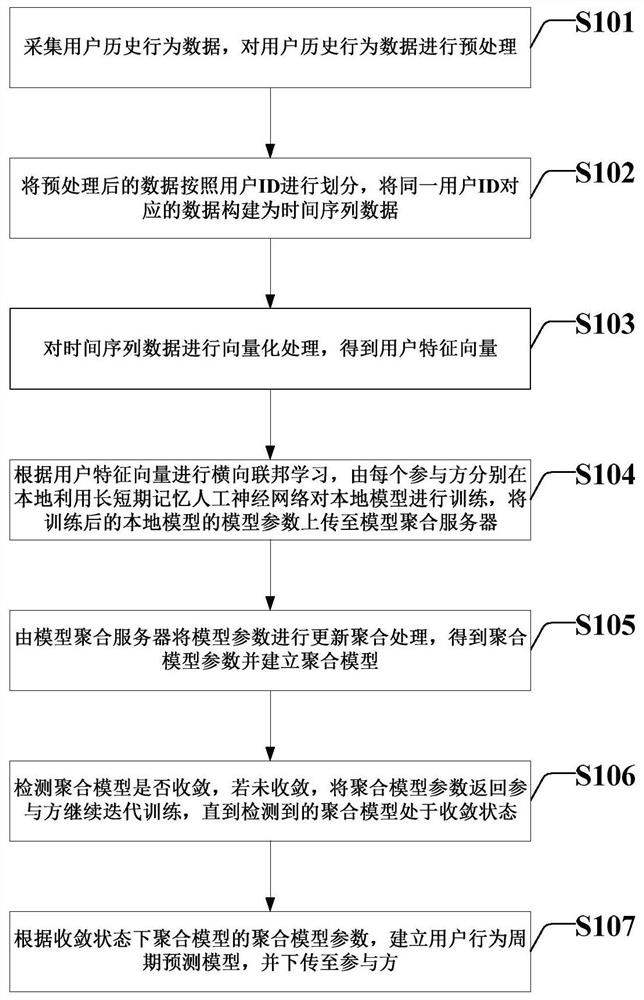
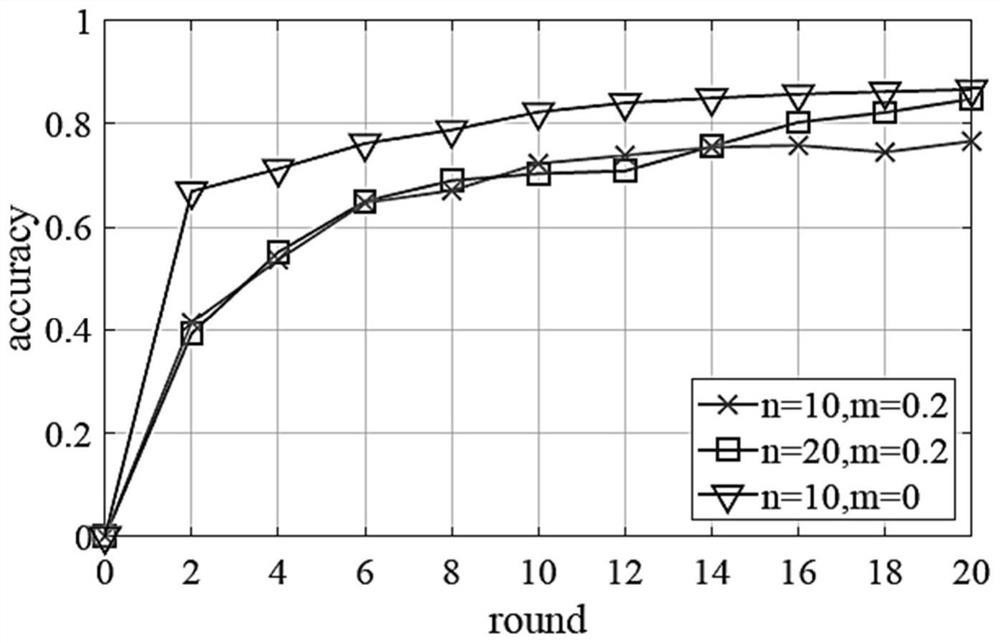
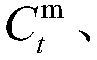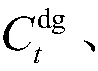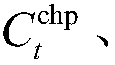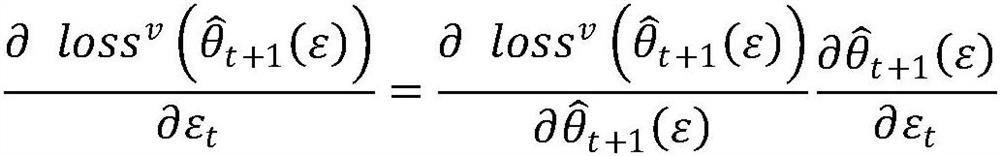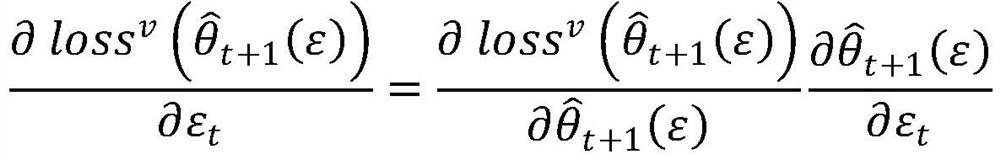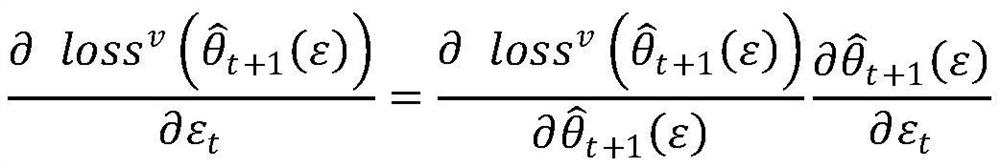Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88 results about "Model aggregation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Equipment evaluation and federated learning importance aggregation method, system and equipment based on edge intelligence and readable storage medium
ActiveCN112181666AReduce consumptionReduce latencyDigital data information retrievalResource allocationEdge serverResource information
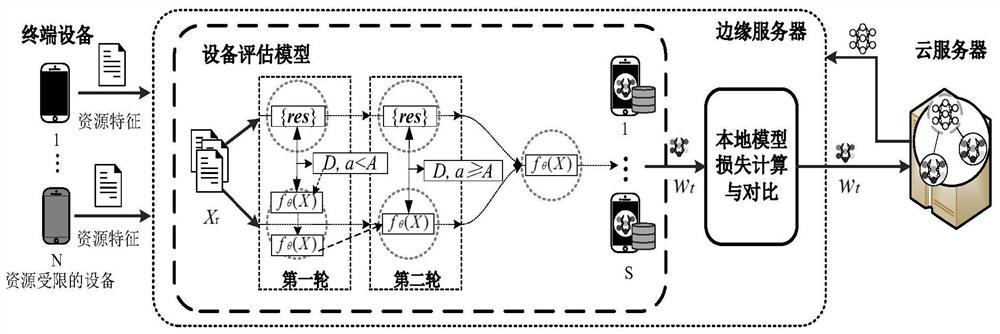
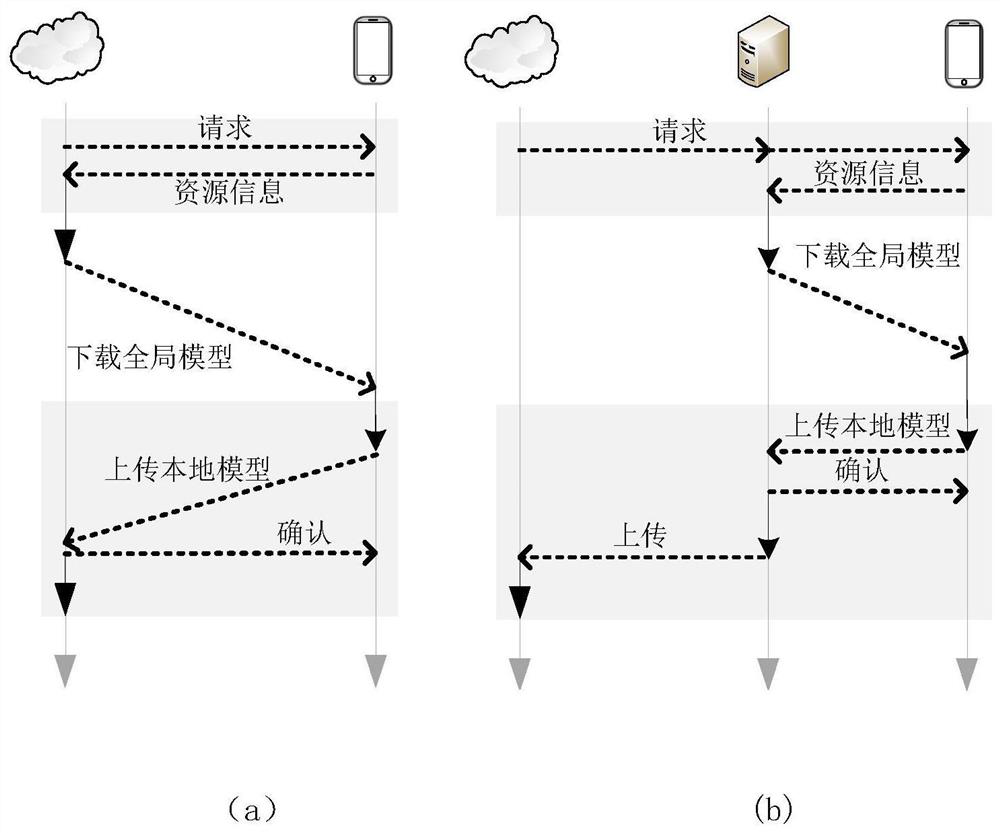
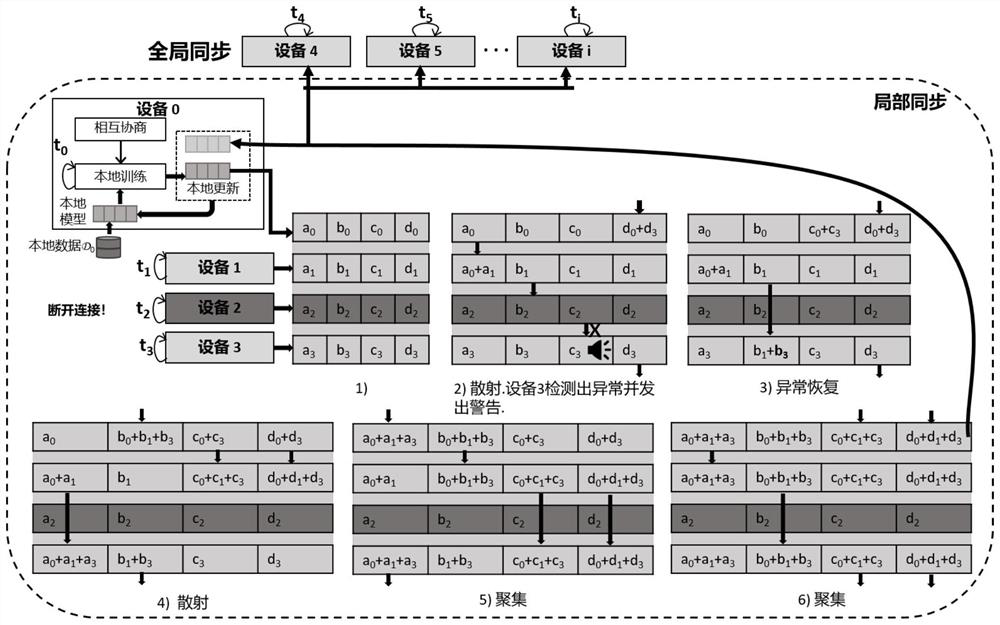
The invention provides an equipment evaluation and federated learning importance aggregation method based on edge intelligence, which comprises the following steps of cloud server initialization: generating an initial model by a cloud server, equipment evaluation and selection: receiving resource information of terminal equipment by an edge server, generating a resource feature vector, and inputting the resource feature vector to the evaluation model, local training: after the edge server selects the intelligent equipment, sending the transferred initial model to the intelligent equipment, andenabling the intelligent equipment to carry out local training on the initial model in federated learning to obtain a local model, local model screening: sending the local model to an edge server, and judging whether the local model is an abnormal model or not by comparing the loss values of the local model and a previous round of global model, and global aggregation: performing global aggregation by using a classical federated average algorithm. According to the method provided by the invention, on one hand, the training bottleneck problem with resource constraint equipment is solved, and onthe other hand, the model aggregation effect is improved so as to reduce redundant training and communication consumption.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Random convolutional neural network-based high-resolution image scene classification method
InactiveCN106250931AImprove generalization abilityImprove training efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNerve networkAlgorithm
The invention discloses a random convolutional neural network-based high-resolution image scene classification method. The method comprises the steps of performing data mean removal, and obtaining a to-be-classified image set and a training image set; randomly initializing a parameter library of model sharing; calculating negative gradient directions of the to-be-classified image set and the training image set; training a basic convolutional neural network model, and training a weight of the basic convolutional neural network model; predicting an updating function, and obtaining an addition model; and when an iteration reaches a maximum training frequency, identifying the to-be-classified image set by utilizing the addition model. According to the method, features are hierarchically learned by using a deep convolutional network, and model aggregation learning is carried out by utilizing a gradient upgrading method, so that the problem that a single model easily falls into a local optimal solution is solved and the network generalization capability is improved; and in a model training process, a random parameter sharing mechanism is added, so that the model training efficiency is improved, the features can be hierarchically learned with reasonable time cost, and the learned features have better robustness in scene identification.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Virtual power plant combined heat and power scheduling robust optimization model
InactiveCN106127389ASolve modeling problemsReduce riskEnergy industryResourcesRobustificationDistributed generator
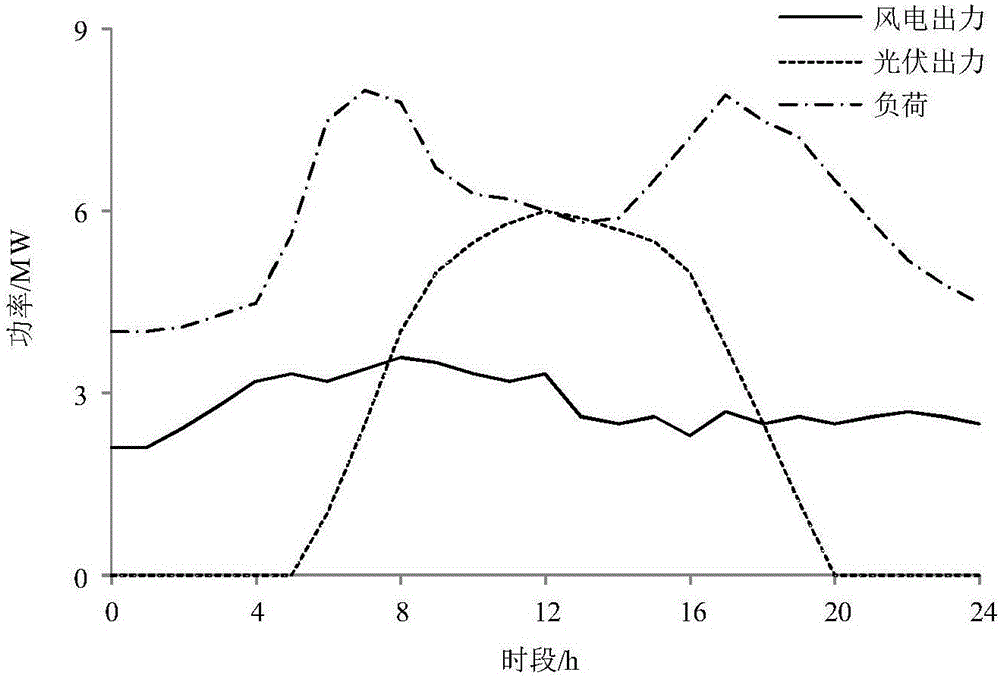
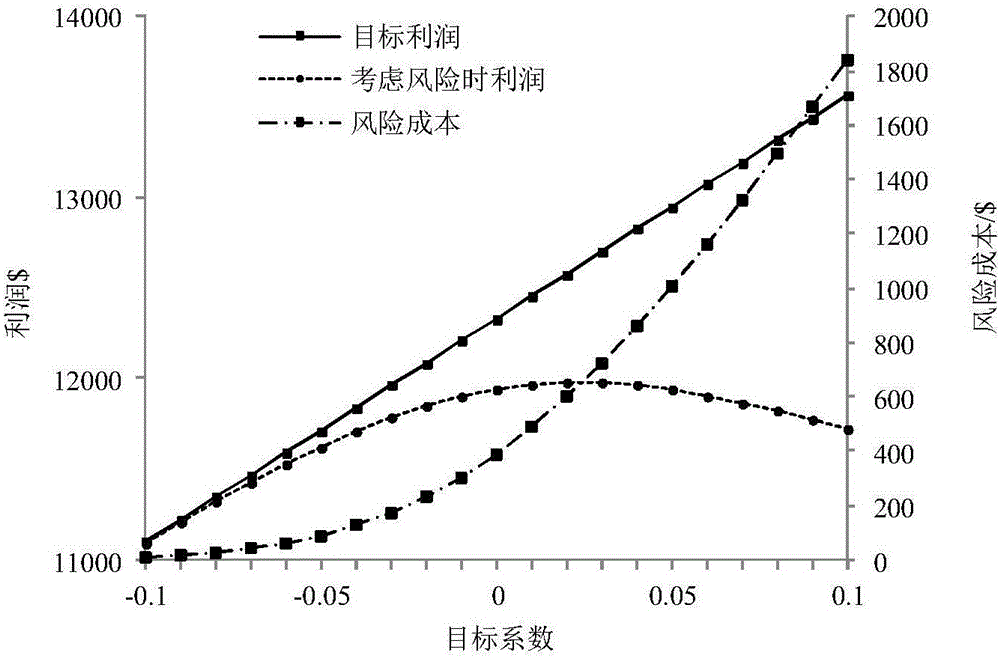
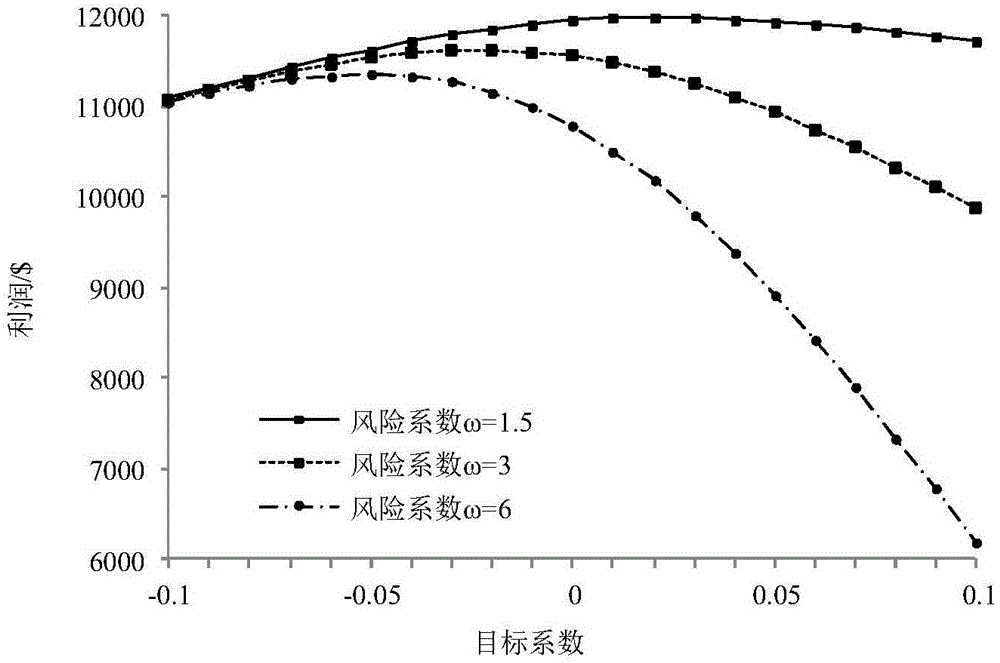
The invention provides a virtual power plant combined heat and power scheduling robust optimization model. A model aggregation unit comprises a distributed generating set, a wind turbine generator set, a photovoltaic set, a combined heat and power (CHP) set, a boiler, electric energy storage, heat energy storage, an electric load and a heat load. Participation of the CHP set in the SRM (Spinning Reserve Market) situation is considered. Aiming at the facing uncertain problem of a virtual power plant (VPP) and resulting risks, robust optimization (RO) is utilized to process uncertainty of the EM electricity price, the SRM electricity price, the wind power capacity, the photovoltaic capacity, the electric load and the heat load, and risk quantification indexes are established, and thus robustness and economical efficiency of a RO model are balanced. The model provided by the invention well solves the existing combined heat and power scheduling optimization model establishment problem of the VPP when participating EM and SRM at the same time, and improves flexibility of decision making, and thus the profit of the VPP is increased. Meanwhile, the introduction of the RO model effectively reduces system risks, and thus the effective reference is provided for a decision maker to select a proper robust factor.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
