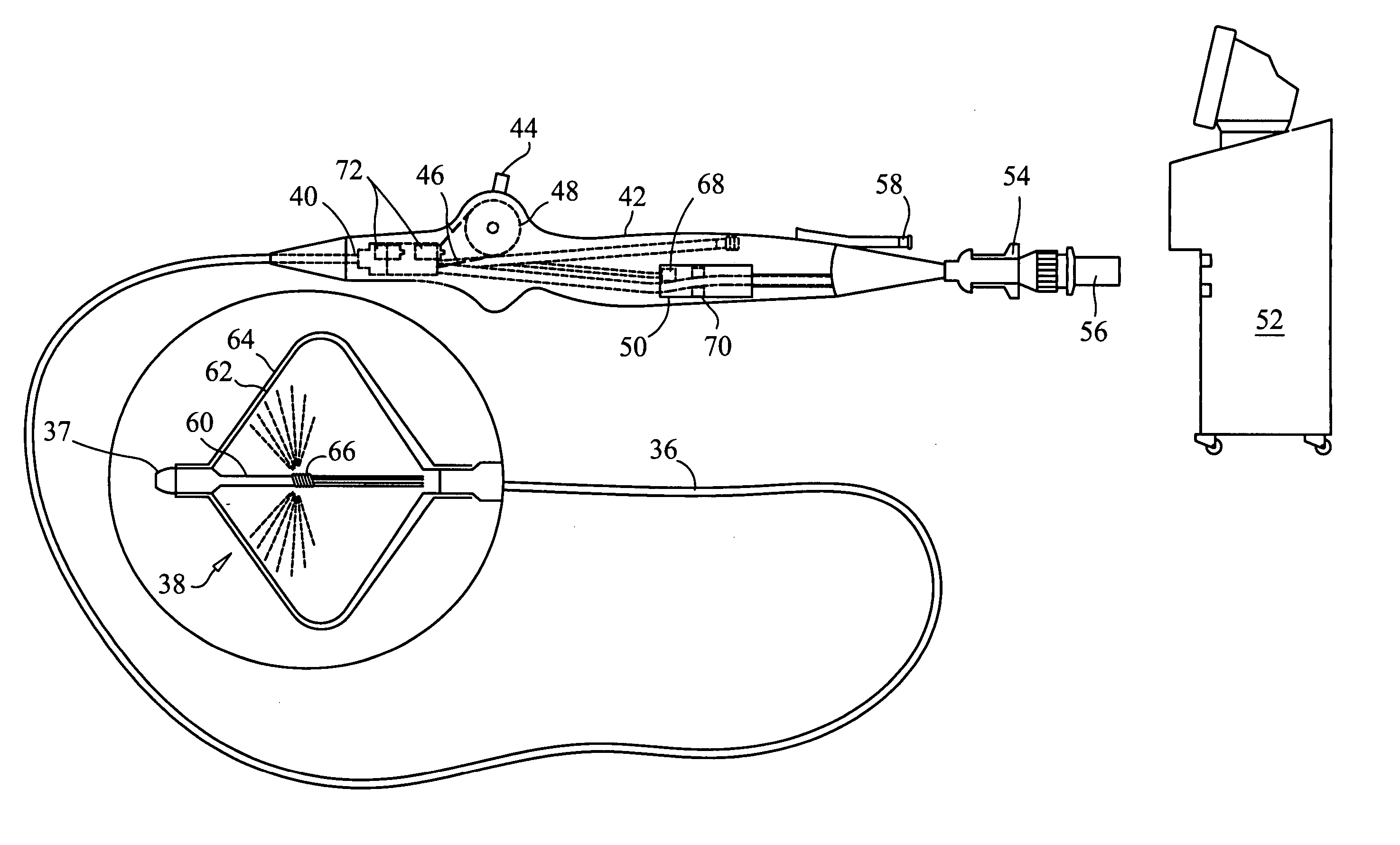
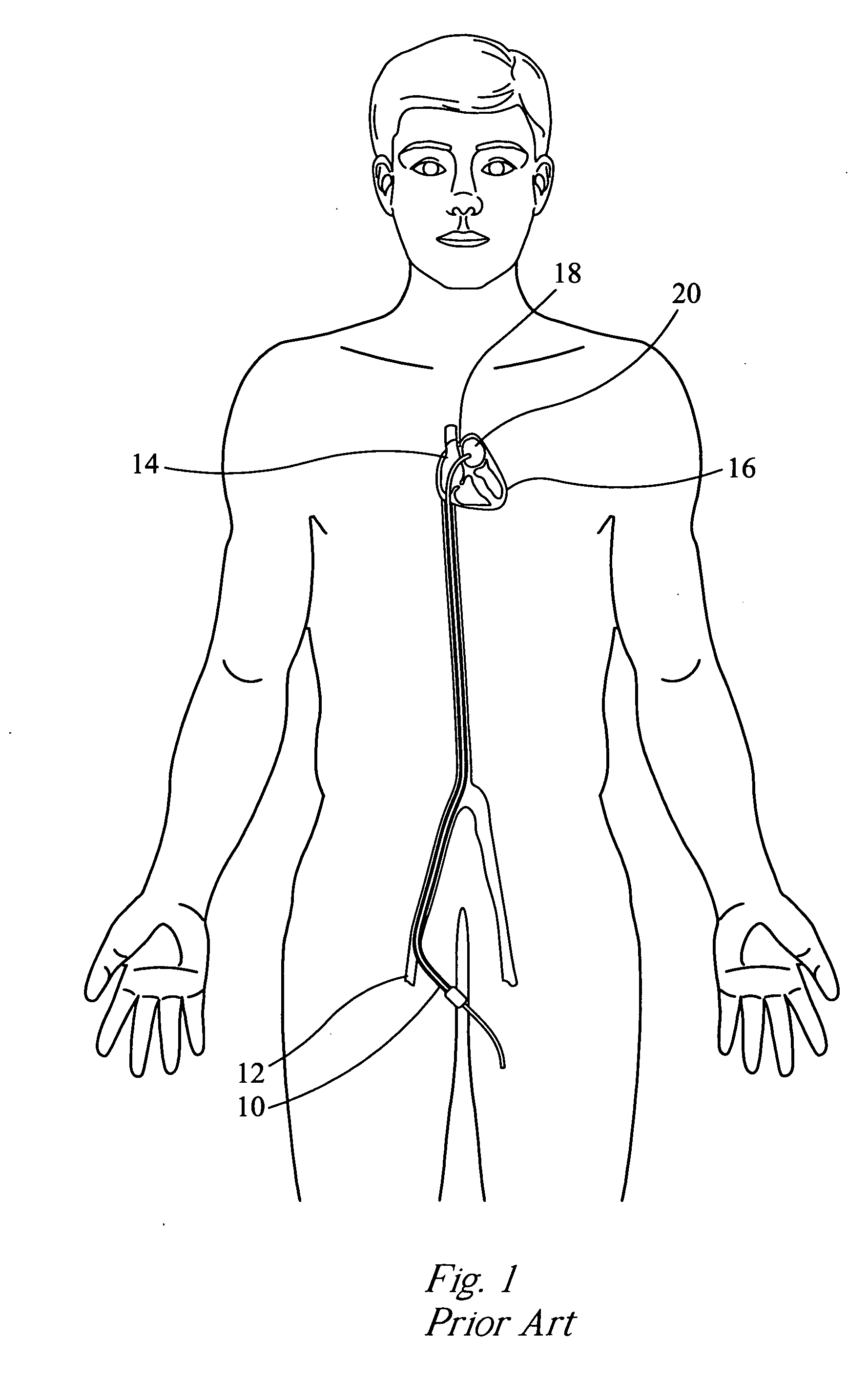
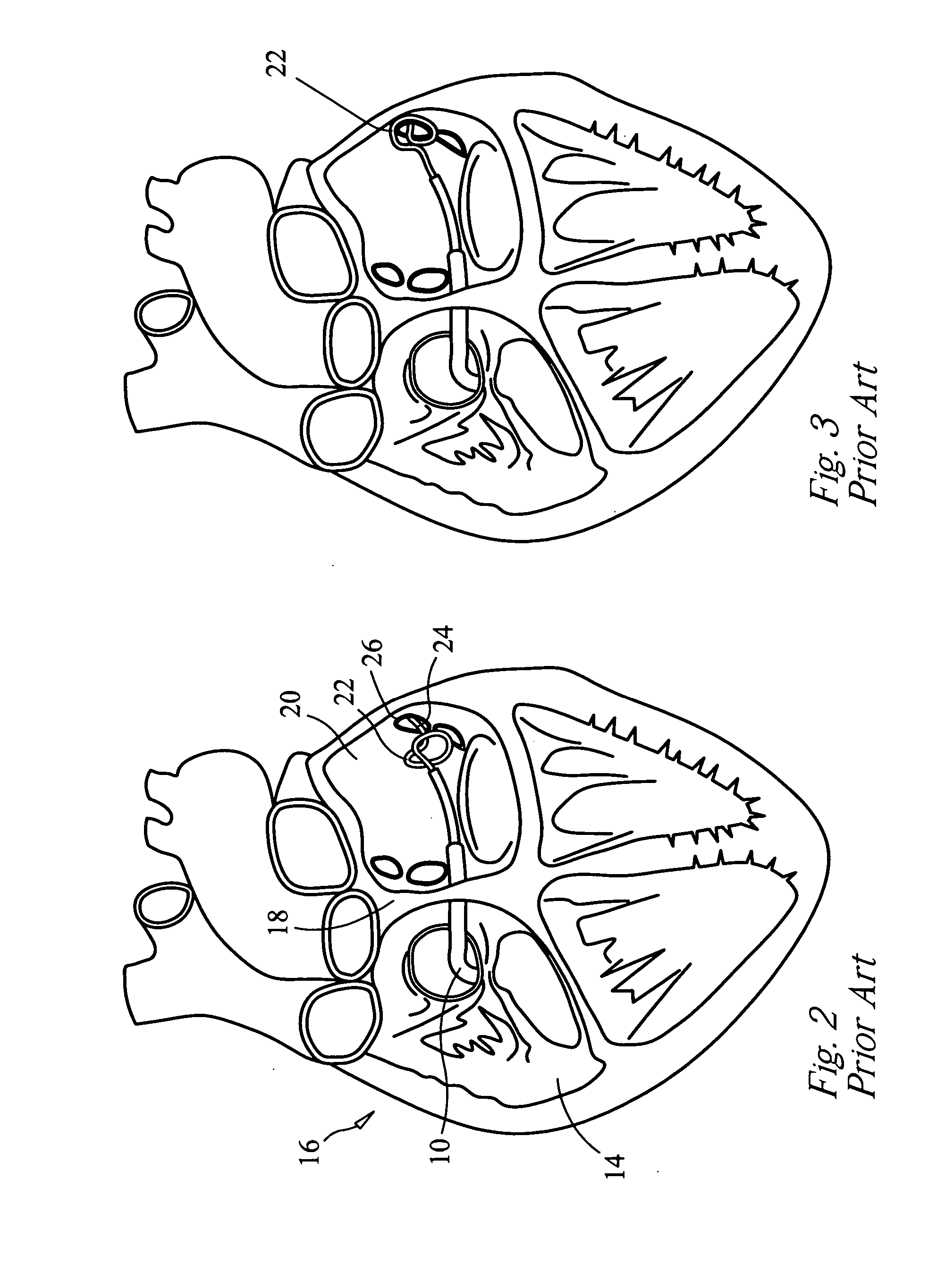
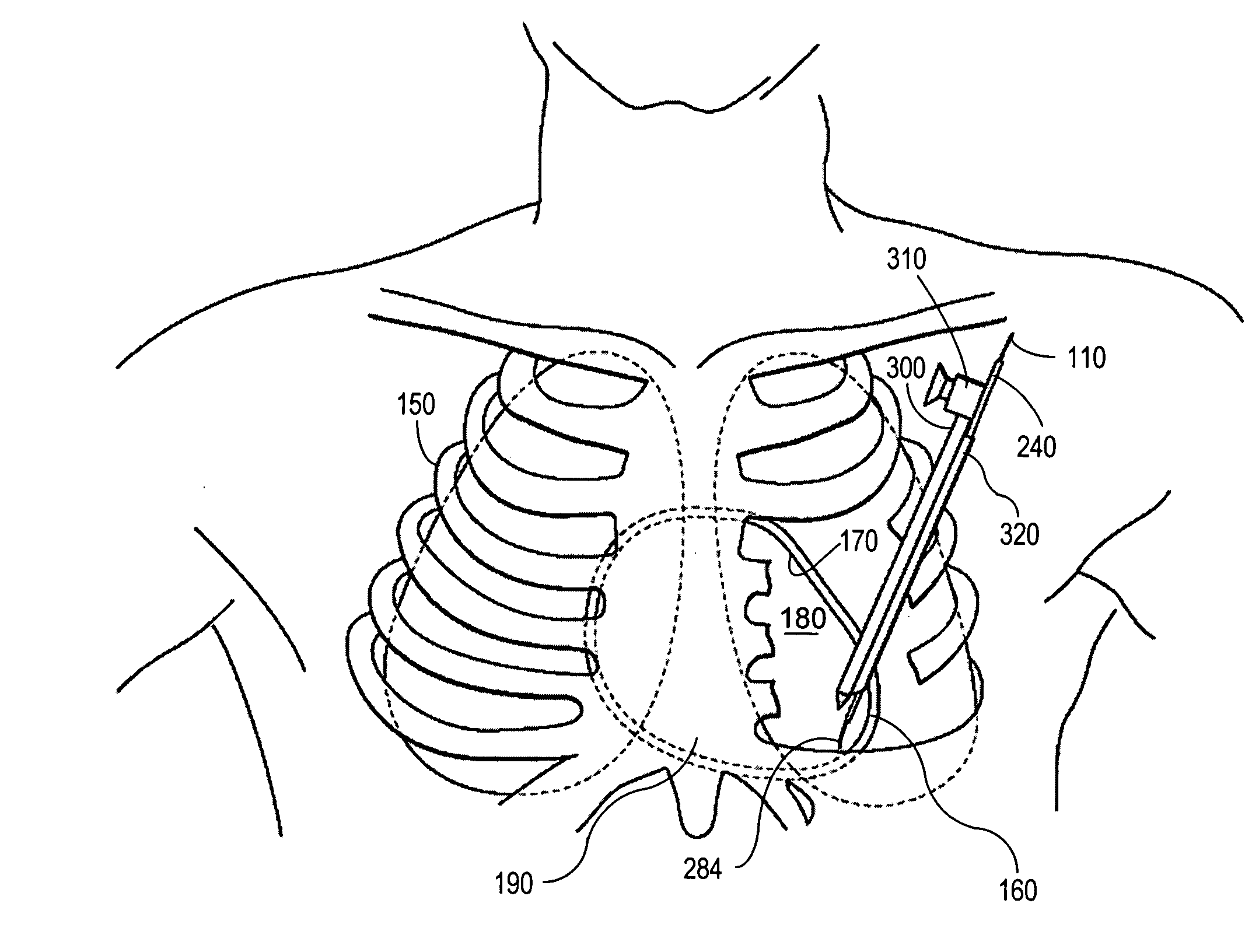
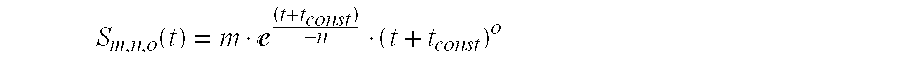Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
376 results about "Myocardial tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
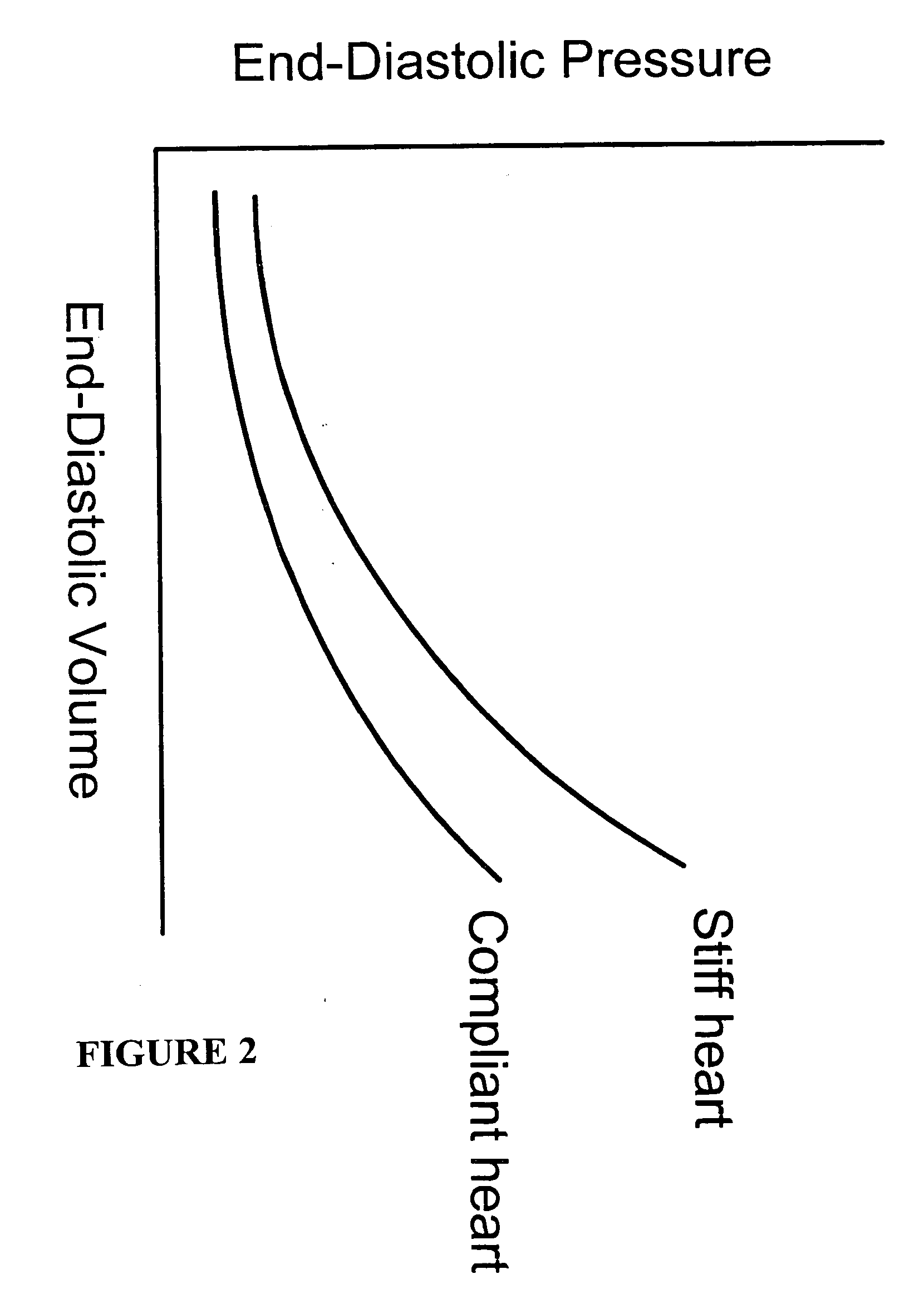
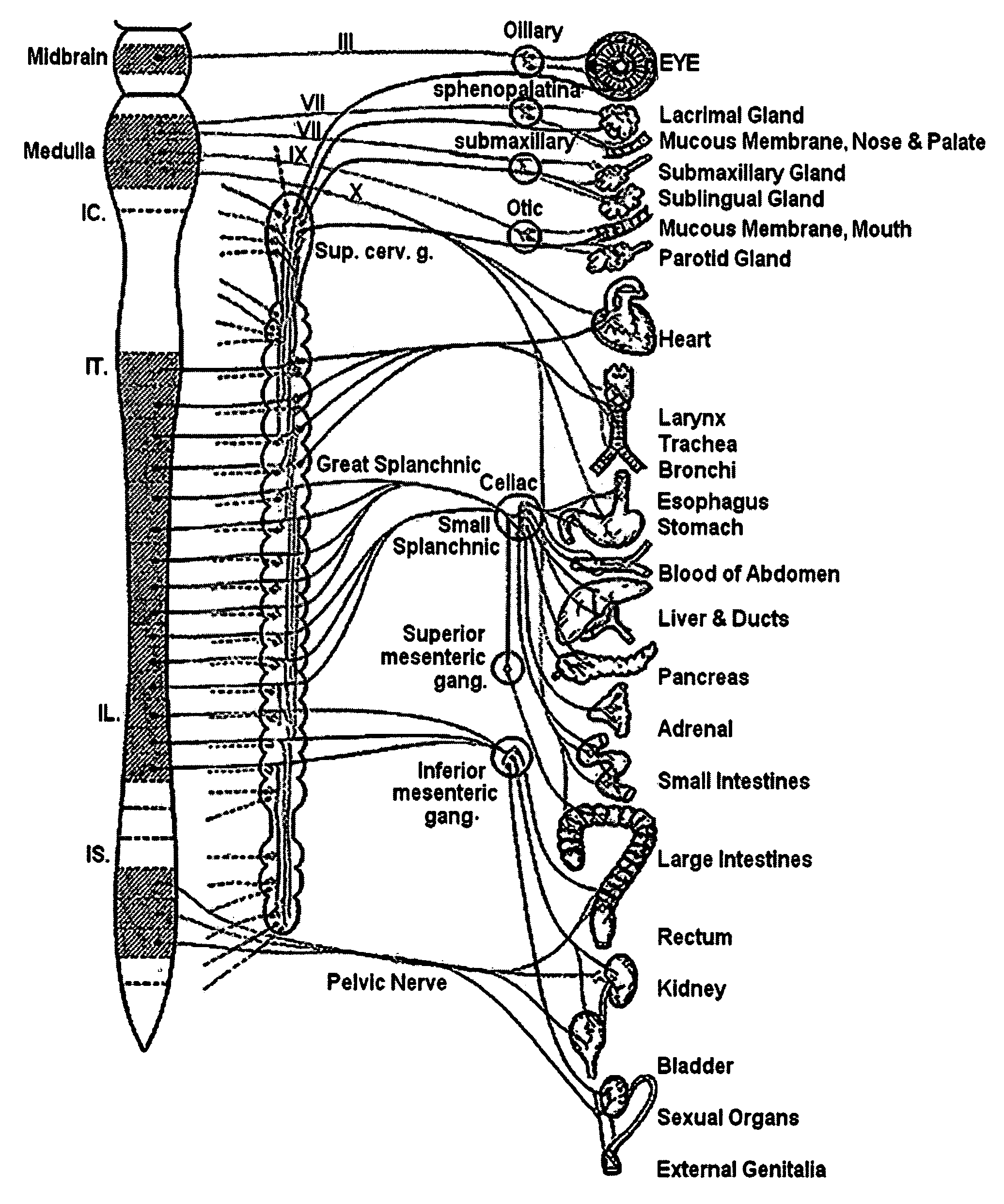
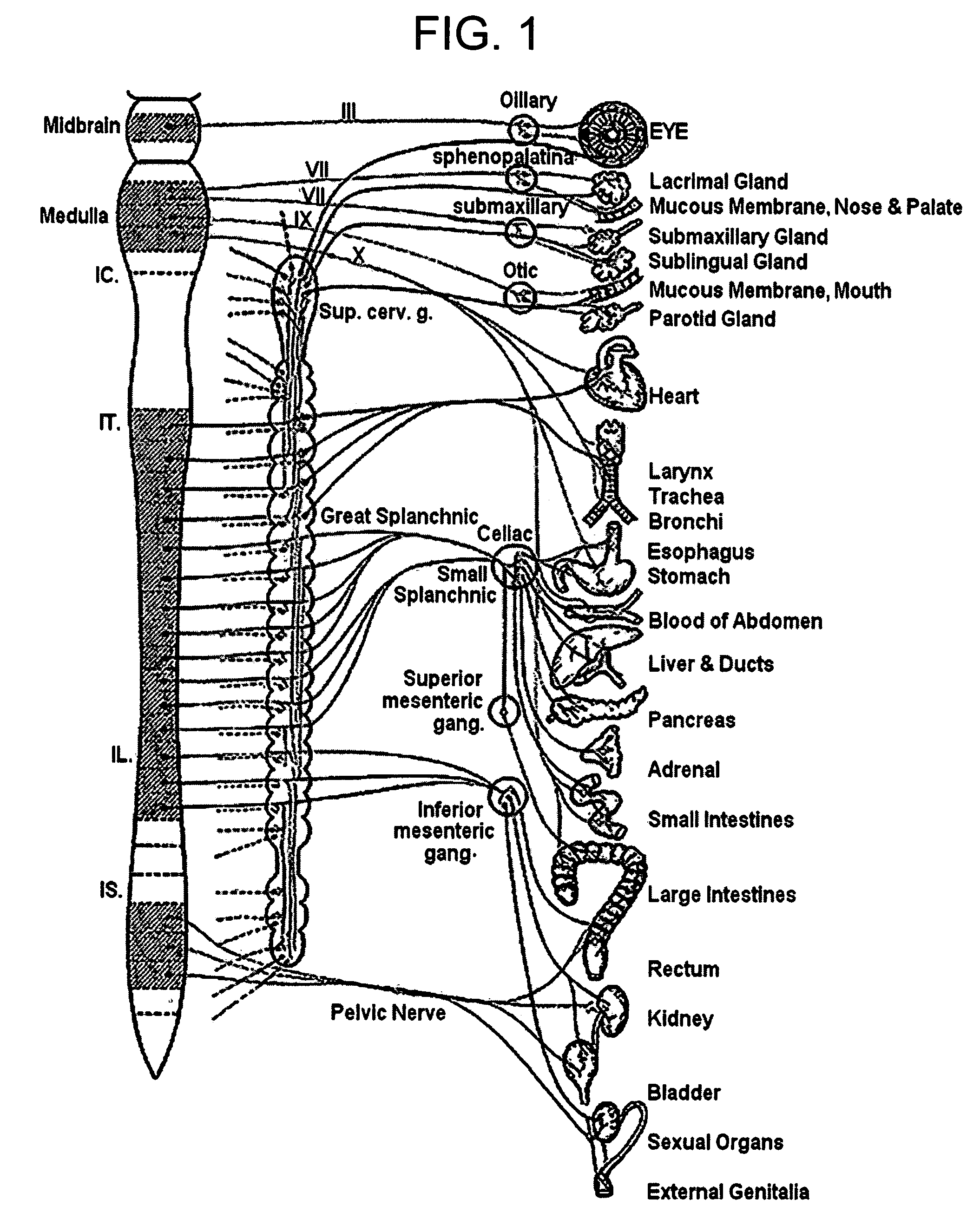
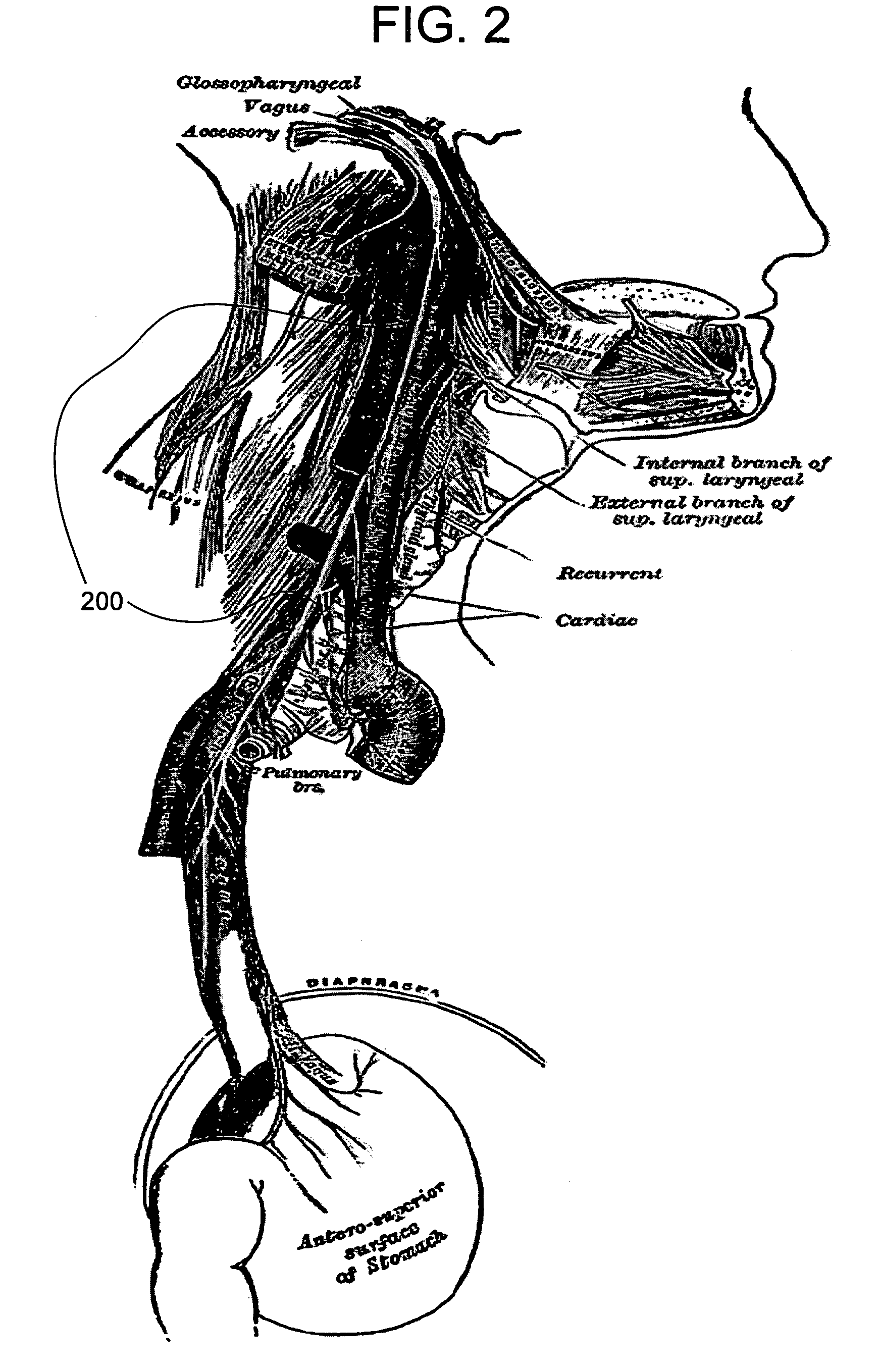
Definition of Myocardium. The muscle tissue that forms the walls of the heart. Myocardial cells are unique in their structure, blending muscle and nerve structures so they can both contract and conduct electrical impulses. Myocardial cells thus can contract independent of external stimulation.
