Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135 results about "Tissue protection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
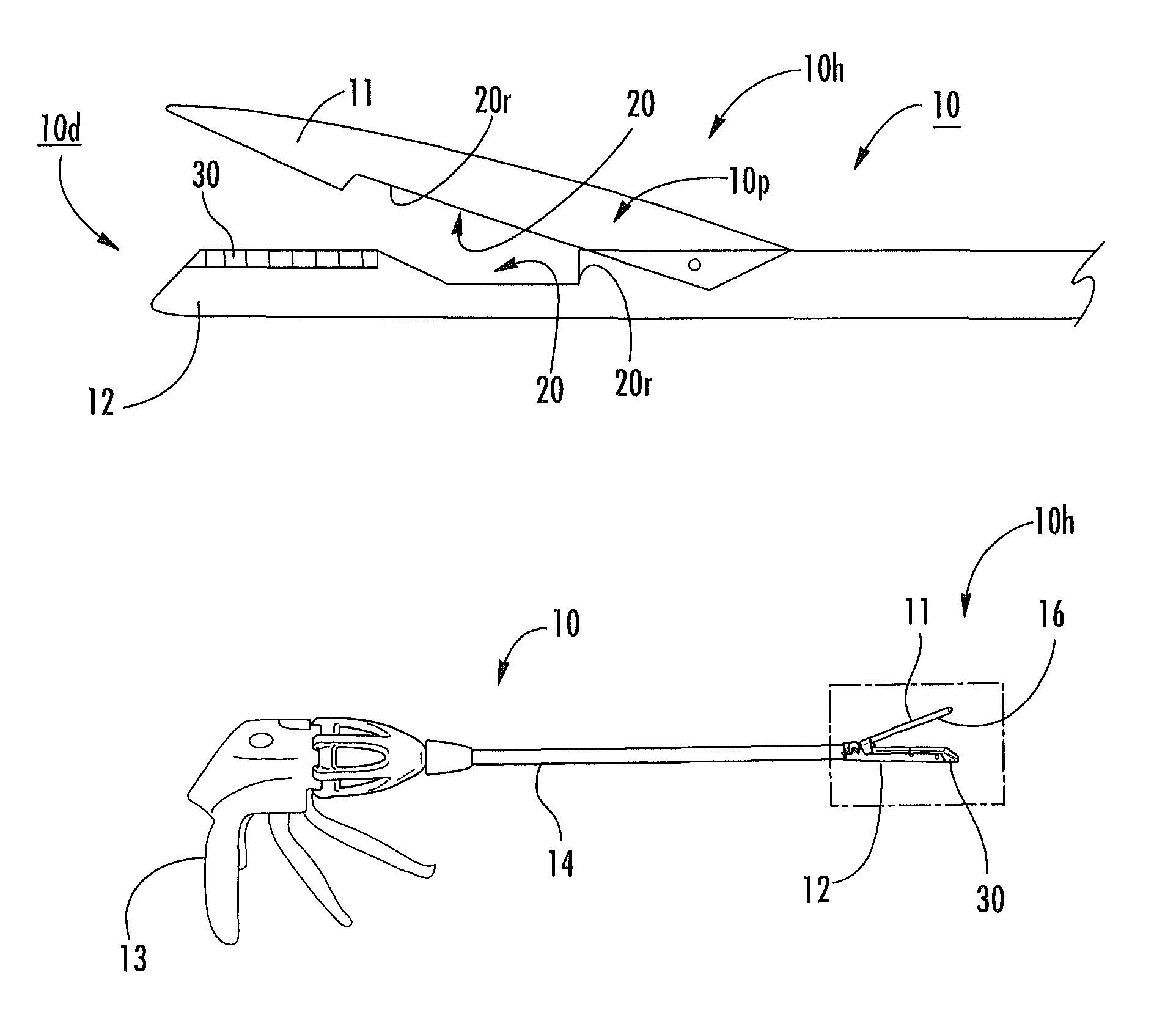
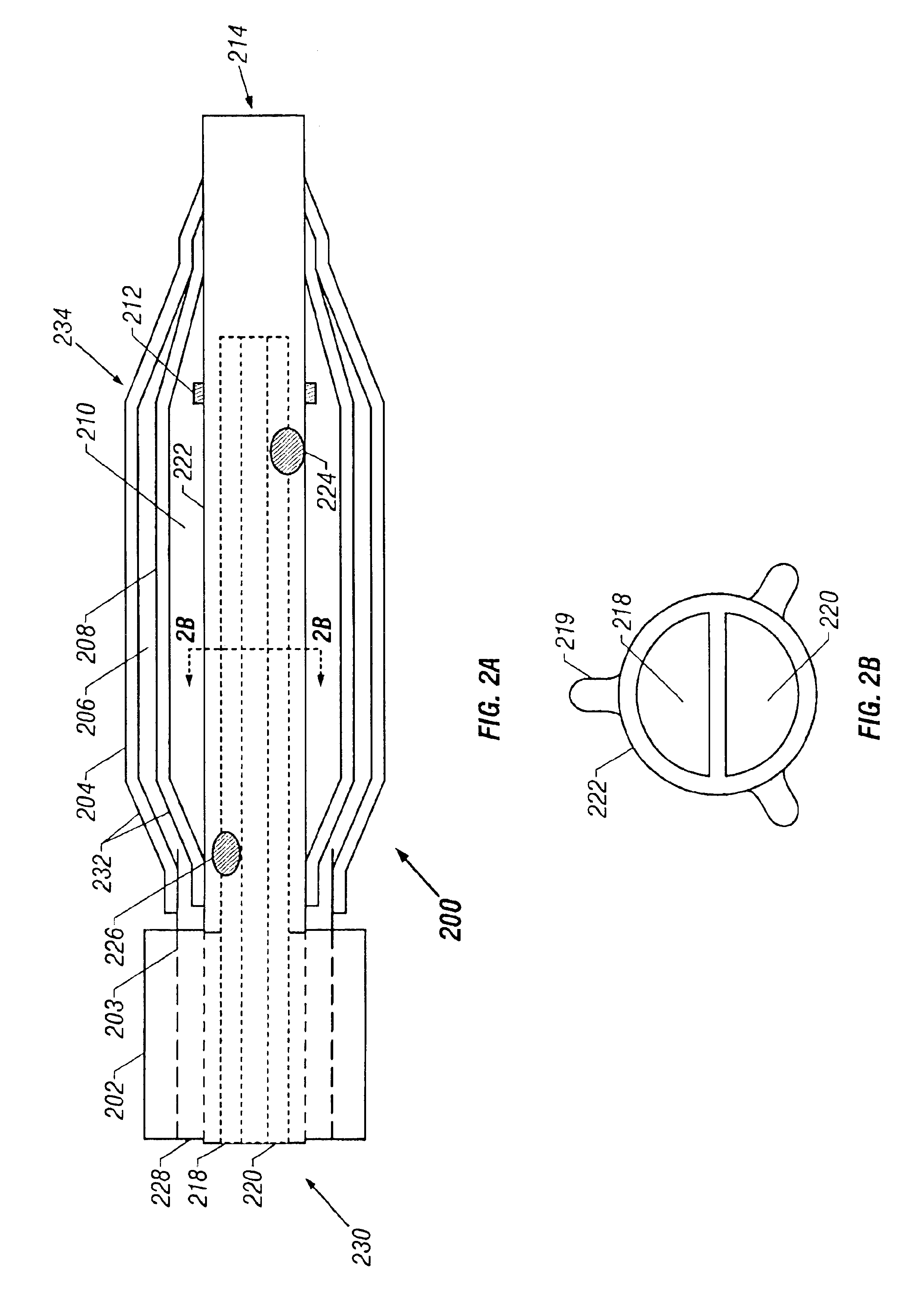
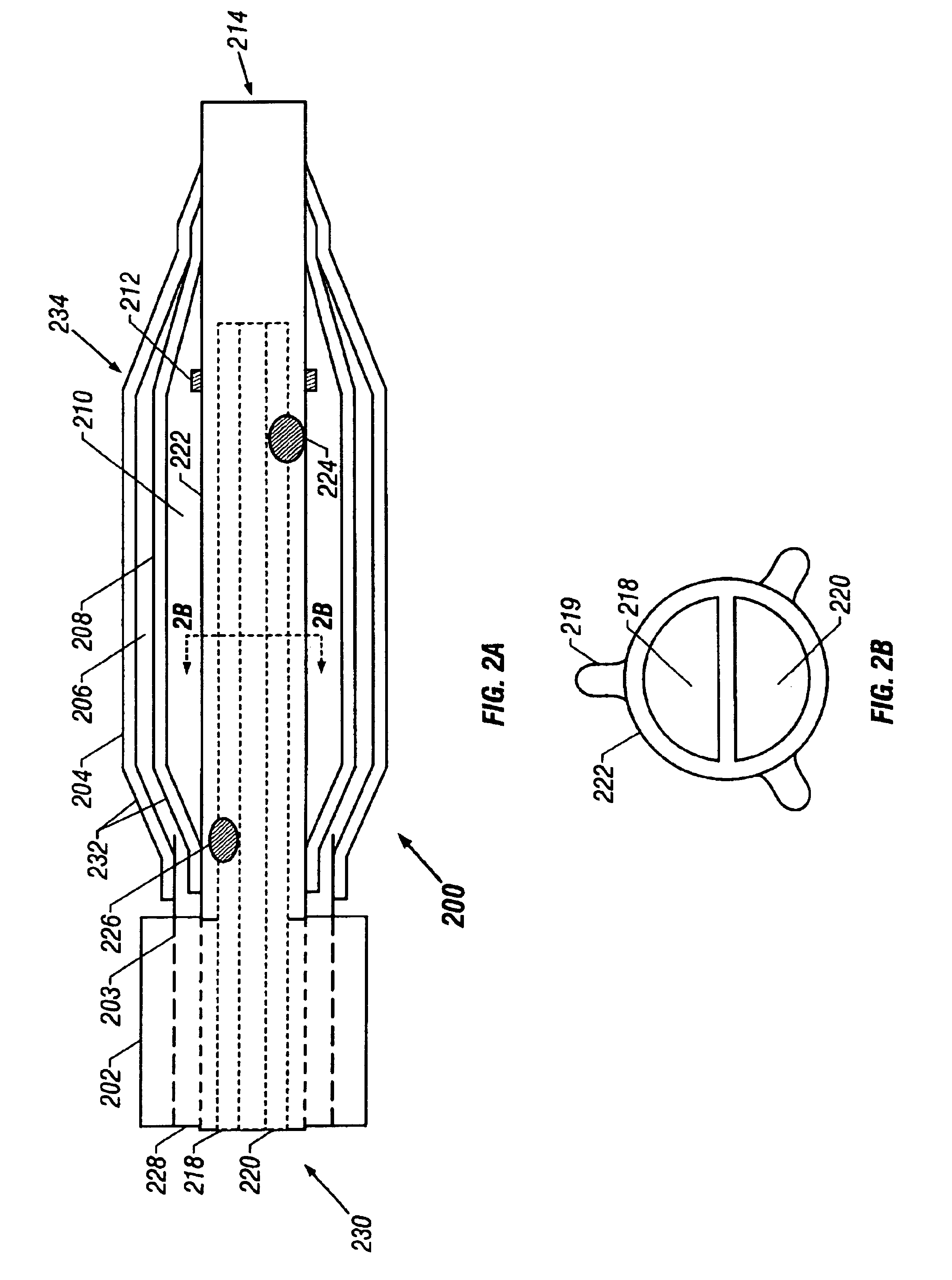
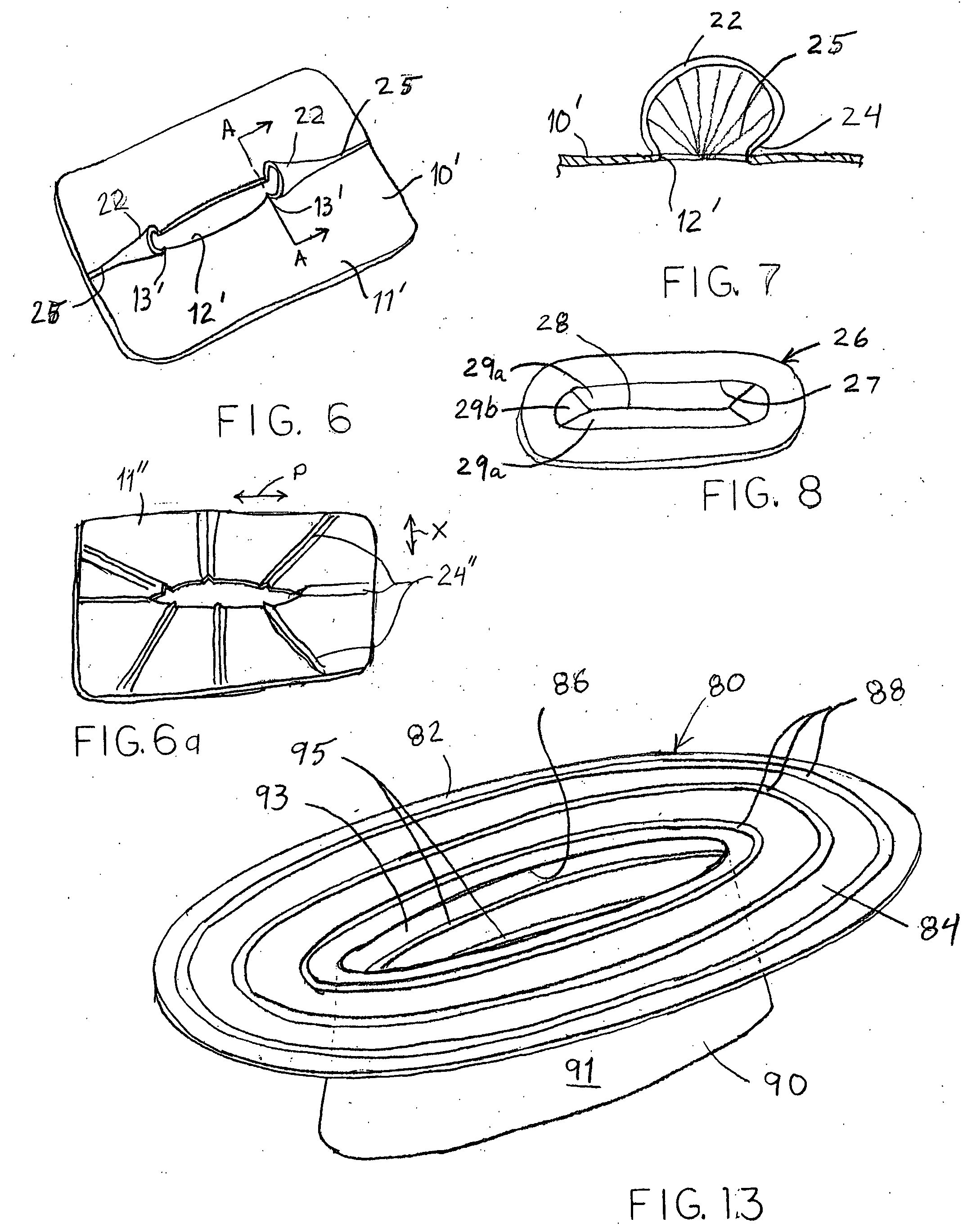
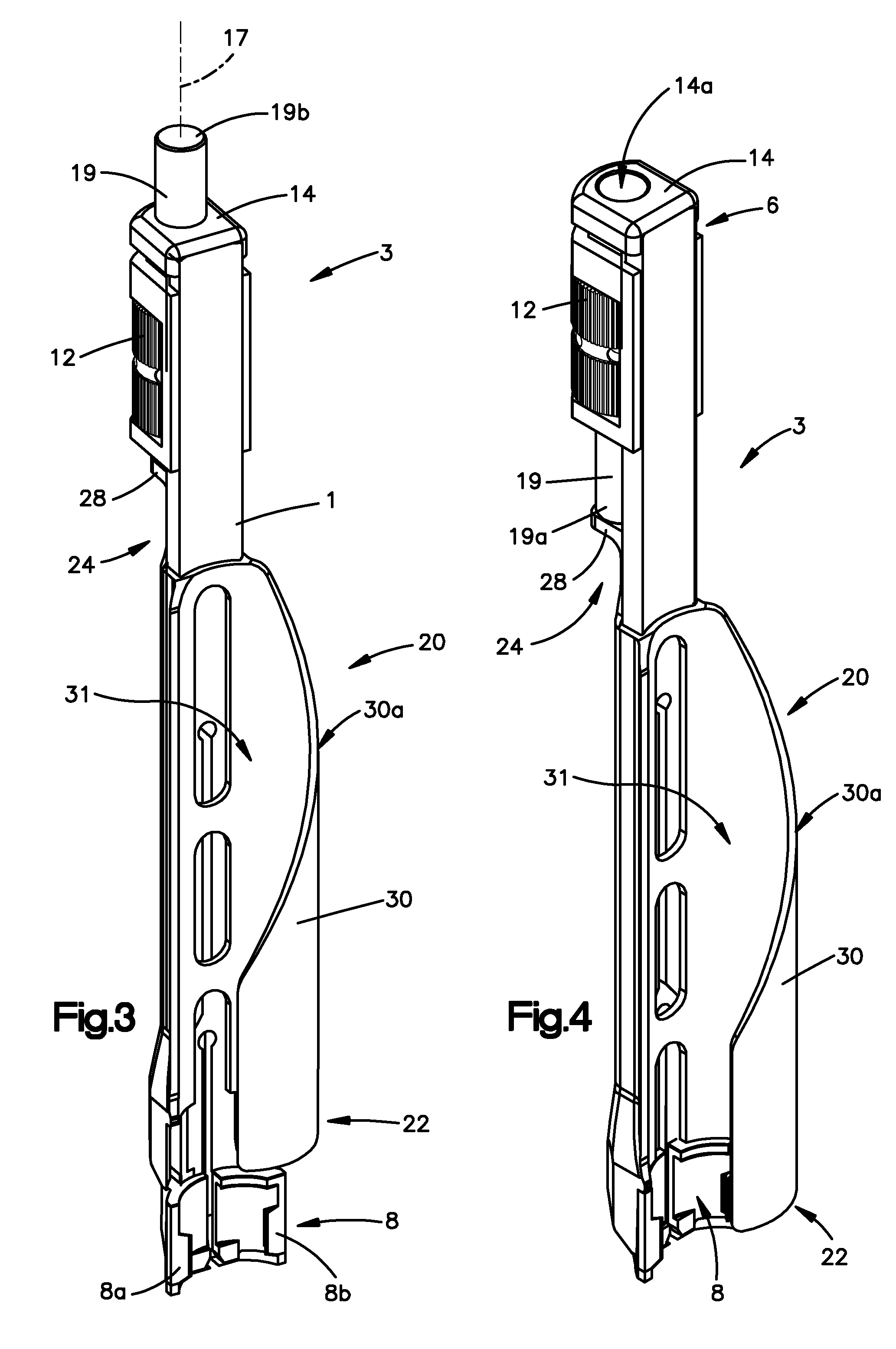
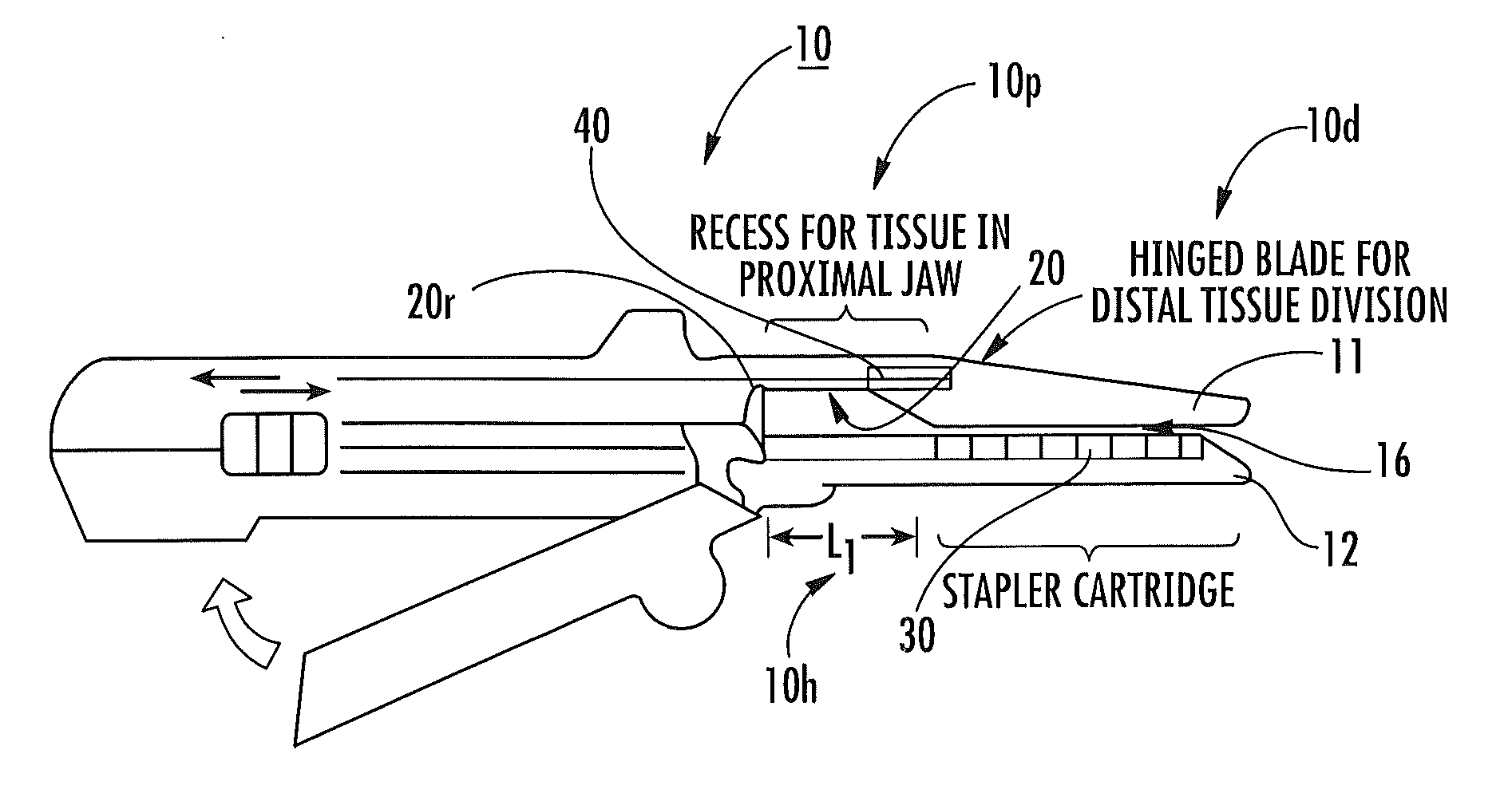
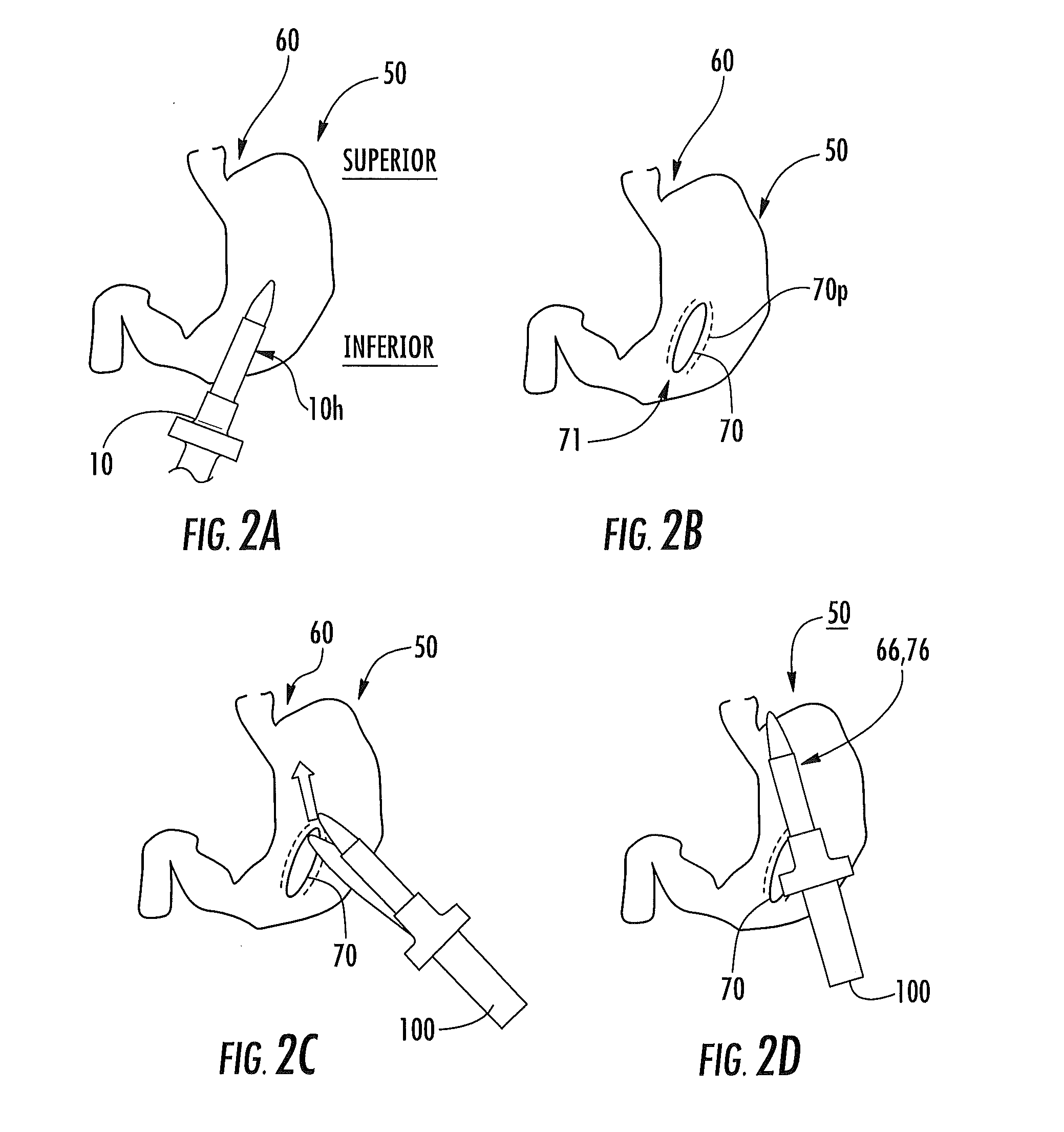
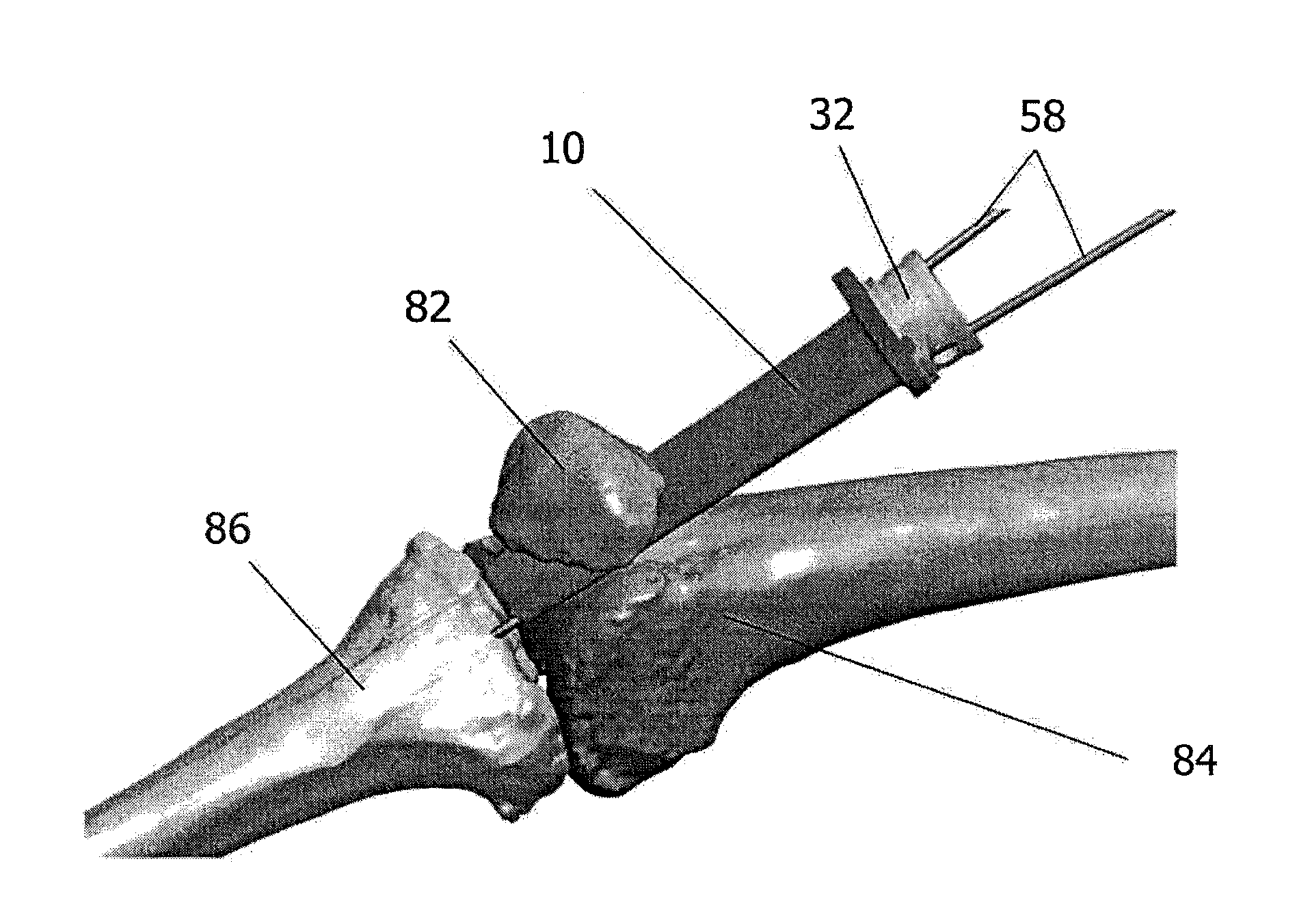
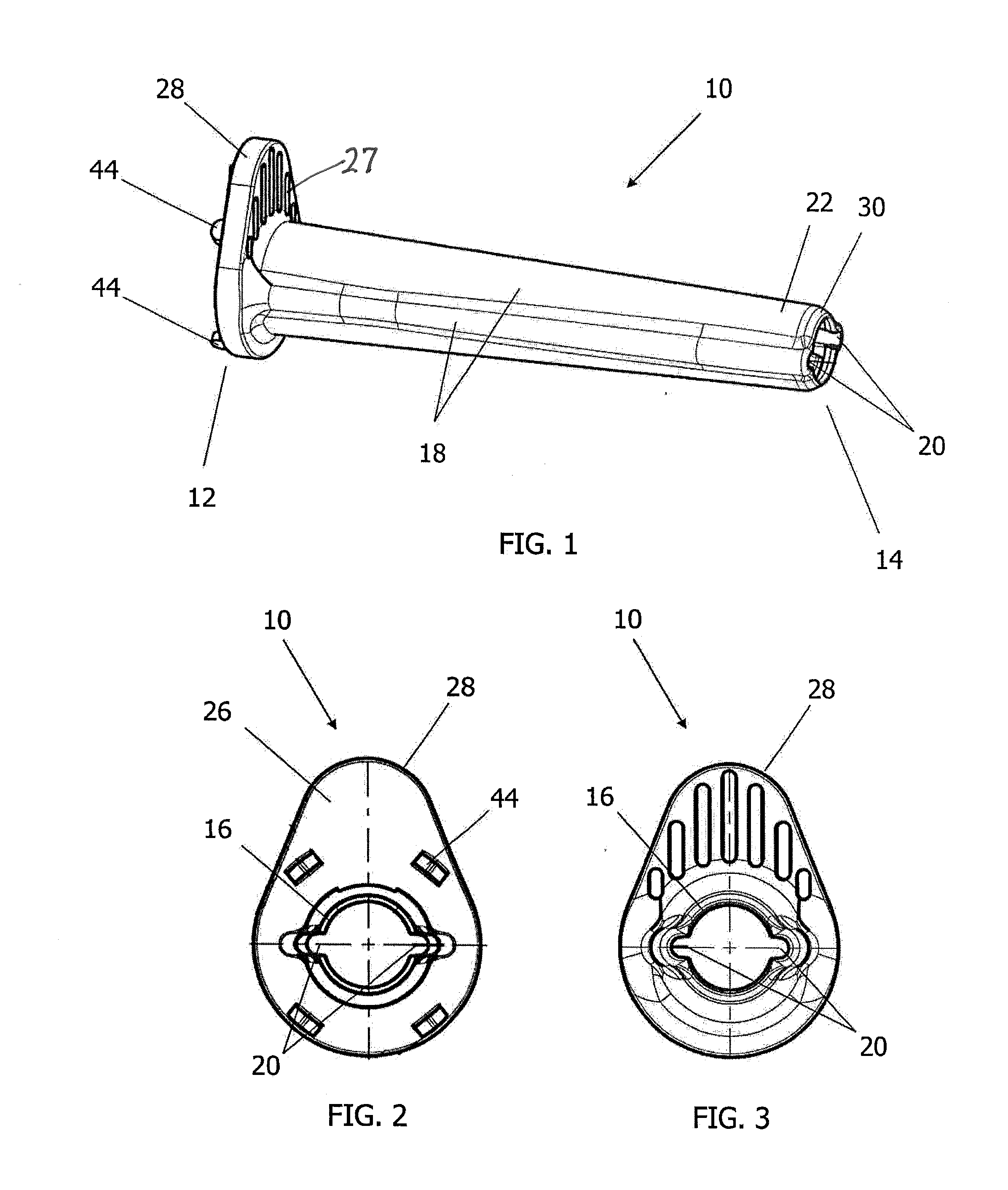
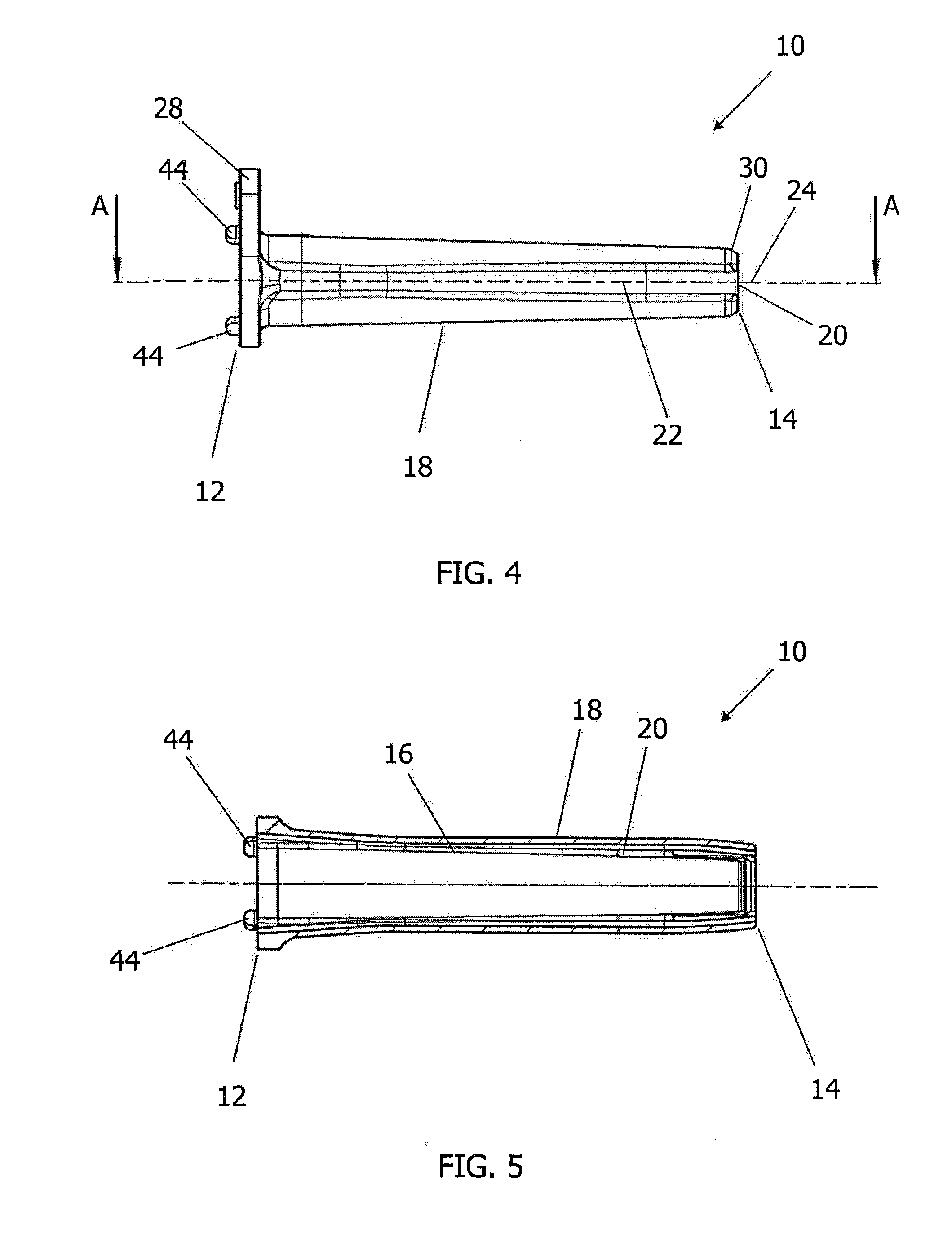
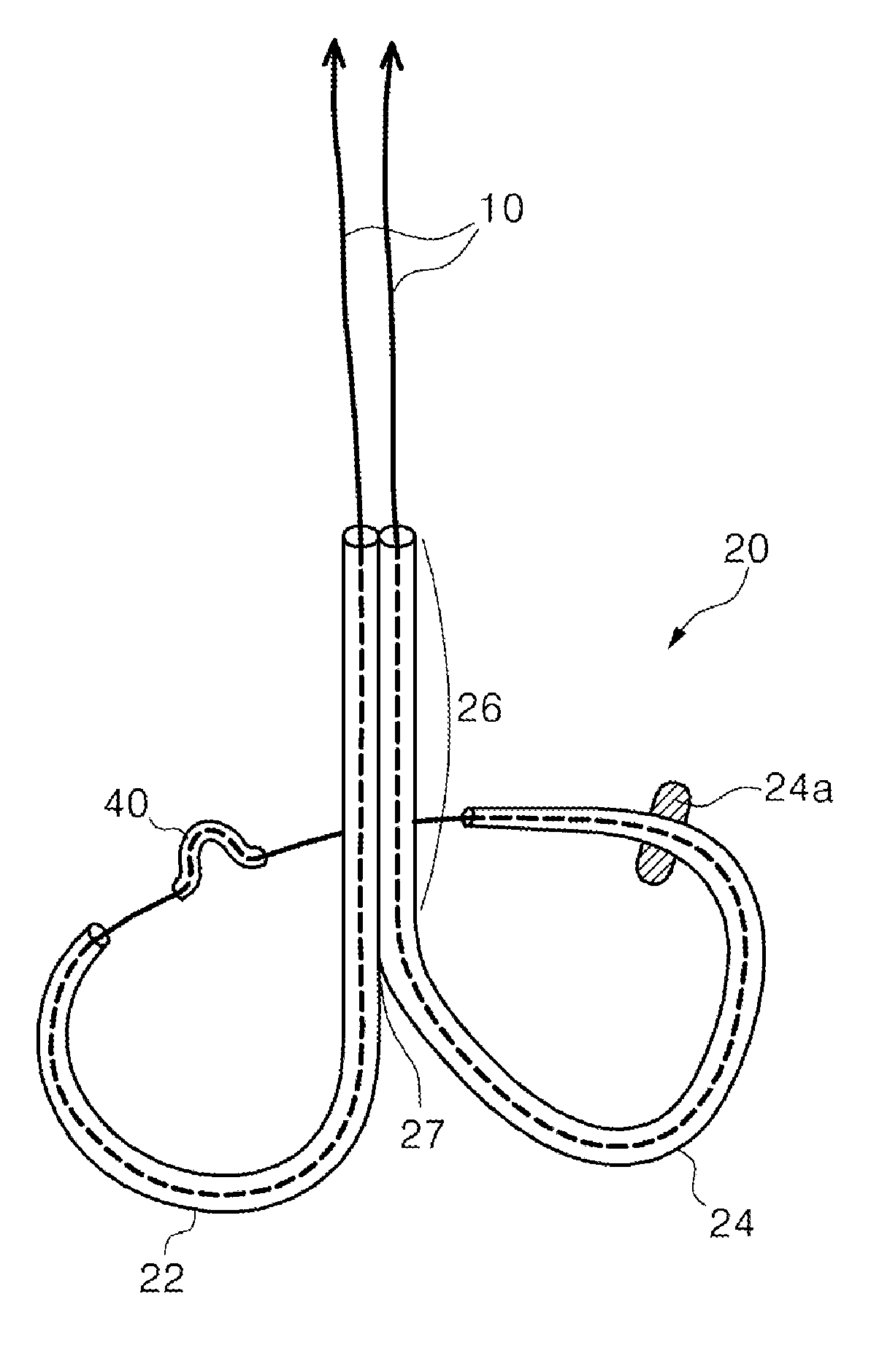
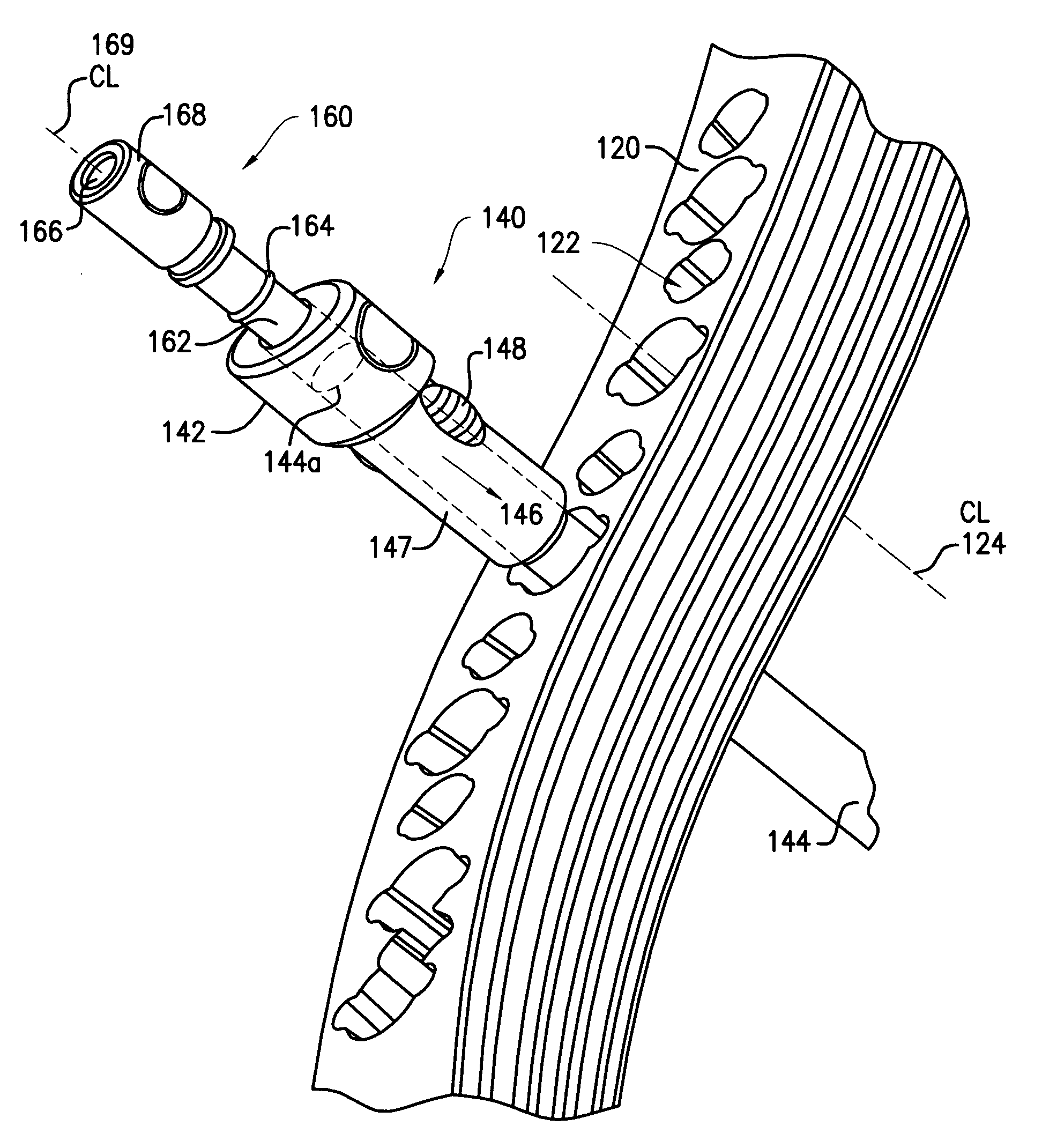
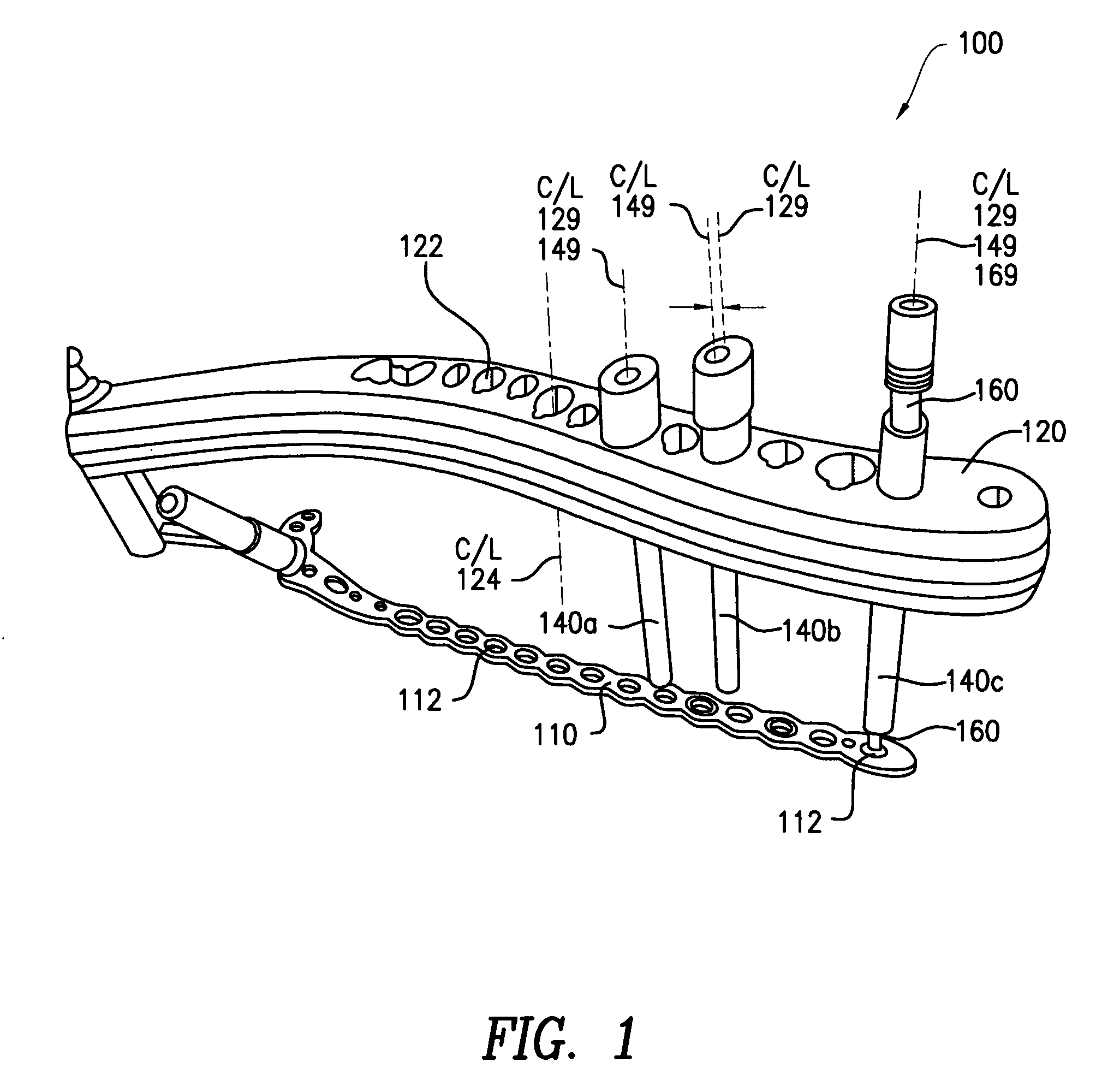
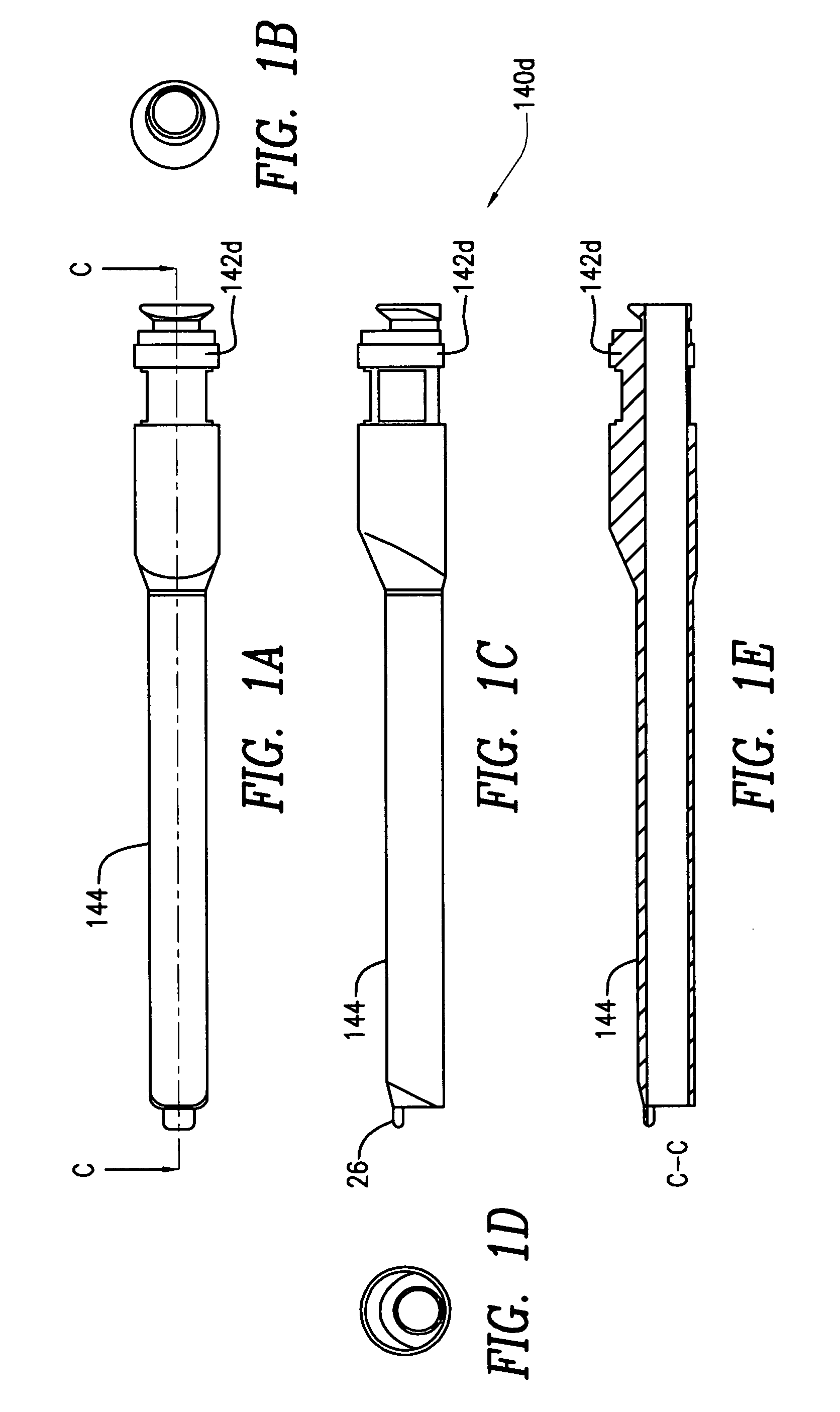
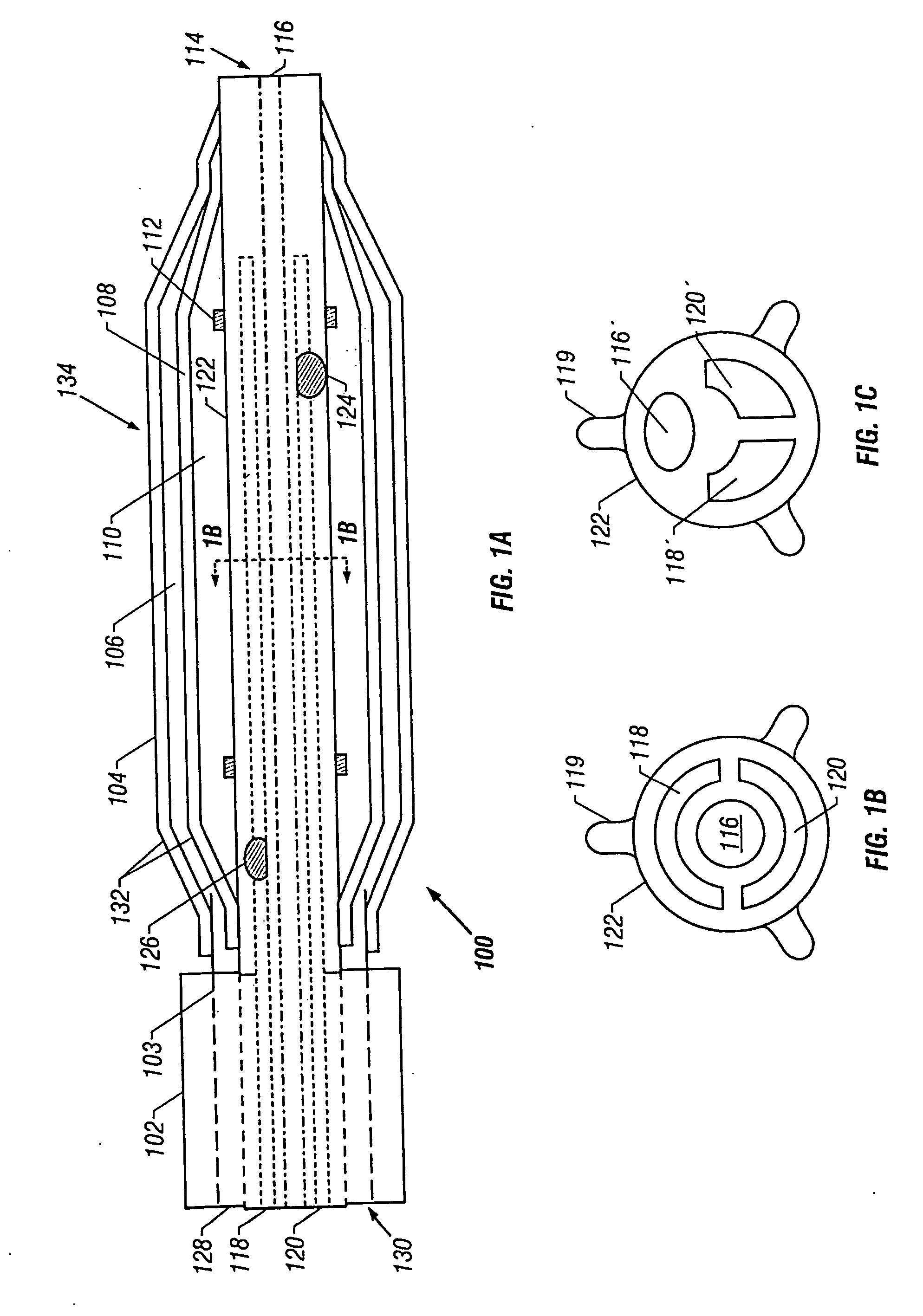
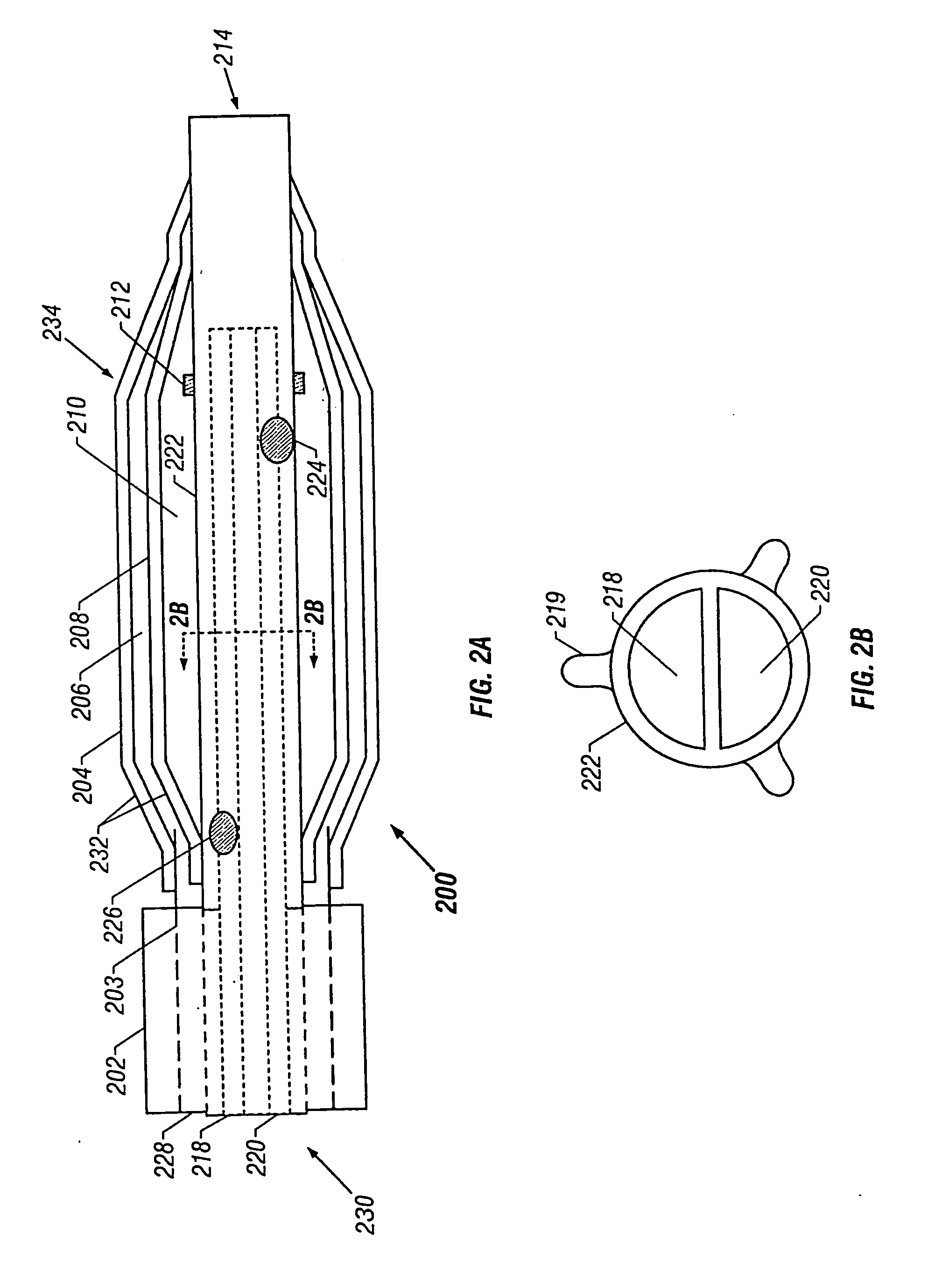
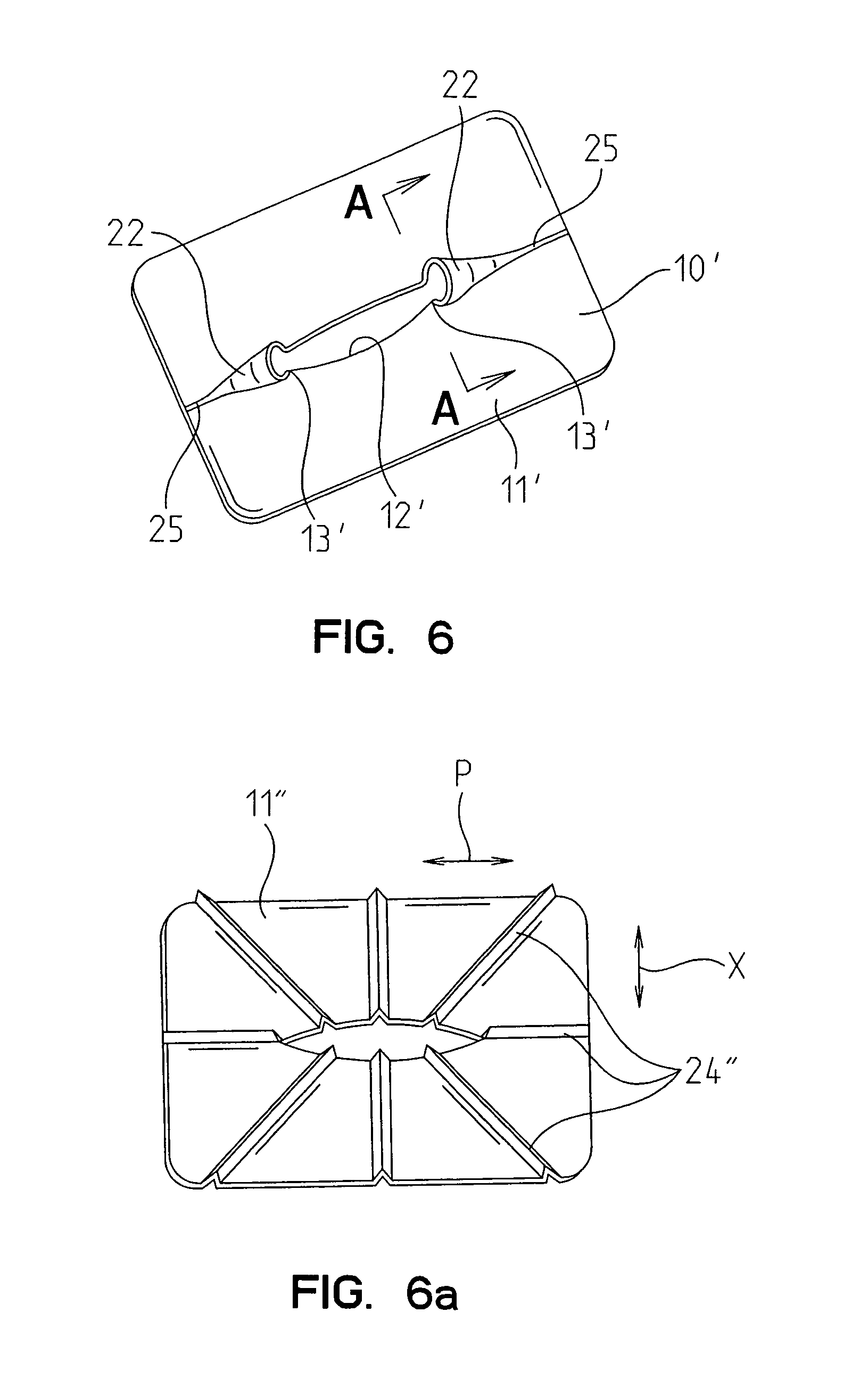
Surgical staplers with tissue protection and related methods
Surgical staplers include: (a) a stapler head having opposed first and second elongate jaws with opposing proximal and distal end portions; (b) a staple cartridge held in at least one of the first and second jaws, the stapler cartridge configured to concurrently deliver a plurality of parallel rows of staples; and (c) a tissue protection segment held in a proximal portion of at least one of the first and second jaws. The jaws are configured to close against target tissue and, at stapler firing, staples are delivered to a subset of tissue held inside the jaws so that tissue held by the tissue protection segment adjacent the proximal end portion of the stapler is not stapled.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
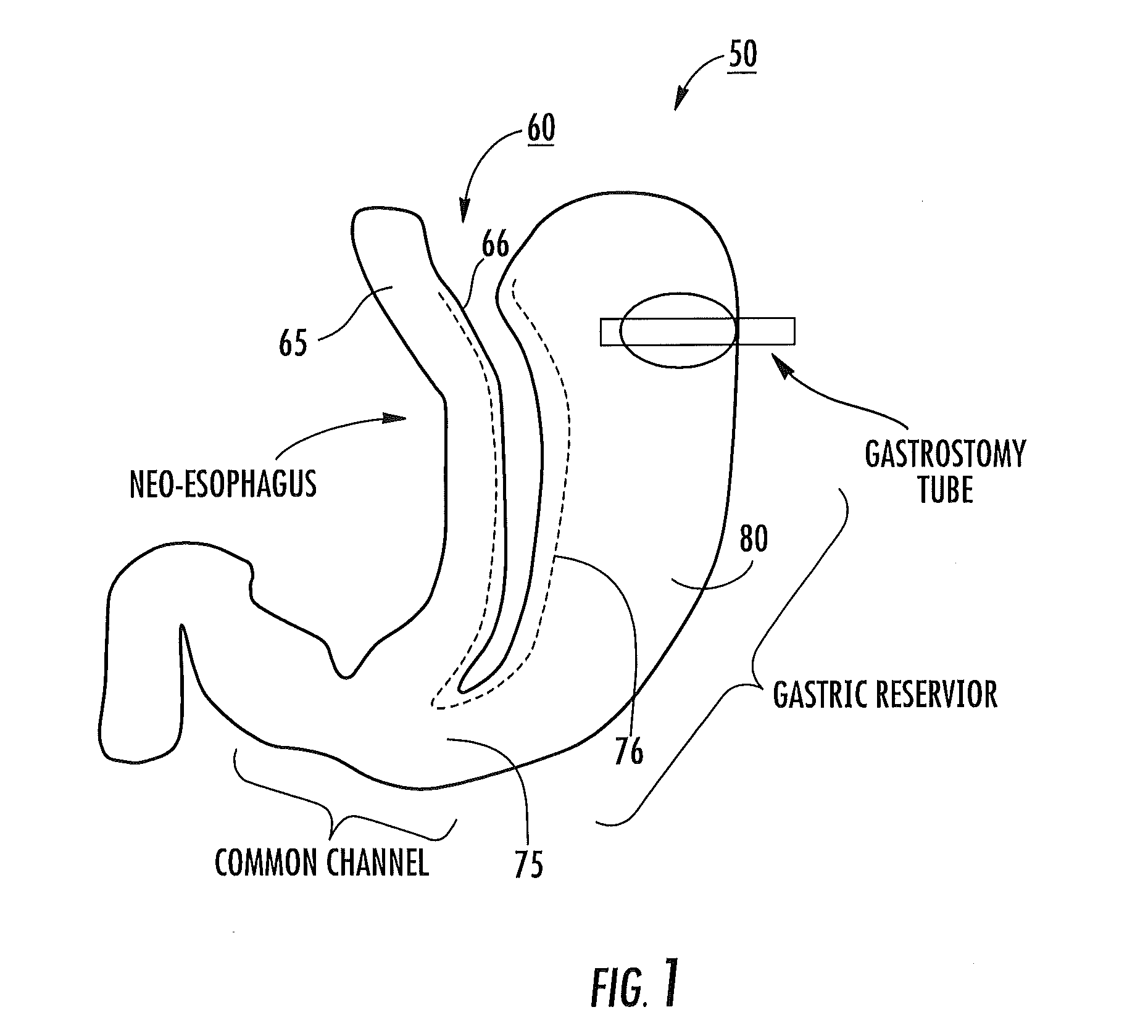
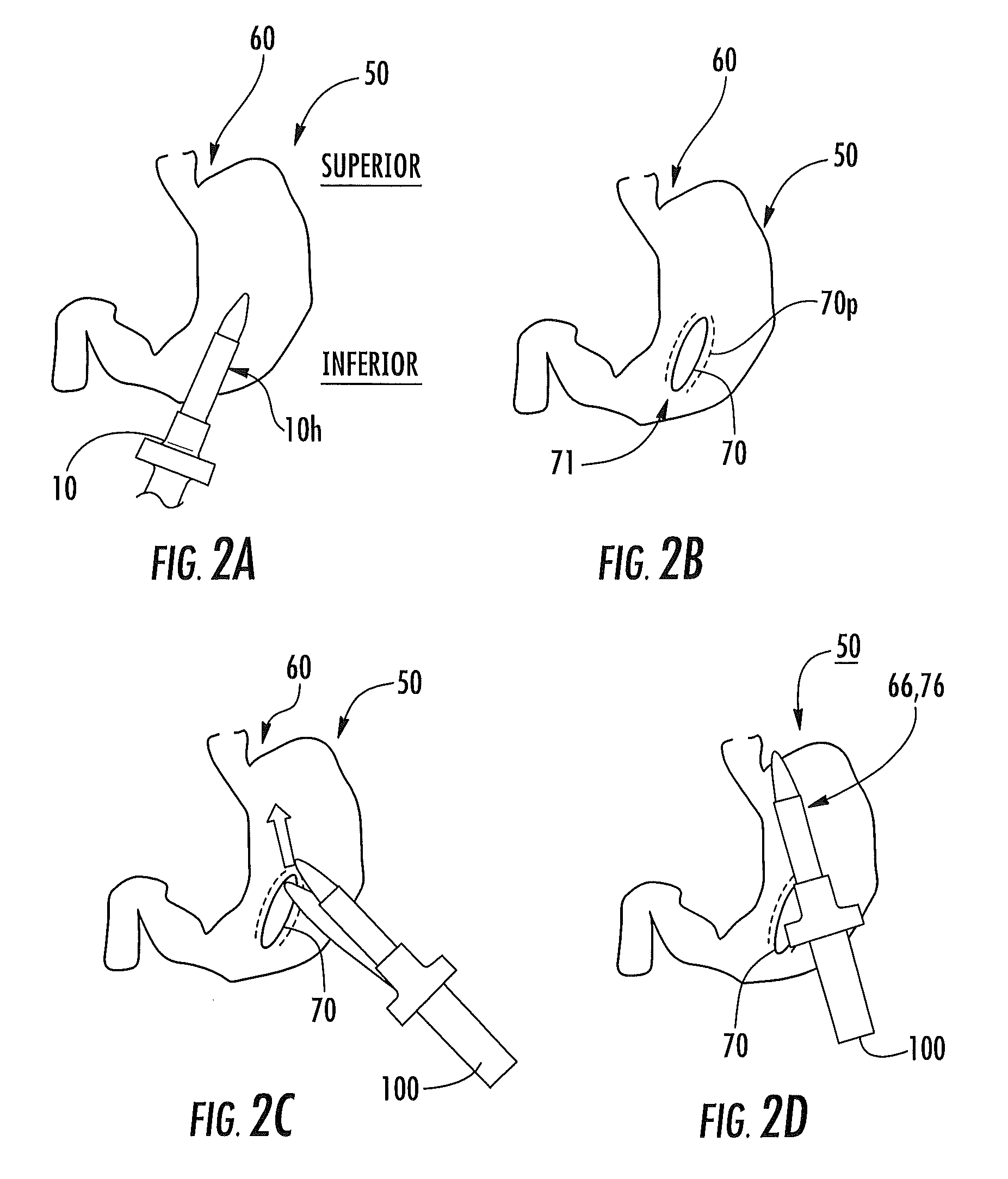
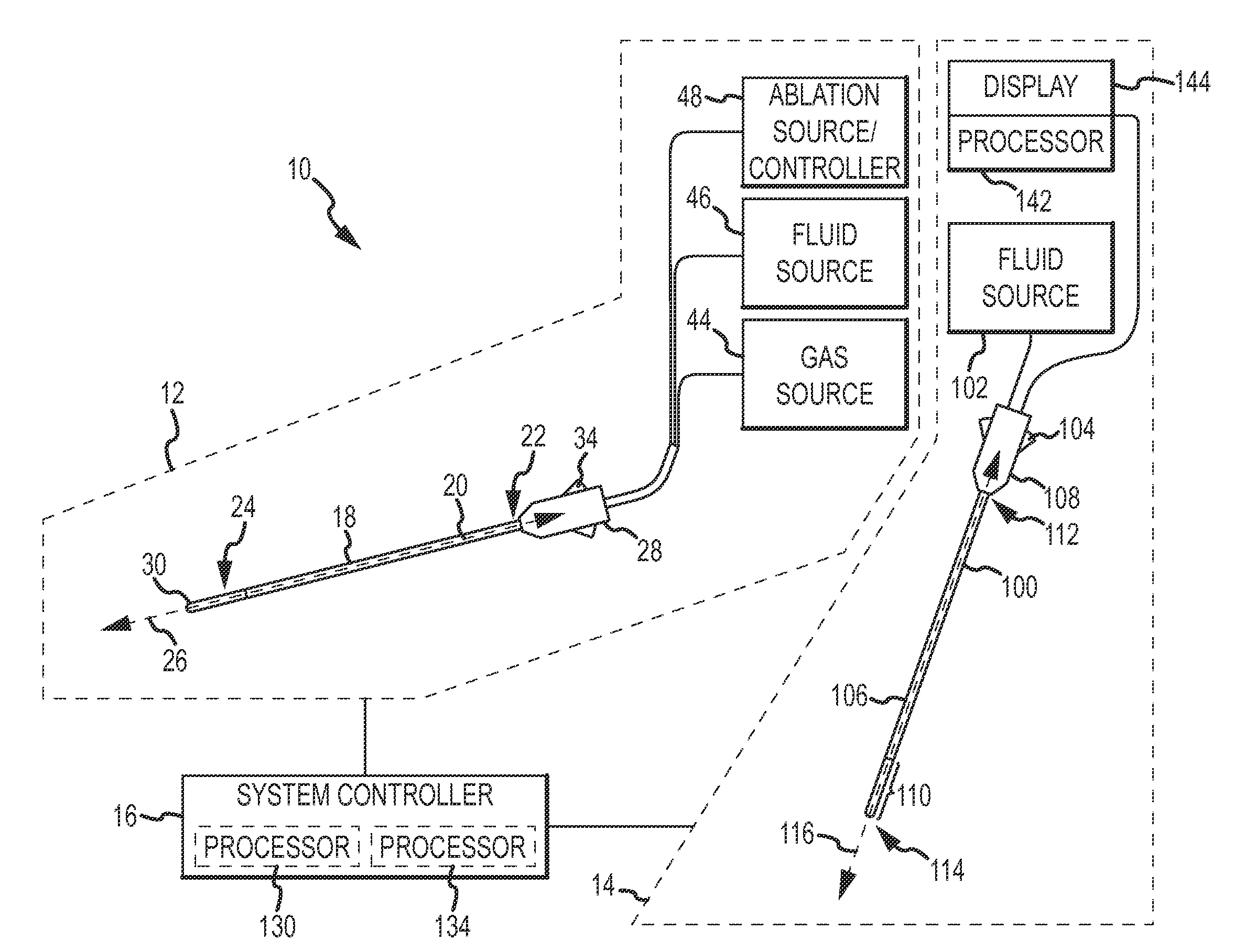
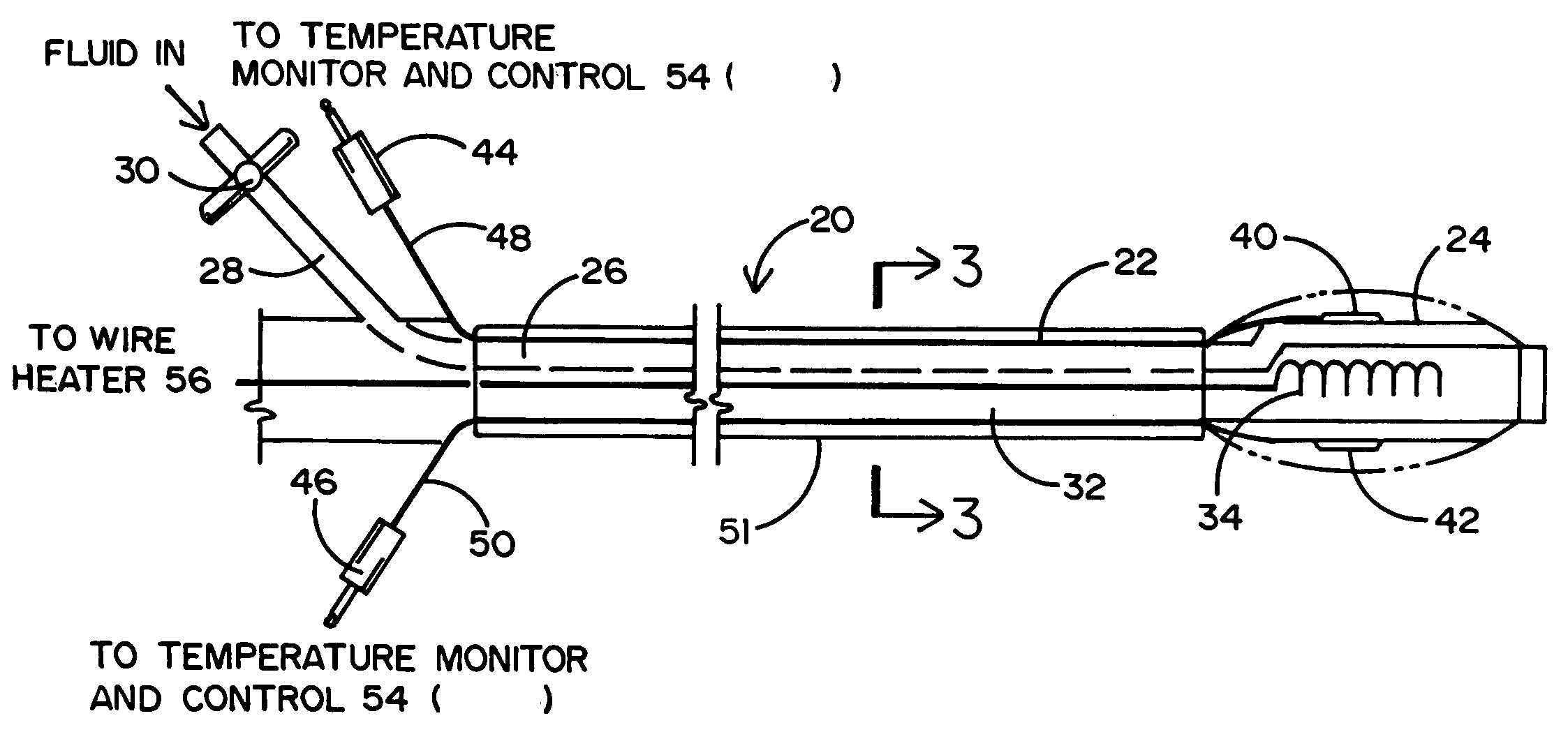
Method and device for performing cooling or cryo-therapies, for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS7001378B2Minimize and inhibit bio-chemical eventRobust designCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
