Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2724 results about "Obstetrics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynaecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN) which is a surgical field.
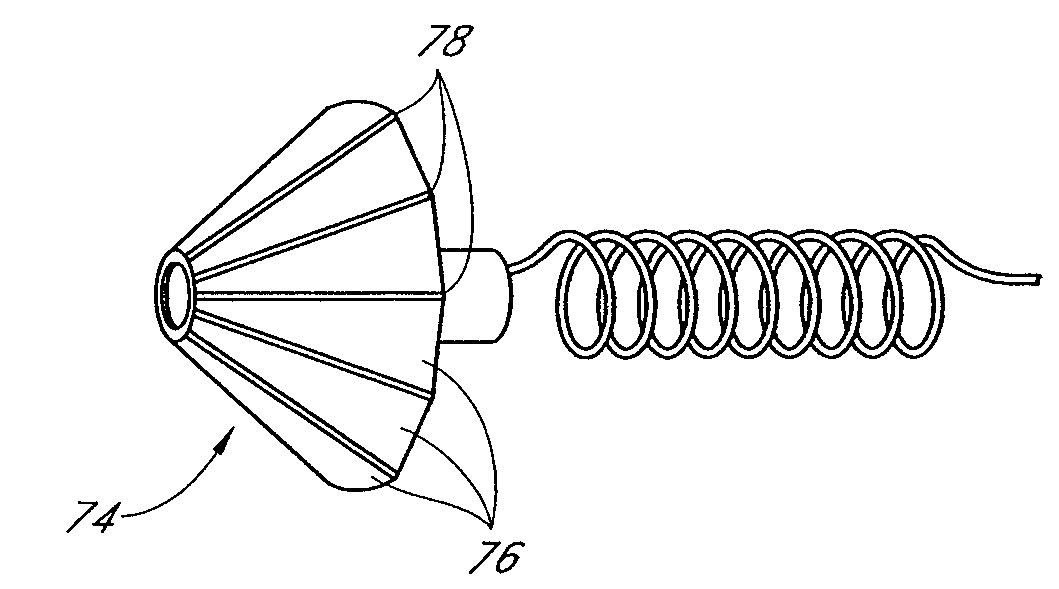
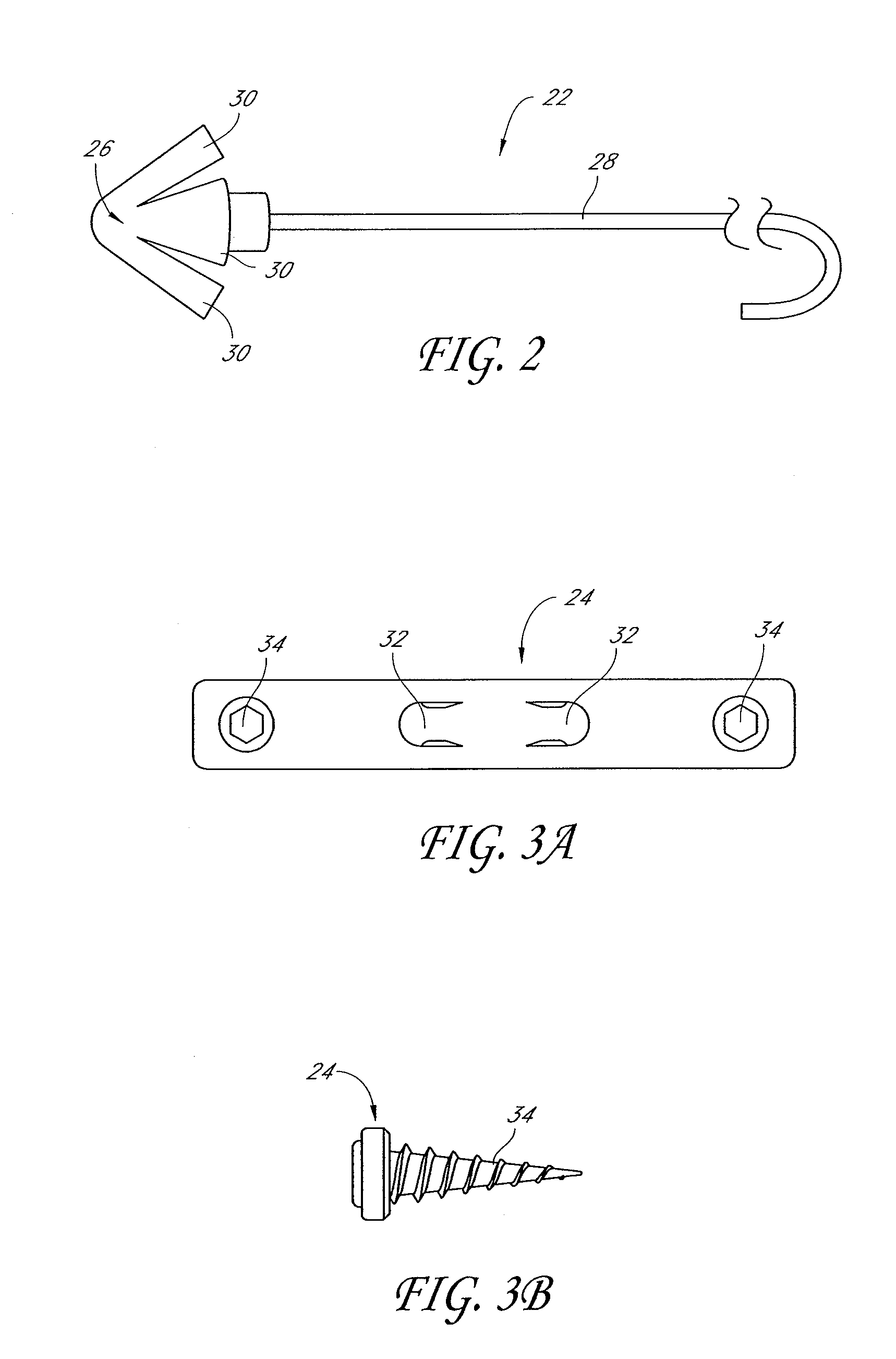
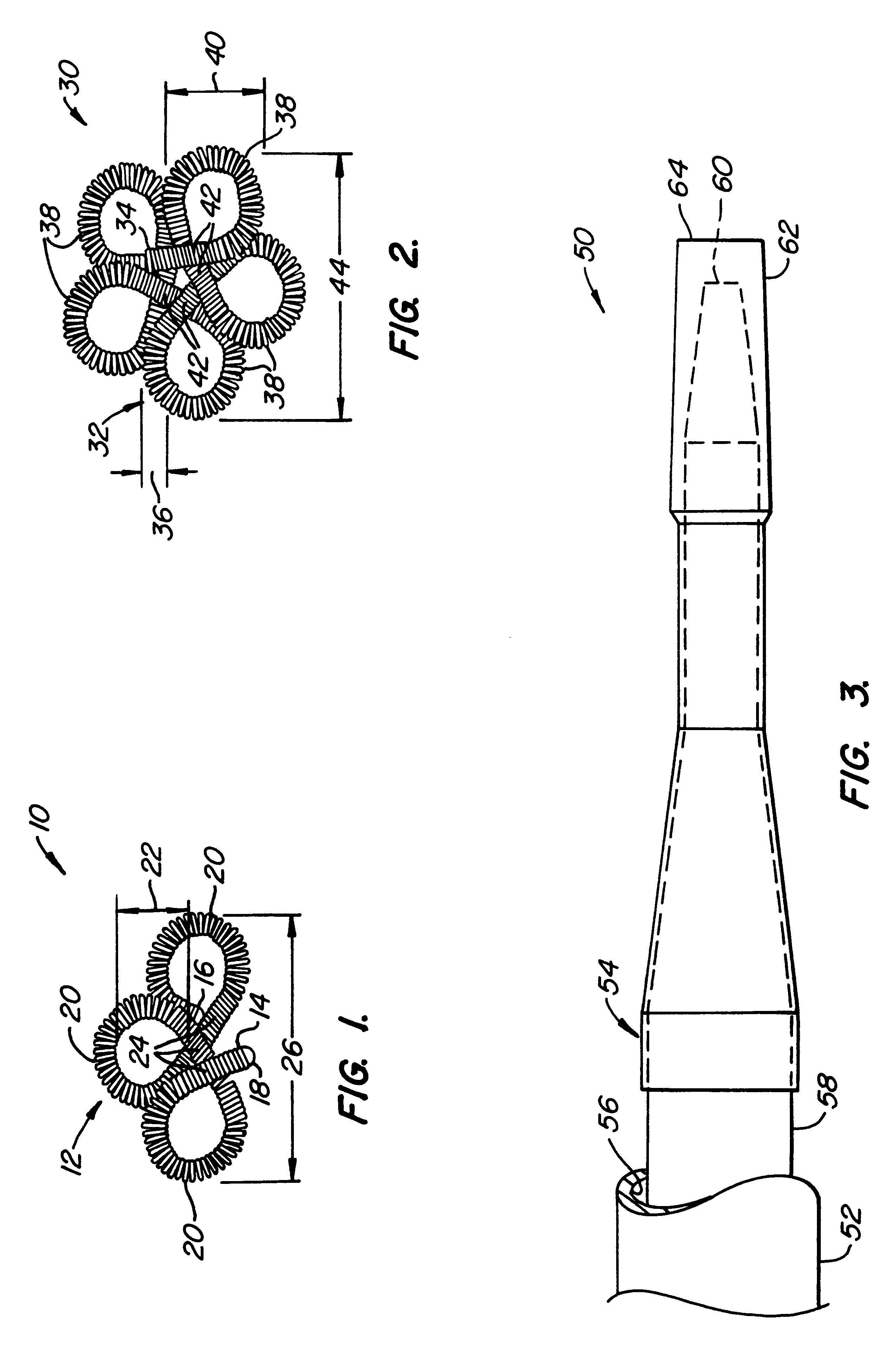
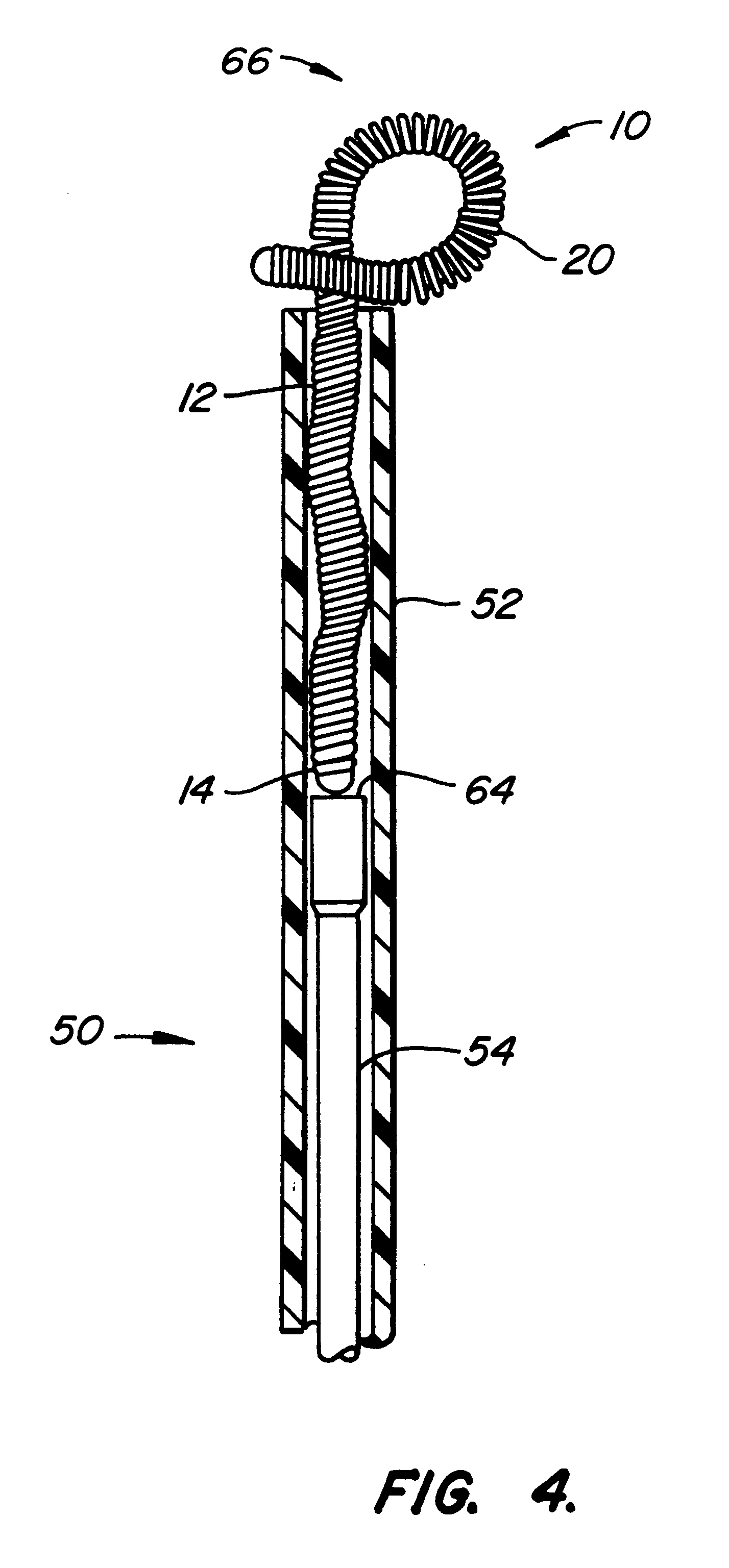
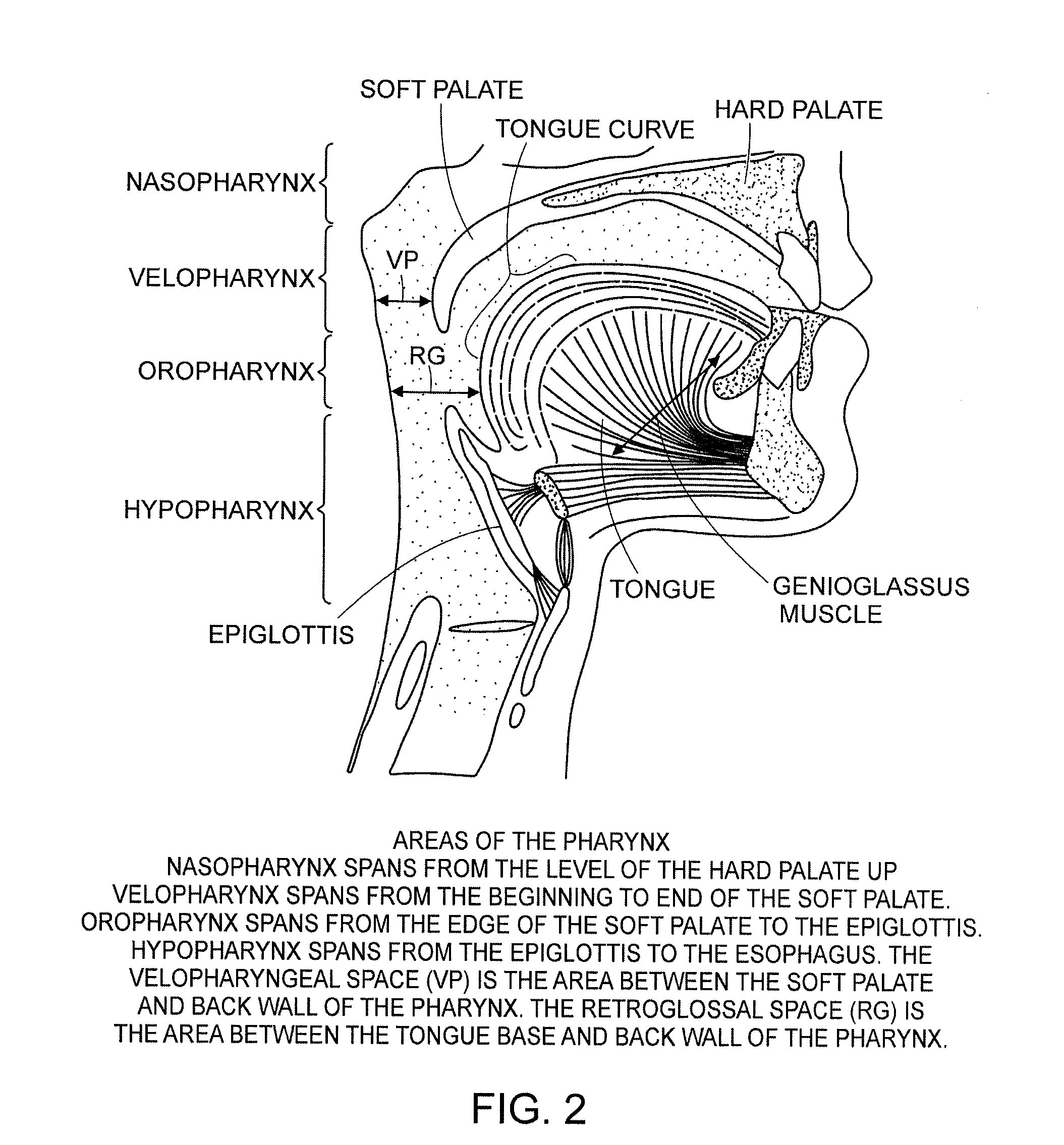
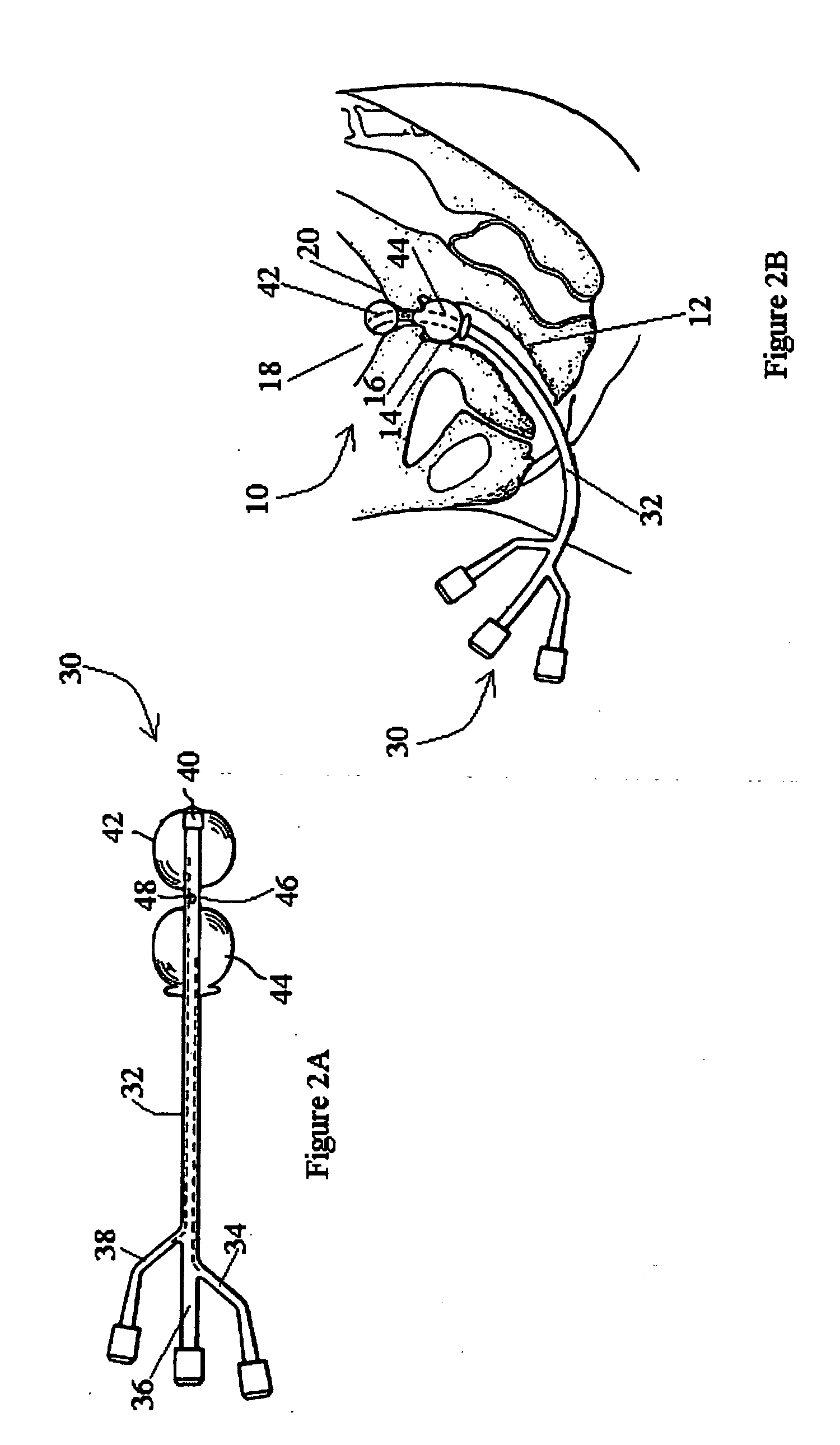
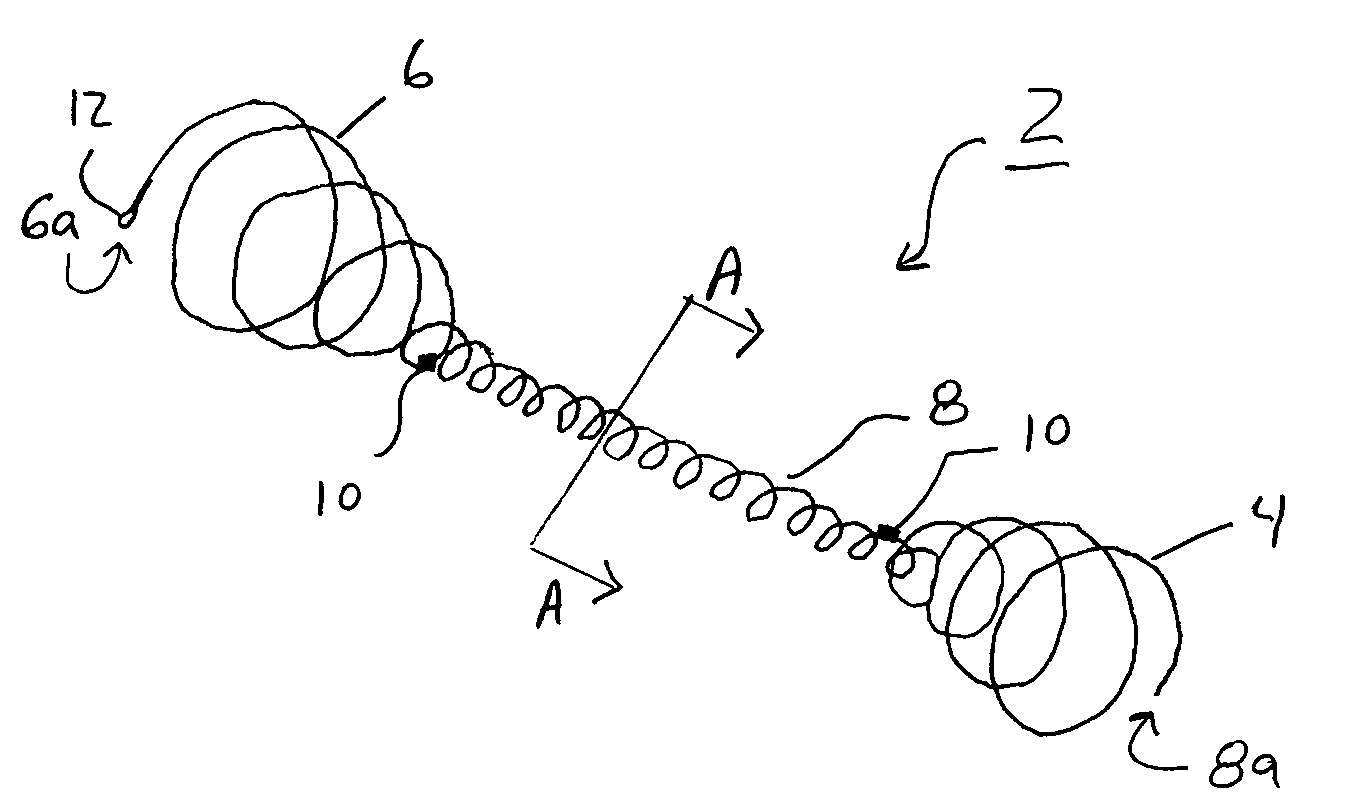
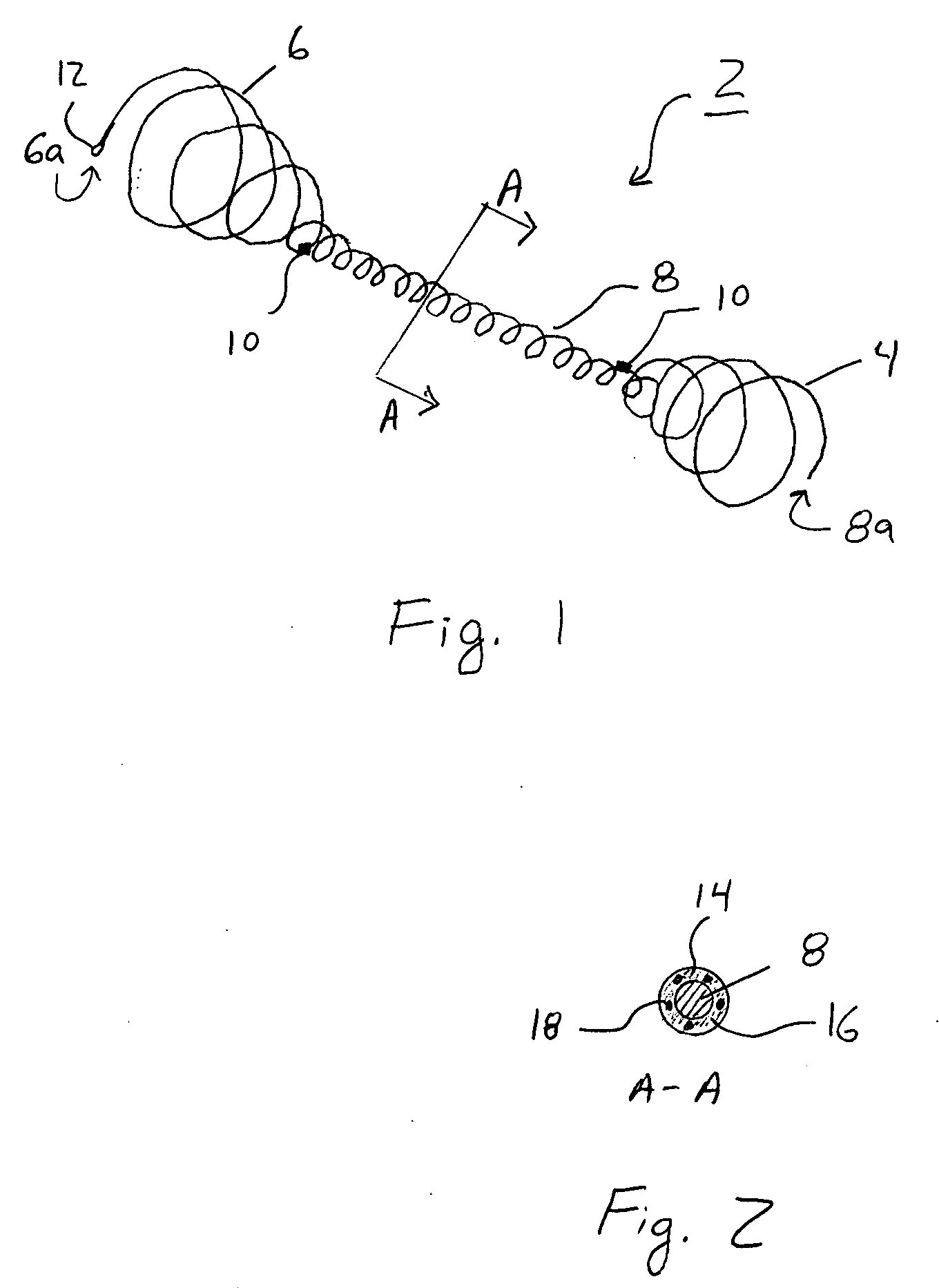
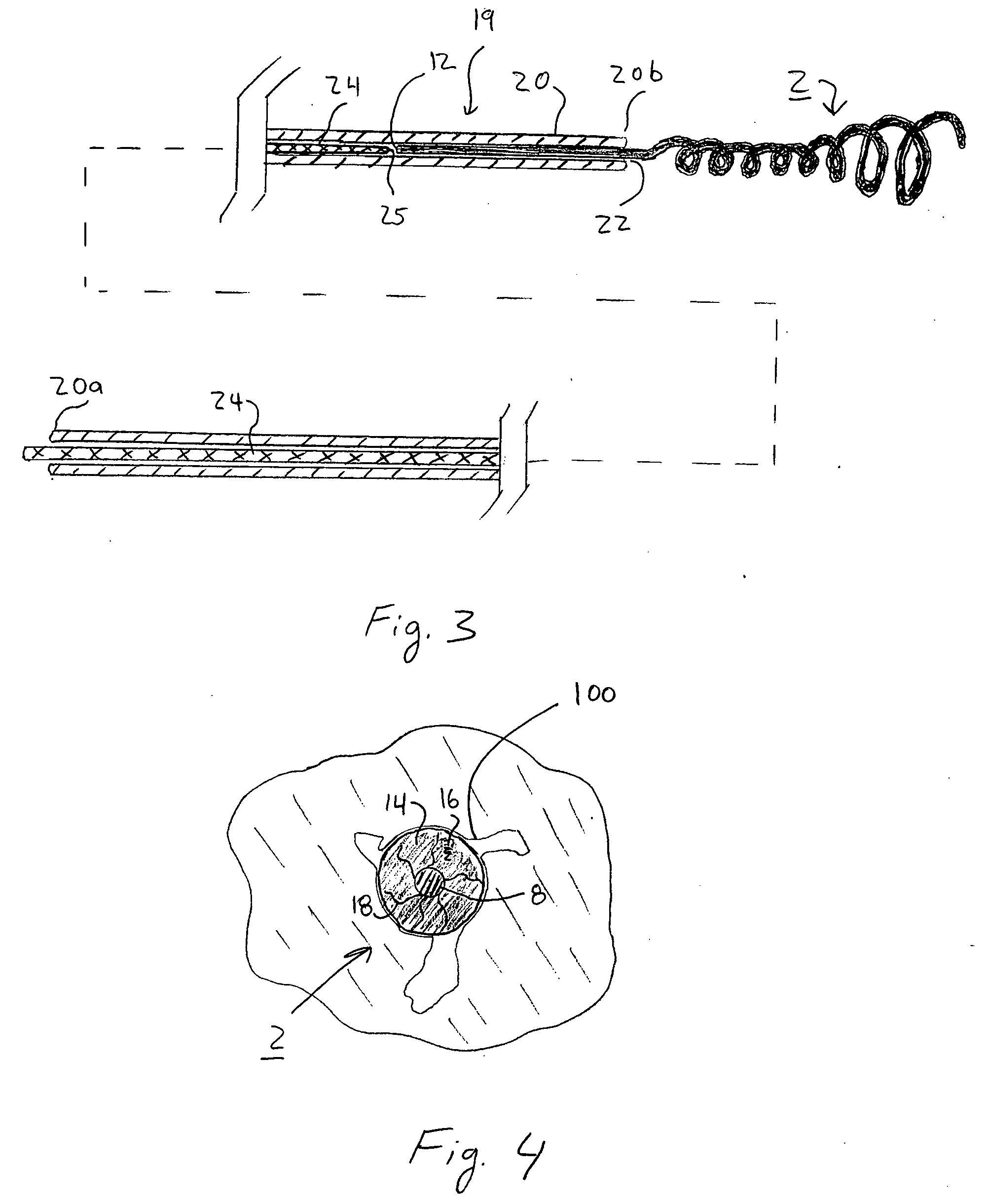
System and method for percutaneous palate remodeling
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating the palatal tissue. An implant is positioned within at least a portion of the soft palate and may be secured to other surrounding, less mobile structures such as the hard palate or the mucosa overlying the hard palate. The implant may be manipulated to displace at least a portion of the soft palate in an anterior or lateral direction, or to alter the tissue tension or compliance of the soft palate.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
