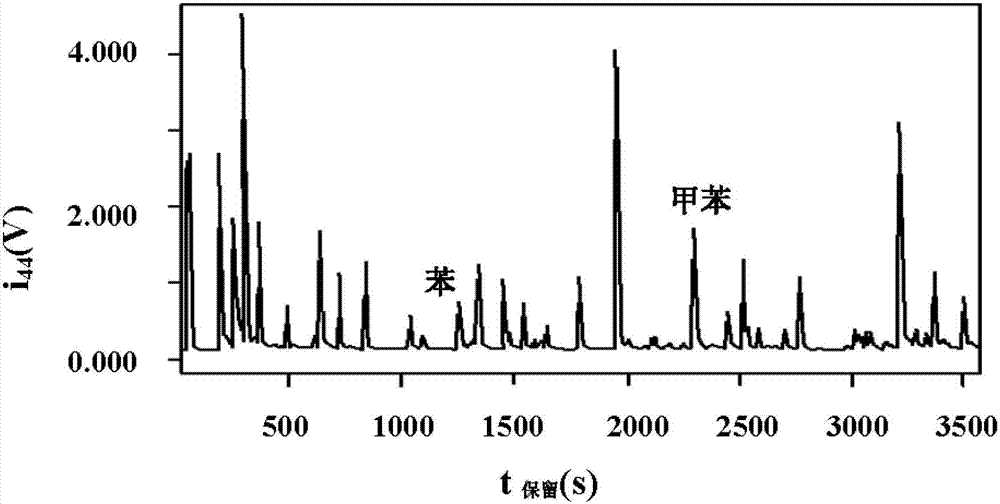
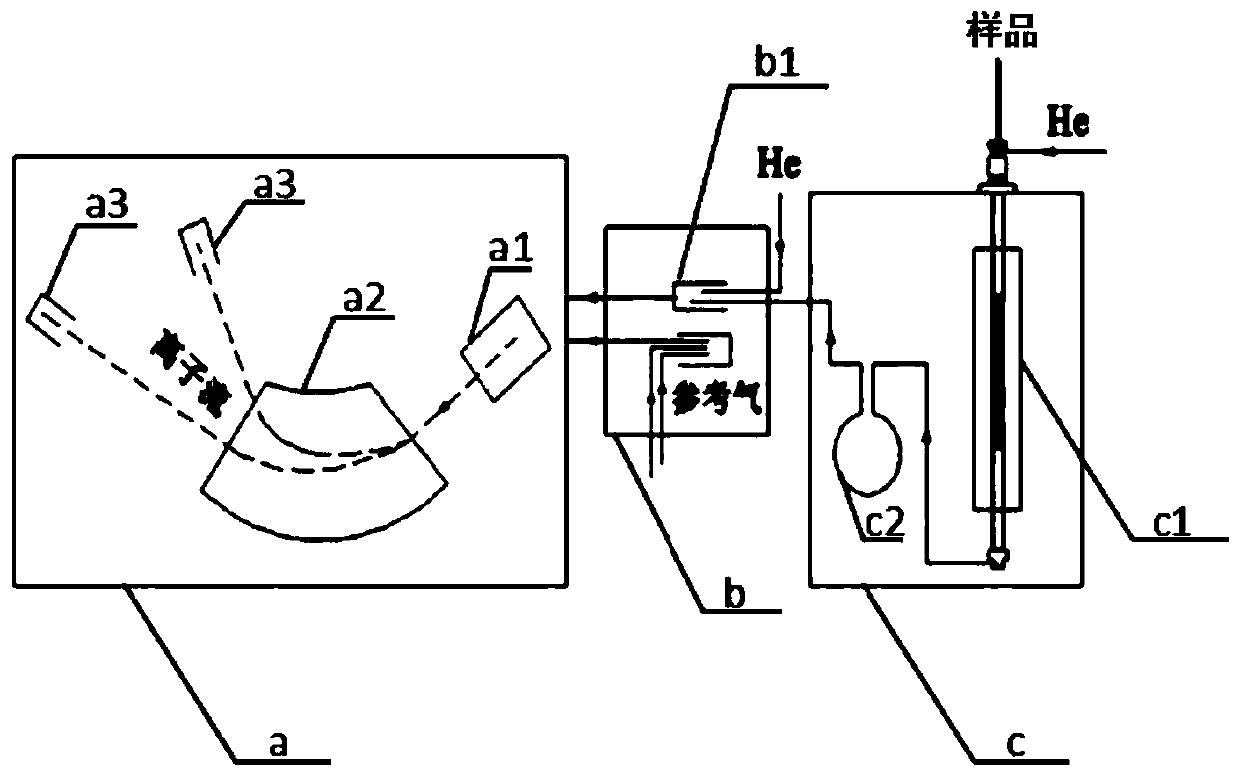
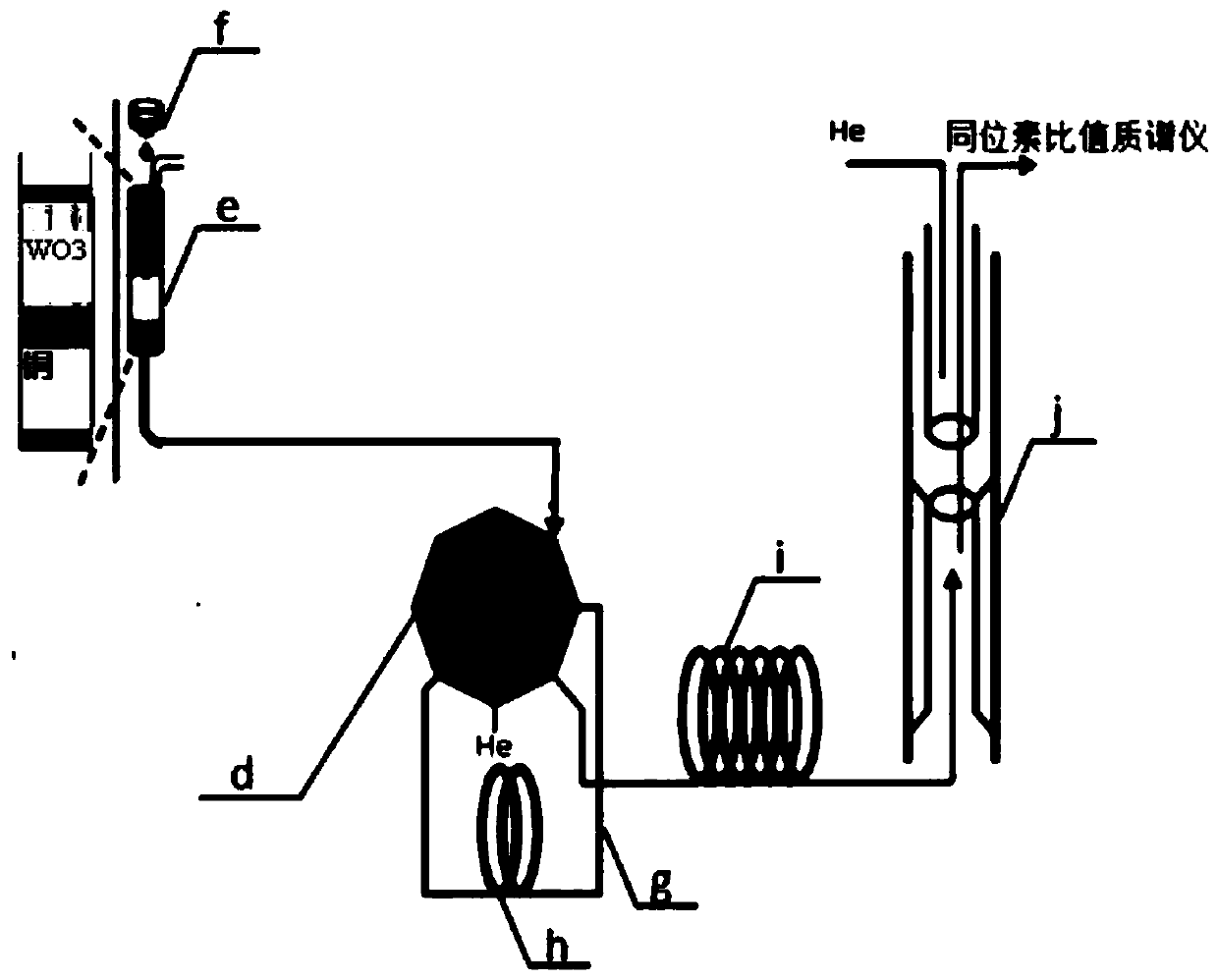
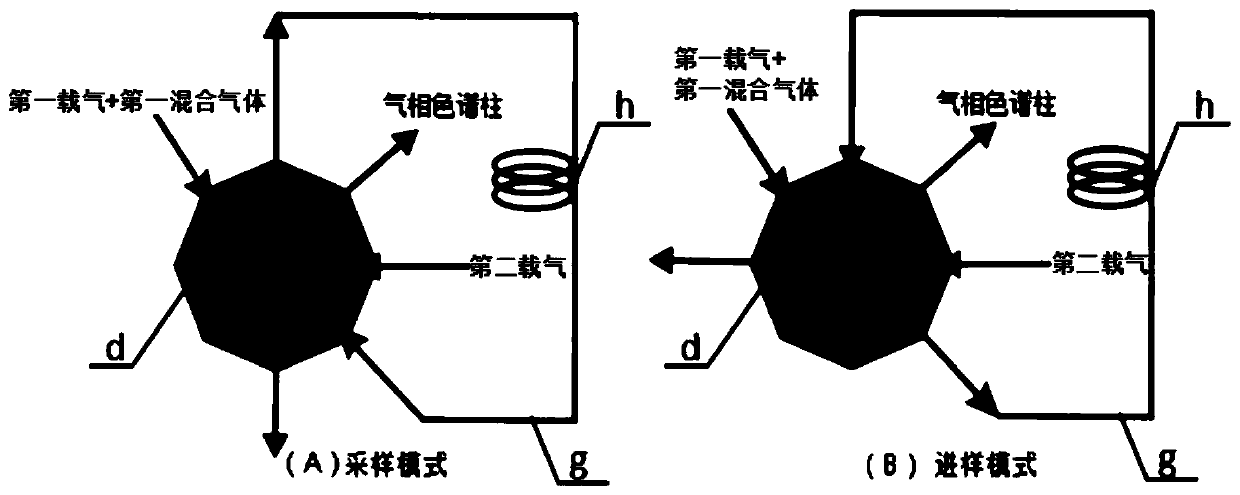
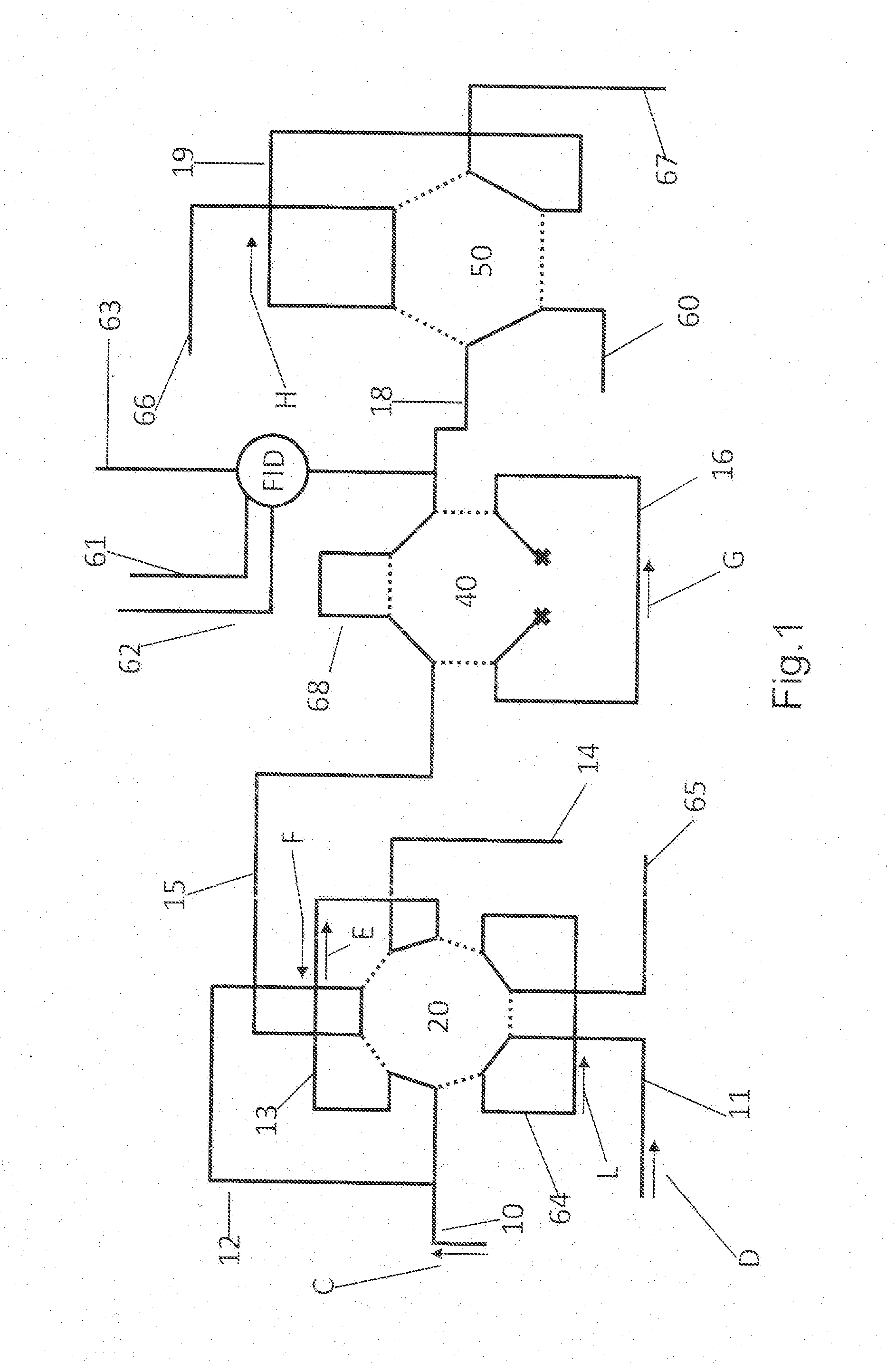
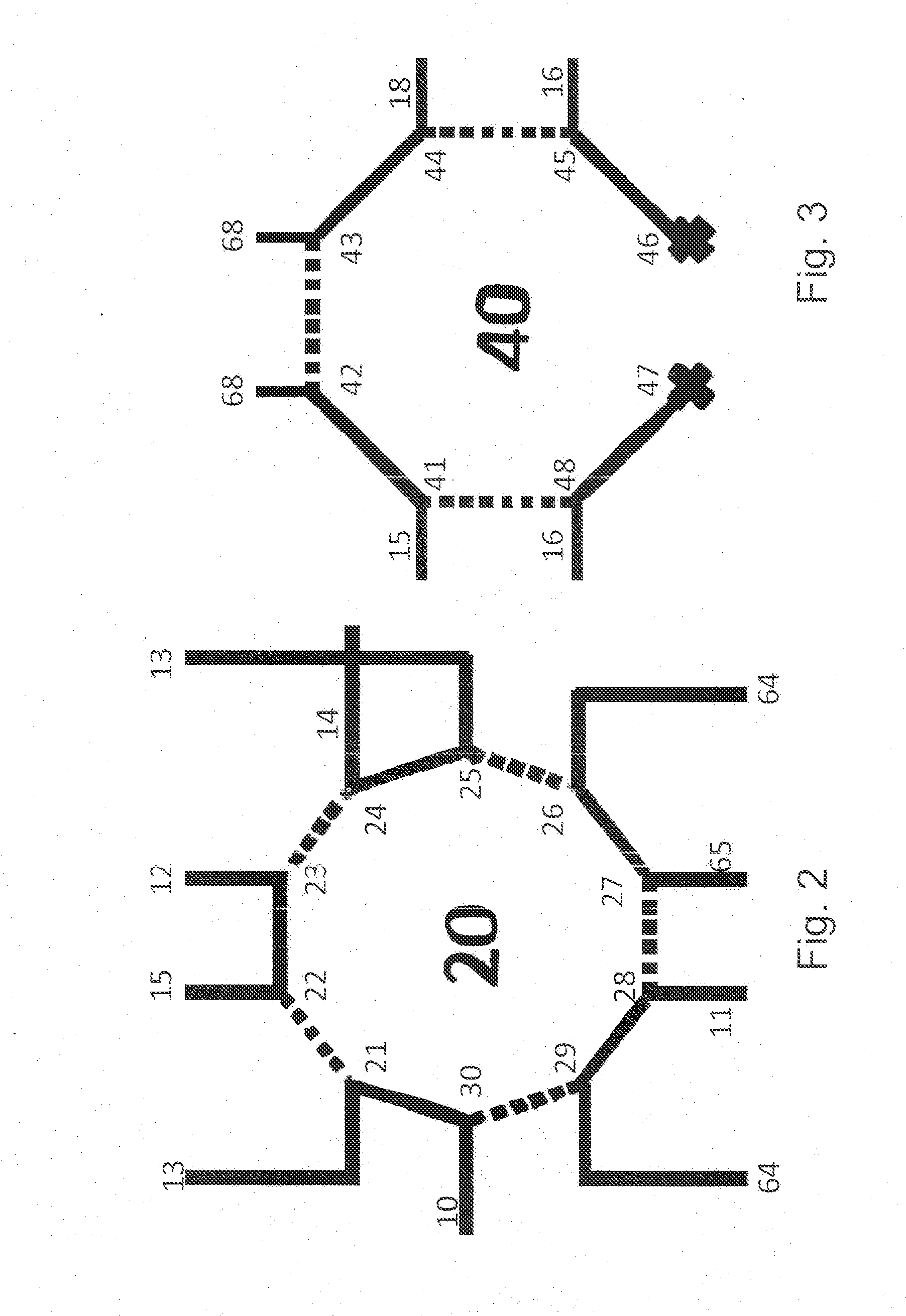
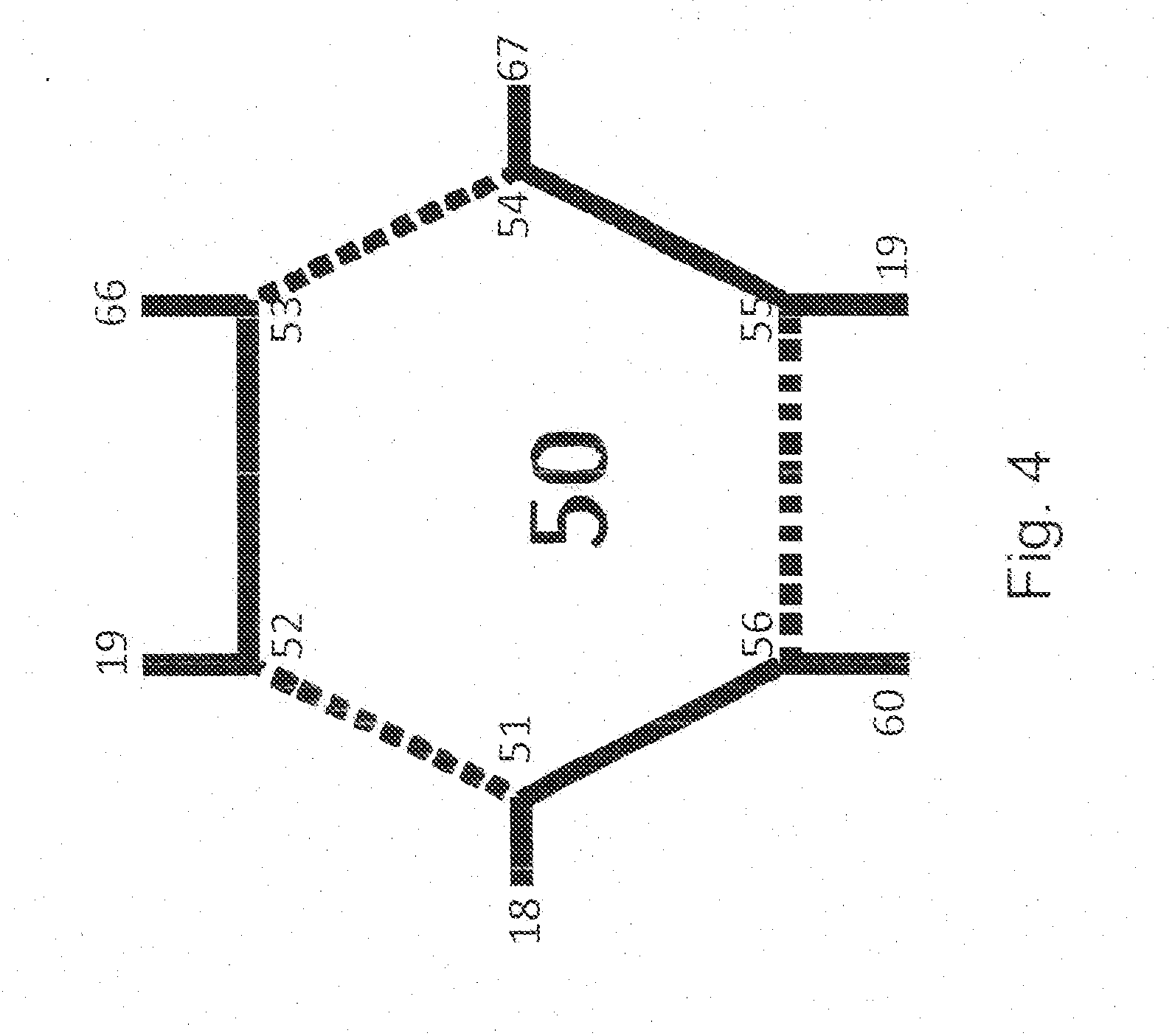
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
149 results about "Isotopic ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition. Isotopic ratio refers to the ratio of the atomic abundances of two isotopes of the same element, e.g., 18 O/ 16 O or 143 Nd/ 144 Nd. An advantage of using ratios rather than absolute abundances of a particular nuclide is a better precision. Comparing the two signals 143 Nd and 144 Nd can be done at the ppm (one part in one million)...
