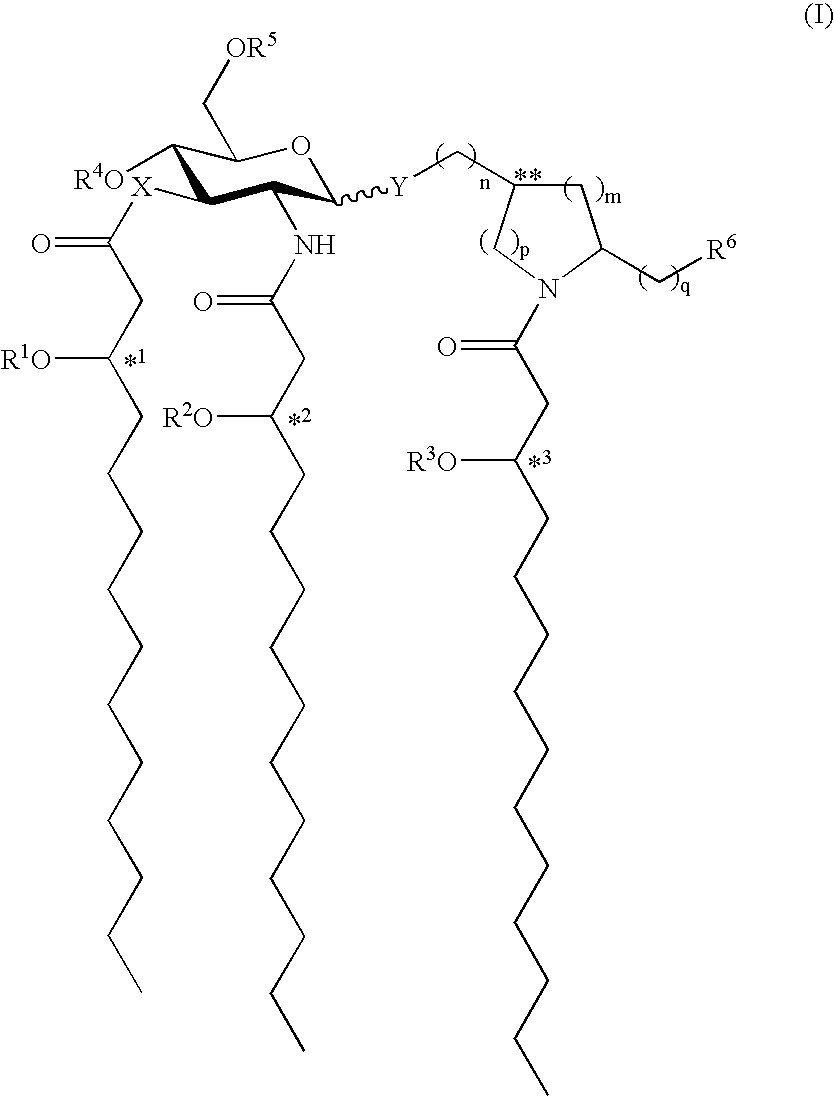
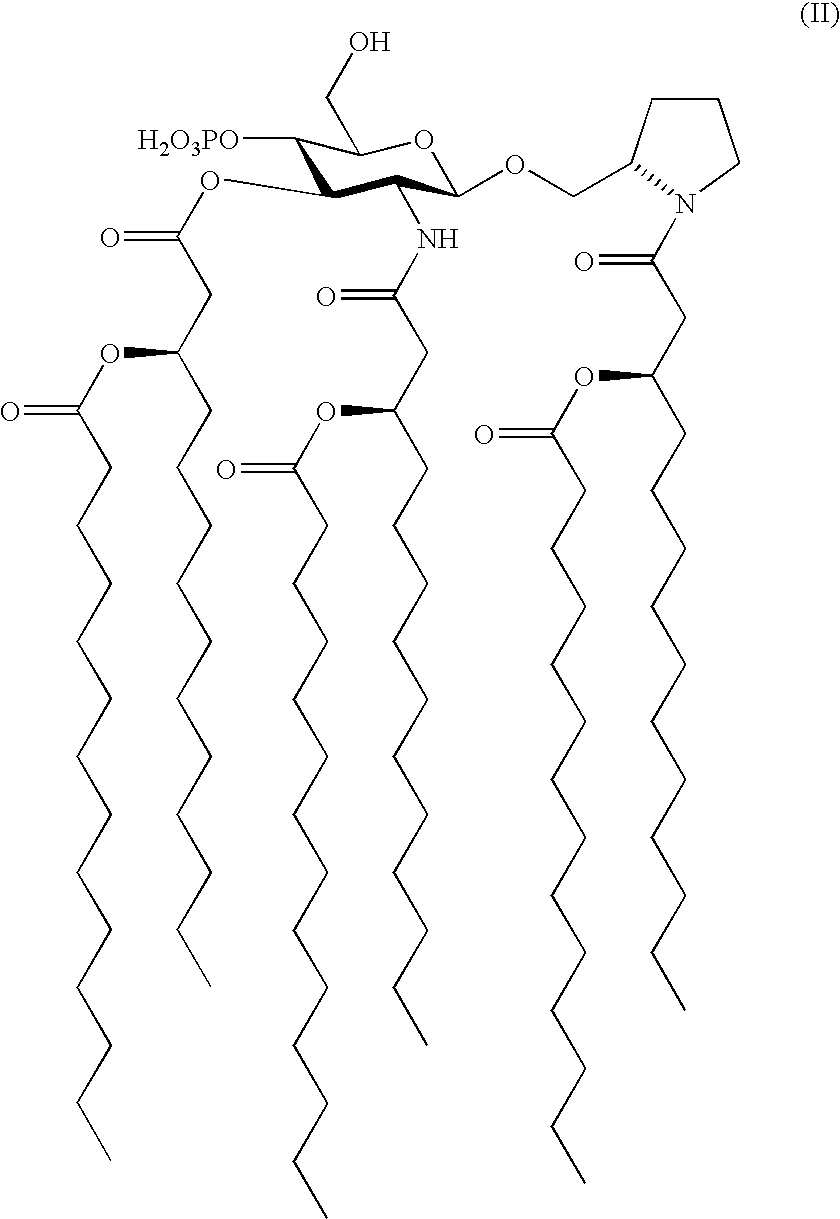
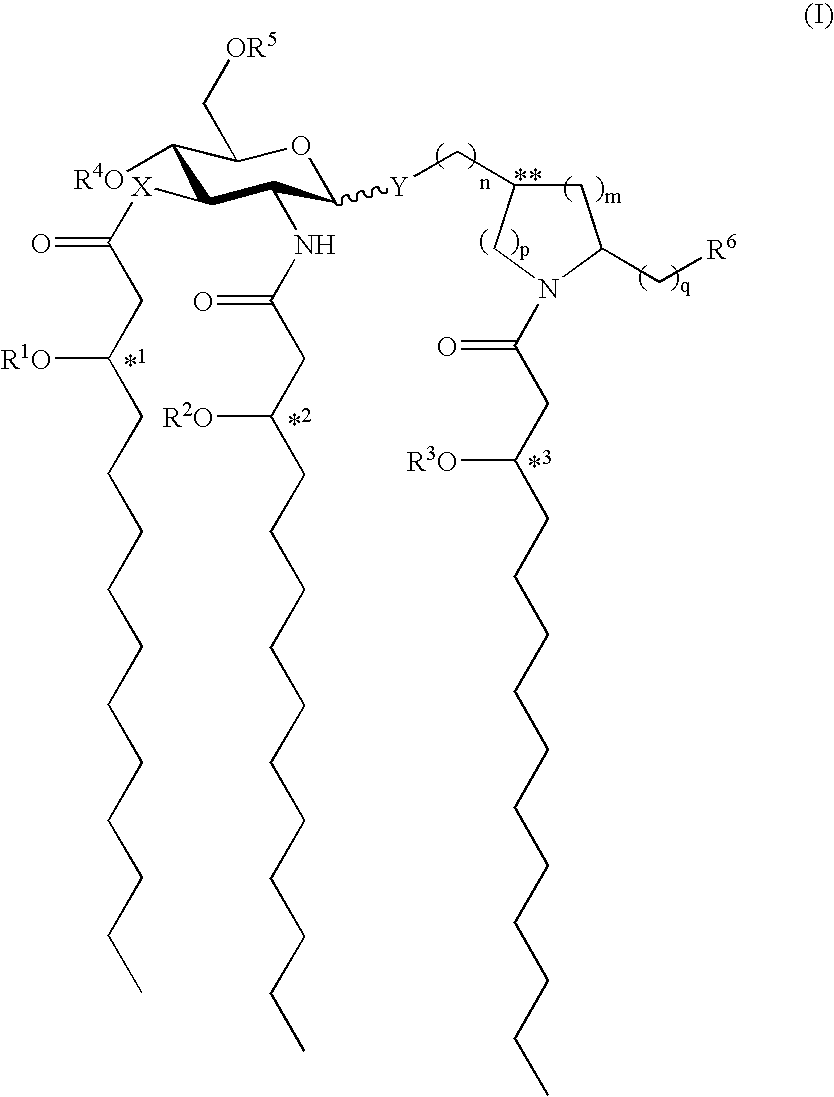
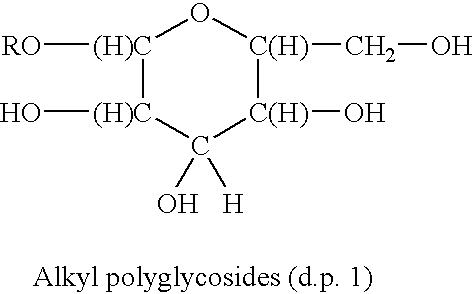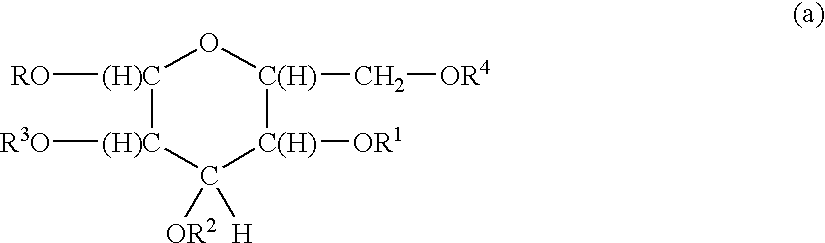Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
575results about "Antibiotics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
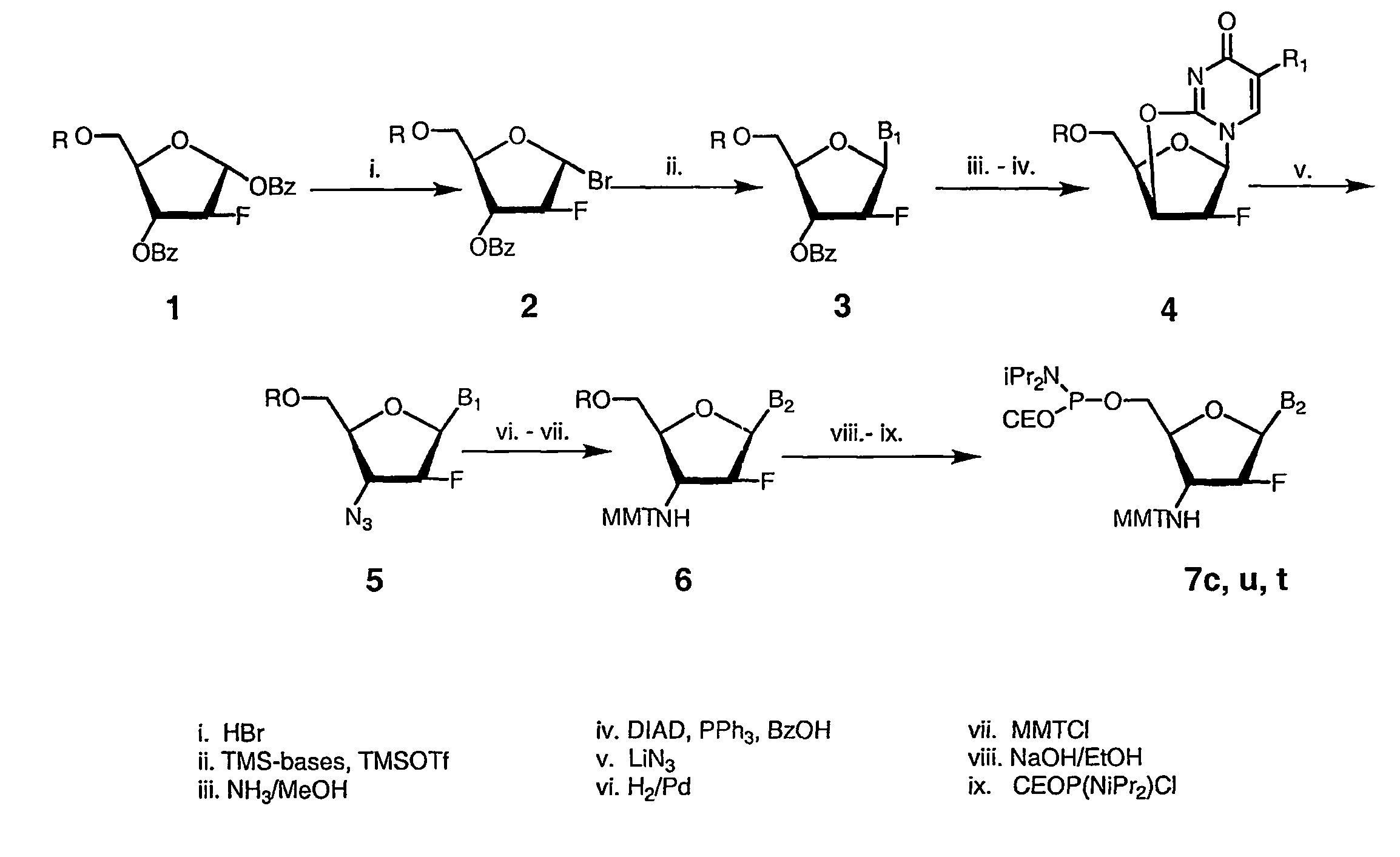
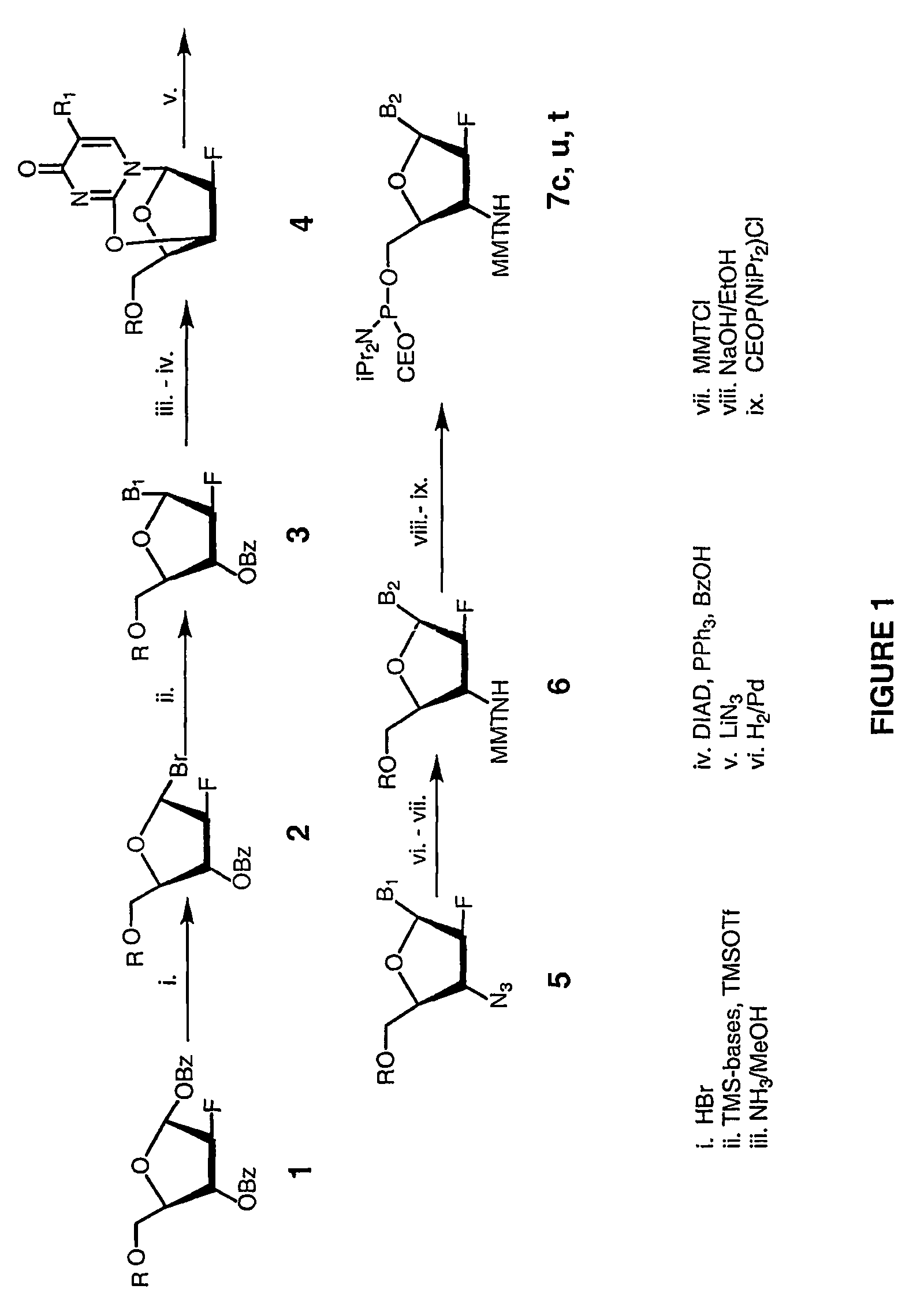
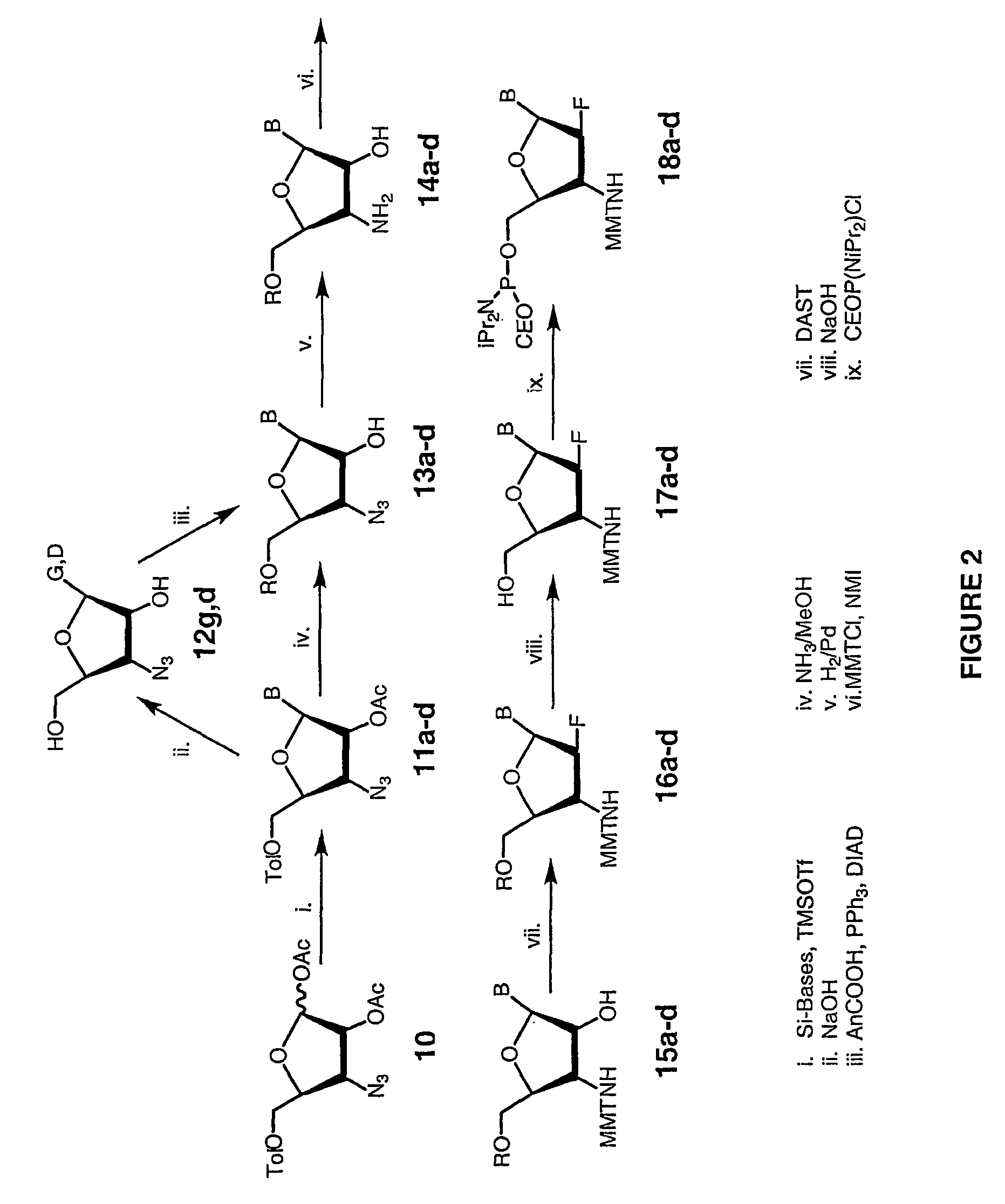
2'-arabino-fluorooligonucleotide N3'->P5' phosphoramidates: their synthesis and use
Oligonucleotides with a novel sugar-phosphate backbone containing at least one 2′-arabino-fluoronucleoside and an internucleoside 3′-NH—P(—O)(OR)—O-5′ linkage, where R is a positively charged counter ion or hydrogen, and methods of synthesizing and using the inventive oligonucleotides are provided. The inventive phosphoramidate 2′-arabino-fluorooligonucleotides have a high RNA binding affinity to complementary nucleic acids and are base and acid stable.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
