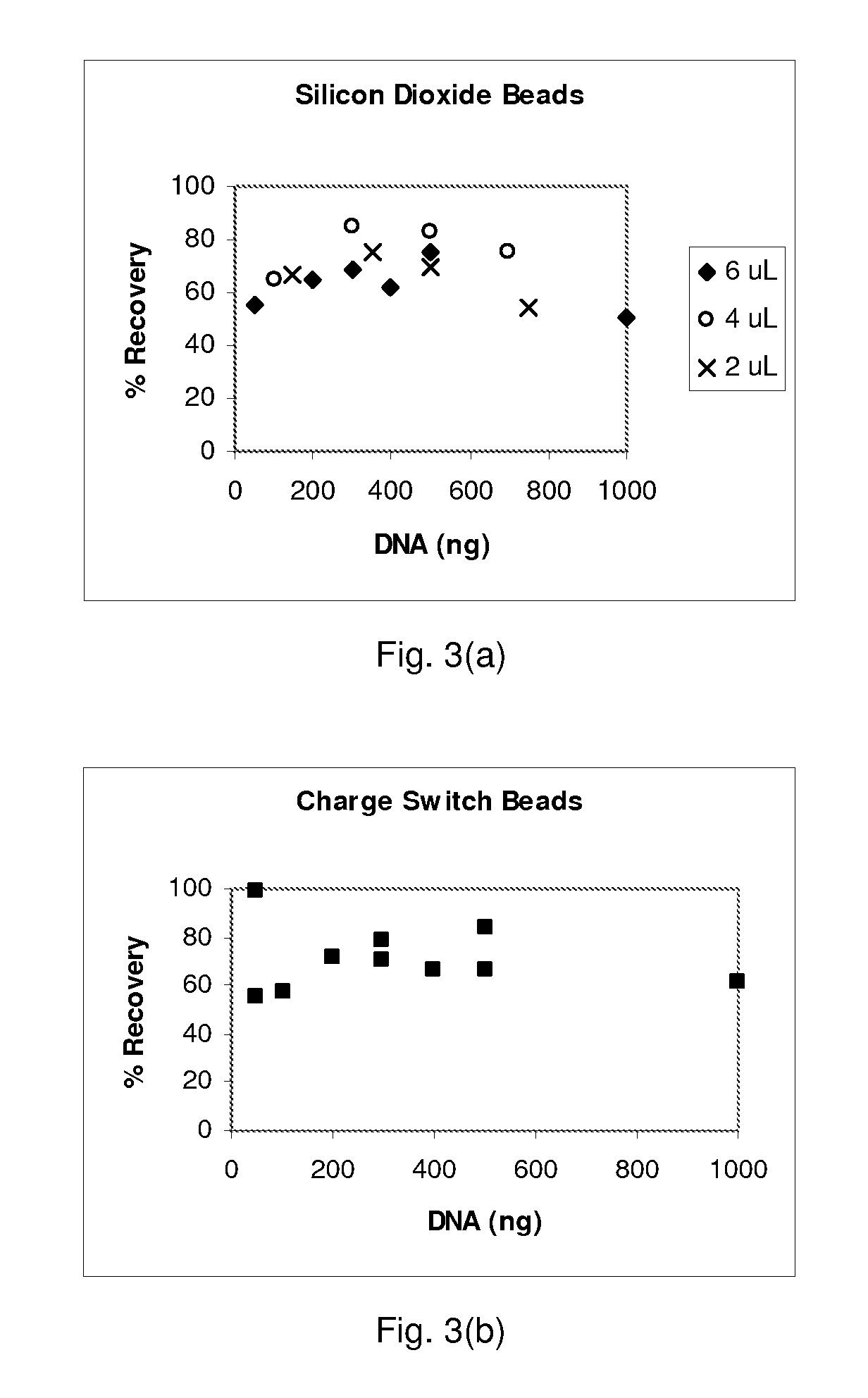
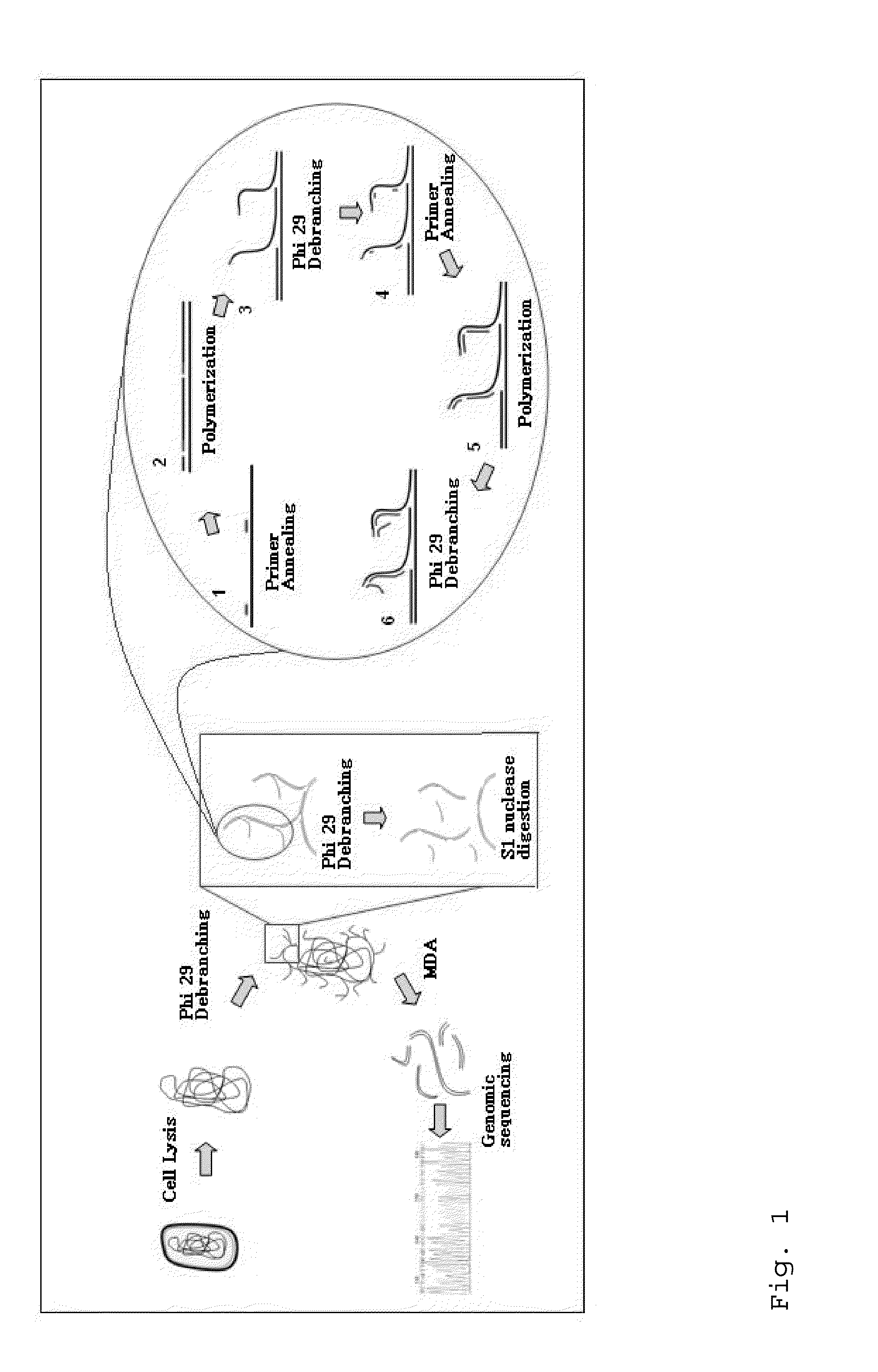
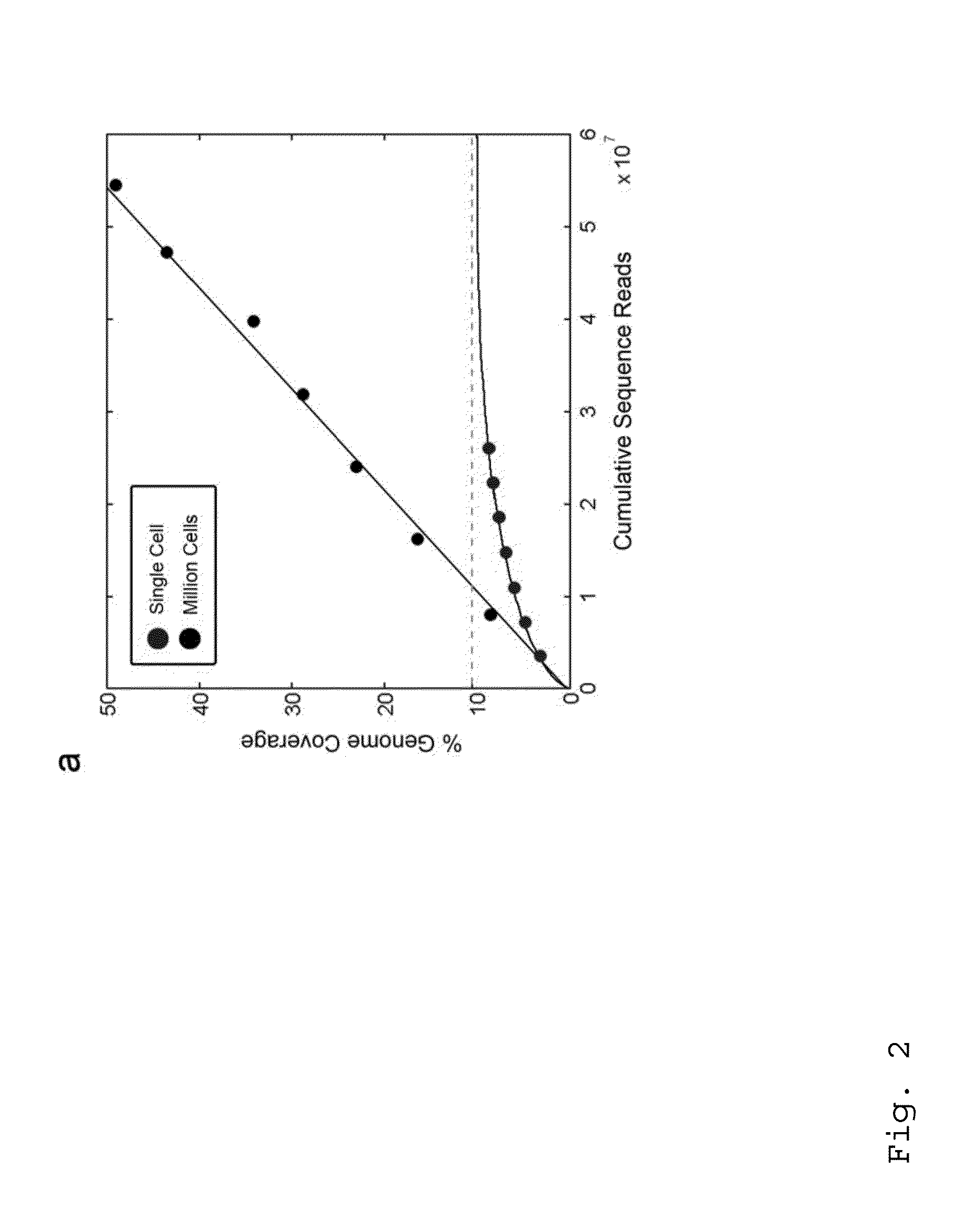
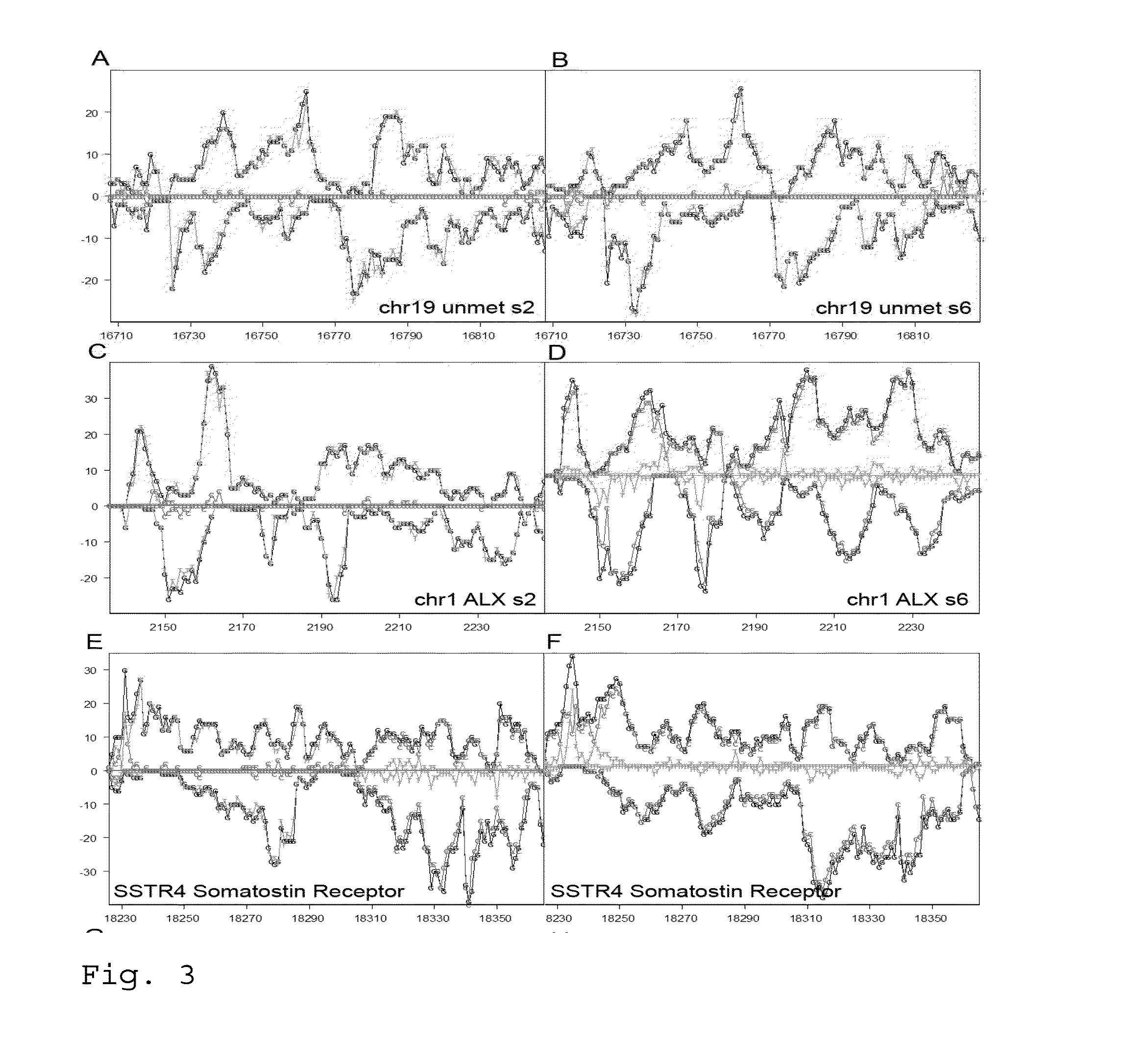
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6695 results about "Polymerase chain reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
<ul><li>A normal result is negative and a positive result indicates presence of a pathogen/an infection.</li></ul>
Polynucleotide sequencing
InactiveUS6833246B2Efficient and fast determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
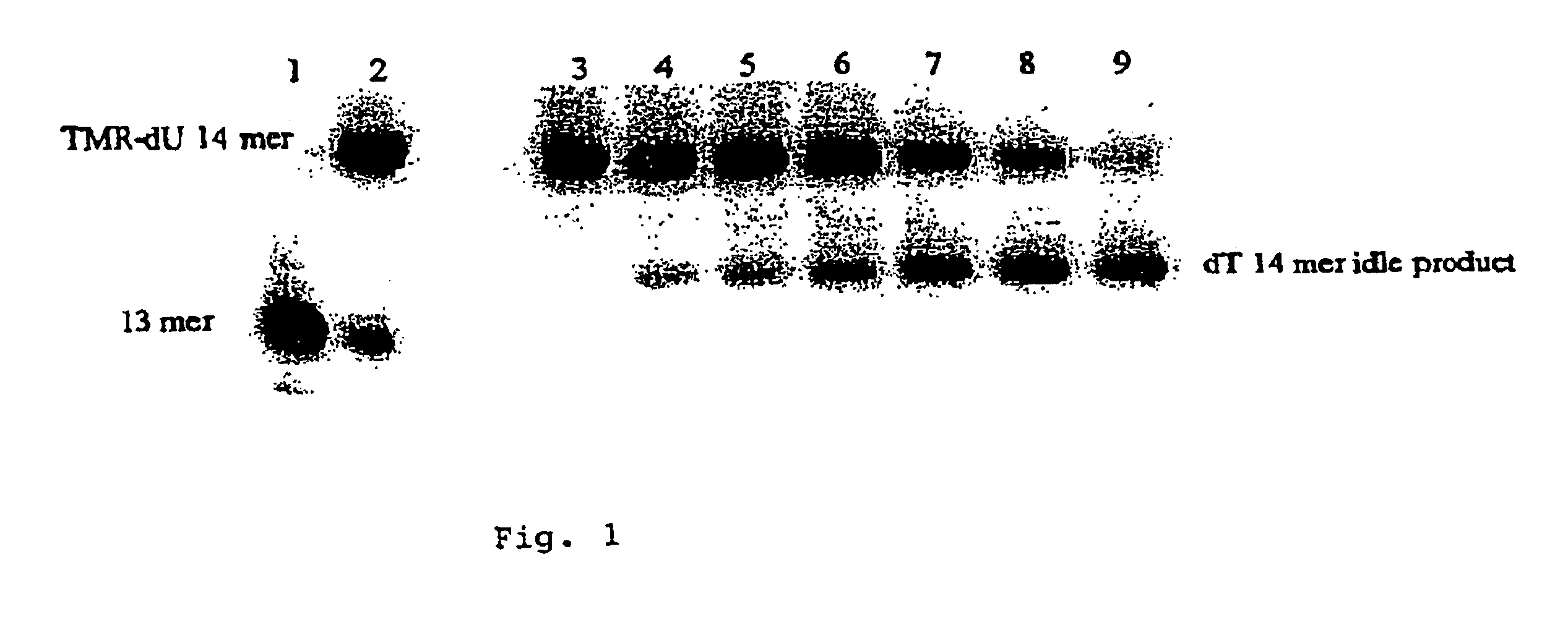
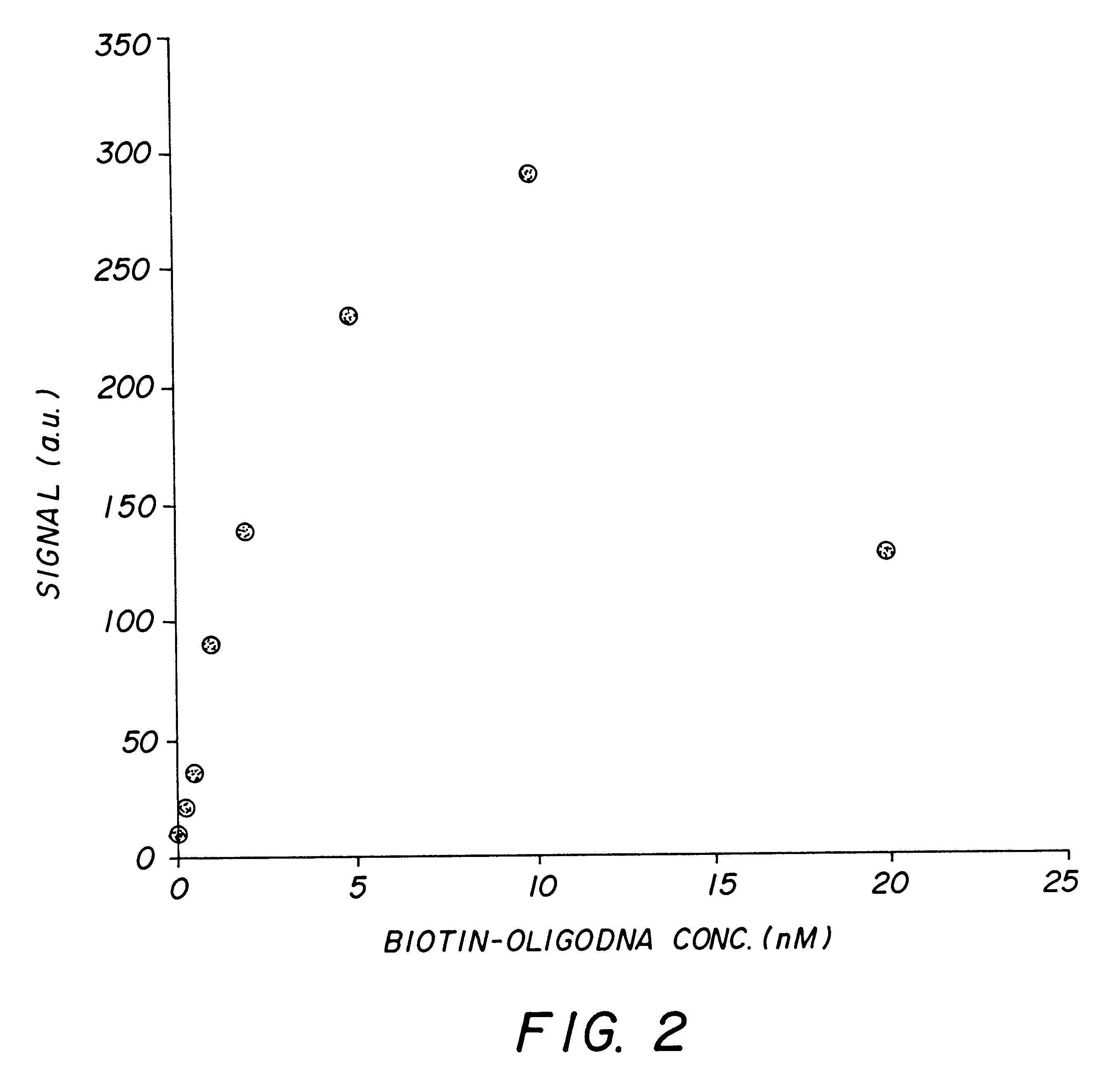
The invention relates to the sequencing of a target polynucleotide sequence, immobilized on a solid support, using the polymerase reaction to extend a suitable primer and characterizing the sequential addition of labelled bases. The present invention further relates to the presence of a polymerase enzyme that retains a 3' to 5' exonuclease function, which is induced to remove an incorporated labelled base after detection of incorporation. A corresponding non-labelled base may then be incorporated into the complementary strand to allow further sequence determinations to be made. Repeating the procedure allows the sequence of the complement to be identified, and thereby the target sequence.
