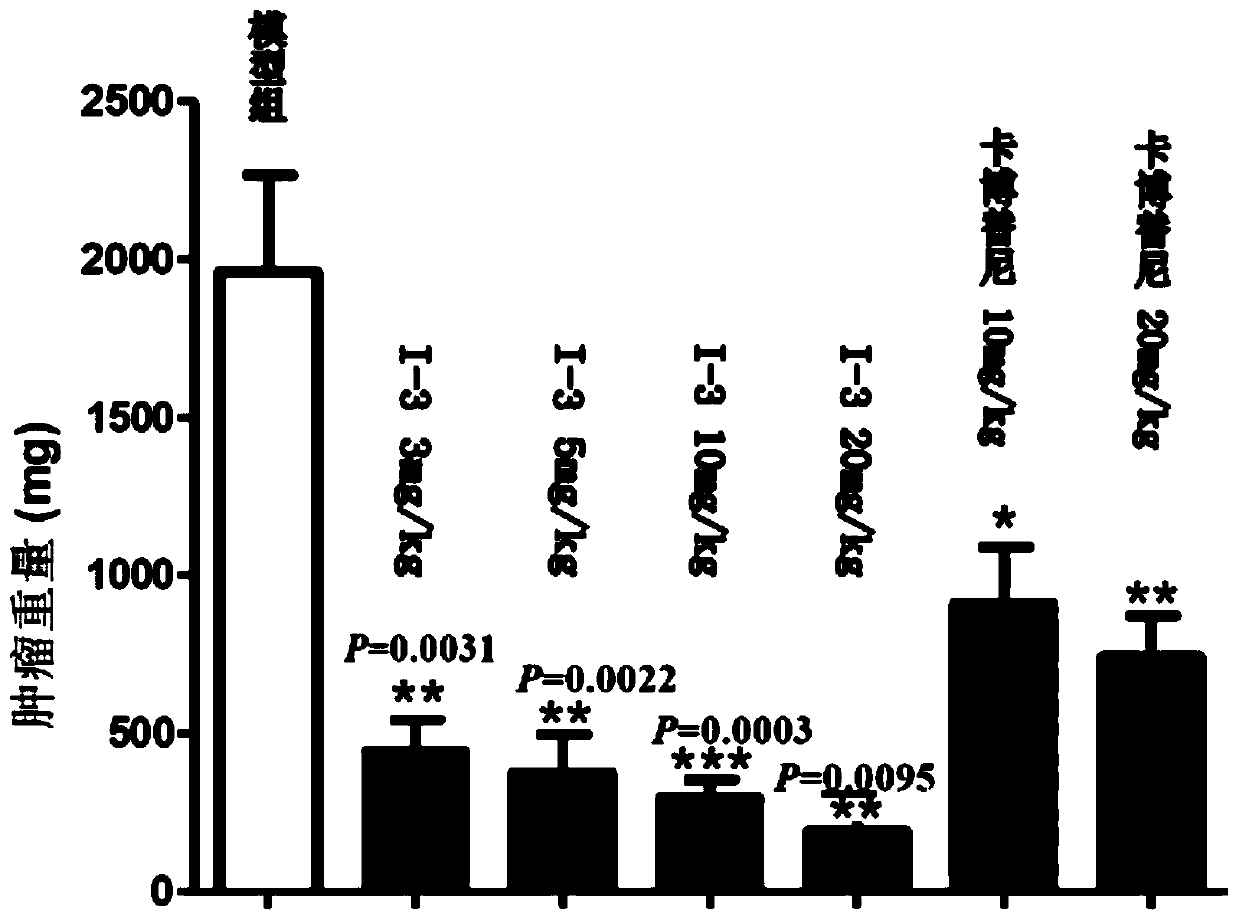
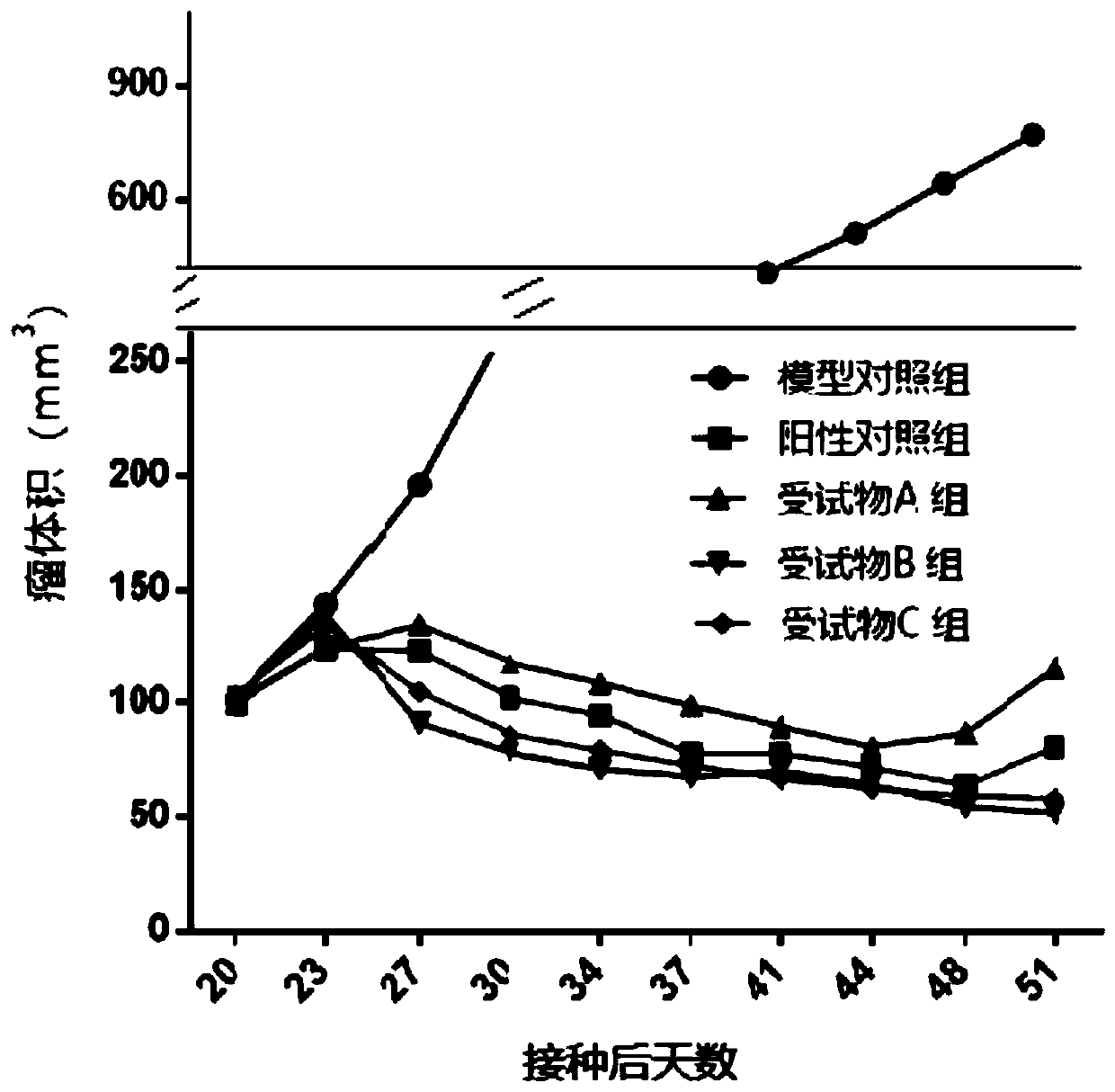
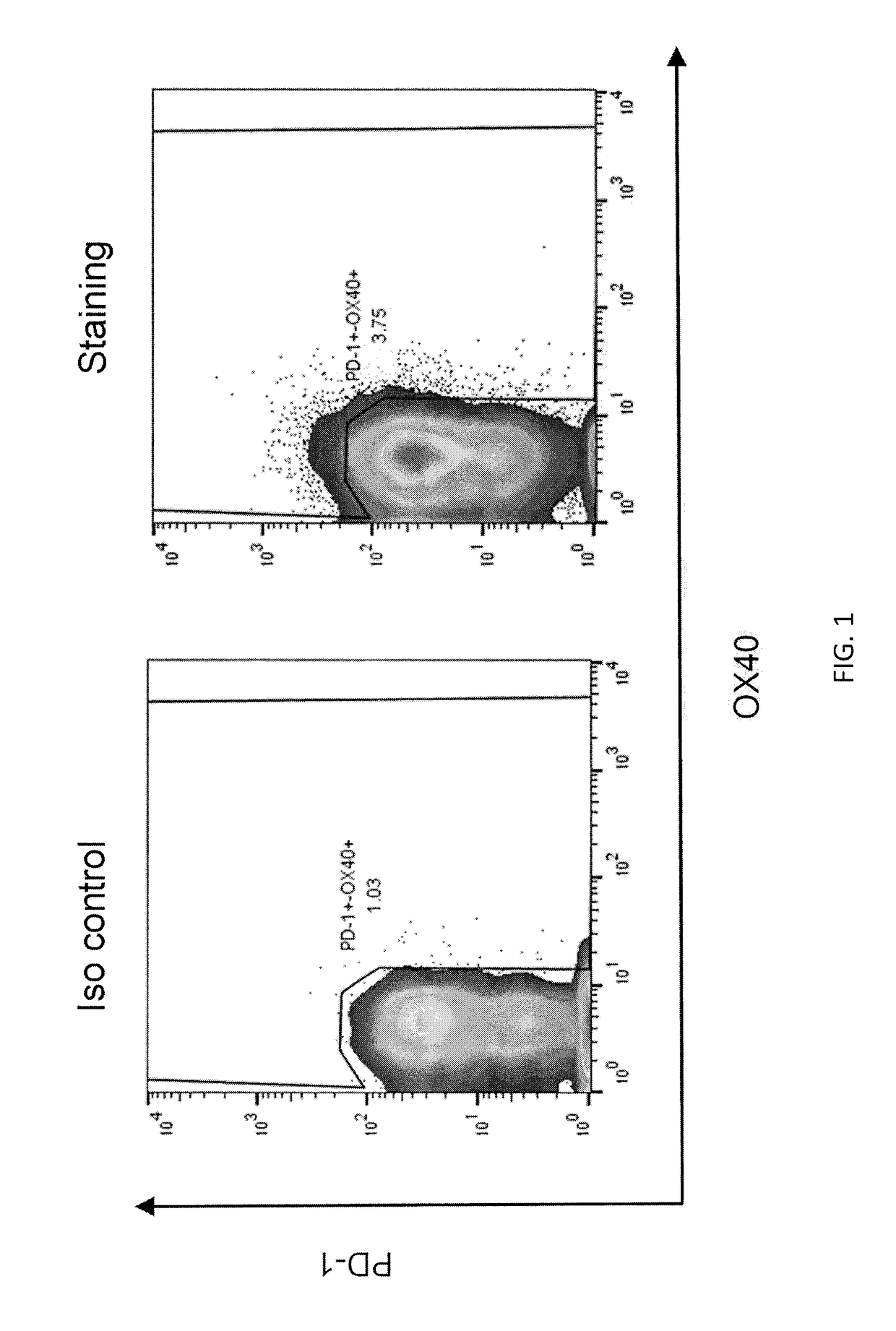
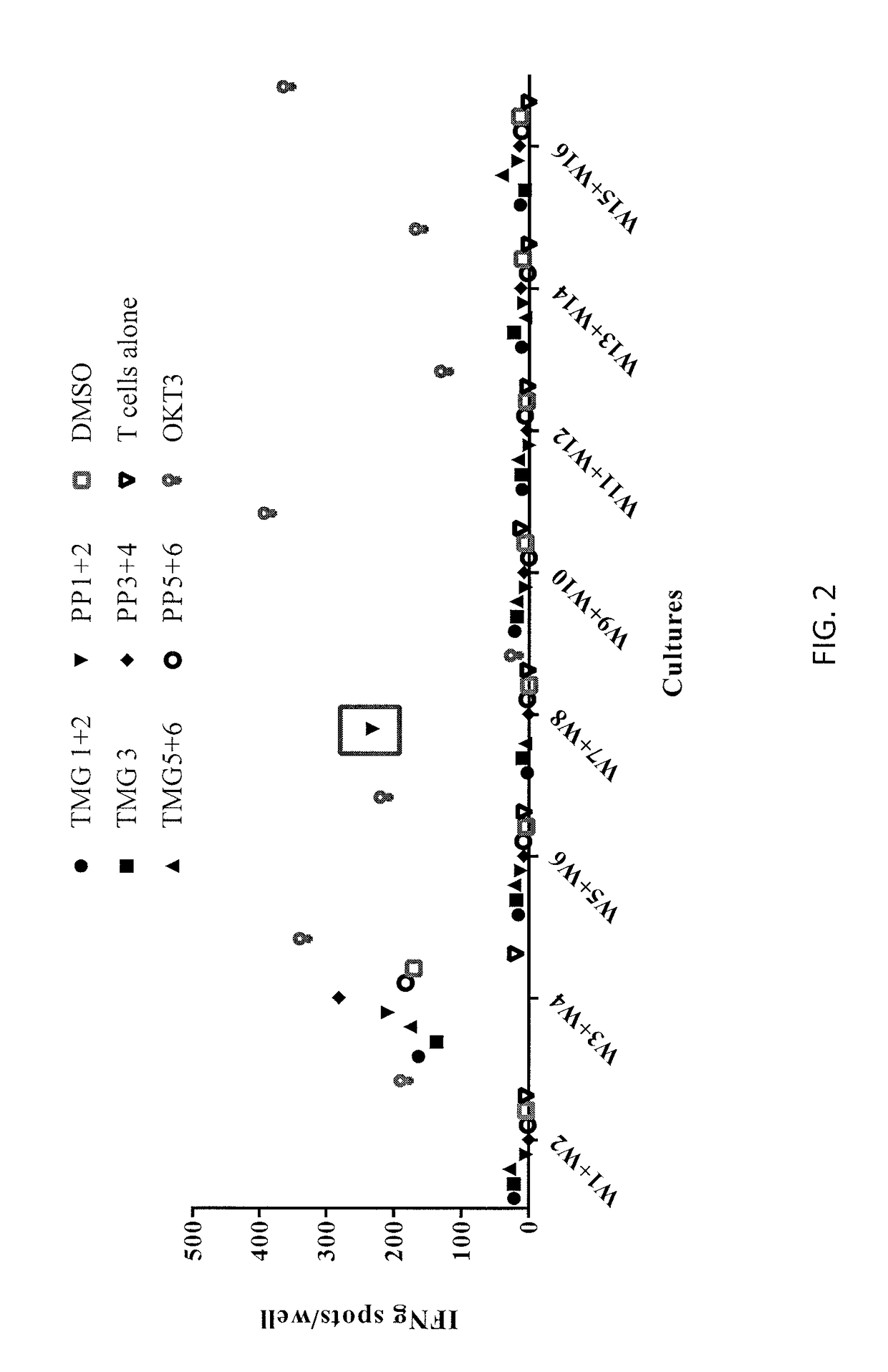
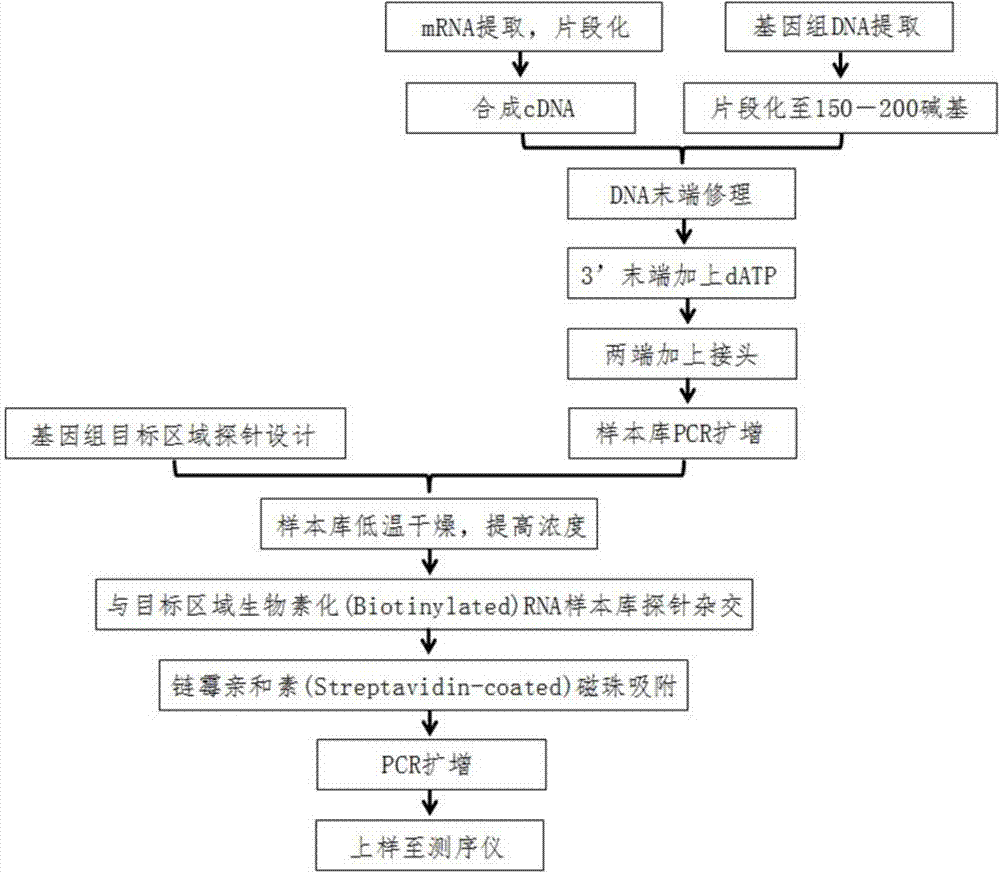
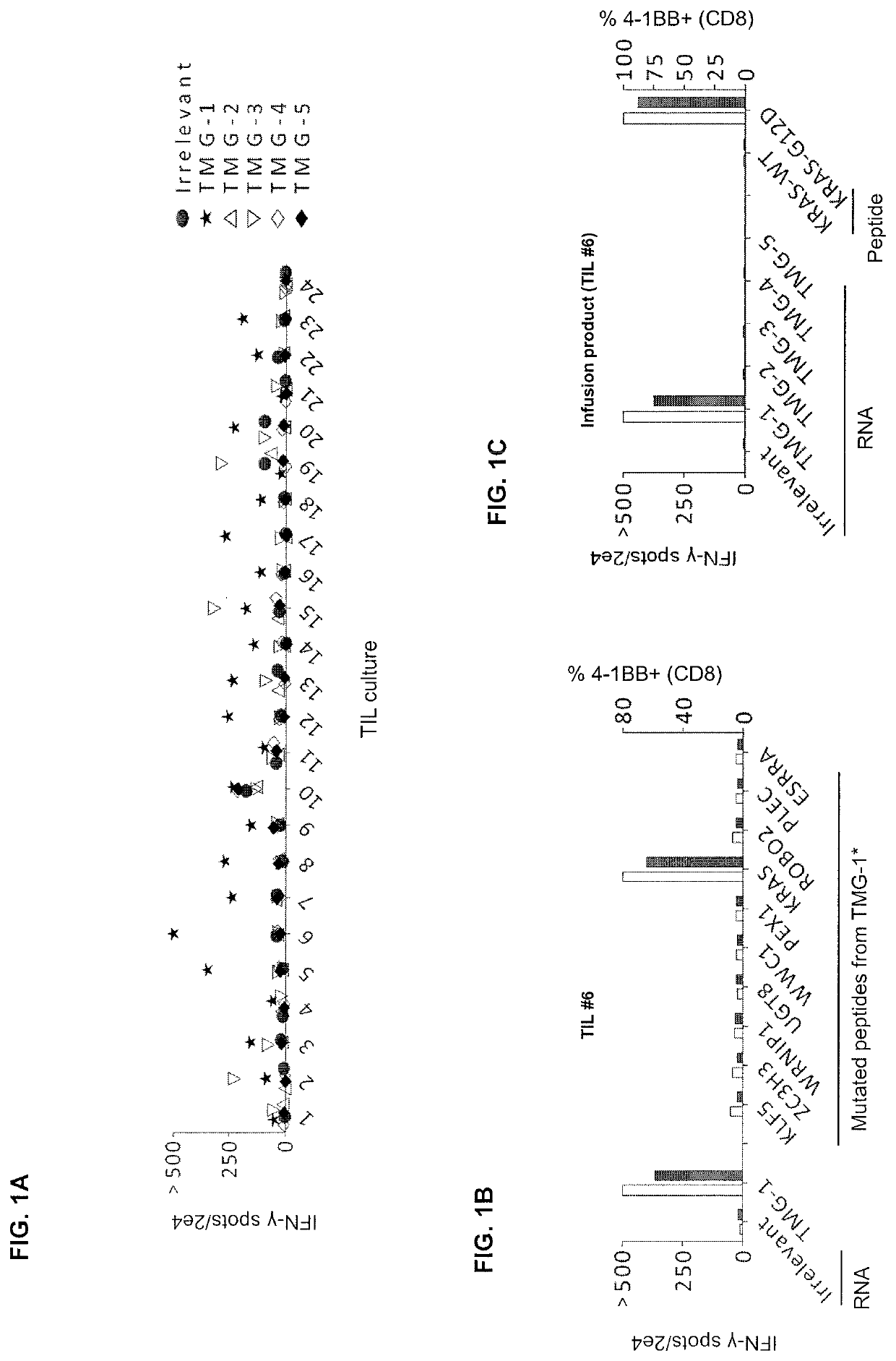
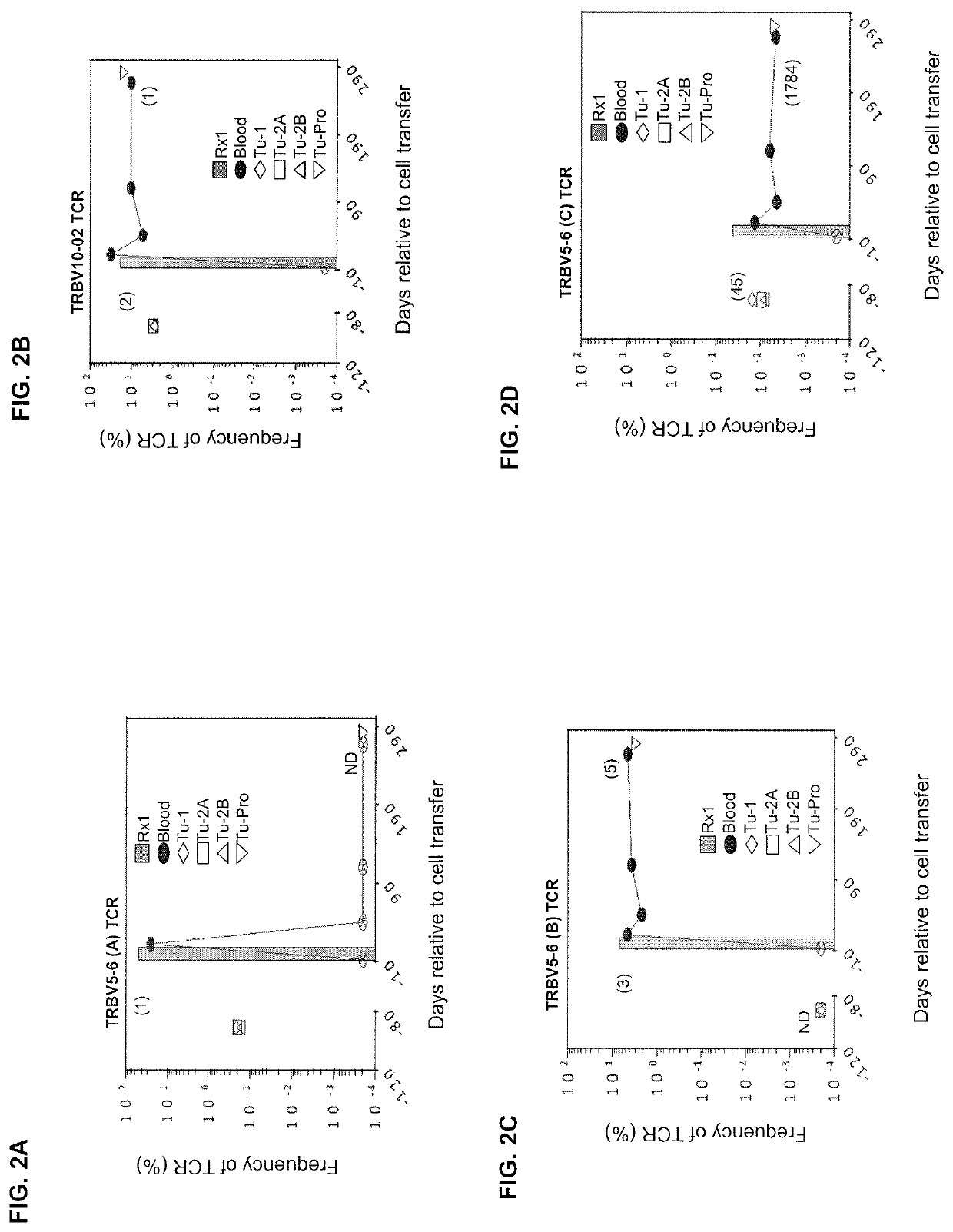
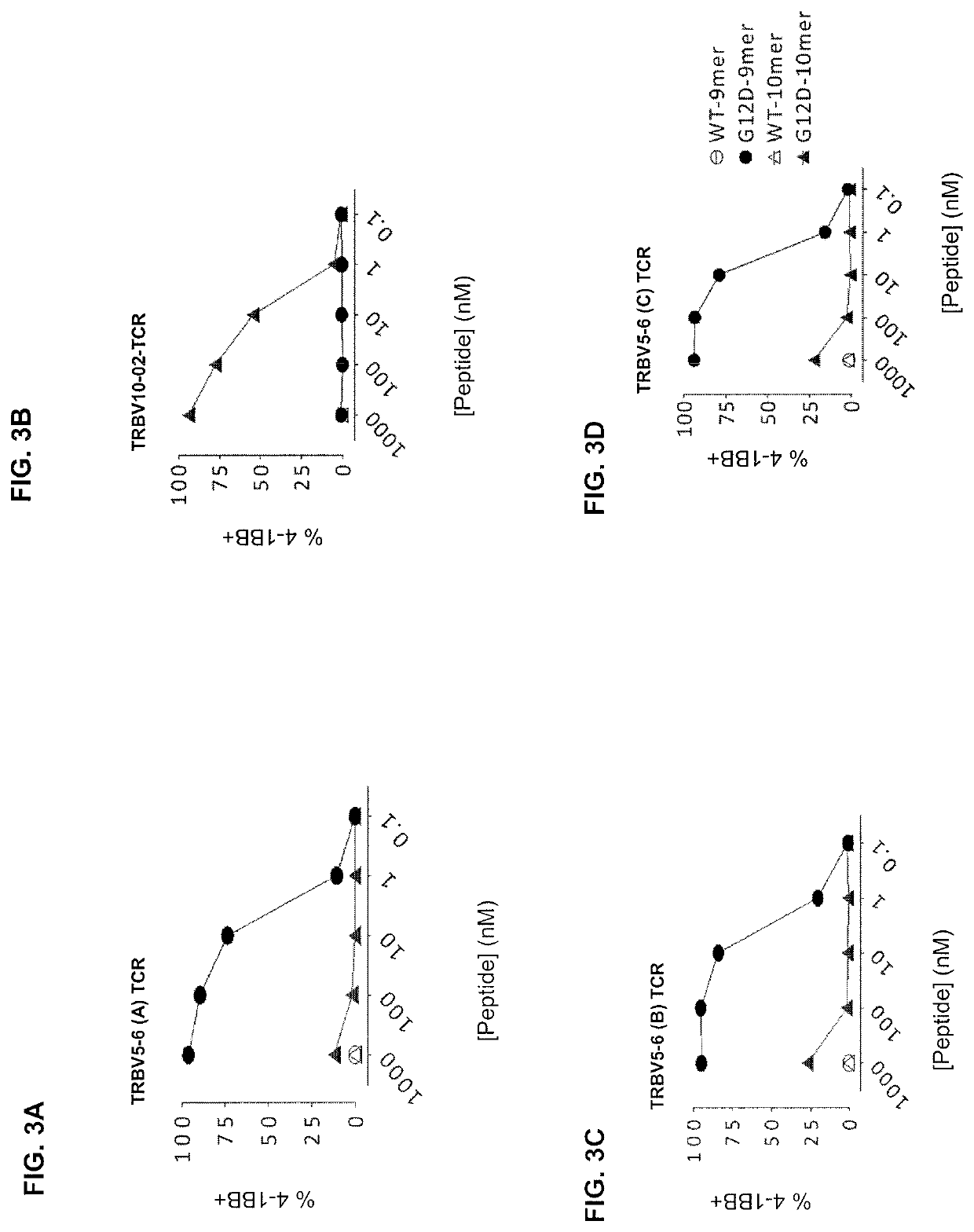
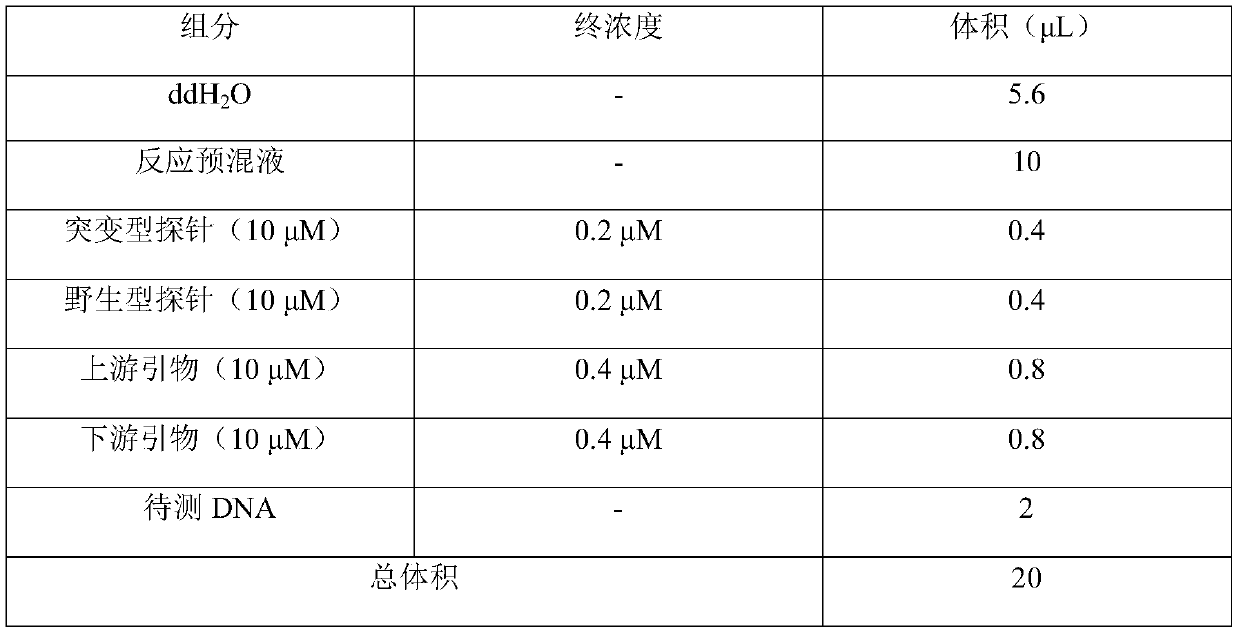
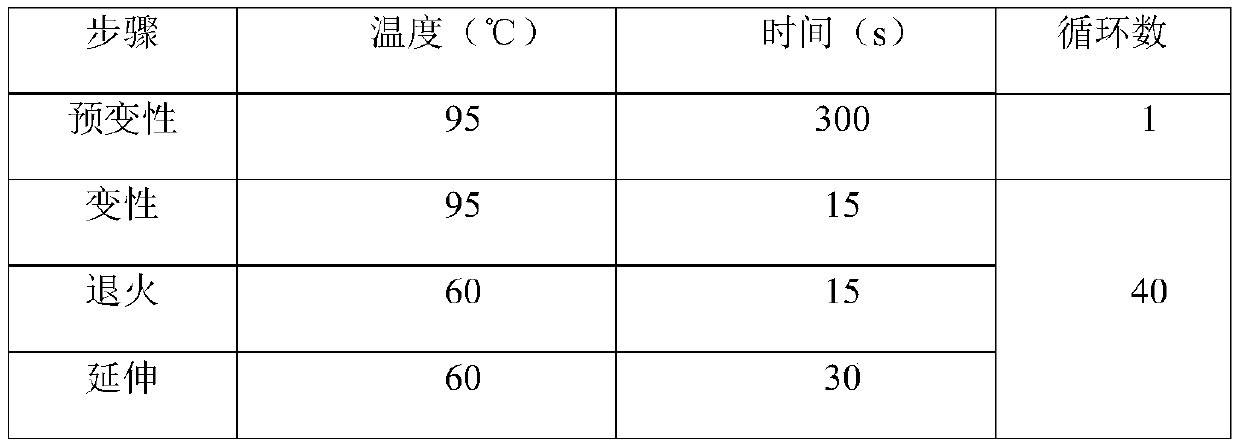
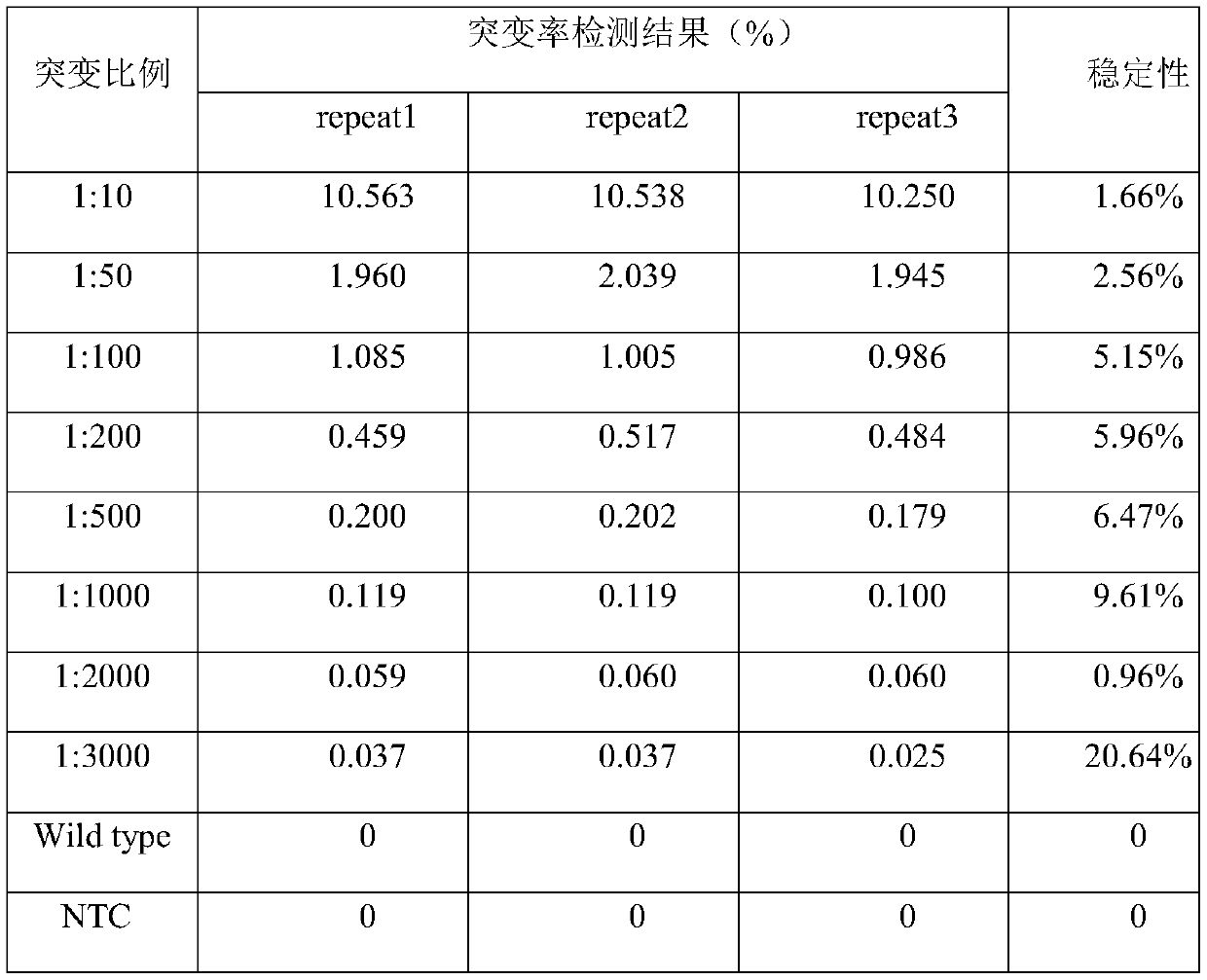
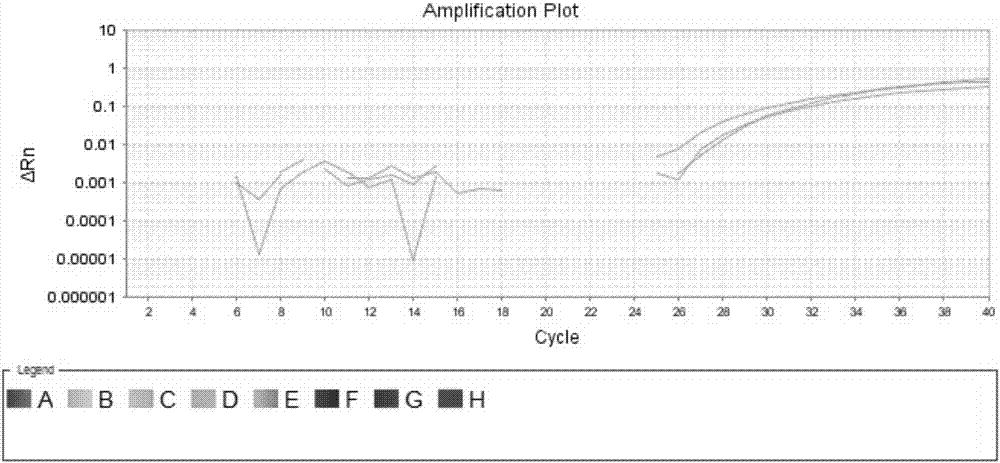
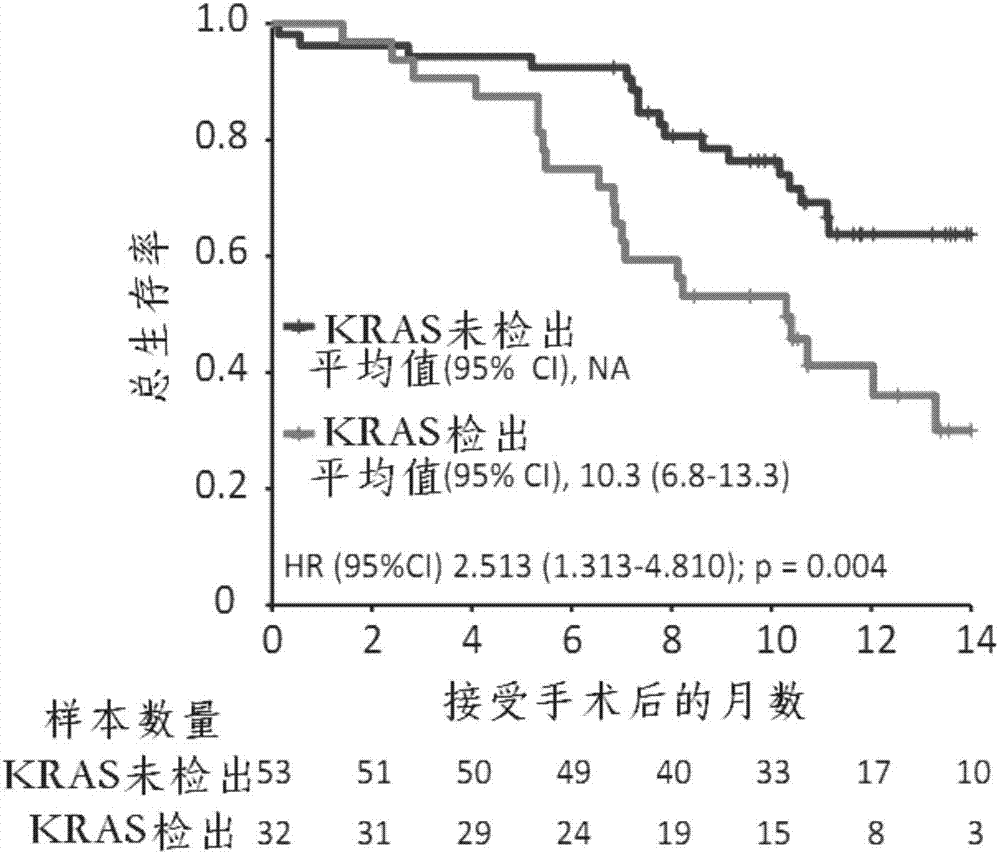
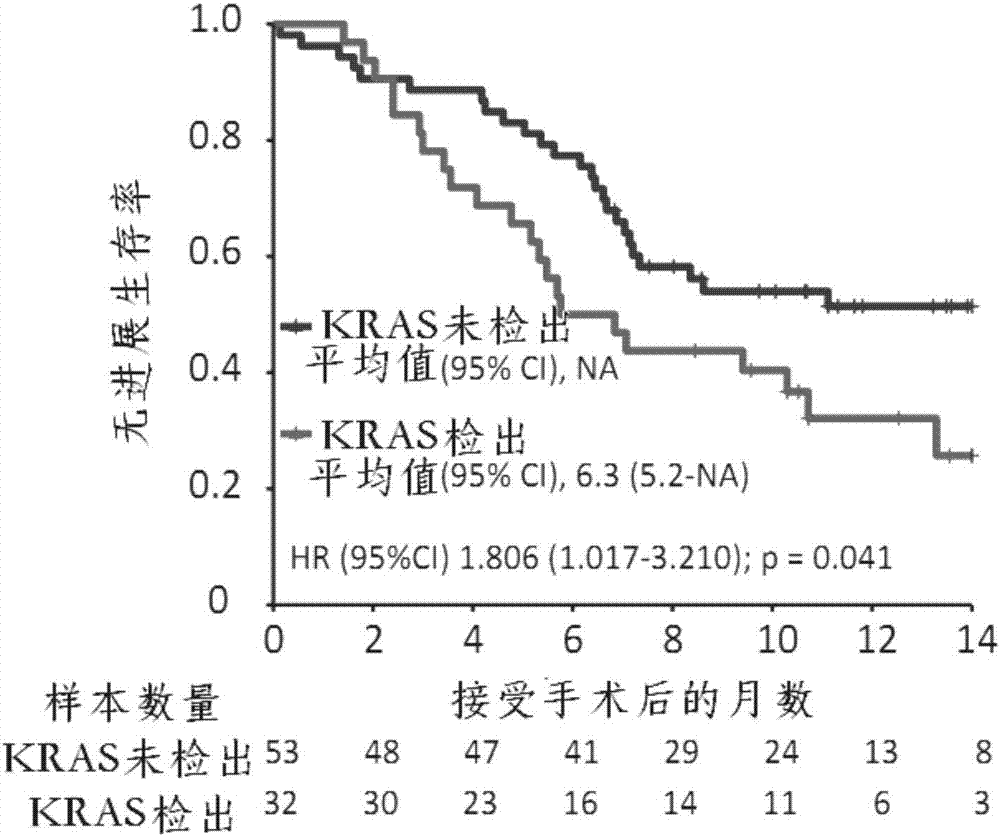
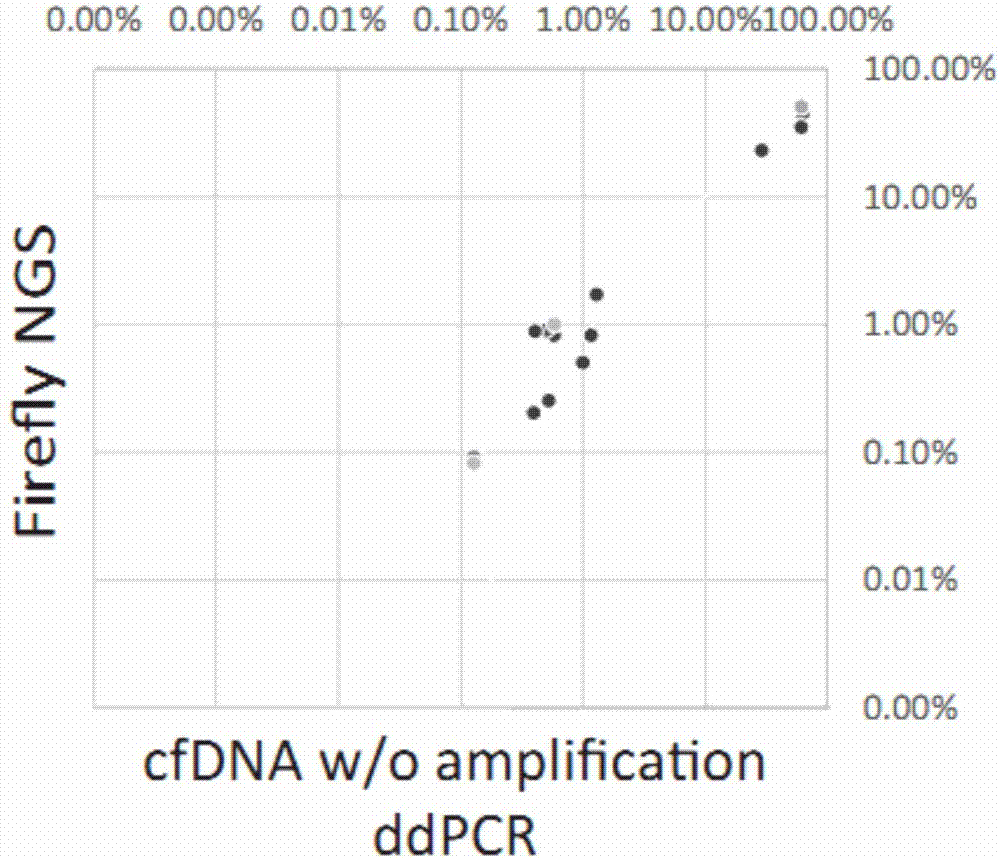
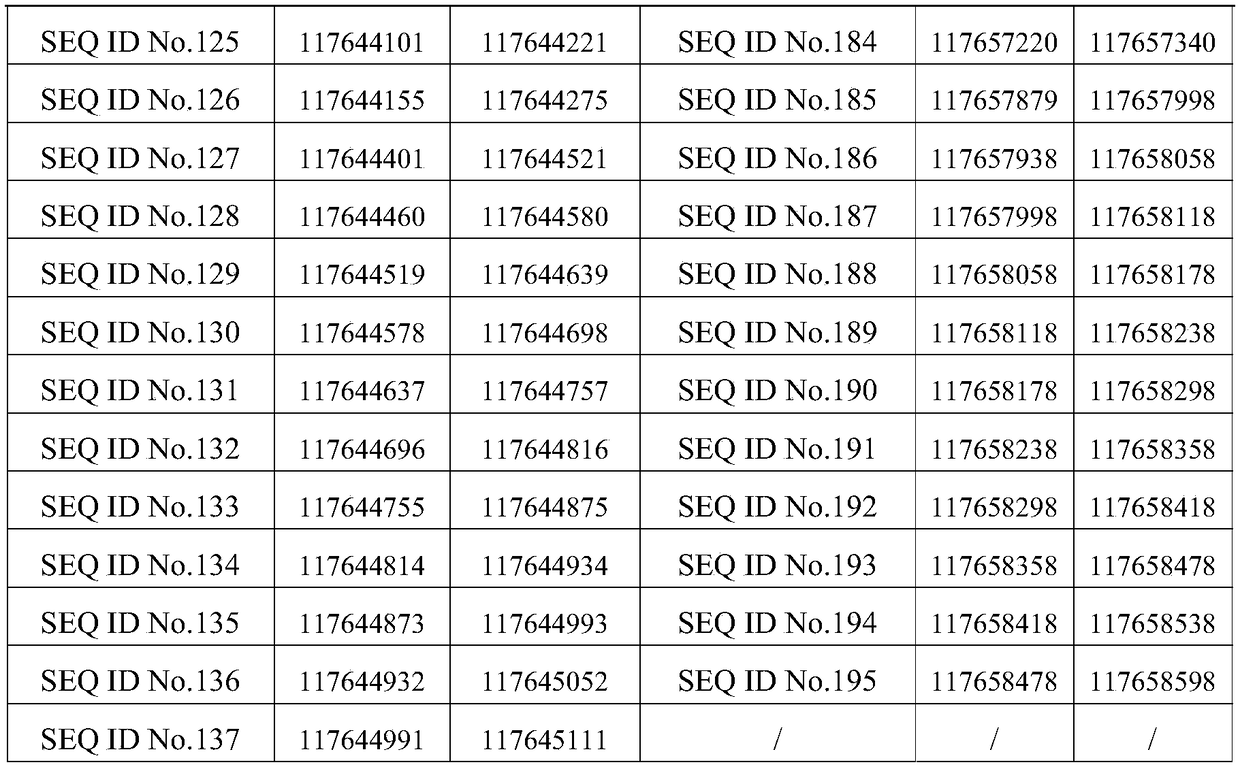
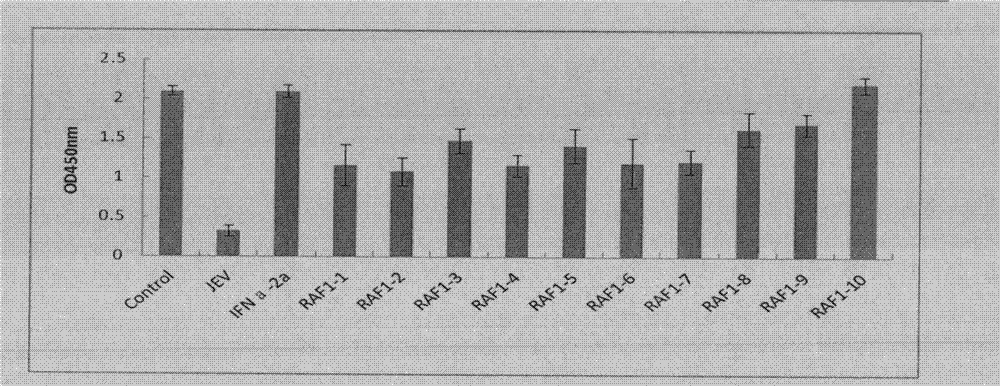Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Viral Oncogene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cancer-causing genes encoded in viral genomes. Usually denoted v-onc.
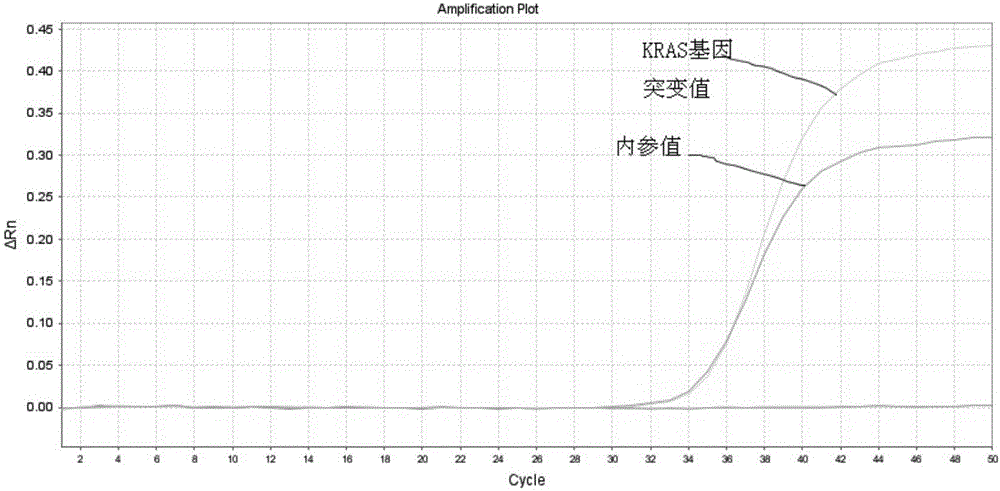
ARMS-qPCR (Allele Refractory Mutation System-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for KRAS (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene mutation subtype and detection method
