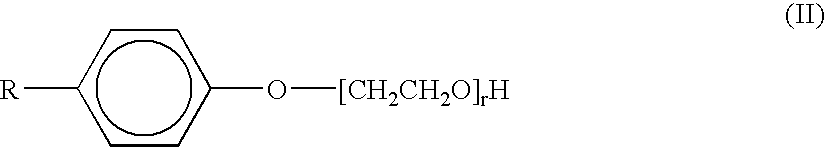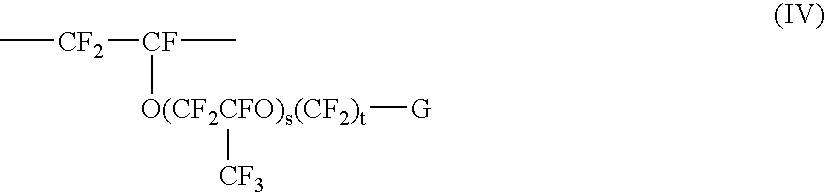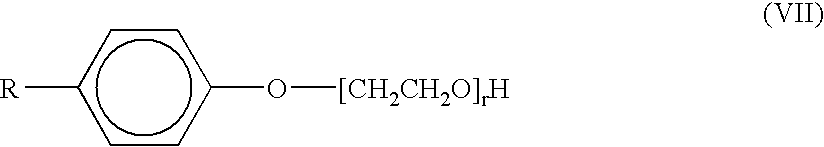Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3818 results about "Fluoropolymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A fluoropolymer is a fluorocarbon-based polymer with multiple carbon–fluorine bonds. It is characterized by a high resistance to solvents, acids, and bases. The best known fluoropolymer is polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon).
Aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers using a perfluoropolyether surfactant
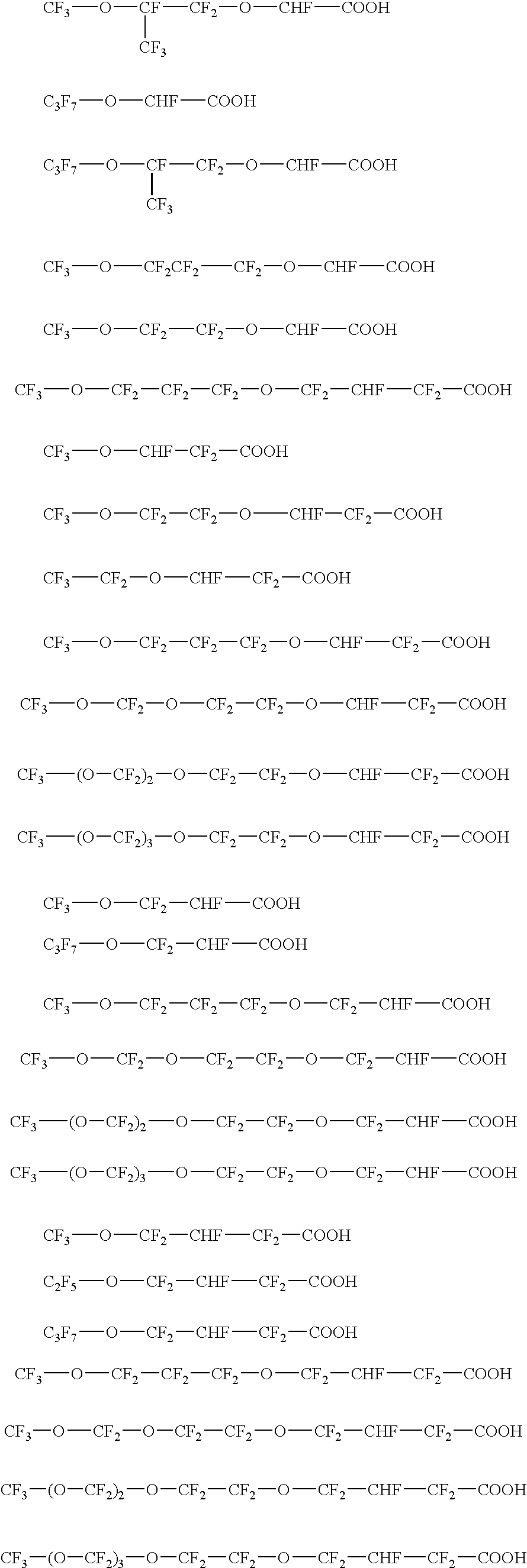
The invention relates to an aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers using perfluoropolyethers of the following formula (I) or (II). In particular, the perfluoropolyether surfactants correspond to formula (I) or (II) CF3—(OCF2)m—O—CF2—X (I) wherein m has a value of 1 to 6 and X represents a carboxylic acid group or salt thereof, CF3—O—(CF2)3—(OCF(CF3)—CF2)z—O-L-Y (II) wherein z has a value of 0, 1, 2 or 3, L represents a divalent linking group selected from —CF(CF3)—, —CF2— and —CF2CF2— and Y represents a carboxylic acid group or salt thereof. The invention further relates to an aqueous dispersion of a fluoropolymer having the aforementioned perfluoropolyether surfactant(s).
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Fluorinated surfactants for making fluoropolymers
ActiveUS20070142541A1Easy to preparePrepared cost-effectivelyLiquid surface applicatorsTransportation and packagingEmulsion polymerizationFluoropolymer
The invention provides a fluorinated surfactant having the general formula: [Rf—(O)t—CHF—(CF2)n—COO—]iXi+ (I) wherein Rf represents a partially or fully fluorinated aliphatic group optionally interrupted with one or more oxygen atoms, t is 0 or 1 and n is 0 or 1, Xi+ represents a cation having a valence i and i is 1, 2 or 3. The surfactant can be used in emulsion polymerization of fluoromonomers to prepare fluoropolymers.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers using a fluorinated surfactant
InactiveUS20070015866A1Low toxicityGood chemical stabilityLiquid surface applicatorsFibre treatmentEmulsion polymerizationEther
The present invention provides an aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers including gaseous fluorinated monomers using a perfluoro ether surfactant as an emulsifier. The perfluoro ether surfactants correspond to formula (I) Rf—O—CF2CF2—X (I) wherein Rf represents a linear or branched perfluoroalkyl group having 1, 2, 3 or 4 carbon atoms and X represents a carboxylic acid group or salt thereof. In a further aspect, the invention also provides an aqueous fluoropolymer dispersion comprising the perfluoro ether surfactant and the use of such dispersion in the coating or impregnation of substrates.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
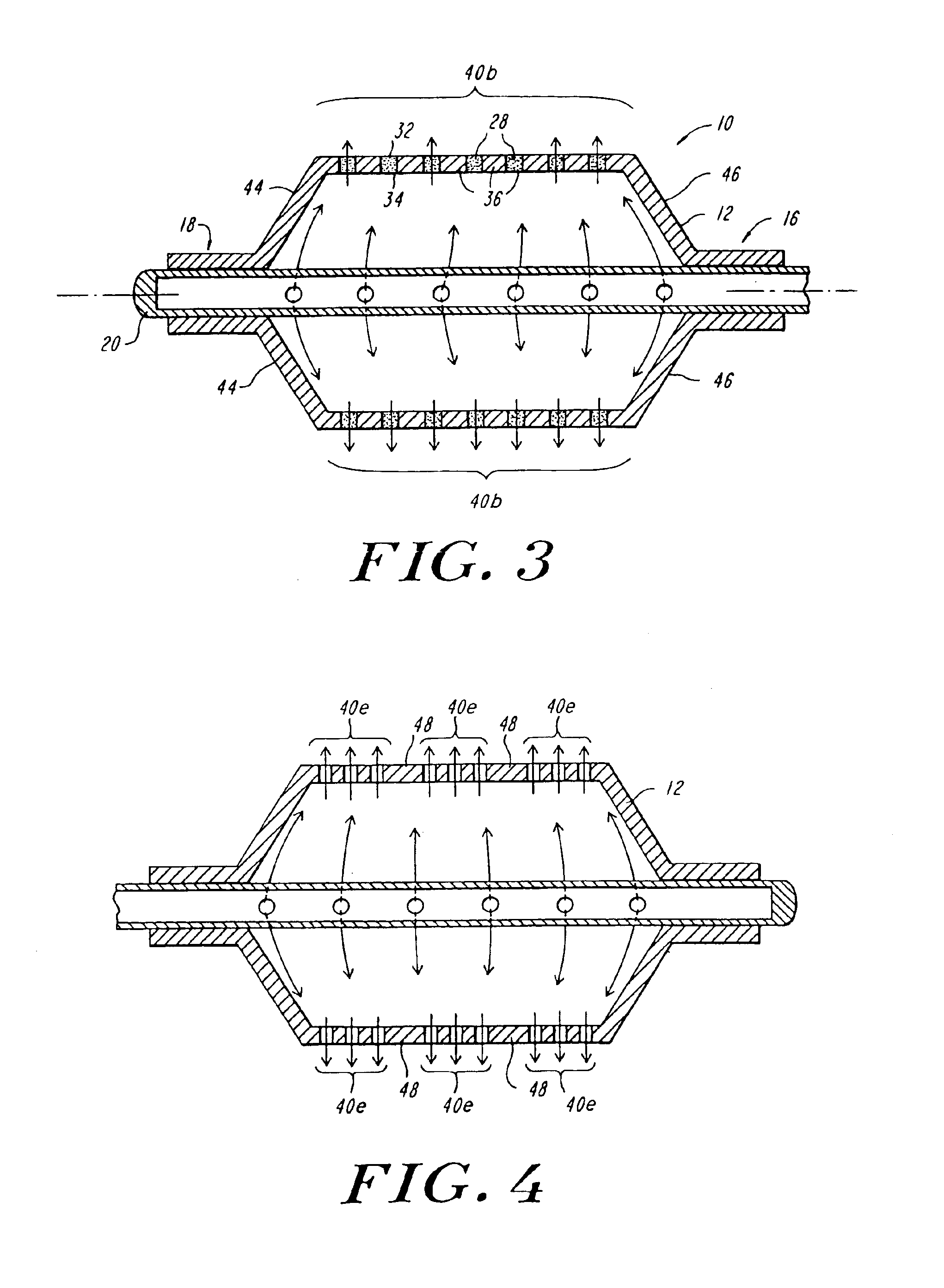
Circumferential ablation device assembly and methods of use and manufacture providing an ablative circumferential band along an expandable member
InactiveUS6954977B2Strong connectionConsistent positionElectrotherapyDiagnosticsFluoropolymerBalloon catheter