Owner:SOLEXA
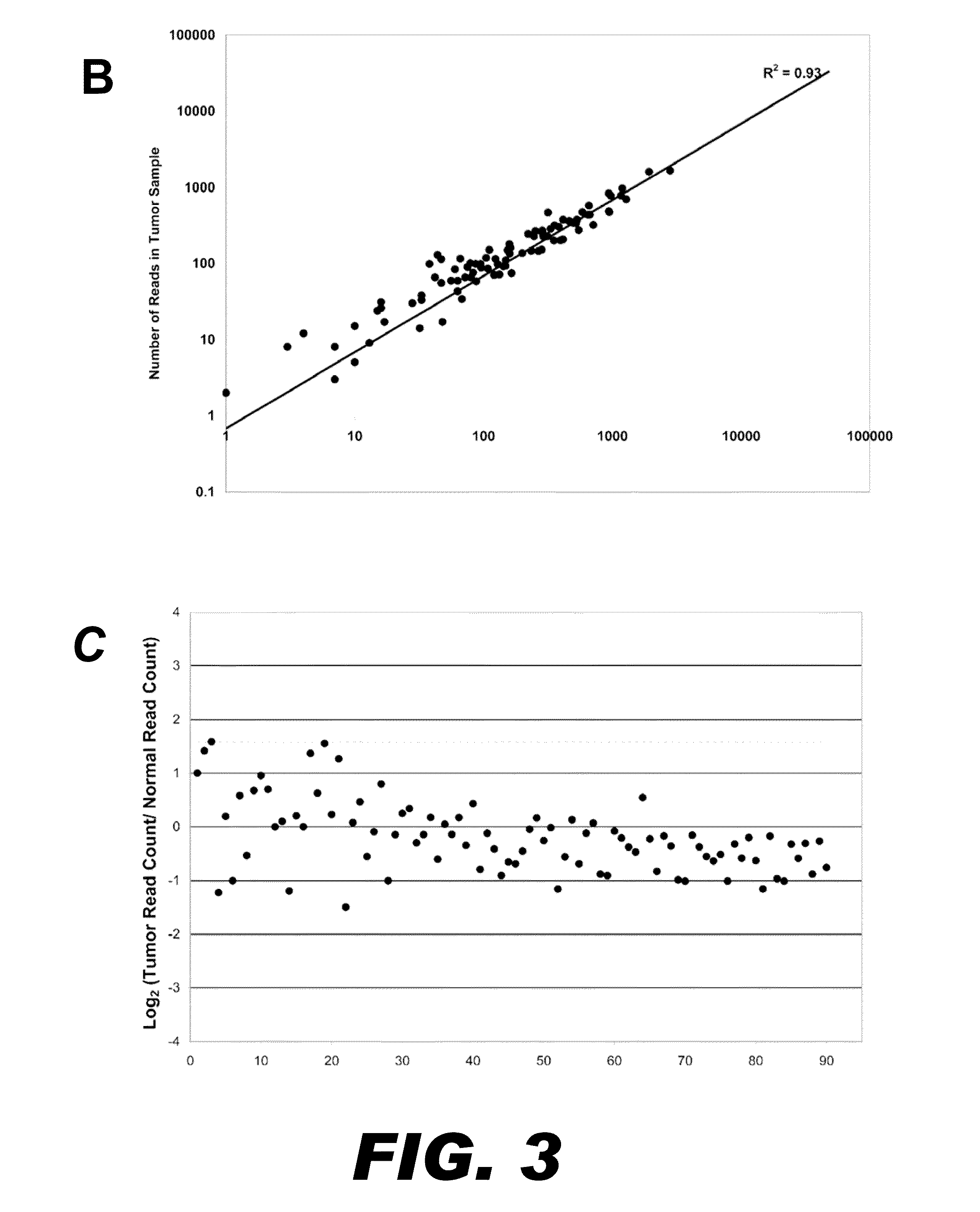
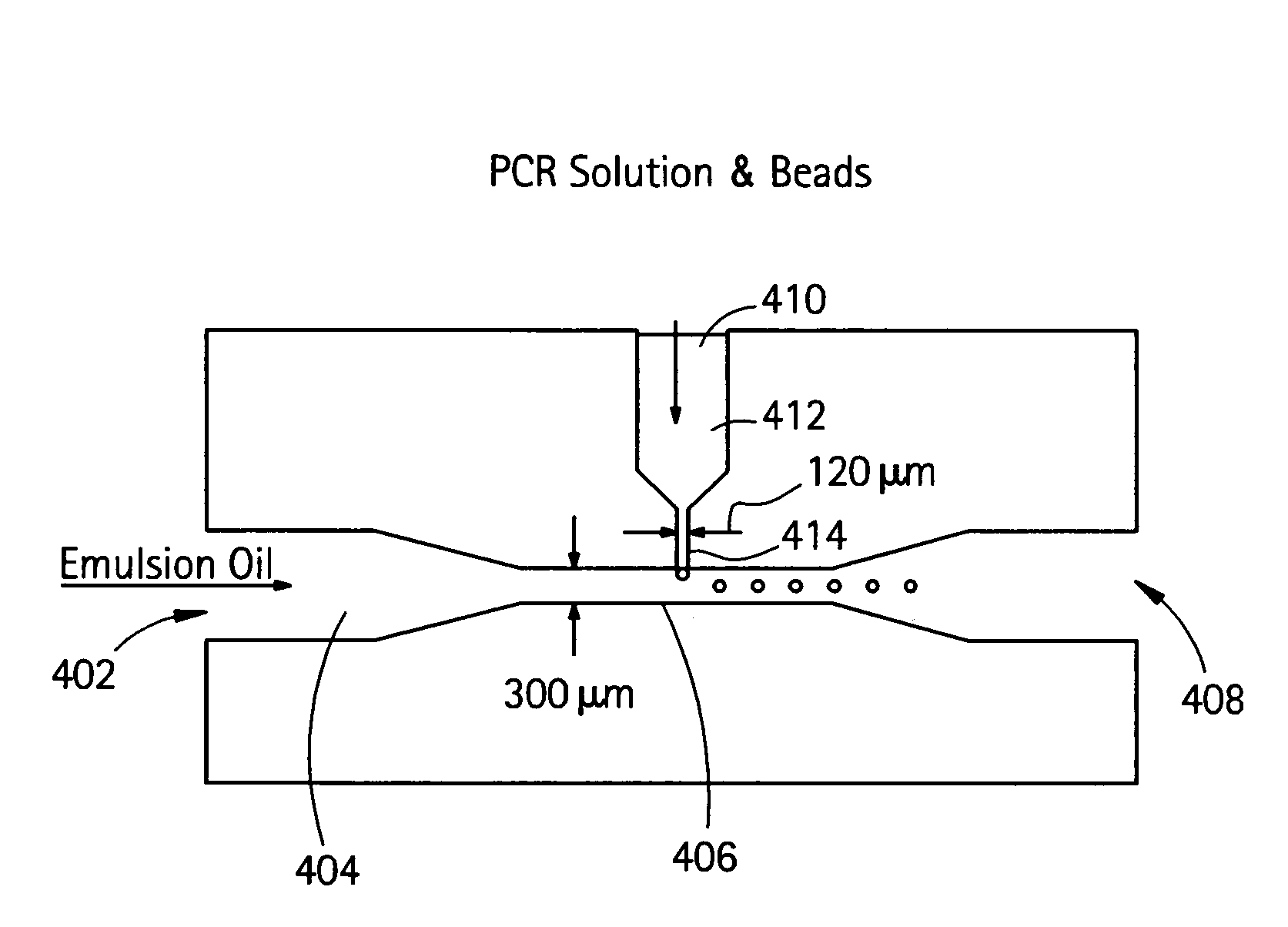
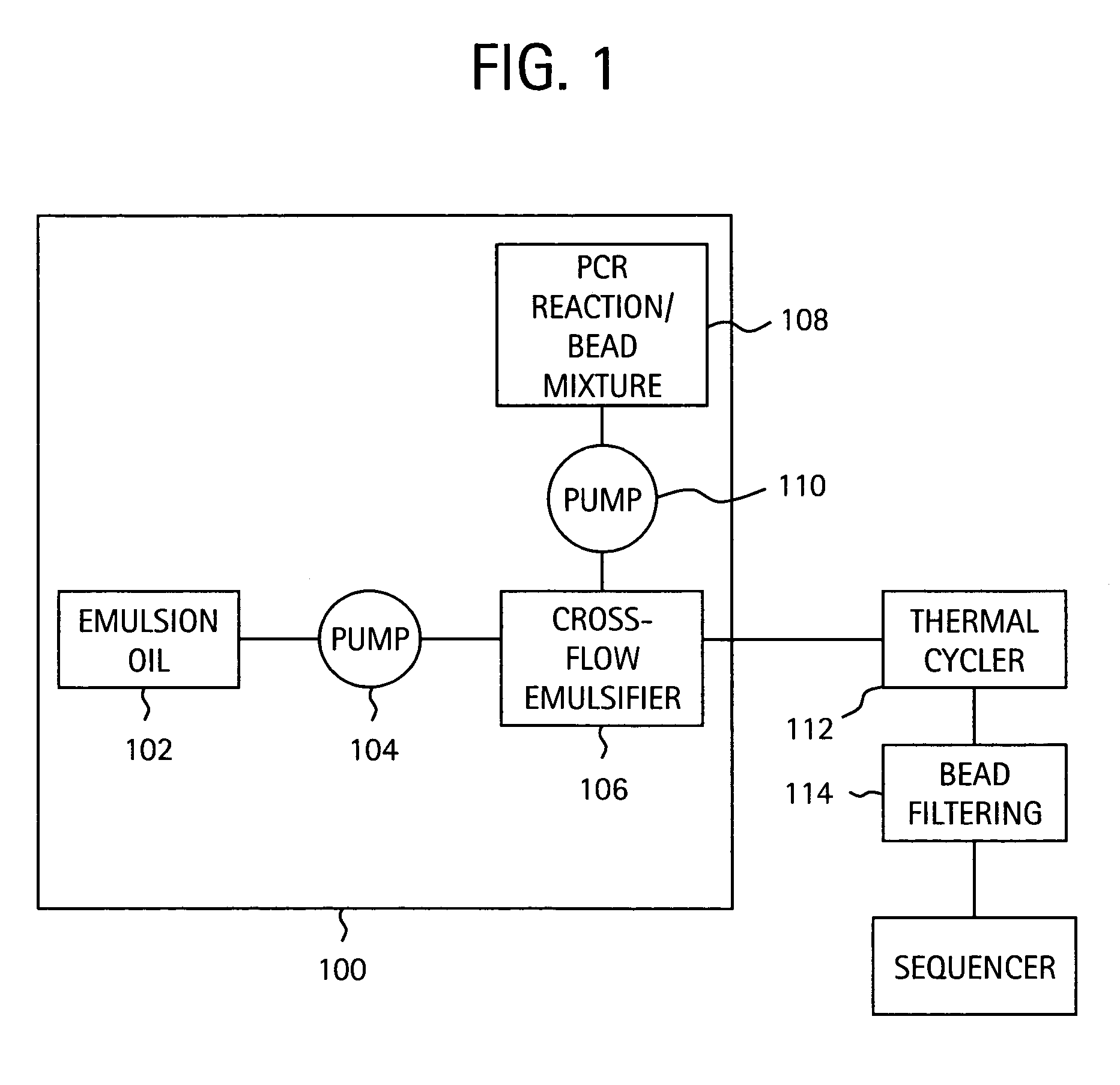
Nucleic acid amplification with continuous flow emulsion
InactiveUS20050227264A1Rapid and economical mannerReduce nozzle cloggingHeating or cooling apparatusFlow mixersMicroreactorGenetic Materials
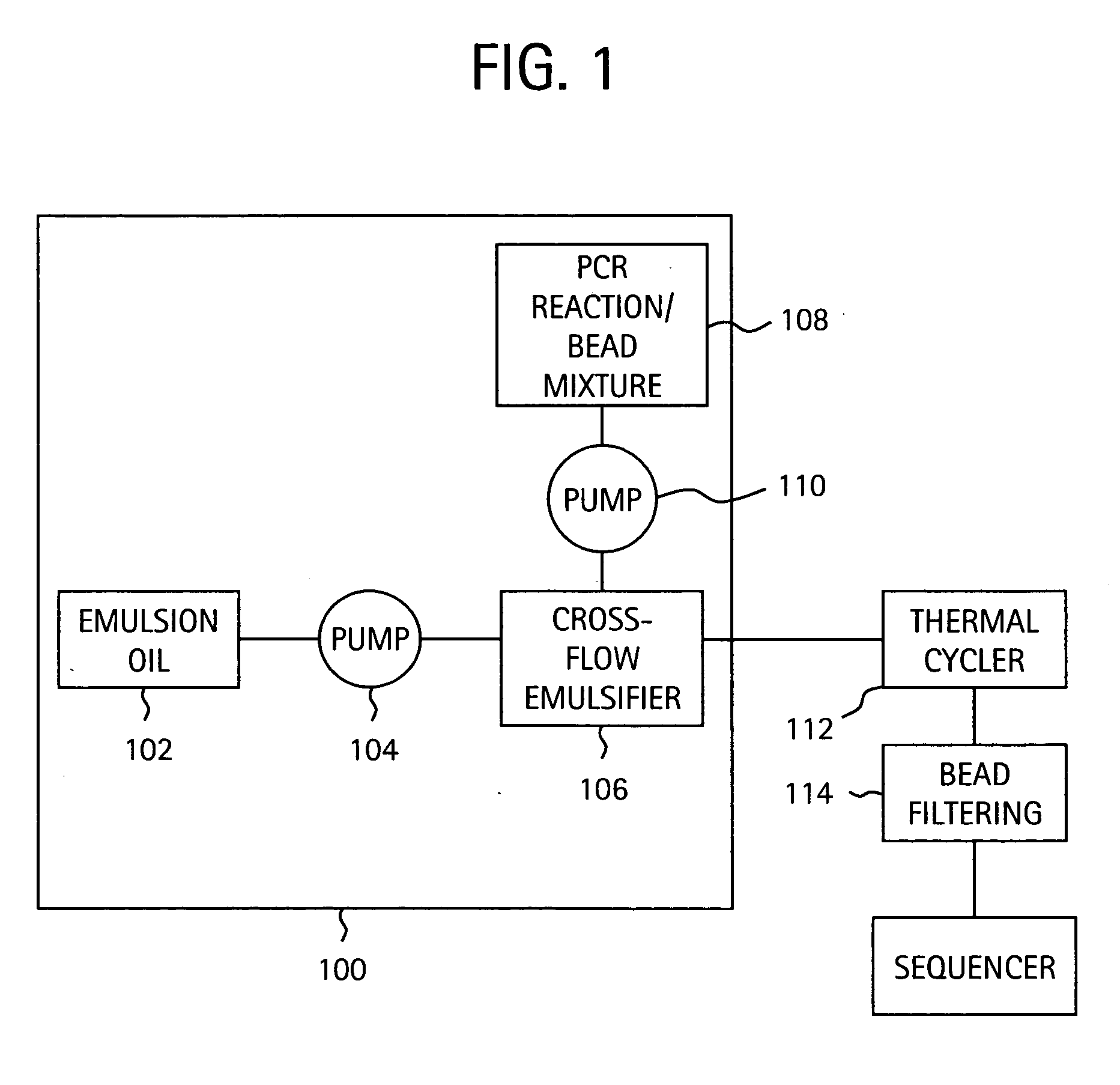
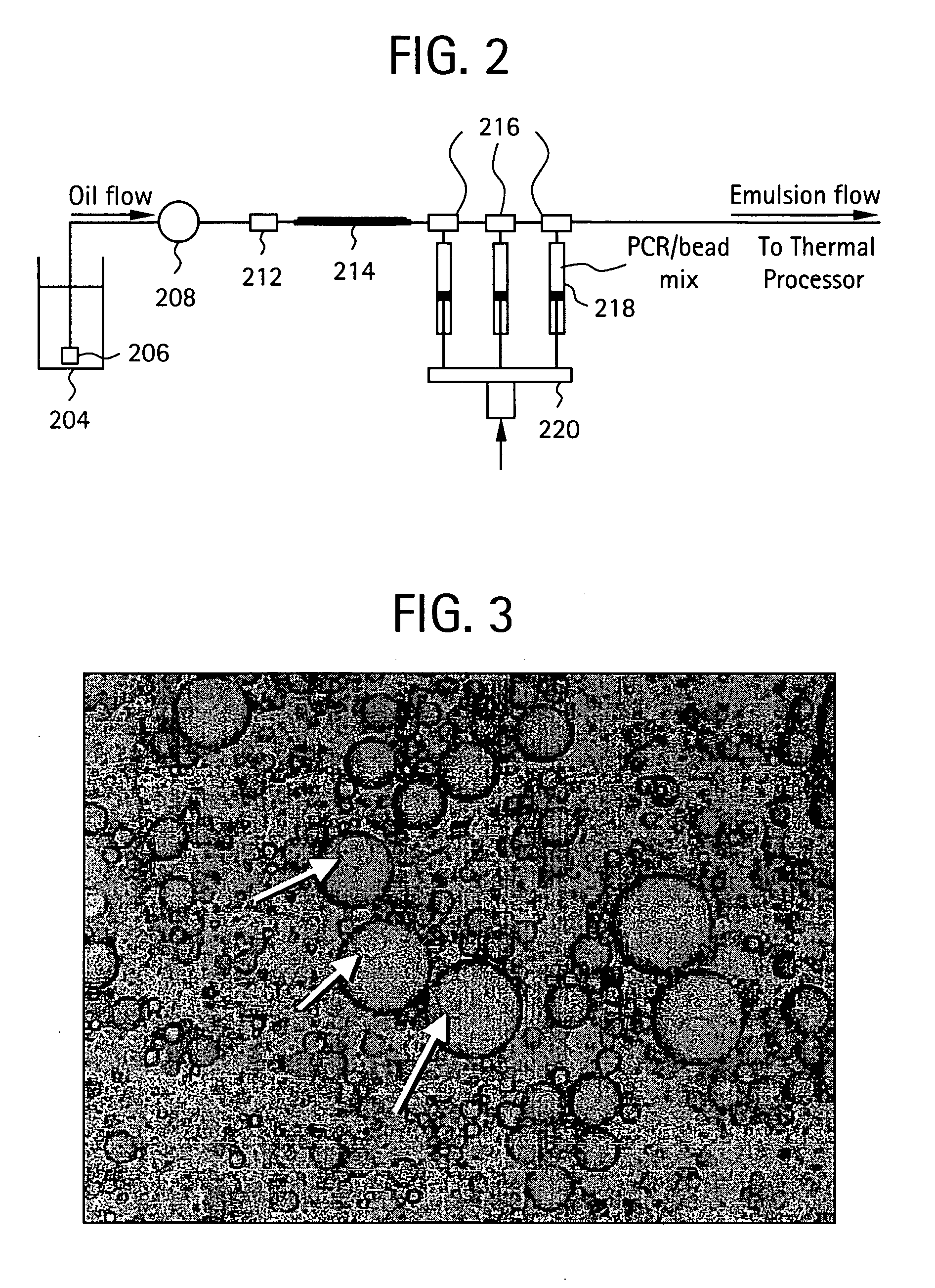
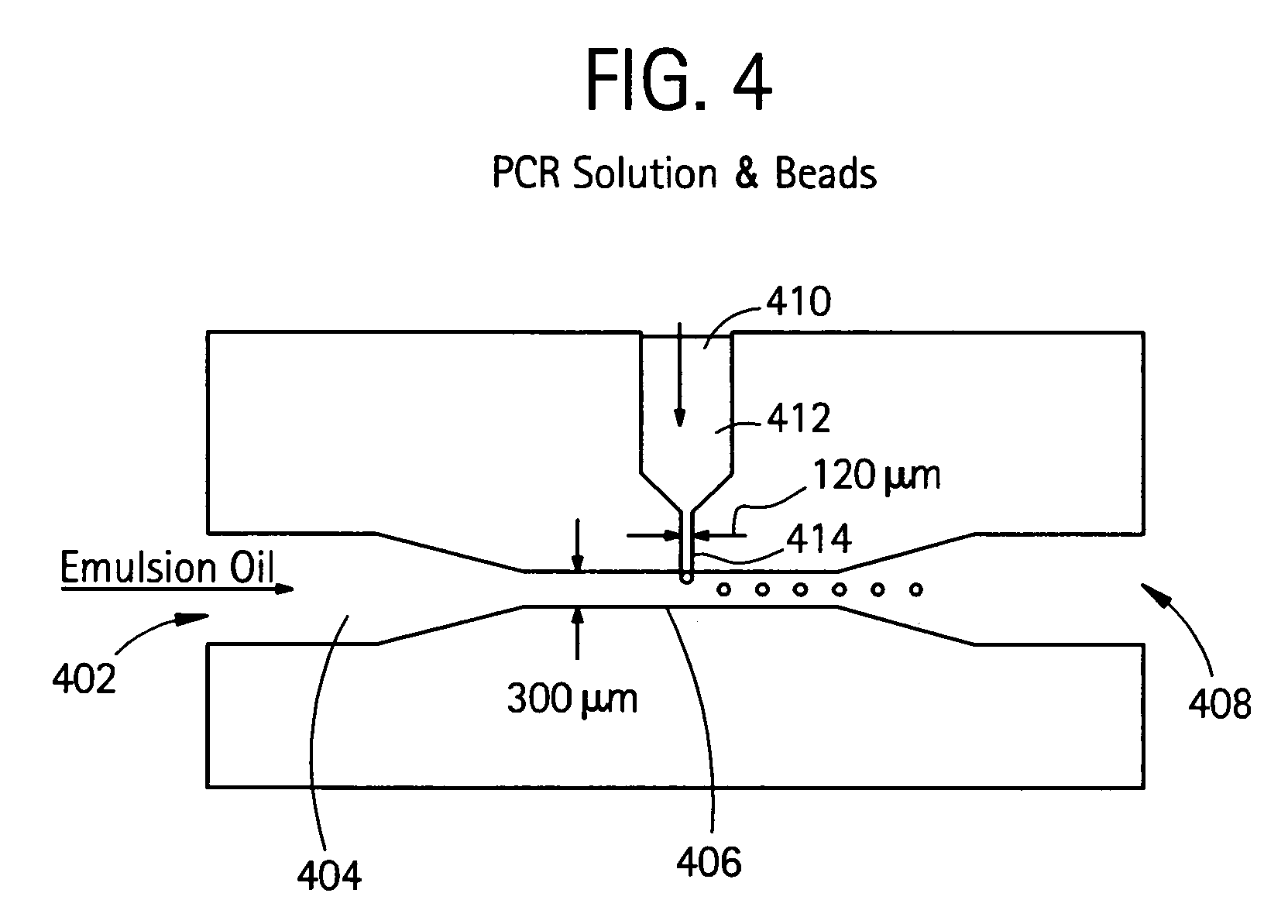
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods and devices / systems for amplifying genetic material and may include providing a water-in-oil emulsion in a continuous flow. The emulsion may include a plurality of water droplets comprising microreactors. Each of the plurality of microreactors may include a single bead capable of capturing a nucleic acid template, a single species nucleic acid template and sufficient reagents to amplify the copy number of the nucleic acid template. The method also includes flowing the emulsion across a first temperature zone and a second lower temperature zone to thermally process the microreactors to amplify the nucleic acid template by polymerase chain reaction.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
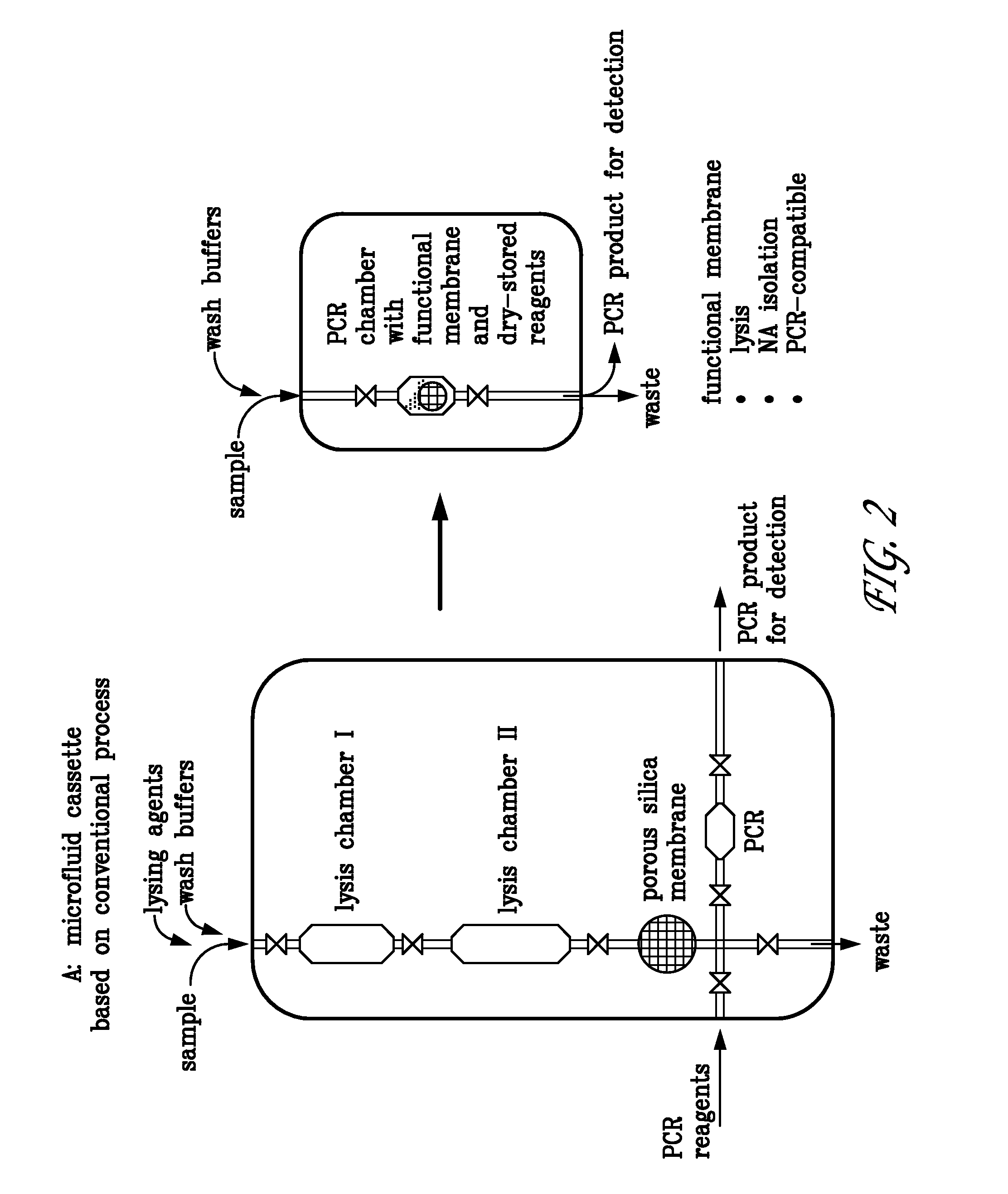
Devices and methods for the performance of miniaturized in vitro amplification assays
InactiveUS6706519B1Optimize thermal cycling parametersEfficient use ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCentripetal forcePolymerase chain reaction
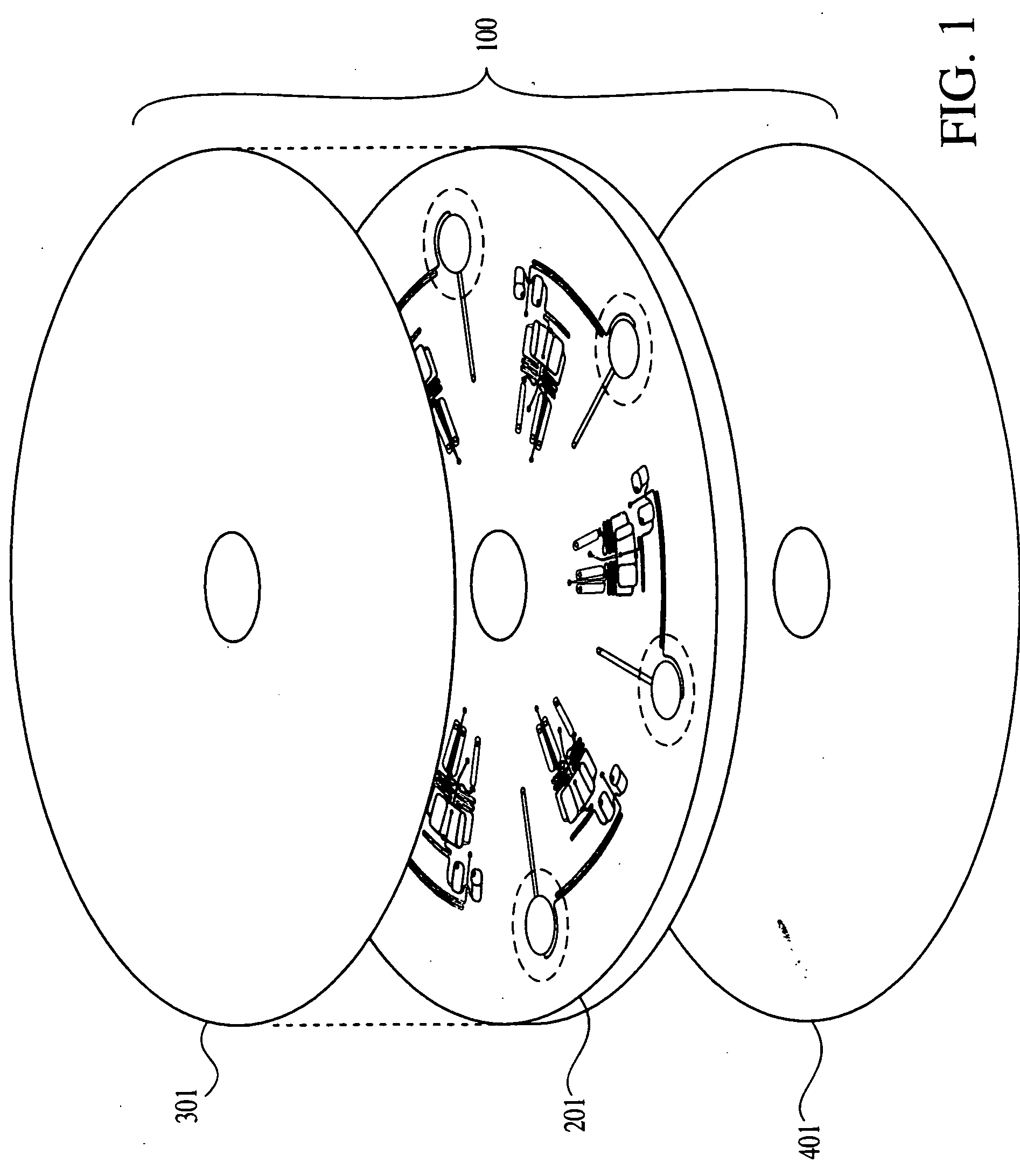
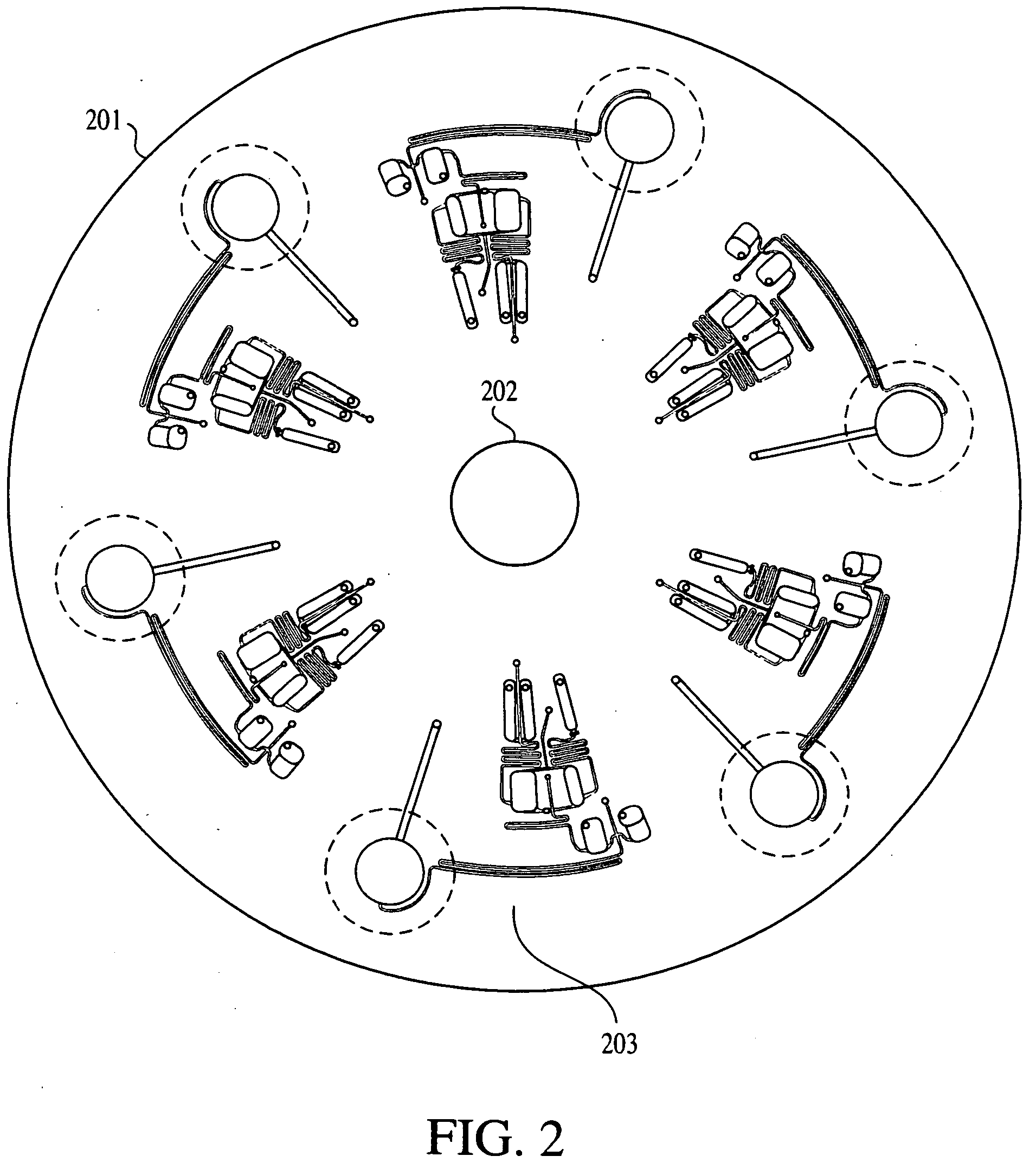
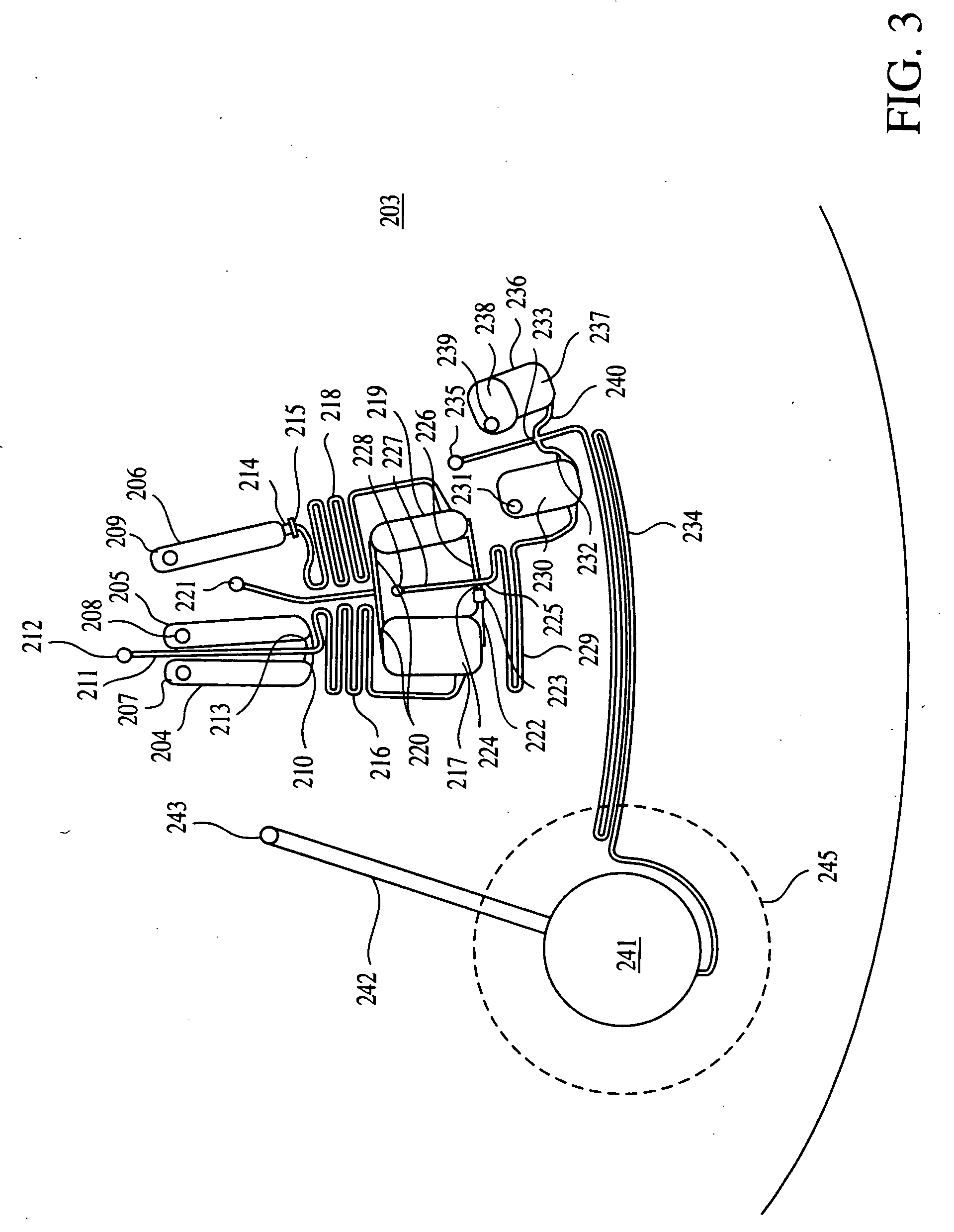
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for performing microanalytic and microsynthetic analyses and procedures. The invention provides a microsystem platform and a micromanipulation device for manipulating the platform that utilizes the centripetal force resulting from rotation of the platform to motivate fluid movement through microchannels. The invention specifically provides devices and methods for performing miniaturized in vitro amplification assays such as the polymerase chain reaction. Methods specific for the apparatus of the invention for performing PCR are provided.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG +1
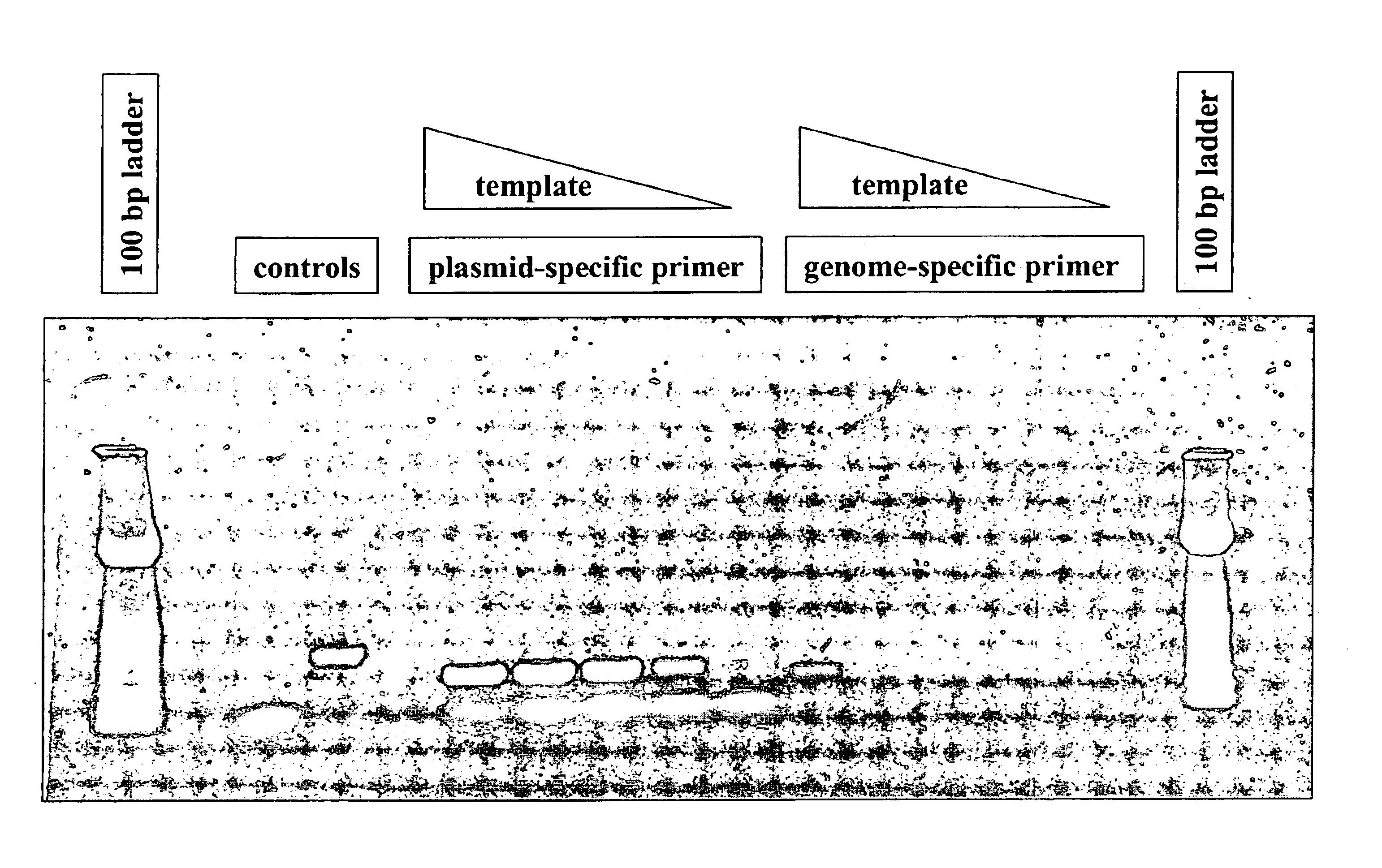
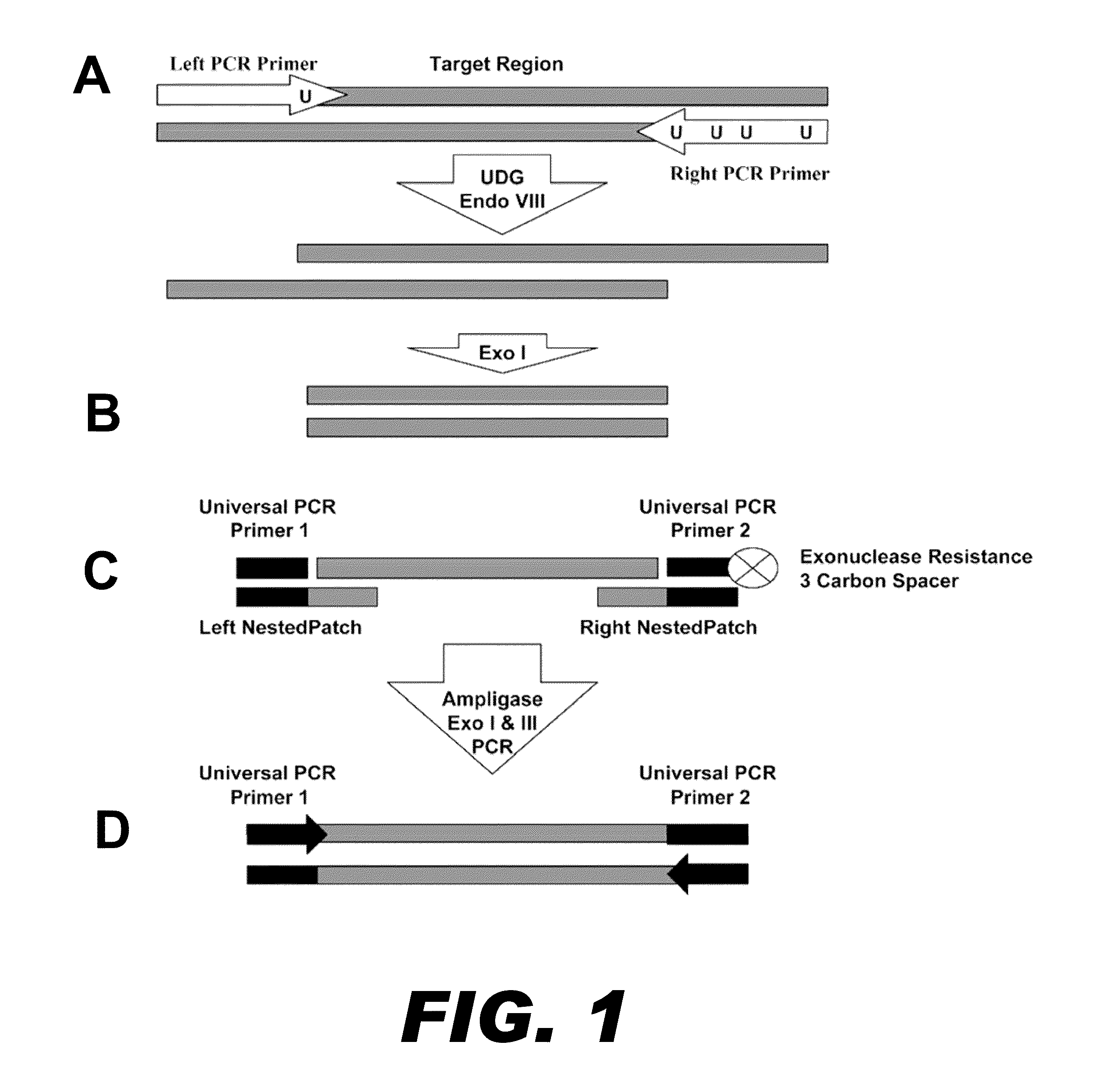
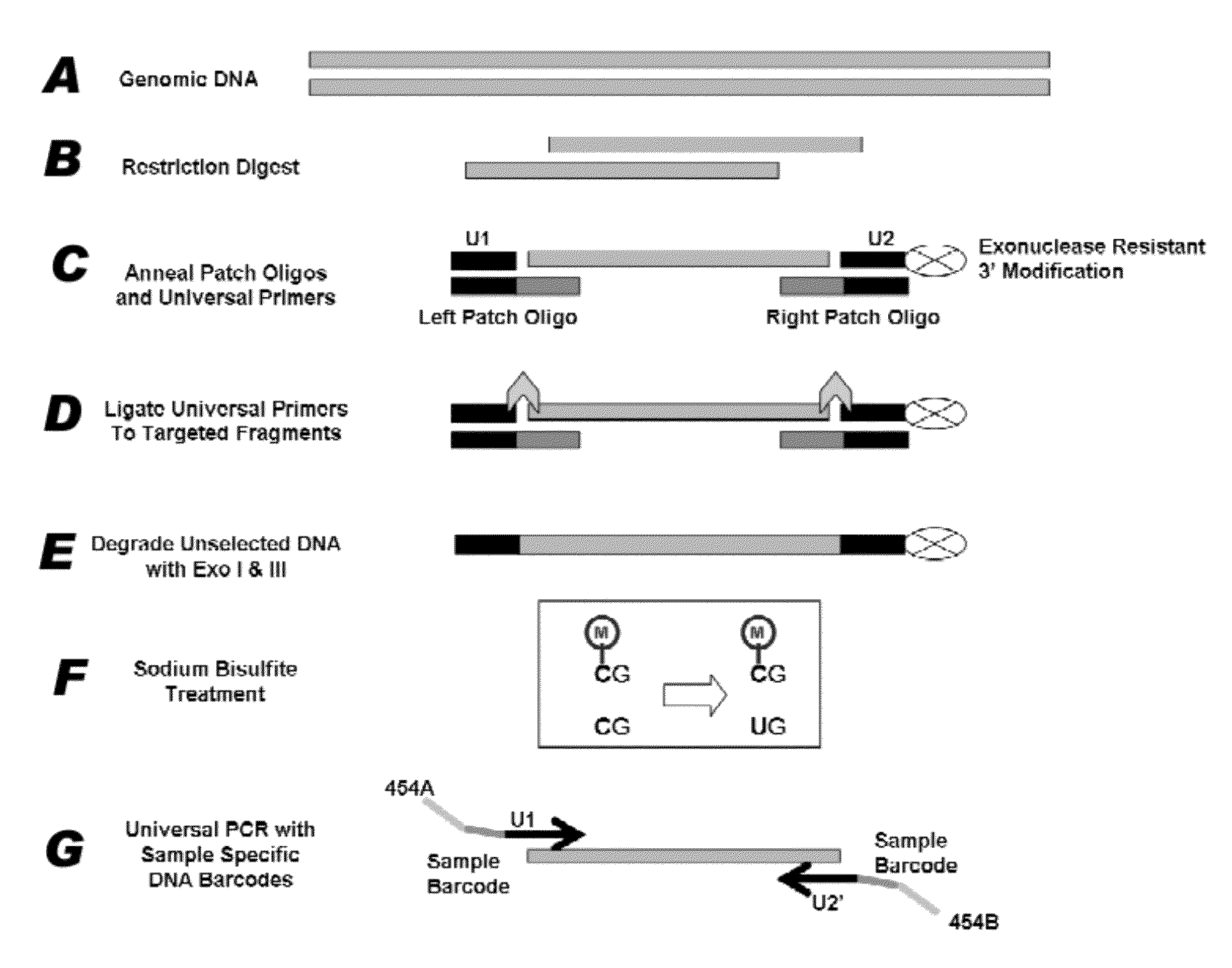
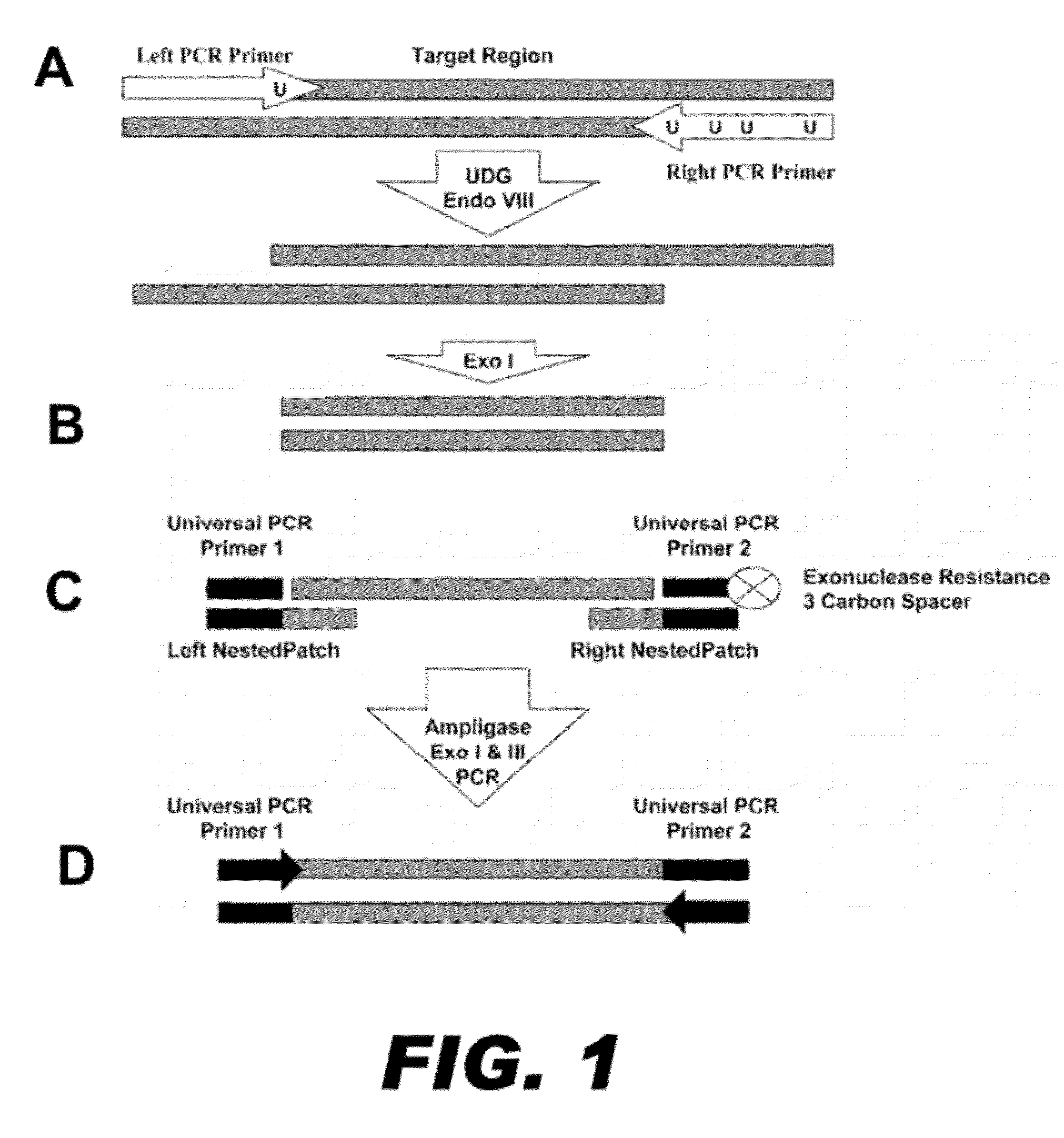
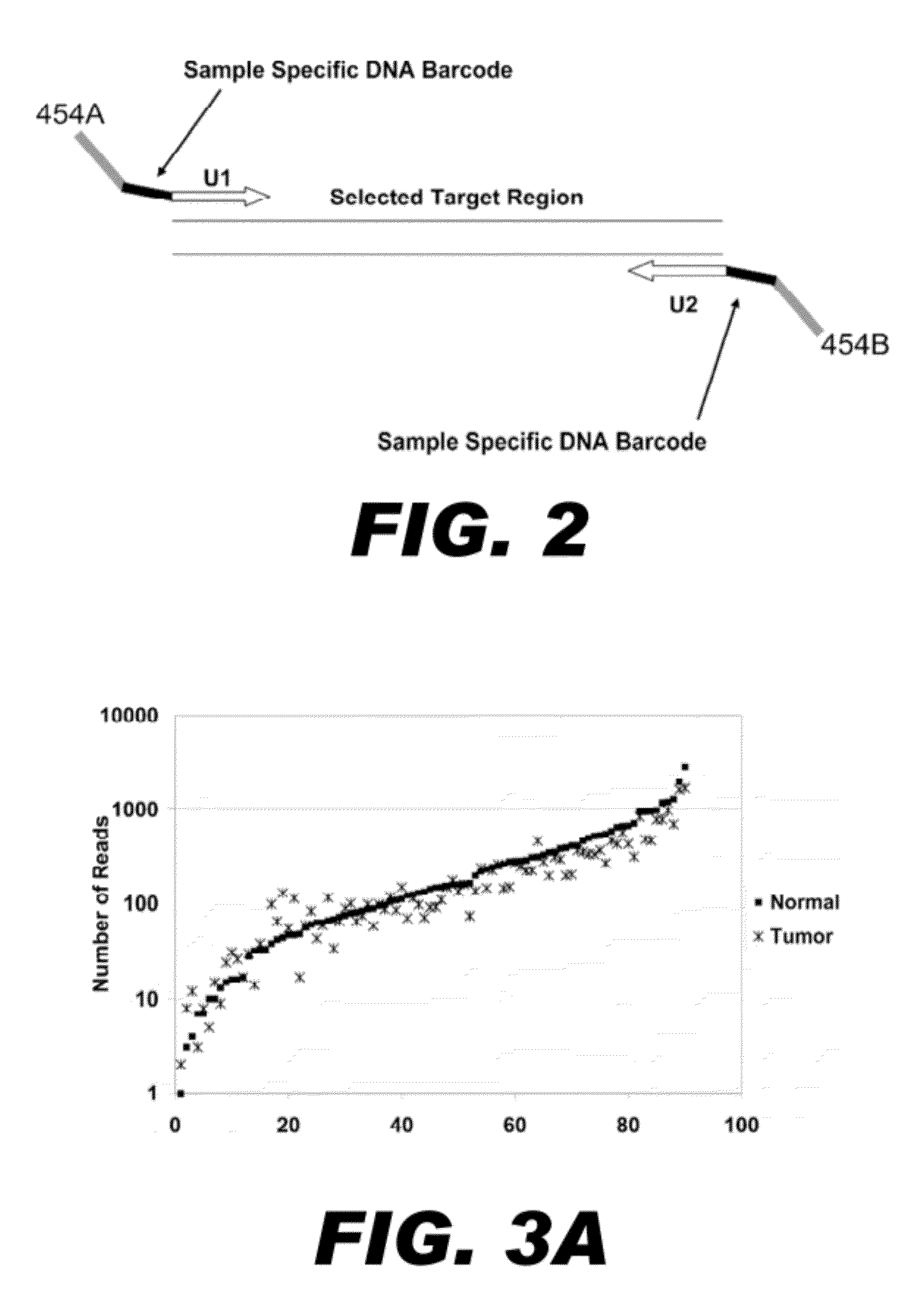
Method for multiplexed nucleic acid patch polymerase chain reaction
ActiveUS20100129874A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
The invention encompasses a method for amplifying at least two different nucleic acid sequences. In particular, the method encompasses a multiplexed nucleic acid patch polymerase chain reaction.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Nucleic acid amplification with continuous flow emulsion
InactiveUS7927797B2Rapid and economical mannerReduce nozzle cloggingHeating or cooling apparatusFlow mixersMicroreactorGenetic Materials
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods and devices / systems for amplifying genetic material and may include providing a water-in-oil emulsion in a continuous flow. The emulsion may include a plurality of water droplets comprising microreactors. Each of the plurality of microreactors may include a single bead capable of capturing a nucleic acid template, a single species nucleic acid template and sufficient reagents to amplify the copy number of the nucleic acid template. The method also includes flowing the emulsion across a first temperature zone and a second lower temperature zone to thermally process the microreactors to amplify the nucleic acid template by polymerase chain reaction.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
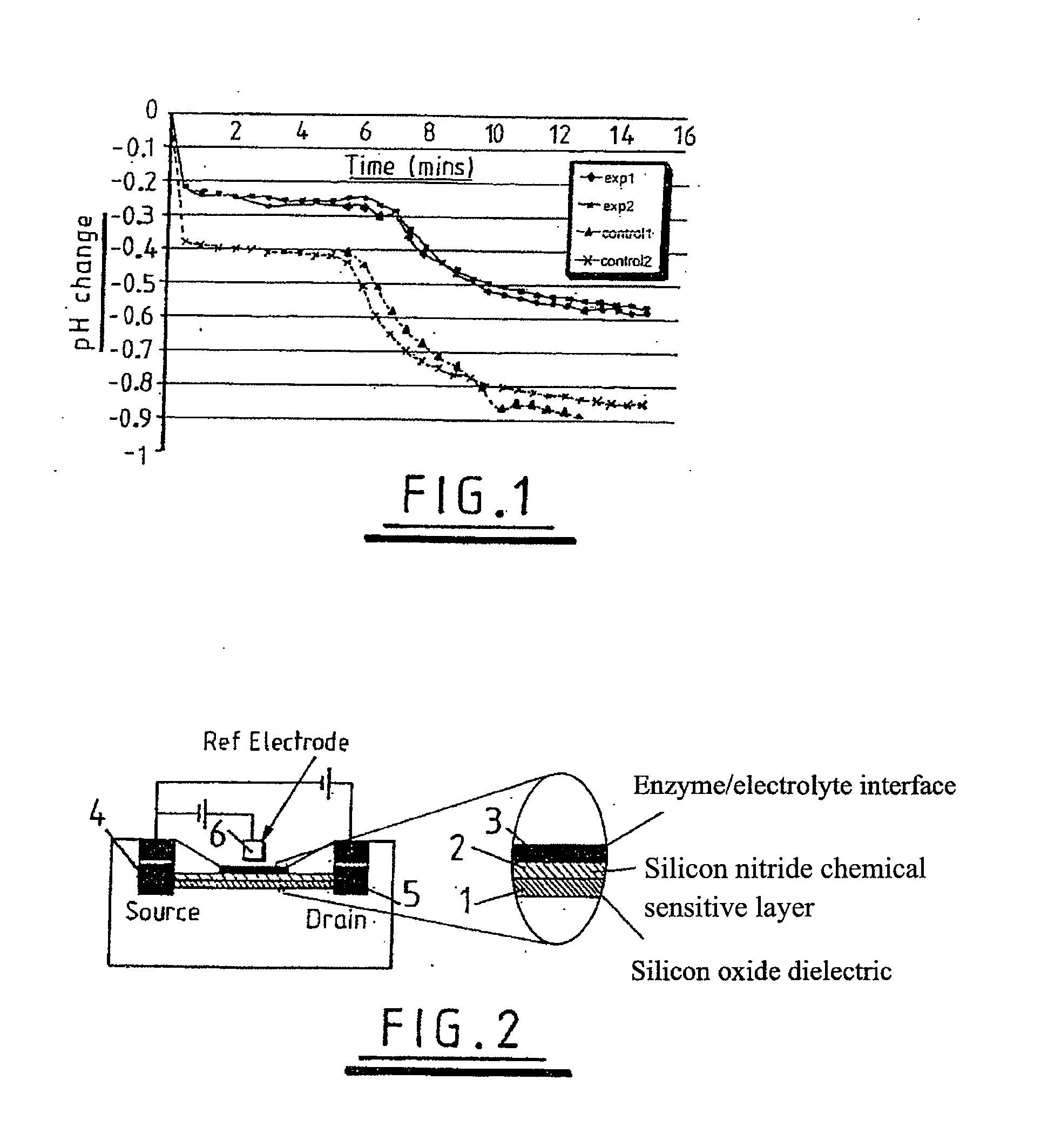
