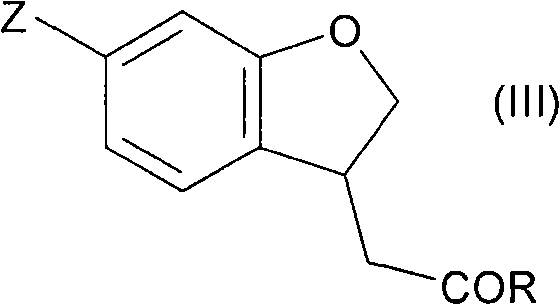
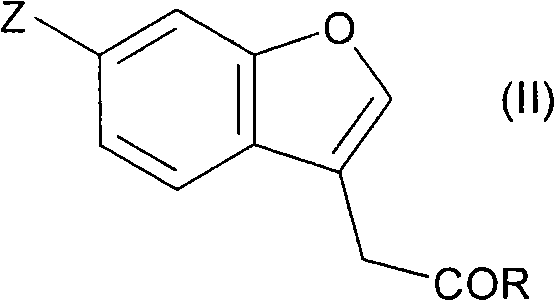
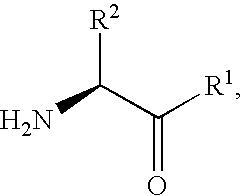
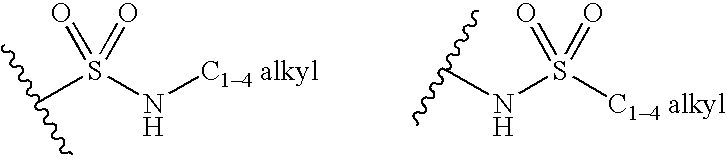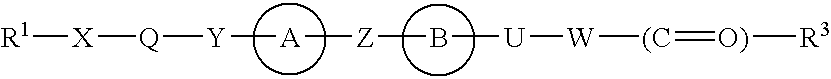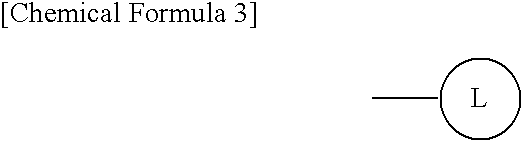Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
123 results about "Secretagogue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A secretagogue is a substance that causes another substance to be secreted. One example is gastrin, which stimulates the H/K ATPase in the parietal cells (increased gastric acid production by the stomach). Pentagastrin, a synthetic gastrin, histamine, and acetylcholine are also gastric secretagogues.
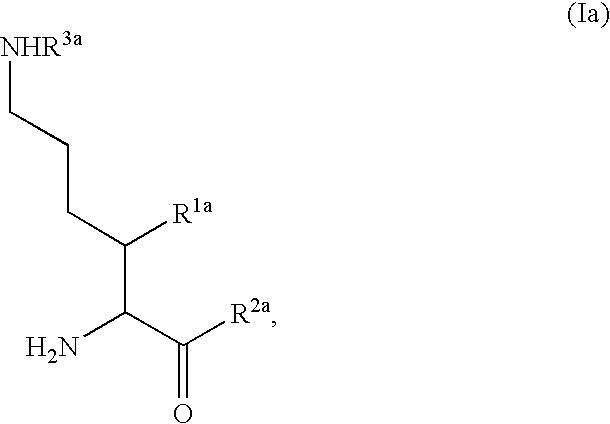
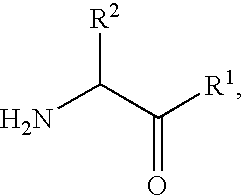
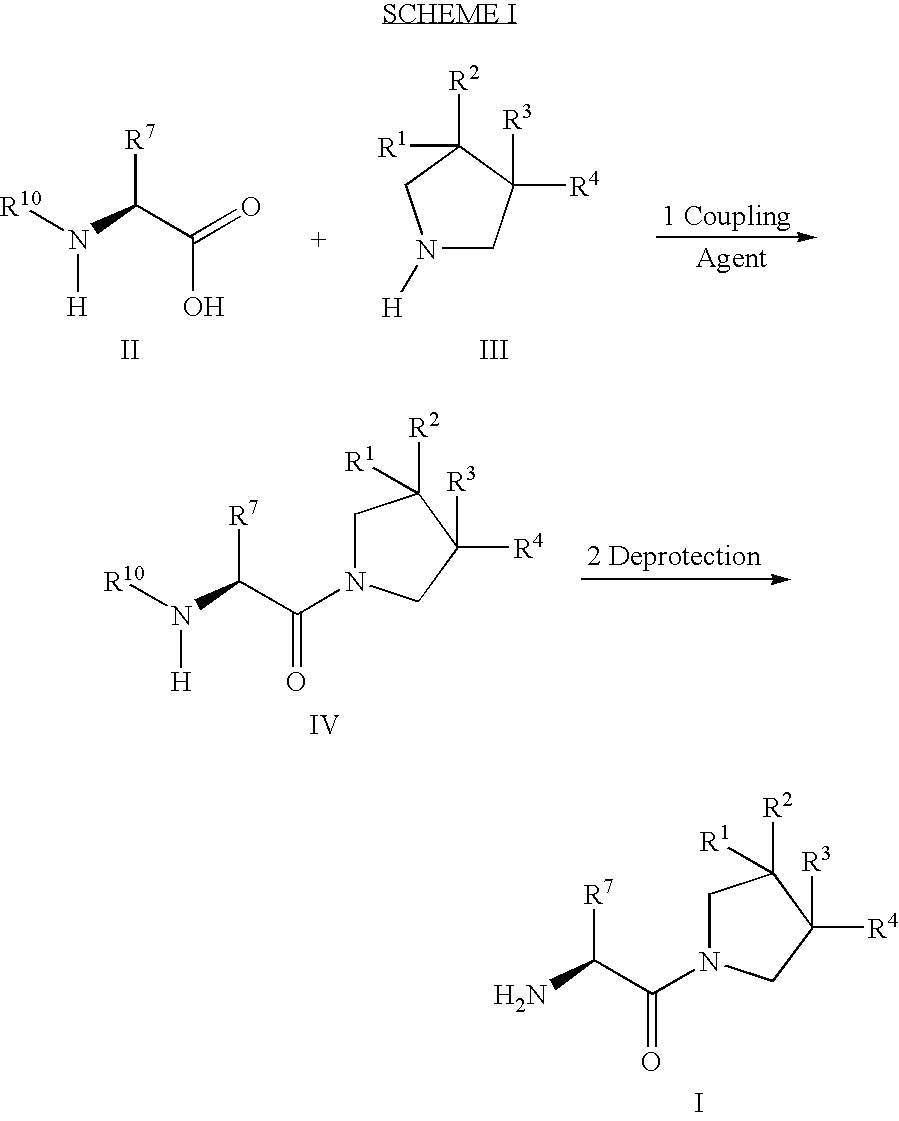
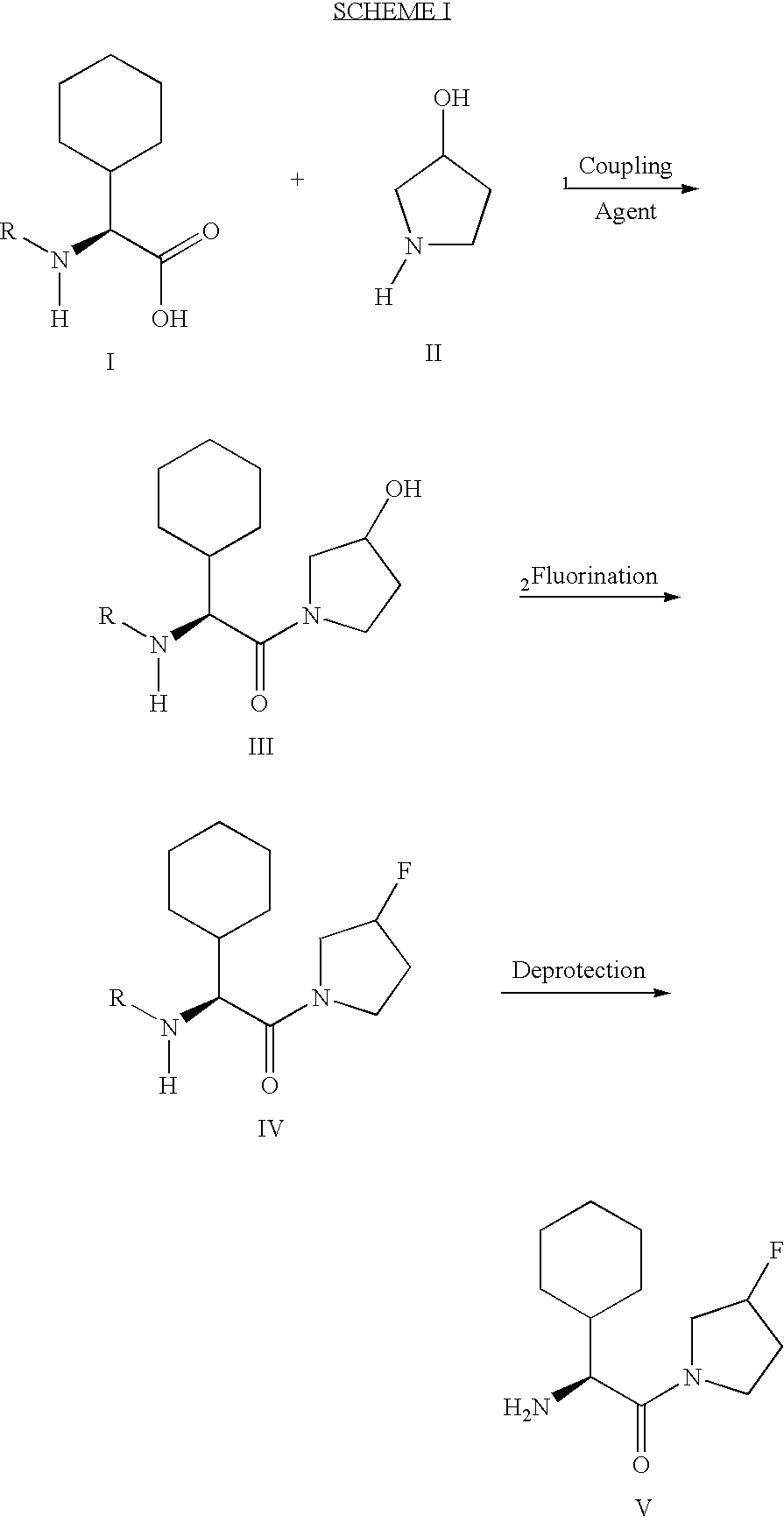
Fluorinated lysine derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors
InactiveUS20050043292A1Ease of preparation and detectabilityGood metabolic stabilityBiocideOrganic chemistryDiabetic retinopathyArthritis
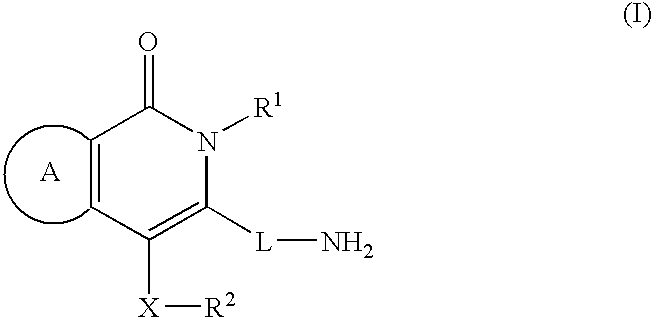
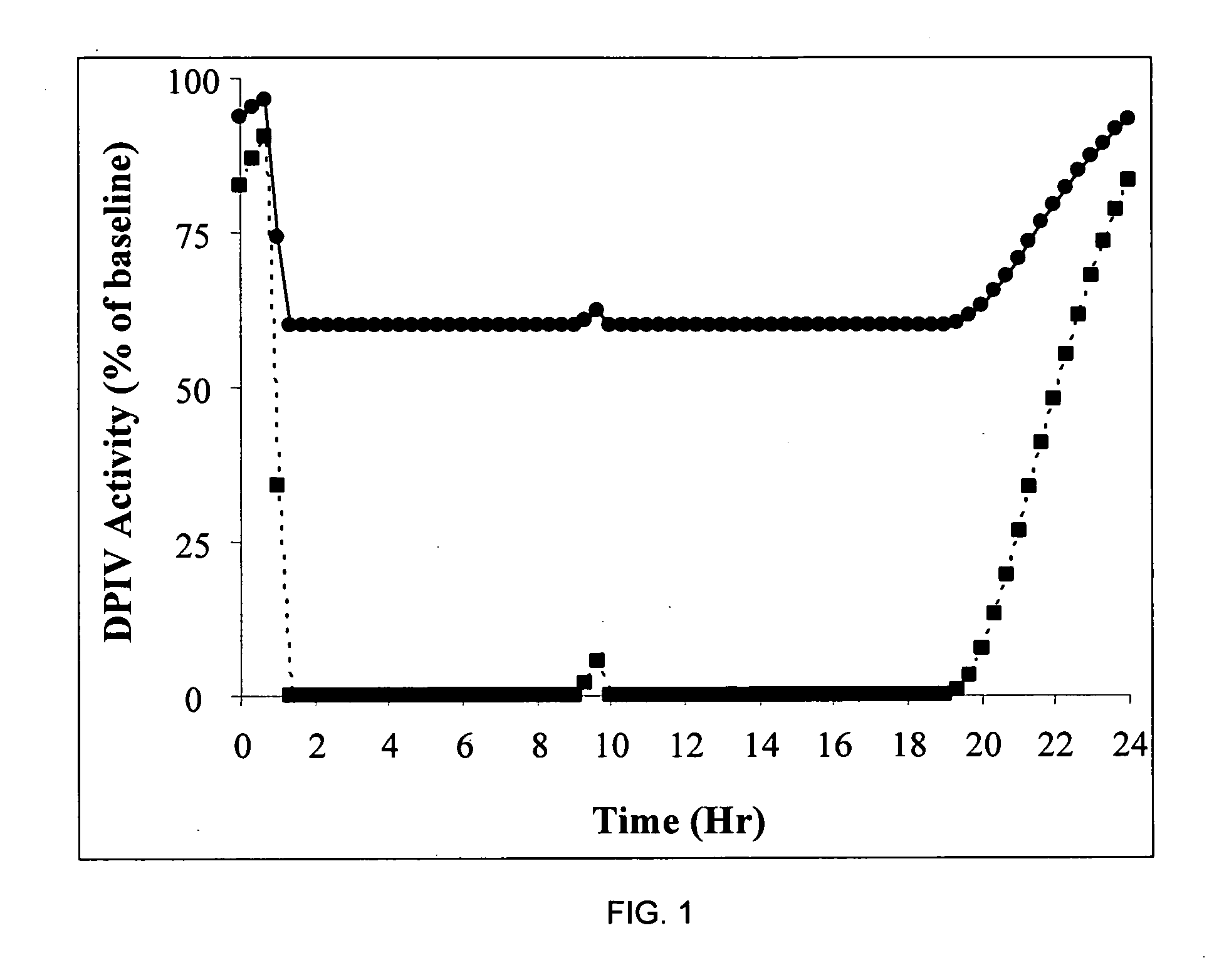
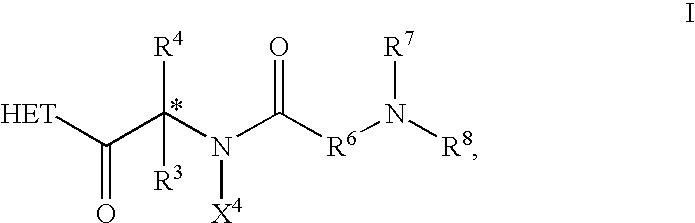
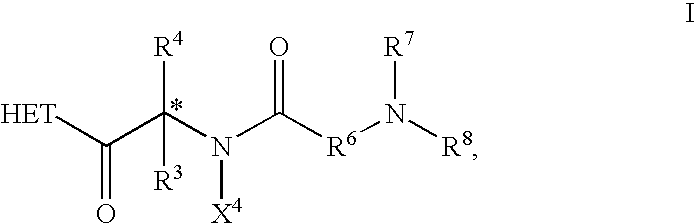
The invention relates to new therapeutically active and selective inhibitors of the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (“DPP-IV”), pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds and the use of such compounds for treating diseases that are associated with proteins that are subject to processing by DPP-IV, such as Type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome (syndrome X or insulin resistance syndrome), hyperglycemia, impaired glucose tolerance, glucosuria, metabolic acidosis, arthritis, cataracts, diabetic neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic cardiomyopathy, Type 1 diabetes, obesity, conditions exacerbated by obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis, osteopenia, frailty, bone loss, bone fracture, acute coronary syndrome, infertility due to polycystic ovary syndrome, short bowel syndrome, anxiety, depression, insomnia, chronic fatigue, epilepsy, eating disorders, chronic pain, alcohol addiction, diseases associated with intestinal motility, ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel syndrome and to prevent disease progression in Type 2 diabetes. The invention also relates to a method of identifying an insulin secretagogue agent for diabetes.