InactiveCN102367478AIncreased sensitivityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementViral OncogenePositive control
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and aims to provide an ARMS-qPCR (Allele Refractory Mutation System-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for KRAS (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene mutation subtype and a detection method. The kit comprises a qPCR hybrid reaction solution, a locked nucleic acid retardant probe, a reference primer, an ARMS primer and a positive control sample, wherein the qPCR hybrid reaction solution comprises a PCR buffer solution, dNTPs (Deoxynucleotide Triphosphates), MgCl2, GoldStarbest Taq enzyme, a universal PCR reverse primer and a universal TaqMan probe. The kit provided by the invention can be used for rapidly and accurately detecting specific locus mutation of KRAS genes in various cancer tissues with high sensitivity, has high sensitivity, and can be used for detecting genome DNA with various tissue origins, specially free DNA segments adopting cell-free systems, such as blood serum and blood plasma, orother body fluid origins, wherein the genome DNA is derived from cell systems. Compared with direct sequencing and other mutation detection technologies, the kit and the detection method thereof havethe advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simplicity and rapidness in operation, high throughput, safety, definiteness and objectivity in result identification and the like for detecting the KRAS gene mutation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
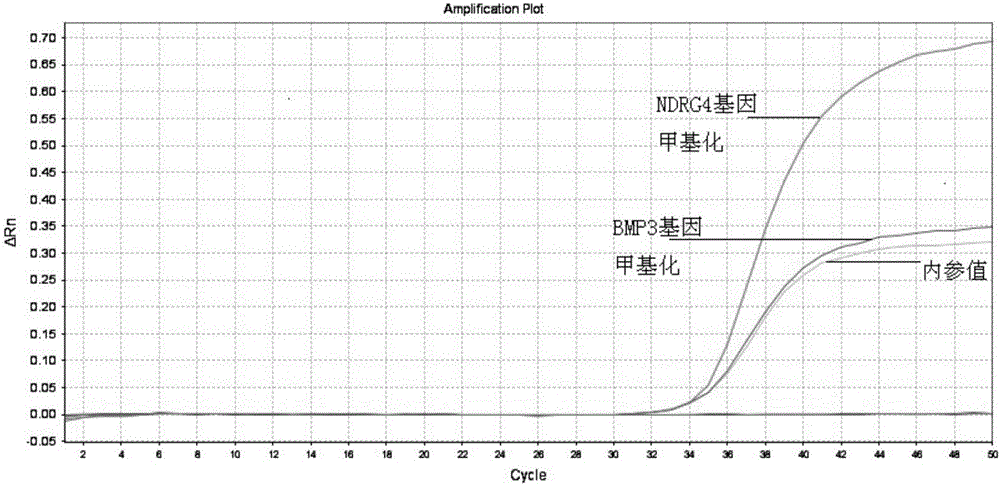
Kit for early stage colorectal cancer auxiliary diagnosis and use method and detection system thereof
InactiveCN106399570ANo detection blind zoneHigh test acceptanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisViral OncogeneGenes mutation
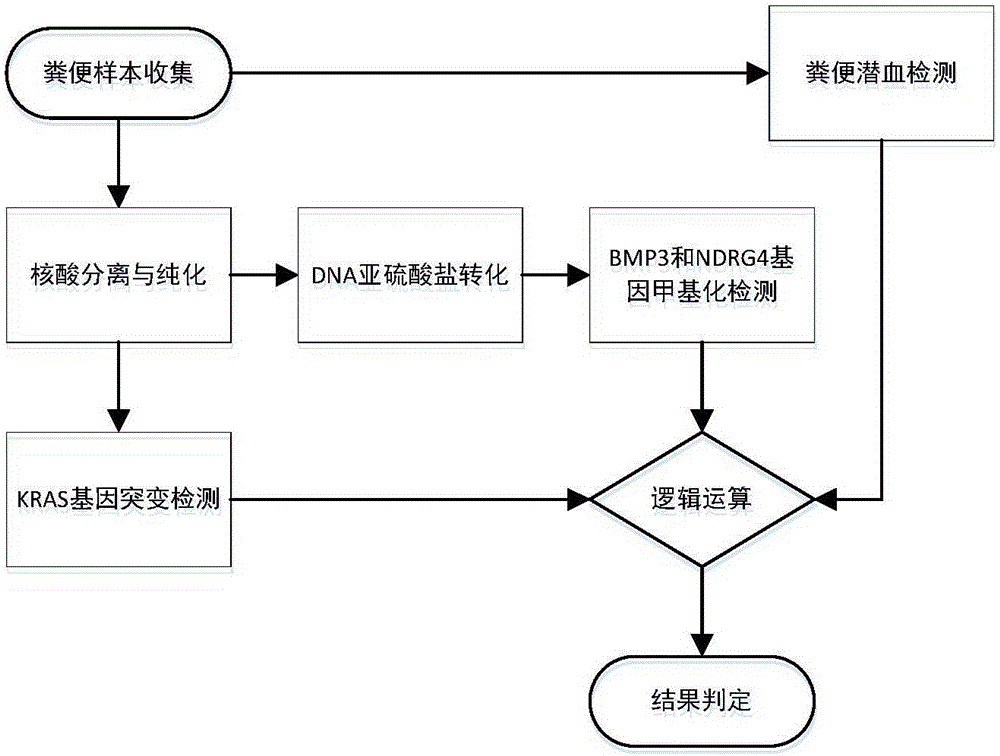
The invention provides a kit for early stage colorectal cancer auxiliary diagnosis and a use method and a detection system thereof. The kit comprises a nucleic acid isolation and purification reagent, a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sulfite conversion reagent, a KRAS (kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog) gene mutation detection reagent, a BMP3 (bone morphogenetic protein 3) and NDRG4 (N-myc downsteam regulated gene 4) gene methylation detection reagent and a fecal occult blood detection reagent, wherein the nucleic acid isolation and purification reagent is used for separating and purifying the human DNA in a faeces sample; the DNA sulfite conversion reagent is used for performing sulfite conversion on the purified partial human DNA, and is used for subsequent BMP3 and NDRG4 gene methylation detection. Through detecting two kinds of indexes of DNA and fecal occult blood in the faeces sample in a combined way, the kit provided by the invention is used for the early stage screening of the colorectal cancer. Compared with an FOBT (fecal occult blood test) detection method, the kit provided by the method can realize higher sensitivity on the detection of colorectal cancer, particularly the developing period tumor.