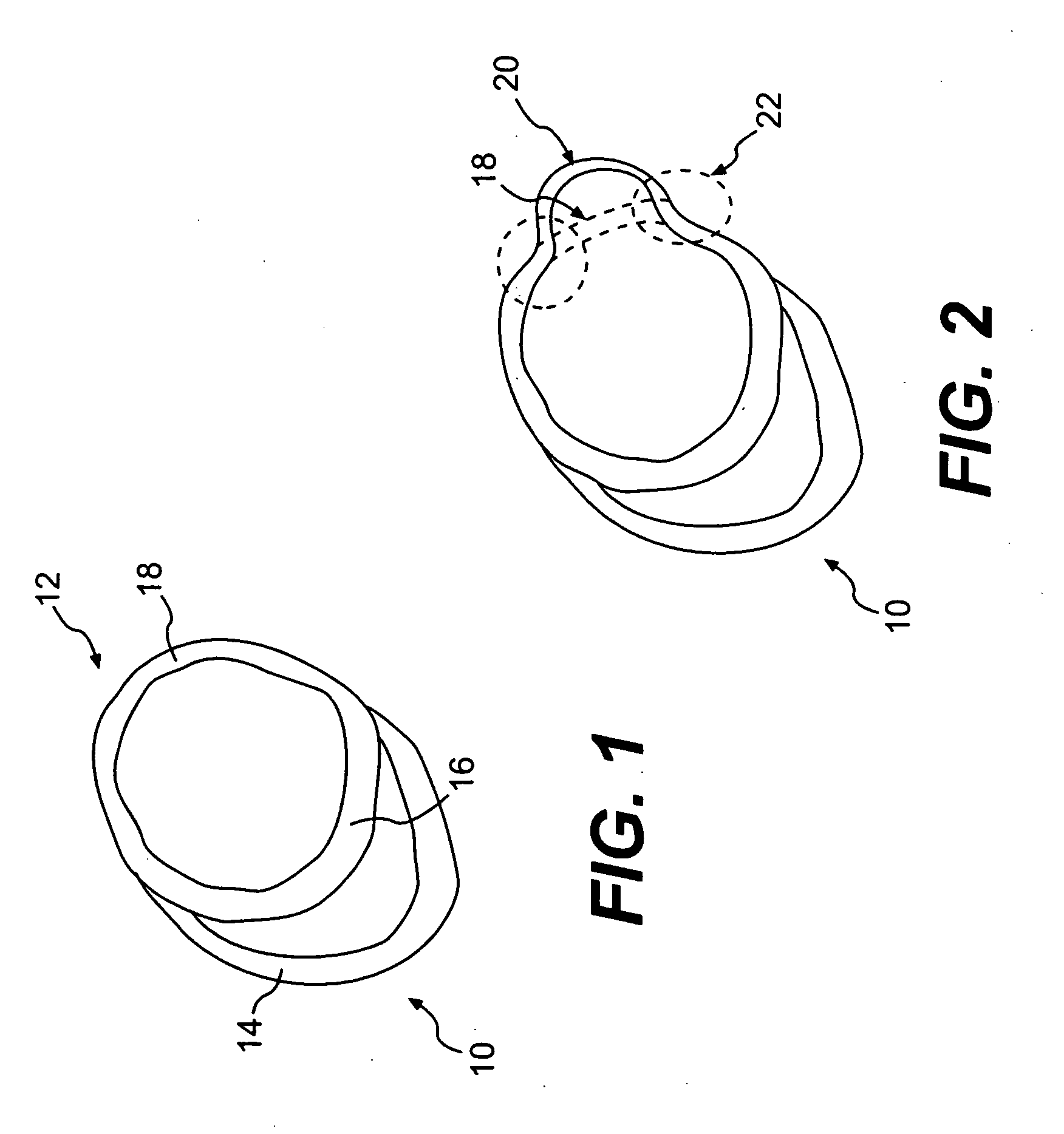
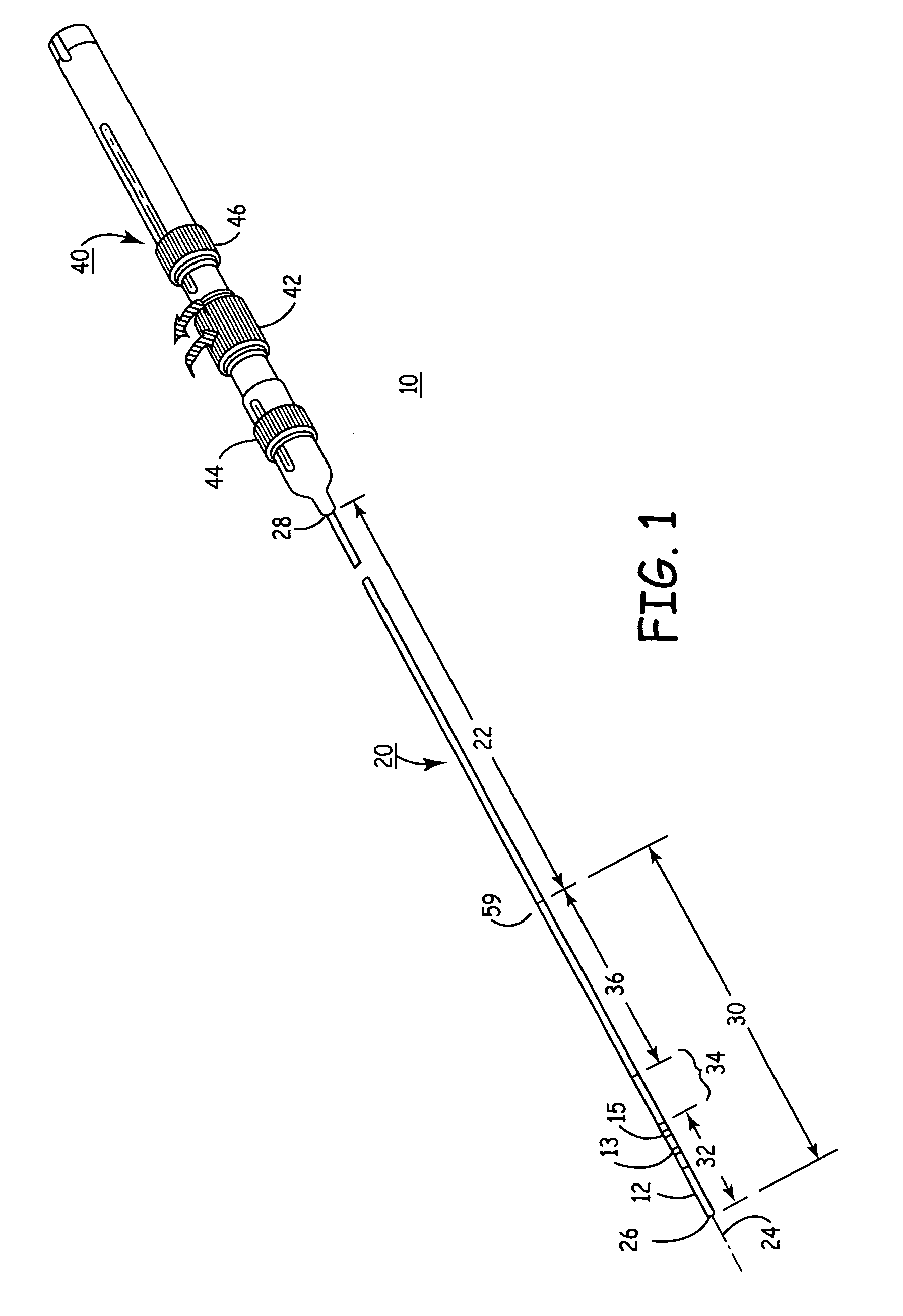
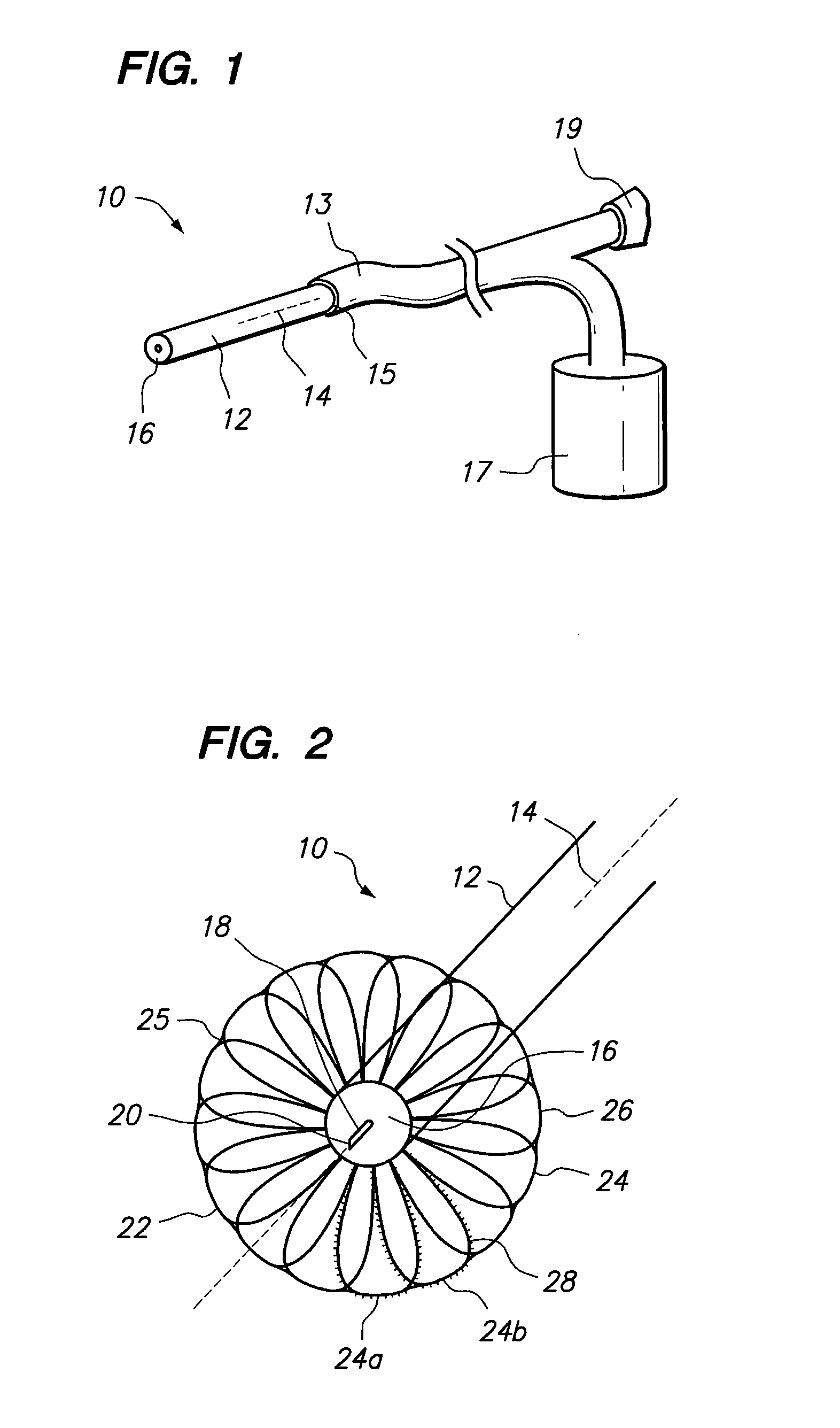
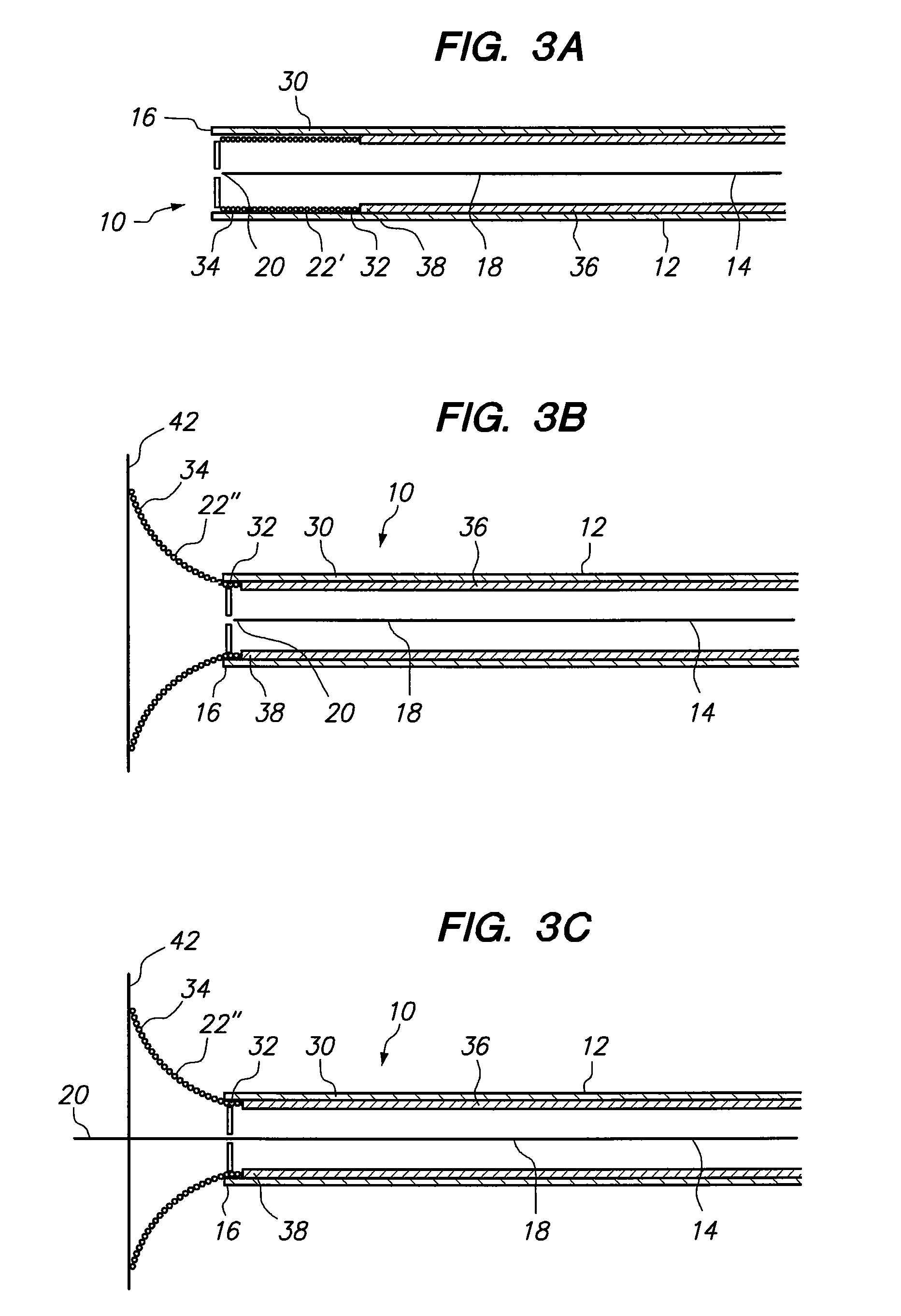
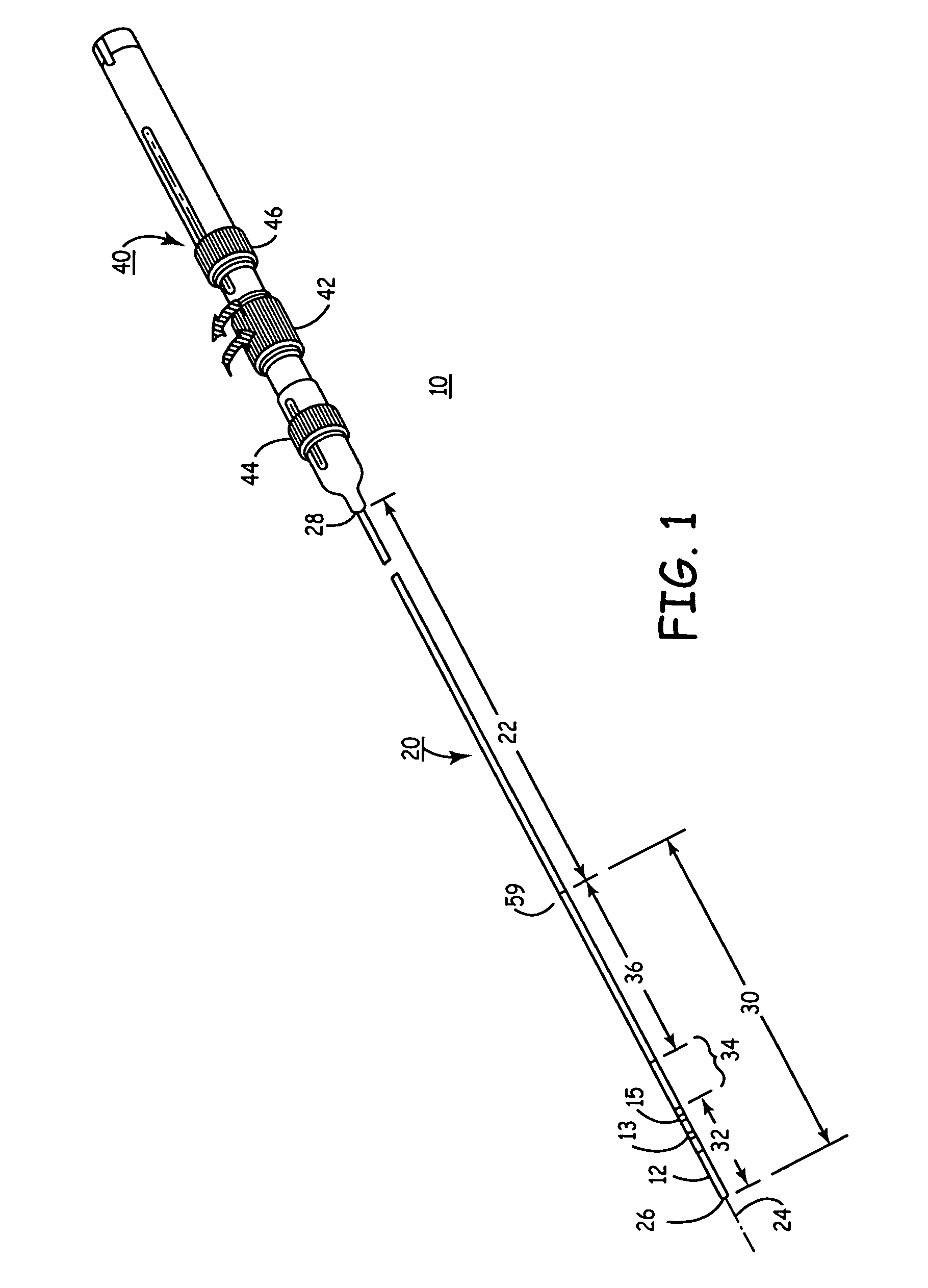
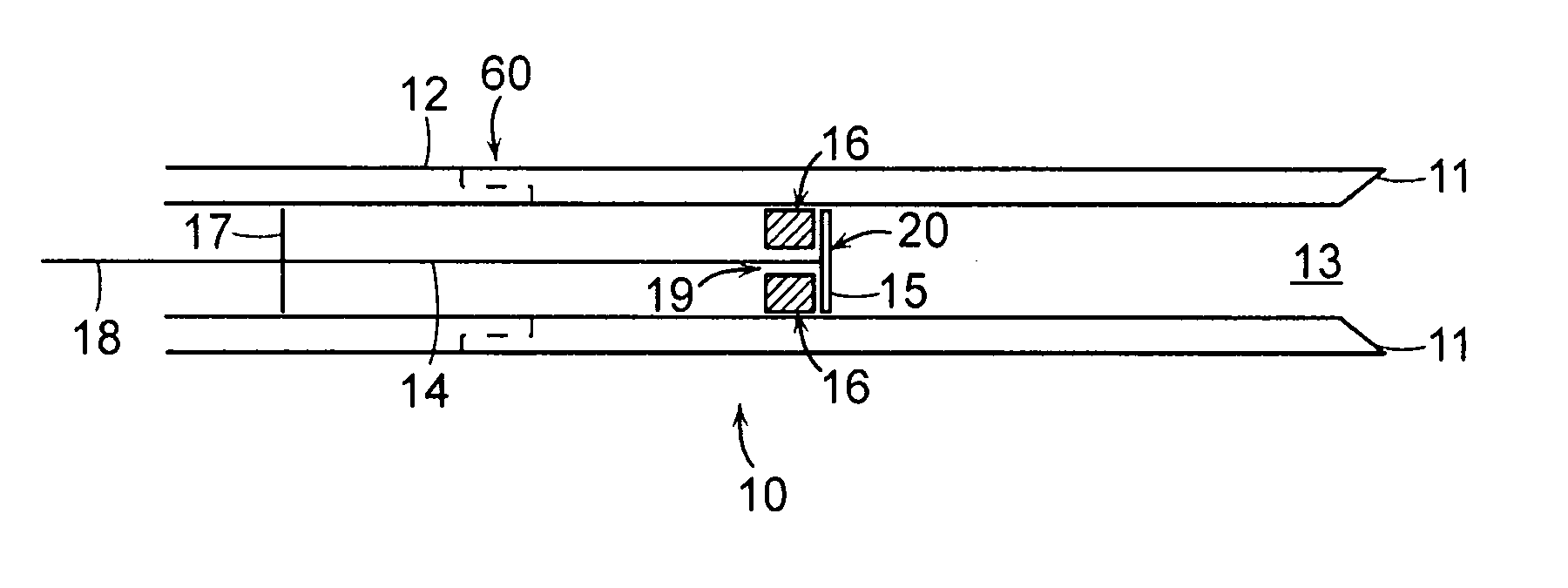
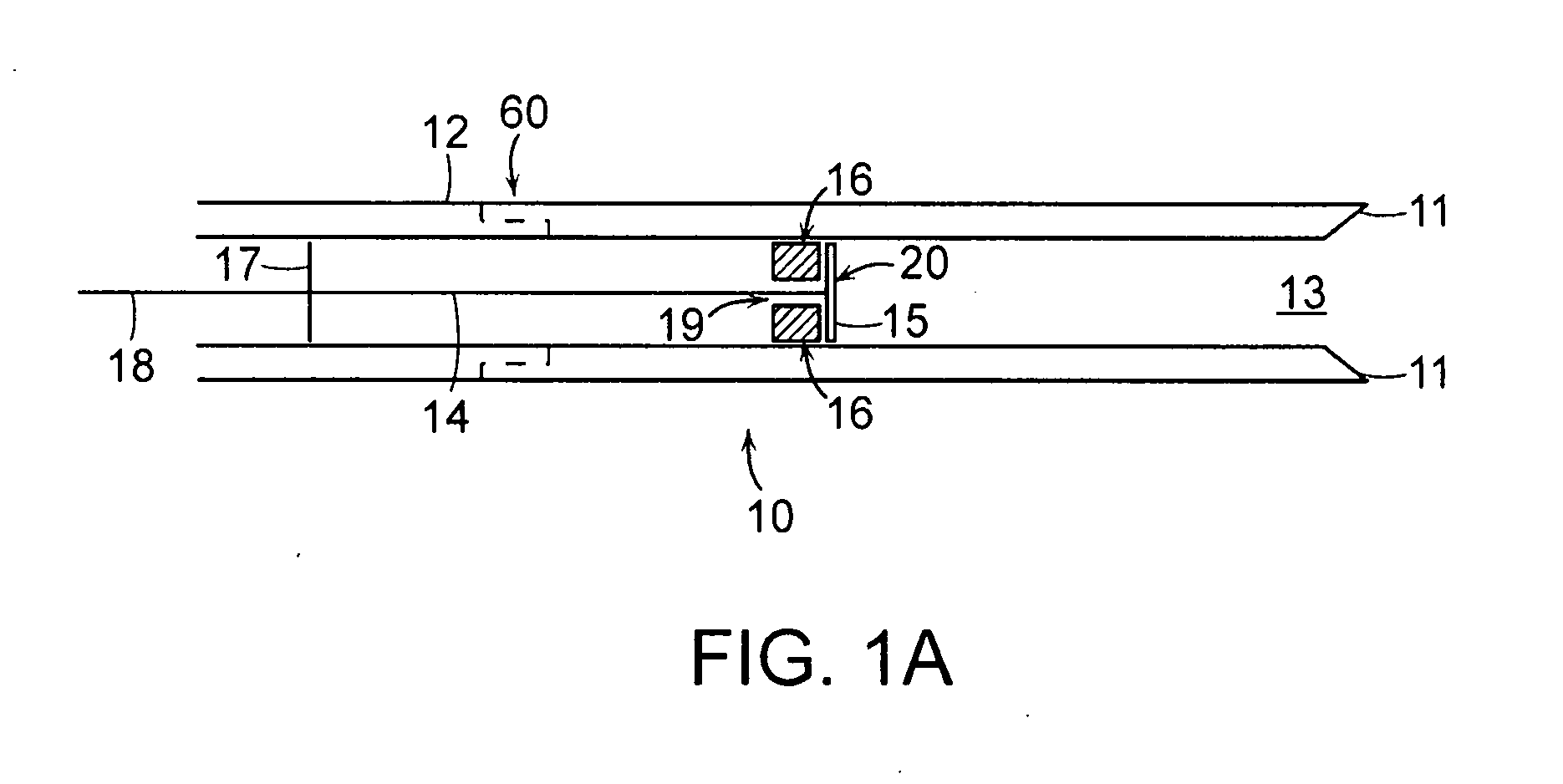
Prevention of myocardial infarction induced ventricular expansion and remodeling
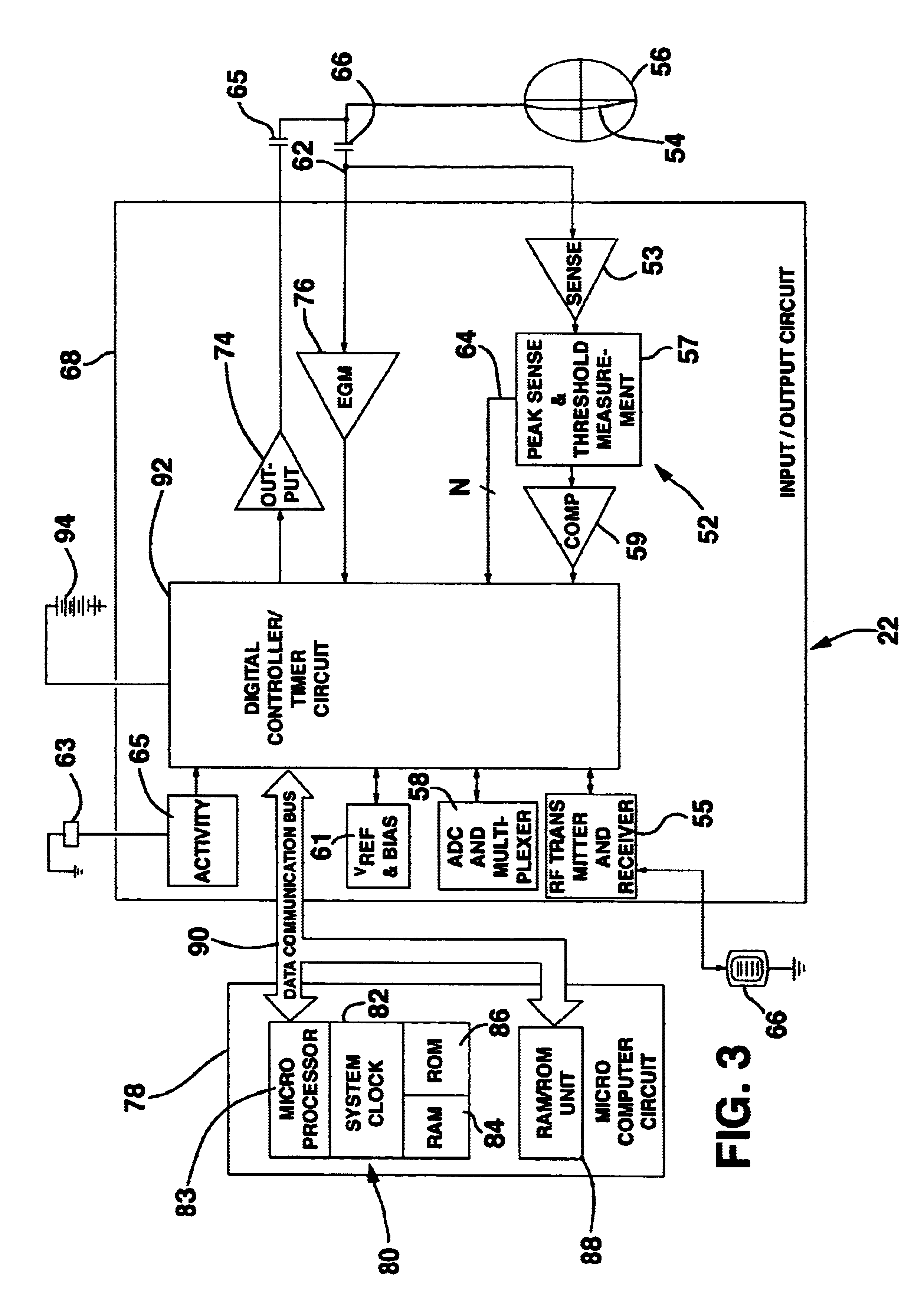
ActiveUS20050080402A1Prevent further deteriorationInhibit swellingSuture equipmentsPowder deliveryCardiac muscleTherapeutic treatment
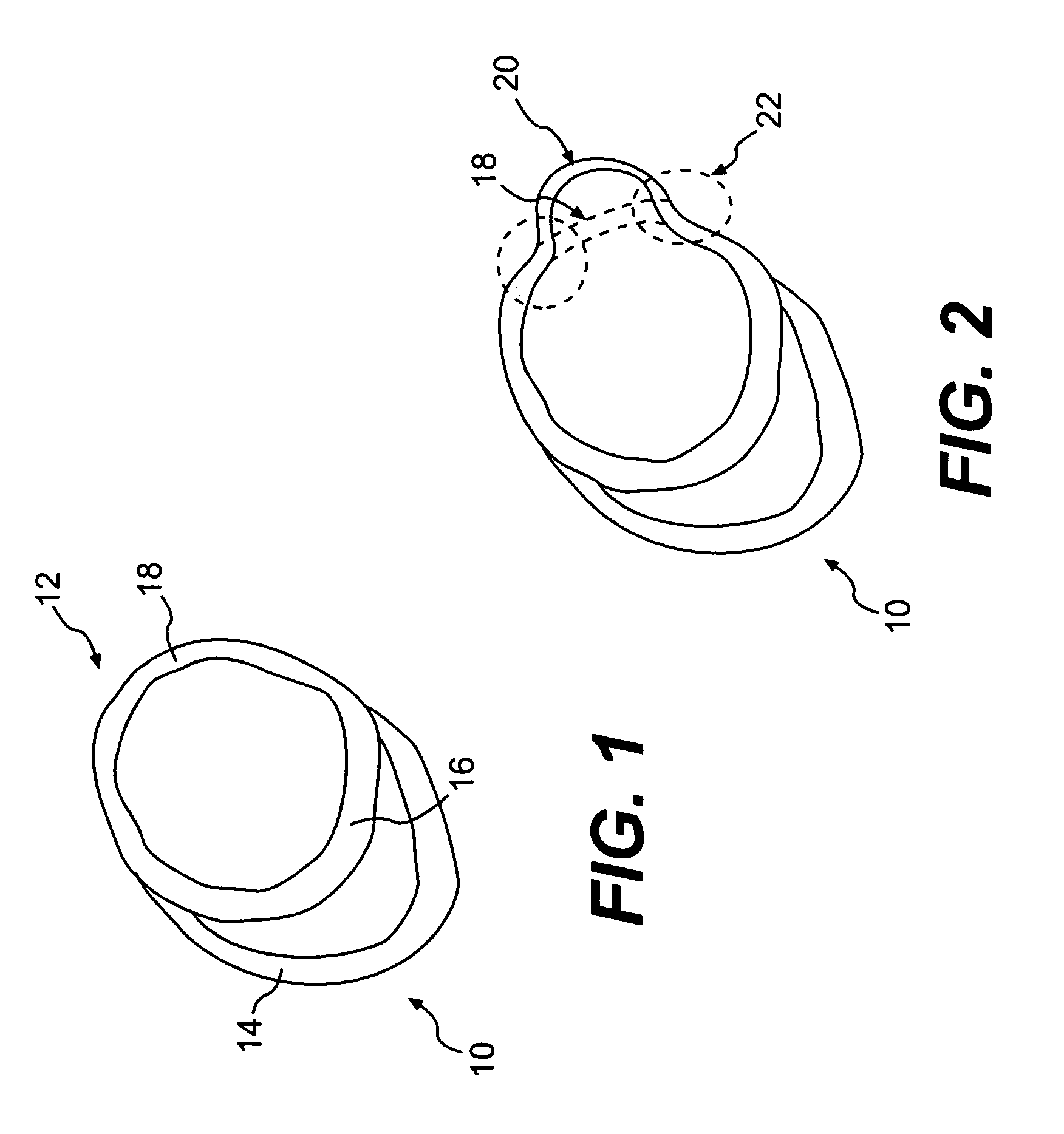
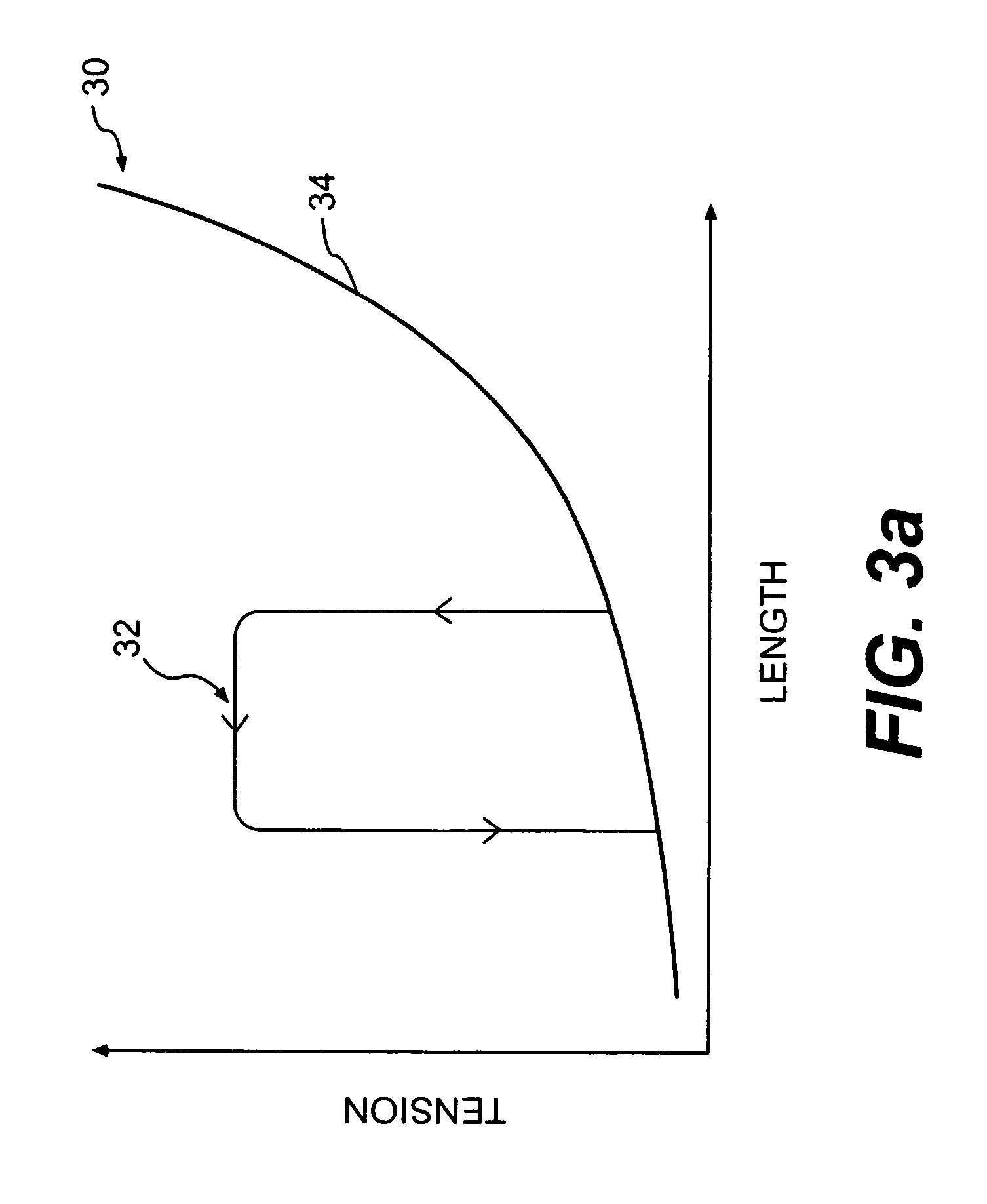
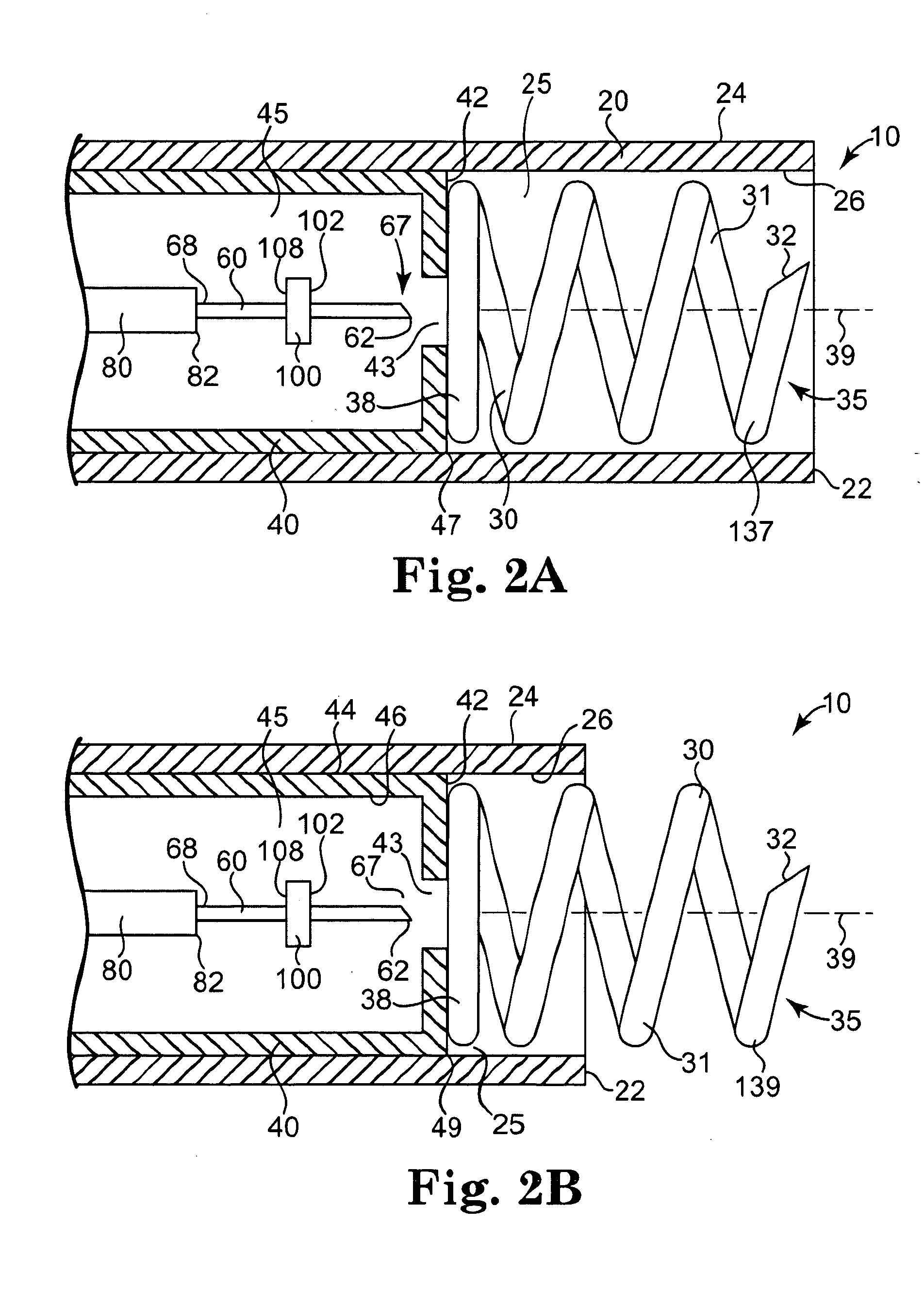
A method for direct therapeutic treatment of myocardial tissue in a localized region of a heart having a pathological condition. The method includes identifying a target region of the myocardium and applying material directly and substantially only to at least a portion of the myocardial tissue of the target region. The material applied results in a physically modification the mechanical properties, including stiffness, of said tissue. Various devices and modes of practicing the method are disclosed for stiffening, restraining and constraining myocardial tissue for the treatment of conditions including myocardial infarction or mitral valve regurgitation.