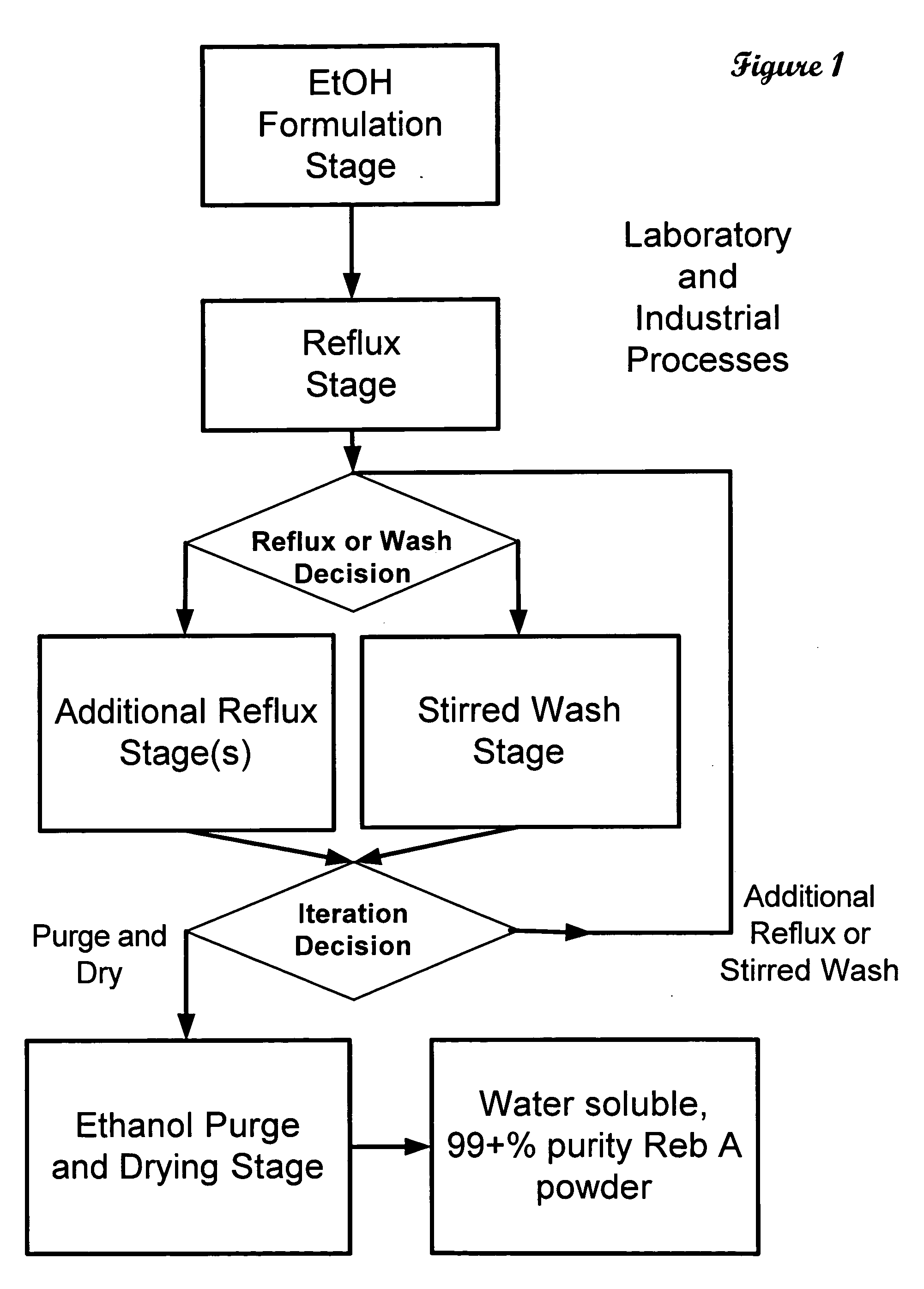
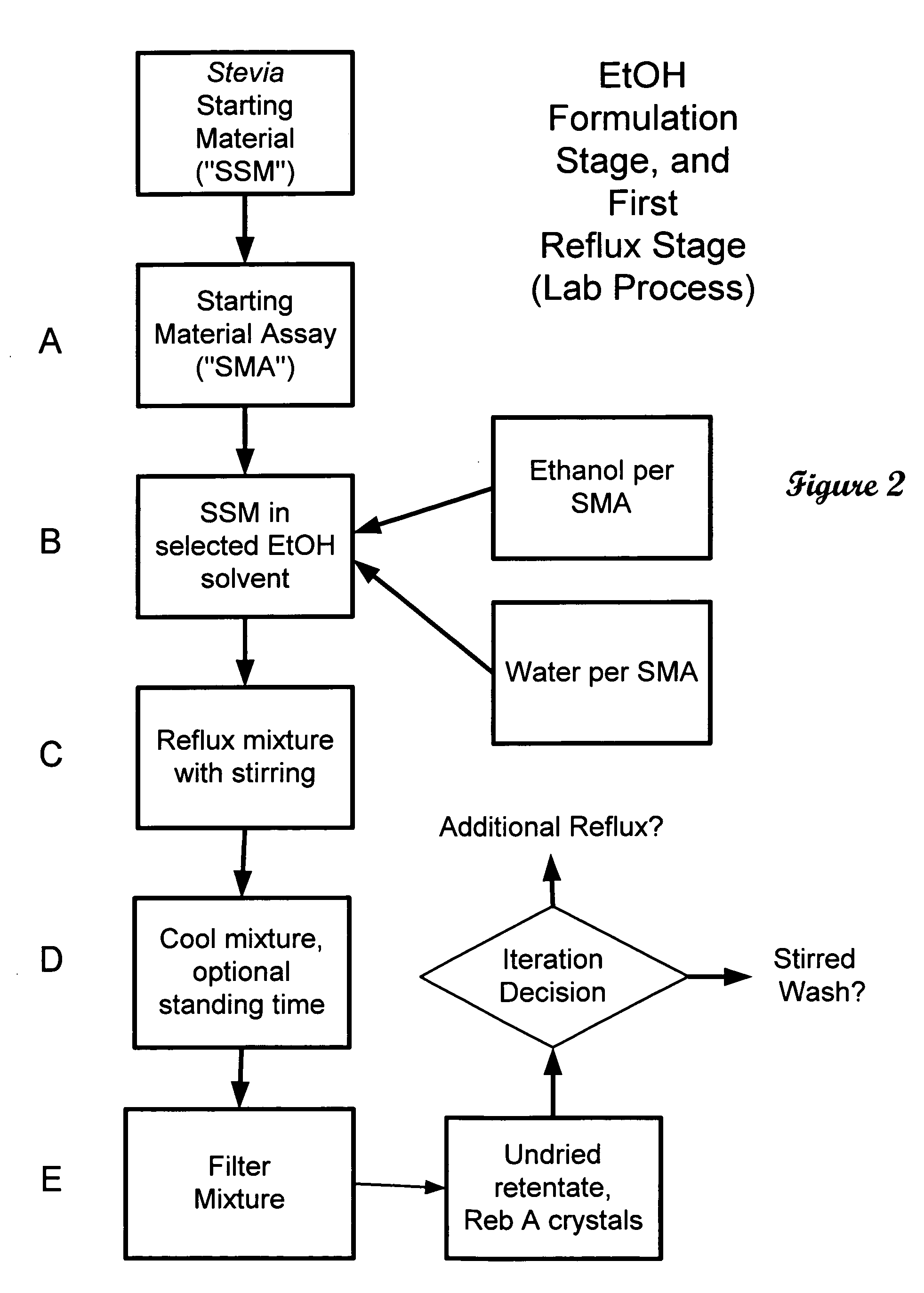
High yield method of producing pure rebaudioside A
ActiveUS20060083838A1Reduction in yieldQuality improvementSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderSolubilityAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a high throughput, high purity, high yield system and method of isolating and purifying rebaudioside A (“Reb A”), with acceptable water solubility for all commercial uses, from commercially available Stevia rebaudiana starting material. The invention also provides a means of maximizing yields of 99+% purity Reb A based on the attributes of a given batch of Stevia starting material. The Reb A produced by the invention is water soluble, devoid of bitterness heretofore associated with rebaudioside sweeteners, non-caloric, and suitable for use as a reagent and as an ingredient in orally consumed products, e.g., as a sweetener, flavor enhancer, and flavor modifier.
