Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1774 results about "Mixing ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry and physics, the dimensionless mixing ratio is the abundance of one component of a mixture relative to that of all other components. The term can refer either to mole ratio or mass ratio.
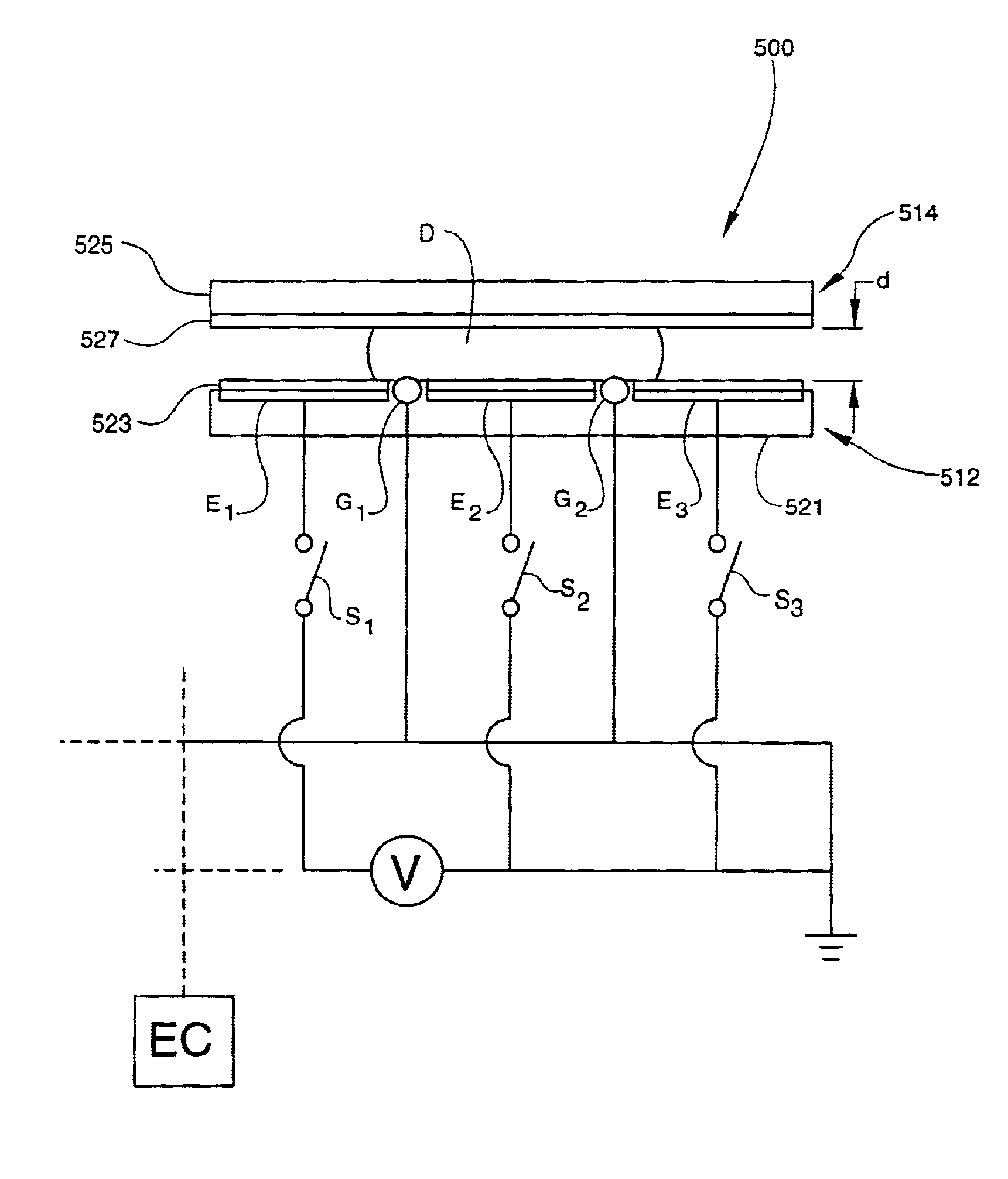
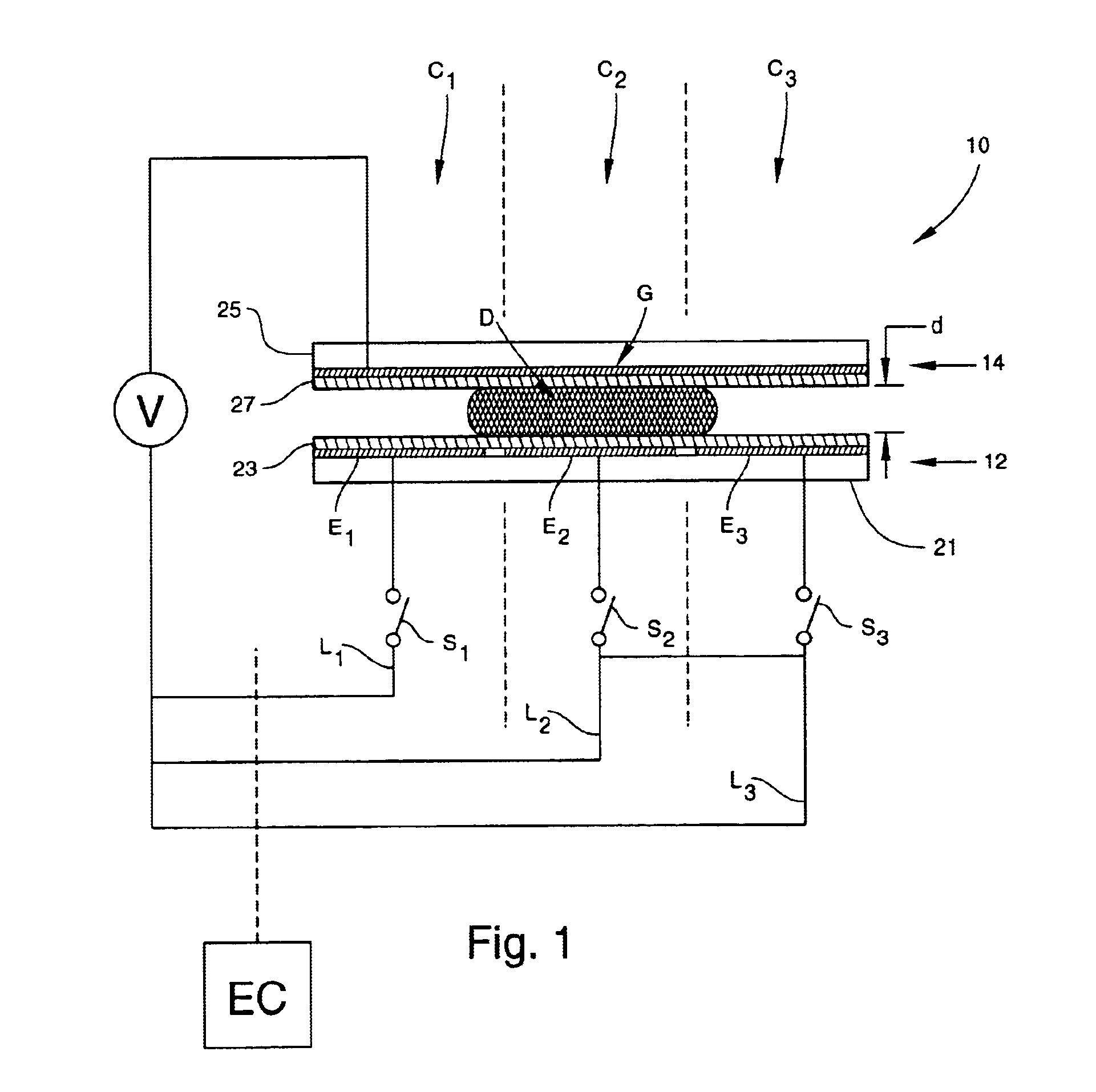
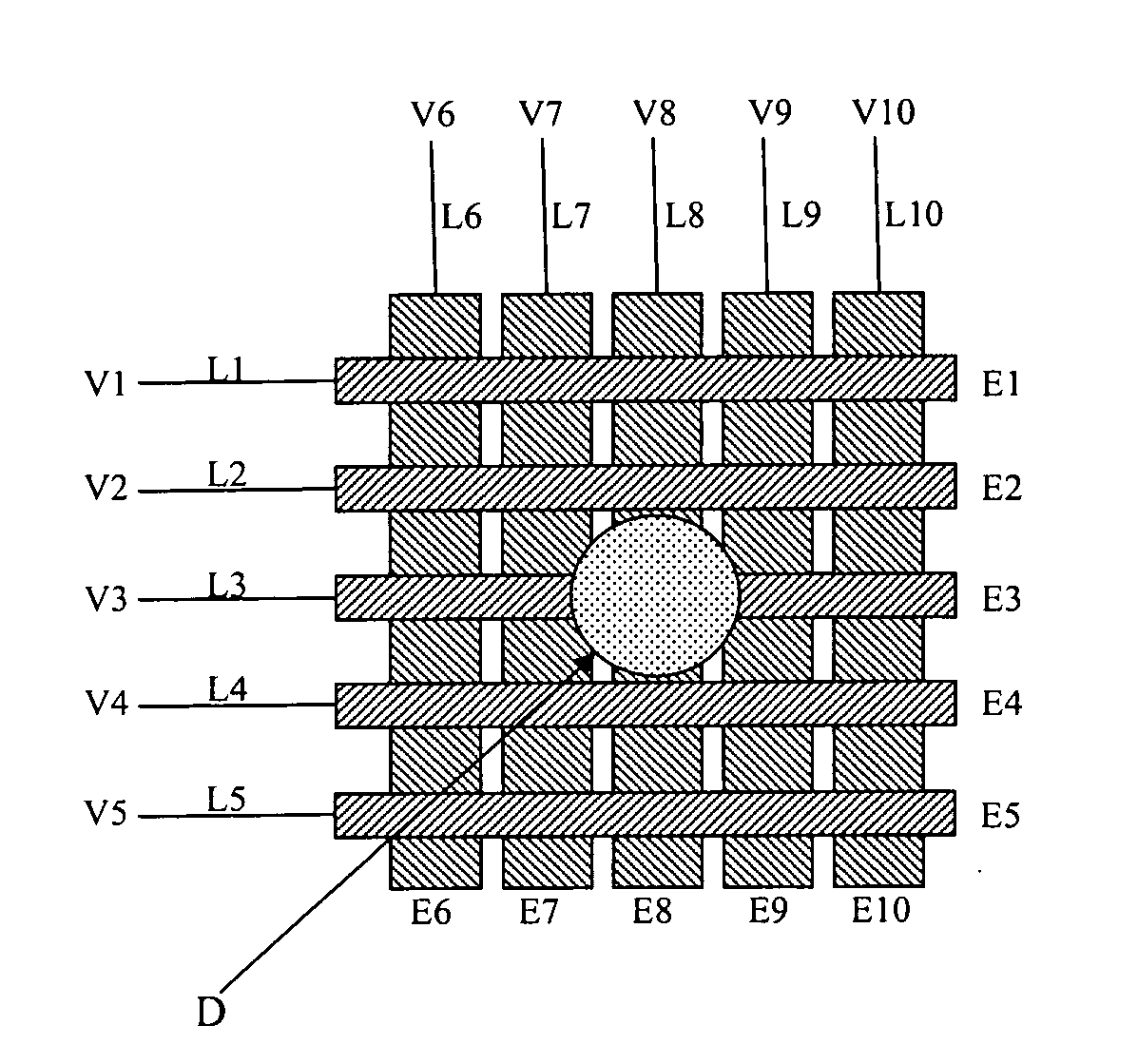
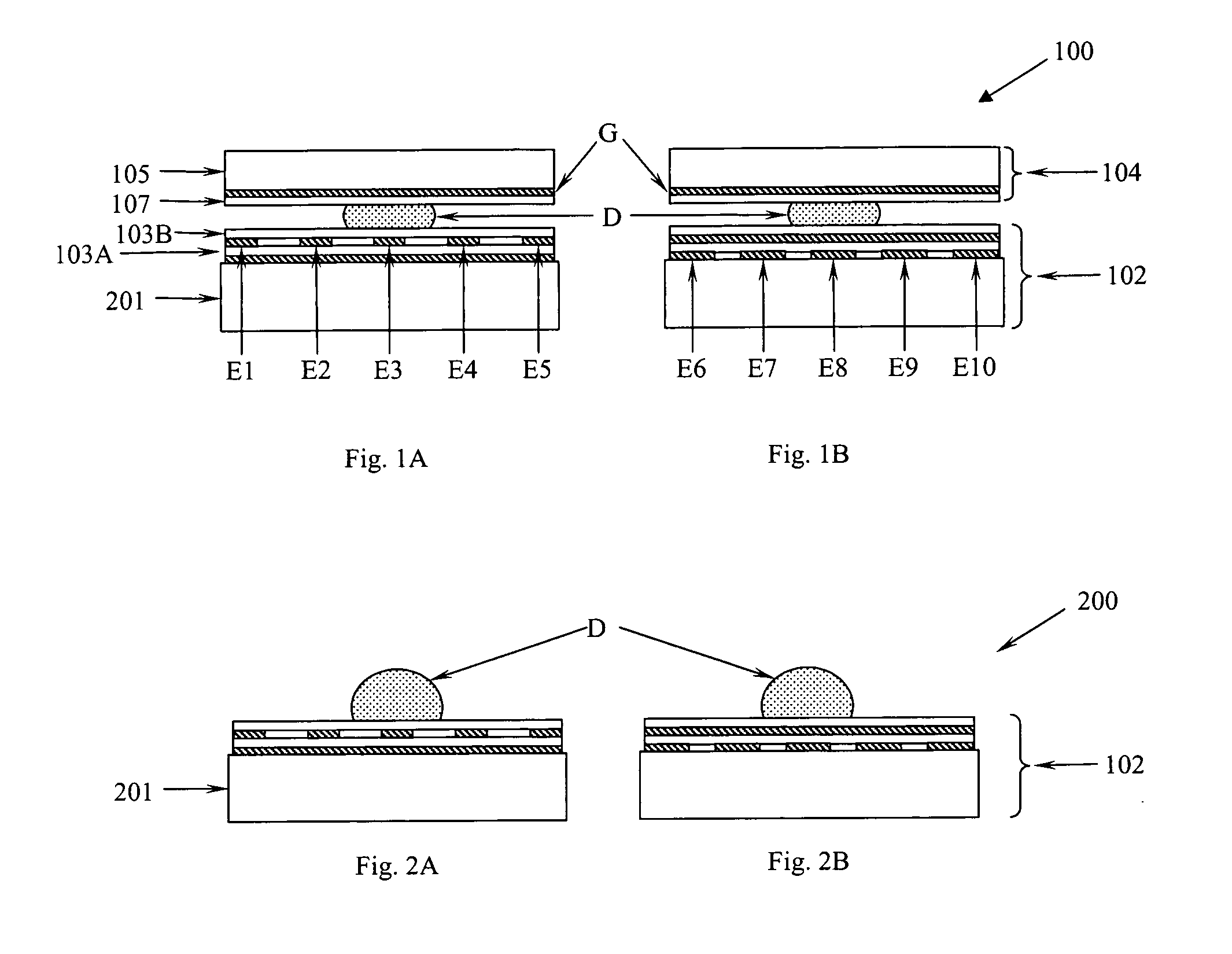
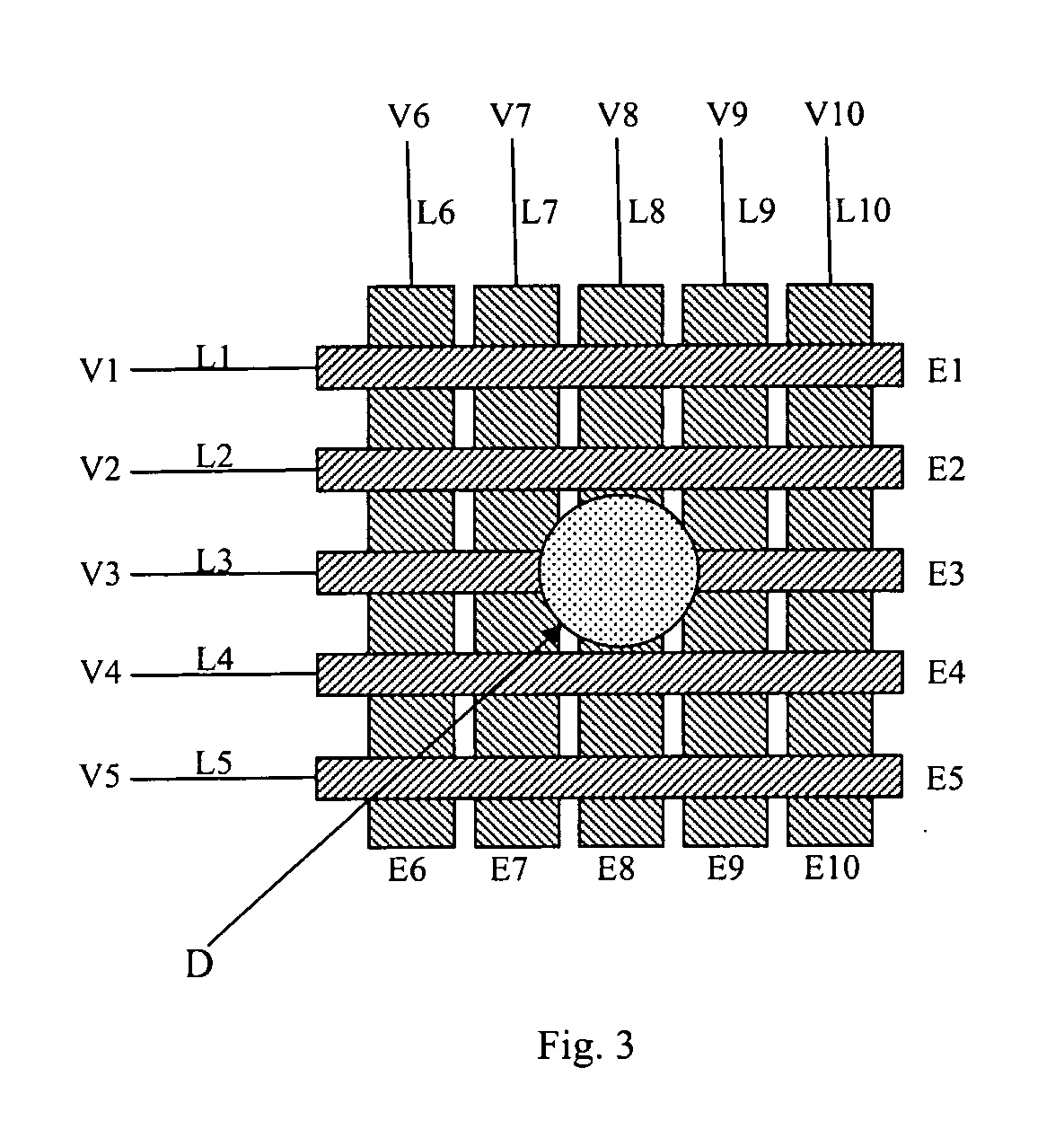
Apparatus for manipulating droplets by electrowetting-based techniques
InactiveUS6911132B2Improve controllabilityImprove accuracyBurnersElectrostatic separatorsElectricityControl manner
An apparatus is provided for manipulating droplets. The apparatus is a single-sided electrode design in which all conductive elements are contained on one surface on which droplets are manipulated. An additional surface can be provided parallel with the first surface for the purpose of containing the droplets to be manipulated. Droplets are manipulated by performing electrowetting-based techniques in which electrodes contained on or embedded in the first surface are sequentially energized and de-energized in a controlled manner. The apparatus enables a number of droplet manipulation processes, including merging and mixing two droplets together, splitting a droplet into two or more droplets, sampling a continuous liquid flow by forming from the flow individually controllable droplets, and iterative binary or digital mixing of droplets to obtain a desired mixing ratio.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
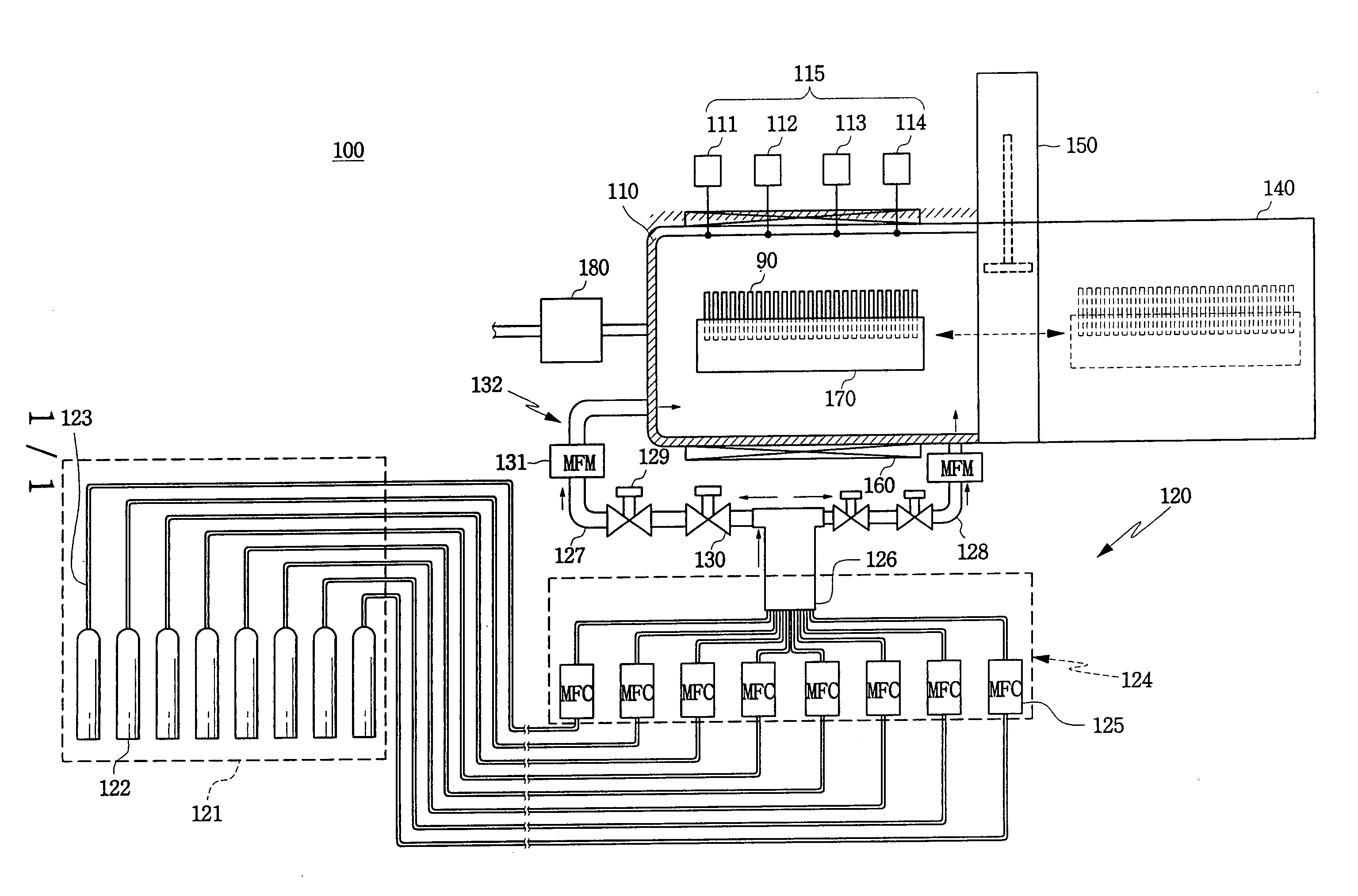
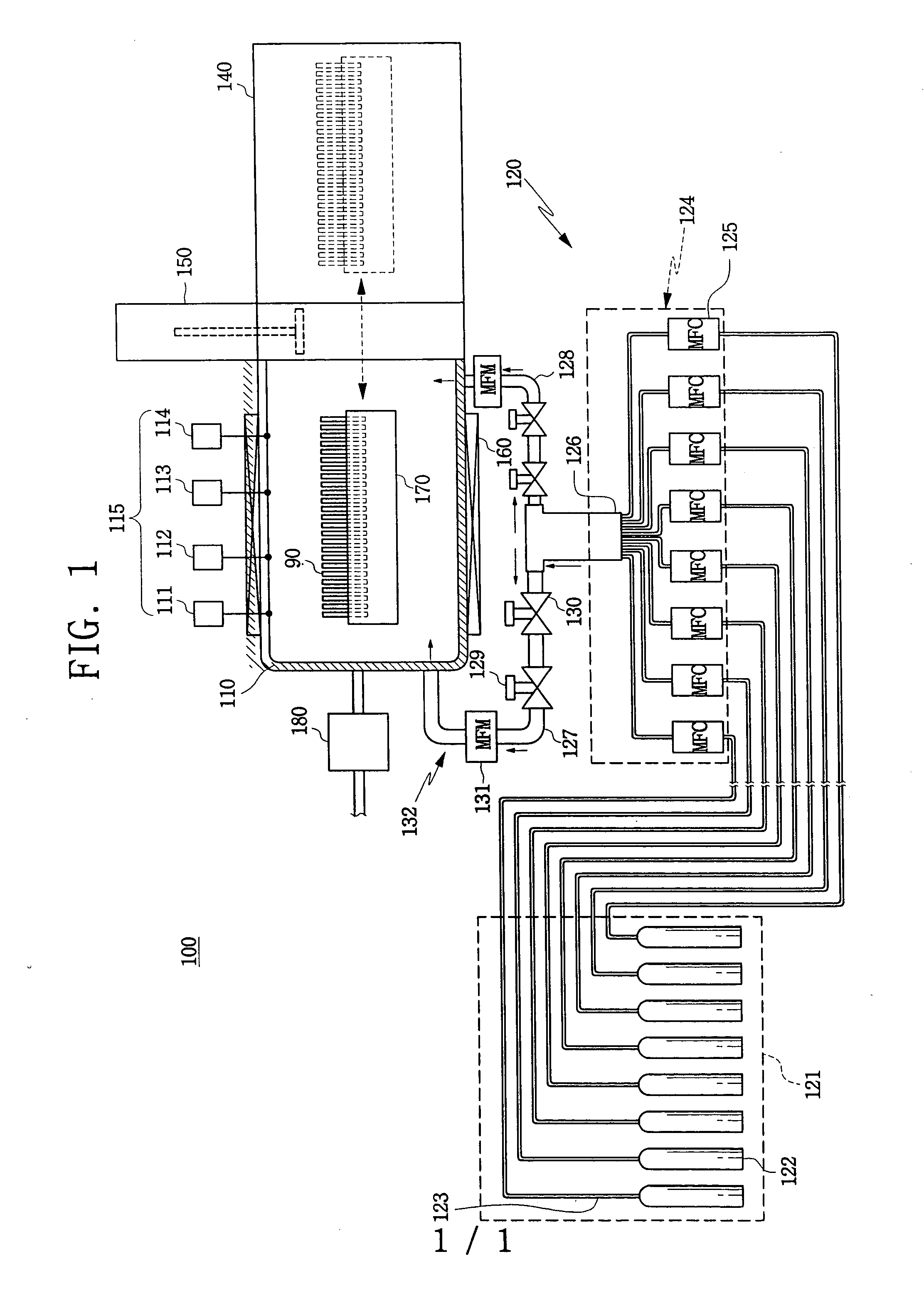
Gas supply unit and semiconductor device manufacturing apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20050016452A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDevice materialManufactured apparatus
