Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
497 results about "Leaching (metallurgy)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Leaching is a process widely used in extractive metallurgy where ore is treated with chemicals to convert the valuable metals within into soluble salts. These can then be washed out and processed to give the pure metal; the material left over is commonly referred to as tailings. Compared to pyrometallurgy leaching is easier to perform, requires less energy and is potentially much less harmful as no gaseous pollution occurs. Drawbacks of leaching include its lower efficiency and the often significant quantities of waste effluent and tailings produced, which are usually either highly acidic or alkali as well as toxic (e.g. Red mud).
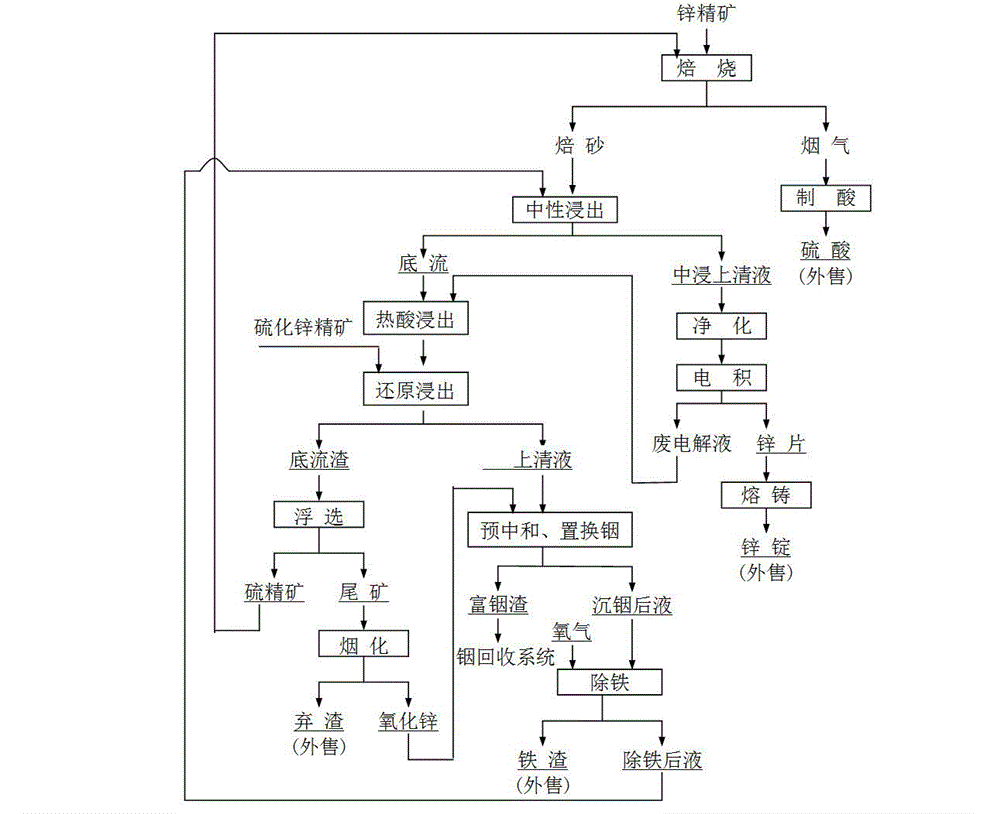
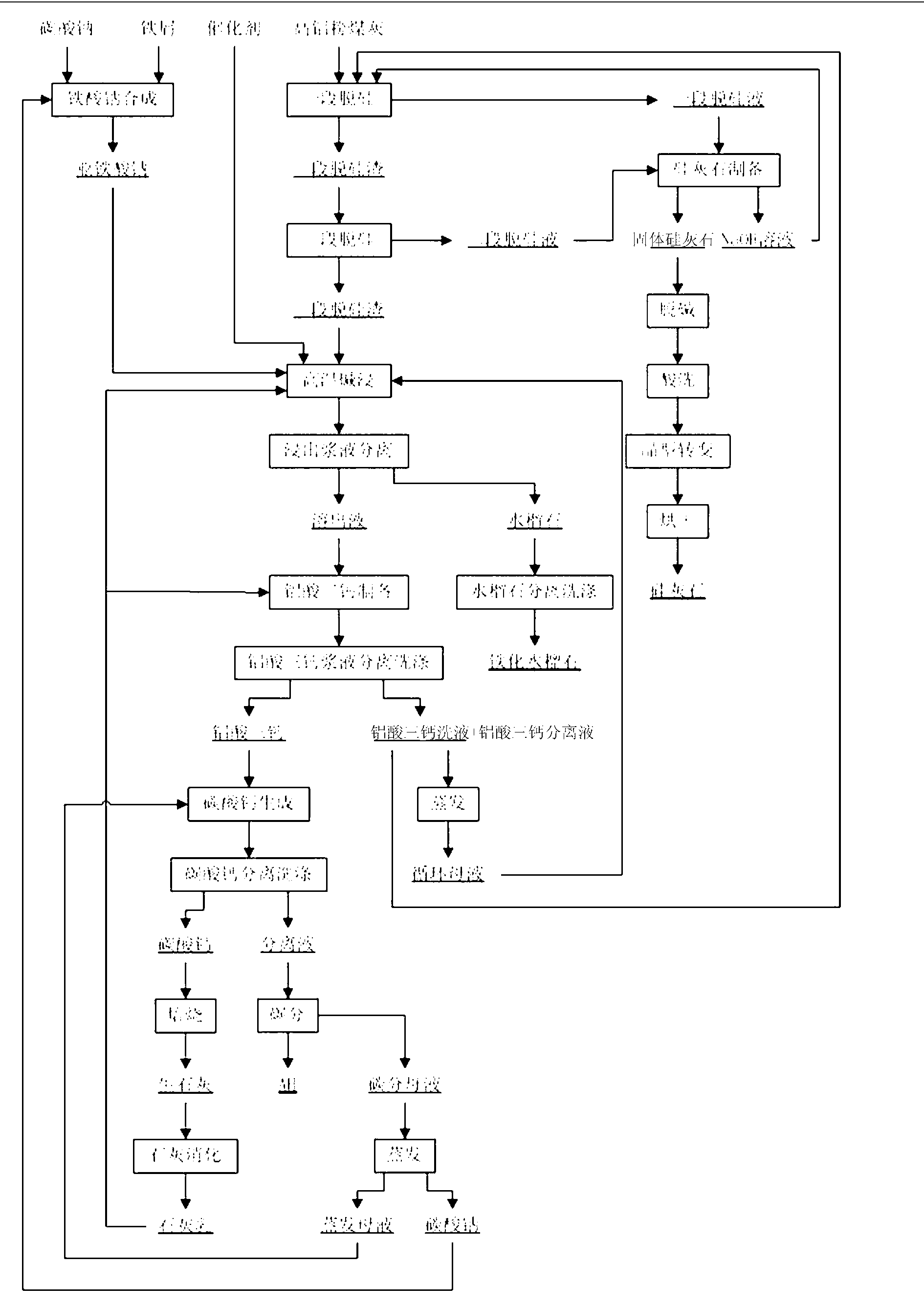
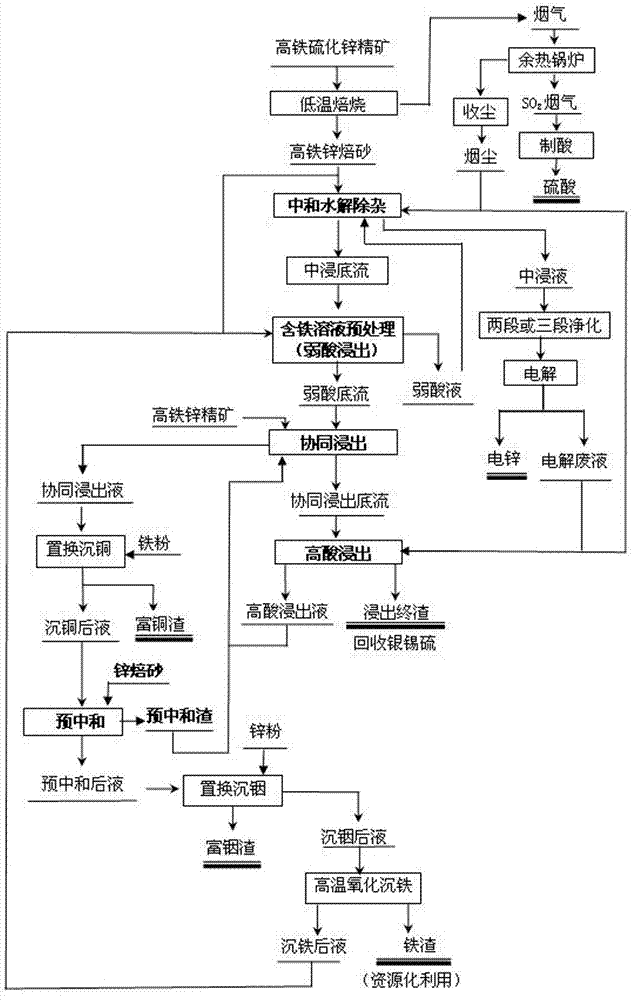
Method for individually processing high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate
ActiveCN103409622AThe process is highly targetedHigh enrichment ratioProcess efficiency improvementIndiumHydrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for individually processing high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate. The method comprises a step of subjecting the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate to calcination in a fluidized bed combustion boiler to obtain zinc calcine; a step of subjecting the zinc calcine to neutral leaching to produce neutral leaching solution and neutral leaching residue; a step of, after the neutral leaching residue and the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate are mixed, successively performing reduction leaching and oxidation leaching, and circulating oxidation leaching solution to the reduction leaching to produce reduction leaching solution and silver-rich sulfur residue; a step of replacing the reduction leaching solution by using iron powder to precipitate copper and to produce copper-rich slag and solution after copper precipitation; a step of subjecting the solution after copper precipitation to pre-neutralization by using the zinc calcine, and then replacing by using zinc powder to precipitate indium and to produce indium-rich slag and solution after indium precipitation; and a step of bubbling oxygen into the solution after indium precipitation, heating and removing iron to obtain iron removal solution and hematite slag. The hematite slag can be utilized as a raw material for ironmaking. The method has strong pertinence, short technological process and high metal recovery yield, and the method is clean, efficient, energy-saving and environmental friendly. Separation and comprehensive utilization of zinc, indium, copper and iron are achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH TECH IND SALES MANAGEMENT
Zinc hydrometallurgy production process
InactiveCN102876888AReduce lossesHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementCement factoryIndium
The invention relates to a zinc hydrometallurgy production process. According to the zinc hydrometallurgy production process provided by the invention, reduction leached supernate is subjected to preneutralization, then zinc dust is added for replacing indium, after the indium is separately removed, oxygen with the concentration being not lower than 98 percent is filled into liquid obtained after the indium is deposited, controlling the temperature in the range of 160 to 200 DEG C and controlling the pressure in the range of 1,000 to 2,000kPa, so that iron precipitates in the liquid obtained after the indium is deposited enter slags. The iron removed liquid obtained by the zinc hydrometallurgy production process has the iron content being lower than 1.2g / l, the iron removed liquid can be directly returned to be subjected to neutral leaching, and the system has stable production working conditions and is beneficial to stable production; in the iron slags obtained by the zinc hydrometallurgy production process, the zinc content is lower than 1 percent, the zinc loss is low and the zinc recovery rate is high; the iron slags can be directly sold to a cement plant and an iron and steel plant to be used as the raw materials without being stacked in a slag field, so that the zinc hydrometallurgy production process is beneficial to environmental-protection and the comprehensive utilization of resources and mineral resources are saved.
