Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Tissue phantom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
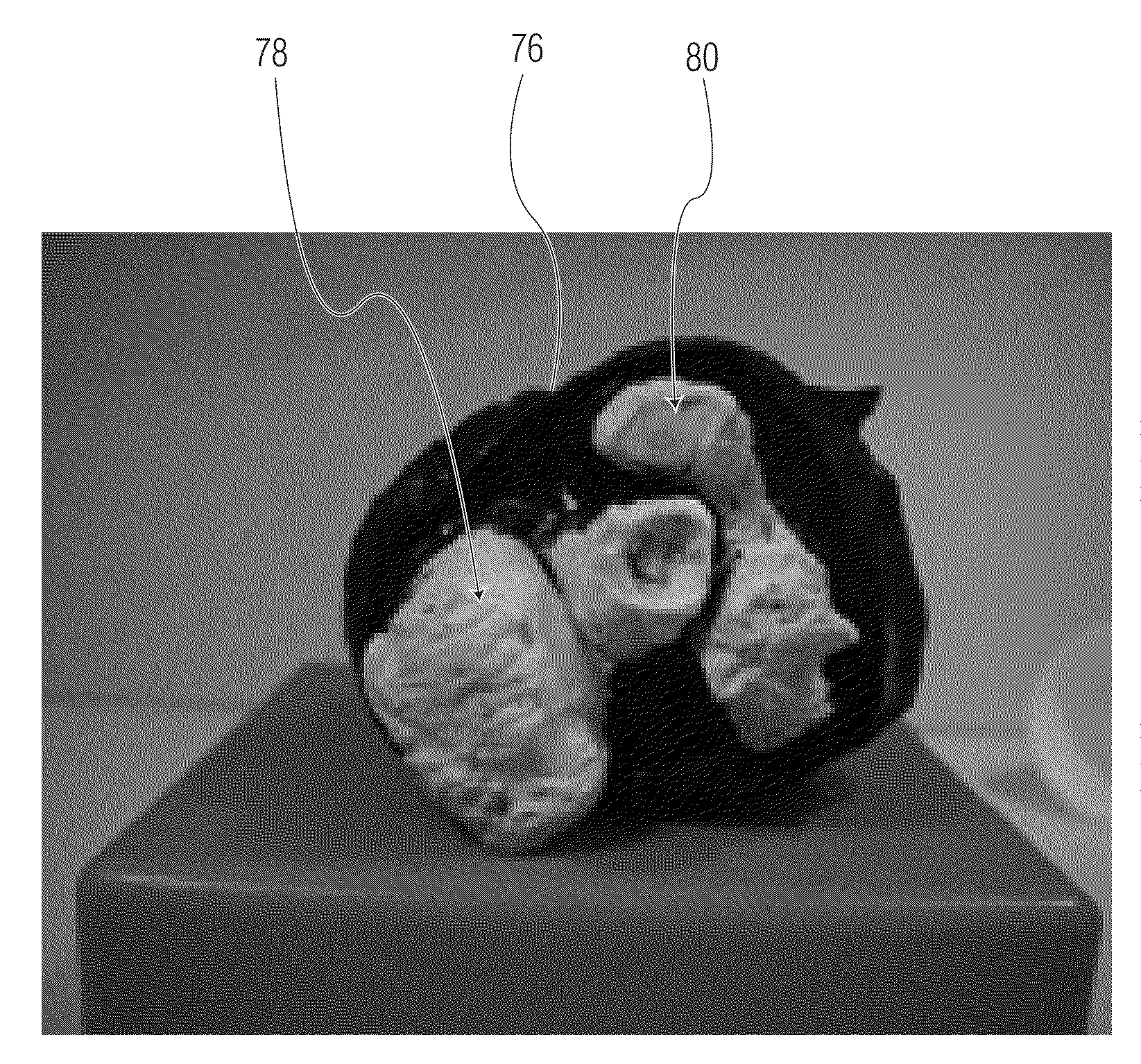
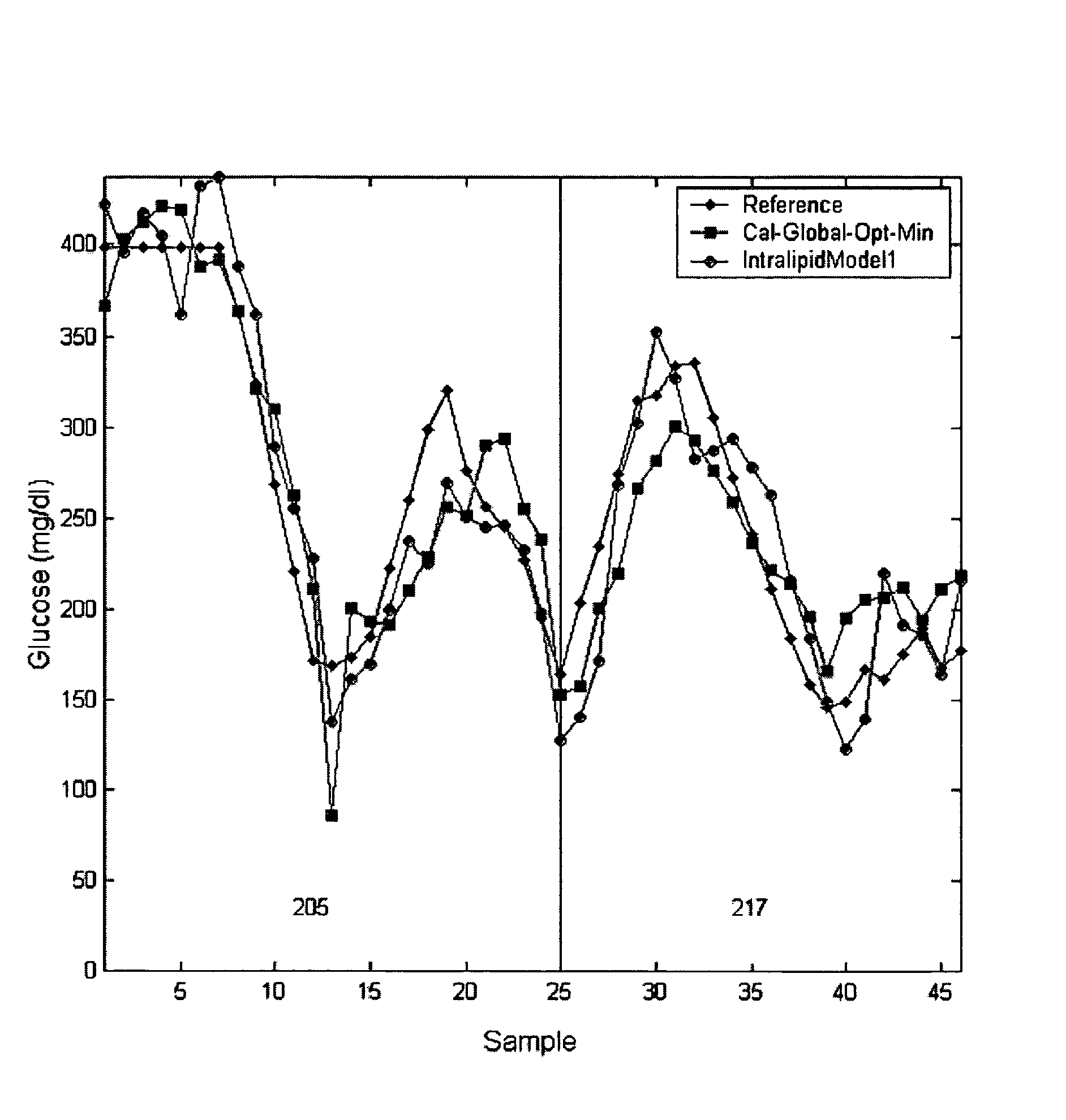
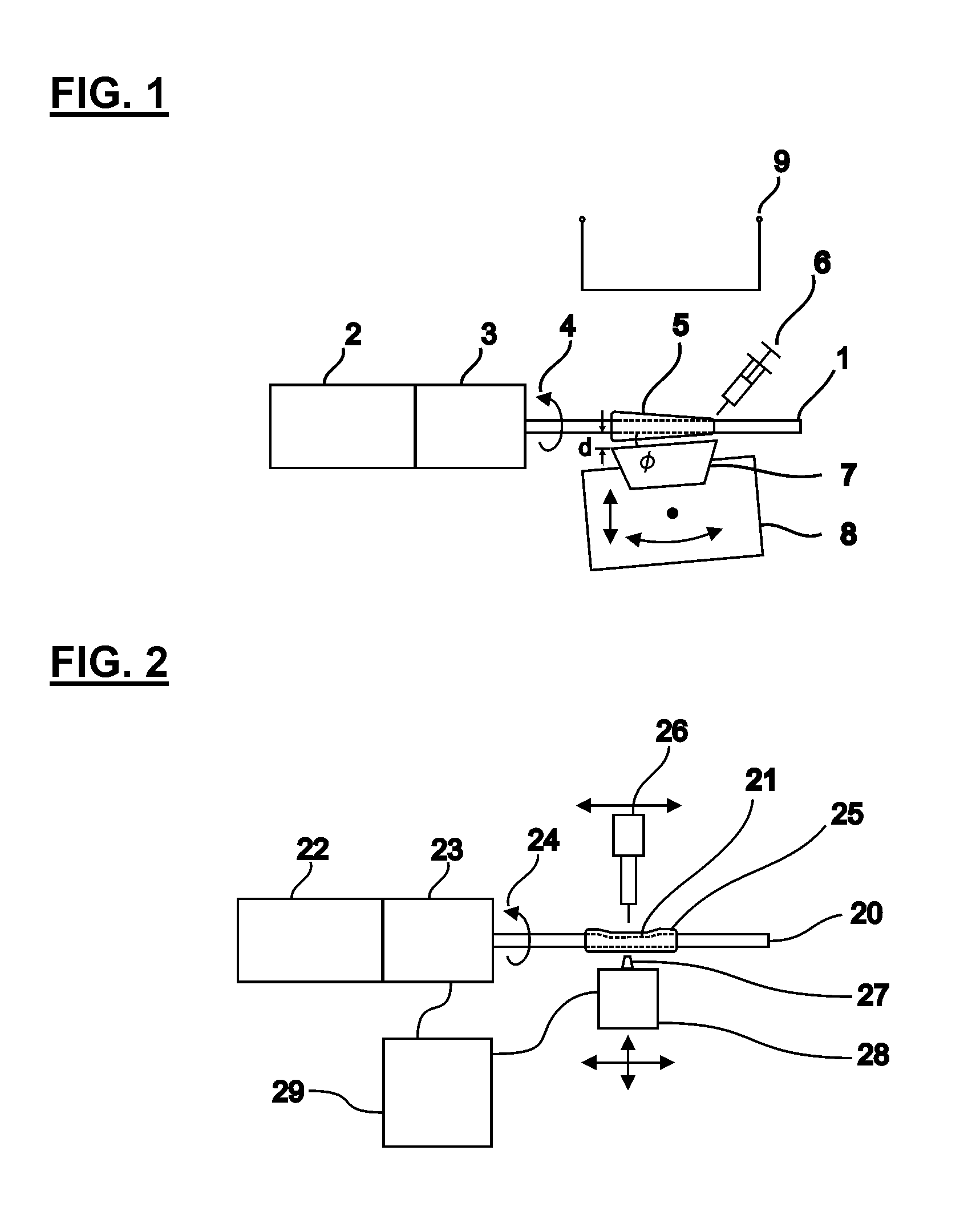
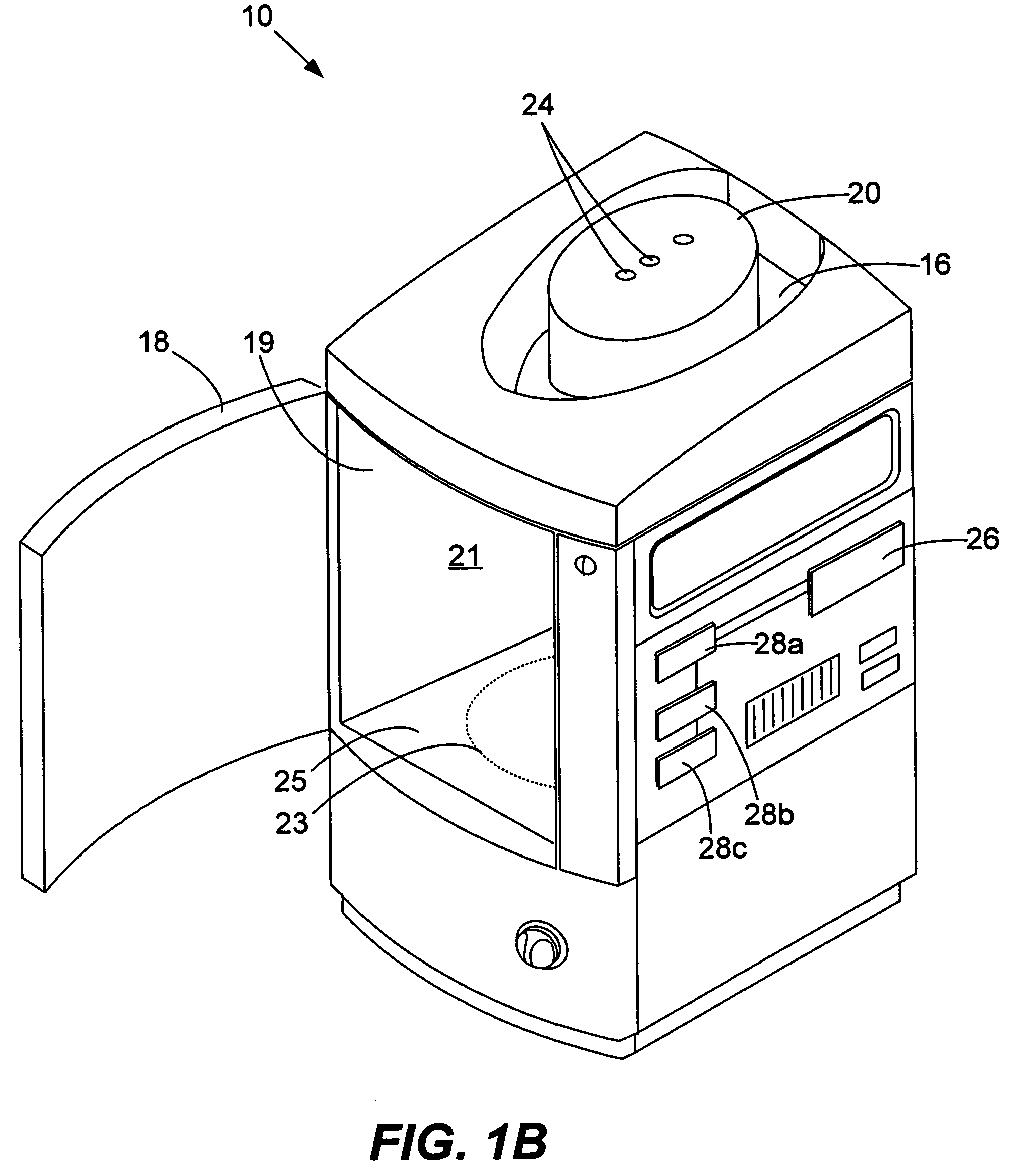
Method of adapting in-vitro models to aid in noninvasive glucose determination
InactiveUS7317938B2Easy to controlStrict controlDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsConcentrations glucoseNon invasive
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
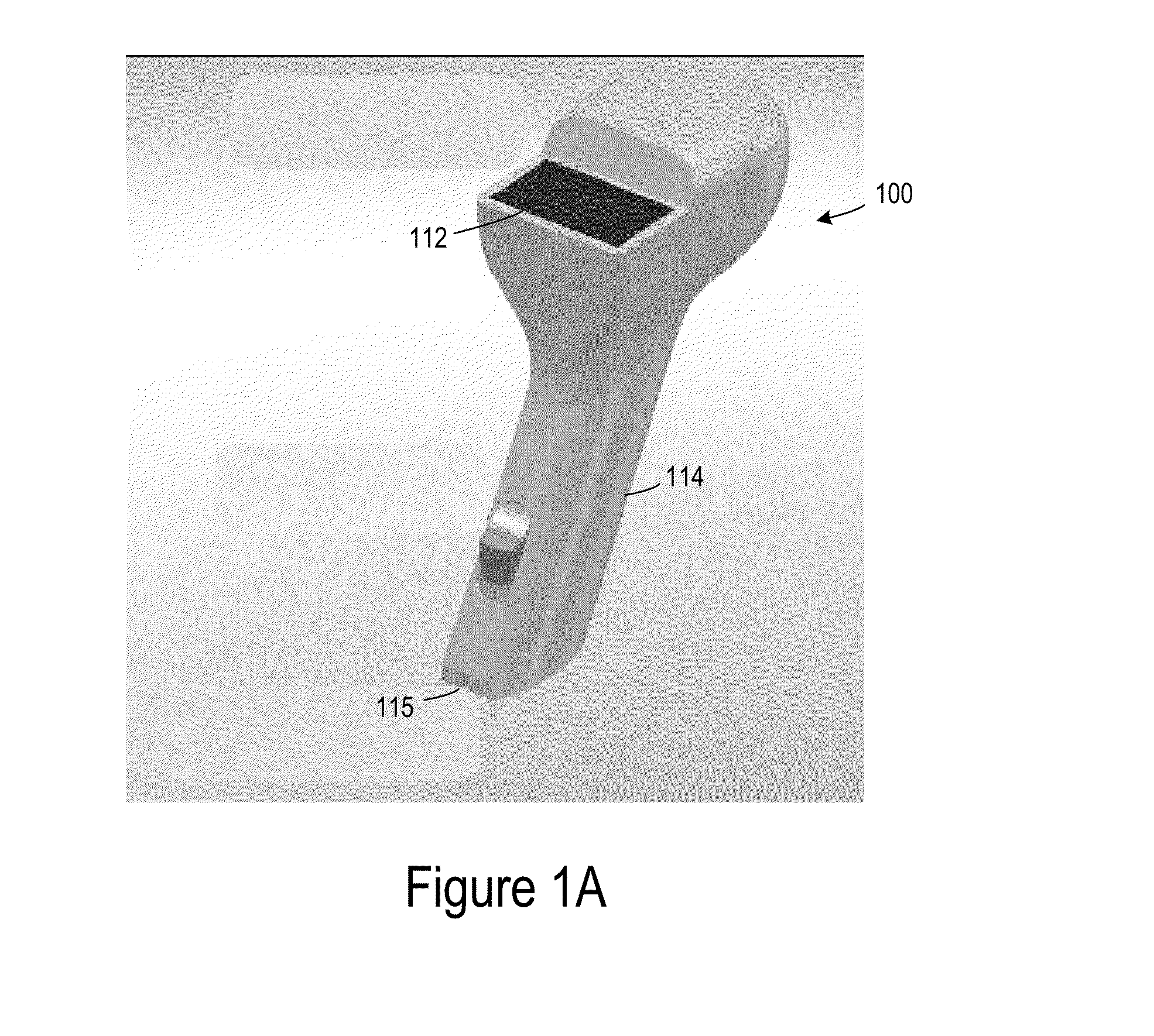
In vivo port wine stain, burn and melanin depth determination using a photoacoustic probe
ActiveUS7322972B2Avoid introducingSurgical instrument detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringBurning tissueBurn tissue
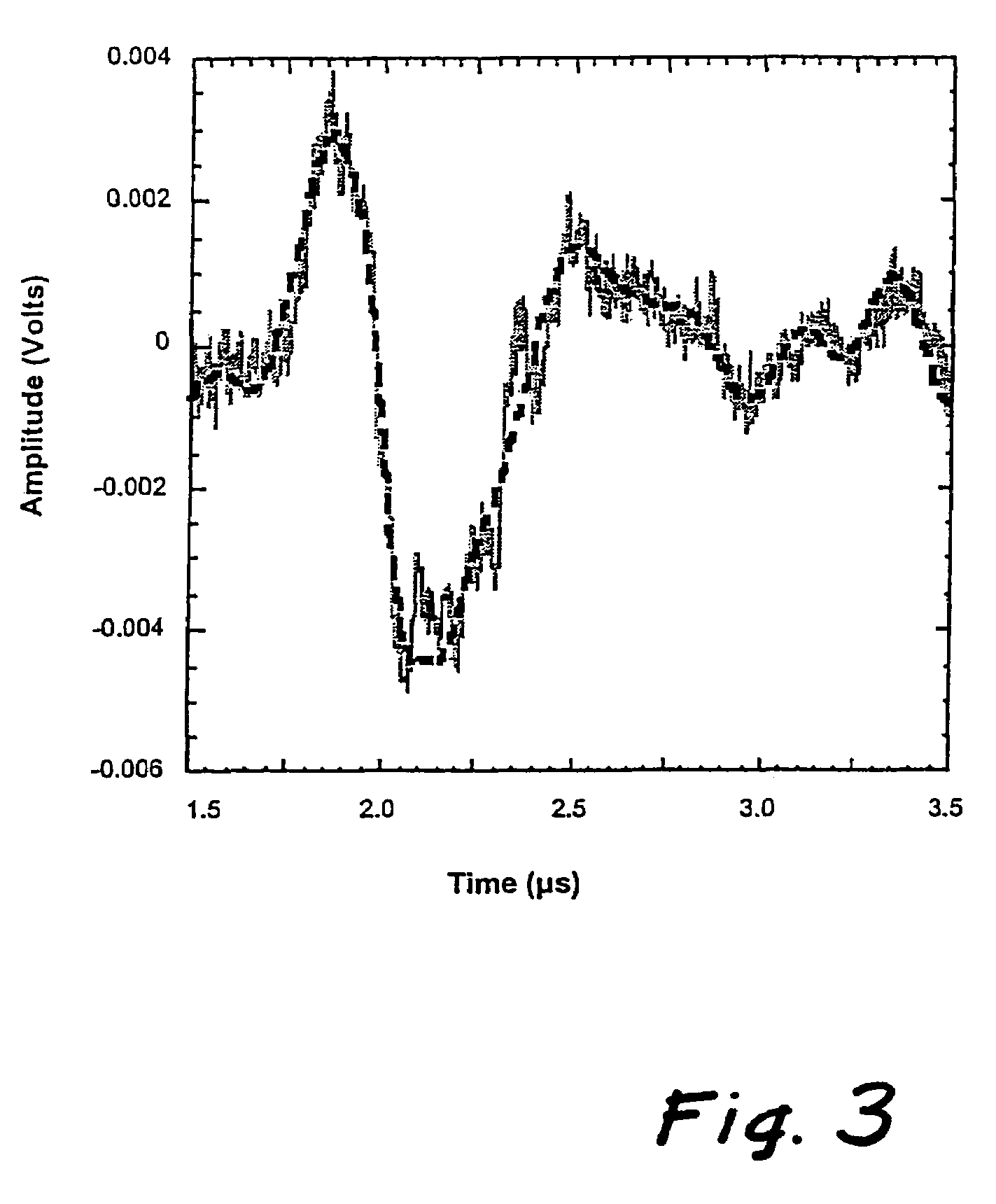
A photoacoustic probe for port wine stain (PWS), burn and melanin depth measurements is comprised of optical fibers for laser light delivery and a piezoelectric element for acoustic detection. The probe induced and measured photoacoustic waves in acryl amide tissue phantoms and PWS skin in vivo. Acoustic waves were denoised using spline wavelet transforms, then deconvolved with the impulse response of the probe to yield initial subsurface pressure distributions in phantoms and skin. The waves were then analyzed for epidermal melanin concentration, using a photoacoustic melanin index (PAMI) related to the amount of laser energy absorbed by melanin. Propagation time of the photoacoustic wave was used to determine the depth of blood perfusion underlying necrotic, burned tissue. Thus, the photoacoustic probe can be used for determining PWS, burn and melanin depth for most patients receiving laser therapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
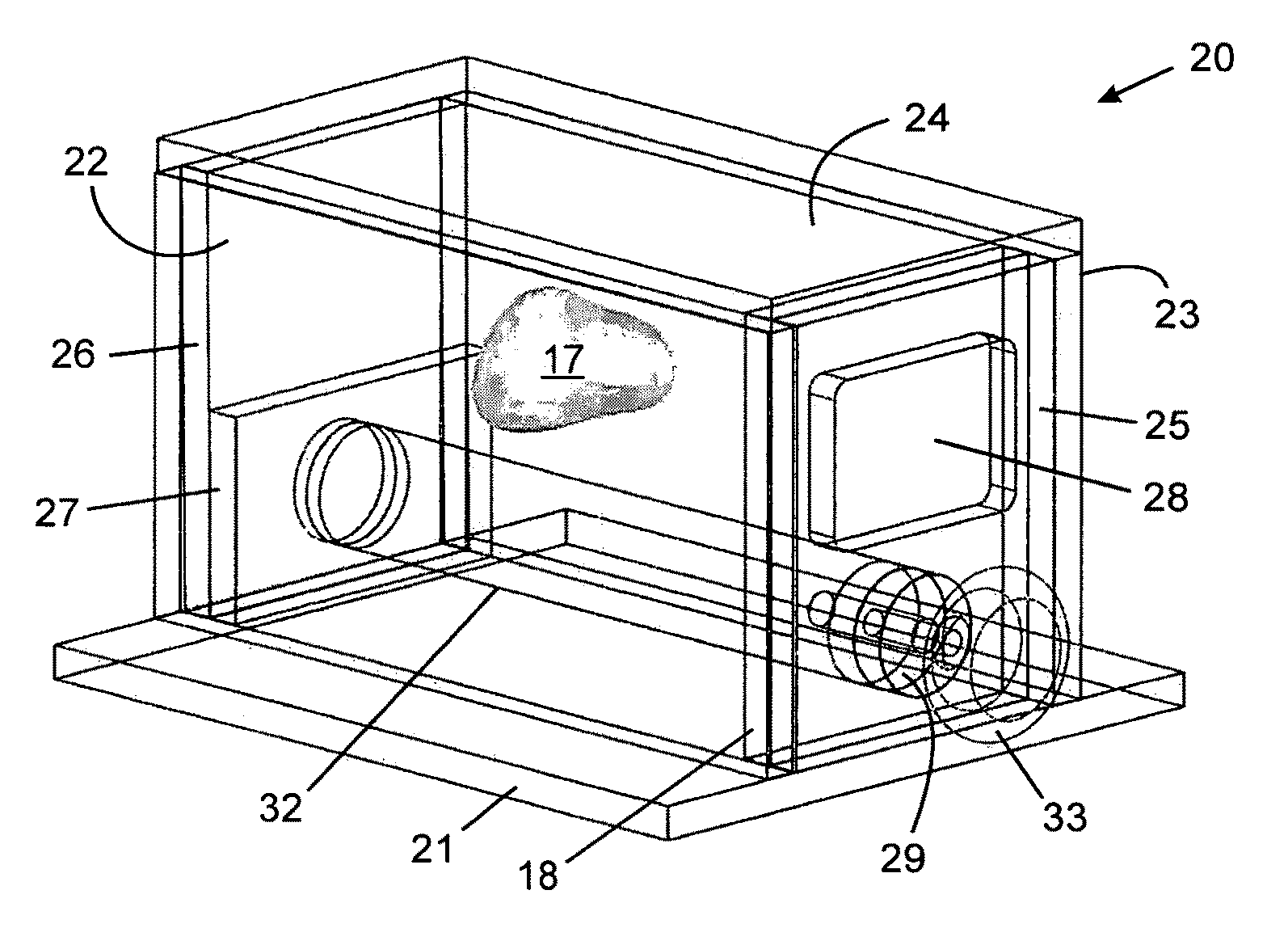
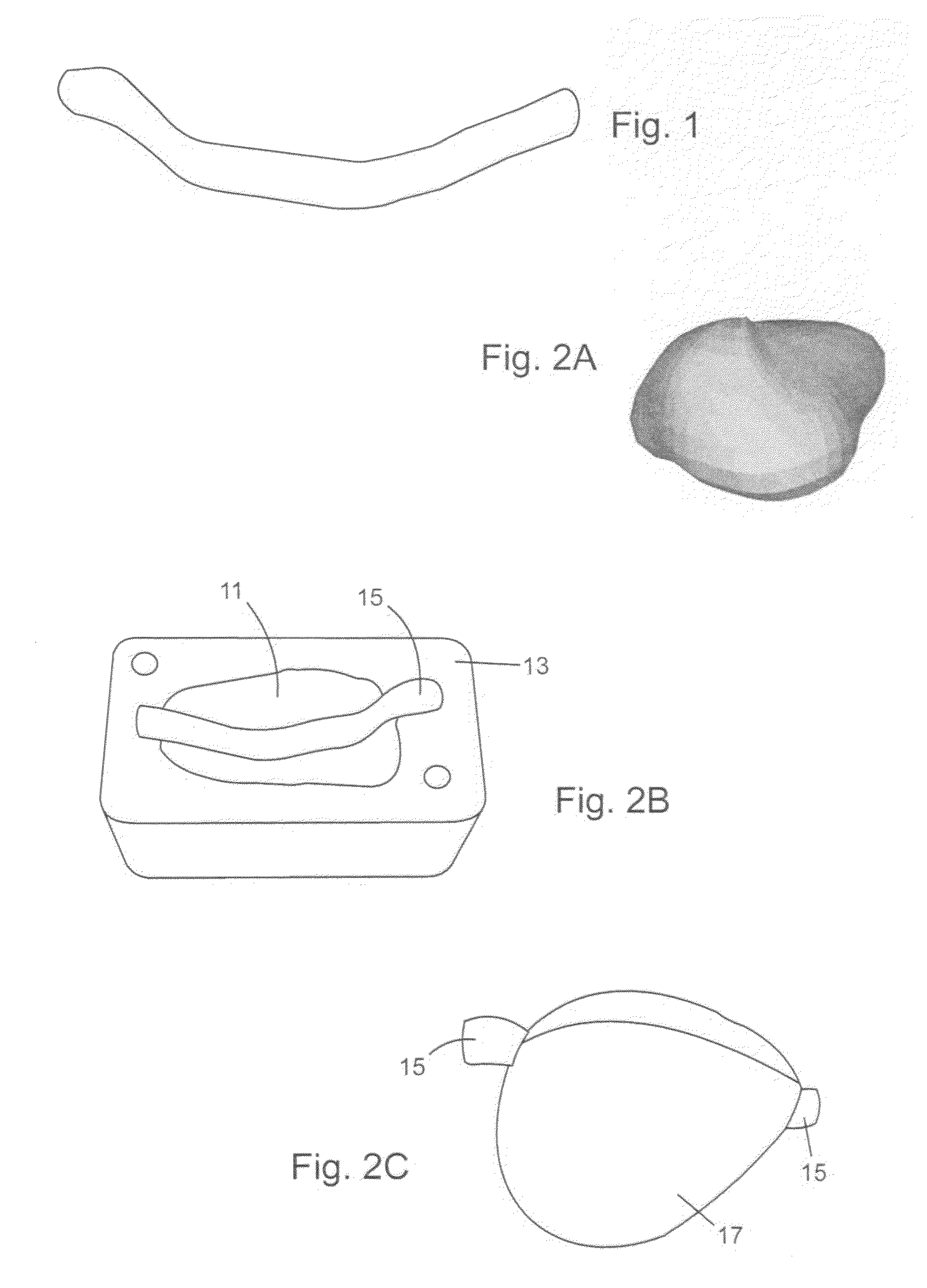
Tissue-mimicking phantom for prostate cancer brachytherapy
A phantom for prostate cancer brachytherapy has a prostate tissue phantom shaped like a real prostate gland, a perineal tissue phantom surrounding the prostate tissue phantom, a skin tissue phantom separating the perineal tissue phantom from an outside environment, and an enclosure. The prostate tissue phantom is a polyvinyl alcohol cryogel (PVA-C) having undergone 3-5 freeze-thaw cycles and having 10-20% w / w PVA in a solvent (e.g. water), 4-8% w / w oil and an amount of acoustic scattering particles to ultrasonically distinguish the prostate-tissue phantom from its surroundings. The perineal tissue phantom is a PVA-C having undergone 1-2 freeze-thaw cycles and having 10-20% w / w PVA in a solvent, 4-8% w / w oil and an amount of acoustic scattering particles to ultrasonically distinguish the perineal tissue phantom from its surroundings. The skin tissue phantom is a PVA-C having undergone at least 6 freeze-thaw cycles and having 15-25% w / w PVA in a solvent. The phantom mimics the imaging and mechanical properties of the prostate and surrounding tissues, providing a realistic phantom for prostate cancer brachytherapy.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
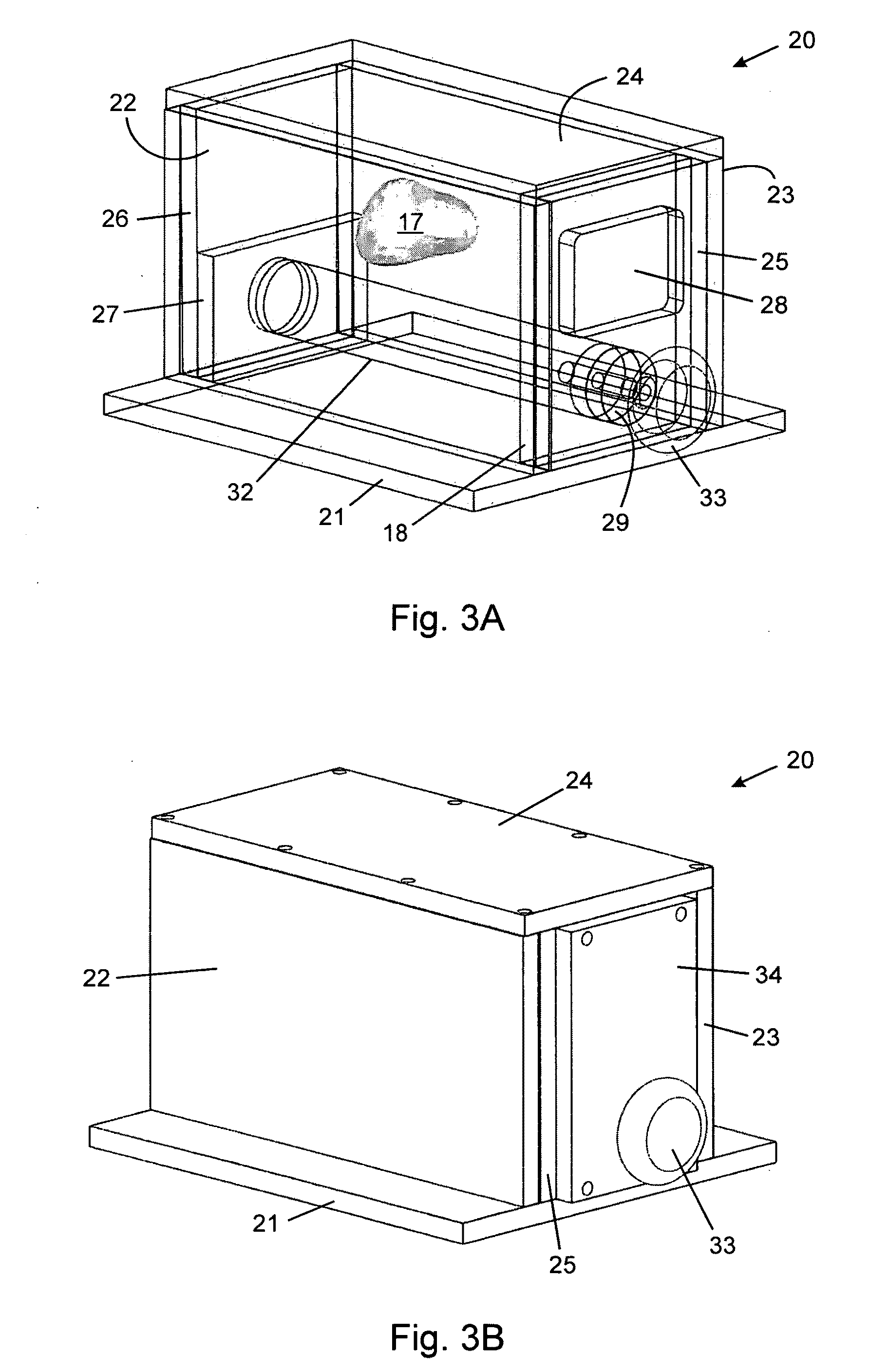
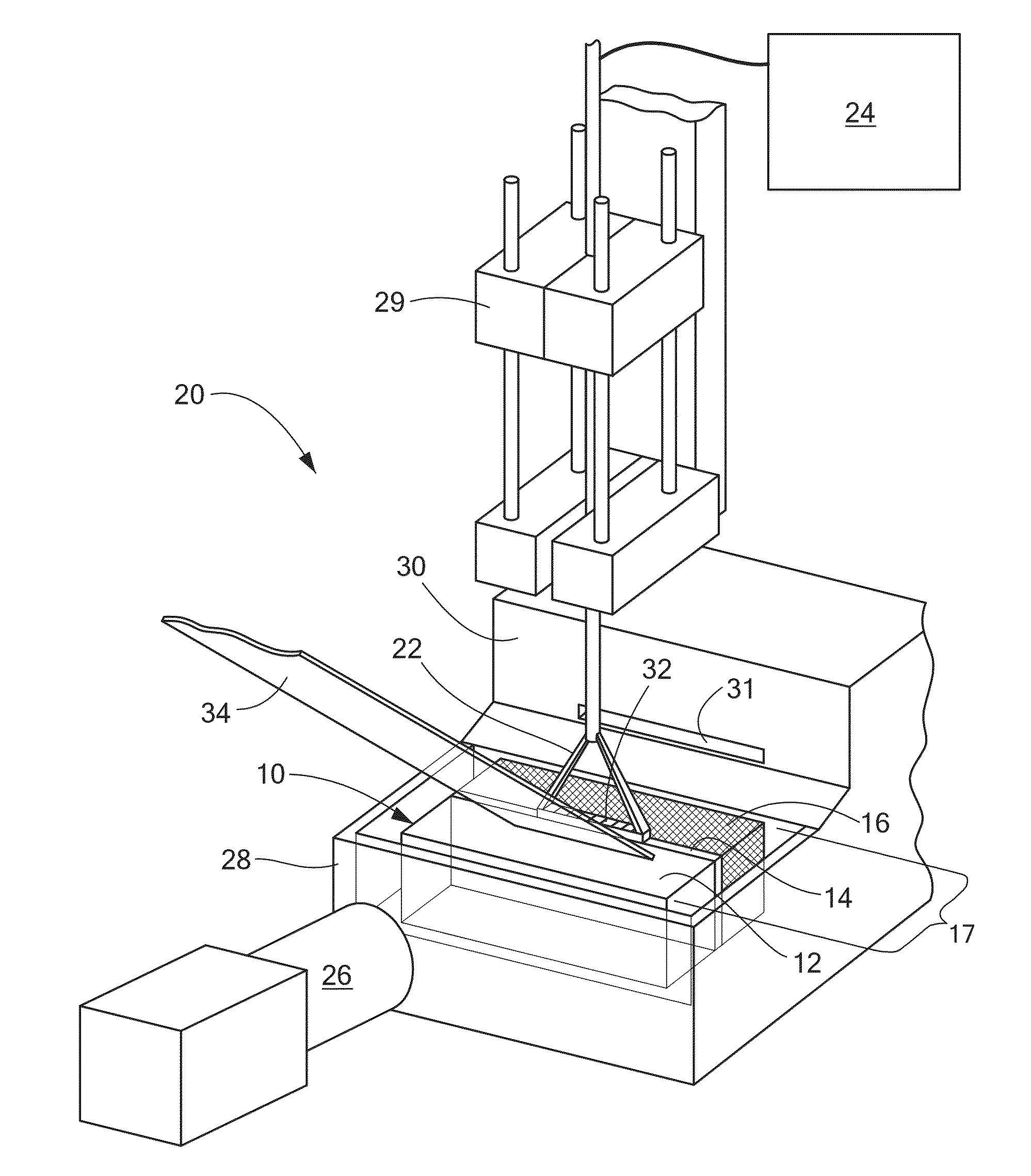
Anatomically and functionally accurate soft tissue phantoms and method for generating same
InactiveUS20100047752A1Efficient use ofEfficient replicationLamination ancillary operationsLaminationElastomerTissue phantom
