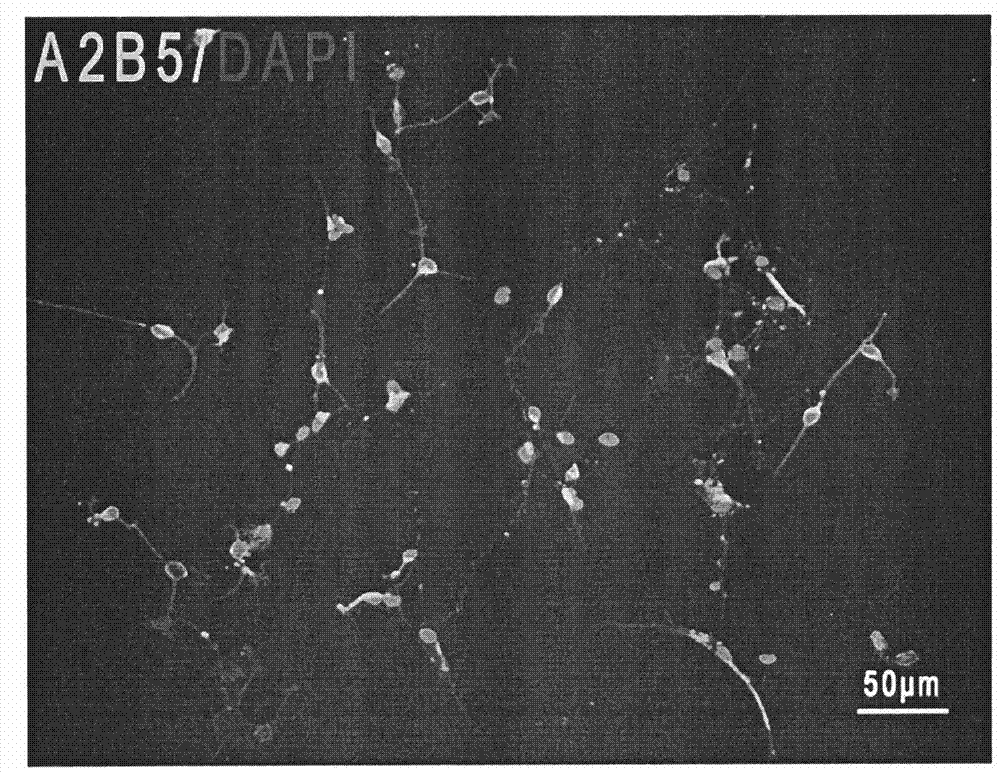
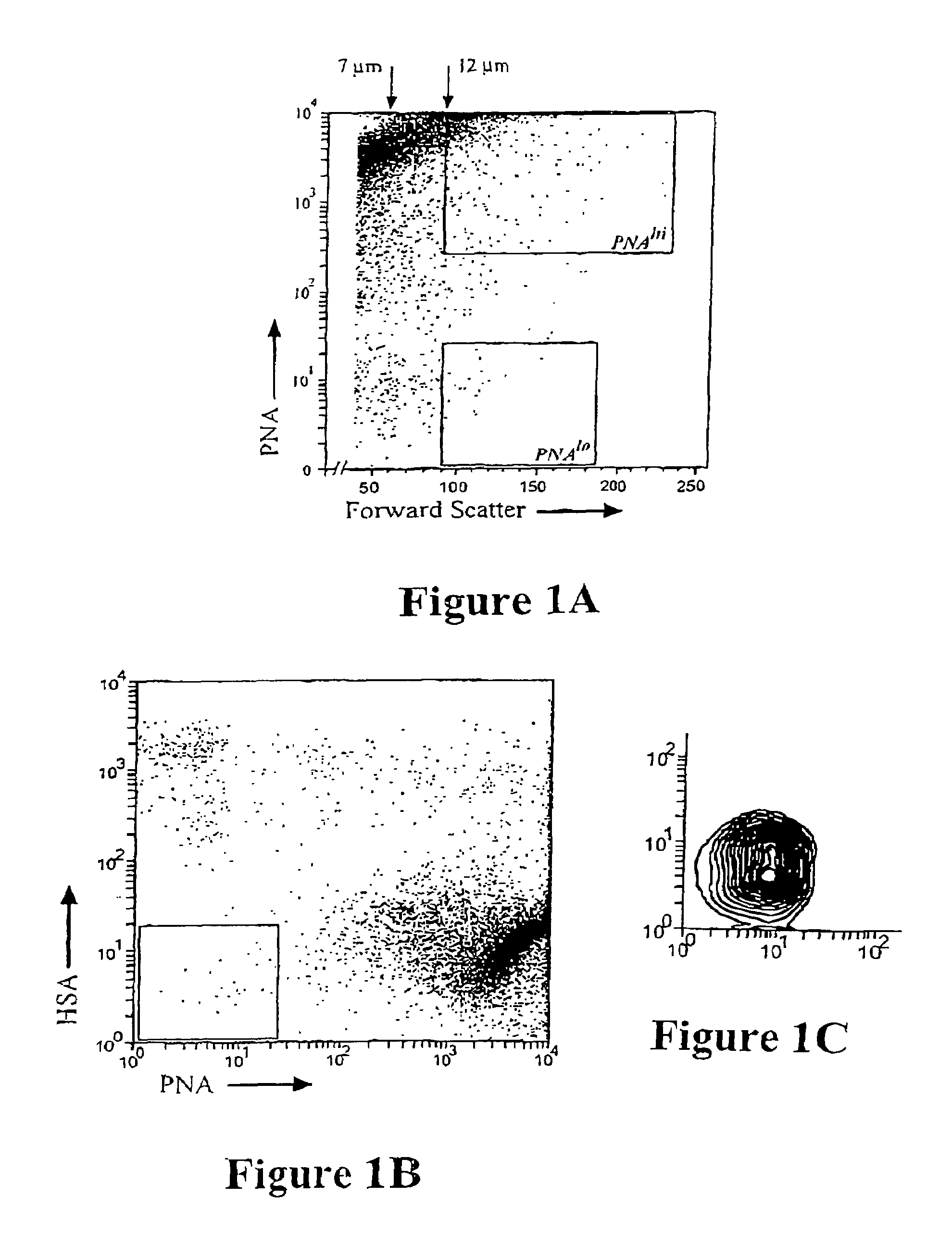
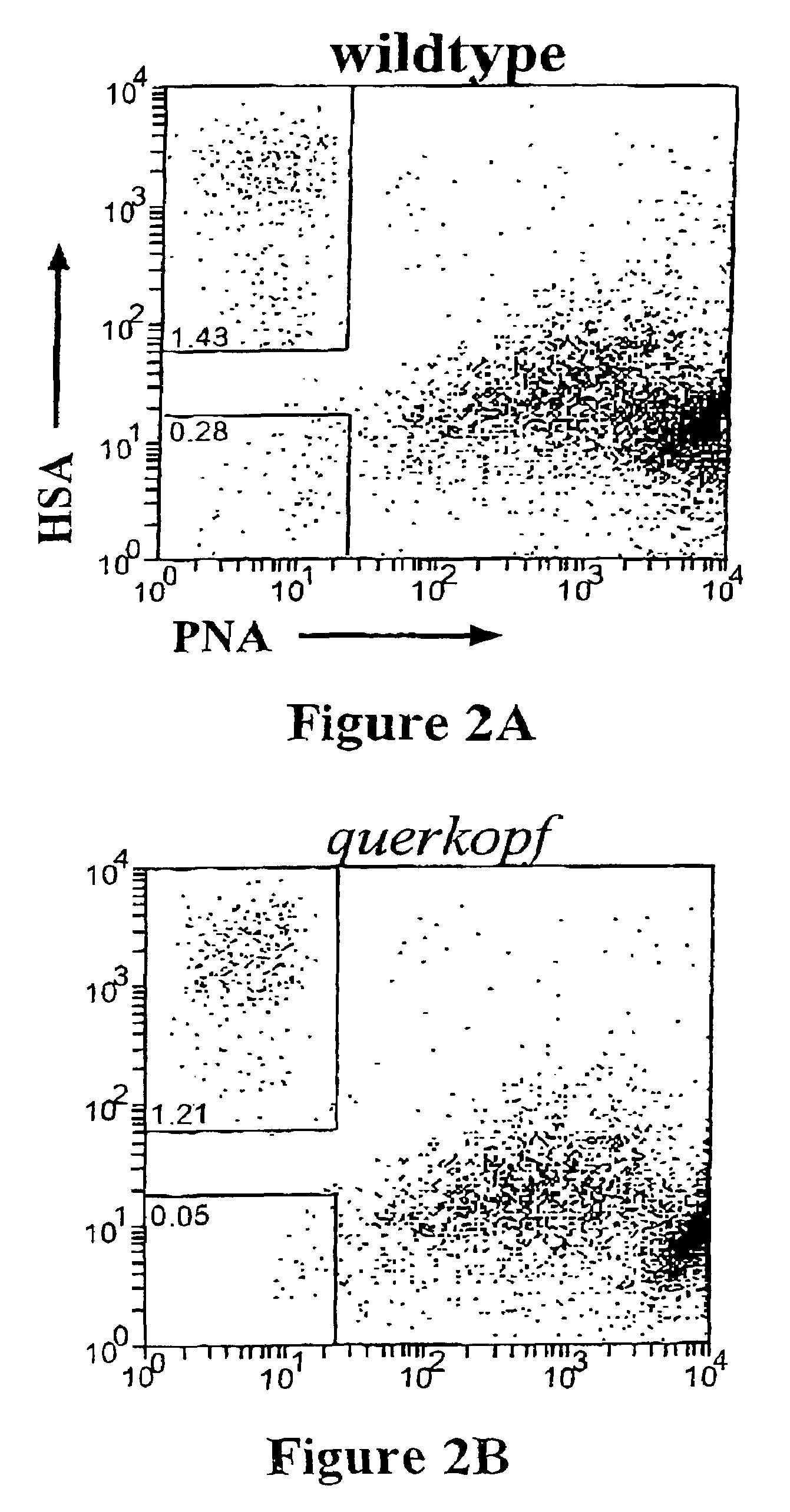
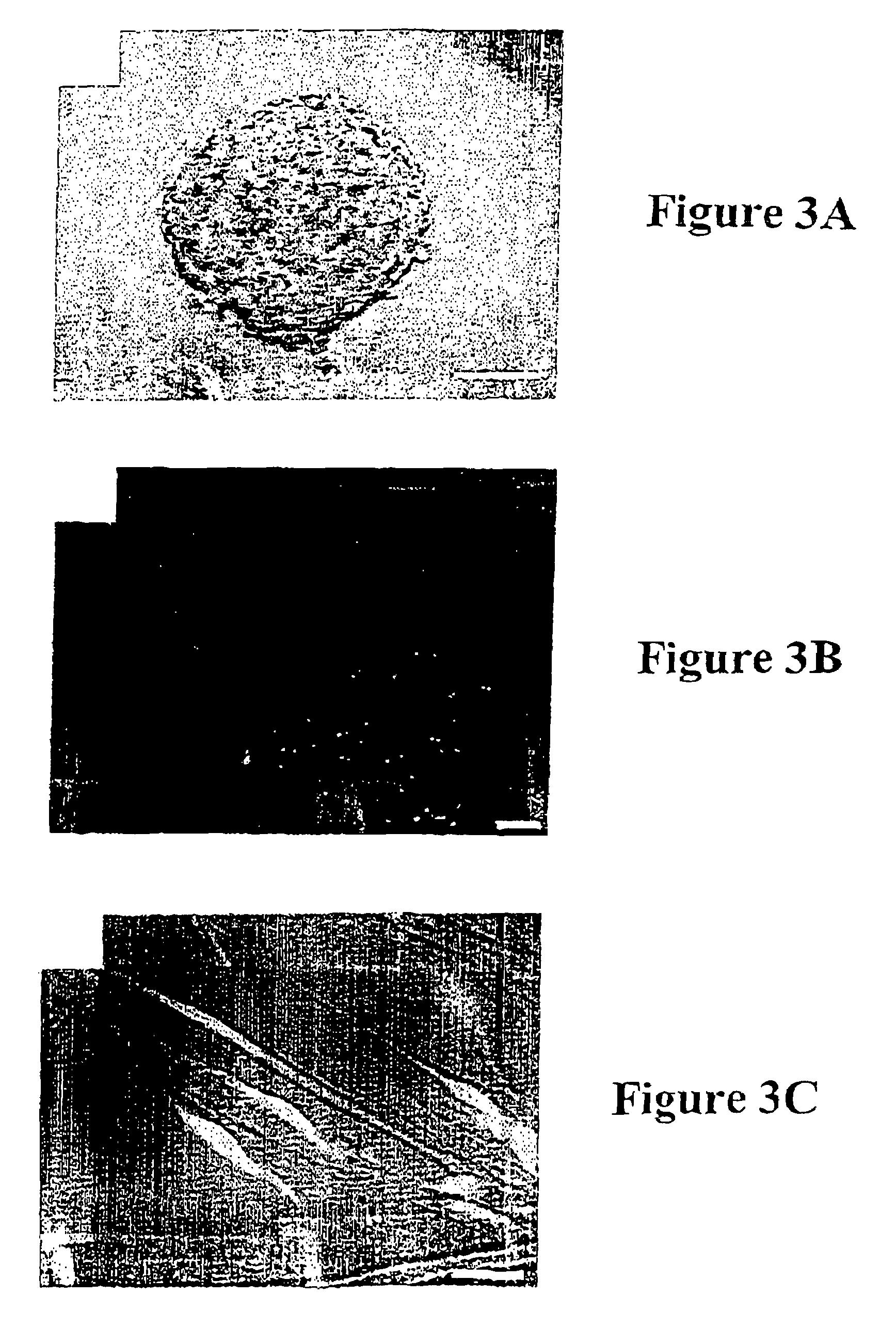
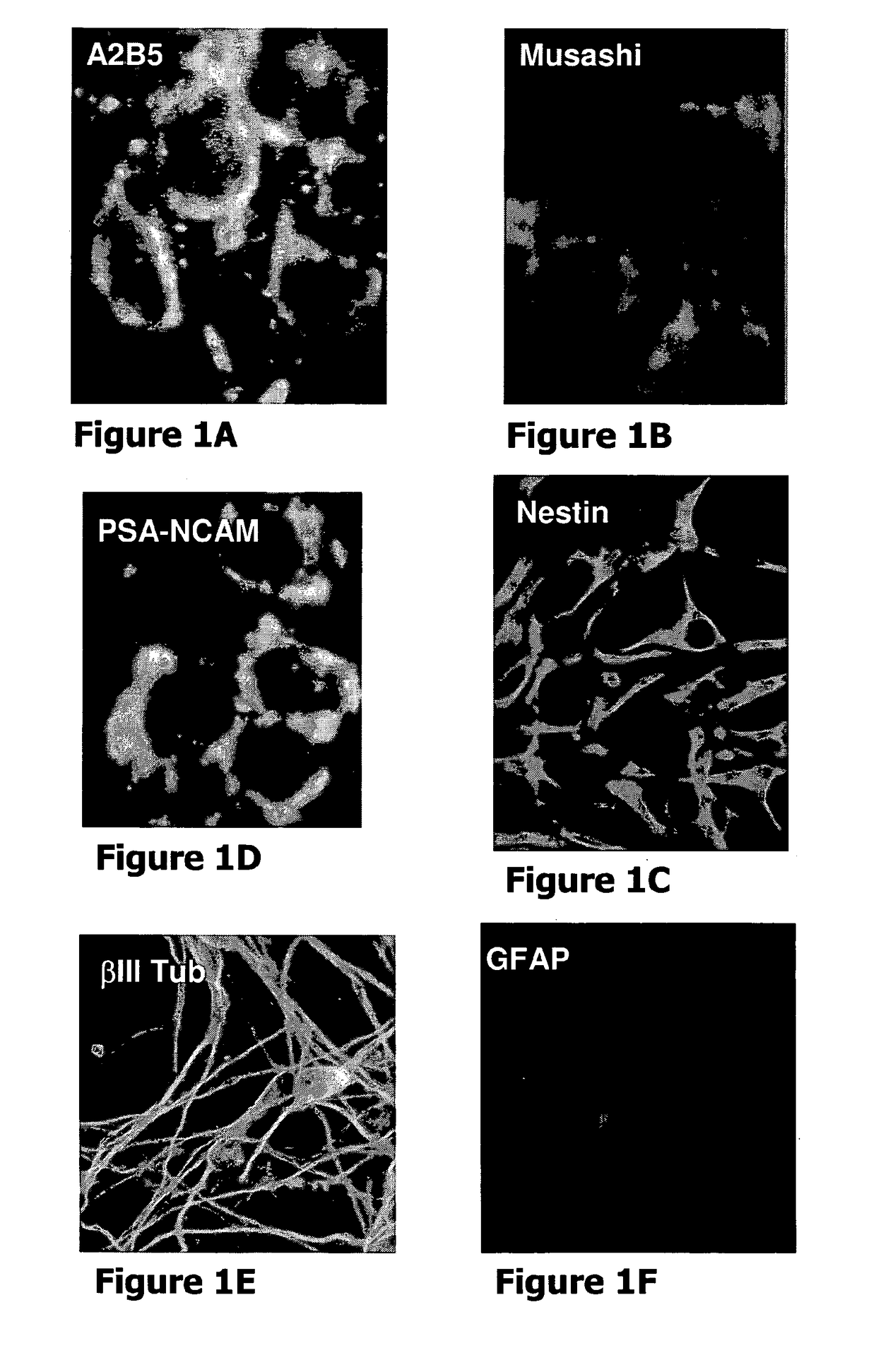
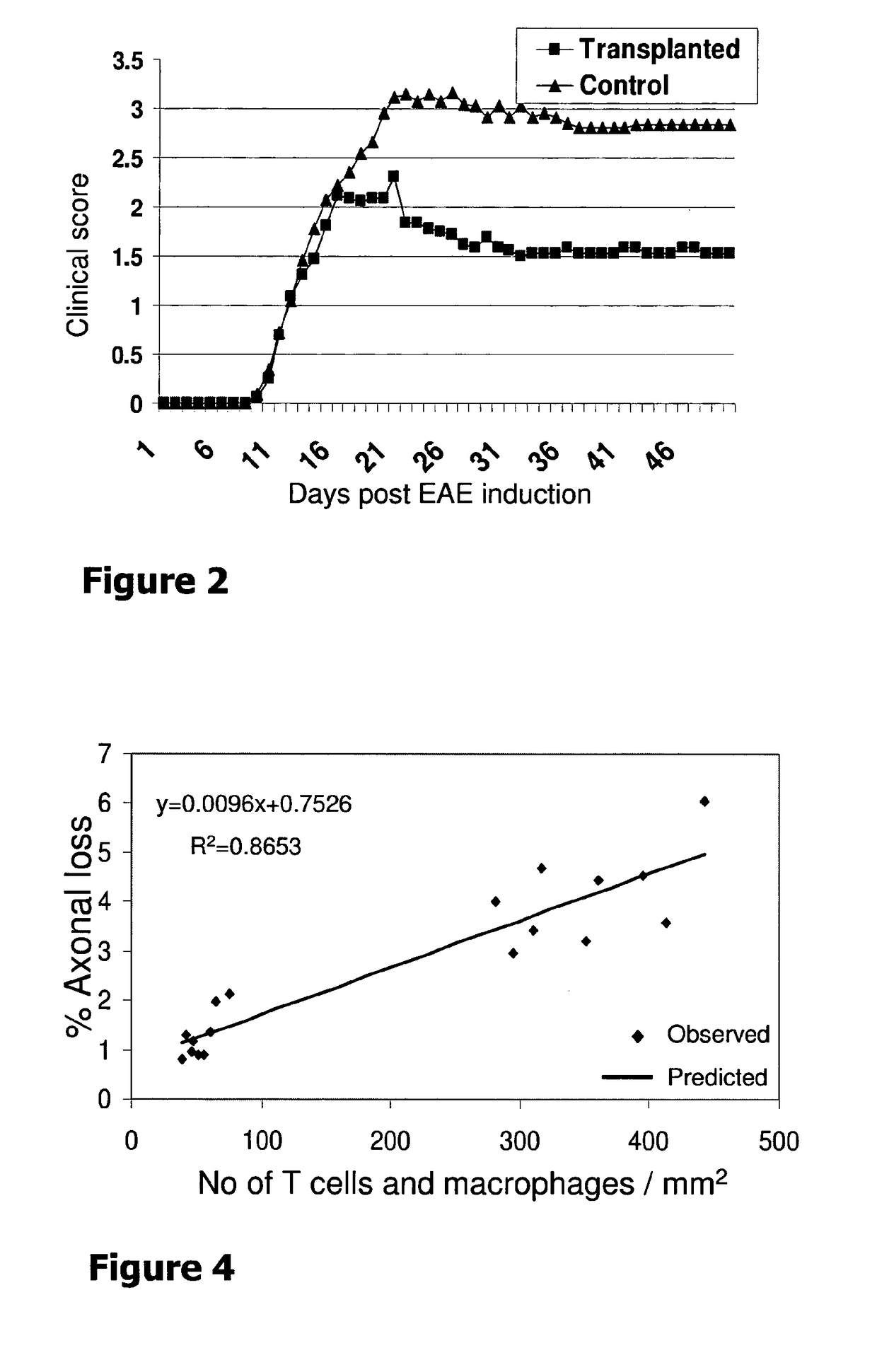
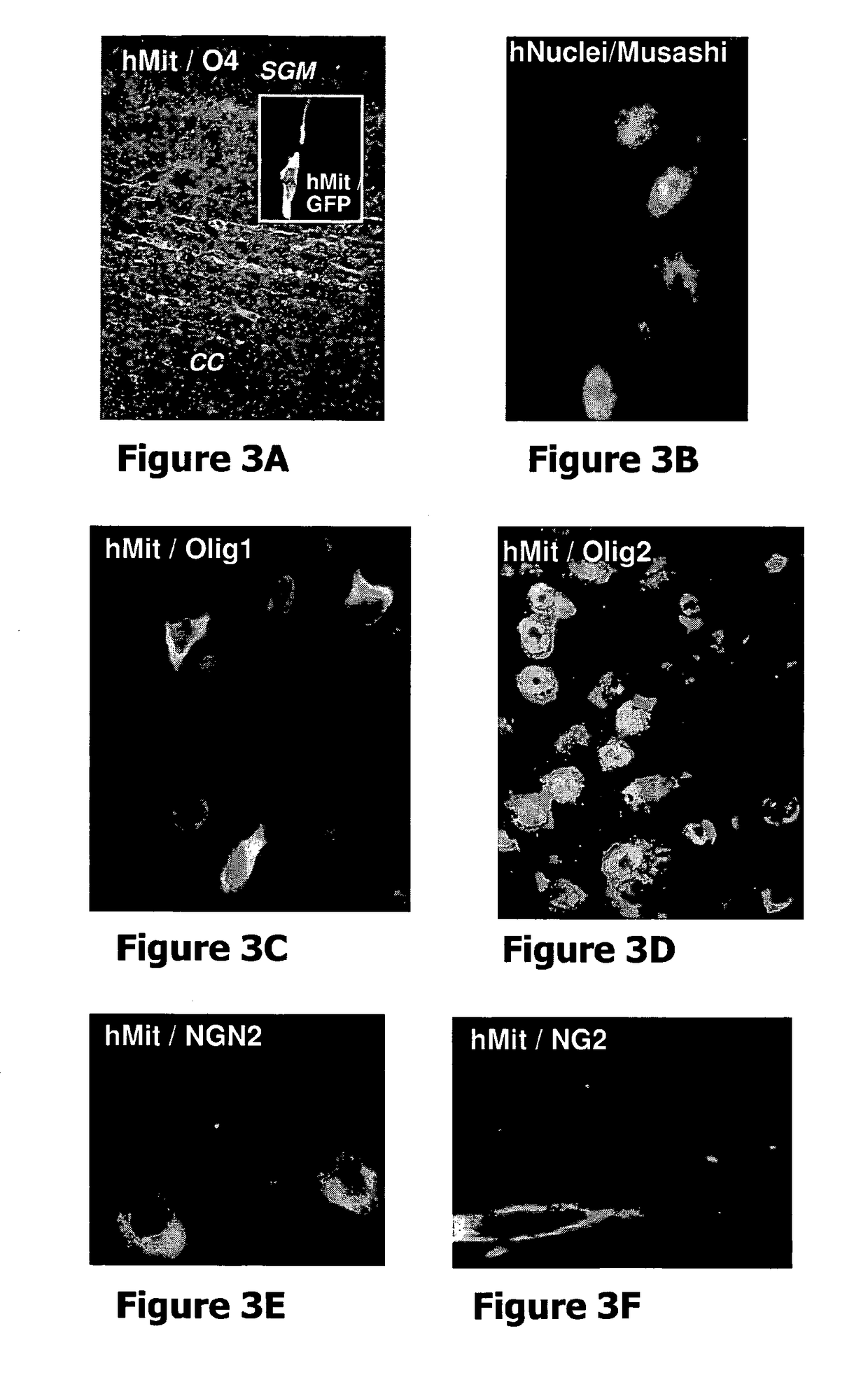
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135 results about "Oligodendrocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
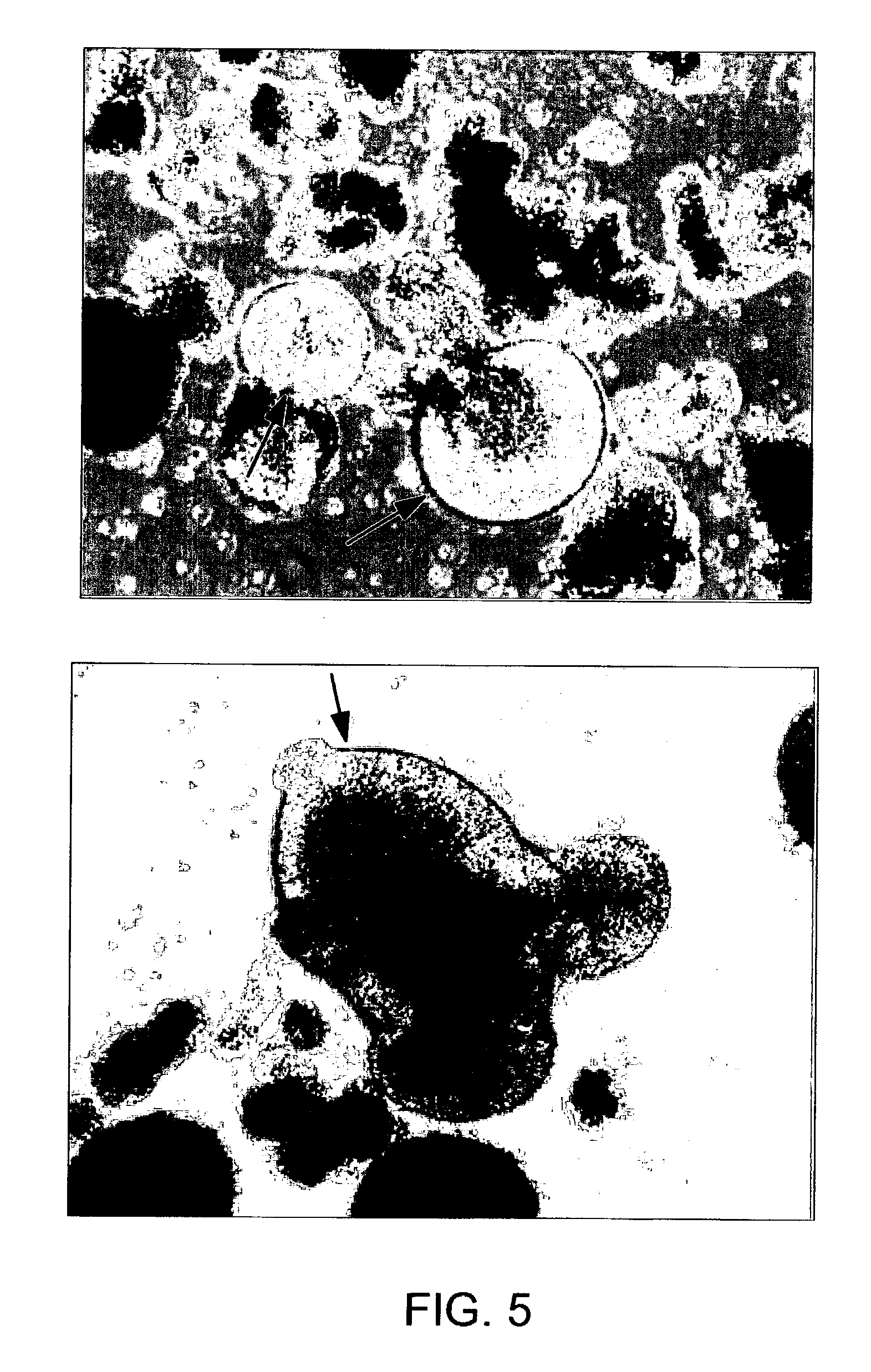
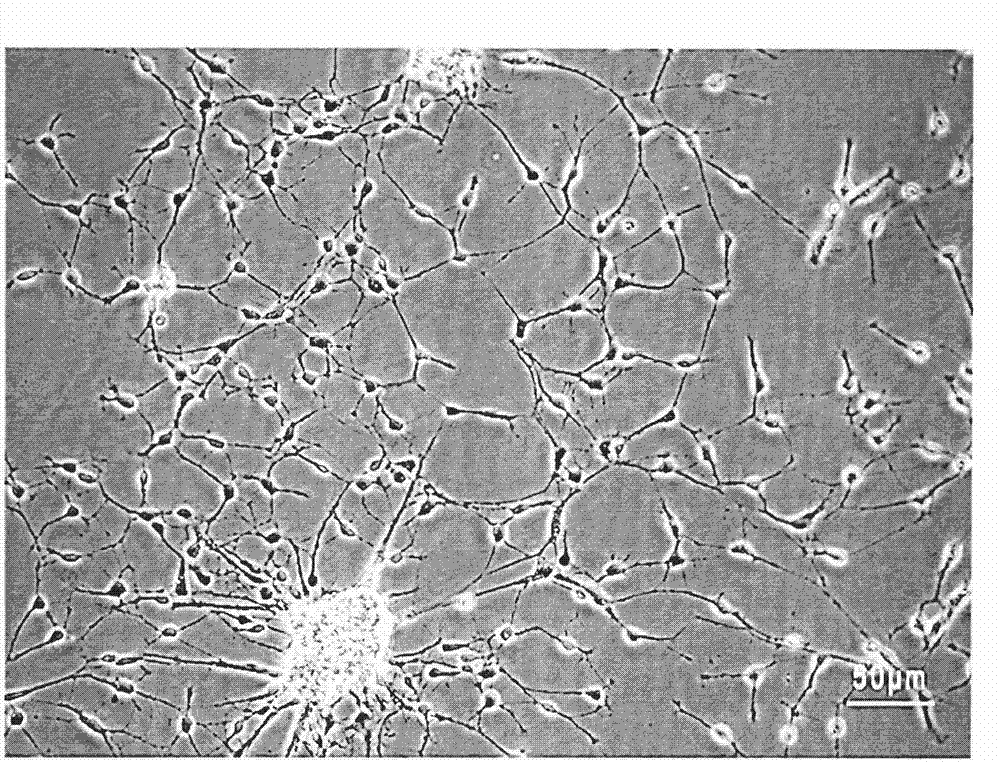
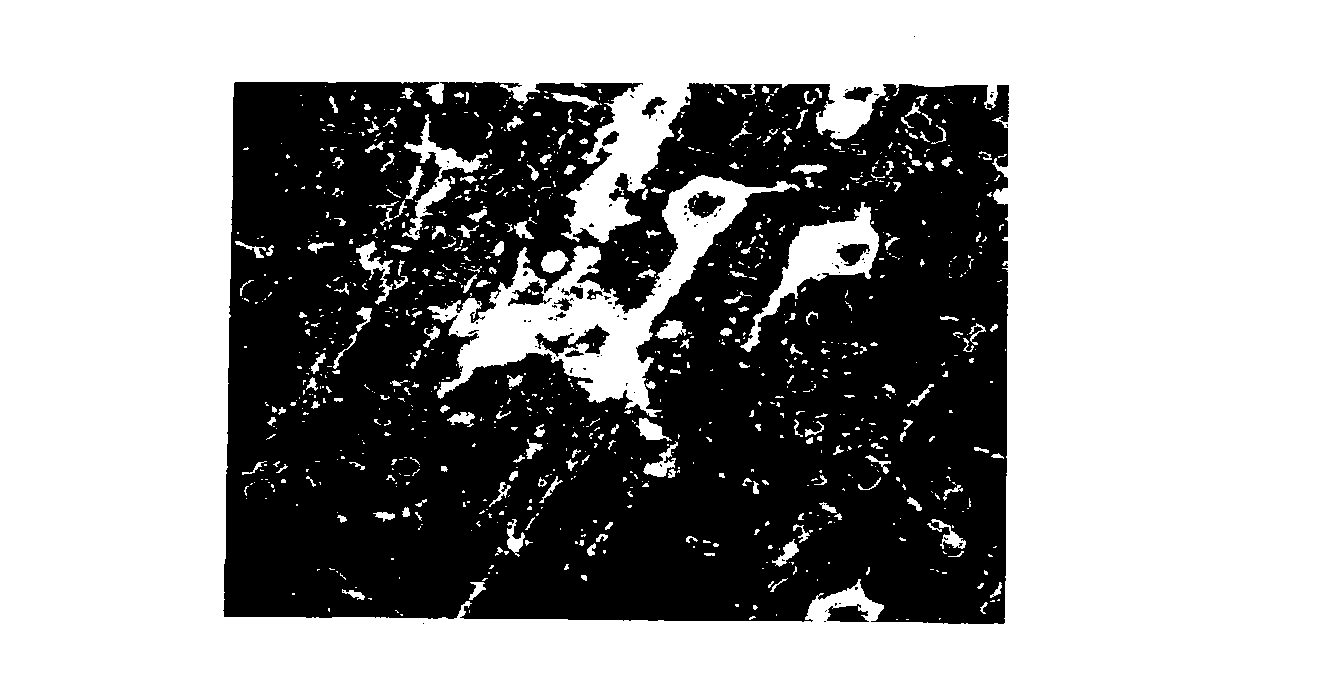
Oligodendrocytes (from Greek, meaning 'cells with a few branches'), or oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main functions are to provide support and insulation to axons in the central nervous system of some vertebrates, equivalent to the function performed by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. Oligodendrocytes do this by creating the myelin sheath, which is 80% lipid and 20% protein. A single oligodendrocyte can extend its processes to 50 axons, wrapping approximately 1 μm of myelin sheath around each axon; Schwann cells, on the other hand, can wrap around only one axon. Each oligodendrocyte forms one segment of myelin for several adjacent axons.
