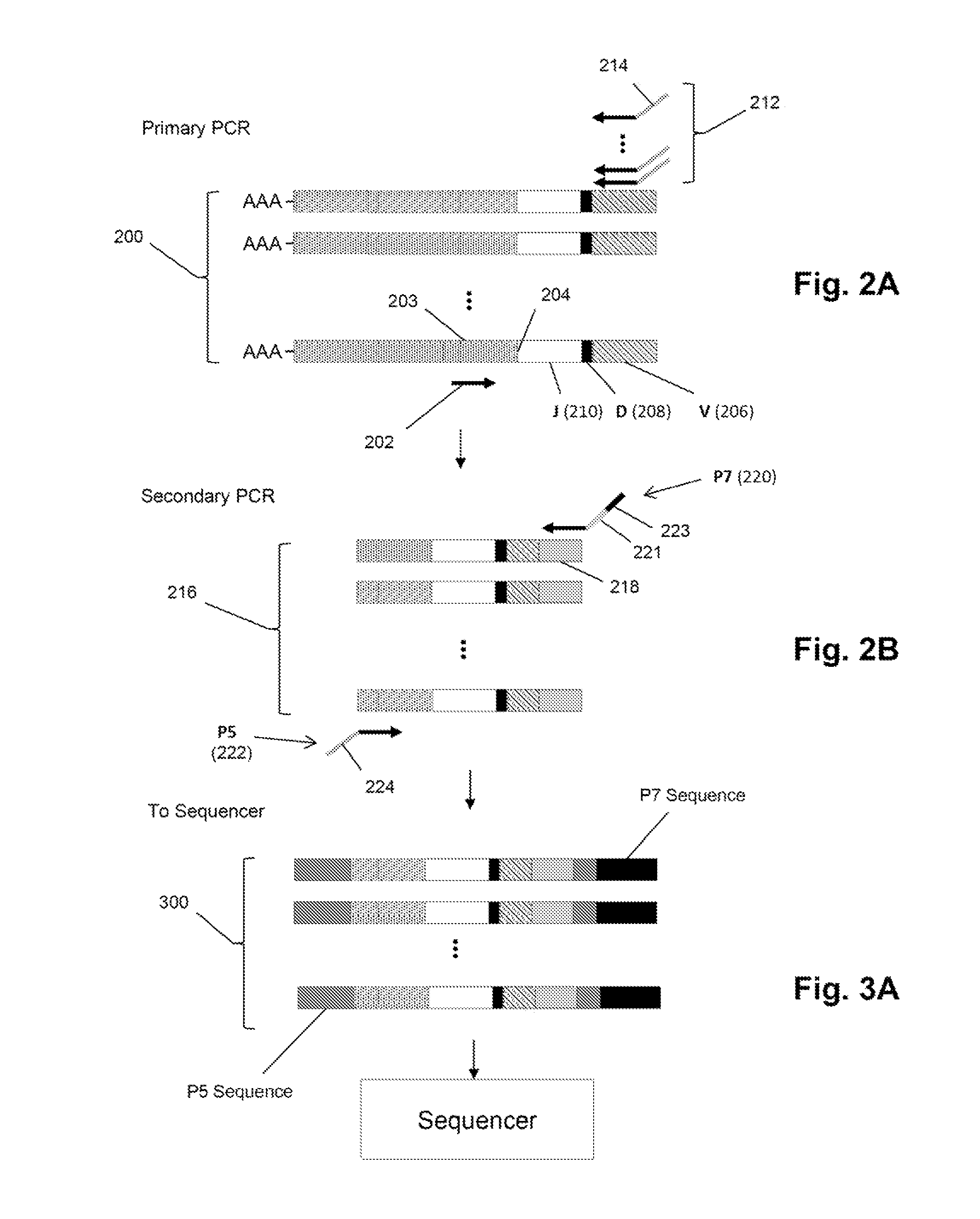
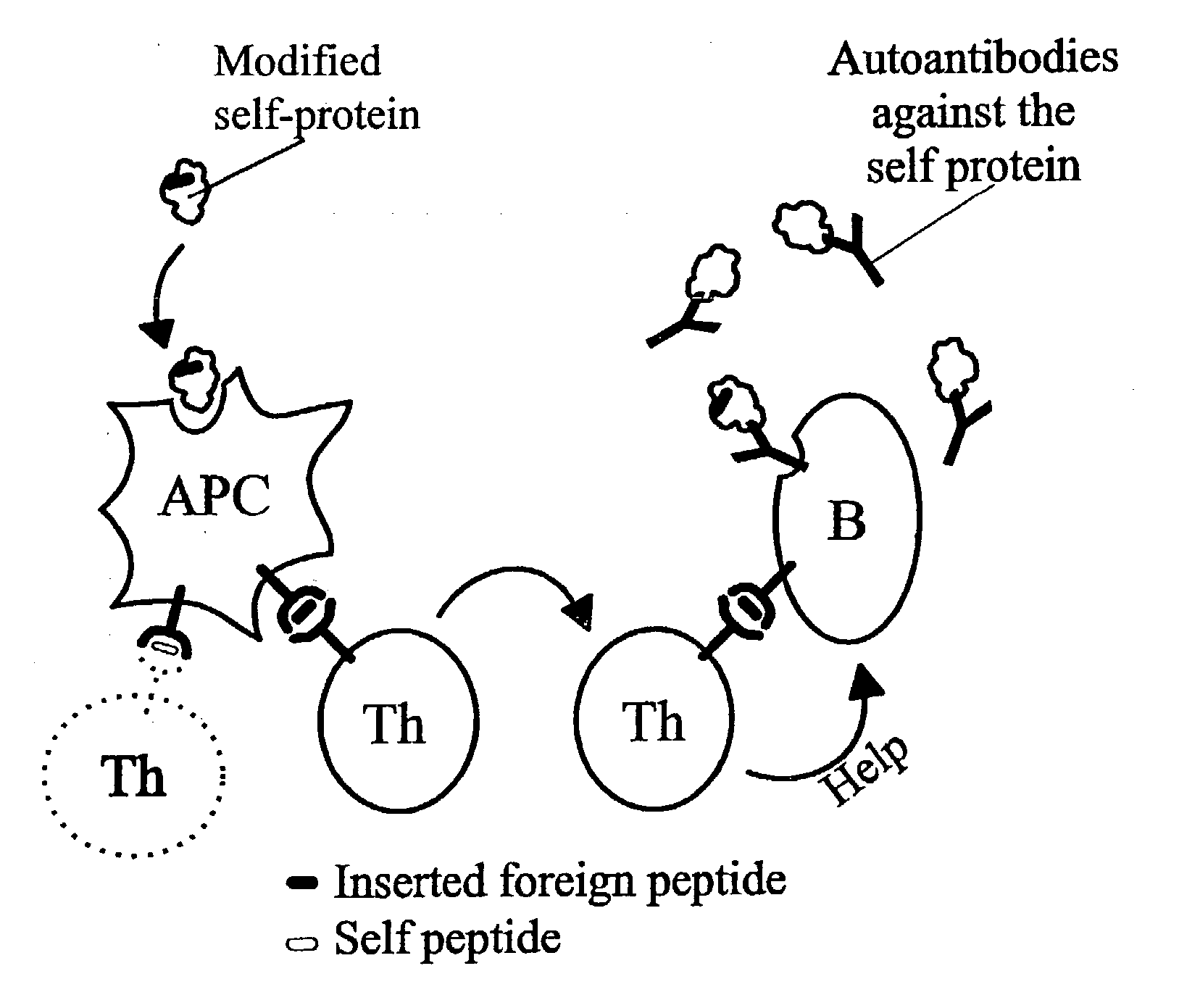
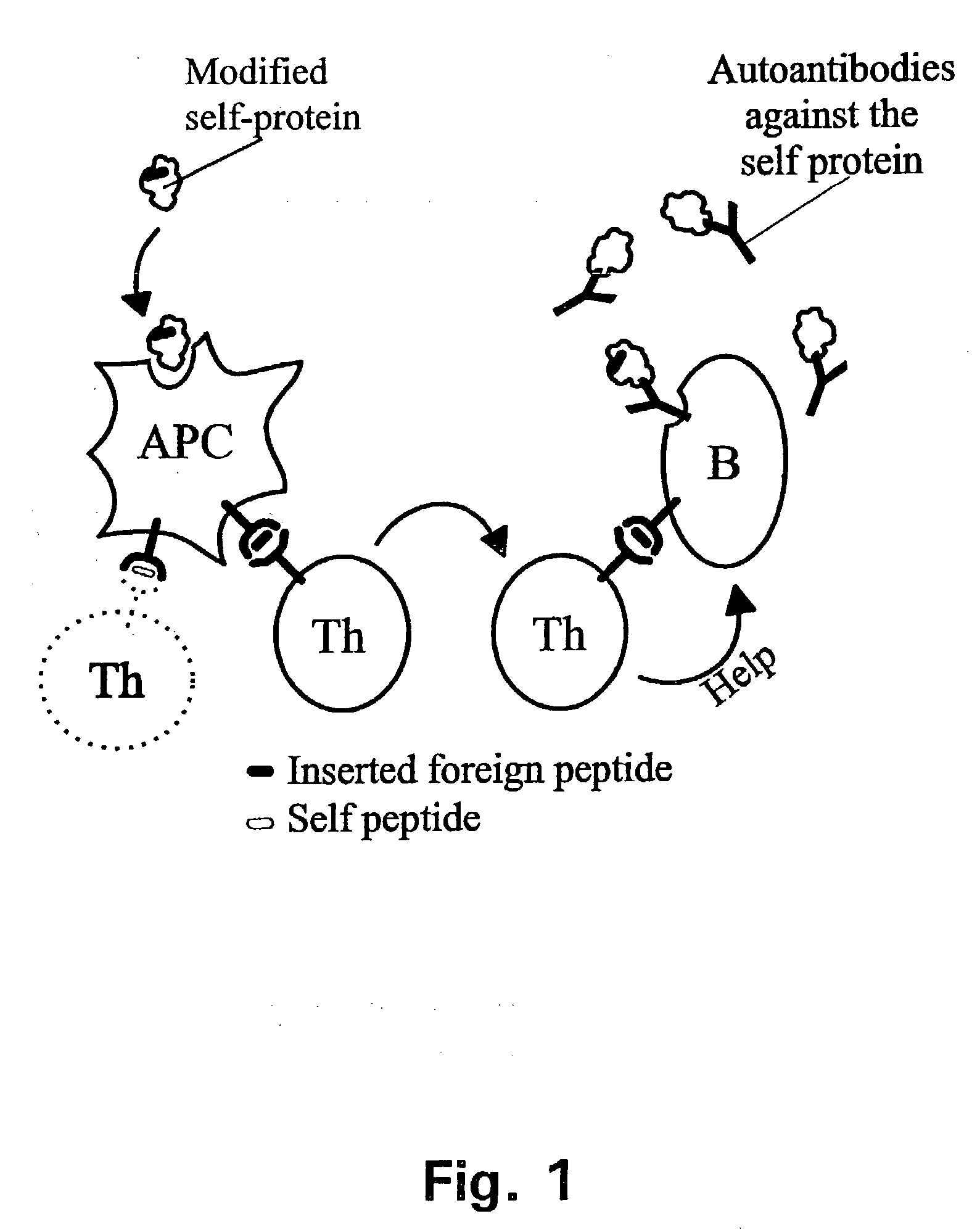
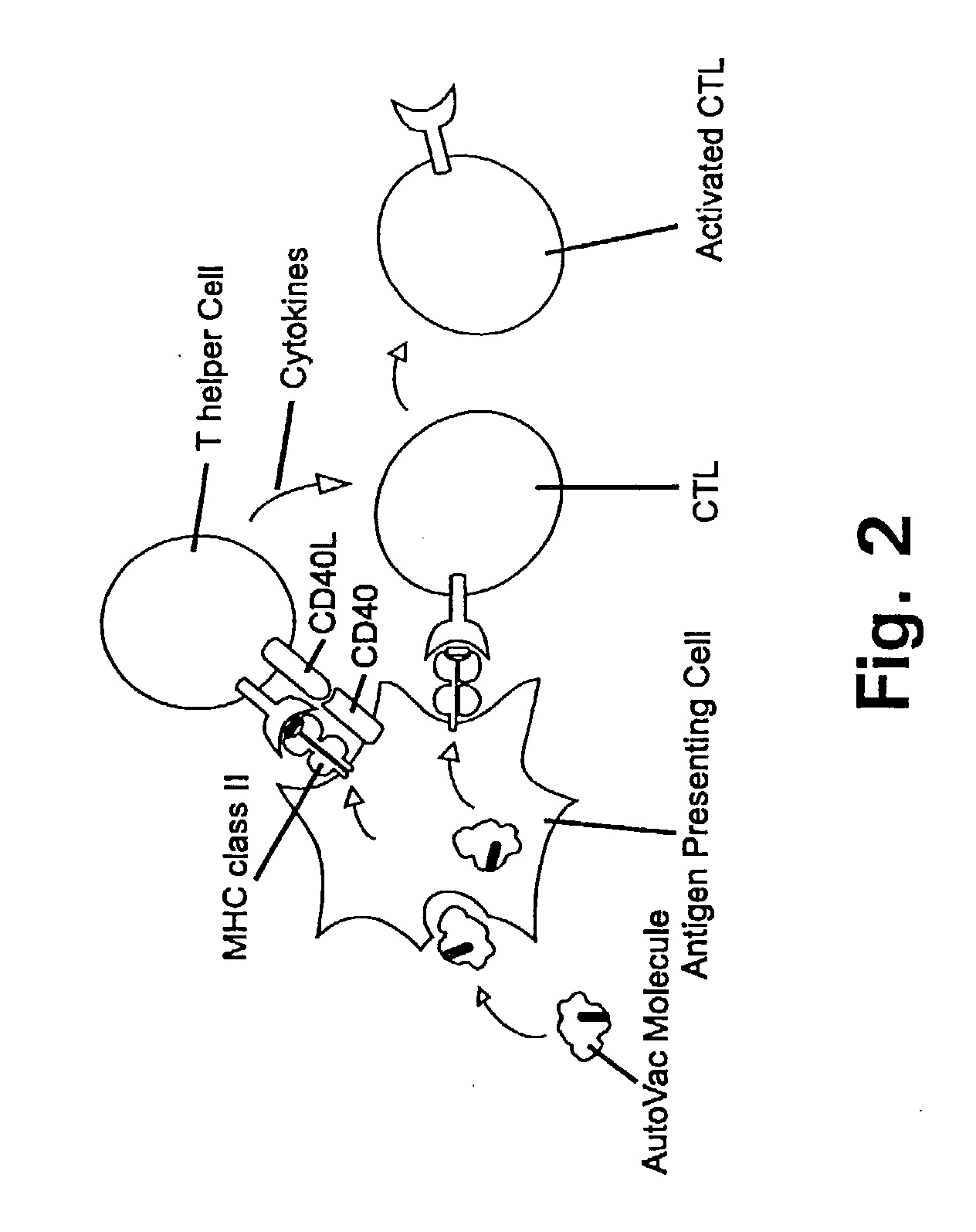
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1911 results about "Lymph" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lymph (from Latin, lympha meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to the central circulation. Interstitial fluid – the fluid which is between the cells in all body tissues – enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood.