Owner:HANGZHOU NEW HORIZON HEALTH TECH CO LTD
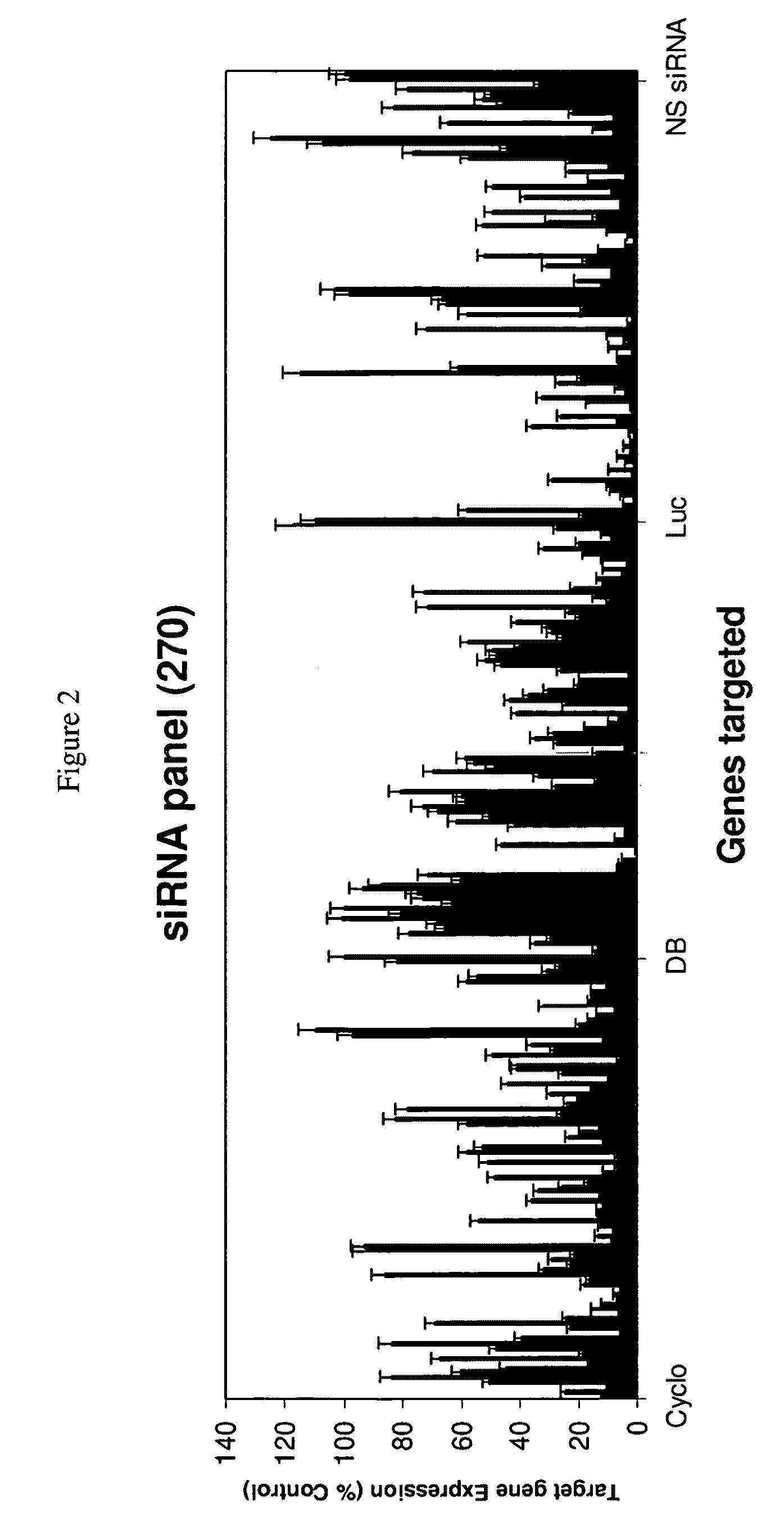
siRNA targeting v-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (MYC)
InactiveUS7951935B2Improve efficiencyGood curative effectSugar derivativesActivity regulationViral OncogeneSilent gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed including those directed to MYC.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Detection chip for tumor driving gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a detection chip for a tumor driving gene and application thereof. The detection chip for the tumor driving gene comprises an ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) fusion detection agent, an EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) fusion detection agent, an RET (reticulocyte) fusion detection agent and an ROS1 (reactive oxygen species 1) fusion detection agent. Proofed by the results of clinical detect, after fusion probes corresponding to the ALK, the EGFR, the RET and the ROS1 are specifically designed, the detection chip has the advantages that the sensitivity is high, and the gene fusion between a particular site area of the ALK, the EGFR, the RET and the ROS1 and fusion segments is specifically detected. The invention further discloses a detection chip for detecting a second sequence group of the gene mutation and a third sequence group of the gene amplification; after detecting once, the gene fusion, gene mutation and gene amplification of the multiple tumor driving genes, such as the ALK, BRAF (aserine / theroninespecific kinases), DDR2 (discordin domain receptor 2), the EGFR, ERBB2 (receptor tyrosine kinase 2), FGFR1 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 1), KRAS (kirstenrat sarcoma viral oncogene), MET (methionine), NRAS, PIK3CA (phosphatidylino-sitol 3-kinases), the RET and the ROS1.
Owner:常州桐树生物科技有限公司
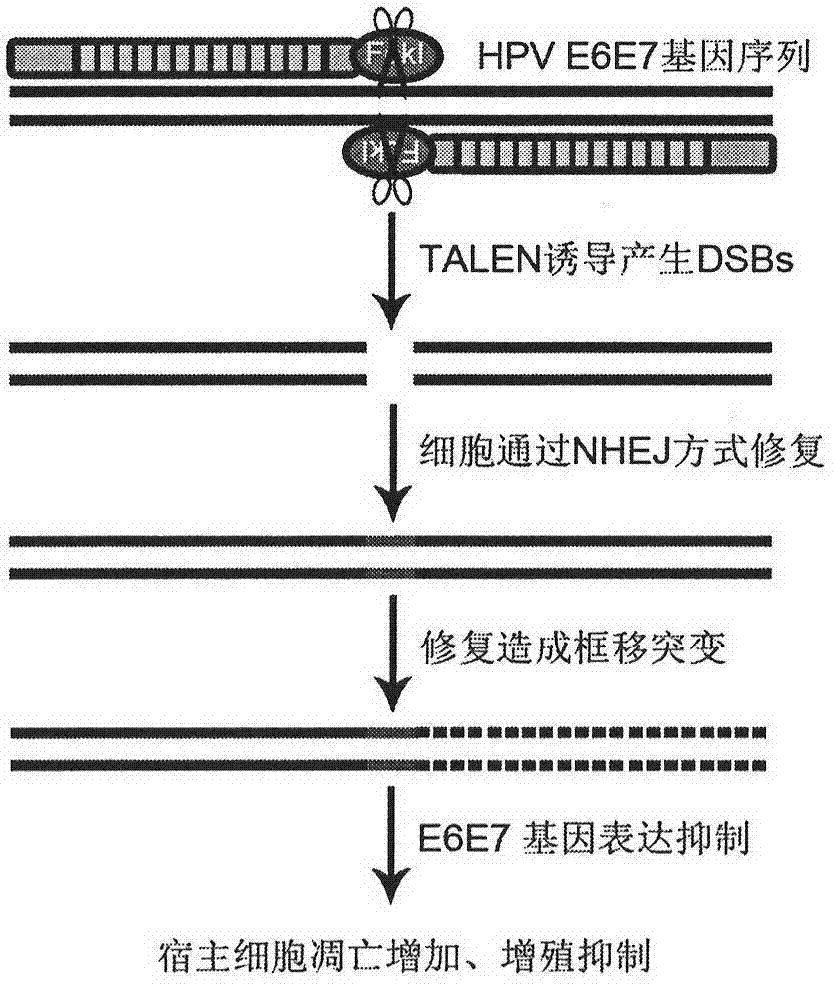
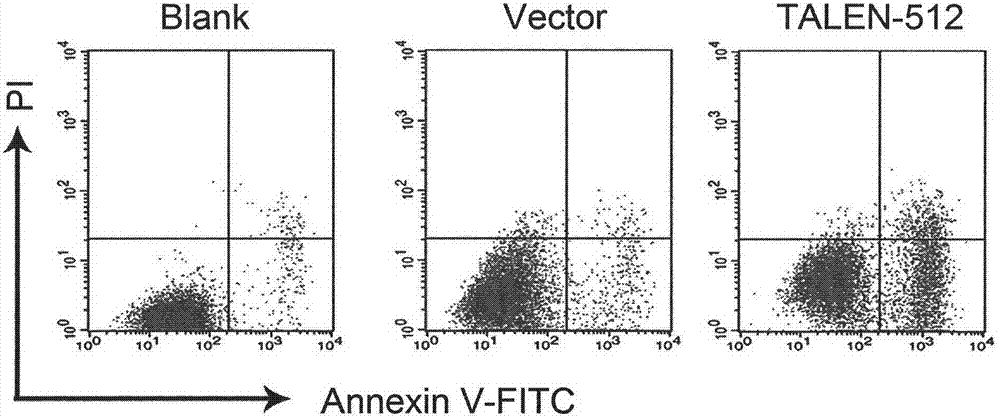
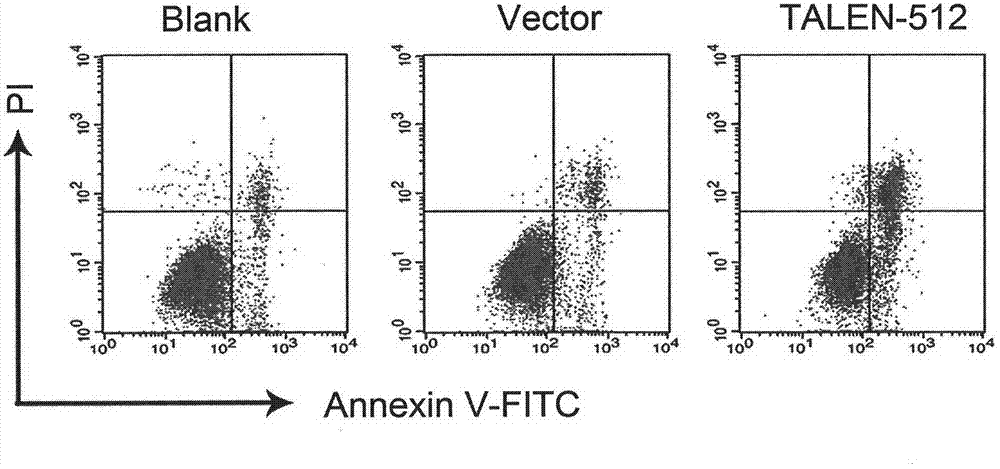
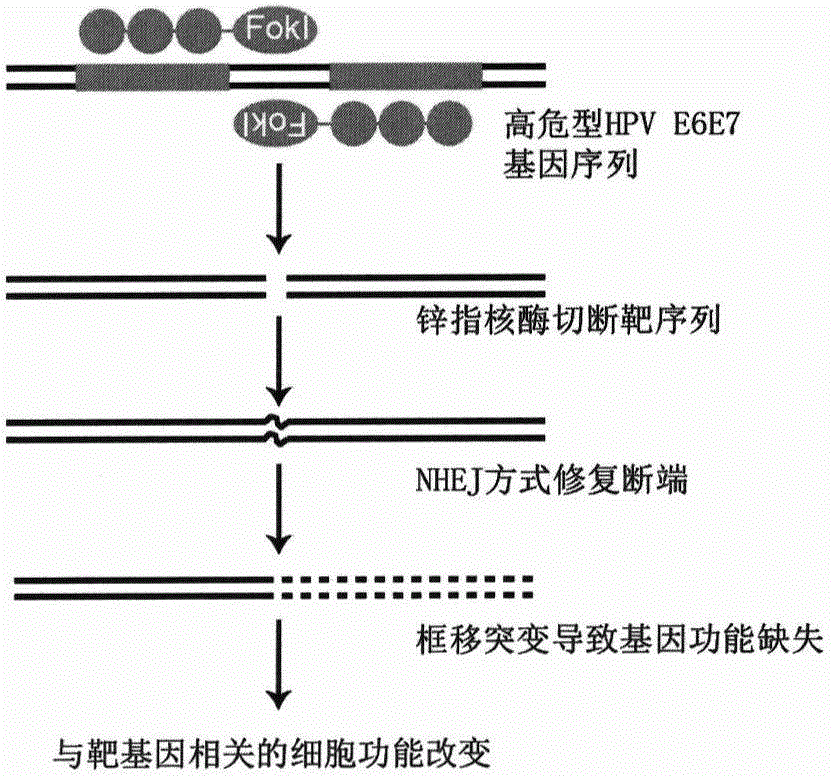
Method for knocking out HPV (human papilloma virus) E6E7 oncogene by use of TALEN (transcription activator-like effector nuclease)
The invention relates to the field of gene therapy and discloses a fixed-point knockout system for high-risk HPV (human papilloma virus) E6E7 gene, namely targeted cutting of TALENs (transcription activator-like effector nucleases) of HPV E6E7 gene, wherein a TALENs expression vector of the target specific site is designed according to the high-risk HPV E6E7 gene sequence, and the HPV E6E7 gene sequence in the cells are cut in a targeted manner so as to knock out the target gene and induce the apoptosis increase and proliferation inhibition of corresponding subtype cells while the TALENs do not act on the HPV positive or HPV negative cells of other subtypes. By transfecting the TALEN expression vector in a subcutaneous tumor model of HPV positive cervical cancer cells, the growth of subcutaneous tumor can be obviously inhibited, and the tumor weight is reduced. According to the method for targeted knockout of high-risk HPV E6E7 gene using TALEN provided by the invention, the virus oncogene can be efficiently broken on the DNA level so as to cause apoptosis and proliferation inhibition of the HPV infected cells, and the method is of tremendous therapeutic value on HPV infection related diseases and particularly precancerous lesions such as cervical intraepithelial neoplasias.