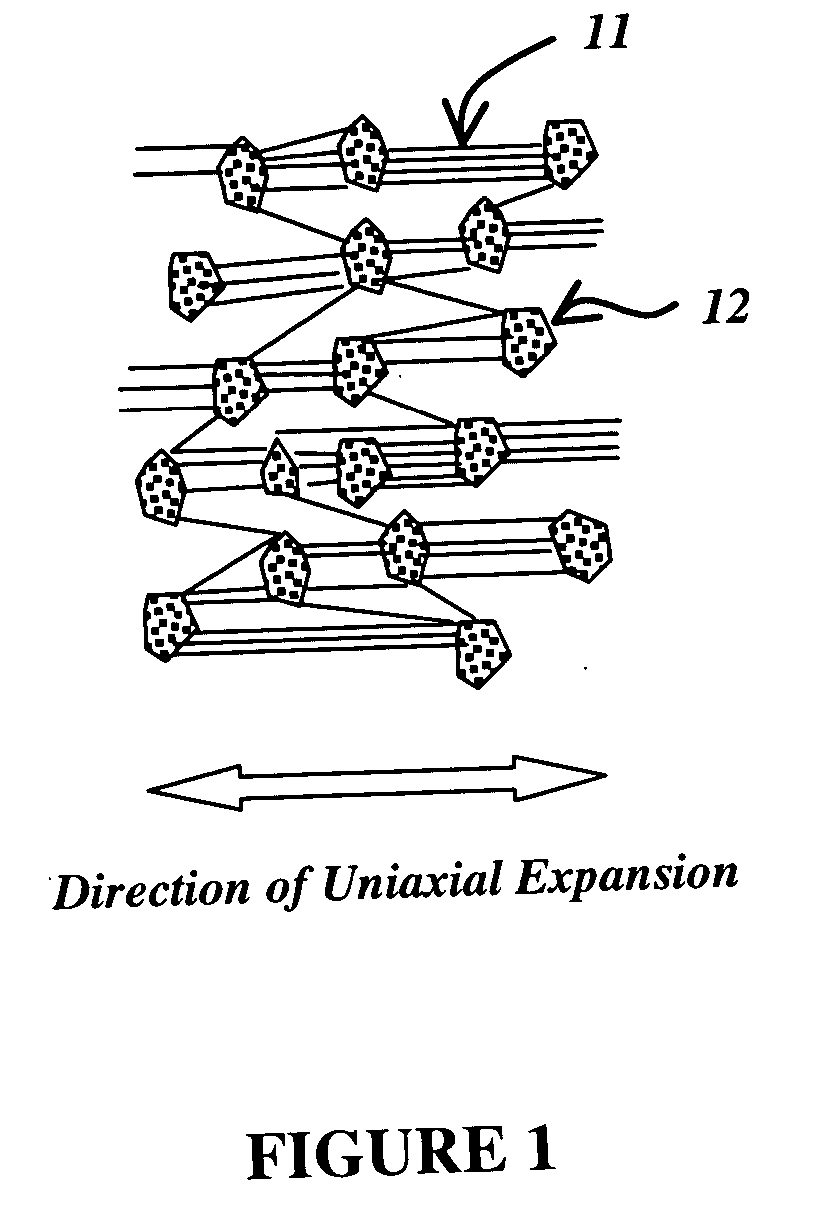
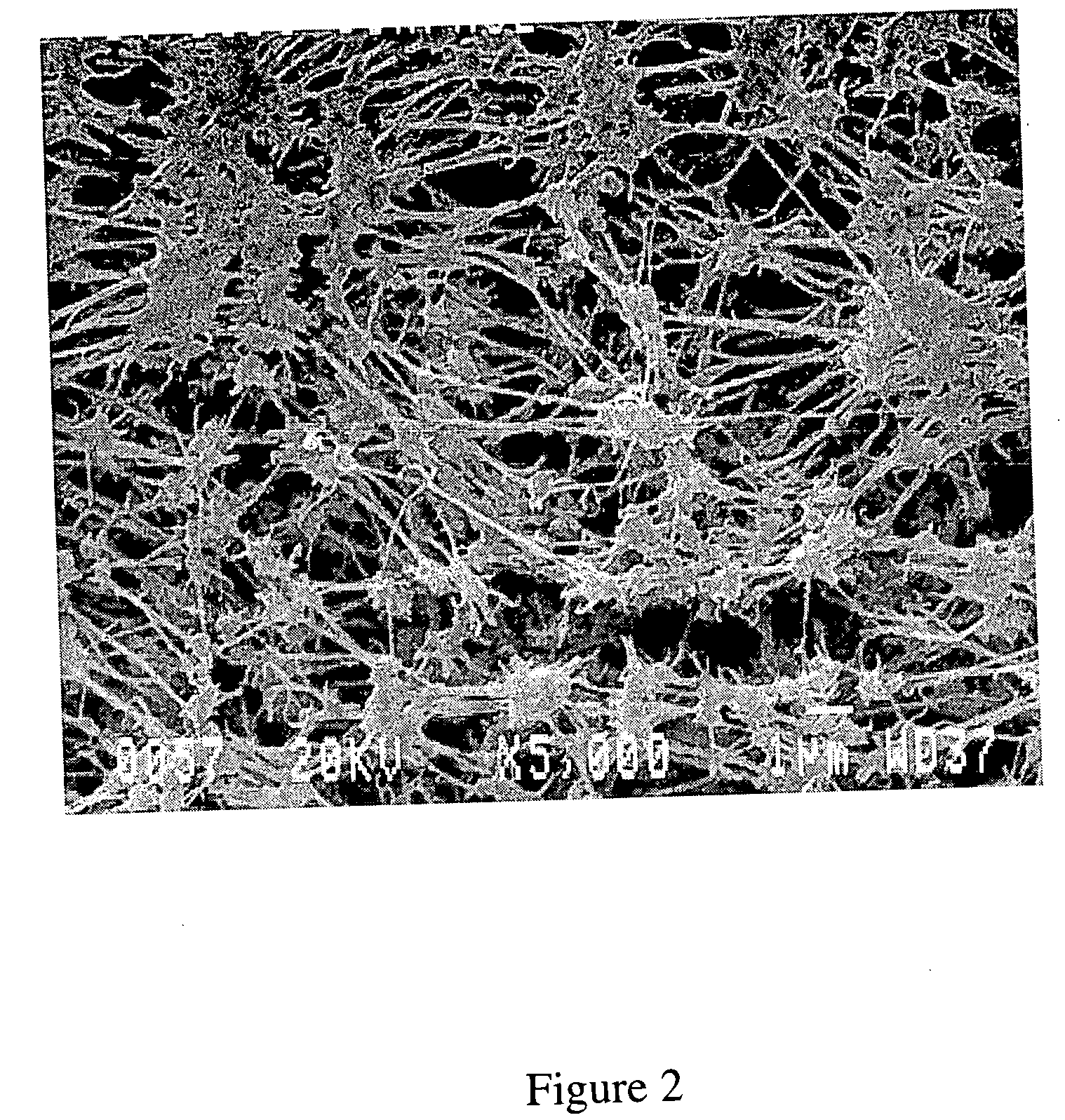
A medical balloon catheter assembly includes a balloon having a permeable region and a non-permeable region. The balloon is constructed at least in part from a fluid permeable tube such that the permeable region is formed from a porous material which allows a volume of pressurized fluid to pass from within a chamber formed by the balloon and into the permeable region sufficiently such that the fluid may be ablatively coupled to tissue engaged by the permeable region. The non-permeable region is adapted to substantially block the pressurized fluid from passing from within the chamber and outwardly from the balloon. The porous material may be a porous fluoropolymer, such as porous polytetrafluoroethylene, and the pores may be created by voids that are inherently formed between an interlocking node-fibril network that makes up the fluoropolymer. Such voids may be created according to one mode by expanding the fluoropolymer. The balloon may be formed such that the porous material extends along both the permeable and non-permeable regions. In one mode of this construction, the porous material is porous along the permeable region but is non-porous along the non-permeable region, such as for example by expanding only the permeable region in order to render sufficient voids in the node-fibril network to provide permeable pores in that section. The voids or pores in the porous material may also be provided along both permeable and non-permeable sections but are substantially blocked with an insulator material along the non-permeable section in order to prevent fluid from passing therethrough. The insulator material may be dip coated, deposited, or extruded with the porous material in order to fill the voids. The insulator material may in one mode be provided along the entire working length of the balloon and then selectively removed along the permeable section, or may be selectively exposed to only the non-permeable sections in order to fill the voids or pores there.
Owner:MAGUIRE MARK A +1
Methods for Obtaining Hydrophilic Fluoropolymers
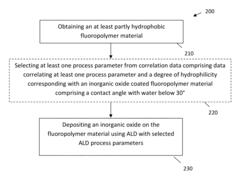
InactiveUS20150345018A1Rendering fluoropolymers hydrophilicSimple methodSynthetic resin layered productsChemical vapor deposition coatingFluoropolymerPlasma activation
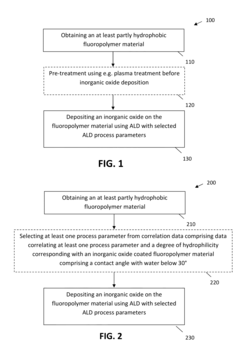
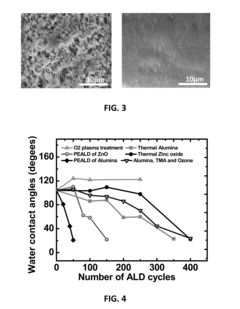
A method is described for providing a hydrophilic effect to a fluoropolymer, e.g. polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) material. The method comprises obtaining an at least partly hydrophobic fluoropolymer material, applying a plasma and / or ozone activation step and depositing an inorganic coating using an atomic layer deposition process. Plasma activation step and / or said atomic layer deposition process thereby comprises using process parameters determining a high interaction probability between one or more precursors for the atomic layer deposition process and the fluoropolymer material so as to obtain a coated fluoropolymer material having a contact angle with water below 30°.
