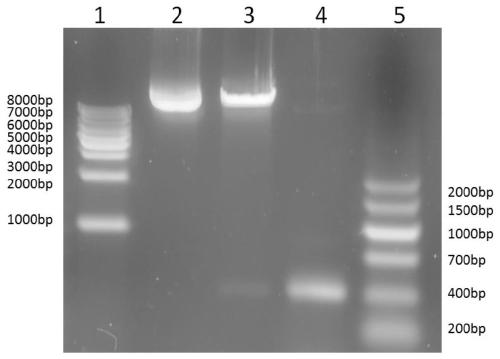
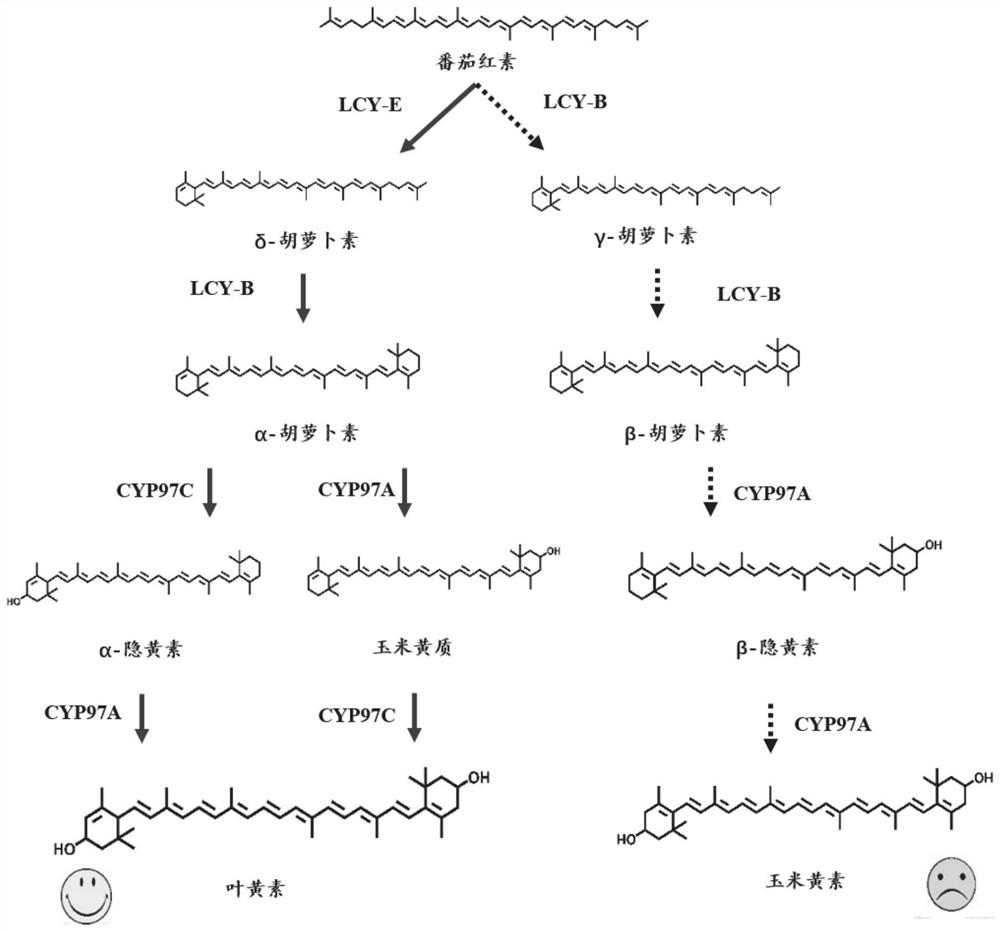
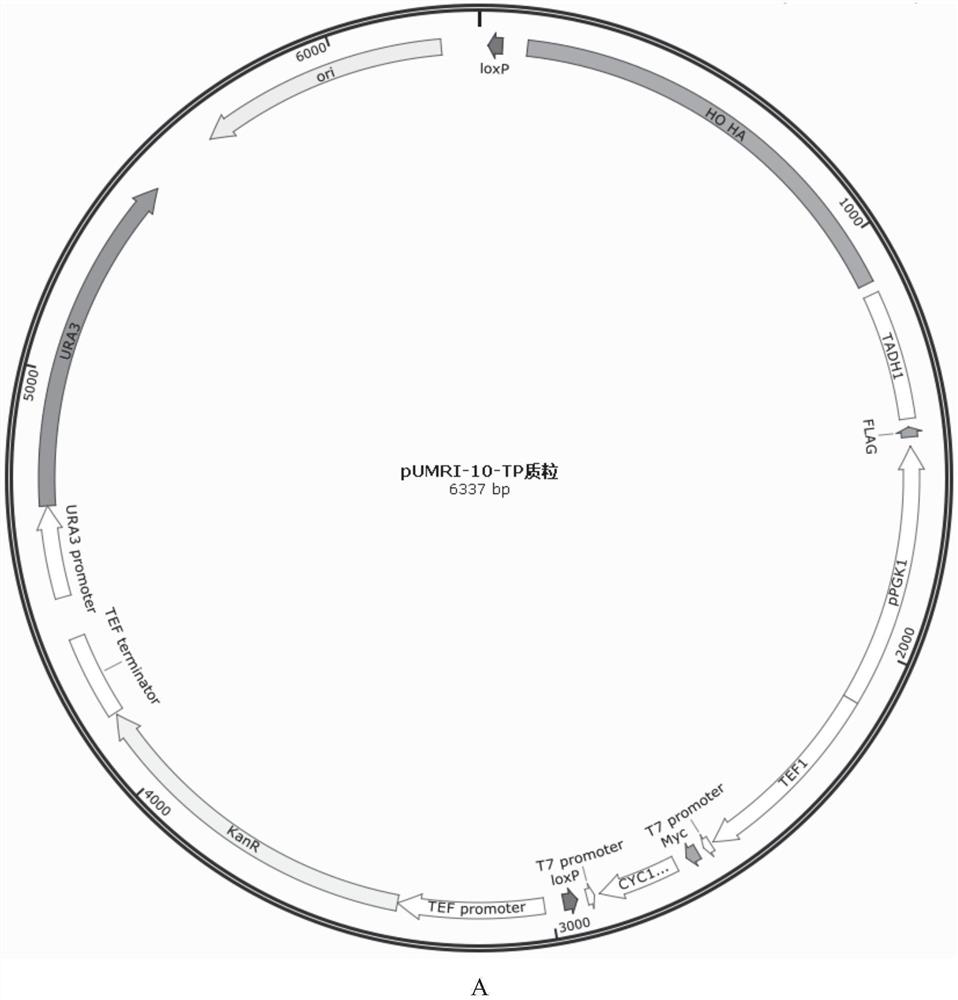
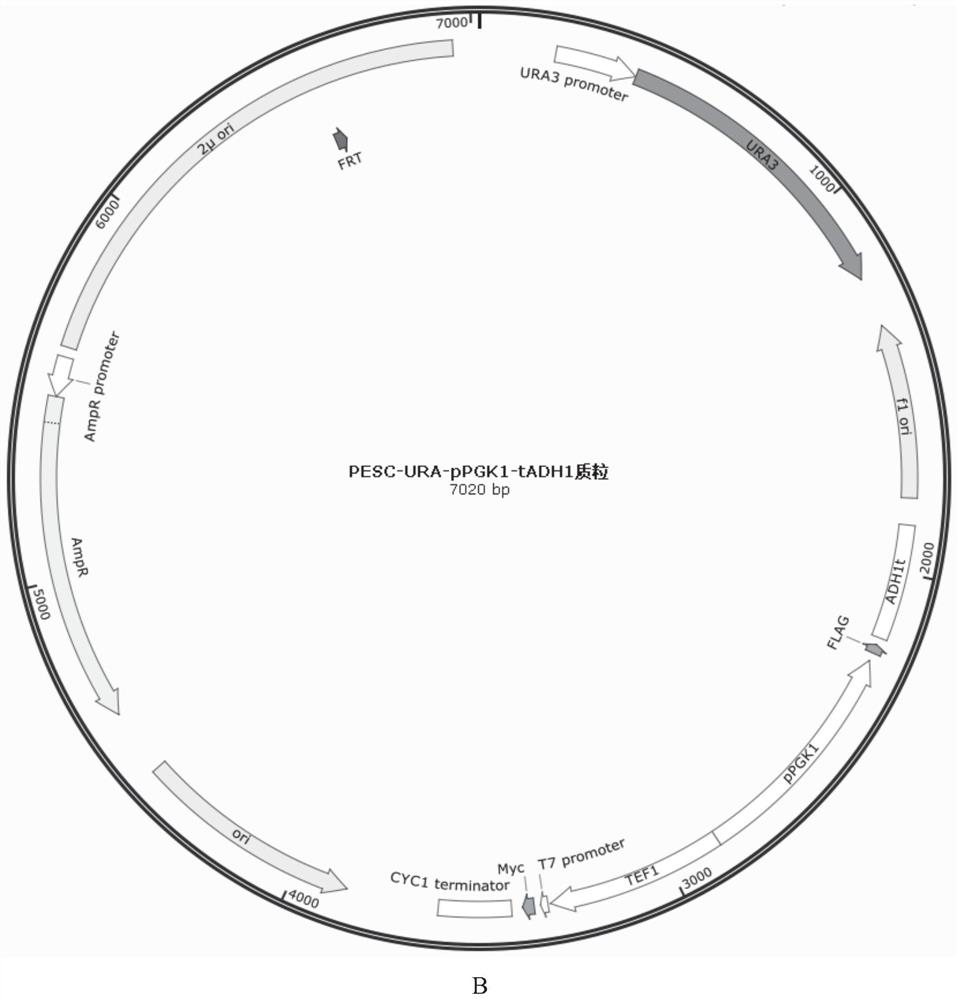
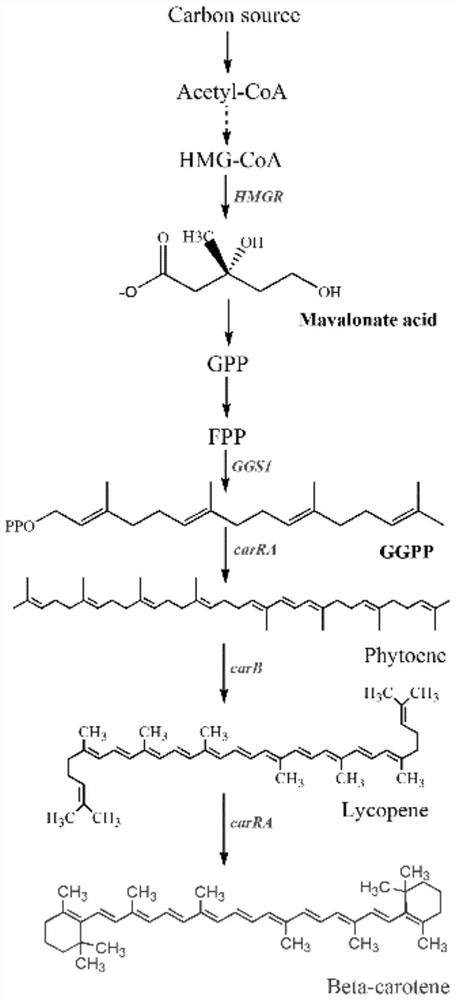
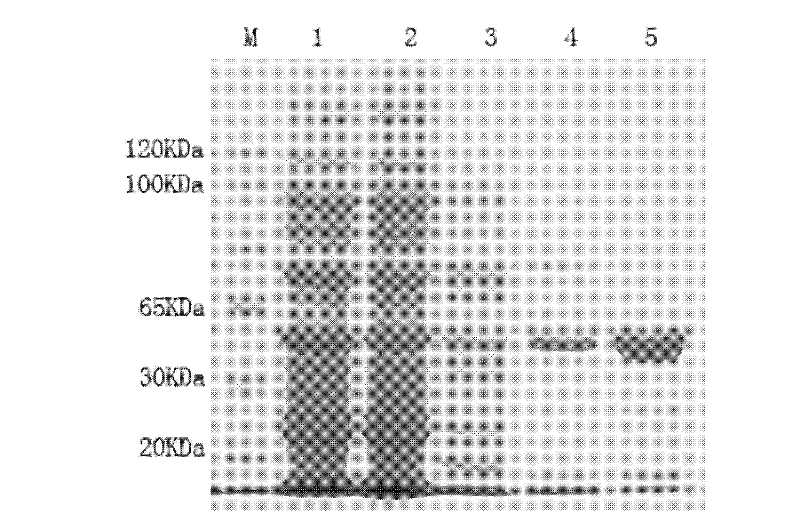
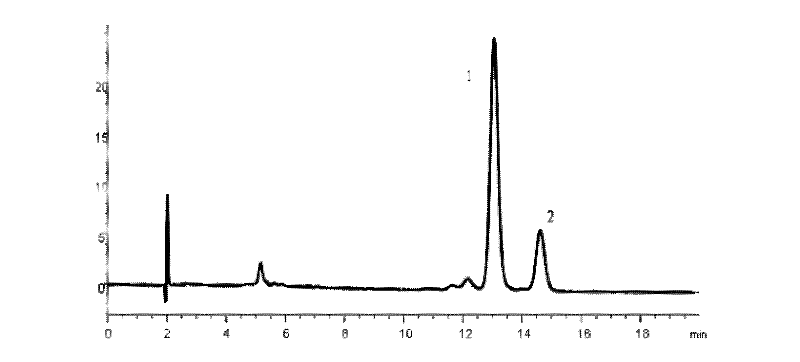
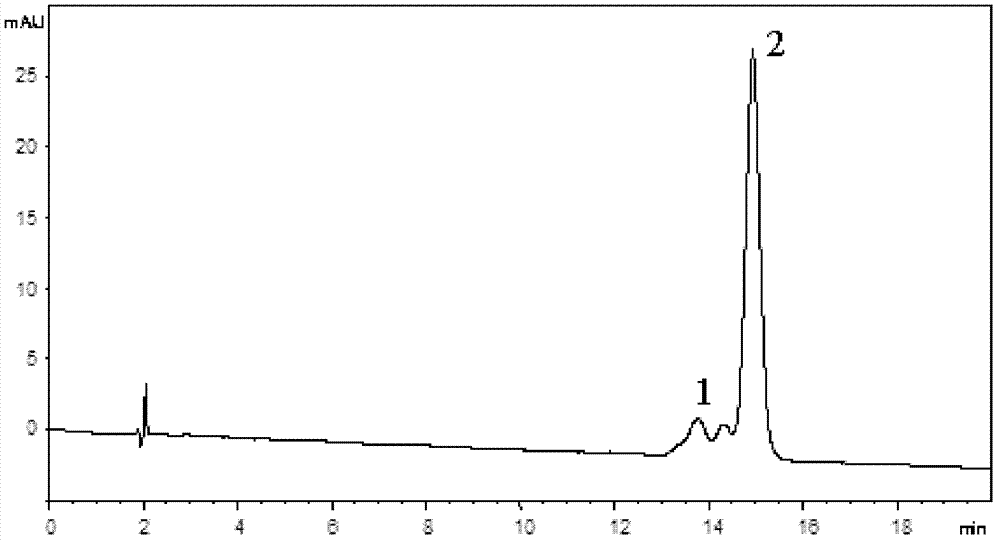
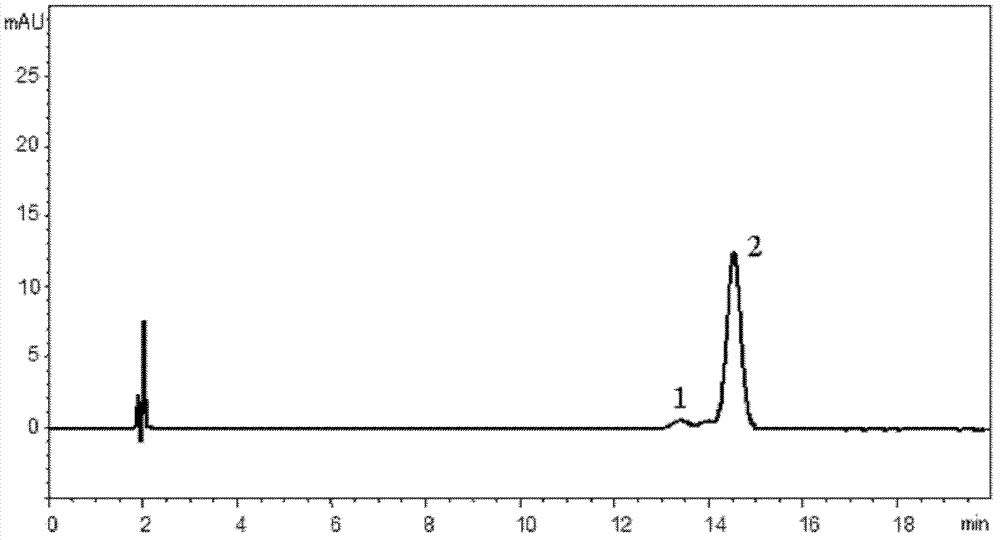
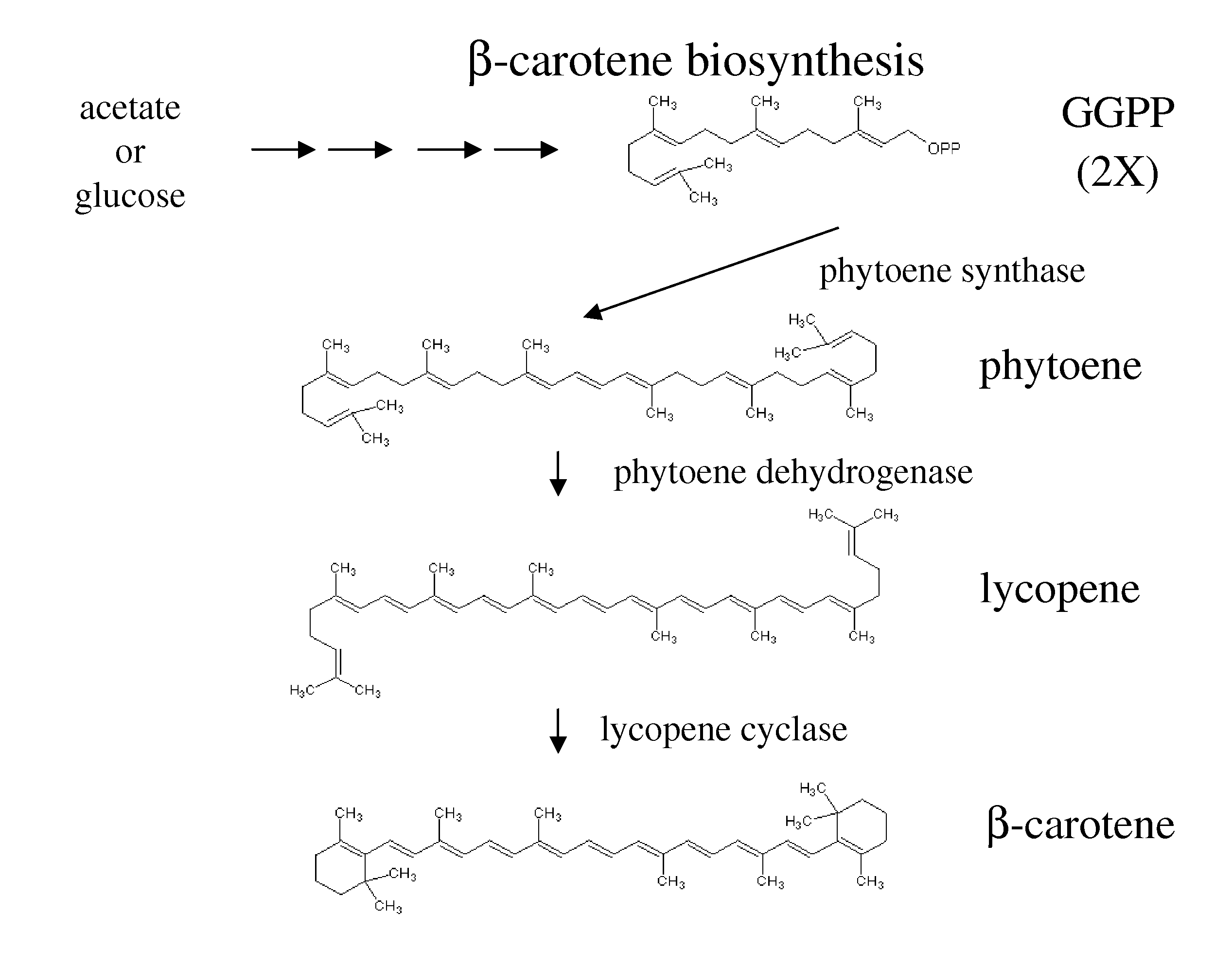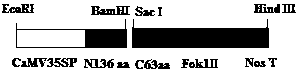Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Phytoene dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
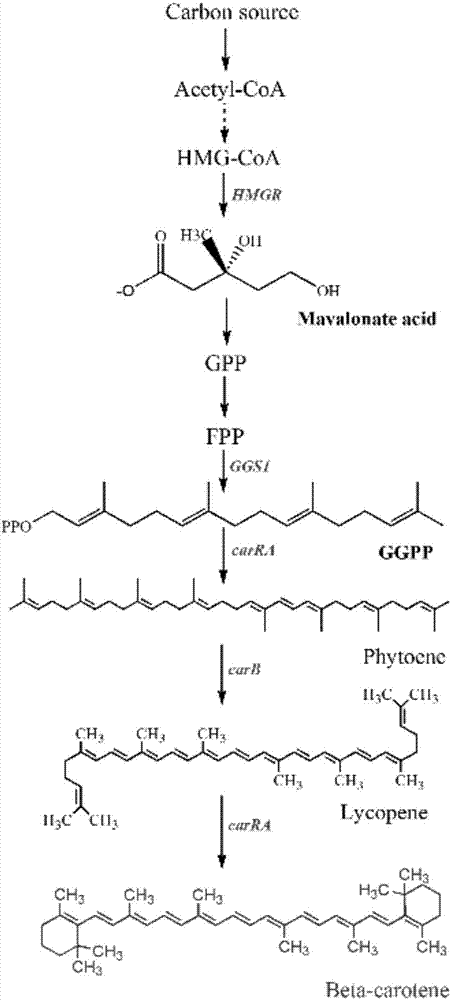
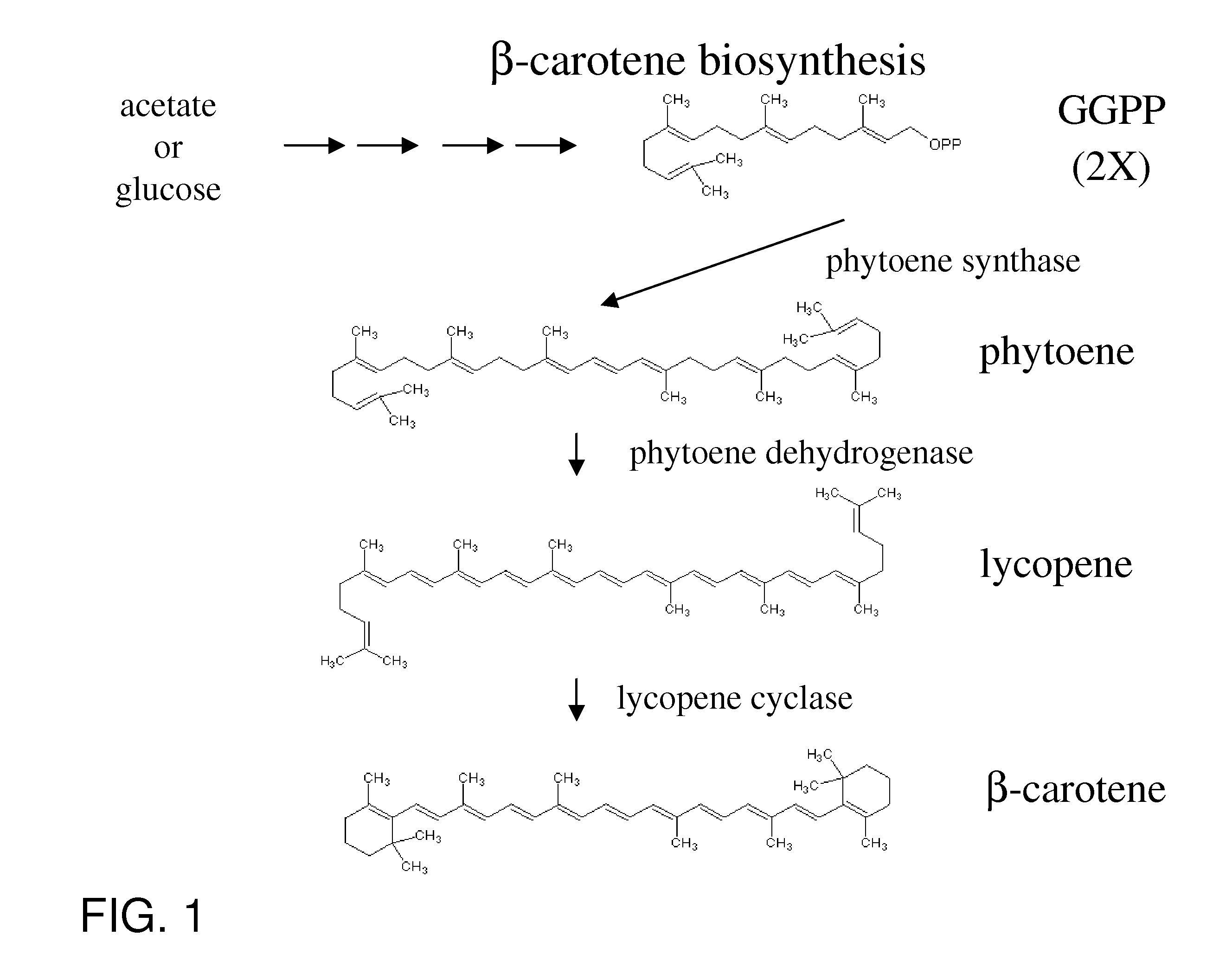
Recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacterium
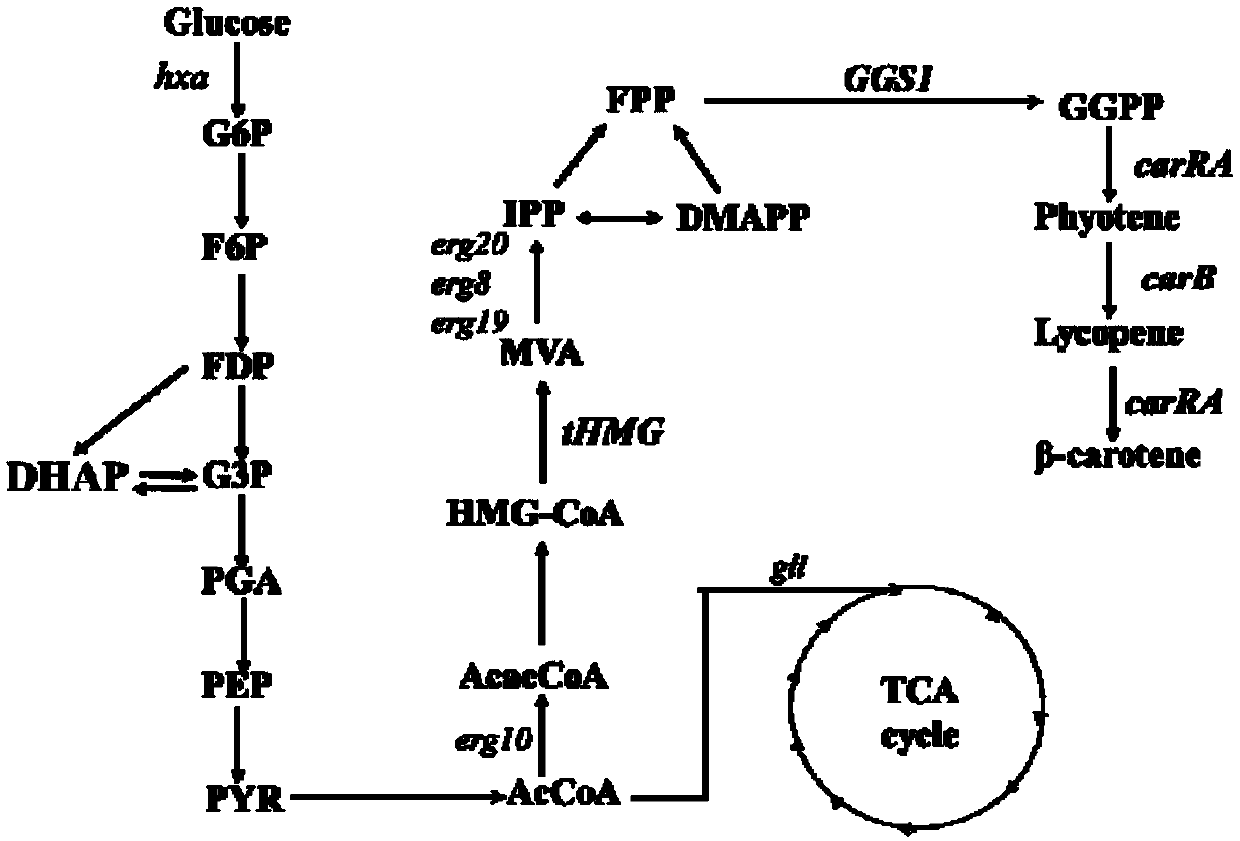
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacterium. The construction method comprises the following steps: respectively constructing superstrong gene expression modules of protein phytoene synthetase / lycopene cyclase coded by beta-carotene synthetic genes optimized by codons, phytoene dehydrogenase, protein geranyl diphosphate synthase coded by MAV (micro aerial vehicle) pathway genes and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; assembling the gene expression modules in vitro, so as to obtain four plasmids of the gene expression modules, integrating the plasmids into a host bacteria genome which does not produce beta-carotene and screening orange single colonies, so as to obtain the recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene. The recombinant bacterium disclosed by the invention is adopted for producing beta-carotene by fermental cultivation, and the yield of beta-carotene can reach 26.03mg / g DCW. Therefore, the recombinant bacterium has high performance of producing beta-carotene.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
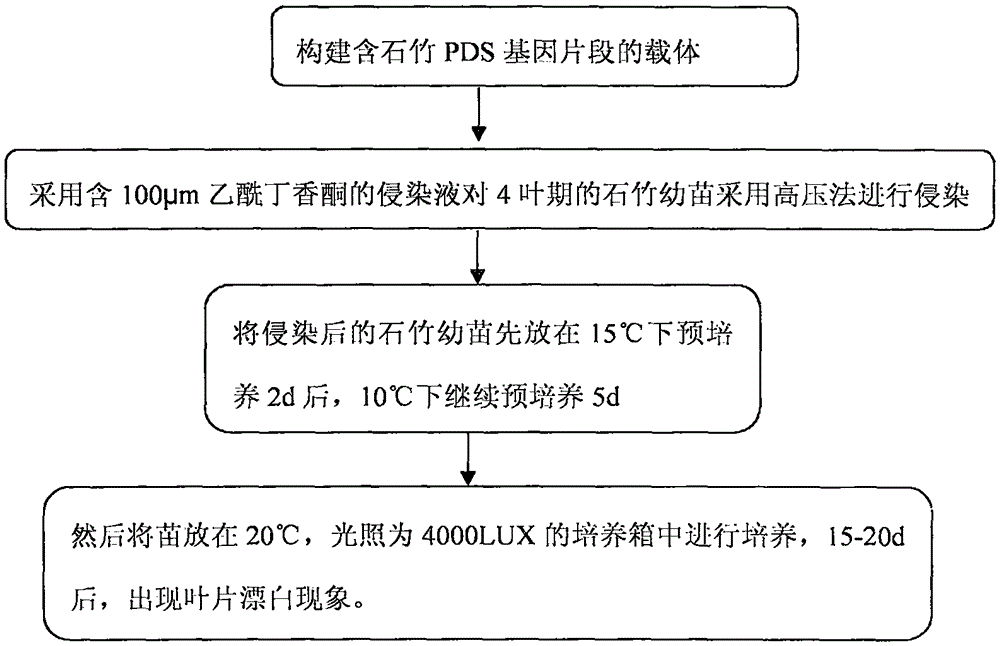
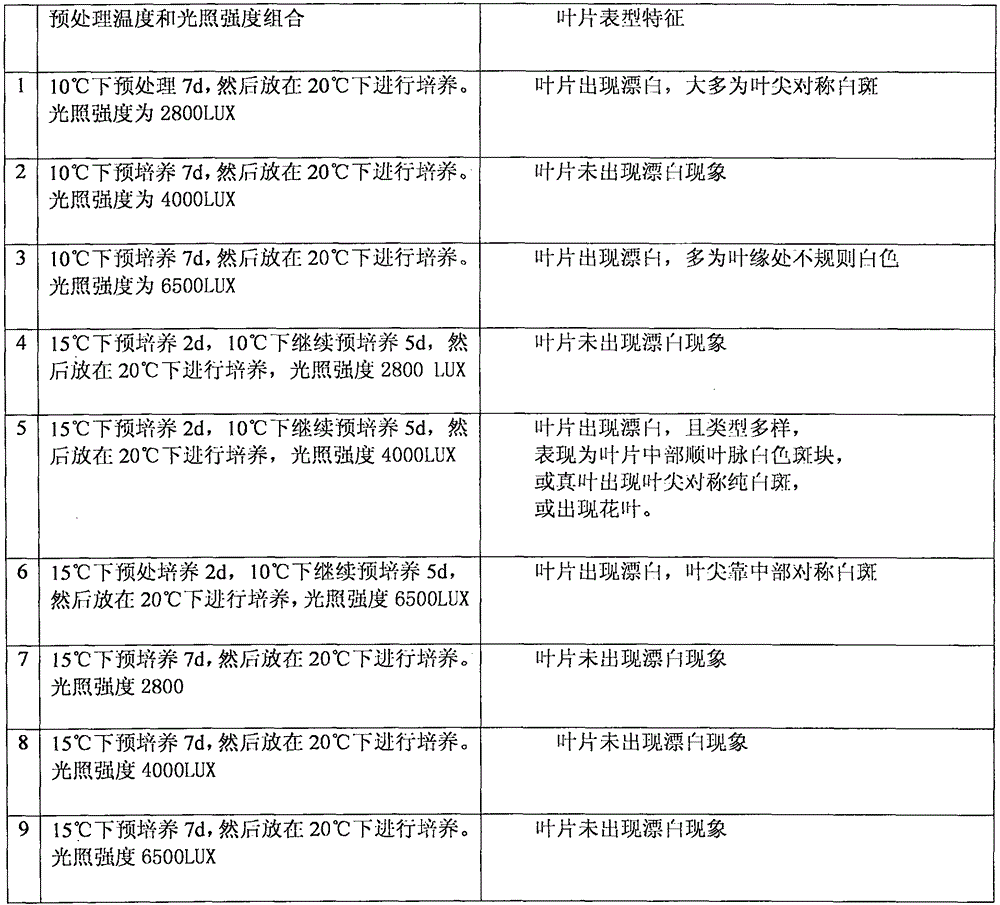
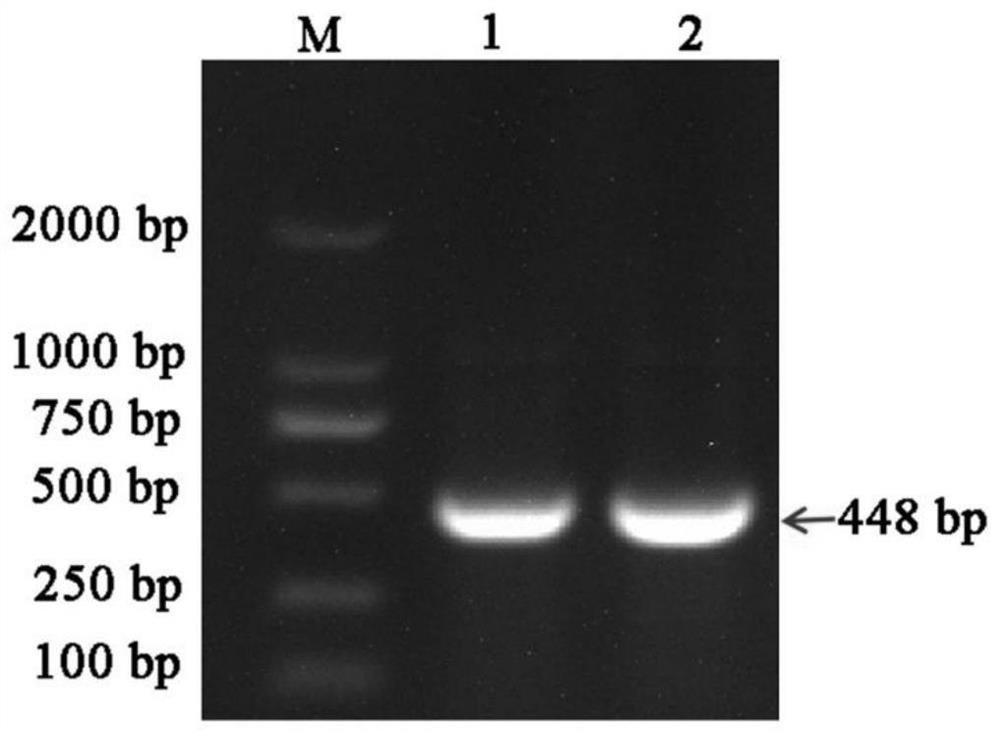
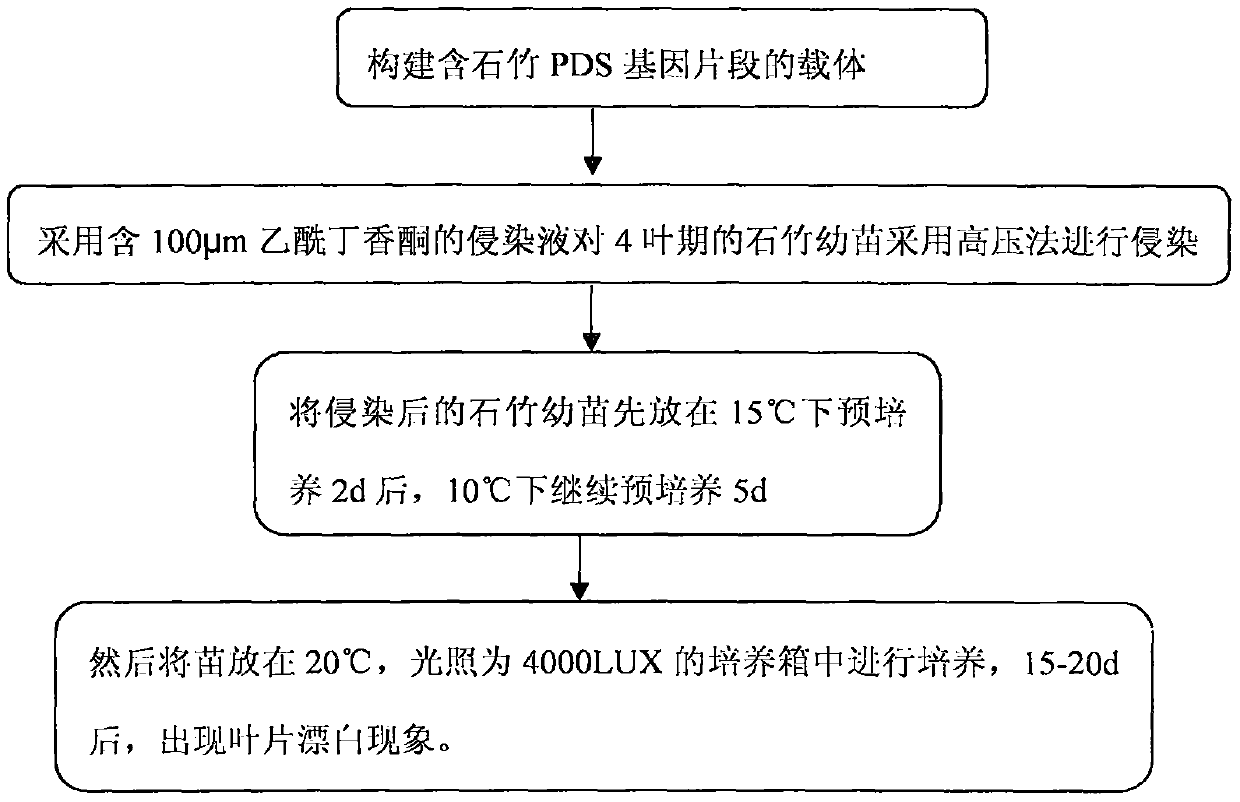
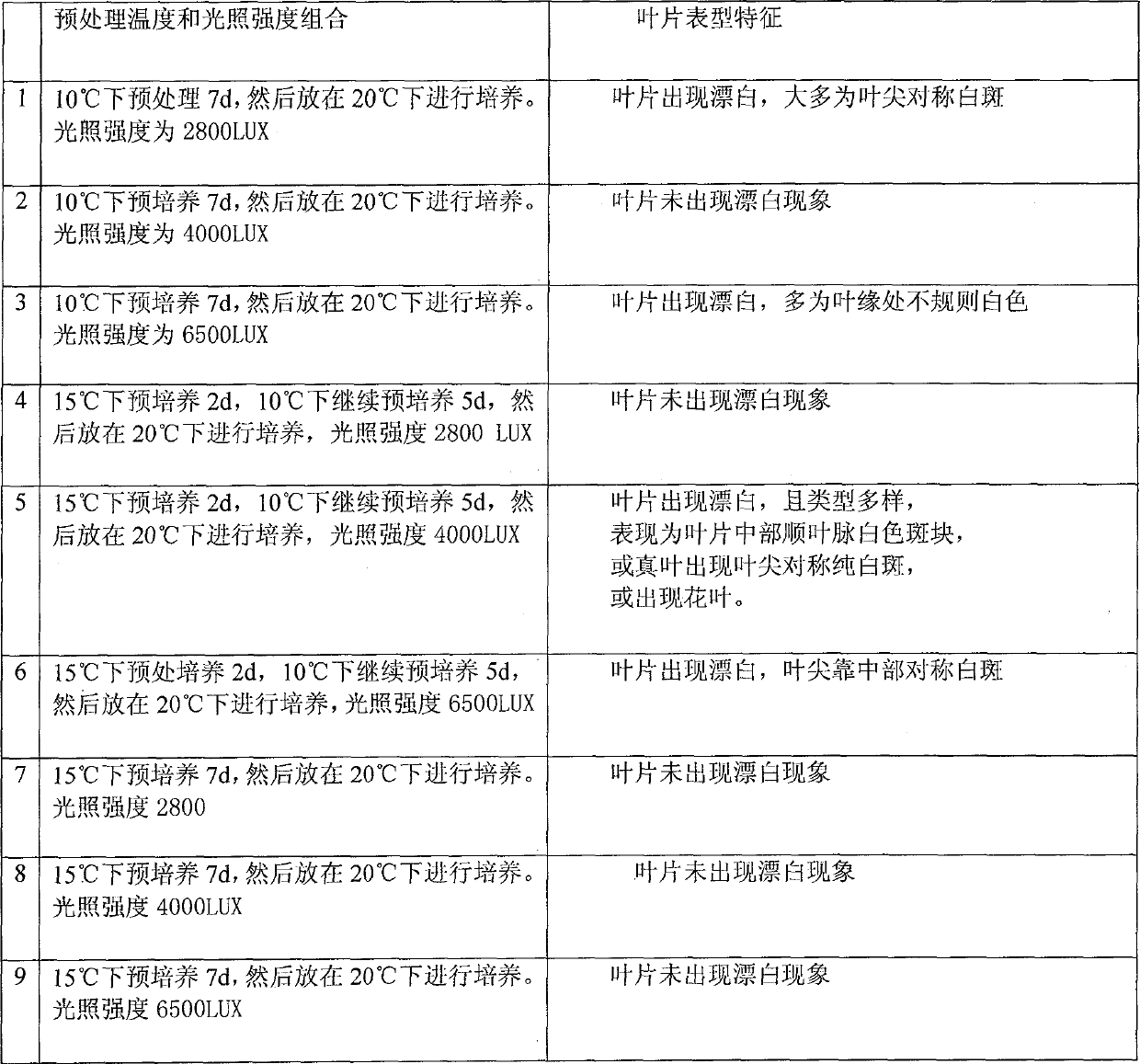
Efficient virus-induced phytoene desaturase gene silence system for Chinese pink
InactiveCN105296535ASolving questions about gene functionGenetic engineeringFermentationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidMultiplex polymerase chain reaction
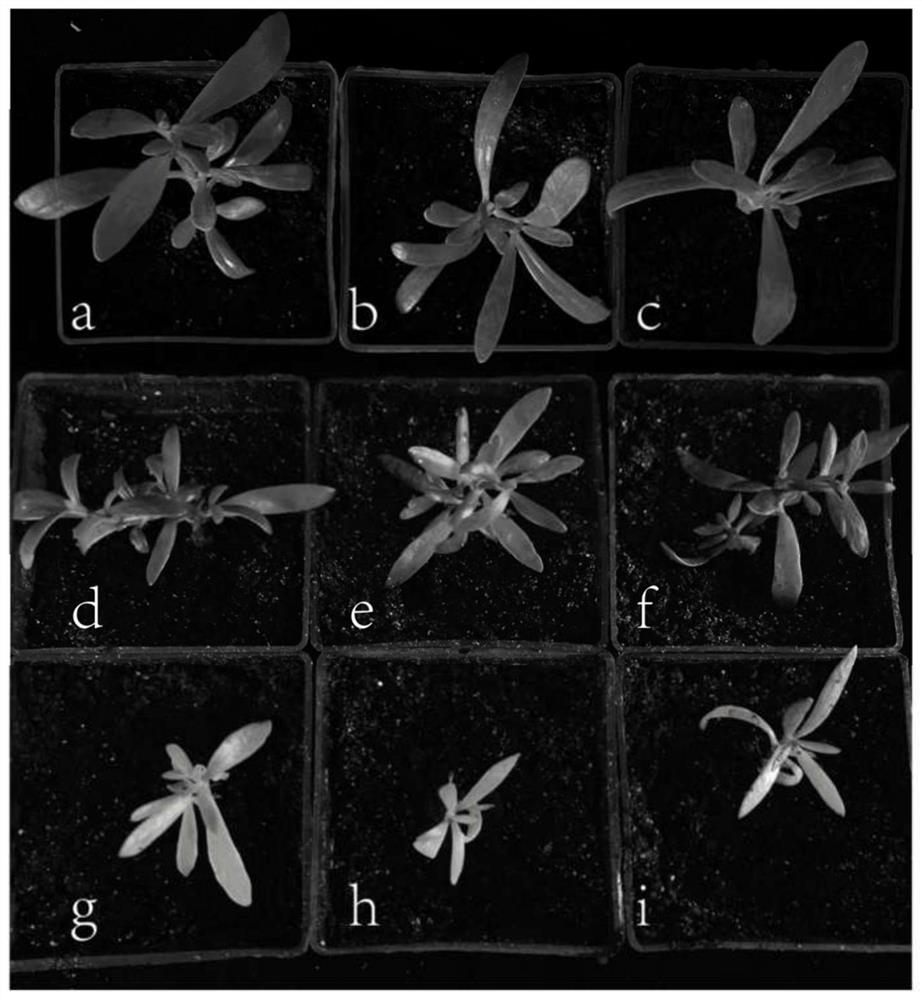
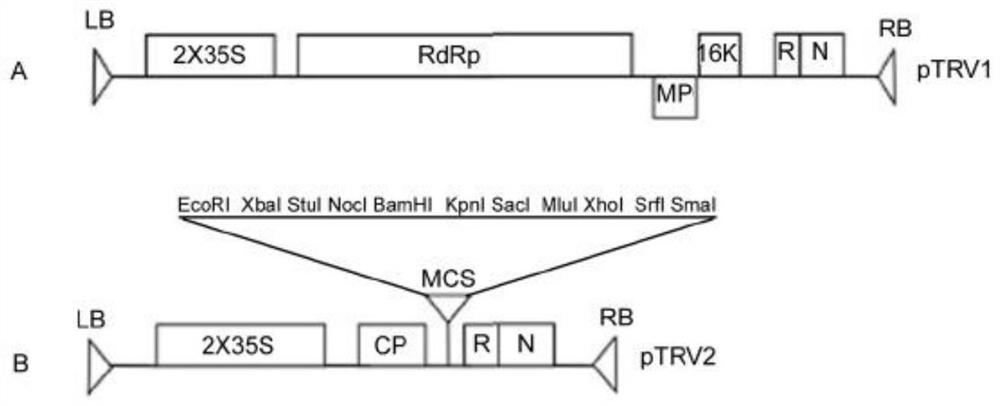
The invention discloses an efficient virus-induced phytoene desaturase gene silence system for Chinese pink. A specific primer is designed according to a coding gene sequence of PDS (phytoene desaturase), and about 500bp cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments are amplified in the Chinese pink through RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction). Obtained PDS cDNA fragments are connected to TRV2, and acetosyringone concentration, seedling age and preculture temperature after infection as well as light conditions for plants after preculture are integrated in an assorted manner by optimizing an agrobacterium-mediated virus-induced gene silence system according to photobleaching frequency, bleached leaf area and bleached conditions of the plants, so that the rapid efficient virus-induced silence system is established, virus-induced gene silence character can be obtained, and further, the problem that Chinese pink gene functions are verified effectively is solved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of phytoene dehydrogenase gene and its application
ActiveCN102260692AEfficient productionHydrocarbon active ingredientsMicroorganism based processesRhodobacter azotoformansFhit gene
The invention relates to a phytoene dehydrogenase gene, in particular to a phytoene dehydrogenase gene for efficiently synthesizing lycopene and application thereof, belonging to the field of gene engineering. The nucleotide sequence of the phytoene dehydrogenase gene is shown by SEQ ID No.1. The amino acid sequence of the phytoene dehydrogenase coded with the gene is shown by SEQ ID No.2. The phytoene dehydrogenase gene provided by the invention can be used for efficiently producing lycopene. The examination results in that the yield of lycopene in a fermentation liquor is 0.269 mg / L and thecontent of lycopene in the dry weight of bacteria is 0.256 mg / g and accounts for 73.5% the total content of carotenoid; the phytoene dehydrogenase recombinase catalysate of rhodobacter azotoformans uses lycopene as the main pigment component and provides a new enzyme source for producing lycopene.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
