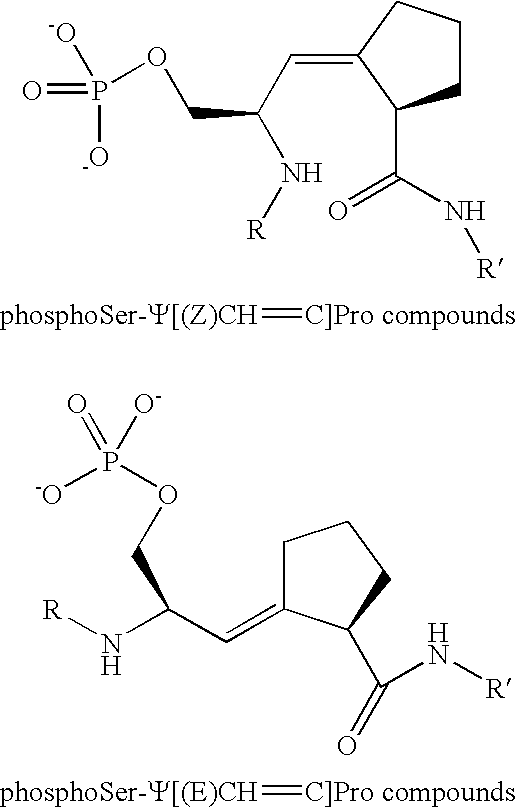
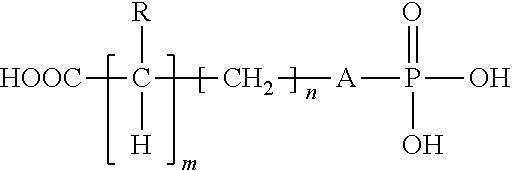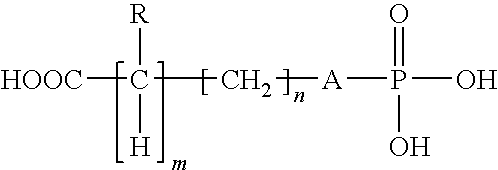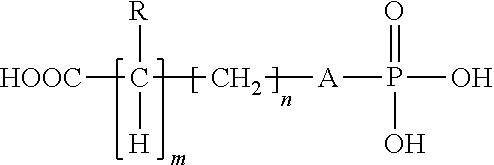Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Phosphoserine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
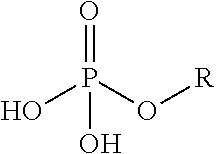
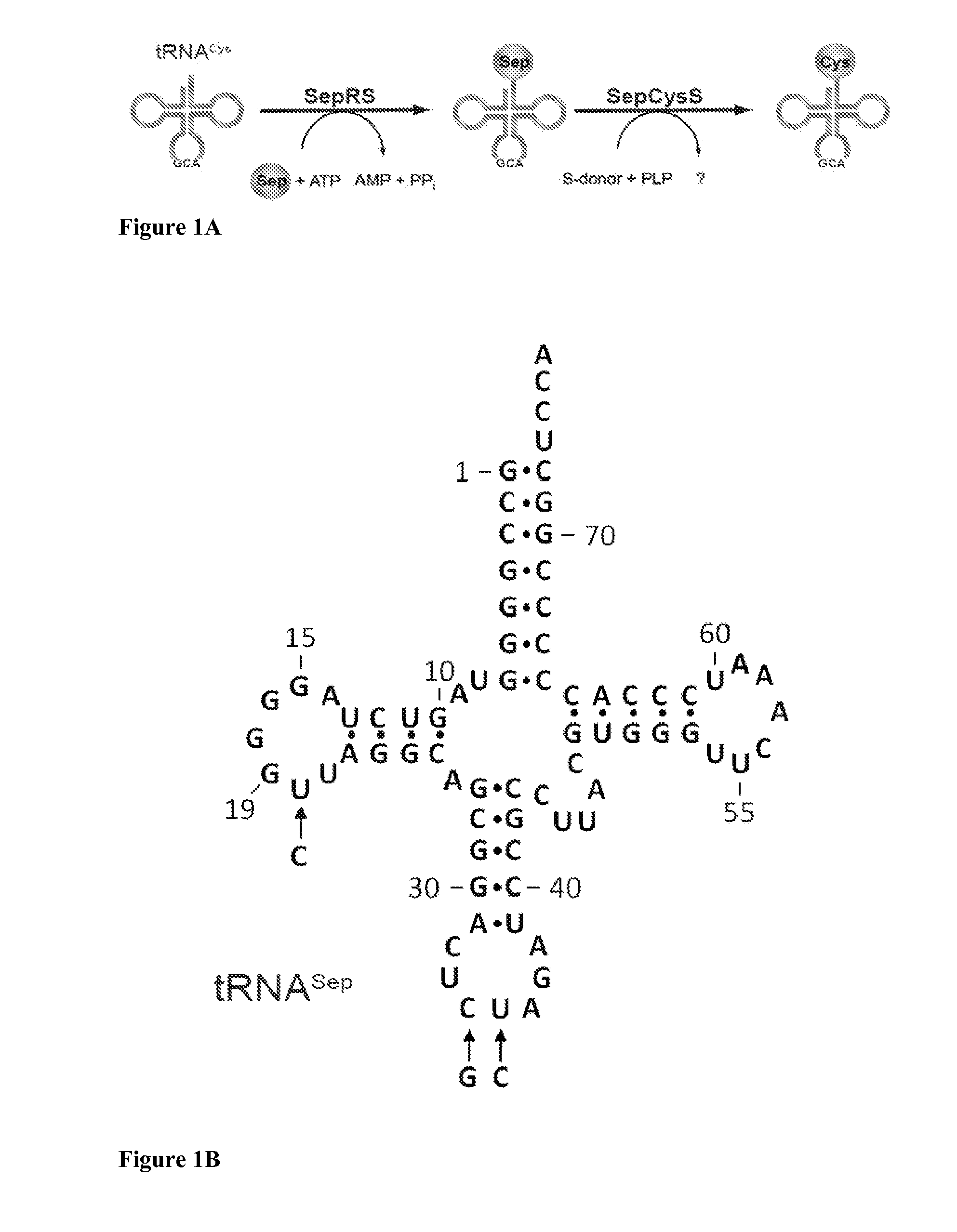
Phosphoserine (abbreviated as SEP or J) is an ester of serine and phosphoric acid. Phosphoserine is a component of many proteins as the result of posttranslational modifications. The phosphorylation of the alcohol functional group in serine to produce phosphoserine is catalyzed by various types of kinases. Through the use of technologies that utilize an expanded genetic code, phosphoserine can also be incorporated into proteins during translation.
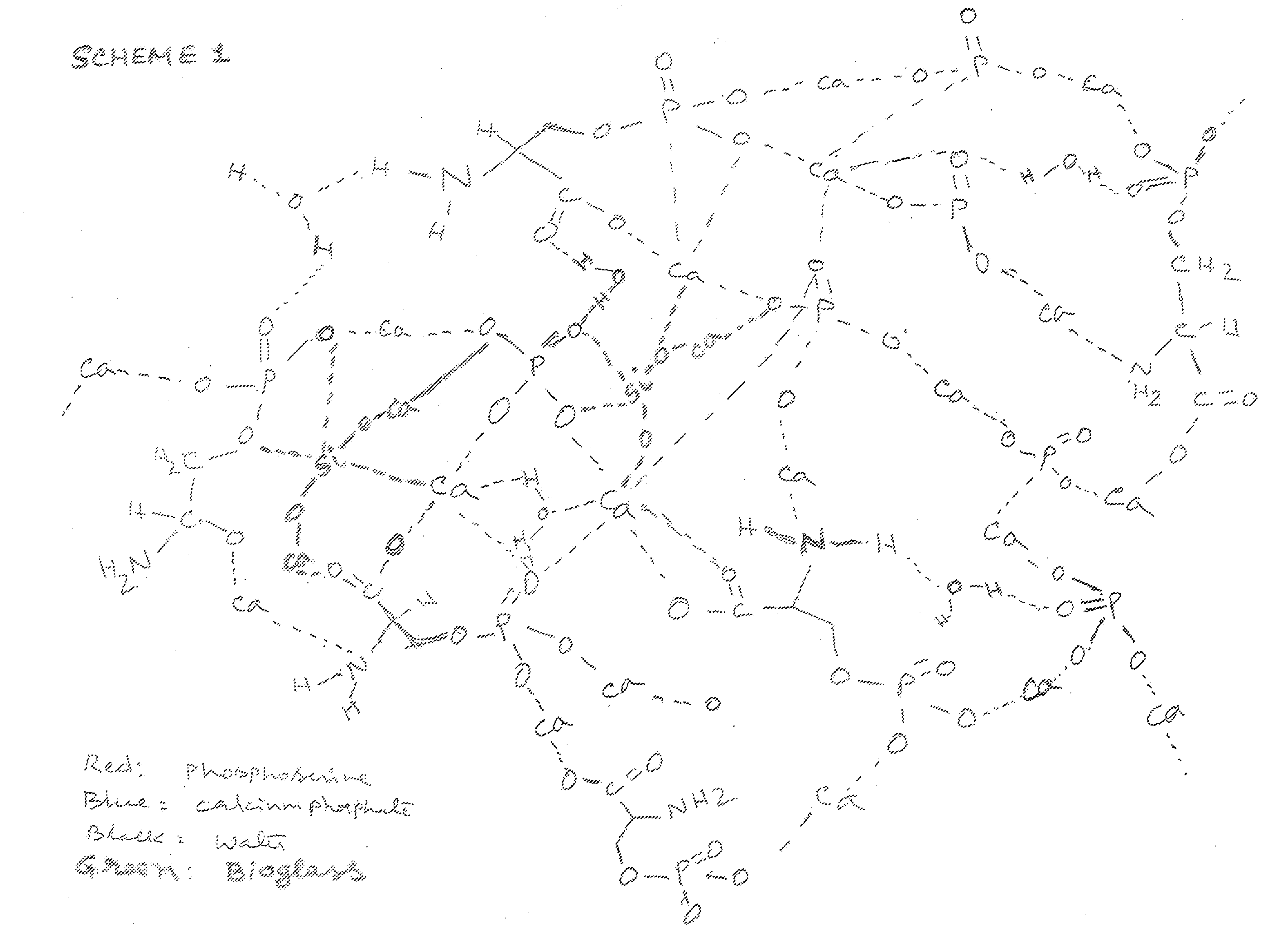
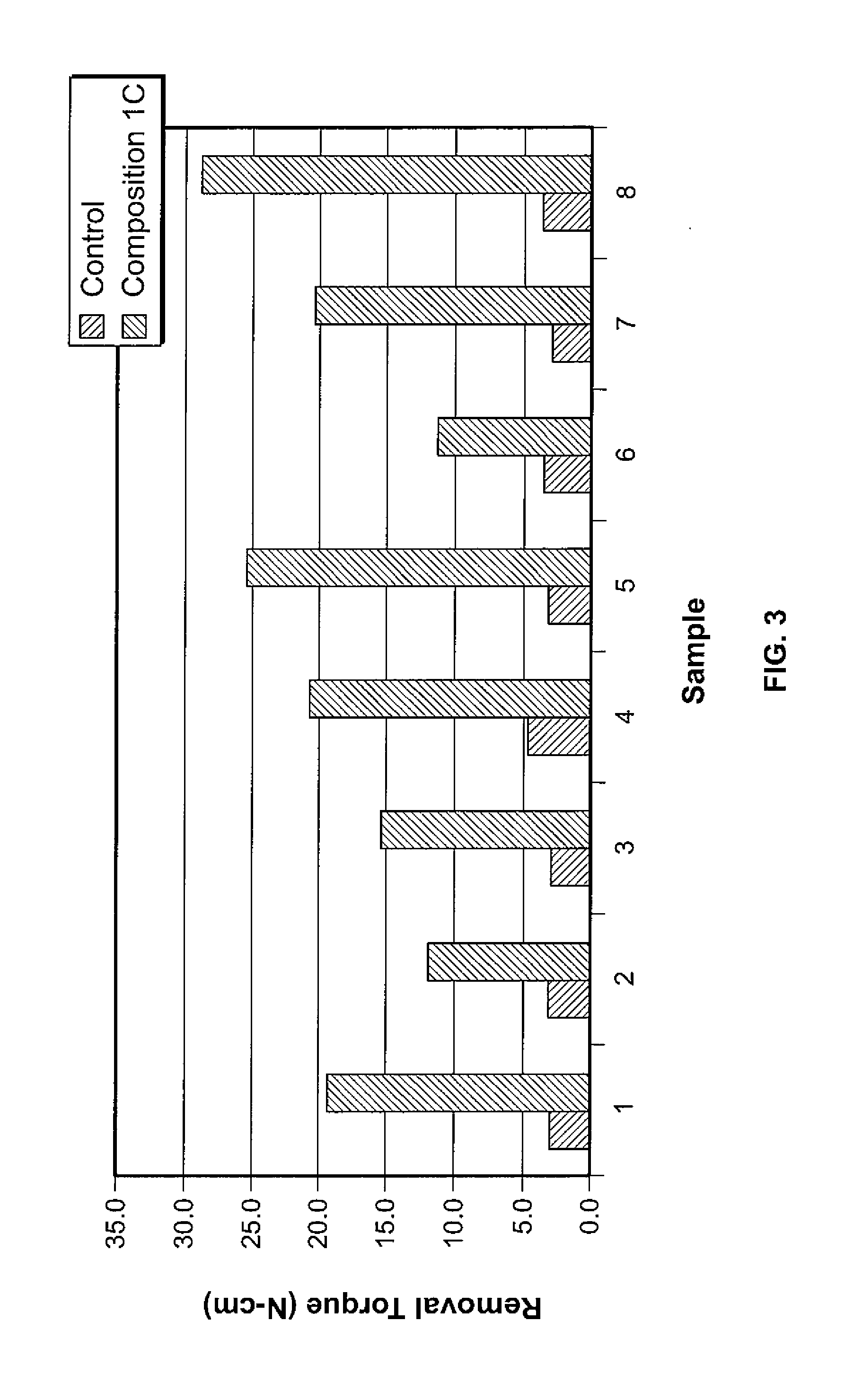
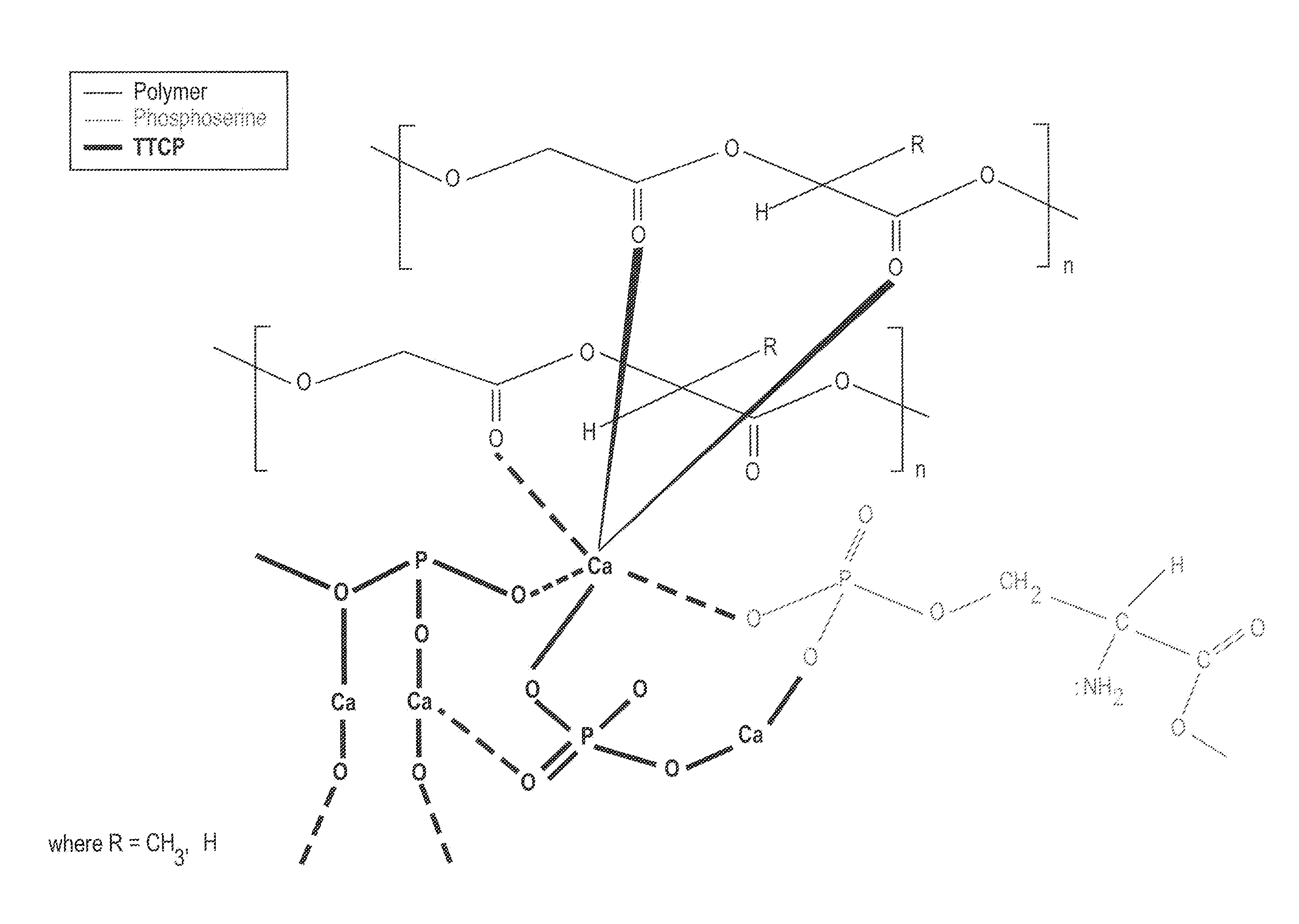
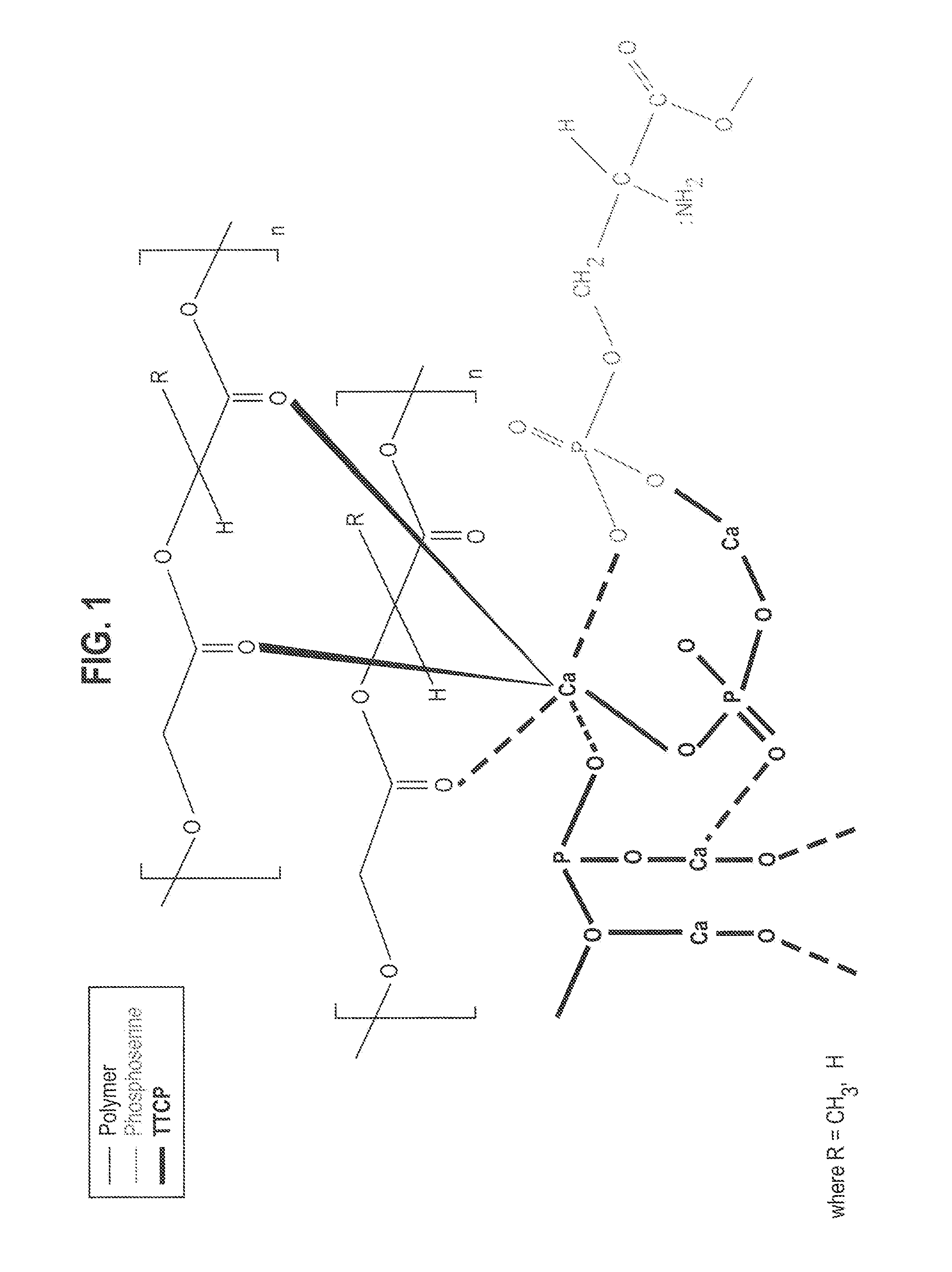
Organophosphorous, Multivalent Metal Compounds, and Bioactive Glass Material Macromolecular Network Compositions and Methods
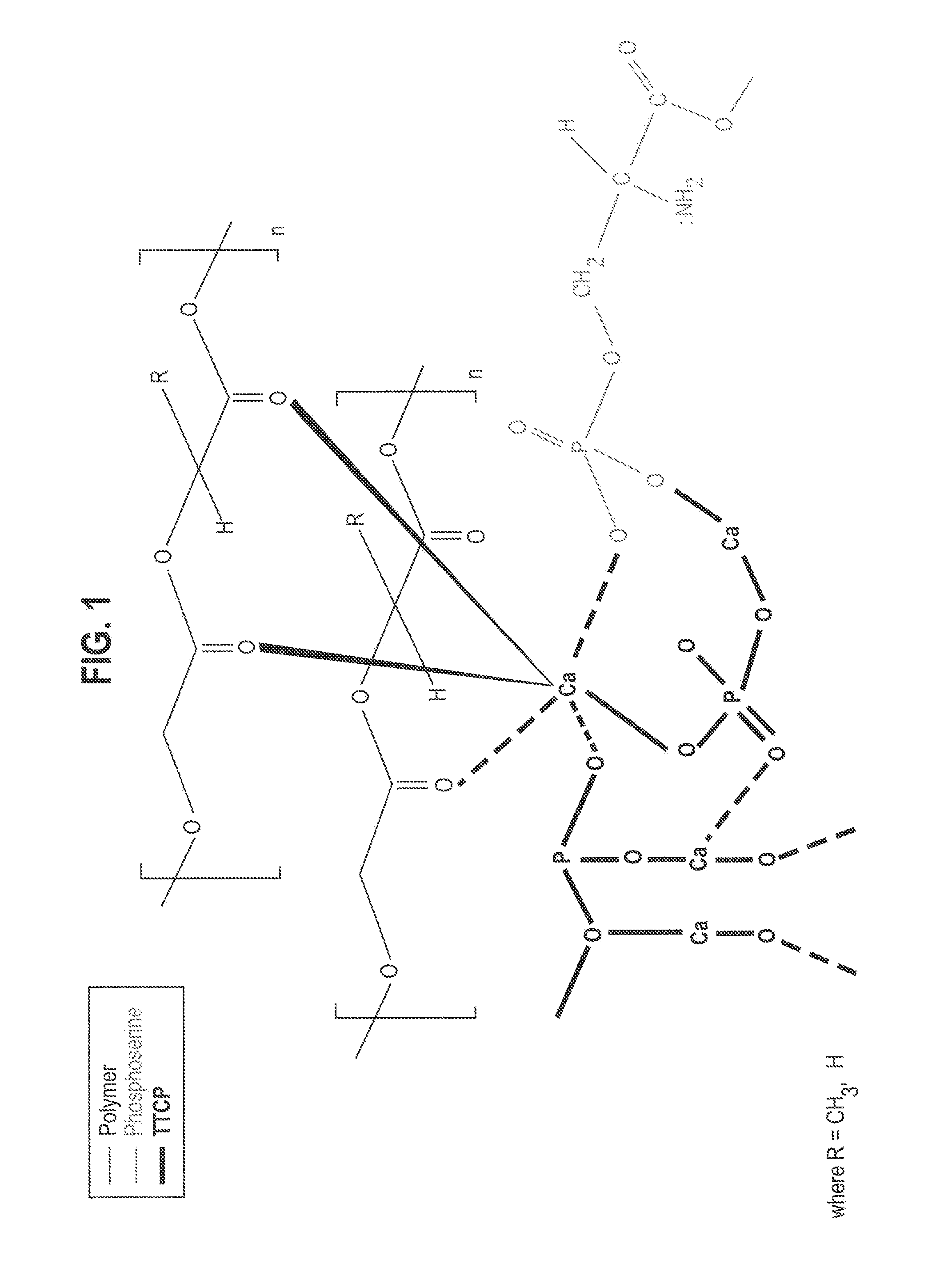
Cements containing certain small molecule amino acid phosphate compounds such as phosphoserine and certain multivalent metal compounds such as but not limited to calcium phosphate have been found to have improved properties and form a macromolecular network in the presence of a bioactive glass material that contain silicates, phosphates, and calcium salts which can be involved in the formation of bonding sites.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
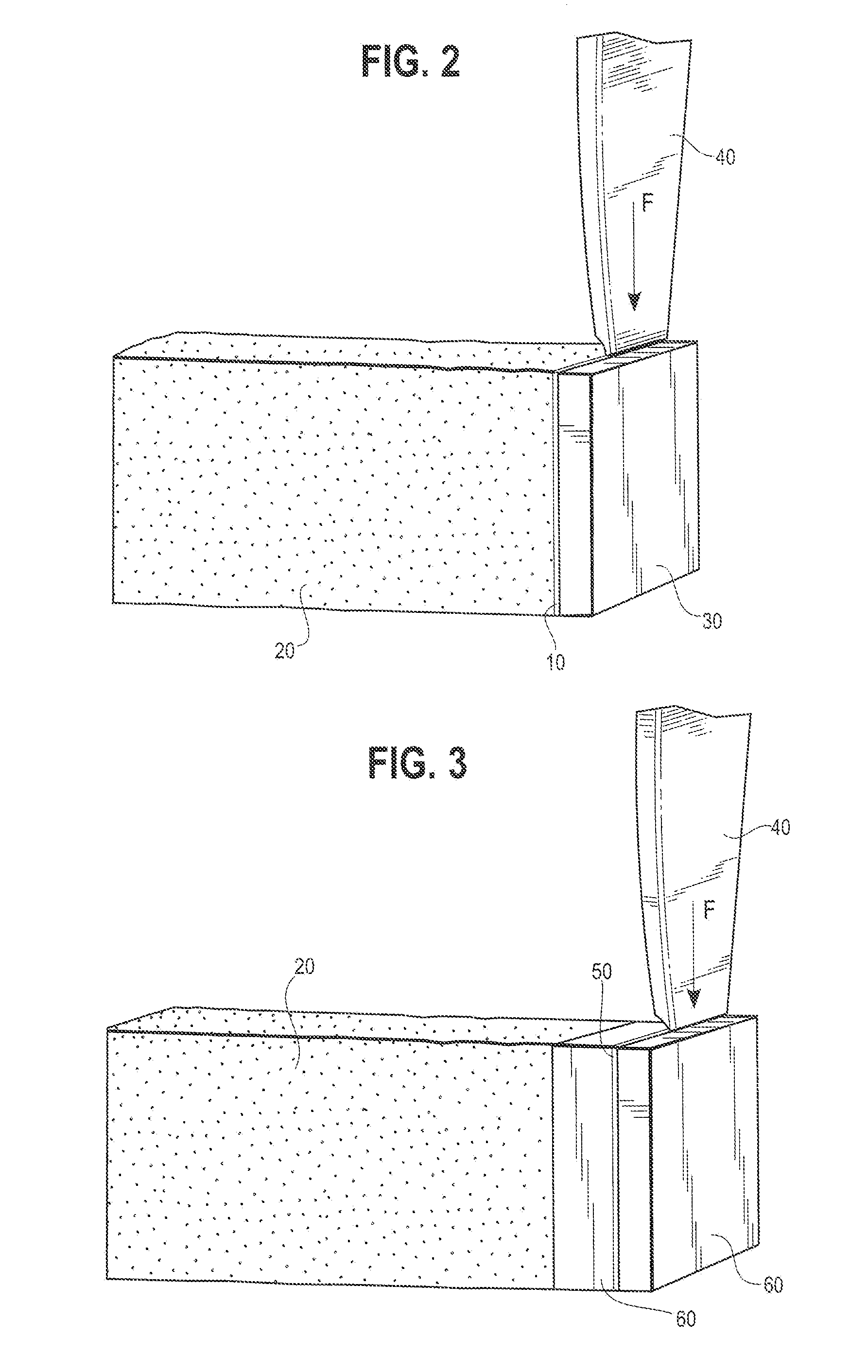
Tetra Calcium Phosphate Based Organophosphorus Compositions and Methods
Compositions and methods of their use to adhere a variety of materials together are disclosed herein. The compositions include at least tetra calcium phosphate, an effective amount of a compound that is structurally similar to phosphoserine, and can be mixed with an aqueous solution. The compositions provide adhesive and cohesive strength in both wet and dry environments and exhibit significant bond strength upon curing.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Organophosphorous, Multivalent Metal Compounds, & Polymer Adhesive Interpenetrating Network Compositions & Methods
