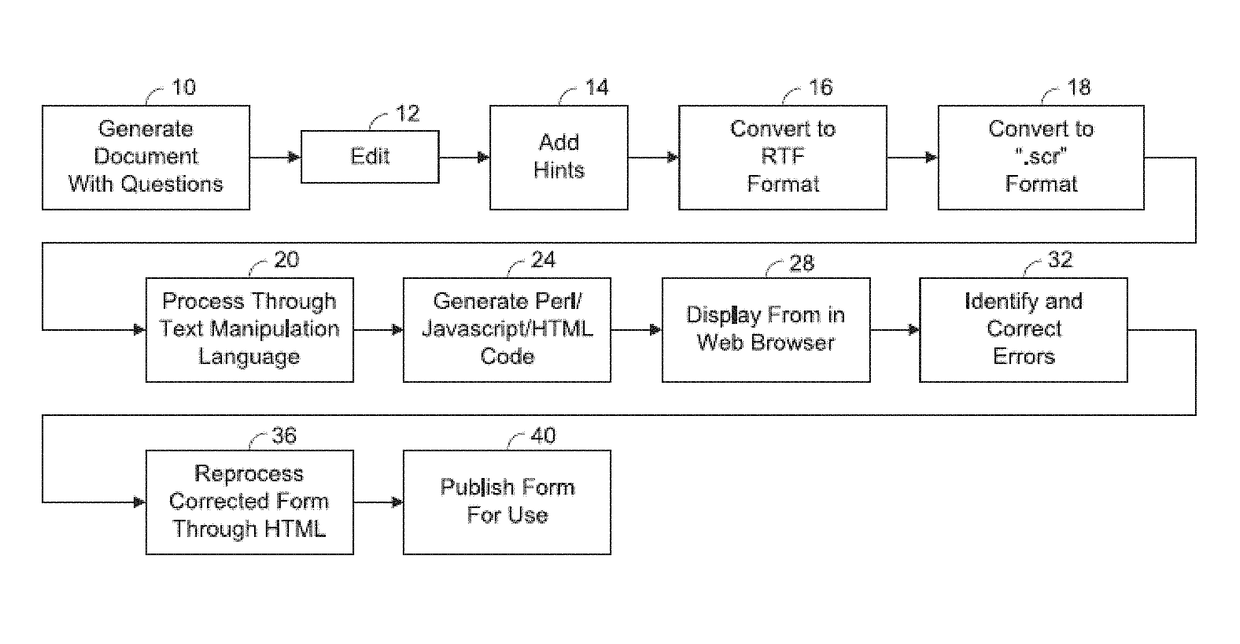
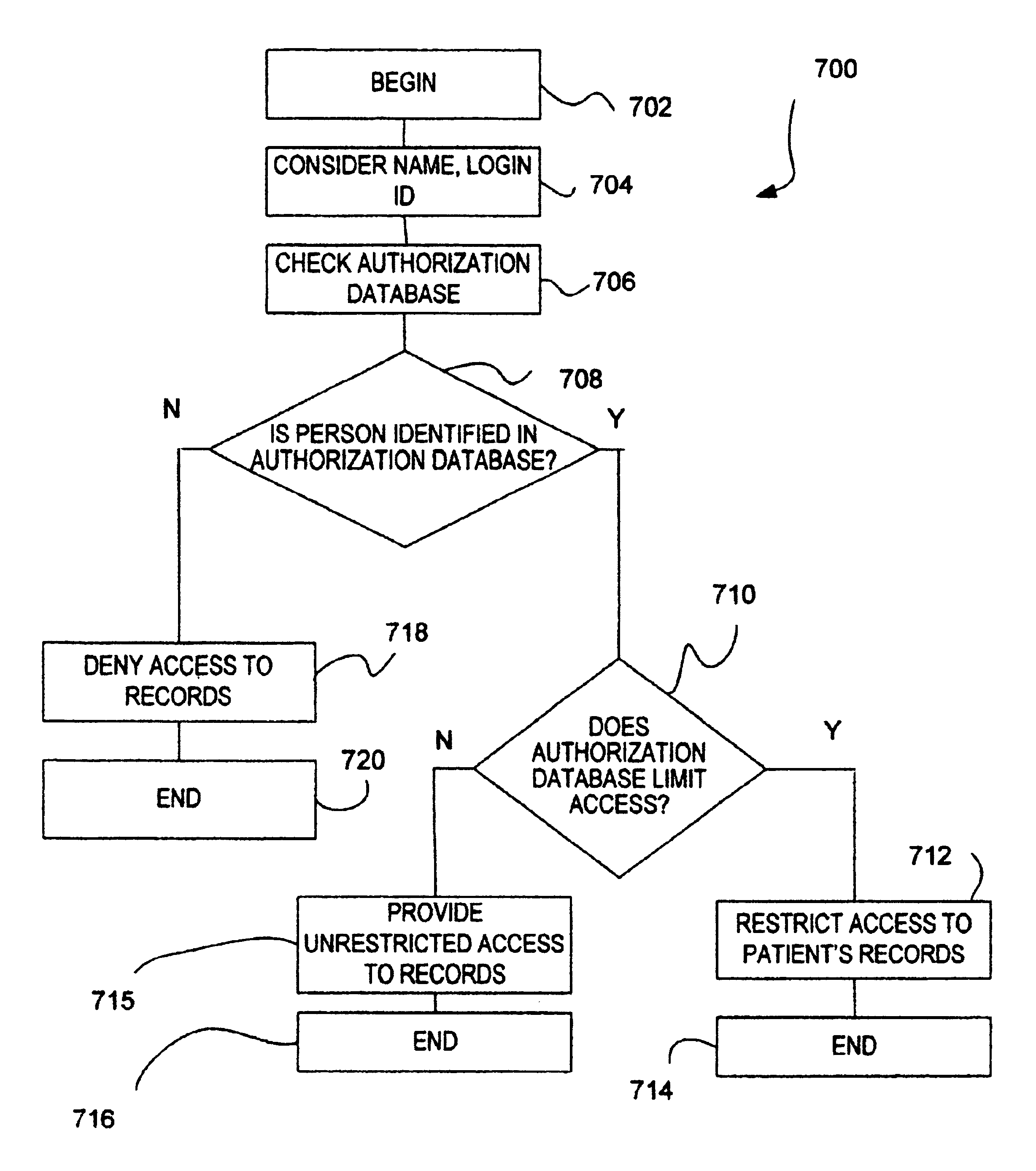
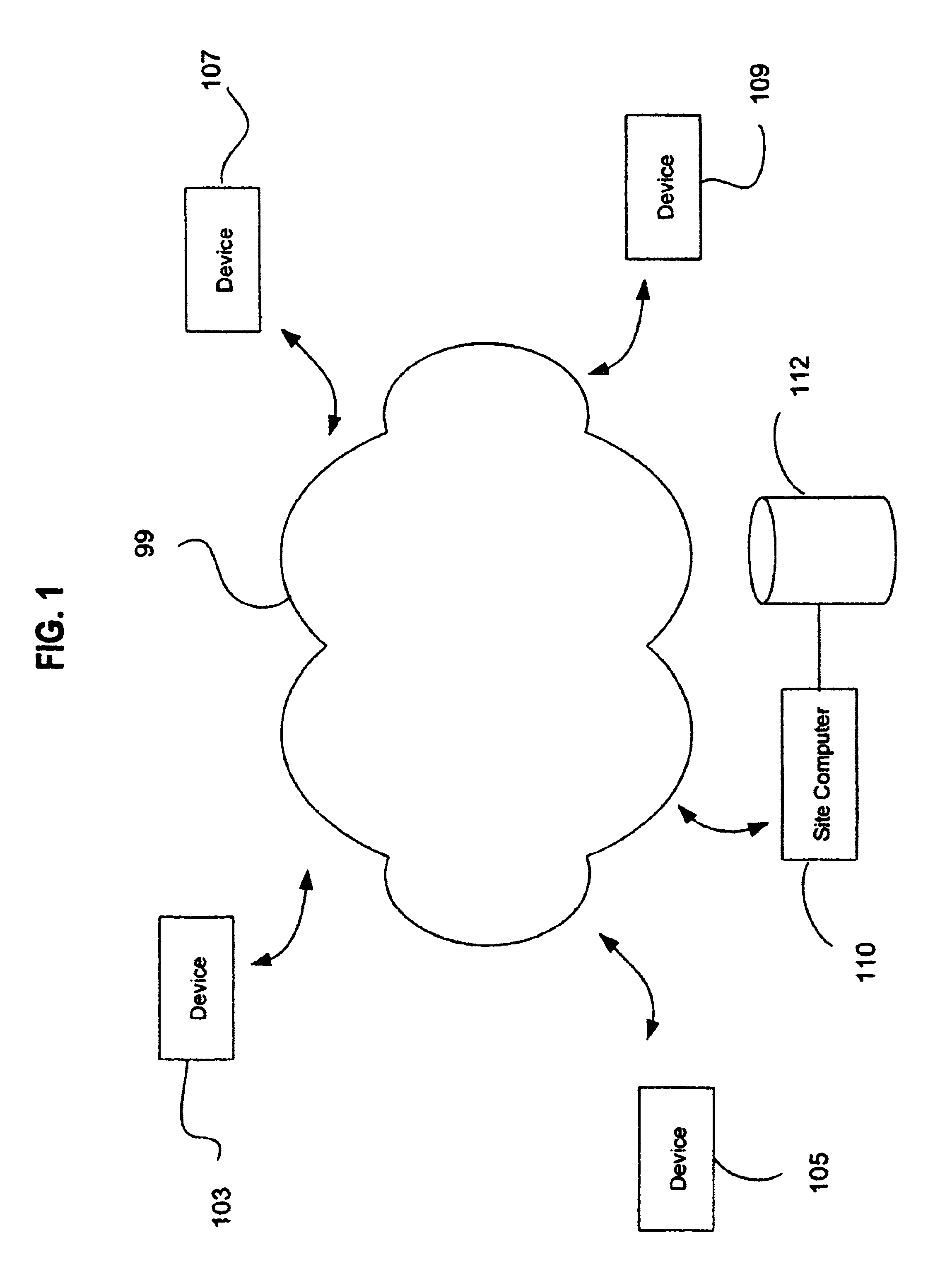
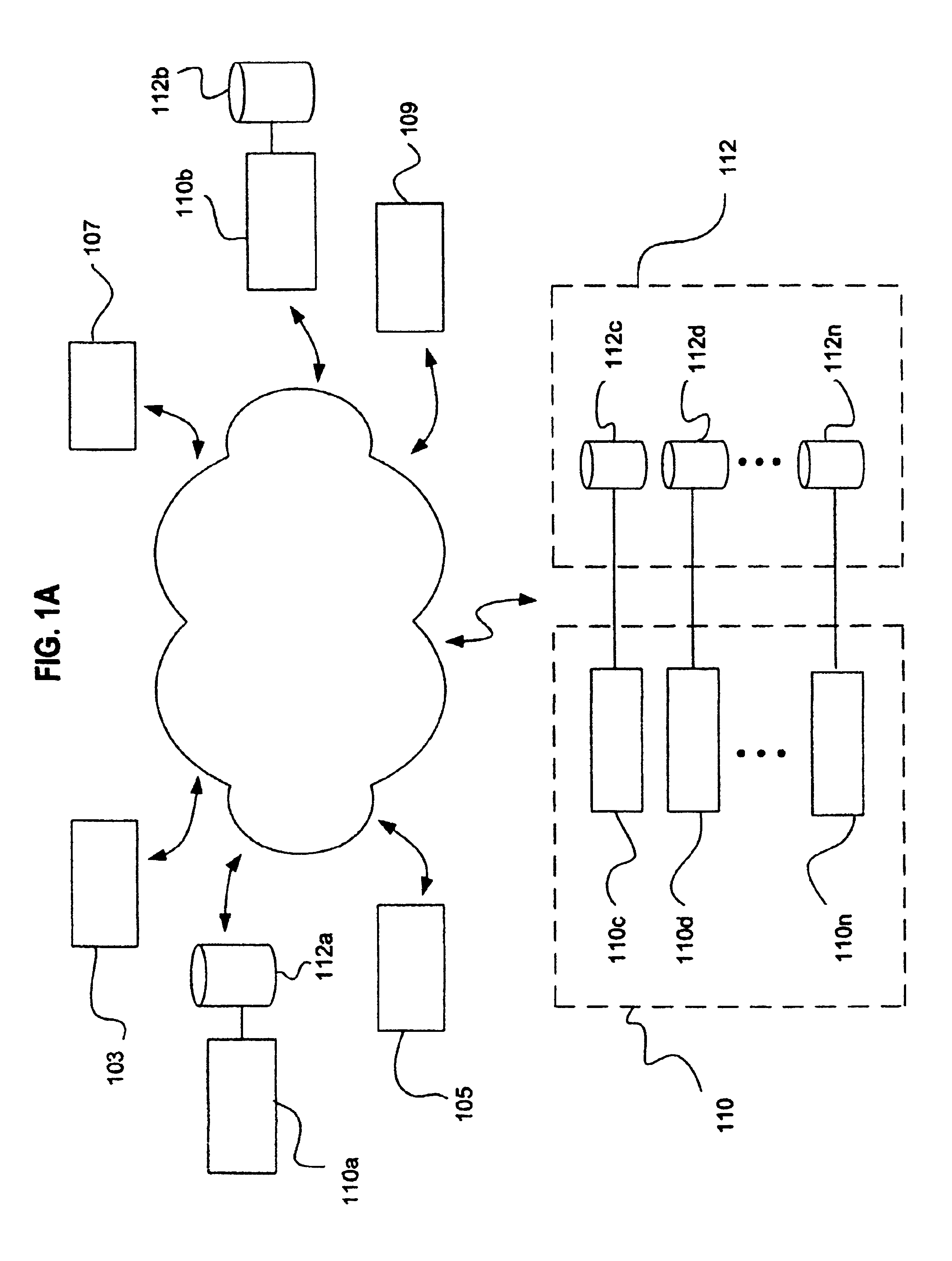
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2219 results about "Patient information" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Patient information. A non-specific term for any information about a condition or procedure which is intended for consumption by a non-professional audience.
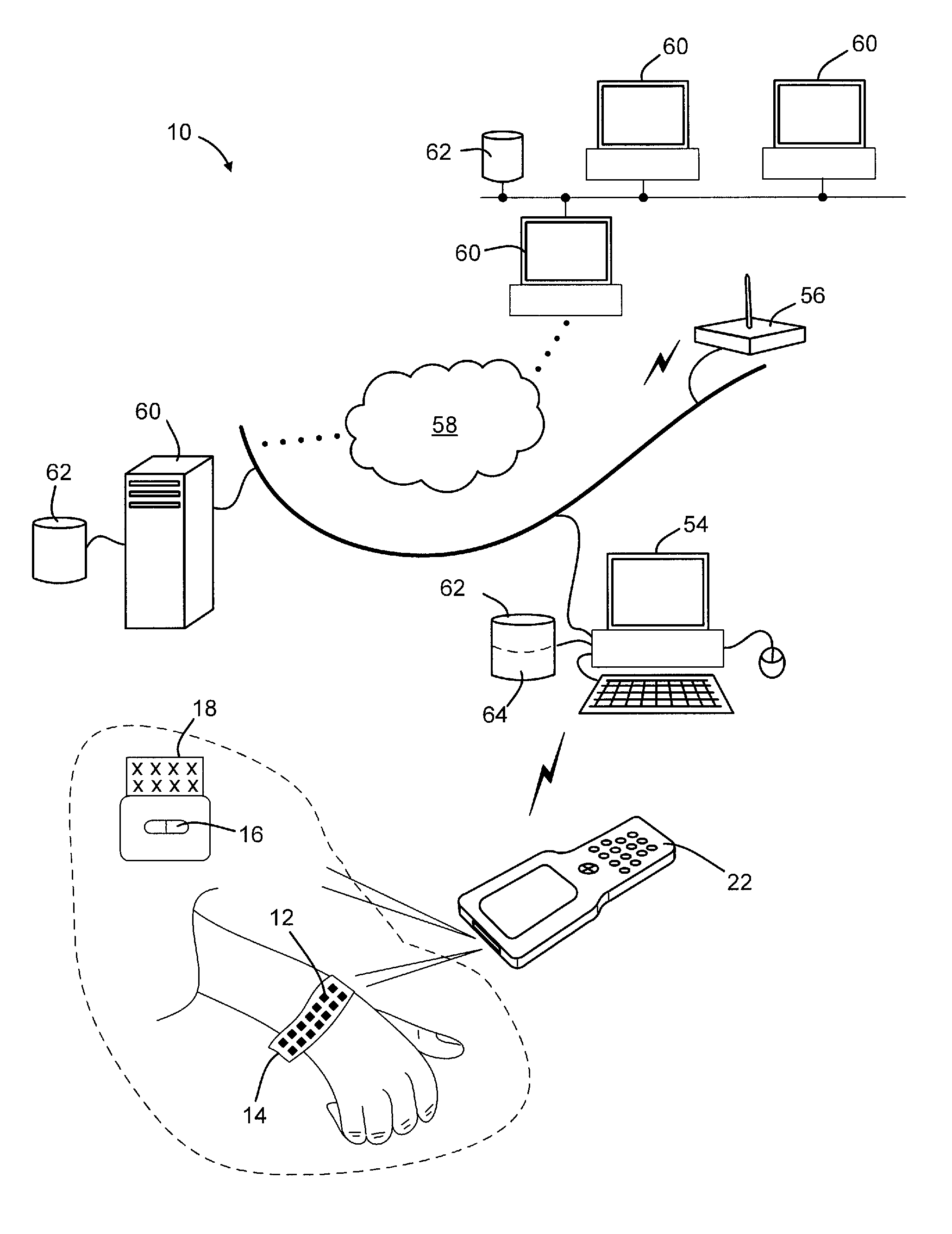
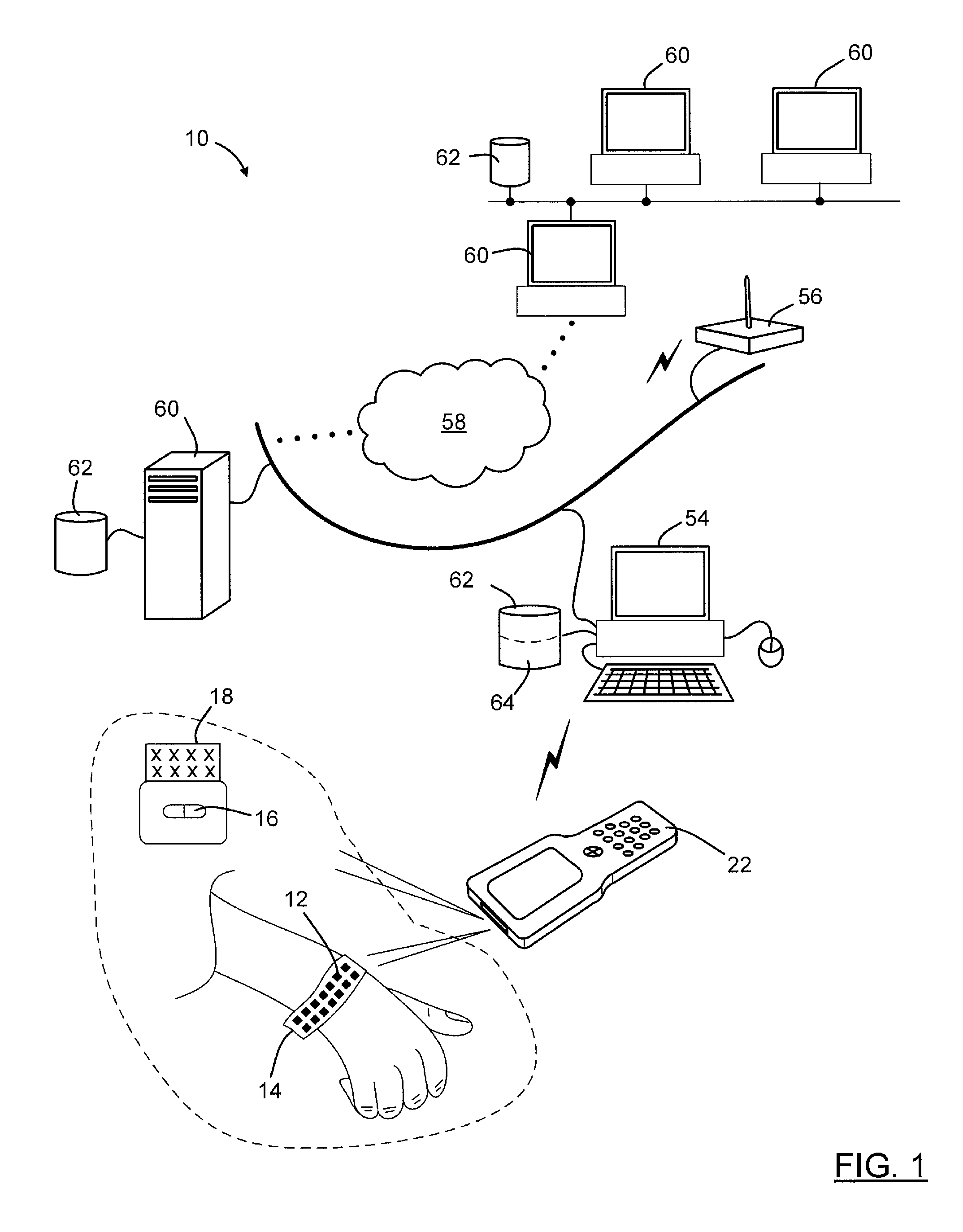
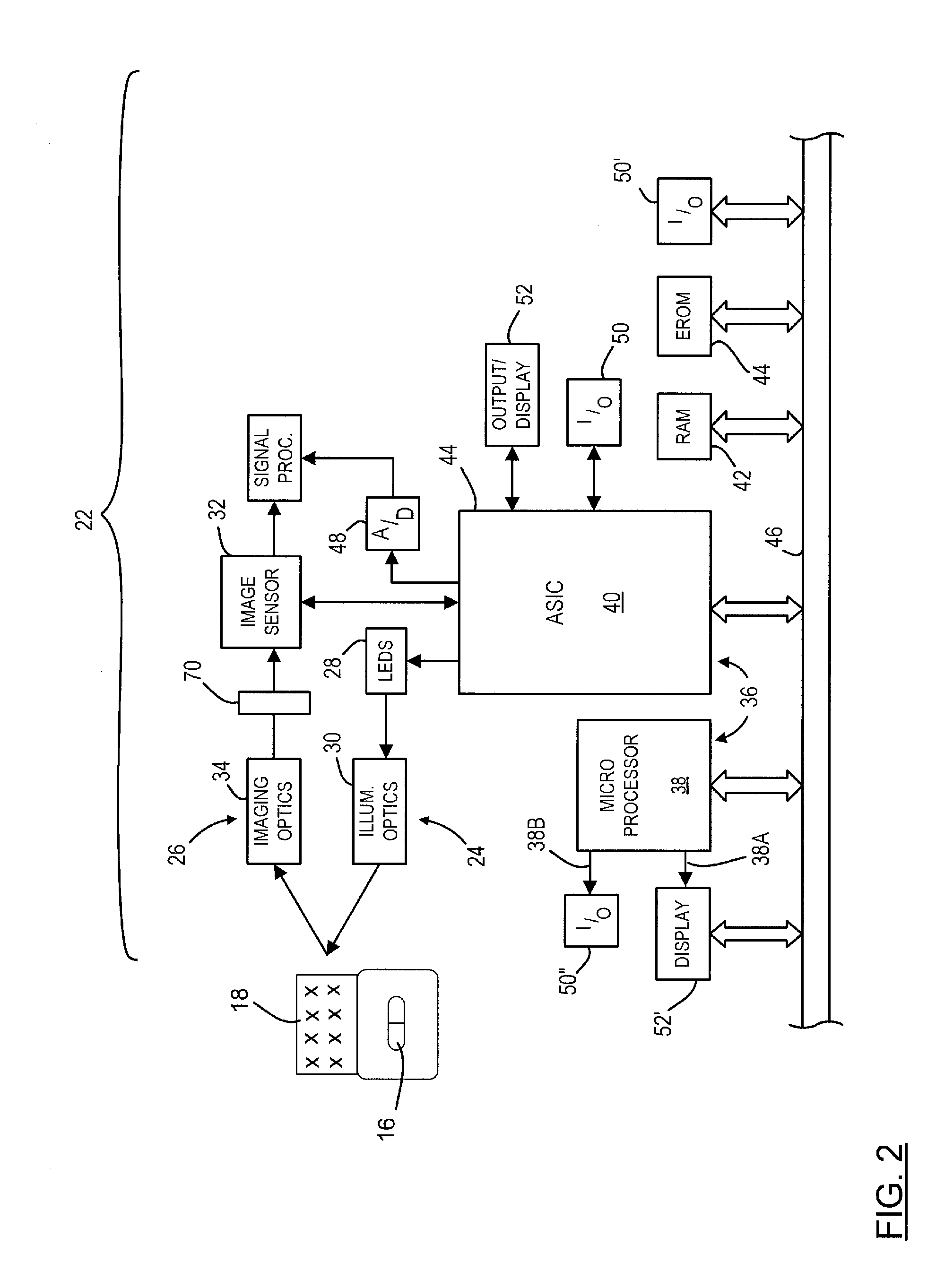
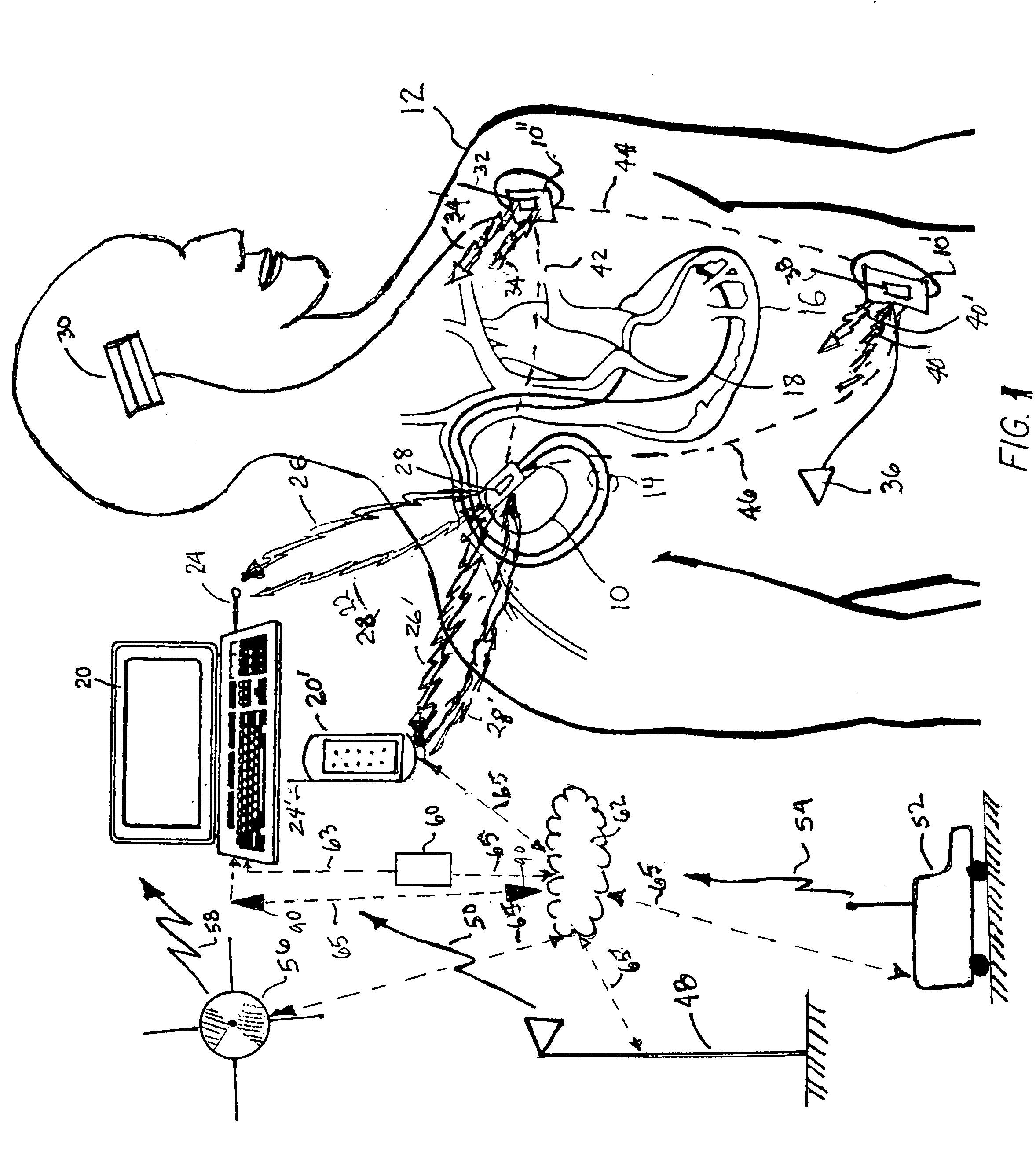
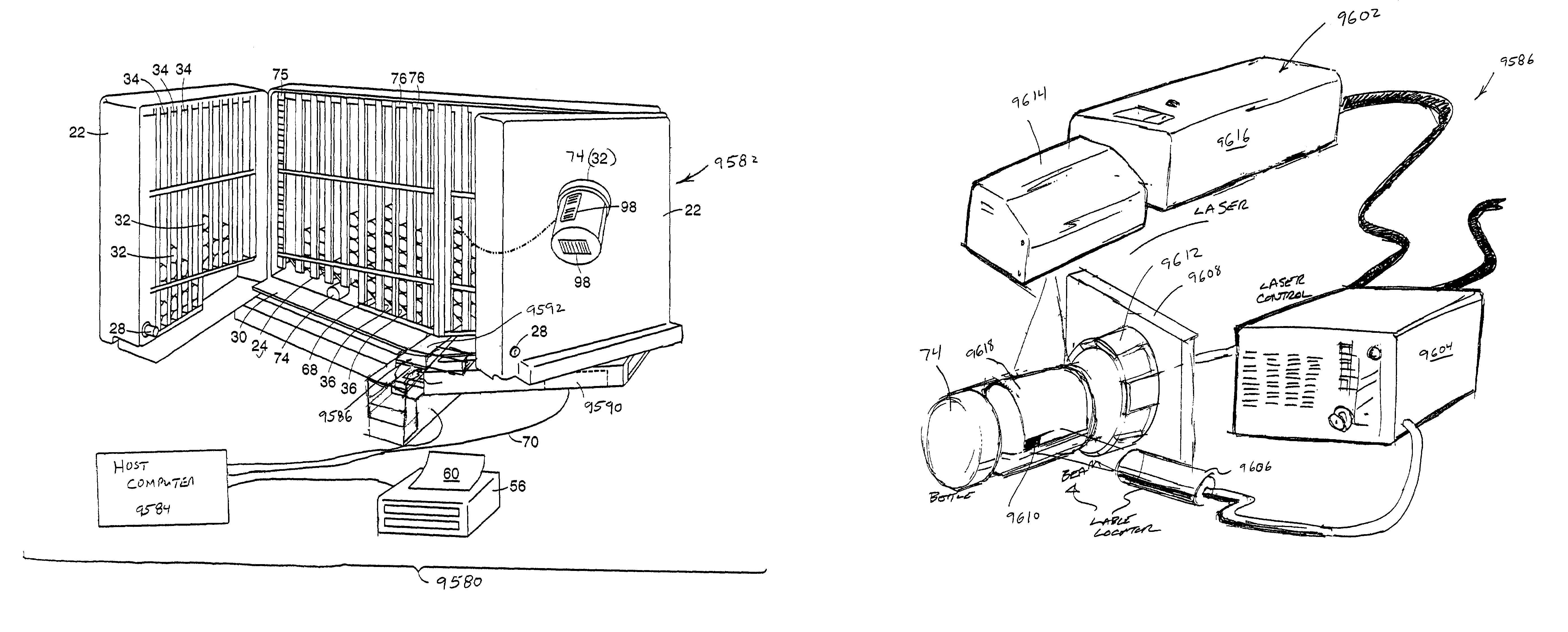
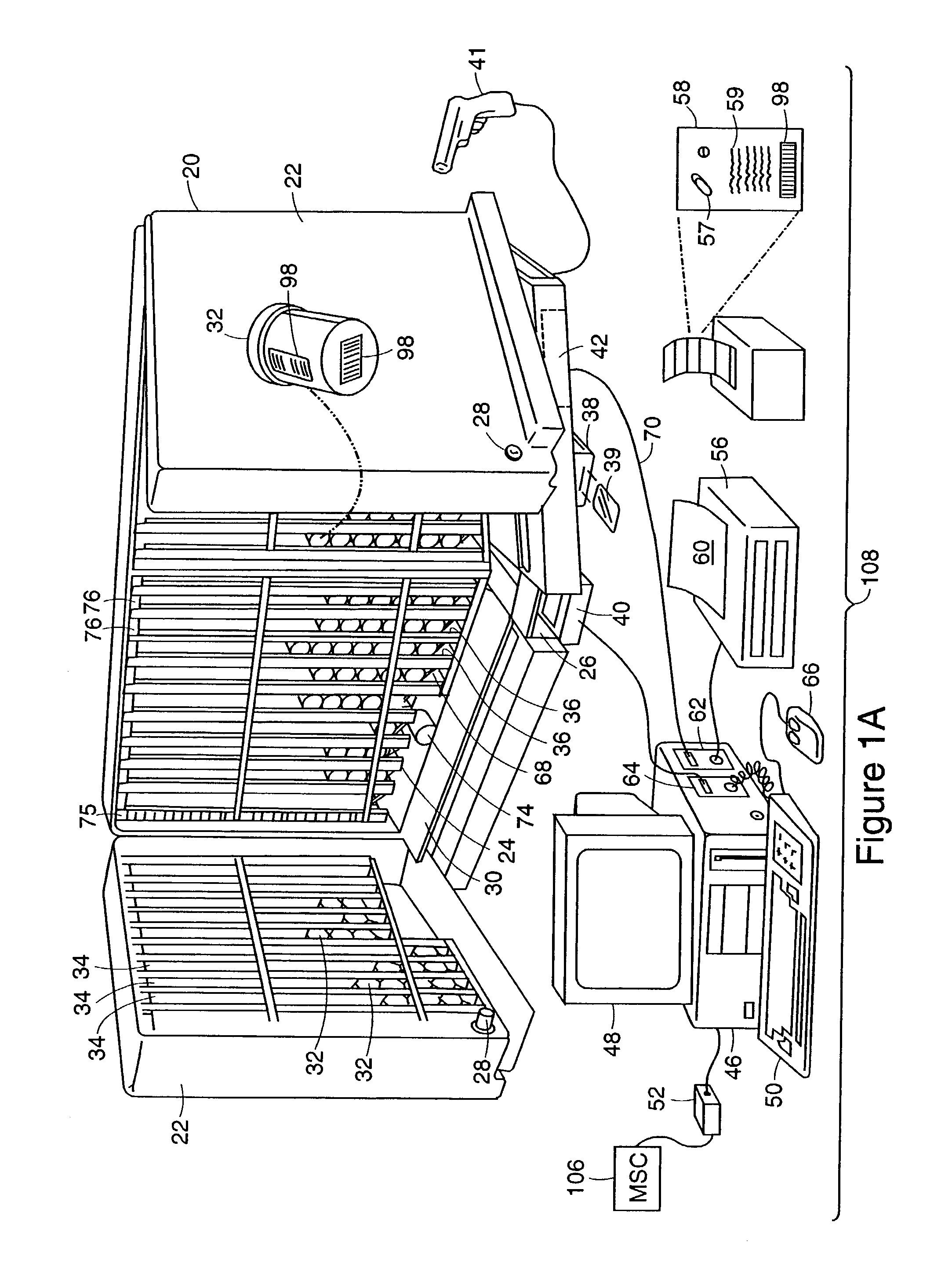
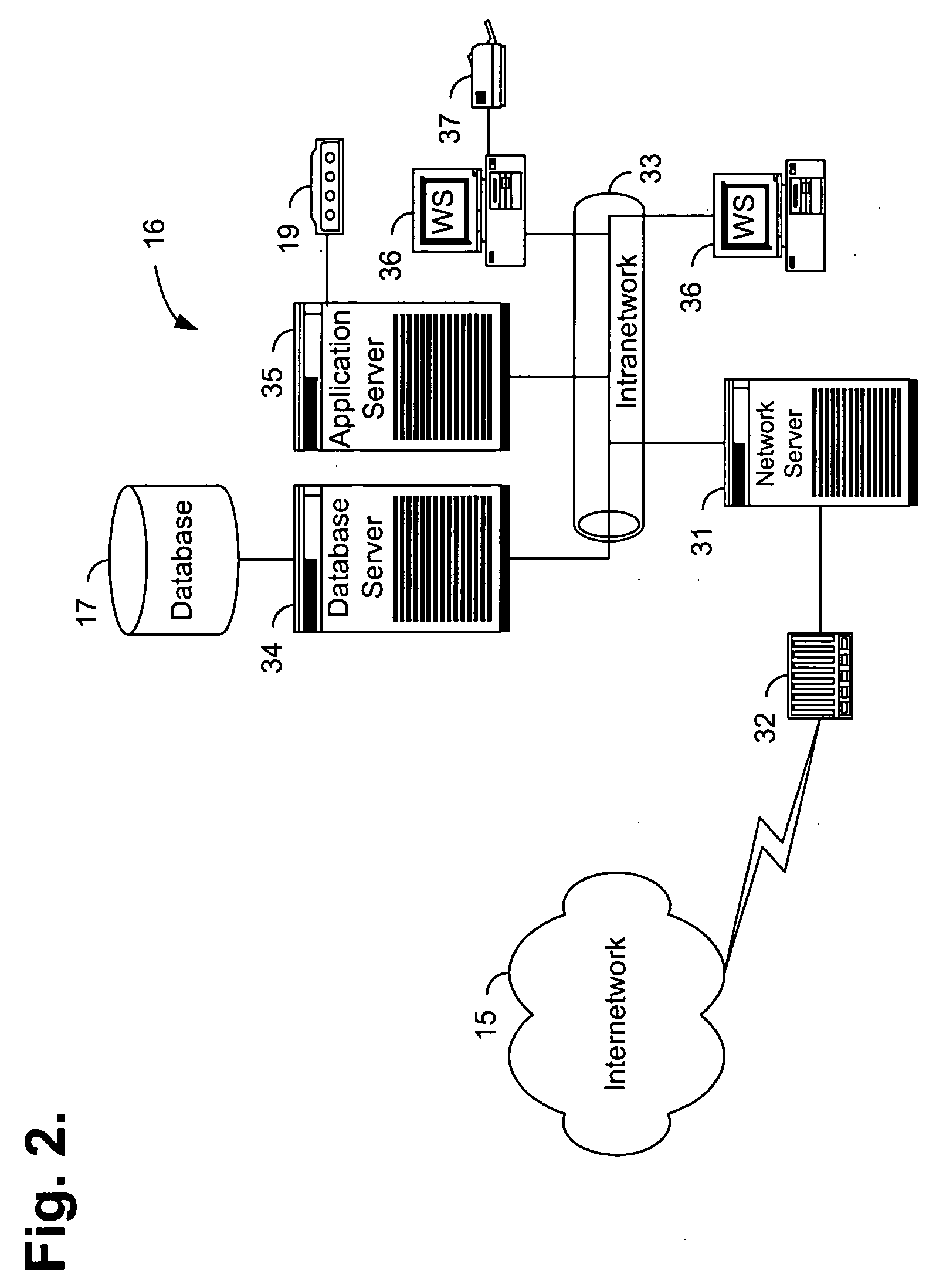
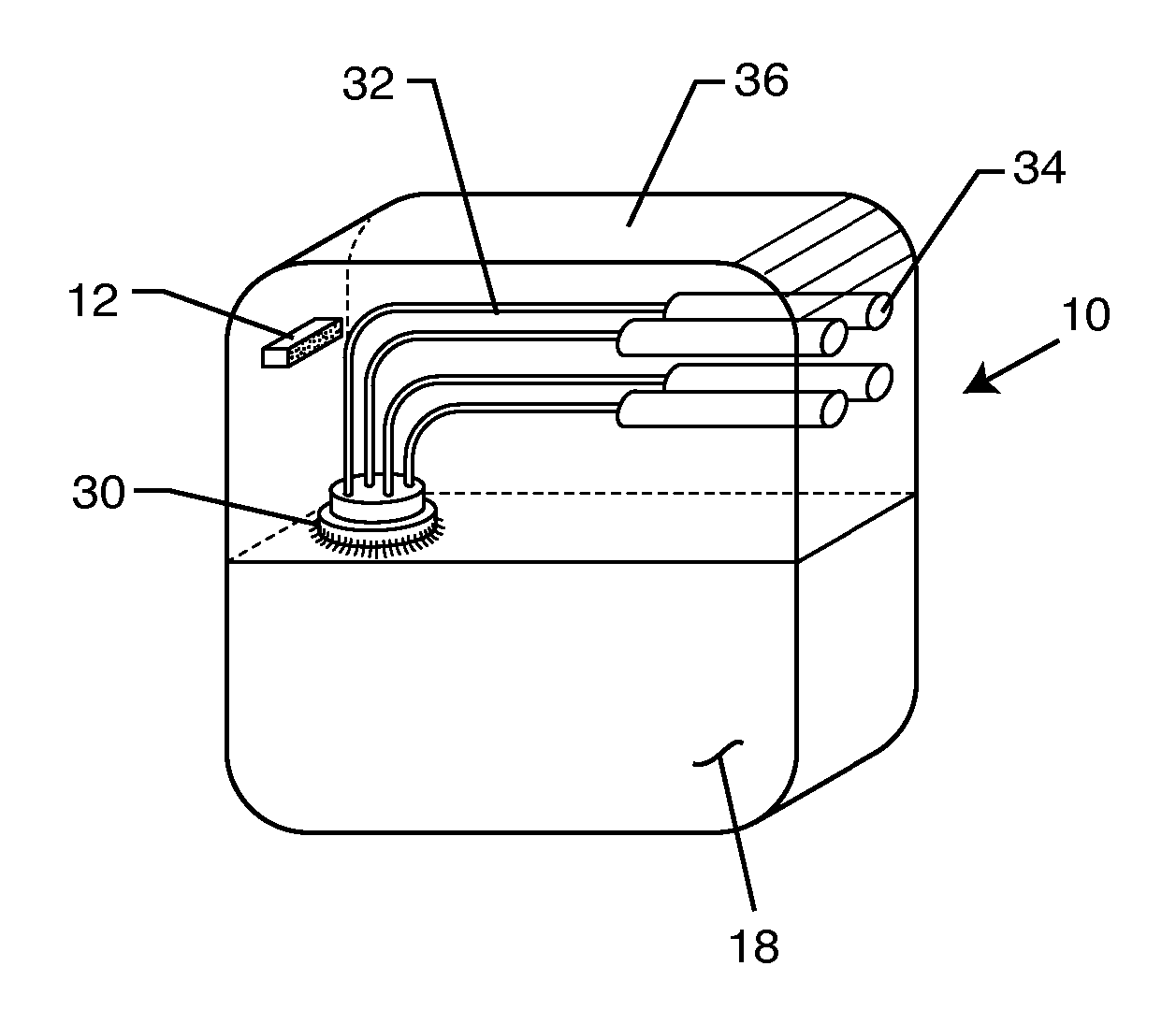
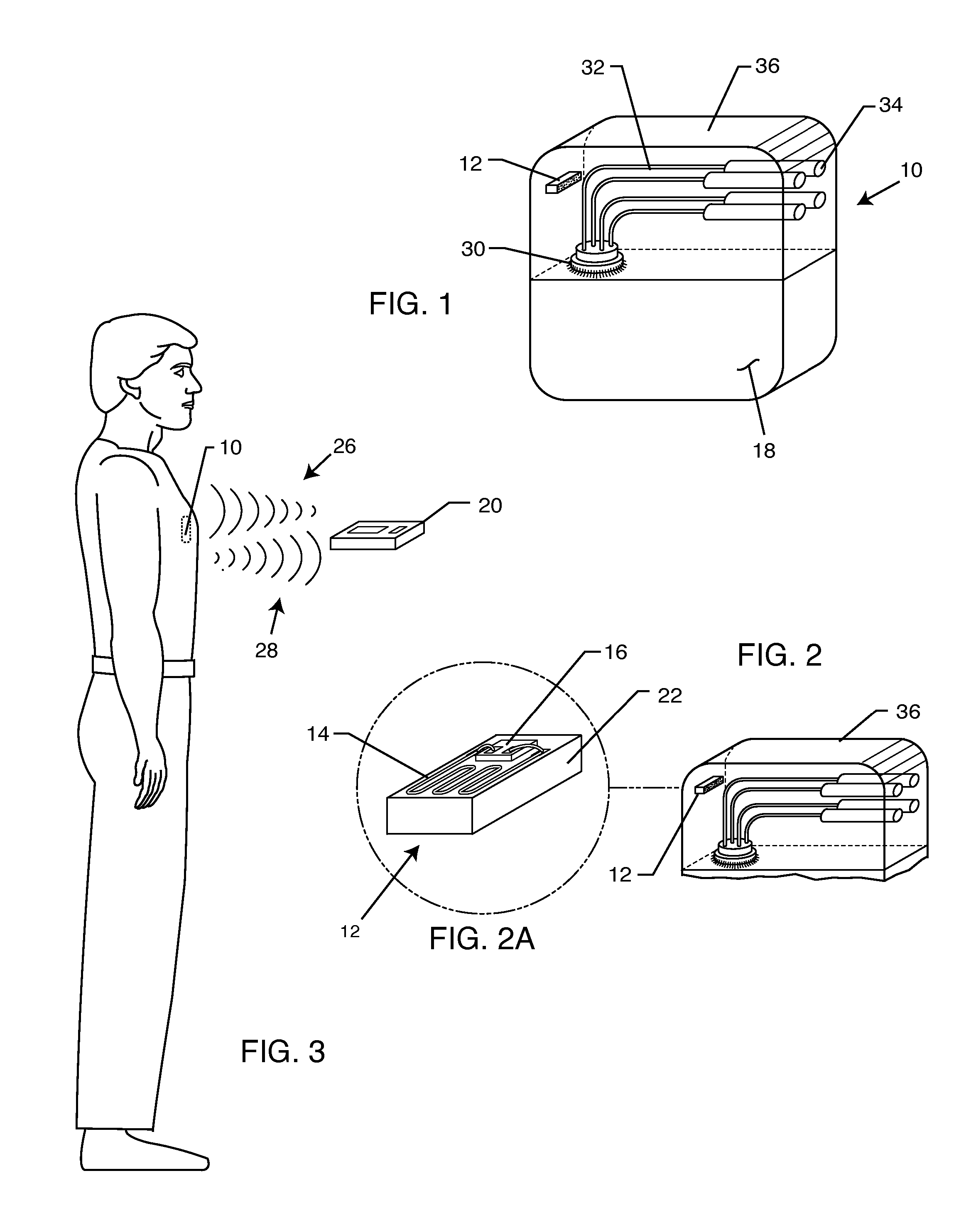
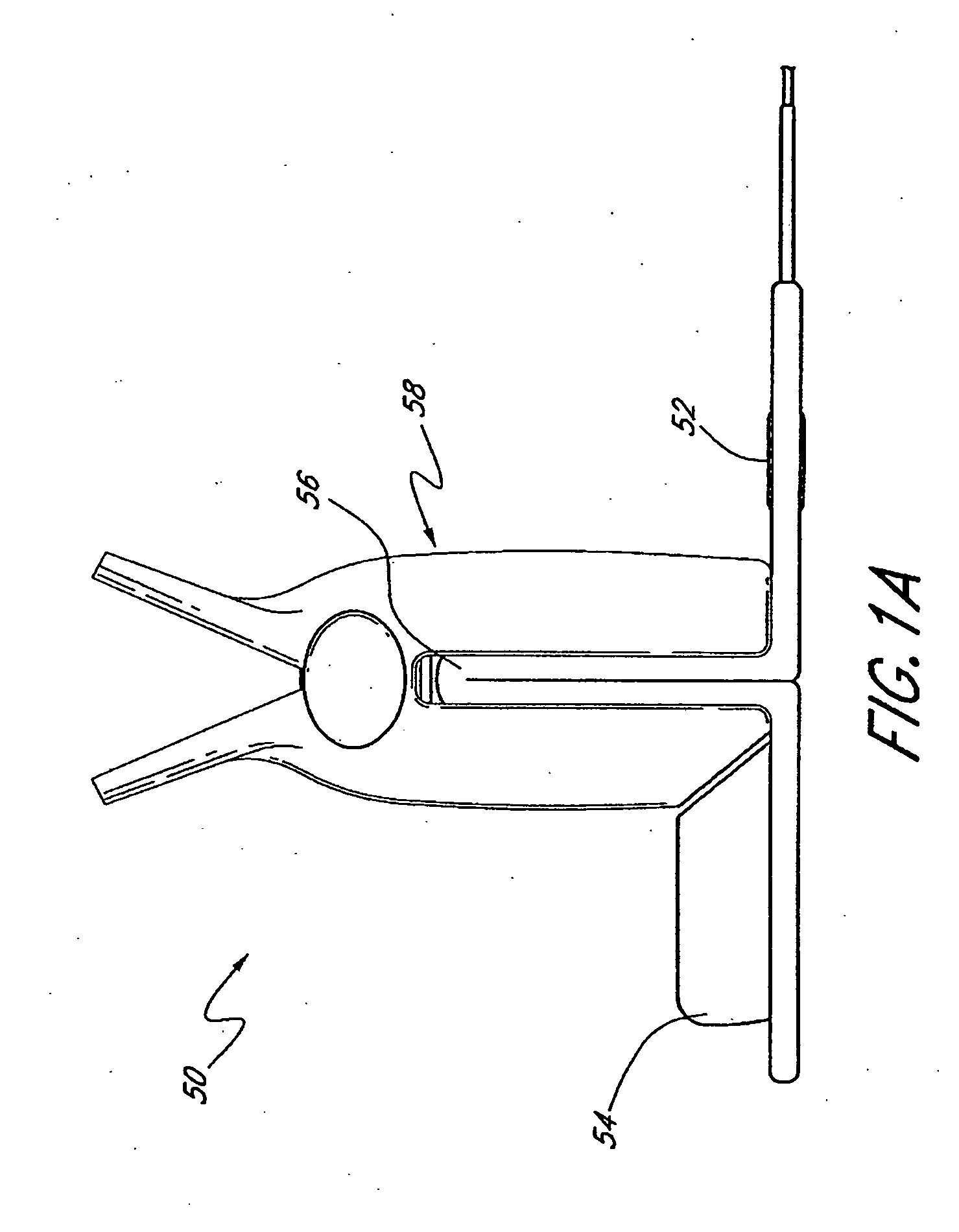
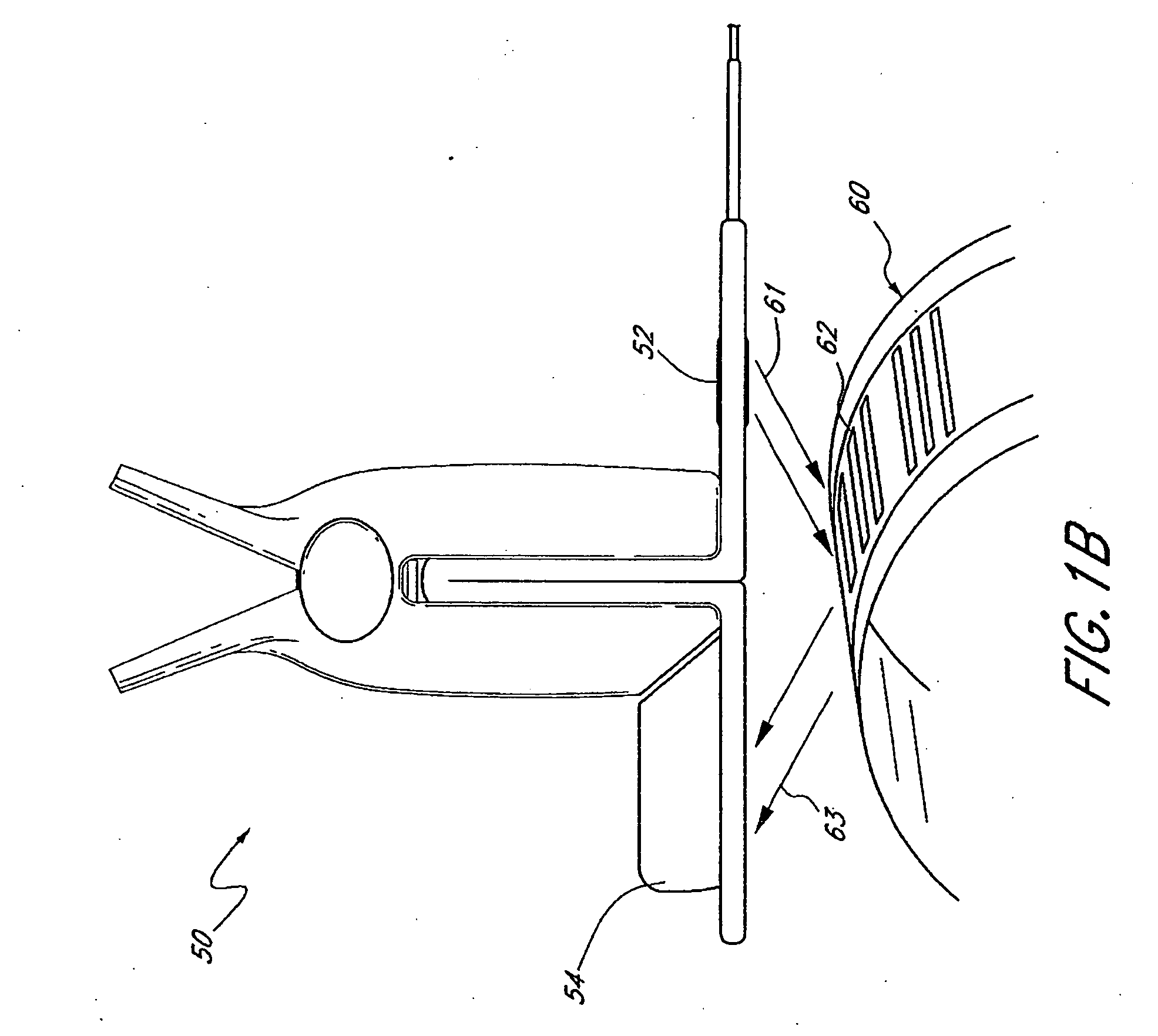
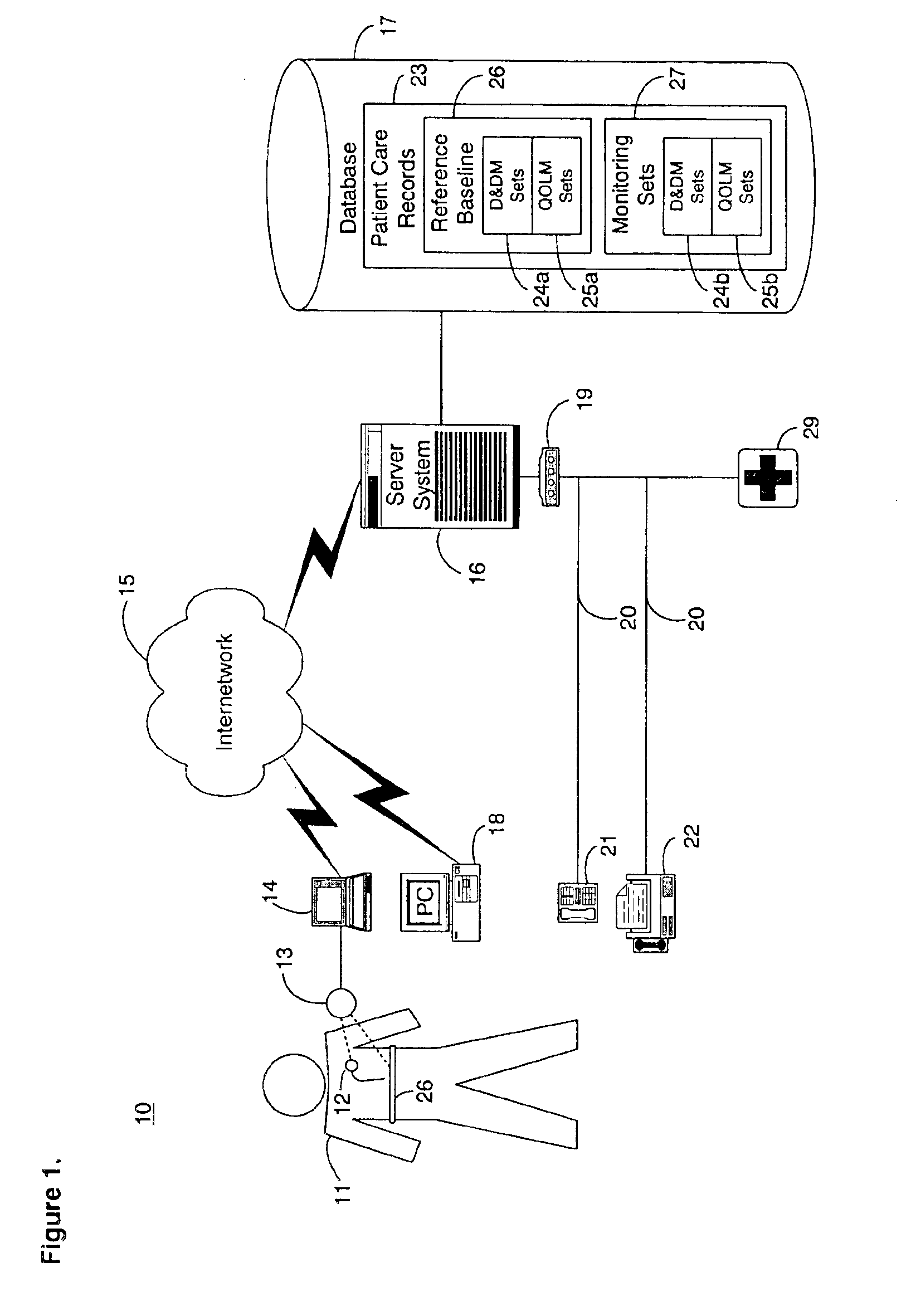
Optical imager and method for correlating a medication package with a patient
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
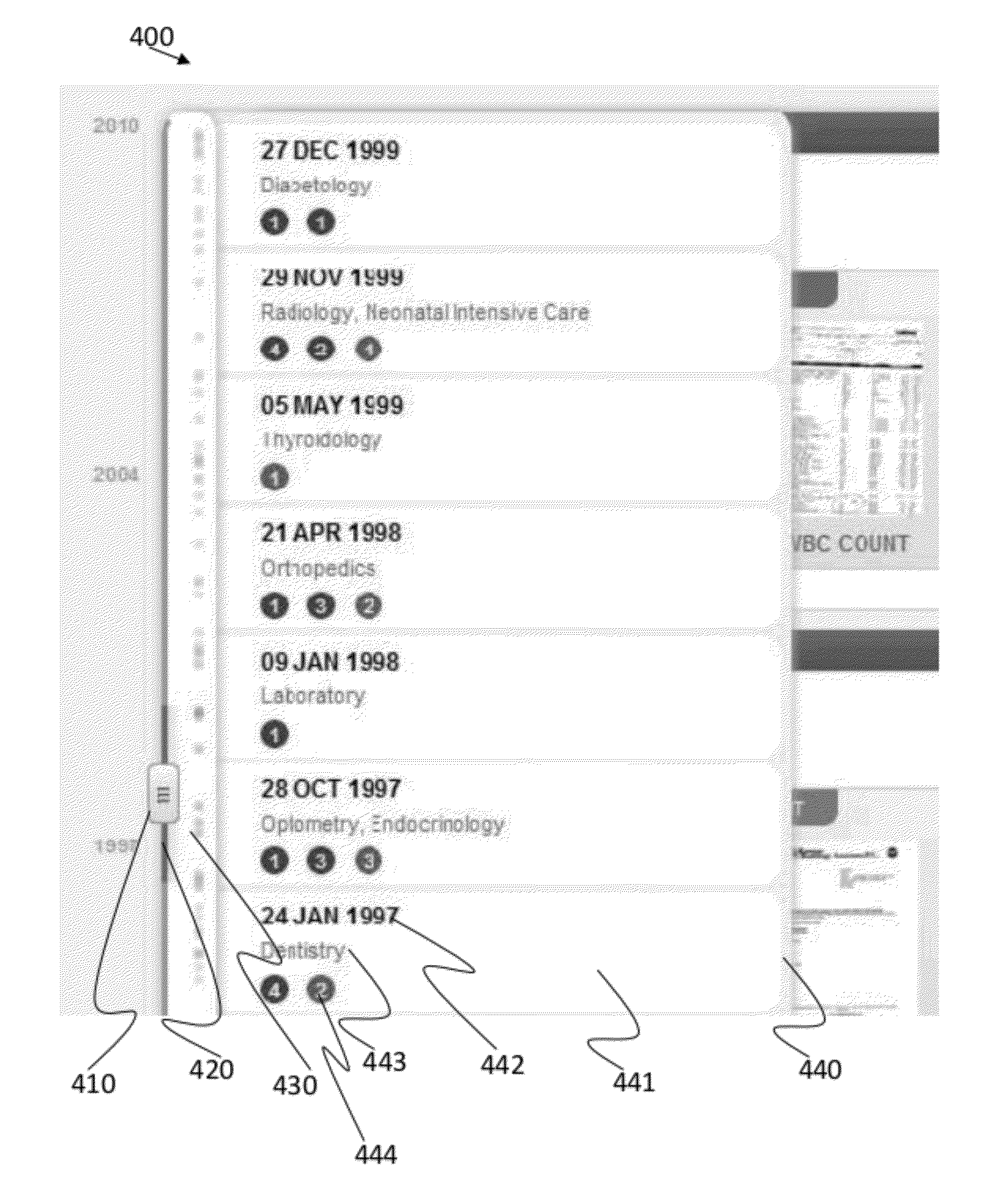
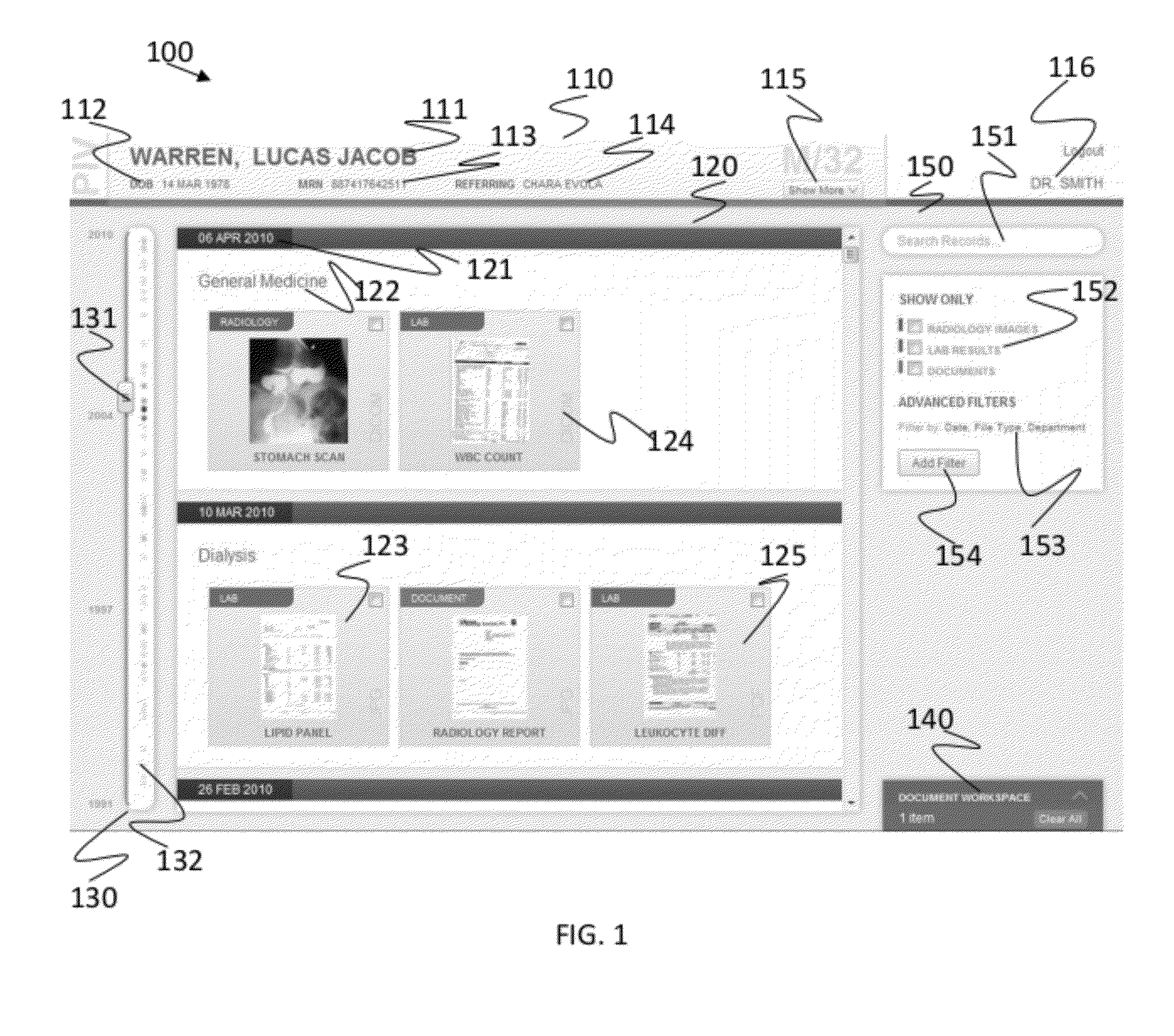
Patient information timeline viewer
InactiveUS20120131507A1Facilitate user navigationPatient personal data managementPatient-specific dataGraphicsEngineering
An example patient information viewer timeline includes a timeline arranged to provide a longitudinal visualization of a patient's record. The timeline provides visual indicators of clusters of patient encounters. The timeline expands to provide further detail on a patient encounter based on user input. The timeline includes a plurality of graphical indicators along the timeline, each