Owner:武汉雅马生物工程有限公司
Quinoline derivative, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, application thereof, medicines and pharmaceutical compositions
ActiveCN109761899AInhibit enzyme activityStrong anti-tumor effectSenses disorderOrganic chemistrySolventQuinoline
The invention provides a quinoline derivative, and pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof. The invention further provides the application of the quinoline derivative, and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof as one inhibitor of MET (Mesenchymal to epithelial transition factor), VEGFR (Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor), BRAF (V-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1), PDGFR (Platelet-derived growth factor receptor) and RET (RET proto-oncogene) or the application in the preparation of two or more multi-target inhibitors of MET, VEGFR, BRAF, PDGFRand RET, and the application of the quinoline derivative, and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof in the preparation of medicines or pharmaceutical compositions used for regulatingand controlling kinase activity or treating kinase related diseases. The invention further provides a medicine or a pharmaceutical composition used for treating angiogenesis abnormal diseases. A structure of the quinoline derivative is shown in a formula (I) (shown in the description), wherein R1 is selected from any one of structure of methyl, deuterated methyl and two chemical elements shown inthe description; R2 is selected from any one of F, Cl, Br, I and H; R3 is selected from any one of F, Cl, Br, I, H, CH3, CHX2, CH2X and CX3; and X is halogen.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LIUSHUN BIO TEC CO LTD
HLA class ii-restricted t cell receptors against mutated ras
ActiveUS20190085046A1Highly avid recognitionIncrease the number ofImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsViral OncogeneHla class ii
Disclosed is an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR), wherein the TCR has antigenic specificity for mutated Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) presented by a human leukocyte antigen (HLA) Class II molecule. Related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. Also disclosed are methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a mammal and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Multiplex immunoassay for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases
Rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases are diagnosed by multiplex assays for antibodies to a panel of antigens that includes cyclic citrullinated peptide and at least five members of a list that includes BRAF1 506-525, BRAF2 656-675, Vimentin (protein) citrullinated, Vimentin 415-433 cit cyclic, Vimentin 58-77 cit3 cyclic, Clusterin 231-250 cit sm1 cyclic, Fibrinogen A 556-575 cit sm cyclic, Fibrinogen A 616-635 cit sm cyclic, Histones2A H2A / a 1-20 cit sm2 cyclic, Filaggrin 48-65 cit2v1 cyclic, BRAF (catalytic domain from v raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homologue B1, amino acids 416-766).
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Safflower MYB (v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)) gene and application thereof
InactiveCN104845978AIncrease contentFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyViral Oncogene
The invention discloses a safflower MYB (v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)) gene. The safflower MYB gene has the advantages that the expression characteristic of a transcriptional modulatory gene is realized; by utilizing the transcription to modulate the expression of the related flavone metabolism gene, the content of total flavone in the safflower is improved, and a firm foundation is laid for culturing new products with high flavone contents.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Primer, probe and assay kit for detecting v-ros avian UR2 sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 1 (ROS1) gene fusion mutation
ActiveCN102776286AWide detection rangeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceViral OncogeneROS1
The invention discloses a primer, a probe and an assay kit for detecting v-ros avian UR2 sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 1 (ROS1) gene fusion mutation, wherein the primer and the probe comprises the following sequences of SEQ ID NO 1 to SEQ ID NO 8. A specific primer and probe technique is adopted, and can specifically detect the human ROS1 gene fusion mutation. The method has the advantages that (1) a real-time fluorescent polymerase chain reaction (PCR) system is built to simultaneously detect four types of ROS1 gene fusion mutation; (2) the sensitivity is high, the mutation of 10-20kb can be detected; (3) the method is simple to operate and low in detection, and has a wide clinical application scope; (4) the sample detection scope is wide, and the sample can be fresh pathological tissues and paraffine-embedded tissues; and (5) the detection speed is fast, and the detection process can be completed within 90 minutes.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) probe library hybridized with BRAF (v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1) gene, and method for enriching BRAF gene segments by adopting same
ActiveCN103667268AIncreased sensitivityGuaranteed accuracyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementViral OncogeneGenes mutation
The invention provides a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) probe library hybridized with BRAF (v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1) gene. The DNA probe library comprises one or more DNA probes which can be hybridized with the BRAF gene, each DNA probe comprises the following sequences: SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3, SEQ ID NO.4, SEQ ID NO.5, OR SEQ ID NO.6. The invention also provides a method for enriching BRAF gene segments by adopting the same. Based on this, the invention further provides a method for detecting the gene mutation of the BRAF gene. The BRAF gene segments can be enriched by thousands of times through adopting the method, the BRAF gene segments can be used for next-generation sequencing technology for detecting gene structure mutation including single base mutation, mRNA deficiency or increase, mRNA structure transversion and mRNA splicing change.
Owner:GENESEEQ TECH INC
Method for knockout of human papillomavirus E6E7 gene by zinc finger nucleases
ActiveCN104404076ANo knockout effectPromote proliferation inhibitionHydrolasesFermentationDiseaseViral Oncogene
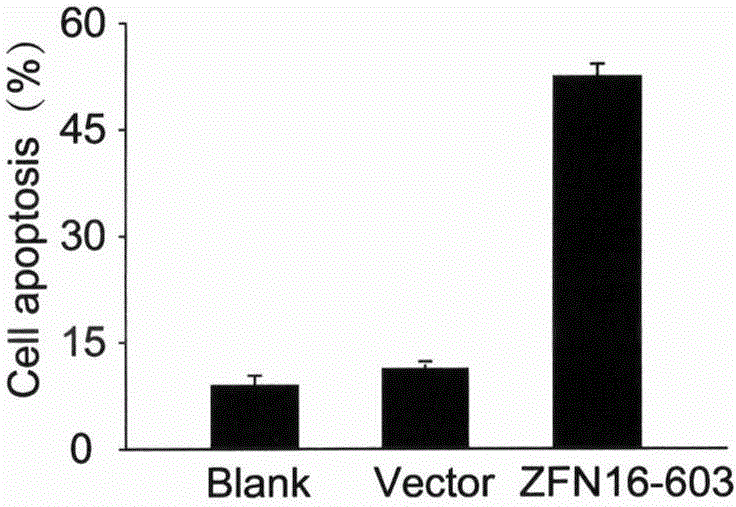
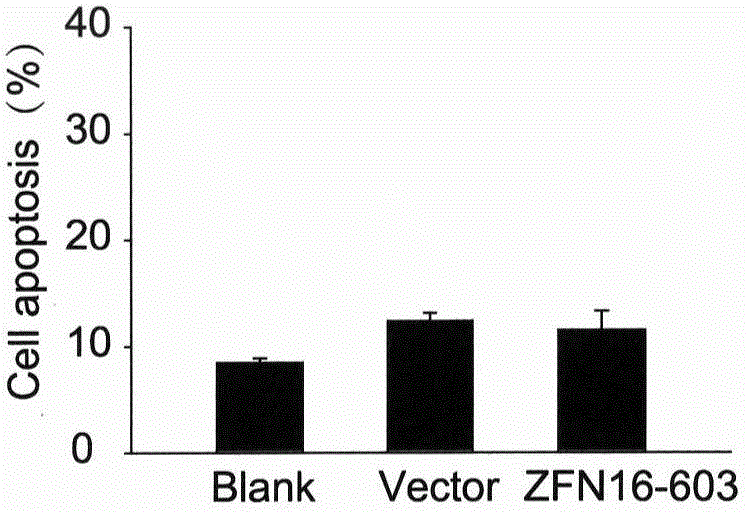
Relating to the field of gene therapy, the invention provides a method for knockout of a high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) E6E7 gene by zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs). According to a high-risk type HPV E6E7 gene sequence, the method designs ZFNs expression vectors of a targeted specific site to targetedly cut the HPVE6E7 gene sequence in cells, thereby knocking out a target gene. In corresponding subtype HPV infected cells, the ZFNs can significantly induce cell apoptosis and proliferation inhibition, and has no effect on other subtype HPV positive cells and HPV negative cells. Transfection of the ZFNs expression vectors in a subcutaneous tumor model of HPV positive cervical cancer cells can obviously inhibit the growth rate of subcutaneous tumors and alleviate tumors. The method for targeted knockout of the high-risk HPV E6E7 gene by ZFNs can efficiently destroy virus oncogenes at the DNA level so as to make HPV infected cells undergo apoptosis and proliferation inhibition, and has enormous treatment value to HPV infection related diseases, especially cervical intraepithelial neoplasias and other precancerous lesions.