Certain small molecule amino acid phosphate compounds such as phosphoserine and certain multivalent metal compounds such as calcium phosphate containing cements have been found to have improved properties and form an interpenetrating network in the presence of a polymer that contain either an electronegative carbonyl oxygen atom of the ester group or an electronegative nitrogen atom of the amine group as the bonding sites of the polymer surfaces to the available multivalent metal ions.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
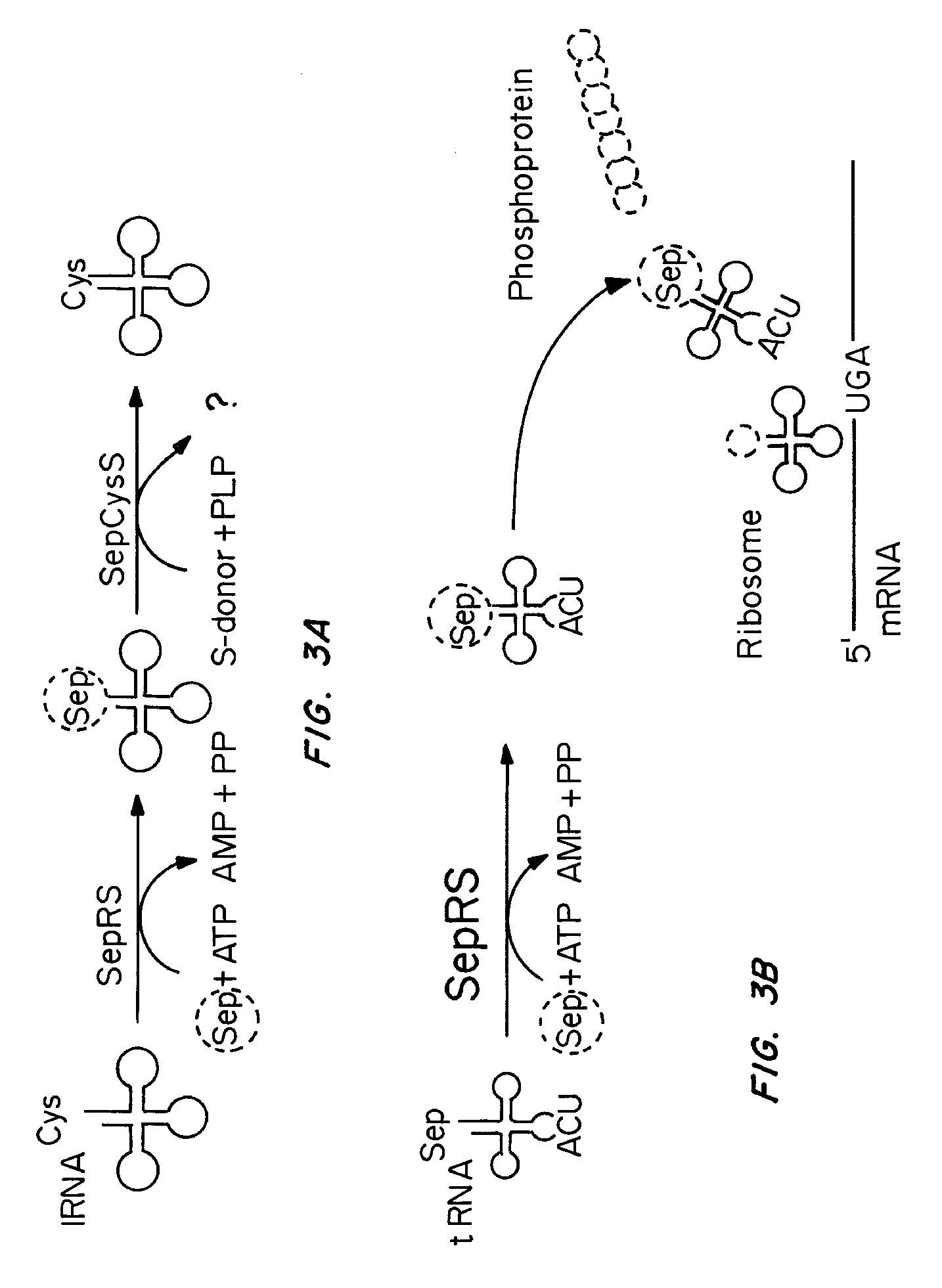
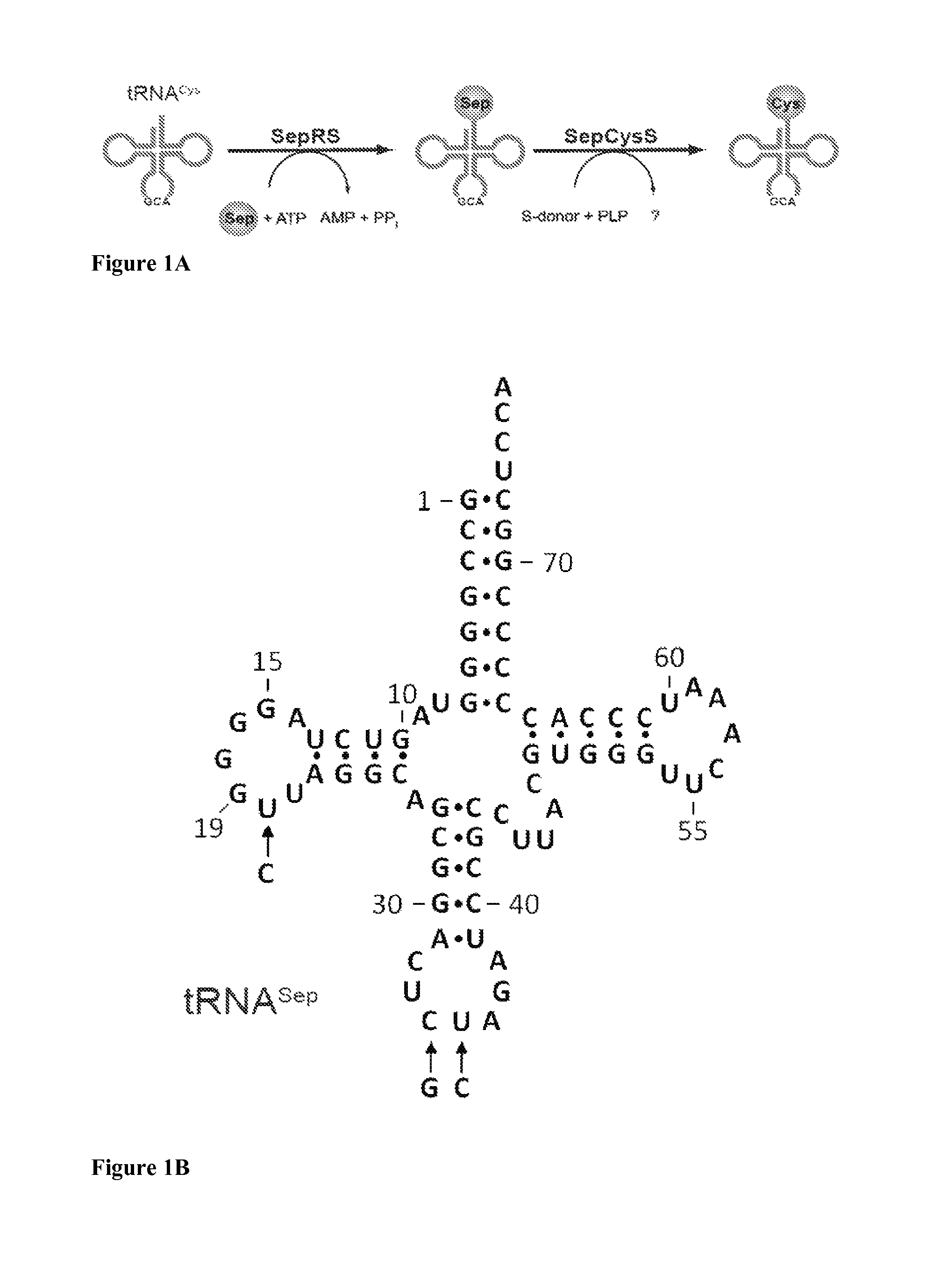
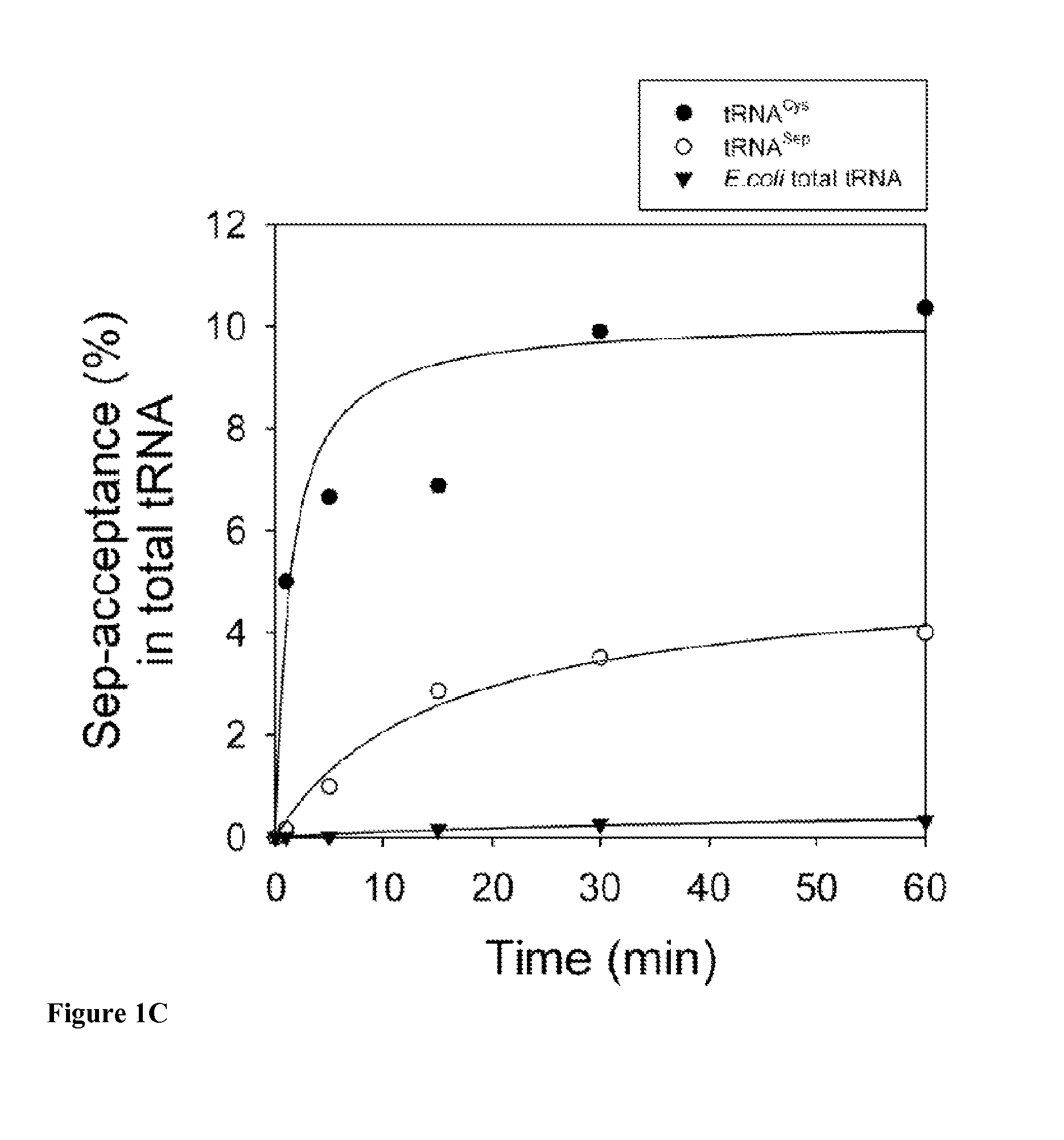
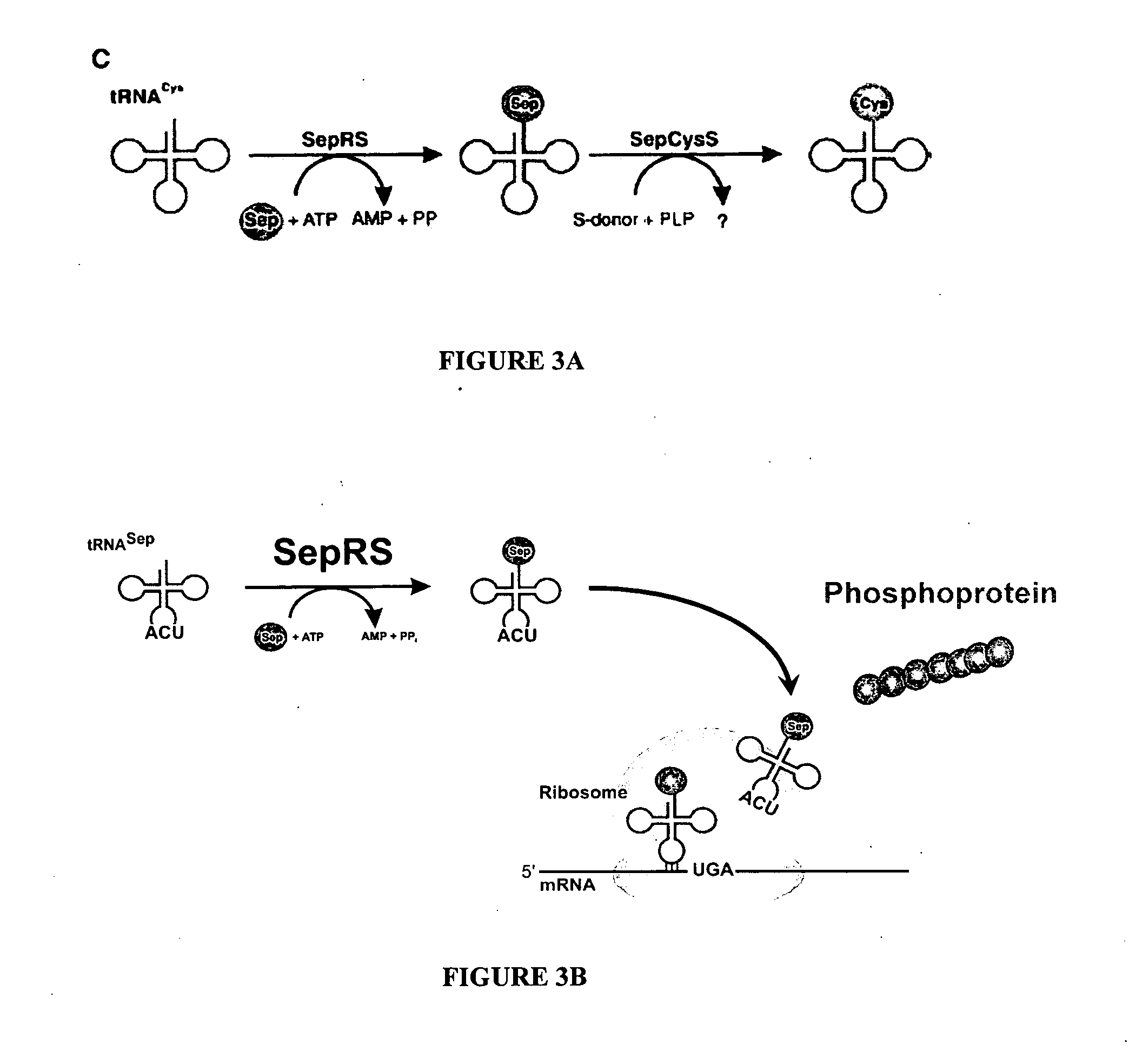
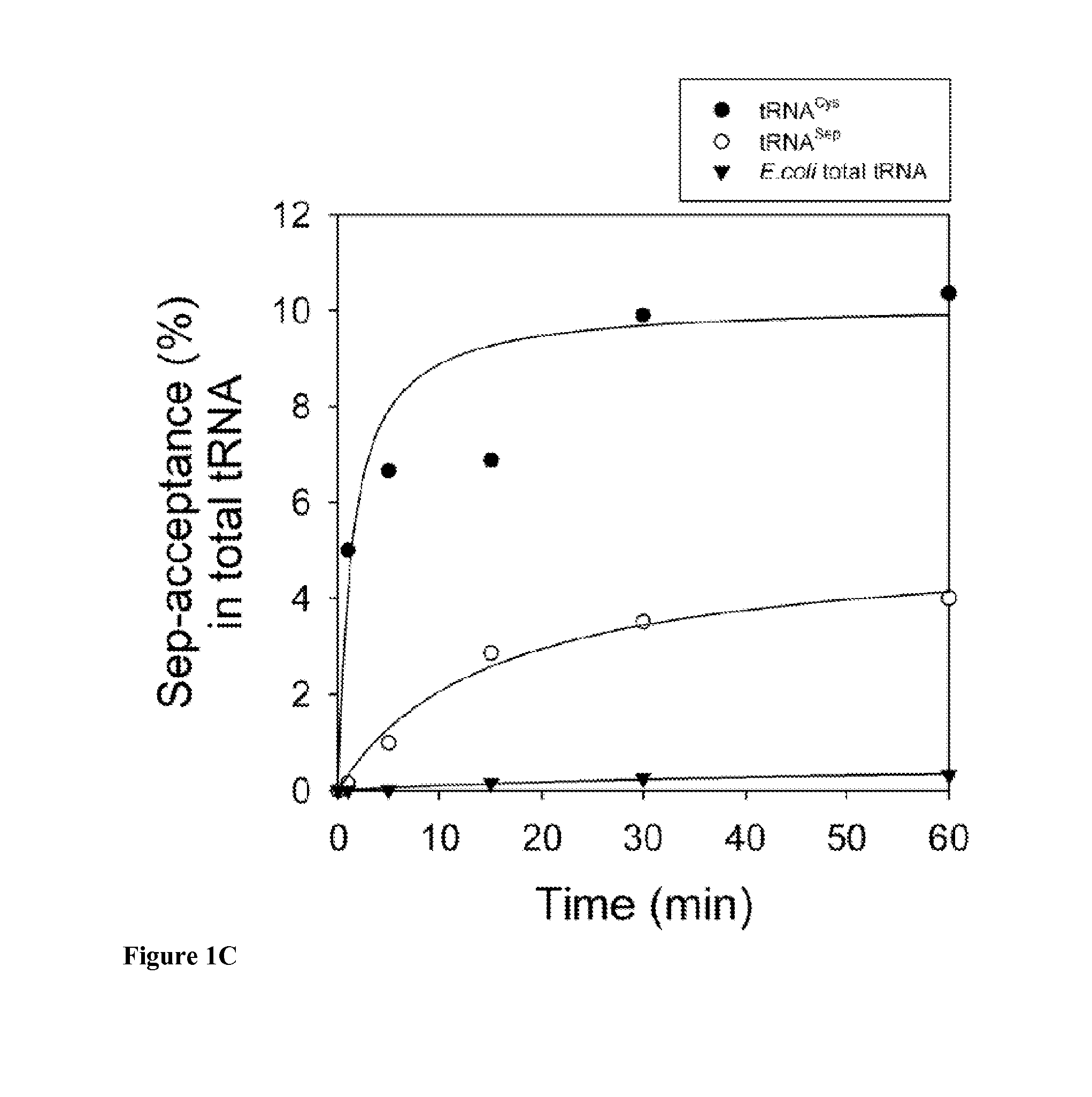
Site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into polypeptides using phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase
Nucleic acids encoding genes with SepRS and tRNASep activity for site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into a protein or polypeptide and methods of use thereof are described. Typically, SepRS preferentially aminoacylates tRNASep with O-phosphoserine and the tRNASep recognizes at least one codon such as a stop codon. In a preferred embodiment the nucleic acids are on vectors. In one embodiment, the vectors are expressed in cells such as bacterial cells, archeaebacterial cells, and eukaryotic cells. In an alternative embodiment, the vectors are expressed in an in vitro transcription / translation system. Proteins or polypeptides containing phosphoserine produced by the methods described herein can be used for a variety of applications such as research, antibody production, protein array manufacture and development of cell-based screens for new drug discovery.