graphical indicator corresponding to a patient encounter. The timeline includes a slider to facilitate user navigation along the timeline to view patient encounters. The timeline includes a scroll line associated with the slider to indicate a subset of patient encounters currently viewable in a detail view area of the timeline. The scroll line and associated detail view area are scalable based on available display real estate. The detail view area provides an expanded view of one or more encounters corresponding to a time period in the timeline encompassed by the scroll line.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
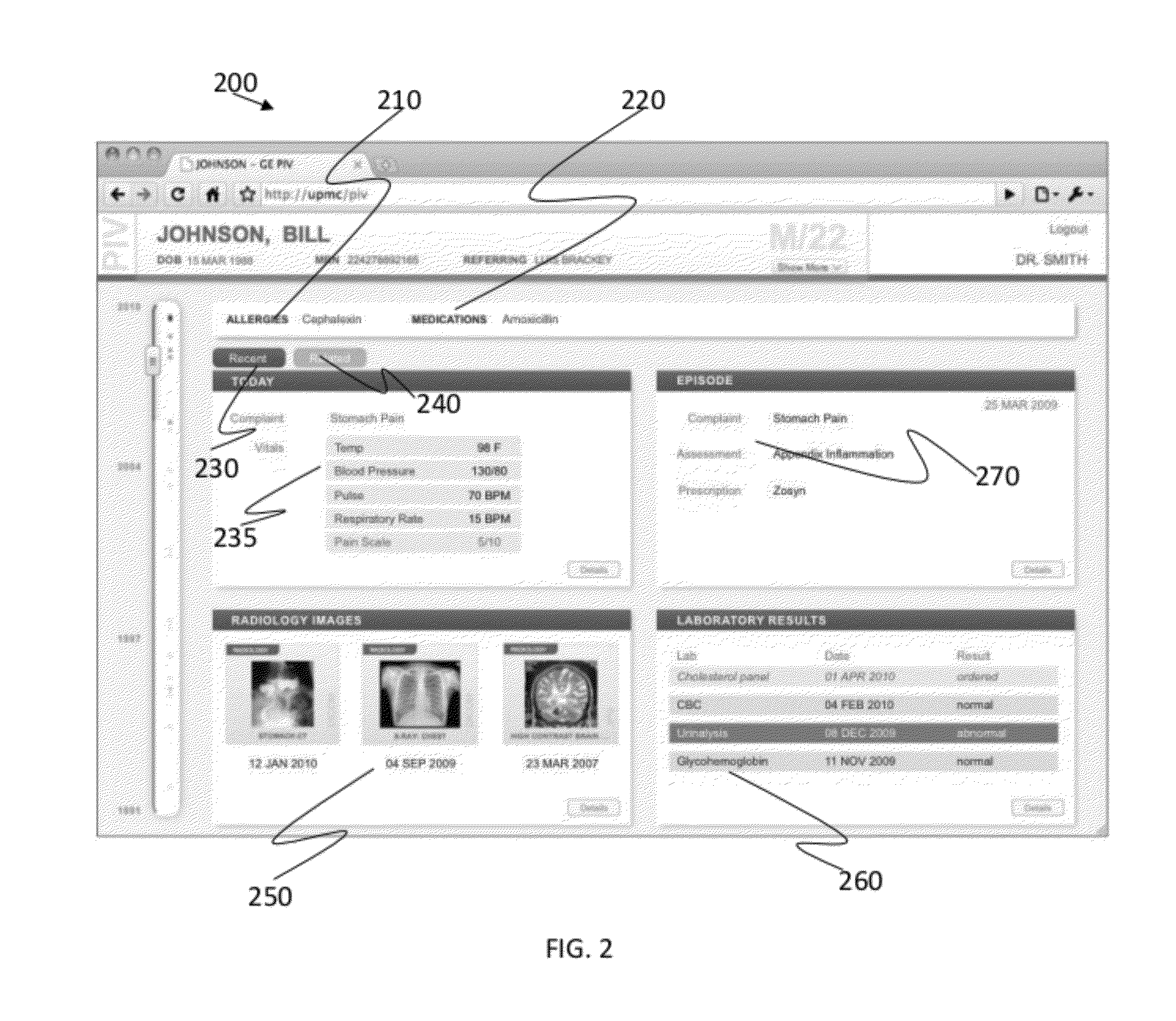
Handheld device graphical user interfaces for displaying patient medical records
ActiveUS7343565B2Improved patient careShorten the lengthInput/output for user-computer interactionLocal control/monitoringMedical recordGraphics
Ergonomic graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for displaying medical record information obtained from various sources within handheld devices are provided. A GUI for display within a touch screen display of a handheld device includes adjacent first and second portions. A list of patient names is displayed within the first portion of the GUI, along with medical facility location information, means for indicating when new clinical data for a patient is available, means for removing patient names from the displayed list, and means for sorting the displayed list of patient names. A plurality of ergonomically designed GUI controls are displayed within the second portion of the GUI. At least some of the displayed information is responsive to user touching for displaying additional patient information.