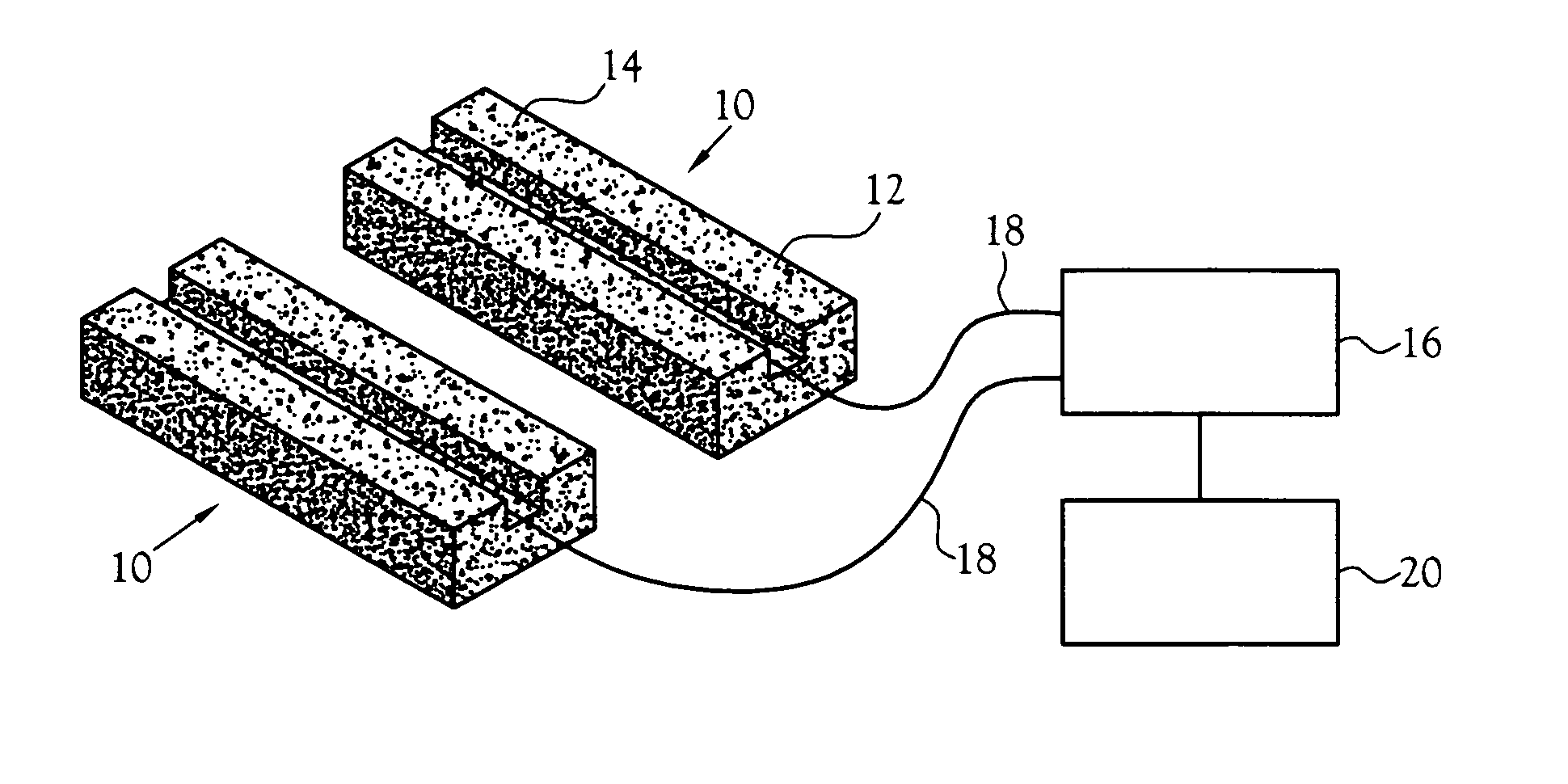
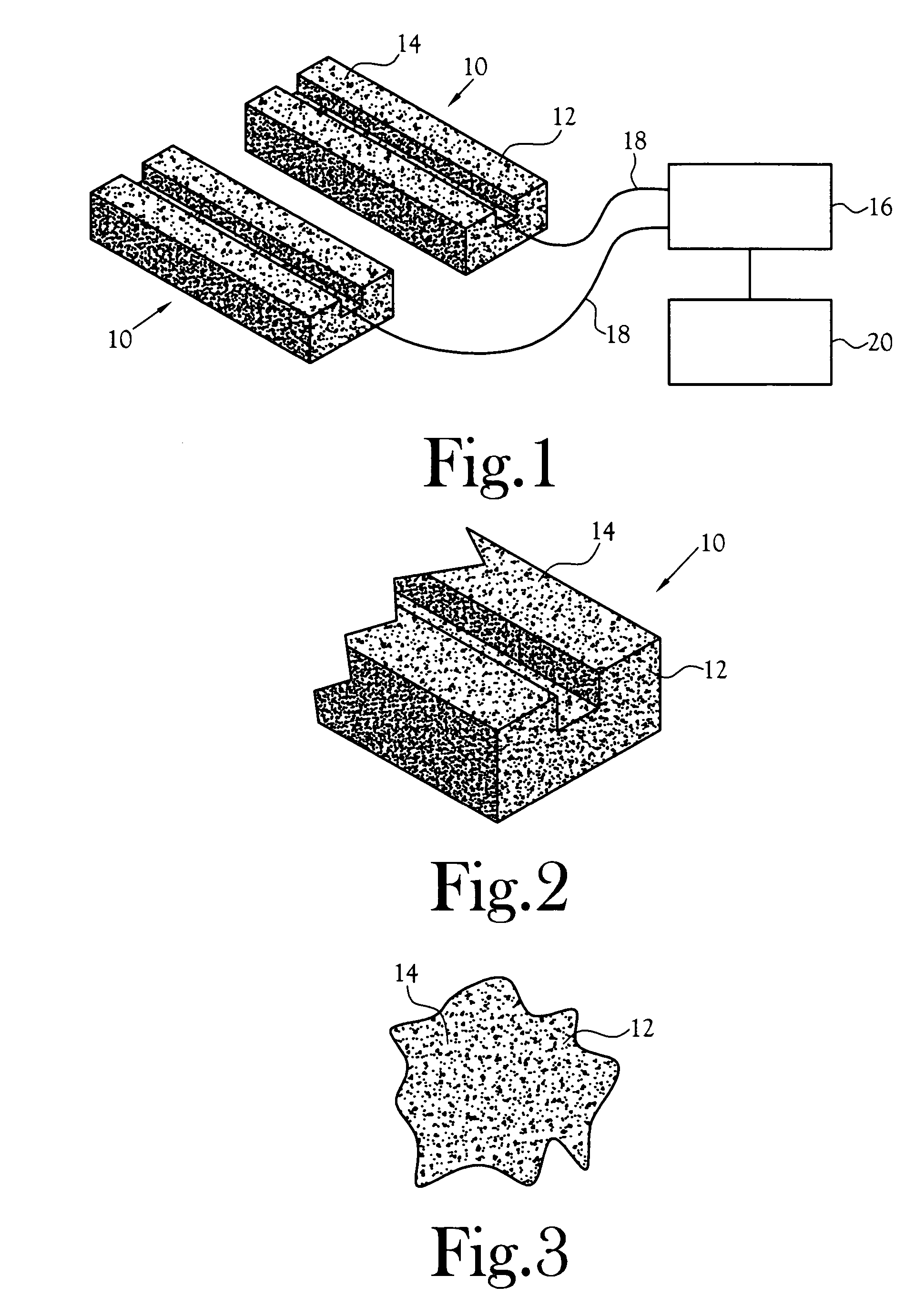
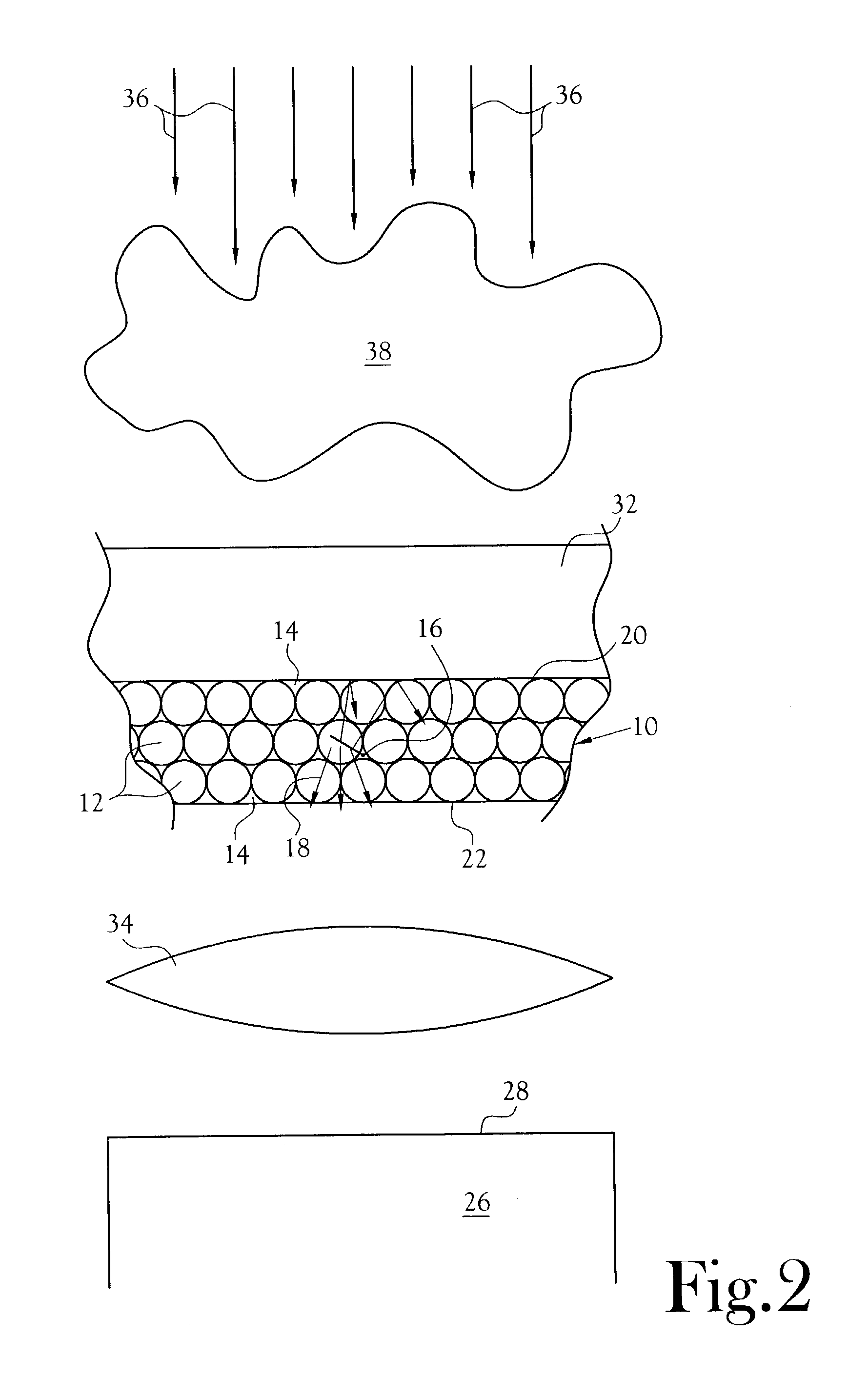
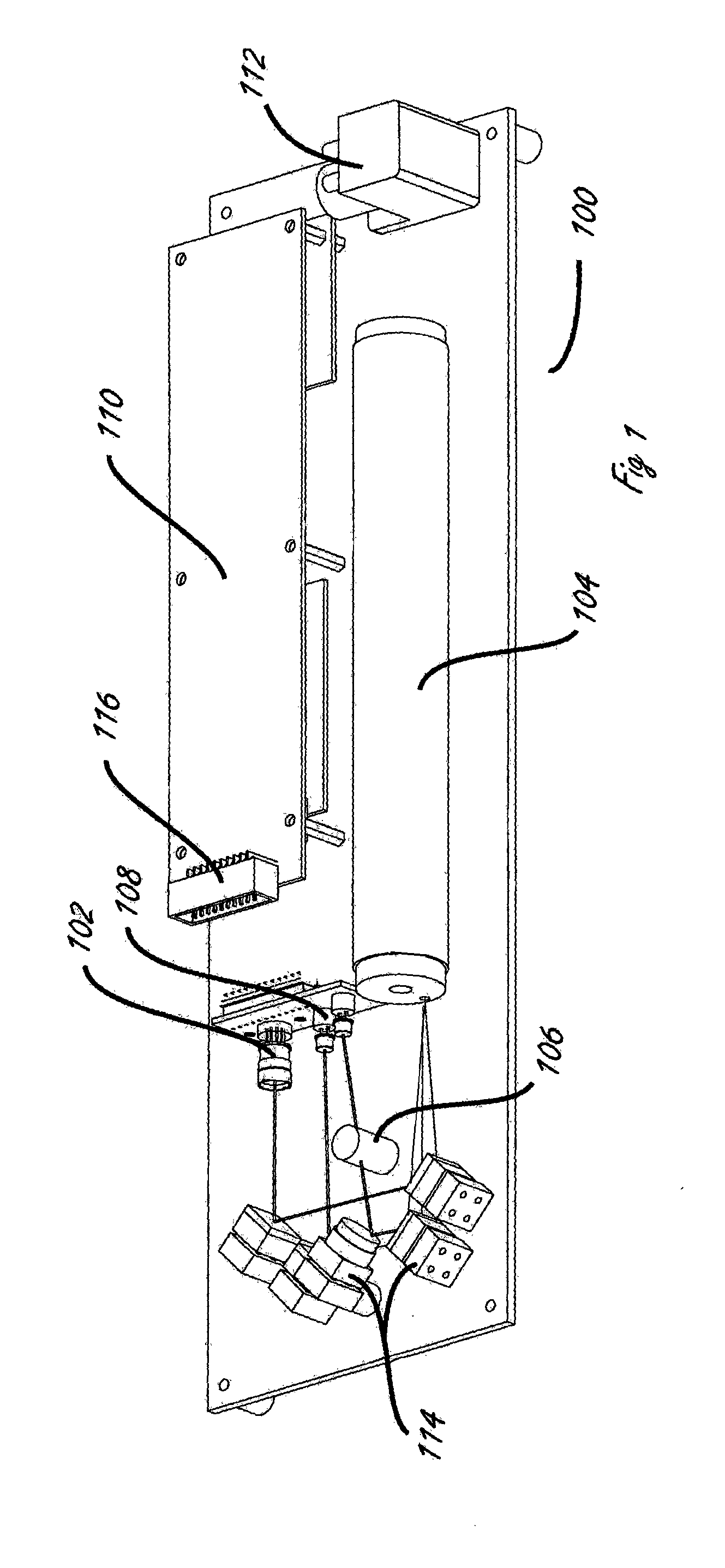
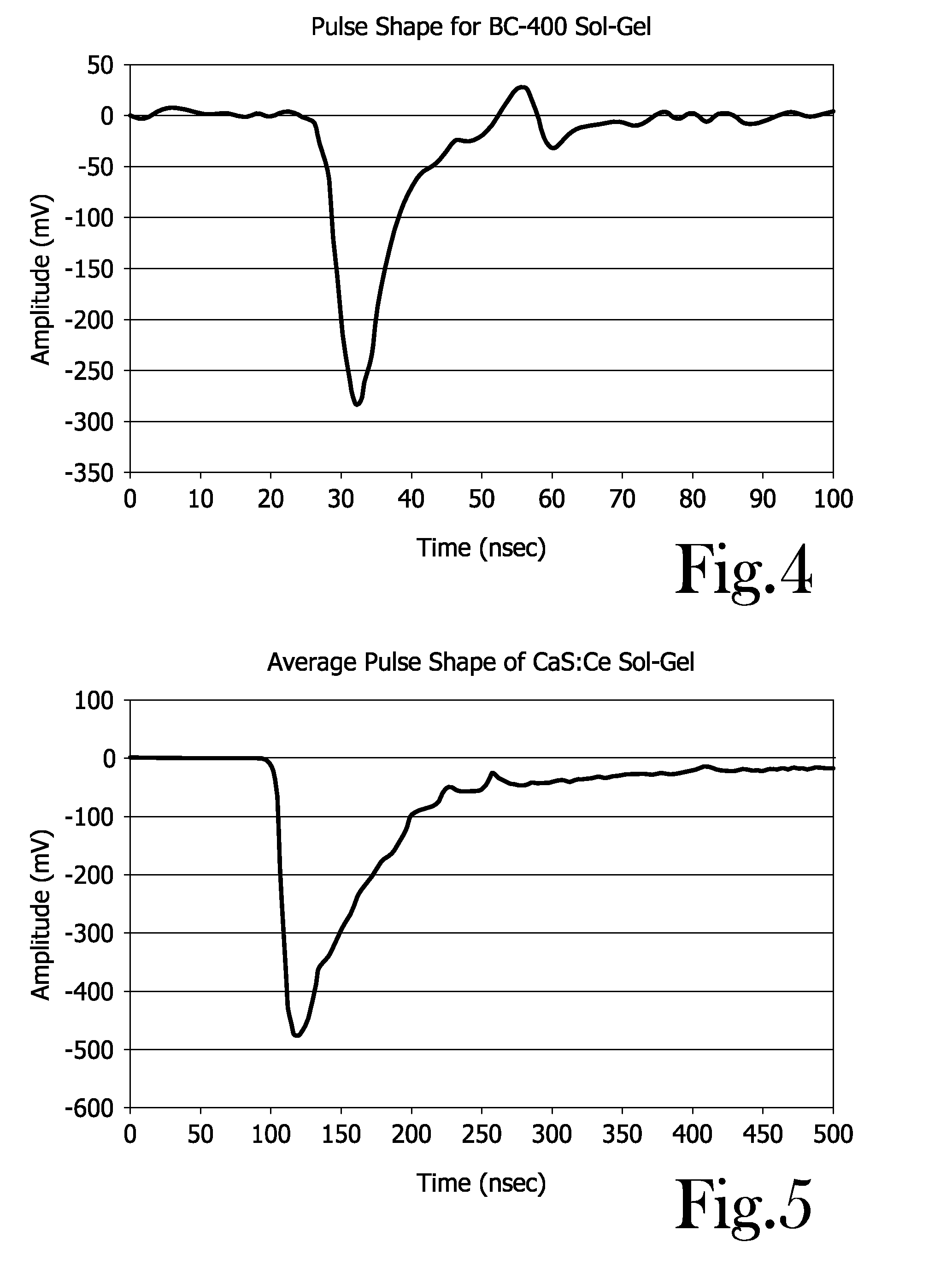
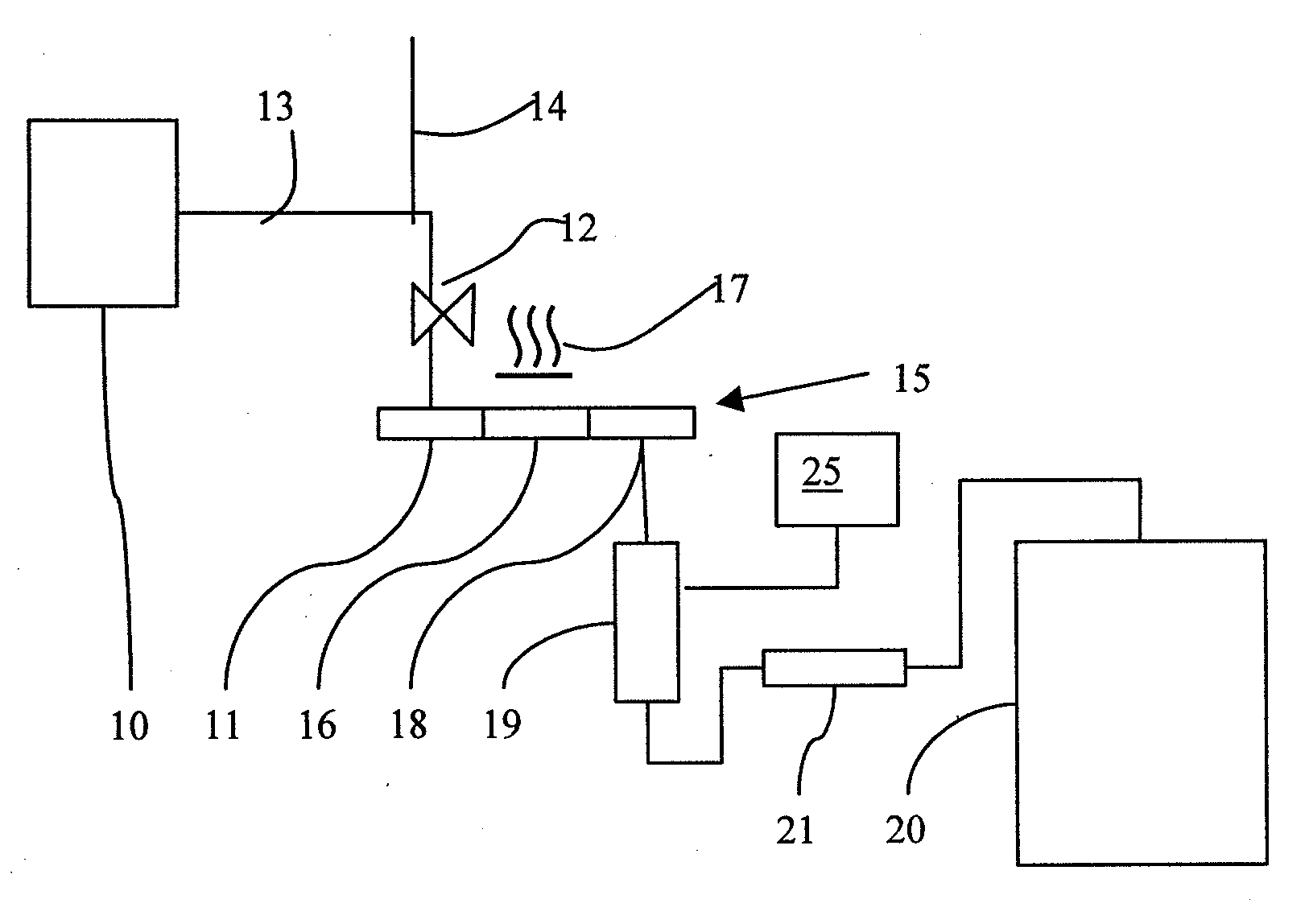
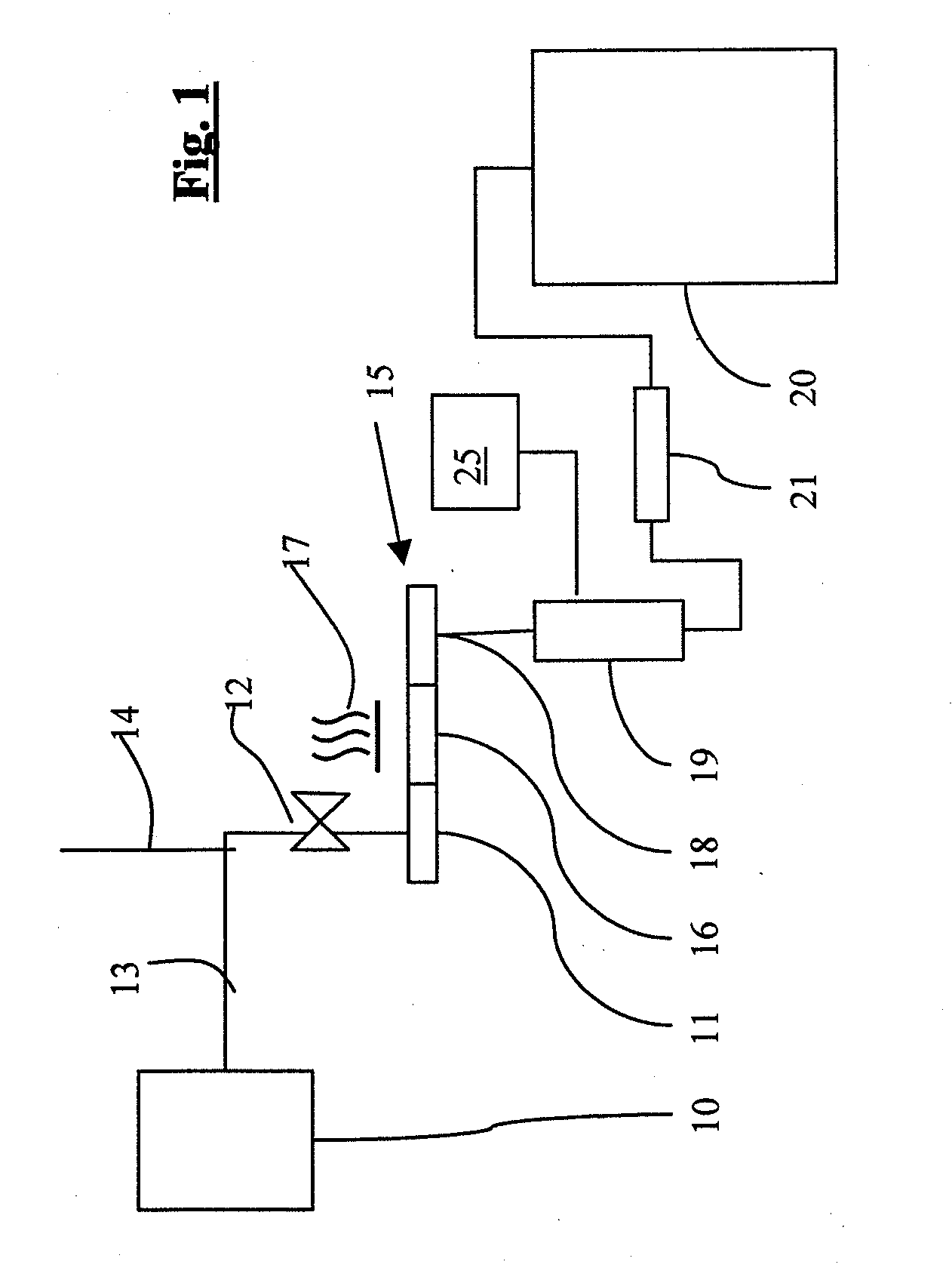
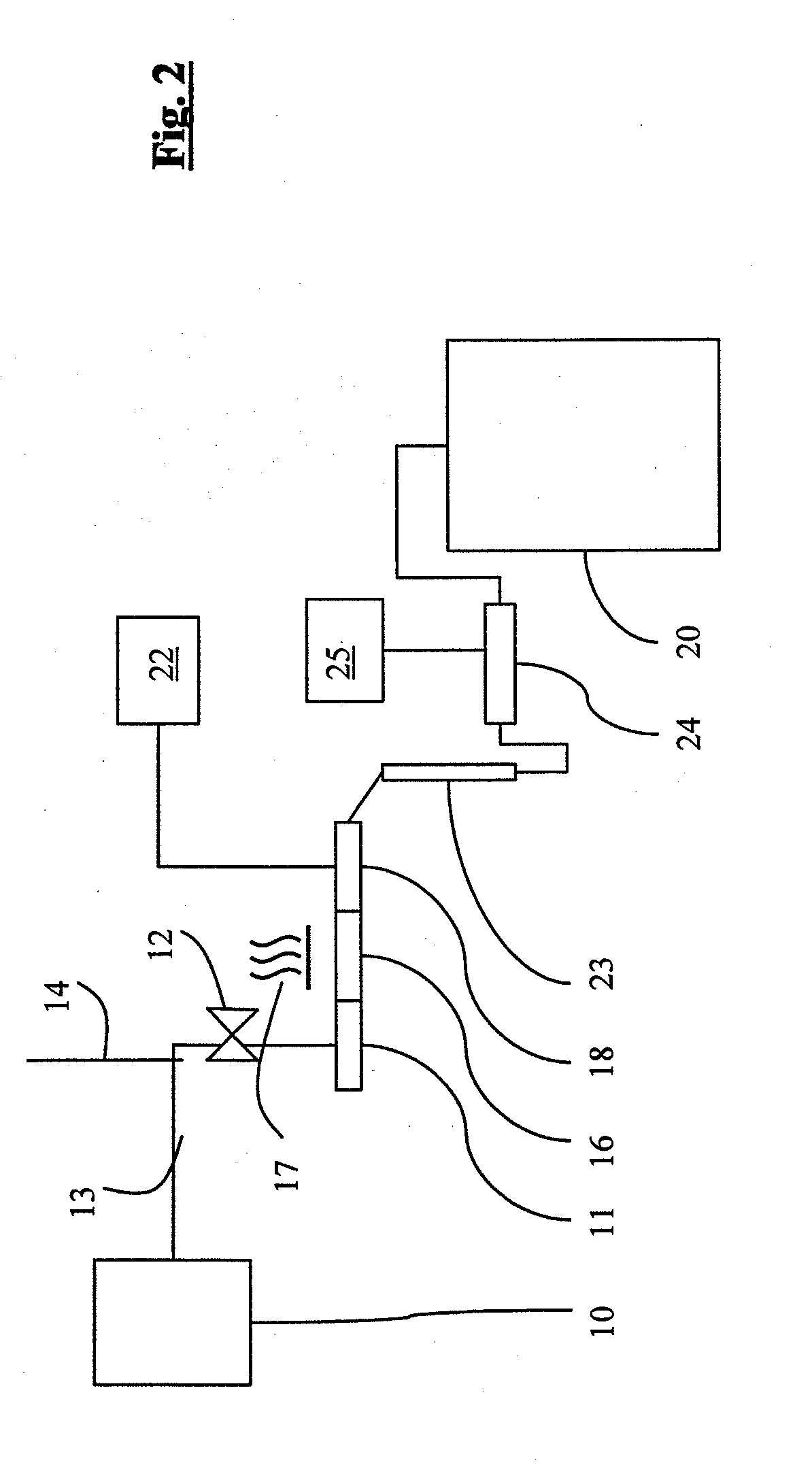
Neutron detector using neutron absorbing scintillating particulates in plastic
InactiveUS20050135535A1Low costIncrease in sizeMeasurement with scintillation detectorsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentParticulatesNinetieth percentile
A neutron detector composed of a matrix of scintillating particles imbedded in a lithiated glass is disclosed. The neutron detector detects the neutrons by absorbing the neutron in the 6Li isotope which has been enriched from the natural isotopic ratio to a commercial ninety five percent. The utility of the detector is optimized by suitably selecting scintillating particle sizes in the range of the alpha and the triton. Nominal particle sizes are in the range of five to twenty five microns depending upon the specific scintillating particle selected.