Production of oligodendrocytes from placenta-derived stem cells
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the production of glial cells and oligodendrocytes from placenta stem cells. The invention further provides for the use of these glia and oligodendrocytes in the treatment of, and intervention in, for example, trauma, ischemia and degenerative disorders of the central nervous system (CNS), particularly in the treatment of demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Direct Conversion of Cells to Cells of Other Lineages
Methods, compositions and kits for producing functional neurons, astroctyes, oligodendrocytes and progenitor cells thereof are provided. These methods, compositions and kits find use in producing neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and progenitor cells thereof for transplantation, for experimental evaluation, as a source of lineage- and cell-specific products, and the like, for example for use in treating human disorders of the CNS. Also provided are methods, compositions and kits for screening candidate agents for activity in converting cells into neuronal cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and progenitor cells thereof.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Medicinal product and method for treatment of conditions affecting neural stem cells or progenitor cells
InactiveUS20050032702A1Modulate proliferationModulate differentiationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsOligodendrocytePharmacy medicine
Use of a substance that upon administration will lead to increased concentrations of growth hormone, such as growth hormone, a functionally equivalent analogue thereof or a substance that will increase the release of endogenous growth hormone, for the production of a medicinal product for treatment of abnormal conditions affecting neural stem cells, progenitor cells and / or cells derived from neural stem cells or progenitor cells, especially conditions affecting the oligodendroglia, astroglia, and / or neuronal cells. In vitro and in vivo methods for inducing lineage determination, propagating and / or inducing or maintaining the genesis of neurons, oligodendrocytes, astroglial cells from progenitor cells, stem cells and / or cells derived from said cells by administrating to the cells a substance that increases the concentration of growth hormone. Also a method of reducing the genesis of oligodendrocytes, neurons, astroglial cells from progenitor cells or stem cells, wherein a pharmaceutically effective amount of a substance that will lead to a decreased concentration of growth hormone or a functionally equivalent analogue thereof is administered to said patient.
Owner:ERIKSSON PETER
Pharmaceutical for prevention and treatment of demyelinating disease
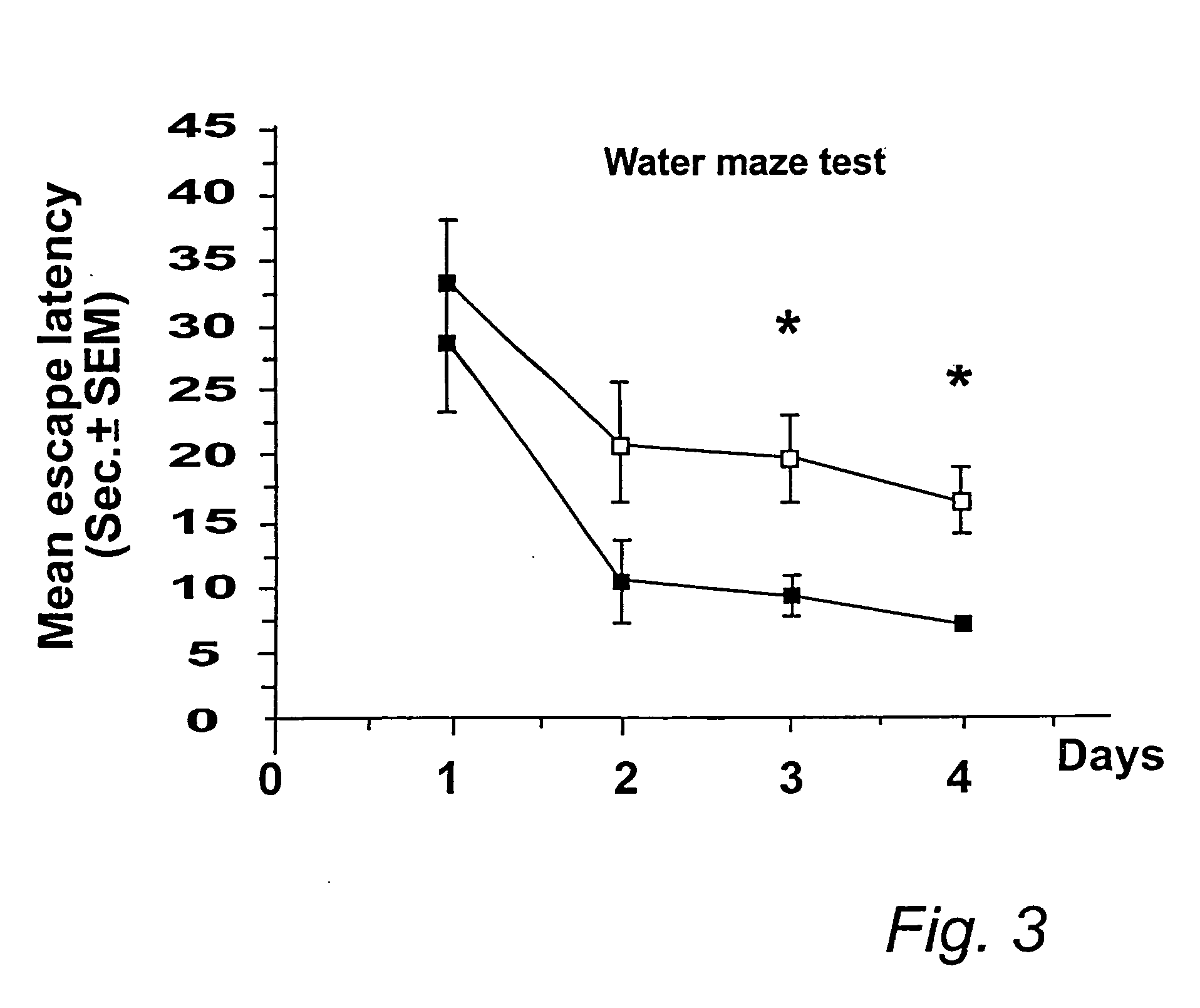
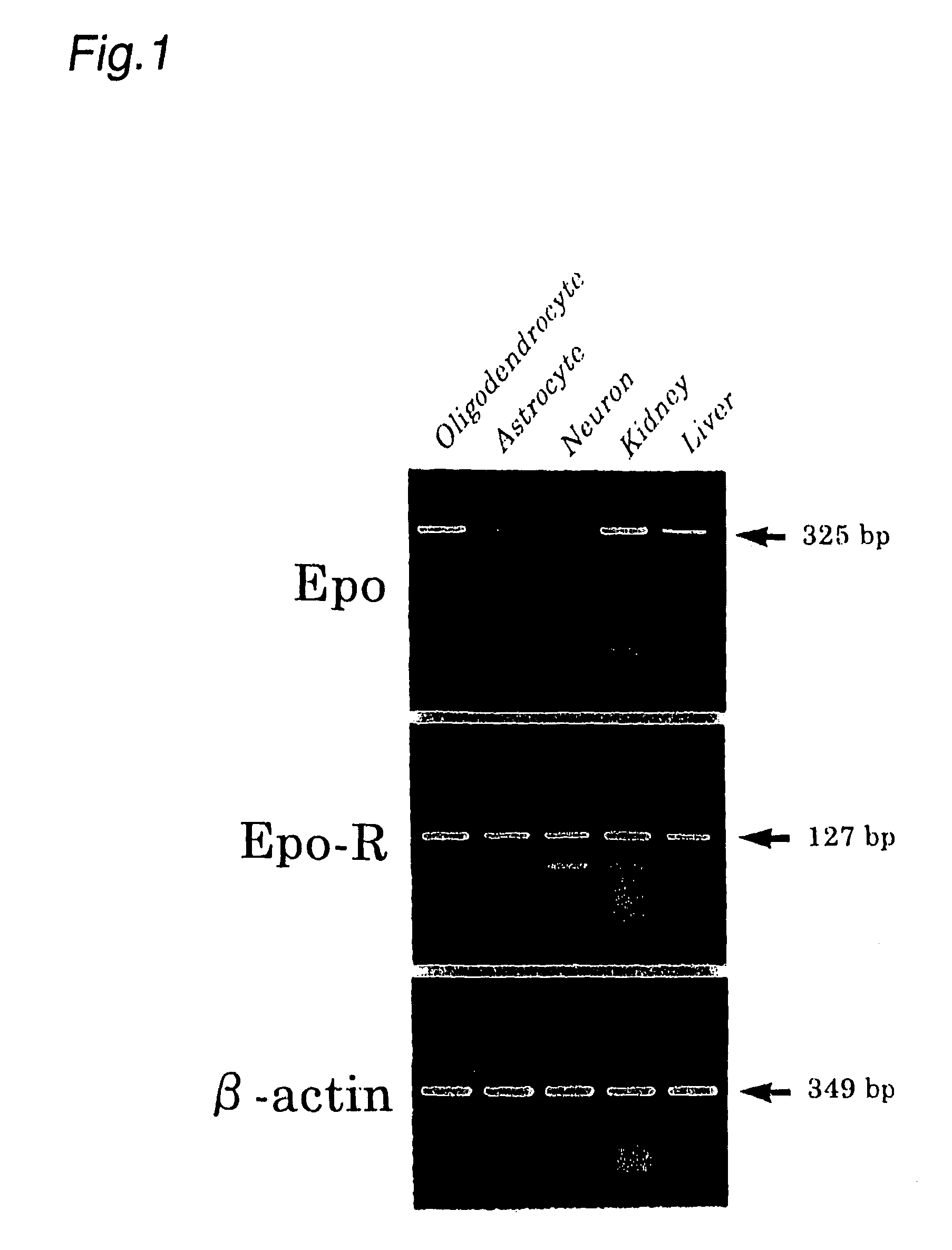
A pharmaceutical for prevention and treatment of demyelination-associated neural function impairing diseases contains erythropoietin as an active ingredient, and protectively act on the survival of oligodendrocytes, which form a myelin sheath, in cerebrovascular dementia typified by multiple sclerosis and Binswanger disease, diseases involving demyelination. The pharmaceutical and method also promote maturation of undifferentiated oligodendrocytes present in the brain, activating remyelination. Through these mechanisms, the pharmaceutical and method can prevent and treat demyelination-associated neural function impairing diseases.
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN FOUND FOR RES ON AGING & PROMOTION OF WELFARE +1
Production of oligodendrocytes from placenta-derived stem cells
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Human IgM antibodies, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses thereof particularly in the central nervous system
InactiveUS7473423B2Promote reproductionPromote safer self-therapiesNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNervous systemIgm antibody
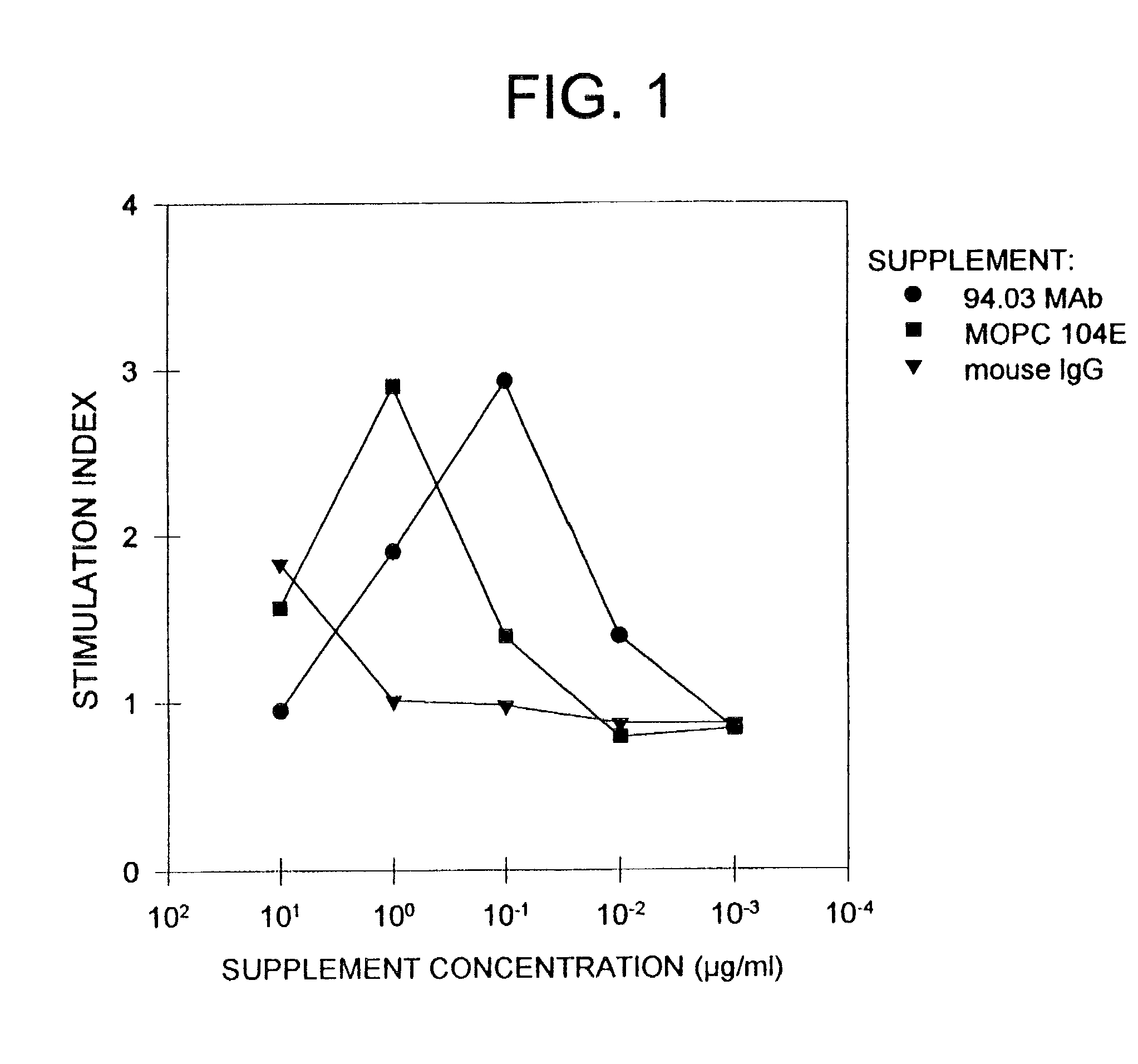
