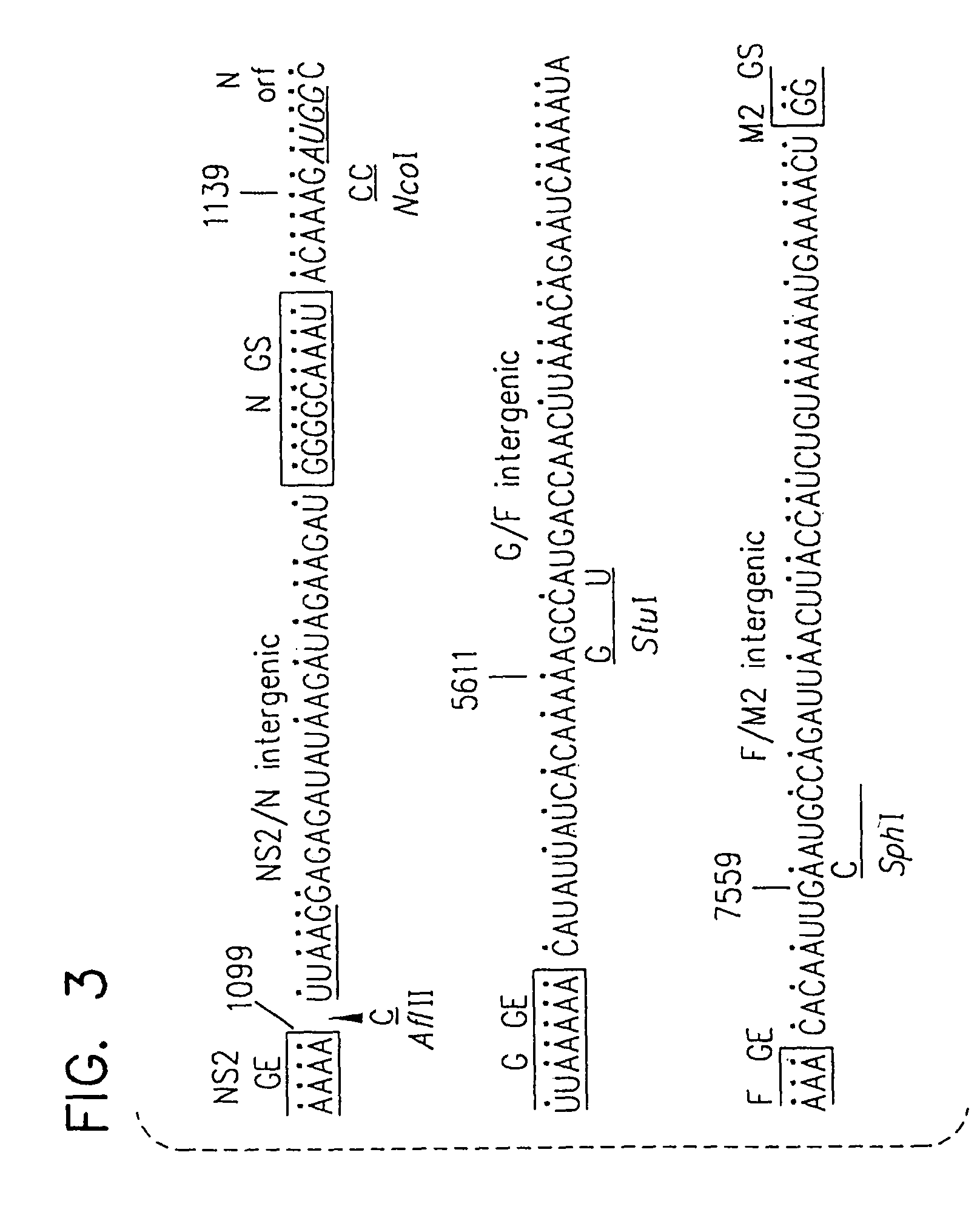
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
888 results about "Vaccine strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
For trivalent (three-strain) vaccine formulations, the group recommended including the Victoria lineage influenza B vaccine strain. H3N2 has been the dominant strain in the Northern Hemisphere over the past several months, but circulation has varied widely by country and region.
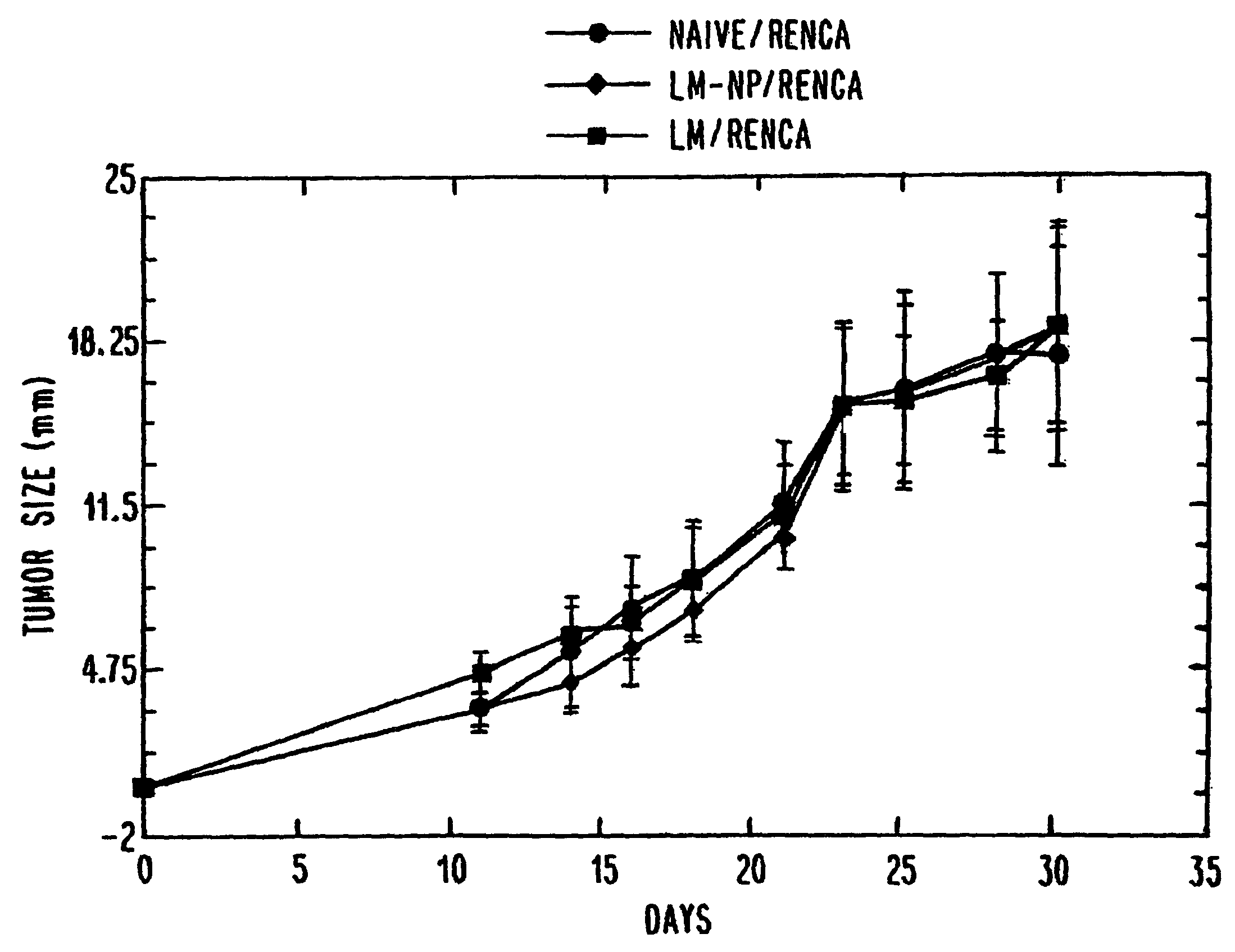
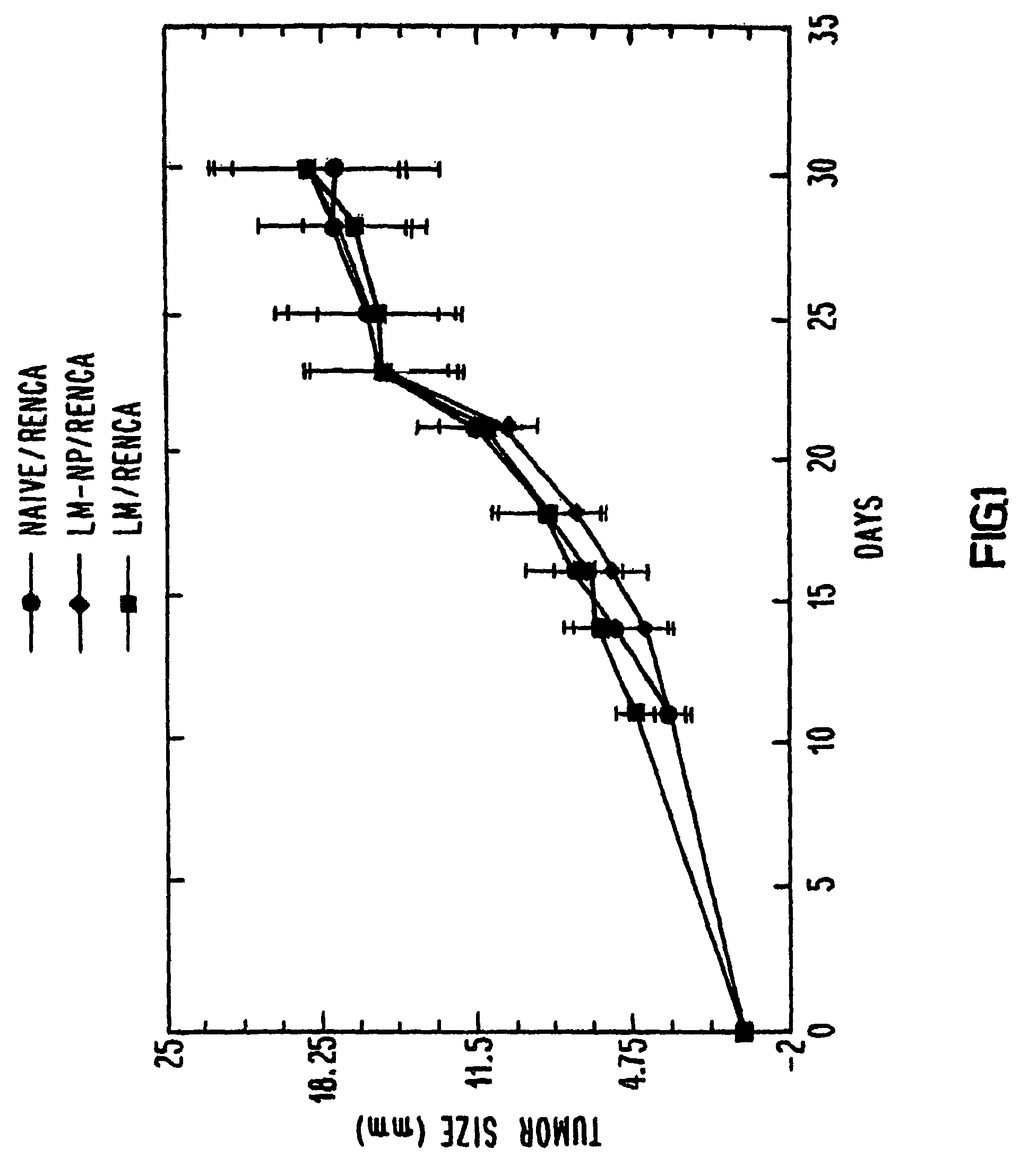
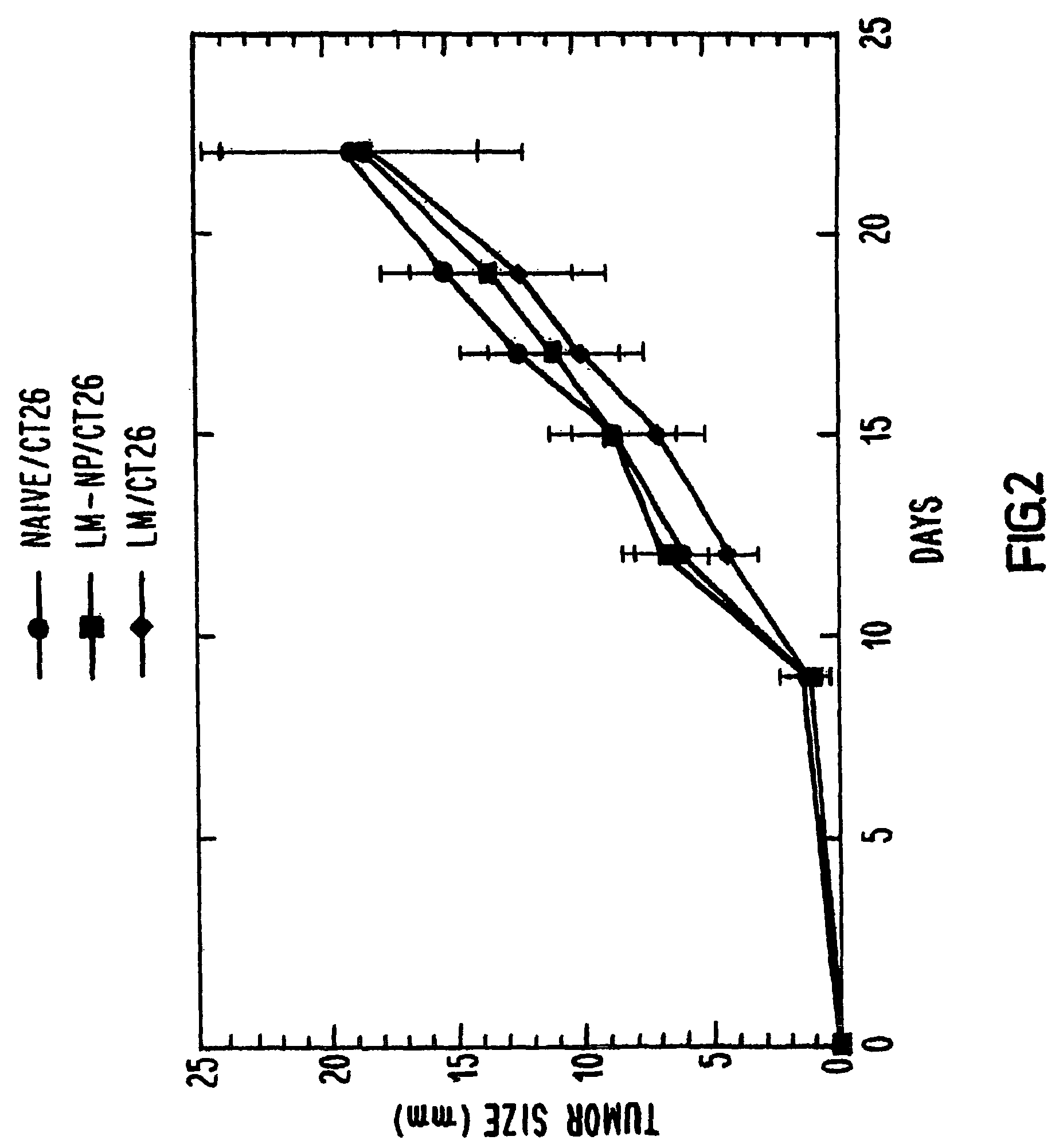
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy of cancer
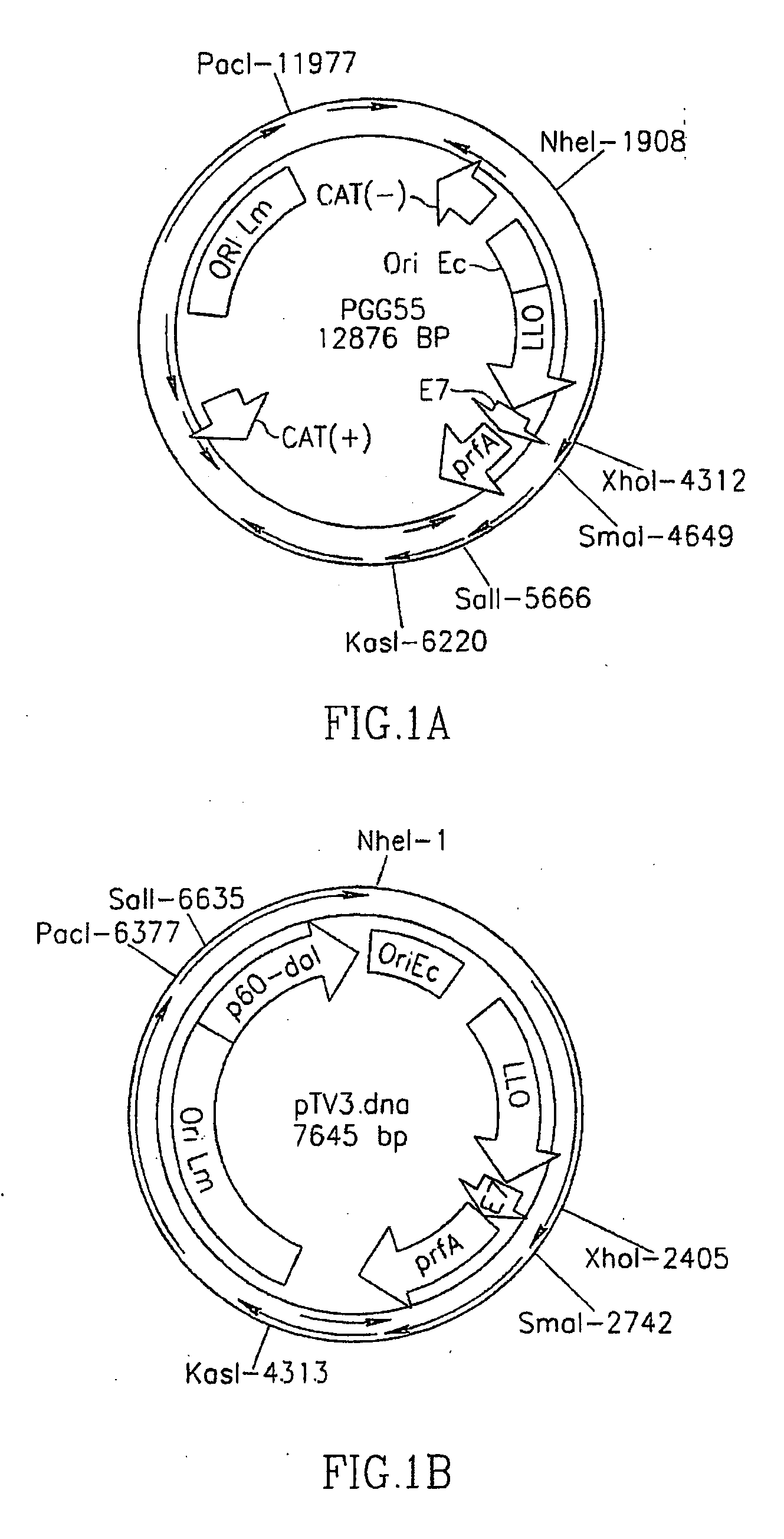
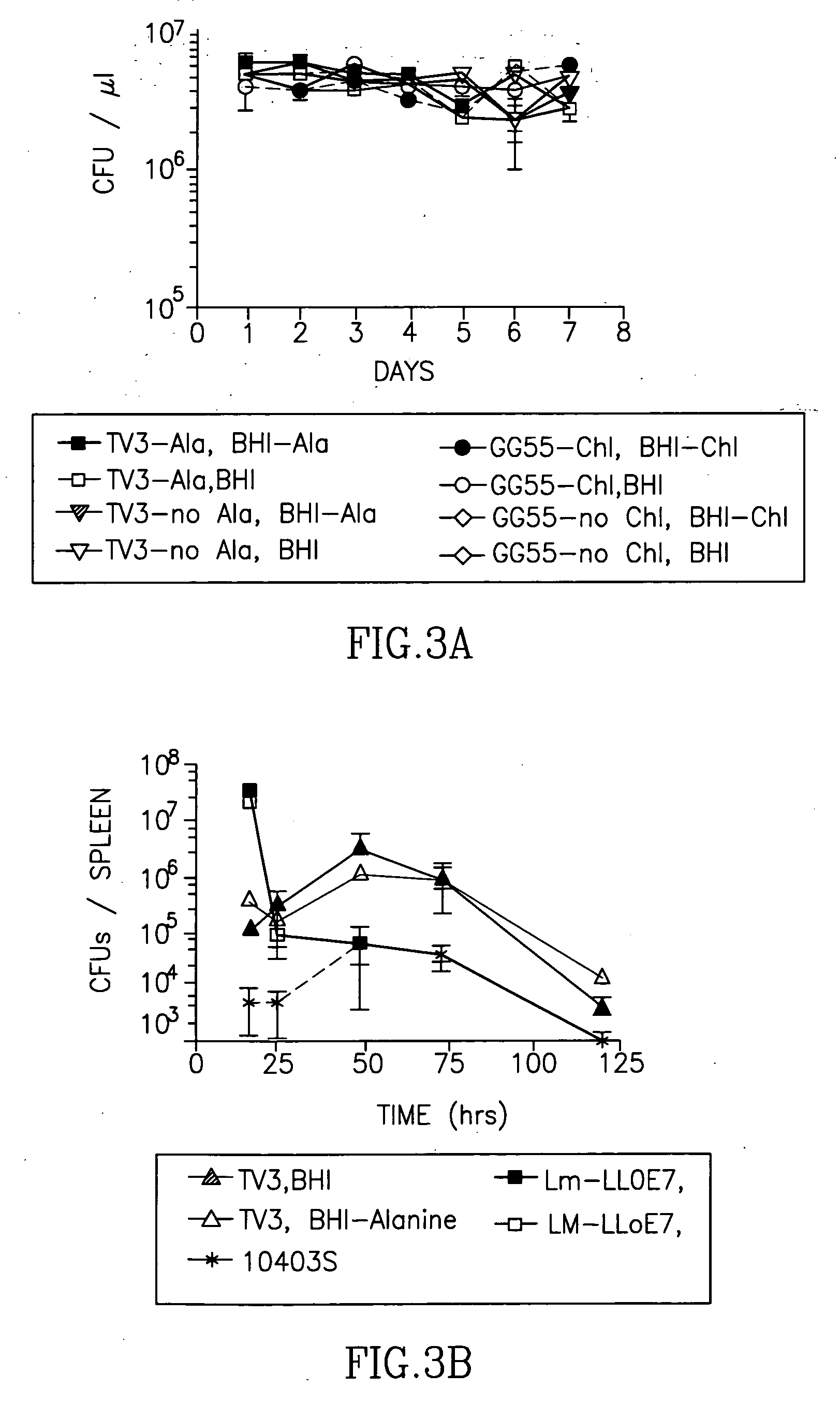
The present invention includes compositions, methods and kits for inducing an immune response to a tumor and for treating cancer with a Listeria vaccine strain expressing an antigen fused to a truncated LLO protein.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
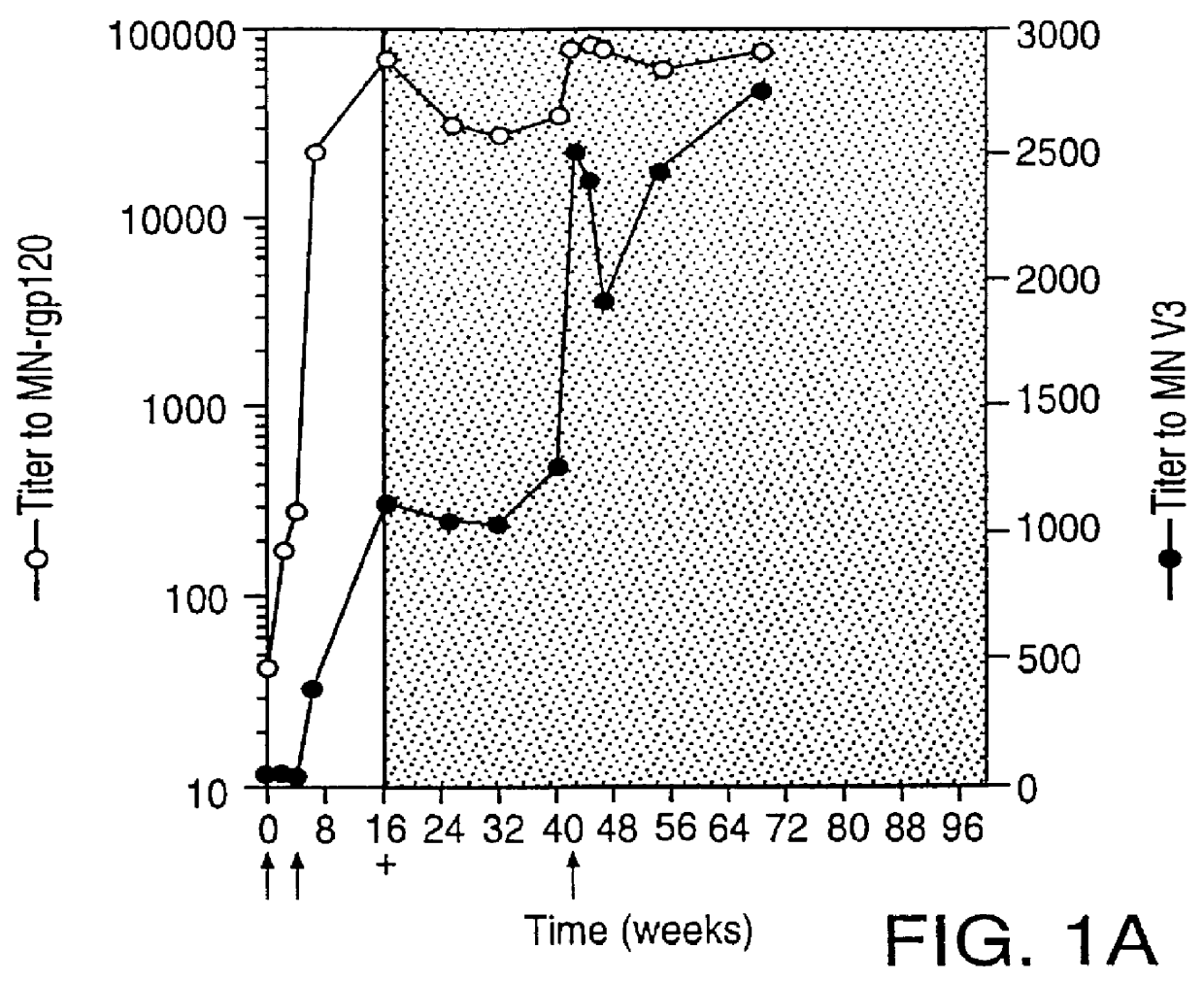
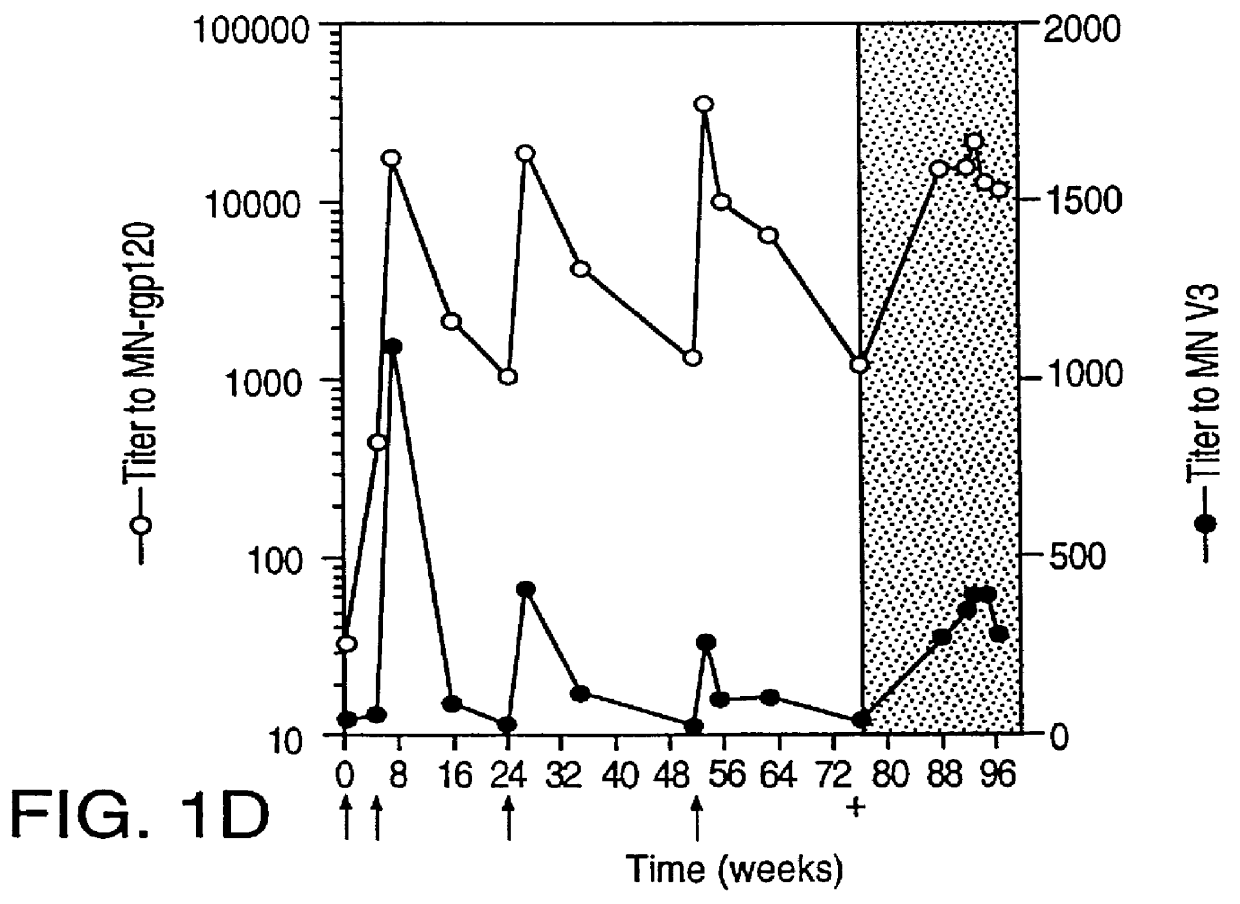
HIV envelope polypeptides and vaccine
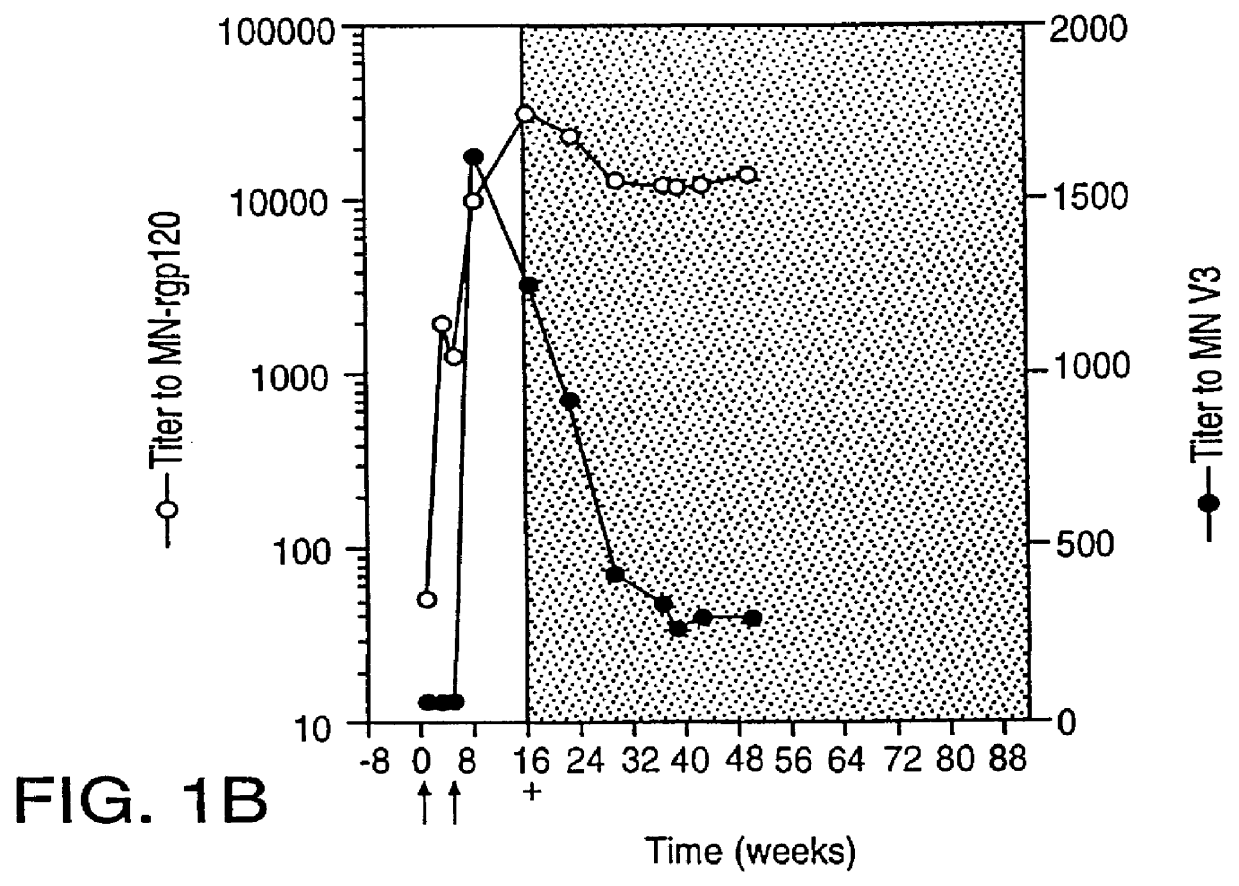
Oligonucleotide sequences encoding gp120 polypeptides from breakthrough isolates of vaccine trials using MN-rgp120 and the encoded gp120 polypeptides are provided. Use of the gp120 polypeptides from one or more of the isolates in a subunit vaccine, usually together with MN-rgp120, can provide protection against HIV strains that are sufficiently different from the vaccine strain (e.g.; MN-rgp120) that the vaccine does not confer protection against those strains. Antibodies induced by the polypeptides are also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