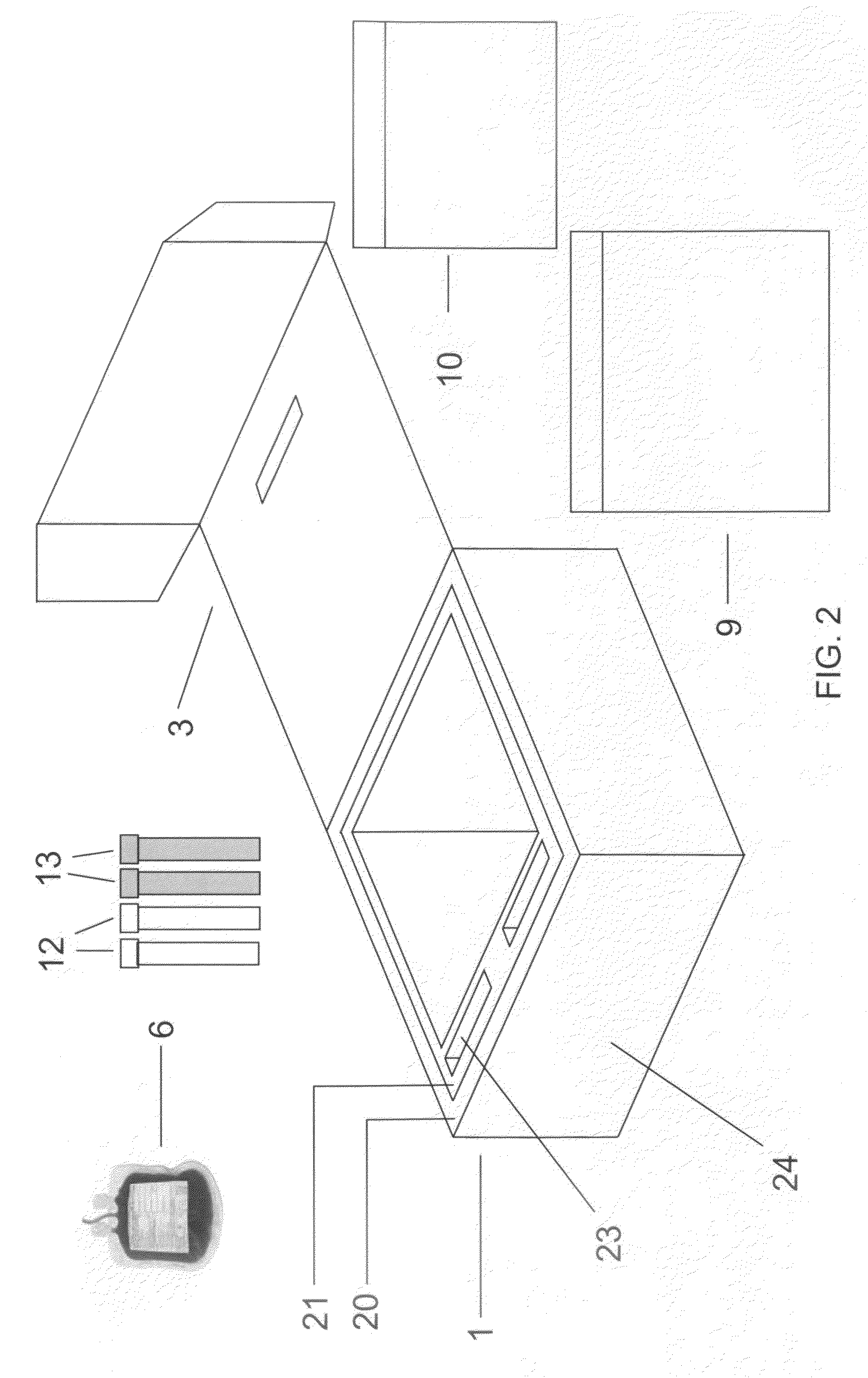
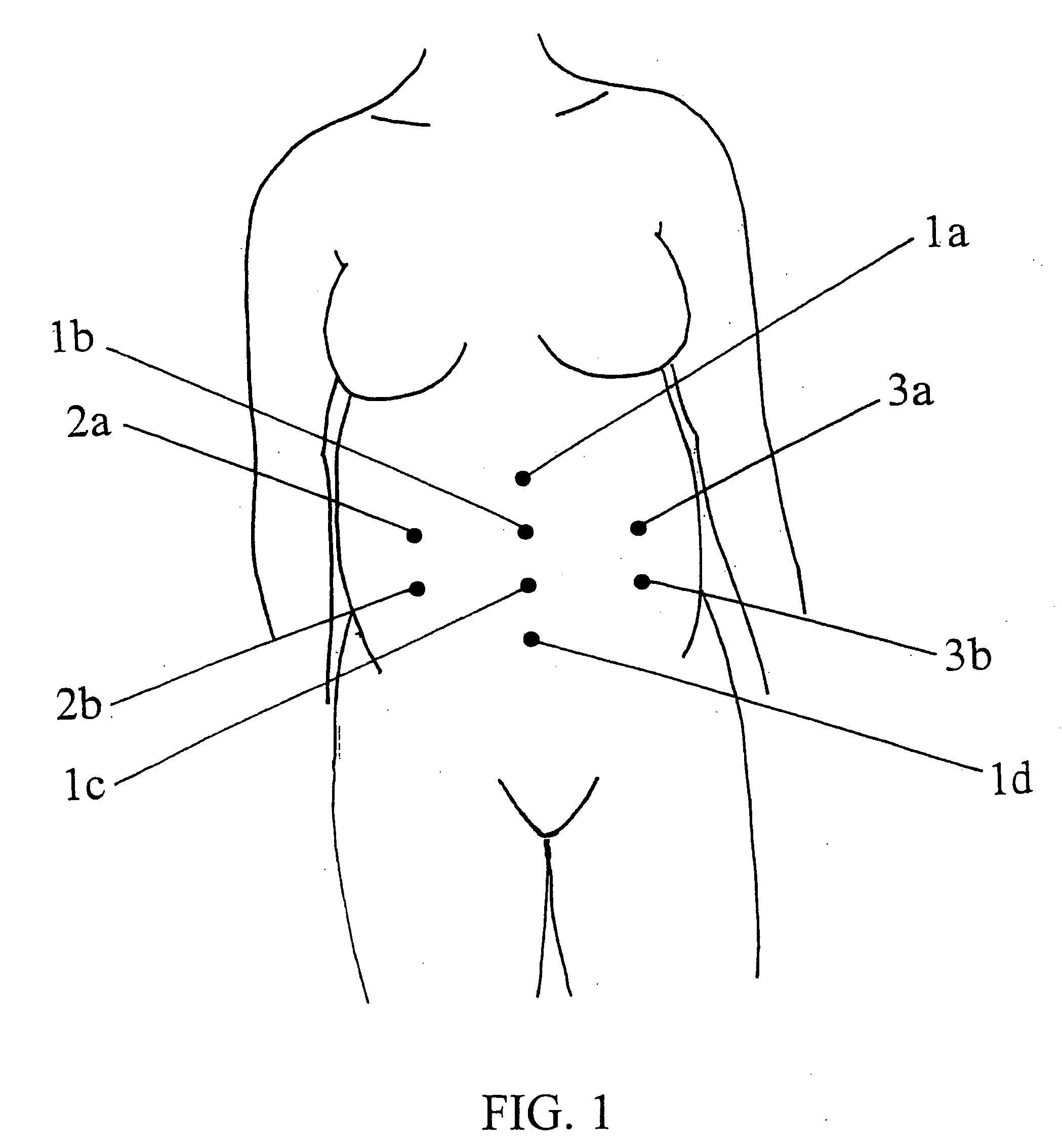
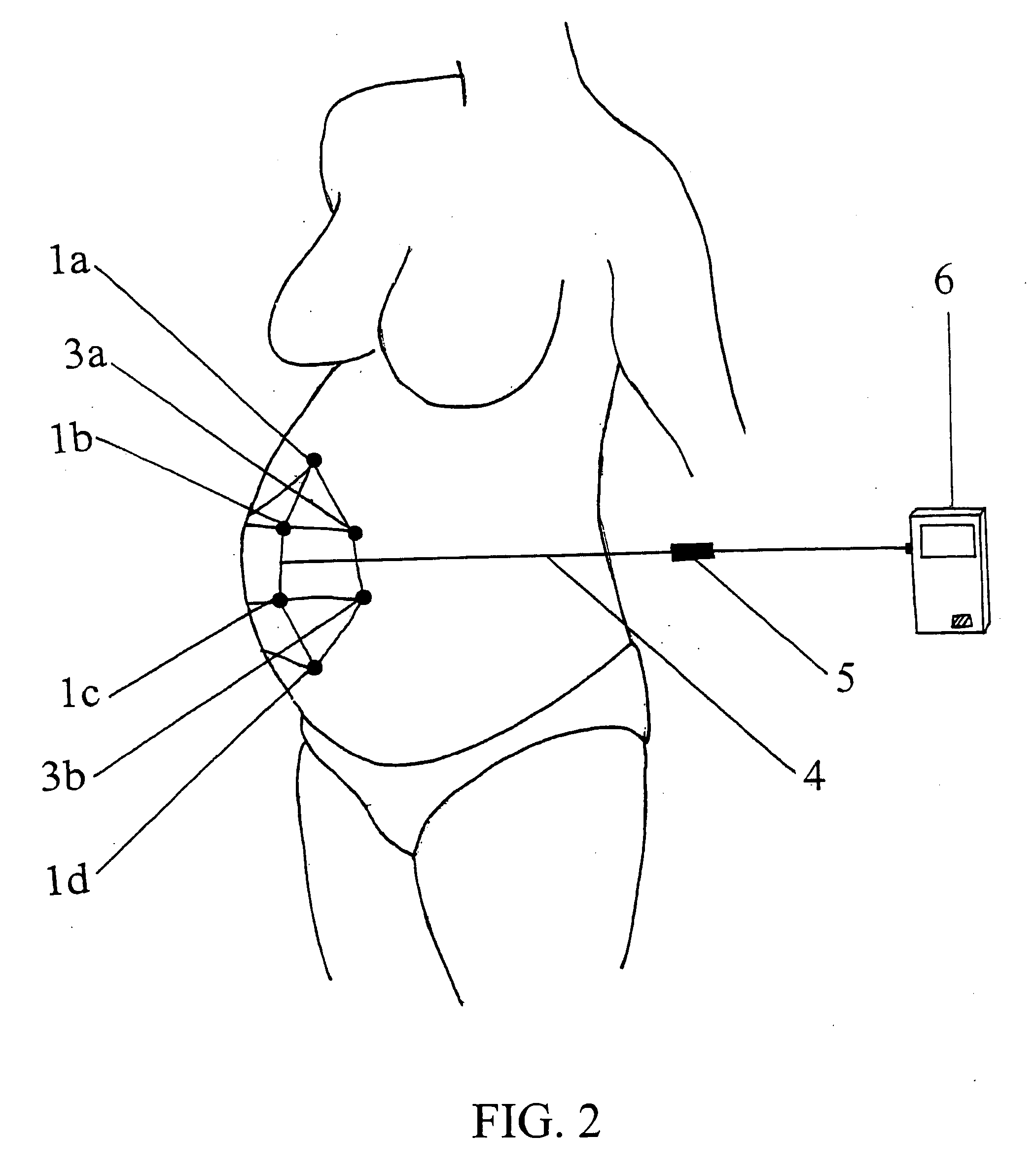
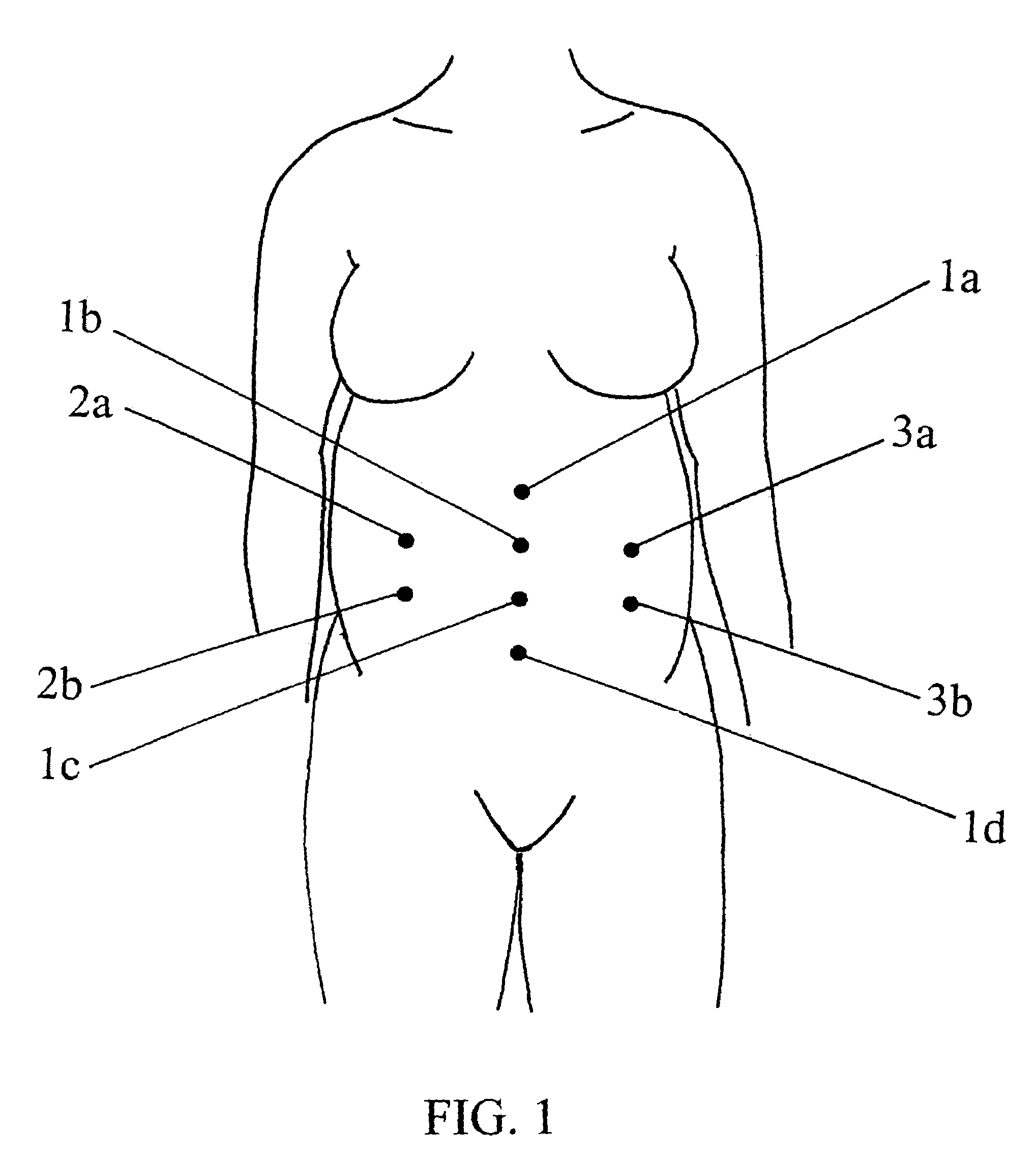
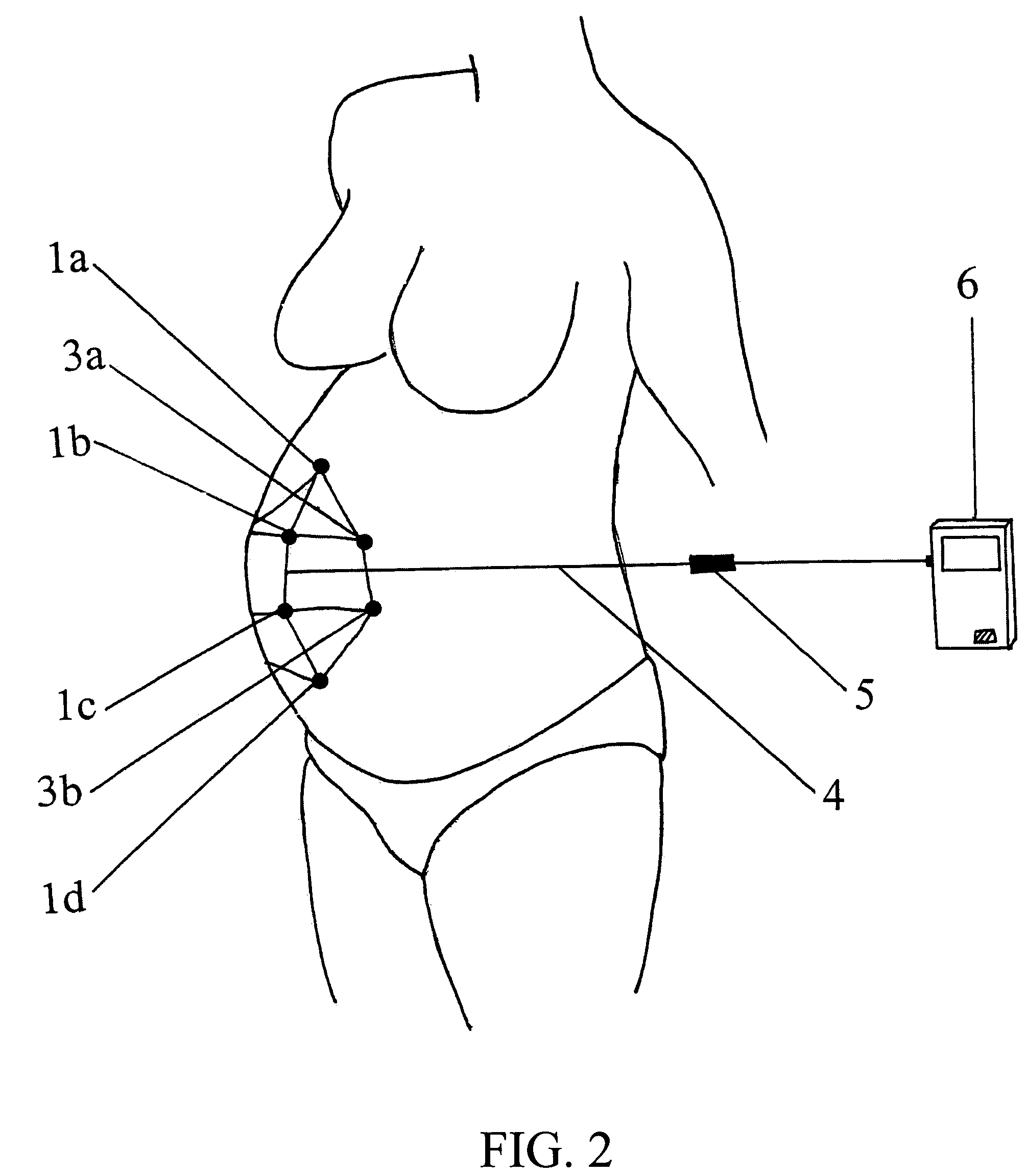
Maternal-fetal monitoring system
ActiveUS20050267376A1Less riskEliminate the problemElectrocardiographyElectromyographyObstetricsNeural network system
A maternal-fetal monitoring system for use during all stages of pregnancy, including antepartum and intrapartum stages. The maternal-fetal monitoring system of the subject invention comprises (1) a set of sensors; (2) an amplifying / filtering means; (3) a computing means; and (4) a graphical user interface. Accurate clinical data, which can be extracted and provided to the user in real-time using the system of the invention, include without limitation, maternal electrocardiogram (ECG) signals, maternal uterine activity signals (EHG), maternal heart rate, fetal ECG signals, and fetal heart rate. In a preferred embodiment, the maternal-fetal monitoring system of the invention includes an intelligence means, such as a neural network system, to analyze and interpret clinical data for use in clinical diagnosis antepartum, intrapartum and postpartum, as well as delivery strategy.