Owner:广西华锡集团股份有限公司 +1
Method for continuously leaching sulfide ore by using synergy of autotrophic ore leaching bacteria and heterotrophic ore leaching bacteria
ActiveCN102329957AEliminate static clingImprove leaching efficiencyPregnant leach solutionSulfidation
The invention discloses a method for continuously leaching sulfide ore by using the synergy of autotrophic ore leaching bacteria and heterotrophic ore leaching bacteria, which comprises two main steps of preparing a compound ore leaching strain and leaching ore by using the compound strain. The step of preparing the compound ore leaching strain comprises the steps of selecting a strain, preparing a culture medium, compositely culturing the strain and domesticating the compound ore leaching strain. The step of leaching ore by using the compound strain comprises the steps of pretreating an ore sample, preparing an ore leaching culture medium, leaching the ore by using the compound ore leaching strain, selecting and adding semiconductor sulfide ore and extracting metals in the leaching liquids. In the method, the characteristic of the semiconductor sulfide ore to provide electrons to promote the ore leaching action of microbes in the electron transition process is utilized, so that the operating cost of the whole process is lowered, the ore leaching efficiency of the process is improved, and the method has broad application prospect in the field of metallurgy.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
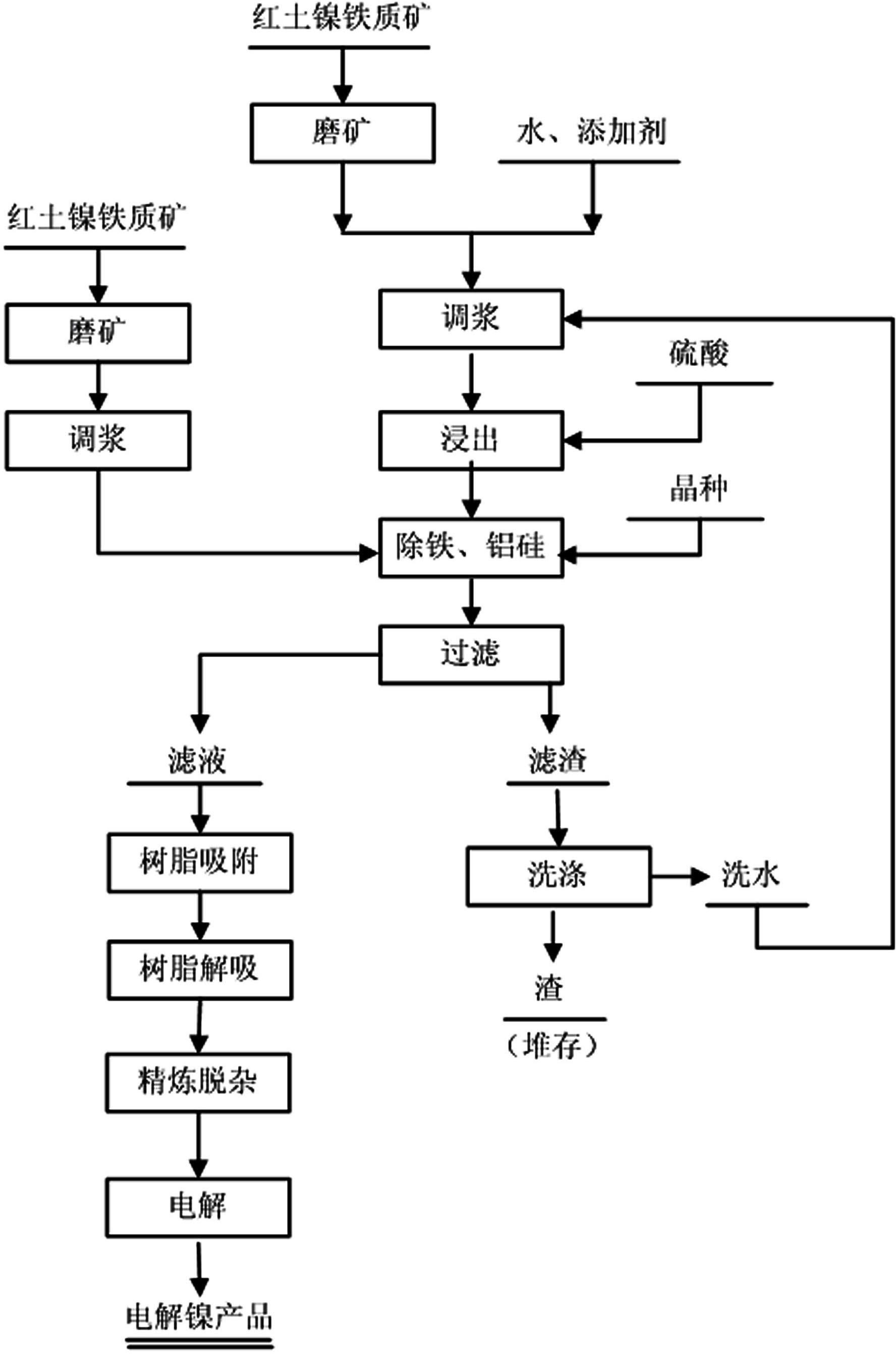
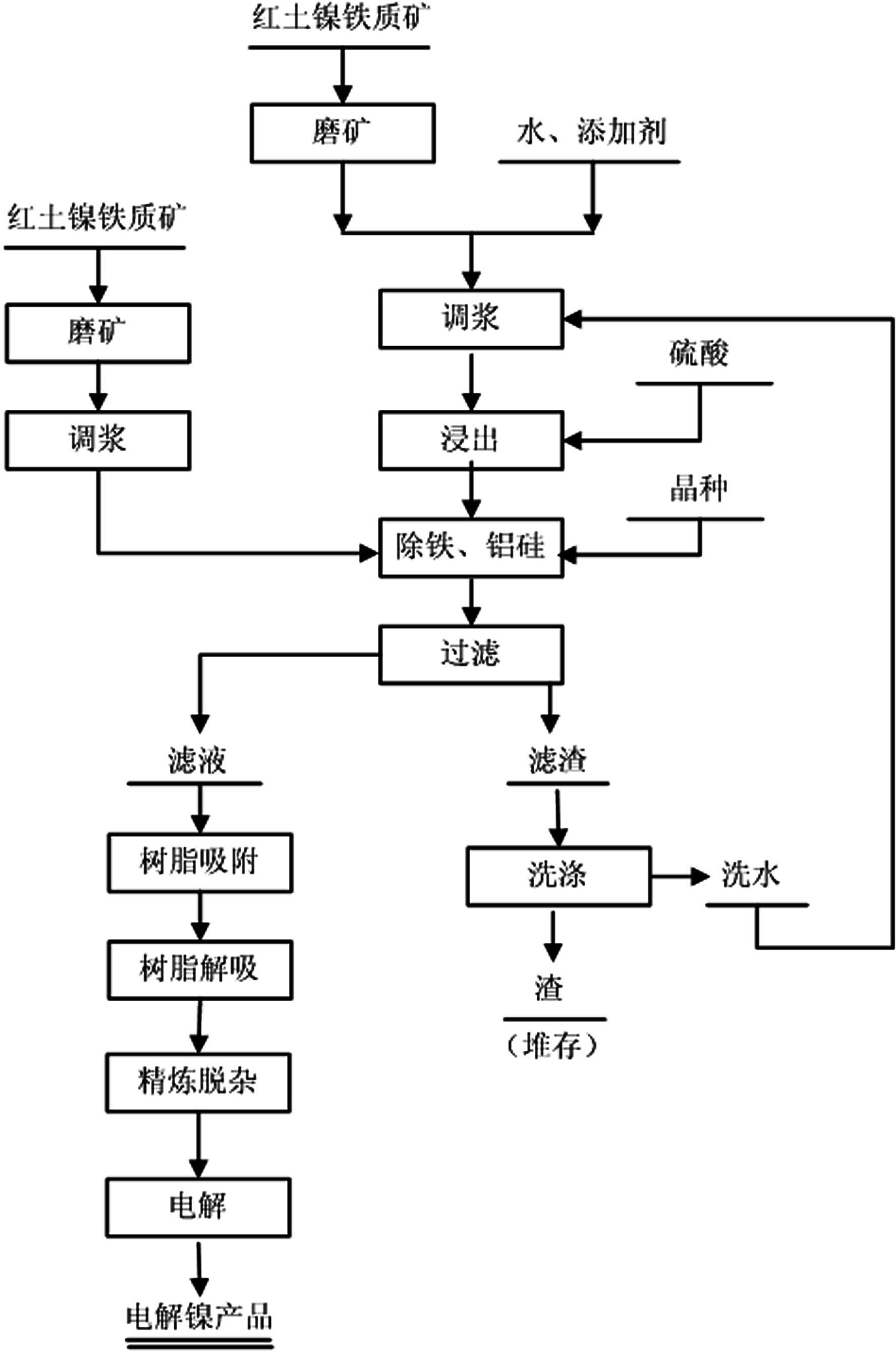
A kind of method of direct electrolysis of sulfuric acid leaching of laterite nickel ore
InactiveCN102286661AFully oxidizedEasy to leachPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisIon exchange
A method for directly electrolyzing laterite nickel ore with sulfuric acid leaching, the invention relates to a method for leaching low-grade laterite nickel ore with sulfuric acid at normal pressure, and belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy. The steps of the method are: separately grinding and pulping the iron ore and magnesia ore in the laterite nickel ore, leaching the iron ore with sulfuric acid under high acidity and high acid ore ratio, adding magnesia ore slurry to adjust the pH value to precipitate jarosite Alkaline neutralizer is added to the mother liquor to remove aluminum and silicon. The filtered leachate is used to absorb nickel ions with ion exchange resin. The electrolytic nickel product is produced by electrolysis, and the magnesium sulfate-containing solution after the ion exchange resin is added with calcium hydroxide to precipitate, and the magnesium and calcium are separated by carbonization to obtain magnesium carbonate. The present invention solves the disadvantages of long process flow, large amount of magnesium-containing wastewater and difficult treatment, and makes the magnesium open to become a product, and the wastewater can be directly discharged or reused, and at the same time, part of the recovered magnesium can be returned to the process for recycling. agent.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN GROUP HLDG
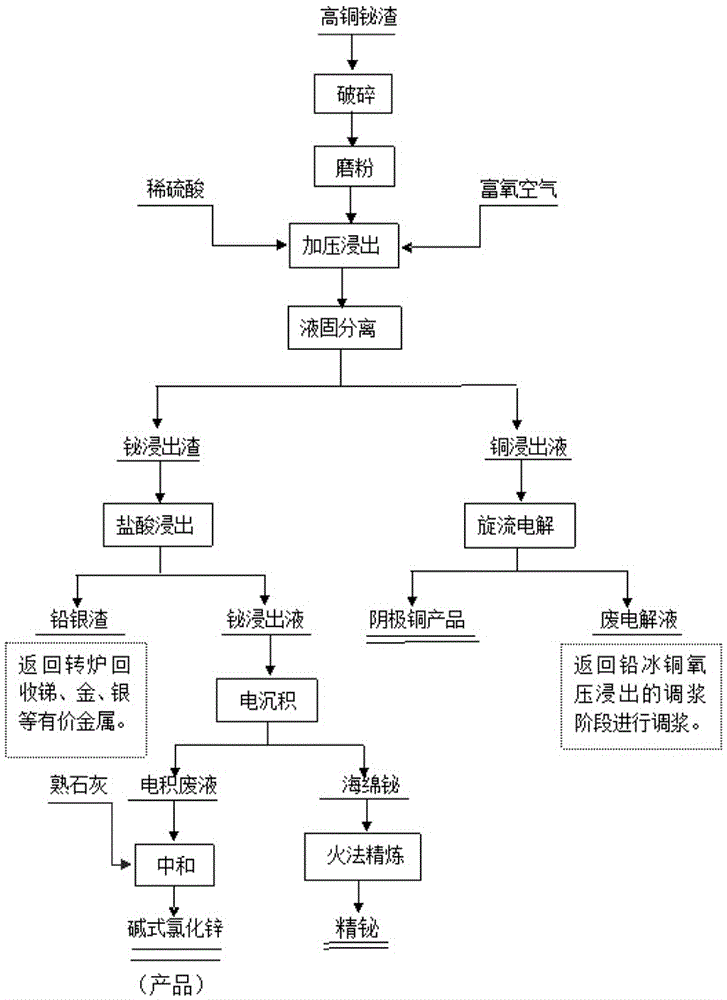
Method used for selective high-efficiency extraction of copper and bismuth from high-copper bismuth slag
InactiveCN106566928AStrong raw material adaptabilityEasy to operateProcess efficiency improvementBismuthPyrometallurgy
The invention discloses a method used for selective high-efficiency extraction of copper and bismuth from high-copper bismuth slag. According to the method, high-copper bismuth slag is taken as a raw material; high-copper bismuth slag powder obtained via smashing, grinding, and sieving and a sulfuric acid solution are subjected to size mixing at a certain ratio, and are delivered into a high-pressure autoclave; rich oxygen is introduced into the high-pressure autoclave, and oxygen pressure in the high-pressure autoclave is controlled for oxidizing leaching, wherein in the oxidizing leaching process, leaching of Cu in the form of Cu2+ is realized, and selective separation of copper with other non-zero valent elements is realized; a copper-containing leachate is subjected to acid adjusting, and is subjected to rotational flow electrolysis directly so as to extract copper in the copper-containing leachate and obtain copper products; a leaching residue is subjected to leaching separation of bismuth with concentrated hydrochloric acid, sponge bismuth is obtained via electro-deposition, and product refined bismuth is obtained via refining of sponge bismuth; and the rest slag is delivered into a lead pyrometallurgy system for comprehensive recycling of non-zero valent elements such as Pb, Ag, and Au. No environment pollution is caused by the method, no three wastes are discharged, and the method is a clean metallurgy technology.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
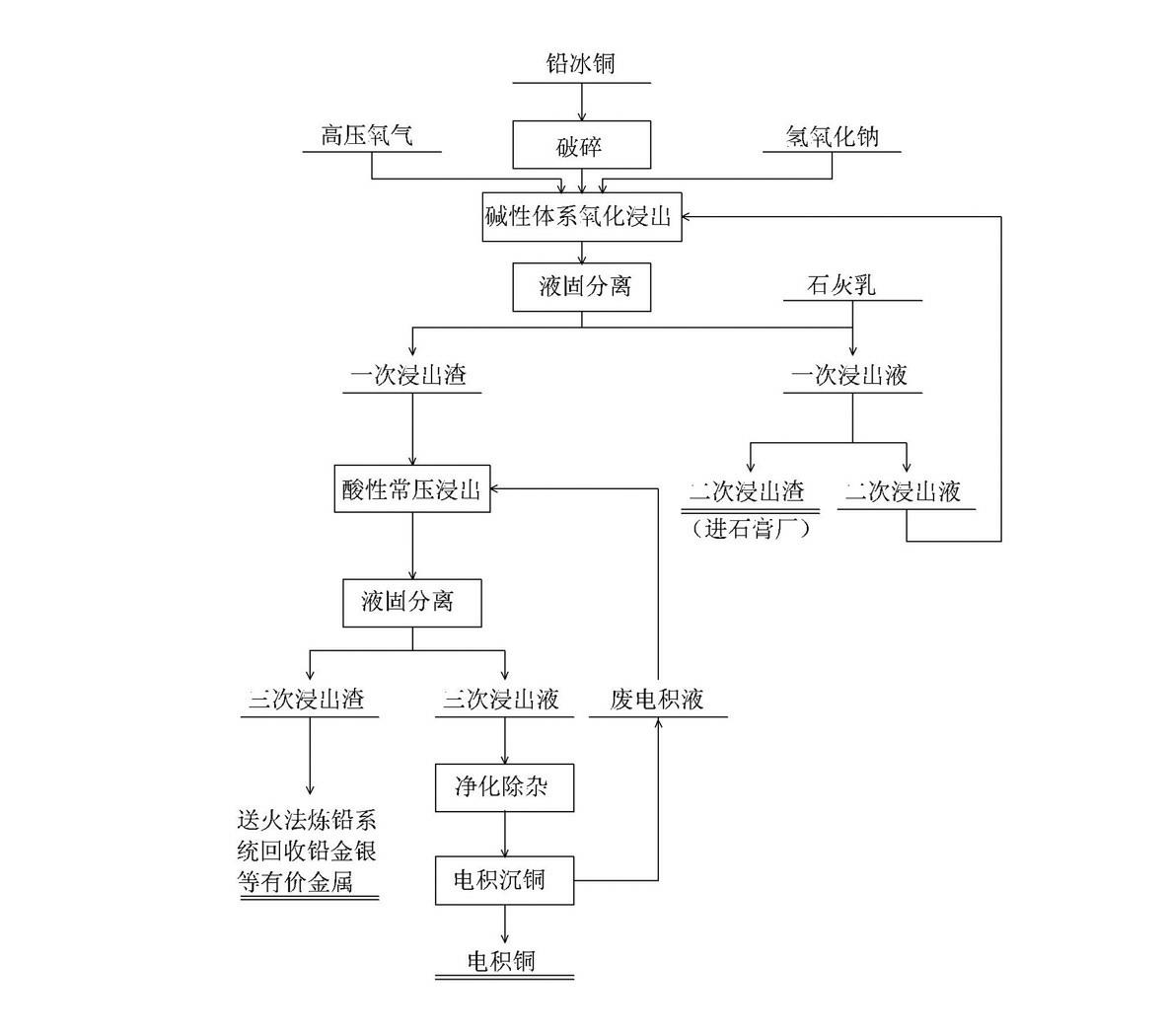
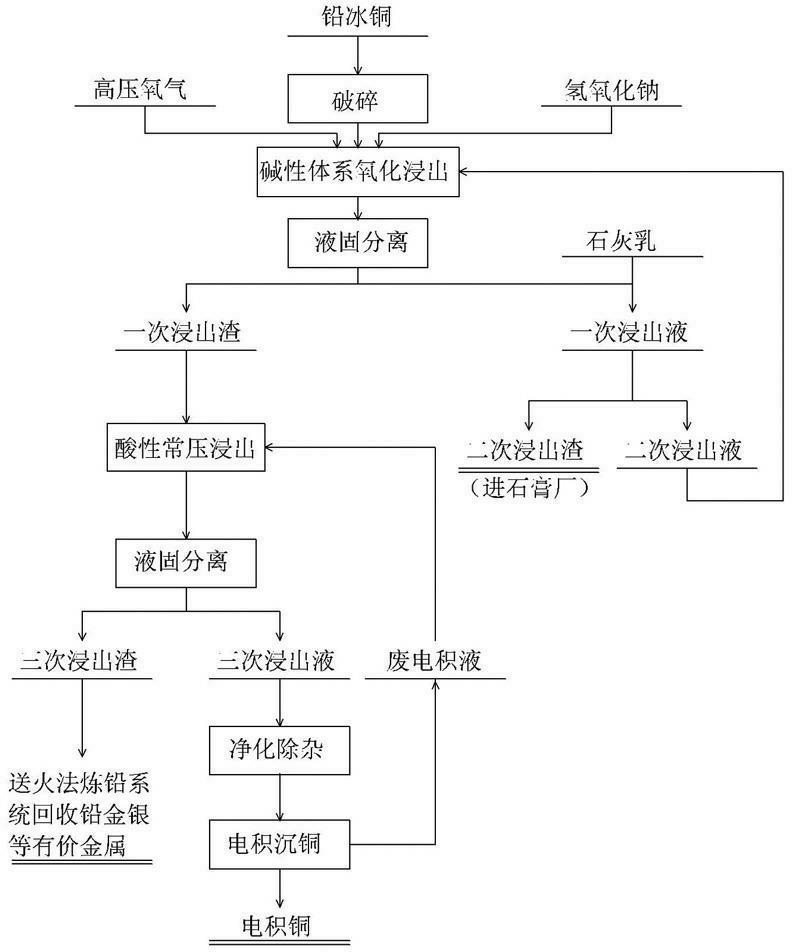
Process for recycling valuable metal from lead copper matte
ActiveCN102586600AHigh recovery rateHigh purityPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSulfateHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a process for recycling valuable metal from lead copper matte, which belongs to the field of nonferrous metallurgy hydrometallurgy. The process adopts pressurization oxidation leaching in an alkalic system to convent sulfur into sulfate to be desorbed, then atmospheric pressure copper leaching is performed through diluted acid, and copper electro-deposition is further performed through purification and impurity removal to obtain cathode copper. The process is a real metallurgy cleaning process, is low in requirement for corrosion resisting conditions of device material quality, basically free of sewage discharge, free of environment pollution, short in process flow, high in comprehensive recovery rate of metal and changeable in scale, and has the advantages of having strong practical applicability and adaptability to the scale and raw materials and the like.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Wet-method process for reclaiming zinc from zinc leaching residue
InactiveCN1837380AIncrease loadReduce the amount of acid used for leachingProcess efficiency improvementKeroseneSlag
This invention relates to wet process of recovering zinc from leach slag containing zinc. It belongs to a wet process for zinc ore, in particular to a process for slag containing zinc produced from the systerm of wet zinc metallurgy. This method comprises the following steps: washing residue with water or diluted acid to get slag, selecting P204 as extractant and coal oil as thinner to extract them to water phase, configuring the solution containing zinc and sulfuric acid, eluting the impurity loaded in organic phase, back extracting the load organic phase with depleted electrolyte and sulfuric acid, transferring zinc in organic phase to water phase, deoiling all water phases which contact with organic phase, finally, taking the liquid which has been back extracted as fresh liquid, and adding it into zinc electrodeposition systerm. The invention has high metal recovery ratio, and can recovery zinc from leach slag containing zinc, save resource, avoid environmental contamination. And it perfectly joins with the process of wet processing of zinc oxide ore, decreases the consumption of acid in the leaching of zinc oxide, and reduces the cost.