Owner:PFIZER INC
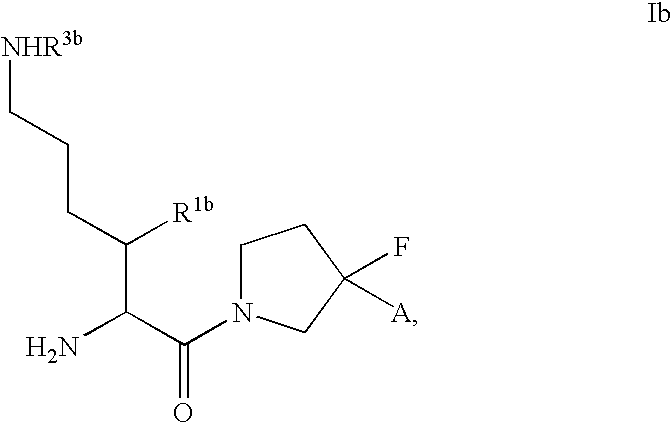
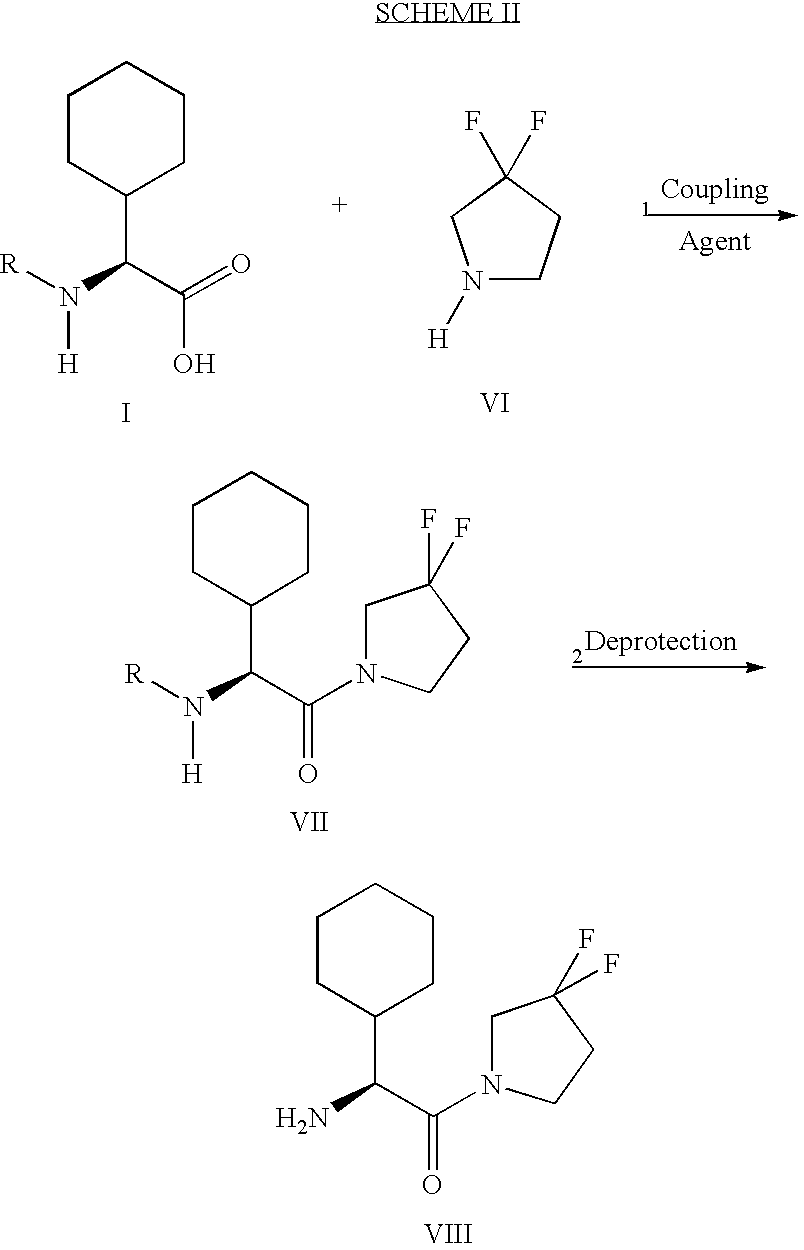
Fluorinated cyclic amides as dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors
InactiveUS6710040B1Easy to prepareEase of detectabilityBiocideOrganic chemistryAcute coronary syndromeDisease progression
The invention relates to new therapeutically active and selective inhibitors of the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-IV, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds and the use of such compounds for treating diseases that are associated with proteins that are subject to processing by DPP-IV, such as Type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, impaired glucose tolerance, metabolic syndrome (Syndrome X or insulin resistance syndrome), glucosuria, metabolic acidosis, cataracts, diabetic neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic cardiomyopathy, Type 1 diabetes, obesity, conditions exacerbated by obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis, osteopenia, frailty, bone loss, bone fracture, acute coronary syndrome, infertility due to polycystic ovary syndrome, short bowel syndrome, anxiety, depression, insomnia, chronic fatigue, epilepsy, eating disorders, chronic pain, alcohol addiction, diseases associated with intestinal motility, ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel syndrome and to prevent disease progression in Type 2 diabetes. The invention also relates to a method of identifying an insulin secretagogue agent for diabetes.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Remedy for Diabetes
ActiveUS20080319077A1Good secretion effectGood hypoglycemic effectBiocideMetabolism disorderAgonistDiabetic patient
The present invention relates to a therapeutic agent for diabetes with sulfonylurea secondary failure, which contains a GPR40 agonist. According to the present invention, a therapeutic agent for diabetes with sulfonylurea secondary failure that affords a superior insulin secretion effect and a superior hypoglycemic effect even in diabetic patients for whom a sulfonylurea compound or a fast-acting insulin secretagogue fails to provide an insulin secretion effect and therefore, fails to provide a sufficient hypoglycemic effect can be provided.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibiting fluorinated cyclic amides
InactiveUS20040110817A1Ease of preparation and detectabilityGood metabolic stabilityBiocideSenses disorderDiabetic retinopathyDisease progression
The invention relates to new therapeutically active and selective inhibitors of the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-IV, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds and the use of such compounds for treating diseases that are associated with proteins that are subject to processing by DPP-IV, such as Type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, impaired glucose tolerance, metabolic syndrome (Syndrome X or insulin resistance syndrome), glucosuria, metabolic acidosis, cataracts, diabetic neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic cardiomyopathy, Type 1 diabetes, obesity, conditions exacerbated by obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis, osteopenia, frailty, bone loss, bone fracture, acute coronary syndrome, infertility due to polycystic ovary syndrome, short bowel syndrome, anxiety, depression, insomnia, chronic fatigue, epilepsy, eating disorders, chronic pain, alcohol addiction, diseases associated with intestinal motility, ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel syndrome and to prevent disease progression in Type 2 diabetes. The invention also relates to a method of identifying an insulin secretagogue agent for diabetes.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Combination therapy for the treatment of diabetes and conditions related thereto and for the treatment of conditions ameliorated by increasing a blood GLP-1 level
