Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1081 results about "Window function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
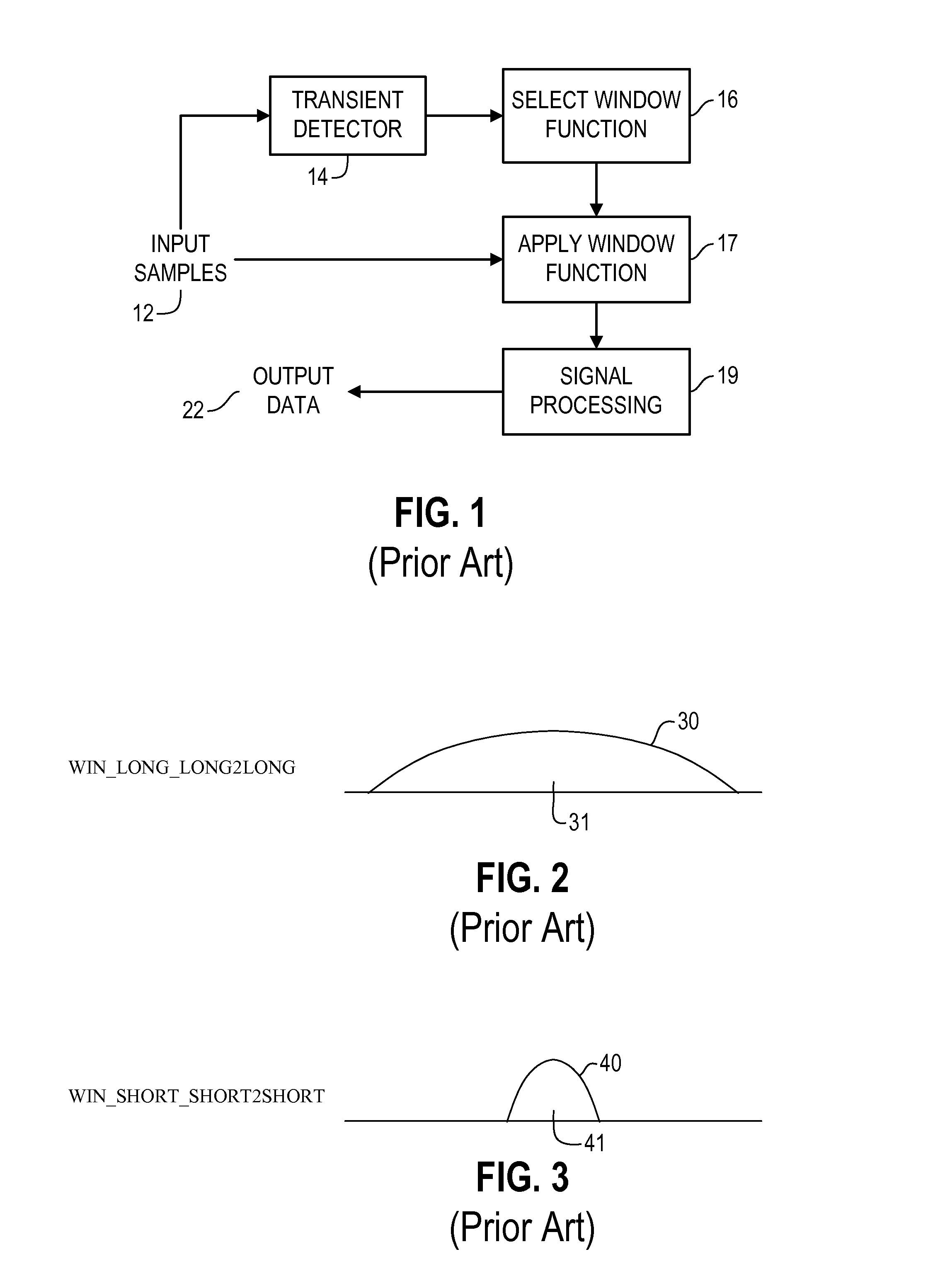
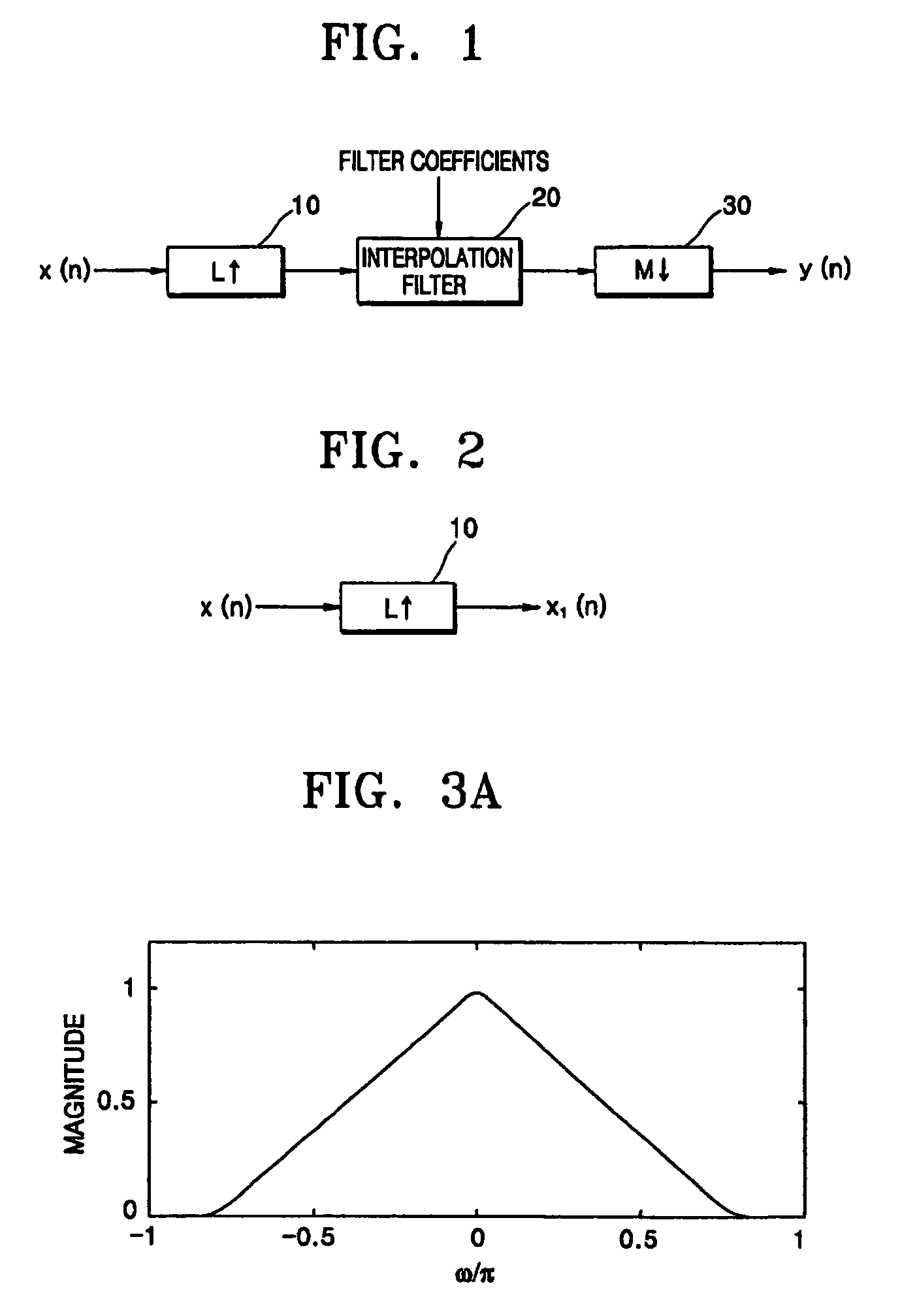
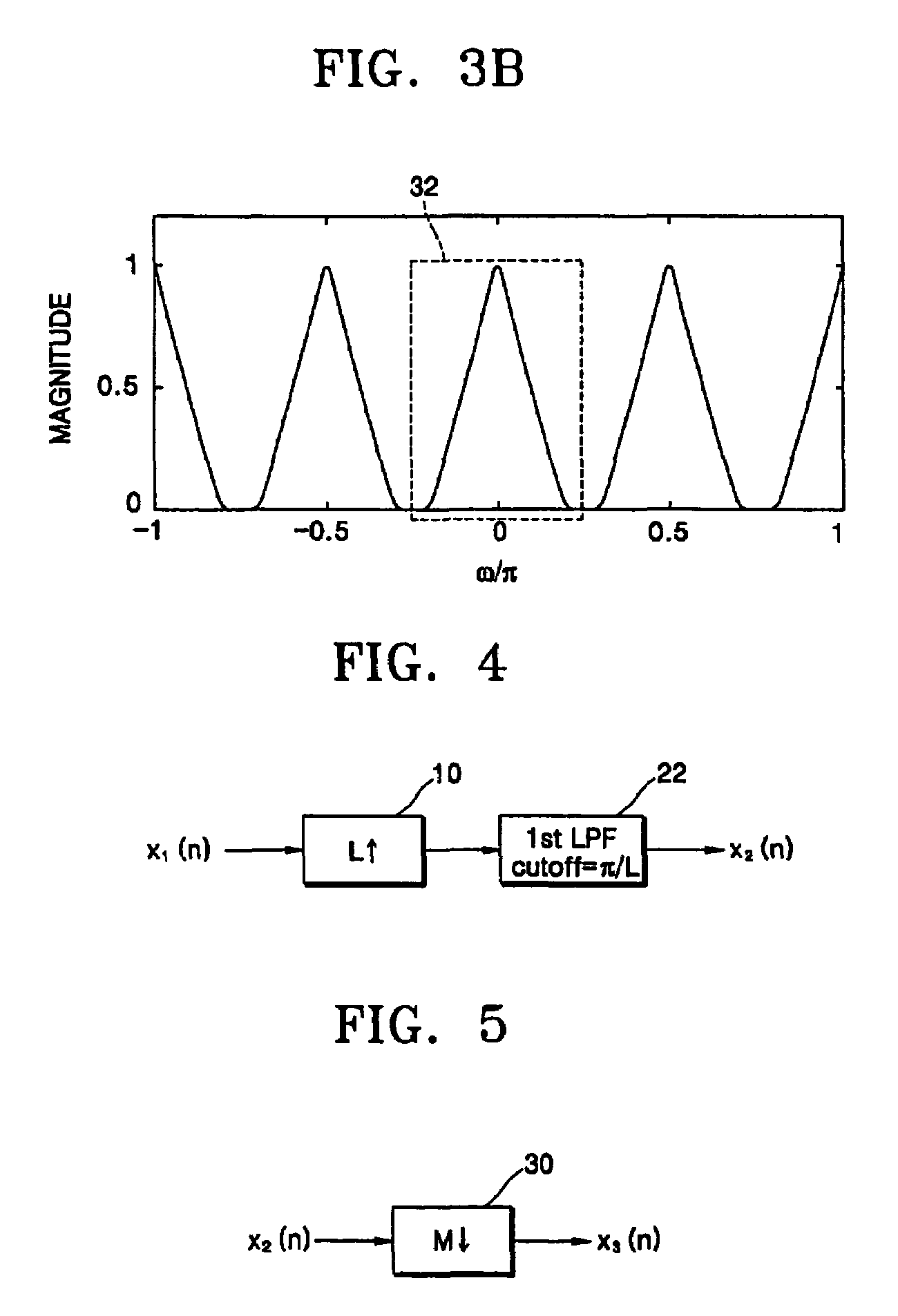
In signal processing and statistics, a window function (also known as an apodization function or tapering function) is a mathematical function that is zero-valued outside of some chosen interval, normally symmetric around the middle of the interval, usually near a maximum in the middle, and usually tapering away from the middle. Mathematically, when another function or waveform/data-sequence is "multiplied" by a window function, the product is also zero-valued outside the interval: all that is left is the part where they overlap, the "view through the window". Equivalently, and in actual practice, the segment of data within the window is first isolated, and then only that data is multiplied by the window function values. Thus, tapering, not segmentation, is the main purpose of window functions.
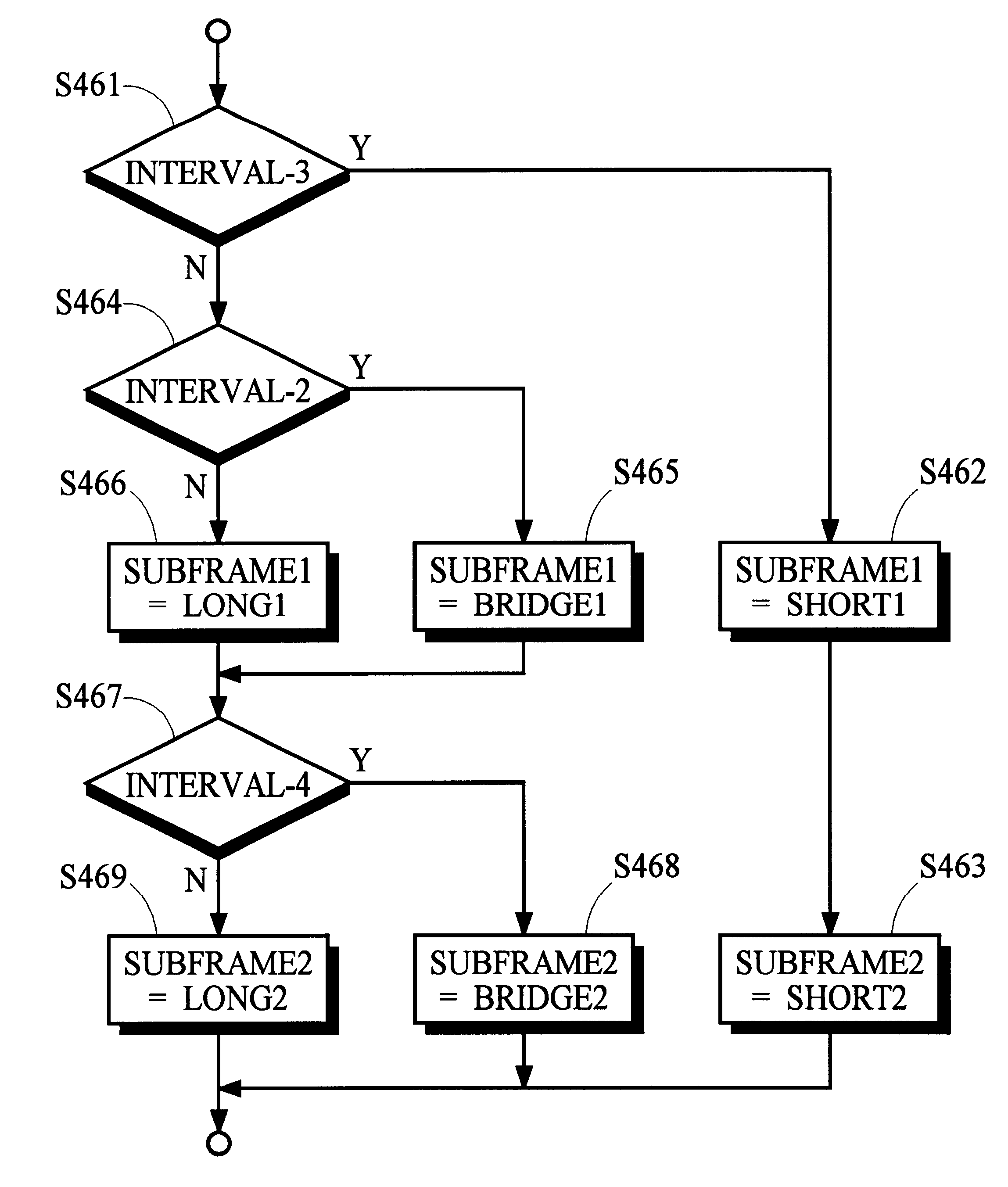
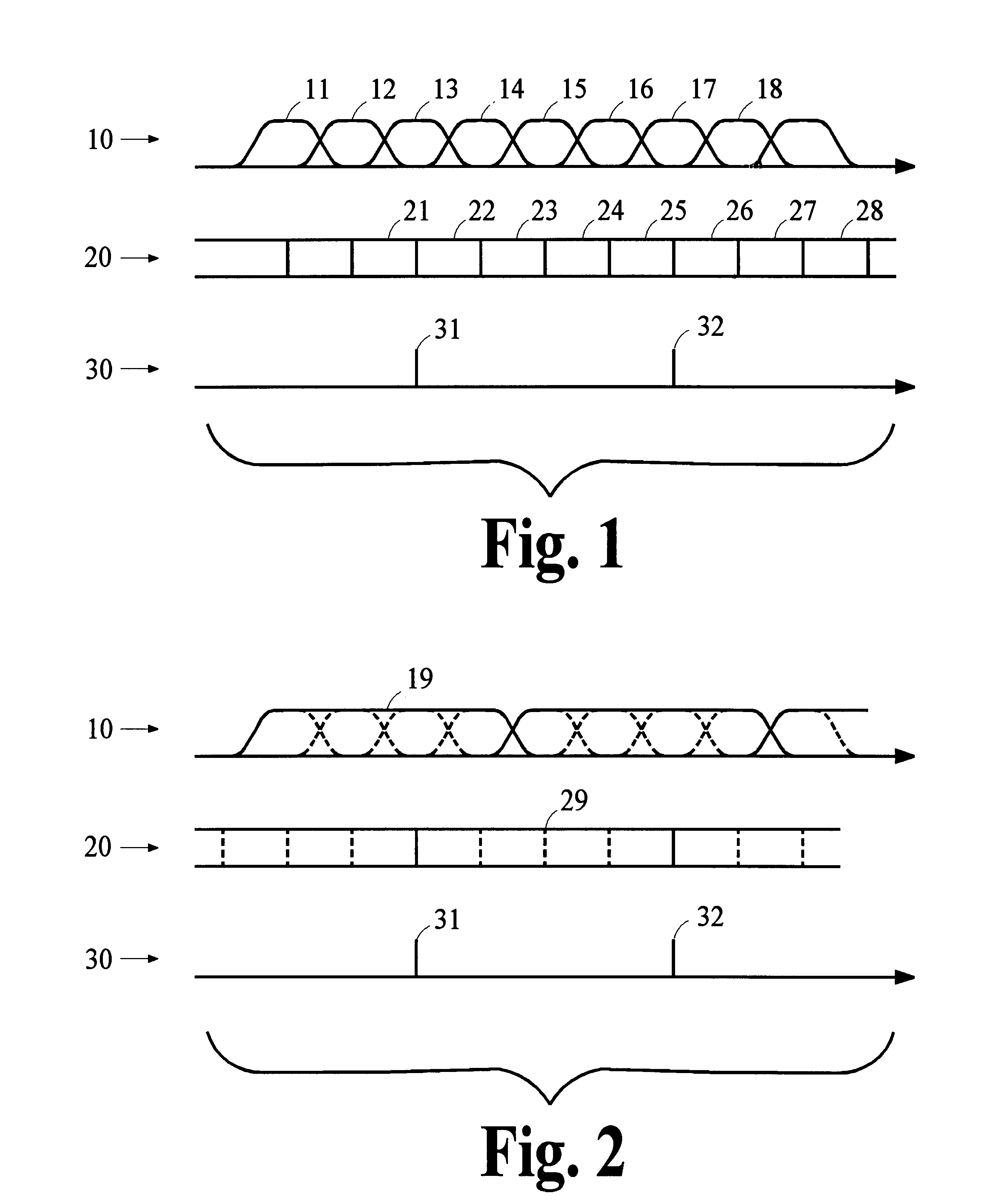
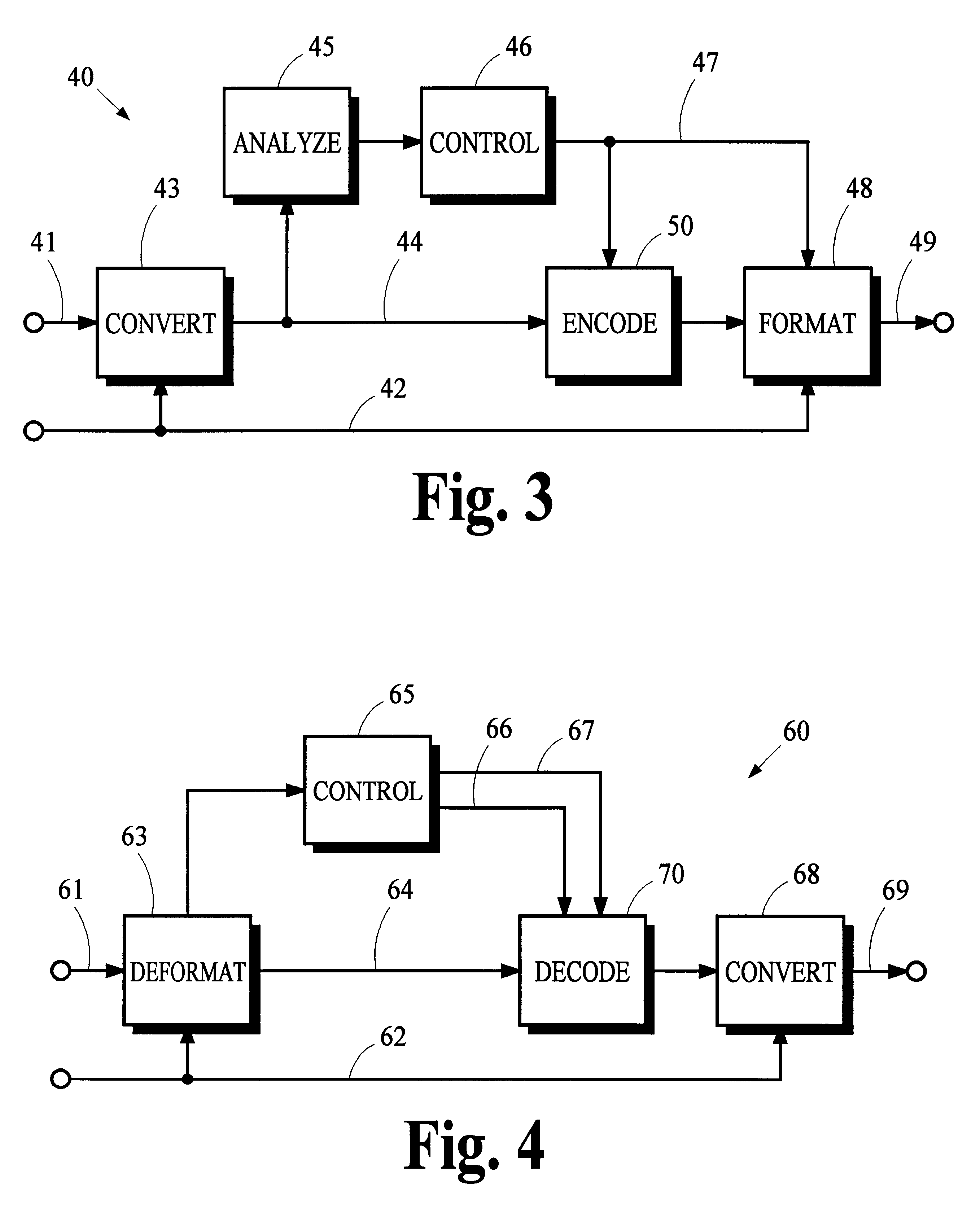
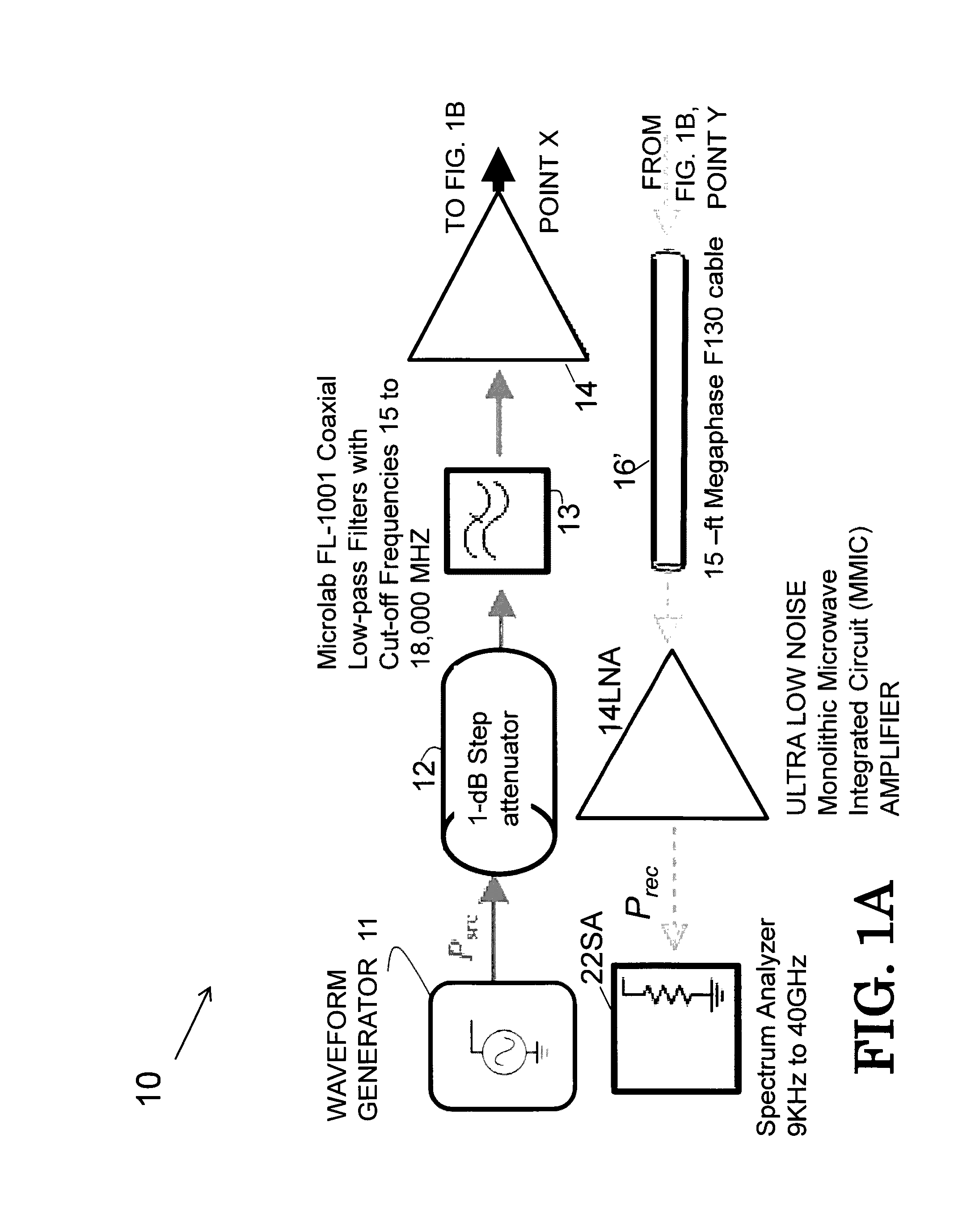
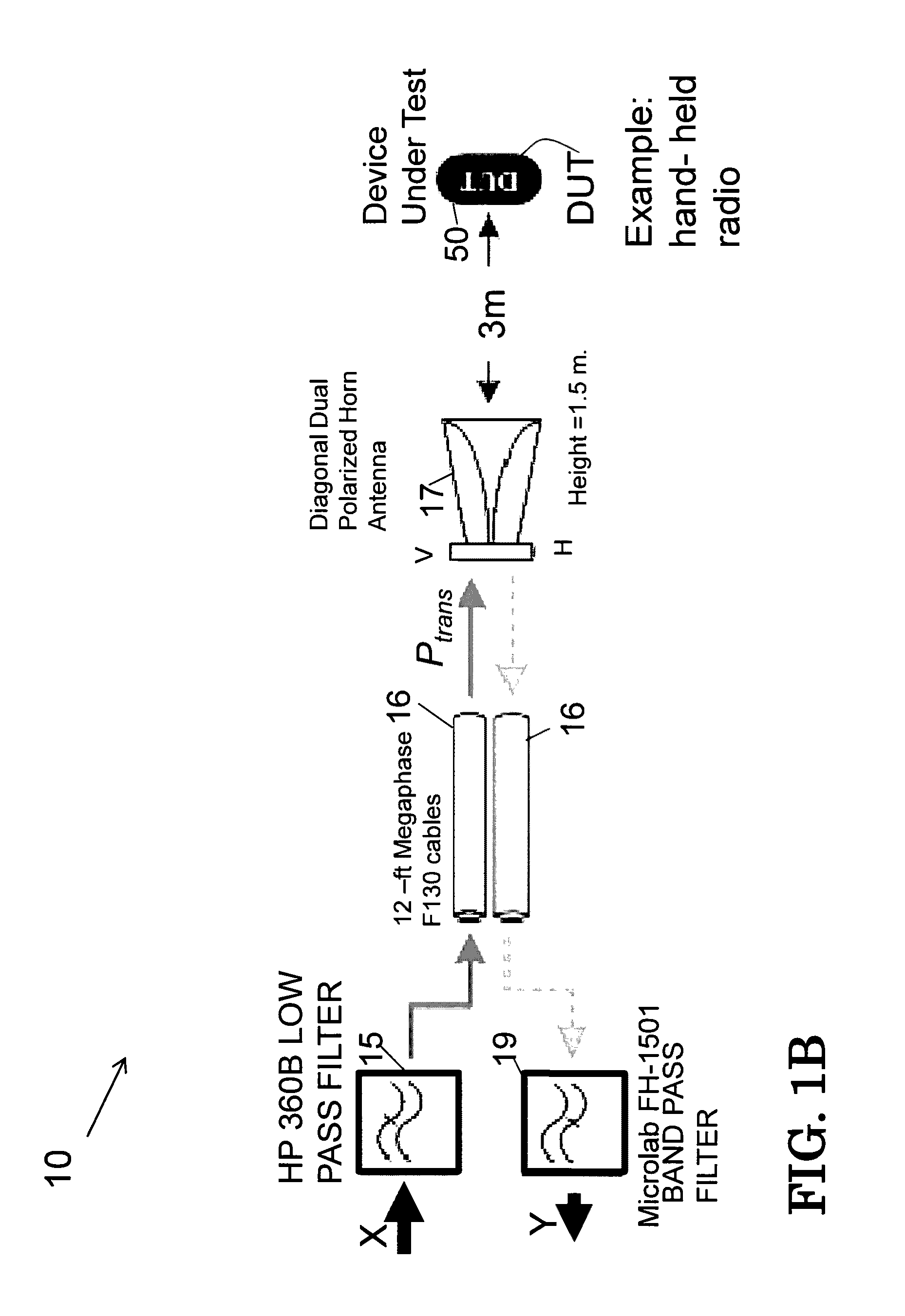
Data framing for adaptive-block-length coding system
InactiveUS6226608B1Easily maintain video/audio synchronizationMinimize artifactElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsColor television signals processingTime domainControl signal
An audio encoder applies an adaptive block-encoding process to segments of audio information to generate frames of encoded information that are aligned with a reference signal conveying the alignment of a sequence of video information frames. The audio information is analyzed to determine various characteristics of the audio signal such as the occurrence and location of a transient, and a control signal is generated that causes the adaptive block-encoding process to encode segments of varying length. A complementary decoder applies an adaptive block-decoding process to recover the segments of audio information from the frames of encoded information. In embodiments that apply time-domain aliasing cancellation (TDAC) transforms, window functions and transforms are applied according to one of a plurality of segment patterns that define window functions and transform parameters for each segment in a sequence of segments. The segments in each frame of a sequence of overlapping frames may be recovered without aliasing artifacts independently from the recovery of segments in other frames. Window functions are adapted to provide preferred frequency-domain responses and time-domain gain profiles.