Owner:SWEET GREEN FIELDS INT CO LTD
3-β-D-ribofuranosylthiazolo[4-5-d]pyridimine nucleosides and uses thereof
Owner:ANDADYS PHARMA INC
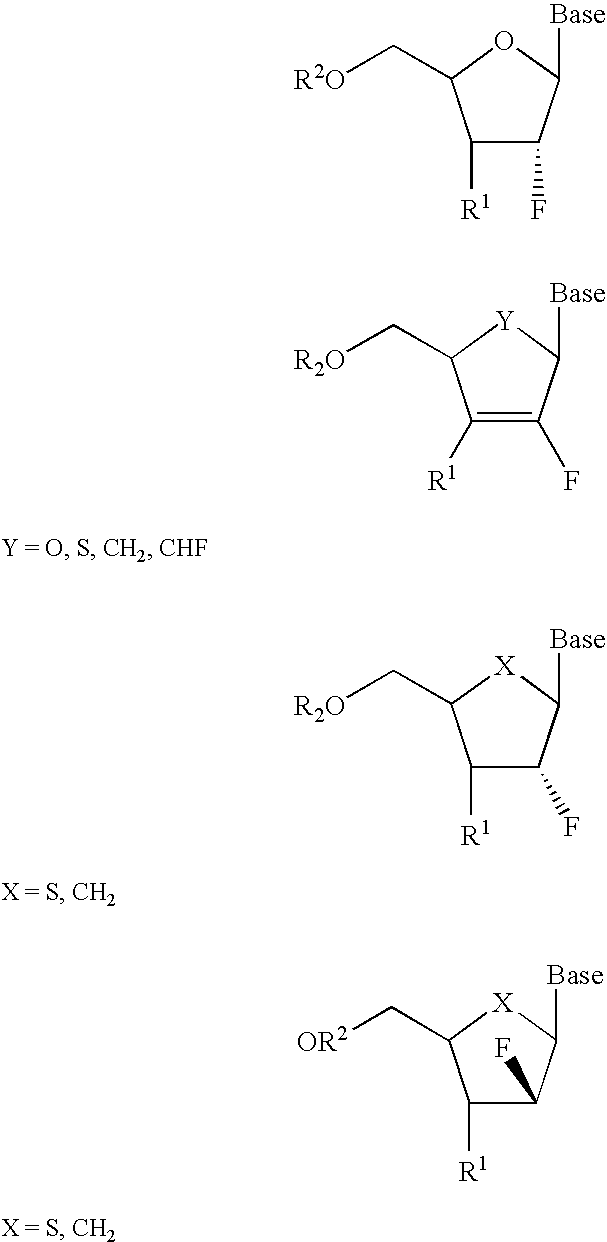
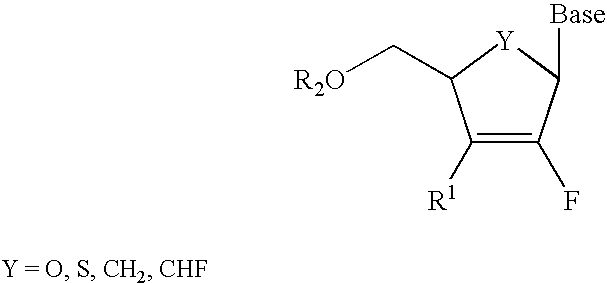
2′-fluoronucleosides
InactiveUS6911424B2Sure easyUseful in treatmentBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphoric Acid EstersPurine
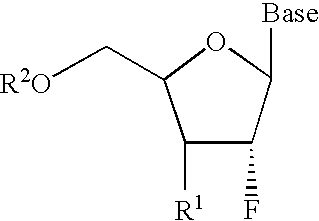
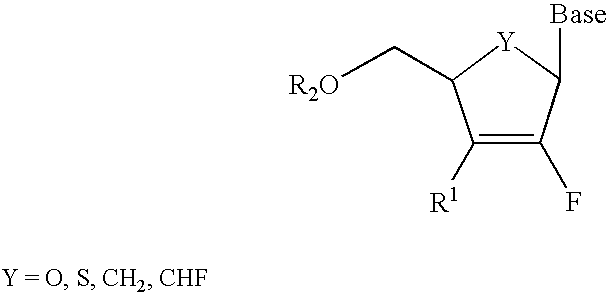
A class of 2′-fluoro-nucleoside compounds are disclosed which are useful in the treatment of hepatitis B infection, hepatitis C infection, HIV and abnormal cellular proliferation, including tumors and cancer. The compounds have the general formulae: wherein[0001]Base is a purine or pyrimidine base;[0002]R1 is OH, H, OR3, N3, CN, halogen, including F, or CF3, lower alkyl, amino, loweralkylamino, di(lower)alkylamino, or alkoxy, and base refers to a purine or pyrimidine base;[0003]R2 is H, phosphate, including monophosphate, diphosphate, triphosphate, or a stabilized phosphate prodrug; acyl, or other pharmaceutically acceptable leaving group which when administered in vivo, is capable of providing a compound wherein R2 is H or