A method, system and apparatus for manufacturing anatomically and functionally accurate soft tissue phantoms with multimodality characteristics for imaging studies is disclosed. The organ / tissue phantom is constructed by filling a container containing an organ having inner vasculature therein with a molten elastomeric material; inserting a plurality of rods with bumps thereupon through the container and the organ; allowing the molten elastomeric material to harden and cure; removing the organ; replacing the organ with a plurality of elastomeric segments; and removing an elastomeric segment and replacing the void created thereupon with molten PVA to create a PVA segment; allowing the molten PVA segment to harden and cure; and repeating the creation of PVA segments until all the elastomeric segments have been removed, such that each successive molten PVA segment adheres to and fuses with the previous hardened PVA segment so as to form an approximately complete organ phantom cast. The organ / tissue phantom is completed by inserting the approximately complete organ phantom cast inserting upside-down into a fixture made from the bottom-most elastomeric segment, which contains molten PVA; and allowing the molten PVA to harden and cure.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
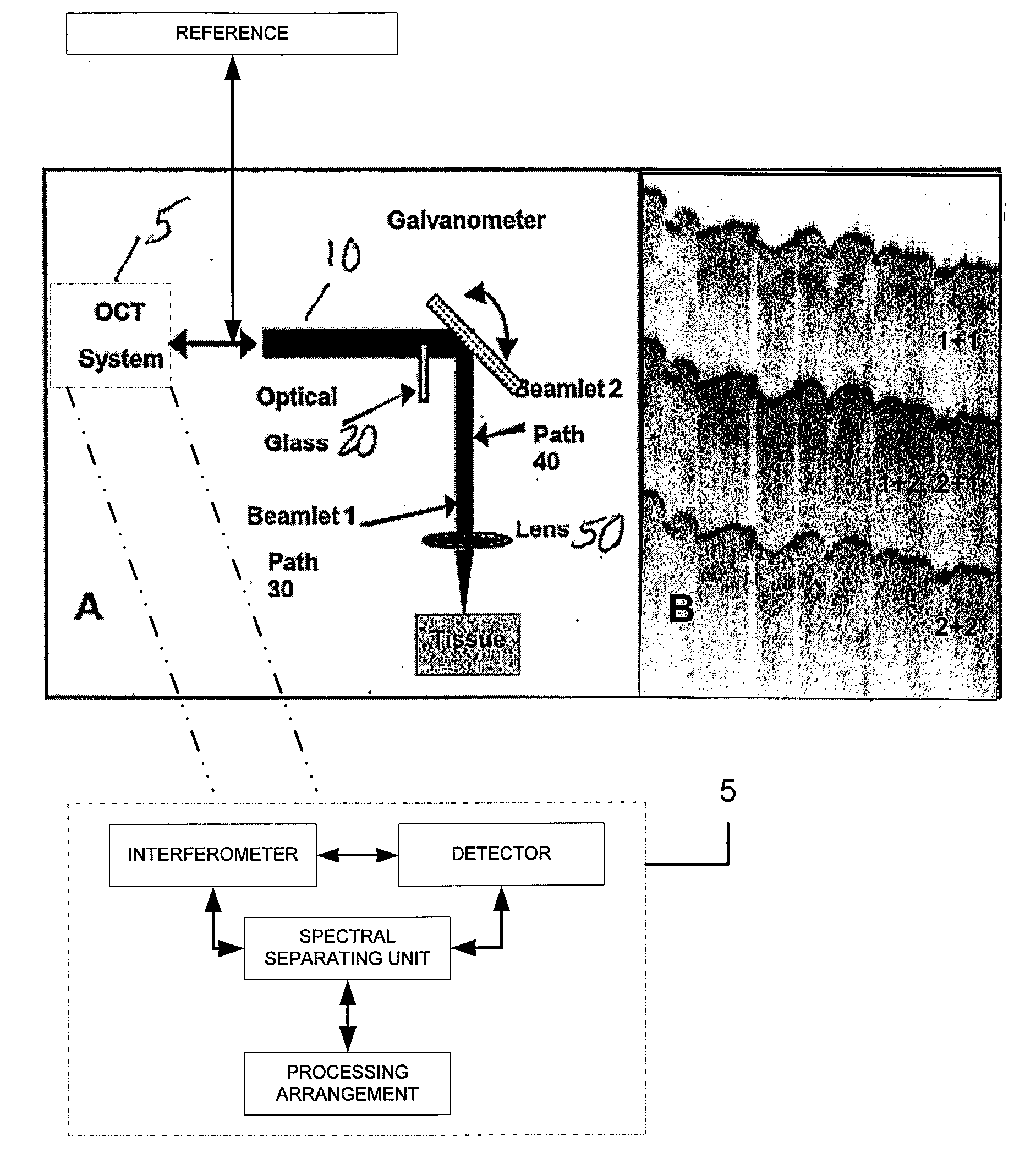
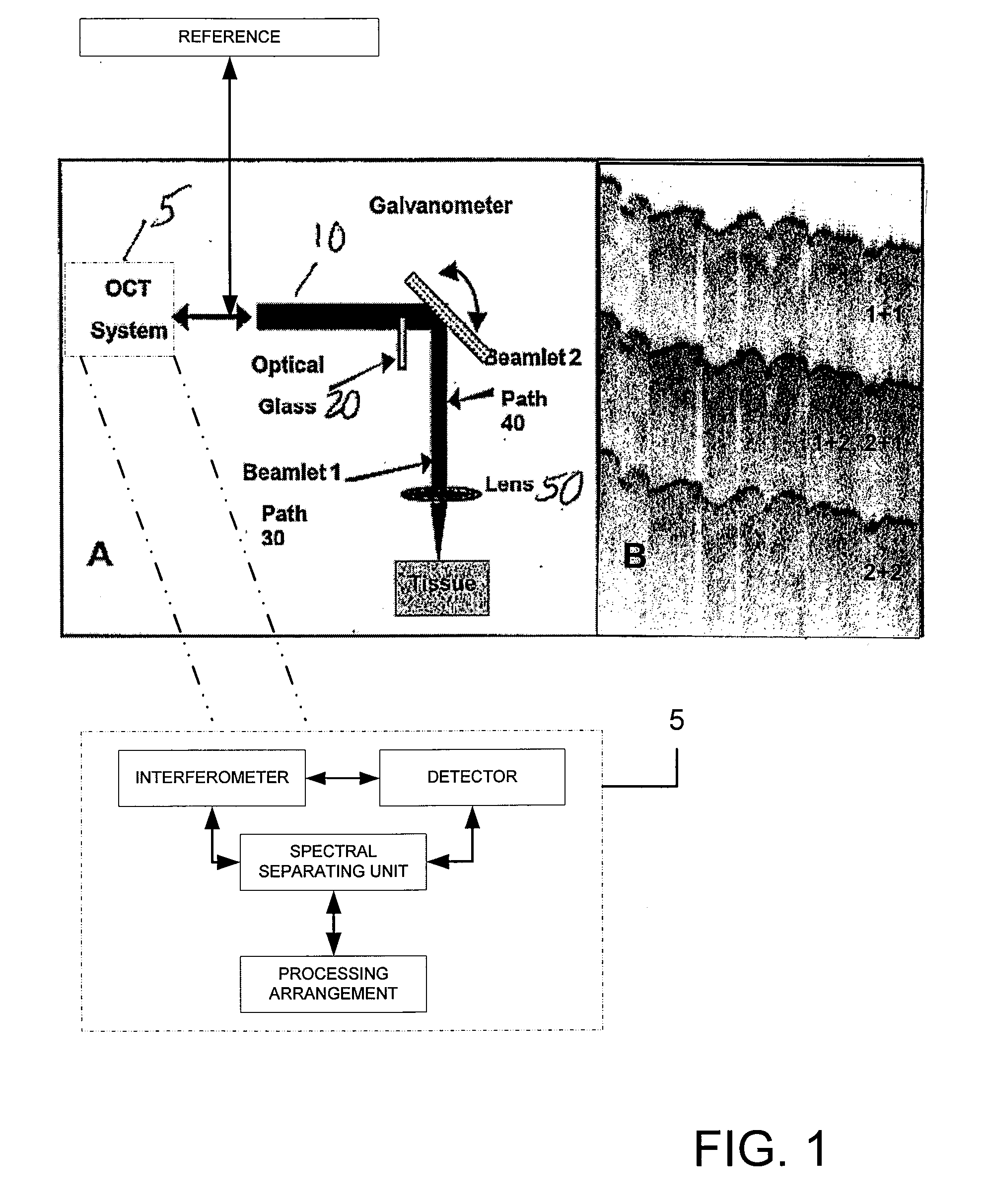
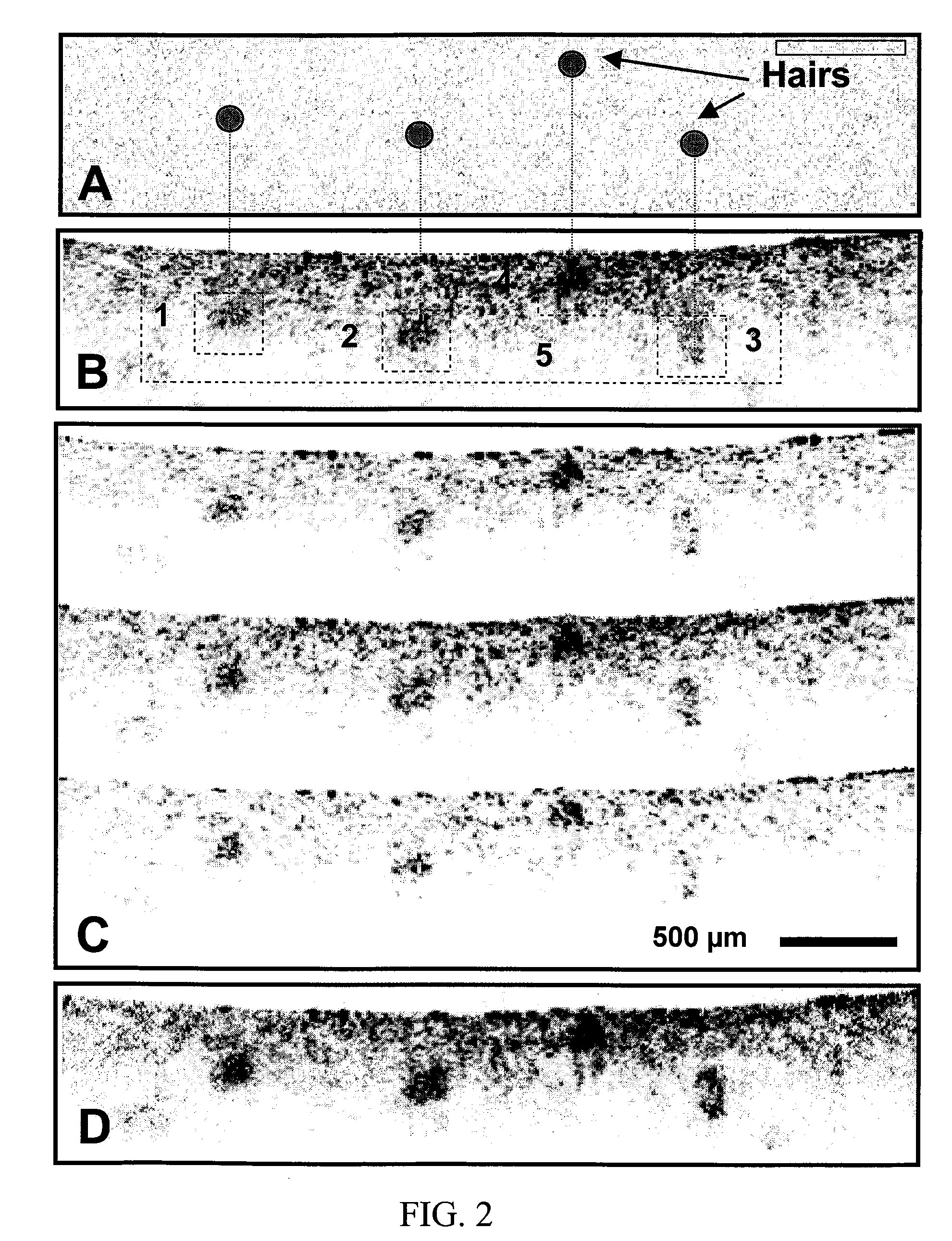
Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by path length encoded angular compounding
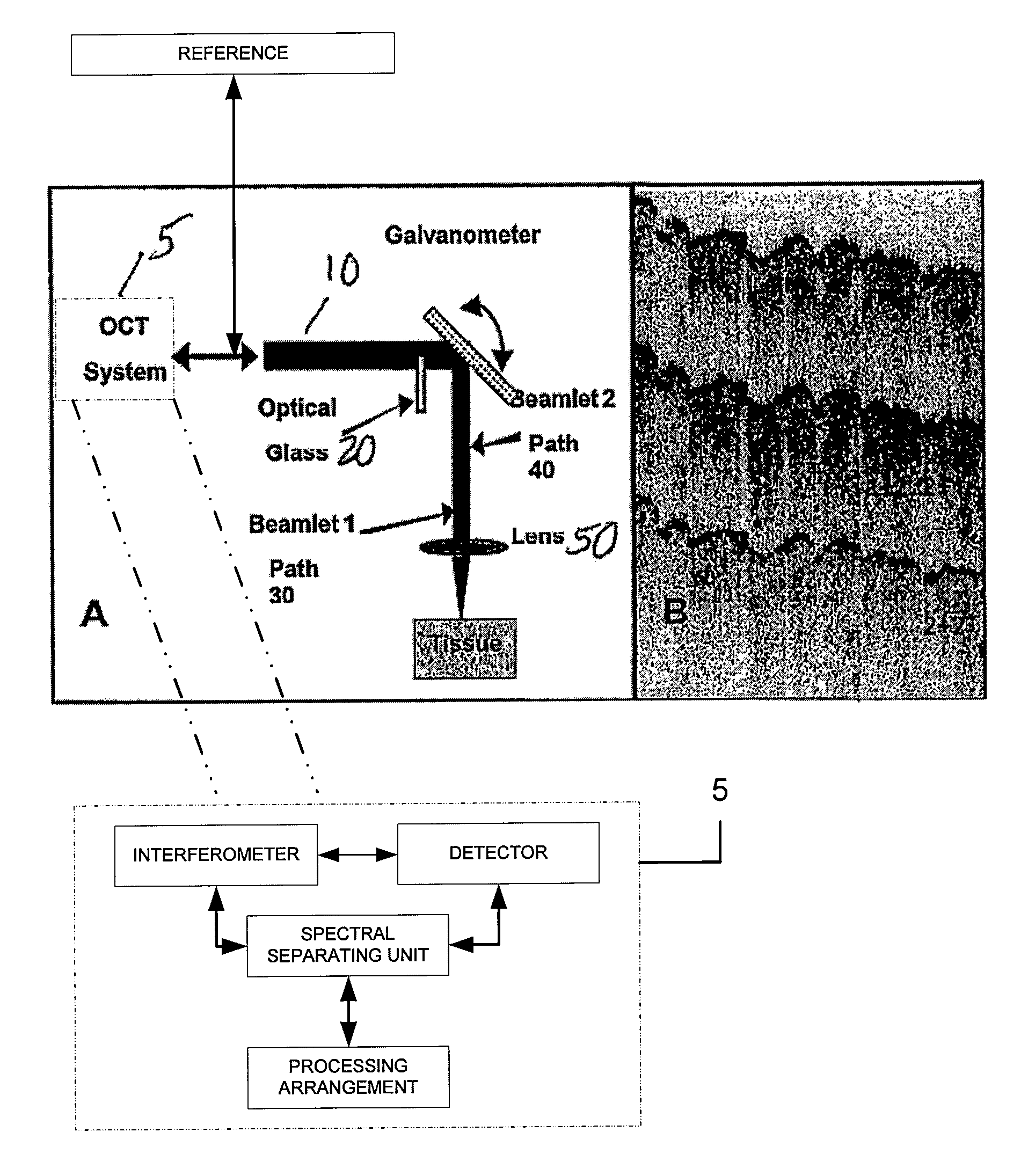
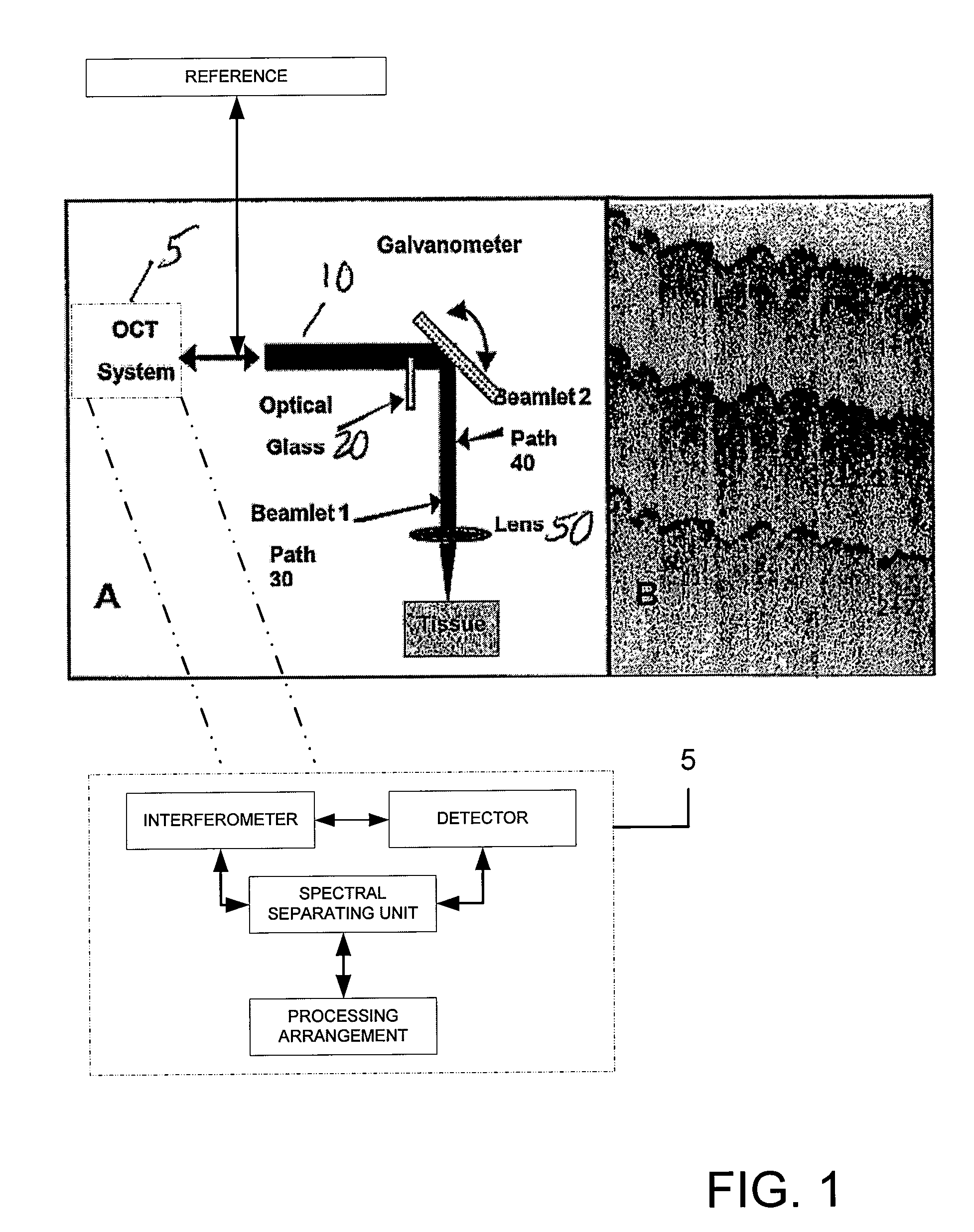
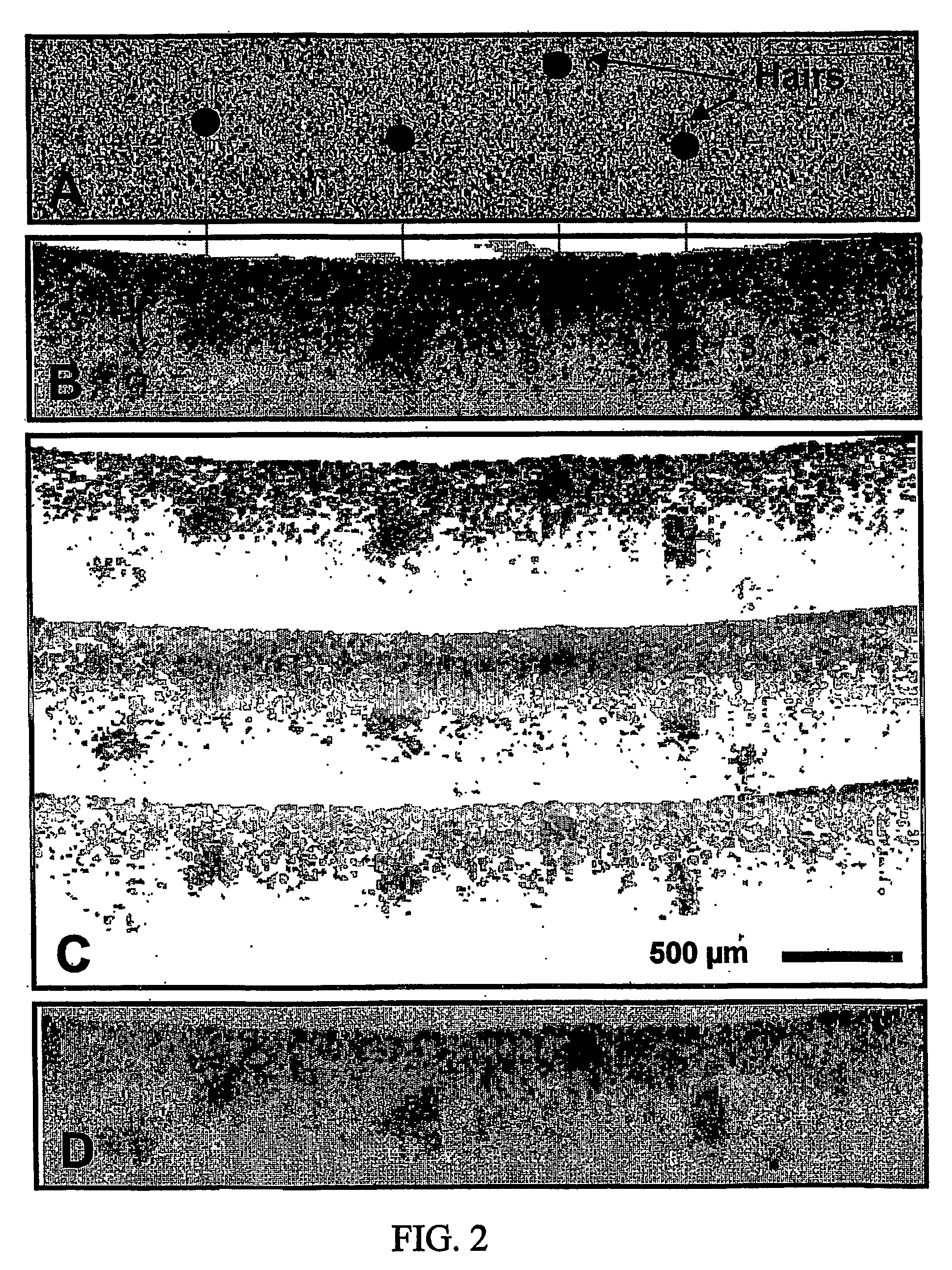
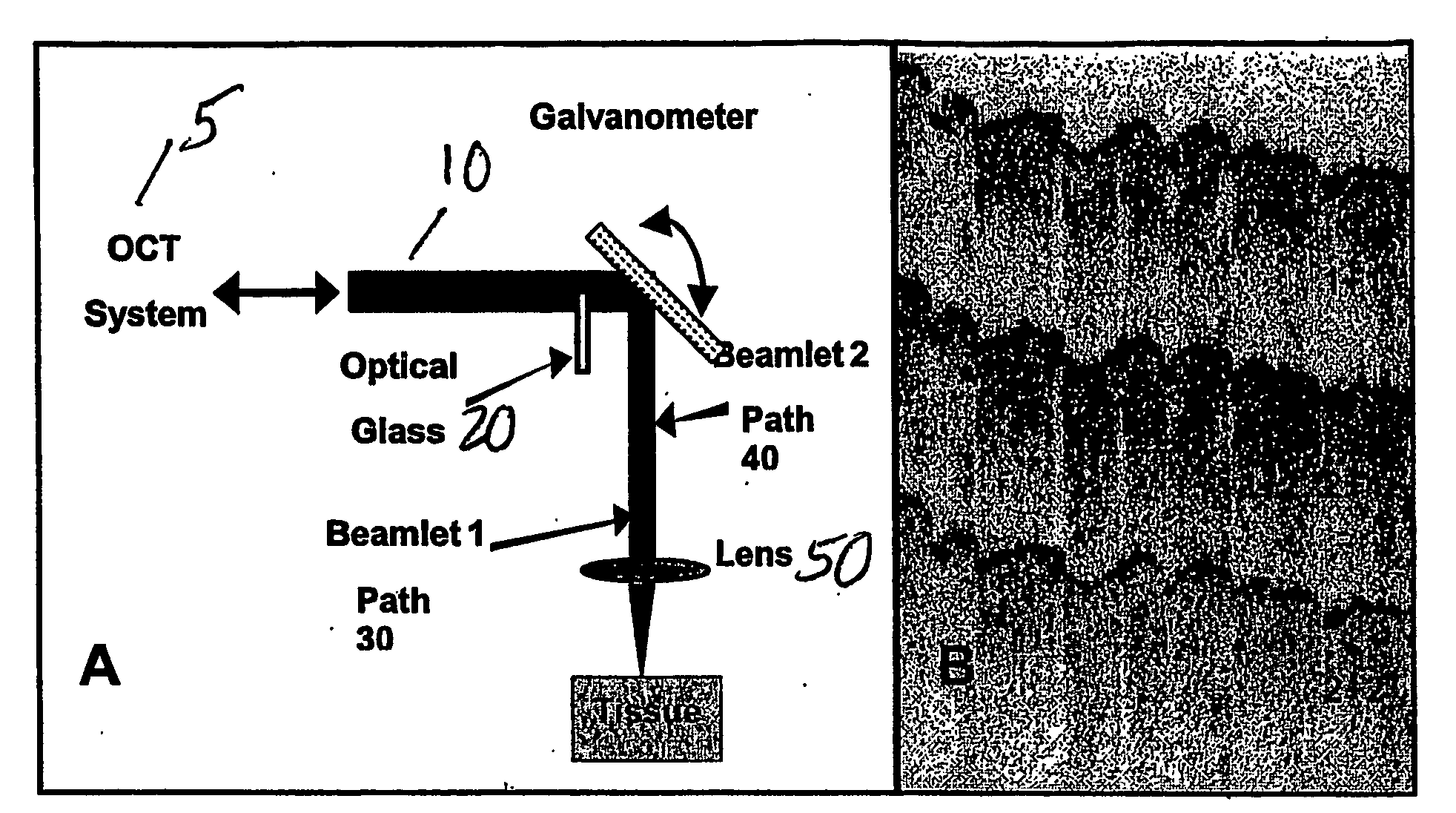
ActiveUS7567349B2Speckle reductionMinimal modificationOptical measurementsDiagnostics using lightDiseasePath length
Speckle, a factor reducing image quality in optical coherence tomography (“OCT”), can limit the ability to identify cellular structures that are important for the diagnosis of a variety of diseases. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention can facilitate an implementation of an angular compounding, angular compounding by path length encoding (“ACPE”) for reducing speckle in OCT images. By averaging images obtained at different incident angles, with each image encoded by path length, ACPE maintains high-speed image acquisition and implements minimal modifications to OCT probe optics. ACPE images obtained from tissue phantoms and human skin in vivo demonstrate a qualitative improvement over traditional OCT and an increased signal-to-noise ratio (“SNR”). Accordingly, exemplary embodiments of an apparatus probe catheter and method can be provided for irradiating a sample. In particular, an interferometer may forward forwarding an electromagnetic radiation. In addition, a sample arm may receive the electromagnetic radiation, and can include an arrangement which facilitates a production of at least two radiations from the electromagnetic radiation so as to irradiate the sample. Such exemplary arrangement can be configured to delay a first radiation of the at least two radiations with respect to a second radiation of the at least two radiations.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Modular radiation bean analyzer
InactiveUS7193220B1Rapid and accurate setupReduced measurement timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesAs DirectedTissue phantom
The instant invention is a modular radiation beam analyzer for measuring the distribution and intensity of radiation produced by a radiation source. More specifically, the instant invention is a modular radiation scanning device that includes up to three modules. By selecting and assembling a predetermined number of modules a radiation detector may be manipulated through up to three axes for radiation beam scans as well as direct Tissue Maximum Ratio (TMR) and / or Tissue Phantom Ratio (TPR) scans.