Sensing apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080032295A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical physicsProton
Use of a pH sensor comprising an ion-sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) to perform real time detection / quantification of nucleic acid amplification, e.g. polymerase chain reaction (PCR) nucleic acid amplification, based on detection of protons released during the primer extension phase.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
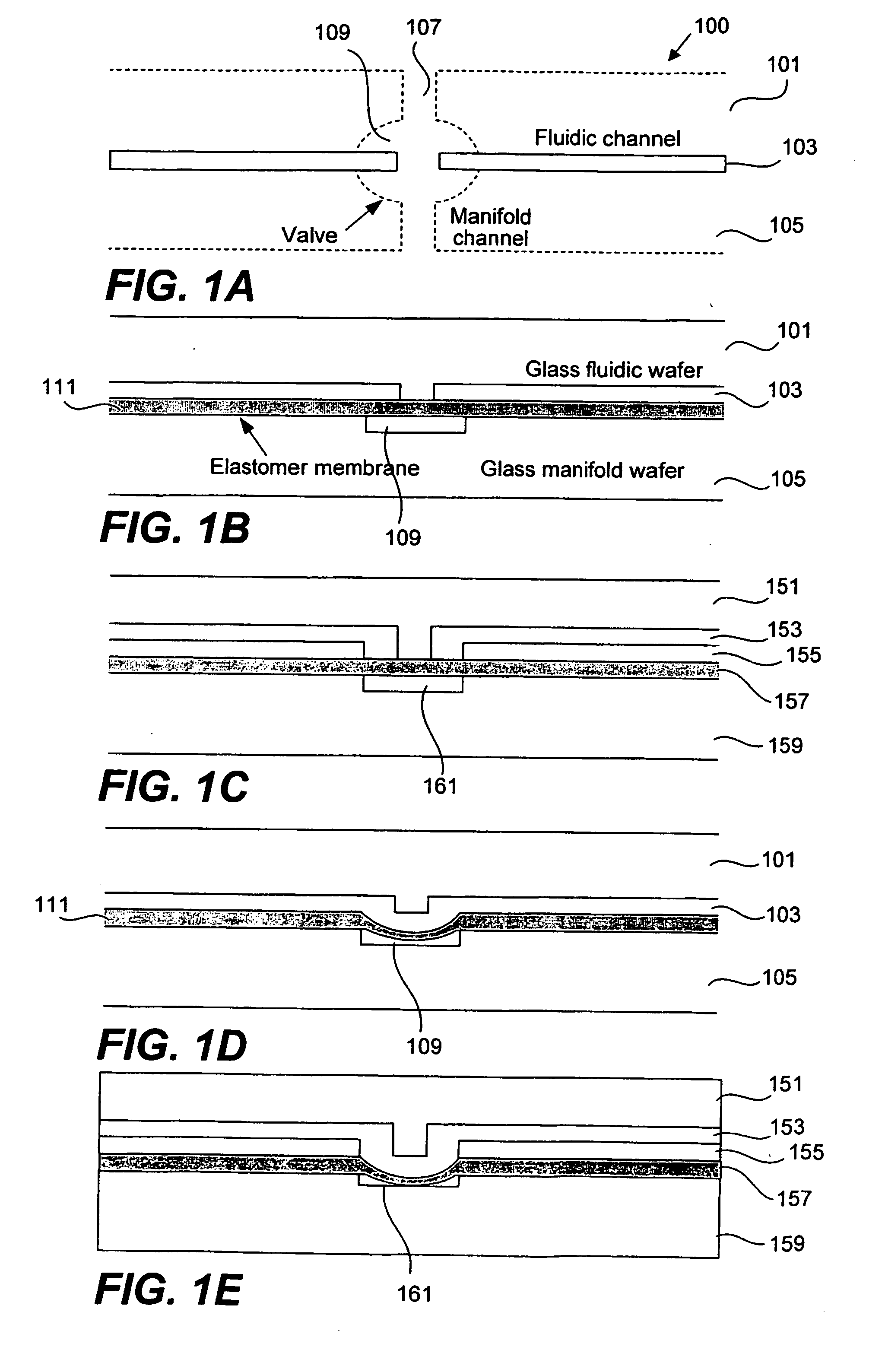
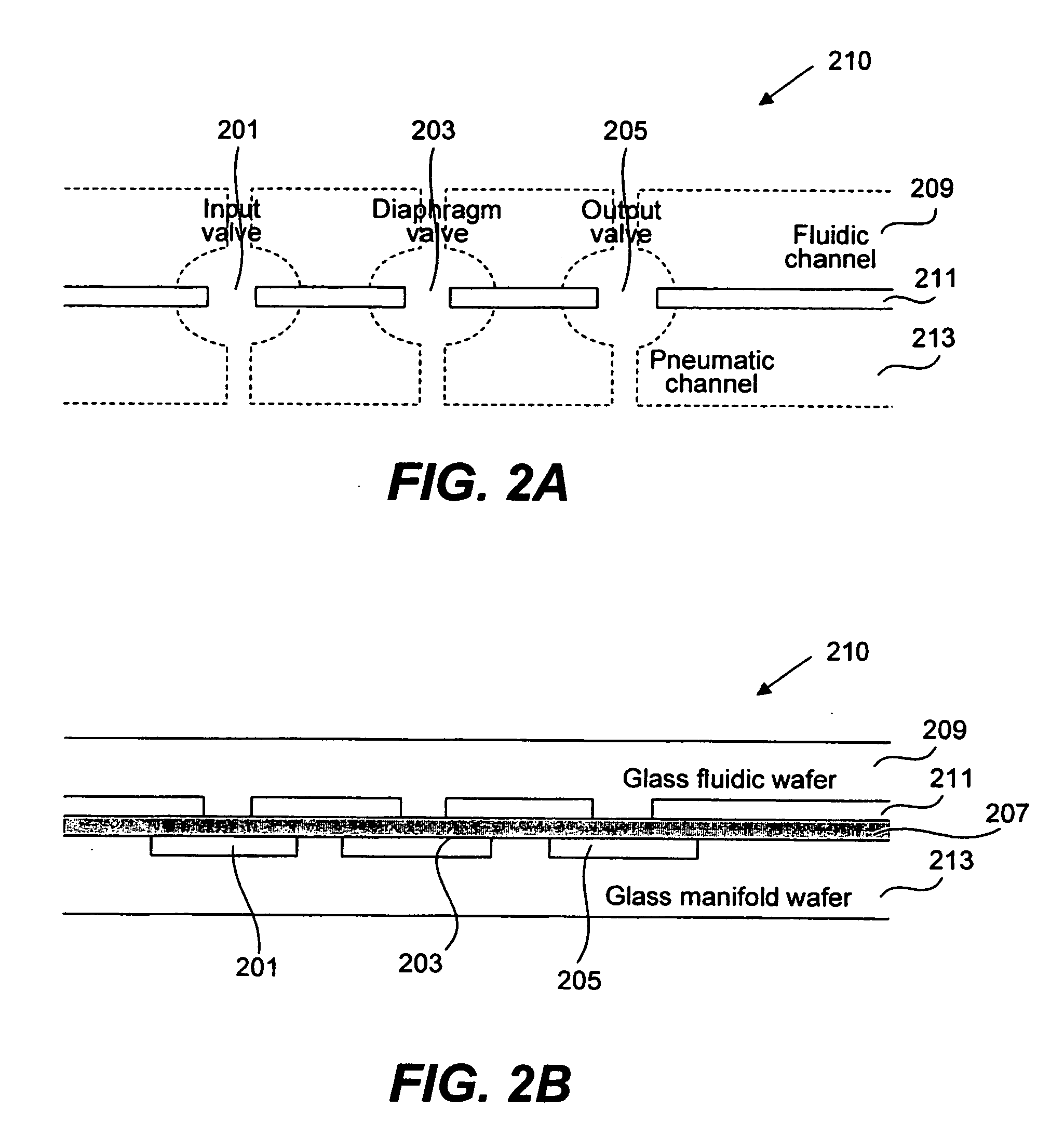
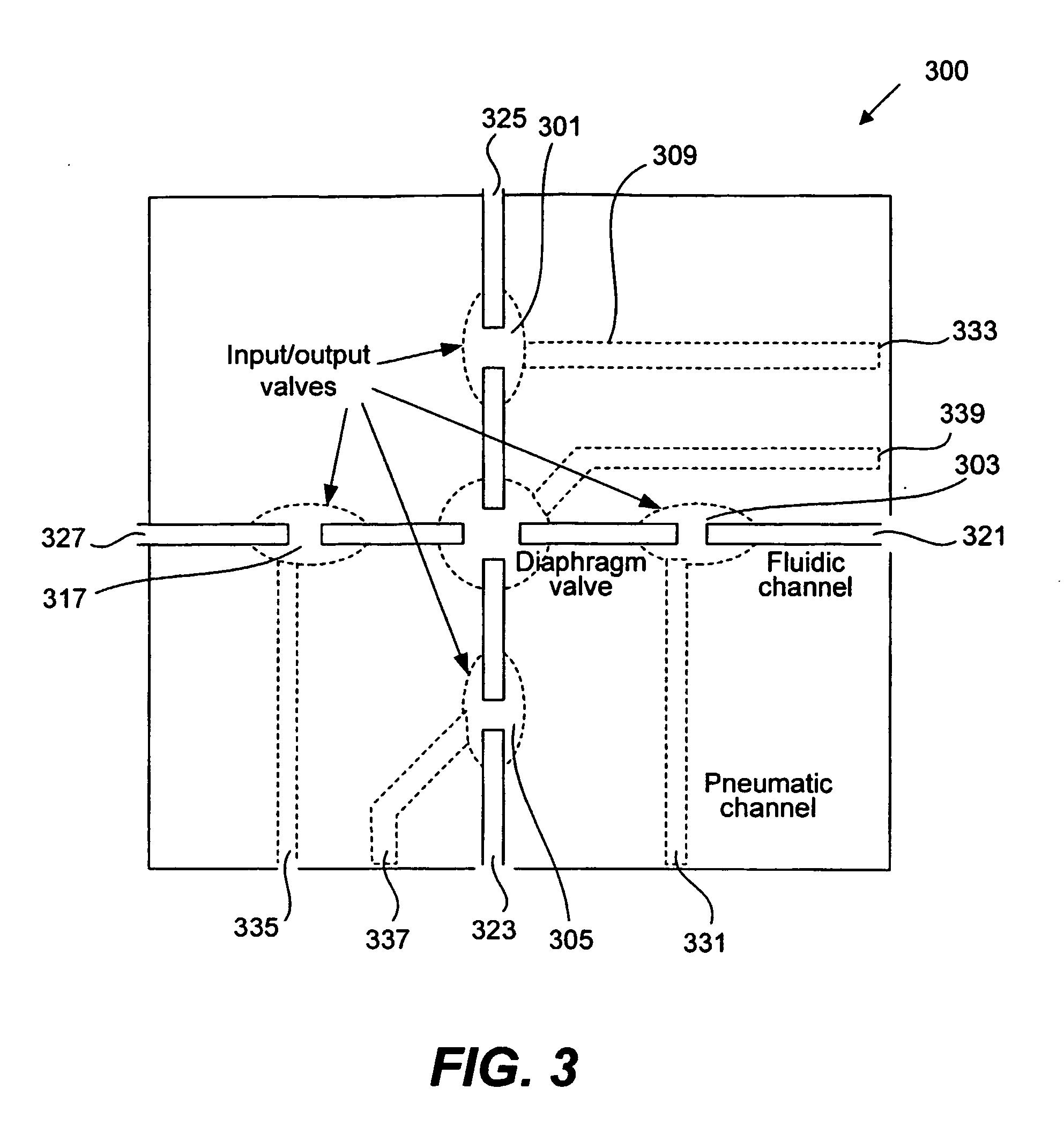
Methods and apparatus for pathogen detection and analysis
Methods and apparatus for implementing microfluidic analysis devices are provided. A monolithic elastomer membrane associated with an integrated pneumatic manifold allows the placement and actuation of dense arrays of a variety of fluid control structures, such as structures for isolating, routing, merging, splitting, and storing volumes of fluid. The fluid control structures can be used to implement a pathogen detection and analysis system including integrated immunoaffinity capture and analysis, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and capillary electrophoresis (CE) analysis. An analyte solution can be input into the device and pumped through a series of immunoaffinity capture matrices in microfabricated chambers having antibodies targeted to the various classes of microbiological organisms such as bacteria, viruses and bacterial spores. The immunoaffinity chambers can capture, purify, and concentrate the target for further analysis steps.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
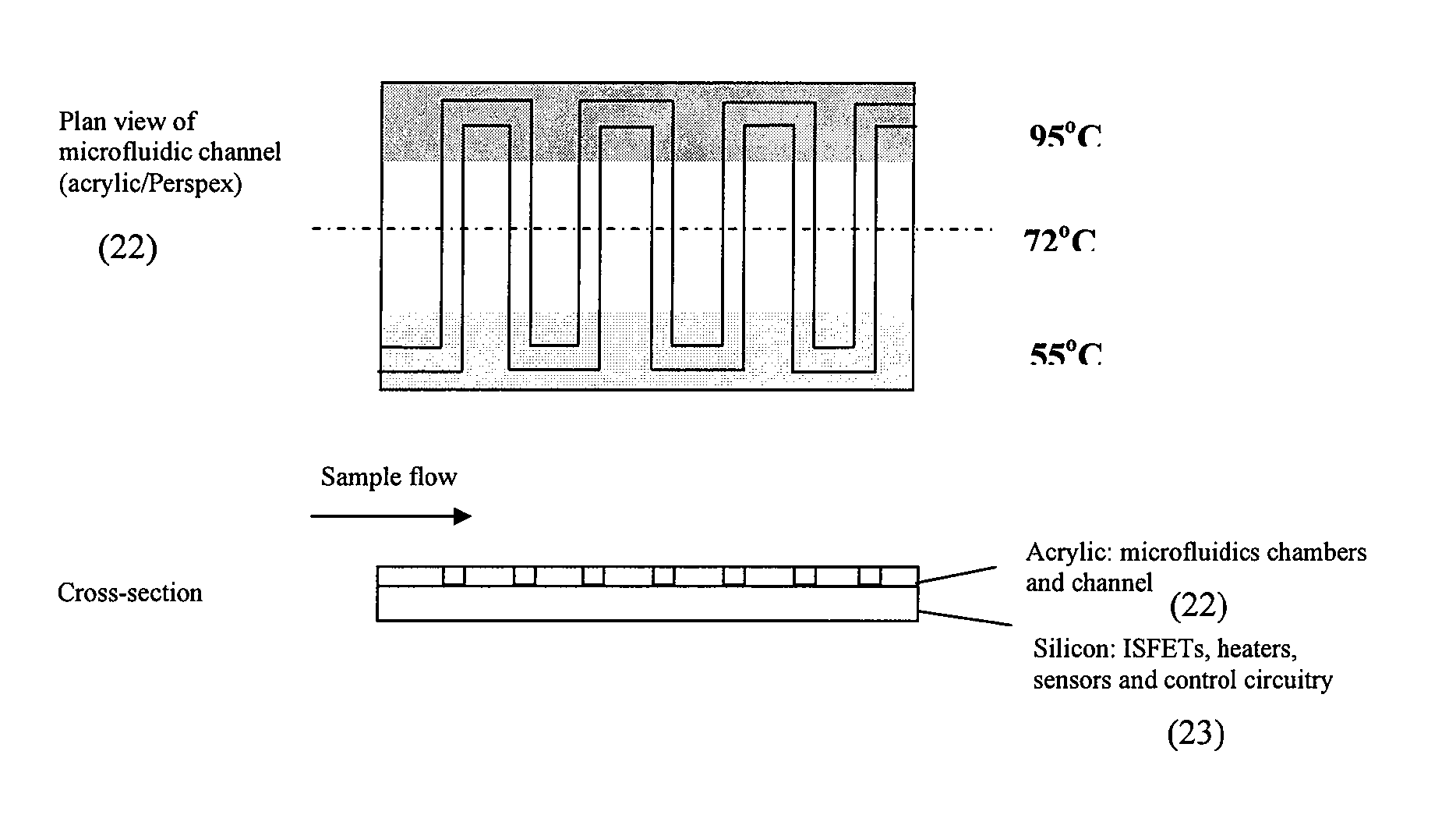
Real-time PCR in micro-channels
The present invention relates to methods for amplifying nucleic acids in micro-channels. More specifically, the present invention relates to methods for performing a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in a continuous-flow microfluidic system and to methods for monitoring real-time PCR in such systems.
Owner:CANON USA
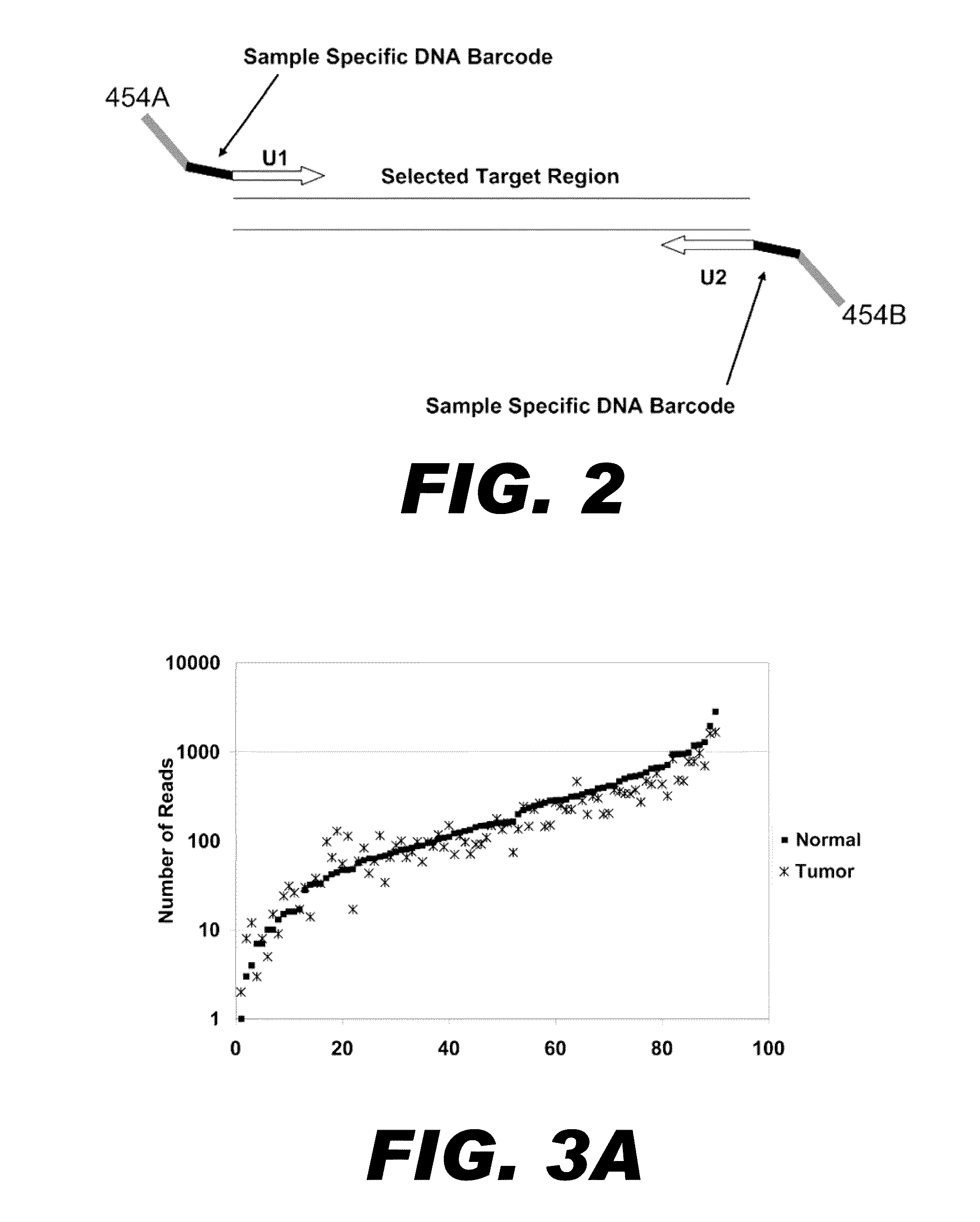
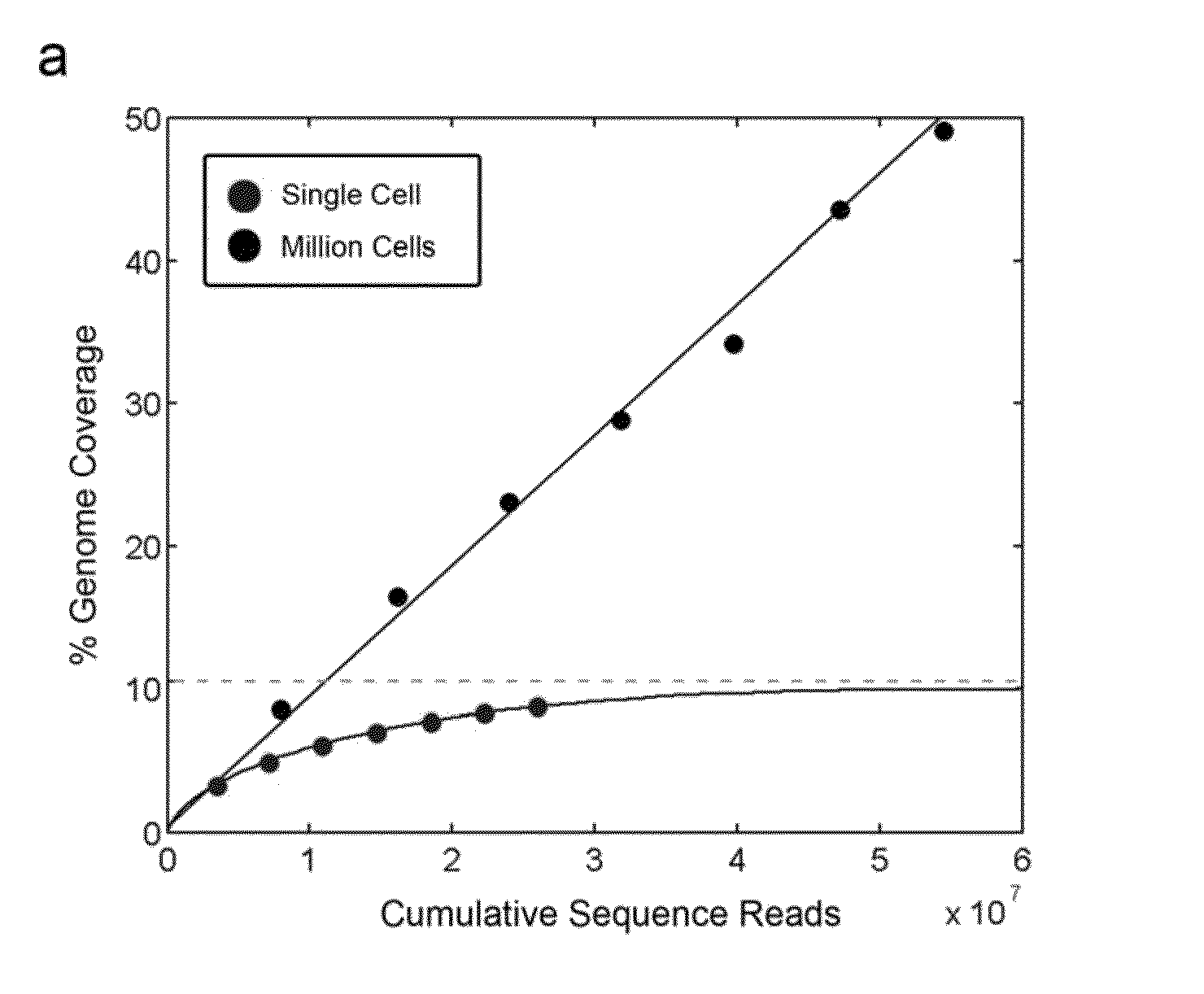
Varietal counting of nucleic acids for obtaining genomic copy number information
A method for obtaining from genomic material genomic copy number information unaffected by amplification distortion, comprising obtaining segments of the genomic material, tagging the segments with substantially unique tags to generate tagged nucleic acid molecules, such that each tagged nucleic acid molecule comprises one segment of the genomic material and a tag, subjecting the tagged nucleic acid molecules to polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, generating tag associated sequence reads by sequencing the product of the PCR reaction, assigning each tagged nucleic acid molecule to a location on a genome associated with the genomic material by mapping the subsequence of each tag associated sequence read corresponding to a segment of the genomic material to a location on the genome, and counting the number of tagged nucleic acid molecules assigned to the same location on the genome having a different tag, thereby obtaining genomic copy number information unaffected by amplification distortion.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Detection of chromosomal disorders
InactiveUS20050250111A1Improve accuracyFast and accurate and simple and inexpensive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseGenomic DNA