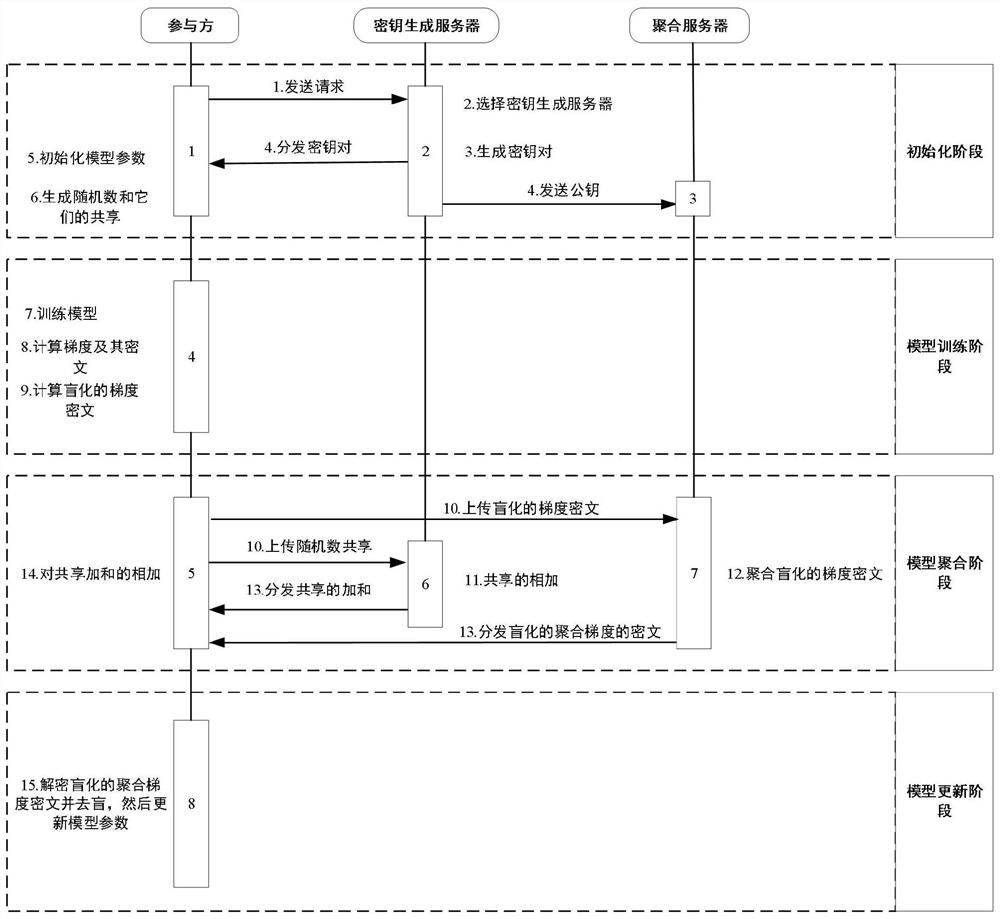
Federal learning privacy protection method based on homomorphic encryption and secret sharing
ActiveCN113037460AResistant to Collusion AttacksKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data protectionAlgorithmCiphertext
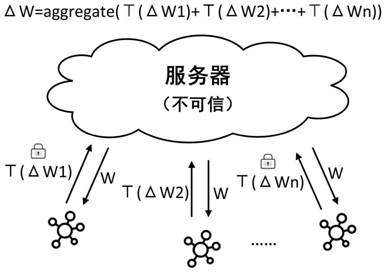
The invention discloses a federal learning privacy protection method based on homomorphic encryption and secret sharing, wherein the method comprises two parts: a gradient protection method based on homomorphic encryption and a random number protection method based on secret sharing, and mainly aims at four stages: an initialization stage, a model training stage, a model aggregation stage and a model updating stage. The gradient protection method based on homomorphic encryption is adopted, gradient protection is achieved, meanwhile, aggregation of gradient ciphertexts can be completed, leakage of gradient privacy information is effectively prevented, and safe aggregation of the gradient can be achieved; through the random number protection method based on secret sharing, the gradient ciphertext is protected, and meanwhile, the random number protected by the gradient ciphertext is protected, so that collusion attacks among the aggregation server, the key generation server and the participants can be effectively prevented, and the security of gradient information in the interaction process of the aggregation server, the key generation server and the participants is further guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Wireless service flow prediction method based on weighted federated learning
ActiveCN111369042AImprove forecast accuracyAvoid forecast inaccuraciesForecastingData switching networksService flowTraffic prediction
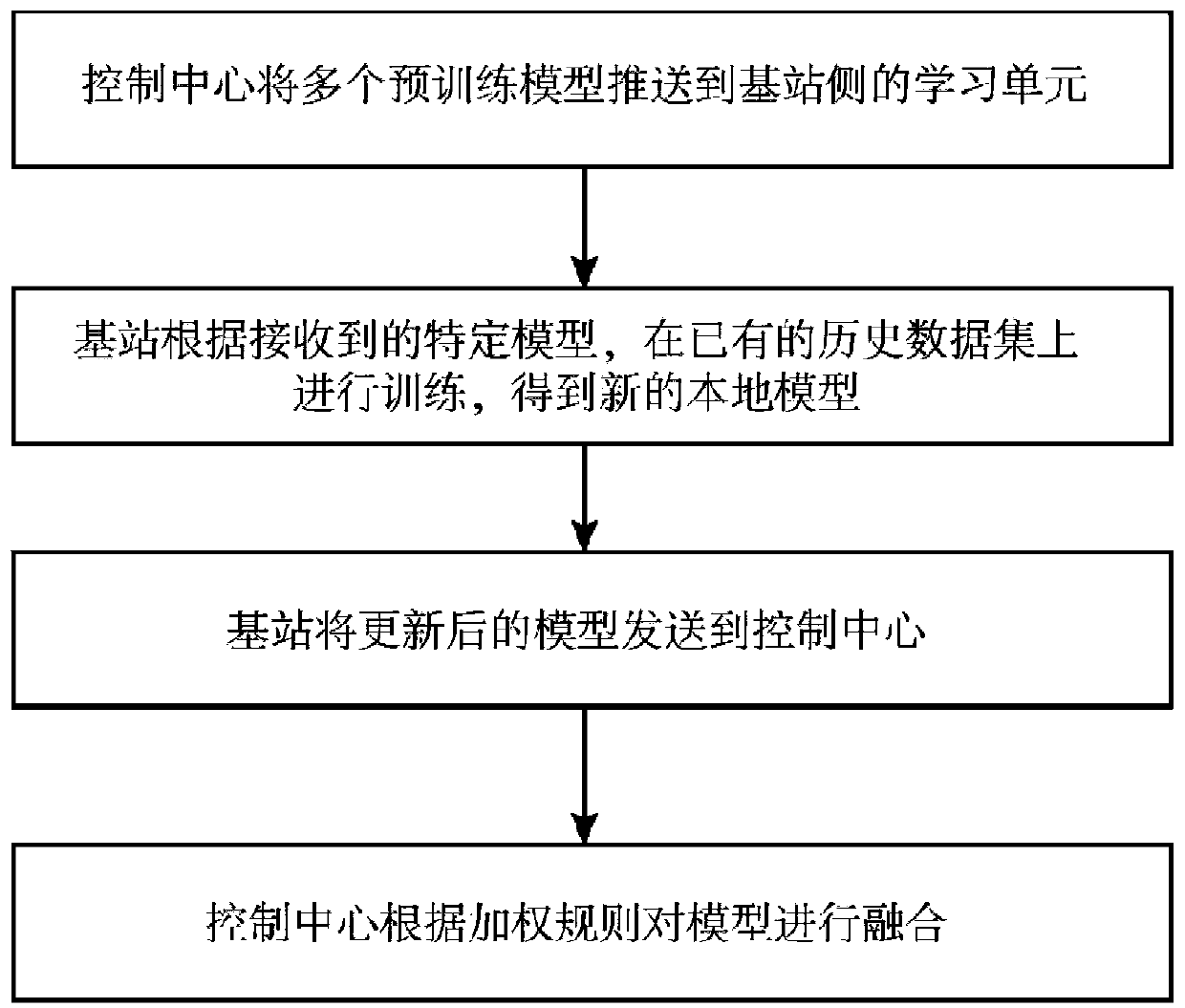
The invention relates to a wireless service flow prediction method based on weighted federated learning. The method comprises the following steps: a control center pushes a plurality of pre-training models to a base station side; the base station side performs model training according to the local data and transmits the trained model to a control center; the control center fuses the models according to a weighting rule and feeds back the fused models to the base station, and more weights are given to the local model in the weighting rule; and the base station predicts the wireless service flowat the future moment according to the obtained final model. According to the wireless service flow prediction method provided by the invention, on the basis of a control center model aggregation strategy, the weighted aggregation rule is used for replacing an average strategy, so that the phenomenon of inaccurate prediction caused by data isomerism can be avoided, and the overall prediction precision of distributed wireless service flow prediction is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Federal learning method and device
ActiveCN114091356AEfficient identificationReduce adverse effectsDesign optimisation/simulationMachine learningEngineeringVerification
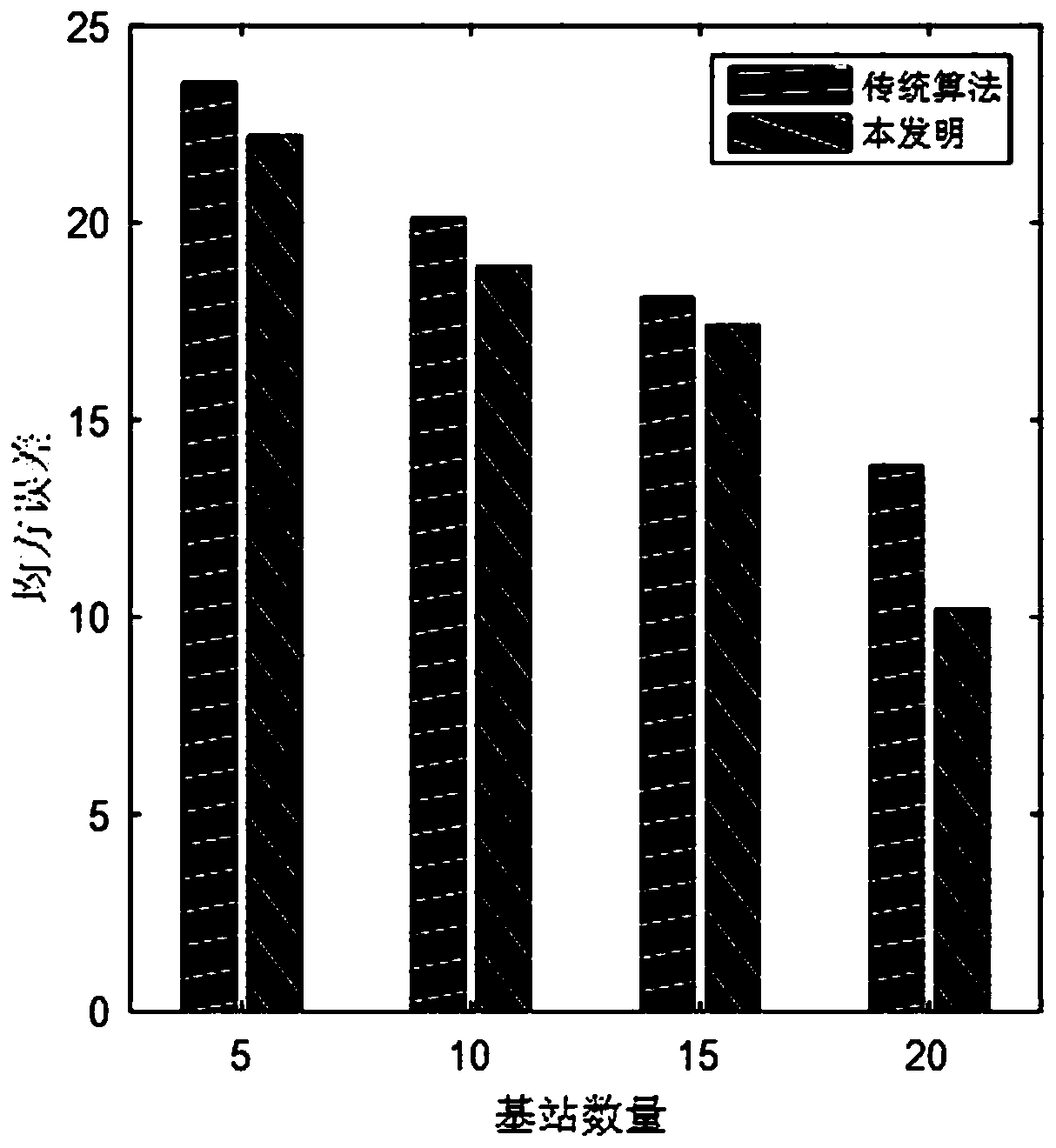
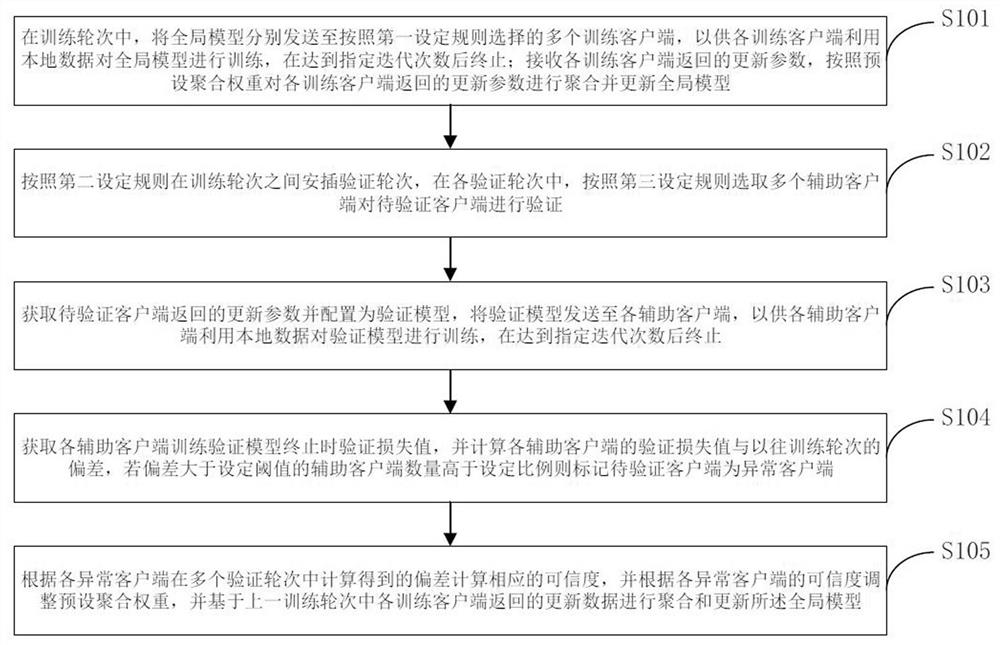
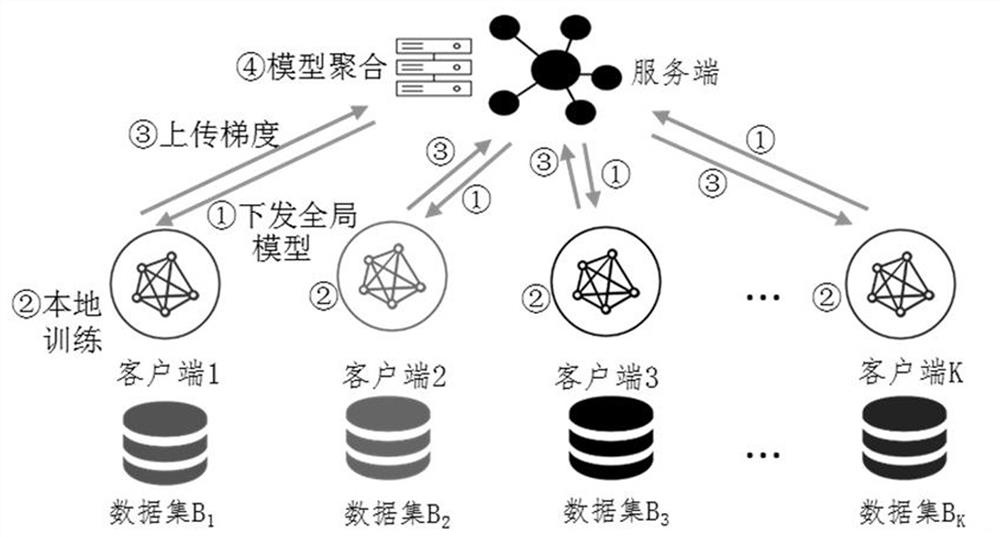
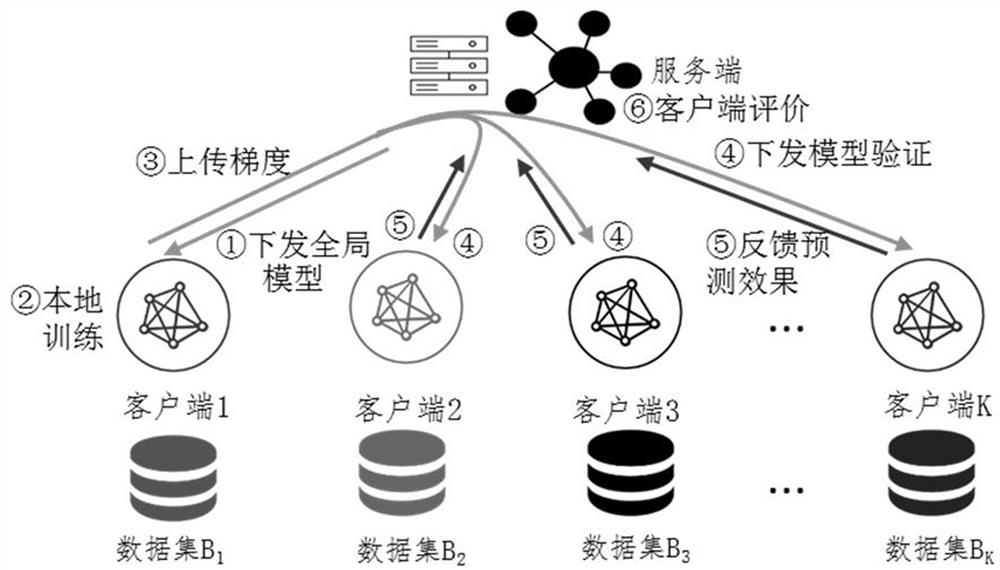
The invention provides a federal learning method and device, and the method comprises the steps: adding a verification round in a federal learning process, enabling a server to transmit a model updating parameter returned by a to-be-verified client last time to an auxiliary client, and carrying out the training through the local data of the auxiliary client, and calculating the deviation between the loss value when training of each auxiliary client in the verification round is terminated and the previous round, and if the number of the auxiliary clients with the deviation greater than a set threshold is greater than a set proportion, marking the client to be verified as an abnormal client. According to the method, the abnormal client can be quickly and effectively identified under the condition that each client is not informed, and furthermore, the weight in the model aggregation process is adjusted according to the deviation in each verification round corresponding to the abnormal client, so that the adverse effect of the abnormal client on global model updating is prevented.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Virtual power plant day-ahead scheduling optimization model