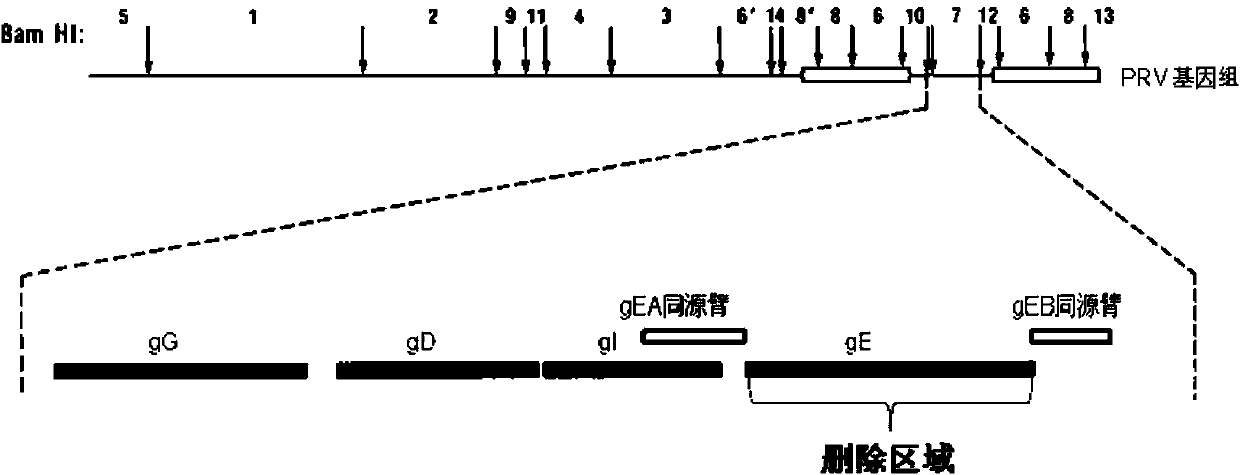
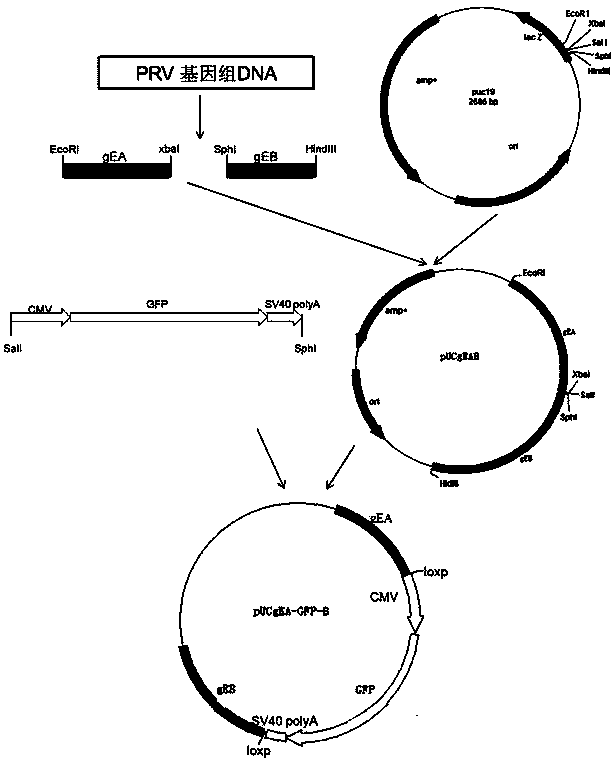
Porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain, and gene deletion vaccine strain thereof and applications thereof
ActiveCN102994458AEffective preventionEffective therapeuticMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsRabiesMicrobacterium
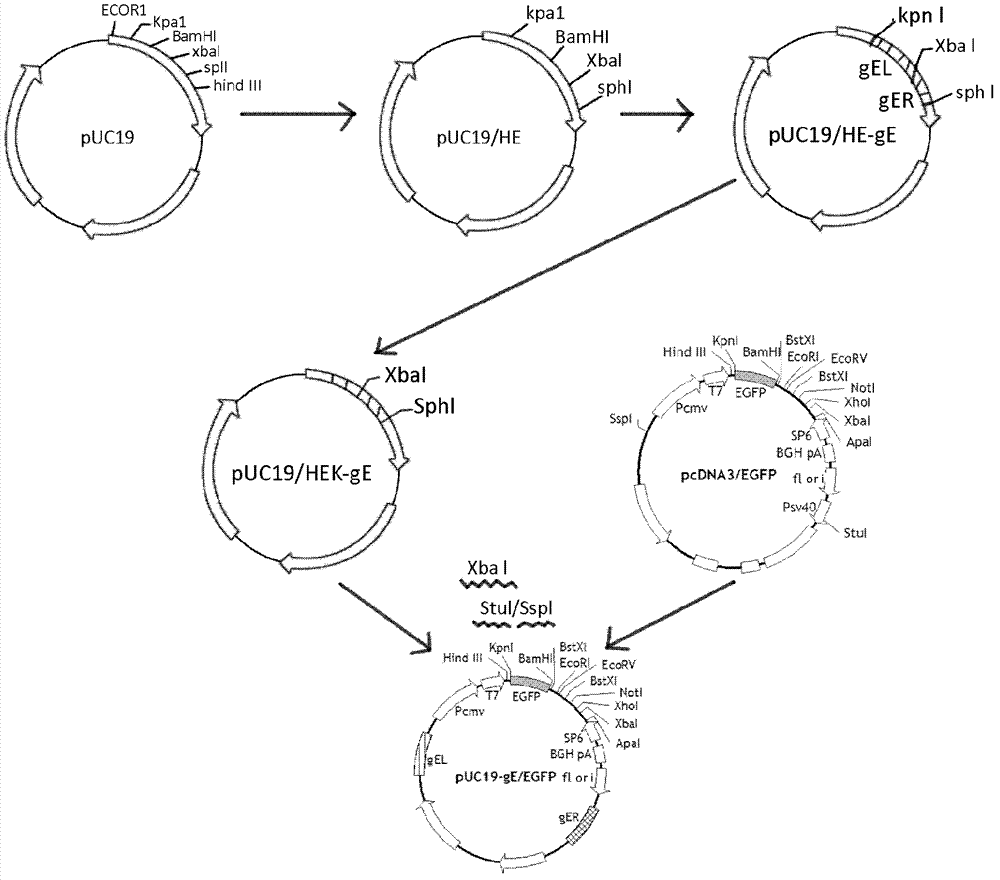
The invention discloses a porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain, and a gene deletion vaccine strain thereof and applications thereof. The porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain is named as HeN1, the microbial preservation number of the porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain is CGMCC NO.6656, the deleted gE gene obtaines the gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ on the basis of the virulent strain HeN1, and the microbial preservation number is CGMCC NO.6657. The virulent strain can be prepared into inactivated vaccine (single vaccine or combined vaccine), the gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ can be prepared into activated vaccine or inactivated vaccine (single vaccine or combined vaccine) and the like, so that porcine pseudorabies can be effectively prevented or cured, or the gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ can be prepared into a diagnosis reagent for diagnosing the porcine pseudorabies. The gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ has the advantages of being good in safety, high in protection efficiency, beneficial to differential diagnosis.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Methods for constructing antibiotic resistance free vaccines