Antibodies, and particularly human antibodies, are disclosed that demonstrate activity in the treatment of demyelinating diseases as well as other diseases of the central nervous system that are of viral, bacterial or idiopathic origin, including neural dysfunction caused by spinal cord injury. Neuromodulatory agents are set forth that include and comprise a material selected from the group consisting of an antibody capable of binding structures or cells in the central nervous system, a peptide analog, a hapten, active fragments thereof, agonists thereof, mimics thereof, monomers thereof and combinations thereof. The neuromodulatory agent has one or more of the following characteristics: it is capable of inducing remyelination; binding to neural tissue; promoting Ca++ signaling with oligodendrocytes; and promoting cellular proliferation of glial cells. Amino acid and DNA sequences of exemplary antibodies are disclosed. Methods are described for treating demyelinating diseases, and diseases of the central nervous system of humans and domestic animals, using polyclonal IgM antibodies and human monoclonal antibodies sHIgm22(LYM 22), sHIgm46(LYM46) ebvHIgM MSI19D10, CB2bG8, AKJR4, CB2iE12, CB2iE7, MSI19E5 and MSI10E10, active fragments thereof and the like. The invention also extends to the use of human antibodies, fragments, peptide derivatives and like materials, and their use in diagnostic and therapeutic applications, including screening assays for the discovery of additional antibodies that bind to cells of the nervous system, particularly oligodendrocytes.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
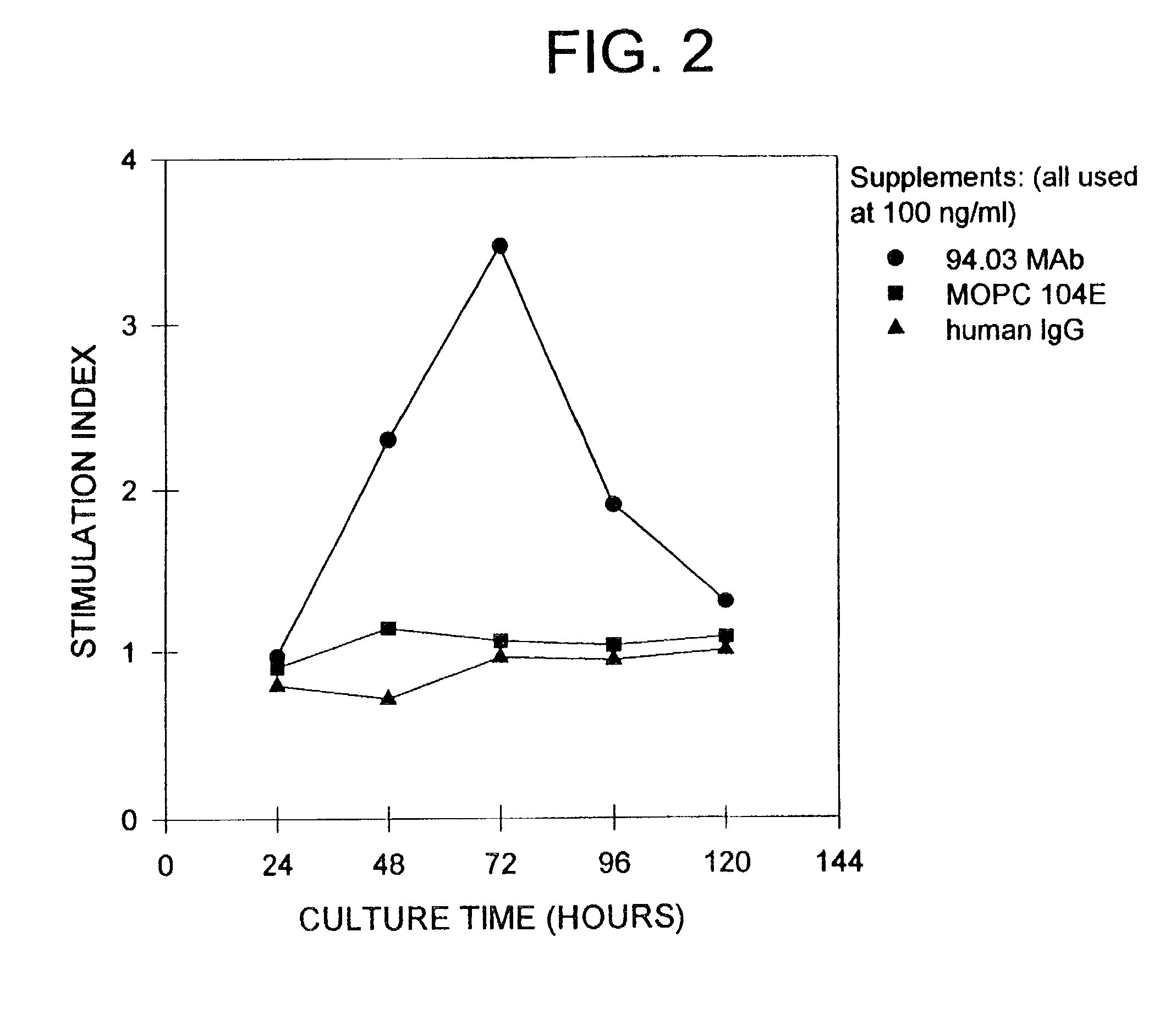
Bioactive peptides and unique ires elements from myelin proteolipid protein plp/dm20
InactiveUS20060173168A1Positively effect myelin repairIncrease secretionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseSpinal cord
Three novel low molecular weight (LMW) polypeptide fragments of a proteolipid protein human PLP / DM20 are designated PIRP-M, PIRP-L and PIRP-J, and are growth factors for oligodendrocytes with anti-apoptotic activity. They are encoded by mRNA from an IRES. Fusion polypeptides of such a LMW polypeptide, DNA encoding the LMW polypeptide and fusion polypeptide, expression vectors comprising such DNA, and cells expressing such polypeptides, or pharmaceutical compositions thereof, are useful for stimulating neural stem cell differentiation, maturation along the oligodendrocytic pathway and proliferation of oligodendrocytes or precursors. These compositions can protect oligodendrocytes (and nonneural cells) from apoptotic death. Thus, the present composition is used to treat a disease or condition in which such differentiation, maturation and proliferation or inhibition of cell death, including remyelination or stimulation of oligodendroglia or Schwann cells, is desirable. Disorders include multiple sclerosis, trauma with Parkinson's-like symptoms, hypoxic ischerriia and spinal cord trauma.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
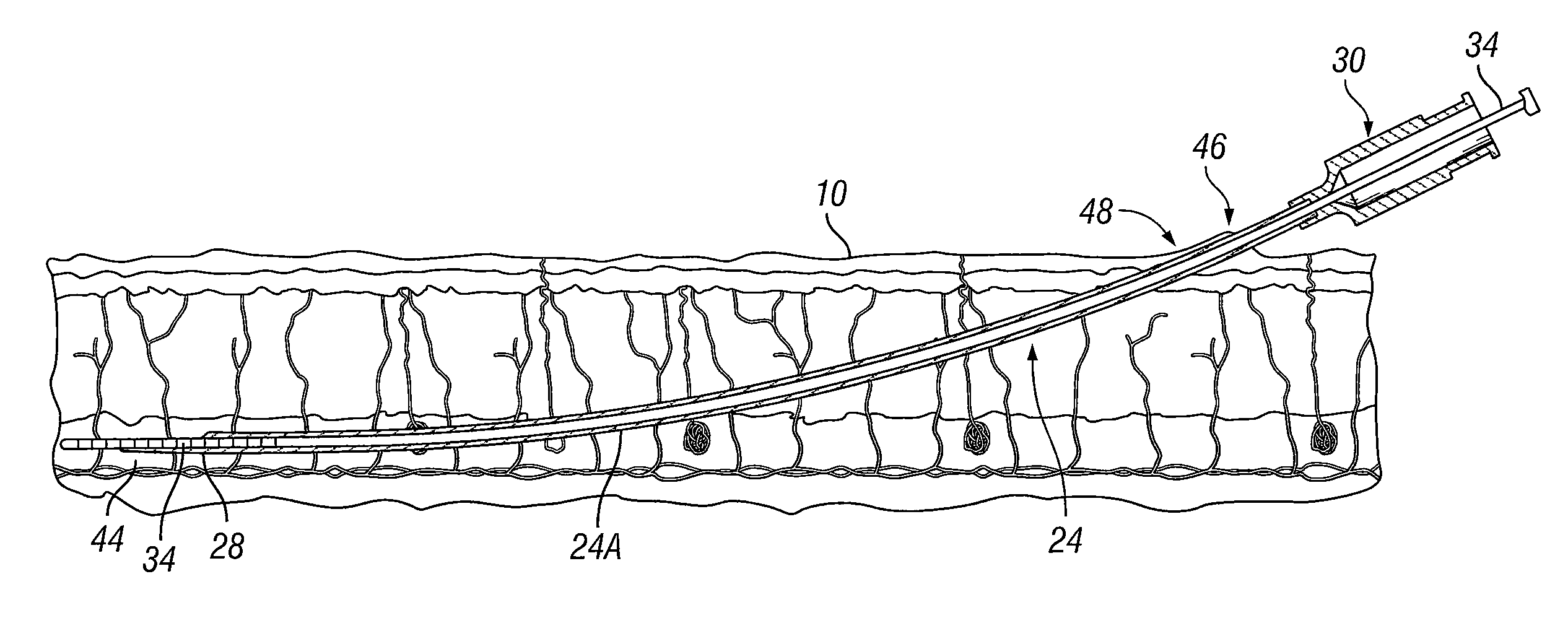
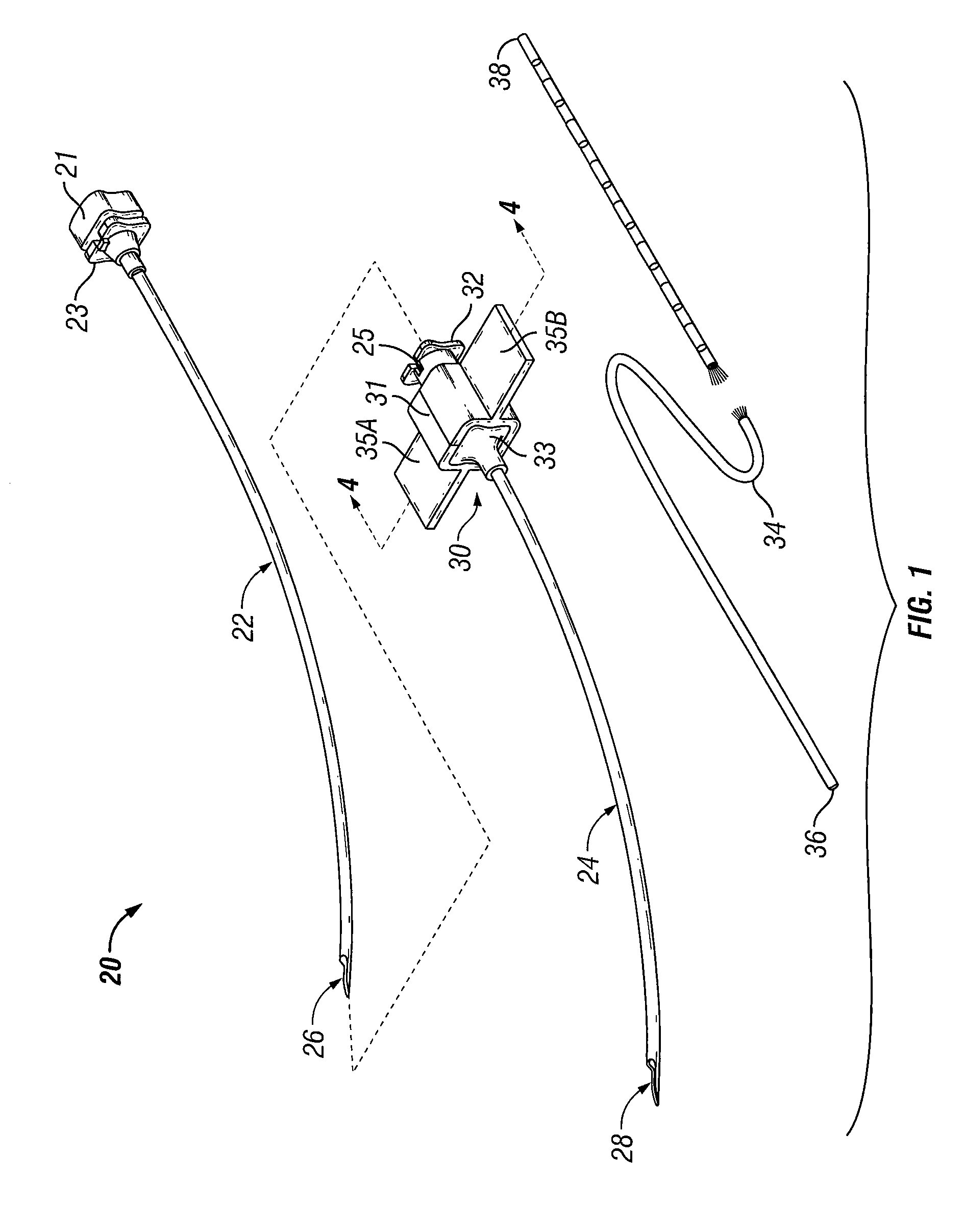
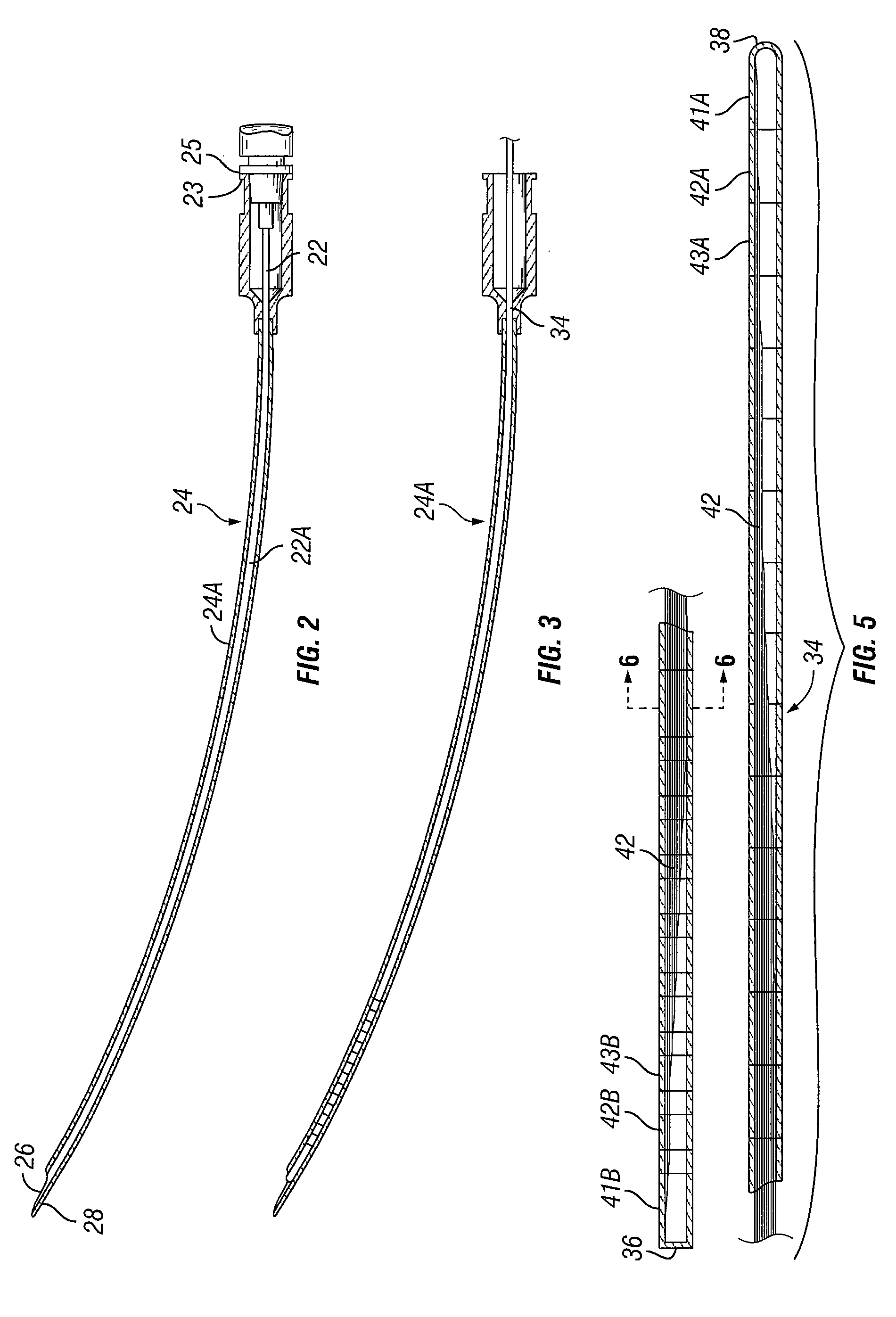
Peripheral nerve field stimulator curved subcutaneous introducer needle with wing attachment specification
An apparatus for use in peripheral nerve field stimulation (PNFS) whereby a plurality of curved introducer needles, of varying curvatures, are provided to permit the physician to best locate the region of oligodendrocytes that contain the A Beta fibers by matching the lumbar lordosis. A wing device is also provided that is attachable to the hub of the curved needle introducer which gives the physician better ability to maneuver the needle during insertion as well as permitting tenting of the skin. The invention benefits a large number of painful disorders arising from pathology in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine. In addition, this invention can also help a large number of other conditions including but not limited to failed back surgery syndrome / post-laminectomy pain, occipital / suboccipital headaches, scar pain, post herpetic neuralgia pain, mononeuritis multiplex, and pain following joint surgery (e.g., knee, hip, shoulder).