Owner:NEUTRON SCI
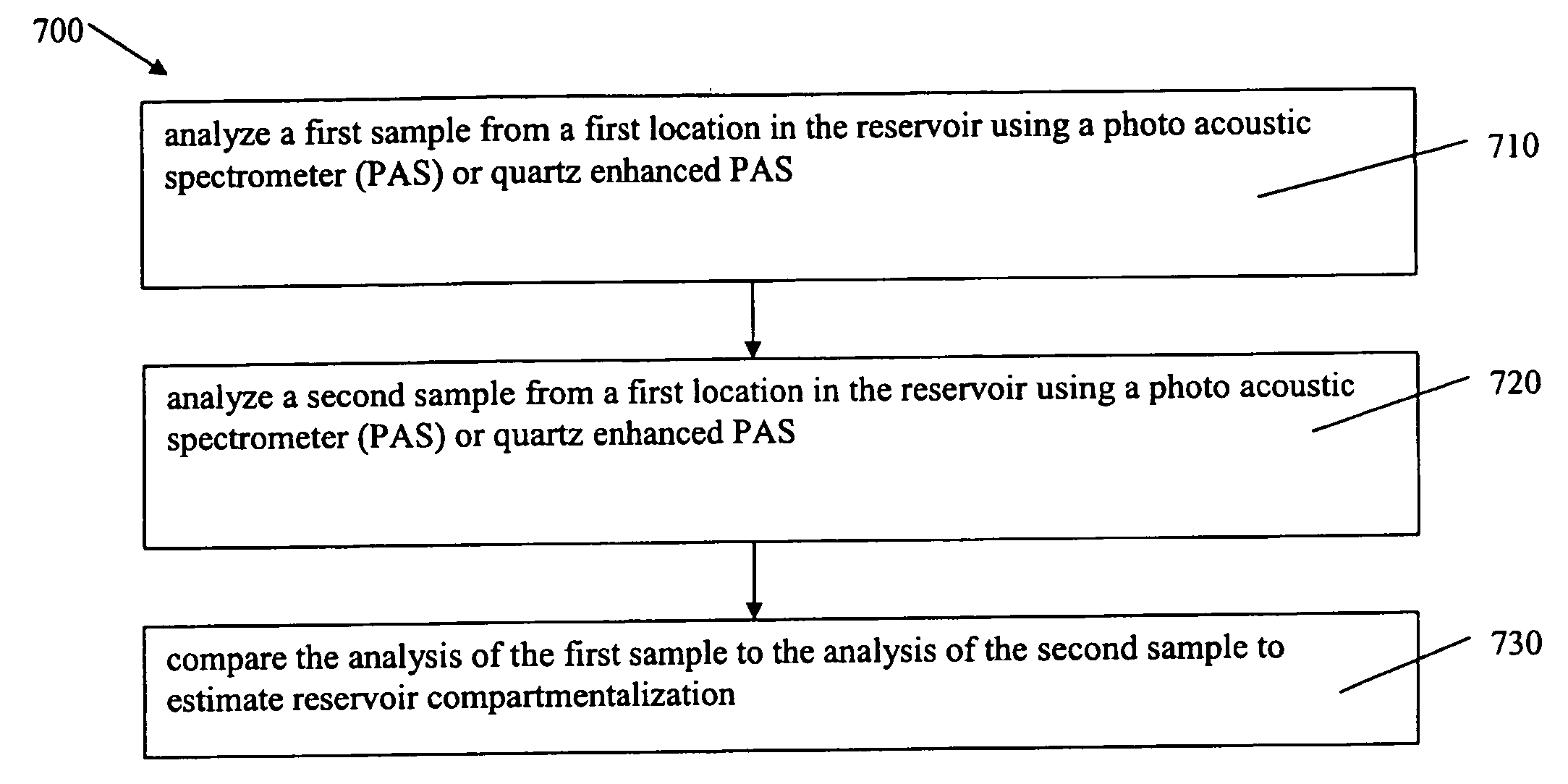
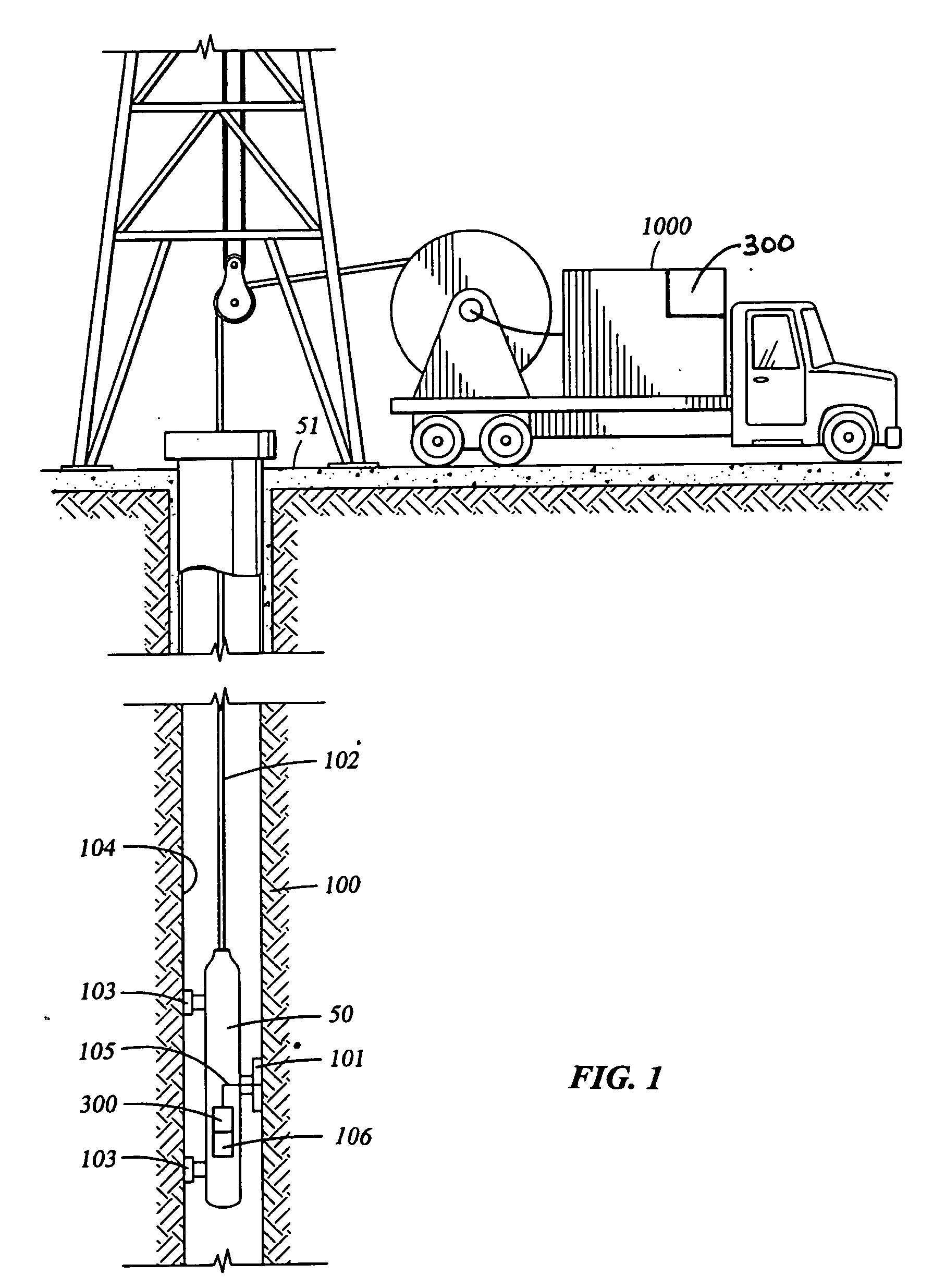
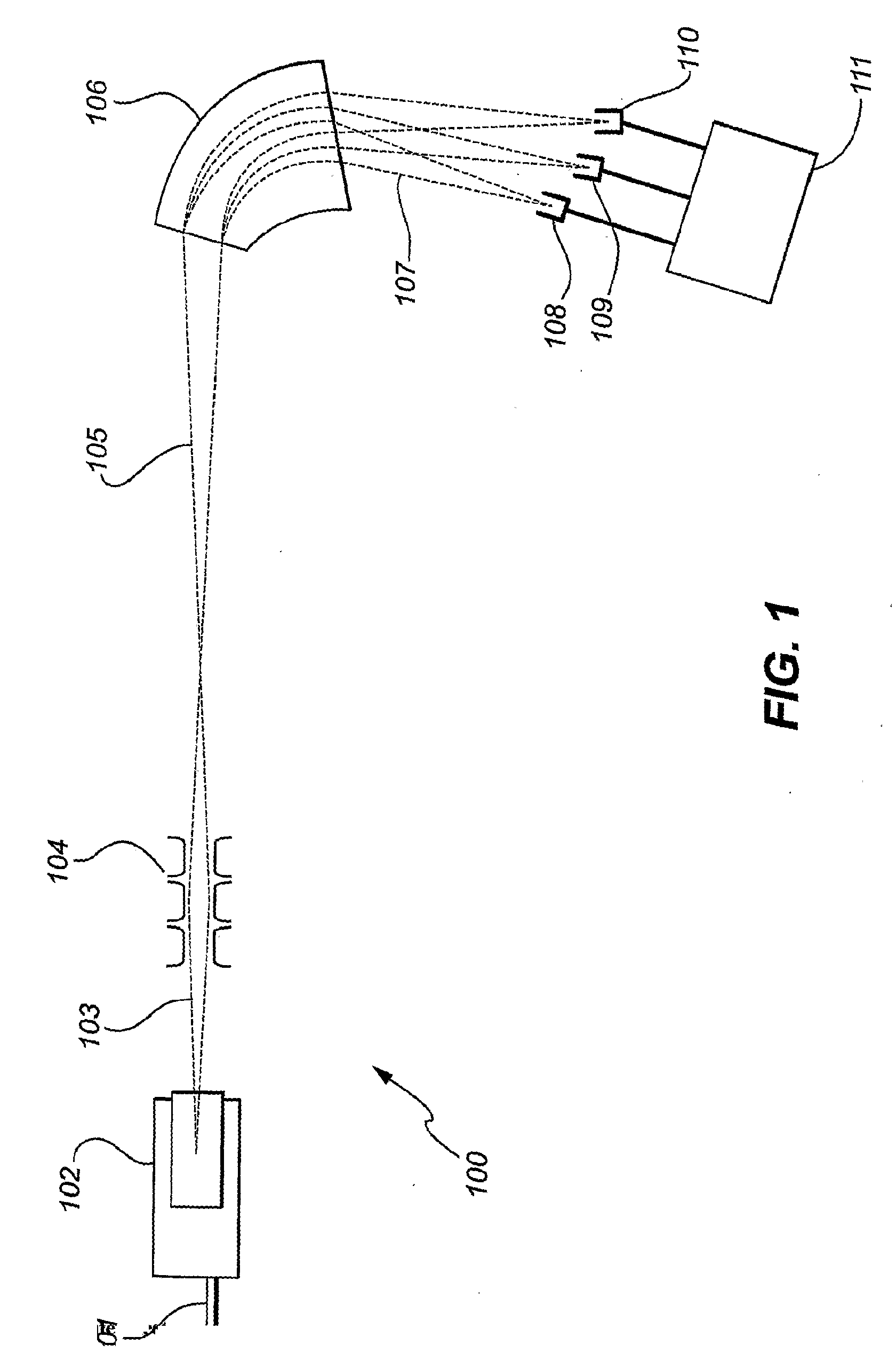
Method and apparatus for reservoir characterization using photoacoustic spectroscopy
InactiveUS20060266109A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurveyCompositional differenceEngineering
A method and apparatus are provided that assess reservoir compartmentalization by determining whether there are compositional differences such as whether the isotopic ratios of carbon (13C / 12C) or of oxygen (17O / 18O) are the same or different in various parts of the reservoir. A quartz enhanced photoacoustic spectrometer is provided for analysis of reservoir samples taken in various parts of the reservoir for comparison of geochemical composition to estimate reservoir compartmentalization.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for reservoir characterization using photoacoustic spectroscopy
InactiveUS7520158B2SurveyMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCompositional differenceEngineering
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for reservoir characterization using photoacoustic spectroscopy
InactiveUS7387021B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurveyCompositional differenceEngineering
A method and apparatus are provided that assess reservoir compartmentalization by determining whether there are compositional differences such as whether the isotopic ratios of carbon (13C / 12C) or of oxygen (17O / 18O) are the same or different in various parts of the reservoir. A quartz enhanced photoacoustic spectrometer is provided for analysis of reservoir samples taken in various parts of the reservoir for comparison of geochemical composition to estimate reservoir compartmentalization.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Neutron detector using lithiated glass-scintillating particle composite
InactiveUS7582880B2Improve overall utilizationPhotosensitive materialsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsLithiumNinetieth percentile
A neutron detector composed of a matrix of scintillating particles imbedded in a lithiated glass is disclosed. The neutron detector detects the neutrons by absorbing the neutron in the lithium-6 isotope which has been enriched from the natural isotopic ratio to a commercial ninety five percent. The utility of the detector is optimized by suitably selecting scintillating particle sizes in the range of the alpha and the triton. Nominal particle sizes are in the range of five to twenty five microns depending upon the specific scintillating particle selected.
Owner:NEUTRON SCI +2
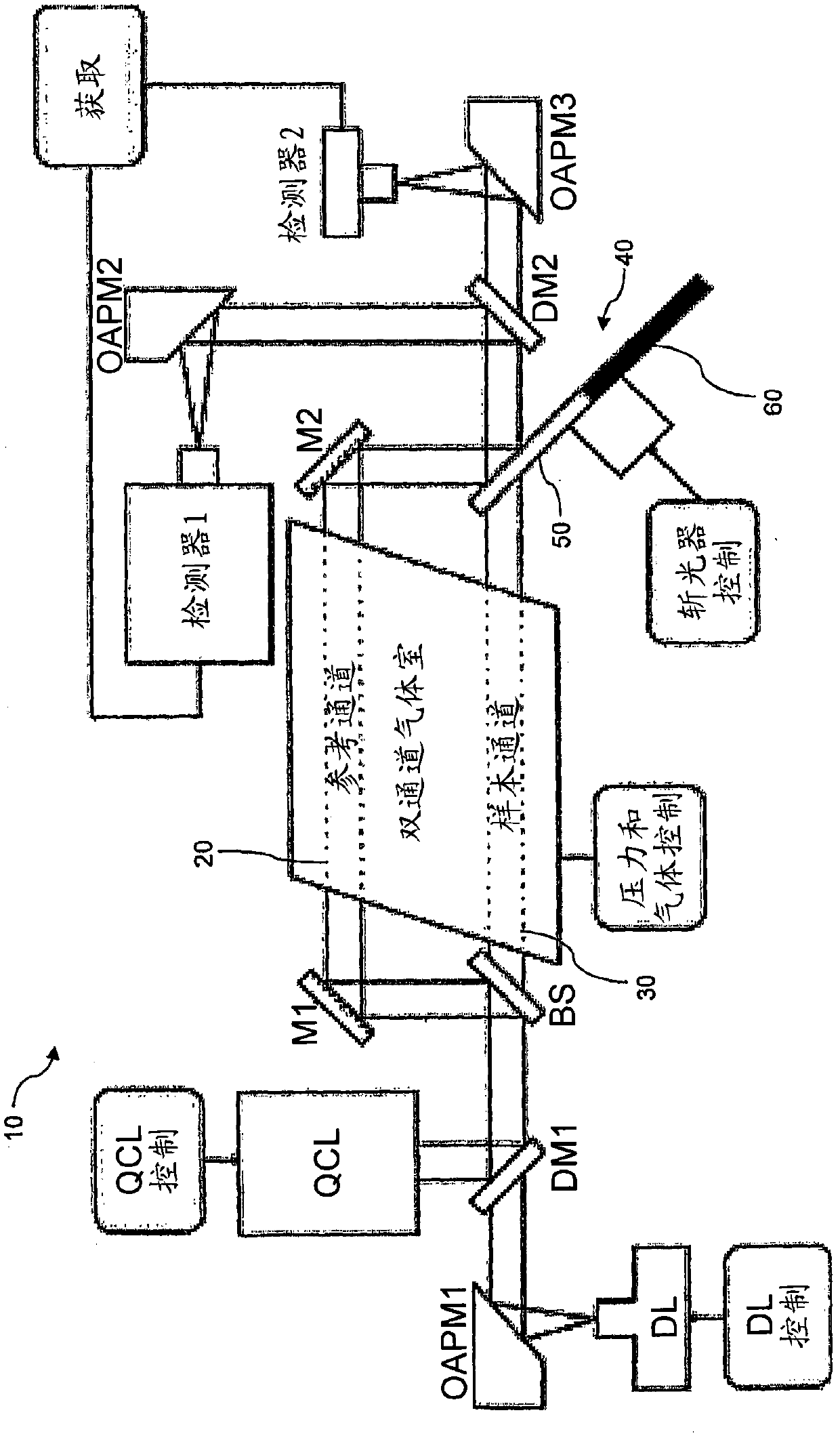
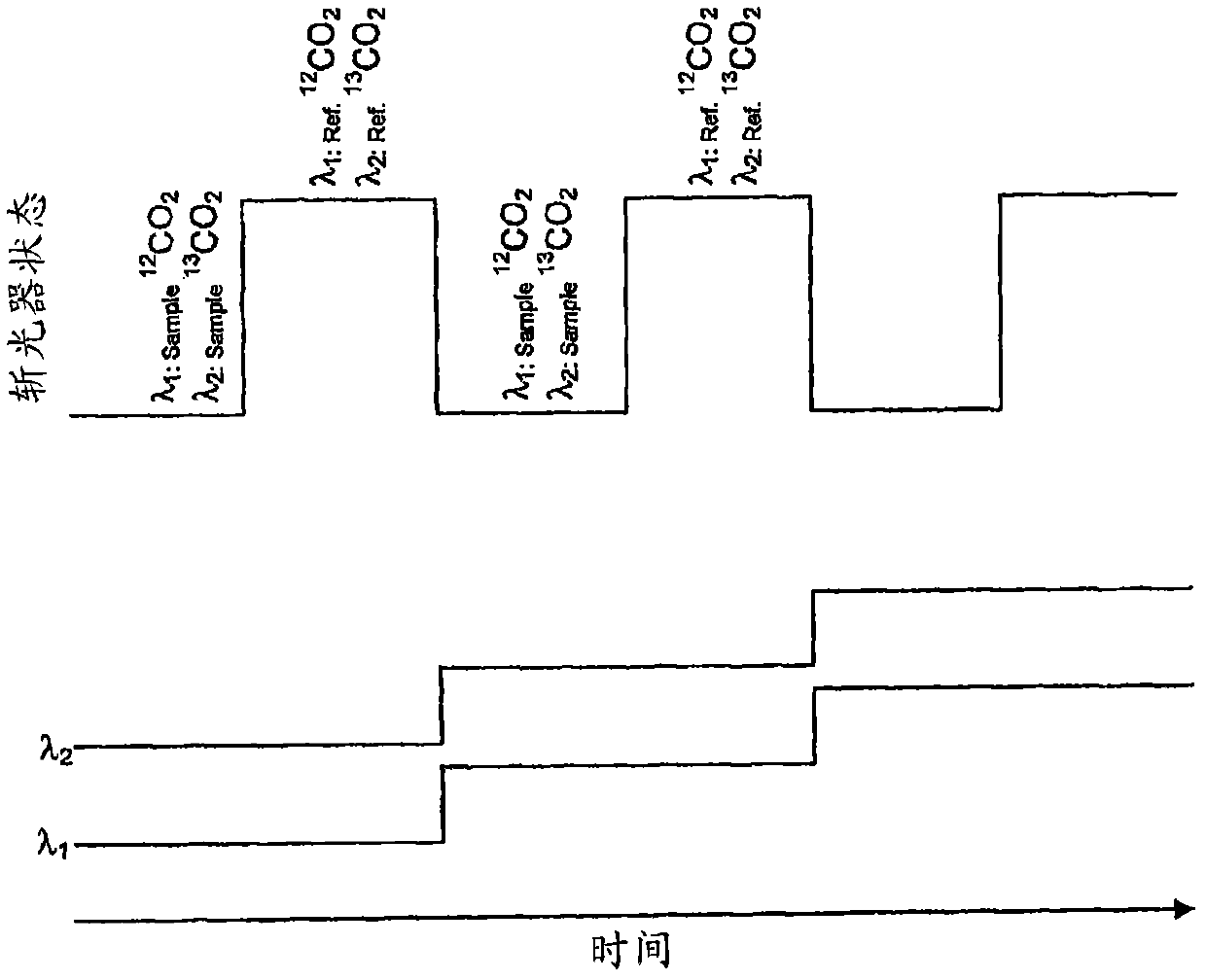
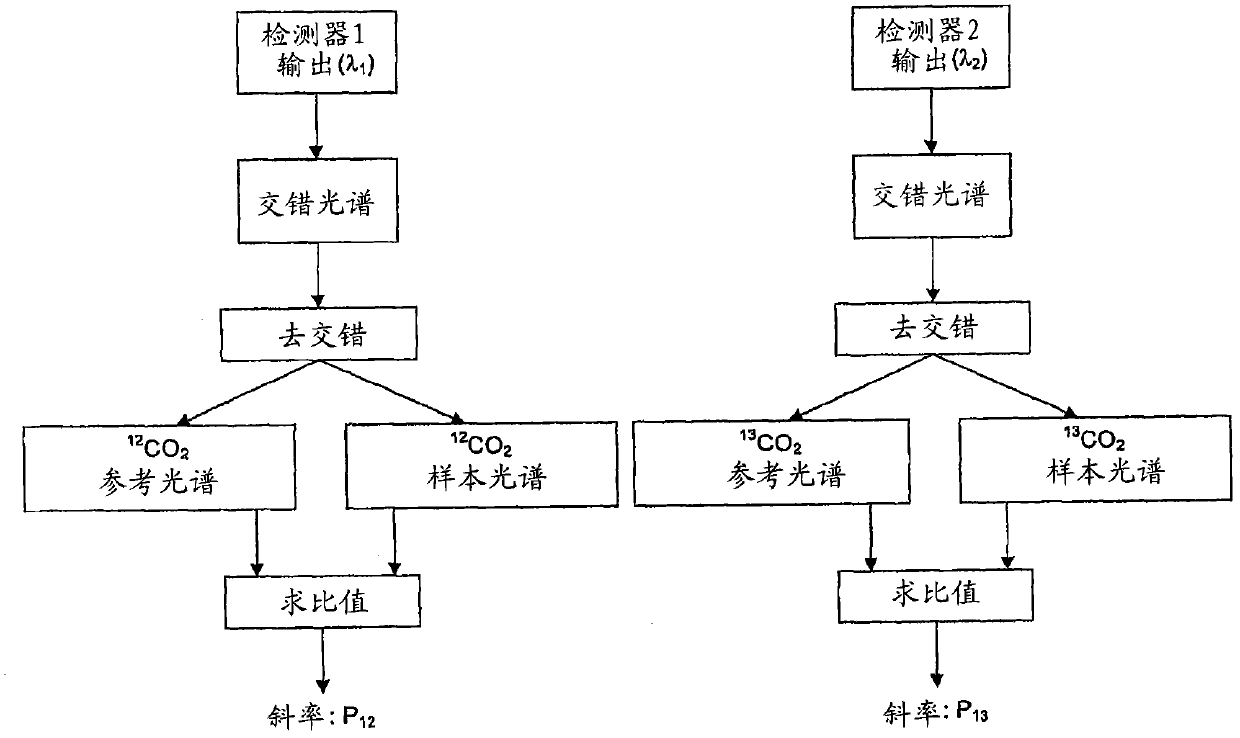
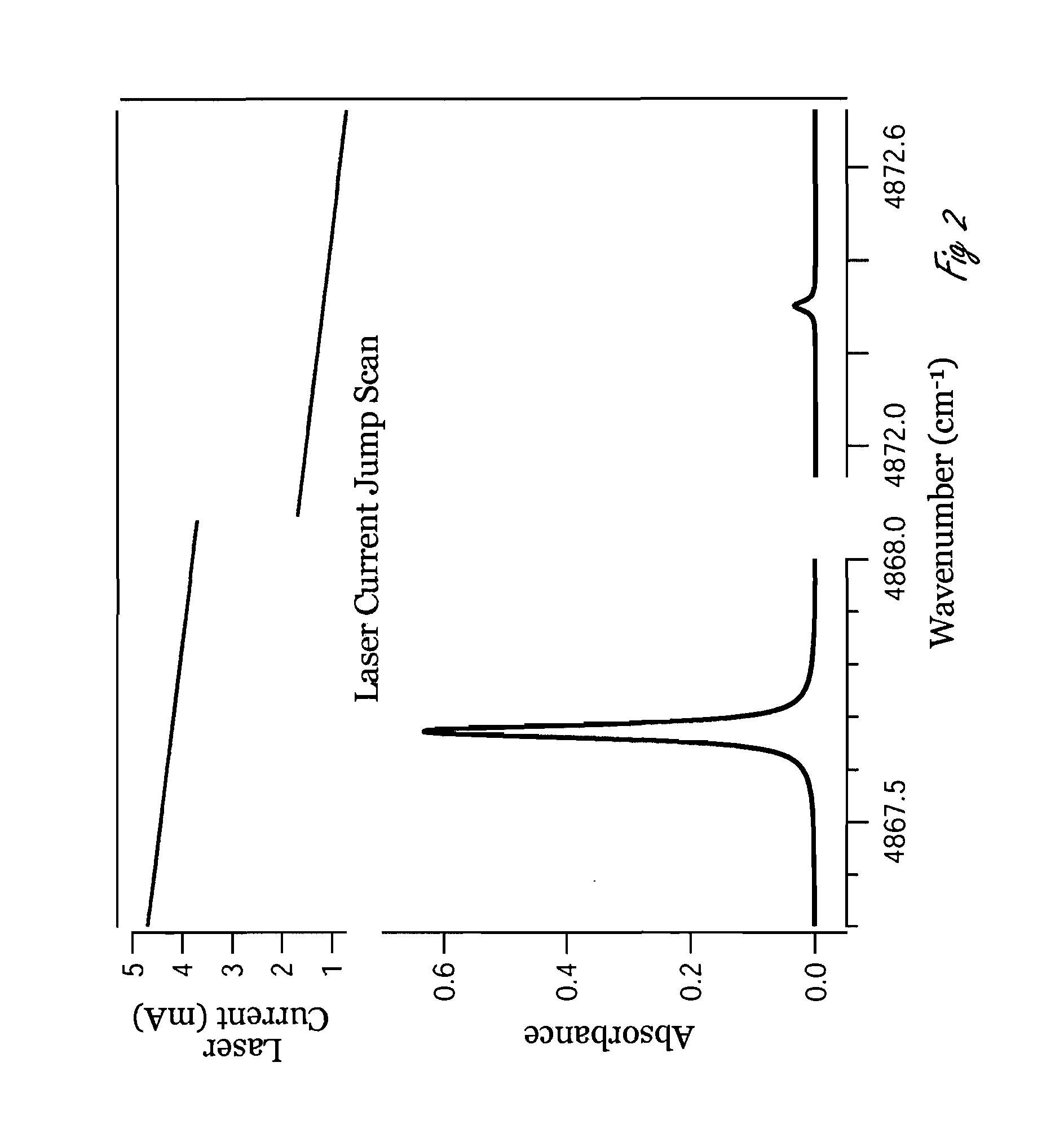