phosphate; sulfonate ester including alkyl or arylalkyl sulfonyl including methanesulfonyl, benzyl, wherein the phenyl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents as described in the definition of aryl given above, a lipid, an amino acid, peptide, or cholesterol; and[0004]R3 is acyl, alkyl, phosphate, or other pharmaceutically acceptable leaving group which when administered in vivo, is capable of being cleaved to the parent compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
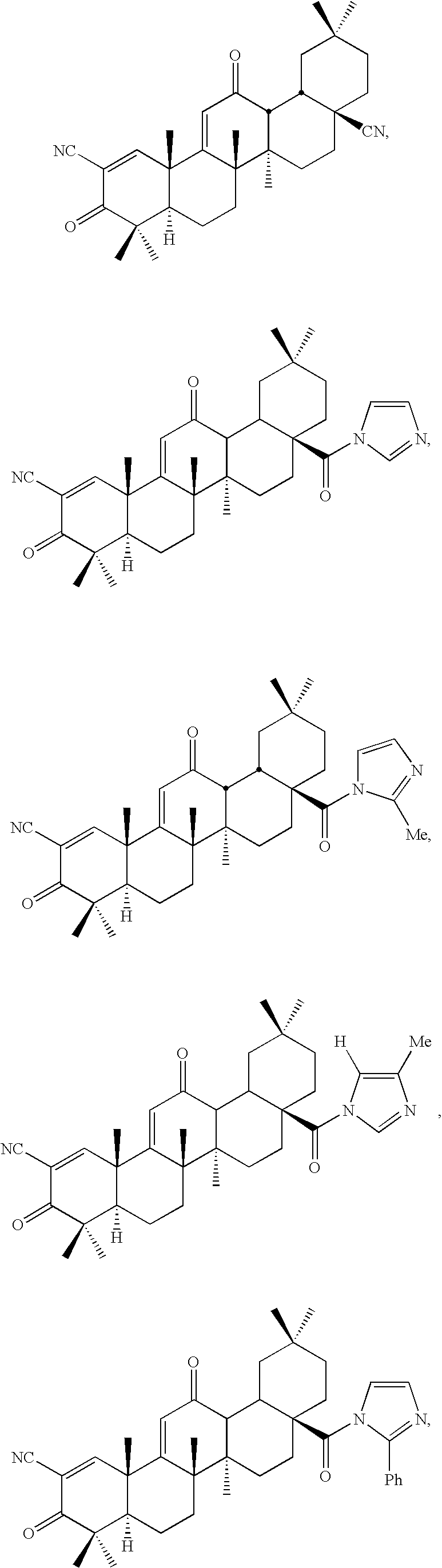
Inhibitors and methods of use thereof
New triterpenoid derivatives with various substituents at the C-17 position of 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO) were synthesized. Among them, 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-onitrile (CNDDO), 1-(2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oyl) imidazole, 1-(2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oyl)-2-methylimidazole, 1-(2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oyl)-4-methylimidazole show extremely high inhibitory activity (IC50=0.01-1 pM level) against production of nitric oxide induced by interferon-γ in mouse