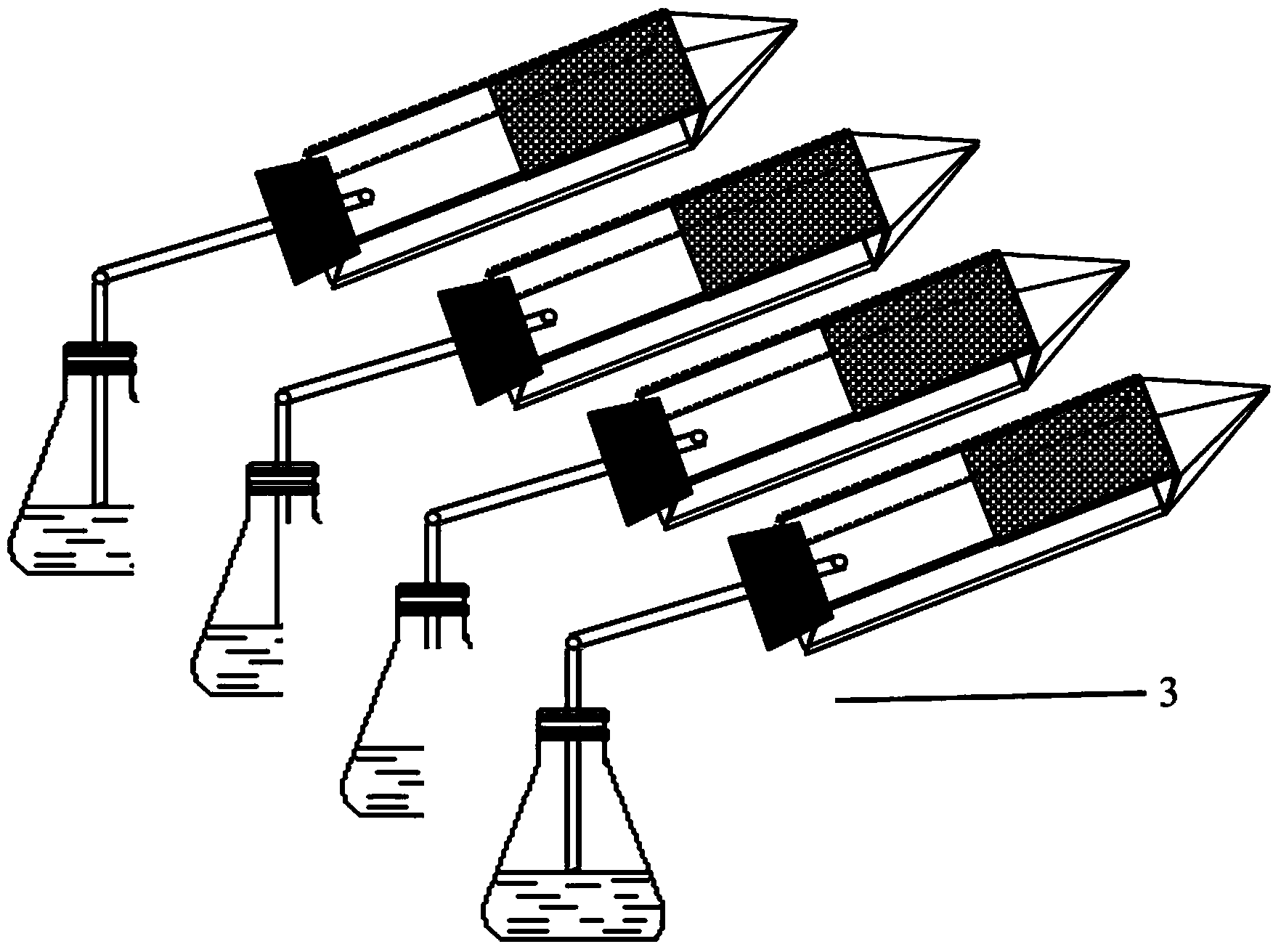
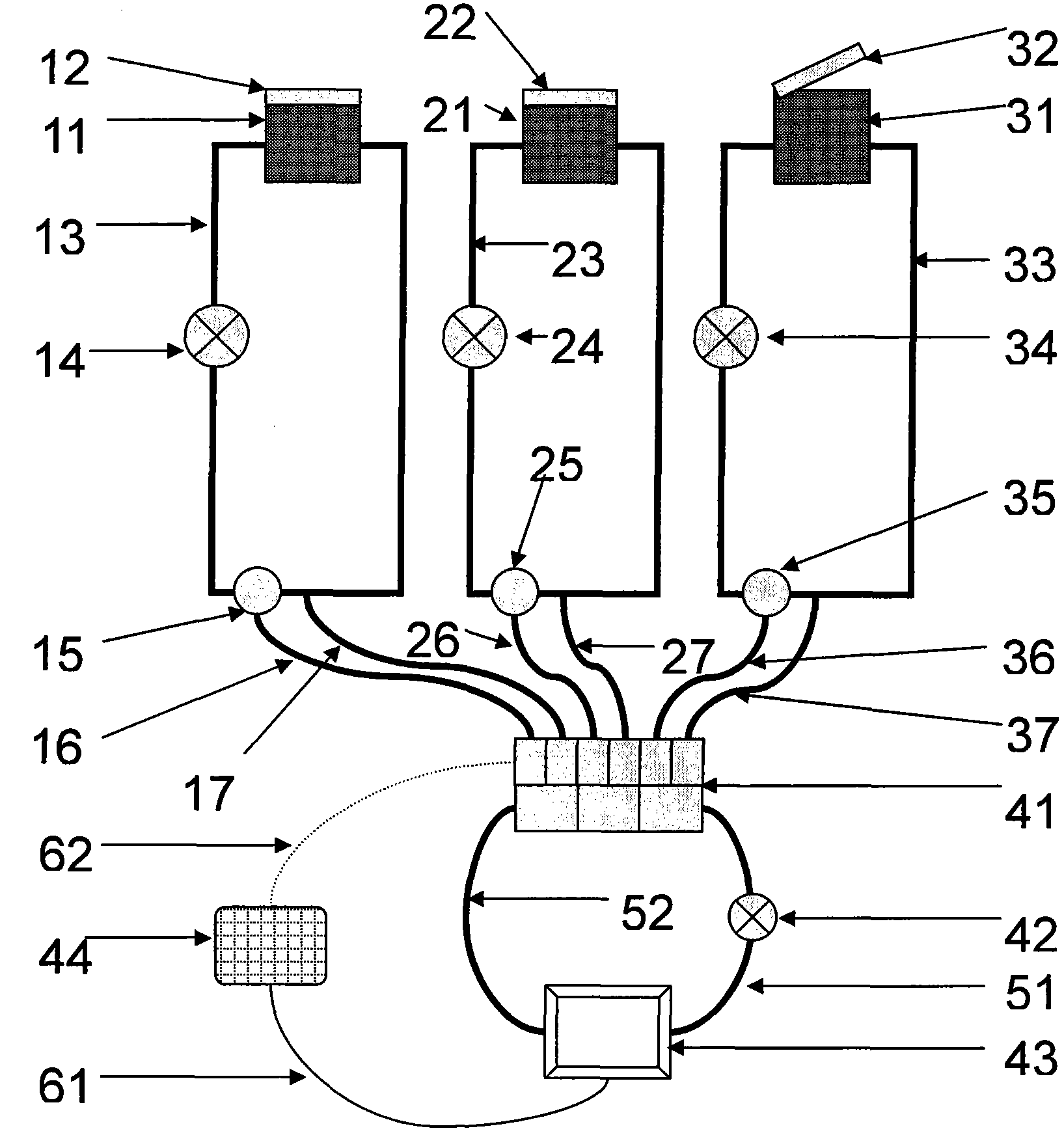
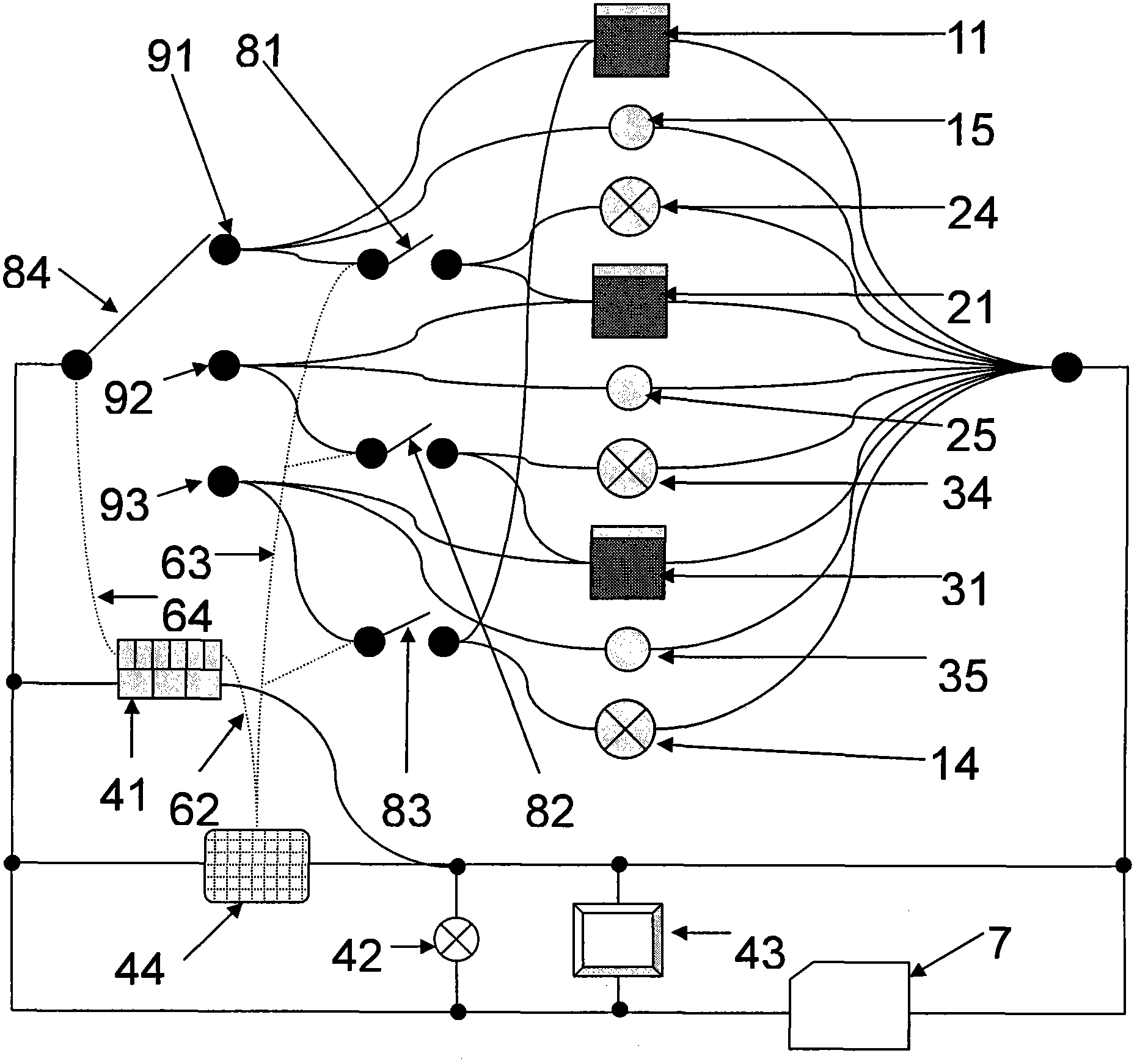
Multichannel double-circulation soil carbon discharge delta13C observing system
The invention relates to the field of ecological study, and provides a multichannel double-circulation soil carbon discharge delta13C observing system. The multichannel double-circulation soil carbon discharge delta13C observing system consists of a gas analyzing system and a circuit control system. The gas analyzing system comprises a discharging box, a box cover, a sampling pipe, an air pump, a three-way solenoid valve, a multichannel solenoid valve, a delta13C analyzer and a single chip microcomputer. The circuit control system is formed by connecting a power source, a control line, a switch and a contact according to a given circuit. With the adoption of the multichannel double-circulation soil carbon discharge delta13C observing system, automatic conversion and circular observation among a plurality of channels are realized, so as to remove interference of 'dead air' on an observing result, save observing time of each channel, and improve the efficiency and the accuracy of soil carbon discharge delta13C observation.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
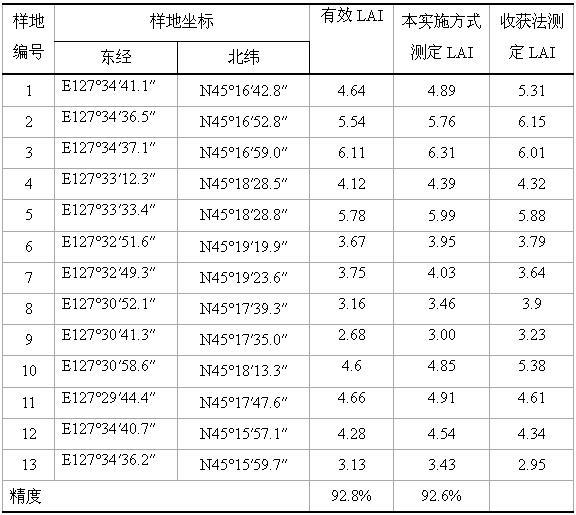
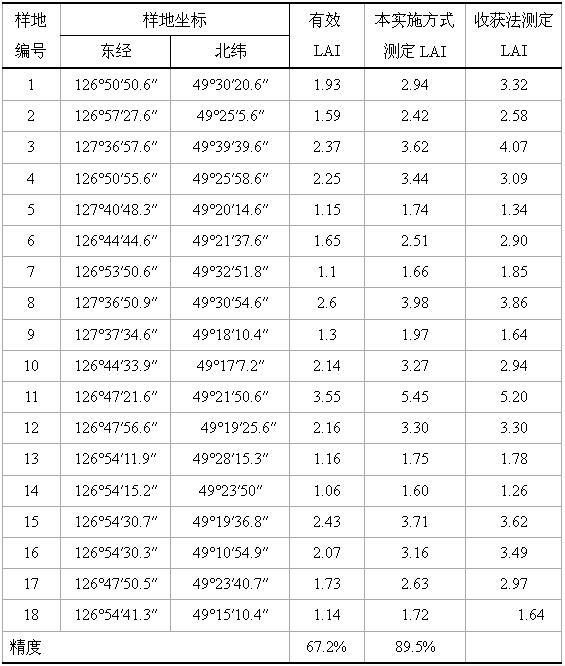
Measuring method of leaf area index
InactiveCN101788283AImprove measurement efficiencyReduce labor intensityMeasurement devicesEcologic studySoil science
The invention relates to a measuring method of leaf area index, belonging to the ecological study field. The invention solves the problems of the prior art that the leaf area index measured by LAI-2000 has low accuracy, and the harvest method for measuring the leaf area index has large labor intensity and low efficiency. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: 1. placing an LAI-2000 plant canopy analyzer 3.5 away from the edge of a leaf, measuring under the condition that the measuring time is 10:00-14:00, the light Intensity is 8000-10000Lux, the wide speed is 7-level and the air humidity is 10-90%; 2. obtaining an effective leaf area index; and 3. substituting the effective leaf area index in the following formula: leaf area index of broad-leaved forest=1.5457*effective leaf area index-0.0414 or leaf area index of coniferous forest=0.9651*effective leaf area index+0.4115, thus completing the measurement of leaf area index. The method can increase the measuring efficiency, reduce the labor intensity and increase the accuracy.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for extracting prawn intestinal microbial DNA
