Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
386 results about "Numerically controlled oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
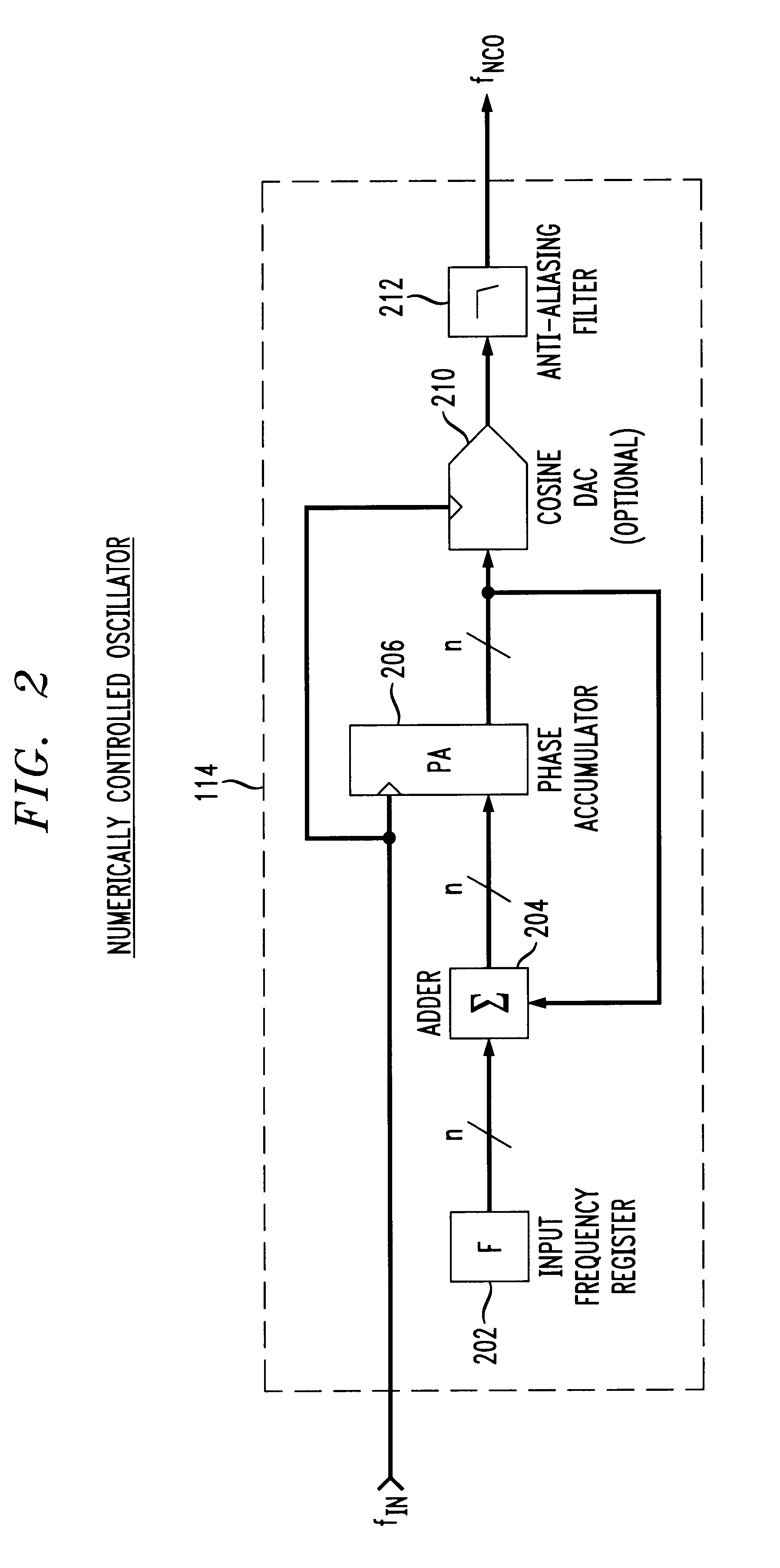
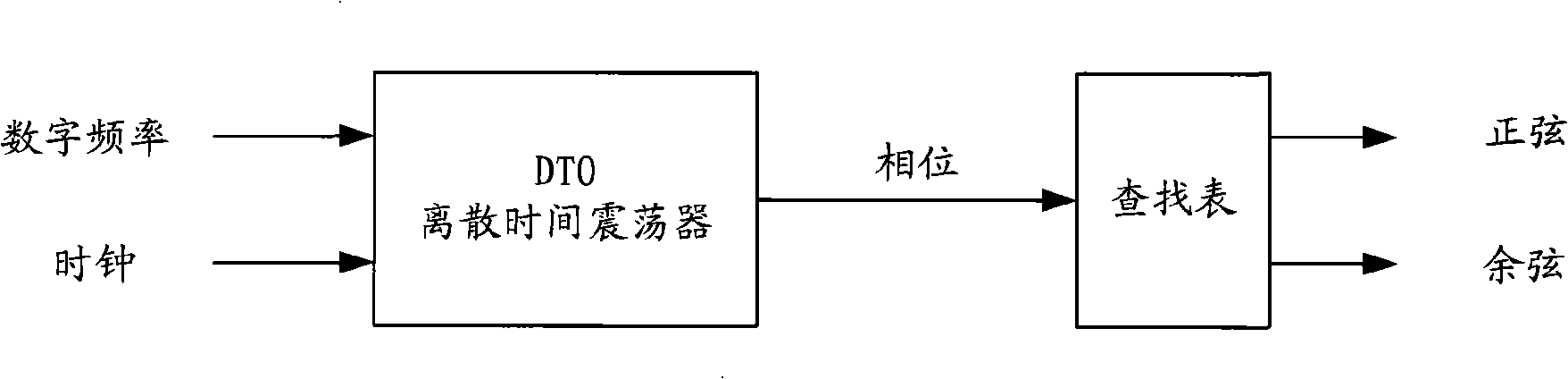
A numerically-controlled oscillator (NCO) is a digital signal generator which creates a synchronous (i.e. clocked), discrete-time, discrete-valued representation of a waveform, usually sinusoidal. NCOs are often used in conjunction with a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) at the output to create a direct digital synthesizer (DDS).
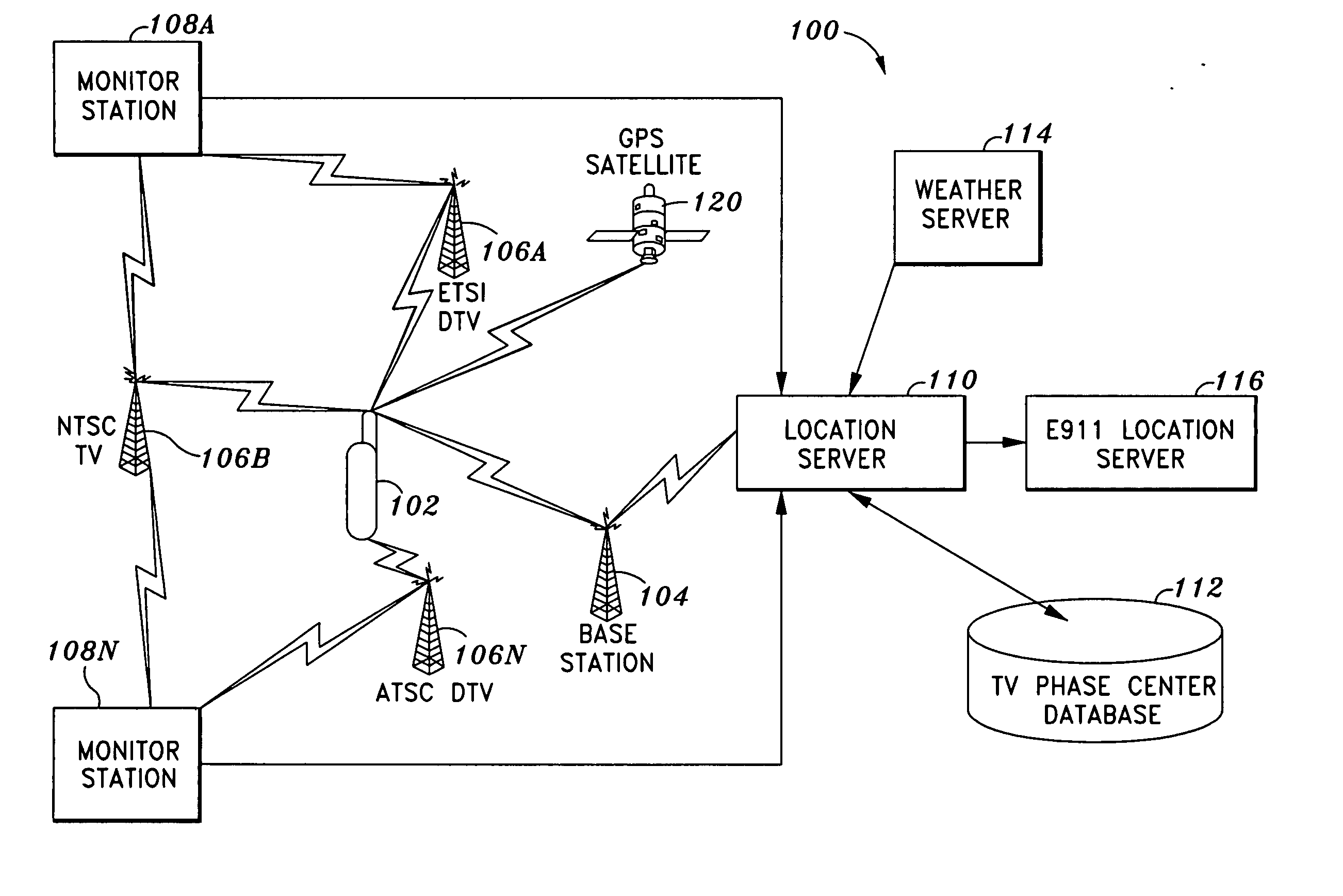
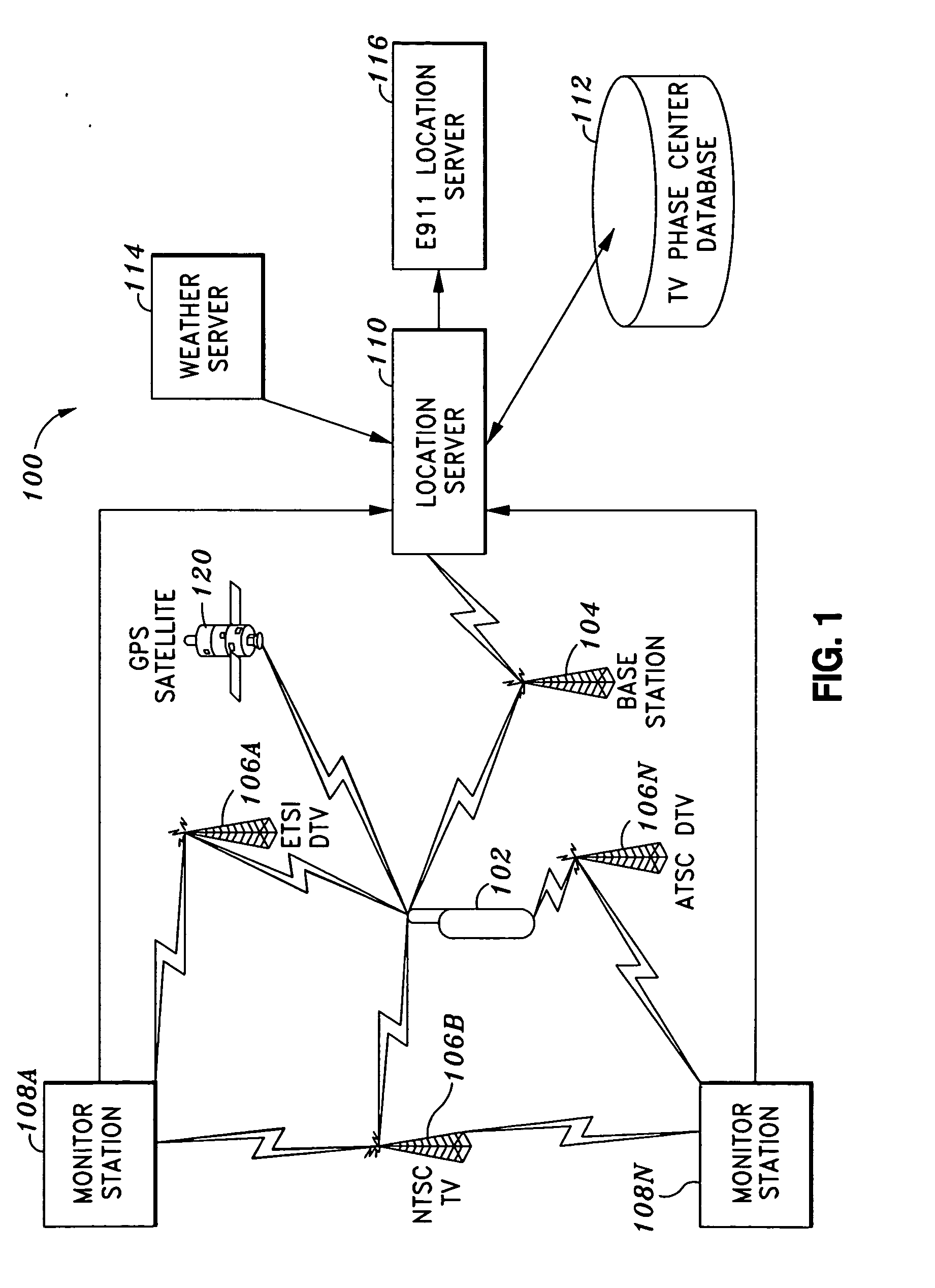
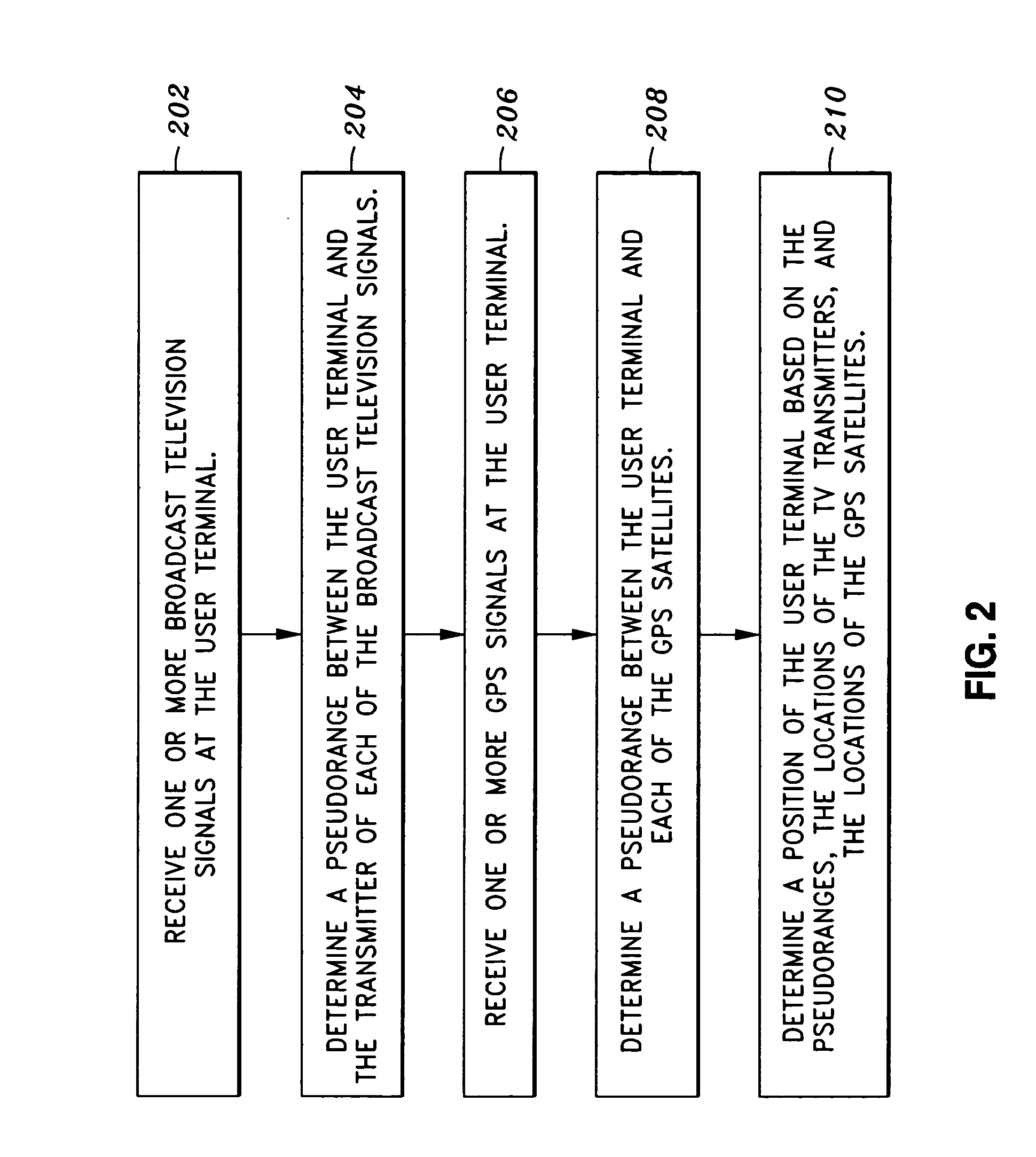
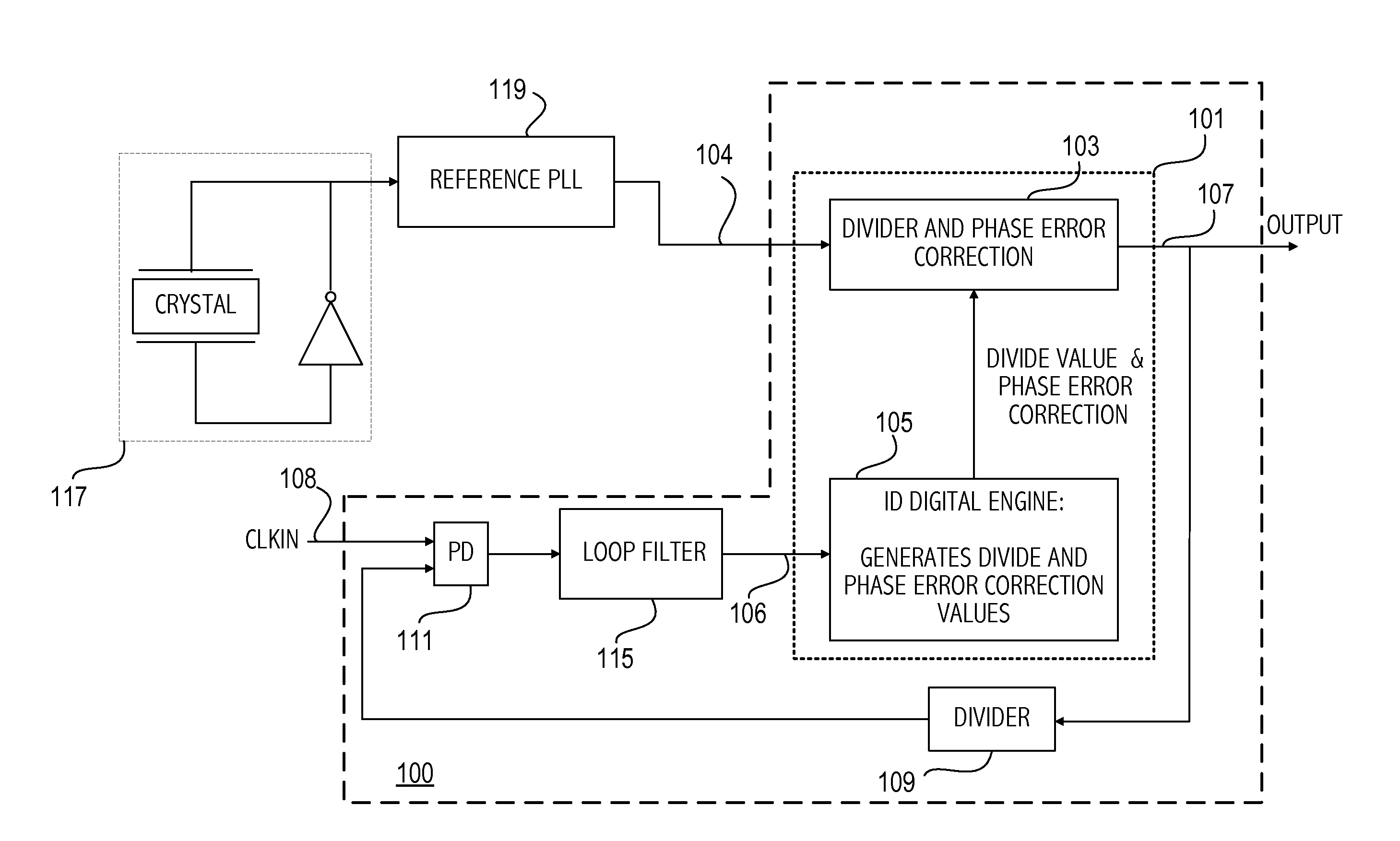
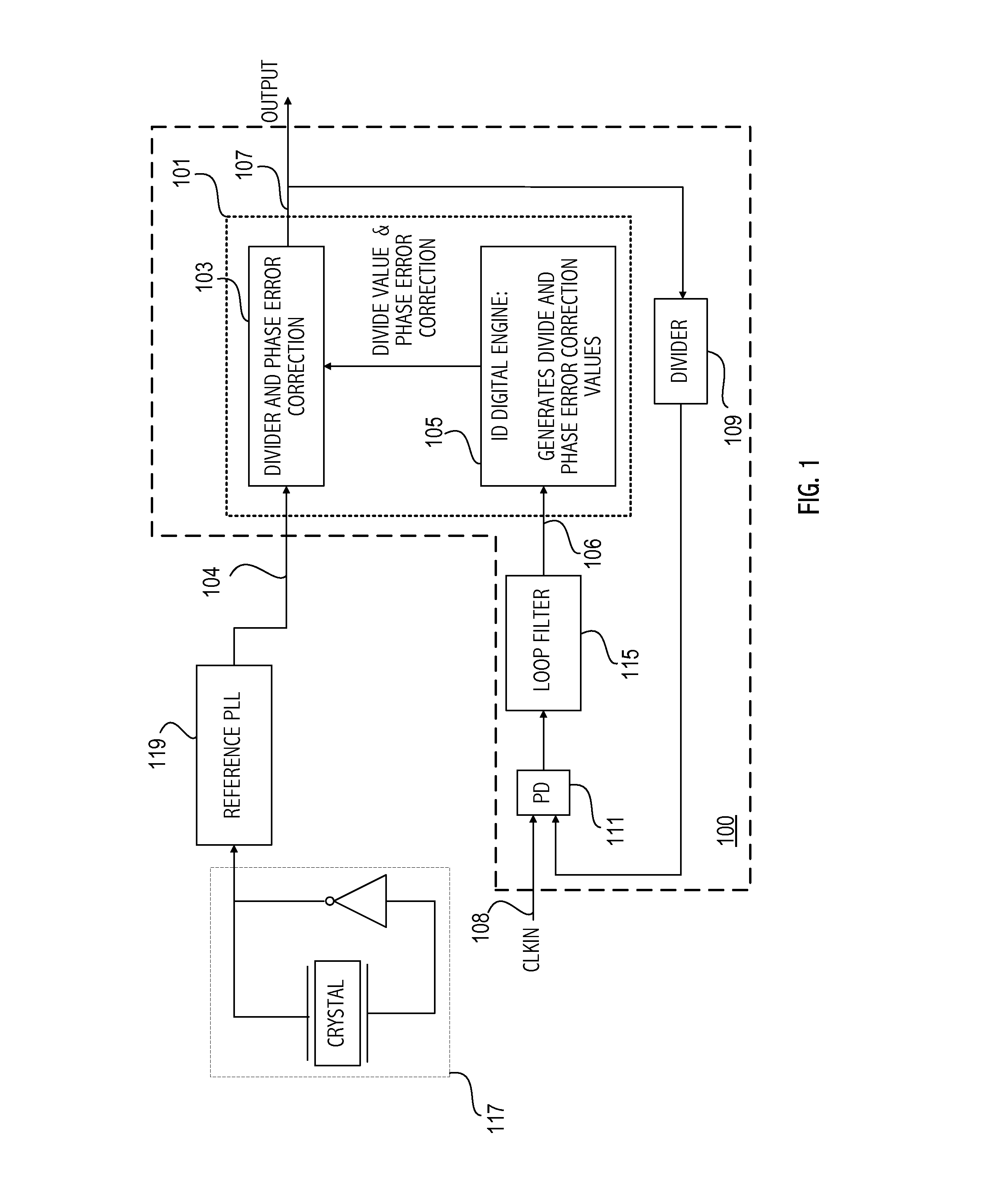
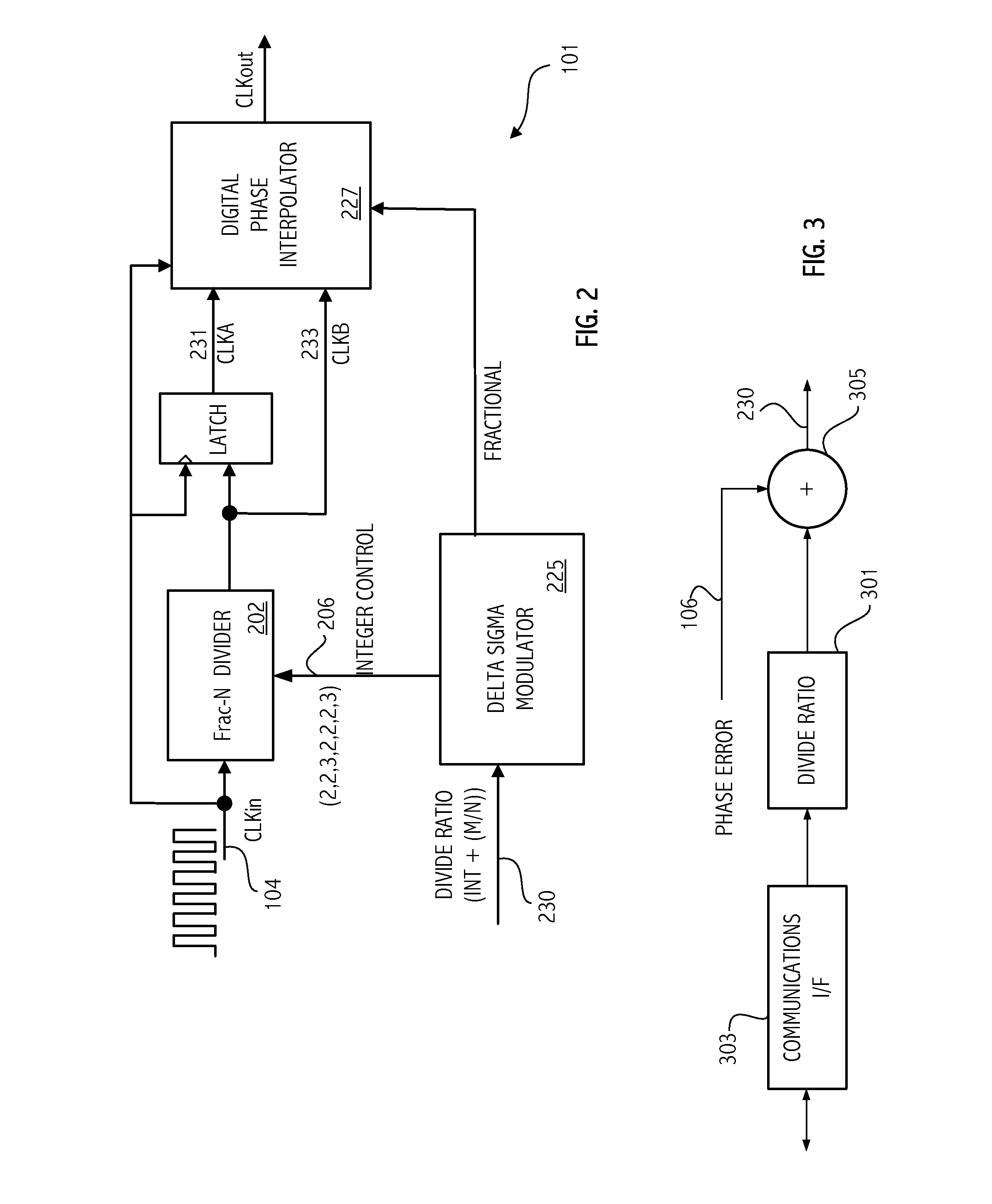
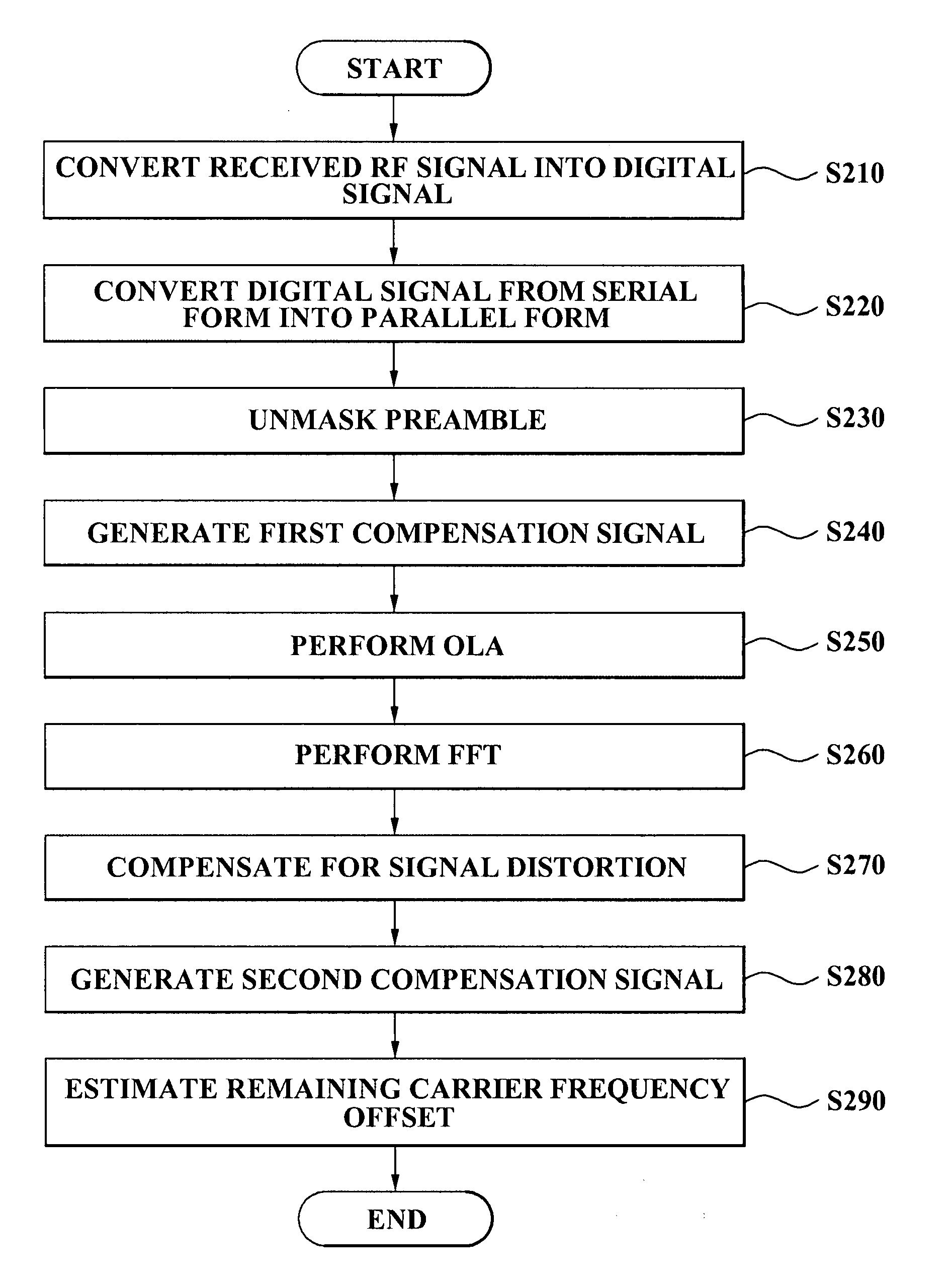
Pilot acquisition and local clock calibration with reduced MIPS
The present invention provides a method, system, and apparatus for estimating a pilot frequency of a television broadcast signal at a receiver. In one aspect, the receiver constitutes a mobile device that uses the estimated pilot frequency to facilitate the determination of position location of the mobile device. The receiver includes a processor which estimates the pilot frequency by computing a baseband version of the pilot signal relative to a reference frequency, defining time-shifted segments for the pilot signal and its baseband version, computing phase correction terms using the pilot signal and its baseband version, phase correcting each received signal segment, and estimating the pilot frequency. In another aspect of the invention, a phase-locked-loop is used to track the phase of the incoming pilot signal. The loop filter and / or the phase of the numerically controlled oscillator is scaled to account for the non-integer nature of samples within the received segments.