InactiveCN106169102ASolve the problem of dealing with the uncertainty of wind power output at the same timeIncrease profitForecastingSystems intergating technologiesDecision schemeOptimal decision
The invention provides a virtual power plant day-ahead scheduling optimization model. A model aggregation unit comprises a gas turbine, a wind turbine generator set, a photovoltaic set, a water drawing energy storage power station and loads. For the characteristics that the electricity price probability distribution description is relatively accurate and the prediction is relatively high, random programming is adopted to process the uncertainty of the electricity price; and for the characteristics that the wind power and photovoltaic output probability distribution is difficult to precise describe and the prediction precision is relative low, an information gap decision theory (IGDT) is adopted to process the uncertainty of wind power and photovoltaic output, different weights are provided to wind power and photovoltaic output deviation coefficients, and the IGDT is enabled to simultaneously process the uncertainty of wind power and photovoltaic output. In addition, for the blindness of uncertainty decisions and the different risk degrees of different strategies, the risk cost is introduced, and the risks corresponding to different decision schemes are quantified. According to the invention, a larger decision making space is provided for a decision maker, and the VPP is enabled to make the optimal decision under more conditions, so that the benefit of the virtual power plant (VPP) is increased.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
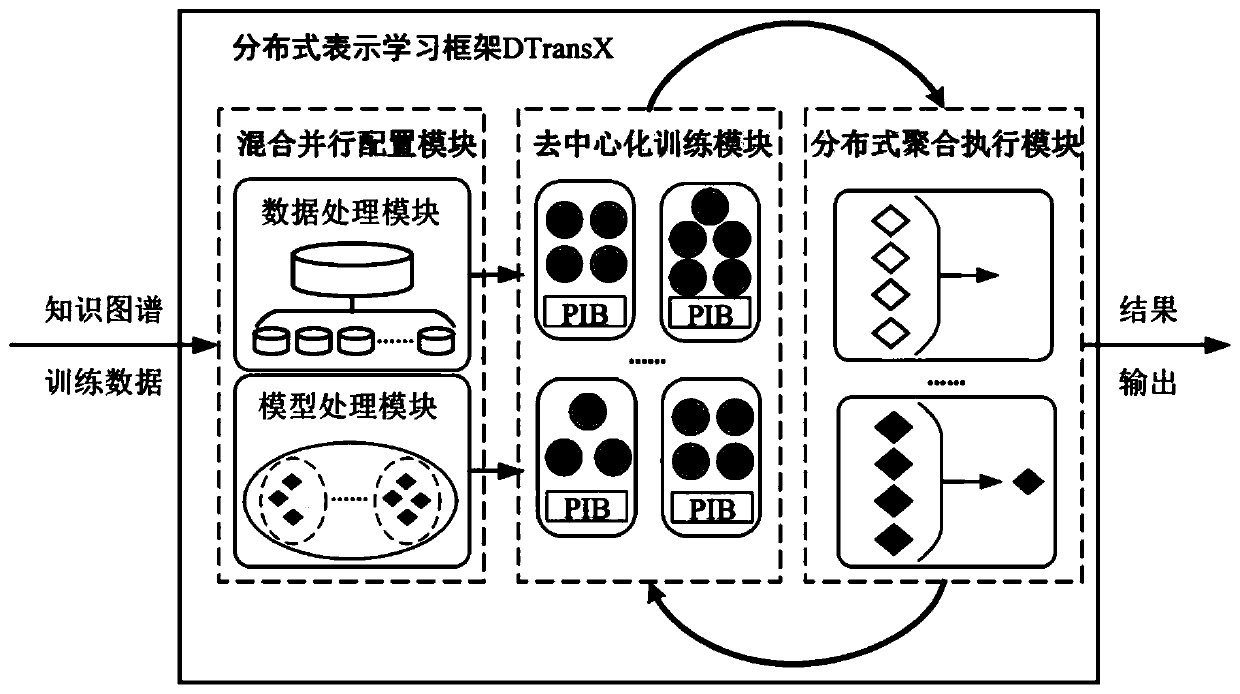
Knowledge graph representation learning-oriented distributed framework construction method
InactiveCN111241301AImplement build workIncreased training scaleSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic tool creationTheoretical computer scienceEngineering
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
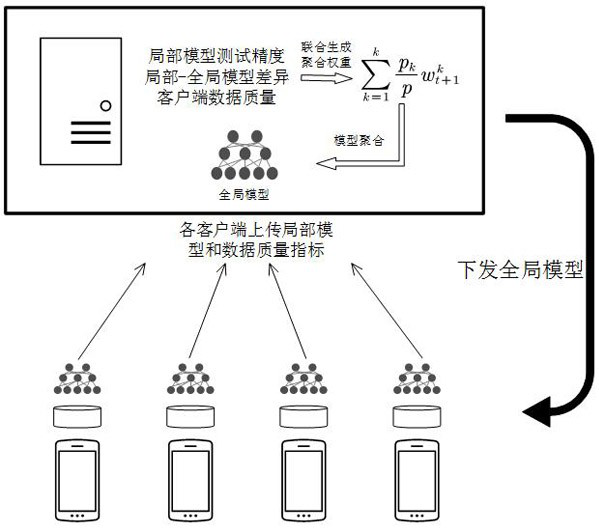
Federal learning method based on dynamic adjustment model aggregation weight
The invention discloses a federal learning method based on a dynamic adjustment model aggregation weight, and the method comprises the steps that: a cloud server receives a local training model and a data quality index from each client, and if a client weight updating condition is reached, a contribution score for each client is calculated according to the contribution of the data quality, the model precision and the model difference index to the model training precision, and weighted average is performed to generate a global model; and the cloud server issues the updated global model to the clients, each client carries out model training on the local training data after receiving the global model, and uploads the local model and the data quality index to the cloud server again after training is finished. According to the method, client training data such as data distribution, model precision and model difference are reasonably utilized, the dynamic aggregation weight is generated, available features in the client training process are fully mined, and a global model with higher quality is formed, so that the model precision and convergence efficiency are improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
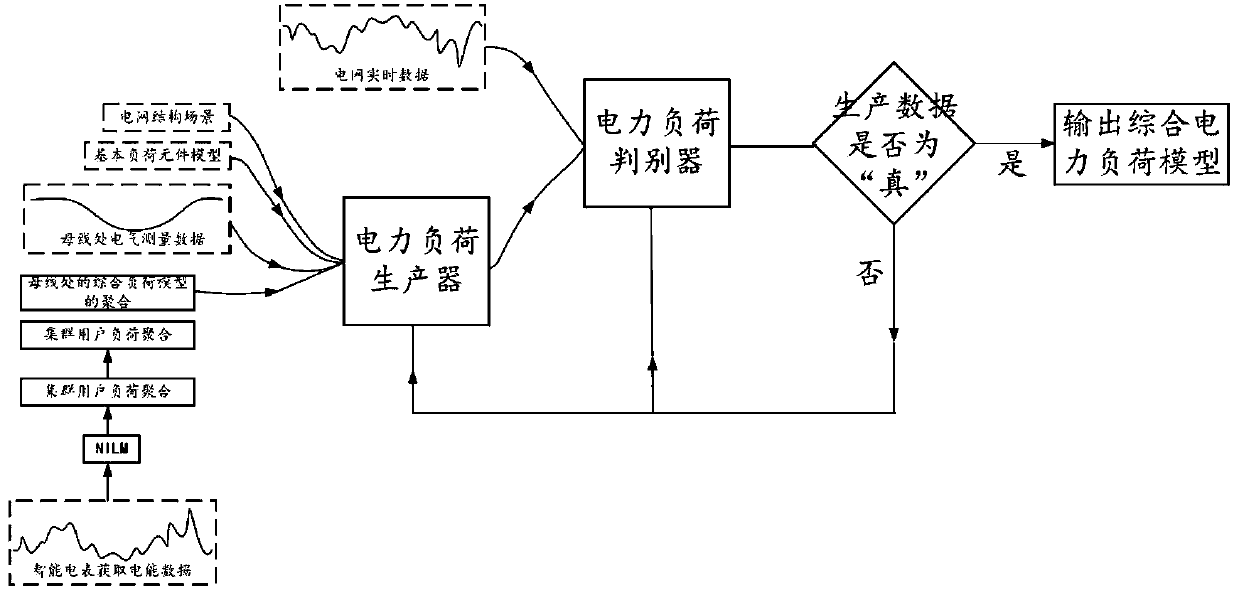
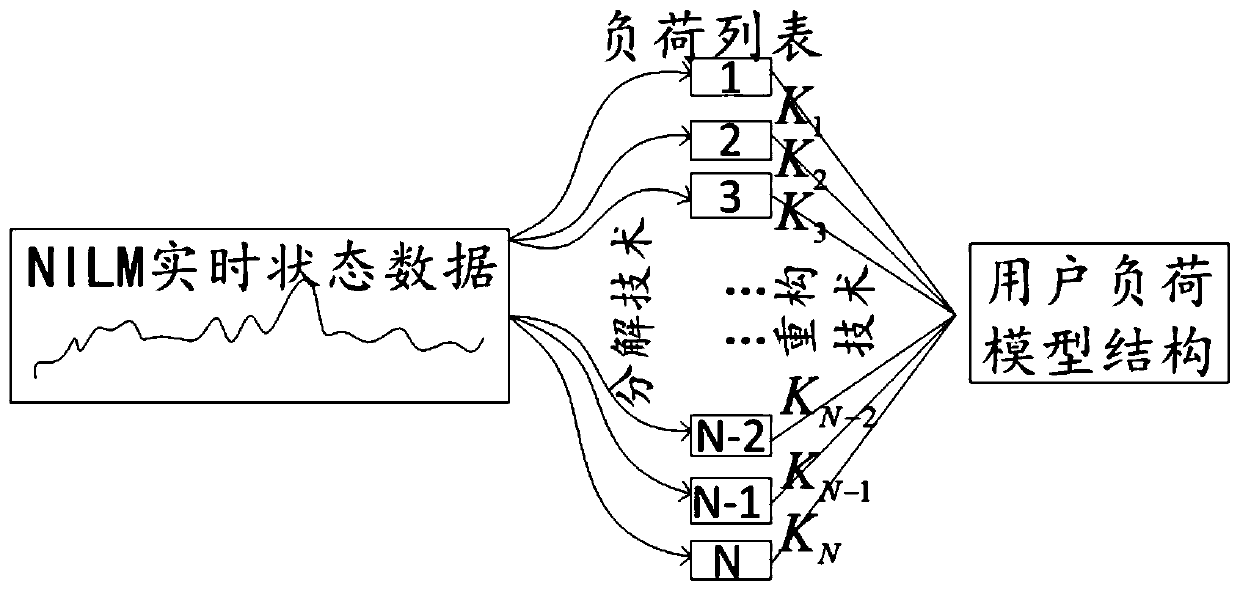
Intelligent comprehensive modeling method for power load digital statistics
PendingCN111428355ARealize online operationIncrease diversityDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingElement modelSimulation
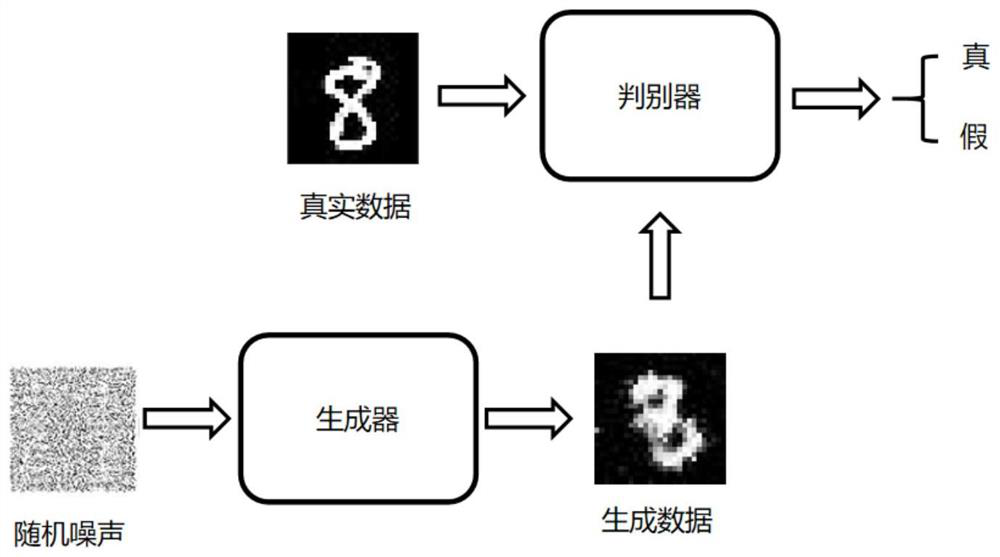
The invention discloses an intelligent comprehensive modeling method for power load digital statistics. The method comprises a non-invasive load monitoring technology. According to the technology, anelectric energy metering device is used for collecting electric load information, deep learning, reinforcement learning and other technologies are used for identifying and classifying user electric loads, a load element model and parameters based on data are formed, and the proportion of energy consumed by a single load element to total consumed energy is calculated. The load element model and theenergy consumption proportion are combined into a load model and the load model is summarized to a bus node, and data such as load element types, parameters and proportions are acquired by adopting methods such as digital statistics and intelligent synthesis. Then, a deep learning algorithm framework such as a production adversarial network generates a power load model and a load discrimination model for accuracy verification of the power load model. The digital statistical intelligent comprehensive modeling method for the power load has the potential of online operation and real-time modeling.