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Vegf-C or Vegf-D Materials and Methods for Stimulation of Neural Stem cells
InactiveUS20080057028A1Easy to identifyTherapy is simpleOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsOligodendrocytePrecursor cell
The present invention relates to VEGF-C or VEGF-D materials and methods for promoting growth and differentiation of neural stem cells, neuronal and neuronal precursor cells, oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocyte precursor cells and materials and methods for administering said cells to inhibit neuropathology.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Oligodendrocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells for remyelination and treatment of spinal cord injury
ActiveUS7285415B2Enhances late-stage differentiationEfficient productionBiocideSenses disorderNeural cellRemyelination
This invention provides populations of neural cells bearing markers of glial cells, such as oligodendrocytes and their precursors. The populations are generated by differentiating pluripotent stem cells such as human embryonic stem cells under conditions that promote enrichment of cells with the desired phenotype or functional capability. Various combinations of differentiation factors and mitogens can be used to produce cell populations that are over 95% homogeneous in morphological appearance, and the expression of oligodendrocyte markers such as GalC. The cells are capable of forming myelin sheaths, and can be used therapeutically improve function of the central nervous system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bioactive peptides and unique ires elements from myelin proteolipid protein plp/dm20
InactiveUS20080227707A1Conducive to survivalIncrease secretionCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsVectorsApoptosisRemyelination
Three novel low molecular weight (LMW) polypeptide fragments of a proteolipid protein human PLP / DM20 are designated PIRP-M, PIRP-L and PIRP-J, and are growth factors for oligodendrocytes with anti-apoptotic activity. They are encoded by mRNA from an IRES. Fusion polypeptides of such a LMW polypeptide, DNA encoding the LMW polypeptide and fusion polypeptide, expression vectors comprising such DNA, and cells expressing such polypeptides, or pharmaceutical compositions thereof, are useful for stimulating neural stem cell differentiation, maturation along the oligodendrocytic pathway and proliferation of oligodendrocytes or precursors. These compositions can protect oligodendrocytes (and nonneural cells) from apoptotic death. Thus, the present composition is used to treat a disease or condition in which such differentiation, maturation and proliferation or inhibition of cell death, including remyelination or stimulation of oligodendroglia or Schwann cells, is desirable. Disorders include multiple sclerosis, trauma with Parkinson's-like symptoms, hypoxic ischerriia and spinal cord trauma.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Culture method to obtain and maintain a pure or enriched population of mammalian neural stem cells and/or neural/progenitor cells that are prone to differentiate into oligodendrocyte-lineage cells in vitro
An isolated expandable human neural stem or progenitor cell wherein the cell is a progenitor cells or stem cell, maintains its capability to differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes, maintains its ability to differentiate into oligodendrocyte lineage cells efficiently throughout subsequent passages, and the cell expresses at least cell surface antigens CD133 and CD140α. Also provided is a method of in vitro culturing an expandable neural progenitor or stem cell isolated from a mammalian central nervous system, and the culture itself, wherein said cell maintains its capability to differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes and its ability to differentiate into oligodendrocyte-lineage cells efficiently. In addition, a method of treating a condition caused by a loss of myelin or a loss of oligodendrocytes is provided as is a composition comprising an isolated expandable neural stem cell or one cultured by the methods of the invention.
Owner:KIDO TSUNEO
Pharmaceuticals containing multipotential precursor cells from tissues containing sensory receptors
Current sources of neural stem and progenitor cells for neural transplantation are essentially inaccessible in living animals. This invention relates to neural precursor cells (stem cells, progenitor cells or a combination of both types of cells) isolated from the olfactory epithelium of mammals that can be passaged and expanded, and that will differentiate into cell types of the central nervous system (CNS), including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and tyrosine-hydroxylase-positive neurons. These precursor cells provide an accessible source for autologous transplantation in CNS, PNS, spinal cord and other damaged tissues.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Oligodendrocyte-Myelin Glycoprotein Compositions and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090175846A1Promoting neuronalPromoting oligodendrocyte survivalOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseMyelin glycoprotein
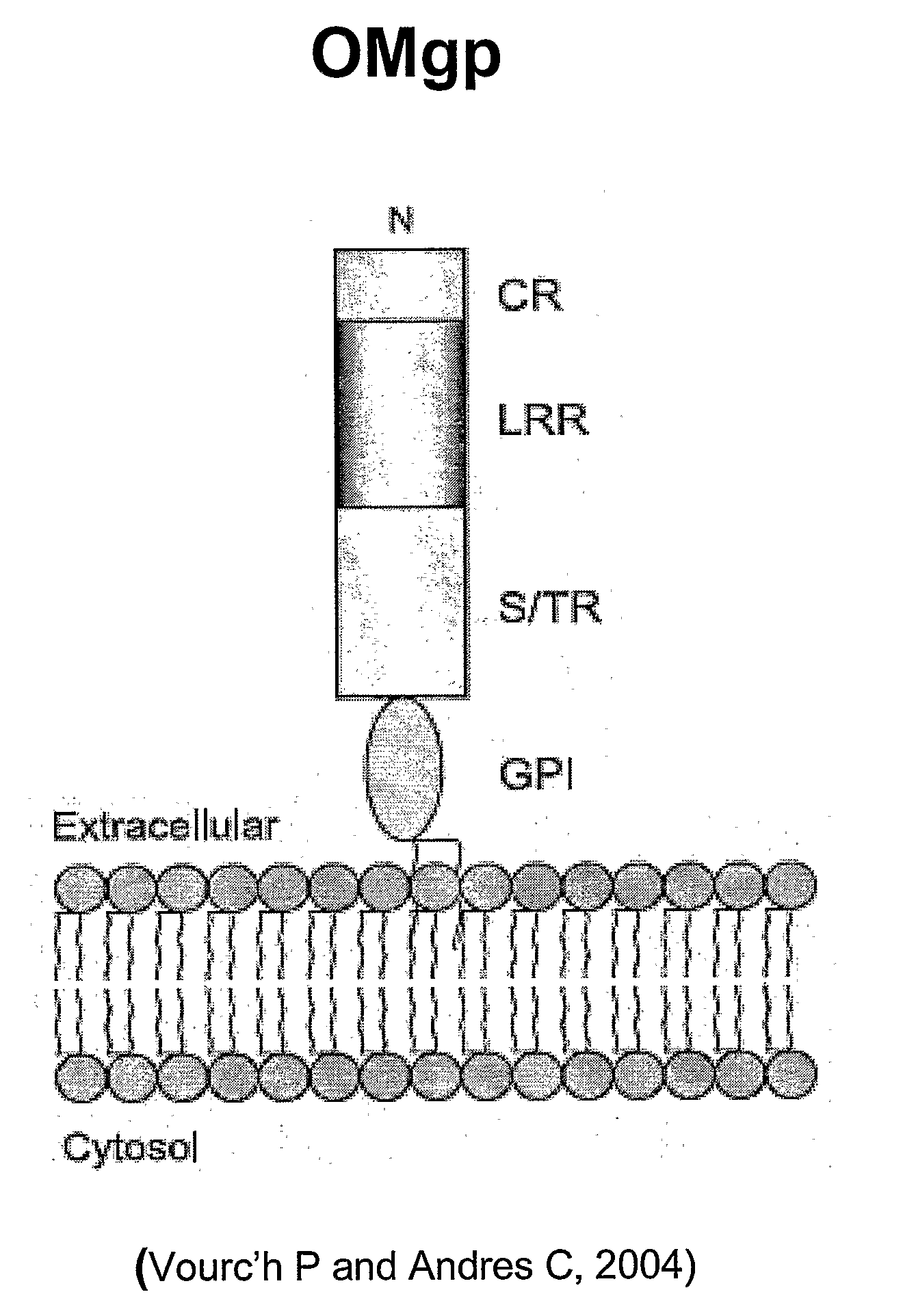
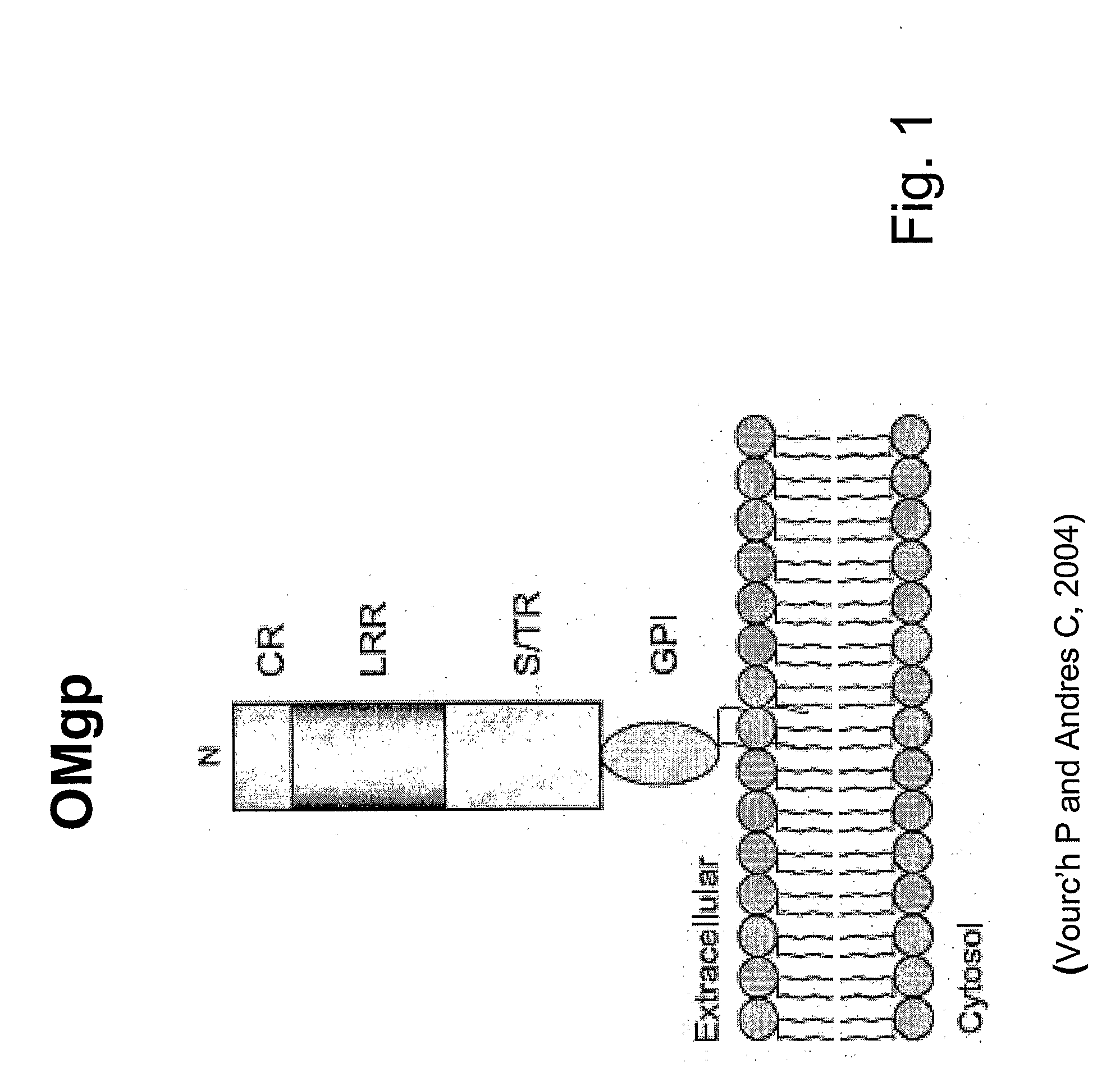
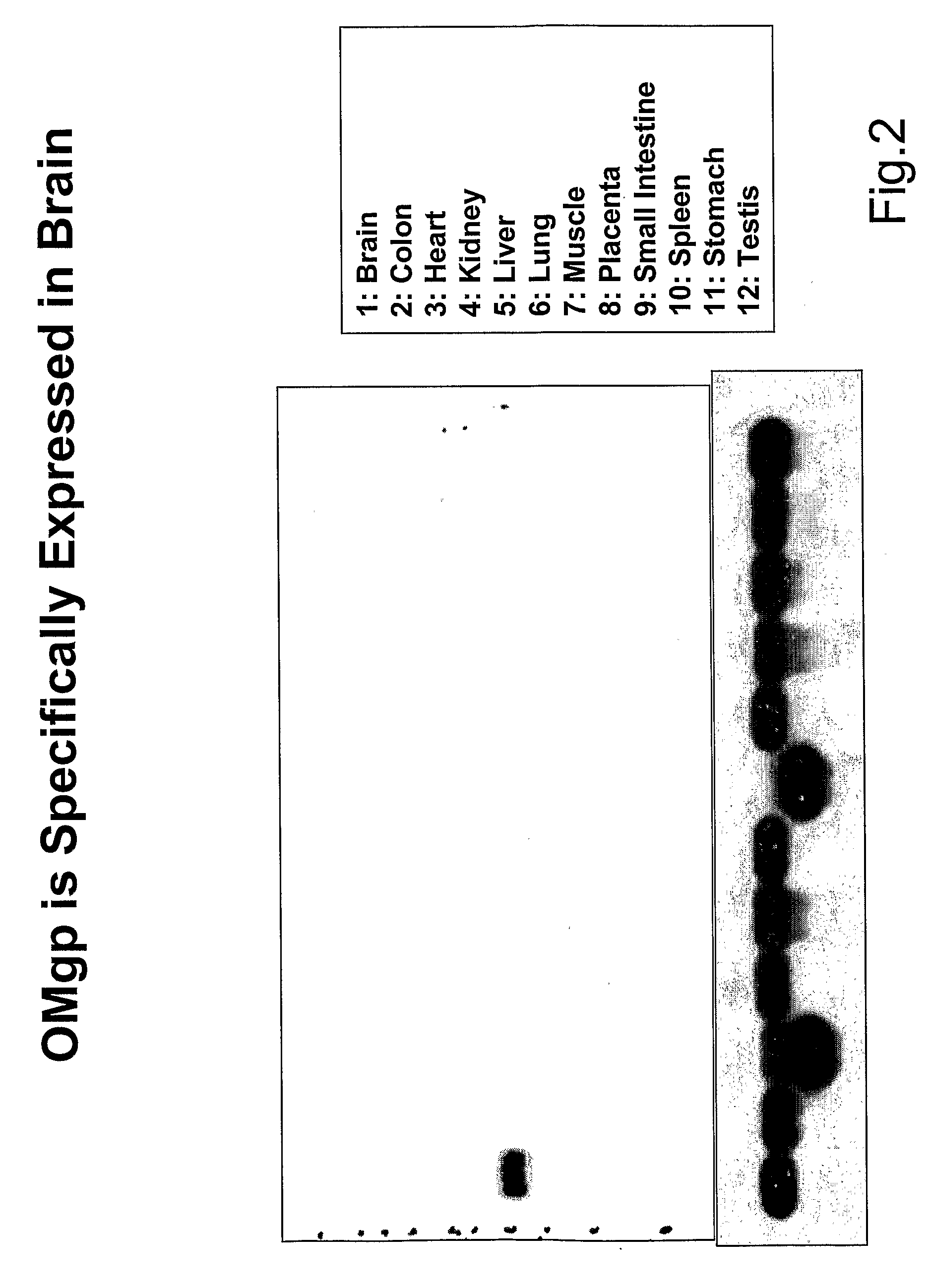
The present invention is based on the discovery that oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein (OMgp), which is ex-pressed by oligodendrocytes and CNS myelin, negatively regulates oligodendrocyte and neuronal differentiation and survival. Based on these discoveries, the invention relates generally to methods of promoting neuronal and oligodendrocyte survival and differentiation by administration of an OMgp anatagonist. Additionally, the invention generally relates to methods of treating various diseases, disorders or injuries associated with demyelination, dysmyelination, oligodendrocyte / neuronal cell death, axonal injury and / or differentiation by the administration of an OMgp antagonist.