Owner:WUHAN KDWS BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
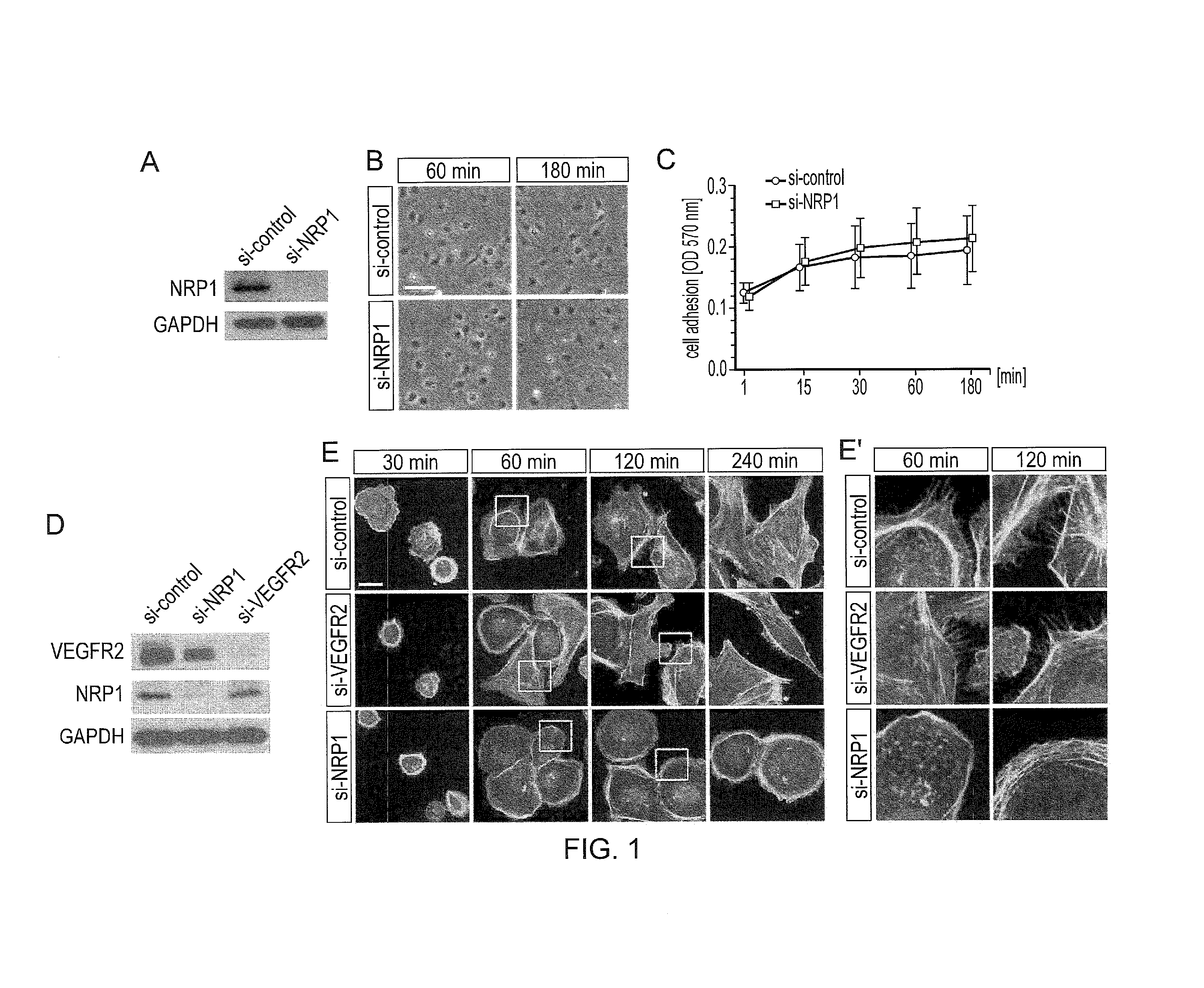
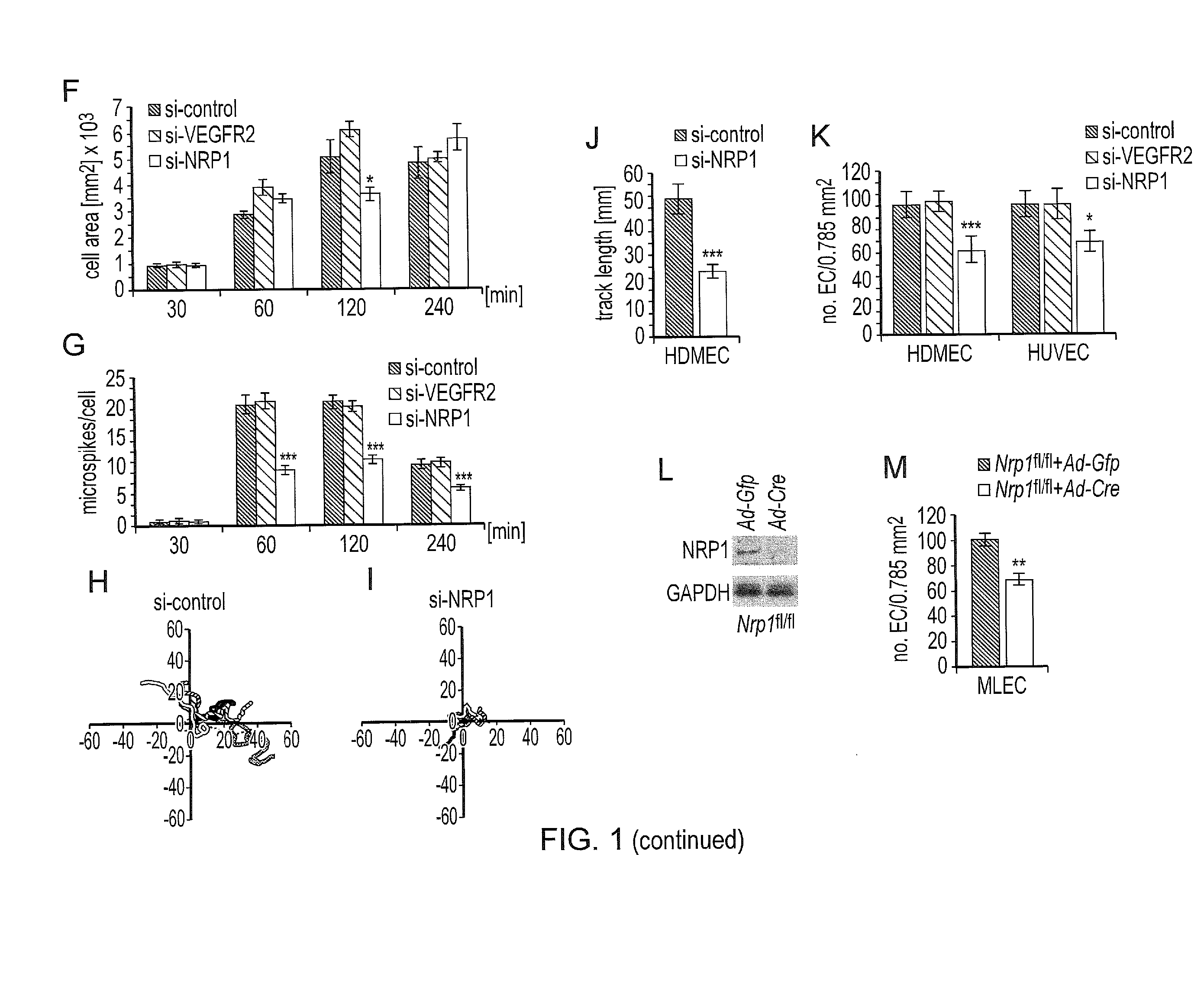
Abl1 inhibitor for treating and preventing ocular neovascularisation
InactiveUS20170027936A1Inhibit angiogenesisInhibit cell migrationOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderViral OncogeneVEGF receptors
The present invention relates to an Abelson murine leukaemia viral oncogene homolog 1 (ABL1) inhibitor for use in the treatment of ocular neovascularisation associated with a non-cancerous condition. The invention also relates to the use of an ABL1 inhibitor as a complementary therapy with VEGF or VEGF receptor inhibitor treatment and provides pharmaceutical compos itions and kits comprising one or both inhibitors.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
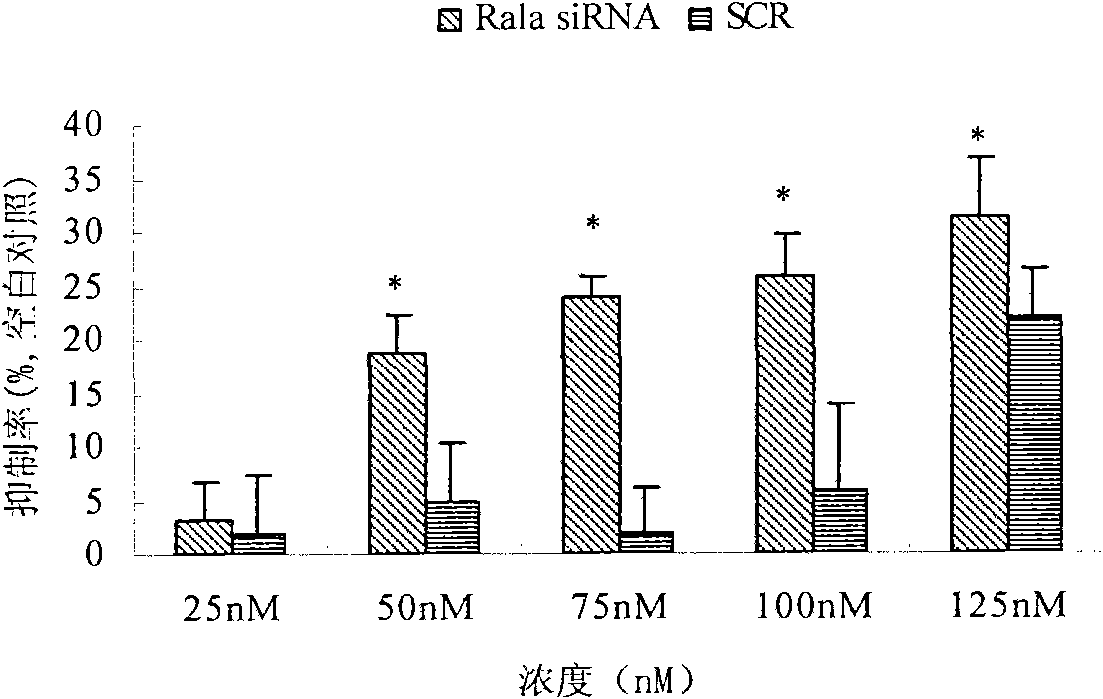
Application of small interfering RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of RALA (v-ral simian leukemia viral oncogene homolog A) gene in preparing medicaments for resisting leukemia
ActiveCN101812452AGrowth inhibitionReduced expression levelGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsViral OncogeneAntileukemic agent
The invention discloses a small interfering RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of an RALA (v-ral simian leukemia viral oncogene homolog A) gene and application thereof in preparing medicaments for resisting leukemia. The sequence of the small interfering RNA is as follows: the positive-sense strand is 5'-CGUGGAAACAUCUGCUAAATT-3', and the antisense strand is 5'-UUUAGCAGAU GUUUCCACGTA-3'. The small interfering RNA of the RALA gene can be used for preparing the medicaments for resisting the leukemia. The RALAsiRNA can suppress the growth of human leukemia k562 cells through down regulating the expression of a cancer RALA, has potential application values to oncogene treatment and is expected to be applied to the treatment of the leukemia. Moreover, on the basis of the small interfering RNA, new medicines for resisting the leukemia are developed to make a contribution to the prevention and cure of clinical leukemia.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Gene joint detection method and kit
ActiveCN104480215AStrong specificityNo non-specific interfering signalsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationViral OncogeneMultiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification
The invention relates to a joint detection method for gene mutation. The joint detection method is characterized in that 16 gene mutations, including KRAS (Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog), PIK3CA (phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, catalytic subunit alpha), BRAF (B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine / threonine kinase) and EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) genes can be detected synchronously by using 20-50ng of DNA as a sample. The method comprises the steps of designing a specific probe; building a reaction system for an MLPA (Multiplex Ligation Dependent Probe Amplification) mutant gene sequences; largely amplifying the targeted gene sequences by PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). The joint detection method for gene mutation has the advantages that the specificity is high, and 10-100ng of wild type DNA do not generate nonspecific interference signals; the selectivity is outstanding, and 0.1 to 1.0% of mutation can be detected under the background of 99-99.9% of wild type DNA.
Owner:南宁维尔凯生物科技有限公司
T cell receptors recognizing hla-cw8 restricted mutated kras
ActiveUS20190040111A1Highly avid recognitionIncrease the number ofImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsViral OncogeneMammal
Disclosed is an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for mutated Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) presented in the context of an HLA-Cw*0802 molecule. Related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. Also disclosed are methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a mammal and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
T cell receptors recognizing hla-cw8 restricted mutated kras
ActiveUS20200148739A1Highly avid recognitionIncrease the number ofImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsViral OncogeneCancer research
Disclosed is an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for mutated Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) presented in the context of an HLA-Cw*0802 molecule. Related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. Also disclosed are methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a mammal and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Anti-kras-g12d t cell receptors
ActiveUS20190177395A1Highly avid recognitionIncrease the number ofImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsViral OncogeneMammal
Disclosed is an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for mutated Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) presented in the context of an HLA-Cw*0802 molecule. Related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. Also disclosed are methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a mammal and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Anti-KRAS-G12D T cell receptors
ActiveUS10611816B2Highly avid recognitionIncrease the number ofImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsViral OncogeneCancer prevention
Disclosed is an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for mutated Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) presented in the context of an HLA-Cw*0802 molecule. Related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. Also disclosed are methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a mammal and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Kit for detecting mutation of V600E locus of BRAF (v-taf mourine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1) gene
PendingCN111304329AAchieving High Sensitivity DetectionVarious sources of samplesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationViral OncogeneNucleotide
Owner:宁波胤瑞生物医学仪器有限责任公司
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection method for mutation of human BRAF (v-raf Murine Sacoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene V600E, primer, probe and kit
InactiveCN107400716AAchieving Specific DetectionEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationViral OncogeneBraf genes
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOCHIP
Method and kit for detecting BRAF (v-raf mourine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1) gene mutation
ActiveCN103451289AStrong specificityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationViral OncogeneBRAF Gene Mutation
The invention discloses a primer, a kit and a method for detecting BRAF (v-raf mourine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1) gene mutation. The primer for detecting the BRAF gene mutation comprises a forward amplification primer with a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1, a backward amplification primer with a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2 and a sequencing primer with a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:3, wherein the 5' tail end of the forward amplification primer and / or the backward amplification primer is provided with a biotin label. The method and the kit for detecting the BRAF gene mutation have the advantages of simplicity and rapidness for operation, high flux, low detection cost and the like, especially have good specificity, high sensitivity and high accuracy and have wide application prospect.