Owner:LIYANG RES INST OF SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
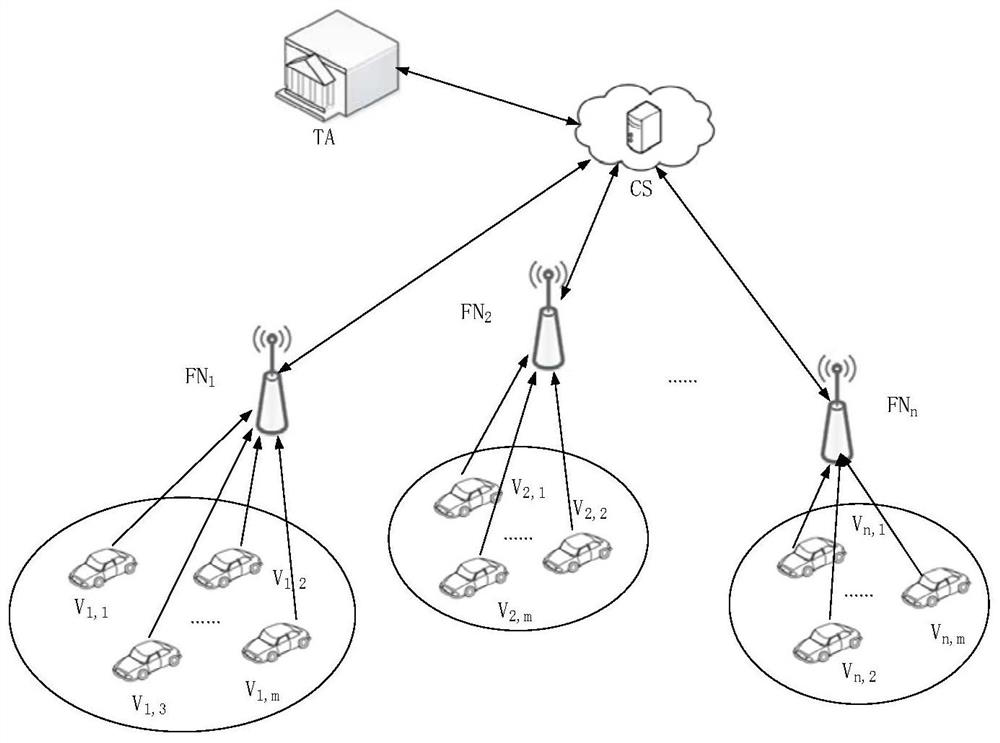
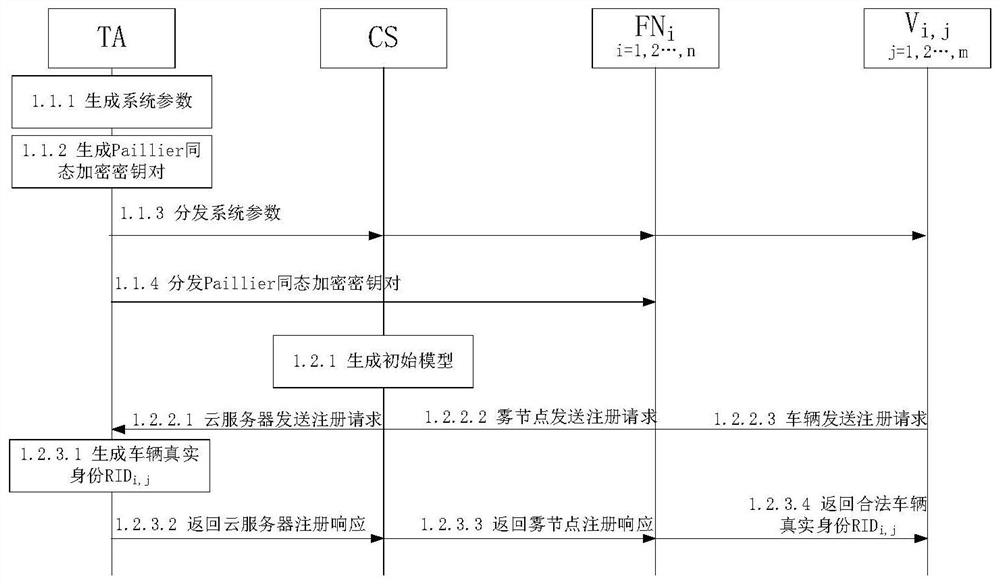
Federal learning-based privacy protection model aggregation system and method in Internet of Vehicles
ActiveCN113163366ACompatible with actual application scenariosImprove practicalityDetection of traffic movementParticular environment based servicesTrusted authorityIntelligent transportation system its
The invention discloses a privacy protection model aggregation system and method based on federated learning in the Internet of Vehicles. The system comprises a TA (Trusted Authority), a CS (Cloud Server), a Fog Node FN (Fog Node) and a V (Vehicle). The method comprises the four steps of system initialization, vehicle data collection, training to generate a local model and aggregation to generate a global model. According to the invention, under the condition that the privacy information of the vehicle is not leaked, the cloud server can effectively generate the global model of the Internet of Vehicles, Meanwhile, the privacy of the local model and the global model in the aggregation process is ensured. The method can promote stable operation of the intelligent traffic system and has good practicability.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
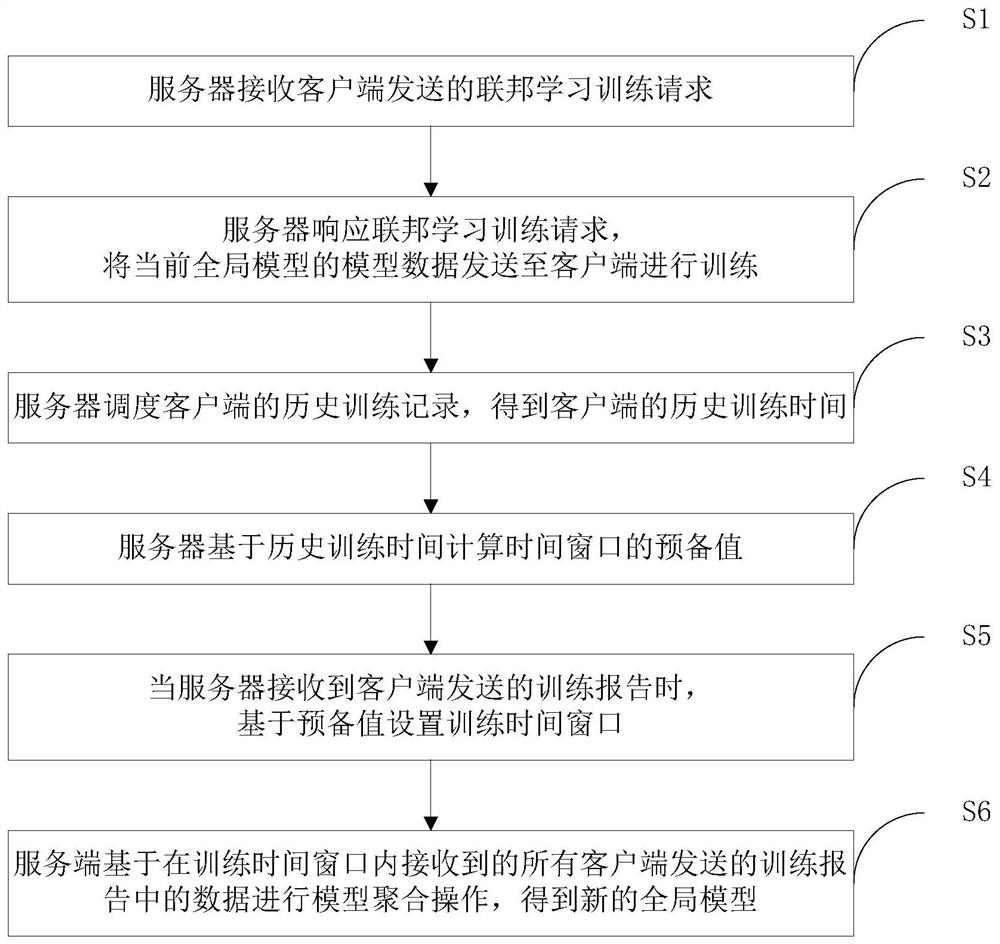
Federal learning scheduling method and device and system
PendingCN112508205AEasy to set upImprove accuracyEnsemble learningCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringModel aggregation
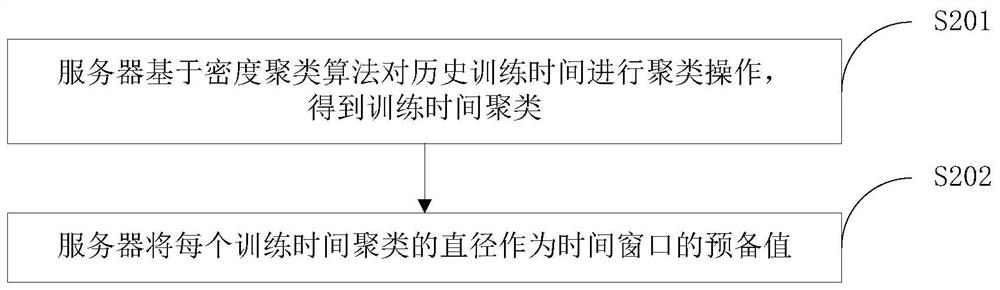
The embodiment of the invention belongs to the technical field of information, and relates to a federated learning scheduling method, which comprises the steps that a server receives a federated learning training request sent by a client; the server responds to the federated learning training request and sends the model data of the current global model to the client for training; the server schedules the historical training record of the client to obtain the historical training time of the client; the server calculates a preparation value of the time window based on the historical training time; when the server receives a training report sent by the client, setting a training time window based on the preparation value; and the server performs model aggregation operation based on the data in the training reports sent by all the clients and received in the training time window to obtain a new global model. The invention further provides a federated learning scheduling device and system.According to the method, the server can flexibly schedule the client, the accuracy of the training model can be improved, and the training time can be saved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Precision feedback federated learning method for privacy protection
PendingCN113762530AImprove impactImprove performanceDigital data protectionNeural architecturesData setPrivacy protection
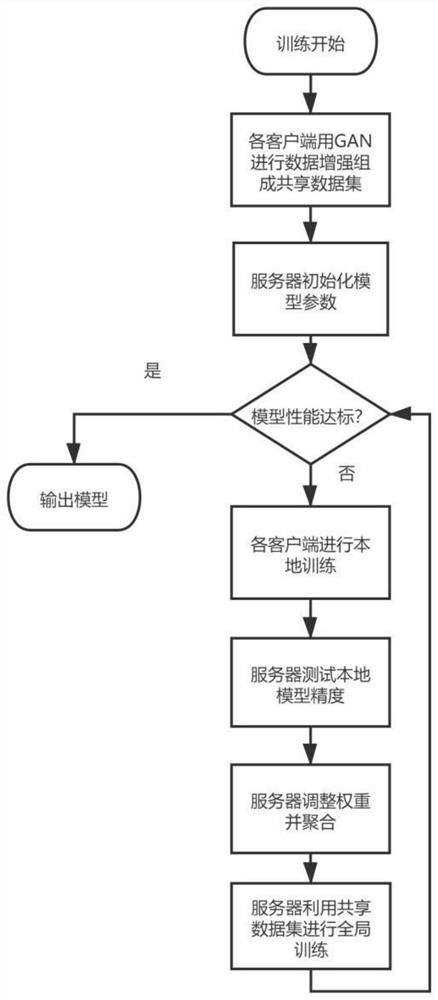
The invention discloses a precision feedback federated learning method for privacy protection. The method comprises the following steps that: 1, each client performs data enhancement on a local data set by using a GAN, and uploads the obtained generated data to a server to form a shared data set; 2, the server initializes the model parameters and broadcasts the model parameters to each client; 3, each client performs local model training by using the downloaded global parameters, and uploads the parameters to the server after training; 4, the server tests each local model to obtain model precision and then generate a new aggregation weight; 5, the server performs model aggregation on the local model by using the aggregation weight; 6, the server performs global training on the aggregated parameters by using the shared data set, and broadcasts the parameters to each client after obtaining a global model; and 7, steps 3-6 are repeated until the model performance meets the requirement. According to the method, the influence on the global model performance caused by non-independent identical distribution of the client data and the training weight of the client can be improved on the premise of protecting the client data.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
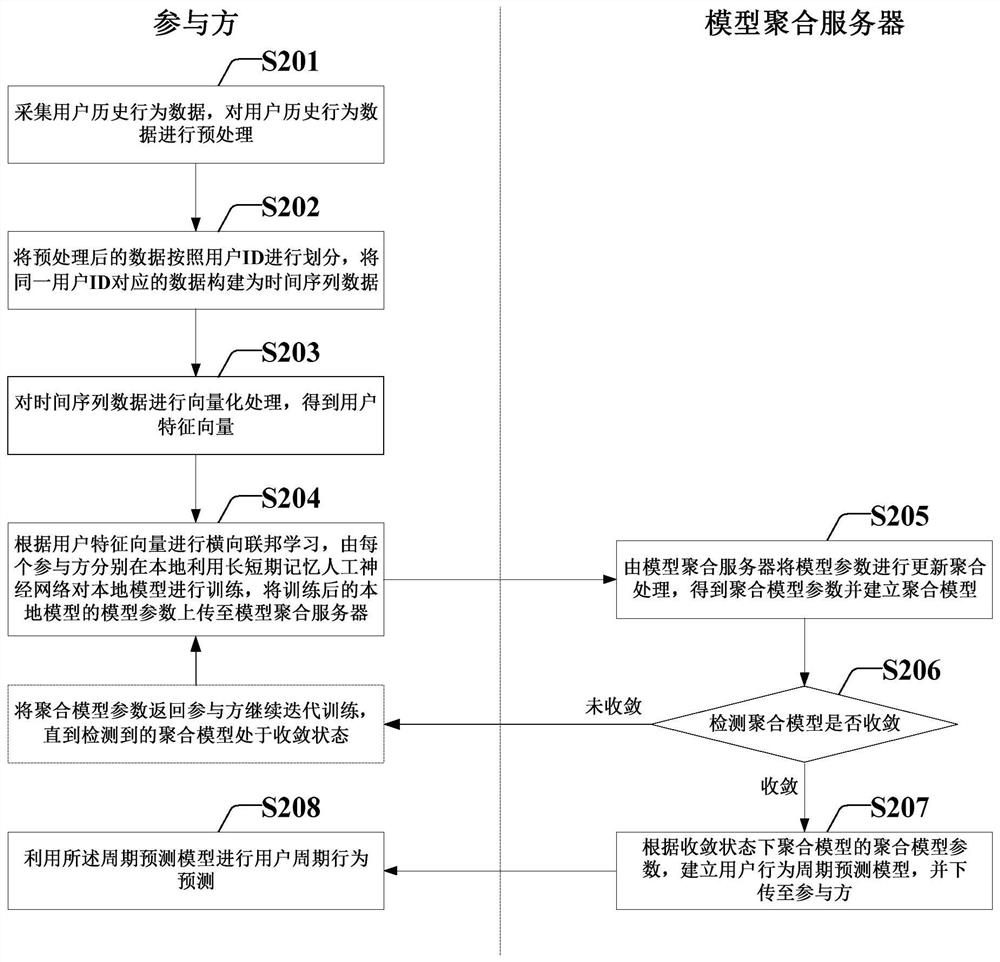
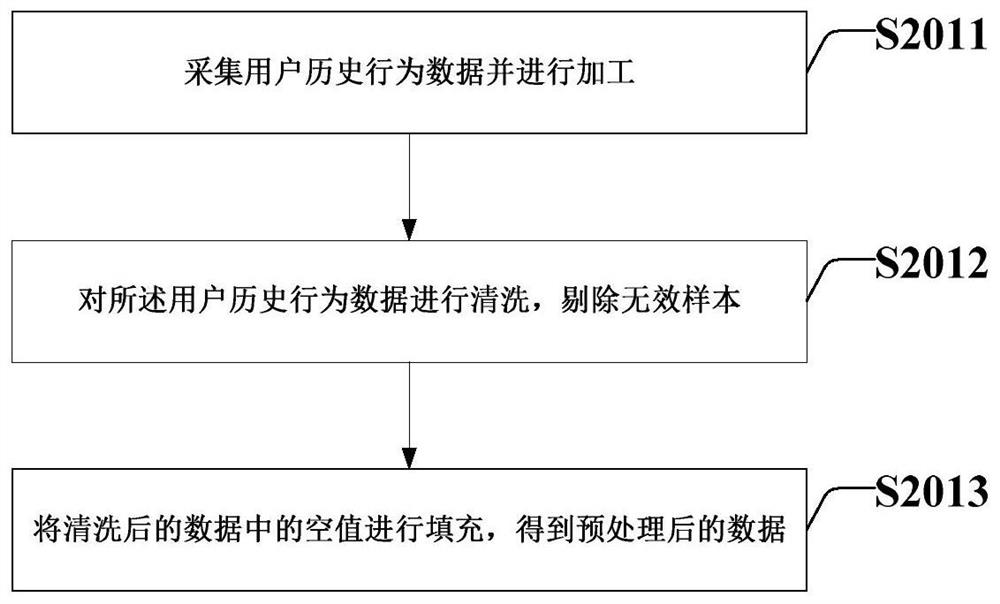
Method and system for establishing user behavior periodic model based on transverse federated learning
PendingCN111898769AImprove accuracyBreaking the data silo dilemmaEnsemble learningNeural architecturesFeature vectorEngineering
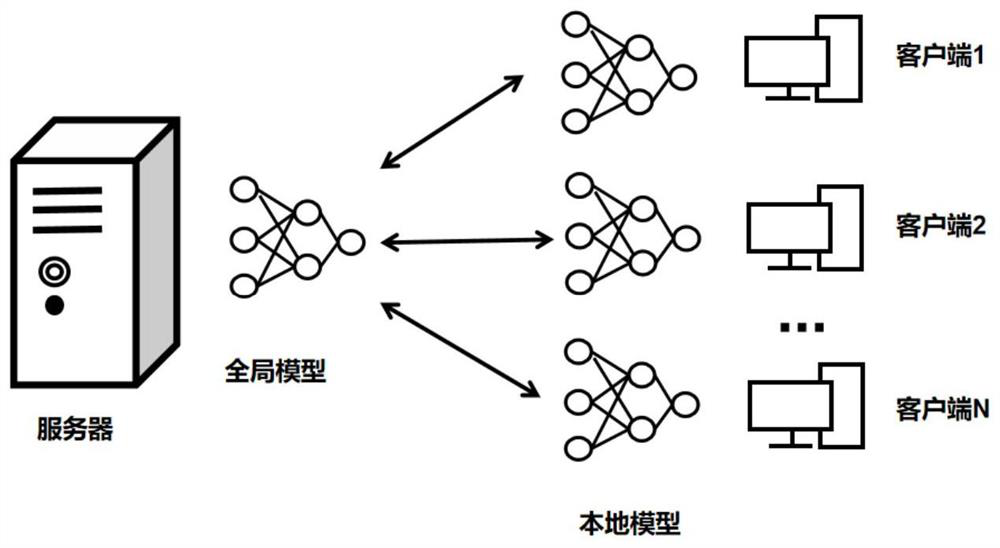
The invention provides a method and system for establishing a user behavior period model based on transverse federated learning. The method comprises steps of collecting the historical behavior data of a user, and carrying out the preprocessing of the historical behavior data of the user; dividing the preprocessed data according to user IDs, and constructing time series data; performing vectorization processing on the time series data; transverse federation learning being carried out according to the user feature vectors, each participant training a local model locally by using a long-term andshort-term memory artificial neural network, and trained model parameters being uploaded to a model aggregation server; updating and aggregating the model parameters to obtain aggregated model parameters; detecting whether the aggregation model is converged or not, and if not, returning aggregation model parameters to the participant to continue iterative training until the detected aggregation model is in a convergence state; and establishing a user behavior period prediction model according to the aggregation model parameters of the aggregation model in the convergence state, and downloading the user behavior period prediction model to the participant.