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
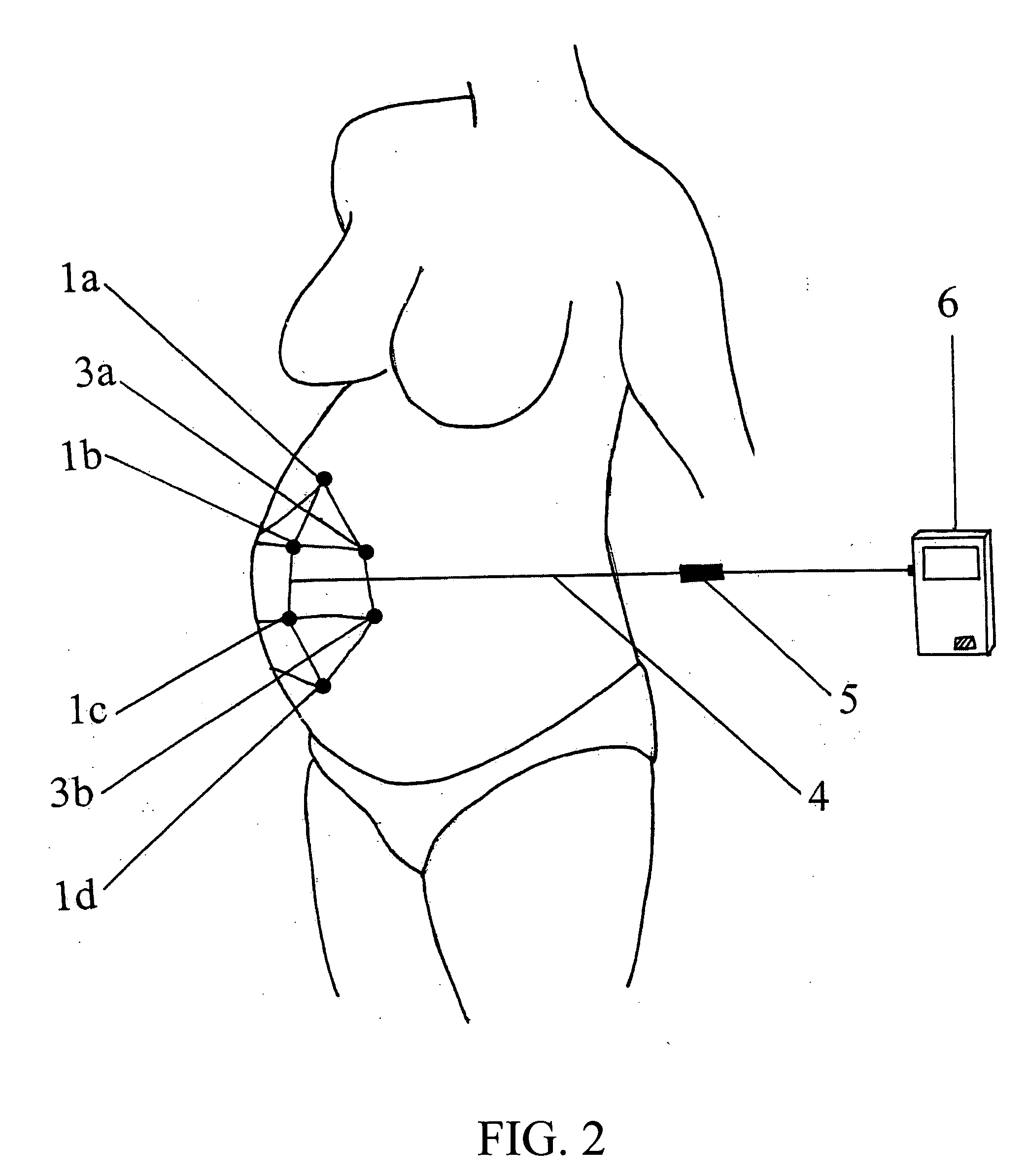
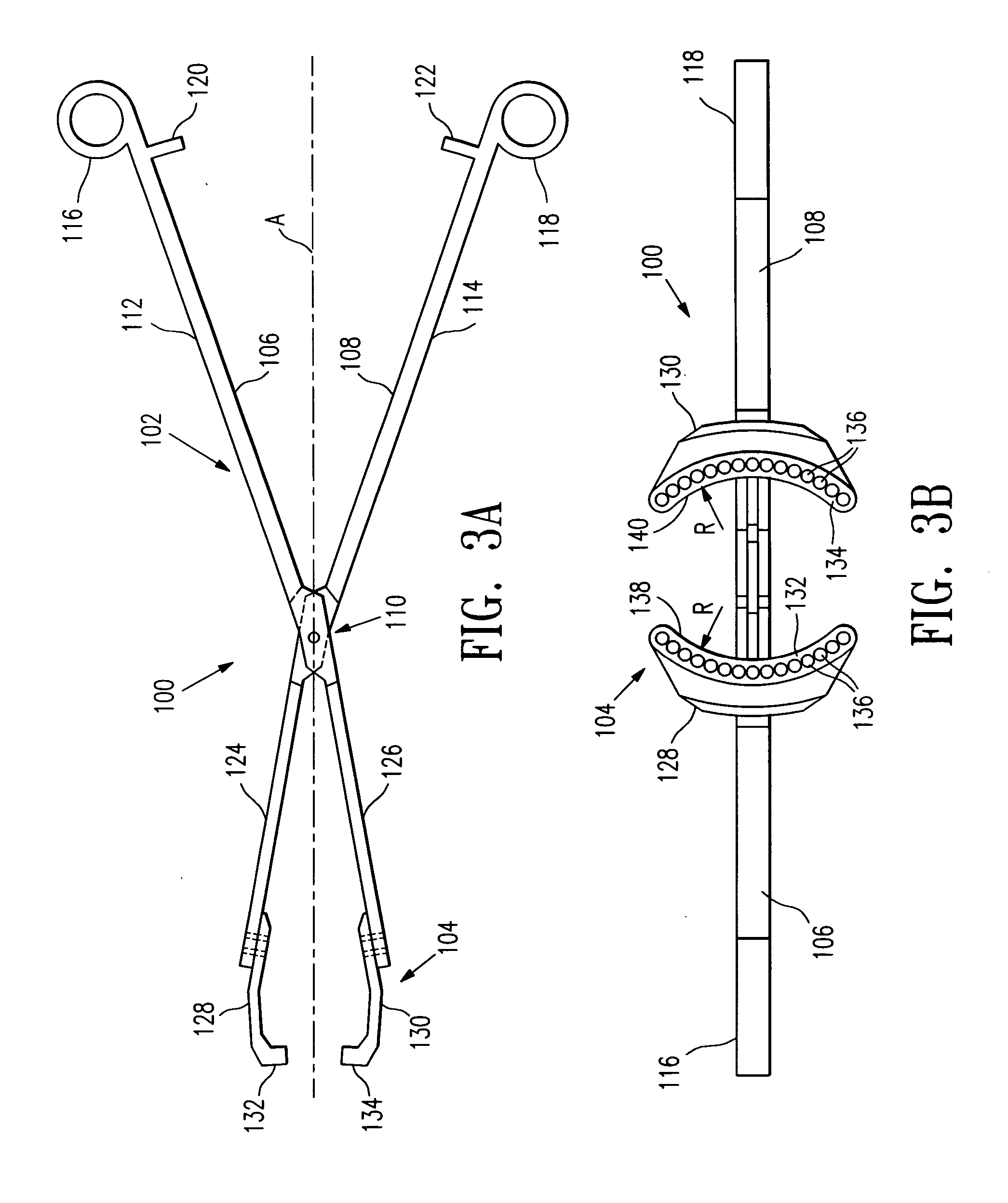
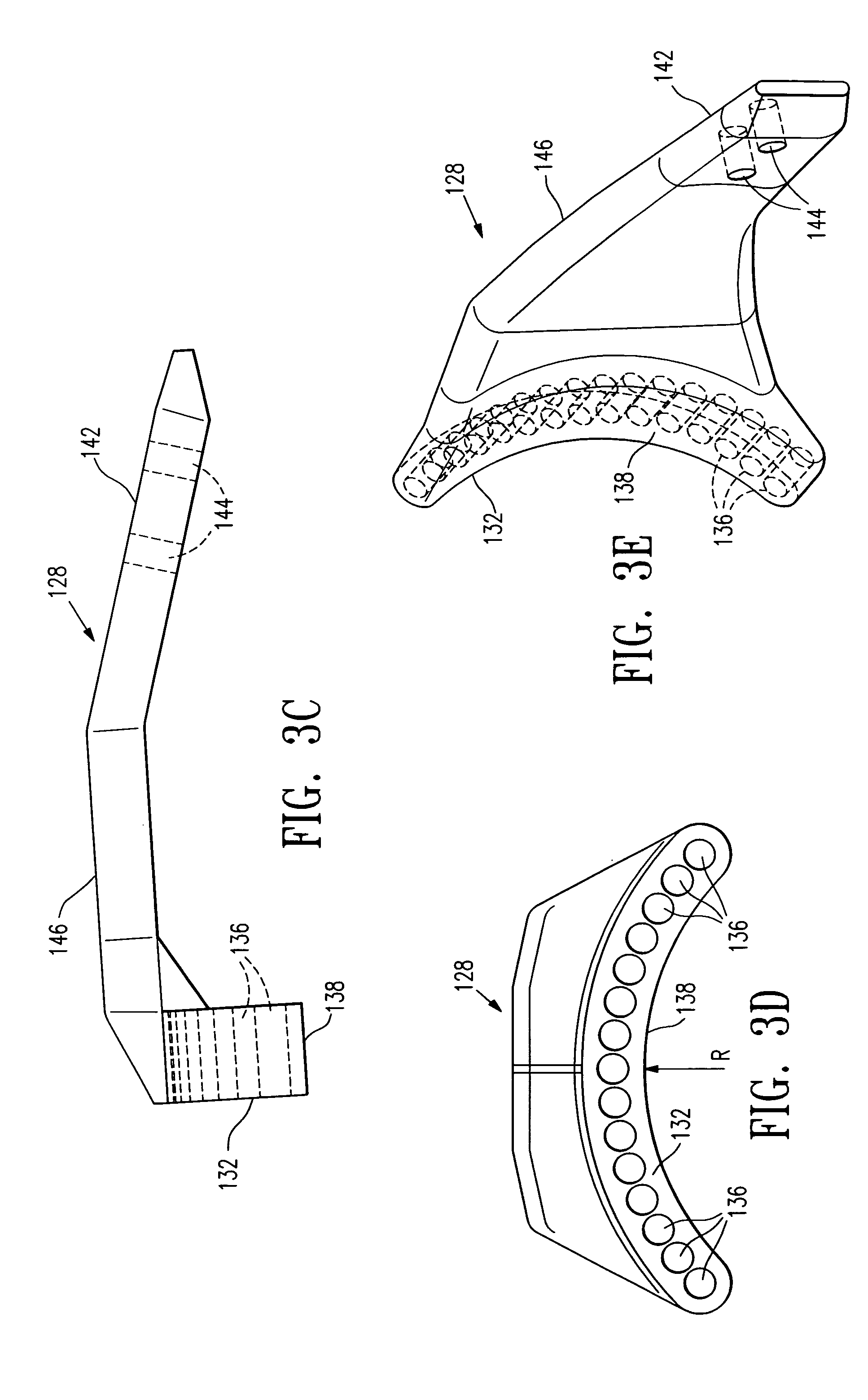
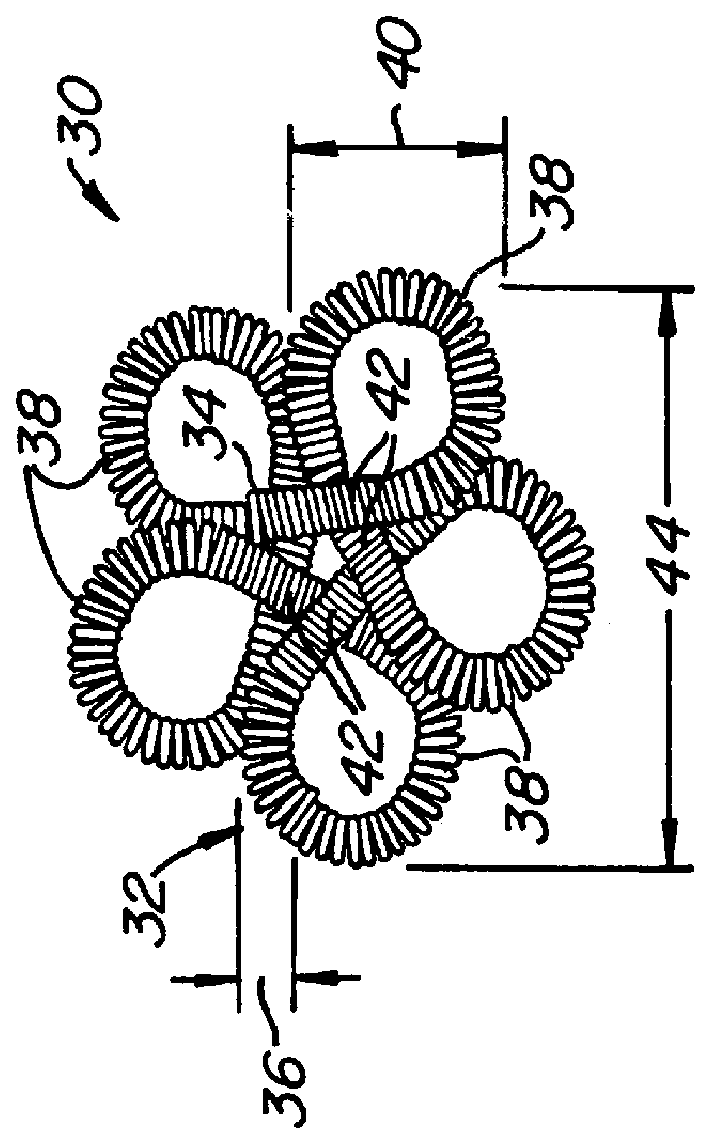
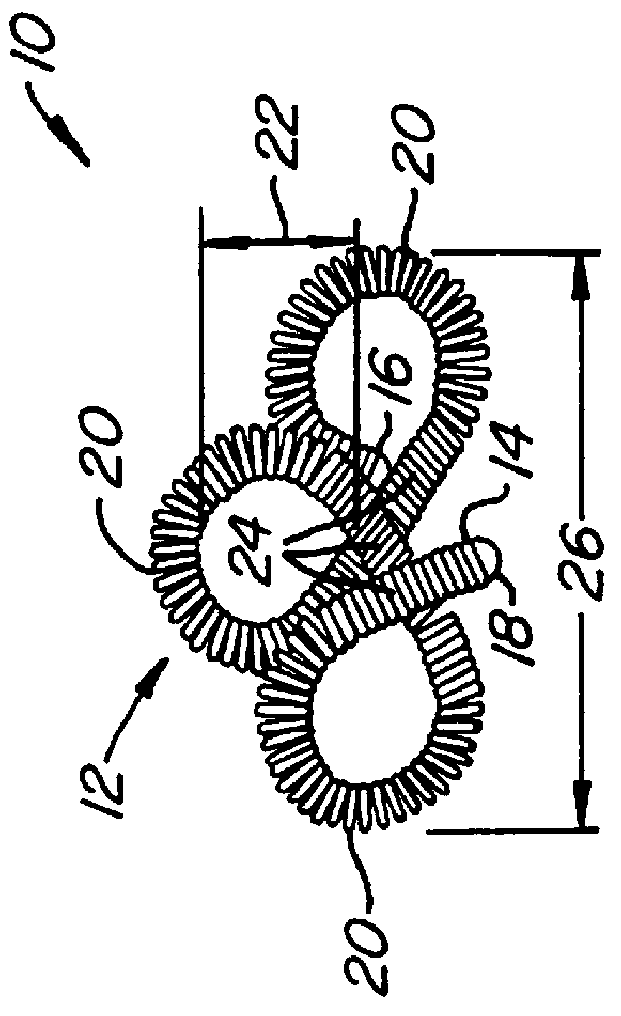
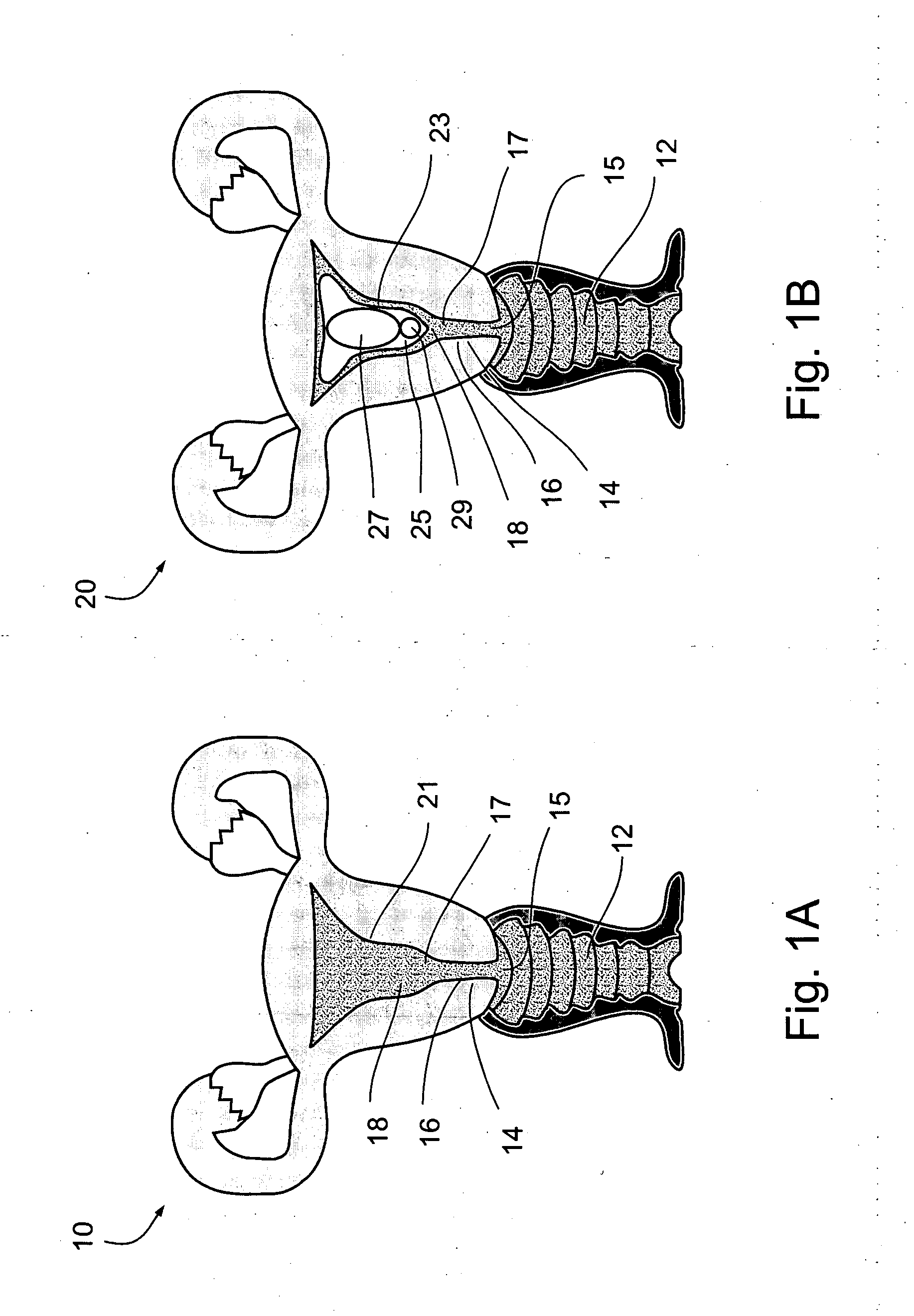
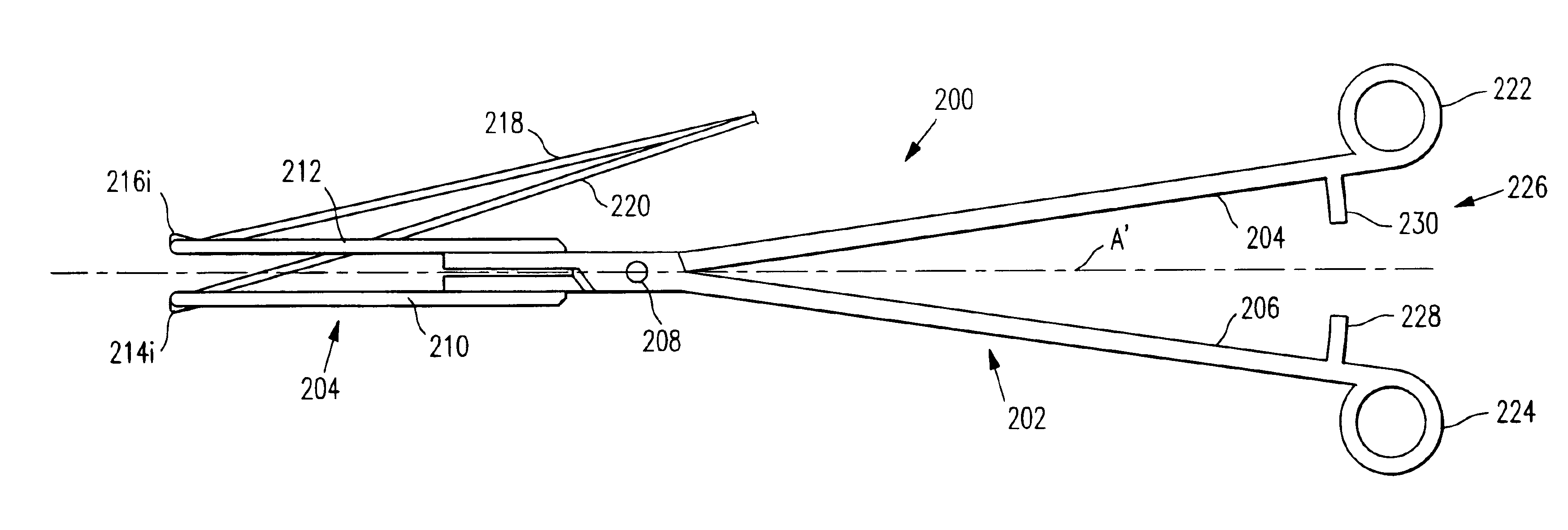
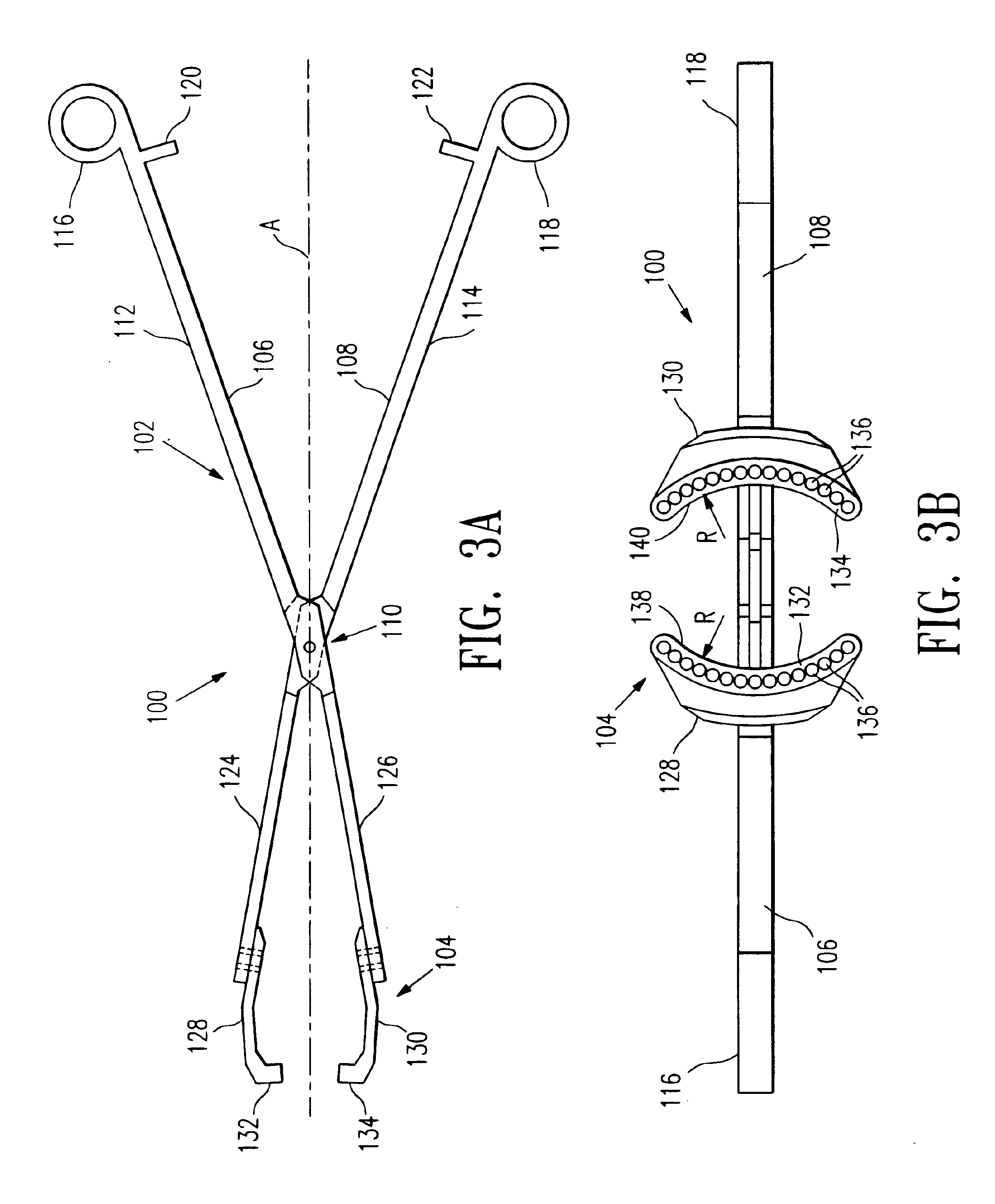
Multi-axial uterine artery identification, characterization, and occlusion pivoting devices and methods
A system is provided for compressing one or both of the uterine arteries of a patient which is at least in part shaped to complement the shape of the exterior of the cervix, which allows the system to be self-positioning. One or more Doppler chips can be mounted or incorporated into the system which permit the practitioner to better identify the uterine artery and monitor blood flow therein. The system includes a pair of pivotally joined elements which can be moved toward and away from the cervix to compress a uterine artery.