Owner:YUNNAN XIANGYUNFEILONG RESOURCES RECYCLING TECH CO LTD +1
Multisection acid leaching, multistage countercurrent washing and filter pressing integrated system and method
InactiveCN102071311AWater-soluble zinc content is reducedReduce environmental risksFiltration separationProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSlag
The invention relates to a multisection acid leaching, multistage countercurrent washing and filter pressing integrated system and method which are applicable to industries such as the metallic zinc electrolysis industry, hydrometallurgy and the like. The system provided by the invention comprises a membrane filter press, wherein the feed port end of the membrane filter press is connected with a zinc calcine acid leaching liquor feed pool, and the discharge port end of the membrane filter press is respectively connected with a filtrate pool and a collection liquor pool; and a waste electrodeposit liquor circulation pool, a circulation washing pool and a clean washing water pool are connected in parallel between the feed port end and discharge port end of the membrane filter press. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) feeding materials; (2) carrying out multisection acid leaching by using the waste electrodeposit liquor at different temperature gradients; (3) carrying out multistage countercurrent washing by using zinc-containing washing water of different concentrations; and (4) carrying out filter pressing on the filter cake. According to the invention, the content of water-soluble zinc (in terms of Zn) in zinc waste slag in the mainstream technique in metallic zinc electrolysis industry at present can be reduced from 3.5-6.0% to below 0.5%; and the acid leaching and washing efficiency are greatly enhanced, and the acid leaching recovery rate of zinc ore can be higher than 97%.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Penicillium, as well as preparation method and application
InactiveCN101434909AReach pollutionReduce pollutionFungiMicroorganism based processesEcological environmentPhosphate
The invention discloses a Penicillium, a preparation method and applications thereof, Penicillium fungus PSM11-5 is separated from a vanadium ore sample; insoluble tricalcium phosphate, sodium metavanadate, cobalt hydroxide and basic nickel carbonate are taken as indicating compounds; and a fungal strain is screened by testing the capability of decomposing the tricalcium phosphate, the sodium metavanadate, the cobalt hydroxide and the basic nickel carbonate. The Penicillium PSM11-5 is Penicillium sp.PSM11-5 CCTCCM208207. The strain is utilized for carrying out biological leaching of phosphorus and biological metallurgy, metals of phosphorus, vanadium, nickel, cobalt and the like are leached from lean ores, discarded ores, submarginal ores, difficult-to-mine ores, difficult dressing ores and refractory ores, thereby fully utilizing the mineral resources, reducing the metallurgical costs and protecting the ecological environment. The PSM11-5 is utilized for leaching the phosphorus from low-grade phosphate rock powder, a biological fertilizer is prepared to be applied to the soil, thereby leading the soil to contain higher content of soluble phosphorus which can be utilized by crops; the strain further leaches insoluble phosphorus which is deposited in the soil before, thereby reducing phosphorus fertilizer and reducing gas pollution caused by the phosphorus fertilizer and water pollution caused by the phosphorus fertilizer.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Technology for recovering metallic copper from high-lead copper matte
ActiveCN102994747ANo external emissionsHigh recovery ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a technology for recovering metallic copper from high-lead copper matte, and belongs to the nonferrous metallurgy and wet metallurgy fields. The technology comprises the following steps: breaking and grinding high-lead copper matte to below 100 meshes, mixing the ground high-lead copper matte with an ammonium carbonate solution to prepare a pulp, adding a proper amount of ammonia water, and pre-leaching under a controlled pH value condition; pumping the ore pulp obtained after the above reaction into an autoclave, and adjusting the liquid-solid ratio to 6-10:1; letting in ammonia and high-pressure oxygen, and controlling the oxygen pressure between 0.1MPa and 1.2MPa and the total pressure between 1.0MPa and 3.7MPa; carrying out high-pressure ammonia system oxidizing leaching at a leaching temperature of 160-240DEG C; carrying out liquid-solid separation, and allowing the obtained solution to undergo ammonia steaming in order to recover ammonia and carbon dioxide; floating the obtained filter residues to recover lead sulfate; and sending the precipitate obtained after the ammonia steaming operation to a solution tank, carrying out dilute acid leaching treatment to recover copper sulfate in the precipitate, purifying to remove impurities, sending to an electro-deposition system, and recovering to obtain a product cathode copper.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
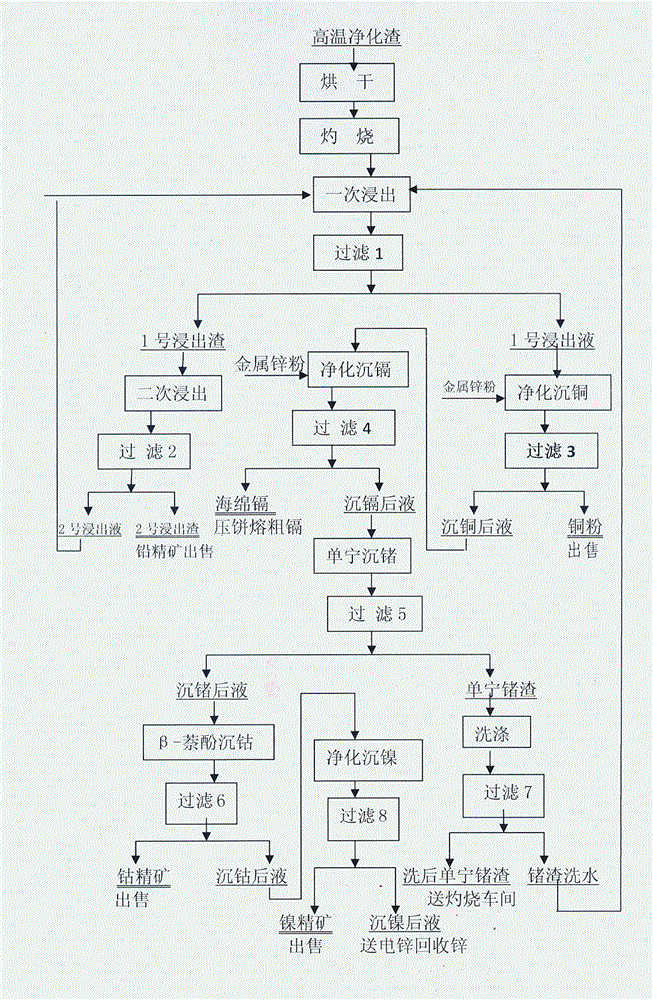
Method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from zinc hydrometallurgy high-temperature purification slags
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from zinc hydrometallurgy high-temperature purification slags. The method comprises the following steps: (1) drying and firing of the high-temperature purification slags; (2) first leaching; (3) second leaching; (4) purification and deposition of copper; (5) purification and deposition of cadmium; (6) deposition of tannin germanium; (7) deposition of cobalt; and (8) deposition of nickel and recovery of zinc by returning liquid obtained by deposition of nickel to a zinc hydrometallurgy system. The invention provides a method for leaching the zinc hydrometallurgy high-temperature purification slags twice after drying and firing to obtain the produced leaching slags, namely silver lead ore concentrate for sales, and comprehensively recovering copper, cadmium, germanium, cobalt, nickel and zinc from filtering liquid subjected to first leaching; the method is easy to carry out and simple in process; the recovery rate of the valuable metals is high, as the recovery rate of lead, silver, copper, cadmium, germanium, cobalt, nickel and zinc respectively reaches 98.50-99.50 percent, 99.10-99.70 percent, 94.40-97.80 percent, 95.10-96.90 percent, 93.50-96.70 percent, 94.70-95.70 percent, 94.80-96.80 percent, and 96.00-97.00 percent; moreover, the recovery of the valuable metals is more comprehensive, scientific and reasonable; waste water, waste gas and waste slags are avoided, and the requirement on national circular economy and sustainable development is met.