Owner:BIOGEN IDEC MA INC
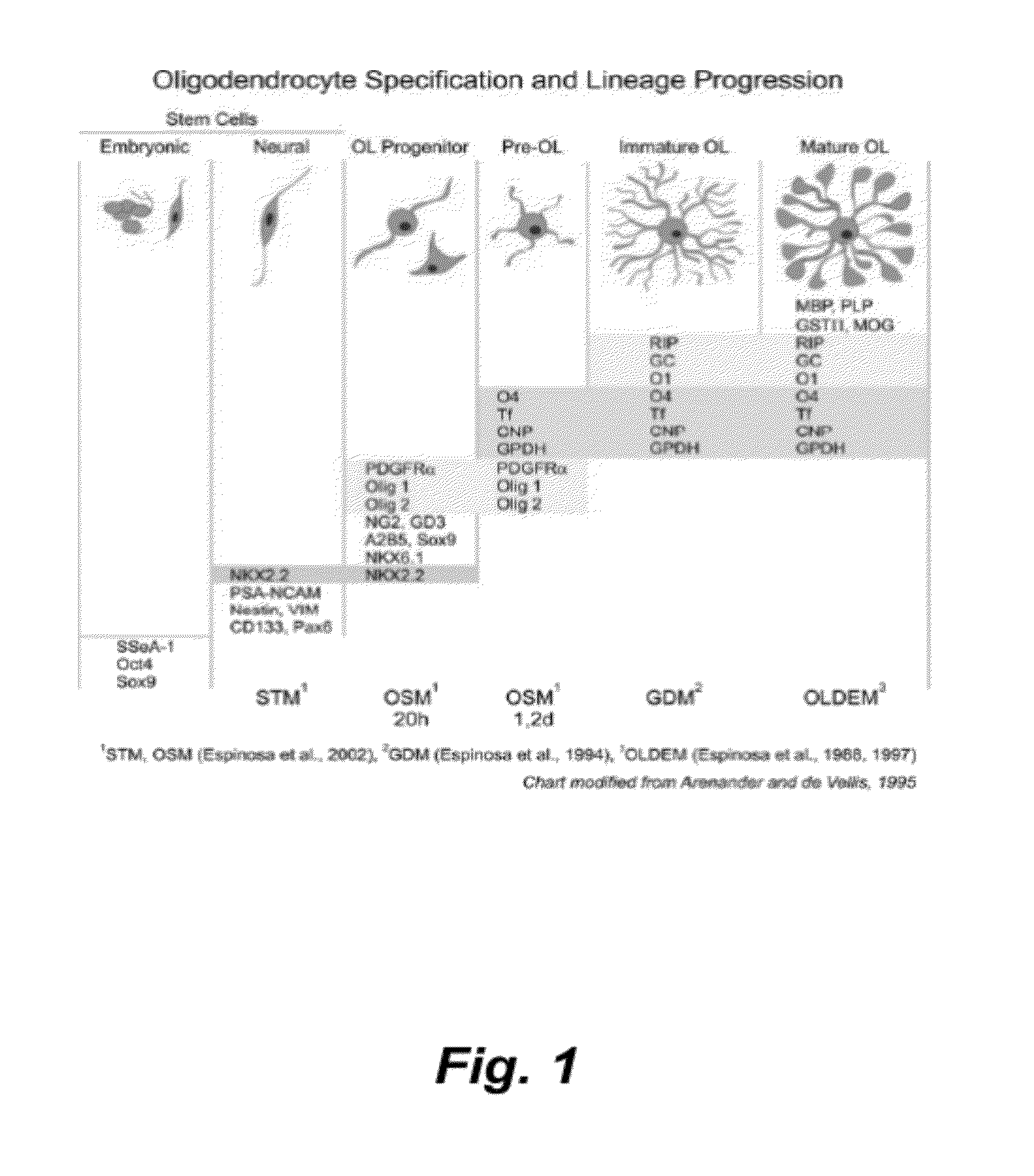
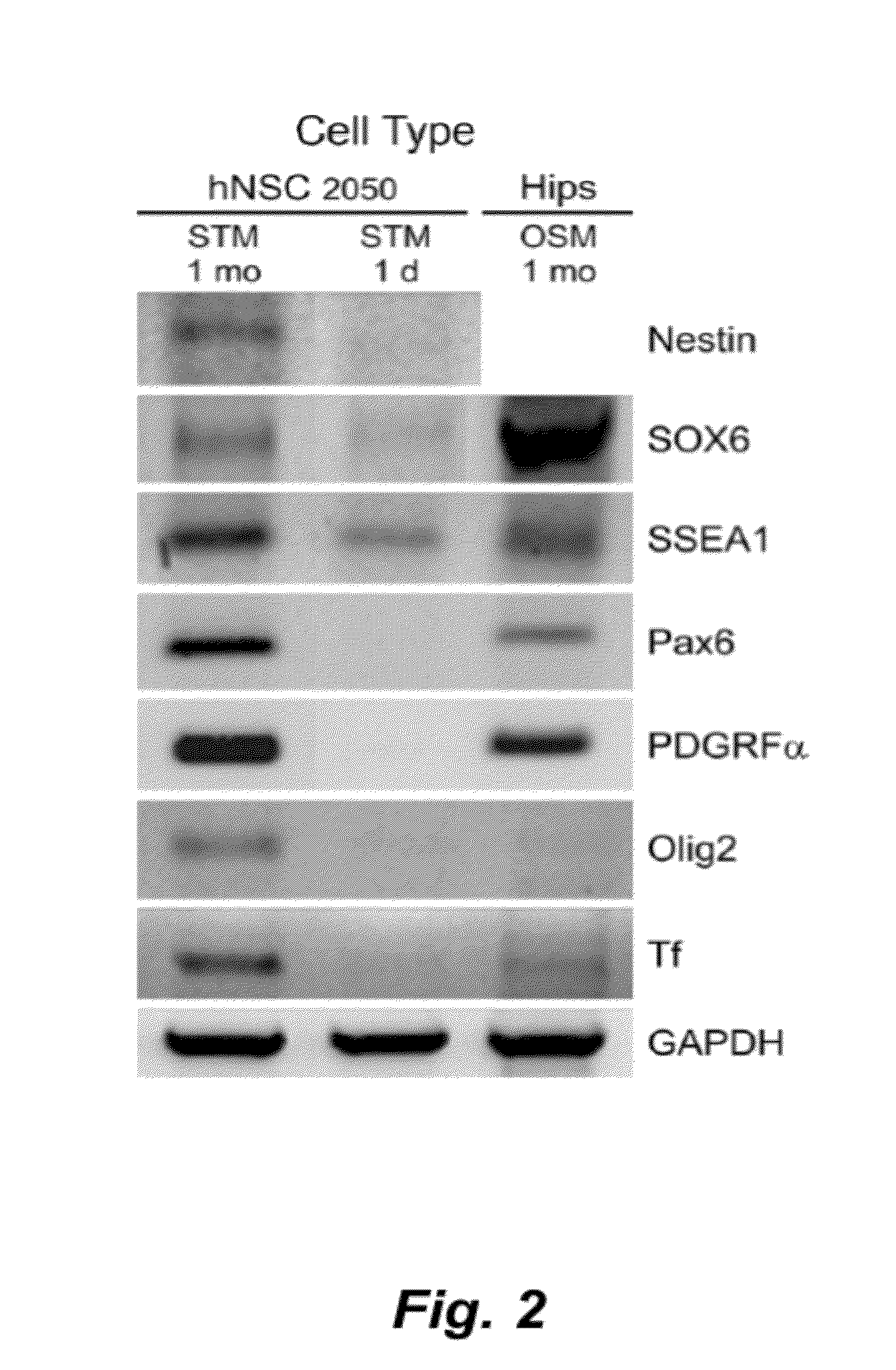
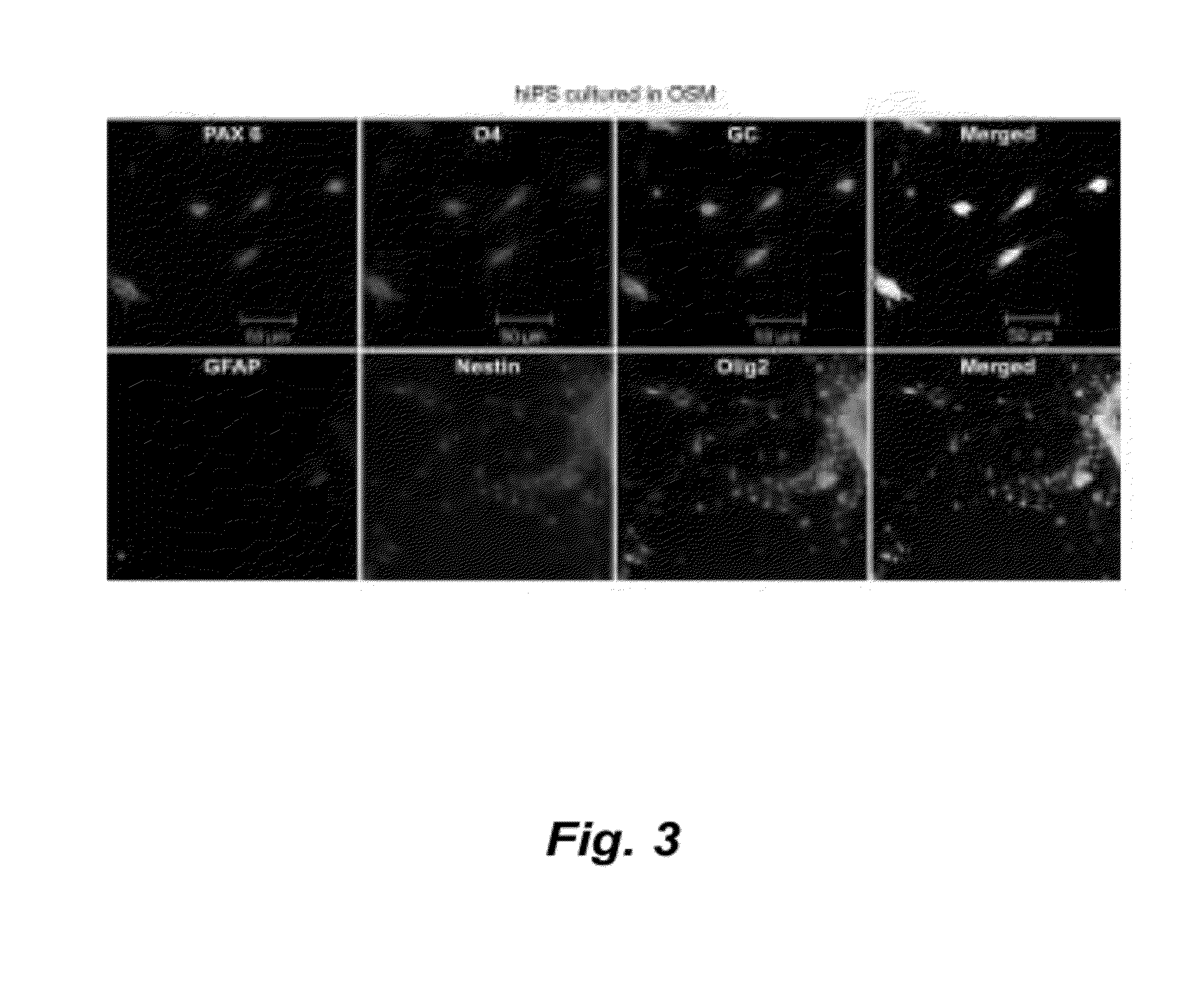
Culture system for stem cell propagation and neural and oligodendrocyte specification
The present invention provides methods and compositions for culturing stem cells, such as neural stem cells, and includes inducing the specification of neural stem cells to the oligodendrocyte phenotype and specification of multipotent cells ie. iPS cells and ES cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
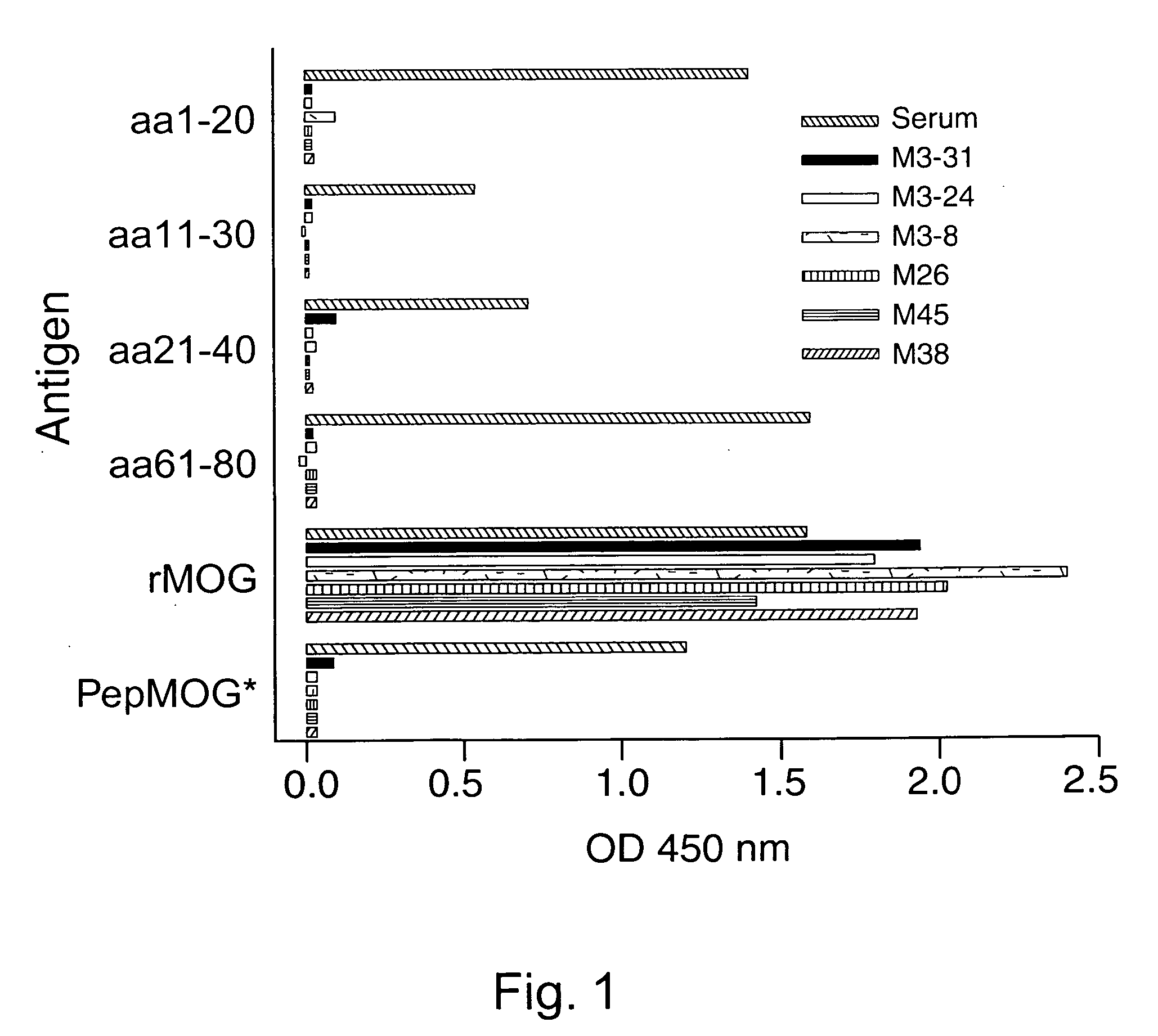
Method for diagnosis and prognosis of multiple sclerosis
This invention provides methods utilizing detection / quantification of autoantibodies to specific epitopes of myelin components (e.g. to conformational epitope of myelin / oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)) for the definitive diagnosis, and / or staging or typing, and / or prognosis of multiple sclerosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Direct conversion of cells to cells of other lineages
Methods, compositions and kits for producing functional neurons, astroctyes, oligodendrocytes and progenitor cells thereof are provided. These methods, compositions and kits find use in producing neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and progenitor cells thereof for transplantation, for experimental evaluation, as a source of lineage- and cell-specific products, and the like, for example for use in treating human disorders of the CNS. Also provided are methods, compositions and kits for screening candidate agents for activity in converting cells into neuronal cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and progenitor cells thereof.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Therapeutic uses for mesenchymal stromal cells
InactiveUS20040208858A1BiocideGenetic material ingredientsMetachromatic leukodystrophyTay-Sachs disease
Human mesenchymal stromal cells can be induced to differentiate into oligodendrocytes and neurons, respectively. For these cell types, therefore, MSCs can be a therapeutic source, either in vitro or in vivo, in the context of treating pathologies of the central nervous system which are characterized by neuron loss, such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and stroke, as well as head trauma, or by dysfunction in ganglioside storage or demyelinization, such as Tay-Sachs disease, G1 gangliosidosis, metachromatic leukodystrophy, and multiple sclerosis.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Oligodendrocyte precursor cells and method of obtaining and culturing the same
InactiveUS20060172415A1High degree of survivalAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderOligodendrocyteDevelopmental stage
The invention describes a self-renewing, phenotypically homogeneous population of oligodendrocyte precursor cells having a synchronized developmental stage and methods of obtaining a self-renewing phenotypically homogeneous population of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Other methods include methods of maintaining and storing a homogeneous population of oligodendrocyte precursor cells for a prolonged period of time without change in the characteristics of the cells and methods of dedifferentiating oligodendrocyte precursor cells. The self-renewing, phenotypically homogeneous population of oligodendrocyte precursor cells or homogeneous population of oligodendrocytes may be useful for treating a patient having a CNS disorder or condition.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Induction medium for inducing neural stem/progenitor cells to be differentiated into oligodendrocyte precursor cells and induction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103484432AAids in healingAids in drug screeningNervous disorderNervous system cellsProgenitorNervous system
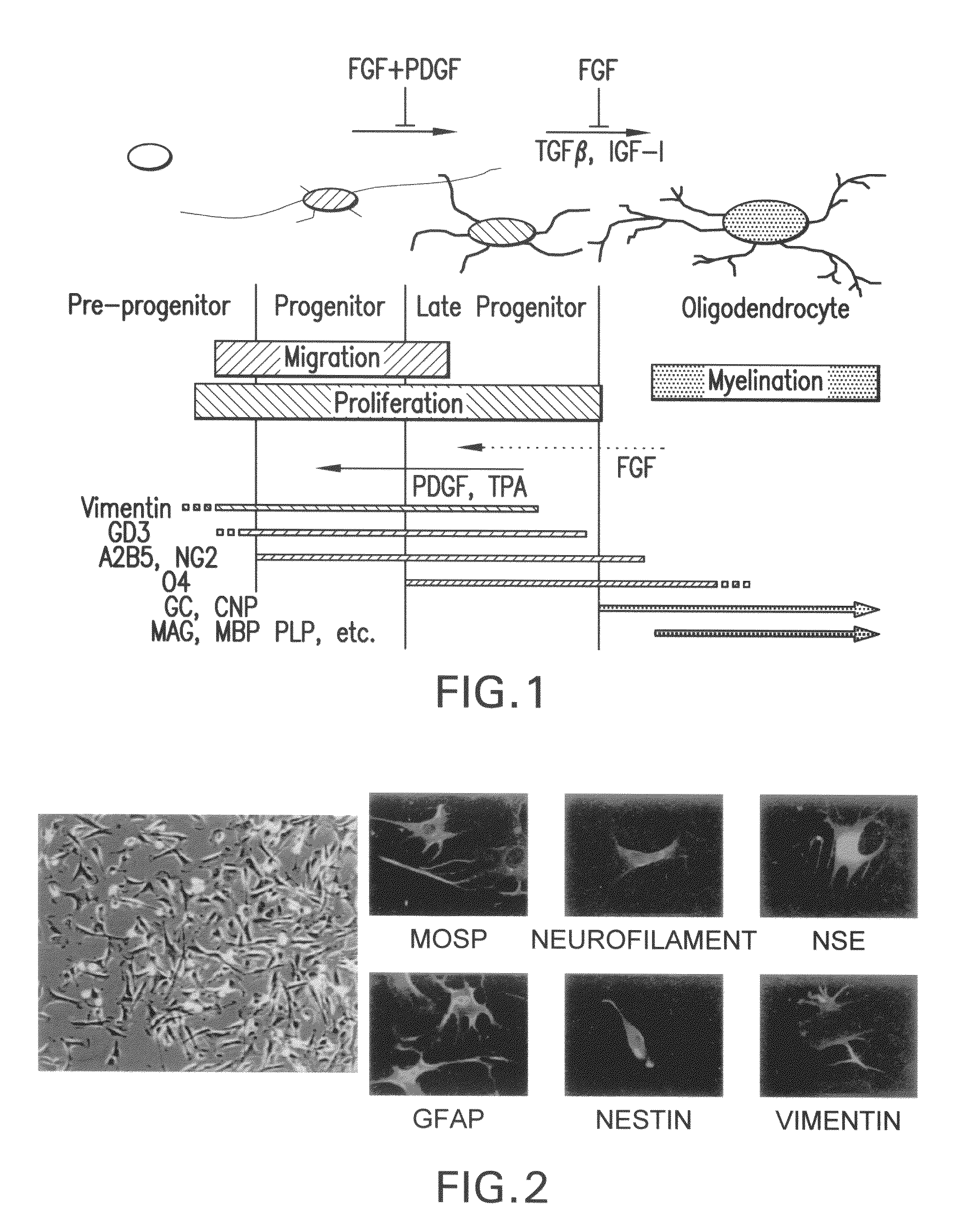
The invention relates to the field of cytobiology and neurobiology, in particular to an induction medium for inducing neural stem / progenitor cells to be differentiated into oligodendrocyte precursor cells and an induction method and application thereof. The invention adopts the technical scheme that after subjected to preprocessing culture for a certain time by a preprocessing medium, the human neural stem / progenitor cells are rapidly differentiated into the oligodendrocyte precursor cells for expressing oligodendrocyte precursor cell markers such as O4, A2B5, NG2, SOX10, PDGFR (Platelet Derived Growth Factor Receptor) and the like at a high purity under the action of the induction medium; and the key ingredients of the induction medium are bFGF (Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor), PDGF-AA and NT-3 (neurotrophins-3). The method disclosed by the invention and the obtained oligodendrocyte precursor cells can be applied to preparation of a medicament for treating the nervous system injury disease and have wide prospect on the aspects of experiment research and clinical treatment.