macrophages. These compounds can be used in the prevention or treatment of diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory diseases. All the new triterpenoid derivatives are more potent than previously known CDDO.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
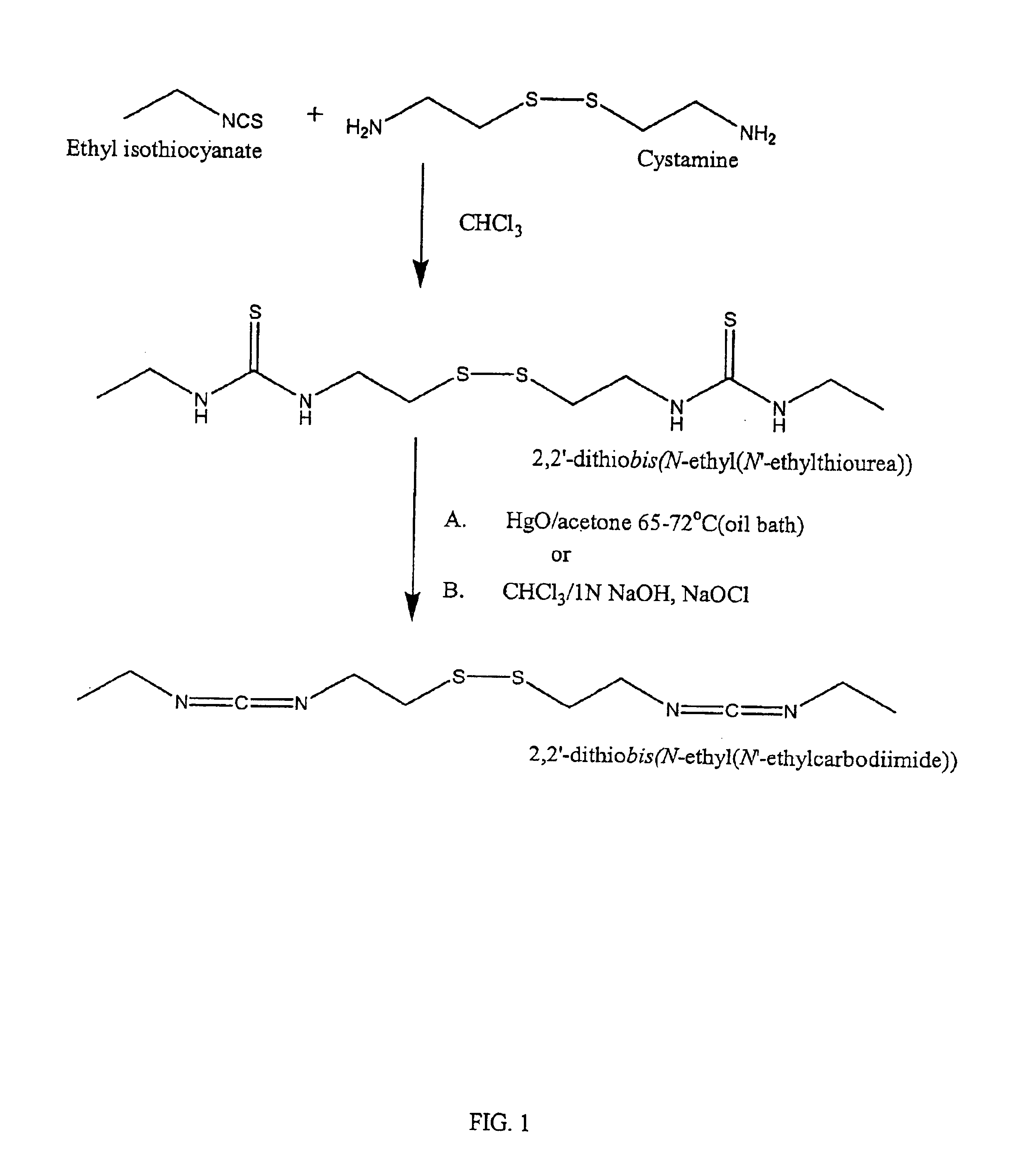
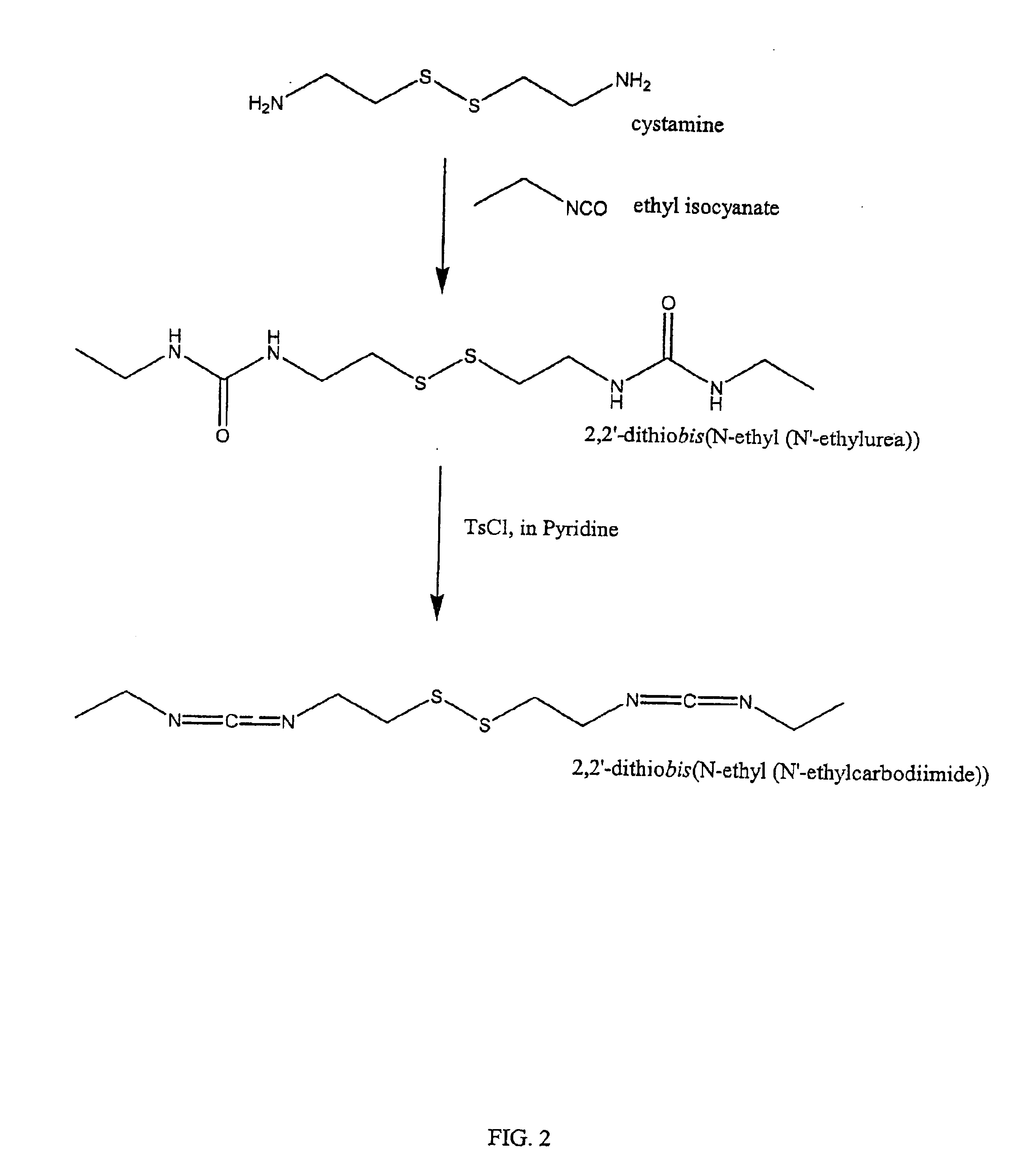
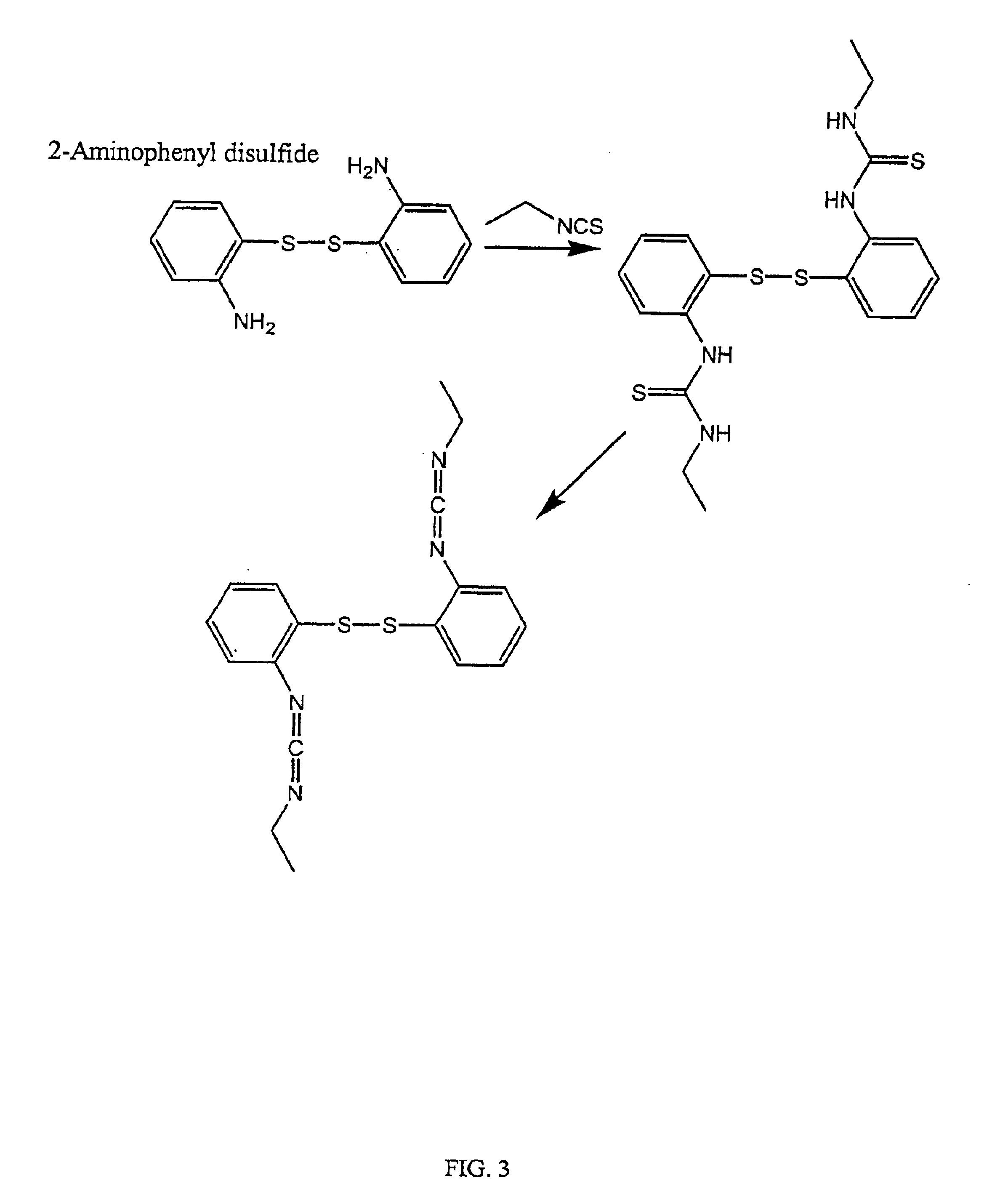
Thiol-modified hyaluronan
InactiveUS6884788B2High activityControl moreBiocideOrganic active ingredientsUrea derivativesCross-link
The present invention relates to biscarbodiimides, thiourea derivatives, urea derivatives, and cross-linked hyaluronan derivatives having at least one intramolecular disulfide bond, and methods of preparation thereof. The invention also includes thiolated hyaluronan derivatives and salts thereof having at least one pendant thiol group or a modified pendant thiol group, and methods of preparation thereof. An example of a modified pendant thiol group is a sulfhydryl group linked to a small molecule such as a bioactive agent, for example a drug or pharmaceutically active moiety. A hyaluronan derivative having a sulfhydryl group linked to a pharmaceutically