Infrared spectrometer
ActiveCN102027344ARadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyInfraredIr absorption
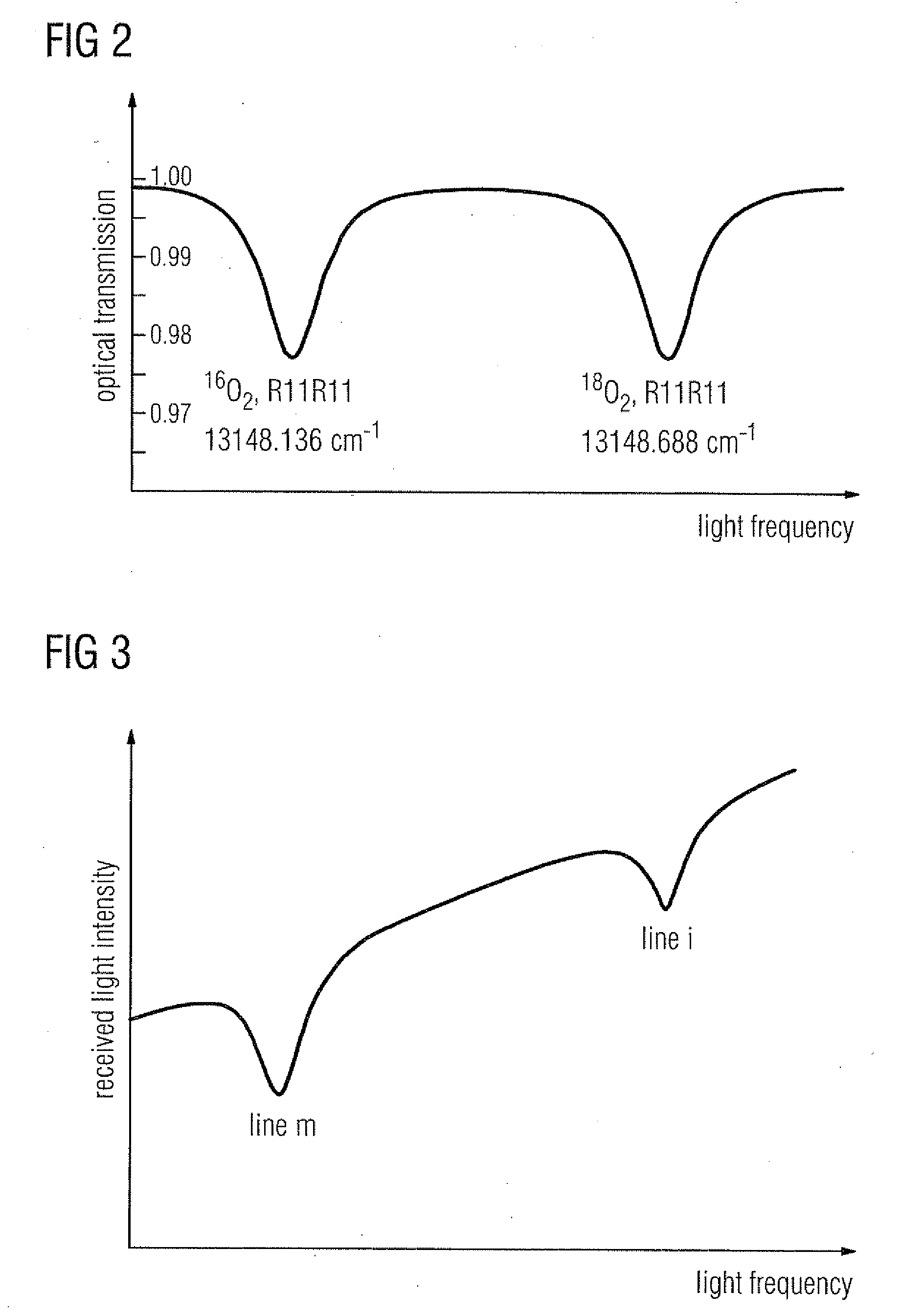
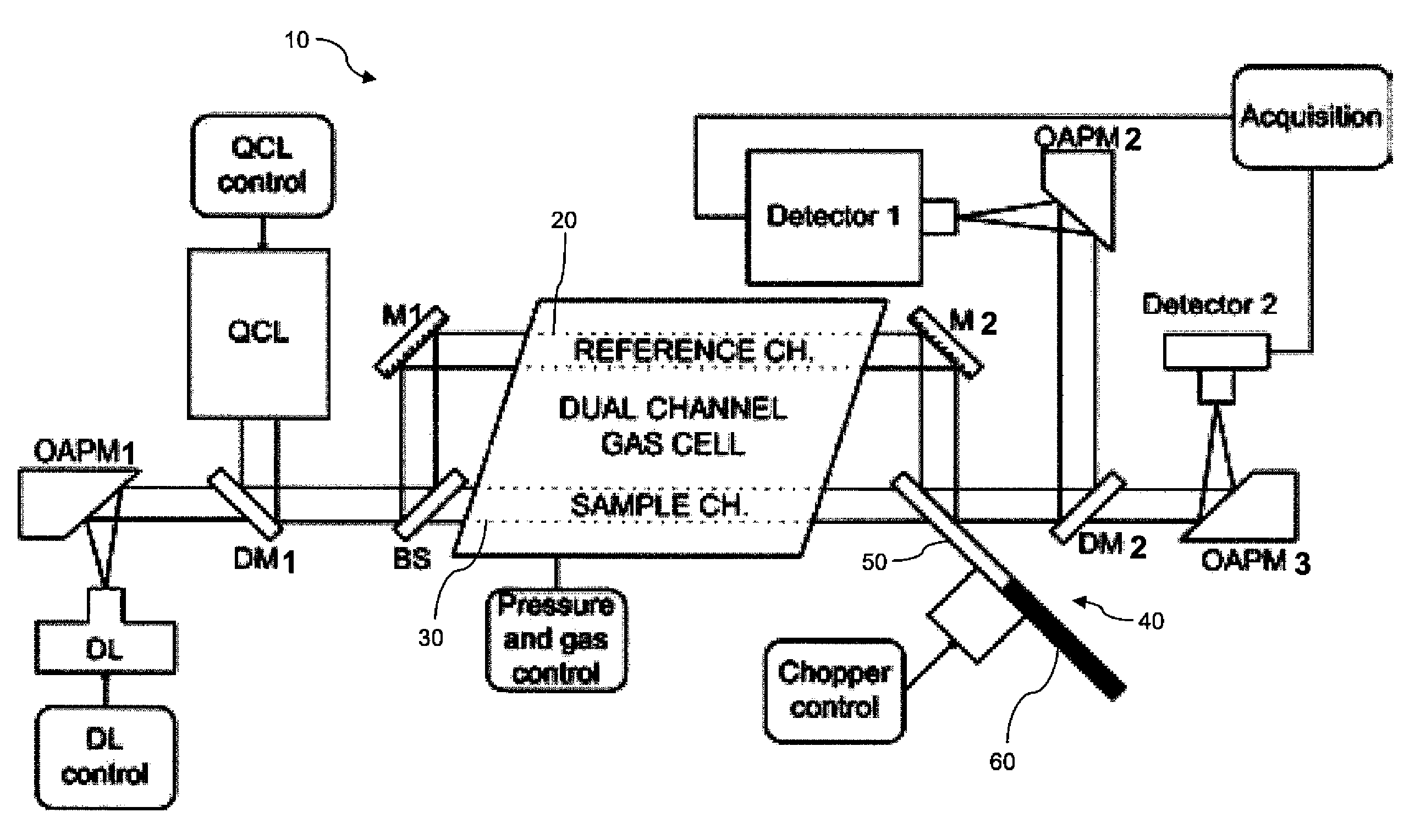
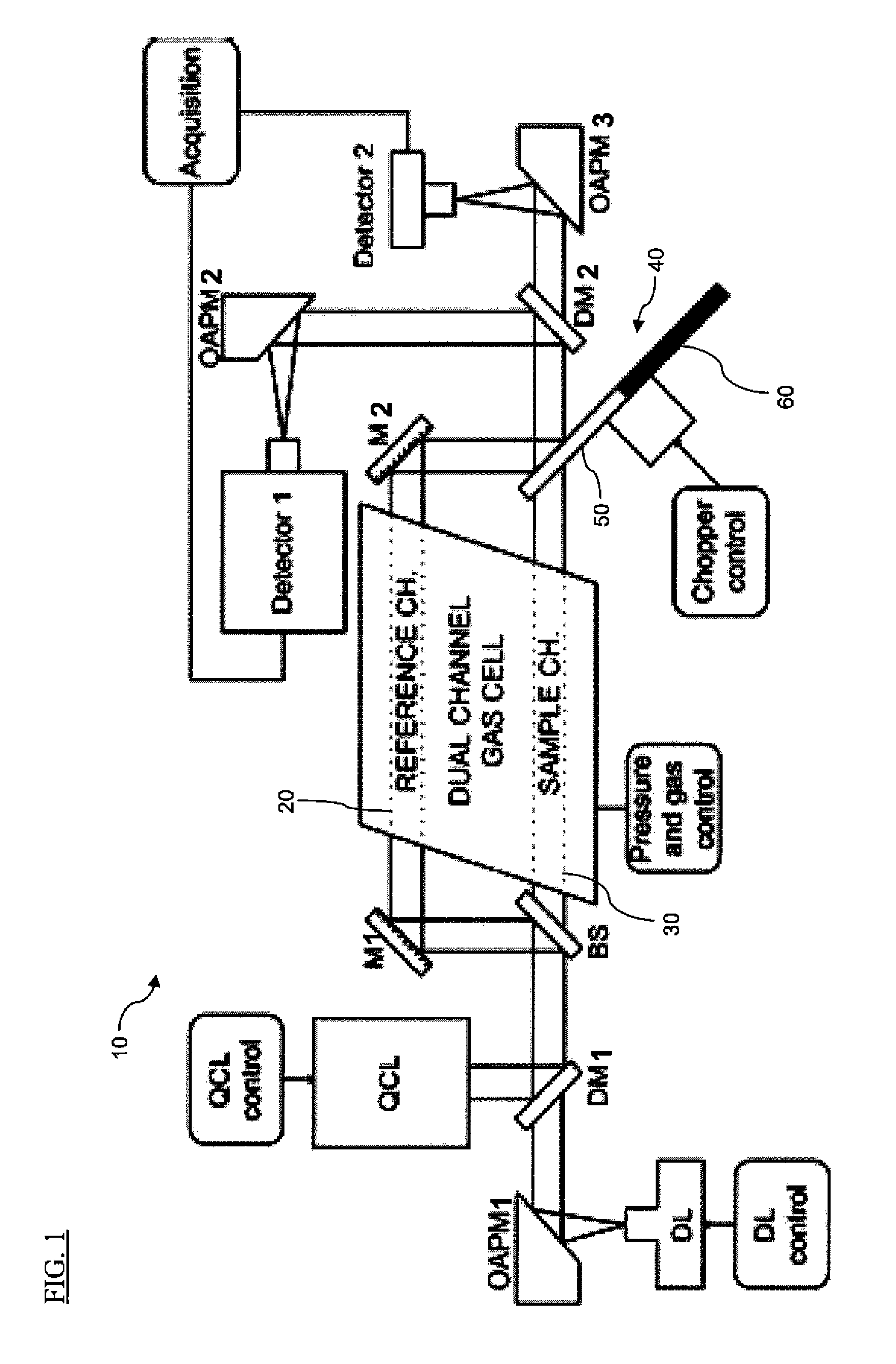
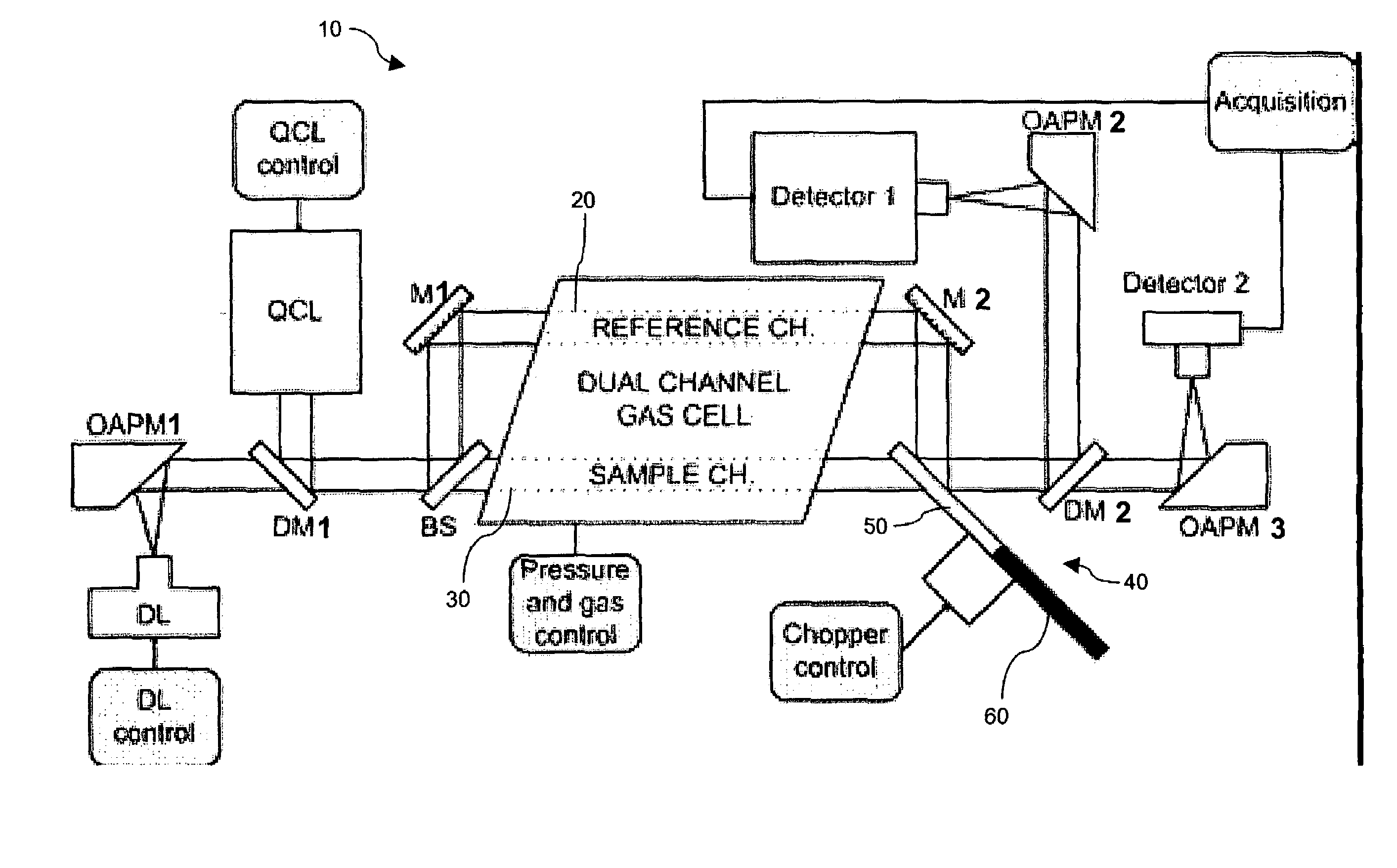
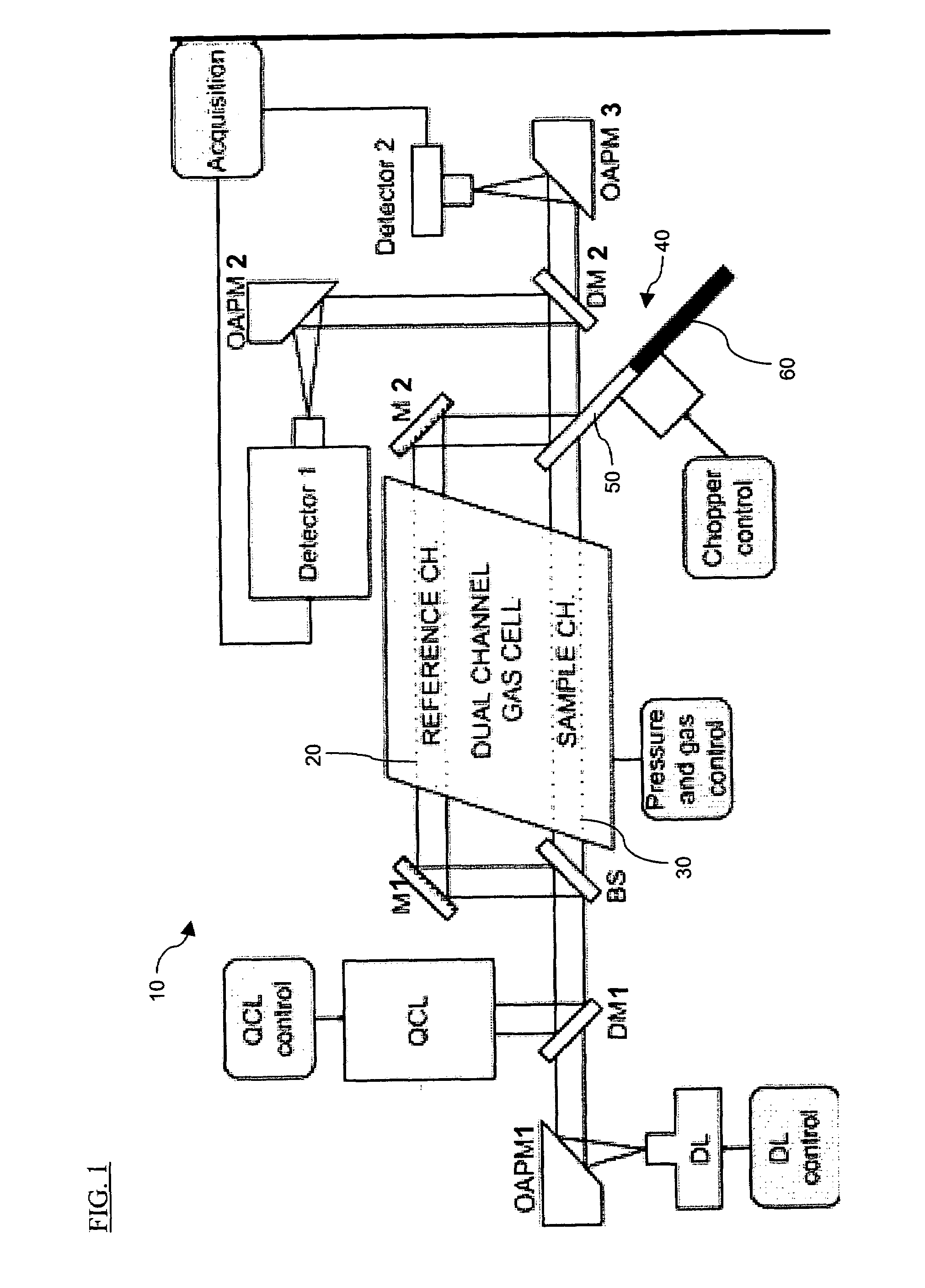
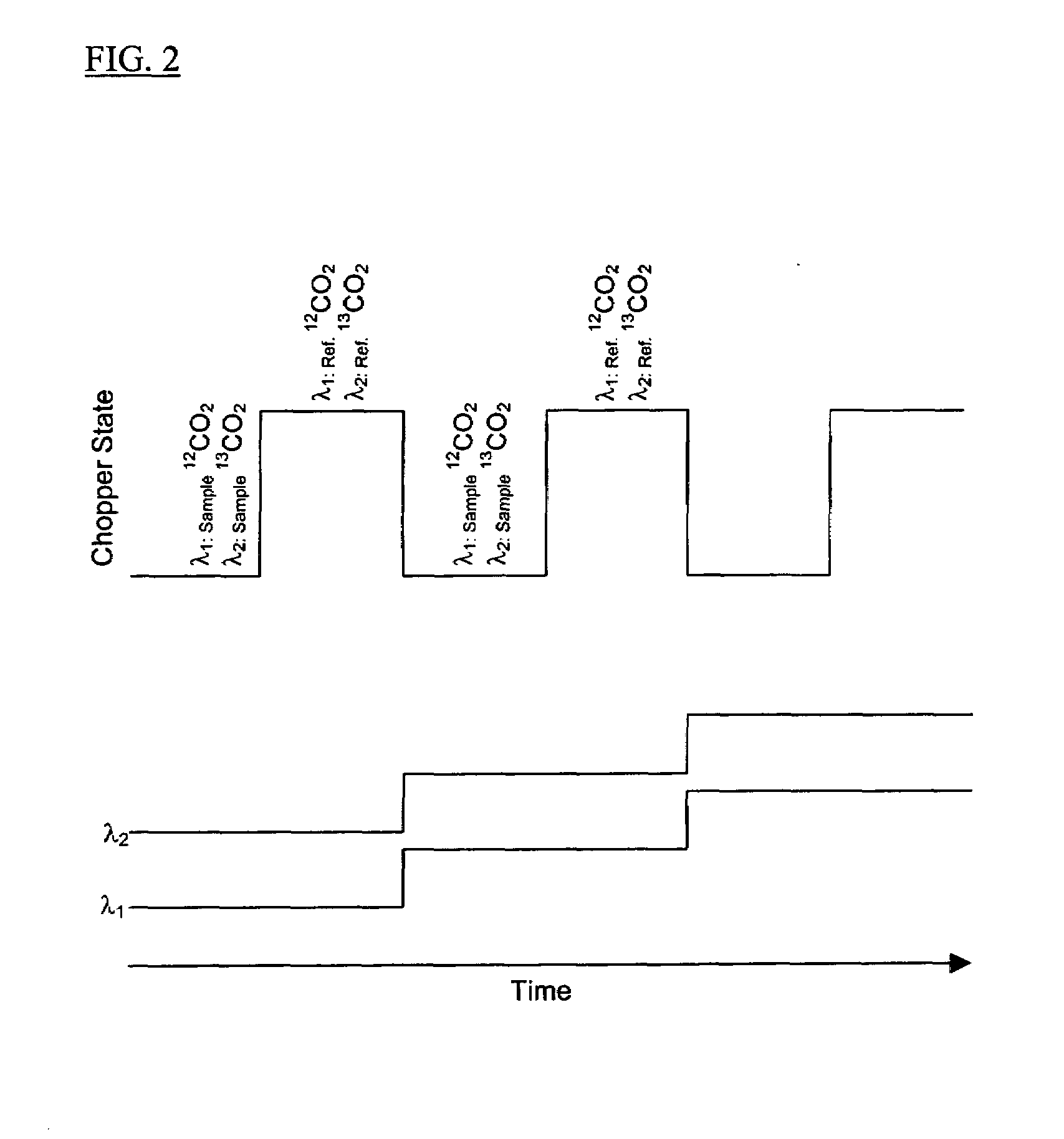
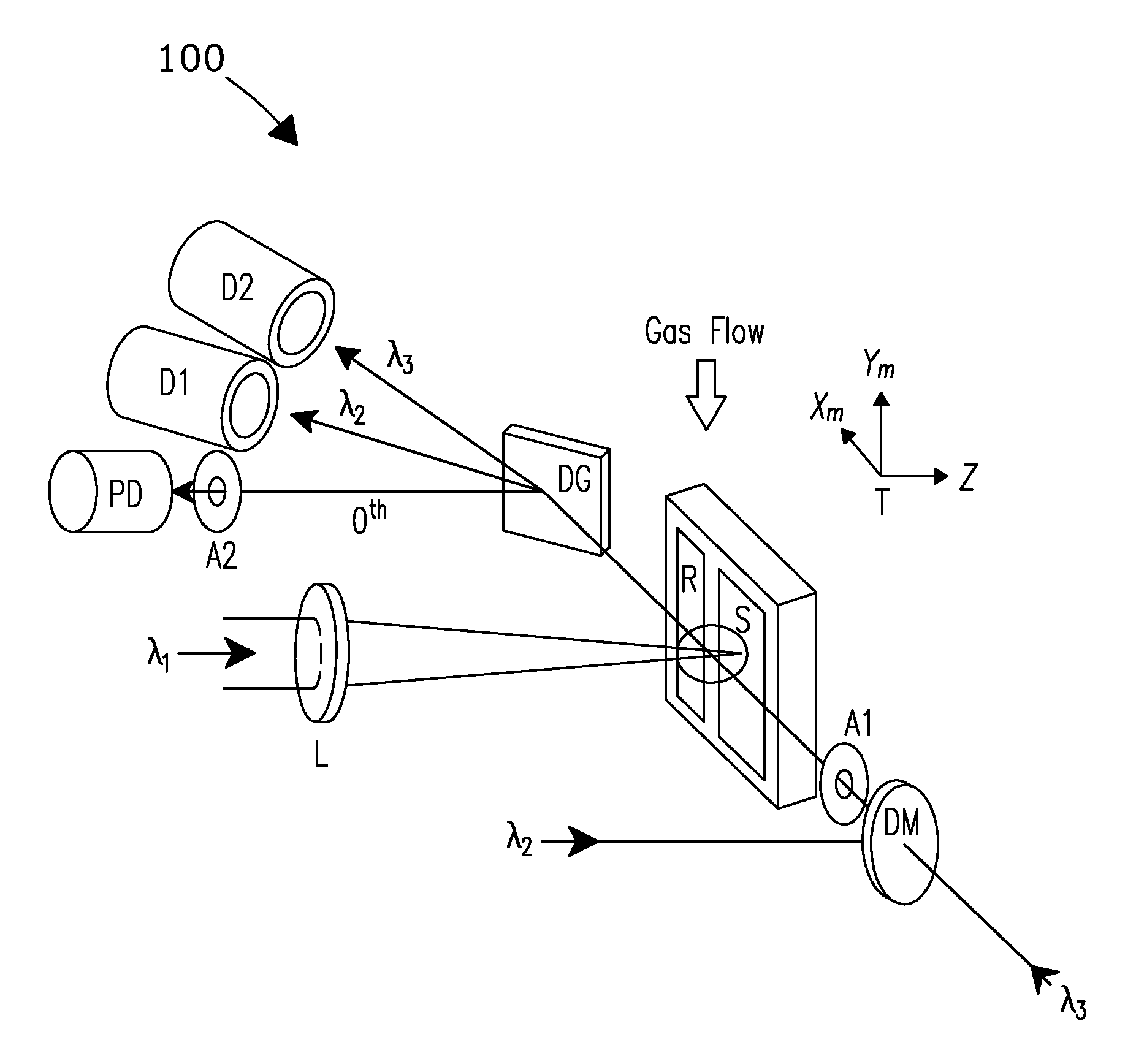
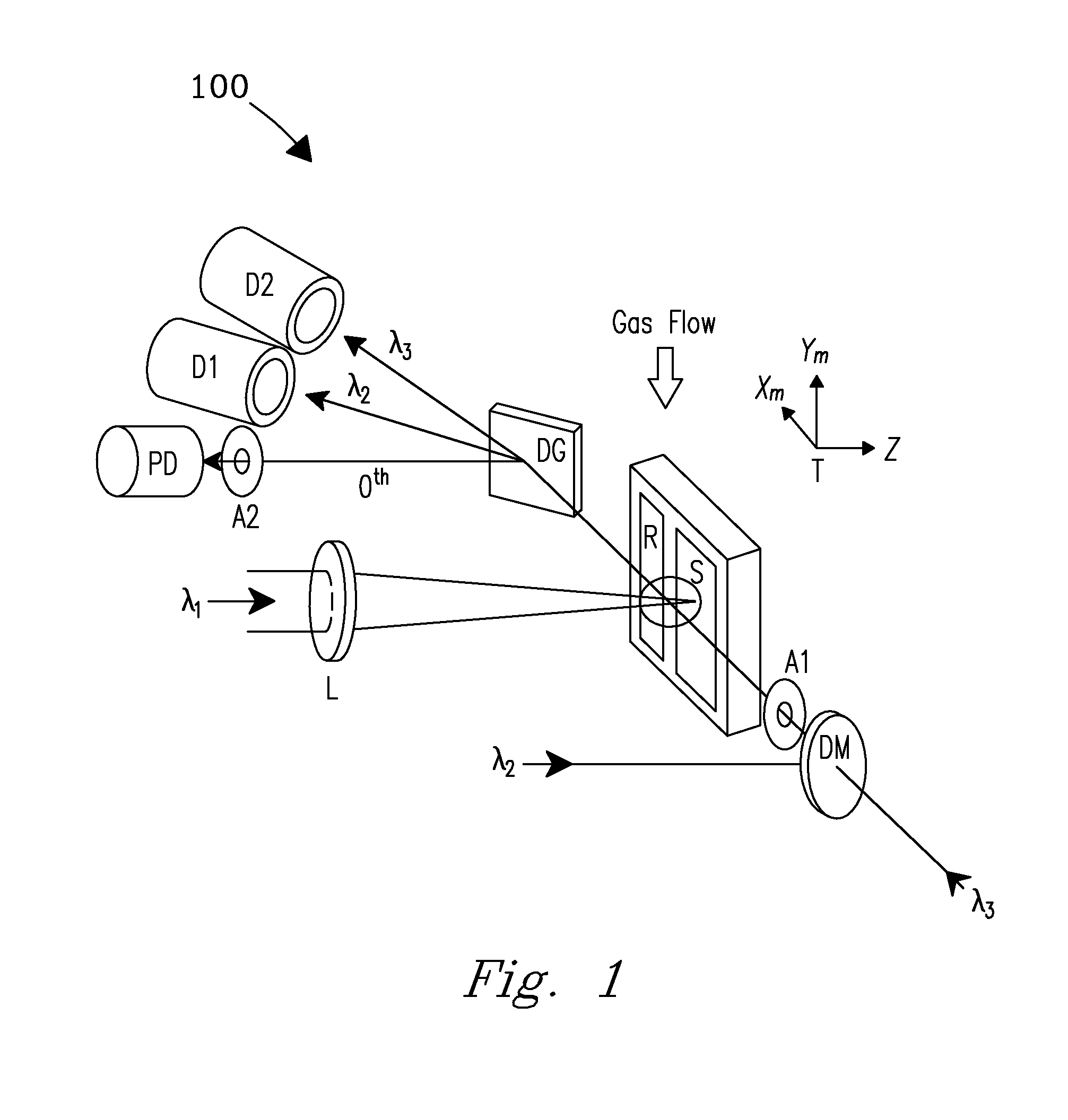
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for detecting, by absorption spectroscopy, an isotopic ratio of a sample, by passing first and second laser beams of different frequencies through the sample. Two IR absorption cells are used, a first containing a reference gas of known isotopic ratio and the second containing a sample of unknown isotopic ratio. An interlacer or reflective chopper may be used so that as the laser frequencies are scanned the absorption of the sample cell and the reference cell are detected alternately. This ensures that the apparatus is continuously calibrated and rejects the baseline noise when phase sensitive detection is used.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Method and apparatus for reservoir characterization using photoacoustic spectroscopy
InactiveUS20060266108A1Accurately determineSurveyMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCompositional differenceEngineering
A method and apparatus are provided that assess reservoir compartmentalization by determining whether there are compositional differences such as whether the isotopic ratios of carbon (13C / 12C) or of oxygen (17O / 18O) are the same or different in various parts of the reservoir. A quartz enhanced photoacoustic spectrometer is provided for analysis of reservoir samples taken in various parts of the reservoir for comparison of geochemical composition to estimate reservoir compartmentalization.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Isotope ratio mass spectrometer and methods for determining isotope ratios
The present invention relates to a method for determining at least one ratio of different isotopes of at least one element in a sample. The method comprises ionizing the sample to produce ions of the different isotopes of the at least one element, the ions being selected from the group consisting of: multiply charged atomic positive ions, single charged positive ions for hydrogen and single charged positive ions for deuterium, separating the charged positive ions of the different isotopes of the at least one element according to their mass-to-charge ratios, and determining at least one ratio of the different isotopes of said at least one element separated in the previous step. The invention also relates to an apparatus for performing the above method.