InactiveUS20060154866A1Lower blood sugar levelsImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderGpr119 agonistG protein-coupled receptor
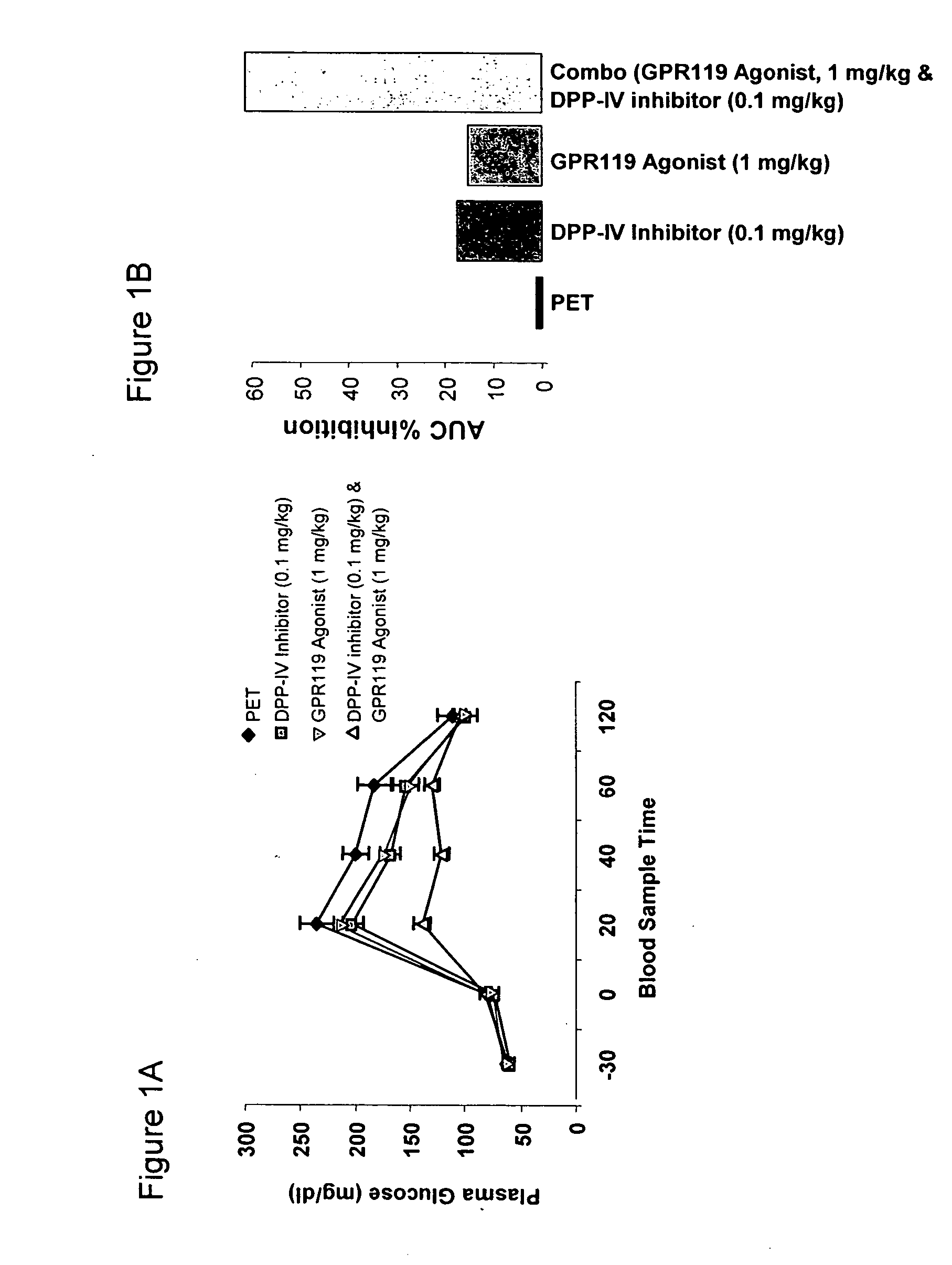
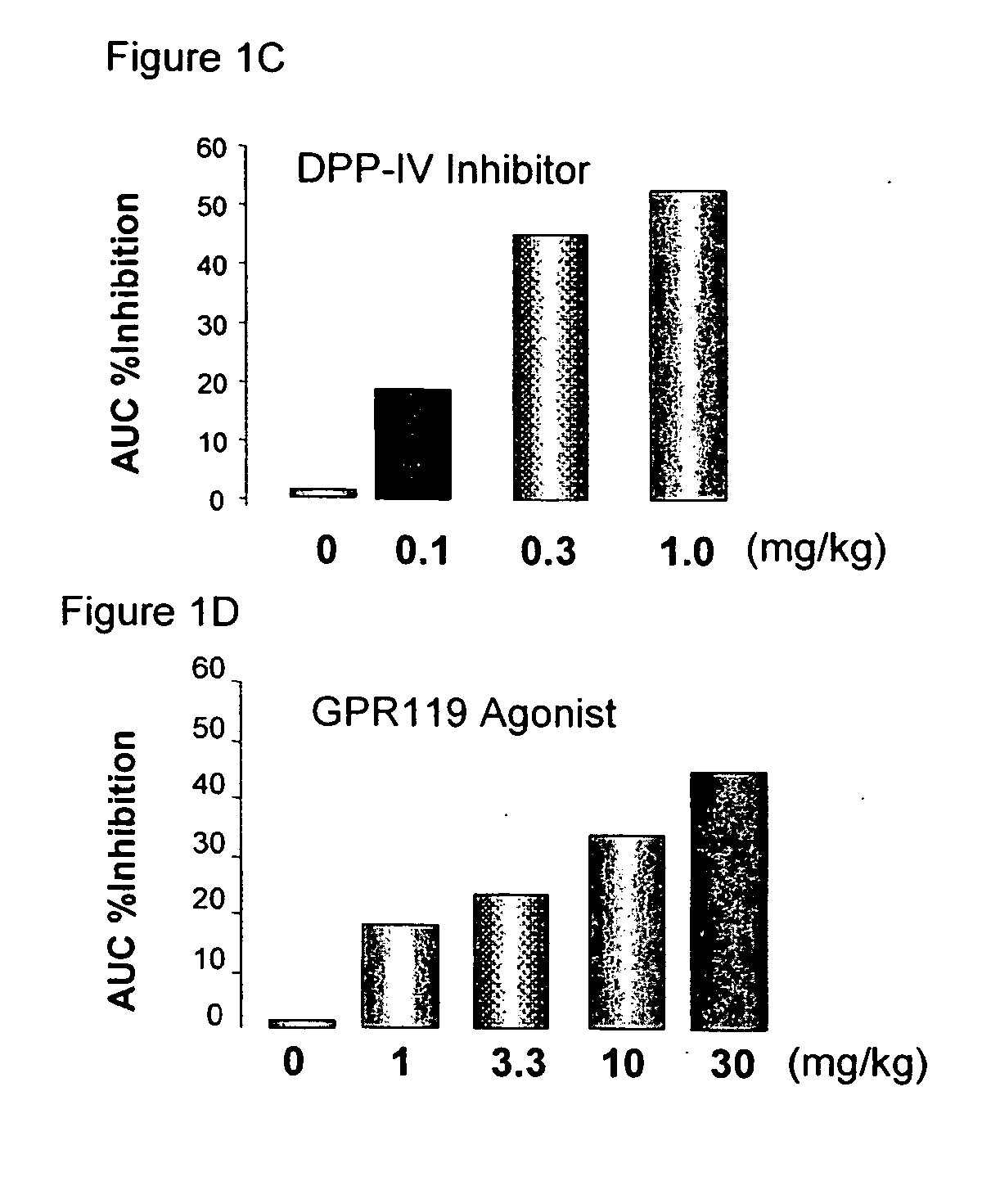
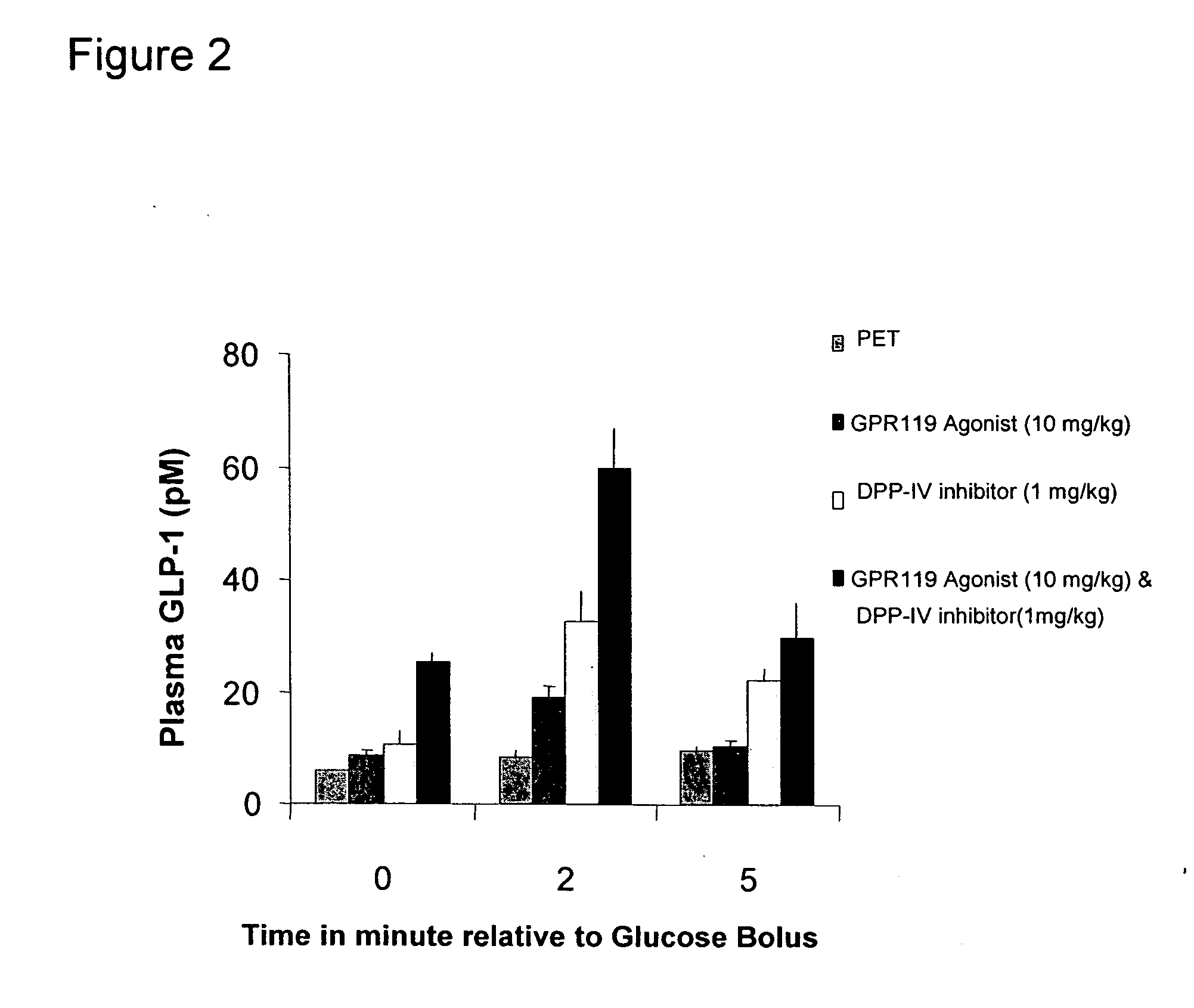
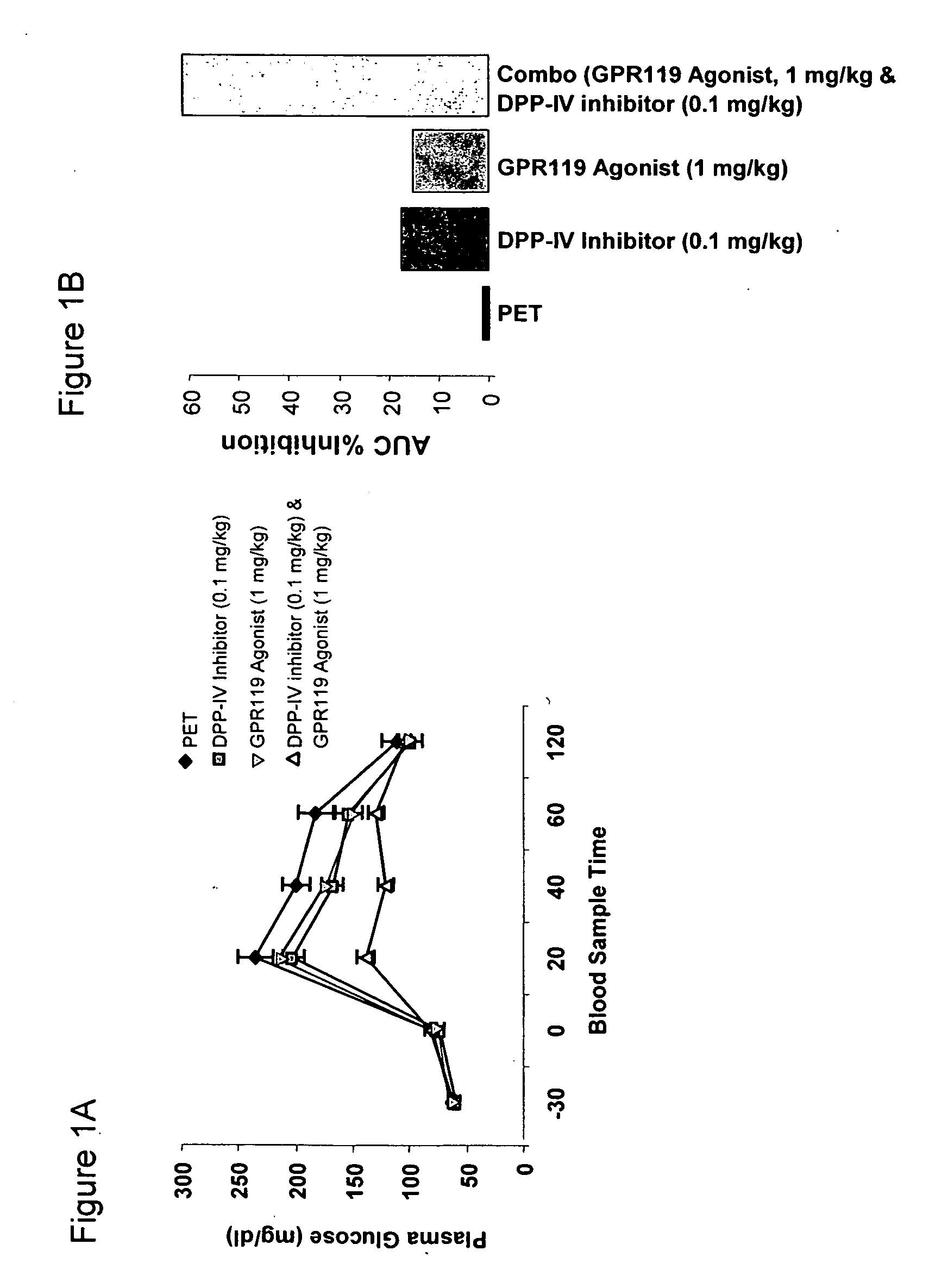
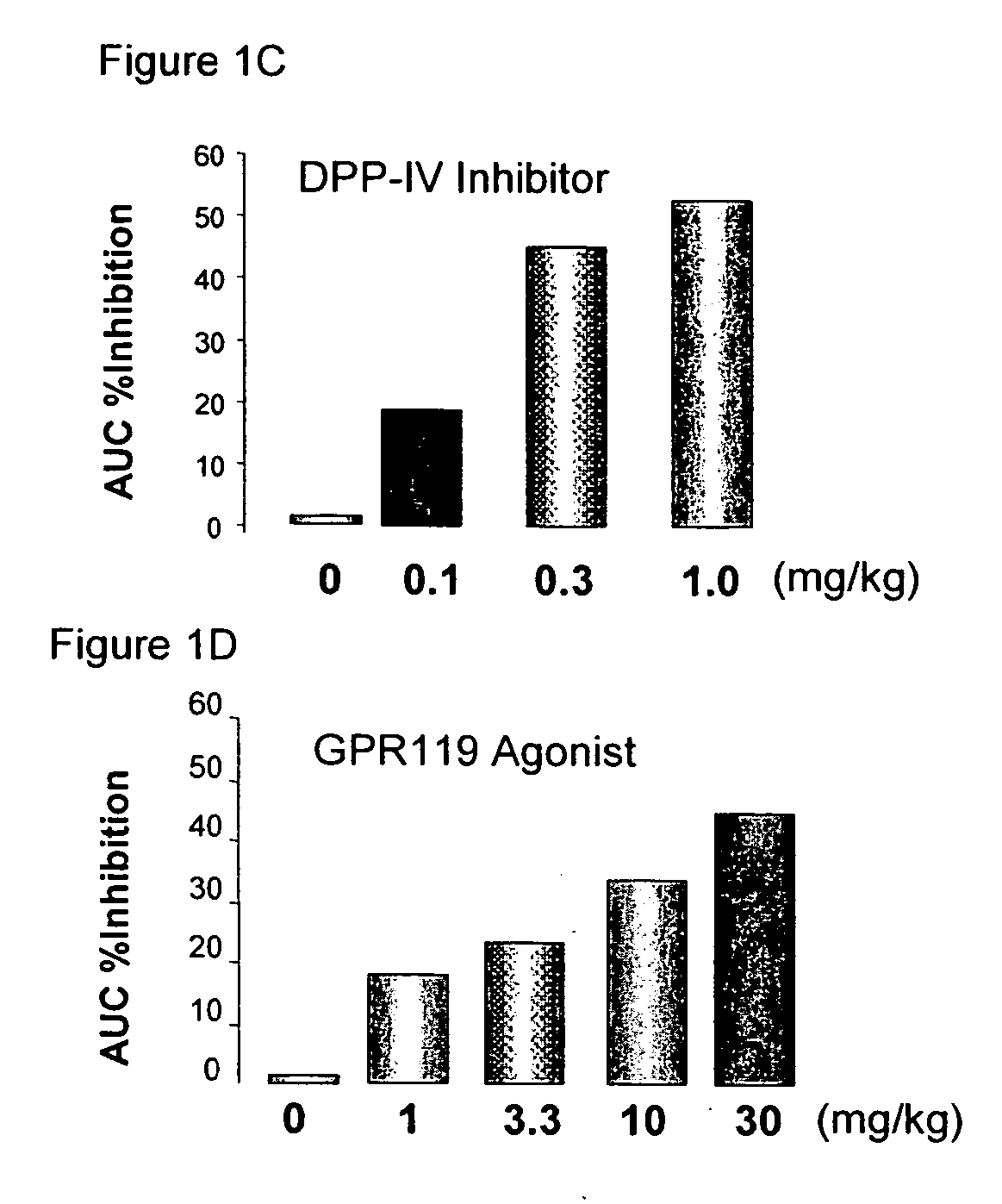
The present invention concerns combination of an amount of a GPR119 agonist with an amount of a dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitor such that the combination provides an effect in lowering a blood glucose level or in increasing a blood GLP-1 level in a subject over that provided by the amount of the GPR119 agonist or the amount of the DPP-IV inhibitor alone and the use of such a combination for treating or preventing diabetes and conditions related thereto or conditions ameliorated by increasing a blood GLP-1 level. The present invention also relates to the use of a G protein-coupled receptor to screen for GLP-1 secretagogues.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
Combination therapy for the treatment of diabetes and conditions related thereto and for the treatment of conditions ameliorated by increasing a blood GLP-1 level
InactiveUS20070072803A1Lower blood sugar levelsImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderGpr119 agonistG protein-coupled receptor
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
Concomitant drugs
InactiveUS20050197376A1Good treatment effectReduce the amount requiredBiocideMetabolism disorderConcomitant drugGlycosidase inhibitor
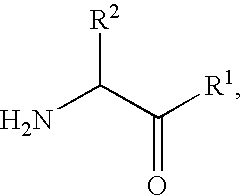
This invention provides a pharmaceutical agent containing, in combination, a sulfonamide compound and other therapeutic agent, preferably, at least one compound represented by the formula (I): R1—SO2—NH—CO-A1-CH2—R2 [each symbol is as defined in the specification] or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and at least one pharmaceutical agent selected from the group consisting of an α-glucosidase inhibitor, an insulin secretagogue, a sulfonylurea and a biguanide, which has a superior therapeutic effect.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Agent for treating diabetes
InactiveUS20070072810A1Excellent insulin-secretingGood hypoglycemic effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDipeptidyl peptidaseDipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitors
An agent for treating diabetes with sulfonylurea secondary failure which comprises a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor. The agent of the present invention is an agent for treating diabetes with sulfonylurea secondary failure showing excellent insulin-secreting and hypoglycemic effects on even diabetic patients on whom a sulfonylurea compound or a fast-acting insulin secretagogue has no insulin-secreting effect and therefore no sufficient hypoglycemic effect.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Treating diabetes with glucagon-like peptide-1 secretagogues
InactiveUS20070032420A1Increase basal GLP- levelDecrease DPP-IV activityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaDipeptidyl peptidase
In general this invention can be viewed as encompassing novel methods of treating diabetes and insulin resistance. The inventors have made the discovery that increasing secretion of endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in combination with inhibiting the activity of dipeptidyl peptidase I (DPP-IV) can have a significant impact on hyperglycemia and insulin secretion in subjects suffering from diabetes and / or insulin resistance. Further the invention encompasses methods of identifying subjects having elevated secretion of GLP-1, methods of assessing sensitivity to a GLP-1 secretagogue, and methods of treating diabetes in these subjects by administering a GLP-1 secretagogue to alleviate at least one symptom of diabetes.