Owner:VASCULAR CONTROL SYST
Contraceptive transcervical fallopian tube occlusion devices and their delivery
InactiveUS6176240B1Good curative effectLess readily restrainedFallopian occludersFemale contraceptivesObstetricsSalpingostomy
The invention provides intrafallopian devices and non-surgical methods for their placement to prevent conception. The efficacy of the device is enhanced by forming the structure at least in part from copper or a copper alloy. The device is anchored within the fallopian tube by imposing a secondary shape on a resilient structure, the secondary shape having a larger cross-section than the fallopian tube. The resilient structure is restrained in a straight configuration and transcervically inserted within the fallopian tube, where it is released. The resilient structure is then restrained by the walls of the fallopian tube, imposing anchoring forces as it tries to resume the secondary shape.
Owner:BAYER ESSURE
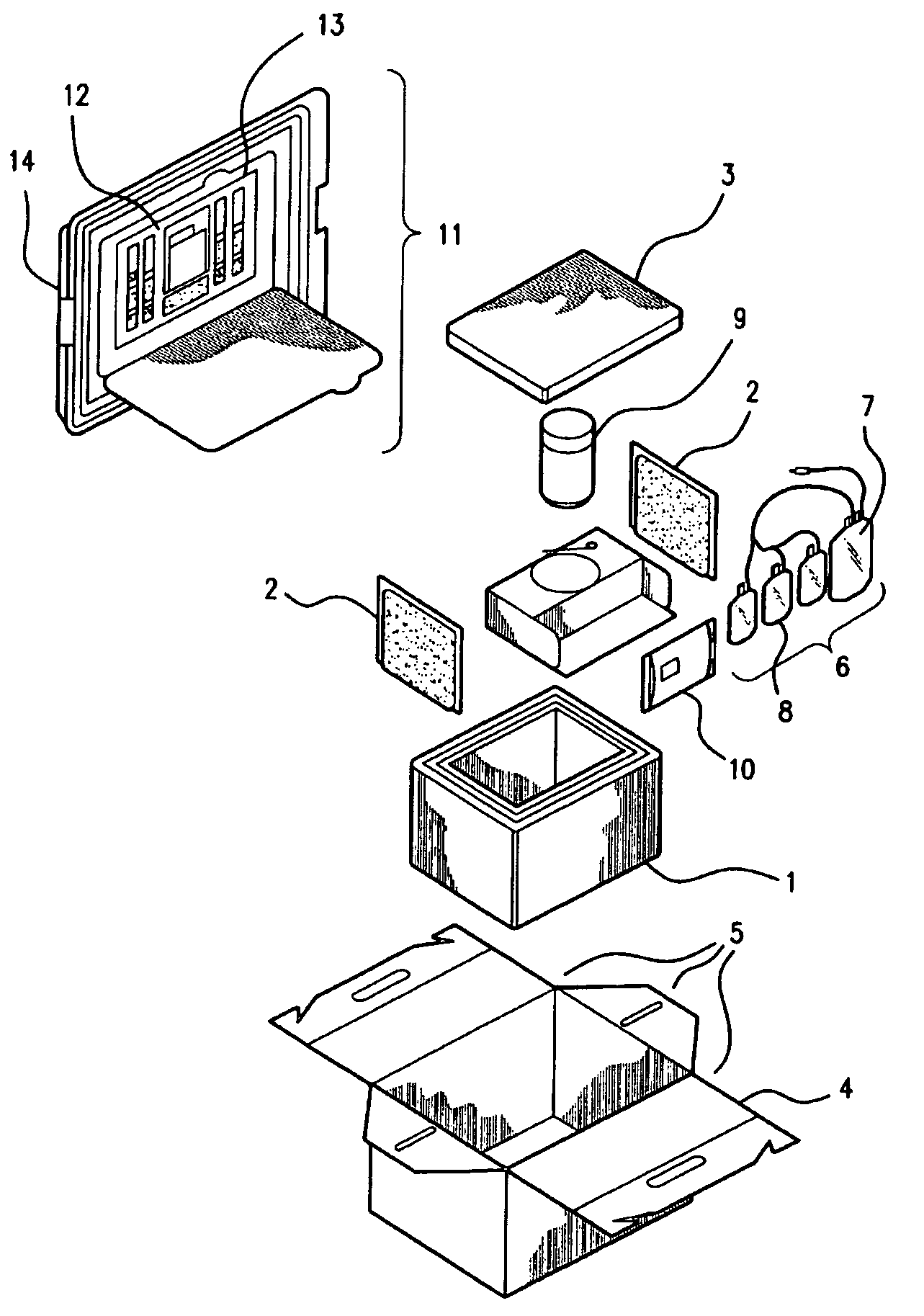
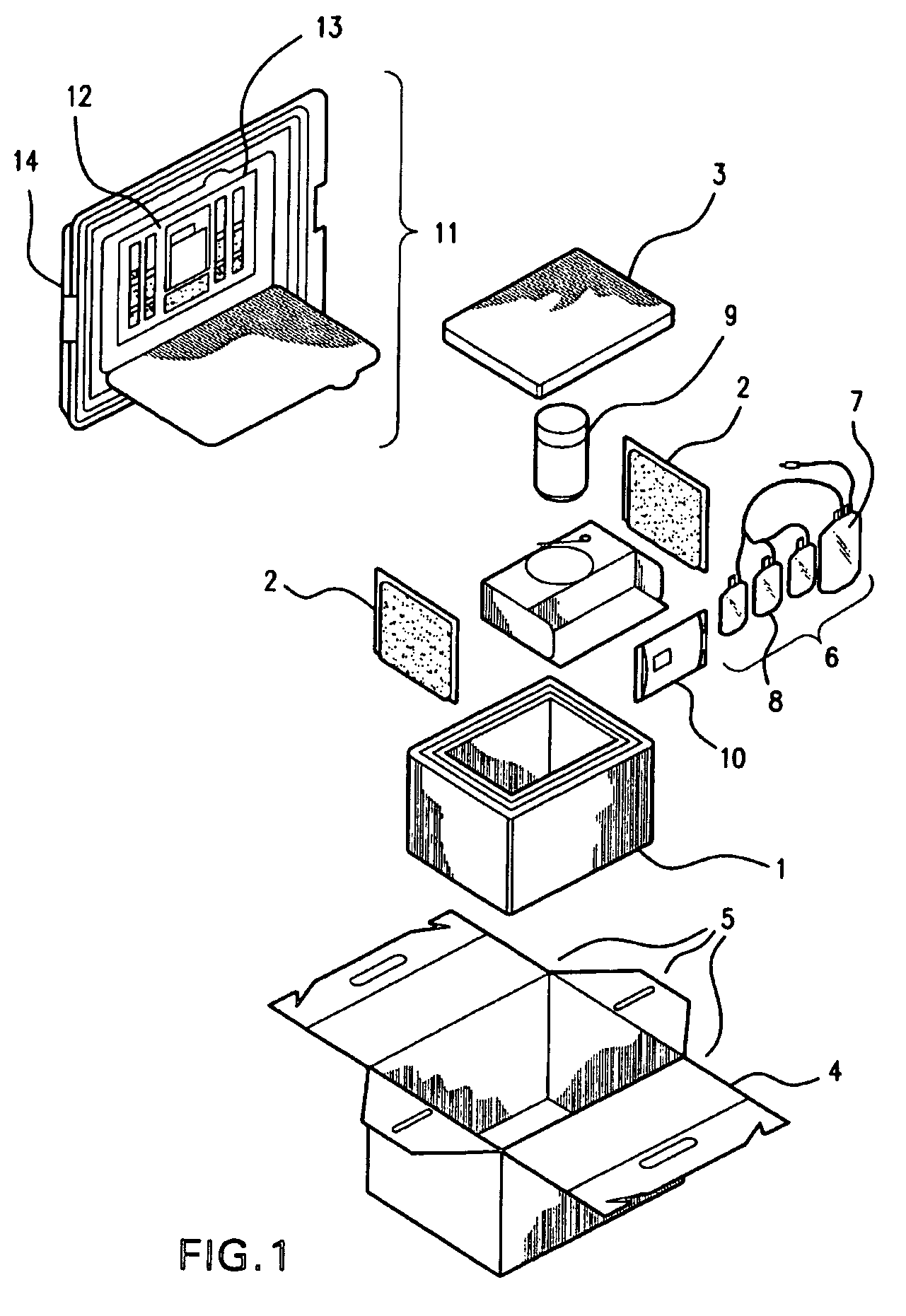
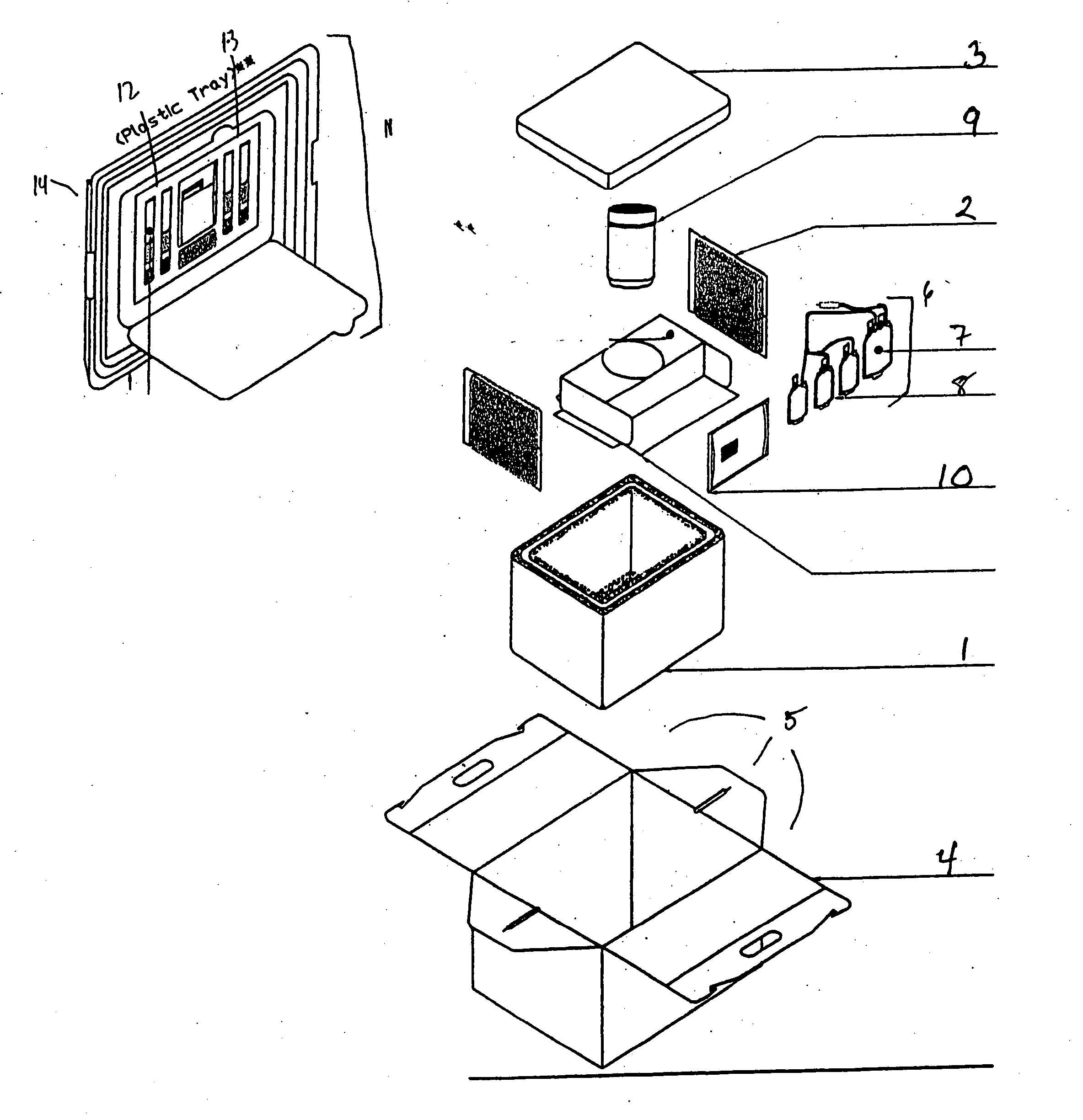
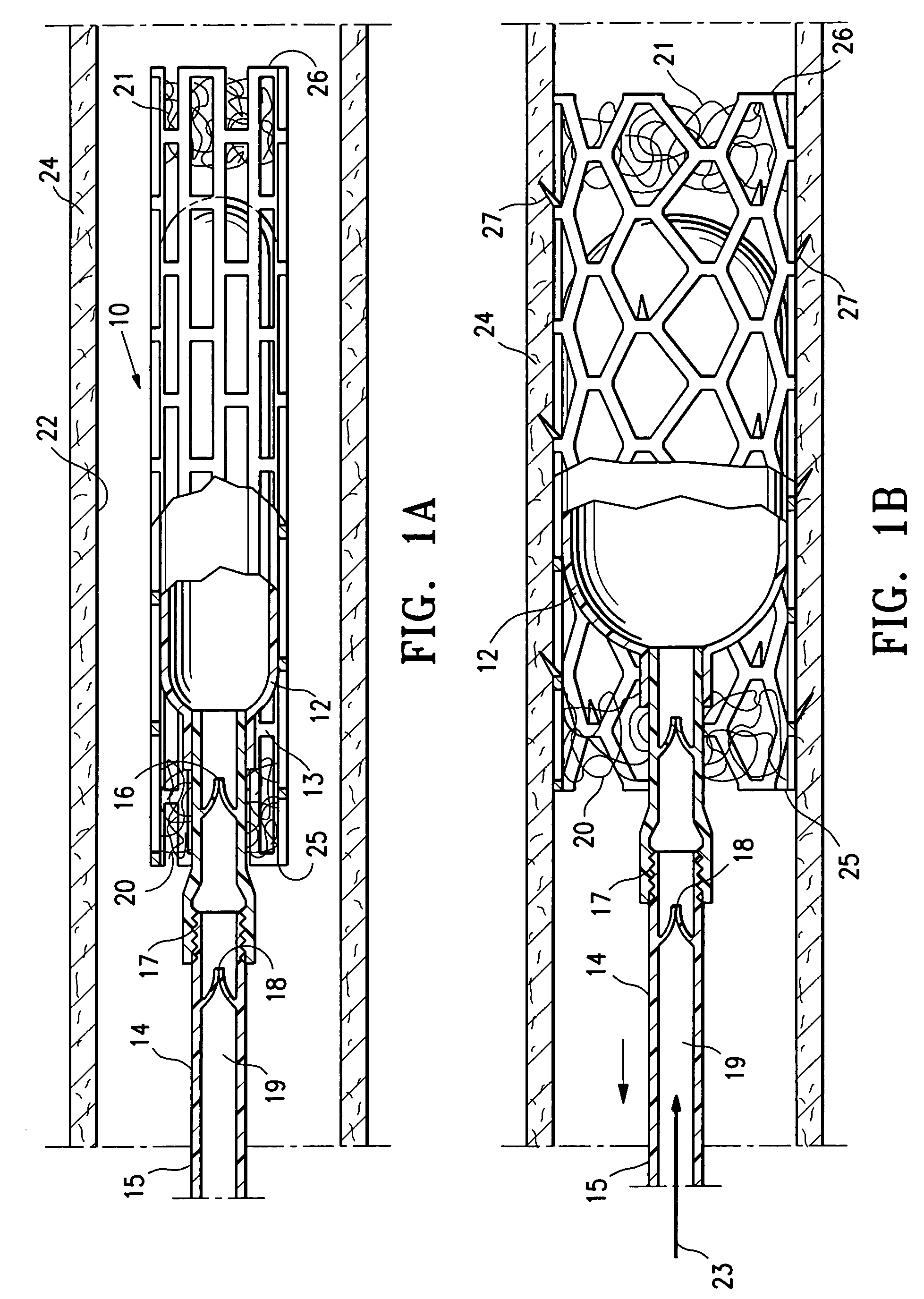
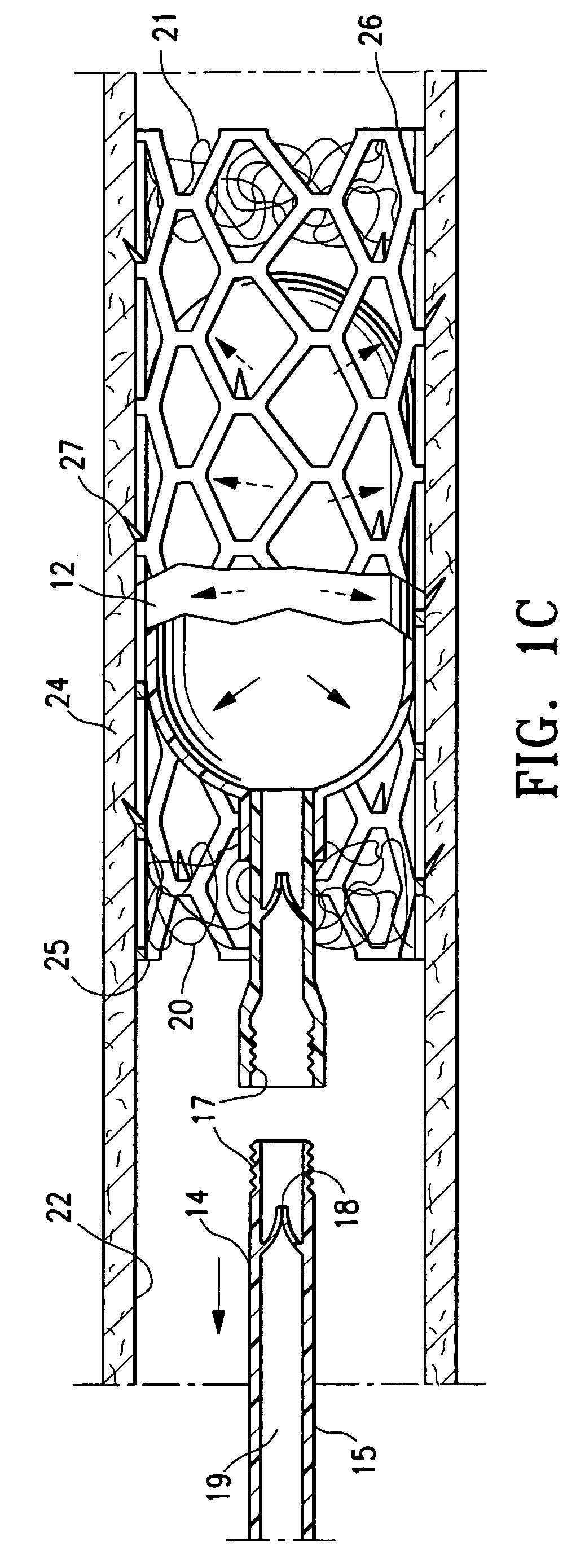
Cord blood and placenta collection kit
ActiveUS7909806B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCord blood stem cellObstetrics
The present invention provides an improved kit for the collection of umbilical cord blood and placental blood, and collection of the placenta from which such blood is obtained. The kit improves upon existing kits in that it provides for improved user convenience, provides for the collection of the placenta itself, and better maintains the internal temperature of the container in which the collected blood and placenta are shipped to a blood bank or registry. The invention further provides a method of collecting umbilical cord and placental blood, and the placenta from which such blood is obtained, comprising using the kit described herein.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Maternal-fetal monitoring system
ActiveUS20050267377A1Accurate repeatabilityImprove signal qualityElectrocardiographyElectromyographyObstetricsNeural network system
A maternal-fetal monitoring system for use during all stages of pregnancy, including antepartum and intrapartum stages. The maternal-fetal monitoring system of the subject invention comprises (1) a set of sensors; (2) an amplifying / filtering means; (3) a computing means; and (4) a graphical user interface. Accurate clinical data, which can be extracted and provided to the user in real-time using the system of the invention, include without limitation, maternal electrocardiogram (ECG) signals, maternal uterine activity signals (EHG), maternal heart rate, fetal ECG signals, and fetal heart rate. In a preferred embodiment, the maternal-fetal monitoring system of the invention includes an intelligence means, such as a neural network system, to analyze and interpret clinical data for use in clinical diagnosis antepartum, intrapartum and postpartum, as well as delivery strategy.