Owner:AUSTRALIAN NUCLEAR SCI & TECH ORGANISAT
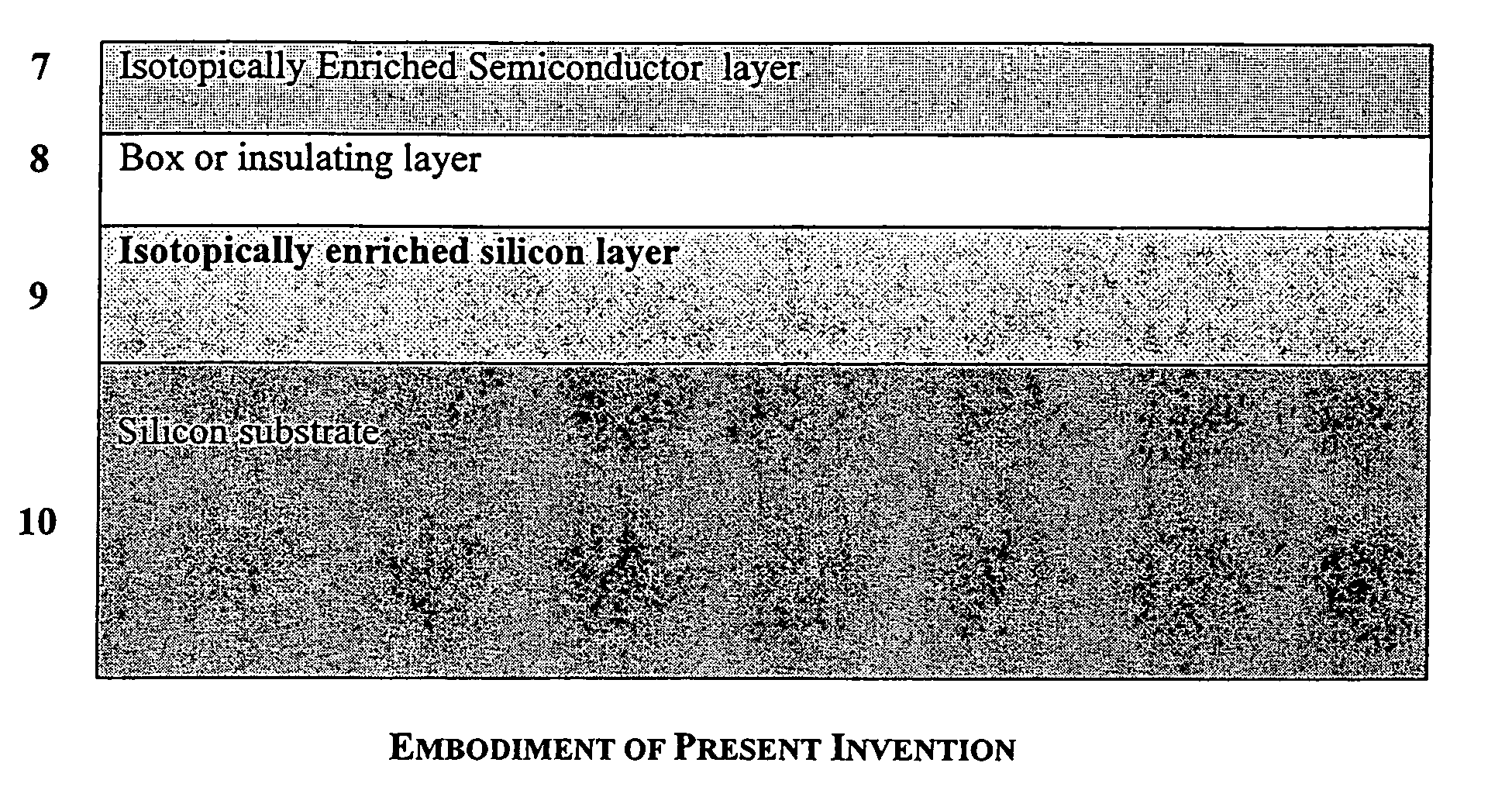
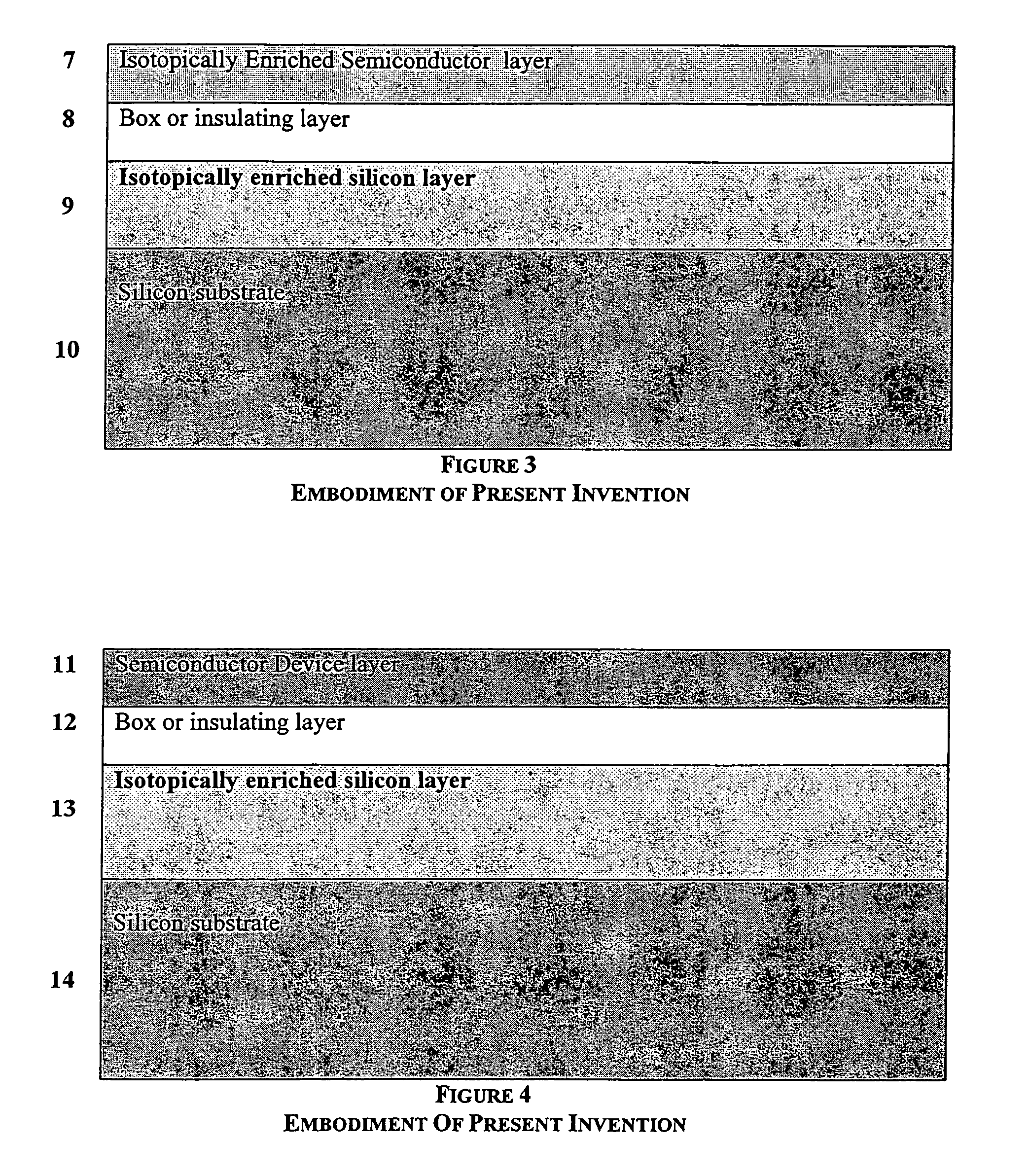
Isotopically pure silicon-on-insulator wafers and method of making same
InactiveUS7119400B2Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsWaferingSemiconductor materials
A semiconductor wafer structure having a device layer, an insulating layer, and a substrate which is capable of supporting increased semiconductor device densities or increased semiconductor device power. One or more of the layers includes an isotopically enriched semiconductor material having a higher thermal conductivity than semiconductor material having naturally occurring isotopic ratios. The wafer structure may be formed by various techniques, such as wafer bonding, and deposition techniques.
Owner:TENOROC
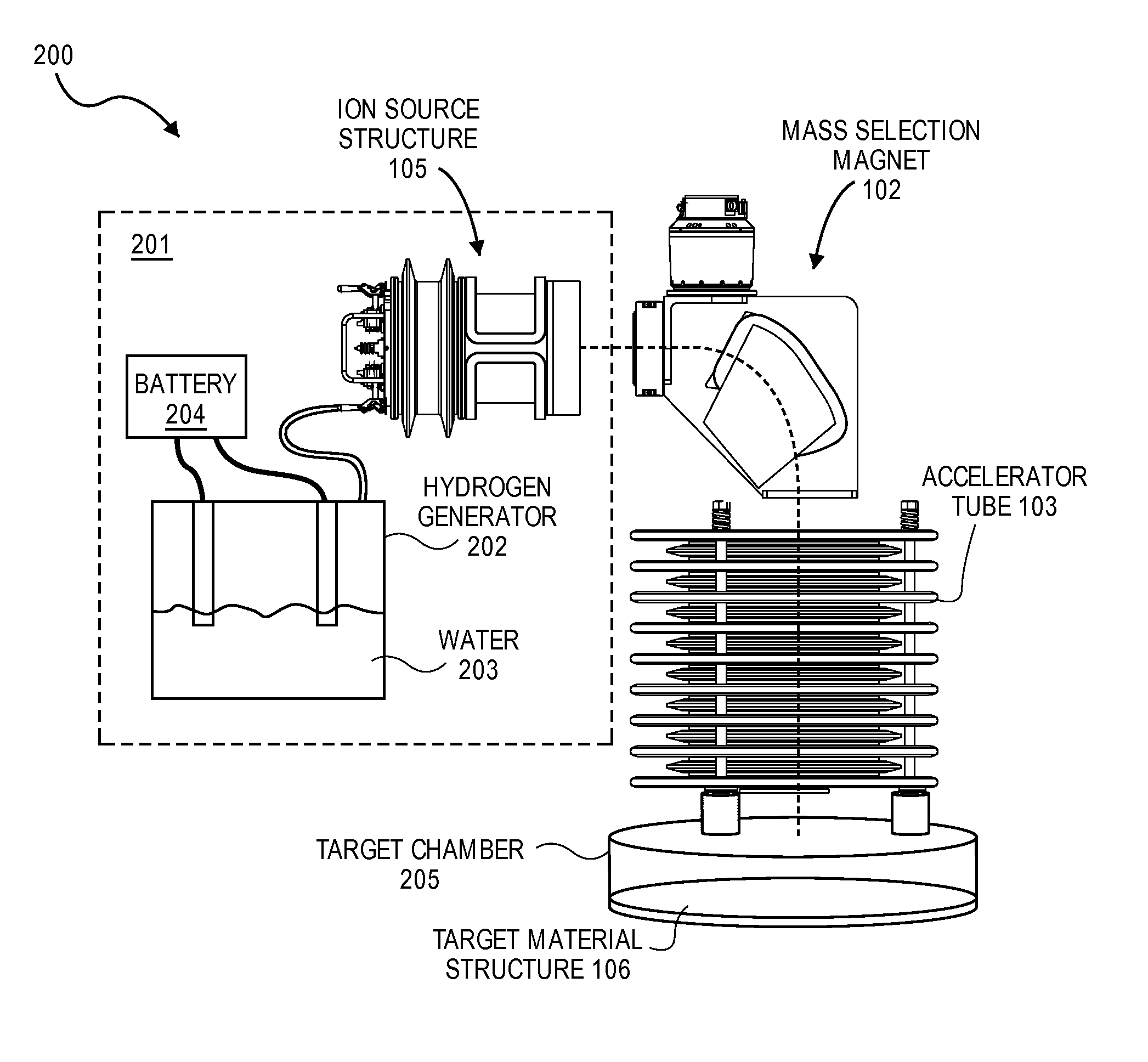
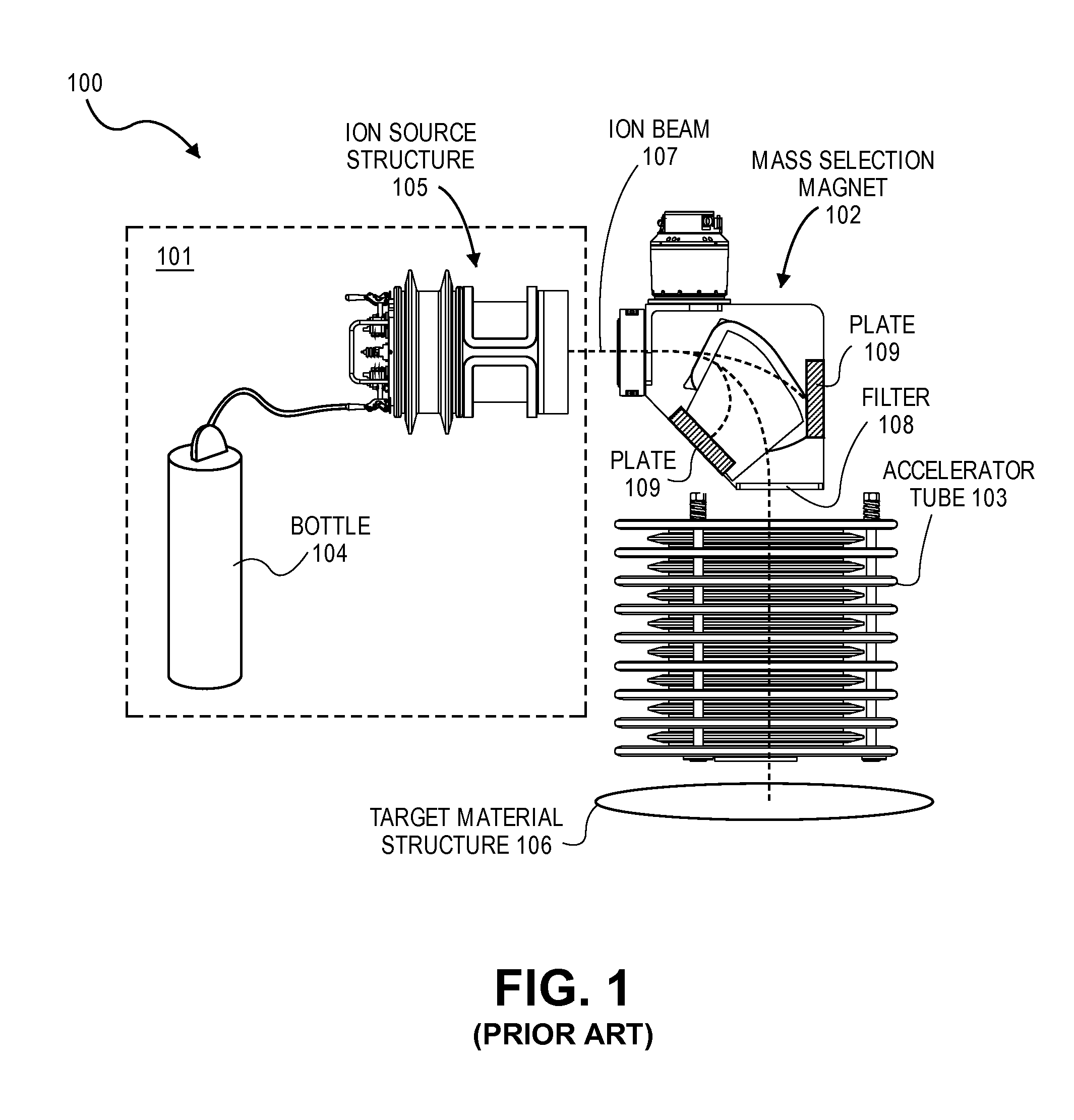
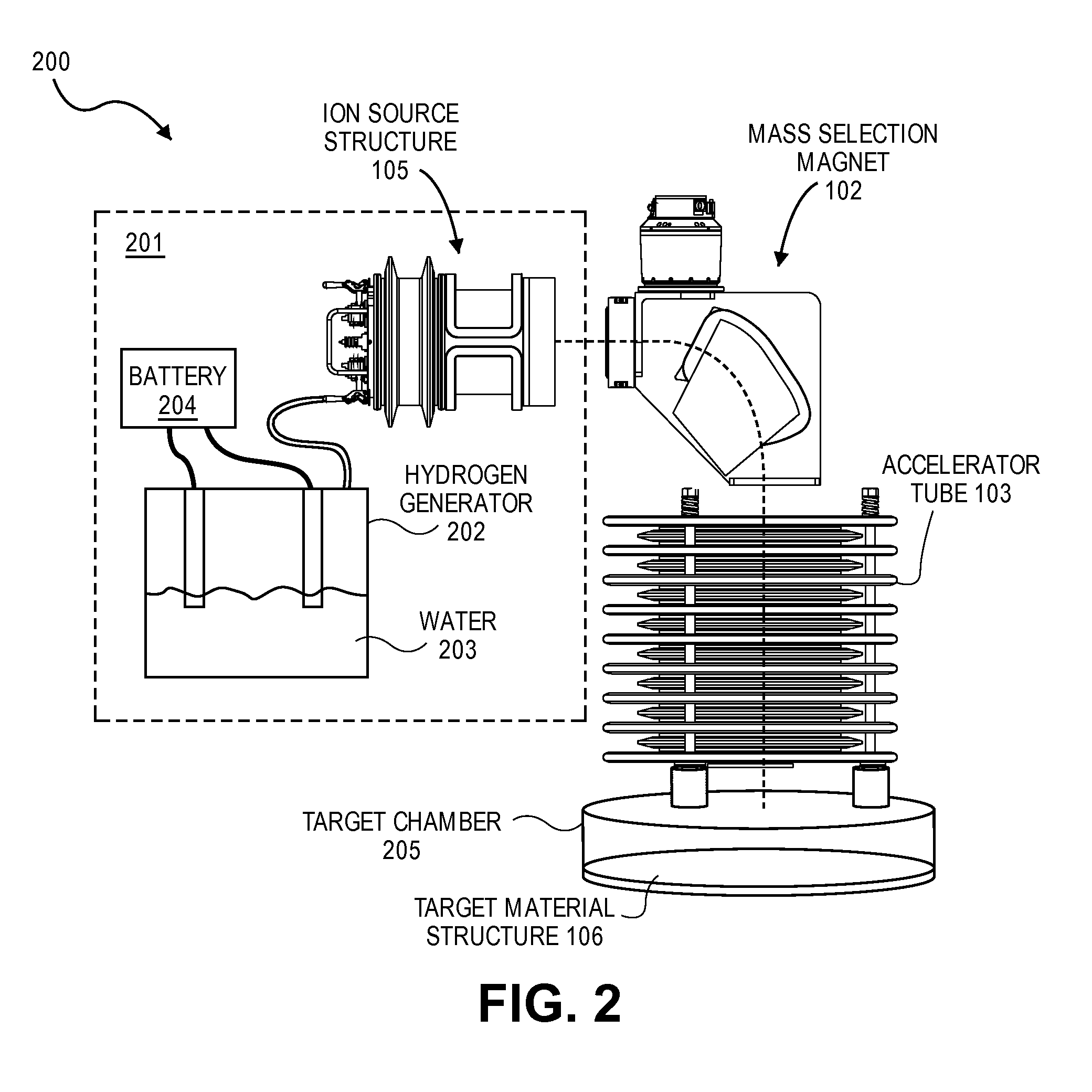
Hydrogen implantation with reduced radiation
ActiveUS8101488B1Electric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansHydrogenVienna Standard Mean Ocean Water
Embodiments of the present invention provide for a system for accelerating hydrogen ions. A hydrogen generator holding a supply of water is configured to generate a flow of hydrogen gas from the supply of water. An ion source structure is configured to generate a plurality of hydrogen ions from the flow of hydrogen gas. An accelerator tube is configured to accelerate the plurality of hydrogen ions. The supply of water has an isotopic ratio of deuterium that is smaller than the isotopic ratio of deuterium in Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water.