Owner:UNIV GENT
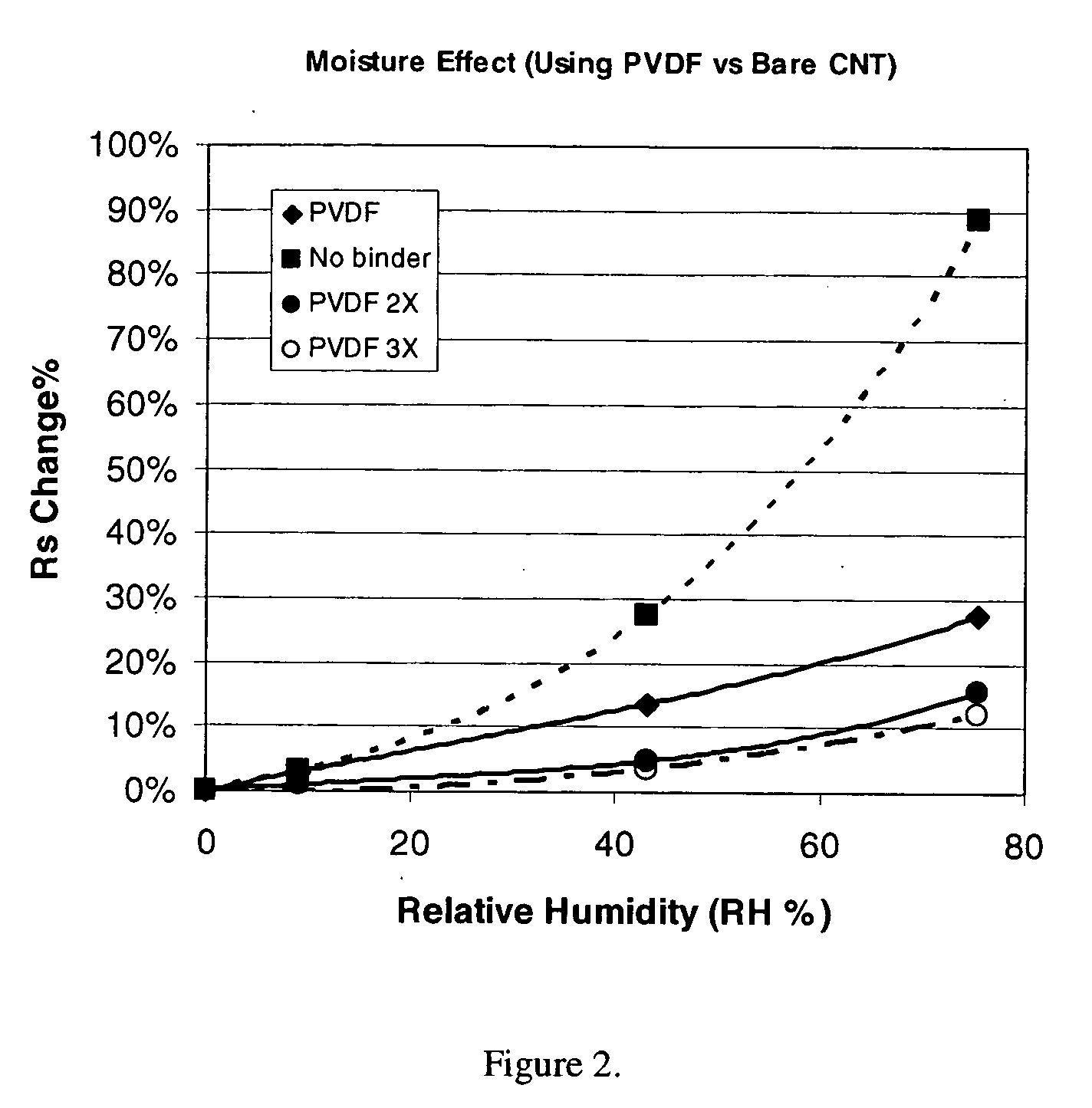
Fluoropolymer binders for carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coatings
InactiveUS20060113510A1Reduce conductivityFunction increaseNanoinformaticsConductive materialThermoplasticOptical transparency
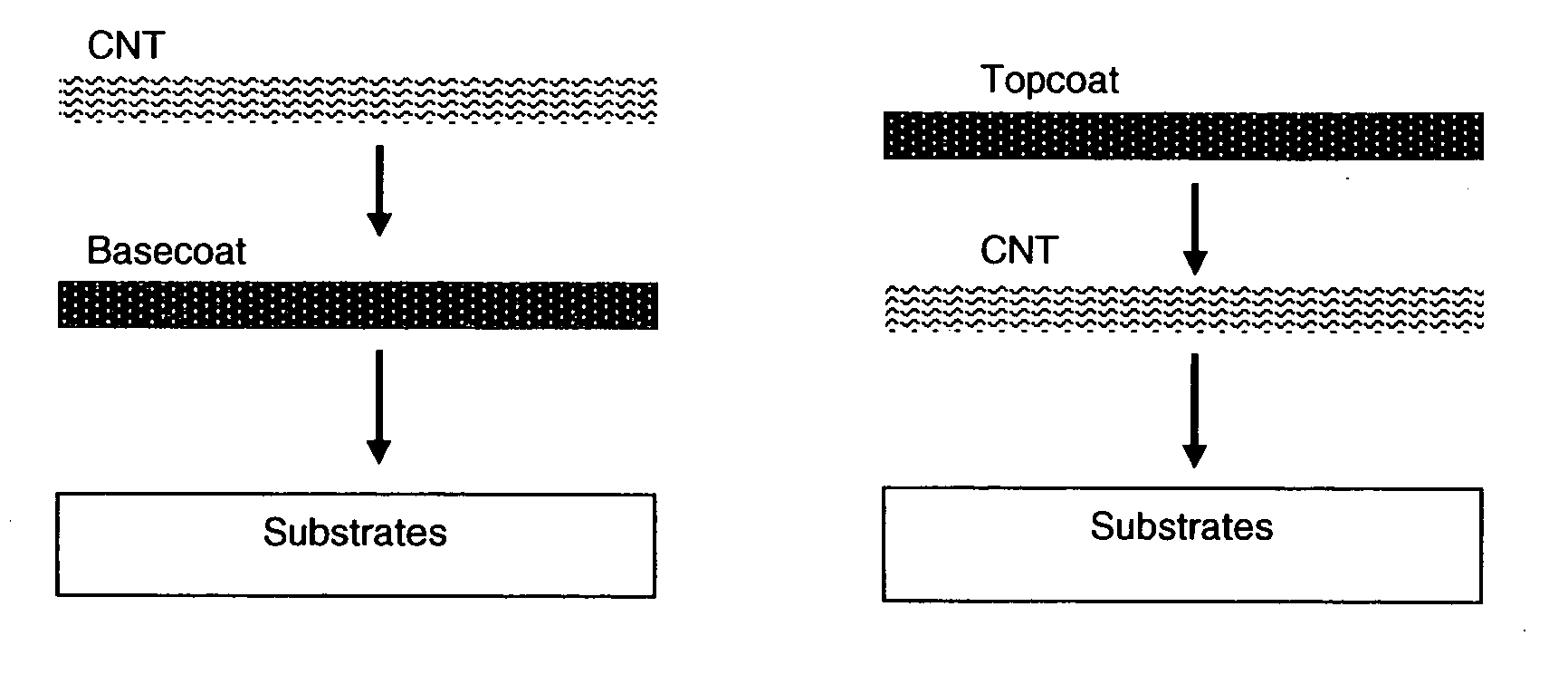
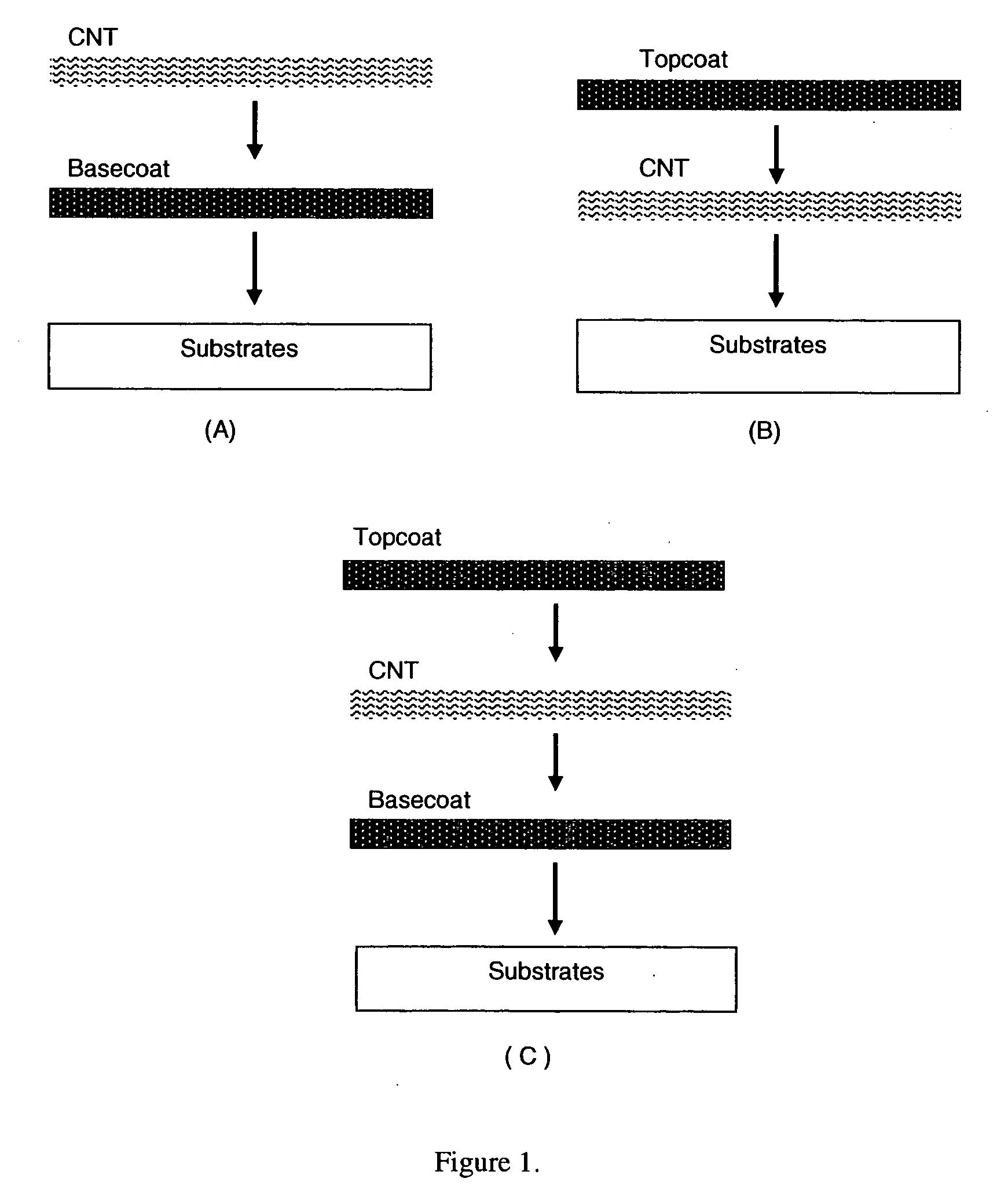
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using carbon nanotubes (CNT) and, in particular, single wall carbon nanotubes, with polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or a combination thereof. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. A fluoropolymer containing binder, which is a solution of one fluoropolymer or a blend of fluoropolymers, which may be formulated with additives, is applied onto a carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coating at nanometer level of thickness on a clear substrate such as PET and glass. The fluoropolymers or blend can be either semi-crystalline (with low level of crystallinity) or amorphous, preferably to be amorphous with low refraction index. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. This binder coating significantly improves optical transparency, and also maintain or increases conductivity of the CNT-based coating. With other benefits such as abrasion, thermal and moisture resistance, this binder coating and the resulting products is used for display and electronic applications.