Owner:CONVERGENT ENG +1
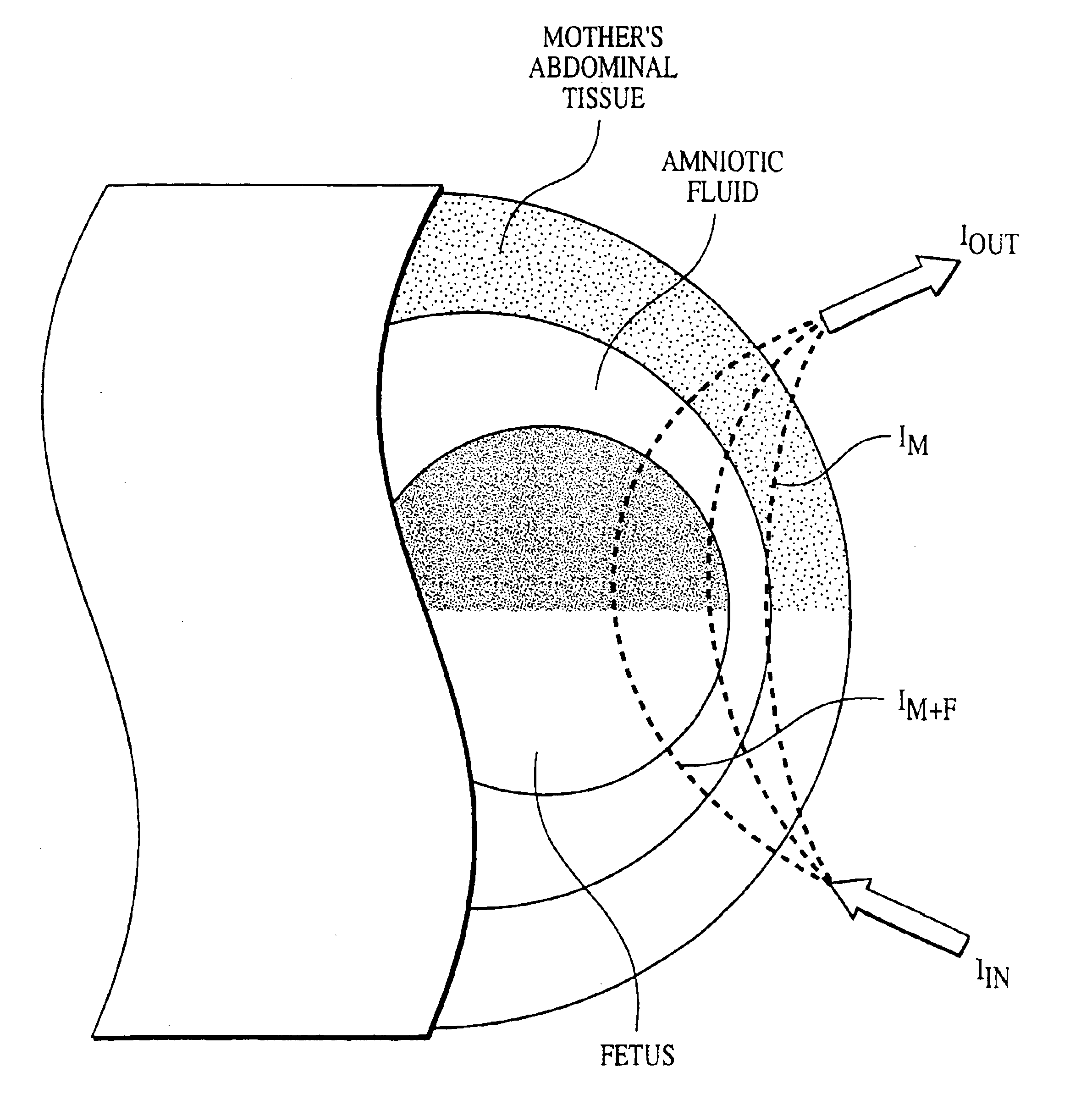
Fetal pulse oximetry
InactiveUS7047055B2Minimize measurement errorDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsObstetricsPulse oximetry
A fetal blood pulse oximetry method and apparatus using a first wavelength of light at about 655 to 705 nm and a second wavelength of light at about 820 to 900 nm. Measurements are taken through a mother's abdomen. Processing is performed to extract absorption information related to fetal arterial blood with calculation of fetal oxygen saturation from the extracted data.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for recognizing and determining a position and robot including such an apparatus
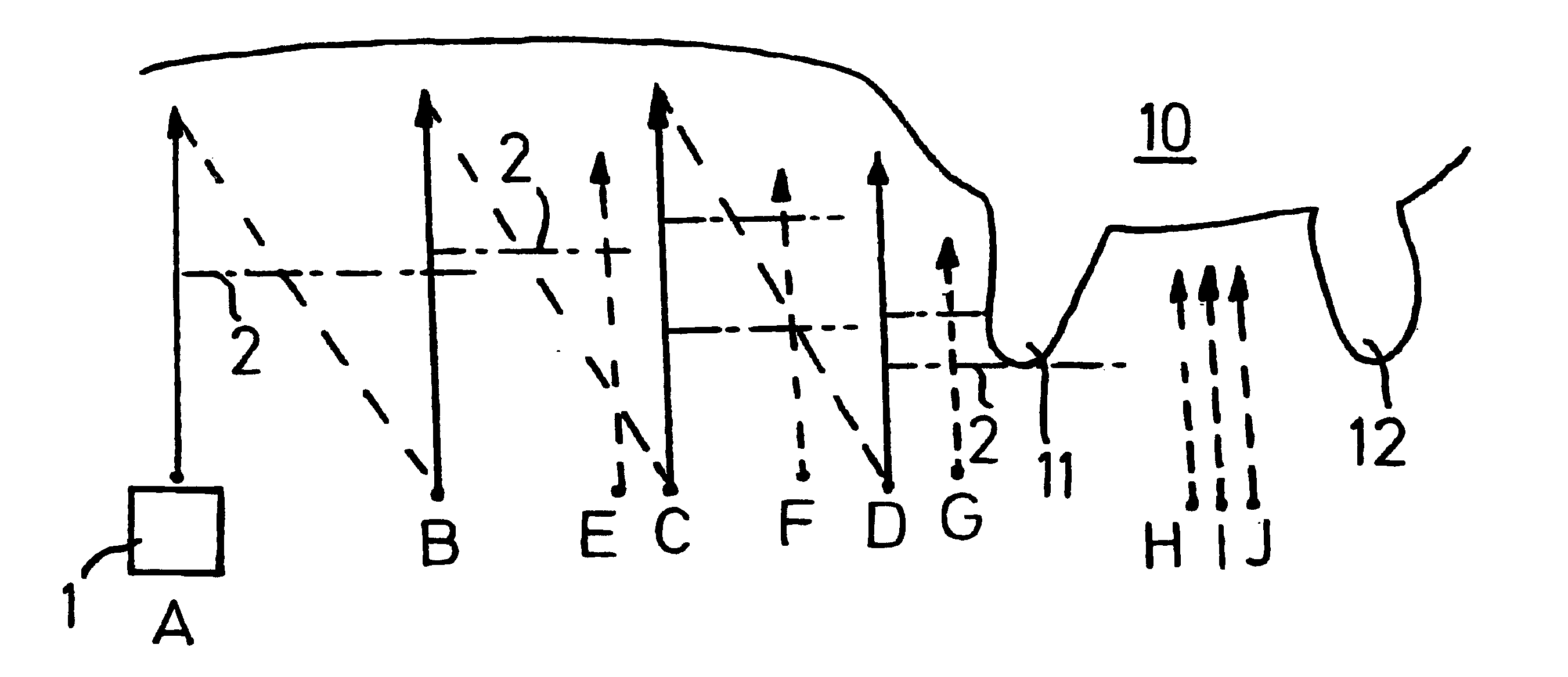
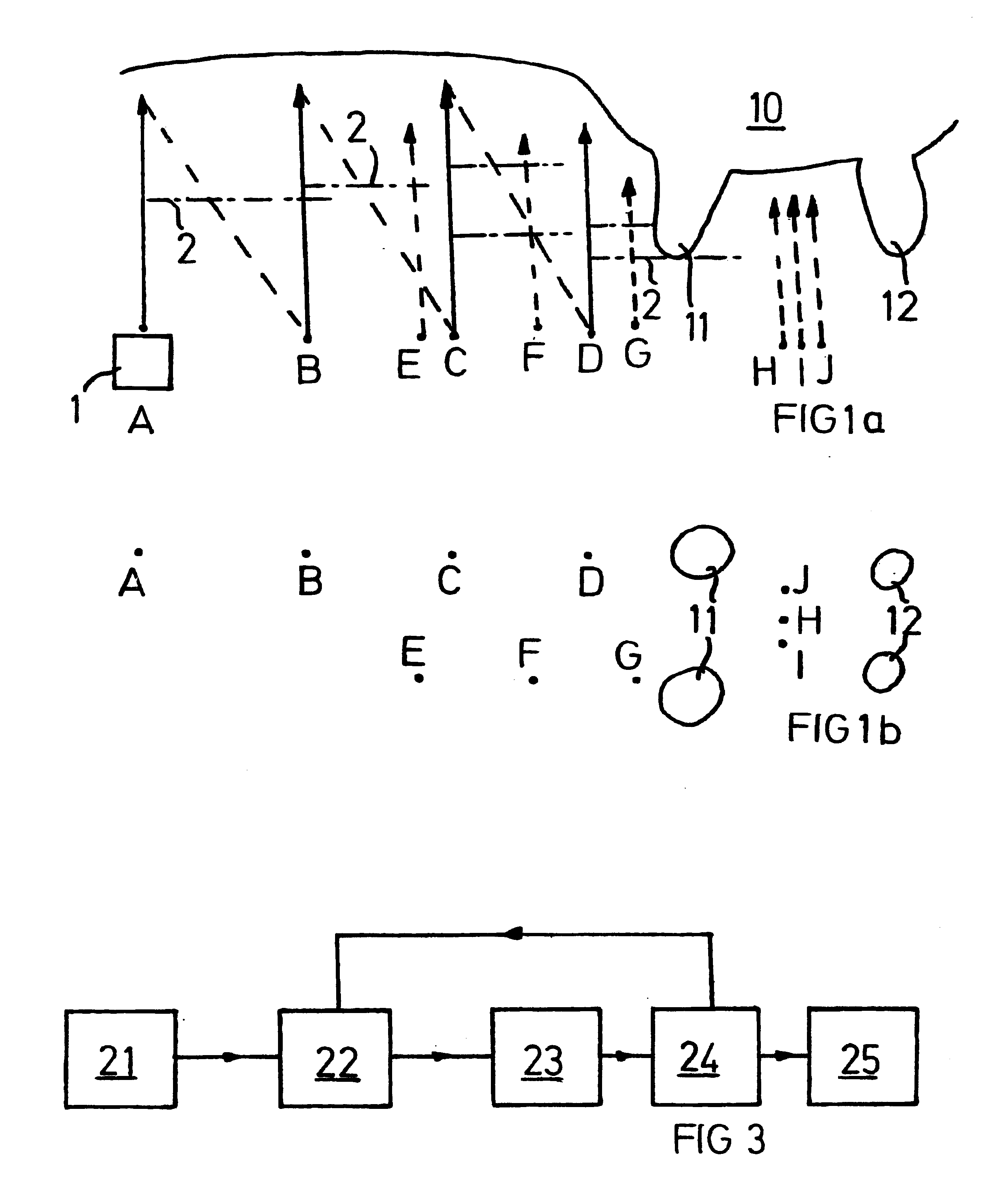
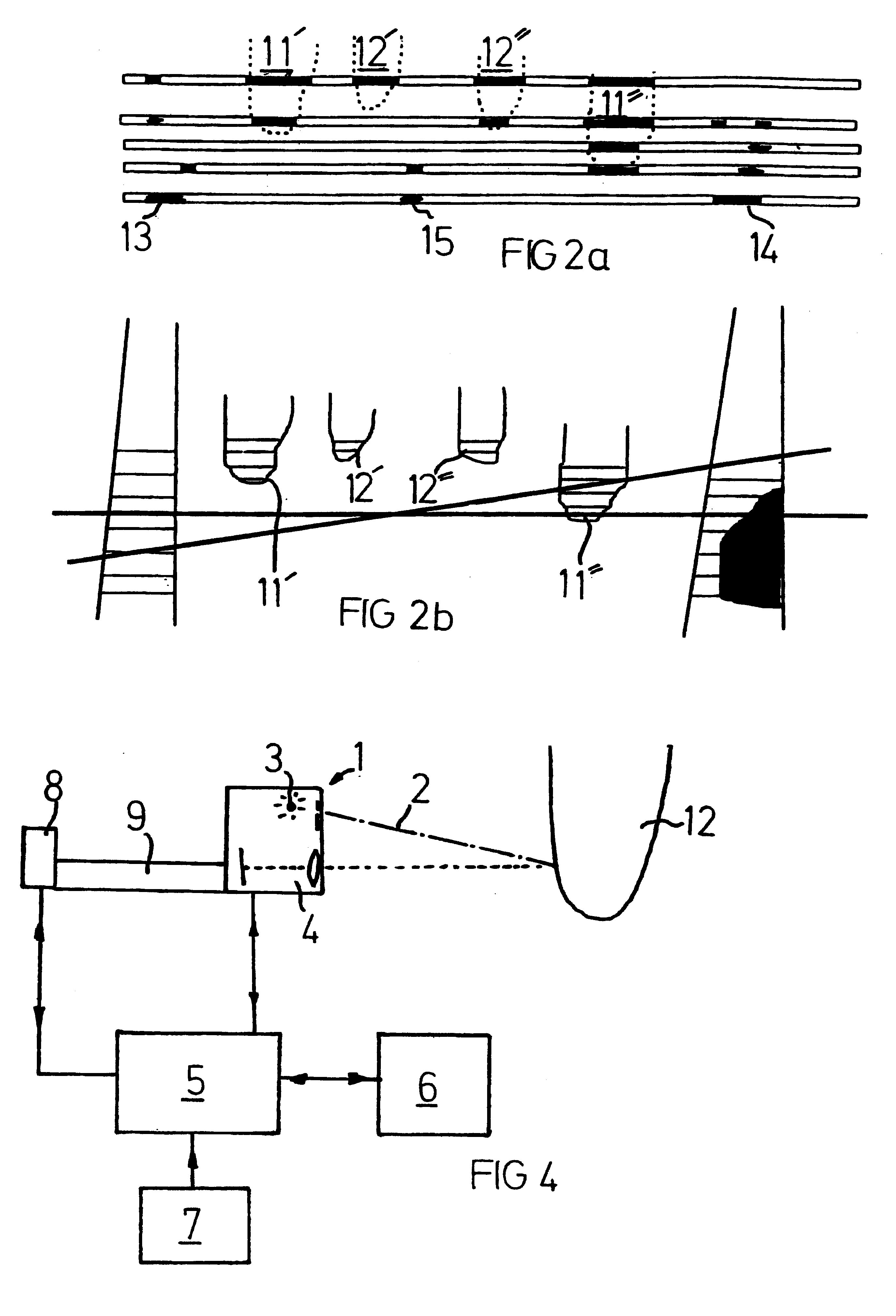
A method for recognizing and determining the position of at least one teat of a milking animal, including the steps: moving a scanning head including a light source to a region containing the teat or teats, capturing at least one image formed by said light, evaluating the image or images so as to determine if each image describes said teat or teats. The scanning head (1) is moved to a fixed initial position (A) in the room which is under the animal and clearly in front of an udder and thereby the teats of all known relevant animals, thereafter the scanning head is moved in determined steps (A-J) under the animal: upwards towards the animal, downwards, backwards towards the udder, upwards, downwards etc., while carrying out the scanning procedure. The invention also concerns an apparatus carrying out the process and a milking robot including such an apparatus.
Owner:DELAVAL HLDG AB
Nucleic acids for the prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases
The invention relates to methods and products for preventing and / or treating sexually transmitted diseases. A nucleic acid and optionally an anti-STD agent, a birth control agent and / or a birth control device are administered, optionally in the context of a sustained release device to a subject to prevent or treat STD.
Owner:COLEY PHARMA GRP INC
Methods and Devices for Delivery of Compositions to Conduits
The present invention comprises systems, methods and devices for the delivery of visualizable or treatment compositions or therapeutic agents comprising device elements for diagnosis and / or treatment of conduits. A delivery system comprising an introducer shaft having at least one exit port and at least one delivery catheter for placement of compositions into the conduit, such as a fallopian tube.
Owner:FEMASYS INC
Electrically affixed transcervical fallopian tube occlusion devices
InactiveUS6145505AGood curative effectLess readily restrainedFallopian occludersFemale contraceptivesObstetricsSalpingostomy
The invention provides intrafallopian devices and non-surgical methods for their placement to prevent conception. The efficacy of the device is enhanced by forming the structure at least in part from copper or a copper alloy. The device is anchored within the fallopian tube by imposing a secondary shape on a resilient structure, the secondary shape having a larger cross-section than the fallopian tube. The resilient structure is restrained in a straight configuration and transcervically inserted within the fallopian tube, where it is released. The resilient structure is then restrained by the walls of the fallopian tube, imposing anchoring forces as it tries to resume the secondary shape.