Owner:ROSUM CORP
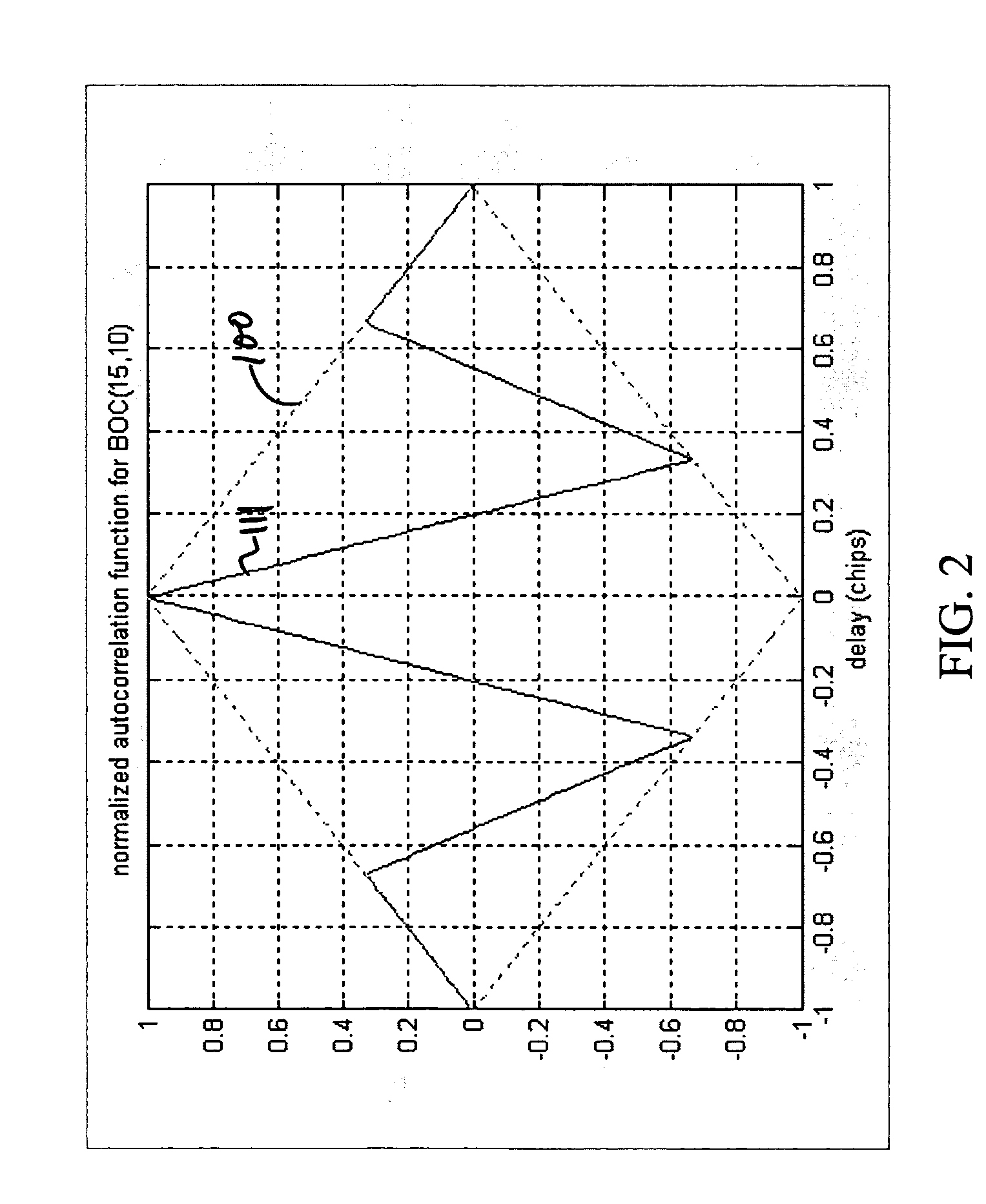
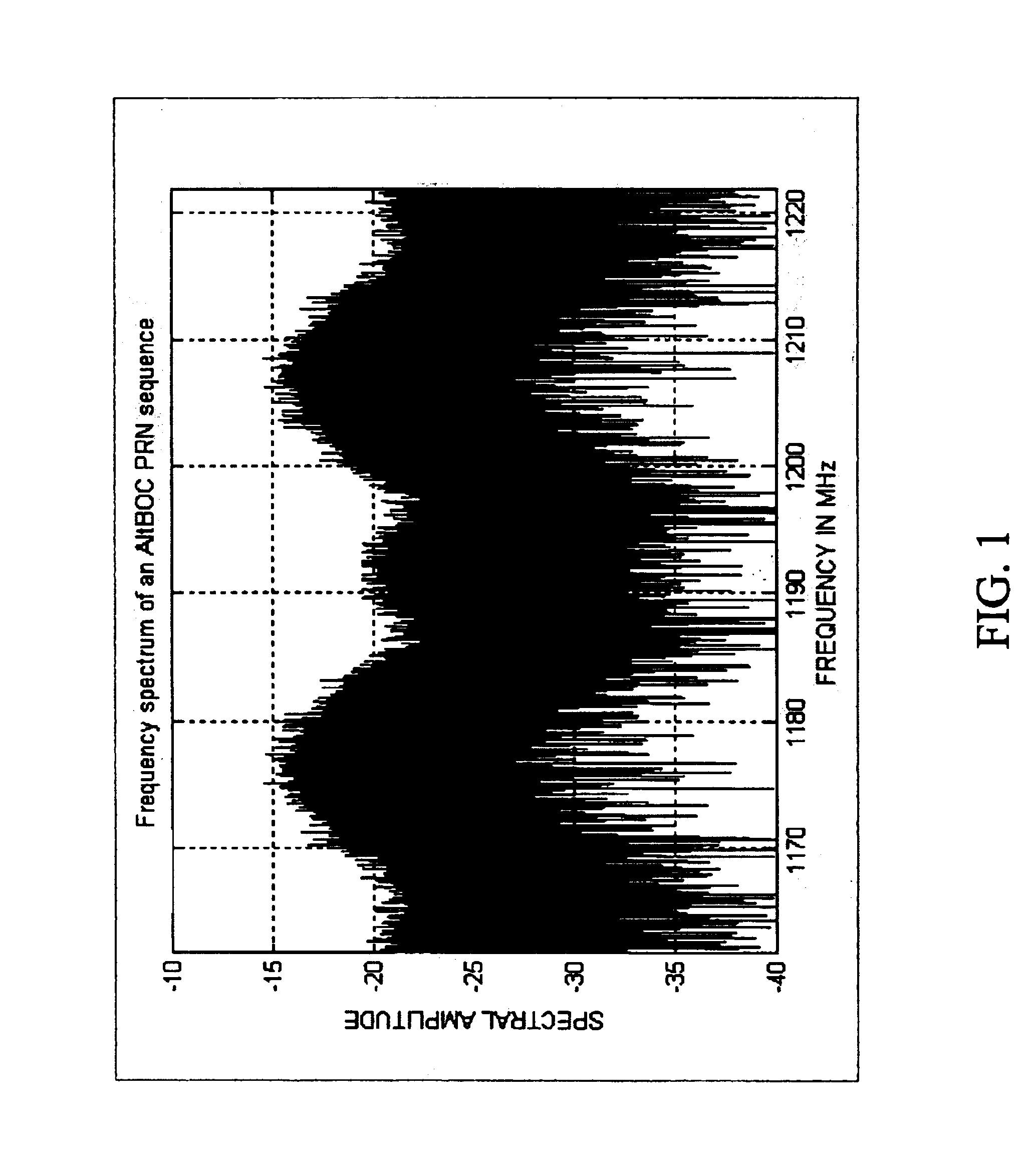
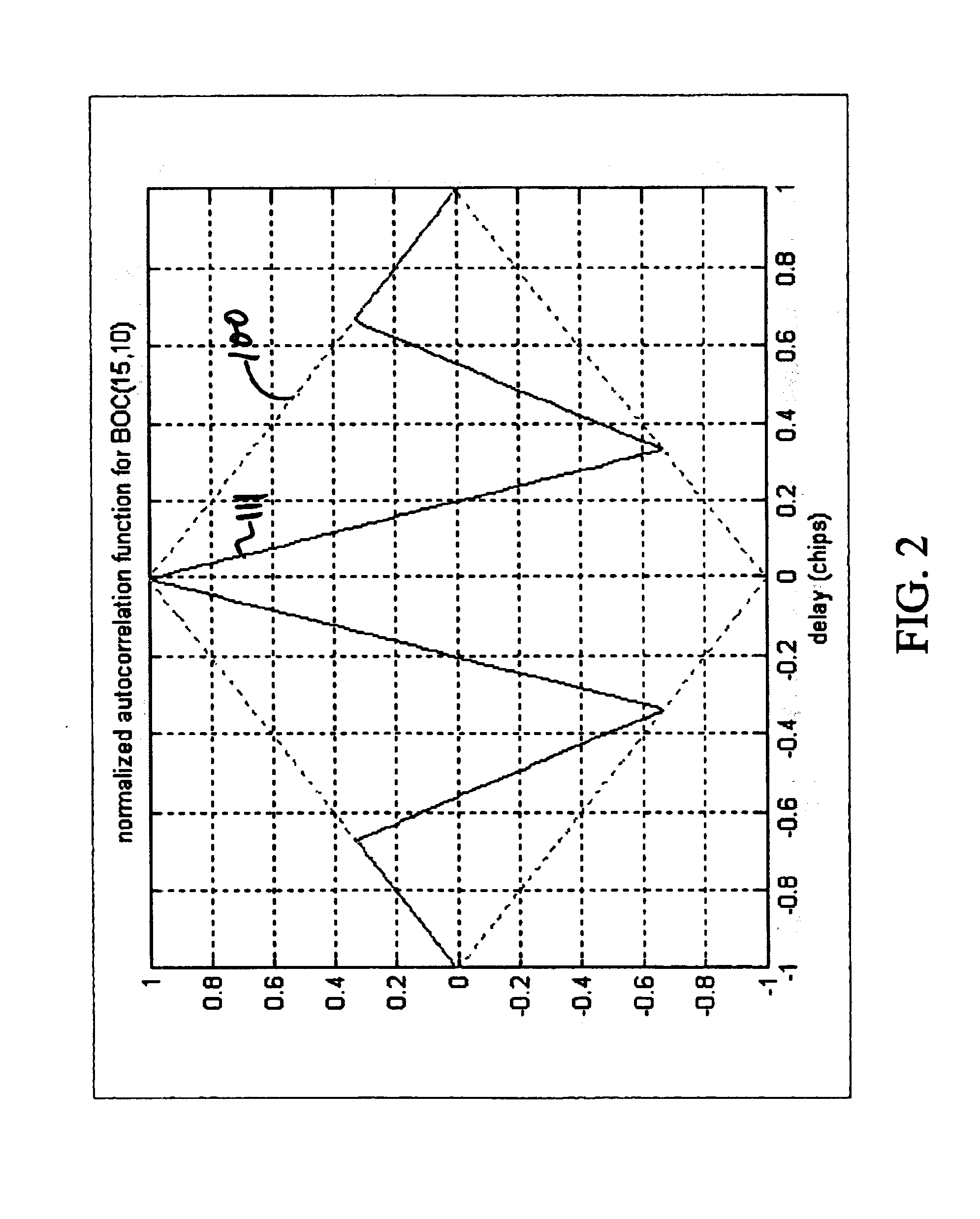
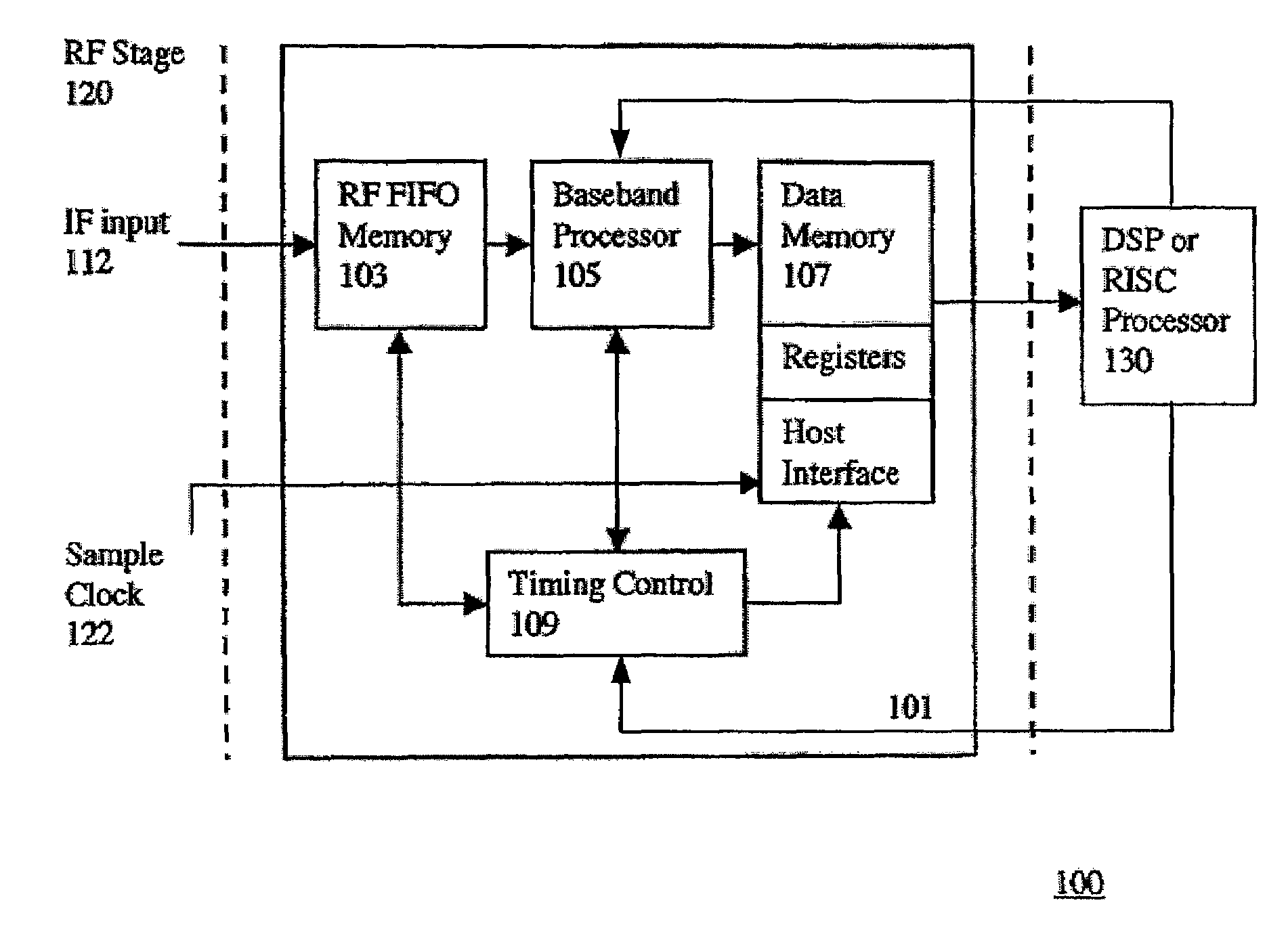
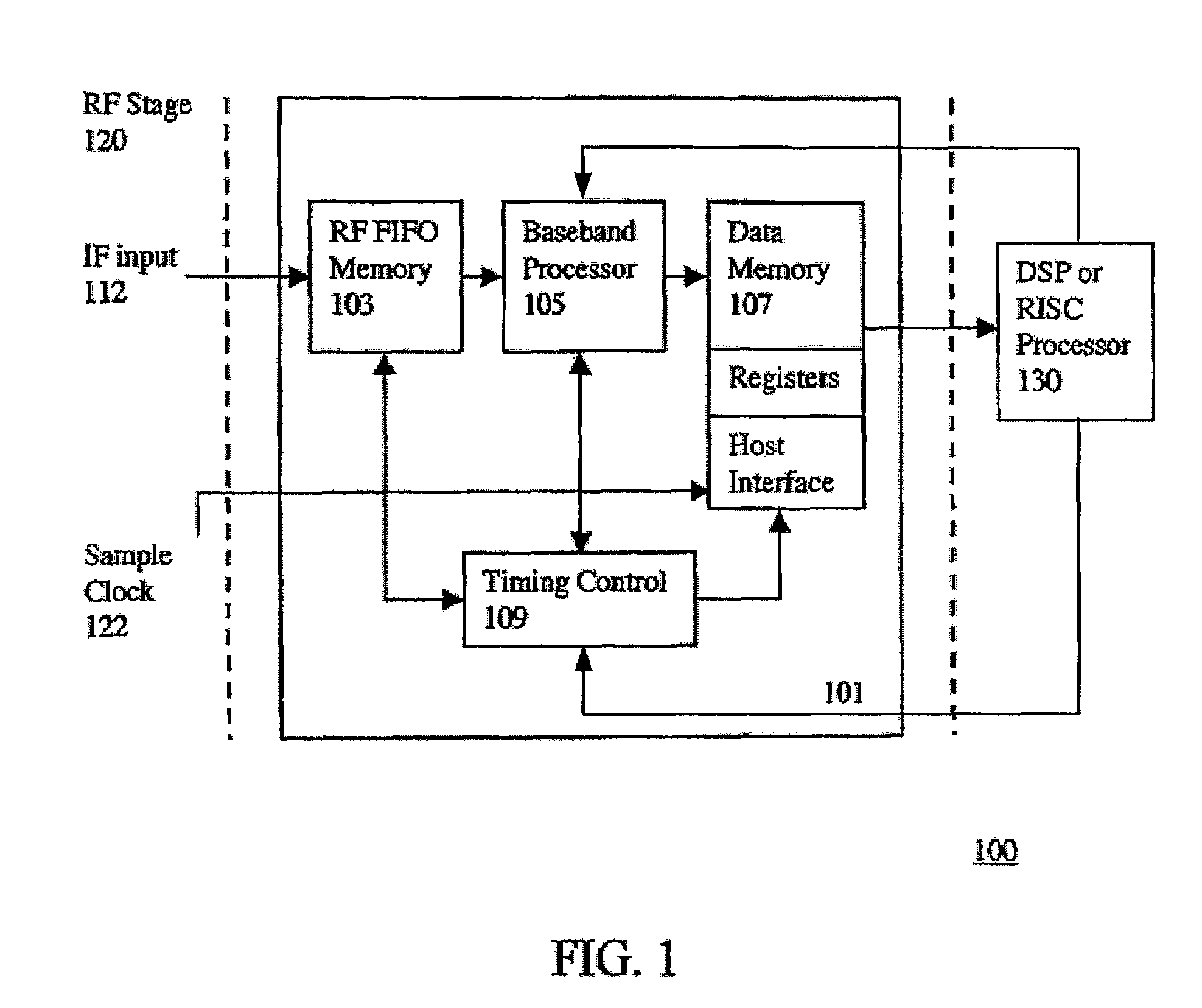
Hardware architecture for processing galileo alternate binary offset carrier (altboc) signals
InactiveUS20050012664A1Polarisation/directional diversityBeacon systems using radio wavesCarrier signalNumerically controlled oscillator
A GNSS receiver tracks the AltBOC (15,10), or composite E5a and E5b, codes using hardware that locally generates the complex composite signal by combining separately generated real and the imaginary components of the complex signal. To track the dataless composite pilot code signals that are on the quadrature channel of the AltBOC signal, the receiver operates PRN code generators that produce replica E5a and E5b PRN codes and square wave generators that generate the real and imaginary components of the upper and lower subcarriers, and combines the signals to produce a locally generated complex composite code. The receiver removes the complex composite code from the received signal by multiplying the received signal, which has been downconverted to baseband I and Q signal components, by the locally generated complex composite code. The receiver then uses the results, which are correlated I and Q prompt signal values, to estimate the center frequency carrier phase angle tracking error. The error signal is used to control a numerically controlled oscillator that operates in a conventional manner, to correct the phase angle of the locally generated center frequency carrier. The receiver also uses early and late versions of the locally generated complex composite pilot code in a DLL, and aligns the locally generated composite pilot code with the received composite pilot code by minimizing the corresponding DLL error signal. Once the receiver is tracking the composite pilot code, the receiver determines its pseudorange and global position in a conventional manner. The receiver also uses a separate set of correlators to align locally generated versions of the in-phase composite PRN codes with the in-phase channel codes in the received signal, and thereafter, recover the data that is modulated thereon.
Owner:EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY
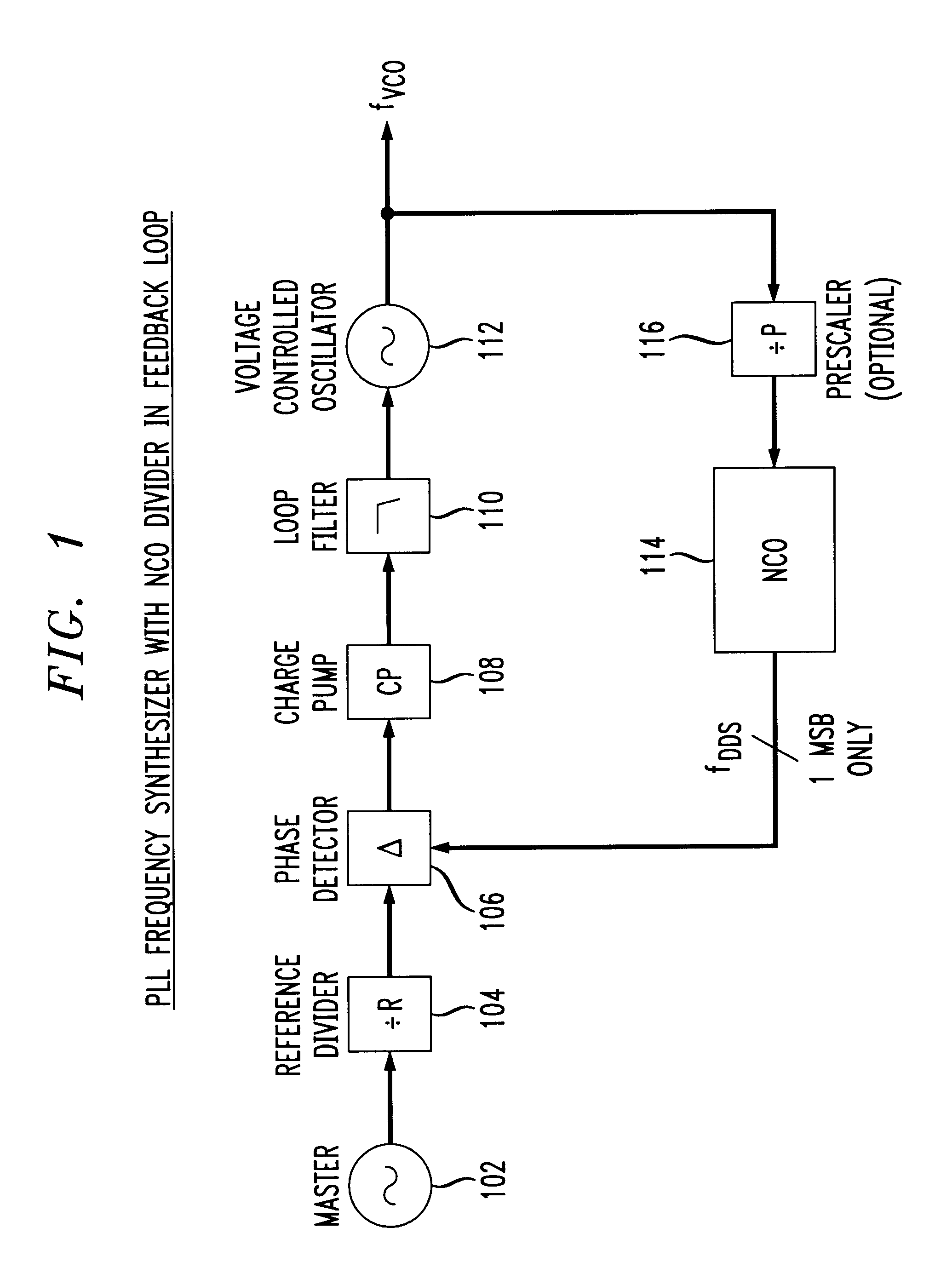
Phase locked loop with numerically controlled oscillator divider in feedback loop
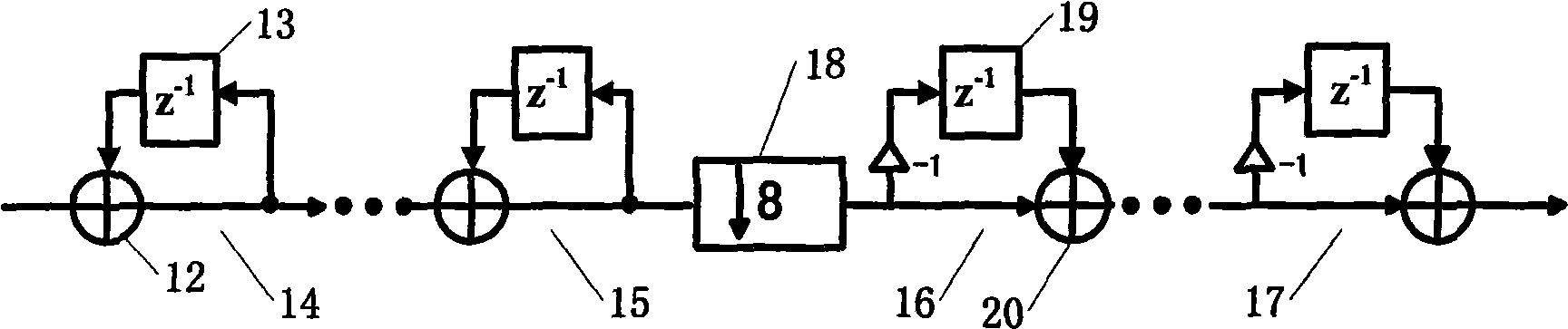
A digital phase locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer includes a 1-bit numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) to negate the requirement that a VCO frequency be an integer multiple of its reference frequency. Thus, in accordance with the principles of the present invention, a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) or numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) is used to form a frequency divider in a feedback path of a PLL. Thus, a synthesizer with fine frequency control and very fast settling time is disclosed. The conventional integer-ratio relationship between the reference frequency fREF and the synthesized output frequency signal fVCO is overcome by replacement of a conventional VCO divider in a feedback path of a digital PLL with a 1-bit NCO. This allows the reference frequency fREF to be greater than the channel spacing, i.e., the channel spacing can be smaller than the reference frequency fREF. Thus, a much quicker settling time and improved VCO phase noise are provided, either of which results in a significant improvement in the performance of virtually any communications system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
Hardware architecture for processing galileo alternate binary offset carrier (AltBOC) signals
InactiveUS6922167B2Beacon systems using radio wavesPolarisation/directional diversityNumerically controlled oscillatorCarrier signal
A GNSS receiver tracks the AltBOC (15,10), or composite E5a and E5b, codes using hardware that locally generates the complex composite signal by combining separately generated real and the imaginary components of the complex signal. To track the dataless composite pilot code signals that are on the quadrature channel of the AltBOC signal, the receiver operates PRN code generators that produce replica E5a and E5b PRN codes and square wave generators that generate the real and imaginary components of the upper and lower subcarriers, and combines the signals to produce a locally generated complex composite code. The receiver removes the complex composite code from the received signal by multiplying the received signal, which has been downconverted to baseband I and Q signal components, by the locally generated complex composite code. The receiver then uses the results, which are correlated I and Q prompt signal values, to estimate the center frequency carrier phase angle tracking error. The error signal is used to control a numerically controlled oscillator that operates in a conventional manner, to correct the phase angle of the locally generated center frequency carrier. The receiver also uses early and late versions of the locally generated complex composite pilot code in a DLL, and aligns the locally generated composite pilot code with the received composite pilot code by minimizing the corresponding DLL error signal. Once the receiver is tracking the composite pilot code, the receiver determines its pseudorange and global position in a conventional manner. The receiver also uses a separate set of correlators to align locally generated versions of the in-phase composite PRN codes with the in-phase channel codes in the received signal, and thereafter, recover the data that is modulated thereon.