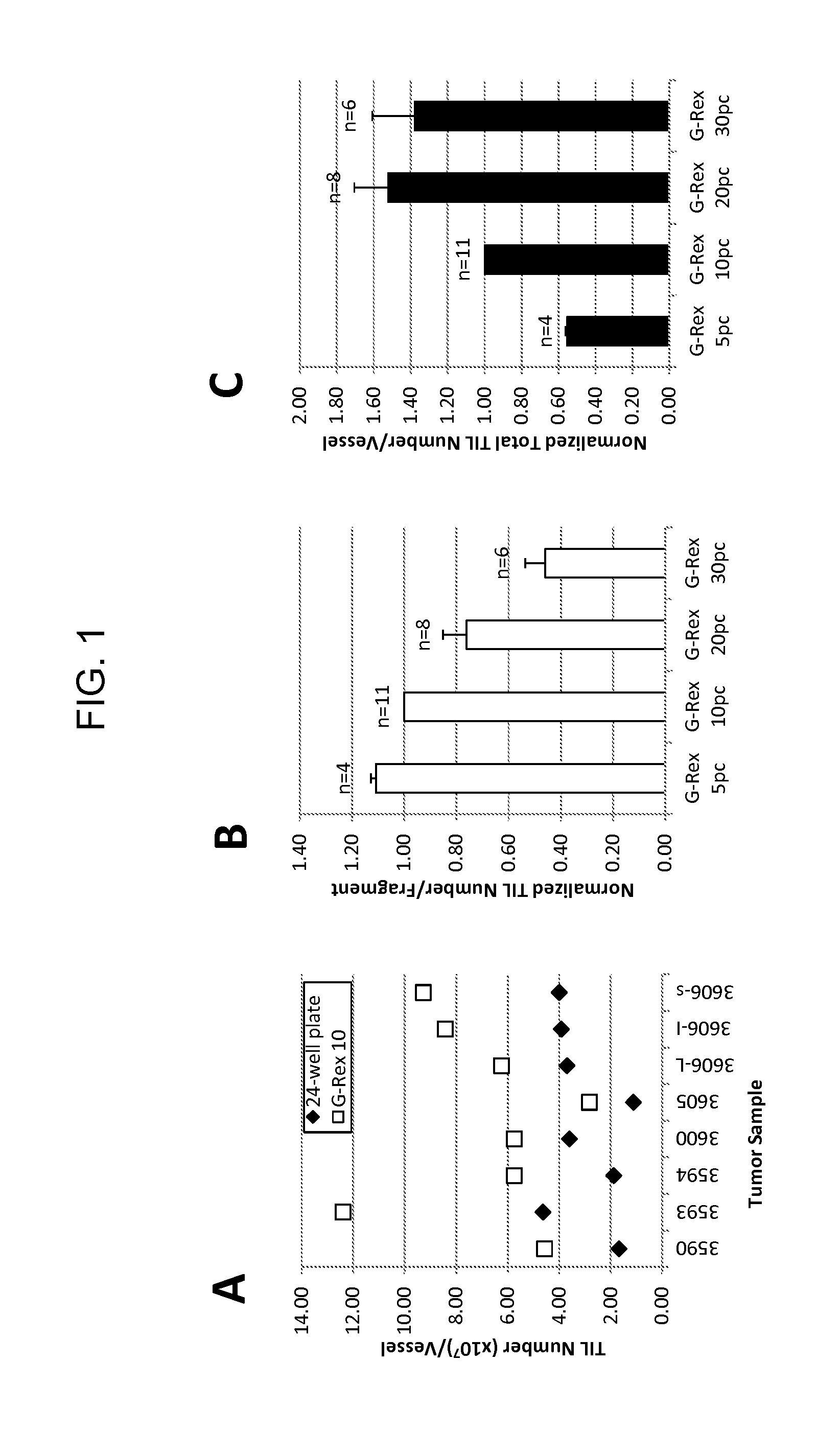
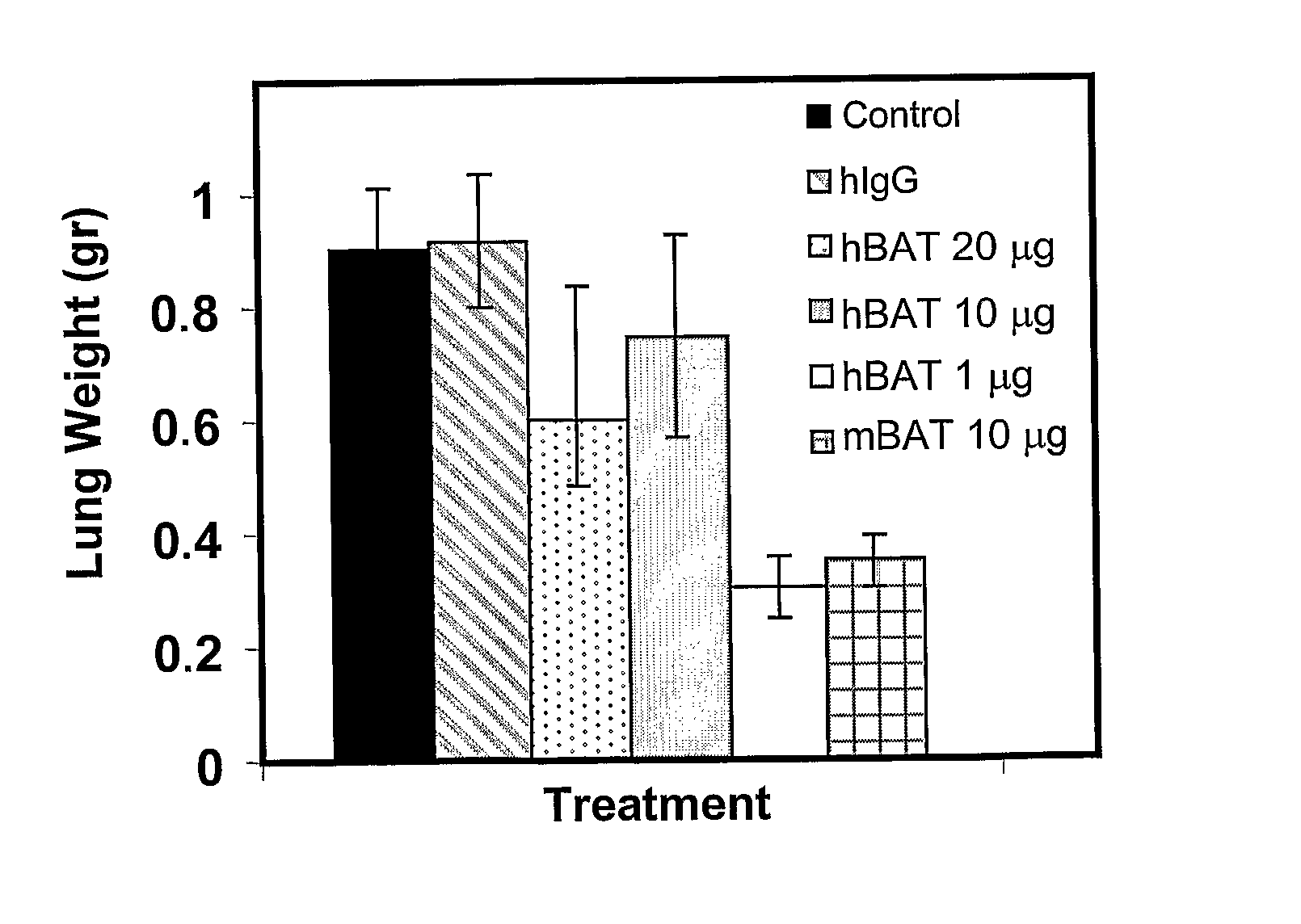
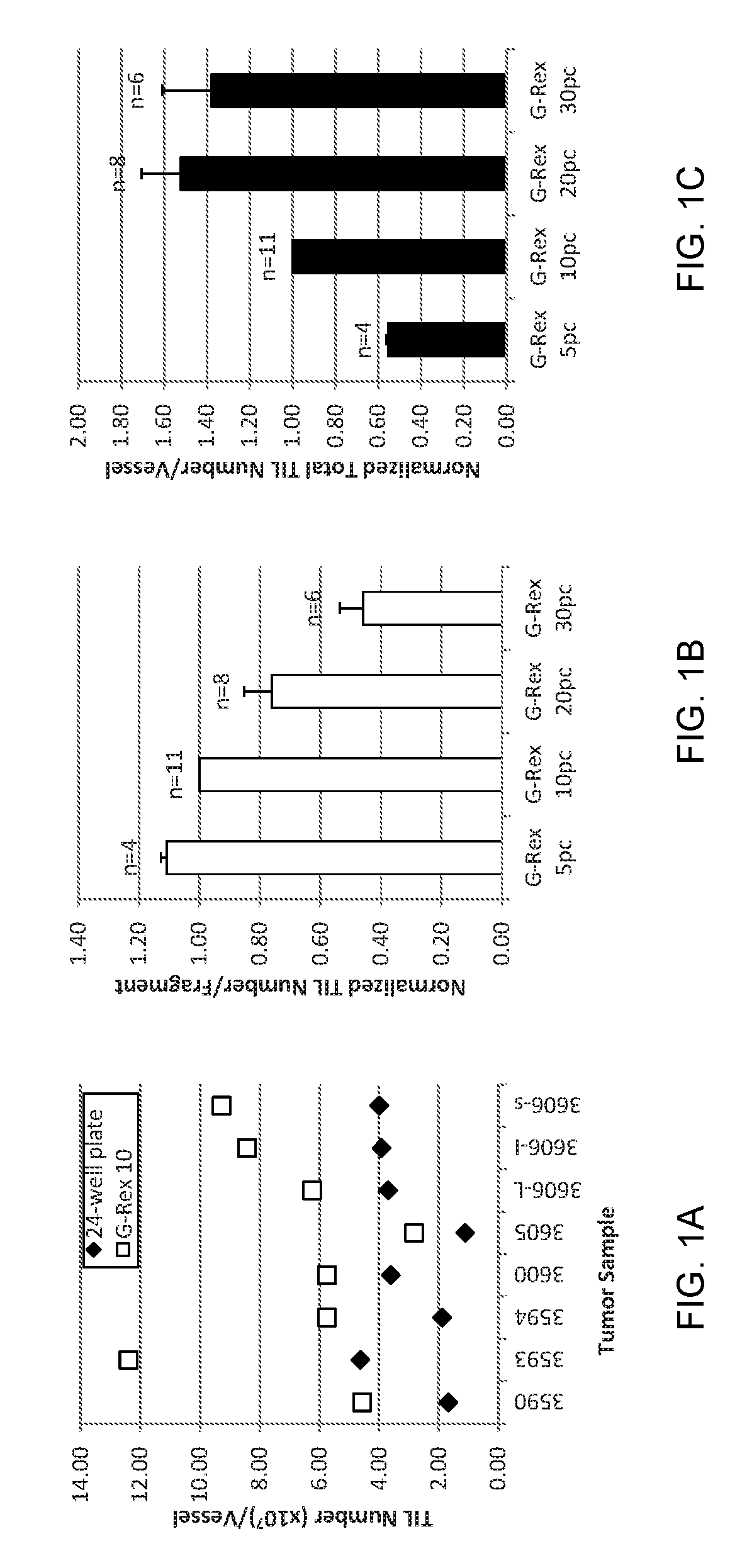
Methods of growing tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in gas-permeable containers
InactiveUS20120244133A1Increase the number ofBiocideArtificial cell constructsTumour tissueCell culture media
An embodiment of the invention provides a method of promoting regression of cancer in a mammal comprising obtaining a tumor tissue sample from the mammal; culturing the tumor tissue sample in a first gas permeable container containing cell medium therein; obtaining tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) from the tumor tissue sample; expanding the number of TIL in a second gas permeable container containing cell medium therein using irradiated allogeneic feeder cells and / or irradiated autologous feeder cells; and administering the expanded number of TIL to the mammal. Methods of obtaining an expanded number of TIL from a mammal for adoptive cell immunotherapy are also provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
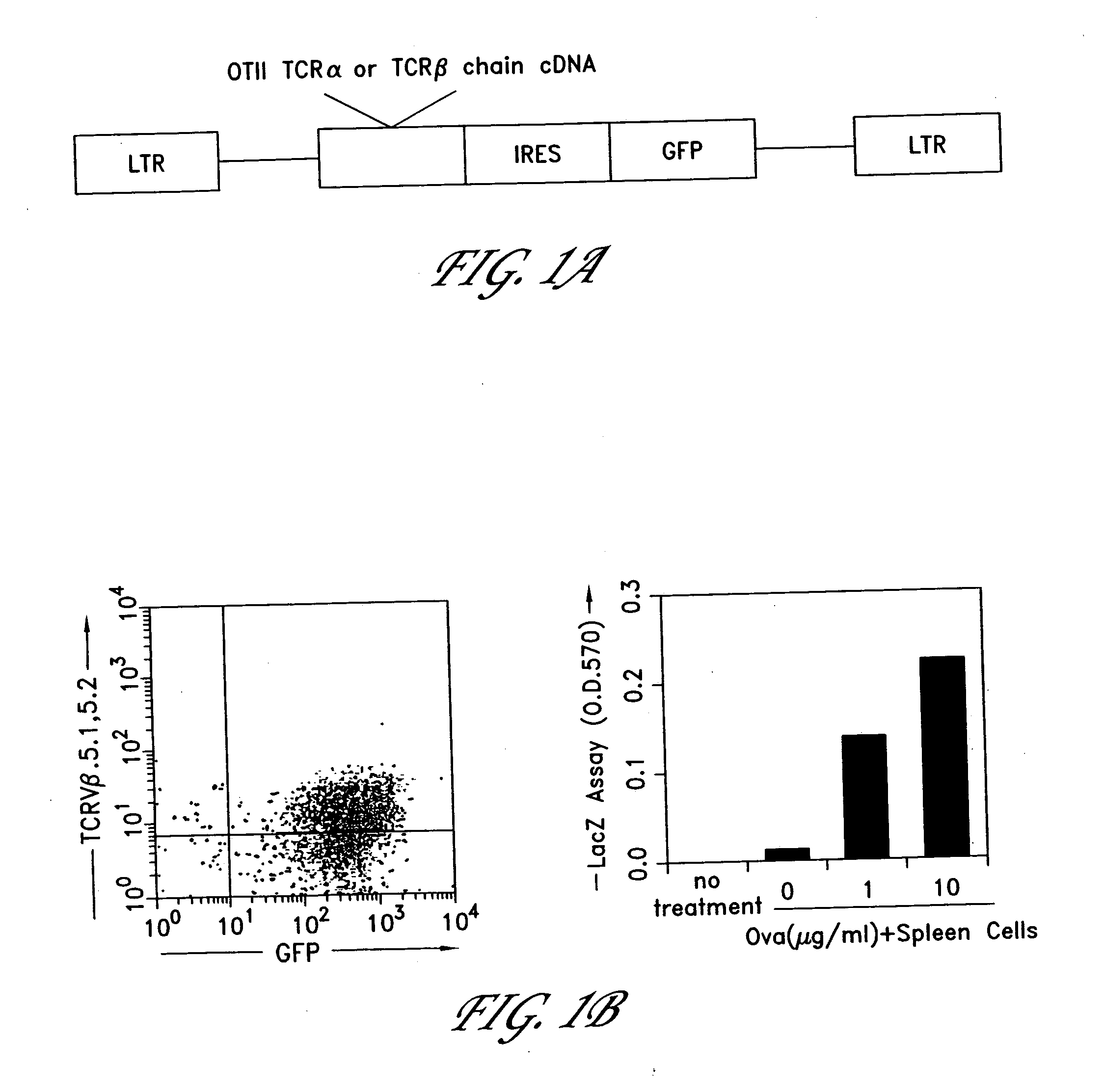
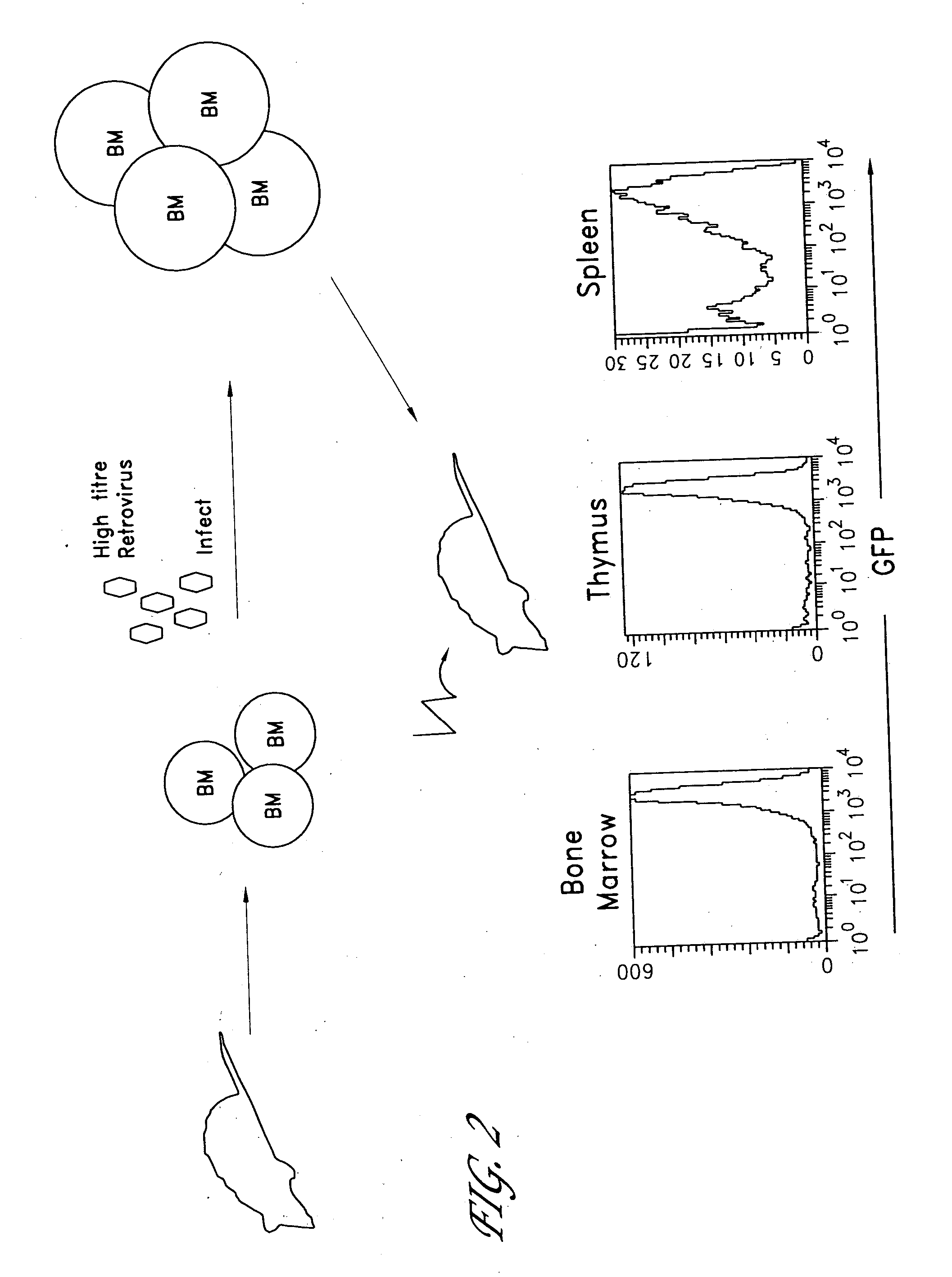
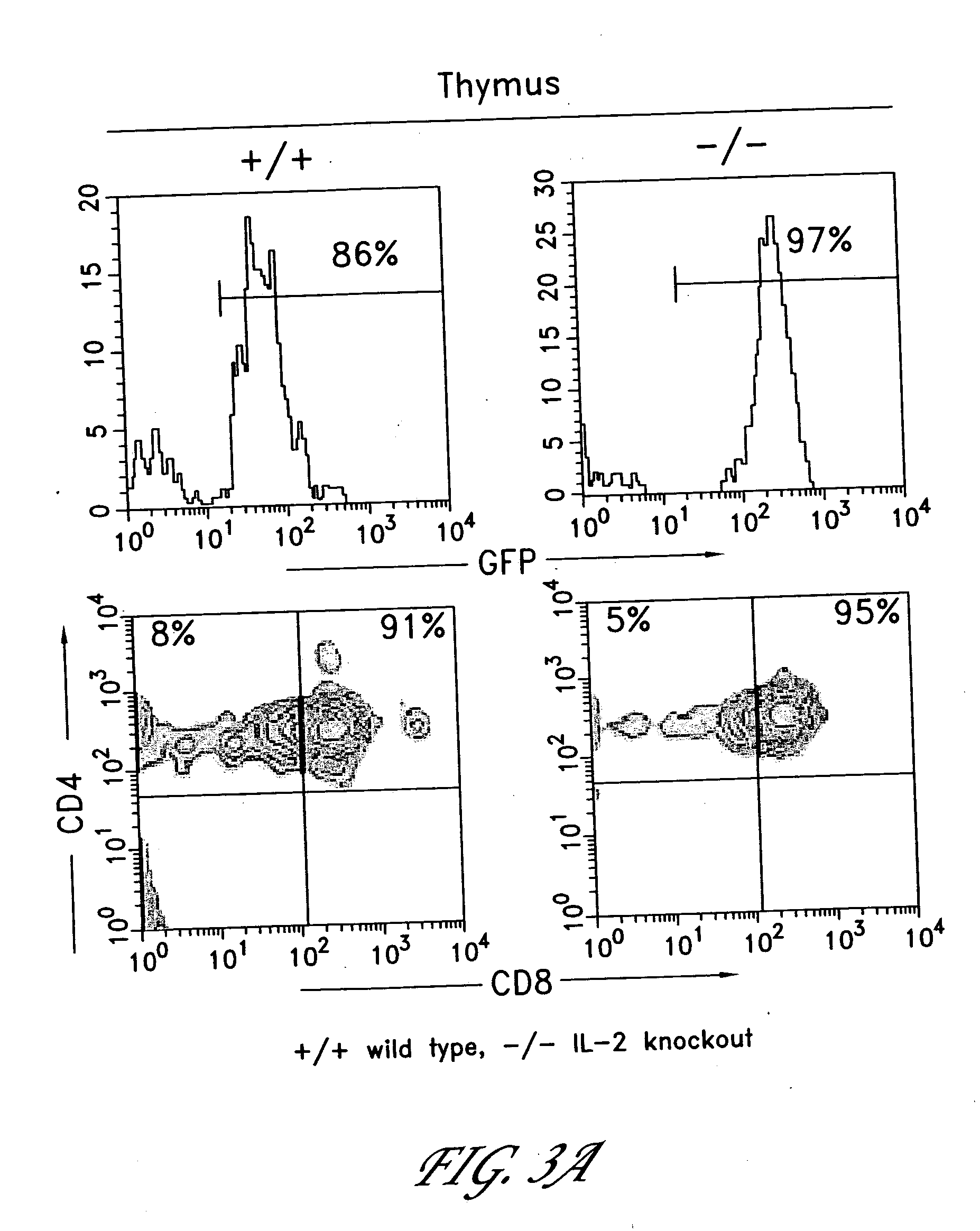
Method for the generation of antigen-specific lymphocytes
InactiveUS20070116690A1Function increaseEnhancing function of T cellBiocideVirusesAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The invention provides systems and methods for the generation of lymphocytes having a unique antigen specificity. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides methods of virally infecting cells from bone marrow with one or more viral vectors that encode antigen-specific antibodies for the production of, for example B cells and T cells. In some embodiments, the viral vectors include an IRES or 2A element to promote separation of, for example, the α subunit and β subunit of a T cell receptor (TCR) or heavy and light chains of a B-cell antibody. The resulting lymphocytes, express the particular antibody that was introduced in the case of B cells and TCR in the case of T cells. The lymphocytes generated can be used for a variety of therapeutic purposes including the treatment of various cancers and the generation of a desired immune response to viruses and other pathogens. The resulting cells develop normally and respond to antigen both in vitro and in vivo. We also show that it is possible to modify the function of lymphocytes by using stem cells from different genetic backgrounds. Thus our system constitutes a powerful tool to generate desired lymphocyte populations both for research and therapy. Future applications of this technology may include treatments for infectious diseases, such as HIV / AIDS, cancer therapy, allergy, and autoimmune disease.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Chimeric immunoreceptor useful in treating human gliomas