The invention relates to a method for extracting prawn intestinal microbial DNA, and belongs to the fields of microbiology and molecular ecology. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding by using liquid nitrogen; breaking cell walls by using mechanical force; cracking cells by adopting lysozyme and SDS lysate; obtaining DNA deposit through separation and precipitation; and finally dissolving the DNA deposit with TE to obtain the DNA with good quality. The product DNA fragment obtained by the method is greater than 20Kb; and can be subjected to gene magnification and sequencing. The method has good generality and is used for extracting the intestinal microbial DNA of various crustacean aquatic animals. High-quality template DNA can be obtained through extraction at one time without repeated experiment; and the obtained DNA can be applied to the research of molecular ecology, system evolution and the like.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for determining micro-ecological imbalance of human intestinal tract and electronic equipment
The invention provides a method and device for determining micro-ecological imbalance of the human intestinal tract and electronic equipment, and relates to the technical field of microbial ecology. The method for determining the micro-ecological imbalance of the human intestinal tract comprises the steps that intestinal flora data of the target human body is obtained, wherein the intestinal floradata is sample data containing markers of multiple species; the intestinal flora data is input into an intestinal random forest prediction model for prediction, and an output result is obtained; theintestinal random forest prediction model is correspondingly provided with a threshold used for judging the phenotypes of samples, the intestinal random forest prediction model comprises a random forest OTU model or a Shannon exponential random forest model; based on the output result, whether or not the micro-ecology of the intestinal tract of the target human body is in an unbalanced state is judged. The method and device for determining the micro-ecological imbalance of the human intestinal tract and the electronic equipment can judge whether or not the target human body is in an intestinalmicro-ecological imbalance state through the prediction model.