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Frame-based audio coding with video/audio data synchronization by dynamic audio frame alignment
InactiveUS6124895AQuality improvementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionUltrasound attenuationData synchronization
Several audio signal processing techniques may be used in various combinations to improve the quality of audio represented by an information stream formed by splice editing two or more other information streams. The techniques are particularly useful in applications that bundle audio information with video information. In one technique, gain-control words conveyed with the audio information stream are used to interpolate playback sound levels across a splice. In another technique, special filterbanks or forms of TDAC transforms are used to suppress aliasing artifacts on either side of a splice. In yet another technique, special filterbanks or crossfade window functions are used to optimize the attenuation of spectral splatter created at a splice. In a further technique, audio sample rates are converted according to frame lengths and rates to allow audio information to be bundled with, for example, video information. In yet a further technique, audio blocks are dynamically aligned so that proper synchronization can be maintained across a splice. An example for 48 kHz audio with NTSC video is discussed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Time warped modified transform coding of audio signals
ActiveUS20070100607A1Decrease of bit rate demandHighly robustCode conversionSpeech recognitionWindow functionAudio signal
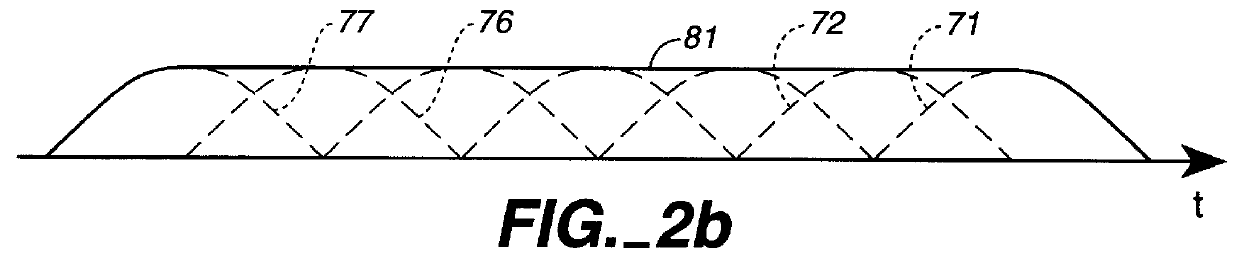
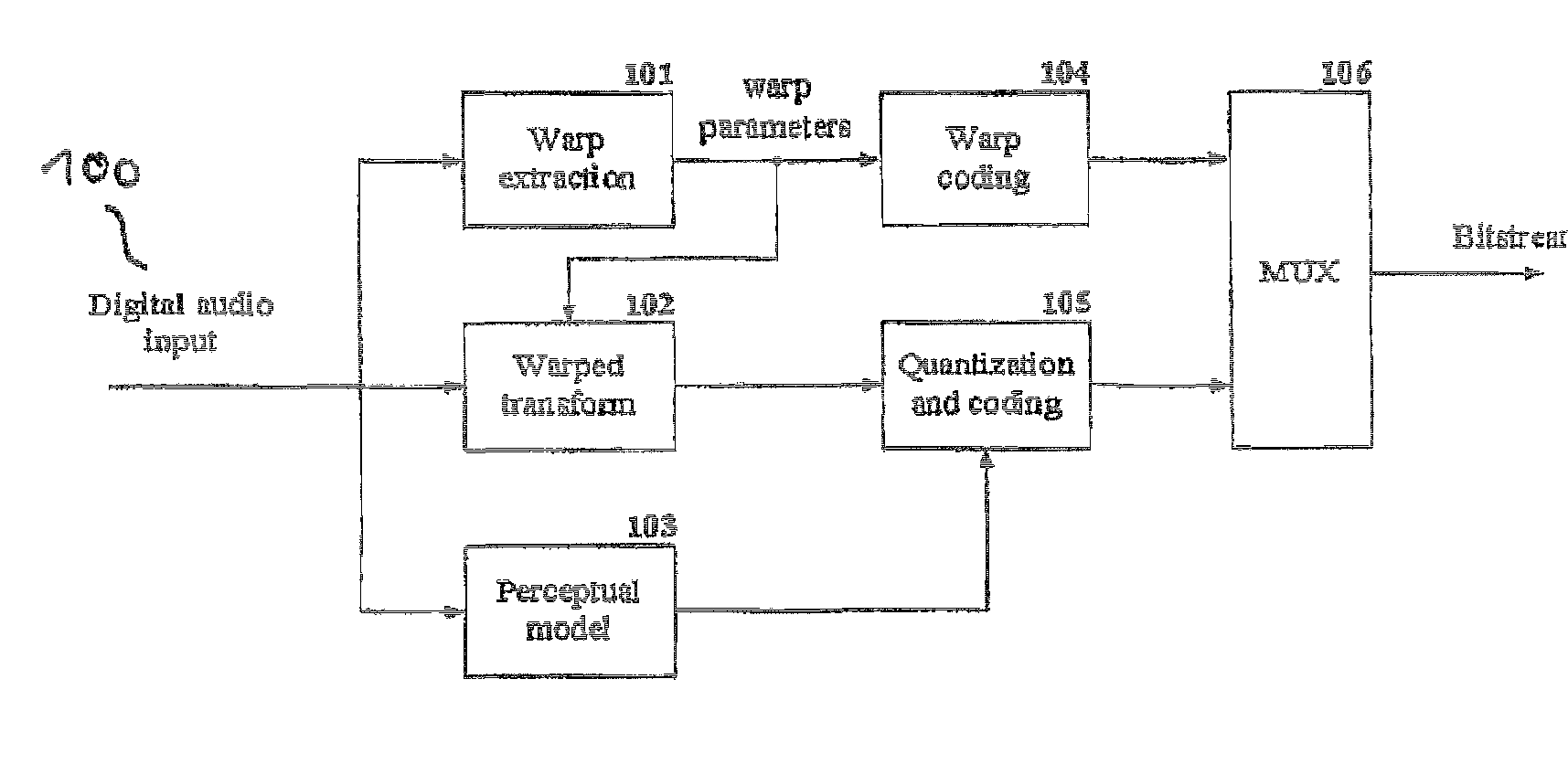
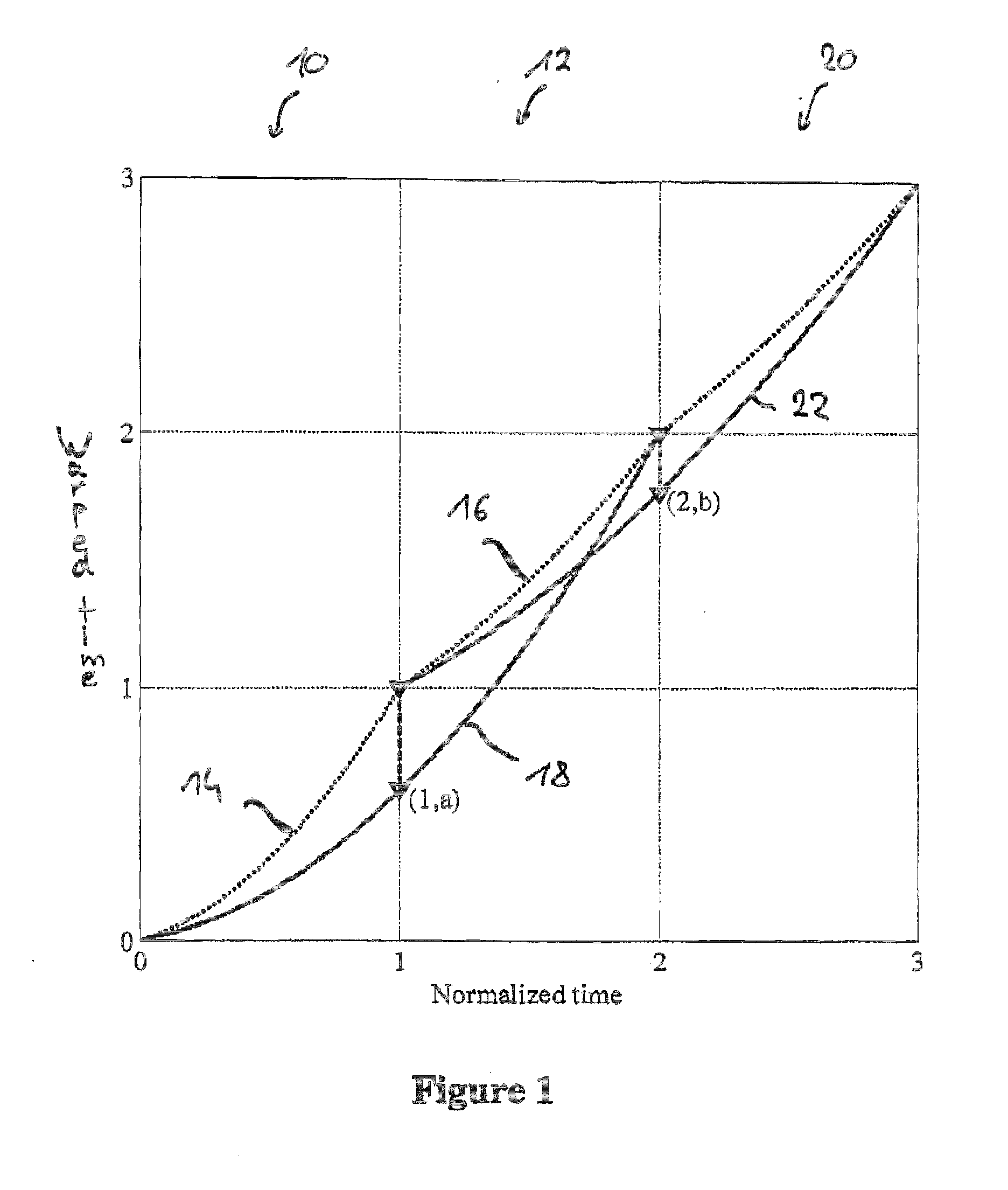
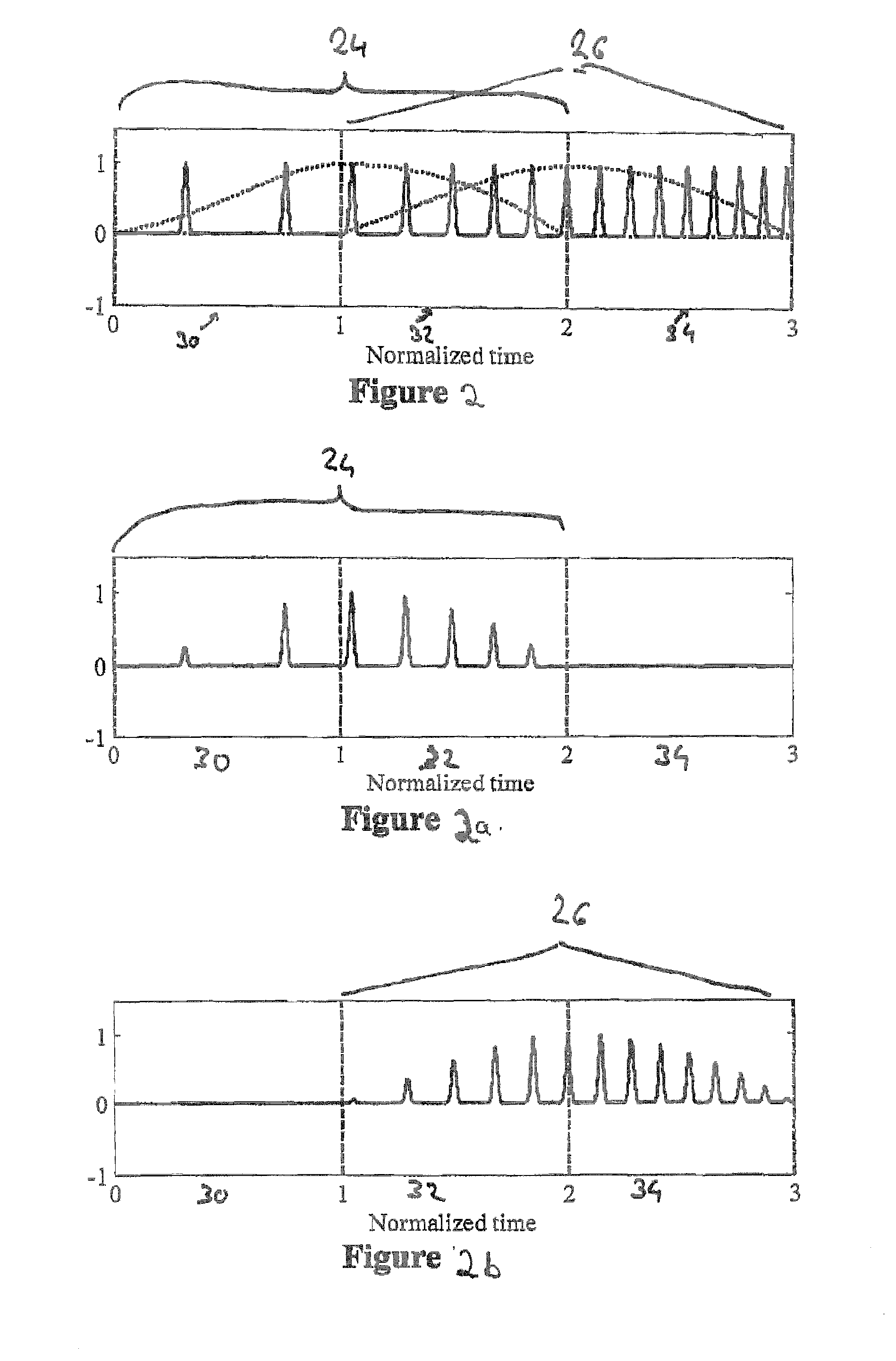