Owner:YALE UNIV
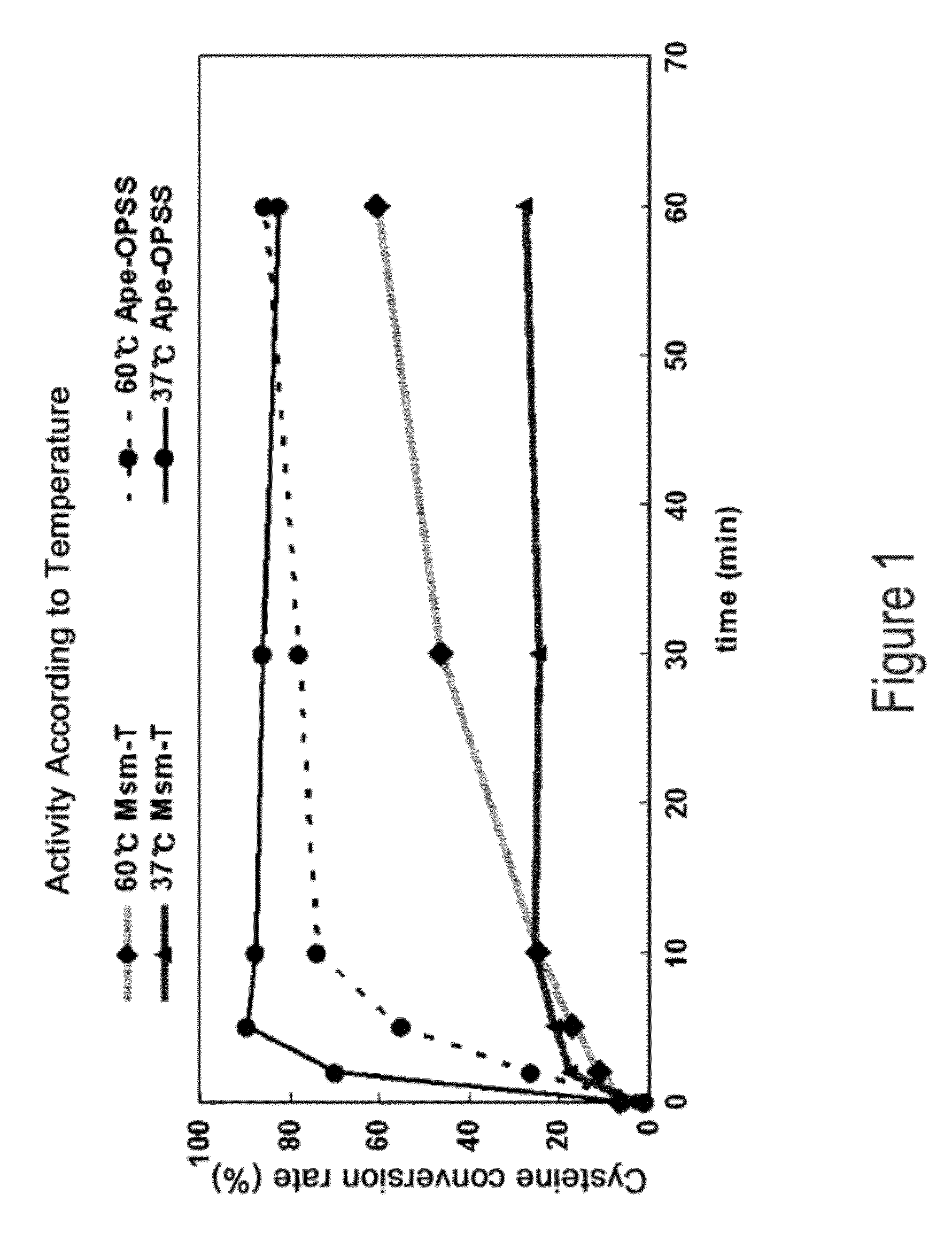
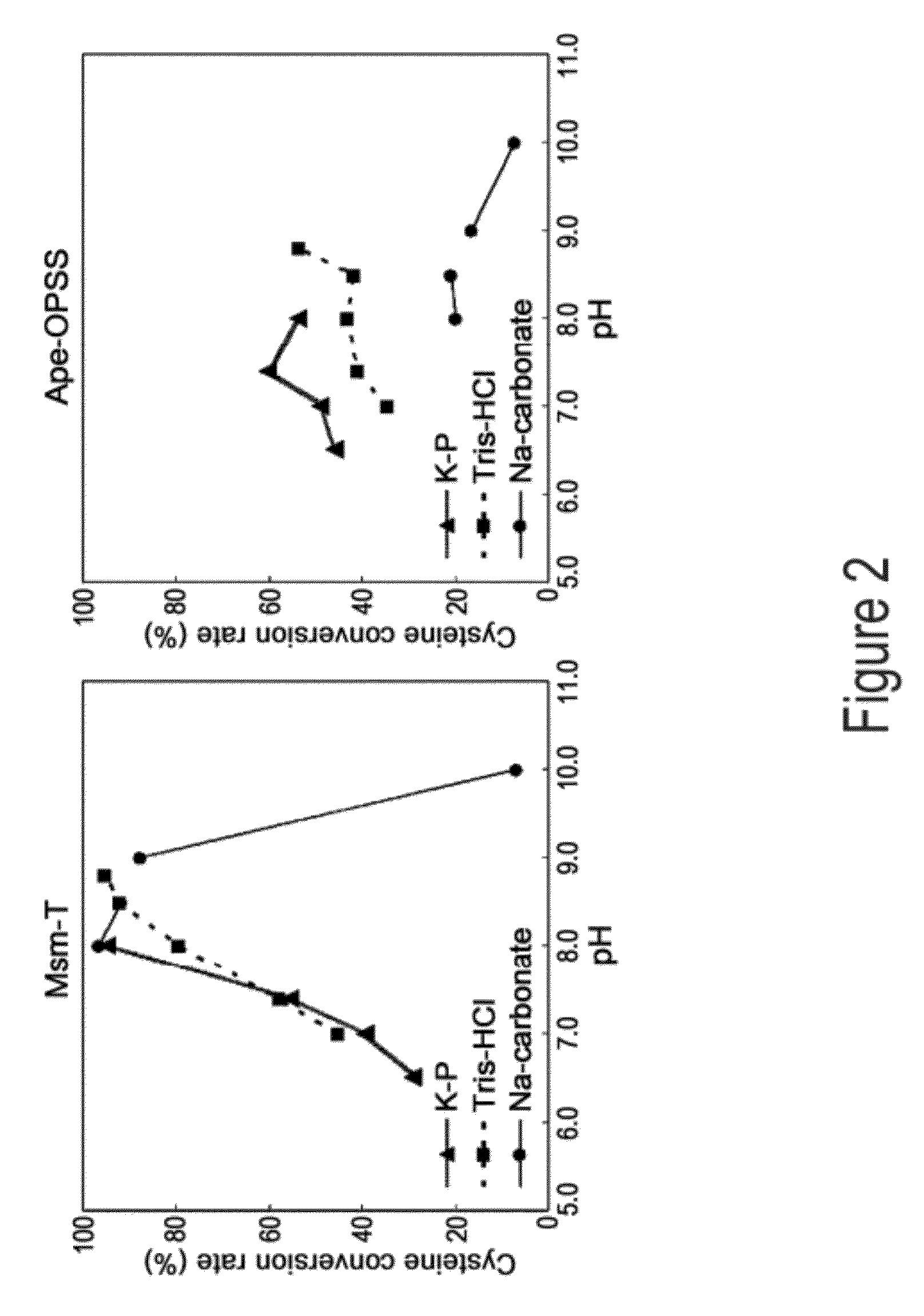
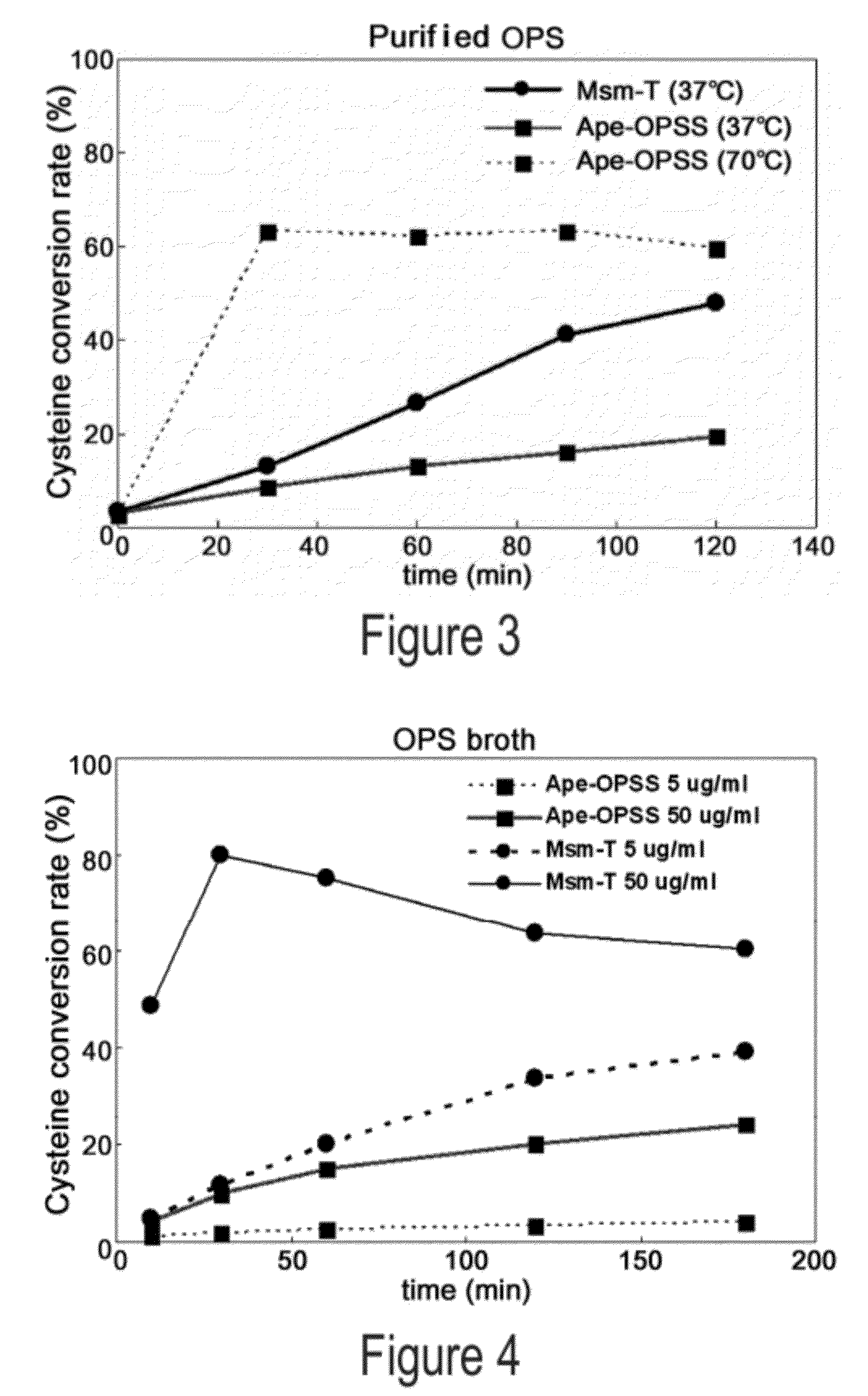
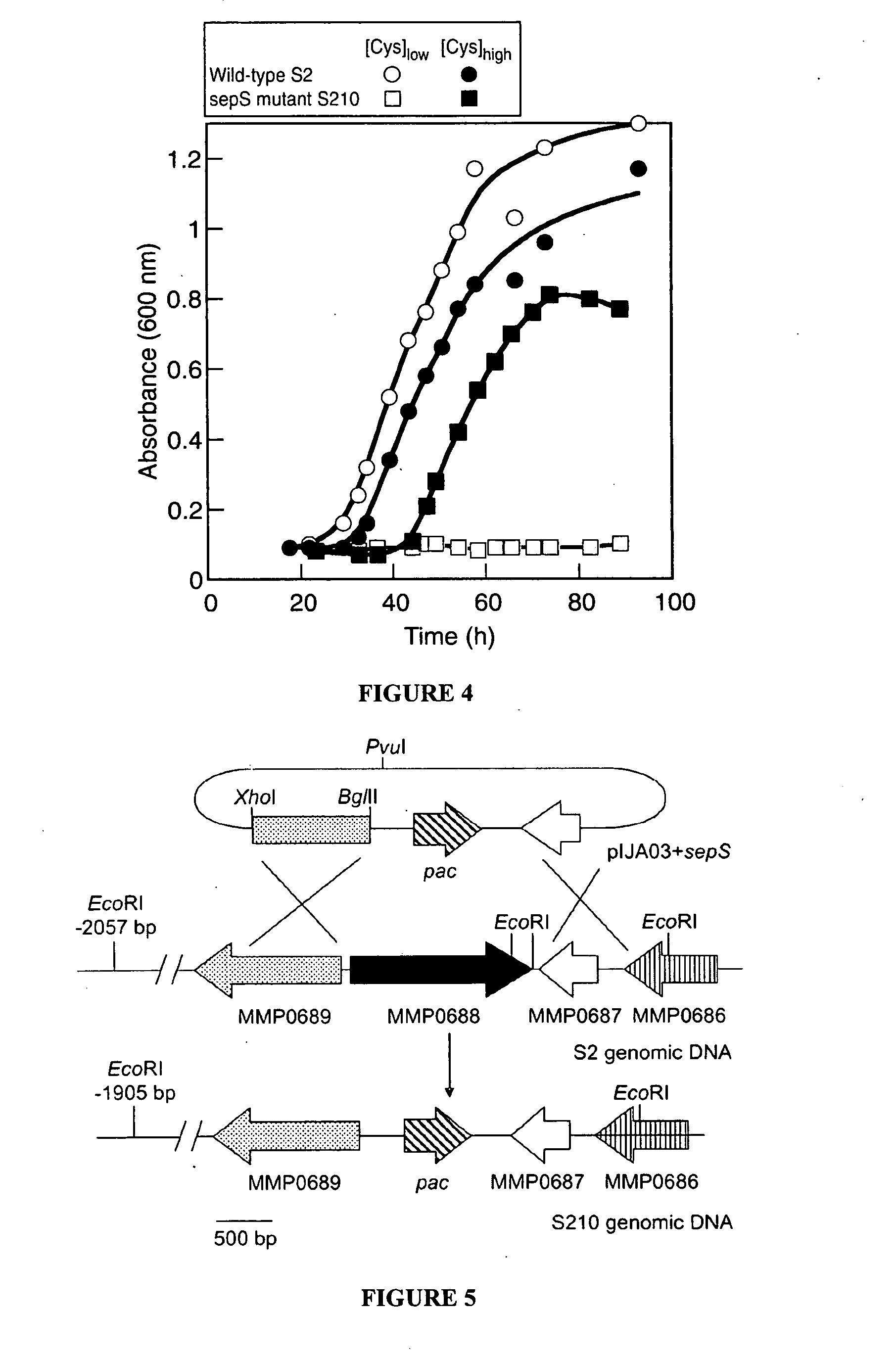
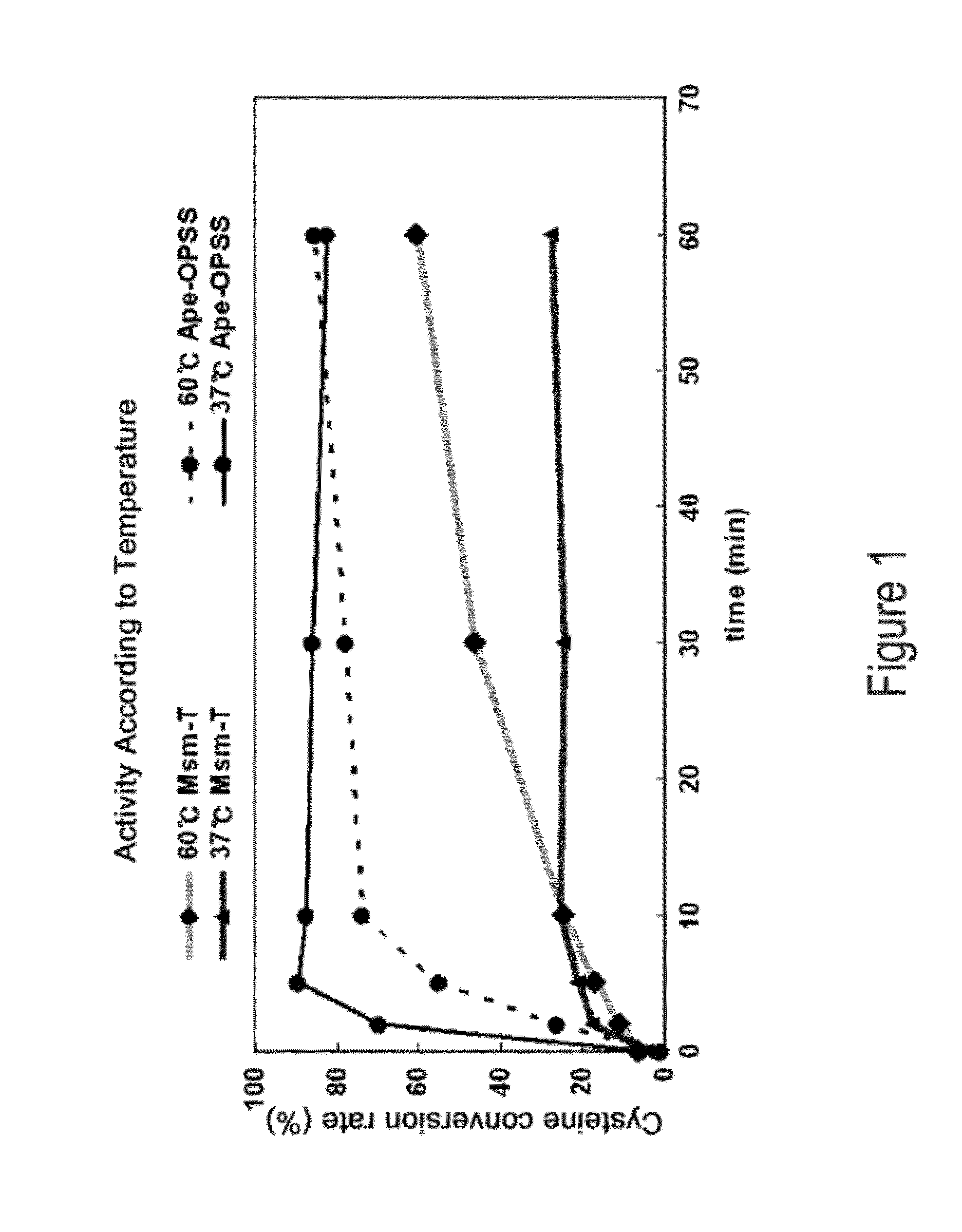
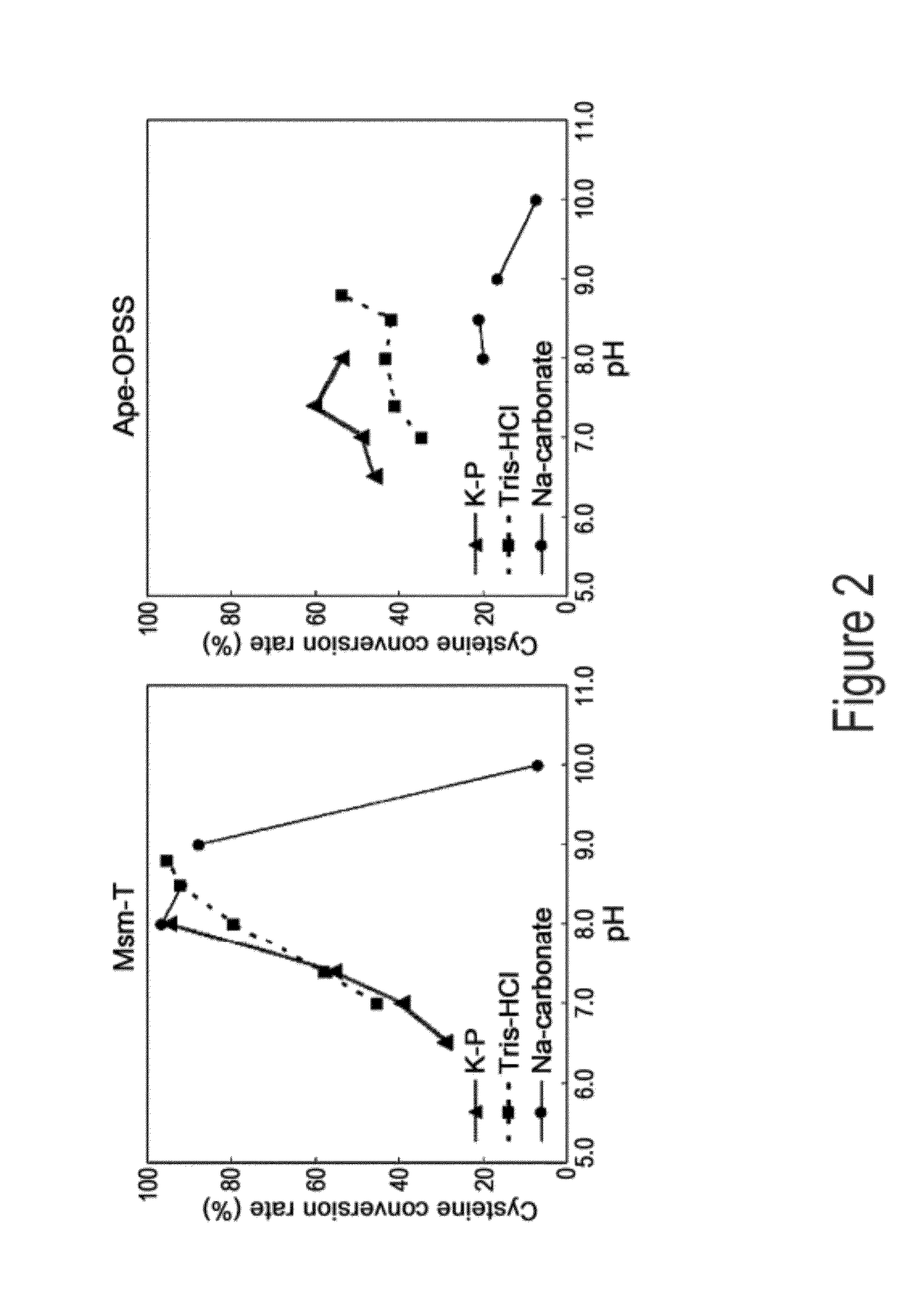
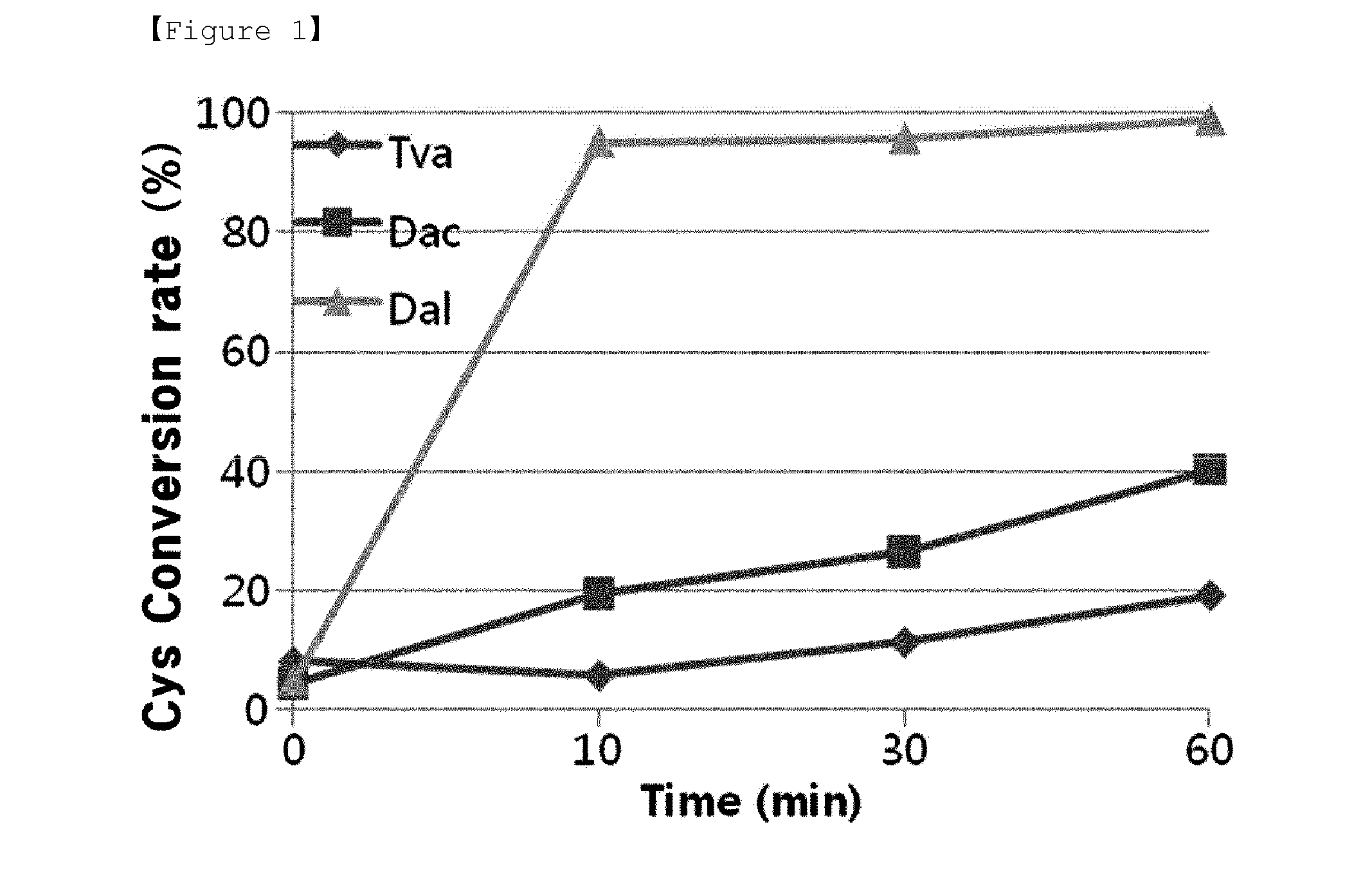
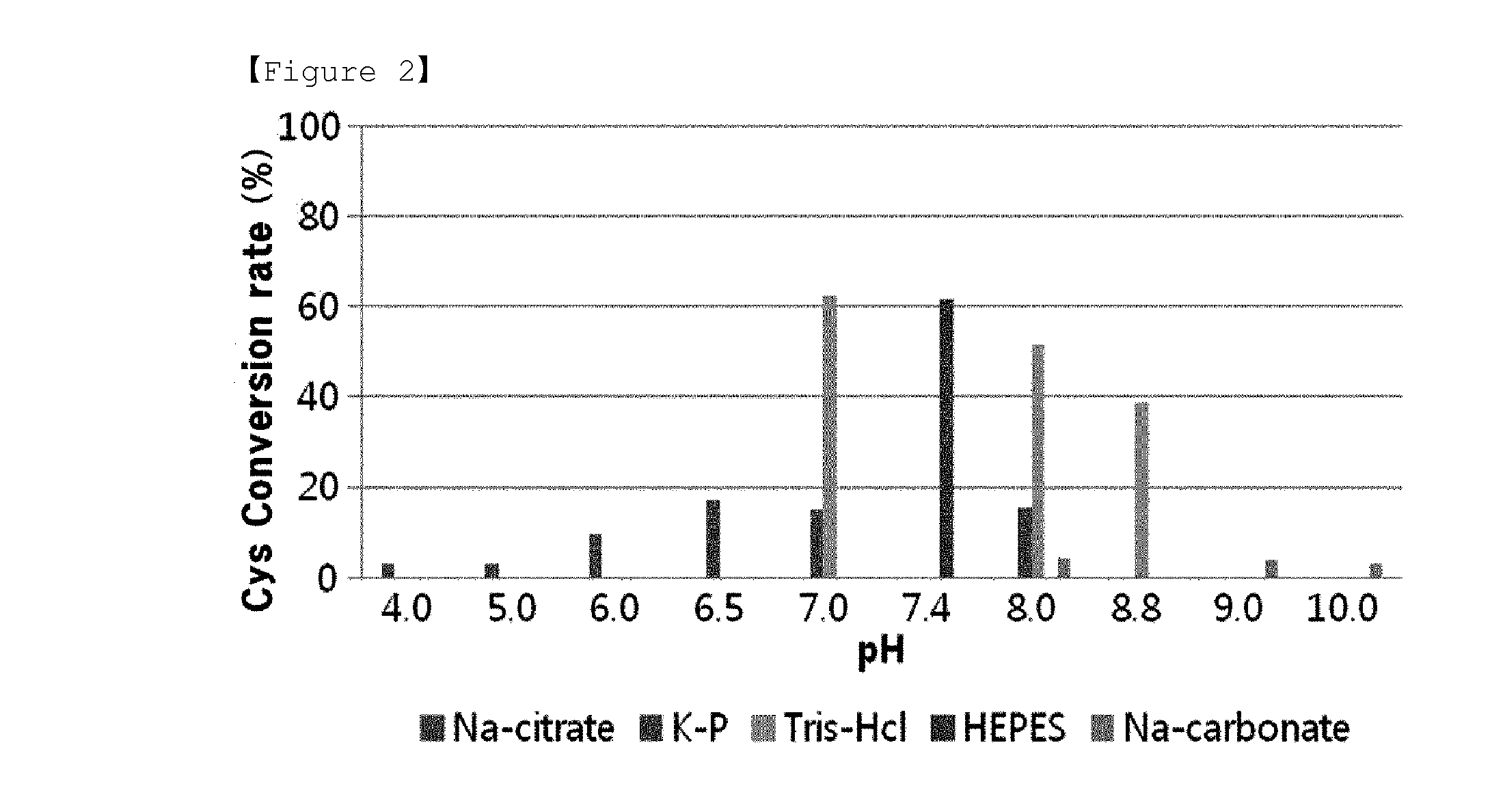
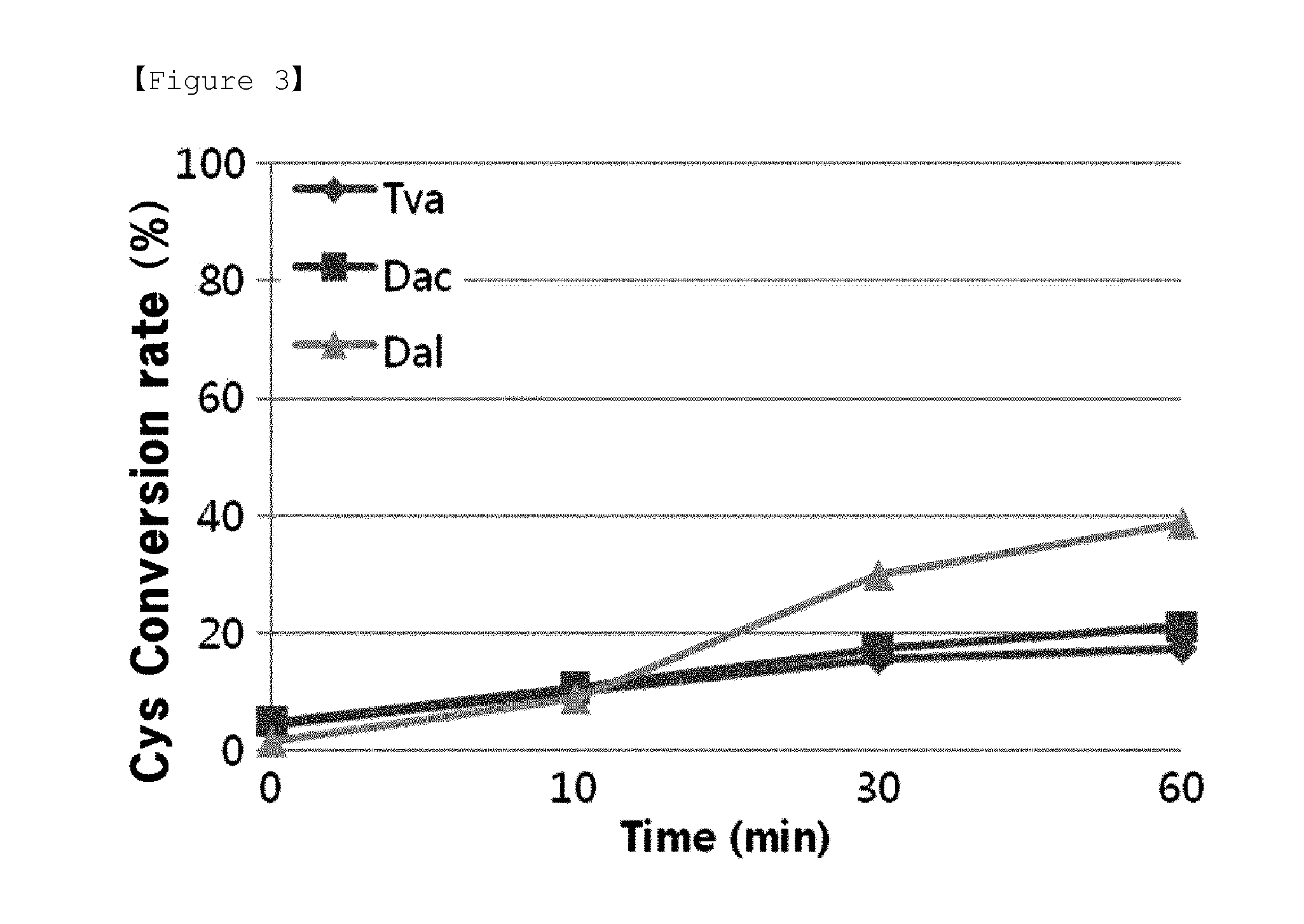
O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase mutants and method for production of cysteine using the same
ActiveUS9127324B2Improve enzymatic activityHigh yieldSugar derivativesBacteriaMycobacterium smegmatisO-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase
Disclosed is an O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase (OPSS) mutant which has a Mycobacterium smegmatis-derived amino acid sequence corresponding to that of SEQ ID NO: 1 which is devoid of three to seven C-terminal amino acid residues. Also, a nucleic acid molecule encoding the OPSS mutant, an expression vector carrying the nucleic acid molecule, and a transformant transformed with the expression vector are disclosed. In addition, a method is provided for producing cysteine in which O-phospho-L-serine (OPS) is reacted with a sulfide in the presence of the OPSS mutant. The OPSS mutant has improved enzymatic activity and can be applied to the environmentally friendly production of L-cysteine through a simple enzymatic conversion reaction.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Immunopotentiators
InactiveUS20050220801A1High activityImprove securityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPeptidePhosphoserine
An object of the present invention is to provide a peptide with superior immuno-enhancing activities, which comprises particular amino acid sequence, and an immuno-enhancing agent comprising such a peptide. The present invention relates to the immuno-enhancing agent comprising a peptide consisting of the following amino acid sequence (I): Q1-SerP-X-SerP-Q2 (I); wherein, SerP represents the phosphoserine residue, X represents one to three of any amino acid residues, and either of Q1 or Q2 dose not exist or neither of them exists, or Q1 and Q2 are independently at least one of any amino acid residue.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Tetra Calcium Phosphate Based Organophosphorus Compositions and Methods
Compositions and methods of their use to adhere a variety of materials together are disclosed herein. The compositions include at least tetra calcium phosphate, an effective amount of a compound that is structurally similar to phosphoserine, and can be mixed with an aqueous solution. The compositions provide adhesive and cohesive strength in both wet and dry environments and exhibit significant bond strength upon curing.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Site-specific incorporation of phosphoserine into proteins in Escherichia coli