Owner:NAVARRO DANIEL
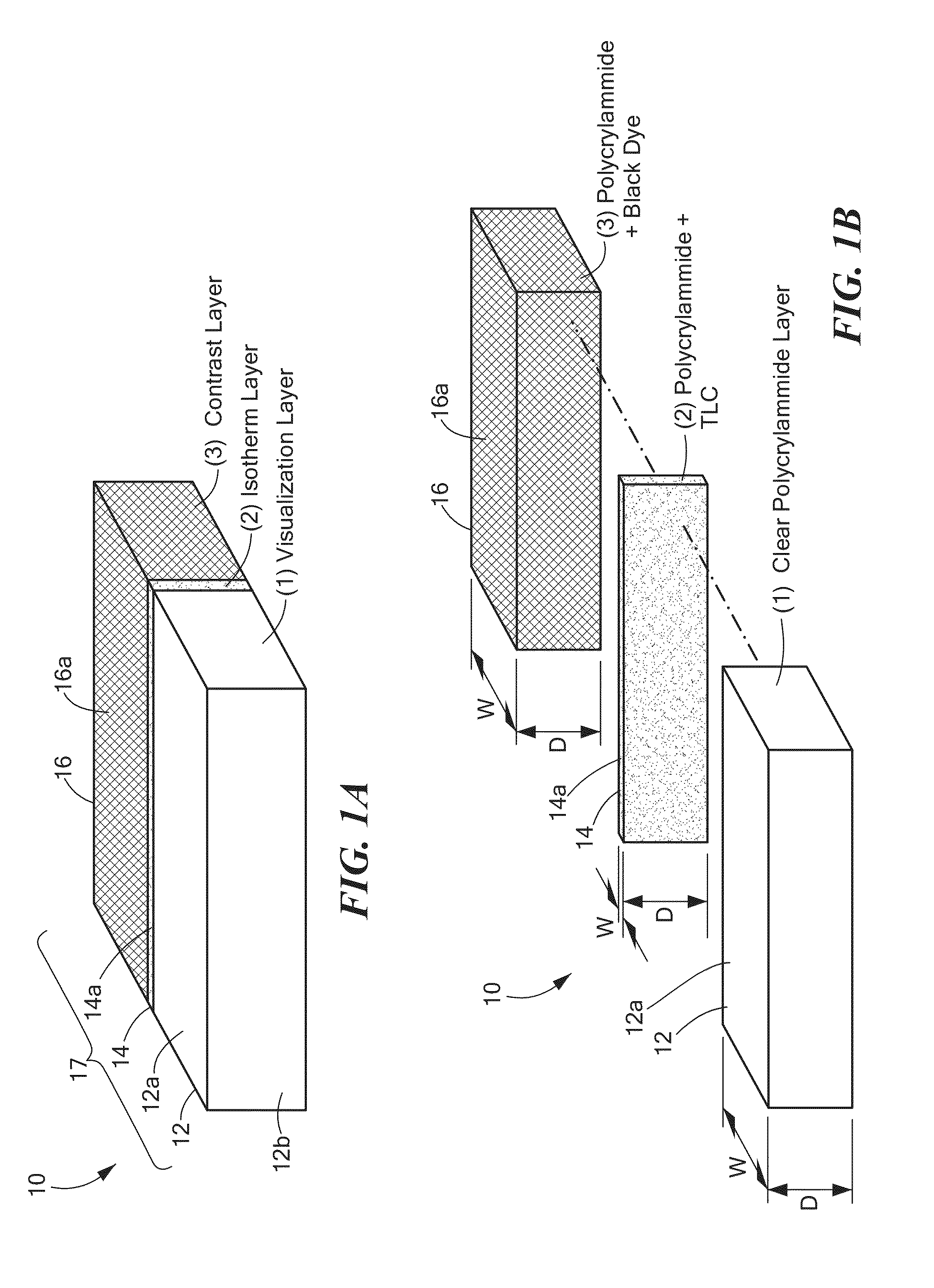
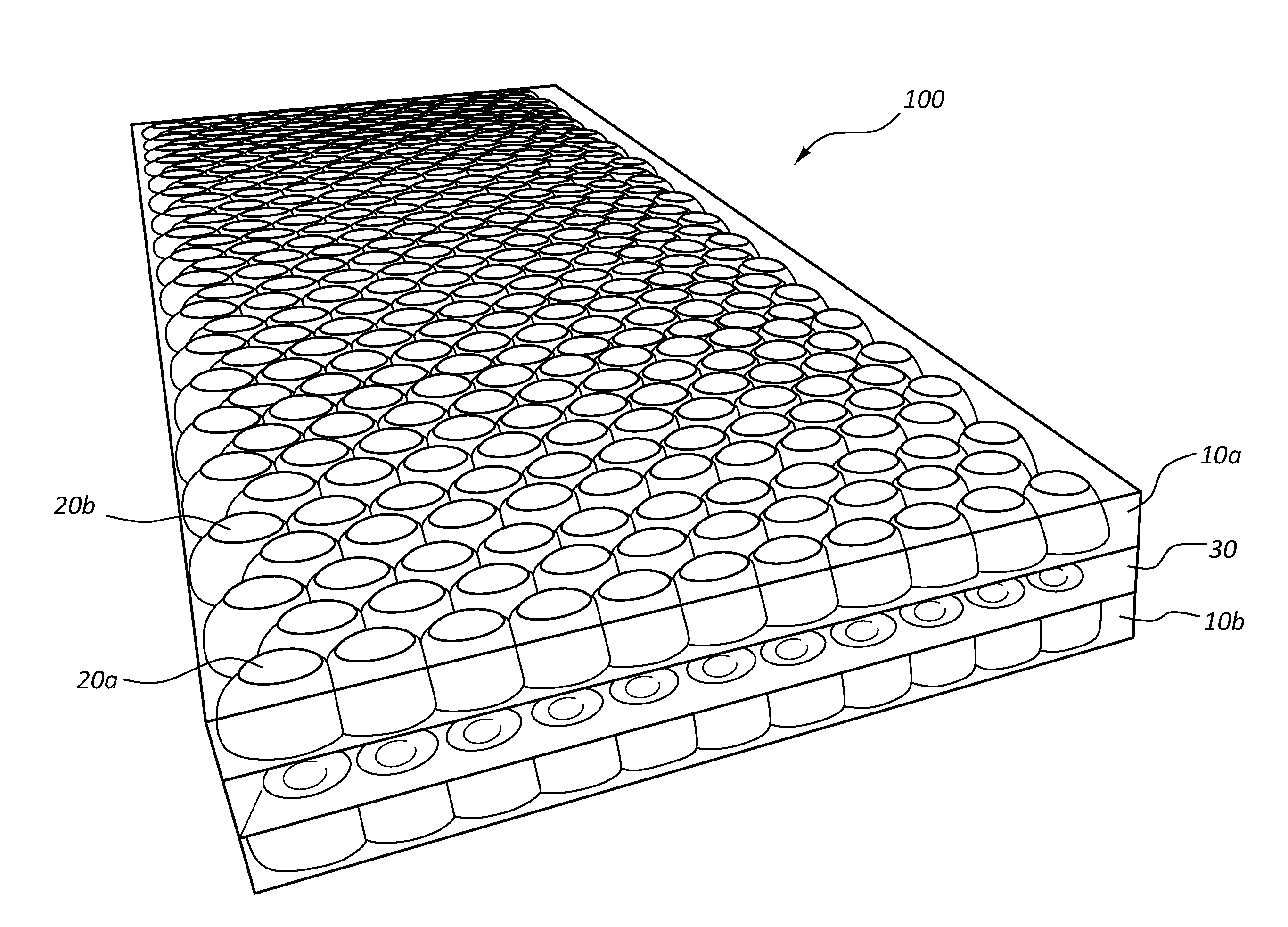
Multilayered tissue phantoms, fabrication methods, and use
InactiveUS8888498B2Efficiently formedStructure morePreparing sample for investigationPretreated surfacesOptical propertyEngineering
A method for producing a multilayer tissue phantom involves successively forming at least two layers, each layer formed by depositing a viscous flowable material over a supporting element or over a previously formed layer of the phantom supported by the supporting element, selectively redistributing the material while material is solidifying to control a thickness distribution of the layer, and allowing the material to solidify sufficiently to apply a next layer. The supporting element supports the material in 2 or 3 directions and effectively molds a lumen of the tissue. The neighboring layers are of different composition and of chosen thickness to provide desired optical properties and mechanical properties of the phantom. The phantom may have selected attenuation and backscattering properties to mimic tissues for optical coherence tomography imaging.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Method of adapting in-vitro models to aid in noninvasive glucose determination
InactiveUS20050119541A1Easy to controlStrict controlDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsConcentrations glucoseNon invasive
The invention relates to a noninvasive analyzer and a method of using information determined at least in part from in-vitro spectra of tissue phantoms or analyte solutions to aid in the development of a noninvasive glucose concentration analyzer and / or in the analysis of noninvasive spectra resulting in glucose concentration estimations in the body. The preferred apparatus is a spectrometer that includes a base module and a sample module that is semi-continuously in contact with a human subject and that collects spectral measurements which are used to determine a biological parameter in the sampled tissue, such as glucose concentration. Collection of in-vitro samples is, optionally, performed on a separate instrument from the production model allowing the measurement technology to be developed on a research grade instrument and used or transferred to a target product platform or production analyzer for noninvasive glucose concentration estimation.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Robust Calibration and Self-Correction for Tissue Oximetry Probe
ActiveUS20130324816A1Increase probabilityReduce data redundancyDiagnostic signal processingDiagnostics using lightTissue phantomSelf correction
A method for calibrating detectors of a self-contained, tissue oximetry device includes emitting light from a light source into a tissue phantom, detecting in a plurality of detectors the light emitted from the light source, subsequent to reflection from the tissue phantom, and generating a set of detector responses by the plurality of detectors based on detecting the light emitted from the light source. The method further includes determining a set of differences between the set of detector responses and a reflectance curve for the tissue phantom, and generating a set of calibration functions based on the set of differences. Each calibration function in the set of calibration functions is associated with a unique, light source-detector pair. The method further includes storing the set of calibration function in a memory of the self-contained, tissue oximetry device.
