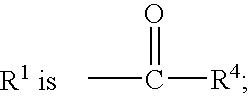
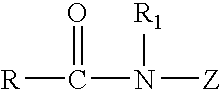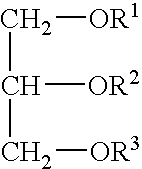Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
156 results about "Fluid gel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
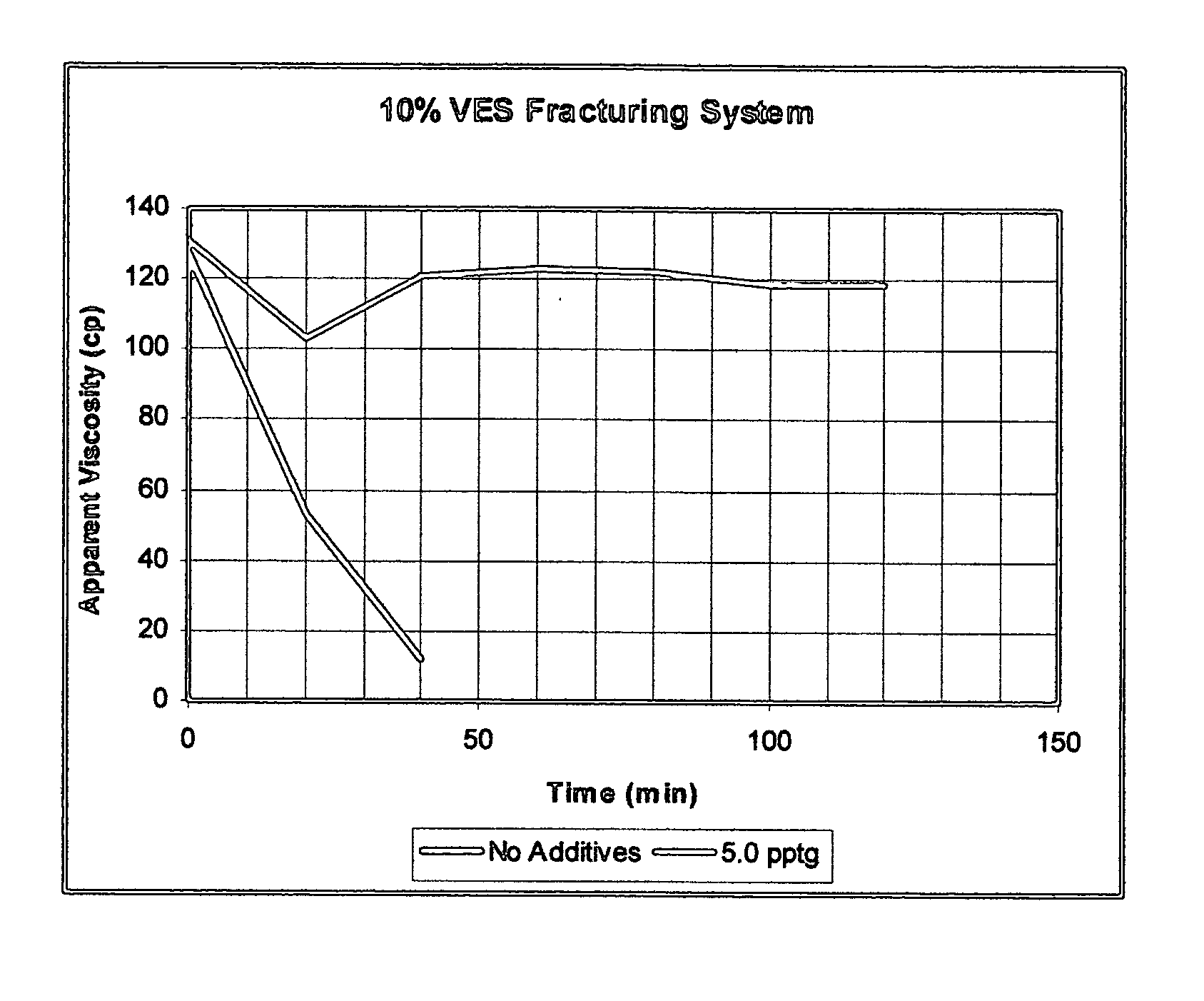
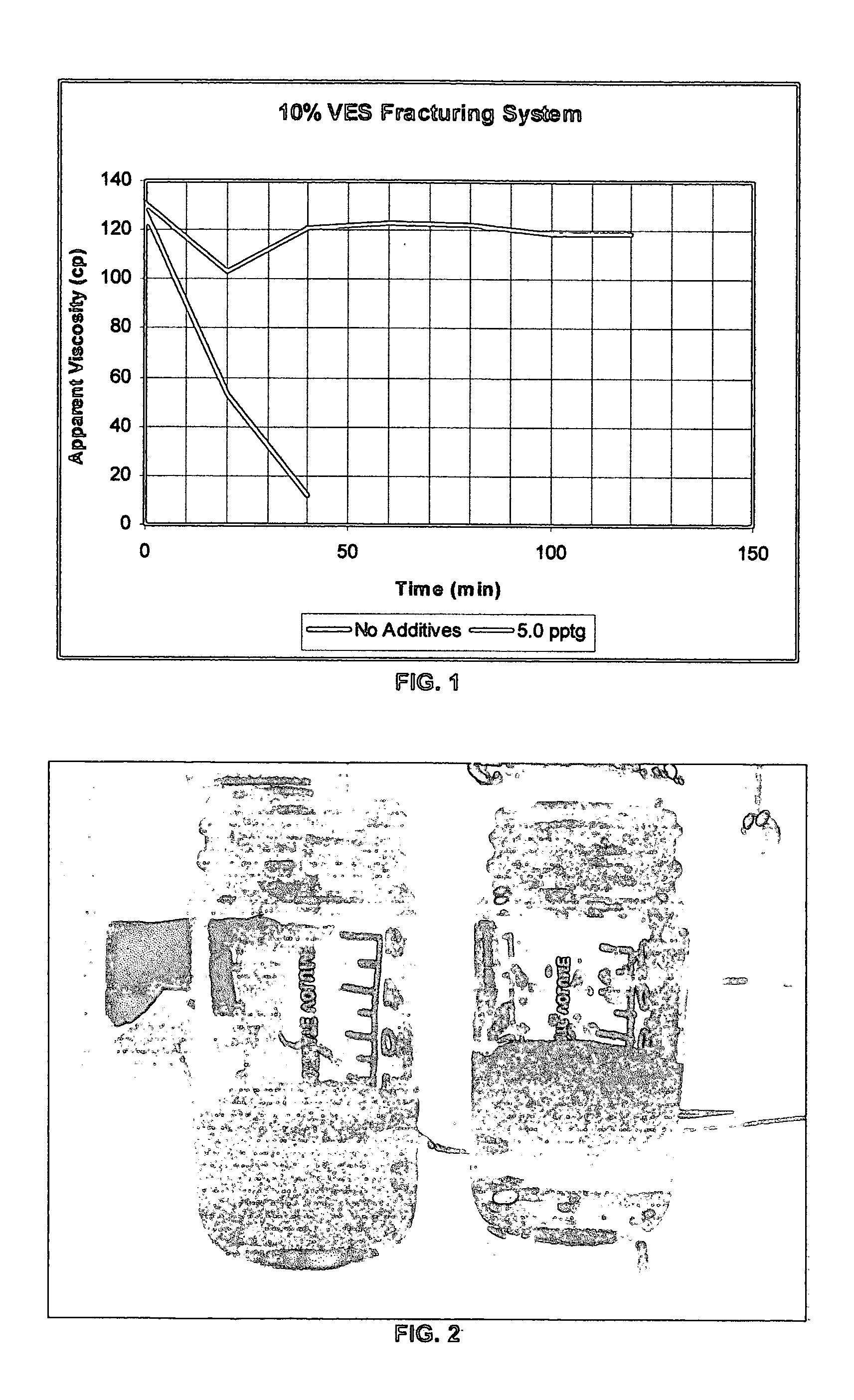
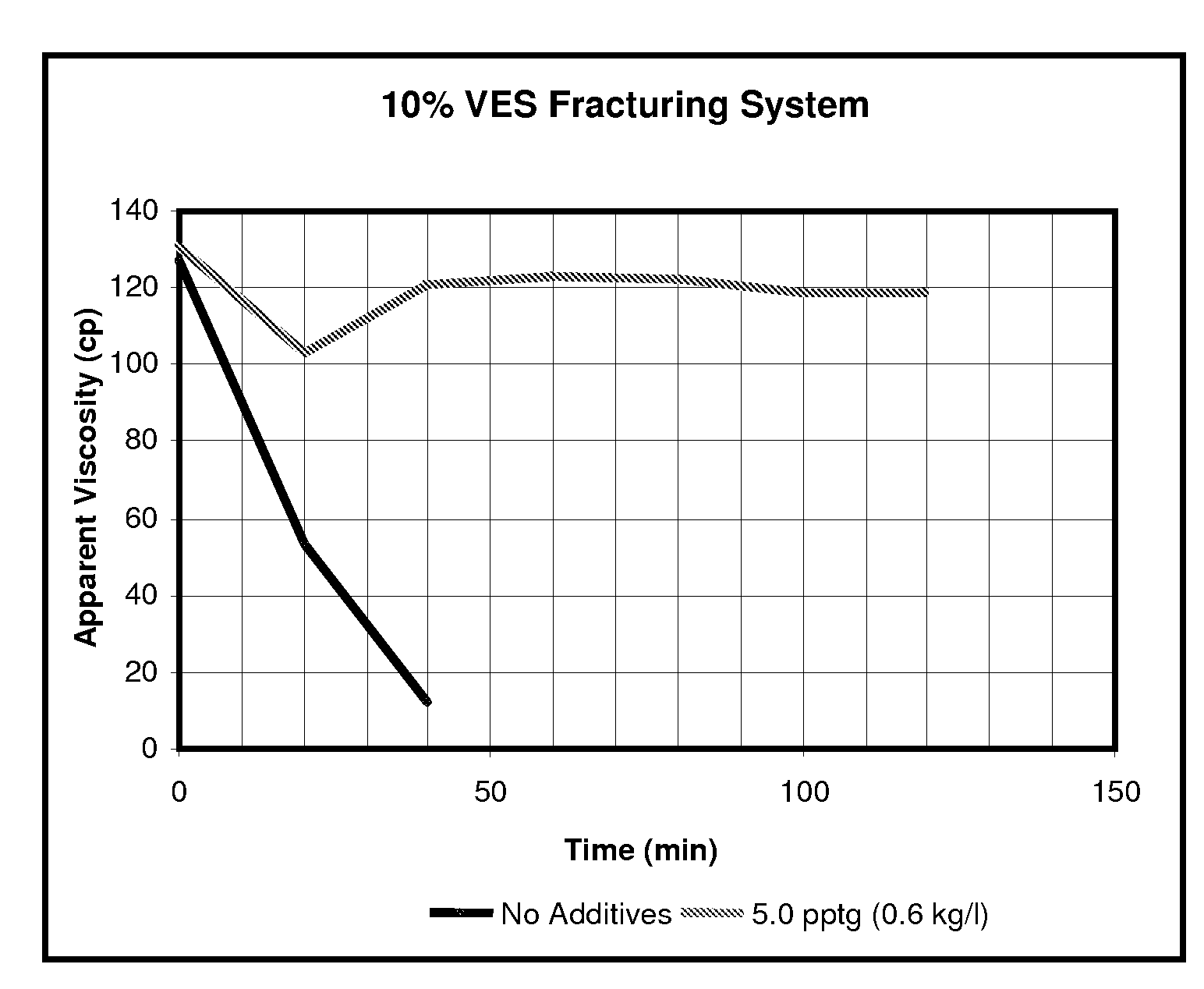
System stabilizers and performance enhancers for aqueous fluids gelled with viscoelastic surfactants
InactiveUS20050252658A1Improve stabilityReduce precipitationFluid removalDrilling compositionFluid gelHydraulic fracturing
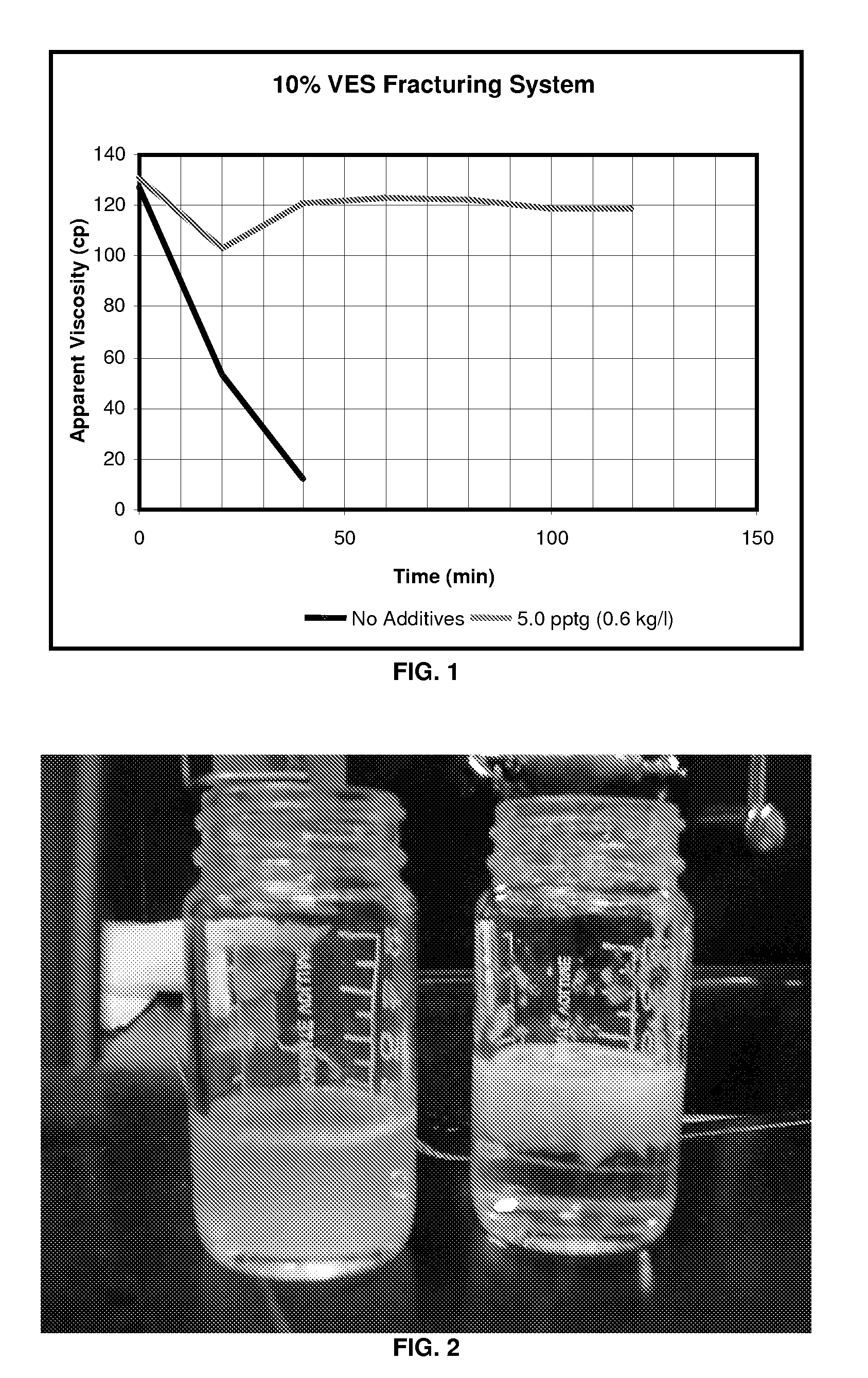
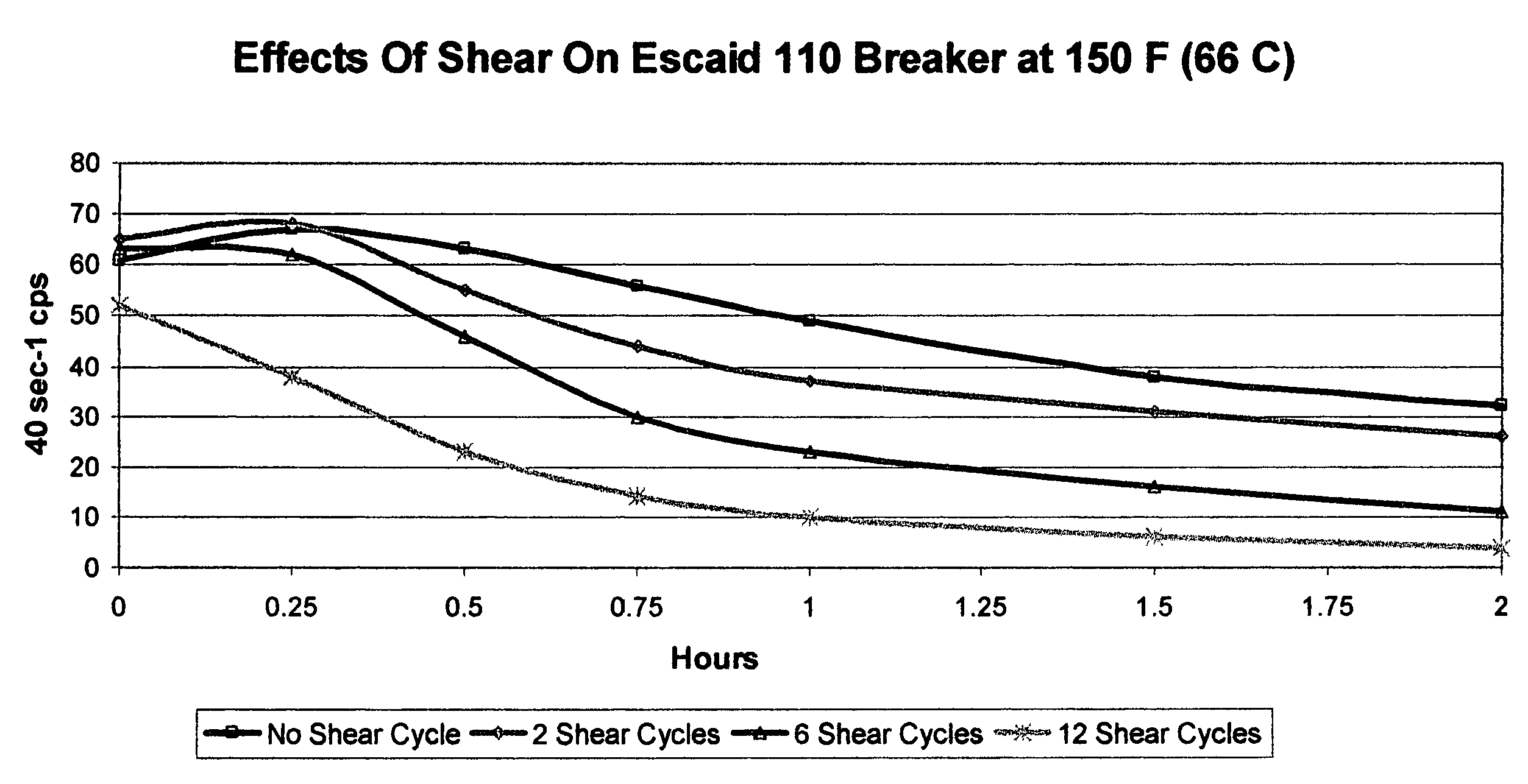
An aqueous, viscoelastic fluid gelled with a viscoelastic surfactant (VES) is stabilized and improved with an effective amount of an alkali earth metal oxide and / or alkali earth metal hydroxide. These fluids are more stable and have reduced or no tendency to precipitate, particularly at elevated temperatures. The additives may also increase viscosity to the point where less VES is required to maintain a given viscosity. These stabilized, enhanced, aqueous viscoelastic fluids may be used as treatment fluids for subterranean hydrocarbon formations, such as in hydraulic fracturing.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
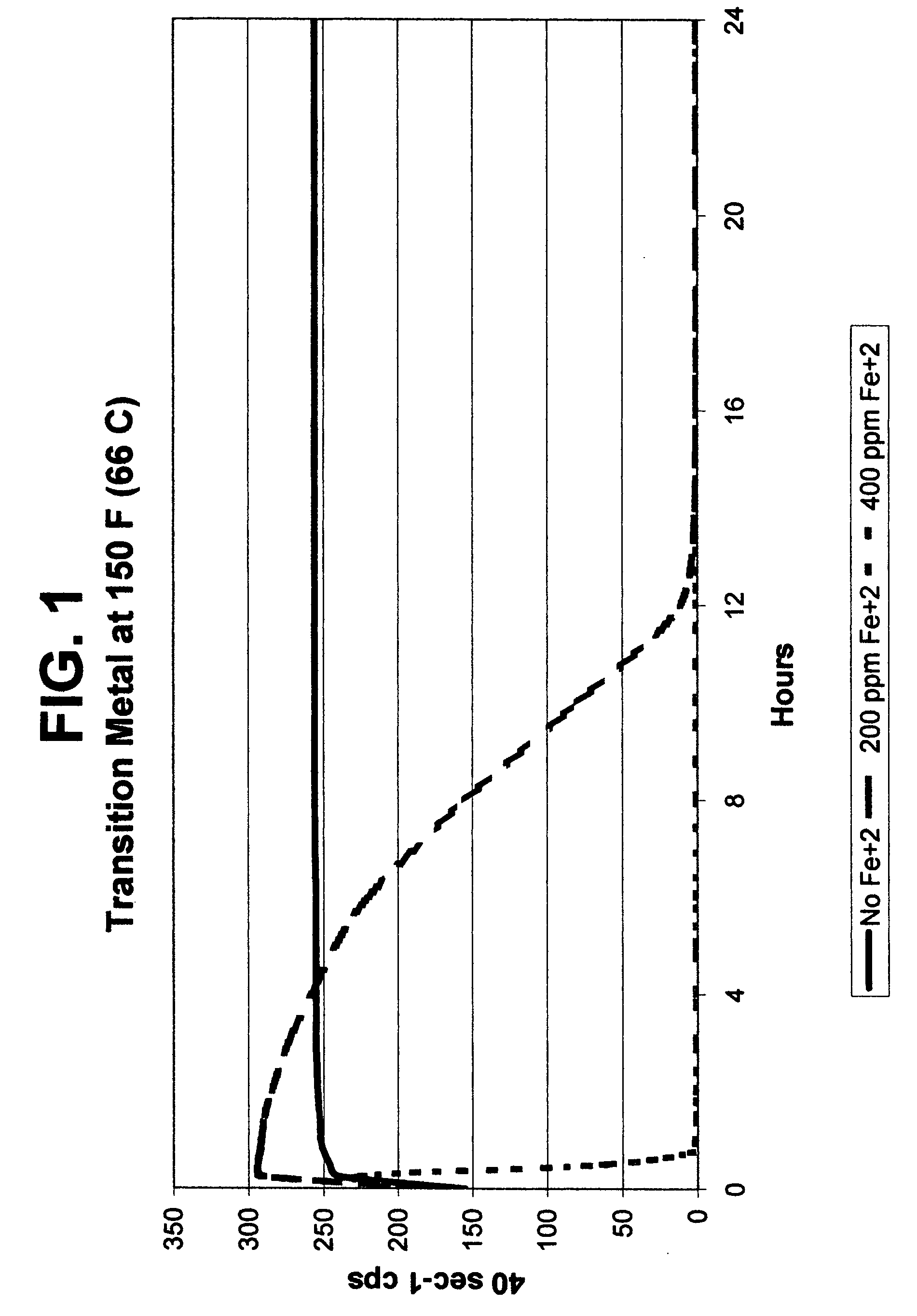
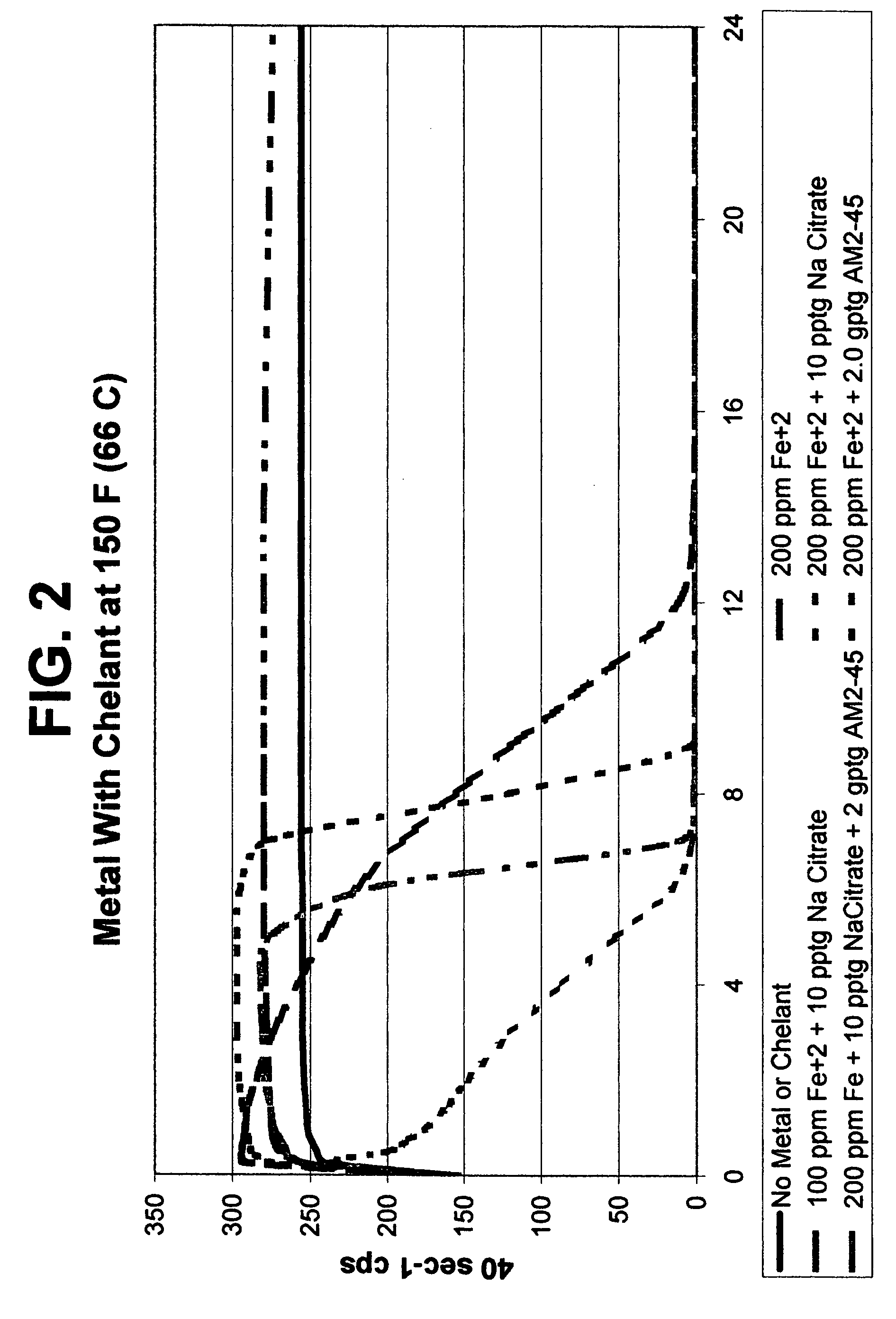
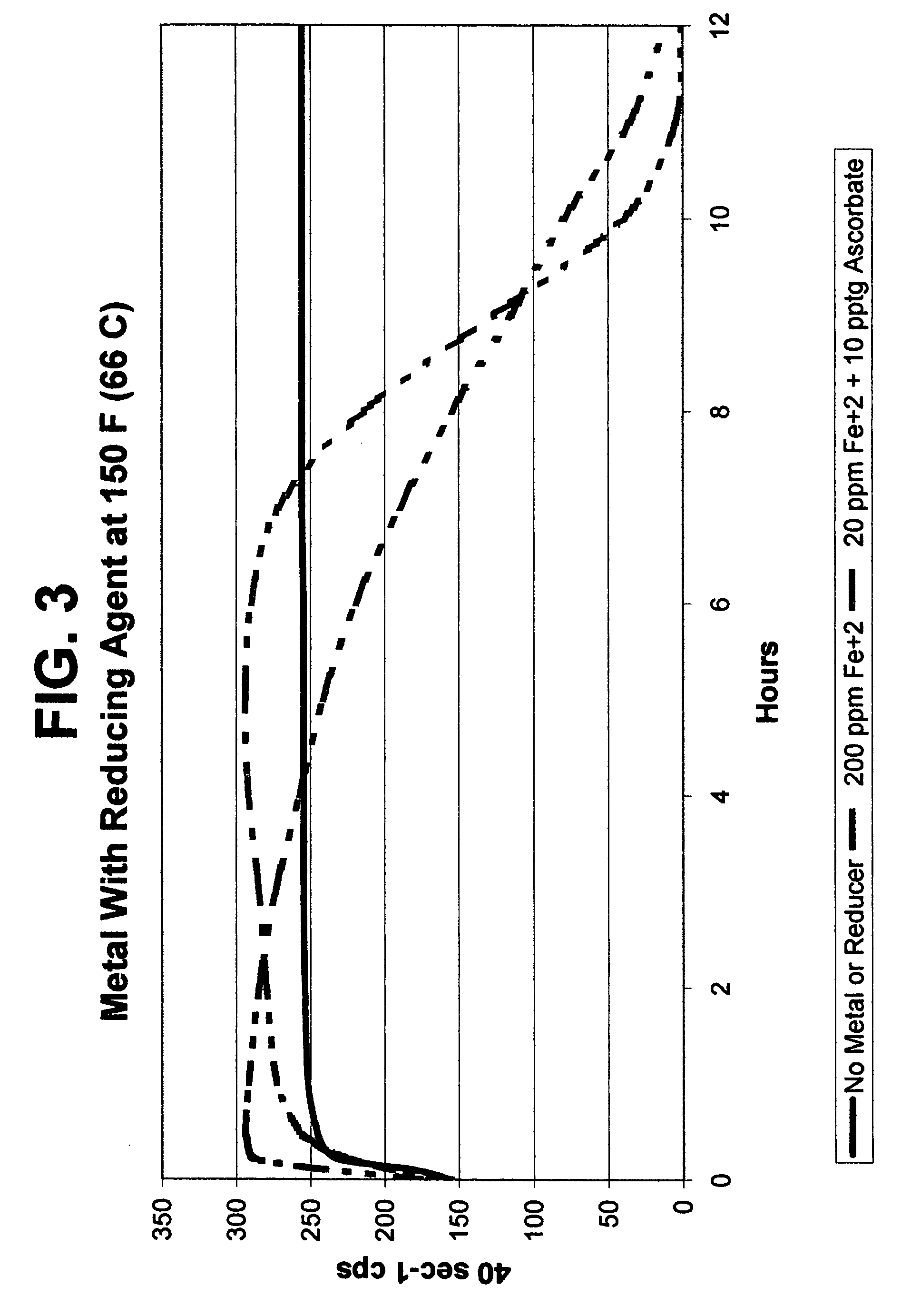
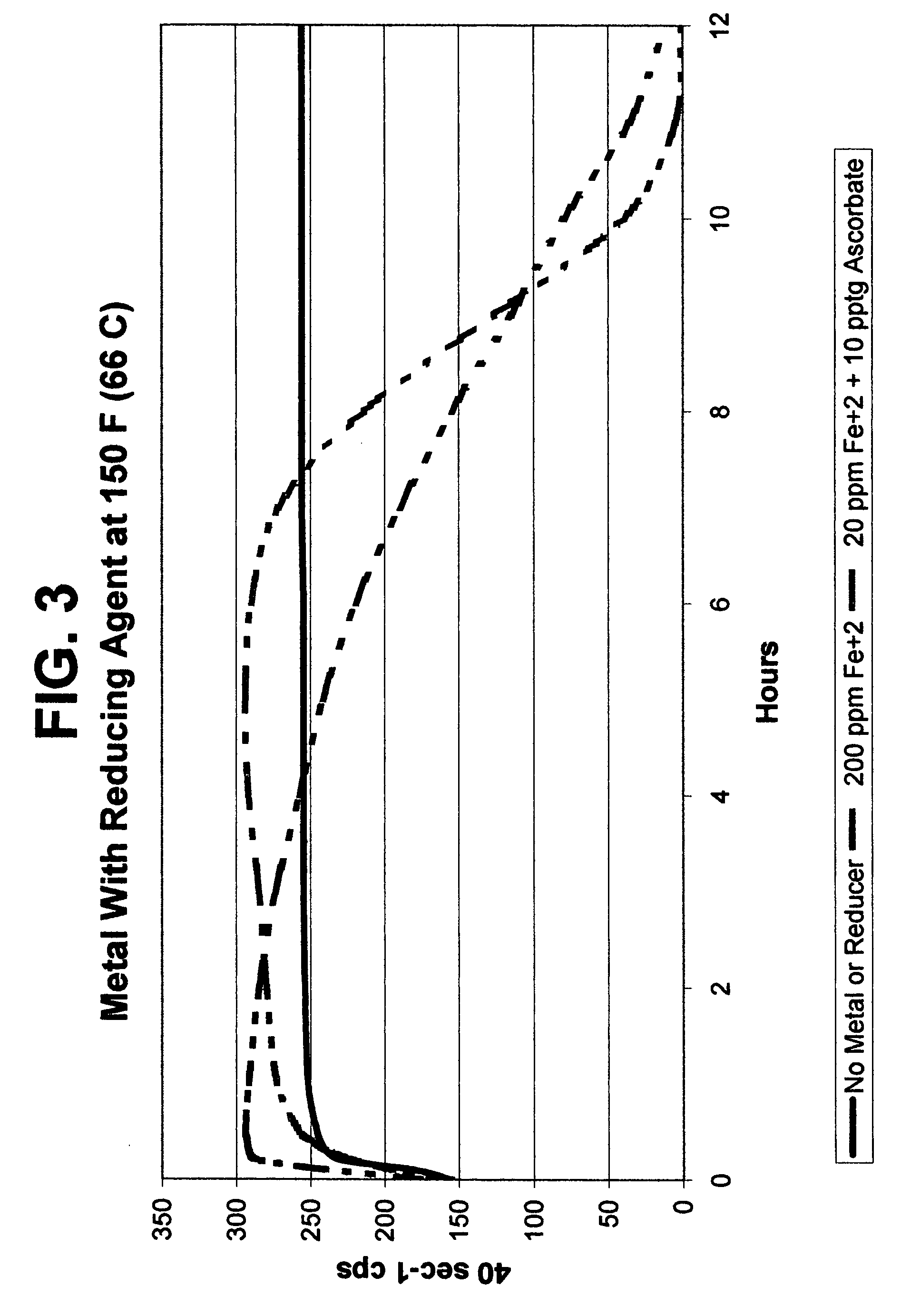
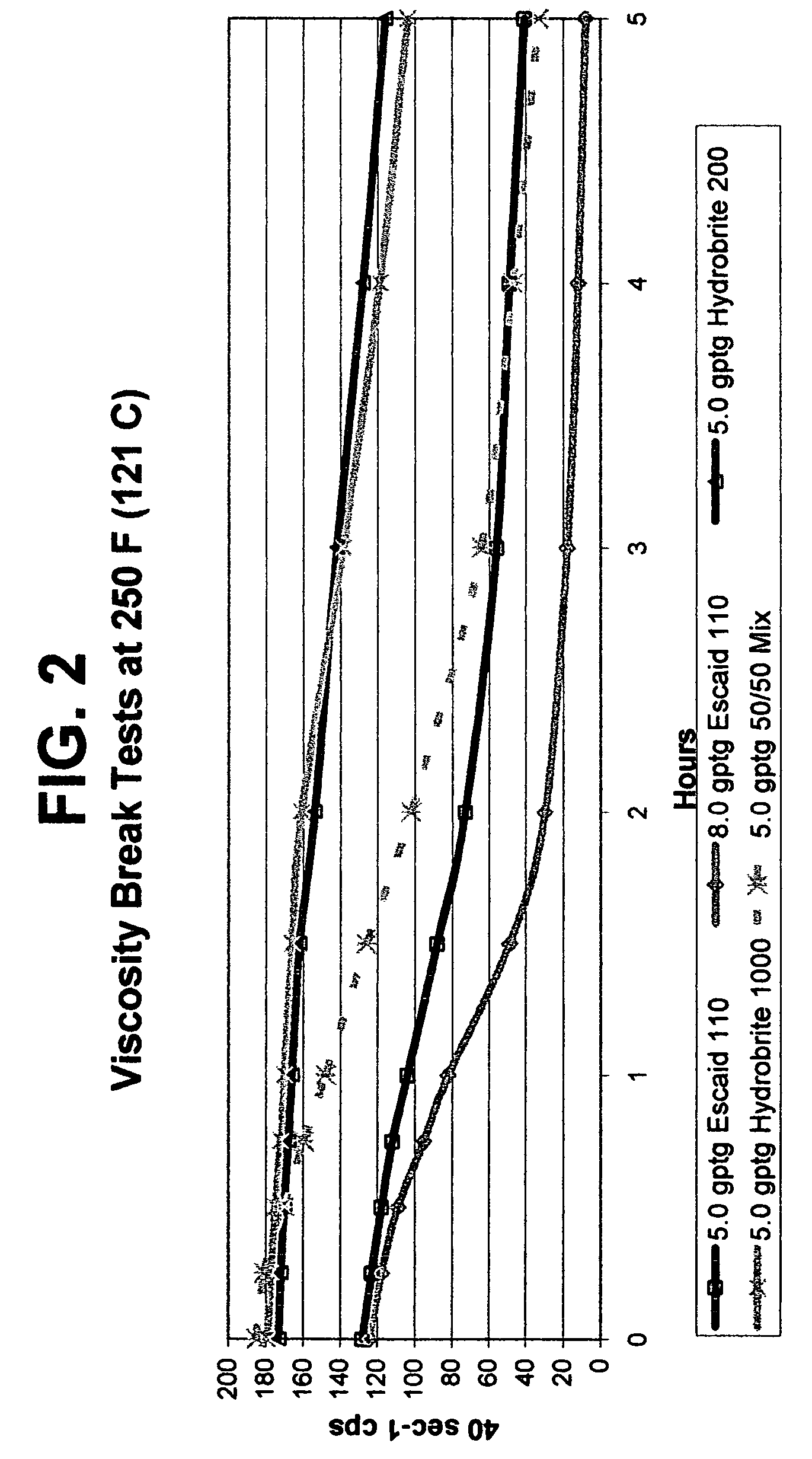
Metal-mediated viscosity reduction of fluids gelled with viscoelastic surfactants
ActiveUS20060041028A1Break viscosityQuick breakOther chemical processesFluid removalChemical structureFluid gel