Owner:MERATIVE US LP
Medical information management system and patient interface appliance
A medical information management system and method that stores and manages patient information and that enables a patient and an authorized third party, such as a friend or family member, to access the patient's medical information. The presentation format, substance of the patient's medical information provided, or both are customized depending on whether the patient, a healthcare professional or the third party is accessing the patient's medical information. The present invention also pertains to a method of subsidizing such a medical information system by selling advertising space in the presentation shown to the third party, patient, or the healthcare professional. The present invention further pertains to a patient interface appliance that includes a display containing multiple viewing fields, one of which is a general information field and one of which is an advertising field, to present information and advertisements to a user during a patient interactive session. Patient participation in conducting the survey is fostered by offering a survey completion reward to the patient upon completing the survey.
Owner:SUN JIANGUO +6
Physician-centric health care delivery platform
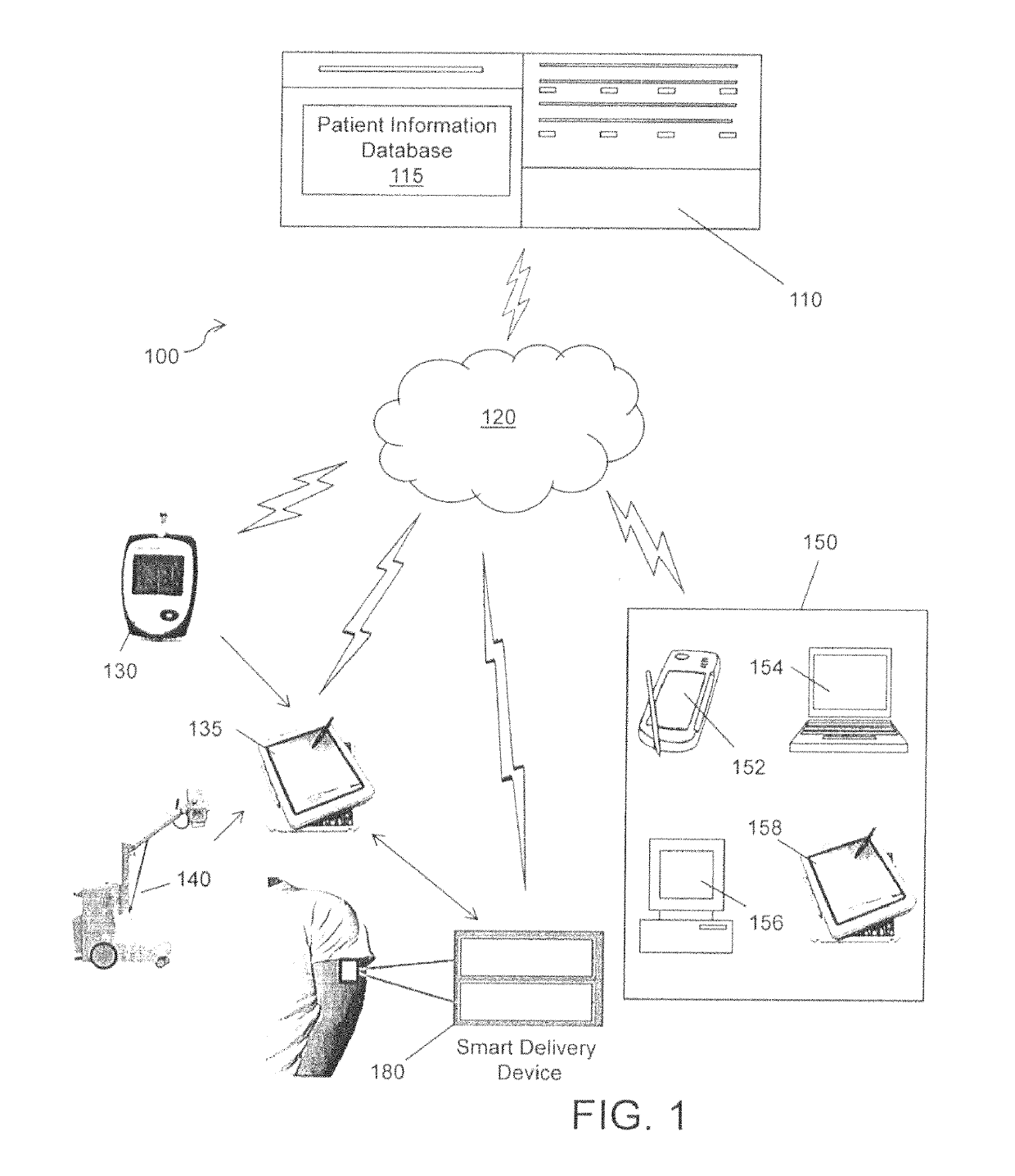
A system for diagnosing and / or treating a patient comprising a patient information database for storing and retrieving patient health data related to the patient. The data includes one or more of real-time patient health information, at least one clinical practice guideline, at least one patient questionnaire and a patient medical history. At least one server is operative to access the patient information database. A computing device remotely located from the server, including a microprocessor, configured to store a computer application and is configured for communication with the server for retrieving of the patient health data. The computer application generates at least one of a patient diagnosis or a patient treatment recommendation using the retrieved patient health data.
Owner:MD24 PATENT TECH LLC
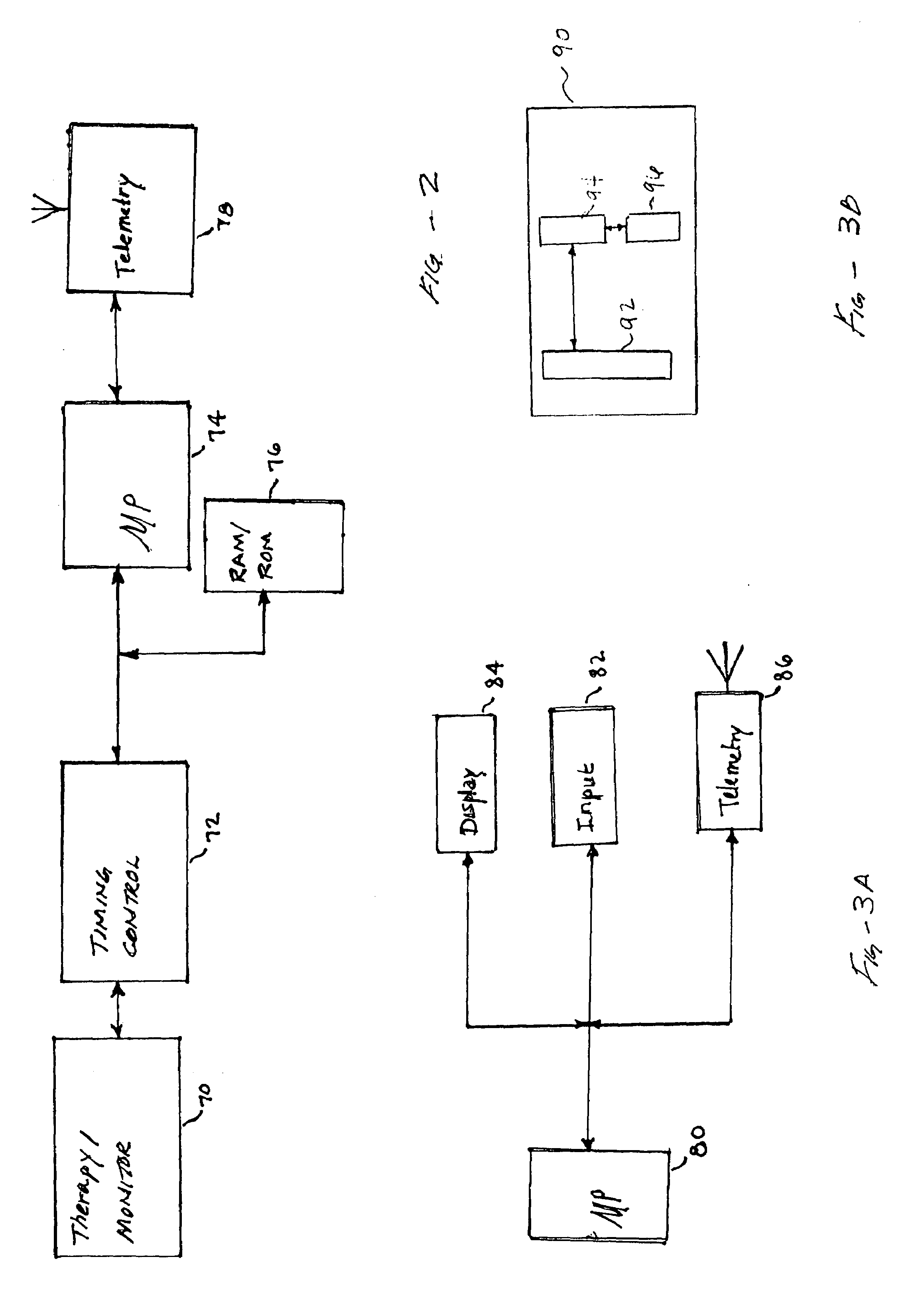
Method and apparatus to secure data transfer from medical device systems
InactiveUS7039810B1Key distribution for secure communicationElectrotherapyCommunications systemData center
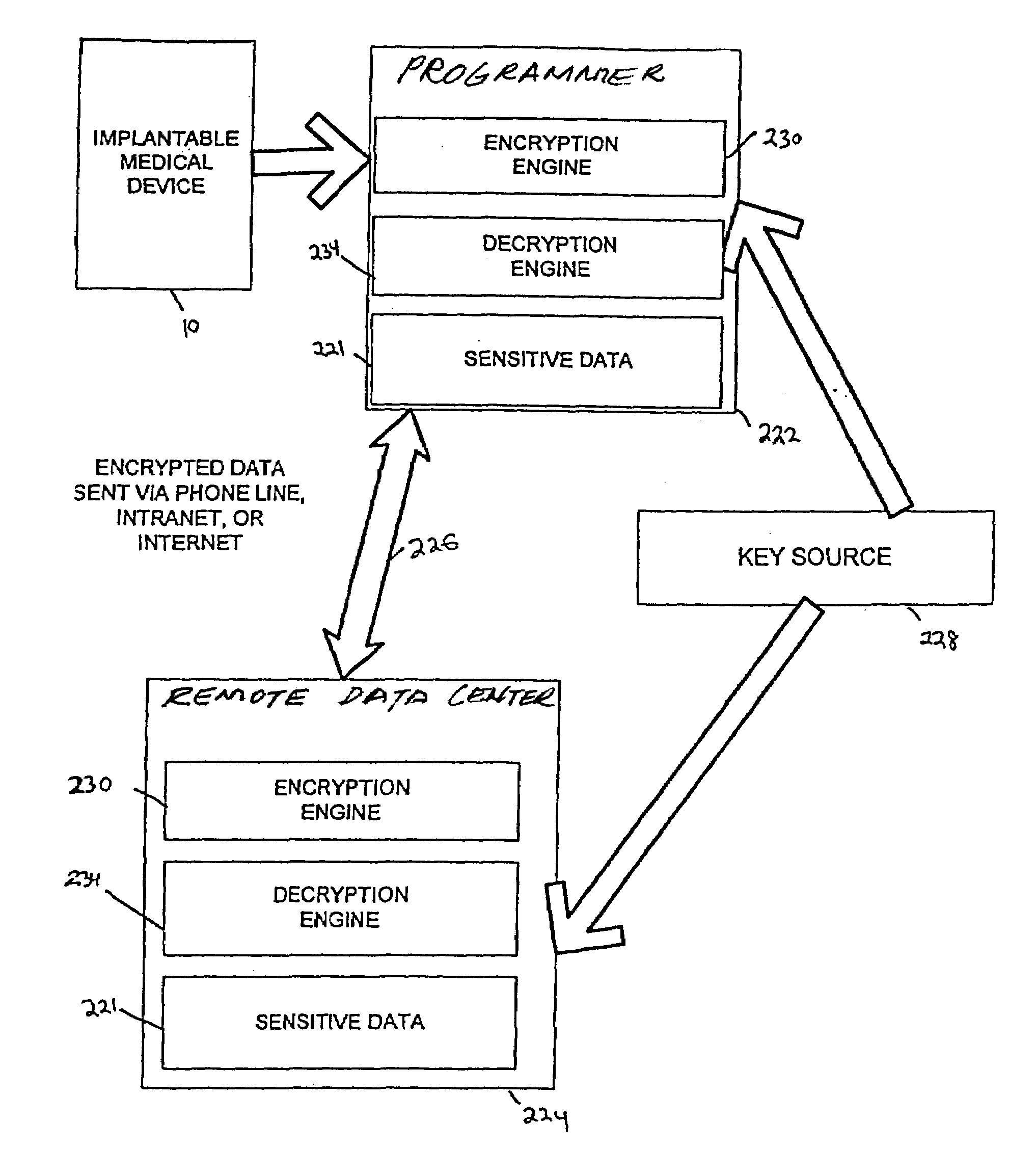
Sensitive data such as patient records are securely transferred between a programmer and a data encryption. A database residing on the programmer contains patient information obtained by at least one implantable medical device. A key source provides the programmer with a first key and the remote expert data center with a second key to be used in the encryption / decryption process. An encryption engine residing within the programmer encrypts the sensitive patient information contained within the database, using the first key. The programmer transmits the encrypted patient information to the remote expert data center via a data communications system such as a public network. A decryption engine residing within the remote expert data center decrypts the encrypted sensitive patient information using the second key.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
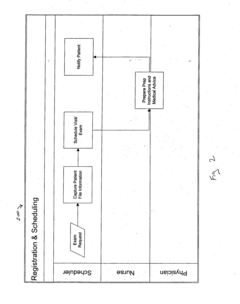
System and method for managing an endoscopic lab
A system designed to support and manage the workflow for all user roles pertaining to an endoscopic laboratory, from registration and scheduling of patient information through pre-procedure, procedure and post-procedure phases of an endoscopic examination, including support for the entry, by various users associated with an endoscopic laboratory, of information and data including the processing and storage of endoscopic images captured during an endoscopic exam of a patient, for association with a patient record stored in a database, and including the entry of procedure notes and generation of reports that include the stored images, all via an integrated user interface.
Owner:OLYMPUS AMERICA +1
Systems for dispensing medical products
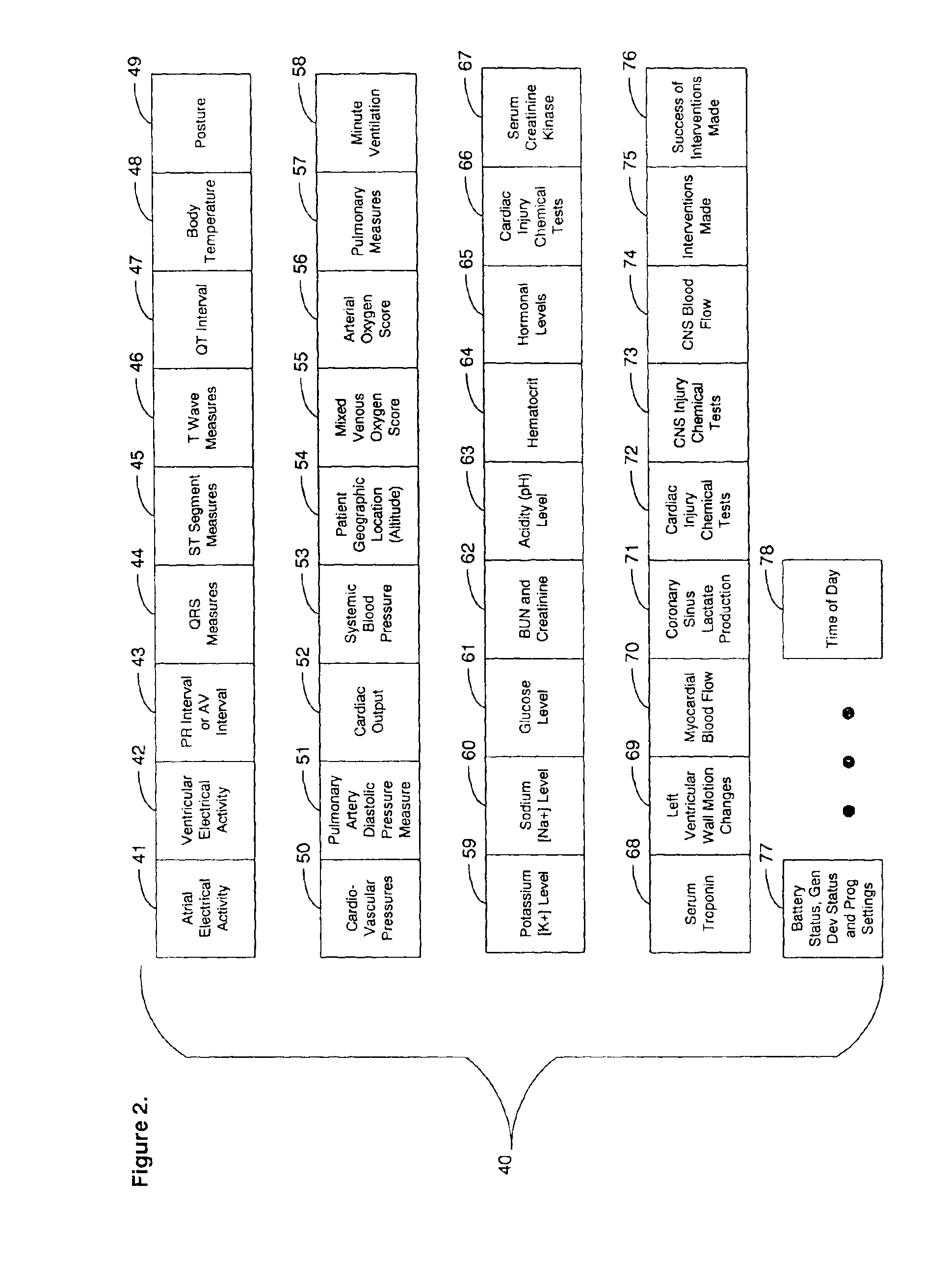
InactiveUS7006893B2Safe and convenientPreserving confidentialityControlling coin-freed apparatusDrug and medicationsCommunications systemMedical product
Owner:ARXIUM INC
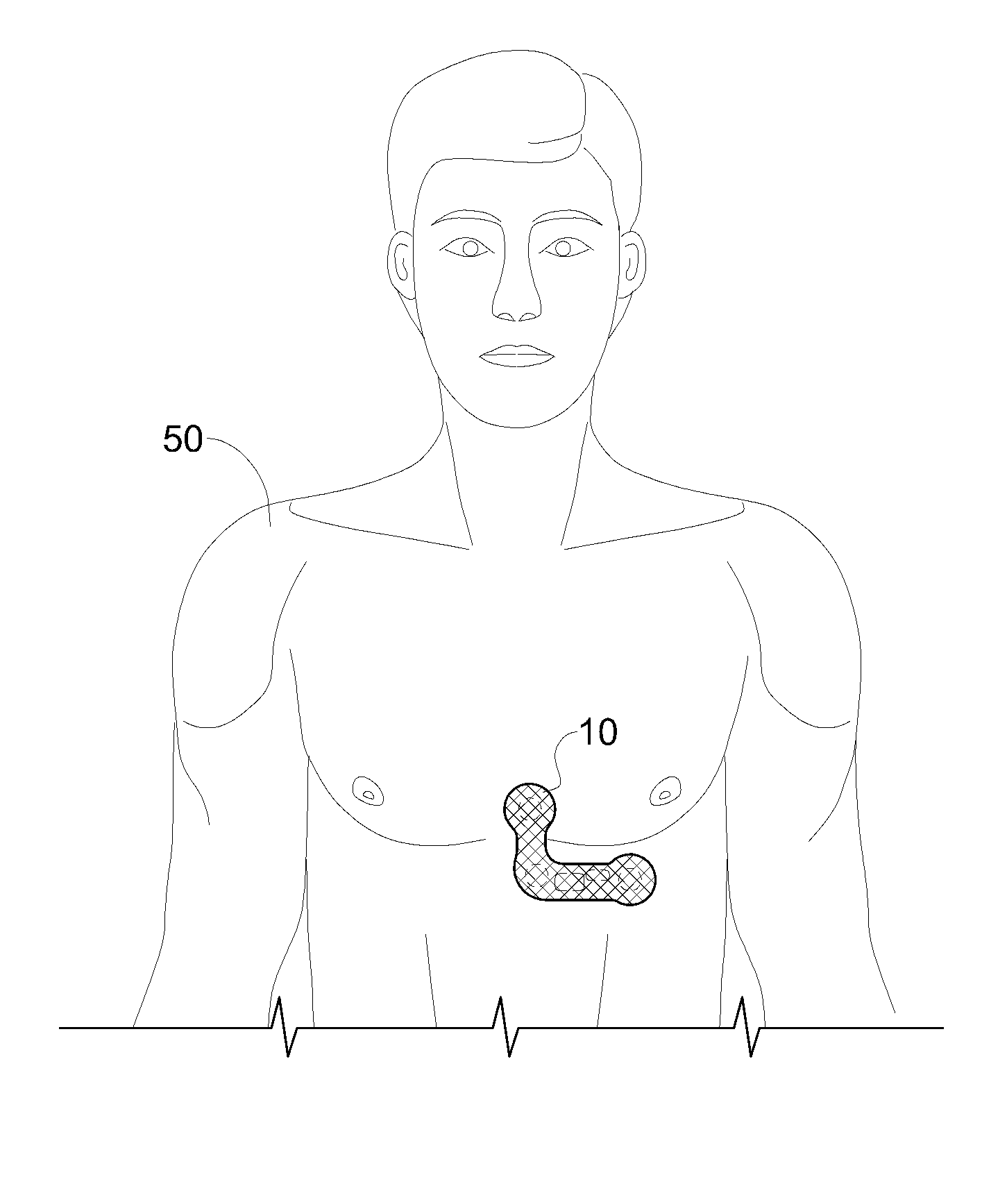
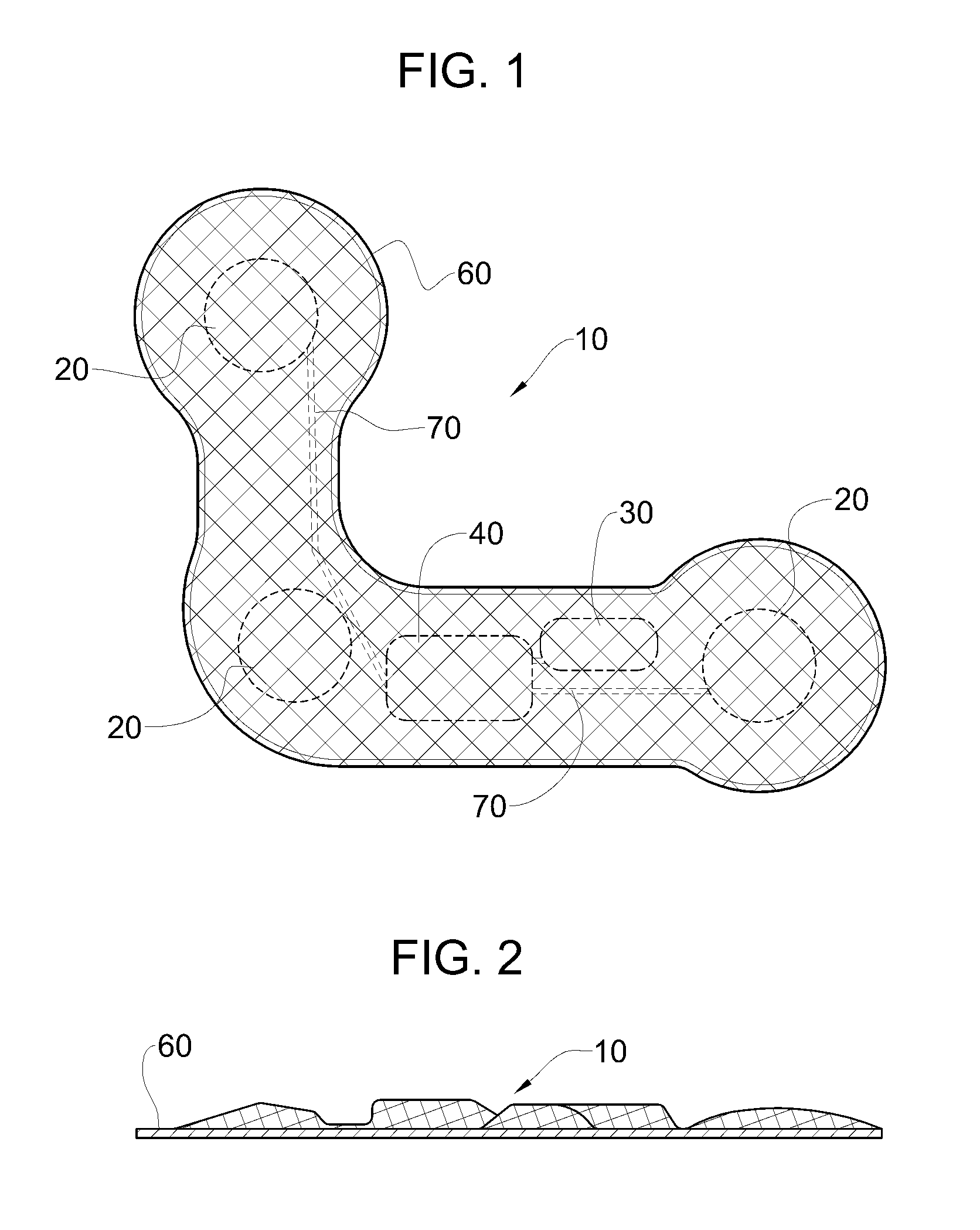
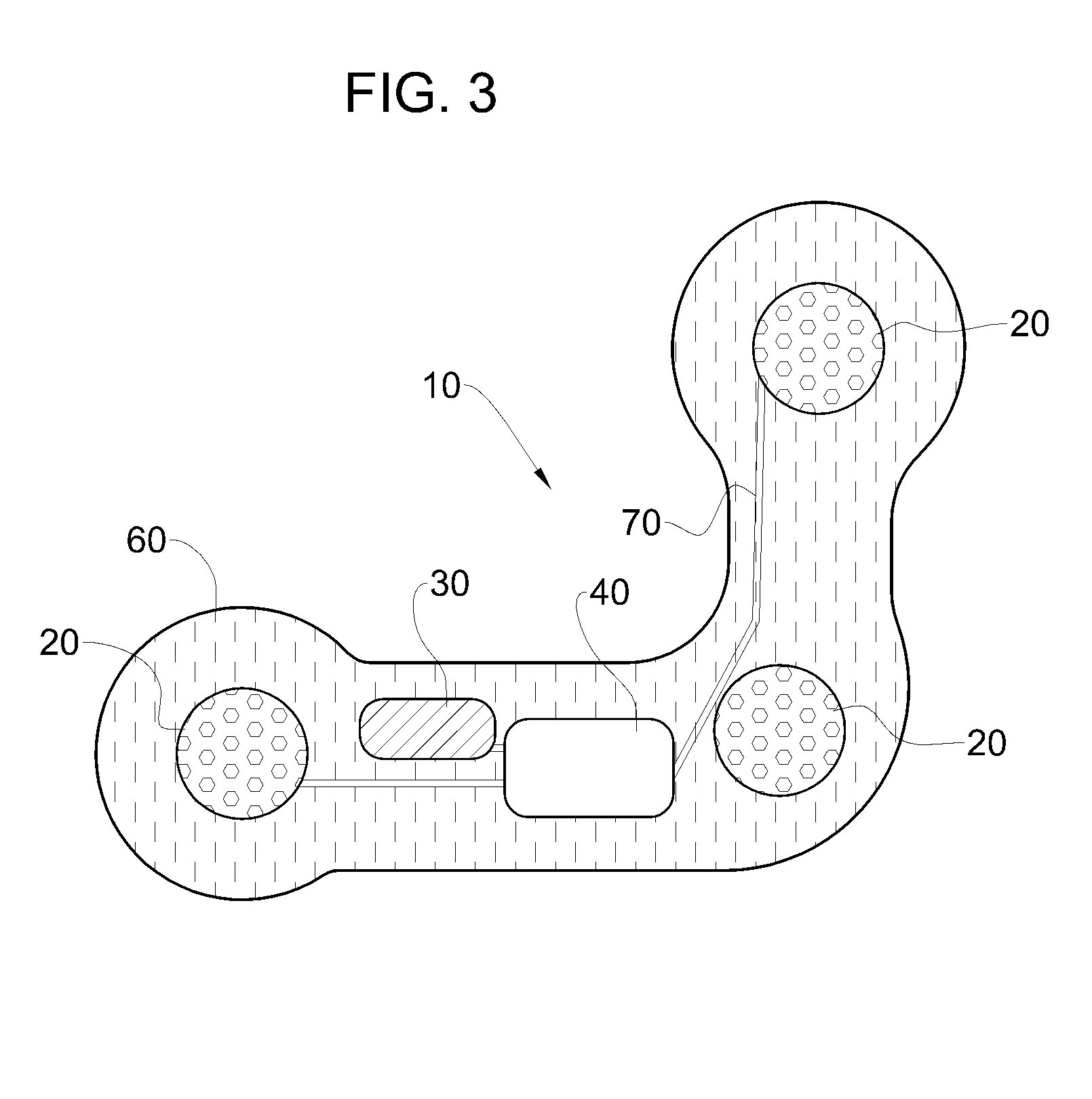
Heart monitoring body patch and system
InactiveUS20090062670A1Good adhesionEasily attached to patientElectrocardiographySensorsTransceiverHeart monitoring
Provided is a diagnostic patch system for monitoring and storing patient information, which includes sensors, a data storage unit, and a transceiver. Each of the sensors is attached to a skin to detect a patient data. The data storage unit is configured to store stream of the detected patient data from the plurality of sensors. The transceiver, connected with the sensors and the data storage unit, communicates the stream of the patient data with an analyzer, and the analyzer is configured to process and analyze the stream of the patient data. Two or more diagnostic patch systems can communicate with each other.