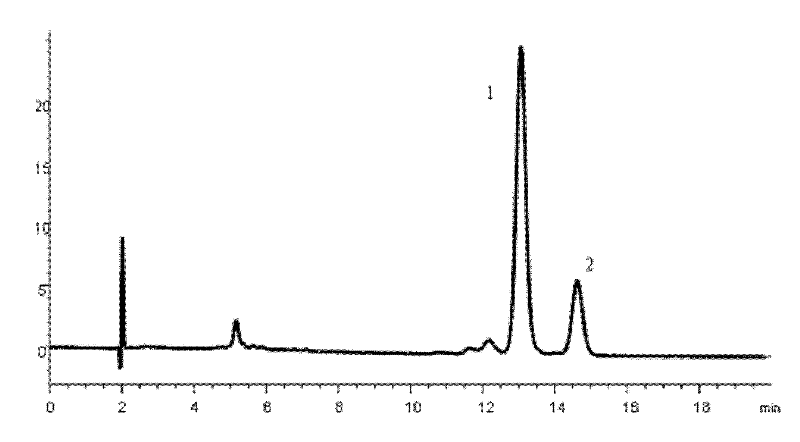
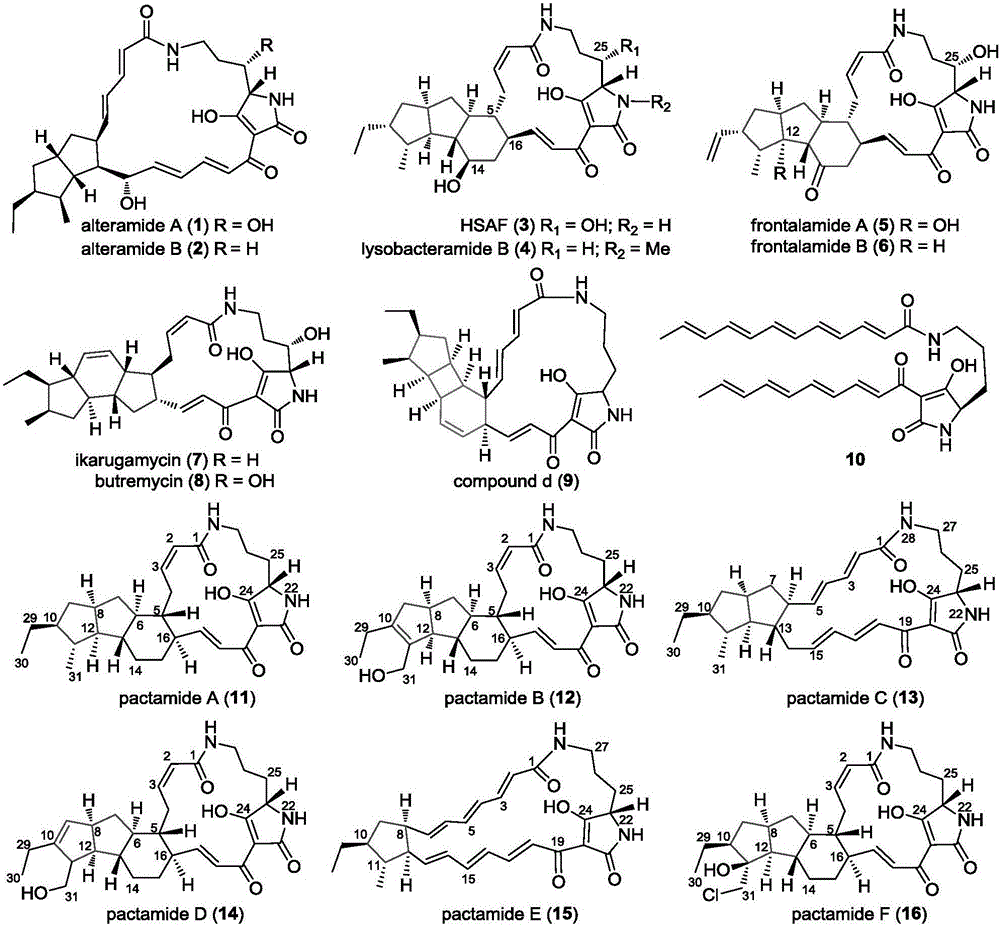
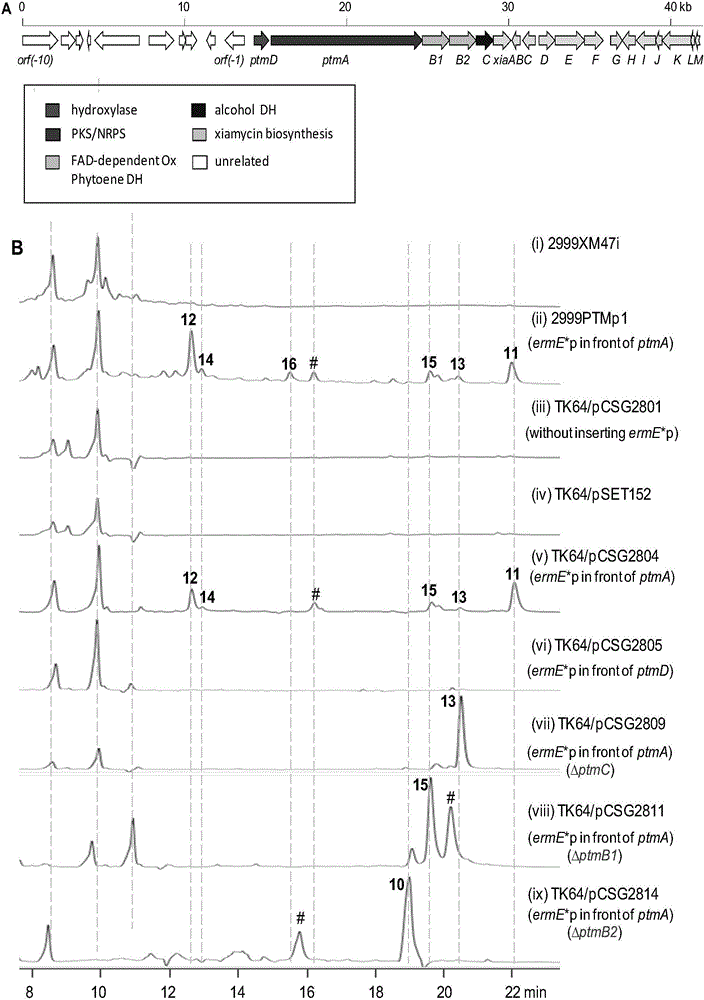
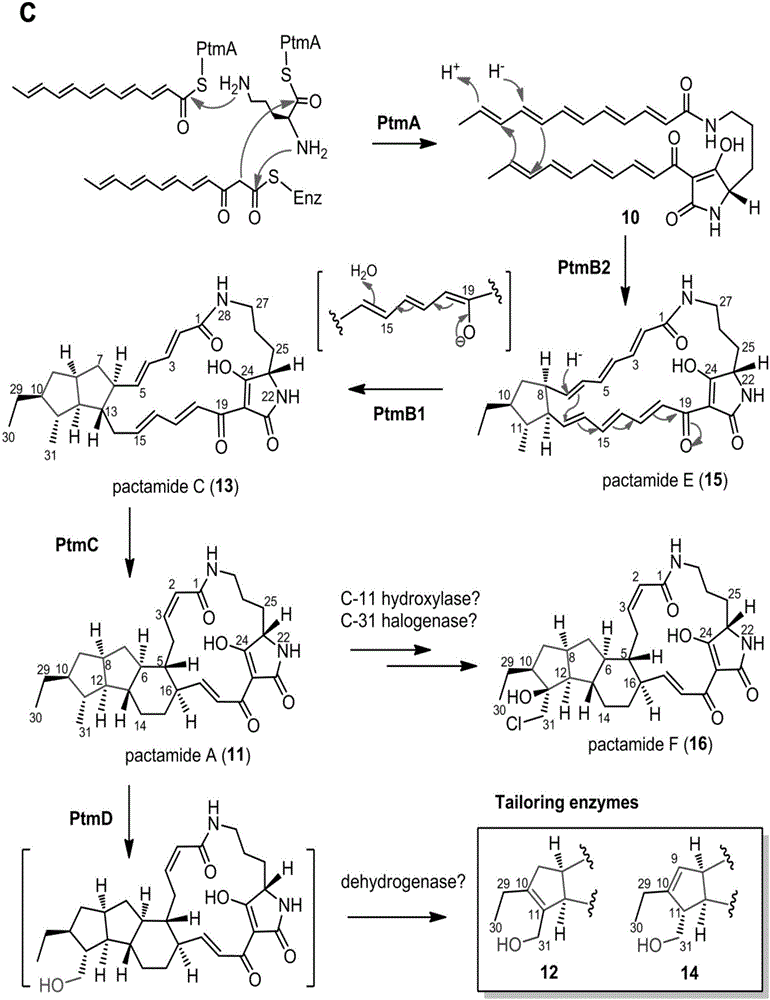
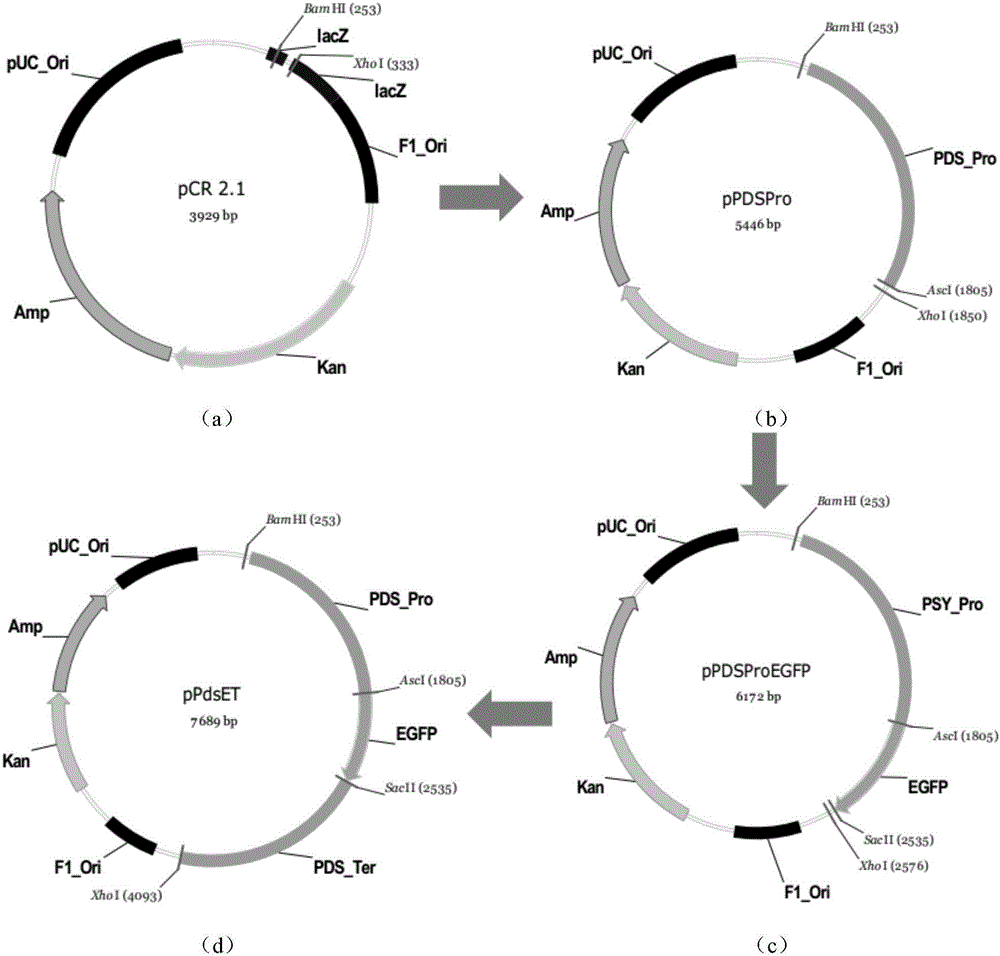
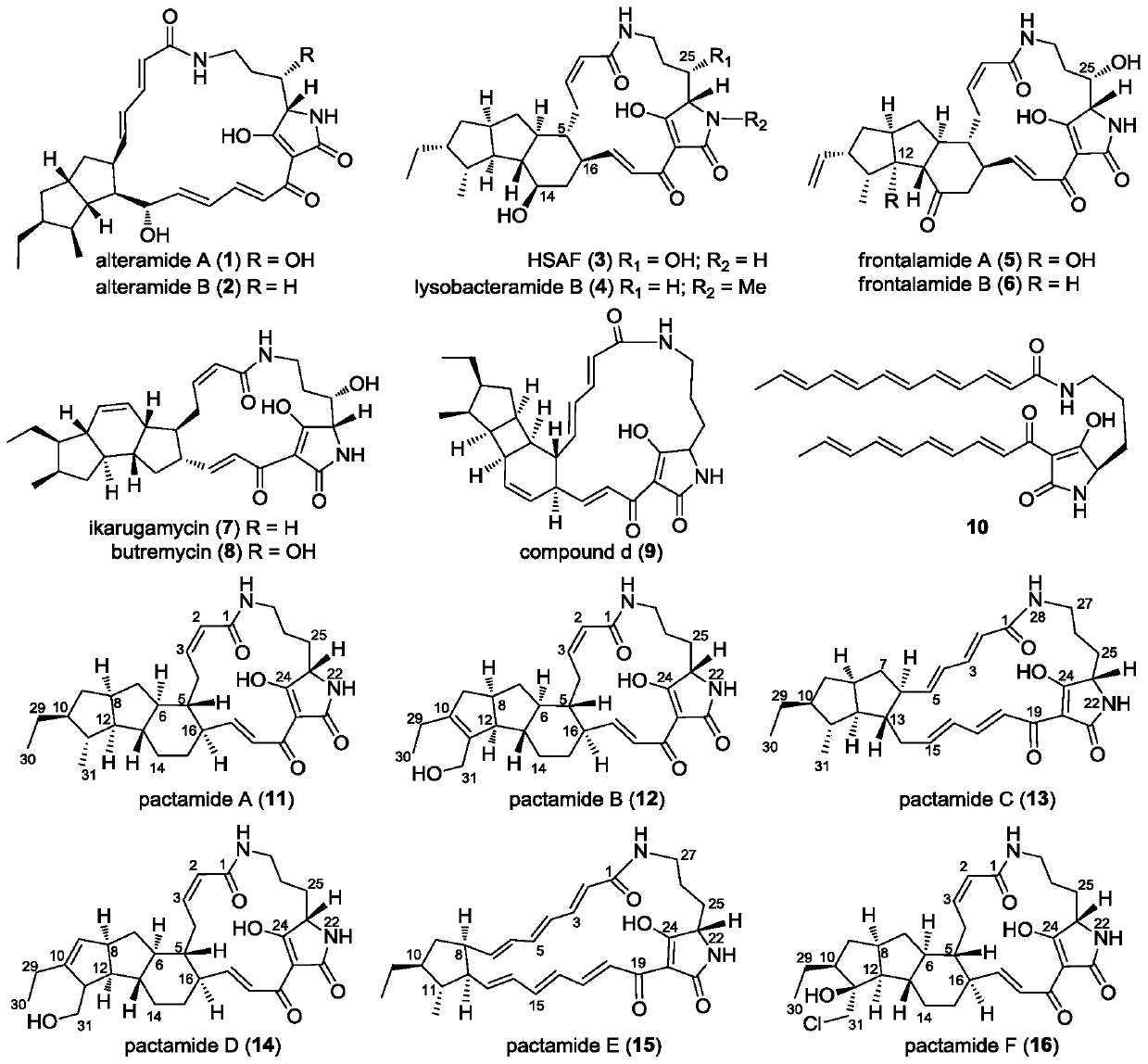
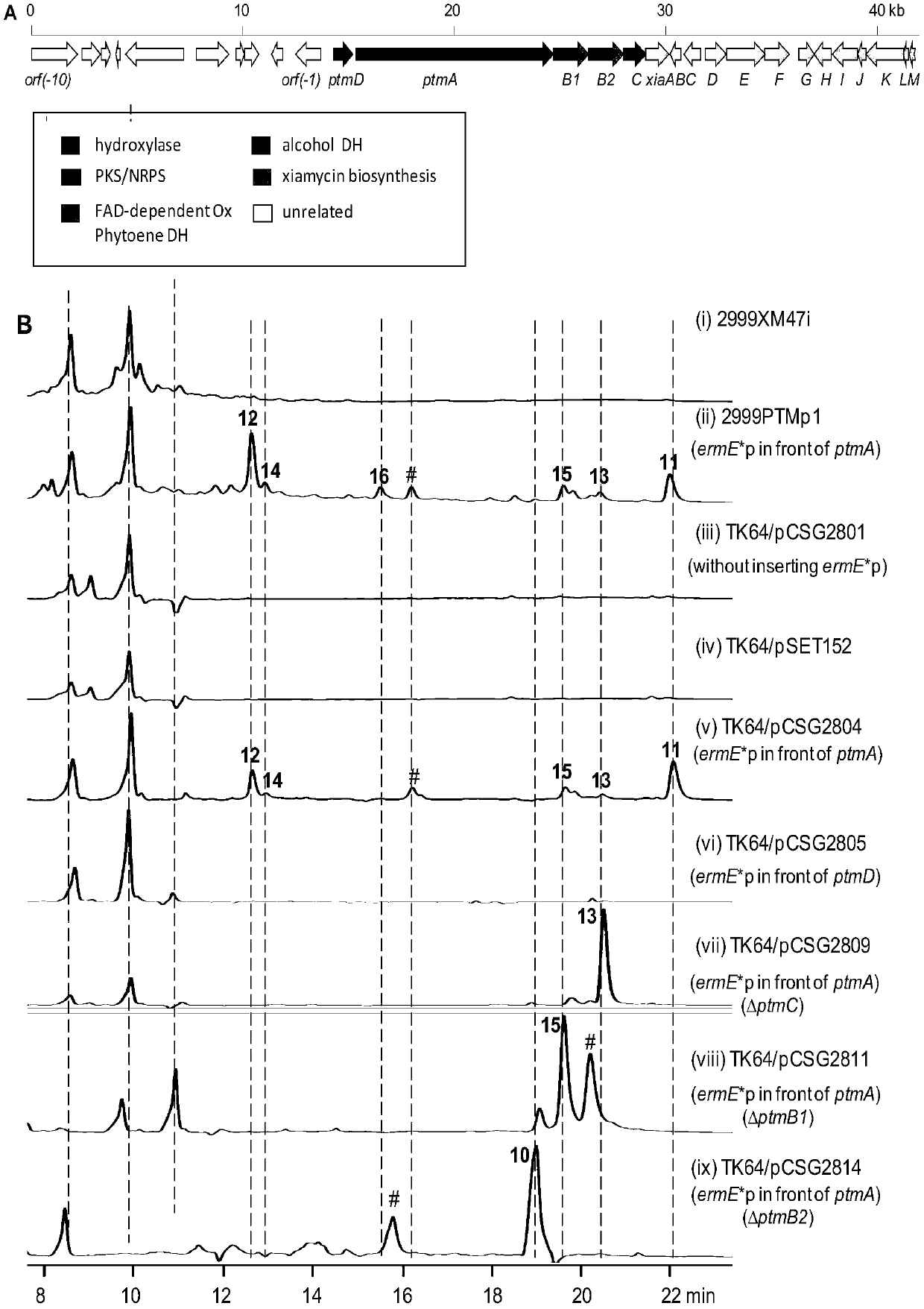
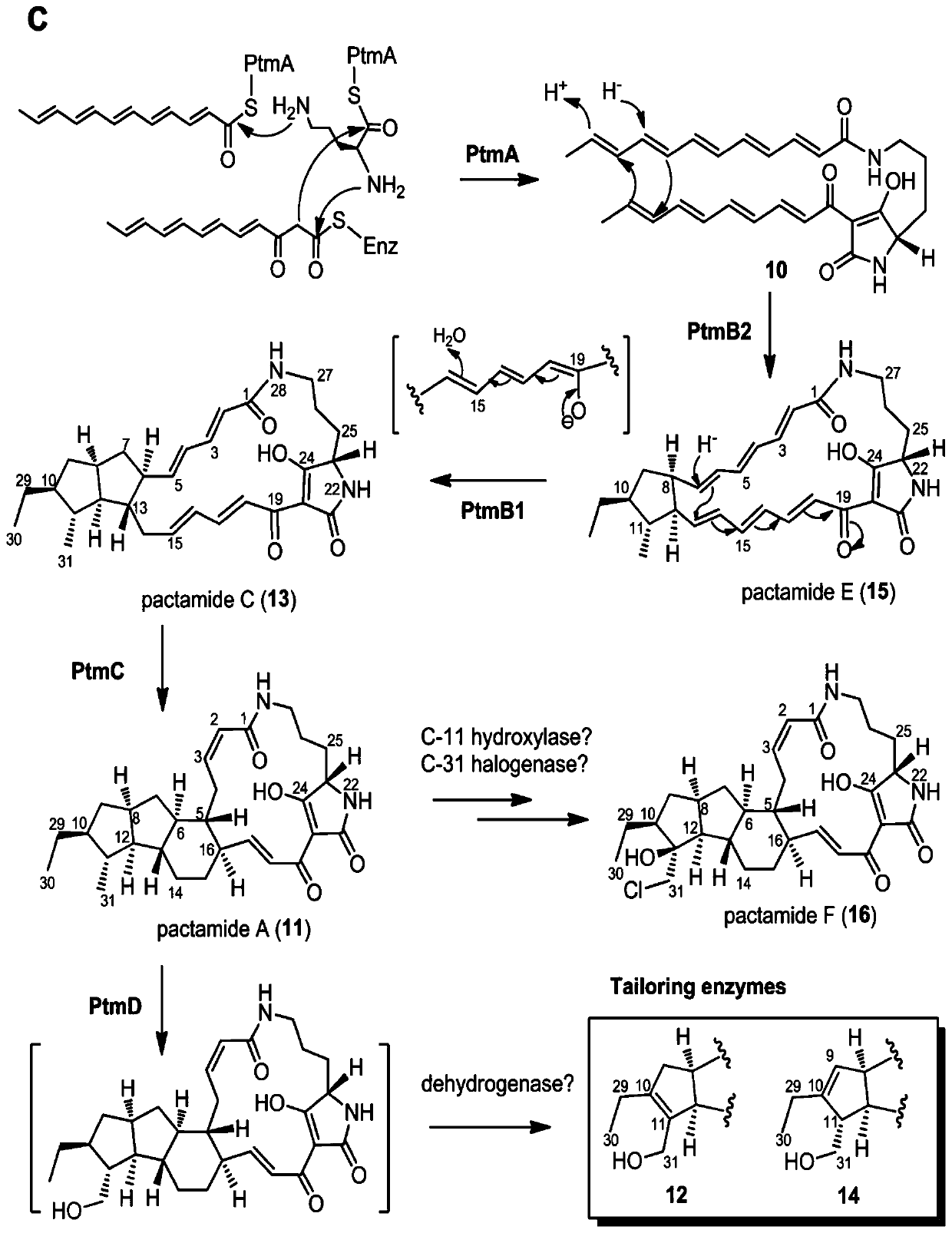
Biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and application thereof
ActiveCN106434702ABiosynthetic gene cluster activationHas antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCyclasePolyketide
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and an application thereof. The biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide comes from (Streptomyces pactum)SCSIO 02999, and the cluster comprises five genes including heterozygous polyketone / nonribosomal peptide synthetases genes ptmA, FAD dependent redox enzyme genes ptmB1, phytoene dehydrogenase genes ptmB2, cyclase genes ptmC and hydroxylase genes ptmD. According to the biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and the application thereof, information in genes and proteins related to biosynthesis of the paquete amide provides theoretical foundations and materials for conducting genetic modification on the biosynthesis of multi-ring tetramate macrocylic lactam family. By conducting genetic modifications on the biological synthetic genes, 6 new structures antineoplastic paquete amide compounds pactamide A-F are obtained, and thus effective compound entities are provided for research and development of antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
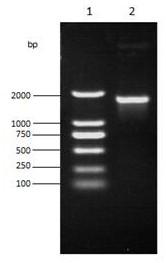
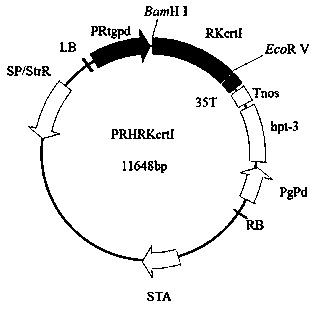
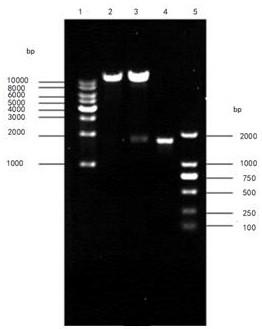
Phytoene dehydrogenase gene RKcrtI and application thereof
InactiveCN109536518AIncreased transcript levelsIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyYeast
The invention discloses a phytoene dehydrogenase gene RKcrtI having the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1; the amino acid sequence encoded by the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The gene is derived from rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235; the gene is connected with a vector and then is transferred into yeast cells. The rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235 can be promoted to produce beta-carotenoid, and a foundation is laid for large-scale commercial production of beta-carotenoid.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Phytoene dehydrogenase mutant gene and application thereof in carotenoid synthesis
InactiveCN108034665AIncrease productionOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsColor changes
The invention discloses a phytoene dehydrogenase mutant gene and application thereof in carotenoid synthesis. The mutant gene is obtained by performing multiple rounds of mutation on a phytoene dehydrogenase coding gene by means of iterative orthogenesis and through a high-throughput screening method based on bacterial colony color change. When the phytoene dehydrogenase mutant gene is used to synthesize lycopene, A178S mutant is obtained in the first round of orthogenesis, and lycopene yield is increased by 27.3%; A178S / N280T mutant and A178S / M234I mutant are obtained by using the A178S mutant as a base for orthogenesis, and lycopene yield is further increased by 51.4% and 18.3% while the lycopene yield is not further increased by combining A178S, N280T and M234I; A178S / N280T / E239P mutantis obtained by performing orthogenesis on the A178S / N280T mutant, and A178S / N280T / E239P mutant is finally obtained through three rounds of orthogenesis and screening.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Phytoene desaturase gene of sphingomonas sp. and application thereof
InactiveCN101979587AReduce manufacturing costReduce dosageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideA-DNA