Owner:BANK OF CHINA
Efficient contribution evaluation method in federated learning scene
ActiveCN112506753AFast convergenceImprove performanceHardware monitoringSoftware testing/debuggingAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses an efficient contribution evaluation method in a federated learning scene. The method comprises the steps of calculating a weight according to a training log: the weight of each user during model aggregation is calculated by using the training log of federated learning by a server, wherein in common federated learning, in the (t + 1) th epoch, the server aggregation model can be formalized as description, wherein theta t + 1 represents the global model of the (t + 1) th round, and theta t is the global model of the tth epoch. According to theinvention, contribution is calculated through the weight of a user during model aggregation, the calculation overhead is greatly reduced, the index-level overhead is reduced into linear overhead, model convergence can be accelerated, and the performance is improved; 2) the used training log is inherent information of federated learning, and extra privacy protection cost is avoided;.
Owner:德清阿尔法创新研究院
Method and system for detecting abnormal nodes in federated learning
ActiveCN112749392AGuaranteed credibilityGuaranteed accuracyEnsemble learningPlatform integrity maintainanceTrusted authorityUser privacy
The invention discloses a method and a system for detecting abnormal nodes in federated learning. The detection method comprises the following steps of: initializing a system, performing user registration, generating system parameters and performing key negotiation; generating a mask local model; malicious user detection: the server side carries out local model aggregation and generates a confusion aggregation model, the user side verifies the confusion aggregation model to generate a verification result, and the server side carries out malicious user detection according to the verification result of the user side; and the server performs model aggregation by using a mask local model uploaded by a non-malicious user to obtain a global model of a current iteration round and send the global model to the user, and the user performs local model updating according to the received global model. The detection system is composed of an aggregation server, a trust authority and a plurality of users. According to the method, the credibility and the accuracy of the global model can be improved while the privacy of each user is ensured, and safe and reliable federal learning is realized.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
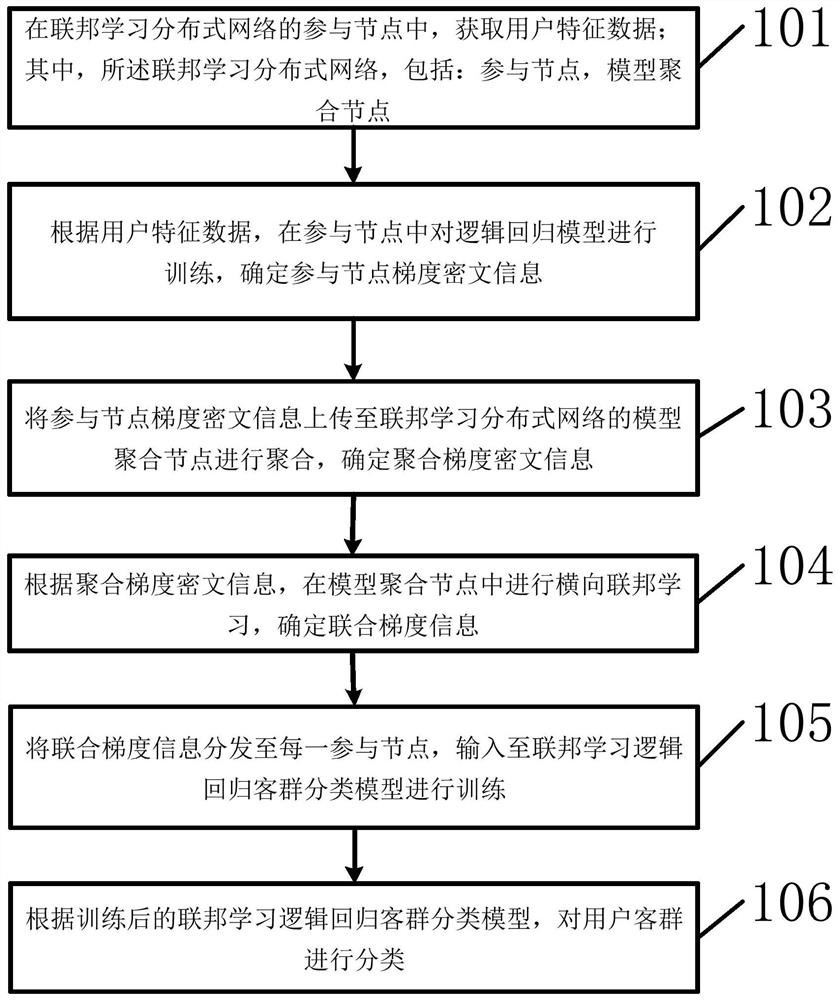
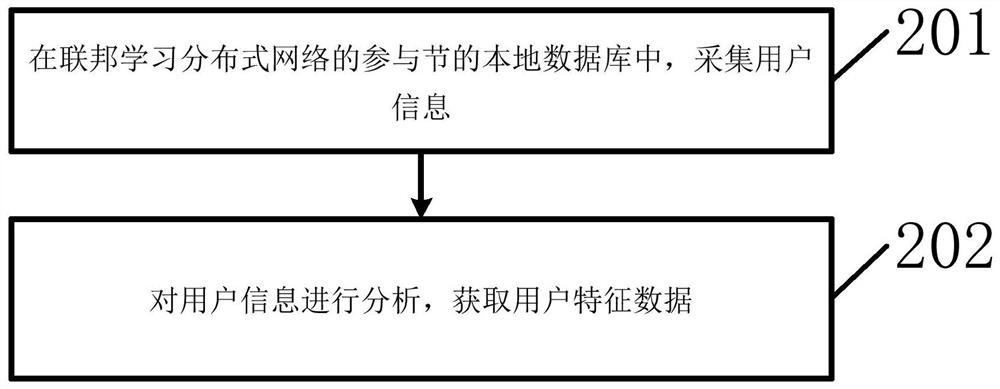
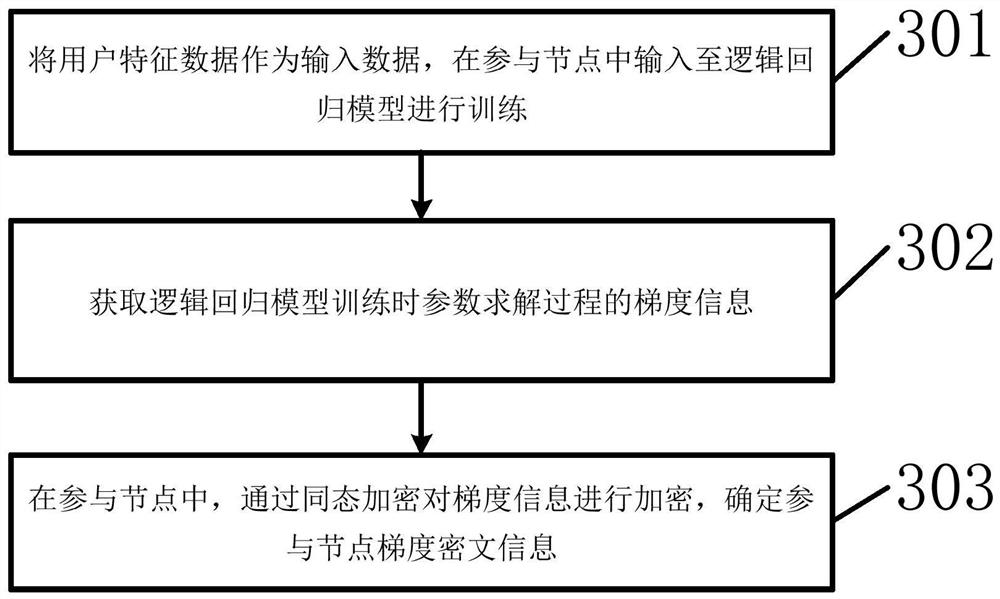
User customer group classification method and device
PendingCN111967910AEnsure safetyAchieve sharingFinanceCharacter and pattern recognitionCiphertextClassification methods
The invention provides a user customer group classification method and device, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining user feature data in participation nodes of a federated learning distributed network, wherein the federated learning distributed network comprises participation nodes and model aggregation nodes; training a logistic regression model in the participation nodes according to the user characteristic data, and determining participation node gradient ciphertext information; uploading the participation node gradient ciphertext information to a model aggregation node of the federated learning distributed network for aggregation, and determining aggregation gradient ciphertext information; according to the aggregation gradient ciphertext information, carrying out transverse federated learning in model aggregation nodes, and determining joint gradient information; distributing the joint gradient information to each participation node, and inputting the joint gradient information to a federated learning logistic regression customer group classification model for training; and classifying the user customer groups according to the trained federated learning logistic regression customer group classification model. According to the invention, the accuracy of user customer group classification can be improved.
Owner:BANK OF CHINA
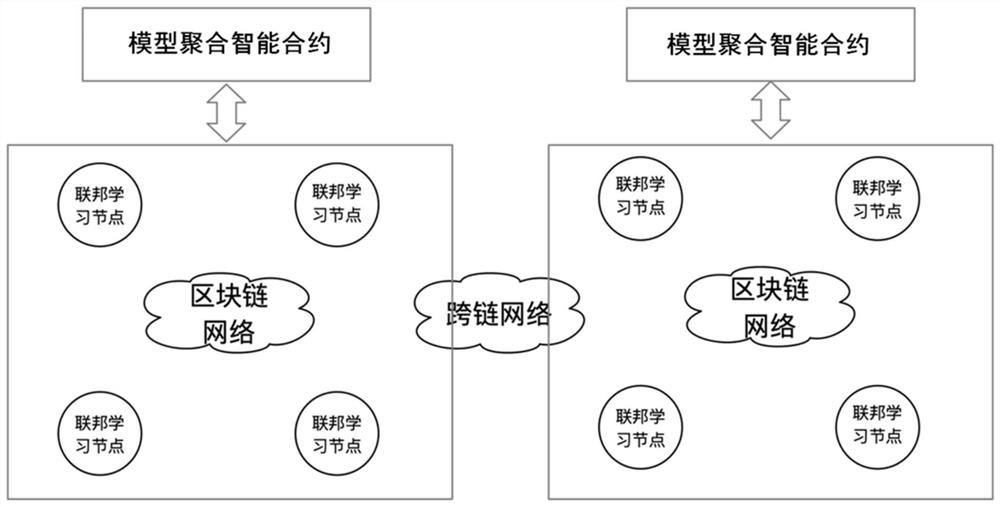
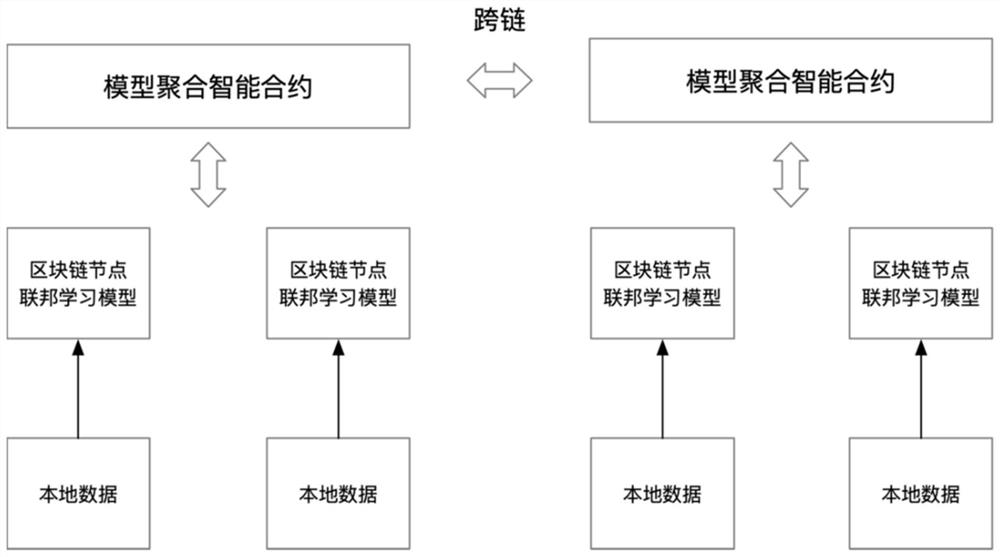
Block chain cross-chain-based federated learning method and device
PendingCN113992360ARealize privacy securityGuaranteed privacy and securityMachine learningSecuring communicationData setEngineering
The invention discloses a block chain cross-chain-based federated learning method and device, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the training of a federated learning model through local data in a single block chain network, and transmitting model parameters to a model aggregation smart contract through a private transaction, thereby achieving the aggregation of different node model parameters in a single chain, synchronizing model parameters at each node; the model aggregation smart contract sending the latest model parameters to a cross-chain network through cross-chain private transaction to realize model synchronization between different chains. In the whole process, data of a single network node and data of a cross-chain network node are not exchanged, it is ensured that model parameters of each node are not leaked through a private transaction mode, training of different node data of different block chain networks on a federated learning model is achieved while data privacy security is ensured, a trained data set is expanded, and the accuracy of the model is improved. An integral mechanism is adopted to improve the enthusiasm of each member to contribute to a data training model, and the model training effect is further improved.