Owner:ENTELOS INC
Compositions and methods for stimulating gastrointestinal mobility
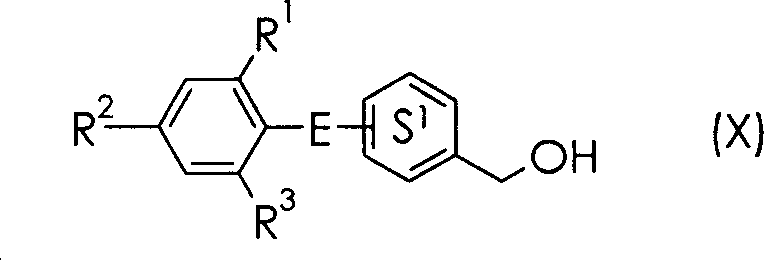
The present invention is directed to methods for stimulating the motility of the gastrointestinal system in a patient which comprises administering a growth hormone secretagogue, a prodrug thereof or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of said secretagogue or said prodrug. More particularly, the present invention provides methods for stimulating the motility of the gastrointestinal system in a patient which comprises administering a compound of Formula I: a prodrug thereof or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of said secretagogue or said prodrug.
Owner:RAQUALIA PHARMA INC
Fused cyclic compounds
ActiveCN101616913AImprove stabilityLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiabetes mellitusCyclic compound
The present invention provides a compound represented by the formula (I): wherein each symbol is as defined in the description, or a salt thereof. The compound or a salt thereof or a prodrug thereof has a GPR40 receptor function modulating action and is useful as an insulin secretagogue or an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of diabetes and the like.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Epidermal growth factor increasing insulin secretion and lowering blood glucose
InactiveUS20090312250A1Lower Level RequirementsEGF treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderD-GlucoseGlycemic
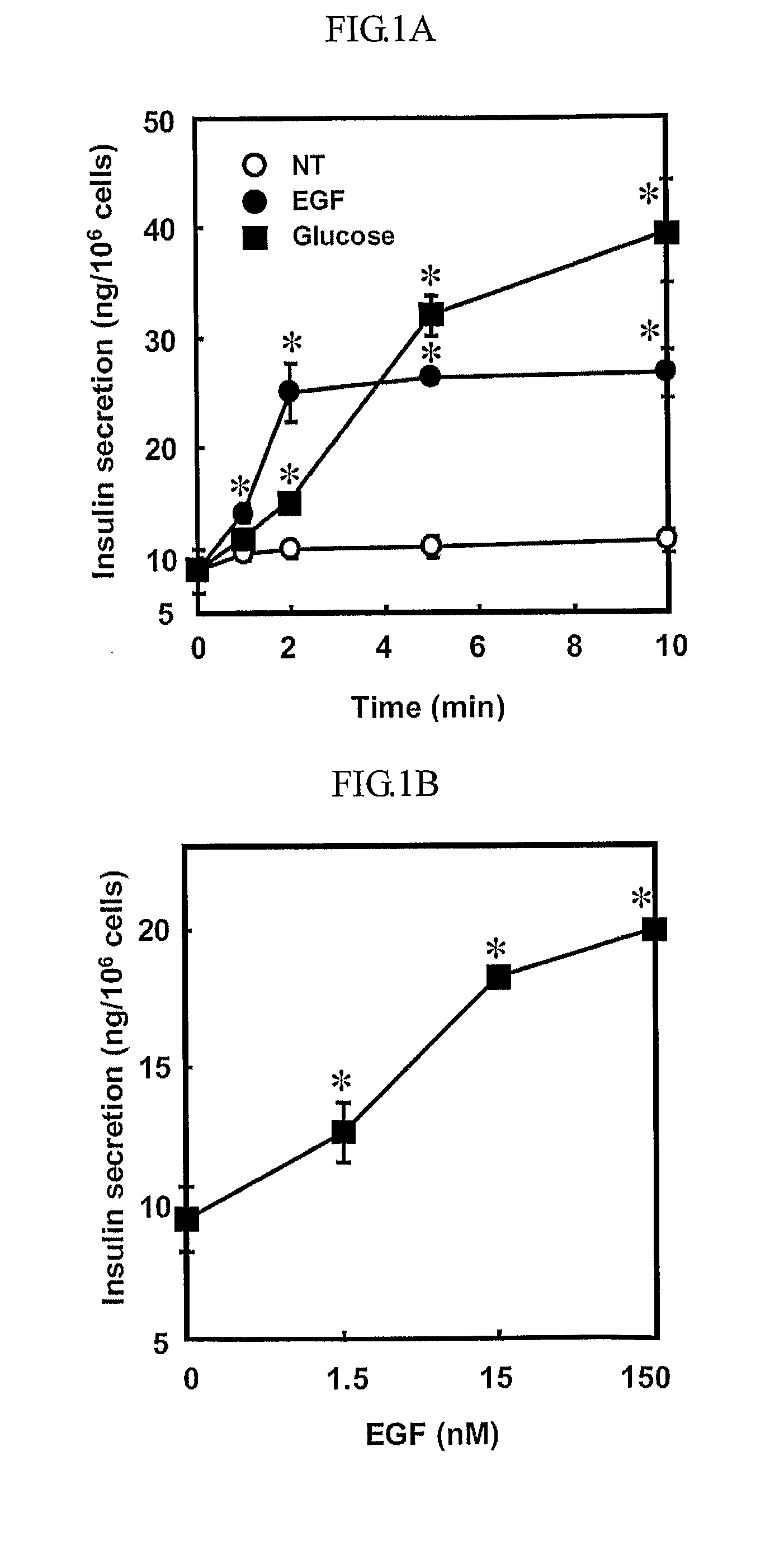
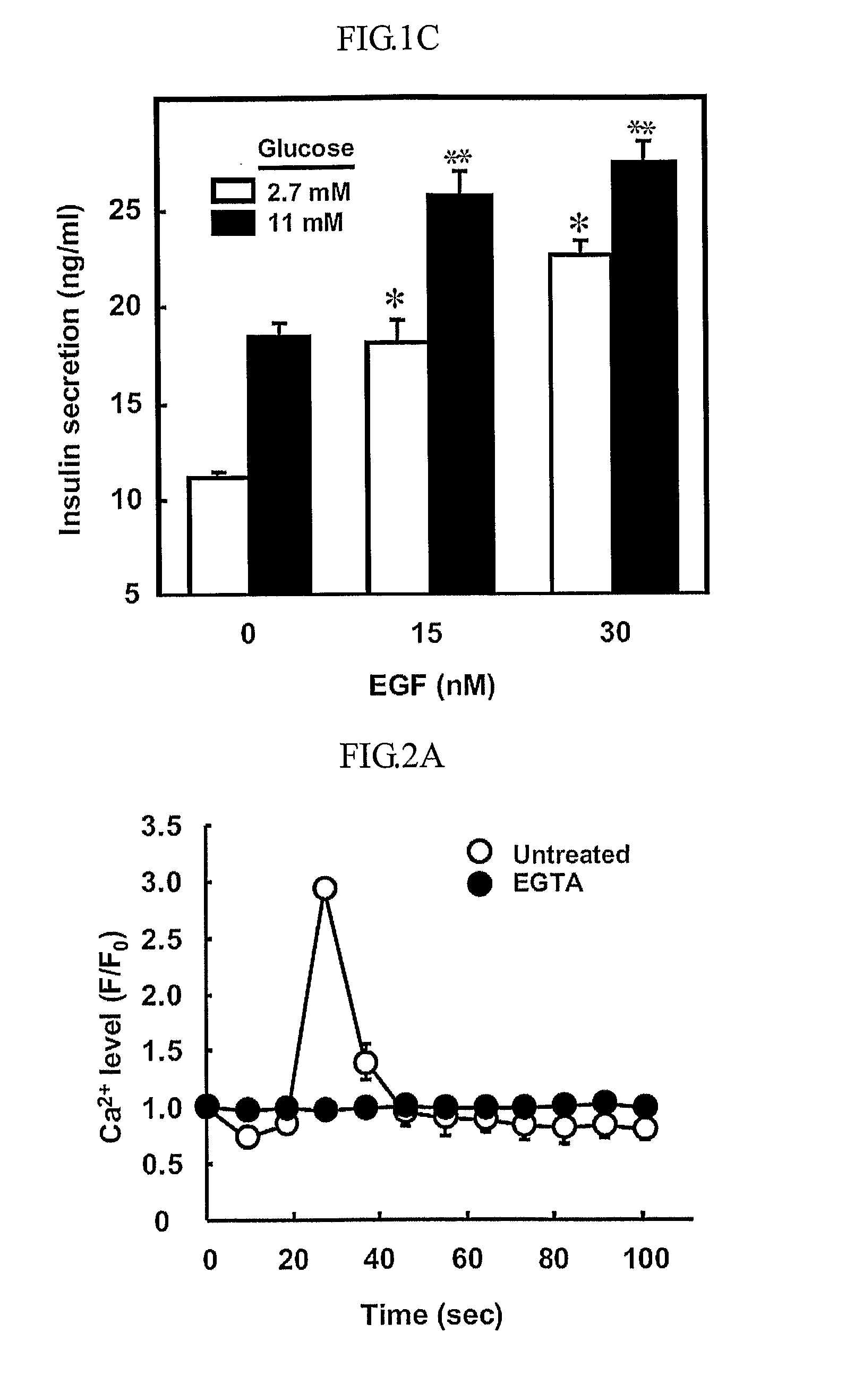
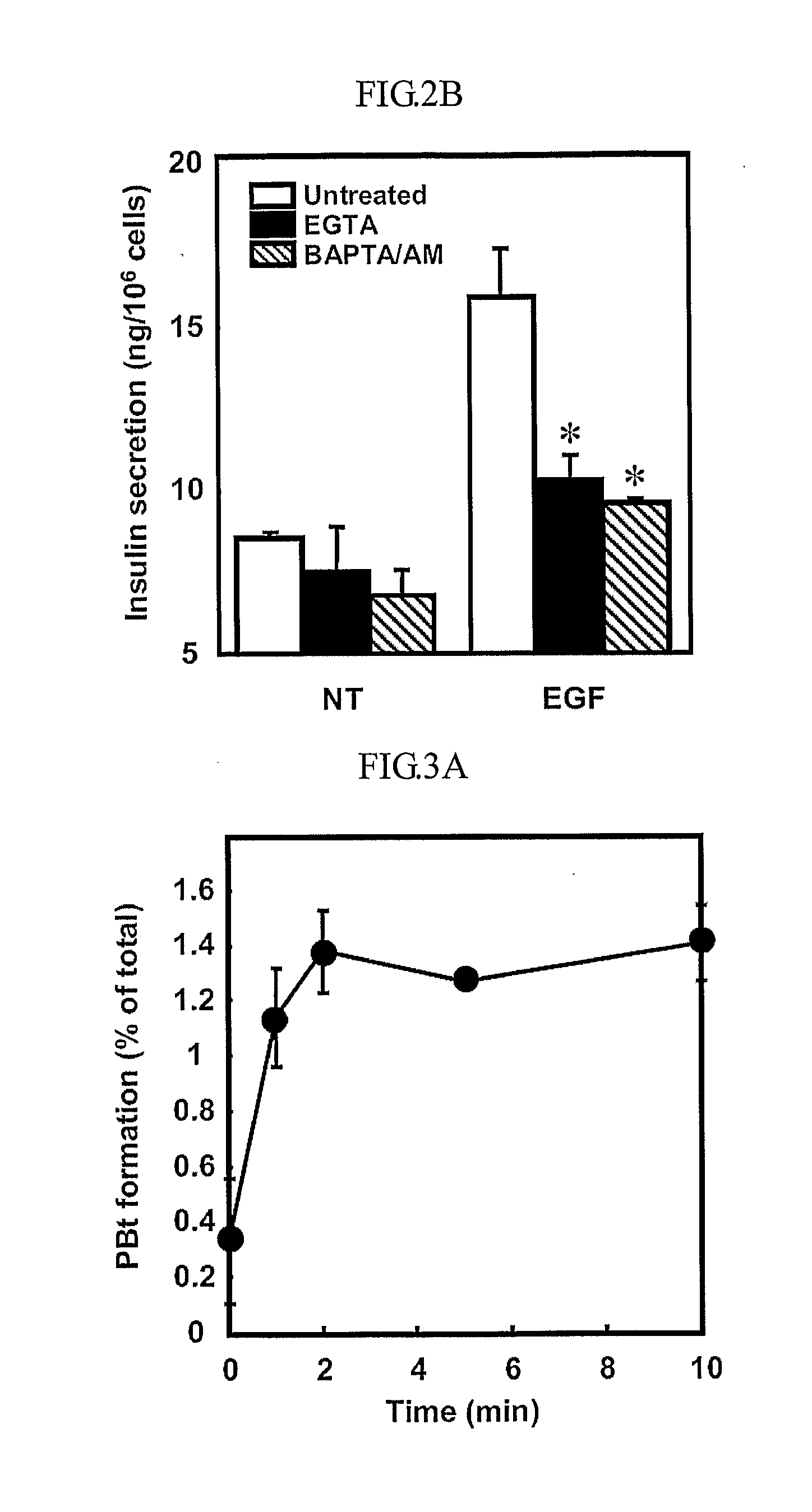
The present inventors show that a brief exposure to EGF stimulates insulin secretion glucose-independently via a Ca2+ influx- and PLD2-dependent mechanism. Furthermore, the present invention shows that EGF is a novel secretagogue that lowers plasma glucose levels in normal and diabetic mice, suggesting the potential for EGF treatment in diabetes.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Combination therapy for the treatment of diabetes and conditions related thereto and for the treatment of conditions ameliorated by increasing a blood GLP-1 level
InactiveUS20070072804A1Lower blood sugar levelsImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderGpr119 agonistG protein-coupled receptor
The present invention concerns combination of an amount of a GPR119 agonist with an amount of a dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitor such that the combination provides an effect in lowering a blood glucose level or in increasing a blood GLP-1 level in a subject over that provided by the amount of the GPR119 agonist or the amount of the DPP-IV inhibitor alone and the use of such a combination for treating or preventing diabetes and conditions related thereto or conditions ameliorated by increasing a blood GLP-1 level. The present invention also relates to the use of a G protein-coupled receptor to screen for GLP-1 secretagogues.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
Fluorinated cyclic amides as dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors
InactiveUS20040132713A1Ease of preparation and detectabilityGood metabolic stabilityBiocideOrganic chemistryDisease progressionDiabetic nephropathy
The invention relates to new therapeutically active and selective inhibitors of the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-IV, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds and the use of such compounds for treating diseases that are associated with proteins that are subject to processing by DPP-IV, such as Type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, impaired glucose tolerance, metabolic syndrome (Syndrome X or insulin resistance syndrome), glucosuria, metabolic acidosis, cataracts, diabetic neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic cardiomyopathy, Type 1 diabetes, obesity, conditions exacerbated by obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis, osteopenia, frailty, bone loss, bone fracture, acute coronary syndrome, infertility due to polycystic ovary syndrome, short bowel syndrome, anxiety, depression, insomnia, chronic fatigue, epilepsy, eating disorders, chronic pain, alcohol addiction, diseases associated with intestinal motility, ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel syndrome and to prevent disease progression in Type 2 diabetes. The invention also relates to a method of identifying an insulin secretagogue agent for diabetes.