InactiveUS7514537B2Negligible toxicityPotent and selectiveBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIntracellular signallingHuman glioma
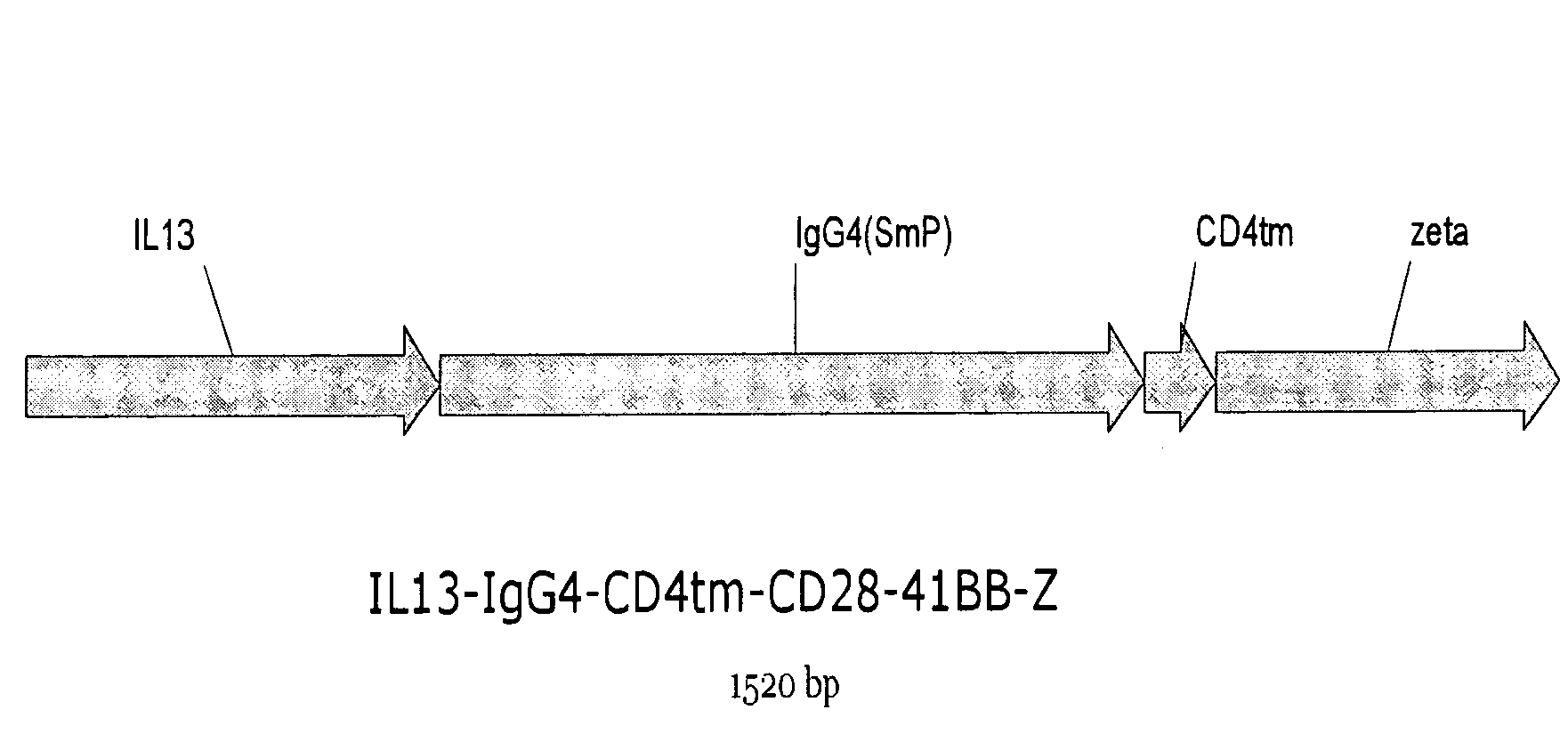
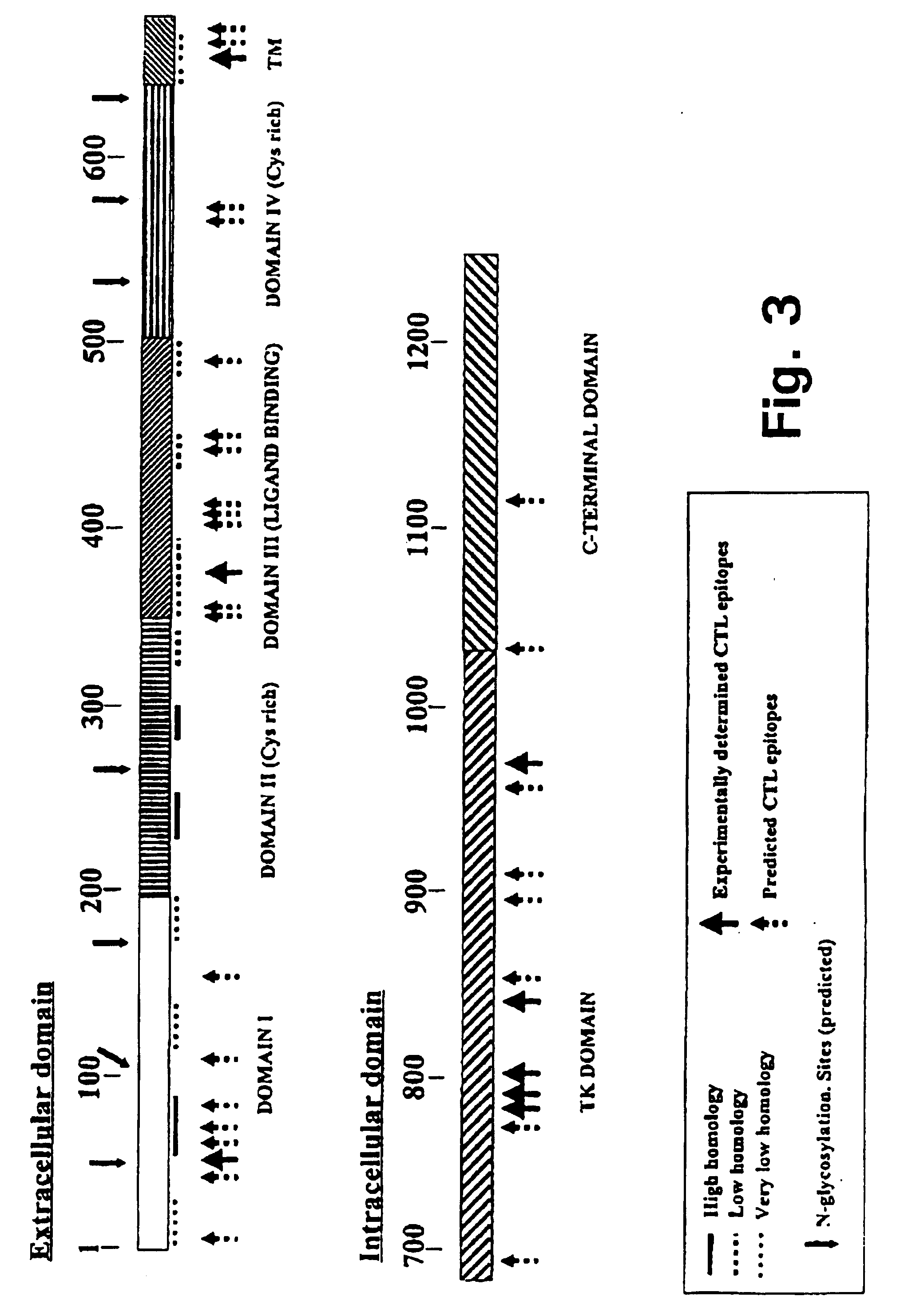
The present invention relates to chimeric transmembrane immunoreceptors, named “zetakines,” comprised of an extracellular domain comprising a soluble receptor ligand linked to a support region capable of tethering the extracellular domain to a cell surface, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signaling domain. Zetakines, when expressed on the surface of T lymphocytes, direct T cell activity to those specific cells expressing a receptor for which the soluble receptor ligand is specific. Zetakine chimeric immunoreceptors represent a novel extension of antibody-based immunoreceptors for redirecting the antigen specificity of T cells, with application to treatment of a variety of cancers, particularly via the autocrin / paracrine cytokine systems utilized by human maligancy. In a preferred embodiment is a glioma-specific immunoreceptor comprising the extracellular targeting domain of the IL-13Rα2-specific IL-13 mutant IL-13(E13Y) linked to the Fc region of IgG, the transmembrane domain of human CD4, and the human CD3 zeta chain.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
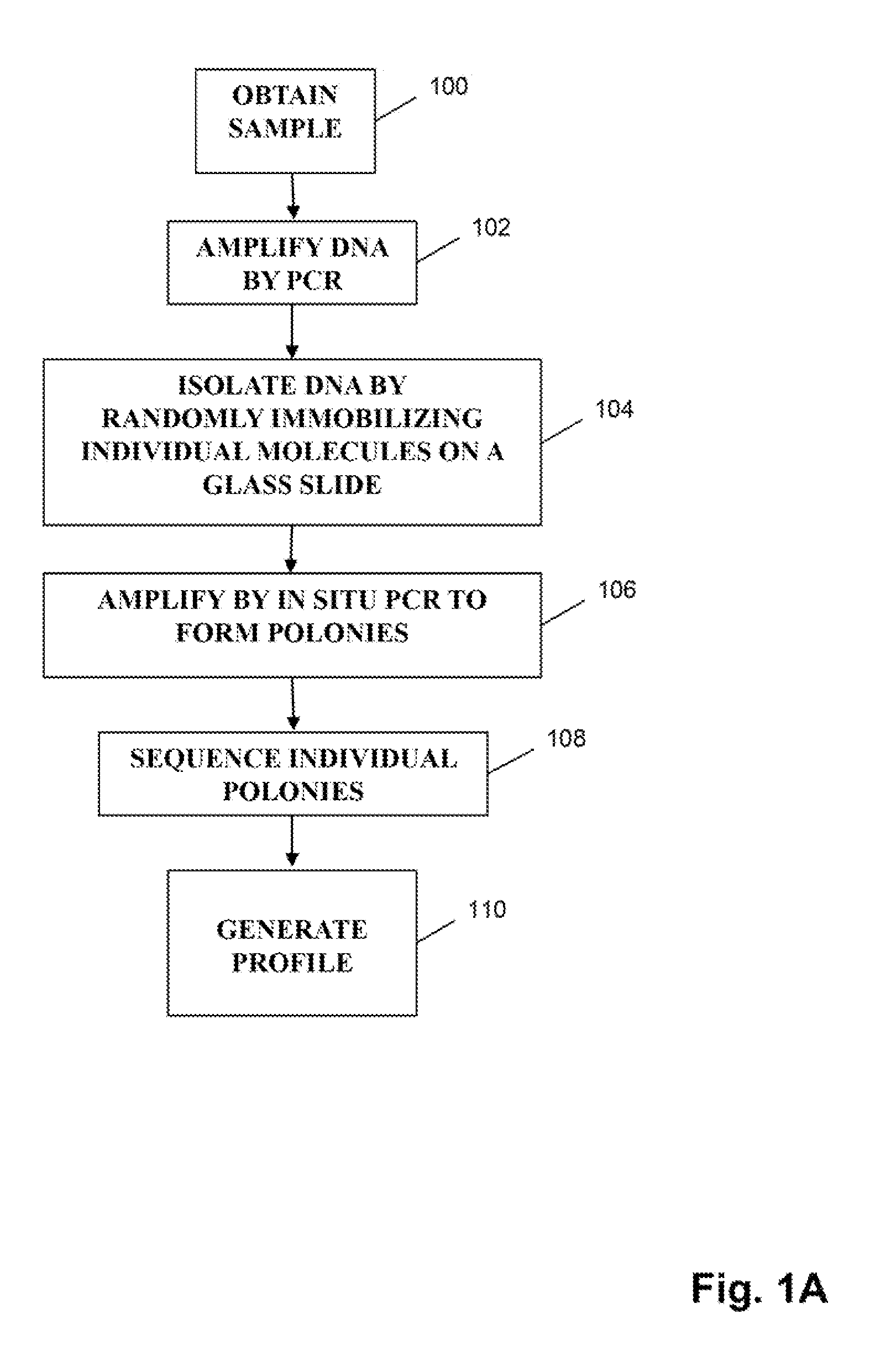
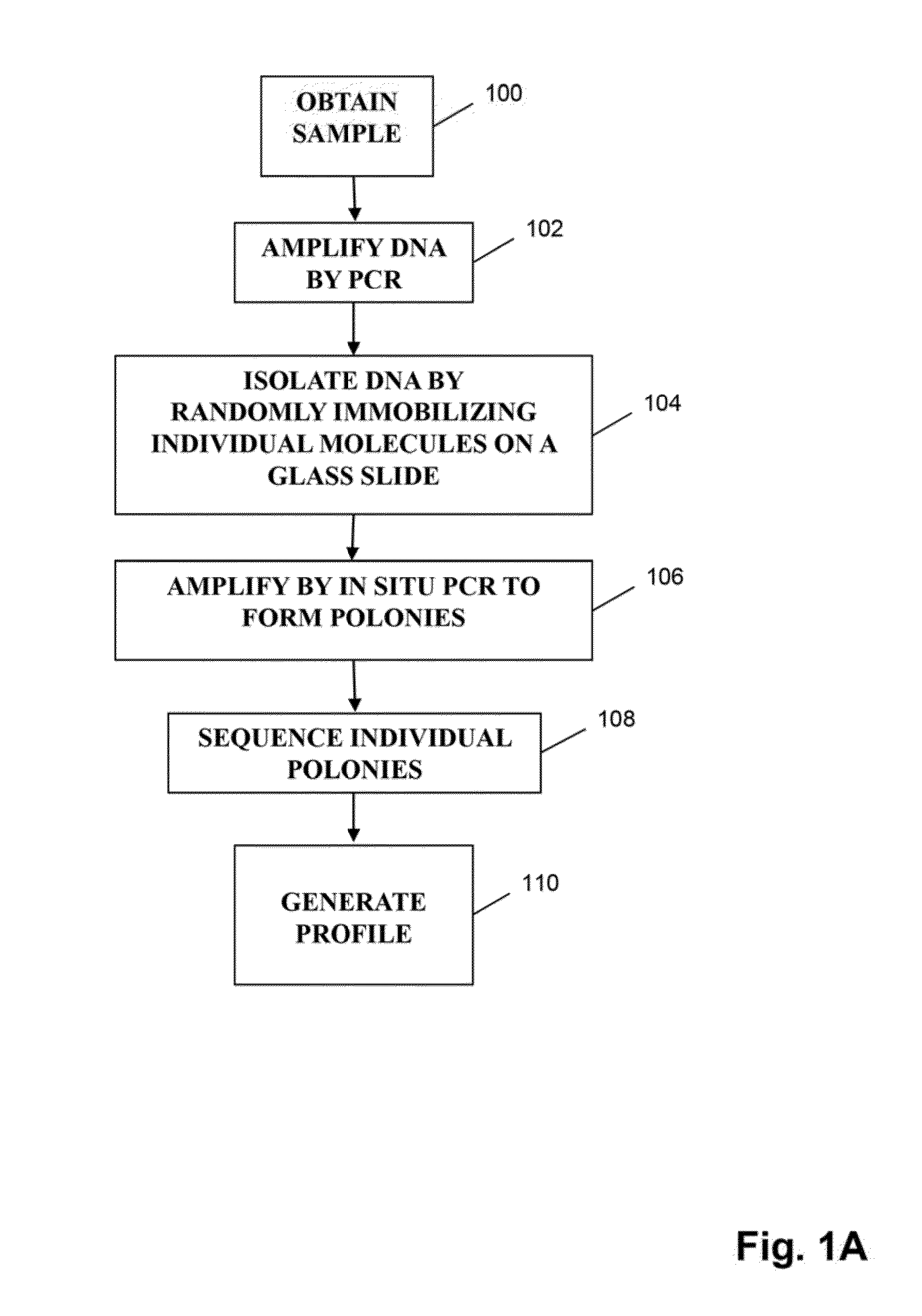
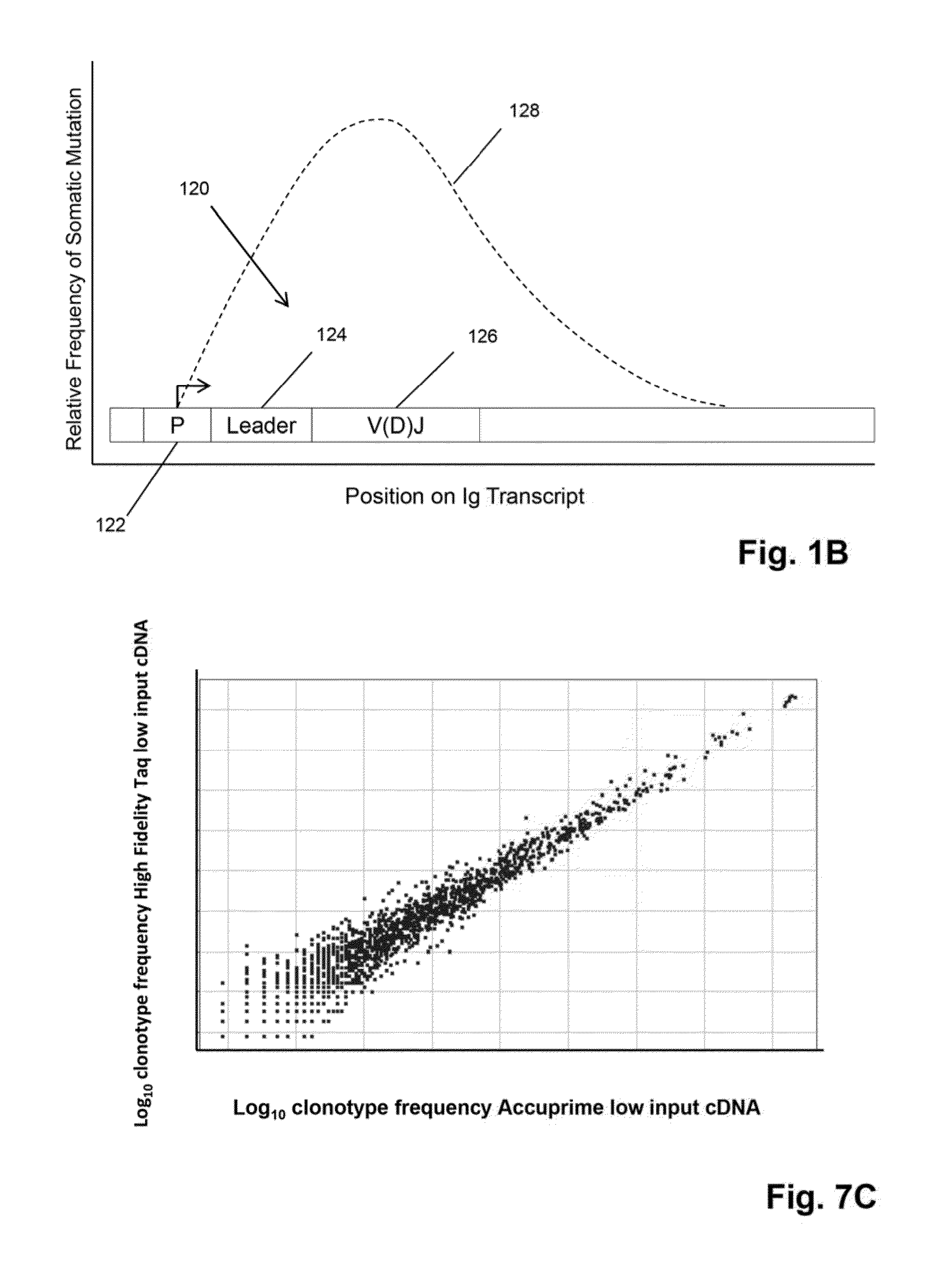
Monitoring health and disease status using clonotype profiles
ActiveUS20110207134A1High sensitivityOvercome deficienciesMicrobiological testing/measurementAutoimmune diseaseBiomarker (petroleum)
There is a need for improved methods for determining the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with conditions, including autoimmune disease and cancer, especially lymphoid neoplasms, such as lymphomas and leukemias. Provided herein are methods for using DNA sequencing to identify personalized, or patient-specific biomarkers in patients with lymphoid neoplasms, autoimmune disease and other conditions. Identified biomarkers can be used to determine and / or monitor the disease state for a subject with an associated lymphoid disorder or autoimmune disease or other condition. In particular, the invention provides a sensitive method for monitoring lymphoid neoplasms that undergo clonal evolutions without the need to development alternative assays for the evolved or mutated clones serving as patient-specific biomarkers.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
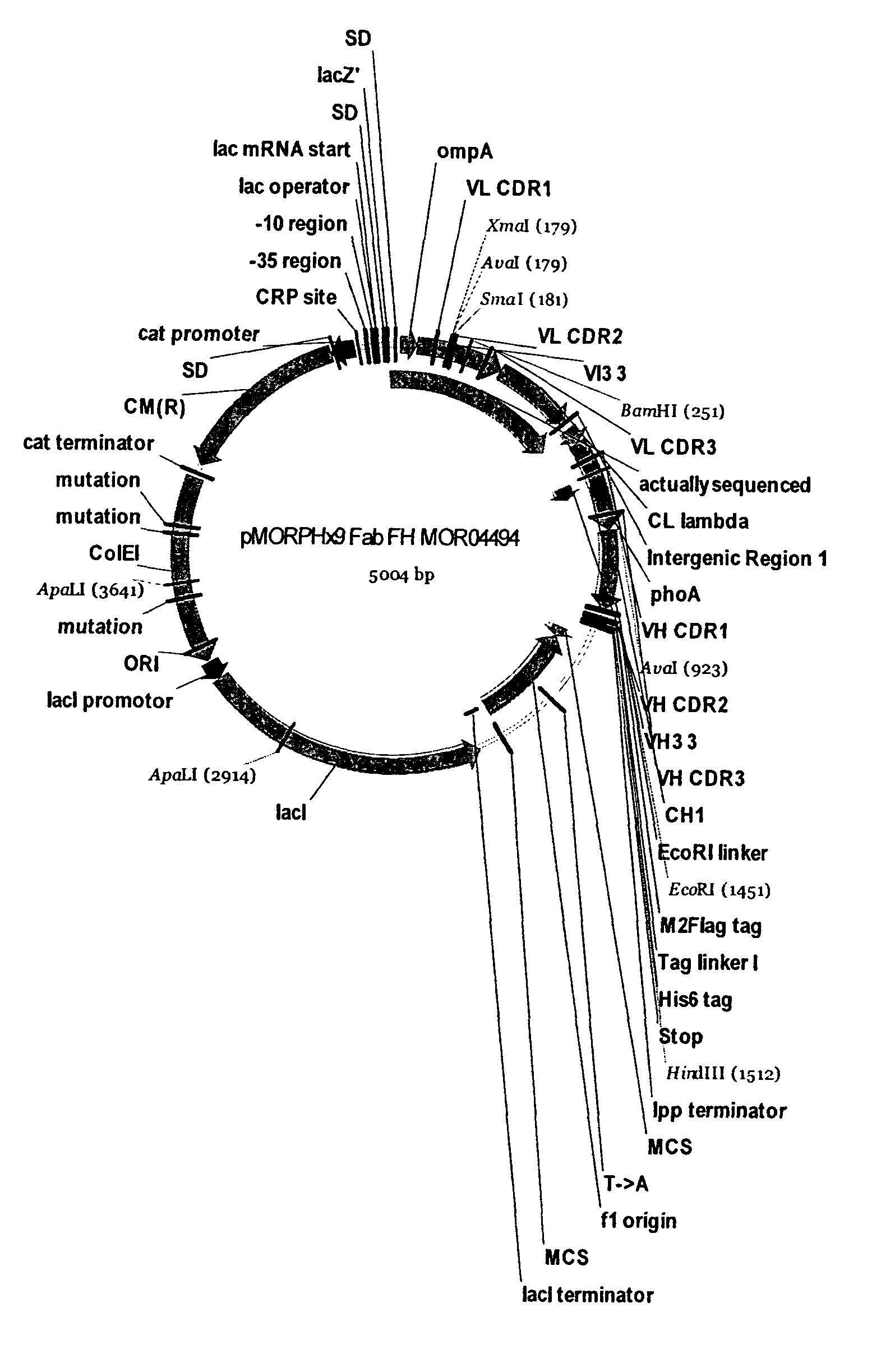
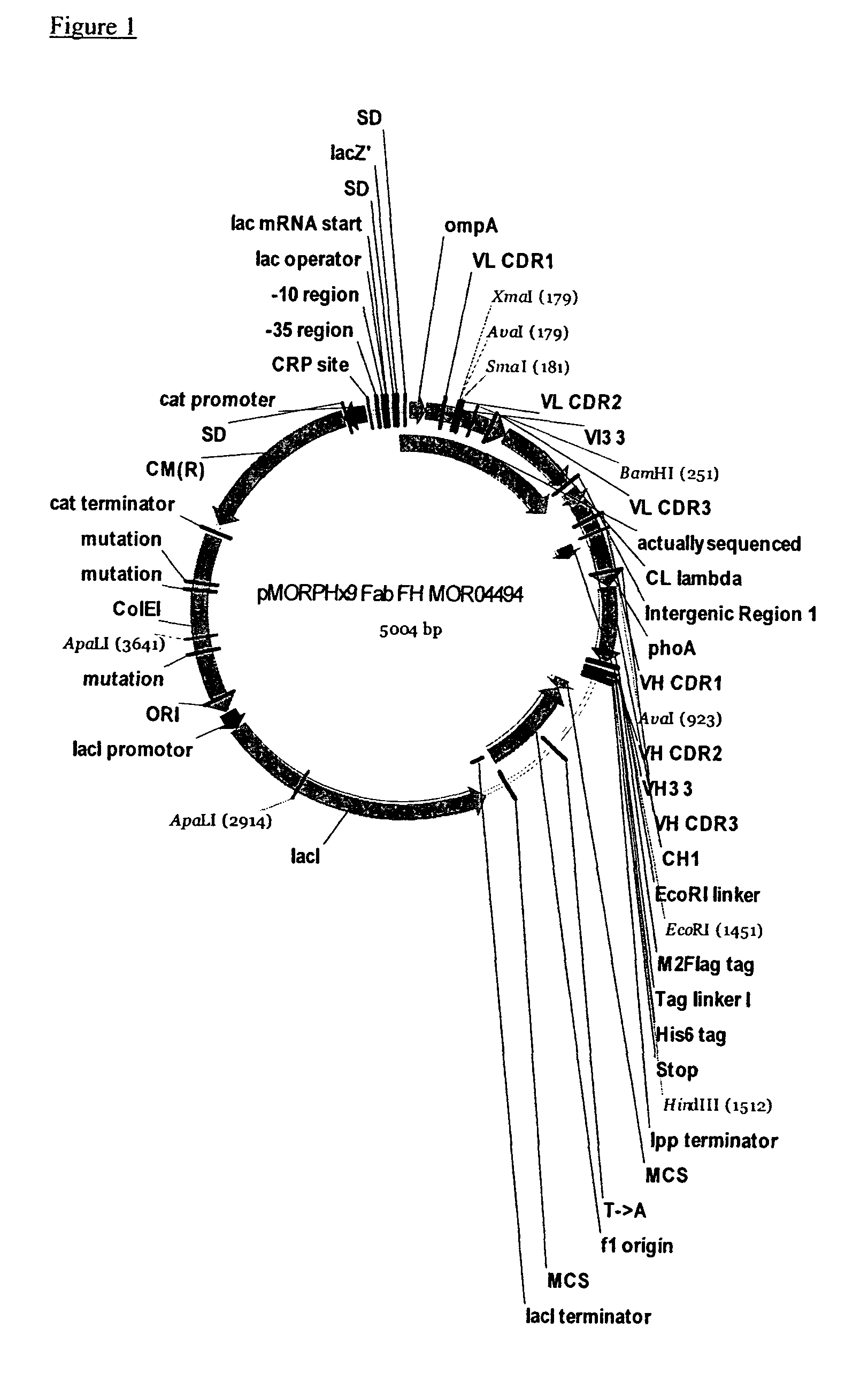