Methods for detecting in a single assay any one of multiple chromosomal disorders that result from aneuploidy or certain mutations, particularly microdeletions, and kits for use therein. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is carried out to amplify eukaryotic genomic DNA using a plurality of primer oligonucleotide pairs wherein one primer of each pair has a detectable label attached 5′ thereto. A plurality of the primer pairs are targeted to DNA segments of different chromosomes of interest which are indicative of potential chromosomal disorders, and one pair is targeted for a control gene. The amplified PCR products are purified, and single-stranded DNA having the detectable labels is obtained therefrom and hybridized with spots on a microarray that each contain DNA oligonucleotide probes having nucleotide sequences complementary to a nucleotide sequence of one strand of each segment. The microarray is imaged for presence of labels on its respective spots, and the absence or presence of chromosomal disorders as indicated by one or more of the targeted DNA segments of interest is diagnosed by first comparing the imaging results to the imaging of spots specific to the control gene and then to results obtained from imaging normal DNA.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
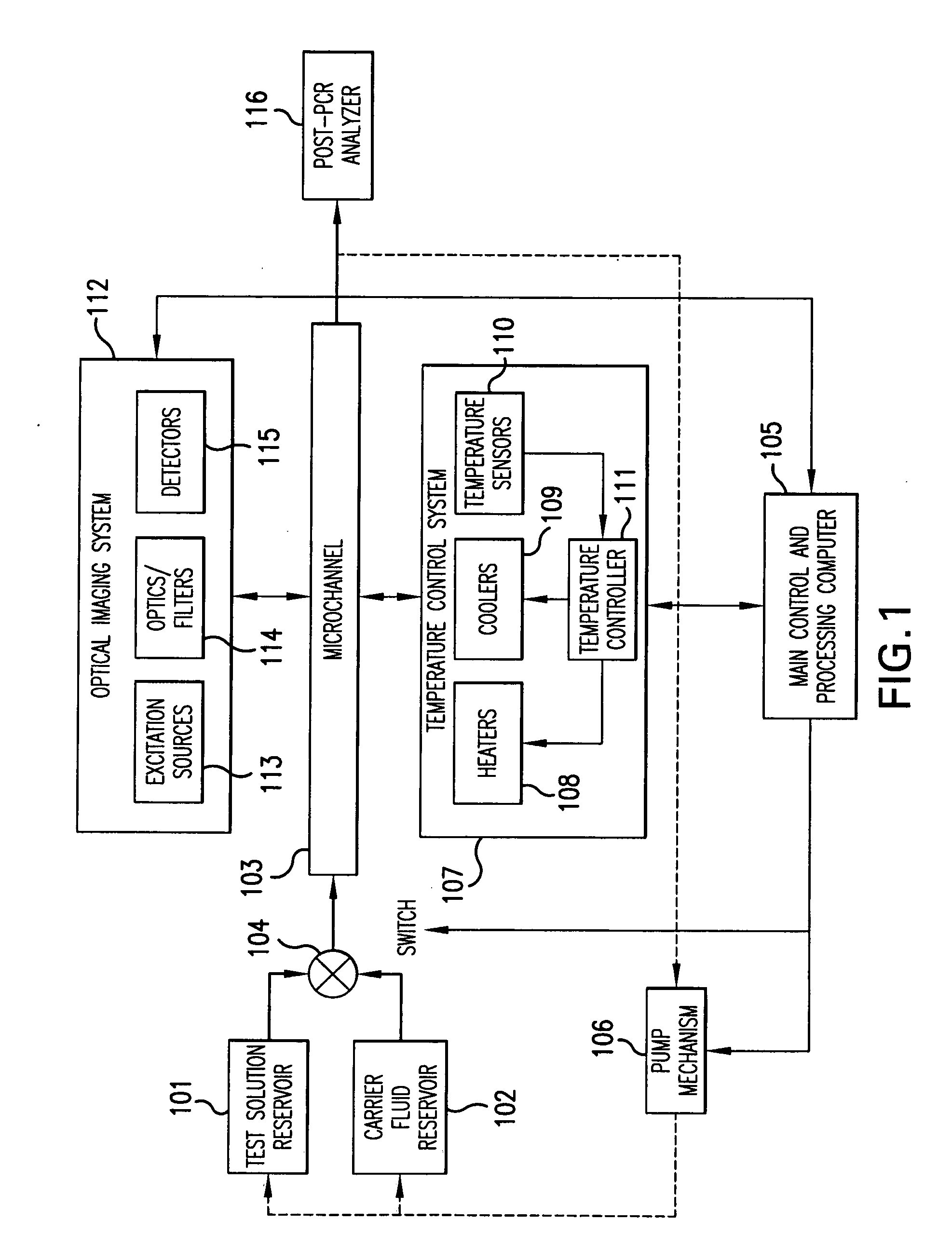
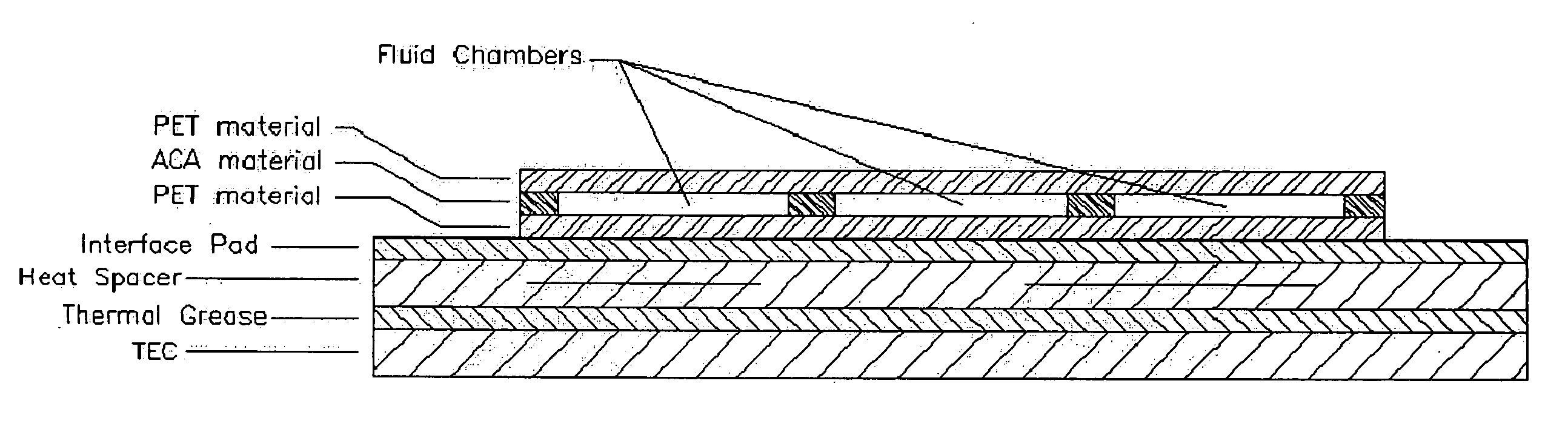
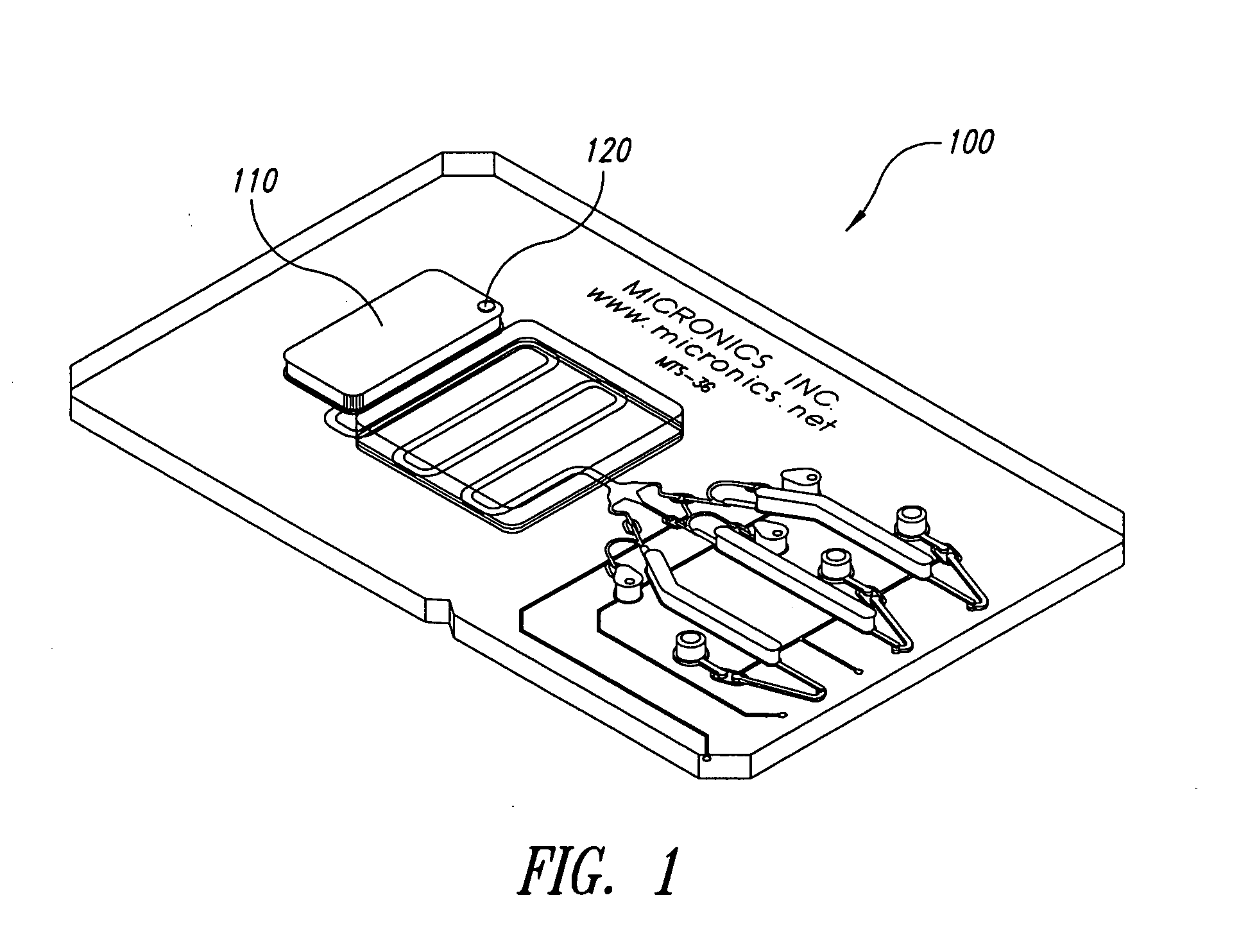
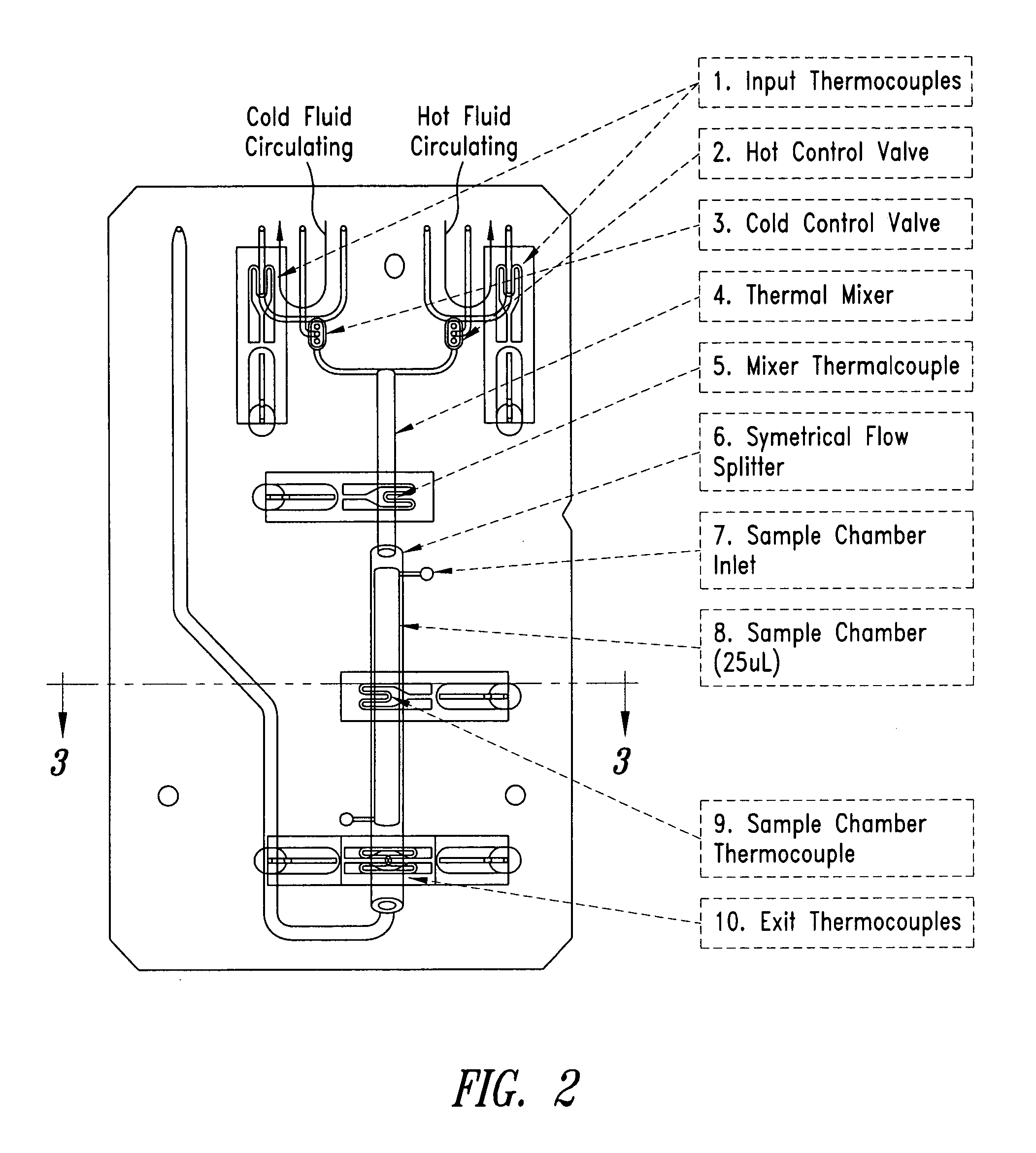
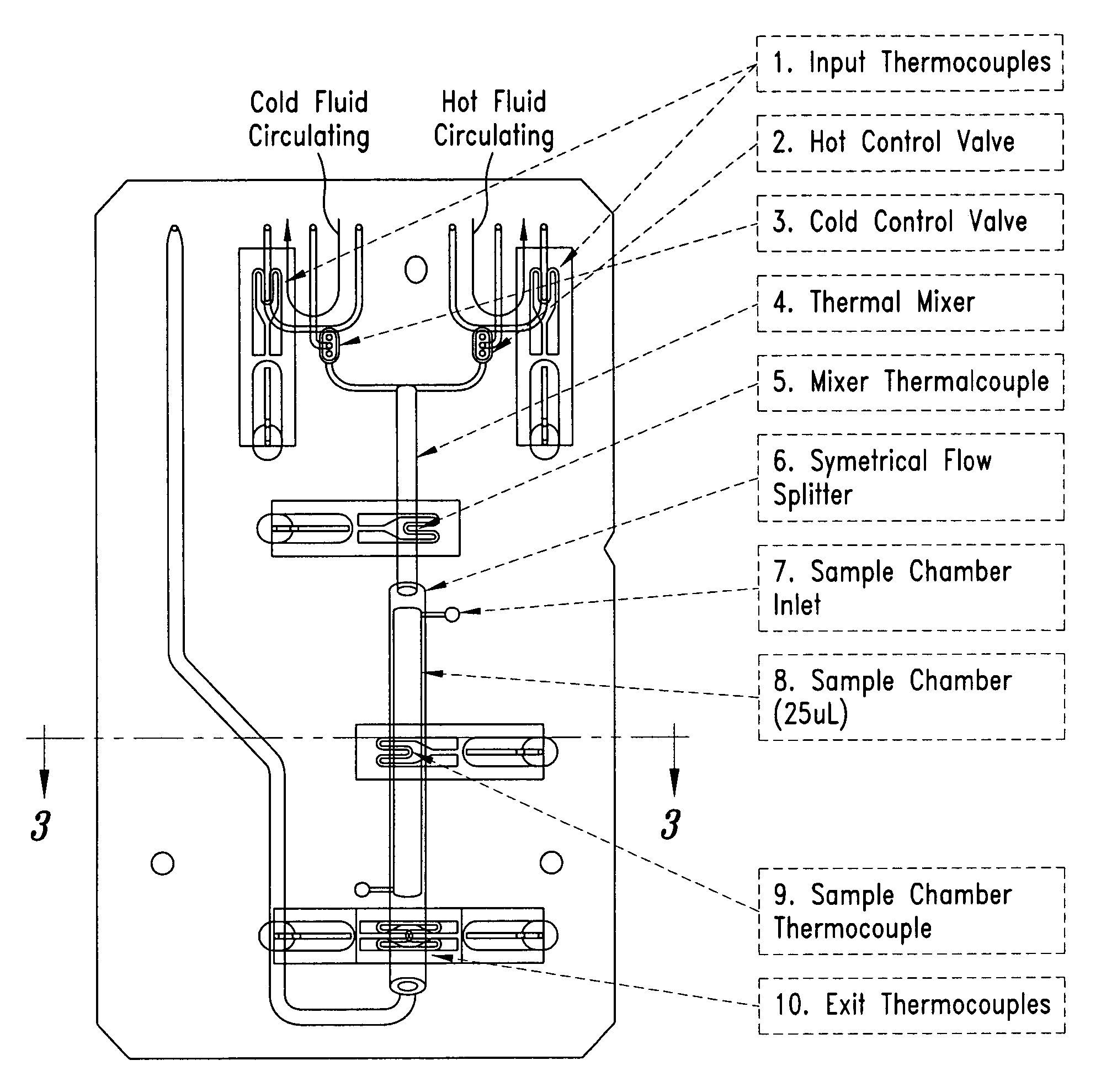
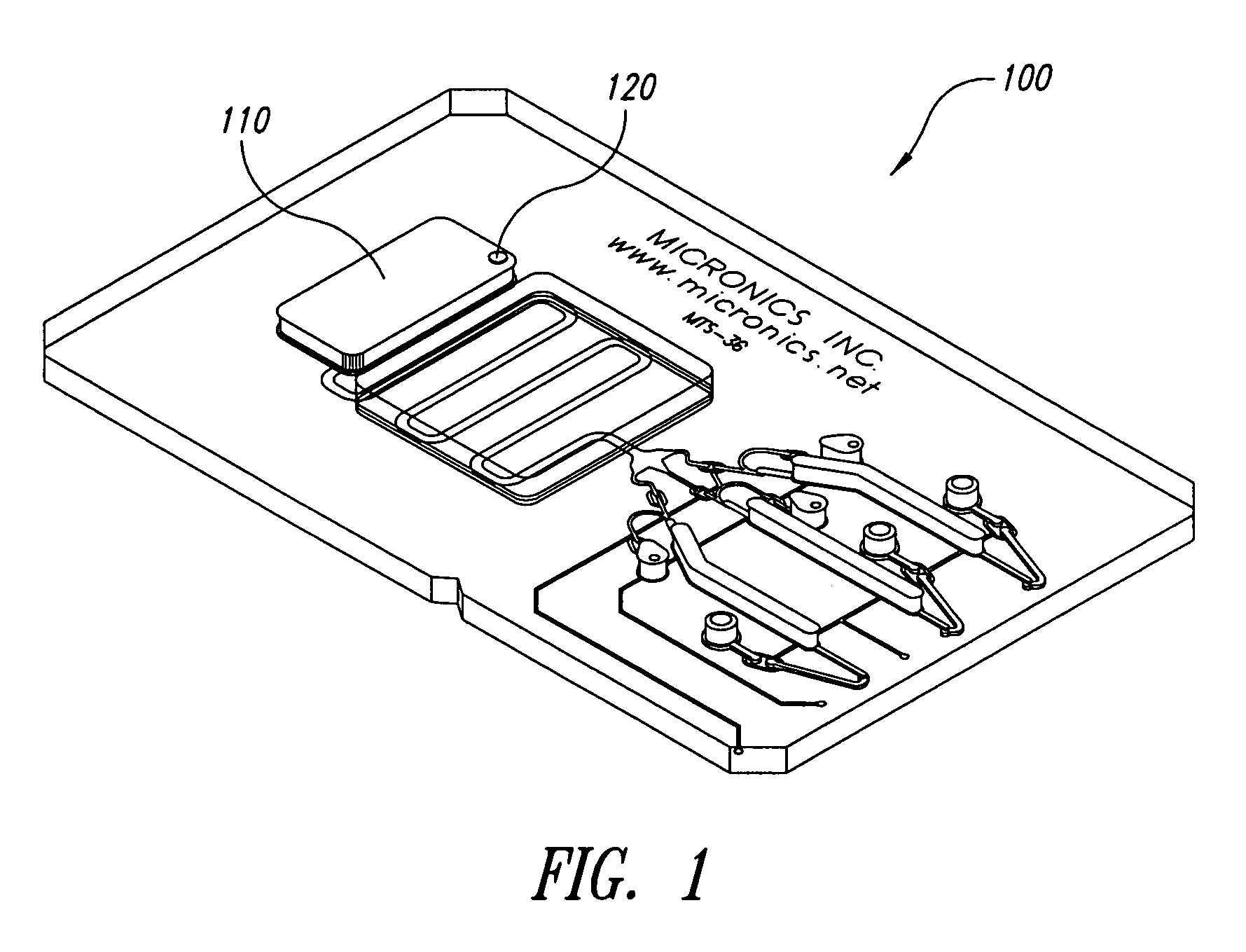
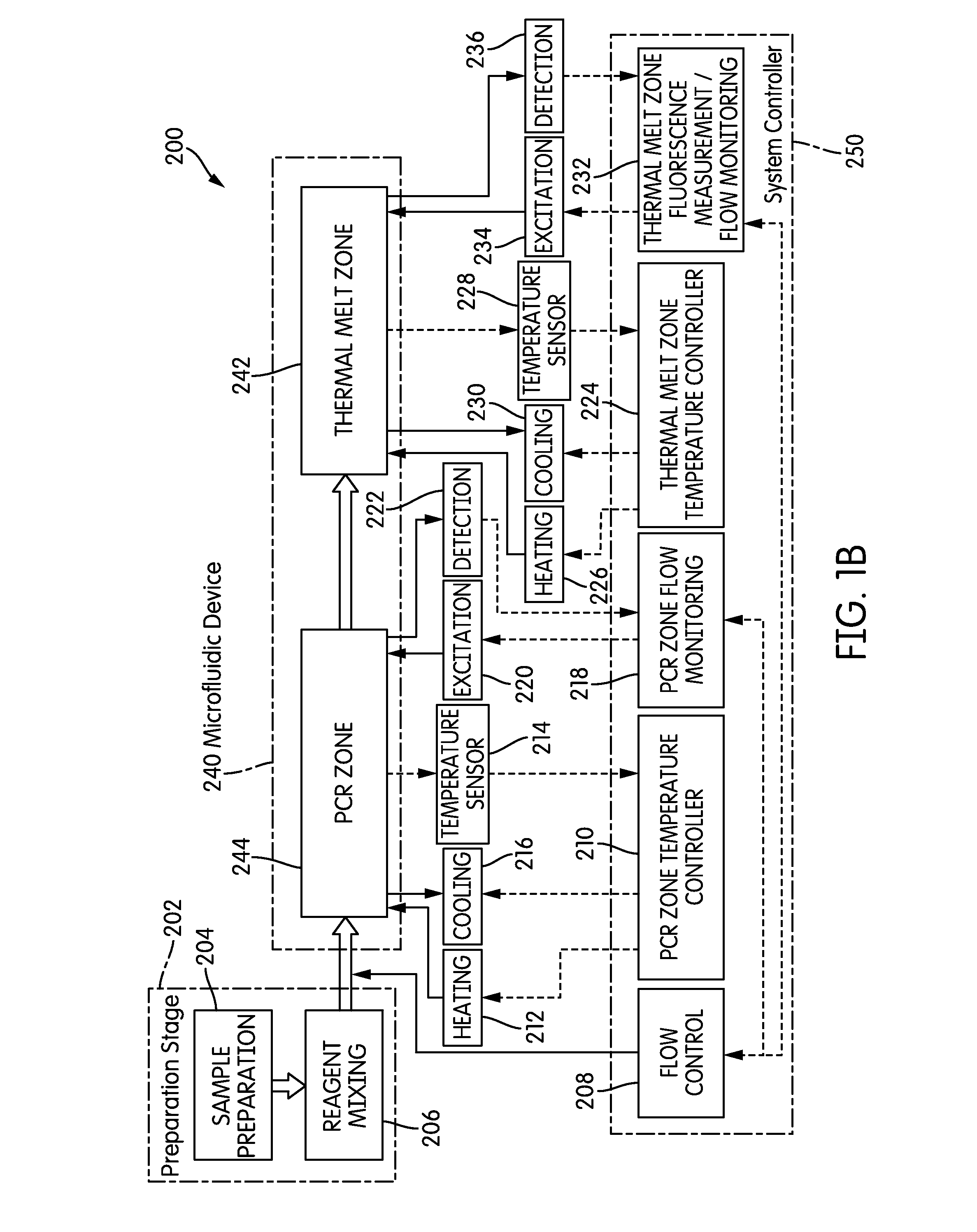
System and method for heating, cooling and heat cycling on microfluidic device
ActiveUS20050129582A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsThermoelectric coolingOn board
An integrated heat exchange system on a microfluidic card. According to one aspect of the invention, the portable microfluidic card has a heating, cooling and heat cycling system on-board such that the card can be used portably. The microfluidic card includes one or more reservoirs containing exothermic or endothermic material. Once the chemical process of the reservoir material is activated, the reservoir provides heat or cooling to specific locations of the microfluidic card. Multiple reservoirs may be included on a single card to provide varying temperatures. The assay chemicals can be moved to the various reservoirs to create a thermal cycle useful in many biological reactions, for example, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) or rtPCR. According to another aspect of the invention, the integrated heat exchanger is an adjacent microfluidic circuit containing fluid that is either independently heated or cooled, or is an exothermic or endothermic material, such that the fluid in the adjacent circuit imparts a change in temperature to the assay fluid in an independent circuit. According to yet another aspect of the invention, a thermal electric cooler (TEC) is used for thermocycling the amplification chamber of a disposable microfluidic card.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Automated sample-to-microarray system
InactiveUS20070092901A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLysisOligonucleotide
An apparatus having within or as part of a housing; a sample port; a microarray port; a lysis module; a purification module for containing a solid phase for binding of oligonucleotides; a thermocycling module for containing a polymerase chain reaction; a fragmentation module; and a microarray module for holding a microarray and a liquid in contact with the microarray. The apparatus is configured to be coupled to a device for: pumping a liquid through, in order, the lysis, purification, thermocycling, fragmentation, and microarray modules; sonicating any contents of the lysis module; thermocycling the thermocycling module to perform the polymerase chain reaction; heating the fragmentation module to fragment any oligonucleotides contained therein; circulating a fluid over the surface of the microarray; and performing one or more washing or staining steps on the microarray.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Varietal counting of nucleic acids for obtaining genomic copy number information
ActiveUS20140065609A1Microbiological testing/measurementHybridisationDistortionComputational biology