Fluids viscosified with viscoelastic surfactants (VESs) may have their viscosities reduced (gels broken) by the direct or indirect action of a composition that contains at least one metal ion source and optionally at least one second source. An optional second source may be a chelating agent where at least one reducing agent source may be additionally optionally used. Another optional component with the metal ion source includes a second, different metal ion source. The breaking composition is believed to directly attack the VES itself, possibly by disaggregating or otherwise attacking the micellar structure of the VES-gelled fluid, and / or possibly by changing the chemical structure of the VES to give two or more products.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Thermoreversible pharmaceutical formulation for anti-microbial agents comprising poloxamer polymers and hydroxy fatty acid ester of polyethylene glycol
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical formulation having thermoreversible properties, comprising: a) an anti-microbial agent; b) a poloxamer mixture containing at least two poloxamer polymers; and c) a hydroxy fatty acid ester of polyethylene glycol, wherein the formulation is a solid at room temperature and is a liquid-gel at body temperature. The thermoreversible pharmaceutical formulation has a viscosity of about 8,500 cP to about 400,000 cP at room temperature, and a viscosity of about 1,000 cP to about 8,000 cP at body temperature and exhibits a hysteresis loop behavior. The present invention further provides a process of preparing as well as a method of treating a microbial infection in a mammal using the same.
Owner:TARO PHARMA INDS
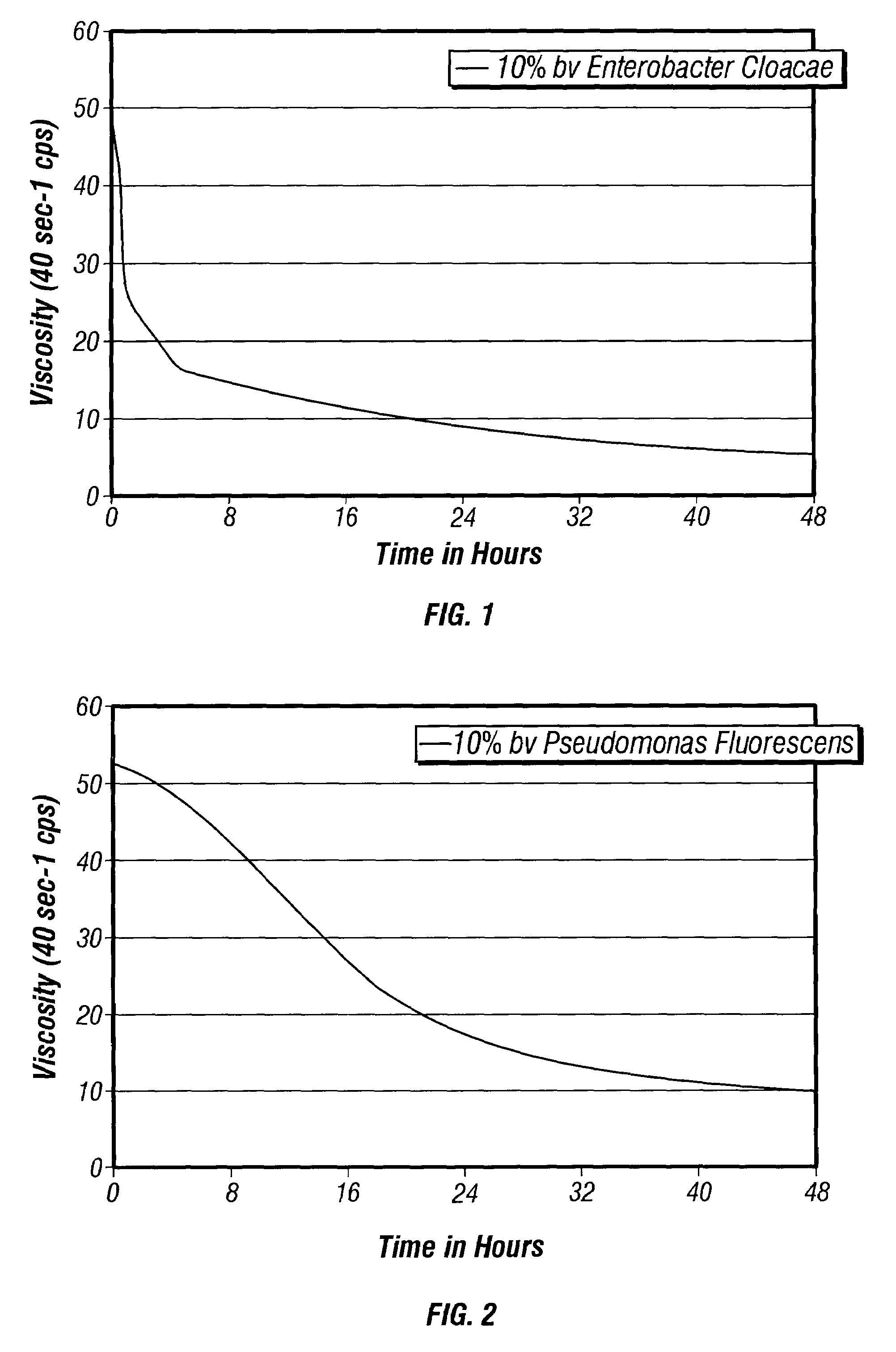
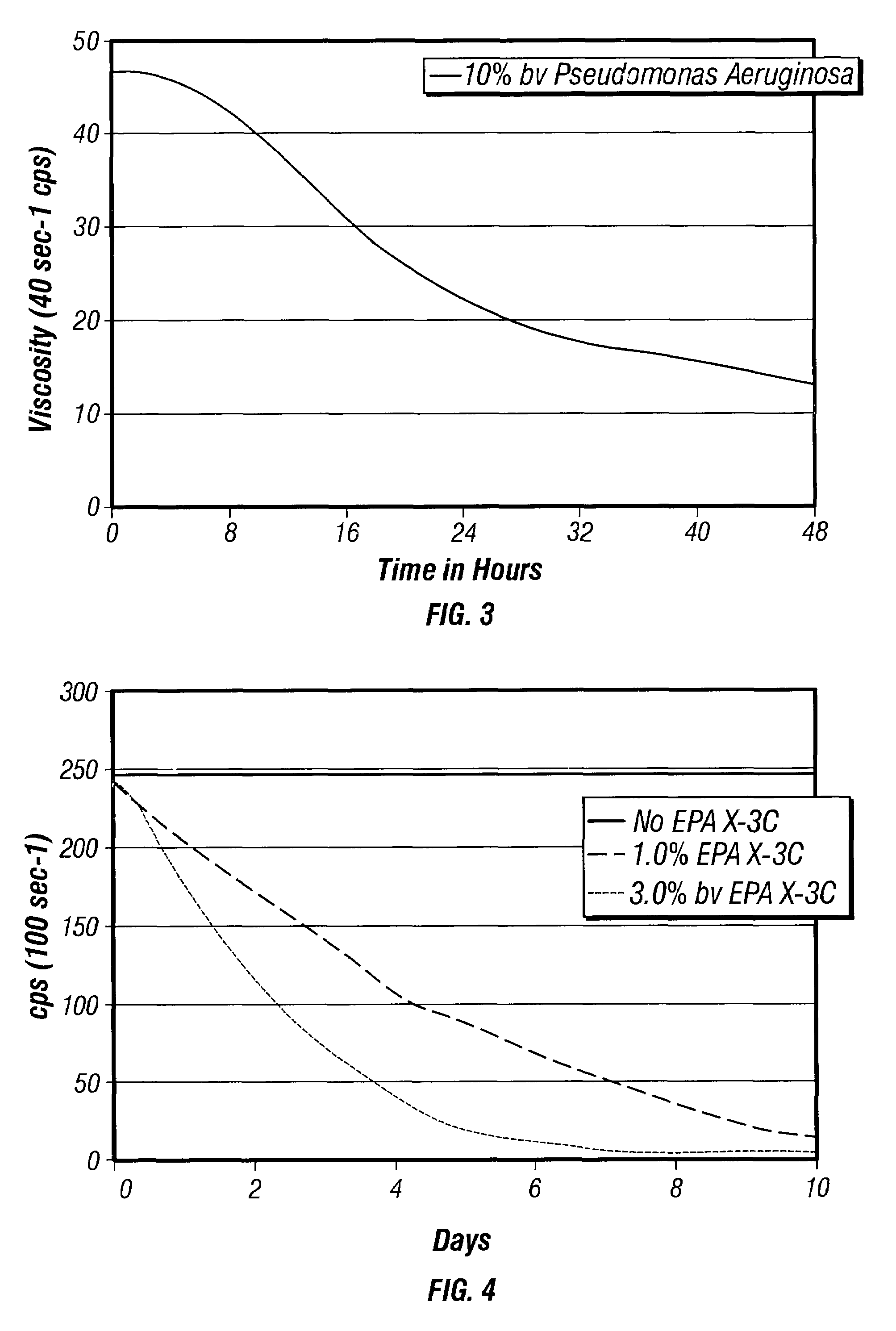
Bacteria-based and enzyme-based mechanisms and products for viscosity reduction breaking of viscoelastic fluids
ActiveUS7052901B2Low viscosityBreak viscosityDeodrantsFlushingIndirect actionPseudomonas fluorescens
It has been discovered that fluids viscosified with viscoelastic surfactants (VESs) may have their viscosities reduced (gels broken) by the direct or indirect action of a biochemical agent, such as bacteria, fungi, and / or enzymes. The biochemical agent may directly attack the VES itself, or some other component in the