Owner:EIKOS
Circumferential ablation device assembly and methods of use and manufacture providing an ablative circumferential band along an expandable member
A medical balloon catheter assembly includes a balloon having a permeable region and a non-permeable region. The balloon is constructed at least in part from a fluid permeable tube such that the permeable region is formed from a porous material which allows a volume of pressurized fluid to pass from within a chamber formed by the balloon and into the permeable region sufficiently such that the fluid may be ablatively coupled to tissue engaged by the permeable region. The non-permeable region is adapted to substantially block the pressurized fluid from passing from within the chamber and outwardly from the balloon. The porous material may be a porous fluoropolymer, such as porous polytetrafluoroethylene, and the pores may be created by voids that are inherently formed between an interlocking node-fibril network that makes up the fluoropolymer. Such voids may be created according to one mode by expanding the fluoropolymer. The balloon may be formed such that the porous material extends along both the permeable and non-permeable regions. In one mode of this construction, the porous material is porous along the permeable region but is non-porous along the non-permeable region, such as for example by expanding only the permeable region in order to render sufficient voids in the node-fibril network to provide permeable pores in that section. The voids or pores in the porous material may also be provided along both permeable and non-permeable sections but are substantially blocked with an insulator material along the non-permeable section in order to prevent fluid from passing through. The insulator material may be dip coated, deposited, or extruded with the porous material in order to fill the voids. The insulator material may in one mode be provided along the entire working length of the balloon and then selectively removed along the permeable section, or may be selectively exposed to only the non-permeable sections in order to fill the voids or pores there.
Owner:ATRIONIX
Fluoroalkyl carboxylic acid derivative, method for producing fluorine-containing polymer, and aqueous dispersion of fluorine-containing polymer
ActiveUS20060281946A1Improve efficiencyImprove stabilityPreparation from carboxylic acid halideOrganic compound preparationHydrogen atomAcid derivative
This invention provides a novel compound which can be properly used as a surfactant, a method of producing a fluoropolymer, surfactant and a fluoropolymer aqueous dispersions using the novel compound. This invention is a fluoroalkylcarboxylic acid derivative which is represented by the general formula (i): Rf1(OCH2CF2CF2)n1OCX1X2CF2(Rf2)n2COOM (i) wherein Rf1 represents a straight or branched fluoroalkyl group containing 1 to 20 carbon atoms, which fluoroalkyl group may optionally contain 1 to 5 oxygen atoms in the principal chain thereof, Rf2 represents a straight or branched fluoroalkylene group containing 1 to 25 carbon atoms, said fluoroalkylene group may optionally contain 1 to 5 oxygen atoms in the principal chain thereof, n1 represents an integer of 0 to 3, n2 represents an integer of 0 or 1, X1 and X2 are the same or different and each represents hydrogen atom or fluorine atom, and M represents NH4 or a monovalent metal element.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Resist composition
The following resist composition which is excellent particularly in transparency to light beams and dry etching properties and gives a resist pattern excellent in sensitivity, resolution, evenness, heat resistance, etc., as a chemical amplification type resist, is presented. A resist composition which comprises a fluoropolymer (A) having repeating units represented by a structure formed by the cyclopolymerization of one molecule of a fluorinated diene and one molecule of a monoene, in which the monoene unit in each repeating unit has a blocked acid group capable of regenerating the acid group by the action of an acid, an acid-generating compound (B) which generates an acid upon irradiation with light, and an organic solvent (C).
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Polymer compositions, method of manufacture, and articles formed therefrom
ActiveUS20060142455A1High tensile modulusImprove ductilityPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyPolymer scienceFluoropolymer
A polymer composition is disclosed, which comprises a matrix polymer, a fluoropolymer that may be at least partially encapsulated by an encapsulating polymer, and a filler. Methods for making the polymer compositions and articles made of such compositions are also disclosed. The compositions and article can have improved tensile modulus, ductility, and / or impact properties.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Fluorinated surfactants for use in making a fluoropolymer
InactiveUS20070117914A1Convenient and easy preparationPrepared cost-effectivelyOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationEmulsion polymerizationCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a fluorinated surfactant having the general formula:[Rf—(O)t—CQH—CF2—O]n—R-G (I)wherein Rf represents a partially or fully fluorinated aliphatic group optionally interrupted with one or more oxygen atoms, Q is CF3 or F, R is an aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbon group, G represents a carboxylic or sulphonic acid or salt thereof, t is 0 or 1 and n is 1, 2 or 3. The surfactant is particularly useful in polymerizing fluorinated monomers in an aqueous emulsion polymerization.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Fluoropolymer dispersion containing no or little low molecular weight fluorinated surfactant