Owner:VIOPTIX
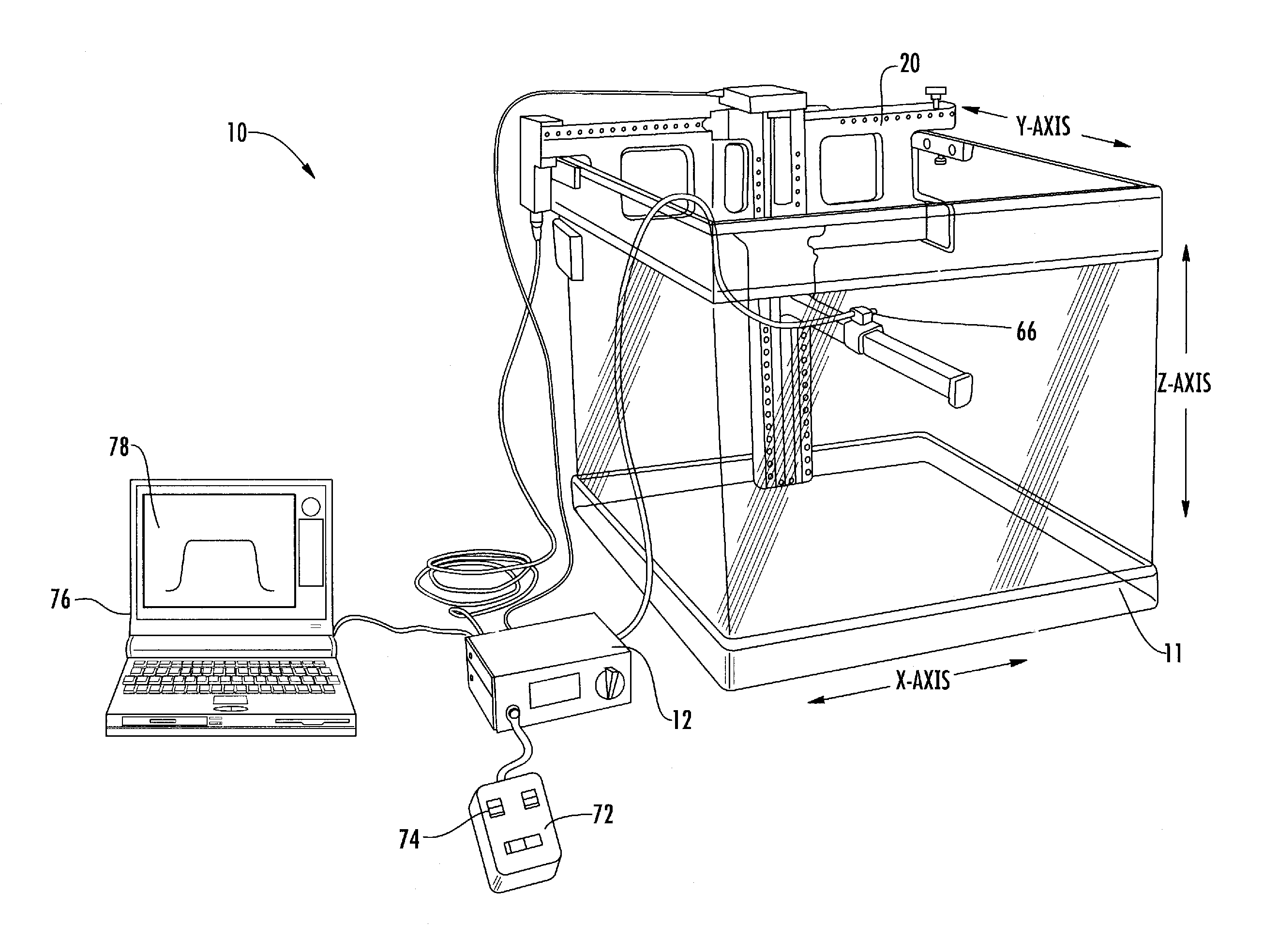
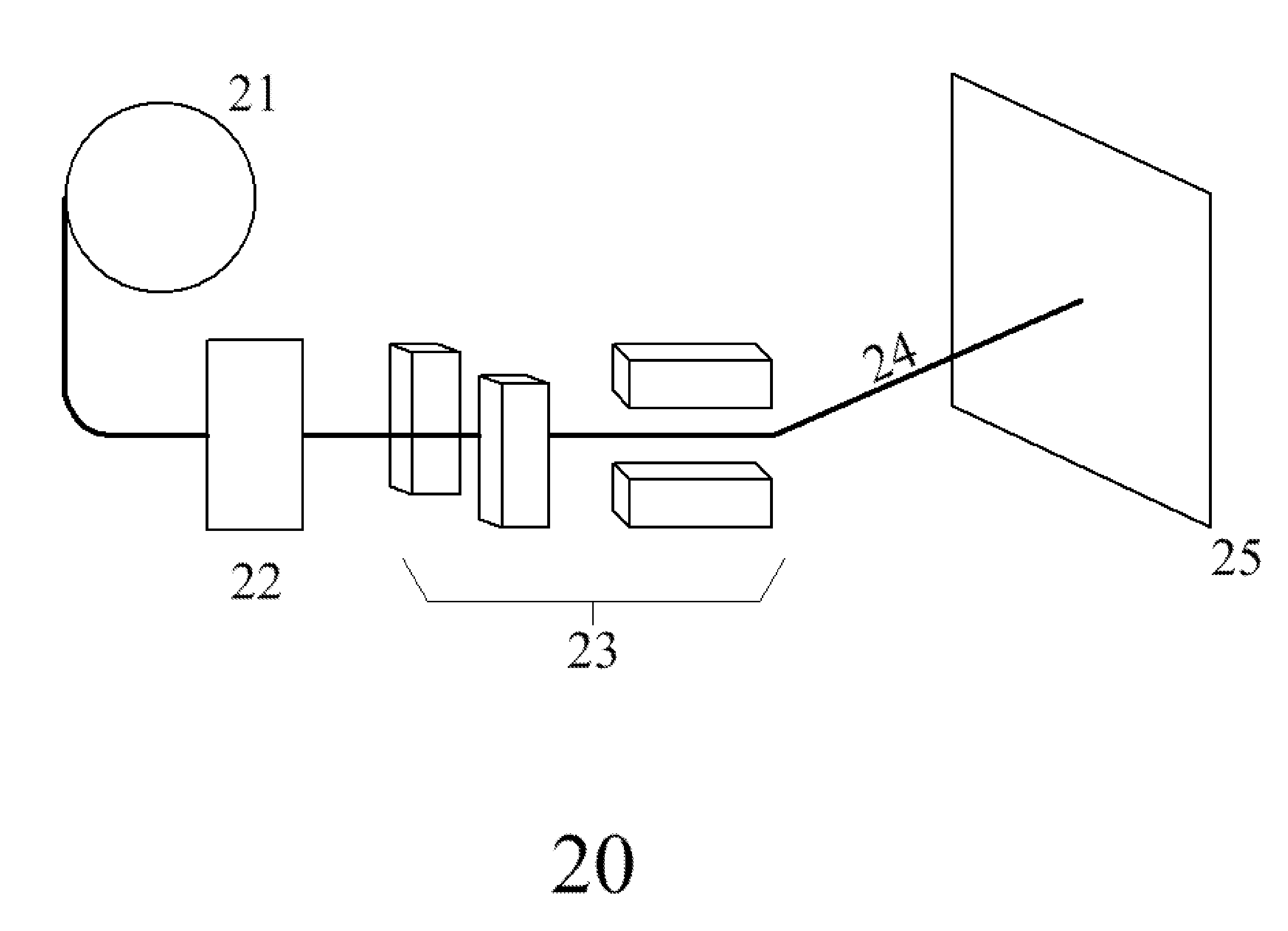
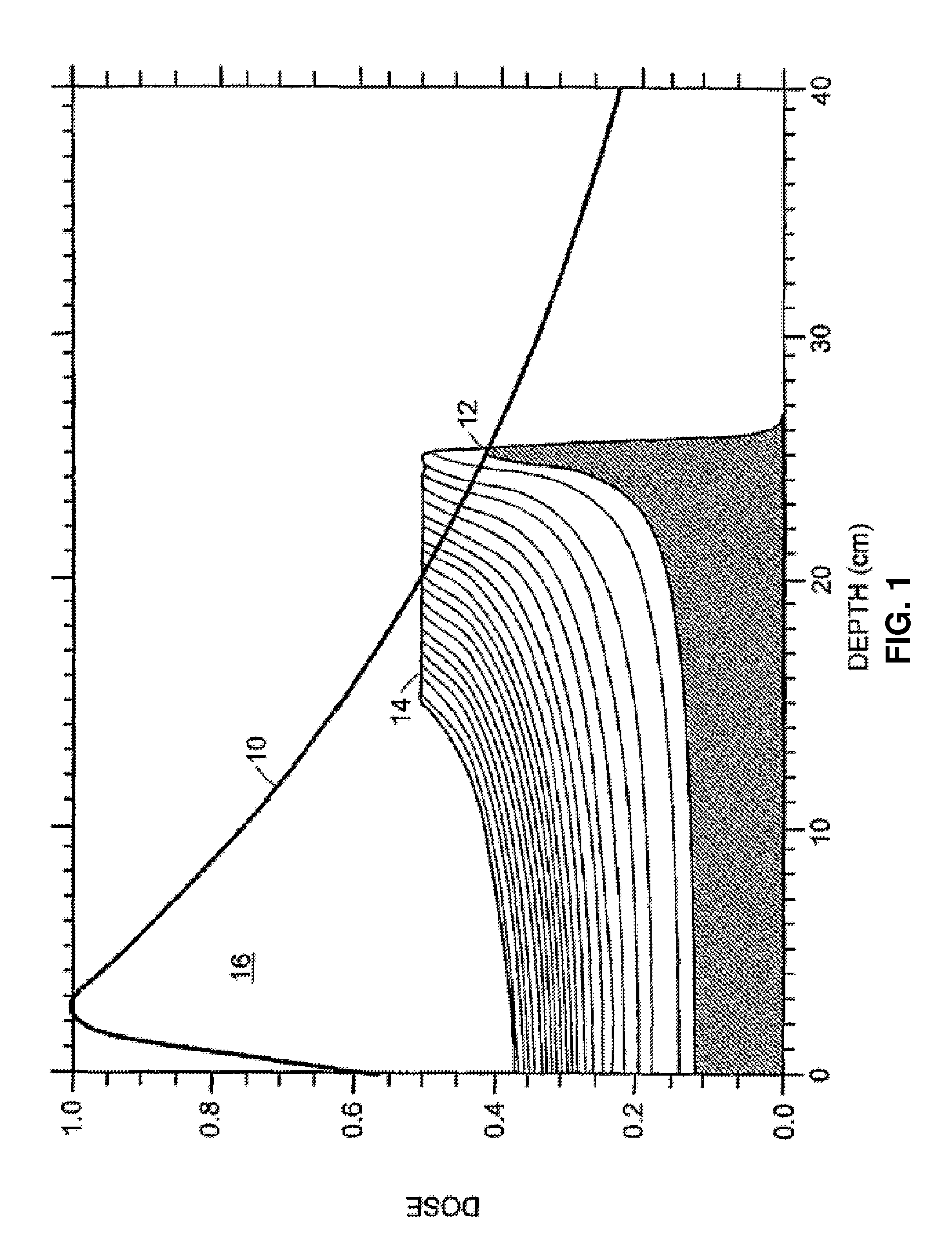
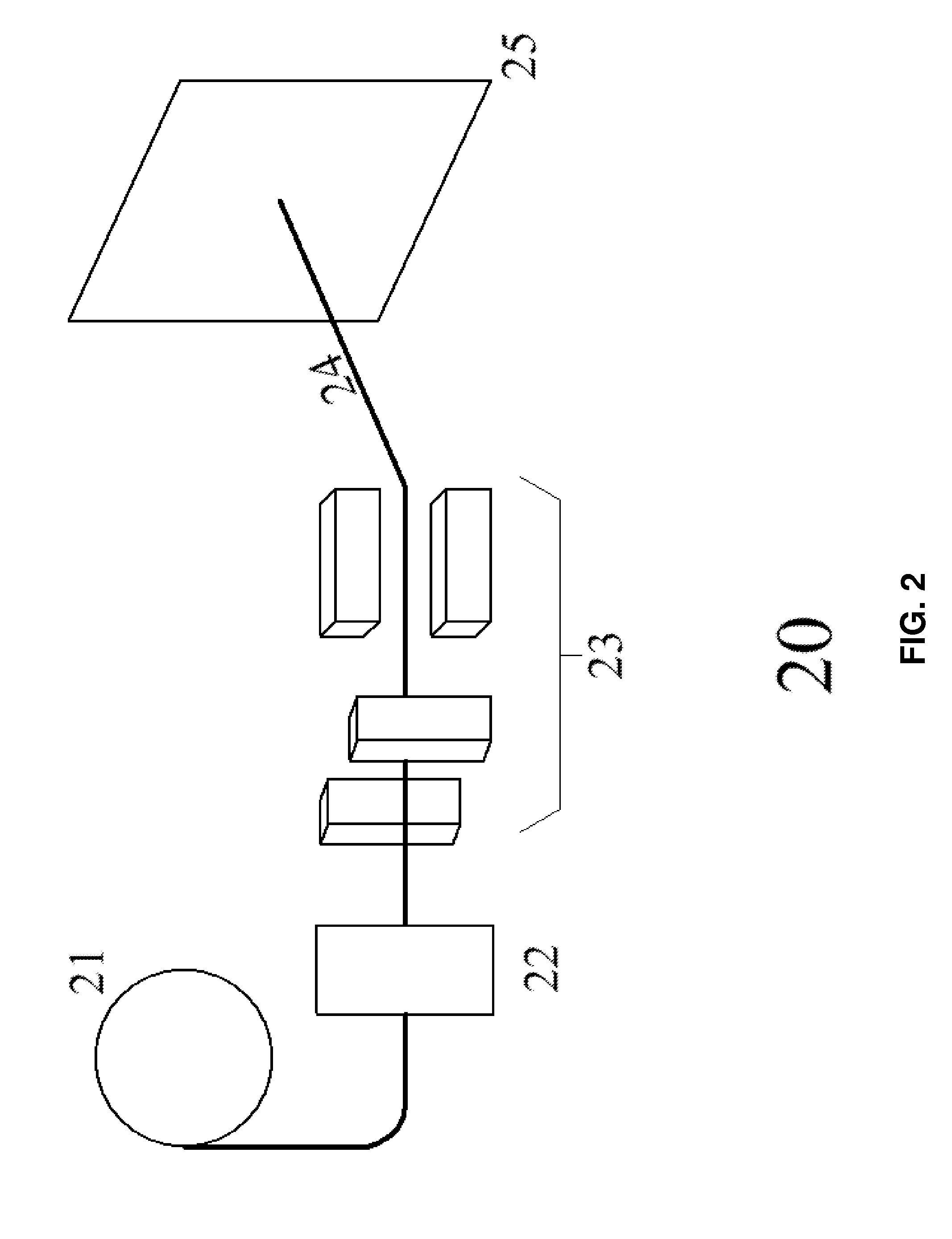
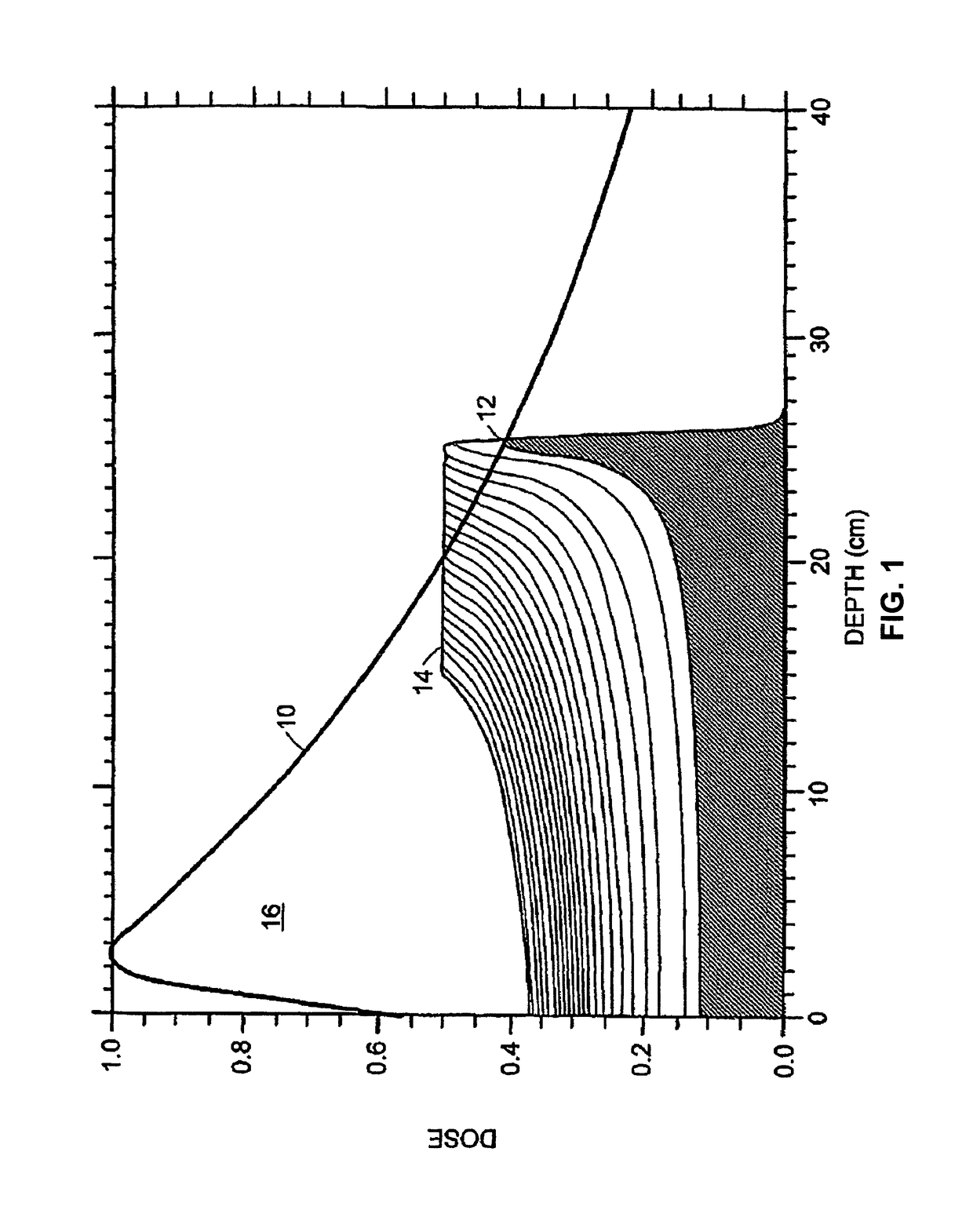
Dosimetric scintillating screen detector for charged particle radiotherapy quality assurance
ActiveUS20150071408A1High resolutionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyCharacteristic responseCharged particle radiotherapy
An apparatus and method are provided for performing Quality Assurance of complex beams of penetrating radiation inside a patient. A detector with a transverse scintillating screen images the radiation inside a tissue phantom with high spatial resolution. The scintillator is comprised of a mixture of two or more scintillators emitting different spectra of light and having different characteristic responses as a function of the beam LET value. The optics relaying the scintillation output have variable transmission with wavelength, further shaping the spectrum of light transmitted to the imaging sensor which also has spectrally varying sensitivity. Parameters of the scintillator construction, the optics, and the imaging sensor are chosen so the output of the composite detector is proportional to a characteristic of the input beam, for example the dose deposited as a function of depth inside the tissue phantom.
Owner:EBSTEIN STEVEN M
Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by path length encoded angular compounding
ActiveUS20060227333A1Easy to produceSpeckle reductionOptical measurementsDiagnostics using lightDiseasePath length
Speckle, a factor reducing image quality in optical coherence tomography (“OCT”), can limit the ability to identify cellular structures that are important for the diagnosis of a variety of diseases. The present invention allows for an implementation of an angular compounding, angular compounding by path length encoding (“ACPE”) for reducing speckle in OCT images. By averaging images obtained at different incident angles, with each image encoded by path length, ACPE maintains high-speed image acquisition and implements minimal modifications to OCT probe optics. ACPE images obtained from tissue phantoms and human skin in vivo demonstrate a qualitative improvement over traditional OCT and an increased signal-to-noise ratio (“SNR”). Accordingly, apparatus probe catheter, and method are provided for irradiating a sample. In particular, an interferometer may forward forwarding an electromagnetic radiation. In addition, a sample arm may receive the electromagnetic radiation, and can include an arrangement which facilitates a production of at least two radiations from the electromagnetic radiation so as to irradiate the sample. Such arrangement can be configured to delay a first radiation of the at least two radiations with respect to a second radiation of the at least two radiations.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Tissue-mimicking phantom for prostate cancer brachytherapy
ActiveUS20100041005A1Additive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsPolyvinyl alcoholFreezing thawing
A phantom for prostate cancer brachytherapy has a prostate tissue phantom shaped like a real prostate gland, a perineal tissue phantom surrounding the prostate tissue phantom, a skin tissue phantom separating the perineal tissue phantom from an outside environment, and an enclosure. The prostate tissue phantom is a polyvinyl alcohol cryogel (PVA-C) having undergone 3-5 freeze-thaw cycles and having 10-20% w / w PVA in a solvent (e.g. water), 4-8% w / w oil and an amount of acoustic scattering particles to ultrasonically distinguish the prostate-tissue phantom from its surroundings. The perineal tissue phantom is a PVA-C having undergone 1-2 freeze-thaw cycles and having 10-20% w / w PVA in a solvent, 4-8% w / w oil and an amount of acoustic scattering particles to ultrasonically distinguish the perineal tissue phantom from its surroundings. The skin tissue phantom is a PVA-C having undergone at least 6 freeze-thaw cycles and having 15-25% w / w PVA in a solvent. The phantom mimics the imaging and mechanical properties of the prostate and surrounding tissues, providing a realistic phantom for prostate cancer brachytherapy.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
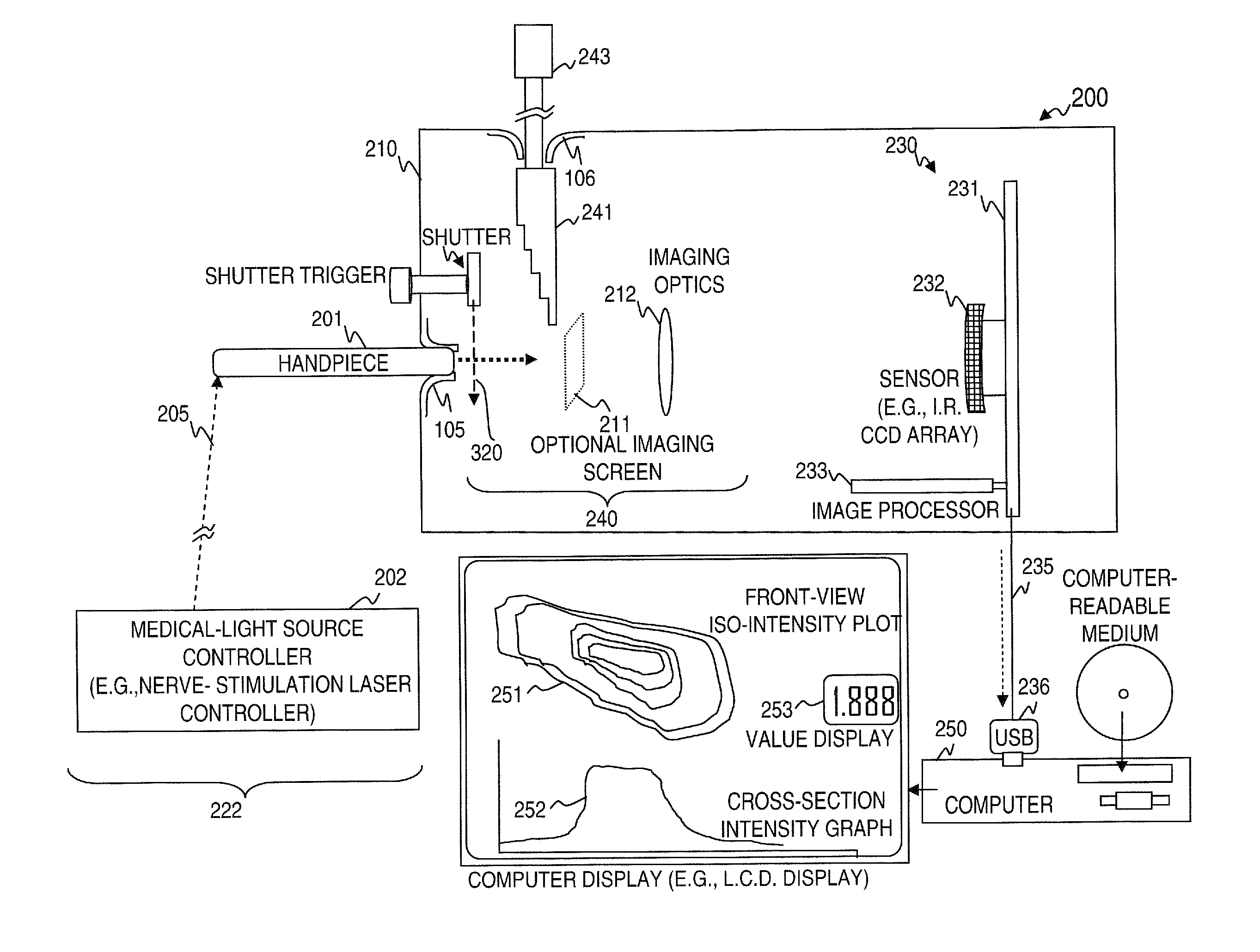
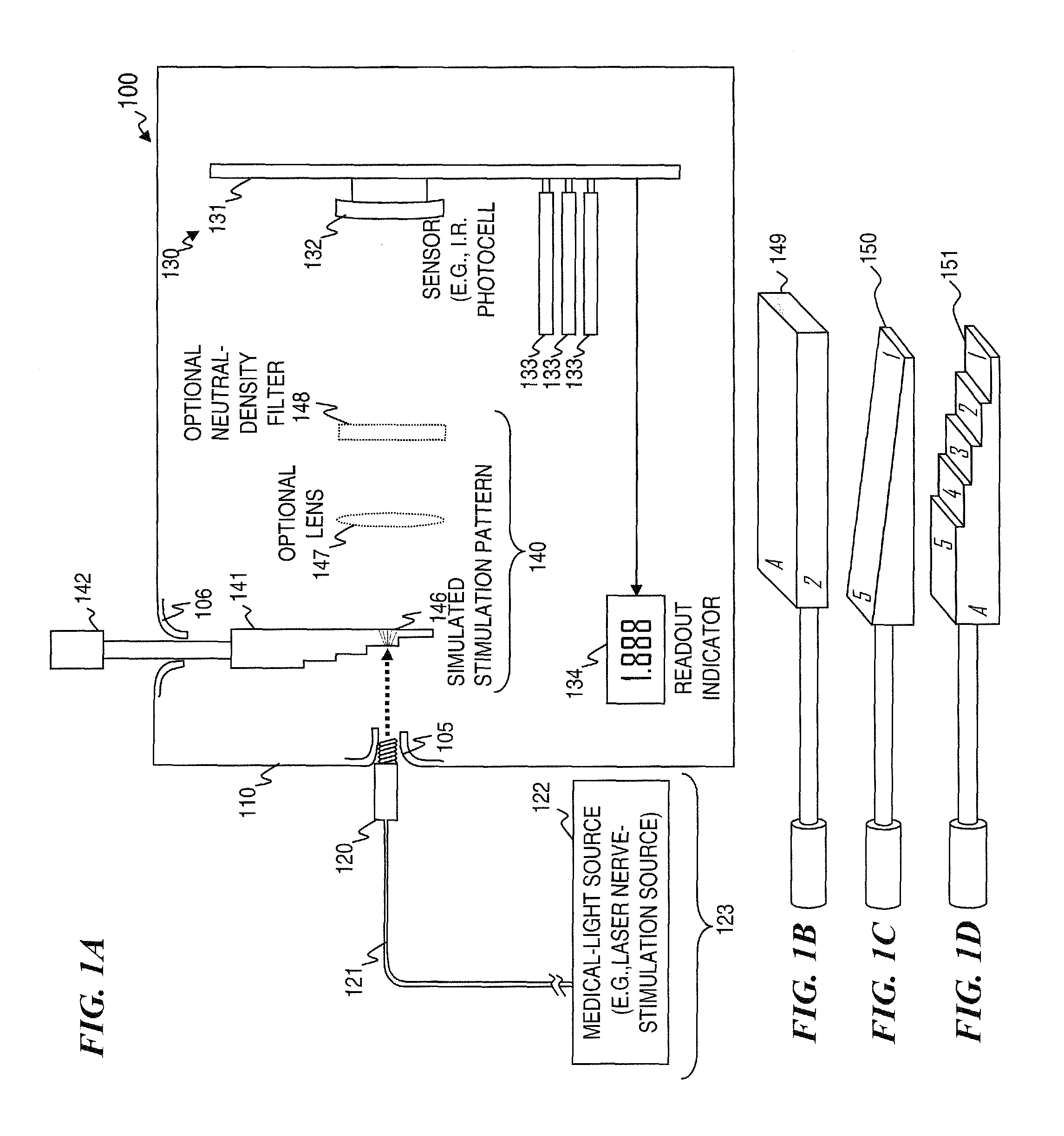
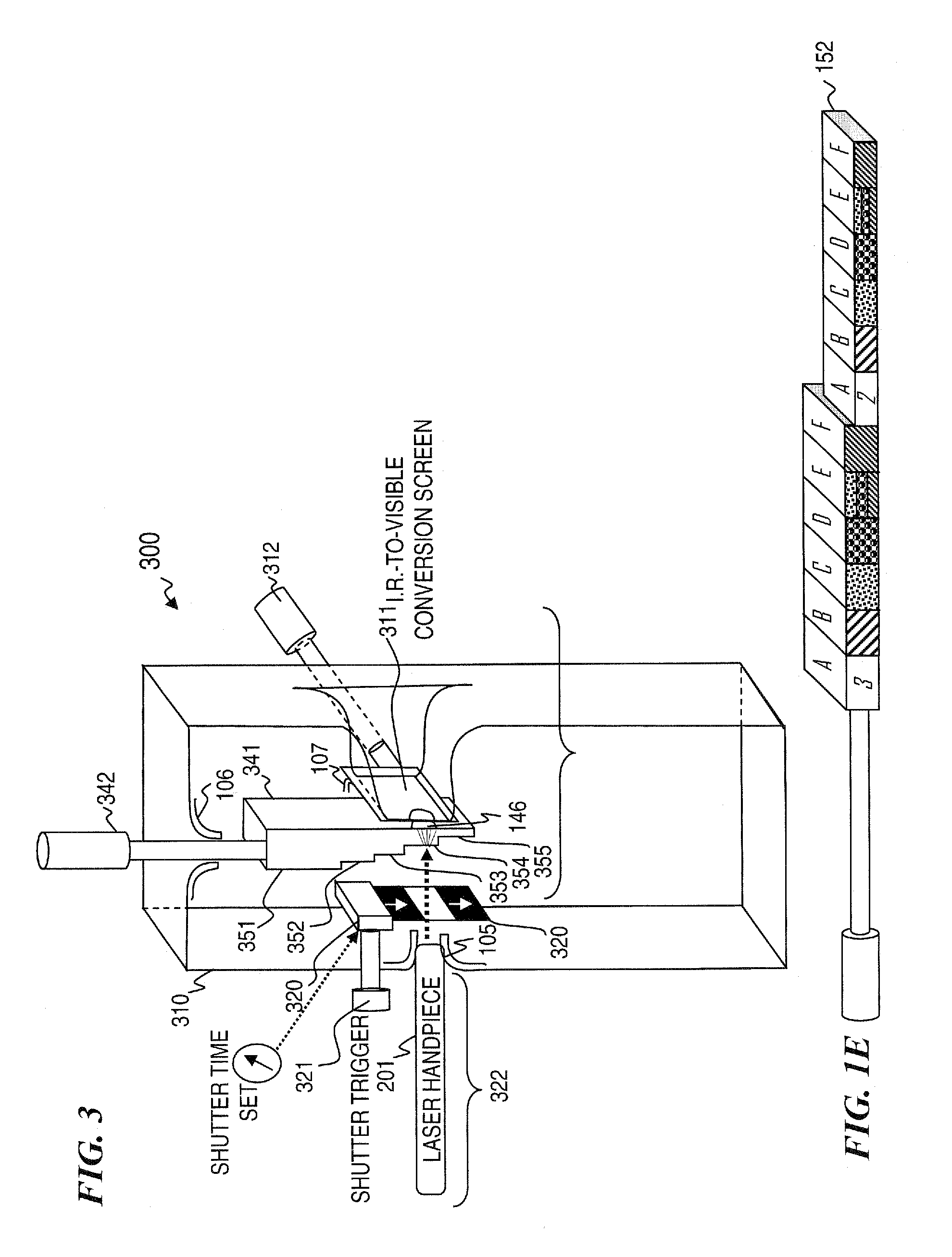
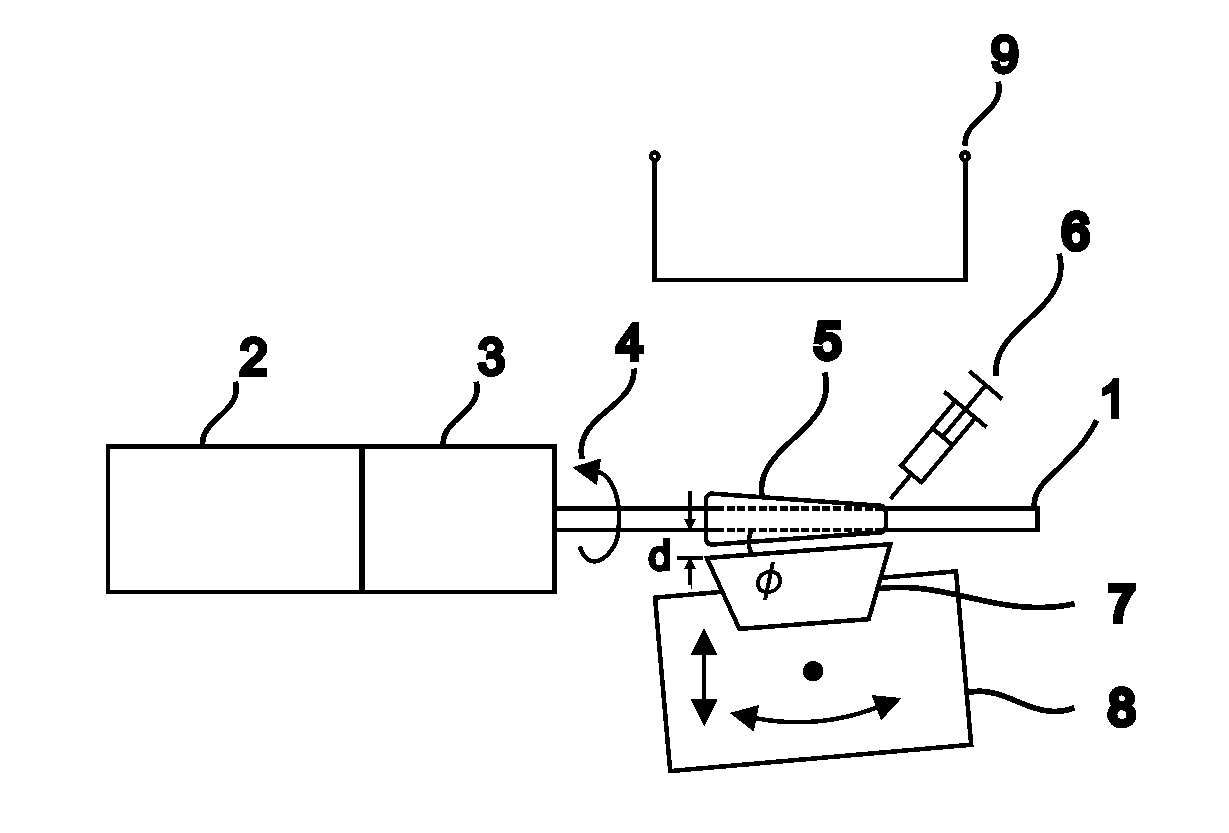