fluid that produces a by-product that then causes viscosity reduction. The biochemical agent may disaggregate or otherwise attack the micellar structure of the VES-gelled fluid. The biochemical agent may produce an enzyme that reduces viscosity by one of these mechanisms. A single biochemical agent may operate simultaneously by two different mechanisms, such as by degrading the VES directly, as well as another component, such as a glycol, the latter mechanism in turn producing a by-product (e.g. an alcohol) that causes viscosity reduction. Alternatively, two or more different biochemical agents may be used simultaneously. In a specific, non-limiting instance, a brine fluid gelled with an amine oxide surfactant can have its viscosity broken with bacteria such as Enterobacter cloacae, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and the like.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Use of mineral oils, hydrogenated polyalphaolefin oils and saturated fatty acids for breaking ves-gelled fluids
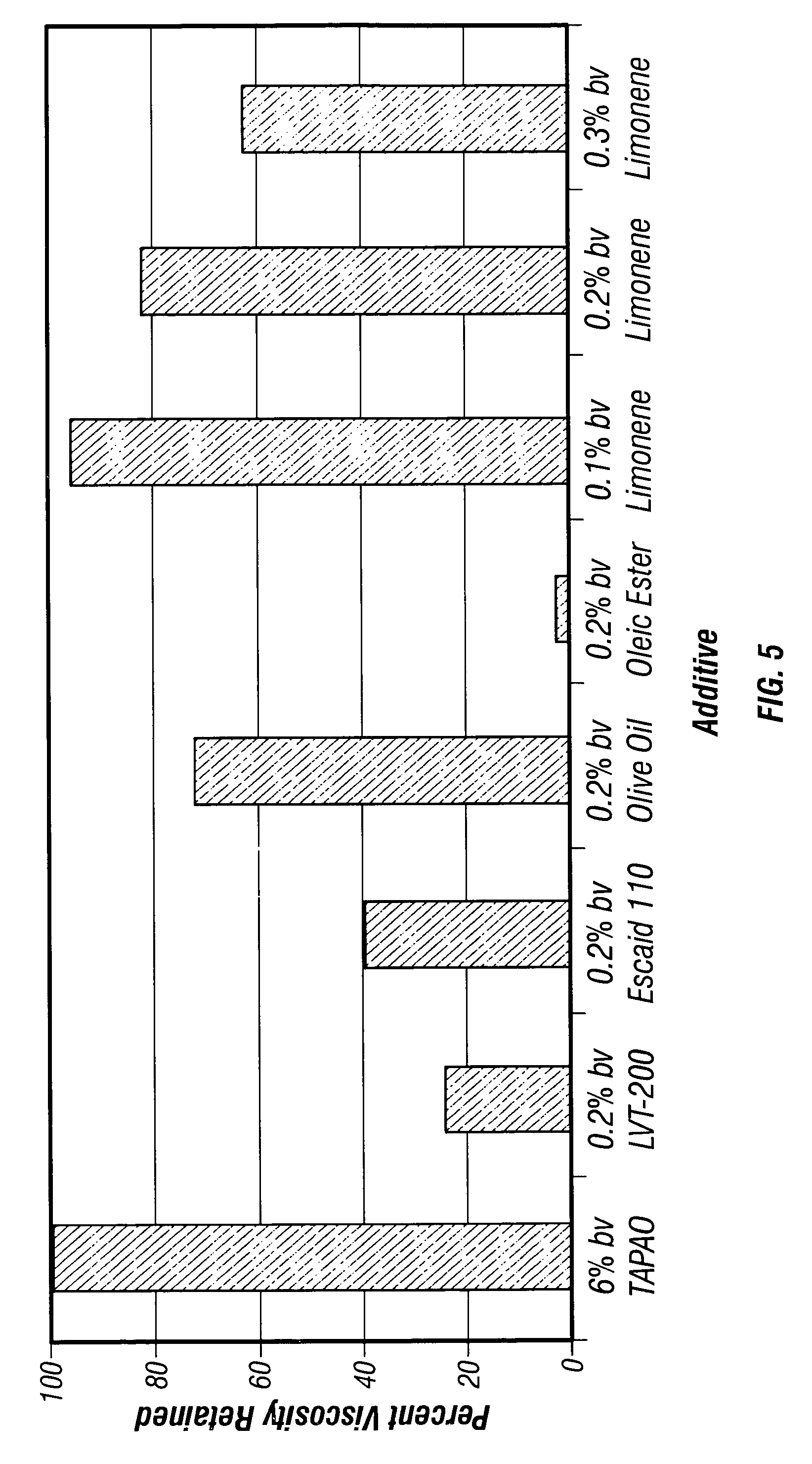
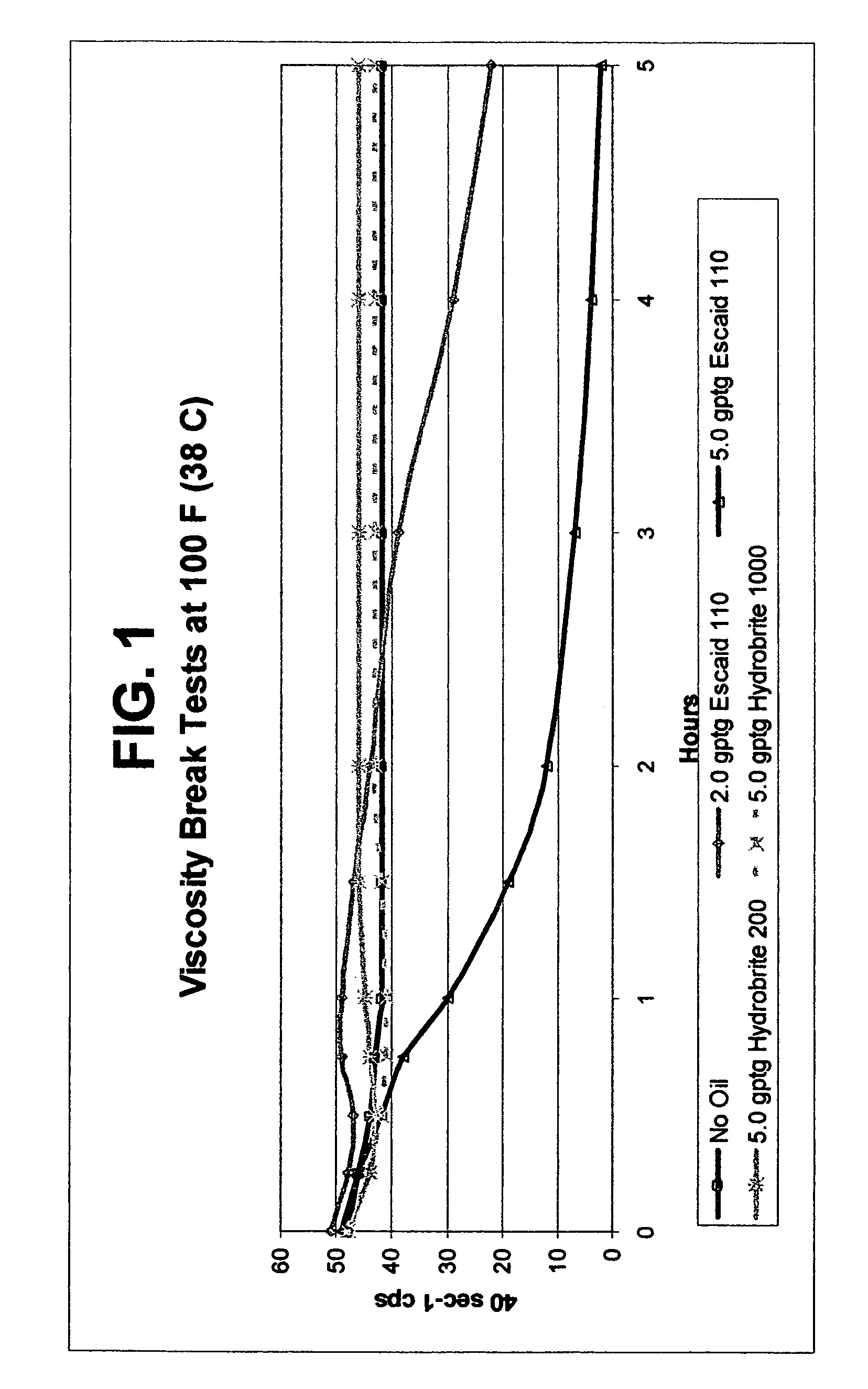
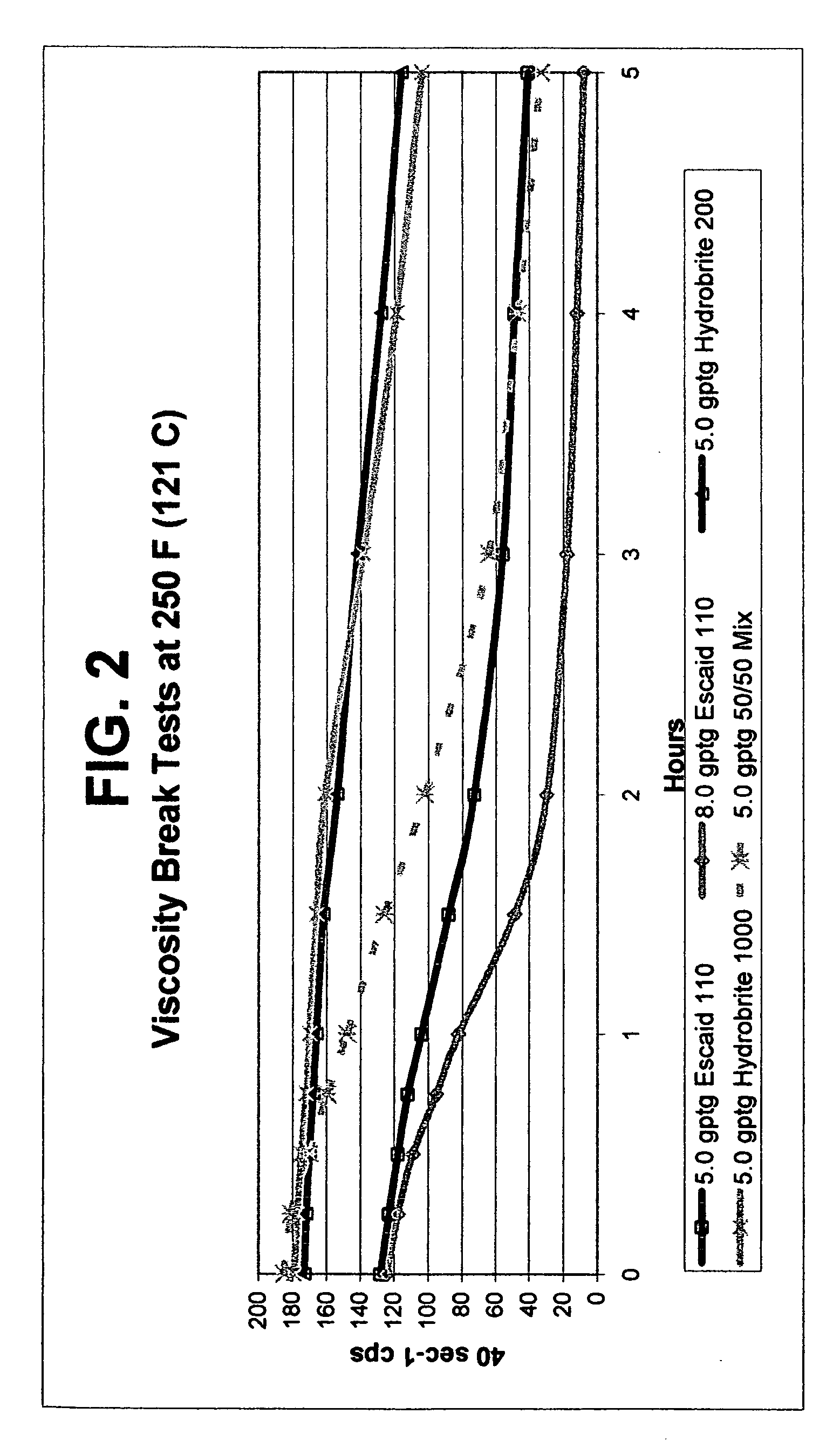
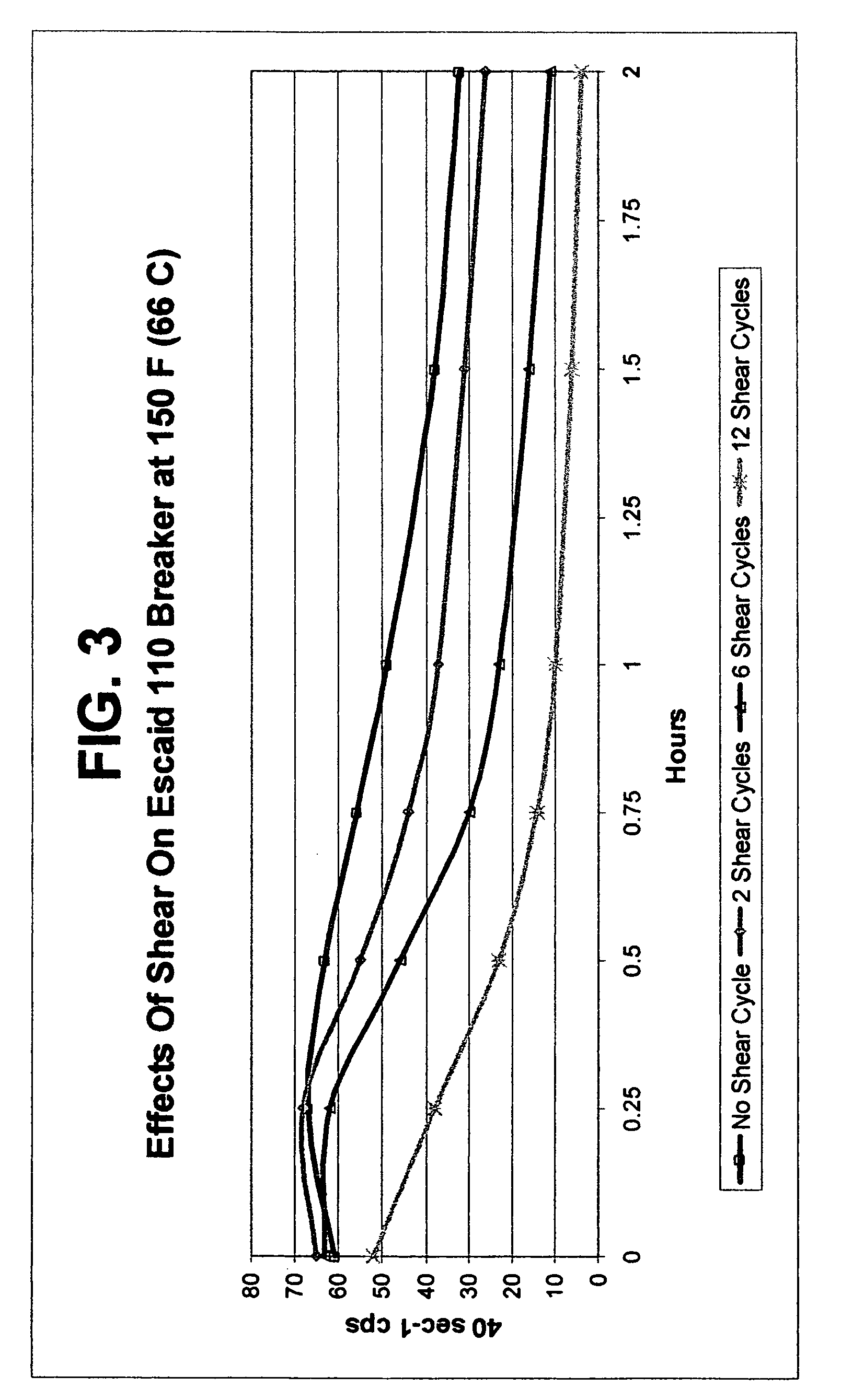
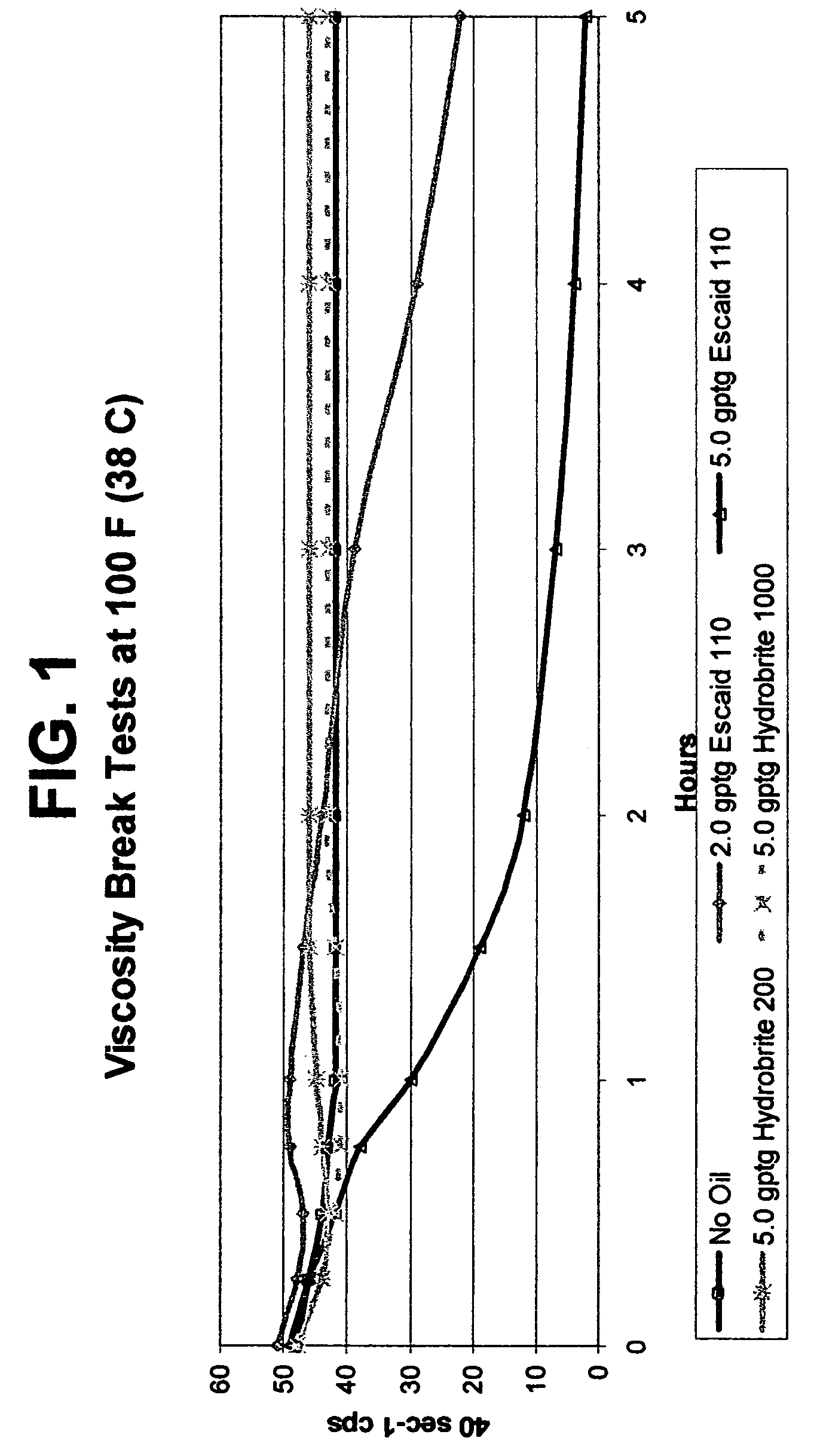
Fluids viscosified with viscoelastic surfactants (VESs) may have their viscosities reduced (gels broken) by the direct or indirect action of a breaker composition that contains at least one mineral oil, at least one polyalphaolefin oil, and / or at least one saturated fatty acid. The breaker may initially be dispersed oil droplets in an internal, discontinuous phase of the fluid. In one non-limiting embodiment, the breaker, e.g. mineral oil is added to the fluid after it has been substantially gelled. The breaking composition is believed to act possibly by rearranging, disaggregating or otherwise attacking the micellar structure of the VES-gelled fluid in a non-spontaneous, rate controlled manner at elevated fluid temperatures. In a specific, non-limiting instance, a brine fluid gelled with an amine oxide surfactant can have its viscosity broken with a light, low viscosity paraffinic mineral oil.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Laundry detergent compositions comprising amphiphilic graft polymers based on polyalkylene oxides and vinyl esters