Owner:MYOMEND
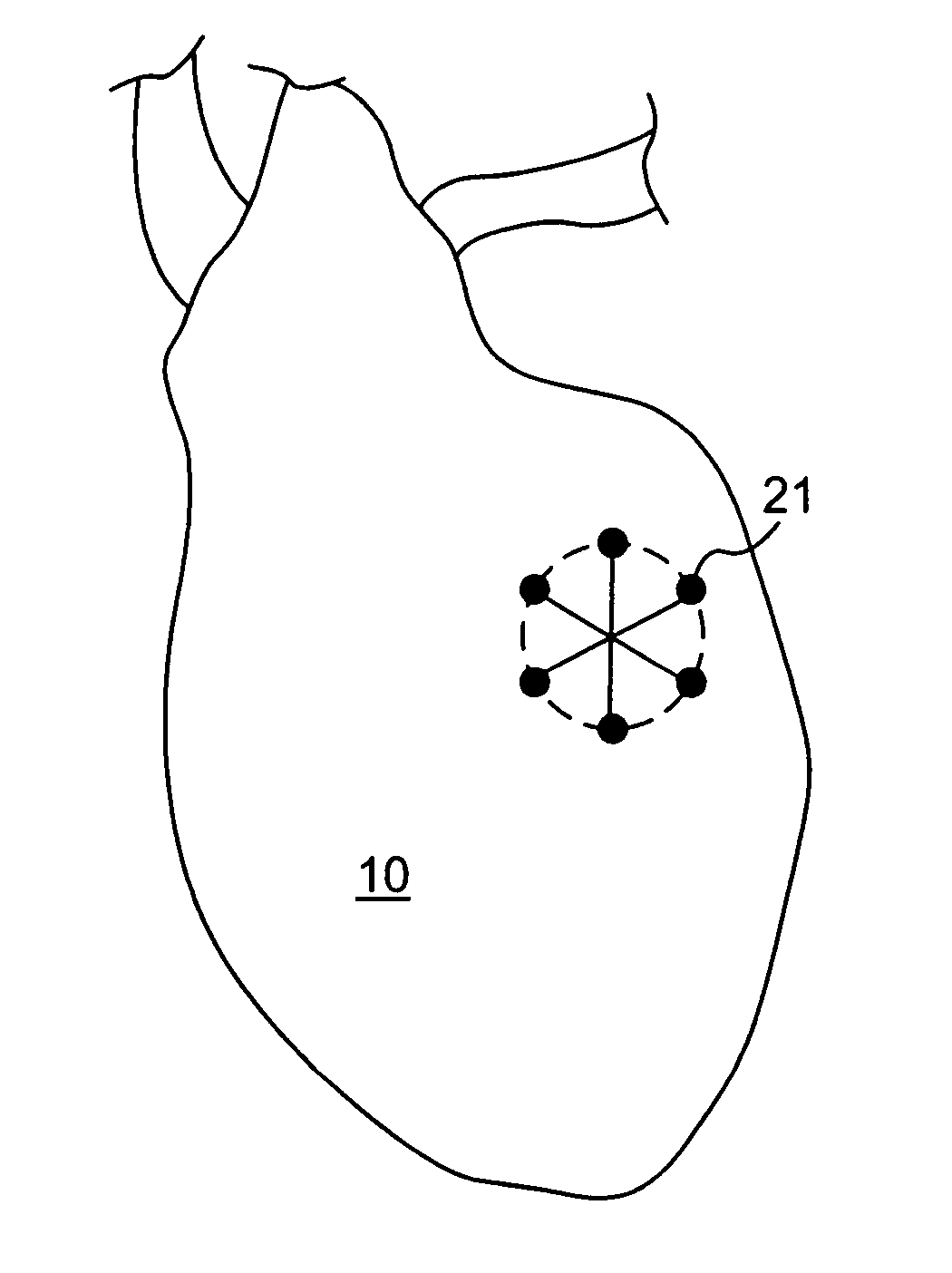
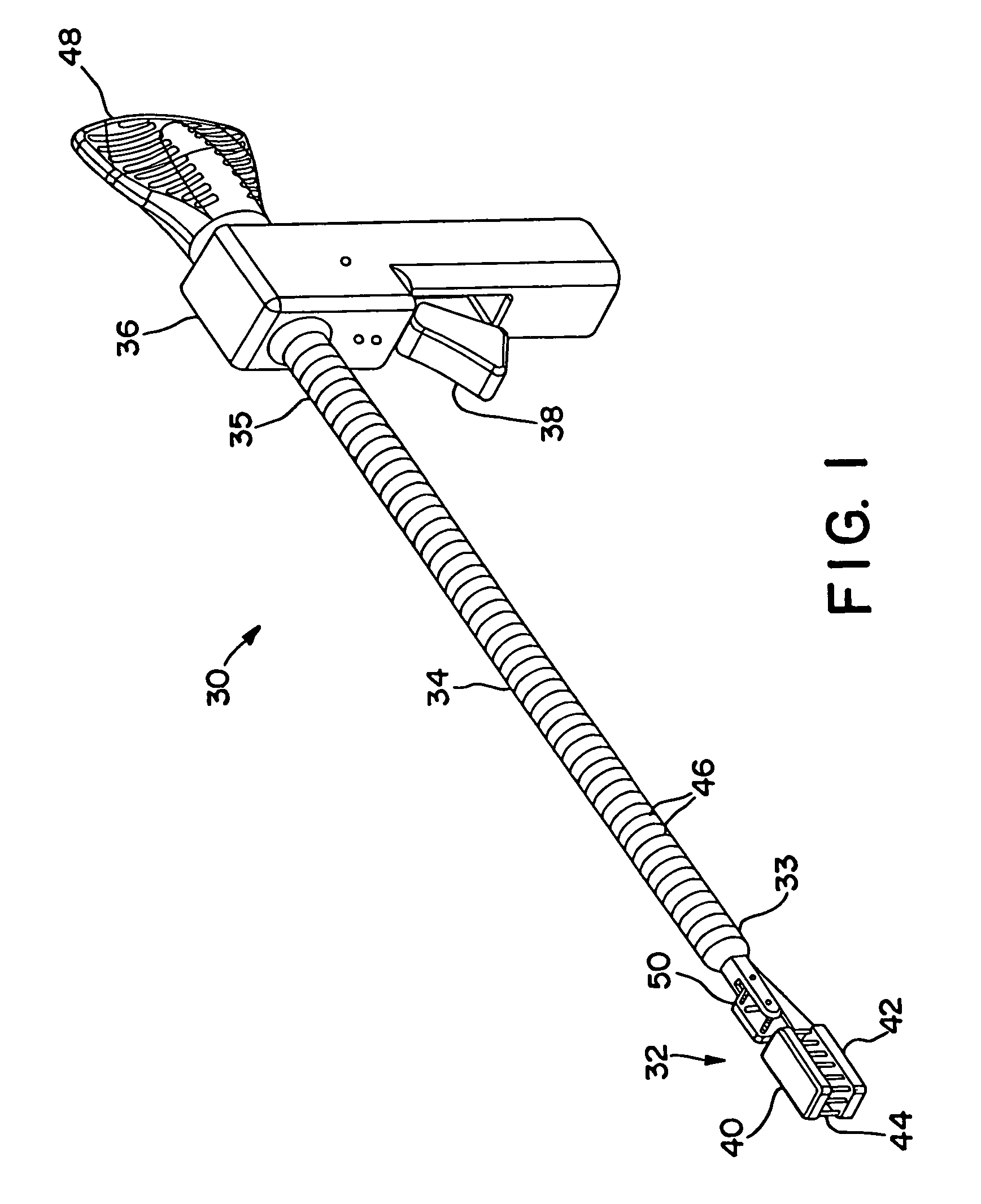
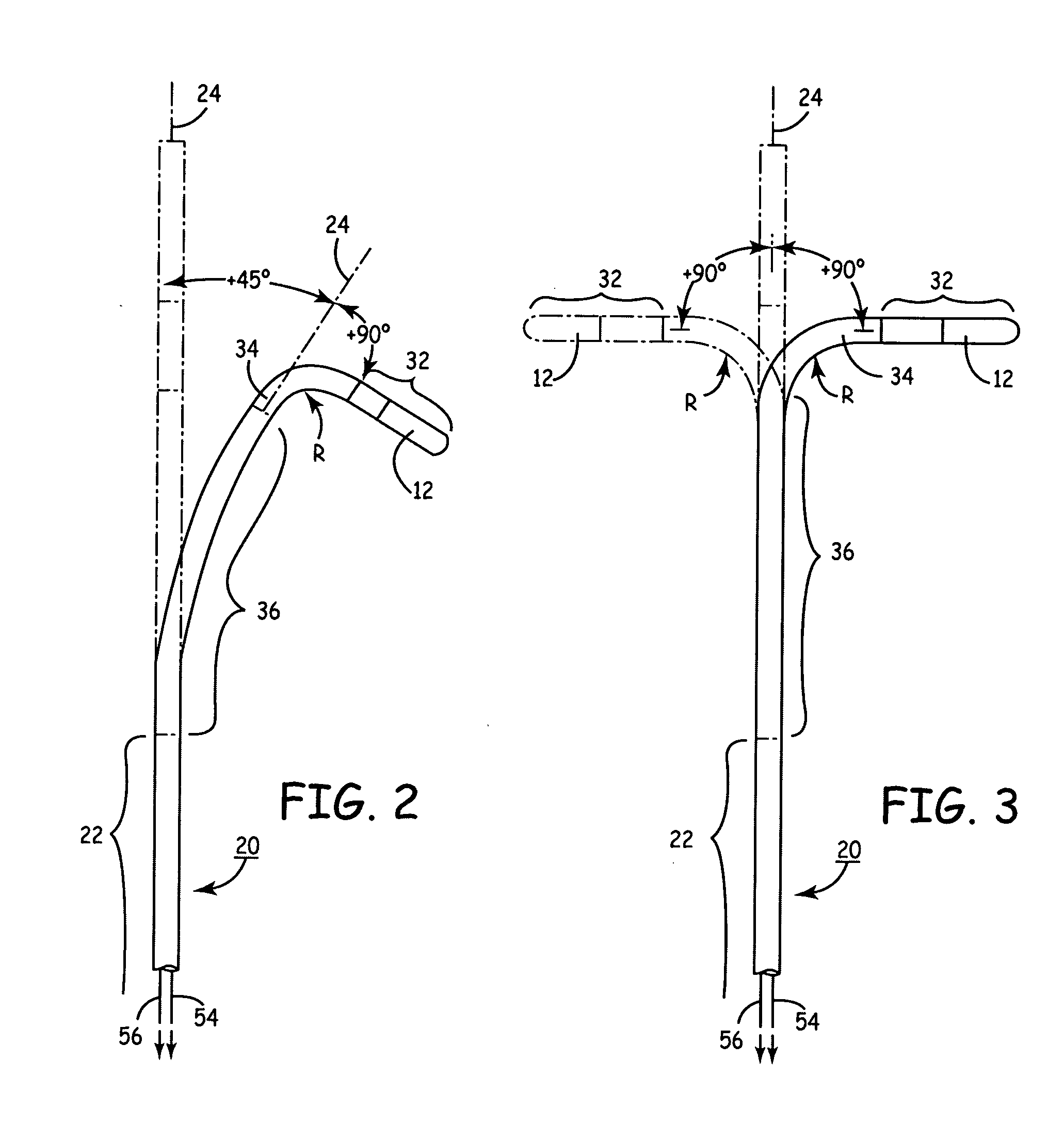
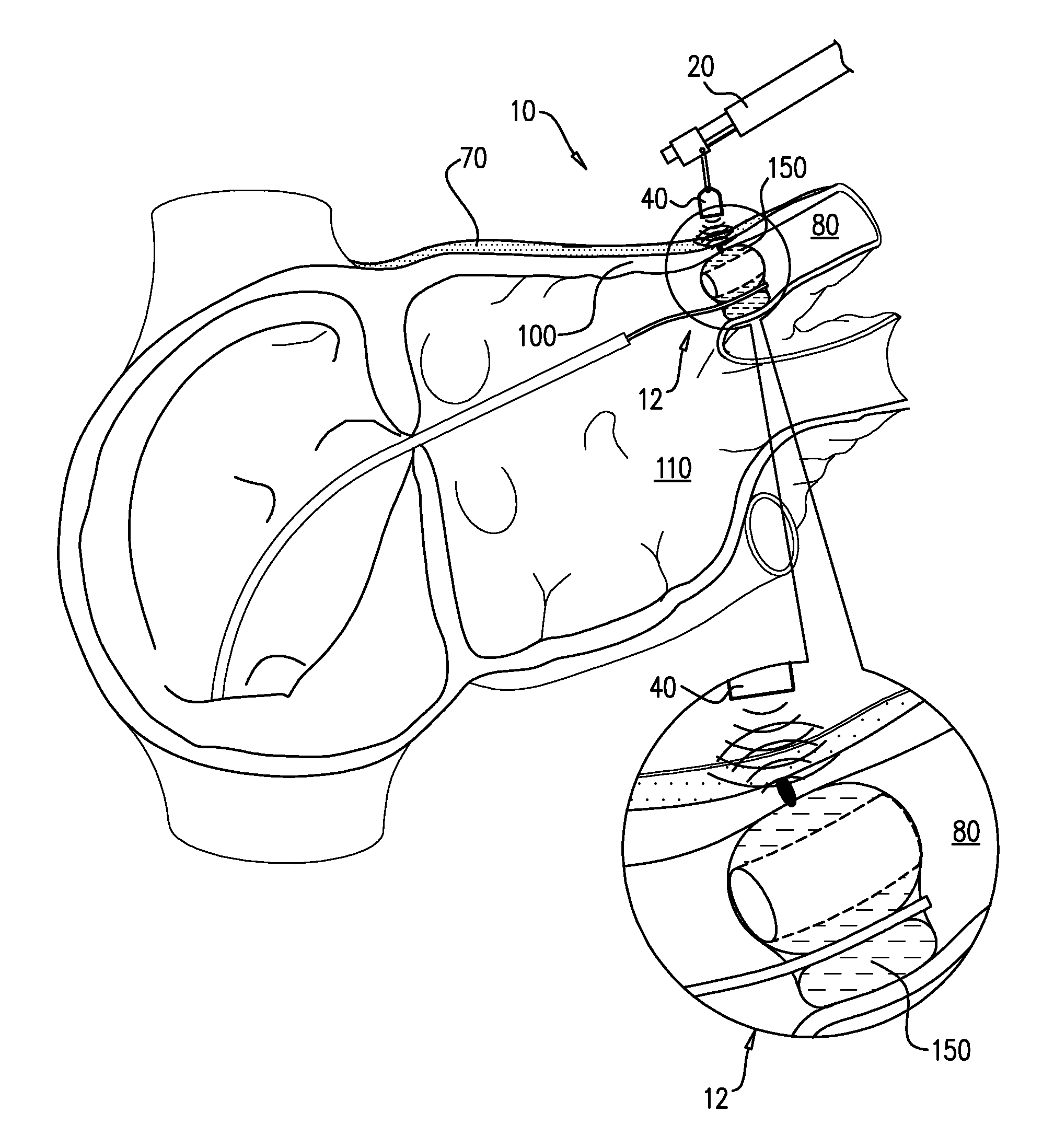
Heart wall ablation/mapping catheter and method
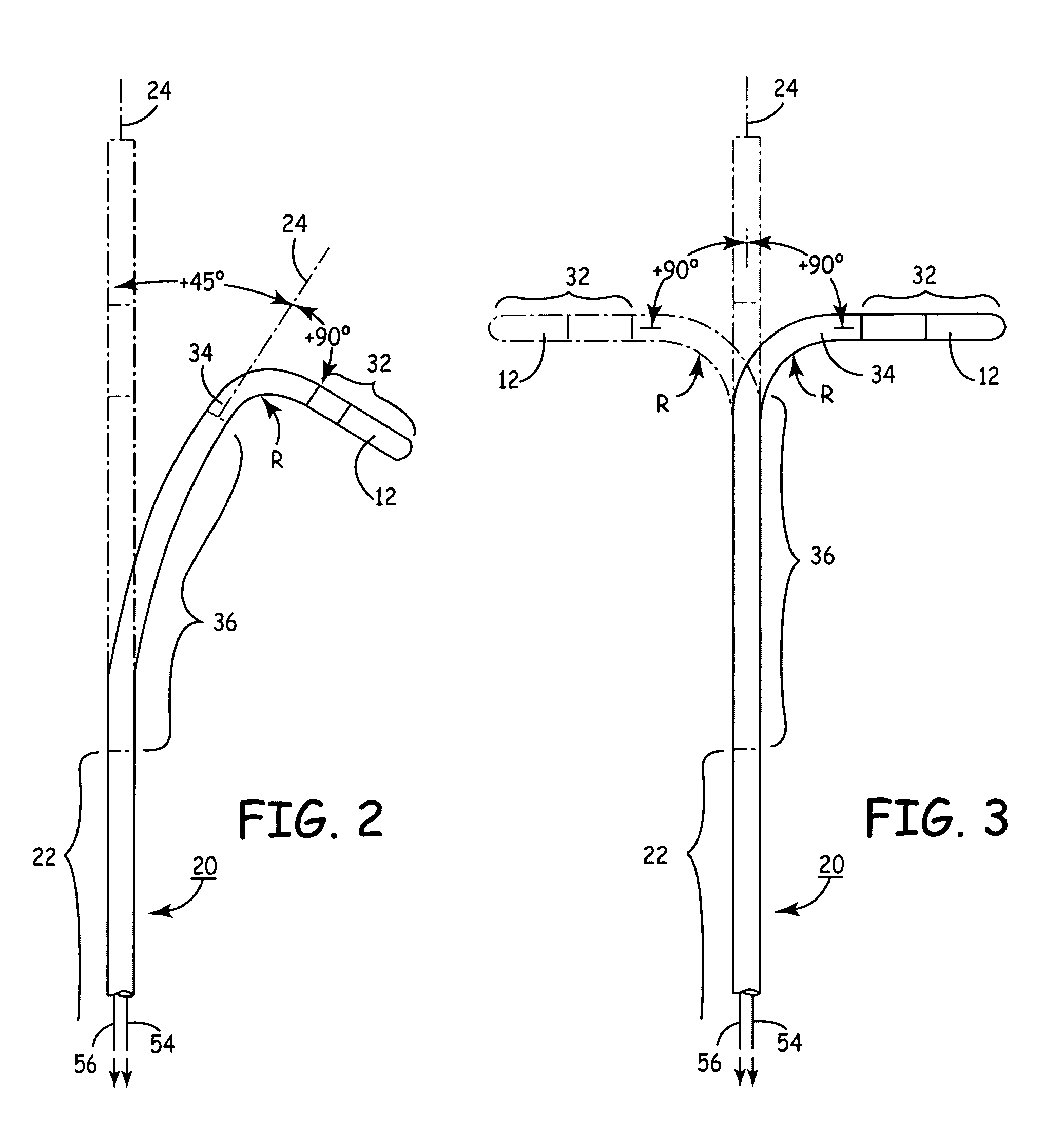
InactiveUS6926669B1Wide angleSmall knuckle curveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesCardiac wallAngular orientation
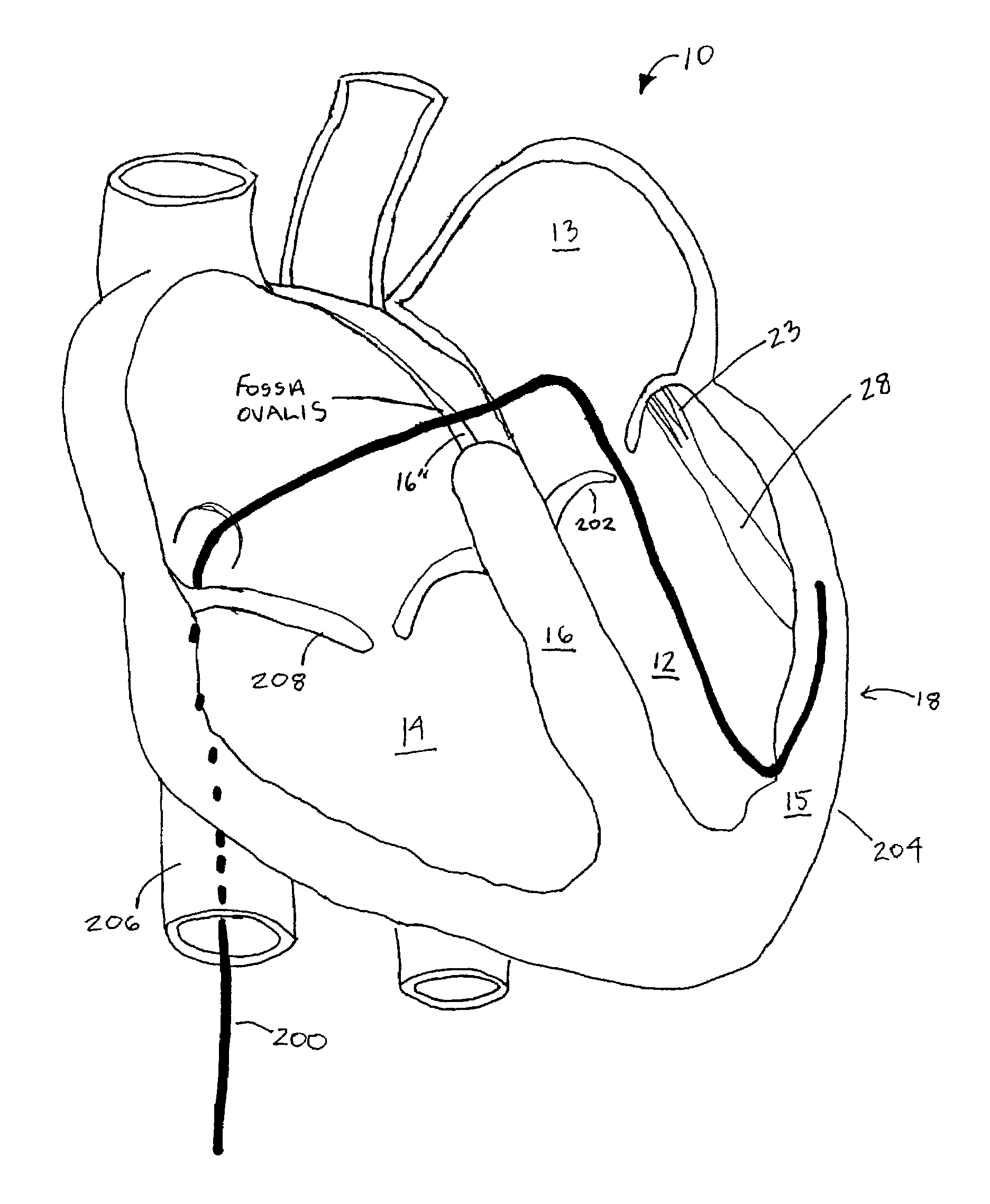
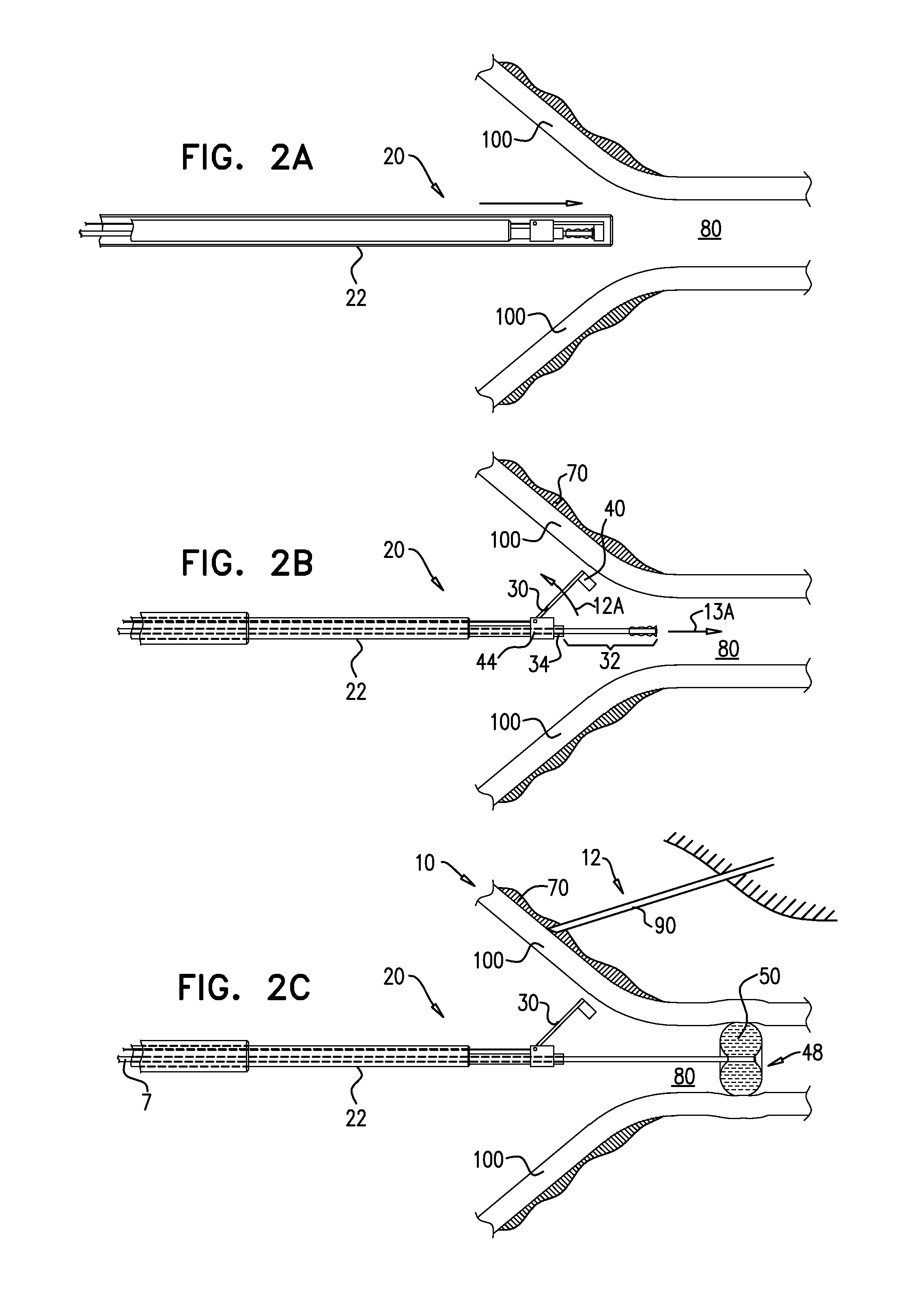
Steerable electrophysiology catheters for use in mapping and / or ablation of accessory pathways in myocardial tissue of the heart wall and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The catheter comprises a catheter body and handle, the catheter body having a proximal section and a distal section and manipulators that enable the deflection of a distal segment of the distal tip section with respect to the independently formed curvature of a proximal segment of the distal tip section through a bending or knuckle motion of an intermediate segment between the proximal and distal segments. A wide angular range of deflection within a very small curve or bend radius in the intermediate segment is obtained. At least one distal tip electrode is preferably confined to the distal segment which can have a straight axis extending distally from the intermediate segment. The curvature of the proximal segment and the bending angle of the intermediate segment are independently selectable. The axial alignment of the distal segment with respect to the nominal axis of the proximal shaft section of the catheter body can be varied between substantially axially aligned (0° curvature) in an abrupt knuckle bend through a range of about −90° to about +180° within a bending radius of between about 2.0 mm and 7.0 mm and preferably less than 5.0 mm. The proximal segment curve can be independently formed in a about +180° through about +270° with respect to the axis of the proximal shaft section to provide an optimum angular orientation of the distal electrode(s). The distal segment can comprise a highly flexible elongated distal segment body and electrode(s) that conform with the shape and curvature of the heart wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS7022077B2Maximize tissue displacementEasy diagnosisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound techniques
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Method and apparatus to modulate cellular regeneration post myocardial infarct
InactiveUS20050288721A1Easy to adjustModulate tissue growthMedical devicesPressure infusionCardiac muscleWorkload
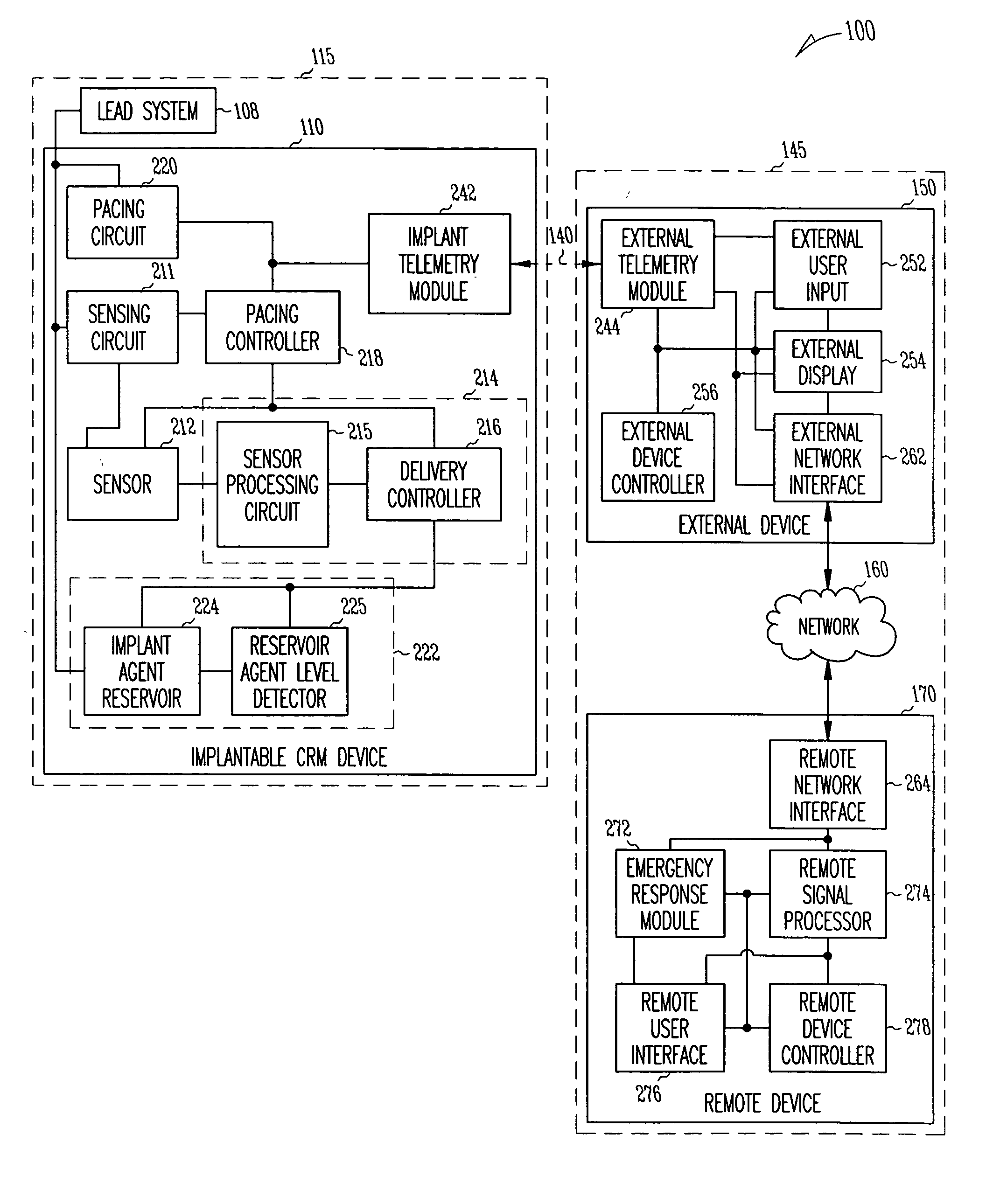
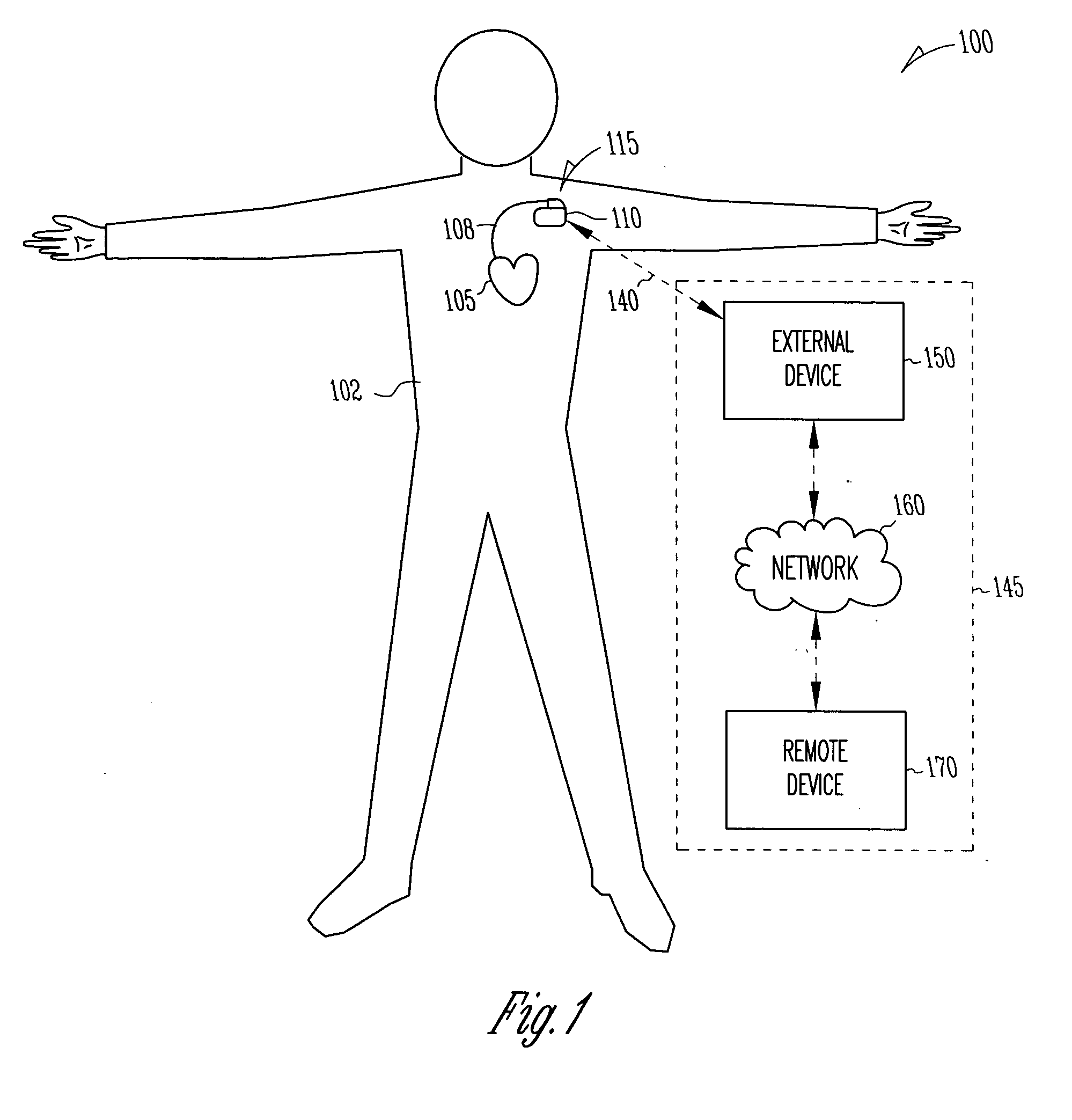
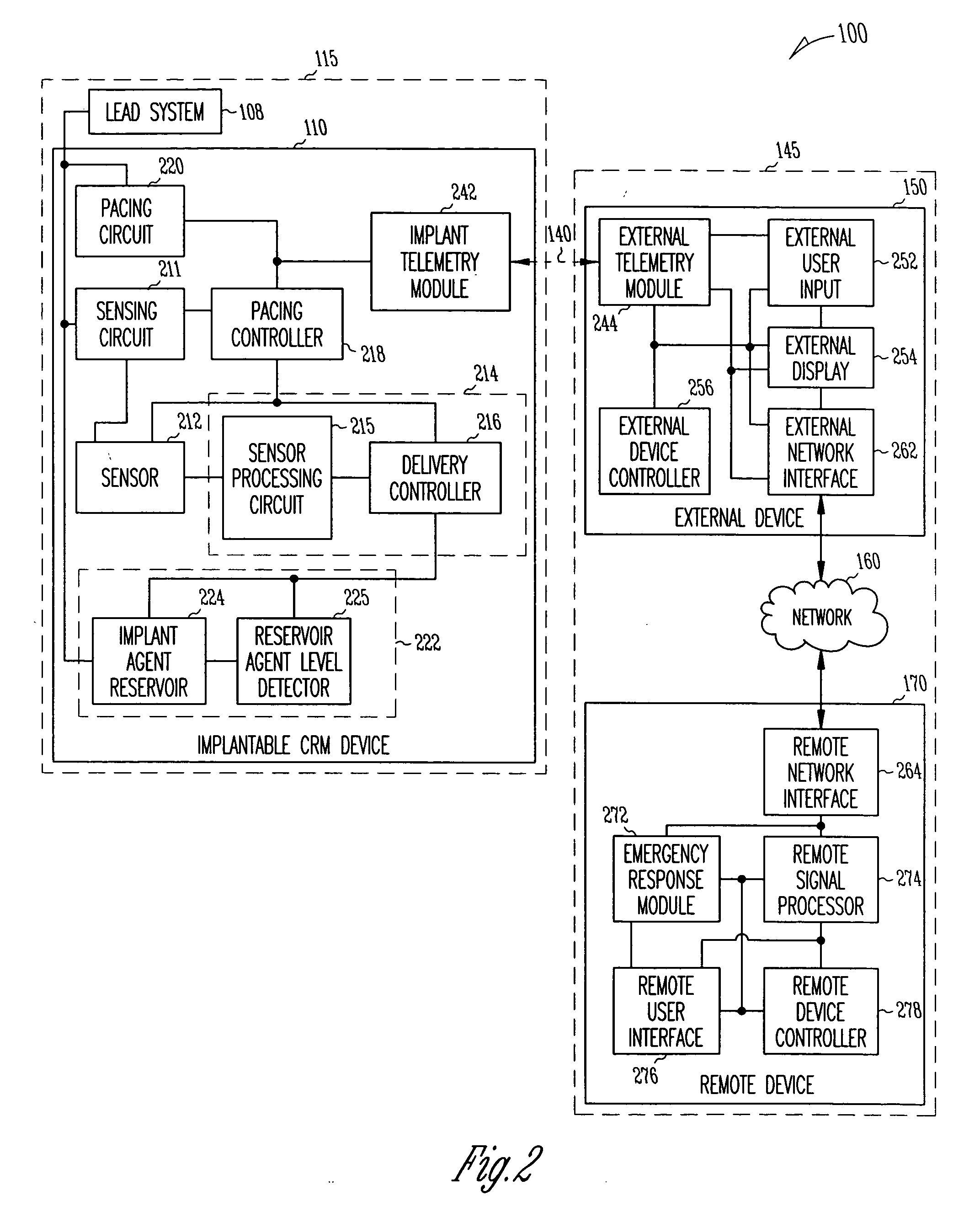
A system delivers cardiac pacing therapy and chemical and / or biological therapy to modulate myocardial tissue growth in a heart after myocardial infarction (MI). The system includes an agent delivery device to release one or more agents to an MI region to modulate myocardial tissue growth in that region, and a cardiac rhythm management (CRM) device to deliver pacing pulses to enhance the effects of the one or more agents by altering myocardial wall stress and cardiac workload. In one embodiment, the system is an implantable system including an implantable agent delivery device and an implantable CRM device.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS20070016031A1Easy diagnosisLimited successBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationVentricular filling