active moiety is useful as a sustained or controlled release drug delivery vehicle. Compositions containing the hyaluronan derivatives of the invention can reversibly viscosify in vivo or in vitro, in response to mild changes in condition, and are thus useful in ophthalmic surgery and in tissue engineering.
Owner:ANIKA THERAPEUTICS INC
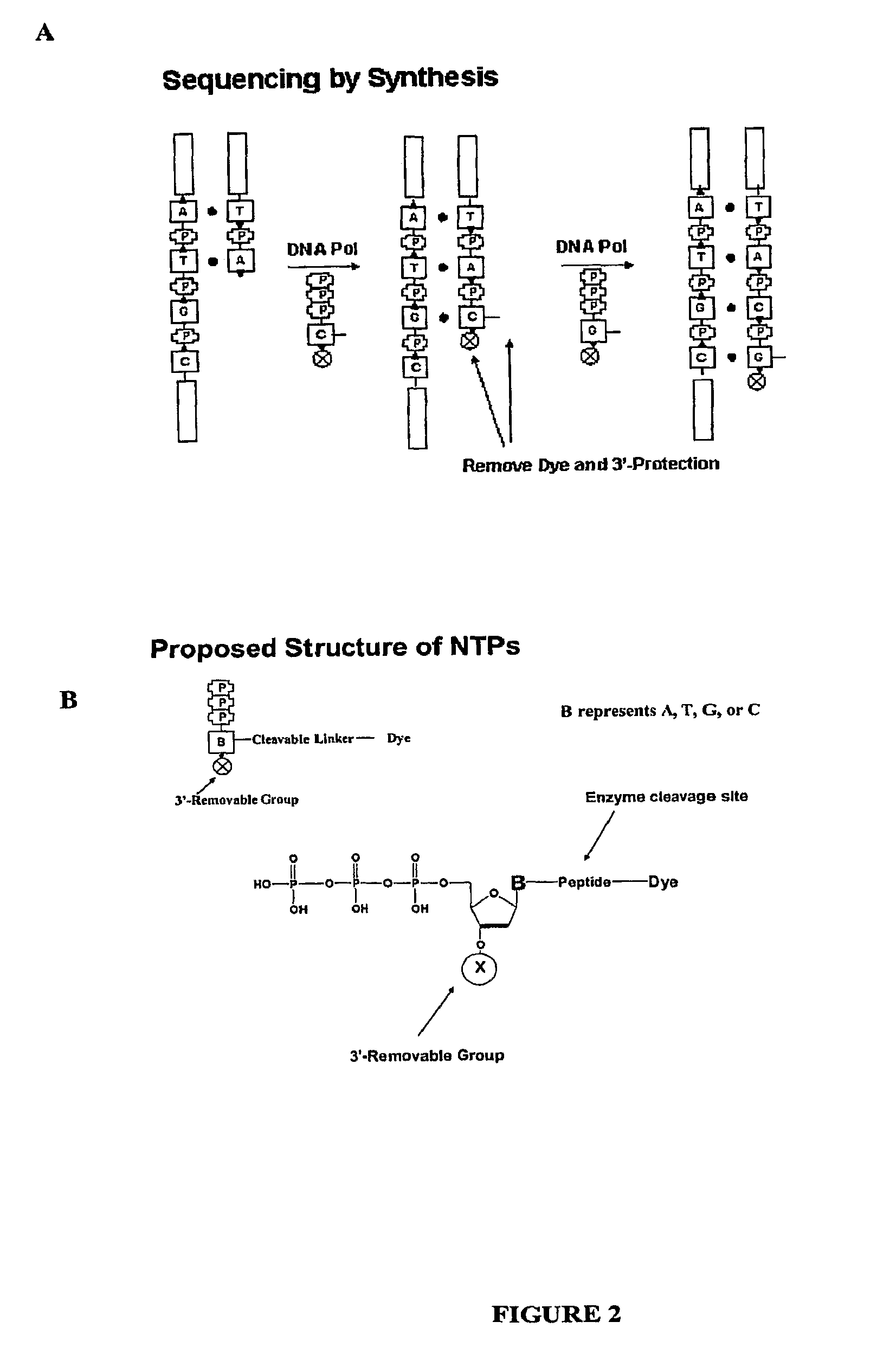
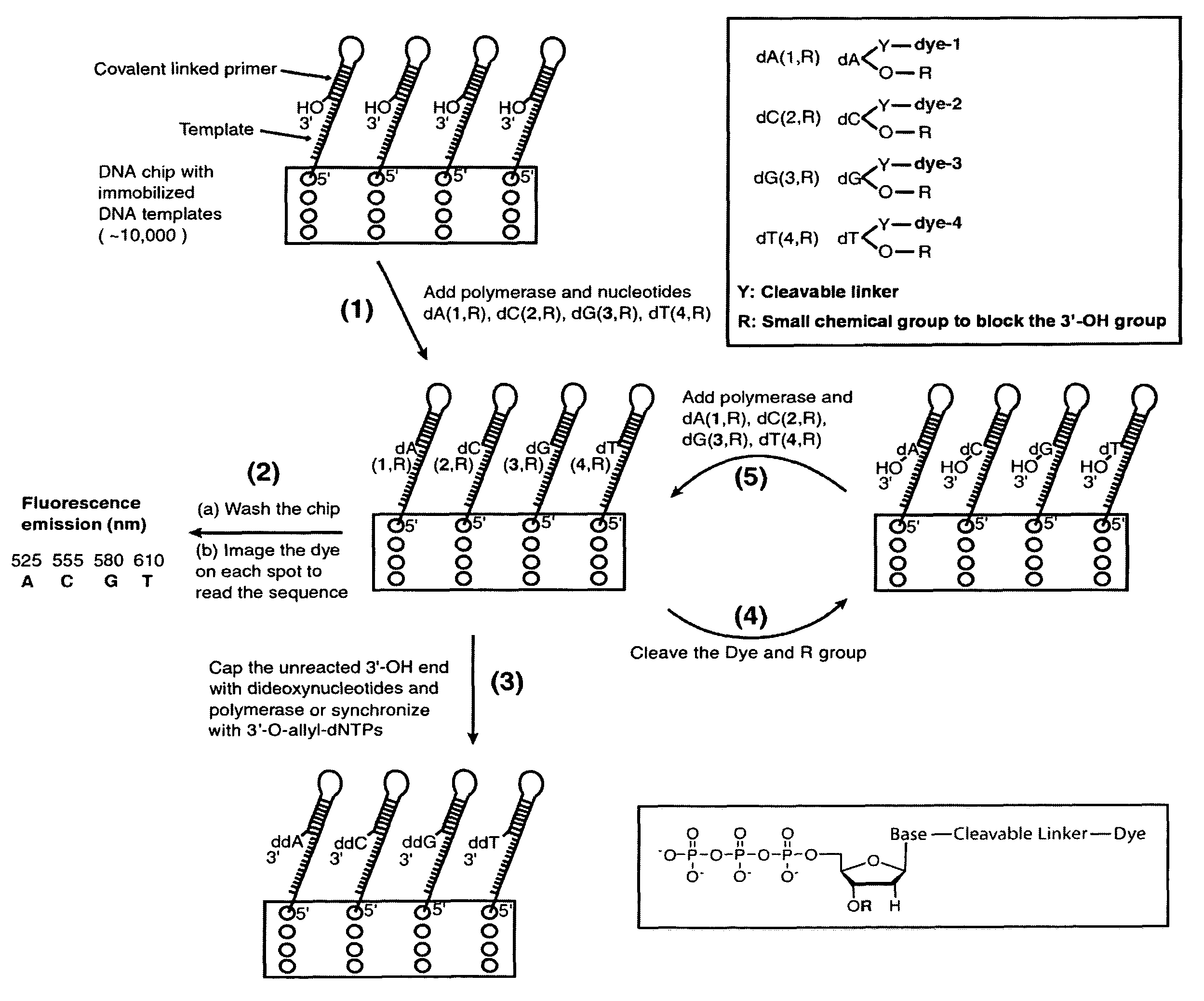
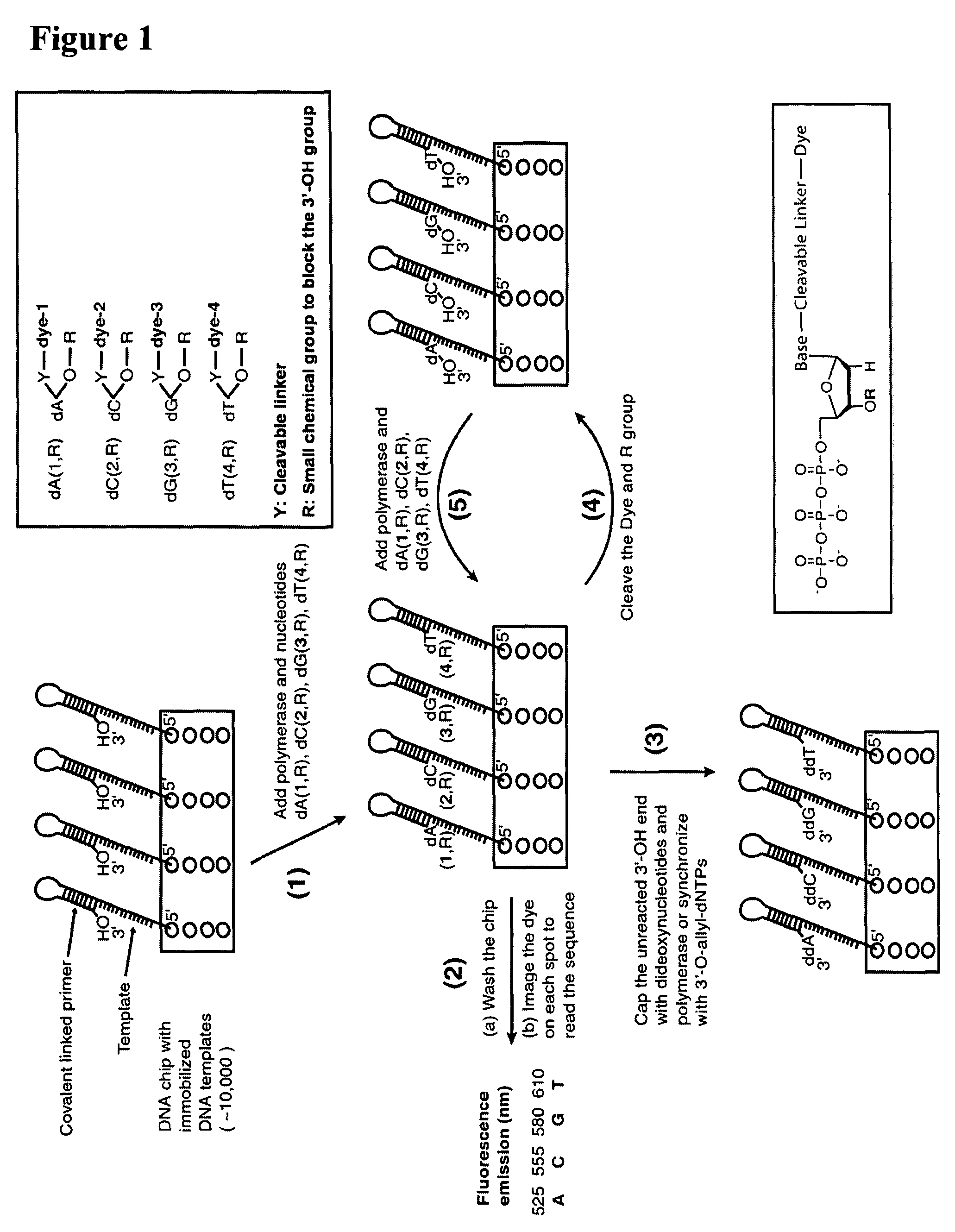
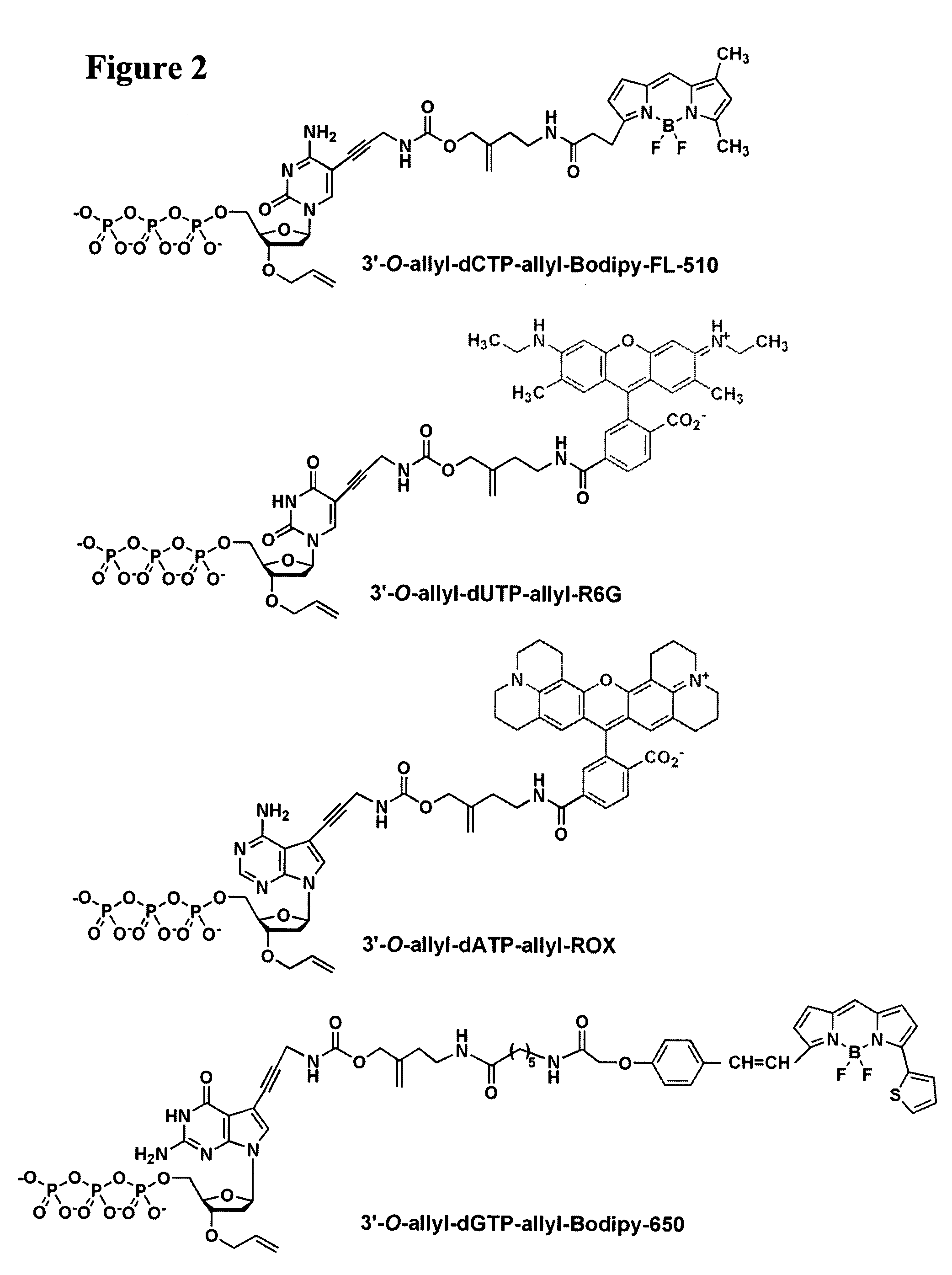
Four-color DNA sequencing by synthesis using cleavable fluorescent nucleotide reversible terminators
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
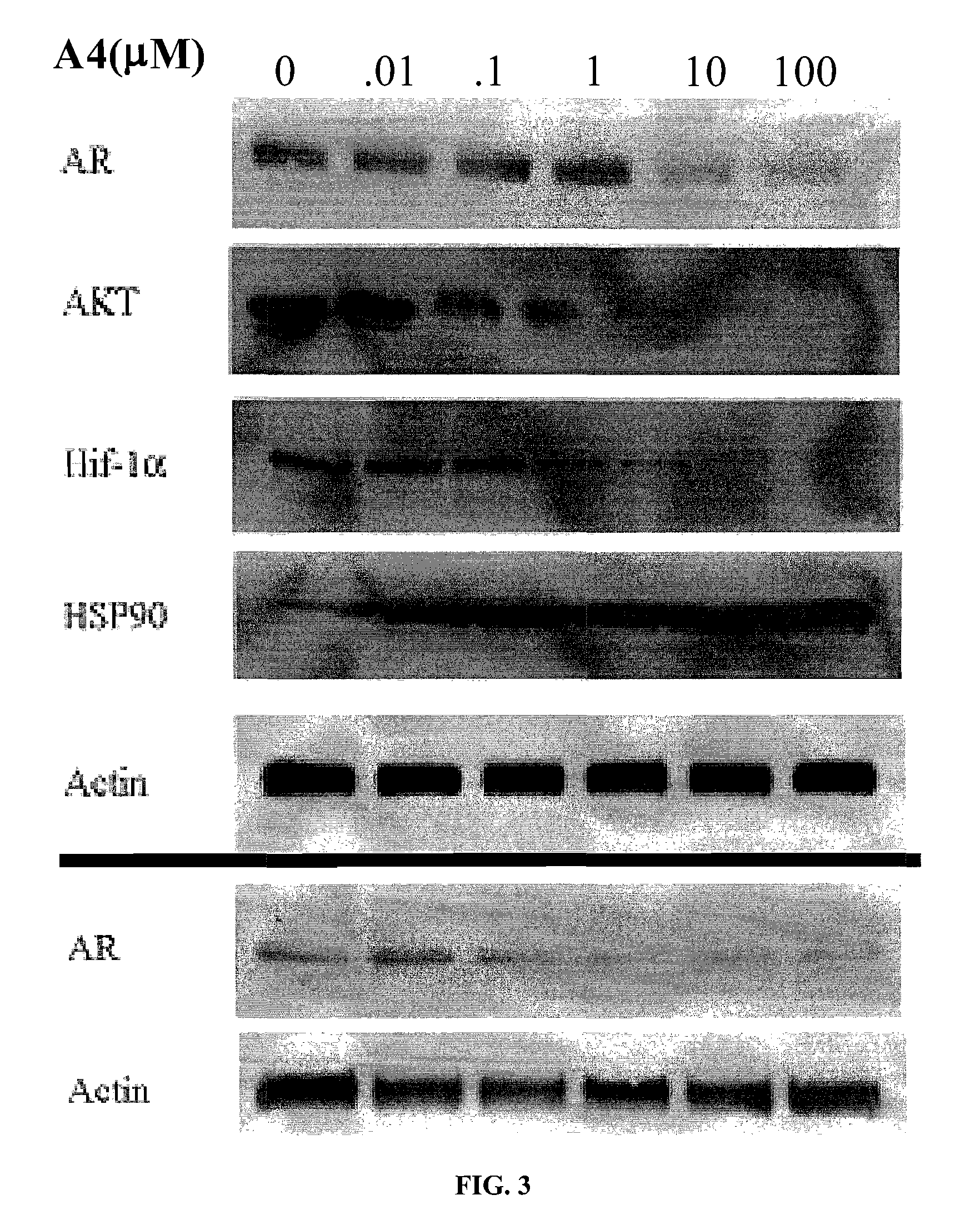
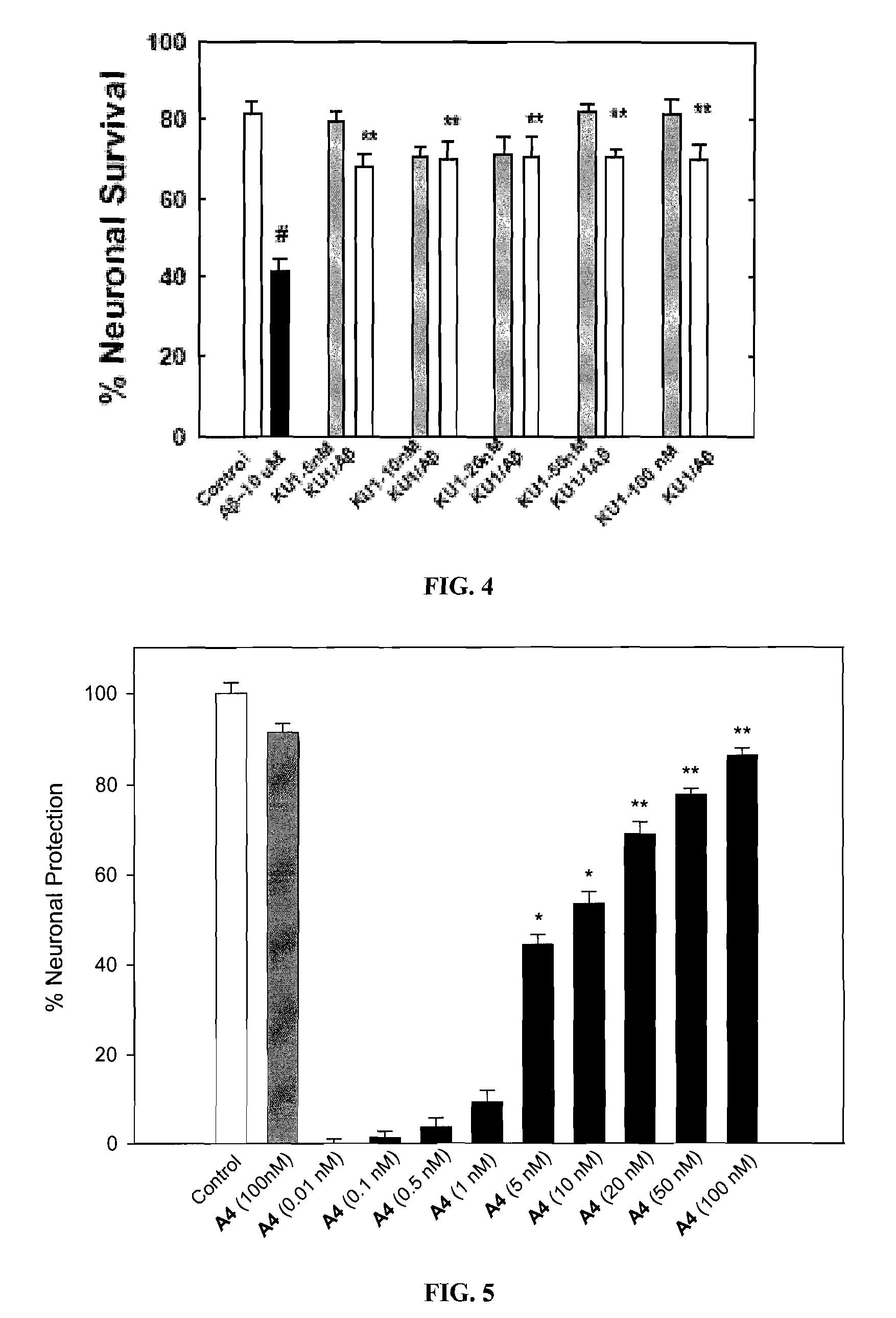
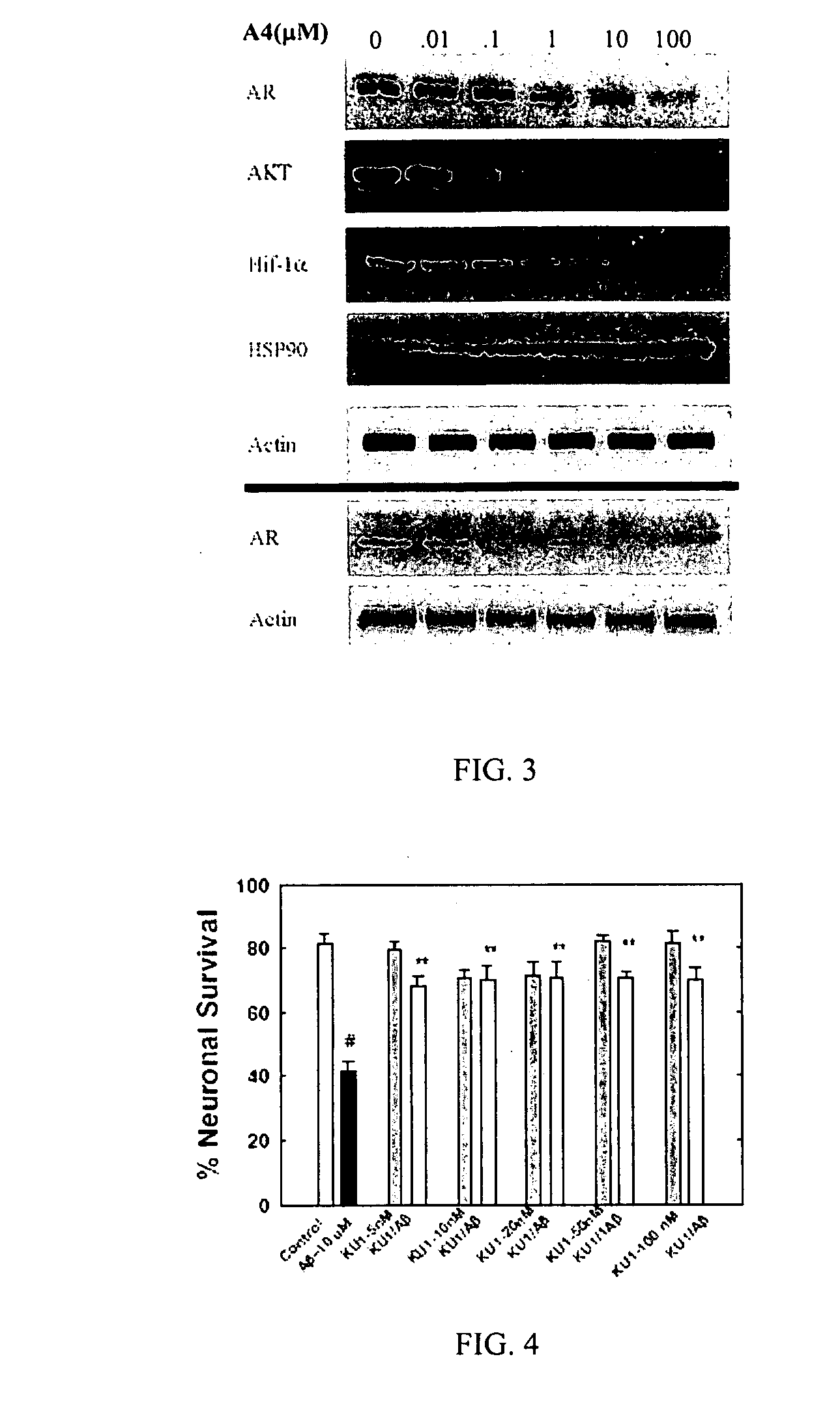
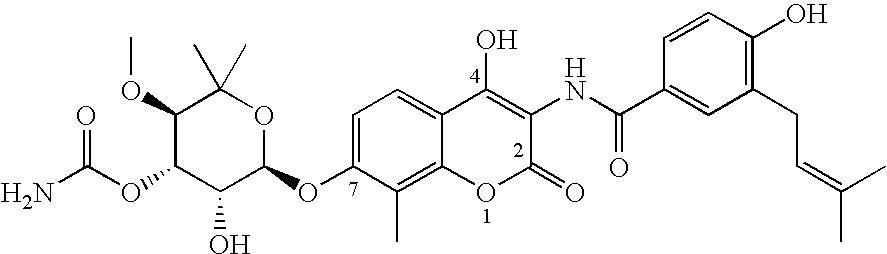
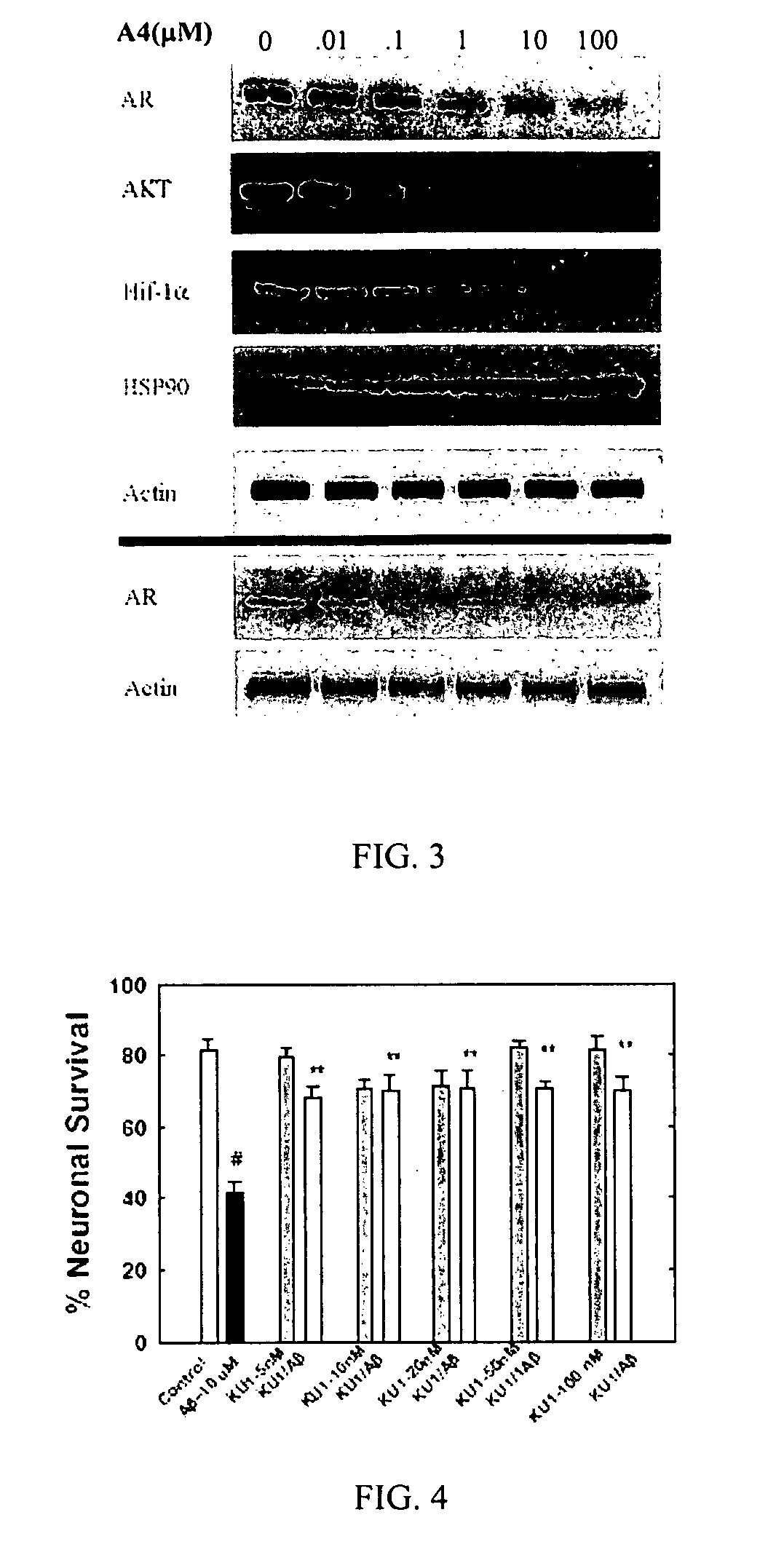
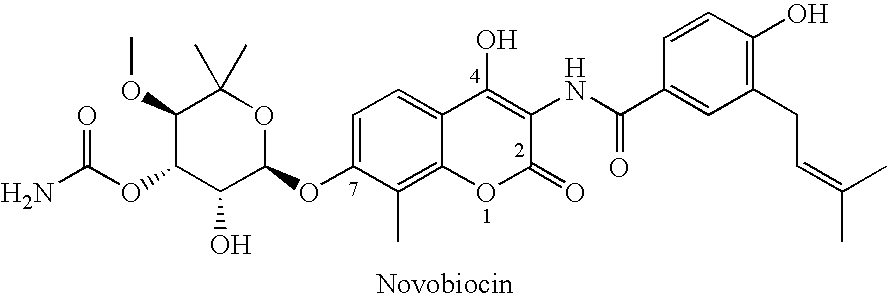
Novobiocin analogues as neuroprotective agents and in the treatment of autoimmune disorders
Novobiocin analogues and pharmaceutical composition containing such compounds useful for the treatment and / or prevention of neurodegenerative disorders and autoimmune disorders.