The invention provides a DNA sequence of a phytoene desaturase gene of sphingomonas sp., a recombinant strain with phytoene desaturase lost and application thereof. The phytoene desaturase gene (crtI) of the sphingomonas sp. has a nucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID No.1. The DNA sequence of the phytoene desaturase gene (crtI) of the sphingomonas sp. provided by the invention lays a foundation for the genetic transformation of a biological synthesis manner of sphingomonas sp. carotene. Moreover, compared with the wild strains, the sphingomonas sp. recombinant strain with the phytoene desaturase lost, which is constructed by a gene knockout method, has gellan glue yield unchanged, generates no uranidin, reduces the amount of ethanol or isopropanol which is used during gellan glue extraction and therefore reduces the production cost of the gellan glue; meanwhile, the strain can also be applied to the further gene knockout or metabolic engineering transformation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
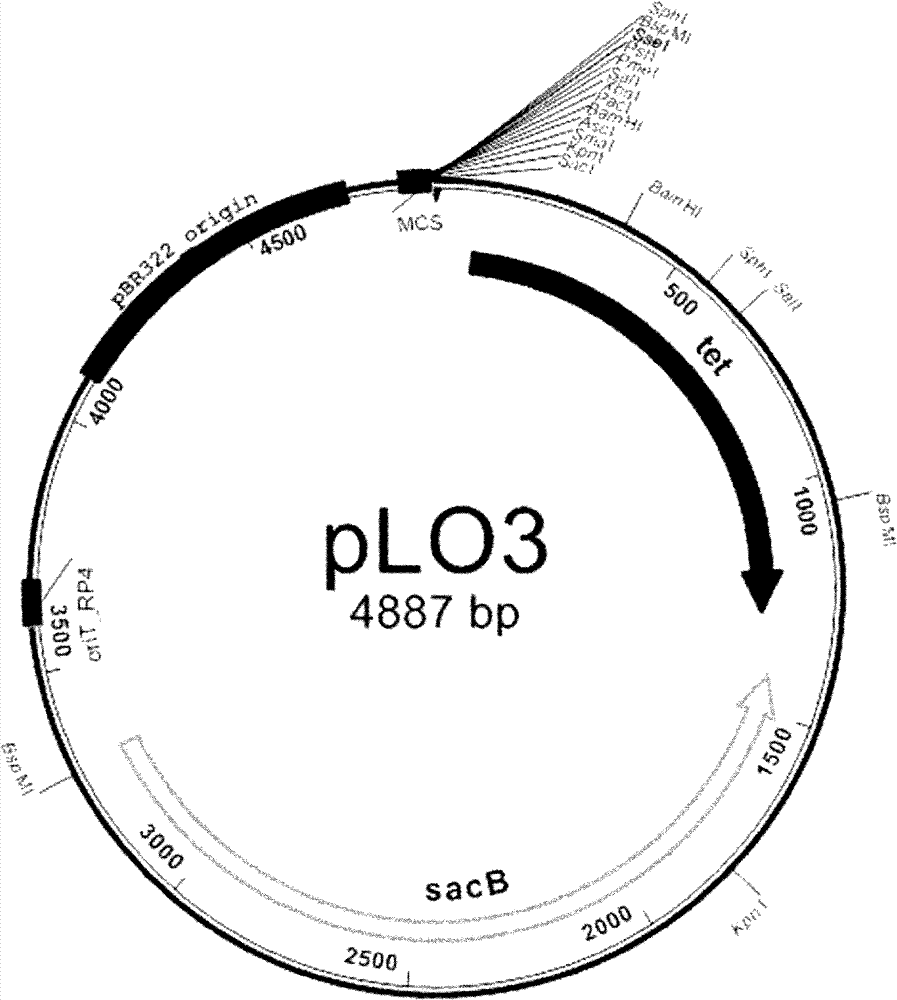
Construction and application of gene silencing vector induced by Chinese wheat yellow mosaic virus
InactiveCN108517332ARich varietyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsRibosomal proteinTriticeae
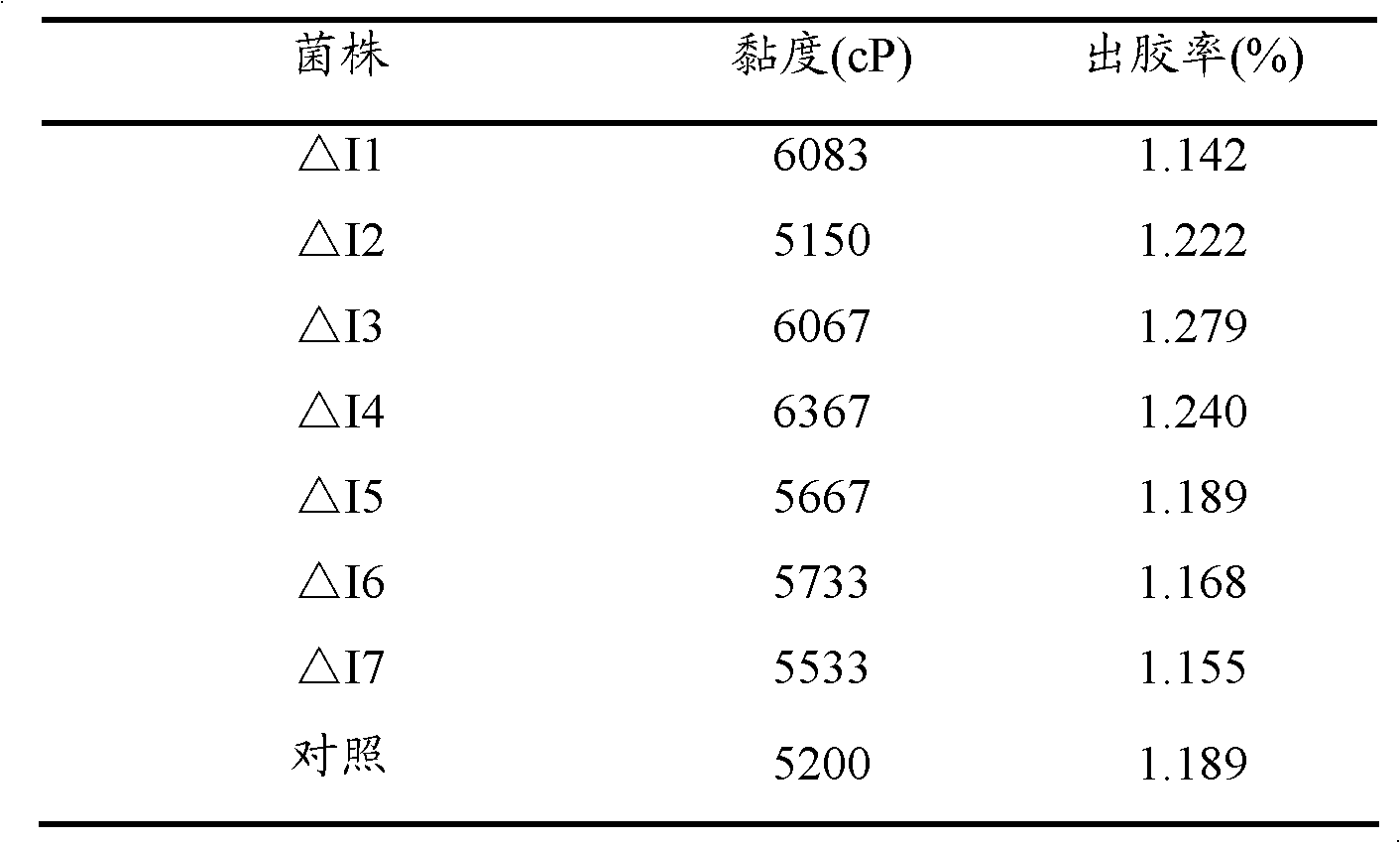
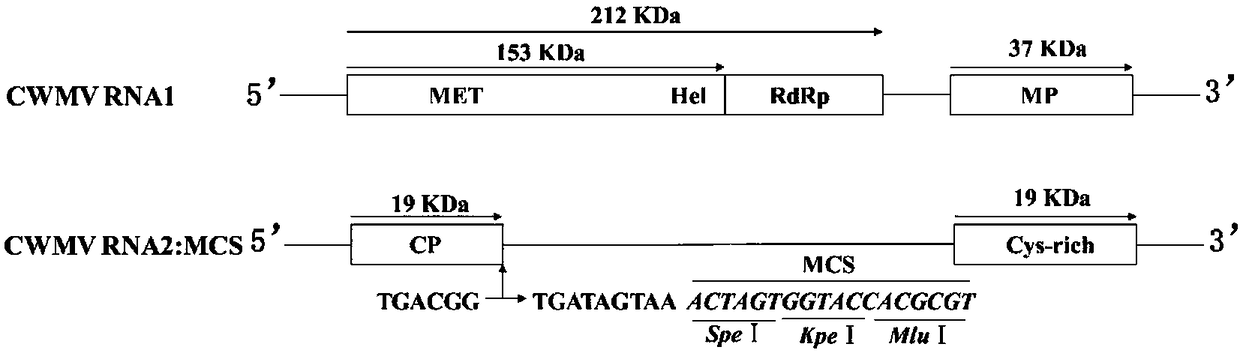
The invention mainly relates to construction of a gene silencing vector induced by Chinese wheat yellow mosaic virus, and application thereof to nicotiana benthamiana. The biological active analysis results show that the constructed CWMV-VIGS can successfully infect the nicotiana benthamiana and can realize the silencing after the effective transcription on relevant genes such as phytoene desaturase and 50S ribosomal protein L12. The types of the VIGS vectors are enriched; in addition, the effective technical measures are provided for the gene function study.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Recombinant bacteria used for producing beta-carotene and construction method utilizing Crispr-Cas9 technology
PendingCN109666596AIncrease the efficiency of homologous recombinationImprove stabilityFungiStable introduction of DNABeta-CaroteneKu70
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria used for producing beta-carotene and a construction method utilizing a Crispr-Cas9 technology. A Ku70 gene is subjected to knockout from yarrowia lipolytica, and then phytoene synthase / lycopene cyclase (carRA), phytoene desaturase (carB), geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGS1) and a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (tHMG) gene take snfas a target point and are integrated in a yarrowia lipolytica gene set after knockout of the ku70 gene, wherein the phytoene synthase / lycopene cyclase (carRA) and phytoene desaturase (carB) are from blakeslea trispora, and the geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGS1) and the 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (tHMG) gene are from the yarrowia lipolytica; the Crispr-Cas9 technology isutilized for regulating the copy number of the carRA, the carRA, the GGS1 and the tHMG, and the recombinant bacteria capable of producing the high-yield beta-carotene is constructed. After the recombinant bacteria is fermented, cultured, extracted and separated, the content of the beta-carotene can reach the dry cell weight of 35 mg / g, and the bacterial strain stability is high.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Carotene Synthase Gene and Uses Therefor
Described herein is a novel three domain gene from Schizochytrium, denoted carotene synthase, that encodes a protein with three different enzymatic activities: phytoene dehydrogenase (PD), phytoene synthase (PS), and lycopene cyclase (LC). Also described is the isolated gene encoding the carotene synthase, homologues thereof, the enzyme encoded by such gene, biologically active portions and homologues thereof, recombinant nucleic acid molecules, microorganisms and plants that have been genetically modified to increase or decrease the action of such gene, and methods of producing carotenoids and derivatives thereof or methods of producing microorganisms and lipid products lacking pigmentation using the knowledge of the carotene synthase described herein.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