Owner:BIOSEVEN
System and method for collection and analysis of patient information for automated remote patient care
InactiveUS7134996B2Easy to gatherEasy to storePhysical therapies and activitiesElectrotherapyDatabase serverPatient status
A system for collection and analysis of patient information for automated remote patient care is presented. A medical device adapted to be implanted for an individual patient regularly records and stores measures sets containing individual measures which each relate to patient information. A database collects one or more patient care records organized to include a plurality of the collected measures sets, and stores the collected measures set into a patient care record for the individual patient within a database. A server periodically receives a set of the collected measures from the medical device adapted to be implanted, and analyzes one or more of the collected measures sets in the patient care record for the individual patient relative to one or more other collected measures sets stored in the database server to determine a patient status indicator.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and method for transacting an automated patient communications session
InactiveUS20050171411A1Facilitates gathering and storage and analysisBurden to of minimizedMedical communicationData processing applicationsSpoken languagePatient characteristics
A system and method for transacting an automated patient communications session is described. A patent health condition is monitored by regularly collecting physiological measures through an implantable medical device. A patient communications session is activated through a patient communications interface, including an implantable microphone and an implantable speaker in response to a patient-provided activation code. An identification of the patient is authenticated based on pre-defined uniquely identifying patient characteristics. Spoken patient information is received through the implantable microphone and verbal system information is played through the implantable speaker. The patient communications session is terminated by closing the patient communications interface. The physiological measures and the spoken patient information are sent.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
RFID detection and identification system for implantable medical lead systems
A system for identifying active implantable medical devices (AIMD) and lead systems implanted in a patient using a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag having retrievable information relating to the AIMD, lead system and / or patient. The RFID tag may store information about the AIMD manufacturer, model number, serial number; lead wire system placement information and manufacturer information; MRI compatibility due to the incorporation of bandstop filters; patient information, and physician and / or hospital information and other relevant information. The RFID tag may be affixed or disposed within the AIMD or lead wires of the lead system, or surgically implanted within a patient adjacent to the AIMD or lead wire system.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
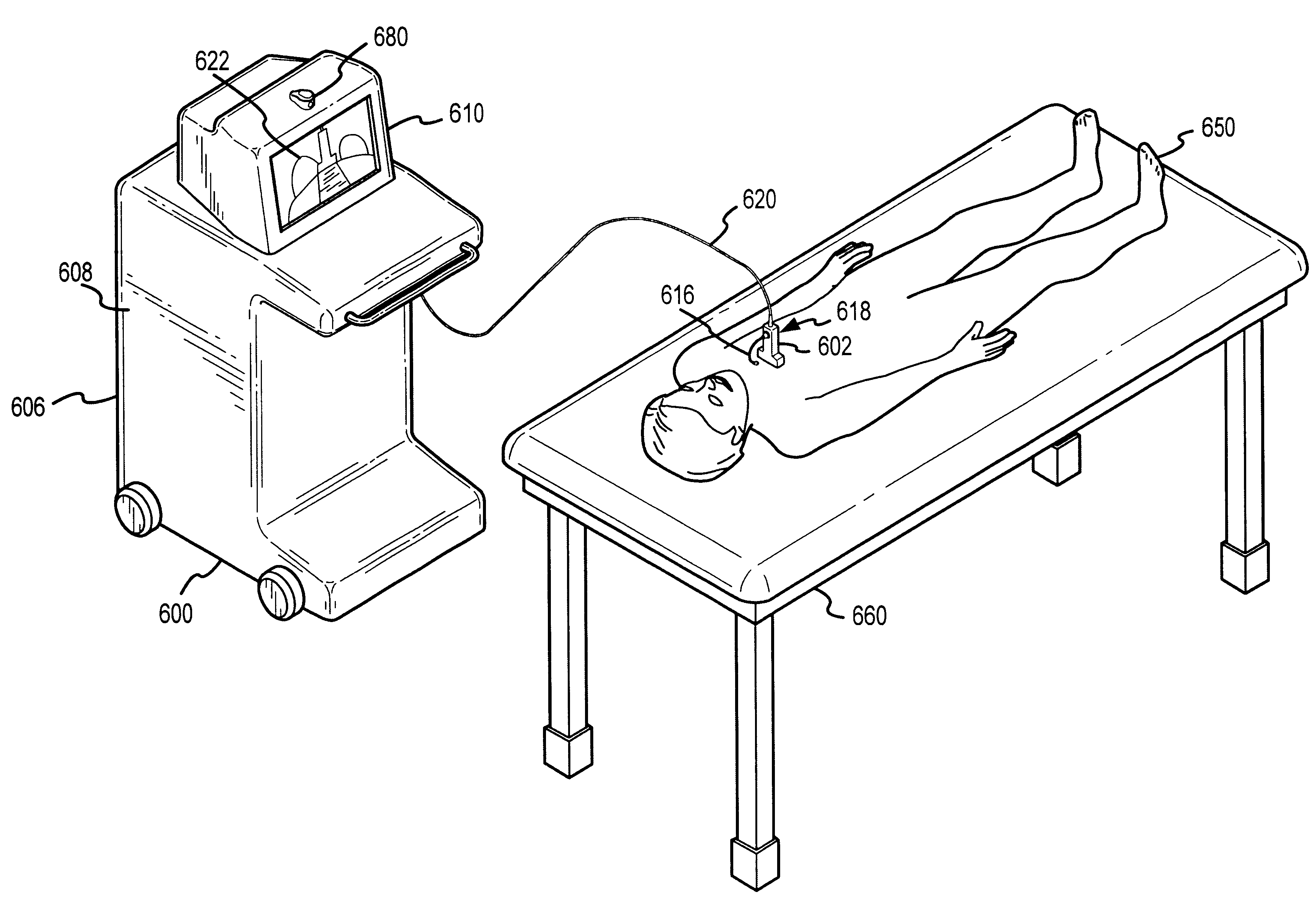
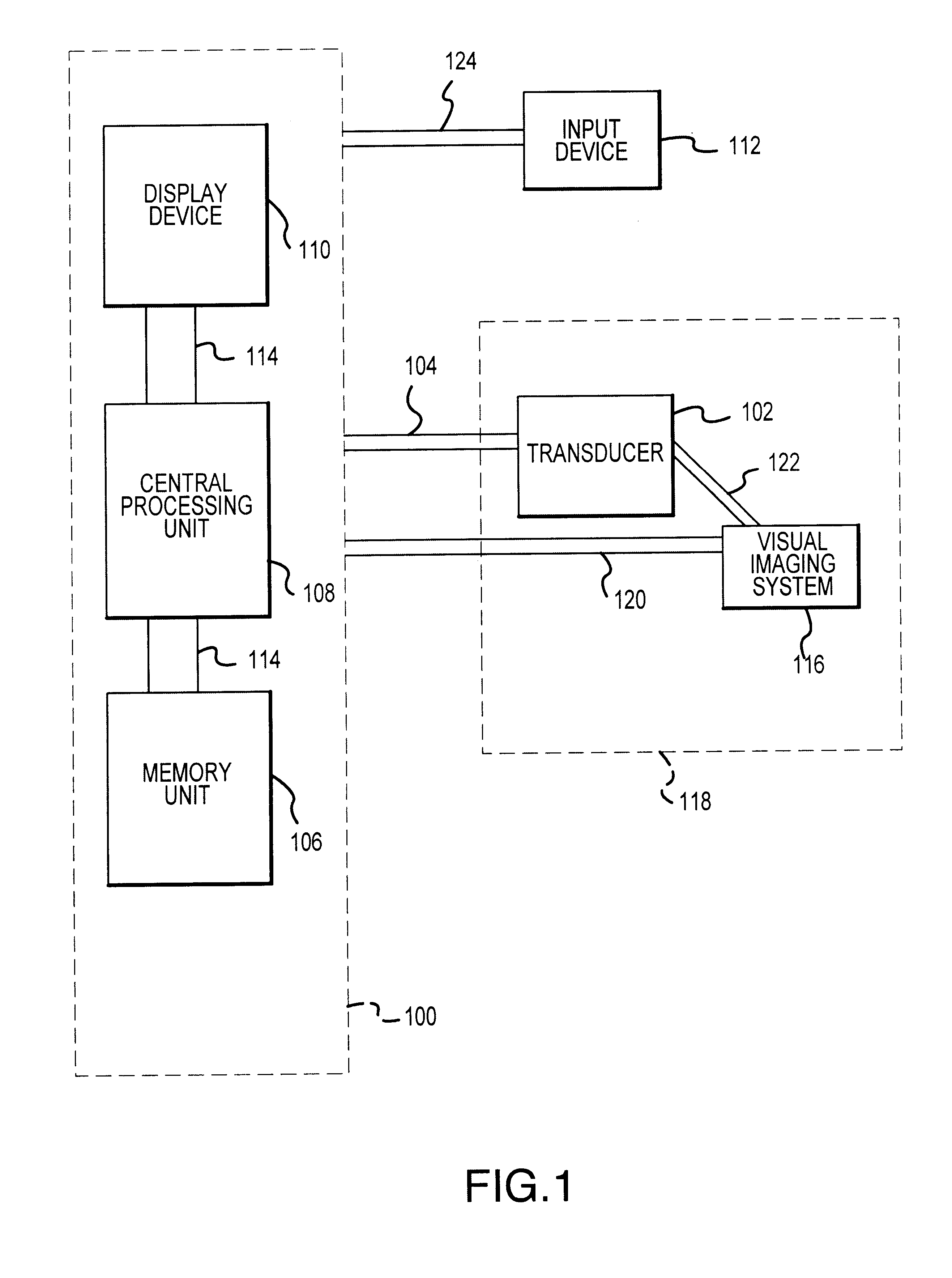
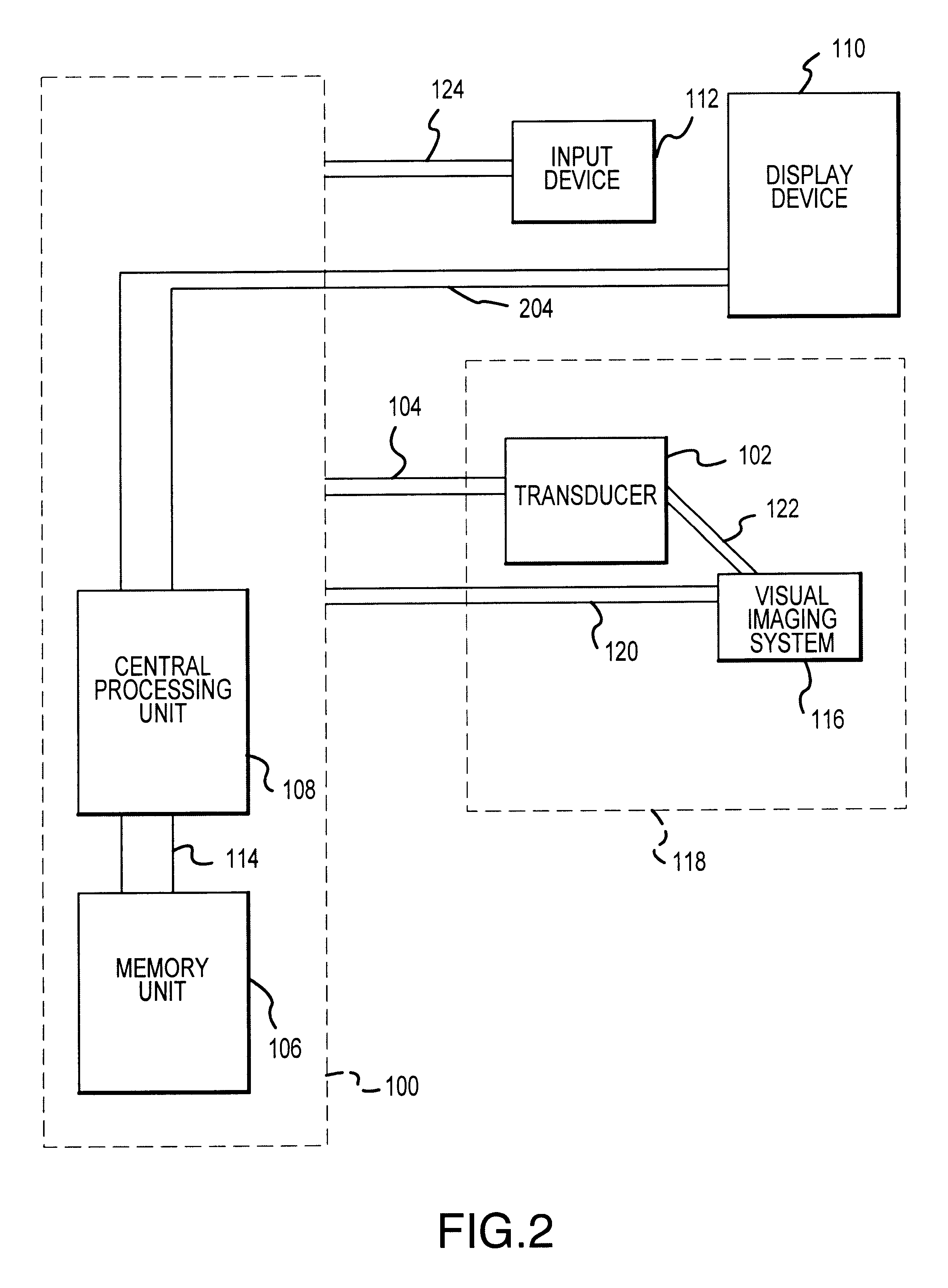
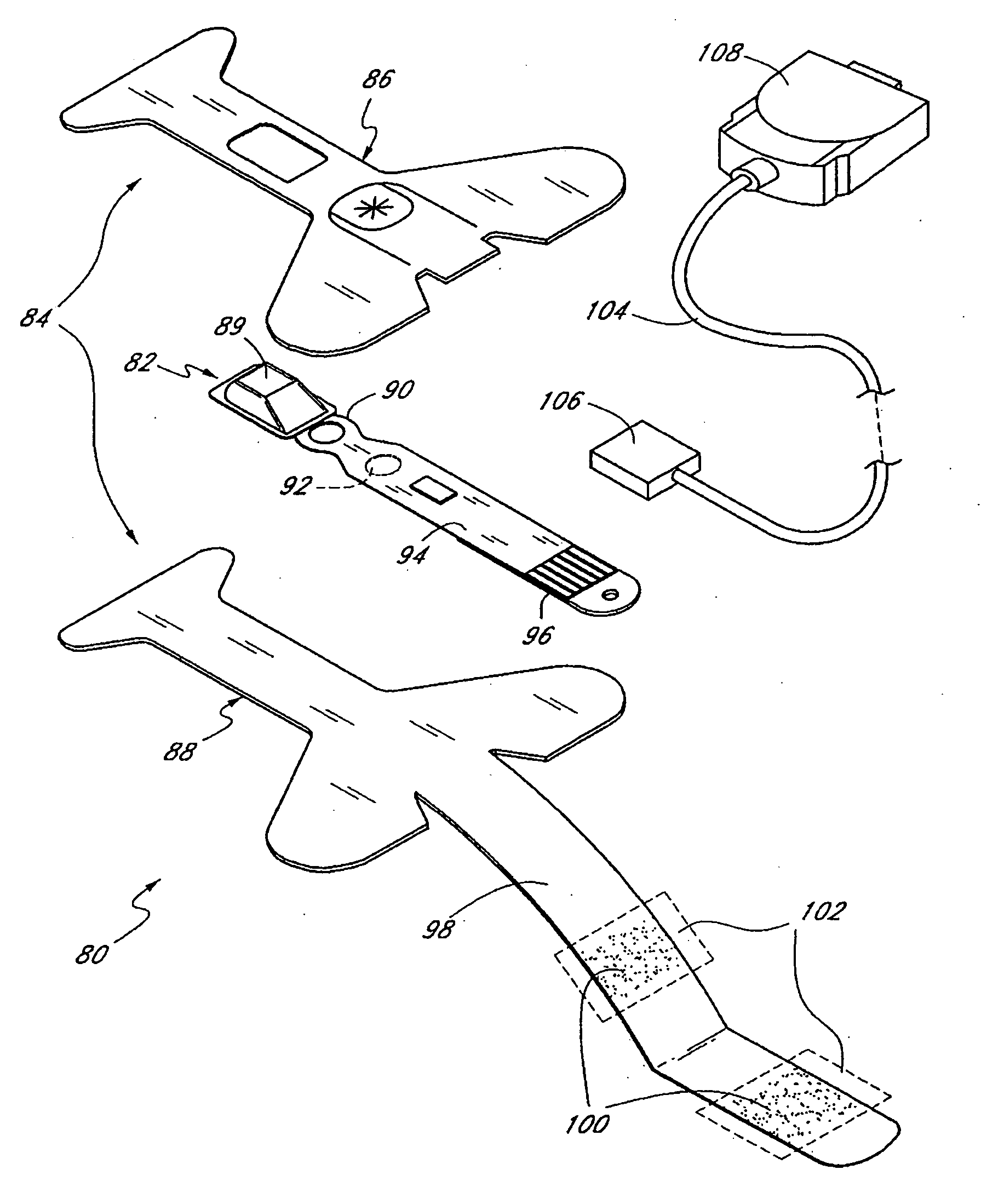
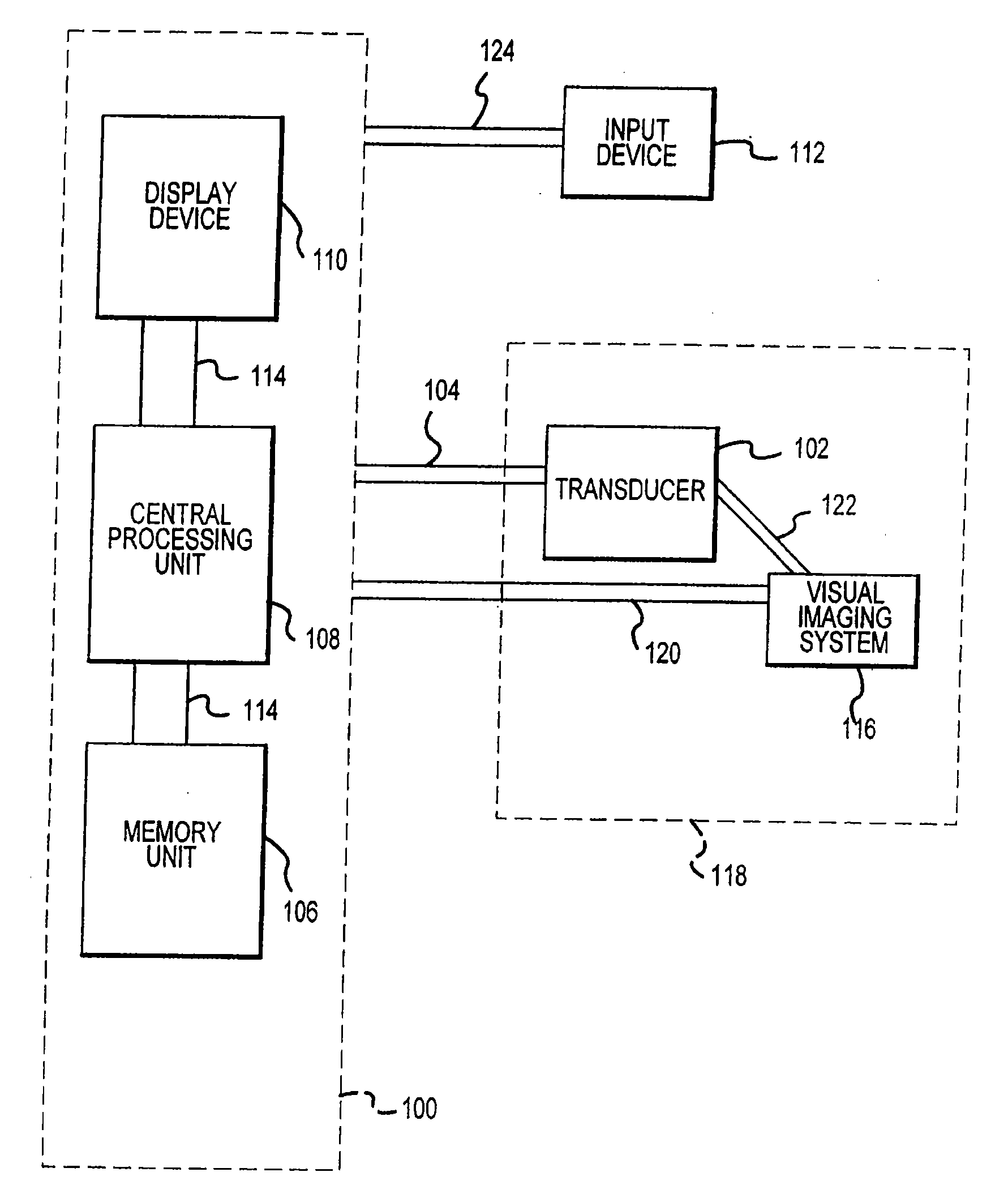
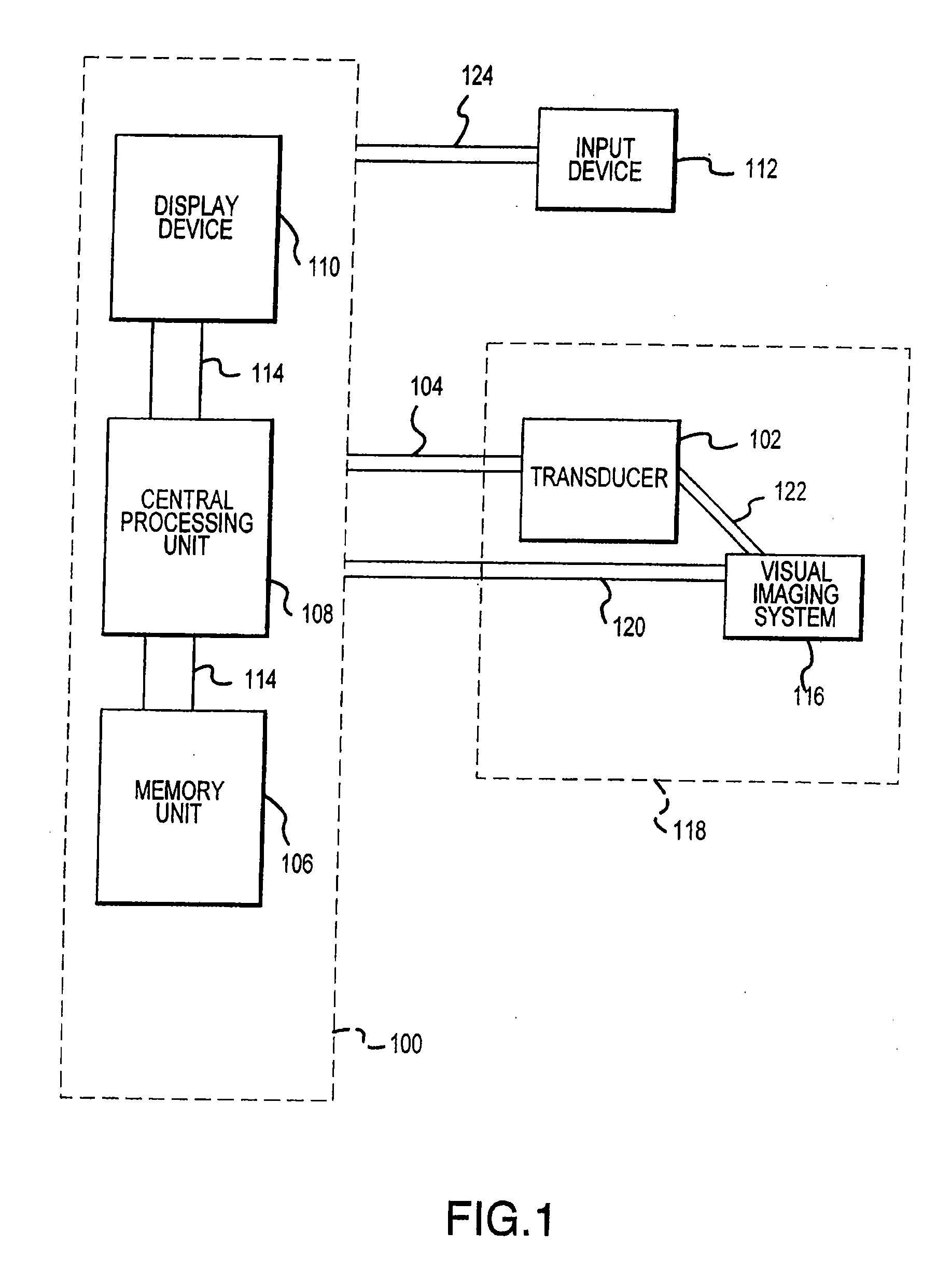
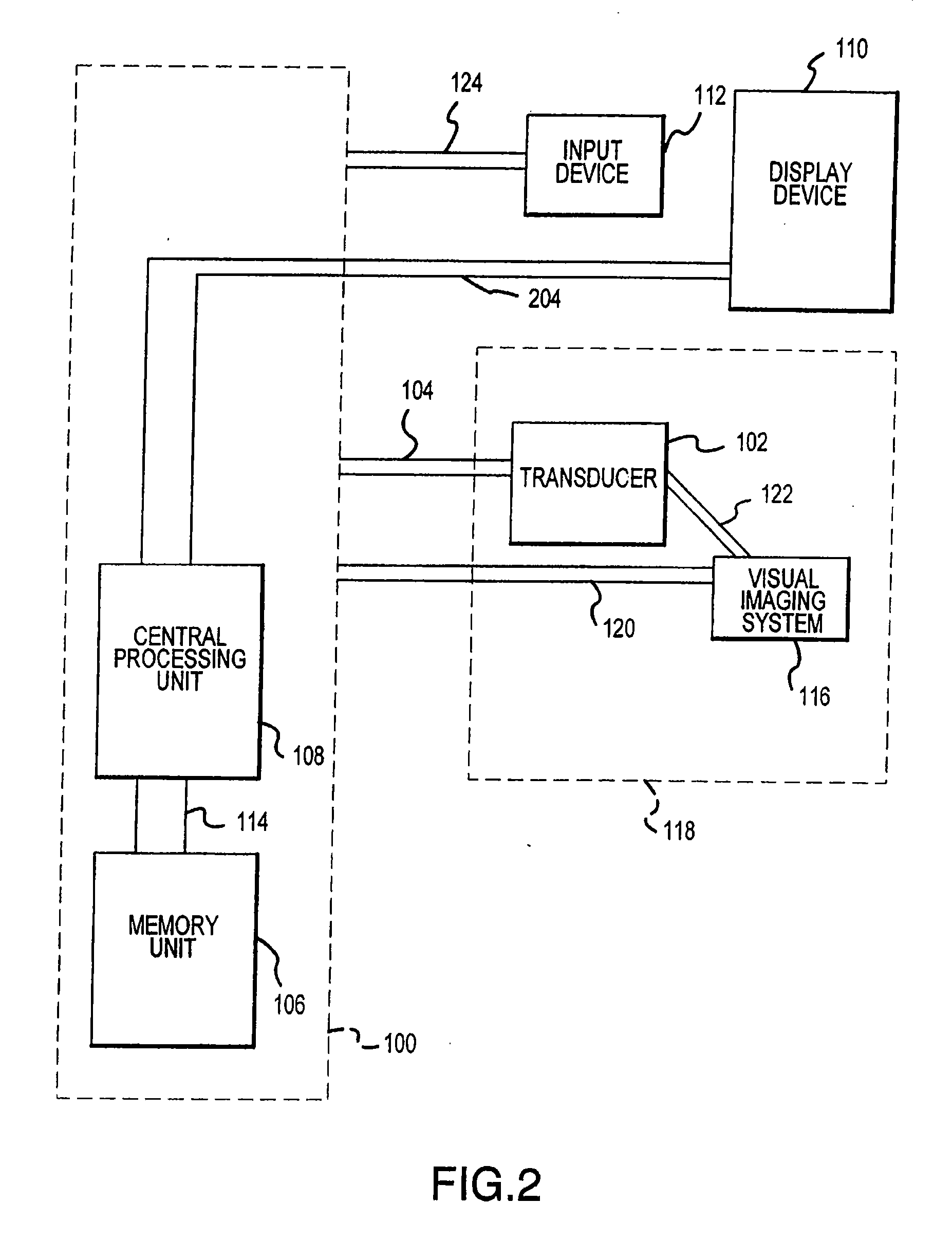
Visual imaging system for ultrasonic probe
InactiveUS6540679B2Optimize locationDiagnostic probe attachmentInfrasonic diagnosticsTherapeutic treatmentNon invasive
A non-invasive visual imaging system is provided, wherein the imaging system procures an image of a transducer position during diagnostic or therapeutic treatment. In addition, the system suitably provides for the transducer to capture patient information, such as acoustic, temperature, or ultrasonic images. For example, an ultrasonic image captured by the transducer can be correlated, fused or otherwise combined with the corresponding positional transducer image, such that the corresponding images represent not only the location of the transducer with respect to the patient, but also the ultrasonic image of the region of interest being scanned. Further, a system is provided wherein the information relating to the transducer position on a single patient may be used to capture similar imaging planes on the same patient, or with subsequent patients. Moreover, the imaging information can be effectively utilized as a training tool for medical practitioners.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