A semiconductor device manufacturing apparatus is provided. The semiconductor device manufacturing apparatus comprises a furnace having a closed predetermined space for seating a wafer, a loading device located at one side of the furnace to load the wafer on which a prior process may have been performed, a gate valve interposed between the furnace and the loading device to selectively open / close a pathway between the furnace and the loading device, a heater for heating an interior of the furnace, a vacuum pump for maintaining the interior of the furnace with a suitable pressure necessary to the process, a gas reservoir for storing individually various kinds of reaction gases supplied from an exterior of the space, a gas mixing device connected to the gas reservoir to mix the various kinds of reaction gases supplied from the gas reservoir with an even mixing ratio, at least two mixed gases supply pipes connected to the gas mixing device to supply the reaction gases mixed in the gas mixing device to each direction of the furnace, and a mixed gases flow control unit installed at the mixed gases supply pipe to control the flow of the reaction gases supplied through the mixed gases supply pipe.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
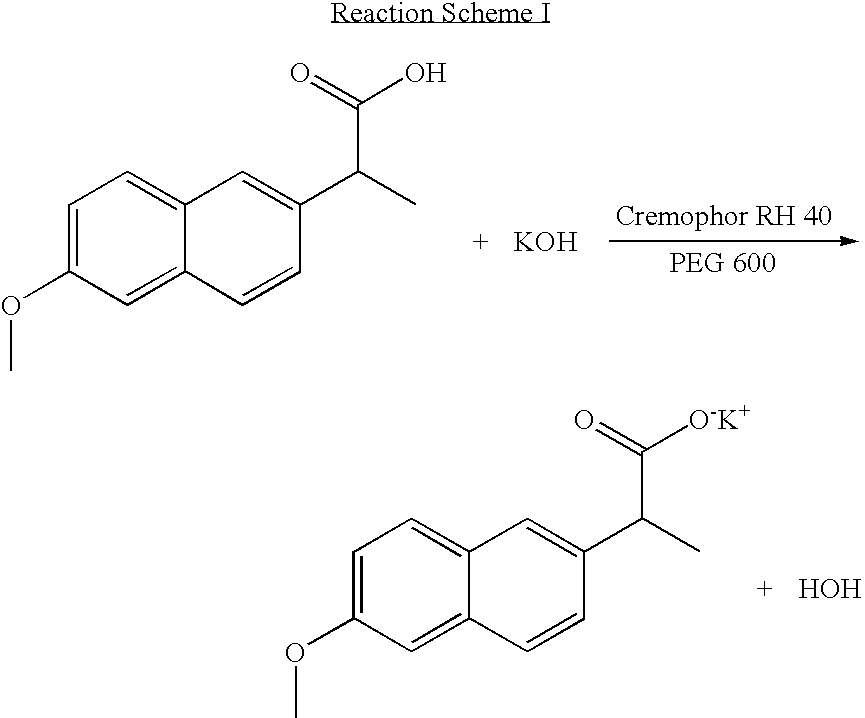
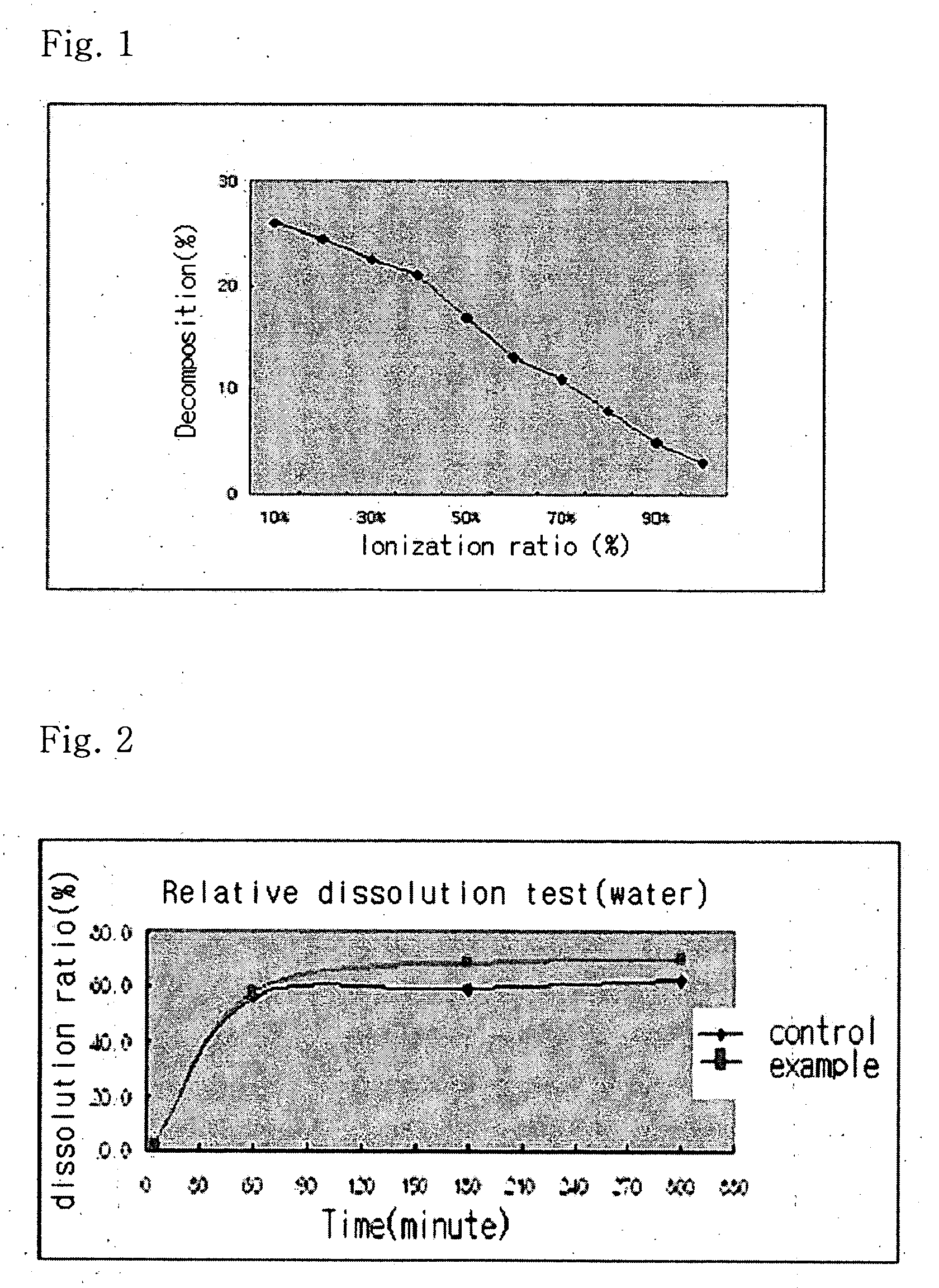
Solvent system of hardly soluble drug with improved dissolution rate
InactiveUS20040157928A1Good disintegrationPromote dissolutionBiocideAntipyreticDissolutionIonization
The present invention relates to a solvent system with improved disintegration degree and dissolution ratio of a hardly soluble drug by highly concentrating the drug through partial ionization, and by establishing optimal conditions for enhancing bioavailability of the drug, such as the co-relation between the acid drug and the accompanied components, ionization degree of a solvent system, use of an appropriate cation acceptance, water content, selection of optimal mixing ratio of the respective components and use of specific surfactants, and to a pharmaceutical preparation comprising the same. The solvent system of the invention has advantages in that it can enhance bioavailability by improving the disintegration degree and dissolution ratio of a hardly soluble drug and also provide a capsule with a sufficiently small volume to permit easy swallowing.