InactiveUS20090005288A1Negatively impacting general cleaning capabilityLower surfactant levelOrganic detergent compounding agentsDetergent solventsOrganic solventPolybutylene
A laundry detergent composition comprising a graft copolymer of polyethylene, polypropylene or polybutylene oxide with vinyl acetate in a weight ratio of from about 1:0.2 to about 1:10; from about 0.2% to about 8% of organic solvent; and from about 2% to about 20% of a surfactant system; wherein said detergent composition is in a form selected from: liquid; gel; and combinations thereof.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method and composition for preventing tooth hypersensitivity when using passive bleaching agents
InactiveUS20060013778A1Avoid allergiesLonger contact/coating periodCosmetic preparationsGum massageZinc peroxidePotassium nitrate
Dental bleaching compositions, for example in the form of liquids, gels, creams, pastes and ointments, comprising a peroxide releasing compound and from 1% to 35% by weight of a potassium-containing compound such as potassium nitrate, wherein the potassium nitrate is present in a safe and effective amount to prevent tooth hypersensitivity in the patient during the bleaching process. The potassium nitrate contemplated by the invention is compatible with peroxide yielding bleaching compounds such as peroxide, carbamide peroxide, calcium peroxide, zinc peroxide, magnesium peroxide and sodium perborate. Potassium nitrate is complimentary and synergistic with the peroxide bleaching agents contemplated by the invention and enhances the release of oxygen to the tooth enamel. Also contemplated are methods of bleaching teeth comprising application of the dental bleaching compositions of the invention.