Owner:PFIZER INC
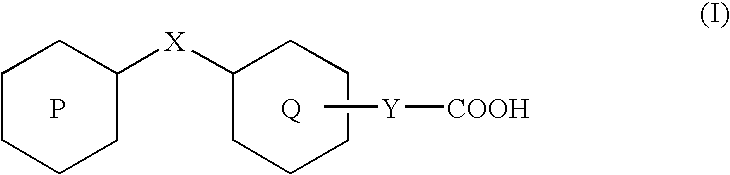
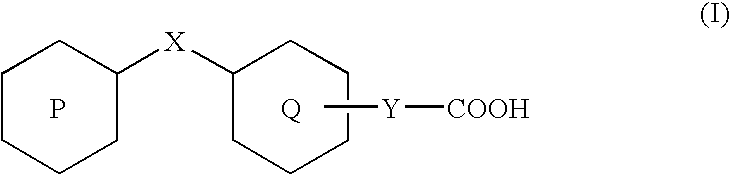
3-(4-Benzyloxyphenyl) propanoic acid derivatives
InactiveUS20070149608A1Superior agonist activityEasy to useBiocideGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsDiabetes mellitusMammal
The present invention provides a novel compound represented by the formula (I) wherein each symbol is as defined in the specification, a salt thereof and a prodrug thereof having a superior GPR40 receptor function modulating action, which can be used as an insulin secretagogue, an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of diabetes and the like. They unexpectedly show superior GPR40 receptor agonist activity, and also show superior properties as a pharmaceutical product, such as stability and the like. Thus, they can be safe and useful pharmaceutical agents for the prophylaxis or treatment of GPR40 receptor related diseases in mammals.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Combination therapy for endothelial dysfunction, angina and diabetes
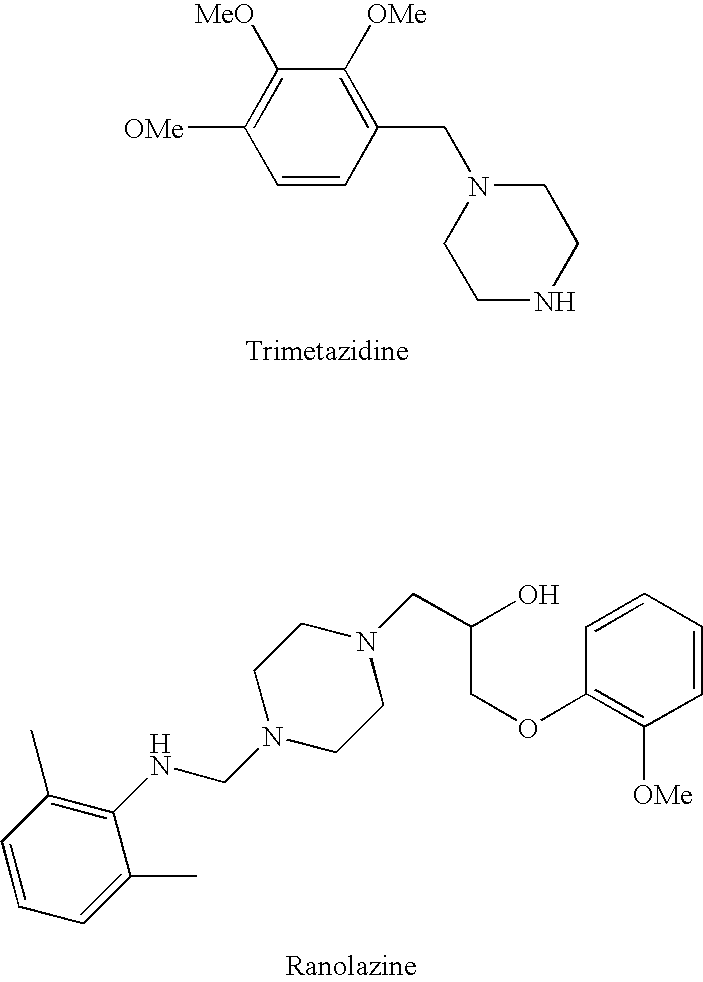
InactiveUS20060205727A1Control blood sugar levelsIncrease productionBiocideMetabolism disorderHMG-CoA reductaseTrimetazidine
The combination of a HMG CoA reductase inhibitor like a statin, such as simvastatin, with a pFox inhibitor such as trimetazidine (“Simetazidine”) is particularly advantageous for treatment of end-stage complications, such as acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and chronic angina, especially in type II diabetics. The combination therapy is also useful in the treatment and / or prevention of chronic heart failure (CHF) and peripheral arterial disease (PAD). The combination of a nitric oxide (NO) mechanism with increased NO production with pFox inhibition simultaneously treats both the effect and the cause of angina. One or more oral hypoglycemic compounds (biguanides, insulin sensitizers, such as thiazolidinediones, α-glucosidase inhibitors, insulin secretagogues, and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors), protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors can also be used in combination with the HMG CoA reductase inhibitors and / or pFox inhibitors, especially in type II diabetics, to control glucose levels and treat endothelial dysfunction. The drugs can be given in combination (e.g. a single tablet) or in separate dosage forms, administered simultaneously or sequentially. In the preferred form the statin is given in a dose of between 5 and 80 mg / day in two separate doses, and the pFox inhibitor is administered in a sustained or extended dosage formulation at a dose of 20 mg three times a day or 35 mg two times a day. The dose of the oral hypoglycemic, PKC inhibitor, or acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitor varies with the type of drug used.
Owner:HONG KONG NITRIC OXIDE
Alkoxyphenylpropanoic Acid Derivatives
InactiveUS20070213364A1Superior agonist activityMaintain good propertiesBiocideOrganic chemistryAcid derivativeMedicinal chemistry
The present invention aims at provision of a novel compound having a GPR40 receptor function modulating action, which is useful as an insulin secretagogue, an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of diabetes and the like. The compound represented by the formula: wherein each symbol is as defined in the description, a salt thereof, and a prodrug thereof of the present invention unexpectedly have a superior GPR40 receptor agonistic activity and superior properties as pharmaceutical products such as stability and the like, and can be safe and useful pharmaceutical agents as agents for the prophylaxis or treatment of GPR40 receptor-related pathology or diseases in mammals.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
GH secretagogues and uses thereof
The invention relates to use of a GH secretagogue (e.g. GRF or an analog thereof) for (1) altering a lipid parameter in a subject; (2) altering a body composition parameter in a subject, (3) treating a condition characterized by deficient or decreased bone formation in a subject (4) improving daytime vigilance and / or cognitive function in a subject, (5) improving a metabolic condition in a subject, (6) improving anabolism in a catabolic condition in a subject, and / or (7) improving and / or reconstituting immune function in a subject.
Owner:THERATECHONOLGIES INC
Co-formulations or kits of bioactive agents