A method for obtaining from genomic material genomic copy number information unaffected by amplification distortion, comprising obtaining segments of the genomic material, tagging the segments with substantially unique tags to generate tagged nucleic acid molecules, such that each tagged nucleic acid molecule comprises one segment of the genomic material and a tag, subjecting the tagged nucleic acid molecules to polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, generating tag associated sequence reads by sequencing the product of the PCR reaction, assigning each tagged nucleic acid molecule to a location on a genome associated with the genomic material by mapping the subsequence of each tag associated sequence read corresponding to a segment of the genomic material to a location on the genome, and counting the number of tagged nucleic acid molecules assigned to the same location on the genome having a different tag, thereby obtaining genomic copy number information unaffected by amplification distortion.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
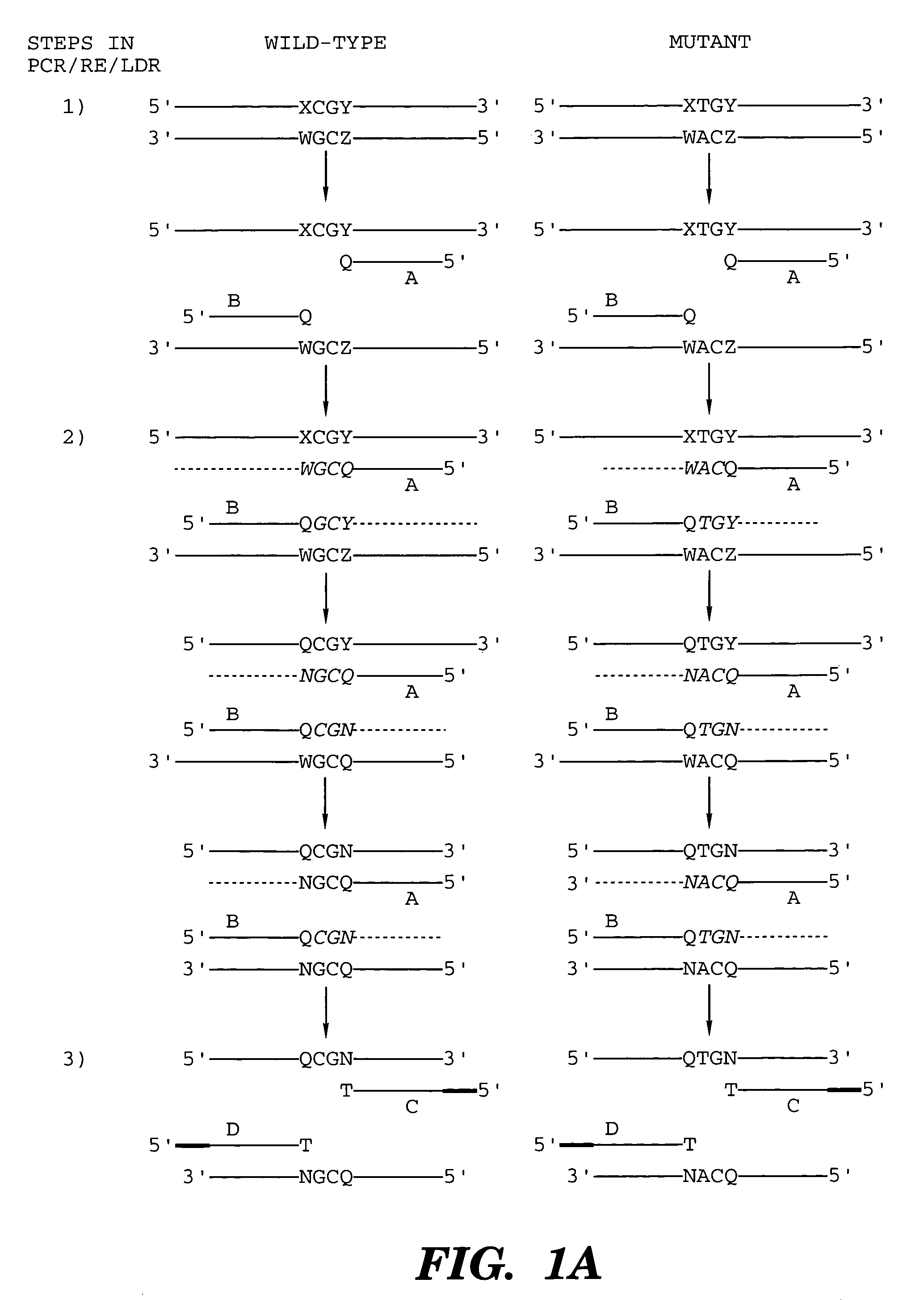
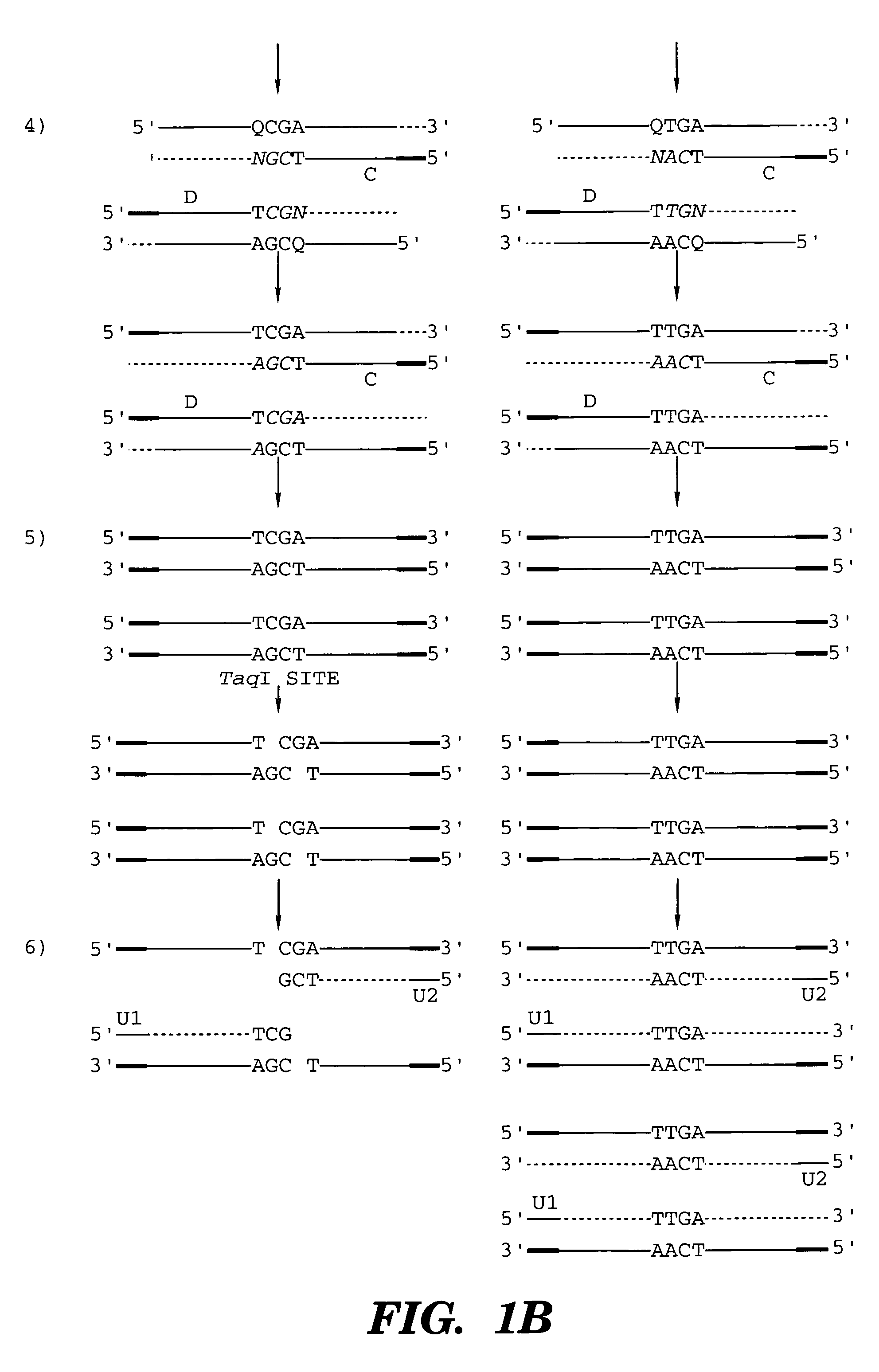
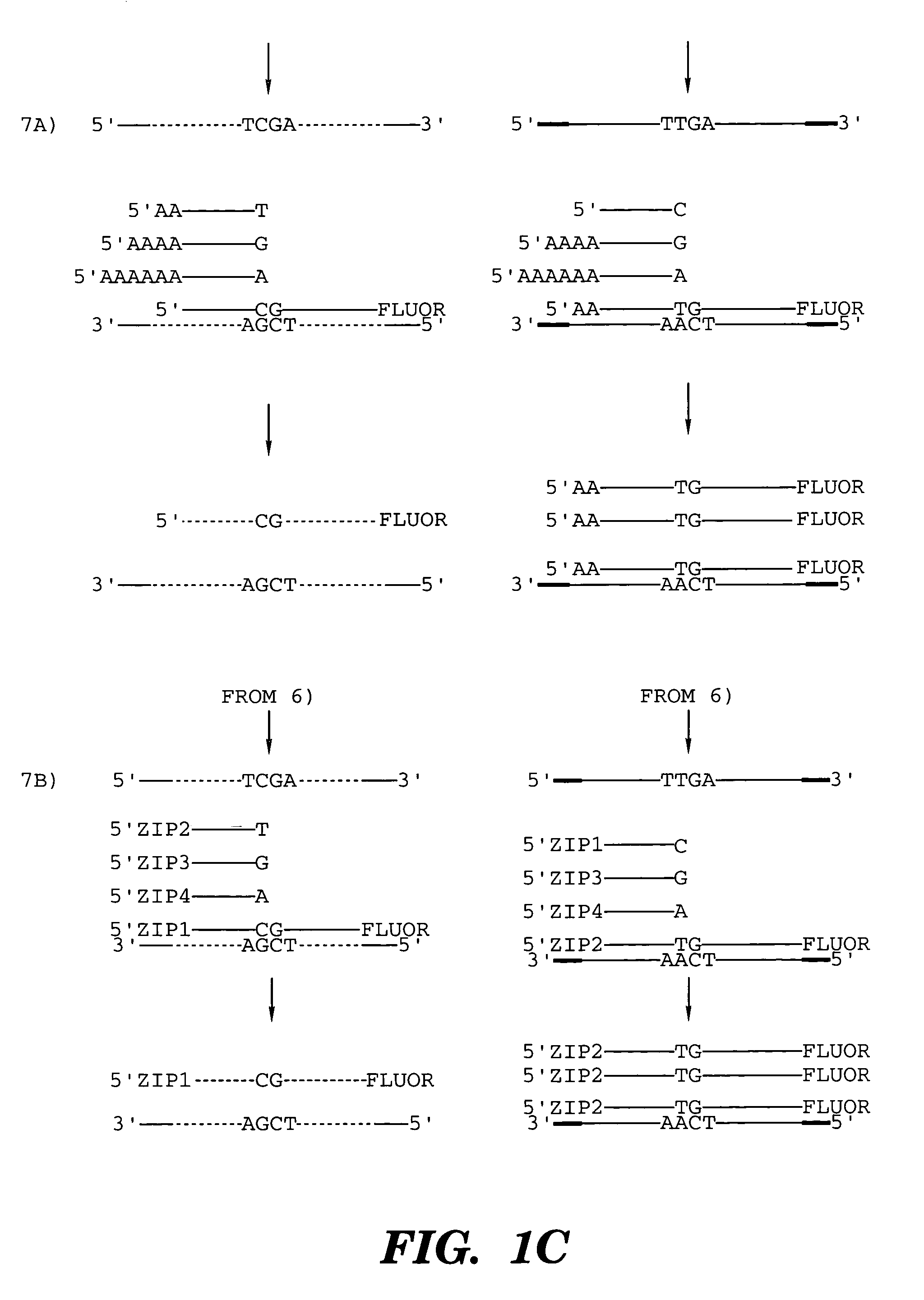
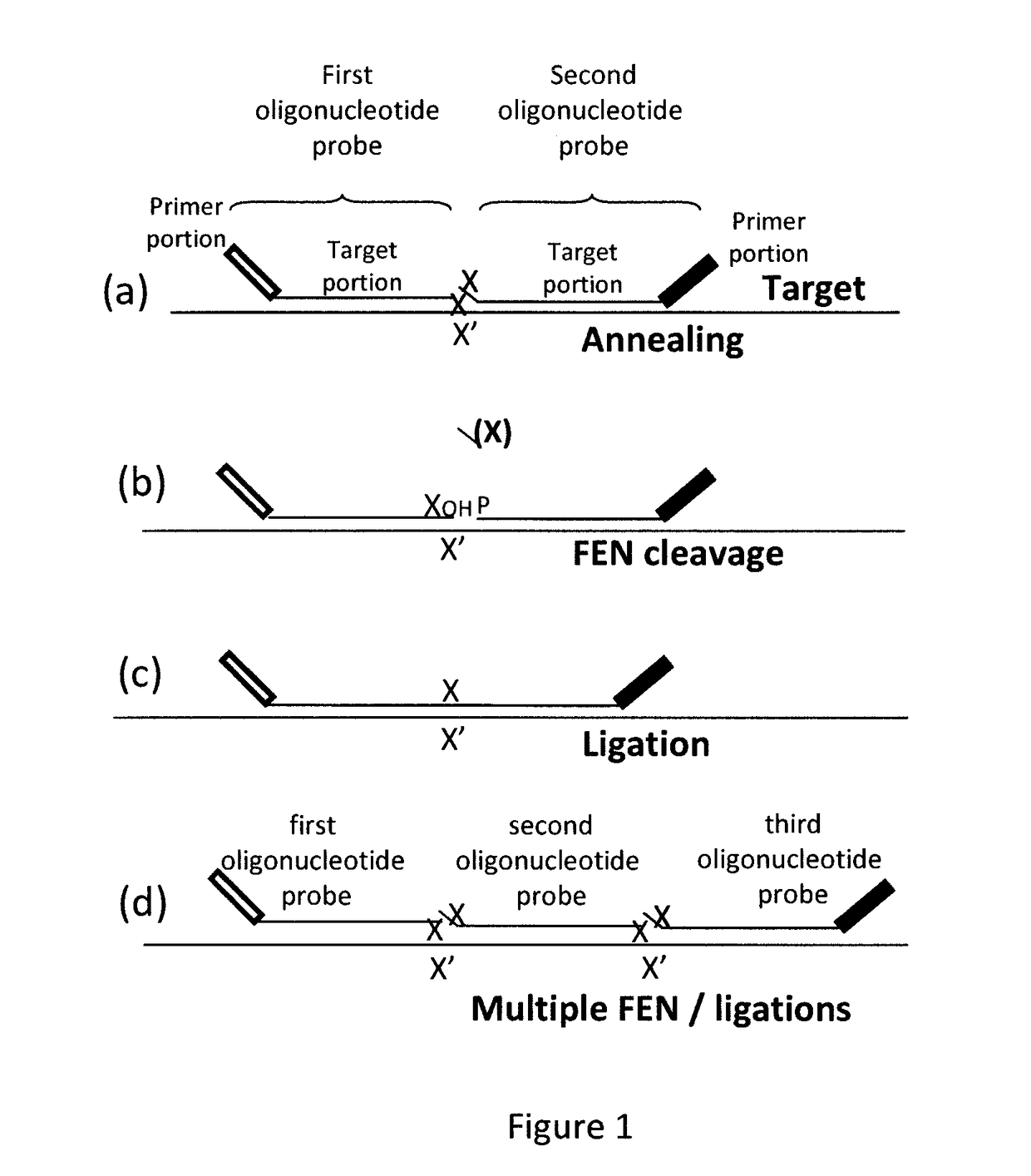
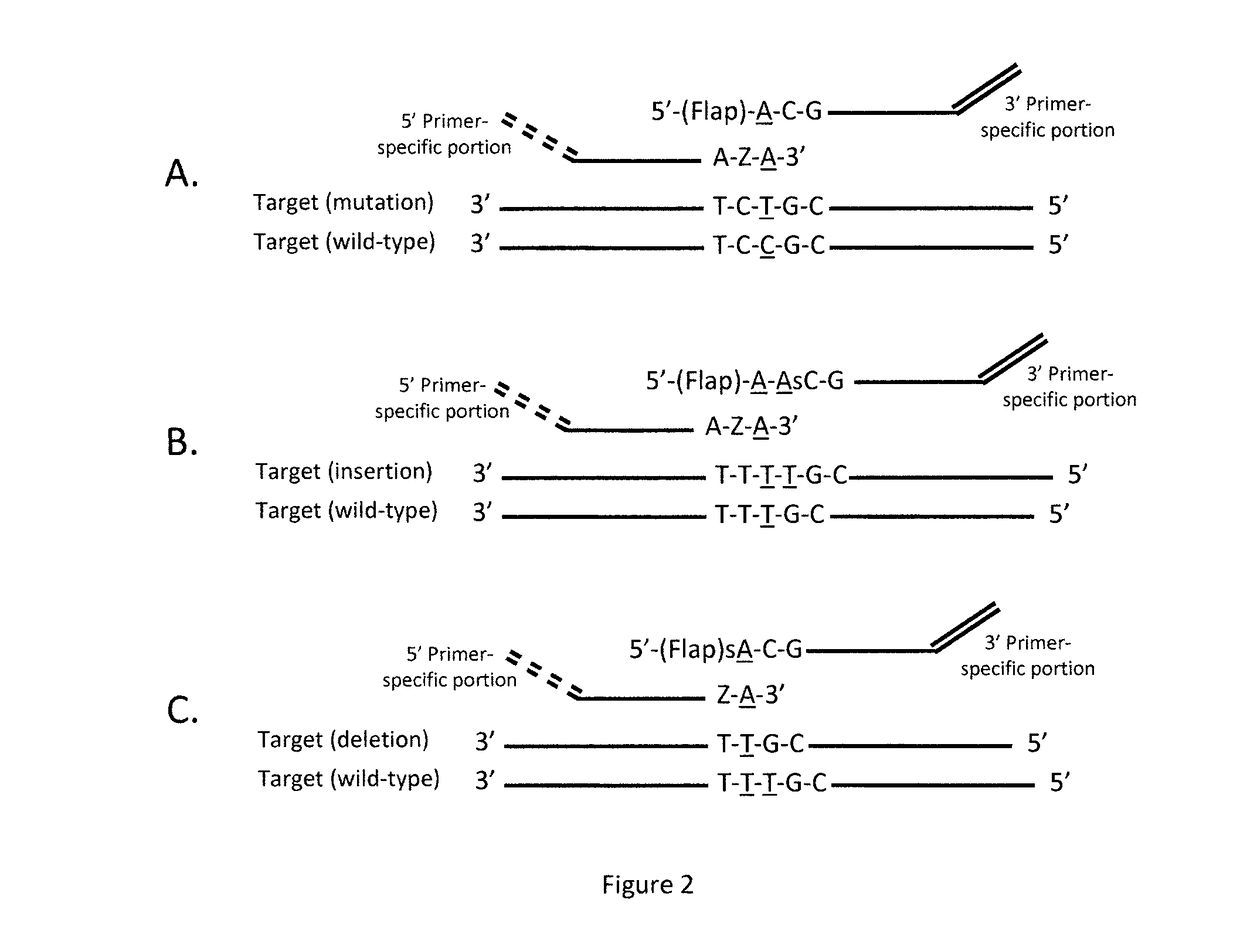
Coupled polymerase chain reaction-restriction-endonuclease digestion-ligase detection reaction process
InactiveUS7014994B1Sensitive highOptimizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideWild type
The present invention provides a method for identifying one or more low abundance sequences differing by one or more single-base changes, insertions, or deletions, from a high abundance sequence in a plurality of target nucleotide sequences. The high abundance wild-type sequence is selectively removed using high fidelity polymerase chain reaction analog conversion, facilitated by optimal buffer conditions, to create a restriction endonuclease site in the high abundance wild-type gene, but not in the low abundance mutant gene. This allows for digestion of the high abundance DNA. Subsequently the low abundant mutant DNA is amplified and detected by the ligase detection reaction assay. The present invention also relates to a kit for carrying out this procedure.
Owner:LOUISIANA STATE UNIV +1
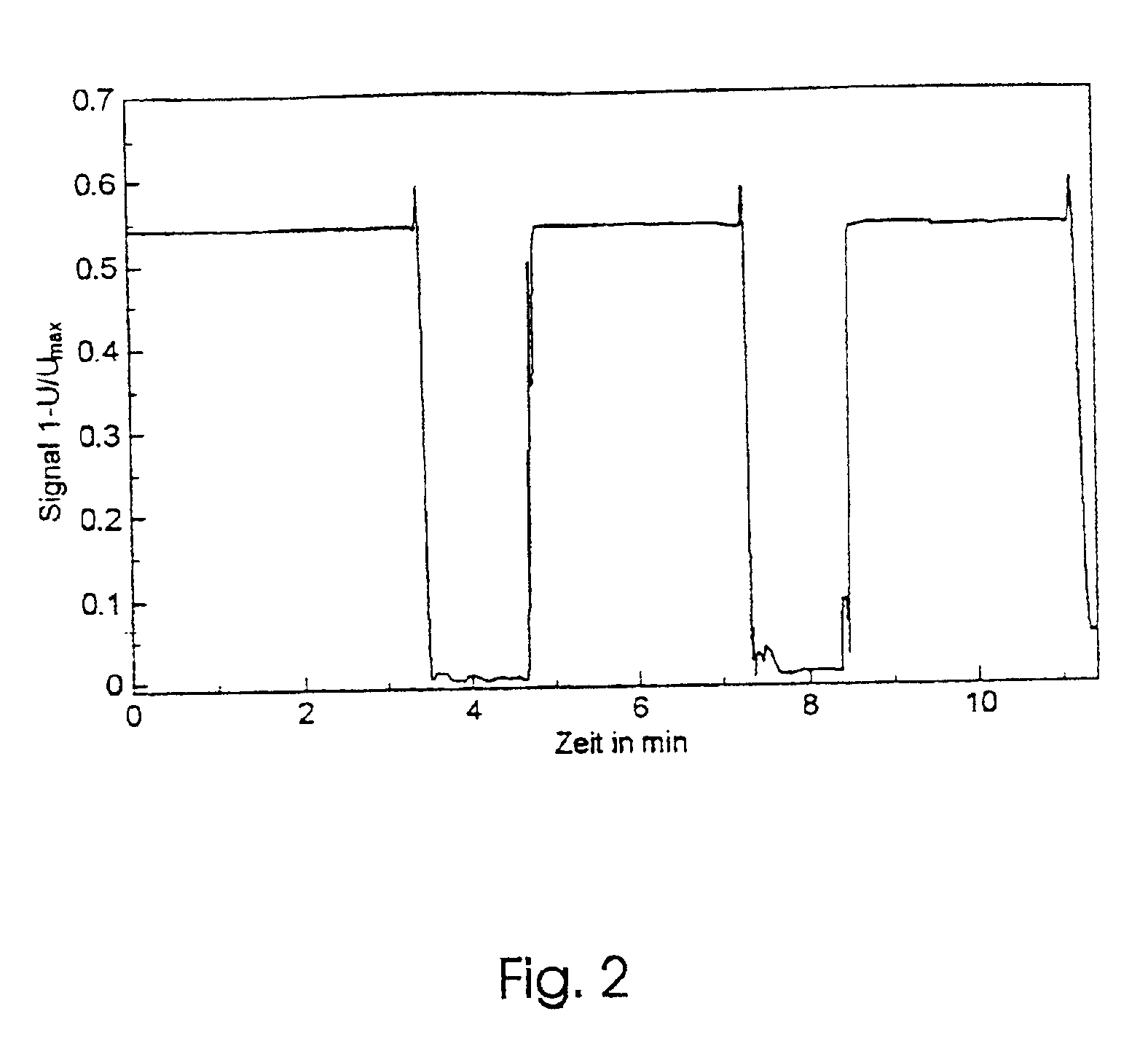
Method and a device for monitoring nucleic acid amplification reactions
InactiveUS6310354B1Continuous measurementSimply performedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvetteMicroparticle
A method for quantitatively measuring nucleic acid amplification reactions, especially the polymerase chain reaction, employing microparticles as hybridization solid phase, a probe sequence labeled with a fluorescent label and a fluorescence detection system which is based on two-photon fluorescence excitation, contacting all the amplification reaction components and the solid phase simultaneously in a closed cuvette, performing the amplification reactions in the same cuvette, focusing a two-photon exciting laser beam into the cuvette during the amplification cycles and measuring the fluorescence signal emitted by the microparticles from one particle at a time when they randomly float through the focal volume of the laser beam. The features of this invention allow a method and device for performing a fast quantitative nucleic acid amplification assay of single or multiple target sequences in a very small closed sample volume.
Owner:SOINI ERKKI
Devices and methods for the performance of miniaturized in vitro amplification assays
InactiveUS20040259237A1Temperature controlEfficient use ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayBiomedical engineering