Apparatus and method for characterizing optical sources used with human and animal tissues
Medical researchers use various optical devices for diagnosis, detection, treatment, and therapy. In some embodiments, they do not have the equipment necessary to determine how much light is emitted by the optical device or how far it penetrates tissue. The present invention provides for a method and apparatus for characterizing light from an optical device by using a tissue phantom. The method includes coupling light from an optical source into a device, transmitting the light through a tissue phantom, detecting a transmitted light, optionally electrically processing the detected output, and displaying the corresponding optical characterization. In some embodiments, the apparatus obtains input light from an optical source, and may include a tissue phantom, an optical detector, an electrical processing unit, and a display for displaying the corresponding optical characterization.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
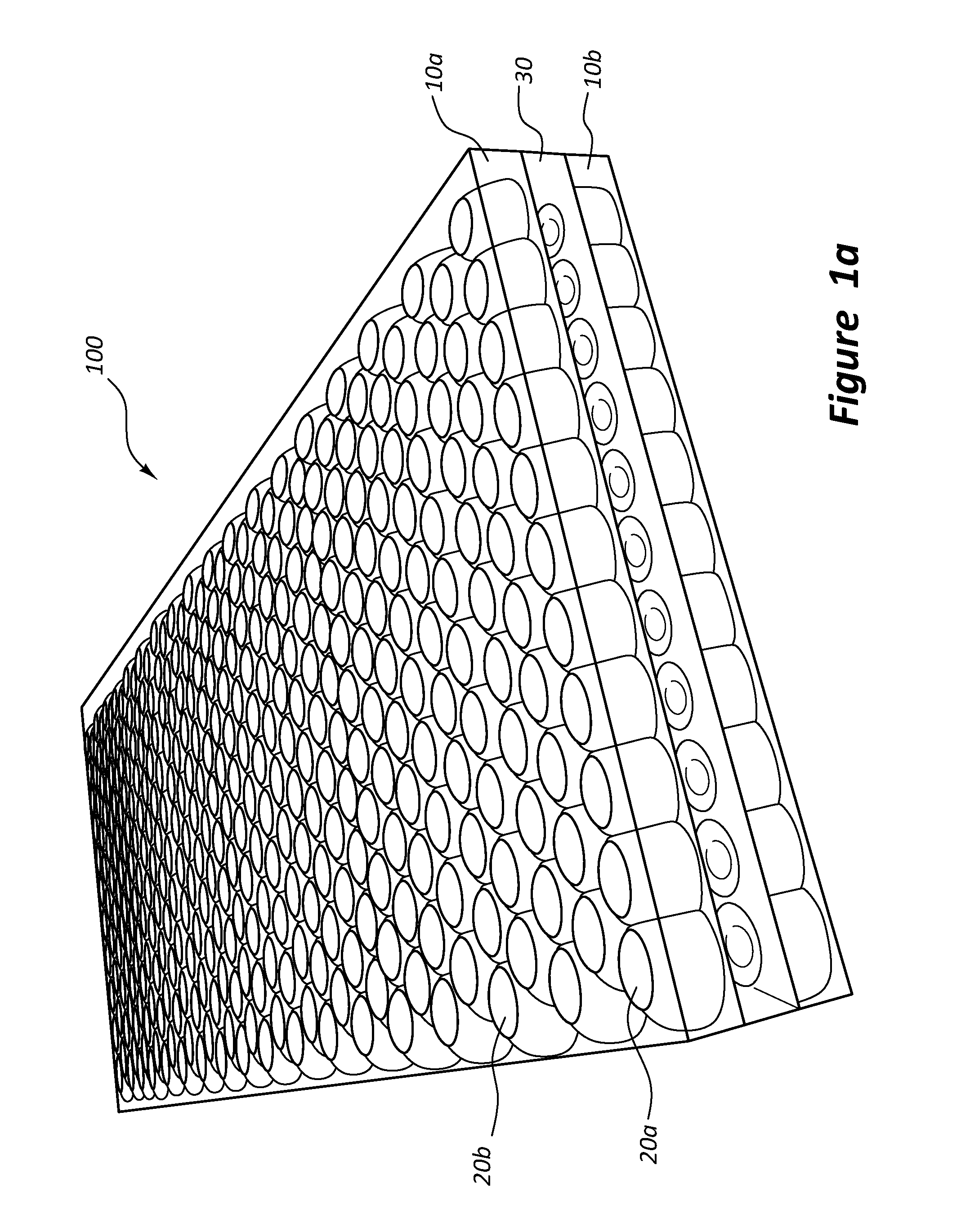
Multilayered Tissue Phantoms, Fabrication Methods, and Use
InactiveUS20110062318A1Easy to useReproduce geometrical deformationPreparing sample for investigationPretreated surfacesUltrasound attenuationOptical property
A method for producing a multilayer tissue phantom involves successively forming at least two layers, each layer formed by depositing a viscous flowable material over a supporting element or over a previously formed layer of the phantom supported by the supporting element, selectively redistributing the material while material is solidifying to control a thickness distribution of the layer, and allowing the material to solidify sufficiently to apply a next layer. The supporting element supports the material in 2 or 3 directions and effectively molds a lumen of the tissue. The neighbouring layers are of different composition and of chosen thickness to provide desired optical properties and mechanical properties of the phantom. The phantom may have selected attenuation and backscattering properties to mimic tissues for optical coherence tomography imaging.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
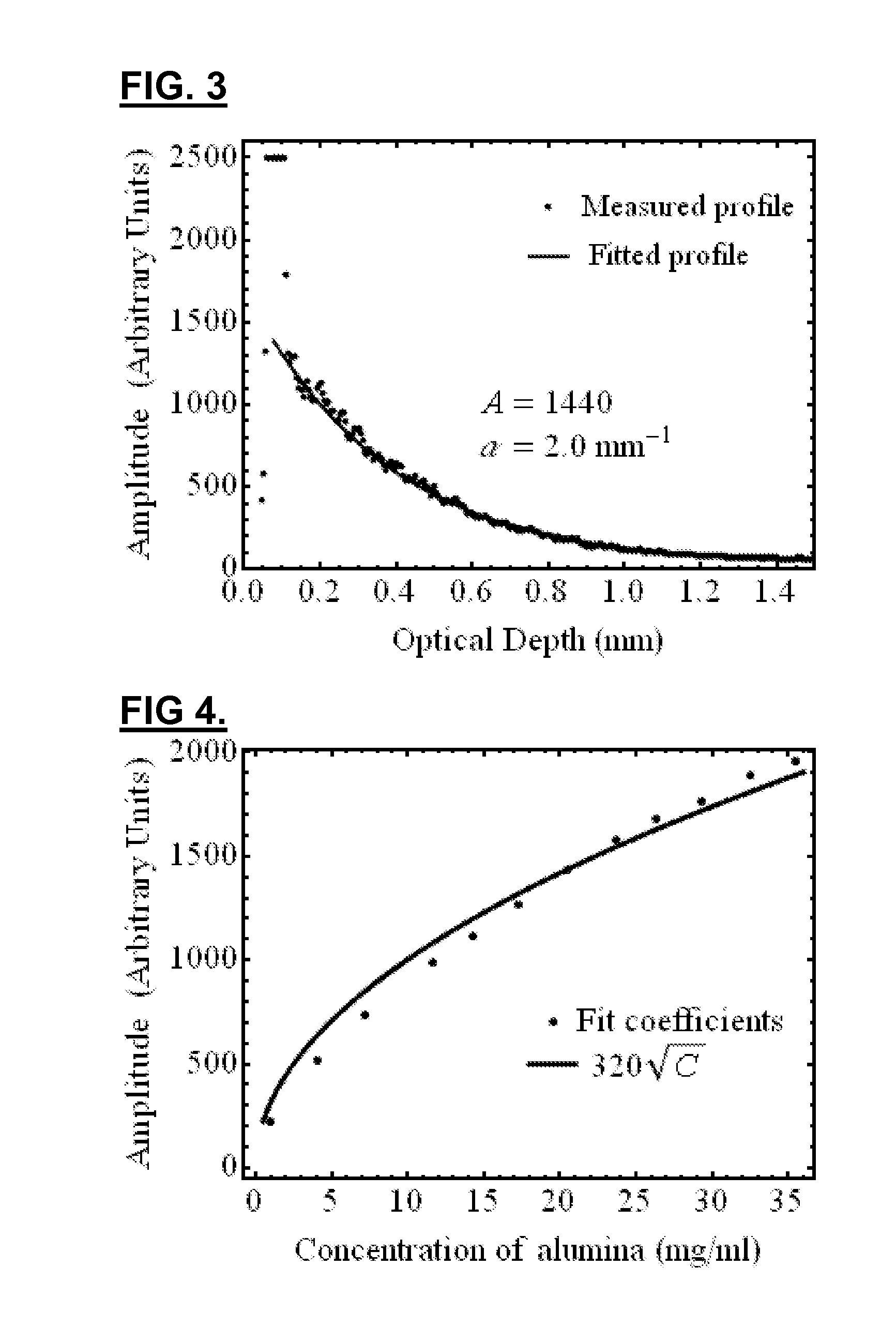
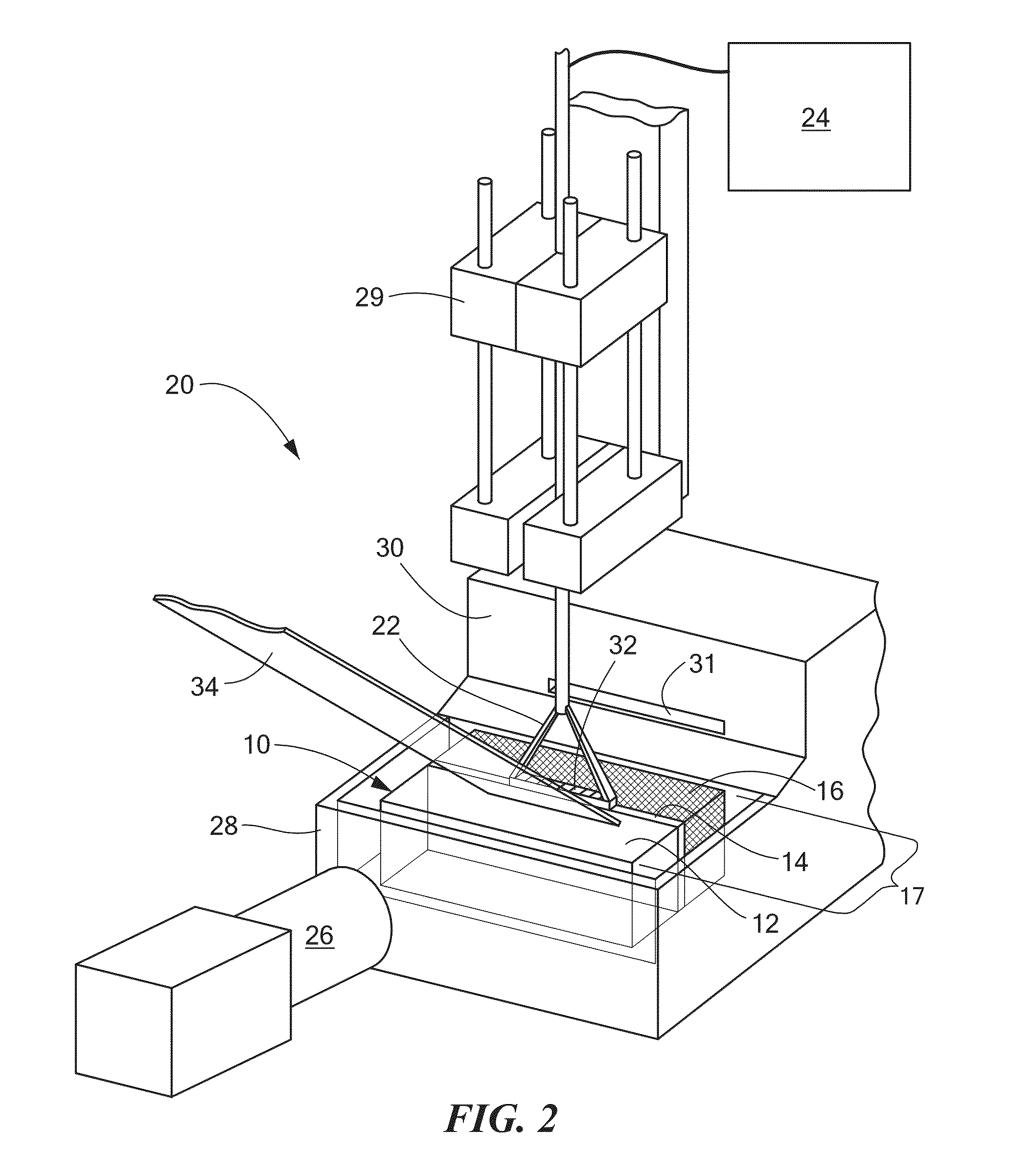
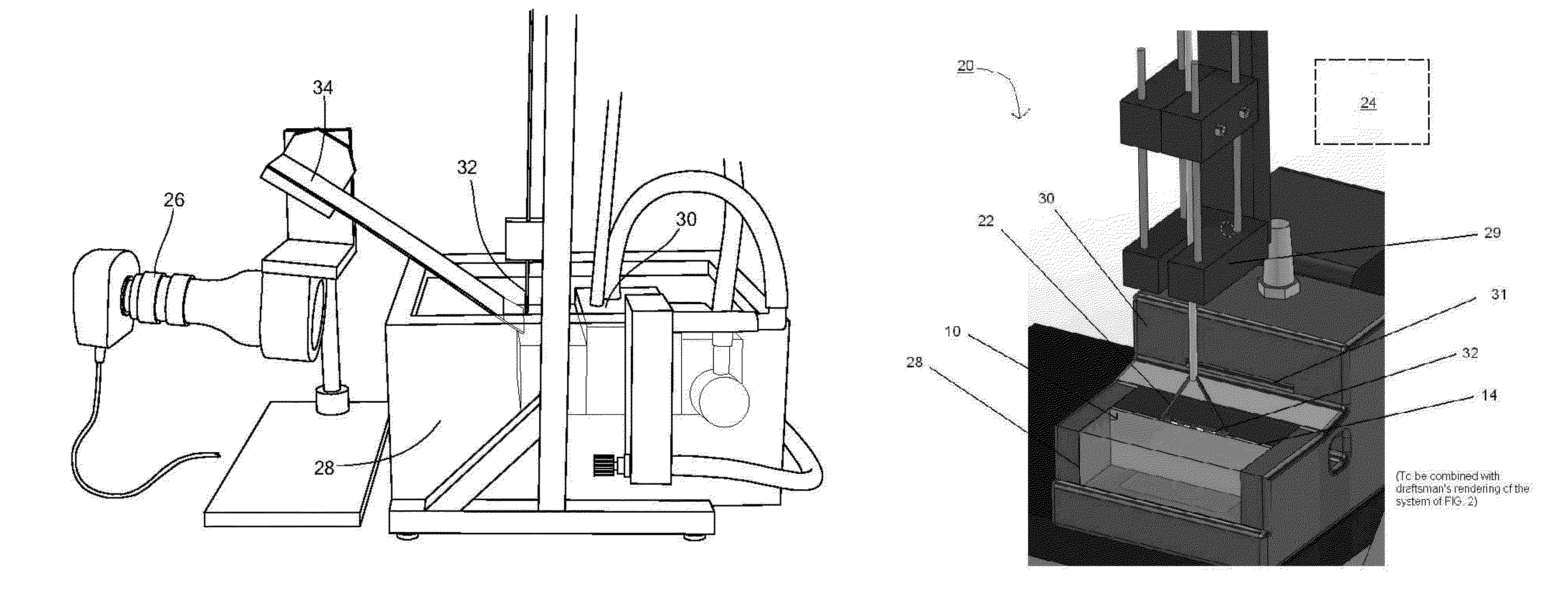
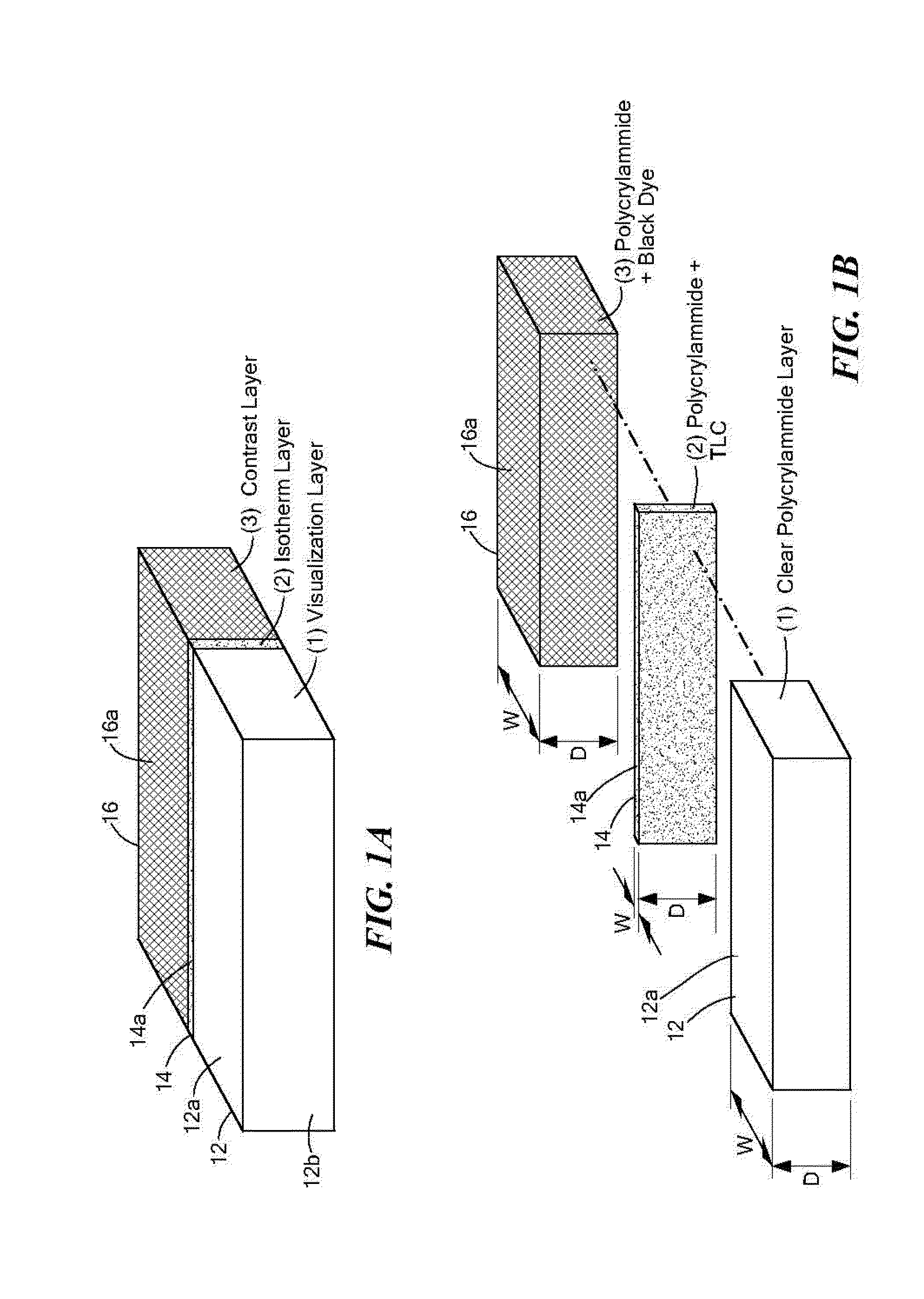
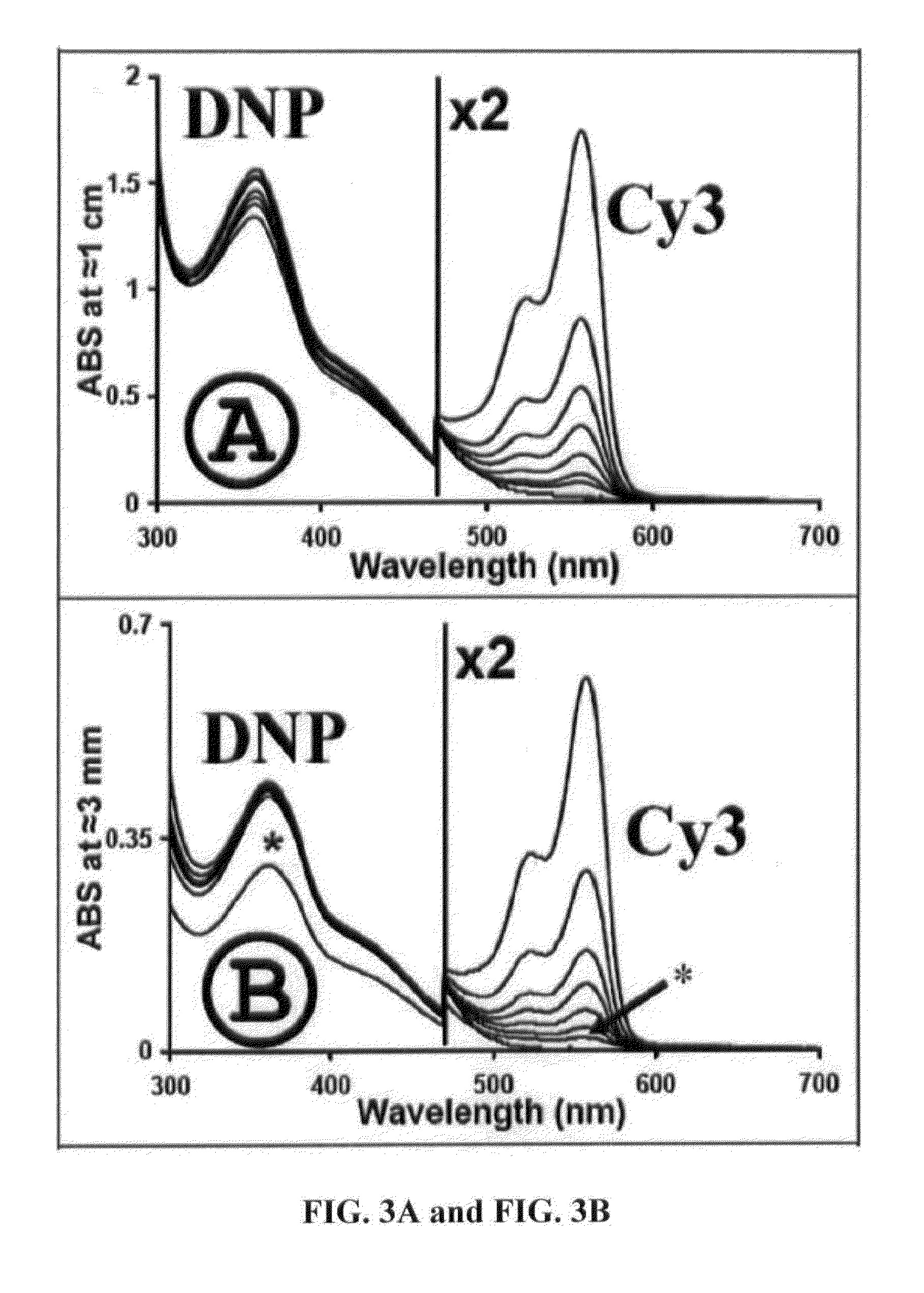
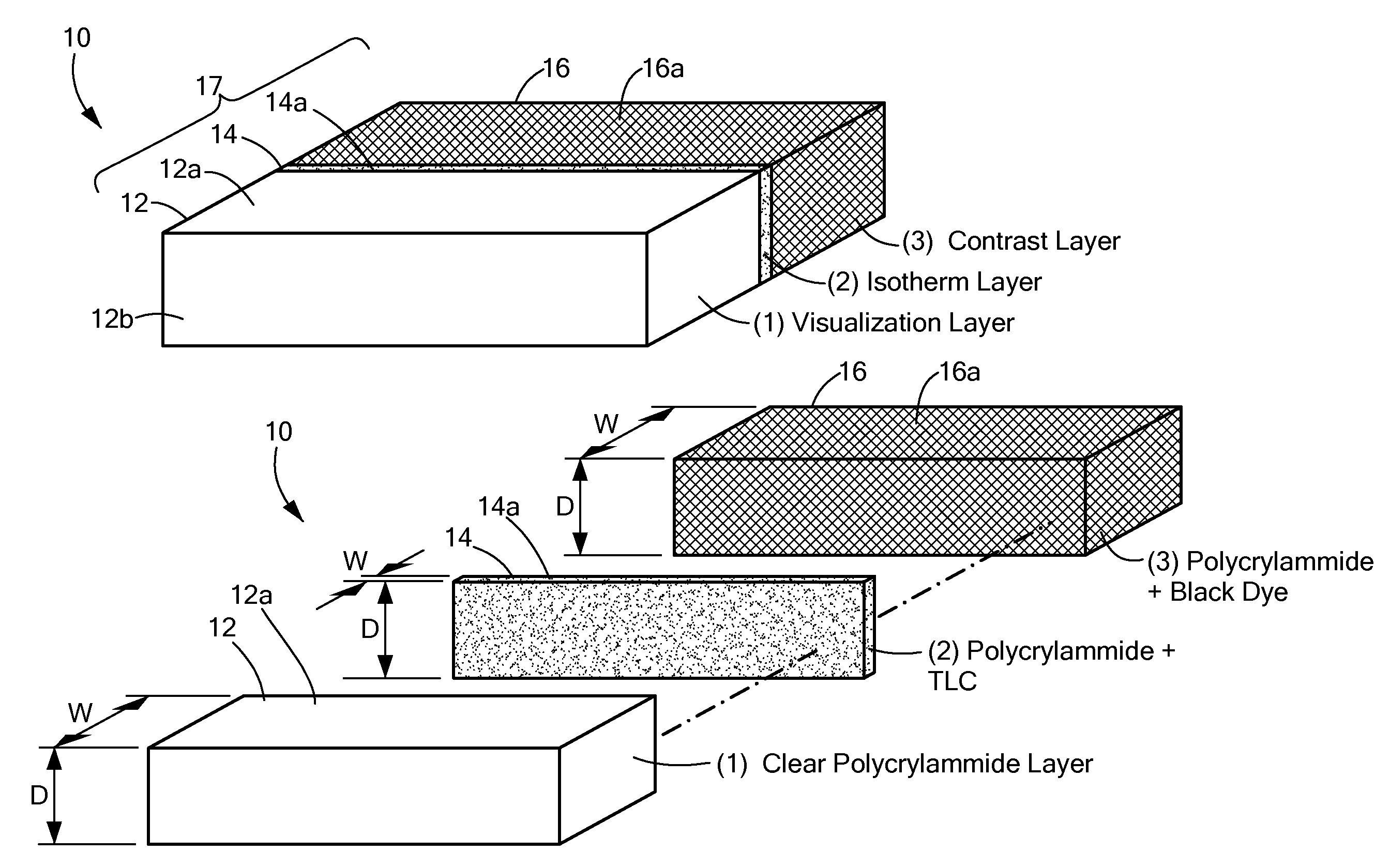
Thermochromic polyacrylamide tissue phantom and its use for evaluation of ablation therapies
ActiveUS20150168227A1Ultrasound therapyThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsRf ablationTissue phantom
A polyacrylamide tissue phantom embedded with multi-formulated thermochromic liquid crystals for use in the evaluation of RF ablation therapies is provided. The tissue phantom approximates the properties of biological tissue, and therefore provides a suitable substitute for use in testing the effects of RF and other energy-emitting devices on biological tissue. Also provided is a system for using the tissue phantom in the evaluation of RF therapies.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Thermochromic polyacrylamide tissue phantom and its use for evaluation of ablation therapies
ActiveUS20130192392A1Ultrasound therapyThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsRf ablationTissue phantom
A polyacrylamide tissue phantom embedded with multi-formulated thermochromic liquid crystals for use in the evaluation of RF ablation therapies is provided. The tissue phantom approximates the properties of biological tissue, and therefore provides a suitable substitute for use in testing the effects of RF and other energy-emitting devices on biological tissue. Also provided is a system for using the tissue phantom in the evaluation of RF therapies.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
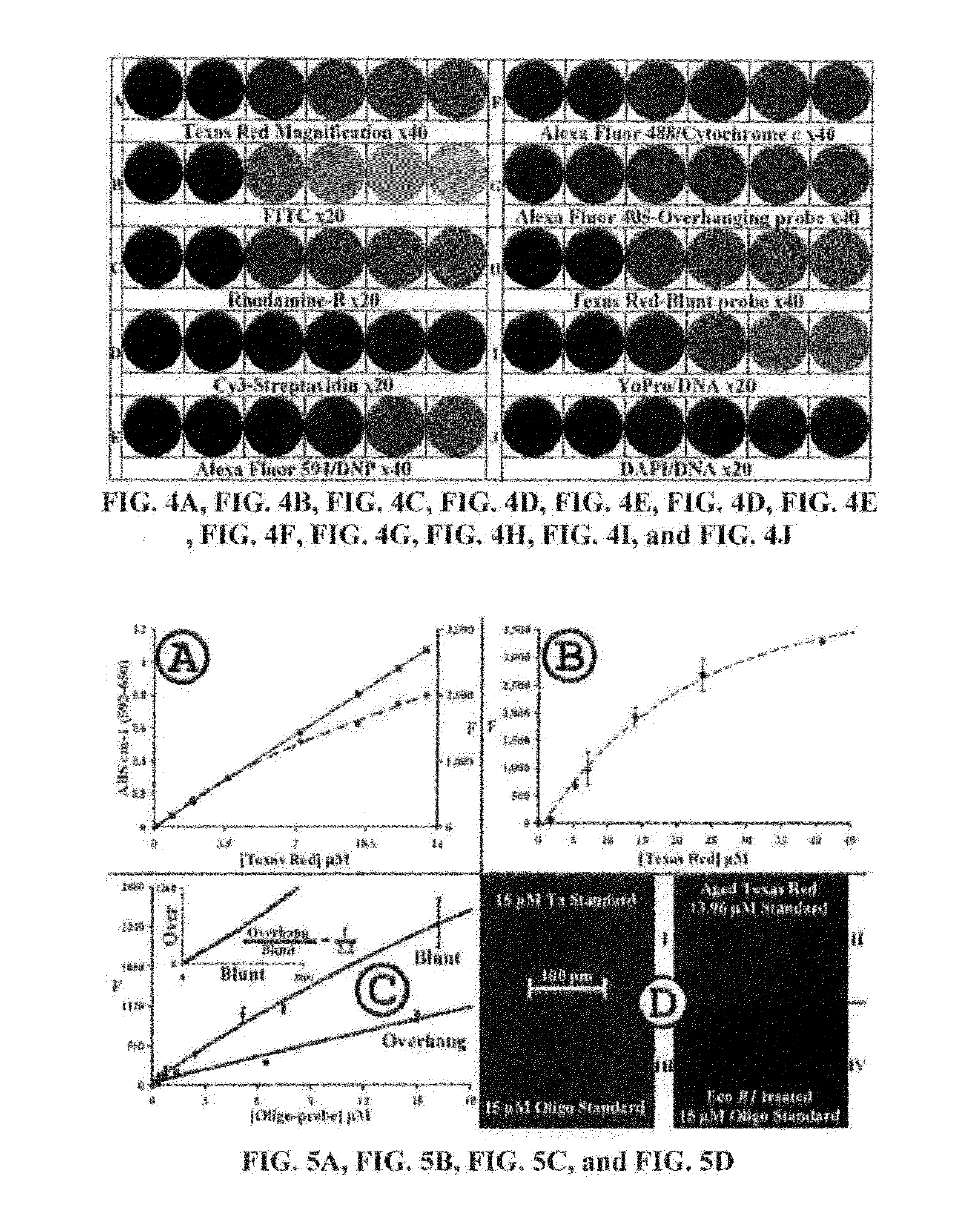
Compositions and Methods for Quantitative Histology, Calibration of Images in Fluorescence Microscopy, and ddTUNEL Analyses
InactiveUS20130157261A1Effectively used as labeling mediumInherent limitationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorophoreTissue phantom
Disclosed are compositions and methods for quantitation and calibration of images in fluorescence microscopy. Also provided are tissue phantoms that contain known amount(s) of fluorophore standard(s), as well as components and diagnostic kits containing the same for use in various histological analyses. In certain embodiments, three distinct nucleic-acid based assays provide improvements over conventional TUNEL methods to facilitate precise quantitation of a variety of nucleic acids obtained from a biological sample.