Nucleic acids encoding mutant elongation factor proteins (EF-Sep), phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase (SepRS), and phosphoseryl-tRNA (tRNASep) and methods of use in site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into a protein or polypeptide are described. Typically, SepRS preferentially aminoacylates tRNASep with O-phosphoserine and the tRNASep recognizes at least one codon such as a stop codon. Due to the negative charge of the phosphoserine, Sept-tRNASep does not bind elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu). However, mutant EF-Sep proteins are disclosed that bind Sep-tRNASep and protect Sep-tRNASep from deacylation. In a preferred embodiment the nucleic acids are on vectors and are expressed in cells such as bacterial cells, archeaebacterial cells, and eukaryotic cells. Proteins or polypeptides containing phosphoserine produced by the methods described herein can be used for a variety of applications such as research, antibody production, protein array manufacture and development of cell-based screens for new drug discovery.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Organophosphorous and multivalent metal compound compositions and methods
ActiveUS8765189B2Heavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsCohesive strengthAqueous solution
Compositions and methods of their use to adhere a variety of materials together are disclosed herein. The compositions include at least multivalent metal compound, an effective amount of a compound that is structurally similar to phosphoserine, and can be mixed with an aqueous solution. The compositions provide adhesive and cohesive strength in both wet and dry environments which exhibit bond strength upon curing with the possible usage as bone cement for bone filler applications.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
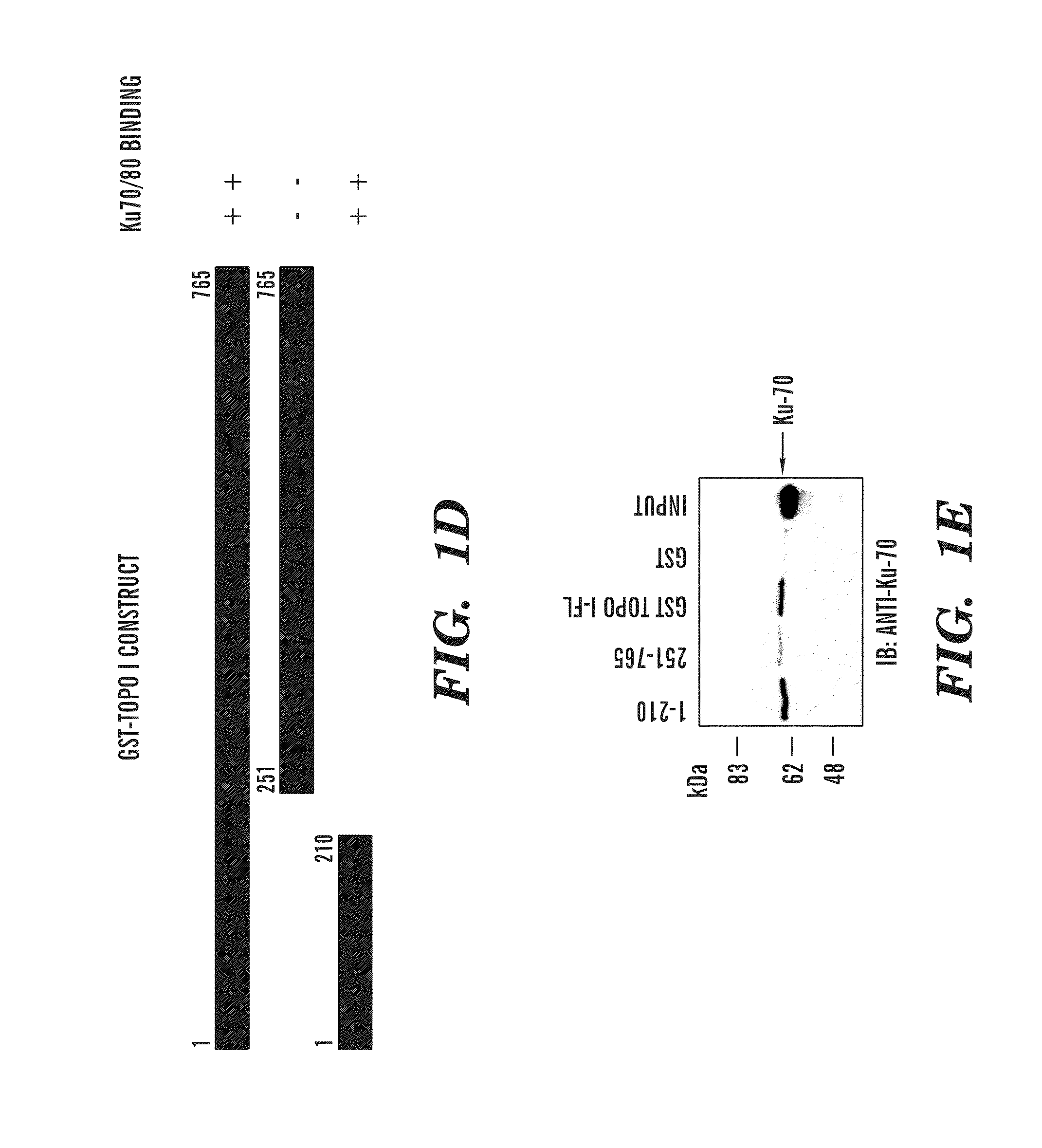
Predictive marker for topoisomerase I inhibitors
ActiveUS8993309B2Organic active ingredientsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCancer preventionPredictive marker
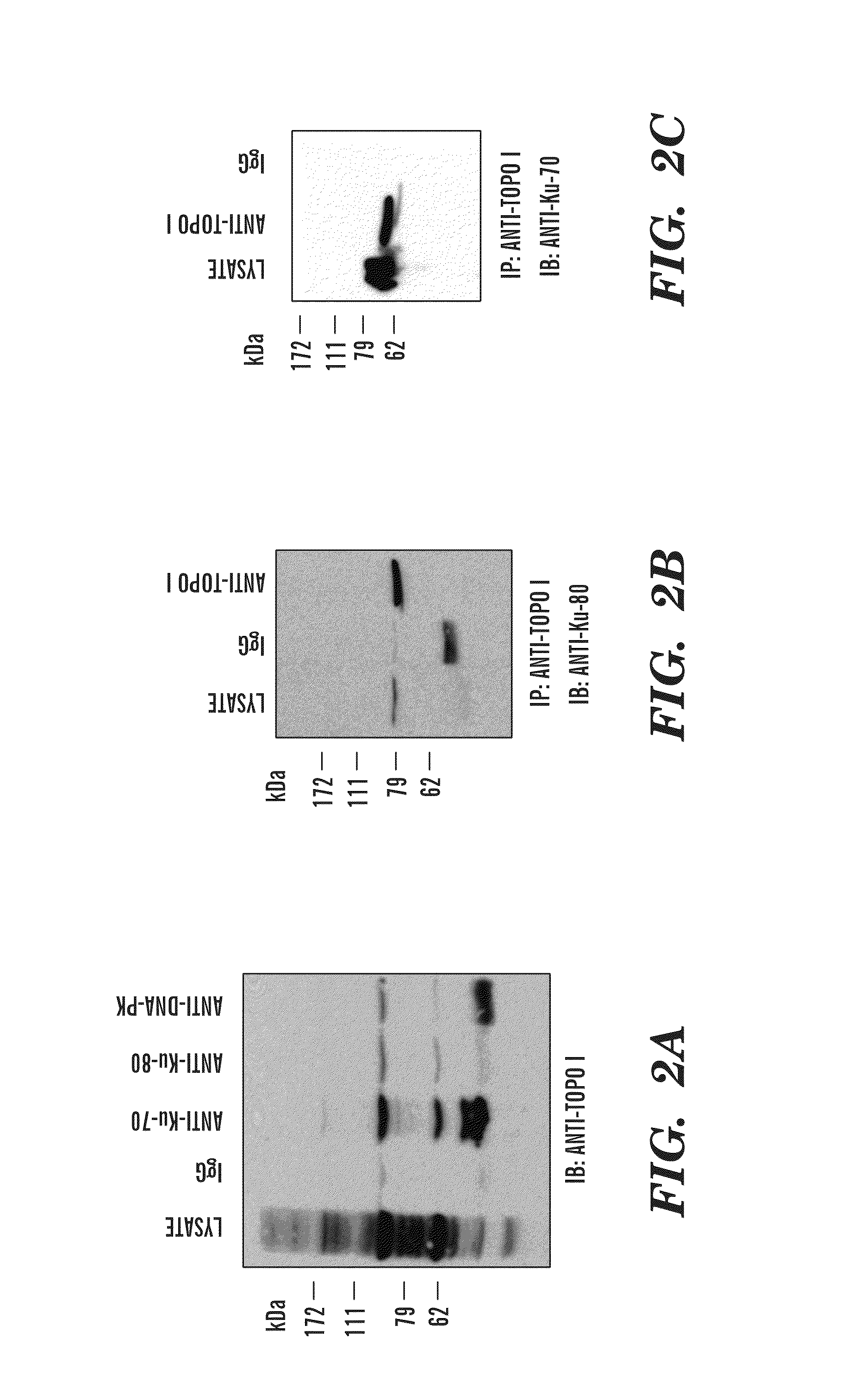
The present invention generally relates to the fields of cancer therapy and cancer prevention. More particularly, the present invention generally relates to a diagnostic marker for predicting the efficacy of topoisomerase I (topo I) inhibitors in the treatment of cancers. More specifically, the present invention relates to methods, machines, computer systems, computable readable media and kits which can be used to identify and determine the effectiveness of topoisomerase I (topo I) inhibitors in the treatment of cancers, and in some embodiments, the level of sensitivity or resistance of a tumor cell to a topoisomerase I inhibitor, such as camptothecin (CPT), or CTP analogues such as topotecan and irinotecan and derivatives thereof. More specifically, the present invention related to methods, machines, computer systems, computable readable media and kits which can be used to determine the presence of phosphorylation of topoisomerase I polypeptide, in some embodiments phosphorylation at residue serine 10 (S10) of a topoisomerase I polypeptide, wherein the presence of phosphorylation, in particular the phosphorylation at serine 10 of a topoI polypeptide indicates a cancer is likely to be unresponsive to a topo I inhibitor, whereas the absence of phosphorylation, in particular, the absence of phosphorylation at residue serine 10 (S10) identifies a cancer is likely to be responsive to a topo I inhibitor. Other aspect of the present invention relate to phospho-serine 10 topoisomerase I antibodies and other protein binding moieties, and uses thereof.