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for performing microanalytic and microsynthetic analyses and procedures. The invention provides a microsystem platform and a micromanipulation device for manipulating the platform that utilizes the centripetal force resulting from rotation of the platform to motivate fluid movement through microchannels. The invention specifically provides devices and methods for performing miniaturized in vitro amplification assays such as the polymerase chain reaction. Methods specific for the apparatus of the invention for performing PCR are provided.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
Method for multiplexed nucleic acid patch polymerase chain reaction
ActiveUS20120289414A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Use of uracil-DNA glycosylase in genetic analysis
InactiveUS6090553AImprove hybridization efficiencyIntensity of signal may decreaseHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic analysisPolymerase chain reaction
The present invention relates to a process for detecting the presence of at least one specific nucleic acid sequence in a sample containing a nucleic acid or a mixture of nucleic acids by amplifying the nucleic acid using polymerase chain reaction, cleaving the amplified products with uracil DNA glycosylase to obtain short DNA segments and detecting the DNA fragments by using reverse blot hybridization.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
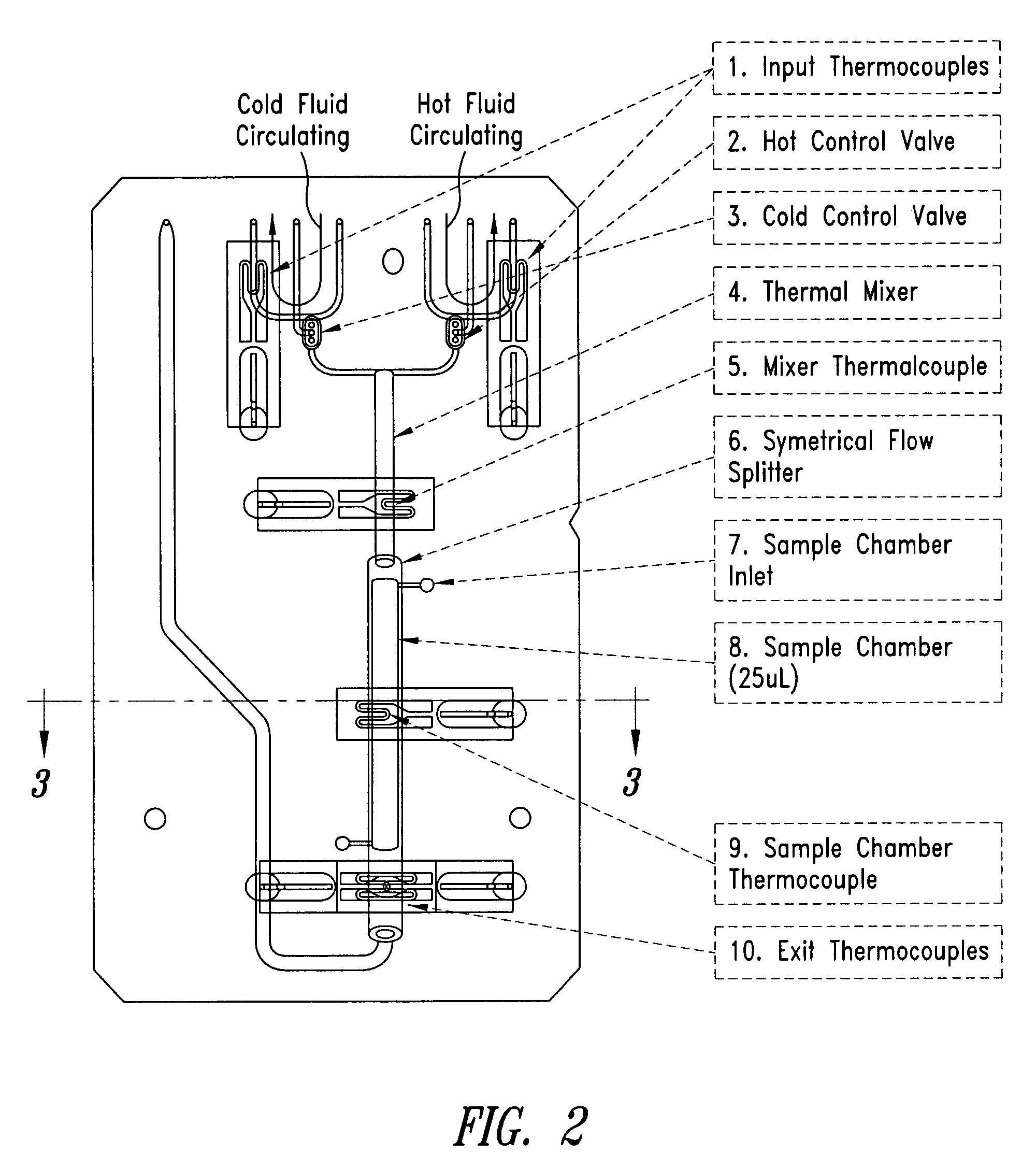
System and method for heating, cooling and heat cycling on microfluidic device
ActiveUS7544506B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusThermoelectric coolingOn board
An integrated heat exchange system on a microfluidic card. According to one aspect of the invention, the portable microfluidic card has a heating, cooling and heat cycling system on-board such that the card can be used portably. The microfluidic card includes one or more reservoirs containing exothermic or endothermic material. Once the chemical process of the reservoir material is activated, the reservoir provides heat or cooling to specific locations of the microfluidic card. Multiple reservoirs may be included on a single card to provide varying temperatures. The assay chemicals can be moved to the various reservoirs to create a thermal cycle useful in many biological reactions, for example, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) or rtPCR. According to another aspect of the invention, the integrated heat exchanger is an adjacent microfluidic circuit containing fluid that is either independently heated or cooled, or is an exothermic or endothermic material, such that the fluid in the adjacent circuit imparts a change in temperature to the assay fluid in an independent circuit. According to yet another aspect of the invention, a thermal electric cooler (TEC) is used for thermocycling the amplification chamber of a disposable microfluidic card.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
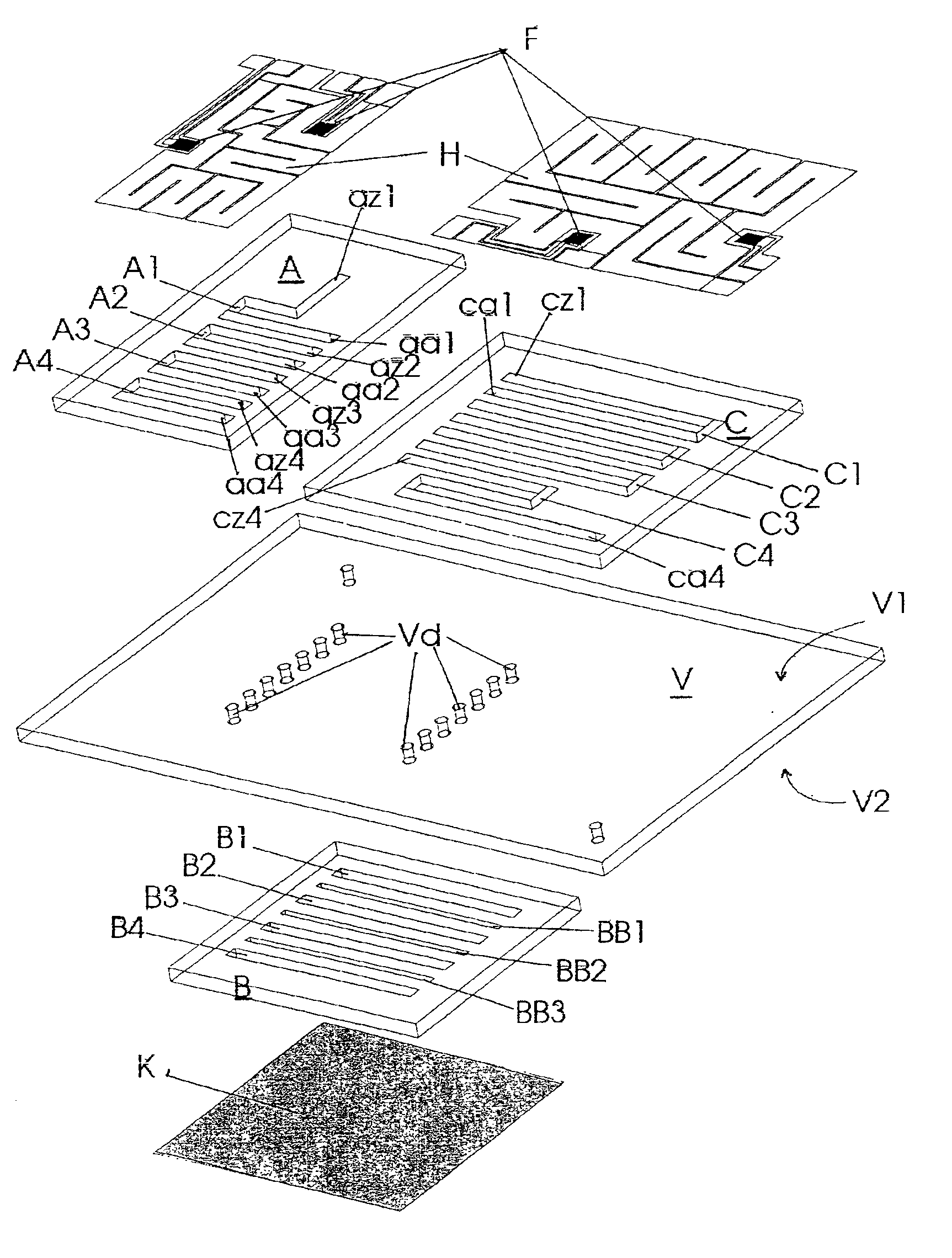
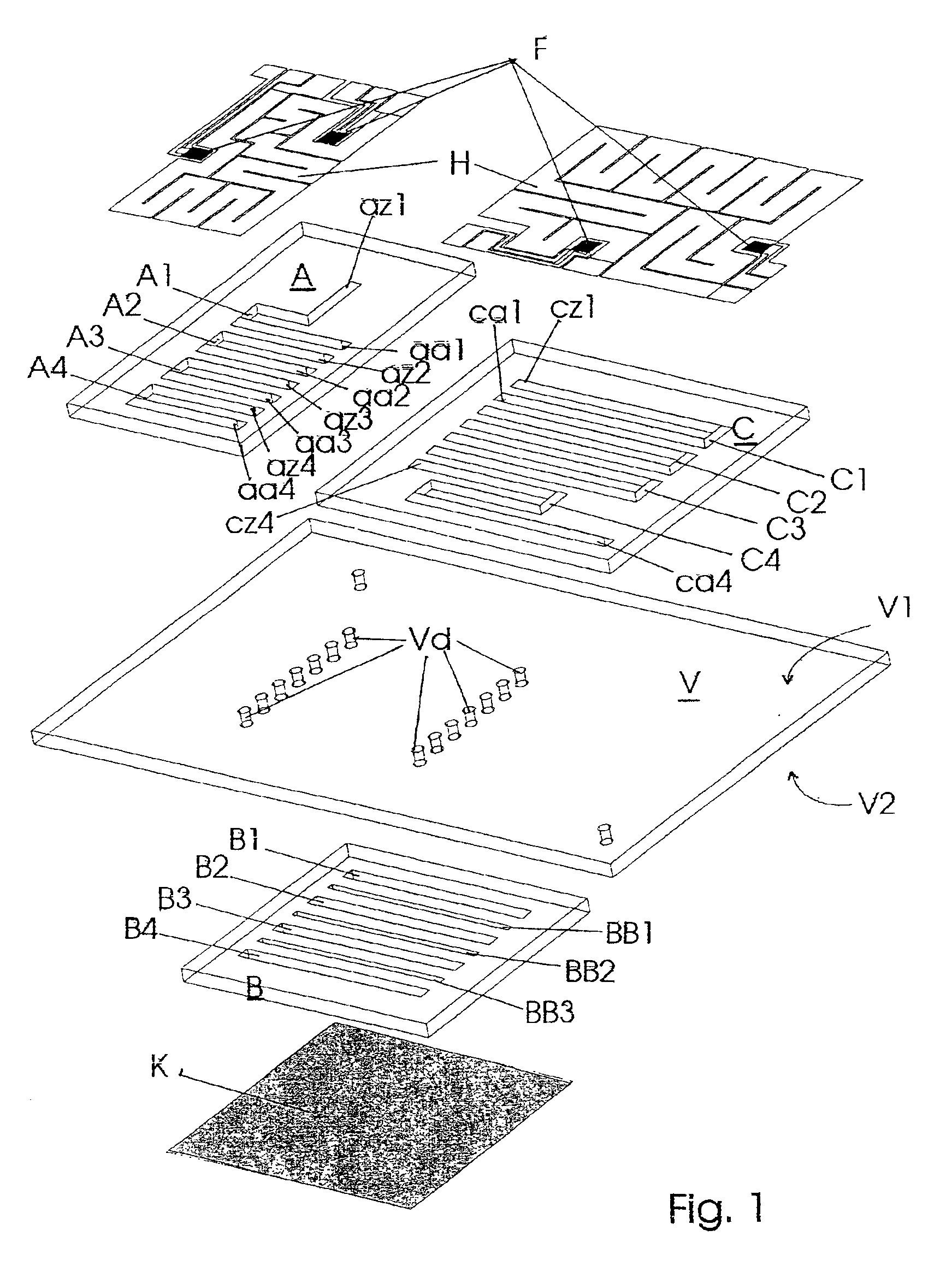
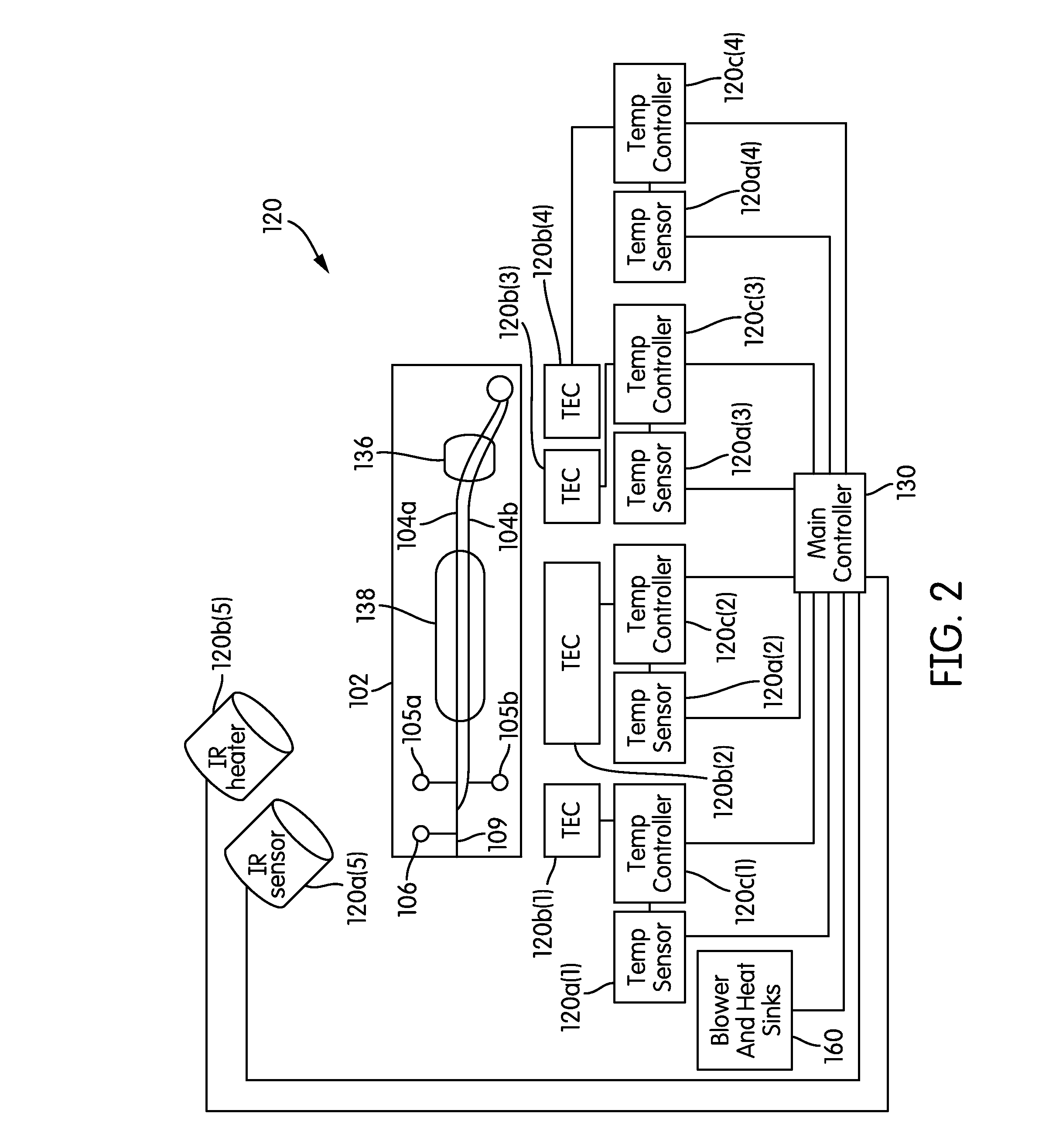
Miniaturized temperature-zone flow reactor
InactiveUS6896855B1Efficient executionHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementMiniaturizationPartial path
A miniaturized temperature-zone flow reactor, used for thermally controlled biochemical or molecular-biological processes, especially polymerase chain reaction (PCR) enables more efficient reactions by providing at least one closed flow path which is divided into three partial paths (A1 . . . An; B1 . . . Bn and BB1 . . . BBn−1; C1 . . . Cn) with the reactor having three substrate chips (A; B; C) which are made of a material having a high heat conductivity, and which have defined channel sections that are spaced apart relative to each other, and are connected by a connecting chip (V) made of a poor heat-conductive material. The substrate chips (A; B; C) are maintained at different temperatures by various means, including the use of controlling heating elements in contact with the chips.