Owner:THE METHODIST HOSPITAL RES INST
Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by path length encoded angular compounding
ActiveUS20100157309A1Speckle reductionMinimal modificationOptical measurementsDiagnostics using lightDiseasePath length
Speckle, a factor reducing image quality in optical coherence tomography (“OCT”), can limit the ability to identify cellular structures that are important for the diagnosis of a variety of diseases. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention can facilitate an implementation of an angular compounding, angular compounding by path length encoding (“ACPE”) for reducing speckle in OCT images. By averaging images obtained at different incident angles, with each image encoded by path length, ACPE maintains high-speed image acquisition and implements minimal modifications to OCT probe optics. ACPE images obtained from tissue phantoms and human skin in vivo demonstrate a qualitative improvement over traditional OCT and an increased signal-to-noise ratio (“SNR”). Accordingly, exemplary embodiments of an apparatus probe catheter and method can be provided for irradiating a structure. In particular, an interferometer may forward forwarding an electromagnetic radiation. In addition, a sample arm may receive the electromagnetic radiation, and can include an arrangement which facilitates a production of at least two radiations from the electromagnetic radiation so as to irradiate the structure. Such exemplary arrangement can be configured to delay a first radiation of the at least two radiations with respect to a second radiation of the at least two radiations.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Anatomically and functionally accurate soft tissue phantoms and method for generating same
InactiveUS20110291321A1Efficient use ofEfficient andEducational modelsDomestic articlesElastomerImage Study
A method, system and apparatus for manufacturing anatomically and functionally accurate soft tissue phantoms with multimodality characteristics for imaging studies is disclosed. The organ / tissue phantom is constructed by filling a container containing an organ having inner vasculature therein with a molten elastomeric material; inserting a plurality of rods with bumps thereupon through the container and the organ; allowing the molten elastomeric material to harden and cure; removing the organ; replacing the organ with a plurality of elastomeric segments; and removing an elastomeric segment and replacing the void created thereupon with molten PVA to create a PVA segment; allowing the molten PVA segment to harden and cure; and repeating the creation of PVA segments until all the elastomeric segments have been removed, such that each successive molten PVA segment adheres to and fuses with the previous hardened PVA segment so as to form an approximately complete organ phantom cast. The organ / tissue phantom is completed by inserting the approximately complete organ phantom cast inserting upside-down into a fixture made from the bottom-most elastomeric segment, which contains molten PVA; and allowing the molten PVA to harden and cure.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
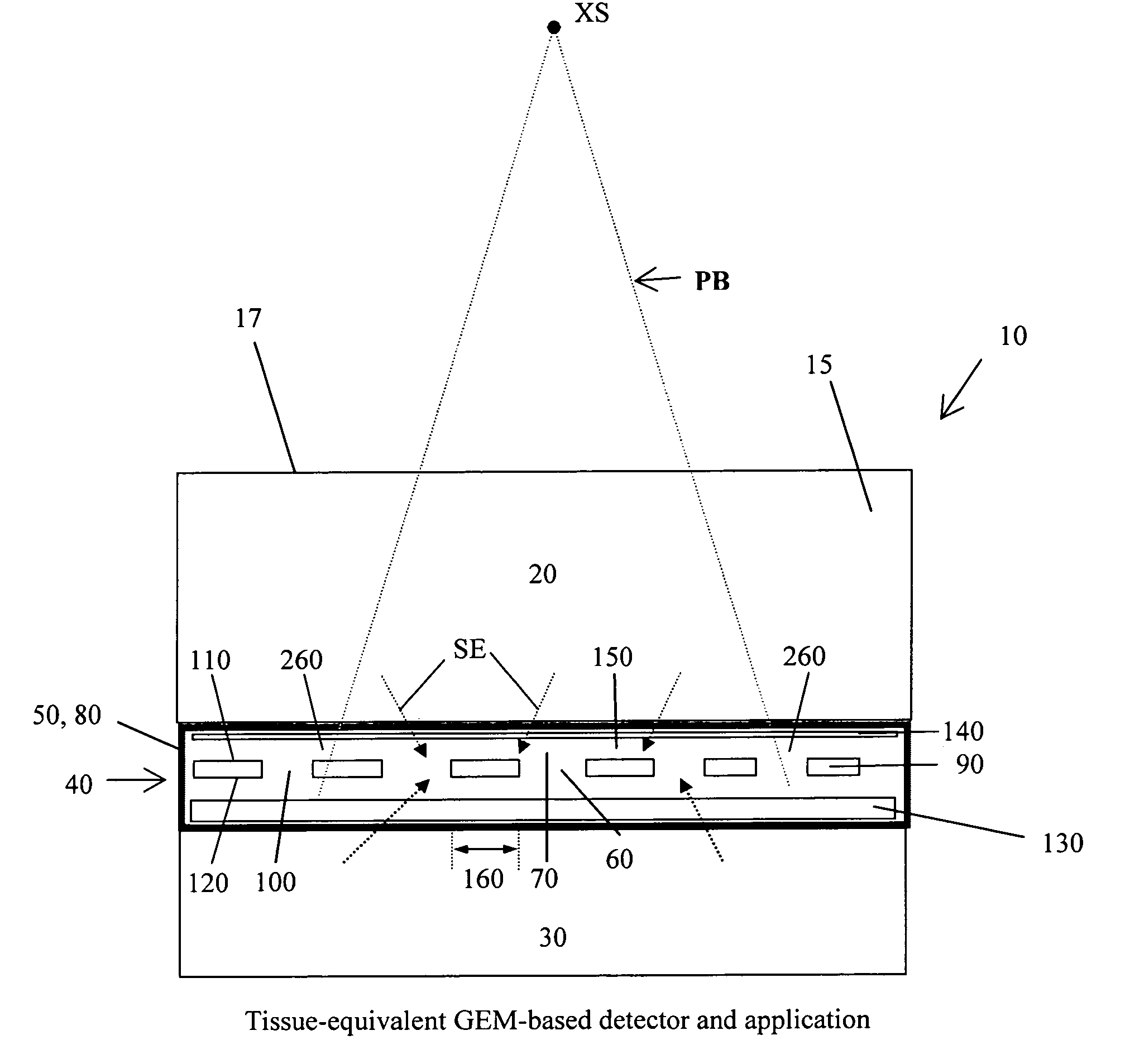
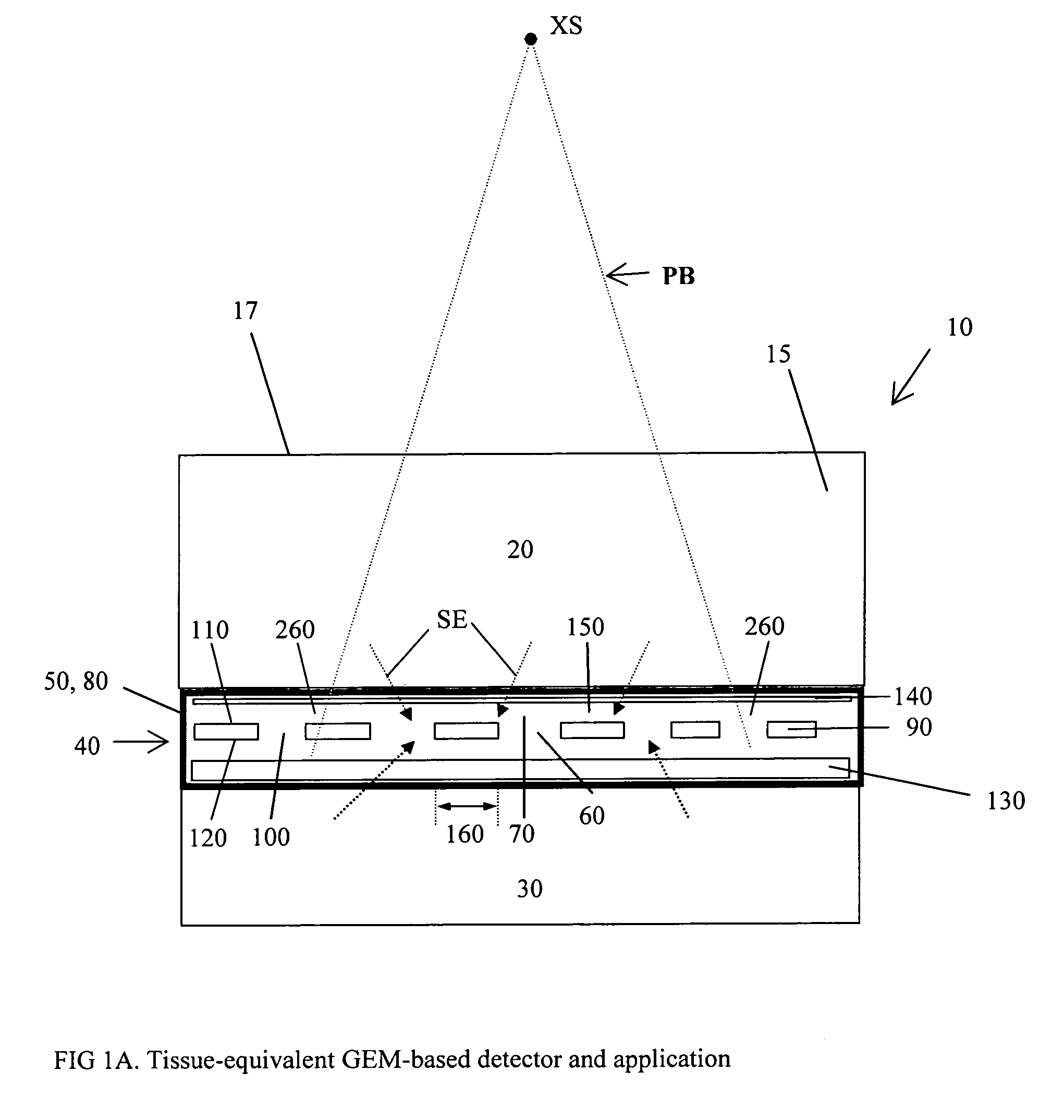
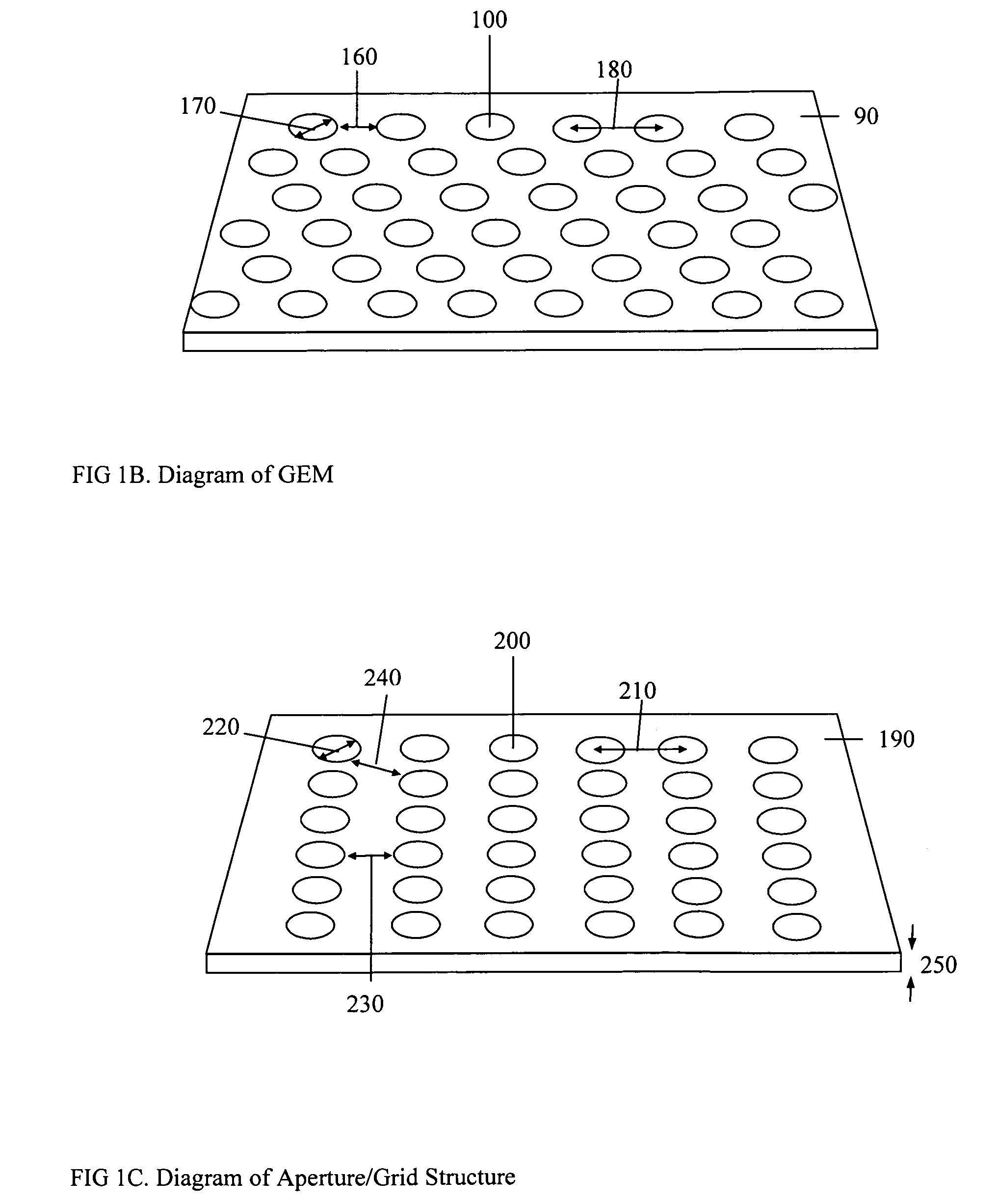
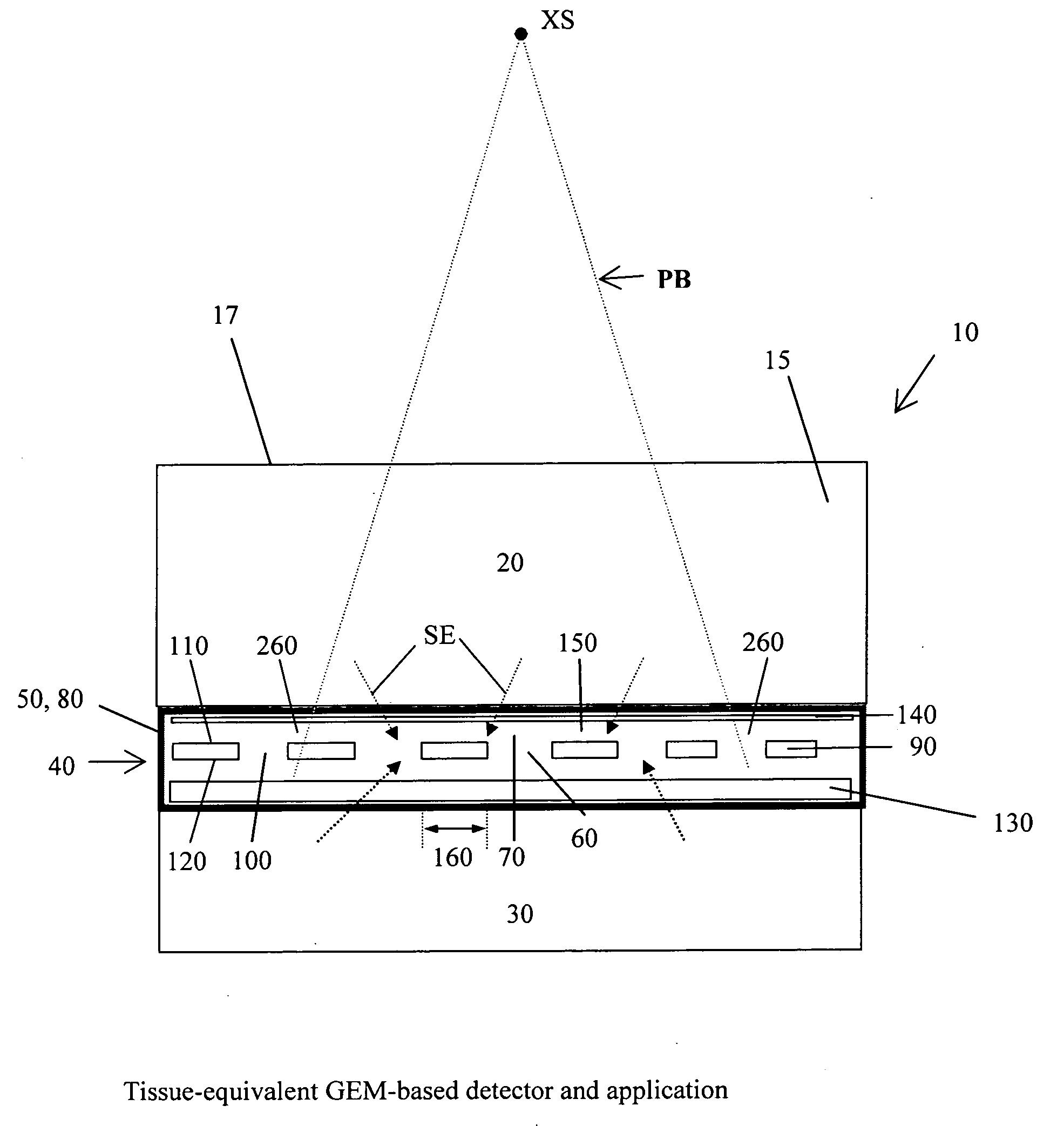
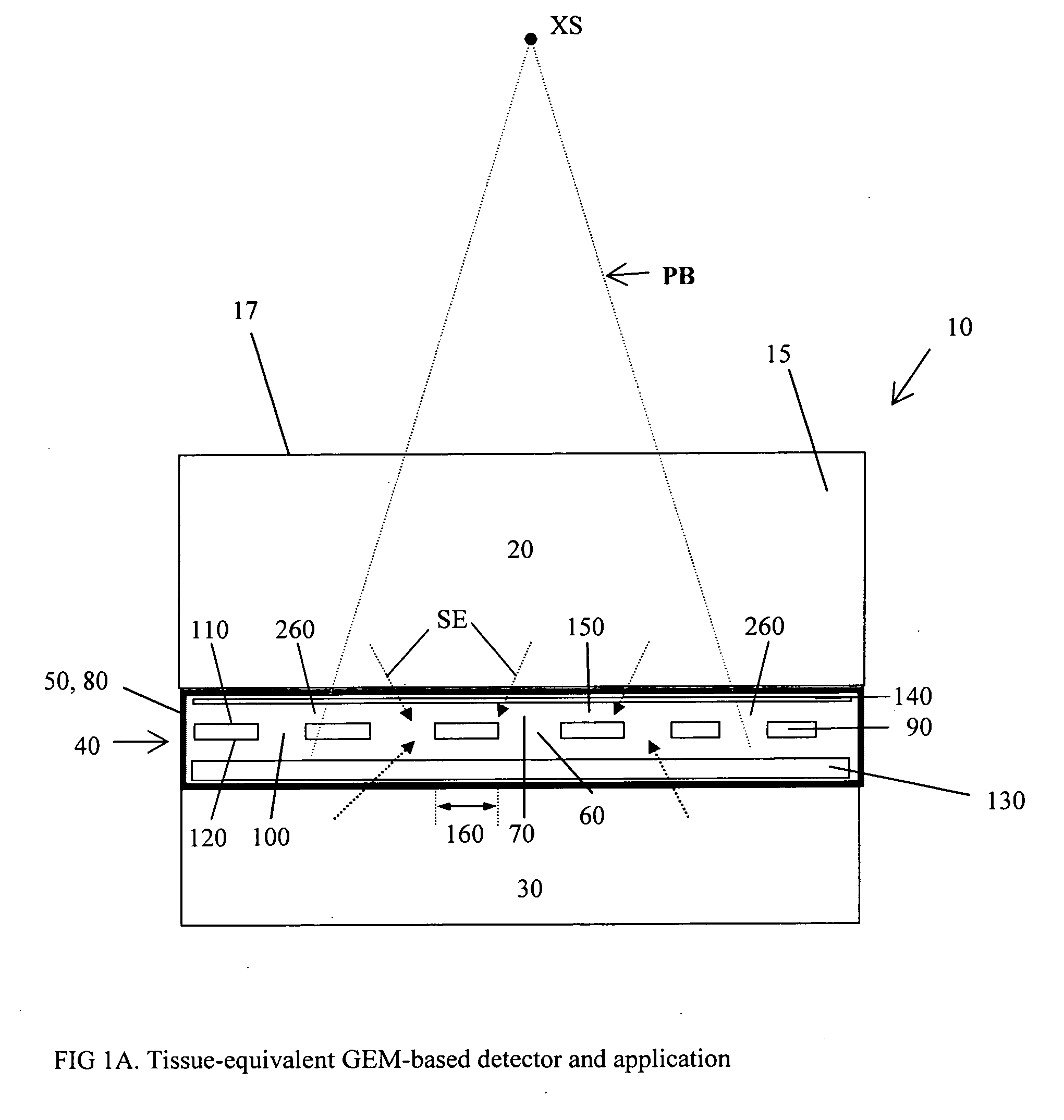
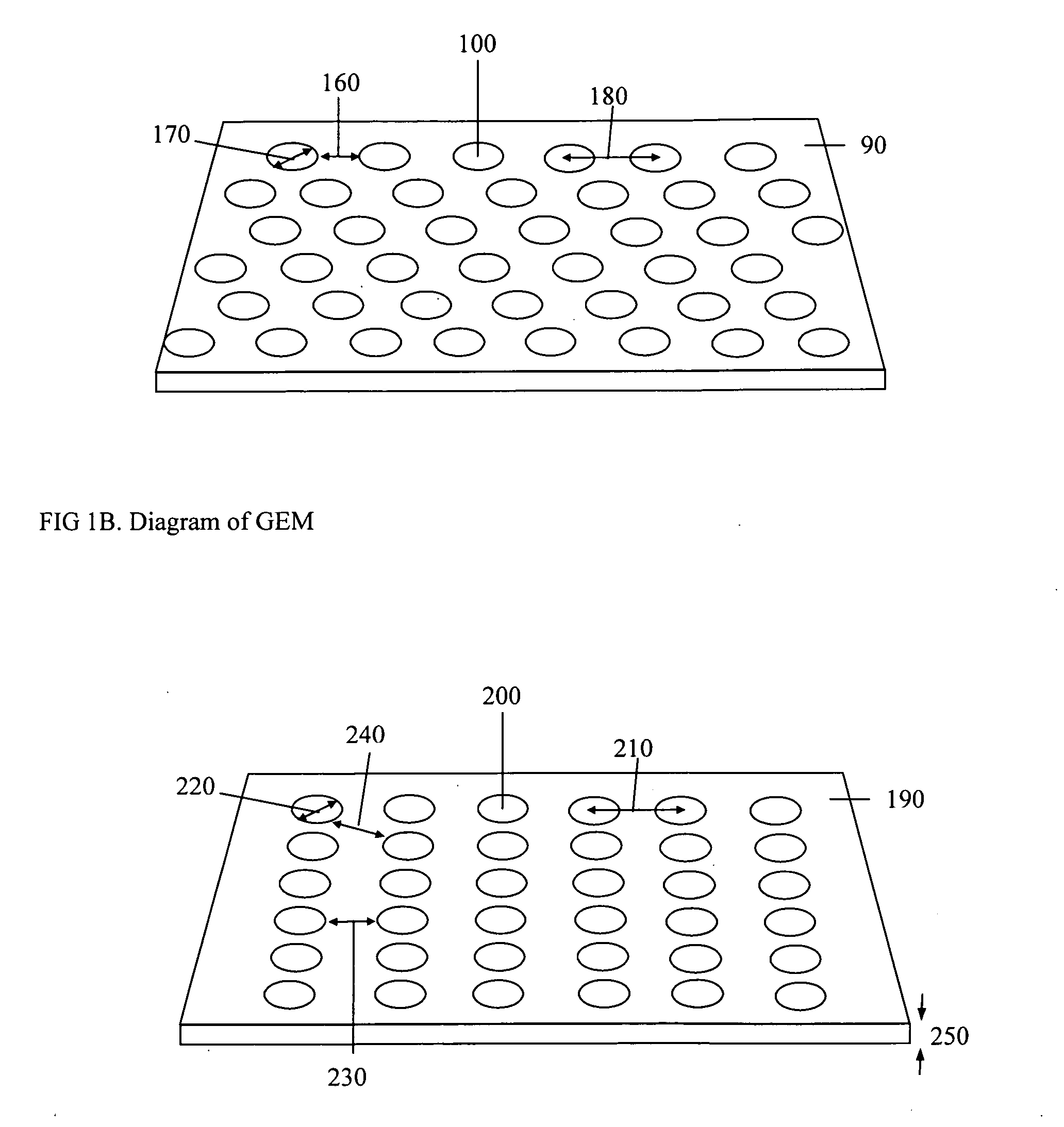
Dosimeter based on a gas electron multiplier for dose measurements of therapeutic radiation
InactiveUS7432510B2Facilitate sandwichingElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansDosimeterTherapeutic radiation
A dosimeter based on a gas electron multiplier and method of use thereof for measurement of doses of therapeutic radiation to which a tissue-phantom is exposed. Subsequent to the in-phantom measurement and verification of radiation beam delivery, radiation can be effectively delivered to a human target organ, based on the verification of radiation quantities to which the phantom was exposed. Use of a gas electron multiplier-based dosimeter facilitates precise and accurate verification of the radiation dose within a phantom by taking measurements in real time, with no need for subsequent film processing.