Owner:R & P KOREA
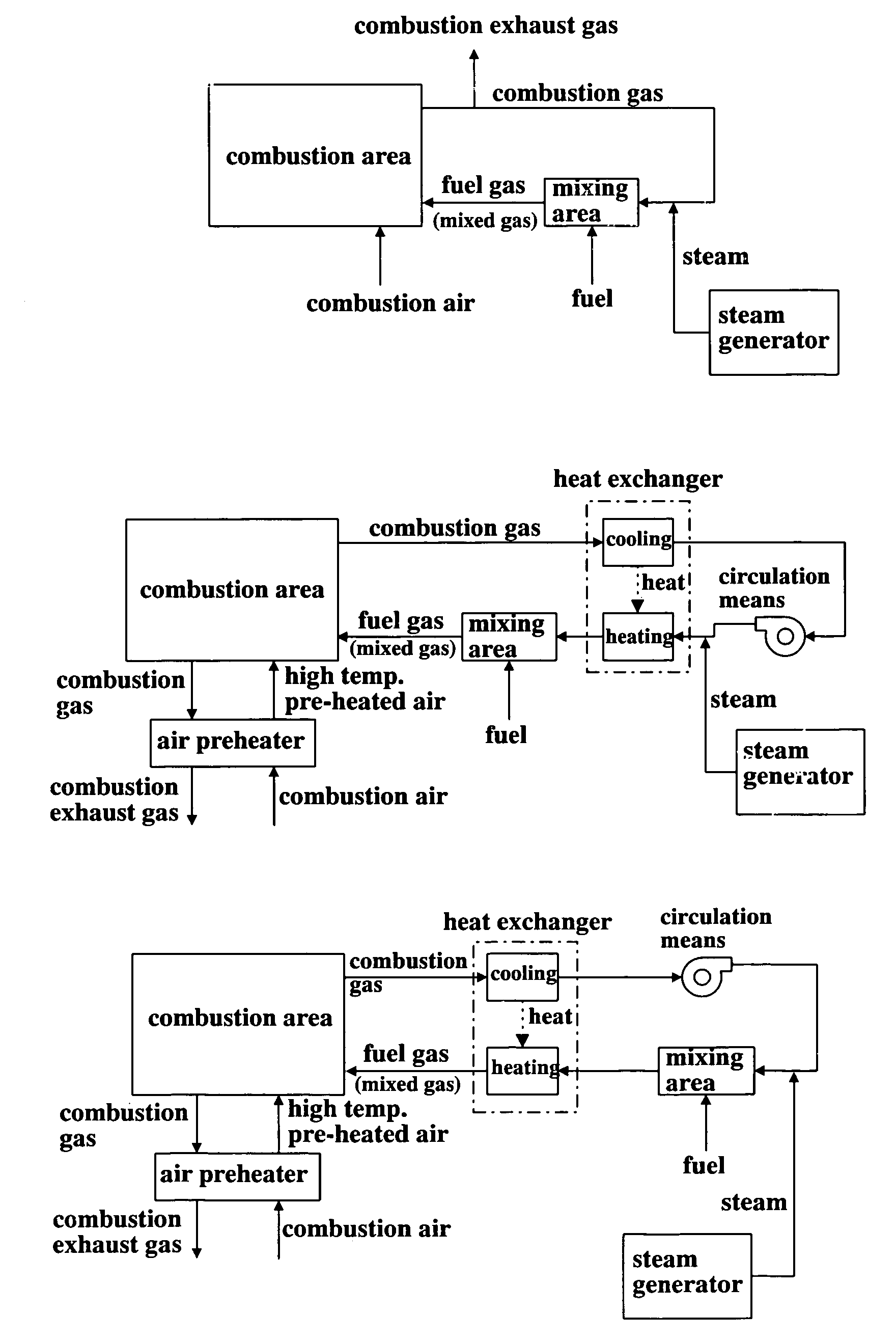
Device and method for feeding fuel
InactiveUS7104784B1Control of combustionReduced flexibilityGaseous fuel pretreatmentCombustion using multiple fuelsCombustion systemProduct gas
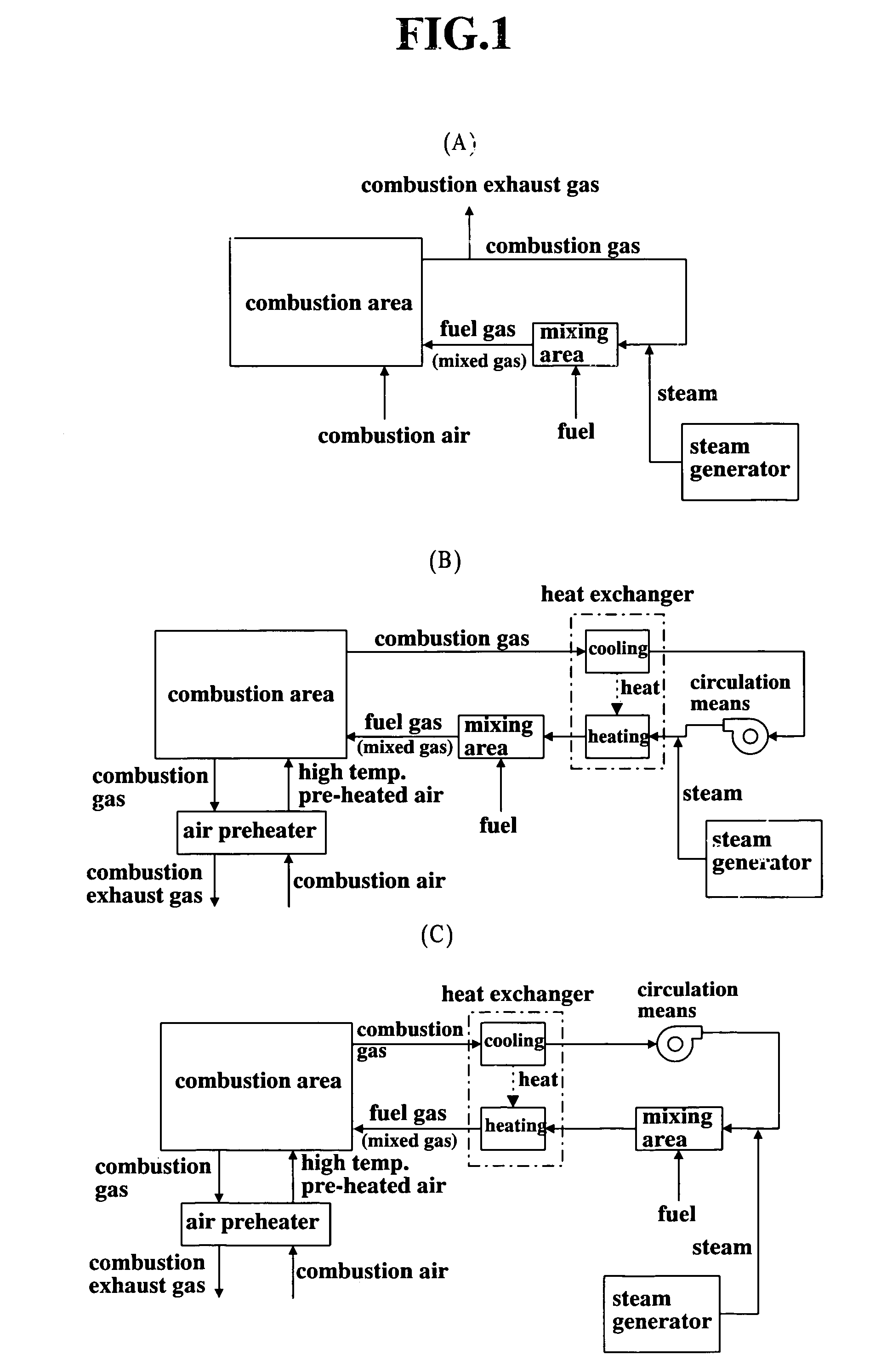
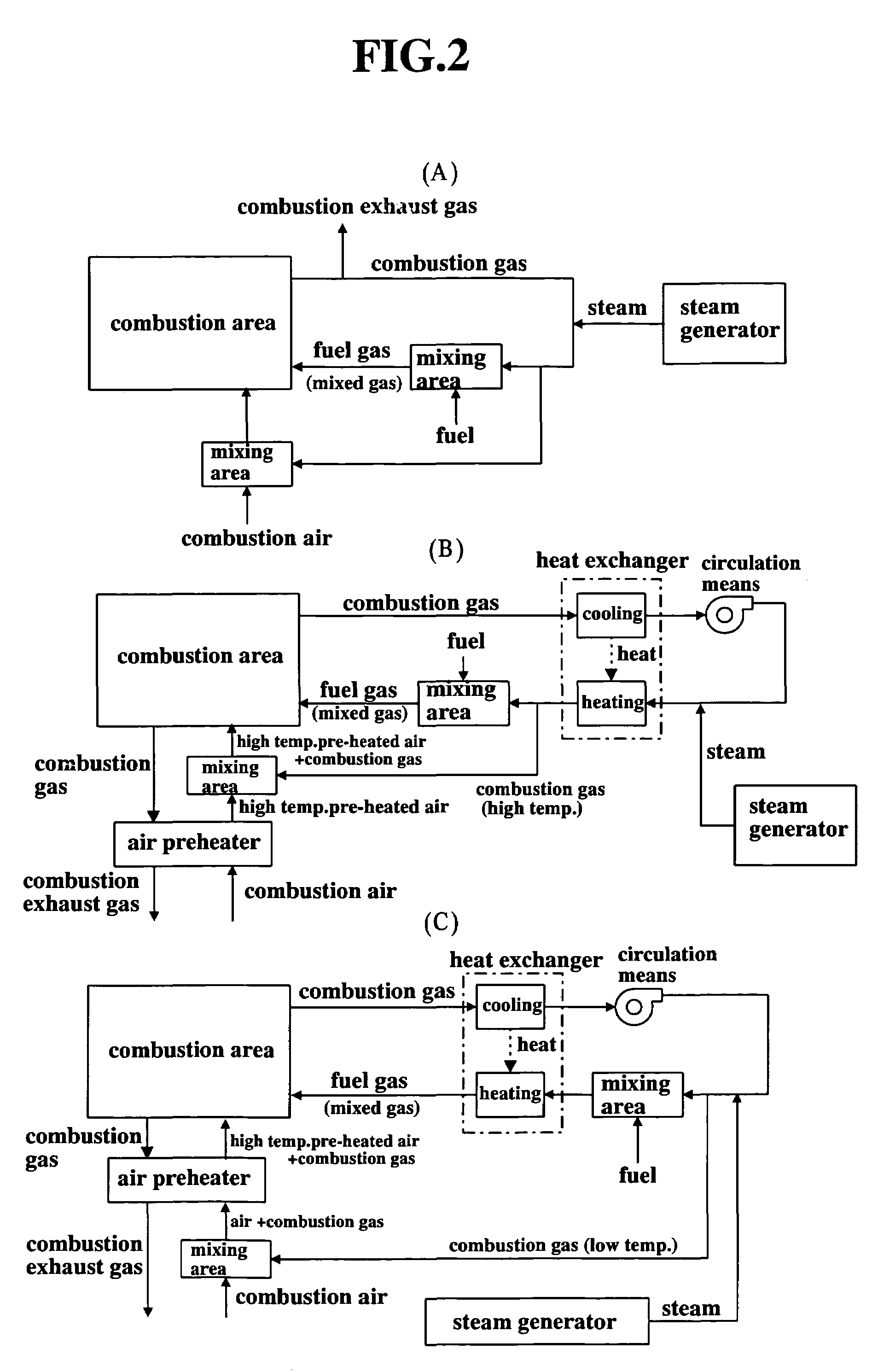
The present invention provides a fuel feeding apparatus and method for improving the controllability of mixing process and mixing ratio of fuel and combustion air, and a combustion system and method for effecting new combustion properties. The fuel feeding apparatus of the combustion system has fuel feeding means, combustion gas extraction means, steam supply means, mixing means and fuel gas introduction means. The combustion gas extraction means extracts combustion gas of a combustion area therefrom. The mixing means mixes the fuel of fuel feeding means with at least one of combustion gas extracted from the furnace and steam of a steam generator. The fuel gas introduction means introduces a mixed fluid of combustion gas, steam and fuel to the combustion area as a fuel gas, and allows the fuel gas to be mixed with the combustion air. A step of mixing the fuel with the combustion gas after extracted from the furnace and a step of mixing the fuel gas with the combustion air are stepwisely carried out, so that the controllability of mixing process and ratio of the air and fuel is improved. Such a control of fuel gas flow enables control of characteristics of flame and production of flame with new properties in the combustion area.