Owner:CHINA ZHESHANG BANK +1
Edge privacy protection method based on federal learning
PendingCN114169010AAchieve sharingDigital data protectionMachine learningPrivacy protectionDifferential privacy
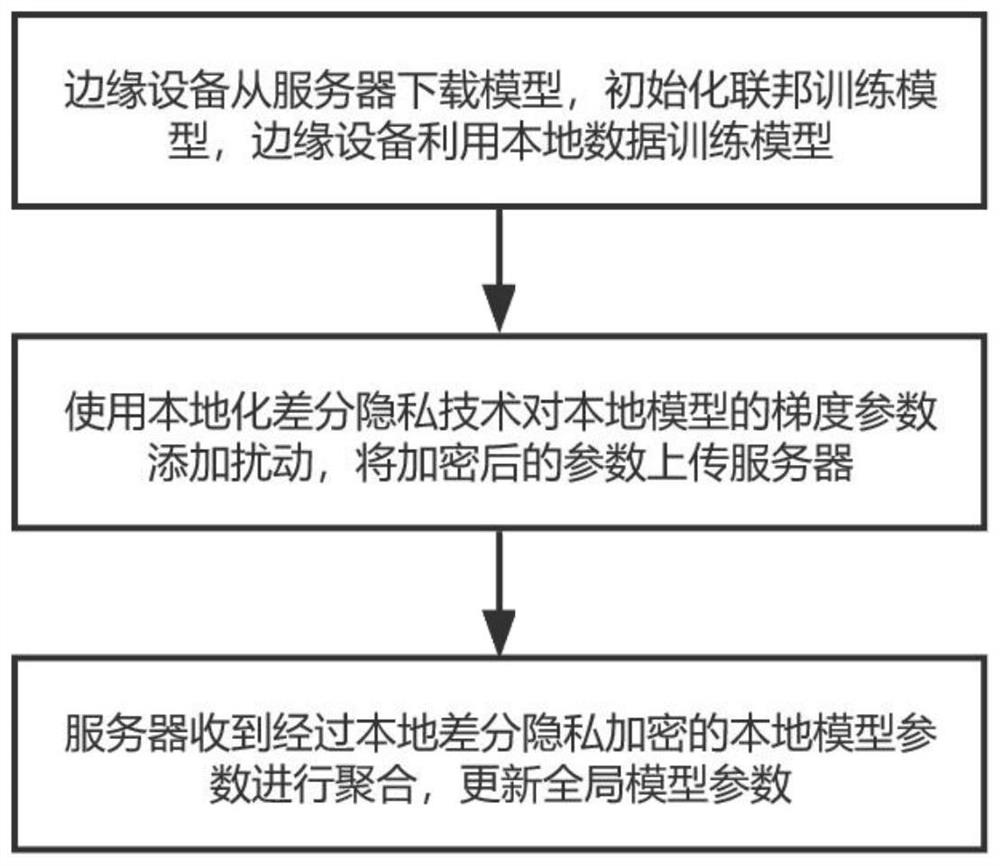
The invention relates to an edge privacy protection method based on federated learning, and the method comprises the steps: an edge device downloads a model from a server, initializes a federated training model, and employs local data to train the model; adding disturbance to gradient parameters of a local model by using a localized differential privacy technology, and uploading the encrypted parameters to a server; and the server receives the local model parameters subjected to local differential privacy encryption, aggregates the local model parameters and updates global model parameters. According to the method, local differential privacy is applied to federated learning, localized training and model aggregation of data in edge equipment can be completed while safe data sharing of edge users is guaranteed, data does not need to be uploaded in the whole process, privacy safety of the data of the edge users is guaranteed, and the purpose of protecting model parameters is achieved while the accuracy of the model is guaranteed.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Power system fast transient stability simulation method based on real-time dynamic equivalence
InactiveCN105375475AAdaptableFast convergenceAc network circuit arrangementsTransient stability analysisModel aggregation
The invention discloses a power system fast transient stability simulation method based on real-time dynamic equivalence. According to the method, real-time grouping and model aggregation are performed on power generator sets by a short period of whole system numerical integration calculation after a fault occurs, then equivalent system network parameters are obtained by applying a proposed equivalent system nodal admittance matrix rapid identification method, and finally transient stability calculation is completed on an obtained dynamic equivalent system. Compared with existing power system transient stability analysis methods which have disadvantages that calculation amount is high and calculation speed cannot meet the online calculation requirement, the method has advantages of high precision and great convergence of a conventional numerical integration method due to low number of grouping and low time consumption of identification of an equivalent system admittance matrix, and a calculation system is greatly simplified and calculation amount is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
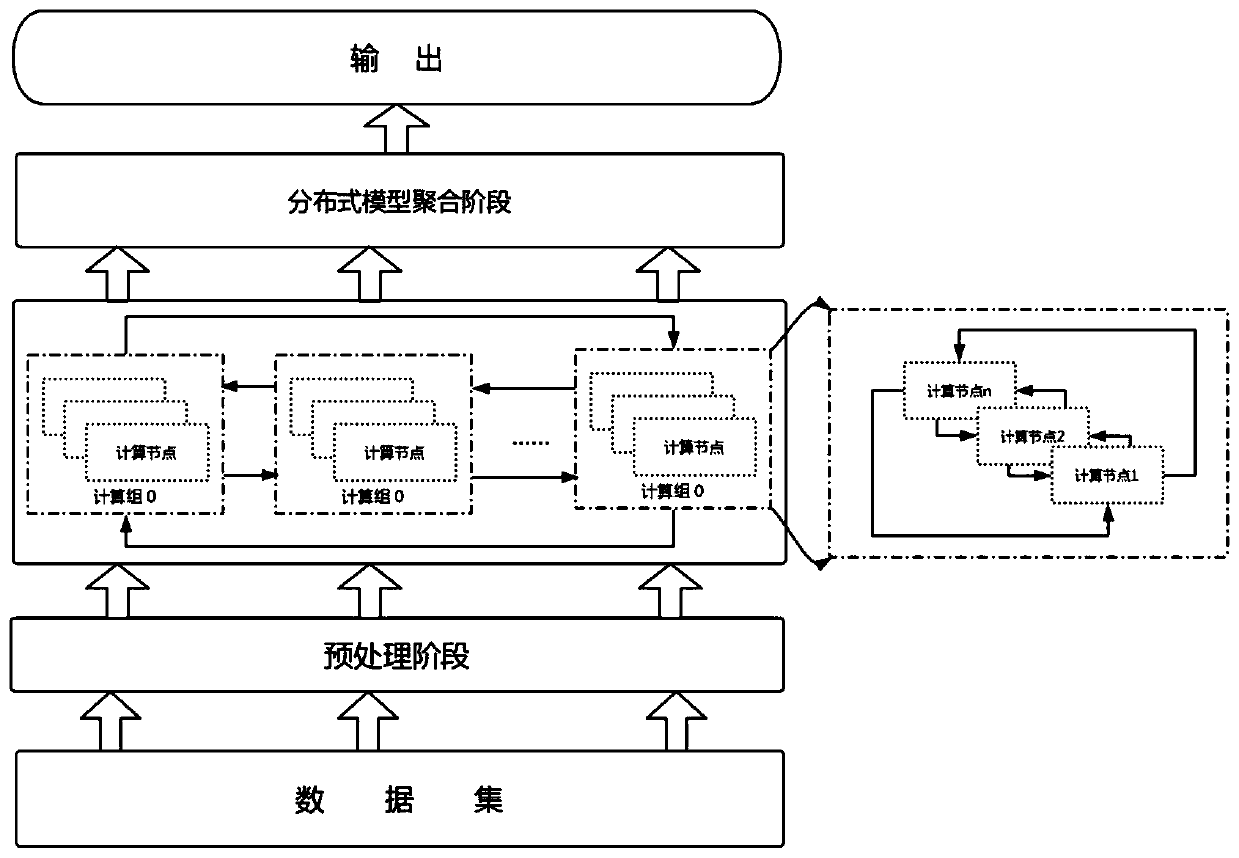
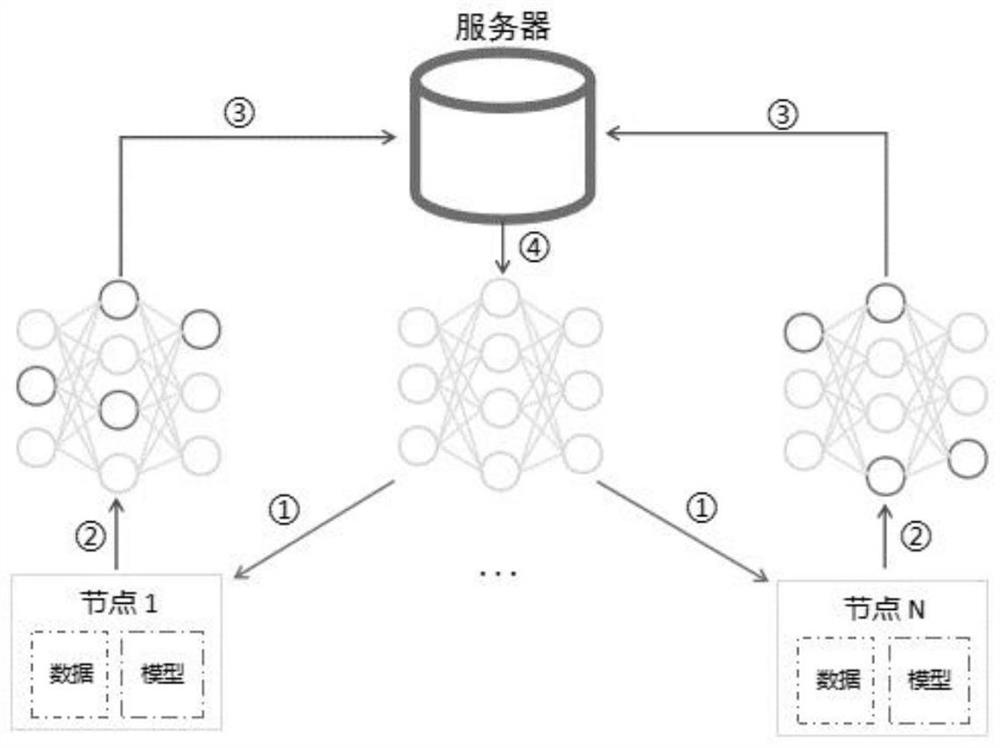
Decentralized federated learning framework based on heterogeneous computing power perception and modeling method
ActiveCN113033082AFast trainingRelieve stressEnsemble learningDesign optimisation/simulationManagement trainingModel aggregation
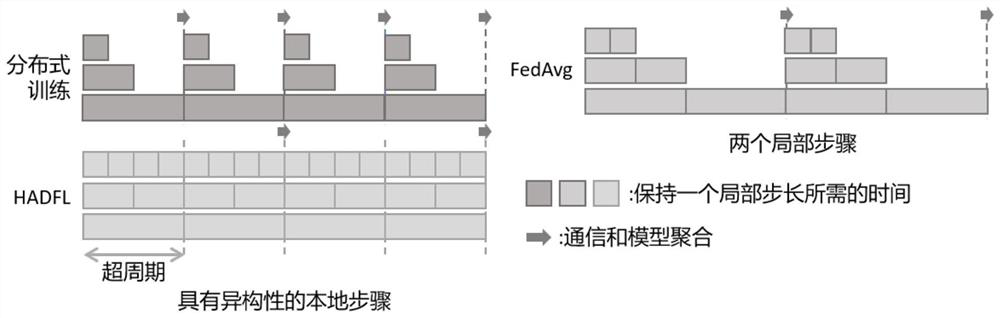
The invention discloses a decentralized federated learning framework based on heterogeneous computing power perception. The decentralized federated learning framework comprises a cloud coordinator and a plurality of equipment ends. The cloud coordinator is used for management, training and parameter updating scheme generation during operation and regular model backup. The equipment end is used for transmitting equipment information to the cloud coordinator, operating a model locally and updating equipment end parameters. The cloud coordinator acquires the least common multiple of the one-time training time of the equipment end as a super cycle, the equipment end calculates different step lengths in the super cycle, and the model is aggregated in the integral multiple of the super cycle. Different local steps are operated according to different computing capabilities of equipment, and in the model aggregation process, negative effects of slow nodes are reduced; and a distributed point-to-point communication mode is adopted, and the communication pressure of the central server in the distributed training process can be eliminated under the condition that the overall communication traffic is not increased.
Owner:SUZHOU INST FOR ADVANCED STUDY USTC
Smart campus-oriented distributed machine learning model parameter aggregation method
PendingCN110929885AImprove utilization efficiencyReduce trafficData processing applicationsMachine learningLocal optimumEngineering
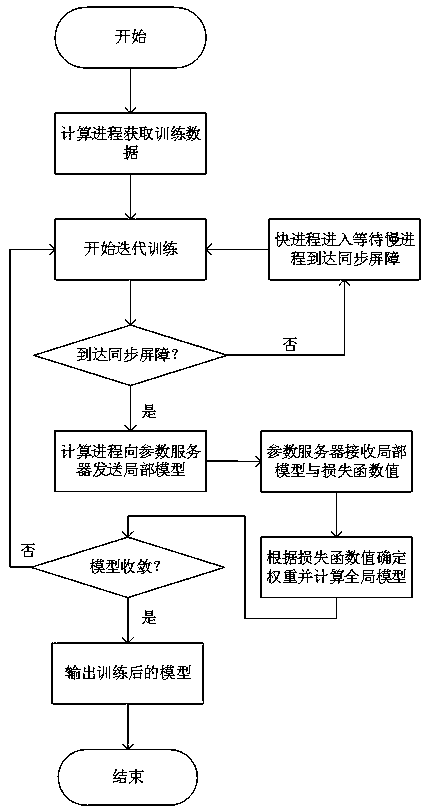
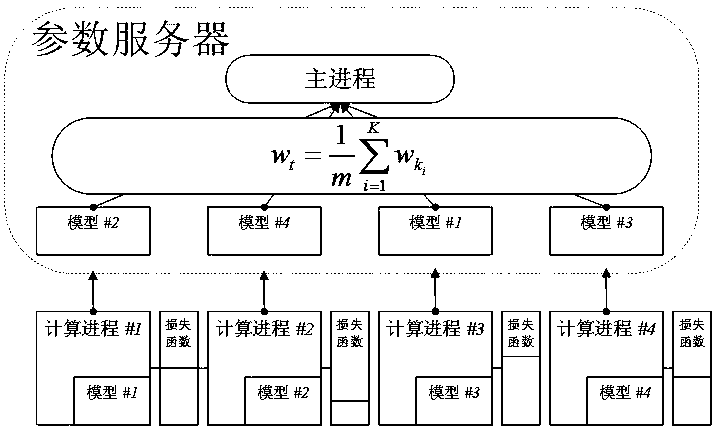
The invention discloses a smart campus-oriented distributed machine learning model parameter aggregation method, and aims to solve the problem that model training falls into a local optimal solution under a data parallel strategy. Starting from a model aggregation method of a distributed machine learning algorithm, the proportion of each calculation process local model when the parameter server aggregates the local model parameters is determined through the loss function value of each calculation process, so that the training precision is improved; training data are obtained by using a methodof directly extracting the data without putting back in a calculation process, so that the communication overhead is reduced. When the method is applied to synchronization models such as an overall synchronization parallel model and a delay synchronization parallel model, the training precision can be effectively improved, the training speed is not influenced, and the service recommendation accuracy can be effectively improved when the training result is applied to the smart campus.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV +1