Owner:JIANGXI PRECISION GENE CO LTD
Sustainable grassland desertification control method
InactiveCN108990456ASustainable governanceRestore fluencyOther chemical processesOrganic fertilisersWoody plantEcological study
The invention discloses a sustainable grassland desertification control method. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out closing, concretely enclosing a desertification grassland area, and banning grazing; supplying water, concretely digging gullies through nearby water systems, and laying a plurality of strip-shaped water collecting strips; carrying out conditioning, concretely carrying out spraying conditioning on the desertification grassland by using a soil conditioner; carrying out sowing, concretely sowing seeds of drought-resistant plants, mesophyte herbaceous plants and pasture grass; carrying out irrigation, concretely carrying out irrigation for once every 1-2 months after irrigation is carried out for the first time in spring; carrying out reseeding, concretely carrying reseeding by using seeds of the drought-resistant plants, mesophyte herbaceous plants and pasture grass according to conditions; and carrying out recuperation, concretely carrying out recuperation and rehabilitation, sowing seeds of the mesophyte herbaceous plants, and carrying out irrigation and reseeding. According to the sustainable grassland desertification control method, hydrological and soil foundations are constructed on the basis of ecology, and biotic communities are constructed on the hydrological and soil foundations, so that a concept of sustainable development is implemented, and an inestimable profound influence is achieved on treatment of grassland desertification.
Owner:JIANGSU DONGZHU LANDSCAPE CONSTR
Quantification method for denitrifying microorganisms in aquaculture environment sediments
InactiveCN105132553AShorten the timeGood effectMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceEcological study
The invention discloses a method for real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (qPCR) detection of denitrifying microorganisms in aquaculture environment sediments, and belongs to the technical field of environmental microbial ecology. The method comprises the following contents: metagenome DNA extraction and concentration determination of sediment samples in various stations, PCR amplification of nirK and nirS genes, construction of a standard plasmid, preparation of a standard curve, qPCR amplification and calculation of the number of denitrifying microorganisms in the samples according to a qPCR result in accordance with the standard curve. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for determining the number of the denitrifying microorganisms in an aquaculture environment through quantitative analysis on two genes, namely nirK and nirS, so as to overcome the shortcoming that 16S rRNA gene cannot be used in the quantification of the denitrifying microorganisms as well as the shortcoming that the prior art, which focuses on some functional gene only, is incomplete in quantification; and the provided method for detecting the number of the denitrifying microorganisms in the aquaculture environment is good in specificity, high in repeatability and high in accuracy. According to the method disclosed by the invention, logarithm values of nirK and nirS gene copy numbers keep a good linear relation with Ct value of a luminescence threshold, and the regression coefficient of the standard curve is above 0.99.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
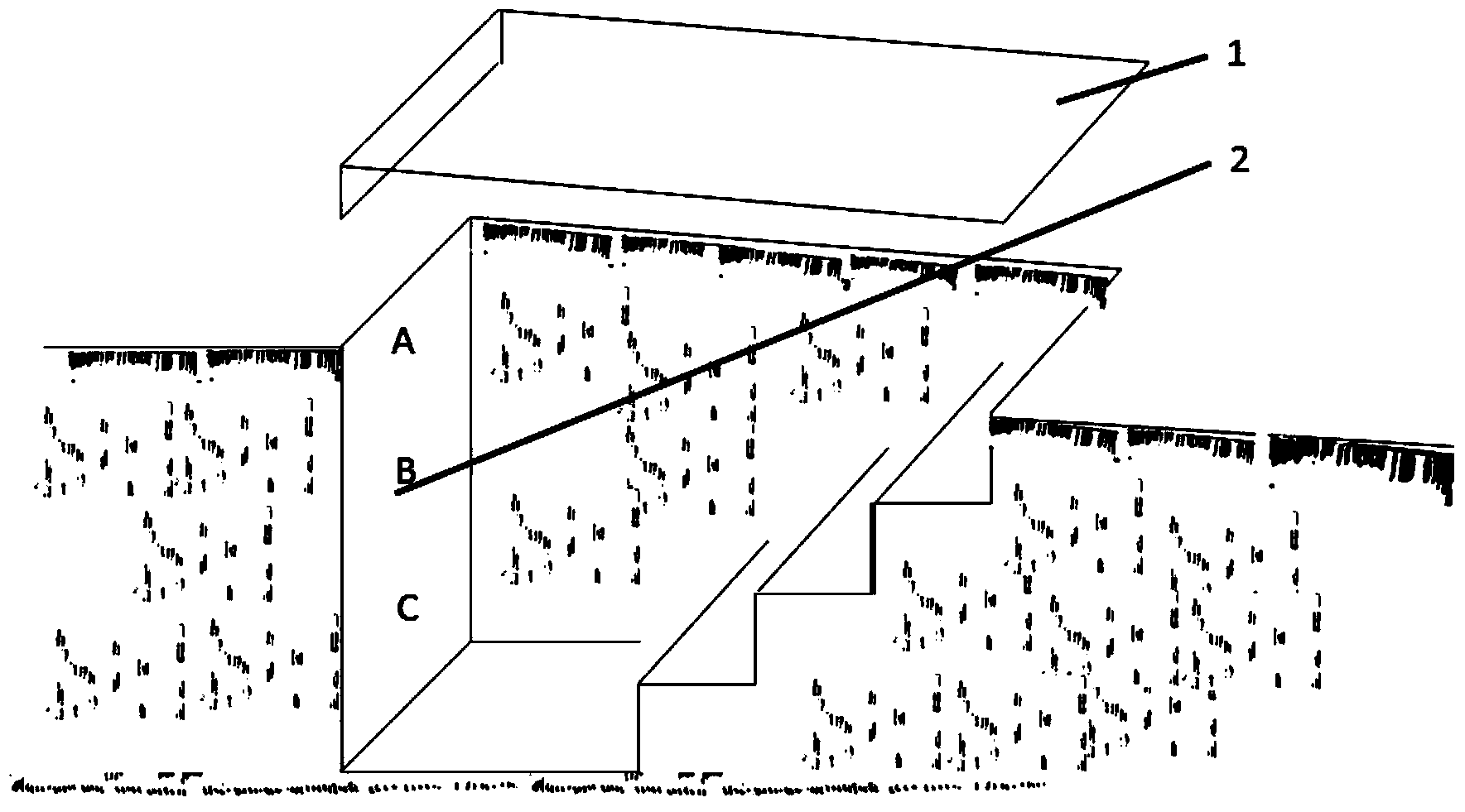
Method for measuring interflow in forest soil
The invention discloses a method for measuring interflow in forest soil, and belongs to the field of forest soil ecological study. The method is characterized in that the system utilizes the soil profile and consists of an interflow flow collecting groove, a flow guide pipe and an interflow collector, wherein the flow collecting groove is embedded into a soil body in different layers of the soil profile, the interflow is collected, and the interflow is guided into the collector for completing the collection of the interflow. The method has the advantages that the structure is compact, the system is reasonable, the method is simple, the realization is easy, a scientific and reasonable small-dimension measuring system is provided for the study of the forest soil hydrology process, the moisture and nutrient balance and moving and the like, and greater popularization and application values are realized in the fields of forest soil ecology, forest hydrology, water and soil conservation and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mixed culture system for sea cucumber, shrimp and shellfish based on deep-water net cage
InactiveCN104686403AIngenious designEasy to operateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMixed cultureEcological study
The invention relates to the technical field of aquaculture, specifically to a mixed culture system for sea cucumber, shrimp and shellfish based on a deep-water net cage. The mixed culture system of the invention comprises a stereo bracket, wherein the upper part of the stereo bracket is provided with at least two layers of culture areas; the periphery of each layer of the culture area is surrounded with a netting; the bottom layer of the culture area is used for the culture of the sea cucumber; a plurality of sea cucumber blindages are fixedly arranged on the netting of the bottom layer of the culture area; other layers of the culture areas are used for culture of Patinopecten yessoensis; a plurality of longitudinal nettings are fixedly arranged between the nettings at two opposite side surfaces of the Patinopecten yessoensis culture areas; and a plurality of stereo string bags are arranged on each longitudinal netting. The mixed culture system provided by the invention is designed according to biological and ecological characteristics of the Patinopecten yessoensis and the sea cumber, can promote growth of the sea cucumber and improve culture yield per unit of the Patinopecten yessoensis, has the characteristics of simple operation and strong on-site operability and can improve culture yield and reduce environmental pressure by making full use of maritime space and complementarity of ecological niches of different varieties.