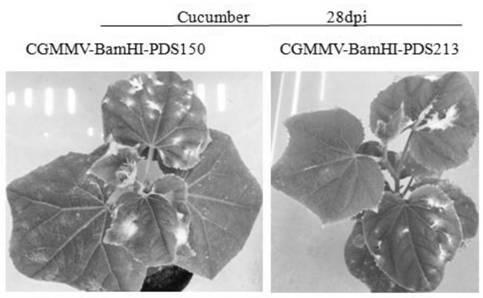
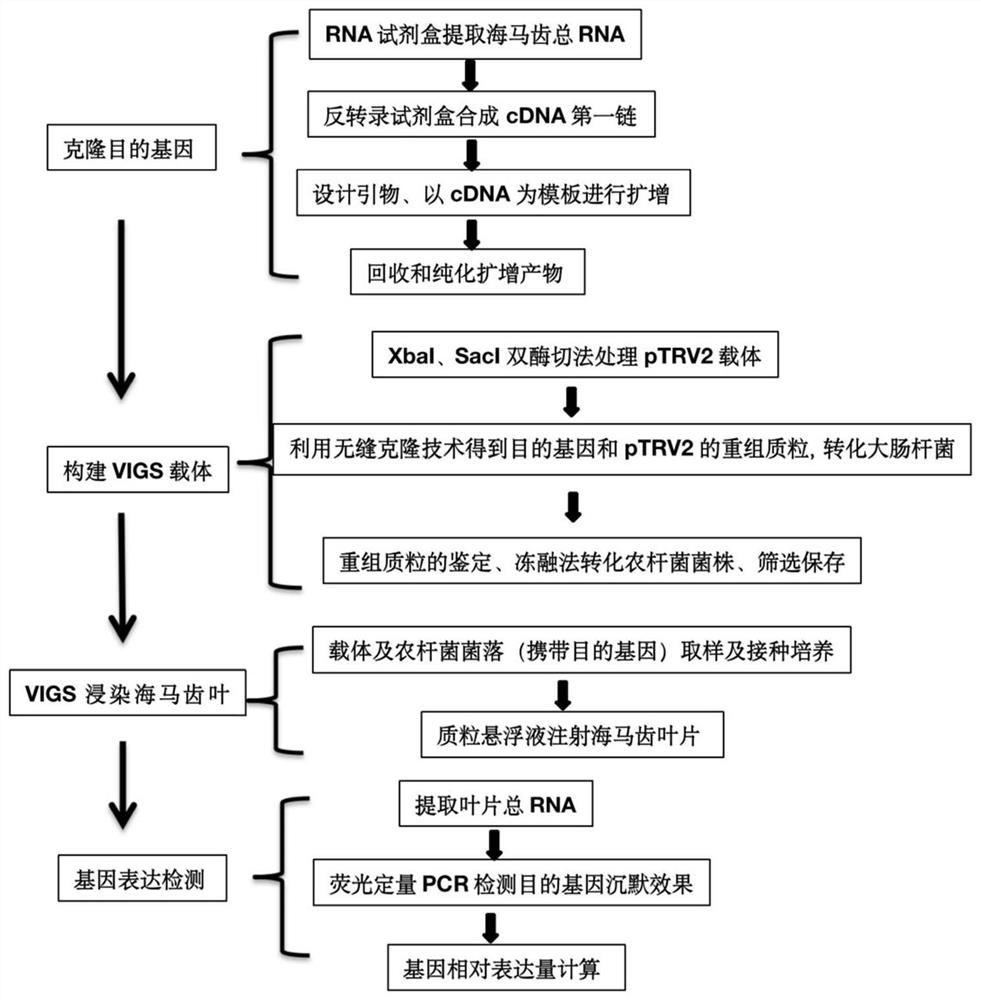
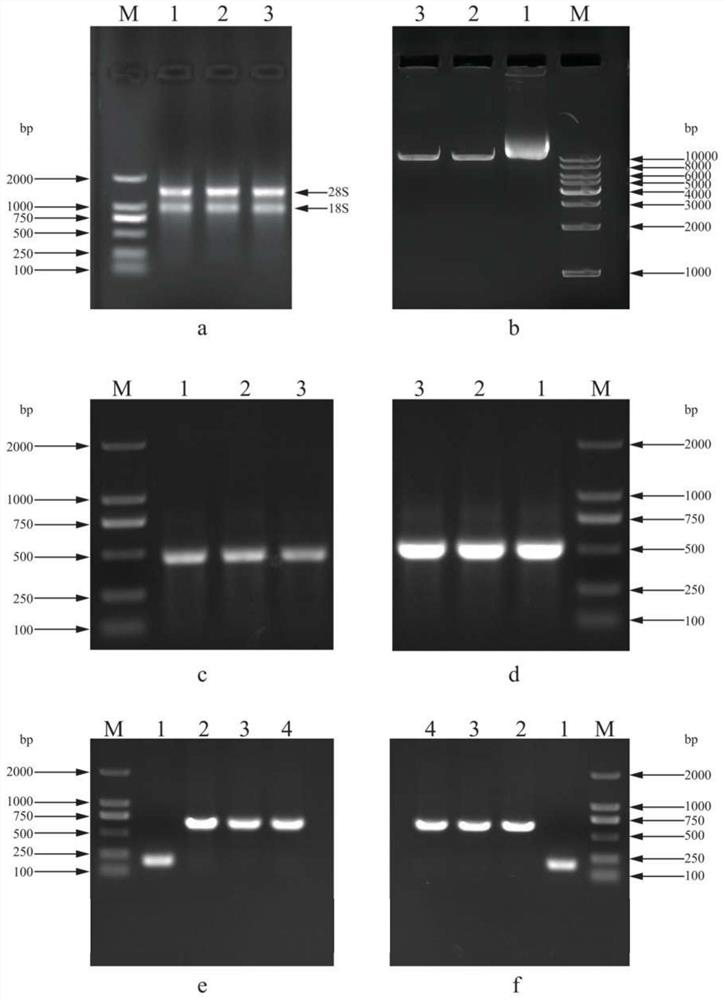
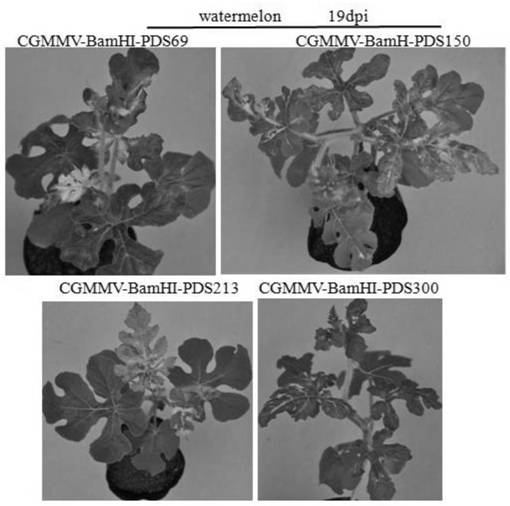
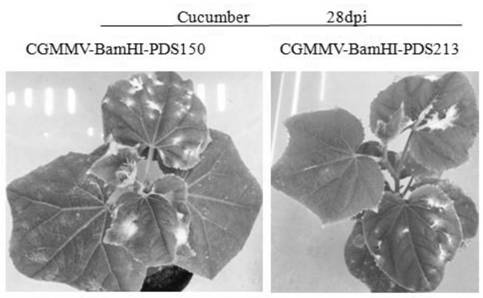
CGMMV (cucumber green mottle mosaic virus) induced gene silencing vector as well as building method and application thereof
ActiveCN109576303AReduced expression levelVector-based foreign material introductionGene silencingCucumber green mottle mosaic virus
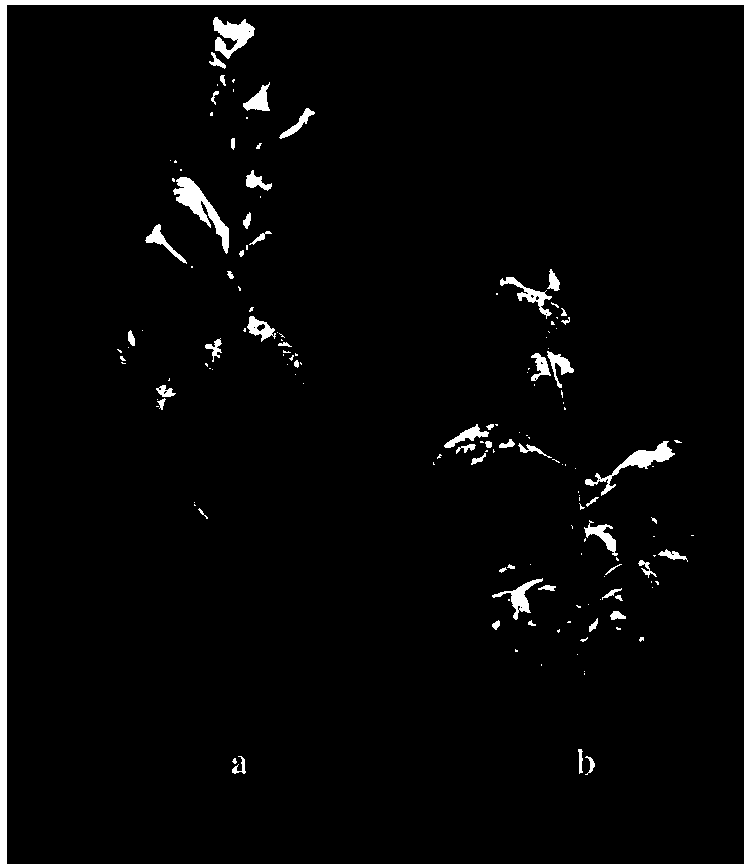
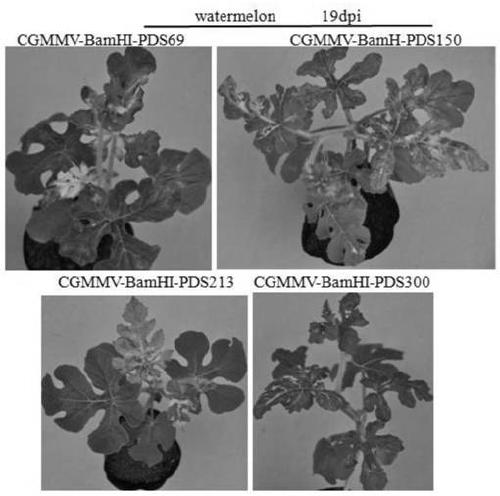
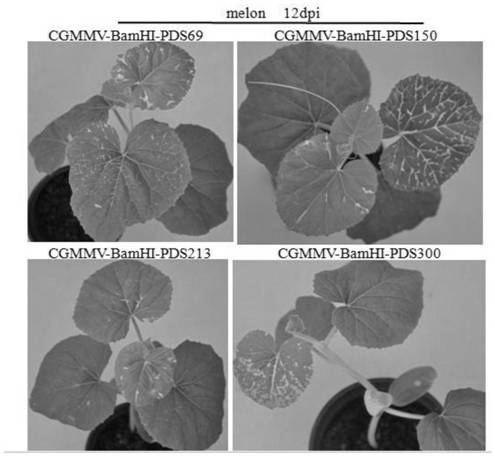
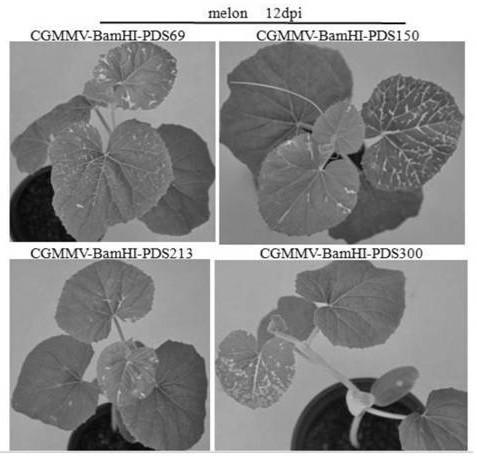
The invention builds a new VIGS vector capable of being applied to cucurbit plants based on a CGMMV (cucumber green mottle mosaic virus), and provides a CGMMV recombinant vector carrying PDS (phytoenedesaturase) gene segments. The cucurbit plants such as watermelons, sweet melons, cucumbers and bottle gourds are natural hosts of the CGMMV. The recombinant vector can effectively reduce the expression level of a PDS gene in the cucurbit plants, so that the plant generates a PDS gene silenced light bleaching phenotype. The successful building of the recombinant vector can be used for researchingthe gene function; the foundation is laid for digging a cucurbit plant gene with important agronomic trait, and culturing excellent, disease-resistant and specific varieties.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU FRUIT RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
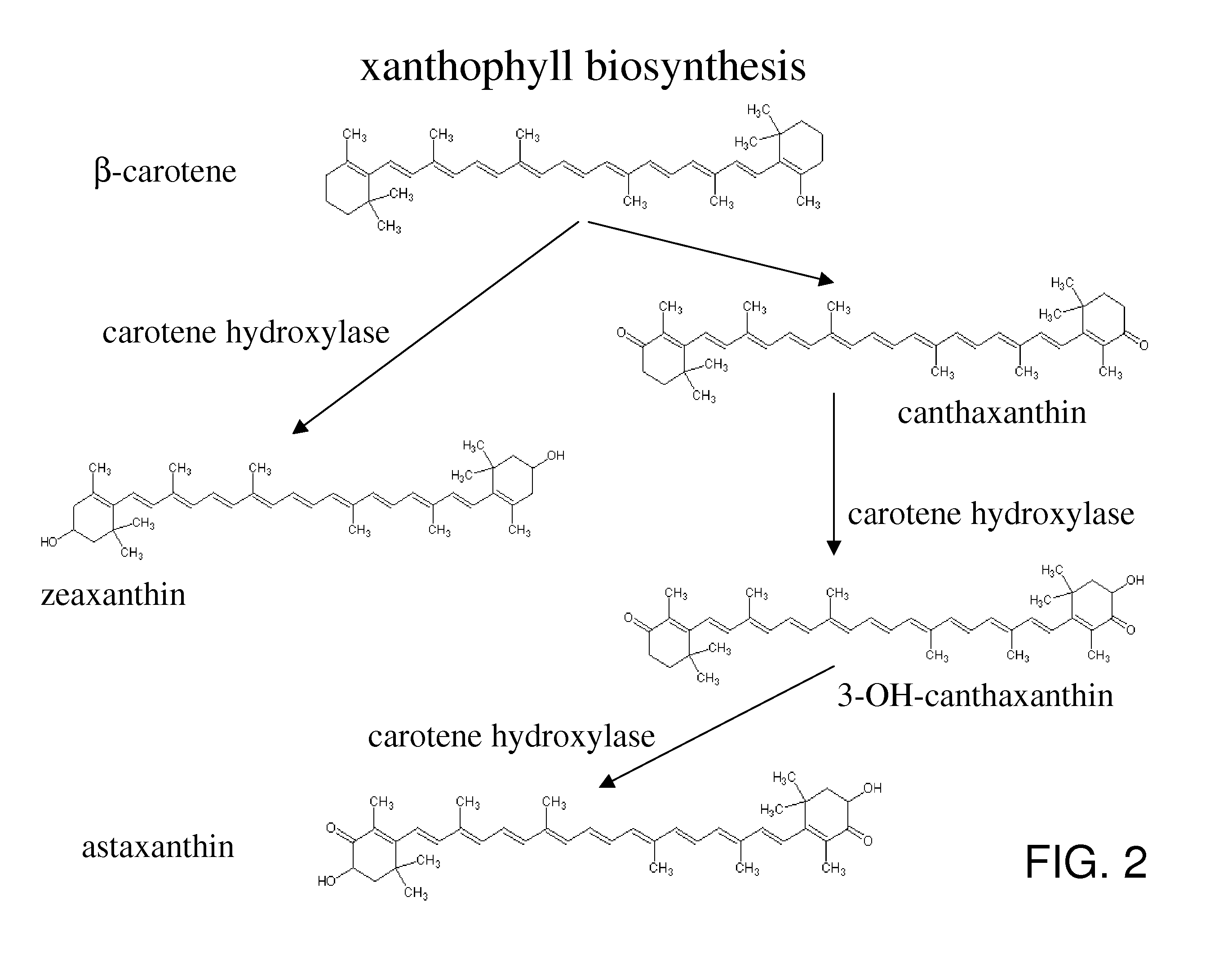
Methods of production of products of metabolic pathways
A plurality of isolated polynucleotide sequences encoding enzymes of the astaxanthin pathway is disclosed. The polynucleotides include:(i) a polynucleotide which encodes Phytoene dehydrogenase (crtI) and a first transcriptional regulatory sequence;(ii) a polynucleotide which encodes Beta-lycopene cyclase (lcy-B) and a second transcriptional regulatory sequence;(iii) a polynucleotide which encodes Beta-carotene ketolase (crtW) and a third transcriptional regulatory sequence; andwherein the first, second and third regulatory sequence are selected such that the expression of the Icy-B and the crtW is greater than a level of expression of the crtI. Methods of generating astaxanthin using the plurality of polynucleotide are also disclosed as well as bacterial cells comprising high levels of astaxanthin.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Octahydrolycopene dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111849932AIncrease diversityOxidoreductasesFermentationLycopersenePrincipal component analysis
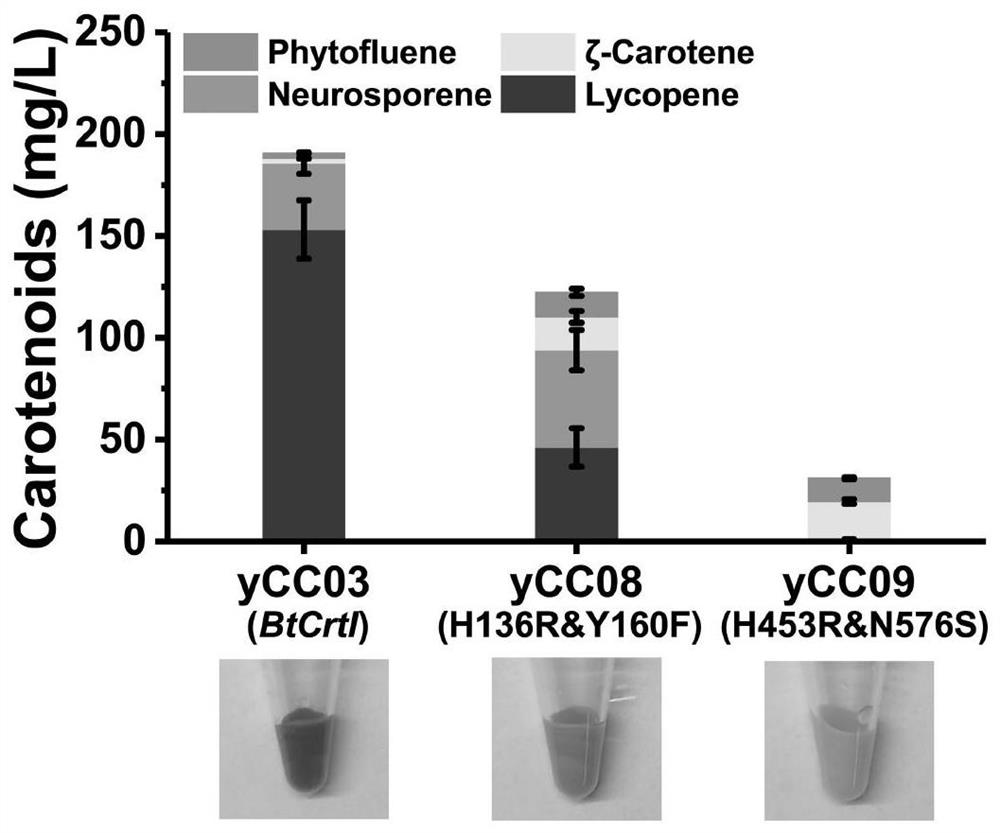
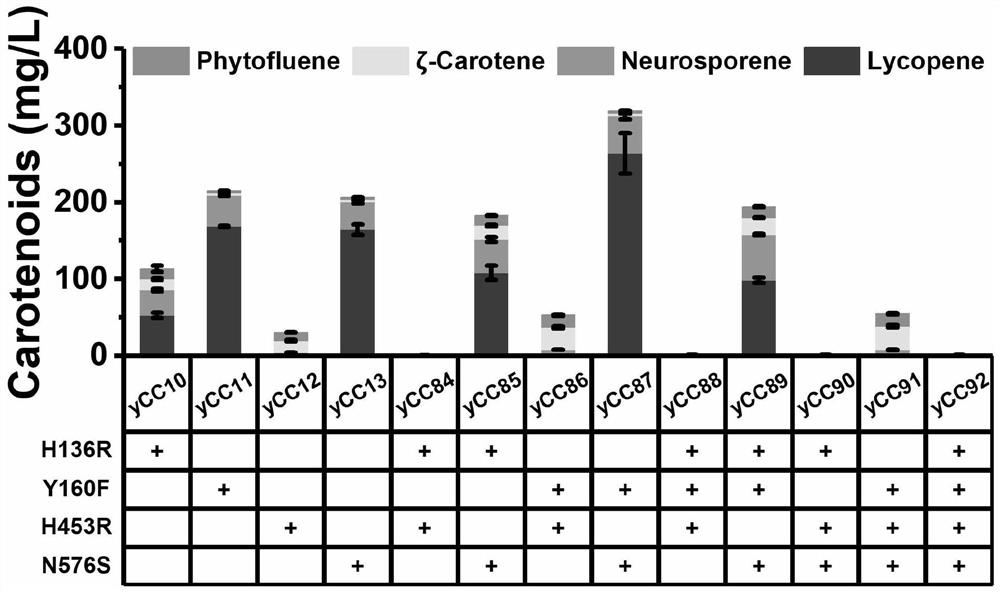
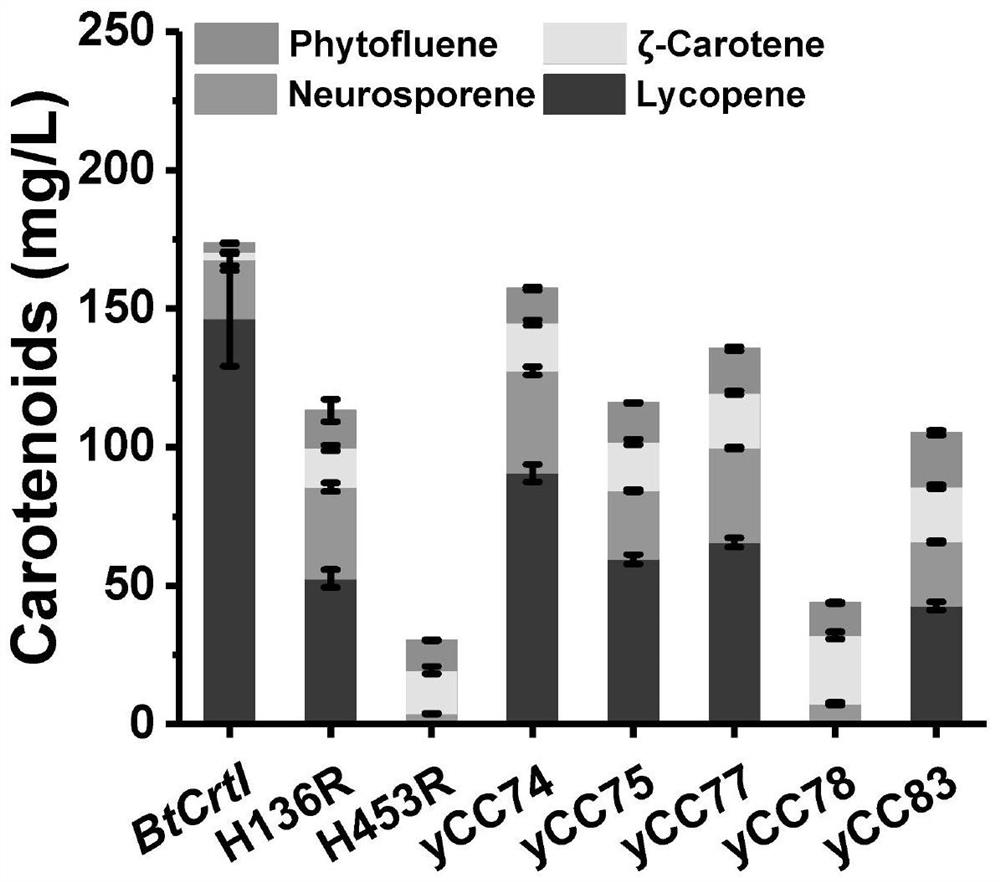
The invention relates to the field of biosynthesis, in particular to an octahydrolycopene dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof. Based on a BtCrtI mutant strain screened through error-prone PCRin the earlier stage, single-point and multi-point recombination verification is conducted on contained mutation sites, and key sites influencing BtCrtI catalytic specificity are determined; saturation mutation is performed on the screened BtCrtI key sites so as to increase the functional diversity of the BtCrtI mutant; principal component analysis (PCA) and K-means clustering analysis are performed on a BtCrtI single-point saturated mutation result, the single-point mutants are classified, and different types of representative single-point mutations are combined to further analyze the diversity of a BtCrtI catalytic function.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
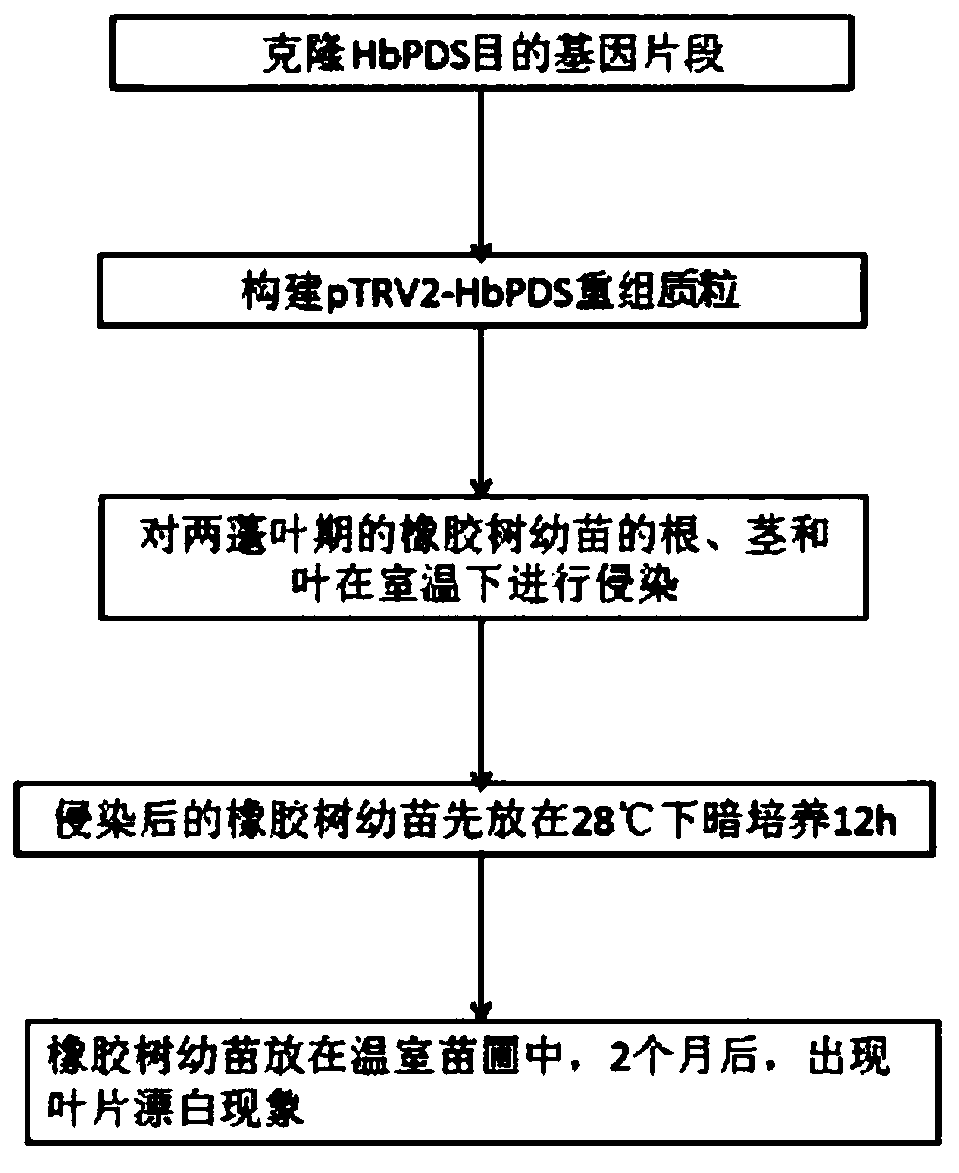
Rubber tree phytoene dehydrogenase gene VIGS silencing system, and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111593065AReduced expression levelEasy to operateOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyLycopersene
The embodiment of the invention discloses a rubber tree phytoene dehydrogenase gene VIGS silencing system, and a construction method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The rubber tree phytoene dehydrogenase gene VIGS silencing system has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The method in the invention is simple to operate; a set of rapid and effective virus induced silencing system is established; and the defects that the traditional genetic transformation needs heavy labour and is low in efficiency are effectively avoided. The system can effectively reduce the expression level of a HbPDS gene in a rubber tree, can obtain virus-induced gene silencing traits, further solves the problem of effectively verifying functions of rubber tree genes, and lays a foundation for excavating the rubber tree genes with important agronomic traits and cultivating excellent rubber tree varieties.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Recombinant yeast for producing xanthophyll and application of recombinant yeast
The invention discloses a recombinant yeast for producing xanthophyll. An octahydro-lycopene synthase gene, an octahydro-lycopene dehydrogenase gene, a lycopene epsilon cyclase gene, a lycopene beta cyclase gene, a carotene beta hydroxylase gene and a carotene epsilon hydroxylase gene are exogenously introduced into the yeast. The six enzymes capable of being successfully expressed in yeast are obtained through gene cloning and codon optimization, and a genetically engineered yeast strain for producing xanthophyll is constructed. The delta carotene is produced under the catalysis of phytoene synthase, phytoene dehydrogenase and lycopene epsilon cyclase, and then the delta carotene is converted into xanthophyll under the catalysis of lycopene beta cyclase, carotene beta hydroxylase and carotene epsilon hydroxylase.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A recombinant bacterium producing β-carotene and its construction method and application
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Yarrowia lipolytica with high yield of beta-carotene and application thereof
PendingCN114806914ASteps to remove the speed limitEfficient synthesisFungiTransferasesLycoperseneCyclase
The invention discloses yarrowia lipolytica with high yield of beta-carotene and application of the yarrowia lipolytica. The recombinant strain is prepared by the following steps: inserting geranyl geranyl diphosphate synthase, phytoene dehydrogenase, phytoene synthetase / phytoene cyclase, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase into a genome of an initial strain po1f to construct a strain yarrowia lipolytica Yli-CAH; and inserting at least one expression cassette of crtE, crtI, crtYB, citrate lyase (ACL) or tHMGR again to obtain the recombinant expression vector. The construction method of the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica is simple to operate, efficient and capable of removing the speed limiting step of an MVA pathway, more acetyl CoA transfer flux flows to synthesis of beta-carotene, cell growth can be improved by overexpressing a citrate lyase coding gene, and industrial utilization is facilitated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Crispr/cas9 system to knock out the pds gene of Populus alba and its application
ActiveCN111235177BFacilitate the study of gene functionKnockout EfficientVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyLycopersene
The invention relates to a CRISPR / Cas9 system knockout PDS gene of Populus alba and its application, and belongs to the technical field of molecular breeding. The nucleotide sequence of the Populus alba phytoene dehydrogenase (PDS) gene of the present invention is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The target site described in the present invention can realize site-directed editing of the PDS gene, and the nucleotide sequence of the target site is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The invention provides a new scheme for gene function research of woody model plants, establishes a molecular breeding platform for native tree species of my country's poplar, and provides technical support for the directional cultivation of new forest species that meet the needs of my country's economic development.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Dunaliella phytoene dehydrogenase gene promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN106367418AAchieve instant expressive effectsHigh electrical conversion efficiencyNucleic acid vectorOxidoreductasesVisual field lossGreen fluorescent protein