The present invention provides Listeria vaccine strains that express a heterologous antigen and a metabolic enzyme, and methods of generating same.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
HIV envelope polypeptides
A method for the rational design and preparation of vaccines based on HIV envelope polypeptides is described. In one embodiment, the method for making an HIV gp120 subunit vaccine for a geographic region comprises determining neutralizing epitopes in the V2 and / or C4 domains of gp120 of HIV isolates from the geographic region and selecting an HIV strain having gp120 a neutralizing epitope in the V2 or C4-domain which is common among isolates in the geographic region. In a preferred embodiment of the method, neutralizing epitopes for the V2, V3, and C4 domains of gp120 are determined. At least two HIV isolates having different neutralizing epitopes in the V2, V3, or C4 domain are selected and used to make the vaccine. The invention also provides a multivalent HIV gp120 subunit vaccine. A DNA sequence encoding gp120 from preferred vaccine strains of HIV, GNE8 and GNE16, expression constructs comprising the GNE8-gp120 and GNE16-gp120 encoding DNA under the transcriptional and translational control of a heterologous promoter, and isolated GNE8-gp120 and GNE16-gp120 are also described.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Porcine pseudorabies virus gene deletion strain, vaccine composition, and preparation method and application of vaccine composition
ActiveCN103923884ASymptoms relieved or improvedMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsVirus antigenTGE VACCINE
The invention provides a porcine pseudorabies virus gene deletion strain, a vaccine composition, and a preparation method and an application of the vaccine composition. The vaccine composition comprises an immunizing dose of an attenuated livetotivirus antigen and an inactivated totivirus antigen of the porcine pseudorabies virus gene deletion strain or its culture. The vaccine composition can effectively induce the antibody production, can effectively protect pigs, and can be used as a marking vaccine to effectively differentiate wild strains and vaccine strains.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Attenuated live vaccine strain for preventing pig-pig infection breeding and respiratory syndrome
ActiveCN101633909AAvoid breedingPrevention of Respiratory SyndromeViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyAttenuated Live Vaccine
The invention provides an attenuated live vaccine strain for preventing pig-pig infection breeding and respiratory syndrome, a formulation thereof and a preparation method of the attenuated live vaccine strain and the formulation thereof. The attenuated live vaccine strain has obvious immunity protection effect on the pig-pig infection breeding and respiratory syndrome. The vaccine formulation also has long protection period and stable storage.