An enhanced method and device are provided to treat atrial fibrillation or inhibit or reduce restenosis following angioplasty or stent placement. A balloon-tipped catheter is disposed in the area treated or opened through balloon angioplasty immediately following angioplasty. The balloon, which can have a dual balloon structure, may be delivered through a guiding catheter and over a guidewire already in place. A fluid such as a perfluorocarbon flows into the balloon to freeze the tissue adjacent the balloon, this cooling being associated with reduction of restenosis. A similar catheter may be used to reduce atrial fibrillation by inserting and inflating the balloon such that an exterior surface of the balloon contacts at least a partial circumference of the portion of the pulmonary vein adjacent the left atrium. In another embodiment, blood perfusion is performed simultaneously. In another embodiment, tissue contacted by the cryoablation catheter, undesired to be ablated, is protected against damage by a separate heating step.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
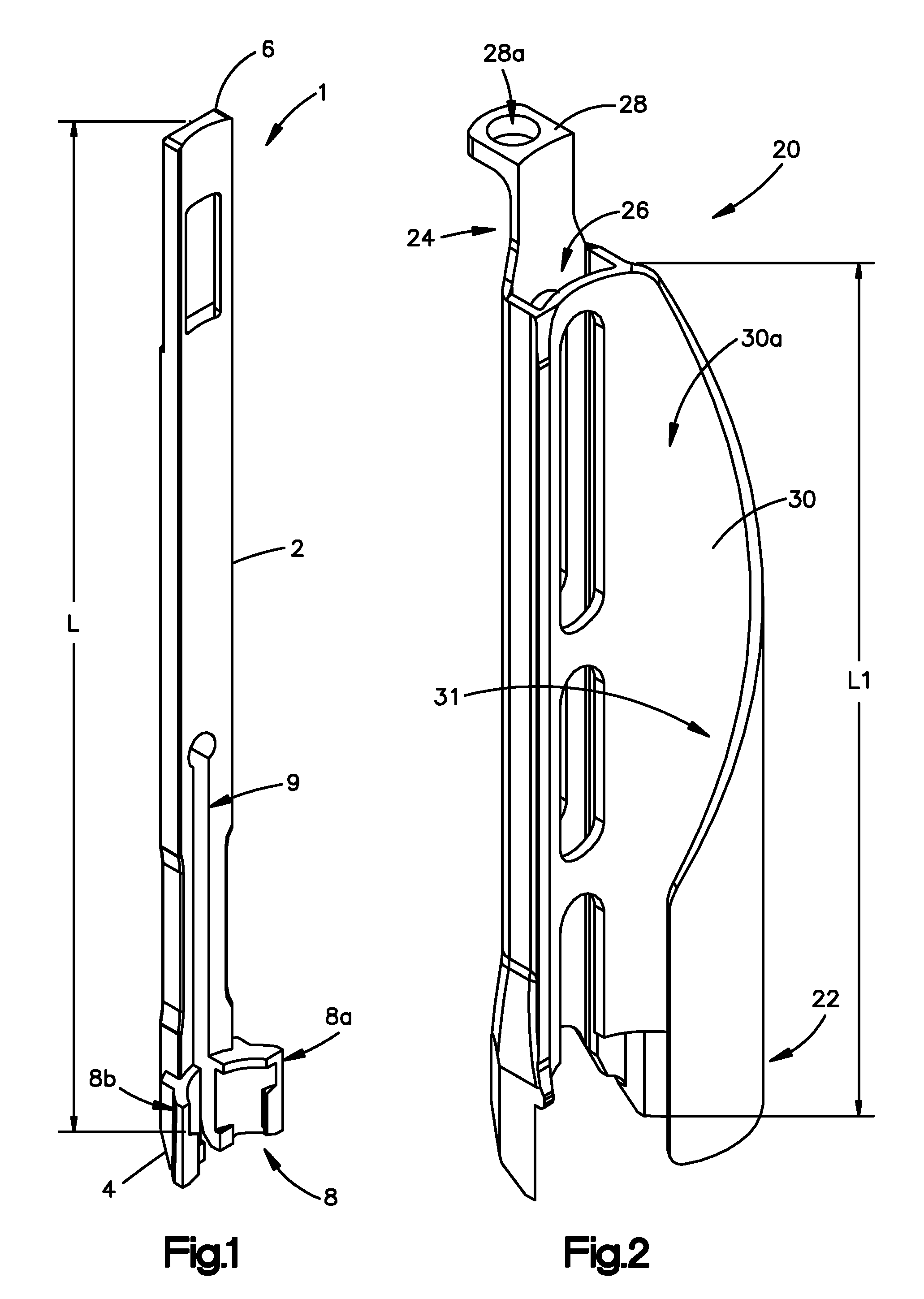
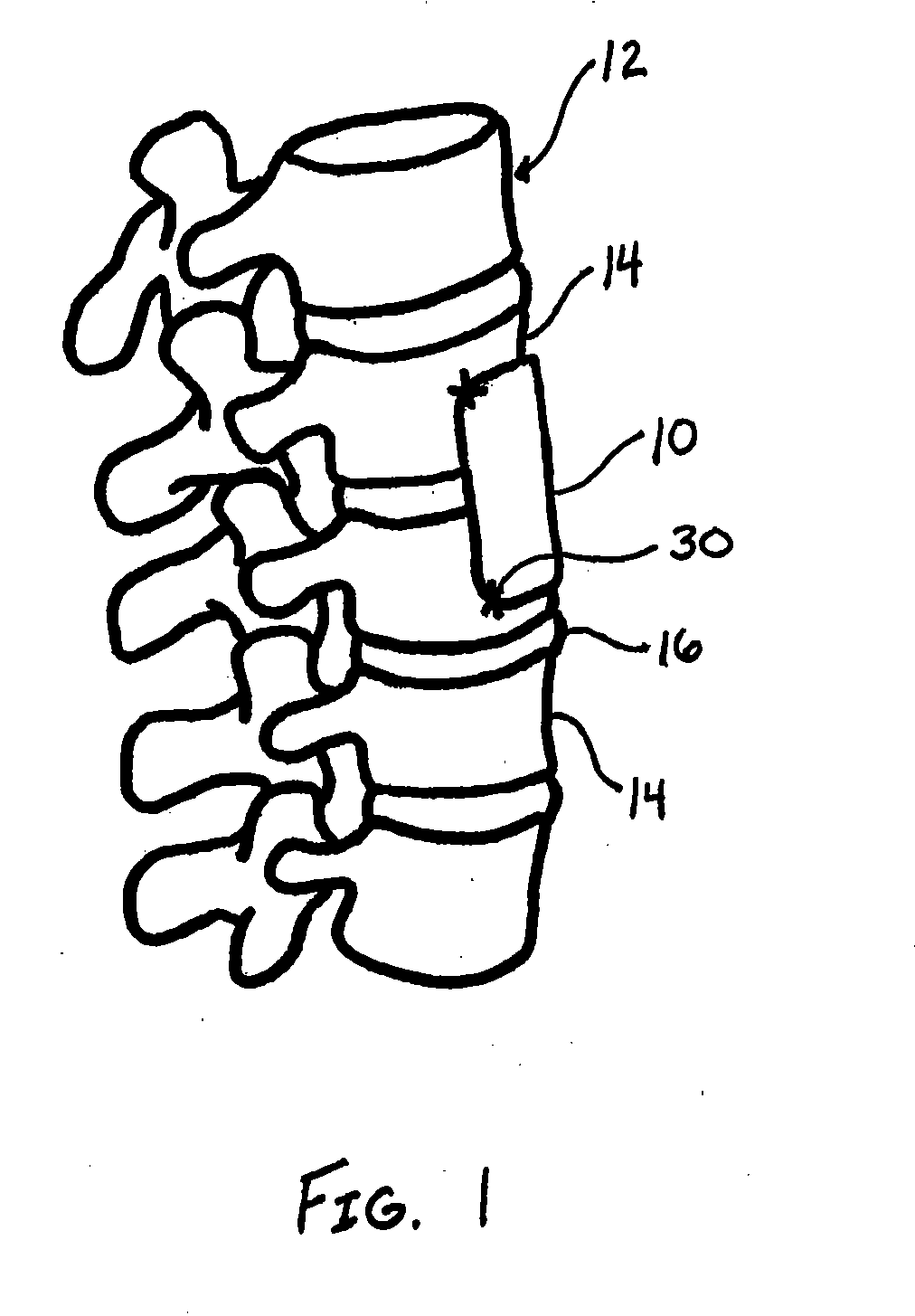
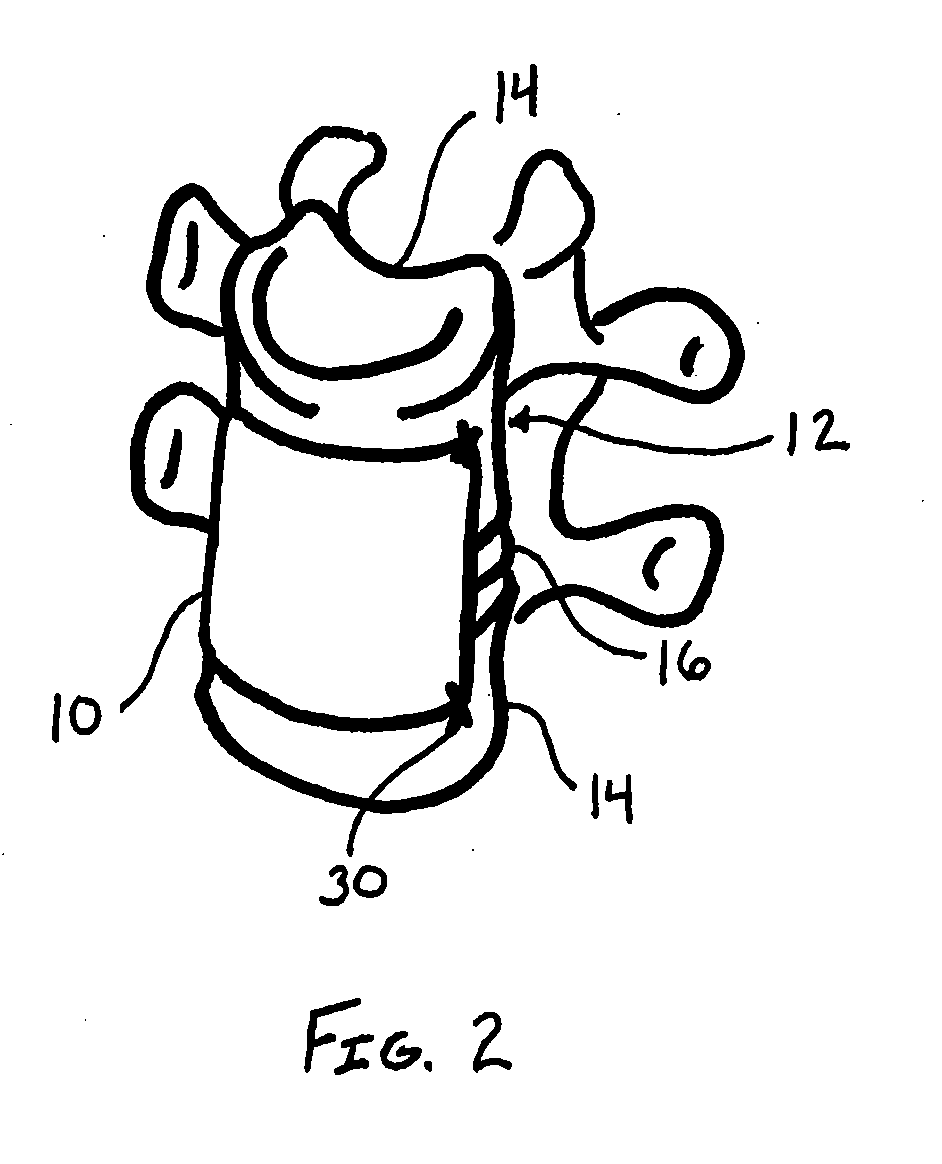
Minimally invasive fixation sysyem
ActiveUS20070270842A1Reduce the amount of noiseInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSet screwSurgical site
A minimally invasive fixation system and method for providing access to a surgical site. The fixation system may include a holding assembly, the holding assembling preferably including a lateral implant holder which may be attached to a pedicle screw and a sleeve positioned in connection with the lateral implant holder to prevent the lateral implant holder from separating from the pedicle screw. The sleeve may further include a tissue protection portion to keep the tissue out of the surgical site. A holding sleeve may be operably connected to the holding assembly and pedicle screw and may be used to insert the pedicle screw into the body. Multiple constructs may be inserted into the body so that a portion of the holding assembly extends from the body and provides access to and visualization of the surgical site. A rod holder may also be used to insert a rod into the head of the screw. The rod may be held by the rod holder so that the rod may be angulated as the rod is inserted into the screw heads. Once the rod is positioned in the screw heads, locking caps and / or set screws may be positioned over the rod and engage the screw heads so that the position of the rod may be fixed with respect to the screws. In some embodiments, a movement mechanism may be used to move the screws relative to each other to compress and / or distract the vertebrae.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Method and device for performing cooling- or cryo-therapies for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS6905494B2Minimize and inhibit biochemical eventRobust designCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