Owner:EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY
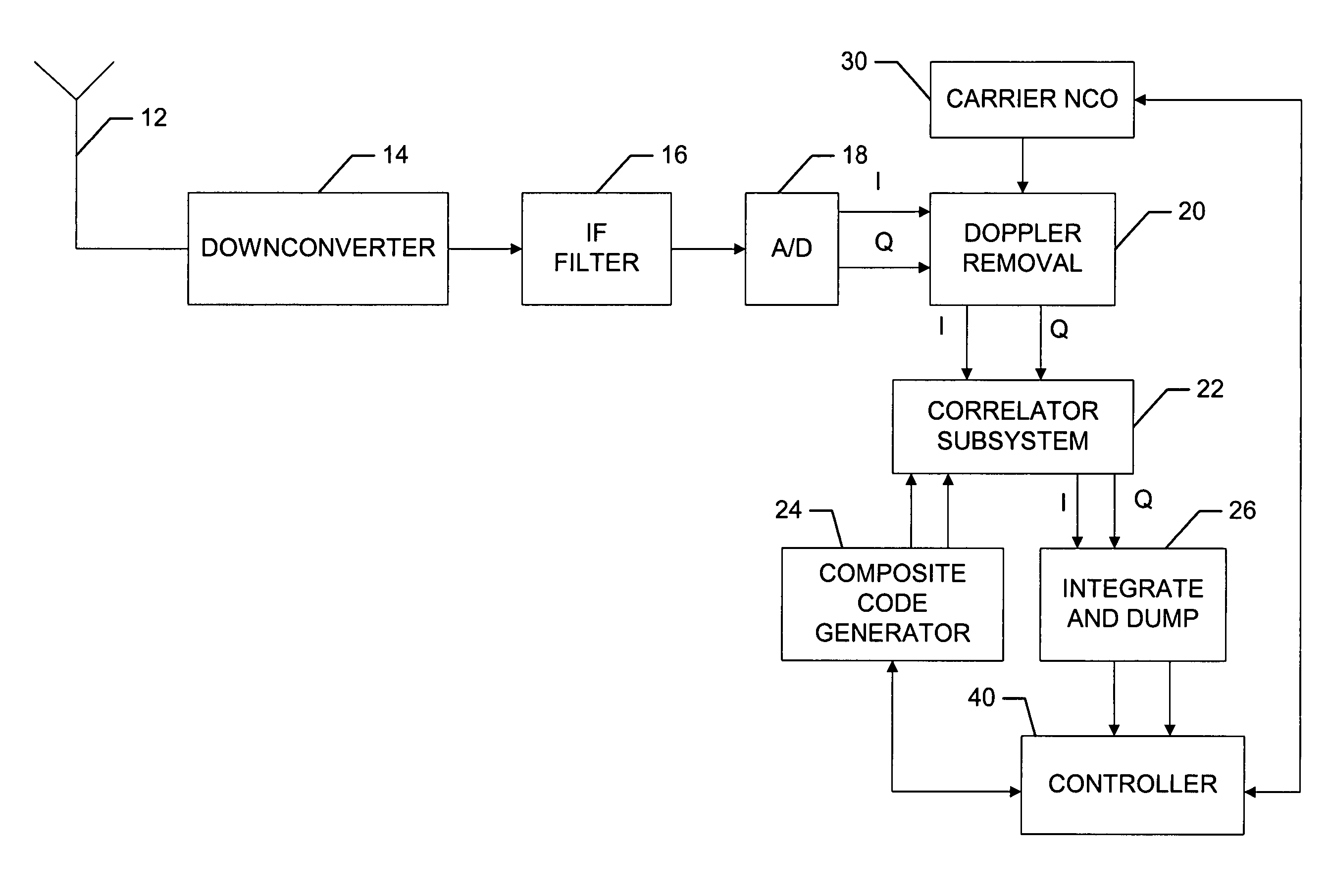
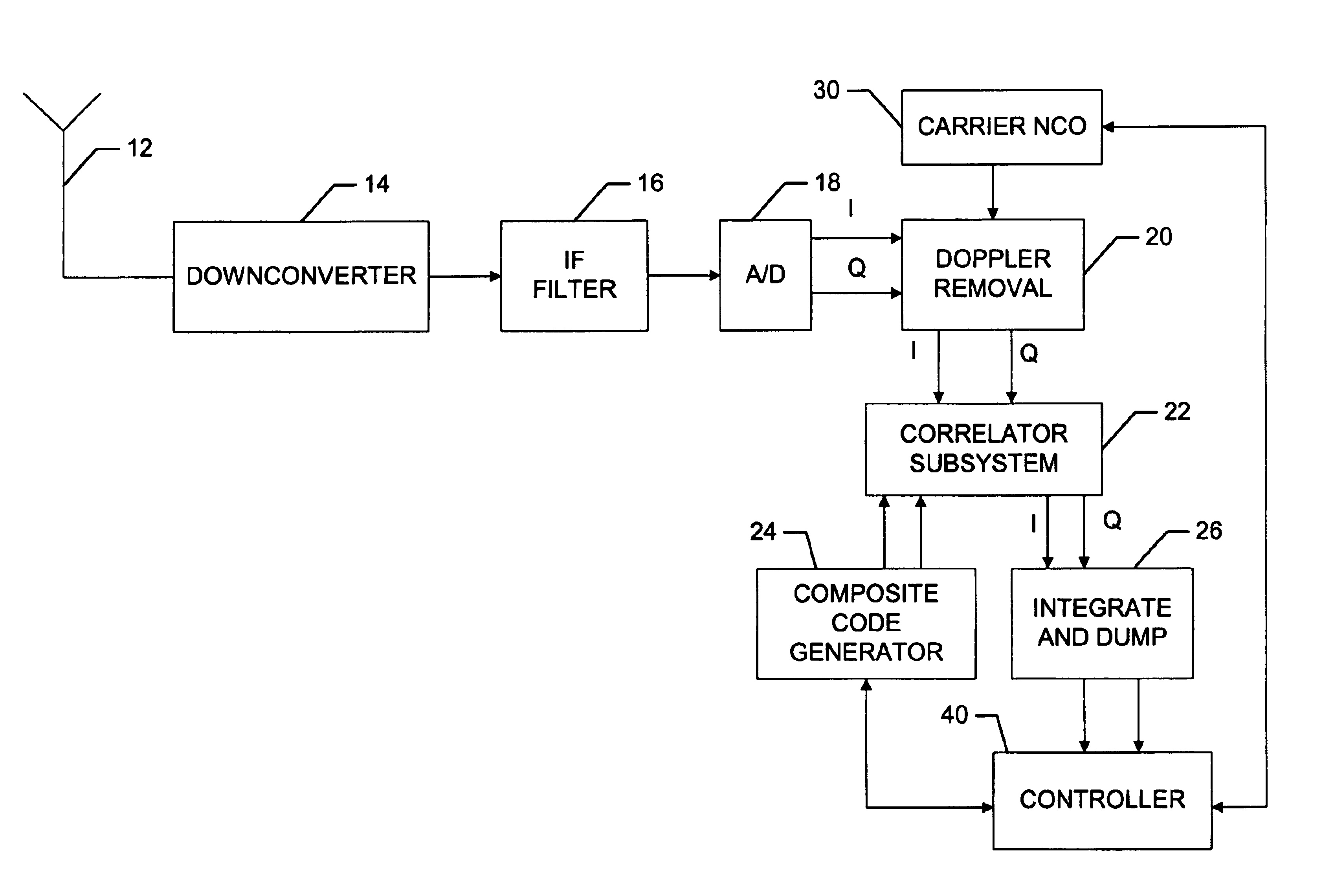
Efficient and flexible GPS receiver baseband architecture
ActiveUS7428259B2Minimize the numberEfficient powerColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNCOSNumerically controlled oscillator
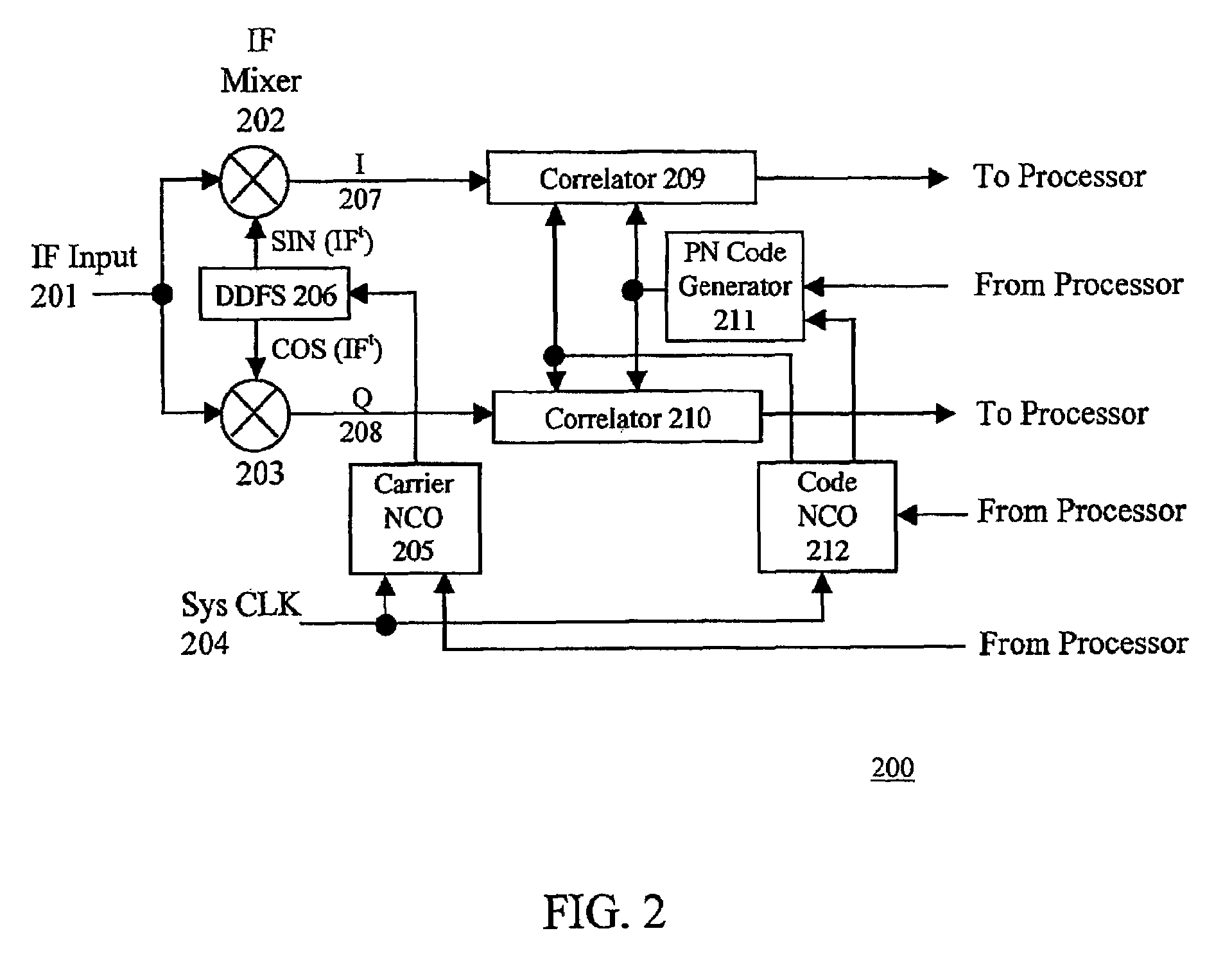
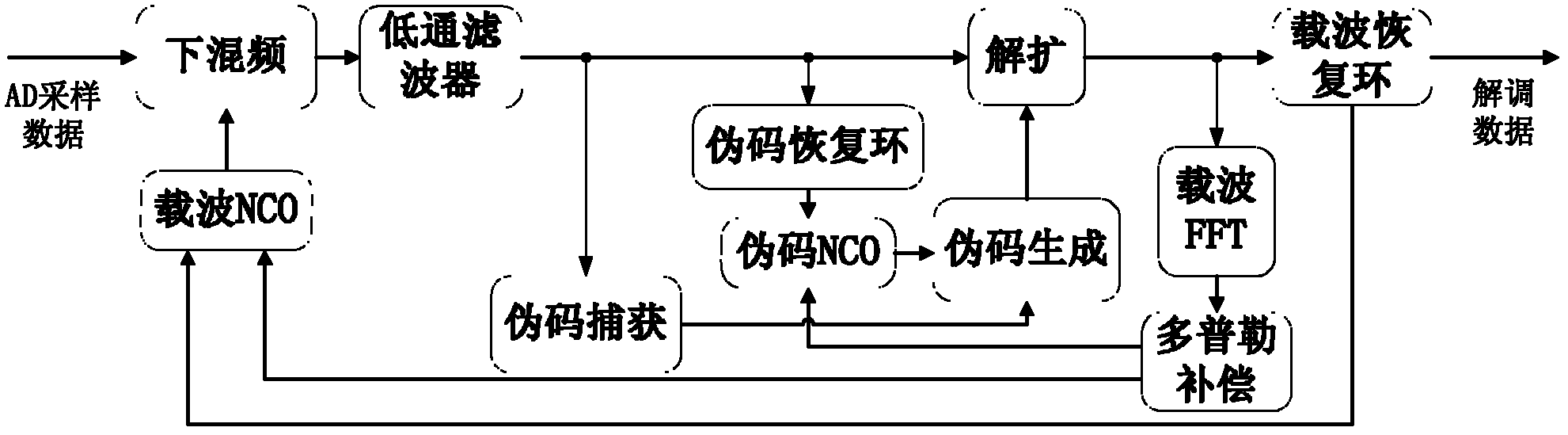
The present invention provides a new baseband integrated circuit (IC) architecture for direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) communication receivers. The baseband IC has a single set of baseband correlators serving all channels in succession. No complex parallel channel hardware is required. A single on-chip code Numerically Controlled Oscillator (NCO) drives a pseudorandom number (PN) sequence generator, generates all code sampling frequencies, and is capable of self-correct through feedback from an off-chip processor. A carrier NCO generates corrected local frequencies. These on-chip NCOs generate all the necessary clocks. This architecture advantageously reduces the total hardware necessary for the receiver and the baseband IC thus can be realized with a minimal number of gate count. The invention can accommodate any number of channels in a navigational system such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), GLONASS, WAAS, LAAS, etc. The number of channels can be increased by increasing the circuit clock speed.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
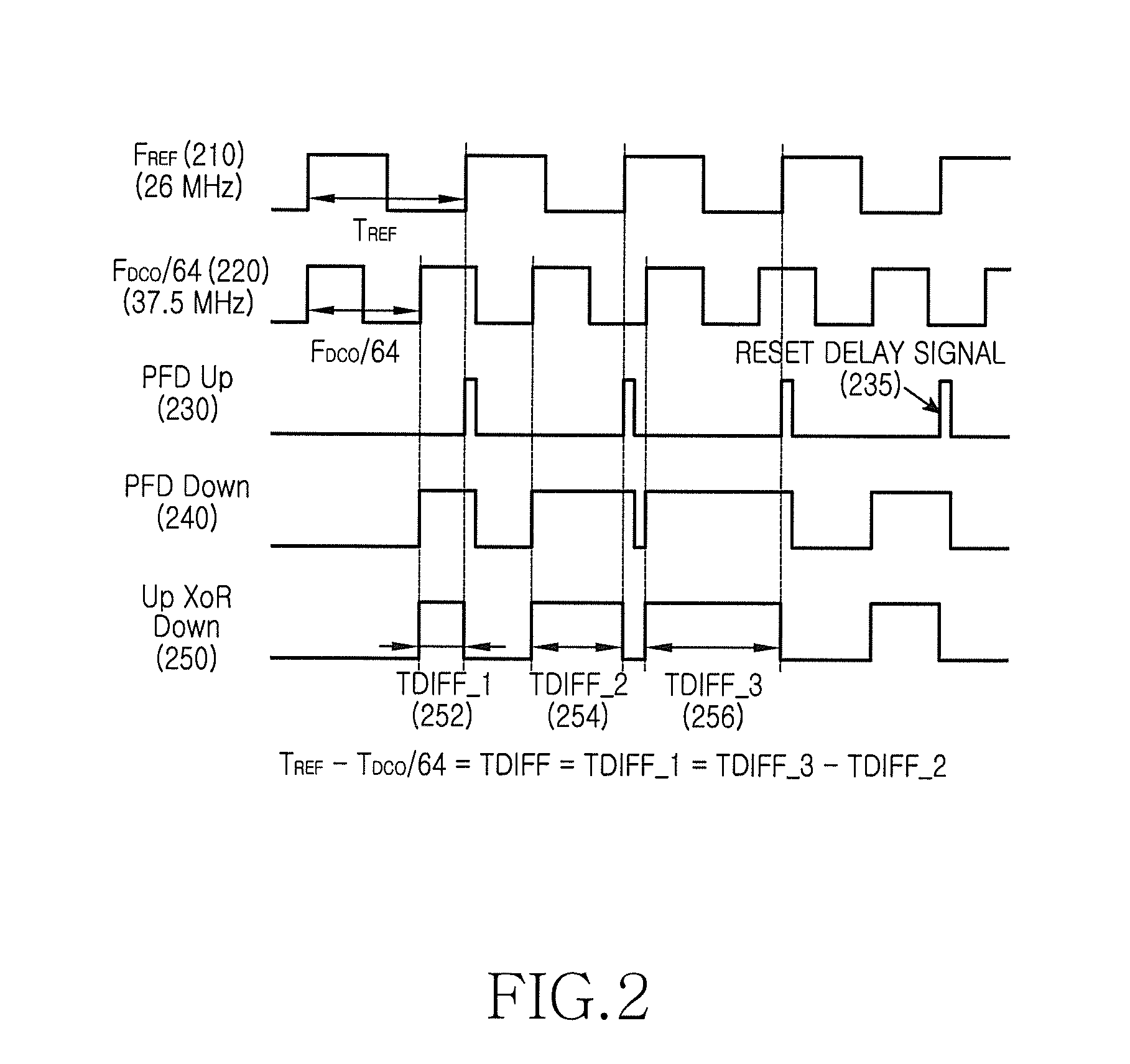
Rapid locking method for full digital phase-locked loop
ActiveCN101640533AShort lock timeReduce forecast errorPulse automatic controlDiscriminatorPhase difference
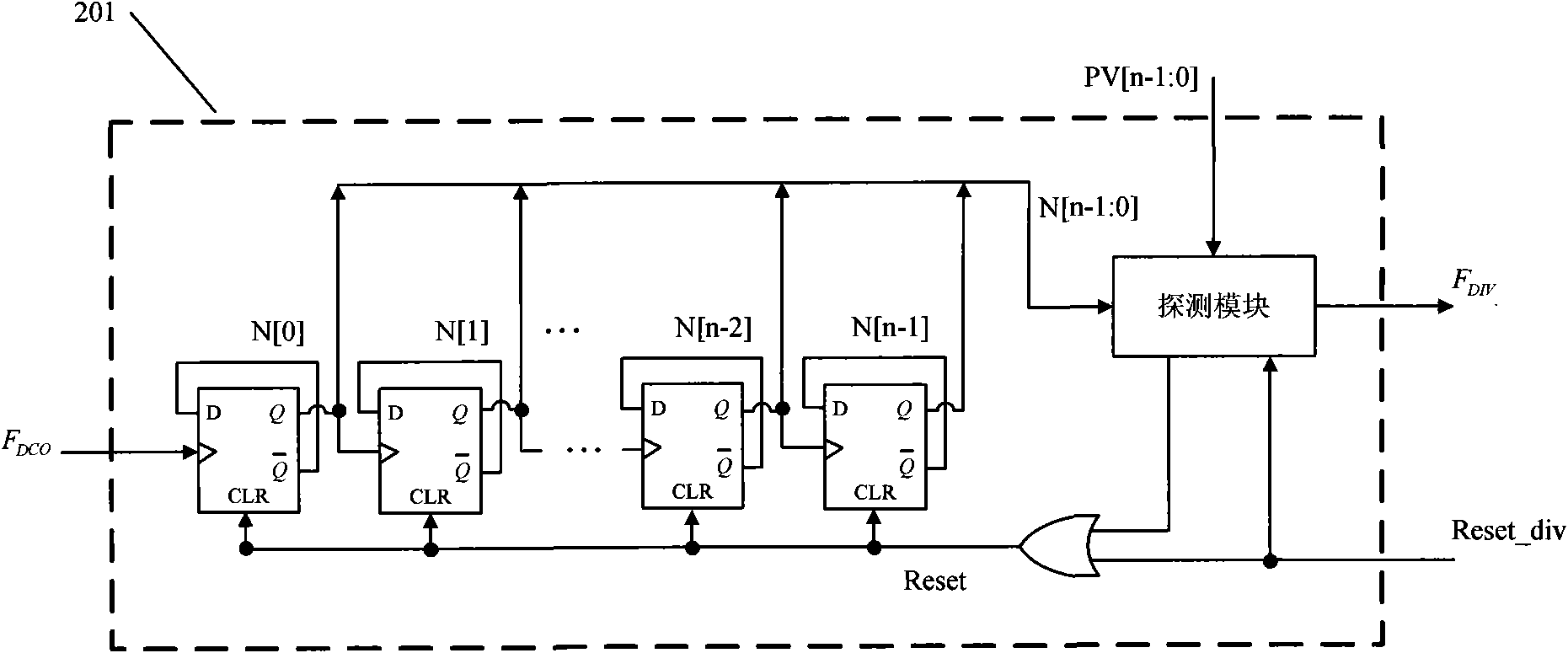
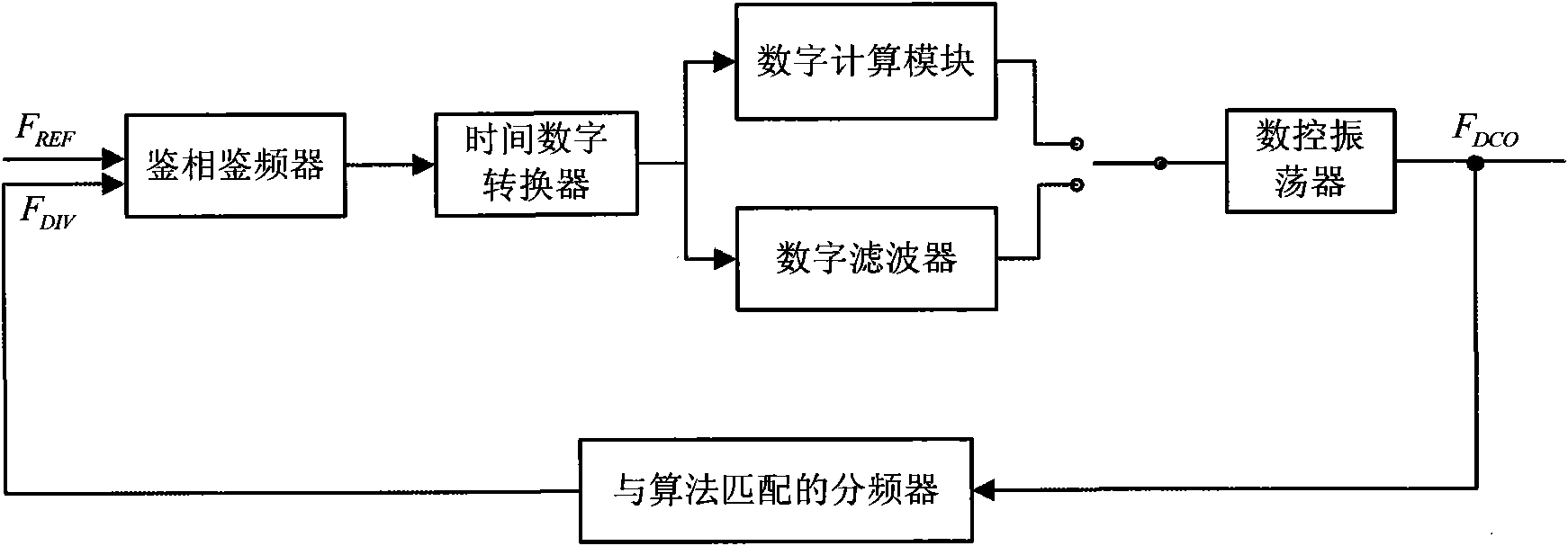
The invention relates to a rapid locking method for a full digital phase-locked loop, which is used for locking the frequency of the full digital phase-locked loop comprising a phase detection discriminator, a time-to-digit converter, a digital filter, a digital controlled oscillator and a frequency divider in a short time. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: finding a control word controlling the frequency of the digital controlled oscillator by a designed algorithm; dividing the frequency of a clock output by the digital controlled oscillator which is controlled bythe control word to obtain a divided-frequency clock with the frequency approximate to a reference clock frequency; and then, controlling the digital controlled oscillator to lock based on a phase difference between the reference clock and the divided-frequency clock which are distinguished by the phase detection discriminator. The full digital phase-locked loop is provided with a rapid frequencycapture loop and a phase-locked loop which alternately work, i.e. firstly, the rapid frequency capture loop finishes frequency capture, and then, the phase-locked loop finishes accurate locking.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Fully-digital direct sequence spread spectrum communication system and rapid pseudo code capturing method thereof
ActiveCN102571137ASimple designReduce power consumptionTransmissionDigital signal processingFpga implementations
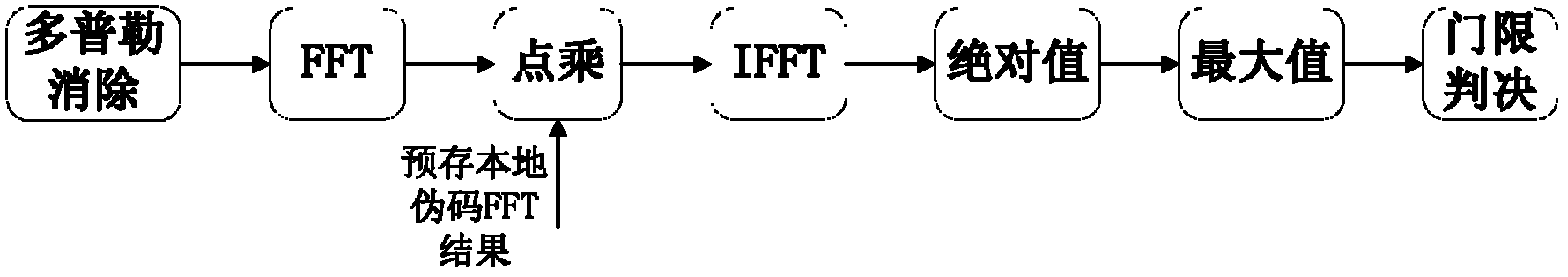
The invention discloses a fully-digital direct sequence spread spectrum communication system and a rapid pseudo code capturing method thereof. A digital signal is processed by using an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) which comprises a pseudo code capturing module, a sampling signal of an ADC (Analog To Digital Converter) is subjected to frequency mixing with a signal of a local carrier NCO (Numerically Controlled Oscillator) and filtered to obtain a baseband signal, residual carrier Doppler frequency is eliminated from the baseband signal by adopting a differential multiplying mode, thus the phase deviation of a receiving signal and a local pseudo code is further obtained through an FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) algorithm without scanning on a carrier frequency domain; and when the phase deviation of the pseudo code is obtained, a local pseudo code phase is modified and is subjected to correlation degree of dissociation with the receiving signal, and the carrier Doppler frequency is figured out by using the FFT algorithm, and is compensated to a carrier NCO and a pseudo code NCO, thus carrier frequency capturing and pseudo code capturing are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
All-digital frequency synthesis with non-linear differential term for handling frequency perturbations
ActiveUS7483508B2Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDigital tuningNumerically controlled oscillator
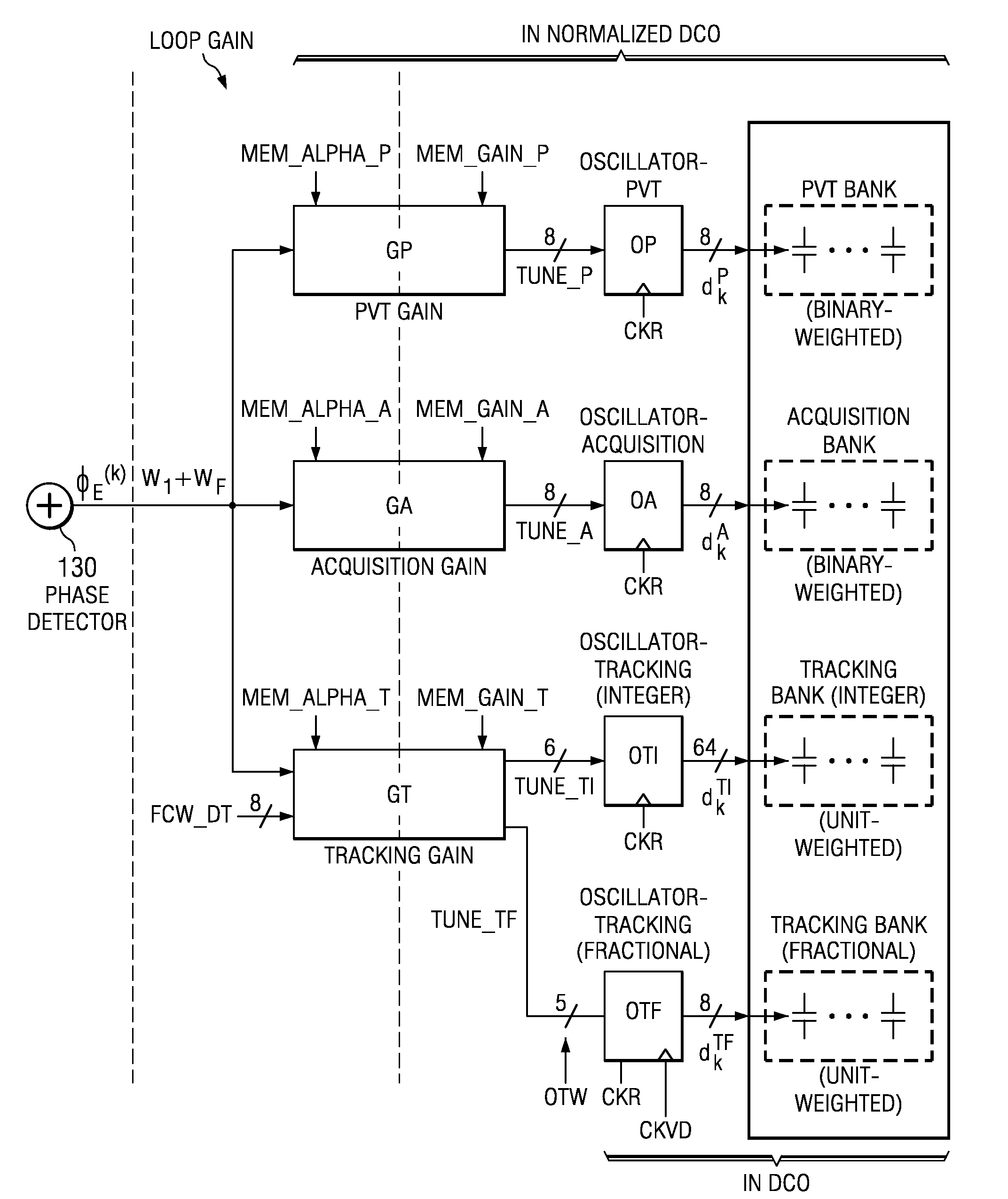
An all-digital frequency synthesizer architecture is built around a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) that is tuned in response to a digital tuning word (OTW). In exemplary embodiments: (1) a gain characteristic (KDCO) of the digitally controlled oscillator can be determined by observing a digital control word before and after a known change (Δfmax) in the oscillating frequency; (2) a portion (TUNE_TF) of the tuning word can be dithered (1202), and the resultant dithered portion (dkTF) can then be applied to a control input of switchable devices within the digitally controlled oscillator; and (3) a non-linear differential term (187, 331) can be used to expedite correction of the digitally controlled oscillator when large phase error changes (335) occur.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Pseudolite-based precise positioning system with synchronised pseudolites
InactiveUS20050015198A1Accurate synchronizationInstruments for road network navigationBeacon systemsNumerical controlLoop filter
Pseudolite-based precise positioning system with synchronised pseudolites that can compute the position of a mobile station with slave pseudolites synchronised to master pseudolite is provided. Therefore pseudolite-based precise positioning system according to present invention does not need correction information of a reference station. A pseudolite-based precise positioning system for computing the position of a mobile station without correction information of a reference station, the pseudolite-based precise positioning system includes: master pseudolite with reference clock of the positioning system; at least one slave pseudolite having digitally controlled numerical controlled oscillator means; mobile station computing the position of itself based on the clock-synchronised signal from the master pseudolite and the slave pseudolite without correction information of a reference station; and clock synchronisation loop filter means having the digitally controlled numerical controlled oscillator means synchronise the clock of the slave pseudolite to the clock of the master pseudolite by transmitting synchronisation information U k? of the slave pseudolite to the digitally controlled numerical controlled oscillator means, clock synchronisation loop filter means generating the synchronisation information U k? based on the pseudorange information and carrier phase information received from the master pseudolite and the slave pseudolite.