Owner:华威特(江苏)生物制药有限公司
Reverse genetic operation system of New castle disease LaSota vaccine strain and its applciation
The present invention is reverse genetic operation system of Newcastle disease Lasota low virulent vaccine strain and its application. The system includes one transcription plasmid including the genome cDNA sequence of the low virulent vaccine strain; one or several transcription aiding plasmids including the cDNA sequence coding the nucleoprotein of the low virulent vaccine strain, the cDNA sequence coding the phosphoprotein of the low virulent vaccine strain and the cDNA sequence coding the large polymerase protein of the low virulent vaccine strain; and the host cell of the Newcastle disease Lasota low virulent vaccine strain. Wild viral strain is obtained by means of the reverse genetic operation system. The present invention lays firm foundation for further development of Newcastle disease virus live carrier vaccine and Newcastle disease virus related research.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Chicken infectivity bronchitis virus attenuated vaccine strain and application thereof
ActiveCN101514334AImprove securityNo side effectsInactivation/attenuationMicroorganism based processesInfectious bronchitisMicroorganism
The invention discloses a infectivity bronchitis attenuated vaccine strain LDT3-A strain, and discloses application and application effect thereof in preventing and curing chicken infectivity bronchitis. The microorganism accession number of the attenuated vaccine strain is CGMCC-2902. The attenuated vaccine strain of the present invention has good safety and good immunization protection effect to the chicken infectivity bronchitis. The attenuated strain can be prepared into single vaccine or combined vaccine for preventing or curing infectivity bronchitis virus.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
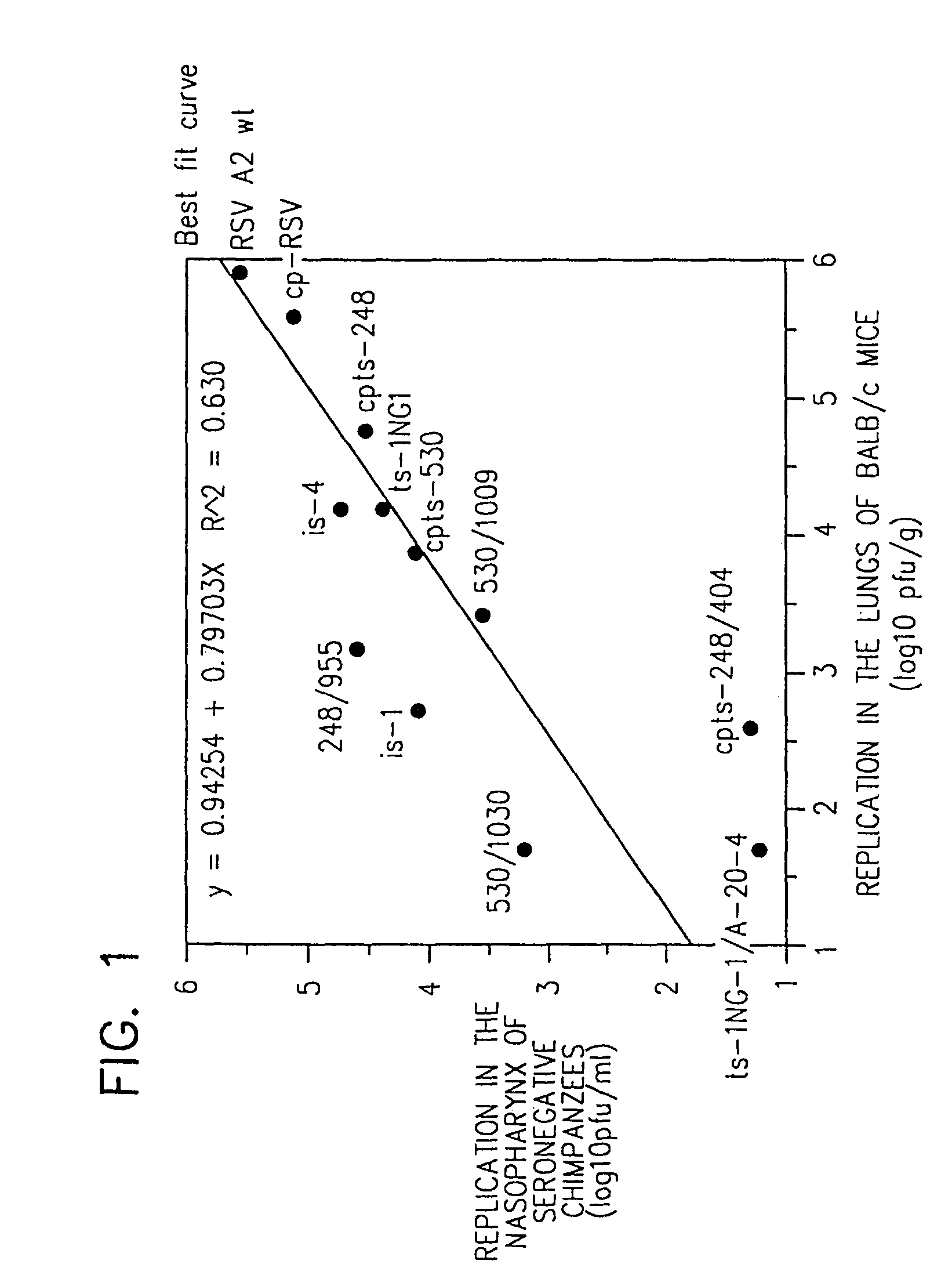
Attenuated chimeric respiratory syncytial virus
InactiveUS7846455B2Reduce the possibilityDesired characteristicSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHeterologousProtective antigen
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
A type foot-and-mouth disease recombinant vaccine strains and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103266091AMultiple phenotype improvements and enhancedPhenotype Improvement and EnhancementMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsAntigenDisease
The invention relates to A type foot-and-mouth disease recombinant vaccine strains prepared by using a reverse genetic manipulation technology and a preparation method and application of the strains. One strain is an A type foot-and-mouth disease recombinant vaccine strain with high titer, antigen matching property and immune protection rate, and the other strain is an A type foot-and-mouth disease recombinant non-pathogenic vaccine strain with high titer, antigen matching property and immune protection rate and without pathogenicity for a host; an antigen nucleotide sequence of each of the vaccine strains is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; eukaryotic plasmids of viruses can be saved by using a reverse genetic manipulation system; after pigs and cattle are immunized by using the inactivated vaccines prepared from the prepared recombinant vaccine strains, the bodies can be effectively stimulated to produce immune response, and an immune protection effect is provided for the bodies of the pigs and the cattle; through a 10,000-times cattle median infectious dose (BID50) challenge assay of A type AISA topological strains, the immune protection rate reaches 100 percent, and the median protective dose (PD50) is 10.81 to 13.59; and the recombinant vaccine strains can be applied to prevention and control of A type foot-and-mouth disease viruses of China and neighboring countries.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant porcine pseudorabies virus TK/gE double-gene deletion strain
The invention separates a porcine pseudorabies virus GDXX strain, and a separating strain is served as a female parent for deleting a thymidylate kinase (TK) gene and a gE gene through a molecular biology means in sequence, thus obtaining recombinant virus PRV / TK- / gE-. The recombinant virus provided by the invention is used as a vaccine strain for preparing safe and efficient porcine pseudorabies live vaccine.
Owner:GUANGDONG WENS DAHUANONG BIOTECH +1
Virus velogen strain for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome, attenuated vaccine strain thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN101280292AImprove securityNo side effectsViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMicroorganism
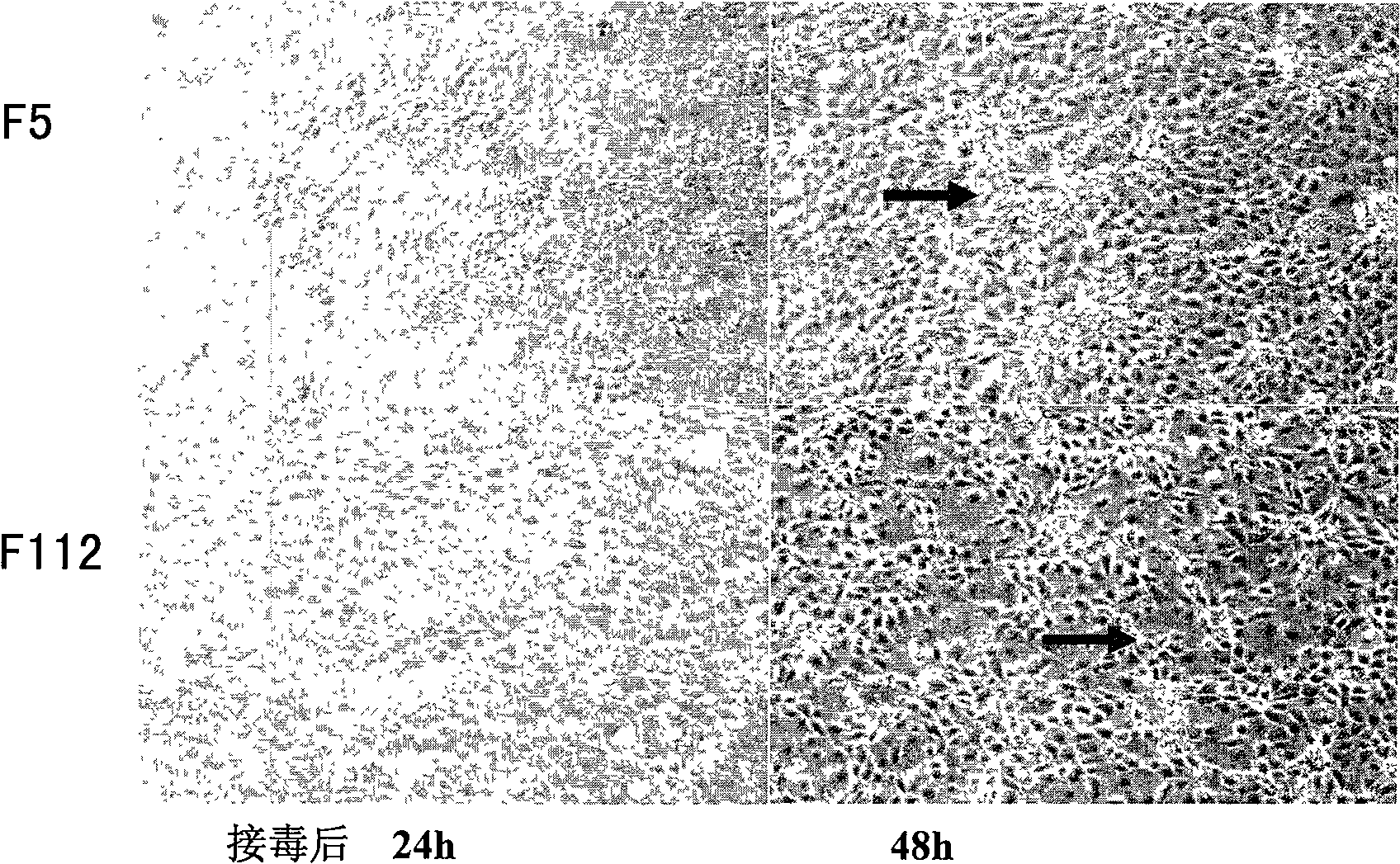
The invention discloses a virulent strain HuN4 for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome, and an attenuated vaccine strain HuN4-F112 (the collection number of microorganism: CGMCC No.2484) attenuated because of virulent strain HuN4 passage, and also discloses the application of the attenuated vaccine strain in preventing or curing the highly pathogenic blue-ear disease, which belongs to the biomedical field. The attenuated vaccine strain HuN4-F112 can be prepared into single-vaccine or combined strain (live vaccine or inactivated vaccine), can effectively prevent or cure the highly pathogenic blue-ear disease, and also can be prepared into diagnostic reagent for the highly pathogenic blue-ear disease diagnosis. The attenuated vaccine strain HuN4-F112 of the invention has the advantages of good security and high protection efficiency.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Avian influenza virus marking vaccine, preparation process and application thereof
The invention discloses a vaccine strain H5N1 / PR8-5B19 marked by H5N1 hypotype poultry influenza virus, which also provides the application to prevent and monitor poultry influenza.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant novel coronavirus as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111560354ASolve the shortage problemSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntigen epitopeAntigen
The invention discloses a recombinant novel coronavirus as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The invention firstly discloses a recombinant virus. Any one of an NS gene of an influenza virus, an HA gene of the influenza virus and an NA gene of the influenza virus of the recombinant virus is replaced. The invention further discloses application of the recombinant virus in preparation of a product for preventing and / or treating diseases caused by influenza virus and / or SARS-CoV-2. According to the invention, the SARS-CoV-2 antigen epitope and the influenza virus genome are operated from the gene level; the recombinant SARS-CoV-2 vaccine strain taking the influenza virus as the carrier is prepared on the basis of an RG technology, so that the problem of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine shortage is solved. The recombinant novel coronavirus will be a new milestone in the field of coronavirus vaccines, and the SARS-CoV-2 chimeric vaccine can protect more people from being harmed by theinfluenza virus and SARS-CoV-2.