Owner:夏雪飞
Ecology regulation and control method for delaying sex reversal time of eels
InactiveCN103004649AImprove group fecundityMeet seedling requirementsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaHigh densityEcological study
The invention relates to an ecology regulation and control method for delaying the sex reversal time of eels. The ecology regulation and control method for delaying the sex reversal time of the eels is characterized in that under an ecology imitation condition, young eels with the same specification are massively produced, and moreover, with the adoption of a pond net cage breeding method, the young eels obtained in the same year are bred and overwinter to grow into 30-40g 1-full-age eels; and after the overwintering, the 30-40g 1-full-age eels are fed for one year with high protein nutrients at a high density in a pond net cage, wherein the feeding density is 50-80 eels per square meter and the feed protein content is 40% to 42%. Through the method, 2-winter-age female eel parents with great brood amount and an individual specification of more than 100g can be produced; the colony reproductive capacity of the female eel parents can be improved by 200% to 300%; the quantity of the produced young eels is correspondingly improved by 200% to 300%; and therefore, the demand on the large-scale breeding of the young eels can be met.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
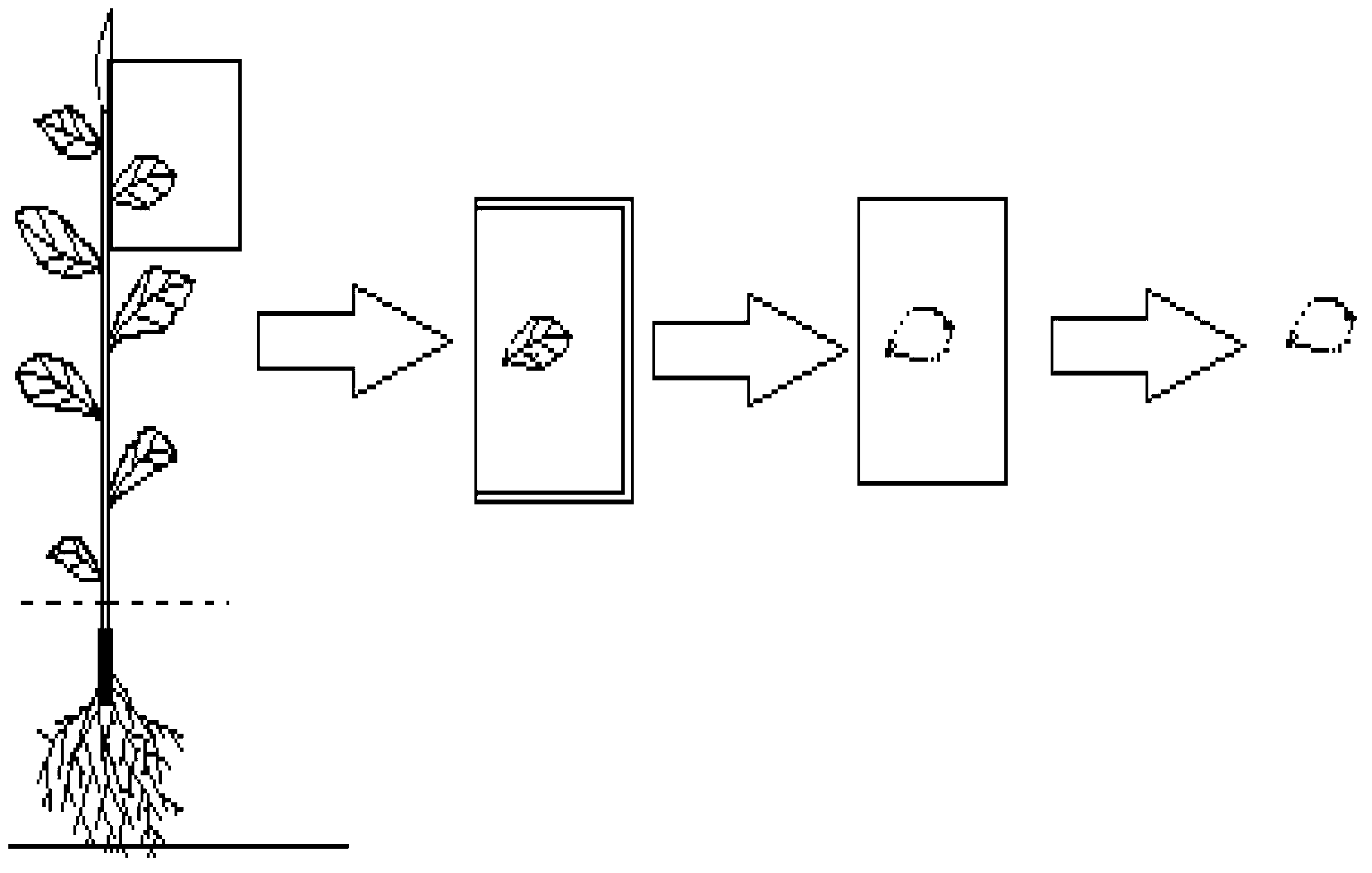
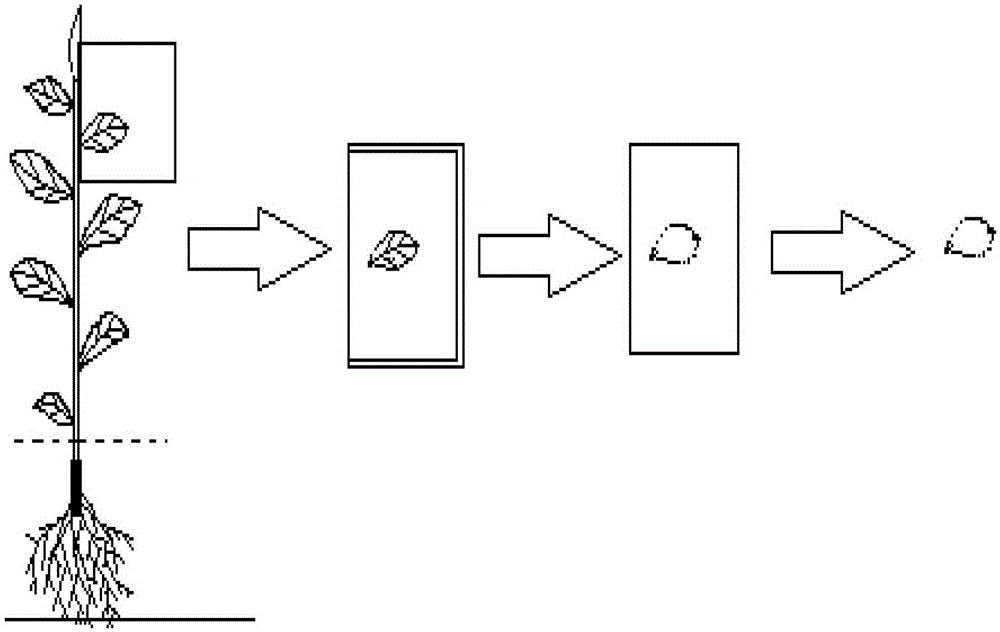
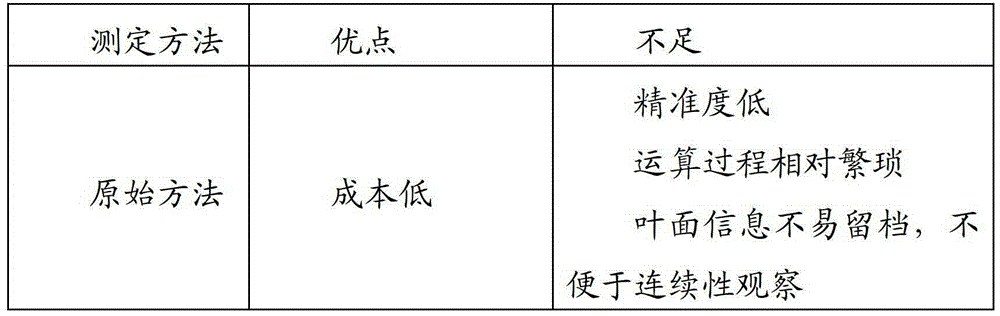
Plant leaf area print weighing in-vivo testing method
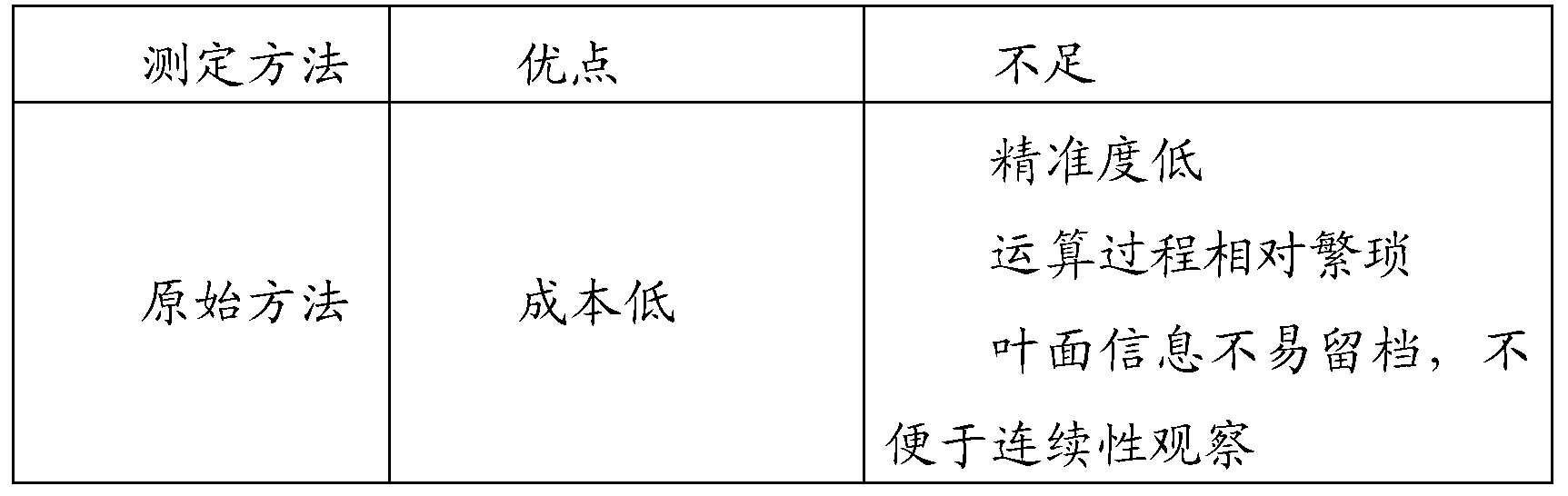
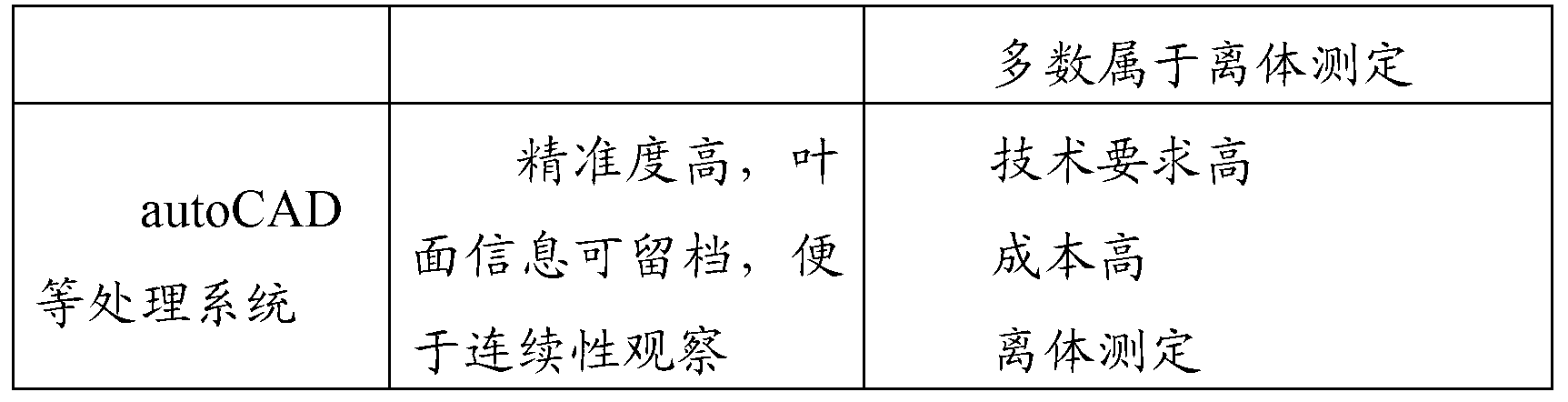
The invention belongs to the field of ecological studies and particularly relates to a plant leaf area print weighing in-vivo testing method. The method has no significant difference with an autoCAD (auto computer aided design) method in testing accuracy and can replace the autoCAD method to be used for plant leaf area testing. The technical scheme includes that the method includes the following steps: detecting and calculating paper density rho, coating markers on the whole back of a plant leaf to be tested, printing the whole shape of the leaf onto paper A to acquire a print graph of the leaf, cutting another empty paper B to make paper C in the shape of the print graph of the leaf, weighing the paper C to acquire mass m, and calculating to acquire area s of the leaf. Compared with conventional algorithms like a basic testing method or the autoCAD method, the plant leaf area print weighing in-vivo testing method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, low cost, no need to pick off the leaf, freeness of leaf damaging, conduciveness to sustainability studies and the like.