Owner:BOSTON MEDICAL CENTER INC
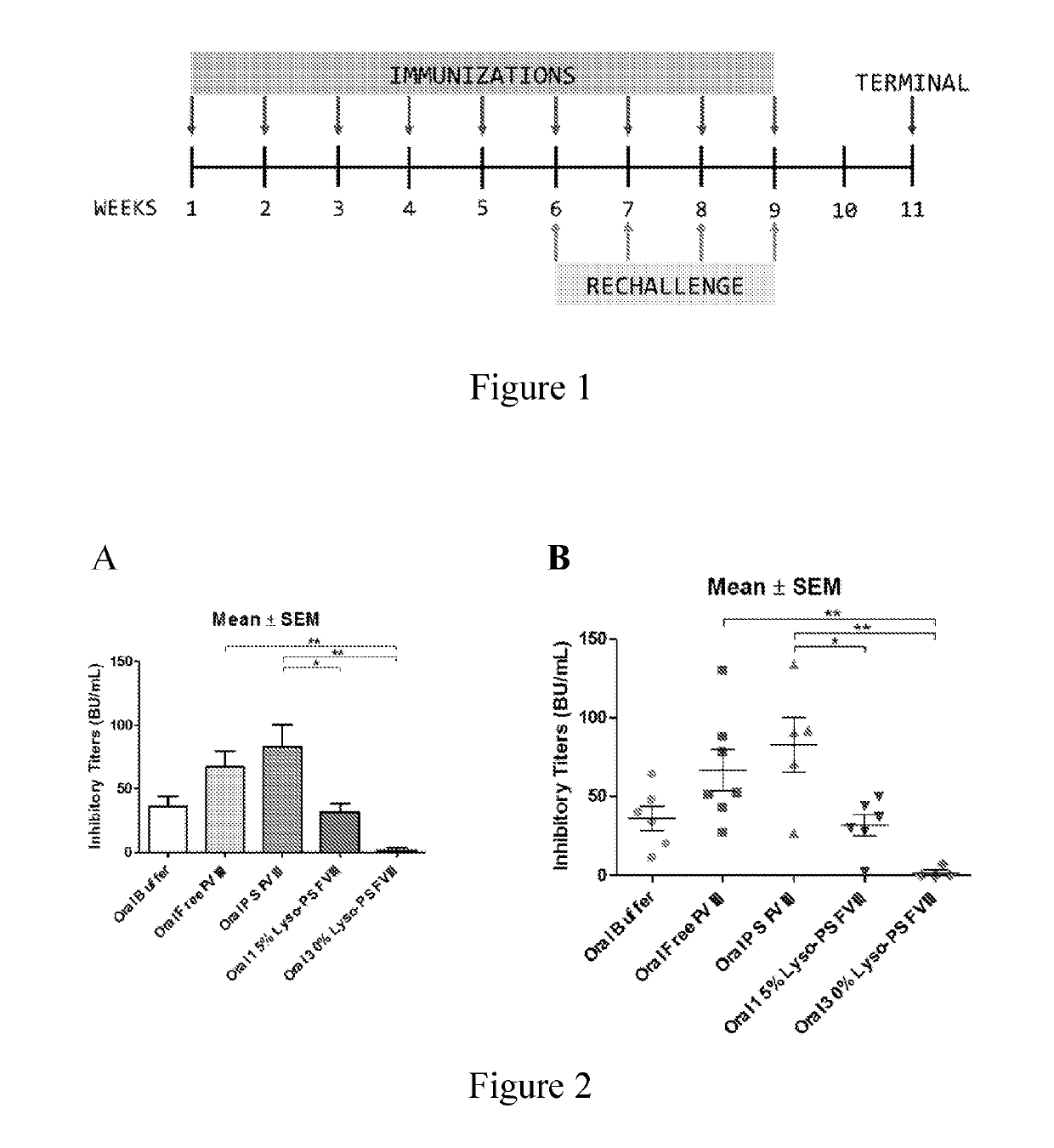
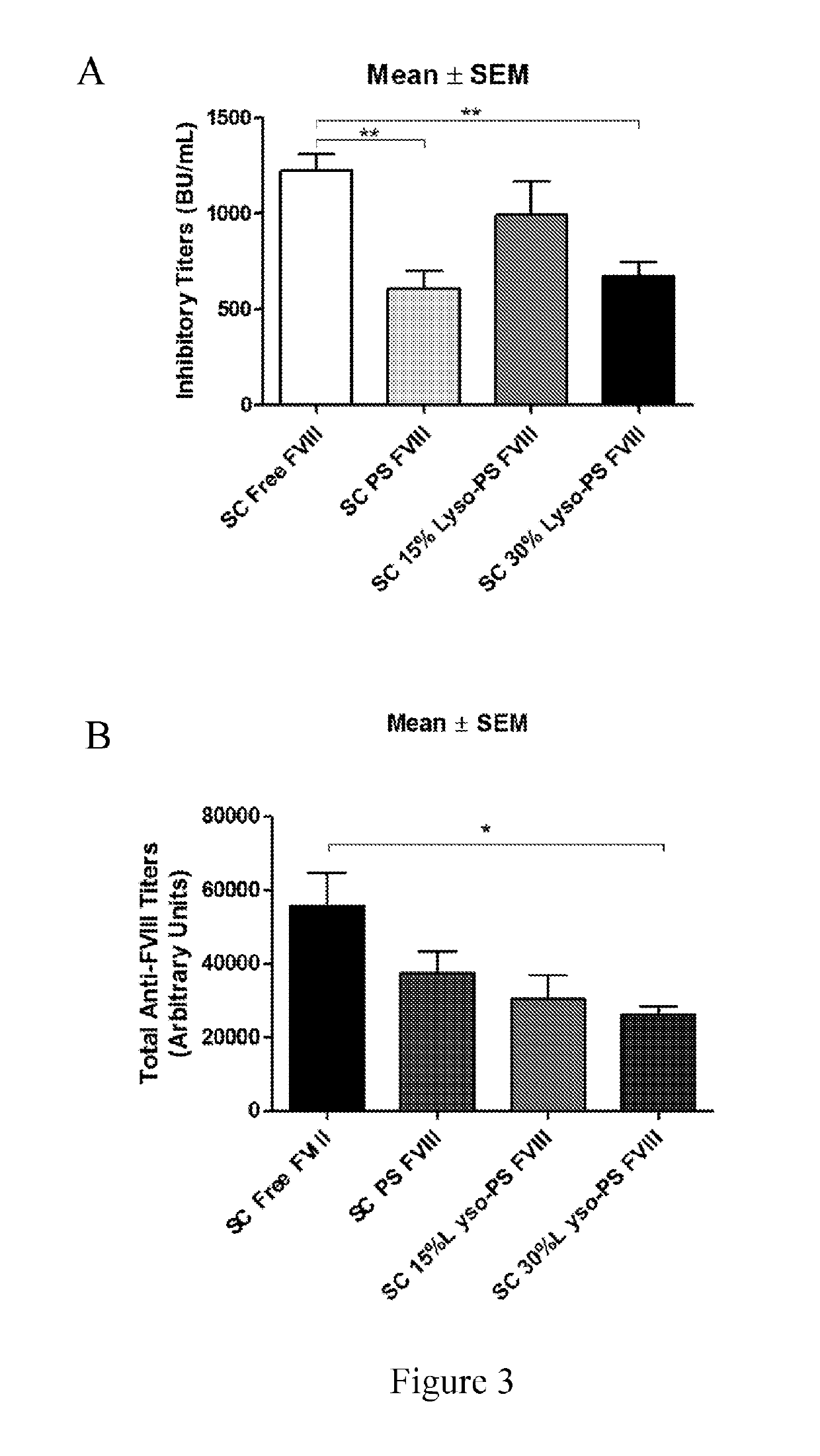
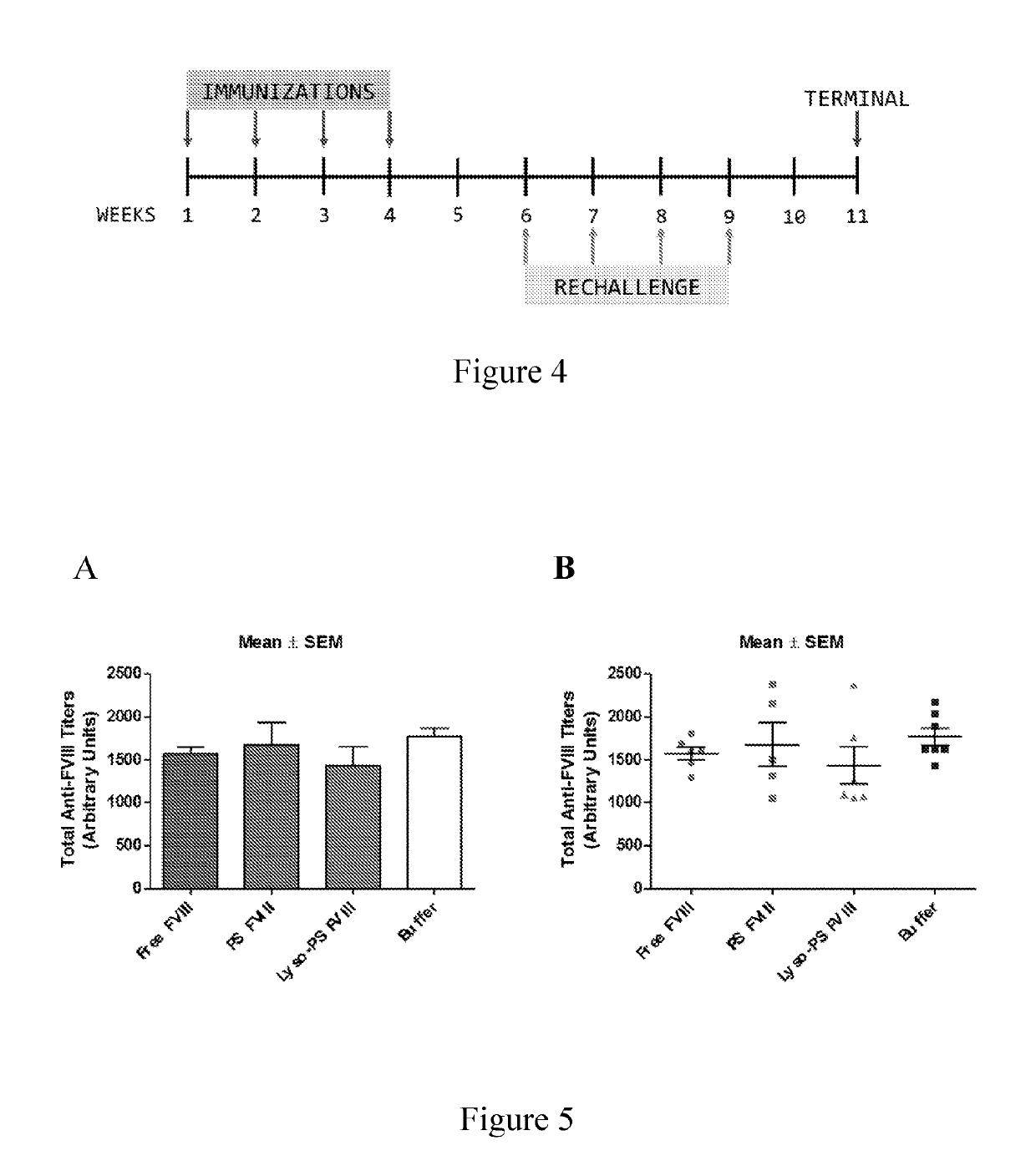
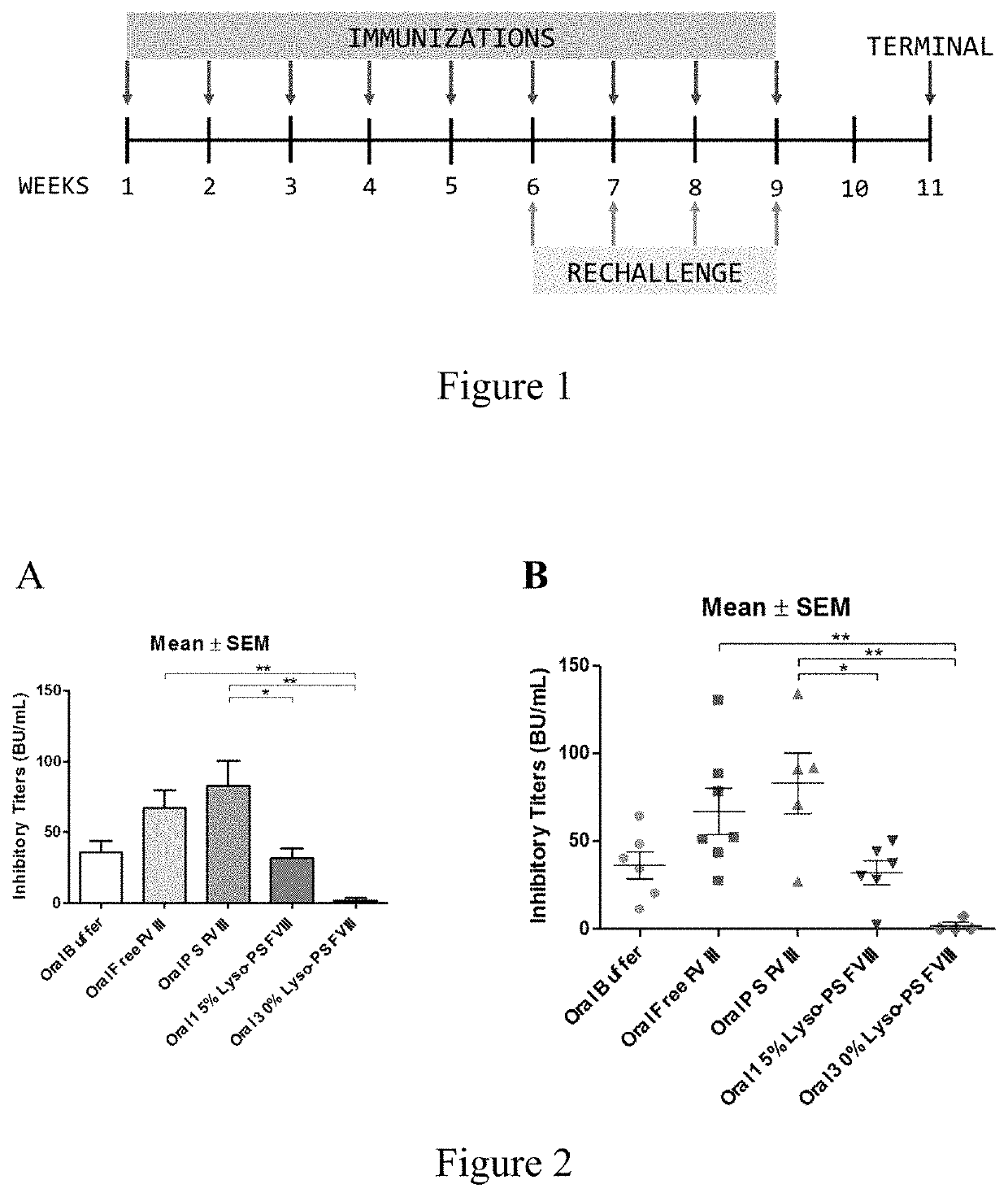
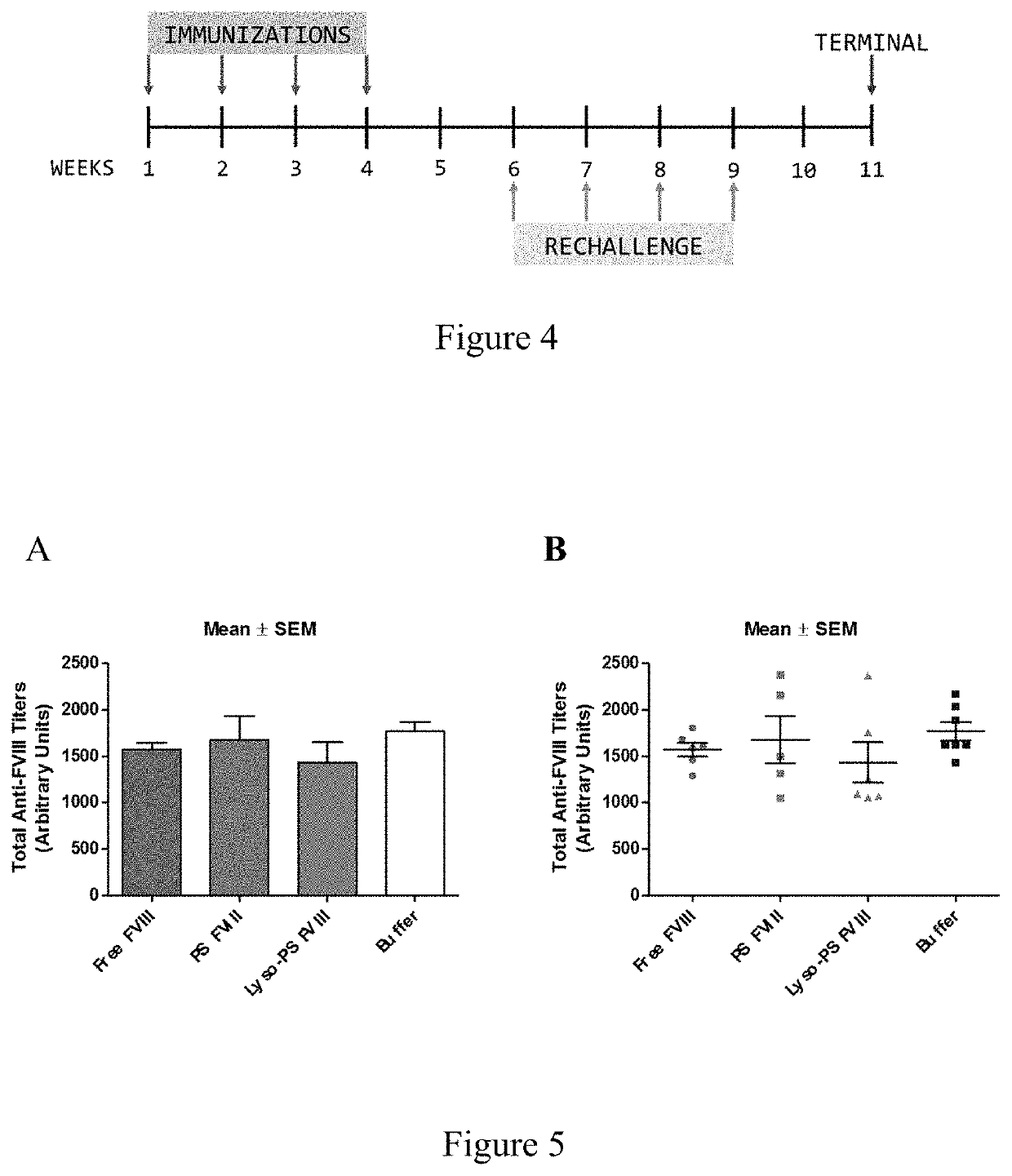
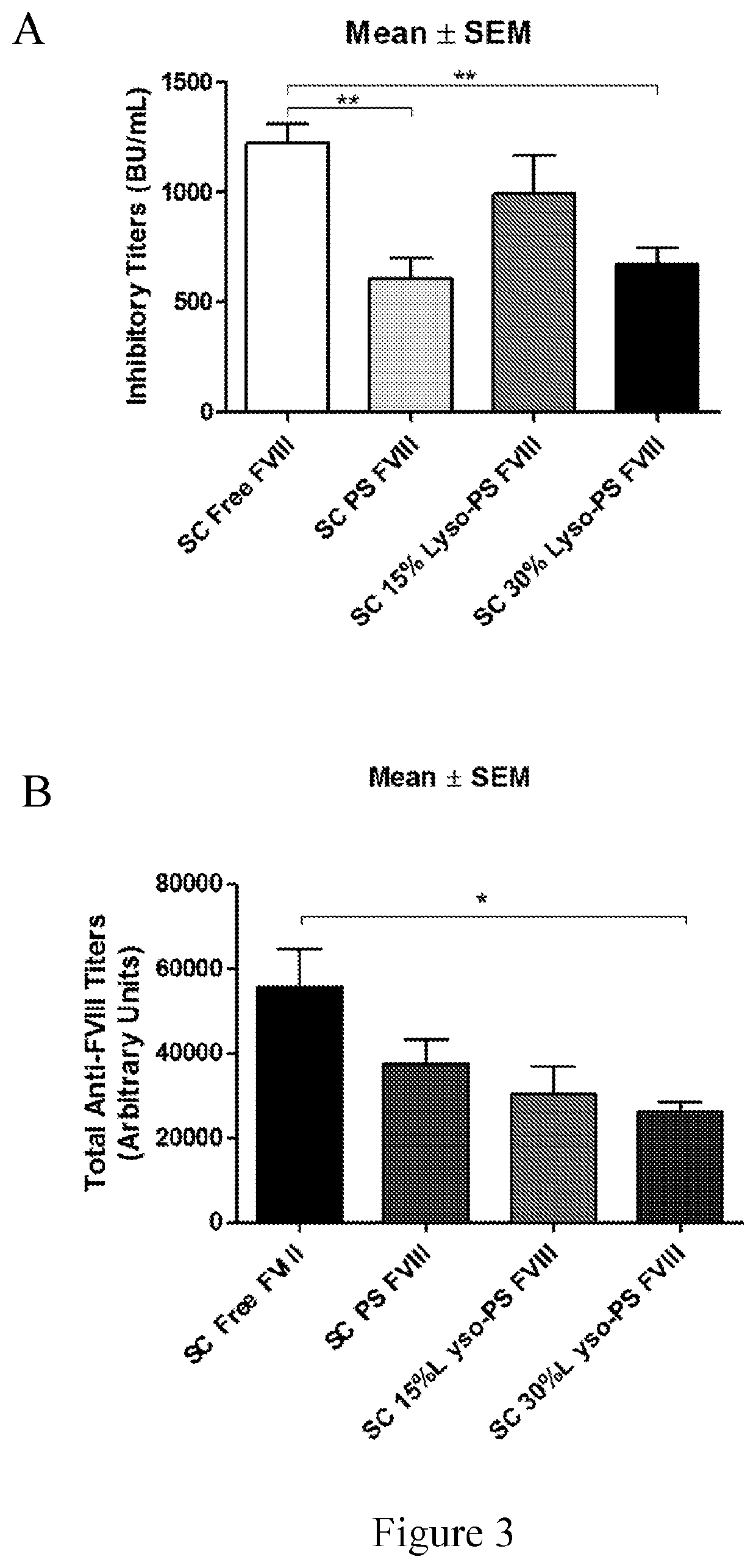
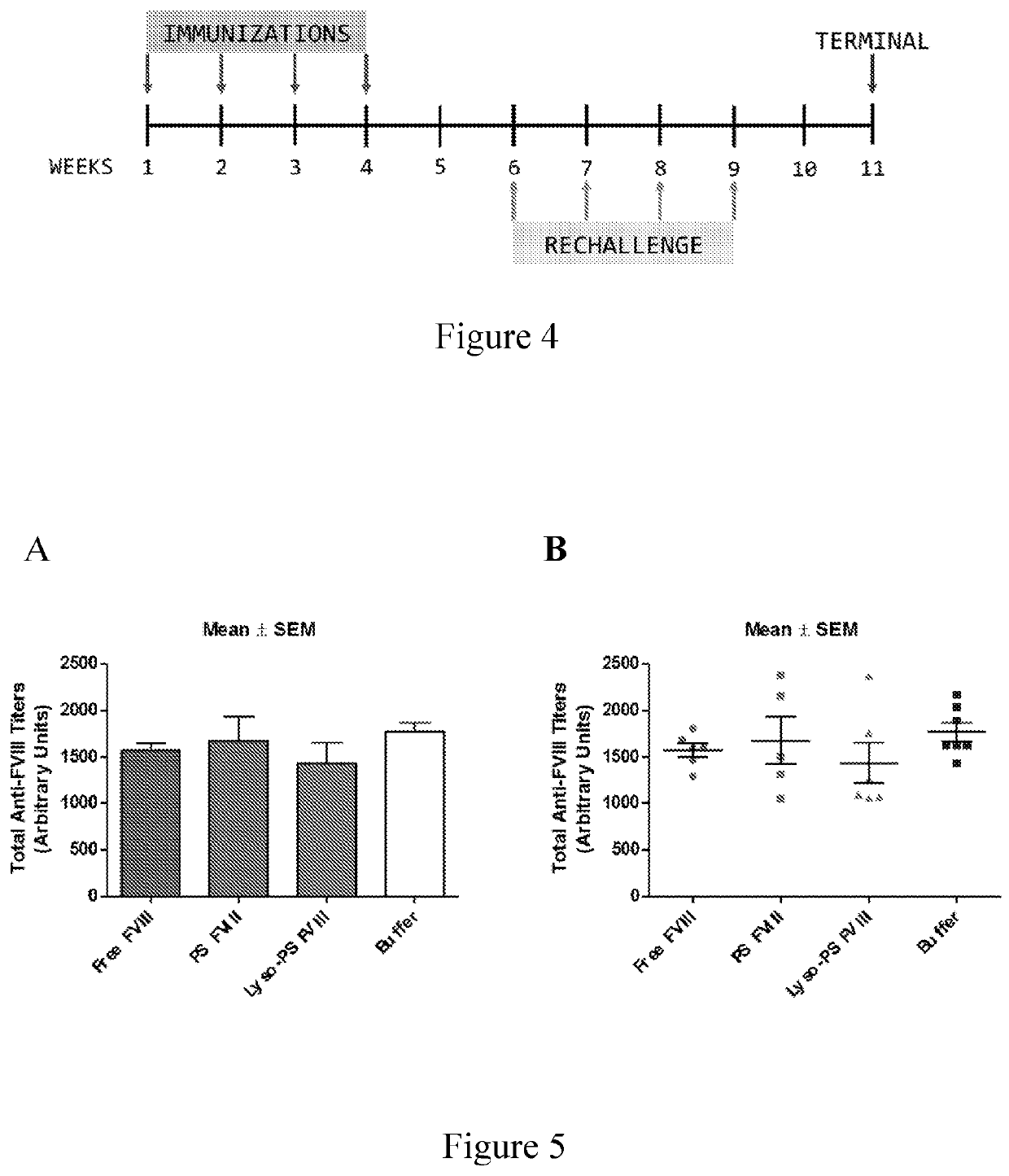
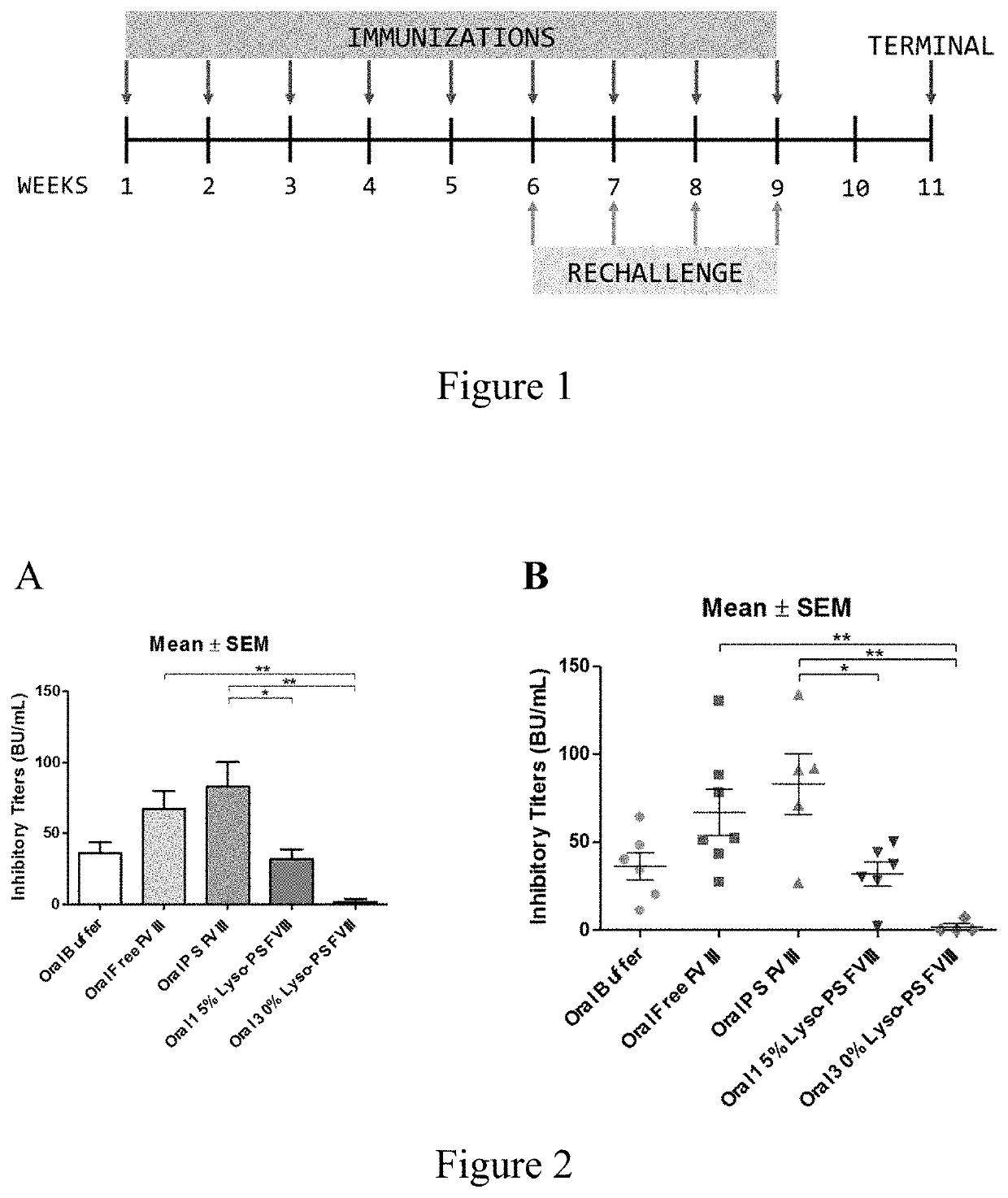
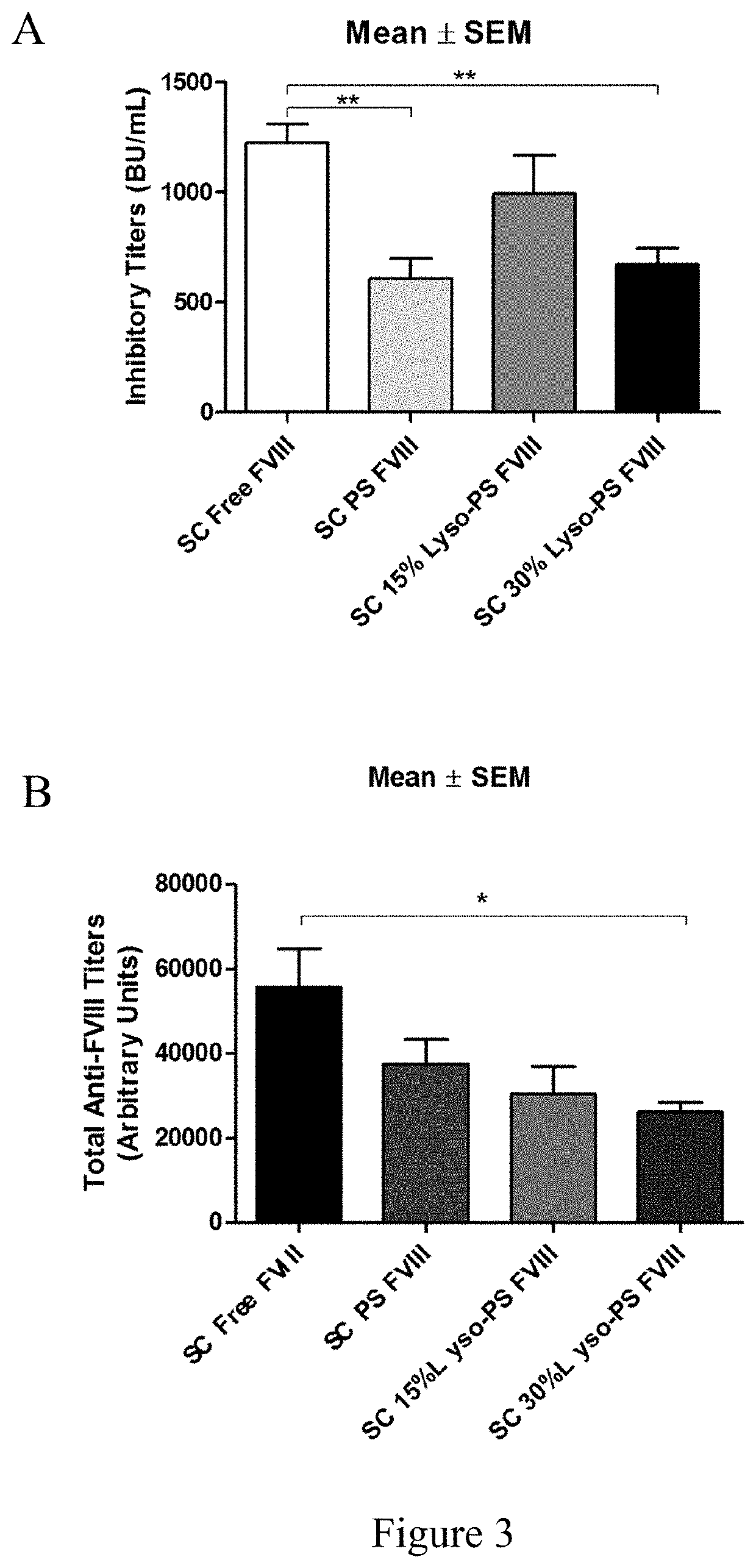
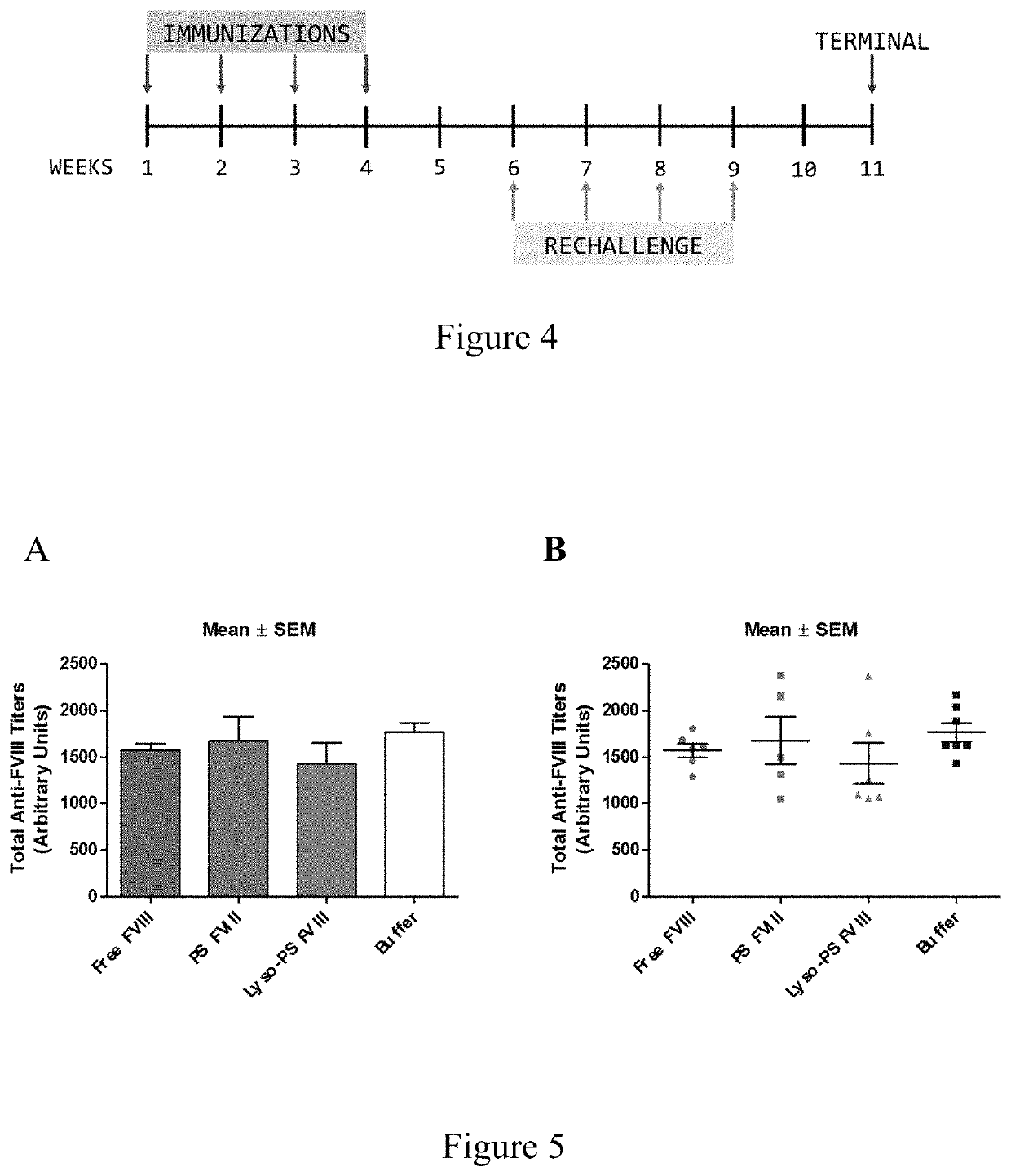
Phosphoserine containing compositions for immune tolerance induction
ActiveUS20190151426A1More effectivenessInduction of immune toleranceOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryImmune toleranceLiposome
Compositions and methods for inducing immune tolerance to proteins and subsequence administration of the proteins are disclosed. Compositions comprise proteins complexed with liposomes comprising PS and PC, wherein at least part of the PS is present as lyso-PS.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Parkinson's disease specific serum endogenous small molecule marker and application thereof
InactiveCN111366651AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityComponent separationDisease diagnosisPropanoic acidAklanonic acid
The invention discloses a Parkinson's disease specific serum endogenous small molecule marker and application thereof. The marker contains 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyl-3-methoxyphenyl) propionic