Owner:NEUTRON THERAPEUTICS LLC
Mass Spectrometer and Method for Direct Measurement of Isotope Ratios
InactiveUS20120211651A1Wide concentration rangeIsotope separationMass spectrometersMass analyzerSpectrometer
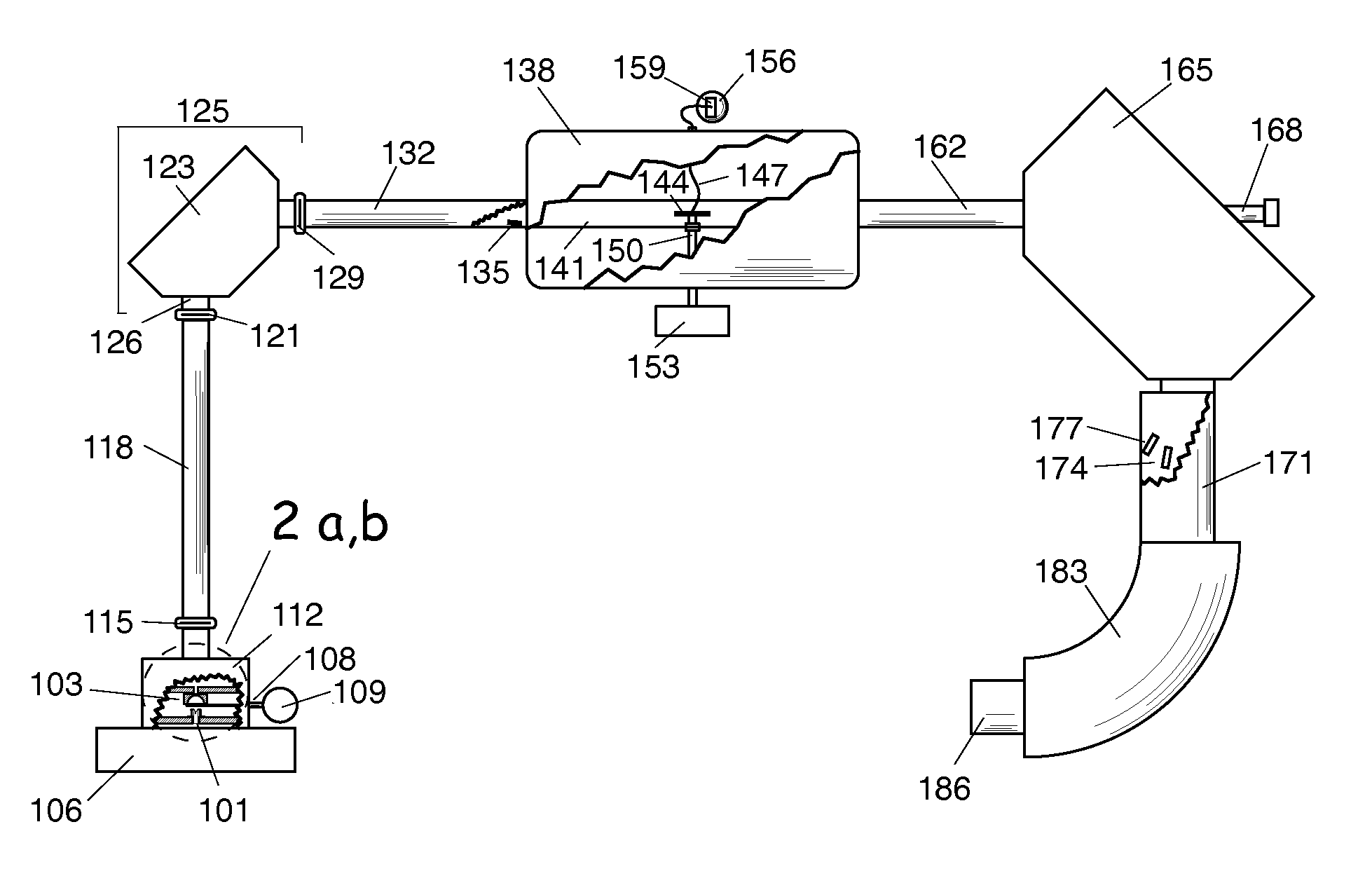
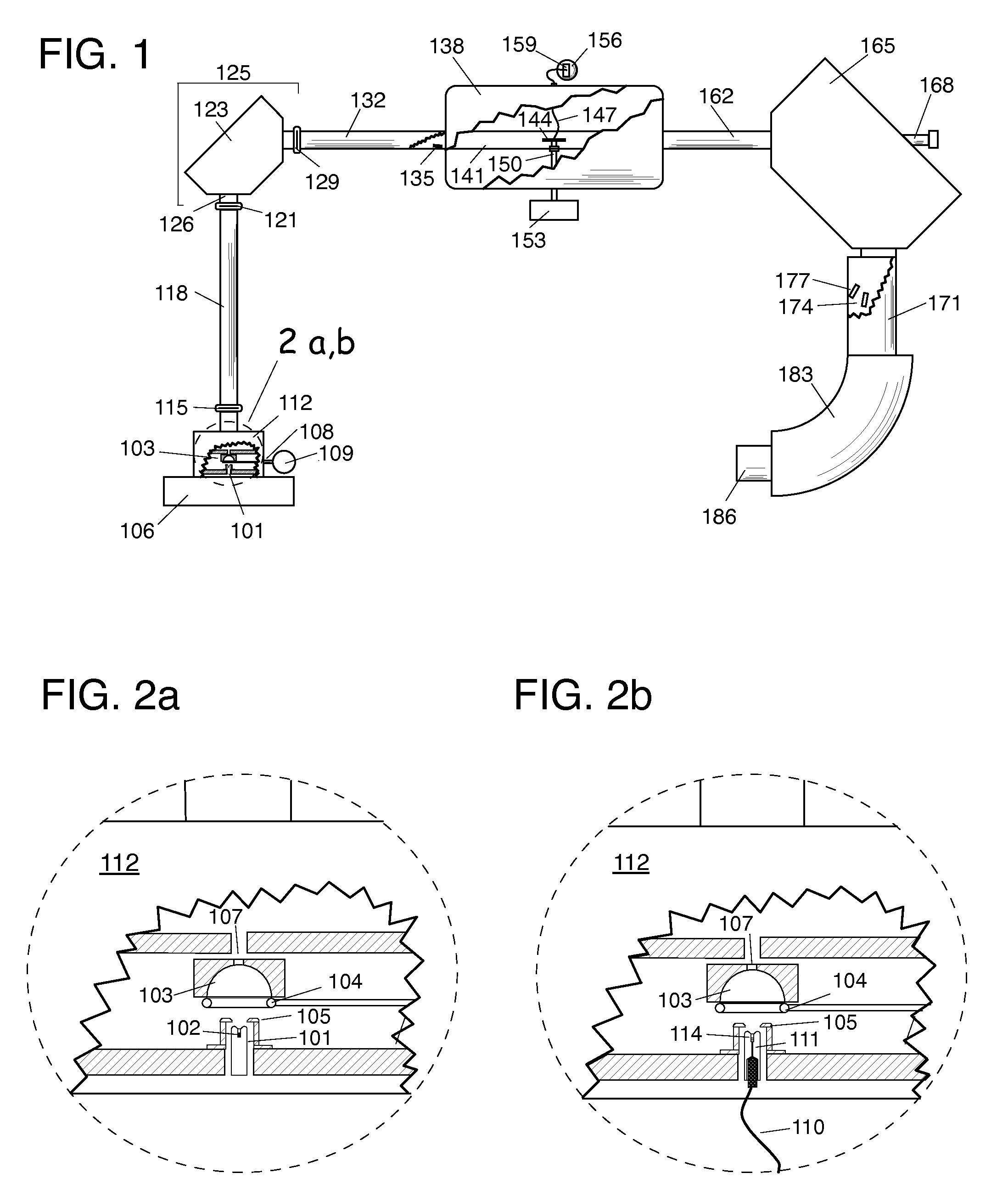
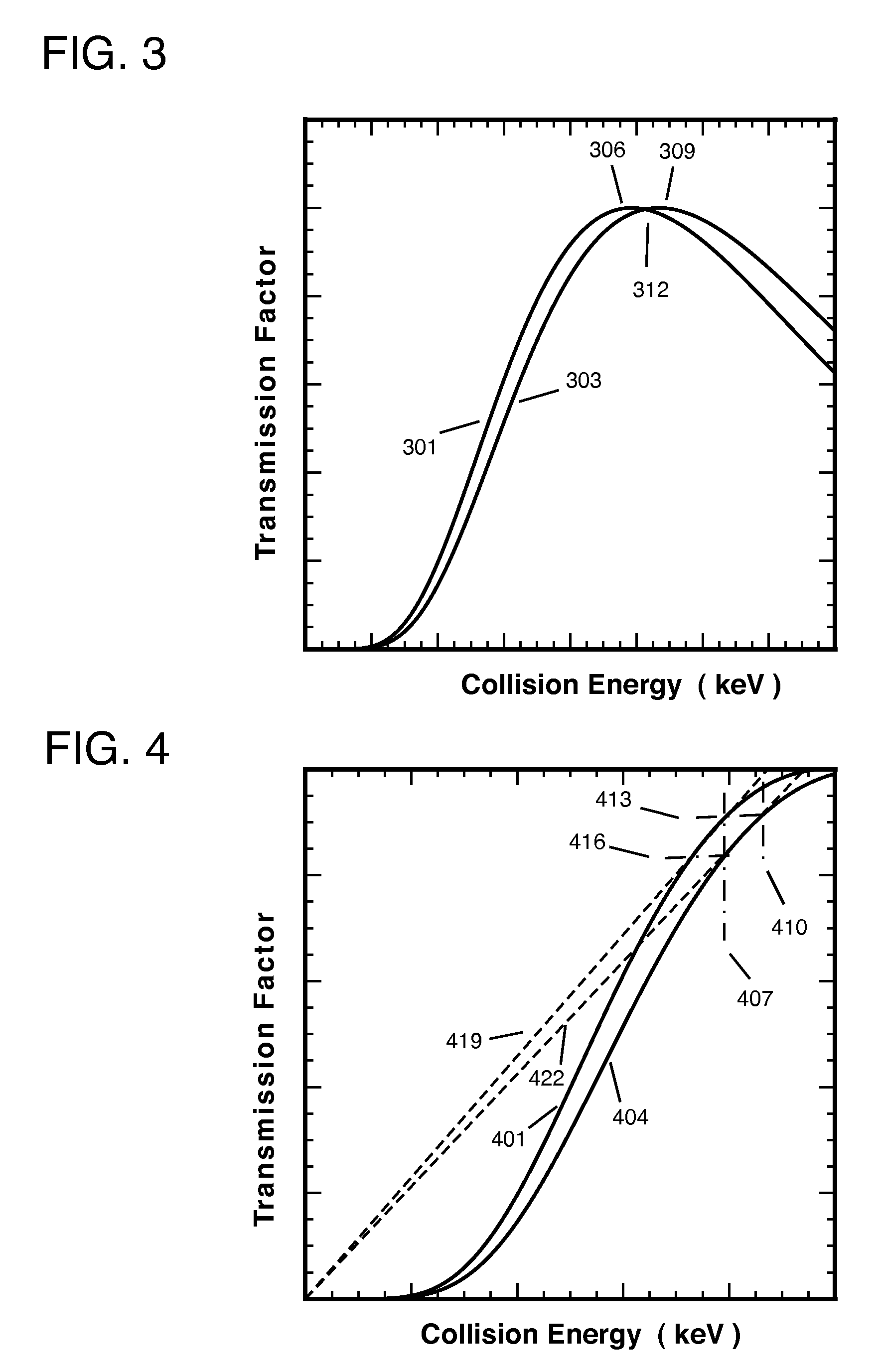
An isotope ratio mass spectrometer is described that obtains direct ratios of atomic isotopes in a monoenergetic beam of negative ions by passing them through a collision cell at specific kinetic energies for which the relative production of positive ions from the negative ions is calculable from the isotopic masses.
Owner:VOGEL JOHN STEPHEN
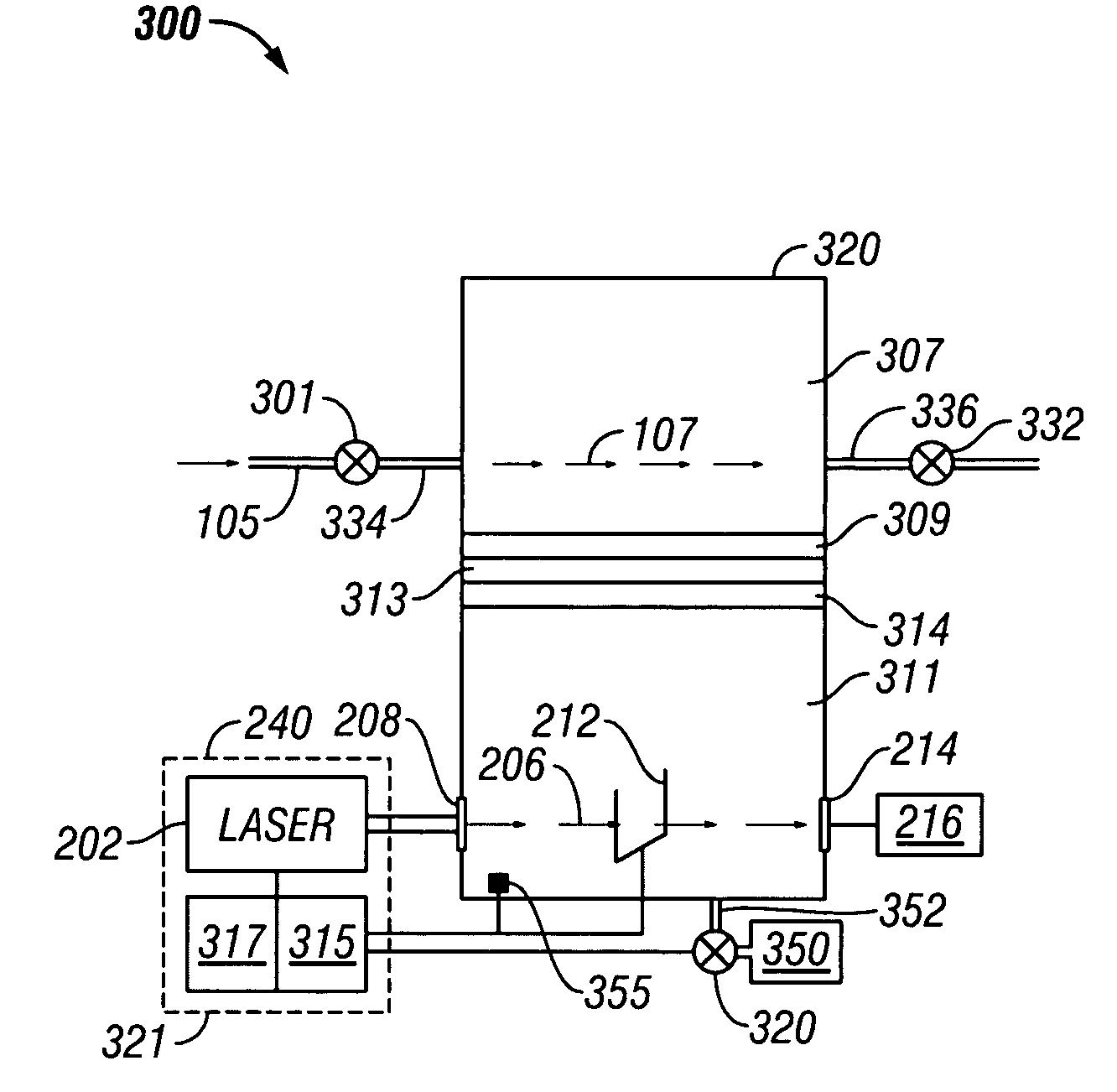
Laser Based, Temperature Insensitive, Carbon Dioxide Isotope Ratio Measurement
InactiveUS20120298868A1Radiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsRatio measurementLaser light
An apparatus and method (and related kit) for determination of the isotopic ratio of 13C to 12C in a gas sample containing carbon dioxide comprising introducing gas into a gas sample chamber, directing light into the sample chamber from a laser light source, the laser light source being capable of accessing one or more of the wavelength pairs 2054.37 and 2052.42; 2054.96 and 2051.67; or 2760.53 and 2760.08 nanometers, and with a detector detecting the laser light energy after passage through the sample chamber.
Owner:SOUTHWEST SCI
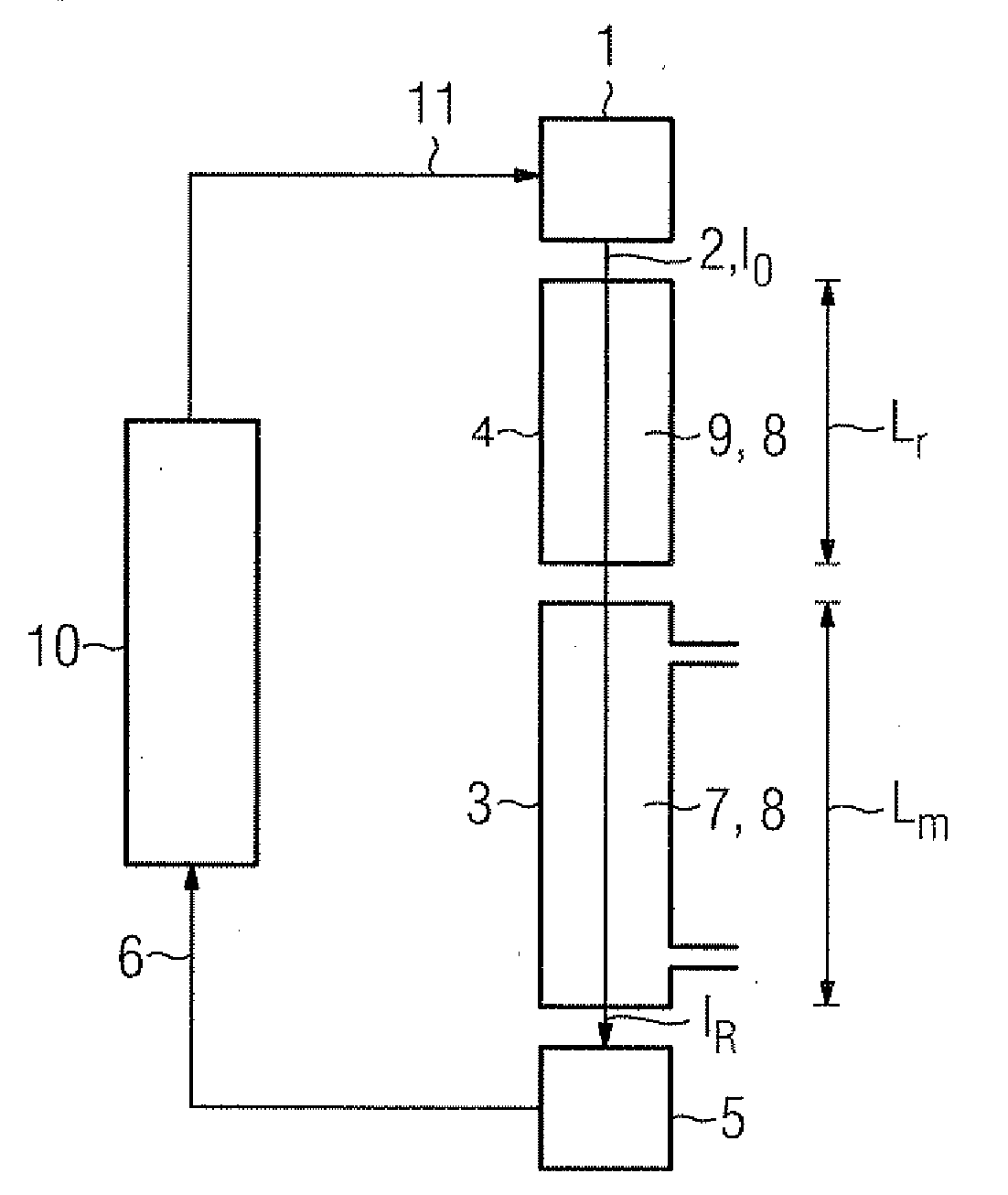
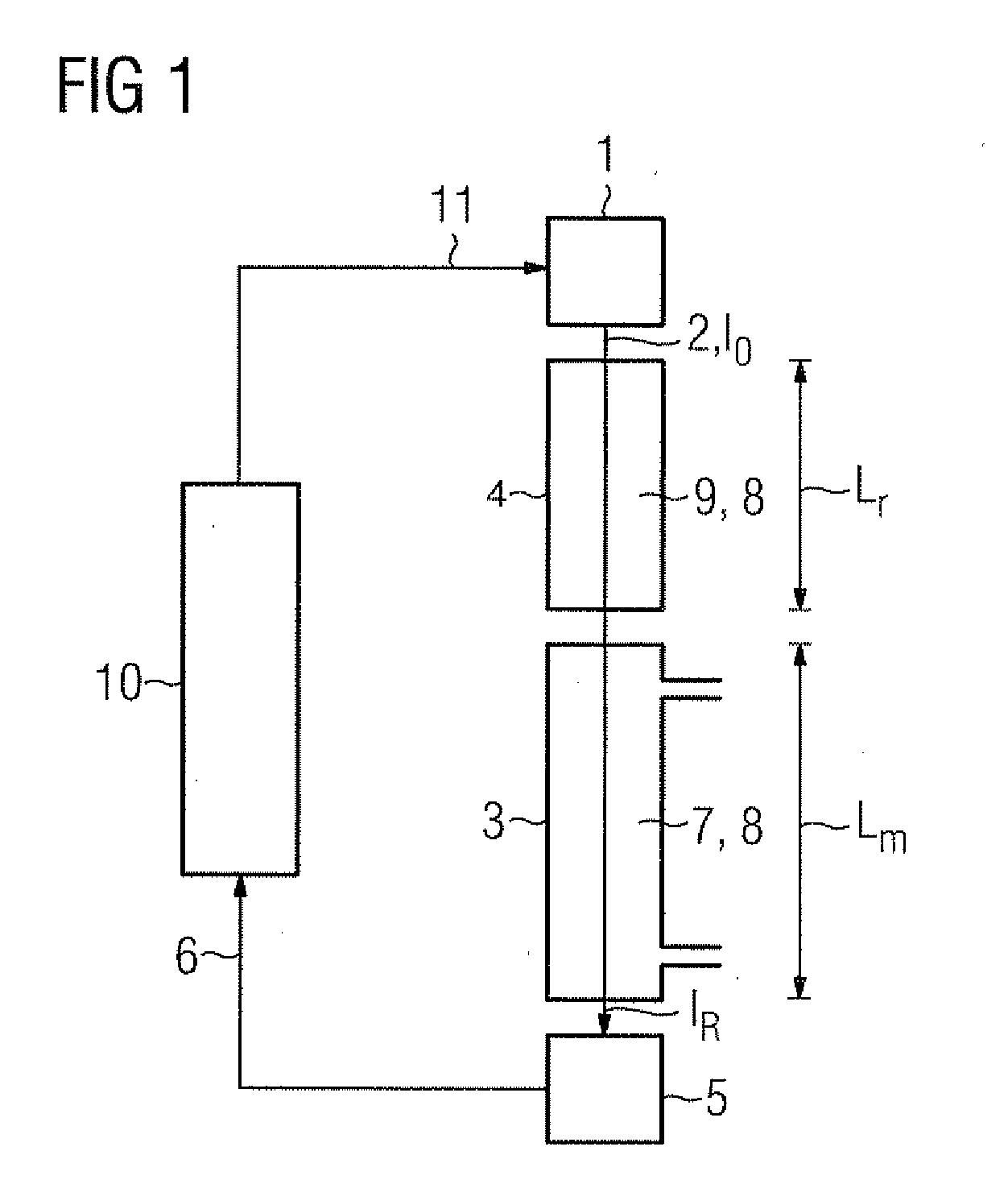
Method for measuring the concentration of a gas component in a measuring gas
ActiveUS20080304066A1Simple methodRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsGas compositionProduct gas
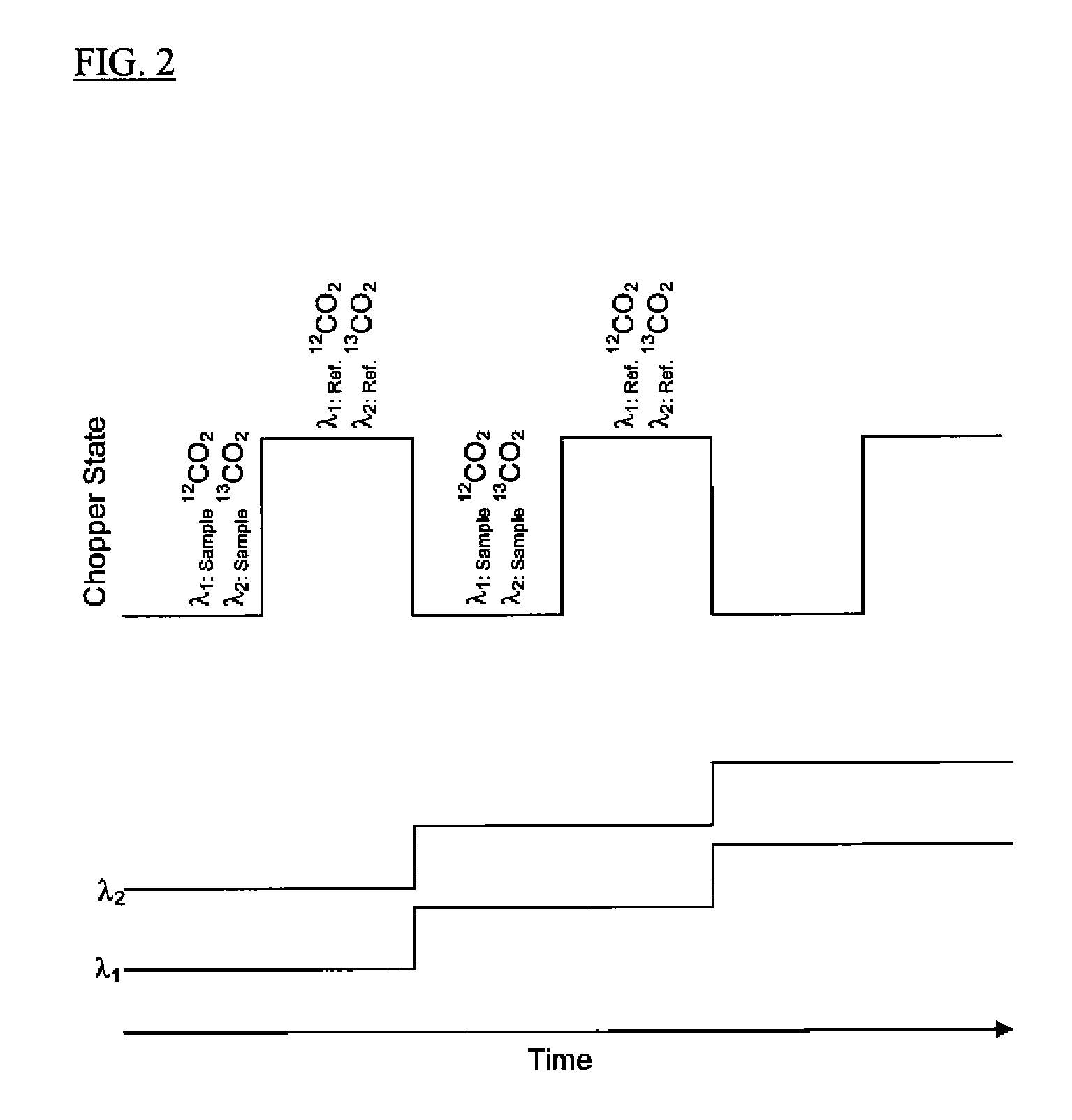
There is described a method for measuring a concentration of a gas component in a measuring gas, wherein the light of a wavelength tunable light source is passed along a single optical path through a measuring volume containing the measuring gas and a reference cell containing a reference gas to a detector. The reference cell is selected to contain a selected isotope of the gas component to be measured in a known abundance ratio higher than the known natural-abundance isotope ratio of the gas component in the measuring volume; the light source is tuned to sweep the wavelength of the light over the absorption lines of the selected isotope and the remaining gas component; and the concentration of the gas component in the measuring volume is calculated from the ratio of the detector signals at the peaks of the absorption lines, based on Lambert's law and taking into account the known abundance isotope ratios.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
System and method for isotopic signature and mass analysis
Mass intensity values, isotopic ratios and exact mass differences between isotopes may be obtained and analyzed to determine if there are one or more masses of interest. In one implementation, a method will look among the mass intensity values for peaks of interest. The mass intensity values, representative of isotopic signatures, will be compared to a criteria in order to determine which of the masses are of interest. Although the invention is not so limited, examples of such criteria include mass intensity values above a specified threshold, within a certain ratio of another mass intensity value, and / or separation between the masses themselves. Optionally, a tolerance may be applied to the criteria. If masses are found to be of interest, MS / MS can automatically be triggered for one or all of the masses of interest, when an analyzing system such as an LC-MS-MS, GC-MS-MS or MALDI-MS-MS system is used.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Infrared spectrometer
ActiveUS20080315102A1Increased signal noiseImprove system signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyIr absorptionPhase sensitive
Method and apparatus for detecting, by absorption spectroscopy, an isotopic ratio of a sample, by passing first and second laser beams of different frequencies through the sample. Two IR absorption cells are used, a first containing a reference gas of known isotopic ratio and the second containing a sample of unknown isotopic ratio. An interlacer or reflective chopper may be used so that as the laser frequencies are scanned the absorption of the sample cell and the reference cell are detected alternately. This ensures that the apparatus is continuously calibrated and rejects the baseline noise when phase sensitive detection is used.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
A sem-icp-ms method for measuring single particle uranium isotope ratio
InactiveCN102288671AIncrease concentrationFast dissolutionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansParticulatesRatio measurement
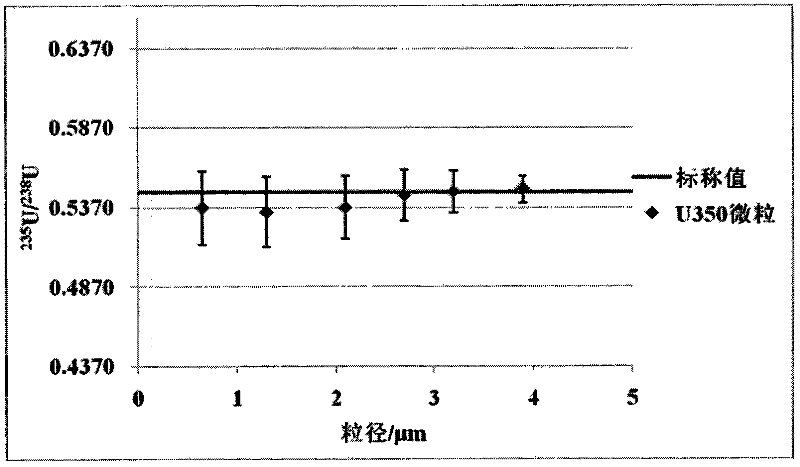
The invention discloses a method for measuring the uranium isotope ratio of a single particle by SEM-ICP-MS. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of a uranium particle sample; (2) search, identification and transfer of the uranium particle; (3) Dissolution of uranium particles; (4) determination of uranium isotope ratio, described step (3) is to put the silicon chip with uranium particles into the reagent bottle, add HNO3, heat on the electric heating plate to dissolve the particles, and then add Deionized water is used to adjust the acidity; in the step (4), a multi-receiver inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (MC-ICP-MS) is used to simultaneously receive 235U and 238U signals for sample measurement. The invention provides a SEM-ICP-MS method for determining the uranium isotope ratio of a single particle with fast particle dissolution rate, large sample processing capacity, small amount of sample required for measurement, relatively high measurement precision and short measurement time.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Mineral exploration method for judging mineralization of granite body by using zircon