A spectral representation of an audio signal having consecutive audio frames can be derived more efficiently, when a common time warp is estimated for any two neighbouring frames, such that a following block transform can additionally use the warp information. Thus, window functions required for successful application of an overlap and add procedure during reconstruction can be derived and applied, the window functions already anticipating the re-sampling of the signal due to the time warping. Therefore, the increased efficiency of block-based transform coding of time-warped signals can be used without introducing audible discontinuities.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
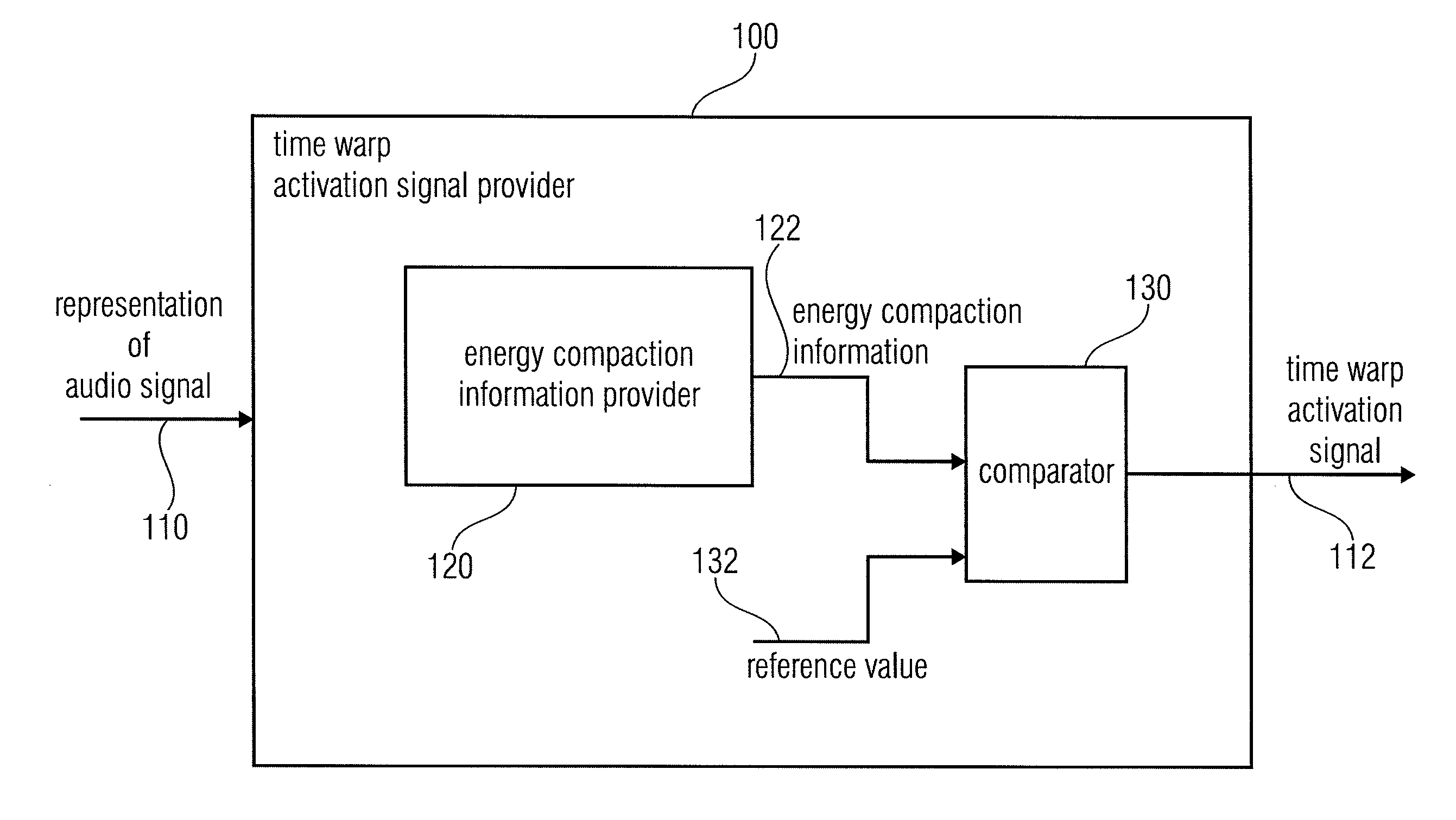
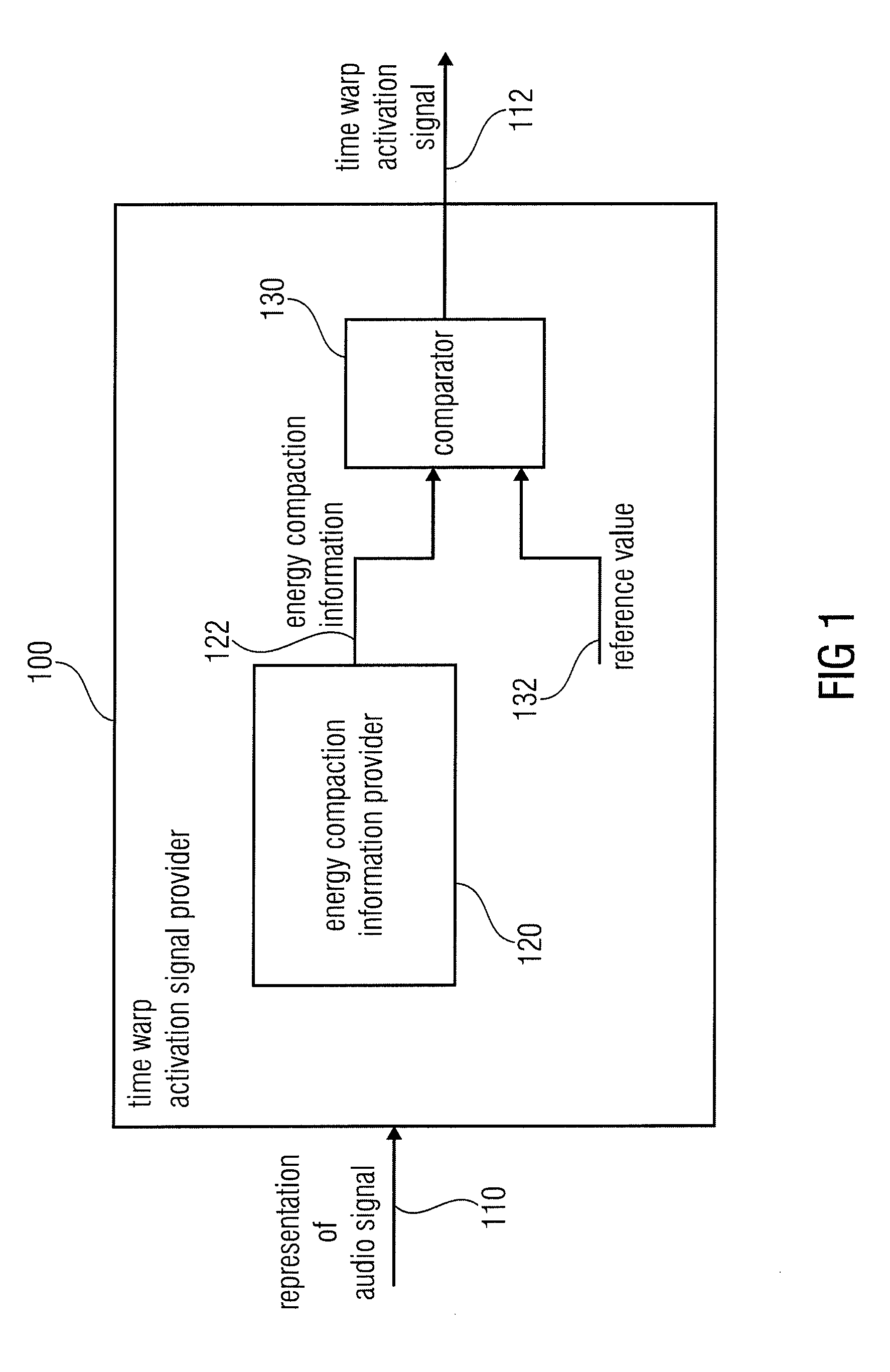
Time warp activation signal provider, audio signal encoder, method for providing a time warp activation signal, method for encoding an audio signal and computer programs
An audio encoder has a window function controller, a windower, a time warper with a final quality check functionality, a time / frequency converter, a TNS stage or a quantizer encoder, the window function controller, the time warper, the TNS stage or an additional noise filling analyzer are controlled by signal analysis results obtained by a time warp analyzer or a signal classifier. Furthermore, a decoder applies a noise filling operation using a manipulated noise filling estimate depending on a harmonic or speech characteristic of the audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and system for seamless integration of preprocessing and postprocessing functions with an existing application program
InactiveUS6874139B2Function increaseWithout compromising file securityHardware monitoringPlatform integrity maintainanceGraphicsOperational system
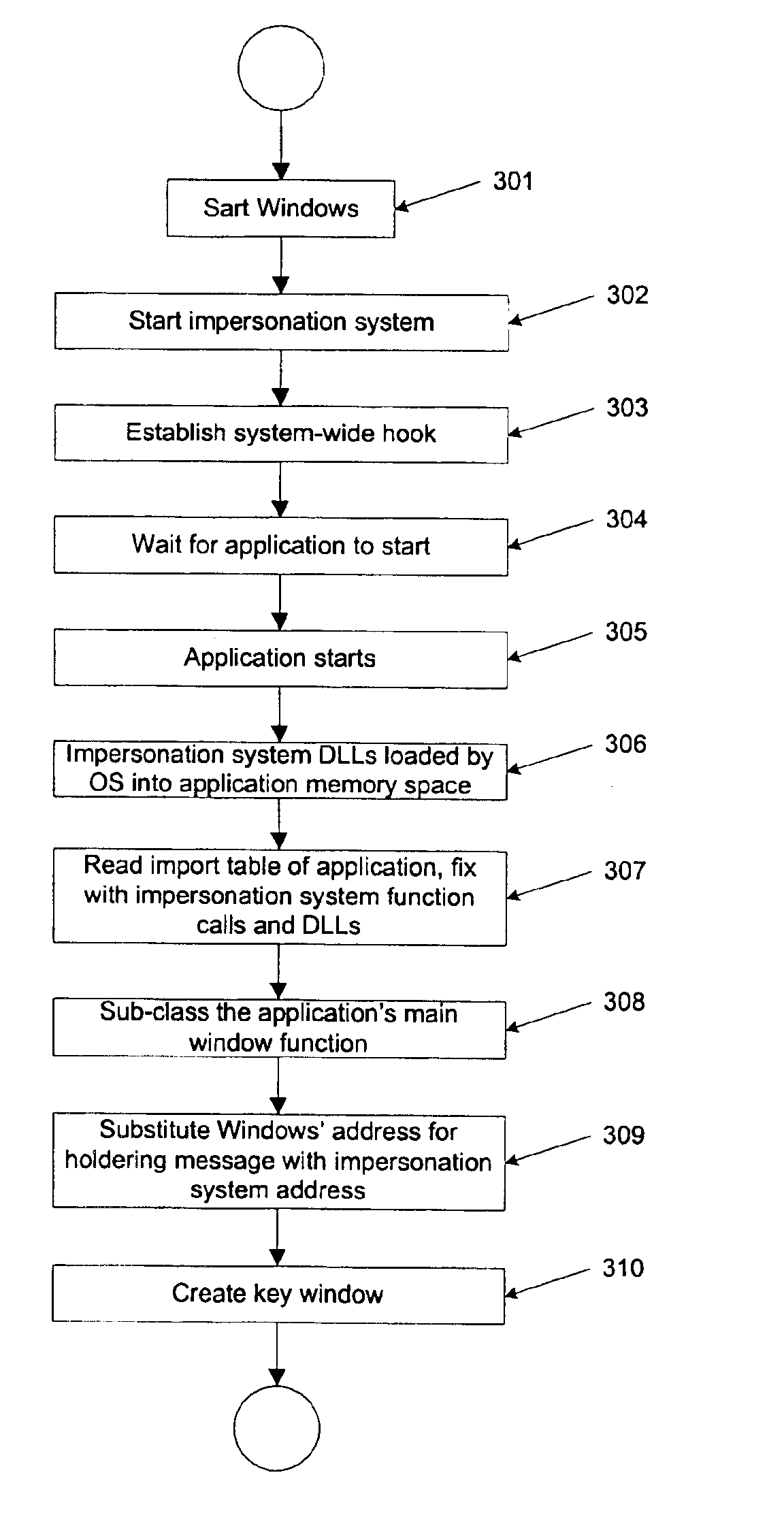
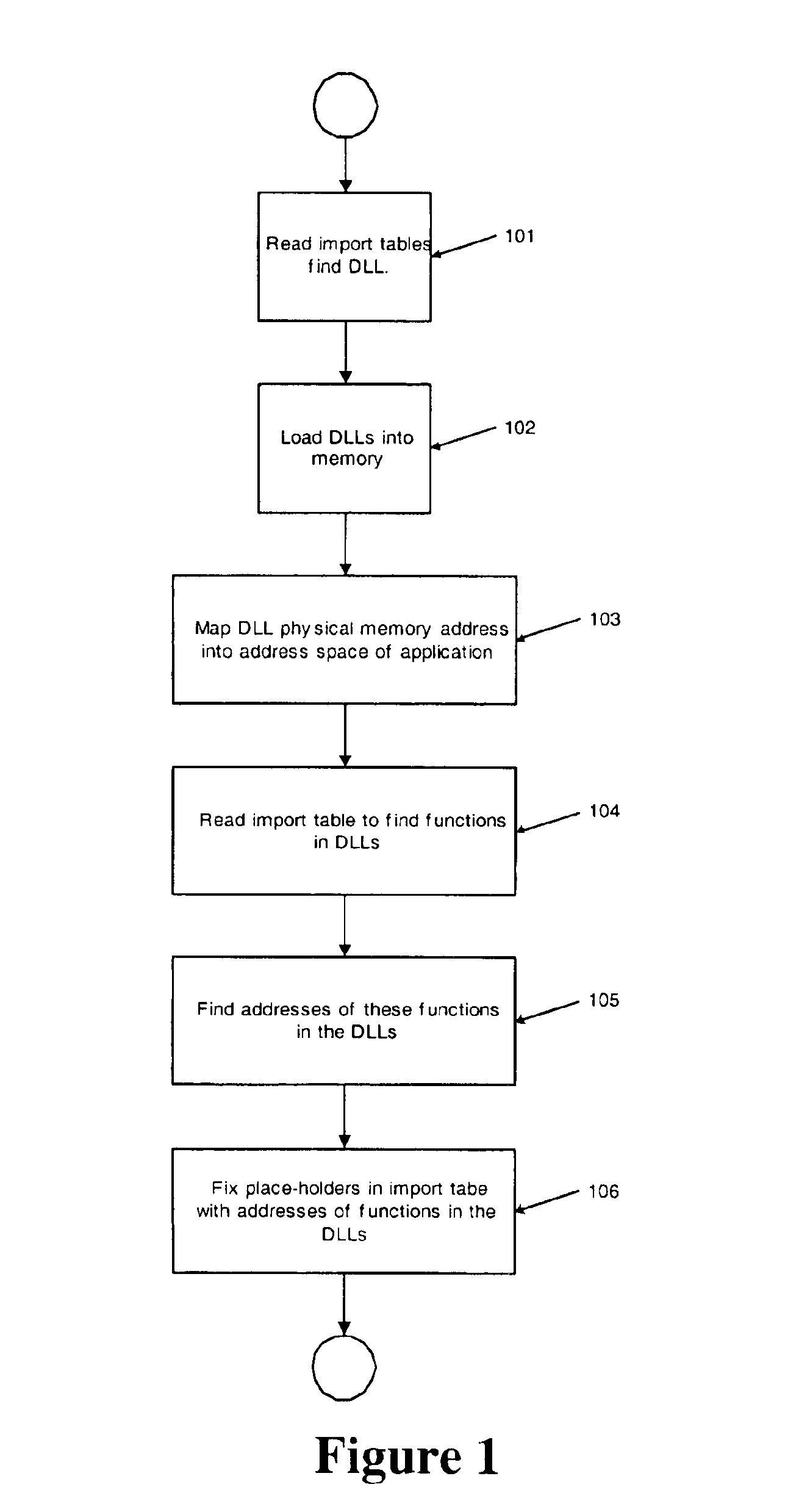
A method for associating file activity of an application with the graphical display of the file on a screen comprises loading by an operating system an executable code of a message monitoring program adapted to monitoring a message sent by an operating system to a document display window. The message monitoring program establishes a system-wide window hook using available operating system API functions associated with one or more functions in a library of the message monitoring program. The message monitoring program library is loaded into the memory space of a newly started application program, the import table of the application is fixed with addresses of functions from the message monitoring program library, and the application's main window function is substituted with a message monitoring program window function.