Owner:INSTITUT FUER PHYSIKALISCHE HOCHTECH
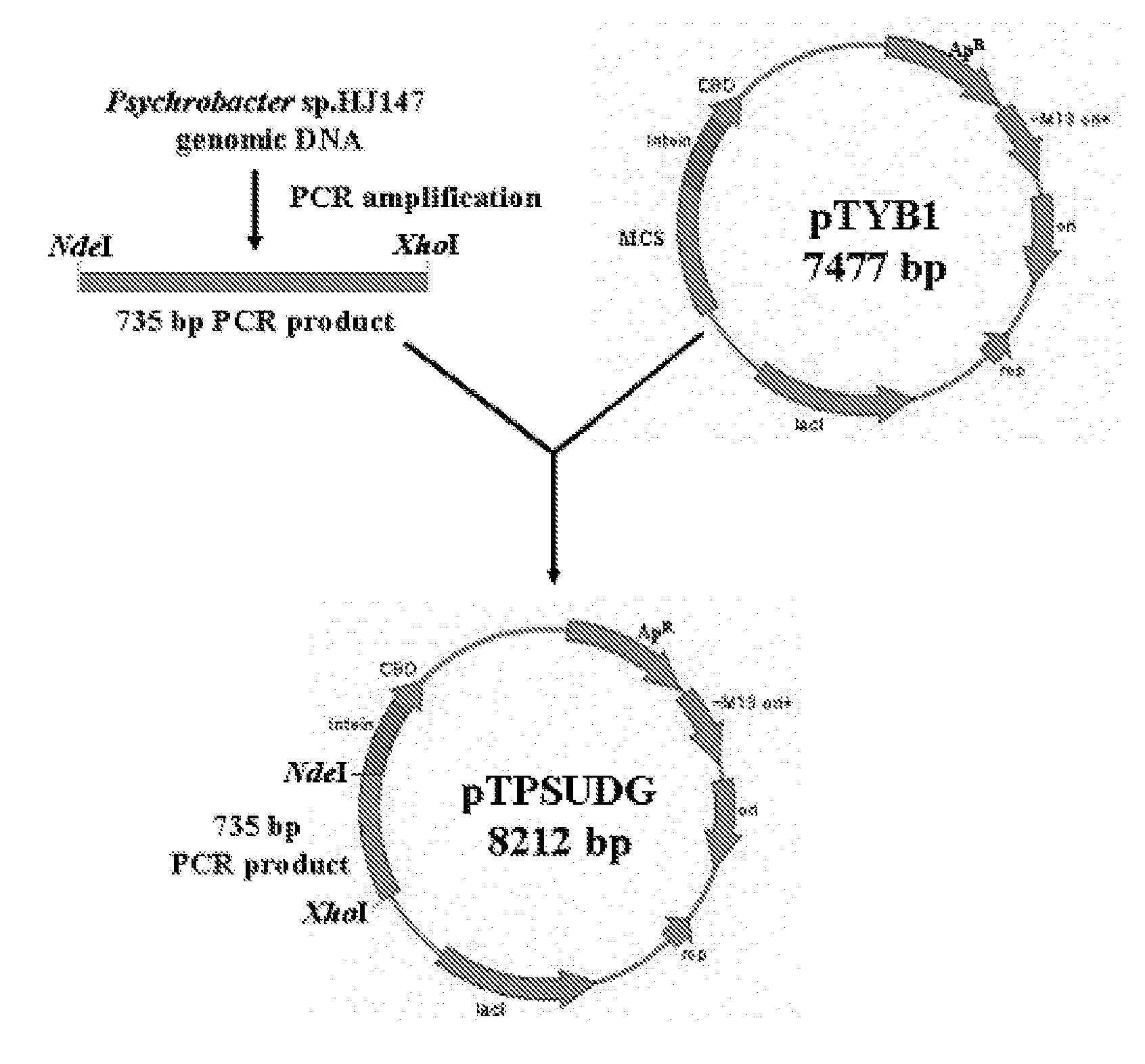
Uracil-DNA glycosylase of psychrobacter sp. HJ147 and use thereof
ActiveUS20080299609A1Eliminating contamination carry-overEliminating cross contaminationBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coliPsychrobacter sp.
The present invention provides uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) gene originating from Psychrobacter sp. HJ147, and amino acid sequences deduced from the gene; expression and purification of Psp HJ147 UDG gene in Escherichia coli; and characterization of UDG obtained therefrom, and the use thereof in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The UDG according to the present invention has a specific activity of excising uracil bases in a uracil-containing DNA substrates at a low temperature, and is easily heat-inactivated. It thus can effectively eliminate cross contamination and carry-over contamination of PCR templates often occurring after a PCR process using dUTP. Therefore, it is useful for increasing preciseness (elimination of false positives), purity and amplification efficiency of PCR.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Gene expression profiles to predict breast cancer outcomes
ActiveUS20110145176A1Evaluating prognosisEvaluating treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDigital computer detailsTreatment optionsIntrinsics
Methods for classifying and for evaluating the prognosis of a subject having breast cancer are provided. The methods include prediction of breast cancer subtype using a supervised algorithm trained to stratify subjects on the basis of breast cancer intrinsic subtype. The prediction model is based on the gene expression profile of the intrinsic genes listed in Table 1. This prediction model can be used to accurately predict the intrinsic subtype of a subject diagnosed with or suspected of having breast cancer. Further provided are compositions and methods for predicting outcome or response to therapy of a subject diagnosed with or suspected of having breast cancer. These methods are useful for guiding or determining treatment options for a subject afflicted with breast cancer. Methods of the invention further include means for evaluating gene expression profiles, including microarrays and quantitative polymerase chain reaction assays, as well as kits comprising reagents for practicing the methods of the invention.
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA CANCER AGENCY BRANCH +3
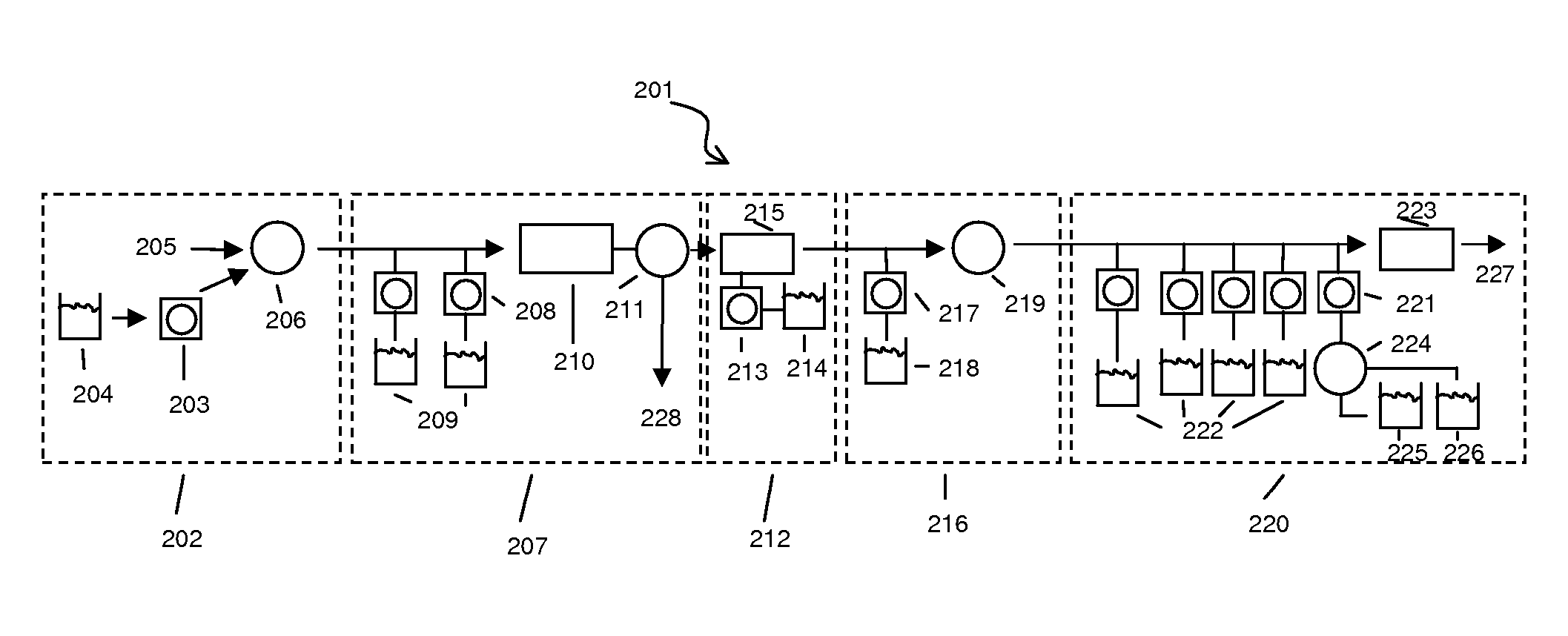
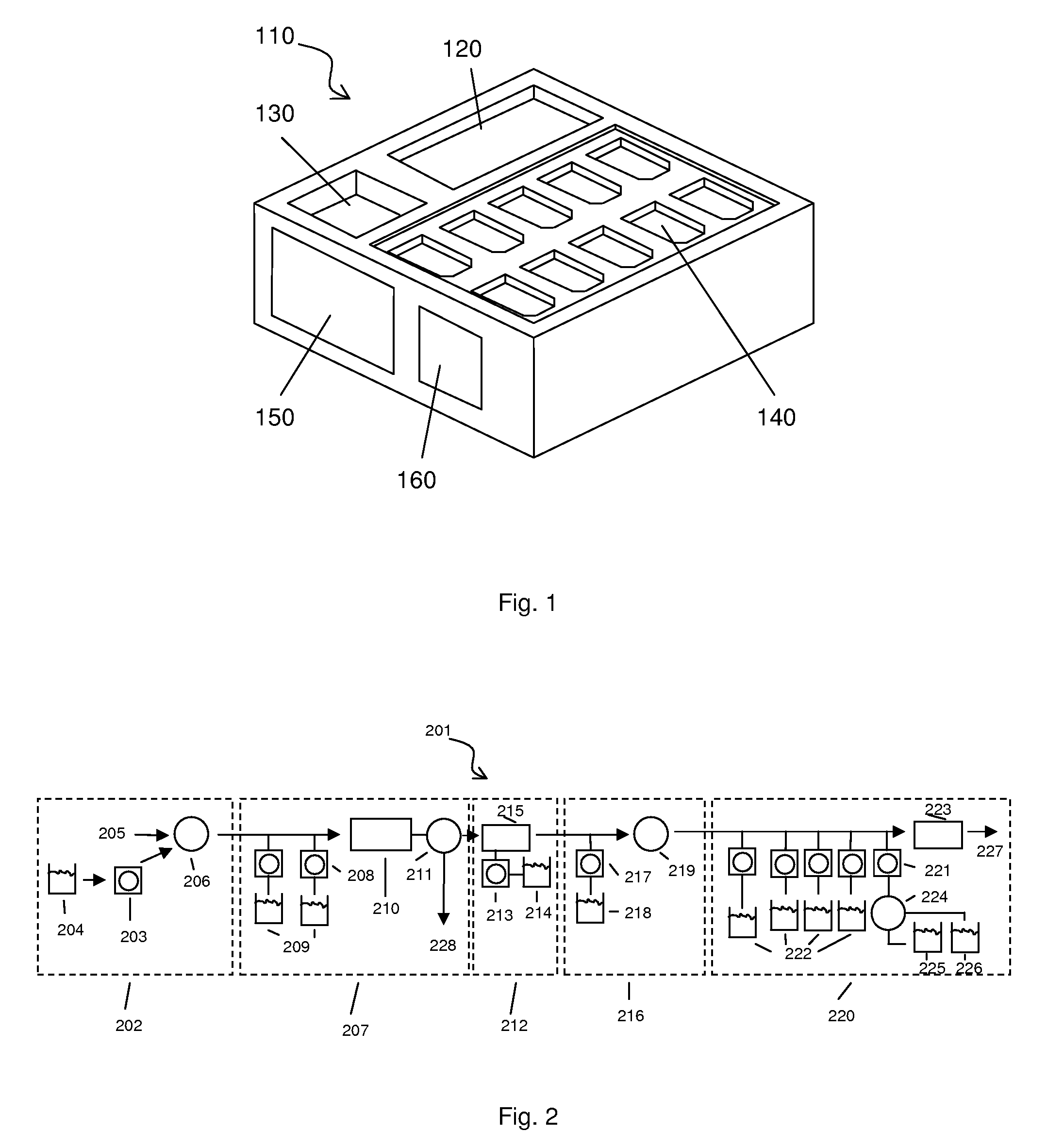
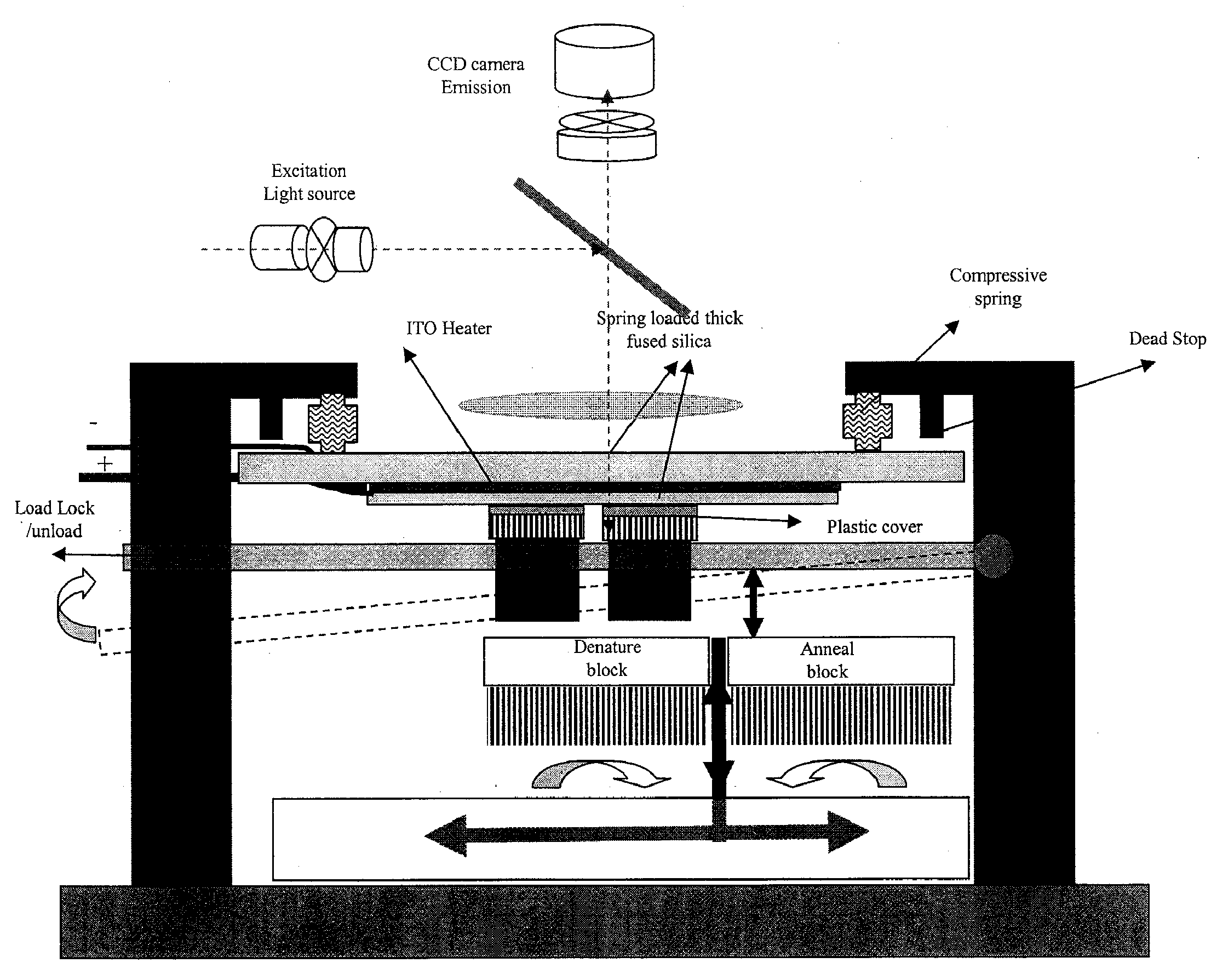
System and method for serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS20120052560A1Rapid serial processingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHandling systemData store
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays. More particularly, the present invention provides for the real time processing of nucleic acid during polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and thermal melt applications. According to an aspect of the invention, a system for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays is provided. In one embodiment, the system includes, but is not limited to: a microfluidic cartridge having microfluidic (flow-through) channels, a fluorescence imaging system, a temperature measurement and control system; a pressure measurement and control system for applying variable pneumatic pressures to the microfluidic cartridge; a storage device for holding multiple reagents (e.g., a well-plate); a liquid handling system comprising at least one robotic pipettor for aspirating, mixing, and dispensing reagent mixtures to the microfluidic cartridge; systems for data storage, processing, and output; and a system controller to coordinate the various devices and functions.