Owner:PRECISION DOSIMETRY SYST
Dosimeter based on a gas electron multiplier for dose measurements of therapeutic radiation
InactiveUS20080029709A1Real-time acquisitionFacilitate sandwichingElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansDosimeterTherapeutic radiation
A dosimeter based on a gas electron multiplier and method of use thereof for measurement of doses of therapeutic radiation to which a tissue-phantom is exposed. Subsequent to the in-phantom measurement and verification of radiation beam delivery, radiation can be effectively delivered to a human target organ, based on the verification of radiation quantities to which the phantom was exposed. Use of a gas electron multiplier-based dosimeter facilitates precise and accurate verification of the radiation dose within a phantom by taking measurements in real time, with no need for subsequent film processing.
Owner:PRECISION DOSIMETRY SYST
Modular radiation beam analyzer
InactiveCN101479634ACoupling light guidesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentAs DirectedTissue phantom
The instant invention is a modular radiation beam analyzer for measuring the distribution and intensity of radiation produced by a radiation source. specifically, the instant invention is a modular radiation scanning device that includes up to three modules. By selecting and assembling a predetermined number of modules a radiation detector may be manipulated through up to three axes for radiation beam scans as well as direct Tissue Maximum Ratio (TMR) and / or Tissue Phantom Ratio (TPR) scans.
Owner:丹尼尔纳瓦罗
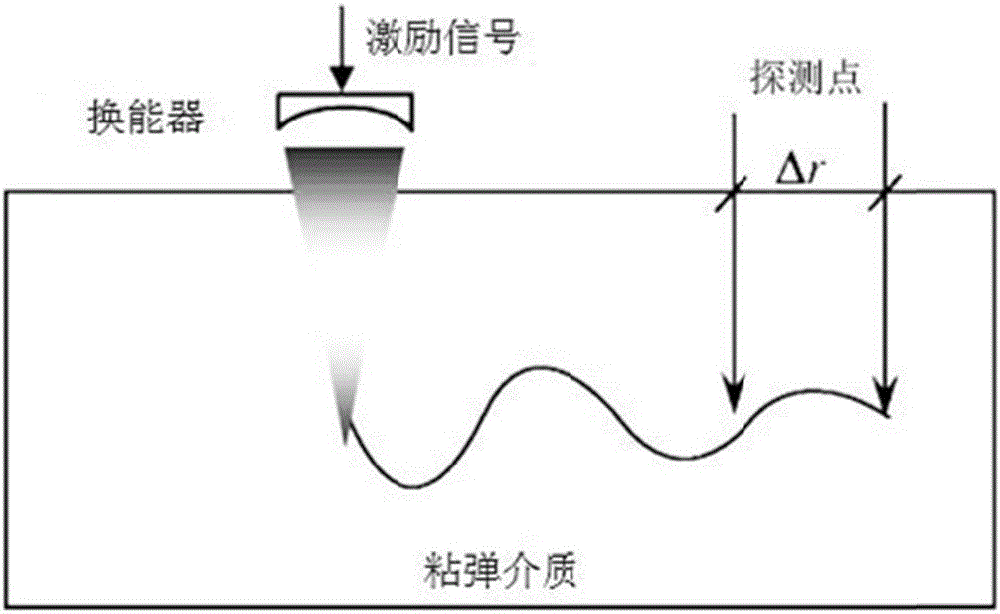
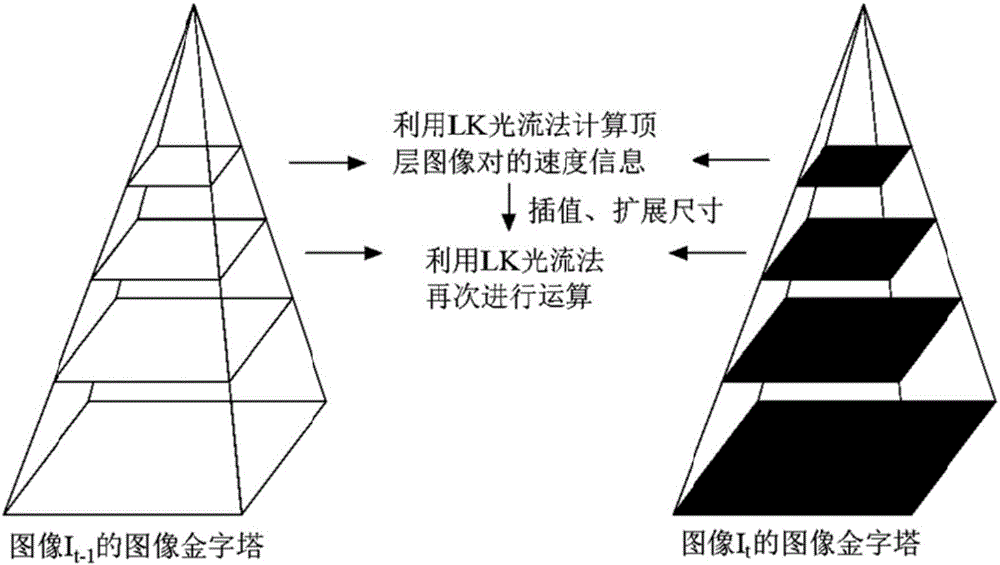
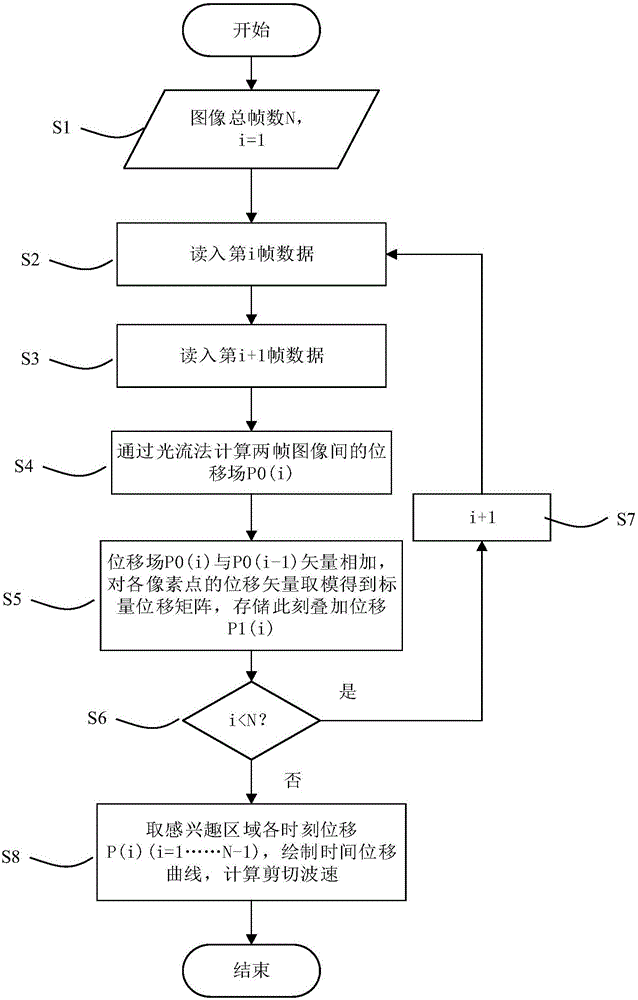
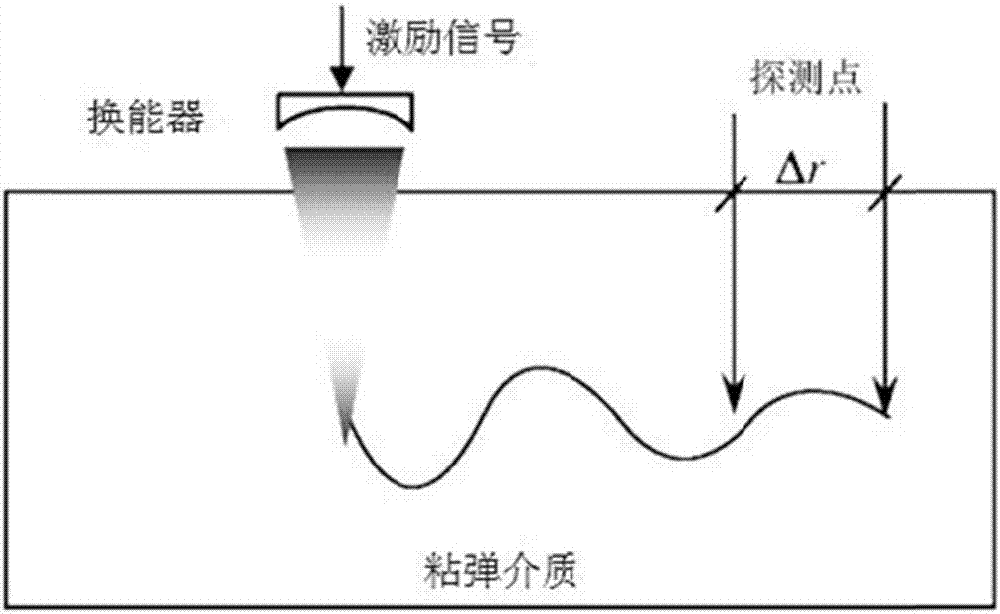
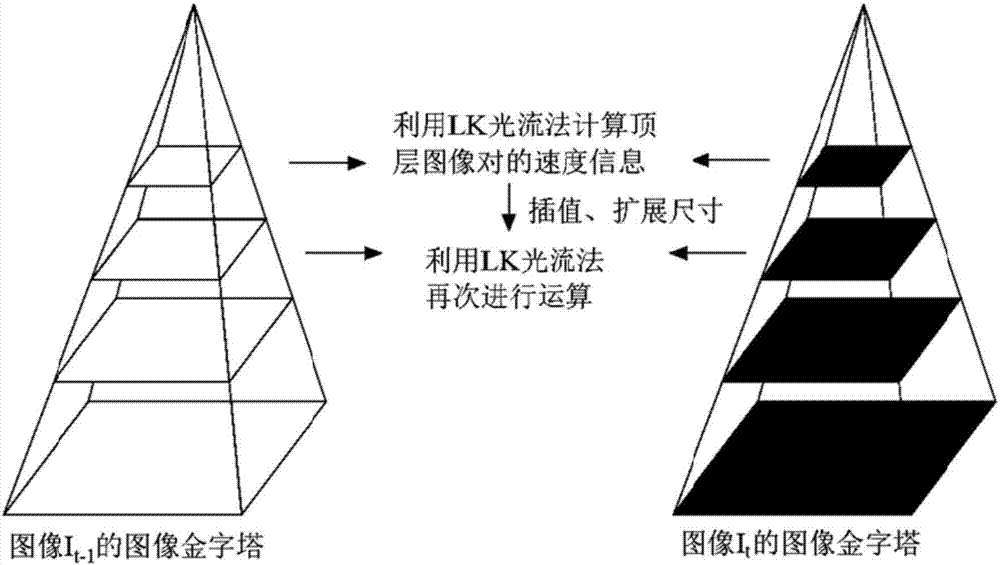
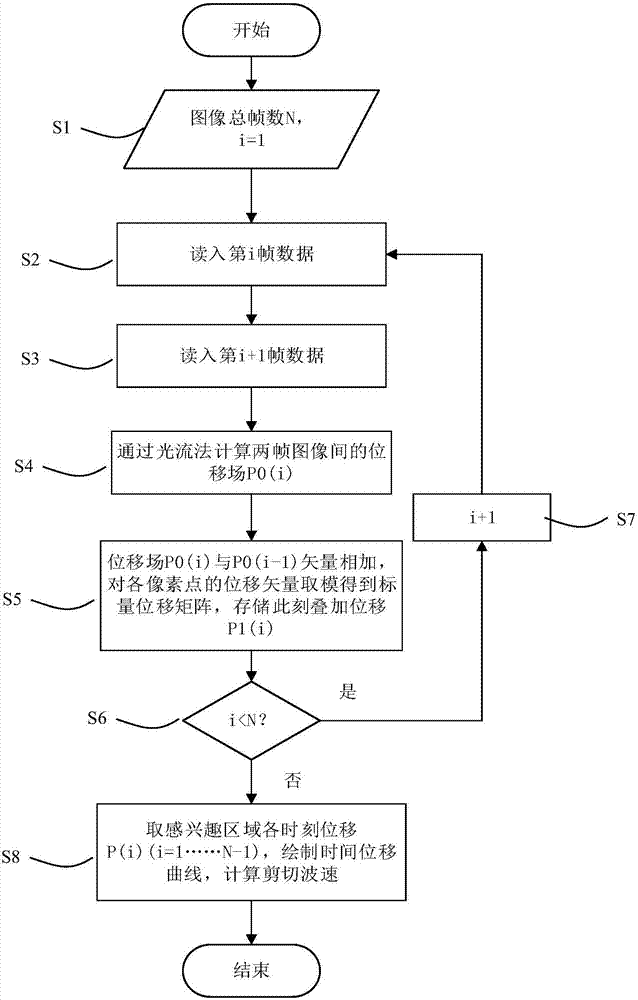
HIFU damage shear wave elastic characteristic estimation method based on LK optical flow
ActiveCN106214182AQuantitative estimation of elastic propertiesHigh sensitivityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsTreatment effectEngineering
The invention discloses an HIFU damage shear wave elastic characteristic estimation method based on LK optical flow. A damage formation and vibration continuous image is obtained with a high-speed camera when HIFU acts on tissue phantom, a vibration displacement curve of damage is obtained with the Lucas-Kanade optical flow method of an image pyramid, the propagation speed of acoustic radiation force shear wave generated on damage under the action of HIFU is calculated with the time-to-peak (TTP) method, quantitative estimation of shear elasticity modulus of damage can be conducted according to the relation among medium density, shear wave velocity in medium and medium shear elasticity modulus, and then the elastic characteristic of target tissue during treatment is monitored in real time and treatment effect is evaluated.