The invention discloses a dunaliella phytoene dehydrogenase gene promoter and application thereof. The gene sequence of the dunaliella phytoene dehydrogenase gene promoter is represented by SEQ ID NO: 1. The phytoene dehydrogenase gene promoter obtained by cloning dunaliella can be applied to starting genes of microalgae such as the dunaliella, and is different from a common CaMV35s general promoter, so that transferring of a dunaliella endogenous promoter is really realized; the promoter can achieve the effect of transient expression of exogenous genes through verification. The promoter disclosed by the invention can be further applied to the research on a regulation factor of the phytoene dehydrogenase gene promoter. Meanwhile, compared with a method, such as Yu Sun, of electric transfer of dunaliella, an electric shock transfer method optimized by the experiment is higher in electric transfer efficiency. The amount of green fluorescent proteins in the optimized transfer effect in the visual field is larger than that of the green fluorescent proteins in the transfer effect which is not optimized, so that the transfer efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A biosynthetic gene cluster of pactamide and its application
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and an application thereof. The biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide comes from (Streptomyces pactum)SCSIO 02999, and the cluster comprises five genes including heterozygous polyketone / nonribosomal peptide synthetases genes ptmA, FAD dependent redox enzyme genes ptmB1, phytoene dehydrogenase genes ptmB2, cyclase genes ptmC and hydroxylase genes ptmD. According to the biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and the application thereof, information in genes and proteins related to biosynthesis of the paquete amide provides theoretical foundations and materials for conducting genetic modification on the biosynthesis of multi-ring tetramate macrocylic lactam family. By conducting genetic modifications on the biological synthetic genes, 6 new structures antineoplastic paquete amide compounds pactamide A-F are obtained, and thus effective compound entities are provided for research and development of antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phytoene desaturase gene of sphingomonas sp. and application thereof
InactiveCN101979587BReduce manufacturing costReduce dosageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideA-DNA
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Construction method and application of iris plant eleutherine eleutherine VIGS silencing system
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a VIGS (Vinyl Insulin Growth Sulfate) silencing system of an iridaceae plant eleutherine eleutherine. The VIGS silence system suitable for the eleutherine eleutherine is successfully created by taking the TRV as a carrier of a VIGS system and taking an eleutherine eleutherine phytoene dehydrogenase gene as a target gene and utilizing a vacuum infiltration treatment method; the system is applied to development of gene function research of Euphorbia elegans pigment synthesis related genes EbMYB5 and EbMYB52, the expression quantity of the EbMYB5 and EbMYB52 genes in infected silence treatment group sample leaves is remarkably reduced, and the expression quantity of key genes related to pigment synthesis routes is remarkably changed to different degrees; the eleutherine americana VIGS silencing system can be successfully applied to eleutherine americana gene function verification. The eleutherine americana VIGS silence system constructed by the invention has important significance on eleutherine americana gene function research.
Owner:GUANGDONG ACAD OF FORESTRY
Virus-induced high-efficiency silencing system of dianthus phytoene dehydrogenase gene