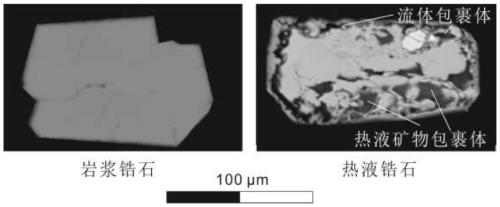
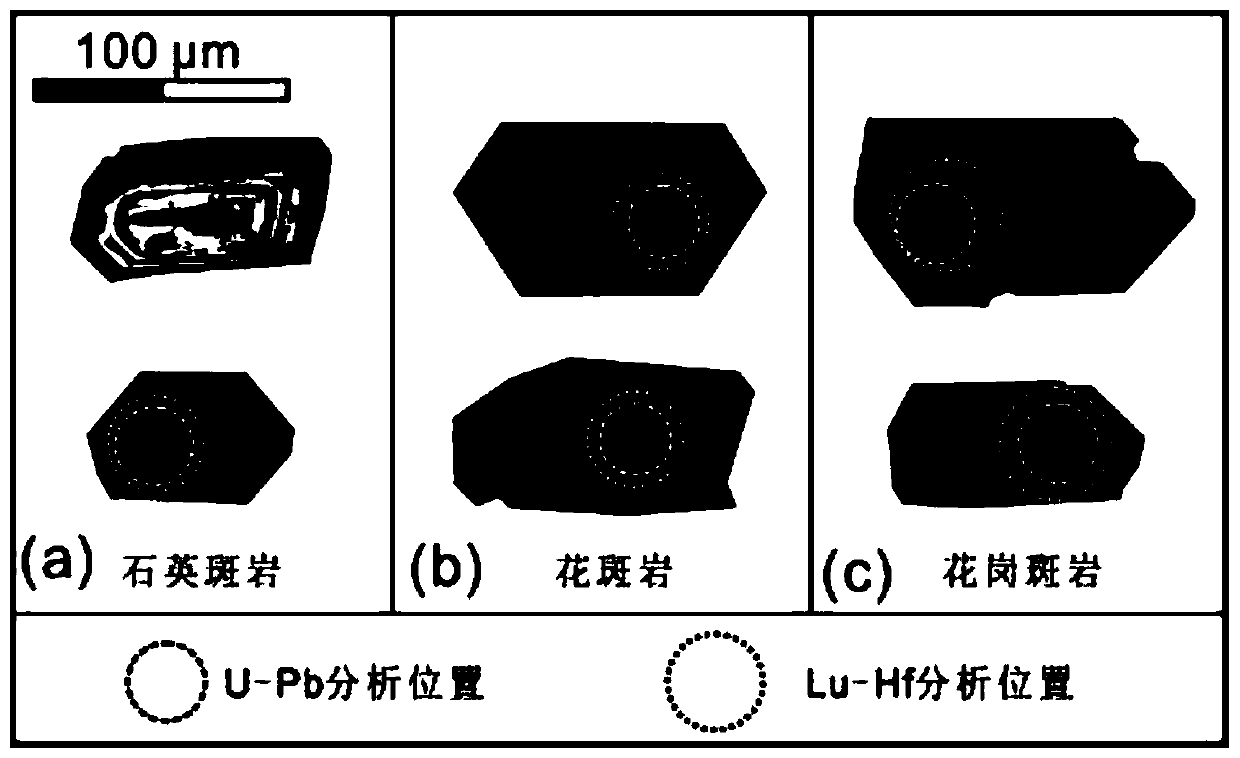
ActiveCN111272797ADetermination of mineralizationShorten the timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationMetallogenyZircon
The invention discloses a mineral exploration method for judging mineralization of a granite body by using zircon. The method comprises the steps of carrying out cathodic luminescence photography, back scattering photography, U-Pb dating, micro-area component analysis, Lu-Hf isotope ratio analysis and the like on zircon obtained by sorting from granite bodies. The mineralization of the granite bodies can be rapidly and accurately judged, and the time is saved by 50% or above compared with that of a traditional exploration method; the occurrence part of the ore body related to the granite can be effectively indicated, and the time is saved by more than 40% compared with that of the traditional prospecting means.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Infrared spectrometer
ActiveUS20080128622A1Radiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyIr absorptionPhase sensitive
Method and apparatus for detecting, by absorption spectroscopy, an isotopic ratio of a sample, by passing first and second laser beams of different frequencies through the sample. Two IR absorption cells are used, a first containing a reference gas of known isotopic ratio and the second containing a sample of unknown isotopic ratio. An interlacer or reflective chopper may be used so that as the laser frequencies are scanned the absorption of the sample cell and the reference cell are detected alternately. This ensures that the apparatus is continuously calibrated and rejects the baseline noise when phase sensitive detection is used.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Isotope based surface water pollution source analytical method
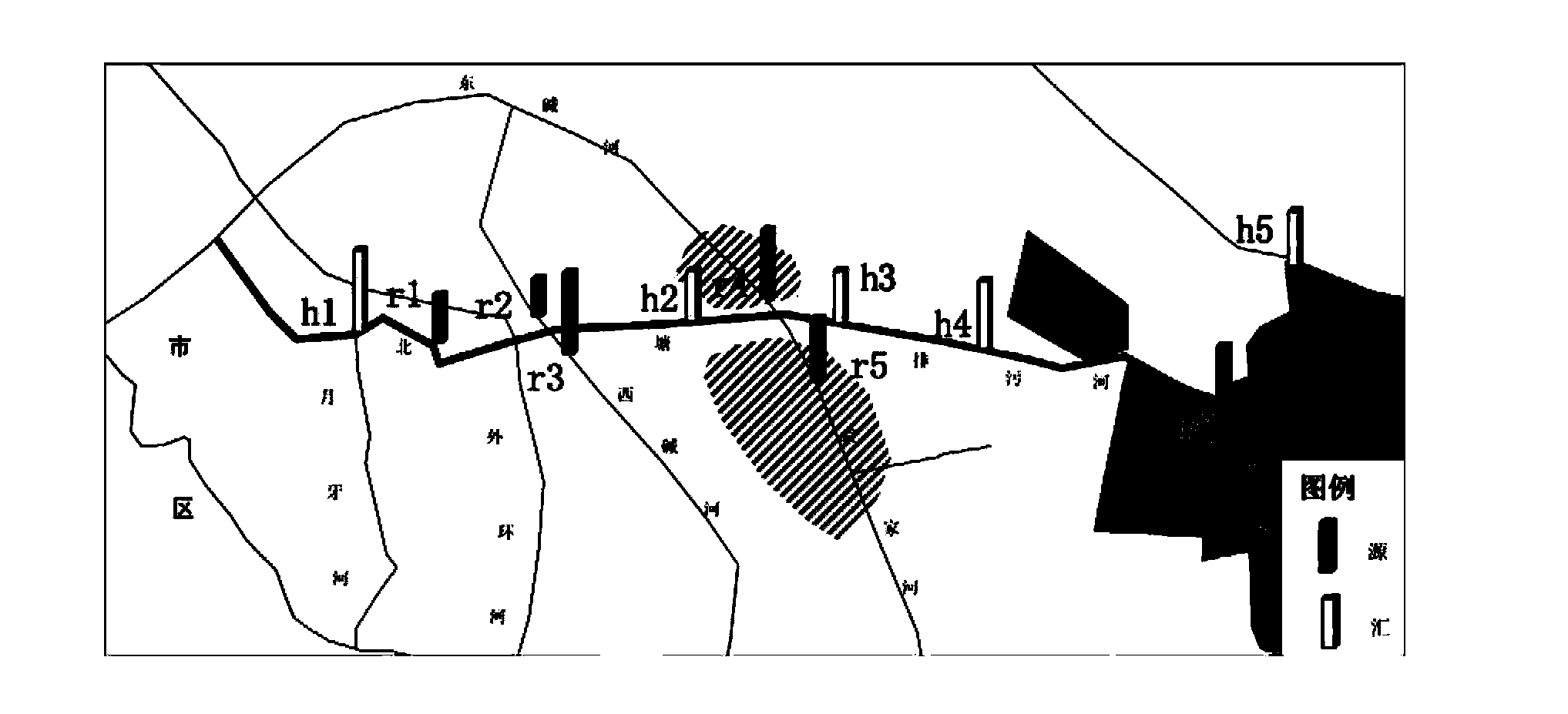
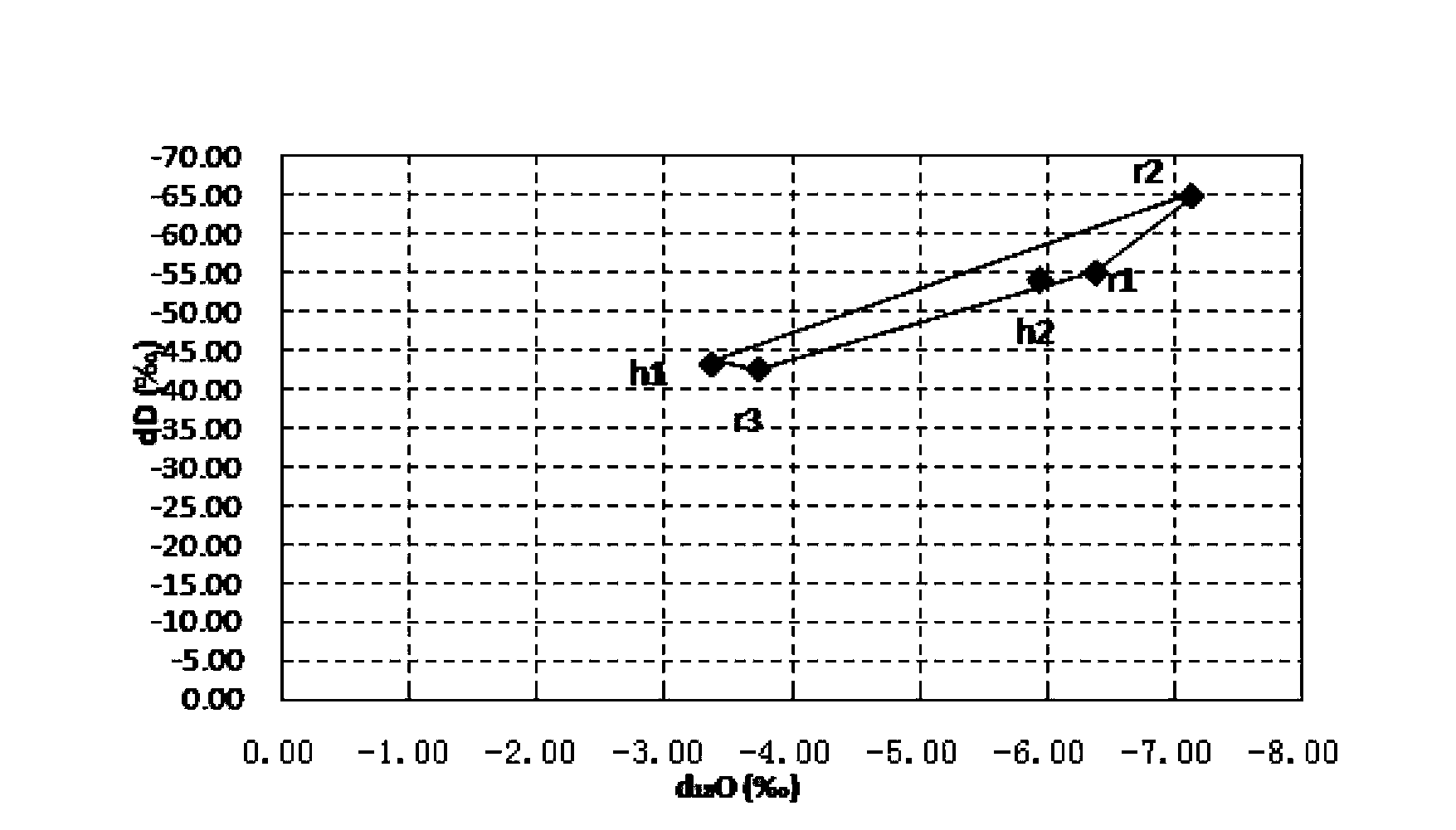
InactiveCN103808790AImprove accuracyImprove work efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInternational standardIsotopes of carbon
The invention relates to an isotope based surface water pollution source analytical method, which comprises the steps of: 1) sampling: laying sampling points and conducting sampling according to industry standards; 2) isotope detection: taking isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen, namely D, <18>O, <13>C, and <15>N as the indexes; employing an isotope ratio mass spectrometer to detect the ratios of isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen, namely D, <18>O, <13>C, and <15>N in samples, and conducting comparison with international standard substances, and working out isotope ratios of the samples; and 3) data analysis: drawing a hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratio diagram according to the ratios of isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen, namely D and <18>O in source and convergence samples; selecting analysis nodes, calculating a pollution source contribution rate through a source convergence isotope ratio of the nodes, and determining a new pollution source by judging whether the source convergence isotope ratio of outflow nodes is balanced, and then making use of analysis of the isotopes of carbon and nitrogen, namely <13>C and <15>N to verify the accuracy of the result. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of improving the accuracy and efficiency.
Owner:TIANJIN ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
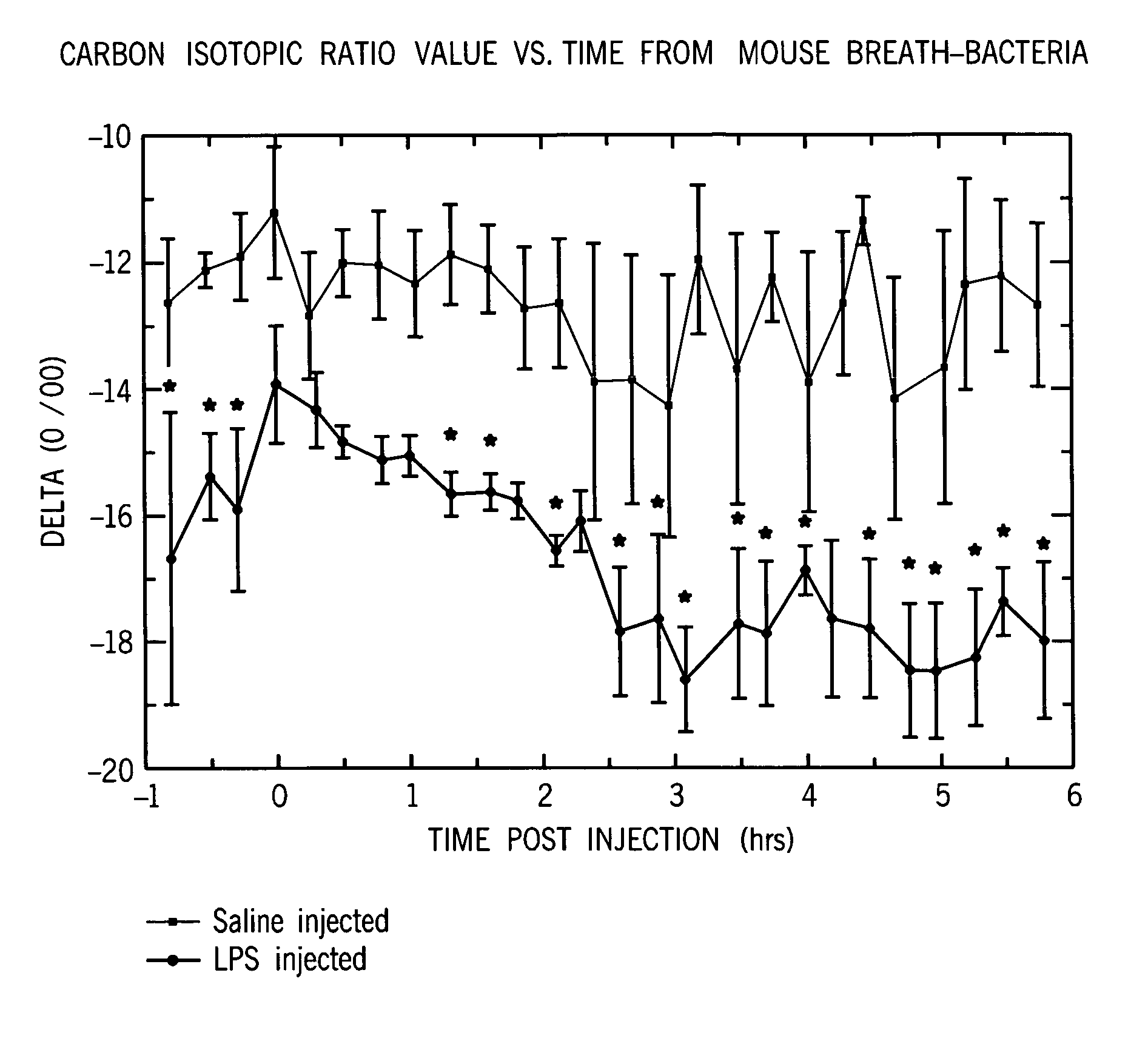
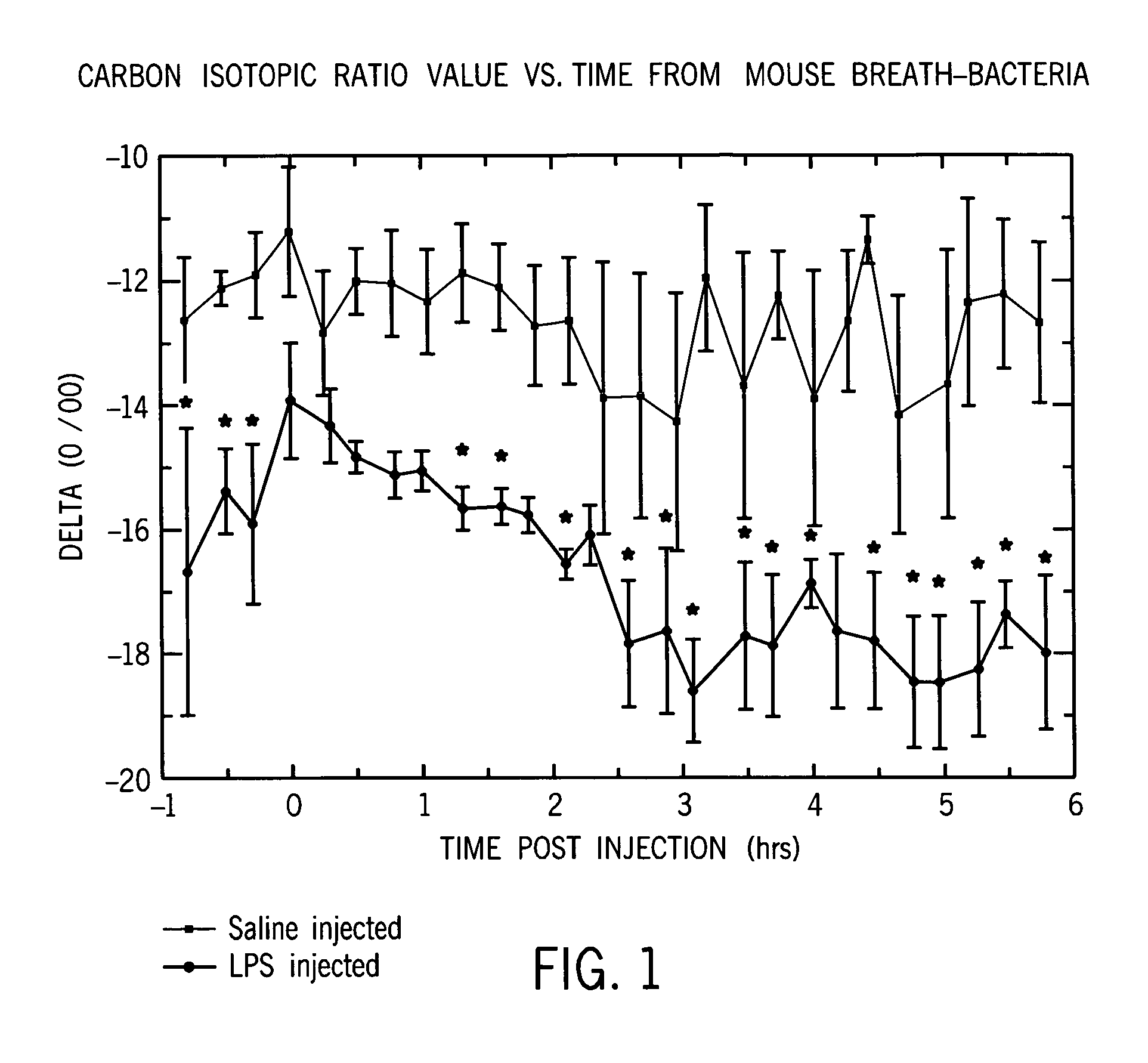
Identification of disease characteristics using isotope ratios in breath
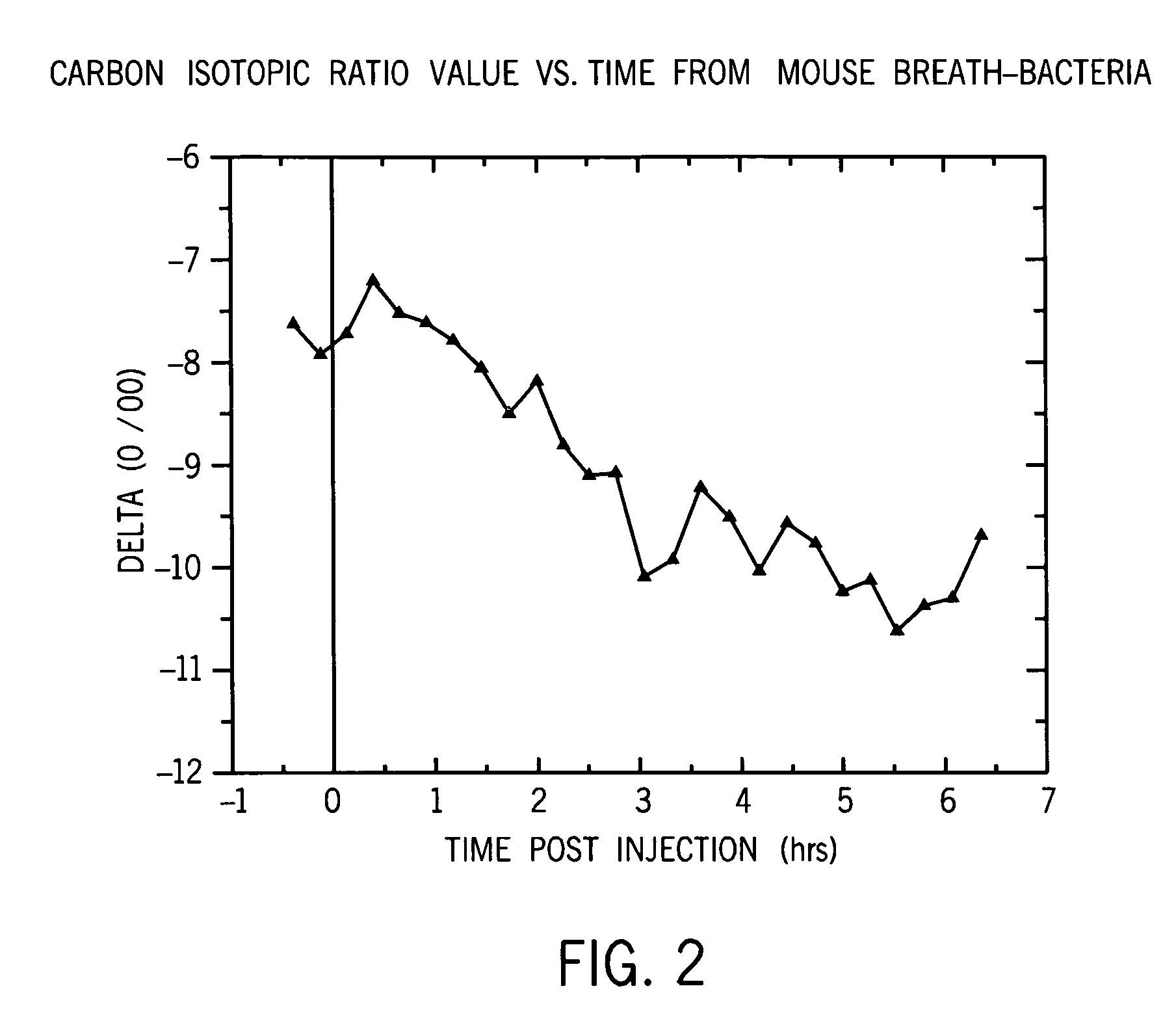
ActiveUS7465276B2Early effective indicatorEasy to detectWithdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationTriageIsotope
Methods are disclosed for distinguishing whether an animal is experiencing a bacterial infection or a viral infection. One monitors breath taken from the animal over time to measure the relative amount of a first breath stable isotope to a second breath stable isotope therein over time. A quick change in the isotope ratios within several hours from the likely infection is indicative of a bacterial infection. A delayed change in the isotope ratios, followed by periodic repeated alterations in the ratios, is indicative of viral infection. The methods are particularly efficient when using cavity ringdown spectroscopy for the monitoring. They may be used for monitoring a patient already admitted to a hospital, or for monitoring a patient initially complaining of adverse symptoms, or for triage, or for collectively monitoring a population of animals.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Neutron Detector Using Neutron Absorbing Scintillating Particulates in Plastic
ActiveUS20100019160A1Low costIncrease in sizeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMeasurement with scintillation detectorsParticulatesNinetieth percentile
A neutron detector composed of a matrix of scintillating particles imbedded in a lithiated glass is disclosed. The neutron detector detects the neutrons by absorbing the neutron in the 6Li isotope which has been enriched from the natural isotopic ratio to a commercial ninety five percent. The utility of the detector is optimized by suitably selecting scintillating particle sizes in the range of the alpha and the triton. Nominal particle sizes are in the range of five to twenty five microns depending upon the specific scintillating particle selected.