Owner:HODOSH MILTON
Compositions for stabilizing DNA, RNA and proteins in saliva and other biological samples during shipping and storage at ambient temperatures
ActiveUS20130209997A1Prevent degradationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSaliva sampleColloid
Compositions and methods are disclosed for substantially liquid, gel, suspension, slurry, semisolid and / or colloid storage of biological samples following admixture with the herein disclosed storage composition, permitting substantial recovery of biological activity following storage without refrigeration. In certain embodiments, unfractionated saliva samples may be stored without refrigeration for weeks, months or years in a form that permits recovery of intact DNA following the storage period.
Owner:BIOMATRICA INC
Metal-mediated viscosity reduction of fluids gelled with viscoelastic surfactants
ActiveUS7595284B2Quick breakLow viscosityOther chemical processesFluid removalChemical structureFluid gel
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
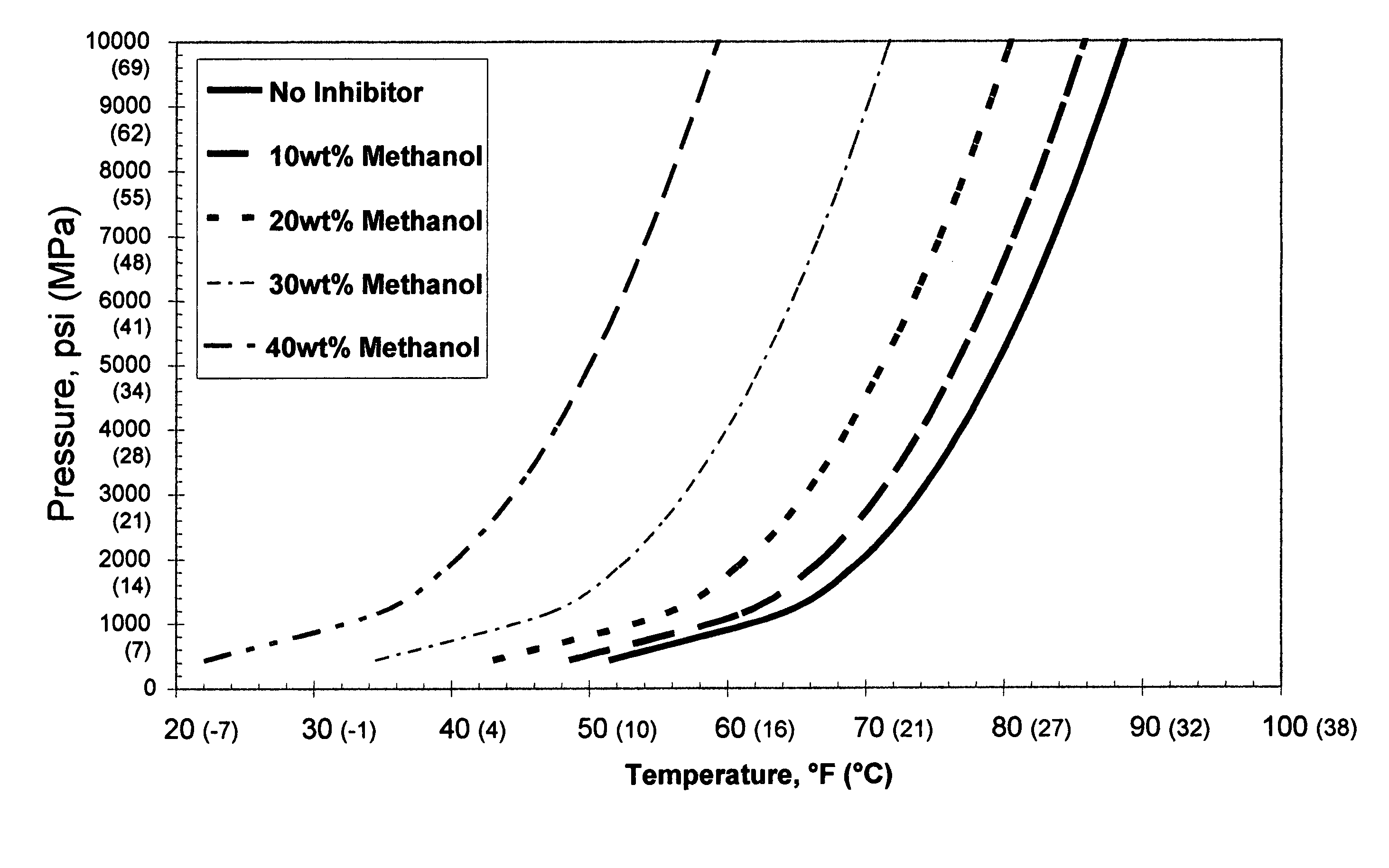
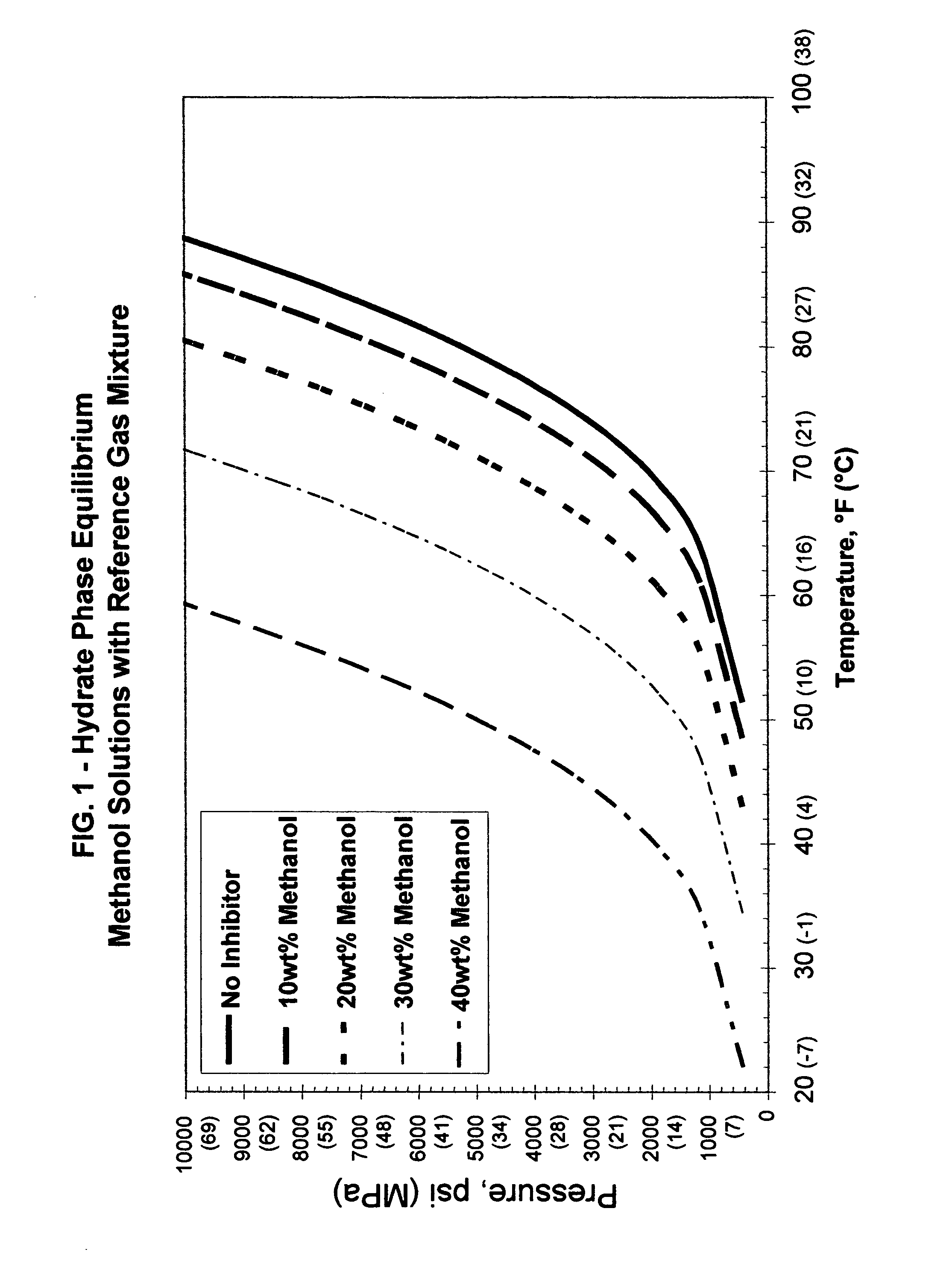
Additives for hydrate inhibition in fluids gelled with viscoelastic surfactants
An aqueous, viscoelastic fluid gelled with a viscoelastic surfactant (VES) is inhibited against hydrate formation with an effective amount of an additive that could be one or more halide salts of alkali metals and alkali earth metals, formate salts, alcohols, glycols, glycol amines, sugars, sugar alcohols, amidoamine oxides, polymers such as polyamines, polyvinylpyrrolidones and derivatives thereof, polyvinyl alcohols and derivatives thereof, polycaprolactams and derivatives thereof, hydroxyethylcellulose, and mixtures thereof. These fluids are inhibited against hydrate formation and may have increased viscosity as well. The additives may increase viscosity to the point where less VES is required to maintain a given viscosity. These inhibited, aqueous, viscoelastic fluids may be used as treatment fluids for subterranean hydrocarbon formations, such as in stimulation treatments, e.g. hydraulic fracturing fluids.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
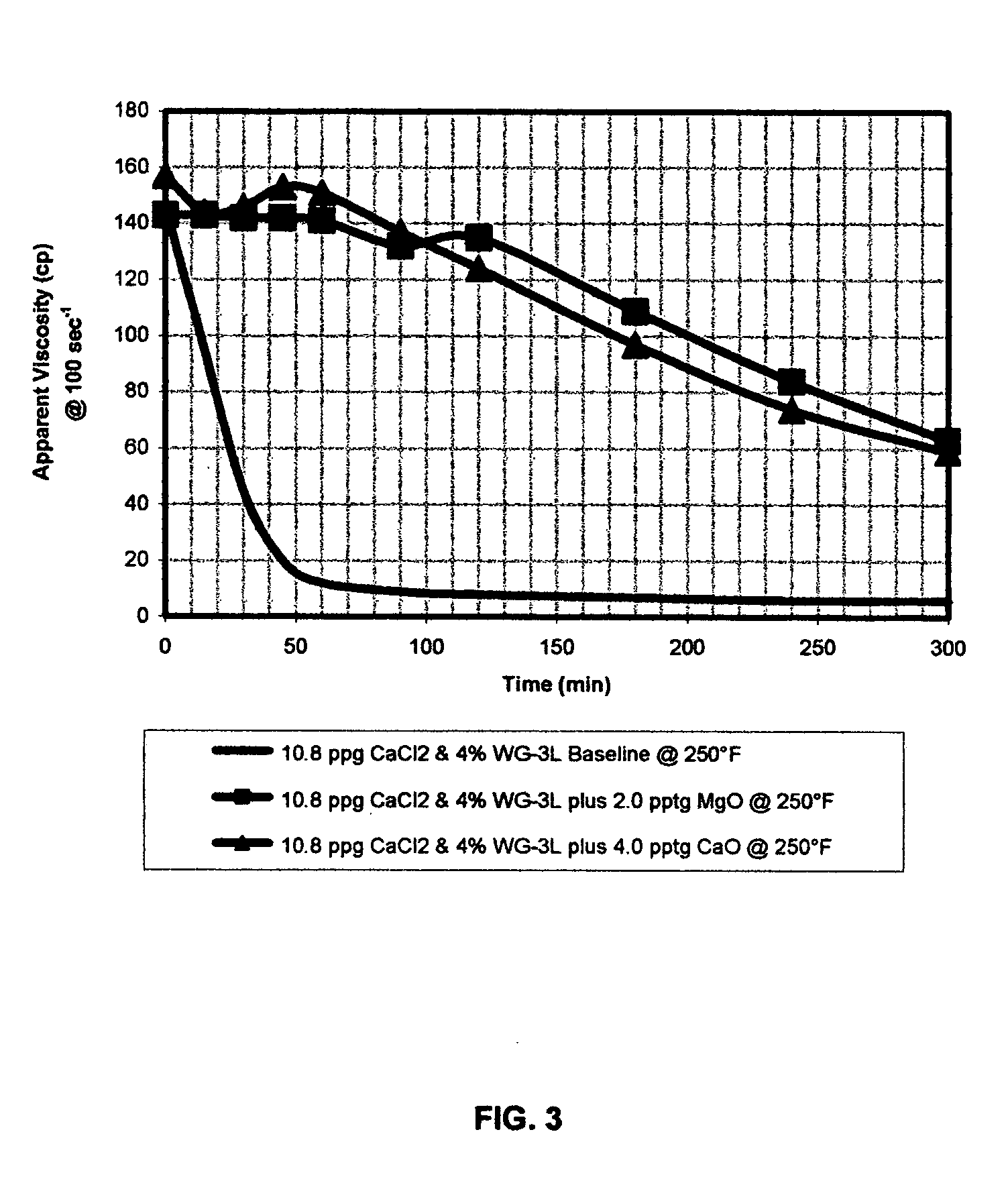
System stabilizers and performance enhancers for aqueous fluids gelled with viscoelastic surfactants
InactiveUS7343972B2Improve stabilityReduce precipitationFluid removalDrilling compositionFluid gelAlkaline earth oxides
An aqueous, viscoelastic fluid gelled with a viscoelastic surfactant (VES) is stabilized and improved with an effective amount of an alkali earth metal oxide and / or alkali earth metal hydroxide. These fluids are more stable and have reduced or no tendency to precipitate, particularly at elevated temperatures. The additives may also increase viscosity to the point where less VES is required to maintain a given viscosity. These stabilized, enhanced, aqueous viscoelastic fluids may be used as treatment fluids for subterranean hydrocarbon formations, such as in hydraulic fracturing.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Use of mineral oils, hydrogenated polyalphaolefin oils and saturated fatty acids for breaking ves-gelled fluids
Fluids viscosified with viscoelastic surfactants (VESs) may have their viscosities reduced (gels broken) by the direct or indirect action of a breaker composition that contains at least one mineral oil, at least one polyalphaolefin oil, and / or at least one saturated fatty acid. The breaker may initially be dispersed oil droplets in an internal, discontinuous phase of the fluid. In one non-limiting embodiment, the breaker, e.g. mineral oil is added to the fluid after it has been substantially gelled. The breaking composition is believed to act possibly by rearranging, disaggregating or otherwise attacking the micellar structure of the VES-gelled fluid in a non-spontaneous, rate controlled manner at elevated fluid temperatures. In a specific, non-limiting instance, a brine fluid gelled with an amine oxide surfactant can have its viscosity broken with a light, low viscosity paraffinic mineral oil.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Liquid Gel Concentrate Compositions and Methods of Use
Certain aspects of the invention are drawn to formulations and methods of making a liquid gel concentrate composition. Such liquid gel concentrates are formed by admixing an alkali-swellable polymer with an alkaline swelling agent in an oil-based suspending agent. The invention also provides for gelled water fire suppressants produced by mixing a liquid gel concentrate composition with water and methods of using such fire suppressants for combating fires.