An enhanced method and device are provided to treat atrial fibrillation or inhibit or reduce restenosis following angioplasty or stent placement. A balloon-tipped catheter is disposed in the area treated or opened through balloon angioplasty immediately following angioplasty. The balloon, which can have a dual balloon structure, may be delivered through a guiding catheter and over a guidewire already in place. A fluid such as a perfluorocarbon flows into the balloon to freeze the tissue adjacent the balloon, this cooling being associated with reduction of restenosis. A similar catheter may be used to reduce atrial fibrillation by inserting and inflating the balloon such that an exterior surface of the balloon contacts at least a partial circumference of the portion of the pulmonary vein adjacent the left atrium. In another embodiment, blood perfusion is performed simultaneously. In another embodiment, tissue contacted by the cryoablation catheter, undesired to be ablated, is protected against damage by a separate heating step.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
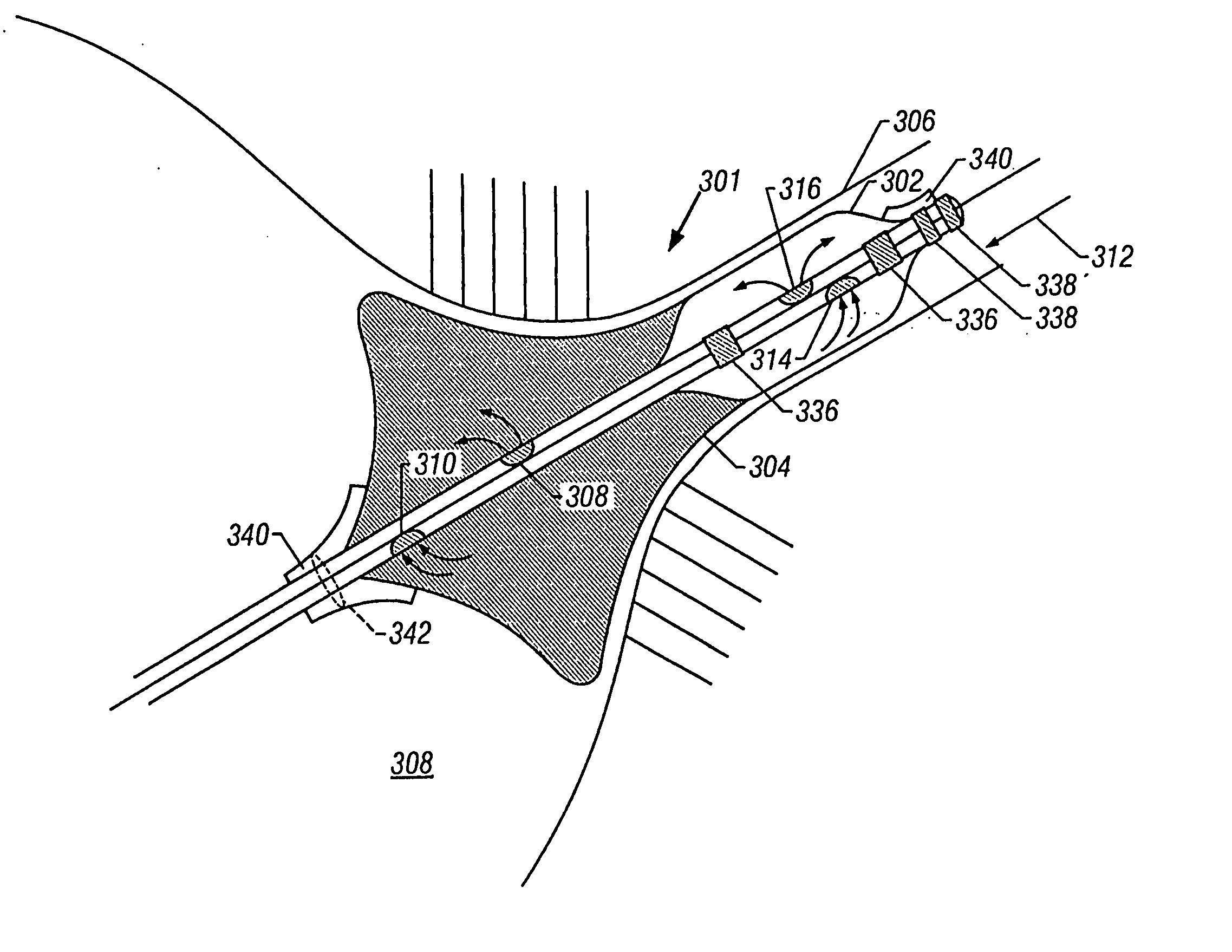
Ablation catheter with tissue protecting assembly
A medical probe includes an elongate member having a proximal end and a distal end, an ablative element mounted to the distal end of the elongate member, and a cage assembly mounted to the distal end of the elongate member, the cage assembly at least partially covers the ablative element. A method of treating tissue in a body includes inserting an ablative element in the body, placing the ablative element adjacent the tissue, and maintaining a distance between the ablative element and the tissue using a protective catheter element that circumscribes at least a portion of the ablative element.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
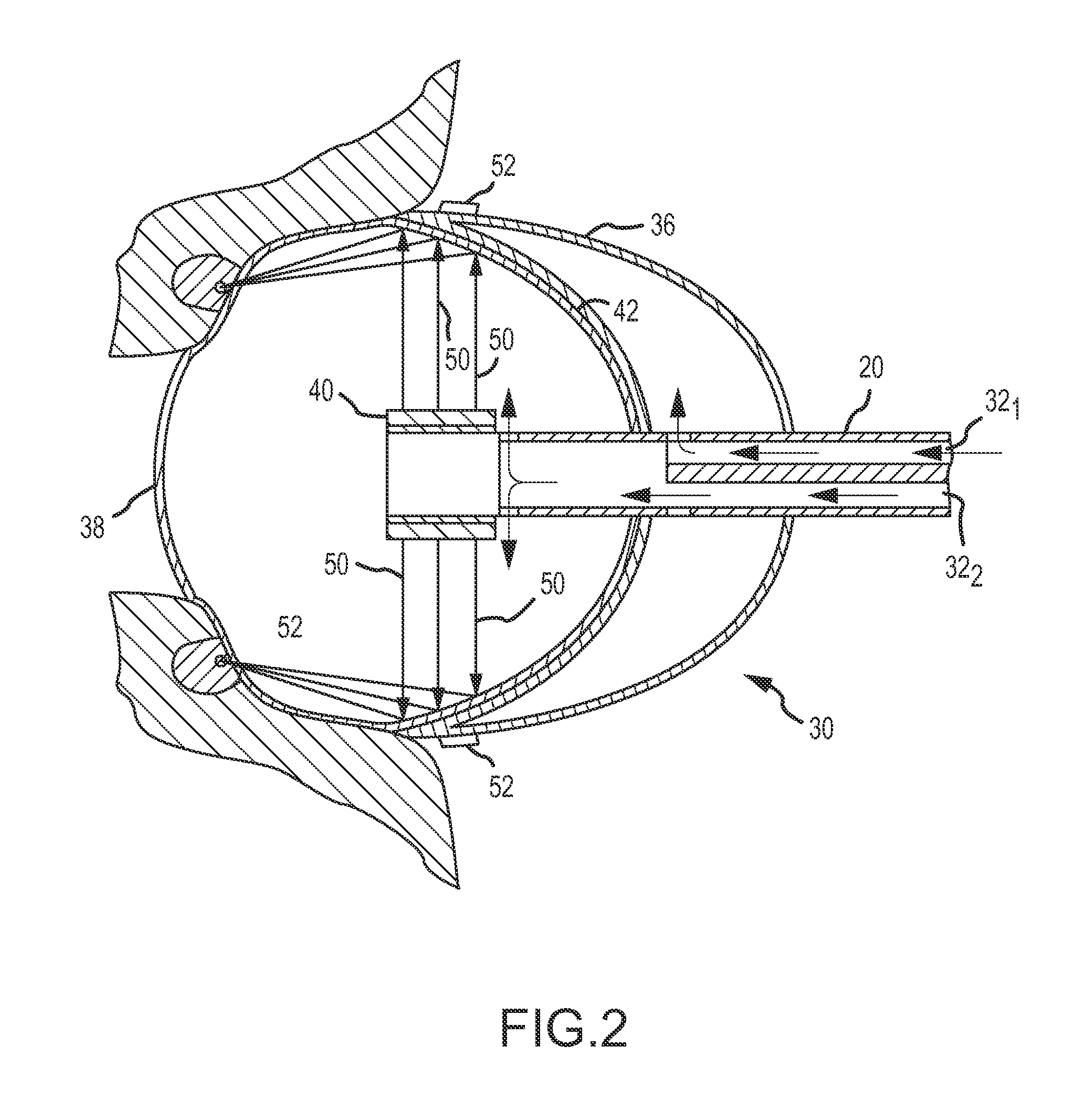
Ablation system with blood leakage minimization and tissue protective capabilities
ActiveUS20100168624A1Controlling energy of instrumentChiropractic devicesUltrasonic sensorTransducer