Owner:NFK HLDG
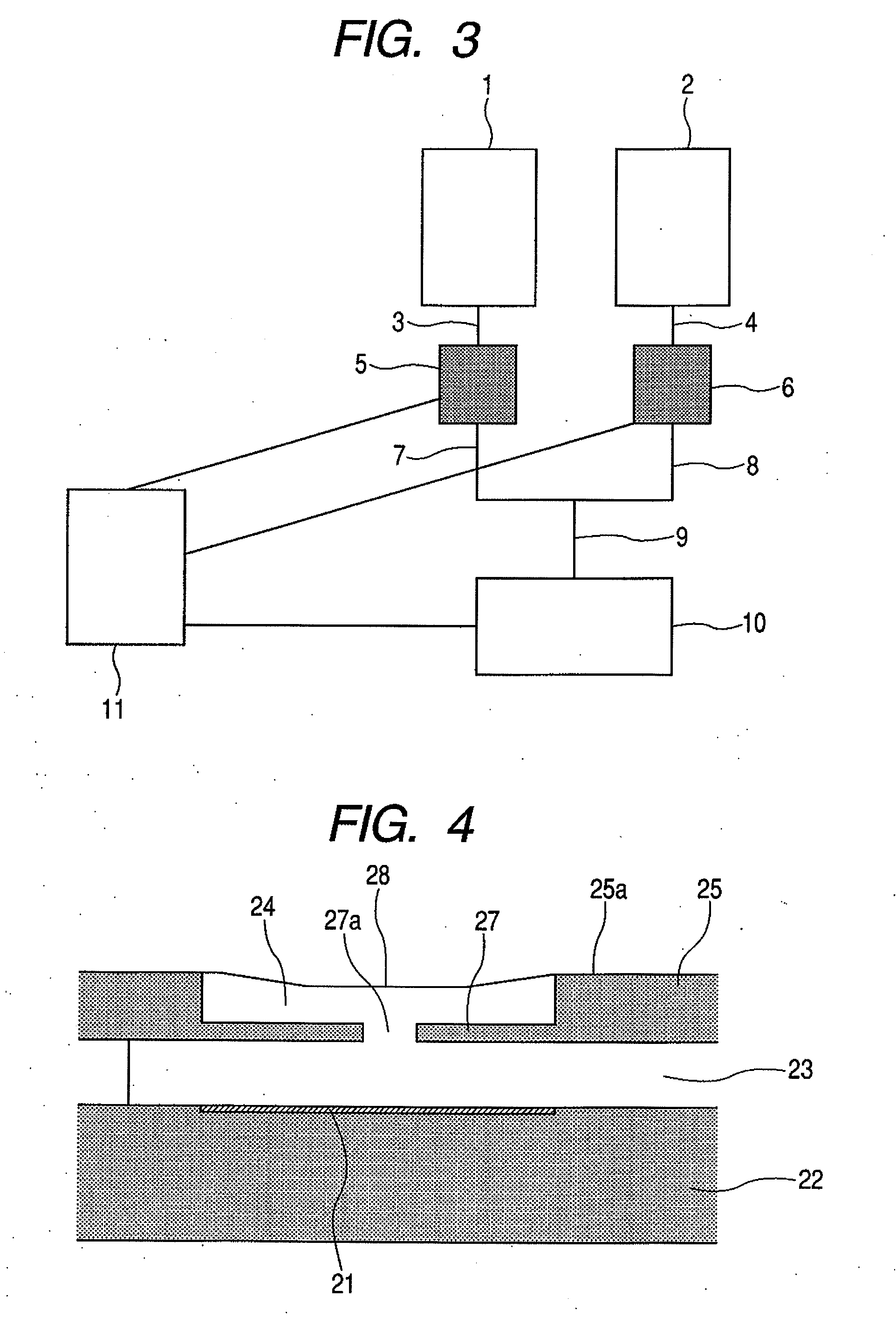
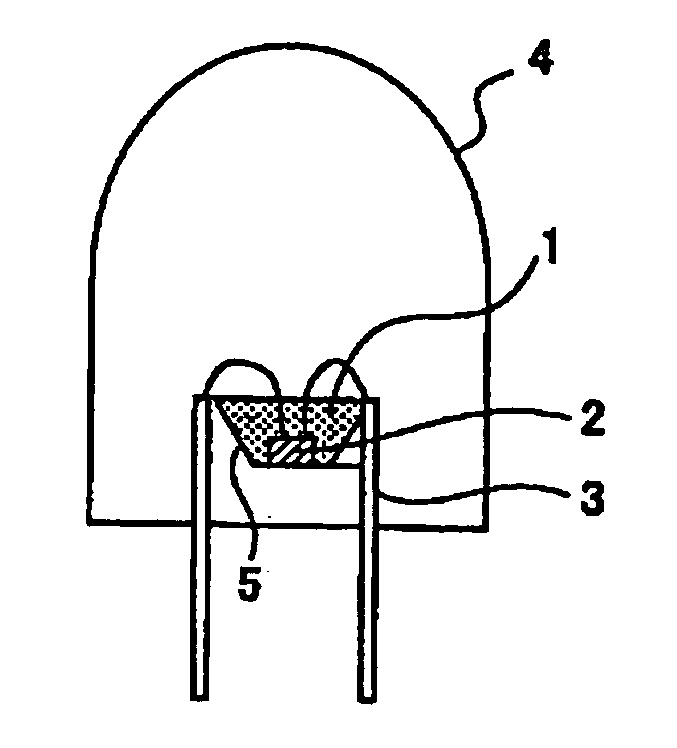
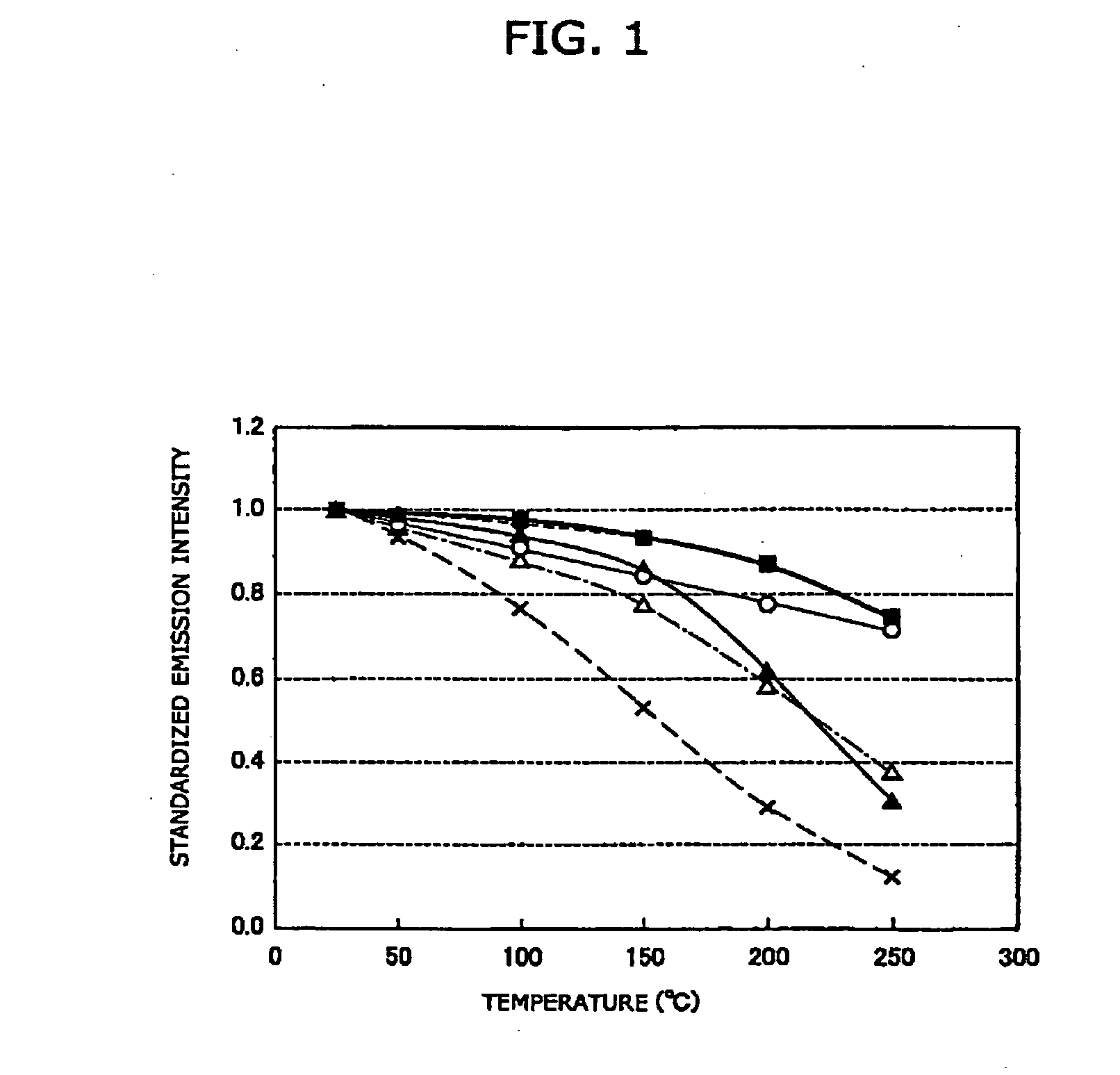
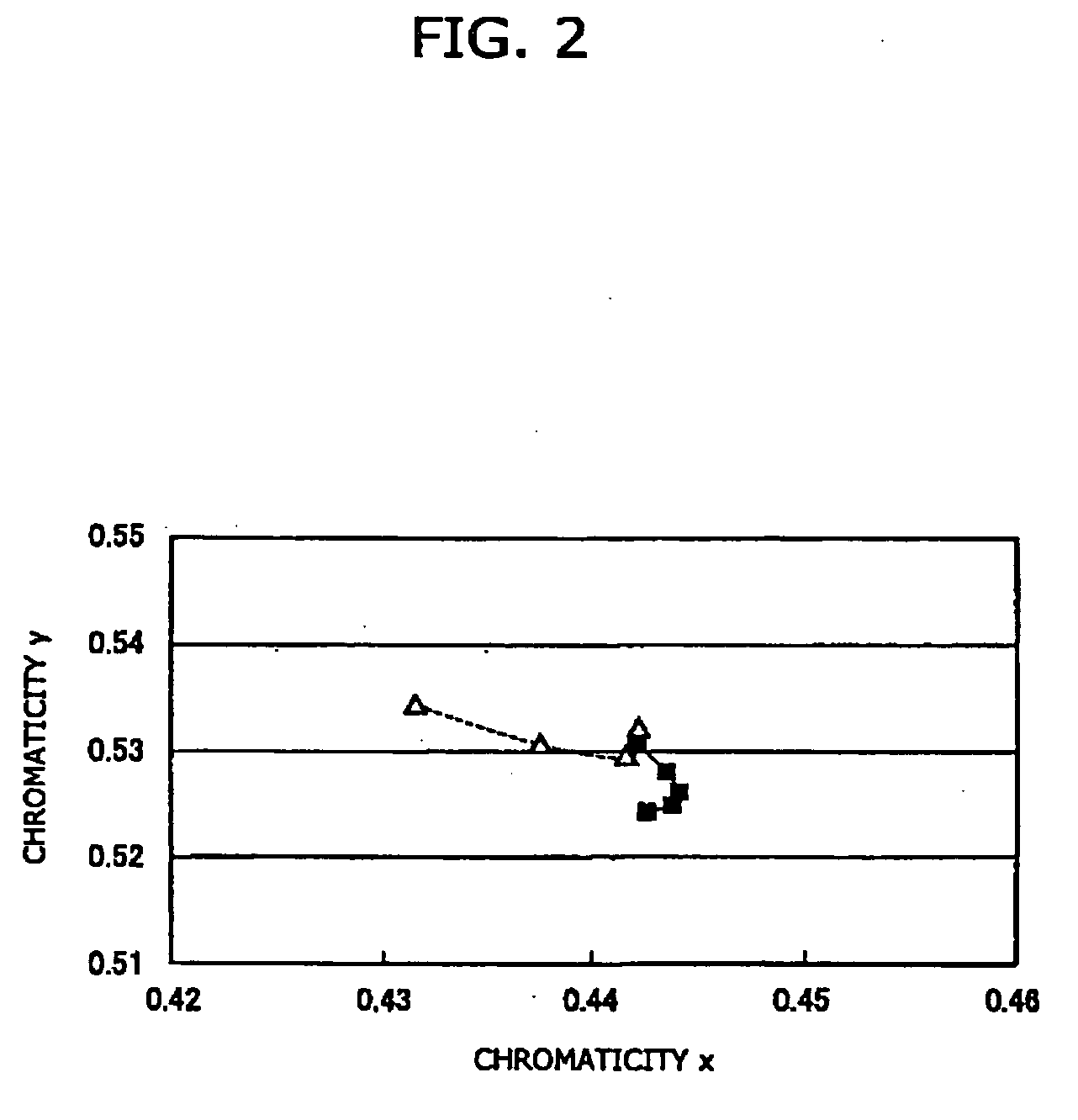
Phosphor mixture and light emitting device
ActiveUS20060091790A1Bright enoughGood color propertiesDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPeak valueLight emitting device
To provide a light emitting device having a phosphor mixture and a light emitting part, the phosphor mixture including a red phosphor and more than one kind of phosphor having an emission spectrum with a peak in a wavelength range from 500 nm to 630 nm, and emitting light having a sufficient luminance and excellent in color rendering properties not only in a white light with high correlated color temperature, but also in a warm white light with low correlated color temperature. CaAlSiN3:Eu manufactured as a red phosphor and and CaAl2Si4N8:Eu manufactured as an orange phosphor, and for example, commercial YAG:Ce as a yellow-green phosphor, are prepared, and emission spectra of these phosphors are measured when excited by excitation light in the wavelength range from 430 nm to 500 nm. Further, the emission spectrum of the light used as an excitation light are measured, by simulation using their emission spectra, a mixing ratio of each phosphor, by which the correlated color temperature of the phosphor mixture becomes a target color temperature, is obtained. And based on the result of the simulation, each phosphor is measured nad mixed, thus obtaining the phosphor mixture.
Owner:CITIZEN ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Liquid ejection device and ejection method
InactiveUS20090126722A1Easy to changeWay accuratePowder deliverySpray deliveryEngineeringMechanical engineering
A liquid ejection device, includes: a plurality of storing parts for storing liquids; a plurality of liquid-feeding parts connected to the respective storing parts; a ejection part for ejecting a liquid; a plurality of flow paths connected to the plurality of liquid-feeding parts, respectively; and a connection part for joining the plurality of flow paths and connecting them as a single flow path to the ejection part. The plurality of liquid-feeding parts are actuated to mix the liquids from the plurality of storing parts in the single flow path joined at the connection part and feed a mixture of the liquids to the ejection part to eject the mixture from the ejection part. According to the ejection device of the present invention, the ejection amount or the mixing ratio can be easily changed in a comparatively precise manner.
Owner:CANON KK
Phosphor mixture and light emitting device
ActiveUS20060197432A1Good color propertiesSmall color shiftDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsColor shiftPhosphor
To provide a phosphor mixture realizing a light emitting device having a phosphor and a light emission element, by which light emission is performed, with a small color shift due to a feeding current and having an excellent color rendering properties. CaAlSin3:Eu as a red phosphor and YAG:Ce as a yellow phosphor are manufactured, and emission spectra thereof are obtained. Meanwhile, the emission spectrum of an excitation light emitted by a light emitting part is obtained. From the emission spectra thus obtained, a relative mixing ratio of each phosphor is obtained by simulation, so that a correlated color temperature of the light emitting device becomes a target temperature. Then, based on the relative mixing ratio thus obtained, each phosphor is measured and mixed, and a phosphor mixture is thereby obtained.
Owner:NICHIA CORP +1
Ink jet recording with mixing and storage of color inks with different mixing ratios
InactiveUS6050680ARational and efficient useRational and efficient and supplyOther printing apparatusEngineeringMixing ratio
Owner:CANON KK
Method of producing fuel oil by coal tar hydrogenation modifying
ActiveCN1903994AReduce temperature riseReduce coking rateTreatment with hydrotreatment processesGasoline stabilisationLow nitrogenSulfur
The present invention relates to a method for producing fuel oil by utilizing coal tar. It is characterized by that said method includes the following steps: after the whole coal tar in which the moisture and ash are removed and diluting oil are mixed according to a certain mixing ratio, making the obtained mixture be successively passed through a shallow hydrogenation unit with hydrogenation protecting agent and prehydrogenation catalyst and a deep hydrogenation unit with main hydrogenation catalyst, then making the product obtained after deep hydrogenation undergo the processes of high-pressure separation, low-pressure separation and fractionation so as to obtain light-oil fraction, medium-oil fraction and tail-oil fraction, namely obtain low-sulfur low-nitrogen fuel oil and light oil product.
Owner:HUNAN CHANGLING PETROCHEM SCI & TECH DEV CO LTD
Elastic body, method for manufacturing the same and mattress including the same
InactiveUS6704962B2Promote absorptionLow elastic modulusStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesElastomerAlcohol
Disclosed are an elastic body having a good elasticity and an impact absorbing efficiency, a method of manufacturing the same and a mattress employing the same. The elastic body is a foamed polyurethane body including polystyrene and has a plurality of foams in which air is contained. The elastic body is prepared by a method comprising the steps of preparing polyether polyol by mixing poly alcohol and a polyether compound in a mixing ratio of 3-5 to 5-7 by weight, obtaining a polyol mixture by adding 2-20 parts by weight of polystyrene and a trace amount of a catalyst and water to 30-50 parts by weight of the obtained polyether polyol, adding and stirring 20-60 parts by weight of an isocyanate compound to 40-80 parts by weight of the polyol mixture at 20-80° C., and pouring the resulting product into a mold to foam cast. A mattress manufactured by using such elastic bodies has a good elasticity and is capable of absorbing pressure, thereby providing comfort for users.