Owner:KEE CHANG DON
Method and device for phase error correction
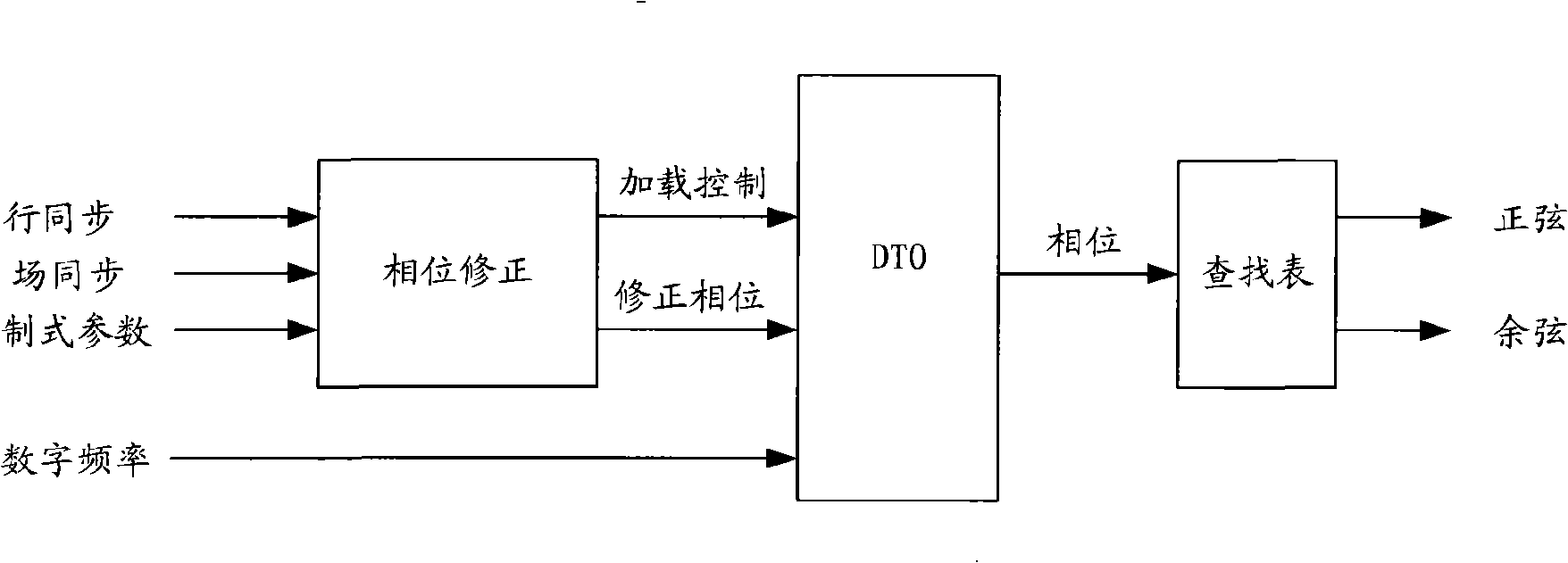
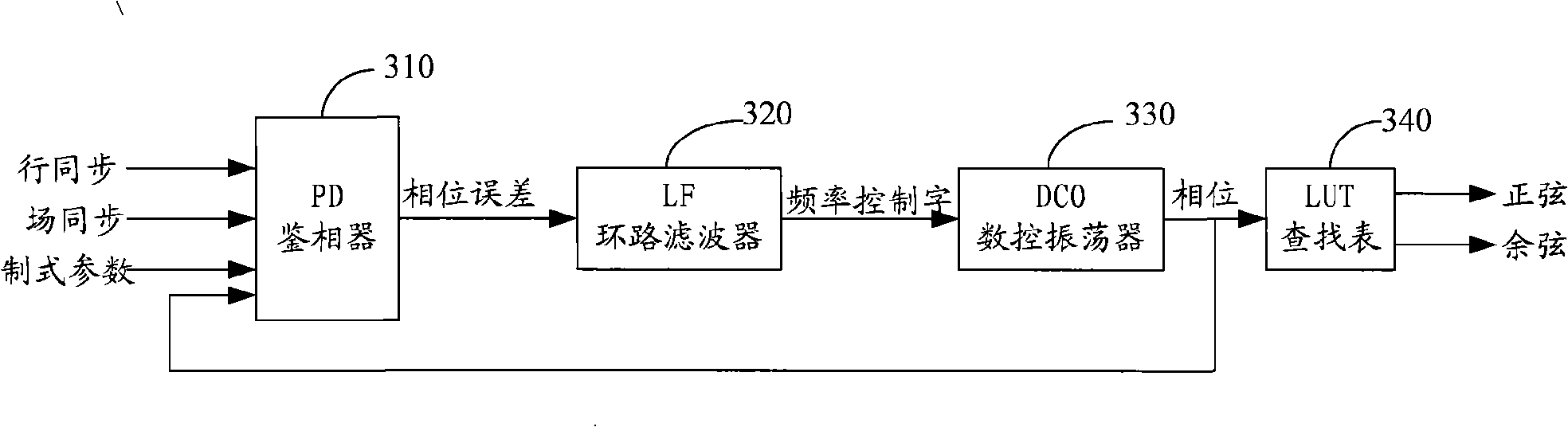
InactiveCN101345886AEliminate long-term accumulationEliminate phase stepsBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsDiscriminatorNumerical control
One embodiment of the invention discloses a device and a method of phase error correction, comprising: a phase discriminator, used for latching a controlled phase position sent by the numerical controlled oscillator when a line synchronizing signal and a field synchronizing signal arrive, and comparing with the moment reference phase position, and outputting phase error; a loop filter, used for receiving the phase error sent by the phase discriminator, performing low-pass filtering, and obtaining a frequency control word signal; a numerical controlled oscillator, used for receiving the frequency control word signal sent by the loop filter, generating controlled phase signal, wherein, the phase signal is transmitted to the phase discriminator, and the high position part of the phase signal is transmitted to the lookup table; a lookup table, used for obtaining a quantized value of corresponding sine and cosine functions according to the high position part of the phase signal. The invention eliminates long term accumulation of DDS to frequency quantized error in a complex video signal coder, cuts the phase error with large granularity into uniform phase error with small granularity, and distributes the phase error uniformly on the time.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Digital signal down variable frequency processing system based on MIMO real time test platform
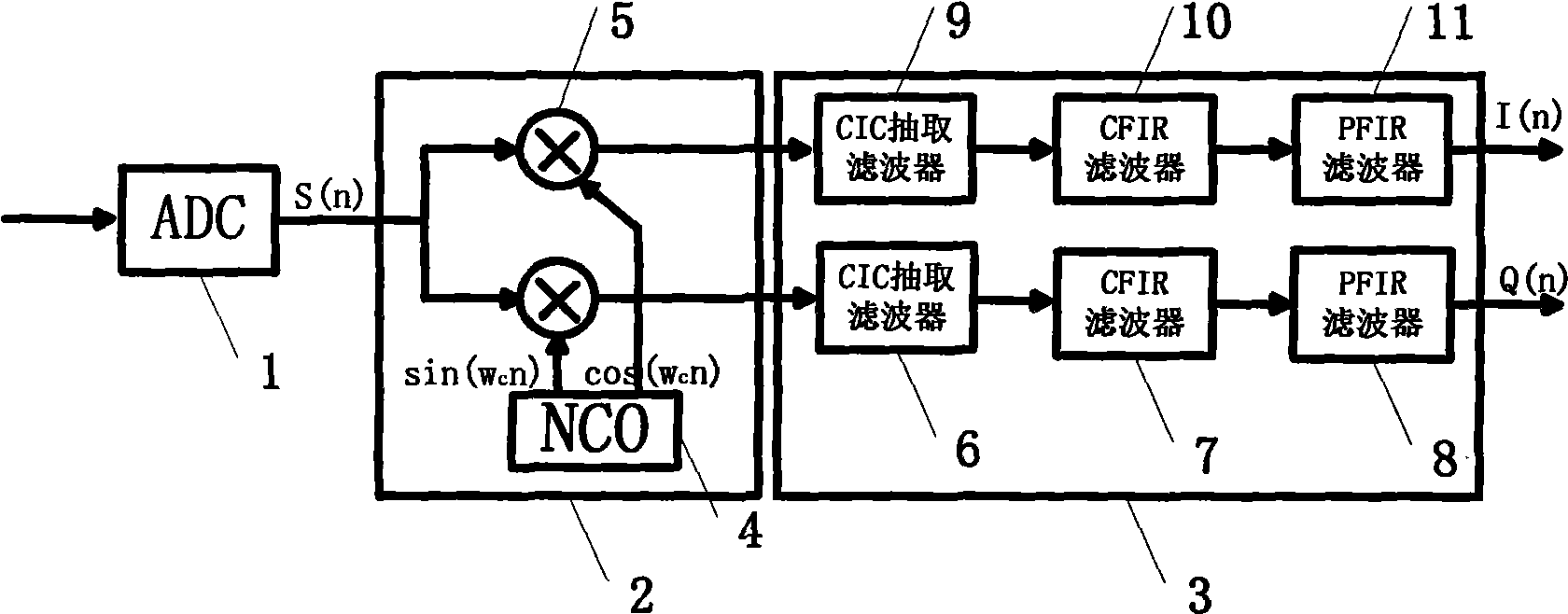
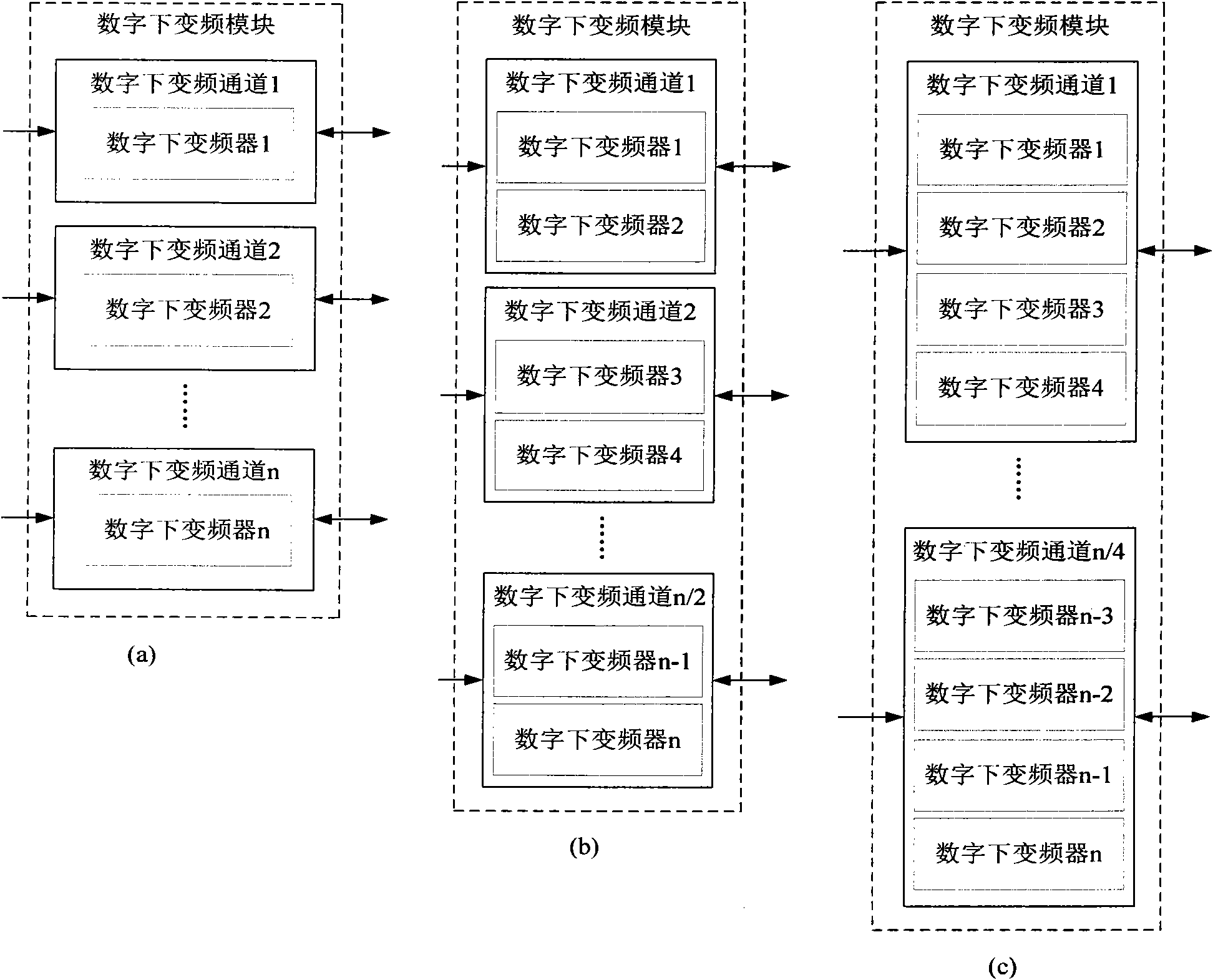
InactiveCN101510756AEasy to implementProcessing speedDigital technique networkTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDigital signal processingNumerically controlled oscillator
The invention discloses a digital signal down-conversion processing system based on an MIMO real-time testing platform, pertaining to the technical field of digital signal processing. The system comprises four DDC modules and each DDC module consists of four independent digital signal down-conversion processing channels. Each channel consists of an analog-to-digital converter, a digital quarter mixer and a digital decimation filter set. The digital quarter mixer consists of a digital controlled oscillator and two paths of multipliers, and the digital controlled oscillator is respectively connected with the two multipliers; the digital decimation filter set consists of two groups of filters with complete same parameters and each filter group respectively comprises a CIC decimation filter, a CFIR compensation filter and a PFIR matched filter which are connected in sequence. The system has good expansibility and modularization and can meet the requirements of real-time and high-speed performance.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Image rejection in logic-based architecture for FSK modulation and demodulation
InactiveUS6265948B1Angle modulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsBandpass filteringModem device
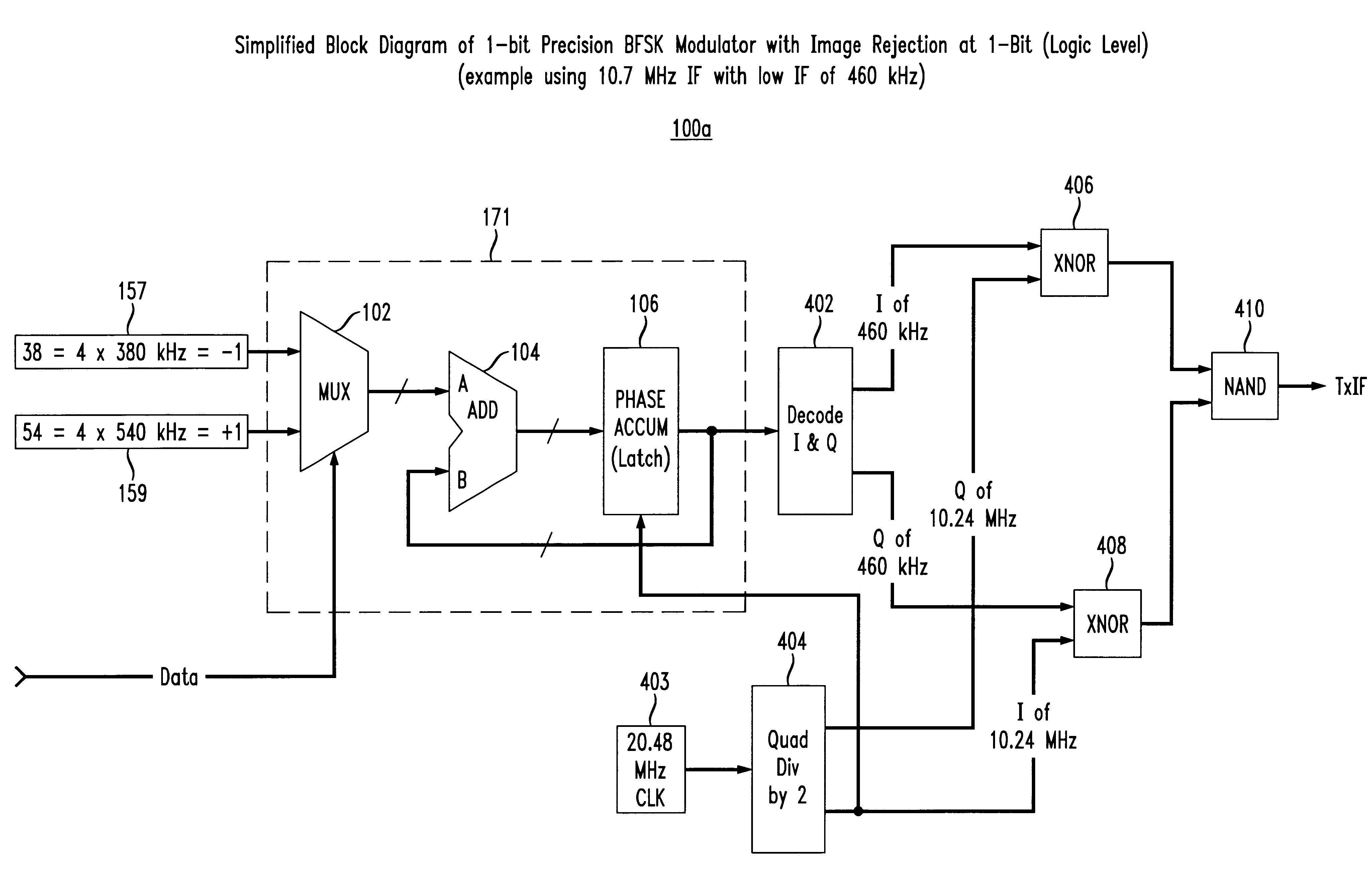
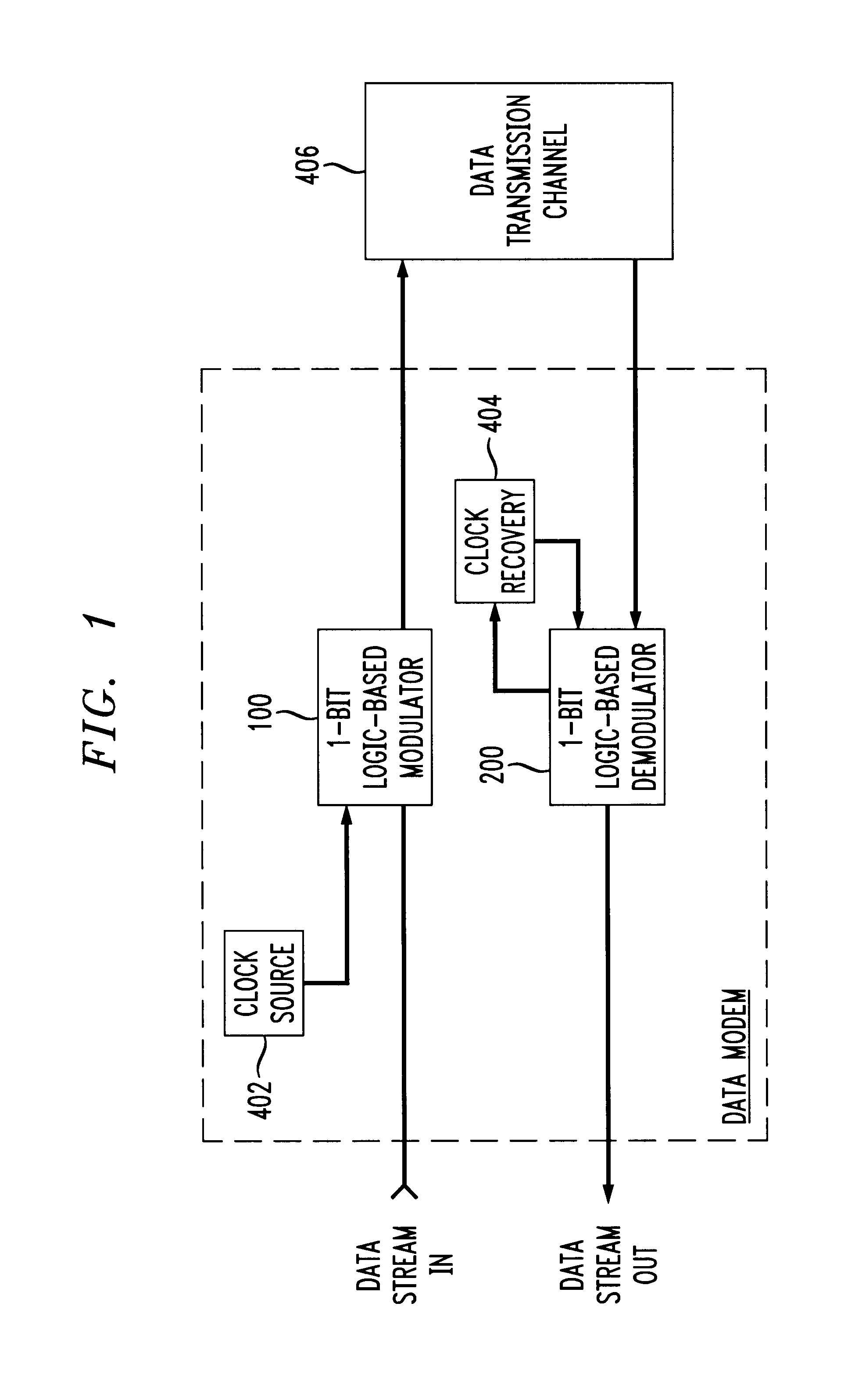
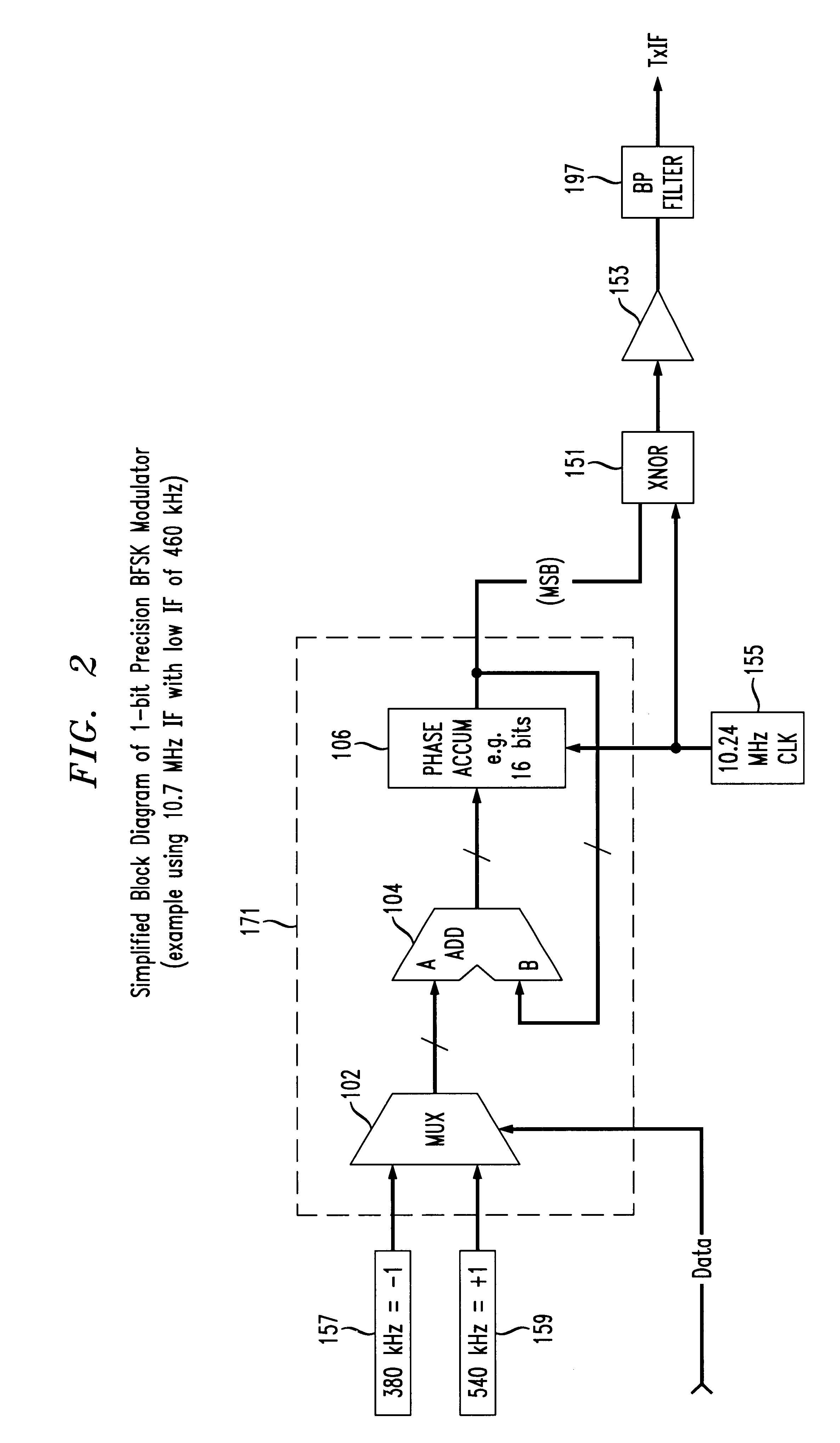
A cost-effective continuous phase logic-based modulator and demodulator are provided to allow communications using binary frequency shift keying (BFSK) as well as M-ary FSK techniques. The modulator of the 1-bit precision modem architecture is based on a 1-bit precision numerically controlled oscillator (NCO), which provides complete programmability with respect to a frequency of the 1-bit precision logic-based modulator and / or demodulator. The 1-bit precision NCO includes an adder and a phase accumulator register which is clocked by a master clock signal. A two-input multiplexer has a single bit symbol value to generate BFSK, or larger input multiplexers can be implemented to provide M-ary FSK. The output of the 1-bit precision NCO is upconverted to an intermediate frequency using a simple logic function, i.e., XNOR logic. Alternatively, the intermediate frequency may be arrived at without the need for upconversion by directly utilizing a harmonic alias at a desired IF frequency. The undesirable portion of the upconverted signal may be suppressed using I / Q image rejection, and / or an appropriate bandpass filter may be used. A band limited, hard limited signal at the high IF is presented to the 1-bit precision demodulator as a receive IF signal, which is treated as a 1-bit quantization of the signal. The receive IF signal is digitally down-converted to a low IF signal to produce an alias signal at the low IF frequency.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
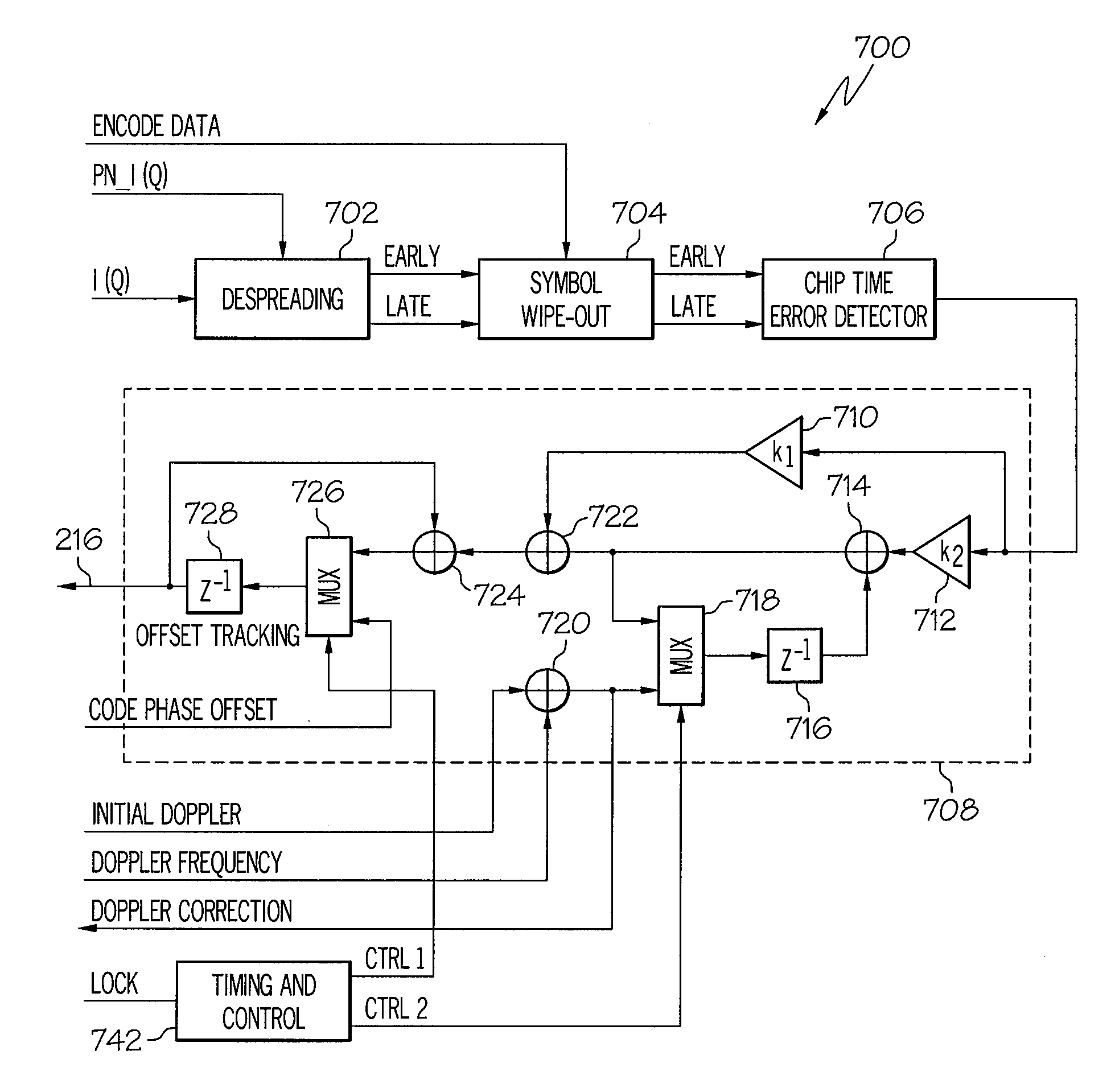
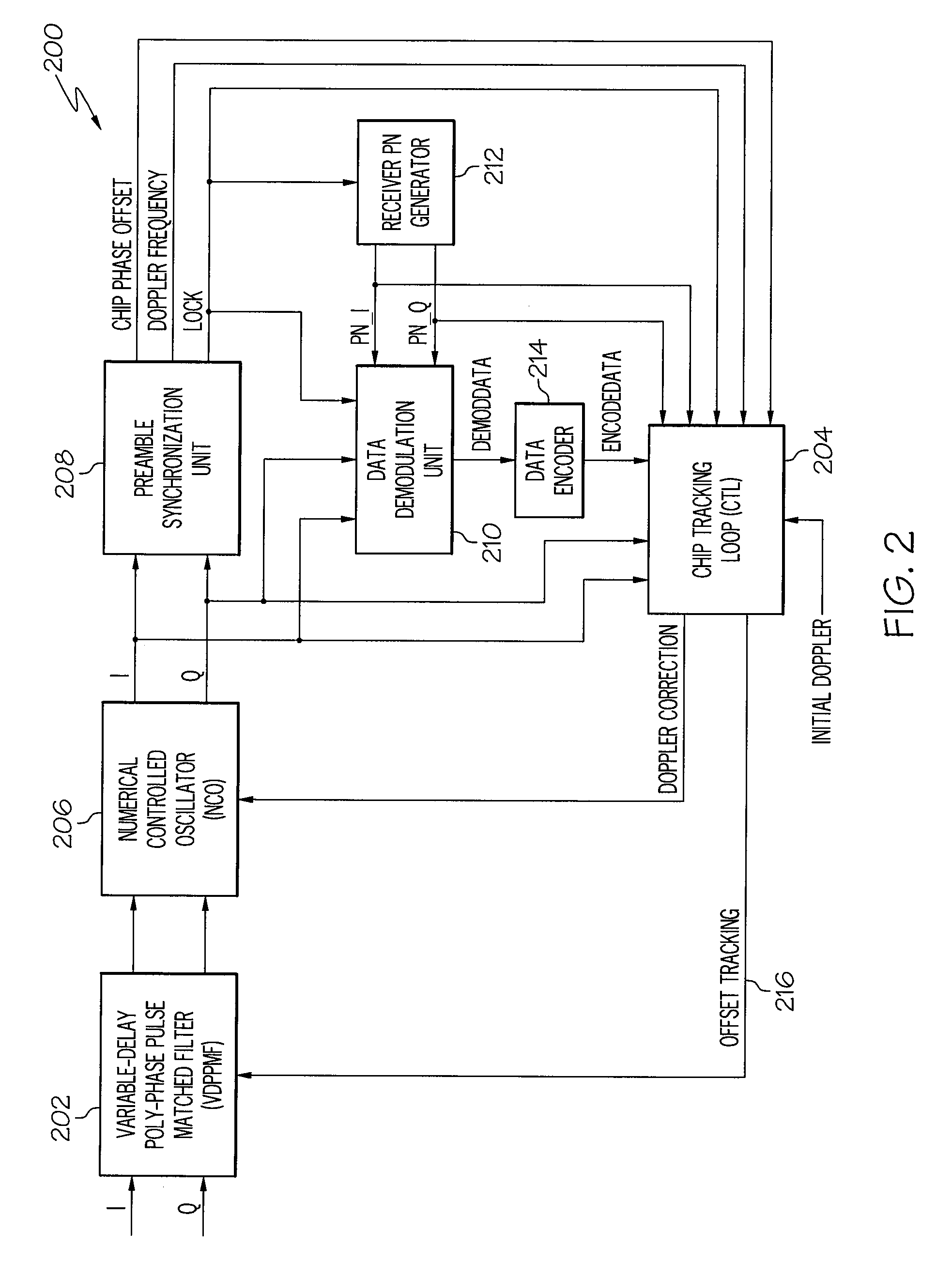
Device and method for fast transition from preamble synchronization to data demodulation in direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) communications
ActiveUS20090180524A1Quick transitionOffset errorTransmissionNumerical controlNumerically controlled oscillator
A device for fast transition from preamble synchronization of a received baseband signal to demodulation of the received baseband signal may include a baseband chip tracking loop to generate an offset tracking value to track any initial chip phase offset and Doppler-caused baseband chip frequency drift associated with the received baseband signal. The device may also include a numerical controlled oscillator to correct any Doppler-caused phase rotation associated with the received signal. The device may additionally include a preamble synchronization unit to detect a preamble of the received baseband signal, and to measure a chip phase offset and a baseband Doppler frequency shift associated with the received baseband signal. The chip phase offset may be used to set an initial chip phase offset value of the chip tracking loop so that the chip tracking loop starts with approximately a zero pull-in error. The baseband Doppler frequency shift may be used to set initial frequency offset values in the chip tracking loop and the numerical controlled oscillator so that both start with substantially near-zero offset errors for substantially immediate demodulation of the received signal. The device may further include an output device to output the data demodulated from the received baseband signal.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