Owner:CONTROLGUARD SOFTWARE TECH +1
Method and apparatus to create a sound field
ActiveUS7515719B2Eliminate the effects ofReduce calculationTelevision system detailsGain controlTransducerVocal tract
The invention generally relates to a method and apparatus for taking an input signal, replicating it a number of times and modifying each of the replicas before routing them to respective output transducers such that a desired sound field is created. This sound field may comprise a directed beam, focussed beam or a simulated origin. In a first aspect, delays are added to sound channels to remove the effects of different travelling distances. In a second aspect, a delay is added to a video signal to account for the delays added to the sound channels. In a third aspect, different window functions are applied to each channel to give improved flexibility of use. In a fourth aspect, a smaller extent of transducers is used top output high frequencies than are used to output low frequencies. An array having a larger density of transducers near the centre is also provided. In a fifth aspect, a line of elongate transducers is provided to give good directivity in a plane. In a sixth aspect, sound beams are focussed in front or behind surfaces to give different beam widths and simulated origins. In a seventh aspect, a camera is used to indicate where sound is directed.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
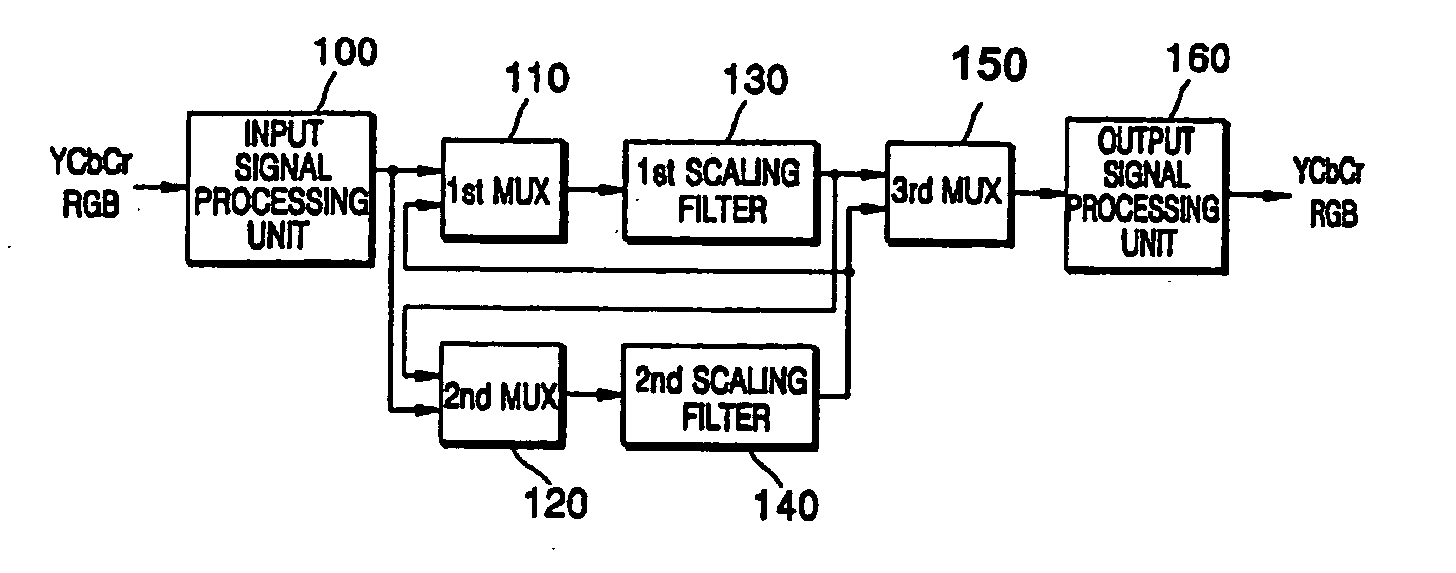
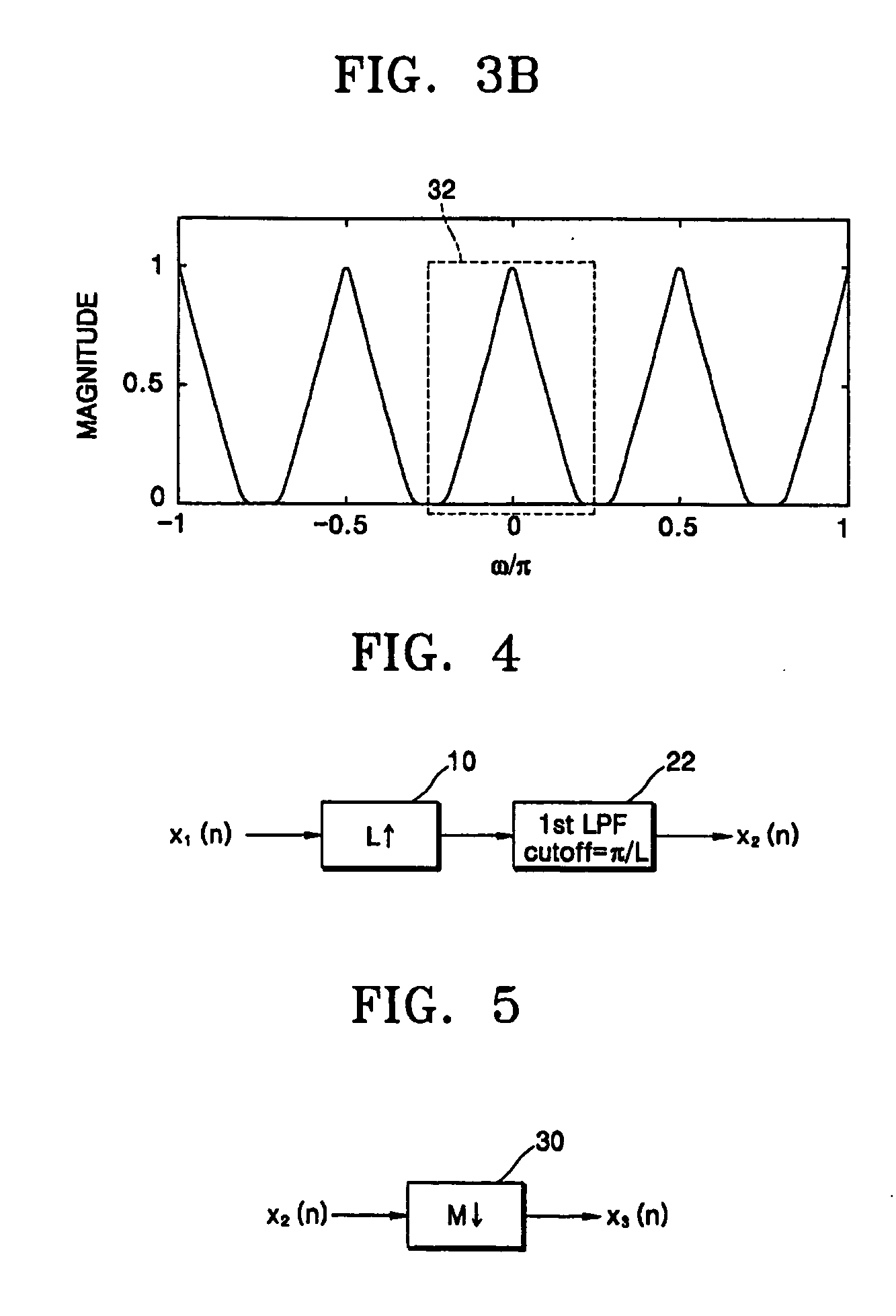
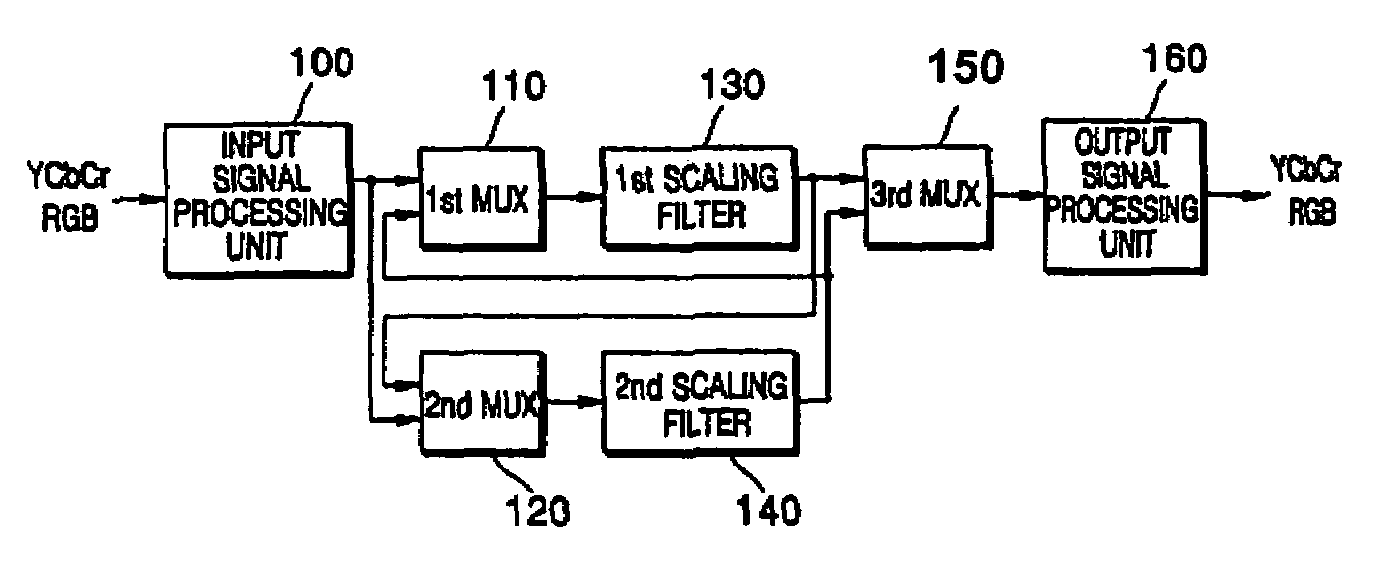
Method of converting resolution of video signals and apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20050134731A1Television system detailsGeometric image transformationImage resolutionGaussian function
A method converts a resolution of video signals, the method including: calculating up-sampling and down-sampling ratios based on a resolution of an input video signal and a desired resolution of an output video signal; calculating a number of filter tabs by multiplying the up-sampling and down-sampling ratios by a number of side lobes; calculating first filter coefficients of a same number of the filter tabs by multiplying a window function by a sinc function; calculating final filter coefficients by subtracting a result of a multiplication of a Gaussian function by a window function from the first filter coefficients, and then normalizing the final filter coefficients; and performing filtering in vertical and horizontal directions based on the final filter coefficients by modifying a sampling rate of an input video signal depending on the up-sampling and down-sampling ratios, to obtain clear video images.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
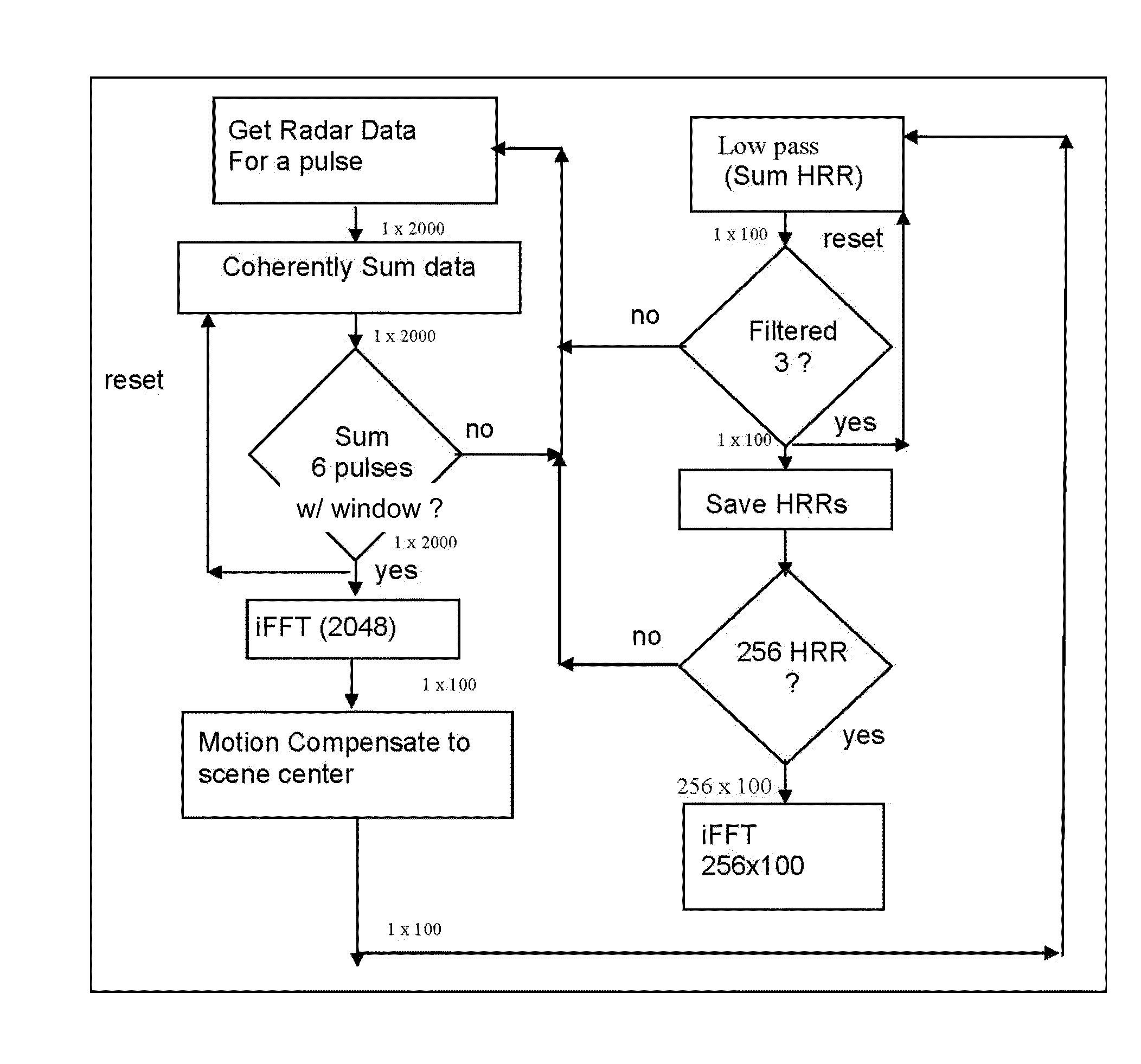
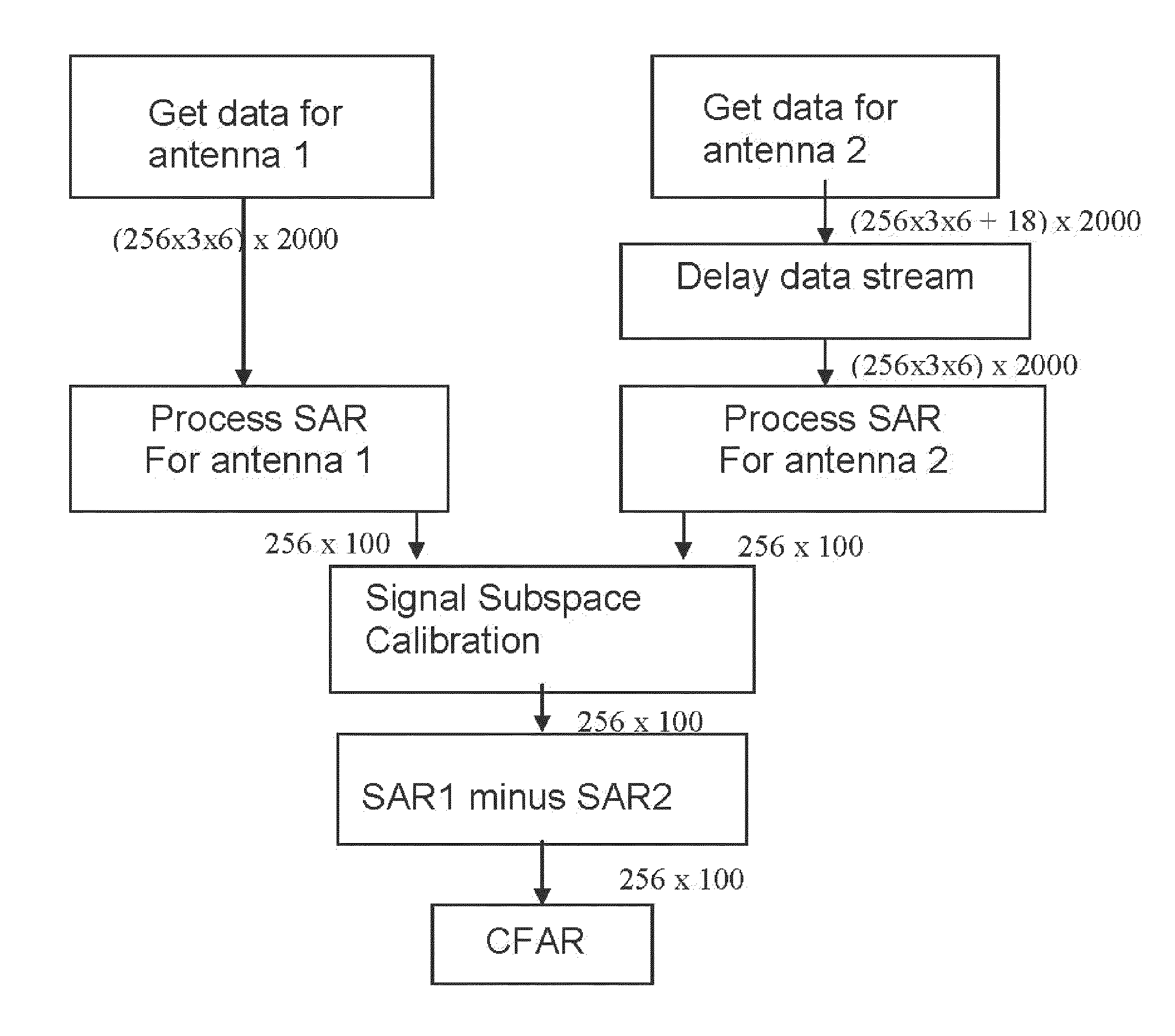
Computationally efficent radar processing method and sytem for SAR and gmti on a slow moving platform
A method and system for processing radar data obtained from a platform which is subjected to non-uniform movement, the distance the platform travels during the formation of an image comprising an aperture; the system comprising software programming for performing a subroutine for building up an average pulse representing a single point on the aperture; the subroutine comprising the steps of inputting radar data from a radar antenna; passing the radar signal through low noise amplifier to reduce impact of electronic noise from the radar system; down converting the signal with a mixer to obtain a lower frequency; filtering out harmonics from the higher frequency range; sampling the radar data using an analog to digital converter at least at Nyquist down range frequency; based upon the IF of the radar; determining a scene center (center of SAR imagery) for the purpose of motion compensation; performing a two stage averaging scheme of the received signals with a variable window function; determining a window function based upon the velocity and acceleration of the platform and scene center; the window function comprising a first stage window; coherently averaging N pulses together to create an average pulse; performing an inverse Fourier transform; compensating to the scene center by multiplying by a complex exponential based upon both the GPS and inertial navigational system; summing the average pulses using low pass filter; the software programming operating to repeat the step of building up an average pulse a first predetermined number of times for a time period that is less than the Nyquist sample time interval; the software programming operating to repeat the step of building an average pulse for a predetermined number of times to generate a second predetermined number of average pulses; the software programming operating to perform a two dimensional inverse Fourier transform to obtain SAR image; outputting the SAR image on a display screen; and a display for displaying the outputted SAR image.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Apparatus and Method for Generating Audio Subband Values and Apparatus and Method for Generating Time-Domain Audio Samples
ActiveUS20090319283A1High energy valueImprove responseDigital technique networkSpeech analysisTime domainAudio frequency
An embodiment of an apparatus for generating audio subband values in audio subband channels has an analysis windower for windowing a frame of time-domain audio input samples being in a time sequence extending from an early sample to a later sample using an analysis window function having a sequence of window coefficients to obtain windowed samples. The analysis window function has a first group of window coefficients and a second group of window coefficients. The first group of window coefficients is used for windowing later time-domain samples and the second group of window coefficients is used for windowing an earlier time-domain samples. The apparatus further has a calculator for calculating the audio subband values using the windowed samples.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and apparatus to create a sound field
InactiveUS20090161880A1Eliminate the effects ofReduce calculationTelevision system detailsMicrophonesVocal tractTransducer
The invention generally relates to a method and apparatus for taking an input signal, replicating it a number of times and modifying each of the replicas before routing them to respective output transducers such that a desired sound field is created. This sound field may comprise a directed beam, focused beam or a simulated origin. In a first aspect, delays are added to sound channels to remove the effects of different travelling distances. In a second aspect, a delay is added to a video signal to account for the delays added to the sound channels. In a third aspect, different window functions are applied to each channel to give improved flexibility of use. In a fourth aspect, a smaller extent of transducers is used top output high frequencies than are used to output low frequencies. An array having a larger density of transducers near the center is also provided. In a fifth aspect, a line of elongate transducers is provided to give good directivity in a plane. In a sixth aspect, sound beams are focused in front or behind surfaces to give different beam widths and simulated origins. In a seventh aspect, a camera is used to indicate where sound is directed.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE MECHATRONICS
Method and system for providing configurable features for graphical user interfaces for electronic trading
A method and system for providing configurable features for a multi-windowed graphical user interface (GUI) for electronic trading. The configurable features include, but are not limited to, creating collective windows comprising plural individual windows, where the collective window functions like an individual window, collapsing plural windows with a single action and changing display characteristics of the plural windows or the collective windows. The method and system allows a user of a target device to customize the multi-windowed GUI based on individual user preferences for electronic trading.
Owner:ROSENTHAL COLLINS GROUP
Apparatus and method for TOL client boundary protection
InactiveUS7065785B1Preventing executionDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionGraphicsGraphical user interface
A telephony-over-LAN (ToL) system having a graphical user interface (GUI) wherein an authorized or guest user may be locked within a ToL window, having full access to the ToL features, but denied access to other parts of the computer system. In such a system, the terminal user or subscriber may click on a “Guest” button on the ToL client GUI screen before leaving the computer. The ToL guest user may then execute the call normally. According to a first embodiment of the invention, the ToL client locks the user into the ToL client screen. Keystrokes and mouse cursor movements which would allow exiting the ToL client are prevented. According to a second embodiment, of the invention, the ToL client screen is “maximized” and the minimize or resize window functions are blocked. When the terminal subscriber returns, a password is entered to regain full access to the computer.