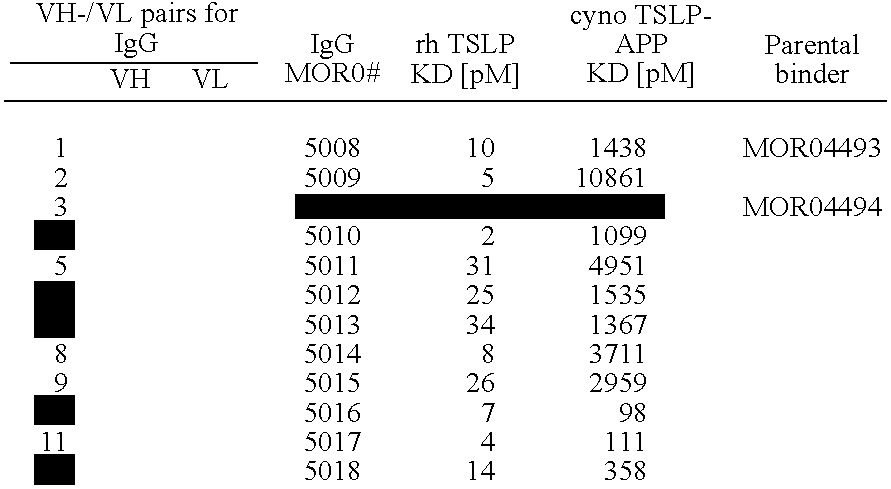
Antigen binding proteins capable of binding thymic stromal lymphopoietin
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods relating to antigen binding proteins which bind to human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), including antibodies. In particular embodiments, the disclosure provides fully human, humanized and chimeric anti-TSLP antibodies and derivatives of such antibodies. The disclosure further provides nucleic acids encoding such antibodies and antibody fragments and derivatives, and methods of making and using such antibodies including methods of treating and preventing TSLP-related inflammatory and fibrotic disorders.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Self-powered compression devices and methods for promoting circulation and therapeutic compression
InactiveUS6589194B1Guaranteed economic efficiencyBlood stagnation preventionAnti-cellulite devicesVenous diseaseCompression device
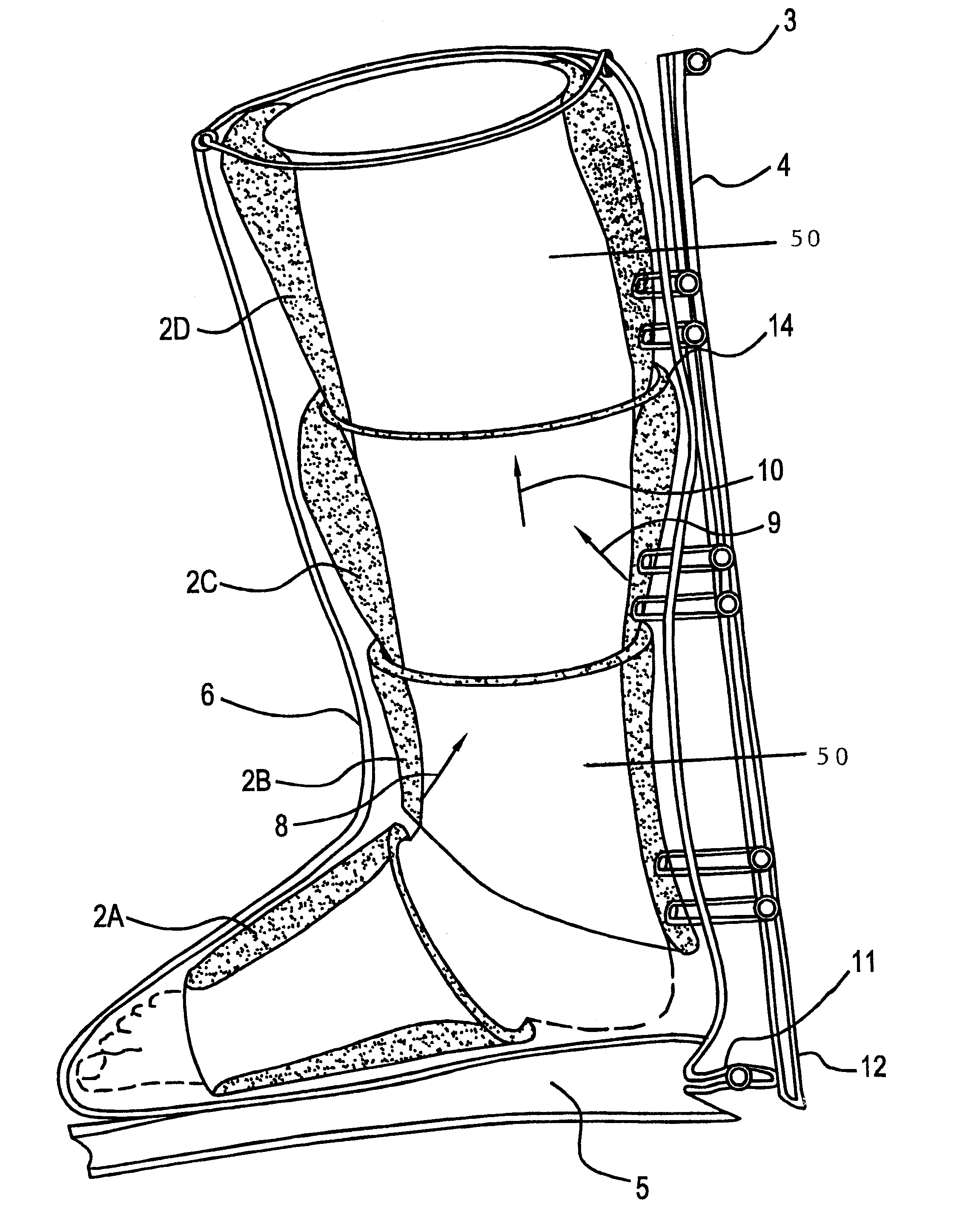
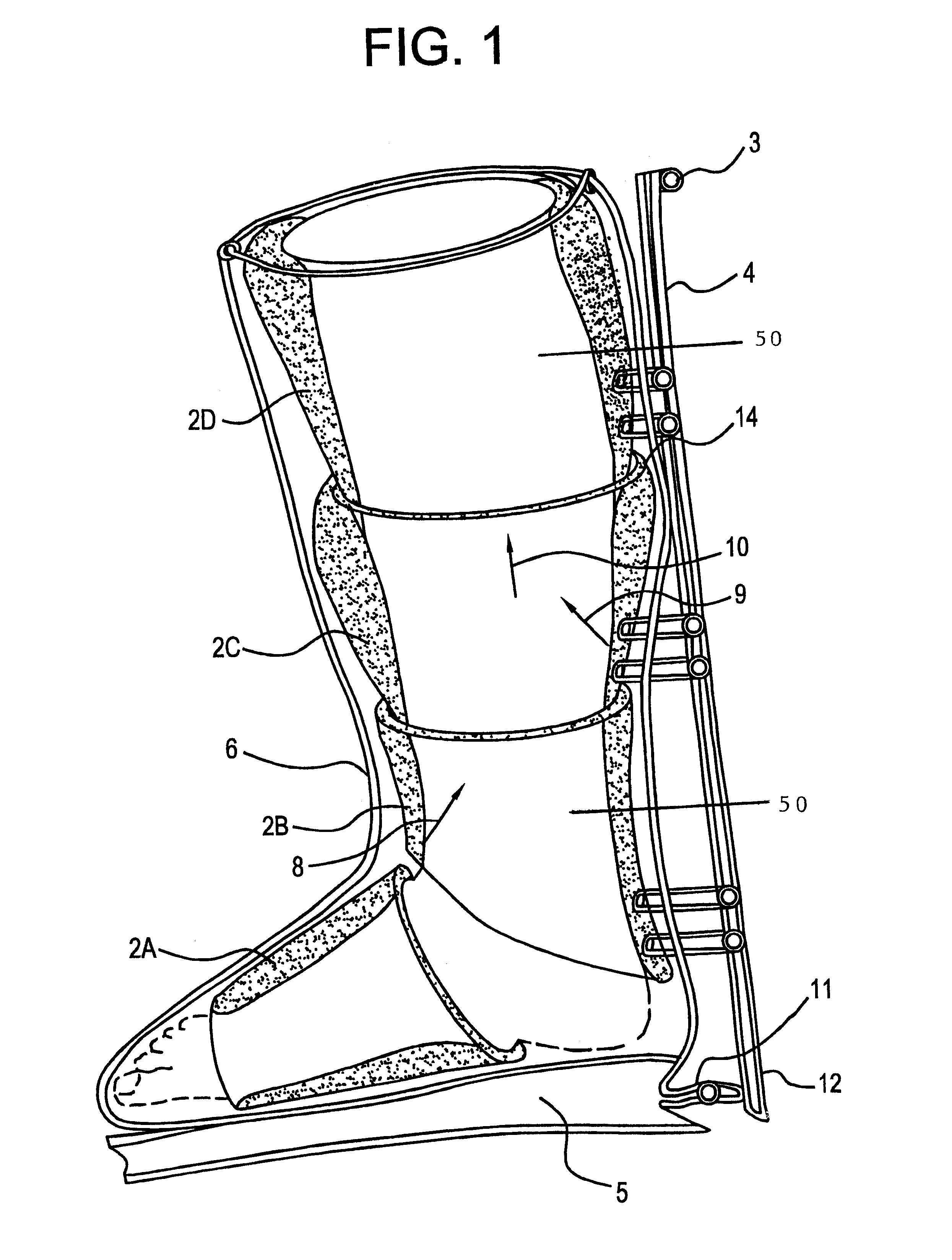
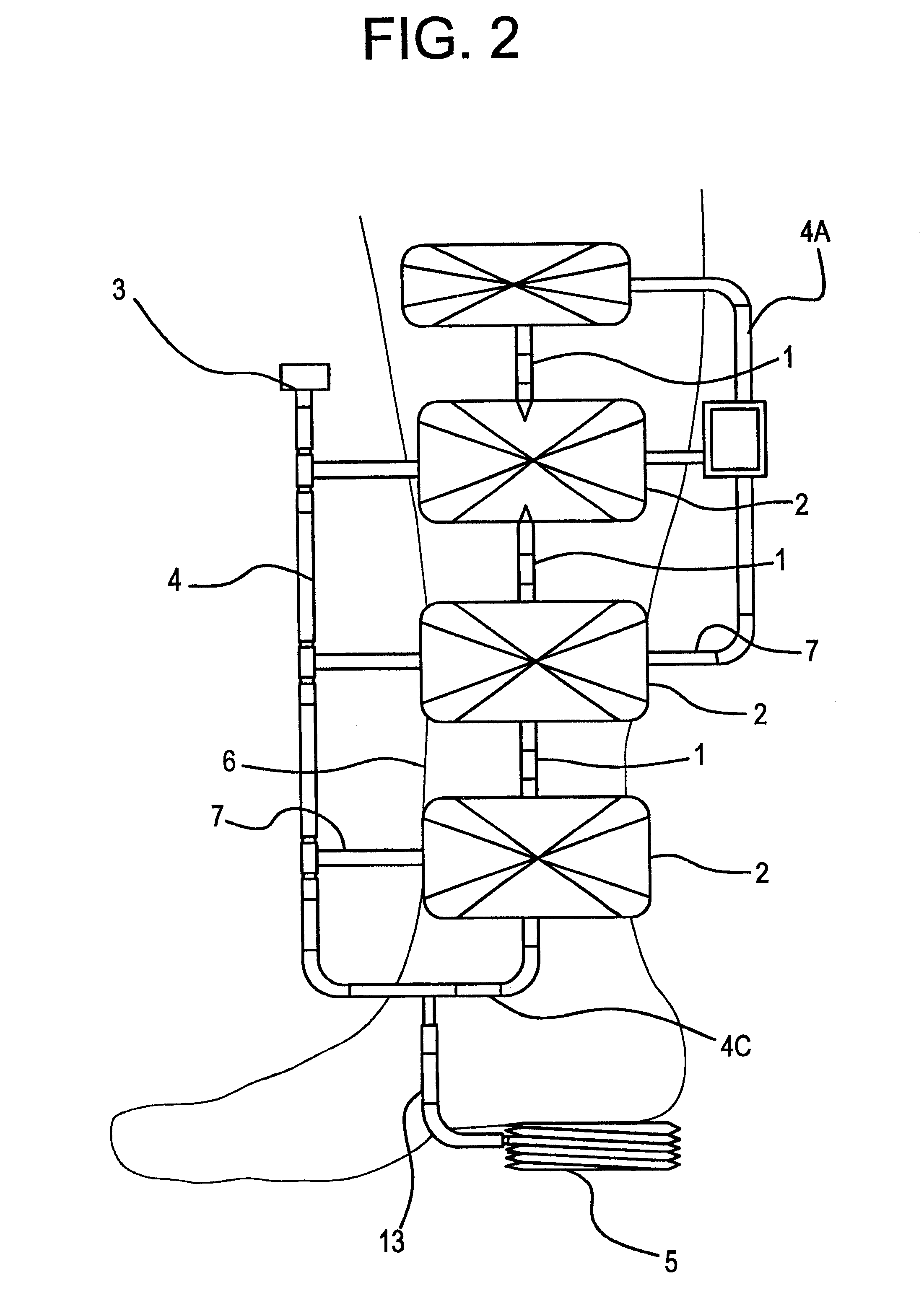
A self-powered compression device for use in promoting circulation, said device embodying a plurality of inflatable sleeves arranged sequentially for applying compression to a body or limb and which further comprises a pump, a piping system and a bandage or boot to enclose the device in its entirety. A method for using self-generated pressure in promoting circulation in conditions including but not limited to, lymphatic and traumatic edemas, venous disorders, limb ulcers, varicose veins, muscle fatigue, sports medicine, cellulite treatment, diabetic feet, feet massage for recreation or cosmetic enhancements.
Owner:C BOOT
Organic Compounds
InactiveUS20090186022A1Reducing required dosagingReduce potential side effectsSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsInflammatory Bowel DiseasesAtopic dermatitis
The present invention relates to human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (hTSLP) antibodies and especially those which neutralize hTSLP activity. It further relates to methods for using anti-hTSLP antibody molecules in diagnosis or treatment of hTSLP related disorders, such as asthma, atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, fibrosis inflammatory bowel disease, and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Cytotoxic t-lymphocyte-inducing immunogens for prevention, treatment, and diagnosis of cancer
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the prevention, treatment, and diagnosis of cancer, especially carcinomas, such as breast carcinoma. The invention discloses peptides, polypeptides, and polynucleotides that can be used to stimulate a CTL response against breast or cancer.