Owner:CHOI YOUN SOO
Digital television transmitter and receiver for transmitting and receiving dual stream using 4 level vestigial side band robust data
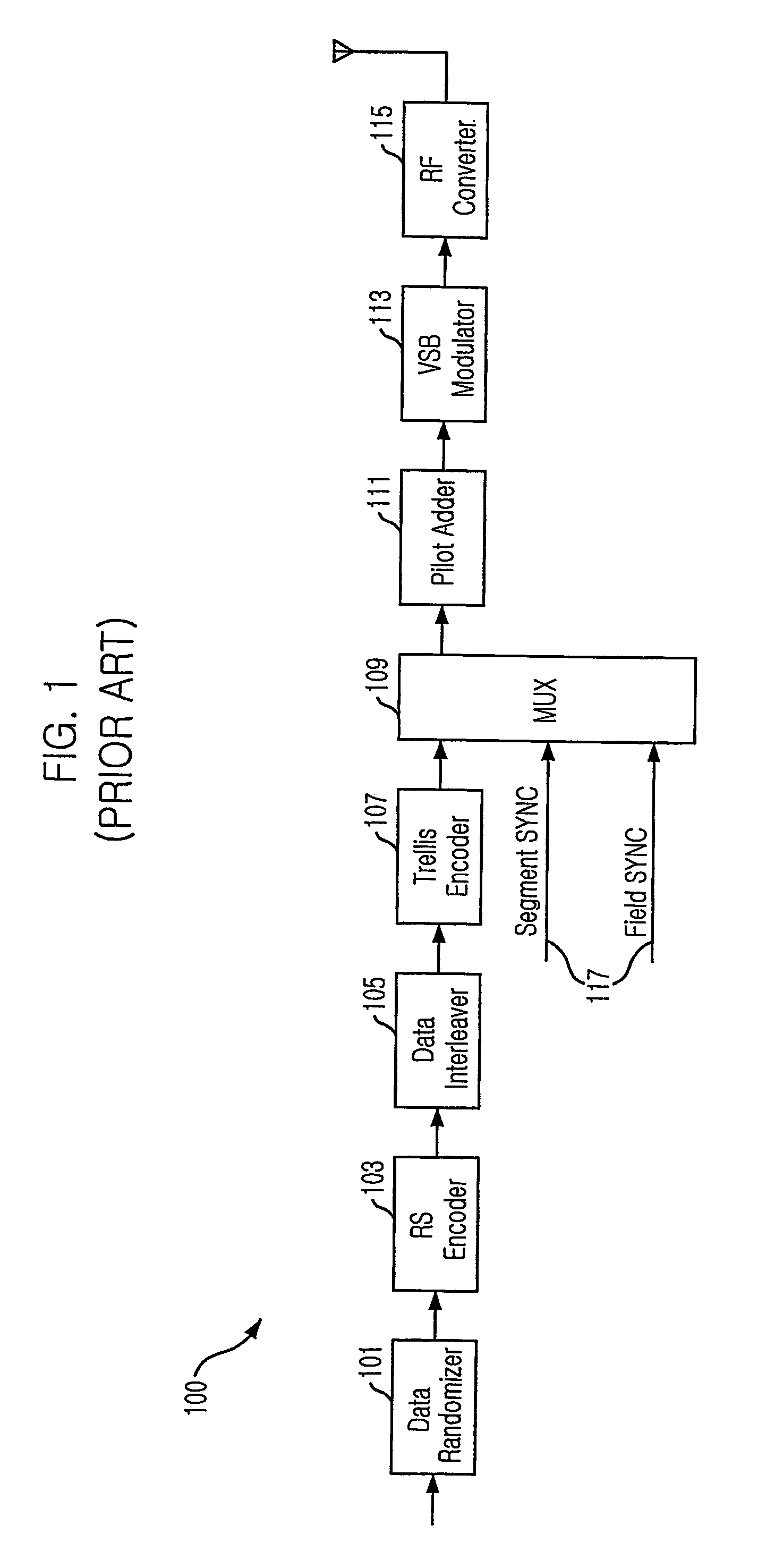
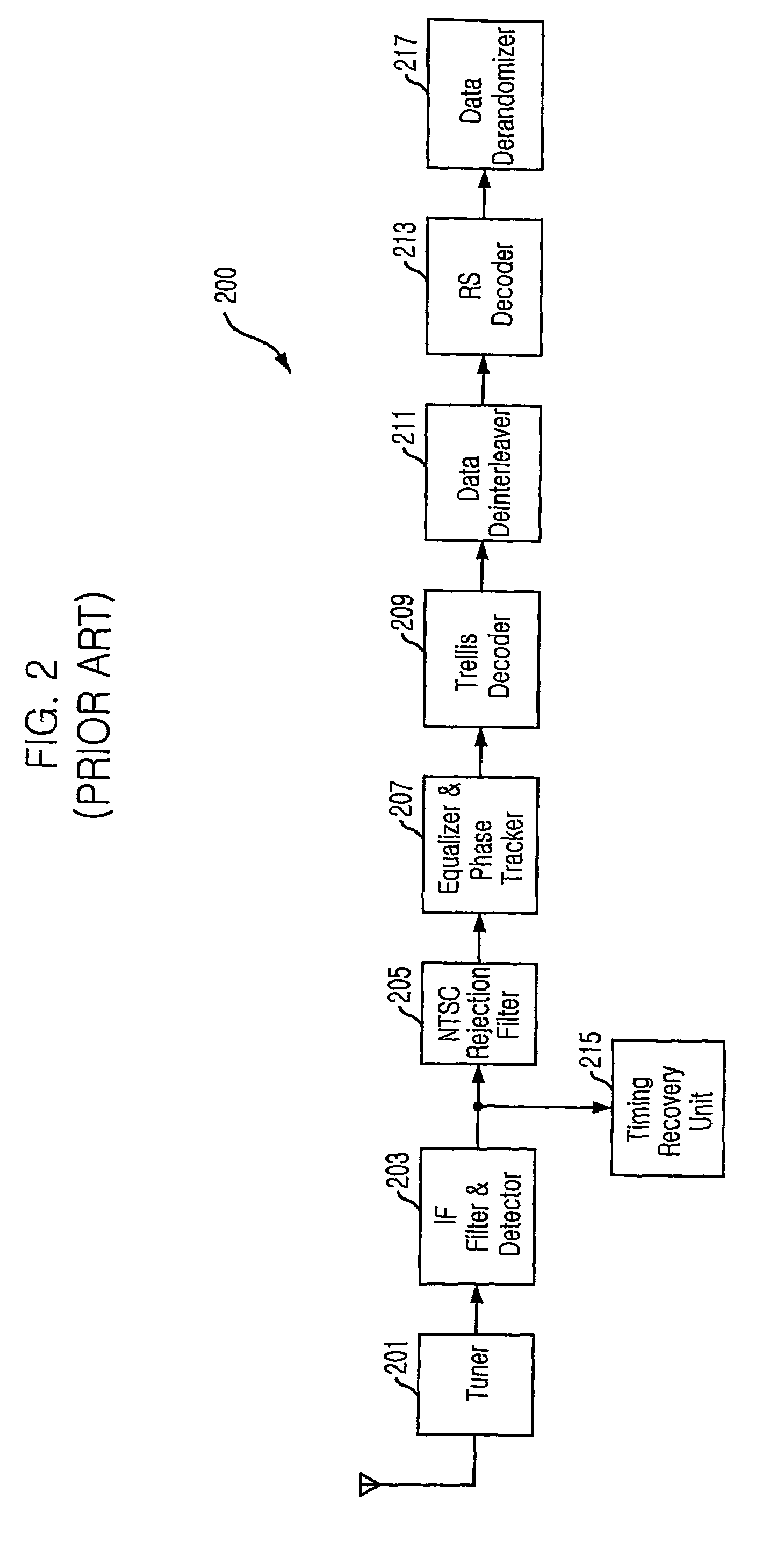
ActiveUS7653143B2Improve decoding performanceReduce signal to noise ratioTelevision system scanning detailsModulated-carrier systemsDigital television transitionTelevision system
The present invention relates to a Vestigial Side Band (VSB) Digital Television (DTV) in agreement with the DTV standards (A / 53) of the Advanced Television System Committee (ATSC), and to a method thereof. More particularly, it provides 4-VSB DTV transceiver that improves reception performance of a receiver by transmitting and receiving dual streams formed of normal data and robust data without increasing average power, regardless of a mixing ratio of the normal and robust data. The 4-VSB DTV transceiver of the present research includes an encoding unit for encoding the robust data to be mapped to one of two groups having 4 levels {−5, −3, 1, 7} and {−7, −1, 3, 5}.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
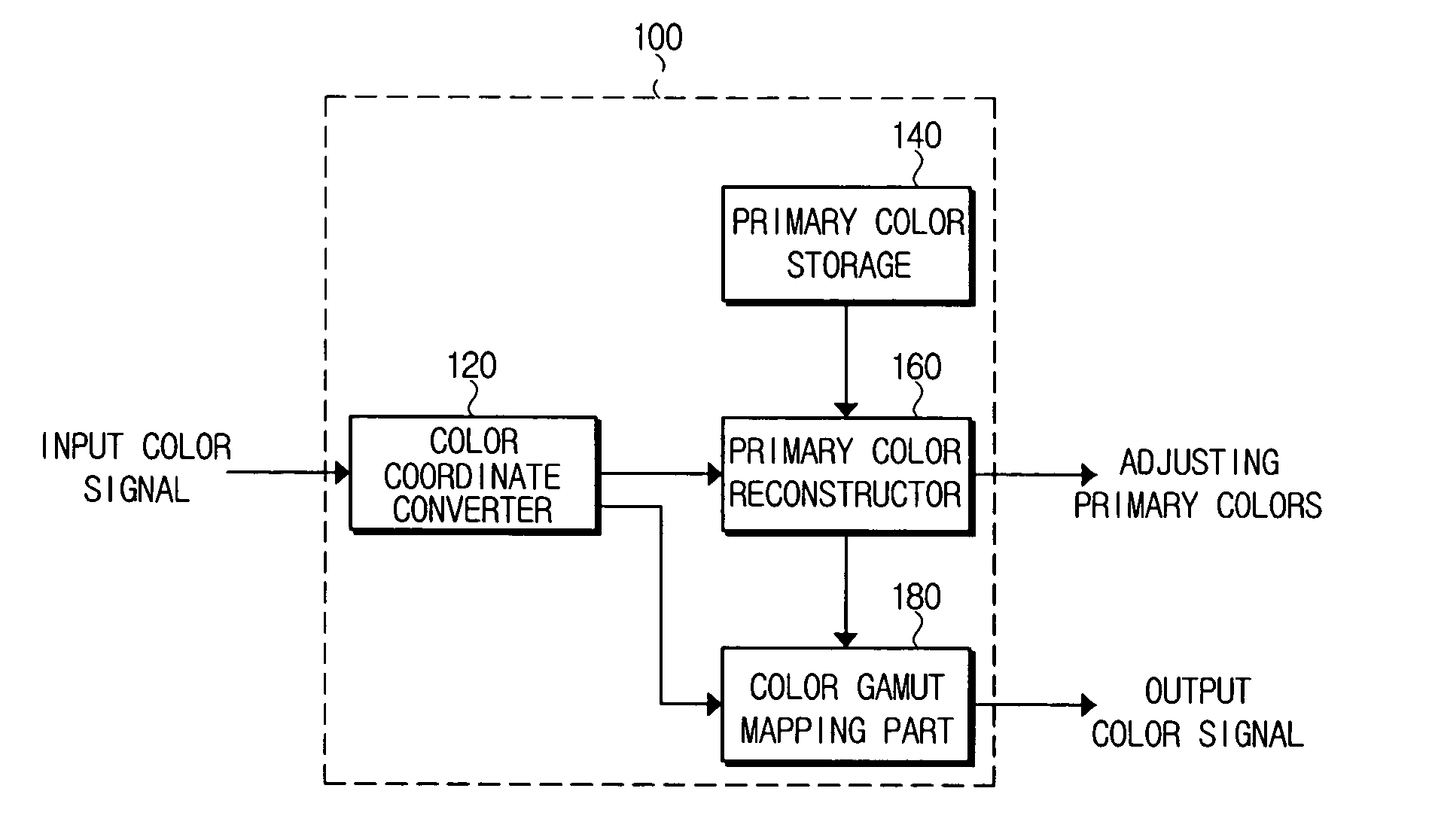
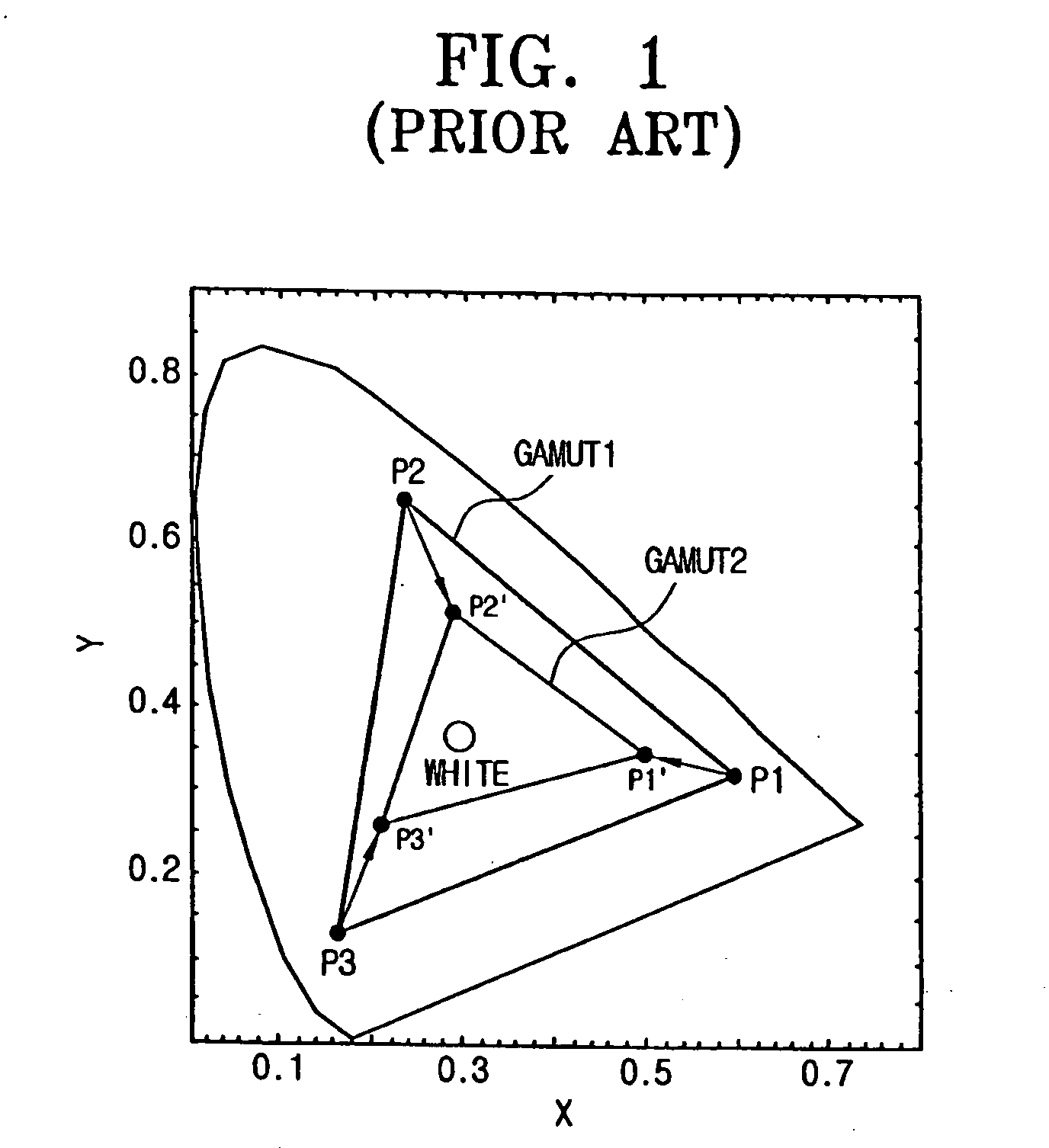
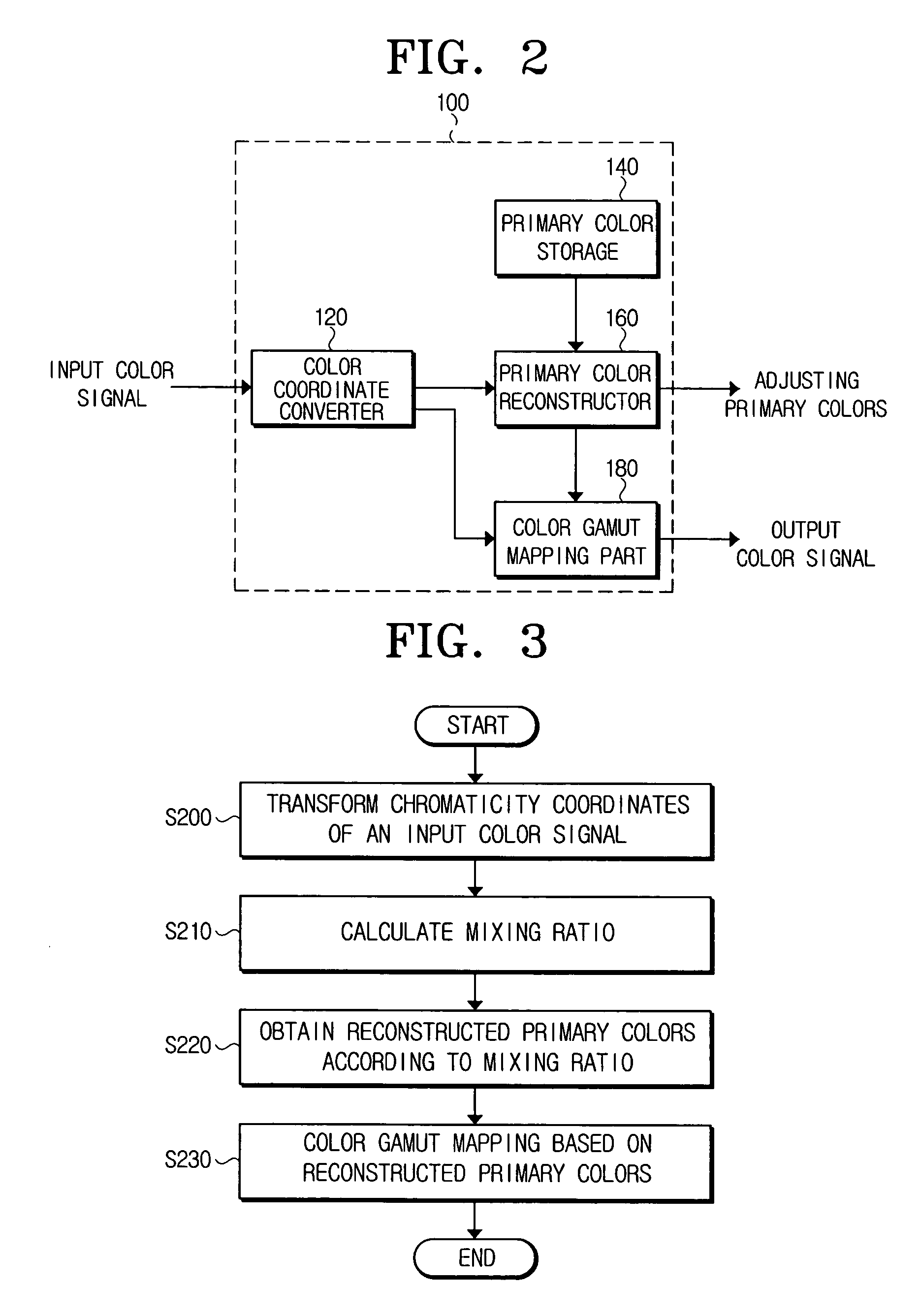
Color signal processing method and apparatus usable with a color reproducing device having a wide color gamut
InactiveUS20050280851A1Wide color gamutSimple algorithmDigitally marking record carriersColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionGamut
A color signal processing method includes calculating a mixing ratio for source primary colors of a color reproducing device through which an input color signal having standard primary colors is reproduced, mixing the source primary colors according to the calculated mixing ratio to obtain reconstructed primary colors, and transforming the input color signal to match a color gamut of the reconstructed primary colors and outputting the transformed color signal. Thus, the color gamut of the color reproducing device can be freely adjusted within a reproduction range thereof according to the input color signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Valve element sealing lubricating agent composition
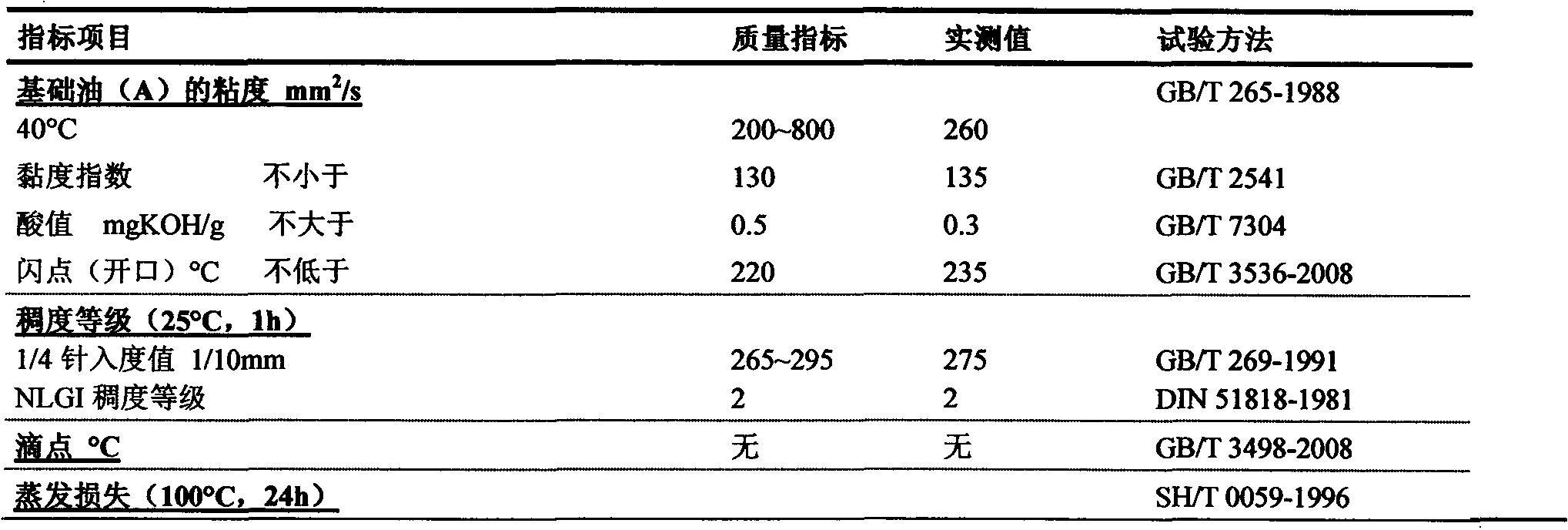
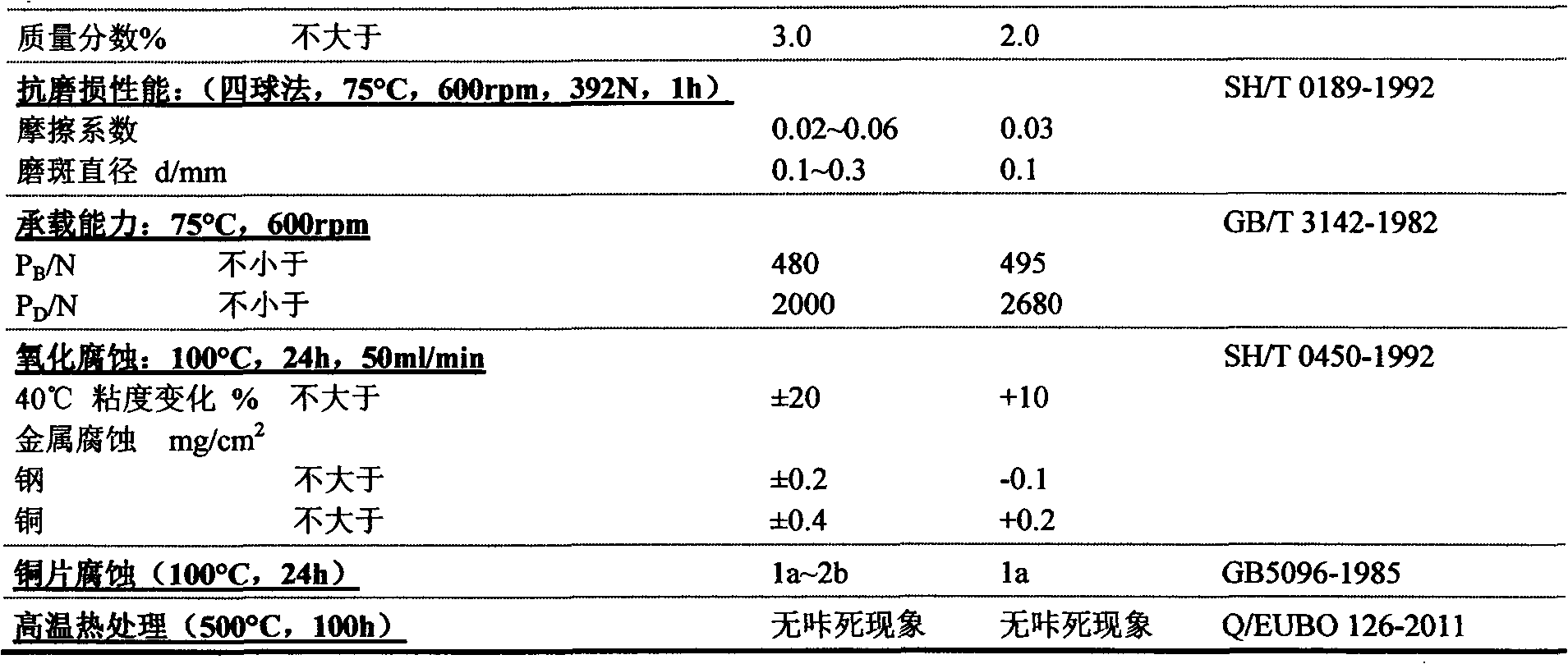
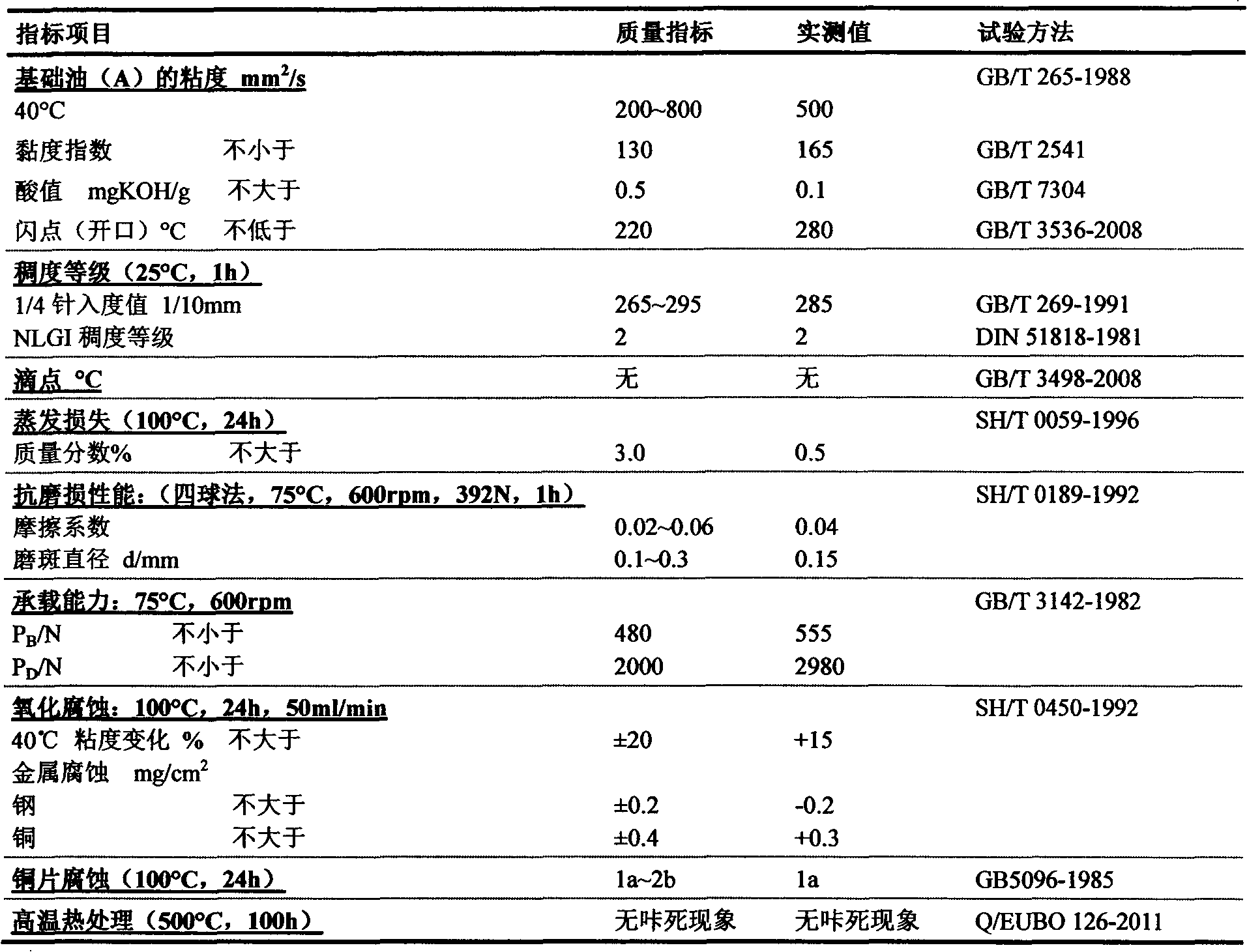
InactiveCN102433204ASimple production methodImprove high temperature resistanceLubricant compositionBase oilWear resistance
The invention relates to the field of lubricating materials, in particular to a valve core sealing lubricating agent composition, which comprises: (A) 100.0 weight parts of base oil; (B) 5.0 to 35.0 weight parts of thickening agent; (C) 3.0 to 55.0 weight parts of solid lubricating agent; (D) 0.1 to 3.0 weight parts of surfactant; (E) 0.1 to 2.5 weight parts of antioxygen; (F) 0.1 to 4.0 weight parts of extreme pressure antiwear agent; (G) 0.1 to 2.0 weight parts of metal passivating agent; and (H) 0.1 to 1.5 weight parts of antimicrobial agent. The finished lubricating agent prepared according to the mixing ratio has high high-temperature resistance, high antiwear and wear-resistance performance and high dead-locking-preventing performance. Meanwhile, the production and preparation method of the lubricating agent are simple, convenient and easy to implement and is suitable for large-scale batch production.