Owner:栾佐
Method of purification of cells
The present invention relates generally to a method for the generation of a substantially homogeneous population of undifferentiated cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to the purification of a substantially homogeneous population of stem cells and their progenitor or precursor cells. Even more particularly, the present invention provides a population of neural stem cells (NSCs). The subject invention is particularly directed to NSCs and precursor cells with the capacity to differentiate into cells and cell lineages required for the development, maintenance or repair of the central nervous system in an animal such as a mammal. The present invention is further directed to NSCs and progenitor and / or precursor cells which are capable of proliferation and differentiation into multiple cell lineages, such as but not limited to neurons, oligodendrocytes, glia and astrocytes. The subject invention further contemplates the use of NSCs and / or precursor cells for the repair or regeneration of tissue, such as tissue associated with the central nervous system, in an animal including a mammal. The NSCs of the present invention may be used to identify naturally occurring molecules such as cytokines as well as molecules obtained from natural product screening or screening of chemical libraries which induce proliferation of the NSCs. Such molecules are useful in the development of therapeutics.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Human stem cell-derived neural precursors for treatment of autoimmune diseases of the central nervous system
Owner:HADASIT MEDICAL RES SERVICES & DEVMENT
Method for separating and purifying oligodendrocyte precursor cells
InactiveCN101735983AAvoid damageIncrease acquisition rateNervous system cellsSingle cell suspensionWhite matter
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying oligodendrocyte precursor cells. The method comprises: digesting cerebral cortex of neonatal rats and part of white matter with trypsin and DNA enzyme; blowing and beating the obtained product to be a single-cell suspension; inoculating the single-cell suspension into a culture flask coated with polylysine in advance by use of a mixed-cell culture medium; performing culture for 3 to 5 days; replacing the culture flask with an oligodendrocyte precursor cell proliferation culture medium when the fusion of bottom-layer cells reaches 65 to 75 percent; performing culture for 3 to 5 days; replacing the oligodendrocyte precursor cell proliferation culture medium with an oligodendrocyte precursor cell separation culture medium; digesting the obtained product at 37 DEG C; isolating oligodendrocyte precursor cells from mixed cells; blowing and beating the obtained product to be the single-cell suspension; inoculating the single-cell suspension into the culture flask coated with polylysine in advance by use of an oligodendrocyte precursor cell inoculation culture medium; replacing the culture flask with an oligodendrocyte precursor cell purification culture medium after the cells adhere to a wall; performing culture for 2 to 4 days; and obtaining adherence cells, namely the oligodendrocyte precursor cells. The method can obtain a large number of high-purity good-activity oligodendrocyte precursor cells conveniently, rapidly, economically and efficiently.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Oligodendrocyte precursor cell composition and methods of use
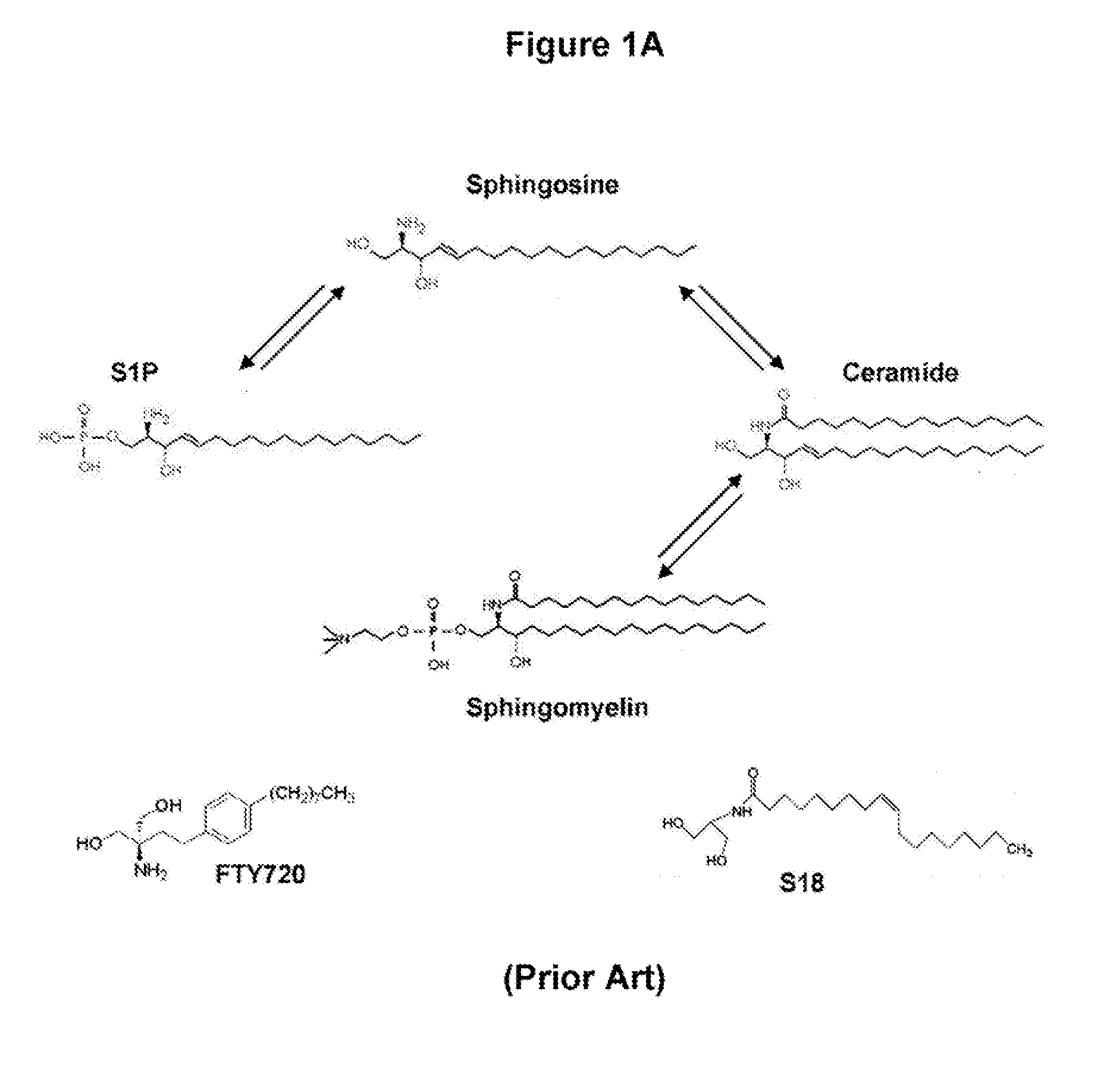
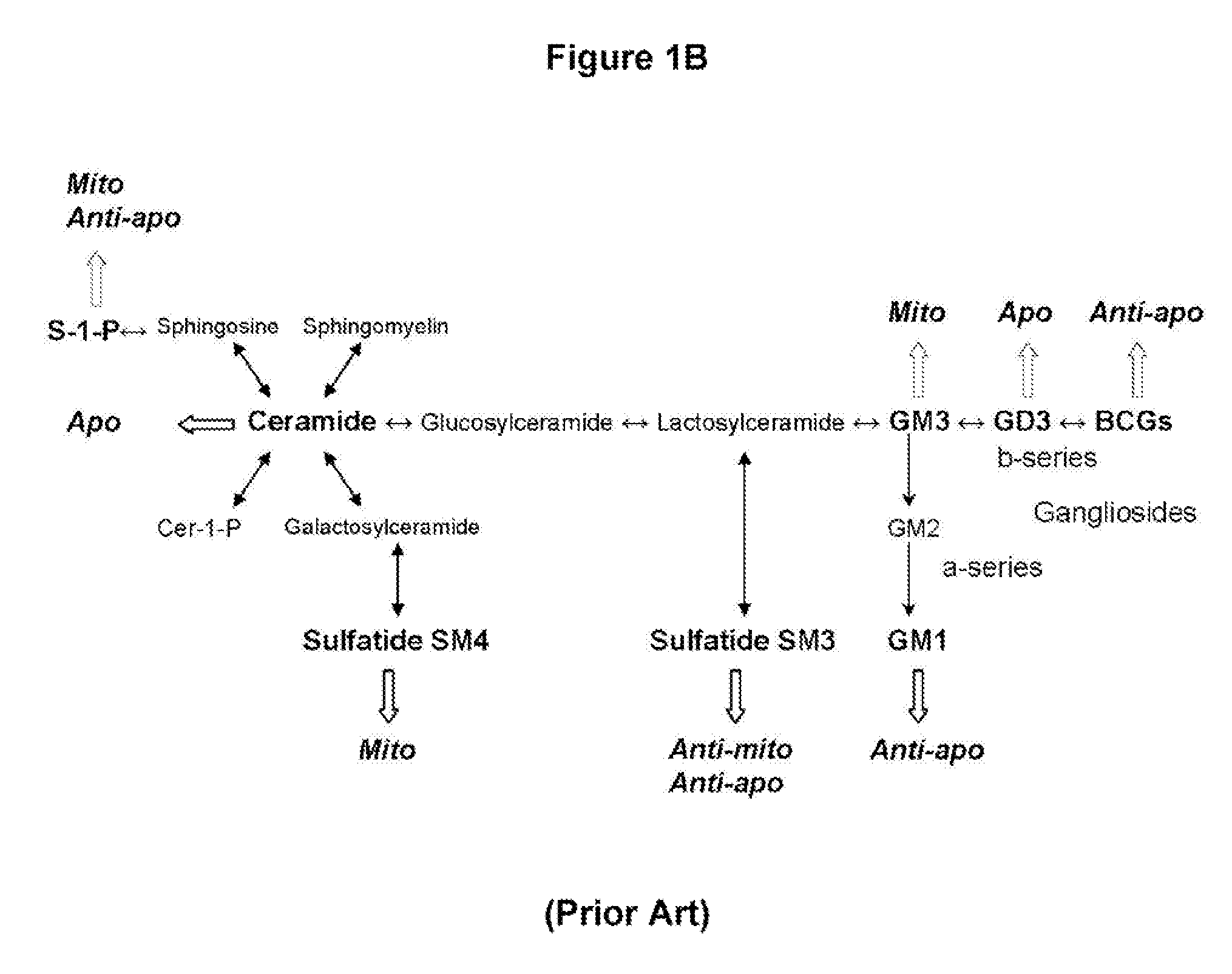
The present invention provides a cell culture enriched for sphingolipid enhances neural stem cells (SENSe), particularly oligodendrocyte precursor cells (ODPCs), that do not form teratomas after transplanted in vivo. Methods for producing and use of the invention ODPCs or the cell culture enriched with these ODPCs for stem cell therapy are also provided. The invention method comprises culturing a stem cell culture with a cell culture medium comprising a ceramide compound and a S1P receptor agonist in sequence, overlapping intervals or concurrent manners. The present invention further provides a cellular or gene therapy using a composition comprising a ceramide compound in conjunction with a S1P1 agonist to proliferate or differentiate endogeneous neural stem cells to ODPCs and further to oligodendrocytes.
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF GEORGIA RES INST
Human stem cell-derived neural precursors for treatment of autoimmune diseases of the central nervous system
The present invention concerns the use of a population of cells comprising: (a) neural precursor cells committed to an oligodendroglial fate; (b) uncommitted neural precursor cells (c) differentiated oligodendrocytes; or (d) a combination of any one of (a) to (c) for the treatment of CNS autoimmune diseases, or for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition for treating CNS autoimmune diseases, the population of cells being derived from human pluripotent stem cells. The invention also provides methods for obtaining such populations of cells, namely, neural precursor cells committed to an oligodendroglial fate as well as differentiated oligodendrocytes which then can be used in the treatment of CNS autoimmune diseases. A preferred autoimmune disease in the context of the present invention is multiple sclerosis where the population of cells is administered to the CNS for local treatment of the disease.