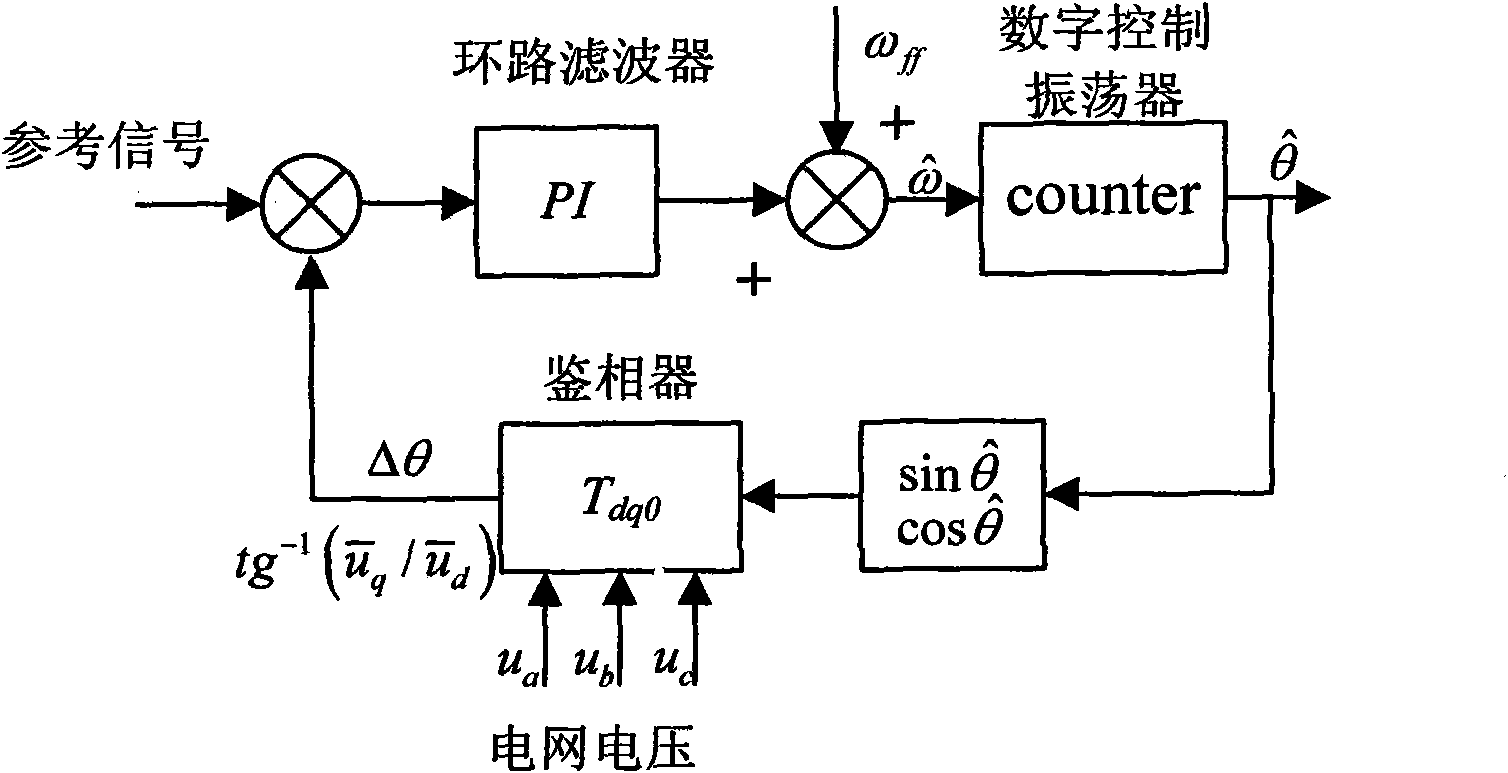
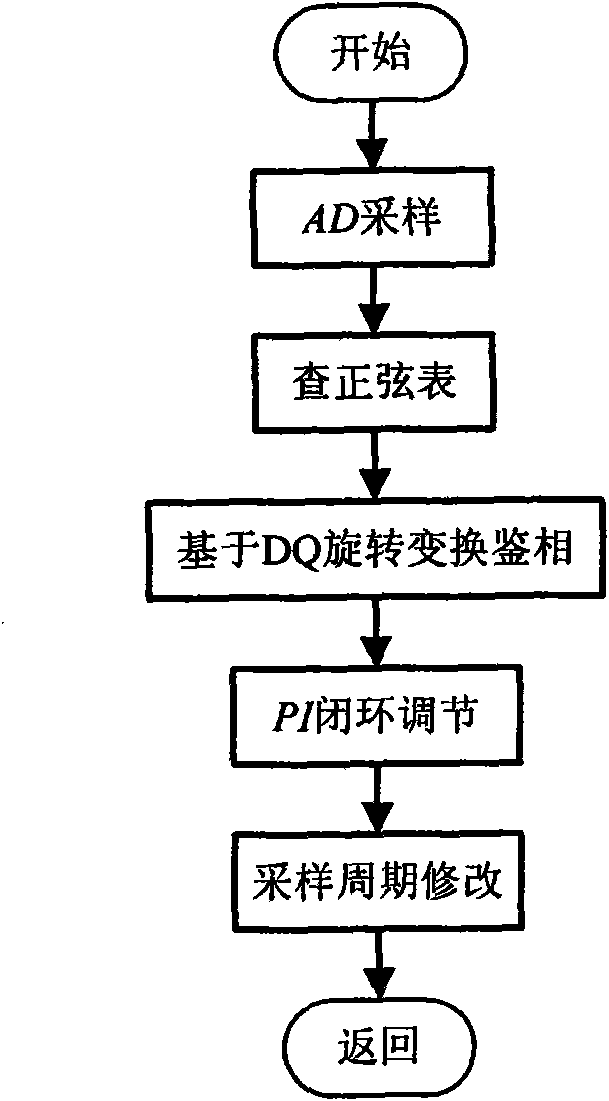
Method for realizing software phase-locked loop with unfixed sampling frequency
InactiveCN101777912ASpeed up developmentImprove calculation accuracyPulse automatic controlNew energyNumerically controlled oscillator
The invention discloses a method for realizing a software phase-locked loop with an unfixed sampling frequency. The method comprises the following steps: firstly adopting an analog phase-locked loop digital controlled oscillator of the DSP period counter to obtain digital controlled oscillator output signals; then working out the phase error between the mains voltage and a reference signals in the DQ-transformation phase demodulation mode by using the digital controlled oscillator output signals as the reference signals; and establishing a closed loop transfer function secular equation of a phase-locked loop system and determining the parameters of the designed loop filter based on the digital controlled oscillator output signals and the phase error between the mains voltage and the reference signals. The invention can maintain the fixed number of the sampling points in the primitive period, and is used for repeatedly controlling various grid-connected converting devices, such as active electric filters, new energy-powered grid-connected converters and the like. By adopting the DQ-transformation phase demodulation mode, the invention can well inhibit the harmonic and unbalanced mains, resist the fluctuation of the mains voltage, and ensure the reliable operation of the phase-locked loop under the conditions of multiple mains voltage zero passage, voltage harmonics, voltage fluctuation and mains voltage imbalance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for estimating carrier, frequency shifts of orthogonal FDM communication system
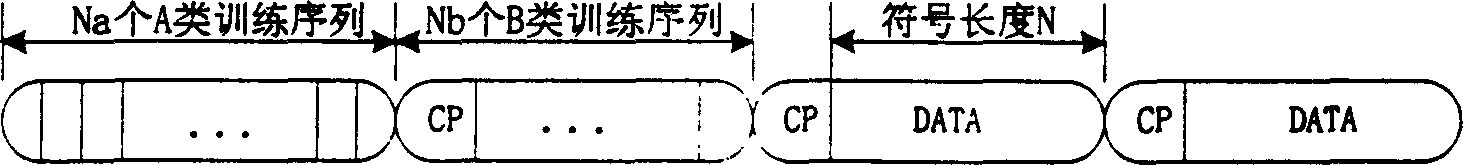
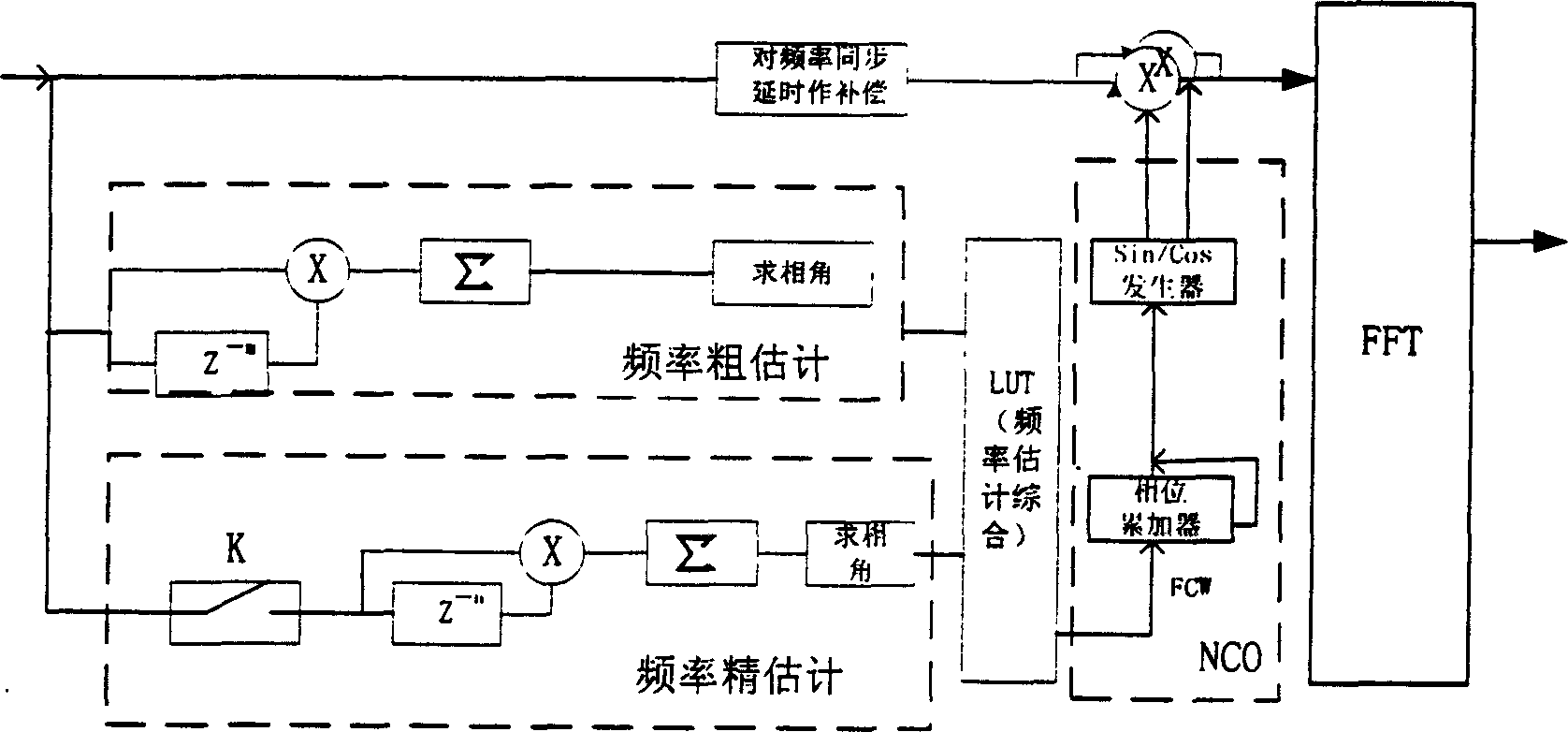
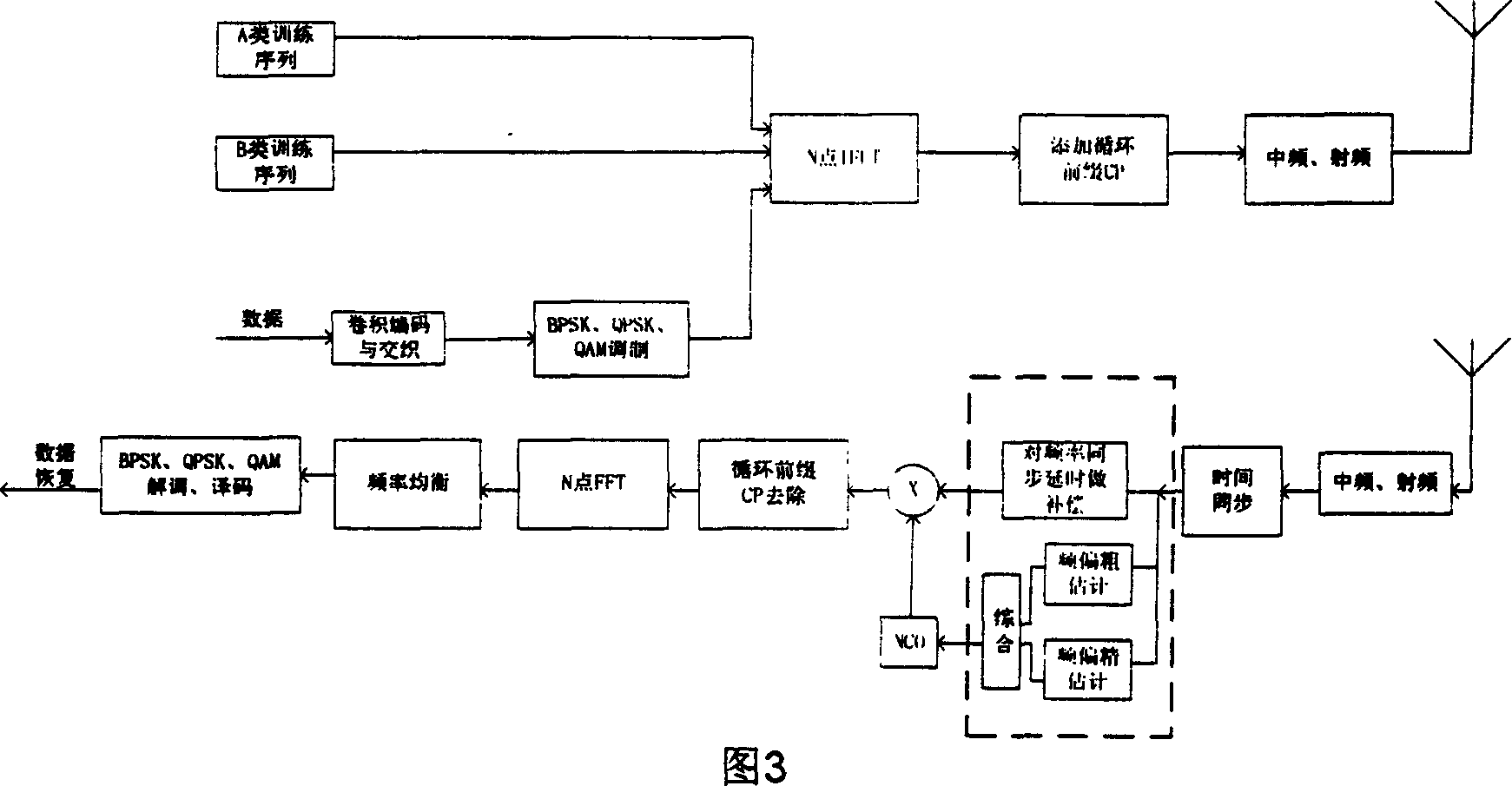
InactiveCN1472900APromote recoveryHigh precisionOrthogonal multiplexMultiple carrier systemsTime domainNumerical control
A estimating method of OFDM communication system carrier frequency excursion, in original place of systems frame adds two training sequence that were designed especially, using the result of cross correlation of class A training sequence estimates original value of frequency excursion, namely to make rough estimation of frequency excursion, then using class B makes autocorrelation, gained frequency deviation signal was estimated precisely in small scale, namely to make frequency excursion precise estimation, then make two estimating value combined to get precise value of system frequency excursion, finally control numerical control oscillator to produce rectify value of system frequency excursion, and put it to multiply with time domain data to make compensation of frequency excursion.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
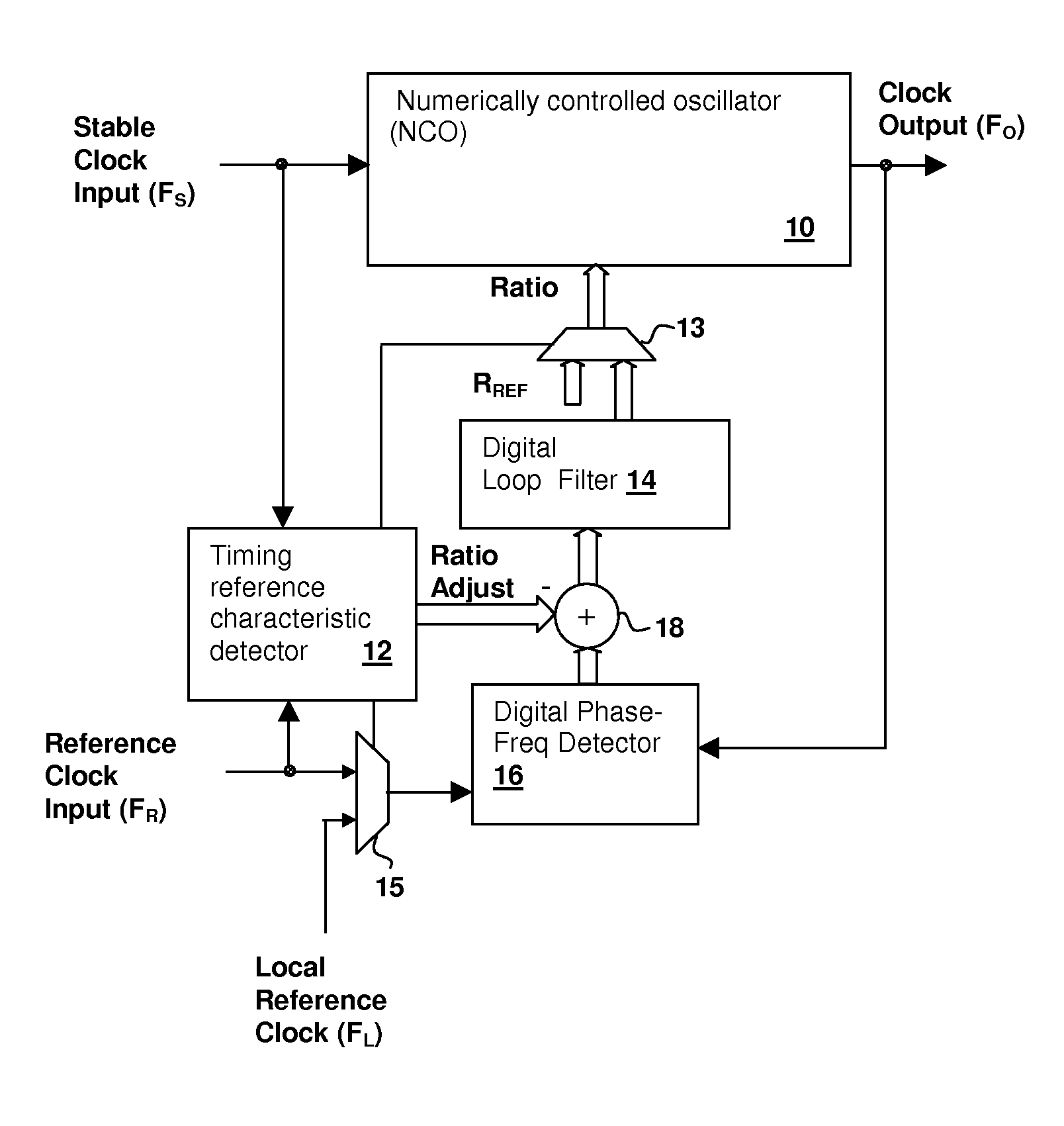
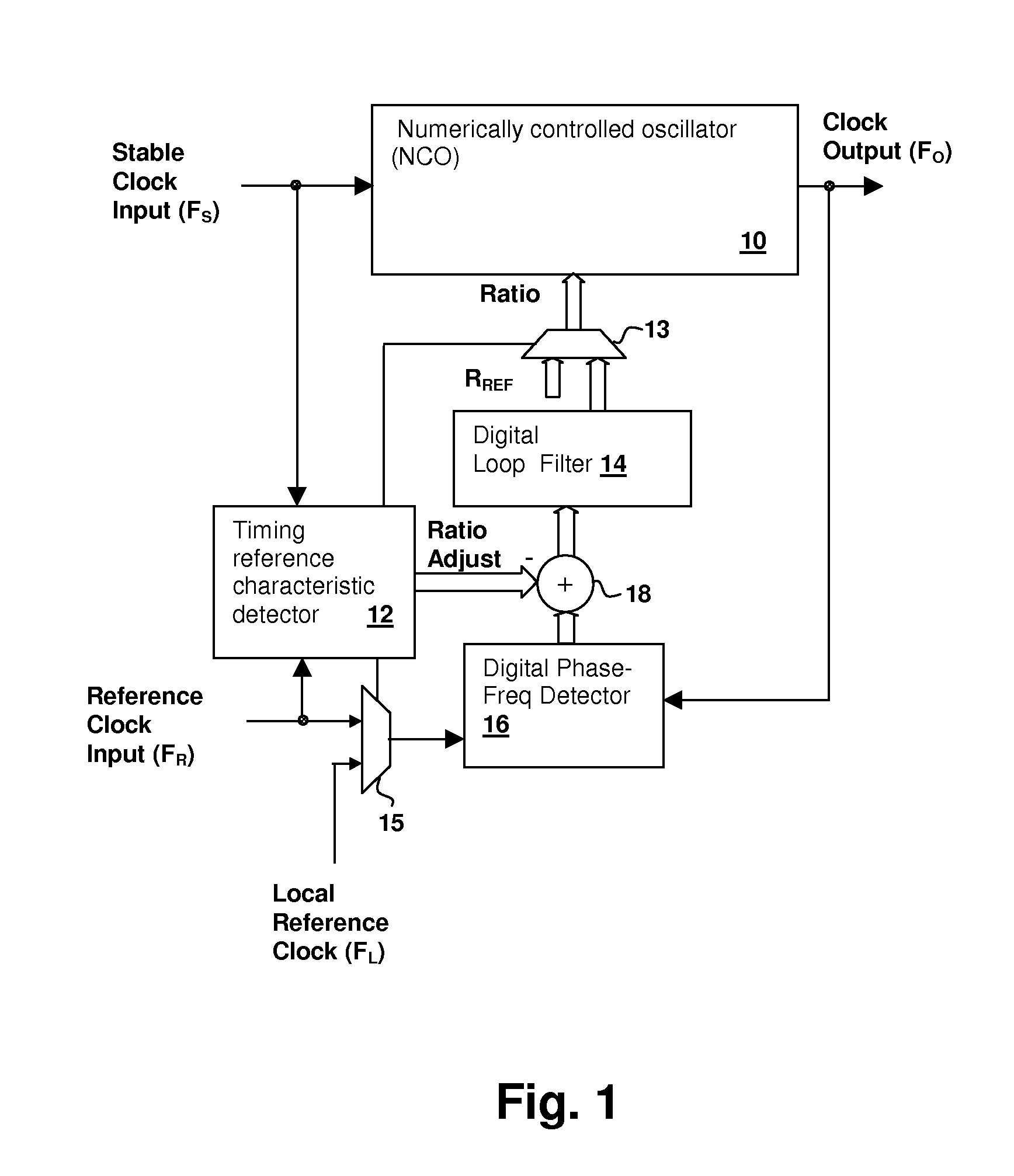
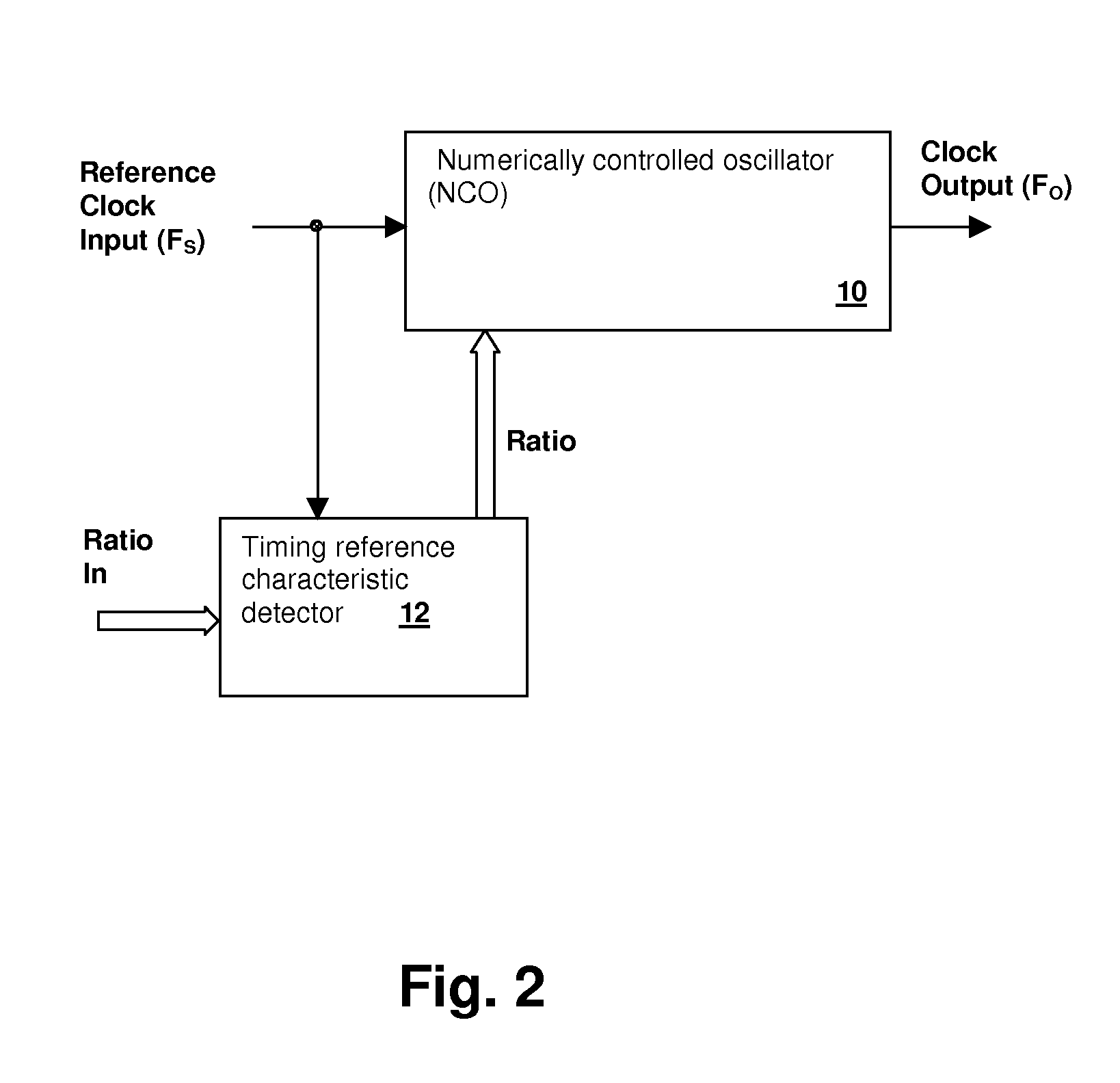
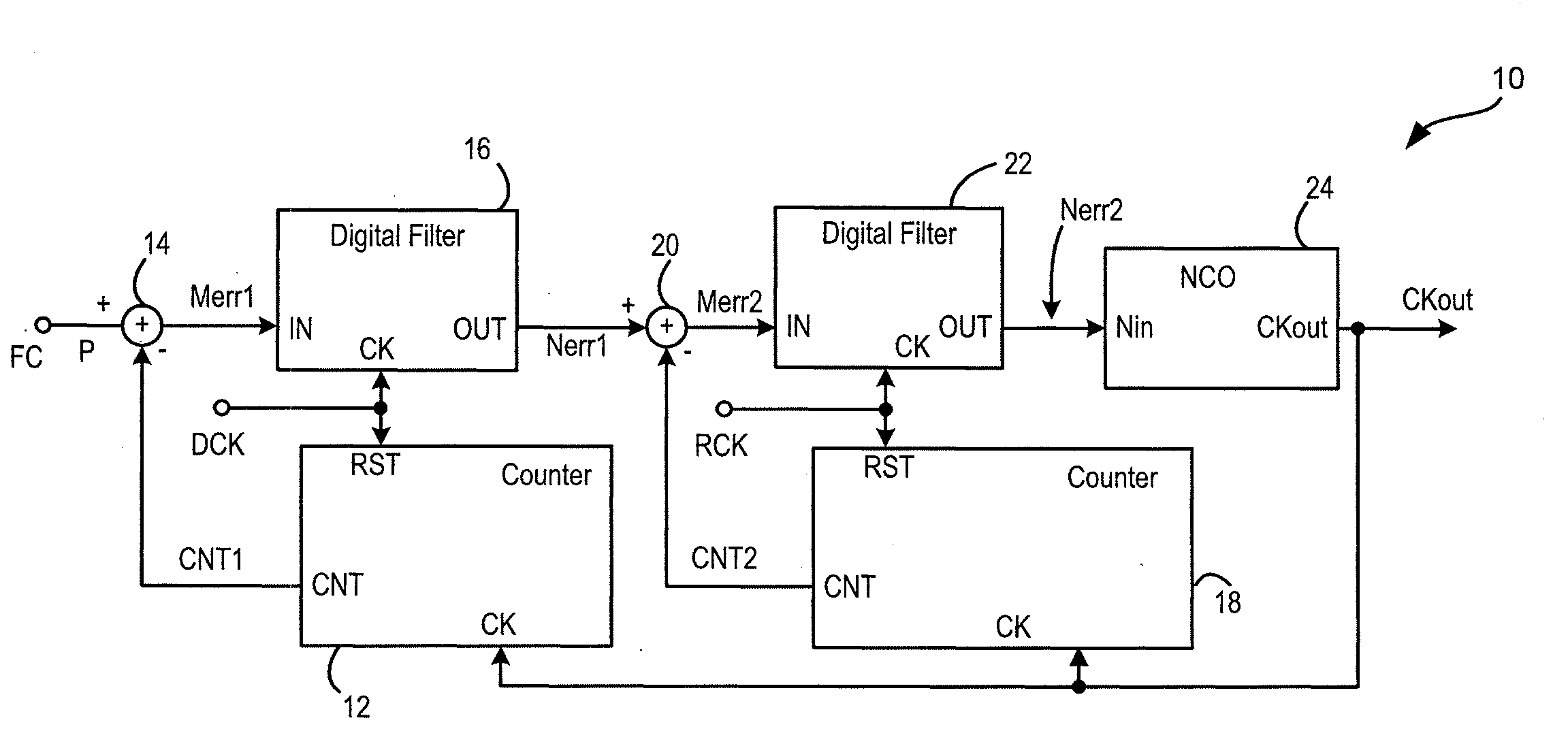
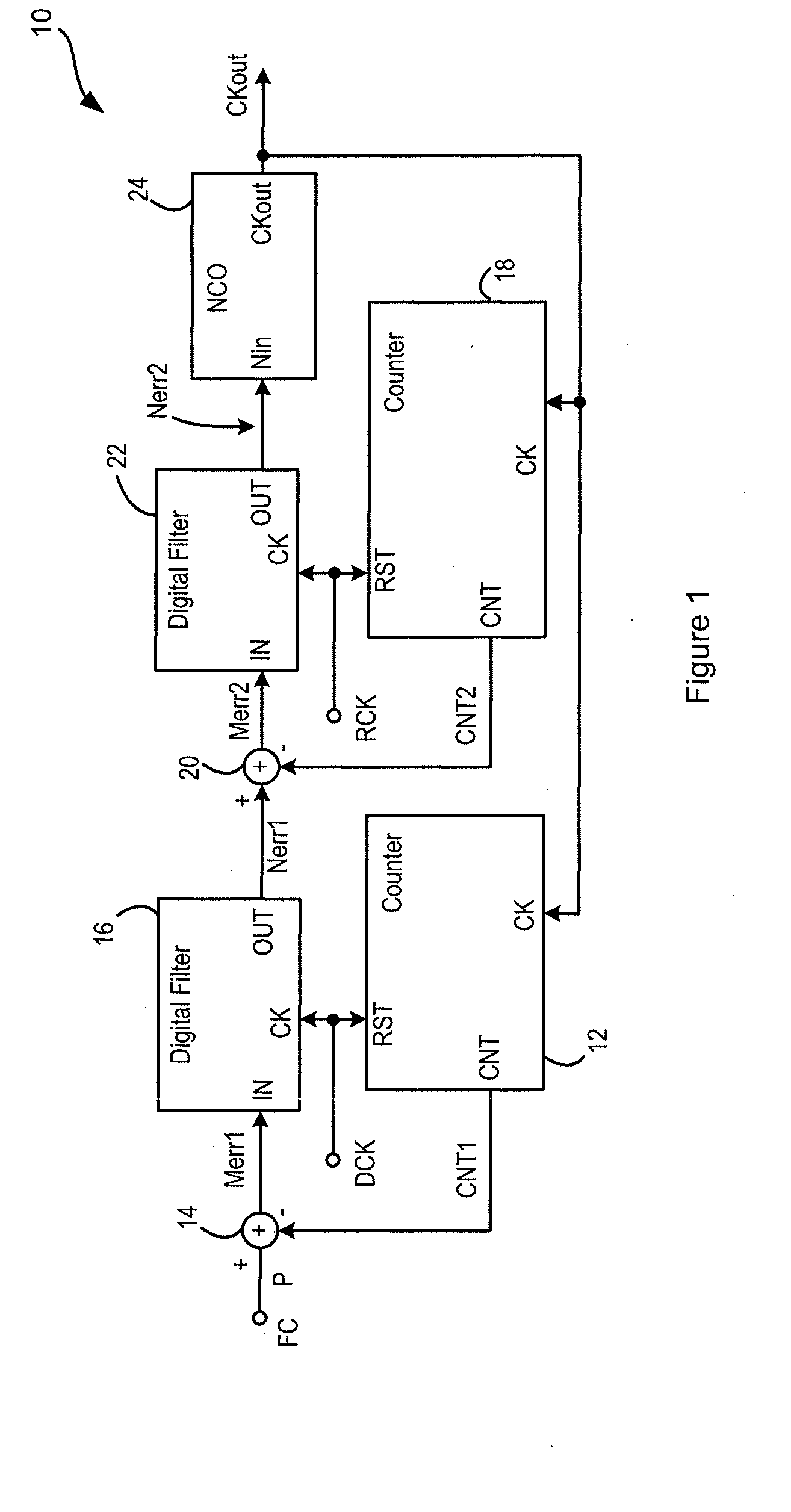
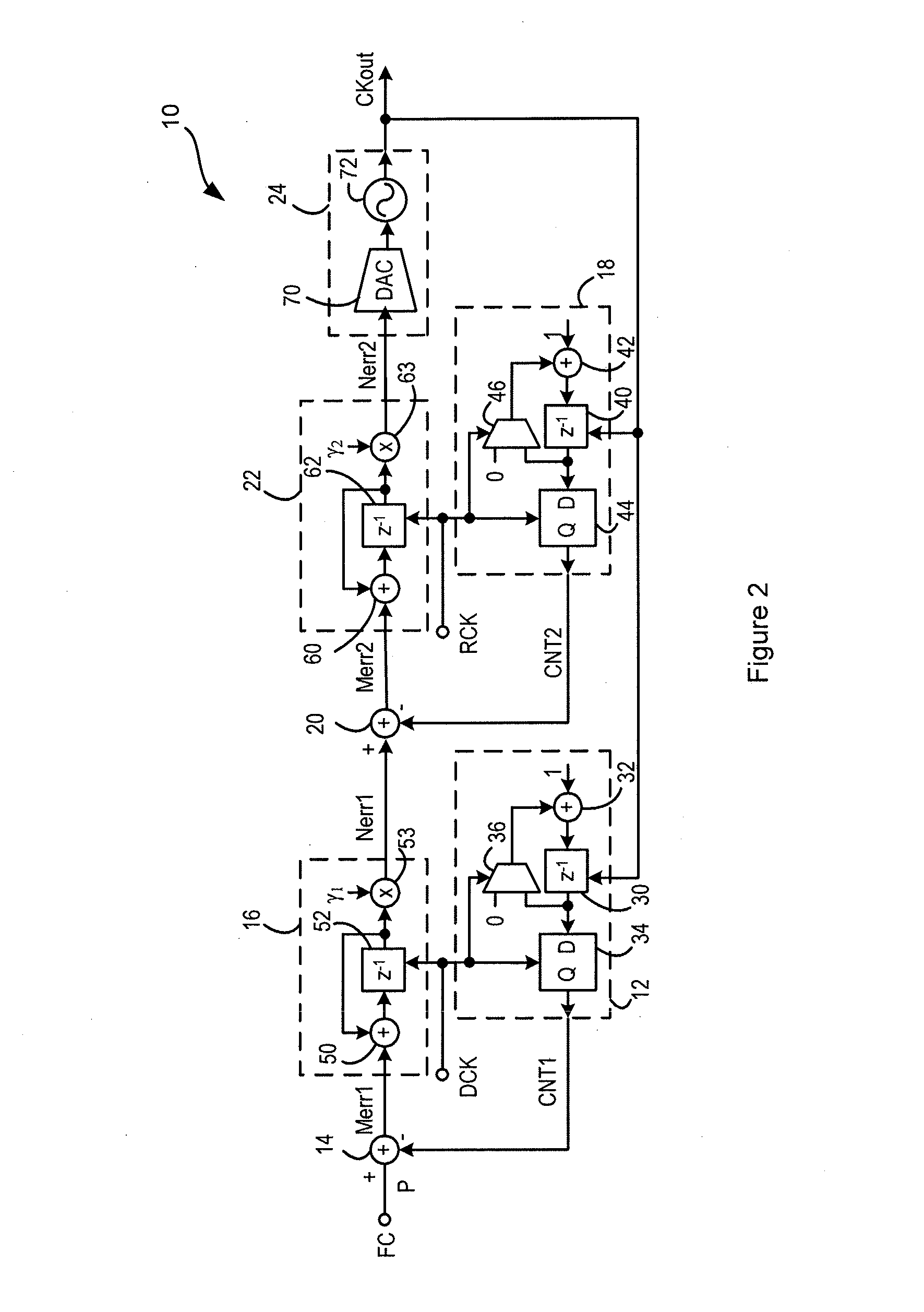
Numerically-controlled phase-lock loop with input timing reference-dependent ratio adjustment
ActiveUS7746972B1Pulse automatic controlRadio transmissionClock rateNumerically controlled oscillator
A numerically-controlled phase-lock loop with input clock dependent ratio adjustment provides for narrower-bandwidth loops that lock to a wide range of frequencies and / or operation with an absent or degraded input timing reference. A timing reference characteristic detector determines an input frequency range of the input timing reference signal, the data type of the timing reference, and / or whether a timing reference signal of sufficient quality is present. A numerically controlled oscillator is controlled by a numeric ratio that is adjusted to provide the desired clock frequency output in conformity with the detected frequency range and / or data type. If the timing reference signal is absent or degraded, then the numeric ratio can be set to a fixed value or a local timing reference can be applied in order to generate the desired clock output frequency.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
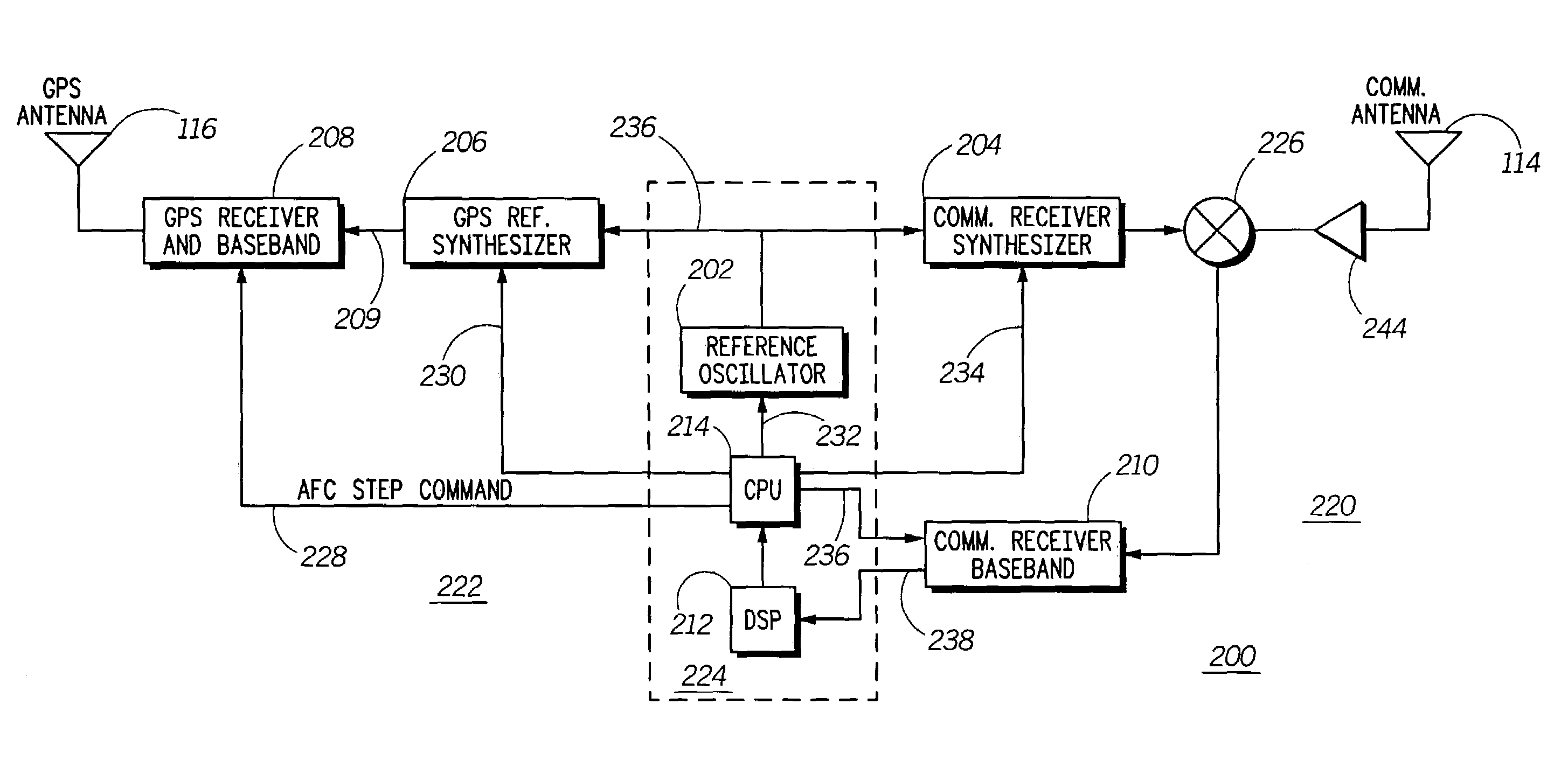
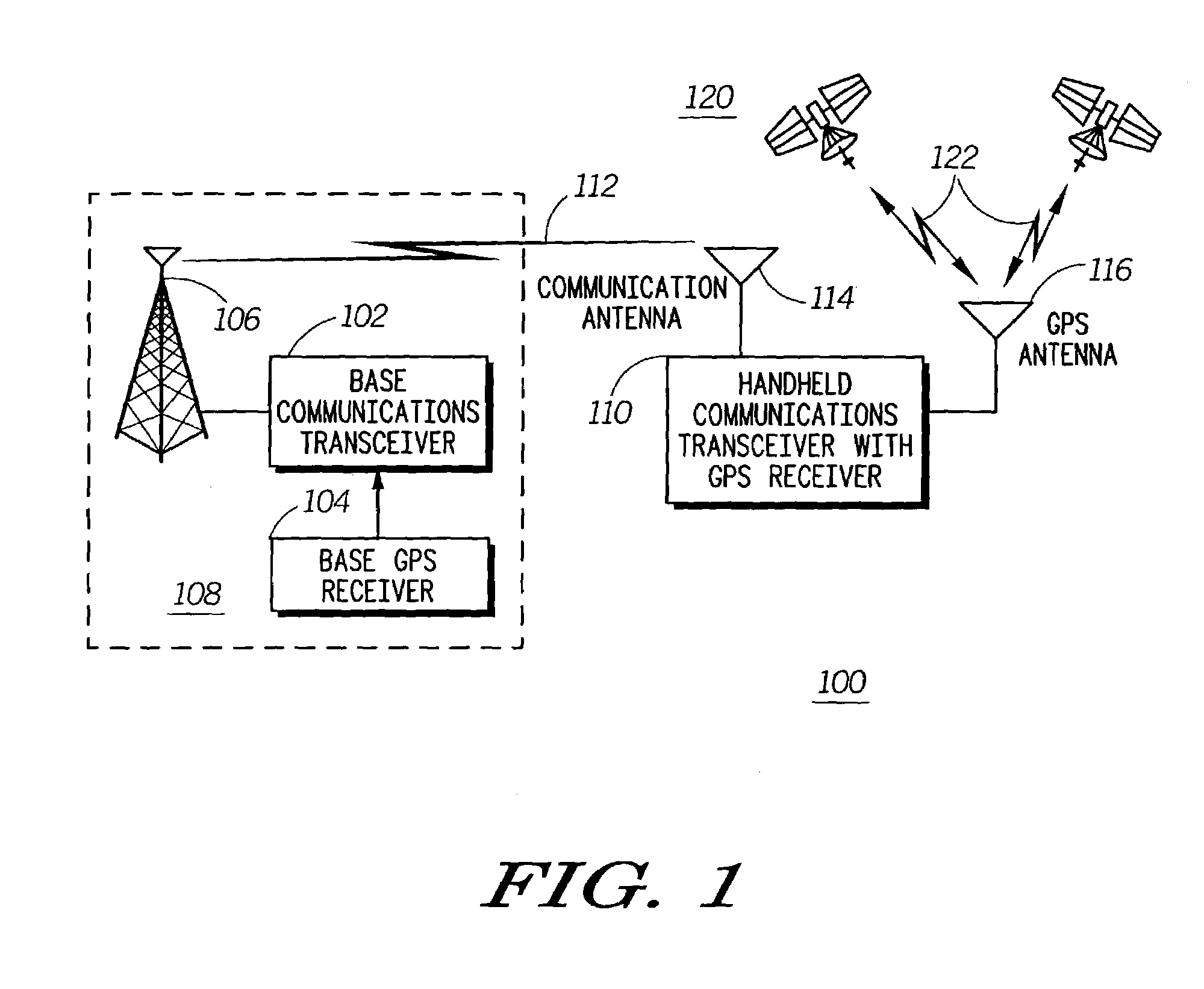
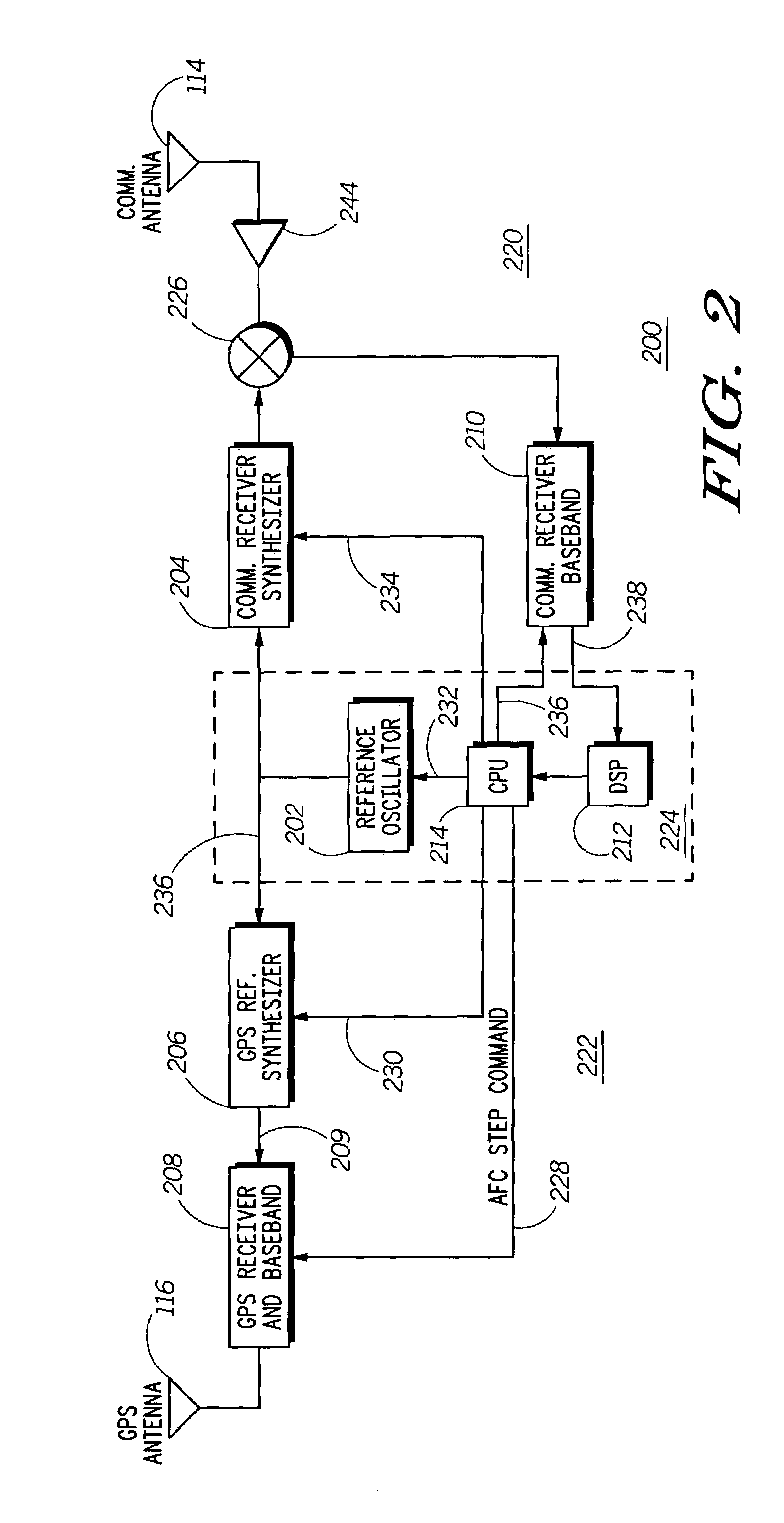
Automatic frequency control processing in multi-channel receivers
InactiveUS7062240B2Continuous tuning detailsResonant circuit detailsLocal oscillator signalConstant frequency
A multiple channel receiver (200) includes a communications receiver synthesizer (204) and at least one numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) (406) that produce local oscillator signals that are derived from a common reference oscillator (202). A DSP (212) and CPU (214) perform automatic frequency control (AFC) by adjustment of the reference oscillator (202) based upon a signal received by a receive channel using the local oscillator signal produced by the communications receiver synthesizer (204). The CPU (214) also provides a synchronous indication of adjustments to the reference oscillator (202) to control circuitry for the at least one NCO (406) so that the configuration of the NCO (406) can be altered so as to maintain a substantially constant frequency output during the adjustment of the reference oscillator (202).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