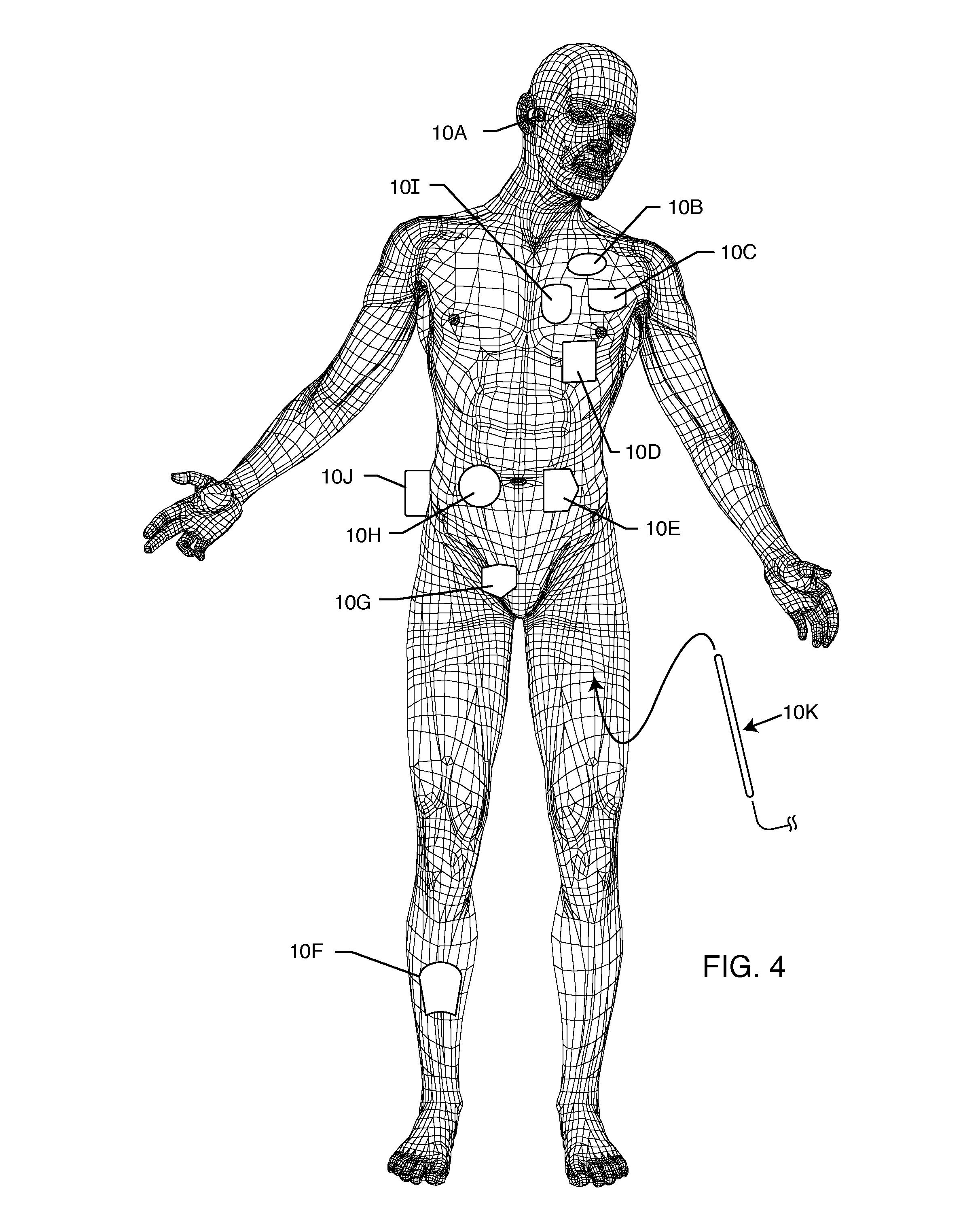
Patient identification using physiological sensor
InactiveUS20070073116A1Help positioningDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A patient information tracking system is disclosed that implements a physiological sensor system used to acquire information related to the wearer of a physiological sensor. The sensor system includes a physiological sensor adapted to be attached to a patient and includes at least one emitter and a photodetector. The sensor system further includes a positioning element to position the sensor such that the at least one emitter is sufficiently proximate the detector to acquire information from an identification element worn by the patient. A method for using a physiological sensor system to acquire information related to the wearer of a sensor is also provided. The sensor may also include a securing portion configured to couple to the sensor portion of the wearer. The sensor may also include a security wire and a memory device for retaining the wearer's information.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
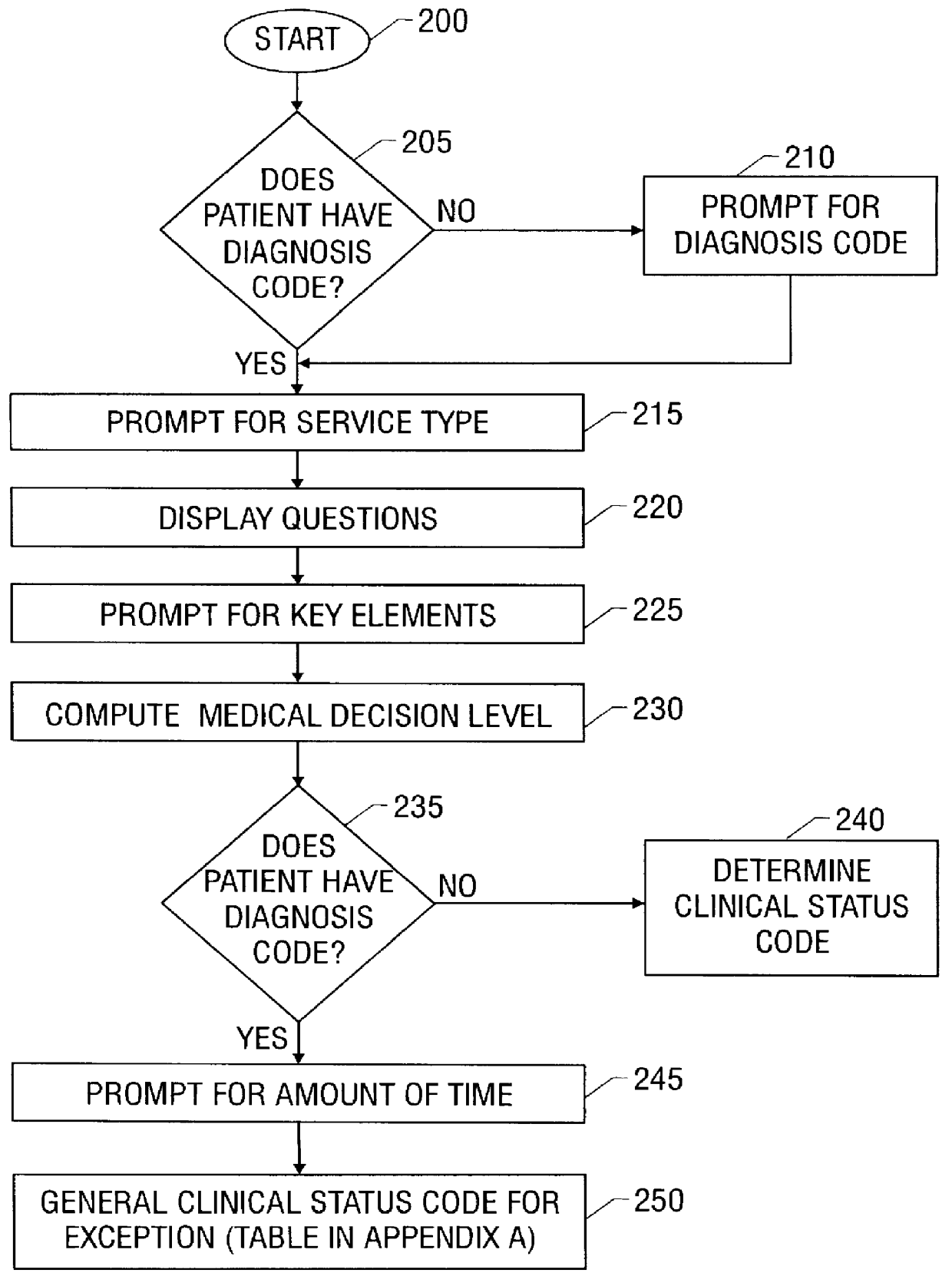
System and method for recording patient history data about on-going physician care procedures
InactiveUS6154726AConvenient recordingOptimize schedulingData processing applicationsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionStaff timeEfficacy
A system and method for processing patient data permits physicians and other medical staff personnel to record, accurately and precisely, historical patient care information. An objective measure of a physician's rendered level of care, as described by a clinical status code, is automatically generated. Data elements used in the determination of the generated clinical status code include a level of history of the patient, a level of examination of the patient, a decision-making process of the physician treating the patient, and a "time influence factor." The quantity and quality of care information for a particular patient is enhanced allowing future care decisions for that patient to be based on a more complete medical history. Enhanced care information can be used in outcome studies to track the efficacy of specific treatment protocols. Archiving of patient information is done in a manner which allows reconstruction of the qualitative aspects of provided medical services. The medical care data can be recorded, saved, and transferred from a portable system to a larger stationary information or database system. Considerable physician and staff time are saved and precision and accuracy are significantly enhanced, by generating these clinical status codes automatically (at the point of service by the care-provider without any intermediary steps) from information recorded simultaneously with the provision of services.
Owner:RENSIMER ENTERPRISES
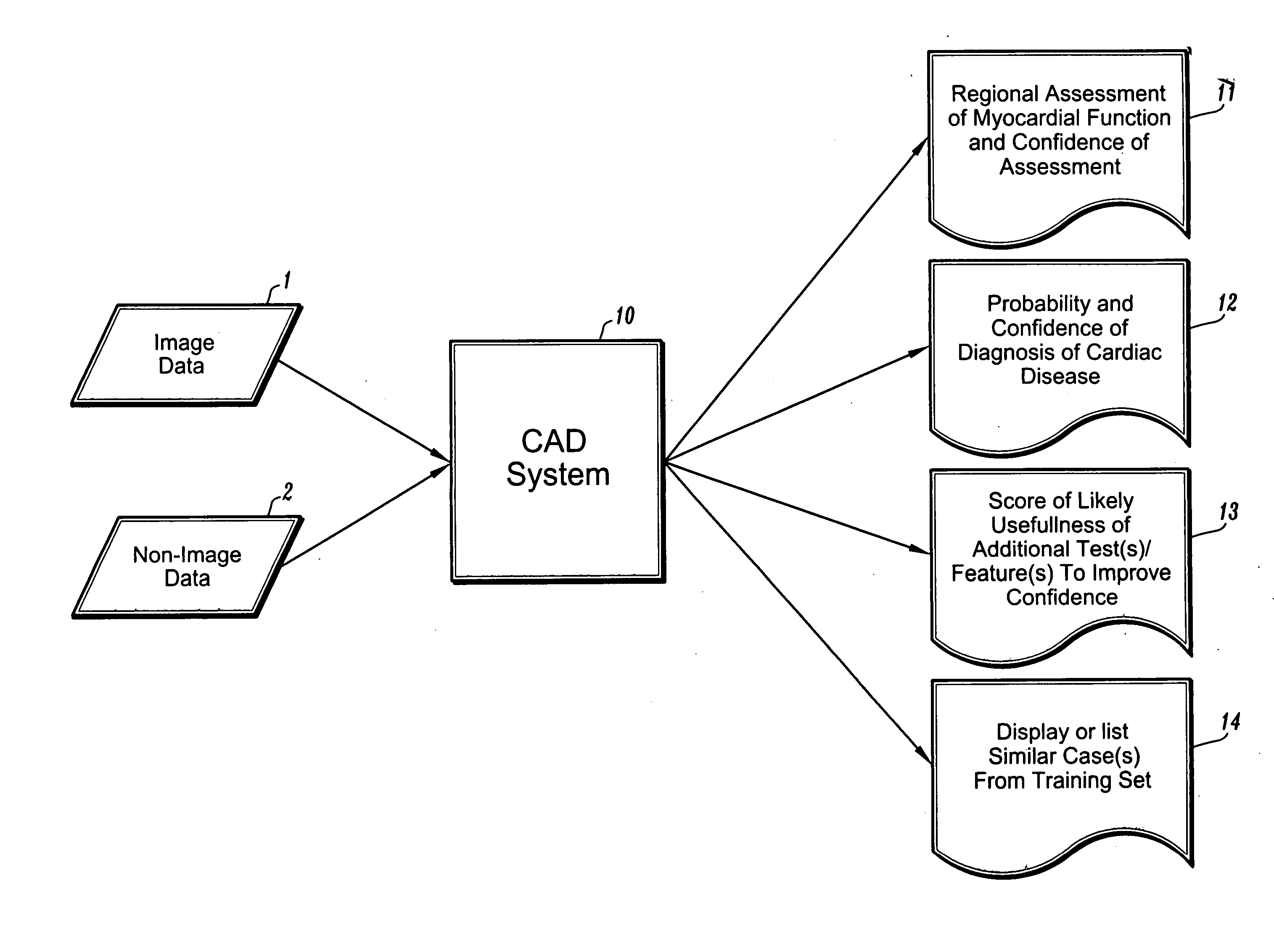
Systems and methods for automated diagnosis and decision support for breast imaging
ActiveUS20050049497A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPatient dataDecision taking
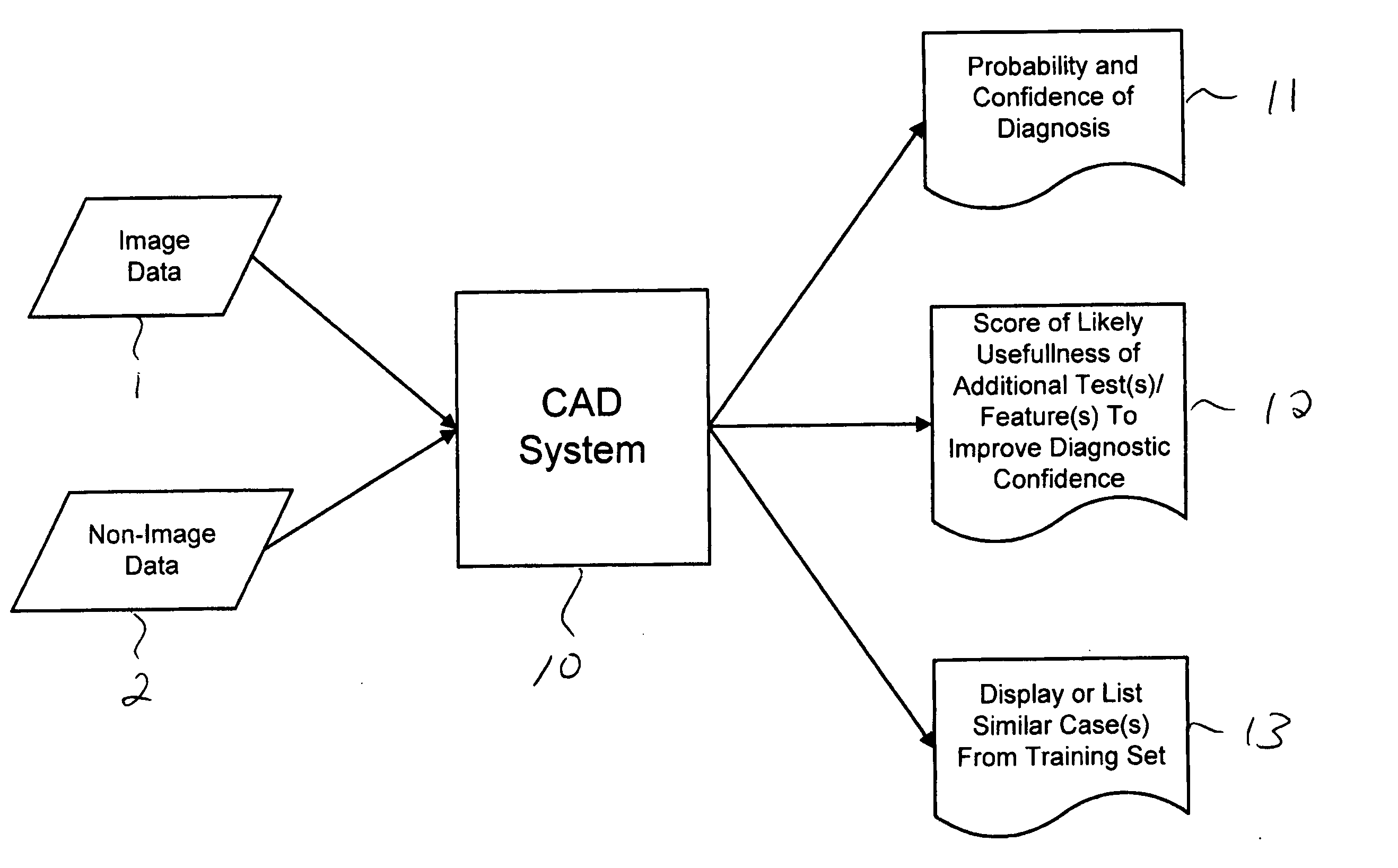
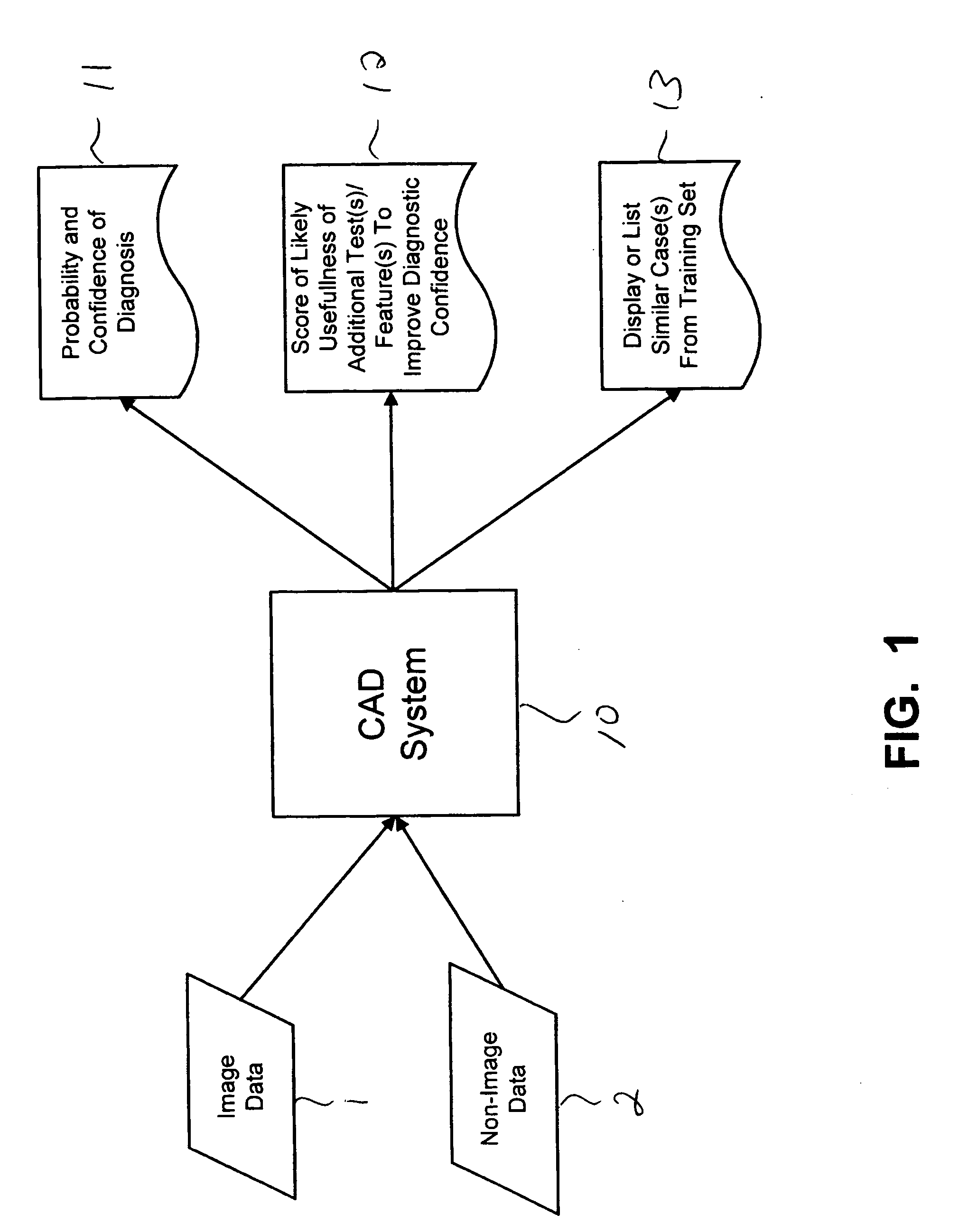
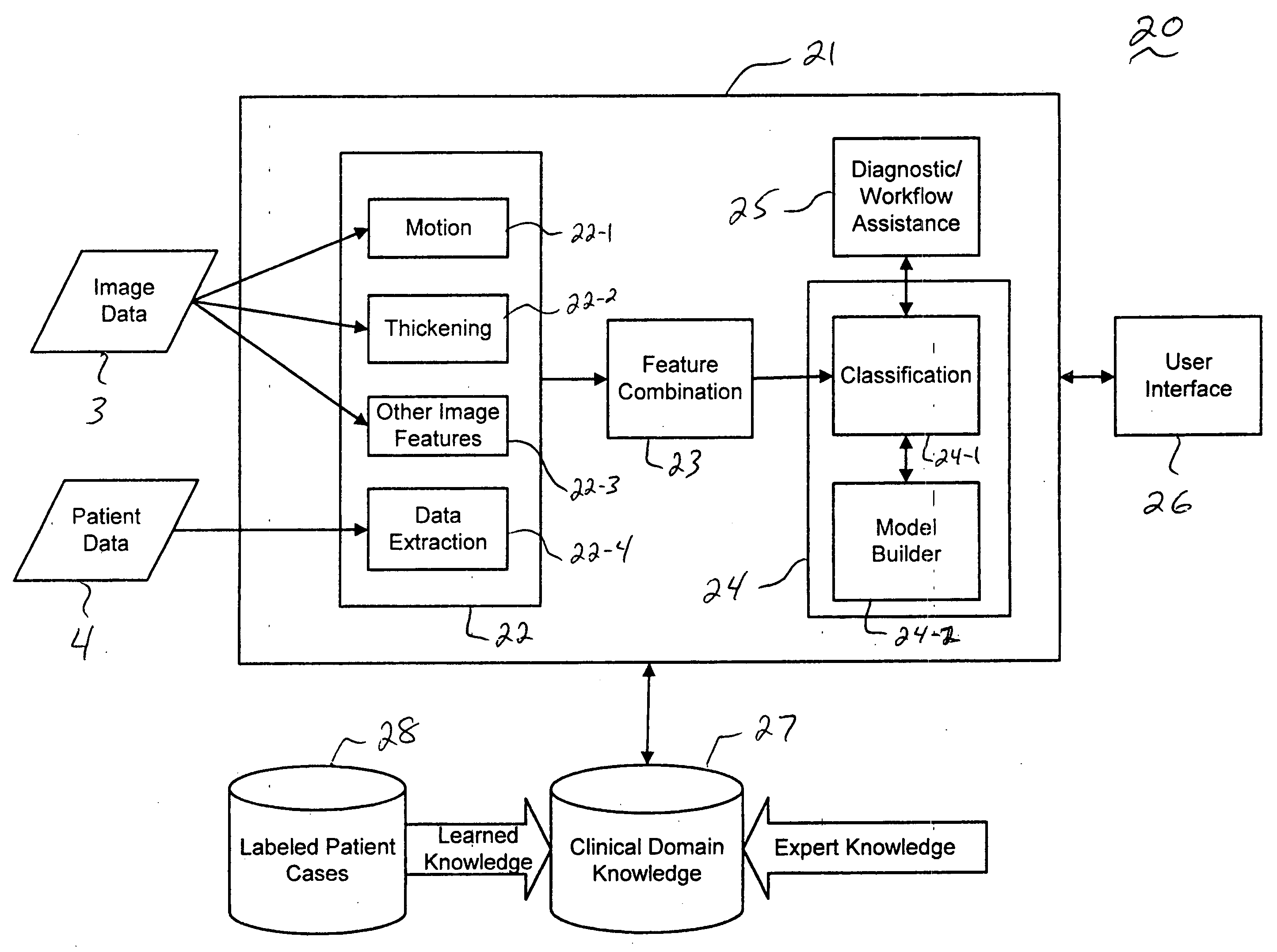
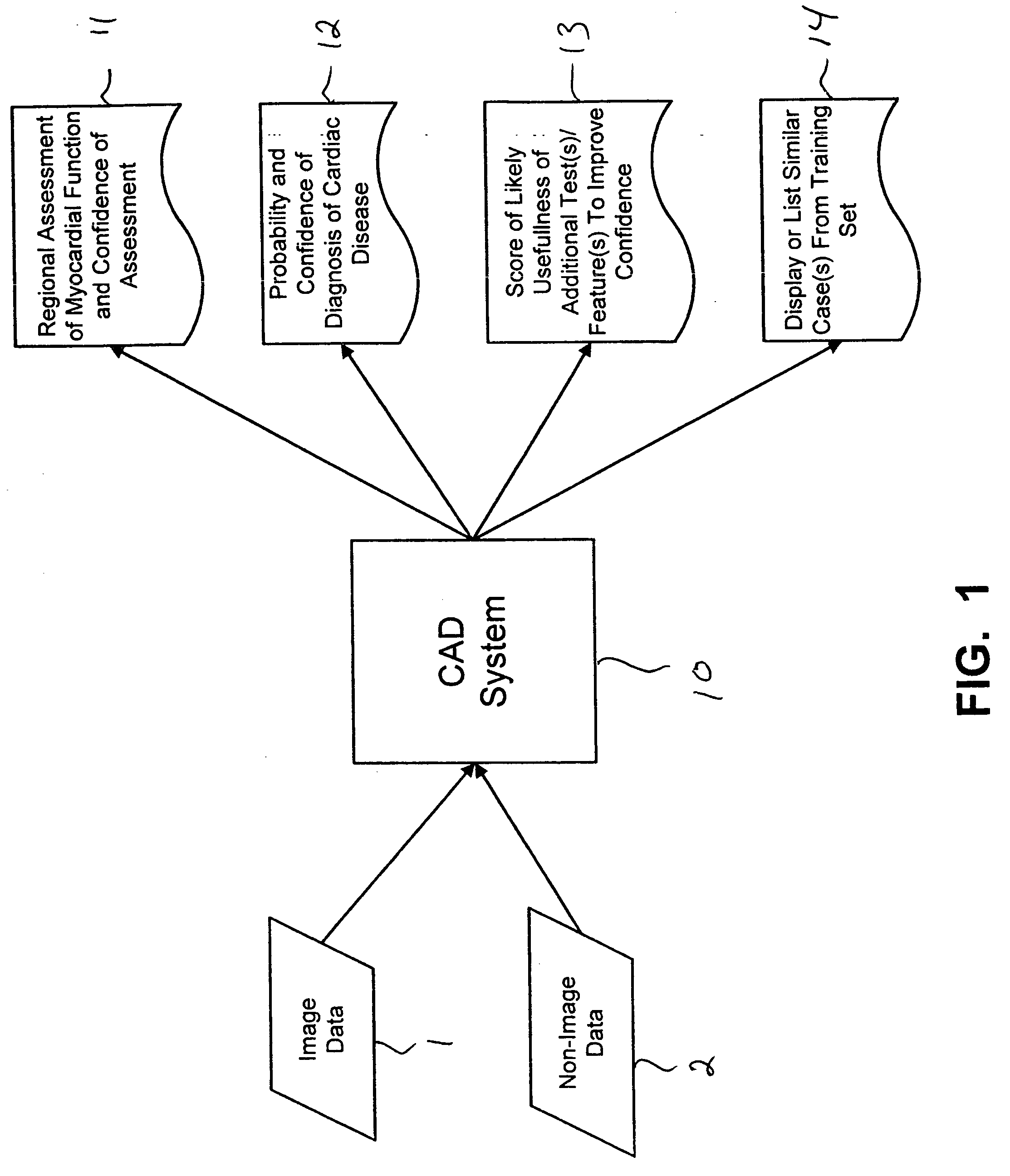
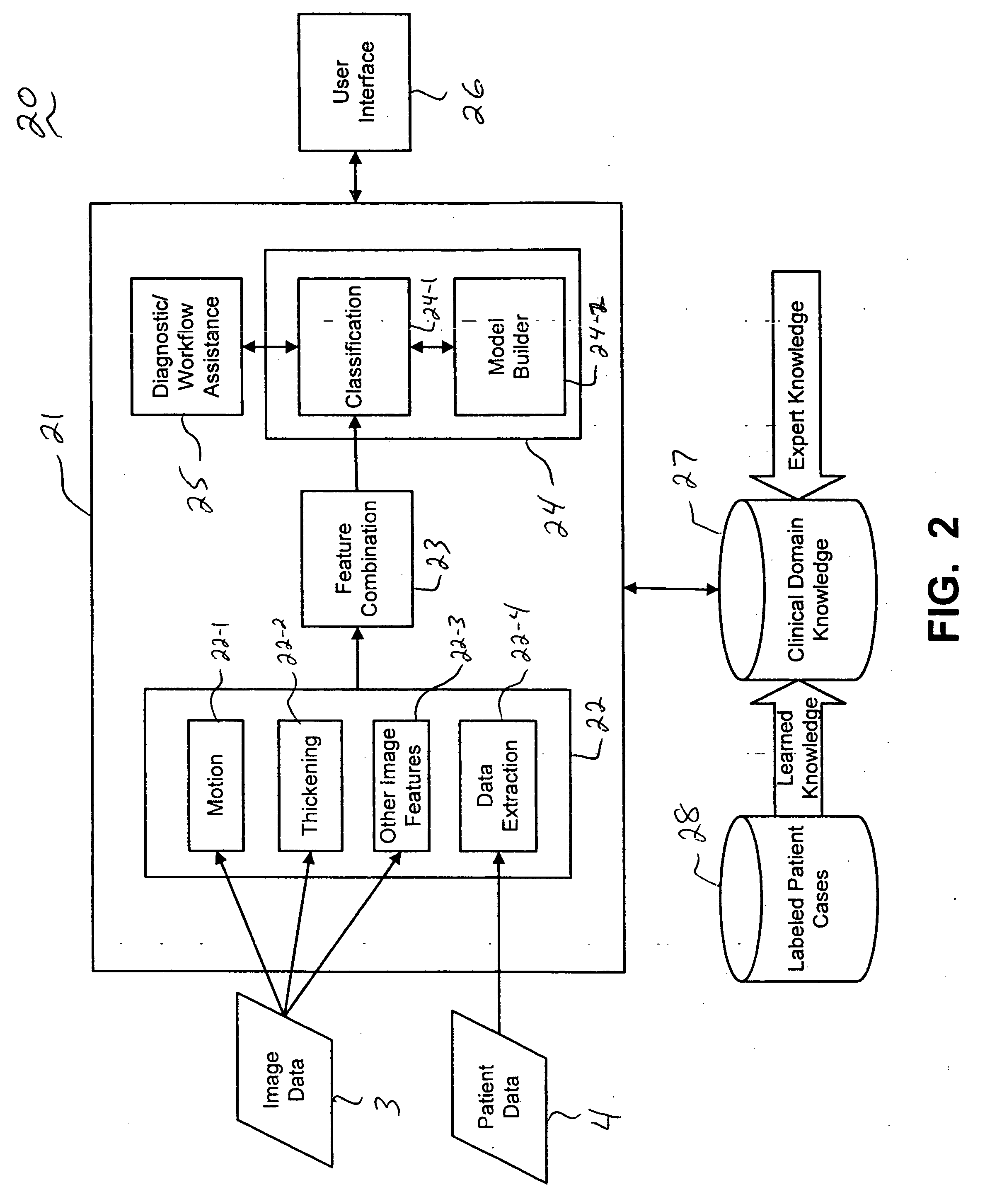
CAD (computer-aided diagnosis) systems and applications for breast imaging are provided, which implement methods to automatically extract and analyze features from a collection of patient information (including image data and / or non-image data) of a subject patient, to provide decision support for various aspects of physician workflow including, for example, automated diagnosis of breast cancer other automated decision support functions that enable decision support for, e.g., screening and staging for breast cancer. The CAD systems implement machine-learning techniques that use a set of training data obtained (learned) from a database of labeled patient cases in one or more relevant clinical domains and / or expert interpretations of such data to enable the CAD systems to “learn” to analyze patient data and make proper diagnostic assessments and decisions for assisting physician workflow.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
System and method for diagnosing and monitoring myocardial ischemia for automated remote patient care
InactiveUS6913577B2Increase productionIncreased serum creatinine kinaseElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesHysteresisHeart muscle extract