An ablation system is provided that includes an ablating device and a probe. The probe is configured to be positioned in close proximity to a region of non-targeted tissue proximate an ablation site of targeted tissue. The probe includes an elongate shaft having proximal and distal ends, with a handle disposed at the proximal end thereof and a tissue protecting apparatus disposed at the distal end thereof. The ablating device includes an elongate shaft having proximal and distal ends, with a handle mounted at the proximal end thereof and an ablation element mounted at the distal end thereof. The ablation element includes an ultrasound transducer and an inflatable balloon surrounding the ultrasound transducer. The balloon includes a layer of gel disposed on its outer surface.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
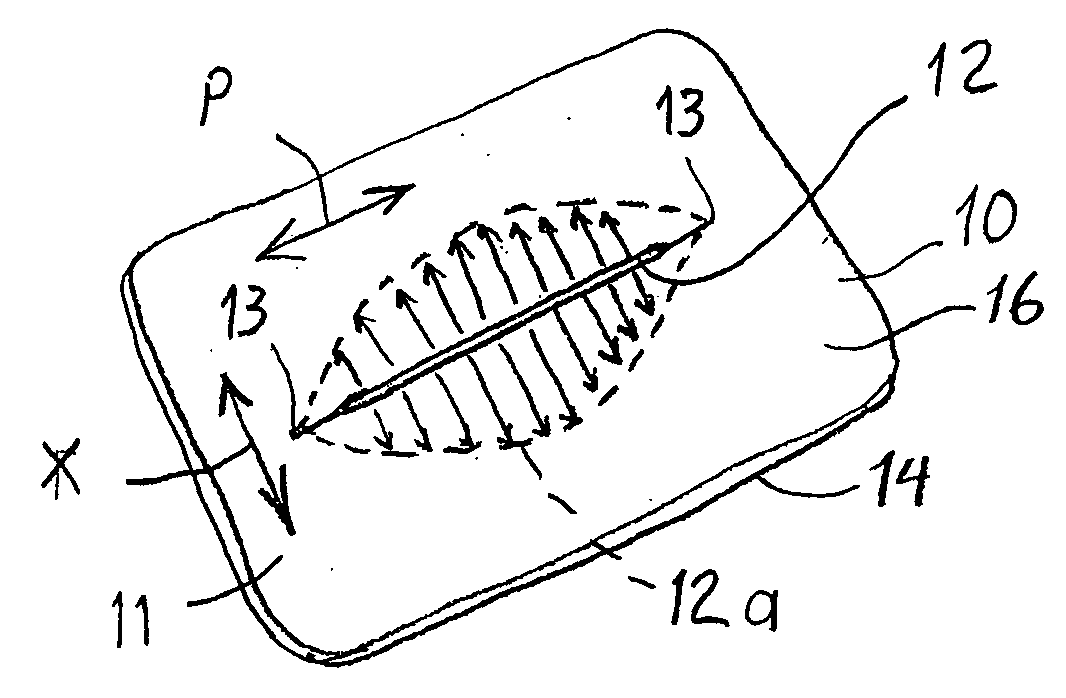
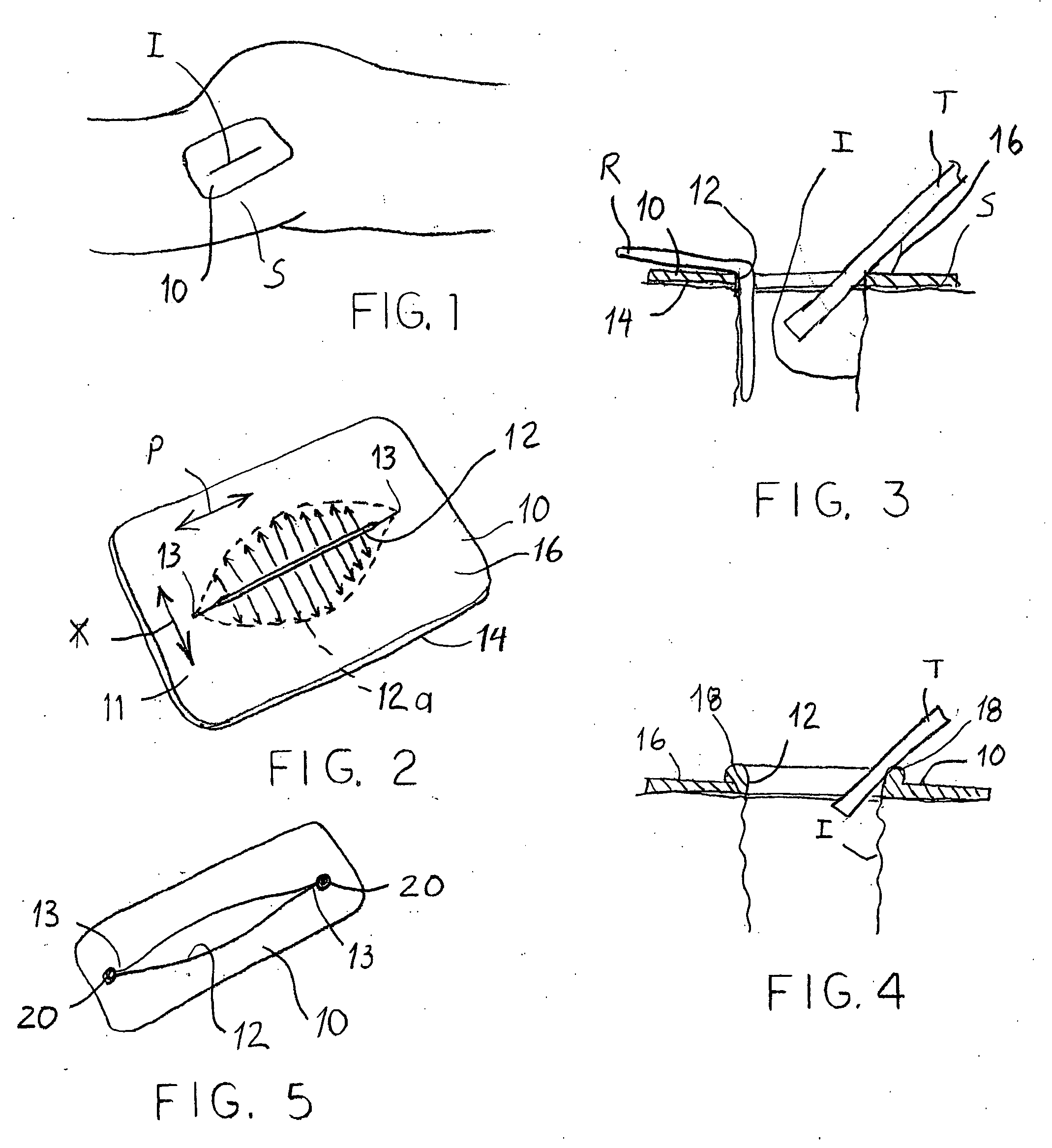
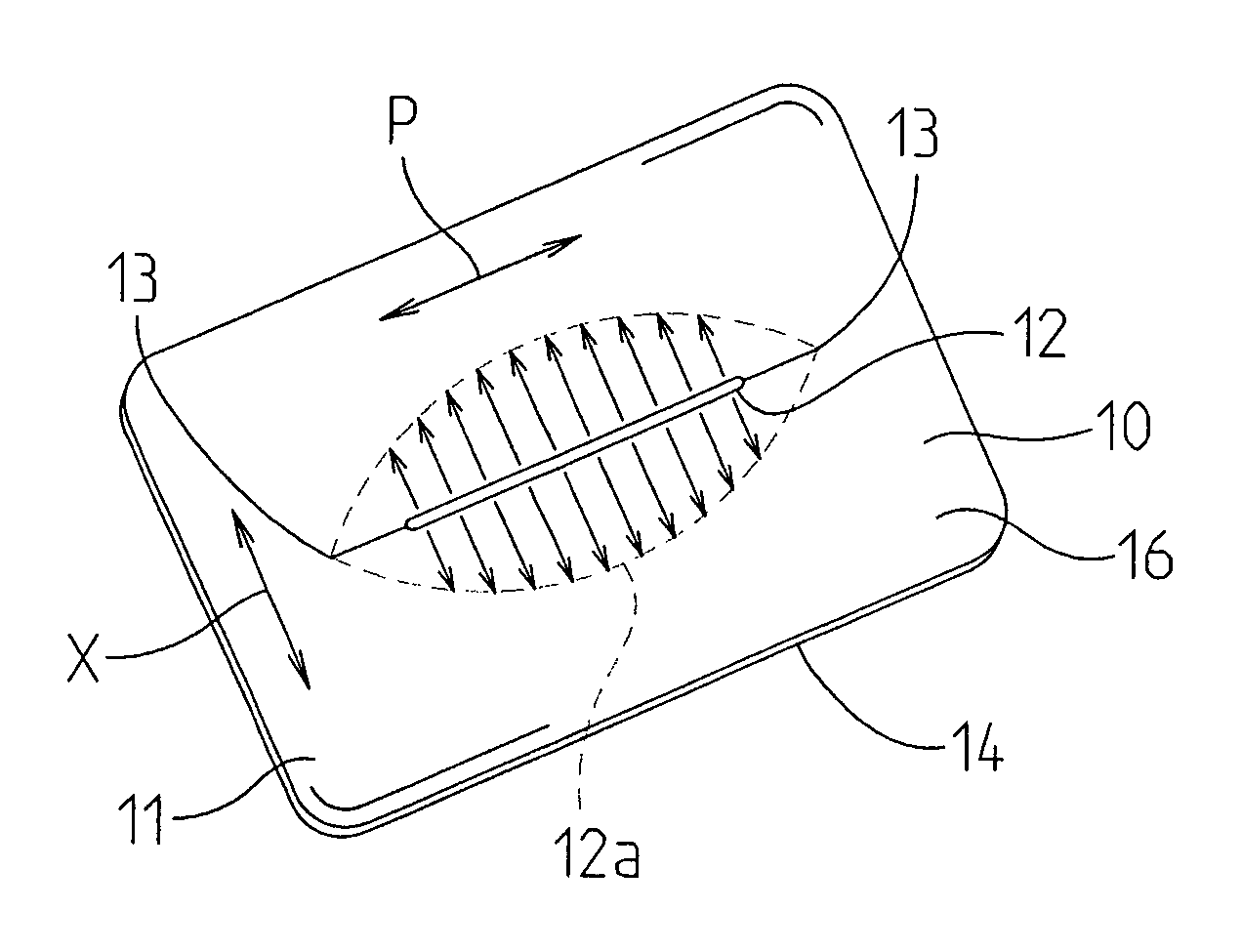
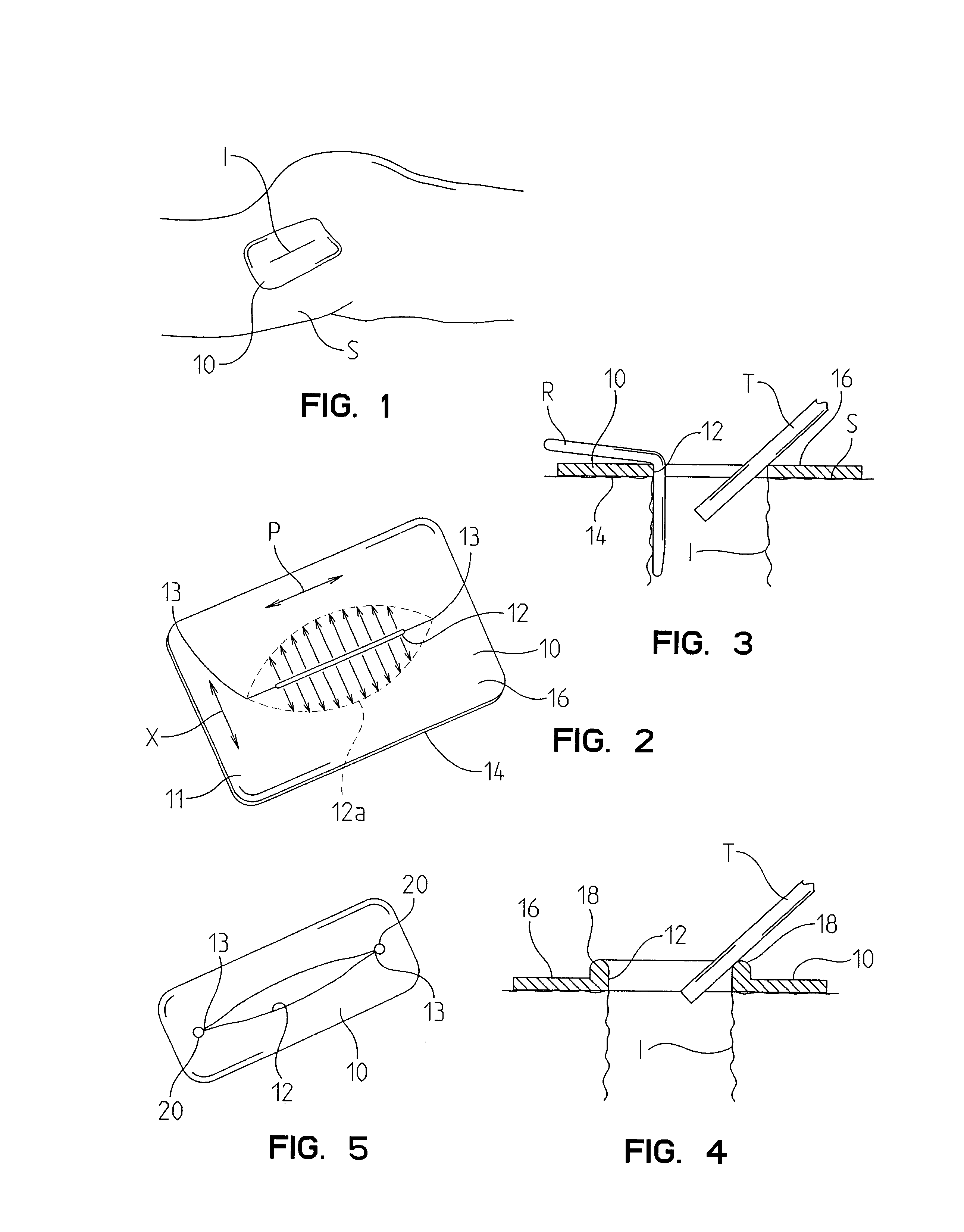
Devices and methods for protecting tissue at a surgical site
ActiveUS20050283050A1Minimize local loadingDissipate forceCannulasDiagnosticsWear resistantSurgical site
A tissue protector is adapted to be positioned on the skin surrounding an incision. The tissue protector provides a load bearing surface for surgical tools and instruments to prevent blunt force and pressure trauma to the skin and soft tissues within the incision. In one embodiment, the tissue protector is a sheet of wear-resistant material having an opening corresponding to the incision and expandable as the incision is retracted. In another embodiment, a tissue protector device includes a continuous expandable arrangement of interconnected L-shaped links. In still another embodiment, a one-piece tissue protector includes a flexible panel supported on the skin and a flexible sleeve extending into the incision. Yet another embodiment of the invention resides in a track that is supported about the incision. An instrument support platform is slidably mounted to the track to support a surgical tool relative to the incision.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
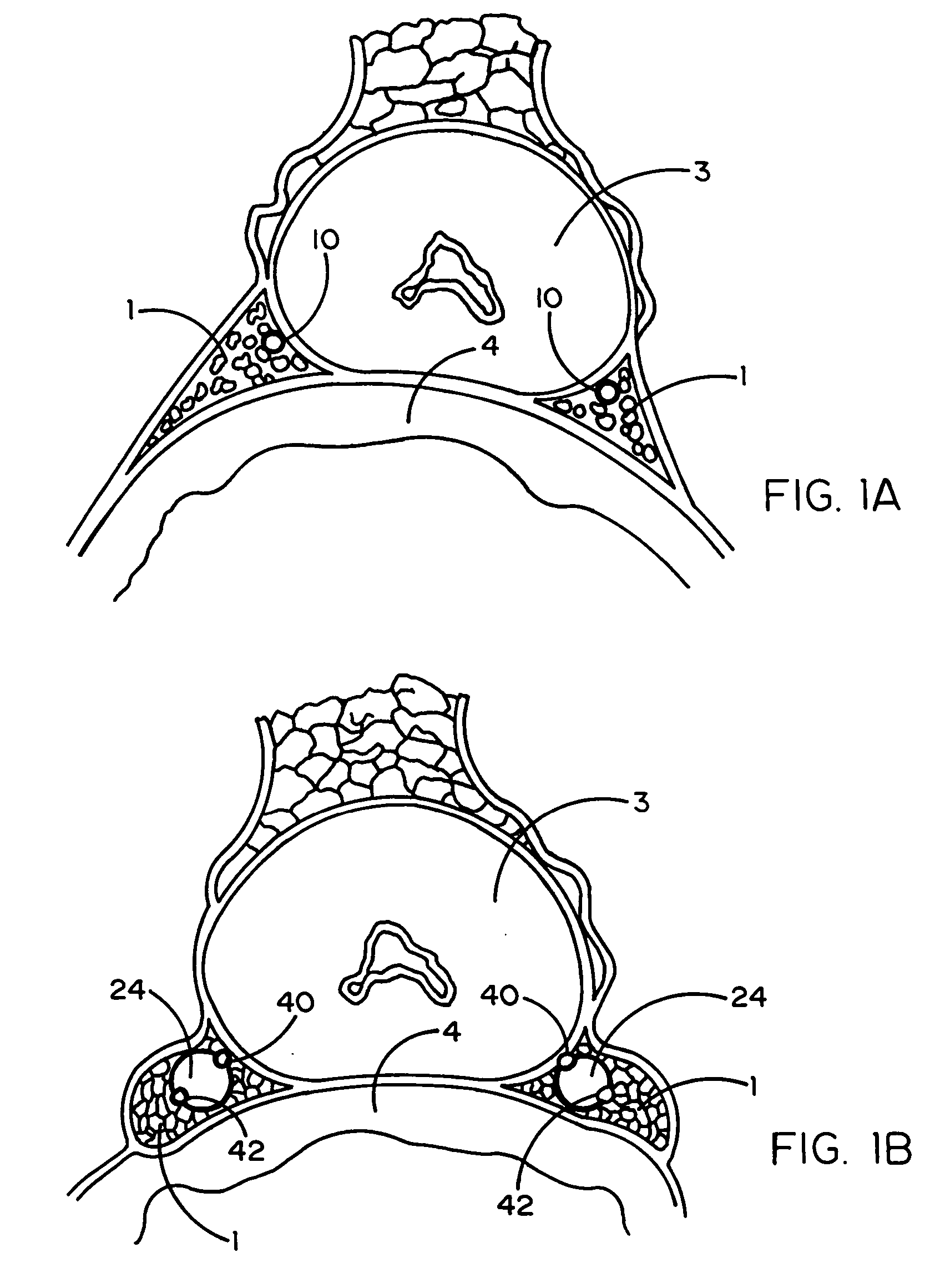
Device and methods useable for treatment of glaucoma and other surgical procedures