Owner:SHENZHEN EUBO NEW MATERIAL TECH
Electrowetting based digital microfluidics
Apparatus and methods are provided for liquid manipulation utilizing electrostatic field force. The apparatus is a single-sided electrode design in which all conductive elements are embedded on the first surface on which droplets are manipulated. An additional second surface can be provided parallel with the first surface for the purpose of containing the droplets to be manipulated. By performing electrowetting based techniques in which different electrical potential values are applied to different electrodes embedded in the first surface in a controlled manner, the apparatus enables a number of droplet manipulation processes, including sampling a continuous liquid flow by forming individually controllable droplets from the flow, moving a droplet, merging and mixing two or more droplets together, splitting a droplet into two or more droplets, iterative binary mixing of droplets to obtain a desired mixing ratio, and enhancing liquid mixing within a droplet.
Owner:DIGITAL BIOSYST
Ink composition and image process using the same
InactiveUS20060158493A1Measurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsUltravioletViscosity
The present invention relates to an ink composition containing a monofunctional monomer at a mixing ratio of 50 to 70% by weight, a bifunctional monomer at a mixing ratio of 10 to 30% by weight and a multifunctional monomer at a mixing ratio of 1 to 10% by weight. According to the invention, there is provided an ultraviolet curing type ink composition which is curable with an ultraviolet ray, high in its curing (polymerization) rate, and low in viscosity and toxicity. Further, an imaging process using the above-mentioned ink composition is also disclosed.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Microporous polyurethane elastomer compound with excellent dynamic performance and preparation method thereof
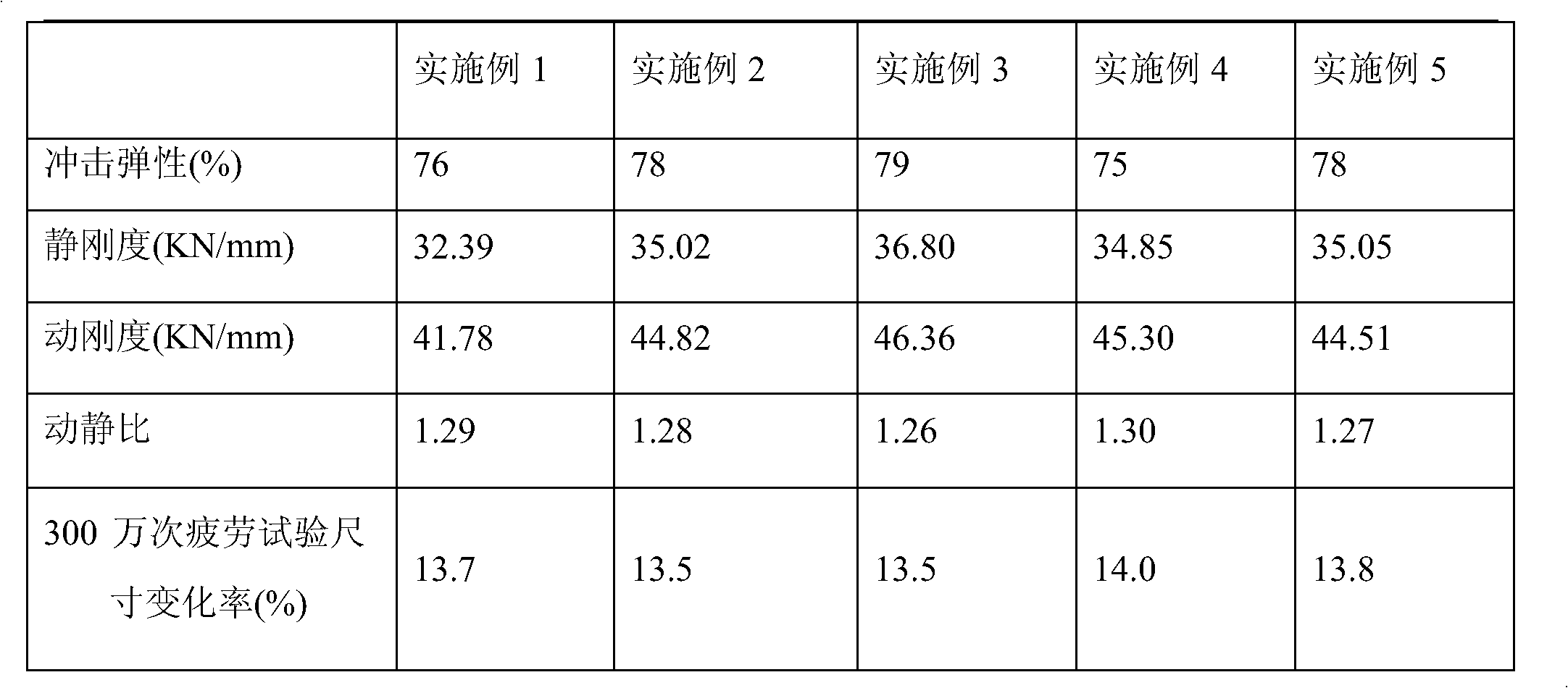
The invention belongs to the field of polyurethane elastomer synthesis, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a microporous polyurethane elastomer compound with excellent dynamic performance. The compound is characterized in that the compound consists of a polyol mixture component and a modified isocyanate component. The preparation method has the advantages as follows: (1) a quasi-prepolymer method is adopted to process microporous polyurethane elastomer material, the two components has similar viscosity and similar mass mixing ratios, the material mixing temperature is low, the materials are easy to mix evenly, the process control condition is simple, and the operation is easy; and (2) the microporous polyurethane elastomer material prepared by using the compound disclosed by the invention has the advantages that a ratio of dynamic stiffness to static stiffness is smaller than or equal to 1.35, the impact elasticity is larger than or equal to 75 percent, the appearance is not damaged after 3,000,000 times of fatigue tests and the dimensional change rate is smaller than or equal to 20 percent, so that the compound can be used for preparing high-performance products such as damping cushion blocks of high-speed railways and damping elements of automobiles.