Owner:ENTERPRISE SYST TECH S A R L
Method for processing sampling value of digitalization protection test control apparatus
InactiveCN101350518AAccurate measurementAccurateCurrent/voltage measurementEmergency protective circuit arrangementsData setDigital filter
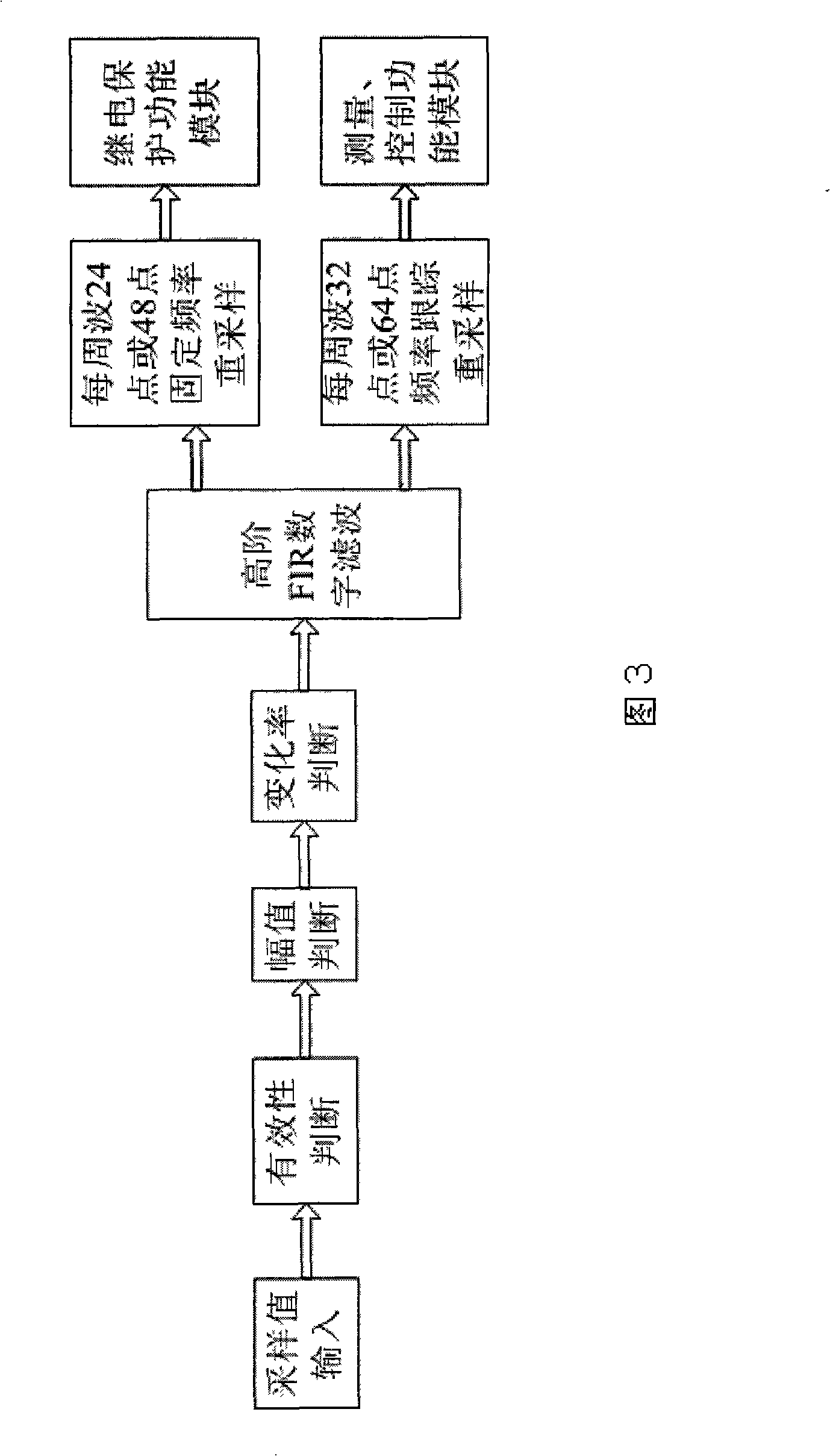
The present invention relates to a sampling value processing method of integrative device based on a sampling value interface, which is used for protecting and monitoring a digital substation. The method is characterized in that the sampling value interface module of the integrative device is used for real-time judgment on the effectiveness and rationality of sampling values which are transmitted from an incorporating unit; the secondary Lagrange interpolation are calculated for a small quantity of broken or lost sampling values; a window function is used for designing a high-order FIR digital filter which is used for filtering the sampling values; the on-line parameters of the threshold and the filter are regulated in a self-adapting way according to the parameters of conventional data sets transmitted by the sampling values; the protection function is resampled by adopting a secondary Lagrange algorithm of fixed frequency according to the requirements of protecting and monitoring functions; the monitoring function is first processed by iterative computation of frequency; the real-time resampling frequency s regulated according to the signal frequency; the sampling values are resampled by adopting the secondary Lagrange algorithm according to the novel sampling frequency, thus the processing method not only satisfies the requirements of protection and application, but also improves the measurement accuracy.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD
Efficient system and method for converting between different transform-domain signal representations
InactiveUS6963842B2Eliminating intermediate time-domain processingInnovative designCode conversionSpeech synthesisTime domainFourier transform on finite groups
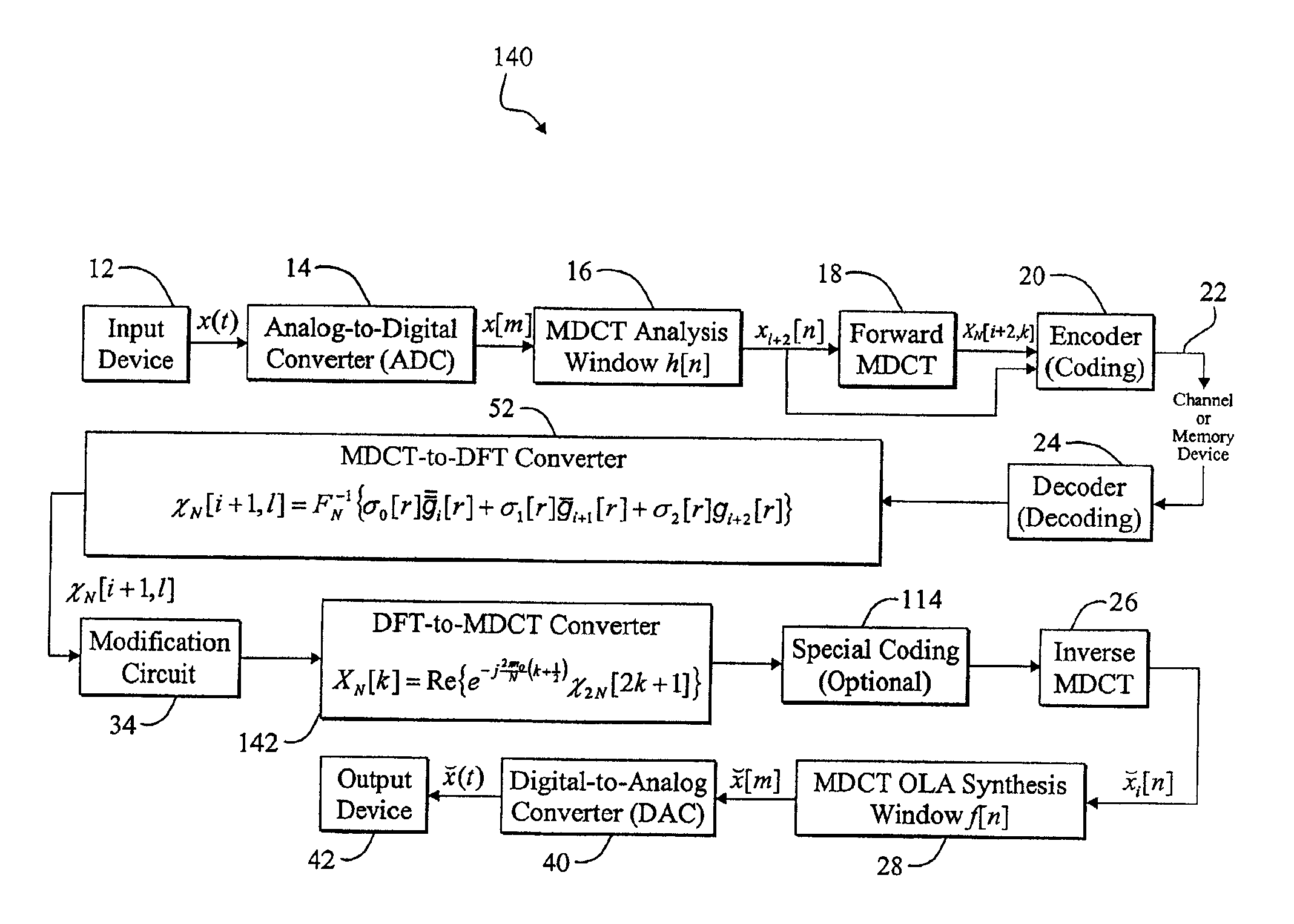
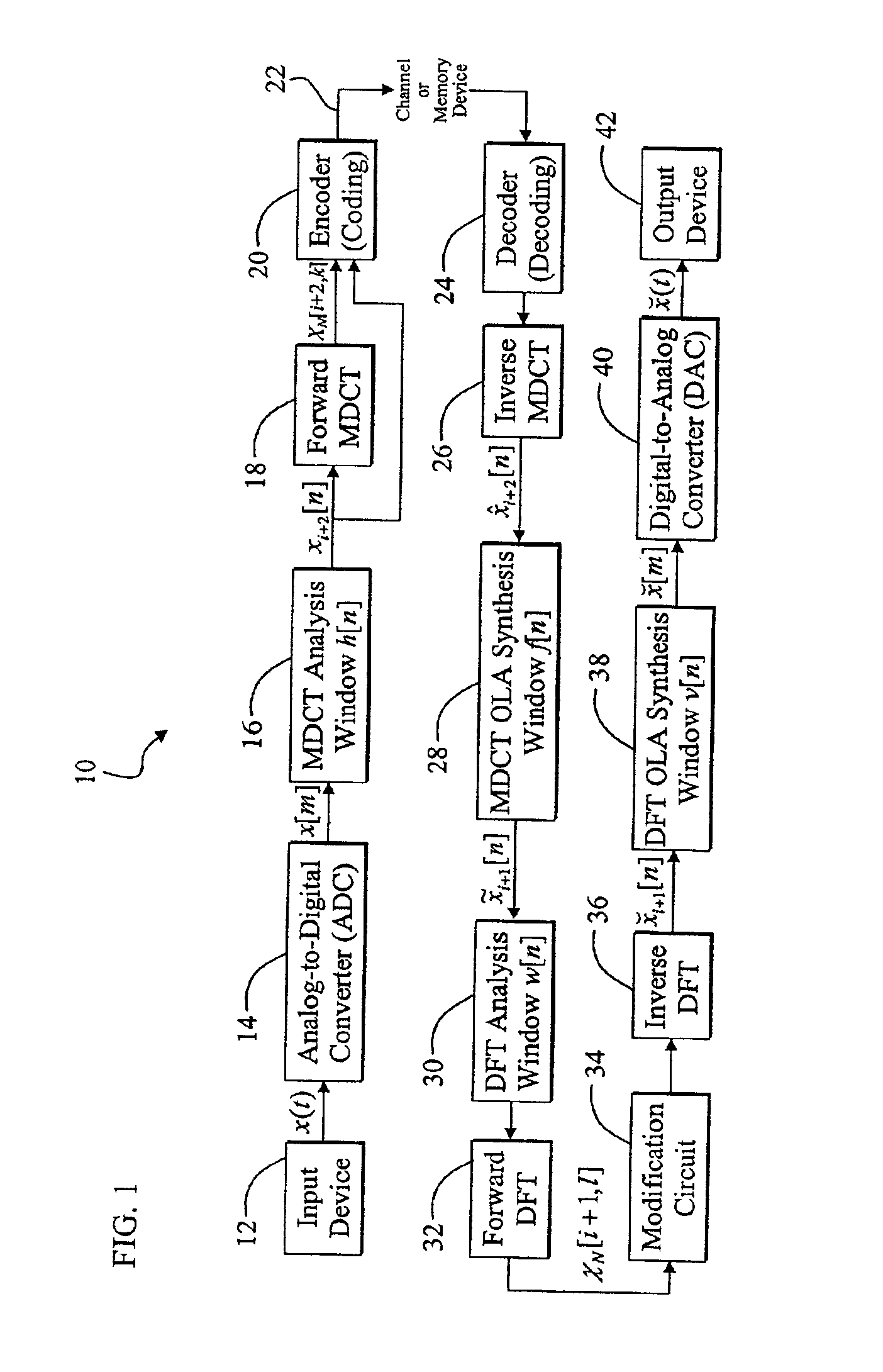
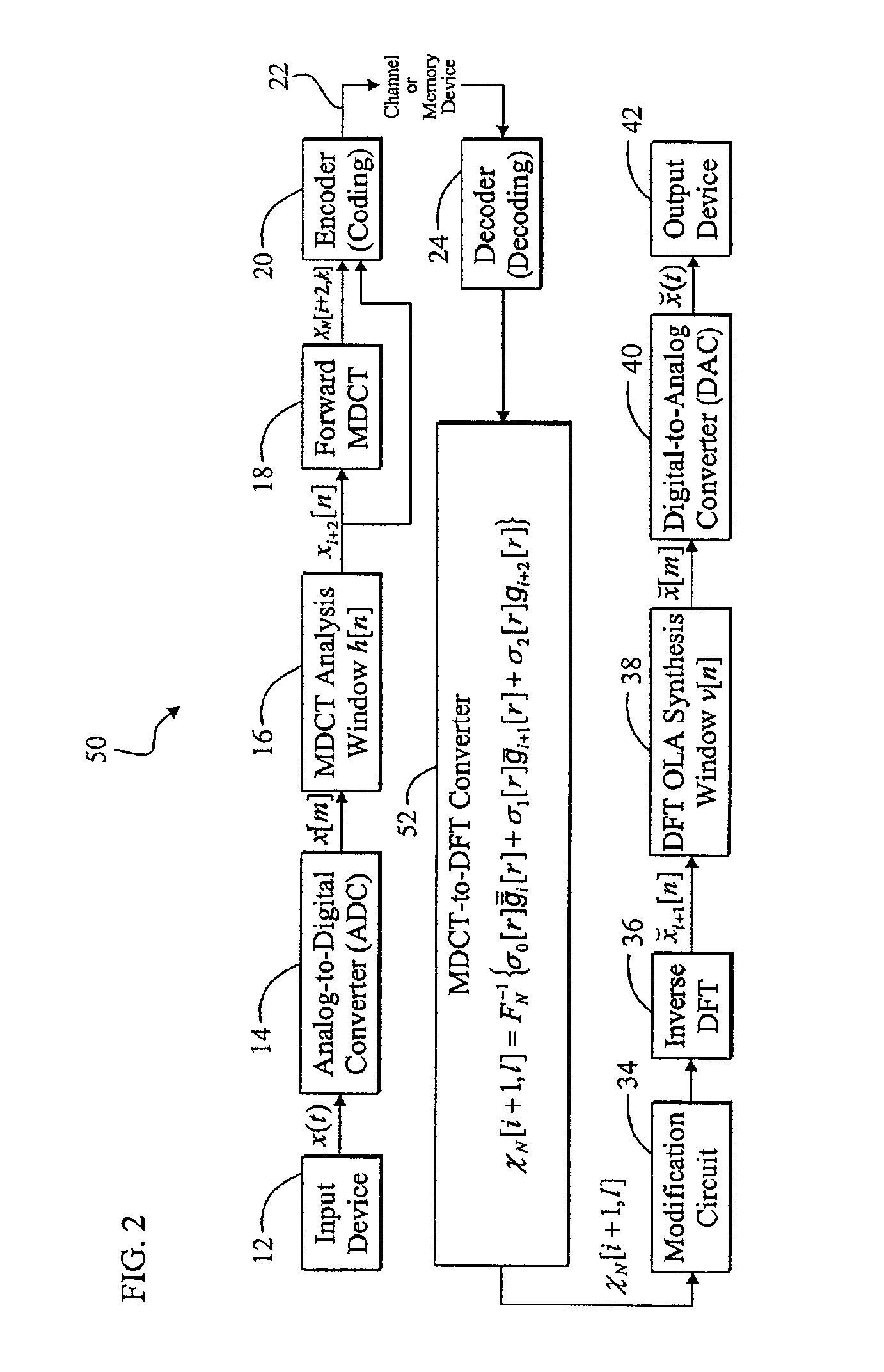
A memory-efficient system converting a signal from a first transform domain to a second transform domain. The system includes a first mechanism that obtains an input signal expressed via a first transform-domain signal representation. A second mechanism expresses the input signal via a second transform-domain signal representation without intermediate time-domain conversion. In the specific embodiment, the input signal is a Modified Discrete Cosine Transform (MDCT) signal. The second transform-domain signal representation is a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) signal. The second mechanism further includes a third mechanism that combines effects of an inverse MDCT, a synthesis window function, and an analysis window function, and provides a first signal in response thereto. A fourth mechanism converts the MDCT signal to the DFT signal based on the first signal. In a more specific embodiment, the synthesis window function is an MDCT synthesis window function, while the analysis window function is a DFT analysis window function. The fourth mechanism includes a mechanism for performing a fast transform on the MDCT signal and providing a first transformed signal in response thereto. The fourth mechanism further includes a mechanism for selectively delaying and updating the first transformed signal to yield second and third transformed signals, respectively, in response thereto. The fourth mechanism further includes a mechanism for operating on the first, second, and third transformed signals via third, second, and first combined window functions, respectively, and providing third, second, and first windowed signals, respectively, in response thereto. An adder adds the first, second, and third windowed functions to provide an added digital signal. An inverse DFT circuit performs an inverse DFT on the added digital signal to provide the DFT signal as output.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
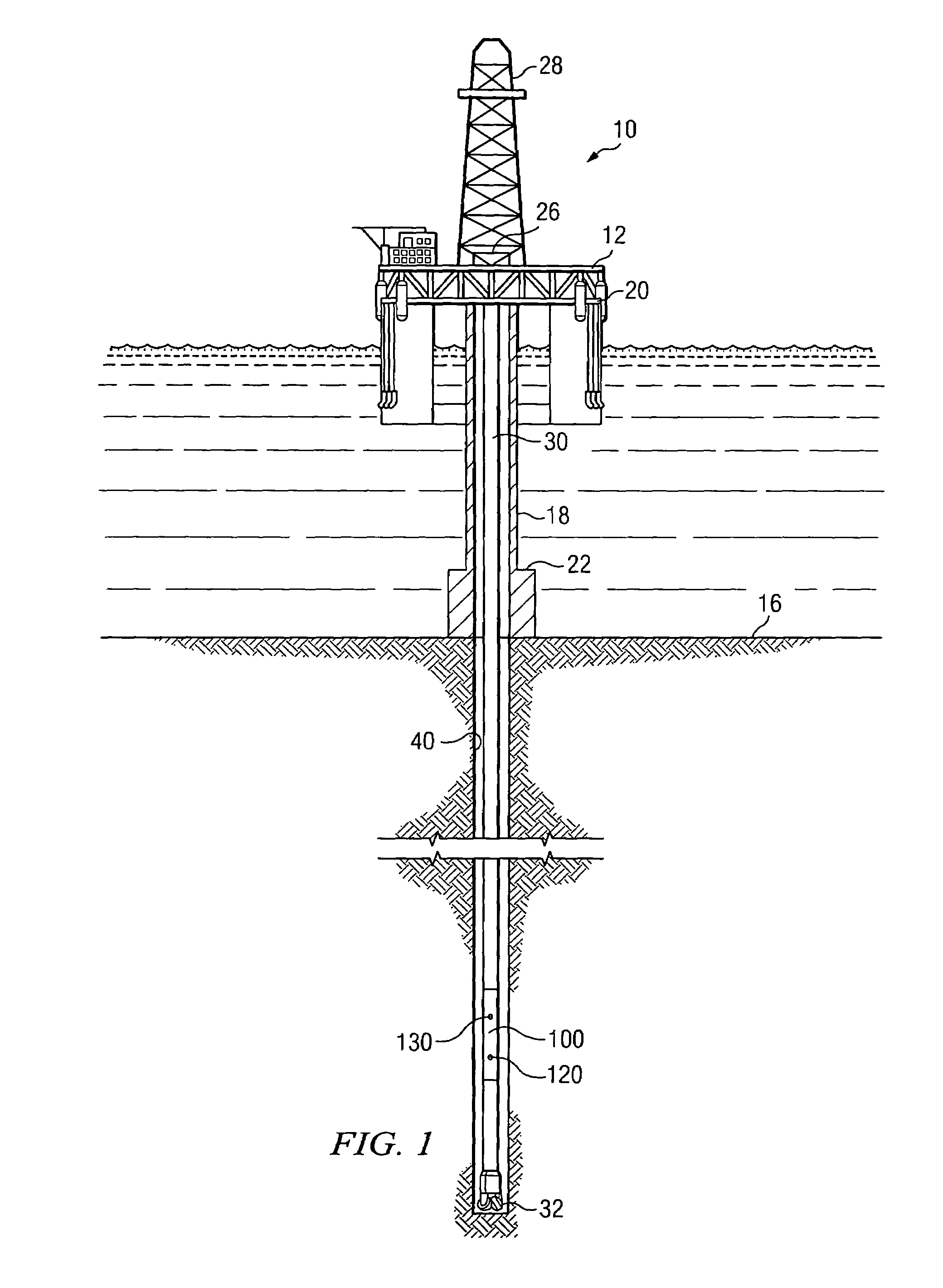
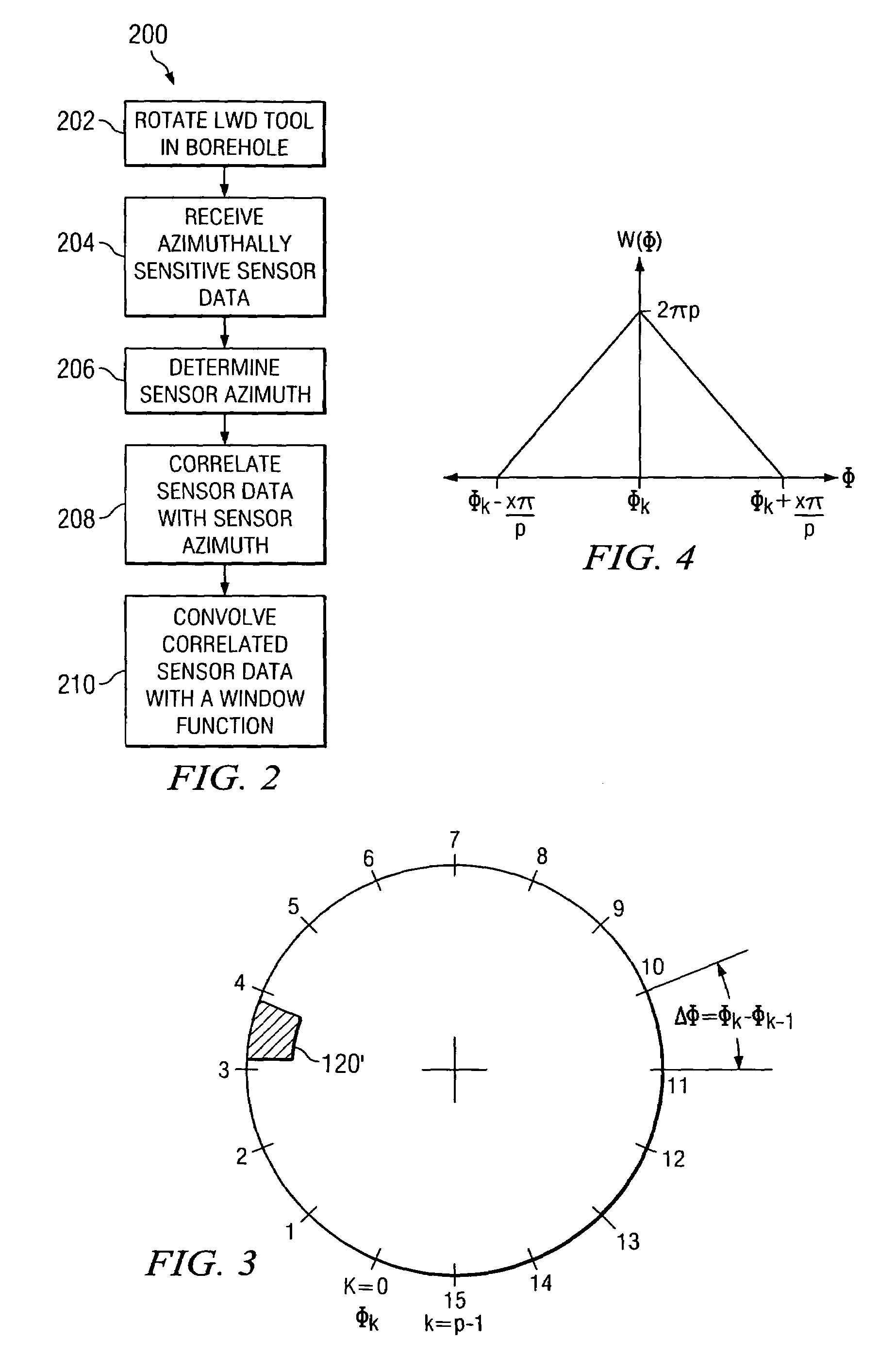
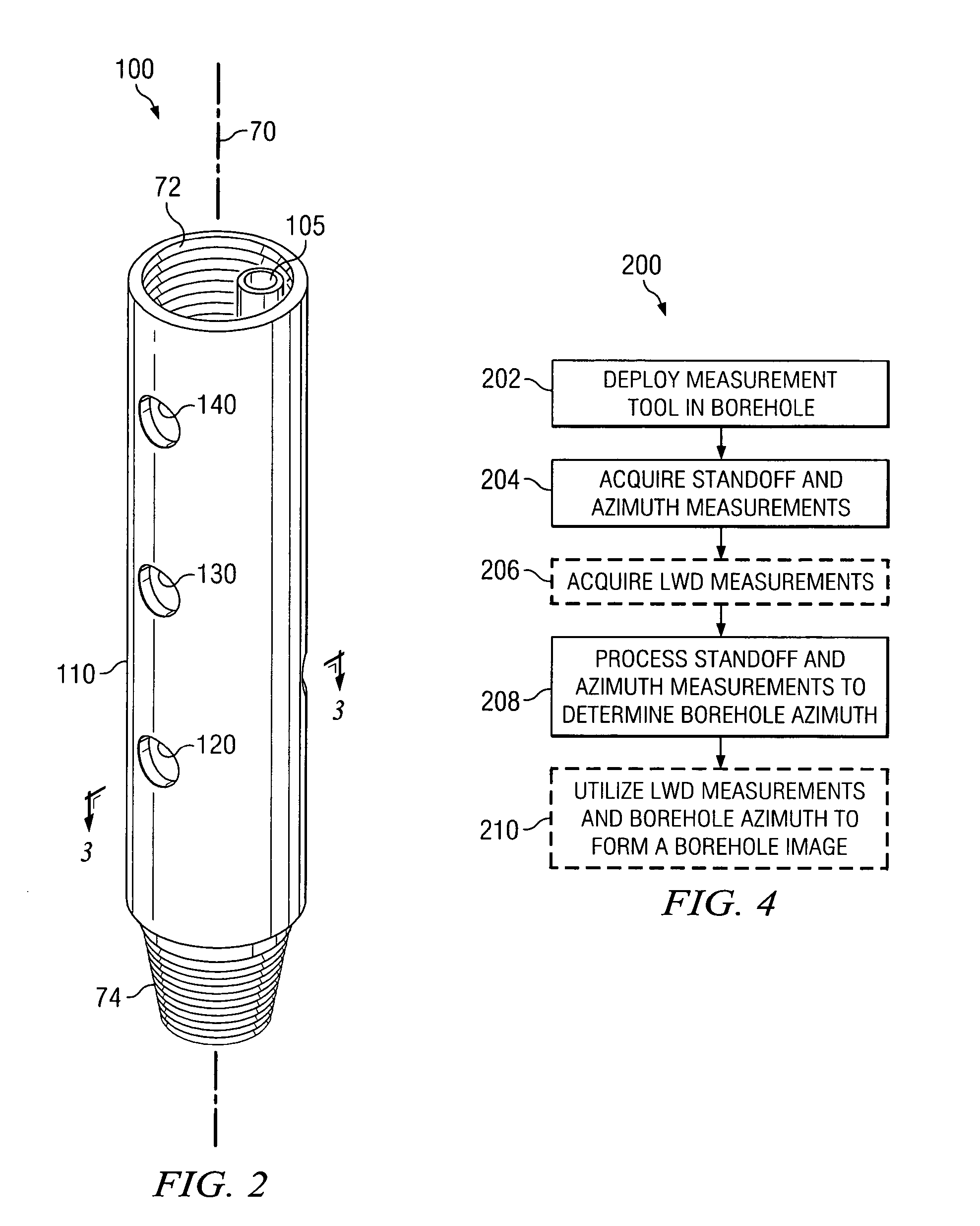
Enhanced measurement of azimuthal dependence of subterranean parameters
ActiveUS7027926B2Improve practicalityImprove noiseElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyImage resolutionNoise suppression
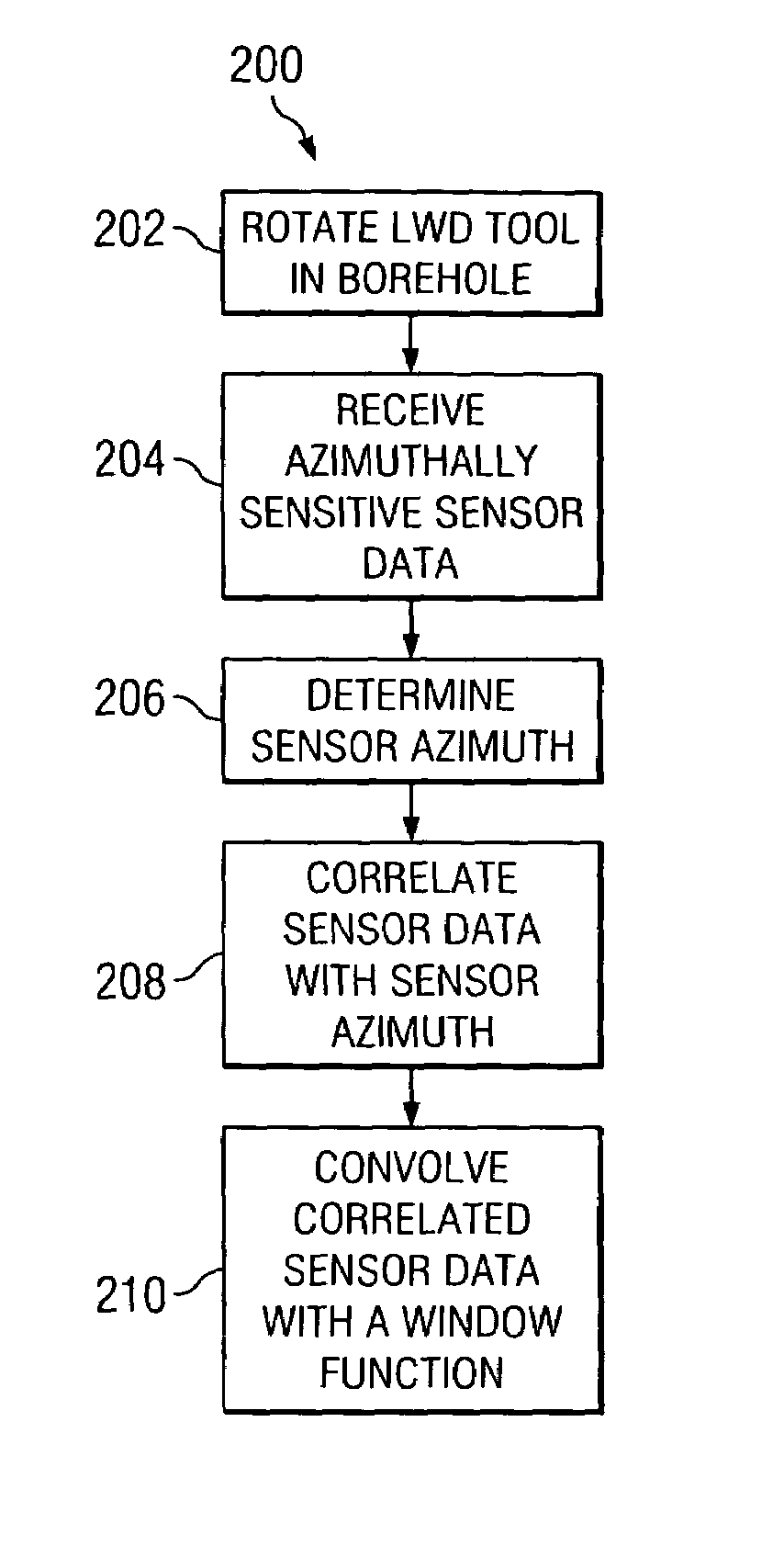