InactiveCN105296535BSolving questions about gene functionFermentationGenetic engineeringComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidReverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
The invention discloses an efficient virus-induced phytoene desaturase gene silence system for Chinese pink. A specific primer is designed according to a coding gene sequence of PDS (phytoene desaturase), and about 500bp cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments are amplified in the Chinese pink through RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction). Obtained PDS cDNA fragments are connected to TRV2, and acetosyringone concentration, seedling age and preculture temperature after infection as well as light conditions for plants after preculture are integrated in an assorted manner by optimizing an agrobacterium-mediated virus-induced gene silence system according to photobleaching frequency, bleached leaf area and bleached conditions of the plants, so that the rapid efficient virus-induced silence system is established, virus-induced gene silence character can be obtained, and further, the problem that Chinese pink gene functions are verified effectively is solved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Phytoene dehydrogenase gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102260692BEfficient productionHydrocarbon active ingredientsMicroorganism based processesLycoperseneEnzyme Gene
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
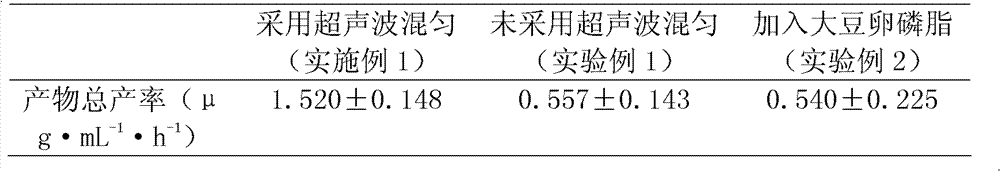
Method for increasing phytoene dehydrogenase in vitro reaction rate
InactiveCN102286593BIncrease exposureIncrease reaction rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDouble phaseReaction rate
The invention relates to a method for increasing water-organic double-phase enzymatic reaction rate, in particular relates to a method for increasing phytoene dehydrogenase in vitro reaction rate and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: adding phytoene acetone solution, glucose, glucose oxidase and hydrogenperoxidase into crushed coarse enzyme solution to ultrasonically mix uniformly; performing dark airtight oscillating reaction at the temperature of between 28 and 30 DEG C; adding methanol; performing warm bath at the temperature of between 55 and 60 DEG C for 15 to 20 minutes; adding petroleum ether with the boiling range of 30 to 60 DEG C to oscillate to extract reaction products; collecting the upper layer of a petroleum ether layer; and performing vacuum rotary evaporation to obtain the product. A phytoene dehydrogenase in vitro reaction system is optimized by utilizing the mechanical effects such as homogeneity, dispersion, emulsification and the like of ultrasonic wave, so probability of a substrate contacting the enzyme is improved, the enzymatic reaction rate is obviously increased, reaction time is shortened, oxidation loss of the product is reduced, and accuracy of data is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Methods of production of products of metabolic pathways
A plurality of isolated polynucleotide sequences encoding enzymes of the astaxanthin pathway is disclosed. The polynucleotides include:(i) a polynucleotide which encodes Phytoene dehydrogenase (crtI) and a first transcriptional regulatory sequence;(ii) a polynucleotide which encodes Beta-lycopene cyclase (lcy-B) and a second transcriptional regulatory sequence;(iii) a polynucleotide which encodes Beta-carotene ketolase (crtW) and a third transcriptional regulatory sequence; andwherein the first, second and third regulatory sequence are selected such that the expression of the Icy-B and the crtW is greater than a level of expression of the crtI. Methods of generating astaxanthin using the plurality of polynucleotide are also disclosed as well as bacterial cells comprising high levels of astaxanthin.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Sea purslane phytoene dehydrogenase gene and construction of VIGS silencing system
ActiveCN114836445AReduced expression levelAchieve the silencing traitOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyLycopersene
The invention discloses construction of a phytoene dehydrogenase gene and a VIGS silencing system, the VIGS silencing system of the phytoene dehydrogenase gene is constructed through a specific fragment, and the silencing system can effectively reduce the expression level of SpPDS gene in the sea horse, can realize virus-induced related gene silencing traits, and has a good application prospect. Meanwhile, the VIGS system constructed by the invention has good stability, can be used for verifying the function of the gene in the sedum lineare, and lays a foundation for excavating the sedum lineare gene with a stress resistance function and cultivating plant varieties with excellent soil remediation and saline-alkali soil transformation potential.
Owner:HAINAN NORMAL UNIV
A gene silencing vector induced by cucumber green mottle mosaic virus and its construction method and application
ActiveCN109576303BReduced expression levelVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyLycopersene
The invention constructs a new VIGS vector that can be applied in cucurbit crops based on CGMMV, and provides a cucumber green mottle mosaic virus recombination vector carrying a phytoene dehydrogenase (PDS) gene fragment. Cucurbitaceae plants such as watermelon, melon, cucumber and gourd are natural hosts of CGMMV. The recombinant vector of the present invention can effectively reduce the expression level of PDS gene in Cucurbitaceae crops, so that the plants produce photobleaching phenotypes in which the PDS gene is silenced. The successful construction of the recombinant vector can be used to study gene functions, and lay the foundation for mining the genes of Cucurbitaceae plants with important agronomic traits and cultivating excellent, disease-resistant and characteristic varieties.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU FRUIT RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant lactococcus lactis used for generating lycopene, and application of recombinant lactococcus lactis
ActiveCN112646764AAnti-cancerImprove antioxidant capacityBacteriaTransferasesLycoperseneStaphylococcus lactis
The invention discloses a recombinant lactococcus lactis bacterial strain used for generating lycopene, and a construction method and application of the recombinant lactococcus lacti. The recombinant lactococcus lactis bacterial strain is constructed in a way that parts of nucleotide sequences of two competition approaches, i.e., a lactic dehydrogenase gene and an [alpha]-acetolactic acid synthetase gene, of a lycopene synthesis precursor are eliminated, and then, plasmids are used to introduce a geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase gene (crtE), a phytoene synthetase gene (crtB) and a phytoene dehydrogenase gene (crtI) of a Pantoea ananatis source. Experiments prove that after the recombinant lactococcus lactis disclosed by the invention is subjected to shaking culture, the lycopene can be generated, and the experiments also predict that the recombinant lactococcus lactis has wide application potential in the development field of health care products and biological medicines.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
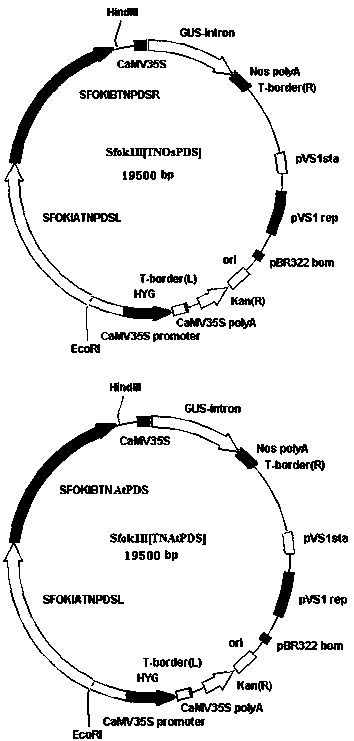
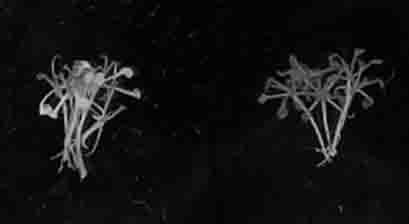
TALE nuclease simplified framework construction for plant gene fixed-site shearing
PendingCN110468148AHigh frequencyEfficient Directional ShearingOxidoreductasesFermentationNucleaseSeedling
The invention discloses a TALE nuclease simplified framework sequence for plant gene shearing. The terminal N of the framework contains 136 amino acids, the terminal C contains 63 amino acids, repetition modules of TALEs for recognizing specific DNA sequences are constructed in the middle of the framework, Fok1 type-II endonucleases are fused at the terminal C, tiny fragments of two different endonucleases are inserted in the terminal N and the terminal C, and through the two endonucleases, the repetition modules of the TALEs can be randomly inserted to construct TALE nucleases capable of shearing the specific DNA sequences. The TALE nucleases are simplified to construct the phytoene dehydrogenase shear nucleases, and after plants are transformed, whitened seedlings are obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com