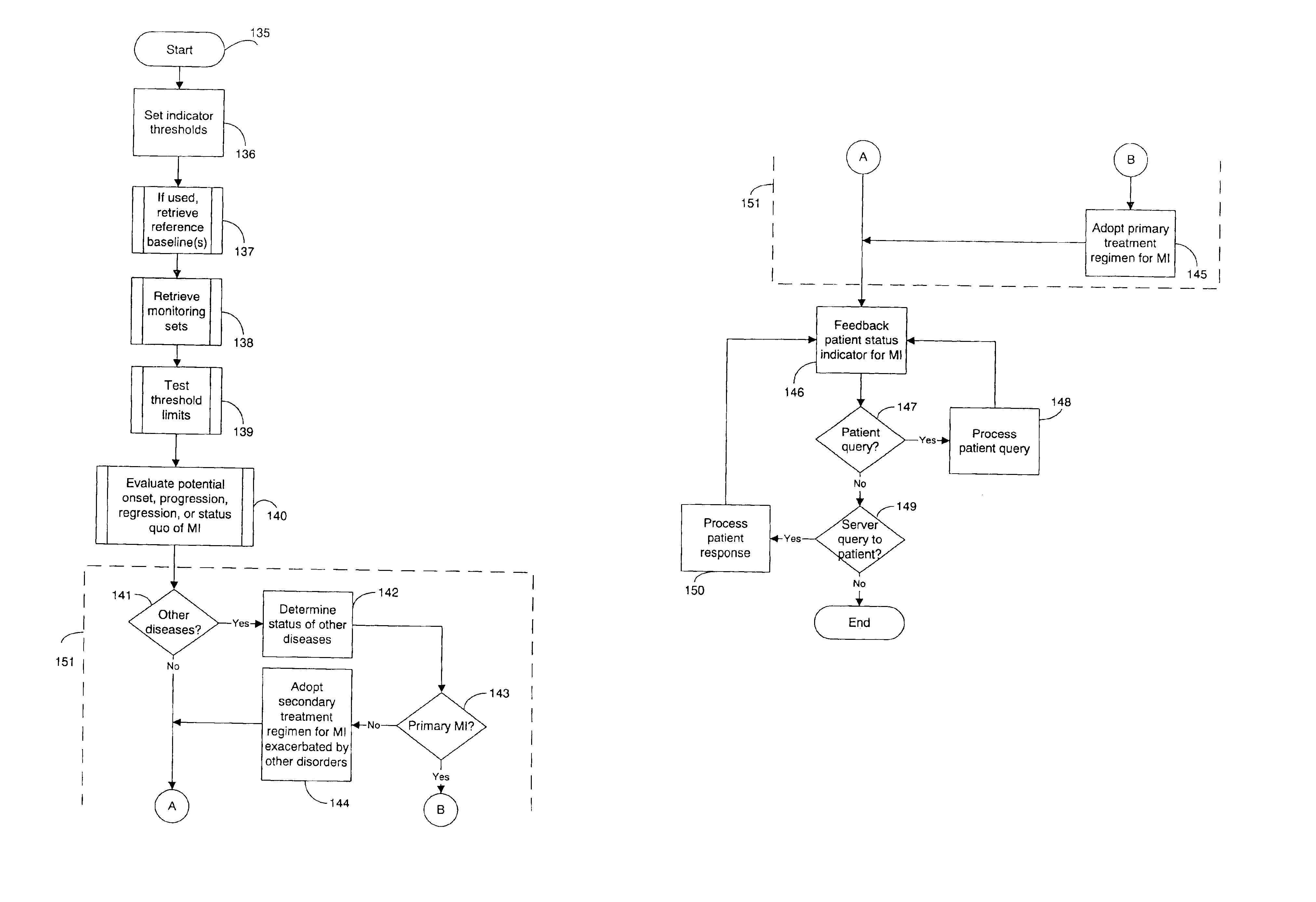
A system for diagnosing and monitoring myocardial ischemia for automated remote patient care is presented. A database stores monitoring sets containing recorded measures relating to patient information recorded on a substantially continuous basis. A server retrieving and processing the monitoring sets includes a comparison module determining a patient status change by comparing recorded measures and time from each of the monitoring sets to other recorded measures and time from another monitoring set with both recorded measures relating to a same type of patient information recorded at different times, and an analysis module testing each patient status change for, an onset, a progression, a regression, and a status quo of myocardial ischemia against a predetermined indicator threshold, including hysteresis threshold, corresponding to same type of patient information as the compared recorded measures.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
Systems and methods for providing automated regional myocardial assessment for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS20050059876A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementMedical recordAcquired characteristic
Systems and methods are provided for automated assessment of regional myocardial function using wall motion analysis methods that analyze various features / parameters of patient information (image data and non-image data) obtained from medical records of a patient. For example, a method for providing automatic diagnostic support for cardiac imaging generally comprises obtaining image data of a heart of a patient, obtaining features from the image data of the heart, which are related to motion of the myocardium of the heart, and automatically assessing regional myocardial function of one or more regions of a myocardial wall using the obtained features.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
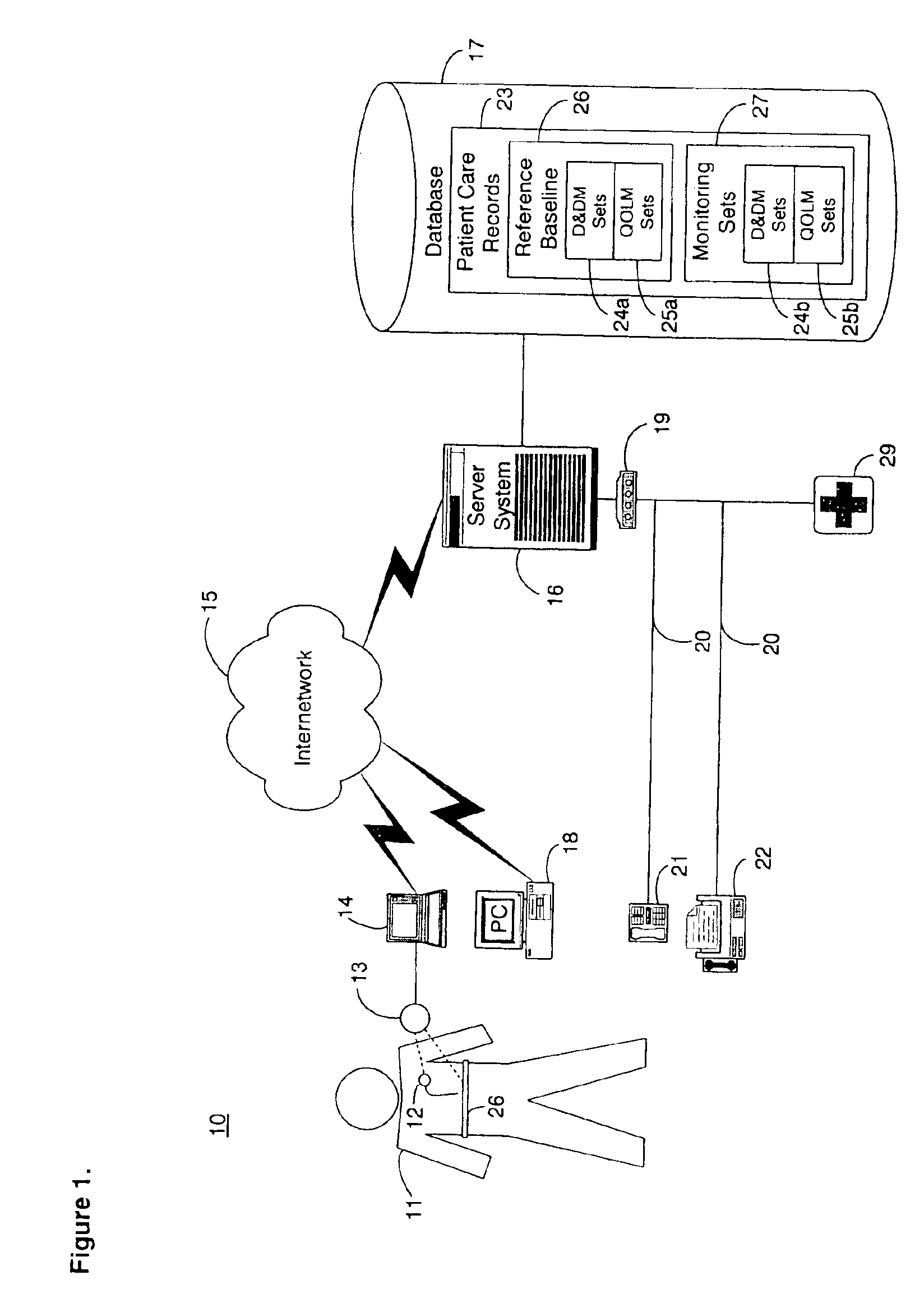
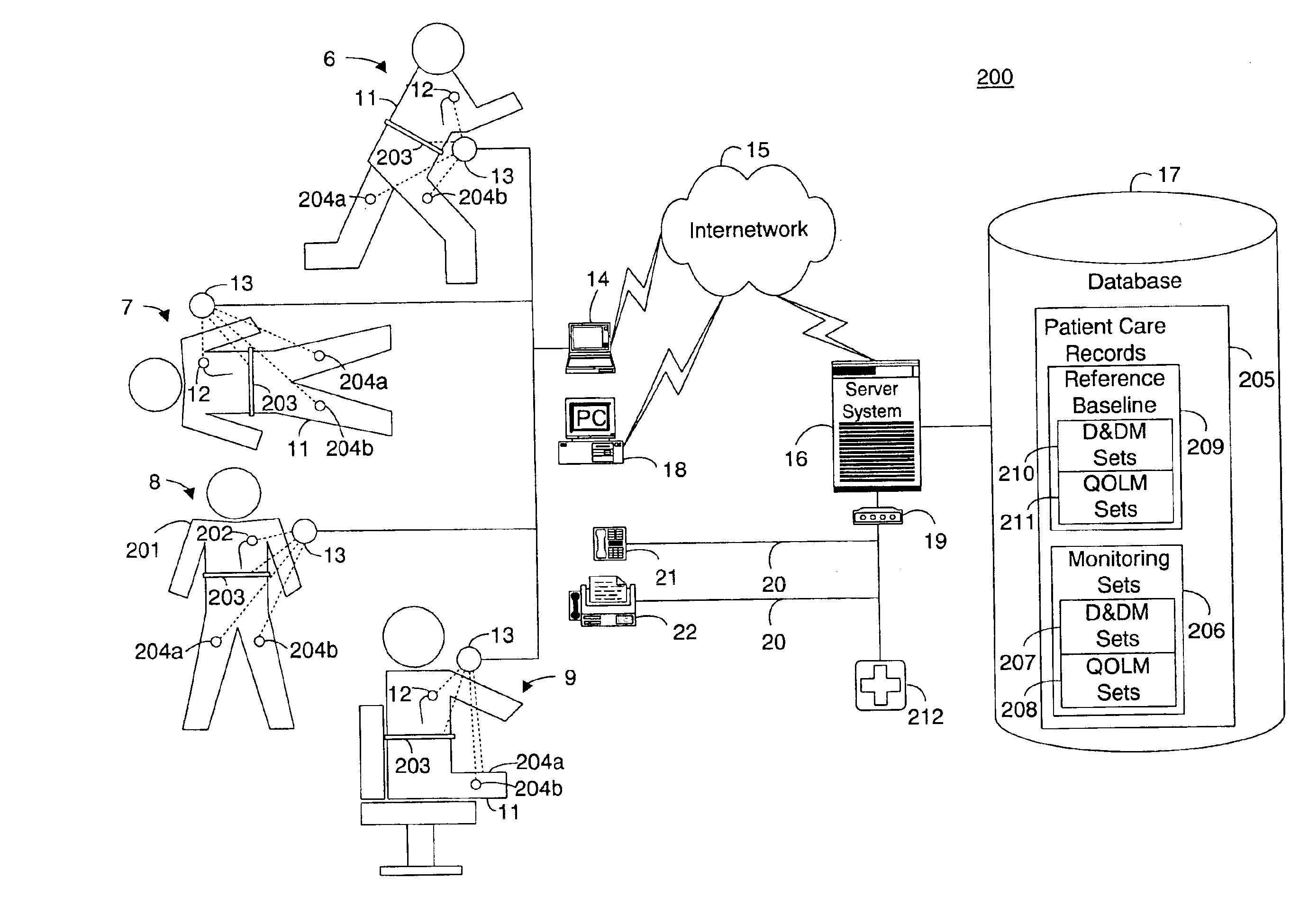
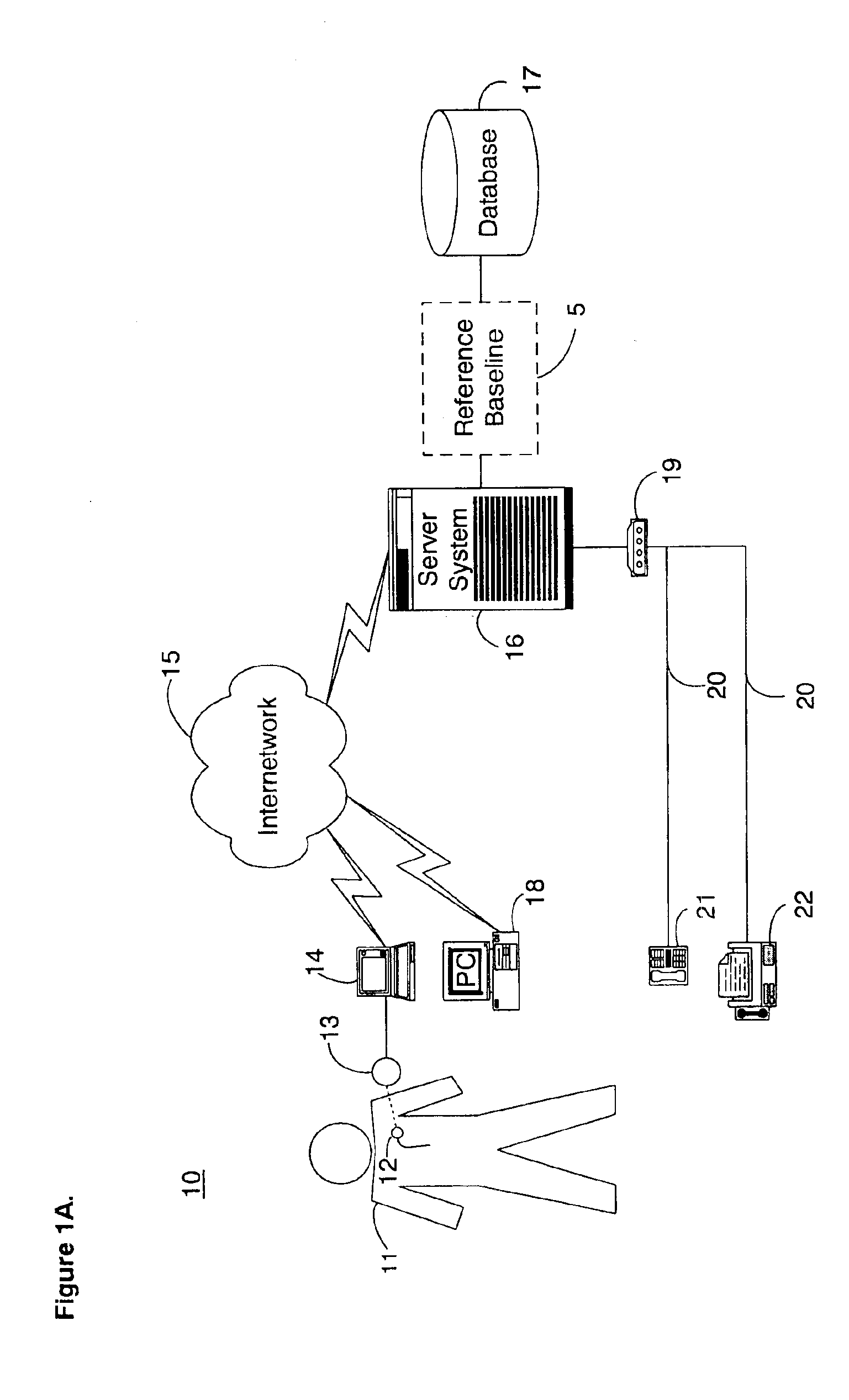
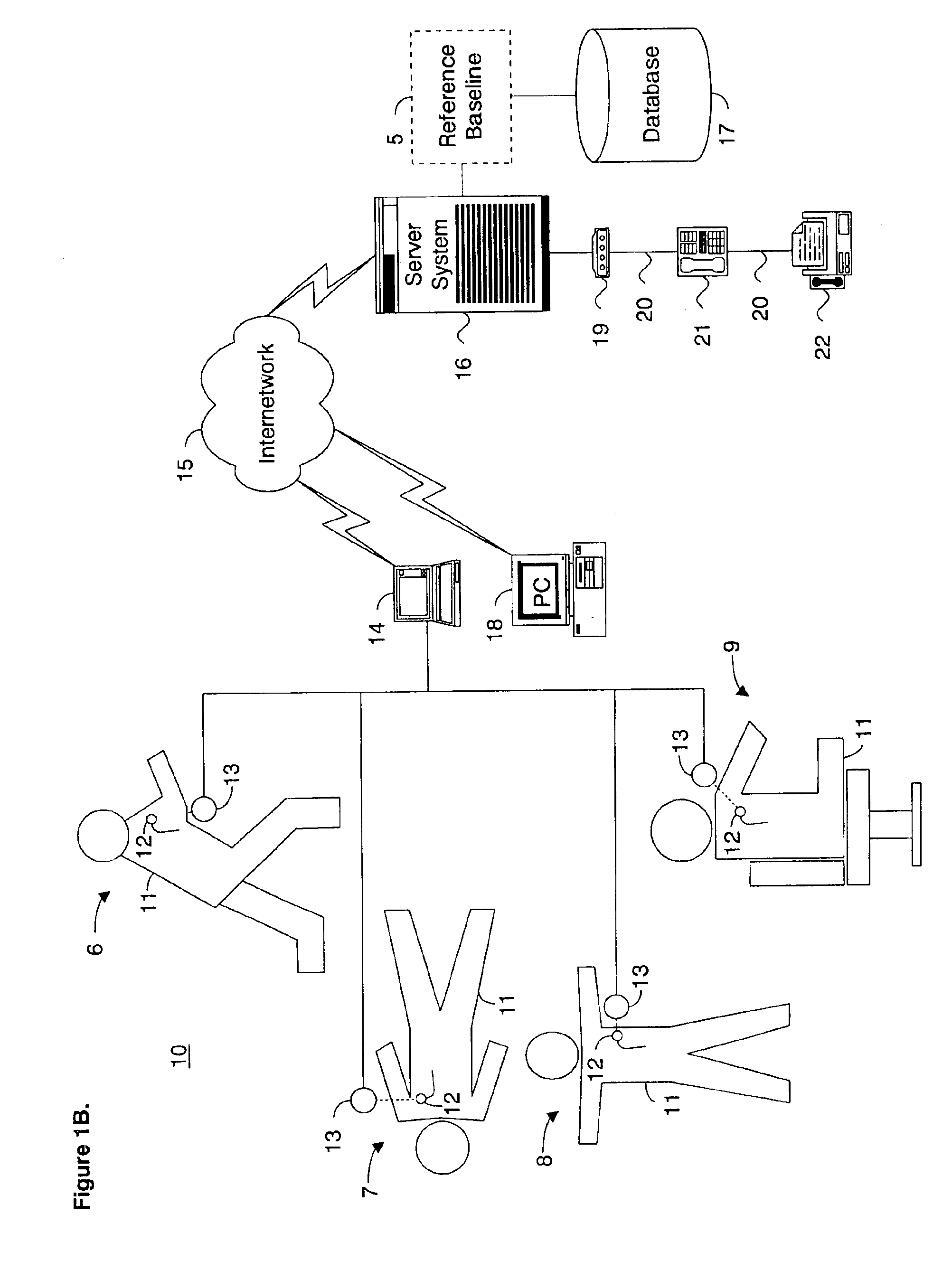
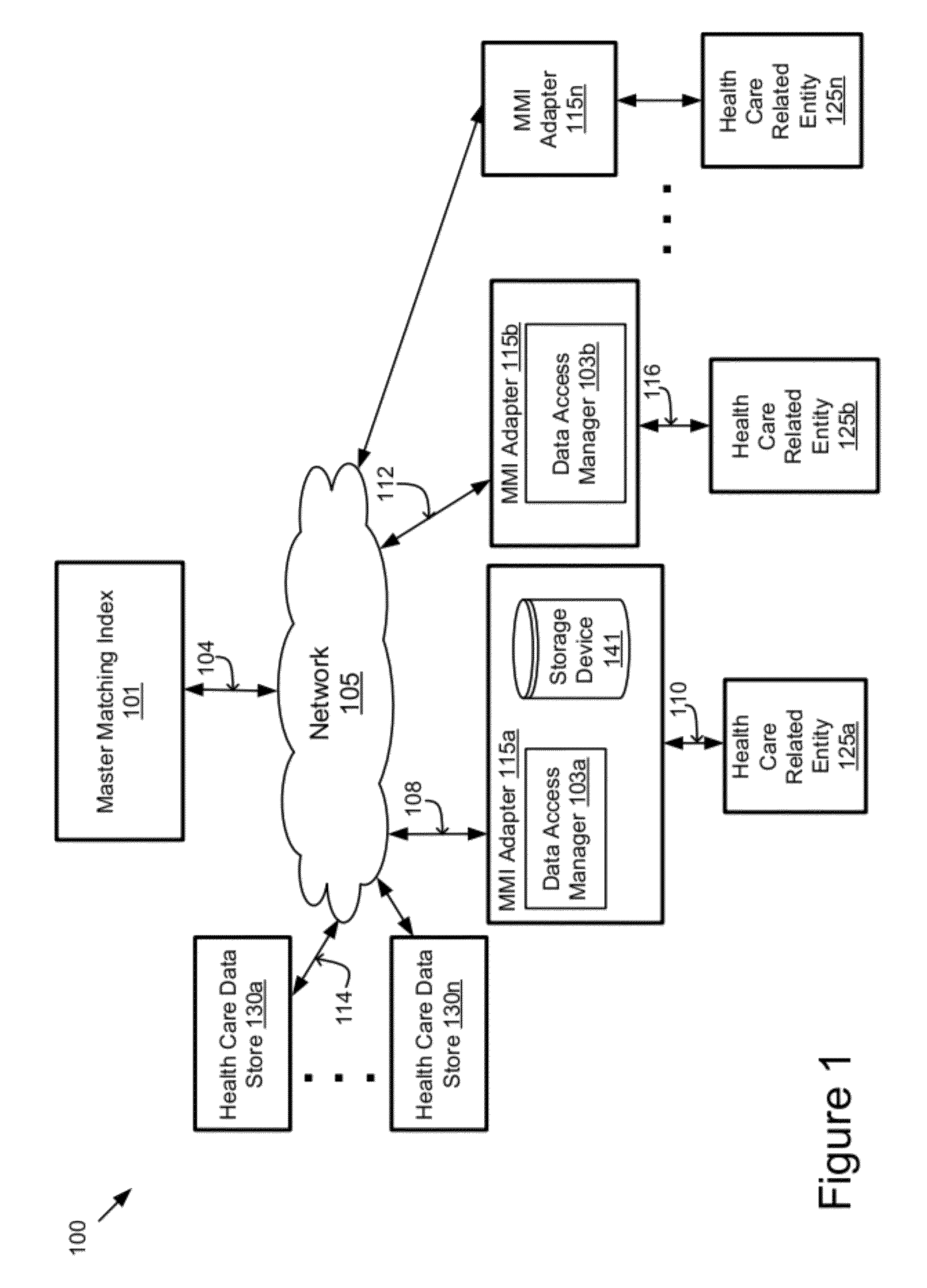
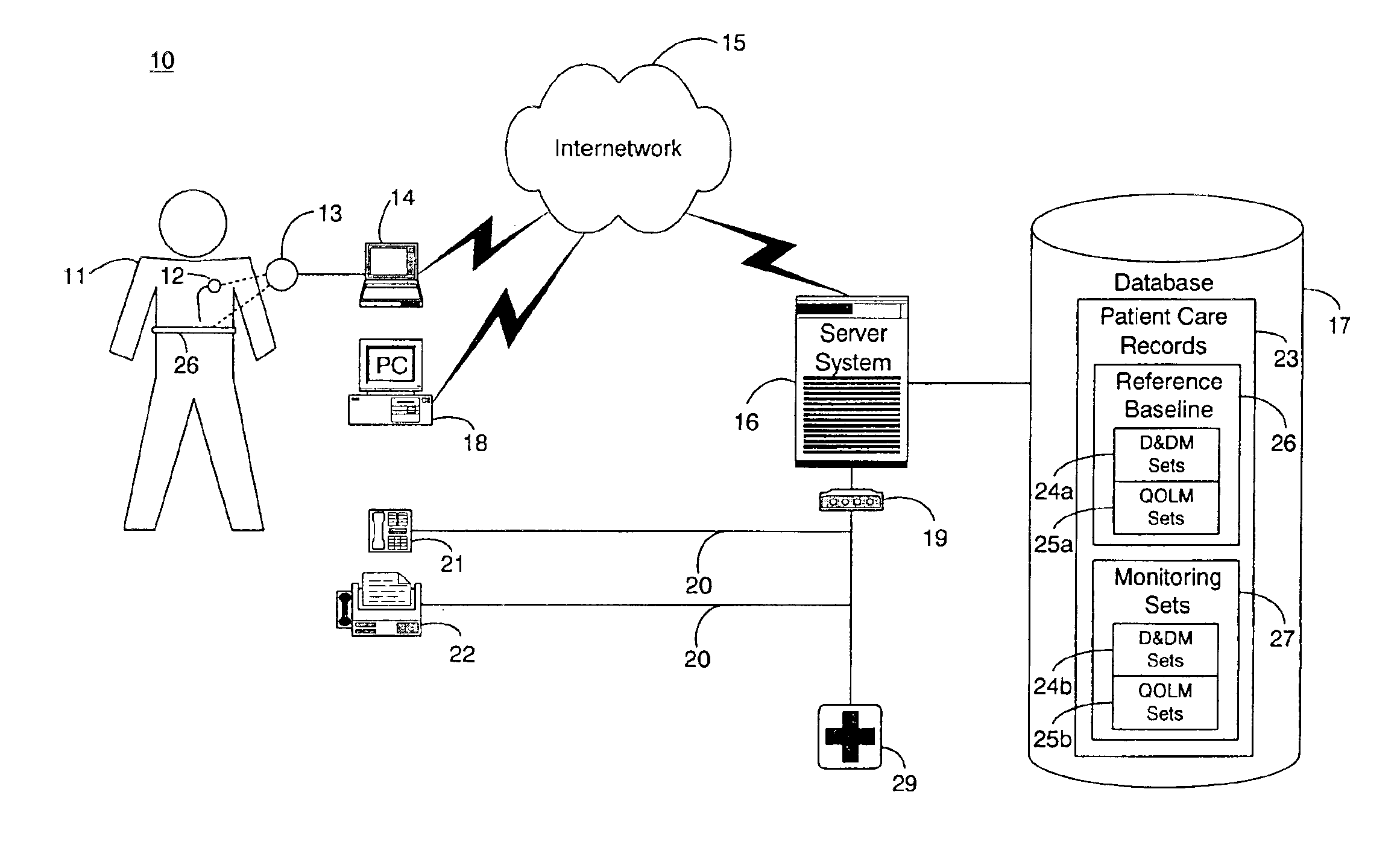
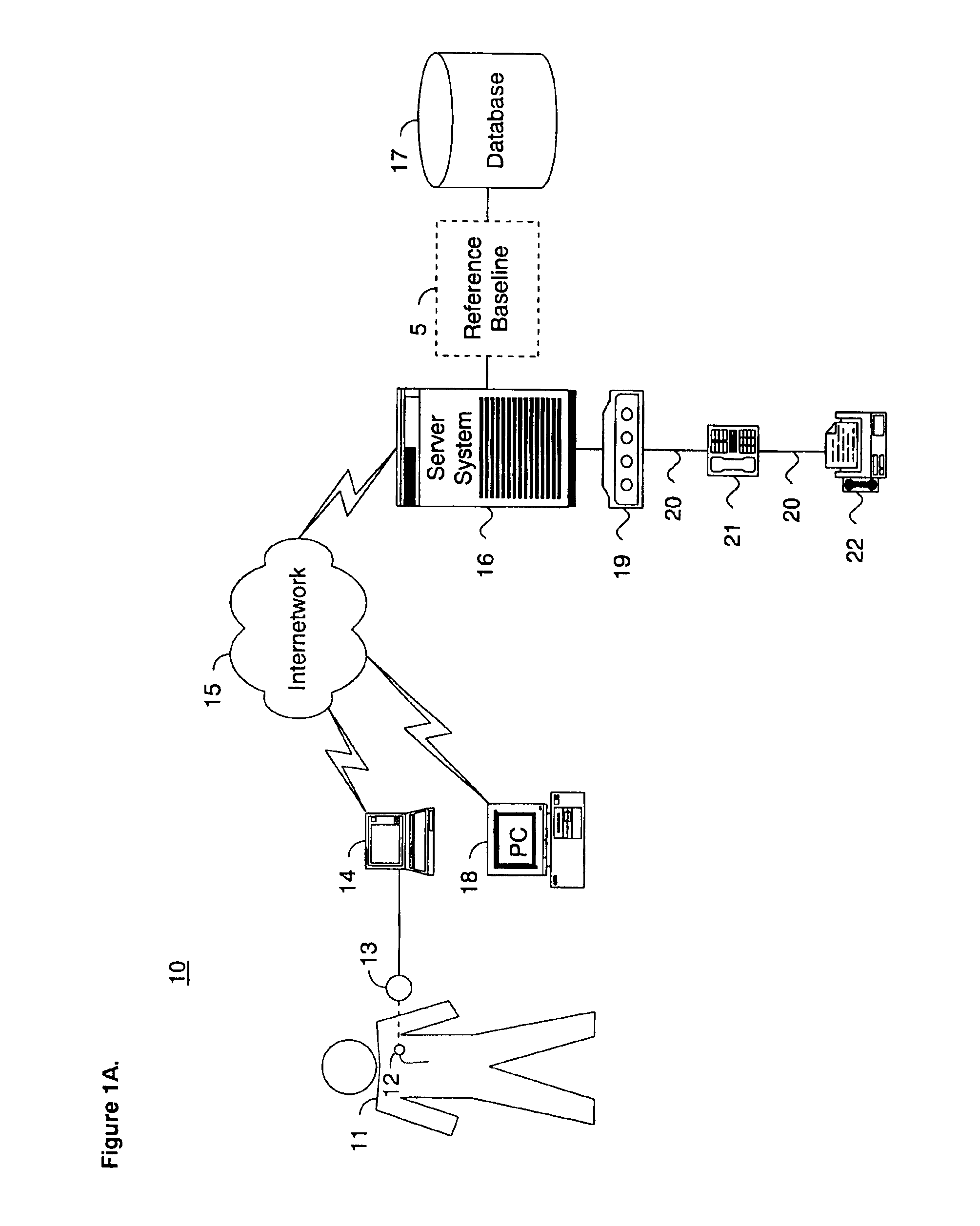
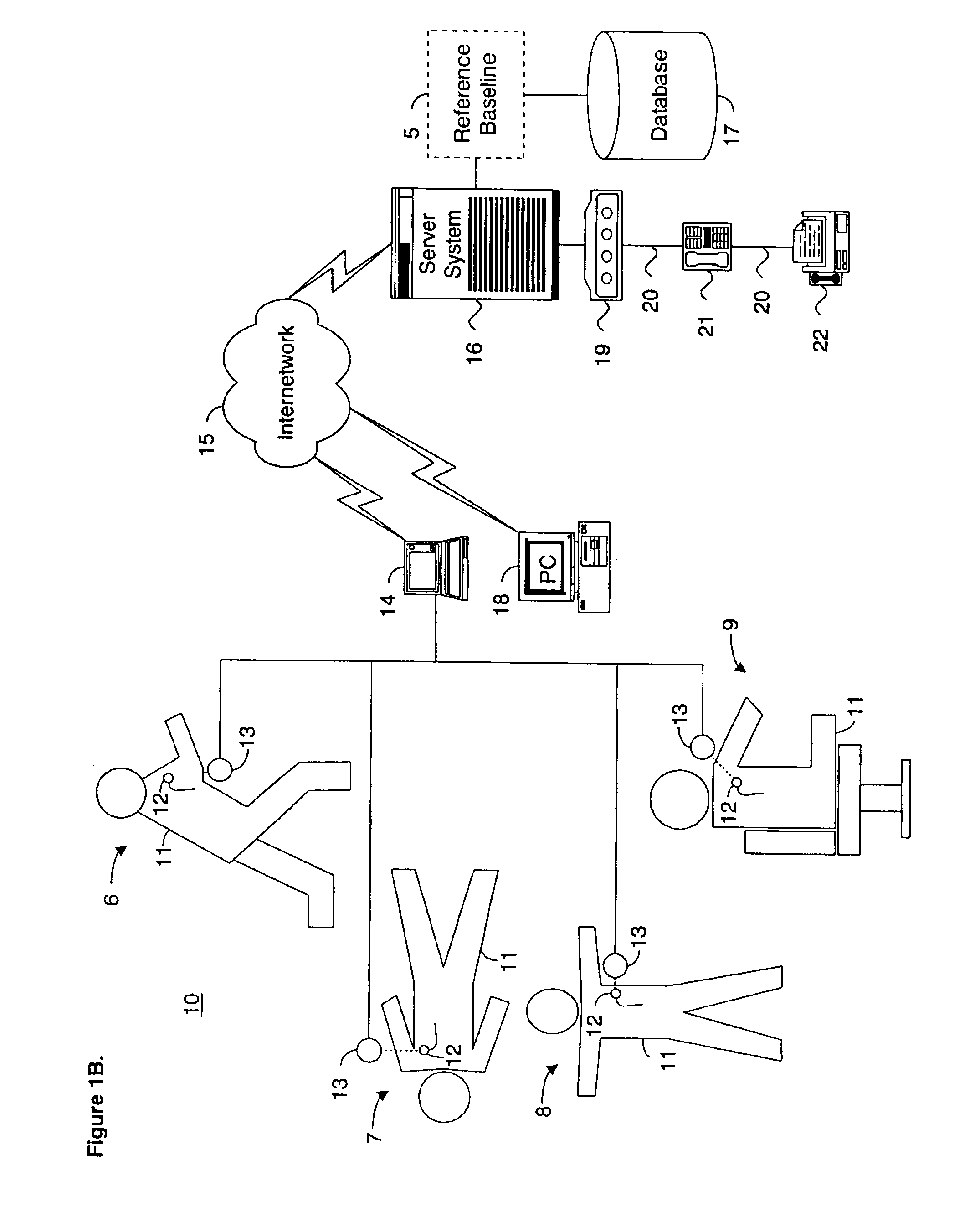
System and method for determining a reference baseline of regularly retrieved patient information for automated remote patient care
InactiveUS6887201B2Improve accuracyImproves chroniclingElectrotherapyHealth-index calculationEmergency medicinePatient status
A system for determining a reference baseline of regularly retrieved patient information for automated remote patient care is presented. A medical device having a sensor for monitoring at least one physiological measure of an individual patient regularly records and stores measures sets relating to patient information during an initial time period. A database collects one or more patient care records by organizing one or more patient care records and storing the collected measures set into such a patient care record for the individual patient. A server receives the collected device measures set from the medical device, processes the collected device measures set into a set of reference measures representative of at least one of measured or derived patient information, and stores the reference measures set into the patient care record as data in a reference baseline indicating an initial patient status.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
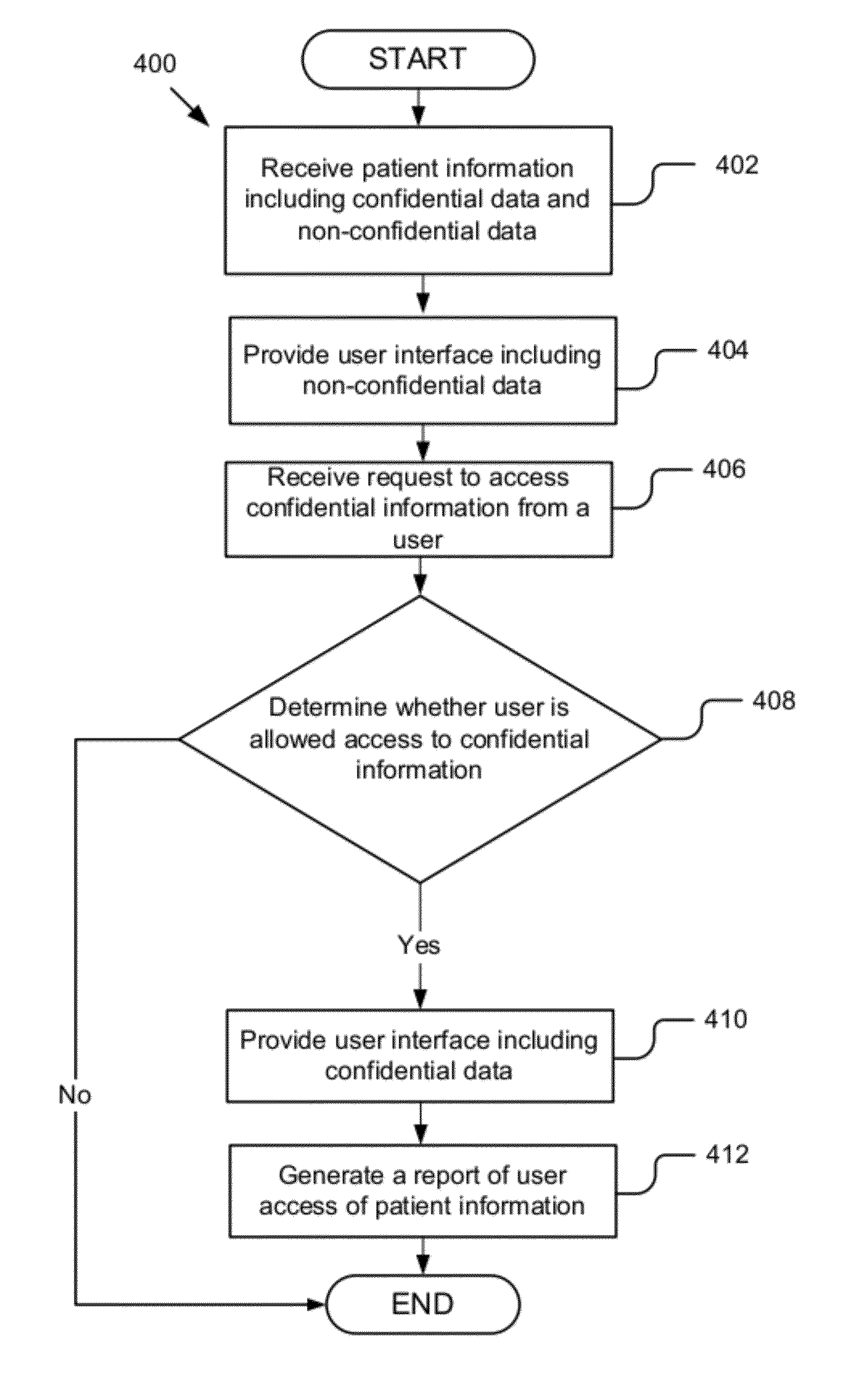
Managing patient consent in a master patient index
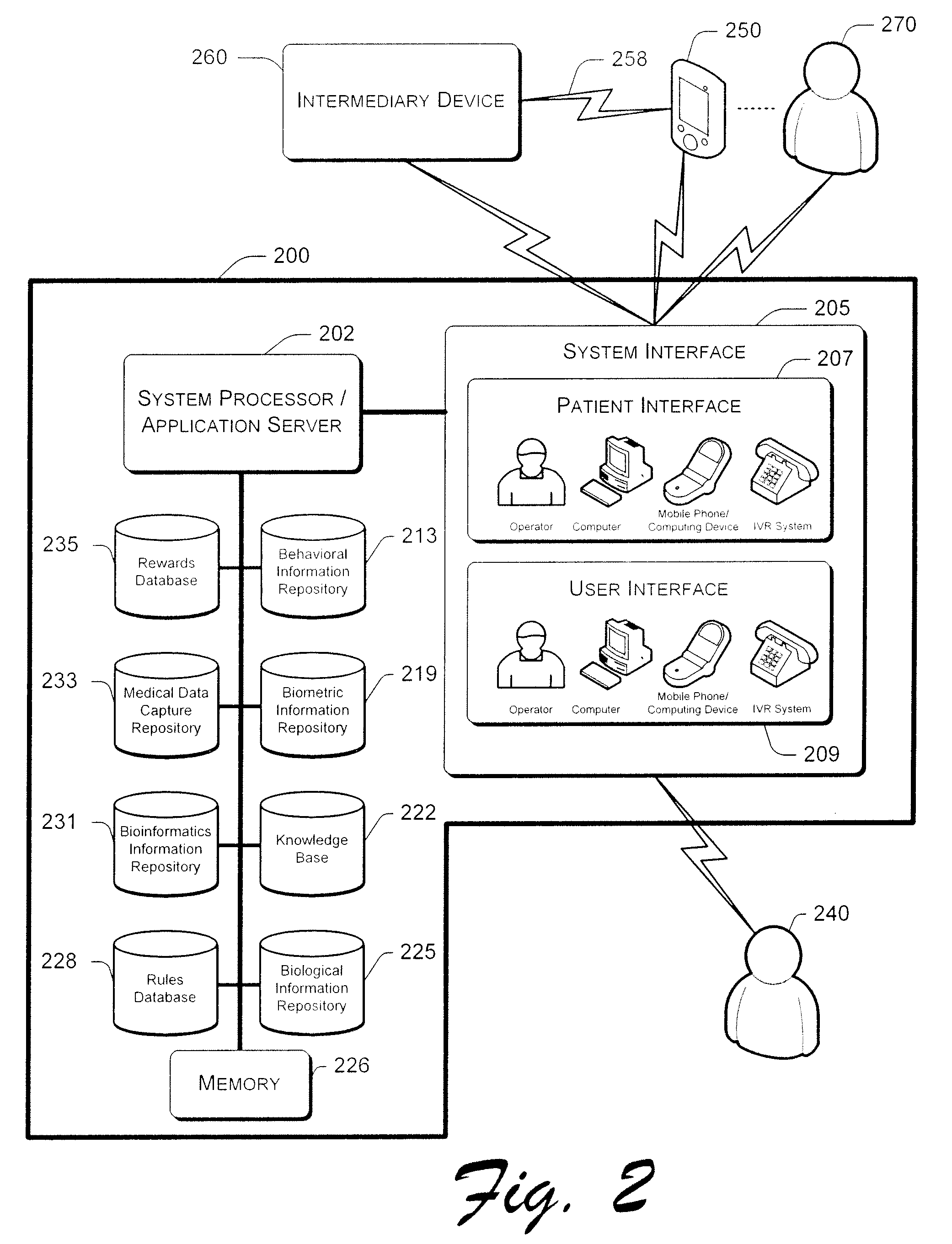
ActiveUS8949137B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCore functionData access
A system and method for managing patient consent. A data access manager includes a controller, a lookup module, a clinical authorization engine, a logging / auditing unit, a user profile engine, a report module and a user interface engine. The controller manages the core functions and the transmission of data between the data access manager components. The lookup module enables a user to query patient data. The clinical authorization engine authorizes access to patient data. The logging / auditing unit logs and monitors user activity. The user profile engine accesses and updates user profile information. The patient profile engine accesses and updates patient profile information. The report module generates reports related to the user activity. The user interface engine generates user interfaces for displaying the user profiles and patient information data.