Provided, among other things, is a formulation or kit comprising: (a) a pharmaceutically effective dosage of one or more a glucose-level-controlling bioactive agents selected from an α-glucodase inhibitor, sulfonylurea, meglitinide, thiazolidinediones, biguanide, insulin, dual PPARα / γ agonist, PPARγ agonist or insulin secretagogue; and (b) a pharmaceutically effective dosage of (i) one or more of an antihypertensive bioactive agent selected from an ACE inhibitor, calcium channel blocker, beta blocker, angiotension II receptor antagonist or diuretic, or (ii) one or more of an anti-dyslipidemia bioactive agent selected from a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, bile acid sequestrant, fibric acid derivative, sterol, cholesterol absorption inhibitor, MTP inhibitor or nicotinic acid derivative; wherein: in the case of (i) a combination of a first bioactive agent of group (a) that is metformin with a second bioactive agent of group (b), or (ii) a combination of a first bioactive agent of group (a) that is a thiazolidinedione or dual PPARα / γ agonist with an angiotension II receptor antagonist, one or more of the following applies: (I) one of the first bioactive agent or the second bioactive agent is formulated for sustained release, and the other is formulated for immediate release, each formulated for once-a-day dosing; or (II) the co-formulation or kit comprises (A) a biguanide and a thiazolidinedione and (B) one or more group (b) bioactive agents.
Owner:ABEILLE PHARMA
Oxadiazolidinedione compound
A pharmaceutical agent having GPR40 receptor agonistic action, particularly a compound which is useful as an insulin secretagogue or an agent for preventing and / or treating diabetes mellitus. The present inventors have examined a compound having GPR40 receptor agonistic action, confirmed that an oxadiazolidinedione compound which has a substituent such as a benzyl group, etc. linked with a substituent such as a phenyl group, etc. through a linker at the 2-position of an oxadiazolidinedione ring, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof has an excellent GPR40 agonistic activity, and thus completed the invention. The oxadiazolidinedione compound has excellent insulin secretagogue action and anti-hyperglycemic action, and therefore can be used as an insulin secretagogue or an agent for preventing and / or treating diabetes mellitus.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
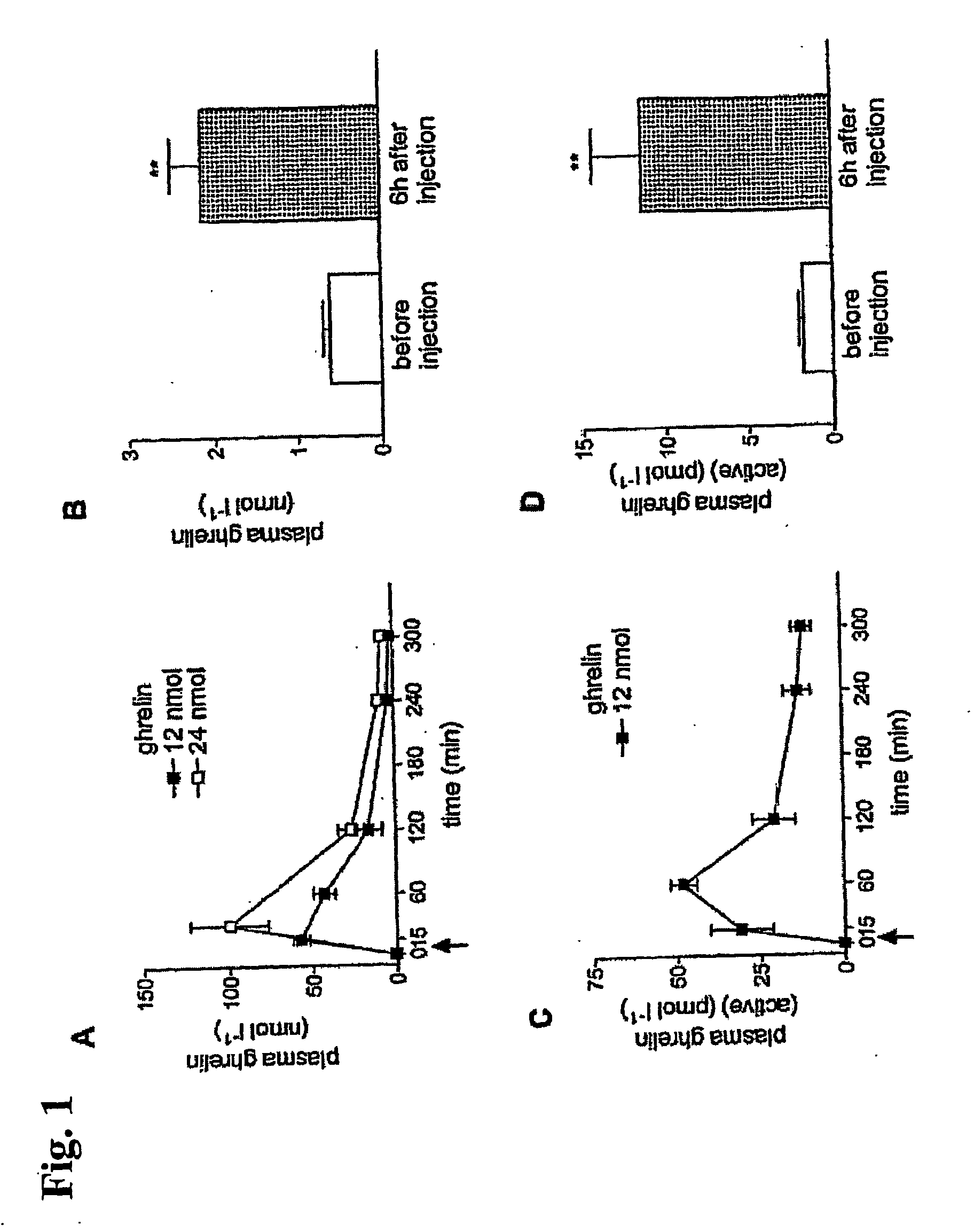
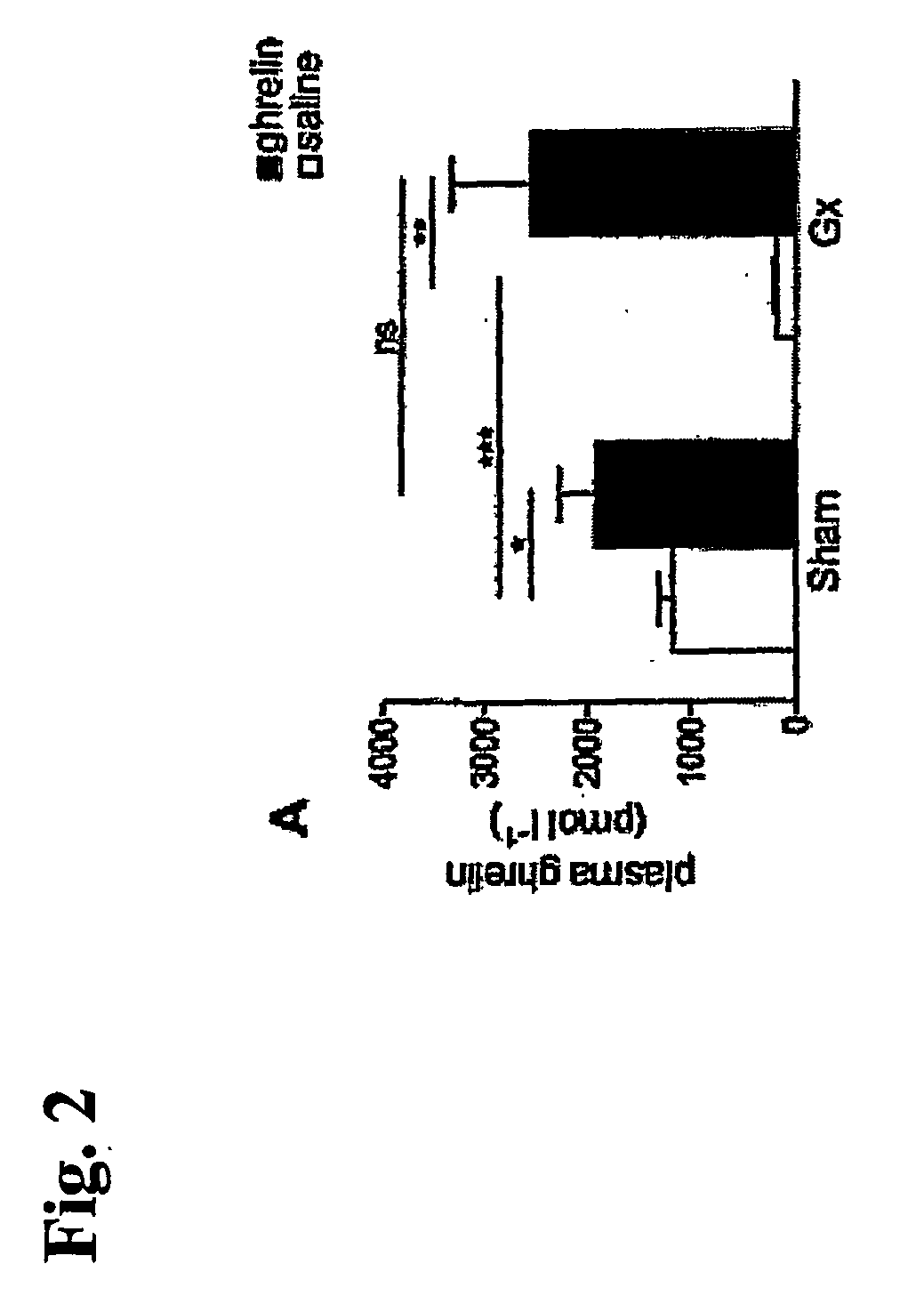
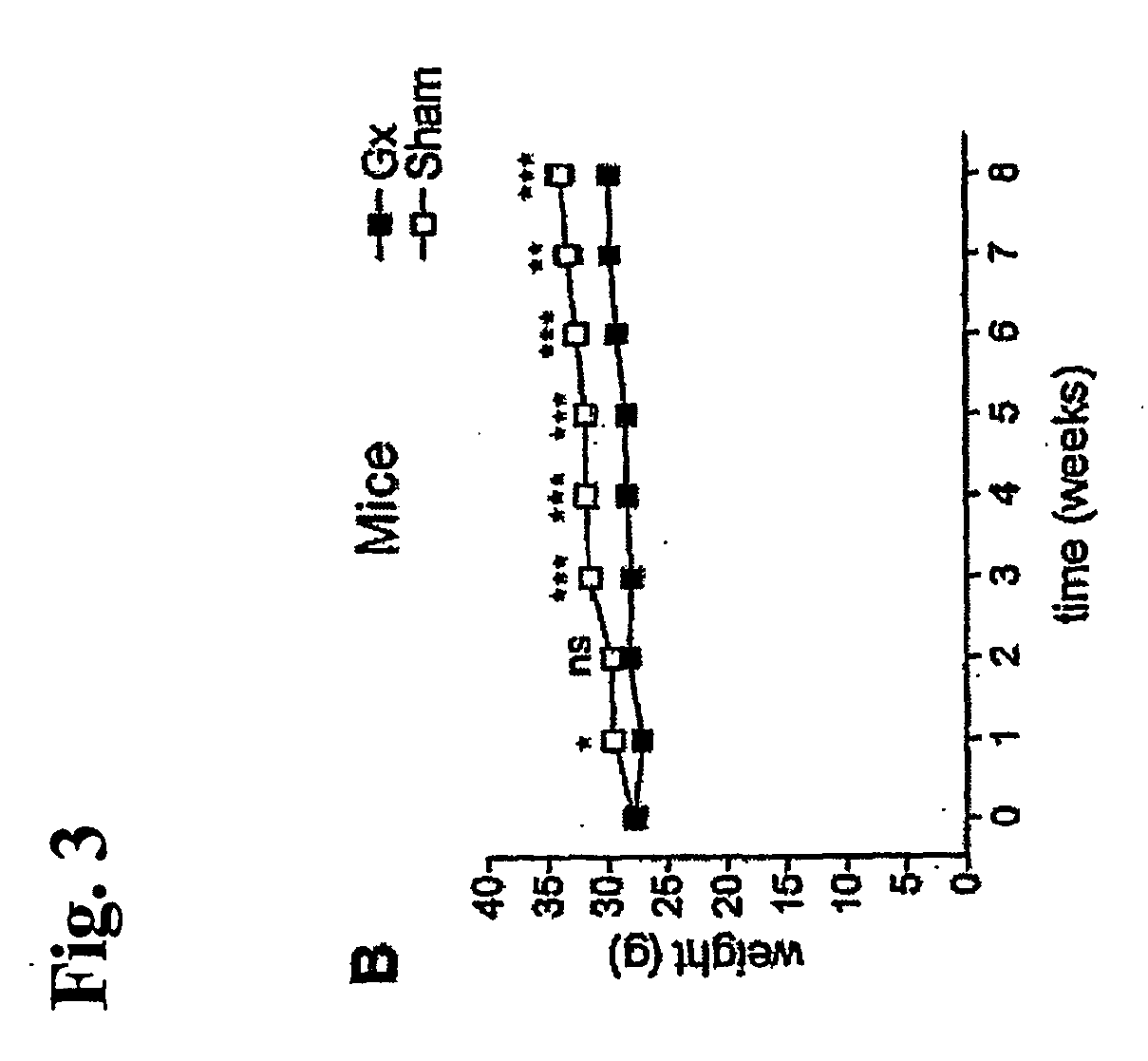
Uses of secretagogues like ghrelin in cancer cachexia and for stimulating appetite
InactiveUS20070037751A1Sufficient effectDipeptide ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicinePharmacology
The present invention relates, in one aspect, to the use of a secretagogue compound for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of cancer cachexia in an individual in need of such treatment. In another aspect, the present invention relates to the use of a ghrelin-like compound for the preparation of a medicament for prophylaxis or treatment of cachexia in an individual by administering a subcutaneous dosage of said medicament to the individual. In a further aspect, the present invention relates to the use of a ghrelin-like compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for the preparation of a medicament for stimulation of appetite in an individual by administering a subcutaneous dosage of said medicament to the individual. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a number of new ghrelin-like compounds and uses thereof, as well as to pharmaceutical compositions and medical packaging comprising the new ghrelin-like compounds.
Owner:GASTROTECH PHARMA AS
Use Of Secretagogue For The Teatment Of Ghrelin Deficiency
InactiveUS20080171700A1Improve the level ofPrevents upregulationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSleep patternsCvd risk
The present invention relates to the use of a growth hormone (GH) secretagogue, such as a ghrelin-like compound, for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of ghrelin deficiency, and / or undesirable symptoms associated therewith, in an individual at risk of acquiring partial or complete ghrelin deficiency resulting from a medical treatment and / or from a pathological condition. The present invention also relates to use of a secretagogue compound for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of one or more of: loss of fat mass, loss of lean body mass, weight loss, cachexia, loss of appetite, immunological dysfunction, malnutrition, disrupted sleep pattern, sleepiness, reduction in intestinal absorption and / or intestinal mobility problems in an individual suffering from, or at risk of suffering from, ghrelin deficiency. Furthermore, the present invention relates to the use of a secretagogue, such as a ghrelin-like compound, for the production of a medicament for preventing weight increase in an individual either: a) being converted from a hyperthyroidic state to euthyroid state, or b) in remission from being converted from a hyperthyroidic state to euthyroid state.