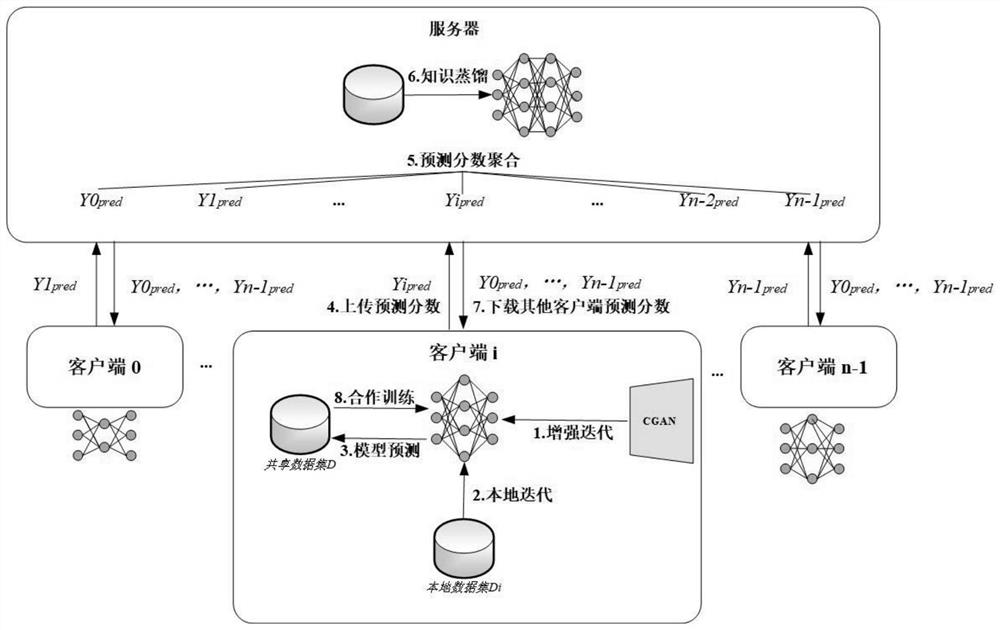
Heterogeneous model aggregation method and system based on federated learning
PendingCN113705610ASolve the problem of data heterogeneityImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setEngineering
The invention relates to the field of federated learning, in particular to a heterogeneous model aggregation method and system based on federated learning, and the method comprises the steps of initializing a neural network model; the method also includes that each client contributes a part of local data and uploads the local data to the server to form a shared data set, and a CGAN model is trained; the client uses a local data set and a data set generated by the CGAN model to train a local model, predicts each data in the shared data set and uploads a prediction score to the server; the server calculates the prediction score deviation degree of each client, takes the reciprocal of a calculation result as a weight, calculates a global prediction score, and uses the global prediction score to perform knowledge distillation on the server model; the client downloads the prediction scores of other client models from the server for cooperative training; and model convergence is performed after multiple iterations. According to the invention, the problem of data heterogeneity of the client side can be solved, the client side model uploads and downloads the prediction score of the shared data set, and the communication traffic between the client side and the server side is reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
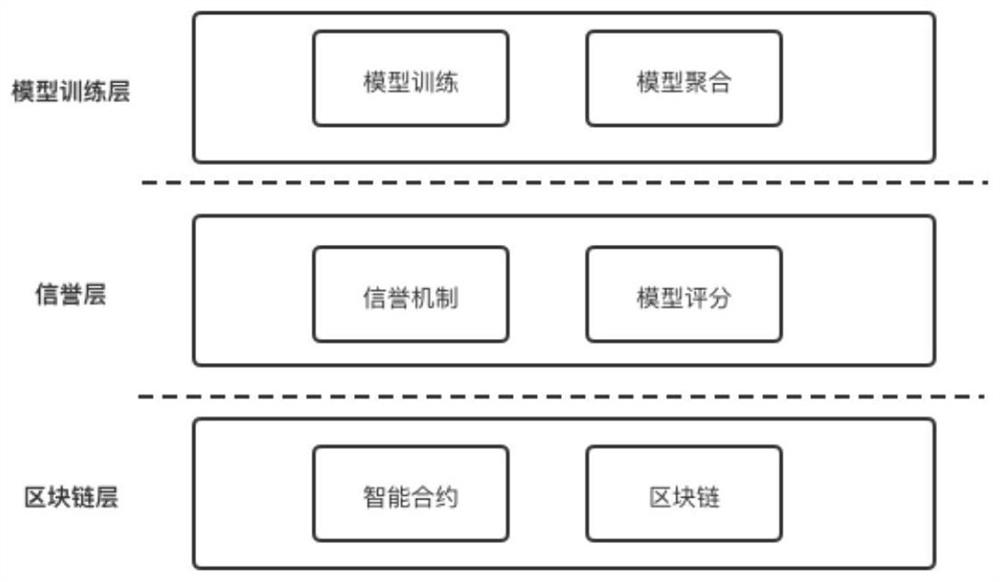
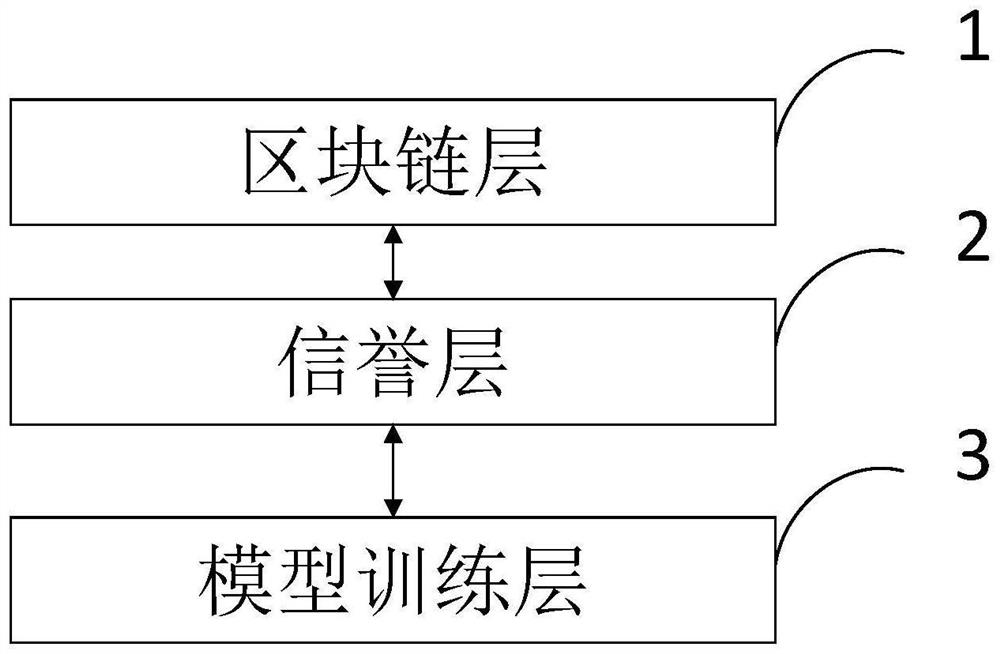
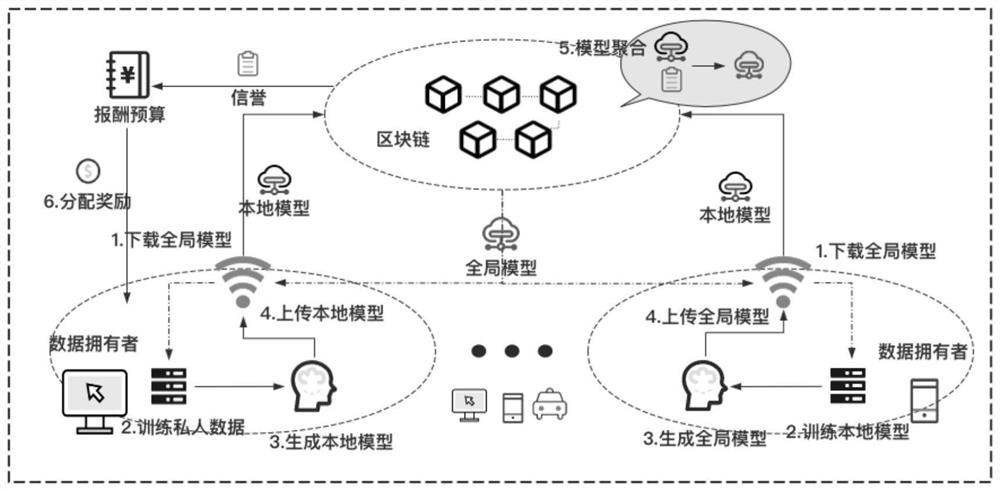
High-quality federal learning system and learning method based on block chain and reputation mechanism
InactiveCN114154649AQuality improvementIncrease motivationDiscounts/incentivesEnsemble learningEngineeringData mining
The invention belongs to the technical field of federal learning, and discloses a high-quality federal learning system and learning method based on a block chain and a reputation mechanism, and a block chain layer shares a global model and reputation evaluation by taking an intelligent contract as a carrier; the reputation layer scores the local models shared by all the data owners by using a model scoring mechanism; reputation evaluation is carried out on each data owner by using a reputation mechanism; a model training layer data owner carries out training of a local model and shares the local model to a model aggregator; and meanwhile, the model aggregator aggregates the collected models in combination with the reputation and awards participating data owners. The federated learning system based on the block chain disclosed by the invention has important guidance and technical significance for realizing a high-quality model aggregation task, is beneficial to improving the security and robustness of federated learning, and is beneficial to promoting the fairness of reward distribution and the enthusiasm of participating in the task.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
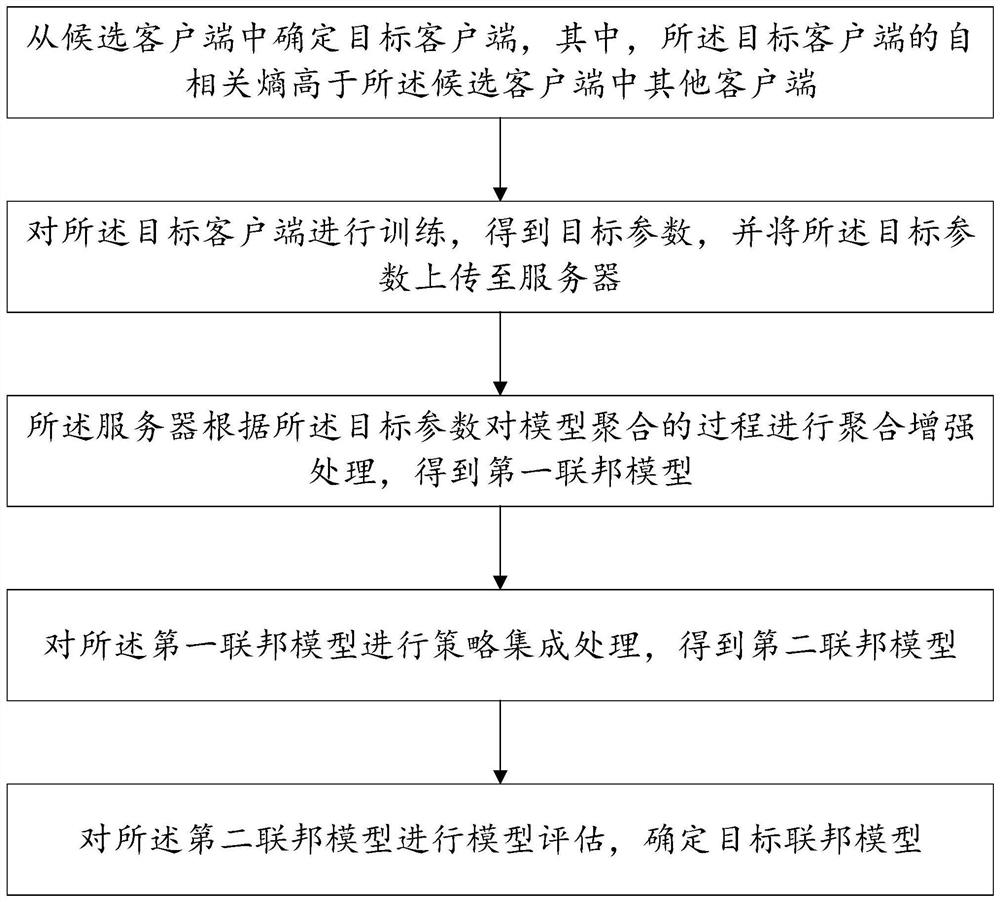
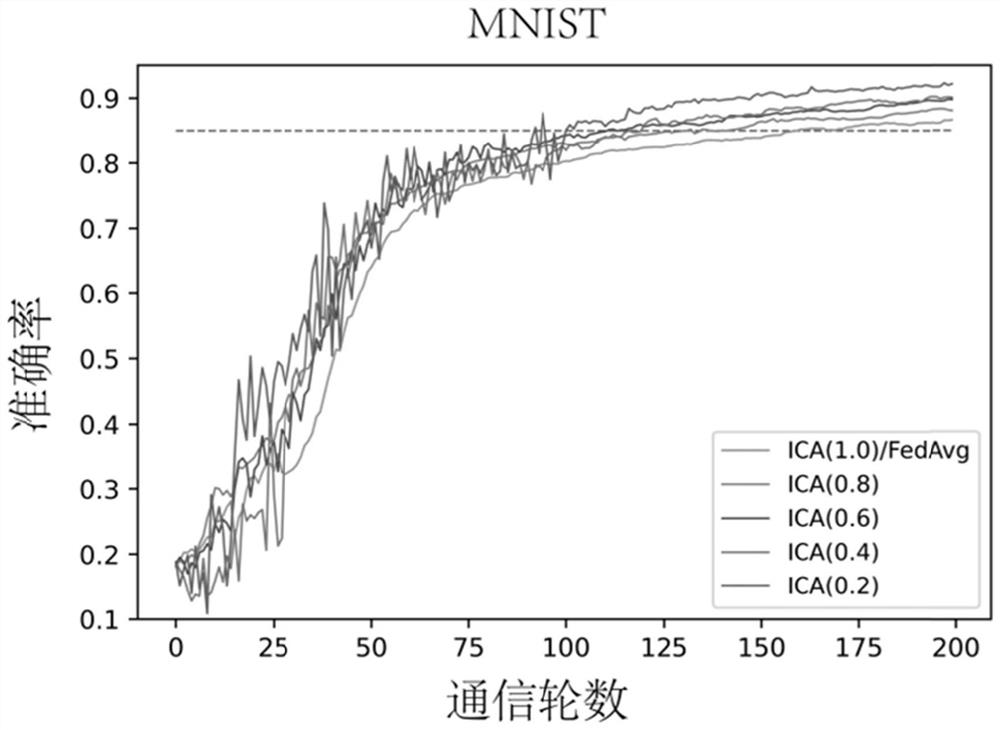
Heterogeneous scene-oriented asynchronous federal learning method and device and storage medium
PendingCN114037089AImprove accuracyReduce communication costsEnsemble learningEngineeringData mining
The invention discloses a heterogeneous scene-oriented asynchronous federal learning method and device and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps of determining a target client from candidate clients, the autocorrelation entropy of the target client being higher than the autocorrelation entropy of other clients in the candidate clients; training the target client to obtain a target parameter, and uploading the target parameter to a server; enabling the server to perform aggregation enhancement processing on a model aggregation process according to the target parameter to obtain a first federated model; performing strategy integration processing on the first federated model to obtain a second federated model; and performing model evaluation on the second federated model to determine a target federated model. The invention can improve the model accuracy and reduce the communication cost, and can be widely applied to the technical field of artificial intelligence.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Edge end bias detection method in federated machine learning environment
PendingCN112183652AEnsure fairnessCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningData setEngineering
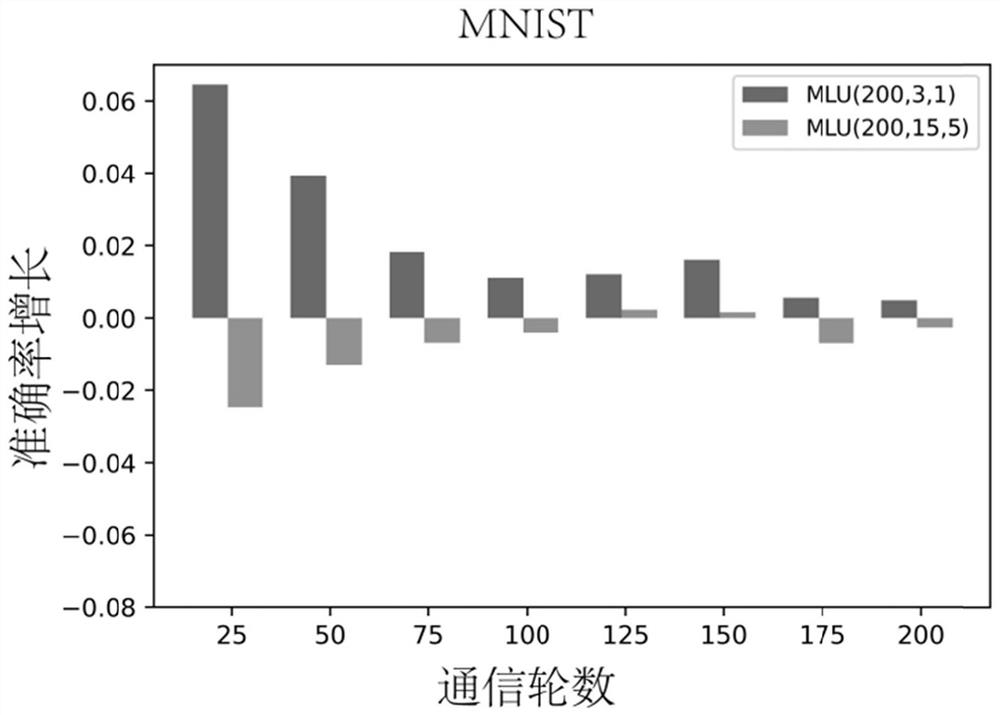
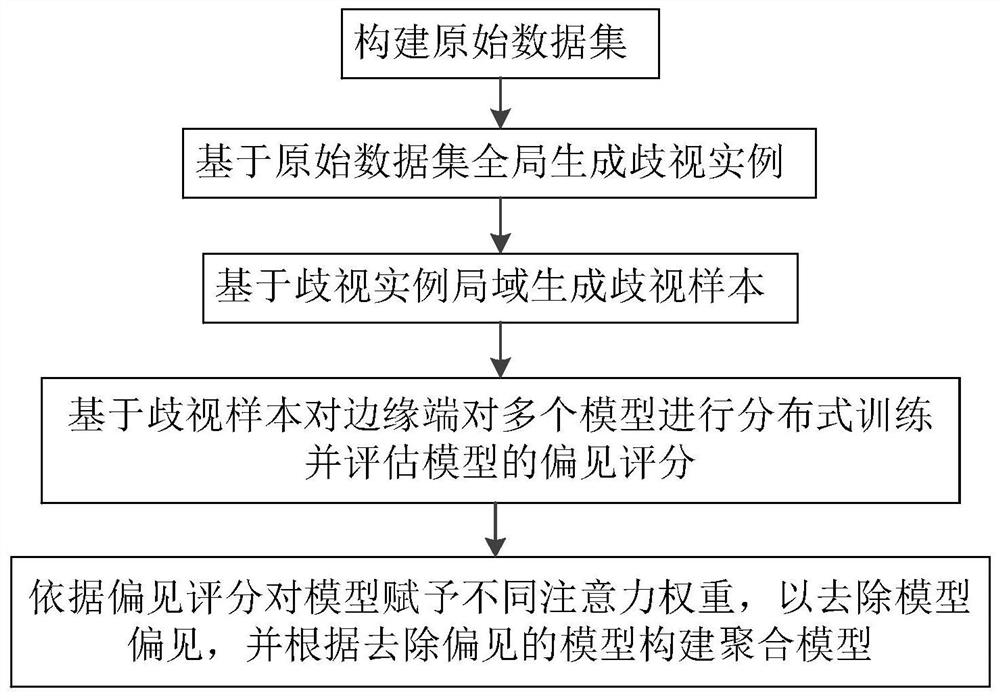
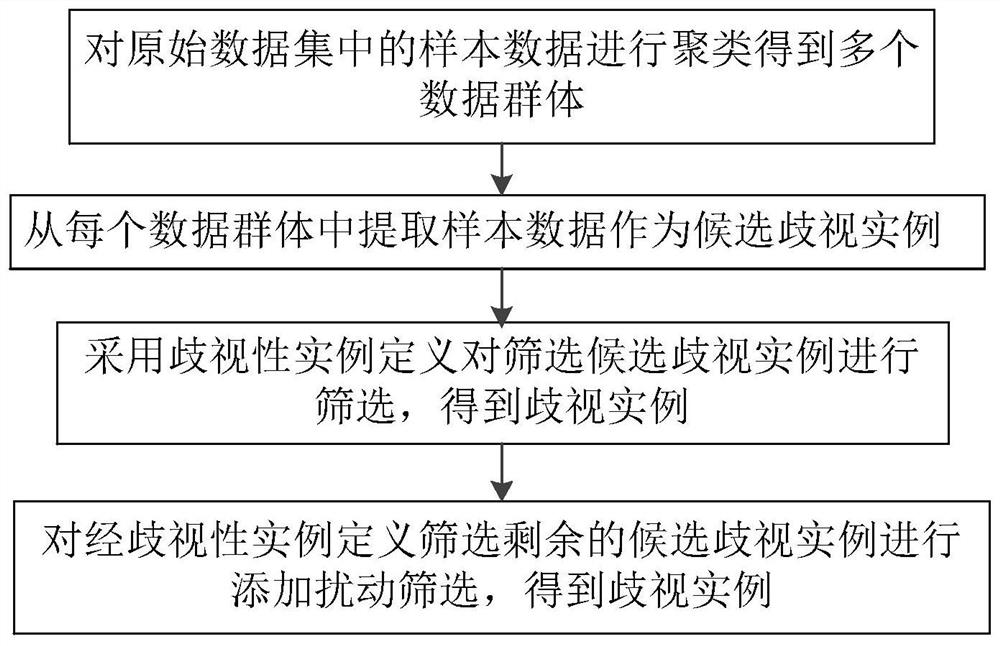
The invention discloses an edge end bias detection method in a federated machine learning environment. The method comprises the following steps of: screening to obtain ambiguous instances, increasingthe proportion of the ambiguous instances in a data set to construct a new data set, carrying out distributed training on a model by utilizing the new data set, obtaining the prejudice degree of eachmodel for sensitive attributes (prejudice information), removing prejudice by endowing each model with different attention weights according to the prejudice degree, and performing model aggregation after the prejudice is eliminated, thereby ensuring the fairness of an edge end in a federated machine learning environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