InactiveUS20060241580A1Not to damageAvoiding significant and irreparable damageEye surgerySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical departmentTissue protection
A device and method for cutting or ablating tissue in a human or veterinary patient includes an elongate probe having a distal end, a tissue cutting or ablating apparatus located adjacent within the distal end, and a tissue protector extending from the distal end. The protector generally has a first side and a second side and the tissue cutting or ablating apparatus is located adjacent to the first side thereof. The distal end is structured to be advanceable into tissue or otherwise placed and positioned within the patient's body such that tissue adjacent to the first side of the protector is cut away or ablated by the tissue cutting or ablation apparatus while tissue that is adjacent to the second side of the protector is not substantially damaged by the tissue cutting or ablating apparatus.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK +1
Tissue protective system and method for thermoablative therapies
InactiveUS20060118127A1Possible removalDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingCancer cellNeurovascular bundle
A tissue protective system and method having particular application in thermoablative surgical therapies where heat or cold is used to create a kill zone for treating cancer cells as well as malignant or benign tumors in a targeted internal tissue area (e.g., the prostate) of a patient while sparing an adjacent benign internal tissue area (e.g., a neurovascular bundle). One of a hollow sheath or a balloon that is carried by a balloon catheter is located within an access opening that is made by a needle trocar inserted between the targeted tissue area in need of treatment and the benign tissue area to be protected in order to hold the protected tissue area off the targeted tissue area and away from the lethal temperature of the kill zone. The balloon of the balloon catheter is inflated in the access opening via a balloon channel which runs longitudinally through the catheter. At least one temperature sensor is mounted on the balloon and responsive to the temperature near the benign tissue area to be protected. Heat or cold is provided to the balloon from a heating wire or a circulating fluid, depending upon the temperature that is sensed by the temperature sensor.