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Prevention of myocardial infarction induced ventricular expansion and remodeling
InactiveUS7988727B2Limited elongationReduce the abnormal geometry and wall stressSuture equipmentsPowder deliveryCardiac muscleTherapeutic treatment
A method for direct therapeutic treatment of myocardial tissue in a localized region of a heart having a pathological condition. The method includes identifying a target region of the myocardium and applying material directly and substantially only to at least a portion of the myocardial tissue of the target region. The material applied results in a physically modification the mechanical properties, including stiffness, of said tissue. Various devices and modes of practicing the method are disclosed for stiffening, restraining and constraining myocardial tissue for the treatment of conditions including myocardial infarction or mitral valve regurgitation.
Owner:MYOMEND
Method and apparatus for modulating cellular growth and regeneration using ventricular assist device
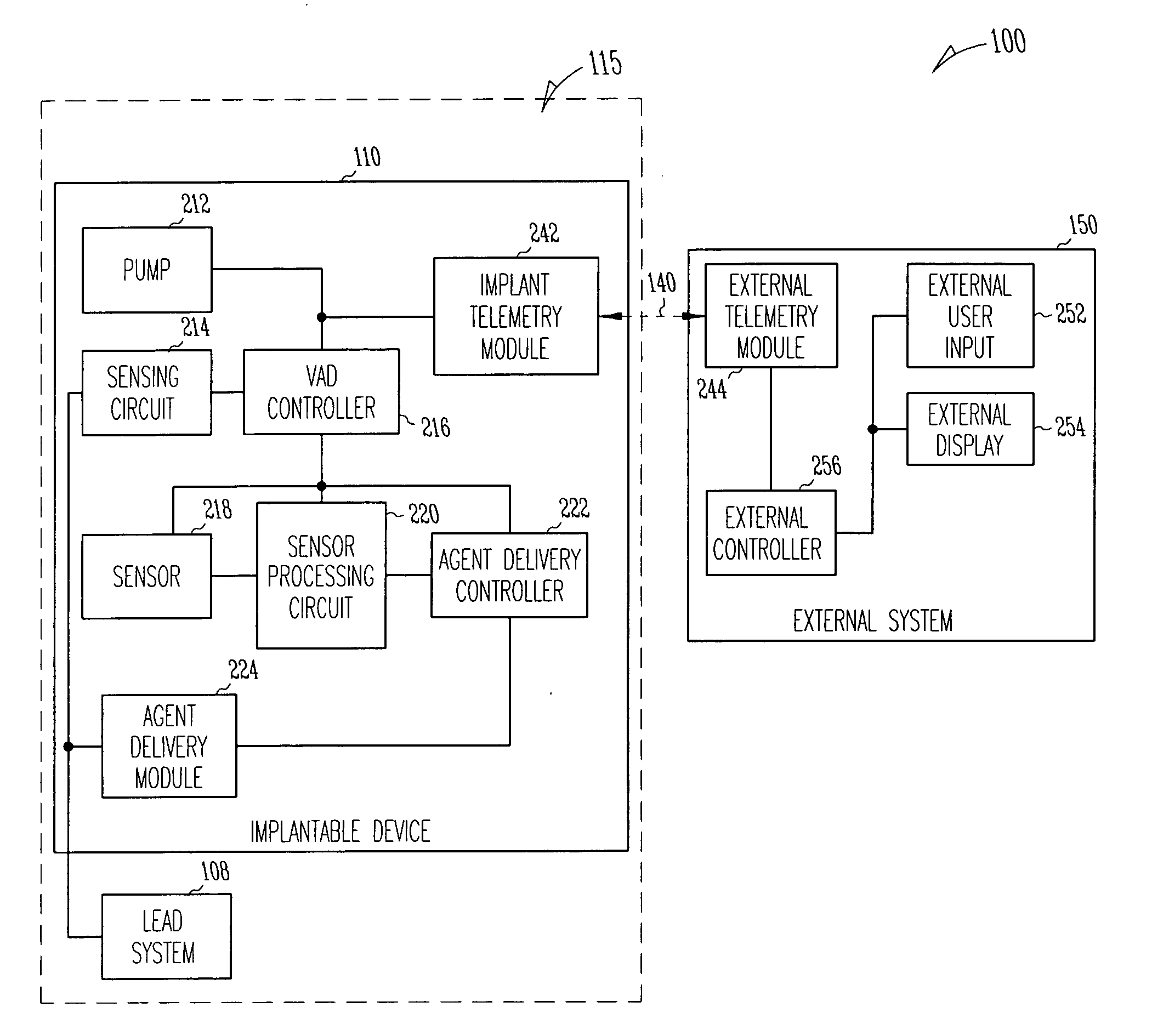
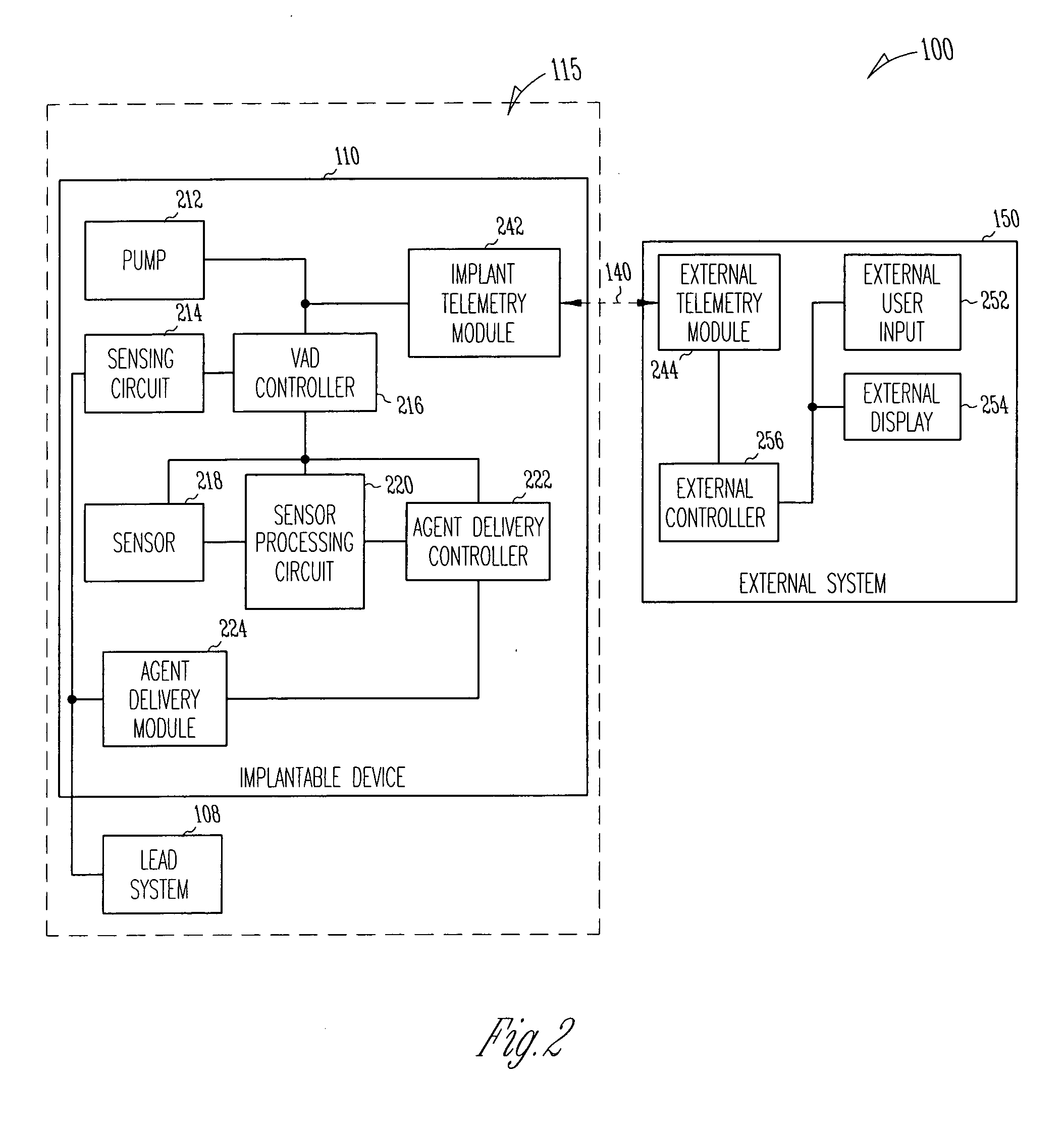
InactiveUS20060036126A1Good effectPromote tissue growthControl devicesBlood pumpsCardiac muscleVentricular assistance
A system delivers combined ventricular assist device (VAD) therapy and chemical and / or biological therapy to modulate myocardial tissue growth in a heart after myocardial infarction (MI). The system includes an agent delivery device to release one or more agents to an MI region to modulate myocardial tissue growth in that region, and a VAD to enhance the effects of the one or more agents by reducing myocardial wall stress and the overall cardiac workload. In one embodiment, the system is an implantable system including an implantable agent delivery device and an implantable VAD for long-term use in a patient.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
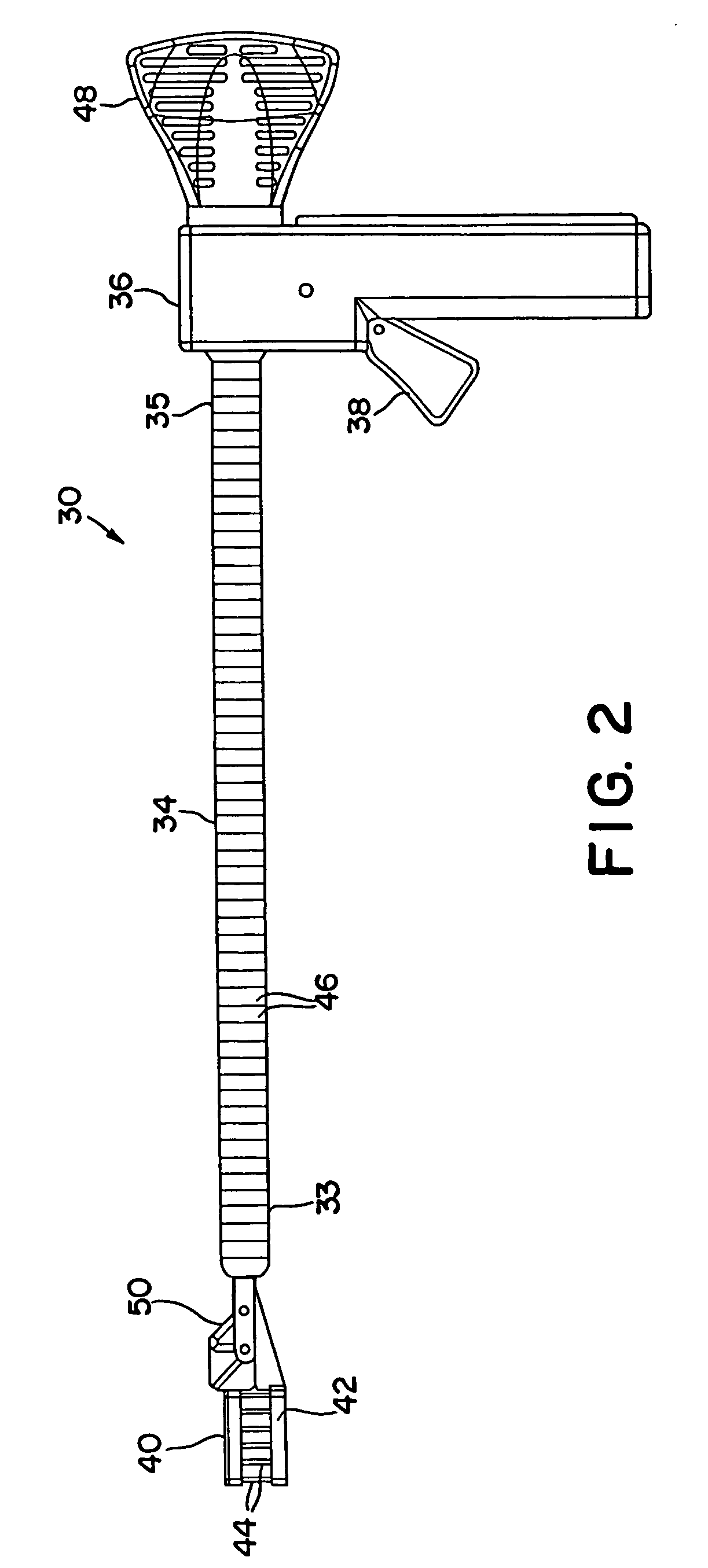
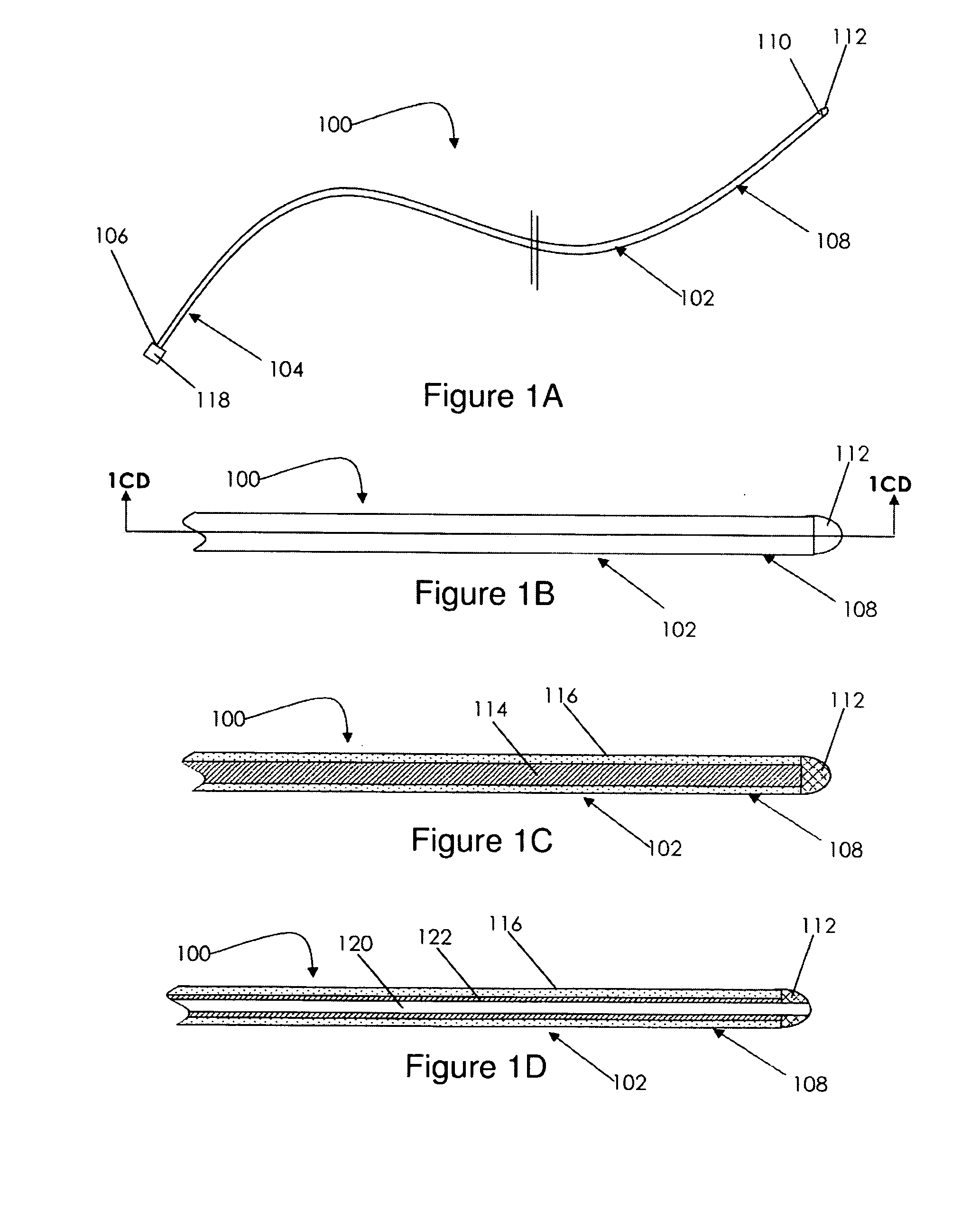
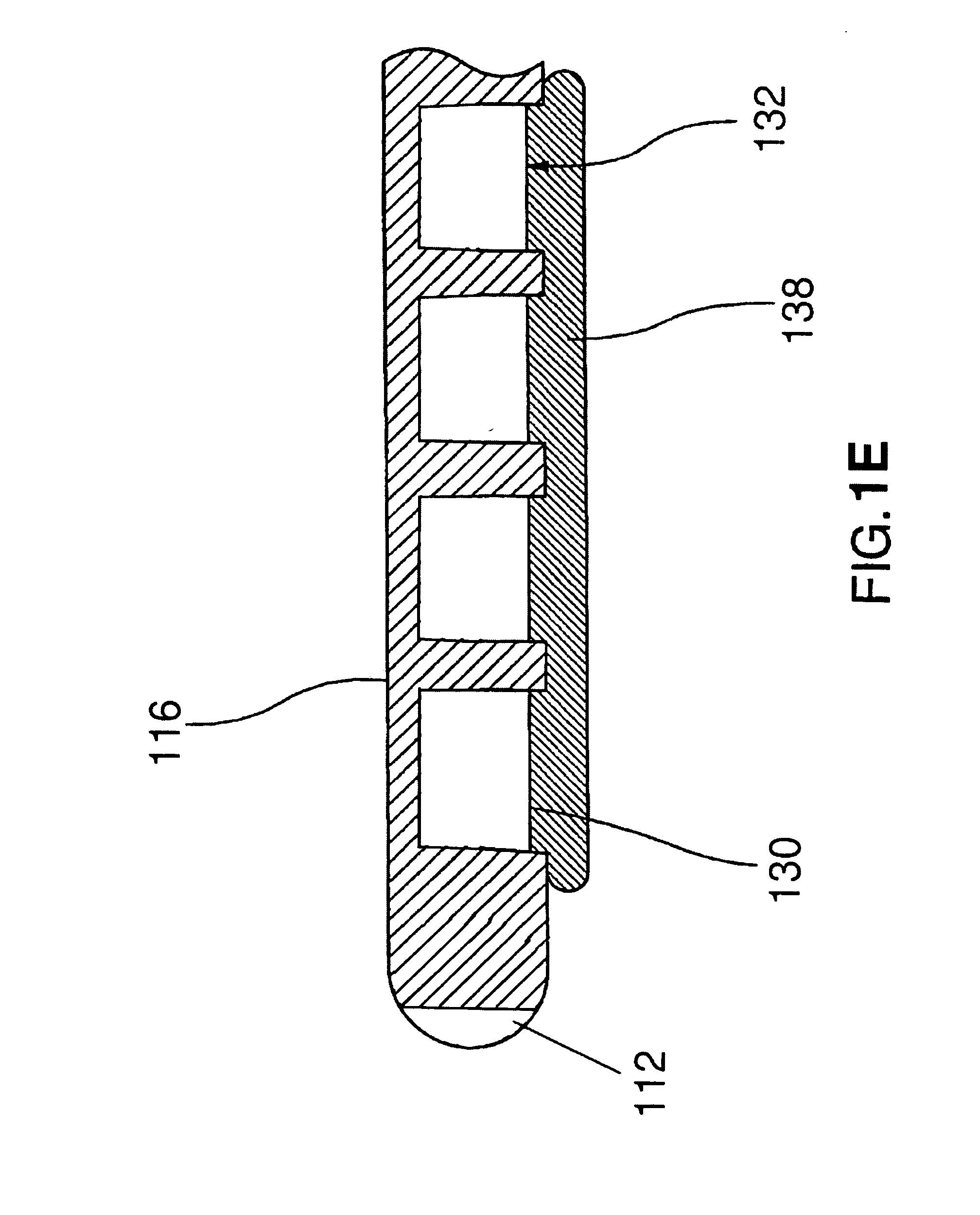
Myocardial injector
ActiveUS7803136B2Preventing unwanted advancementWithout risk of damageGuide needlesInfusion syringesCardiac muscleAbutment
Owner:SCHATZ RICHARD A
Myocardial ablation by irreversible electroporation
InactiveUS20160113709A1Lower the volumeSurgical instruments for heatingEccentric hypertrophyCardiac muscle
Selective cellular ablation by electroporation, applicable, for example, to bulk tissue in the beating heart. Protocol parameters potentially induce tissue loss without thermal damage. Device and method are potentially applicable for myocardial tissue ablation to treat arrhythmias, obstructive hypertrophy, and / or to generate natural scaffolds for myocardial tissue engineering.