Owner:BAYER ESSURE
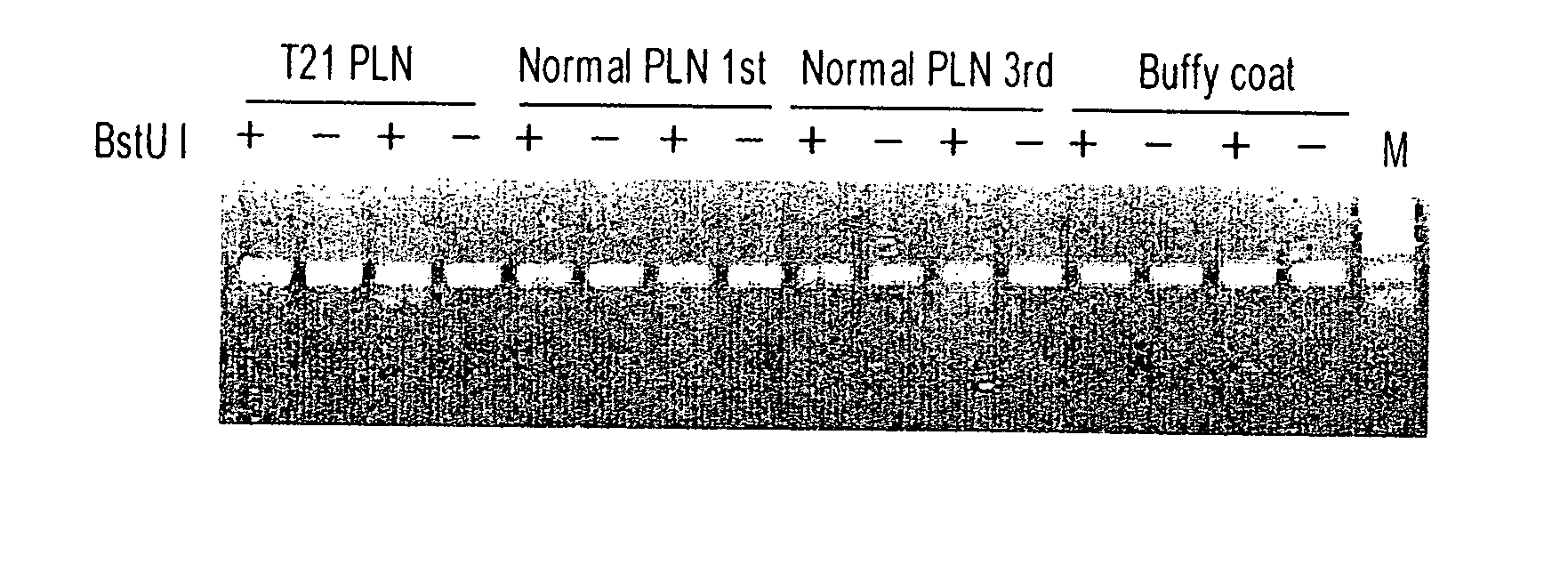
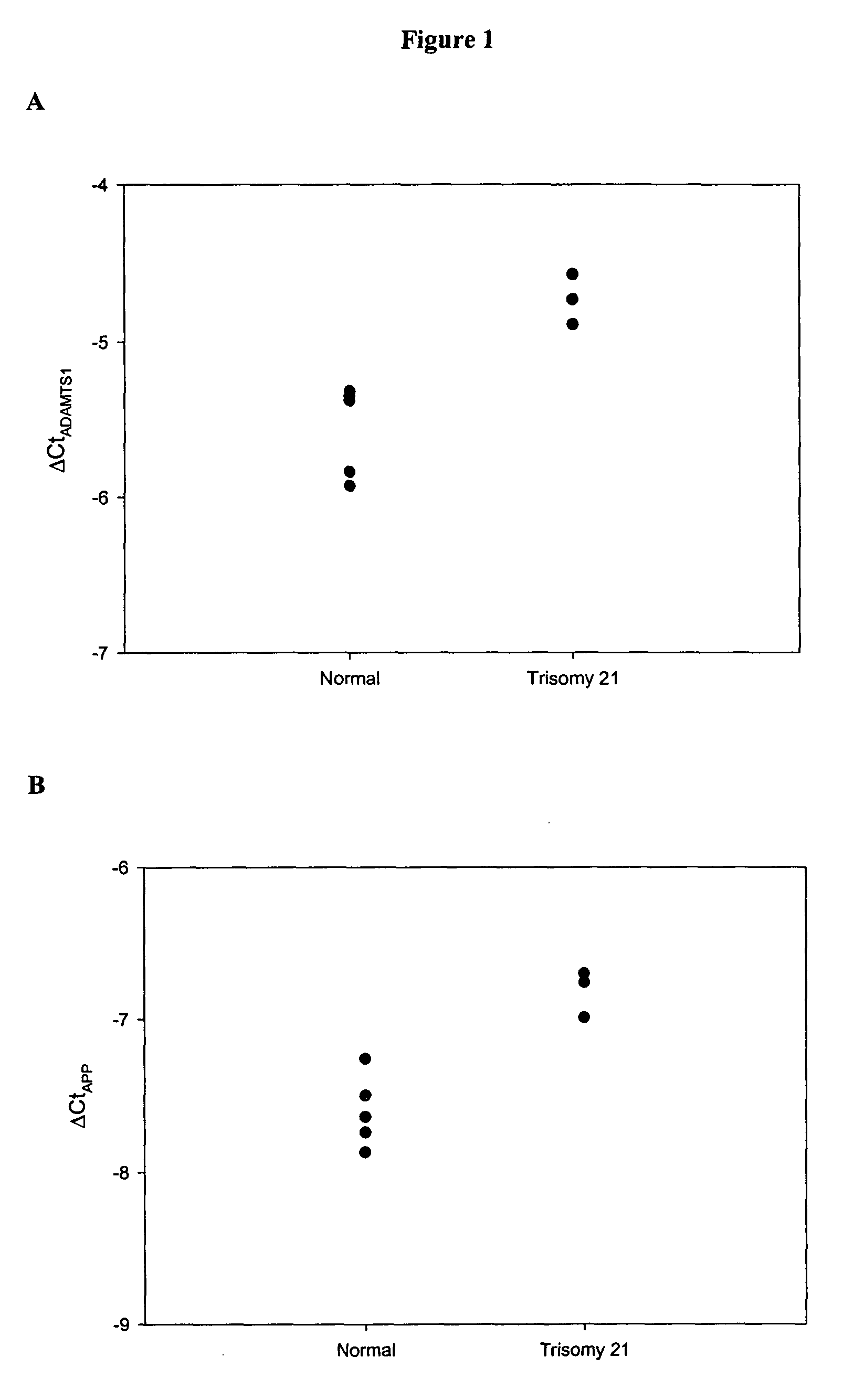
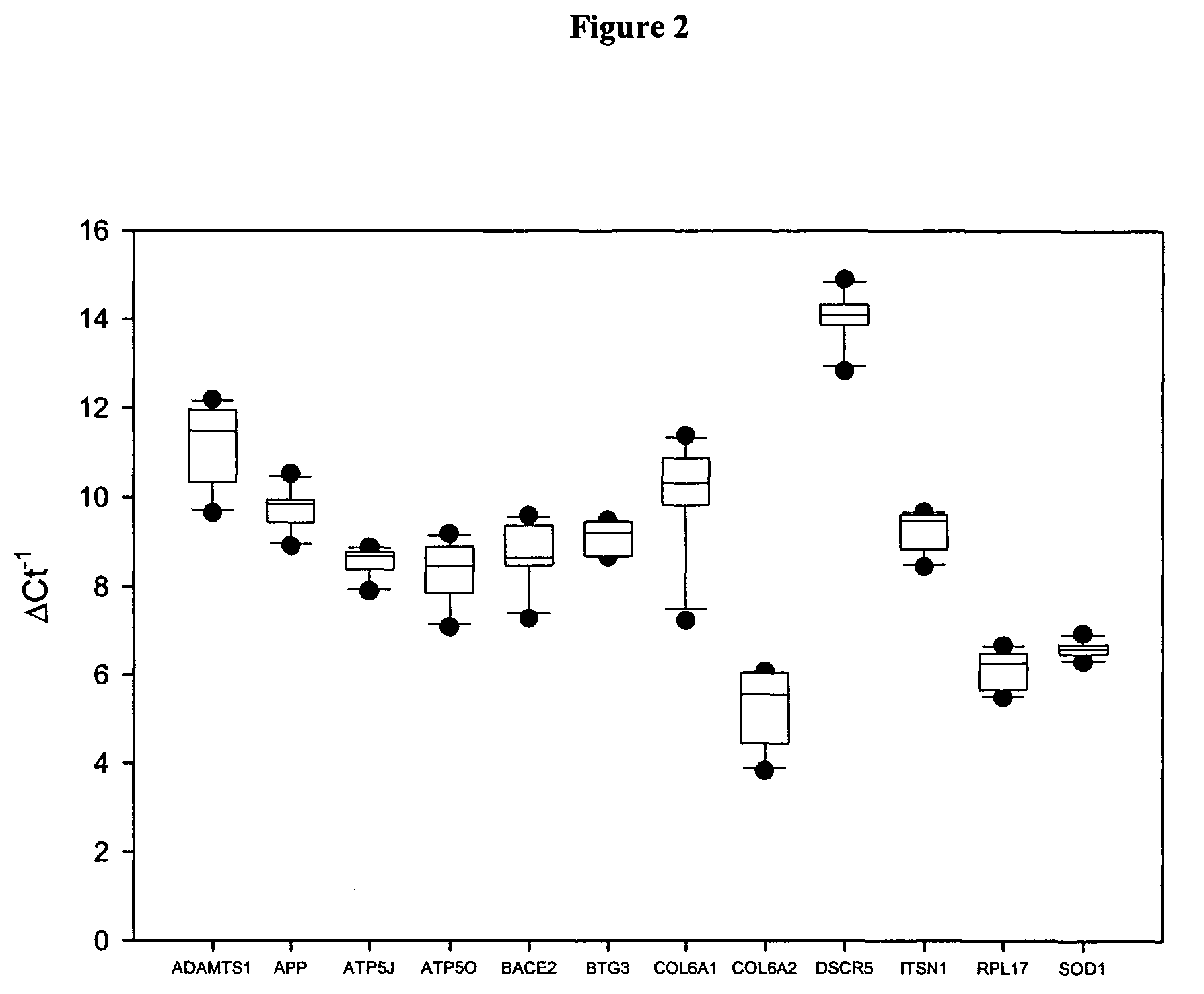
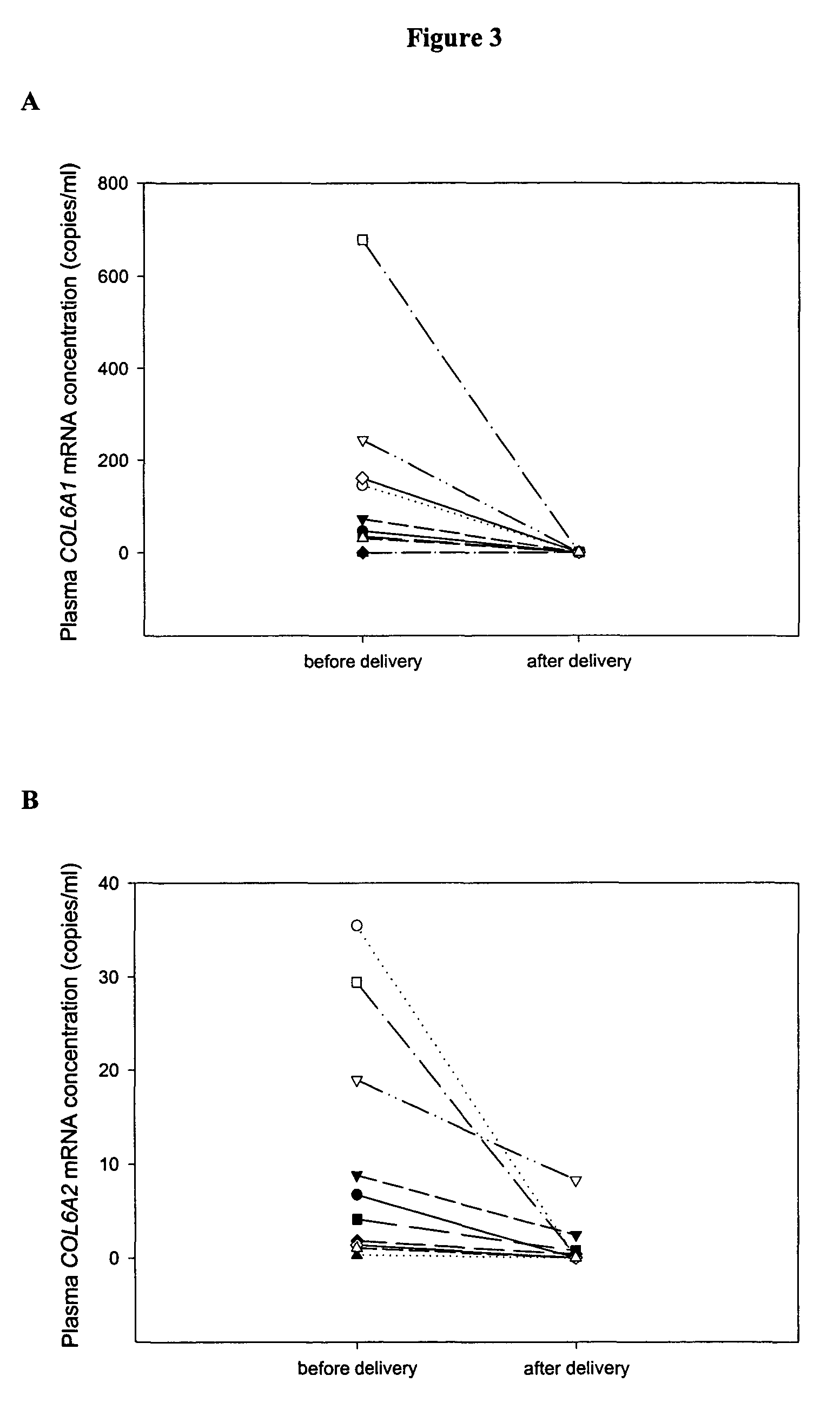
Novel markers for prenatal diagnosis and monitoring
ActiveUS20070275402A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementObstetricsPrenatal diagnosis
This application provides the use of novel fetal markers for prenatal diagnosis and monitoring of certain pregnancy-related conditions. More specifically, the invention resides in the discovery that certain CpG islands located on fetal chromosome 21 demonstrate a methylation profile that is distinct from that of the corresponding CpG islands located on maternal chromosome 21. This application also provides kits for diagnosing or monitoring of the relevant conditions.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Markers for prenatal diagnosis and monitoring
Methods and kits are provided for diagnosing, monitoring, or predicting preeclaimpsia in a pregnant woman, trisomy 18 and trisomy 21 in a fetus, as well as for detecting pregnancy in a woman, by quantitatively measuring in the maternal blood the amount of one or more RNA species derived from a set of genetic loci and comparing the amount of the RNA species with a standard control.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Cord blood and placenta collection kit
ActiveUS20060060494A1Solve insufficient capacitySufficient volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCord blood stem cellObstetrics
The present invention provides an improved kit for the collection of umbilical cord blood and placental blood, and collection of the placenta from which such blood is obtained. The kit improves upon existing kits in that it provides for improved user convenience, provides for the collection of the placenta itself, and better maintains the internal temperature of the container in which the collected blood and placenta are shipped to a blood bank or registry. The invention further provides a method of collecting umbilical cord and placental blood, and the placenta from which such blood is obtained, comprising using the kit described herein.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
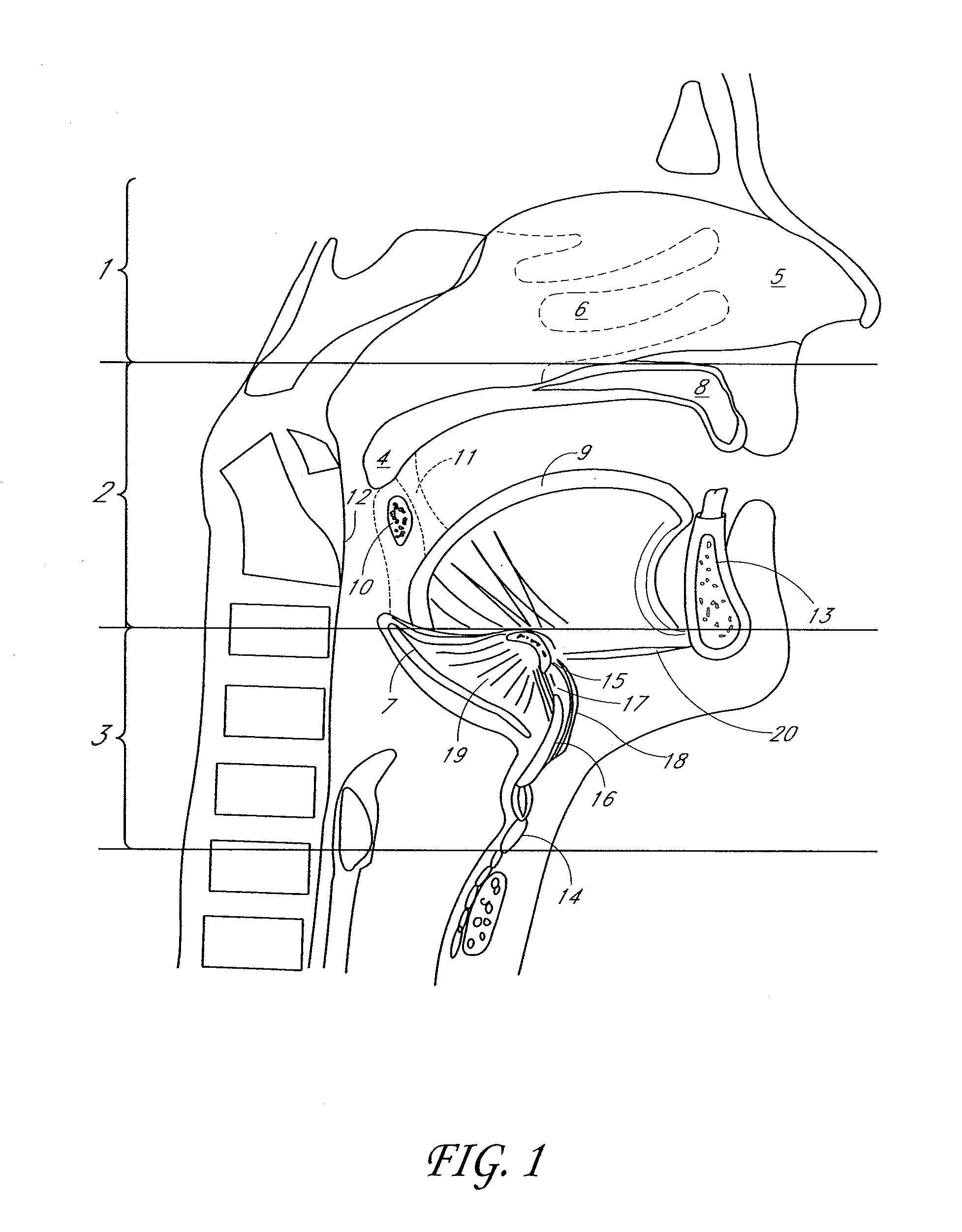
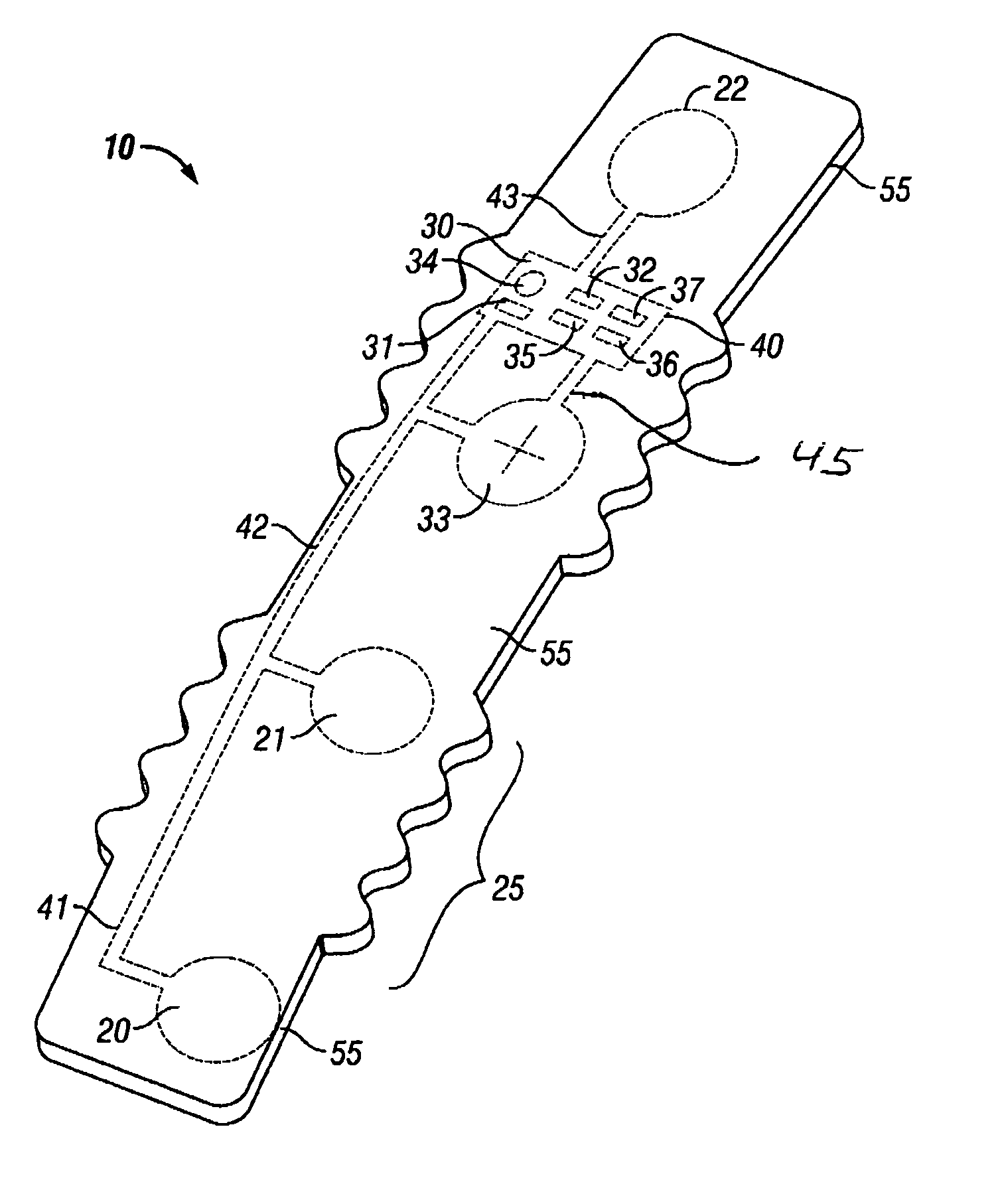
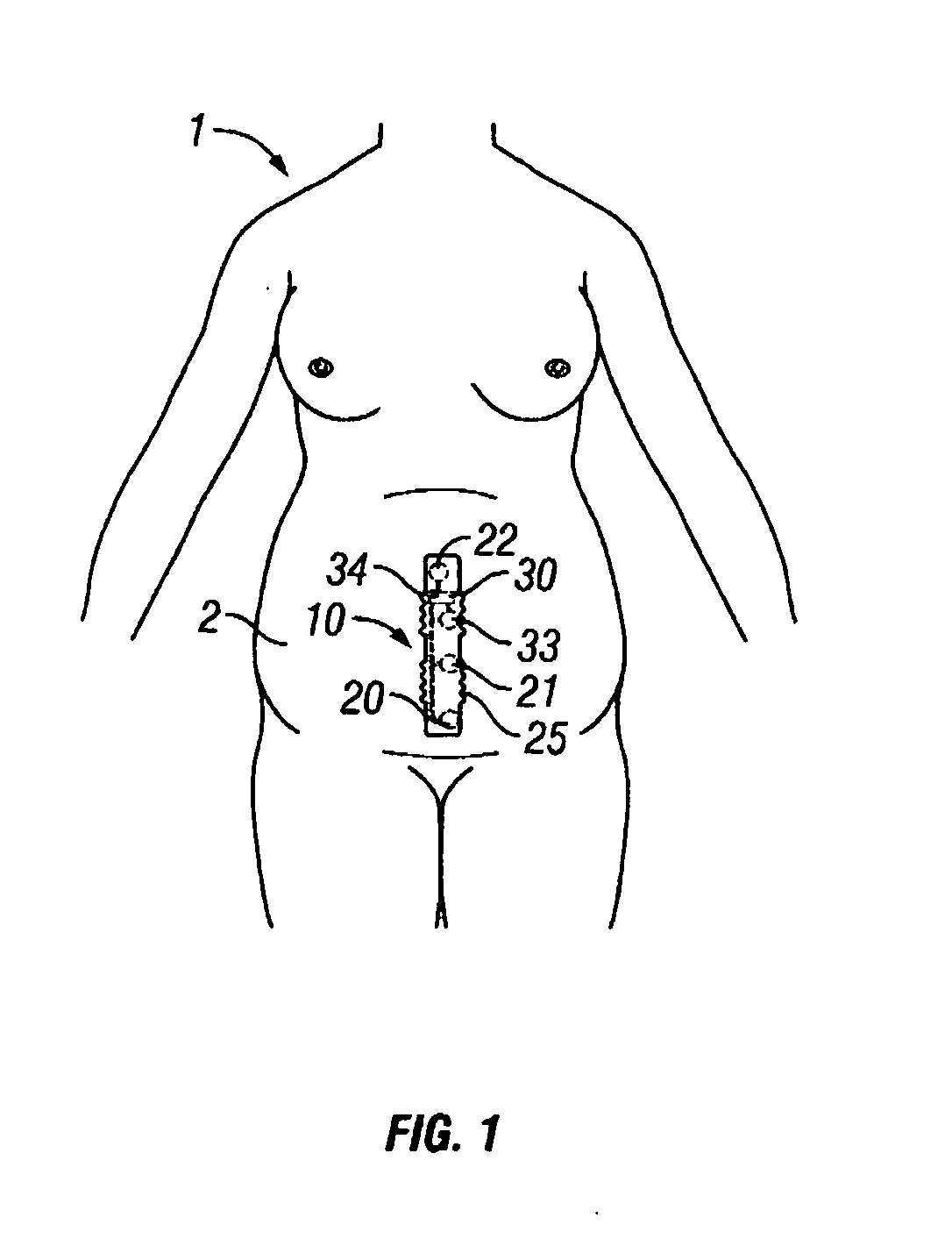
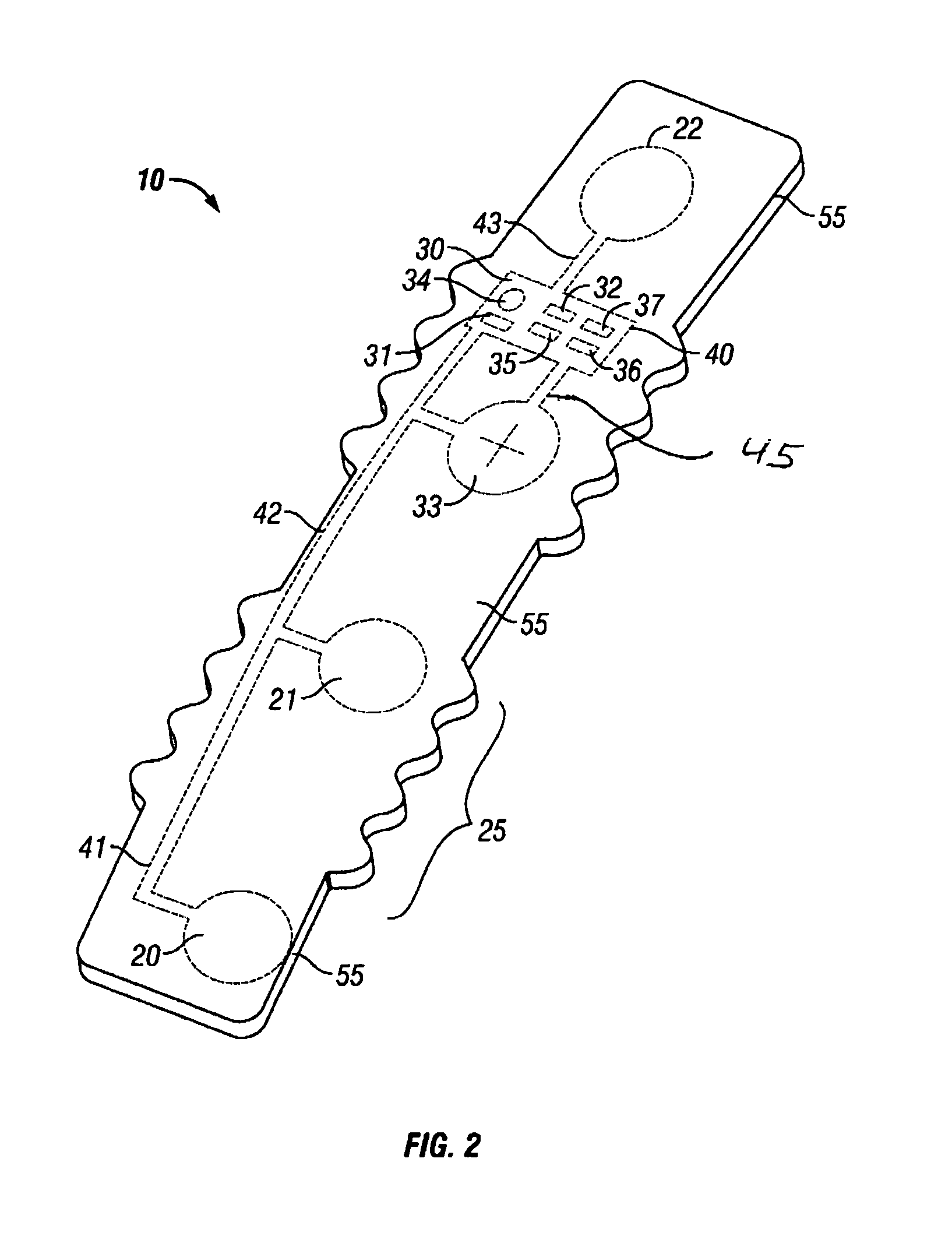
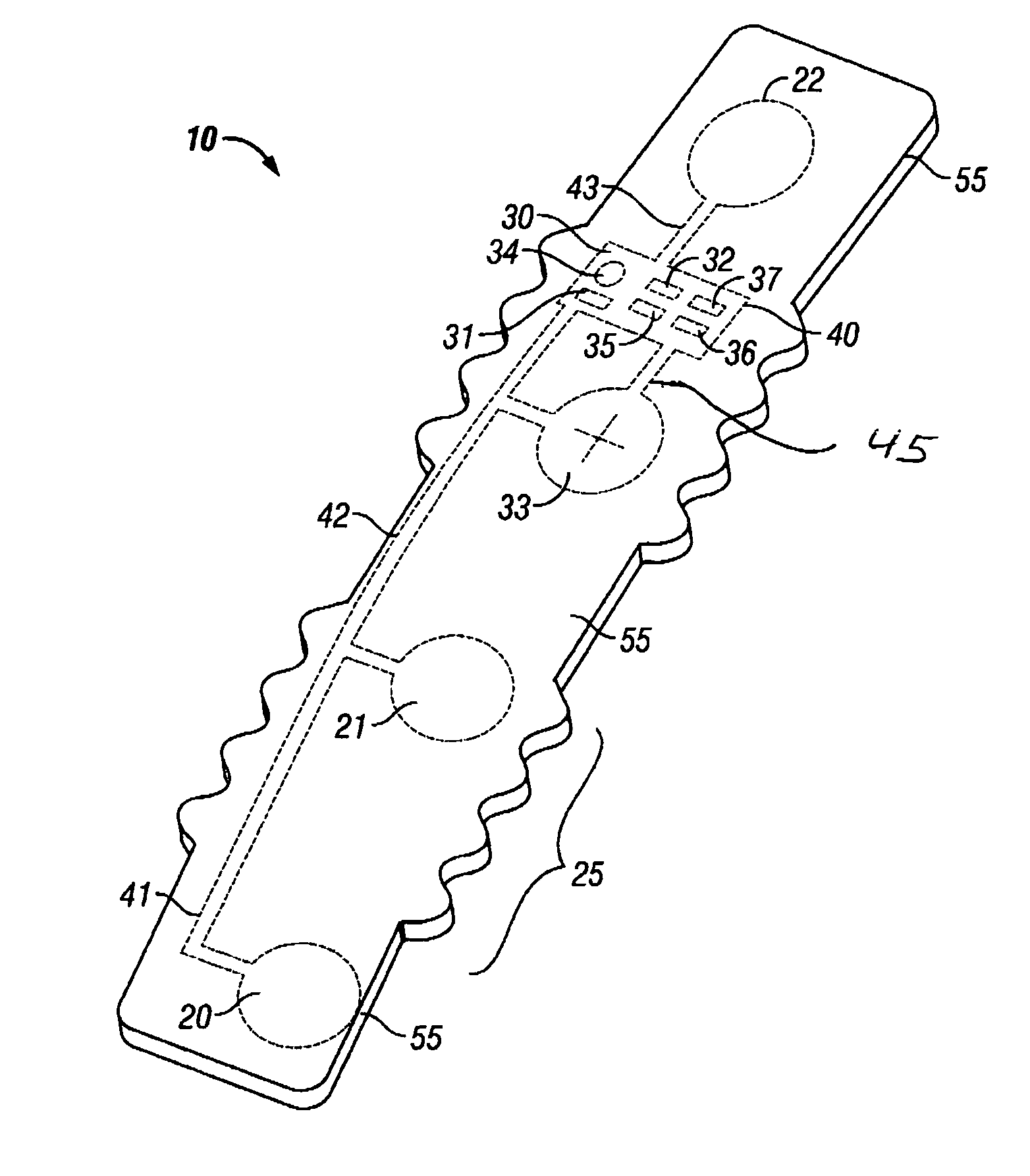
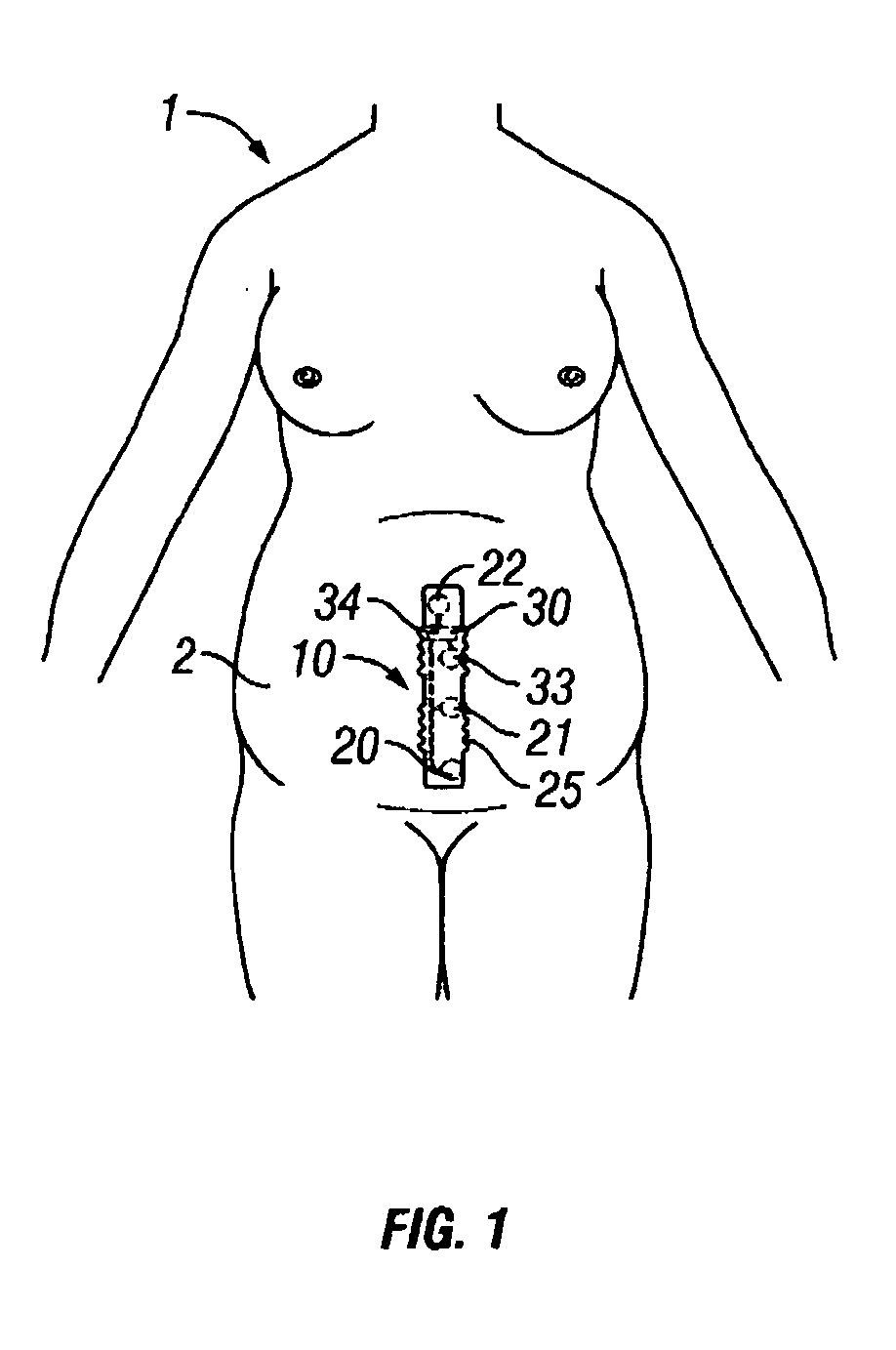
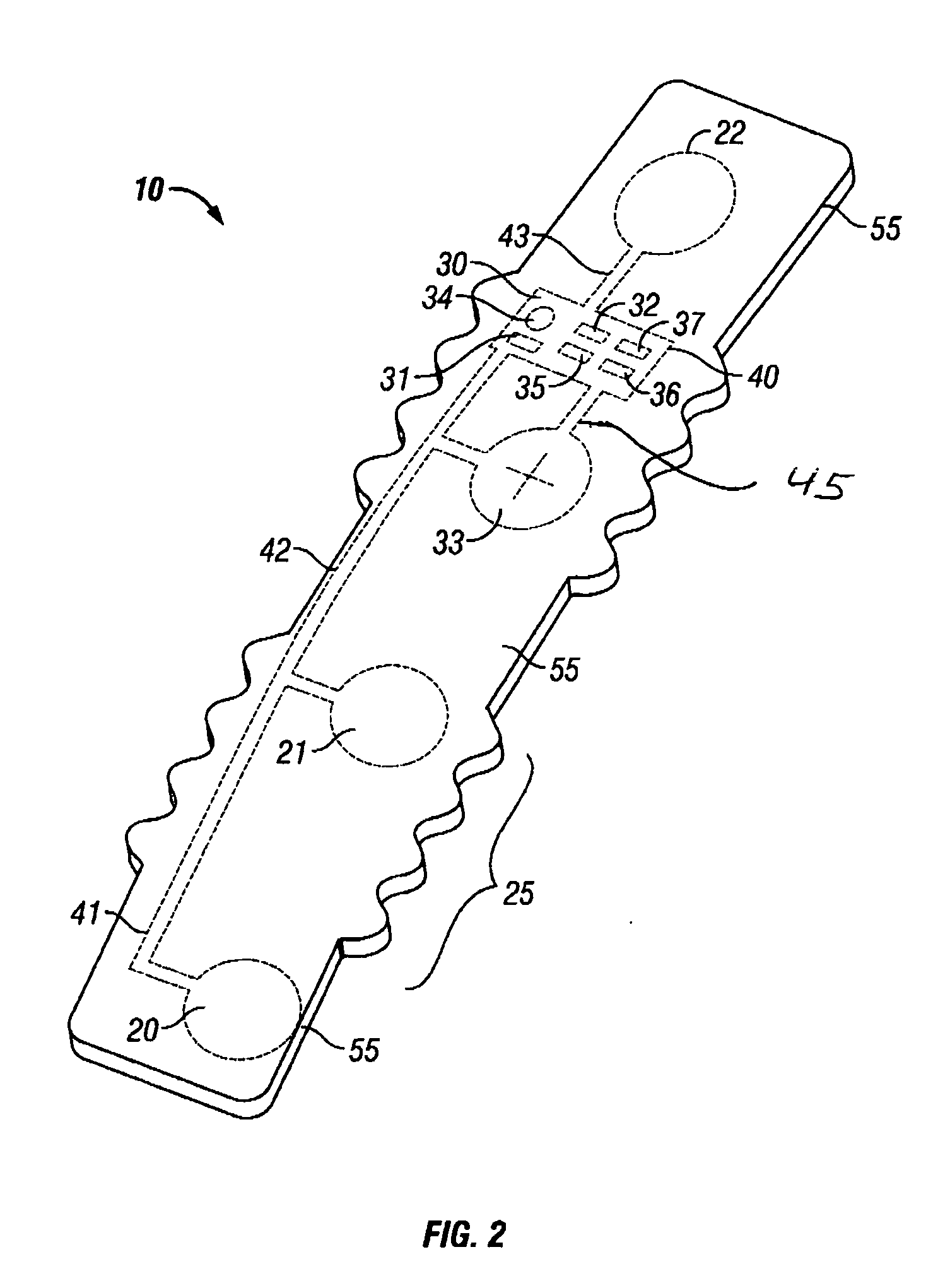
Intrapartum monitor patch
The invention provides an integrated patch for the non-invasive monitoring of a laboring woman. The patch incorporates biopotential electrodes for sensing fetal ECG and EMG indicative of myometrial activity. The patch also incorporates a processor for extracting labor activity and fetal heart activity after filtering out maternal ECG from the composite biopotential signal present on the abdomen of the pregnant woman. The fetal monitor patch is thin, flexible, and incorporates a battery and biopotential amplifier network. In the preferred embodiment, the patch is disposable and worn continuously during labor or later stages of pregnancy. In a hospital embodiment for intrapartum monitoring, the patch wirelessly transmits fetal heart activity and myometrial activity to a bedside monitor or a remote monitoring station.