Owner:CHINN DOUGLAS O
Minimally invasive fixation system
A minimally invasive fixation system and method for providing access to a surgical site. The fixation system may include a holding assembly, the holding assembling preferably including a lateral implant holder which may be attached to a pedicle screw and a sleeve positioned in connection with the lateral implant holder to prevent the lateral implant holder from separating from the pedicle screw. The sleeve may further include a tissue protection portion to keep the tissue out of the surgical site. A holding sleeve may be operably connected to the holding assembly and pedicle screw and may be used to insert the pedicle screw into the body. Multiple constructs may be inserted into the body so that a portion of the holding assembly extends from the body and provides access to and visualization of the surgical site. A rod holder may also be used to insert a rod into the head of the screw. The rod may be held by the rod holder so that the rod may be angulated as the rod is inserted into the screw heads. Once the rod is positioned in the screw heads, locking caps and / or set screws may be positioned over the rod and engage the screw heads so that the position of the rod may be fixed with respect to the screws. In some embodiments, a movement mechanism may be used to move the screws relative to each other to compress and / or distract the vertebrae.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
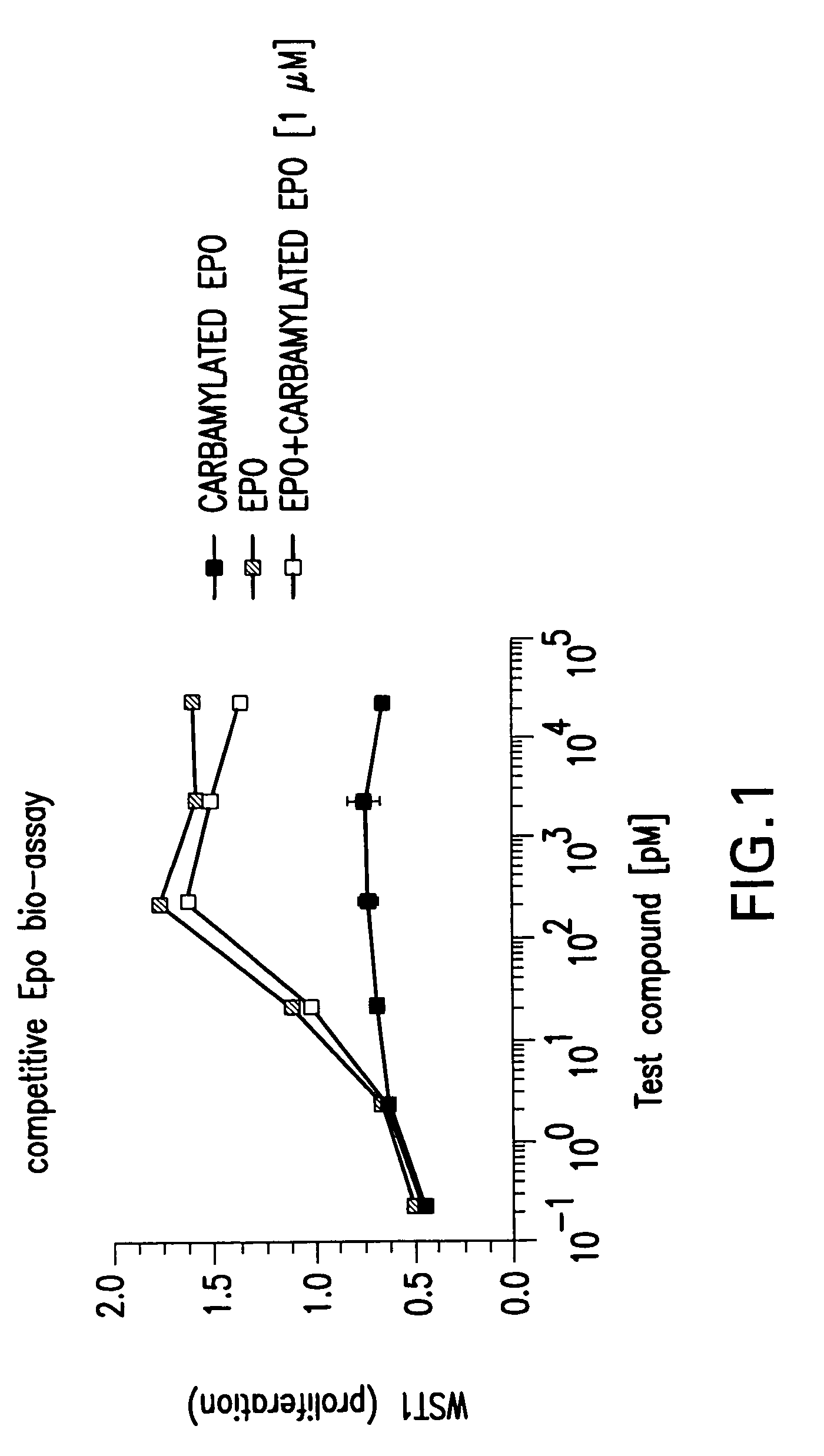
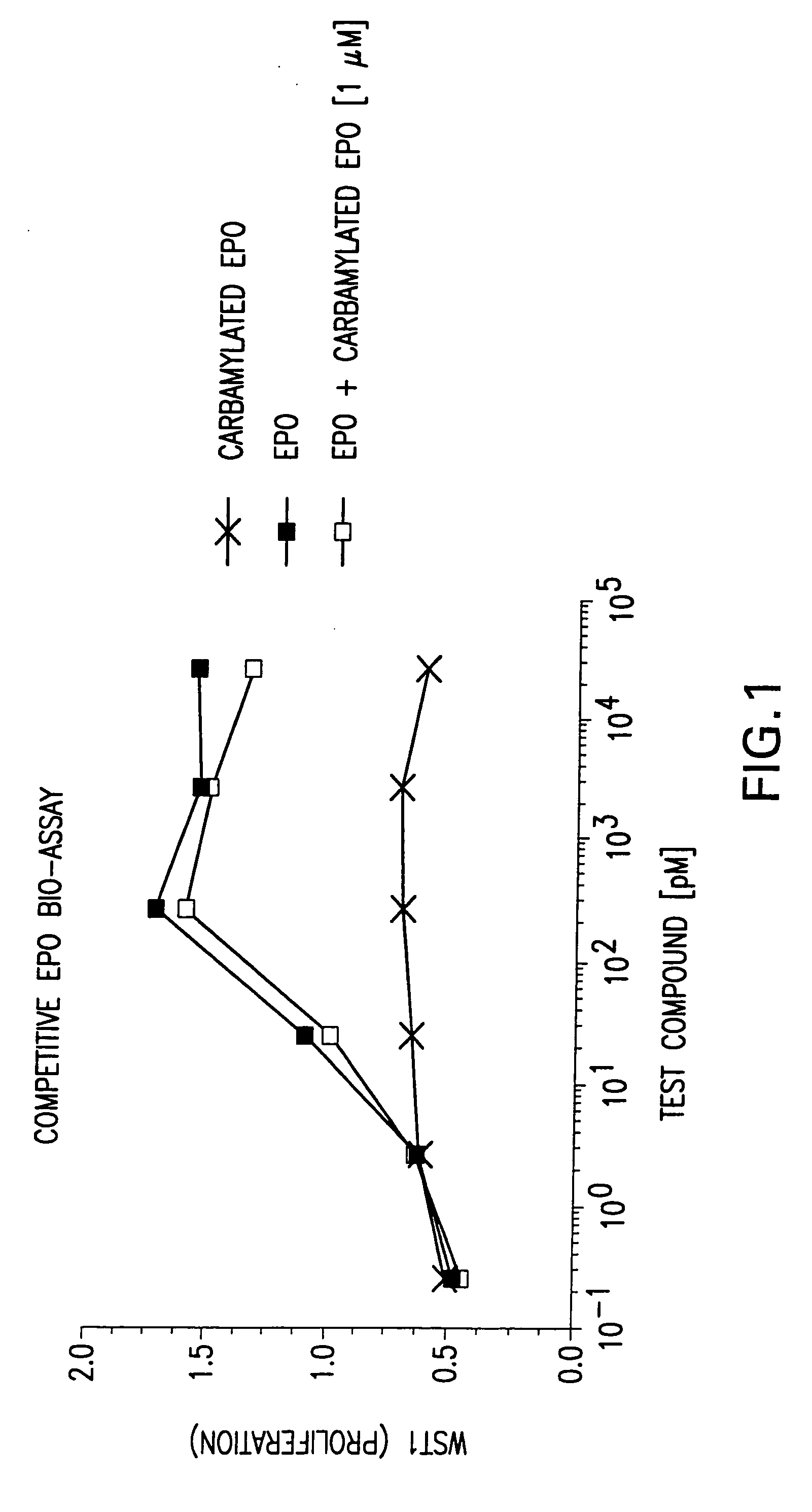
Recombinant tissue protective cytokines and encoding nucleic acids thereof for protection, restoration, and enhancement of responsive cells, tissues, and organs
InactiveUS20040122216A1Increase in hematocritEnhance cell viabilityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderMammalWhole body
Methods and compositions are provided for protecting or enhancing a responsive cell, tissue, organ or body part function or viability in vivo, in situ or ex vivo in mammals, including human beings, by systemic or local administration of an erythropoietin receptor activity modulator, such as an recombinant tissue protective cytokine.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS +1
Surgical staplers with tissue protection and related methods
Surgical staplers include: (a) a stapler head having opposed first and second elongate jaws with opposing proximal and distal end portions; (b) a staple cartridge held in at least one of the first and second jaws, the stapler cartridge configured to concurrently deliver a plurality of parallel rows of staples; and (c) a tissue protection segment held in a proximal portion of at least one of the first and second jaws. The jaws are configured to close against target tissue and, at stapler firing, staples are delivered to a subset of tissue held inside the jaws so that tissue held by the tissue protection segment adjacent the proximal end portion of the stapler is not stapled.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
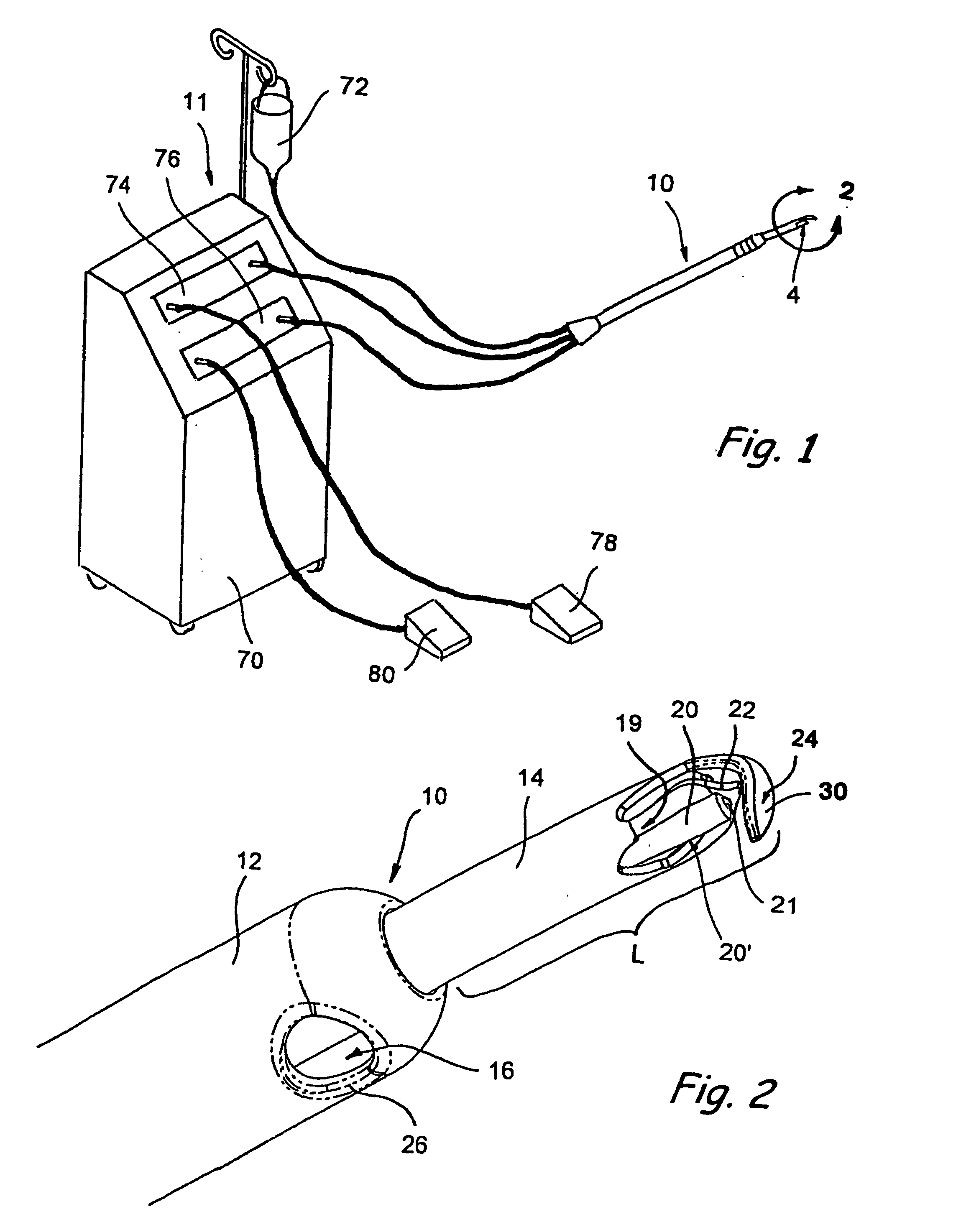
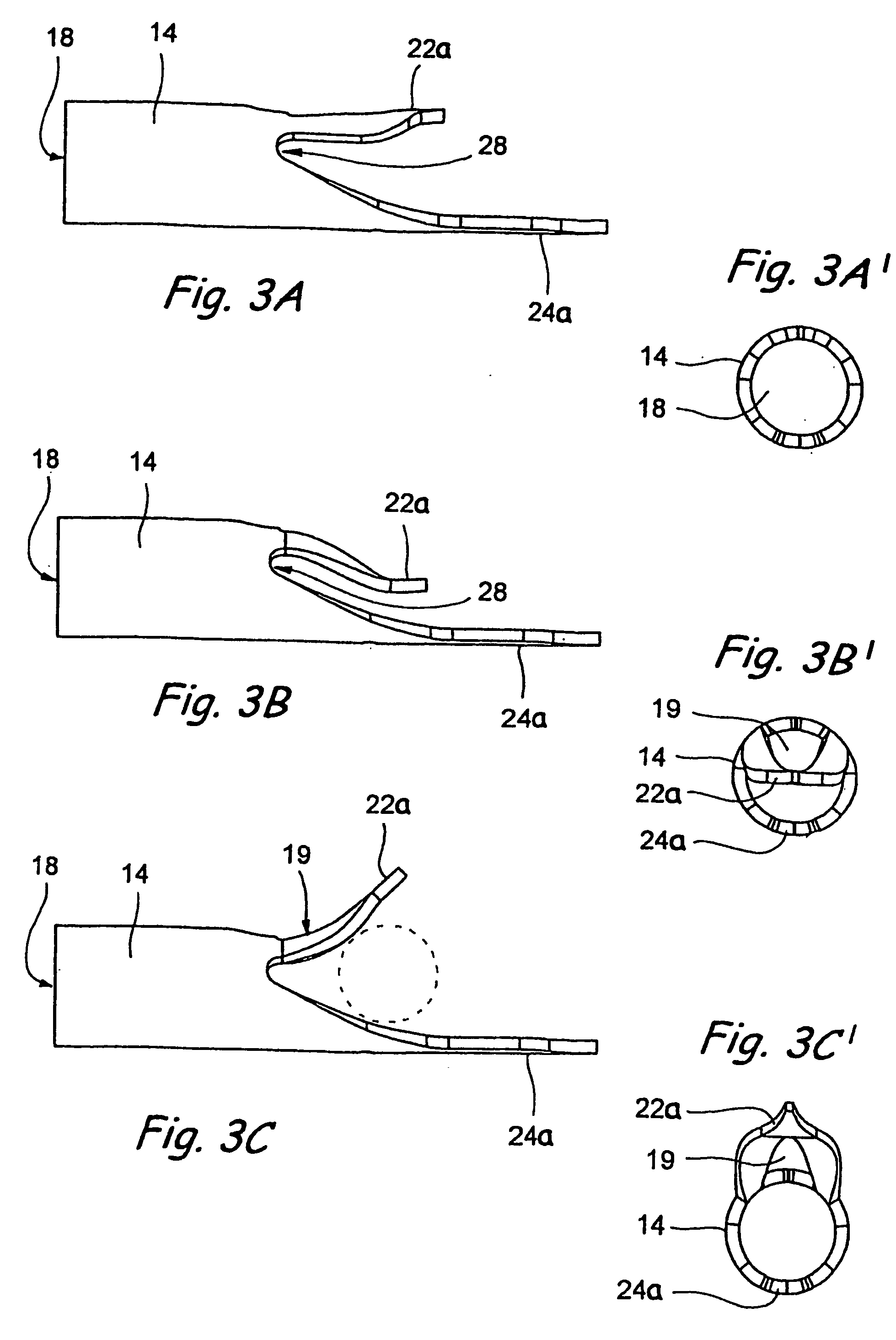
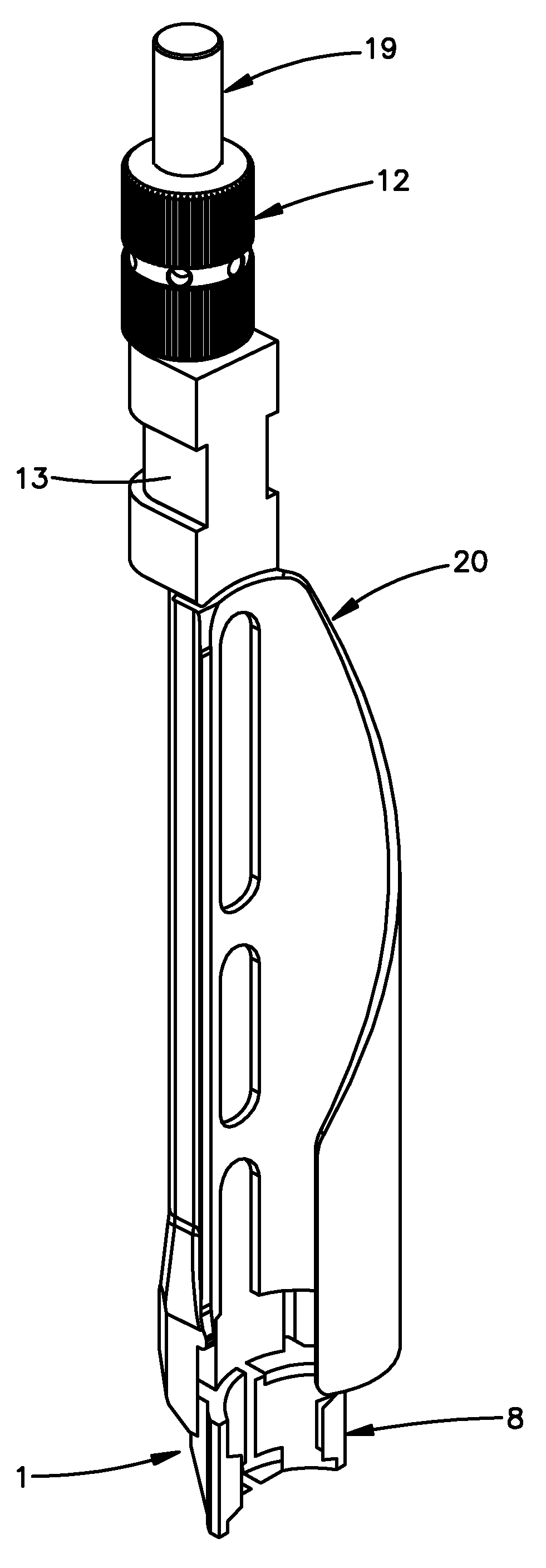
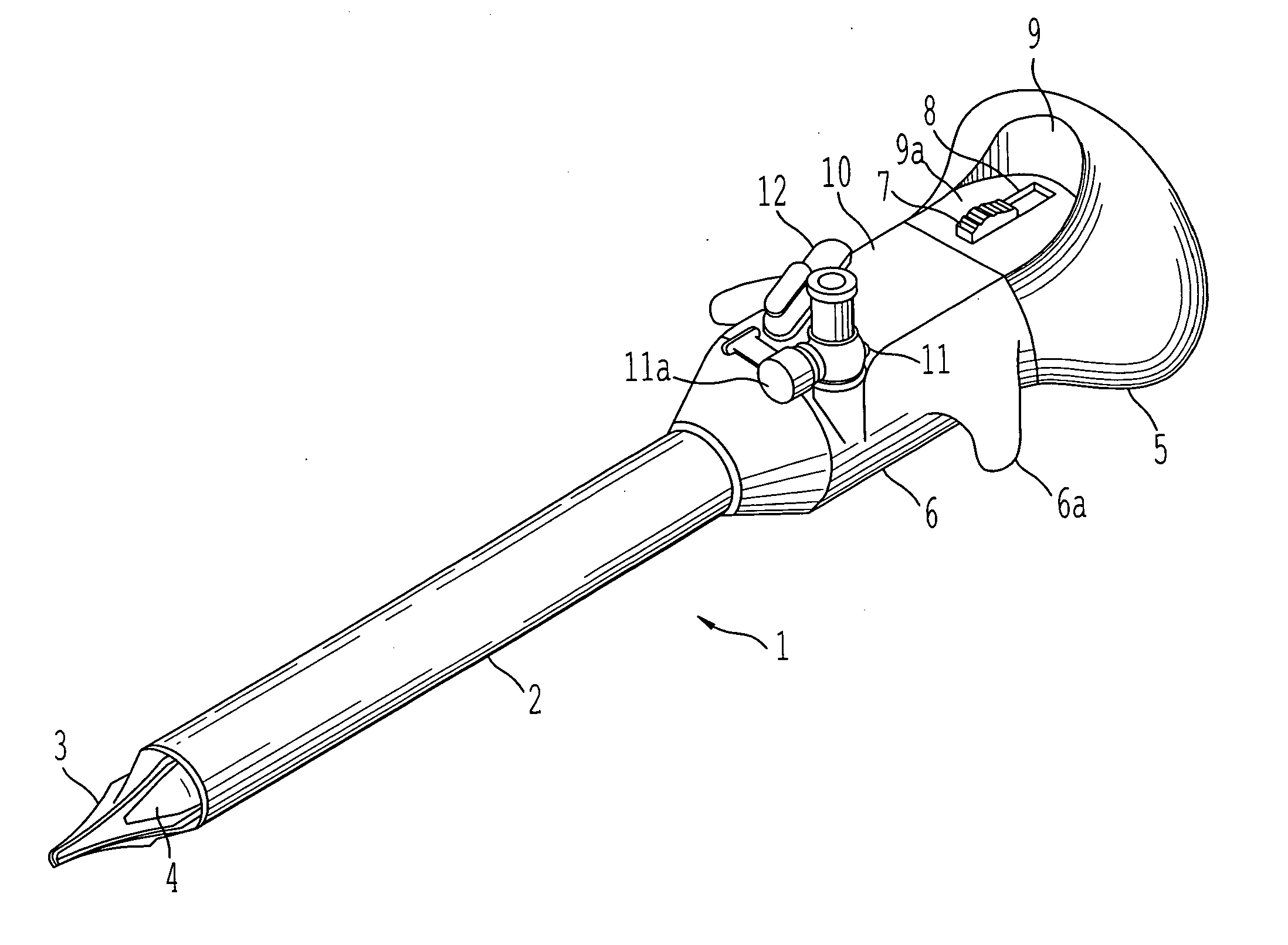
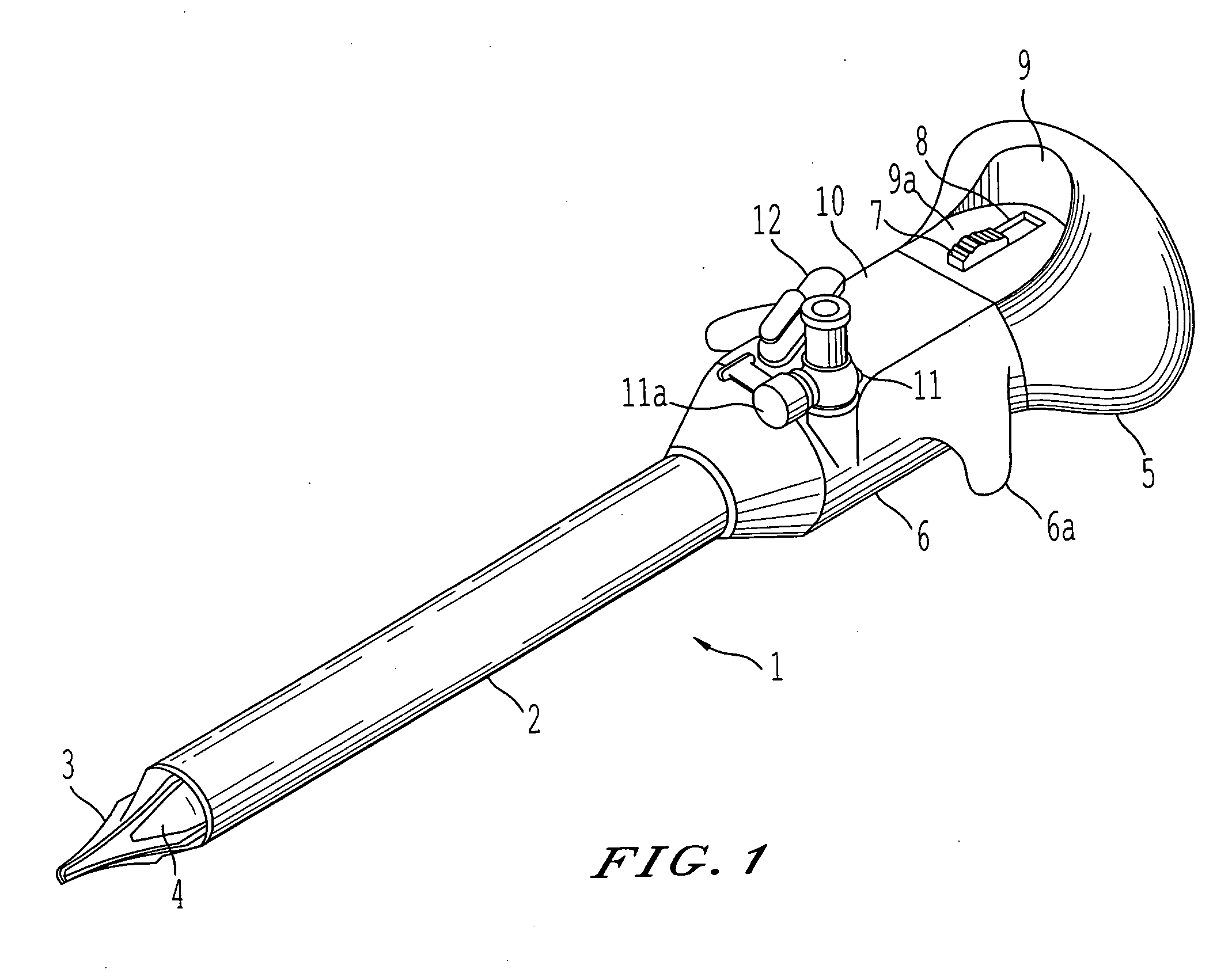
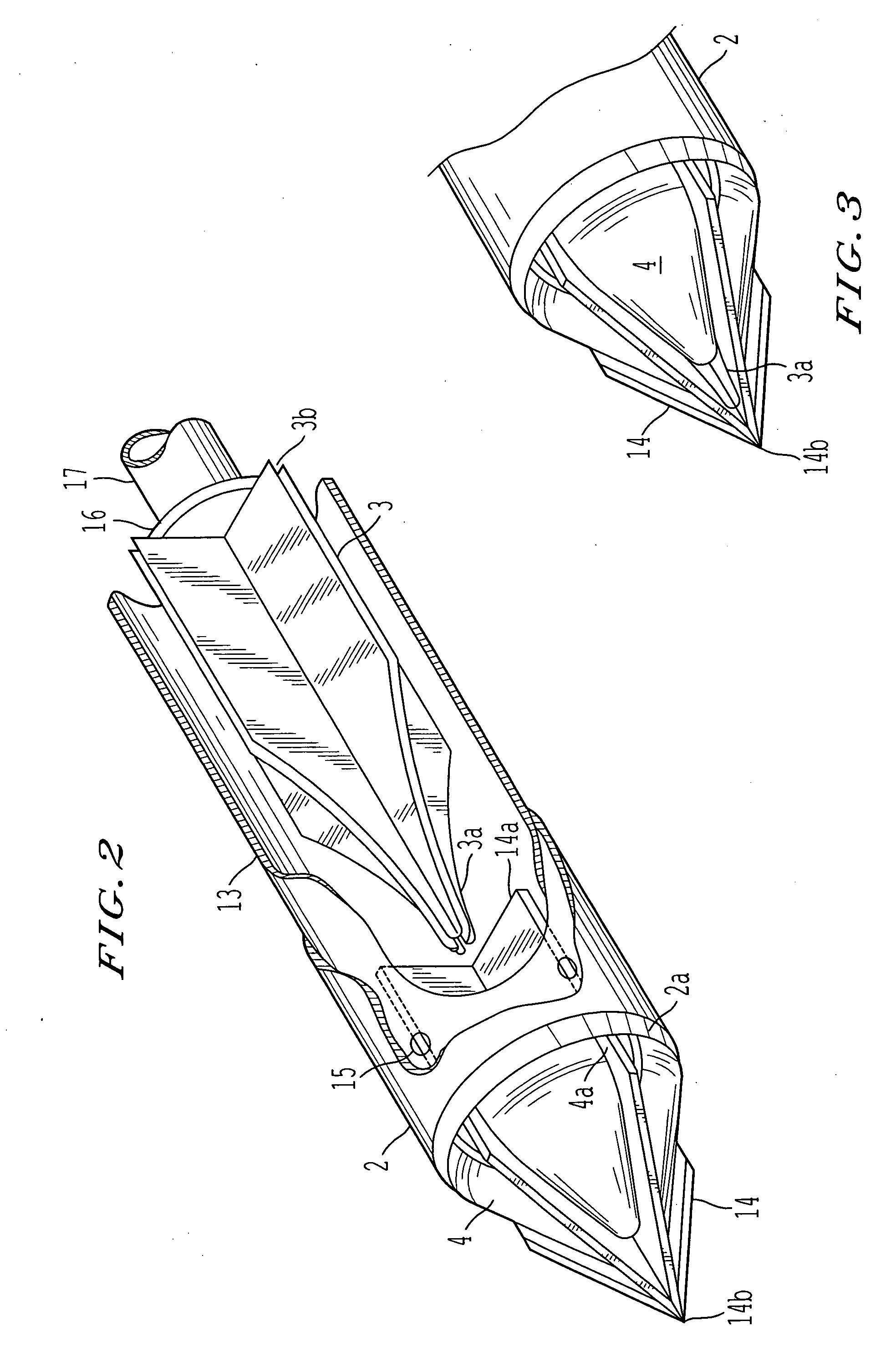
Insufflator and method of use
InactiveUS20040230155A1Reduce probabilitySurgical needlesMedical devicesEngineeringPreventing injury
A surgical device and method for endoscopic surgical procedures capable of preventing injuries to internal organs during insertion. The surgical device can include one or more of the following: a multiple system of sharp blade edges or a single blade, a mechanical tissue protection device that includes a series of thin plastic guards sliding along the sides of the planar knives and having an angle between their edges smaller than that of the cutting knife edges, one or more fixed conical deflectors to expand the cut tissue passage leaving the guards to contact tissue contact only at their tips, an insufflation passage configured to transport fluid into the body cavity during penetration, a locking system for the guards that prevents accidental reuse of the cutting features, and / or an ergonomic design which facilitates handling.