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES
Heart wall ablation/mapping catheter and method
InactiveUS20050273006A1Wide angleSmall knuckle curveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyCardiac wallAngular orientation
Steerable electrophysiology catheters for use in mapping and / or ablation of accessory pathways in myocardial tissue of the heart wall and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The catheter comprises a catheter body and handle, the catheter body having a proximal section and a distal section and manipulators that enable the deflection of a distal segment of the distal tip section with respect to the independently formed curvature of a proximal segment of the distal tip section through a bending or knuckle motion of an intermediate segment between the proximal and distal segments. A wide angular range of deflection within a very small curve or bend radius in the intermediate segment is obtained. At least one distal tip electrode is preferably confined to the distal segment which can have a straight axis extending distally from the intermediate segment. The curvature of the proximal segment and the bending angle of the intermediate segment are independently selectable. The axial alignment of the distal segment with respect to the nominal axis of the proximal shaft section of the catheter body can be varied between substantially axially aligned (0° curvature) in an abrupt knuckle bend through a range of about −90° to about +180° within a bending radius of between about 2.0 mm and 7.0 mm and preferably less than 5.0 mm. The proximal segment curve can be independently formed in a range of about −180° through about +270° with respect to the axis of the proximal shaft section to provide an optimum angular orientation of the distal electrode(s). The distal segment can comprise a highly flexible elongated distal segment body and electrode(s) that conform with the shape and curvature of the heart wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
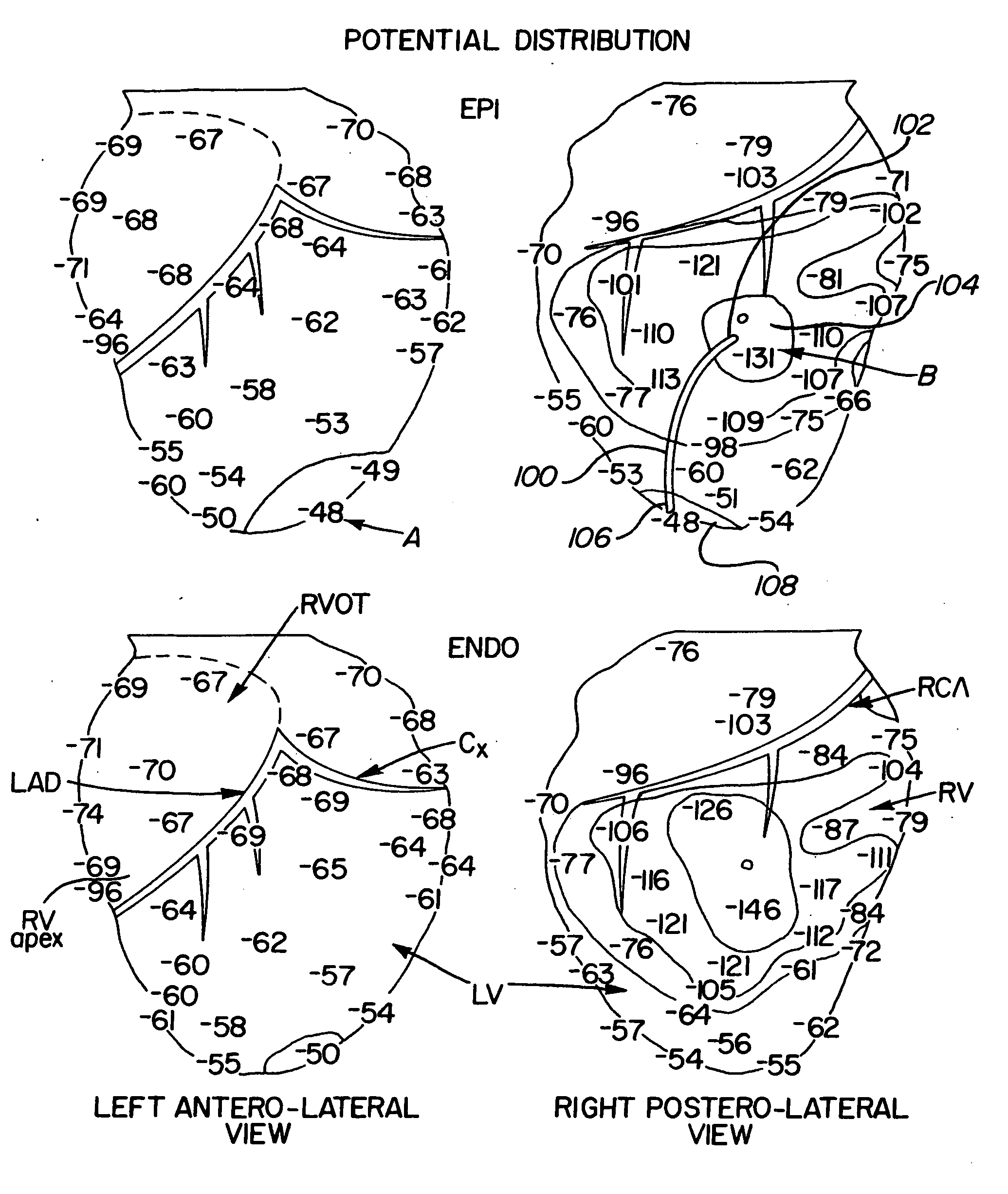
Method and apparatus for representing myocardial tissues in different states of damage
InactiveUS20080038197A1Easy to detectImprove representationDiagnostic recording/measuringTomographyLate phaseComputed tomography
The invention relates to a method for differentially representing myocardial tissue in different states of damage, comprising the following steps: administering a myocardium-suitable contrast agent to a patient under examination; entering at least one patient-specific parameter affecting the speed of uptake by and elimination from the myocardium of said contrast agent; calculating a point in time after administration of the contrast agent at which a difference between a contrast agent content in necrotic myocardial tissue and a contrast agent content in non-necrotic myocardial tissue attains a maximum value, on the basis of the at least one patient-specific parameter, and carrying out, at the point in time calculated, a late-phase CT scan for accentuation of necrotic myocardial tissue compared to non-necrotic myocardial tissue. The invention likewise relates to apparatus, in particular for carrying out the method. A clean copy of the abstract that incorporates the above amendments is provided herewith on a separate page.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Pericardium reinforcing devices and methods of using them
InactiveUS7060023B2Promote endothelializationHeart valvesTubular organ implantsPericardial spaceCardiac muscle
This is a surgical device and a method of using it. In particular, the device is one for reinforcing the pericardial sac surrounding the heart to assist in the treatment of congestive heart failure. The device, generically, is an enclosure having an interior and an exterior. The interior surface is made in such a way that it tends not to or does not form adhesions with or accept ingrowth with the myocardial tissue of the epicardium. The exterior surface of the device, in contrast, is adapted to adhere to or to ingrow with or otherwise attach sufficiently to the pericardium so that it reinforces that membrane or structure. The nature of the device is that it tends not to allow the pericardium to expand further with time. The device, after complete deployment, should envelope some measure of pericardial fluid in its interior separating it from the epicardial surface. This device helps to prevent further declination of the heart during congestive heart failure. The device is preferably introduced into the pericardial space and into the inner surface of the pericardium using transcutaneous or minimally invasive techniques.
Owner:THE FOUNDY LLC
Wide area ablation of myocardial tissue
ActiveUS20060247611A1Modifies its propertyCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingWide areaCardiac muscle
The present invention advantageously provides a method and system for cryogenically ablating large areas of tissue within the left atrium. In an exemplary embodiment a cryotherapy device includes a catheter body having a substantially fixed diameter, a proximal end and a distal end; a first lumen for permitting passage of a cooling fluid from the proximal end to the distal end; a second lumen permitting return of the cooling fluid from the distal end to the proximal end; and an ablation element expandable from a first diameter that is substantially the same as the diameter of the catheter body to a second diameter that is at least twice the diameter of the catheter body, the ablation element having a surface portion that conforms to the uneven surface topography of the cardiac tissue. The ablation element can include one or more balloon and / or a flexible element that is deformed by moving the distal end of the catheter toward the proximal end of the catheter. The surface of the balloon can further be shaped by regulation of pressure within the one or more balloons. In an exemplary method a tissue ablation device is provided and tissue in the antrum of the left atrium is ablated with the device. In an exemplary method, only tissue in the antrum is ablated, and the ablation is created by freezing tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
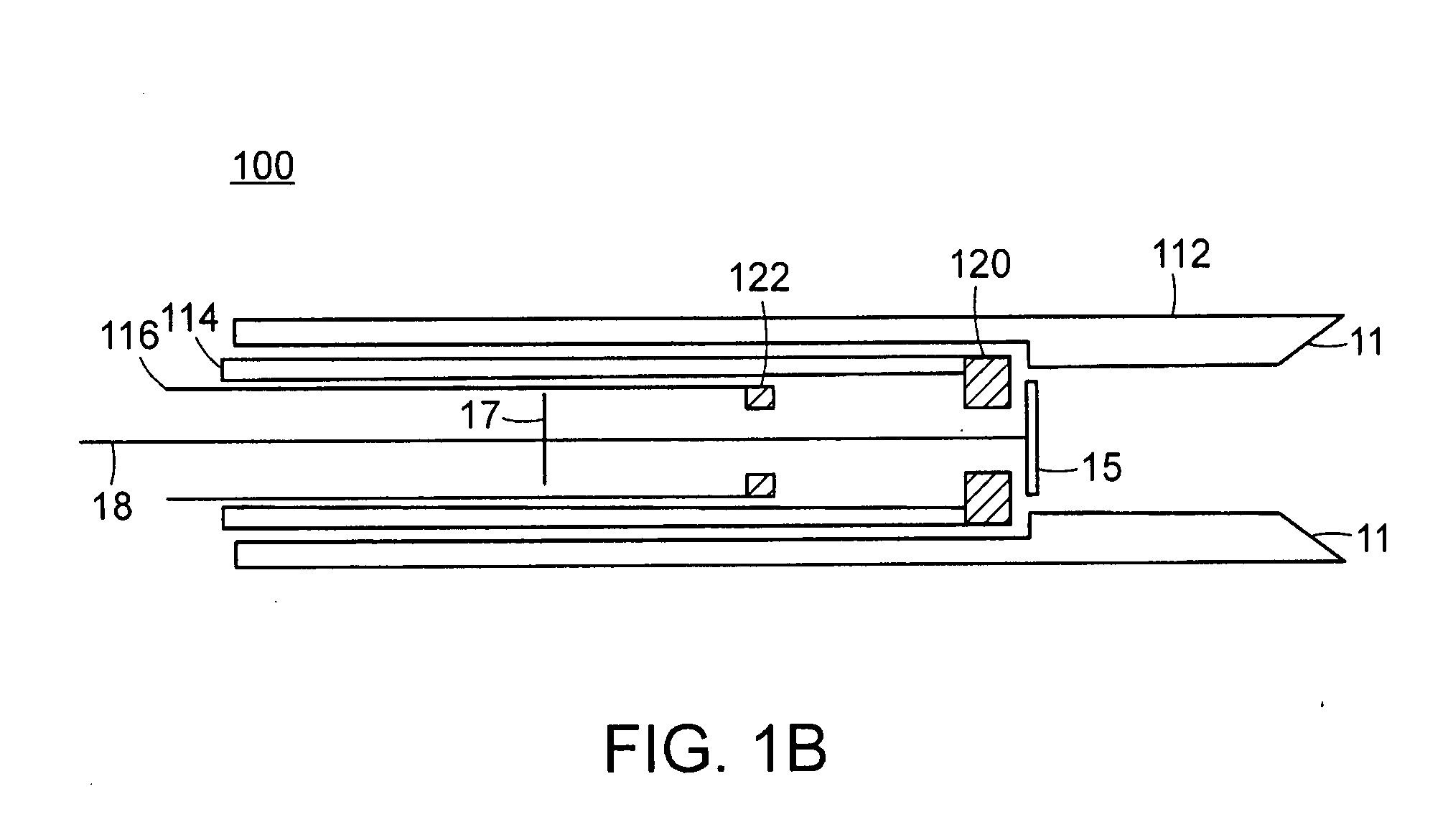
Intramyocardial lead implantation system and method
InactiveUS20050080470A1Facilitates slideable advancementEasy to implantEpicardial electrodesExternal electrodesHelical coilCardiac monitoring
A system and method for placement of cardiac monitoring and stimulation leads. A lead is advanced into a myocardium of the patient's heart through a lead introducing system, and an electrode is implanted within the myocardium. The method may include gaining access with a cannula from an outer chest wall to the myocardium. Space is created in the myocardium using the lead introduction system. Aspects include eluting a steroid from the lead and into the myocardium, affixing the lead into myocardial tissue using an active fixation mechanism, such as a helical coil, and stabilizing the lead by suturing, clipping, stapling, or other method. A dilating sheath may be used to create a space within the myocardium sufficient in size to accommodate an implantable myocardial electrode. The system may include an implantation depth indicator such as a shoulder, a cuff, or a skirt on the lead.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