Owner:IMMUNOTOPE
Monitoring health and disease status using clonotype profiles
ActiveUS8748103B2High sensitivityOvercome deficienciesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAutoimmune diseaseBiomarker (petroleum)
There is a need for improved methods for determining the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with conditions, including autoimmune disease and cancer, especially lymphoid neoplasms, such as lymphomas and leukemias. Provided herein are methods for using DNA sequencing to identify personalized, or patient-specific biomarkers in patients with lymphoid neoplasms, autoimmune disease and other conditions. Identified biomarkers can be used to determine and / or monitor the disease state for a subject with an associated lymphoid disorder or autoimmune disease or other condition. In particular, the invention provides a sensitive method for monitoring lymphoid neoplasms that undergo clonal evolutions without the need to development alternative assays for the evolved or mutated clones serving as patient-specific biomarkers.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Method and system for treating cellulite
ActiveUS8133180B2Good lookingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyThermal injuryUltrasound imaging
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
Methods and apparatus for transesophageal microaccess surgery
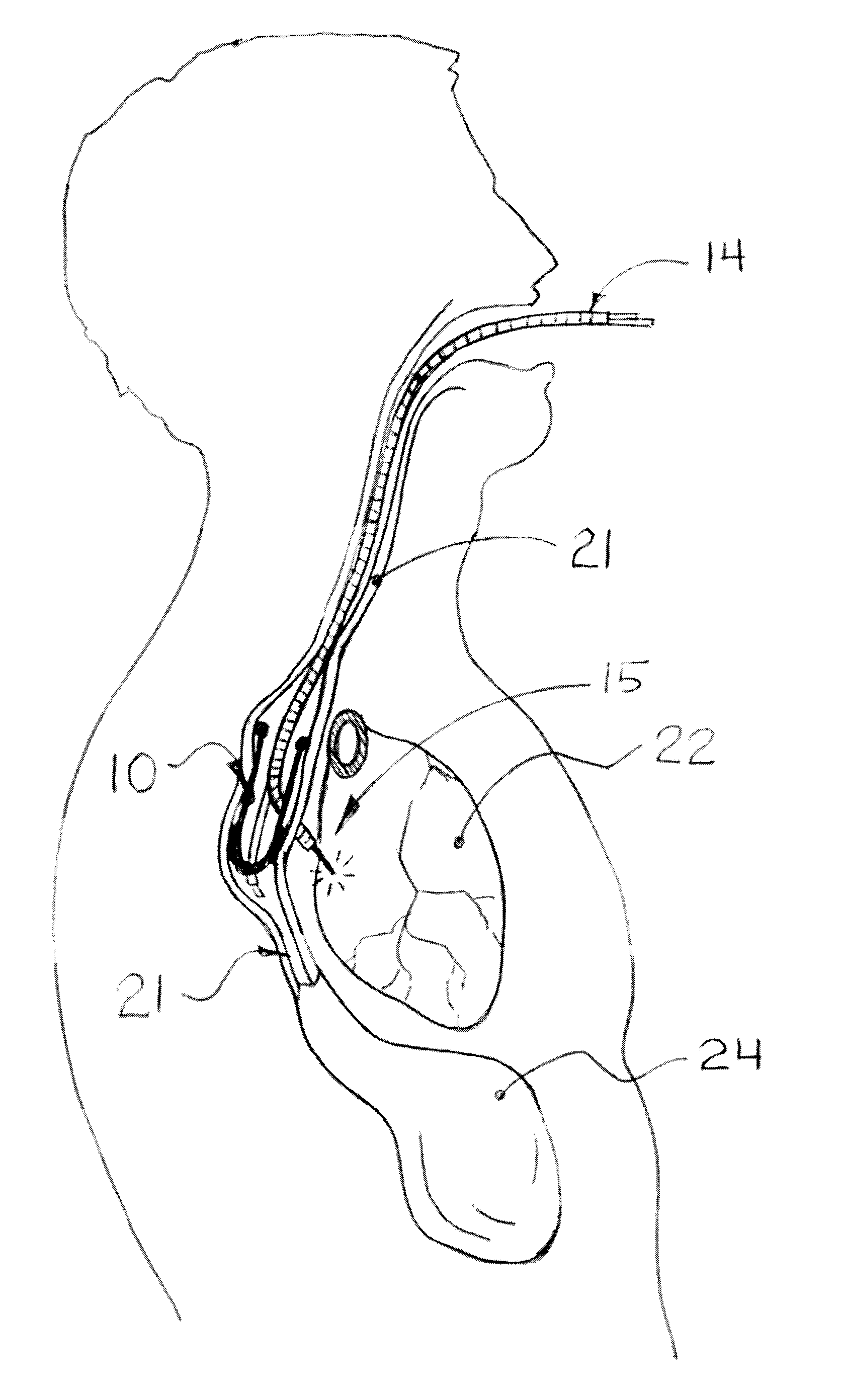
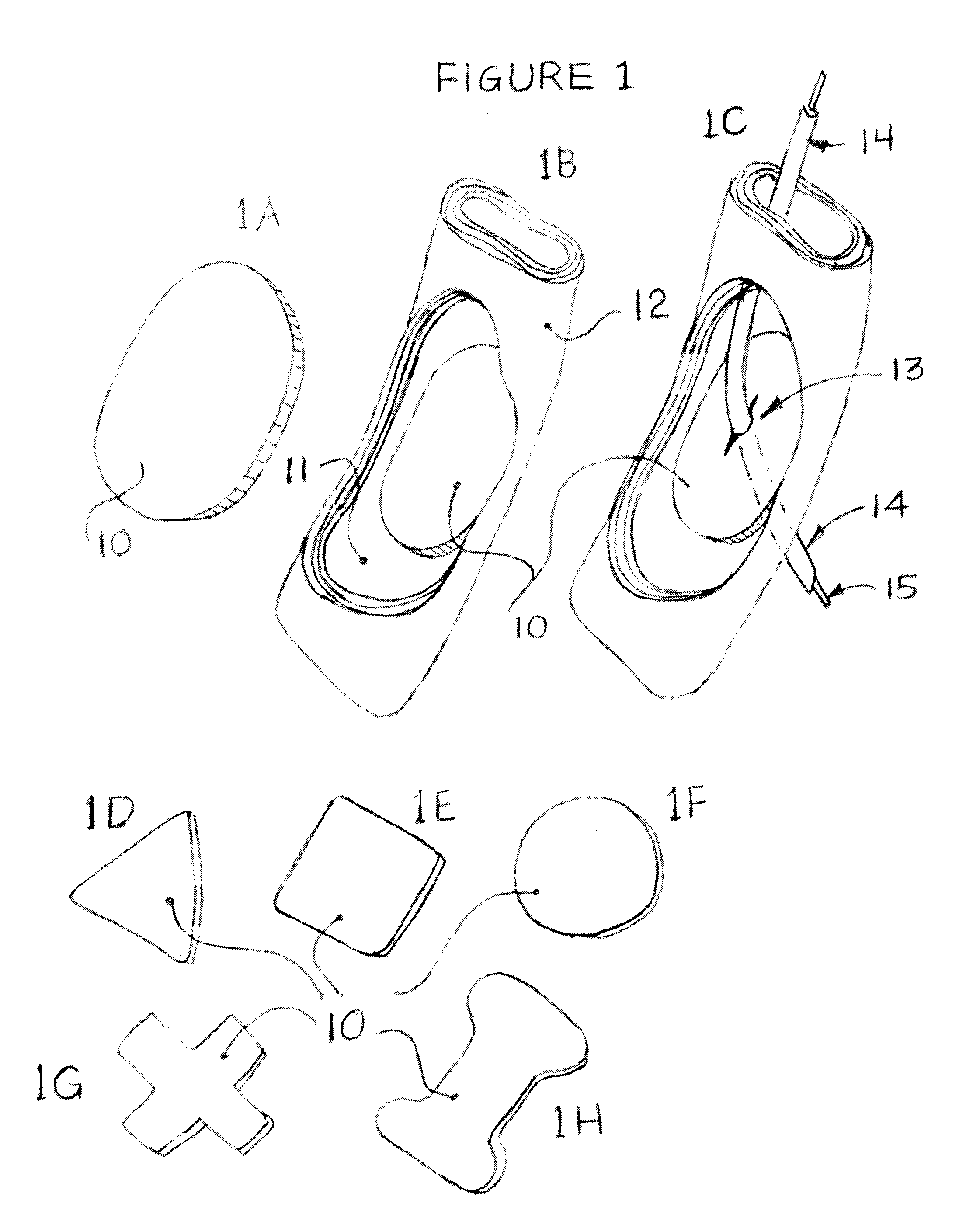
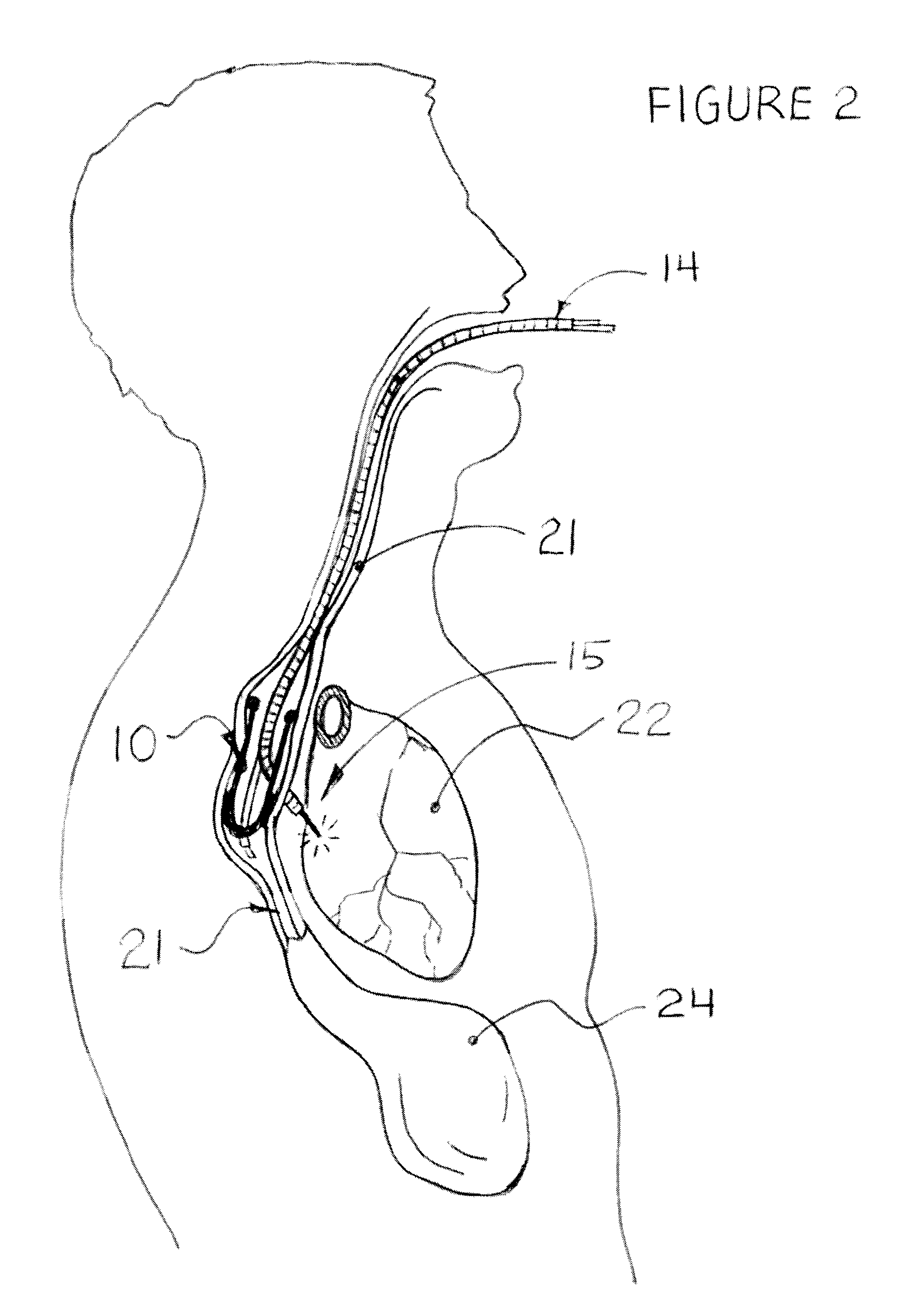
The current invention describes methods of transesophageal access to the neck and thorax to perform surgical interventions on structures outside the esophagus in both the cervical and the thoracic cavity. It describes a liner device made of a complete or partial tubular structure, or a flat plate, the liner having means to facilitate creation of a side opening, which may include a valve. The liner with its side opening form a port structure inside the esophageal lumen. The port structure allows elongated surgical devices to pass through a perforation across the full thickness of the esophageal wall to outside location, in a controlled way. The elongated surgical devices can be diagnostic scopes, therapeutic scopes, manual elongated surgical devices, robotic arms or the like. After being deployed outside the esophagus, the surgical devices can access structures outside the esophagus, in the neck and thorax in 360 degrees of freedom around the esophageal circumference. These structures can be bony, cartilaginous, spinal, vascular, soft tissue, deep tissues, lymph nodal, cardiac, pulmonary, tracheal, nervous, muscular or diaphragmatic, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the neck, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the anterior chest wall, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the skin of the back, and skin and layers of the breast.
Owner:MICROACCESS
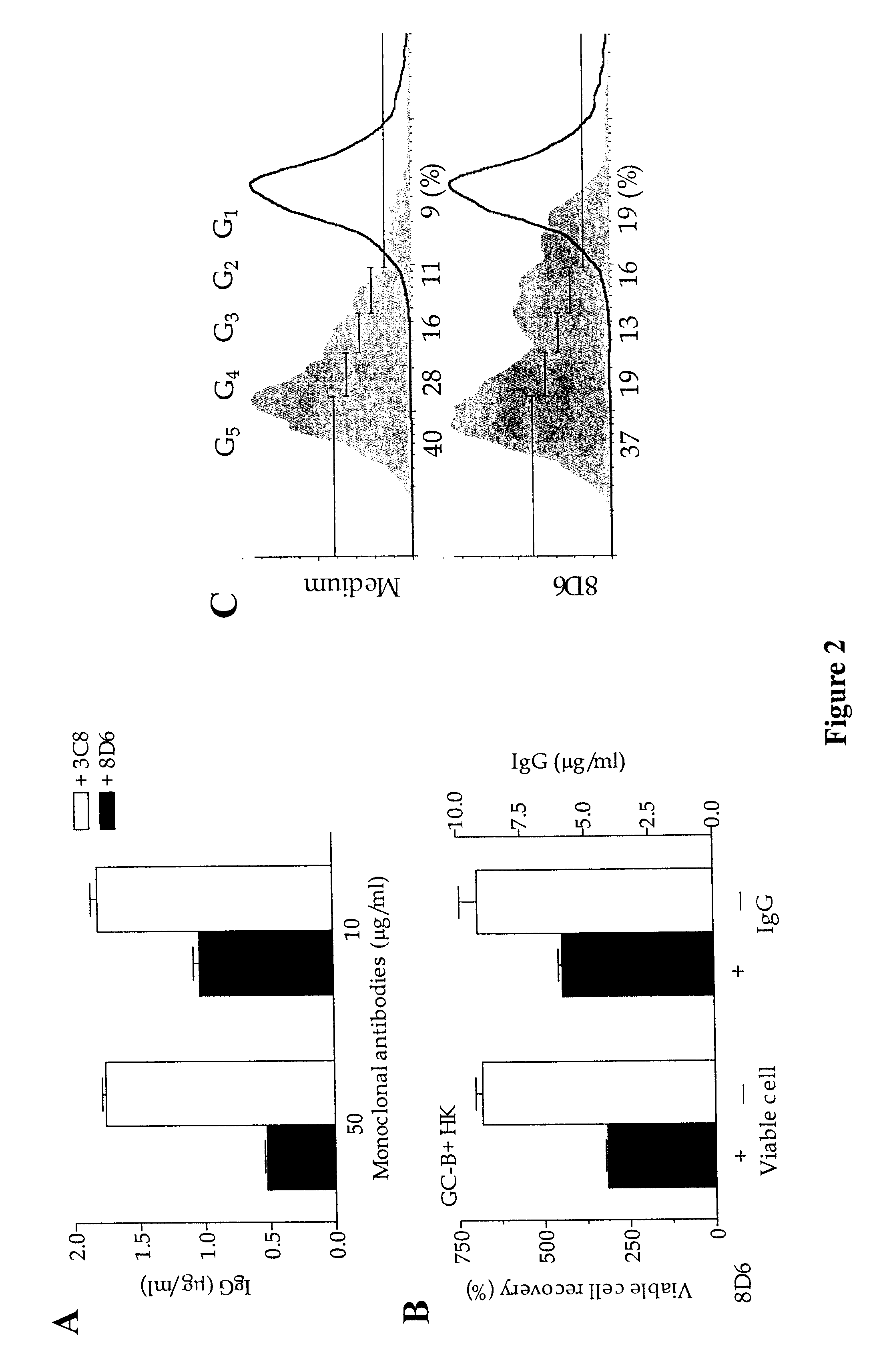
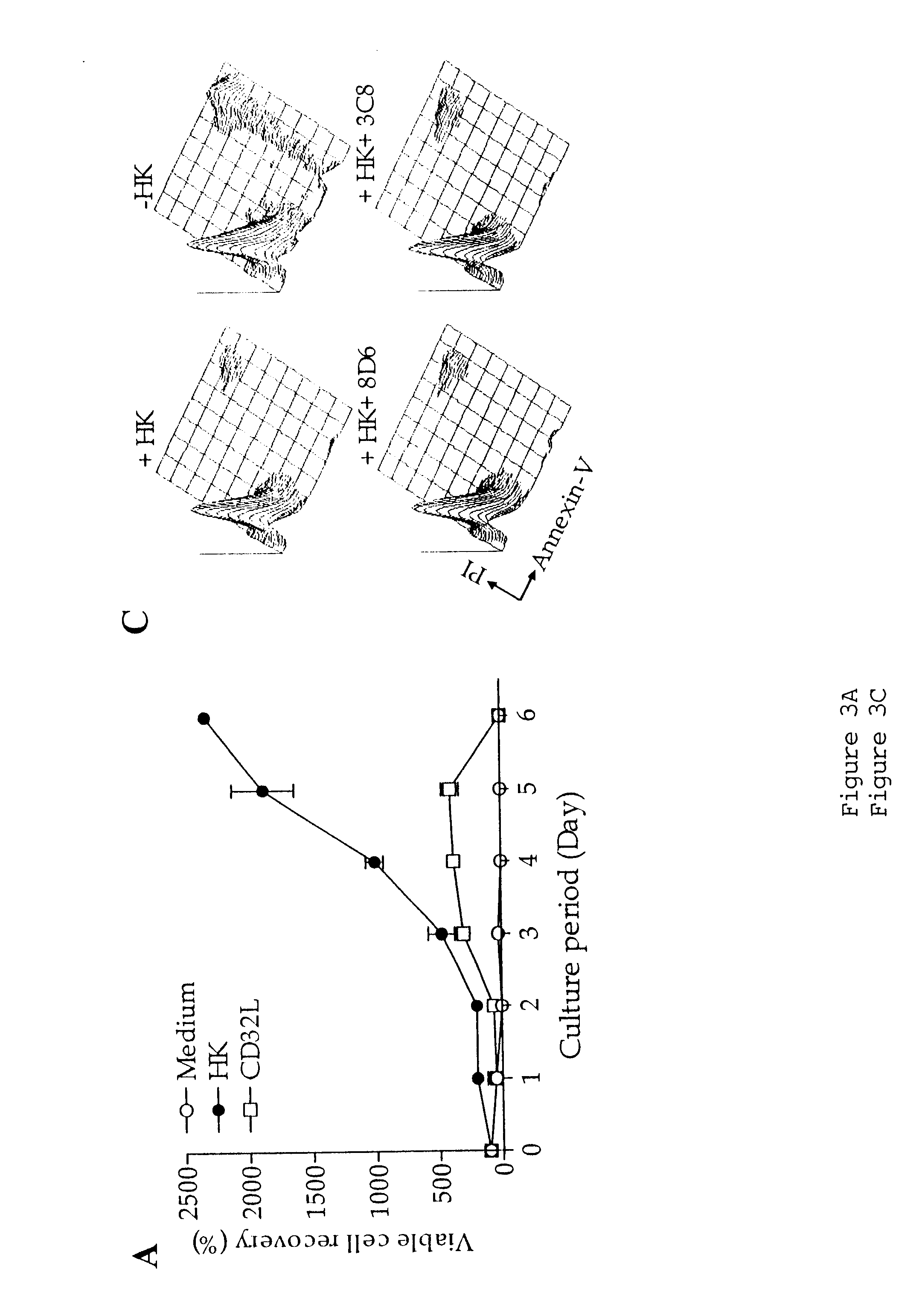
Monoclonal antibodies that suppress B cell growth and/or differentiation
The present invention provides monoclonal antibodies which interfere with the interactions between FDCs and B cells, thereby suppressing the proliferation and / or differentiation of B cells in lymphoid follicles. The monoclonal antibodies of the present invention are useful for treating follicular lymphomas, multiple myeloma as well as autoimmune diseases.