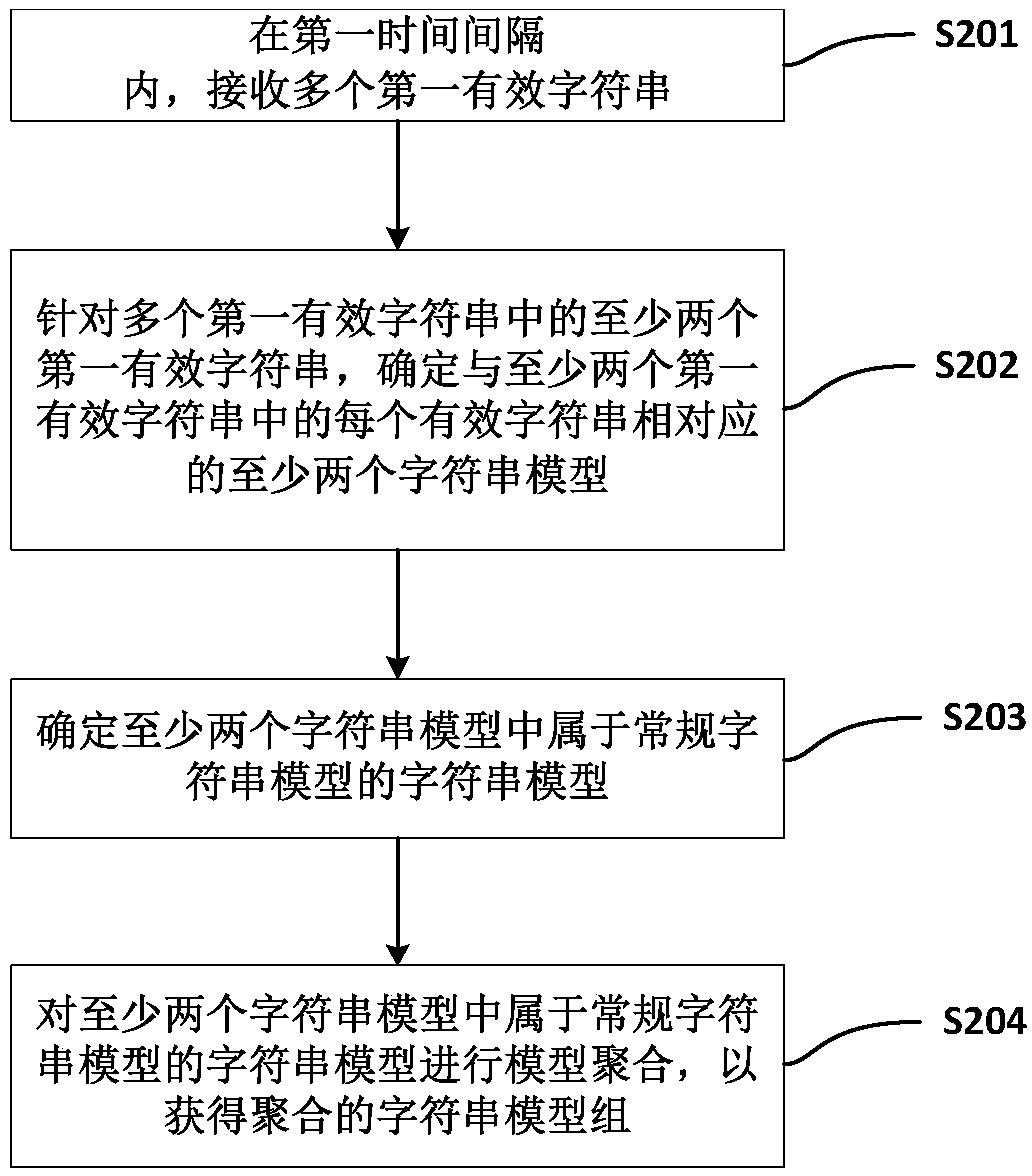
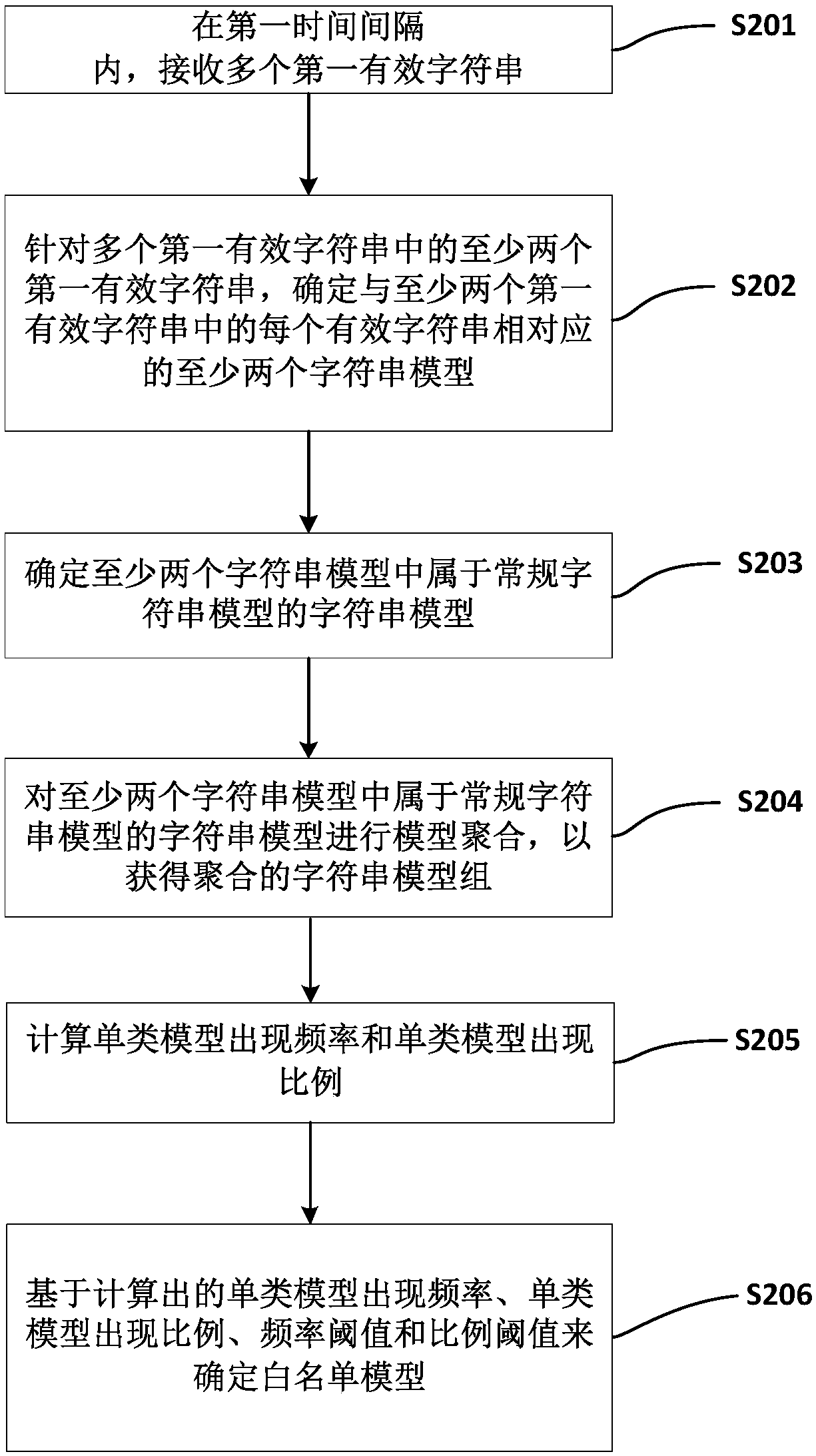
Method and apparatus for processing character string, and computer-readable storage medium
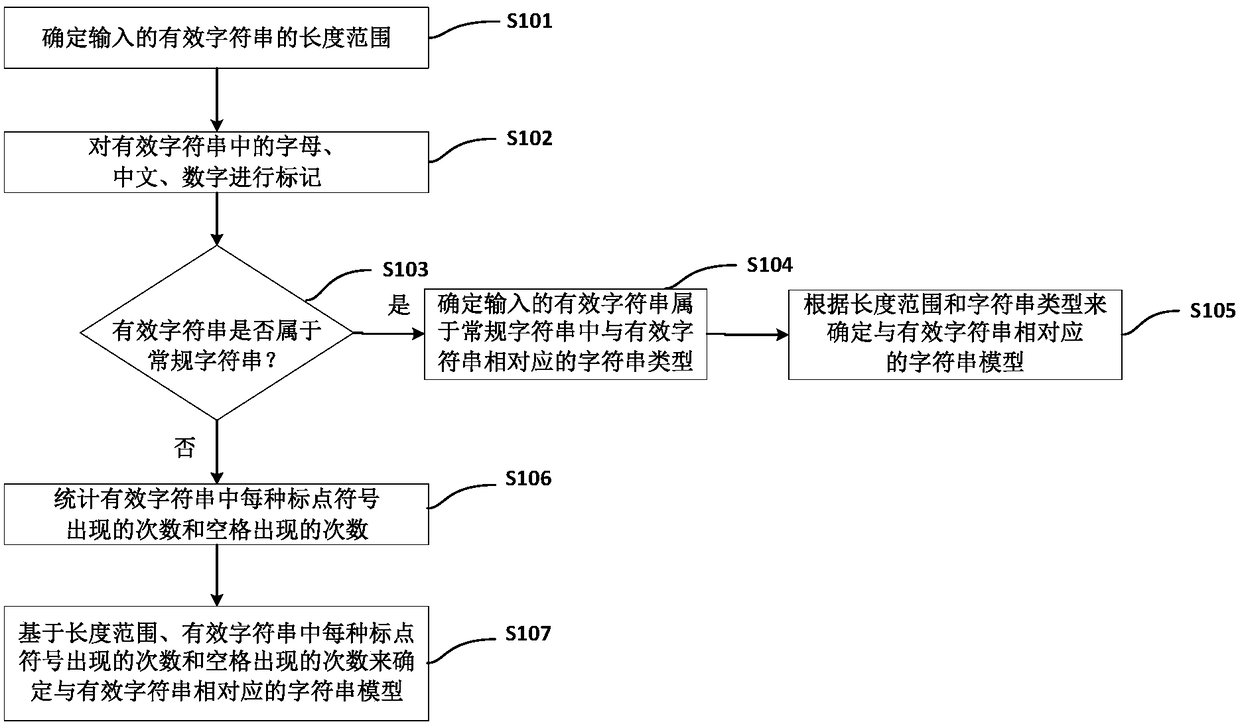
The invention provides a method for processing a character string. The method comprises: a plurality of first valid character strings are received in a first time interval; for at least two of the plurality of first valid character strings, at least two character string models corresponding to each of the at least two first valid character strings are determined; a string model belonging to a regular character string model in the at least two character string models is determined; and model aggregation is carried out on the string model belonging to the regular character string model in the atleast two character string models to obtain an aggregated character string model set. With the method provided by the invention, the efficiency is improved; and avoidance is prevented and thus an undisclosed attack can be found.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANRONG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
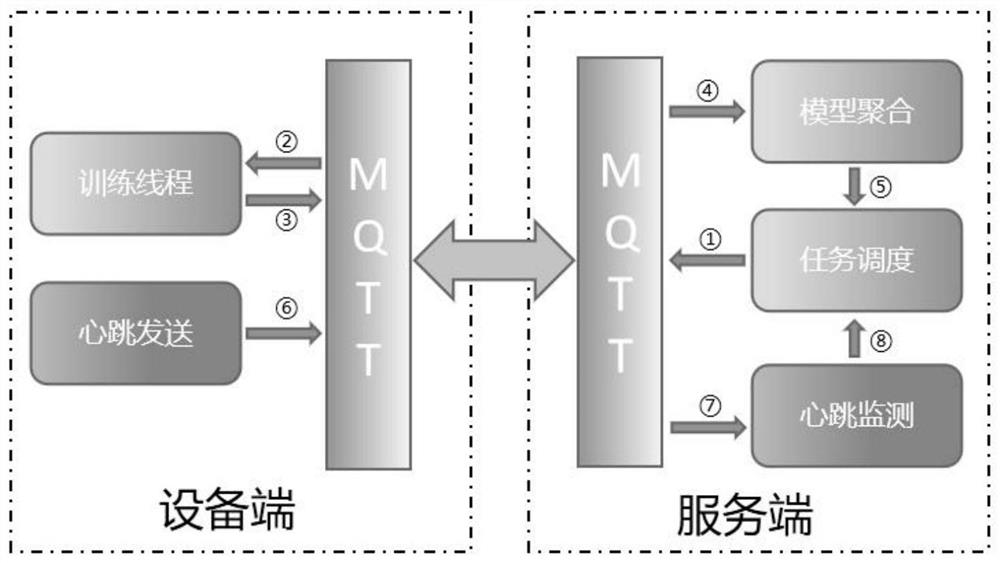
Federal learning system and federal learning training method for smart city Internet of Things belief fusion
The invention discloses a federated learning system oriented to belief fusion of the Internet of Things of a smart city. The federated learning system comprises an equipment end and a server end, the equipment end comprises an MQTT, a training thread and a heartbeat sending thread; the server comprises an MQTT, a model aggregation thread, a task scheduling thread and a heartbeat monitoring thread. The invention also provides a federated learning training method based on the federated learning system, and the method comprises the steps: the server initializes a global model, selects a certain proportion of equipment in a communication round, and sends the global model to the selected equipment; after the equipment receives the message, the model is trained and updated; the updated model is uploaded to the server again and aggregated, a new global model is obtained, and the next communication round is entered; and after the preset number of communication rounds is completed, the device receives the latest global model issued by the server and stores the latest global model for subsequent use. The method has certain equipment expandability, robustness and high efficiency.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Model aggregation using model encapsulation of user-directed iterative machine learning
PendingUS20210342743A1Easy to configureEasy to createDigital data information retrievalEnsemble learningHard codingPersonalization
The present invention relates to model aggregation tools utilizing model encapsulation of user-directed iterative (UDI) machine learning, and the related methods that offer a typical user, without programming expertise, the ability to create and modify machine learning models. In particular, the present invention further provides methods and tools that not only afford machine learning models that are easily created and configured without the necessity of hard coding by the user, but also to afford the user with the ability to share their “know-how” derived from these models to collectively improve the models while maintaining privacy by obscuring the original training data, so that no confidential or proprietary information is shared between users of this collective model. Users may thereby rapidly teach the machine learning models to interpret their data without programming, personalizing the system's analysis and filtering capabilities, and then encapsulate their domain expertise in machine learning models that can be leveraged at scale and shared throughout a single or across multiple enterprises.
Owner:COALESCE
Federal learning method with high communication efficiency in wireless communication scene
PendingCN114580498AAlleviate communication bottlenecksHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningEngineeringLearning methods
The invention discloses a federated learning method with high communication efficiency in a wireless communication scene. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a federated learning framework from three aspects of a federated learning system, a training algorithm and a communication model in the wireless communication scene; s2, aiming at the constructed federal learning framework, carrying out convergence analysis on the training process of the federal learning framework; and S3, constructing an optimization problem about the federated learning framework according to a convergence analysis result, and solving the problem through a joint optimization method for equipment selection and beam forming. According to the method, on the basis of air calculation and a second-order training algorithm, on one hand, low-delay model aggregation is achieved through the waveform superposition characteristic of a channel, on the other hand, the number of iteration rounds needed by training is reduced through the rapid convergence characteristic of the second-order algorithm, and the communication bottleneck problem existing in most wireless federated learning methods at present is solved. Meanwhile, the training accuracy is further improved through the provided joint optimization method for the federated learning framework.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com