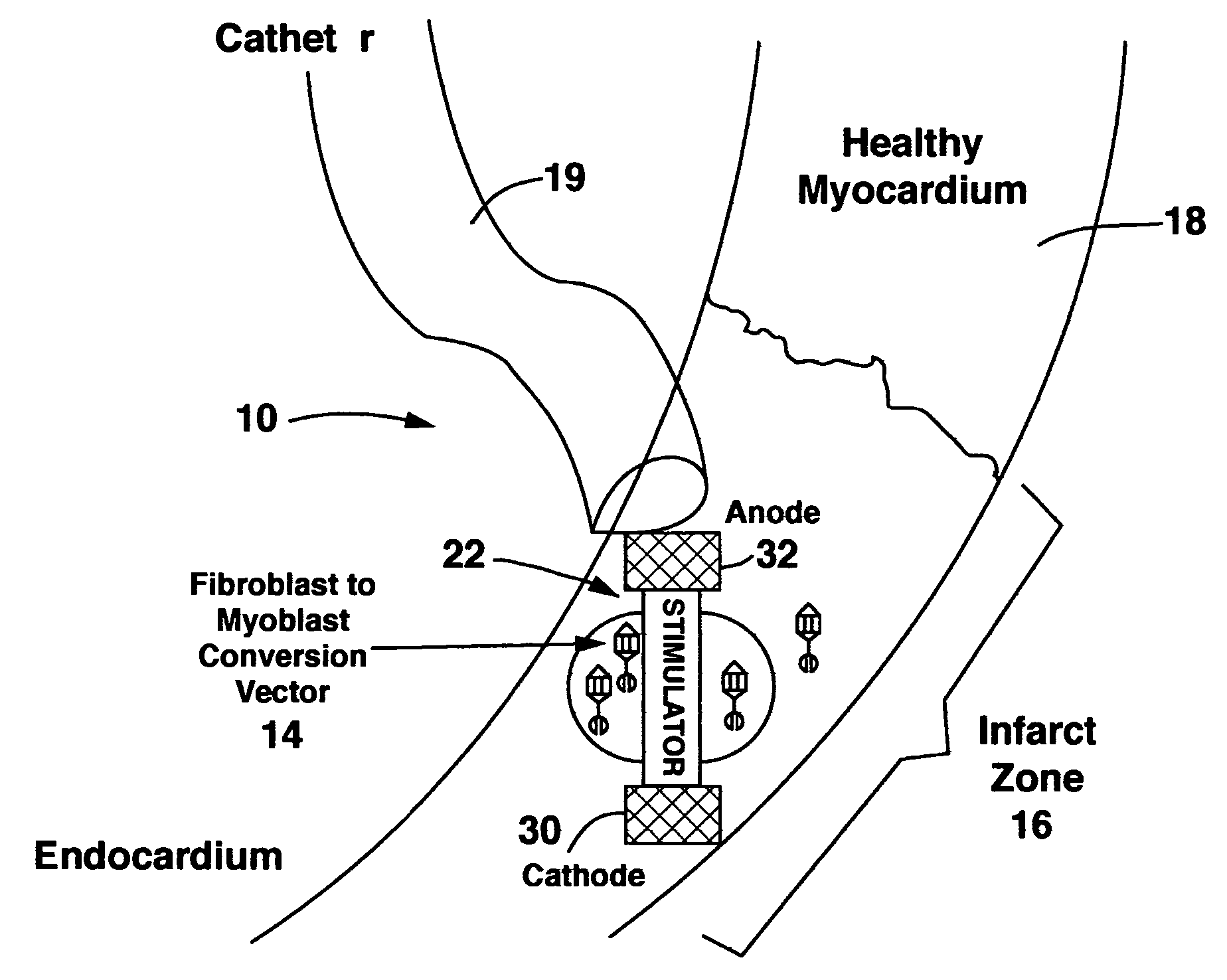
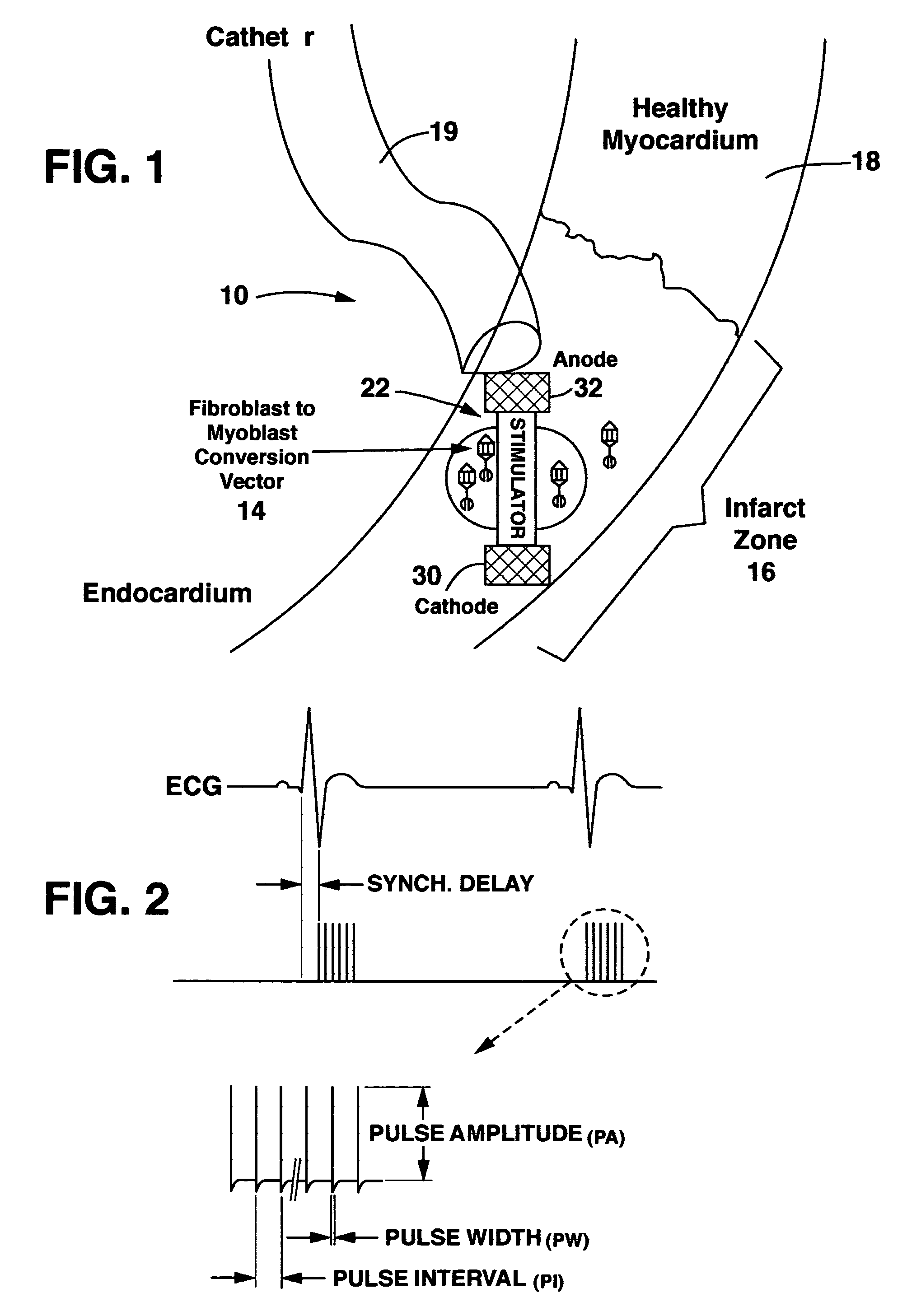
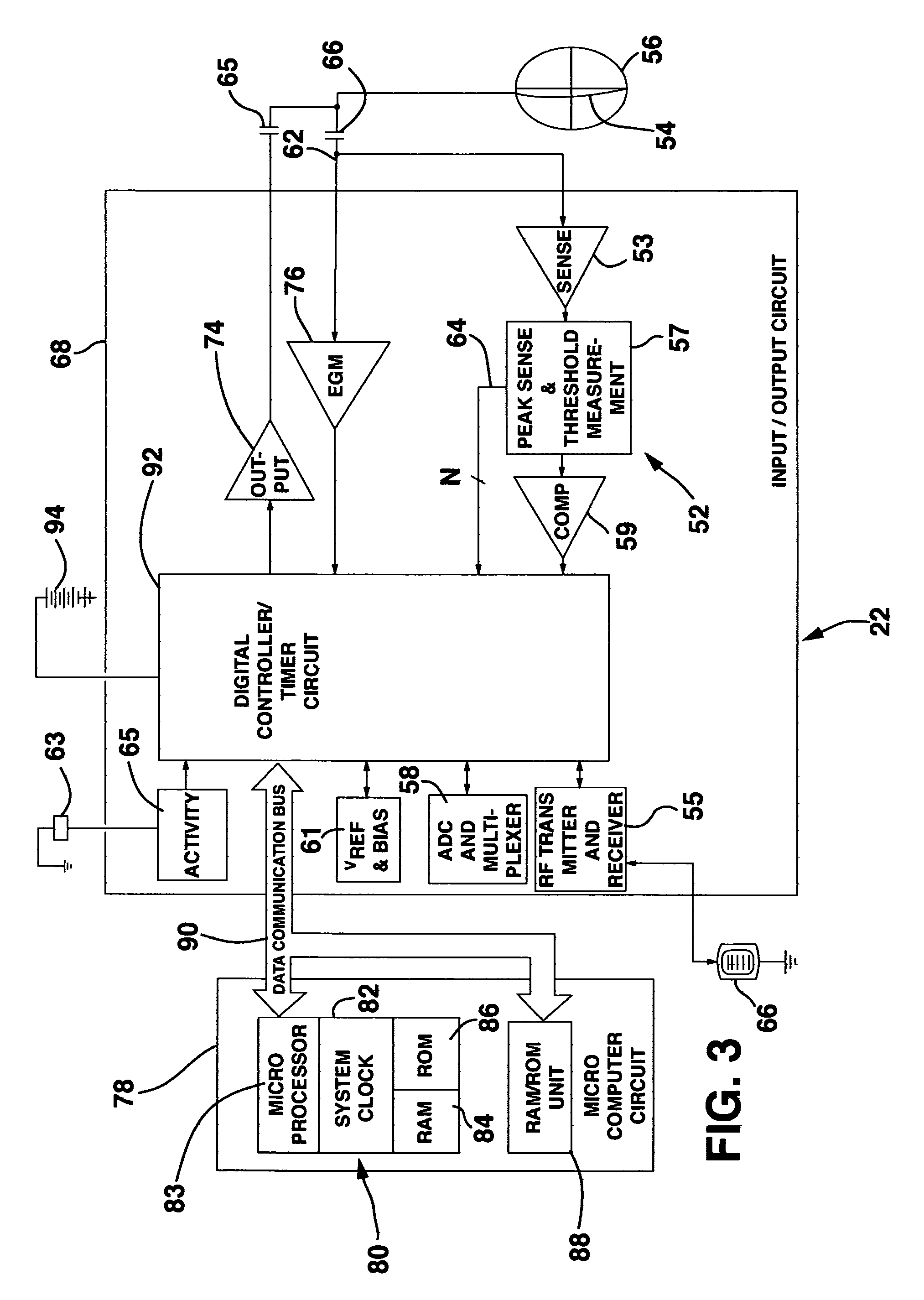
Method and system for myocardial infarction repair
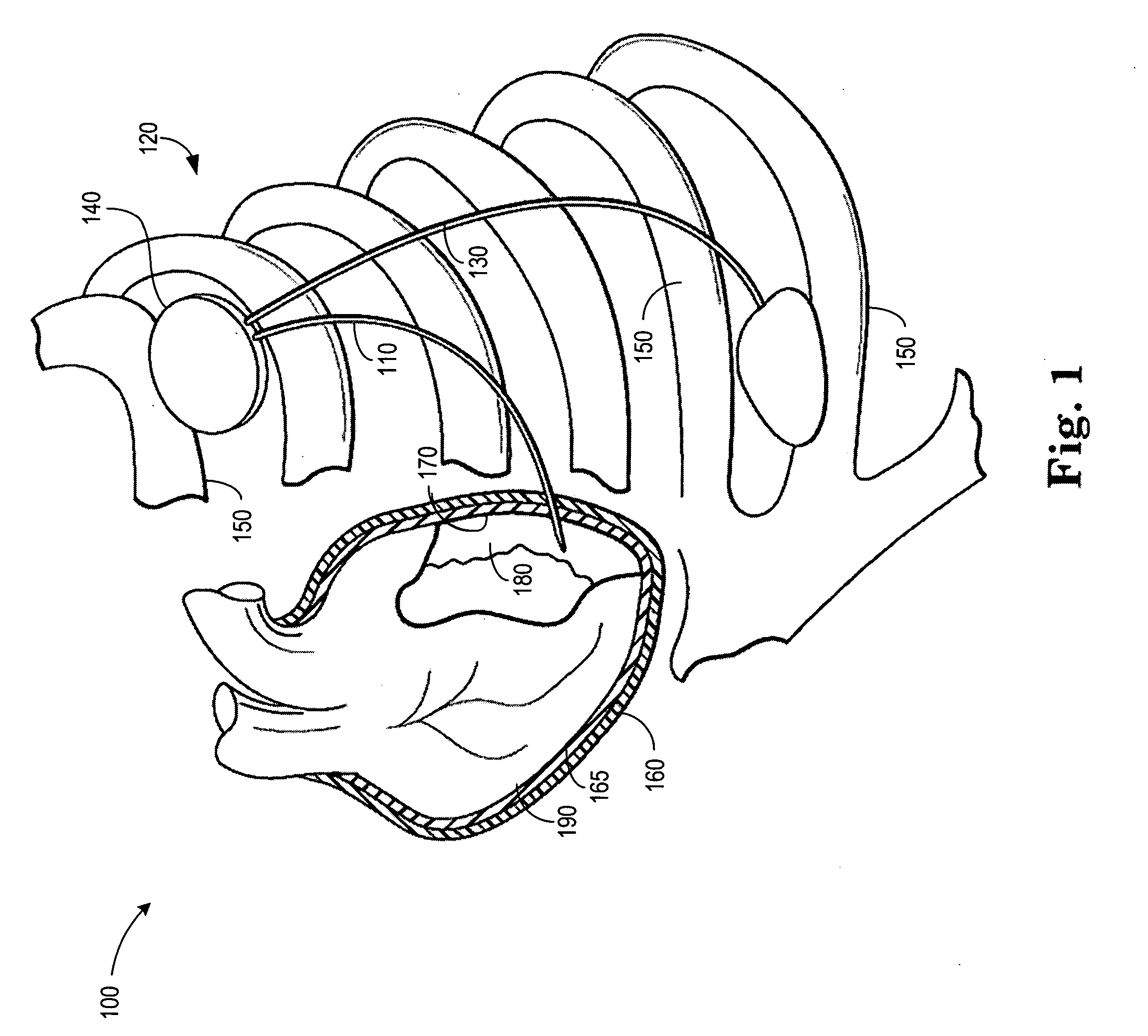
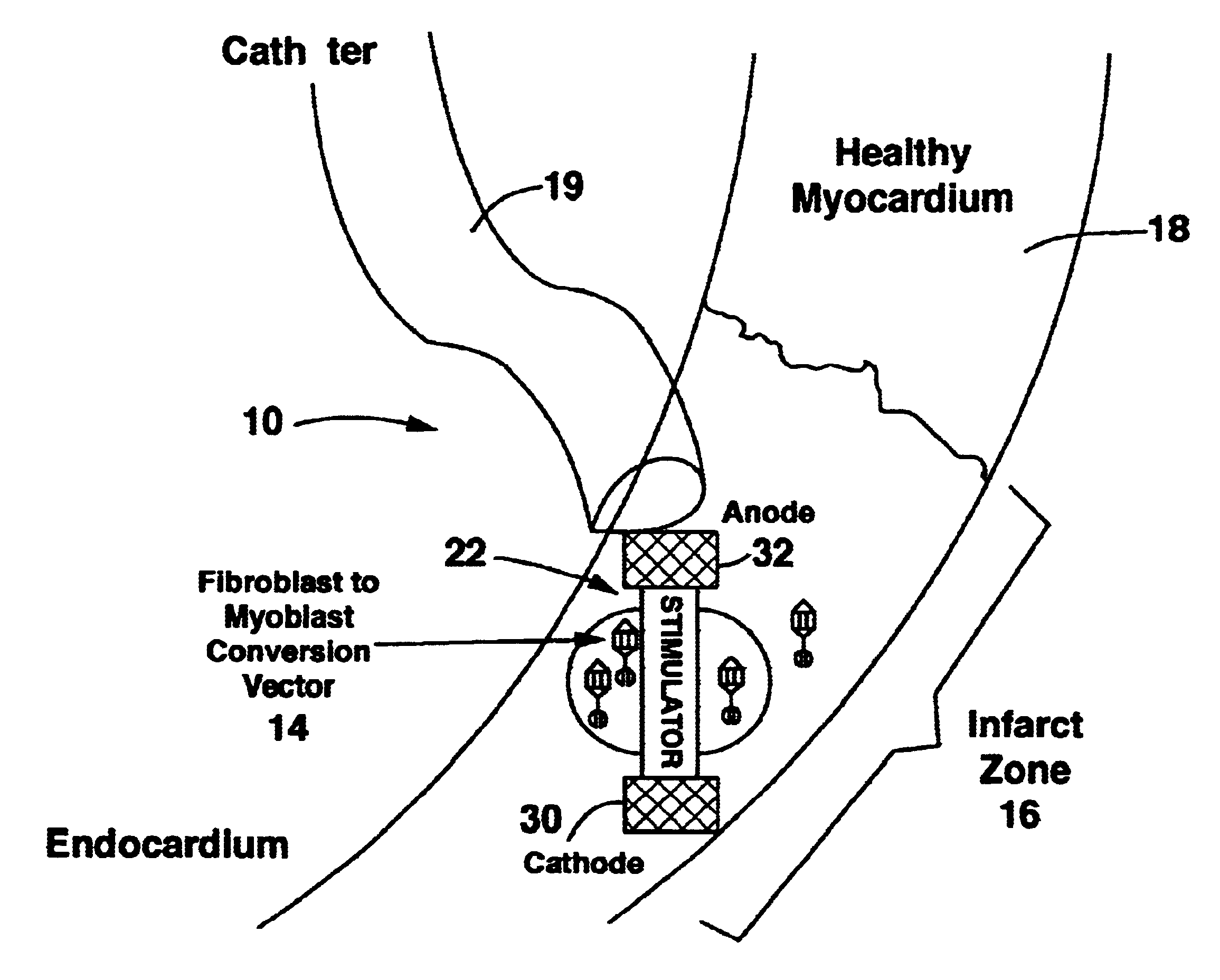
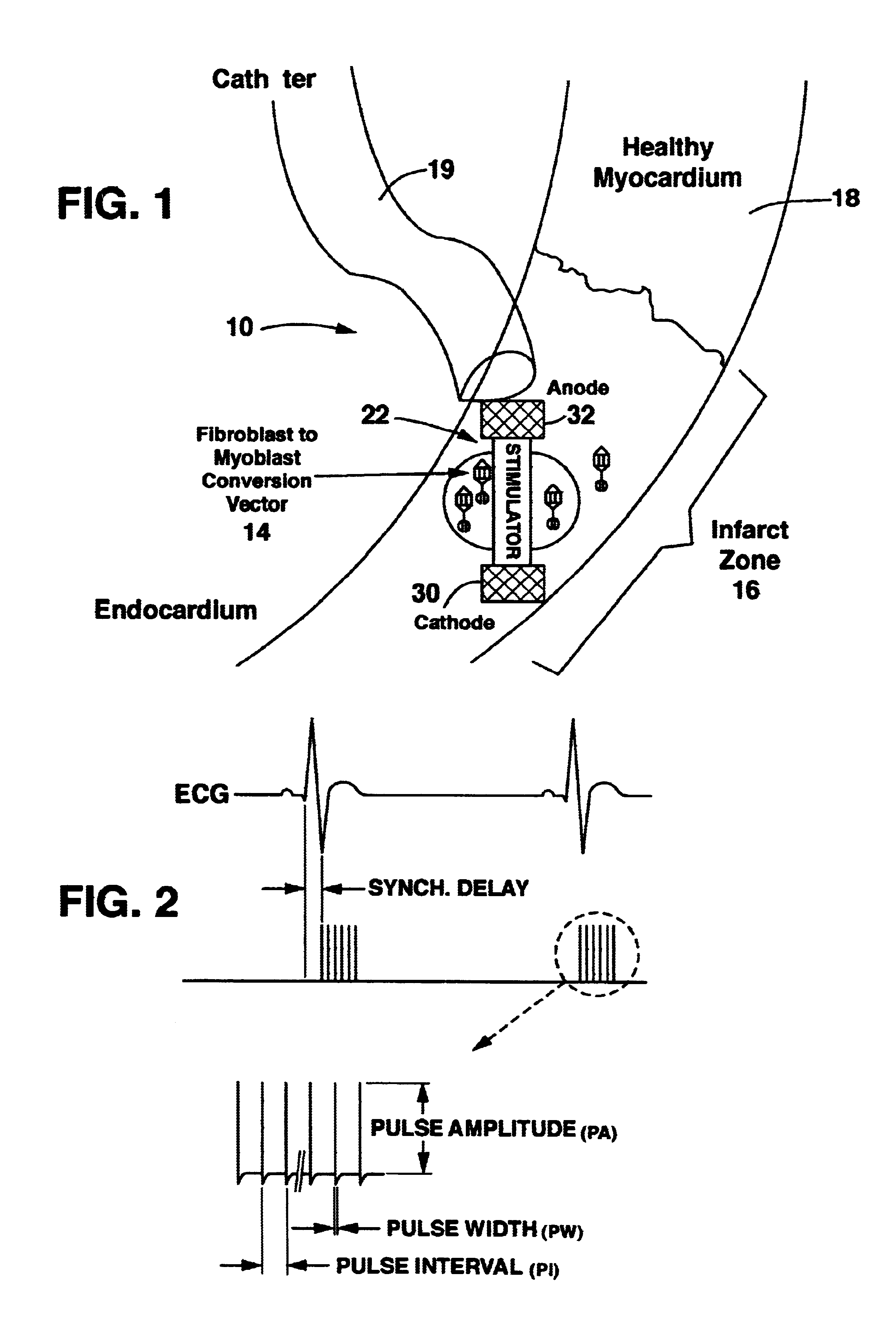
InactiveUS6671558B1Restore elasticityRestoration of contractilityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationGenetic MaterialsCardiac muscle
An implantable system is provided that includes: a cell repopulation source comprising genetic material, undifferentiated and / or differentiated contractile cells, or a combination thereof capable of forming new contractile tissue in and / or near an infarct zone of a patient's myocardium; and an electrical stimulation device for electrically stimulating the new contractile tissue in and / or near the infarct zone of the patient's myocardium or otherwise damaged or diseased myocardial tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and apparatus for treating anaphylaxis using electrical modulation
ActiveUS7711430B2Improve heart functionIncrease pressureSpinal electrodesBronchial tubeCardiac muscle
Owner:ELECTROCORE
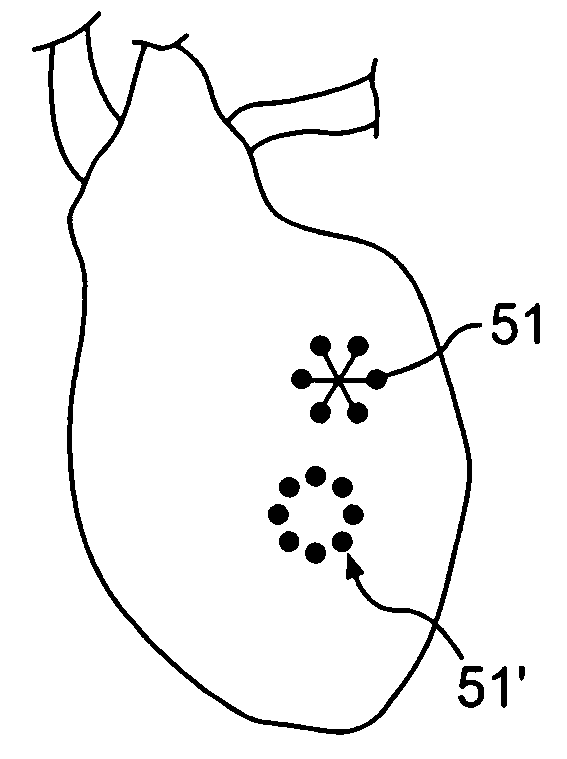
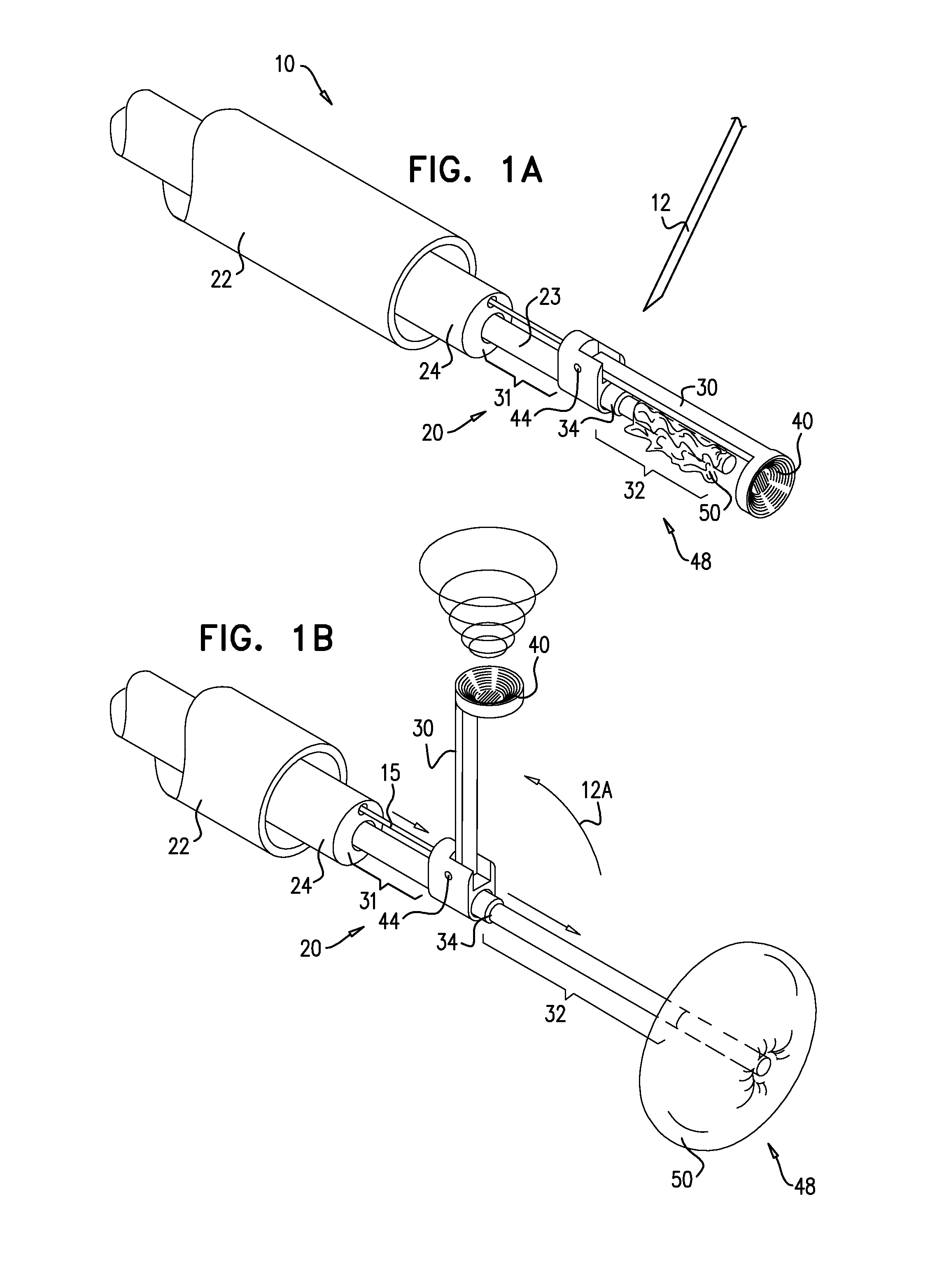
Apparatus and method for controlled depth of injection into myocardial tissue
An injector apparatus and associated methods for safely and repeatedly delivering an injectate at a predefined depth into the myocardium of the heart may be catheter-based or implemented in a handheld unit for use in open chest procedures. The injector includes a body, a stabilizer secured to a distal end of the body for stabilizing the distal end of the body relative to the myocardium, and a needle that may be controllably advanced from the distal end of the body into the myocardium. The stabilizer employs any suitable technique for stabilizing the distal end of the catheter body relative to the myocardium while the heart is beating. An enlarged region disposed along the needle functions as a stop to prevent the needle from being advanced into the myocardium beyond a desired penetration depth. To make an injection, the physician brings the distal end of the body in proximity to the endocardium or the epicardium using any suitable technique, actuates the stabilizer to stabilize the distal end relative to the myocardium; and advances the needle into the myocardium. Advancement of the needle into the myocardium is impeded by the enlarged region, thereby placing the needle tip at the desired penetration depth and avoiding puncturing of the heart. The injection is then made, and the needle and catheter are removed.
Owner:HENRY FORD HEALTH SYST
Prevention of myocardial infarction induced ventricular expansion and remodeling
InactiveUS7311731B2Prevent further deteriorationInhibit swellingSuture equipmentsPowder deliveryTherapeutic TechniqueMedicine
A method for direct therapeutic treatment of myocardial tissue in a localized region of a heart having a pathological condition. The method includes identifying a target region of the myocardium and applying material directly and substantially only to at least a portion of the myocardial tissue of the target region through transseptal delivery. The material applied results in a physically modification the mechanical properties, including stiffness, of said tissue. Various devices and modes of practicing the method are disclosed for stiffening, restraining and constraining myocardial tissue for the treatment of conditions including myocardial infarction or mitral valve regurgitation. The novel treatment may be combined with prior art diagnostic and therapeutic techniques employing transseptal delivery methods.
Owner:MYOMEND
Devices and methods for tissue transplant and regeneration
InactiveUS20070239066A1Promote cell growthIncrease the number ofSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsIntact tissueMedicine
Devices and methods for transplanting tissue for the purpose of regeneration, for treating a patient having injured myocardial tissue, and / or for improving cardiac function through cell regrowth. More specifically, the devices and methods obviate the need for cellular alteration. The devices comprise a hollow tube with a sharp distal end, a stylet that is disposed and movable within the hollow tube, and a stopping device that constrains movement of the stylet. The methods comprise removing intact tissue from a first region of a mammalian organ and implanting the tissue in a second region of the same organ.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Cardiac electrosurgery
A method of accessing a pericardial cavity of a heart is disclosed, comprising delivering electrical energy to a pericardium in a manner which creates a channel substantially through a parietal pericardium and does not substantially affect myocardial tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Reflectance-facilitated ultrasound treatment
ActiveUS20110282249A1Facilitate ablationPromote rapid formationUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesSonificationHeart chamber
Apparatus is provided that includes an ultrasound ablation system, which includes a reflection-facilitation element, configured to be placed at an extramyocardial site of a subject, and to provide an extramyocardial reflective region. The system further includes an ultrasound tool, which comprises at least one ultrasound transducer configured to be positioned within a heart chamber of the subject, and to ablate myocardial tissue by applying ultrasound energy to the myocardial tissue such that at least a portion of the transmitted energy is reflected by the reflective region onto the myocardial tissue. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:RAINBOW MEDICAL LTD
Methods and Devices for Reducing Tissue Damage After Ischemic Injury
InactiveUS20090010987A1Improve efficiencyReduce ischemia-induced tissue damageStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsReperfusion injuryIschemic injury
Methods and devices are provided for the local delivery of anti-ischemic agents which reduce myocardial tissue damage due to ischemia or reperfusion, in combination with compounds that sensitize the response of the tissue to the anti-ischemic agent. The therapeutic agents are delivered to the myocardial tissue over an administration period sufficient to achieve reduction in ischemic or reperfusion injury of the tissue.