Owner:THE FIFTH MEDICAL CENT OF CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL +1
Attenuated Live Vaccine for Prevention of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome
ActiveUS20120189655A1Organic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseBiologyAttenuated Live Vaccine
The present disclosure provides an attenuated live vaccine strain and the formulations thereof, for preventing pigs from infection of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS). The preparation methods for the vaccines and the formulations are also provided. The attenuated live vaccine strain provided herein offers significant immunological protection to pigs against PRRS. The vaccine formulations of the present disclosure also have advantages in long shelf lives as well as good stability during storage.
Owner:WU HUA
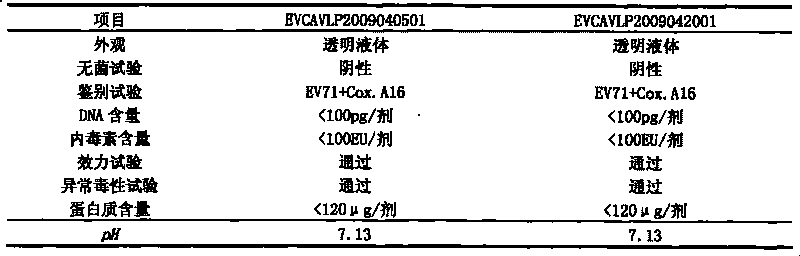
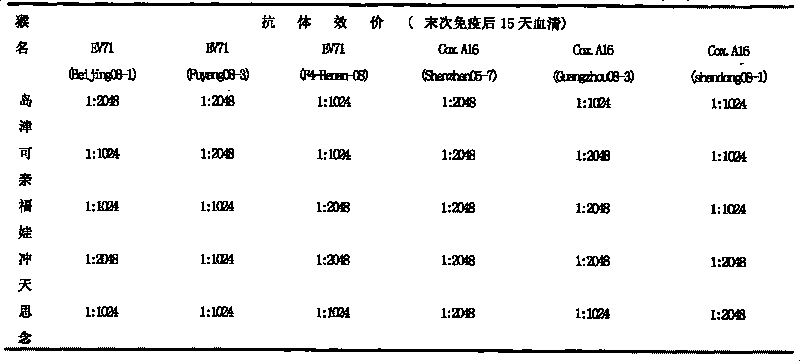
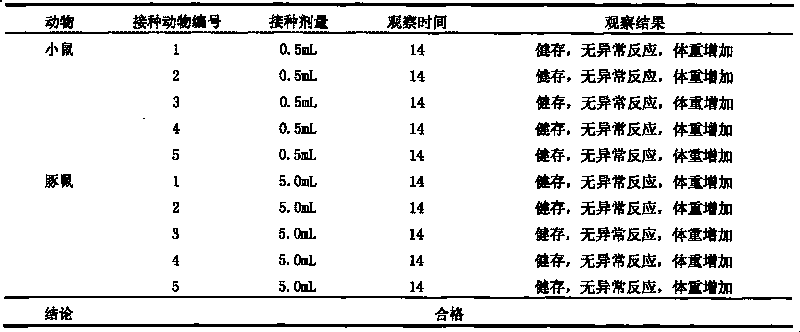
Univalent and bivalent inactivated vaccine for hand-foot-and-mouth disease and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101695570AInactivation/attenuationMicroorganism based processesHand-foot-and-mouth diseaseCoxsackievirus a16
The invention discloses a univalent and bivalent inactivated vaccine for preventing Enterovirus 71 (EV71) and Coxsackie virus A16 (Cox.A16) of hand-foot-and-mouth disease, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: screening vaccine strains for the hand-foot-and-mouth disease; establishing and verifying a vaccine strain third-stage seed lot library; culturing cells; inoculating and propagating virus; collecting virus suspension; inactivating the virus; ultra-filtering, concentrating and purifying the virus suspension to obtain vaccine stock solution; and finally preparing the univalent and bivalent inactivated vaccine. The univalent and bivalent inactivated vaccine has good application prospect for preventing the hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Univalent and bivalent gene engineered subunit vaccine for hand-foot-and-mouth disease and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101695569AInactivation/attenuationMicroorganism based processesHand-foot-and-mouth diseaseCoxsackievirus a16
The invention discloses a univalent and bivalent gene engineered subunit vaccine for preventing Enterovirus 71 (EV71) and Coxsackie virus A16 (Cox.A16) of hand-foot-and-mouth disease, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively obtaining recombinant baculovirus Bac-EV71-P1-3CD and Bac-Cox.A16-P1-3CD by gene engineering means, respectively efficiently coexpressing similar SeQ ID No.1 EV71 P1 and Se Q ID No.2 Cox.A16 P1 and 3CD proteins in insect cells, and respectively self-assembling into EV71 VLP and Cox.A16 VLP; establishing and verifying a vaccine strain third-stage seed lot library; culturing cells; inoculating and propagating virus; lysing the cells, ultra-filtering and purifying virus suspension; and further preparing the univalent and bivalent vaccine. The vaccine has good application prospect for preventing the hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
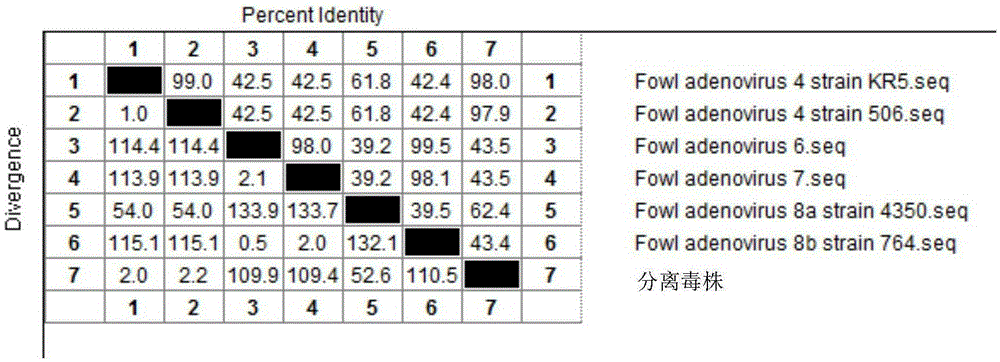
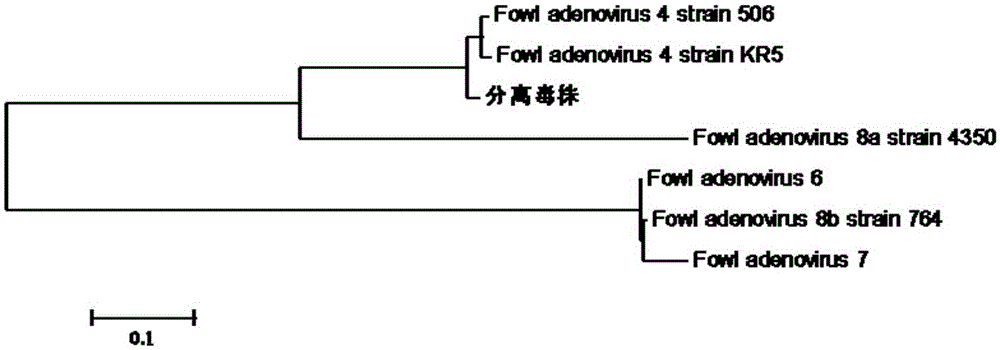
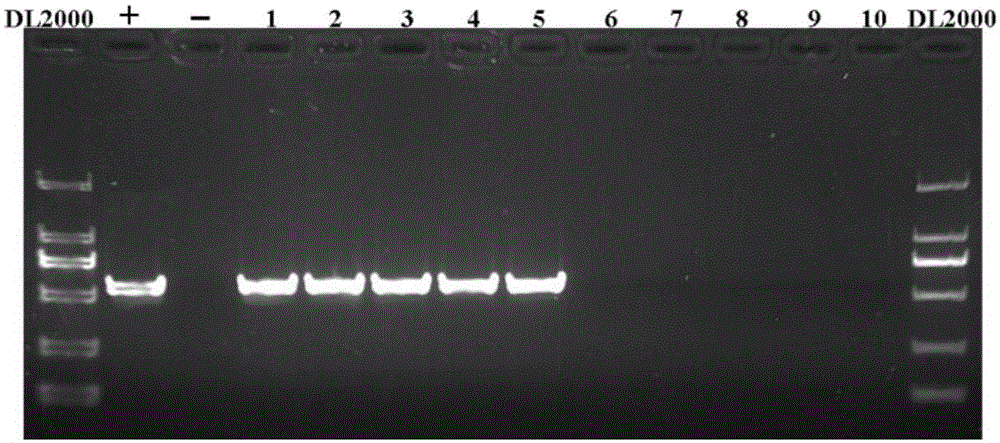
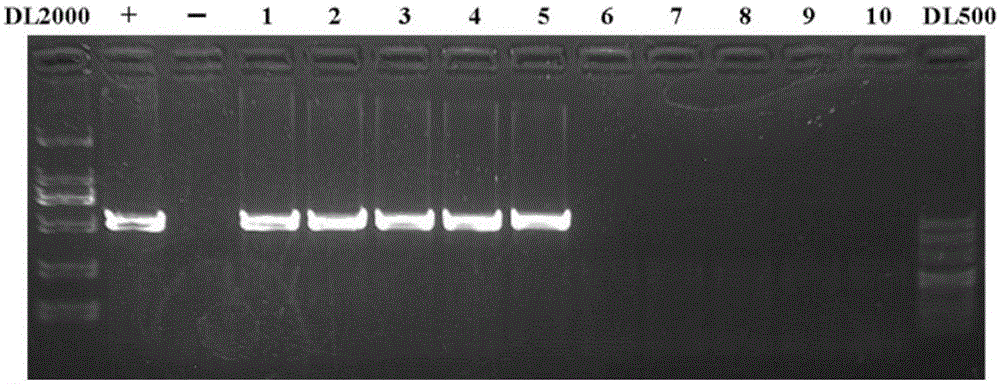
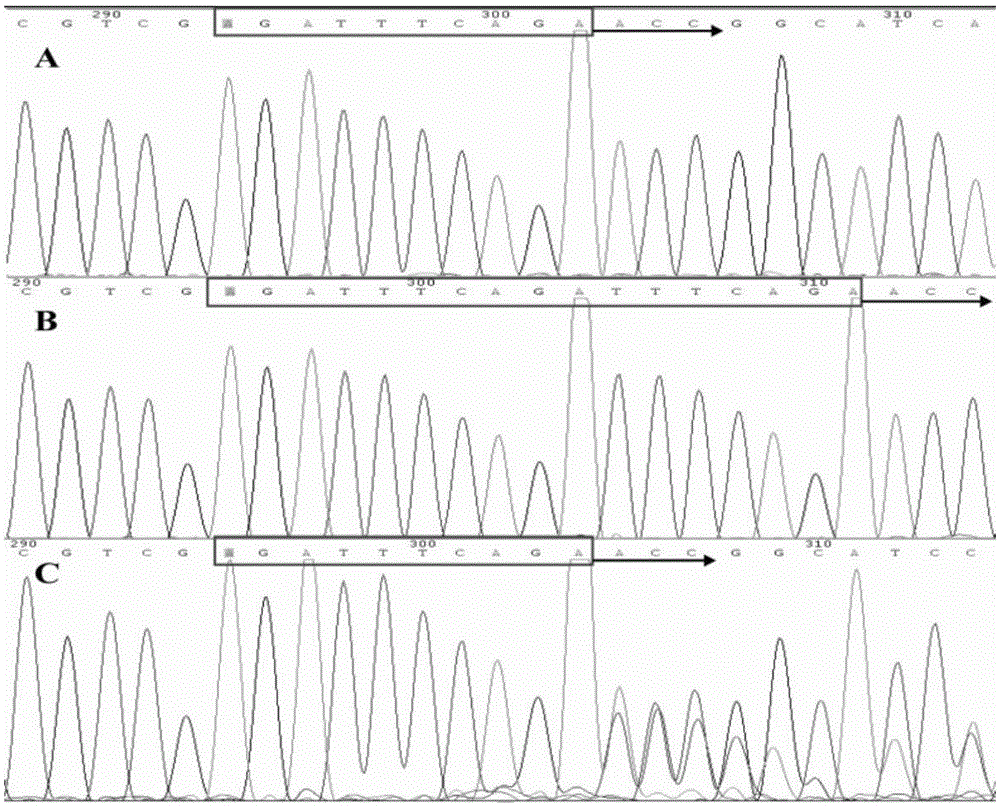
I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 strain and application thereof
ActiveCN105368795AImprove featuresImproving immunogenicityViral antigen ingredientsBiological material analysisInfected cellLaryngotracheitis virus
The invention aims at providing an I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 strain, which is preserved with preservation number of CCTCC No. V201541. The I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 YBAV-4 strain disclosed by the invention is excellent in specificity and immunogenicity; a specific precipitation line does not appear in specific positive serum chicken SPF chicken serum such as infected cell sap and egg drop syndrome resisting virus, chicken infectious bursal disease virus, Newcastle disease virus, chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus, chicken Marek's disease virus, avian influenza and the like, while an obvious specific precipitation line appears in I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 specific serum. The strain disclosed by the invention, as a vaccine strain which is good in manufacturing effect, is capable of preventing chicken hydropericardium syndrome, and the strain is applicable to identification of virus serotype and investigation on epidemiology.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
Kit for recognizing Brucella wild strain and vaccine strains A19 and S2
ActiveCN105018489AEasy to distinguishStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBacteroidesBrucella Vaccine
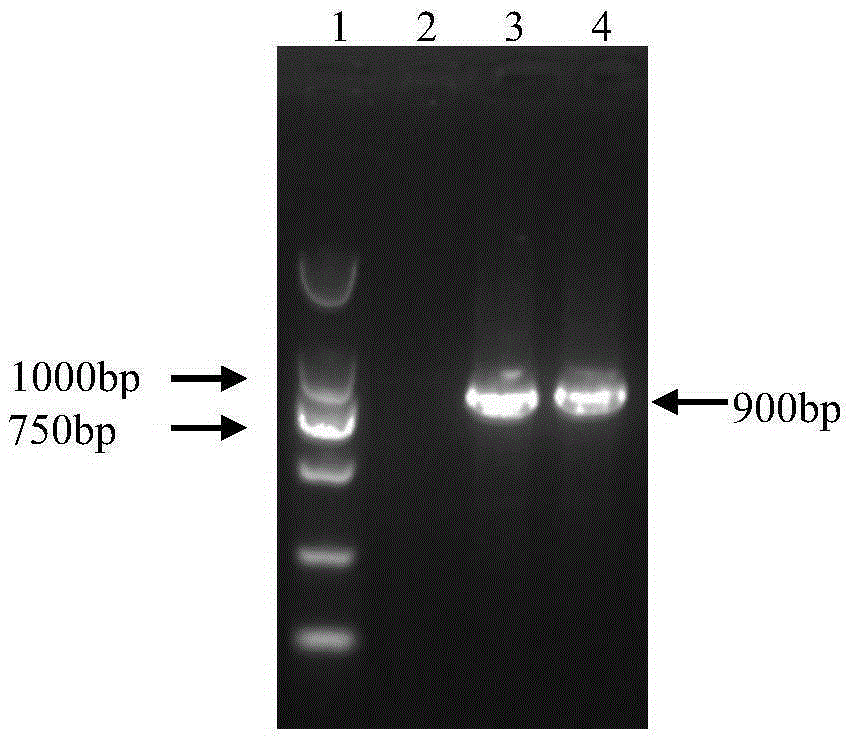
The invention relates to a kit for recognizing a Brucella wild strain and vaccine strains A19 and S2. The kit comprises a special primer pair SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2 for recognizing the Brucella vaccine strain A19 and a special primer pair SEQ ID No.3 and SEQ ID No.4 for recognizing the Brucella vaccine strain S2. The kit is used for conducting further sequencing analysis on a PCR amplification product after the Brucella and other conventional bacterial strains are distributed on a PCR amplification-electrophoresis detection area, and the Brucella A19 and S2 vaccine strains in a clinic sample can be rapidly and effectively recognized and diagnosed according to the sequencing result.
Owner:DAIRY CATTLE RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and application thereof