ActiveUS6861466B2Good film formingTransportation and packagingFibre treatmentPolymer scienceRoom temperature
In an aspect of the invention, a fluoropolymer dispersion, preferably a PTFE dispersion, is provided that comprises fluoropolymer particles having an average particle size of 10 to 400 nm dispersed in water whereby the dispersion has an amount of solids between 35 and 70% by weight. The dispersion is free of fluorinated surfactant having a molecular weight of less than 1000 g / mol (hereinafter called low molecular weight fluorinated surfactant) or contains the low molecular weight fluorinated surfactant in an amount of not more than 0.05% by weight based on the total weight solids of the dispersion. The dispersion further comprises a non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactant or mixture of non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactants and one or more non-fluorinated anionic surfactants. Through the use of a non-fluorinated anionic surfactant, a dispersion is obtained that has a low viscosity at room temperature (20° C.). The dispersion is further free of aromatic group containing non-ionic surfactants and is accordingly environmentally more friendly and can yield coatings that are less susceptible of discoloration. The amount and nature of the non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactant or mixture of non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactants is selected such that the Viscosity Transition Temperature (VTT) (measured as set forth in the examples) of the fluoropolymer dispersion is at least 26, preferably at least 28° C. In a further aspect of the invention, a method is provided to obtain the aforementioned dispersion.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Core-shell fluoropolymer dispersions
InactiveUS6841594B2High shear stabilityExtend elastic lifeSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsTetrafluoroethylenePolymer science
A dispersion of non-melt-processible fluoropolymer particles having an SSG of less than about 2.225 in aqueous medium. The fluoropolymer particles comprise a core of high molecular weight polytetrafluoroethylene having an average melt creep viscosity greater than about 1.5×1010 Pa·s and a shell of lower molecular weight polytetrafluoroethylene or modified polytetrafluoroethylene. The shell has an average melt creep viscosity greater than about 9×109 Pa·s and comprises about 5 to about 30% by weight of the particles. The fluoropolymer in the dispersion of the invention is fibrillating.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Expandable fluoropolymer device for delivery of therapeutic agents and method of making
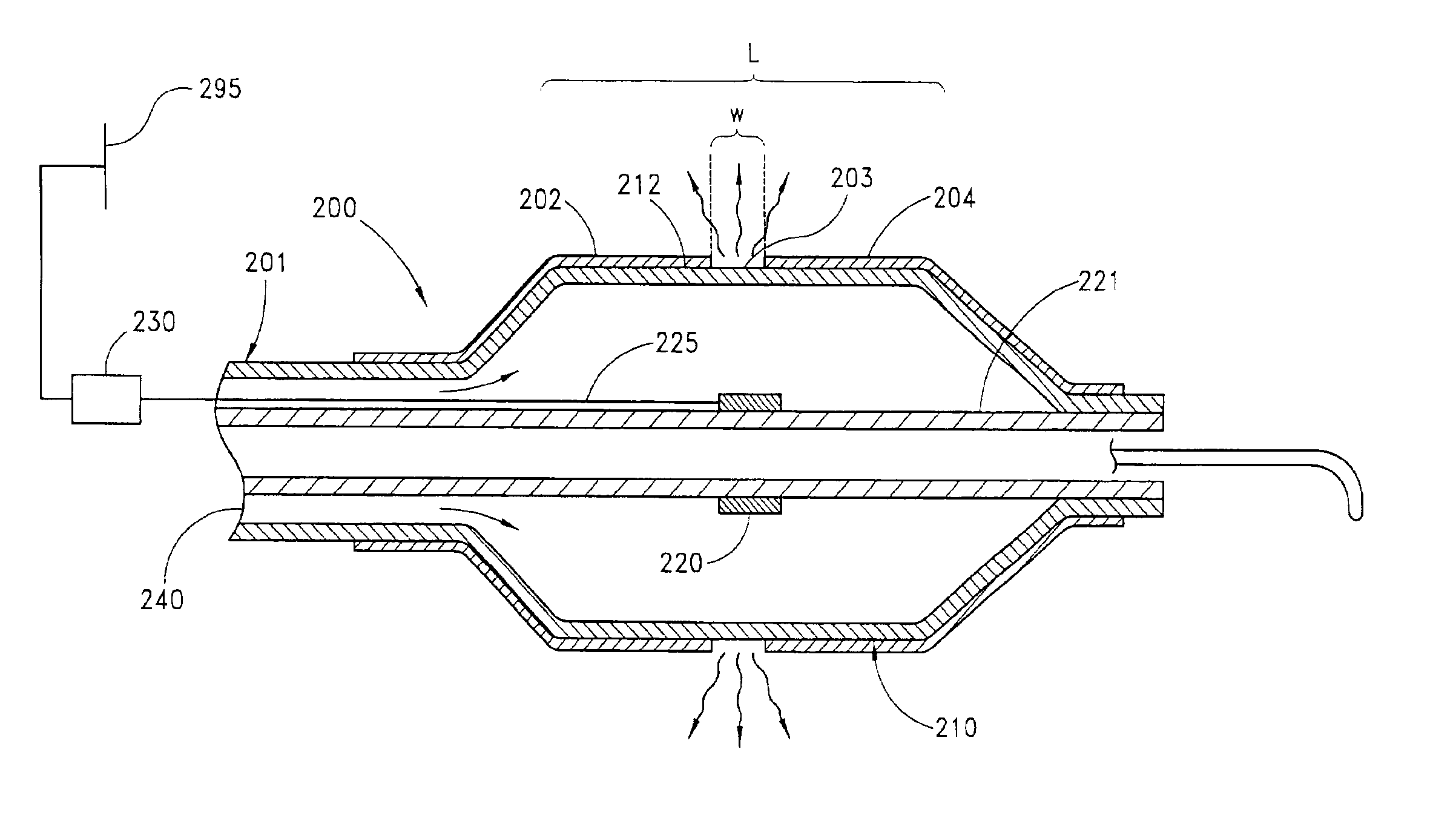
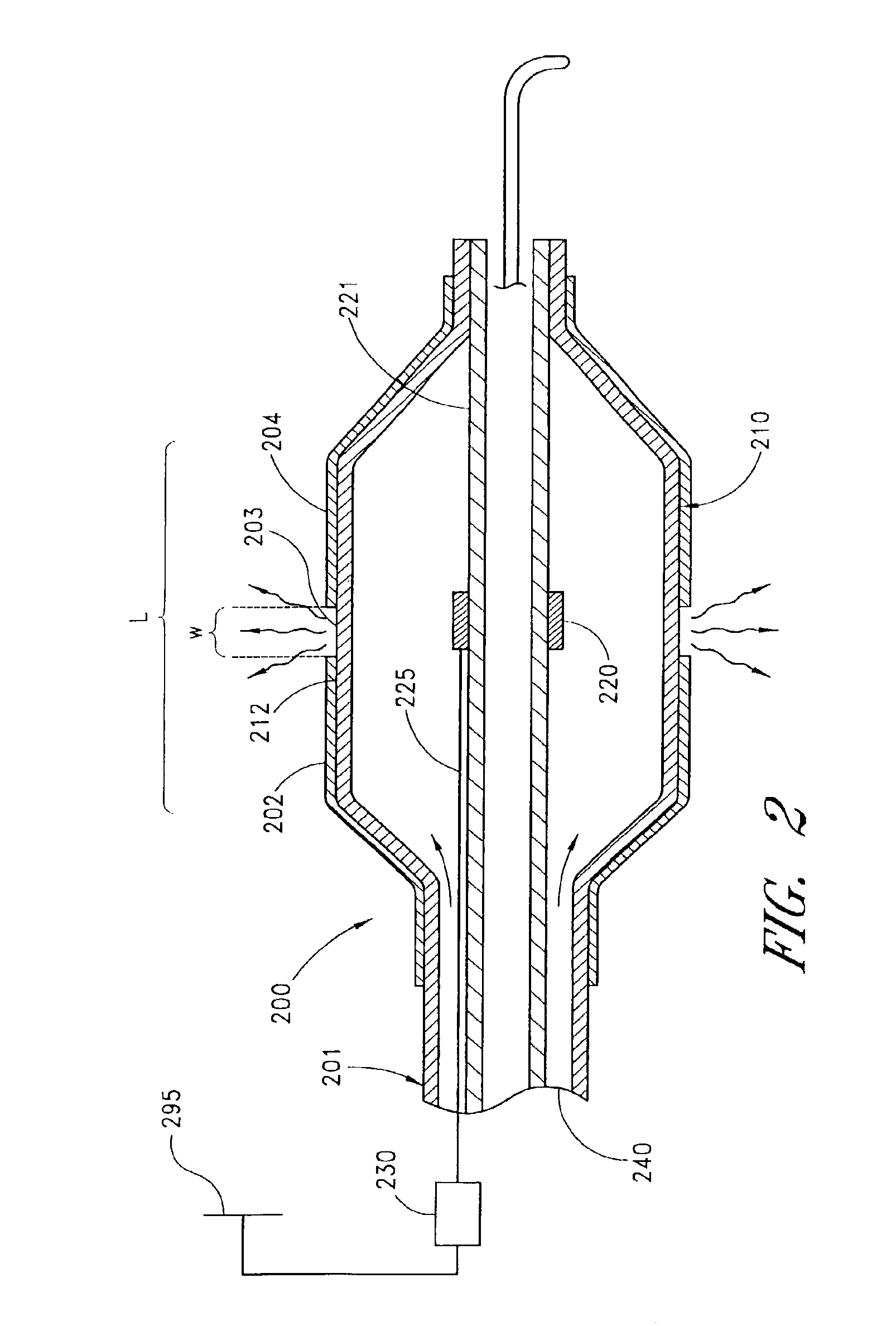
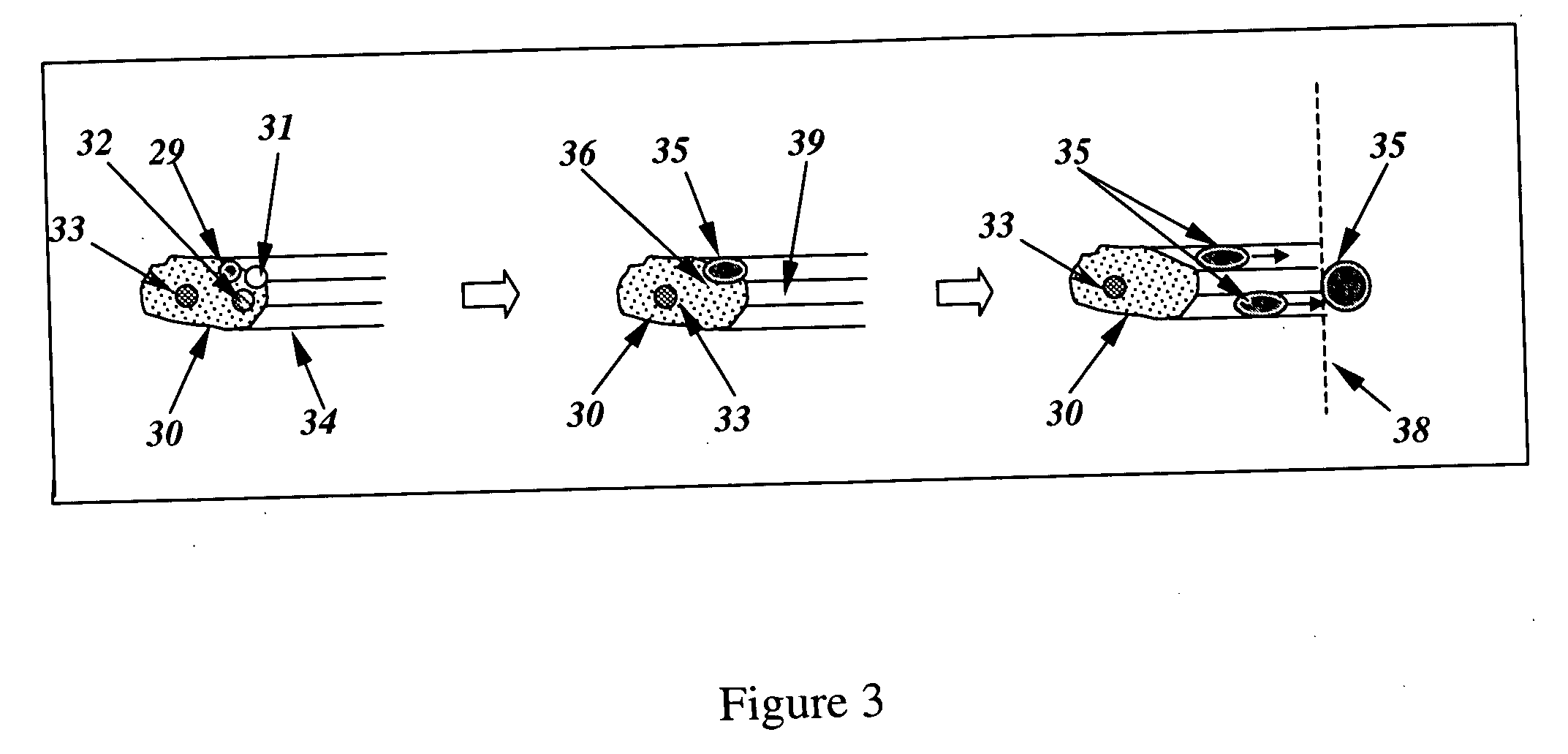
A radially expandable fluid delivery device for delivering a fluid to a treatment site within the body is disclosed. The fluid delivery device is constructed of a microporous, biocompatible fluoropolymer material having a microstructure that can provide a controlled, uniform, low-velocity fluid distribution through the walls of the fluid delivery device to effectively deliver fluid to the treatment site without damaging tissue proximate the walls of the device. The fluid delivery device includes a tubular member defined by a wall having a thickness transverse to the longitudinal axis of the tubular member and extending between an inner and an outer surface. The wall is characterized by a microstructure of nodes interconnected by fibrils. The tubular member is deployable from a first, reduced diameter configuration to a second, increased diameter configuration upon the introduction of a pressurized fluid to the lumen. The tubular member includes at least one microporous portion having a porosity sufficient for the pressurized fluid to permeate through the wall. Substantially all of the nodes within the microporous portion are oriented such that spaces between the nodes form micro-channels extending from the inner surface-to the outer surface of the wall.
Owner:ATRIUM MEDICAL
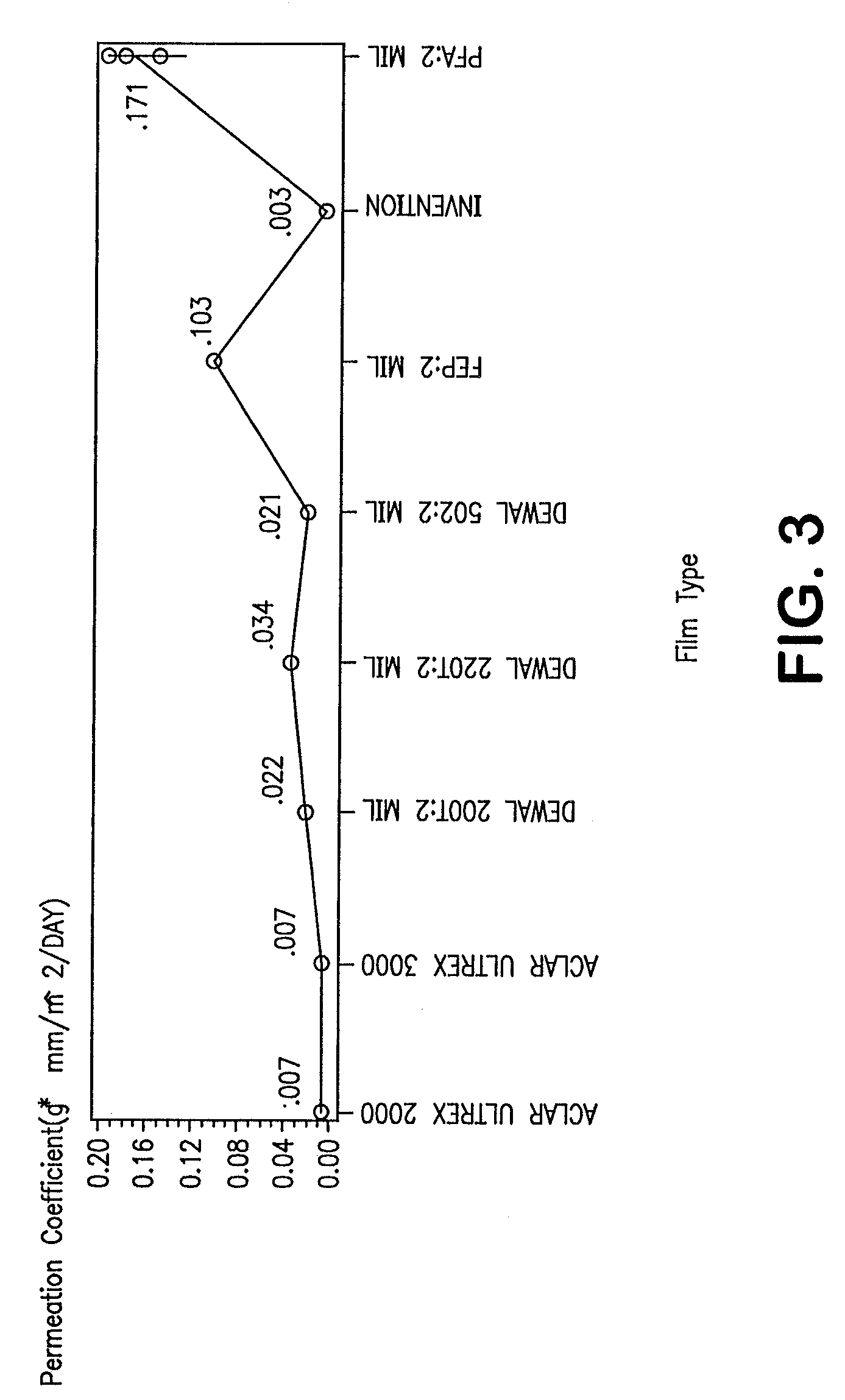
Fluoropolymer barrier material
InactiveUS7521010B2Improve barrier propertiesImprove permeabilitySynthetic resin layered productsCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceWater vapor permeability
A novel densified fluoropolymer article is described which has a water vapor permeation of about 0.015 g-mm / m2 / day or less, and preferably has a matrix tensile strength of at least 10,000 psi in two orthogonal directions. The articles are made by compressing expanded porous PTFE at pressures, temperatures and times which result in elimination of the pores, and subsequent stretching above the crystalline melt temperature.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Fluoropolymer coated films useful for photovoltaic modules
ActiveUS20070154704A1Strong adhesionIncreased durabilitySynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageEpoxyPolymer science
A fluoropolymer coated film comprising polymeric substrate film and fluoropolymer coating on the polymeric substrate film. The fluoropolymer coating comprises fluoropolymer selected from homopolymers and copolymers of vinyl fluoride and homopolymers and copolymers of vinylidene fluoride polymer blended with compatible adhesive polymer comprising functional groups selected from carboxylic acid, sulfonic acid, aziridine, anhydride, amine, isocyanate, melamine, epoxy, hydroxy, anhydride and mixtures thereof. The polymeric substrate film comprises functional groups on its surface that interact with the compatible adhesive polymer to promote bonding of the fluoropolymer coating to the substrate film.