Owner:PRENATEK
Contraceptive with permeable and impermeable components
InactiveUS20050192616A1Facilitate tissue ingrowthFacilitates tissue ingrowthFallopian occludersCannulasObstetricsTissue ingrowth
An device for occluding a body lumen such as a reproductive lumen which includes an occluding component having an impervious barrier to provide initial occlusion of the body lumen and a permeable body to facilitate tissue ingrowth which provides long term occlusion of the body lumen. The device and the method of using the device is particularly suitable for contraception.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
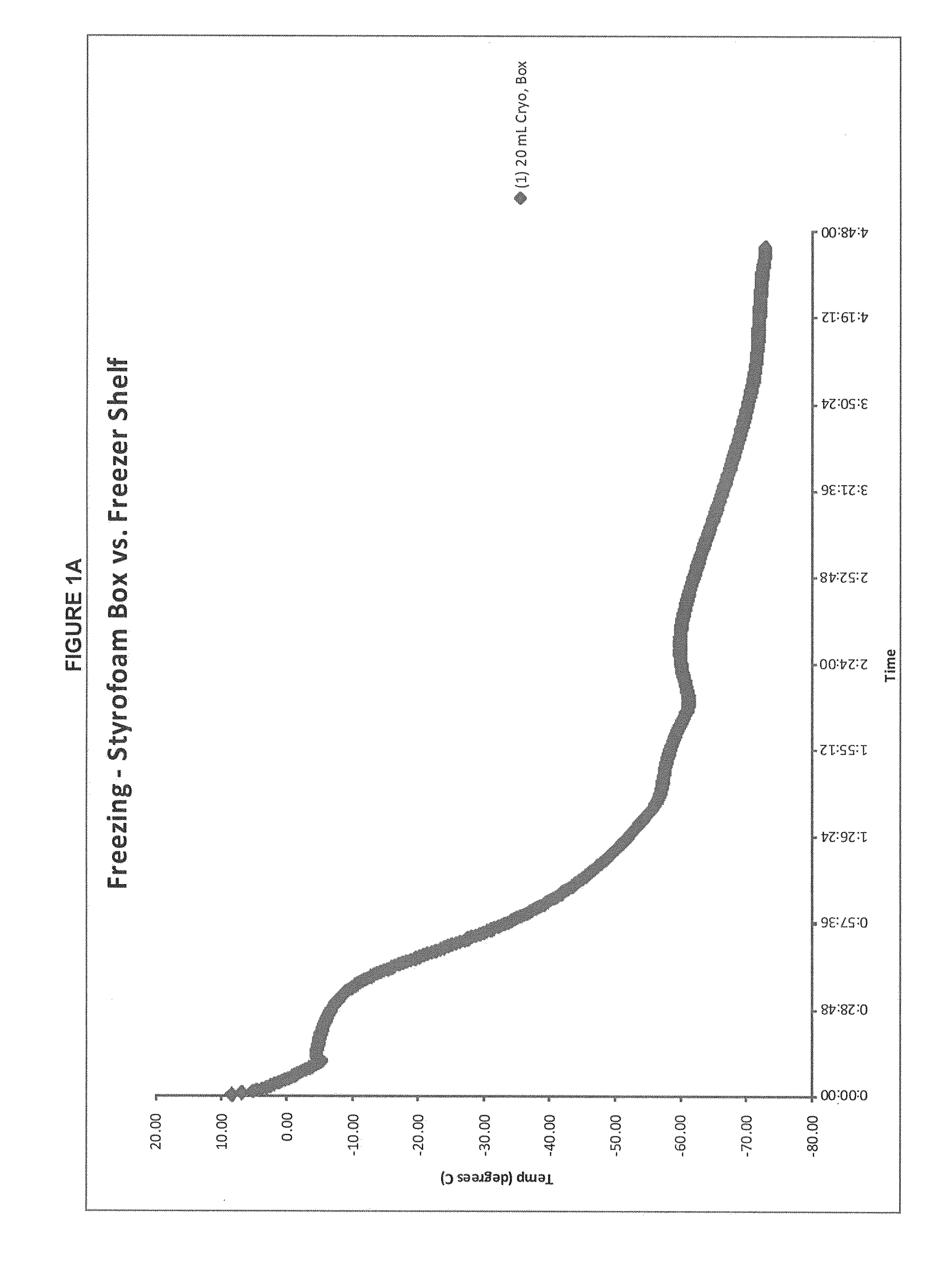
Methods of manufacture of immunocompatible amniotic membrane products
InactiveUS20110206776A1Superior wound healing propertyMaintain good propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsCulture processObstetricsLigament
Provided herein is a placental product comprising an immunocompatible amniotic membrane. Such placental products can be cryopreserved and contain viable therapeutic cells after thawing. The placental product of the present invention is useful in treating a patient with a tissue injury (e.g. wound or burn) by applying the placental product to the injury. Similar application is useful with ligament and tendon repair and for engraftment procedures such as bone engraftment.
Owner:OSIRIS THERAPEUTICS
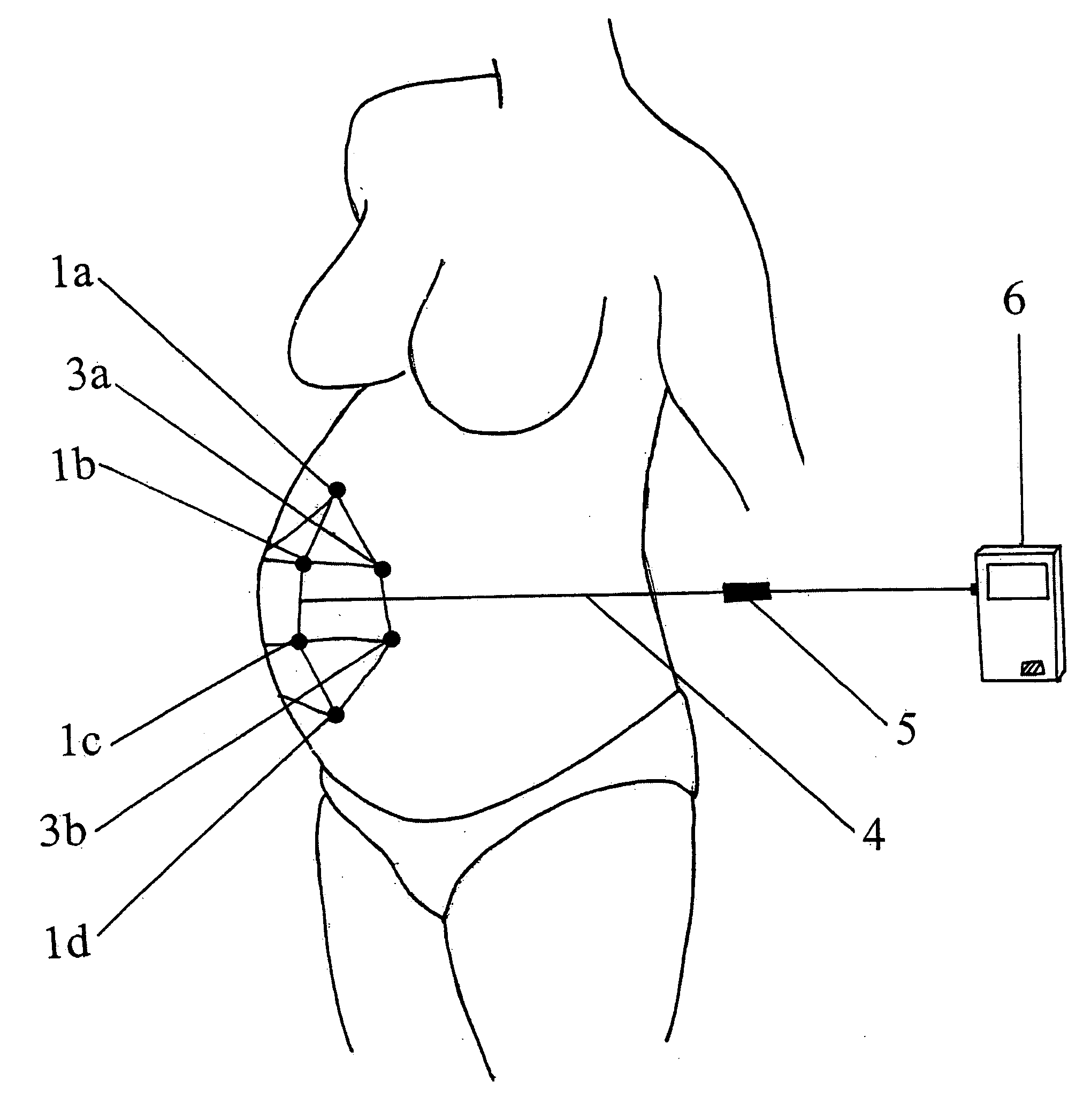
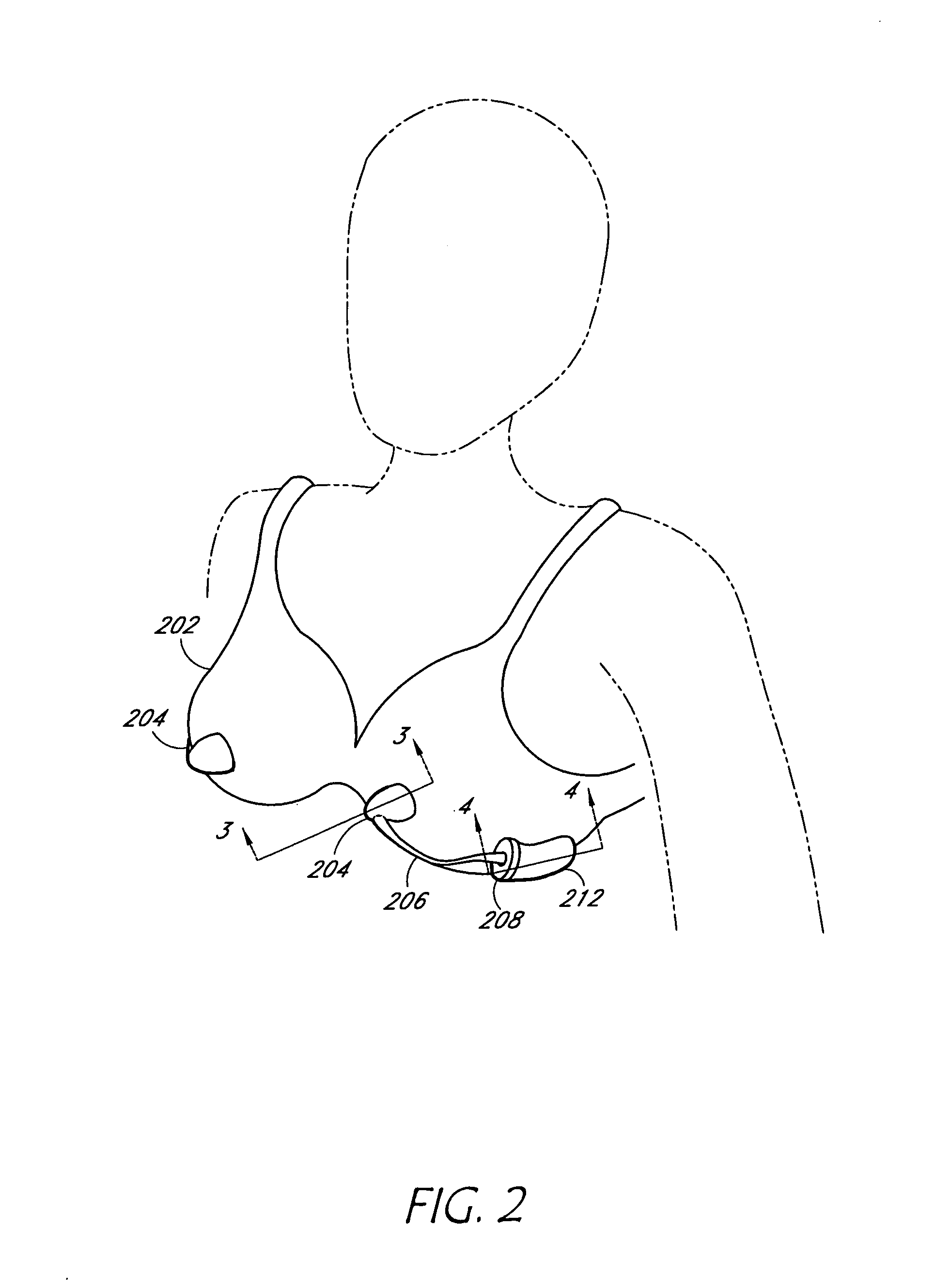
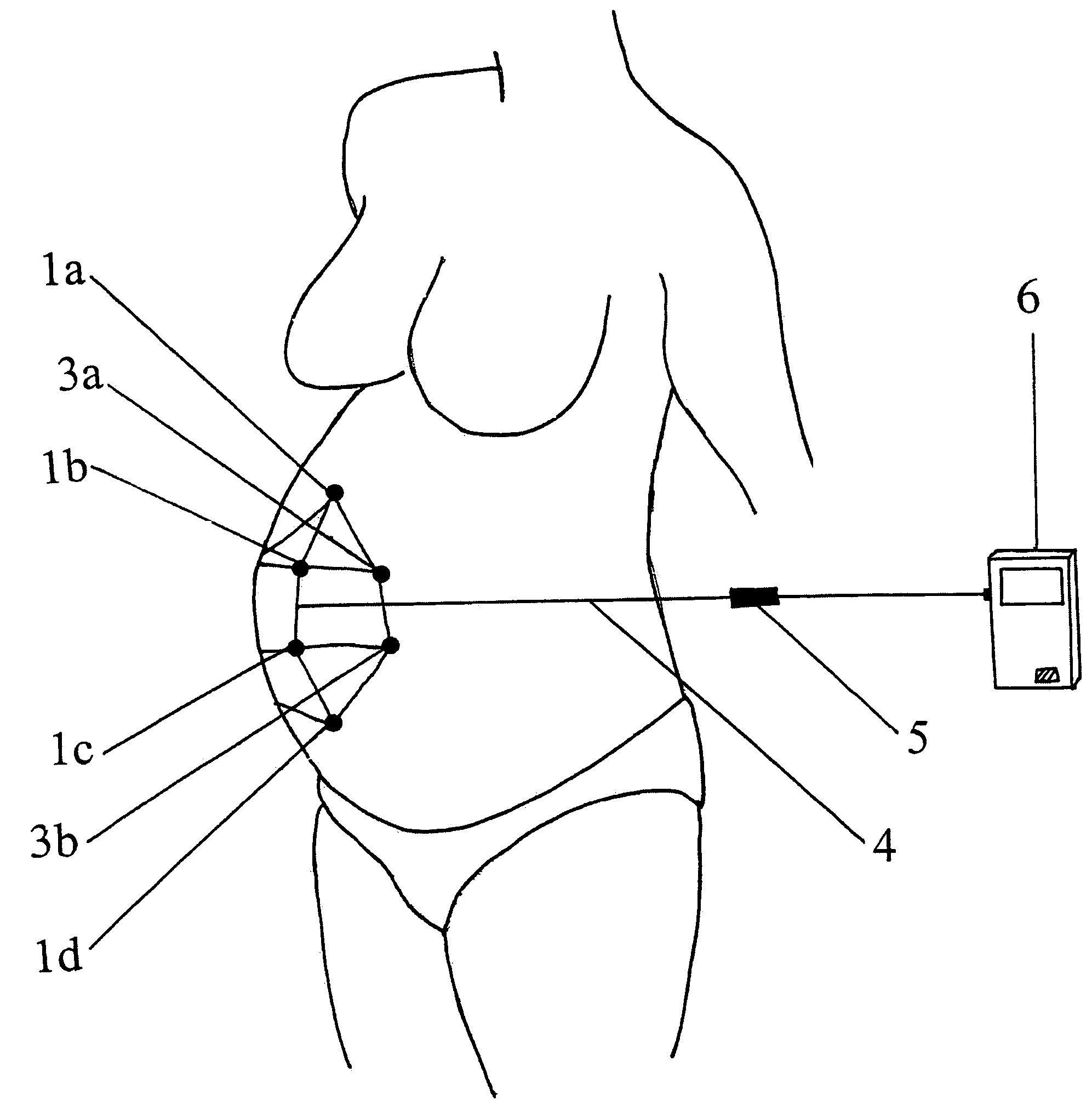
Breast milk expression system and method
A system and for discreetly expressing milk from a woman's breast and storing the milk in a container to the side or underneath the breast. The system contains an expression mechanism including various mechanisms for massaging the breast, thereby stimulating the breast to aid in lactation. Both of the user's hands are free during operation of the system allowing the user to perform other tasks during expression or pumping.
Owner:PURONYX
Methods and devices for treating sleep apnea and snoring
ActiveUS20080188947A1Easy to transformForce is smallSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsObstetricsBreathing disorders
Methods and devices to prevent and / or treat breathing disorders (e.g., upper airways disorders) in mammals related to impaired airflow are described. Methods and devices apply force to soft tissue that avoids obstruction of airflow in the mammel's airway. Breathing disorders that are avoided by the methods and / or devices include apnea.
Owner:LINGUAFLEX INC
Monitoring methods and devices for use therein
InactiveUS6451619B1Reduce unreliabilityLimited usefulnessAnimal reproductionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsBacteriuriaAnalyte
Methods, devices and test kits for monitoring the ovulation cycle, involve testing the body fluid, e.g. urinary, concentration of one or more analytes. Preferably estrone-3-glucuronide and luteinizing hormone are both measured, and a reference concentration for E3G is established at about day 6 of the current cycle. Preferably, disposable testing devices are used, in conjunction with a relatively permanent electronic reader / monitor. The number of "daily" tests required per month can be minimized.
Owner:INVERNESS MEDICAL SWITZERLAND GMBH
Maternal-fetal monitoring system
ActiveUS7333850B2Accurate repeatabilityImprove signal qualityElectrocardiographyElectromyographyObstetricsNeural network system
A maternal-fetal monitoring system for use during all stages of pregnancy, including antepartum and intrapartum stages. The maternal-fetal monitoring system of the subject invention comprises (1) a set of sensors; (2) an amplifying / filtering means; (3) a computing means; and (4) a graphical user interface. Accurate clinical data, which can be extracted and provided to the user in real-time using the system of the invention, include without limitation, maternal electrocardiogram (ECG) signals, maternal uterine activity signals (EHG), maternal heart rate, fetal ECG signals, and fetal heart rate. In a preferred embodiment, the maternal-fetal monitoring system of the invention includes an intelligence means, such as a neural network system, to analyze and interpret clinical data for use in clinical diagnosis antepartum, intrapartum and postpartum, as well as delivery strategy.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Methods for reducing the occurrence of preterm delivery and other pregnancy-related conditions
The present invention relates to methods and kits for reducing the occurrence of preterm delivery and other pregnancy-related conditions in pregnant female subjects exhibiting one or more risk factors for preterm delivery and other pregnancy-related conditions. For example, the present invention relates to methods for reducing the occurrence of preterm delivery in a pregnant female subject having no history of preterm delivery and exhibiting one or more risk factors for preterm delivery (e.g., smoking during pregnancy). The methods and kits provide for the administration of a steroid hormone to the pregnant female subject.
Owner:LUMARA HEALTH IP
Disposable labor detection patch
InactiveUS20070255184A1Low costEasy to detectElectrocardiographyElectromyographyObstetricsAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a low cost, fully integrated, disposable patch for the non-invasive monitoring of labor contractions. The patch monitors EMG bursts present on a pregnant woman's abdomen via a set of electrodes embedded in the invented patch. The contraction monitor patch is thin, flexible, and incorporates EMG amplifiers, a processor, a battery, and an indicator within. The indicator is activated when labor EMG patterns are detected. The labor detection patch is particularly suited for women with risk of premature delivery. The patch is unobtrusively and continuously worn, even during sleep and bathing. In another embodiment, the contraction monitor patch is used in hospitals during labor and delivery to monitor the status of contractions with a wireless link to an external monitoring unit.