Owner:PERIMETER SOLUTIONS LP
Seasonal memory foam pillow
A personal seasonal pillow for accommodating different temperatures occurring during different seasons is disclosed comprising a cool side and a warm side opposite the cool side. A gel layer is associated with the cool side containing a fluid gel, and a layer of insulating fill is associated with the warm side. A cool side indicator is associated with the cool side; and a warm side indicator is associated with the warm side whereby the person may easily identify the desired side.
Owner:SKYTEK
System and method of applying a gel coat brush stroke pattern over an image surface
A system and method for automatically applying a gel coat brush stroke pattern over an image surface secured to a support is described. A liquid gel applicator dispenses a predetermined quantity of transparent liquid gel on the image surface. A brush stroking machine is provided with a plurality of brush head modules which are connected to a reciprocating linkage. The linkage causes reciprocal arcuate displacement of bristles secured to the brush head modules. An adjustable support positions the bristles over the image surface for contact with the liquid gel dispensed thereon by the liquid gel applicator. A conveyor displaces the support with the image surface facing up under the liquid gel applicator and the bristles of the brush head modules along a straight axis whereby reciprocating displacement of the bristles imparts brush stroke patterns in the liquid gel over the image surface.
Owner:7550570 CANADA
Stabilizing crosslinked polymer guars and modified guar derivatives
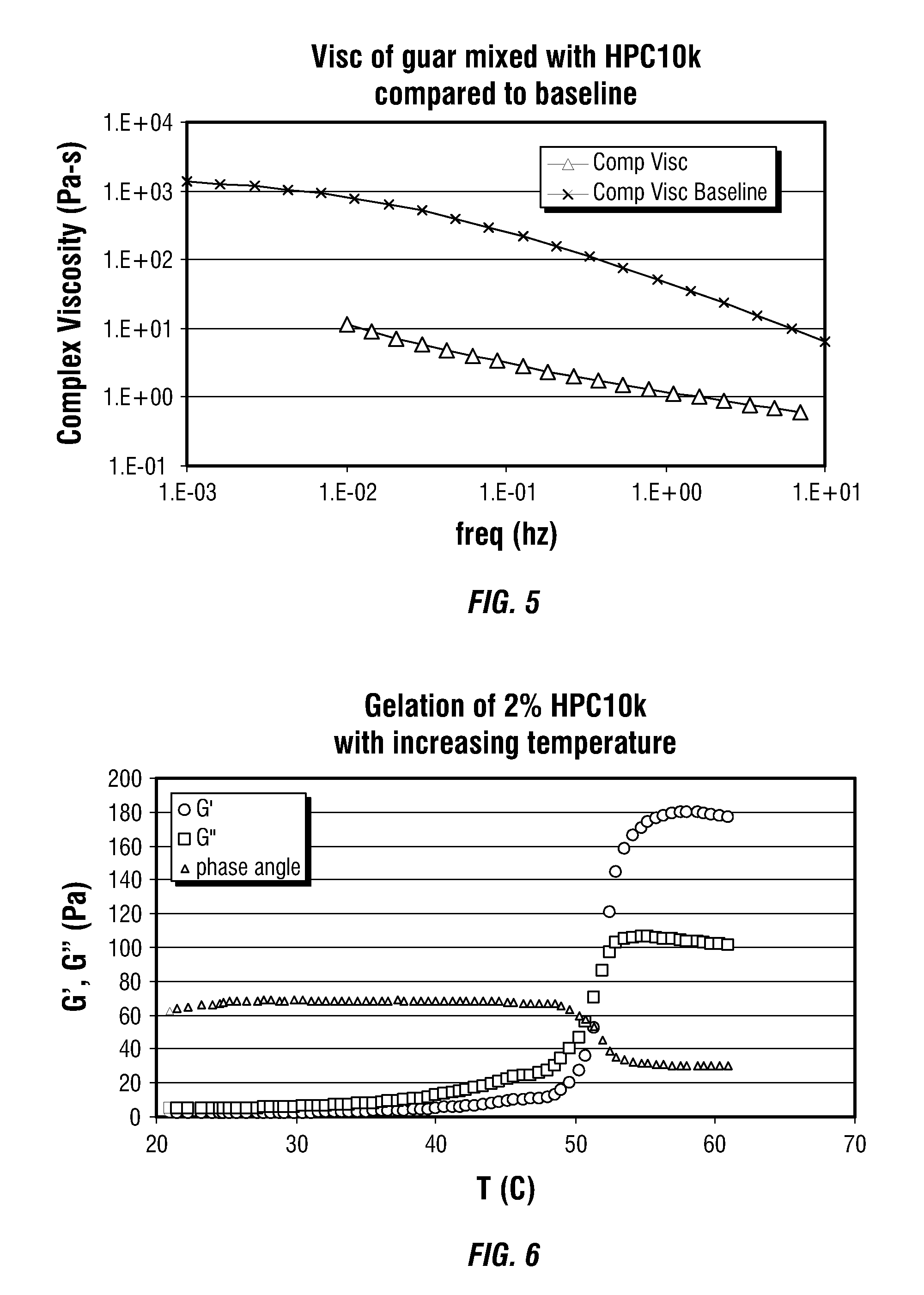
An aqueous, viscoelastic treating fluid gelled with a crosslinked guar or guar derivative is stabilized and improved with an effective amount of a glycol, such as ethylene glycol. These fluids are more stable in that viscosity is maintained, particularly at elevated temperatures. The additives may also increase viscosity to the point where less of a crosslinked guar or guar derivative gelling agent is required to maintain a given viscosity. These stabilized, enhanced, aqueous, viscoelastic fluids may be used as treatment fluids for subterranean hydrocarbon formations, such as in hydraulic fracturing.
Owner:SUPERIOR ENERGY SERVICES LLC
Liquid gelling agent concentrates and methods of treating wells therewith
InactiveUS20050087341A1Improve abilitiesImprove propertiesFluid removalDrilling compositionParticulatesFluid gel
The present invention provides liquid gelling agent concentrates and methods of treating wells therewith. A liquid gelling agent concentrate of this invention comprises an environmentally safe hydrocarbon carrier liquid, an organophillic clay suspending agent, a surfactant for dispersing the organophillic clay suspending agent in the carrier liquid and a particulate aqueous fluid gelling agent suspended in the carrier liquid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Stabilizing crosslinked polymer guars and modified guar derivatives
An aqueous, viscoelastic treating fluid gelled with a crosslinked guar or guar derivative is stabilized and improved with an effective amount of a glycol, such as ethylene glycol. These fluids are more stable in that viscosity is maintained, particularly at elevated temperatures. The additives may also increase viscosity to the point where less of a crosslinked guar or guar derivative gelling agent is required to maintain a given viscosity. These stabilized, enhanced, aqueous, viscoelastic fluids may be used as treatment fluids for subterranean hydrocarbon formations, such as in hydraulic fracturing.
Owner:SUPERIOR ENERGY SERVICES LLC
Packaging and dispensing device
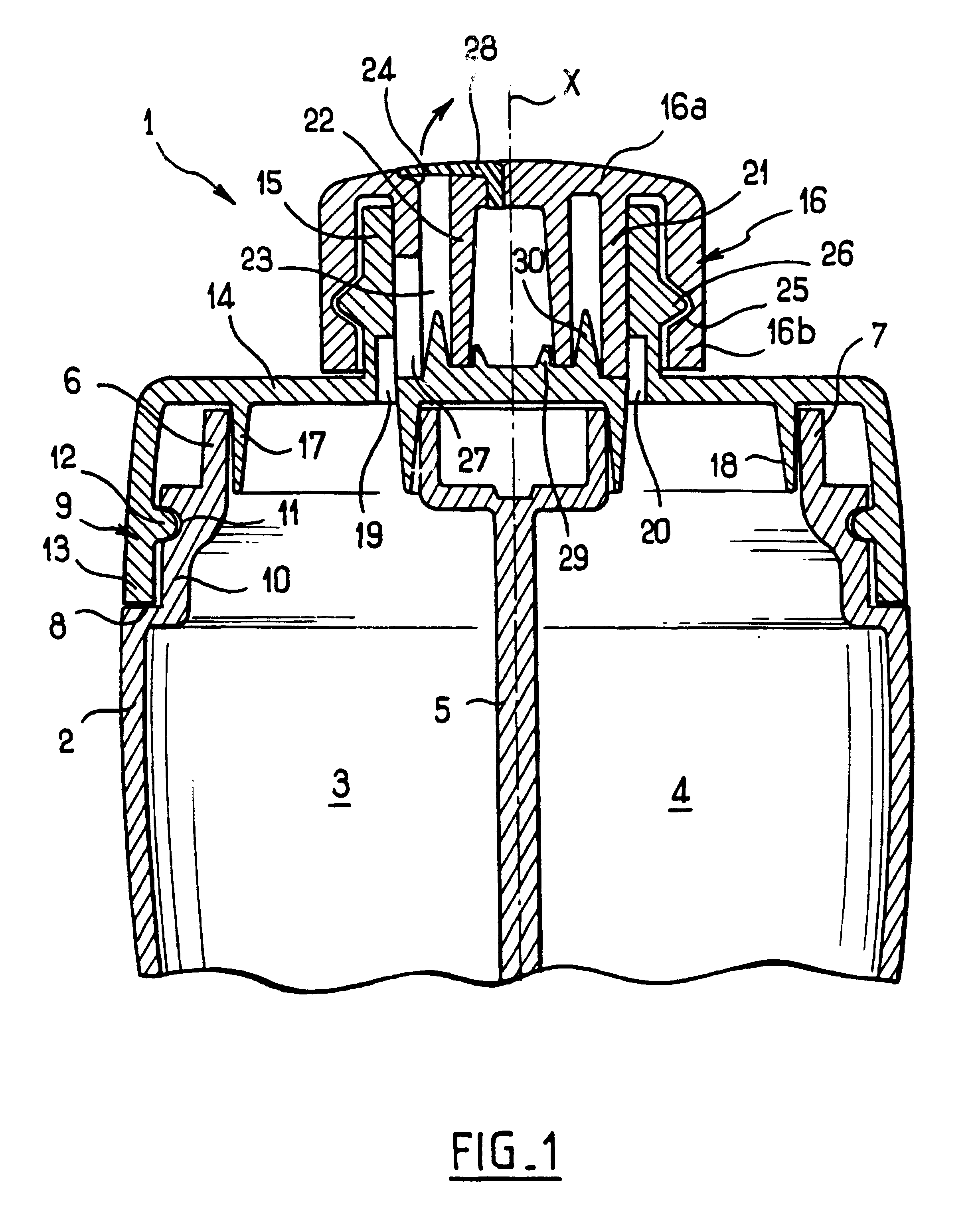
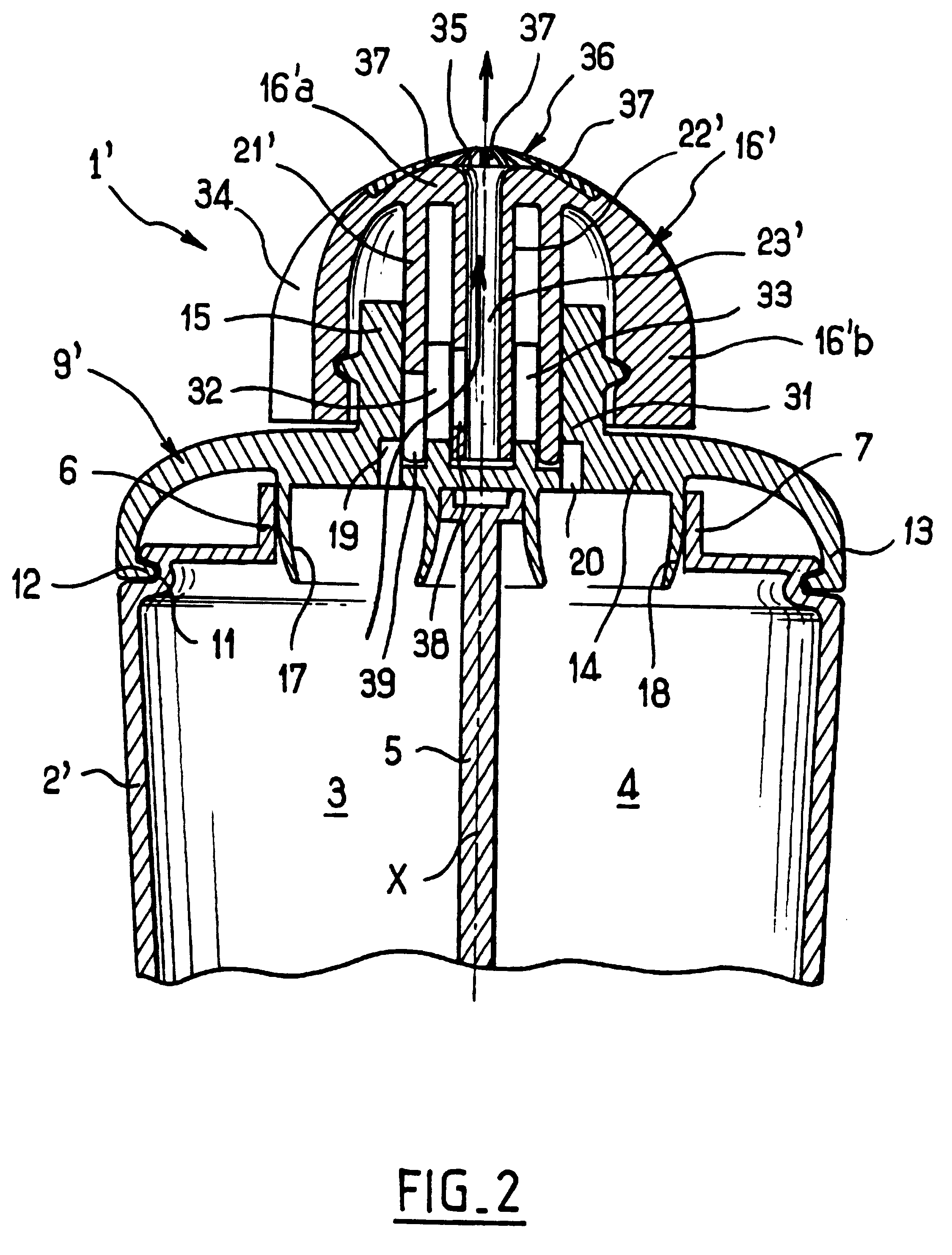
InactiveUSRE38328E1Avoid pollutionAvoid stagnationOpening closed containersBottle/container closureBiomedical engineeringFluid gel
Owner:LOREAL SA
Direct application brush for horses and livestock that releases active ingredients
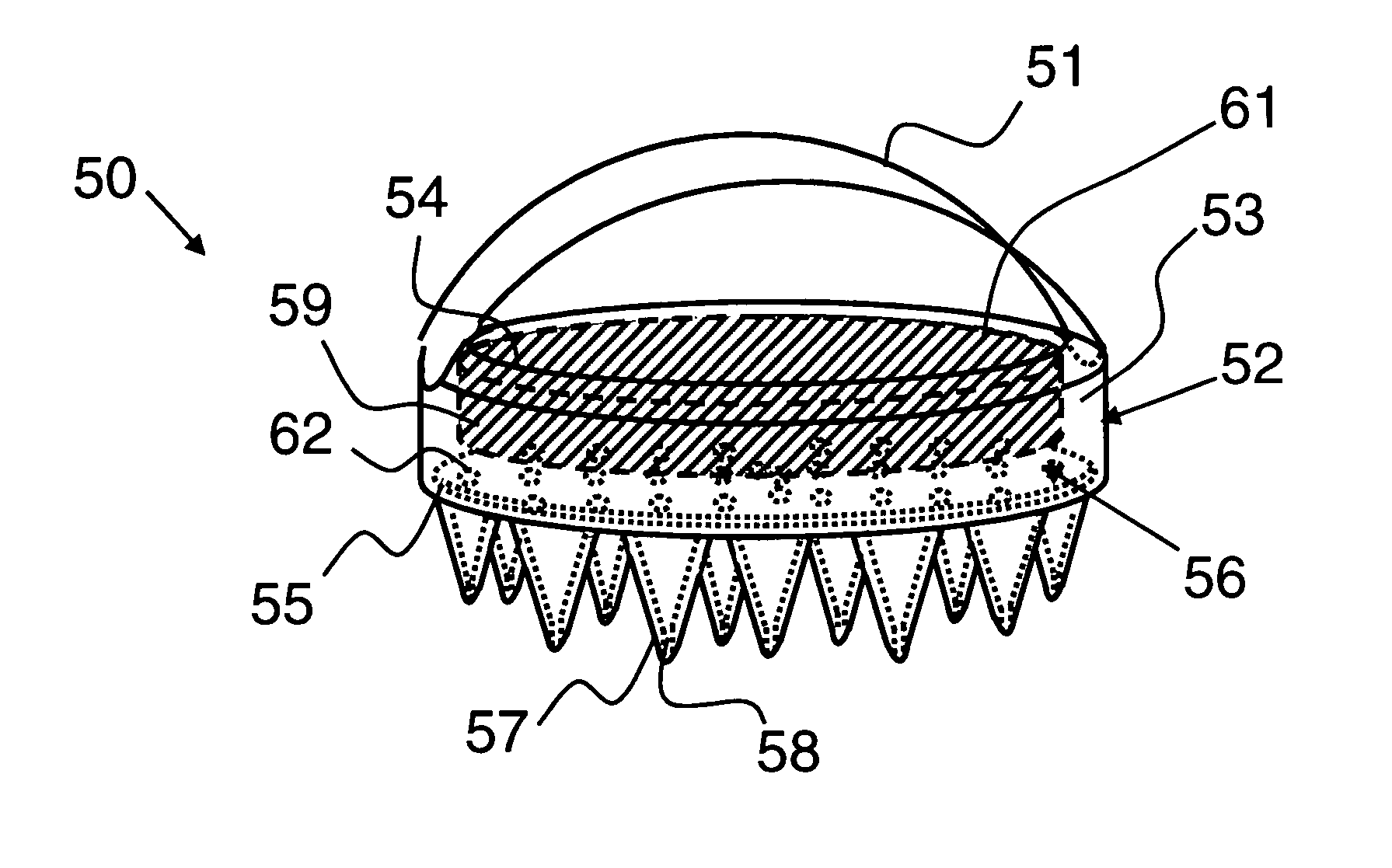
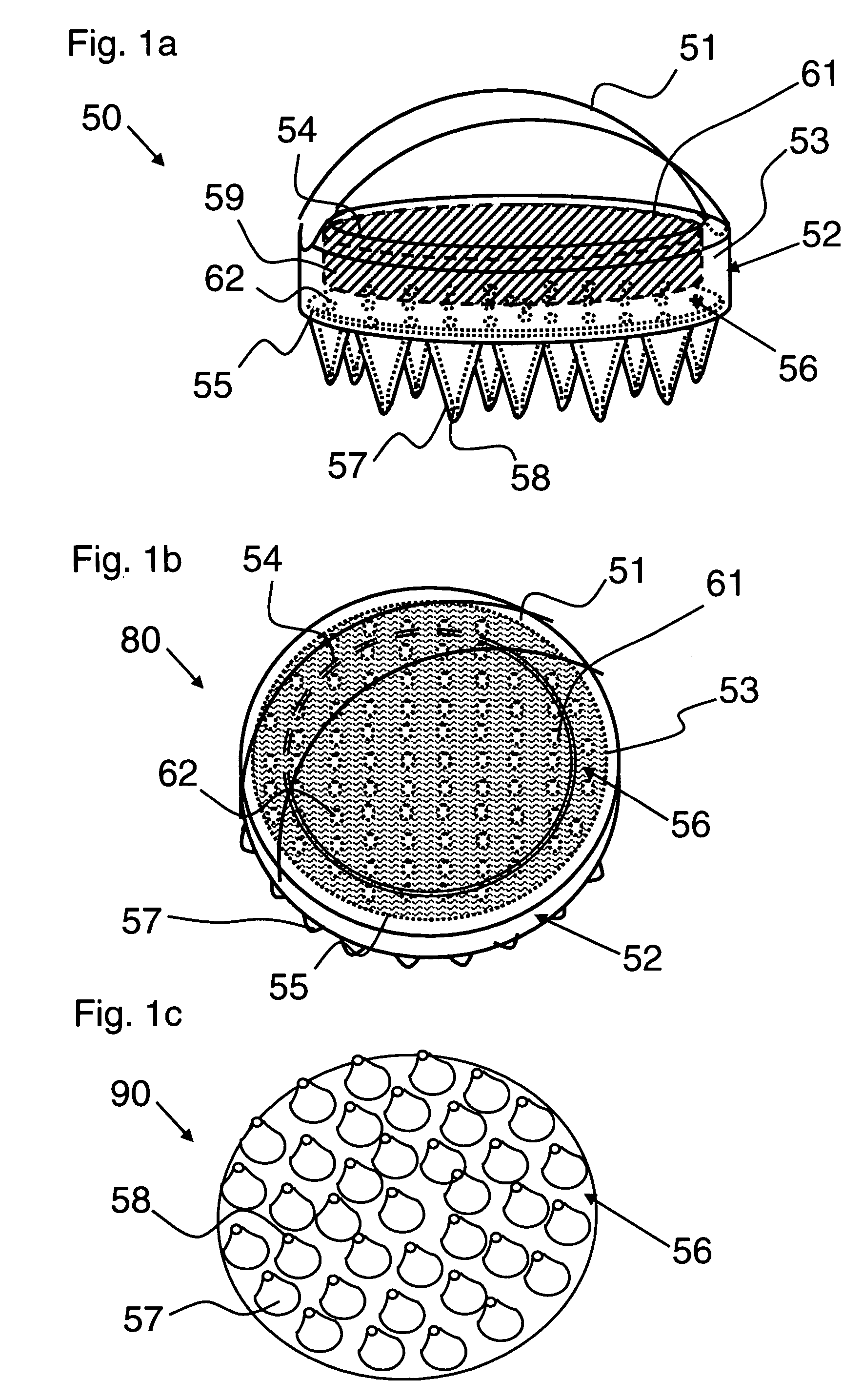
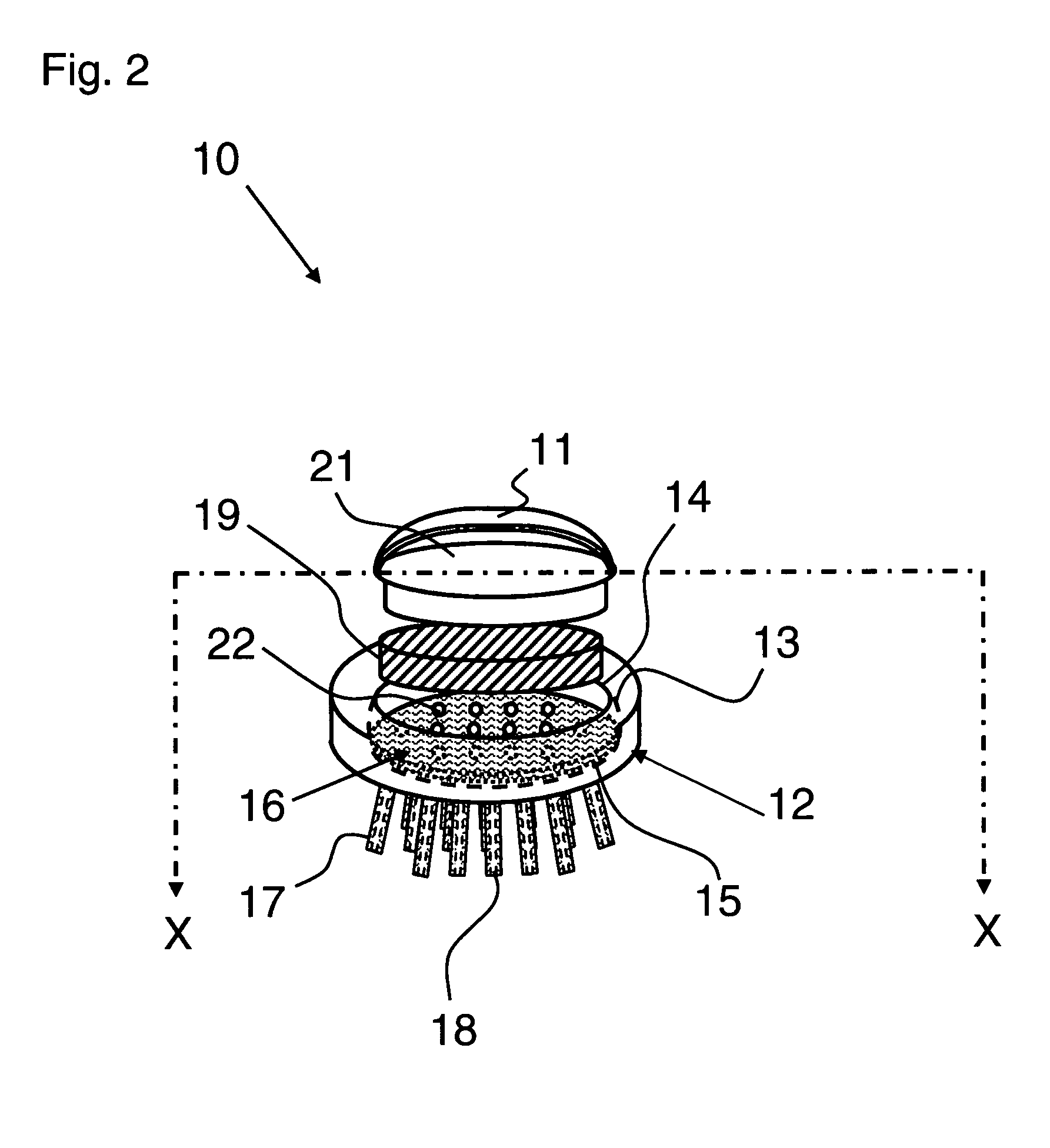
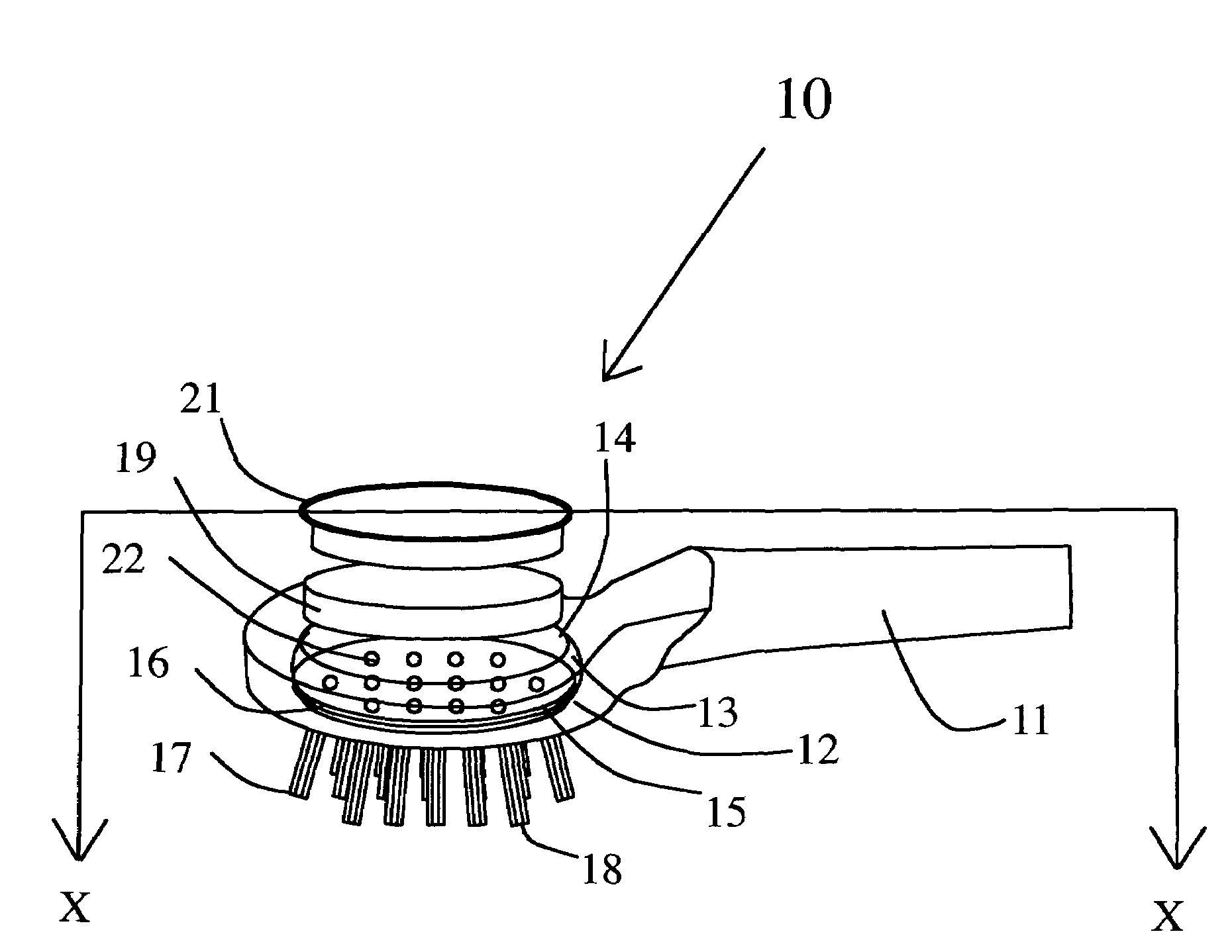
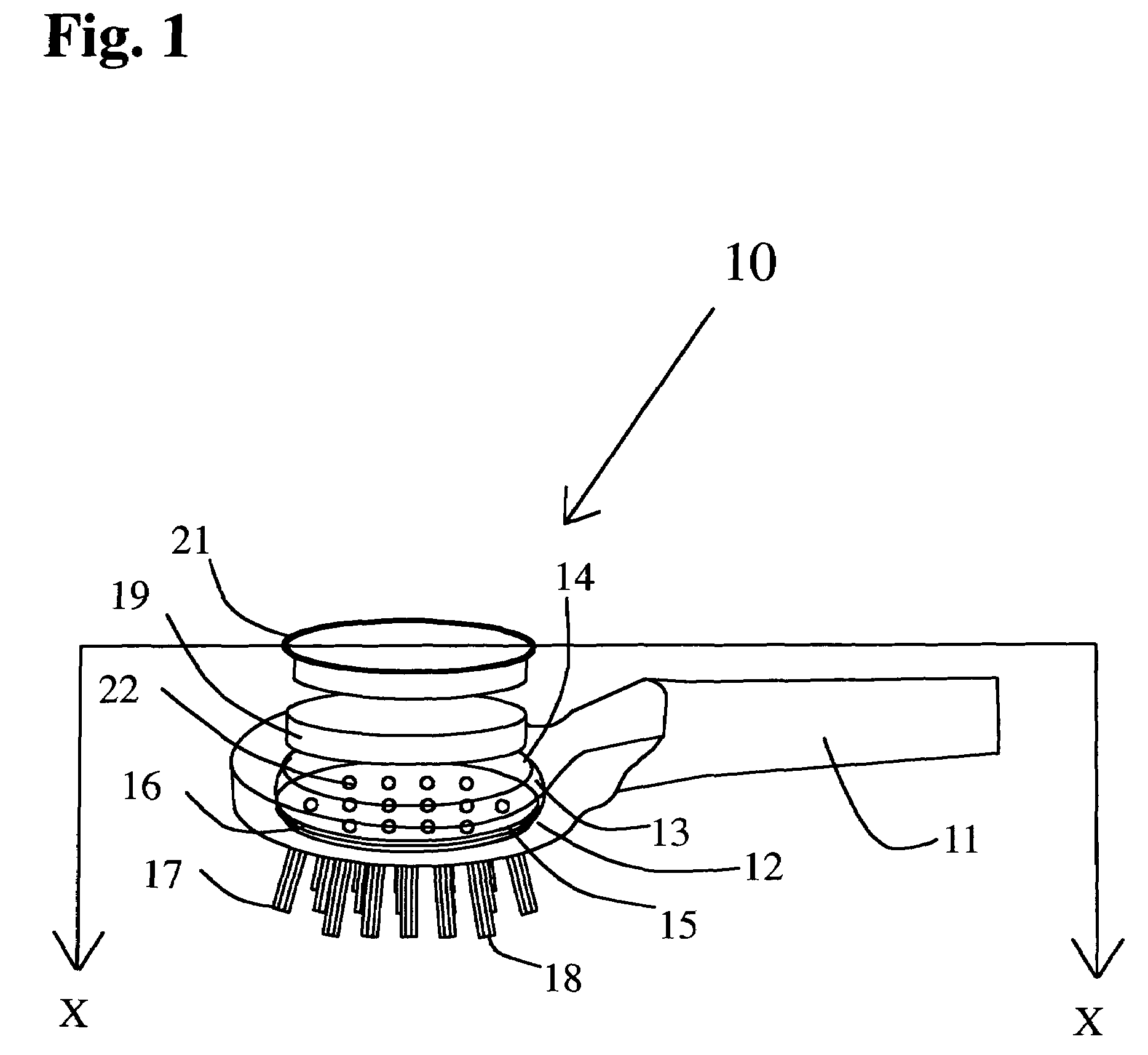
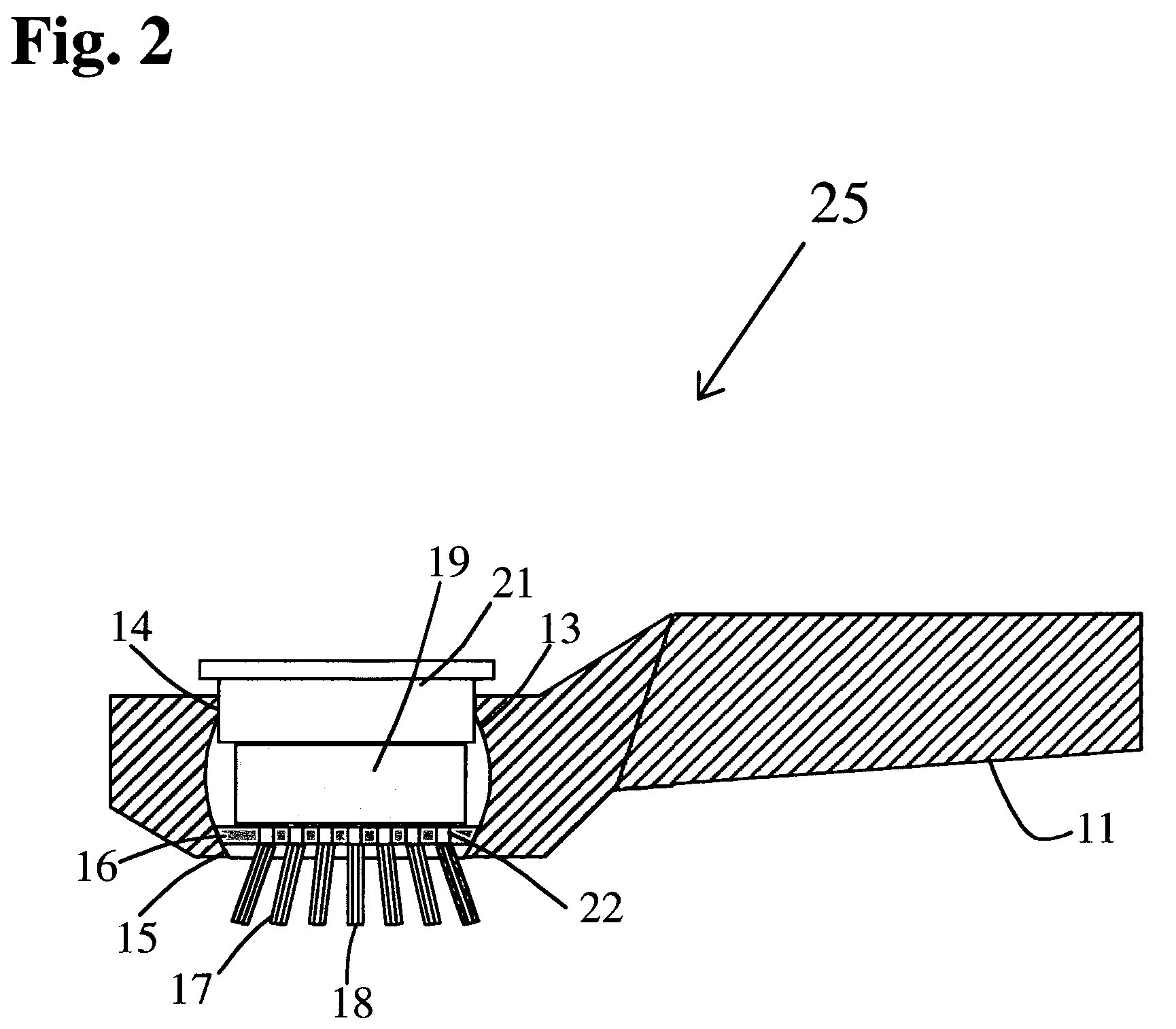
A horse and / or livestock brush releases a liquid gel solution directly onto the coat of an animal during brushing. Delivery of the liquid gel solution is activated by manually depressing the brushes cover. The liquid gel solution includes perfumes, fragrances and other active compositions including insect repellant, hair conditioners, dyes, moisturizers, or antibacterial compounds. The brush includes a flexible deformable membrane with a plurality of apertures that are, optionally, aligned with apertures in brush bristles for delivery of the liquid gel active composition, and is fitted within a first opening of an internal cavity in a brush base. A porous sponge saturated with the liquid gel active ingredient is inserted over the flexible deformable membrane. A cover is inserted through a second opening and rests upon the porous sponge. Brushing action deforms the flexible deformable membrane and squeezes the sponge, releasing the active ingredient during brushing or when the cover is depressed manually.