Owner:INNOVATIONAL HLDG LLC
Method and system for myocardial infarction repair
InactiveUS7031775B2Improve heart functionRestoration of elasticity and contractilityBiocideSkeletal/connective tissue cellsGenetic MaterialsInfarct zone
An implantable system is provided that includes: a cell repopulation source comprising genetic material, undifferentiated and / or differentiated contractile cells, or a combination thereof capable of forming new contractile tissue in and / or near an infarct zone of a patient's myocardium; and an electrical stimulation device for electrically stimulating the new contractile tissue in and / or near the infarct zone of the patient's myocardium or otherwise damaged or diseased myocardial tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
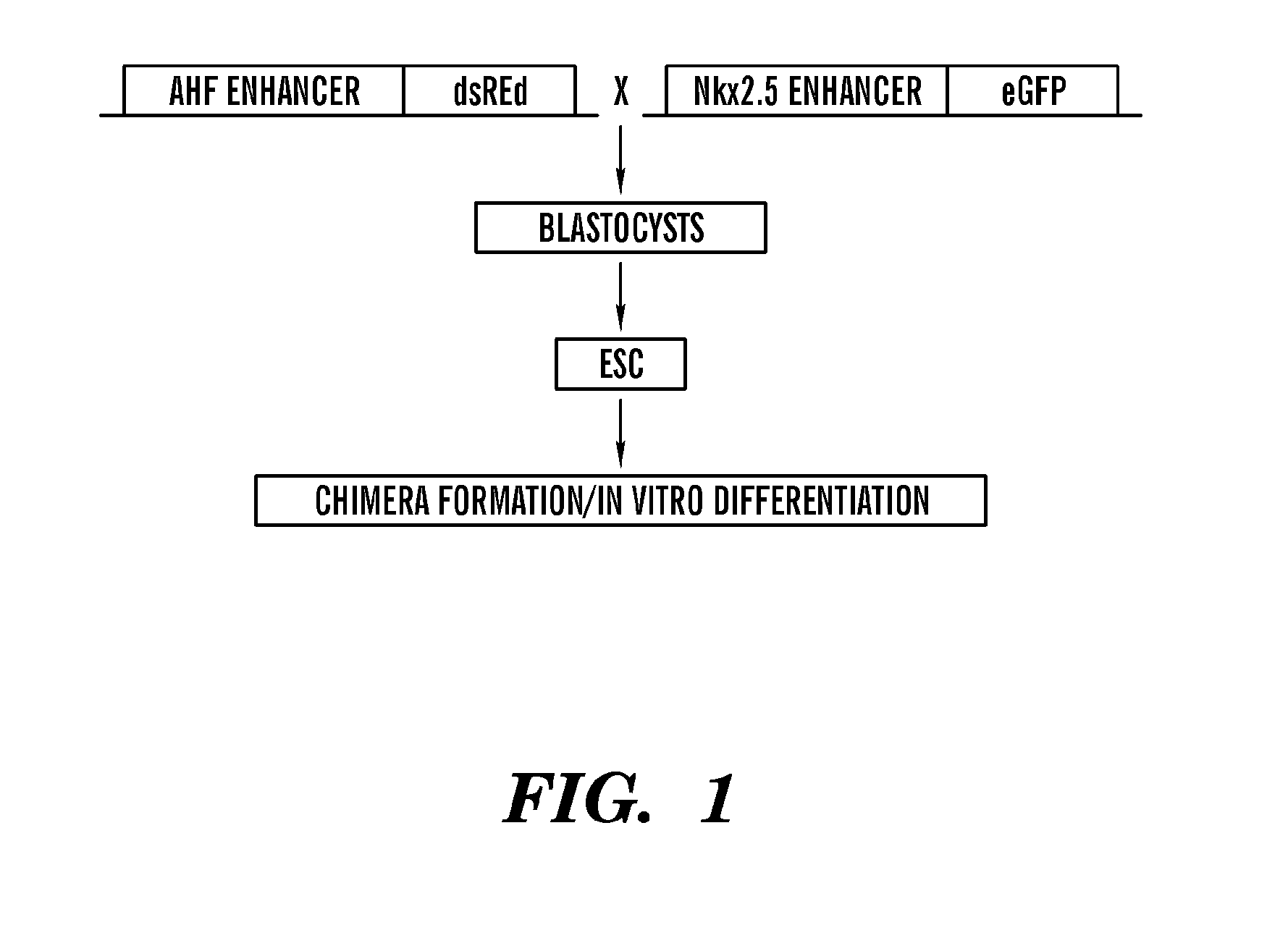
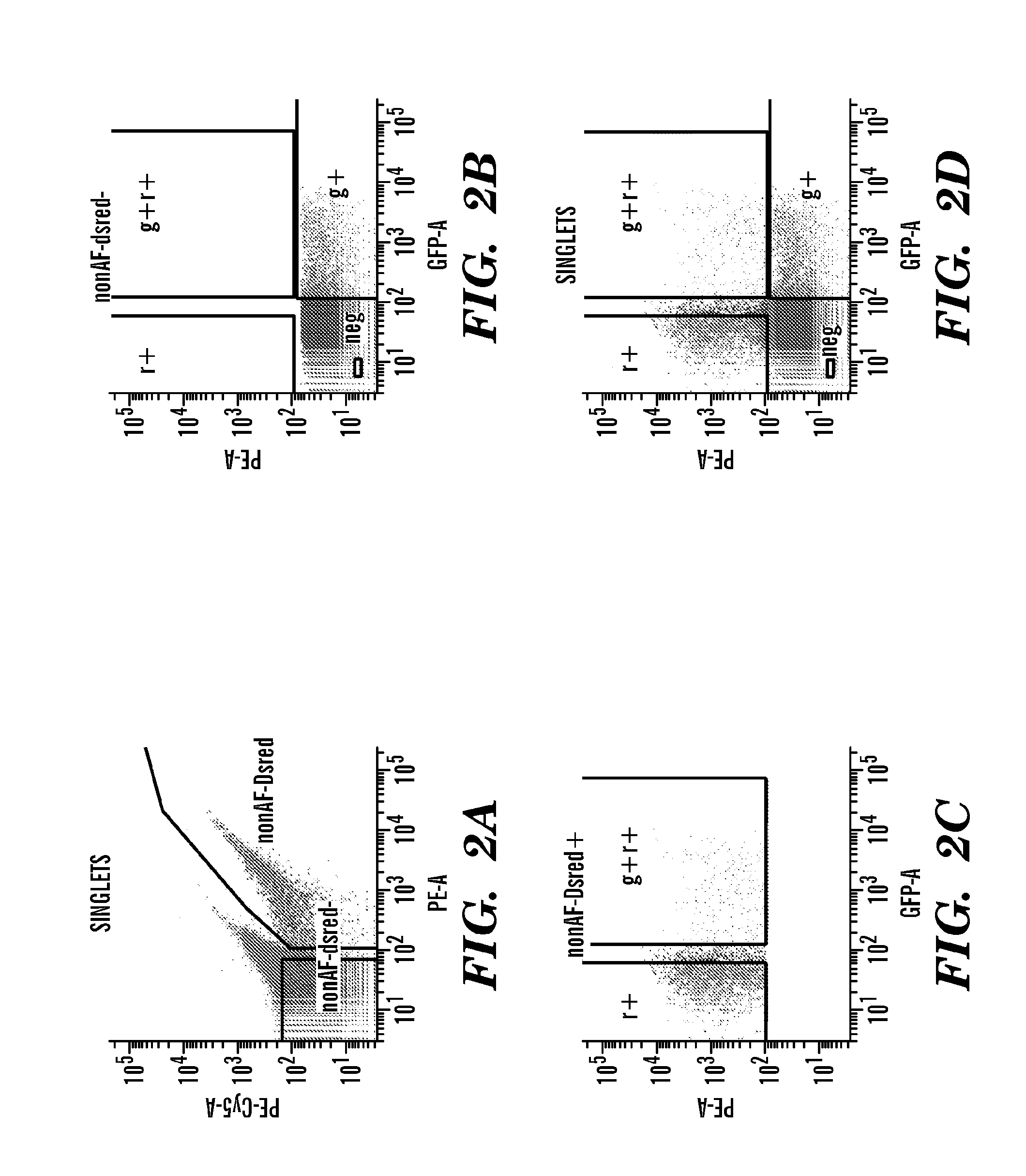
Tissue engineered myocardium and methods of production and uses thereof
The present invention generally relates to a population of committed ventricular progenitor (CVP) cells and their use to generate a tissue engineered myocardium, in particular two dimensional tissue engineered myocardium which is comparable to functional ventricular heart muscle. One embodiment of present invention provides a composition and methods for the production of a tissue engineered myocardium which has functional properties of cardiac muscle, such as contractibility (e.g. contraction force) and numerous properties of mature fully functional ventricular heart muscle tissue. In particular, in one embodiment, a composition comprising the tissue engineered myocardium comprises committed ventricular progenitor (CVP) cells seeded on a free-standing biopolymer structure to form functional ventricular myocardium tissue.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Cell Sheet Containing Mesenchymal Stem Cells
ActiveUS20090053277A1Induce cardiac muscleInduce neovascularizationBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsVascular endotheliumThree vessels
Mesenchymal stem cells are pluripotent cells capable of differentiating into myocardial and vascular endothelial cells. The present invention demonstrates that the mesenchymal stem cell sheet have therapeutic potential for a severely damaged heart due to its pluripotency and in situ self-renewal capability. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue were cultured to prepare a mesenchymal stem cell sheet. Four weeks after induction of myocardial infarction in rats, the mesenchymal stem cell sheet was transplanted to the heart. The mesenchymal stem cell sheet were readily engrafted to the surface of the scarred myocardium, grew gradually in situ, and formed a thick layer (approximately 600 μm) in 4 weeks. The grown transplanted mesenchymal tissue contained newly formed blood vessels, myocardial cells, and undifferentiated mesenchymal cells. The engrafted mesenchymal stem cells inhibited thinning of the myocardial wall in the scar area, and improved cardiac function and survival rate in rats with myocardial infarcts. Thus, mesenchymal stem cell sheet transplantation may represent a novel therapeutic approach for myocardial tissue regeneration.
Owner:H&L MEDICAL CORP
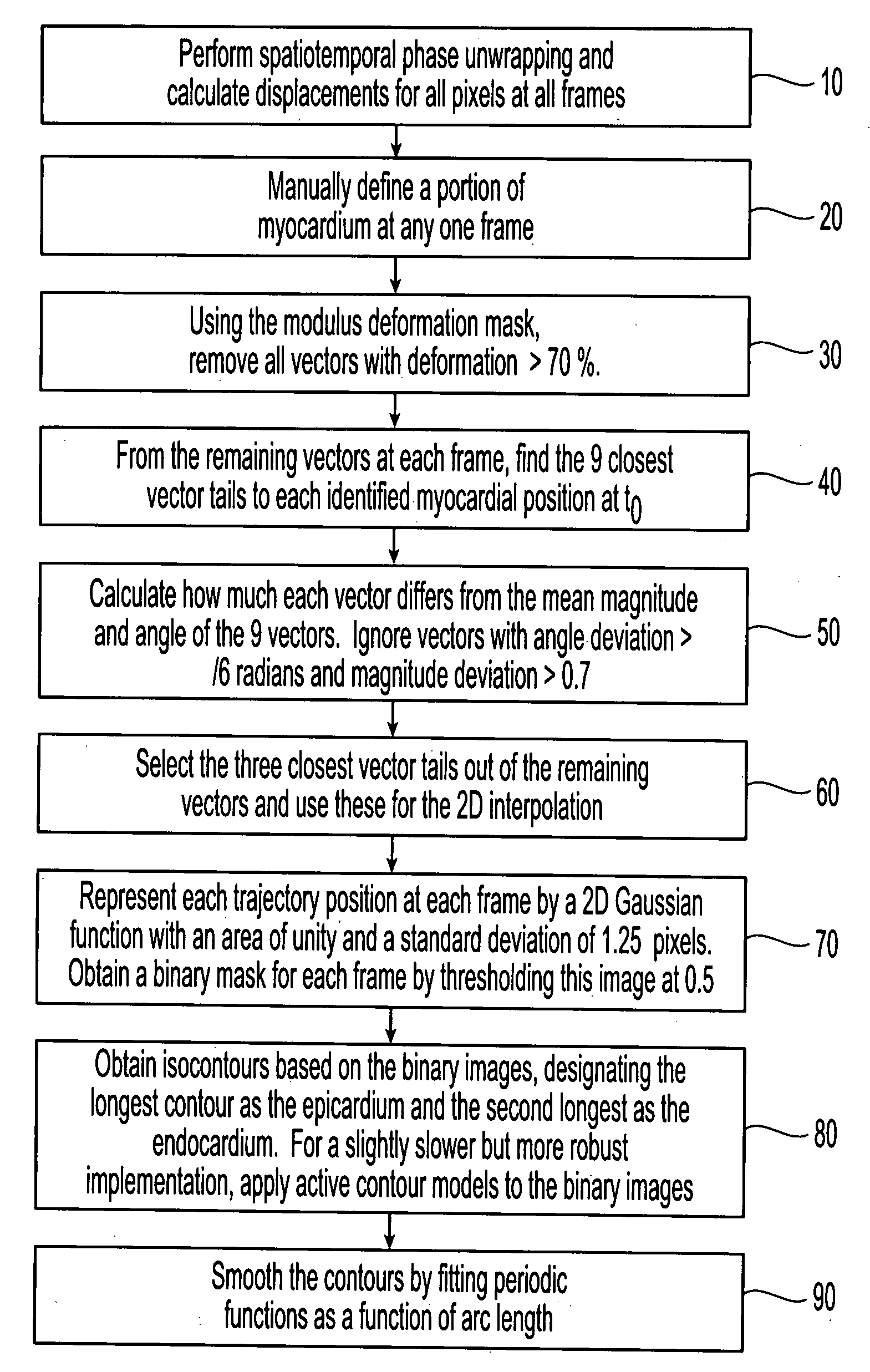
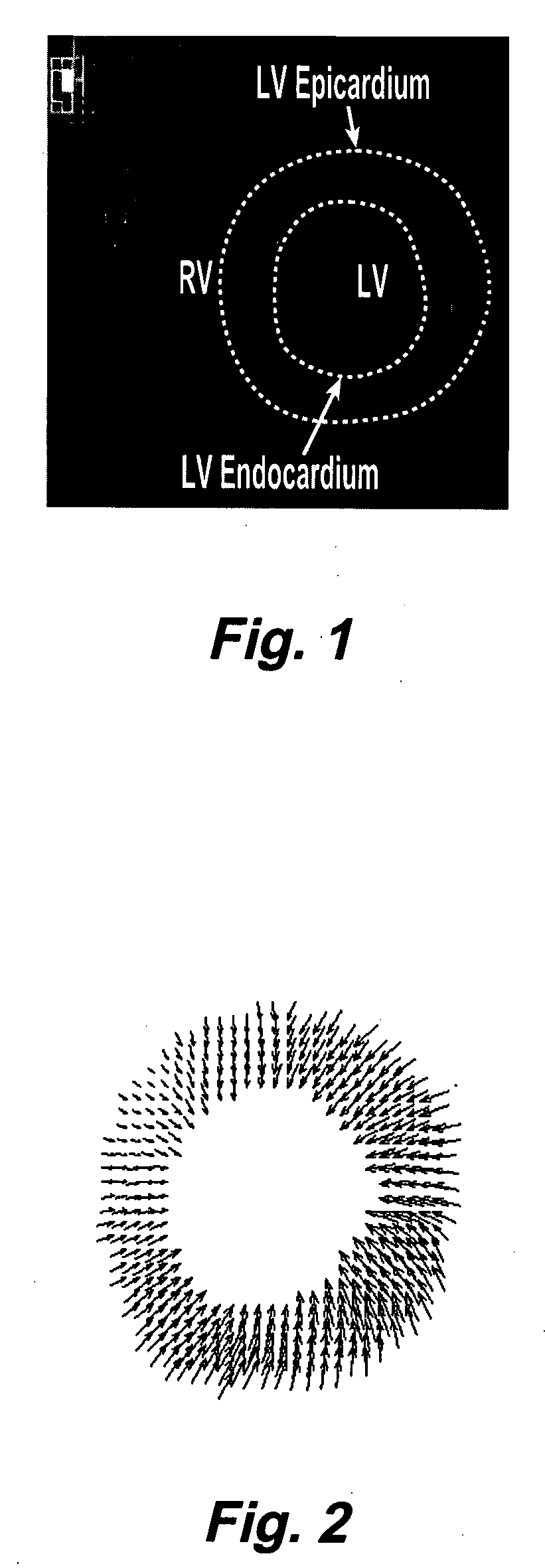
Motion-guided segmentation for cine dense images
Myocardial tissue tracking techniques are used to project or guide a single manually-defined set of myocardial contours through time. Displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE), harmonic phase (HARP) and speckle tracking is used to encode tissue displacement into the phase of complex MRI images, providing a time series of these images, and facilitating the non-invasive study of myocardial kinematics. Epicardial and endocardial contours need to be defined at each frame on cine DENSE images for the quantification of regional displacement and strain as a function of time. The disclosed method presents a novel and effective two dimensional semi-automated segmentation technique that uses the encoded motion to project a manually defined region of interest through time. Contours can then easily be extracted for each cardiac phase.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +2
Myocardial tissue ablation device for treatment of cardiac arrhythmias by ablation of myocardial tissue in a patient as well as associated catheter and associated method
InactiveUS20090076375A1Reduce riskSimple procedureUltrasound therapySurgical navigation systemsCardiac muscleTissue ablation
The invention relates to a myocardial tissue ablation device for treatment of cardiac arrhythmias by ablation of myocardial tissue in a patient, with the myocardial tissue ablation device featuring a catheter which is embodied as an integrated unit with at least one myocardial ablation means and at least one imaging element based on optical coherence tomography and / or intravascular magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
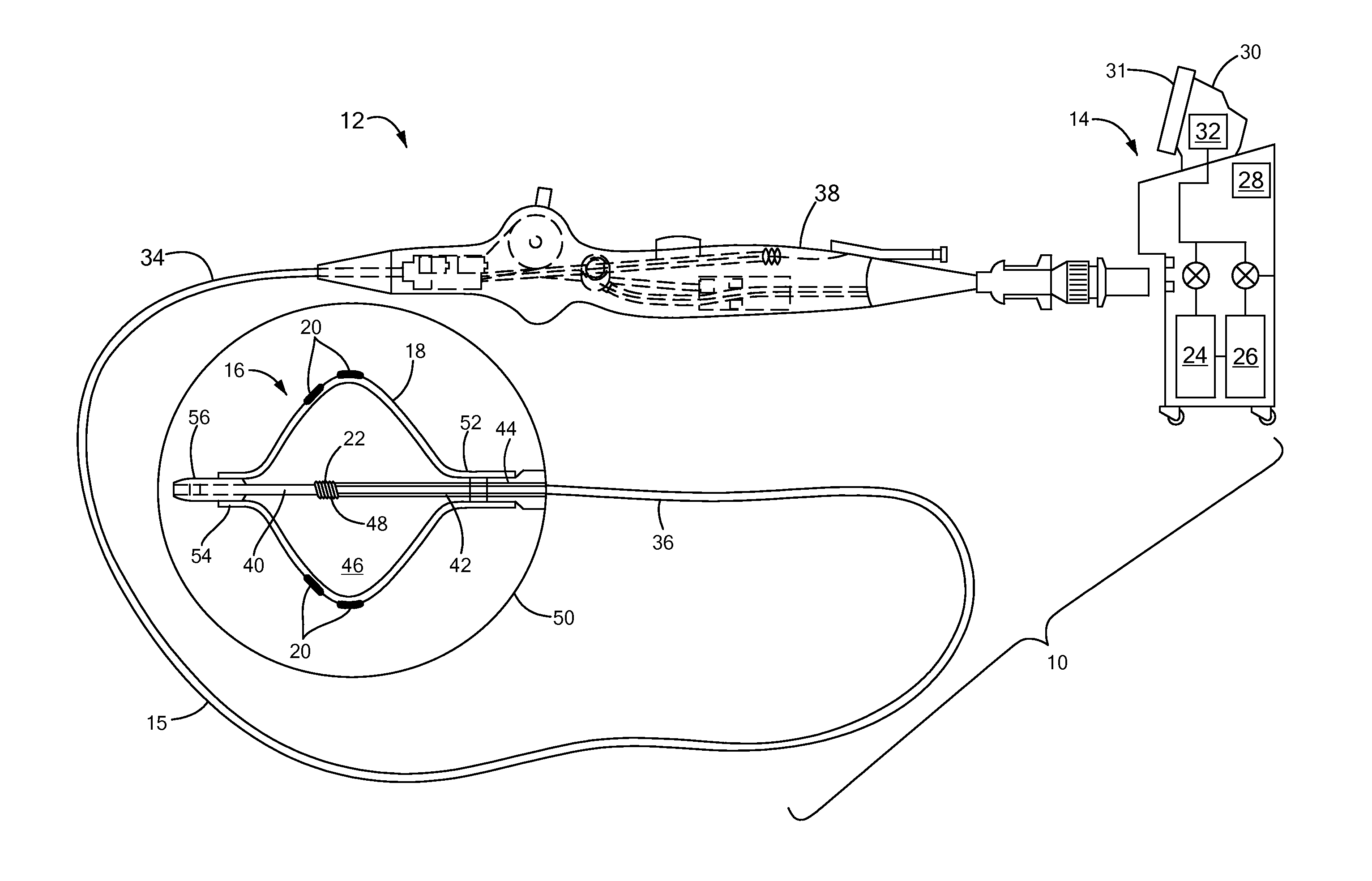
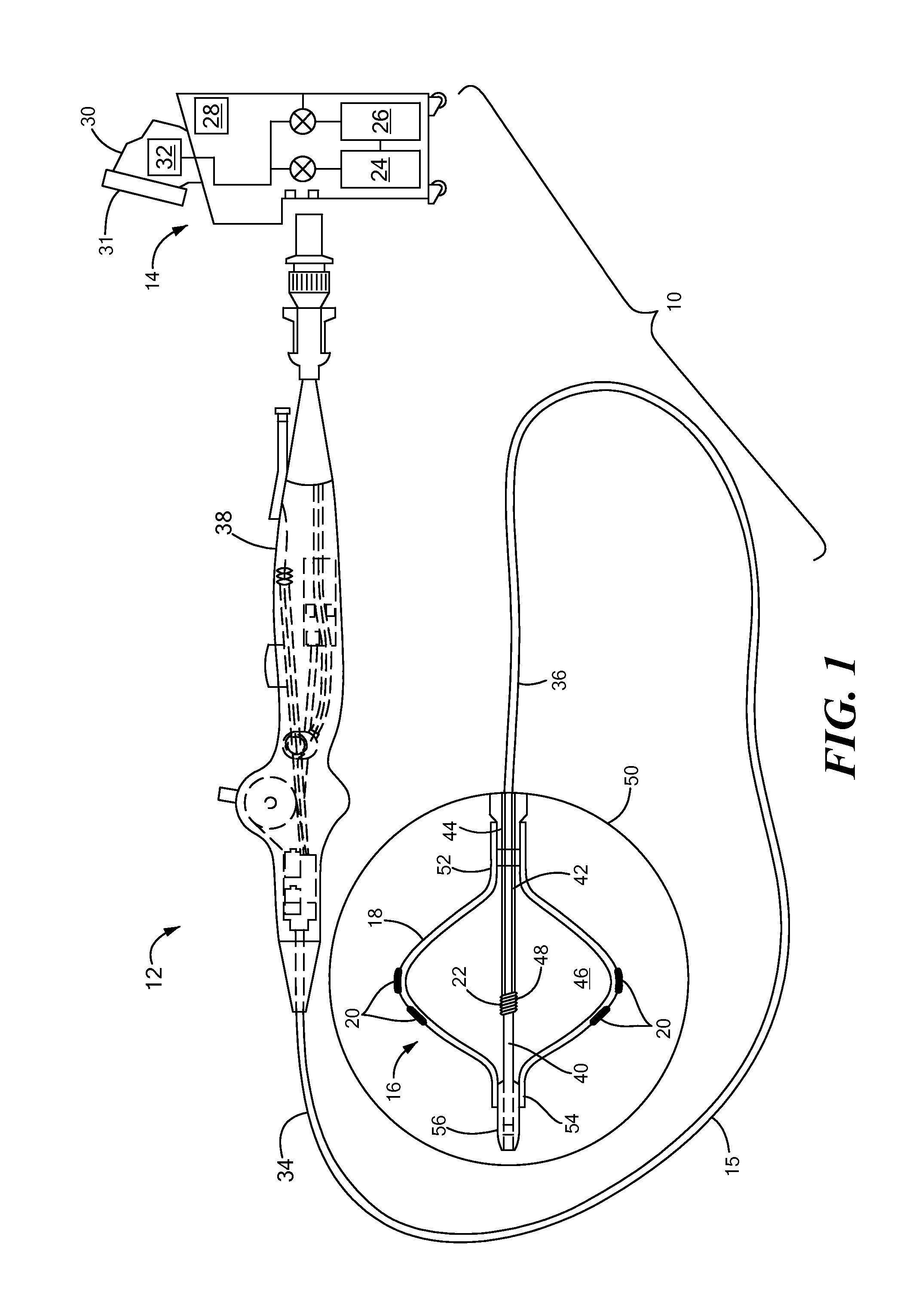
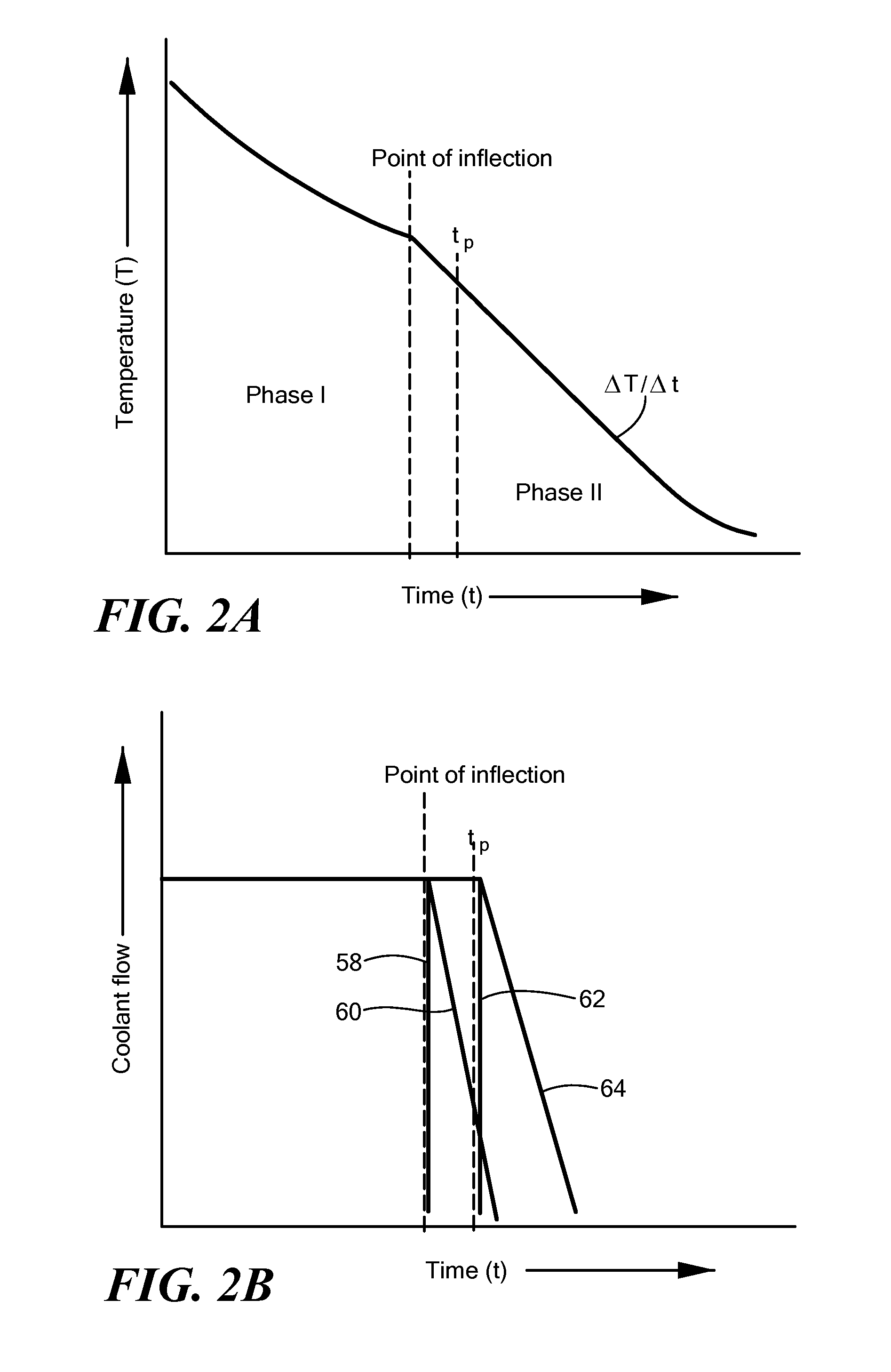
Feedback system for cryoablation of cardiac tissue
A method and system for providing lesion depth feedback during an ablation procedure. In particular, the method and system provide feedback data or information relating to lesion depth in myocardial tissue during a cryoablation procedure. A plurality of tissue temperature measurements may be transmitted from a plurality of thermocouples disposed on a cryotreatment element, which measurements may be used to determine a slope of change in temperature sensed by each thermocouple over time. The circulation of coolant through the treatment element may be adjusted when the slope changes. A change in slope may indicate that the cryoablation temperatures have passed through target myocardial tissue into non-target, non-myocardial tissue, which may result in collateral damage to structures near the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
Method and apparatus for passive cardiac stimulation
A passive conductor assembly for use with an implanted stimulating device having an intracavitarily or transvenously disposed electrode is disclosed. The passive conductor assembly used in combination with the implanted stimulus generator having an intracavitarily or intravenously disposed electrode includes at least one conductive element having a first end and a second end, and / or other contacting sites for contacting a portion of a heart of a subject to be stimulated. The passive conductor is disposed in proximity to the intracavitarily or transvenous electrode which is connected to the implanted stimulus generator such as a pacemaker or defibrillator. Upon discharge of an electrical stimulus or waveform from the implanted stimulus generator, the stimulus is conducted through the myocardial tissue to the conductor assembly where it is passively conducted to a region of the heart in contact with an end or other contacting sites of the conductive element of the passive conductor assembly which have been selected for cardiac stimulation. The passive conductor assembly can include electrical components disposed in electrical communication therewith which provide for the manipulation and / or modification of the electrical stimulus or waveform generated by the implanted stimulus generator which can be designed, for example, to selectively stimulate only neural tissue and not cardiac tissue or vice versa through the same passive conductor assembly.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com