acid, ferulic acid and citraconic acid, altrose, pentadecanoic acid, o-phosphoserine, 4, 6 beta-hydroxymorphine, L-thyroxine, 5[epsilon], 9[epsilon], 16[epsilon]-17-hydroxy peraluminum-19-acid, 8-(1,2,dyhydroxy-3-methylbutyl-3-ene-1-yl)-7-methoxy-2H-chromine-2-2-ketone,10-hydroxydecanoic acid, perfluoro caprylic acid, and Corchorifatty acid F. The Parkinson's disease specific serum endogenous small molecule marker provided by the invention has the characteristics of high accuracy and high sensitivity. The prediction offline prediction area AUC of some markers reaches 0.95 or above, the accuracy and sensitivity of the markers are high, and the markers can be directly used for Parkinson's disease indexes.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sleep inducer and stress insomnia ameliorating agent
InactiveCN101437507ANo side effectsSleep inducingOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderStress inducedLysophosphatidylserine
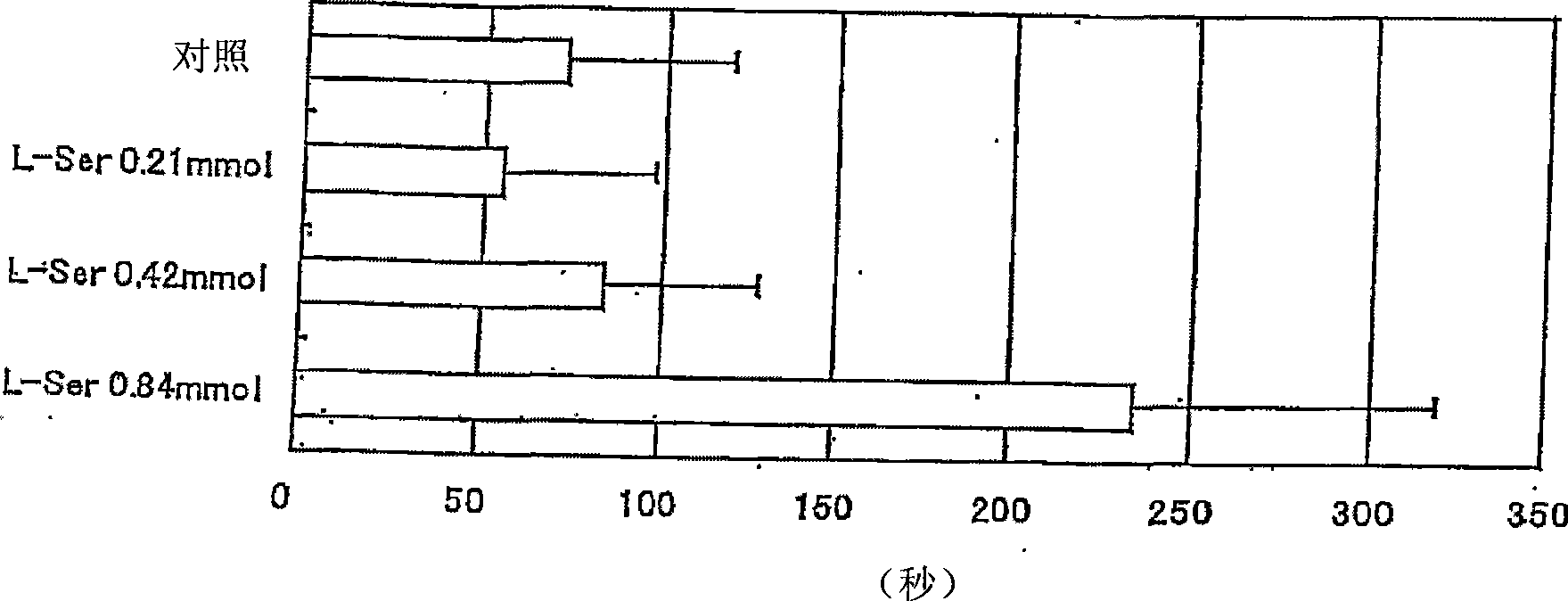
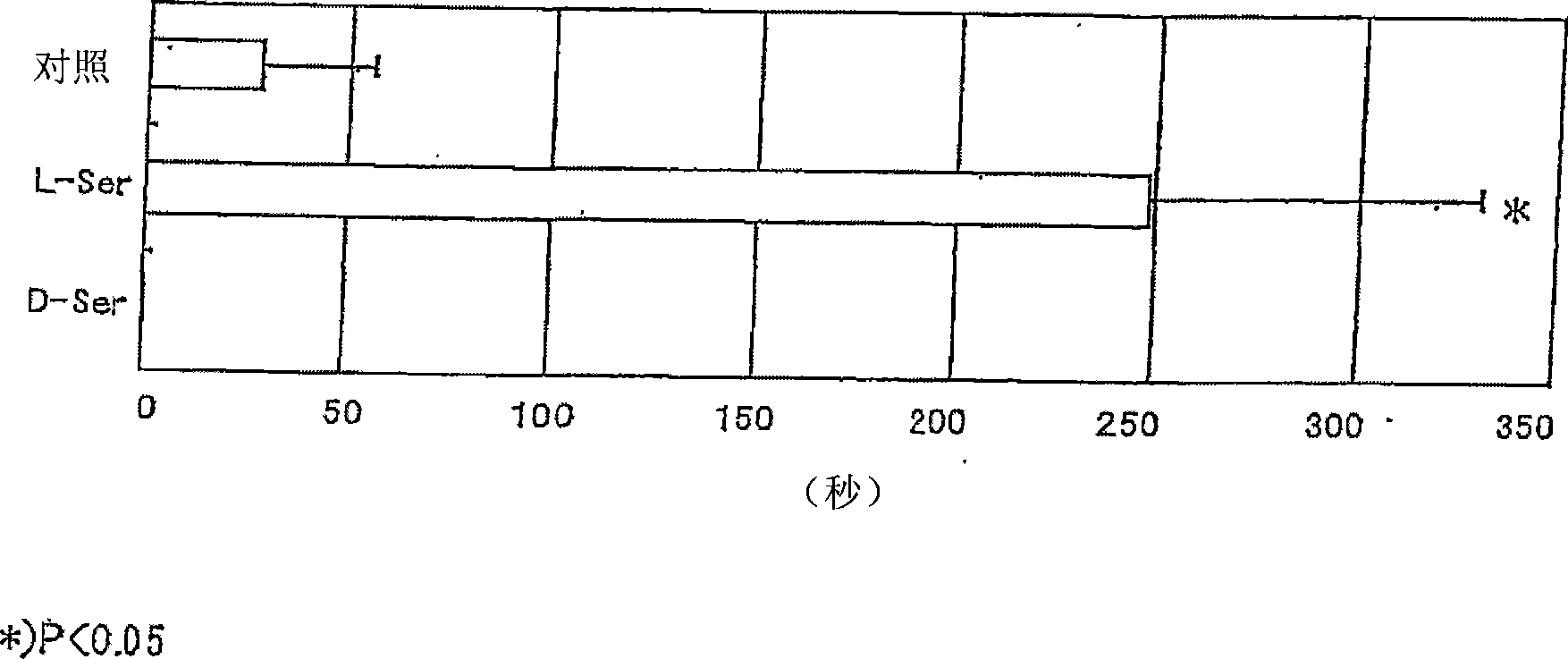
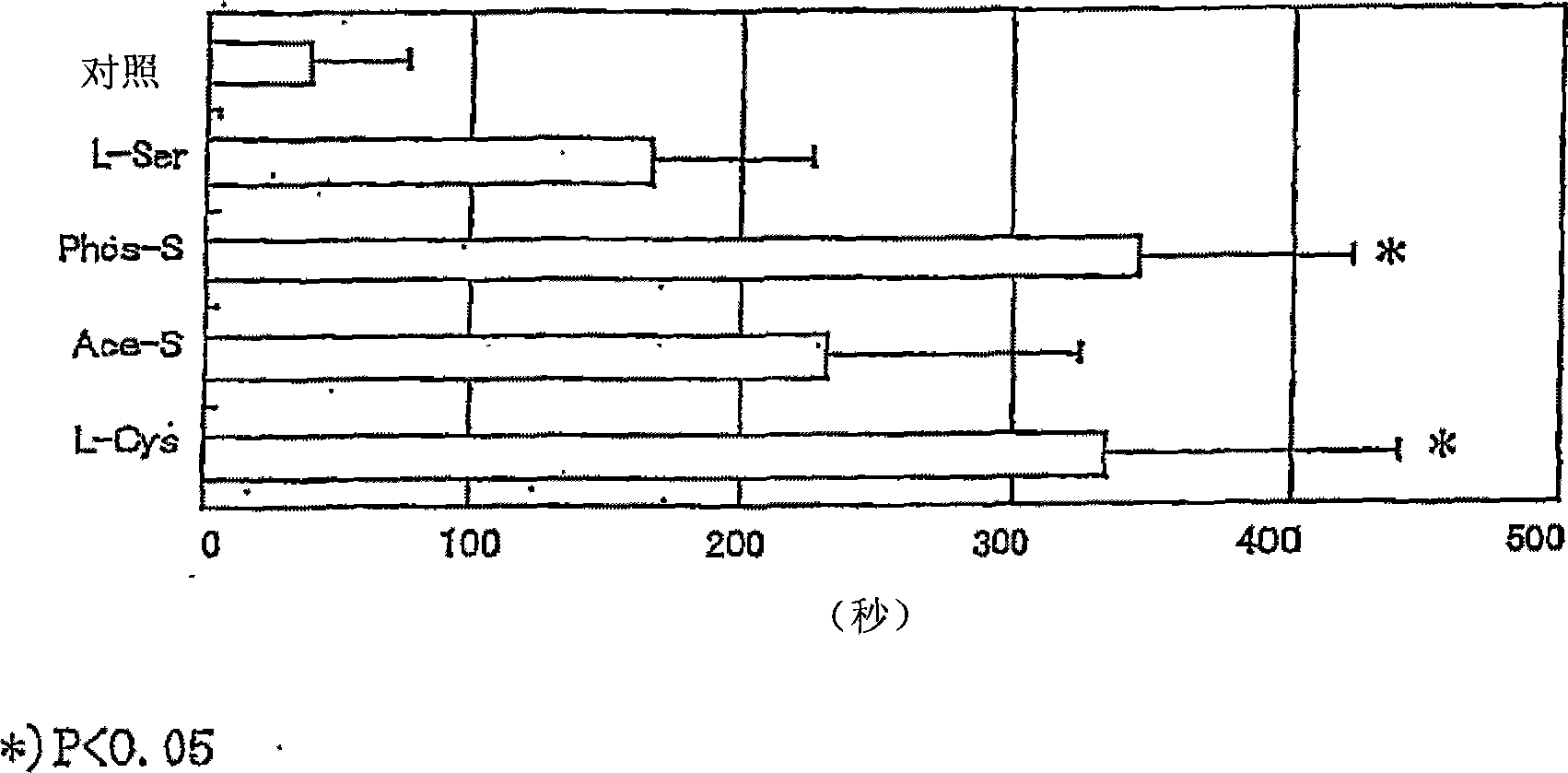
The object is to develop a sleep-inducing agent and an ameliorating agent for stress-induced insomnia. Disclosed is a sleep-inducing oral preparation comprising one or more members selected from serine, phosphoserine, phosphatidylserine, lysophosphatidylserine, acetylserine (which are compounds having a serine unit) and cysteine each in an L-form.