A method for estimating an azimuthal dependence of a parameter of a borehole using logging sensor measurements acquired as a function of azimuth of the logging sensors is provided. The method includes acquiring at least one logging sensor measurement and a corresponding azimuth from a downhole tool. The method further includes processing a convolution of the logging sensor measurement and corresponding azimuth with a predetermined window function to determine convolved logging sensor data for at least one azimuthal position. Certain embodiments of this invention may be advantageously utilized in LWD imaging applications to provide for superior image resolution and noise rejection as compared to prior art imaging techniques.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Computationally efficent radar processing method and sytem for SAR and gmti on a slow moving platform
A method and system for processing radar data obtained from a platform which is subjected to non-uniform movement, the distance the platform travels during the formation of an image comprising an aperture; the system comprising software programming for performing a subroutine for building up an average pulse representing a single point on the aperture; the subroutine comprising the steps of inputting radar data from a radar antenna; passing the radar signal through low noise amplifier to reduce impact of electronic noise from the radar system; down converting the signal with a mixer to obtain a lower frequency; filtering out harmonics from the higher frequency range; sampling the radar data using an analog to digital converter at least at Nyquist down range frequency; based upon the IF of the radar; determining a scene center (center of SAR imagery) for the purpose of motion compensation; performing a two stage averaging scheme of the received signals with a variable window function; determining a window function based upon the velocity and acceleration of the platform and scene center; the window function comprising a first stage window; coherently averaging N pulses together to create an average pulse; performing an inverse Fourier transform; compensating to the scene center by multiplying by a complex exponential based upon both the GPS and inertial navigational system; summing the average pulses using low pass filter; the software programming operating to repeat the step of building up an average pulse a first predetermined number of times for a time period that is less than the Nyquist sample time interval; the software programming operating to repeat the step of building an average pulse for a predetermined number of times to generate a second predetermined number of average pulses; the software programming operating to perform a two dimensional inverse Fourier transform to obtain SAR image; outputting the SAR image on a display screen; and a display for displaying the outputted SAR image.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
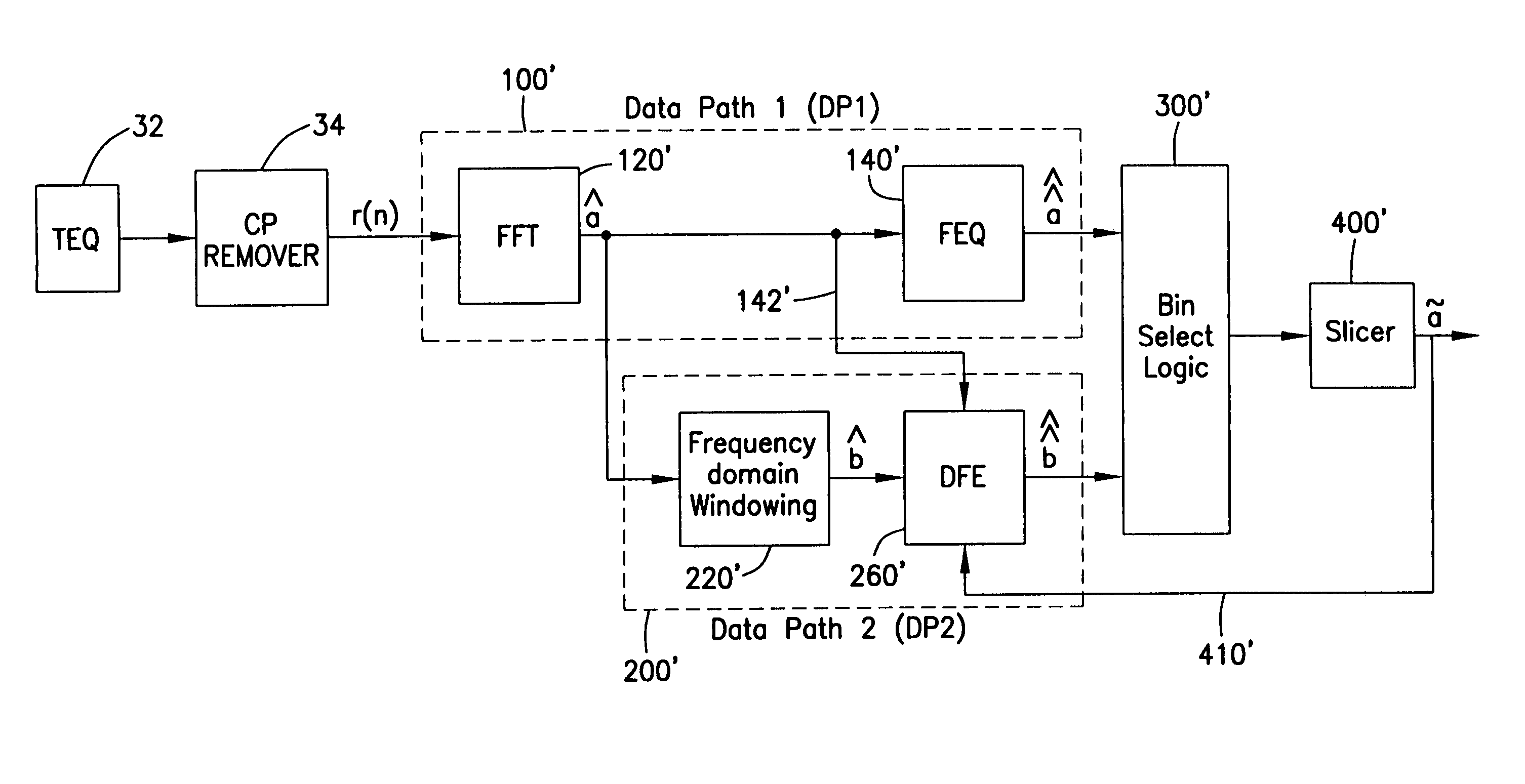
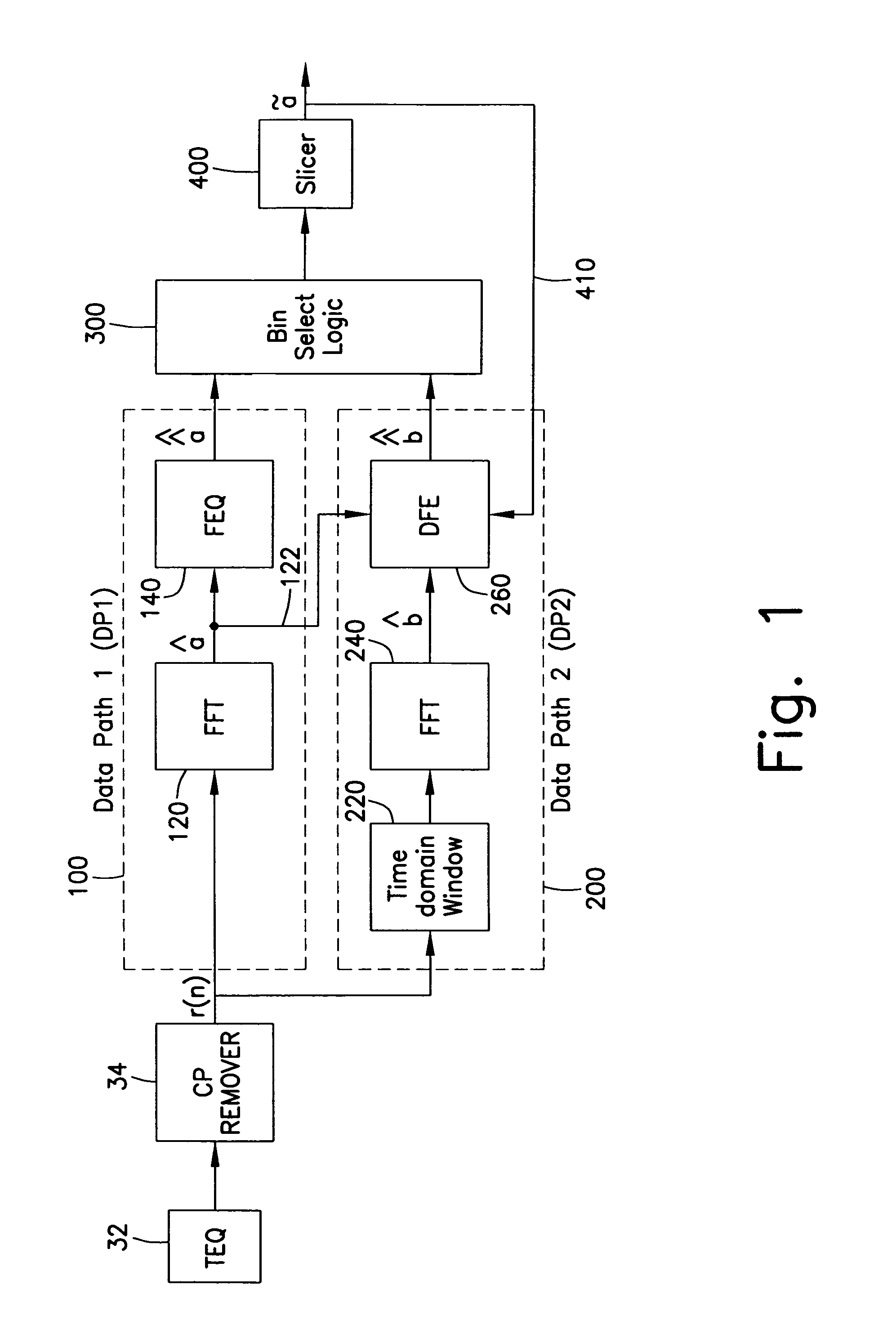
Receiver for discrete multitone modulated signals having window function
InactiveUS7023938B1Reduce threat of error propagationEasy to implementMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationTime domainModem device
A receiver for improving the performance of conventional Discrete Multitone Modulation (DMT) based Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) modems, in the presence of noise and / or interference. A demodulator having an FFT followed by a single-tap-per-bin frequency-domain equalizer is augmented by an additional data-path utilizing windowing or pulse shaping. Windowing is done independently for each symbol over the orthogonality interval and efficiently in the time domain or frequency domain. A decision feedback equalizer at the output of the windowed data-path cancels inter-bin-interference created by windowing.
Owner:NEC CORP
Ultra-directional microphones
ActiveUS20030072461A1Reduced responseImprove responsePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrostatic transducer microphonesOctaveMicrophone signal
The present invention provides a highly directional audio response that is flat over five octaves or more by the use of multiple colinear arrays followed by signal processing. Each of the colinear arrays has a common center, but a different spacing so that it can be used for a different frequency range. The response of the microphones for each spacing are combined and filtered so that when the filtered responses are added, the combined response is flat over the selected frequency range. To improve the response, the output of the microphones for a given array spacing can also be filtered with windowing functions. To receive the response from other directions a "steering" delay may also be introduced in the microphone signals before they are combined. The invention also extends to two and three dimensional arrays.