Owner:北京明谛生物医药科技有限公司
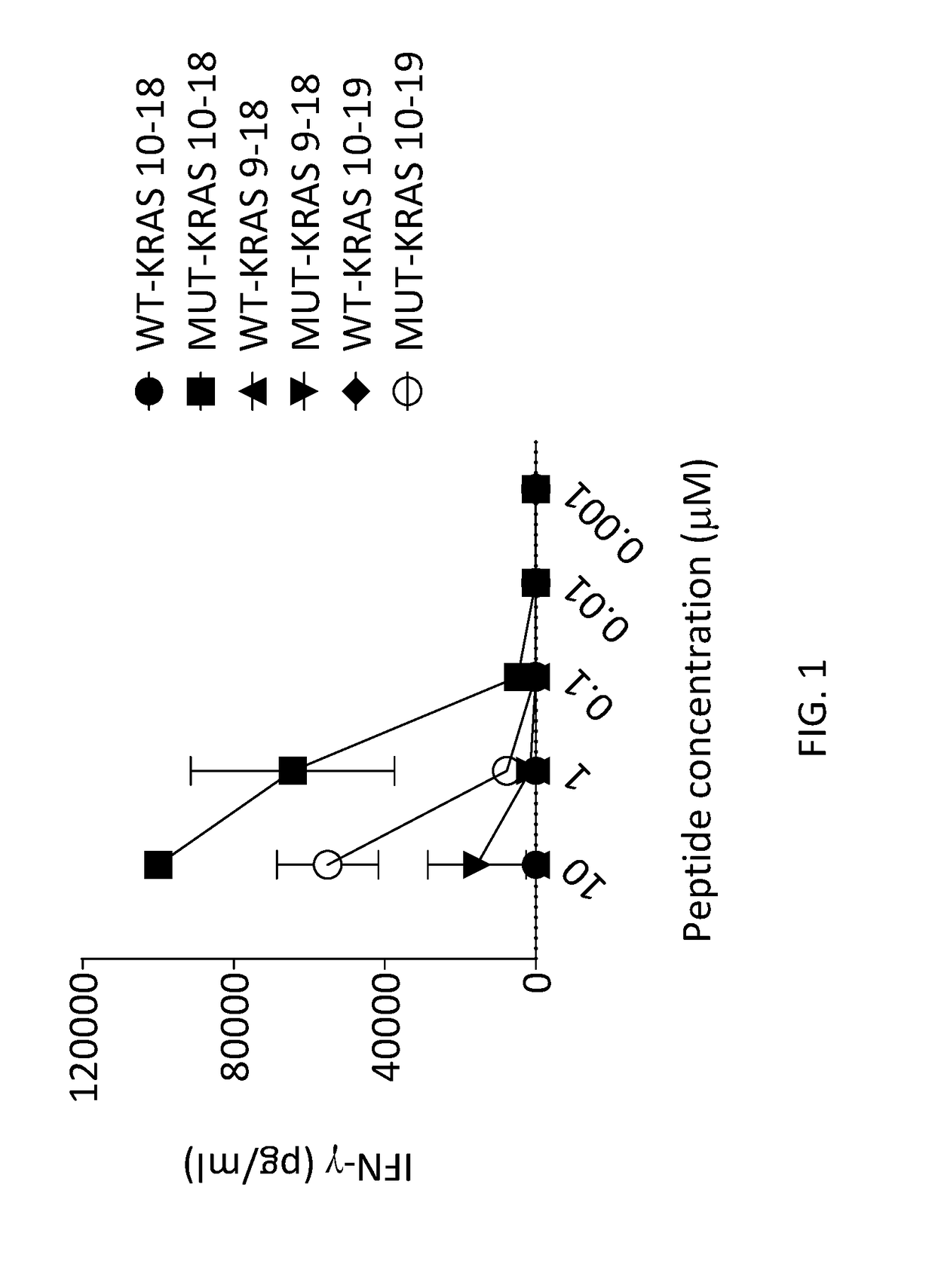
Application of KRAS (kirsten ratsarcoma viral oncogene) serving as biomarker in pancreatic cancer
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to application of KRAS (kirsten ratsarcoma viral oncogene) serving as a biomarker in pancreatic cancer and provides application of a substance for detecting G12V mutation in KRAS gene or active fragments thereof to preparation of a kit used for assessment of pancreatic cancer treatment effects and / or judgment of pancreatic cancer prognosis. According to discovery of remarkable correlation between KRAS mutation in pre-operation cfDNA and shortening of overall survival and progression-free survival, a prognosis value of KRAS cfDNA assessment is revealed, and a method of how to provide information for clinical treatment of patients suffering from the pancreatic cancer on the basis of cfDNA biomarker detection assistance is founded, and accordingly individual treatment of the pancreatic cancer can be promoted.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGHAI HOSPITAL
Compositions for preventing cancers associated with human papilloma viruses
InactiveUS20180200233A1Inhibit specific interactionEffective therapeutic approachOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsViral OncogeneApoptosis
Compositions and methods of treatment are provided for preventing cancers caused by high-risk human papilloma viruses (HPV). Cancers amenable to prevention include cervical cancer, head cancers, neck cancers, and oral cancers. The compositions block interaction between HPV 16 E6, one of two major viral oncogenes, and its partners, thereby resensitizing HPV positive cells to apoptosis.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY
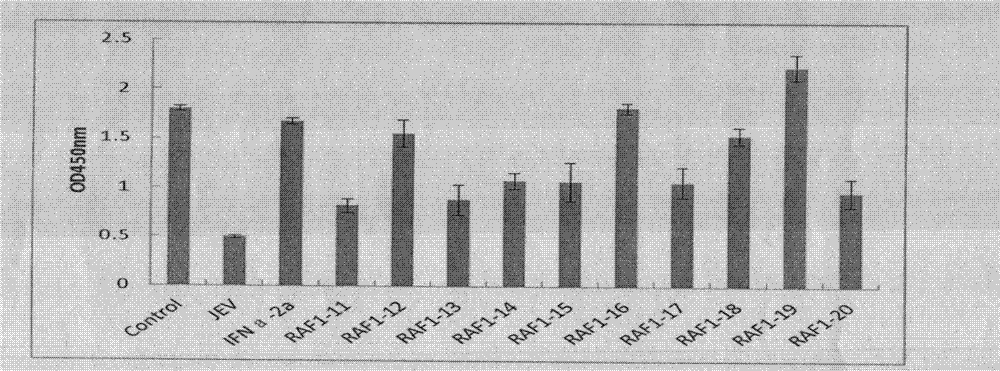
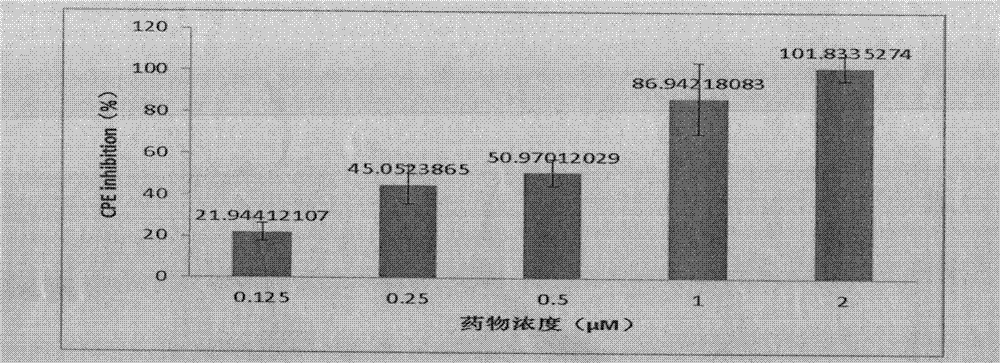
Structure and application of target RAF1 (c-Raf, v-raf-leukemia viral oncogene 1) anti-encephalitis-b-virus oligonucleotides
The invention relates to a structure and application of antisense oligodexynucleotide (ASODN) and particularly relates to a structure of the ASODN discovered with a target RAF1 (c-Raf, v-raf-leukemia viral oncogene 1) and application of the ASODN in preparation of drugs for treating encephalitis b virus infections and related diseases.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
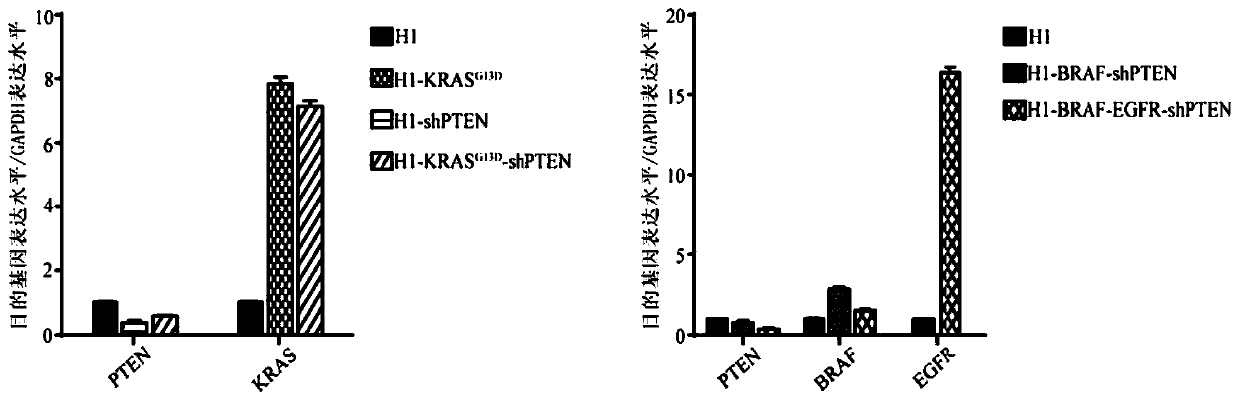
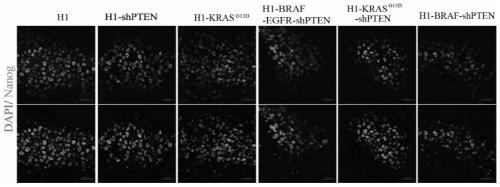
Neural stem cell carrying tumor-related gene and preparation method and application of neural stem cell
ActiveCN111100842AEfficiently simulate dynamic transition processesImportant scientific significanceCompound screeningApoptosis detectionViral OncogeneInduced pluripotent stem cell
The invention discloses a neural stem cell carrying a tumor-related gene and a preparation method and application of the neural stem cell. According to the neural stem cell, a KRAS (kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene) gene mutant as well as an upstream gene EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) and a downstream gene BRAF (V-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1) of a combined over-expression Ras / raf / MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) signal channel are transferred into a human multipotential stem cell, and PTEN (phosphate and tension homology deleted on chromsome ten) gene expression is knocked off or reduced, so that a multipotential stem cell carrying the tumor-related gene is obtained; and the multipotential stem cell is further induced to differentiate to a nerve direction, then the neural stem cell is obtained, the dynamic transformation process of a tumor stem cell and occurrence of a tumor is effectively simulated, and a novel and reliable cell model is provided for research on pathogenesis of neural tumors such as gliomas. By adopting the technology, possibility is provided for dynamic observation on the occurrence and development process of the gliomas in multiple angles, novel research ideas are also brought to glioma treatment medicine screening and targeting treatment, and great scientific significances and application value can be made.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
T cell receptors recognizing HLA-Cw8 restricted mutated KRAS
ActiveUS10556940B2Highly avid recognitionIncrease the number ofImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsViral OncogeneCancer research
Disclosed is an isolated or purified T cell receptor (TCR) having antigenic specificity for mutated Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) presented in the context of an HLA-Cw*0802 molecule. Related polypeptides and proteins, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. Also disclosed are methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a mammal and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Detection chip for tumor driver gene and its application
ActiveCN107022610BNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementViral OncogeneGenes mutation
The invention discloses a detection chip for a tumor driving gene and application thereof. The detection chip for the tumor driving gene comprises an ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) fusion detection agent, an EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) fusion detection agent, an RET (reticulocyte) fusion detection agent and an ROS1 (reactive oxygen species 1) fusion detection agent. Proofed by the results of clinical detect, after fusion probes corresponding to the ALK, the EGFR, the RET and the ROS1 are specifically designed, the detection chip has the advantages that the sensitivity is high, and the gene fusion between a particular site area of the ALK, the EGFR, the RET and the ROS1 and fusion segments is specifically detected. The invention further discloses a detection chip for detecting a second sequence group of the gene mutation and a third sequence group of the gene amplification; after detecting once, the gene fusion, gene mutation and gene amplification of the multiple tumor driving genes, such as the ALK, BRAF (aserine / theroninespecific kinases), DDR2 (discordin domain receptor 2), the EGFR, ERBB2 (receptor tyrosine kinase 2), FGFR1 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 1), KRAS (kirstenrat sarcoma viral oncogene), MET (methionine), NRAS, PIK3CA (phosphatidylino-sitol 3-kinases), the RET and the ROS1.
Owner:常州桐树生物科技有限公司
Method of diagnosing cancer and reagents therefor
ActiveUS9157122B2Degree of reductionMonitor efficacyMicrobiological testing/measurementViral OncogeneHuman genome
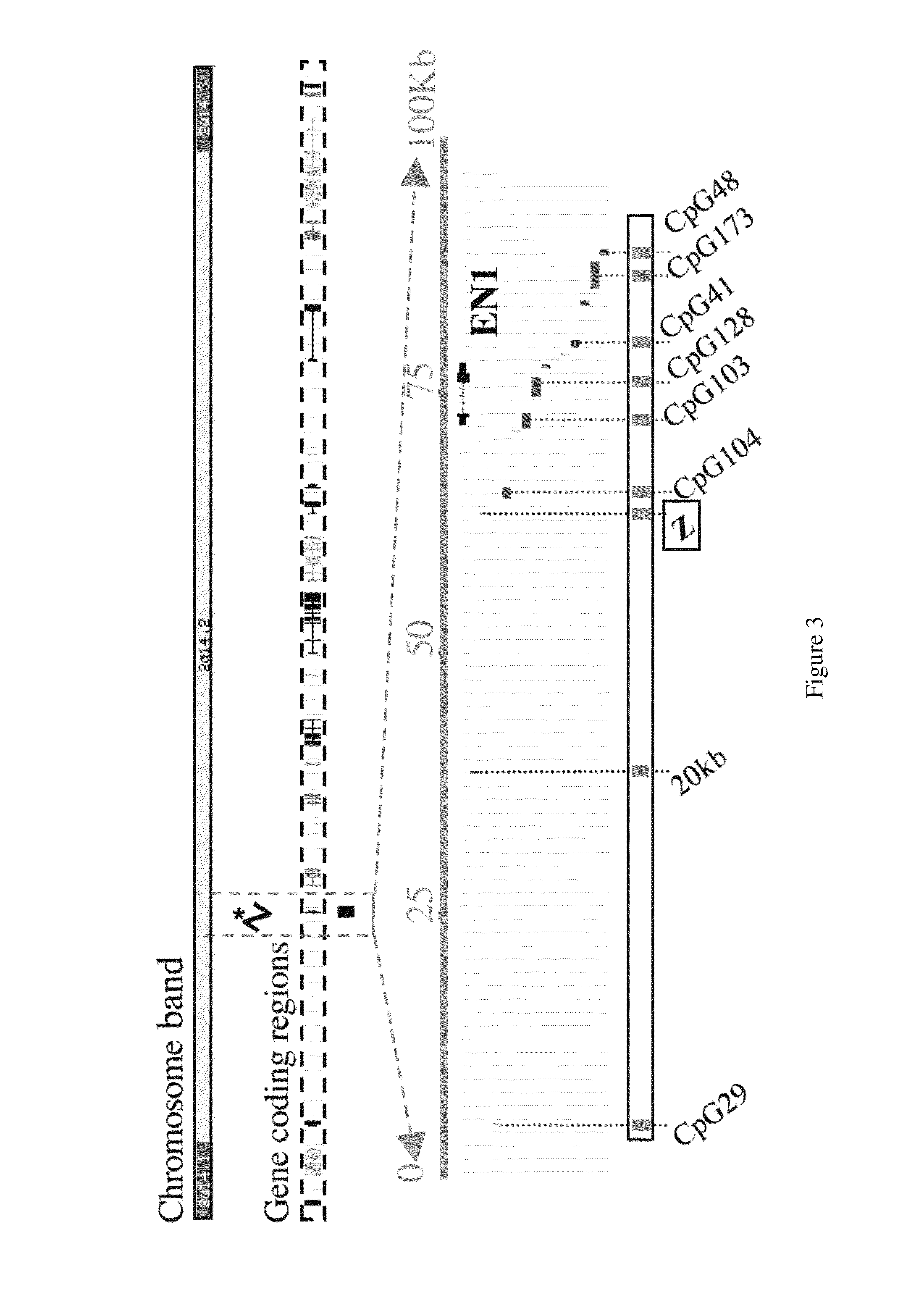
The present invention provides methods for diagnosis and monitoring the efficacy of treatment of a cancer. More particularly, the methods of the invention comprise detecting an enhanced degree of chromatin modification within Chromosome 2 of the human genome from about map position 2q14.1 to about map position 2q14.3 in a sample derived from a subject. The methods include detecting an enhanced level of methylation, or detecting an enhanced level of modification of a histone positioned within the chromatin within the region of about 2q14.1 to 2q14.3 of Chromosome 2. The methods also include detecting a modulated level of expression of a gene within the region of about 2q14.1 to 2q14.3 of Chromosome 2. The gene may be selected from the group consisting of DEAD box polypeptide 18 (DDX18), translin (TSN), v-ral simian leukaemia viral oncogene homolog B (RALB), secretin recepto (SCTR), engrailed homolog 1 (EN1), macrophage receptor with collagenous structure (MARCO), protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 4 (PTPN4), insulin induced gene 2 (INSIG2), inhibin beta B (INHBB), GLI-Kruppel family member 2 (GLI2), FLJ10996, STEAP3, diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI), MGC10993, erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1 like 5 (EPB41L5), FLJ14816, transcription factor CP2-like 1 (TFCP2L1).
Owner:GARVAN INST OF MEDICAL RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com