Owner:OCHSNER CLINIC FOUND
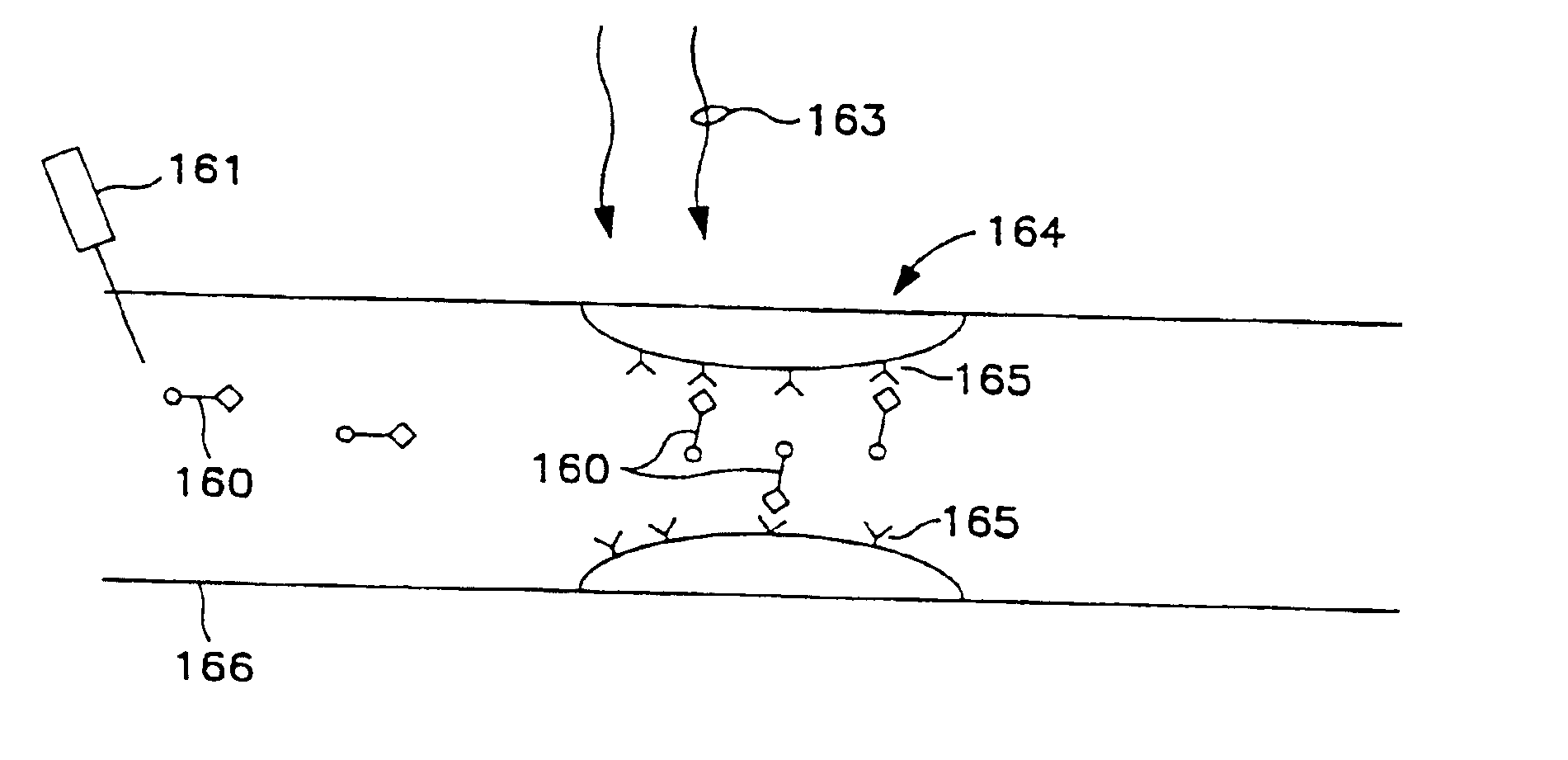
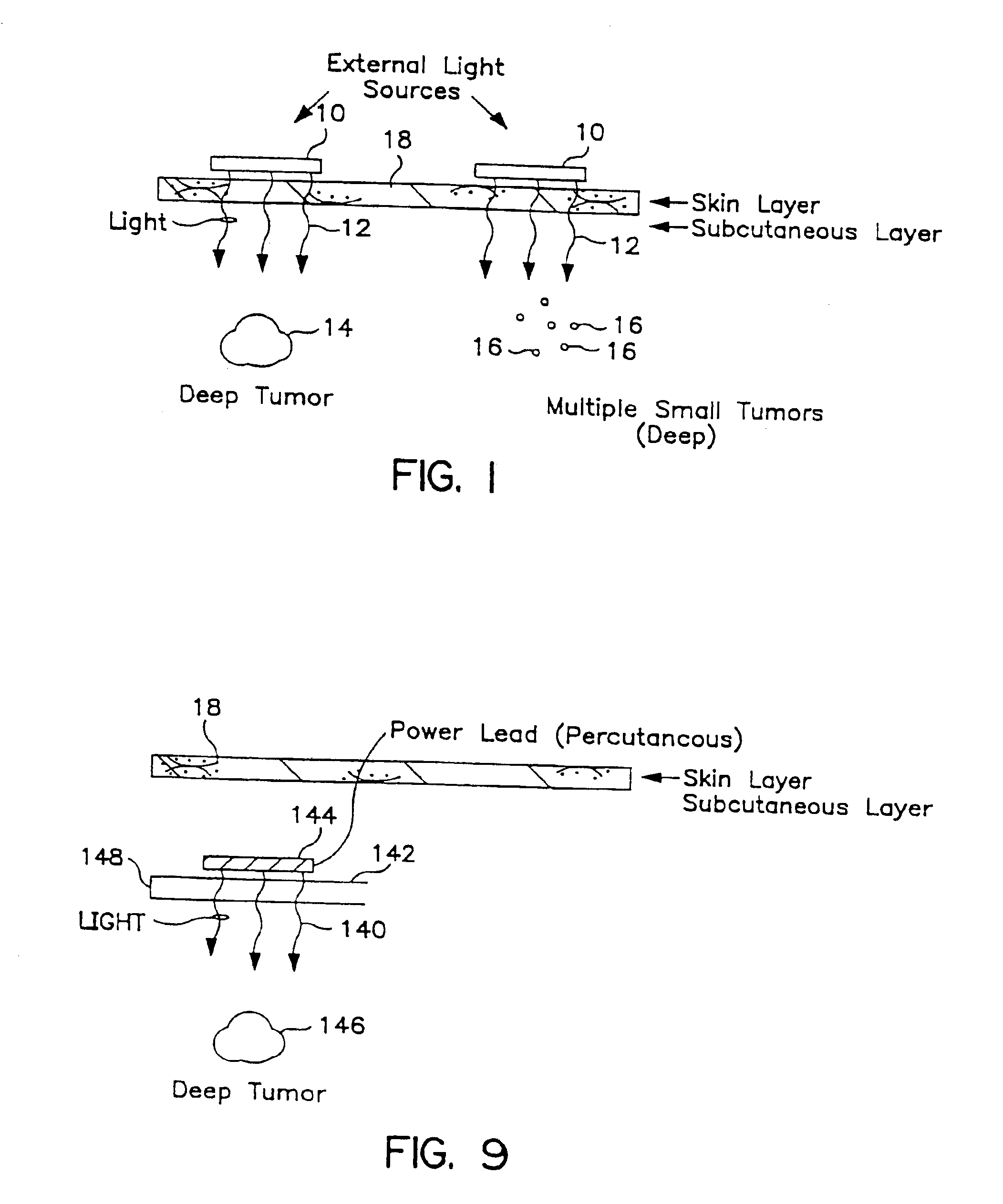
Transcutaneous photodynamic treatment of targeted cells
The present invention is drawn to methods and compounds for photodynamic therapy (PDT) of a target tissue or compositions in a mammalian subject, using a light source that preferably transmits light to a treatment site transcutaneously. The method provides for administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a targeted substance, which is either a targeted photosensitizing agent, or a photosensitizing agent delivery system, or a targeted prodrug. This targeted substance preferably selectively binds to the target tissue. Light at a wavelength or waveband corresponding to that which is absorbed by the targeted substance is then administered. The light intensity is relatively low, but a high total fluence is employed to ensure the activation of the targeted photosensitizing agent or targeted prodrug product. Transcutaneous PDT is useful in the treatment of specifically selected target tissues, such as vascular endothelial tissue, the abnormal vascular walls of tumors, solid tumors of the head and neck, tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, tumors of the liver, tumors of the breast, tumors of the prostate, tumors of the lung, nonsolid tumors, malignant cells of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue and other lesions in the vascular system or bone marrow, and tissue or cells related to autoimmune and inflammatory disease.
Owner:LIGHT SCI ONCOLOGY
Compositions and Methods for Immunomodulation in an Organism
ActiveUS20120177598A1Long half-lifeGood treatment effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsVaccinationHalf-life
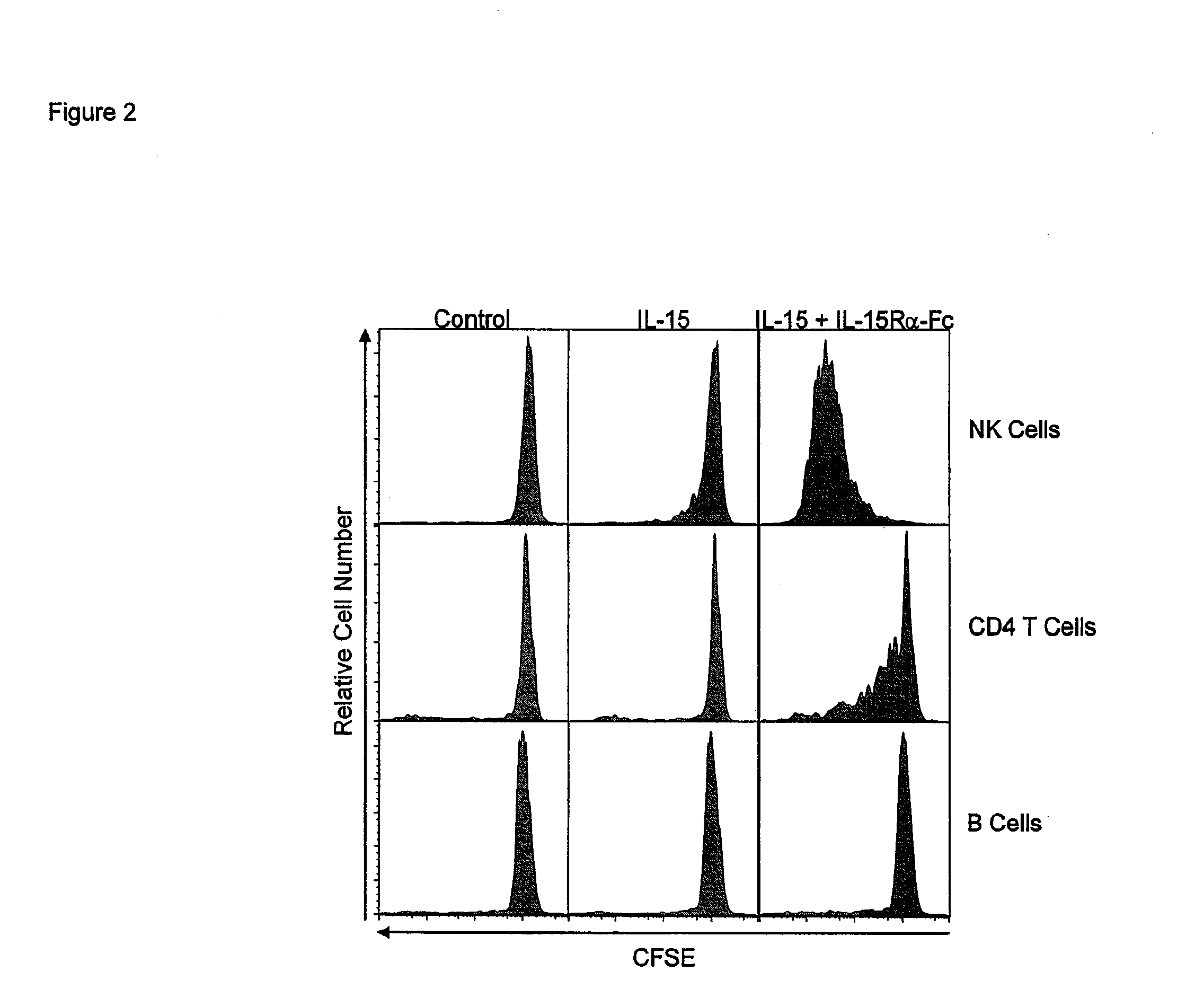
The present invention relates to a therapeutic polypeptide and methods for its creation and use for modulating an immune response in a host organism in need thereof. In particular, the invention relates to the administration to an organism in need thereof, of an effective amount of a pre-coupled polypeptide complex comprising a lymphokine polypeptide portion, for example IL-15 (SEQ ID NO: 5, 6), IL-2 (SEQ ID NO: 10, 12) or combinations of both, and an interleukin receptor polypeptide portion, for example IL-15Ra (SEQ ID NO: 7, 8), IL-2Ra (SEQ ID NO: 9, 11) or combinations of both, for augmenting the immune system in, for example, cancer, SCID, AIDS, or vaccination; or inhibiting the immune system in, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, or Lupus. The therapeutic complex of the invention surprisingly demonstrates increased half-life, and efficacy in vivo.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Compression garment for selective application for treatment of lymphedema and related illnesses manifested at various locations of the body
InactiveUS6852089B2Sufficient flexibilityLimit the amount of flexion of a limbPneumatic massageRestraining devicesDiseaseAfter treatment
A compression garment for selective application for treatment of lymphedema and related illnesses manifested at various locations of the body. The garment includes a pair or series of layers of hermetically sealed material, that can capture pressurized air, when applied therein, and is formed through the patterned sealing of the layers of the garment together, at select locations, to form air pockets that can selectively apply isolated points of pressure to the patient's affected area, without disrupting normal vascular and lymphatic functioning. The garment is design cut, for application to various segments of the body, and applies encompassing pressure over the entire affected area, and includes valves that can allow for the injection of measurable air, to the desired pressure points, or its deflation, after treatment.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEDICAL CORP
Humanized immunomodulatory monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of neoplastic disease or immunodeficiency
InactiveUS20080025980A1Induces proliferation and activationAvoids adverse immunogenic responseHybrid immunoglobulinsAntiviralsDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Owner:CURETECH LTD +1
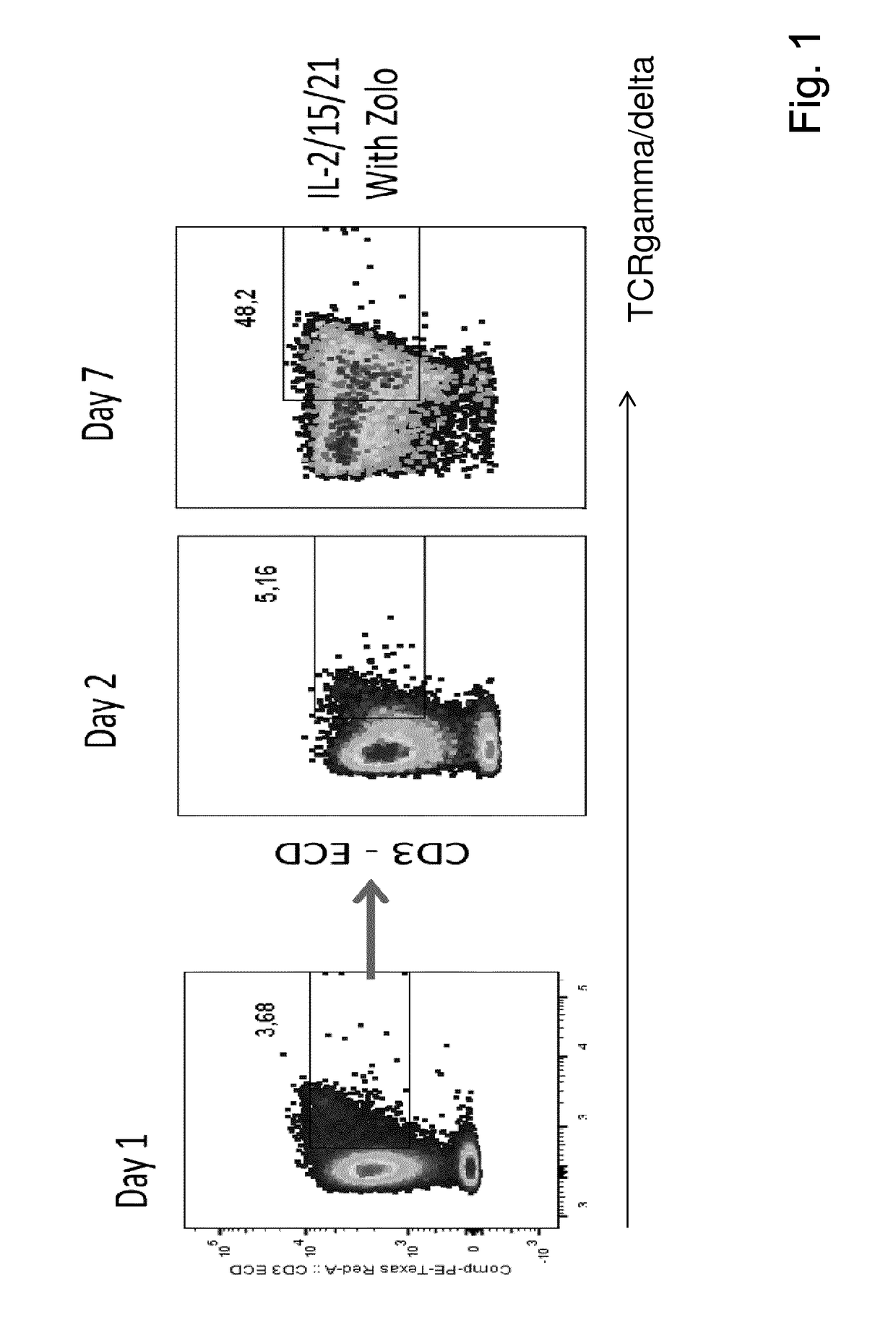
Expansion of lymphocytes with a cytokine composition for active cellular immunotherapy
PendingUS20170107490A1Increase stimulationImprove scalabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisTissue sampleLymphocyte
The present invention relates to a composition for expanding lymphocytes comprising at least two types of cytokines selected from interleukin 2 (IL-2), interleukin 15 (IL-15) and interleukin 21 (IL-21). It further relates to a Method of preparing a population of clinically relevant lymphocytes, comprising the steps of: obtaining a body sample from a mammal in particular a tissue sample or body liquid sample, comprising at least one lymphocyte and optionally separating the cells in the body sample, culturing the body sample in-vitro to expand and / or stimulate lymphocytes in the sample wherein the culturing comprises using IL-2, IL-15 and / or IL-21, and optionally determining the presence of clinically relevant lymphocyte in the cultured sample. The present invention also relates to an immunotherapy and the population of clinically relevant lymphocytes.