Owner:FUAN KERU
Casein phosphopeptide and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110483622APromote absorptionEfficient use ofPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderNeutral proteasePhosphopeptide
The invention relates to the field of polypeptides, in particular to casein phosphopeptide and its preparation method and application. In the invention, casein in cow's milk is used as a raw material.Casein phosphopeptide with strong calcium holding activity is prepared through trypsin and compound protease (trypsin and neutral protease) enzymolysis, enzyme inactivation, centrifugation, adjustment of isoelectric point / alcohol precipitation and impurity removal, and drying processes. The special cluster phosphoserine structure obtained by the invention has the ability of chelating calcium, andcan effectively promote the absorption and utilization of calcium. The molecular weight of the milk-derived casein phosphopeptide prepared by the invention is mainly between 1,000 and 5,000, which isbeneficial to human body absorption. The content of casein phosphopeptide is more than 85%, and its yield can reach 25%. The method is a preparation method with low cost and simple process, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:INFINITUS (CHINA) CO LTD
Site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into polypeptides using phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase
Nucleic acids encoding genes with SepRS and tRNASep activity for site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into a protein or polypeptide and methods of use thereof are described. Typically, SepRS preferentially aminoacylates tRNASep with O-phosphoserine and the tRNASep recognizes at least one codon such as a stop codon. In a preferred embodiment the nucleic acids are on vectors. In one embodiment, the vectors are expressed in cells such as bacterial cells, archeaebacferial cells, and eukaryotic cells. In an alternative embodiment, the vectors are expressed in an in vitro transcription / translation system. Proteins or polypeptides containing phosphoserine produced by the methods described herein can be used for a variety of applications such as research, antibody production, protein array manufacture and development of cell-based screens for new drug discovery.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Microorganism producing o-phosphoserine and a method for producing o-phosphoserine or l-cysteine using the same
ActiveUS20170260556A1Excellent OPS-exporting capabilityHigh yieldFungiBacteriaMicroorganismPhosphoserine
The present invention relates to a microorganism, wherein the activity of a polypeptide capable of exporting O-phosphoserine (OPS) is enhanced, and a method of producing O-phosphoserine, cysteine, or a cysteine derivative using the microorganism.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
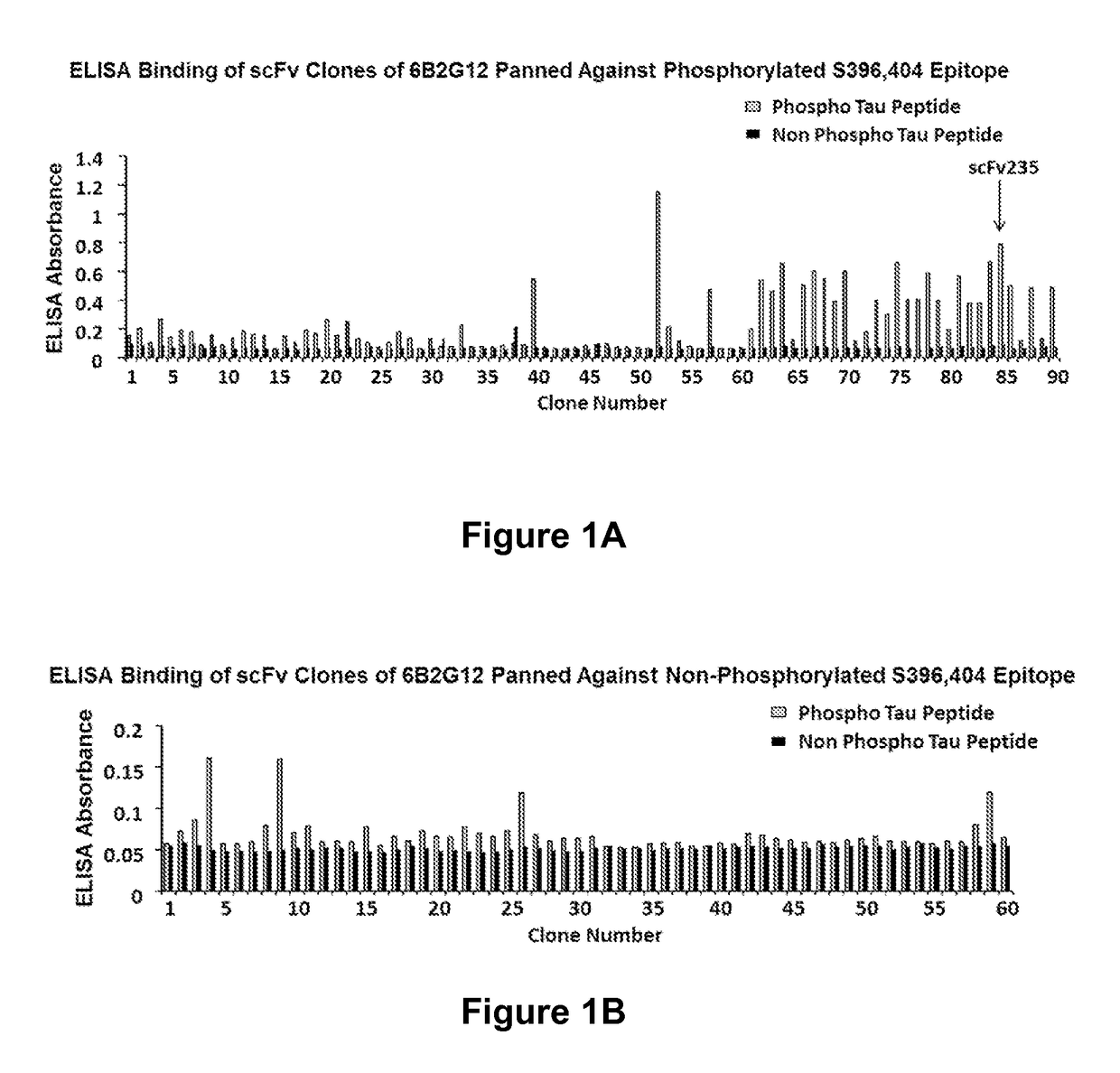
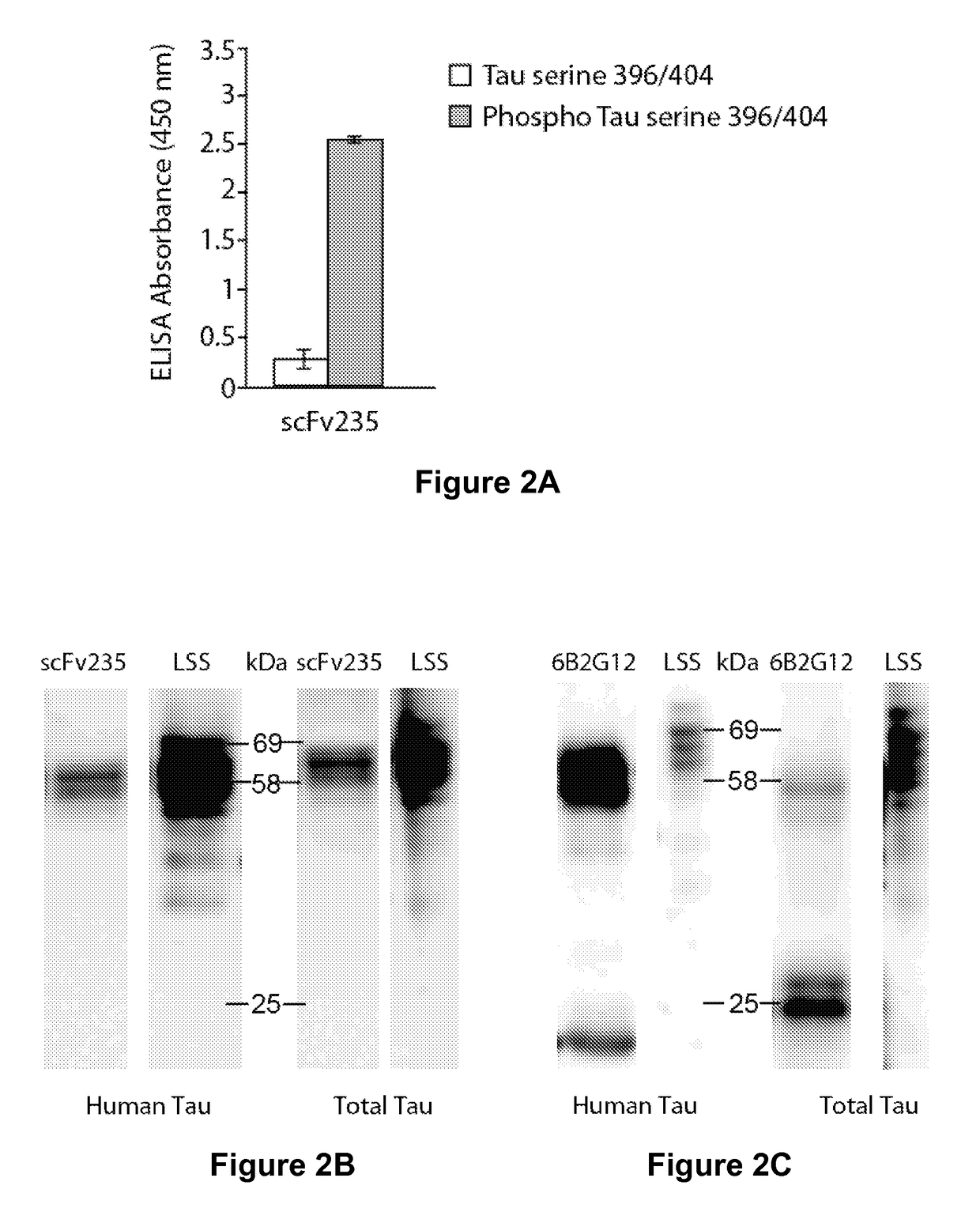
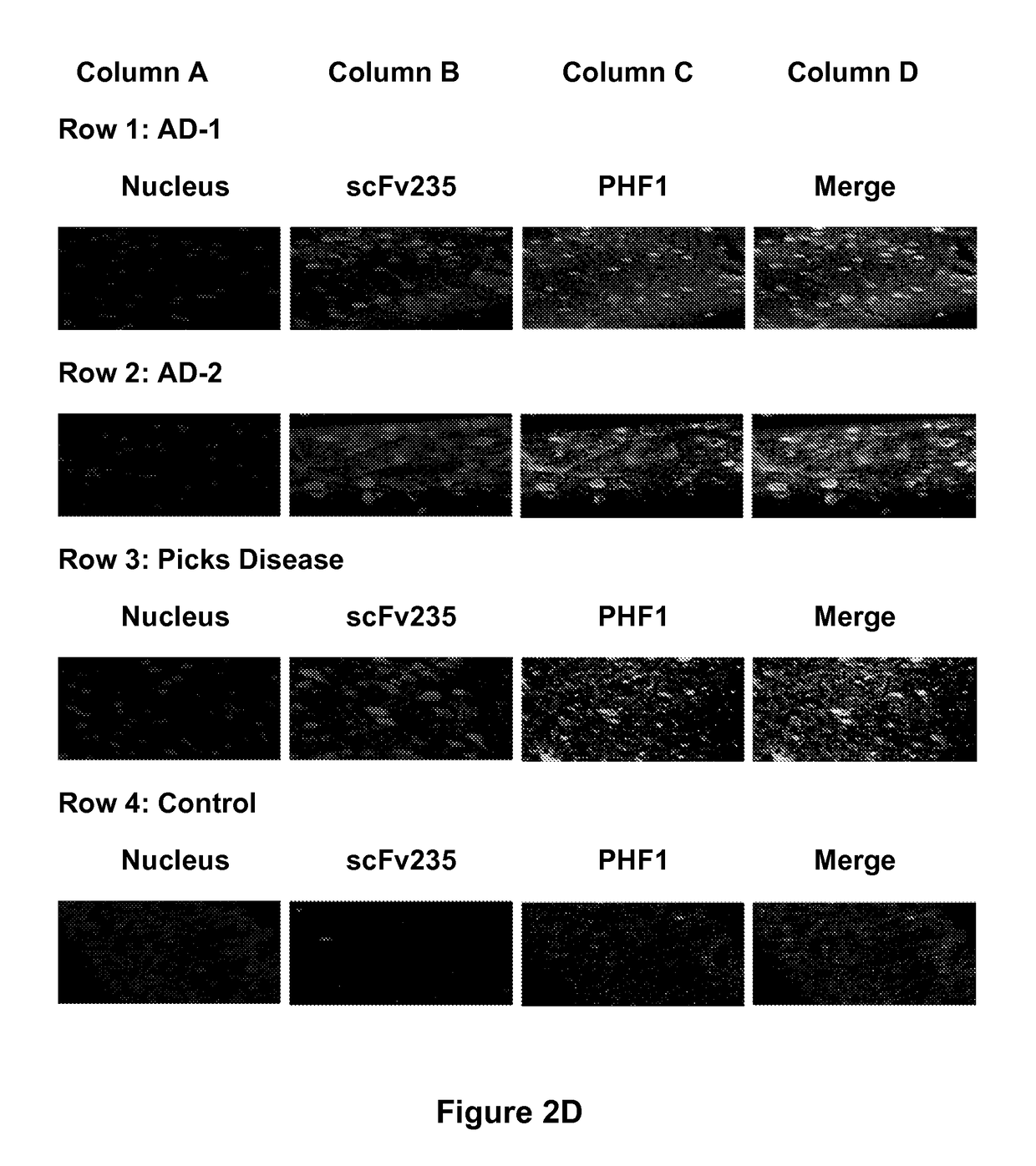
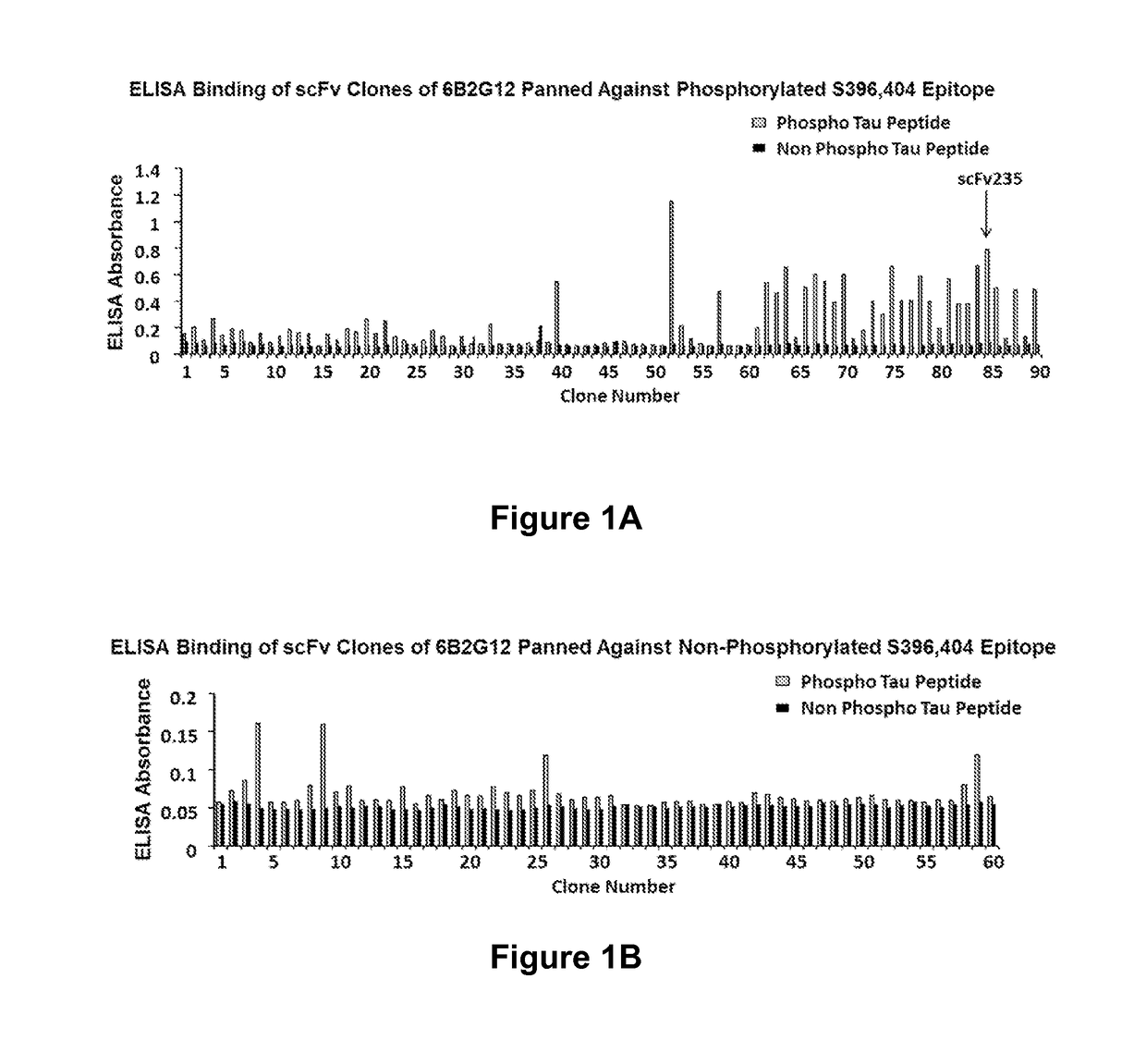
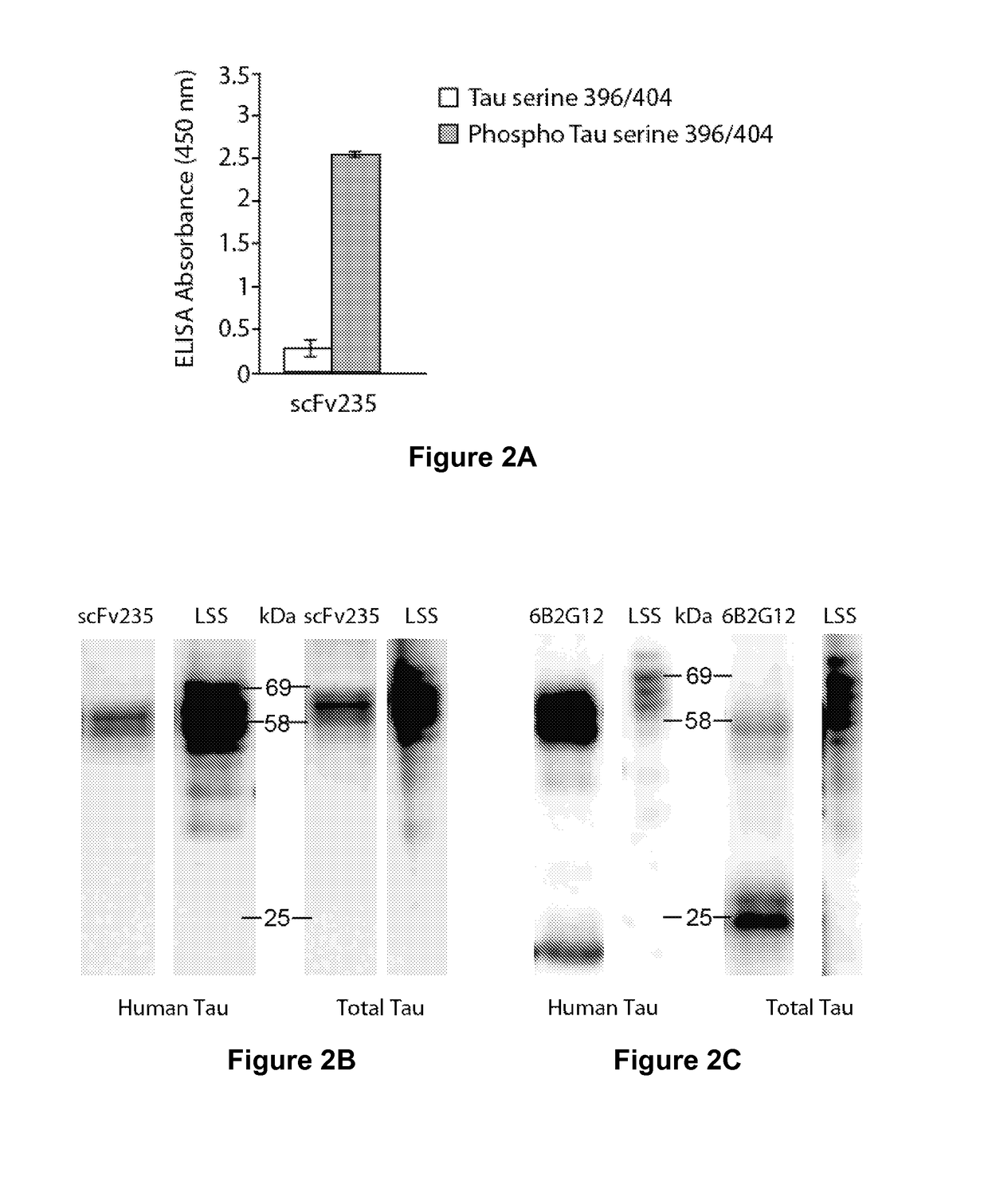
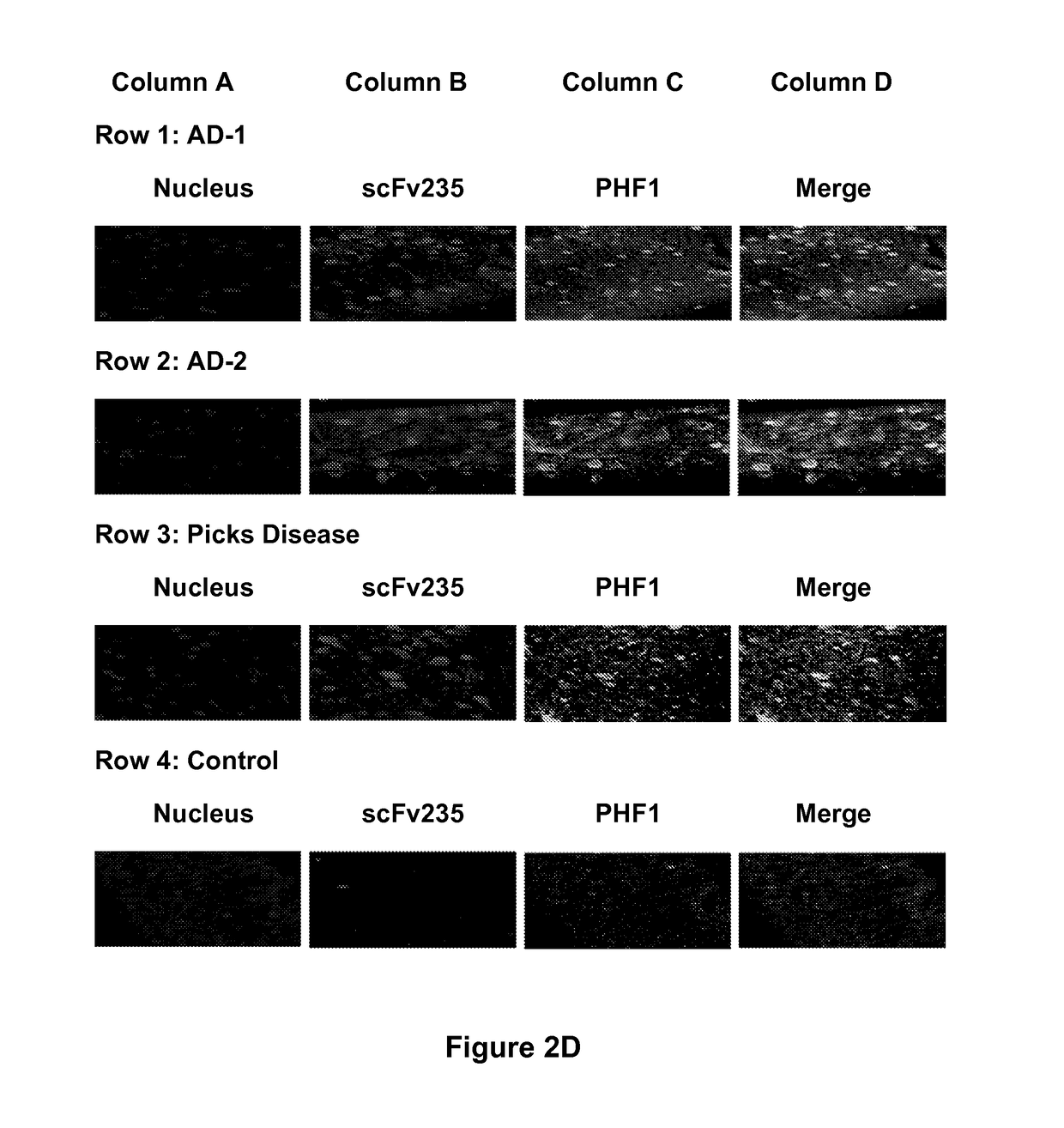
Tau Imaging Ligands and Their Uses in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Tauopathy
ActiveUS20170212131A1Useful in detectionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody fragmentsSingle-domain antibody
The present invention relates to antibody-based probes (including single domain antibody fragment, scFv molecules, antibodies, antibody fragments, diabodies, and the epitope-binding domains thereof) that are capable of immunospecifically and selectively binding to a phospho-serine-containing epitope of Tau, such as, for example, Tau-phospho-serine 396 / 404 peptide. Such imaging ligands are useful to detect pathological Tau protein conformer if present in a biological sample, especially in conjunction with the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease or other tauopathy, and thus provide a diagnostic for Alzheimer's disease and other Tau pathologies. The scFv molecules of the present invention have utility as diagnostic markers for, Alzheimer's disease and related tauopathies and as pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of such conditions.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Alkene Mimics
InactiveUS20080261923A1Growth inhibitionInhibitory activityBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsAlkeneSerine
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography microsphere material as well as preparation and application thereof
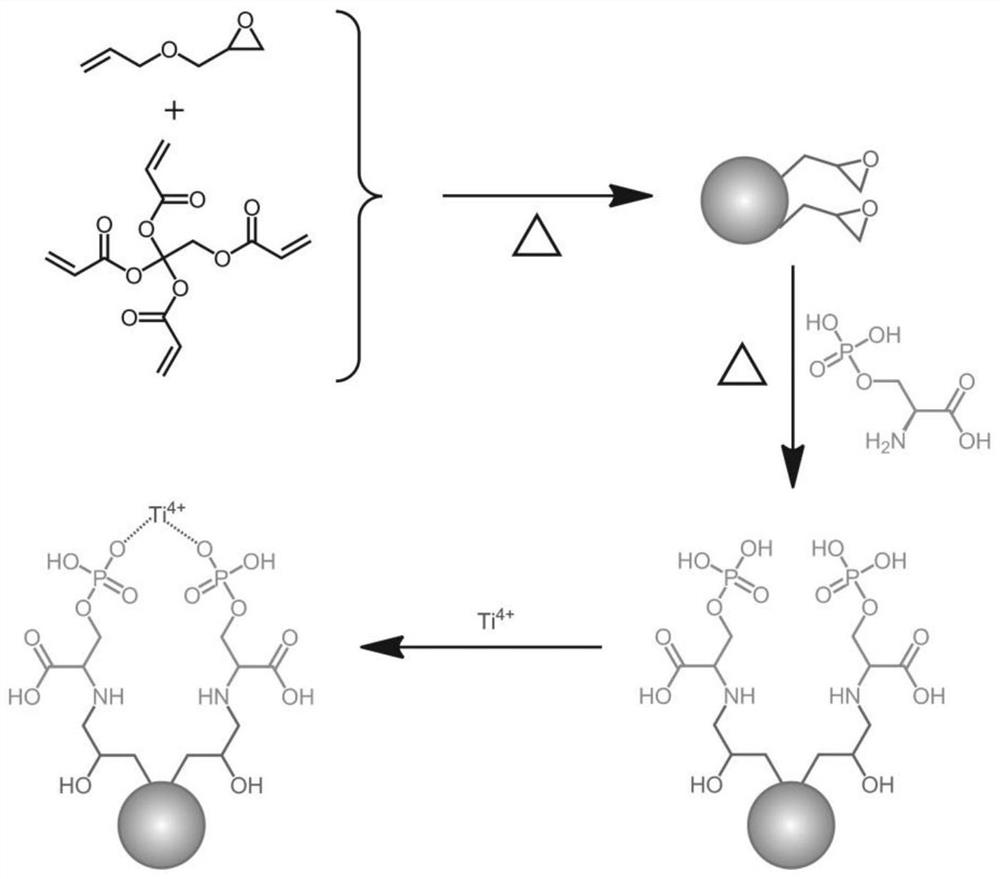
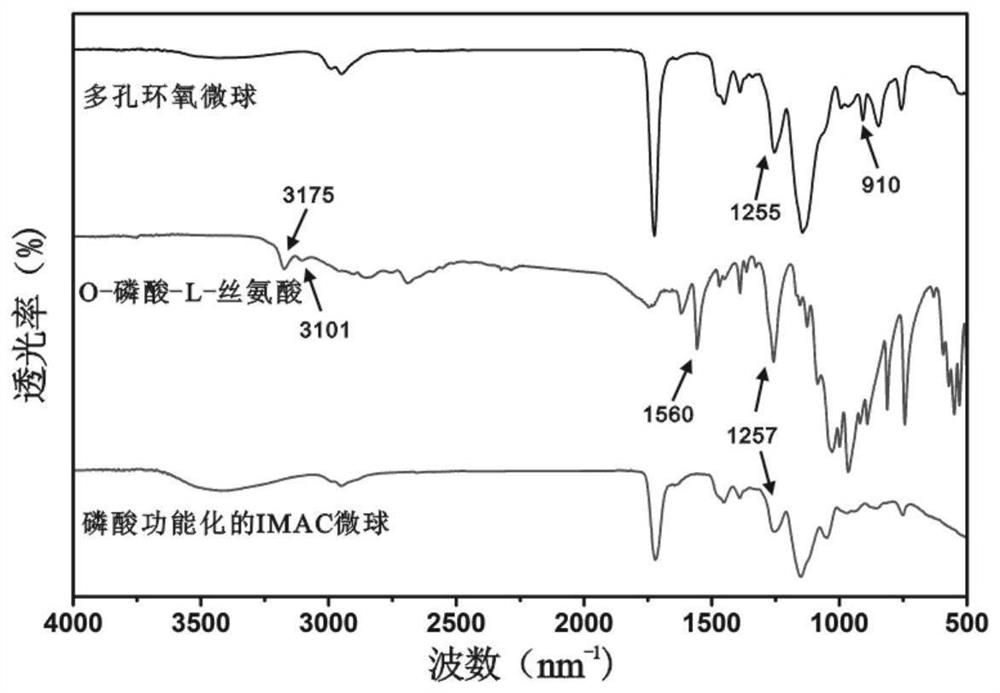
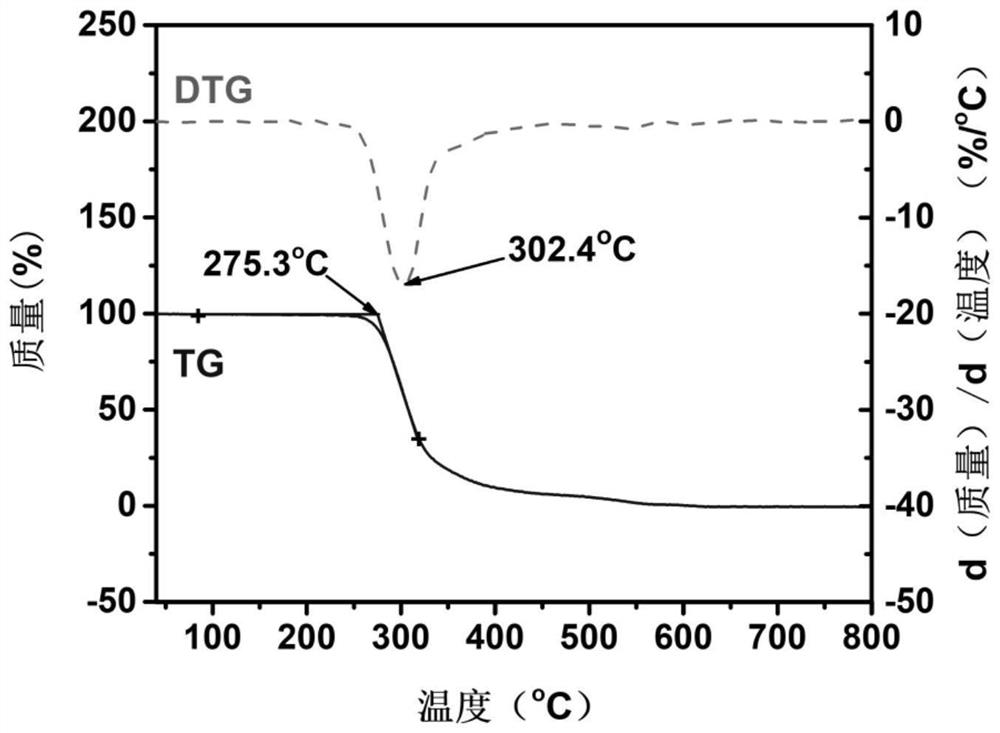
ActiveCN113351190AUniform particle sizeStrong acid and alkali resistanceOther chemical processesComponent separationO-Phosphoric AcidHydrolysate
The invention relates to an immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography material taking epoxy polymer microspheres as a matrix and application of the immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography material in enrichment of phosphorylated peptides. Specifically, firstly, allyl glycidyl ether and pentaerythritol tetraacrylate are used as raw materials, porous polymer microspheres with epoxy groups are prepared through a suspension polymerization method; the porous polymer microspheres are used as a matrix, O-phosphate-L-serine with phosphate radical functional groups is used as a modifier, a phosphoric acid functional group is introduced to the surface of the material through an epoxy-ammonia ring-opening reaction under an alkaline condition, and finally the Ti < 4 + >-IMAC material capable of being used for enriching phosphopeptides is obtained through chelating titanium ions. The obtained Ti < 4 + >-IMAC material has very high selectivity on the phosphopeptides, and can be used for high-sensitivity and high-selectivity enrichment of endogenous phosphopeptides in biological sample beta-casein enzymatic hydrolysate and human serum.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase mutants and method for production of cysteine using the same
ActiveUS20120190080A1Improve enzymatic activityHigh yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesMycobacterium smegmatisO-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase
Disclosed is an O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase (OPSS) mutant which has a Mycobacterium smegmatis-derived amino acid sequence corresponding to that of SEQ ID NO: 1 which is devoid of three to seven C-terminal amino acid residues. Also, a nucleic acid molecule encoding the OPSS mutant, an expression vector carrying the nucleic acid molecule, and a transformant transformed with the expression vector are disclosed. In addition, a method is provided for producing cysteine in which O-phospho-L-serine (OPS) is reacted with a sulfide in the presence of the OPSS mutant. The OPSS mutant has improved enzymatic activity and can be applied to the environmentally friendly production of L-cysteine through a simple enzymatic conversion reaction.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Phosphoserine containing compositions for immune tolerance induction
ActiveUS10617640B2Induction of immune toleranceReducing existing antibody titersPeptide/protein ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsLipofectamineLiposome
Compositions and methods for inducing immune tolerance to proteins and subsequence administration of the proteins are disclosed. Compositions comprise proteins complexed with liposomes comprising PS and PC, wherein at least part of the PS is present as lyso-PS.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Tau imaging ligands and their uses in the diagnosis and treatment of tauopathy
ActiveUS10132818B2Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody fragmentsSingle-domain antibody
The present invention relates to antibody-based probes (including single domain antibody fragment, scFv molecules, antibodies, antibody fragments, diabodies, and the epitope-binding domains thereof) that are capable of immunospecifically and selectively binding to a phospho-serine-containing epitope of Tau, such as, for example, Tau-phospho-serine 396 / 404 peptide. Such imaging ligands are useful to detect pathological Tau protein conformer if present in a biological sample, especially in conjunction with the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease or other tauopathy, and thus provide a diagnostic for Alzheimer's disease and other Tau pathologies. The scFv molecules of the present invention have utility as diagnostic markers for, Alzheimer's disease and related tauopathies and as pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of such conditions.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Site-Specific Incorporation of Phosphoserine Into Proteins in Escherichia Coli
Nucleic acids encoding mutant elongation factor proteins (EF-Sep), phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase (SepRS), and phosphoseryl-tRNA (tRNASep) and methods of use in site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into a protein or polypeptide are described. Typically, SepRS preferentially aminoacylates tRNASep with O-phosphoserine and the tRNASep recognizes at least one codon such as a stop codon. Due to the negative charge of the phosphoserine, Sept-tRNASep does not bind elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu). However, mutant EF-Sep proteins are disclosed that bind Sep-tRNASep and protect Sep-tRNASep from deacylation. In a preferred embodiment the nucleic acids are on vectors and are expressed in cells such as bacterial cells, archeaebacterial cells, and eukaryotic cells. Proteins or polypeptides containing phosphoserine produced by the methods described herein can be used for a variety of applications such as research, antibody production, protein array manufacture and development of cell-based screens for new drug discovery.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Phosphoserine containing compositions for immune tolerance induction
ActiveUS11083782B2Induction of immune toleranceReducing existing antibody titersOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsLipofectamineLiposome
Compositions and methods for inducing immune tolerance to proteins and subsequence administration of the proteins are disclosed. Compositions comprise proteins complexed with liposomes comprising PS and PC, wherein at least part of the PS is present as lyso-PS.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Microorganism producing O-phosphoserine and a method for producing O-phosphoserine or L-cysteine using the same
ActiveUS10323262B2Excellent OPS-exporting capabilityHigh yieldFungiBacteriaMicroorganismPhosphoserine
The present invention relates to a microorganism, wherein the activity of a polypeptide capable of exporting O-phosphoserine (OPS) is enhanced, and a method of producing O-phosphoserine, cysteine, or a cysteine derivative using the microorganism.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Organophosphorous, multivalent metal compounds, and polymer adhesive interpenetrating network compositions and methods
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Method for preparing cysteine or a derivative thereof using a novel o-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase
The present invention relates to a method for producing cysteine or derivatives thereof using novel O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase. According to the present invention, a method for producing cysteine by novel O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase (OPSS) using O-phosphoserine as a substrate is provided, and this method is advantageous in that cysteine can be simply and environmental-friendly produced in a high yield.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
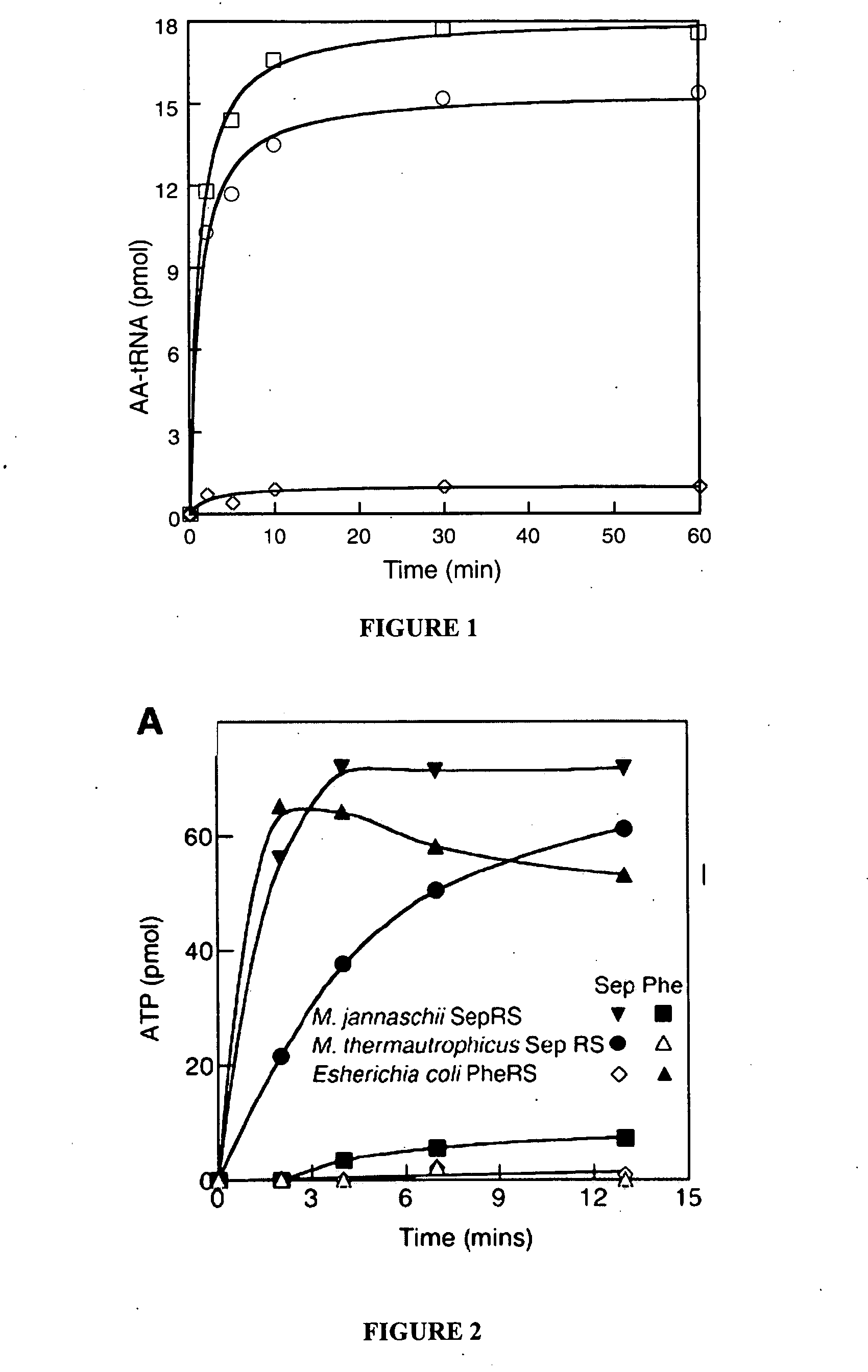
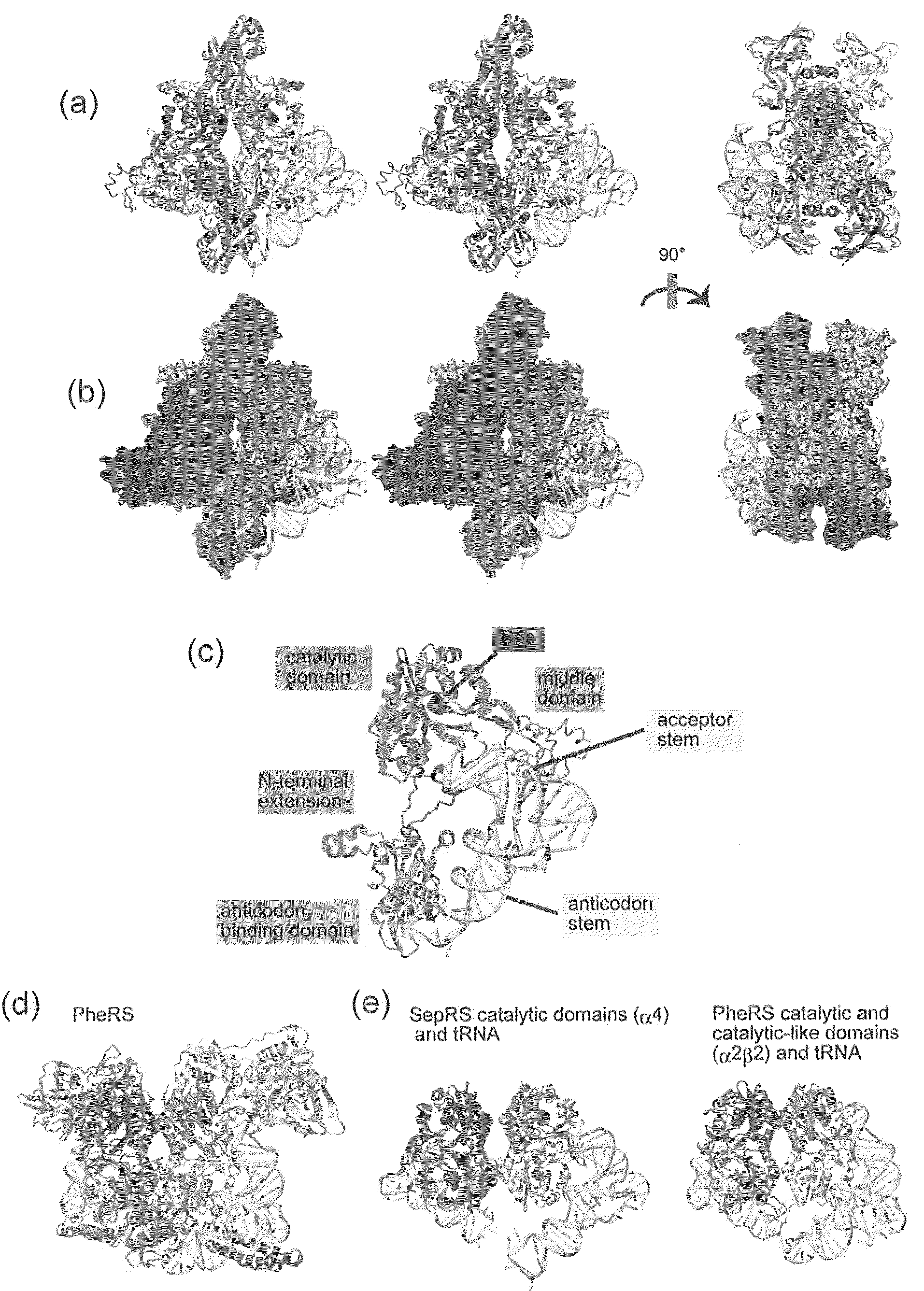
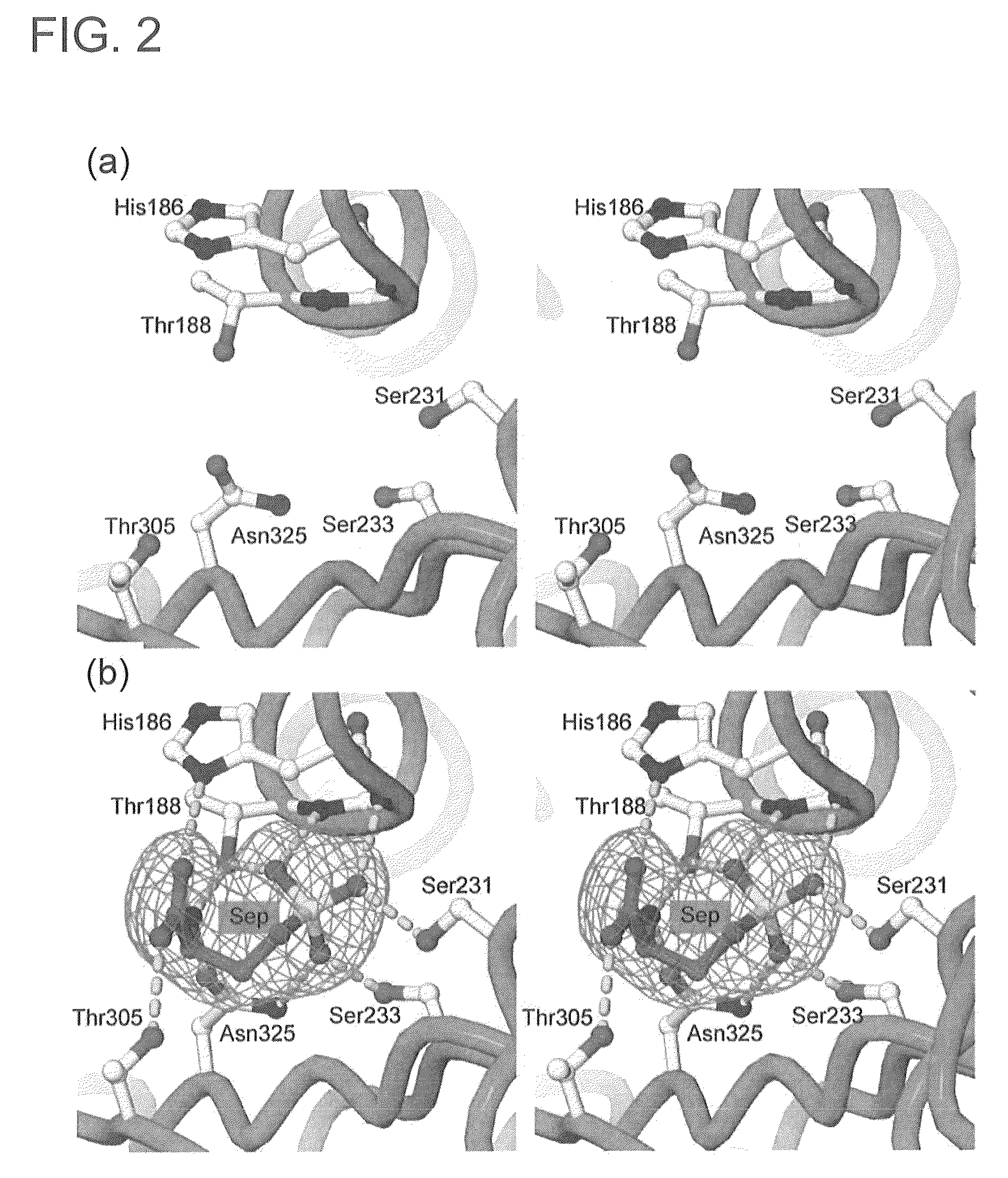
Mutant SepRS, and method for site-specific introduction of phosphoserine into protein using the same
A mutant SepRS which is suitable for a site-specific introduction of phosphoserine into a protein is prepared by analyzing the structure and functions of a phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase (SepRS) derived from an archaebacterium. A mutant SepRS composed of an amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:2, in which any one or more of glutamic acids at position-418 and position-420 and threonine at position-423 are substituted with other amino acid, and having enhanced binding affinity with a suppressor tRNA as compared with a wild type phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase (SepRS) composed of an amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:2 is provided.
Owner:RIKEN
Phosphoserine containing compositions for immune tolerance induction
ActiveUS20200222322A1Induction of immune toleranceReducing existing antibody titersPeptide/protein ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsLipofectamineLiposome
Compositions and methods for inducing immune tolerance to proteins and subsequence administration of the proteins are disclosed. Compositions comprise proteins complexed with liposomes comprising PS and PC, wherein at least part of the PS is present as lyso-PS.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Preparation method of milk powder for infants
The invention belongs to the technical field of milk products, and specifically relates to a preparation method of milk powder for infants. According to the milk powder for the infants, cow milk is used in replacement of breast milk. The cow milk mainly contains casein, beta-casein and [alpha]<s>-casein while the breast milk mainly contains beta-casein and no [alpha]<s>-casein; however, the cow milk is difficult for the infants to digest and absorb due to the [alpha]<s>-casein. And thus, pretreatment is performed on skimmed cow milk. The [alpha]<s>-casein comprises phosphoserine groups, so that, the [alpha]<s>-casein carries net negative charges under alkaline conditions; and thus, the [alpha]<s>-casein has high affinity for calcium ions, and is more likely to precipitate. And therefore, the content of [alpha]<s>-casein in the pretreated cow milk is further reduced so as to make the cow milk easier to digest and absorb; moreover, casein in the cow milk is modified by enzymes extractedfrom egg white so that amido bonds formed by carboxyl of hydrophobic amino acids are primarily catalyzed, and thus, peptide bonds in protein molecules are hydrolyzed so as to produce polypeptides withrelatively small molecular weight. In addition, the prepared milk powder for the infants has certain disease-preventing and disease-resisting functions; and thus, allergenicity of cow milk protein isreduced while safety of the milk powder for the infants is improved.
Owner:仇颖超
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com