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF
Crystalline form of 1-chloro-4-(beta-D-glucopyranos-1-yl)-2-[4-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)-benzyl]-benzene, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments
ActiveUS20070249544A1Prevent degradationImproving and restoring functionalityBiocideAntibiotics chemistryCrystallographyBenzene
The invention relates to a crystalline form of 1-chloro-4-(β-D-glucopyranos-1-yl)-2-[4-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)-benzyl]-benzene, to a method for the preparation thereof, as well as to the use thereof for preparing medicaments.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Absorption Enhancers for Drug Administration
ActiveUS20080299079A1Improve absorption and bioavailabilityToxic effectsBiocideNervous disorderActive agentPancreatic hormone
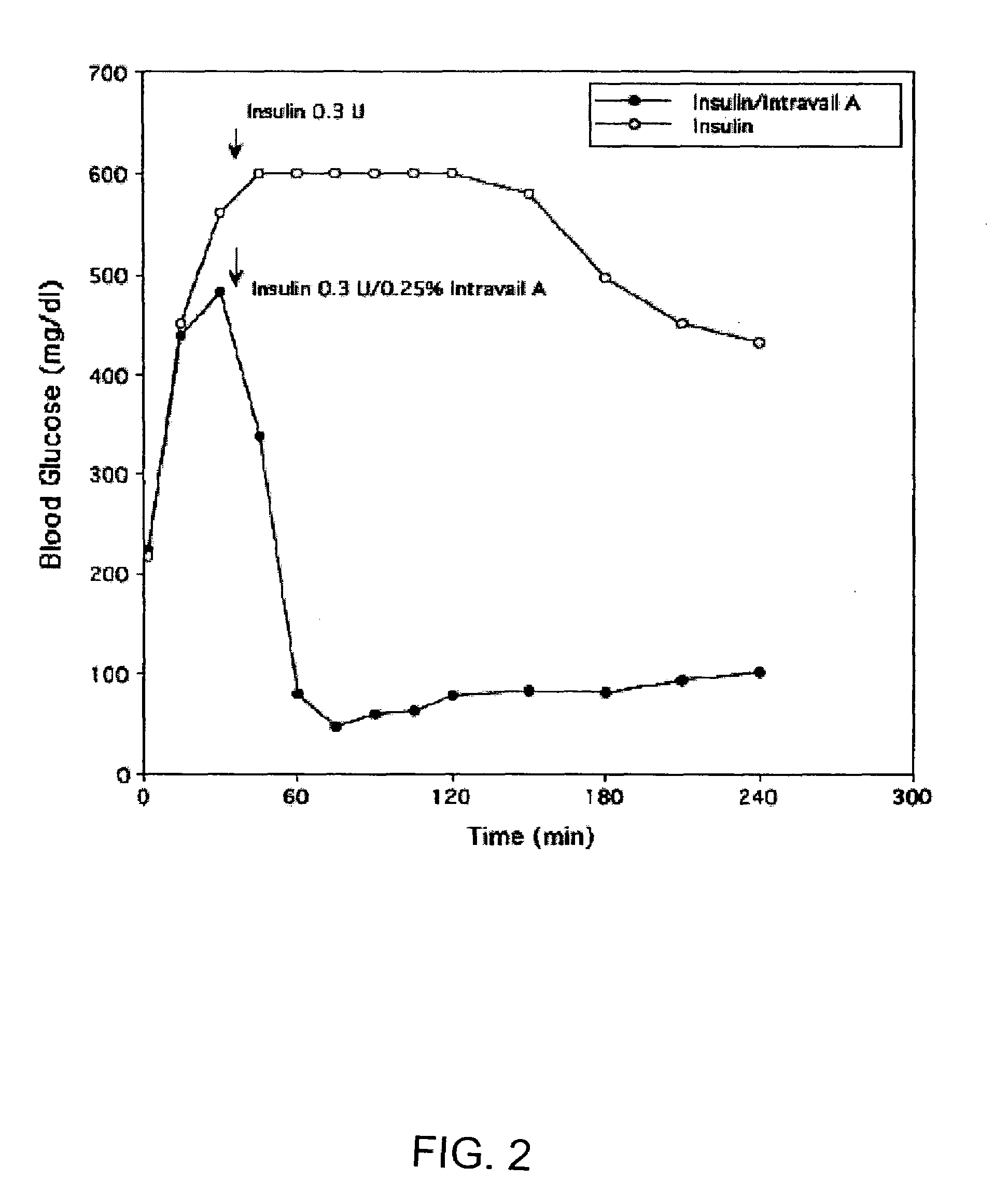
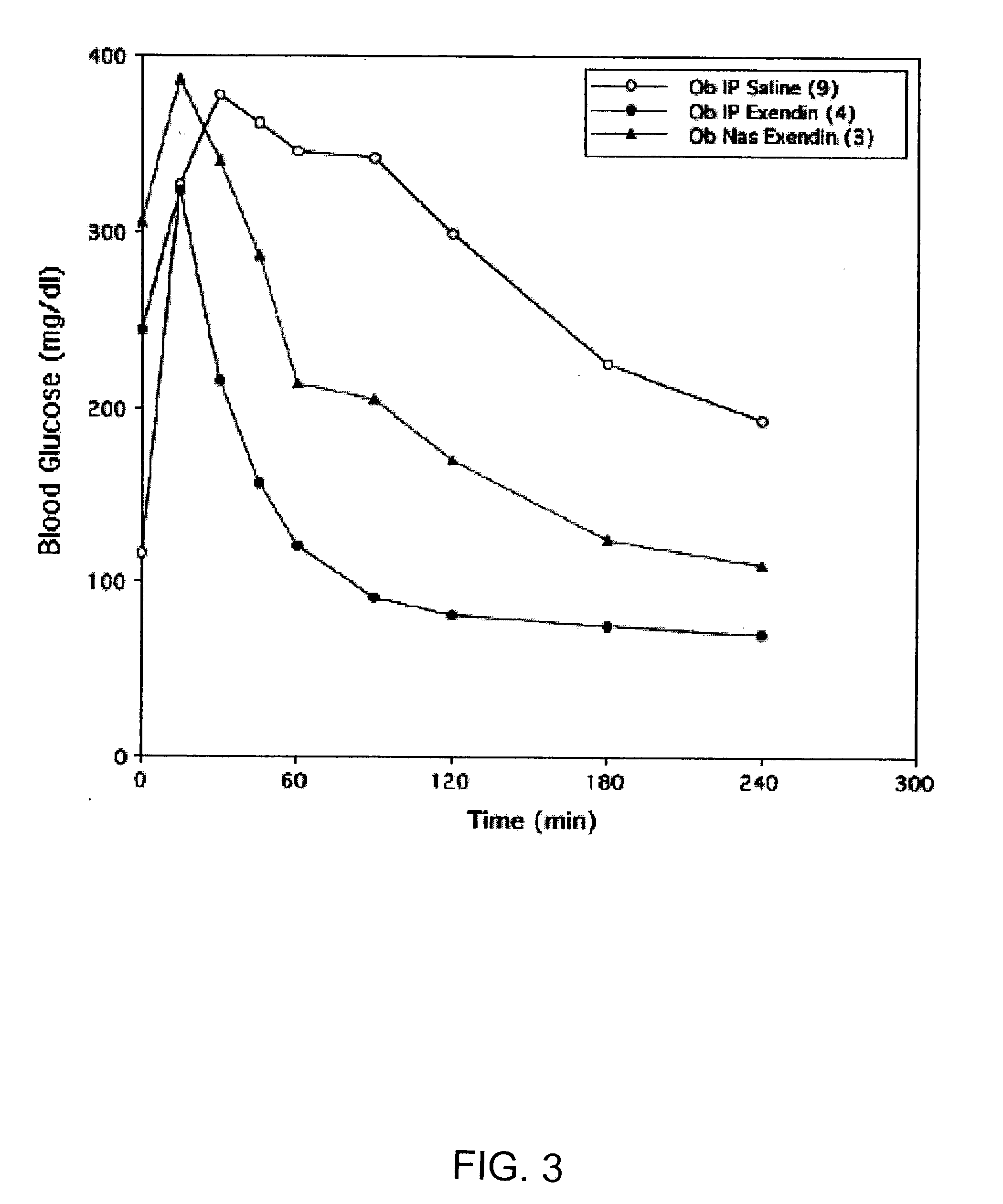
A composition including a surfactant and at least one alkyl glycoside and / or saccharide alkyl ester and a drug. The surfactant composition(s) when admixed with a drug is non-toxic and non-irritating, while stabilizing and increasing the bioavailability of the drug. The invention also provides compositions that enhance absorption of drugs via the oral, ocular, nasal, nasolacrimal, inhalation or pulmonary, oral cavity (sublingual or Buccal cell) or CSF delivery route of a patient, including but not limited to insulin, glucagon and exendin-4.
Owner:AEGIS THERAPEUTICS LLC
Methods for introducing mannose 6-phosphate and other oligosaccharides onto glycoproteins
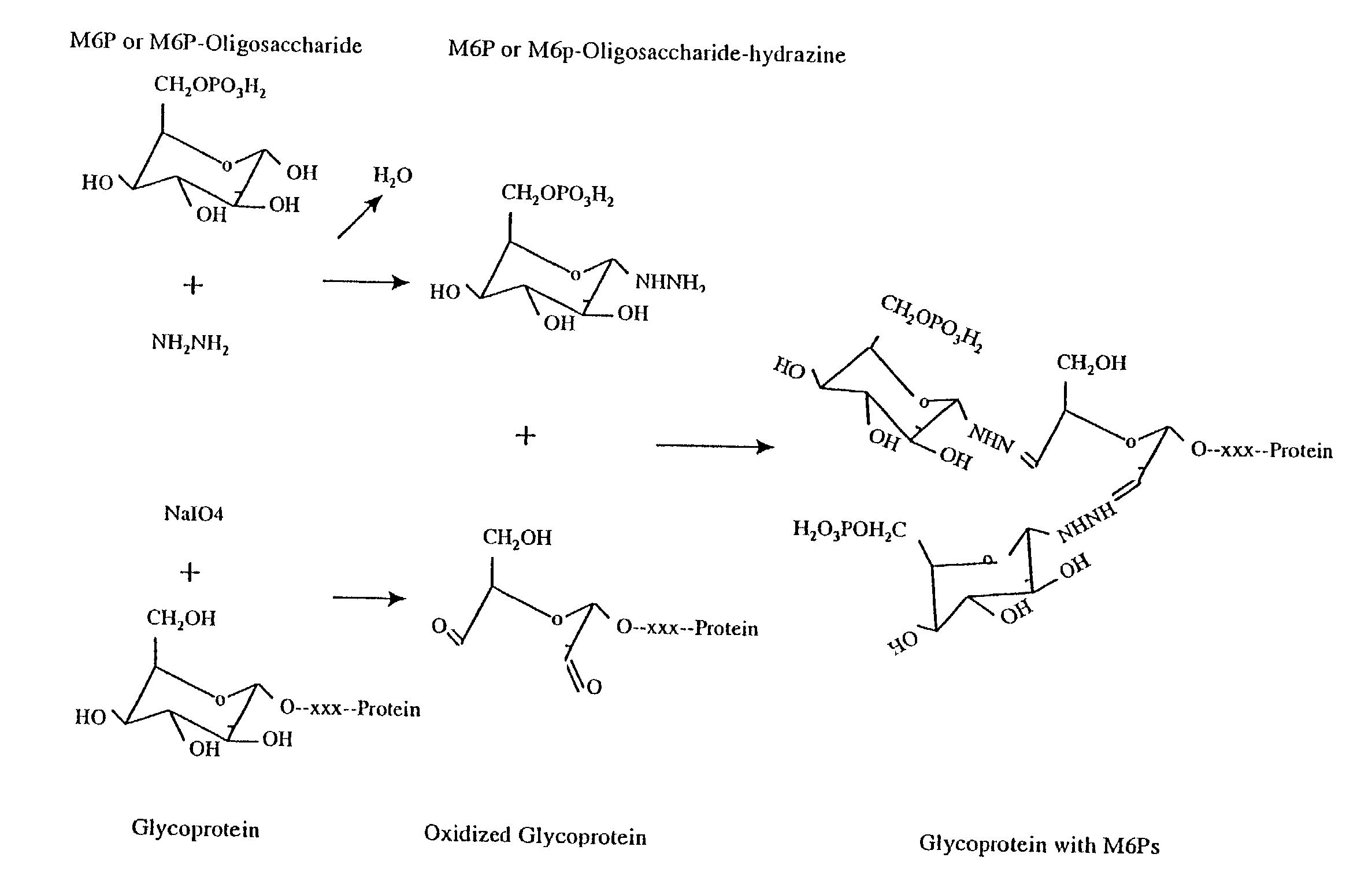
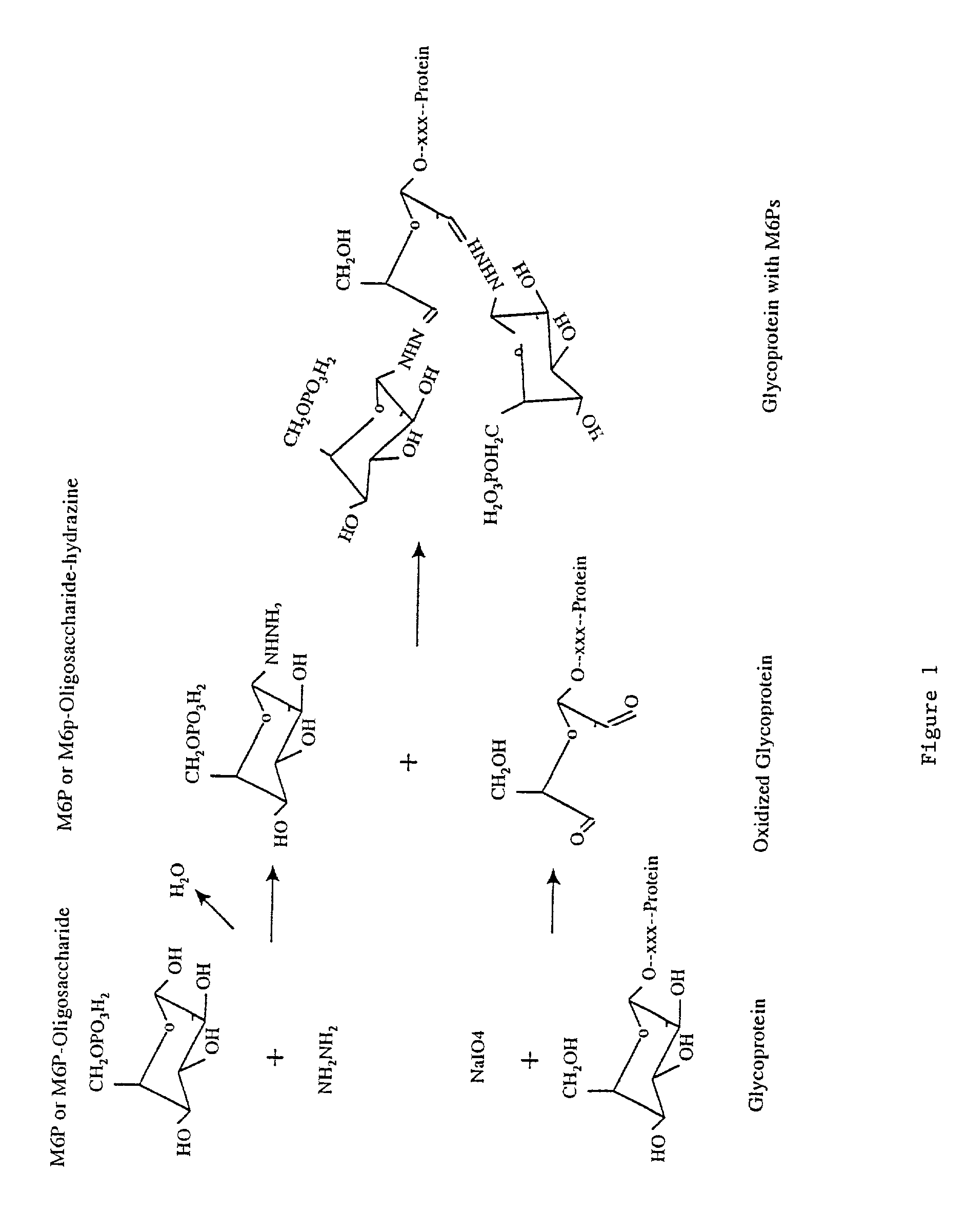
InactiveUS7001994B2Well formedIncrease the cellular uptake of lysosomal enzymesHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphorylationPhosphoric acid
Methods to introduce highly phosphorylated mannopyranosyl oligosaccharide derivatives containing mannose 6-phosphate (M6P), or other oligosaccharides bearing other terminal hexoses, to carbonyl groups on oxidized glycans of glycoproteins while retaining their biological activity are described. The methods are useful for modifying glycoproteins, including those produced by recombinant protein expression systems, to increase uptake by cell surface receptor-mediated mechanisms, thus improving their therapeutic efficacy in a variety of applications.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Novobiocin analogues as neuroprotective agents and in the treatment of autoimmune disorders
Novobiocin analogues and pharmaceutical composition containing such compounds useful for the treatment and / or prevention of neurodegenerative disorders and autoimmune disorders.