Owner:POLYBIOCEPT GMBH
Method of inducing a CTL response
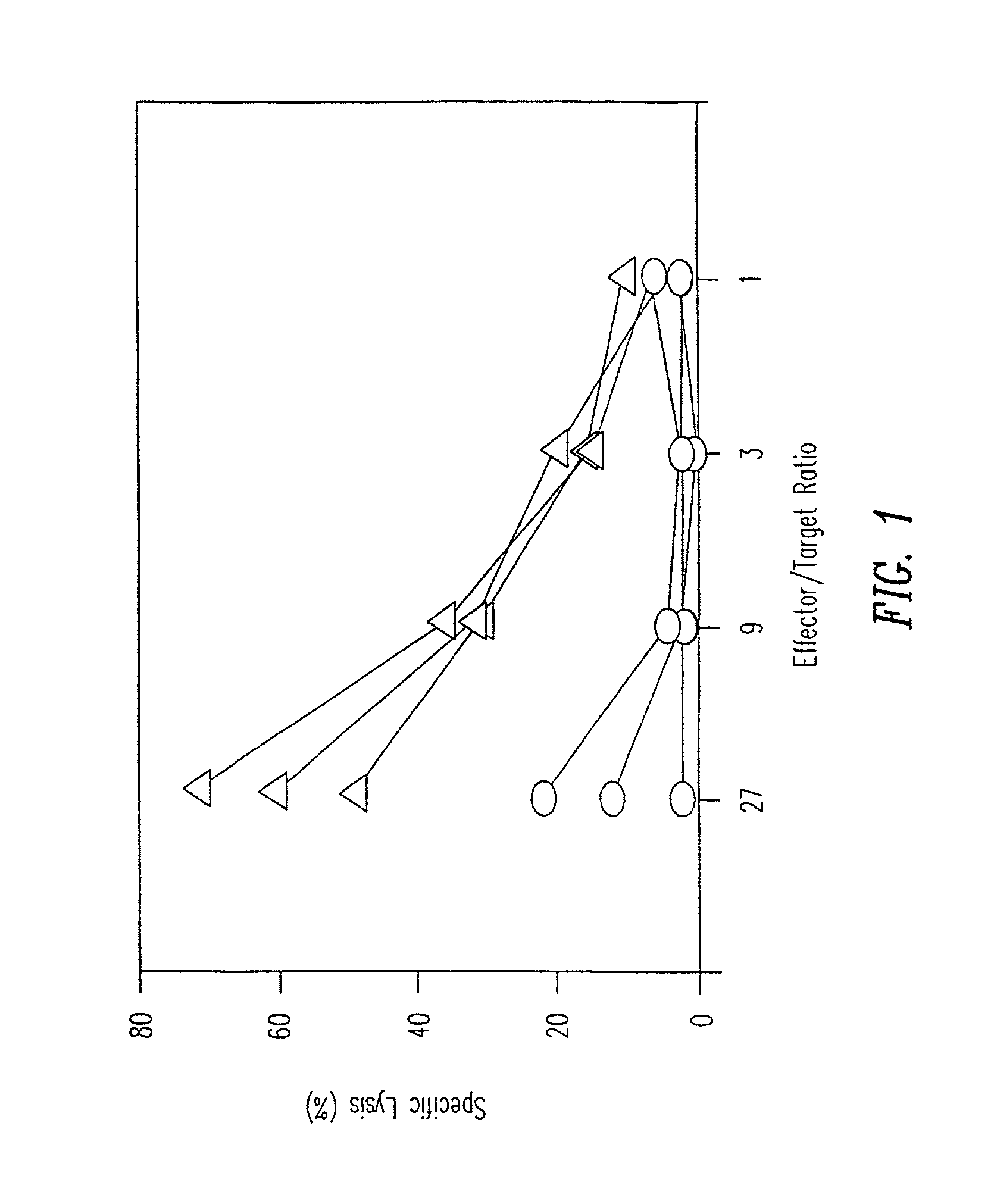
Disclosed herein are methods for inducing an immunological CTL response to an antigen by sustained, regular delivery of the antigen to a mammal so that the antigen reaches the lymphatic system. Antigen is delivered at a level sufficient to induce an immunologic CTL response in a mammal and the level of the antigen in the mammal's lymphatic system is maintained over time sufficient to maintain the immunologic CTL response. Also disclosed is an article of manufacture for delivering an antigen that induces a CTL response in an animal.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Monitoring health and disease status using clonotype profiles
ActiveUS8628927B2High sensitivityOvercome deficienciesMicrobiological testing/measurementUnknown materialsAutoimmune diseaseLymphatic neoplasm
There is a need for improved methods for determining the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with conditions, including autoimmune disease and cancer, especially lymphoid neoplasms, such as lymphomas and leukemias. Provided herein are methods for using DNA sequencing to identify personalized, or patient-specific biomarkers in patients with lymphoid neoplasms, autoimmune disease and other conditions. Identified biomarkers can be used to determine and / or monitor the disease state for a subject with an associated lymphoid disorder or autoimmune disease or other condition. In particular, the invention provides a sensitive method for monitoring lymphoid neoplasms that undergo clonal evolutions without the need to development alternative assays for the evolved or mutated clones serving as patient-specific biomarkers.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Novel methods for therapeutic vaccination
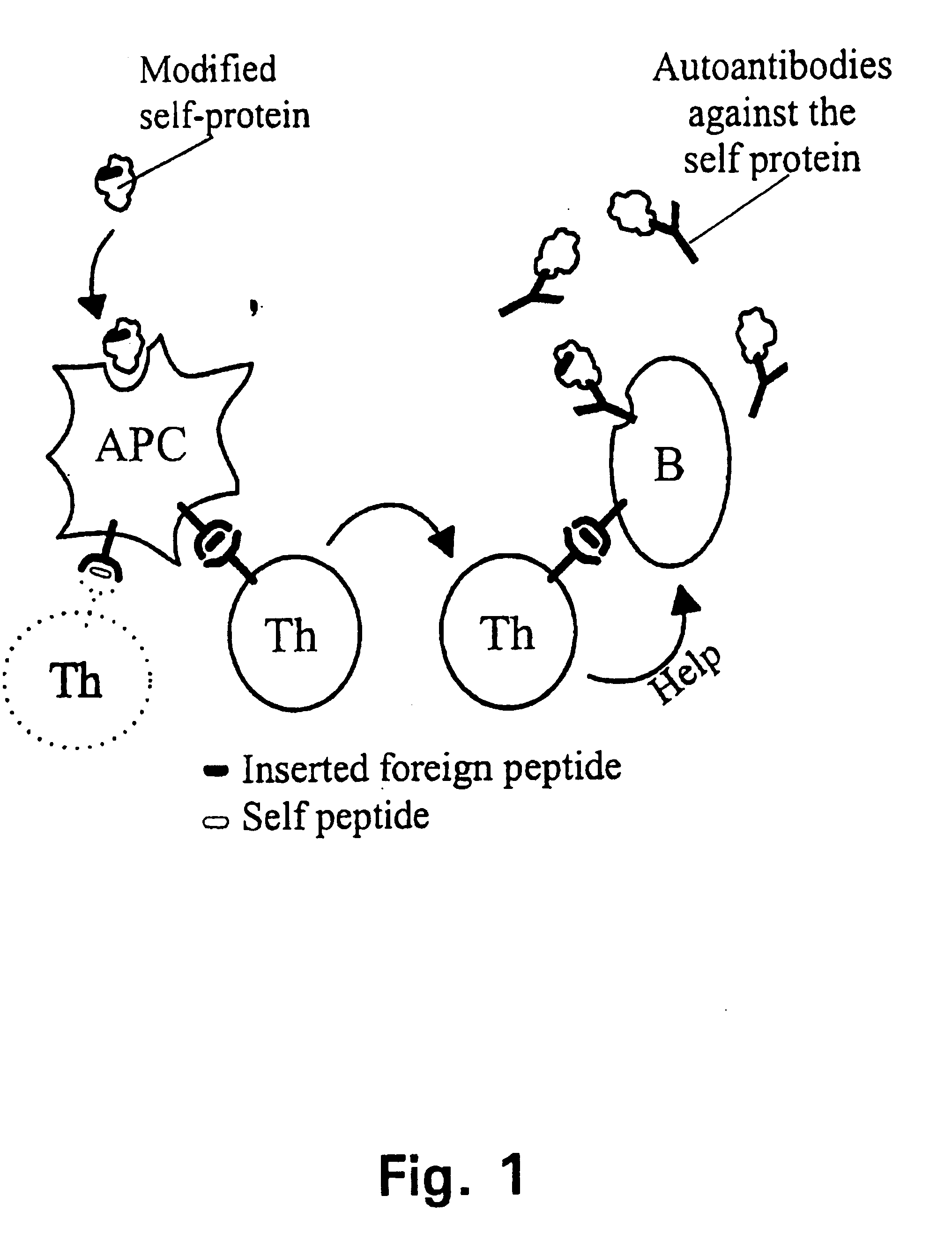
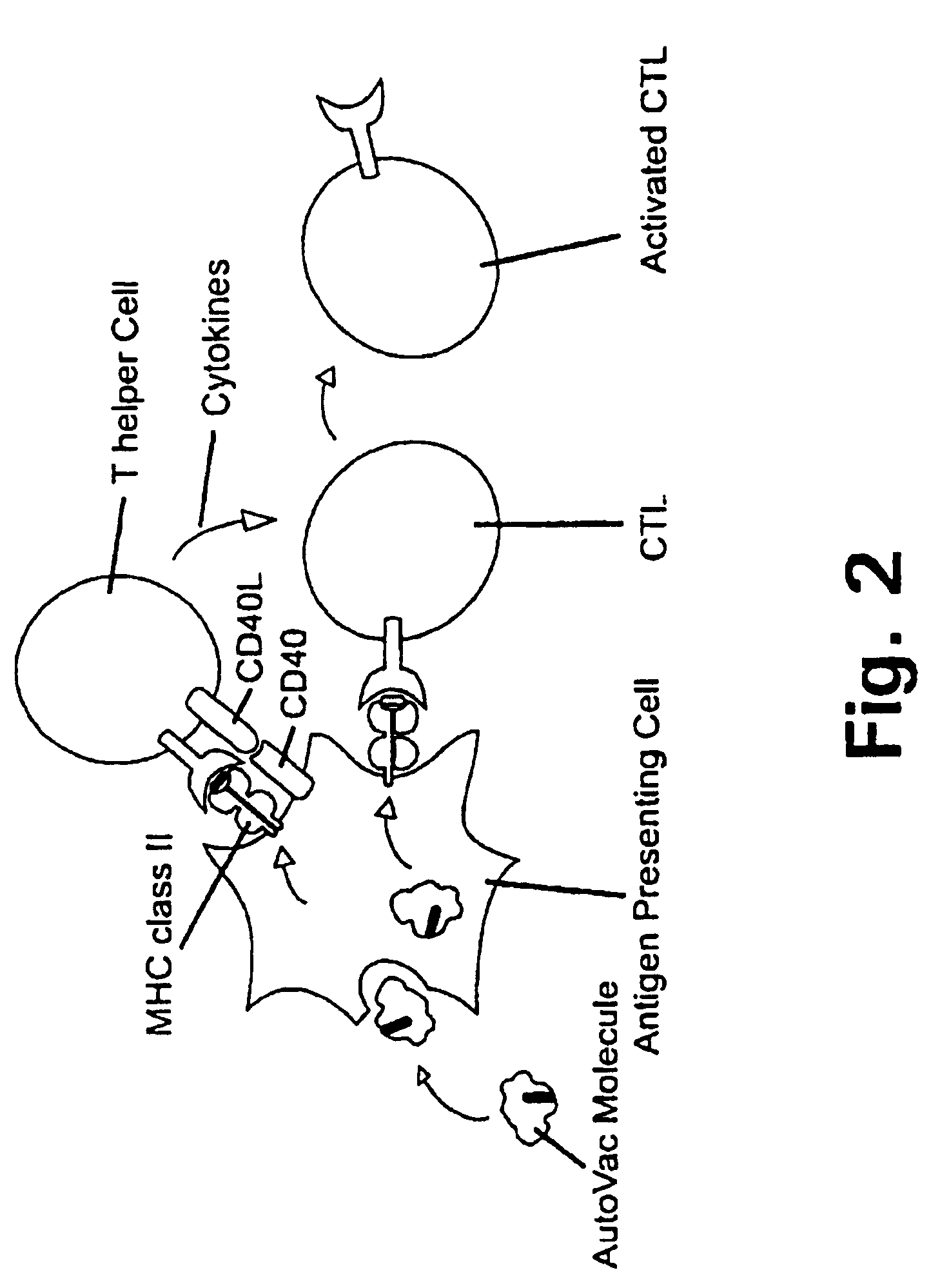
A method is disclosed for inducing cell-mediated immunity against cellular antigens. More specifically, the invention provides for a method for inducing cytotoxic T-lymphocyte immunity against weak antigens, notably self-proteins. The method entails that antigen presenting cells are induced to present at least one CTL epitope of the weak antigen and at the same time presenting at least one foreign T-helper lymphocyte epitope. In a preferred embodiment, the antigen is a cancer specific antigen, e.g. PSM, Her2, or FGF8b. The method can be exercised by using traditional polypeptide vaccination, but also by using live attenuated vaccines or nucleic acid vaccination. The invention furthermore provides immunogenic analogues of PSM, Her2 and FGF8b, as well as nucleic acid molecules encoding these analogues. Also vectors and transformed cells are disclosed. The invention also provides for a method for identification of immunogenic analogues of weak or non-immunogenic antigens.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Method for administering a cytokine to the central nervous system and the lymphatic system
InactiveUS6991785B2Provide effectModulate immune and inflammatory responseBiocideNervous disorderImmunologic disordersInterferon alpha
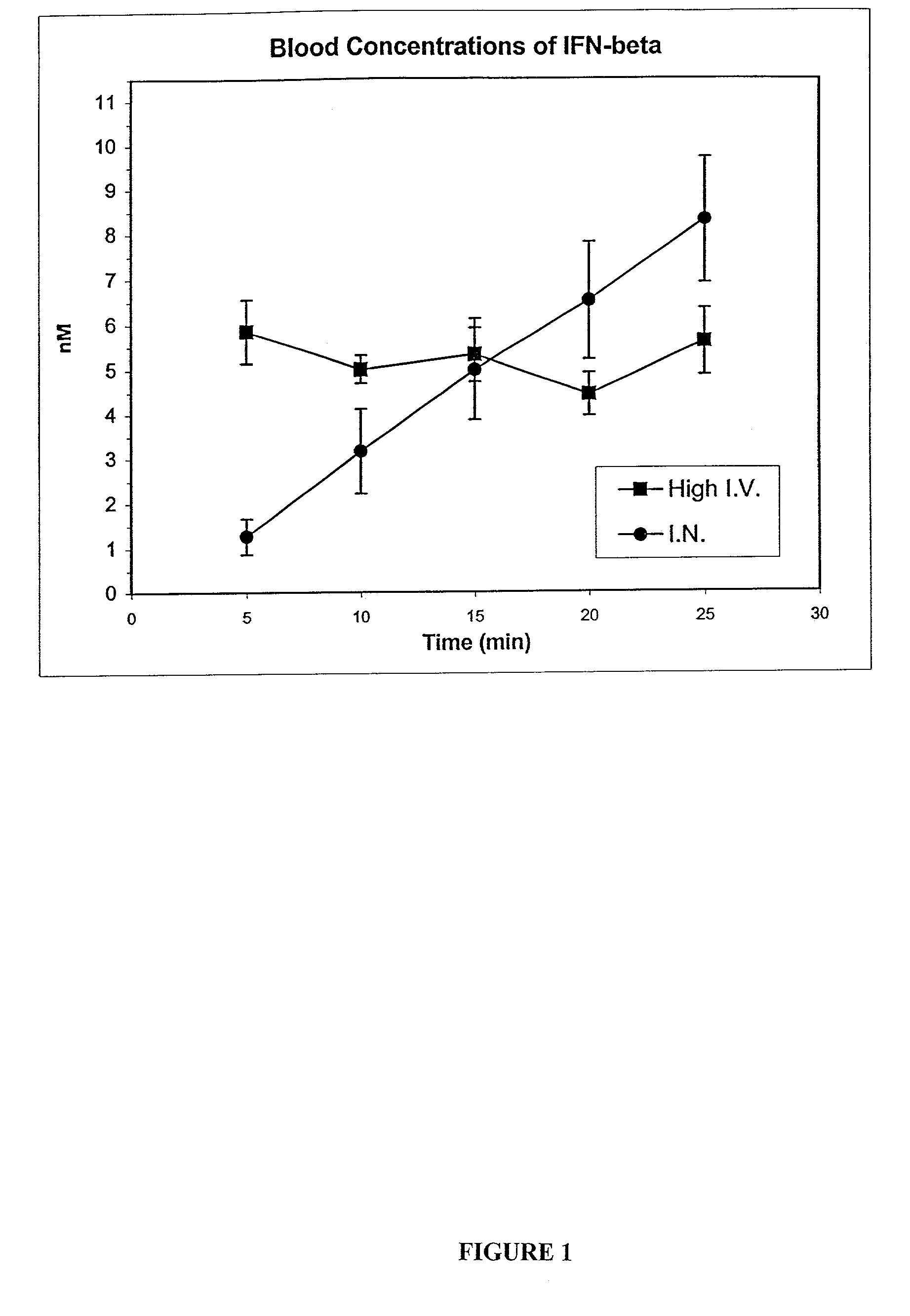
The present invention is directed to a method for delivering cytokines to the central nervous system and the lymphatic system by way of a tissue innervated by the trigeminal nerve and / or olfactory nerve. Cytokines include tumor necrosis factors, interleukins, interferons, particularly interferon-β and its muteins such as IFN-βser17. Such a method of delivery can be useful in the treatment of central nervous system disorders, brain disorders, proliferative, viral, and / or autoimmune disorders such as Sjogren's disorder.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Compositions and methods for the treatment and diagnosis of immune disorders
InactiveUS6084083AReduce in quantityLower Level RequirementsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaClinical trialCell subpopulations
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment and diagnosis of immune disorders, especially T helper lymphocyte-related disorders. For example, genes which are differentially expressed within and among T helper (TH) cells and TH cell subpopulations, which include, but are not limited to TH0, TH1 and TH2 cell subpopulations are identified. Genes are also identified via the ability of their gene products to interact with gene products involved in the differentiation, maintenance and effector function of such TH cells and TH cell subpopulations. The genes identified can be used diagnostically or as targets for therapeutic intervention. In this regard, the present invention provides methods for the identification and therapeutic use of compounds as treatments of immune disorders, especially TH cell subpopulation-related disorders. Additionally, methods are provided for the diagnostic evaluation and prognosis of TH cell subpopulation-related disorders, for the identification of subjects exhibiting a predisposition to such conditions, for monitoring patients undergoing clinical evaluation for the treatment of such disorders, and for monitoring the efficacy of compounds used in clinical trials.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Methods of growing tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in gas-permeable containers
InactiveUS20170152478A1Mammal material medical ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthTumour tissue
An embodiment of the invention provides a method of promoting regression of cancer in a mammal comprising obtaining a tumor tissue sample from the mammal; culturing the tumor tissue sample in a first gas permeable container containing cell medium therein; obtaining tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) from the tumor tissue sample; expanding the number of TIL in a second gas permeable container containing cell medium therein using irradiated allogeneic feeder cells and / or irradiated autologous feeder cells; and administering the expanded number of TIL to the mammal. Methods of obtaining an expanded number of TIL from a mammal for adoptive cell immunotherapy are also provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