Owner:WALLACE STEVEN
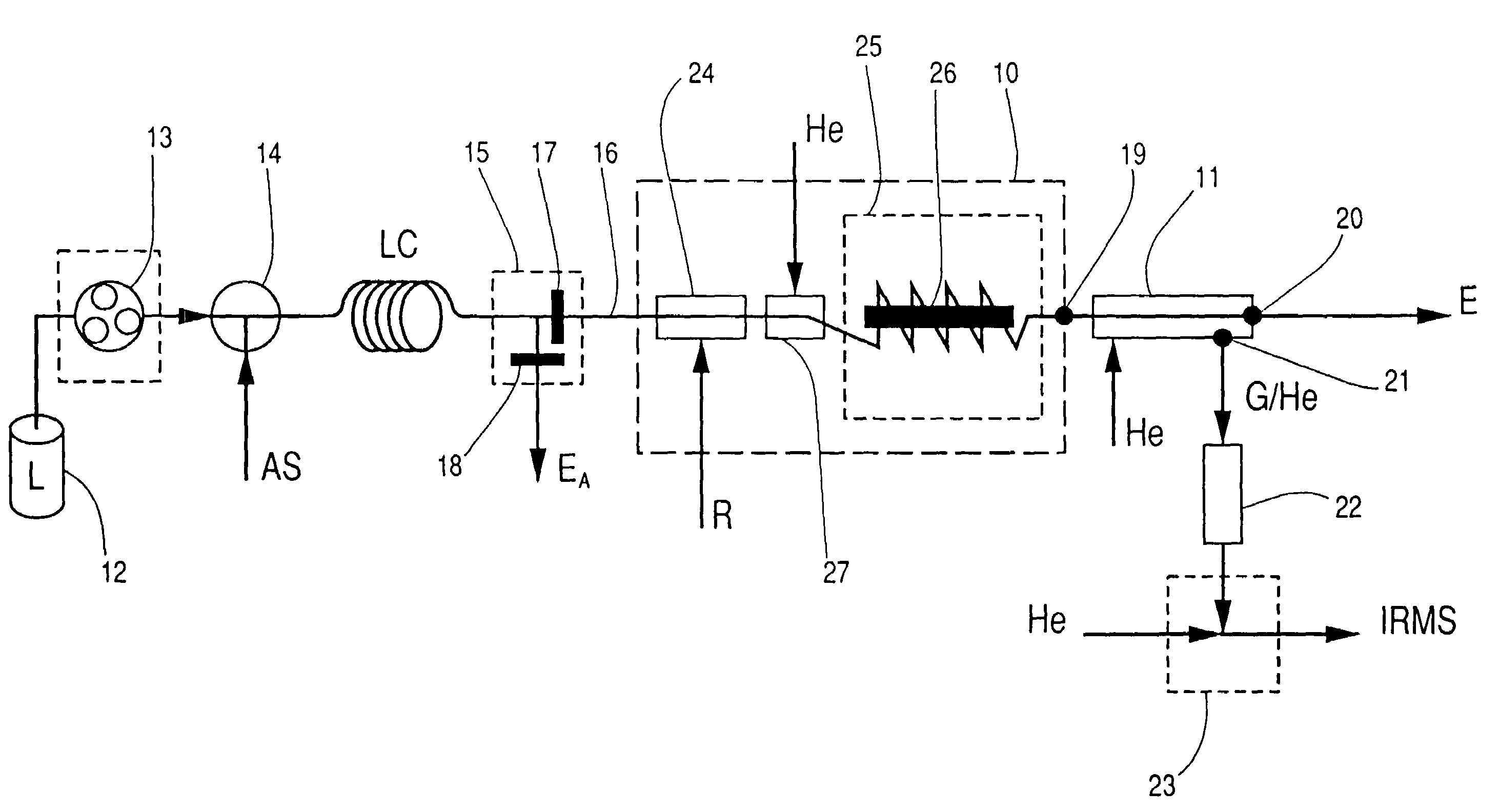
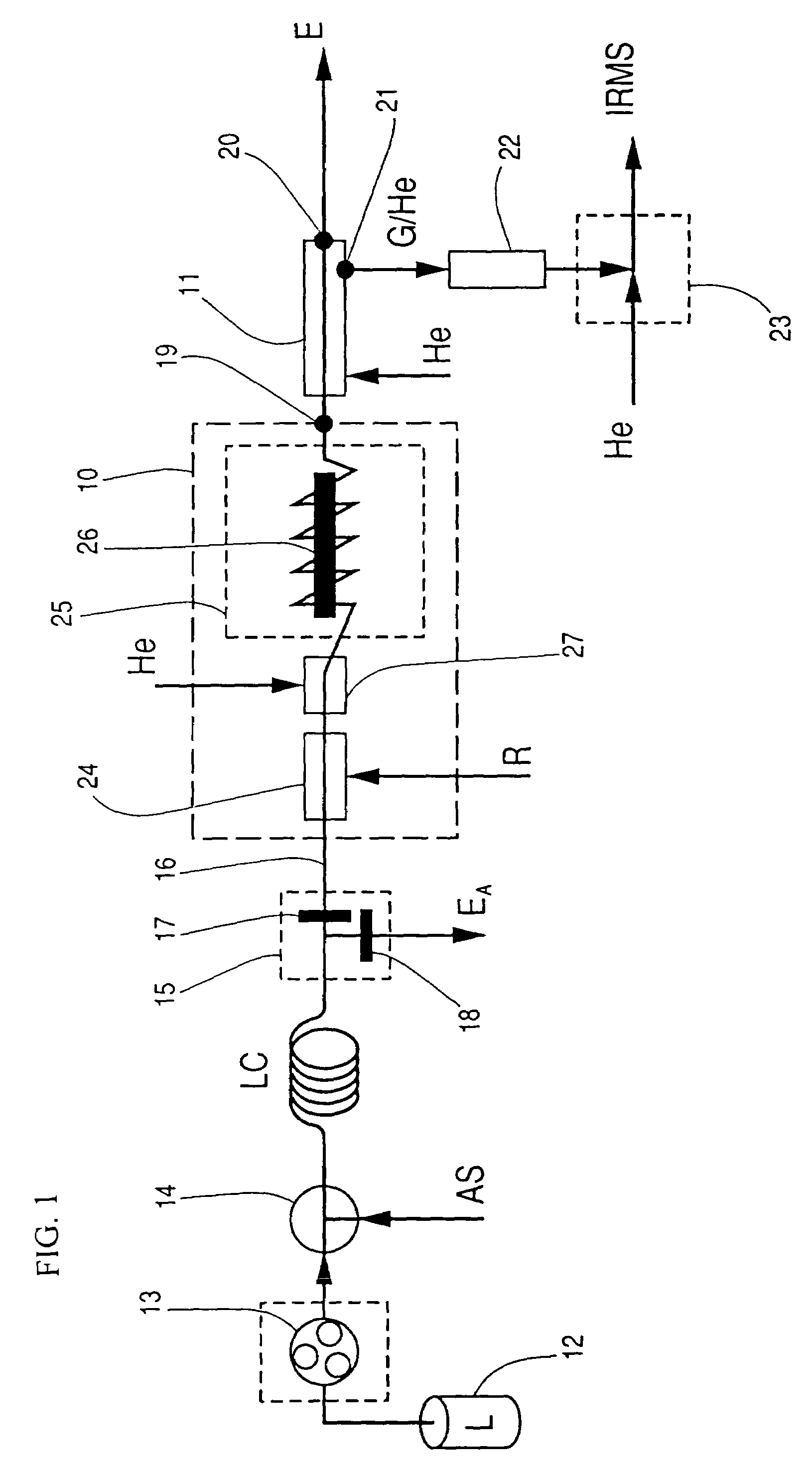
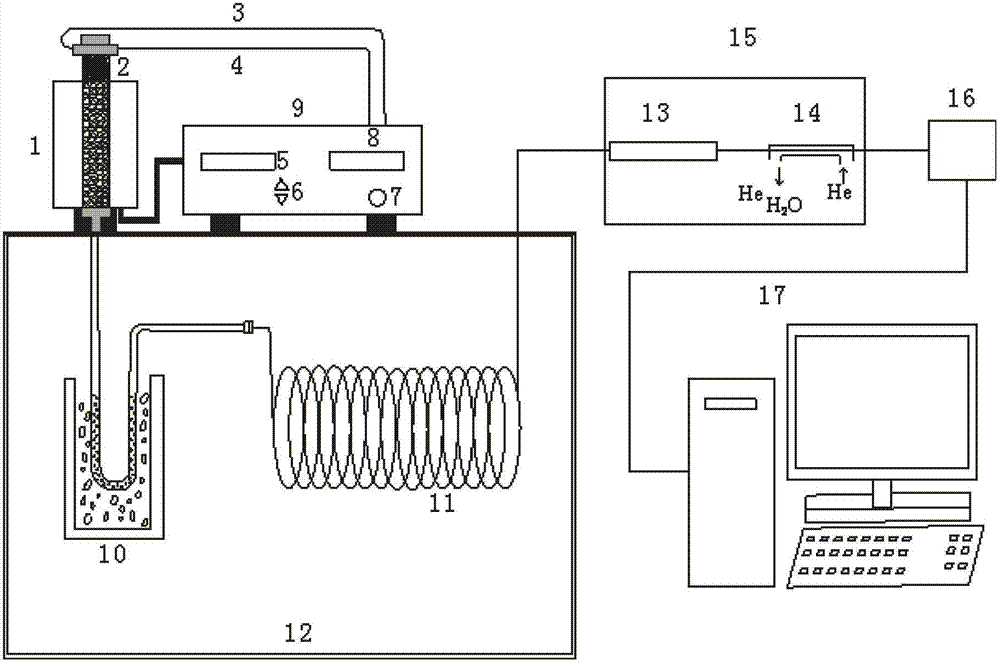
Process and apparatus for providing gas for isotopic ratio analysis
The invention relates to a process and to an apparatus for providing gas for isotopic ratio analysis. According to the invention, a gas is generated from an eluate of a liquid chromatograph (LC). Subsequently, the gas is separated from the eluate. Finally, the gas is fed to an instrument (IRMS) for isotopic ratio analysis.
Owner:BERN UNIV OF
Method for determination of delta-d values of non- exchangeable hydrogen stable isotopes on ethanol' s methyl group by means of irms instrumental technique
InactiveUS20110223629A1Organic compound preparationMicrobiological testing/measurementFruit juiceContinuous flow
The present innovation is related with chemical instrumental analysis, i.e. to the domain of analysis of stable isotopes in food products, and it is related to the method for preparation of ethanol samples and mode for determination of isotopic ratio of non-exchangeable hydrogen stable isotopes sited on the methyl site of ethanol by means of instrumental technique CF-TC / EA-IRMS (Continuous Flow-Temperature Conversion / Elemental Analyzer-Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry), and for the purpose of establishing authenticity and geographical origin of wine and grape must, beer, alcoholic beverages, fruit juices, honey, vinegars and other food products which contain alcohol and / or fermentable sugars. This method is based on full enzymatic (or organic) transformation of ethanol samples to gain ethanoic acid (acetic acid), controlled neutralization of acetic acid and further concentration, purification of prepared acetate salt and its drying to the constant mass and further determination of δD values in prepared samples by means of CF-TC / EA-IRMS.
Owner:SMAJLOVIC IVAN
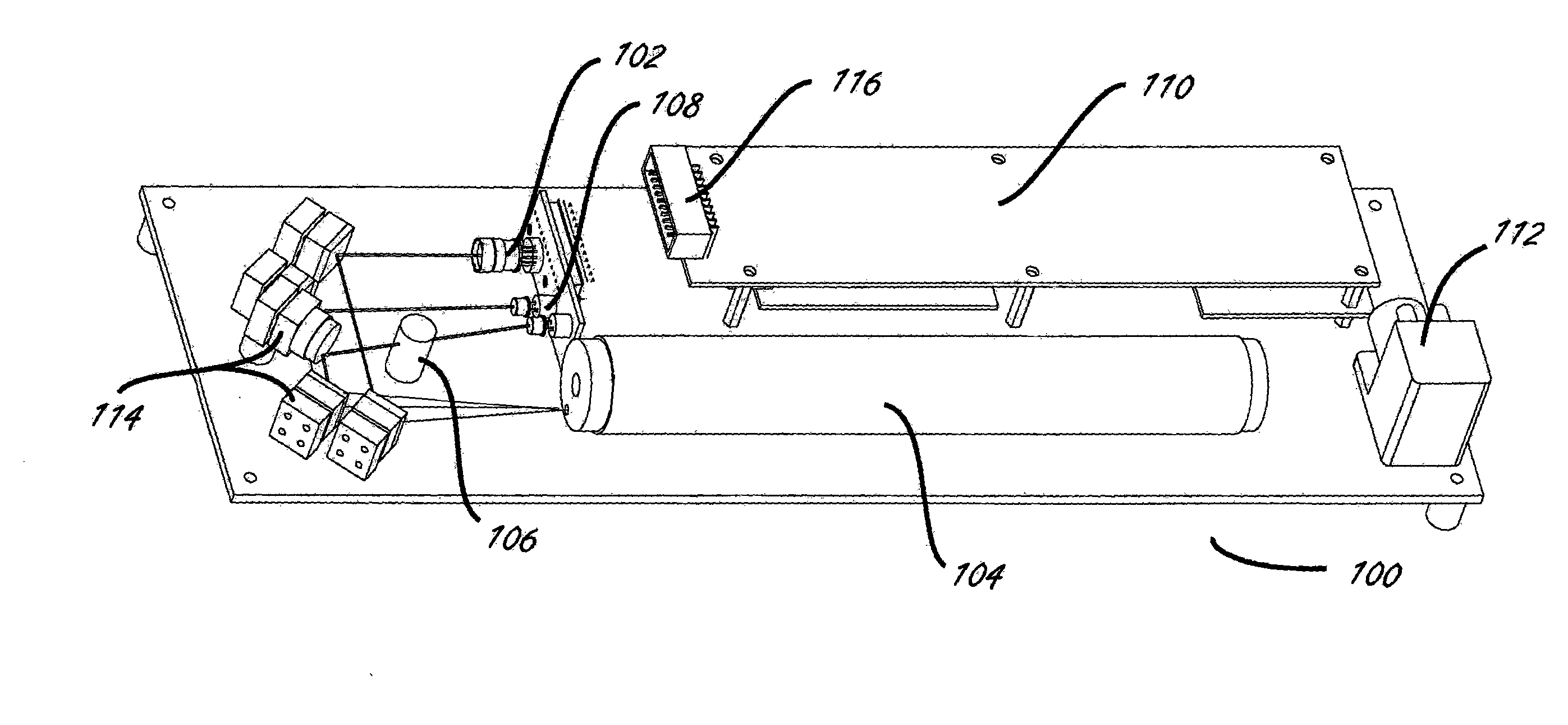
System and method for high precision isotope ratio destructive analysis
ActiveUS20110164248A1Precise proportionImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationRelative standard deviationSingle shot
A system and process are disclosed that provide high accuracy and high precision destructive analysis measurements for isotope ratio determination of relative isotope abundance distributions in liquids, solids, and particulate samples. The invention utilizes a collinear probe beam to interrogate a laser ablated plume. This invention provides enhanced single-shot detection sensitivity approaching the femtogram range, and isotope ratios that can be determined at approximately 1% or better precision and accuracy (relative standard deviation).
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Method and device for isotopic ratio analysis
InactiveUS20110086430A1Reduce complexityComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationAnalyteCarrier fluid
A process and an apparatus for isotope ratio analysis, the process having the following steps: performing a liquid chromatography process and thus providing an eluate which comprises at least one liquid carrier fluid and at least one analytes, collecting a portion of interest from the eluate, processing the eluate portion to form at least one gaseous conversion products of the analytes, and supplying the gaseous conversion products, especially with gaseous carrier fluid, to an isotope analyzer and determining the isotrope ratios.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
Online analysis method for hydrocarbon carbon isotope of light dydrocarbon monomer of source rock pyrolysis product
ActiveCN103245735AGuaranteed representationRealize online analysisComponent separationIsotope-ratio mass spectrometryMonomer
The invention relates to an online analysis method for hydrocarbon carbon isotope of a light dydrocarbon monomer of source rock pyrolysis products. The method comprises the following steps: placing source rock sample particles into a sample pipe; connecting the sample pipe with a sample inlet of a gas chromatograph; adjusting the pressure of carrier gas of a pyrolyzer to 15 to 18psi; introducing the carrier gas to a pyrolyzing furnace for 5 to 10 minutes, and fully filling a liquid nitrogen cold trap with liquid nitrogen; heating the pyrolyzing furnace to be at a preset temperature, keeping the temperature for 30 minutes to obtain a hydrocarbon compound; lowering the temperature of the pyrolyzing furnace to 80 to 85 DEG C, removing the liquid nitrogen cold trap, and starting the gas chromatograph and an isotope ratio mass spectrometry; separating the hydrocarbon compound to single-molecule hydrocarbon compounds by the gas chromatograph; burning the single-molecule hydrocarbon compounds to obtain CO2; measuring the carbon isotope ratio of the CO2 by the isotope ratio mass spectrometry; and recording the carbon isotope ratio and generating a mass spectrum. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of being high in reliability, convenient to operate, quick in analysis, and low in analysis cost.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for analysis of isotopes in bodily fluids
ActiveUS20120021526A1Simplifies and speeds up overall processSimple processTransmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsBlood plasmaOrganic polymer
Biological fluid samples containing proteins (e.g., blood plasma or saliva) are prepared for isotopic analysis by precipitating the proteins while leaving the isotopic ratio unaffected. This precipitation can involve adding metal ions, salts, organic solvents, or organic polymers. The sample is then centrifuged to allow transfer of the supernatant for isotopic analysis, e.g. by tunable diode laser absorption spectrometry to obtain a quantitative measure of the 2H and 18O isotope levels in the water relative to reference standards.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Element isotope analysis system, analysis method of sulfur isotope in trace sulfate sample and application thereof
PendingCN111272917AFast online analysisSolve difficult-to-analyze problemsComponent separationGas liquid chromatographicPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to the field of element isotope analysis, and particularly discloses an element isotope analysis system, an analysis method of sulfur isotopes in a trace sulfate sample and application of the analysis method. The system comprises an element analyzer, an enrichment device, a gas chromatographic column, an isotope ratio mass spectrometer and a heating device which are connectedin sequence, and pipelines for connecting or communicating equipment, wherein the pipeline used for connecting or communicating the equipment is a Teflon pipe, the gas chromatographic column is a chromatographic column made of a Teflon material, the enrichment device comprises a multi-way valve, a sample tube and a cooling trap, at least one part of the sample tube can be arranged in the coolingtrap to realize enrichment, and the heating device is arranged around the sample inlet, the sample inlet valve and the ion source of the isotope ratio mass spectrometer. The analysis method is simple,controllable, easy to operate, capable of utilizing the sample to the maximum extent, low in instrument detection limit, high in sensitivity, small in analysis error and high in accuracy.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring isotope ratio of uranium in single particle
ActiveCN104236978AThe positioning method is simple and fastImprove efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryAdhesive
The invention belongs to the technical field of monitoring of nuclear technology, and discloses a method for measuring the isotope ratio of uranium in a single particle. The method comprises the following steps: firstly seeking a uranium-containing particle by using a scanning electron microscope, using a micro-operation system to transfer the uranium-containing particle to a conductive adhesive with a marked metal mesh on the surface, positioning and fixing the uranium-containing particle, and then analyzing the isotope ratio by using a laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The method has the advantages of simple and quick pre-treatment method, simplified analysis flow, and high analysis precision which can reach to 1%.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Site analysis system for the calculation of the isotope ratio of carbon in several gas species by means of a single analyser
InactiveUS20130064715A1Shorten the timeComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChemical elementMobile laboratory
The present invention relates to a system of analysis, which can be used in a mobile laboratory in a drilling site situation or in a similar situation, suitable for measuring (preferably in relation to at least two partially gaseous species, which derive preferably from a mixture extracted from a drilling mud, for example, methane, ethane, propane and / or any other heavier hydrocarbons) the quantities of the different isotopes of at least a same chemical element (preferably the quantities of 13C, carbon isotope with 6 protons and 7 neutrons, and of 12C, carbon isotope with 6 protons and 6 neutrons, respectively) by means of a laser isotopes analyser regulated for a single, at least partially gaseous species which contains said chemical element.
Owner:CALLERI ANTONIO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com