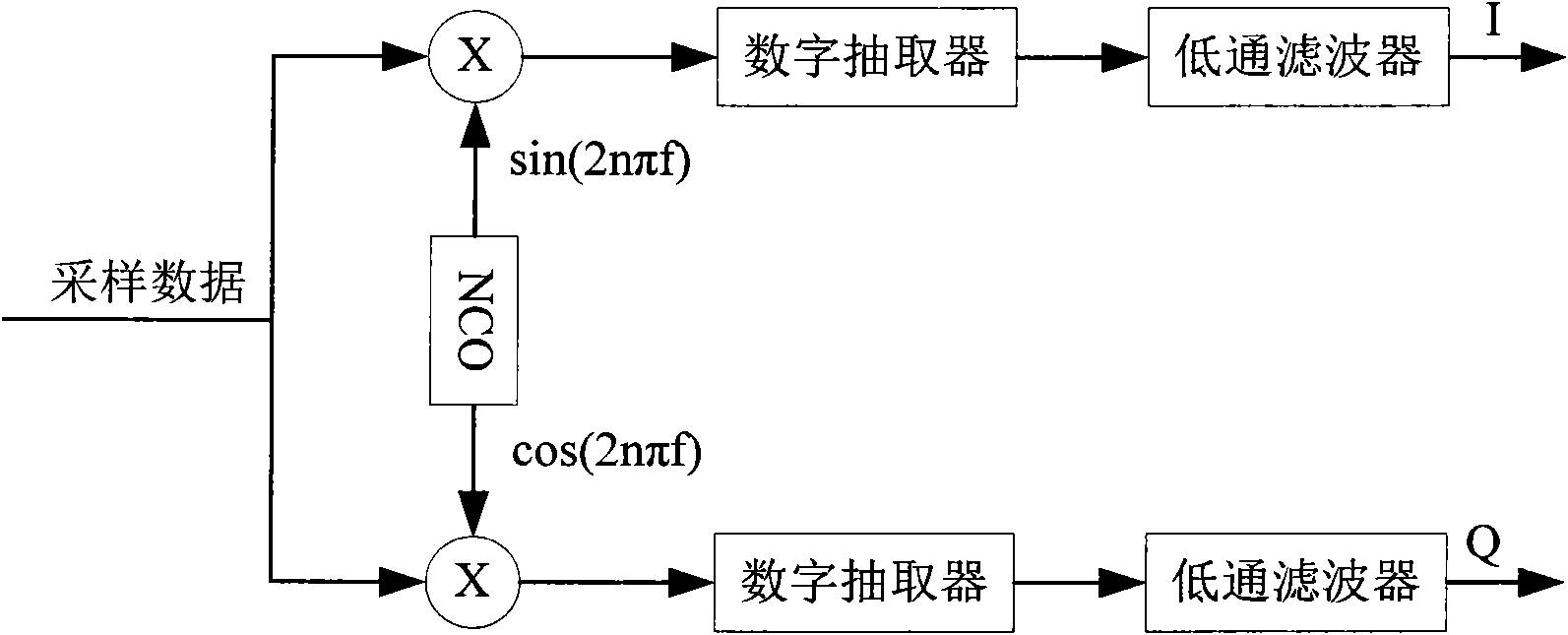
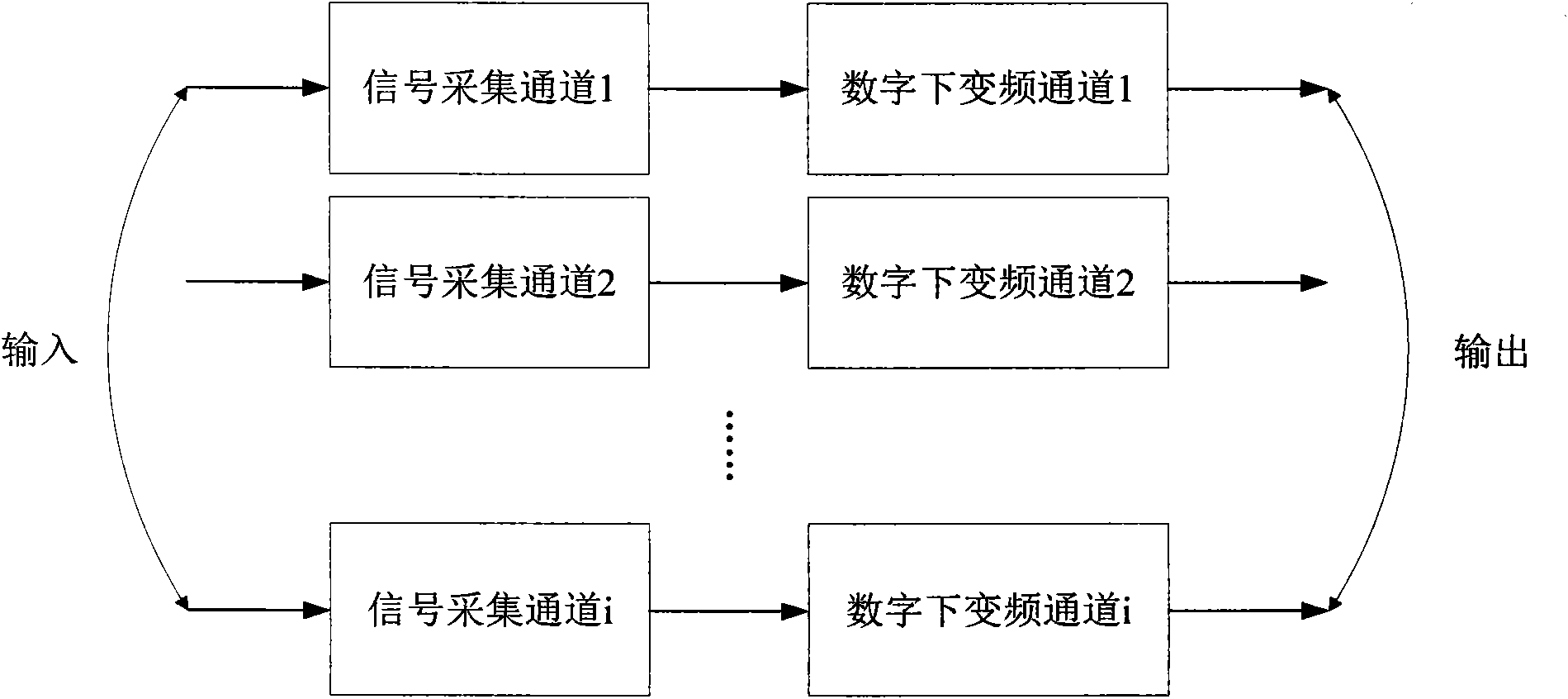
Multi-channel digital down-conversion device
InactiveCN101977021ASolve the limitation of functional structureImprove real-time performanceMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceFrequency changerNumerical control
The invention discloses a multi-channel digital down-conversion device, which comprises a signal acquisition module, an m*n-way switch matrix, a digital down-conversion module and an FPGA controller. Firstly, the FPGA controller controls the digital down-conversion module and determines the working mode of the digital down-conversion module, such as a narrow-band parallel mode, an orthogonal joint mode and an orthogonal alternative joint mode; secondly, the FPGA controller controls the input / output connection state of the m*n-way switch matrix to further finish the paired connection between an m-channel signal acquisition channel and a digital down-conversion channel so as to carry out demodulation according to different down-conversion working modes; and thirdly, the FPGA controller controls each digital down-converter and writes the index parameters of a numerical control oscillator, the index parameters of a digital extractor and the index parameters of a low-pass filter into corresponding internal registers so that each digital down-converter can be independently programmed. The digital down-conversion device of the invention can realize digital down-conversion processing of various band widths and various index parameters for multiple-channel digital intermediate-frequency signals, ensuring better real-time performance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Clock generator
ActiveUS20130129114A1Reduce jitterHigh frequency accuracyPulse automatic controlDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlFrequency ratioNumerically controlled oscillator
A clock generator receives first and second clock signals, and input representing a desired frequency ratio. A comparison is made between frequencies of an output clock signal and the first clock signal, and a first error signal represents the difference between the desired frequency ratio and this comparison result. The first error signal is filtered. A comparison is made between frequencies of the output clock signal and the second clock signal, and a second error signal represents the difference between the filtered first error signal and this comparison result. The second error signal is filtered. A numerically controlled oscillator receives the filtered second error signal and generates an output clock signal. As a result, the output clock signal has the jitter characteristics of the first input clock signal over a useful range of jitter frequencies and the frequency accuracy of the second input clock signal.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Direct digital synthesis using a sine weighted DAC
InactiveUS6281823B1Electric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic control18-bitImage resolution
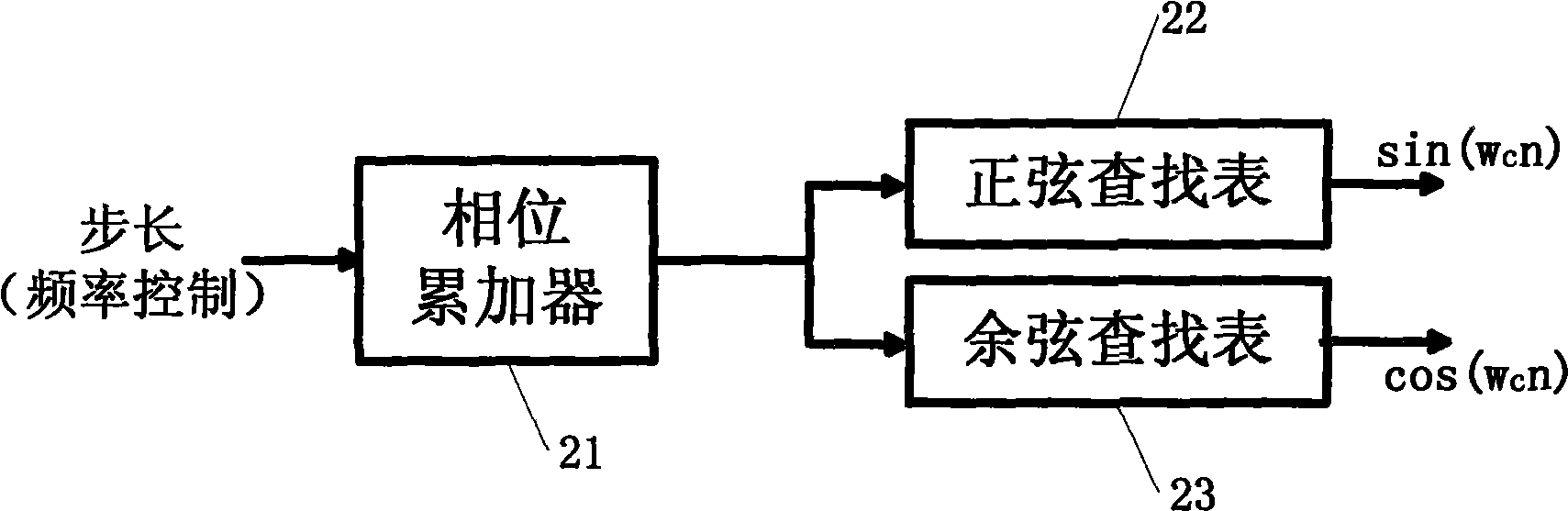
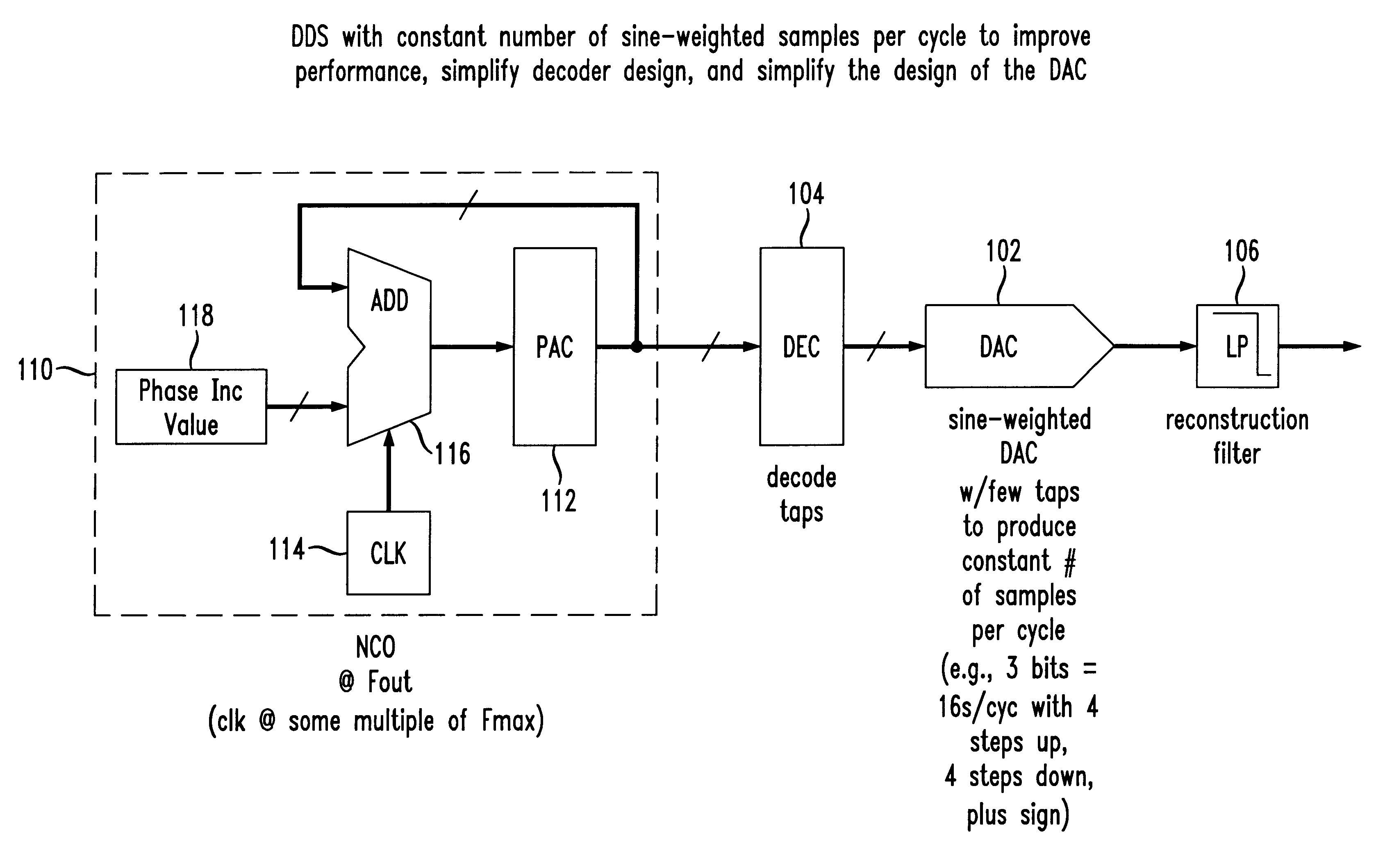
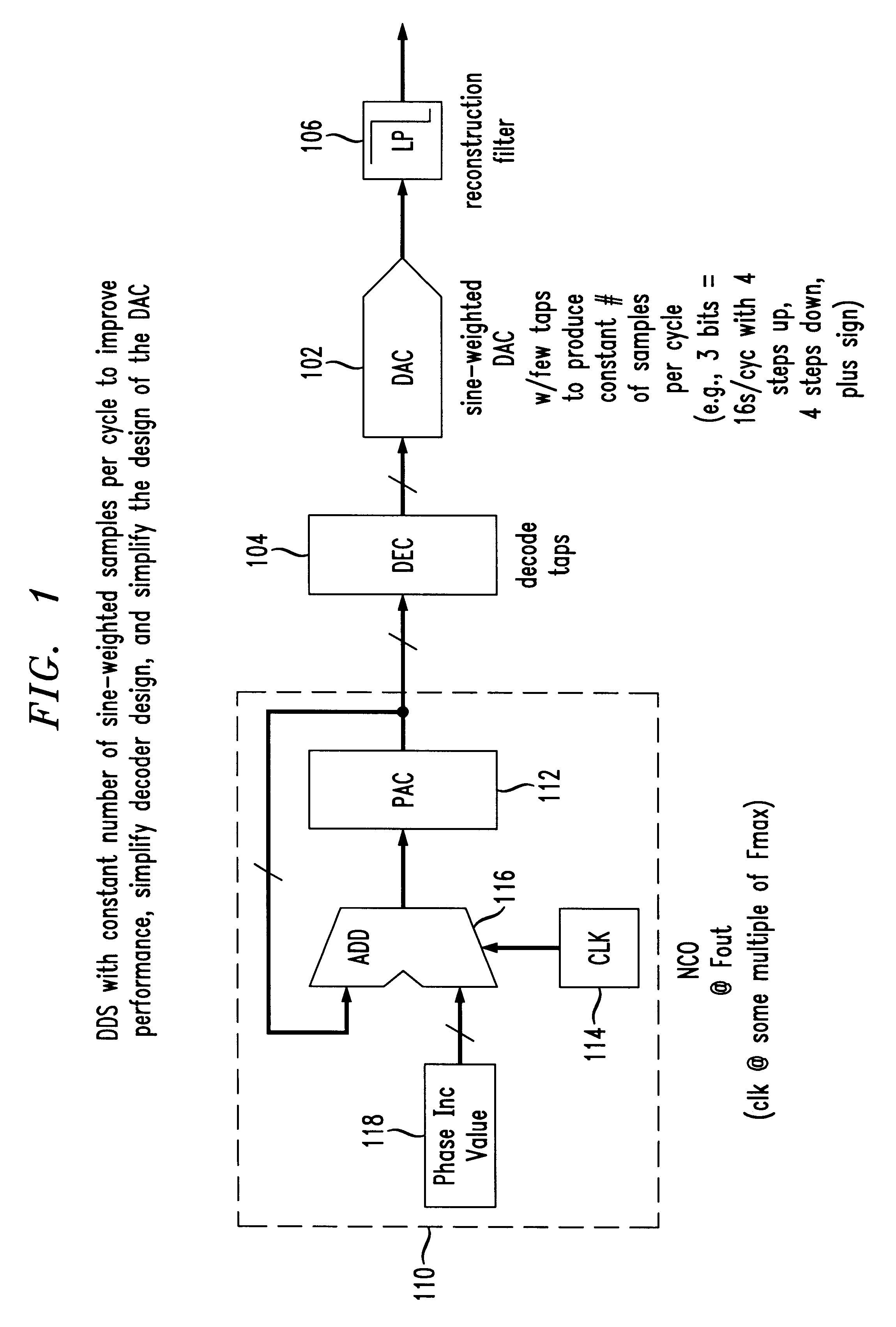
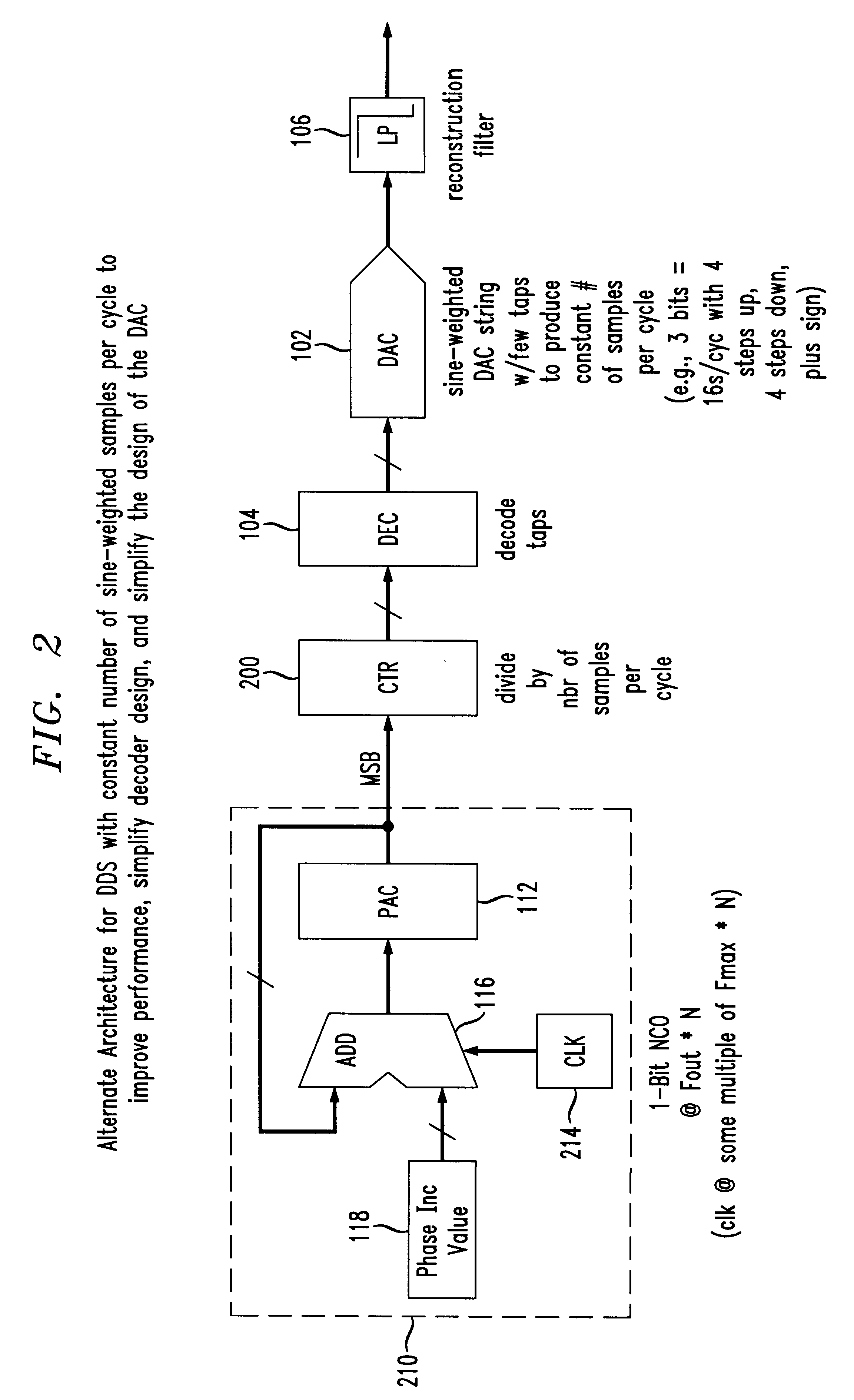
The present invention provides a novel direct digital synthesis system architecture which employs a numerically-controlled oscillator (NCO), some decoding logic, and a sine-weighted digital-to-analog converter (DAC) with significantly fewer output values required than conventional DDS systems to provide improved spurious performance (relative to the number of bits of resolution required of the DAC), extended frequency of operation, reduced chip area, and reduced power consumption relative to conventional DDS techniques. The output of the decoder is input to a sine-weighted digital-to-analog converter (DAC). Importantly, the sine-weighted DAC outputs a constant number of samples per cycle using a relatively few number of taps. Although there are significantly fewer taps in the sine-weighted DAC as compared to the linear DAC in conventional DDS systems, each tap of the sine-weighted DAC has a high degree of accuracy, e.g., 16-18 bits. Accordingly, a constant number of sample values are repetitively used in the stepped approximation of a sine wave, regardless of output frequency, significantly reducing the number of discrete output values that a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) is otherwise required to produce. Unlike conventional direct digital synthesis (DDS) architectures which use linear digital-to-analog converters having many bits of resolution, the present invention provides a sine-weighted digital-to-analog converter having relatively few taps to produce a constant number of samples per cycle, eliminating the conventional need for a memory-based sine wave look-up table.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Carrier tracking circuit and method including dual numerically controlled oscillators and feedforward phase correction coefficient
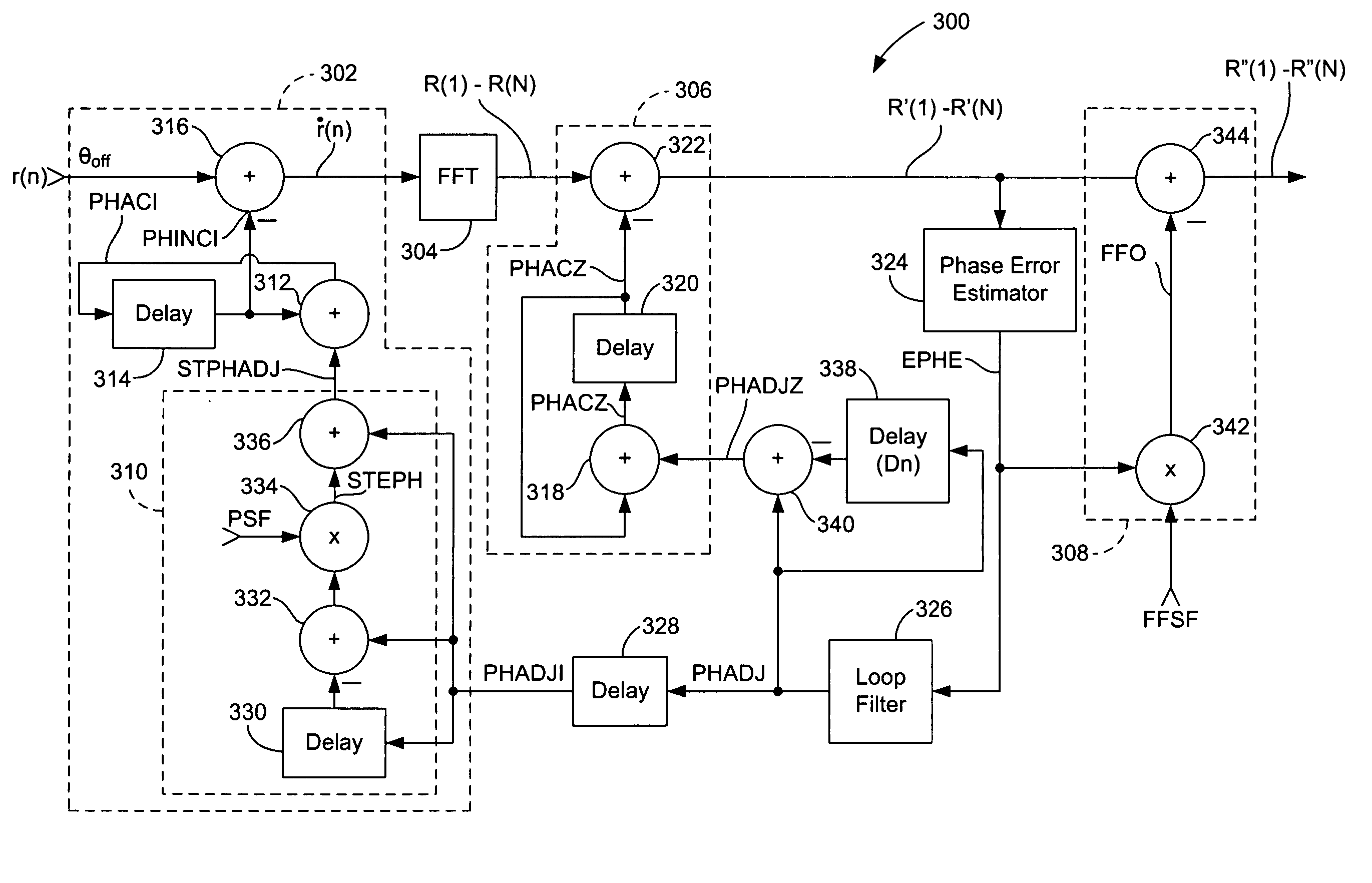
ActiveUS20060140308A1Avoid applicationSecret communicationPhase-modulated carrier systemsPhase correctionCommunications system
A carrier tracking circuit includes a first phase adjustment circuit coupled to an input of a delay element and a second phase adjustment circuit coupled to an output of the delay element. A phase correction circuit is coupled to output of the delay element is operable to generate a phase adjustment value based upon a data symbol output from the delay element. The phase correction circuit includes a double phase correction circuit to prevent double application of the same phase adjustment value to a symbol by both the first and second phase adjustment circuits. The carrier tracking circuit may be used in OFDM communications systems with each data symbol being an OFDM symbol and with the delay element being an FFT. The carrier tracker circuit also may include a feed forward circuit for correcting the phase error of a given data symbol using a phase error generated from that symbol.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