Owner:GASTROTECH PHARMA AS
Combination of dopamine agonists plus first phase secretagogues for the treatment of metabolic disorders
ActiveUS8877708B2Eliminate side effectsImprove blood sugar controlPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPhases of clinical researchDopamine agonist
Owner:VEROSCI
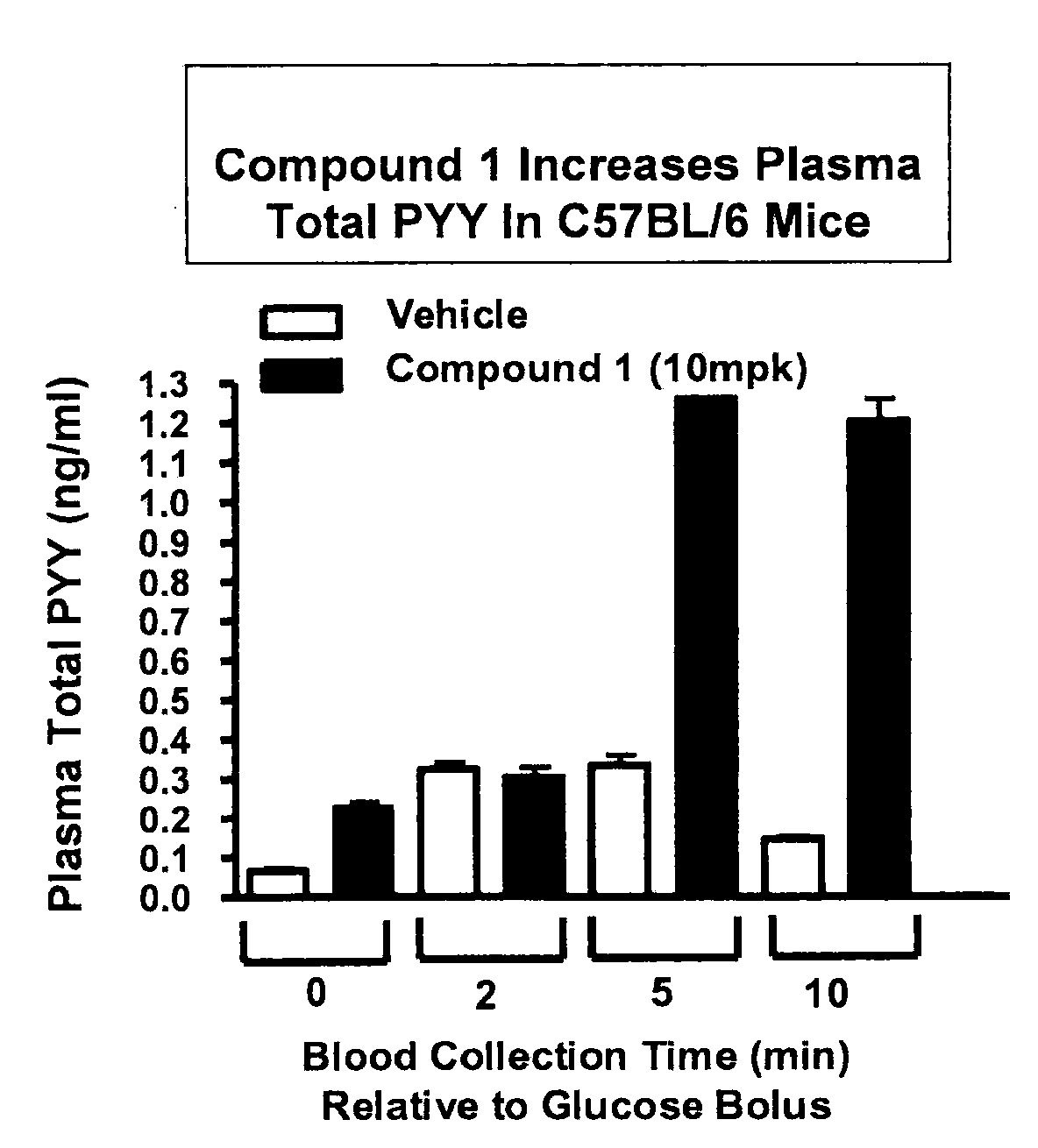
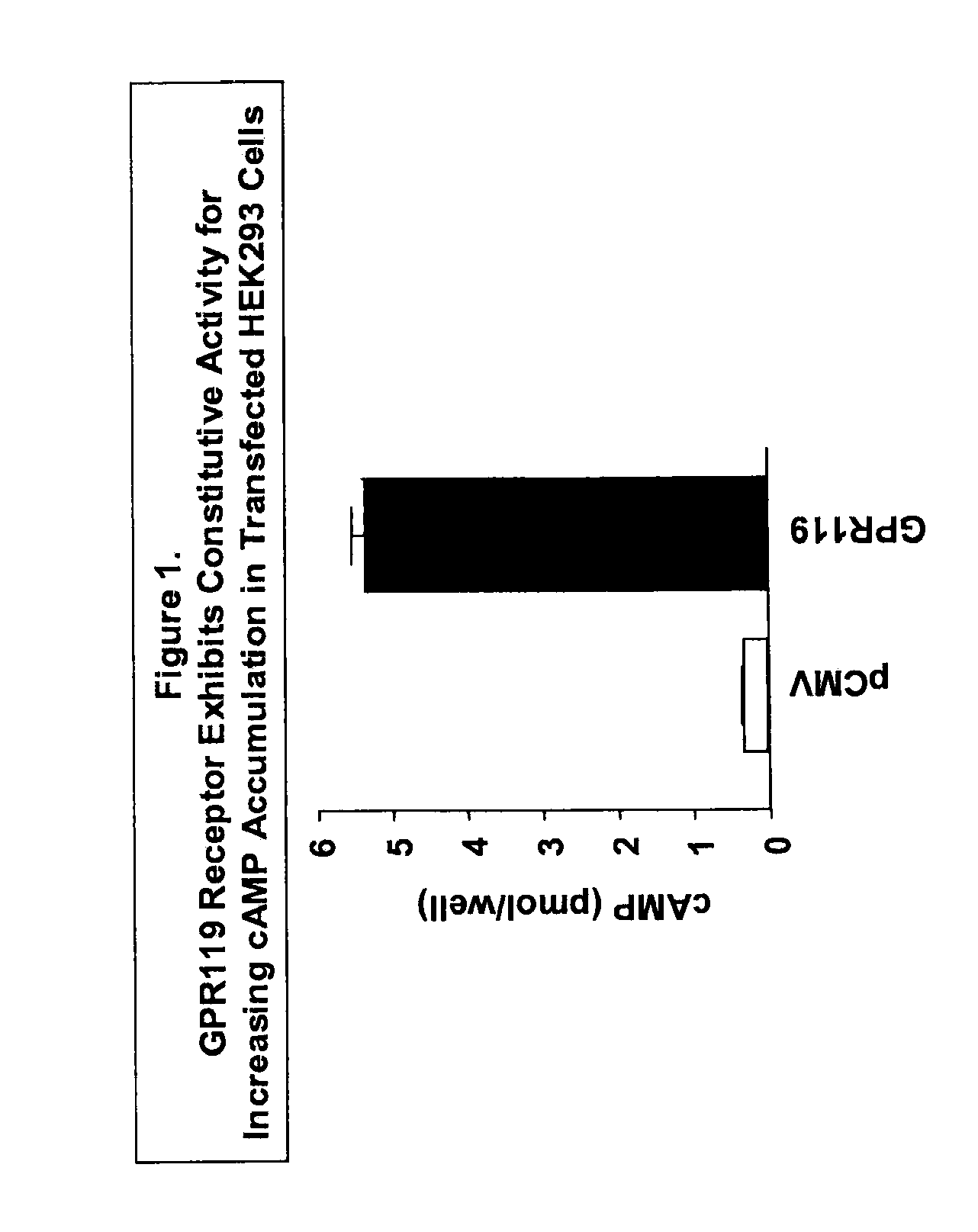
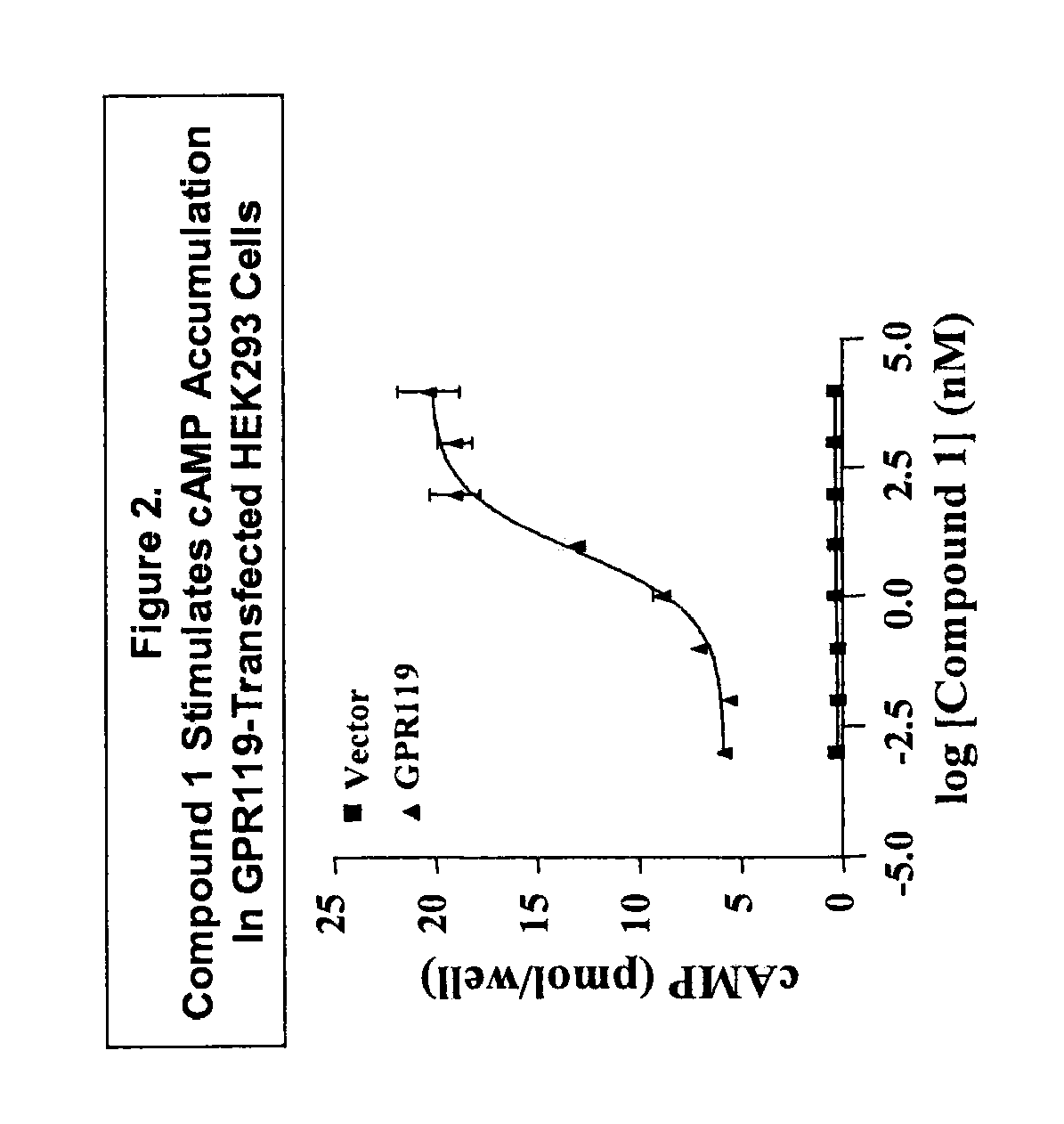
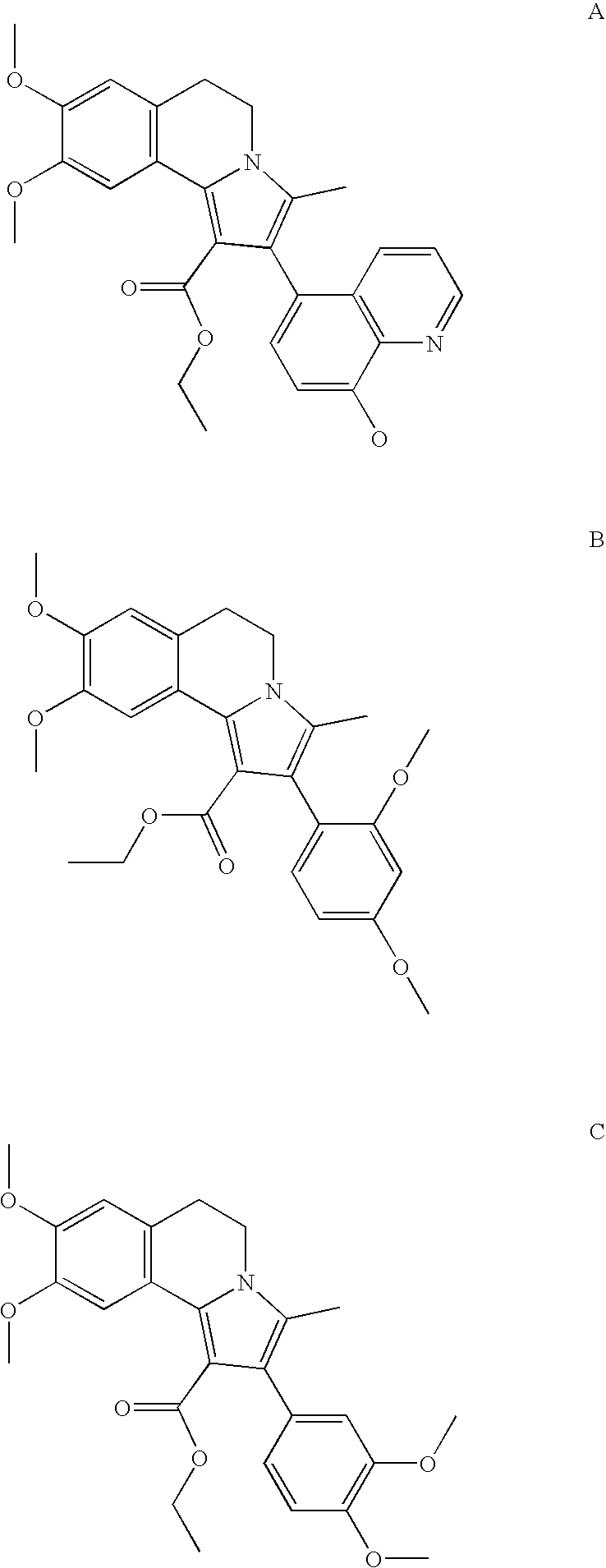
Methods of using a g protein-coupled receptor to identify peptide yy (PYY) secretagogues and compounds useful in the treatment of conditions modulated by pyy
InactiveUS20090253153A1Improve the level ofDetectable level of constitutive activityNervous disorderBacteriaGPR119Malabsorption
The present invention relates to methods of using GPR119 receptor to identify peptide YY (PYY) secretagogues and compounds useful in the treatment of conditions modulated by PYY, such as conditions modulated by stimulation of NPY Y2 receptor (Y2R). Agonists of GPR119 receptor are useful as therapeutic agents for treating or preventing a condition modulated by PYY, such as a condition modulated by stimulation of Y2R. Conditions modulated by PYY such as may be a condition modulated by stimulation of Y2R include bone-related conditions, metabolic disorders, angiogenesis-related conditions, ischemia-related conditions, convulsive disorders, malabsorptive disorders, cancers, and inflammatory disorders.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
Methods for treating diabetes and related disorders using pde10a inhibitors
The methods of the invention relate to the treatment of diabetes, including type 2 diabetes, and related disorders by administration of a PDE10A inhibitor. Such PDE10A inhibitors may be administered in conjunction with alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, insulin sensitizers, insulin secretagogues, hepatic glucose output lowering compounds, B-3 agonist, or insulin. Such PDE10A inhibitors may also be administered in conjunction with body weight reducing agents. Further methods of the invention relate to stimulating insulin release from pancreatic cells, for example, in response to an elevation in blood glucose concentration, by administration of a PDE10A inhibitor.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE AG
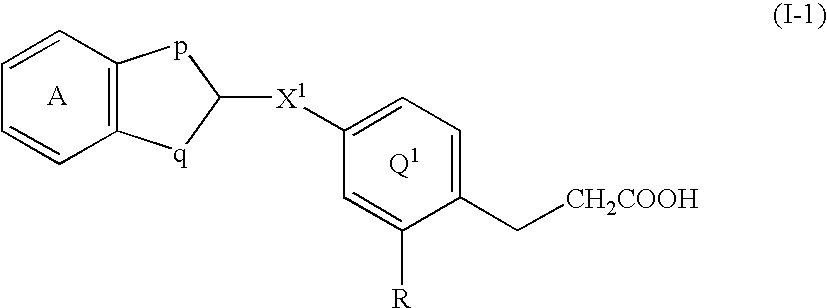
3-hydroxy-5-arylisothiazole derivative
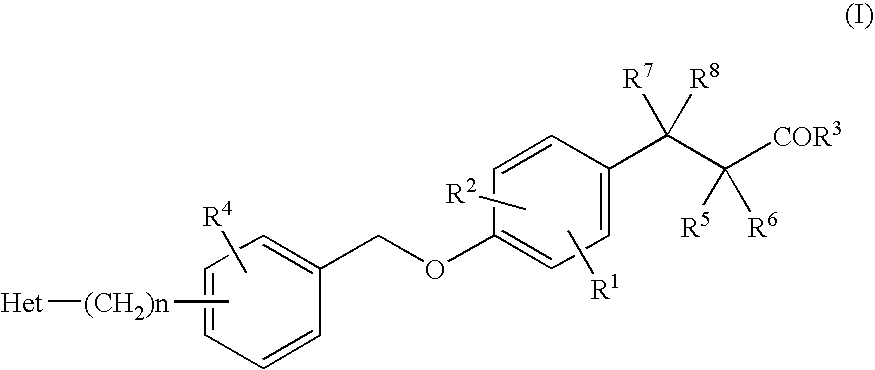
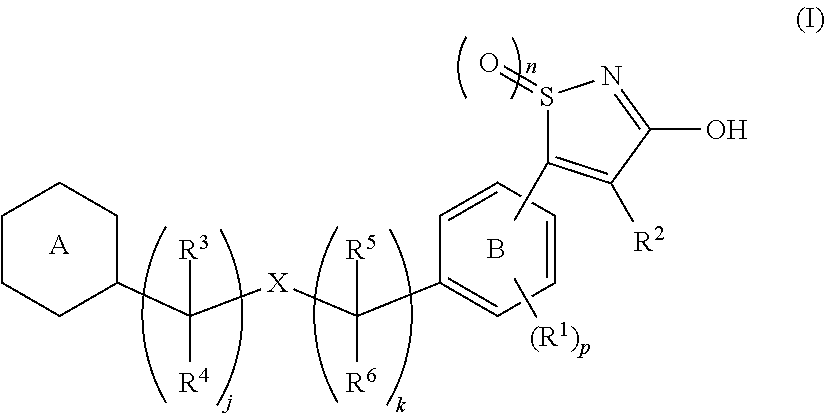
[Problem]To provide a GPR40 activating agent having, as an active ingredient, a novel compound having a GPR40 agonist action, a salt of the compound, a solvate of the salt or the compound, or the like, particularly, an insulin secretagogue and a prophylactic and / or therapeutic agent against diabetes, obesity, or other diseases.[Means of solving the problem]A compound of Formula (I):(where n is 0 to 2; p is 0 to 4; j is 0 to 3; k is 0 to 2; a ring A is an aryl group which is optionally substituted with L or a heterocyclic group which is optionally substituted with L; a ring B is a benzene ring, a pyridine ring, or a pyrimidine ring; X is O, S, —NR7—; and R1 to R7 are specific groups),a salt of the compound, or a solvate of the salt or the compound.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
Method of treating the syndrome of lipodystrophy
Methods of treating a human suffering from the Syndrome of Lipodystrophy or one or more HIV-related abnormalities included therein are provided. One method may include administering, by a pharmaceutically effective mode, a drug composition comprising an opioidergic agent, or alternatively, an opioidergic agent and an insulin secretagogue. The method may also include administering, by a pharmaceutically effective mode, a drug composition comprising an opiate agonist and opiate antagonist, or alternatively, an opiate agonist, opiate antagonist and an insulin secretagogue.