ActiveCN102250843AMeet the differential diagnosisEasy to solveViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsNucleotideGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain of a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). The attenuated vaccine strain comprises a genomic nucleic acid of a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus attenuated vaccine strain HuN4-F112; the HuN4-F112 genome includes a mutation in a genetic region for coding an Nsp2 protein, and the mutation is as follows: a nucleotide sequence for coding a Newcastle disease virus NP protein is inserted to a lacking region of a nucleotide sequence for coding 480-532-site amino acid of the Nsp2 protein; or the nucleotide sequence for coding the Newcastle disease virus NP protein is inserted to the lacking region of a nucleotide sequence for coding 508-532-site amino acid of the Nsp2 protein. The invention also discloses an application of the genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain. The genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus provided by the invention not only can provide completely safe immune protection to resist high-pathogenicity PRRSV after the porcine is immunized, but also can effectively distinguish the immunized porcine of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome vaccine with the naturally infected porcine of the field virus.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy of cancer
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Influenza Virus Vaccines
InactiveUS20080254065A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsFowlInfluenza virus vaccine
The invention provides a vaccine for protecting a human patient against infection by a human influenza virus strain, wherein the vaccine comprises an antigen from an avian influenza virus strain that can cause highly pathogenic avian influenza. The antigen can invoke an antibody response in the patient that is capable of neutralising said human influenza virus strain. Whereas the prior art used known non-pathogenic avian strains to generate antibodies in humans against known pathogenic avian strains, the invention uses known pathogenic avian strains to protect against emerging pathogenic human strains. Furthermore, whereas the prior art focused on achieving a close antigenic match between the vaccine strain and the target strain, the invention selects vaccine strains based on their pathogenicity, regardless of any perceived close antigenic relationship to the target strain. As the invention does not require detailed knowledge of an emerging strain, a vaccine can be provided further in advance to reduce the risk and potential effects of a human pandemic outbreak.
Owner:SEQIRUS UK LTD
Method for expanding antigen spectrum of foot-and-mouth disease vaccine strain by reverse genetic operation and preparation method of vaccine
ActiveCN101948811AHigh protection rateBroad antigen spectrumVirus peptidesMicroorganism based processesImmune effectsSoutheast asia
The invention relates to a method for expanding the antigen spectrum of a foot-and-mouth disease vaccine strain by reverse genetic operation and a preparation method of a vaccine. The amino acid sequence of the VP3 and VP1 structural proteins of the foot-and-mouth disease virus strain of the invention is represented by the amino acid residues from a position 304 to a position 736 in SEQ ID No.4. Experiments show that the vaccine prepared from the mutant virus strain obtained by the invention can resist porcine epidemic viruses of China O / TL / Taiwan / 97 lineage, Pan-Asia O / China / 99 lineage and Southeast Asia Myanmar O / GS / 2010 / 98 lineage, has a characteristic of wide antigen spectrum, can immunize pigs and obviously improve the rate of protection against foot-and-mouth disease viruses which are of the same type and have antigenicity difference, achieves an immune effect of cross protection, and is expected to play an important role in the prevention and control of foot-and-mouth disease.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Porcine epizootic diarrhea virus strain and vaccine composition, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106148287AImprove immune efficiencyImprove securityDigestive systemAntiviralsBiologyDiarrhea
The invention discloses a porcine epizootic diarrhea virus strain with good immunogenicity and an inactivated vaccine prepared through the porcine epizootic diarrhea virus strain. The porcine epizootic diarrhea virus strain is a current epidemic strain, and good immunogenicity and stability are achieved; compared with a commercially available vaccine strain, the vaccine prepared through the strain has the advantages of being good in safety, high in immune protective capability, high in immune efficacy and the like, and porcine epizootic diarrhea can be comprehensively and effectively prevented and treated.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
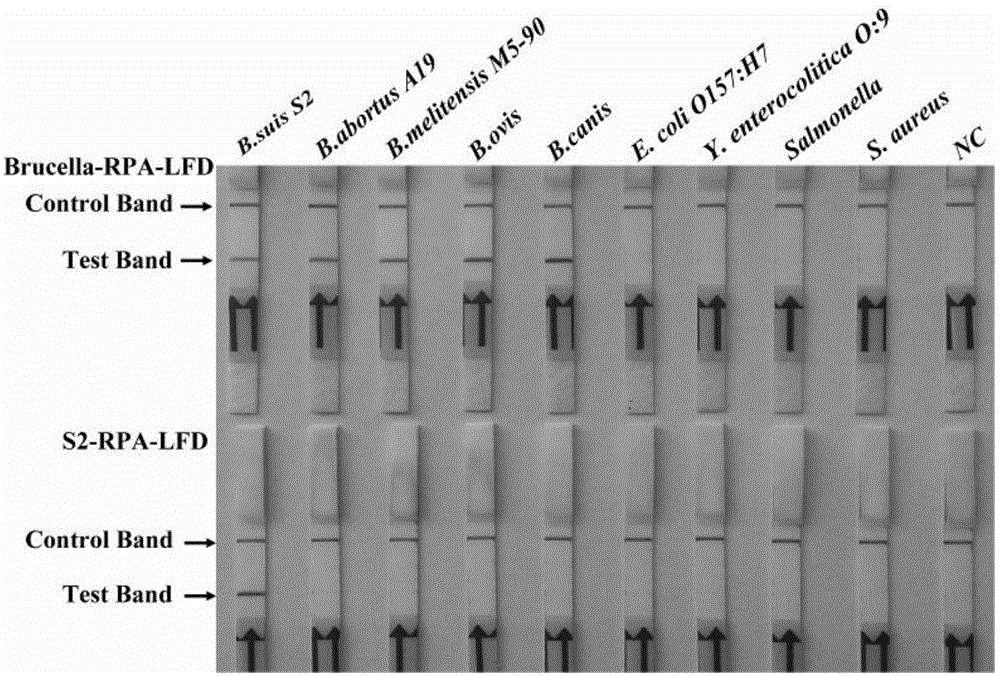
Primer, probe and reagent kit for identifying Brucella S2 vaccine strains in aerocolloid
InactiveCN104862405AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBacteroidesForward primer
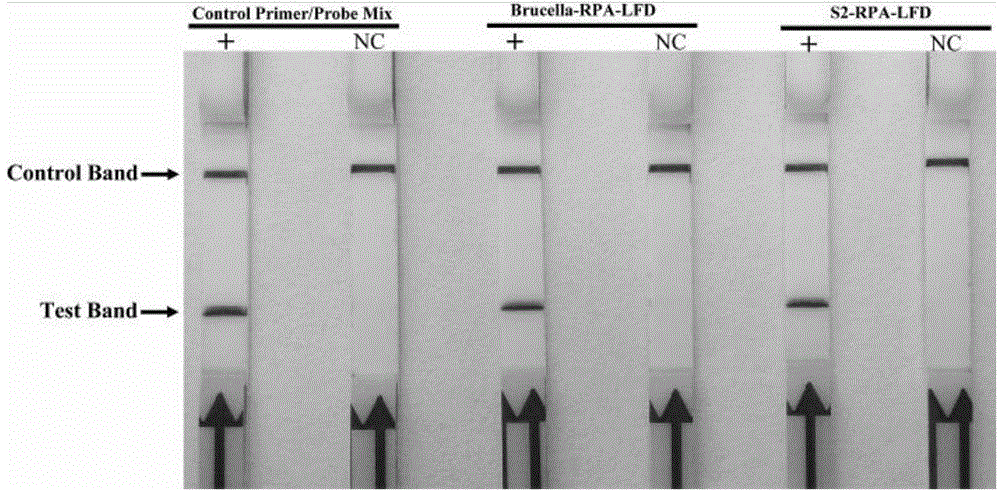
The invention relates to a primer, probe and reagent kit for identifying Brucella S2 vaccine strains in aerocolloid. The forward primer sequence of Brucella-RPA-LFD is shown as SEQIDNo.1, the backward primer sequence of Brucella-RPA-LFD is shown as SEQIDNo.2, and the probe sequence of Brucella-RPA-LFD is shown as SEQIDNo.3; the forward primer sequence of S2-RPA-LFD is shown as SEQIDNo.4, the backward primer sequence of S2-RPA-LFD is shown as SEQIDNo.5, and the probe sequence of S2-RPA-LFD is shown as SEQIDNo.6. The combination of the RPA-LFD primer and the probe, or the reagent kit, for identifying and diagnosing the Brucella S2 vaccine strains, provided by the invention are high in sensitivity and specificity, and can at least detect 2.5*100 cfu of Brucella or the Brucella S2 vaccine strains.