Owner:TEA RES INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for analyzing plankton community DNA polymorphism
InactiveCN101215606AImprove comparabilitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementEcological studyGel electrophoresis
The invention discloses a process of analyzing DNA polymorphism of plankton coenosis, which comprises firstly collecting sample, secondly extracting plankton coenosis DNA, thirdly augmenting the analysis of DNA polymorphism randomly, fourthly carrying out PCR augmentation of ribosome RNA gene of plankton coenosis and degeneration gradient gel electrophoresis analysis, fifthly quantitatively analyzing atlas through utilizing Quantity One software to calculate the similarity of DNA polymorphism of plankton coenosis of each sample. The invention has the characteristics of technical route routinization and comparison and analysis standardization, also has simple operation, and can fast and effectively analyze in parallel a plurality of samples, which overcomes the affect by personal factors, increases comparability among different space-time researches, and provides reliable premise for searching for bio-ecology mechanism.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
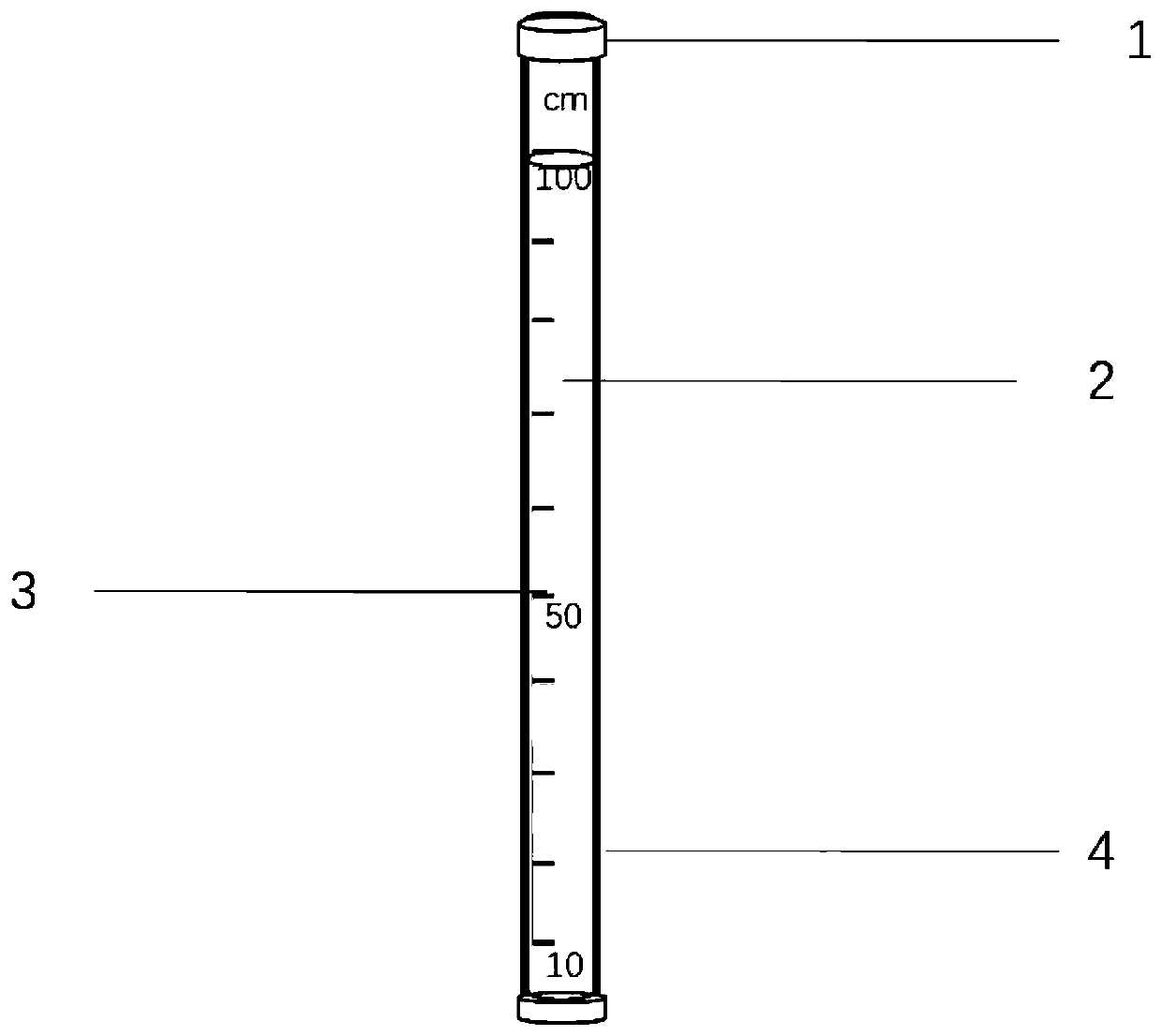
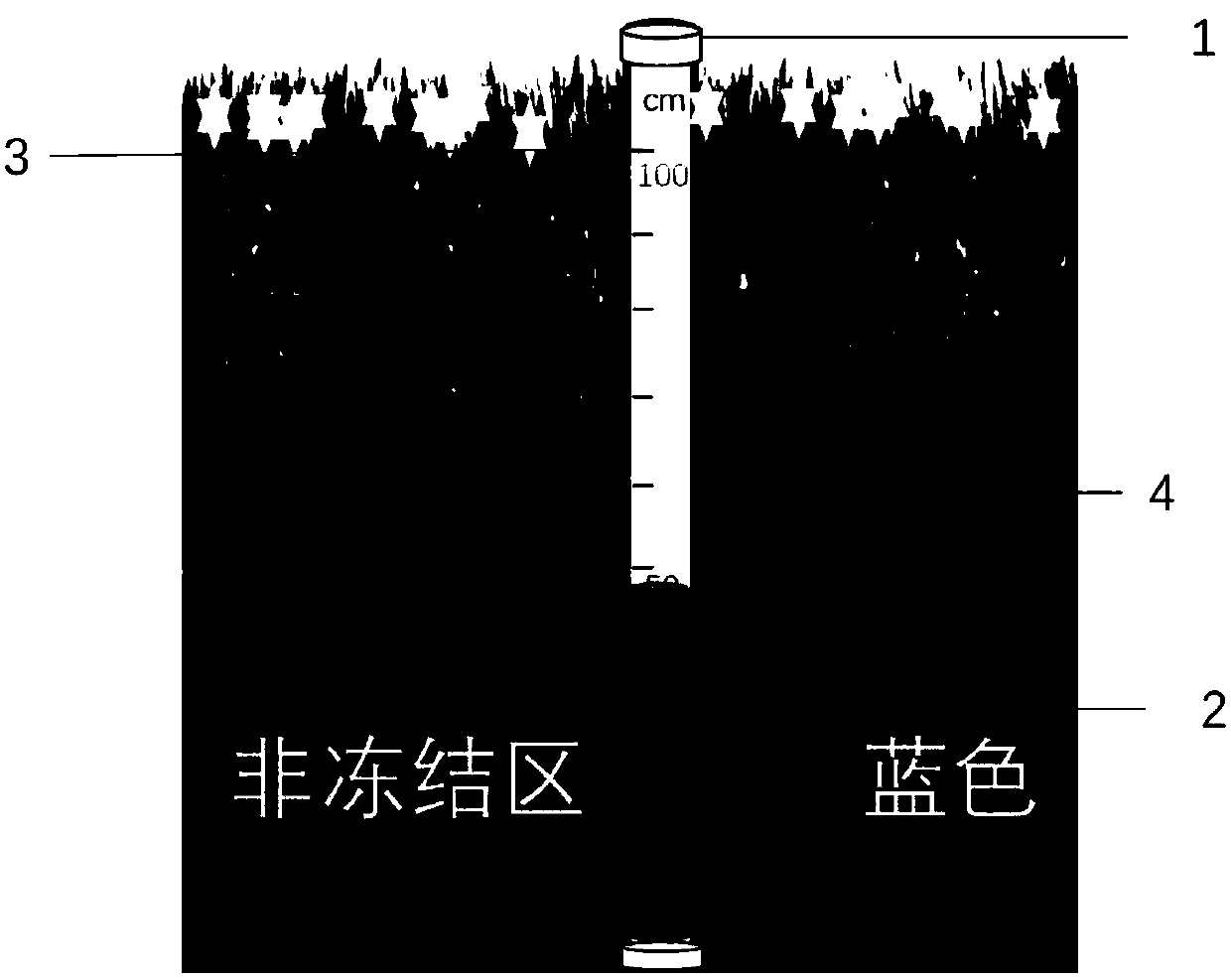
Soil frozen depth measuring device and measuring method
The invention belongs to the field of winter ecological studies, and relates to a soil frozen depth measuring device. The soil frozen depth measuring device comprises a PVC sealing plug 1, a methyleneblue solution 2, a transparent PVC tube 4 and scale lines 3 arranged on the outer wall of the transparent PVC tube 4, wherein the PVC sealing plug 1 plays a sealing role; the concentration of the methylene blue solution 2 is 2 percent; the length of the transparent PVC tube 4 can be selected according to a desired measuring depth; when a measuring depth is within 1 to 2 m, a hard transparent PVCtube 4 can be used for directly measuring the measuring depth; and when a measuring depth is more than 2 m, a soft transparent PVC tube 4 extends into a perforating position, so as to facilitate taking out and measurement. The invention further relates to a soil frozen depth measuring method. The device and the method of the invention are low in cost, good in frozen measuring effect, accurate in data, convenient to use, operate and store, and are suitable for prairie field experiments.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Tool for optimizing chlorinated-solvent bioremediation through integration of chemical and molecular data with electron and alkalinity balances
InactiveUS20130345990A1Maximize accuracyMitigate incomplete reductive dechlorinationContaminated soil reclamationSpecial data processing applicationsAlkalinityOrganismal Process
A prediction and assessment tool for bioremediation performance based on a comprehensive understanding of the link between chemical flow and microbial community interactions includes linking molecular microbial ecology data with electron and alkalinity balances to make it possible to understand dechlorinating microbial communities and their metabolic processes. The interactions of biological processes and site mineralogy result in changes to alkalinity and pH that can lead to incomplete reductive dechlorination resulting from suboptimal pH. Understanding these interactions allows for strategies to predict expected bioremediation outcomes and / or to mitigate incomplete reductive dechlorination.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Biological enhanced functional flora analysis method based on high-flux sequence testing
ActiveCN108486238AGuaranteed repeatabilityGuaranteed comparabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementInformation analysisOriginal data