Owner:NEURENDO PHARMA LLC
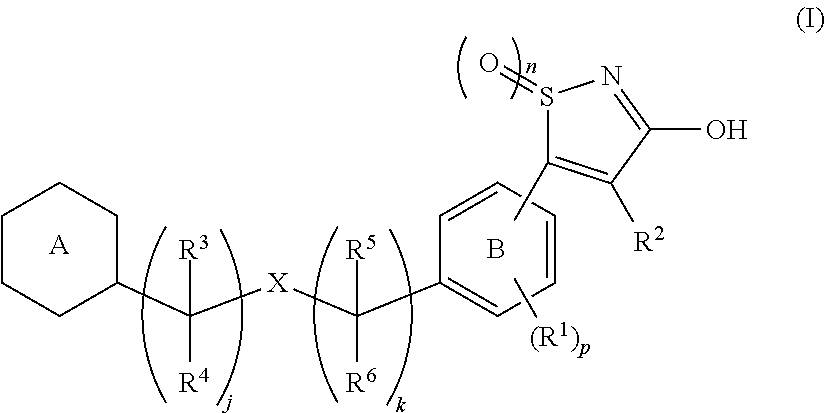
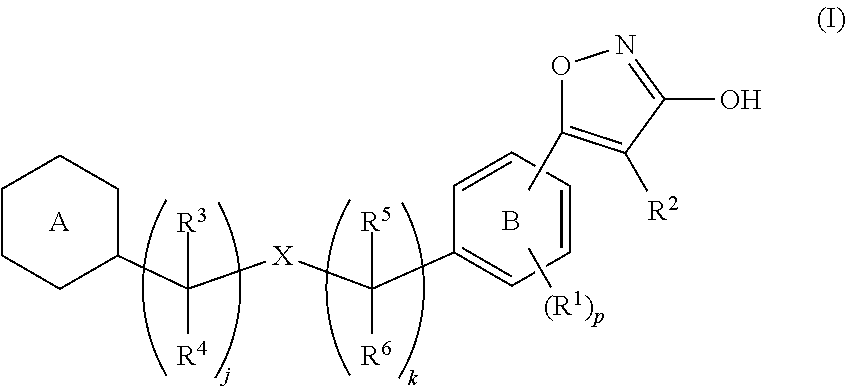
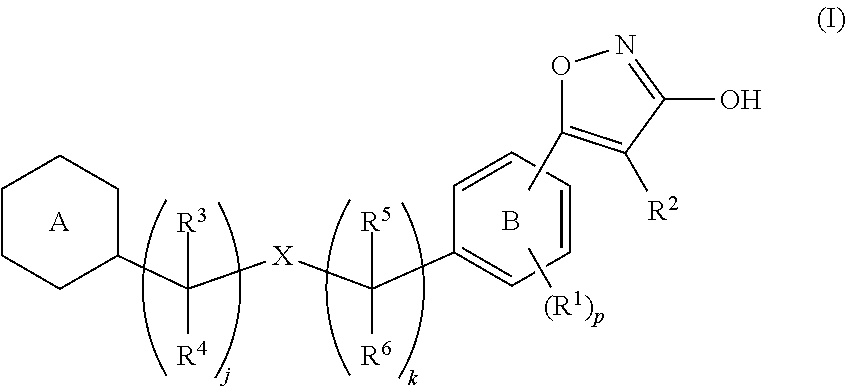
3-hydroxy-5-arylisoxazole derivative
[Problem]To provide a GPR40 activating agent having, as an active ingredient, a novel compound having a GPR40 agonist action, a salt of the compound, a solvate of the salt or the compound, or the like, particularly, an insulin secretagogue and a prophylactic and / or therapeutic agent against diabetes, obesity, or other diseases.[Means of Solving the Problem]A compound of Formula (I):(where p is 0 to 4; j is 0 to 3; k is 0 to 2; a ring A is a specific cyclic group; a ring B is a benzene ring, a pyridine ring, or a pyrimidine ring; X is —CH2—, O, —S(O)i— (i is 0 to 2), or —NR7—; R1 to R6 are specific groups),a salt of the compound, or a solvate of the salt or the compound.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
3-(4-benzyloxyphenyl)propanoic acid derivative
InactiveCN1922165AModulation of high GPR40 receptor functionPrevent diabetesOrganic chemistryDiabetes mellitusDisease cause
The present invention provides a novel compound represented by the formula (I) wherein each symbol is as defined in the specification, a salt thereof and a prodrug thereof having a superior GPR40 receptor function modulating action, which can be used as an insulin secretagogue, an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of diabetes and the like. They unexpectedly show superior GPR40 receptor agonist activity, and also show superior properties as a pharmaceutical product, such as stability and the like. Thus, they can be safe and useful pharmaceutical agents for the prophylaxis or treatment of GPR40 receptor related diseases in mammals.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating peptide (PACAP)receptor 3 (R3) agonists and their pharmacological methods of use
InactiveUS6972319B1Good potencyStimulate insulin releasePeptide/protein ingredientsReceptors for hormonesDiseaseMammal
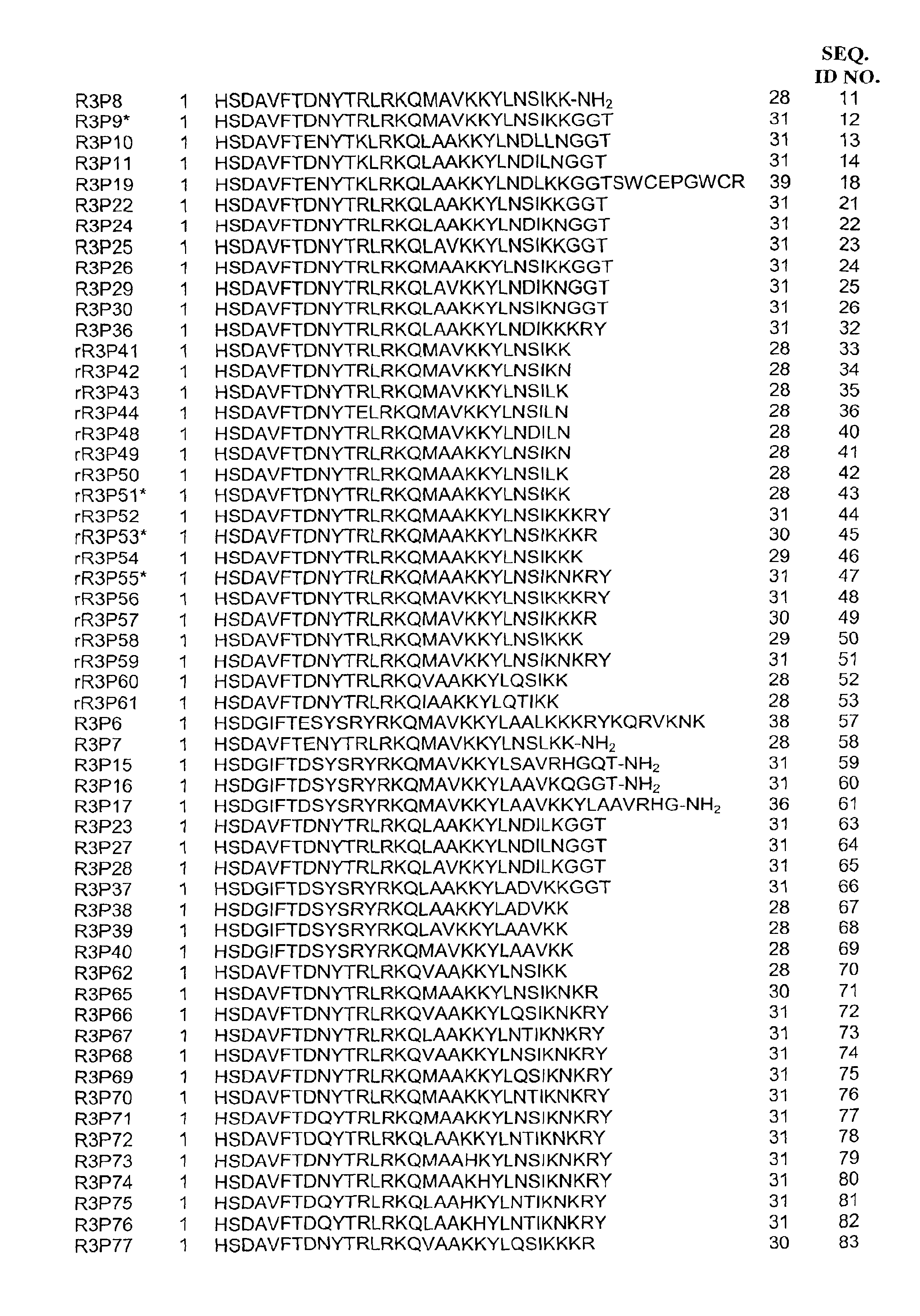
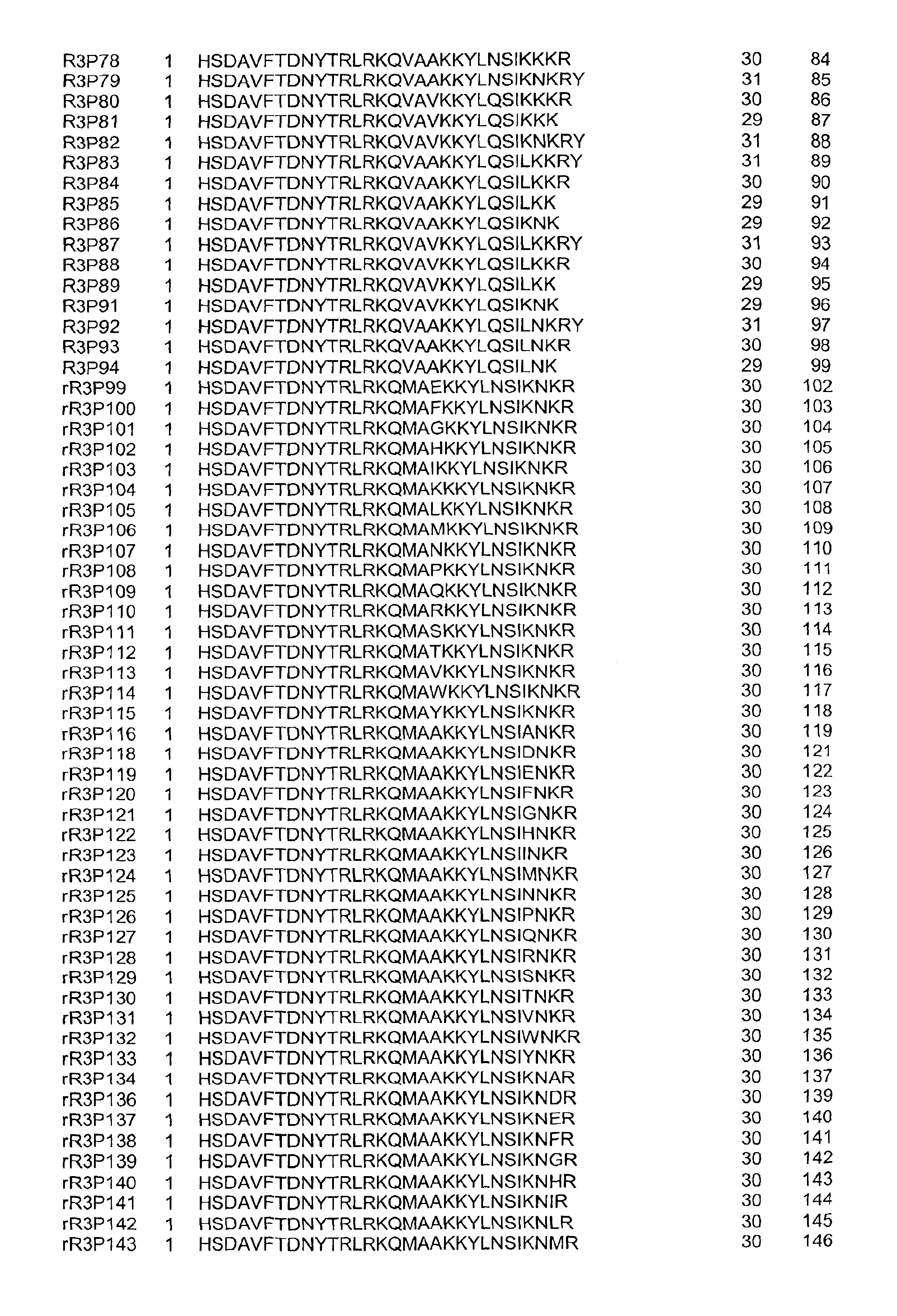
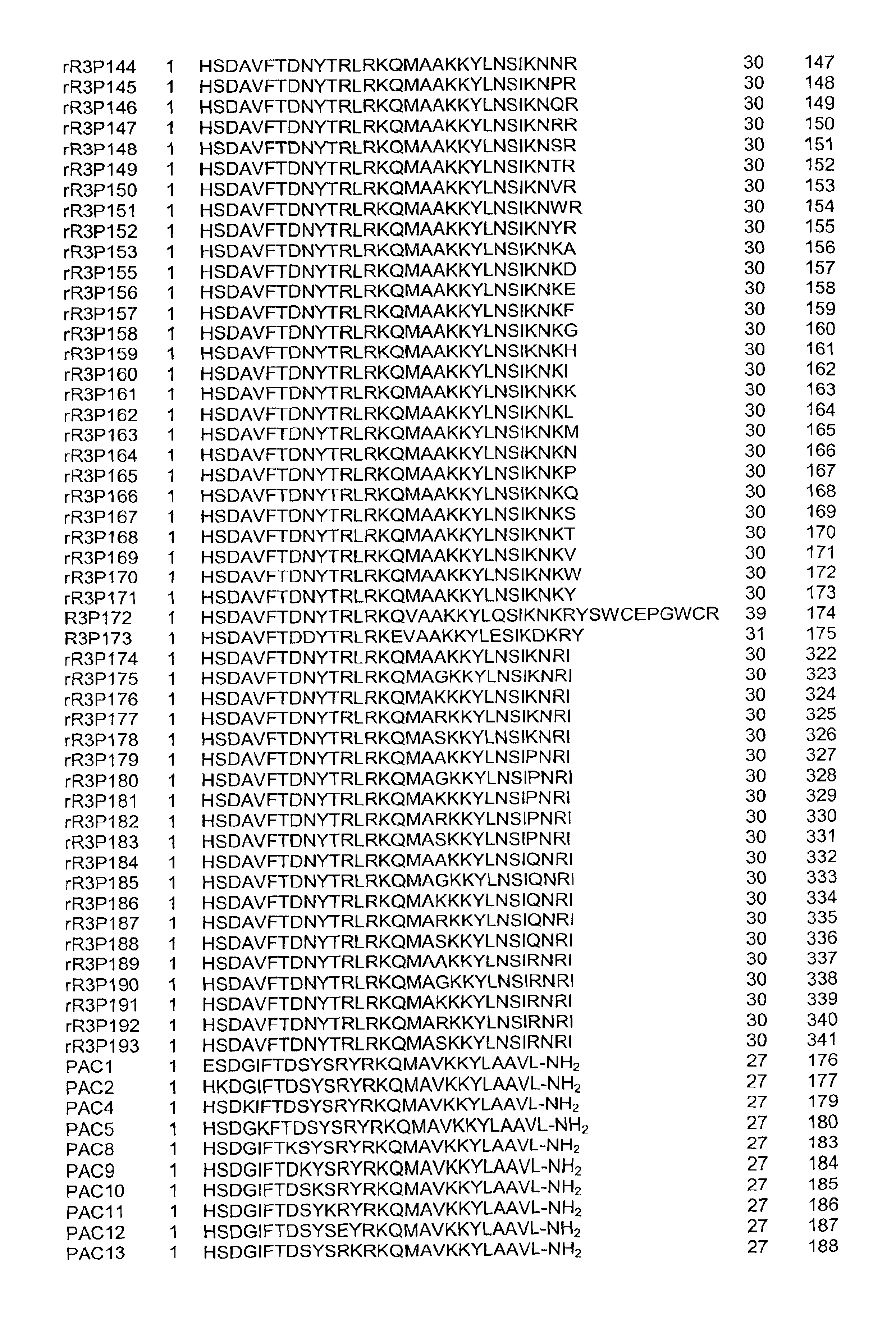
This invention provides novel peptides that function in vivo to stimulate insulin release from pancreatic beta cells in a glucose-dependent fashion. These insulin secretagogue peptides are shown to stimulate insulin release in rat islet cells in vitro, and in vivo. The peptides of the present invention provide a new therapy for patients with decreased endogenous insulin secretion, in particular type 2 diabetics. In particular, the invention is a polypeptide selected from a specific group of VIP / PACAP-related polypeptides, or functional equivalents thereof. The invention is also directed to a method of treating a metabolic disease in a mammal comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of the insulin secretagogue peptides to said mammal. Also disclosed are methods of making the peptides, both recombinant and synthetic.
Owner:BAYER CORPORATION +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com