Owner:HADASIT MEDICAL RES SERVICES & DEVMENT
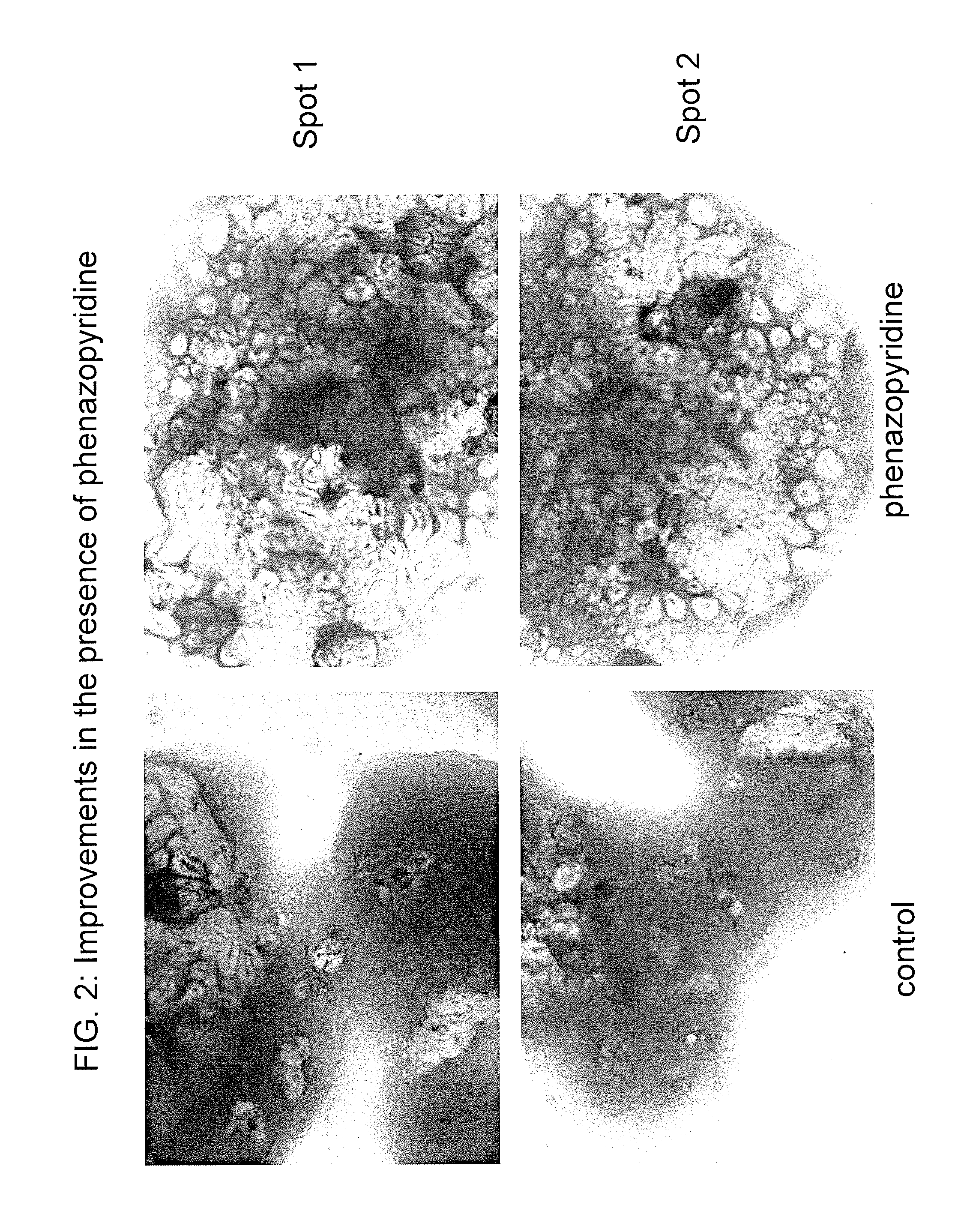
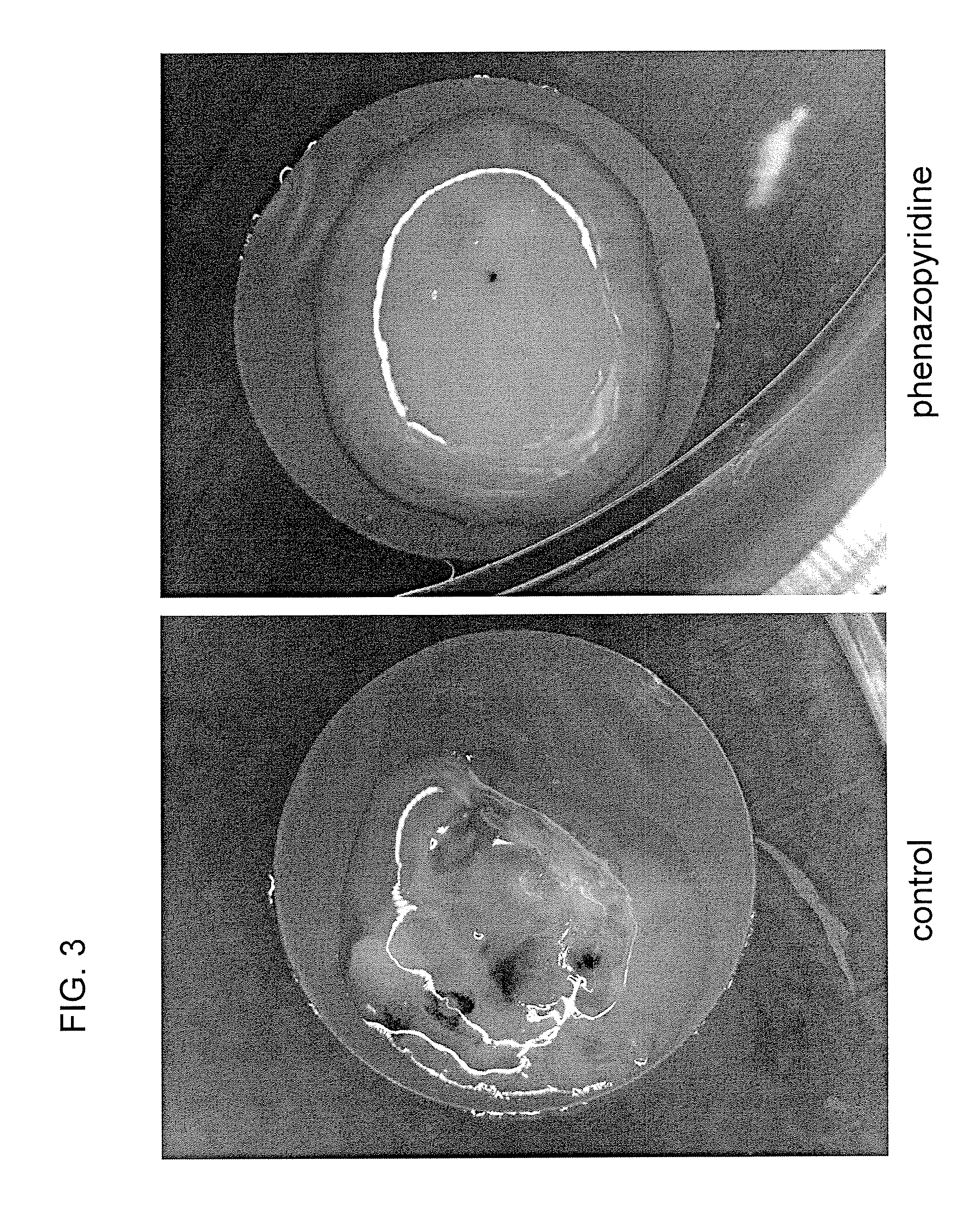
Neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes differentiated from a mammalian pluripotent or neural stem cells exposed to a pyridine deriviative
InactiveUS8609413B2Reduce amountPromote differentiationBiocideNervous disorderPluripotential stem cellOligodendrocyte
A method of preparing neural precursor cells by exposing pluripotent stem cells or neural stem cells to a differentiation agent. The agent is a pyridine analog, which in preferred embodiments is a phenylethynyl-substituted or phenylazo-substituted pyridine. In other embodiments, a method of enhancing neural precursor cell survival is provided in which the survival is enhanced by exposure to the pyridine analog. In further embodiments, a method of preparing neuronal cells is provided in which pluripotent or neural stem cells exposed to the pyridine analog are then incubated without the pyridine analog, resulting in differentiation into neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. These methods may be used in toxicological screens, e.g., to evaluate the neurotoxicity of a test compound.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
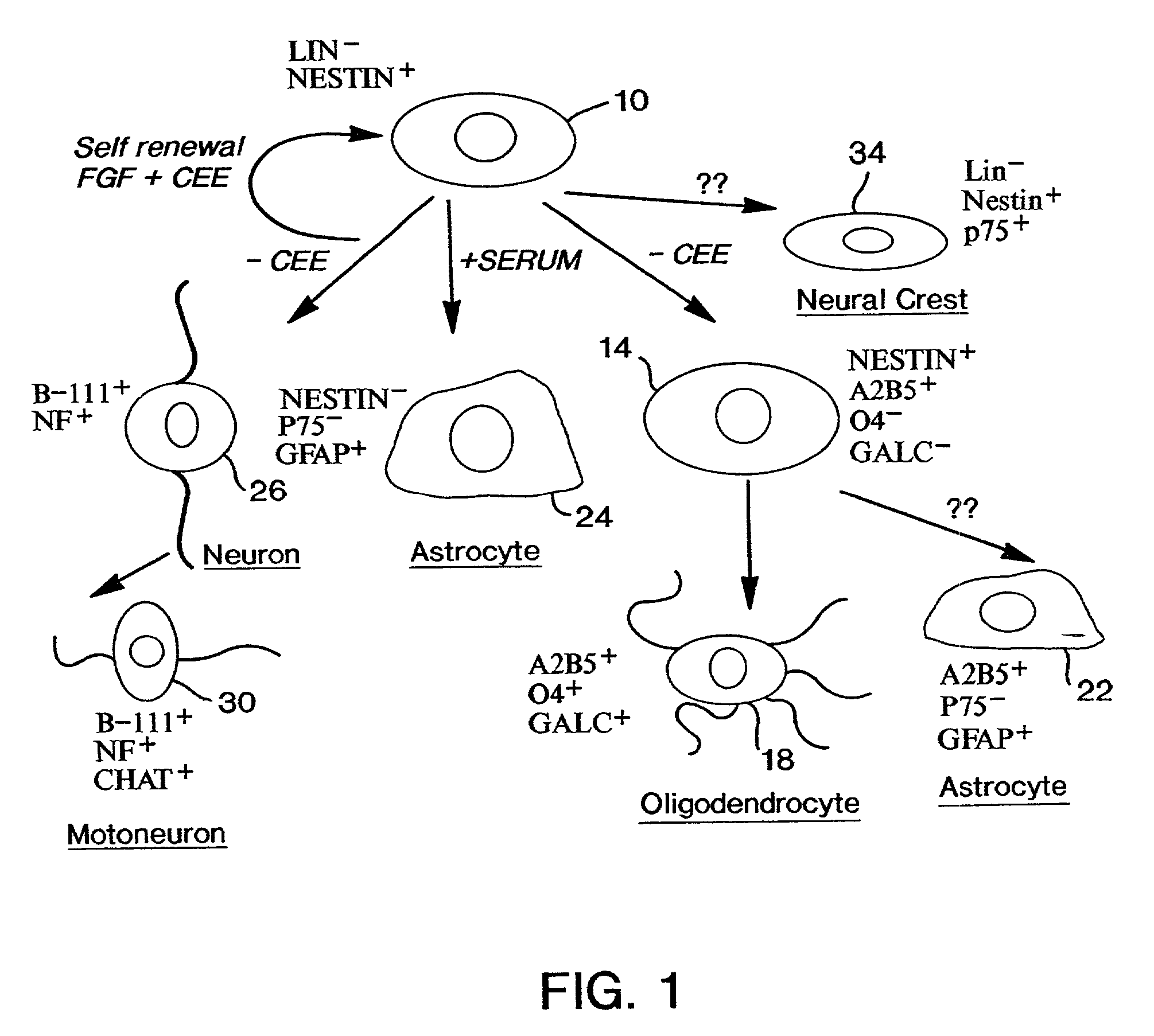
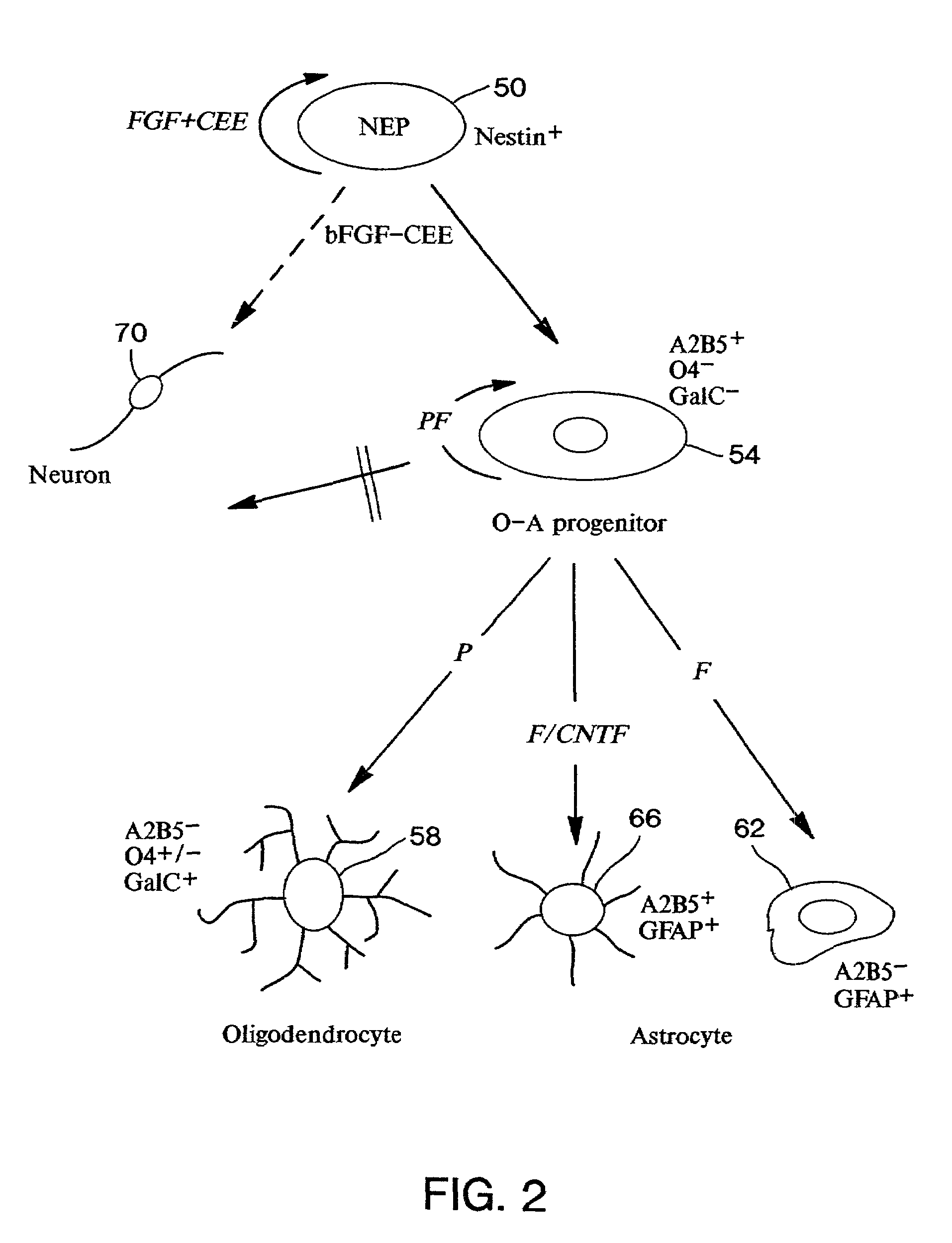
Neuroepithelial stem cells and glial-restricted intermediate precursors
Multipotent neuroepithelial stem cells and lineage-restricted oligodendrocyte-astrocyte precursor cells are described. The neuroepithelial stem cells are capable of self-renewal and of differentiation into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. The oligodendrocyte-astrocyte precursor cells are derived from neuroepithelial stem cells, are capable of self-renewal, and can differentiate into oligodendrocytes and astrocytes, but not neurons. Methods of generating, isolating, and culturing such neuroepithelial stem cells and oligodendrocyte-astrocyte precursor cells are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Therapeutic uses for mesenchymal stromal cells
InactiveUS20070184038A1BiocideGenetically modified cellsMetachromatic leukodystrophyTay-Sachs disease
Human mesenchymal stromal cells can be induced to differentiate into oligodendrocytes and neurons, respectively. For these cell types, therefore, MSCs can be a therapeutic source, either in vitro or in vivo, in the context of treating pathologies of the central nervous system which are characterized by neuron loss, such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and stroke, as well as head trauma, or by dysfunction in ganglioside storage or demyelinization, such as Tay-Sachs disease, G1 gangliosidosis, metachromatic leukodystrophy, and multiple sclerosis.
Owner:TENNEKOON GIHAN +3
Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cell Composition and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20090196859A1Prevents membrane associationReduce phosphorylationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsS1P ReceptorCell culture media
The present invention provides a cell culture enriched for sphingolipid enhances neural stem cells (SENSe), particularly oligodendrocyte precursor cells (ODPCs), that do not form teratomas after transplanted in vivo. Methods for producing and use of the invention ODPCs or the cell culture enriched with these ODPCs for stem cell therapy are also provided. The invention method comprises culturing a stem cell culture with a cell culture medium comprising a ceramide compound and a S1P receptor agonist in sequence, overlapping intervals or concurrent manners. The present invention further provides a cellular or gene therapy using a composition comprising a ceramide compound in conjunction with a S1P1 agonist to proliferate or differentiate endogeneous neural stem cells to ODPCs and further to oligodendrocytes.
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF GEORGIA RES INST
Shortcut method for separation and purification of embryonic cranial neural stem cells
InactiveCN103031271AAchieve separationEfficient separationNervous system cellsEmbryonic cellsOligodendrocyteNeurulation
The invention provides a method able to realize separation, amplification and purification of embryonic cranial neural stem cells rapidly and simply. The invention uses the thermal conversion polymer N-isopropylacrylamide and polyethylene glycol to conduct three-dimensional culture on neural cells, and makes use of the characteristic that neural stem cells can proliferate in a gel environment and form neurospheres to achieve the purposes of separation and purification of the neural stem cells. The formed neurospheres are subjected to immunofluorescent labeling determination, which shows that about 93% of the cells are Nestin positive, so that the method is simple and effective for separation and purification of neural stem cells. The embryonic neural stem cells separated and purified by the method can differentiate in vitro to form neurons, oligodendrocytes and Glias.
Owner:北京清美联创干细胞科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com