Owner:HEALTH CATALYST INC
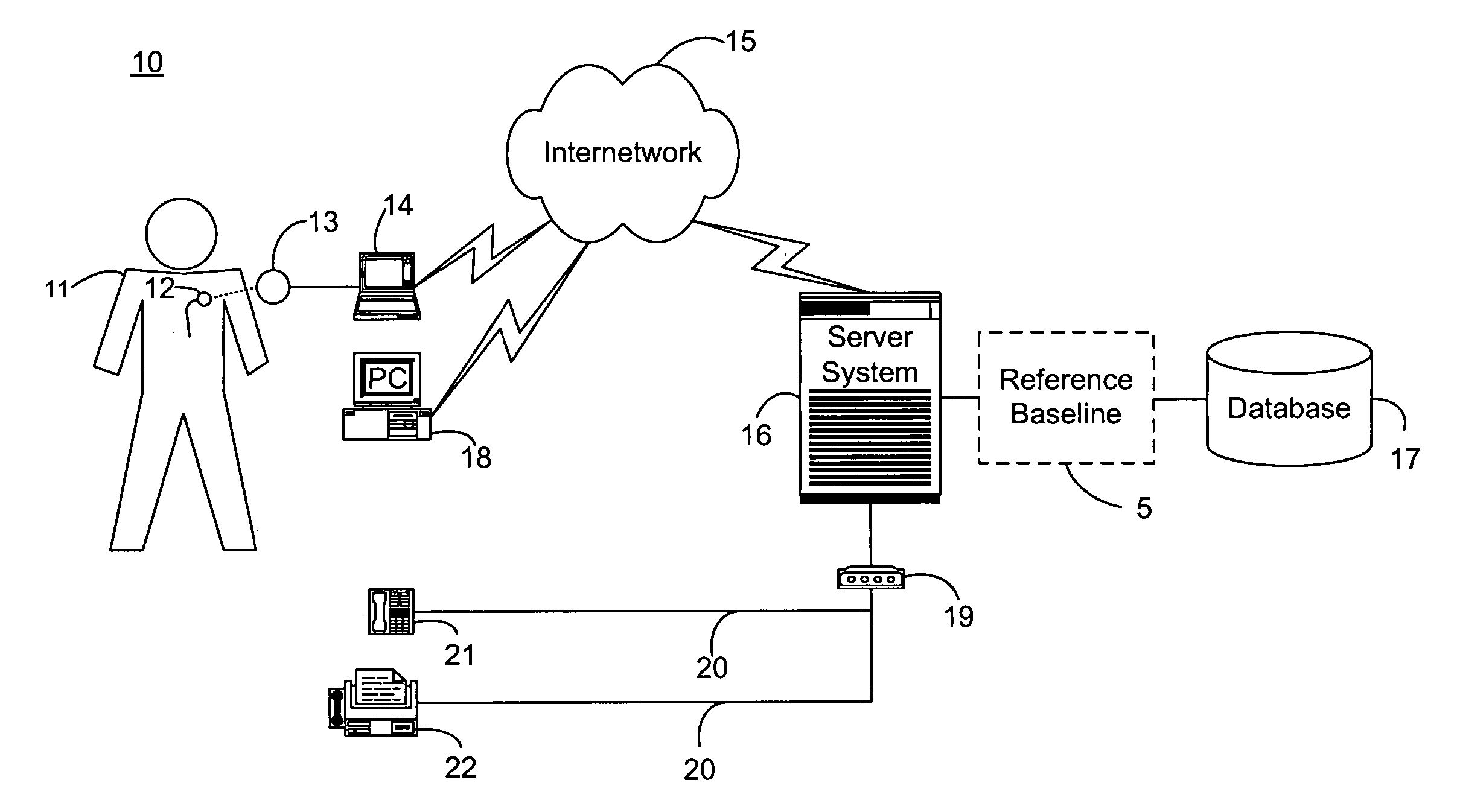
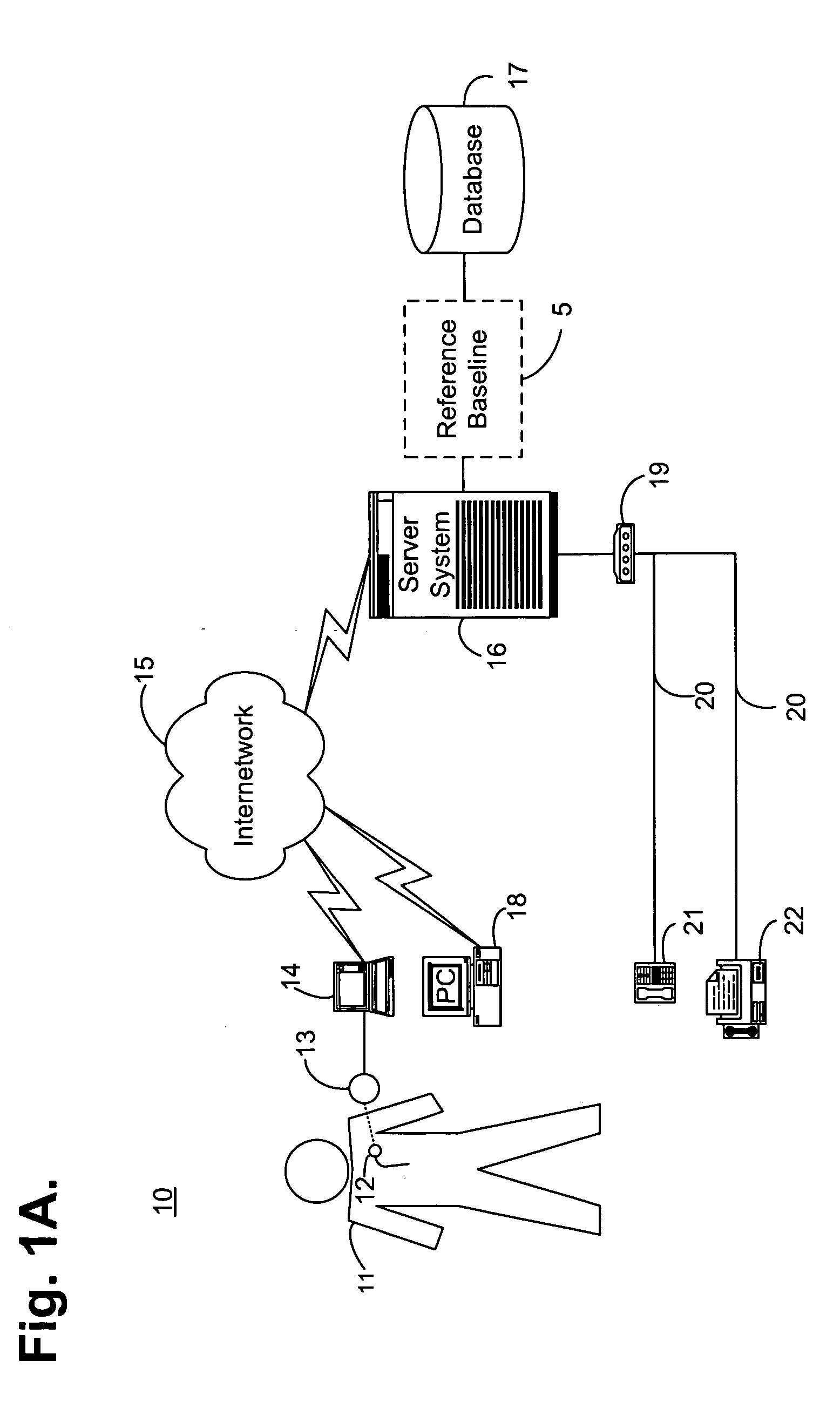
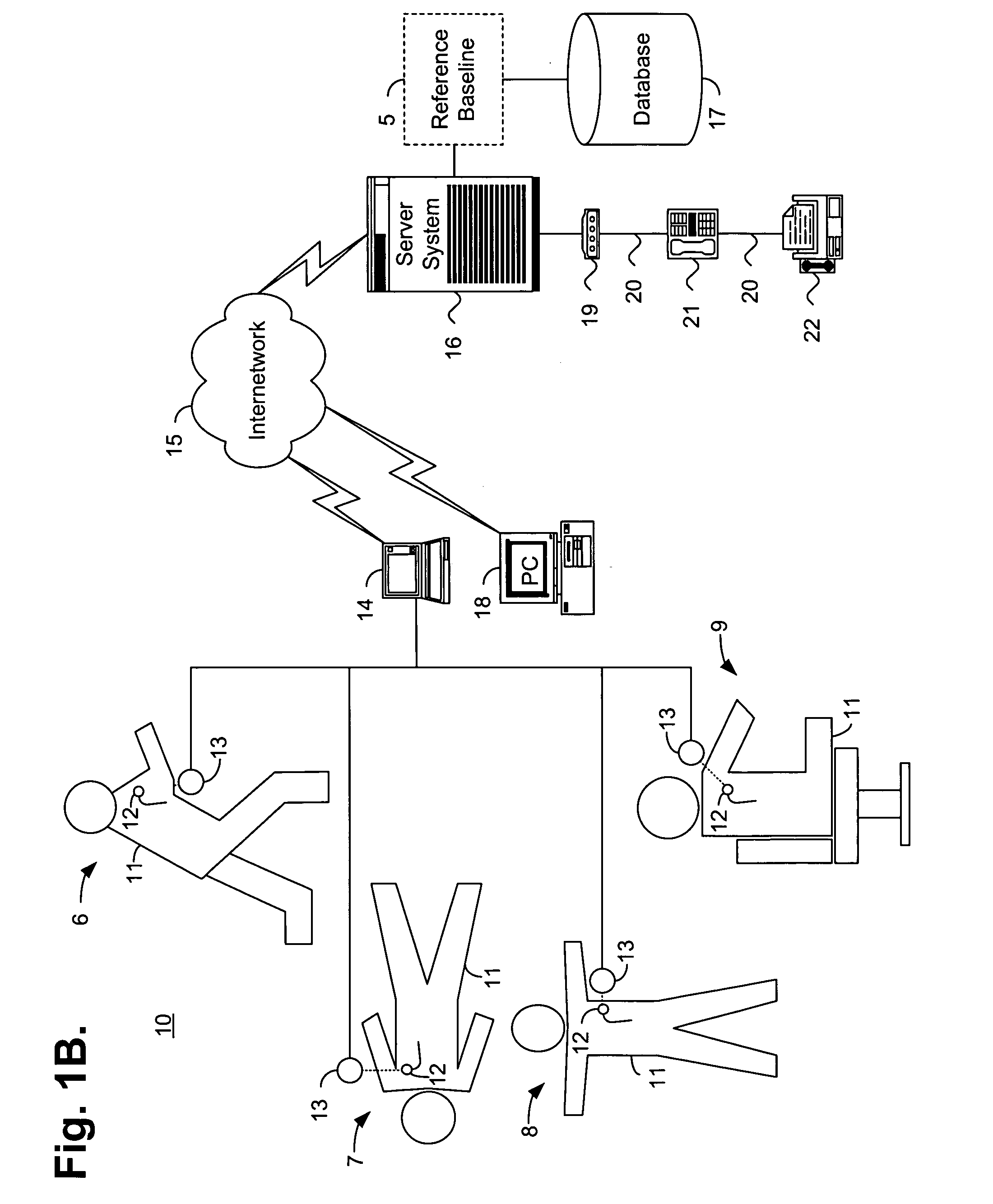
System and method for determining a reference baseline record
InactiveUS20050182308A1Improve accuracyElectrotherapyHealth-index calculationEmergency medicinePatient status
A system and method for determining a reference baseline record for use in automated patient care. One or more physiological measures are retrieved. Each of the measures relates to individual patient information recorded during an initial observation period from a patient care record. One or more reference measures are determined from the physiological measures. Each reference measure is representative of at least one of measured and derived patient information. The reference measures are stored into the patient care record indicating a reference baseline patient status.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Visual imaging system for ultrasonic probe
InactiveUS20070167709A1Optimize locationEasy to determineDiagnostic probe attachmentInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationNon invasive
A non-invasive visual imaging system is provided, wherein the imaging system procures an image of a transducer position during diagnostic or therapeutic treatment. In addition, the system suitably provides for the transducer to capture patient information, such as acoustic, temperature, or ultrasonic images. For example, an ultrasonic image captured by the transducer can be correlated, fused or otherwise combined with the corresponding positional transducer image, such that the corresponding images represent not only the location of the transducer with respect to the patient, but also the ultrasonic image of the region of interest being scanned. Further, a system is provided wherein the information relating to the transducer position on a single patient may be used to capture similar imaging planes on the same patient, or with subsequent patients. Moreover, the imaging information can be effectively utilized as a training tool for medical practitioners.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
System and method for diagnosing and monitoring outcomes of atrial fibrillation for automated remote patient care
A system for diagnosing and monitoring outcomes of atrial fibrillation for remote patient care is presented. A database stores monitoring sets containing recorded measures relating to patient information recorded on a substantially continuous basis. A server retrieving and processing a plurality of the monitoring sets includes a comparison module receiving a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation and determining patient status changes in response to the atrial fibrillation diagnosis by comparing periodically recorded measures from each of the monitoring sets to other recorded measures from another of the monitoring sets with both recorded measures relating to a same type of patient information; and an analysis module evaluating on a periodic basis each patient status change for an absence, an onset, a progression, a regression, and a status quo of atrial fibrillation against a predetermined indicator threshold corresponding to the same type of patient information as the recorded measures which were compared.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
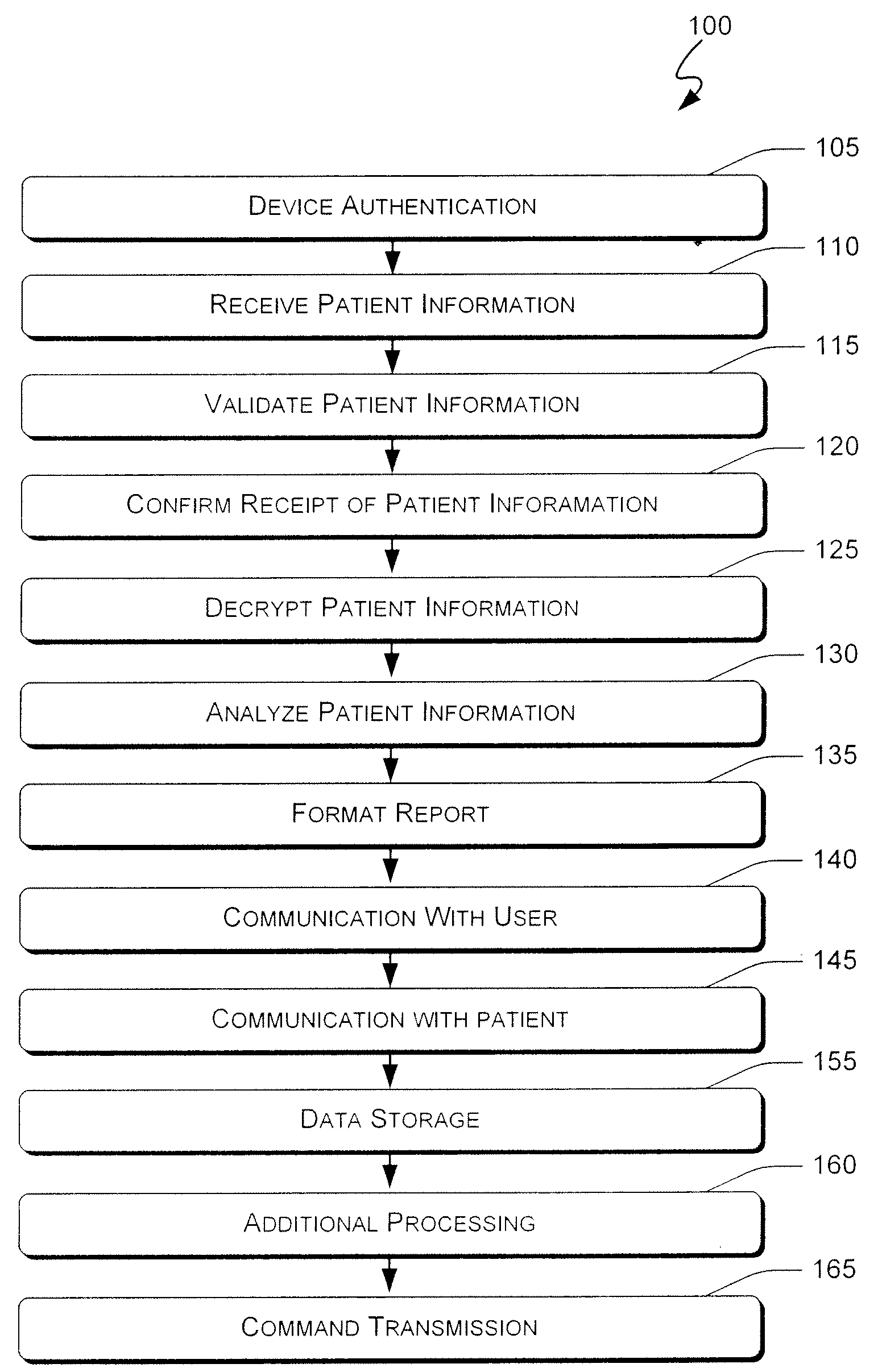
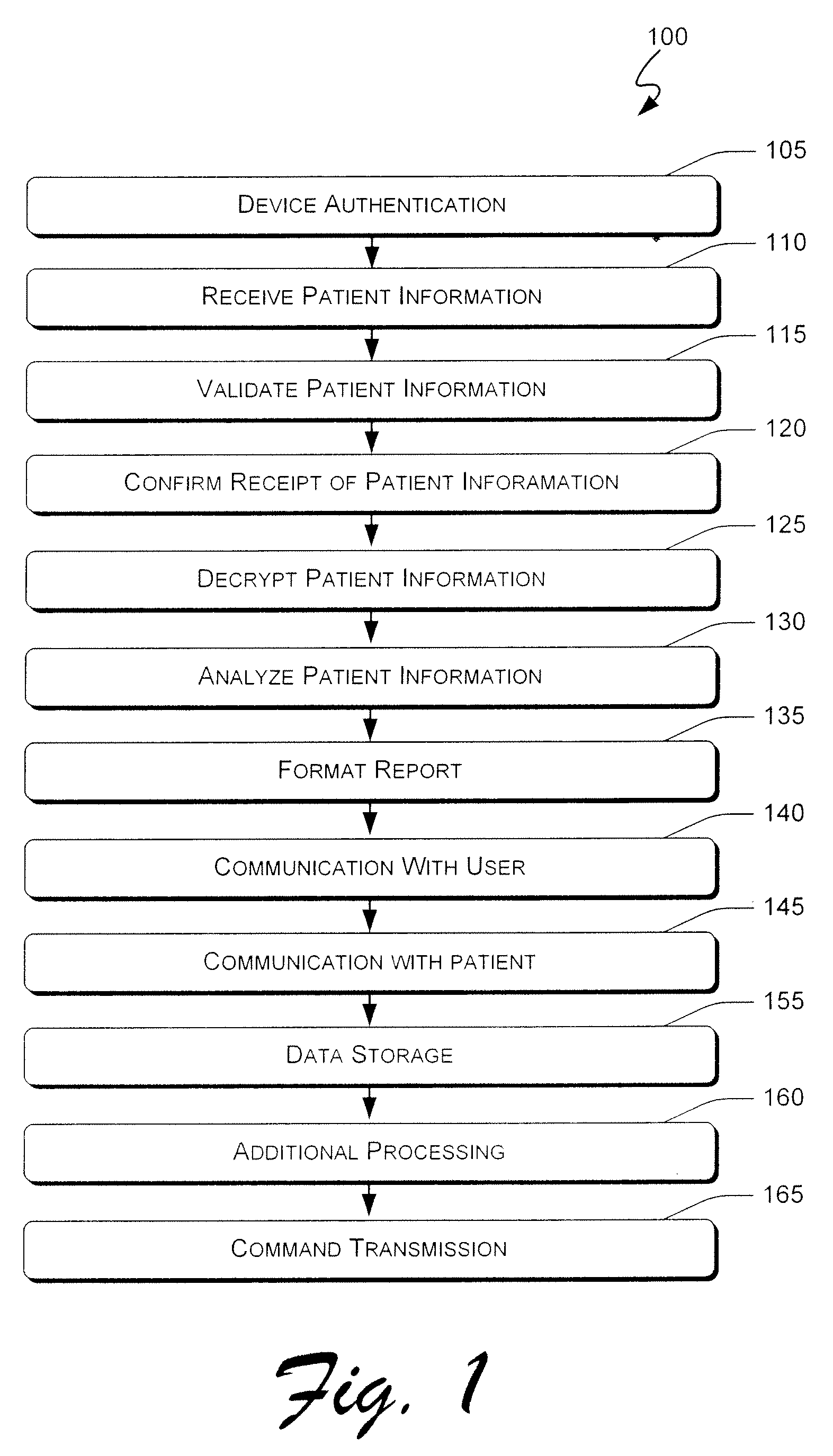
Systems and methods for remote patient monitoring and user interface
ActiveUS20080097793A1Quickly and efficiently provideQuickly and efficiently and retrieveDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPatient monitorMedical device
A method according to one aspect of the present invention includes receiving patient information, analyzing the patient information to identify a condition for the patient, and formatting a report based on the patient information and the patient condition. Embodiments of the present invention may be used to monitor any appropriate medical device from essentially any location from which a communications signal can be sent and received. This enables patients to enjoy an active lifestyle by not being tied to medical device monitoring equipment that is difficult or impossible to transport or having to routinely visit health care facilities. Multiple reports can be formatted to include any desired amount and type of information, and can be transmitted selectively to any number of users.