Owner:SHANDONG INOV POLYURETHANE
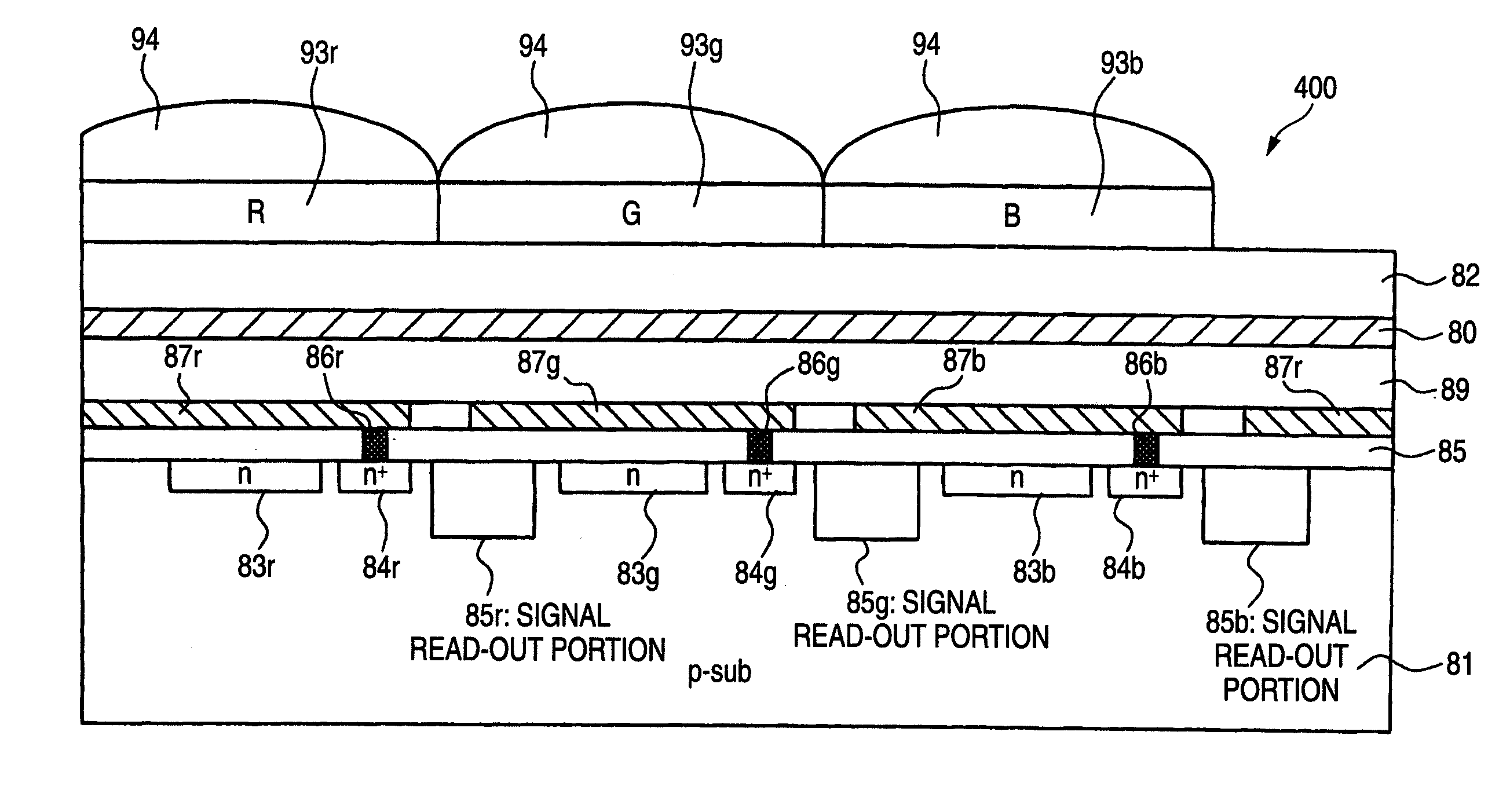
Photoelectric conversion element, method for producing photoelectric conversion element, and solid-state imaging device
ActiveUS20090050881A1Suppress generationImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyTelevision system detailsFinal product manufactureEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric conversion element is provided and includes a photoelectric conversion portion. The photoelectric conversion portion includes: a pair of electrodes; and a photoelectric conversion layer between the pair of electrodes, and at least part of the photoelectric conversion layer includes a mixed layer of a p-type organic semiconductor and a fullerene, and a mixing ratio of the fullerene to the p-type organic semiconductor in terms of thickness ratio is less than 1:1.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Phosphor mixture and light emitting device using the same
ActiveUS7345418B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesPhosphorHigh color
A phosphor mixture containing four or more kinds of phosphors including a red phosphor, an orange phosphor, a blue phosphor, and a green phosphor, to produce emission having excellent color rendering of white light at a high color temperature, and emission in warm white which is low in color temperature, and a light emitting device including the phosphor mixture and a light-emitting section, CaAlSiN3:Eu and CaAl2Si4N8:Eu are manufactured as a red phosphor and an orange phosphor respectively, and ZnS:Cu, Al, and BAM:Eu are prepared as a green phosphor and a blue phosphor respectively. The emission spectrums of these phosphors are measured and a relative mixing ratio at which the correlated color temperature of the phosphor mixture becomes a targeted color temperature is determined from the emission spectrum by simulation, and a phosphor mixture is obtained by weighing and mixing the respective phosphors based on the simulation result.
Owner:NICHIA CORP +1
Modern snuff and its making method
InactiveCN1775117AHarm reductionReduce fatigueTobacco treatmentHydroxy compound active ingredientsAgricultural scienceTar
The present invention discloses a new-type snuff and its preparation method. It is made up by using dried tobacco leaf, dried natural vanilla and functional auxiliary material according to the mixing ratio of 1:0.8:0.2 through a certain preparation process. It can greatly reduce nicotine, tar and other harmful matter contents.
Owner:杨利斌
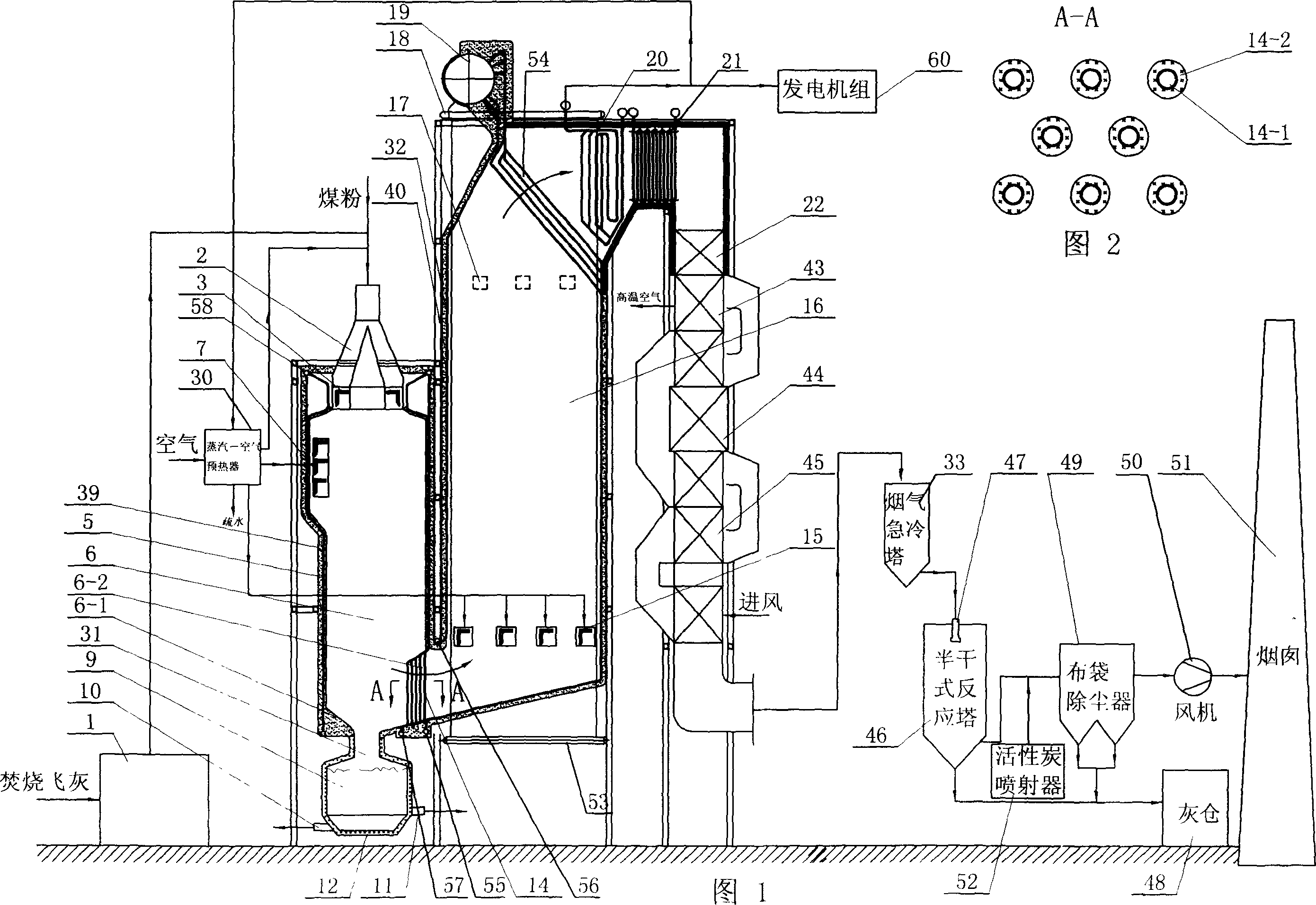
Method of processing refuse burning fly ash through cyclone furnace high temperature melting
The invention relates to a method for processing fly ash after incineration of domestic waste. The high-temperature melting treatment method of fly ash in a garbage incineration is completed by the following steps: 1. The fly ash produced after garbage incineration is mixed with coal powder at a ratio of 15 to 25: 75-85 mixed in a ratio of 75 to 85 and sent to the cyclone furnace 6 for combustion until high-temperature melting; 2. The combustion in the cyclone furnace 6 is in a reduced state; 3. The heavy metals in the fly ash sink to the bottom of the slag pool 9 and are discharged and recovered , and the slag floating on the liquid metal flows out of the slag pool from the slag recovery outlet 11, and is then rapidly cooled by water as cement raw material or building material recycling. The method can not only recover valuable metals in fly ash, decompose dioxin, recover waste heat to generate electricity, but also recycle molten ash as cement raw material or building material after being quenched with water, and has low operating cost. Or the combustion in the cyclone furnace 6 is in an oxidized state, the air excess coefficient is kept at 1.1 to 1.2, and only the quenched glass body is recovered.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Sullage solidifying method
InactiveCN101220590AHigh strengthThe surrounding environment is beautified and tidyRoadwaysSolid waste managementSludgePrice ratio
A sludge solidification method is a method for carrying out solidification treatment to the sludge produced in water conservancy projects and civil engineering. The method is that: a. the liquid water content, the clay content and organic content of dredging sludge are tested. b. curing agent is prepared: the curing agent mainly contains cement and calcium oxide which play the function of solidification; wherein, the weight proportion is between 1 : 1 to 4 : 1; waste gypsum is used as water reducing agent which occupies 1 to 8 percent of the sum of cement and calcium oxide in proportion; mealy sand or pulverized fuel ash are used as concrete aggregate which occupies 3 to 5 percent of the sum of the cement and calcium oxide in proportion; c. the curing agent-mixing ratio which is usually controlled from 5 to 20 percent is determined; sampling respectively is carried out, setting time is tested and the unconfined compressive strength which maintains 7, 14 and 28 days is tested by sampling, and the curing agent-mixing ratio finally is determined according to optimal performance price ratio; d. the sludge is carried out curing and constructing in site; mechanical devices are used for stirring the curing agent and the sludge rapidly and evenly, thereby leading the solidification to be rapid and full.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Elastic body, method for manufacturing the same and mattress including the same
InactiveUS20030101517A1Stay flexibleEasy to manufactureStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesElastomerAlcohol
Disclosed are an elastic body having a good elasticity and an impact absorbing efficiency, a method of manufacturing the same and a mattress employing the same. The elastic body is a foamed polyurethane body including polystyrene and has a plurality of foams in which air is contained. The elastic body is prepared by a method comprising the steps of preparing polyether polyol by mixing poly alcohol and a polyether compound in a mixing ratio of 3-5 to 5-7 by weight, obtaining a polyol mixture by adding 2-20 parts by weight of polystyrene and a trace amount of a catalyst and water to 30-50 parts by weight of the obtained polyether polyol, adding and stirring 20-60 parts by weight of an isocyanate compound to 40-80 parts by weight of the polyol mixture at 20-80° C., and pouring the resulting product into a mold to foam cast. A mattress manufactured by using such elastic bodies has a good elasticity and is capable of absorbing pressure, thereby providing comfort for users.
Owner:CHOI YOUN SOO
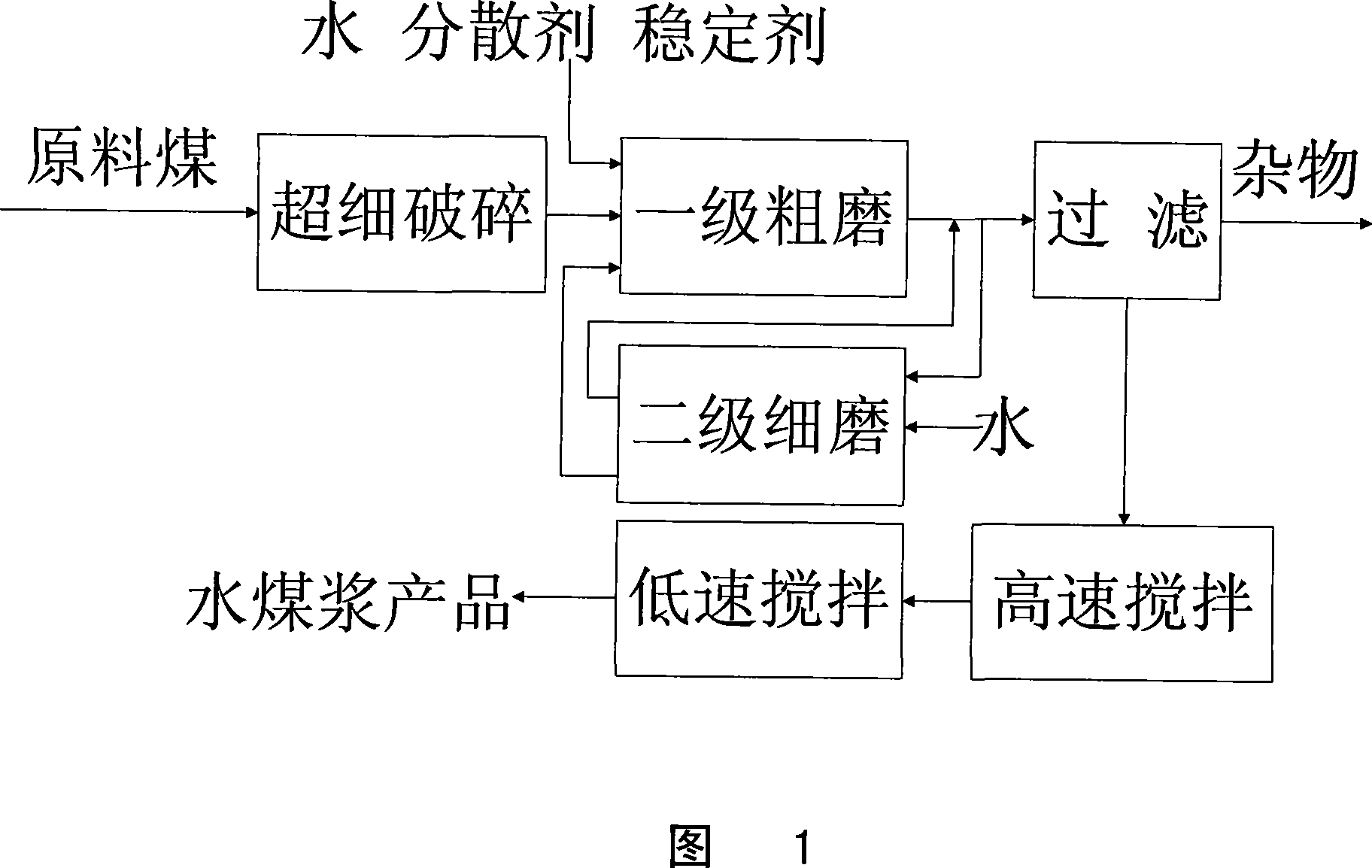
Method for preparing high concentration water-coal-slurry by low-rank coal
ActiveCN101173765AImprove particle size distributionReduce preparation energy consumptionLump/pulverulent fuel preparationHigh concentrationCoal water
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-concentration coal-water slurry by using low-rank coal. The steps include: 1) ultrafine crushing of low-rank coal; 2; 3) wet coarse grinding of the mixture; 4) ① mix 10% to 30% of the total amount of coal slurry after coarse grinding with water in a mass ratio of 5:1 to 2, and then carry out Wet fine grinding; ②The coal slurry after wet coarse grinding other than wet fine grinding is directly sent to the filter device; 5) The coal slurry after step 4) ① fine grinding is processed in the following way: ①Return all the coal slurry to step 3 ) for circulating coarse grinding; or ② return part of the coal slurry to step 3) for circulating coarse grinding, and send another part of finely ground coal slurry directly into the filter device; or ③ directly send all the coal slurry into the filter device; 6) The coal slurry sent to the filter device is filtered through a 18-20 mesh filter, and then stirred at a high speed in the stirring device, left standing, or stirred at a low speed to obtain a high-concentration coal-water slurry product.