Owner:YUNNAN LUOPING ZINC & ELECTRICITY
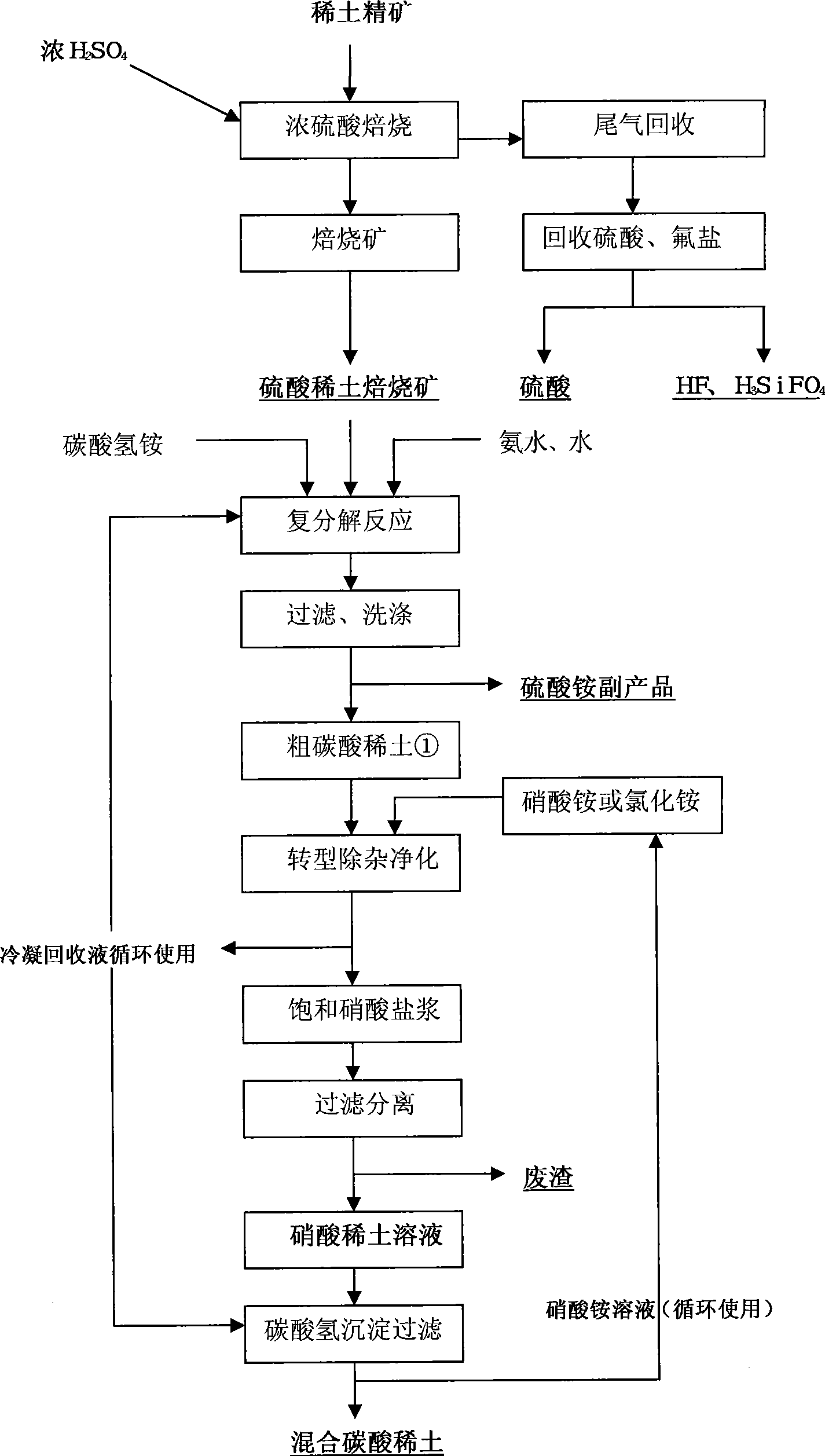
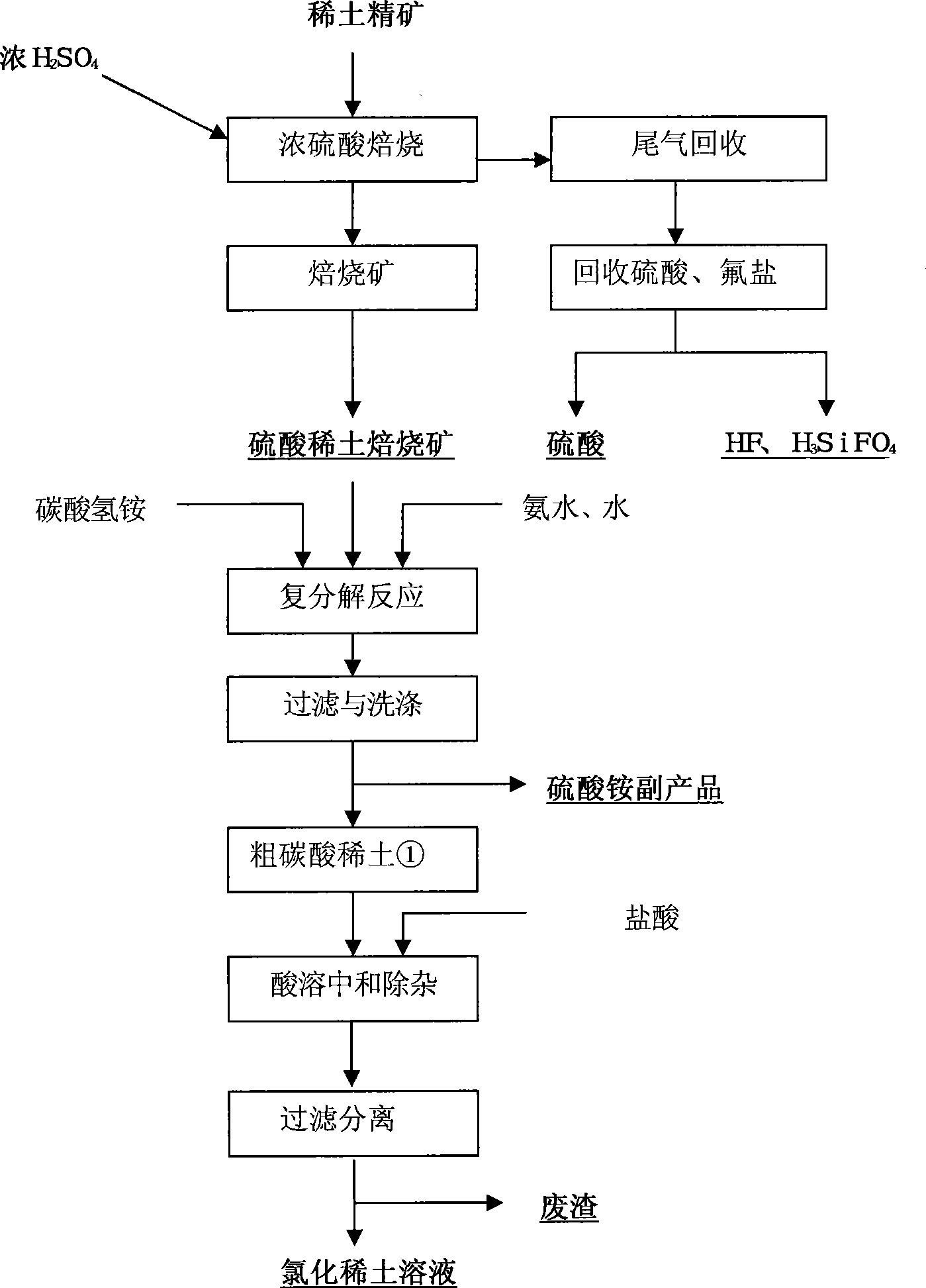
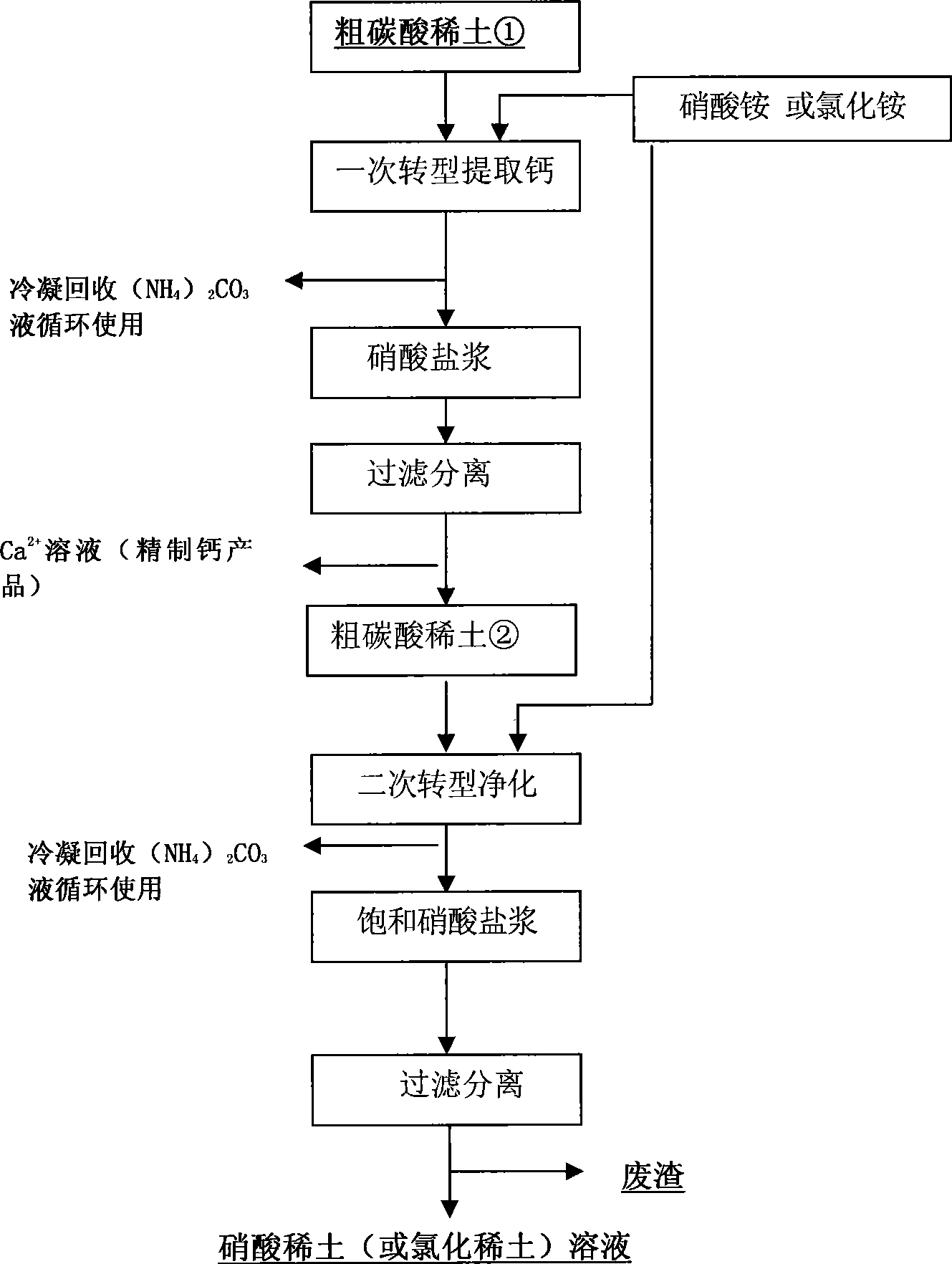
Cleaning production technique for directly transforming rare earth sulfate bake ore to extract rare earth
The invention belongs to the field of rare earth wet metallurgy and industrial chemistry, and relates to a clean production technology for roasting rare earth concentration to leach rare earth by the sulphate method. Aiming at the prior roasting production technology by the sulphate method taking Baotou rare earth concentration as raw materials, the technological process of the clean production technology realizes direct transformation production from sulphate to carbonate by the transformation technology of double decomposition reaction in chemical process and according to the principle of mutual transformation between solid substances with different solubility products. Non-rare-earth compounds (such as ammonium sulphate and ammonium carbonate) and the like are fully recovered with low cost; simultaneously, water can be fully recycled and used; the intermediate impurity removing technology is adopted to recover non-rare-earth substances such as Ca from rare earth ore. Therefore, the purpose of full-recycling and clean production in rare earth leaching process by the sulphate roasting method is realized. The technology has the advantages that the production process of rare earth ore sulphate method fully recovers rare earth elements and valuable elements from mineral products with lower cost, and clean production without sewage emission is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for producing ultrawhite aluminum hydroxide and by-products from high-alumina fly ash by using high-temperature alkaline leaching
ActiveCN103172095AImprove use valueAvoid the problem that the firing temperature is difficult to controlAluminium oxides/hydroxidesAluminium hydroxideWollastonite
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy and in particular relates to a method for producing ultrawhite aluminum hydroxide and by-products from high-alumina fly ash by using high-temperature alkaline leaching. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out two-stage pre-desilicication on the high-alumina fly ash, and then carrying out leaching reaction for 1.5-2.5 hours at 230-280 DEG C to respectively produce the ultrawhite hydroxide as well as wollastonite and ferrugination hydrogarnet as by-products. According to the method, a high-temperature sintering process in which low alumina-silica ratio firing temperature is difficult to control in the process of extracting aluminum hydroxide from the high-alumina fly ash is avoided, the energy consumption is reduced, the comprehensive utilization value of the fly ash is improved, and meanwhile, products in each link can be recycled in each procedure; and an economic and effective technical approach is provided for preparation of the ultrawhite aluminum hydroxide and alumina from the high-alumina fly ash.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV ENG & RES INST CO LTD
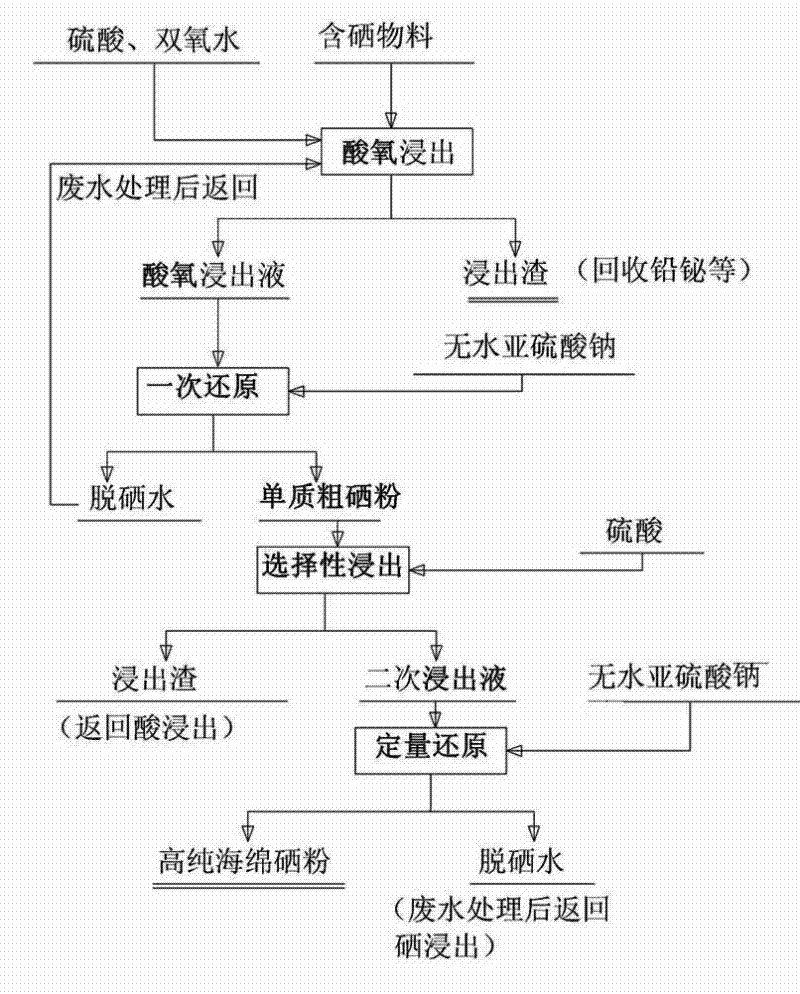
Technology for extracting selenium from low-grade selenium-containing material
ActiveCN102363522AWide variety of sourcesNothing producedElemental selenium/telluriumSulfite saltSulfate
The invention discloses a technology for extracting selenium from a low-grade selenium-containing material, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy. According to the scheme, the technology comprises the following steps of: performing acid-oxygen leaching on the ground low-grade selenium-containing material with heating by using sulfuric acid and oxidant, wherein the selenium enters the acid-oxygen leachate in a form of selenium sulfate; filtering the acid-oxygen leachate, adding anhydrous sodium sulfite into the acid-oxygen leachate, performing primary reduction, filtering after the reduction, and returning the selenium removed water to the acid-oxygen leaching; purifying the obtained elemental crude selenium powder containing certain impurities; performing selective leaching on the crude selenium powder by using 15 percent sulfuric acid solution; filtering, and quantitatively reducing the secondary leachate by using the anhydrous sodium sulfite to obtain sponge selenium; repeatedly cleaning the sponge selenium by using hot water, drying, and thus obtaining high-purity sponge selenium powder. The technology is not limited by the grade of a raw material, is suitable for treating various selenium-containing materials containing 3 to 10 percent of selenium, and is high in selenium recovery rate (reaching over 93 percent) and low in production cost; and the whole production process does not produce waste gas, most waste water can be recycled, and only a little waste water reaching the standard is discharged after being treated, so the technology has no pollution to the environment.
Owner:郴州雄风环保科技有限公司
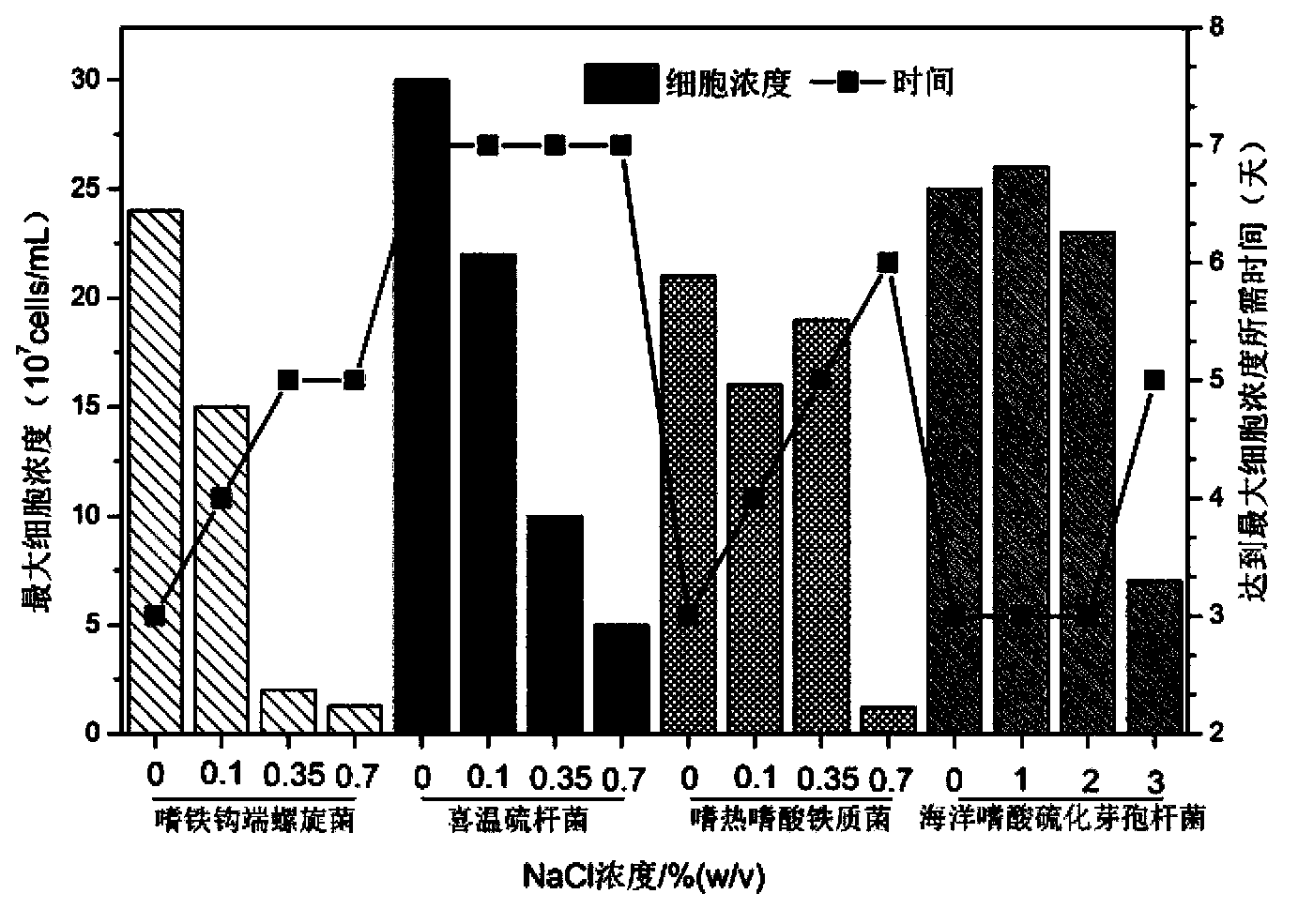
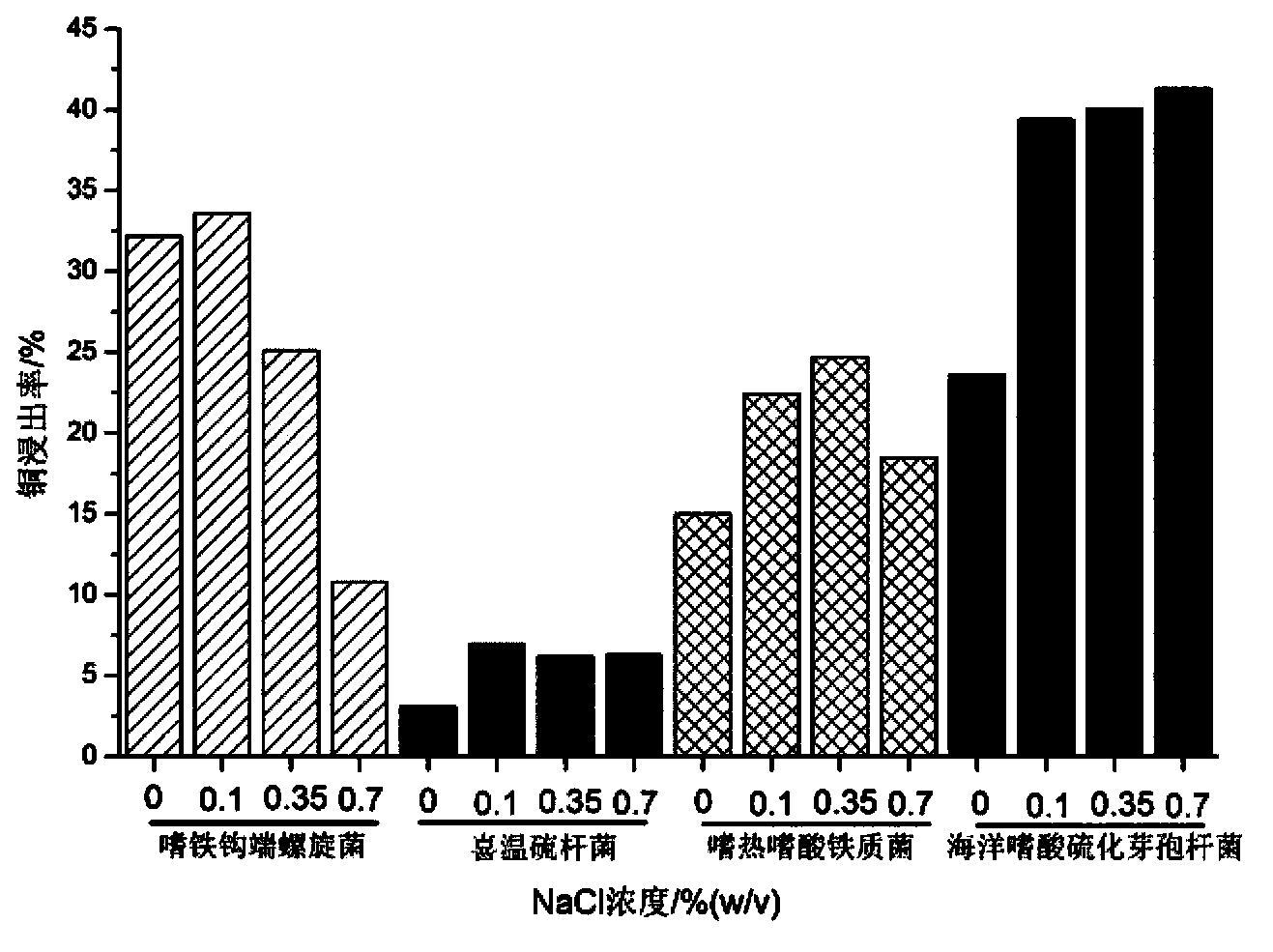
Compound bacterium community capable of efficiently leaching sulphide ore, and compounding method and application method thereof
ActiveCN103396964AIncrease resistanceImprove leaching efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical reactionEngineering
The invention discloses a compound bacterium community capable of efficiently leaching a sulphide ore, and a compounding method and an application method thereof, and belongs to the technical filed of wet-process metallurgy. Aiming at a biological leaching mechanism of the sulphide ore and the physiological-biochemical characteristics of microorganisms, a community capable of efficiently leaching the sulphide ore is compounded by a plurality of mineral leaching microorganisms, wherein the mineral leaching microorganisms comprise marine bacteria which come from deep-sea hydrothermal vents and are capable of enduring high concentration sodium chloride, sulfur-oxidized bacteria, iron-oxidized bacteria and archaea which are from a freshwater environment, autotrophic bacteria and facultative heterotrophic bacteria. Not only can the difficult problem that the mineral leaching microorganisms from the freshwater environment are intolerance of sodium chloride be solved, but also microorganisms required by oxidation and dissolution of the sulphide ore and diversity of chemical reactions are guaranteed. The compound bacterium community can obviously increase leaching efficiency and leaching rate of the sulphide ore such as copper pyrites and can be applied in a leaching process and a dump leaching process of a stirring tank. A certain basis for popularization and application of biological metallurgy of the sulphide ore is provided by the invention.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Method for recycling precious metals from stainless steel acid pickling sludge