Owner:何洪彬
Asia1 type foot-and-mouth disease recombinant virus and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to an Asia1 type foot-and-mouth disease recombinant virus without pathogenicity for a host and a preparation method and application thereof. A saving system is efficient eukaryotic plasmids which are constructed by gene engineering and can express exact foot-and-mouth disease virus genome RNA (Ribonucleic Acid), and therefore the foot-and-mouth disease recombinant virus can be constructed and prepared; vaccine strains with high titer and good antigen matching property can be prepared by using the plasmids, can be prepared into live vaccines or inactivated vaccines and can effectively stimulate bodies to produce immune response after being used for immunizing pigs and cattle, provide an immune protective effect on the pigs and the cattle and effectively protect GV and GII prevalent strains, the immune protection rate can reach 100 percent, and the median protective dose (PD50) is 6.34 to 13.59; and the recombinant virus has the advantages of high titer, high antigen matching property with the prevalent strains, wide antigen spectrum and high immune protection rate, does not have pathogenicity for pig and cattle hosts, does not form toxemia or expel toxin, and can be applied to prevention and control of Asia1 type foot-and-mouth disease viruses of China and neighboring countries.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Site-directed modification method for DNA viral genome
ActiveCN103397018ARealize fixed-point transformationQuick insertRecombinant DNA-technologyFermentationFreeze thawingRecombinant virus
The invention provides a site-directed modification method for DNA viral genome, and the problems in the prior art are solved that induction of site-directed mutagenesis of DNA viral genome is difficult, the operation of inserting an exogenous fragment is complex, and recombination rate is lower. The site-directed modification method comprises: transfecting cells by a plasmid carrying a nuclease system, infecting by a virus, after the cells show pathological changes, collecting the cells with pathological changes, performing freeze-thaw or ultrasonic processing, and centrifuging, separating the liquid supernatant to obtain a progeny virus. The site-directed modification method is capable of realizing applications to screening of virus attenuated vaccine strains, construction of viral genetic carriers and an oncolytic virus, research on virus function sequences, and the like; during modification of the viral genome, the method helps to improve mutagenesis efficiency, accurately control DNA virus for genome site-directed mutagenesis and specific gene knockout, simplify operation steps of inserting the DNA virus carrier by an exogenous gene, and improve efficiency that the exogenous gene is integrated to the viral genome, so that the work of screening high-flux recombination viruses is convenient to conduct.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
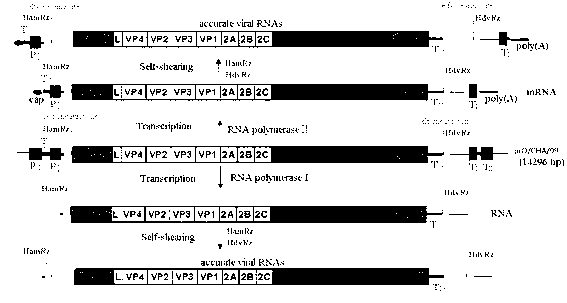
Recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of chicken infectious bursal disease viruses (IBDV) and application thereof
ActiveCN101935637ANon-pathogenicGood spiritsViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesProtective antigenOrganism
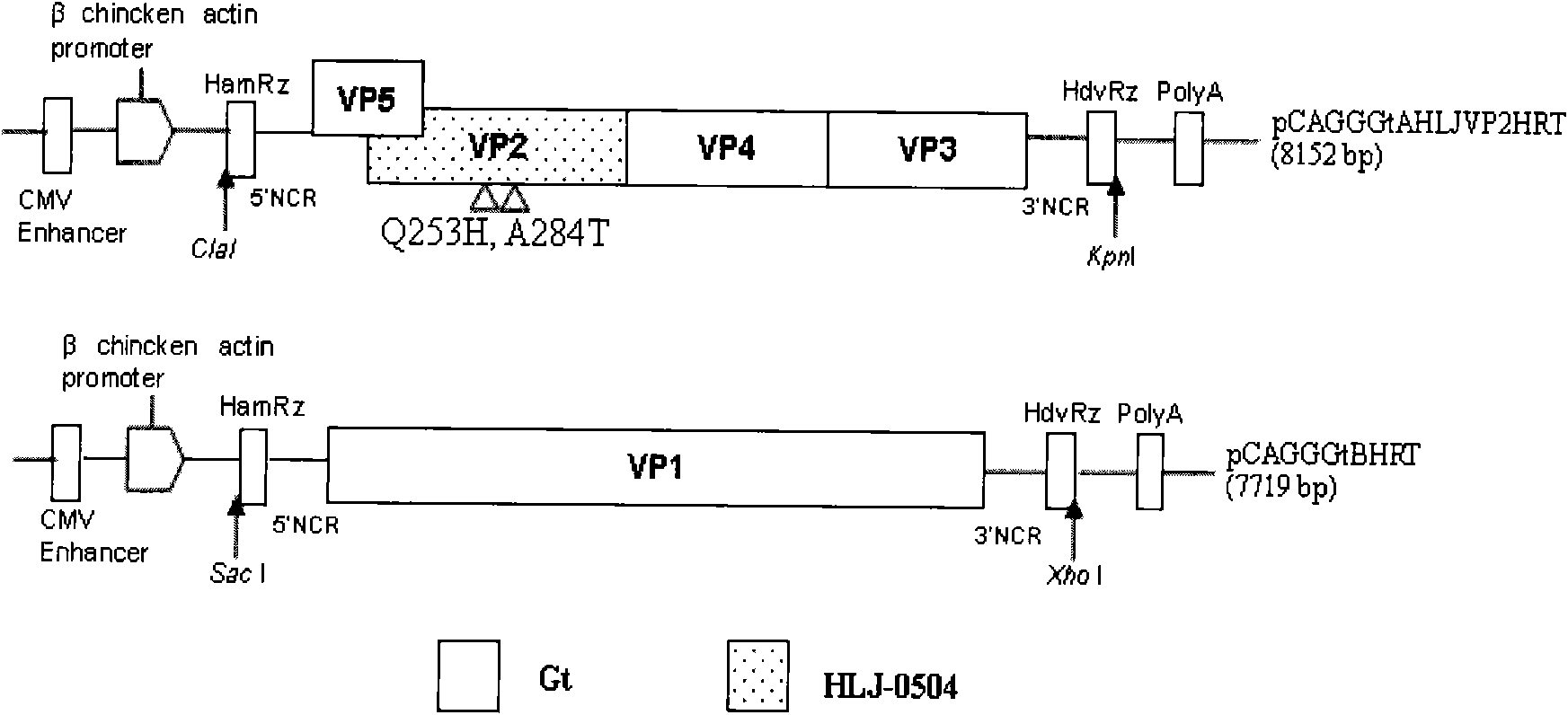
The invention discloses a recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of chicken infectious bursal disease viruses (IBDV) and application thereof. In the invention, a major protective antigen gene VP2 of an epidemic superhigh virulent strain is cloned, the nucleotide of the gene VP2 is modified by mutation and then used for replacing a corresponding segment of a Gt genome of a low-virulent strain of the IBDV, so that the infectious clone of a recombinant genome of the IBDV is constructed, and the recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain is saved and identified by using an IBDV reverse genetic operation system. The microbial collection number of the vaccine strain is CGMCC No.3749. The recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention has high replicability, genetic stability and safety. The immune effect of the low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention is as good as that of the medium-virulent vaccine strain, but is superior to that of the low-virulent vaccine strain. The biological safety of the low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention is superior to that of the medium-virulent vaccine strain. As the vaccine strain, the recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention has the characteristics of high efficiency and low toxicity, is a good candidate vaccine strain and can be used for controlling chicken infectious bursal disease.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
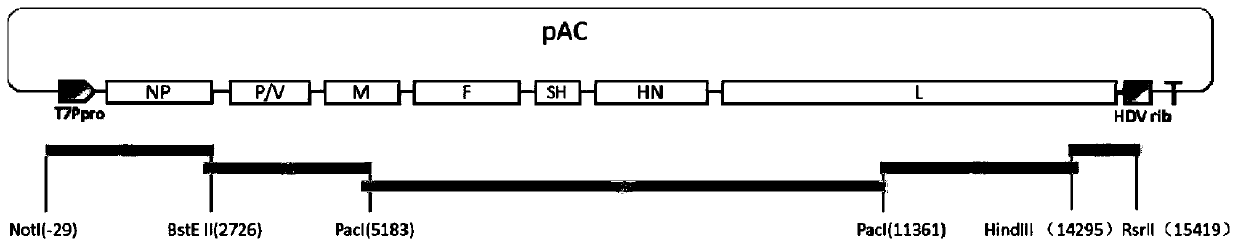
F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention provides an F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain as well as a construction method and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides an F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain and the attenuated strain is a mumps virus QS-F-SH2 with an accession number of CCTCC NO: V201950. The invention also provides a vaccine composition containing the F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain as an active ingredient and a preparation method thereof. The mumps virus attenuated vaccine strain disclosed by the invention can match the F type mumps virus predominantly popular in China, and the level of the mumps virus attenuated vaccine strain is equivalent to that of the current vaccine strain in the aspects of growth characteristics, immunogenicity, neurotoxicity and the like.In addition, the mumps virus genetic engineering attenuated strain screened by the invention can be stably produced in chick embryo cells, and the safety is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING CELL BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com