Owner:I DID IT
Gelable liquid and method for selectively inhibiting the gelation of a gelable liquid
InactiveUS7151078B2Slow-down in overall processingPrevent gelationFlushingDrilling compositionFluid gelAqueous medium
A controlled-gelation aqueous solution is proposed. The solution contains a hydrophobically-aggregating gelling agent, and an effective amount of an inhibitor which suppresses hydrophobic aggregation of the gelling agent. The inhibitor is soluble in water so that when the controlled-gelation aqueous solution contacts aqueous media the inhibitor disperses and gelation occurs. However, the inhibitor is substantially insoluble in hydrocarbons so that when the controlled-gelation aqueous solution contacts hydrocarbon media the inhibitor continues to suppress said hydrophobic aggregation and gelation is suppressed. The solution may be used to control the flow of water into oil wells, making it possible to reduce the water cut.
Owner:THE PHYSICS FACULTY OF MOSCOW UNIV
Ionic liquid gel supporting film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103599707AHigh gas permeation fluxEasy to prepareSemi-permeable membranesSeparation technologyTrapping
The invention relates to an ionic liquid gel supporting film and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of membrane separation techniques. The film is formed by loading ionic liquid gel on a macromolecule microporous membrane, and the mass of the ionic liquid gel accounts for 30-80% of the total mass of the ionic liquid gel supporting film. The preparation method of the film comprises the following steps: firstly, injecting a gel precursor solution into the macromolecule microporous membrane by adopting an impregnation method, and gelatinizing the gel precursor solution through ultraviolet light initiation to prepare the ionic liquid gel supporting film. The ionic liquid gel supporting film prepared by the method provided by the invention has relatively high gas permeation flux and relatively large gas separating factor, and can avoid the liquid leakage of the film under relatively high transmembrane pressure, enhance the performance stability of the film, and prolong the service life of the film. The method is simple and easy to control, the prepared ionic liquid gel supporting film is mainly used in the fields such as trapping of acid gas in industrial discharge exhaust gas, and CO2 separating in spacecrafts, submarines and other confined spaces.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Seasonal Memory Pillow
A personal seasonal pillow for accommodating different temperatures occurring during different seasons is disclosed comprising a cool side and a warm side opposite the cool side. A gel layer is associated with the cool side containing a fluid gel, and a layer of insulating fill is associated with the warm side. A cool side indicator is associated with the cool side; and a warm side indicator is associated with the warm side whereby the person may easily identify the desired side.
Owner:SKYTEK
Improved paint formulations comprising cellulose ether/network building polymer fluid gel thickeners
Paint formulations that exhibit improved performance characteristics due to the presence of a combination of a cellulose ether (carboxymethyicellulose and / or hydroxy ethylcellulose) and a network building polymer (gellan gum, carrageenan, etc.. as examples) as a thickening system therein are provided. Such a combination permits long-term shelf stability of the paint formulation while simultaneously according effective Row. leveling, and other important properties to the final paint formulation. The combination of the cellulose ether and a network building pol\ mer allows for a lower viscositycellulosic compound fo impart the desired.theological behavior therein while also permitting the other desirable characteristics noted above. Such paint compositions also exhibit improved atomizatiopfor spray applications with such a thickening system.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Vascular embolization gelling agent for sustained release of drugs for treating tumors and method for preparing the same
InactiveUS20130195988A1Good curative effectLess side effectsHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideEmbolization AgentDrug treatment
A vascular embolization gelling agent for sustained release of drugs for treating tumors having a drug and a drug carrier. The drugs are antitumor drugs. The drug carrier includes poloxamer polymer and polyvinylpyrrolidone or gel made of the combination, and may be purified before use. The drug carrier accounts for 5-65% of the gel. The particle size of the gel is in the range of 10 nm-150 μm. The embolization agent is a liquid gel at normal temperature, to facilitate direct transcatheter injection, and is rapidly solidified to the gel state in body with the increase of the temperature; it is used to encapsulate different drugs on demand, and can achieve dual efficacy of embolization and drug treatment through local sustained release of the drug. The present invention can be used as the embolization agent for endovascular interventional therapy for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of various benign and malignant tumors.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Direct application brush for horses and livestock that releases active ingredients