InactiveCN103695655AIncrease added valueRealize economic valueProcess efficiency improvementCopper sulfateMaterials science
The invention provides a method for recycling precious metals from stainless steel acid pickling sludge, belonging to the field of non-ferrous metallurgy and waste utilization. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) thickening and filter pressing; 2) leaching; 3) iron removal and filter pressing; 4) P204 extraction: filtering and clarifying the mother liquid and feeding into a P204 extraction box; performing continuous saponification and counter-current extraction, and separating out an organic phase A and a filtrate A; extracting to remove impurity elements such as Zn, Cu, Mn, Ca and the like; 5) P507 extraction: feeding the filtrate A separated by the step 4) into a P507 extraction box, performing continuous saponification and counter-current extraction in the extraction box at room temperature, and separating out an organic phase B and a filtrate B; performing reverse extraction of the organic phase B by use of dilute hydrochloric acid to obtain a high-purity cobalt chloride solution, and enriching nickel in the filtrate B by use of dilute sulphuric acid to obtain a high-purity high-concentration nickel sulfate solution. The method provided by the invention finally obtains products such as copper sulfate, nickel sulfate, high-purity nickel, cobalt oxalate and the like, realizes resource recycling of precious metals in sludge, and has the comprehensive benefits of economic benefits, environmental benefits and social benefits.
Owner:王洪
Wet method smelting process of high silicon zinc oxide crude ore
InactiveCN101418377AEfficient use ofComplex compositionZinc oxides/hydroxidesCopper oxychloridesFlocculationSmelting process
The invention relates to a wet method smelting process for high silicon zinc oxide crude ore. The invention belongs to the field of wet method smelting, and provides a method for the direct leaching of high silicon, high-ferro zinc oxide crude ore. The method comprises the following steps: firstly the high silicon, high ferro zinc oxide crude ore is crushed and undergoes the wet mode ball milling and the acid leaching through the discarded electrolyte used in a zinc hydrometallurgy process; according to the content of ferrous iron ions during the acid leaching, potassium permanganate and / or manganese dioxide are / is added in an extracting stage; the dosage of the potassium permanganate and / or manganese dioxide is controlled 1 to 10 percent of the total weight of the ore; during the leaching, the temperature is controlled 40 to 90 DEG C, and the acidity pH value is 0.5 to 5.2; and a flocculant is added into the leached ore pulp for flocculation and concentration. According to the invention, the direct leaching of the high silicon zinc oxide ore can avoid the formation of silica sol, thereby effectively utilizing the high silicon zinc oxide ore resources. Compared with other high silicon ore treatment processes, the process has the advantages of low acid consumption, low production cost, simple technology, and the like.
Owner:云南金鼎锌业有限公司
Synergistic leaching-copper arsenate removing method for leaching residues in high-iron zinc calcine and high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate
InactiveCN103789544AHigh recovery rateEfficient reductionProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgyCopper sulfate
The invention belongs to the field of wet metallurgy of zinc, and particularly relates to a synergistic leaching-copper arsenate removing method for leaching residues in high-iron zinc calcine and high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the leaching residues in the high-iron zinc calcine with the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate; mixing zinc electrowinning waste liquor and a part of sulfuric acid-containing solution prepared from concentrated sulfuric acid and synergistically leaching; adding a reaction dosage of industrial iron powder into a synergistically-leached copper arsenate-removing primary solution; replenishing a proper amount of copper sulfate as required; reacting; performing liquid-solid separation on reaction ore pulp to obtain cuprous arsenide precipitate serving as a copper-leaching raw material and a copper arsenate-removing secondary solution; returning the copper arsenate-removing secondary solution to a zinc hydrometallurgy process to further recover valuable metals therein. The method is clean and efficient, efficient leaching of copper and efficient reduction of Fe<3+> can be realized, the solution treatment amount is small, the comprehensive recovery rate of valuable metals in a zinc hydrometallurgy process is increased comprehensively, and the smelting flow is simplified.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH TECH IND SALES MANAGEMENT +1
Method for extracting zinc from non-ferrous metal waste residue
InactiveCN102776384AAchieve recyclingGreat tasteProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmental engineeringPyrometallurgy