Owner:ERBLAN SURGICAL
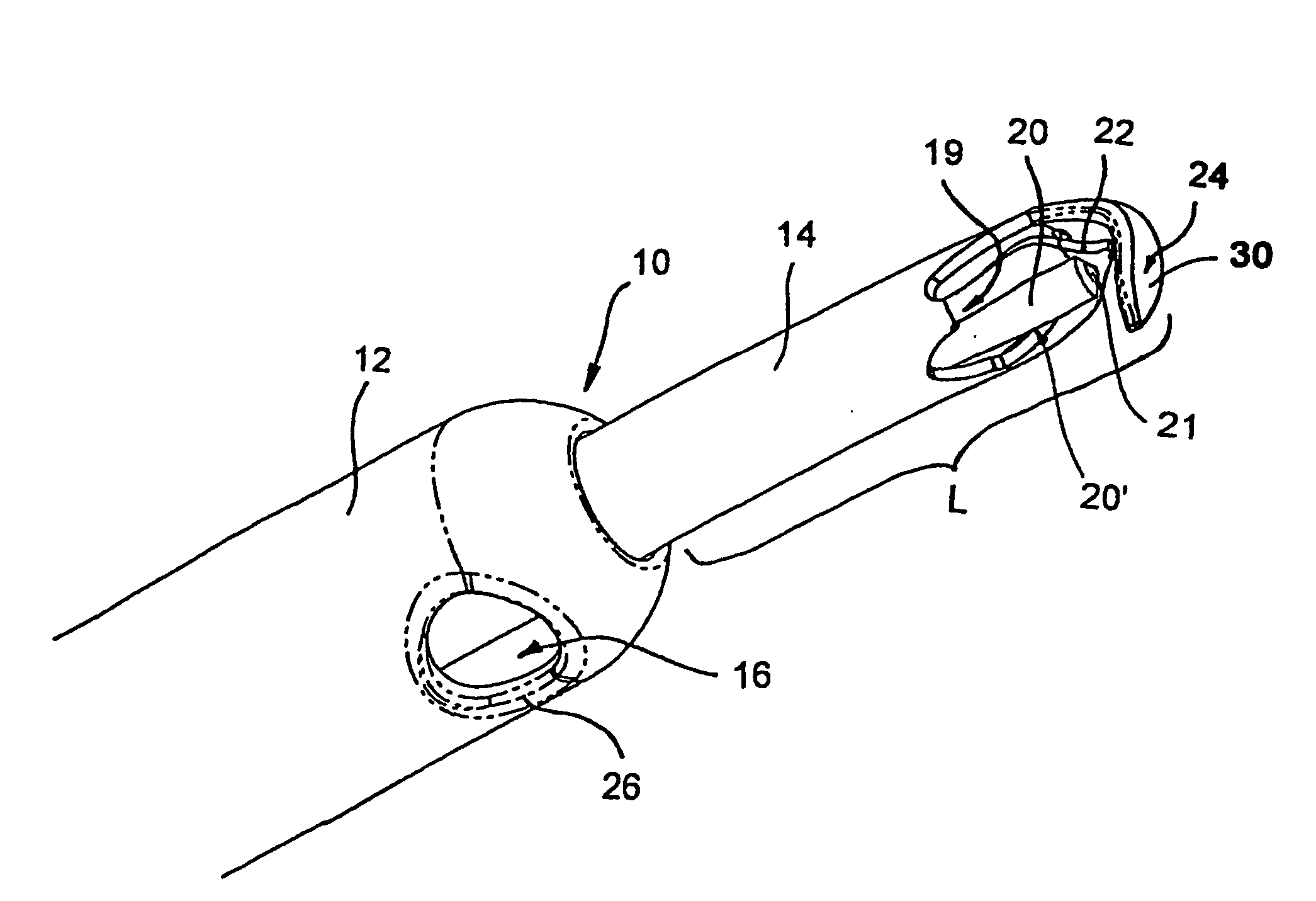
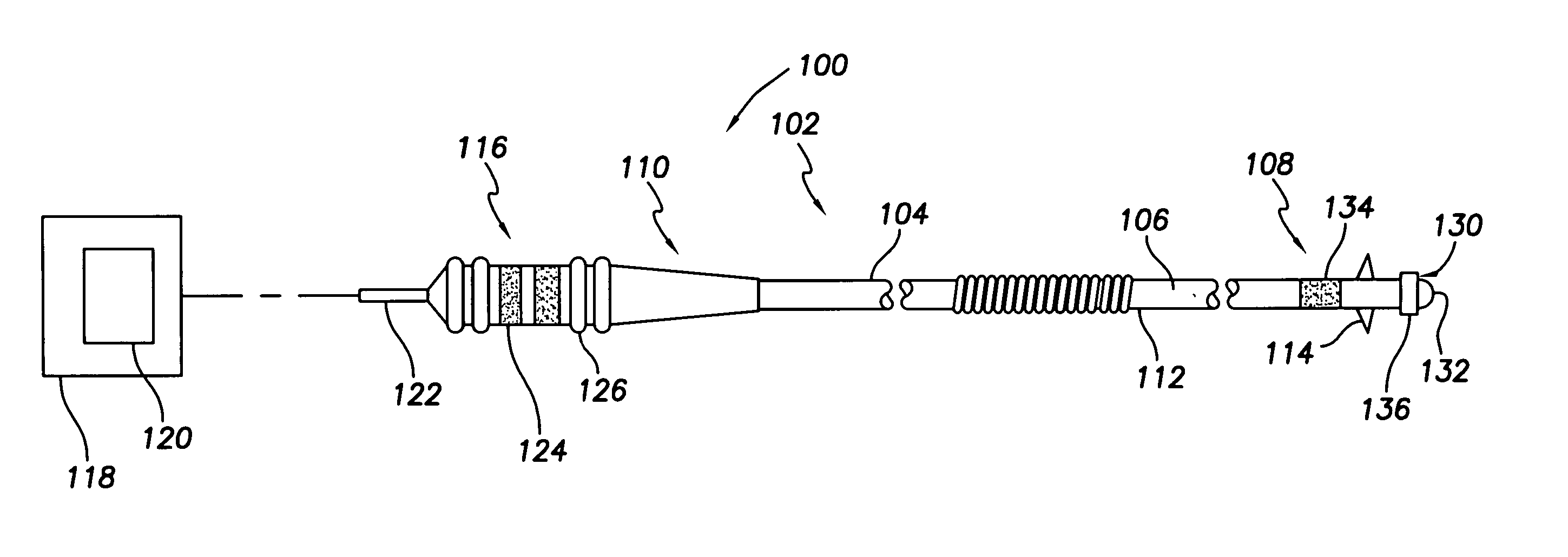
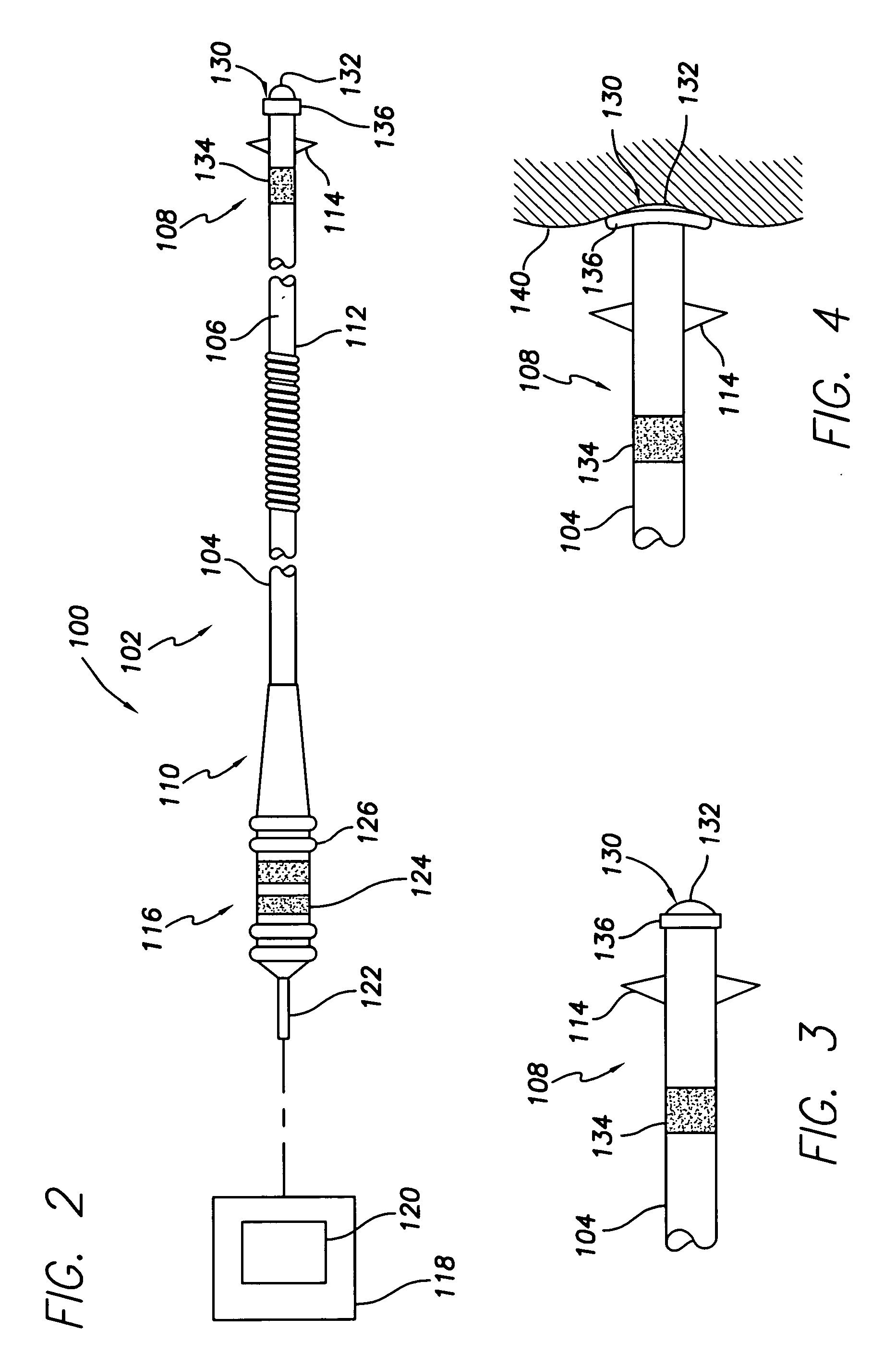
Medical lead with tissue-protecting tip structure
InactiveUS20070208402A1Easy to implantElimination of potentialTransvascular endocardial electrodesVeinCardiac muscle
A transvenous cardiac lead comprises a lead body having a distal end portion comprising a tip adapted to be placed in engagement with cardiac tissue. A protective device is carried by the distal end portion of the lead body in operative association with the tip, the protective device being deployable following placement of the tip to protect the cardiac tissue engaged by the tip. The deployable protective device may be expandable upon implantation to provide a larger surface area or footprint about the lead tip so as to retard or reduce the risk of penetration or perforation of the myocardium by the tip. The protective device may comprise a matrix expandable in response to contact with bodily fluids. Preferably, the expandable matrix comprises hydrogel. Alternatively, the protective device may comprise at least one electroactive polymer element electrically connected to a proximal end of the lead body.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Modular container for medical instruments and implants with extruded flexible bracket and rigid holders
A system for organizing, protecting, sterilizing, storing and delivery of surgical instruments, implants and related devices. Post and button fasteners are removably mounted to a tray and hold rigid and flexible bracketry for securing devices within the assembly. A flexible bar for holding items is mounted by a pair of rigid brackets in turn mounted either directly to the tray floor or to a base wall positioned atop the tray floor.
Owner:CONTAINMED
System AMD method for bone fusing implants and implant insertion tools
A method for fusing two adjacent stacked bones includes the following. First, inserting first and second pins into first and second locations of a first surface of one of the two adjacent stacked bones, respectively. Next, inserting a dilator over each of the first and second pins to dilate tissue around the first and second pins. Next, inserting a tissue protector over the dilator and removing the dilator. Next, inserting a cannulated drill through the tissue protector over each of the first and second pins and drilling first and second openings in the first and second locations, respectively, wherein the first and second opening extend through the two adjacent stacked bones. Next, tapping threads in the first opening and inserting a first bone fusing implant in the first opening, wherein the first bone fusing implant comprises threads configured to engage the threads of the first opening. Next, impacting a broach into the second opening to generate a pattern corresponding to a pattern of a second bone fusing implant and then inserting the second bone fusing implant in the second opening.
Owner:KIC VENTURES LLC
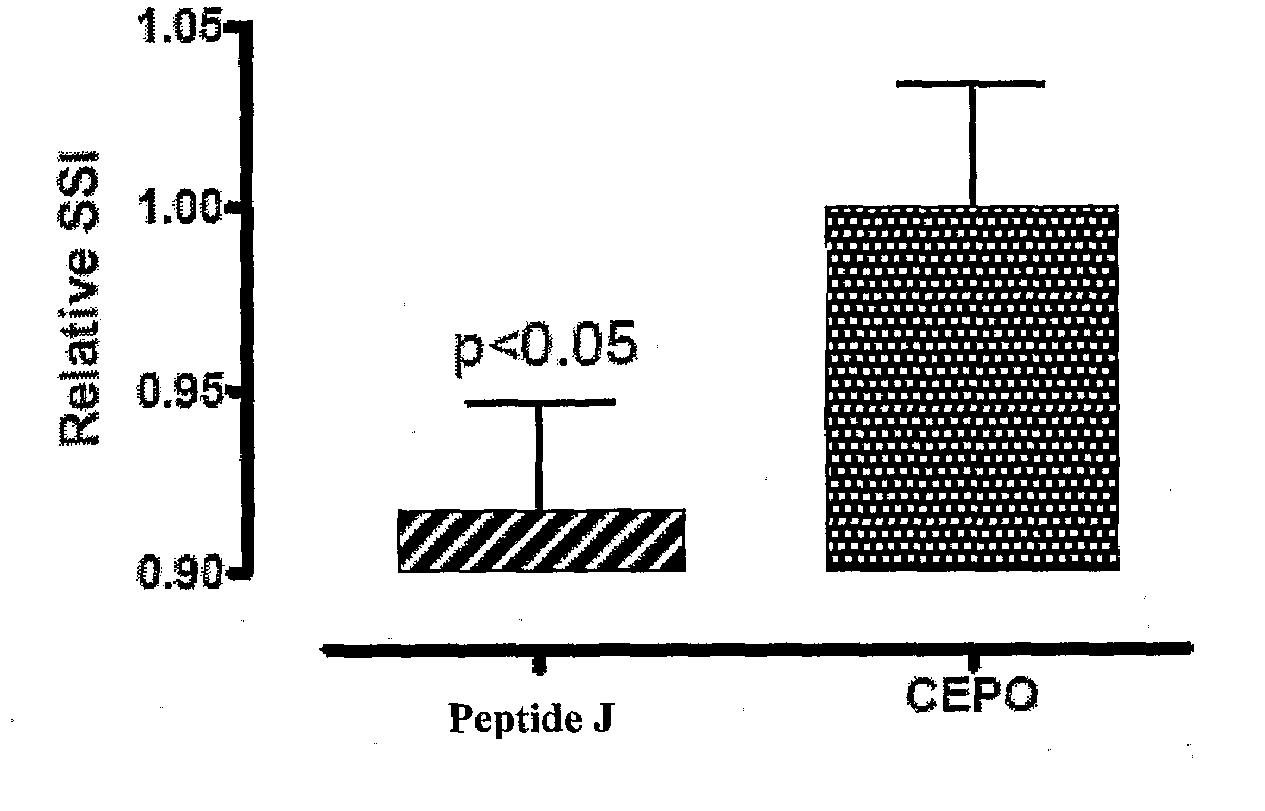
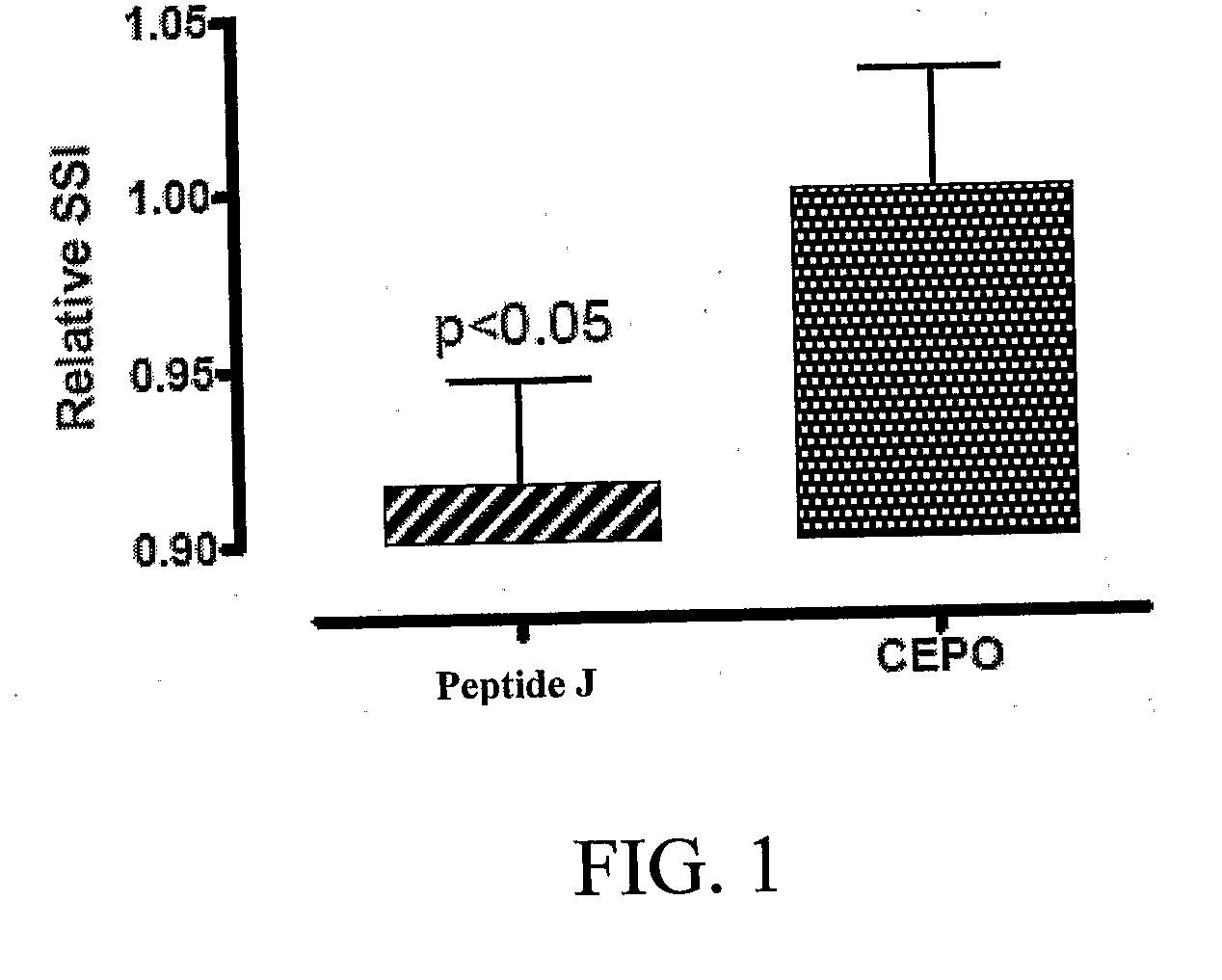
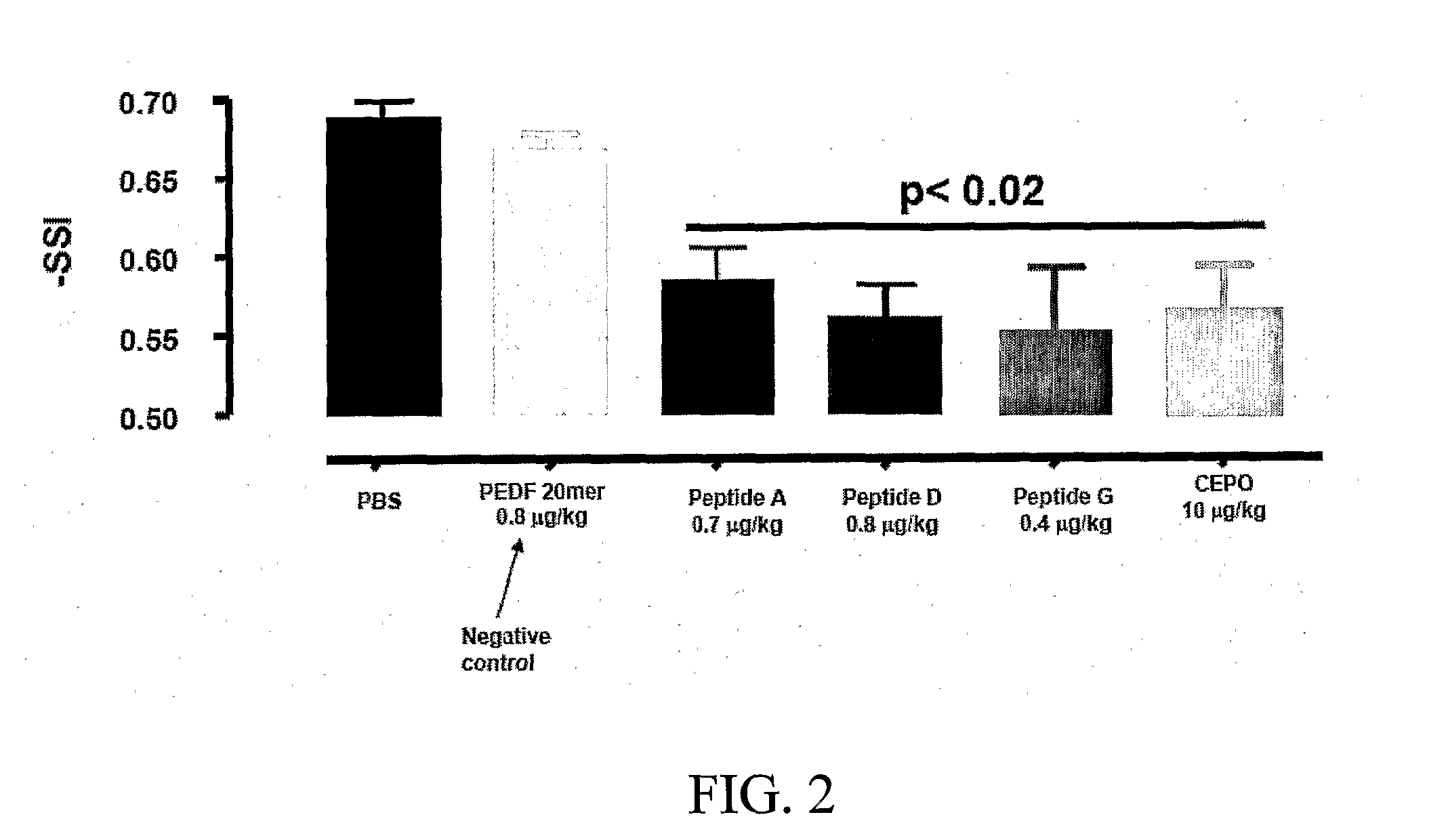
Tissue protective peptides and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090221482A1Avoid damageFacilitate optimal expressionSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTissue protection
The present invention is directed to novel tissue protective peptides. The tissue protective peptides of the invention may bind to a tissue protective receptor complex. In particular, the present invention is drawn to tissue protective peptides derived from or sharing consensus sequences with portions of cytokine receptor ligands, including Erythropoietin (EPO), that are not involved in the binding of the ligand to the receptor complex, e.g., to the EPO receptor homodimer. Accordingly, the tissue protective peptides of the invention are derived from the amino acid sequences of regions of cytokine receptor ligands that are generally located on or within the region of the ligand protein that is opposite of the receptor complex, i.e., are generally derived from amino acid sequences of regions of the ligand protein that face away from the receptor complex while the ligand is bound to the receptor. The invention is further directed to the consensus sequences for use in engineering a synthetic tissue protective peptide. These tissue protective peptides also include fragments, chimeras, as well as peptides designed to mimic the spatial localization of key amino acid residues within the tissue protective receptor ligands, e.g., EPO. The invention further encompasses methods for treating or preventing a disease or disorder using tissue protective peptides of the current invention. The invention also encompasses methods for enhancing excitable tissue function using tissue protective peptides of the current invention.