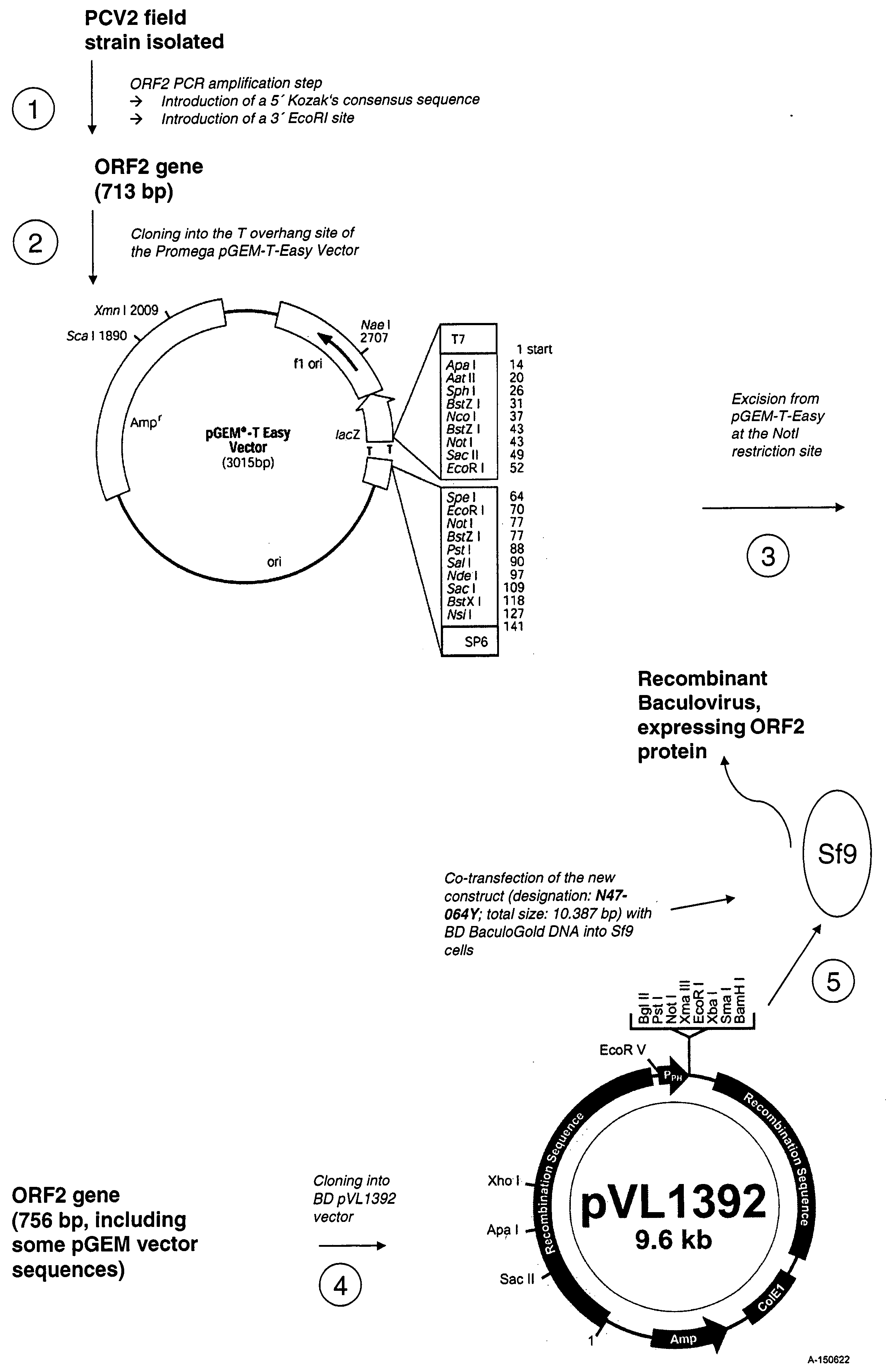
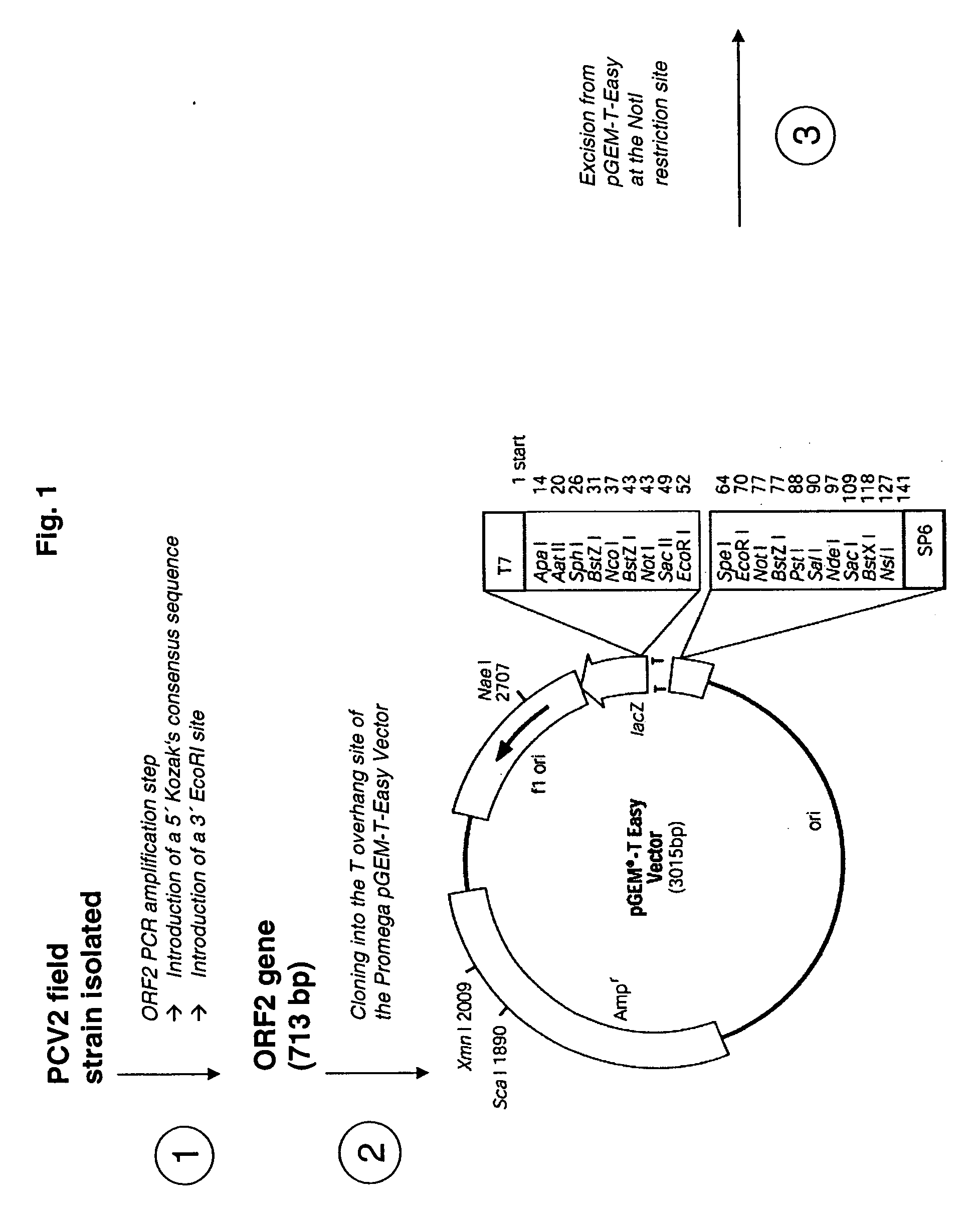
Use of a pcv2 immunogenic composition for lessening clinical symptoms in pigs
InactiveUS20080181910A1Reduces circovirus loadImprove the level ofViral antigen ingredientsDigestive systemClinical manifestationPorcine circovirus
The present invention relates to the use of an immunogenic composition that comprises a porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) antigen for treatment of several clinical manifestations (diseases). Preferably, the clinical manifestations are associated with a PCV2 infection. Preferably, they include lymphadenopathy, lymphoid depletion and / or multinucleated / giant histiocytes. Moreover, the clinical symptoms include lymphadenopathy in combination with one or a multiple of the following symptoms in pigs: (1) interstitial pneumonia with interlobular edema, (2) cutaneous pallor or icterus, (3) mottled atrophic livers, (4) gastric ulcers, (5) nephritis and (6) reproductive disorders, e.g. abortion, stillbirths, mummies, etc. Furthermore the clinical symptoms include Pia like lesions, normally known to be associated with Lawsonia intracellularis infections.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEM VETMADICA INC
Method of inducing a CTL response
InactiveUS20020007173A1Thorough eradicationEasy to useVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenMammal
Disclosed herein are methods for inducing an immunological CTL response to an antigen by sustained, regular delivery of the antigen to a mammal so that the antigen reaches the lymphatic system. Antigen is delivered at a level sufficient to induce an immunologic CTL response in a mammal and the level of the antigen in the mammal's lymphatic system is maintained over time sufficient to maintain the immunologic CTL response. Also disclosed is an article of manufacture for delivering an antigen that induces a CTL response in an animal.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Novel methods for therapeutic vaccination
A method is disclosed for inducing cell-mediated immunity against cellular antigens. More specifically, the invention provides for a method for inducing cytotoxic T-lymphocyte immunity against weak antigens, notably self-proteins. The method entails that antigen presenting cells are induced to present at least one CTL epitope of the weak antigen and at the same time presenting at least one foreign T-helper lymphocyte epitope. In a preferred embodiment, the antigen is a cancer specific antigen, e.g. PSM, Her2, or FGF8b. The method can be exercised by using traditional polypeptide vaccination, but also by using live attenuated vaccines or nucleic acid vaccination. The invention furthermore provides immunogenic analogues of PSM, Her2 and FGF8b, as well as nucleic acid molecules encoding these analogues. Also vectors and transformed cells are disclosed. The invention also provides for a method for identification of immunogenic analogues of weak or non-immunogenic antigens.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Detection of 13q14 chromosomal alterations
InactiveUS7479370B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphocyteChromosomal Alterations
The present invention relates to methods for detection of chromosomal alterations which are associated with the presence of various leukemias and lymphomas. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a biological sample comprising lymphocytes from an individual and assaying the sample to detect chromosomal deletions in the regions of chromosome 13 that corresponds to the region of chromosome 13 present in the RP11-147H23 or RP11-327P2.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
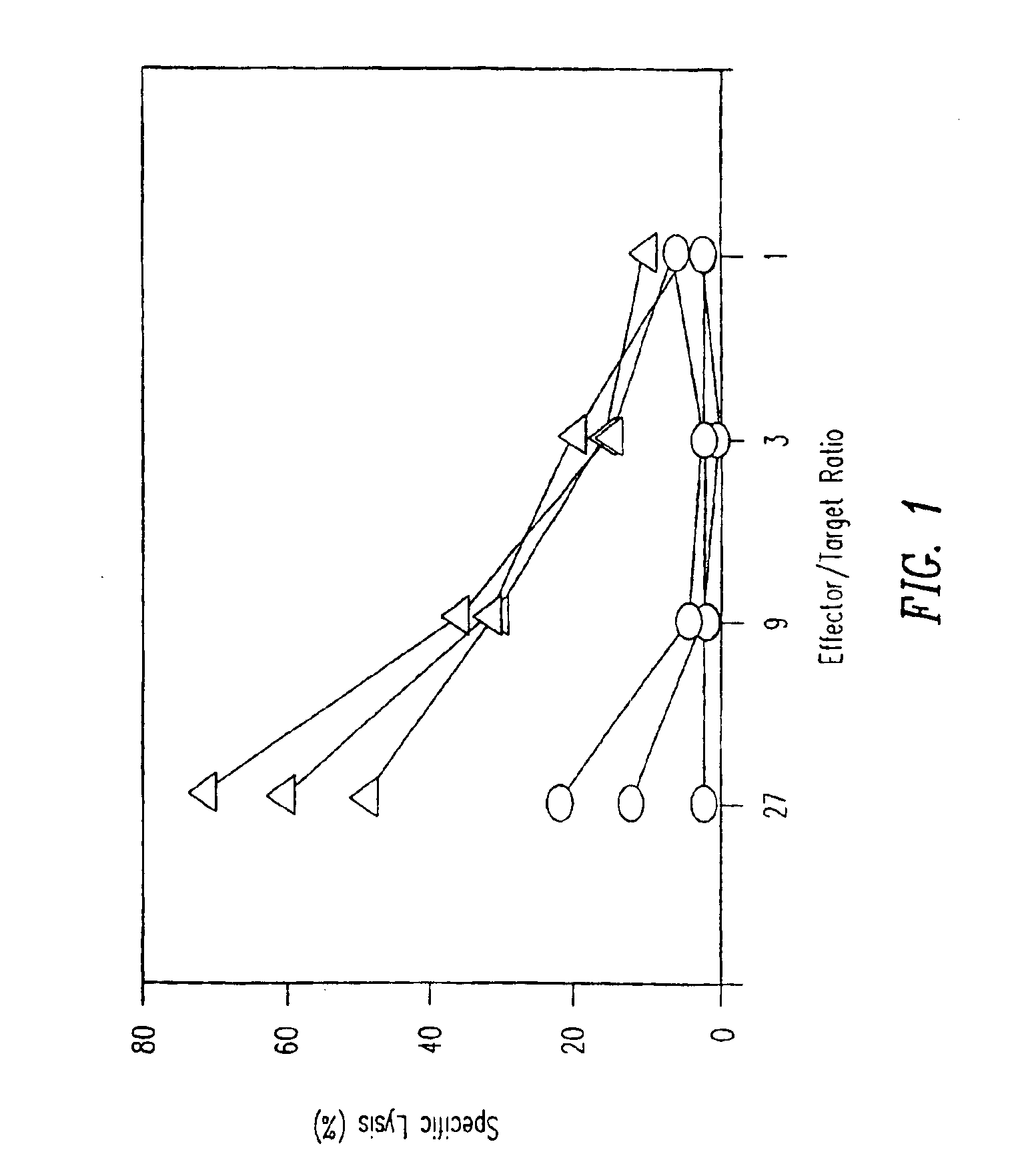
Adoptive transfer of cd8 + t cell clones derived from central memory cells
InactiveUS20080131415A1Increased proliferationBiocideArtificial cell constructsWhite blood cellPharmaceutical formulation
The present invention provides a method of carrying out adoptive immunotherapy in a primate subject in need thereof by administering the subject a cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) preparation in a treatment-effective amount. The method comprises administering as the CTL preparation a preparation consisting essentially of an in vitro expanded primate CTL population, the CTL population enriched prior to expansion for central memory T lymphocytes, and depleted prior to expansion of effector memory T lymphocytes. In some embodiments, the method may further comprise concurrently administering Interleukin-15 to the subject in an amount effective to increase the proliferation of the central memory T cells in the subject. Pharmaceutical formulations produced by the method, and methods of using the same, are also described.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE +1
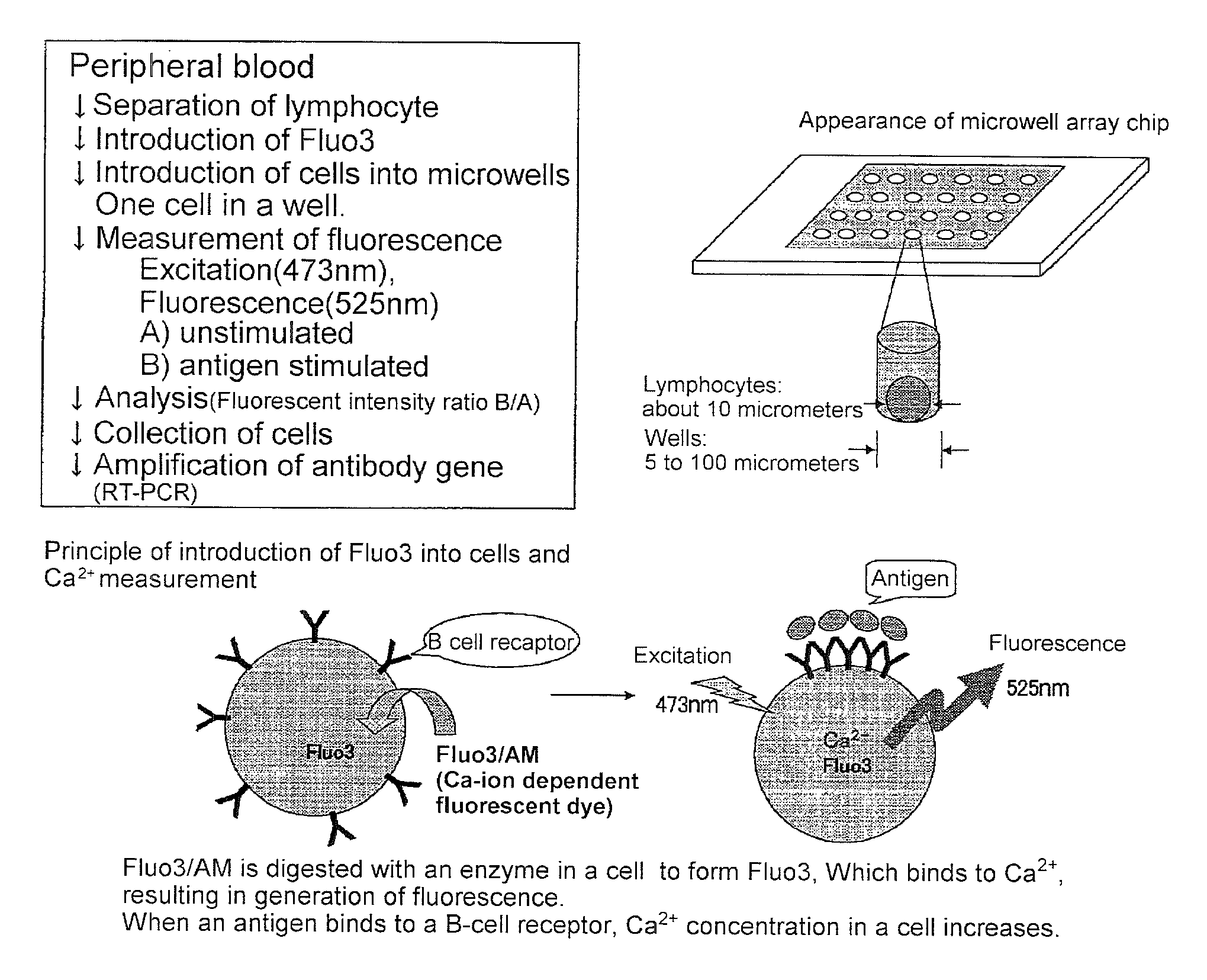
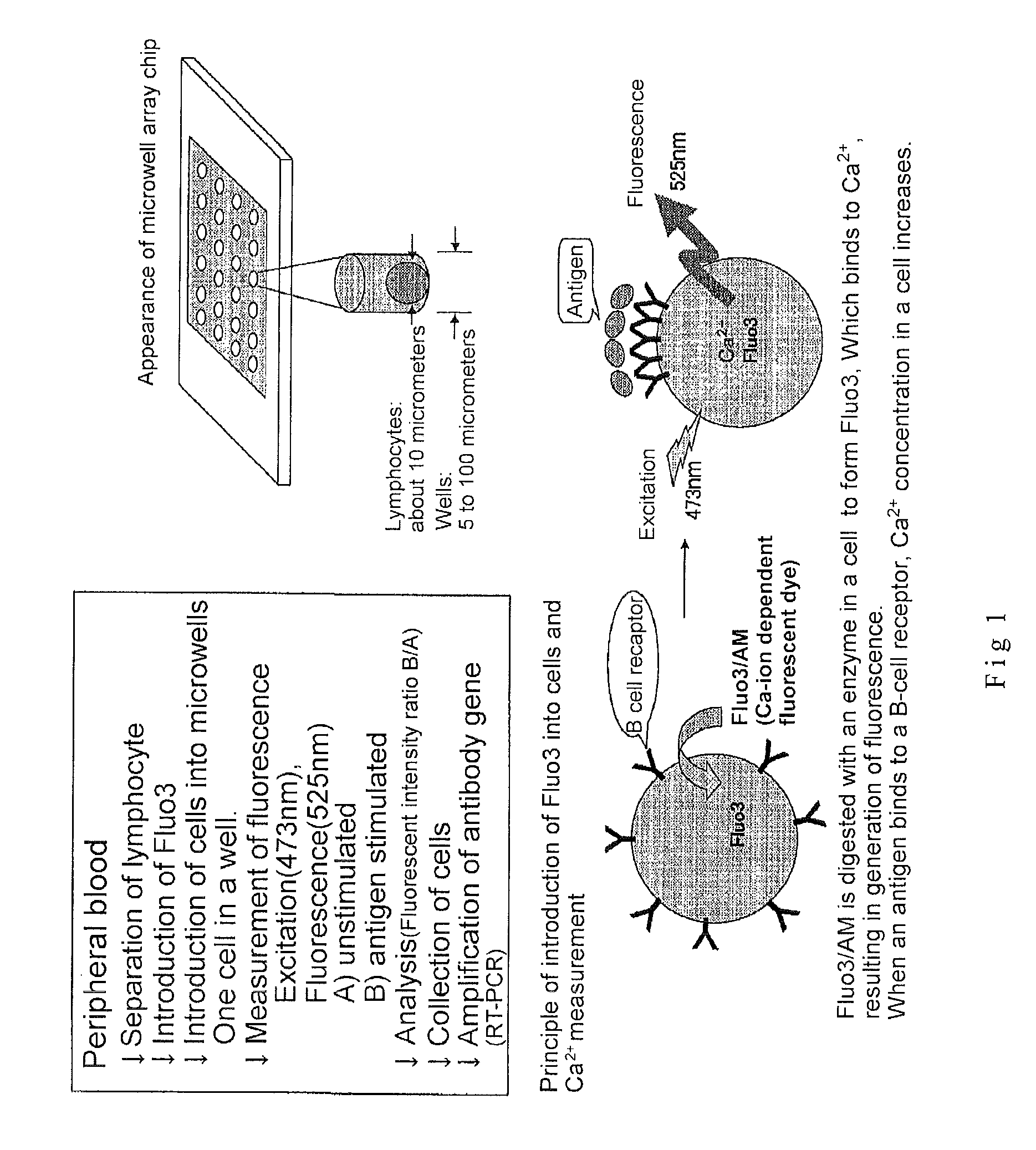
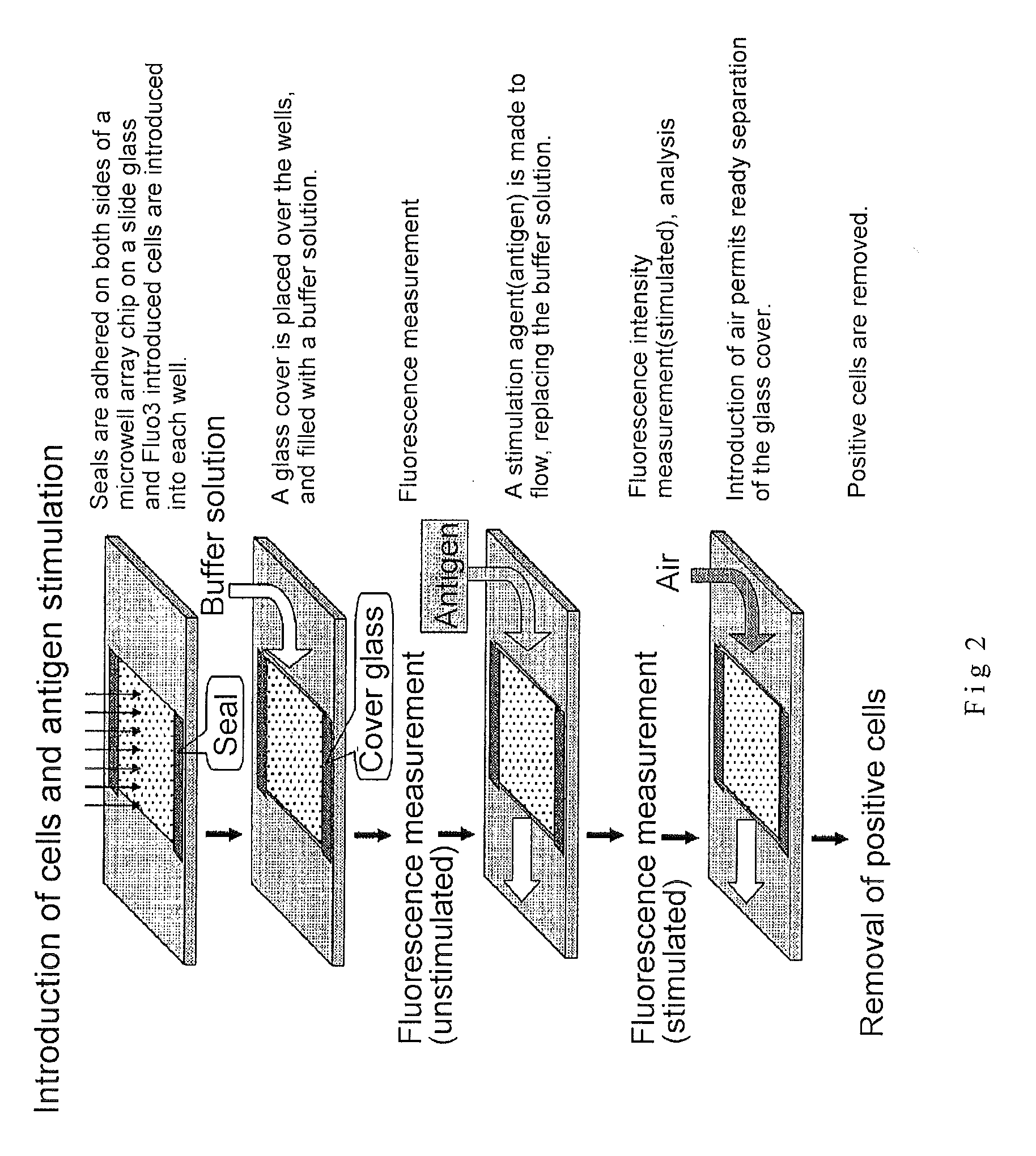
Microwell array chip for detecting antigen-specific lymphocytes, method of detecting and method of manufacturing antigen-specific lymphocytes, and method of cloning antigen-specific lymphocyte antigen receptor genes
ActiveUS20090181859A1Library screeningImmunoglobulins against virusesLymphocyte antigen receptorCellular antigens
A microwell array chip that has multiple microwells and is employed to contain a single lymphocyte specimen in each microwell and detect antigen-specific lymphocytes in single units; wherein the microwell array chip is of a shape and of dimensions where only one lymphocyte is contained in each microwell. A method of detecting antigen-specific lymphocytes comprising the steps of adding antigen to each microwell in the above microwell array chip, stimulating the lymphocyte specimen, and detecting lymphocyte specimens reacting with the antigen.
Owner:BLINK BIOMEDICAL SAS
Modulating agonistic tnfr antibodies
InactiveUS20140010812A1High binding affinityExcellent agonistic activityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell specificLymphocyte
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com