Owner:MEDAPPS
Method and platform/system for creating a web-based form that incorporates an embedded knowledge base, wherein the form provides automatic feedback to a user during and following completion of the form
PendingUS20180301222A1Digital data information retrievalHealth-index calculationMedical recordIcd codes
A web-based platform for guiding a user's encounter with a patient and for generating a medical record of the encounter. The web-based platform comprises a processor in communication with an output display device and an input user interface, a knowledge base. The processor outputs information to the output display device, accesses the knowledge base, and receives information from the input user interface. The output display device requests patient information in response to presented successive prompts for patient medical information. The prompts are responsive to the knowledge base and to prior responses to prior prompts as entered through the input user interface. The output display device presents a patient medical condition report based on responses to requests and prompts. ICD codes are included within the knowledge base and included within the patient medical condition report. The codes are determined, as applicable, as each prompt and response is entered.
Owner:AUTOMATED CLINICAL GUIDELINES
Method for accessing component fields of a patient record by applying access rules determined by the patient
InactiveUS6941271B1Computer security arrangementsDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer scienceMedical care
Owner:SOONG JAMES W
System and method for determining a reference baseline of patient information for automated remote patient care
A system for determining a reference baseline of patient information for automated remote patient care is presented. A medical device regularly records and stores measures sets including individual measures relating to patient information by a medical device adapted to be implanted during an initial time period. A database collects one or more patient care records containing the collected measures sets. A database module stores the collected measures set into a patient care record within the database. A server receives the collected device measures set from the medical device via a receiver. An analysis module within the server processes the collected device measures set into a set of reference measures. Each reference measure is representative of measured or derived patient information. The reference measures set is stored into the patient care record as data in a reference baseline indicating an initial patient status.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
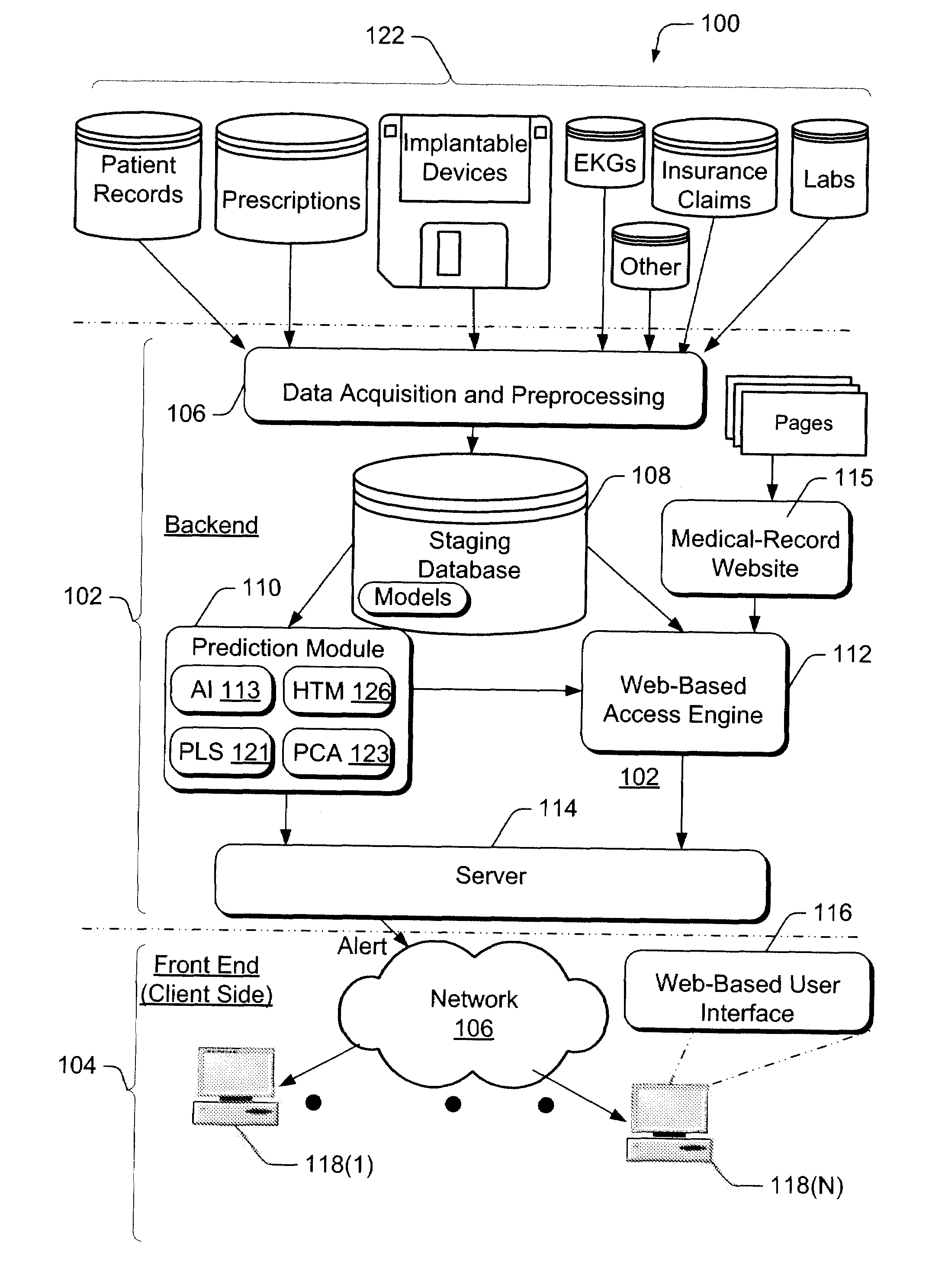
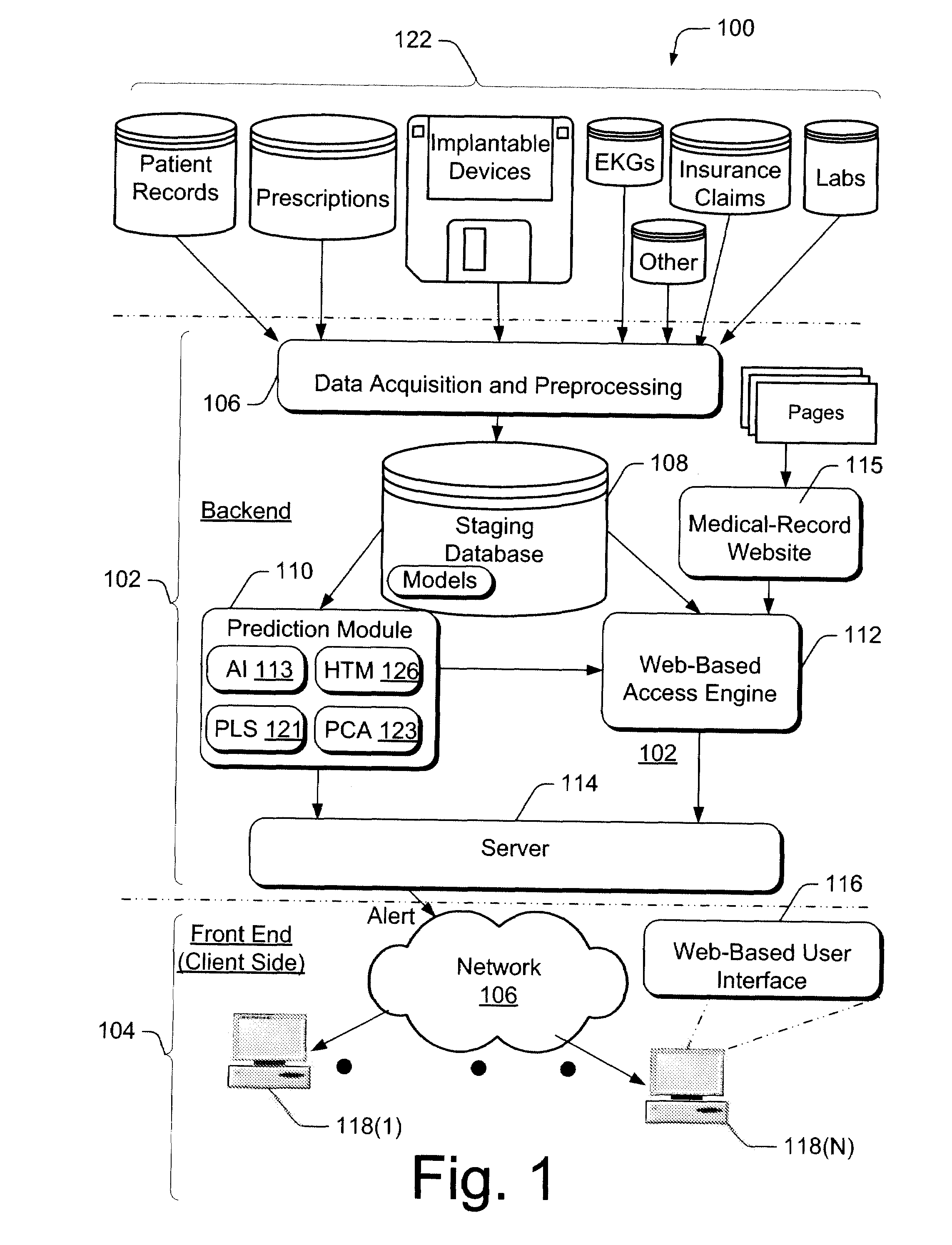
Automated patient-management system for presenting patient-health data to clinicians, and methods of operation thereor
InactiveUS20100131434A1Valid reportHealth-index calculationDigital computer detailsPatient managementPatient data
An automated patient-management system for efficiently reporting patient information to clinicians, and a method of operation thereof is described. The system automatically collects and analyzes historic-physiologic data indicative of a patient's health from a myriad of sources. Based on the historic-physiologic data, the system automatically generates a health-risk score indicative of whether a patient will experience a serious-medical event in the near future (e.g., a predetermined time interval). The system uses a processing model that may rely on Hierarchical-Temporal Memory techniques and other models, for extracting and analyzing patient data. The system also generates an integrated synopsis of a patient's health condition, including the health-risk score. The synopsis is then presented (served) to a clinician in an organized, simplified, and effective manner via a client-side user interface. The synopsis enables a physician to proficiently grasp the patient's most critical health parameters in a short period of time.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Systems and methods for automated diagnosis and decision support for heart related diseases and conditions
InactiveUS20050020903A1Character and pattern recognitionMedical automated diagnosisCoronary artery diseasePatient data
CAD (computer-aided diagnosis) systems and applications for cardiac imaging are provided, which implement methods to automatically extract and analyze features from a collection of patient information (including image data and / or non-image data) of a subject patient, to provide decision support for various aspects of physician workflow including, for example, automated assessment of regional myocardial function through wall motion analysis, automated diagnosis of heart diseases and conditions such as cardiomyopathy, coronary artery disease and other heart-related medical conditions, and other automated decision support functions. The CAD systems implement machine-learning techniques that use a set of training data obtained (learned) from a database of labeled patient cases in one or more relevant clinical domains and / or expert interpretations of such data to enable the CAD systems to “learn” to analyze patient data and make proper diagnostic assessments and decisions for assisting physician workflow.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
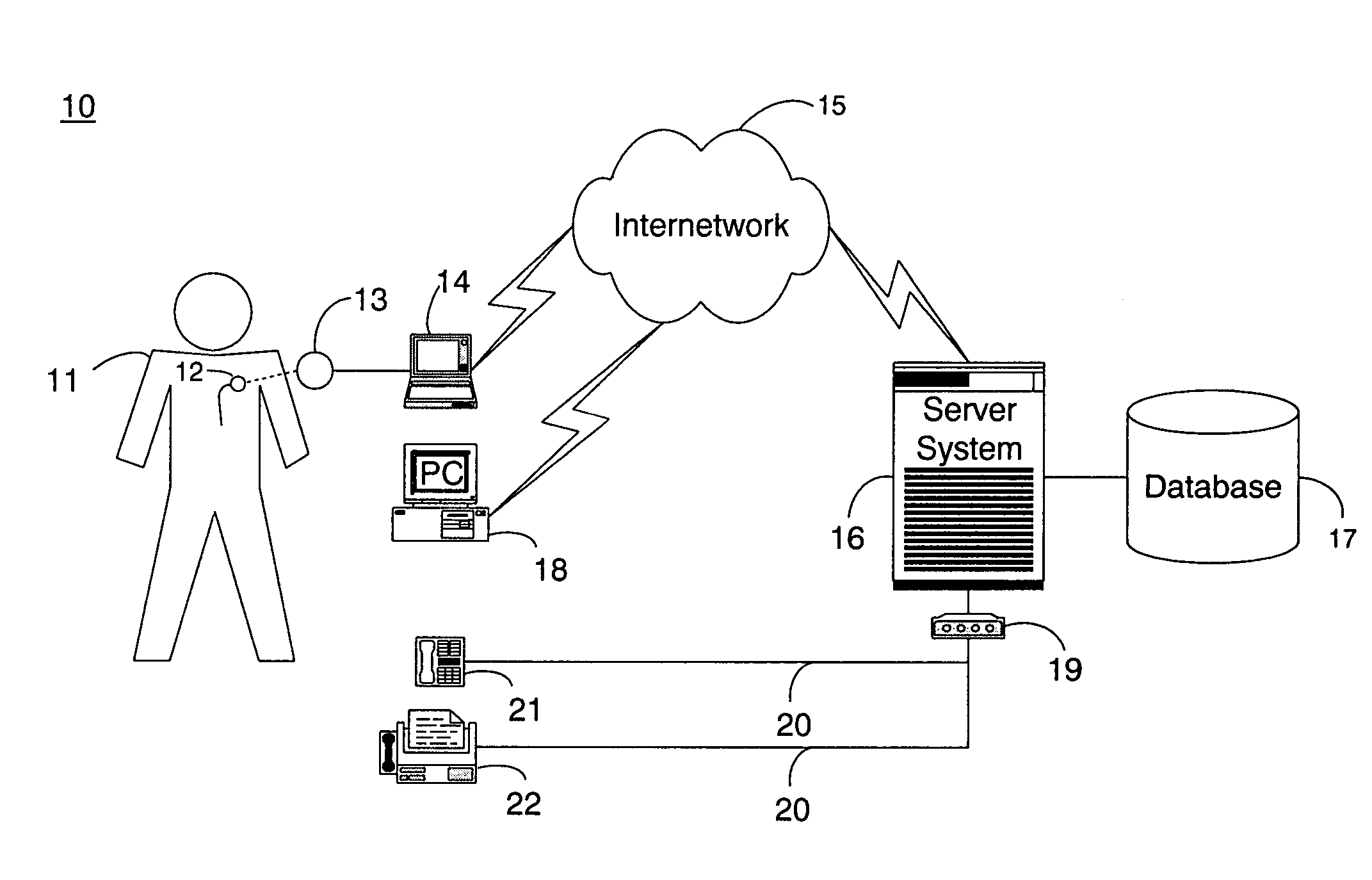
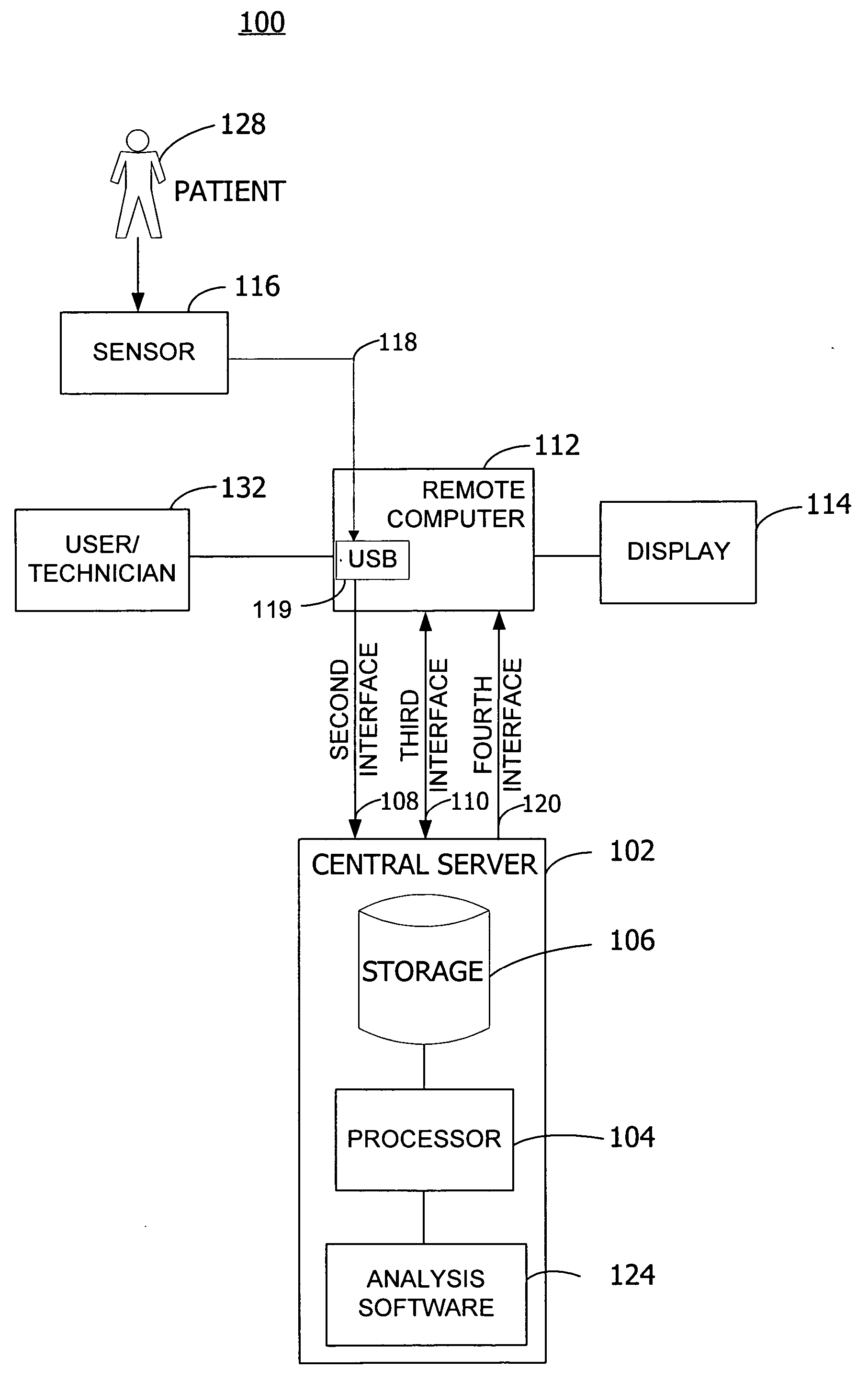
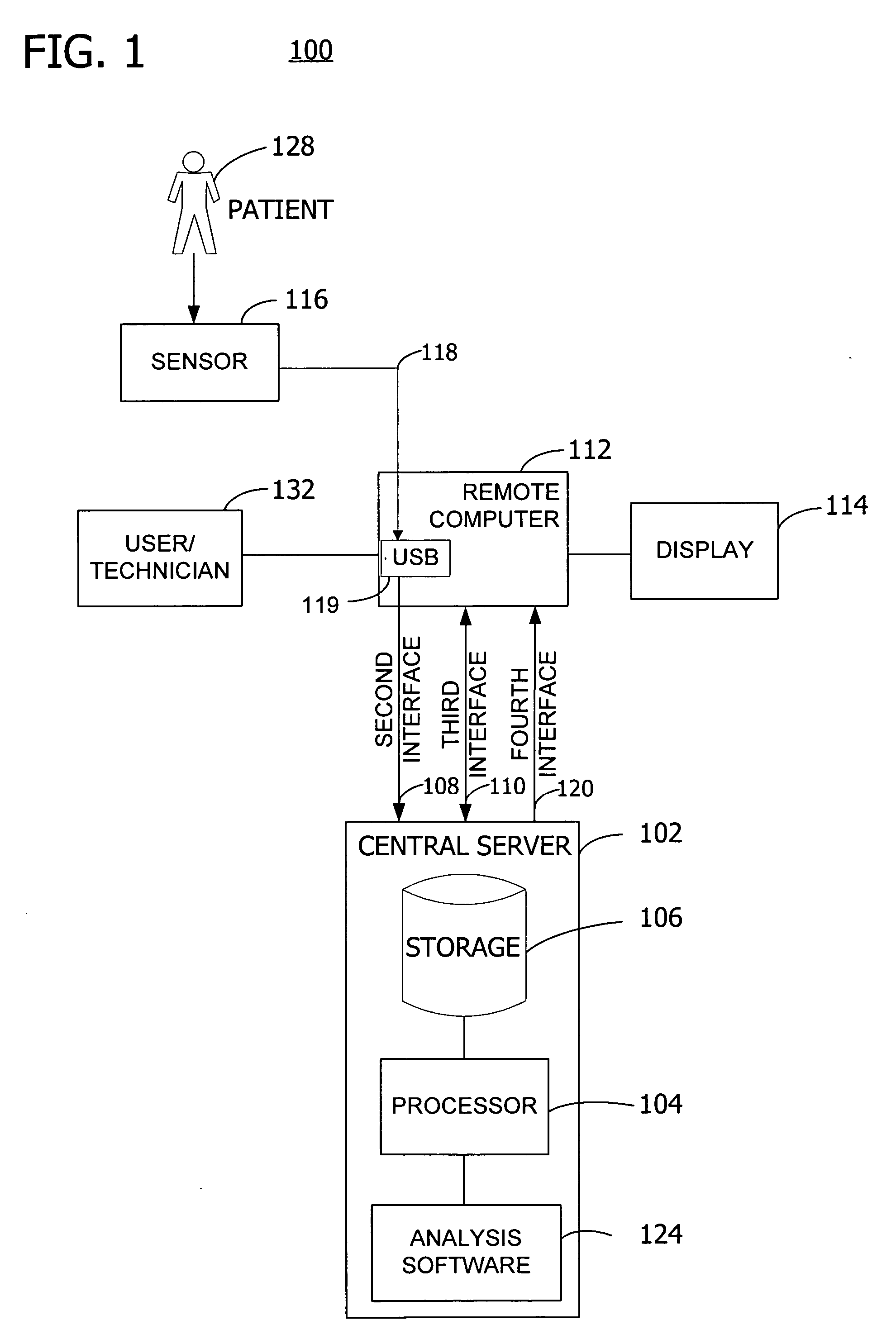
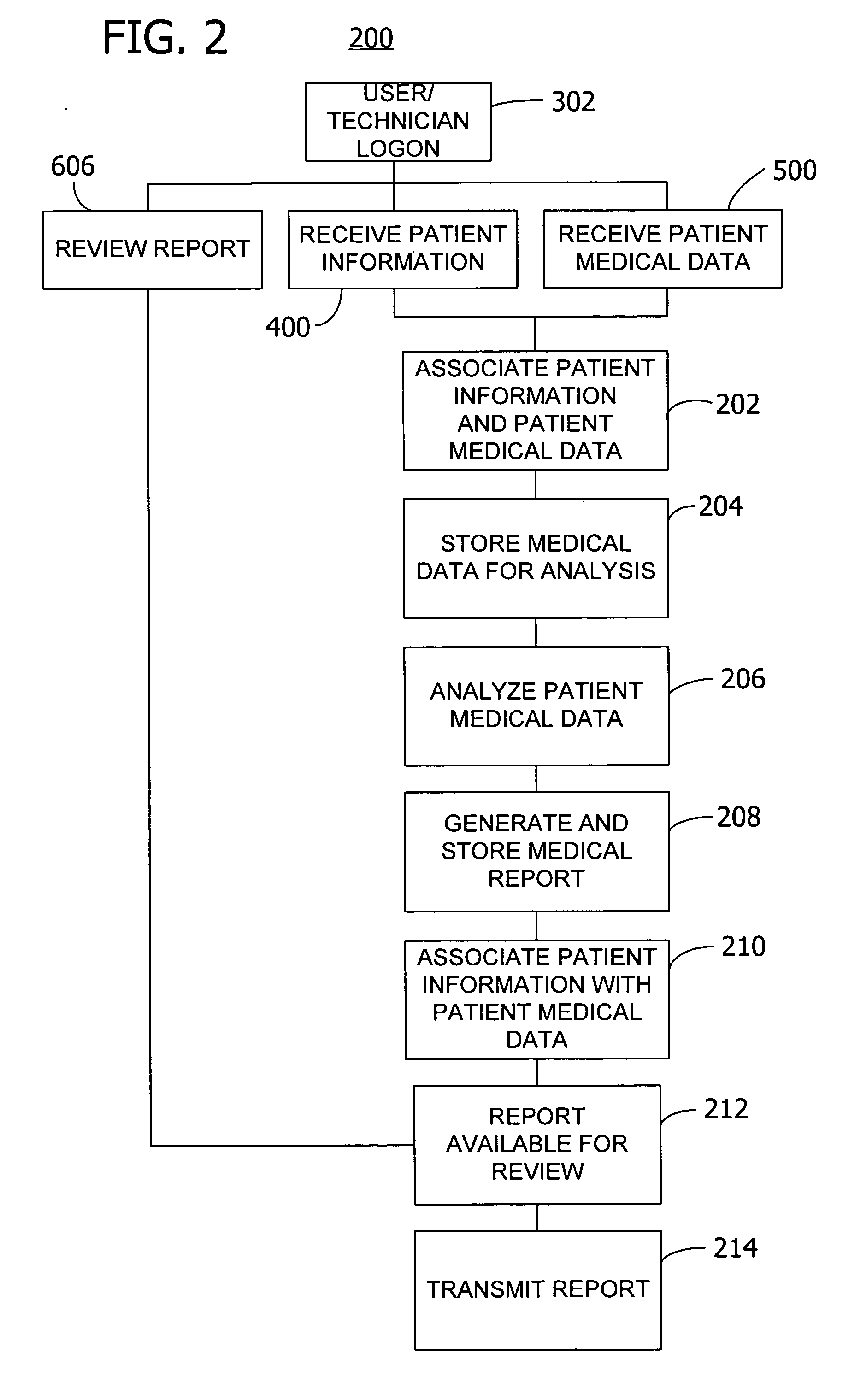
Method and system for collecting and analyzing holter data employing a web site
ActiveUS20050108055A1Secure, timely and efficientMedical communicationLocal control/monitoringWeb siteAnalysis data
A central server controls the receipt and analysis of patient medical data and patient information. The central server receives patient medical data and patient information from a sensor or a remote computer. A storage system of the central server stores the received patient medical data, patient information, and the associated medical report prepared by the analysis software on the central server after analysis of the patient medical data. The medical report associated with the patient medical data is transmitted from the central server to the remote computer. Also, a method controls the acquisition and analysis of patient medical data over a network by a central server from a remote computer operably interconnected by the network with the central server.
Owner:ERESTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com