Owner:ARAIM PHARMA INC
Guide sleeve for suprapatellar surgery
A tissue protection sleeve for use in suprapatellar surgery is provided. The sleeve has a first end, a second end, an inner surface and an outer surface. The sleeve further comprises at least two open grooves that extend along the inner surface from the first end to the second end. The grooves are adapted to accommodate elongated fixation elements inserted into a tibia. A drill guide sleeve and a trocar for inserting a guide wire are also provided and can be accommodated by the tissue protection sleeve.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
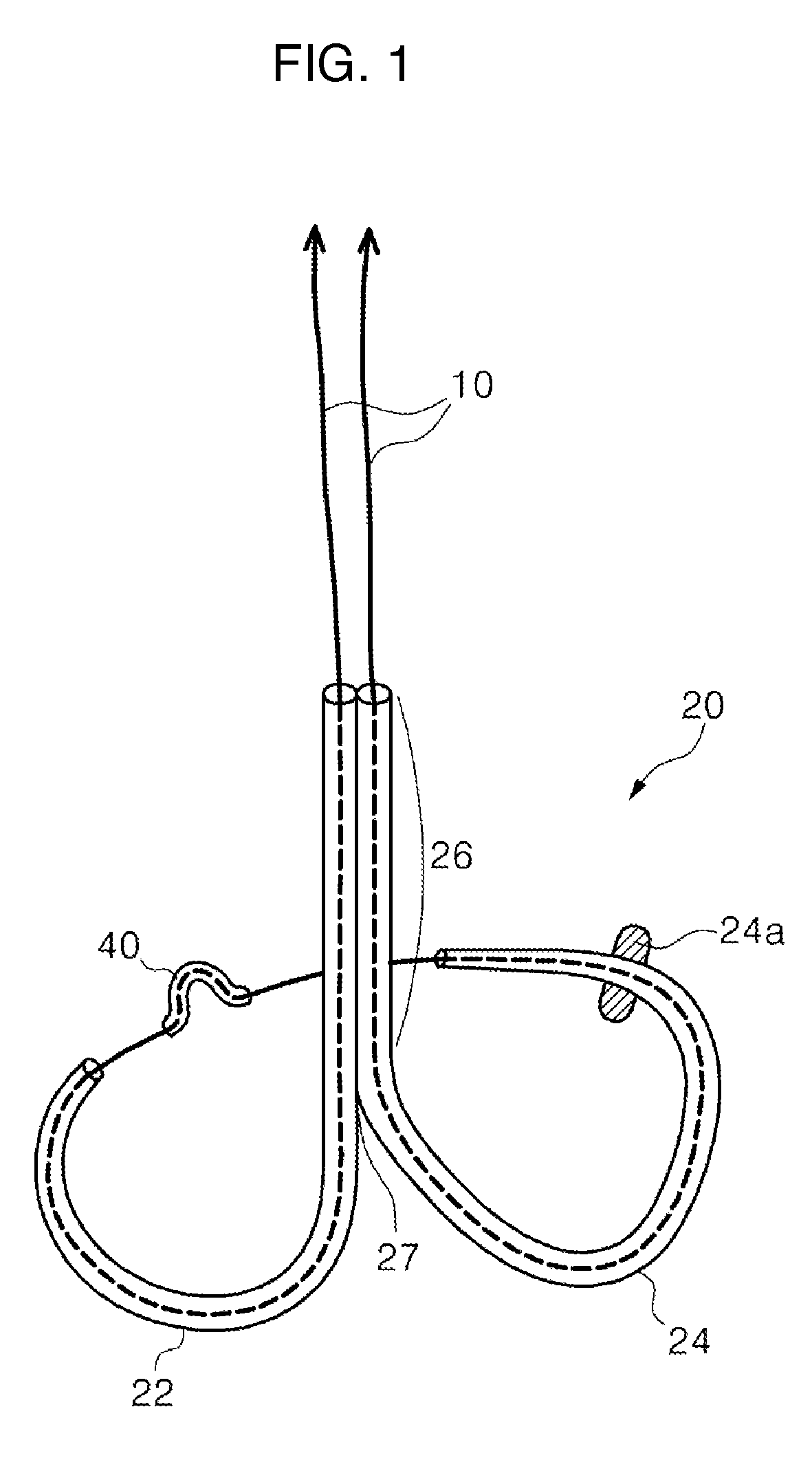
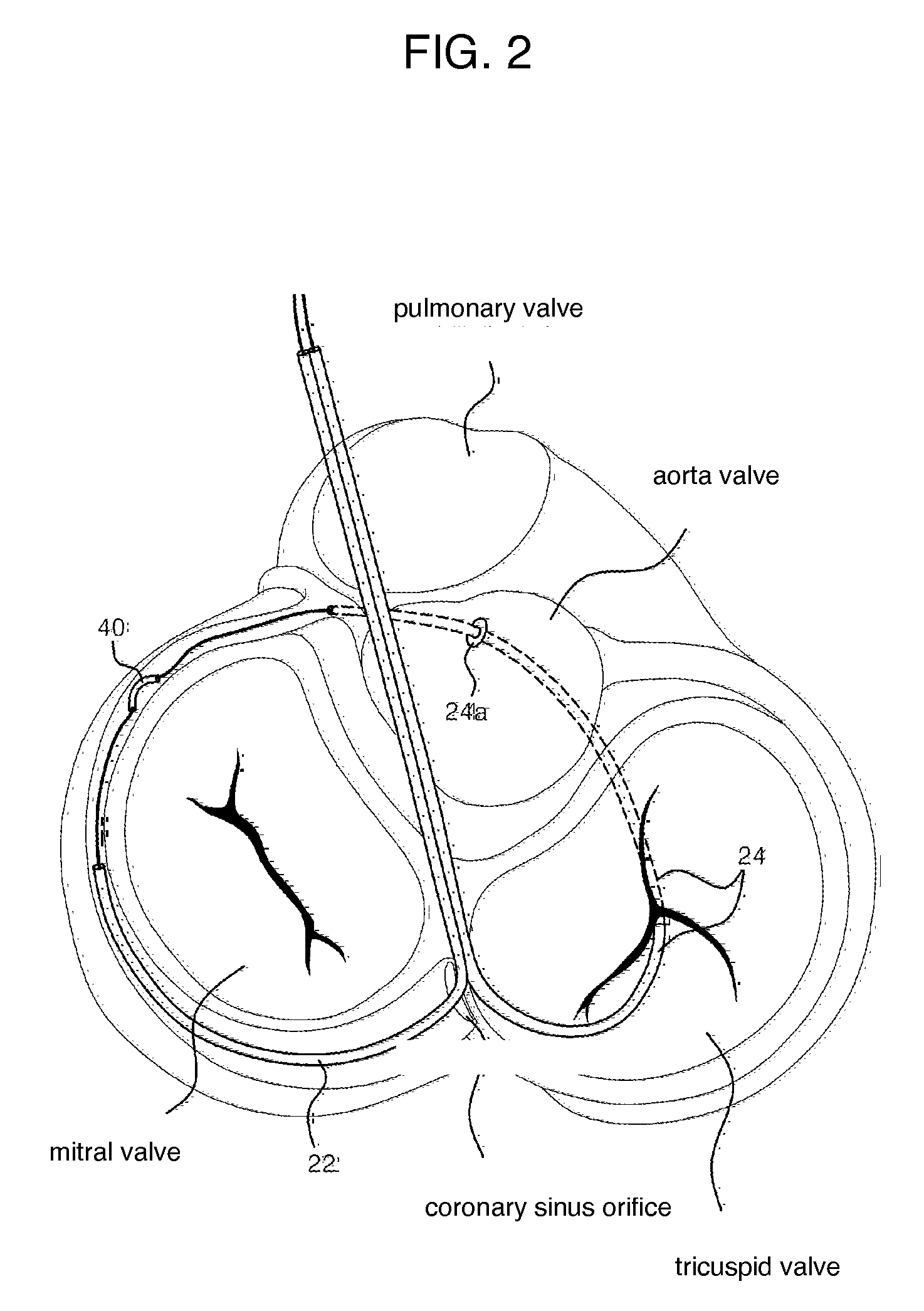
Mitral cerclage annuloplasty apparatus
ActiveUS20110054597A1Avoid damageEasy to adjustSuture equipmentsHeart valvesTissue protectionSurgery
A mitral cerclage annuloplasty apparatus comprises a tissue protective device and a knot delivery device. The tissue protective device comprises a first protective tube and a second protective tube. The knot delivery device comprises a tube wherein a loose knot is looped around its distal end through a hole and wherein tight knot is formed when the distal end of the tube is cut open. Alternatively, the knot delivery device comprises an inner tube and outer tube. The inner tube is insertable and rotatable inside the outer tube. When the tubes are in a closed position by rotating either the outer tube or the inner tube, a hole is created near its distal end. When the tubes are in open position by rotating either the outer tube or the inner tube, the hole joins the opening of the outer tube and lengthens.
Owner:TAU PNU MEDICAL CO LTD
Acidic aqueous chlorite teat dip with improved visual indicator stability, extended shelf life, sanitizing capacity and tissue protection
InactiveUS6699510B2Enhanced softening and smoothing and characterImmobilizes mastitis treatmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideChlorine dioxideTissue protection
The mastitis control teat dip composition having a visible indicator aspect of the invention provides a softening, soothing, smoothing, relaxing property, a rapid initial kill, a useful highly pseudoplastic rheology, a barrier / film-forming capacity, a unique antimicrobial composition that is stable over an extended period of time, and unexpected long term microbial control when compared to the prior art materials disclosed in patents and used in the marketplace. The indicator aspect provides ease of visually detecting the material on the animal skin and can indicate efficacy of the material. The compositions of the invention are made by combining an aqueous liquid composition containing the visual indicator combined with the organic components which can be combined with a simple aqueous solution of a salt of chlorous acid, preferably an alkali metal chlorite. The materials after they are combined and blended into a smooth viscous material containing an emollient package generates active antimicrobial chlorine dioxide and can be immediately contacted with the target animals. The compositions of the invention provide stable visual indication, rapid initial kill, consistent long term kill with chemical and rheological stability.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Methods, compositions, and kits for organ protection during systemic anticancer therapy
InactiveUS6995165B2Reduce concentrationIncrease concentrationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideWhole bodyTissue protection
Owner:ASYMMETRIC THERAPEUTICS
Devices and Methods Useable for Treatment of Glaucoma and Other Surgical Prcedures
ActiveUS20160106589A1Avoiding significant and irreparable damageEye surgeryDisinfectionSurgical departmentTissue protection
A device and method for cutting or ablating tissue in a human or veterinary patient includes an elongate probe having a distal end, a tissue cutting or ablating apparatus located adjacent within the distal end, and a tissue protector extending from the distal end. The protector generally has a first side and a second side and the tissue cutting or ablating apparatus is located adjacent to the first side thereof. The distal end is structured to be advanceable into tissue or otherwise placed and positioned within the patient's body such that tissue adjacent to the first side of the protector is cut away or ablated by the tissue cutting or ablation apparatus while tissue that is adjacent to the second side of the protector is not substantially damaged by the tissue cutting or ablating apparatus.
Owner:MICROSURGICAL TECH INC
Drill alignment assembly for a bone plate using tissue protection sleeves that are fixed in the bone plate
A tissue protection sleeve for use with a drill alignment assembly for a bone plate includes a tubular body having a first end and a second end. A hole extending from the first end to the second end is formed in the tubular body. The hole has a first center line. An expanded section is formed at the second end, the expanded section has a second center line. A first nose is formed at the first end, the first nose is adapted to fit in a screw hole in the bone plate such that the sleeve is rigidly fixed to the bone plate. The drill alignment assembly further includes an aiming arm adapted to mount to a bone plate and a drill guide insertable in the tissue protection sleeve.
Owner:STRYKER TRAUMA GMBH
Tissue protecting spray-on copolymeric film composition
This invention deals with a tissue protecting, spray-on film composition comprising an amphiphilic film-forming, segmented / block copolymer derived form at least one water-soluble monomer and at least another water-insoluble monomer, wherein the film can be formed from a water soluble organic solvent such as 2-propanol, acetone, and ethyl acetate. The film can contain a bioactive agent including those to have antimicrobial, anesthetic, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing activities.
Owner:POLY MED
Method and device for performing cooling- or cryo-therapies for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS20050228368A1Reduce restenosis rateMinimize or inhibit the bio-chemical eventsCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisLeft atrium
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Devices and methods for protecting tissue at a surgical site
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
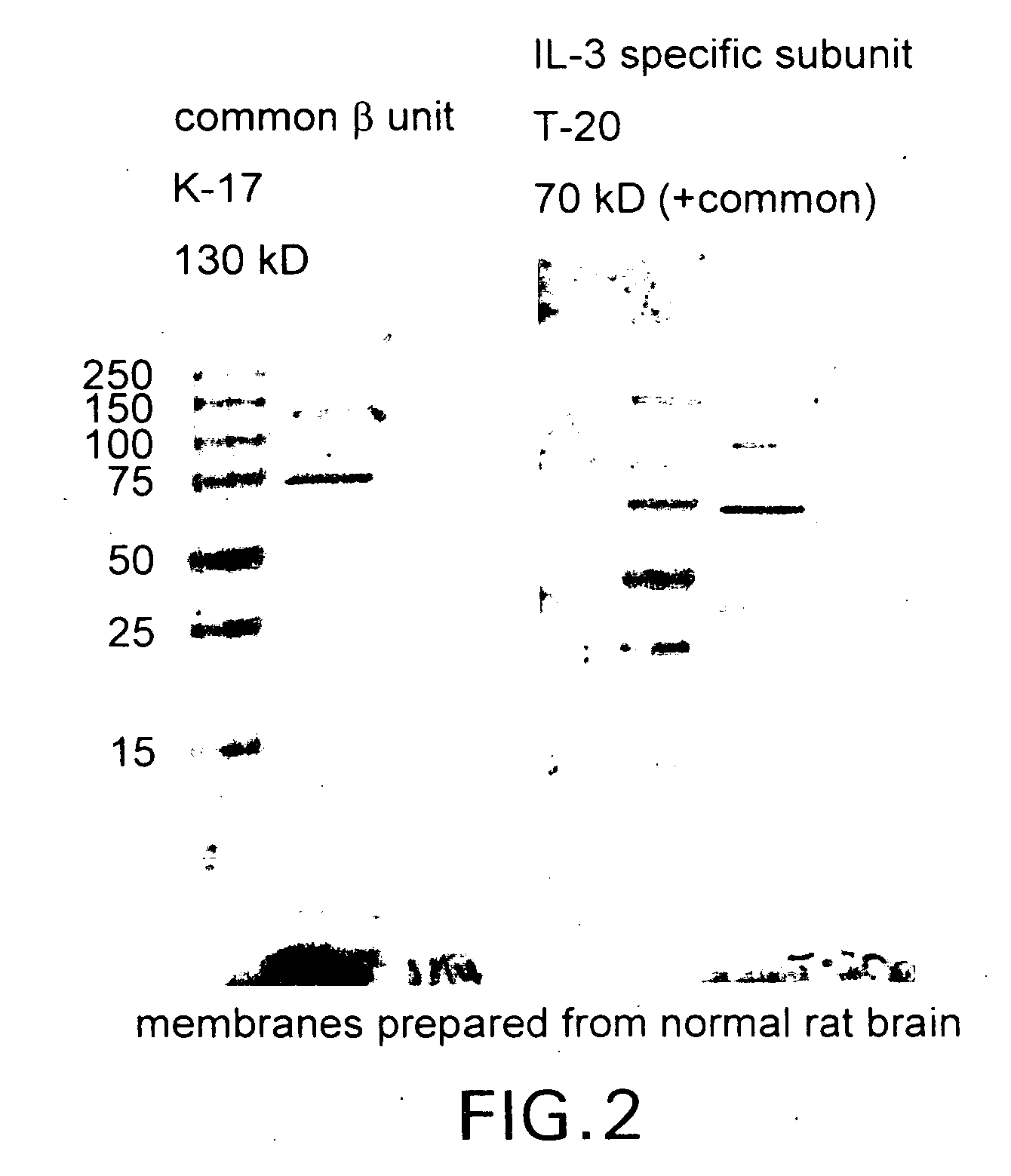
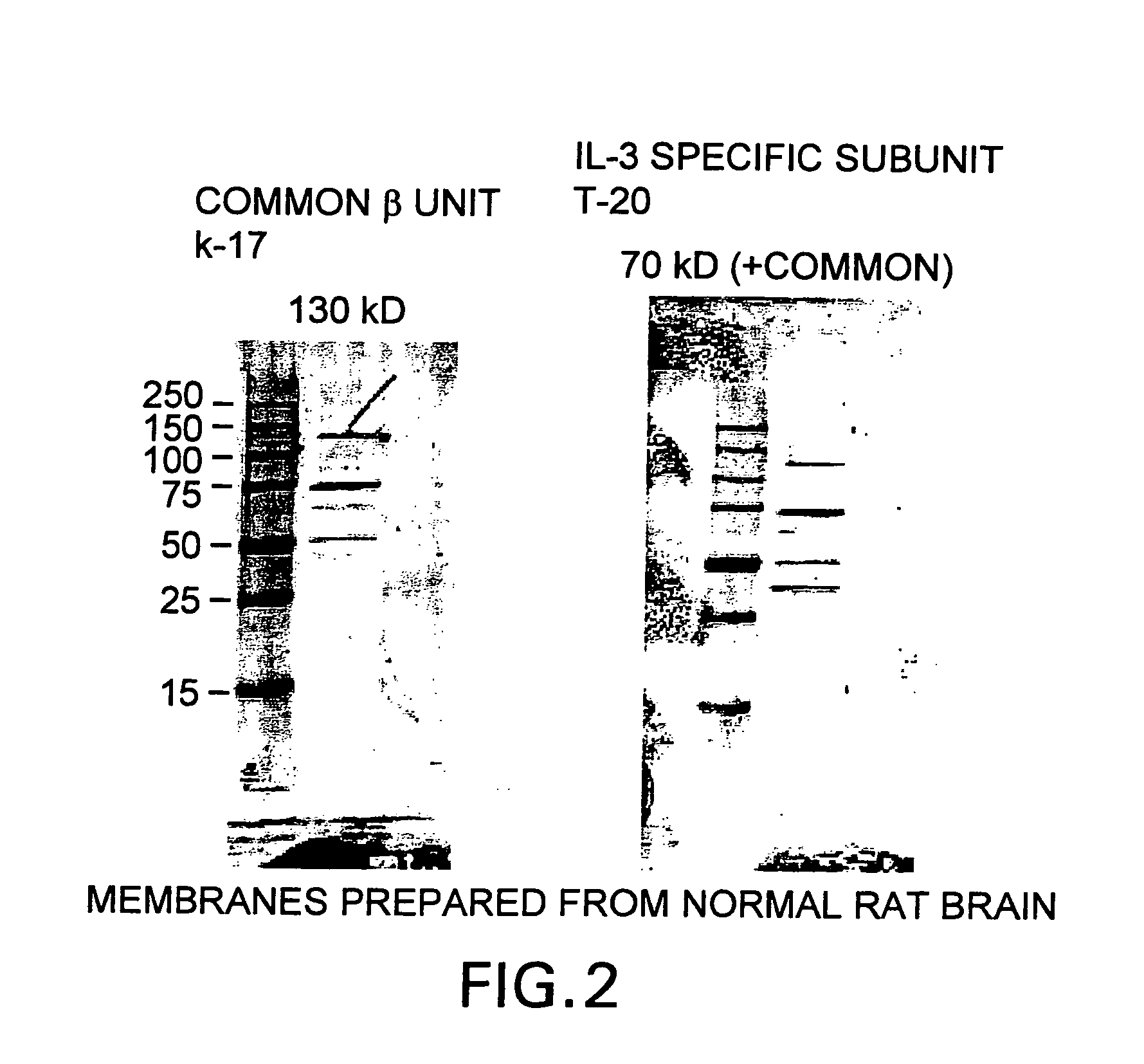
Tissue protective cytokine receptor complex and assays for identifying tissue protective compounds
InactiveUS20040214236A1High activityEnhanced interactionSenses disorderNervous disorderNervous systemExcitable cell
The present invention is directed methods for identifying compounds that have a tissue protective activity using a heteromultimer receptor complex that mediates the tissue protective activities. The complex consists of at least one EPO-R in complex with at least one betac Receptor. These compounds used in the assays to identify tissue protective compounds include, but are not limited to, small molecules and biologics. The compounds identified using these assays can be used to treat various conditions of the central and peripheral nervous systems as well as those of other erythropoietin-responsive or excitable cells, tissues, and organs.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS +2
Vessel protection device
The present disclosure relates to a vessel / tissue protection device having a polymer coated reinforcing layer. The polymer can comprise a biocompatible polymer that will not promote tissue in-growth or attachment, such as segmented polyurethane, polycarbonate urethane, polyether urethane, polyacrylonitrile, etc. The reinforcing layer can comprise any suitable woven, non-woven, knitted, or braided reinforcing polymer, fabric, or foil that is biocompatible and capable of holding a suture, staple, or other attachment device.
Owner:REPLICATION MEDICAL
Tissue protective cytokine receptor complex, assays for identifying tissue protective compounds and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060216757A1Reduce apoptosisPromote recoveryCompound screeningPeptide librariesNervous systemExcitable cell
The present invention is directed methods for identifying compounds that have a tissue protective activity using a heteromultimer receptor complex that mediates the tissue protective activities. The complex consists of at least one EPO-R in complex with at least one βc Receptor. These compounds used in the assays to identify tissue protective compounds include, but are not limited to, small molecules and biologics. The compounds identified using these assays can be used to treat or prevent various diseases, disorders, or conditions of the central and peripheral nervous systems as well as those of other erythropoietin-responsive or excitable cells, tissues, and organs.
Owner:THE KENNETH S WARREN INST
Enhancing treatment of HIF-1 mediated disorders with adenosine A3 receptor agonists
InactiveUS20060194756A1Convenient treatmentReduces and avoids unwanted effectBiocideNervous disorderAdenosine A3 Receptor AgonistsAgonist
The present invention relates to the use of adenosine receptor agonists, preferably A3 receptor agonists, either alone or in combination with other agents for the treatment, prevention and / or management of diseases or disorders associated with under-expression of HIF-1α and / or decreased HIF-1 α activity (e.g., ischemic related disorders). The methods of the invention are directed to methods of reducing tissue damage (e.g., substantially prevention tissue damage, inducing tissue protection) resulting from ischemia orhypoxia. The invention provides methods for treating, preventing and / or ameliorating one or more symptoms of hypoxic or HIF-1α related disorders by administering an A3 receptor agonist either alone or in combination with other agents.
Owner:KING PHARMA RES & DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com