Owner:DUPONT ELECTRONICS INC
Crosslinkable aqueous fluoropolymer based dispersions
Acrylic Modified Fluoropolymers based on vinylidene fluoride polymers are disclosed wherein the acrylic phase is capable of entering into crosslinking reactions. The final cured products provide superior solvent extractability resistance to the fluoropolymer phase.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Removal of fluorinated surfactants from waste water
The present invention provides a method of removing a fluorinated surfactant from waste water comprising fluoropolymer particles. The method comprises (i) adding a non-fluorinated surfactant to the waste water (ii) contacting the thus obtained waste water with adsorbent particles to adsorb at least a portion of the fluorinated surfactant to the adsorbent particles and (iii) separating the waste water and the adsorbent particles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Aqueous polyvinylidene fluoride composition
ActiveUS20100304270A1Dry fastUseful electrodeLiquid electrolytic capacitorsConductive materialInterconnectivityPolyvinylidene difluoride
The invention relates to an aqueous fluoropolymer, and preferably polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), composition for manufacturing electrodes for use in non-aqueous-type electrochemical devices, such as batteries and electric double layer capacitors. The composition contains aqueous PVDF binder, and one or more powdery electrode-forming materials. In one embodiment, the composition is free of fluorinated surfactant In another embodiment, one or more fugitive adhesion promoters are added. The electrode formed from the composition of the invention exhibits interconnectivity and irreversibility that is achieved from the use of aqueous PVDF binder.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Expandable fluoropolymer device for delivery of therapeutic agents and method of making
A method of making a radially expandable fluid delivery device includes providing a tube of biocompatible fluoropolymer material with a predetermined porosity based on an extrusion and expansion forming process, applying a radial expansion force to the tube expanding the tube to a predetermined diameter dimension, and removing the radial expansion force. The tube is radially inelastic while sufficiently pliable to be collapsible and inflatable from a collapsed configuration to an expanded configuration upon introduction of an inflation force, such that the expanded configuration occurs upon inflation to the predetermined diameter dimension. The fluid delivery device is constructed of a microporous, biocompatible fluoropolymer material having a microstructure that can provide a controlled, uniform, low-velocity fluid distribution through the walls of the fluid delivery device to effectively deliver fluid to the treatment site without damaging tissue proximate the walls of the device.
Owner:ATRIUM MEDICAL
Flue gas purification process using a sorbent polymer composite material
ActiveUS20050019240A1Easy to fixImprove removal efficiencyGas treatmentNitrogen compoundsSorbentFluoropolymer
This invention provides a process of removing sulfur oxides, mercury vapor, and fine particulate matters from industrial flue gases that contain such pollutants. The pollutants are removed by modules, which contain microporous adsorbent (i.e., sorbent) material that is held within a polymer matrix. The preferred polymers are fluoropolymers. The composite material that contains the microporous absorbent material held within a polymer matrix removes sulfur oxides by converting them into high concentration sulfuric acids. It also removes mercury vapor by chemically adsorbing the mercury into the matrix. It also removes fine particulate matters by surface filtration. The sulfuric acid that is produced inside the composite material is automatically expelled onto the external surfaces of the composite material and is drained into an acid reservoir together with the fine particulate matters which are washed from the external surfaces of the composite material by the constant dripping of the sulfuric acid along the external surfaces of the composite material.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Fluoropolymer coating compositions with olefinic silanes for anti-reflective polymer films