The invention discloses a method for extracting zinc from non-ferrous metal waste residue. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of pyrometallurgy, acid leaching, zinc depositing, reduction smelting and the like. Firstly, a fire system is utilized to obtain smoke phase secondary zinc oxide products under specific smelting conditions to enable the zinc in the non-ferrous metal waste residue to enter a secondary zinc oxide phase as far as possible, so that good raw material foundation is laid for improving zinc quality; secondly, according to characteristics of the metal zinc, a wet process is utilized to recover the zinc under a certain process condition; and finally, the reduction smelting is performed on the obtained crude zinc to obtain refined zinc. By utilizing a fire-wet combination process to recover the zinc, the recovery rate of the zinc is high, the zinc quality is good, and cyclic utilization of the waste residue is achieved. The existing resources are further recovered, and pollution of the valuable metal to the environment is avoided, so that the method is safe and environment-friendly. Besides, the method is simple in principle, reasonable in flow path and low in cost.
Owner:HANYUAN GUANGCHAO NON FERROUS METALS COMPREHENSIVE RECOVER
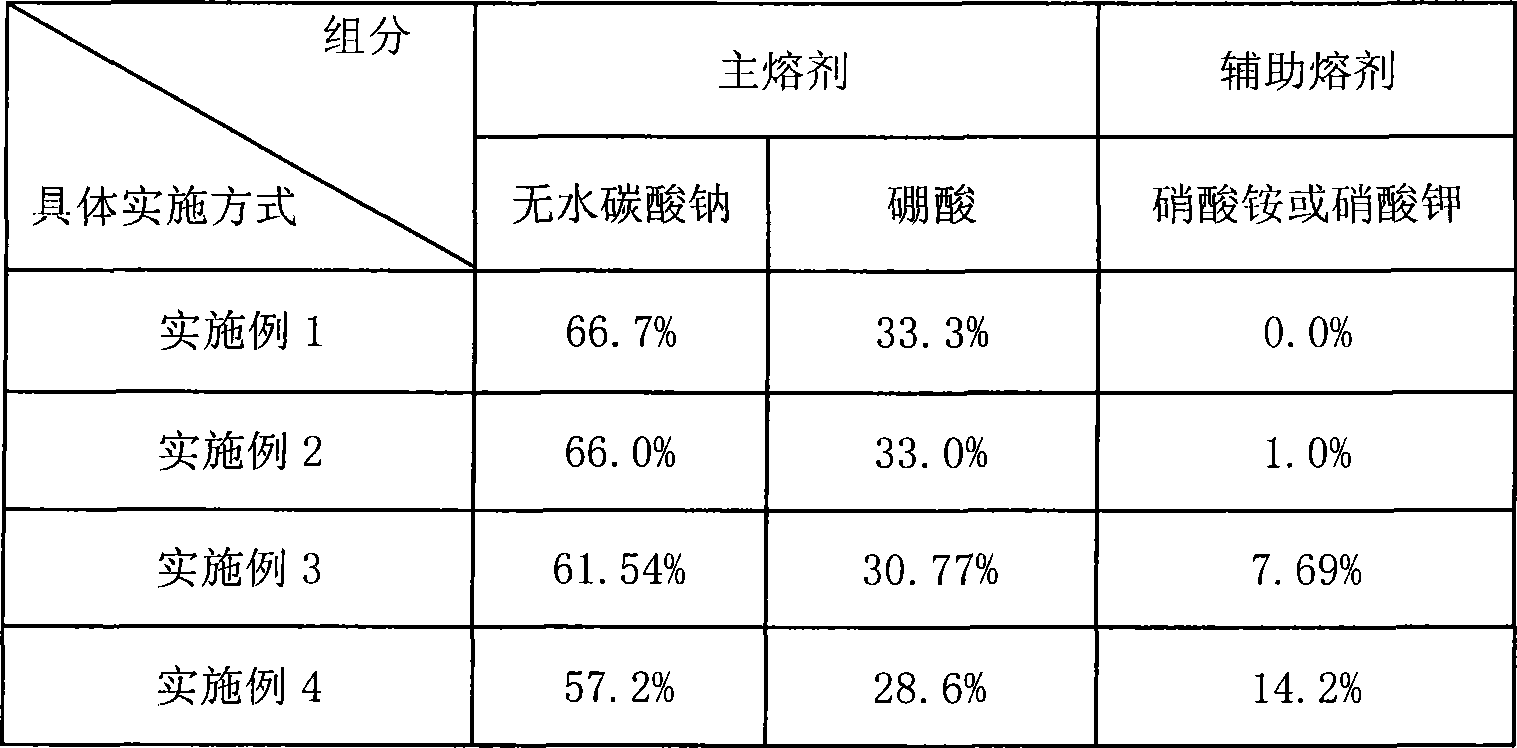
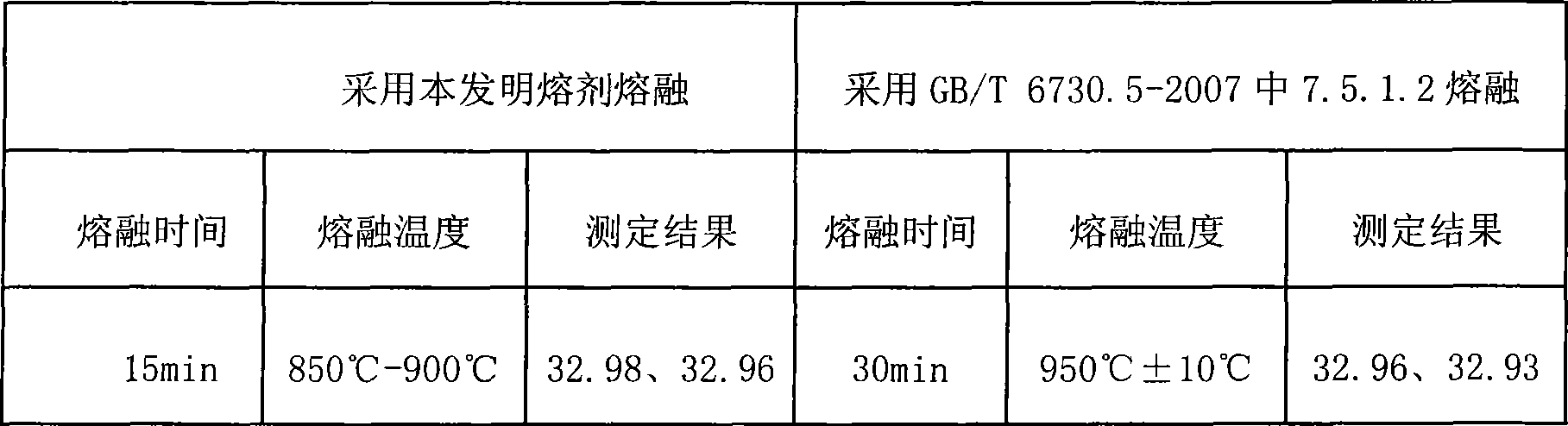
Fusion metallurgy sample analysis fusing agent and its preparation and use method
InactiveCN101368886ALess materialEasy to preparePreparing sample for investigationDecompositionMagnetite
The invention discloses an analysis fluxing agent for melting metallurgical samples, and a preparation and using method thereof; the analysis fluxing agent is prepared with a main fluxing agent and an auxiliary fluxing agent, wherein, the contents of anhydrous sodium carbonate and boric acid reach 85.80% to 100%; the content of the auxiliary flux agent nitrate ammonium or potassium nitrate is 0 to 14.20%; the invention can be used to melt and decompose vanadium-titanium magnetite, vanadium-titanium-bearing slag, high-titanium slag, metallurgical auxiliary material, refractory material, vanadium slag, non-ferrous metal ores and other metallurgical samples; the flux agent of the invention has the advantages of less material adoption, simple preparation method, low cost, simple operation, short melting time, as well as good melting and decomposition effect; the melted samples are of easy acid leaching and decomposition, wide application and convenient using.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +2
Gas-filling temperature-raising leaching tank
ActiveCN102836661AIncrease feed depthImprove impact performanceTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersEnvironmental engineeringHydrometallurgy
The invention discloses a gas-filling temperature-raising leaching tank, and relates to improvement of a leaching tank structure during gas-filling and leaching process of hydrometallurgy. The leaching tank is characterized in that a feed pipe of the leaching tank is opposite to middle portions of stirring blades, a stirring device on a stirring shaft comprises an upper layer and a lower layer of the stirring blades and stirring paddles, a structure of a chlorine gas feed device comprises a chlorine gas inlet pipe and a communicating pipe of an outer pipe, the communicating pipe is in shape like a Chinese character 'bo', the stirring shaft is arranged deviating from the perpendicular axis of the leaching tank, and the structure of a heating gas inlet pipe comprises inner layer titanium steel, a stainless steel pipe layer wrapped outside the inner layer titanium steel, and a rubber pipe layer wrapped outside the stainless steel pipe. The leaching tank can effectively improves anti-swing intensity, prevents a heating shaft from being broken, is long in period, improves safety of operation equipment, effectively ensures leaching temperatures of materials, improves dissolving velocity of the solid particles, accelerates leaching reaction, prolongs use period by 20 times, and is safe and reliable.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Nickel-cobalt precipitation method for hydrometallurgy of lateritic nickel ore
The invention provides a nickel-cobalt precipitation method for hydrometallurgy of lateritic nickel ore. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, the lateritic nickel ore is subjected to acid leaching, and a nickel-cobalt-containing acid leachate is obtained and contains magnesium ions; step 2, the nickel-cobalt-containing acid leachate is subjected to a precipitation reaction, fresh nickel-cobalt-containing acid leachate and a precipitant are added continuously in the precipitation reaction process, and a nickel-cobalt precipitate is obtained; step 3, the nickel-cobalt precipitate is subjected to thickness separation, and nickel-cobalt precipitate underflow is obtained; the nickel-cobalt precipitate underflow is divided into a first part and a second part; step 4, the first part of the nickel-cobalt precipitate underflow is mixed with lime milk, and mixed ore pulp is formed and returned to the step 2 to serve as at least part of the precipitant; the second part of the nickel-cobalt precipitate underflow is subjected to calcium-nickel separation, and nickel cobalt hydroxide is obtained. According to the method, the precipitation performance of nickel cobalt hydroxide is better, thickness separation speed and thick underflow solid content can be increased, and the water content of the nickel cobalt hydroxide product is reduced.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
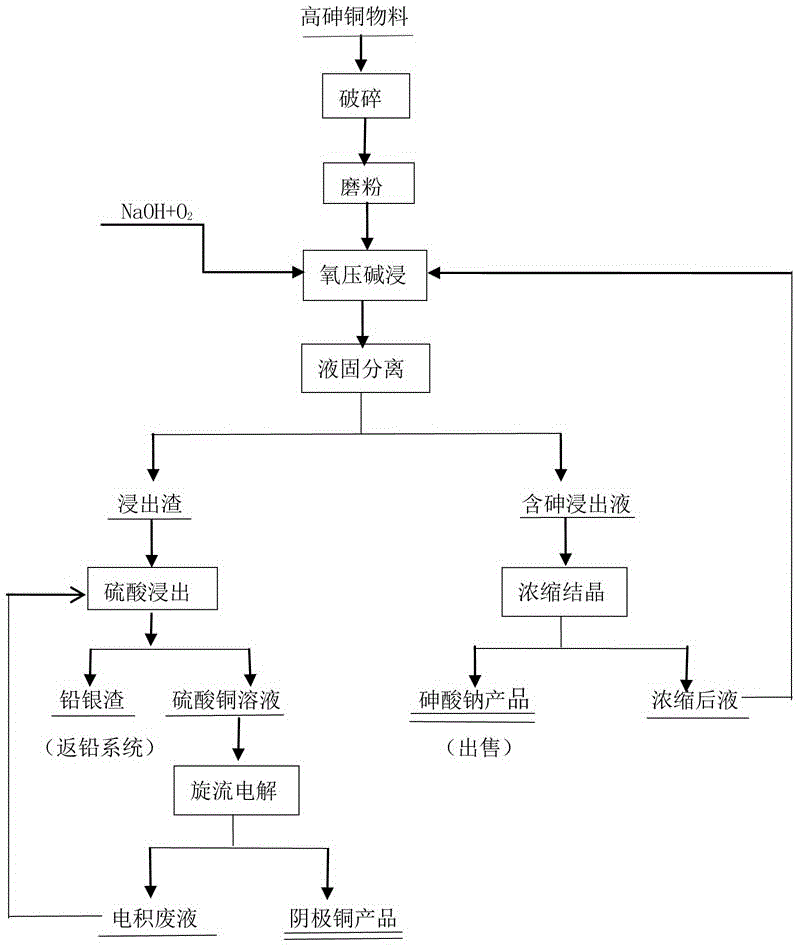
Technology for treating high-arsenic copper material
ActiveCN106555058AEnvironmental pollutionNo pollution to the environmentPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisCopper sulfate
The invention discloses a technology for treating a high-arsenic copper material. The technology comprises the steps that the high-arsenic copper material is subjected to crushing, grinding, sodium hydroxide mixing and oxidizing leaching, copper in the high-arsenic copper material is oxidized and left in residues in a residual mode along with lead and noble metal of gold, silver and platinum, arsenic enters a solution in a sodium arsenate mode, leachate is subjected to concentration and crystallization, a sodium arsenate product is obtained, and a concentrated solution returns to be subject to oxygen-pressure alkali leaching; leached residues are subjected to sulfuric-acid atmospheric pressure leaching, copper enters the solution in a copper sulfate mode, acid adjustment is conducted, and vortex electrolysis is directly conducted for extracting copper; electrodeposited waste liquid is recycled; and lead and the noble metal enter lead and silver residues, and valuable elements of Pb, Ag and Au are comprehensively recycled. The technology belongs to a clean metallurgy process, is low in equipment corrosion-resistant requirement, free of pollution to environment, easy to operate and high in comprehensive recycling degree of metal and has the advantages of being higher in practicability and adaptability to raw materials and the like.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