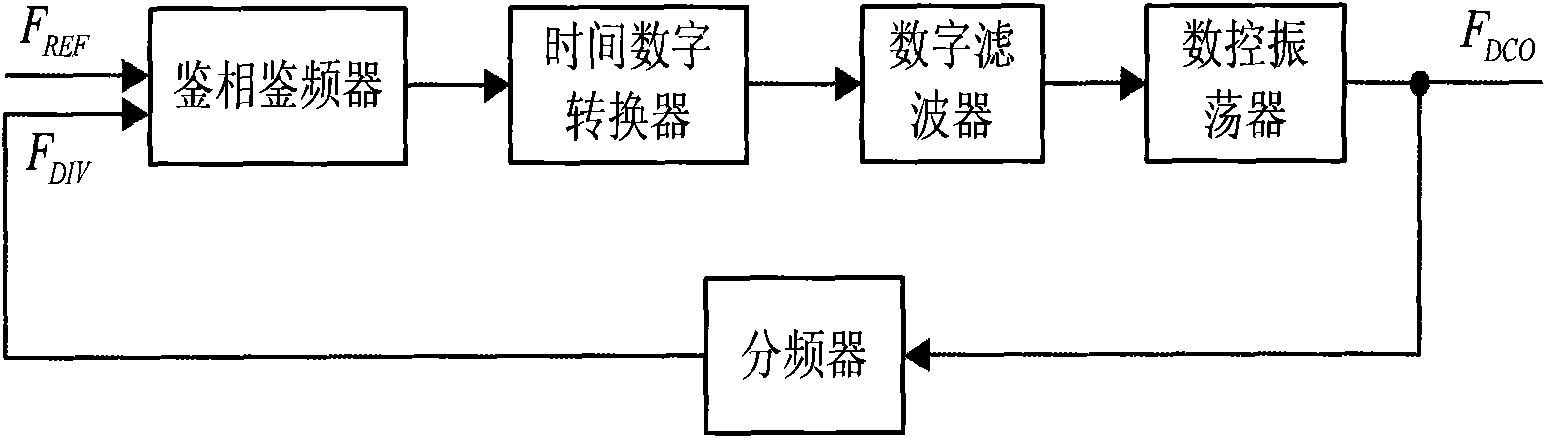
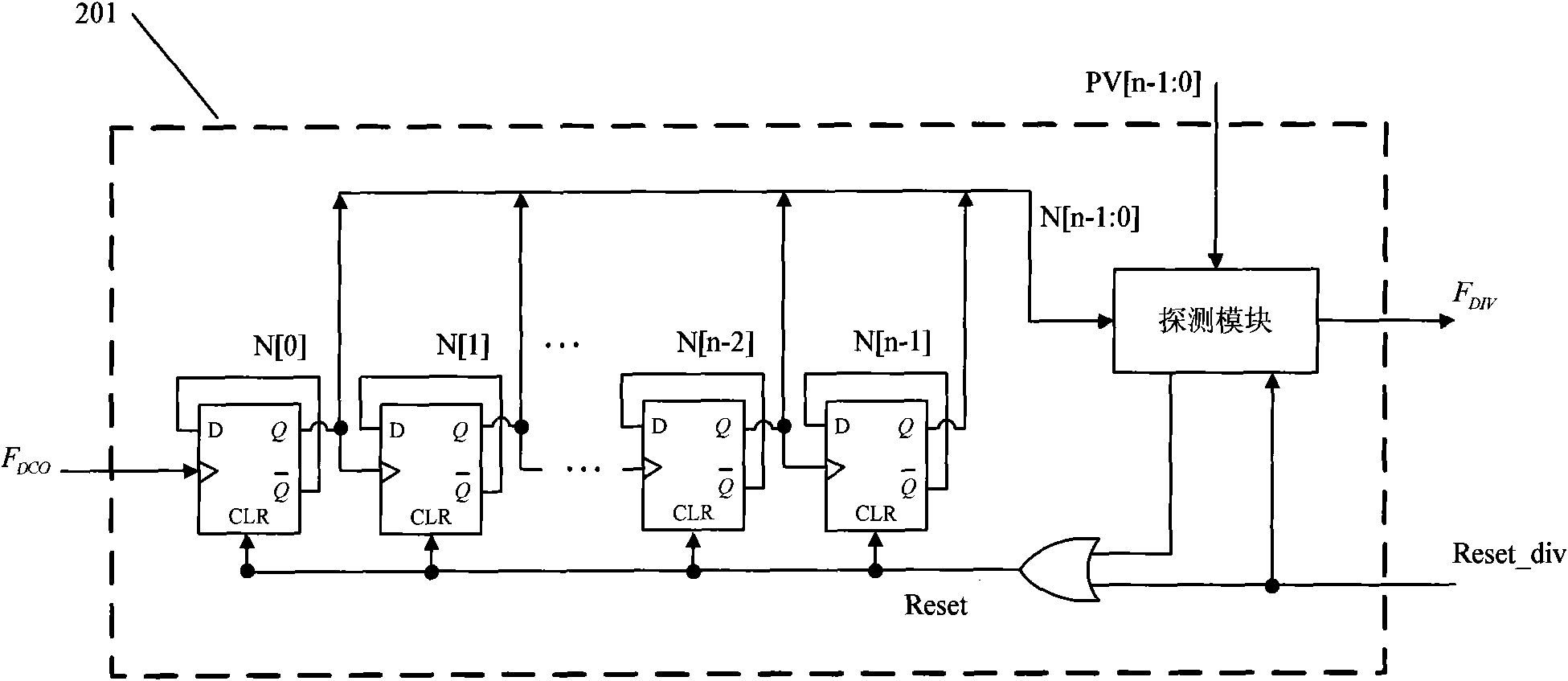
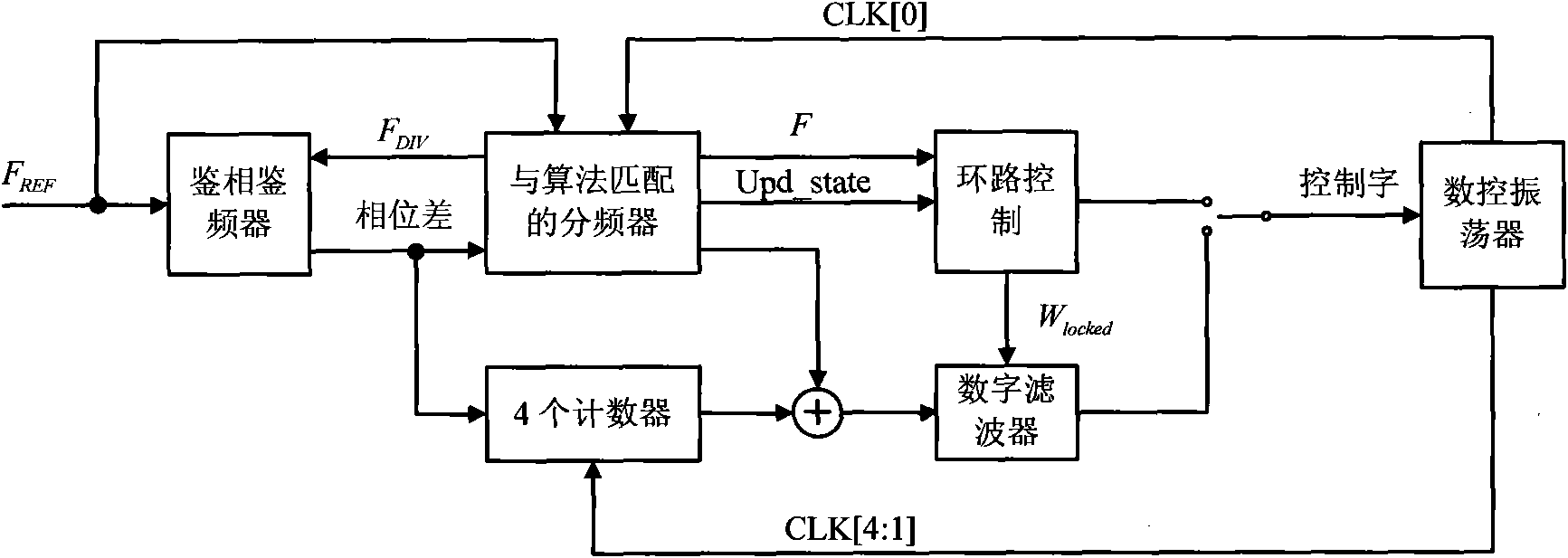
Digital phase locked loop device and method in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20130147531A1Improve performanceLow powerEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlDigital tuningCommunications system
A digital Phase Locked Loop (PLL) in a wireless communication system is provided. The PLL includes a Digitally Controlled Oscillator (DCO), a divider, a Phase Frequency Detector (PFD), a Time to Digital Converter (TDC), a delay comparator, and a level scaler. The DCO generates a frequency signal depending on an input Digital Tuning Word (DTW). The divider divides the frequency signal at an integer ratio. The PFD generates a signal representing a phase difference between a divided frequency signal and a reference signal. The TDC measures a time interval of the phase difference using the signal representing the phase difference. The delay comparator calculates a time interval in the case where rising edges coincide from values measured by the TDC. The level scaler generates a DTW that operates the DCO using a digital code representing the time interval.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Full digital phase-locked loop applying rapid frequency capture method
ActiveCN101640534AShort lock timeReduce forecast errorPulse automatic controlDiscriminatorClock rate
The invention relates to a full digital phase-locked loop applying a rapid frequency capture method for locking the frequency of the full digital phase-locked loop comprising a phase detection discriminator, a time-to-digit converter, a digital filter, a digital controlled oscillator and a frequency divider in a short time. The full digital phase-locked loop is characterized by comprising the following steps: finding a control word controlling the frequency of the digital controlled oscillator by a designed algorithm; and dividing a frequency output by the digital controlled oscillator which is controlled by the control word to obtain a divided-frequency clock with the frequency approximate to a reference clock frequency. The full digital phase-locked loop is provided with a rapid frequency capture loop and a phase-locked loop which alternately work, i.e. firstly, the rapid frequency capture loop finishes frequency capture, and then, the phase-locked loop finishes accurate locking.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Pll using interpolative divider as digitally controlled oscillator
One or more PLLs are formed on an integrated circuit. Each PLL includes an interpolative divider configured as a digitally controlled oscillator, which receives a reference clock signal and supplies an output signal divided according to a divide ratio. A feedback divider is coupled to the output signal of the interpolative divider and supplies a divided output signal as a feedback signal. A phase detector receives the feedback signal and a clock signal to which the PLL locks. The phase detector supplies a phase error corresponding to a difference between the clock signal and the feedback signal and the divide ratio is adjusted according to the phase error.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
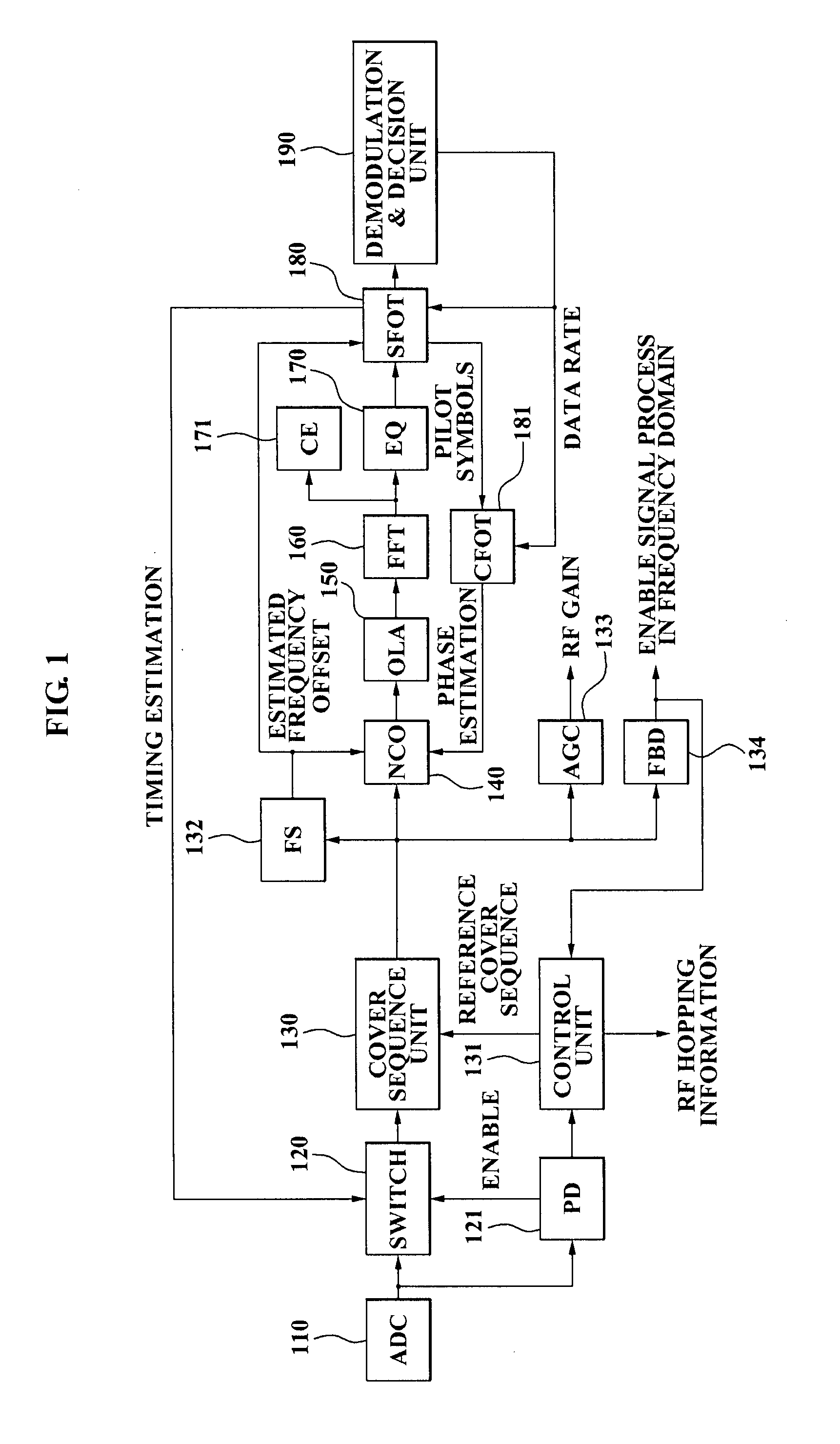
Receiver and method for compensating for frequency offset of receiving signal in multi-band OFDM scheme
InactiveUS20080095250A1Effective compensationSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainMulti band
A multiband Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) receiver, and more particularly, a receiver and method for effectively compensating for a frequency offset of a received signal in a multiband OFDM scheme. The receiver for compensating for a frequency offset of a received signal in an OFDM scheme includes: a numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) which generates a first compensation signal by processing an input signal in a time domain based on a first carrier frequency offset estimated in the time domain, and a second carrier frequency offset estimated in a frequency domain; a sampling frequency offset tracking (SFOT) unit which generates a second compensation signal by estimating a sampling frequency offset from frequency domain pilot symbols contained in the first compensation signal; and a carrier frequency offset tracking (CFOT) unit which estimates the second carrier frequency offset by using pilot symbols contained in the second compensation signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
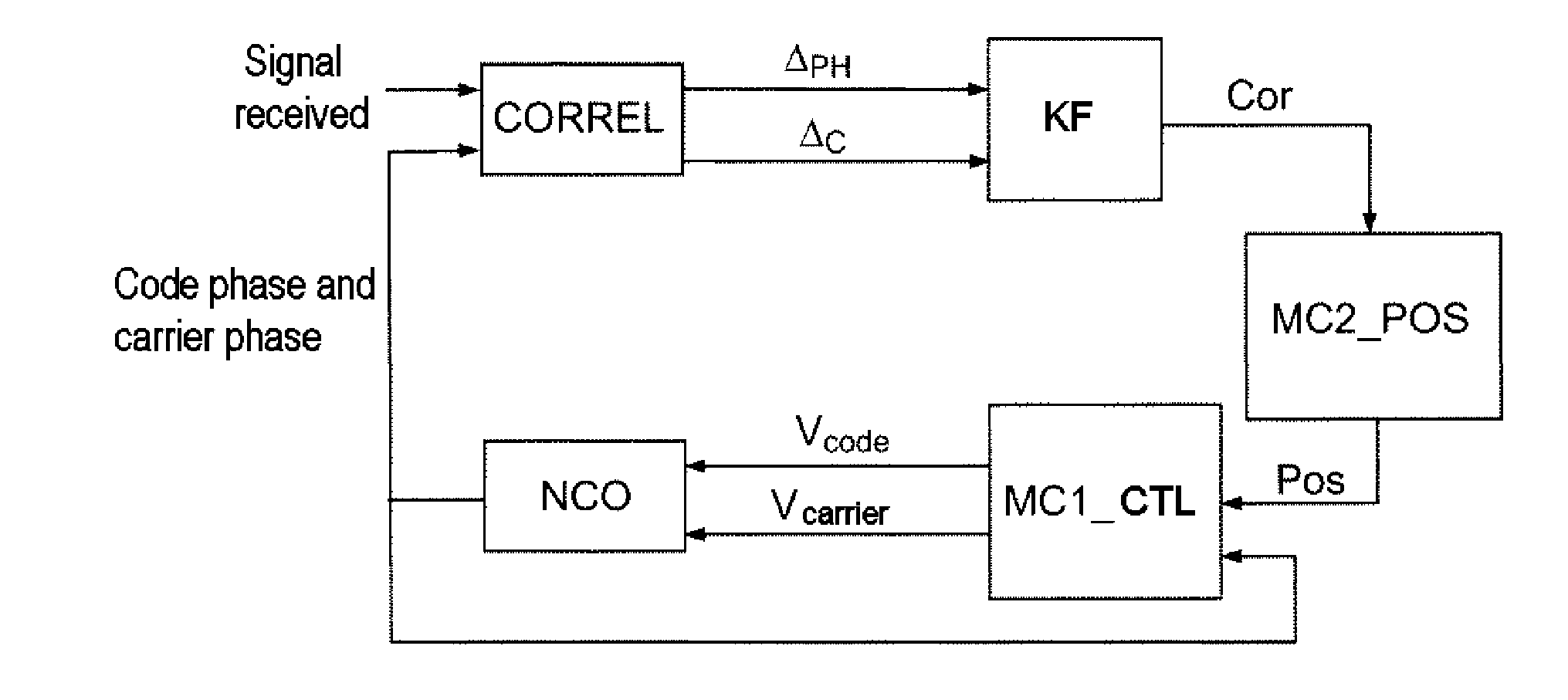
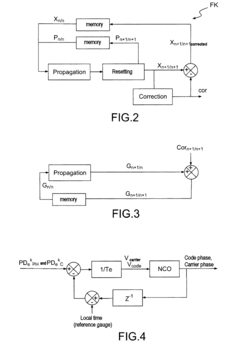
Satellite-based positioning receiver
InactiveUS20110181463A1High precisionBetter quality navigationSatellite radio beaconingDiscriminatorKaiman filter
A satellite-based positioning receiver includes processing channels, each processing channel being associated with a respective satellite from among N satellites, and an extended Kalman filter for performing a vector tracking for the set of satellites using signals received from the satellites. The extended Kalman filter performs a resetting on the basis of the phase error and code error received directly from the phase and code discriminators, of each channel, and the receiver includes first means for calculating the code-wise and carrier-wise control signals for the said code phase and carrier phase numerically-controlled oscillators, on the basis of data provided by the said extended Kalman filter, for each channel.