Owner:S AQUA SEMICONDUCTOR LLC
Targeted speech
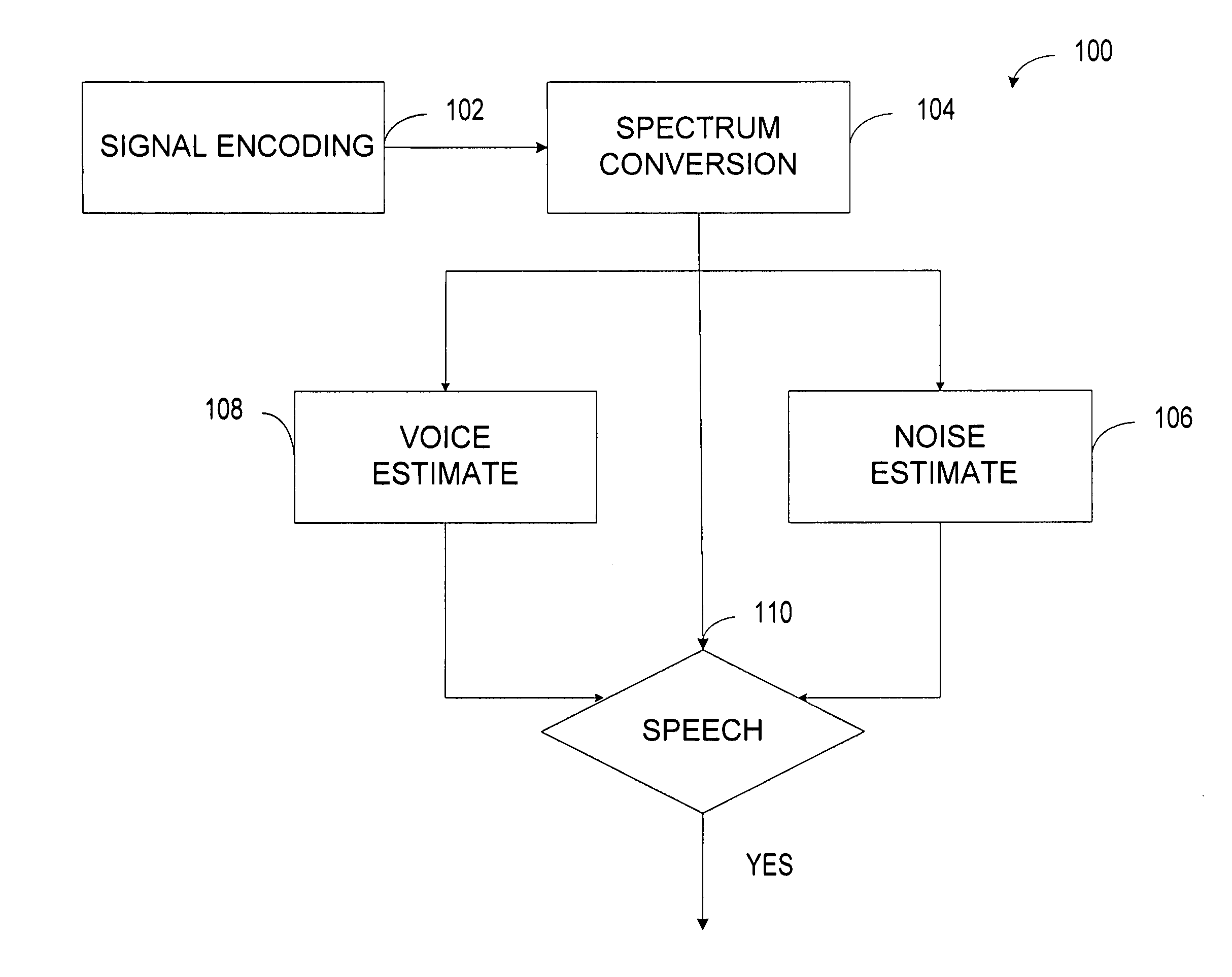
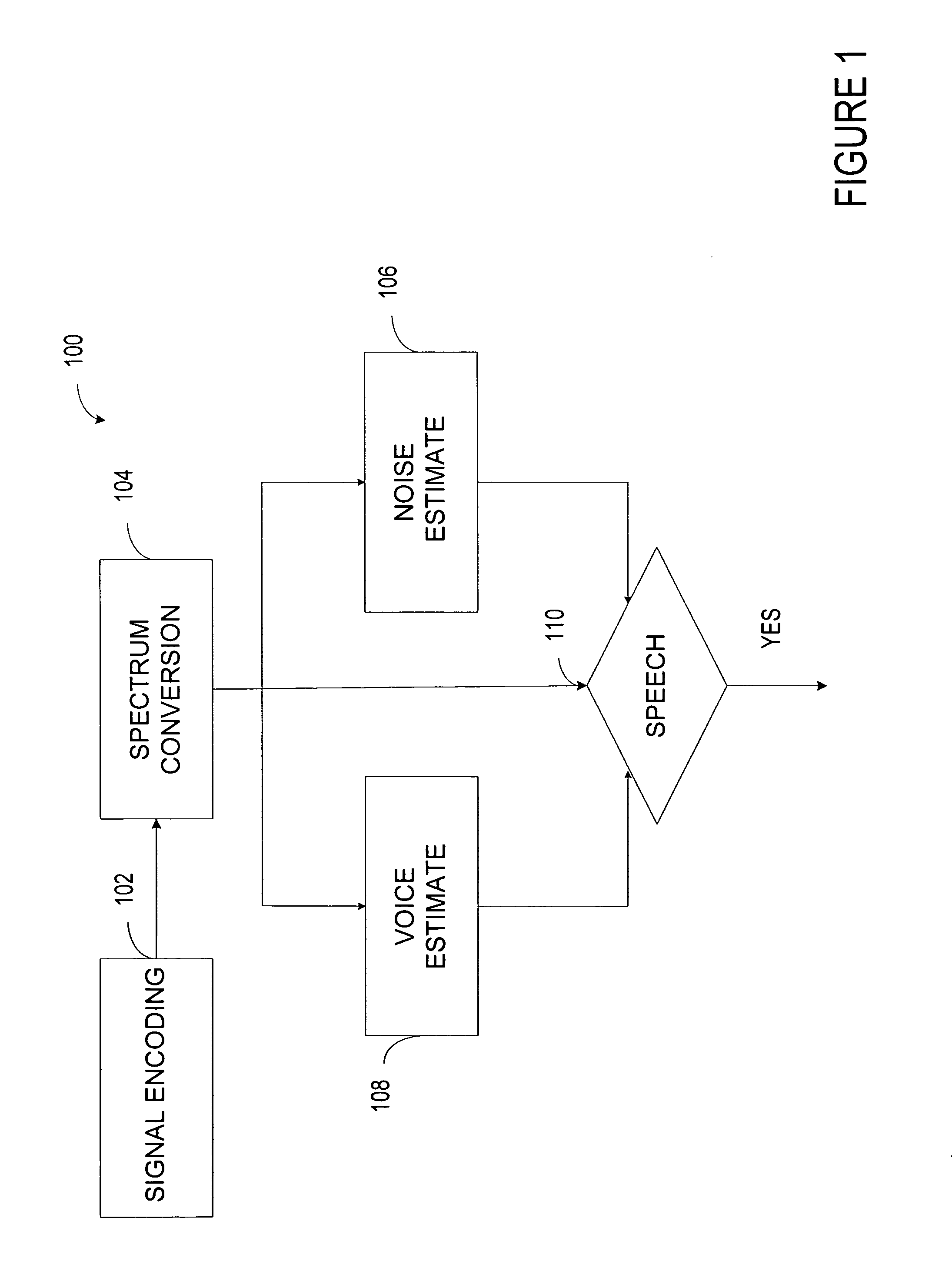
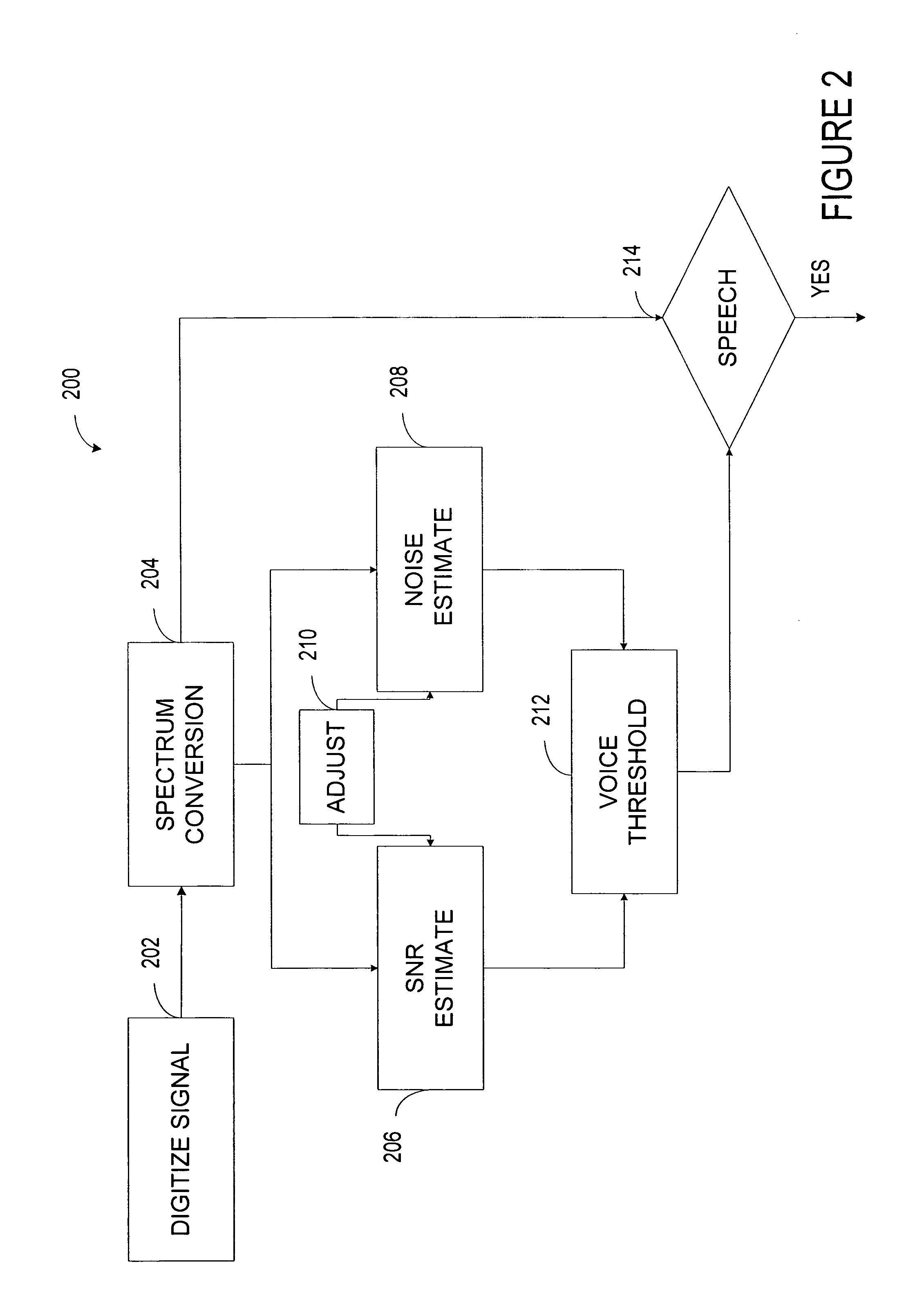
A system detects a speech segment that may include unvoiced, fully voiced, or mixed voice content. The system includes a digital converter that converts a time-varying input signal into a digital-domain signal. A window function passes signals within a programmed aural frequency range while substantially blocking signals above and below the programmed aural frequency range when multiplied by an output of the digital converter. A frequency converter converts the signals passing within the programmed aural frequency range into a plurality of frequency bins. A background voice detector estimates the strength of a background speech segment relative to the noise of selected portions of the aural spectrum. A noise estimator estimates a maximum distribution of noise to an average of an acoustic noise power of some of the plurality of frequency bins. A voice detector compares the strength of a desired speech segment to a criterion based on an output of the background voice detector and an output of the noise estimator.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Multitone Radar with Range Determination and Method of Use
ActiveUS20160282457A1Large system bandwidthRelatively large bandwidthRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFast Fourier transformRadar systems
Method for determining distance to target using a multitone nonlinear radar system comprising providing a transmitter that transmits a signal comprising at least two predetermined frequency components; receiving transmitted signal upon reflection from target; determining the phase relationships of the frequency components when signal strikes target; determining distance the signal has travelled to target based upon the phase relationship of the frequency signal components at the time of reflection from target; computing the distance to target. A system comprising a transmitter subsystem that transmits radar signal comprising at least two frequency components; a receiver subsystem configured to receive a return signal comprising intermodulation and harmonic products; at least one processor configured to extract frequency samples from the return signal within a frequency range, apply a window function to the extracted frequency samples and perform an inverse fast Fourier transform on the resulting function to create a range profile.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
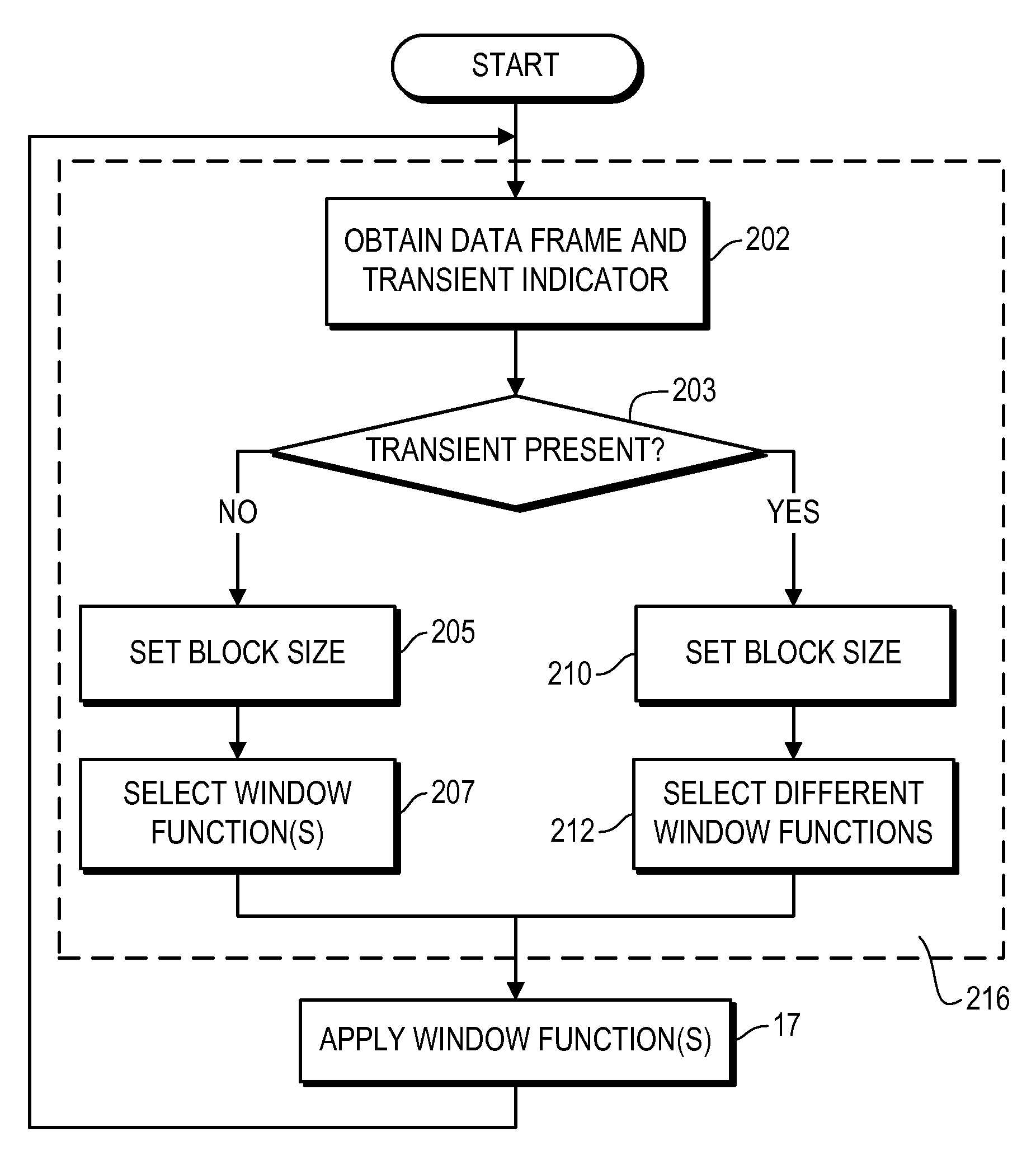
Variable-Resolution Processing of Frame-Based Data
ActiveUS20080059202A1Without complicating processing structureHigh resolutionSpeech analysisCode conversionFrame basedVariable resolution
Provided are systems, methods and techniques for processing frame-based data. A frame of data, an indication that a transient occurs within the frame, and a location of the transient within the frame are obtained. Based on the indication of the transient, a block size is set for the frame, thereby effectively defining a plurality of equal-sized blocks within the frame. In addition, different window functions are selected for different ones of the plurality of equal-sized blocks based on the location of the transient, and the frame of data is processed by applying the selected window functions.
Owner:DIGITAL RISE TECH CO LTD
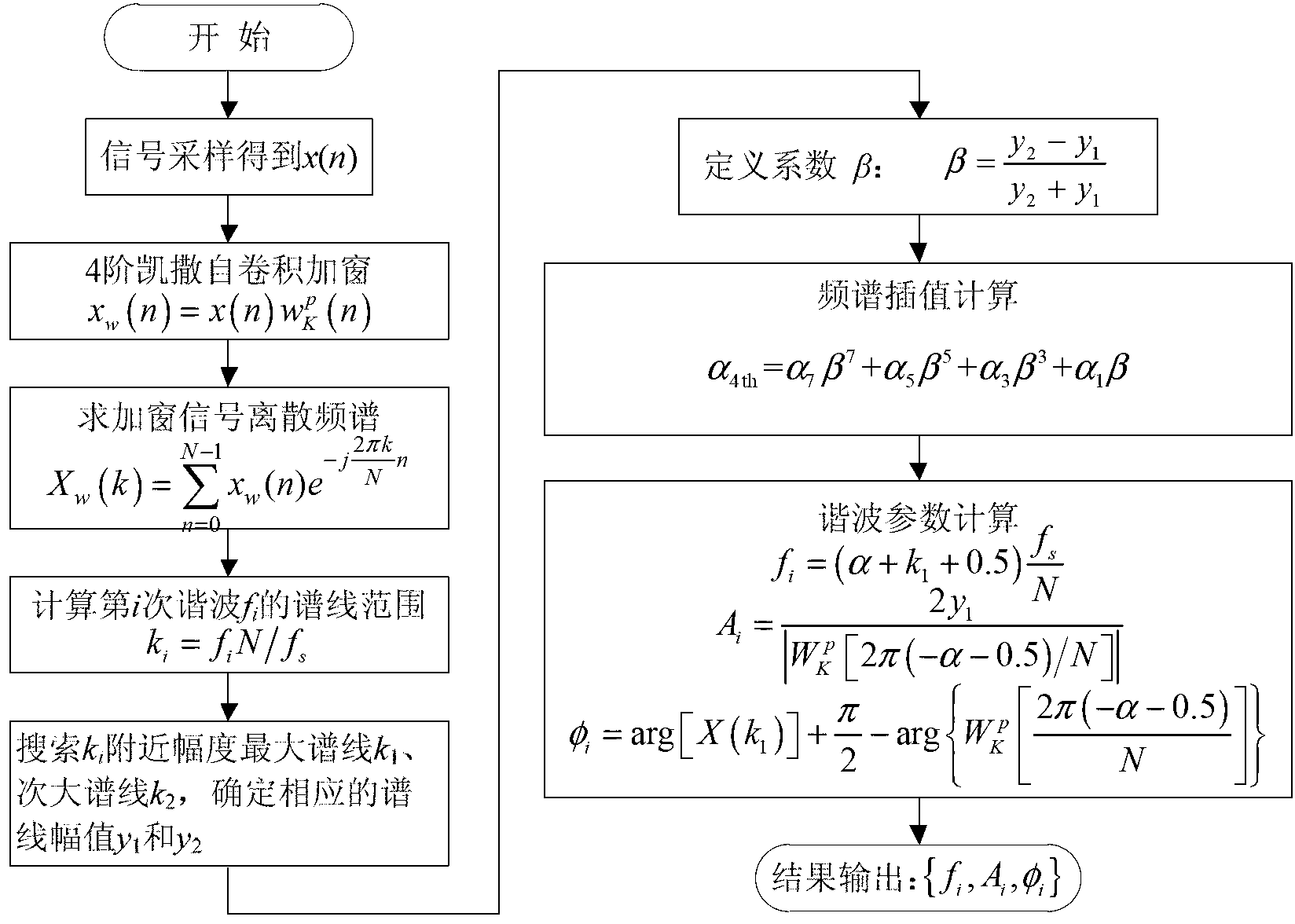
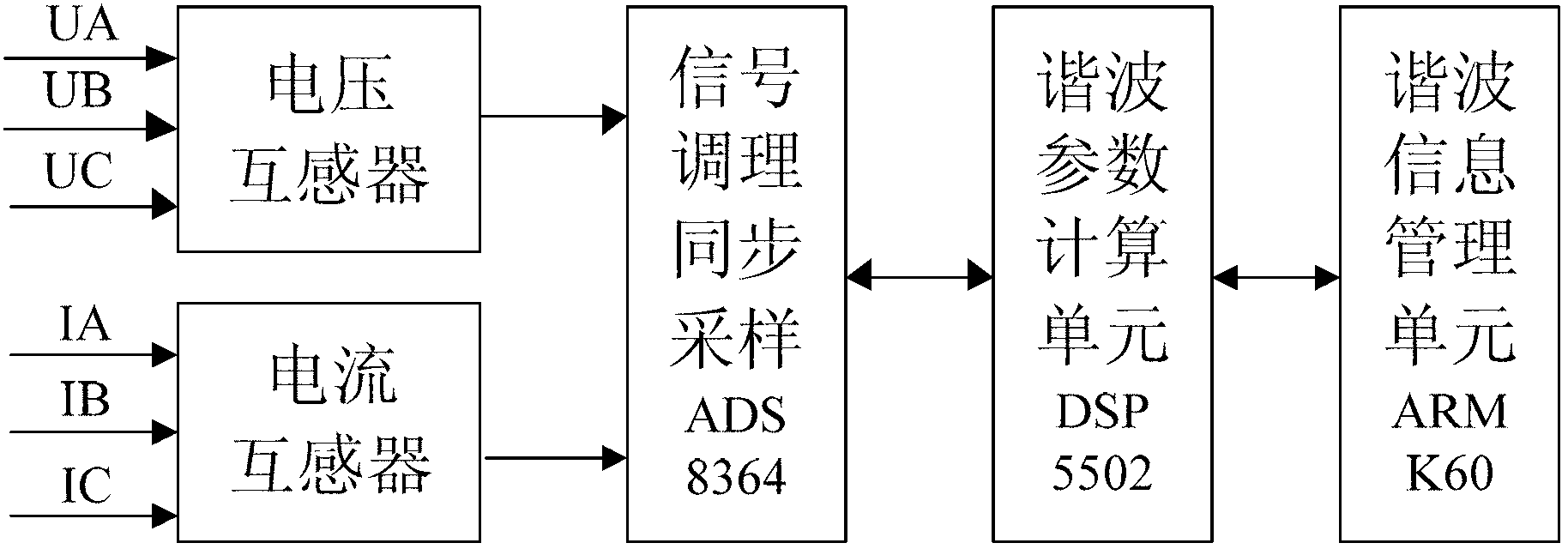
Harmonic analysis method based on Kaiser self-convolution window dual-spectrum line interpolation FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) and device thereof
InactiveCN103308766AQuick checkAccurate detectionFrequency analysisFrequency spectrumFrequency measurements
The invention discloses a harmonic analysis method based on Kaiser self-convolution window dual-spectrum line interpolation FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps of sampling a signal: sampling a time-domain continuous signal, and discretizing to obtain an infinitely long discrete sequence; windowing a four-order Kaiser self-convolution window function: performing four-order Kaiser self-convolution window operation on the infinitely long discrete sequence; performing N-point FFT on a windowed and truncated signal to obtain the discrete spectrum of the signal; determining the peak parameter of the discrete spectrum: searching the local spectrum peak of each integer harmonic frequency around the integer harmonic frequency; and calculating a harmonic parameter: solving a coefficient alpha by adopting a discrete spectrum interpolation correction formula based on an LSM (Least Square Method), and calculating parameters such as a harmonic frequency, an amplitude, an initial phase angle and the like. Due to the adoption of the method, the fundamental and harmonic components of a tested signal can be detected rapidly and accurately, and accurate frequency measurement is realized; and the method is convenient for implementing an embedded system, and the tested signal can be detected continuously for a long time.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Radio ranging using sequential time-difference-of-arrival estimation
A method determines a position of a target object. A window function is applied repeatedly to a first signal and a second signal of a pair of radio signals received at a pair of passive sensors from a target object while time shifting the window function during a correlation interval to produce a first windowed signal and a second windowed signal for each application. The first windowed signals are cross-correlating with the second windowed signals to determine a peak for each cross-correlation. The peaks are compared sequentially in time with a predetermined threshold to detect a first pulse in the first signal and a first pulse in the second signal. A delay between the first pulses indicative of a position of the target object.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
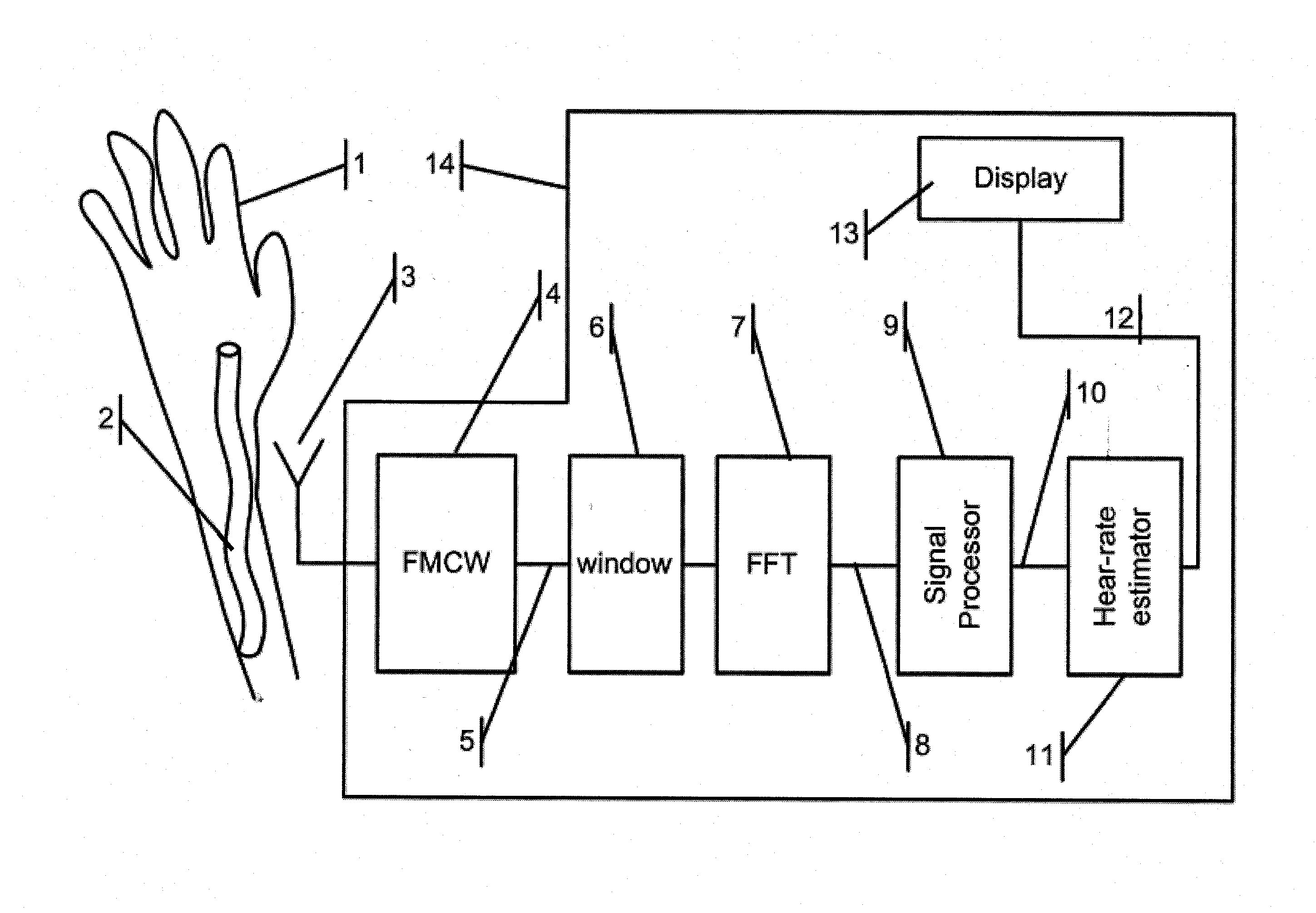
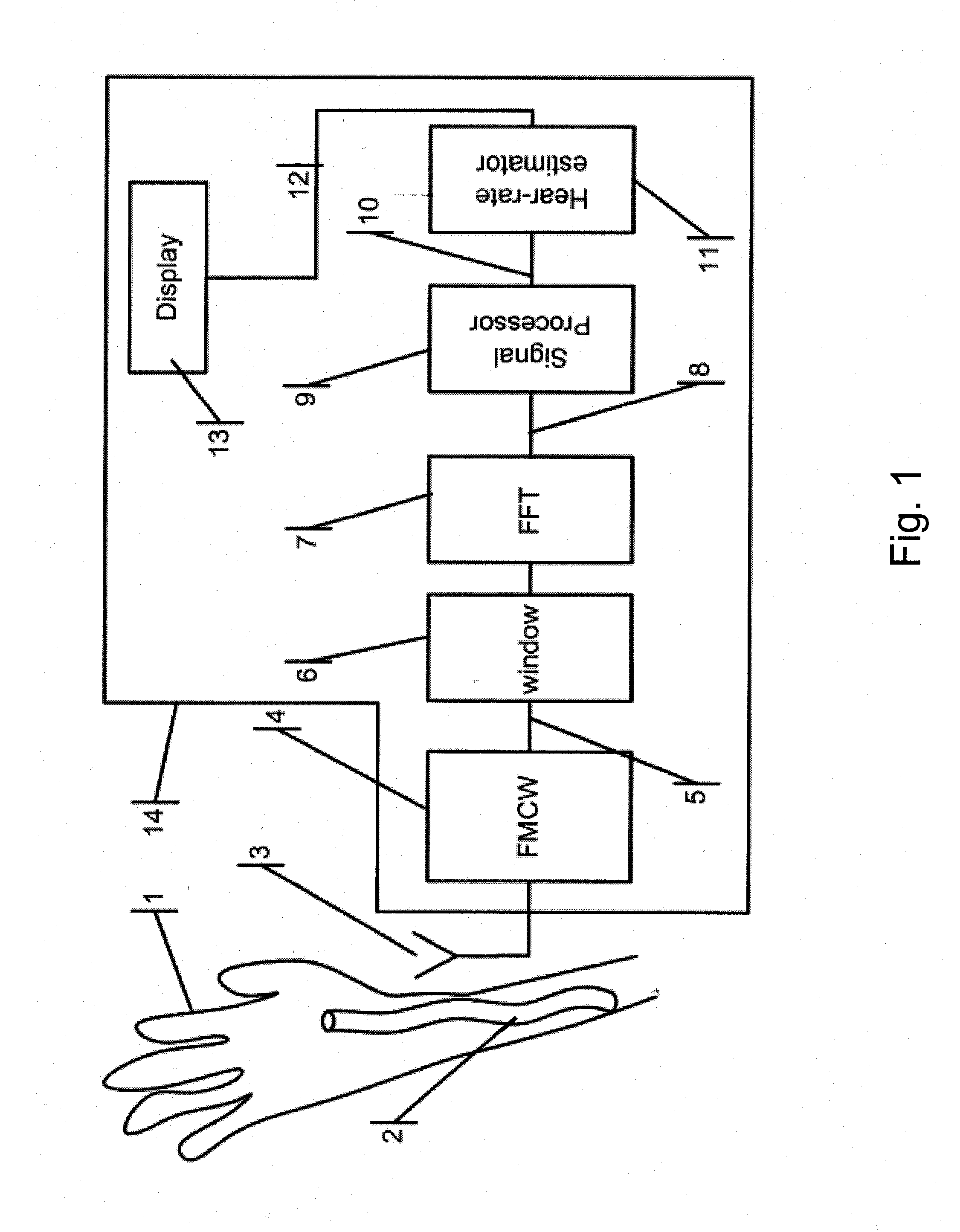
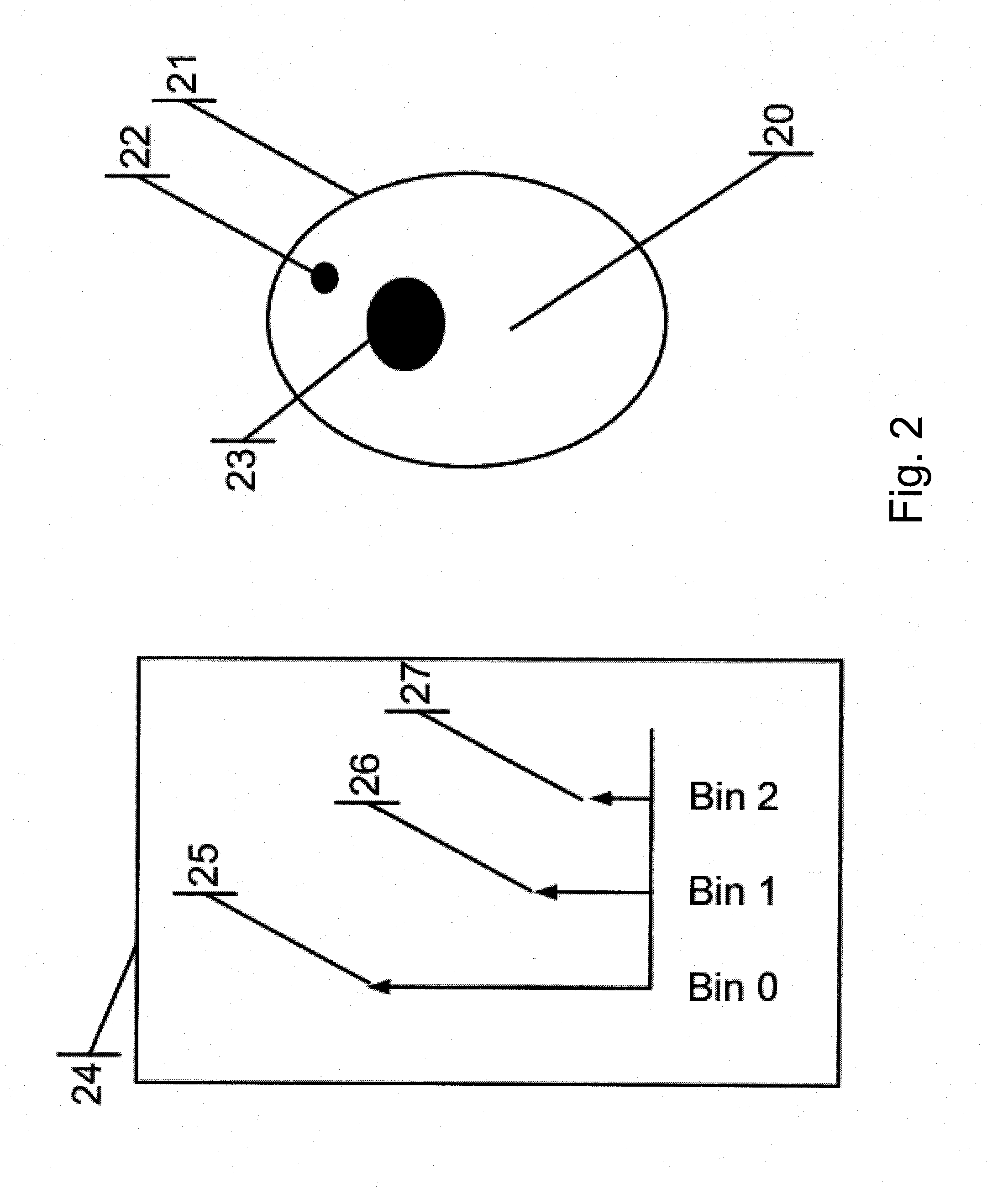
Microwave contactless heart rate sensor
ActiveUS20150018676A1SensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateFrequency spectrumReflection Magnitude
A heart-rate sensor for detecting artery blood-flow volume per unit length change in a human or animal subject, which comprises an antenna for sensing the instantaneous volume of blood in the artery of the subject, to be measured; a RADAR unit for transmitting microwave signals into a subject's body part or limb representing tissue targets. The output of the RADAR unit includes a superposition of signals each of which corresponding to a different tissue target with amplitudes that relate to the target's reflection strength; a sampling circuitry for converting reflected signals to digital; a window function circuitry for suppressing unwanted spectral sidebands originating from the subsequent processor operating on time truncated data; an FFT processor following the window function circuitry, for splitting the superposition according to its relative frequency into a multiplicity of bins, each of which with an amplitude that represents the reflection magnitude of a target at a specific distance from the antenna; a signal processor for filtering out the effect of the sensor movement with respect to the subject body part, or the movement of the body part, and for generating a signal, the amplitude of which is proportional to the artery varying dilatation representing the heart-rate; a heart-rate estimator for measuring the frequency of the artery dilatation variations and for canceling the interference of the amplitude of any signal that does not originate from the artery; a battery for powering the sensor.