Owner:永春县产品质量检验所福建省香产品质量检验中心国家燃香类产品质量监督检验中心福建
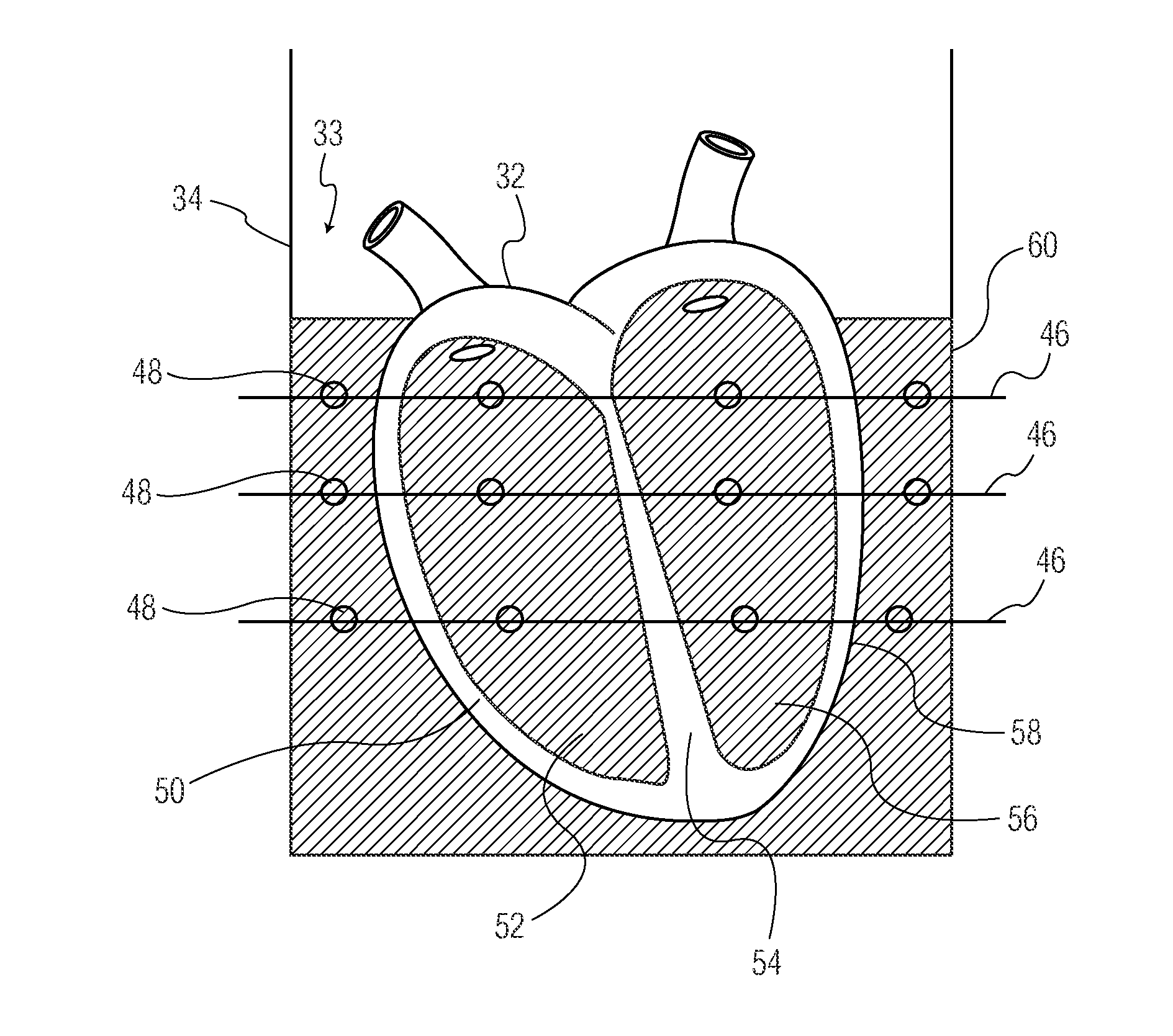
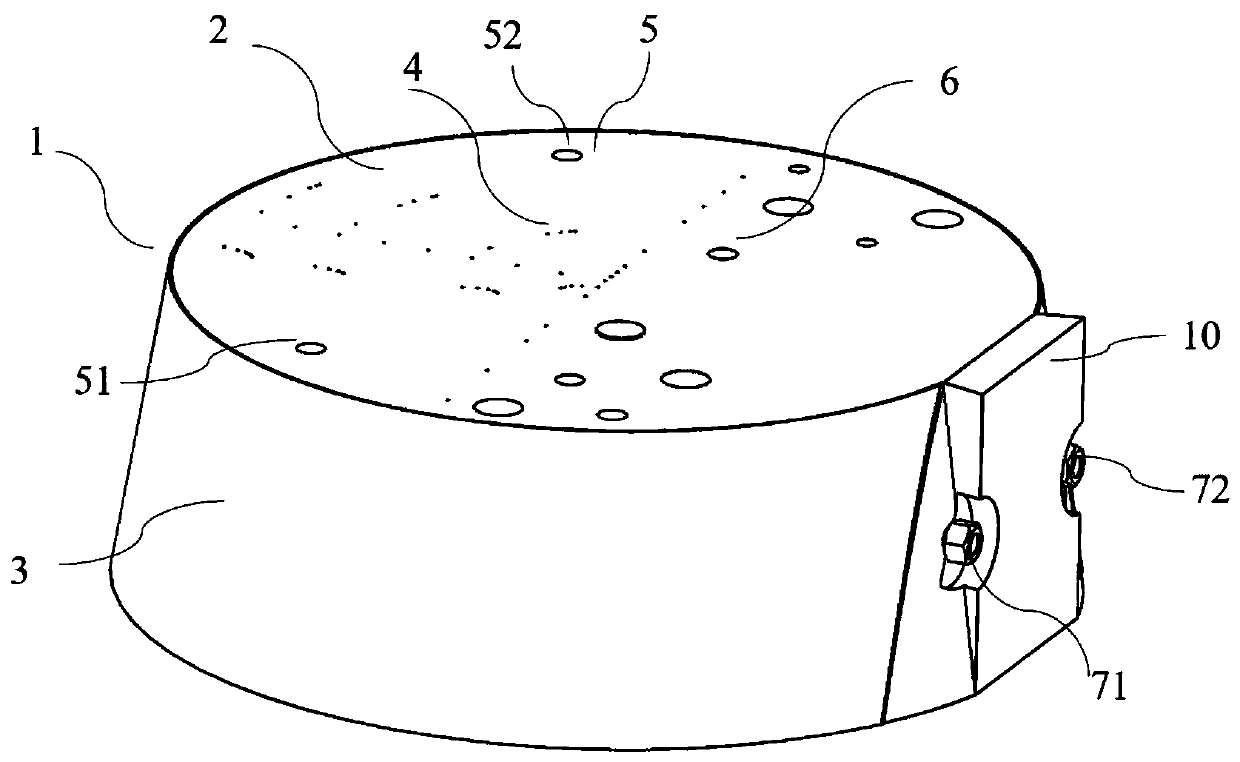
Tissue mimicking body model for detecting imaging distinguishability of ultrasound echotomography scanning equipment
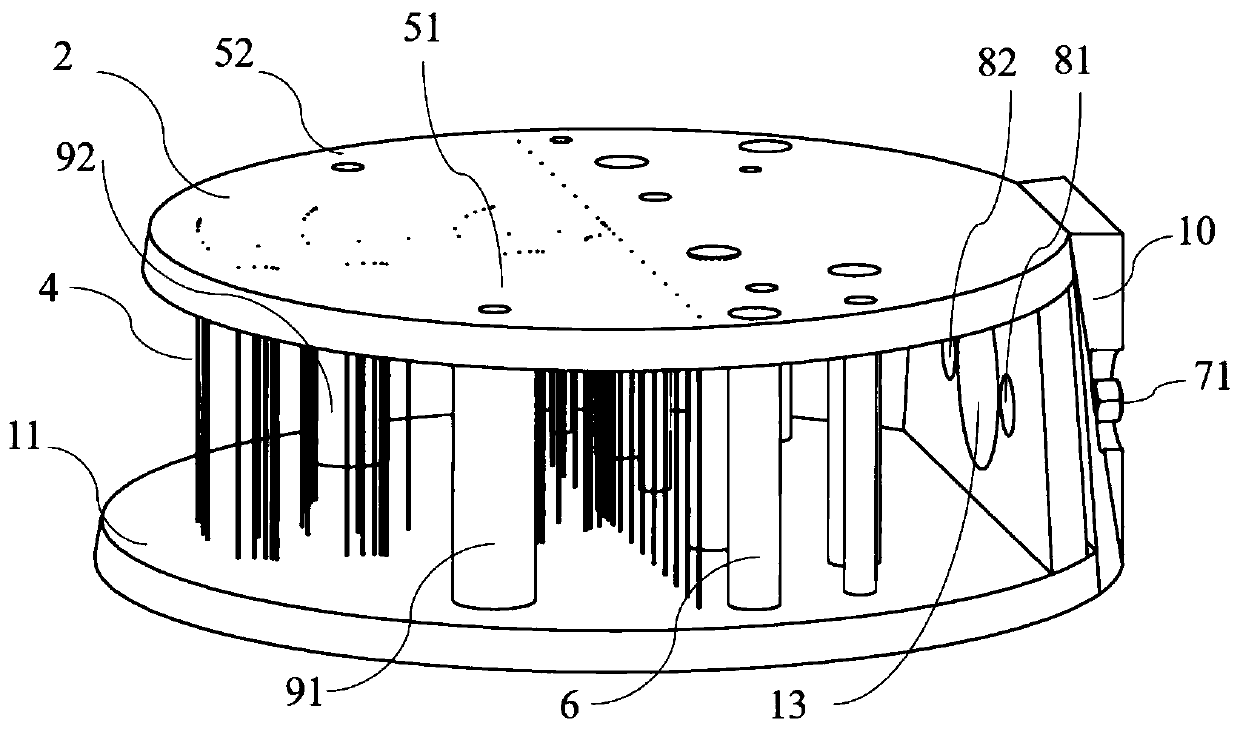
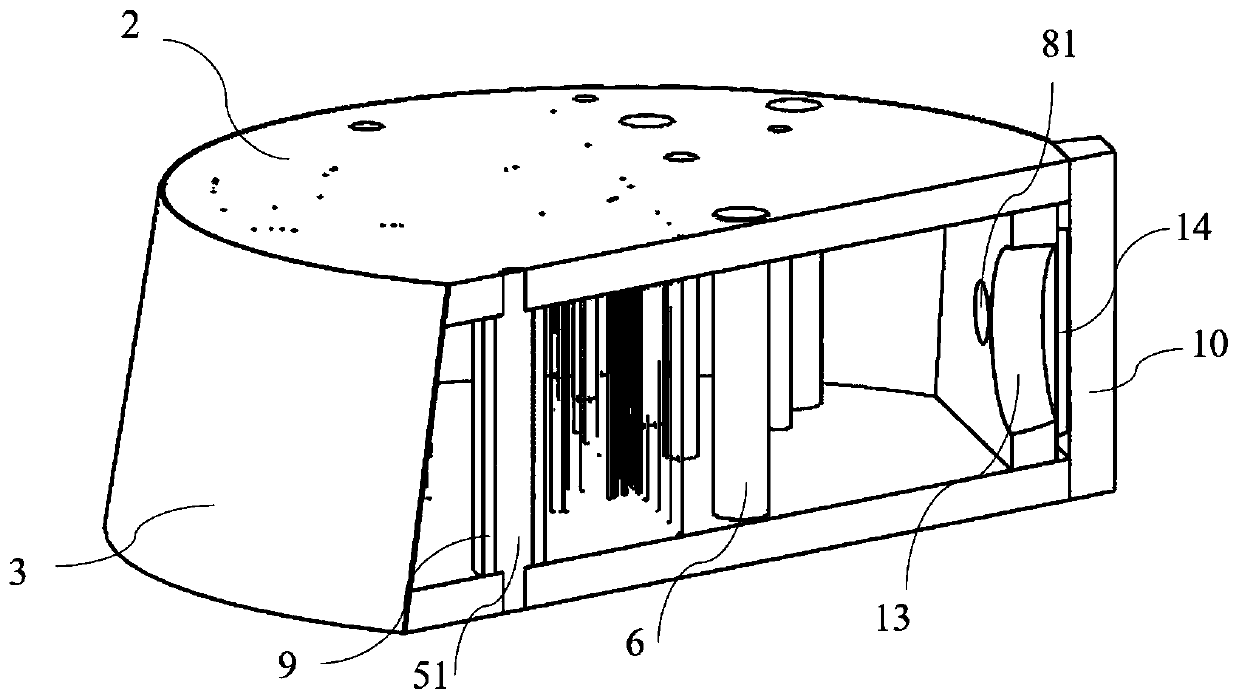
PendingCN110755111AAvoid artifactsLong validity periodOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsTarget lineTissue phantom
The invention discloses a tissue mimicking body model for detecting imaging distinguishability of ultrasound echotomography scanning equipment. The tissue mimicking body model is in the shape of a truncated cone, and comprises a body model housing, an acoustic window (3), a supporting and protecting plate (6), a plurality of target lines (4), a plurality of simulated niduses (6) and background tissue-mimicking materials (12), wherein the body model housing is manufactured by fixed connecting of an upper panel (2), a lower panel (11) and a supporting plate (14); a sealing space is formed by thebody model housing and the acoustic window (3) which is adhered and fixed to the side surface of the truncated cone; the background tissue-mimicking materials (12) are stuffed in the sealing space; the target lines (4) and the simulated niduses (6) are embedded in the background tissue-mimicking materials (12); each target line and each simulated niduse vertically penetrate from the upper panel (2) to the lower panel (11); an inlet for stuffing the background tissue-mimicking materials (12) is formed in the supporting plate (14); a blocking rubber is adhered to the inlet; and the supporting and protecting plate (6) is fixed outside the supporting plate (14).
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three-dimensional construction method for transfer liver cancer tissue models in vitro
InactiveCN101508973AContribute to malignant biological behaviorContribute to the experimental analysis of malignant biological behaviorTumor/cancer cellsBiologic scaffoldIn vivo
The invention provides a method for constructing in-vitro model of 3D metastatic hepatoma-like tissues, characterized in that the method comprises the steps of continuously culturing highly metastatic human hepatoma cell line MHCC97H in a 3D rotary culture system combining an RWM bioreactor and a biologic scaffold PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)) for 15 days to form a metastatic hepatoma-like tissue model which has the characteristics closer to the in-vivo metastatic hepatoma tissues in terms of tissue morphological structure, specific gene expression and protein secretion, thereby better simulating and representing the growth characteristics and pathological changes of the in-vivo metastatic hepatoma solid tumor, therefore, the metastatic hepatoma-like tissue model is superior to the highly metastatic human hepatoma cell line model cultured by the tablet.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Estimation method of HIFU damage shear wave elastic properties based on lk optical flow method
ActiveCN106214182BQuantitative estimation of elastic propertiesHigh sensitivityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsVolumetric Mass DensityEngineering
The invention discloses an HIFU damage shear wave elastic characteristic estimation method based on LK optical flow. A damage formation and vibration continuous image is obtained with a high-speed camera when HIFU acts on tissue phantom, a vibration displacement curve of damage is obtained with the Lucas-Kanade optical flow method of an image pyramid, the propagation speed of acoustic radiation force shear wave generated on damage under the action of HIFU is calculated with the time-to-peak (TTP) method, quantitative estimation of shear elasticity modulus of damage can be conducted according to the relation among medium density, shear wave velocity in medium and medium shear elasticity modulus, and then the elastic characteristic of target tissue during treatment is monitored in real time and treatment effect is evaluated.
Owner:永春县产品质量检验所福建省香产品质量检验中心国家燃香类产品质量监督检验中心福建
Thermochromic polyacrylamide tissue phantom and its use for evaluation of ablation therapies
ActiveUS8984969B2Ultrasound therapyThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsRf ablationTissue phantom
A polyacrylamide tissue phantom embedded with multi-formulated thermochromic liquid crystals for use in the evaluation of RF ablation therapies is provided. The tissue phantom approximates the properties of biological tissue, and therefore provides a suitable substitute for use in testing the effects of RF and other energy-emitting devices on biological tissue. Also provided is a system for using the tissue phantom in the evaluation of RF therapies.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
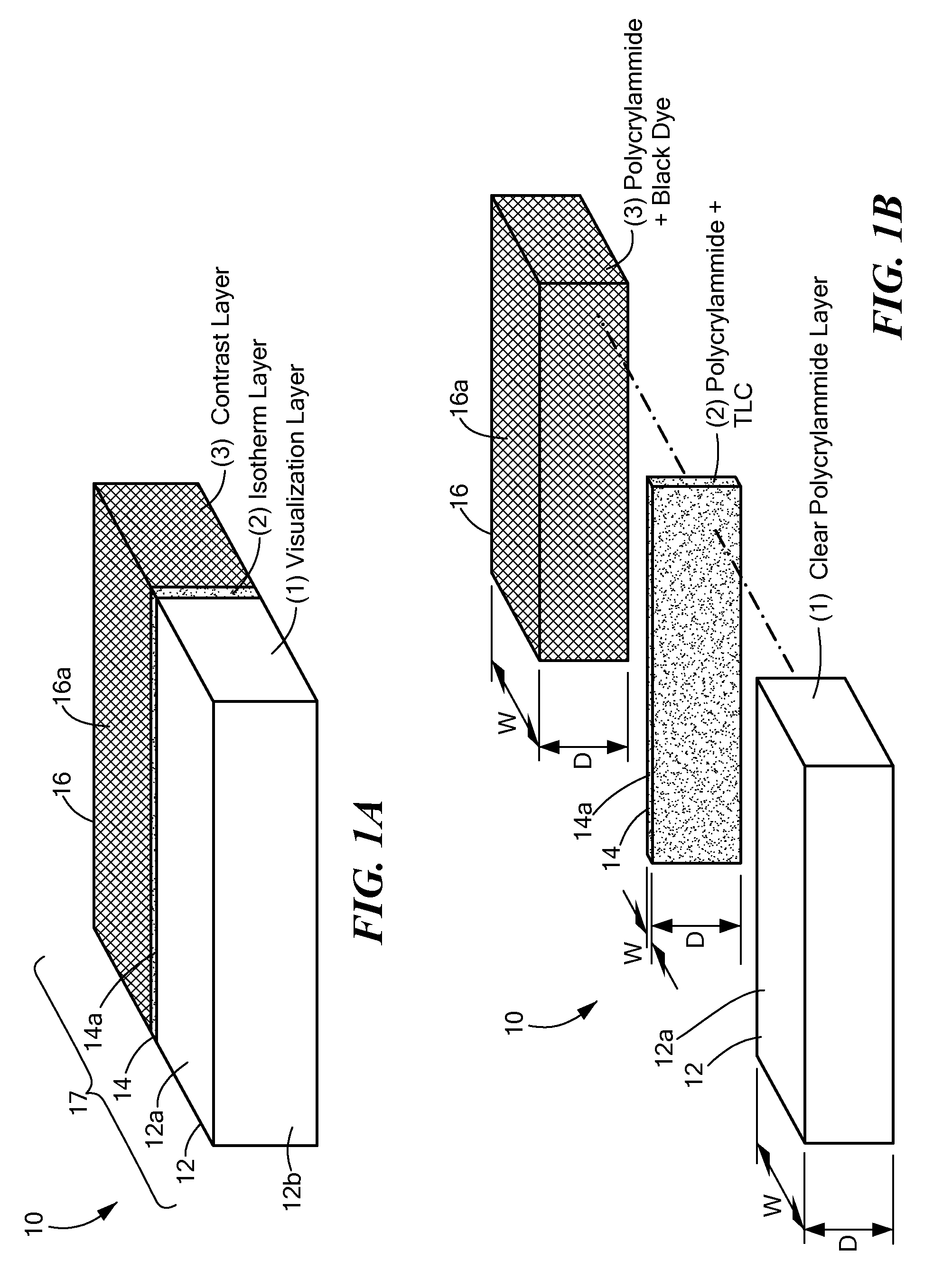
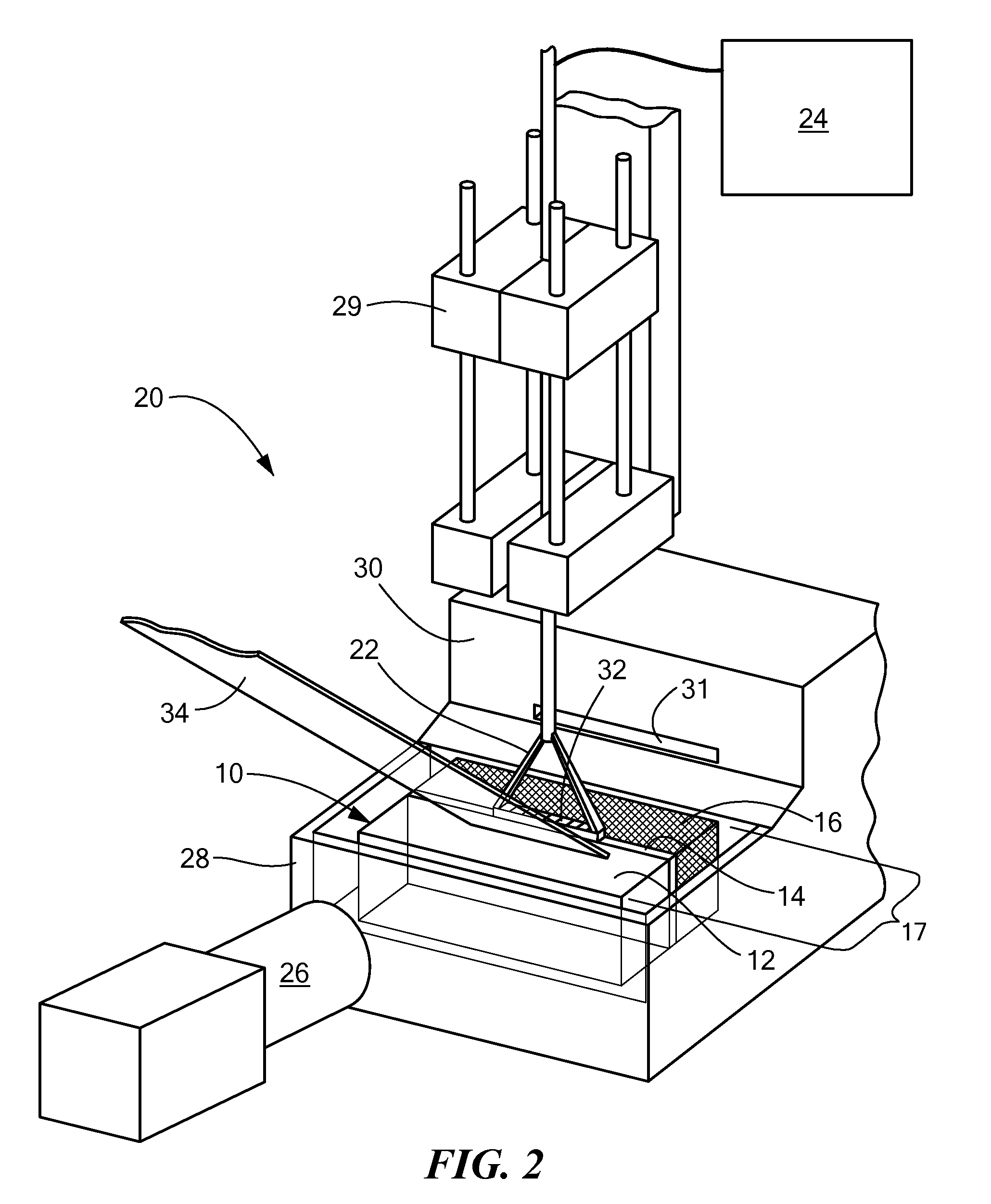
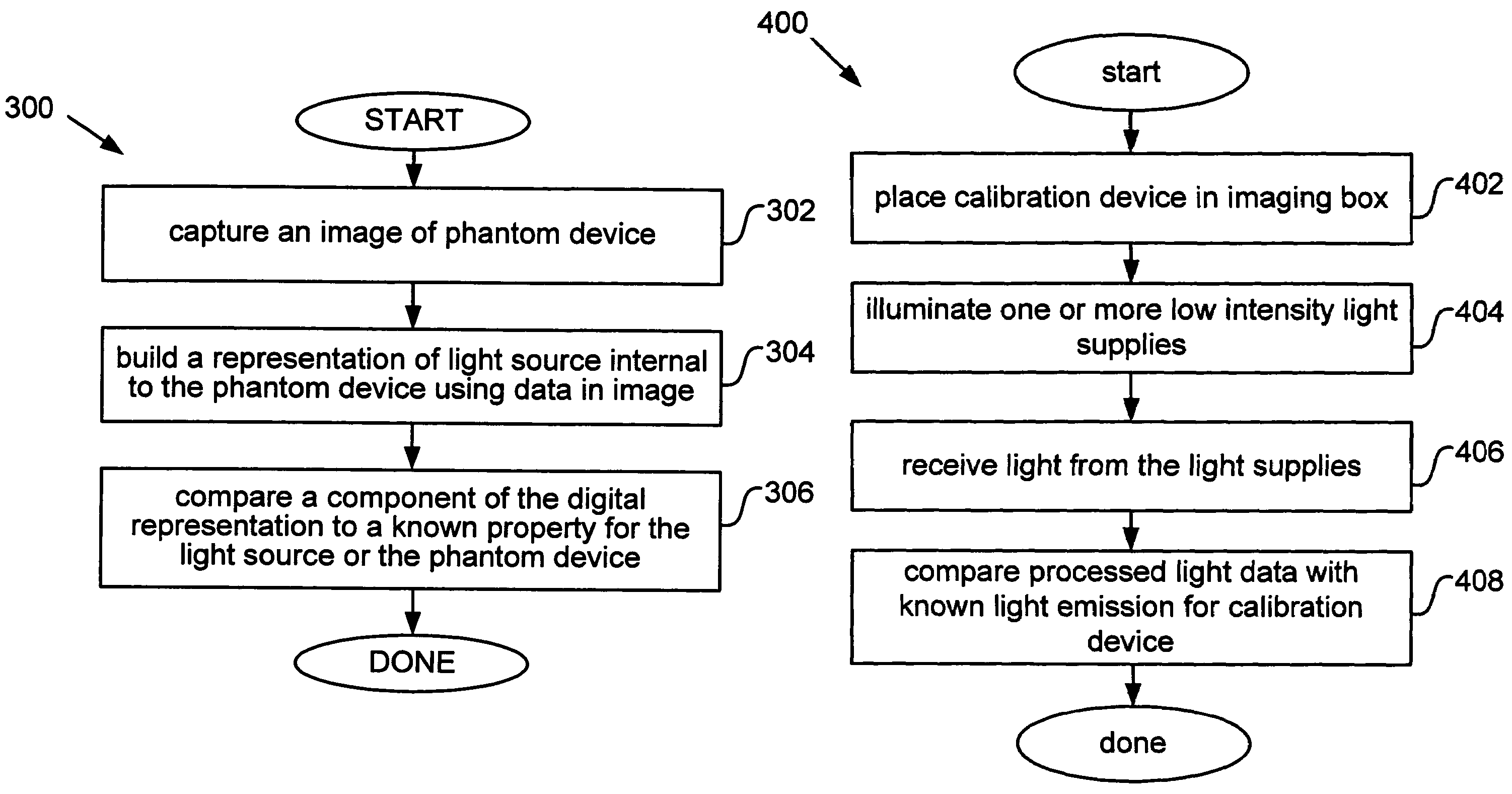
Tissue phantom calibration device for low level light imaging systems
ActiveUS7629573B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLow intensity lightMaterial Design
The present invention relates to a phantom device that simplifies usage and testing of a low intensity light imaging system. The phantom device includes a body and a light source internal to the body. The body comprises an optically selective material designed to at least partially resemble the optical behavior of mammalian tissue. Imaging the light source or phantom device may incorporate known properties of the optically selective material. Testing methods described herein assess the performance of a low-level light imaging system (such as the software) by processing light output by the phantom device and comparing the output against known results. The assessment builds a digital representation of the light source or test device and compares one or more components of the digital representation against one or more known properties for the light source or the test device.
Owner:XENOGEN CORP
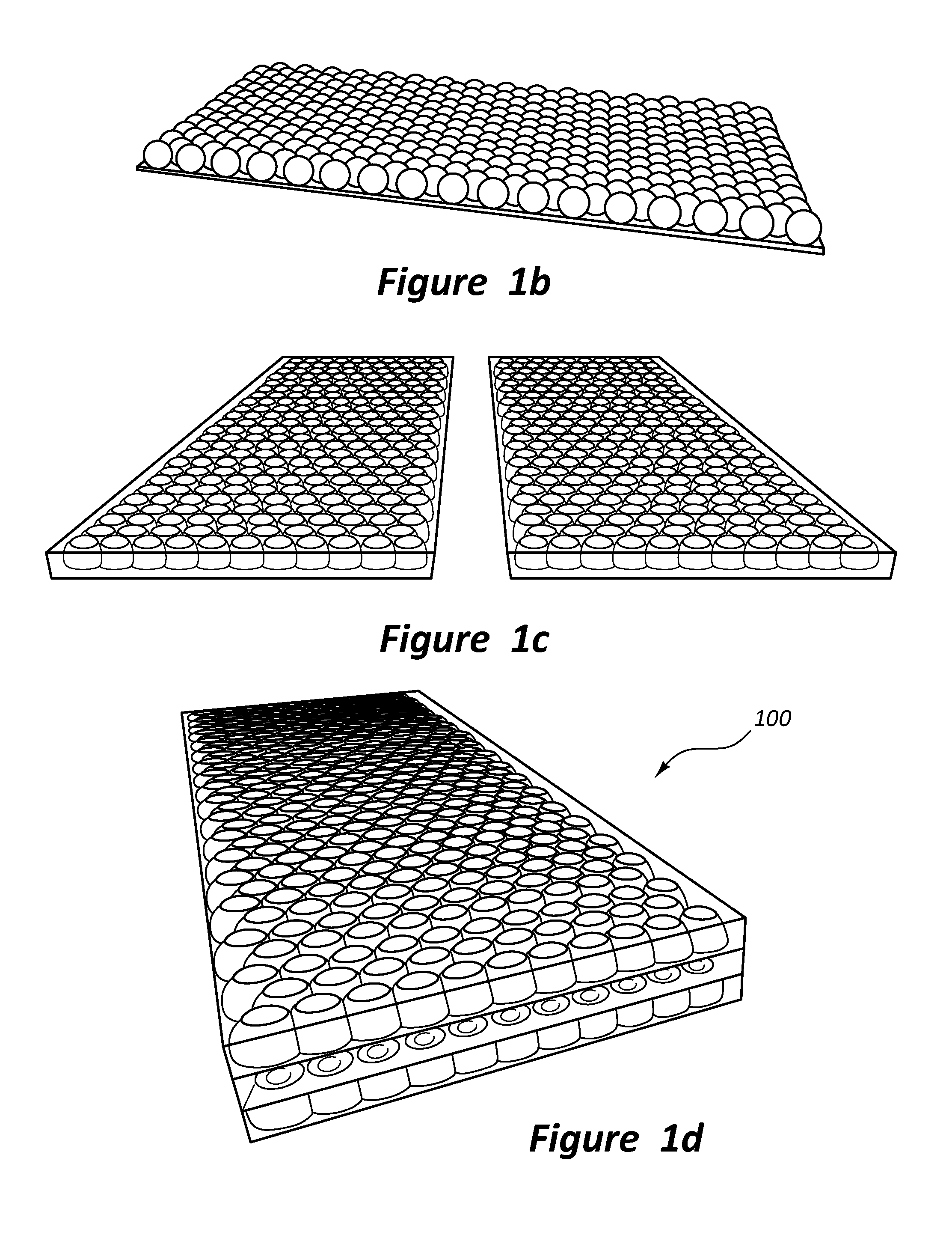
Multilayered Phantom Tissue Test Structure and Fabrication Process
ActiveUS20140072770A1Accurate spacingLamination ancillary operationsLaminationMicrometer scaleMicrosphere
A multilayered optical tissue phantom fabrication approach and inherently produced test target structure which address the issues of optical conformity known in the art by controlling the formation of micrometer scale monolayers embedded with light-scattering microspheres.
Owner:THE UNITED STATS OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE
Dosimetric scintillating screen detector for charged particle radiotherapy quality assurance (QA)
ActiveUS9958402B2PhotometryMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationCharged particle radiotherapyCharged particle
An apparatus and method are provided for performing Quality Assurance of complex beams of penetrating radiation inside a patient. A detector with a transverse scintillating screen images the radiation inside a tissue phantom with high spatial resolution. The scintillator is comprised of a mixture of two or more scintillators emitting different spectra of light and having different characteristic responses as a function of the beam LET value. The optics relaying the scintillation output have variable transmission with wavelength, further shaping the spectrum of light transmitted to the imaging sensor which also has spectrally varying sensitivity. Parameters of the scintillator construction, the optics, and the imaging sensor are chosen so the output of the composite detector is proportional to a characteristic of the input beam, for example the dose deposited as a function of depth inside the tissue phantom.
Owner:EBSTEIN STEVEN M
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com