Owner:THALES SA
Method and system for realizing ultrahigh-speed digital orthogonal down conversion and decimation filtering in FPGA
InactiveCN105915241ANot subject to debuggingStrong upgradeabilityDigital technique networkTransmissionNumerical controlData rate
The invention discloses a method and a system for realizing ultrahigh-speed digital orthogonal down conversion and decimation filtering in an FPGA. The system comprises the components of a plurality of ADC sampling chips, a high-speed ADC data receiving module, an over-clock processing module, a global clock module, a local numerical control oscillator and a multichannel digital decimation filter. The designed working frequency of the traditional FPGA is hard to exceed 200MHz. According to the method and the system, a numerical control oscillator (NCO) and the digital decimation filter as core parts in orthogonal down conversion are improved; furthermore through reasonably restraining layout and wiring of the FPGA, highest sampling rate above 500Msps and output baseband data rate above 125MHz can be ensured on a common FPGA device. Furthermore the method and the device can support simultaneous parallel sampling of multiple paths of ADC data, thereby adapting with a multichannel data receiving occasion.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
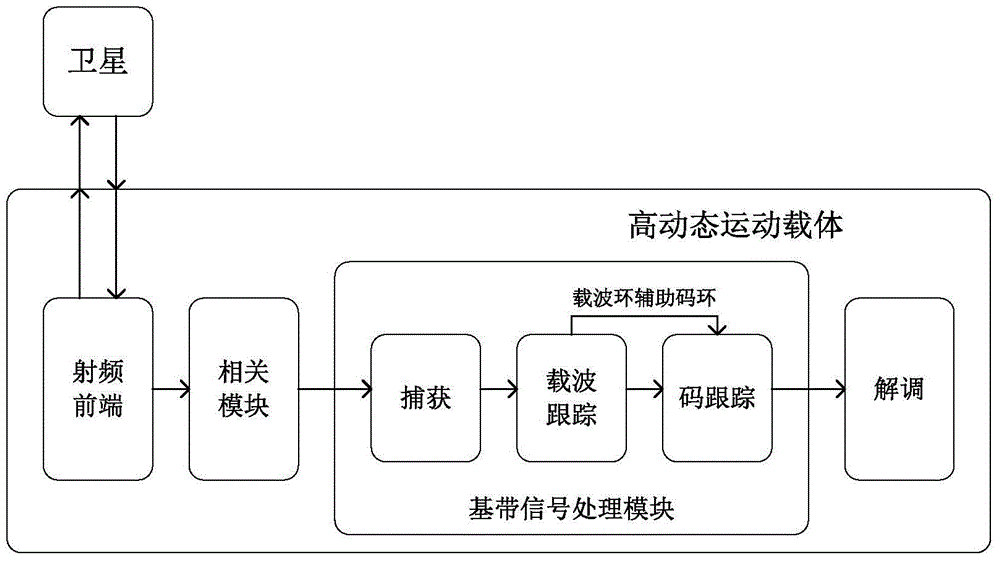
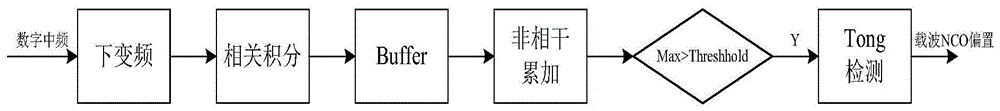
Method for capturing, tracking and receiving Beidou signal of high-dynamic movement carrier
InactiveCN104570016AEliminate DynamicsRealize code phase trackingSatellite radio beaconingNumerically controlled oscillatorCarrier signal
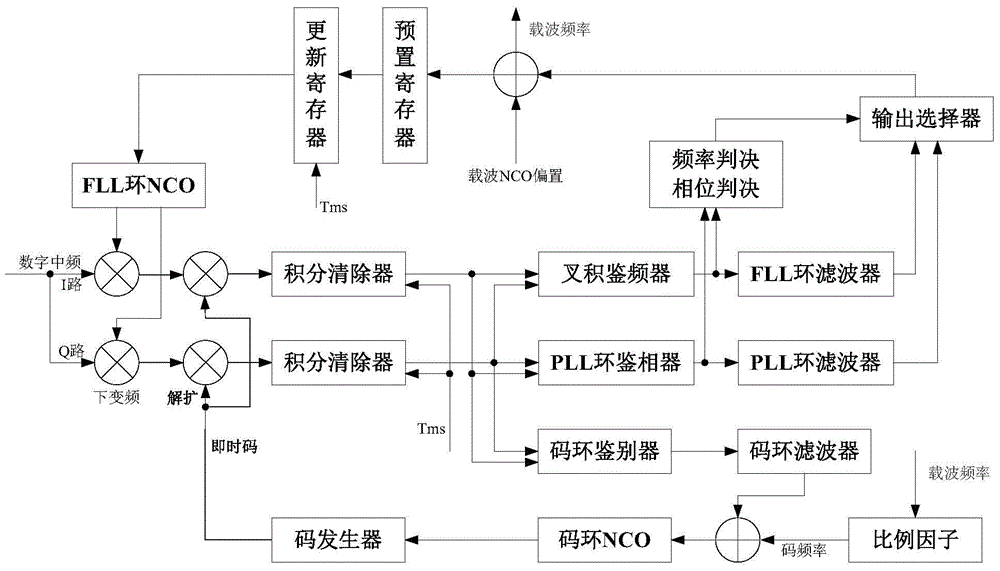
The invention provides a method for capturing, tracking and receiving a Beidou signal of a high-dynamic movement carrier. Through the adoption of the method, a satellite signal can be quickly captured and tracked, the capturing time is shortened, the tracking reliability is ensured, and the signal loss is avoided. The method comprises the following steps: Step 1, capturing a satellite signal of the high-dynamic movement carrier, using repeated uncorrelated accumulation and Tong detection, and obtaining a rough carrier frequency and a pseudo code phase of a received signal; Step 2, using a second-order FLL (frequency locked loop) for tracking the received signal during initial tracking so as to obtain frequency tracking errors, and at the same time, selecting a frequency tracking error for feeding back and rectifying the output carrier wave frequency of a numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) of the FLL by an output selector; Step 3, when the frequency tracking error is smaller than a preset threshold, using a third-order PLL for tracking so as to obtain phase tracking errors, at the same time, selecting the phase tracking error for feeding back and rectifying the output phase of the numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) of the FLL by the output selector, and realizing accurate tracking; Step 4, when the phase tracking error of the third-order PLL is greater than the preset threshold, returning to the Step 2 to perform the second-order FLL tracking, and completing carrier tracking.
Owner:北京航天科工世纪卫星科技有限公司
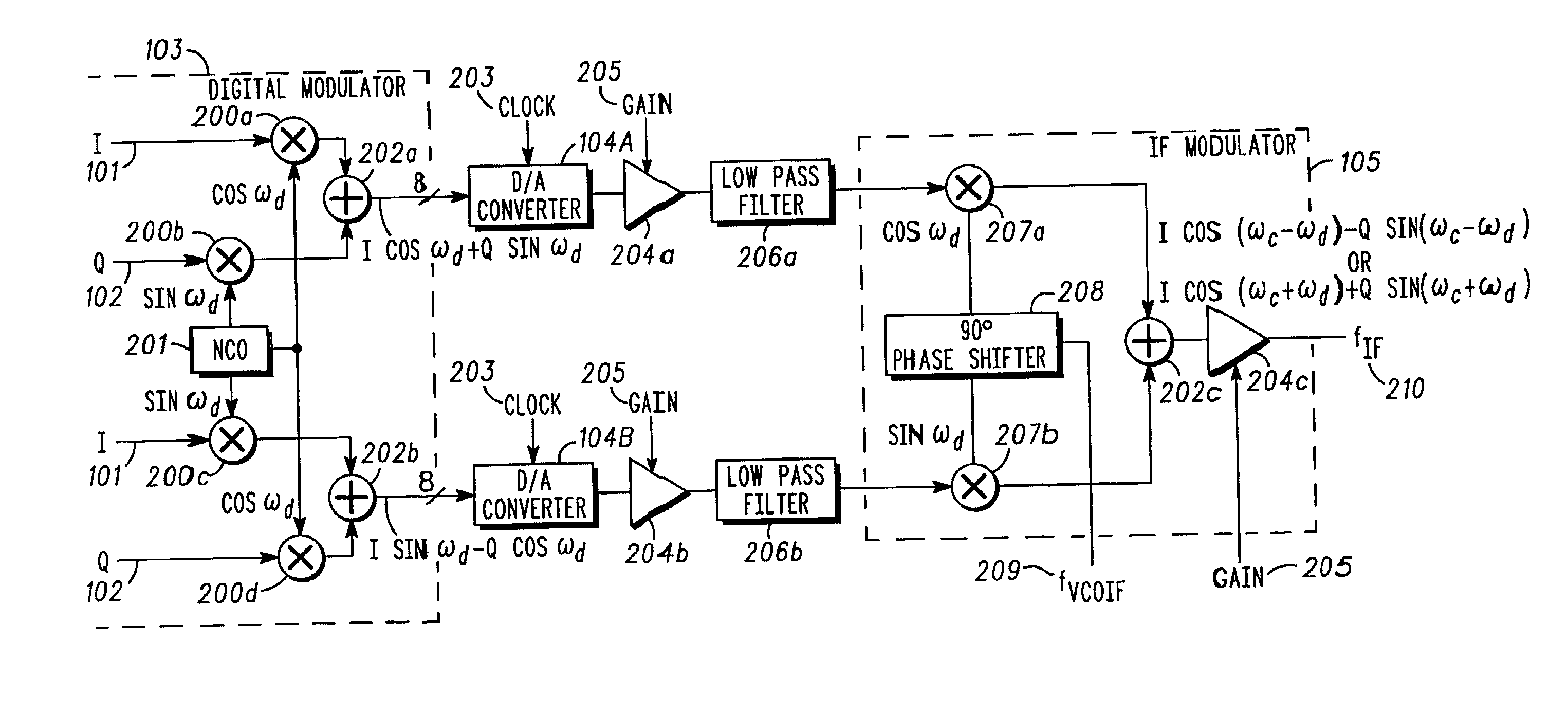
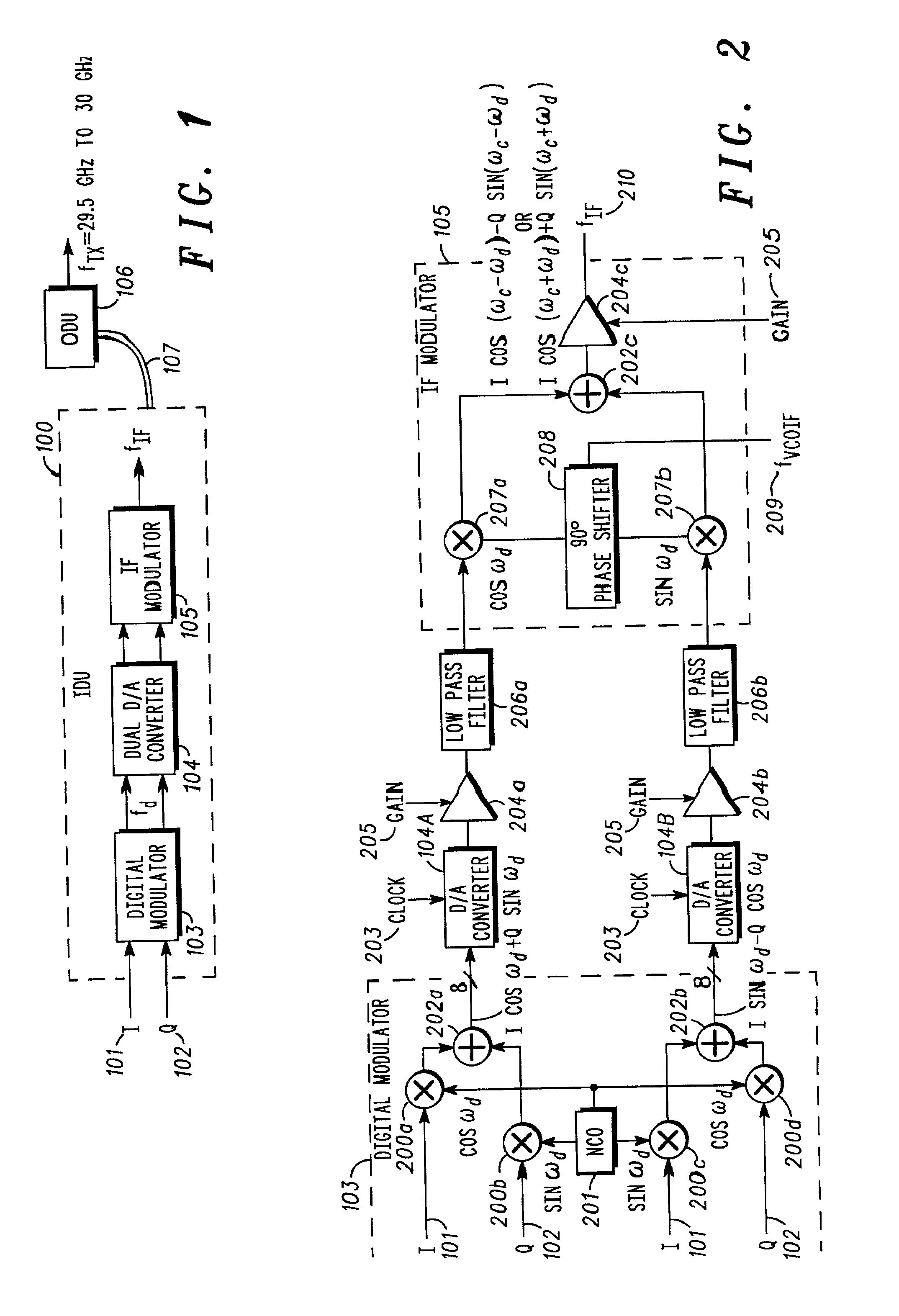
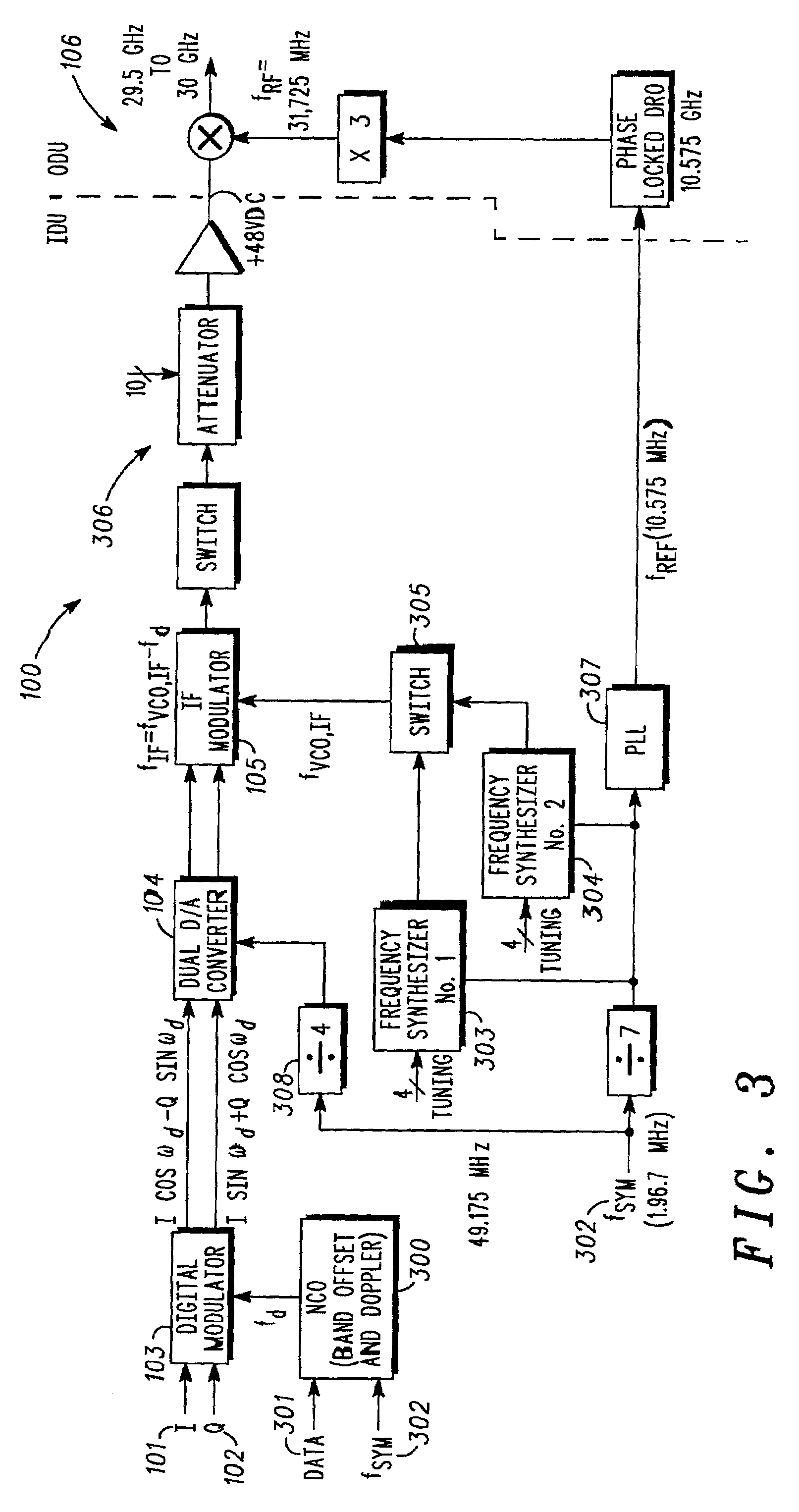
Modulation system for modulating data onto a carrier signal with offsets to compensate for doppler effect and allow a frequency synthesizing system to make steps equal to channel bandwidth
ActiveUS7167528B2Doppler effectFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsIntermediate frequencyCarrier signal
A method and system for modulating data onto a carrier signal in a plurality of channels, each of the channels having a channel bandwidth, can be created for use in any two-way satellite communication system or other wireless communication application where frequency hopping with or without Doppler compensation is desired. The system preferably includes a digital modulator that outputs a modulated baseband signal, an intermediate frequency modulator that receives the modulated baseband signal and outputs an intermediate frequency signal derived from the modulated baseband signal, a frequency synthesizing system that outputs a synthesized intermediate frequency signal to the intermediate frequency modulator, and a circuit (numerically controlled oscillator) connected to the digital modulator which provides a signal to the digital modulator. This signal has a frequency including an offset that allows the frequency synthesizing system and intermediate frequency modulator to make frequency steps equal to the channel bandwidth. The offset can also include a small offset that compensates for the Doppler effect.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC +1
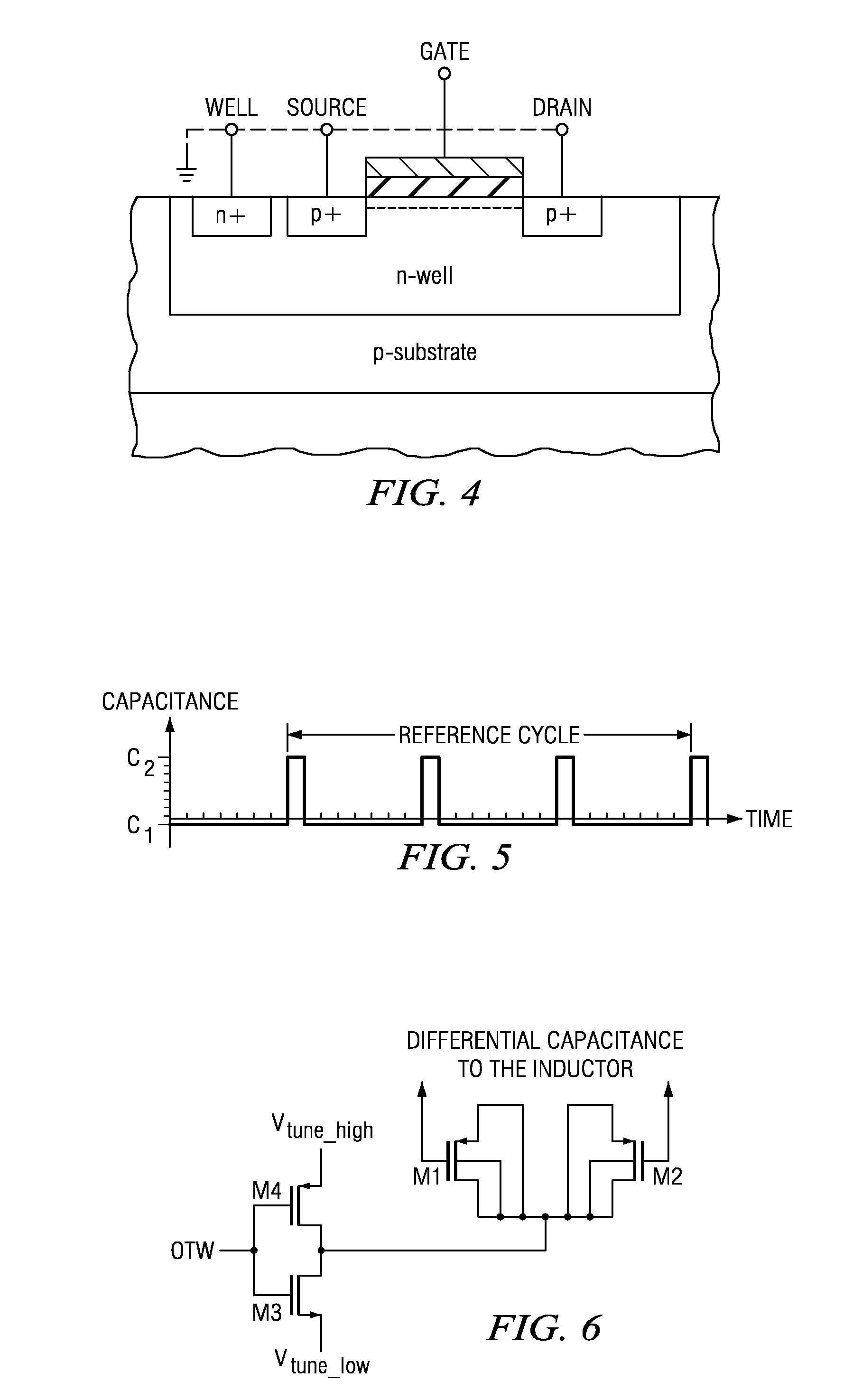
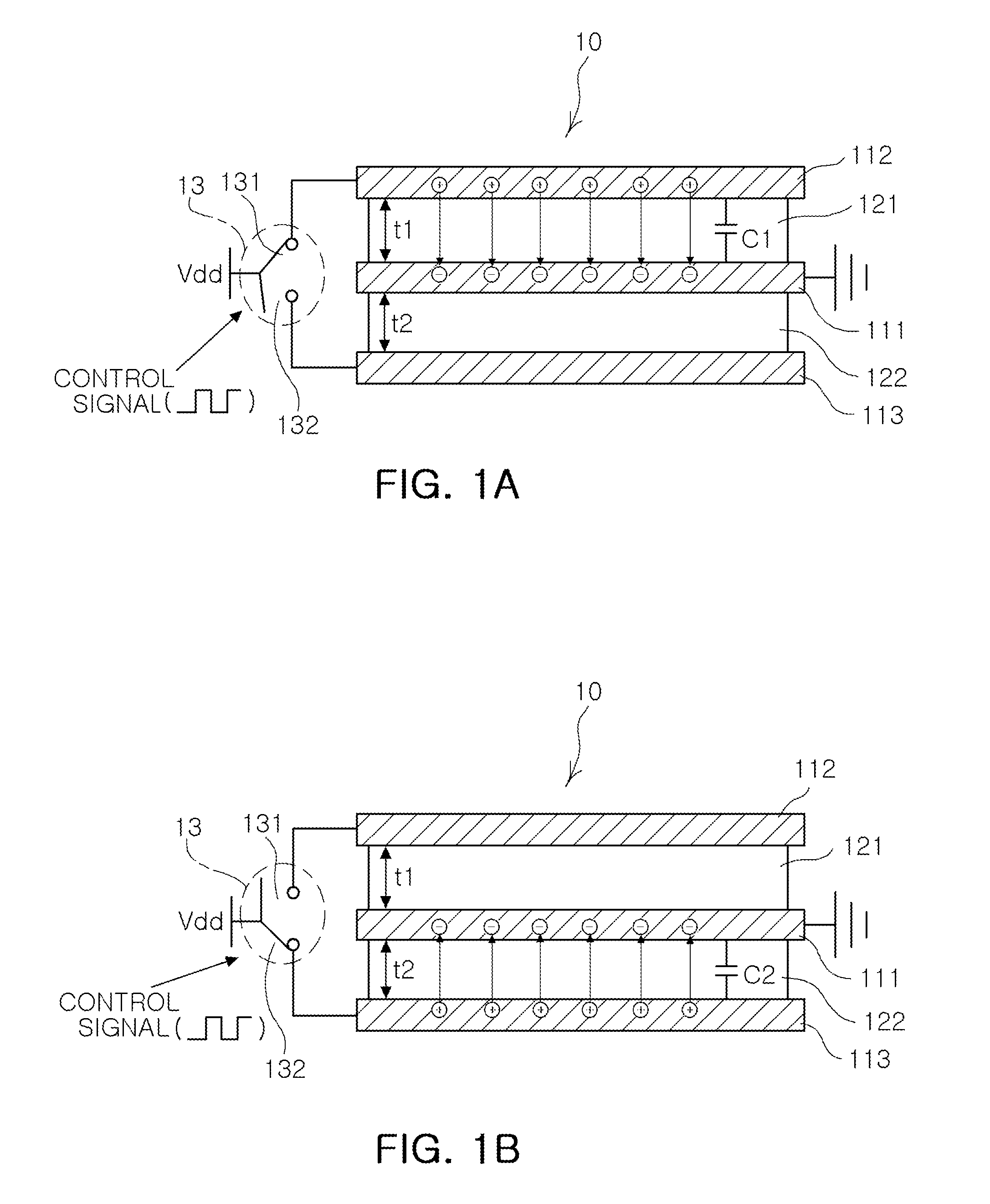
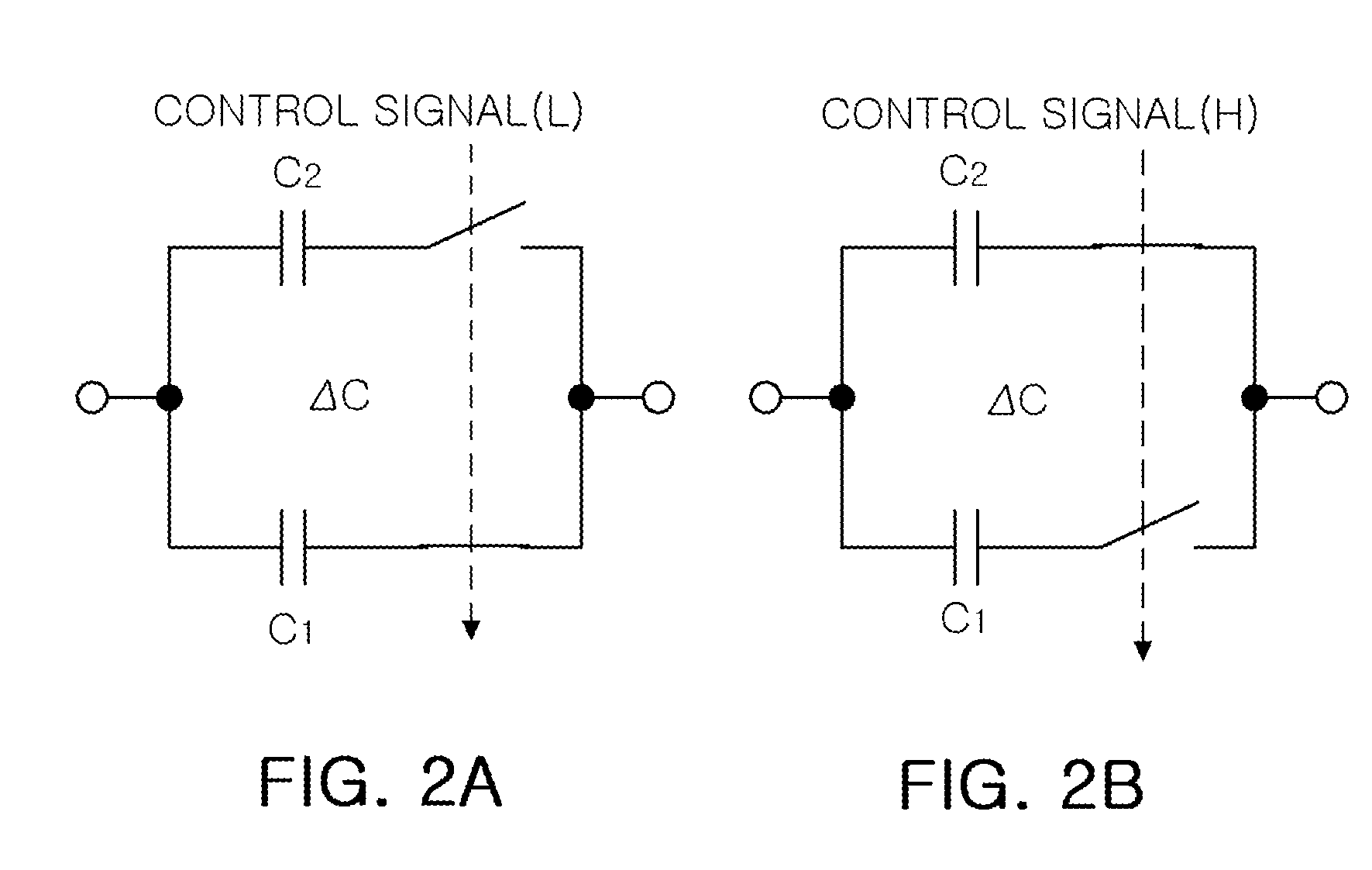
Capacitor having variable capacitance and digitally controlled oscillator including the same
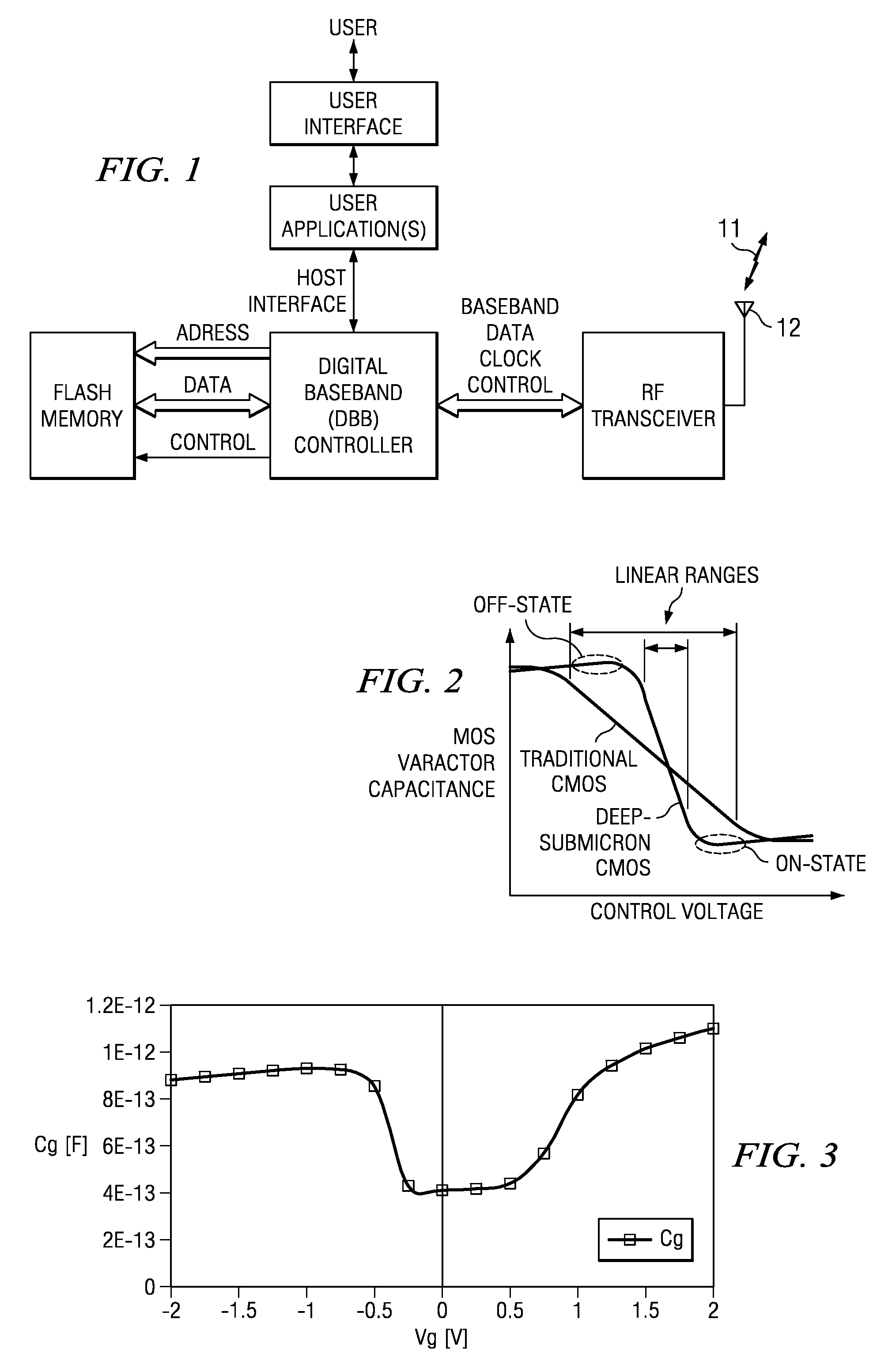
InactiveUS20100134195A1Reduce Capacitance VariationHigh frequency resolutionTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceControl signal
There is provided a capacitor having variable capacitance, which forms different capacitances according to a control signal by applying a switch to a metal-oxide-metal (MOM) structure plate capacitor using a CMOS process. The capacitor includes a stack structure including a plurality of metal layers including a first metal layer, and a plurality of dielectric layers respectively interposed between the plurality of metal layers, and a switch part including at least one switch having one side connected to at least one metal layer among the plurality of metal layers other than the first metal layer. The first metal layer and the other side of the switch serve as both terminals of the capacitor, and at least two capacitances are provided between both terminals of the capacitor upon controlling a short / open of the switch.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com