A horse and / or livestock brush releases a liquid gel solution directly onto the coat of an animal during brushing. Delivery of the liquid gel solution is activated by manually depressing the brushes cover. The liquid gel solution includes perfumes, fragrances and other active compositions including insect repellant, hair conditioners, dyes, moisturizers, or antibacterial compounds. The brush includes a flexible deformable membrane with a plurality of apertures that are, optionally, aligned with apertures in brush bristles for delivery of the liquid gel active composition, and is fitted within a first opening of an internal cavity in a brush base. A porous sponge saturated with the liquid gel active ingredient is inserted over the flexible deformable membrane. A cover is inserted through a second opening and rests upon the porous sponge. Brushing action deforms the flexible deformable membrane and squeezes the sponge, releasing the active ingredient during brushing or when the cover is depressed manually.
Owner:I DID IT
Aqueous Two-Phase Emulsion Gel Systems for Zone Isolation
InactiveUS20090133868A1Easy and accurate deliveryMinimal equipmentFluid removalFlushingEmulsionPolymer science
A low viscosity wellbore polymer fluid gelling system comprising an aqueous medium and a water-in-water emulsion comprising a plurality of polymers or oligomers, including at least one removable polymer or oligomer, and at least one gelling polymer or oligomer, wherein said fluid has a low viscosity when injected, and the gelling polymer forms a gel downhole which has a storage modulus of at least about 60 Pa after the removable polymer is removed from the fluid. The invention also provides a method of isolating at least one zone of a subterranean formation penetrated by a wellbore, including the steps of preparing a water-in-water emulsion comprising a plurality of polymers or oligomers including at least one removable polymer or oligomer, and at least one gellable polymer or oligomer; combining the water-in-water emulsion with an aqueous medium to prepare a low viscosity polymer fluid; introducing the fluid into a zone in the formation, removing the at least one removable polymer or oligomer, and allowing a remaining gellable oligomer, polymer or polymers to form a gel, isolating the zone from at least one other zone in the formation.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Dispenser assembly
A method and a device for preparing a drinking glass, cup, mug or other beverage container, e.g. drink-ware, where any dry granular, flaked, shaved or powder substance (SPICE) is applied to the rim of the drink-ware. Where the drink-ware is inverted and introduced into the SPICE and in order to adhere the SPICE to the rim of the drink-ware, the rim is customarily first moistened with a liquid, gel or other viscous aqueous wetting substance (moistening agent). The dispenser is an all encompassing system to accommodate common large diameter drink-ware, to moisten the rim of the drink-ware, house the SPICE, preserve the moistening agent and preserve the SPICE by separating the moisture of the wetting agent from the SPICE, providing for drink-ware to be introduced into the wetting agent then into the SPICE and to re-close and secure the device and its contents with a screw or snap-on lid.
Owner:SPIGOT RESOURCES INC +1
Blocking method adopting fluid gel for producing blocking valve by formation temperature to block gas reservoir
ActiveCN103361039ASimple processNot easy to formDrilling compositionSealing/packingFluid gelBlocked valves
The invention discloses a blocking method adopting fluid gel for producing a blocking valve by a formation temperature to block a gas reservoir. The blocking method comprises the following steps that a), a gel crosslinked system and a gel initiator are uniformly mixed until the mixed solution has no fish eye-shaped structure so that a fluid solution is obtained; b), the fluid solution is fed into a shaft by a pump and forms gel after gelation waiting; c), after ground operation, a gel breaker aqueous solution is added into the gel in the shaft, wherein the gel breaker aqueous solution comprises 2-5wt% of a gel breaker and the total weight of the gel breaker is 0.1-2% of that of the gel crosslinked system; and d), after the fed gel breaker aqueous solution contacts with the gel, the gel breaker makes the gel lose blocking performances and the broken gel is fed back to the ground. The blocking method has simple processes. The fluid gel for blocking has a low cost and very high pressure resistance.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com