Owner:CANON USA
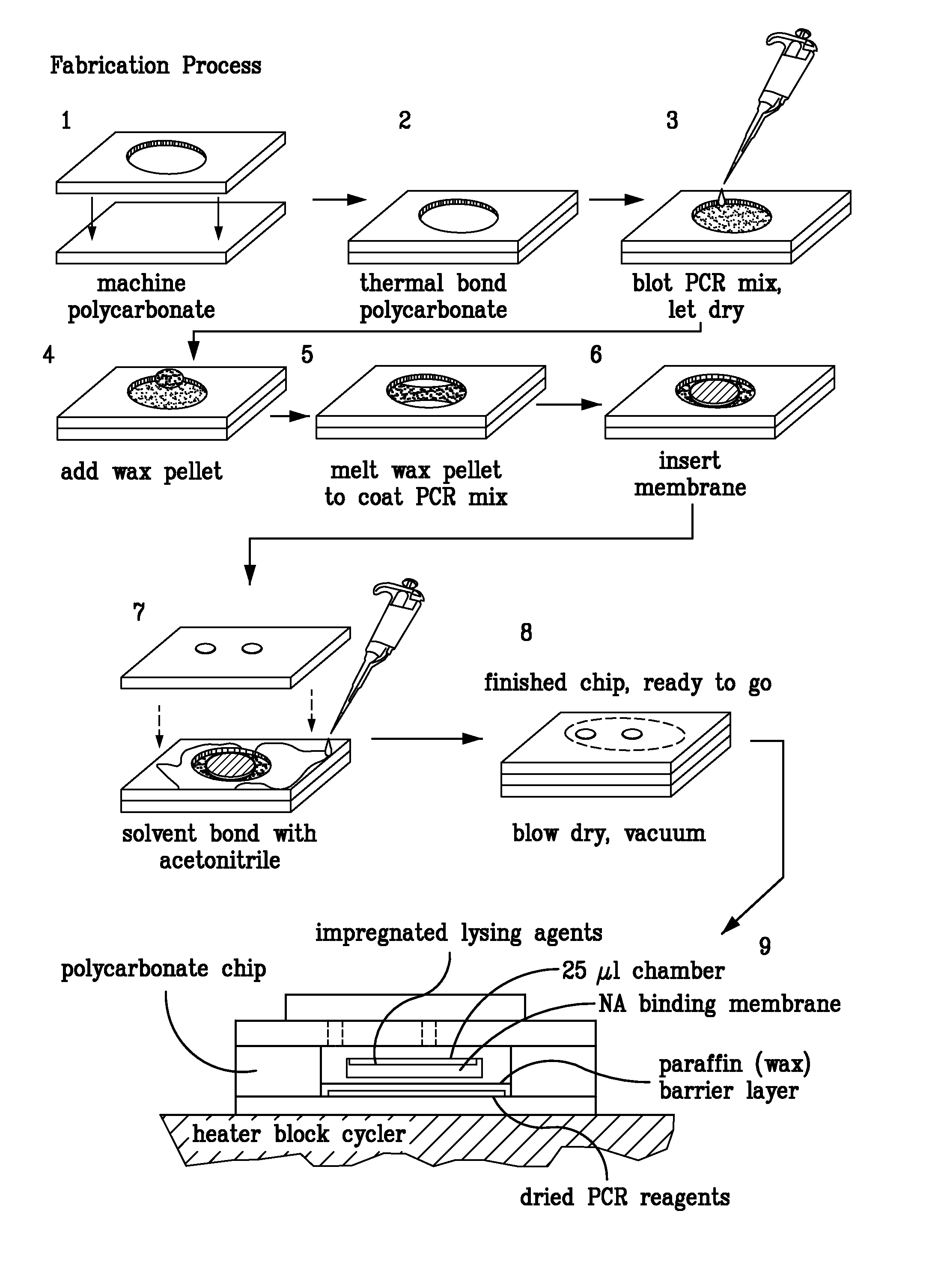
Integrated PCR Reactor for Cell Lysis, Nucleic Acid Isolation and Purification, and Nucleic Acid Amplication Related Applications
ActiveUS20090186357A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle vesselLysis
Disclosed are integrated devices capable of performing a polymerase chain reaction within a single vessel. Also disclosed are related methods of sample analysis.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Apparatus for high throughput chemical reactions
ActiveUS20080176290A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical reactionReaction temperature
Apparatus, systems, chips, and methods of performing a large number of simultaneous chemical reactions are provided herein. The chips of the invention comprise addressable units that can be addressed according to the temperature of the reaction to be run. The subject apparatus, systems, and chips are particularly suited for performing polymerase chain reactions on thousands of nucleic acid sequences, up to and including sequences of an entire genome of an organism of interest.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
Microfluidic analysis system
ActiveUS7622076B2Avoid contactBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusEngineeringCarrier fluid
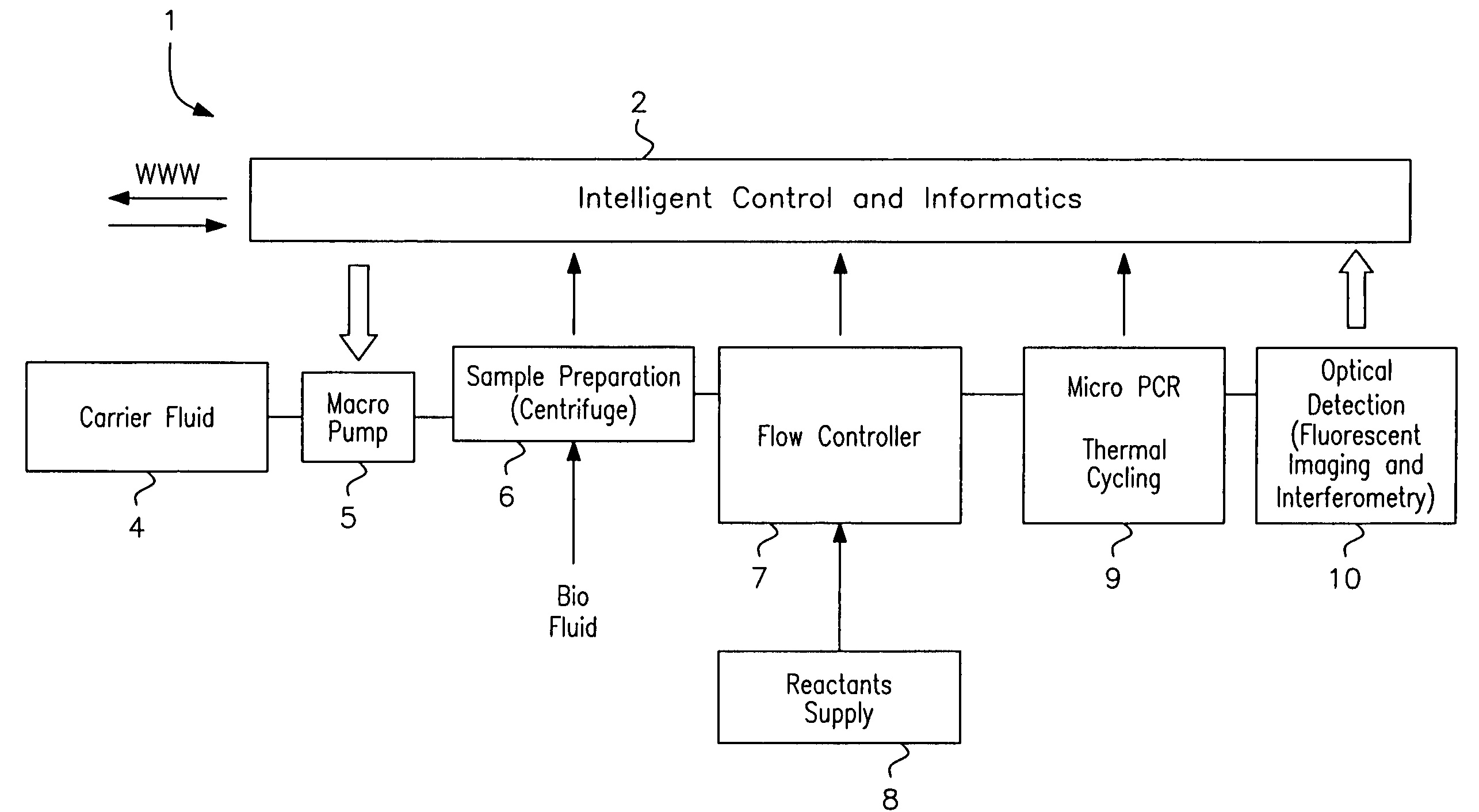
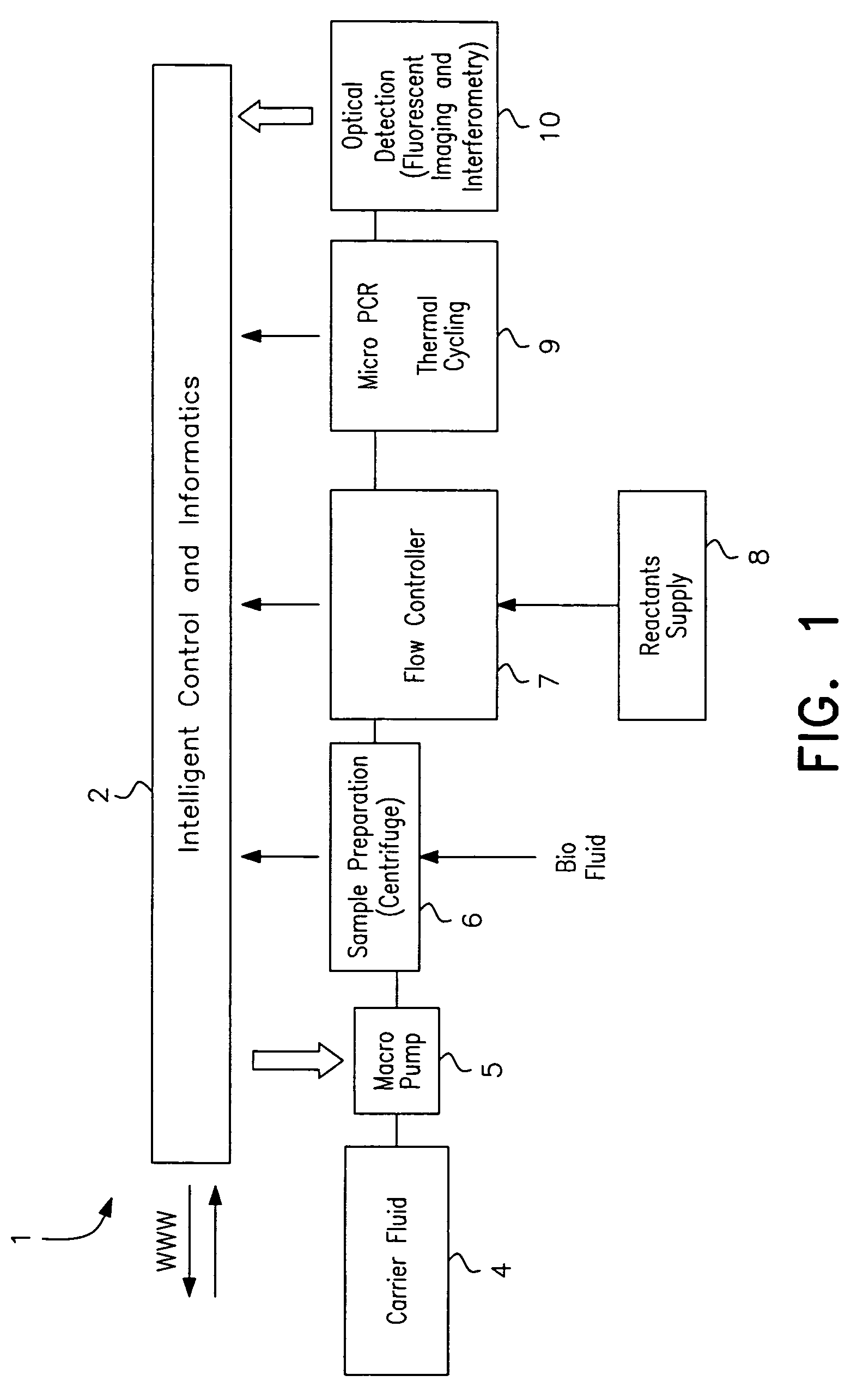
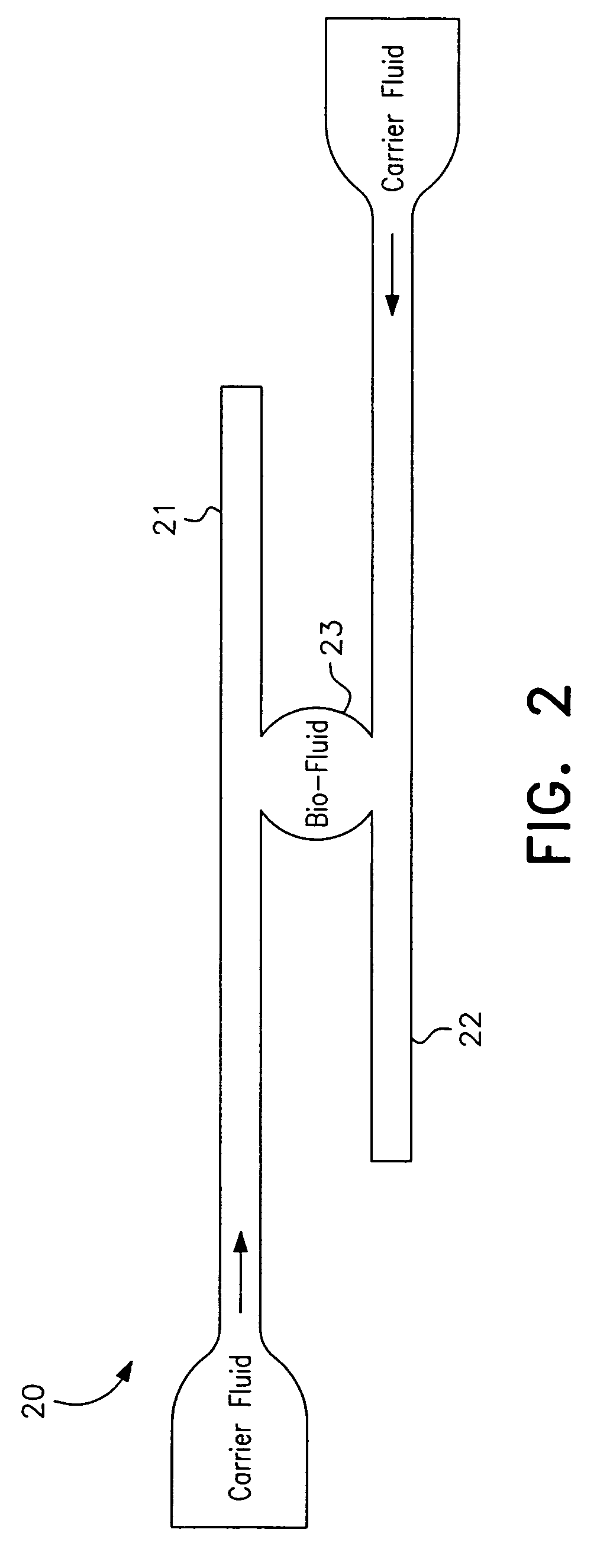
A microfluidic analysis system (1) performs polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis on a bio sample. In a centrifuge (6) the sample is separated into DNA and RNA constituents. The vortex is created by opposing flow of a silicon oil primary carrier fluid effecting circulation by viscous drag. The bio sample exits the centrifuge enveloped in the primary carrier fluid. This is pumped by a flow controller (7) to a thermal stage (9). The thermal stage (9) has a number of microfluidic devices (70) each having thermal zones (71, 72, 73) in which the bio sample is heated or cooled by heat conduction to / from a thermal carrier fluid and the primary carrier fluid. Thus, the carrier fluids envelope the sample, control its flowrate, and control its temperature without need for moving parts at the micro scale.
Owner:STOKES BIO LTD
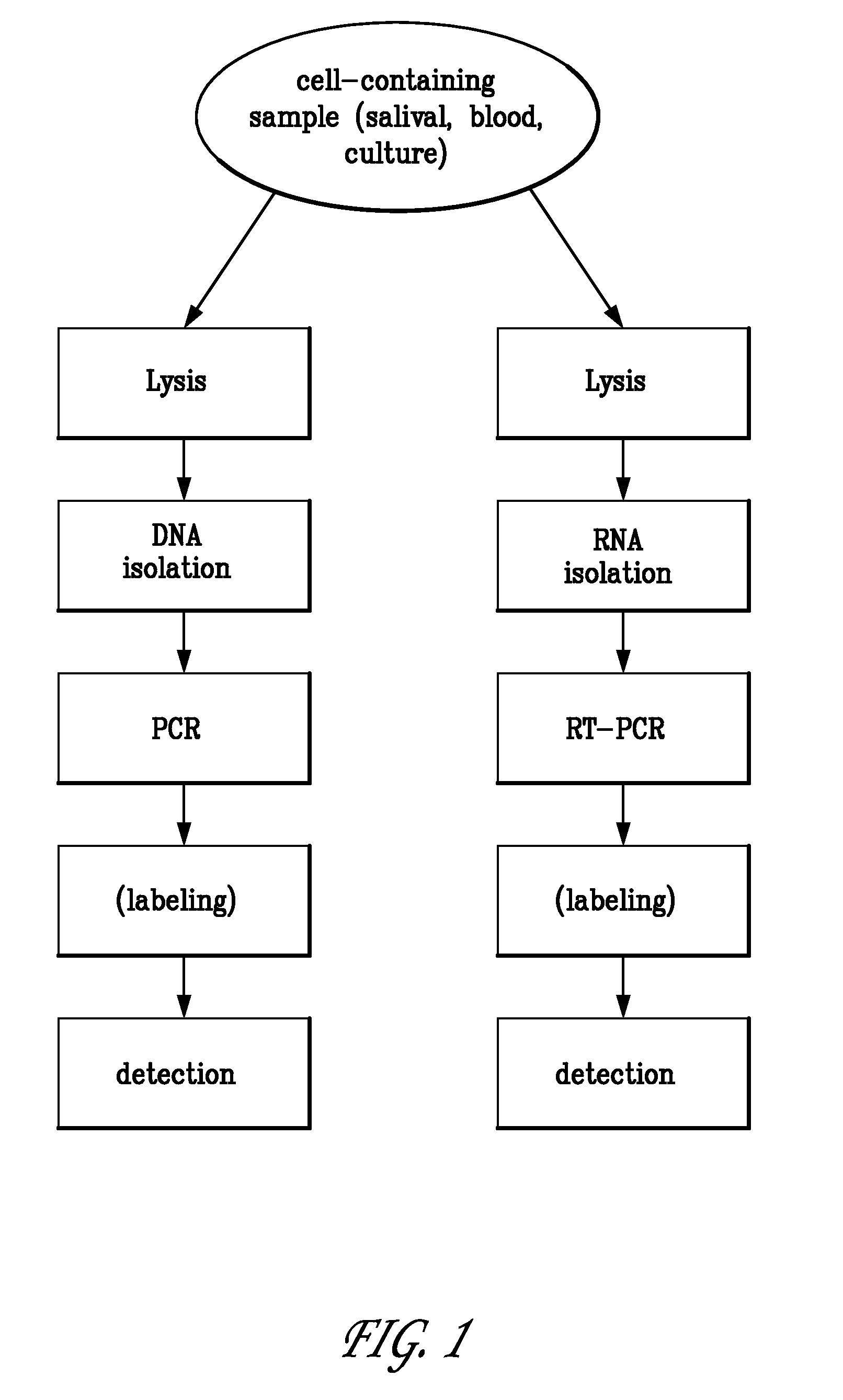
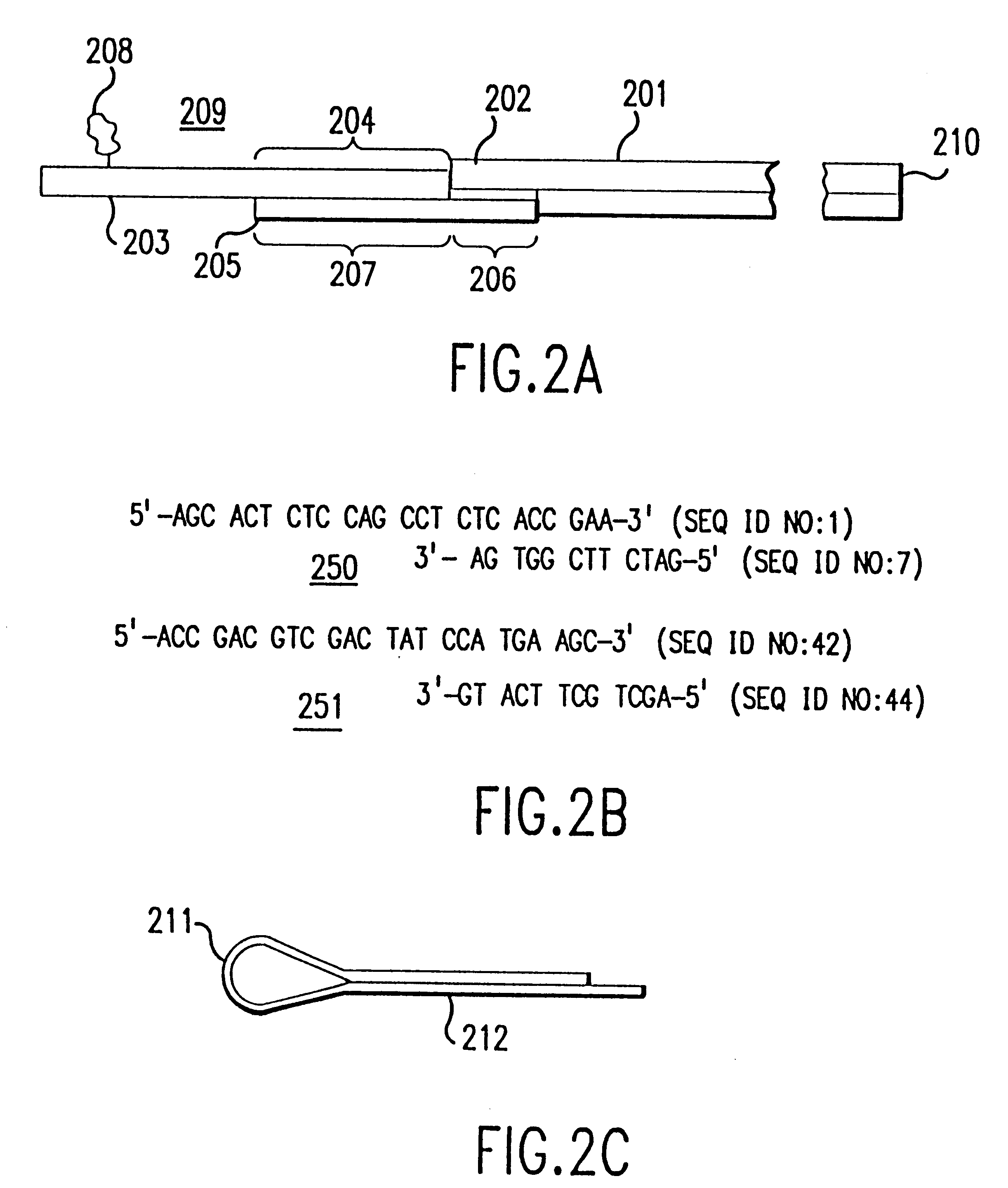
Method and apparatus for identifying classifying or quantifying DNA sequences in a sample without sequencing
InactiveUS6141657ARapid and economical and quantitative and precise determination and classificationSufficient discrimination and resolutionData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSequence databaseDNA Sequence Databases
This invention provides methods by which biologically derived DNA sequences in a mixed sample or in an arrayed single sequence clone can be determined and classified without sequencing. The methods make use of information on the presence of carefully chosen target subsequences, typically of length from 4 to 8 base pairs, and preferably the length between target subsequences in a sample DNA sequence together with DNA sequence databases containing lists of sequences likely to be present in the sample to determine a sample sequence. The preferred method uses restriction endonucleases to recognize target subsequences and cut the sample sequence. Then carefully chosen recognition moieties are ligated to the cut fragments, the fragments amplified, and the experimental observation made. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the preferred method of amplification. Another embodiment of the invention uses information on the presence or absence of carefully chosen target subsequences in a single sequence clone together with DNA sequence databases to determine the clone sequence. Computer implemented methods are provided to analyze the experimental results and to determine the sample sequences in question and to carefully choose target subsequences in order that experiments yield a maximum amount of information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
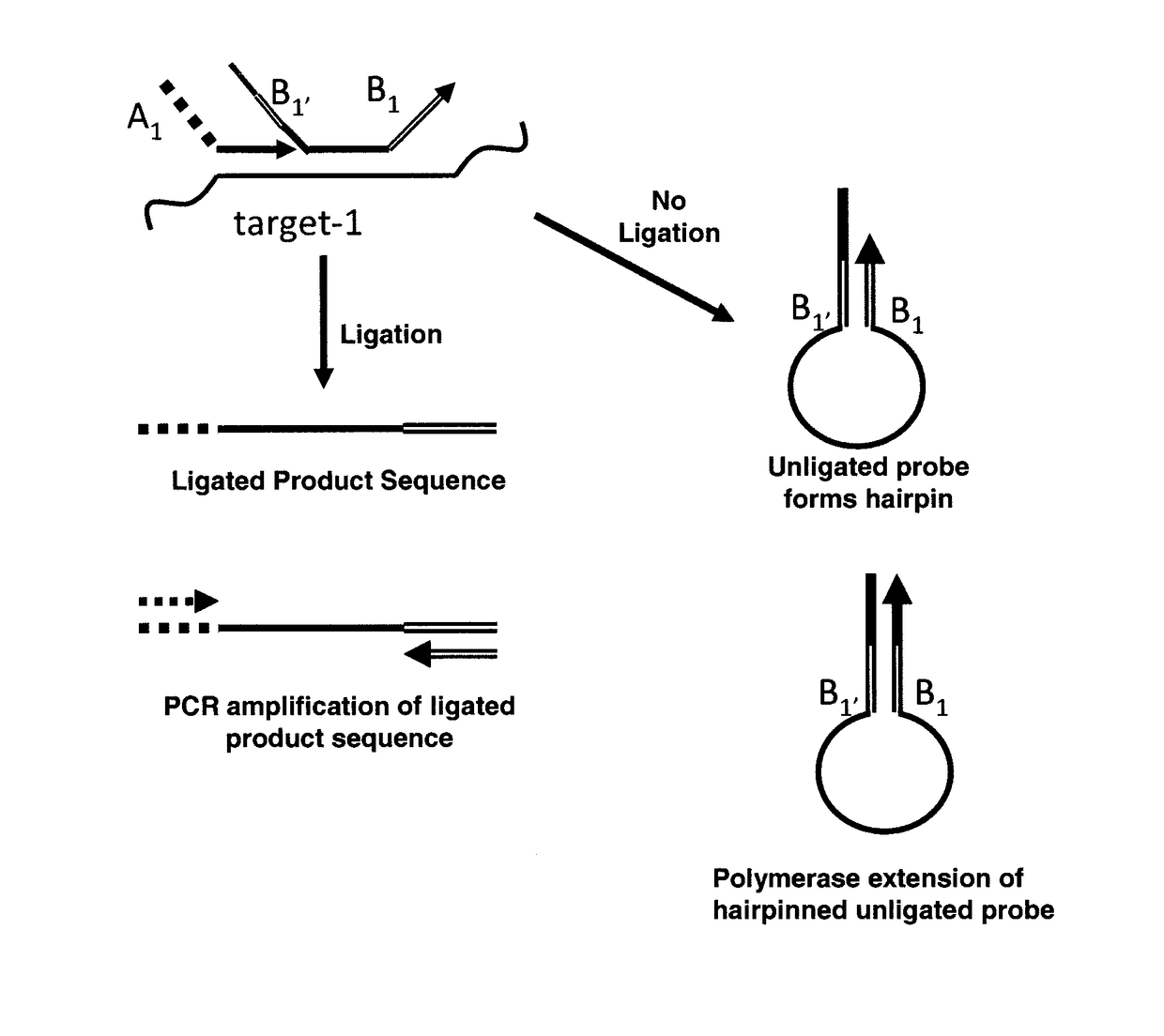
Method for relative quantification of nucleic acid sequence, expression, or copy changes, using combined nuclease, ligation, and polymerase reactions
ActiveUS9598728B2Reduce amountIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to methods for identifying the presence of one or more target nucleotide sequences in a sample that involve a nuclease-ligation reaction. In some embodiments, the ligation products formed in the nuclease-ligation process of the present invention are subsequently amplified using a polymerase chain reaction. The ligated product sequences or extension products thereof are detected, and the presence of one or more target nucleotide sequences in the sample is identified based on the detection.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for identifying, classifying, or quantifying DNA sequences in a sample without sequencing
InactiveUS6418382B2Rapid and economical and quantitative and precise determination and classificationSufficient discrimination and resolutionData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementSample sequenceSingle sequence
This invention provides methods by which biologically derived DNA sequences in a mixed sample or in an arrayed single sequence clone can be determined and classified without sequencing. The methods make use of information on the presence of carefully chosen target subsequences, typically of length from 4 to 8 base pairs, and preferably the length between target subsequences in a sample DNA sequence together with DNA sequence databases containing lists of sequences likely to be present in the sample to determine a sample sequence. The preferred method uses restriction endonucleases to recognize target subsequences and cut the sample sequence. Then carefully chosen recognition moieties are ligated to the cut fragments, the fragments amplified, and the experimental observation made. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the preferred method of amplification. Another embodiment of the invention uses information on the presence or absence of carefully chosen target subsequences in a single sequence clone together with DNA sequence databases to determine the clone sequence. Computer implemented methods are provided to analyze the experimental results and to determine the sample sequences in question and to carefully choose target subsequences in order that experiments yield a maximum amount of information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
Method of de-differentiating and re-differentiating somatic cells using RNA
ActiveUS20110165133A1Efficient transfectionLess time-consumingBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsDiseaseSomatic cell
RNA prepared by in vitro transcription using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-generated template can be introduced into a cell to modulate cell activity. This method is useful in de-differentiating somatic cells to pluripotent, multipotent, or unipotent cells; re-differentiating stem cells into differentiated cells; or reprogramming of somatic cells to modulate cell activities such as metabolism. Cells can also be transfected with inhibitory RNAs, such as small interfering RNA (siRNA) or micro RNA (miRNA), or combinations thereof to induce reprogramming of somatic cells. For example, target cells are isolated from a donor, contacted with one or more RNA's causing the cells to be de-differentiated, re-differentiated, or reprogrammed in vitro, and administered to a patient in need thereof. The resulting cells are useful for treating one or more symptoms of a variety of diseases and disorders, for organ regeneration, and for restoration of the immune system.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com