The invention discloses a biological enhanced functional flora analysis method based on high-flux sequence testing. The method comprises the following operation steps of using a membrane bioreactor; performing functional microbe group domestication by continuously improving the load in inlet water; collecting sludge after the stable operation in each operation stage of the membrane bioreactor; performing centrifugal precipitation so as to enrich microbes; extracting microbe total DNA on sludge samples in each operation stage; performing target fragment PCR amplification; purifying the amplification products; identifying the amplification product quality; mixing different sample PCR amplification products according to the equal mass; performing fragment size and quantitative detection on amixed library; performing high-flux sequence testing; finally performing original data quality control and biological information analysis. The analysis method provided by the invention can be used for systemically analyzing the structure features of the microbe flora in the waste water biochemical treatment process from the ecological aspect, determining the core function flora in the waste watertreatment system and identifying the key water quality parameters influencing the microbe flora structures.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
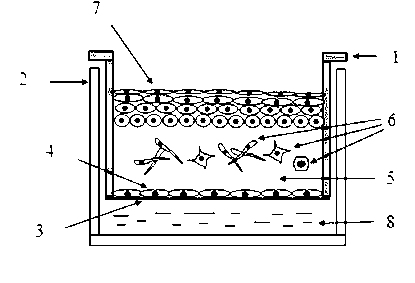
Wetland ecological simulation system
ActiveCN106128231ASimple structureEasy to operateEducational modelsLevel indicators by pressure measurementEcological studyWater level
The invention belongs to the field of ecology, and provides a wetland ecological simulation system. The system comprises a wetland ecological simulation device, a liquid level observation device, and a water pool. The wetland ecological simulation device is used for accommodating the soil and vegetation of a simulation wetland. The liquid level observation device is used for observing the level of water in the wetland ecological simulation device. The water pool is used for supplying water to the wetland ecological simulation device. The system provided by the invention is simple in structure, is convenient to operate, is high in automation degree, and can simulate an actual wetland ecological system in real time.
Owner:NANJING JUNYUAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG CO LTD
Indoor breeding method of fry of rhinogobio ventralis sauvage et dabry
ActiveCN105724288ASolve technical problemsImprove stress resistanceWater treatment parameter controlClimate change adaptationJuvenile fishEcological study
The invention relates to an indoor breeding method of fry of rhinogobio ventralis sauvage et dabry, and belongs to the technical field of breeding of rare and endemic fishes.The method comprises the steps that according to physiological and ecological characteristics of rhinogobio ventralis sauvage et dabry at different development stages of fry, advanced fry and juvenile fishes and differences of sensitivity to main pathogenic microorganisms of ichthyophthirius multifiliis, the whole fry breeding process is divided into three stages of tending barrel micro aeration breeding, tending barrel temperature-control microflow water breeding and glass fiber cylinder imitation-ecology mixed breeding.According to the fry breeding method of the rhinogobio ventralis sauvage et dabry, artificial regulation is conducted on critical water quality environmental factors of plankton communities and water temperature on the basis of intensively studying an influence mechanism of environmental factors causing ichthyophthirius multifiliis, a traditional pond water quality regulation technology is applied to a microflow water breeding mode, a series of technical problems that in the fry breeding process, stress responses of the fry are intense, ichthyophthirius multifiliis occurs frequently, and the fry grow slowly are effectively solved, and a technical support is provided for large-scale breeding of the fry of endemic fishes in the upper Yangtze River.
Owner:CHINESE STURGEON RES INST CHINA THREE GOR
Sustainable method for obtaining tetrodotoxin
InactiveCN102884200AIncrease productionOvercoming resource constraintsBacteriaFermentationBiological bodyEcological study
A sustainable biosynthesizing of tetrodotoxin (TTX) based on seed culture of Vibrio spp is obtained from the mucus of various species of nemerteans (ribbon worms) (phylum Nemertea). The indispensable organisms are kept alive which extends access to crude material and makes the procedure economically and ecologically sustainable.