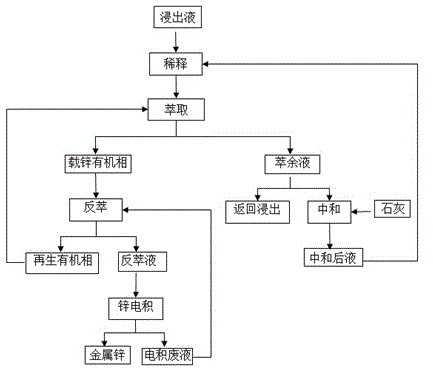
Method for extracting zinc from low-grade zinc-containing material leaching liquid
ActiveCN104531995AEfficient extraction and recoverySolve the problem of incomplete extractionProcess efficiency improvementSulfate zincPregnant leach solution
The invention relates to a method for extracting zinc from a low-grade zinc-containing material leaching liquid and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy. According to the method, di(2-ethylhexyl phosphoric acid) and No. 260 aviation kerosene constitute an extraction organic phase, Zn<2+> is extracted from the low-grade zinc-containing material leaching liquid, reverse extraction is performed with zinc electrodeposition waste liquid and thus the recovery of zinc in the leaching liquid can be effectively achieved. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of firstly preparing a zinc sulfate solution with a certain concentration according to the concentration of zinc in the leaching liquid and the extraction effect of the used extractant, diluting the leaching liquid with the zinc sulfate solution and extracting the diluted solution so that all zinc in the leaching liquid is enriched into the organic phase; returning a part of raffinate for extracting and neutralizing a part of raffinate with lime and recycling for dilution. By the steps of diluting, extracting, neutralizing and recycling, Zn<2+> can be efficiently extracted and enriched and the extraction recovery rate of zinc in the leaching liquid reaches above 98%.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
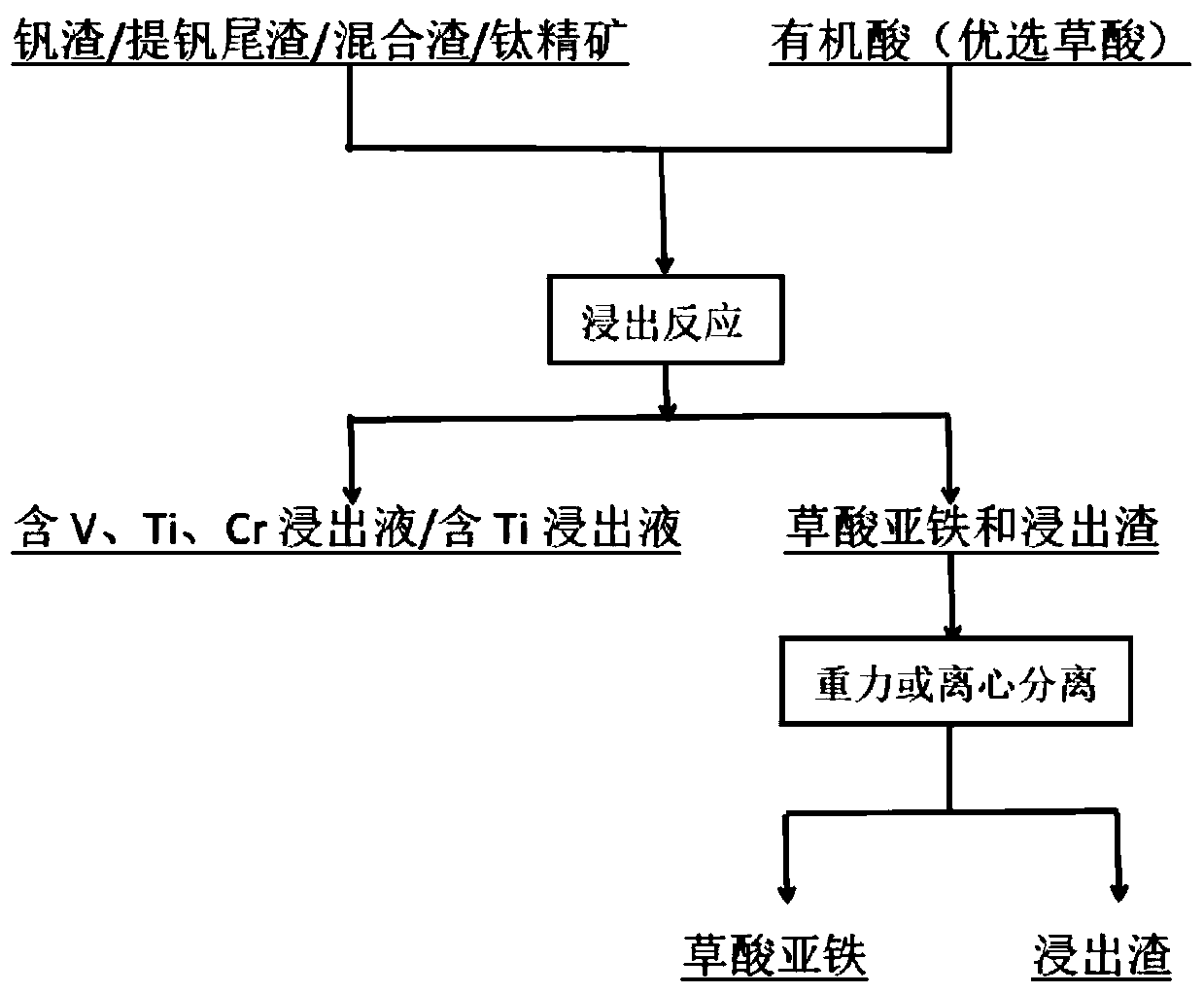
Method for leaching vanadium, titanium and chromium from vanadium, titanium and chromium raw materials by hydrothermal organic acid
ActiveCN111041200AEfficient leachingIncrease added valueProcess efficiency improvementSlagIron(II) oxalate
The invention provides a method for leaching vanadium, titanium and chromium from vanadium, titanium and chromium raw materials by hydrothermal organic acid, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy. The method comprises the steps that vanadium slag, extracted vanadium tailings, vanadium slag-extracted vanadium tailing mixed slag and titanium concentrate are used as raw materials, and organic acid is used as a leaching agent for hydrothermal reaction in a reactor. The vanadium slag, the extracted vanadium tailings and the vanadium slag-extracted vanadium tailing mixed slag are correspondingly leached by the organic acid to obtain an element solution containing vanadium, titanium and chromium and ferrous oxalate; and the titanium concentrate is leached by the organic acid to obtaina solution contacting titanium and ferrous oxalate. According to the method, the acidity and the high complexing ability of the organic acid are utilized to destroy a phase containing vanadium, titanium and chromium, the complex reaction is generated to form a complex ion solution of [V(C2O4)3]3-, [Ti(C2O4)3]3- and [Cr(C2O4)3]3-, and the efficient leaching of vanadium, titanium and chromium elements is achieved; in addition, the method is simple in process and environment-friendly; the added value of the ferrous oxalate is high; and used equipment is common, the energy consumption is low, anda good application prospect is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
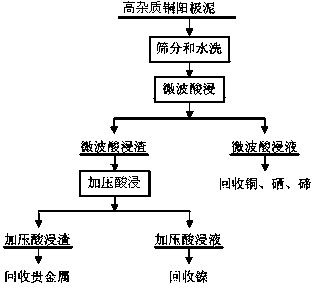
Method for pre-treating high-impurity copper anode slime rich in noble metals
ActiveCN103509953ASimple purification processHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementSeleniumCopper
The invention belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy of non-ferrous metals, and particularly relates to a method for pre-treating high-impurity copper anode slime rich in noble metals. The method comprises the following special steps: adding sulfuric acid in the dried copper anode slime to mix size, placing in a microwave reactor, carrying out the microwave acid leaching for 5-30 min, performing the solid-liquid separation to obtain microwave acid leaching slag and a microwave acid leaching solution, adding dilute sulphuric acid in the microwave acid leaching slag to mix size, placing the microwave acid leaching sizing agent in a high-pressure reaction kettle under the pressure of 0.8-1.2 MPa after oxygen introducing, carrying out pressure acid leaching for 4-6 h to obtain pressure acid leaching slag and a pressure acid leaching solution, recovering gold and silver from the pressure acid leaching slag, and recovering nickel from the pressure acid leaching solution. The method adopting the technical scheme improves the recovery rate of copper, selenium, tellurium and nickel in the impurity copper anode slime, shortens the processing time of the copper anode slime, increases the processing capacity of the copper anode slime, enables the trend of the noble metals to be reasonable and concentrated, and is favorable for comprehensive recovery.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Treatment technique of copper-containing high-indium high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate
ActiveCN104745810AHigh recovery rateHigh enrichment ratioPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionIndium
The invention provides a treatment technique of a copper-containing high-indium high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate, relating to a slag / ore synergic leaching-combined iron precipitation technique of a copper-containing high-indium high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate. The technique comprises the following steps: (1) roasting the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate in a fluidized bed furnace to obtain high-iron zinc calcine; (2) carrying out neutralizing hydrolysis on the high-iron zinc calcine and a zinc-hydrometallurgy electrolysis waste liquid for impurity removal to generate a medium immersion liquid and medium immersion slag; (3) mixing the medium immersion slag with high-iron zinc calcine and a weak acid solution to generate a weak acid solution and weak acid slag; (4) mixing the weak acid slag with the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate and a strong acid solution to perform slag-ore synergic leaching to generate a synergic leach solution and synergic leach slag; (5) carrying out strong acid leaching on the synergic leach slag to generate a strong acid solution and strong acid slag; (6) separating and recovering copper and indium from the synergic leach solution by a two-stage continuous replacement technique to generate copper-rich slag, indium-rich slag and an indium precipitation solution; and (7) carrying out high-temperature oxygen-pressure hydrothermal iron precipitation on the indium precipitation solution to obtain an iron precipitation solution and recoverable iron slag. The technique has high metal recovery rate, and solves the problem of zinc-iron separation.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH TECH IND SALES MANAGEMENT +1
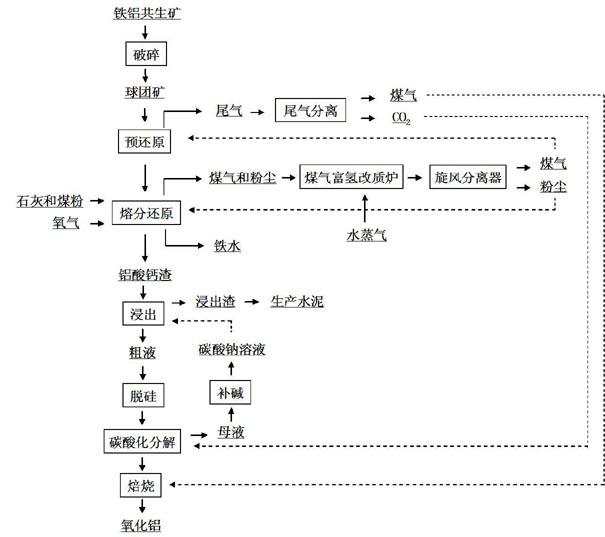
Comprehensive iron-aluminium paragenetic mineral utilization method
ActiveCN102605185AReduce iron oxide contentHigh dissolution rateProcess efficiency improvementRefining (metallurgy)Aluminium hydroxide
A comprehensive iron-aluminium paragenetic mineral utilization method belongs to the technical field of metallurgy. The comprehensive iron-aluminium paragenetic mineral utilization method is carried out according to the following steps: iron-aluminium paragenetic mineral is ground and made into pellets, and reducing gas is filled to pre-reduce the pellets, so that pre-reduced mineral is obtained;the pre-reduced mineral and lime are put into a reduction and melting furnace, and with oxygen as carrier gas, pulverized coal is jetted to carry out melting and reduction, so that molten iron and high-temperature aluminium-containing molten slag are obtained; the high-temperature aluminium-containing molten slag is cooled to normal temperature and naturally powdered, so that slag is obtained, and the slag is put into sodium carbonate solution and leached, so that leachate and leaching residue are obtained; the leachate is desiliconized under normal pressure and desiliconized under medium pressure, so that refined liquor is obtained; CO2 is filled into the refined liquor to carry out carbonation decomposition, so that decomposed mother liquor and aluminium hydroxide are obtained, and the aluminium hydroxide is roasted, so that alumina is produced; sodium carbonate is added into the decomposed mother liquor to replenish alkali, and the produced sodium carbonate solution is used for leaching. The comprehensive iron-aluminium paragenetic mineral utilization method not only can guarantee the high-efficiency dissociation and extraction of iron and aluminium, but also is feasible technically and economically, and the iron-aluminium paragenetic mineral resource in China is effectively and comprehensively utilized.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND +1
Method for recovering cobalt from inverse antimony purified cobalt residue
ActiveCN104726717AAvoid solutionRaise the pHProcess efficiency improvementMetal leachingHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a method for recovering cobalt from inverse antimony purified cobalt residue. The inverse antimony purified cobalt residue of zinc hydrometallurgy is taken as a raw material, and the cobalt concentrate is prepared by use of the processes of leaching, iron removal and cobalt settlement. The reducing atmosphere of leaching the cobalt residue in sulfuric acid is controlled so that metals such as copper and germanium cannot be leached and only zinc, cadmium, cobalt and little iron can be leached; in this way, a relatively high pH value can be controlled during iron removal, the purpose of thorough iron removal can be achieved and the iron can be prevented from being oxidized and hydrolyzed into the cobalt concentrate during cobalt settlement; air serves as an iron removal oxidizing agent, while hydrogen peroxide serves as a cobalt settlement oxidizing agent, and no impurity is imported; and the method is advantageous for increasing the grade of the cobalt concentrate.
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG ZINC & GERMANIUM
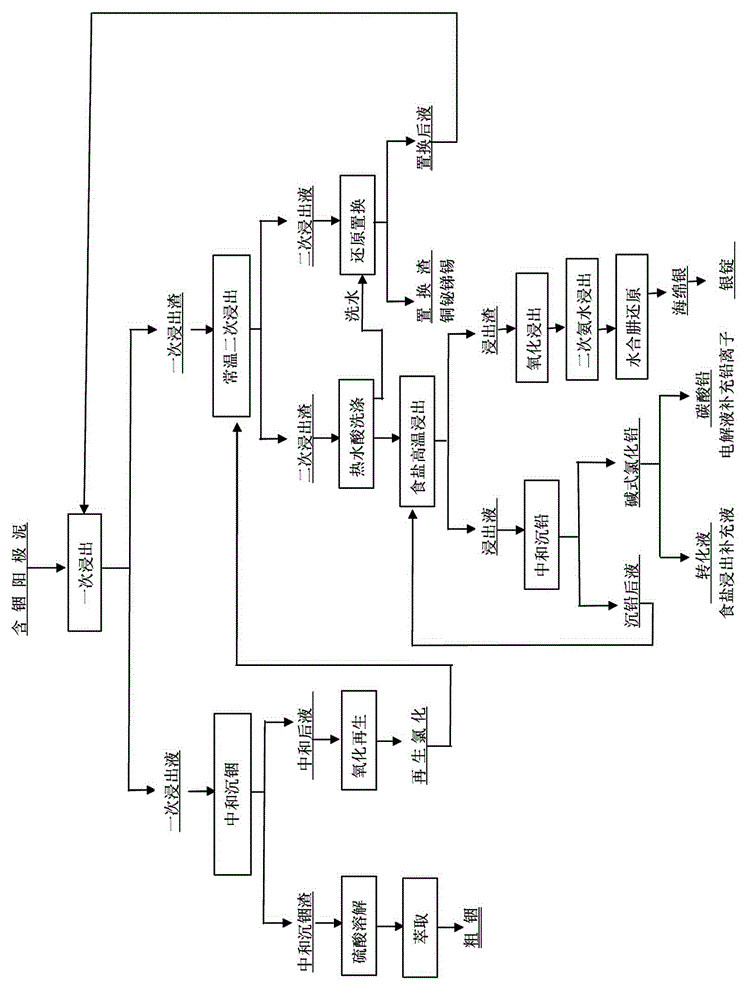
Method for comprehensively treating indium-containing lead anode slime through whole wet process
InactiveCN102912143AEfficient separationHigh economic recycling valueProcess efficiency improvementIndiumWater chlorination
A method for comprehensively treating indium-containing lead anode slime through the whole wet process relates to adoption of the whole wet extraction technology for extracting valuable metals such as indium, silver, lead, copper and bismuth, and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metal metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a chloride solution into anode slime, leaching for the first time at the temperature higher than 80 DEG C, and controlling the final pH value within 2.5-3.0; (2) neutralizing the first leaching solution until the pH value reaches 4.8-5.1, precipitating, then adding sulfuric acid into dregs for dissolution, and extracting to obtain crude indium; (3) oxidizing and chloridizing the neutralized solution of precipitated indium, then leaching the first leached dregs for the second time, and controlling the final acidity within 45-30g / L; (4) the secondary leached dregs are leached at the temperature higher than 90 DEG C, neutralizing the leaching solution for lead precipitation, oxidation leaching the leached dregs, adding ammonia water for leaching, and reducing the ammonia leaching solution by hydrazine hydrate, thereby obtaining silver sponge; and (5) reduction replacing the secondary leaching solution to obtain the valuable metals. The method is low in cost, has higher extraction ratio for the valuable metals, can be used for easily separating the valuable metals, is free from waste liquor and waste residues, and has better economic benefits.
Owner:云南天浩稀贵金属股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com