InactiveUS20060147177A1Low compositionIncreased durabilityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistrySilanesRefractive index
An economic, optically transmissive, stain and ink repellent, durable low refractive index fluoropolymer composition for use in an antireflection film or coupled to an optical display. In one aspect of the invention, the composition is formed from the reaction product of a fluoropolymer, a C═C double bond group containing silane ester agent, and an optional multi-olefinic crosslinker. In another aspect of the invention, the composition further includes surface modified inorganic nanoparticles. In another aspect, the multi-olefinic crosslinker is an alkoxysilyl-containing multi-olefinic crosslinker.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Thermoplastic fluoropolymer-coated medical devices
A medical device provided with at least a partial surface coating of a thermoplastic copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene and perfluoroalkylvinylether that is free of cross-linking monomers and curing agents. The fluoropolymer coating is preferably an amorphous thermoplastic, is highly inert and biocompatible, has elastomeric characteristics that provide desirable mechanical properties such as good flexibility and durability. These characteristics allow the coating to be considered “functionally transparent” because it withstands mechanical deformations required for the assembly, deployment, expansion, and placement of medical devices, without any adverse effect on the mechanical and biological functionality of the coated device. Further, its inertness, derived from the perfluorocarbon structure, contributes to its functionally transparent nature. The coating can be provided with various liquid or solid additives, can be loaded with large quantities of additives including a wide range of therapeutic agents, and has excellent drug elution characteristics when elutable additives are used. The desirable mechanical characteristics are surprising given the absence of cross-linking monomers and curing agents that would otherwise render such materials inadequately biocompatible. The perfluoroalkylvinylether may be perfluoromethylvinylether, perfluoroethylvinylether or perfluoropropylvinylether.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Light-emitting diode (LED) with amorphous fluoropolymer encapsulant and lens
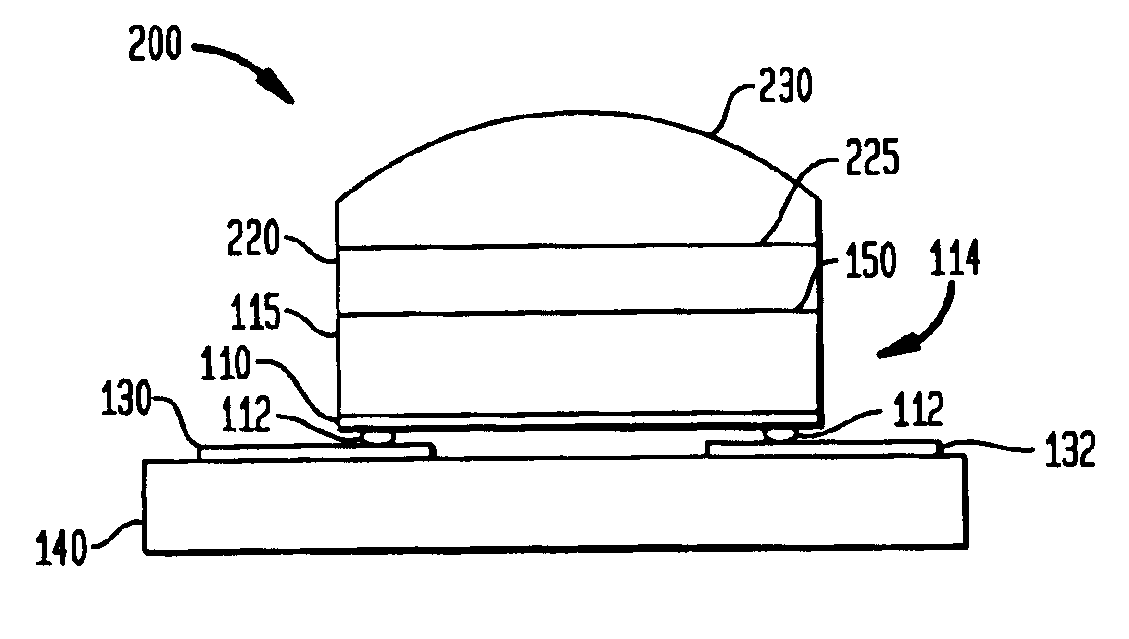
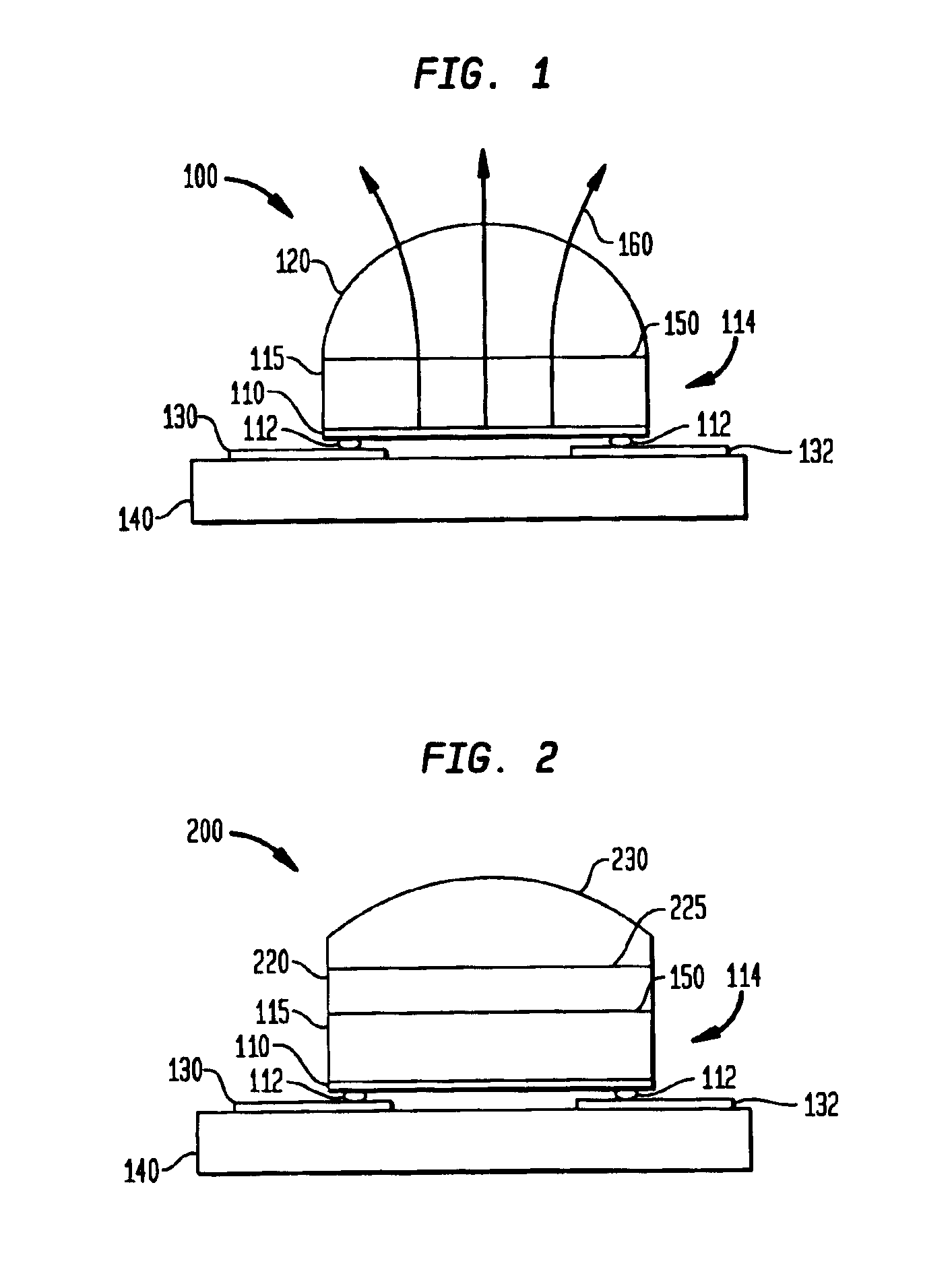
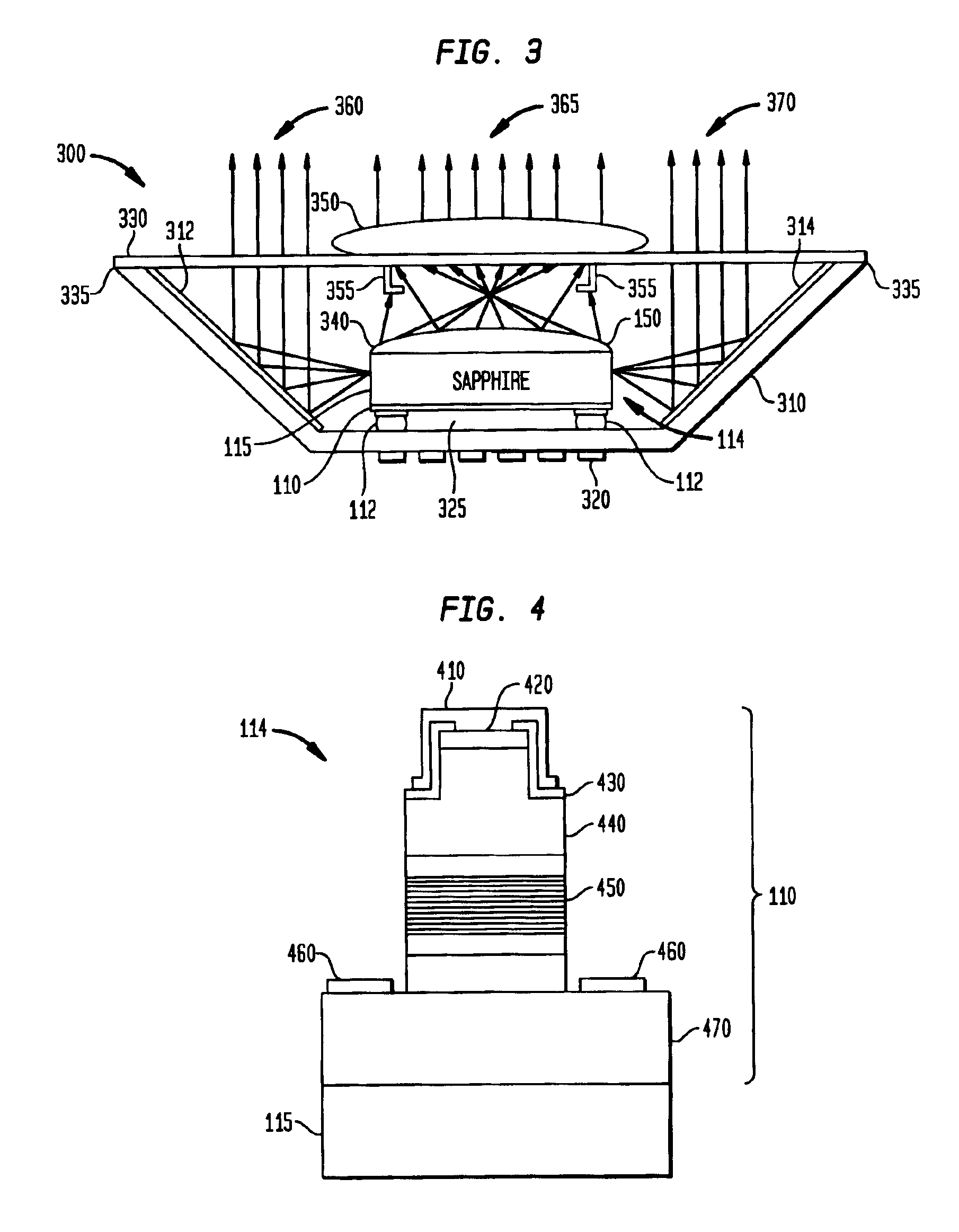
InactiveUS6921929B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesUltravioletFluoropolymer
A lens and encapsulant made of an amorphous fluoropolymer for a light-emitting diode (LED) or diode laser, such as an ultraviolet (UV) LED (UVLED). A semiconductor diode die (114) is formed by growing a diode (110) on a substrate layer (115) such as sapphire. The diode die (114) is flipped so that it emits light (160, 365) through the face (150) of the layer (115). An amorphous fluoropolymer encapsulant encapsulates the emitting face of the diode die (114), and may be shaped as a lens to form an integral encapsulant / lens. Or, a lens (230, 340) of amorphous fluoropolymer may be joined to the encapsulant (220). Additional joined or separate lenses (350) may also be used. The encapsulant / lens is transmissive to UV light as well as infrared light. Encapsulating methods are also provided.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Apparatus and method for easing use of a spectrophotometric based noninvasive analyzer
ActiveUS20070293743A1Easy to detectImprove usabilityScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyAnalyte
A placement guide apparatus with an improved hydration inducing plug used in coupling a noninvasive analyzer to a sampling site to determine analyte in the human body is disclosed. The hydration inducing plug includes at least one fluoropolymer that may be used as a coupling agent. The guide apparatus may further include an automated or semi-automated coupling fluid delivery system. Use of either of these couplers mitigates issues associated with related technology and enhances noninvasive analyte measurements, such as a near-IR diffuse reflectance based noninvasive glucose concentration analyzer.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Method for producing fluorine-containing ploymer, aqueous dispersion of fluorine-containing polymer,2-acyloxycarboxylic acid derivative , and surface active agent
ActiveUS20060223924A1Low residual surfactant contentGood physical propertiesOrganic chemistrySynthetic resin layered productsAcid derivativeCarboxylic salt
The present invention provides a method of producing a fluoropolymer, wherein polymerization using a carboxylate ester bond-containing carboxylic acid derivative as a surfactant in an aqueous medium to give the fluoropolymer is conducted, the above carboxylate ester bond-containing carboxylic acid derivative has a carboxylate ester bond and —COOM (M representing H, NH4, Li, Na or K), the above carboxylate ester bond may optionally be substituted by fluorine atom.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Surfactant, method of producing a fluoropolymer, fluoropolymer aqueous dispersion
The present invention provides a surfactant making it possible to obtain particles comprising a fluoropolymer at a size smaller in diameter in an aqueous dispersion obtained by polymerization in the presence of the same. The present invention is a surfactant comprising a fluorine-containing-sulfobutanedioic-acid-ester derivative represented by the general formula (i): Y—Rf1—(CH2)m—OCOCH(SO3M)-CH2COO—(CH2)n—Rf2—Y (i) wherein Y represents hydrogen atom or fluorine atom; when Y is hydrogen atom, one of Rf1 and Rf2 is —(CF2CF2)3— and the other is —(CF2CF2)2— or —(CF2CF2)3— and, when Y is fluorine atom, Rf1 and Rf2 are the same or different and each is a divalent hydrocarbon group containing 1 to 4 carbon atoms and containing at least one fluorine atom; m and n are the same or different and each represents an integer of 1 to 3; and M represents NH4, Li, Na, K or H.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Fluoropolymer dispersions containing no or little low molecular weight fluorinated surfactant
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Thin film transistor substrate and method of making the same
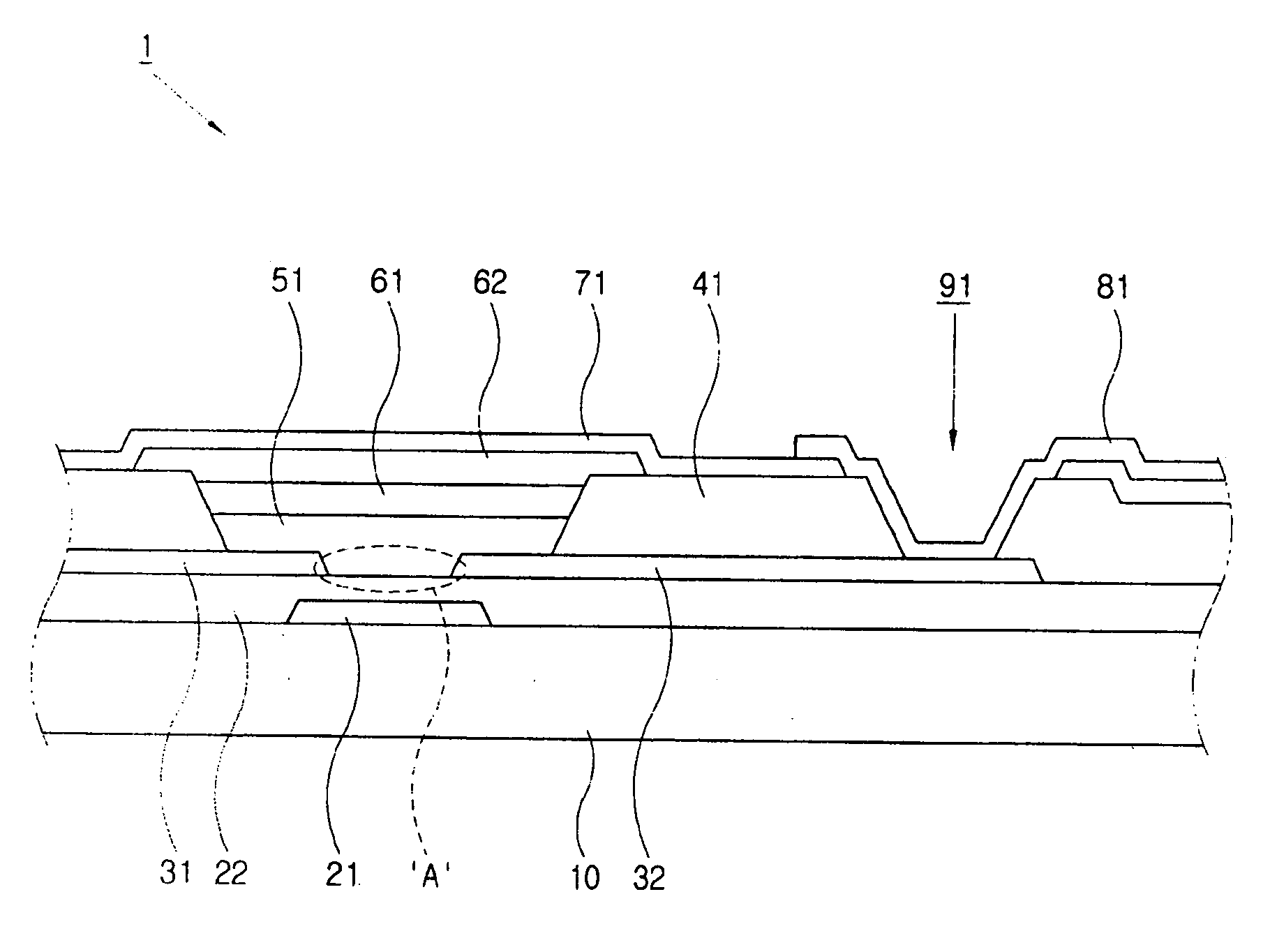
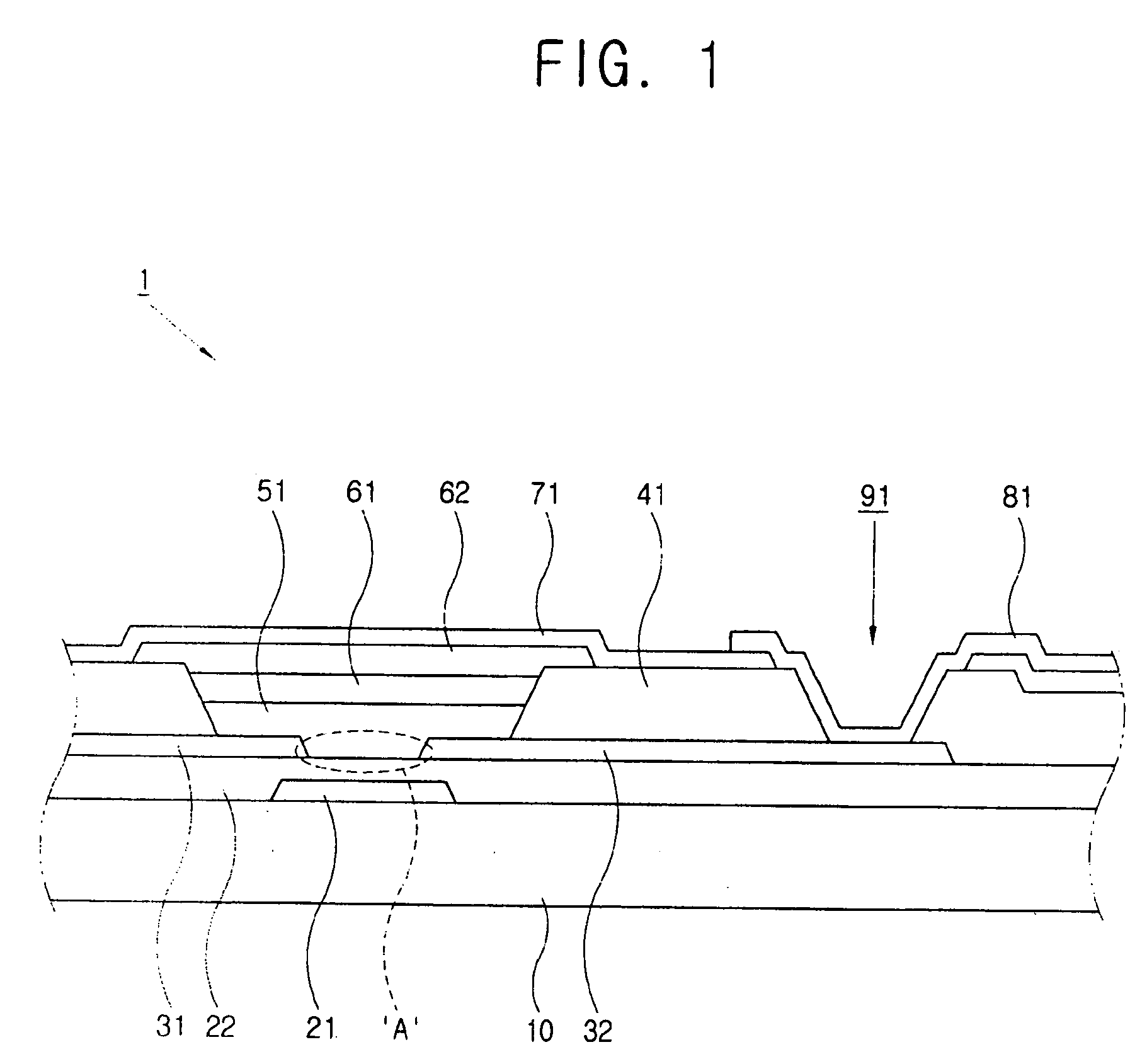
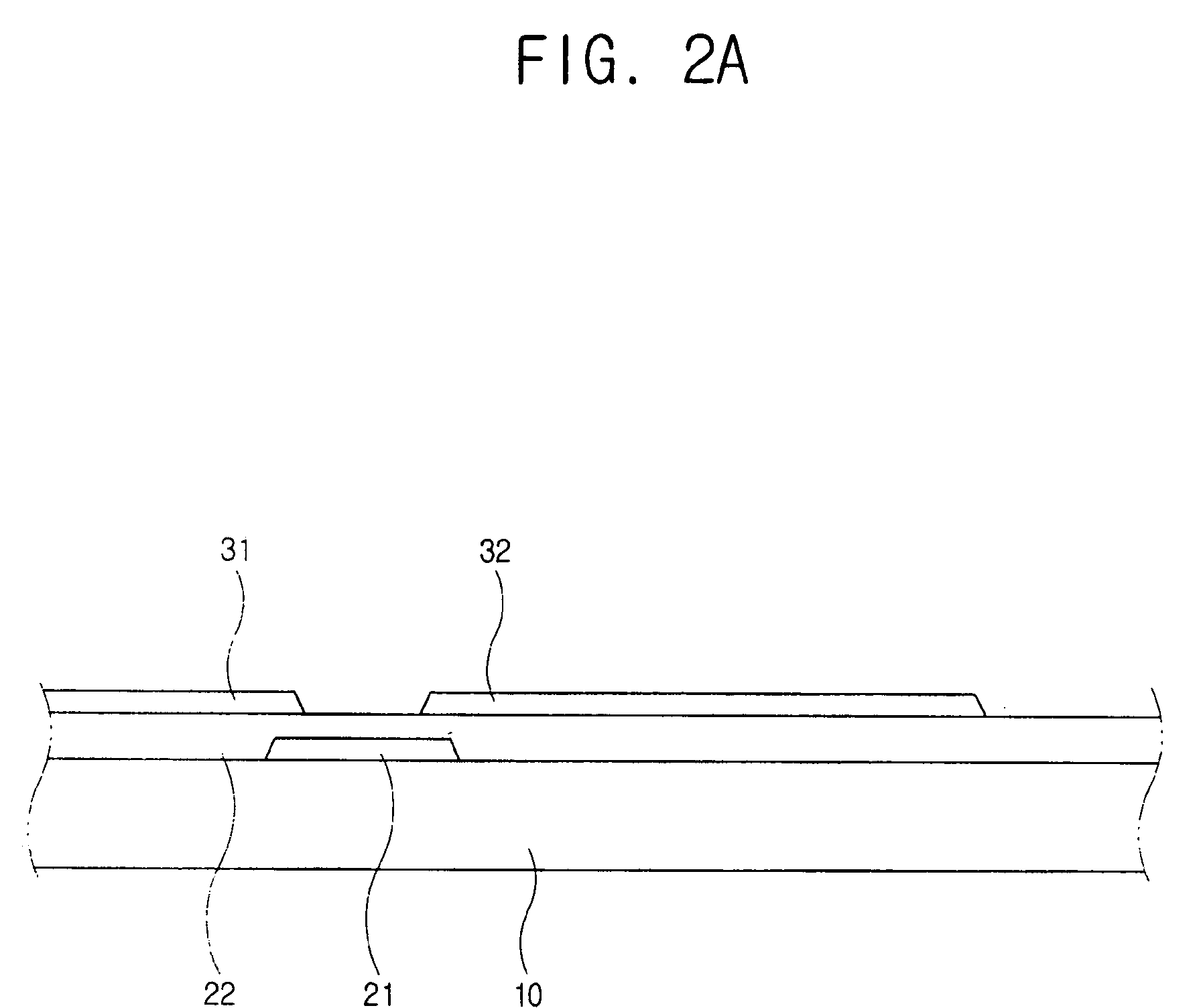
The present invention relates to a thin film transistor substrate comprising: an insulating substrate; a source electrode and a drain electrode which are formed on the insulating substrate and separated from each other and have a channel area therebetween; a wall exposing at least portions of the source electrode and the drain electrode, respectively, encompassing the channel area, and formed of fluoropolymer; and an organic semiconductor layer formed inside the wall. Thus, the present invention provides a TFT substrate where an organic semiconductor layer is planarized. Further, the present invention also provides a method of making a TFT substrate of which an organic semiconductor layer is planarized.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
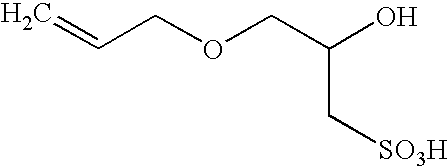
Polymerization of fluoromonomers using a 3-allyloxy-2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonic acid salt as surfactant
InactiveUS6869997B2Reduce the binding forceOrganic chemistryFibre treatmentFluoropolymerBuffering agent
Fluoropolymers are prepared by a process comprising polymerizing at least one fluoromonomer in an aqueous reaction medium containing monomer, a radical initiator and a 3-allyloxy-2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonic acid salt as surfactant. The medium may optionally contain one or more of an antifoulant, a buffering agent and a chain-transfer agent.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com