Owner:CHINA COAL RES INST CCRI ENERGY SAVING TECH CO LTD
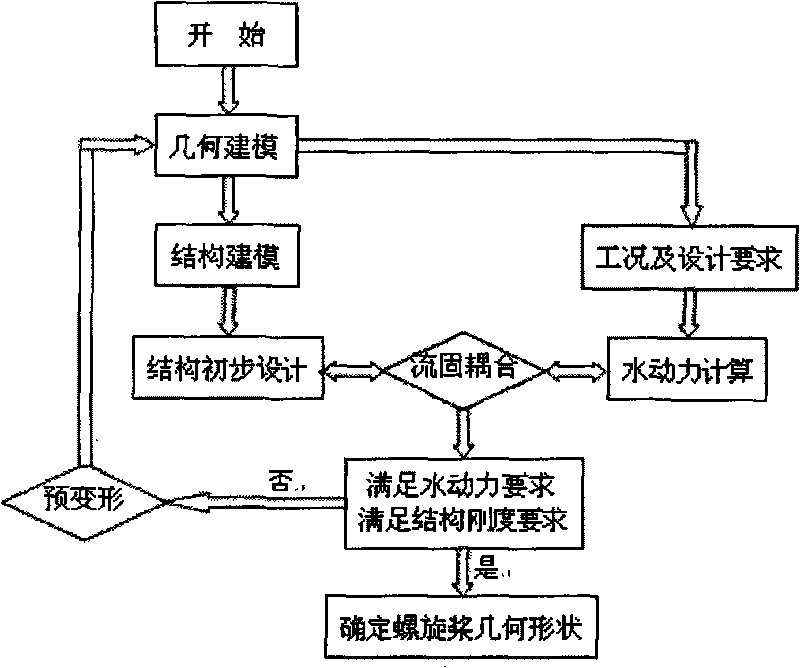
Optimization design method of fibre enhanced composite material marine propeller blade
InactiveCN101706832AAccelerated corrosionImprove impact resistanceRotary propellersSustainable transportationGlass fiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses an optimization design method of fibre enhanced composite material marine propeller blades, which relates to an optimization design method of propeller blades and aims at solving the problem of imperfect design method of the fibre enhanced composite material marine propeller blades. On the basis of offsets data of the original high-speed metal propeller blades, the method is calculated by using a fluid-solid coupling method combining with the implementation of predeformation strategy, a blade structure is composed by mixed fibre composite materials, the surface of a blade adopts fibre glass enhanced composite material, the interior of the blade adopts the mixture of carbon fiber and Kelvar fiber enhanced composite material, and the specific mixed paving mode and the mixing ratio are determined according to the hydro elastic design result of a fibre enhanced composite material marine propeller. The optimization design method is used for designing the propeller blades.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
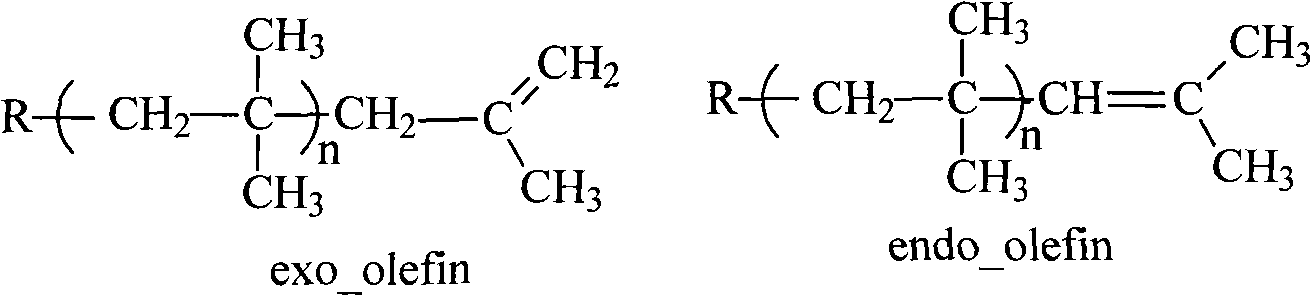
Initiating system for preparing high-reaction activity polyisobutene and copolymer of polyisobutene
ActiveCN101955558ARegulate nucleophilicityReduce formationSimple Organic CompoundsCationic polymerization
The invention relates to an initiating system for preparing high-reaction activity polyisobutene and a copolymer of polyisobutene, which comprises an initiator for initiating the cationic polymerization of an isobutene-containing material, a coinitiator and a compounding ingredient, wherein the coinitiator is FeCl3; the compounding ingredient is an oxygen- or sulfur-containing organic compound; the molar mixing ratio of the FeCl3 and the isobutene raw material ranges from 0.01 to 3.0; the molar mixing ratio of the initiator to the FeCl3 ranges from 0.1 to 2.0; and the molar mixing ratio of the compounding ingredient to the FeCl3 ranges from 0.1 to 3.4. In the invention, the FeCl3 is used as the compounding ingredient to be compounded with the oxygen- or sulfur-containing compounding ingredient to promote a reaction for removing active central carbocations beta-H, thus the high-reaction activity polyisobutene and the copolymer of polyisobutene, which have terminal alpha-double bond content of more than 75mol percent (even over 90 percent) and narrow molecular weight distribution, can be obtained by a one-step method. The process steps are simplified. The production cost is low. Therepeatability is high. The environmental pollution is light. And the industrial application is easy.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
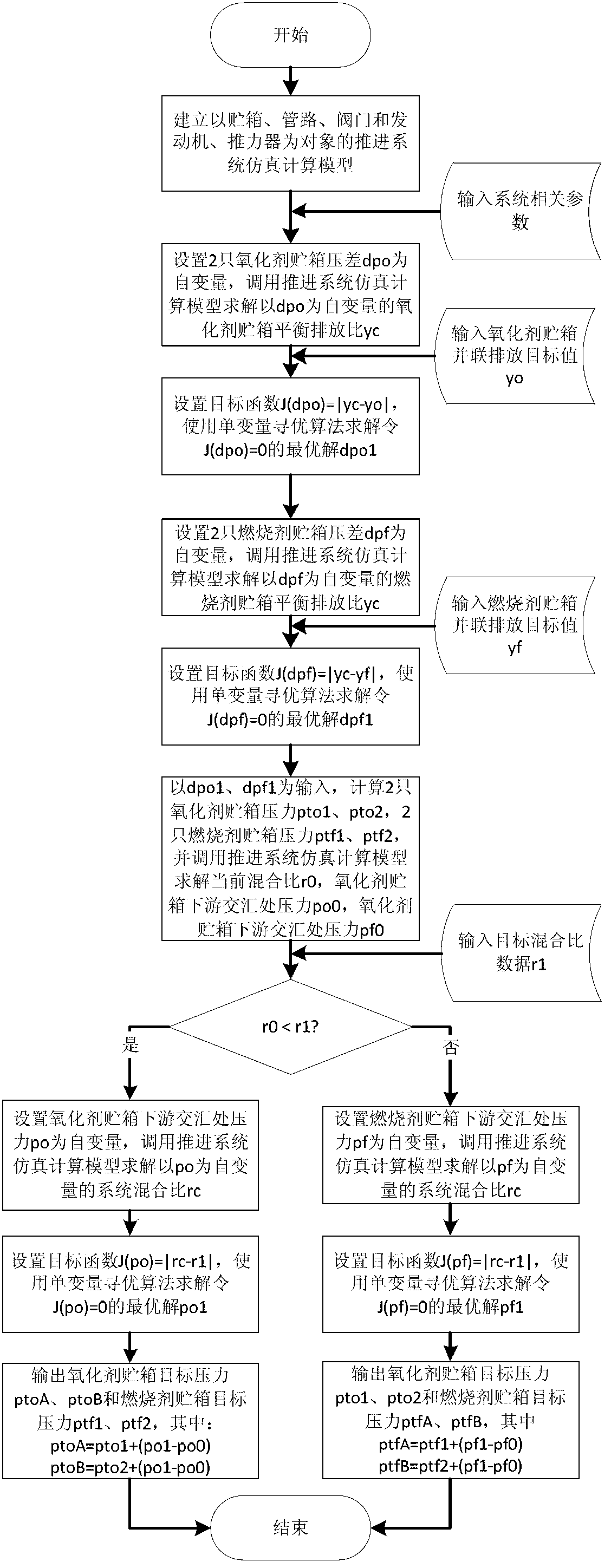
Method of actively adjusting balanced discharging of parallel connection tanks of satellite two component propelling system
ActiveCN103213692ABalanced Emission RegulationThe mixing ratio does not affectCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusPressure differenceOrbit
The invention relates to a method of actively adjusting the balanced discharging of parallel connection tanks of a satellite two component propelling system. A simulation model of a propelling system is firstly established; the current system mixing ratio r0 is calculated according to the current system state data; then the pressure difference dpo1 of oxidant tanks (MON-A and MON-B) and the pressure difference dpf1 of incendiary agent tanks (MMH-A and MMH-B) are calculated through an optimization algorithm according to the target value of the balanced discharging of the parallel connection tanks; the target pressure of each tank is finally calculated through the optimization algorithm by taking the r0 as the target value and the dpo1 and dpf1 as the initial conditions; and the pressure of the tanks can be adjusted to the target pressure point by utilizing gas bypasses when a satellite is in orbit, so that not only is the balanced discharging of the parallel connection tanks adjusted, but also the system mixing ratio is not influenced.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
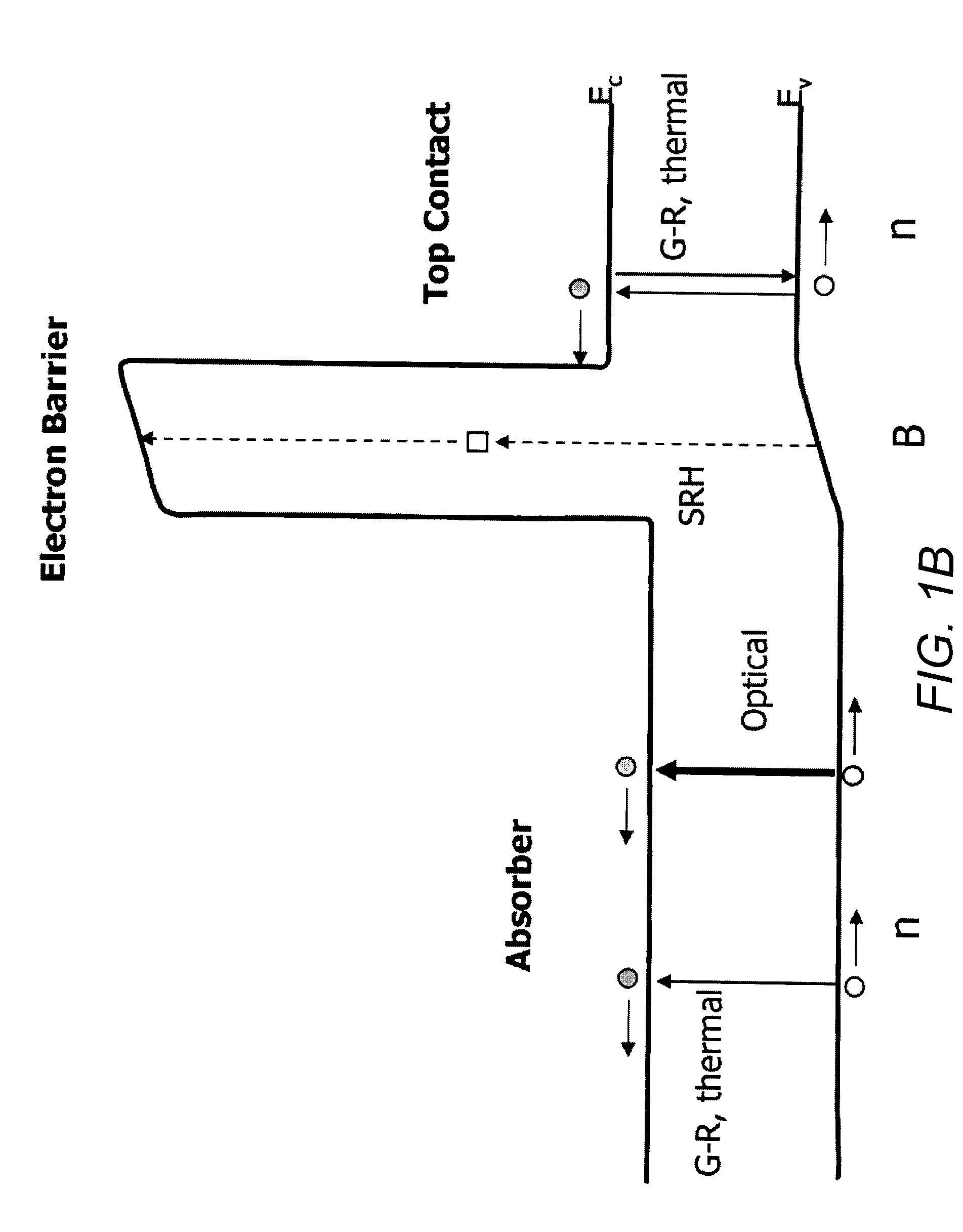
High operating temperature barrier infrared detector with tailorable cutoff wavelength
ActiveUS20100072514A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDetector arrayContact layer
A barrier infrared detector with absorber materials having selectable cutoff wavelengths and its method of manufacture is described. A GaInAsSb absorber layer may be grown on a GaSb substrate layer formed by mixing GaSb and InAsSb by an absorber mixing ratio. A GaAlAsSb barrier layer may then be grown on the barrier layer formed by mixing GaSb and AlSbAs by a barrier mixing ratio. The absorber mixing ratio may be selected to adjust a band gap of the absorber layer and thereby determine a cutoff wavelength for the barrier infrared detector. The absorber mixing ratio may vary along an absorber layer growth direction. Various contact layer architectures may be used. In addition, a top contact layer may be isolated into an array of elements electrically isolated as individual functional detectors that may be used in a detector array, imaging array, or focal plane array.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
An inversion method for laser radar data of atmospheric particulate matter particle size spectrum spatial and temporal distribution
ActiveCN103234877AAchieving Simultaneous ExtractionGet Optical PropertiesParticle size analysisParticulatesExtinction
The present invention discloses an inversion method for laser radar data of atmospheric particulate matter particle size spectrum spatial and temporal distribution. The method comprises: by measuring back scattered echo signal of atmospheric particulate matters via laser radar, accurately inverting to obtain extinction coefficients of atmospheric particulate matters in three wavelengths of infrared, visible and ultraviolet bands at different heights from the ground; building lognormal distribution spectral functions of four aerosol components and parameters thereof, for obtaining refractive indexes at different bands of different aerosols and the mixing ratio of the four aerosol components in different aerosol modes; obtaining the particle size spectrum normalized at 0.55 micron of the extinction coefficient of each aerosol basic component, and comparing with a standard spectrum for authentication; and finally performing iterative calculation to the extinction coefficient spectrums obtained by laser radar surveying to obtain the aerosol mixed volume ratio of each height, thus obtaining atmospheric particulate matter particle size distribution of different heights at different times. According to the inversion method of the invention, valid data are provided for analysis and study of particle properties and variation patterns, especially, an effective means for spatial and temporal change detection for the particle-size spectrum of the atmospheric particulate matters is provided, and active three-dimensional telemetry technology suitable for atmospheric particulate matter particle size distribution is established.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dispensing Assembly for Two Components , Including a Syringe or Dispensing Cartidge and a Mixer
The invention relates to a system for dispensing two components, including a syringe or cartridge and a mixer. The system is characterized in that the edges of the mixer inlet openings on the cartridge end and the transfer channel outlets linked with the cartridge outlets are disposed and configured to allow a vacuum-free replacement of the mixer. The planes of the openings on the adapter outlets or on the cartridge outlets or the planes of the openings of the mixer inlets form an angle, especially an angle of 90°, with the longitudinal axes of the outlets or inlets. The inventive systems allows removal of the mixers without producing a vacuum, thereby preserving the filling level of the two components and allowing a correct mixing ratio from the outset once the new mixer is placed on the syringe or cartridge.
Owner:MEDMIX SYST
Insulating gas insulating performance experiment system and method thereof applied to electrical equipment
InactiveCN103913682ASolve the discharge problemAvoid nudityTesting dielectric strengthDecompositionElectrical devices
The invention provides an insulating gas insulating performance experiment system and a method thereof applied to electrical equipment. The insulating gas insulating performance experiment system and the method thereof applied to the electrical equipment is targeted to the defect of an insulating gas discharging decomposition device. By means of the insulating gas insulating performance experiment system and the method thereof applied to the electrical equipment, an insulating performance experiment of high-low pressure insulating gas in the electrical equipment can be conducted, various defects of a real GIS can be effectively simulated, the insulating performance of various replaced gas and mixed gas of the replaced gas under the experiment condition of different defects, different mixing ratios and different air pressure can be obtained, comparing with SF6 gas under the same experiment condition is conducted, and the experiment basis for replacing the SF6 gas is provided.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com