Owner:PRENATEK
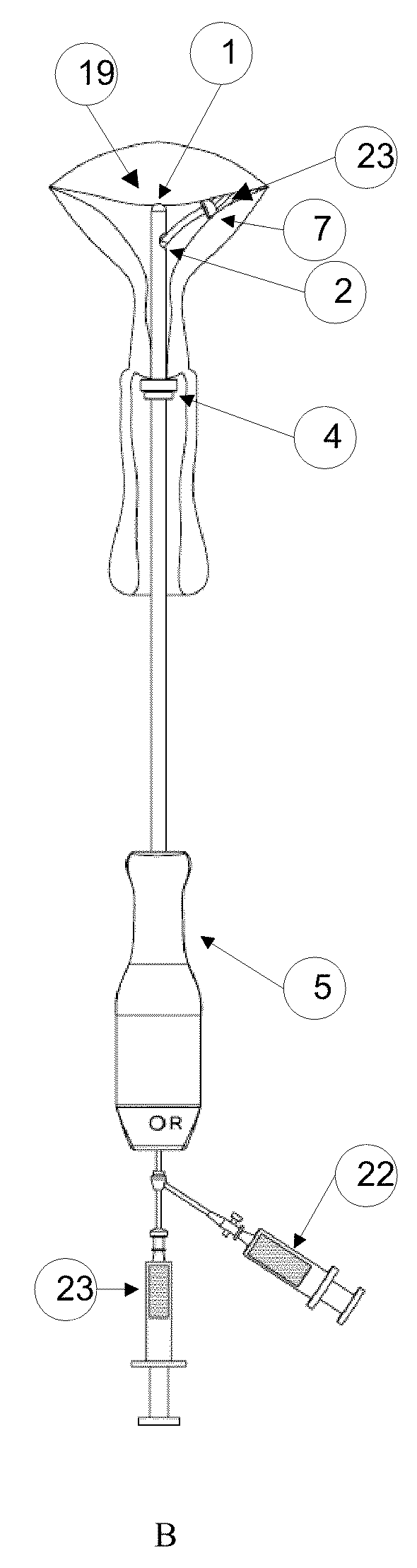
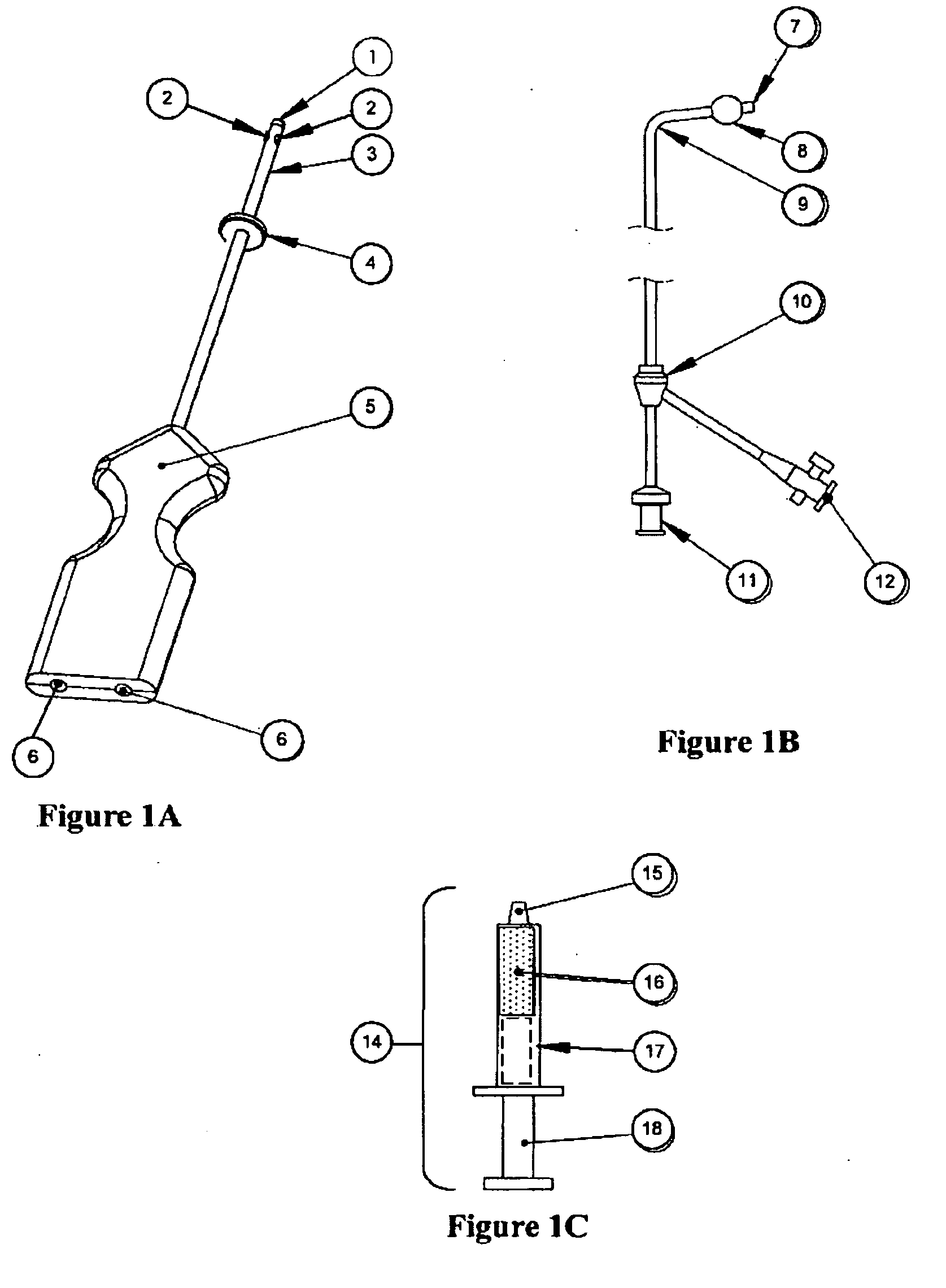
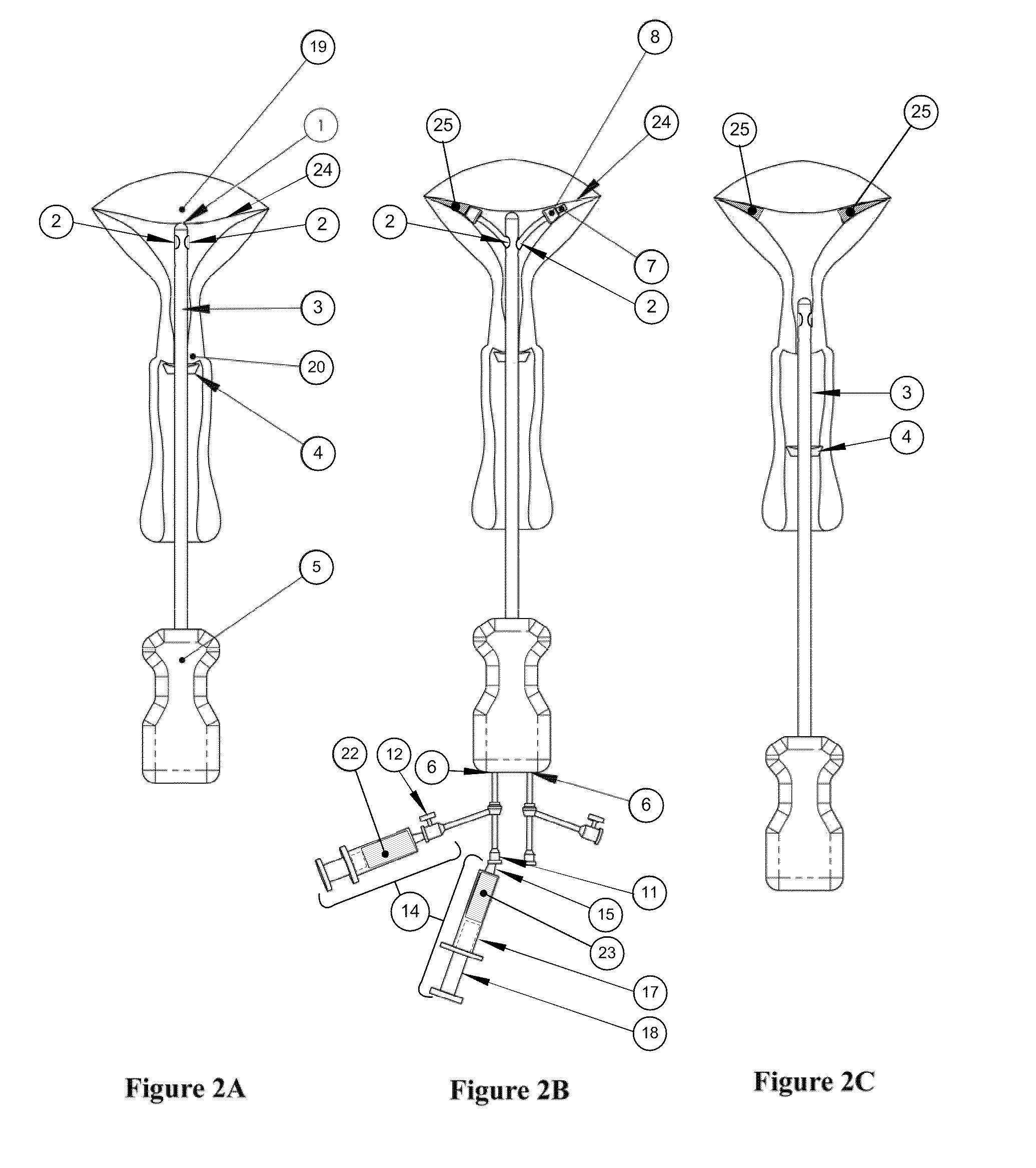
Inflatable system for cervical dilation and labor induction
An inflatable system, of between one and three balloons, for cervical dilation and labor induction is provided. The inflatable system may have a uterine balloon, for positioning at a proximal portion of the uterus, with respect to an operator, adjacent to the cervical internal os, the uterine balloon being shaped so as to maximize the pressure against the decidua and the internal cervical os and so as to minimize the pressure on the fetal head. Additionally or alternatively, the inflatable system may have a vaginal balloon, for positioning in the vagina, for applying pressure on the external cervical os. Additionally or alternatively, the inflatable system may have a cervical balloon, for positioning in the cervical canal, the cervical balloon being shaped so as to maximize the contact area with the cervix. The balloons are operative to stimulate the secretion of hormone, by exerting pressure on the proximal decidual surfaces of the uterus and on the cervix, so as to soften and ripen the cervix, cause the cervix to dilate, and induce labor. The balloons, which may have rough external surfaces, in order to keep them anchored in place, may be inflated by the operator, directly after their insertion, or manually and gradually, by the woman herself. Various sensors and other instruments may be used with the inflatable system, to monitor cervical dilation, fetal well-being, and the woman's conditions.
Owner:ATAD - DEV & MEDICAL SERVICES
Treatment of female sexual dysfunction with vasoactive intestinal polypeptide agonists
InactiveUS7226910B2Good for healthImprove the lubrication effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsObstetricsActive agent
Owner:VIVUS
Device for blood collection from the placenta and the umbilical cord
InactiveUS20130190653A1Optimisation in working timeLow costCatheterSensorsBlood collectionHealth risk
A device is provided for blood extraction and collection from the placenta and / or the umbilical cord through a system that combines the collection of the blood falling under gravity, together with a suction system facilitating this fall. Thus, a larger amount of blood can be extracted than is obtained by conventional gravity systems without posing a health risk to the mother, allowing a controlled suction that prevents premature detachment of the placenta.
Owner:ALVAREZ RAMOS ANGEL GABRIEL
Fallopian tube occlusion devices and methods
InactiveUS20070056591A1Safe and effectiveSafe and effective sterilizationFallopian occludersFemale contraceptivesOvulation timesObstetrics
A contraceptive device for placement in a fallopian tube includes expanding distal and proximal anchor members and an expandable elongate member connecting the distal anchor member to the proximal anchor member. An expandable material is disposed on at least a portion of the contraceptive device, whereupon delivery of the contraceptive device, the expandable material expands to completely occlude the fallopian tube. The expandable material may contain a drug, therapeutic agent, or hormone which is released over time to occlude or otherwise prevent the passage of spermazoa through the fallopian tube, or prevent ovulation. The contraceptive device may be delivered non-operatively and provide complete sterilization within a period of days. The device and delivery method obviates the need for follow-up visits to confirm closure of the fallopian tubes.
Owner:MCSWAIN HUGH
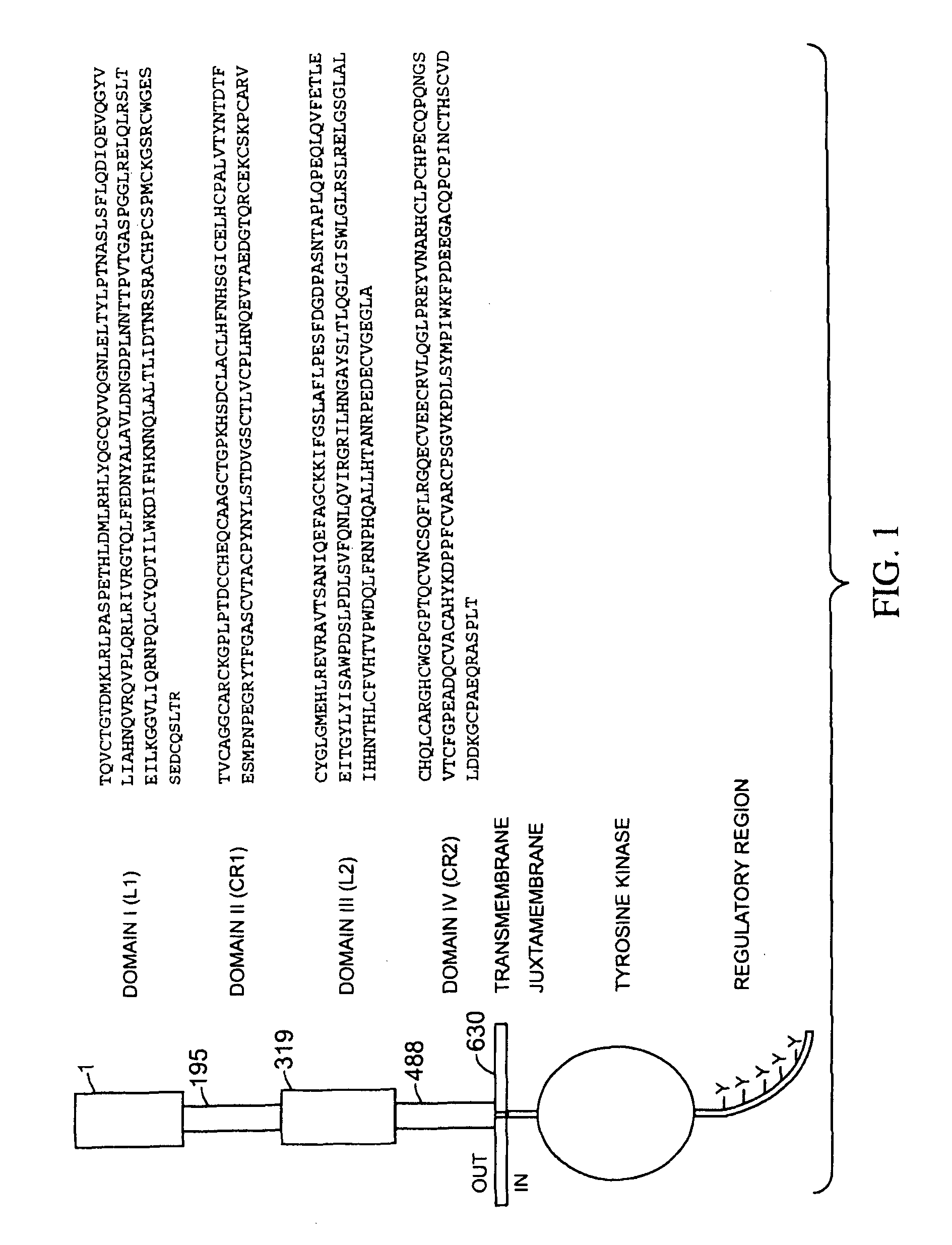
Predicting response to a HER inhibitor
InactiveUS7981418B2Improve responseOrganic active ingredientsData processing applicationsObstetricsSelection criterion
The present application describes the use of low HER3 as a selection criterion for treating patients with a HER inhibitor, such as pertuzumab.It also describes the use of high HER2:HER3 ratio as a selection criterion for treating cancer patients, such as ovarian cancer patients, with a HER inhibitor, such as pertuzumab.In addition, the application describes the use of high HER3 as a selection criterion for treating cancer patients with a chemotherapeutic agent, for instance gemcitabine.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Multi-axial uterine artery identification, characterization, and occlusion pivoting devices and methods
A system is provided for compressing one or both of the uterine arteries of a patient which is at least in part shaped to complement the shape of the exterior of the cervix, which allows the system to be self-positioning. One or more Doppler chips can be mounted or incorporated into the system which permit the practitioner to better identify the uterine artery and monitor blood flow therein. The system includes a pair of pivotally joined elements which can be moved toward and away from the cervix to compress a uterine artery.
Owner:VASCULAR CONTROL SYST
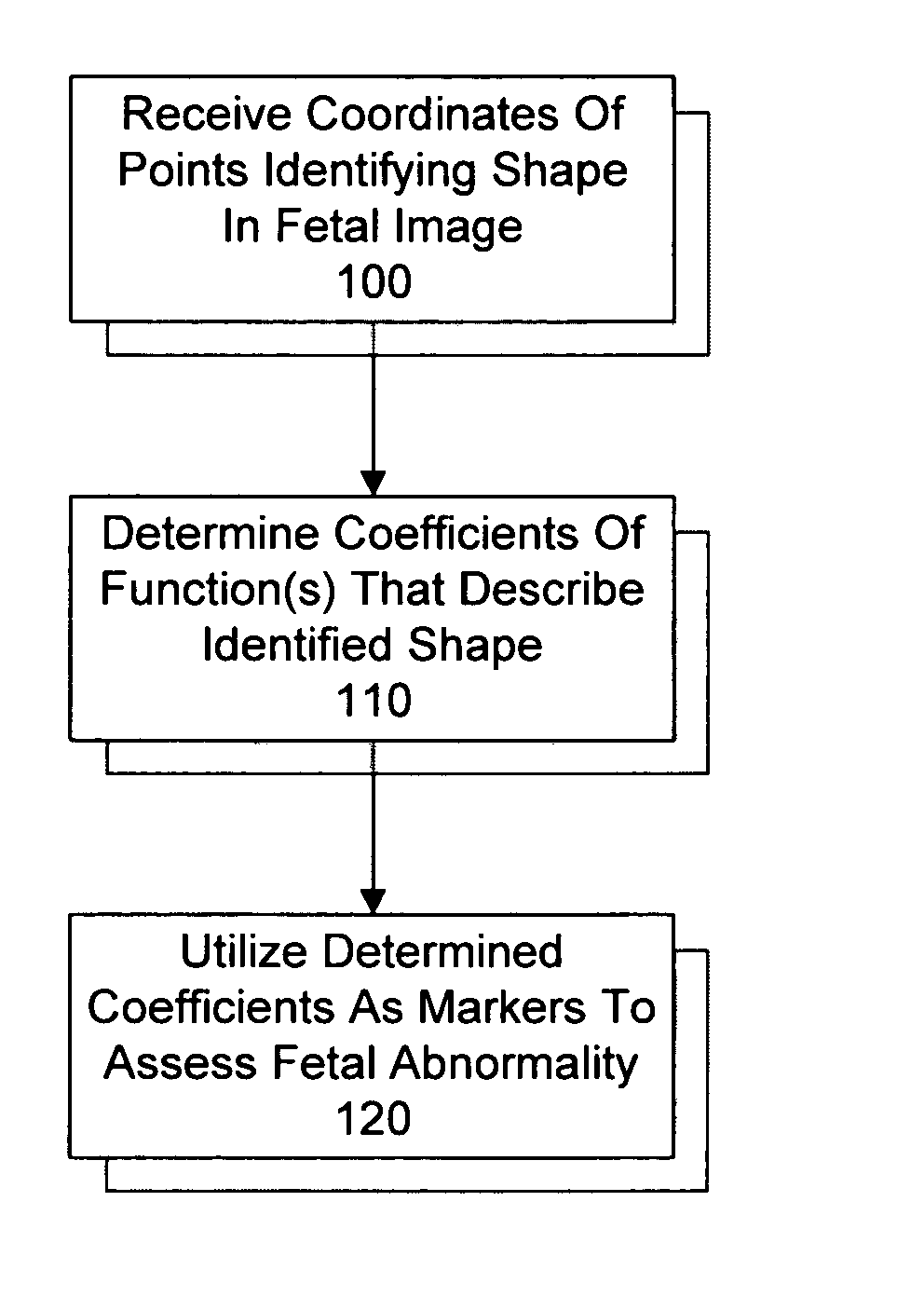
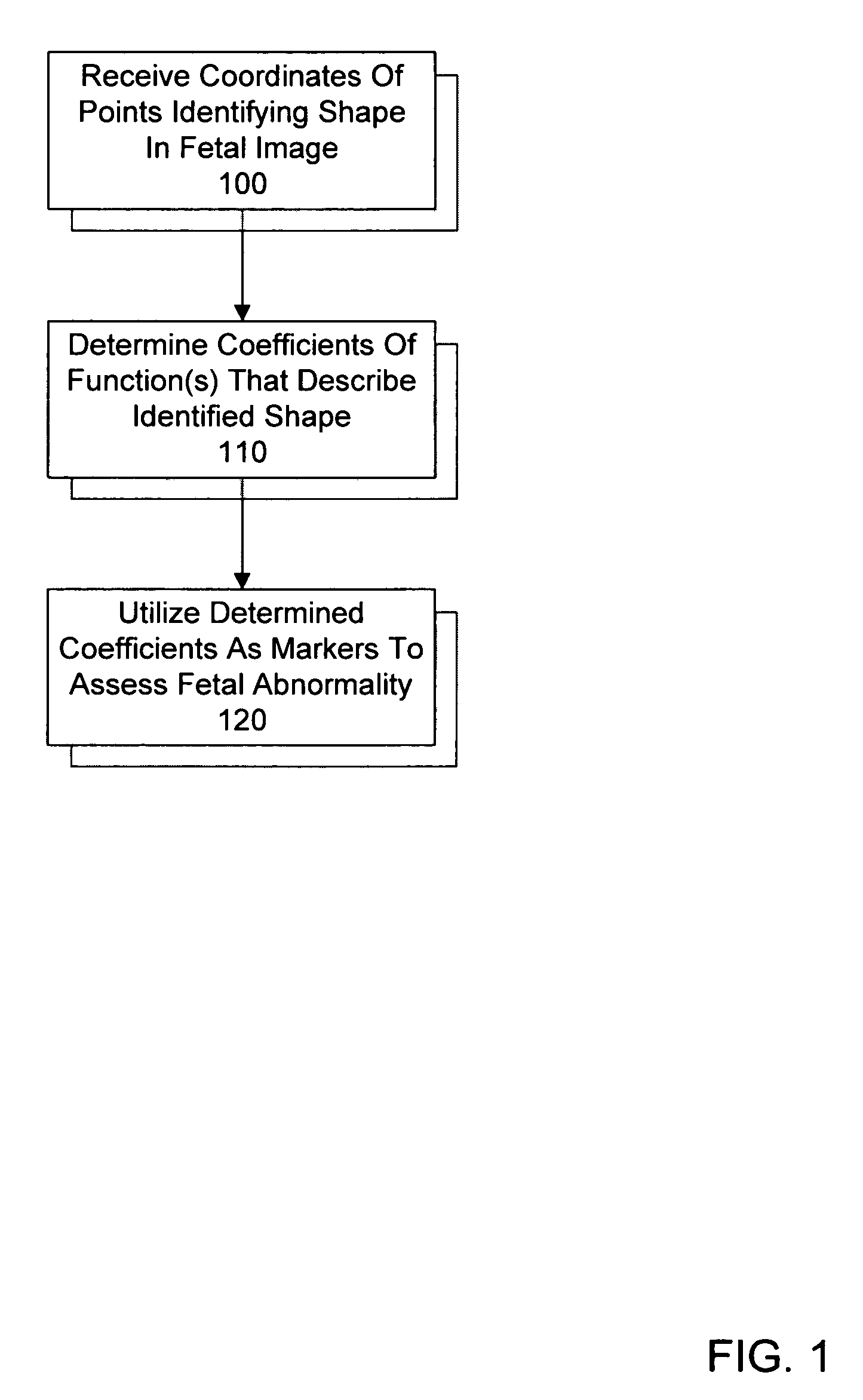
System and method for utilizing shape analysis to assess fetal abnormality
InactiveUS7244233B2Medical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFetal abnormalityObstetrics
A method and system for utilizing shape analysis to assess fetal abnormality. According to one embodiment, coordinates of points identifying a shape in a fetal image are received, coefficients of one or more mathematical functions that describe the identified shape are determined, and the determined coefficients are utilized as markers to assess fetal abnormality.
Owner:NTD LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com