Owner:NEMERPHARMA
Method for predicting microflora structural variation based on power law scaling model of diversity-area-time relationship (DATR)
The invention discloses a method for predicting and evaluating a microbial structure, in particular to a method for predicting distribution variation of microflora diversity on time and space scales based on a power law scaling model of diversity-area-time relationship (DATR). Sampling loci are subjected to random samplesort, species abundance information is accumulated according to the sampling loci and sampling time order, a species diversity index under accumulated time and space is calculated, and a mathematical model is built through the power law scaling model. A sampling and fitting process is repeated, and a set of comprehensive evaluation system is built by utilizing the average parameters of the models. The index can comprehensively and effectively monitor or predict the structural features and distribution rules of various kinds of microbial ecological communities in nature, and is particularly suitable for human body microbial flora. The method can provide reliable quantitative indexes and ecological basis for evaluation of human body health condition and diagnosis and treatment of flora related diseases according to the rule of change of the structure of the specific flora with time and space.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Simulation three-dimensional incubator and culture method for mouth mucosa epithelial cells and applications of incubator and culture method
InactiveCN103255058ATissue/virus culture apparatusEmbryonic cellsOral mucosal epithelial cellEcological study
The invention discloses a simulation three-dimensional incubator and a culture method for mouth mucosa epithelial cells and applications of the incubator and the culture method. The incubator comprises a single or a plurality of basic structural units, wherein each basic structural unit consists of an inner container and an outer container which are tightly nested with each other, and are prepared from an organic material for cell culture; and the bottom of the inner container consists of a permeable supporting film, and a certain gap is formed between the bottom of the inner container and the bottom of the outer container. The incubator takes the factors of nutrient supply of the mouth mucosa epithelial cells, blood vessels and blood vessel endothelial cells into account, and the growing environment of the mouth mucosa epithelial cells in the incubator is close to that in a human body, so that the incubator can be used for physiological, pharmacological, toxicological and micro-ecological studies of mouth mucosas, and can also be used for constructing human tissue engineering mouth mucosas and repairing and reconstructing mucosal coloboma. The new technology of the simulation three-dimensional incubator promotes an in vitro culture model of a mouth mucosa to a new height, so that related studies are closer to clinical practices.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Uniform grid positioning seed sowing method based on crop ecology experiment
InactiveCN108650946AEqual distanceEasy to operateSowingCereal cultivationEcologic studyEcological study
The invention discloses a uniform grid positioning seed sowing method based on crop ecology experiments. The method comprises the following steps: 1) laying out small cell seedling beds; 2) customizing and laying grids; 3) encoding the grids, and confirming a seed sowing scheme; 4) sowing seeds into the grids; 5) thinning seedlings after seedling emergence; 6) carrying out sampling. By adopting the method, positions of individual plants can be accurately positioned through the grids, seeds can be uniformly sown, distances and seed sowing depths of individual seedlings of wheat can be determined, and advantages of uniform and equal seedling distances, uniform individual sizes and accurate individual plant positions after wheat seedling emergence are achieved. The method disclosed by the invention is easy to operate, provides a scientific basis for studying interactions of individuals in a crop population and relationships of population behaviors and studying interactions of individual plants and ecological study on dense planting plants, and has popularization values.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Tetraena mongolica microsatellite locus, as well as amplification primer and application thereof
InactiveCN109371151AGood effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTetraena mongolicaMicrosatellite
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and provides a tetraena mongolica microsatellite locus and a primer sequence thereof. The tetraena mongolica microsatellite locus has a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-10. The tetraena mongolica microsatellite locus can be used in molecular ecological research, pedigree analysis, germplasm resources investigation, assistant breeding and individual recognition of tetraena mongolica, and provides basic materials to studying plant drought resisting mechanisms.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA ENERGY CO LTD +2
A Quantitative Analysis Method for the Effect of Gate and Dam Regulation on the Spatial Characteristics of Fish Habitat
ActiveCN107563610BReflect habitat statusWater resource protectionPisciculture and aquariaHydrometryWater resource planning
The invention discloses a quantification analysis method of fish habitat space characteristics influenced by gate dam regulation and control; the method comprises the following steps: investigating fish resource present situations in a research area, and screening a target fish; aiming at the screened target fish, and using indoor stress experiments and history data to build a quantification response relation curve of the target fish with respect to key habitat factors; gathering research area basic hydrology and landform data so as to build a water-power water environment model, and combiningthe quantification response relation curve of the target fish with respect to key habitat factor so as to build a habitat model facing fish habitats; introducing a landscape ecology theory and methodso as to evaluate the space characteristics of the habitat simulation result facing the fish habitat, and quantitatively analyzing the influences on the fish habitat space characteristics by the gatedam operations. The method can guide multi-gate dam river ecology restorations and protections, thus providing important theory and practice meanings for basin water resource planning and configurations.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
Skeletonema costatum PCNA gene detecting method
InactiveCN101130820BConfirmation of specificitySolve the problem of detection specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDynamic modelsEcological study
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for realizing asymmetric reduction of p-propiophenone compounds by adopting carrot tissue or callus and applications of carrot tissue or callus in asymmetric reduction of p-propiophenone compounds
The invention provides a method for realizing asymmetric reduction of p-propiophenone compounds by adopting carrot tissue and callus cells. The method comprises the following steps: preparing p-propiophenone compound standard substance, extracting the carrot tissue, preparing a culture medium, carrying out reduction on the substrate by adopting the carrot tissue, culturing the carrot callus, buffering the cultured solution, and carrying out asymmetric reduction on the substrate by adopting the carrot callus. The invention further provides applications. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that great economical and ecological significance is obtained for the preparation of chelloral medicines and the realization of green chemistry.
Owner:杨妮
A Plant Leaf Imprint Weighing In Vivo Assay
Owner:TEA RES INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Multichannel double-circulation soil carbon discharge delta13C observing system
The invention relates to the field of ecological study, and provides a multichannel double-circulation soil carbon discharge delta13C observing system. The multichannel double-circulation soil carbon discharge delta13C observing system consists of a gas analyzing system and a circuit control system. The gas analyzing system comprises a discharging box, a box cover, a sampling pipe, an air pump, a three-way solenoid valve, a multichannel solenoid valve, a delta13C analyzer and a single chip microcomputer. The circuit control system is formed by connecting a power source, a control line, a switch and a contact according to a given circuit. With the adoption of the multichannel double-circulation soil carbon discharge delta13C observing system, automatic conversion and circular observation among a plurality of channels are realized, so as to remove interference of 'dead air' on an observing result, save observing time of each channel, and improve the efficiency and the accuracy of soil carbon discharge delta13C observation.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Remote automatic monitoring system for termites based on Internet of Things
InactiveCN105230588BEffective prevention and control methodsImprove the effect of prevention and controlClosed circuit television systemsInsect catchers and killersEcologic studyMonitoring system
Owner:熊忠阳 +1
A method of measuring soil flow in forest soil
The invention discloses a method for measuring interflow in forest soil, and belongs to the field of forest soil ecological study. The method is characterized in that the system utilizes the soil profile and consists of an interflow flow collecting groove, a flow guide pipe and an interflow collector, wherein the flow collecting groove is embedded into a soil body in different layers of the soil profile, the interflow is collected, and the interflow is guided into the collector for completing the collection of the interflow. The method has the advantages that the structure is compact, the system is reasonable, the method is simple, the realization is easy, a scientific and reasonable small-dimension measuring system is provided for the study of the forest soil hydrology process, the moisture and nutrient balance and moving and the like, and greater popularization and application values are realized in the fields of forest soil ecology, forest hydrology, water and soil conservation and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com