Owner:SENSIFREE
Determination of borehole azimuth and the azimuthal dependence of borehole parameters
ActiveUS20060096105A1Improve imaging resolutionSuperior noise rejectionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyImage resolutionImaging technique
A method for determining a borehole azimuth in a borehole is disclosed. In one exemplary embodiment, the method includes acquiring at least one standoff measurement and a tool azimuth measurement at substantially the same time. Such measurements are then processed, along with a lateral displacement vector of the downhole tool upon which the sensors are deployed in the borehole, to determine the borehole azimuth. The computed borehole azimuths may be advantageously correlated with logging sensor data to form a borehole image, for example, by convolving the correlated logging sensor data with a window function. As such, exemplary embodiments of this invention may provide for superior image resolution and noise rejection as compared to prior art LWD imaging techniques.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
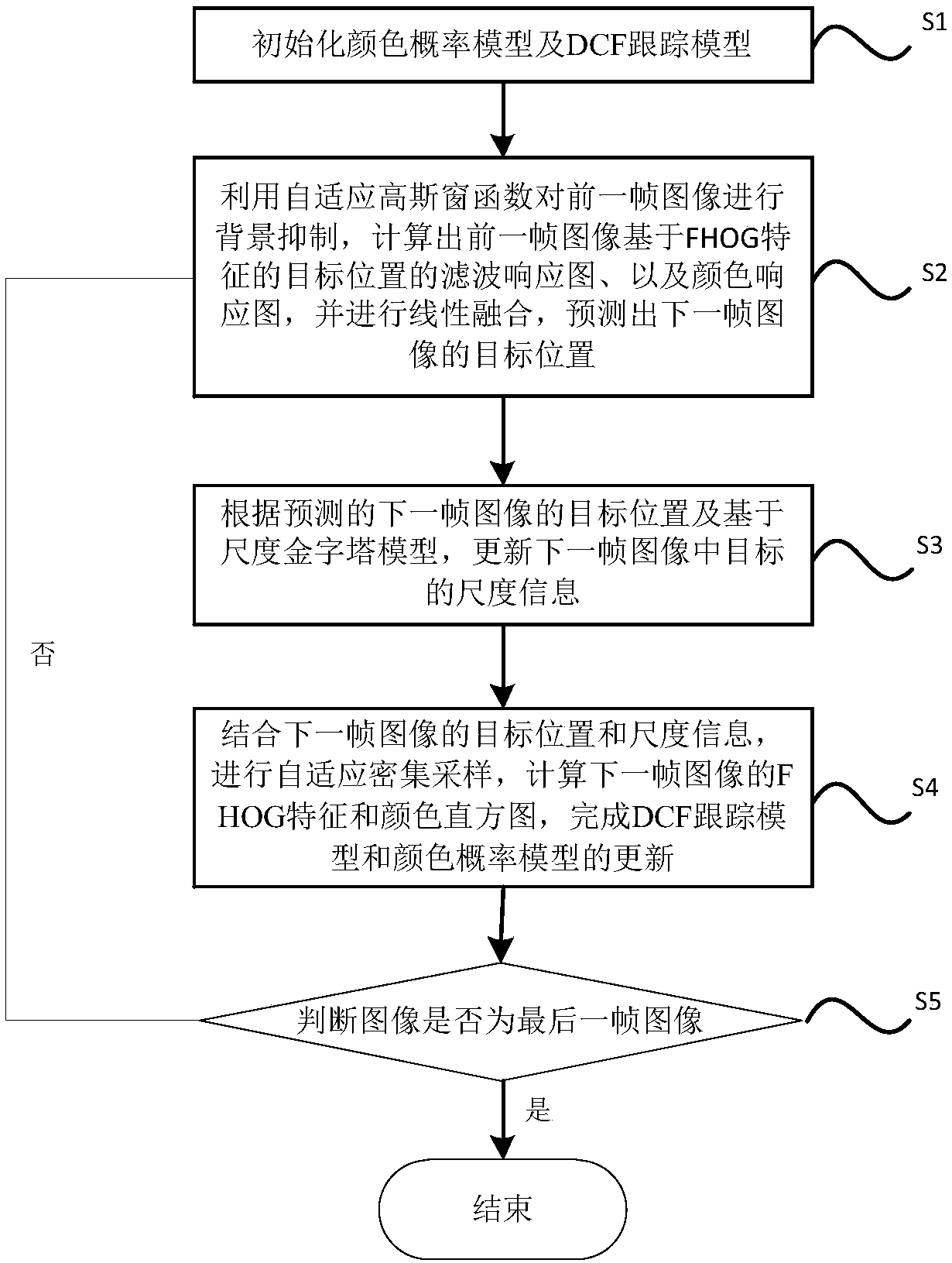
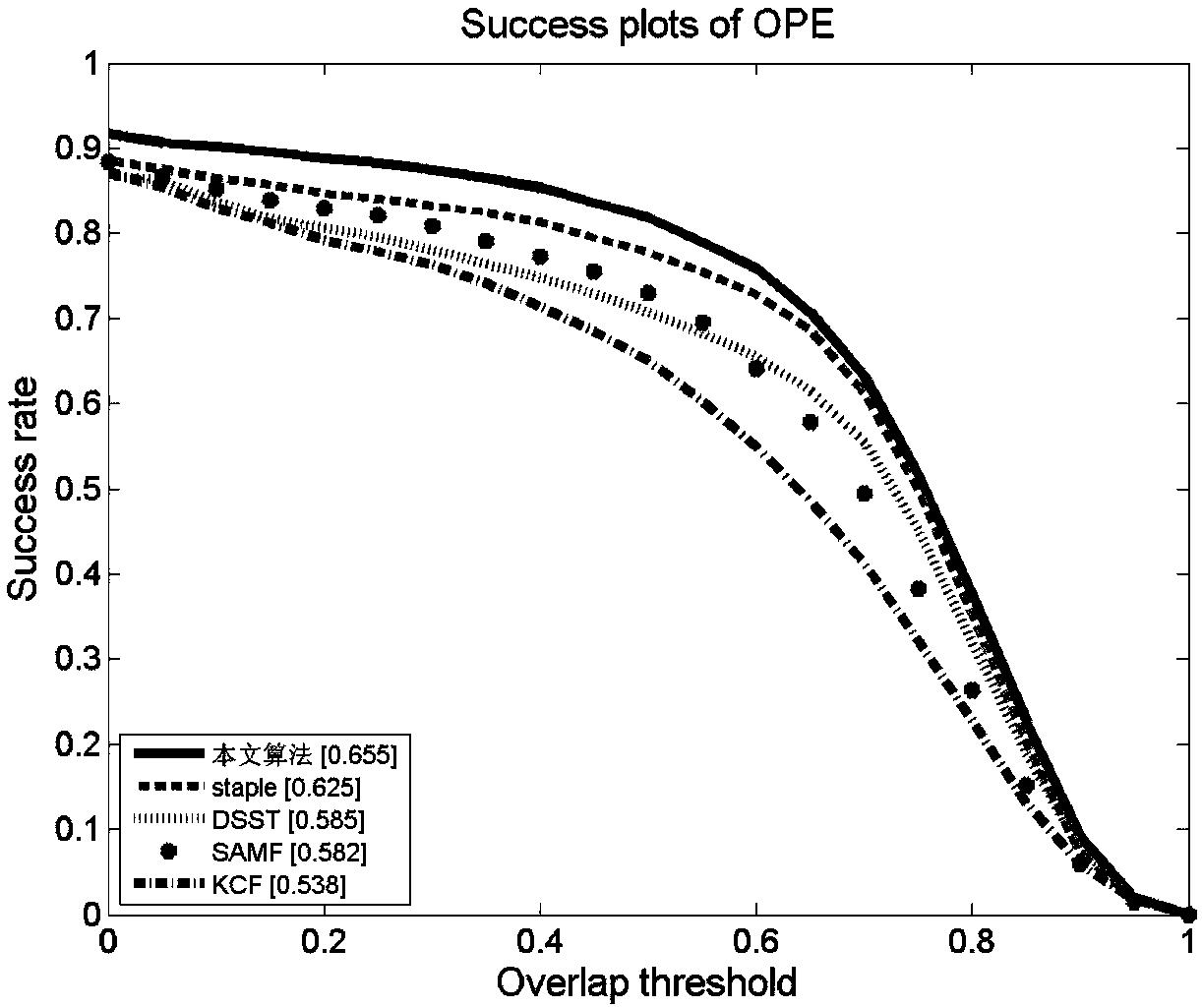
Multi-scale target tracking method based on background suppression and foreground anti-jamming
InactiveCN108053419AGood tracking effectTo achieve the purpose of background suppressionImage enhancementImage analysisAnti jammingWindow function
The invention discloses a multi-scale target tracking method based on background suppression and foreground anti-jamming, which relates to the technical field of target tracking. The method includes the following steps: constructing and initializing a color probability model and a DCF tracking model; using an adaptive Gaussian window function to suppress the background in the previous frame of image, calculating the filter response map of a target position based on FHOG features in the previous frame of image, calculating the color probability distribution of the previous frame of image, obtaining the color response map of the target position, linearly fitting the filter response map and the color response map, and predicting a target position of next frame of image; updating the scale information of the target in the next frame of image according to the predicted target position of the next frame of image and based on a scale pyramid model; and carrying out adaptive dense sampling according to the target position and scale information of the next frame of image, calculating the FHOG features and color histogram of the next frame of image, and updating the DCF tracking model and the color probability model.
Owner:WUHAN DANWAN TECH CO LTD
Method of converting resolution of video signals and apparatus using the same
ActiveUS7375767B2Television system detailsGeometric image transformationImage resolutionGaussian function
A method converts a resolution of video signals, the method including: calculating up-sampling and down-sampling ratios based on a resolution of an input video signal and a desired resolution of an output video signal; calculating a number of filter tabs by multiplying the up-sampling and down-sampling ratios by a number of side lobes; calculating first filter coefficients of a same number of the filter tabs by multiplying a window function by a sinc function; calculating final filter coefficients by subtracting a result of a multiplication of a Gaussian function by a window function from the first filter coefficients, and then normalizing the final filter coefficients; and performing filtering in vertical and horizontal directions based on the final filter coefficients by modifying a sampling rate of an input video signal depending on the up-sampling and down-sampling ratios, to obtain clear video images.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
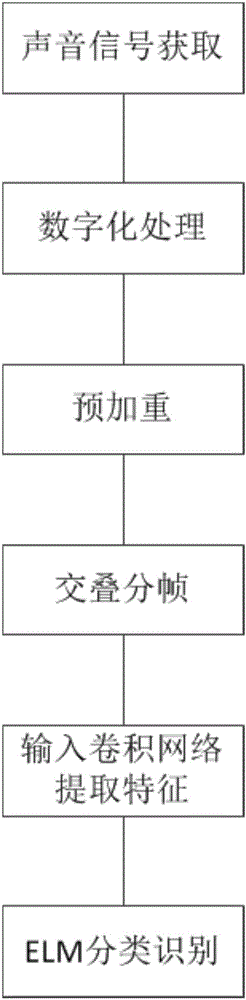
One-dimensional deep convolution network underwater multi-target recognition method
InactiveCN106682574AAvoid lostImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFrequency spectrumGoal recognition
The invention provides a one-dimensional deep convolution network underwater multi-target recognition method. A 6dB / frequency doubling one-order digital filter is adopted to enhance a high-frequency part to enable a signal spectrum to be flattened; a window function is selected to intercept signals, and signals with the duration of 170 ms are acquired as the best input frame length for a convolutional neural network; the one-dimensional deep convolution network is adopted to carry out feature extraction on sound signals; a training sample set is used for learning the convolution network to obtain network structure parameters with the best features; and an extreme learning machine is selected to carry out classification and recognition on output features of the convolution network. the deep convolution network in the deep learning is used for carrying out feature extraction on the sound signals, the traditional manual feature extraction is replaced, the automatically-extracted sound features contain richer recognition information, the extreme learning machine is used for carrying out classification and recognition on features automatically extracted by the convolution network, features different from those obtained in the traditional manual analysis mode can be effectively found out, and the underwater sound signal recognition rate is improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Application startup optimization method and apparatus, storage medium and intelligent terminal
ActiveCN107748686AImprove interactivityAvoid the situation where the application interface is displayed againProgram loading/initiatingExecution for user interfacesMan machineApplication software
Embodiments of the invention disclose an application startup optimization method and apparatus, a storage medium and an intelligent terminal. The method comprises the steps of obtaining startup operation for an application; when the application does not run in a background, judging whether the application enables a startup window function or not; when the application does not enable the startup window function, loading a preset picture, creating a startup window according to the preset picture, and displaying the startup window; and when a preset condition is met, switching to operation of displaying an application interface corresponding to the application. By adopting the technical scheme, when the startup operation for the application is detected, the startup window is displayed, thereby intuitively showing that a system starts the application in response to the startup operation; and when the preset condition is met, the startup window is switched to the application interface of the application, so that the situation that the application interface is displayed after stay for a period of time on a desktop in related technologies is avoided and the man-machine interactive performance is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Acoustic communication device and acoustic signal communication method
The present invention provides an acoustic transmitter for sequentially transmitting a plurality of pulse signals by sound. Each of the plurality of pulse signals is a signal of at least one modulated carrier wave, which has a predetermined frequency. The carrier wave of each of the pulse signals has a mutually different frequency. The transmitter performs amplitude modulation and / or phase modulation based on transmission information, and modulation by a signal indicating a window function, for the carrier wave of each of pulse signals. Then the transmitter sequentially transmits the plurality of pulse signals by sound.
Owner:TOKYO GAS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com