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF
2′-Fluoronucleosides
InactiveUS7307065B2Sure easyUseful in treatmentBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphoric Acid EstersPhosphate
A class of 2′-fluoro-nucleoside compounds are disclosed which are useful in the treatment of hepatitis B infection, hepatitis C infection, HIV and abnormal cellular proliferation, including tumors and cancer. The compounds have the general formulae:whereinBase is a purine or pyrimidine base;R1 is OH, H, OR3, N3, CN, halogen, including F, or CF3, lower alkyl, amino, loweralkylamino, di(lower)alkylamino, or alkoxy, and base refers to a purine or pyrimidine base;R2 is H, phosphate, including monophosphate, diphosphate, triphosphate, or a stabilized phosphate prodrug; acyl, or other pharmaceutically acceptable leaving group which when administered in vivo, is capable of providing a compound wherein R2 is H or phosphate; sulfonate ester including alkyl or arylalkyl sulfonyl including methanesulfonyl, benzyl, wherein the phenyl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents as described in the definition of aryl given above, a lipid, an amino acid, peptide, or cholesterol; andR3 is acyl, alkyl, phosphate, or other pharmaceutically acceptable leaving group which when administered in vivo, is capable of being cleaved to the parent compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
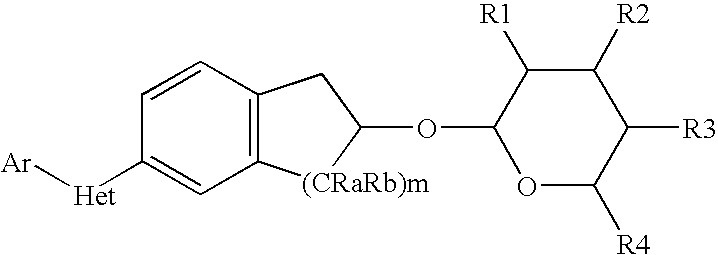
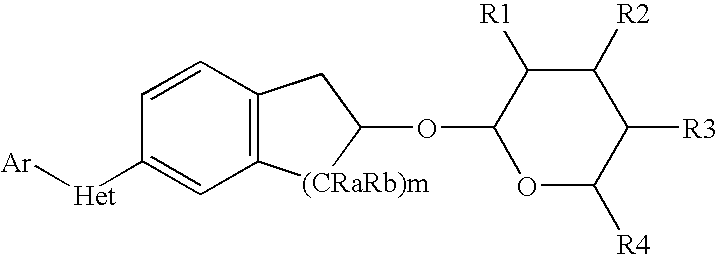
Novobiocin Analogues Having Modified Sugar Moieties
Novobiocin analogues useful as Hsp90 inhibitors in the treatment of cancer, neuroprotection, and autoimmune disorders.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Immunoeffector compounds
Owner:CORIXA CORP
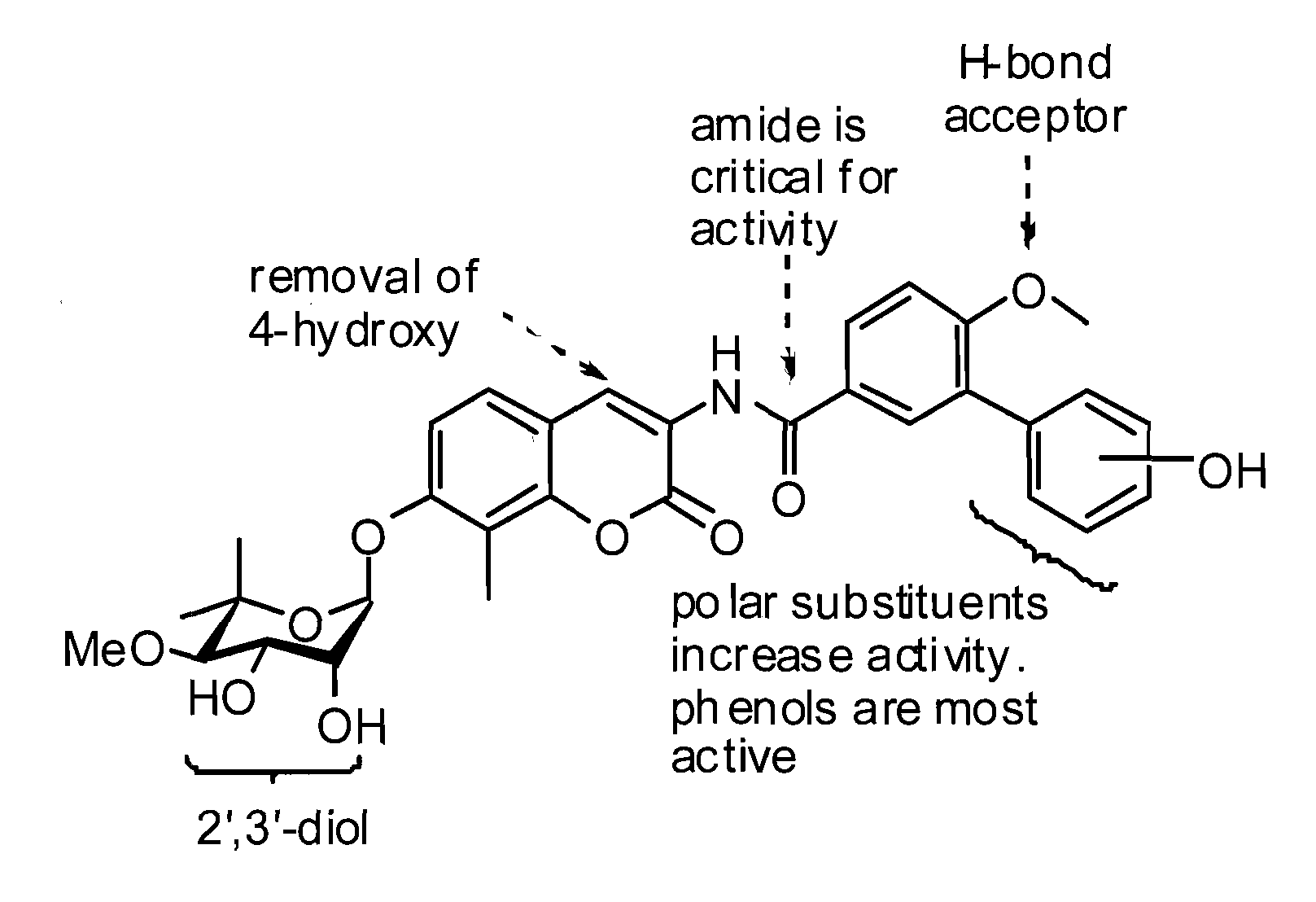
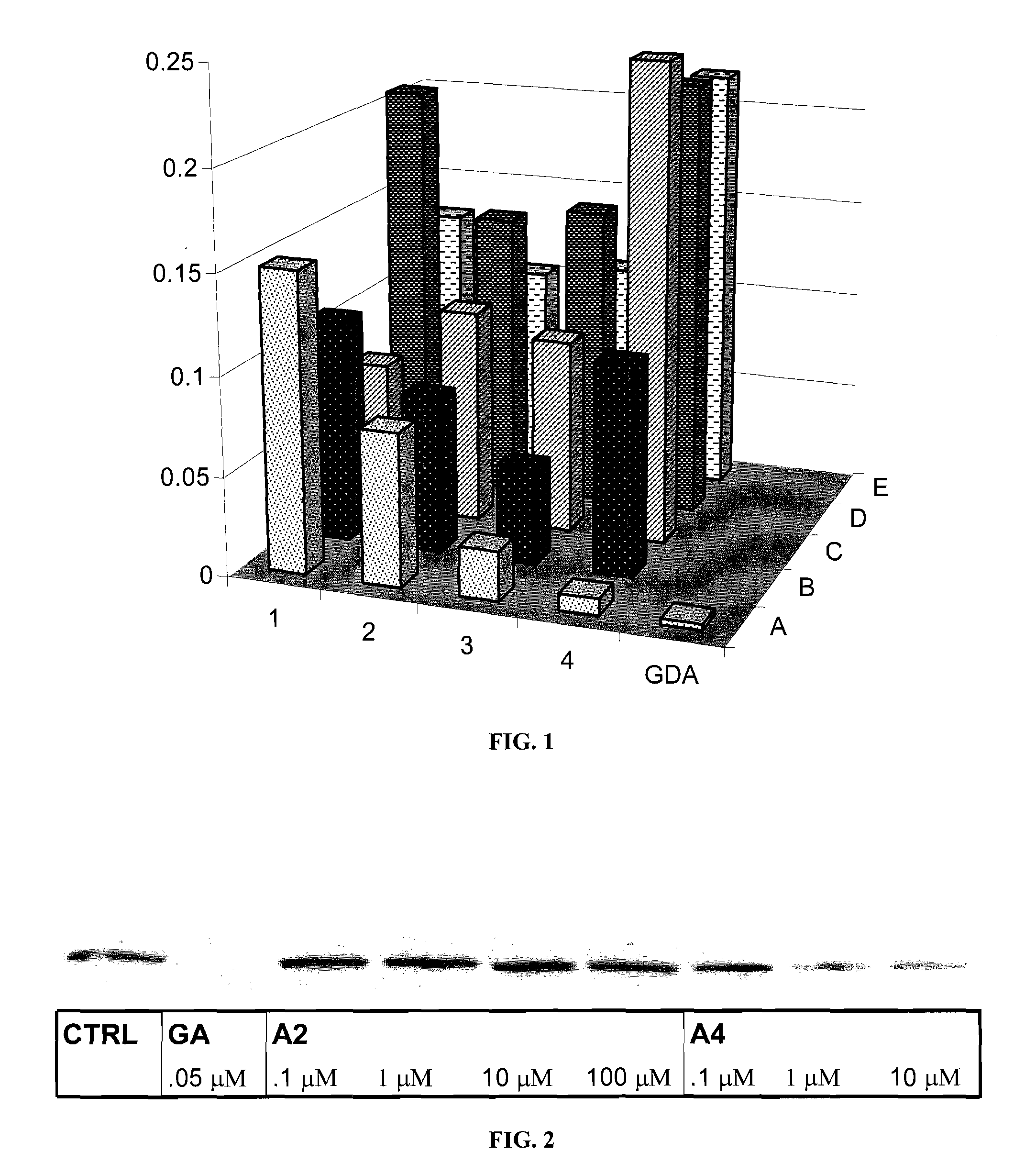
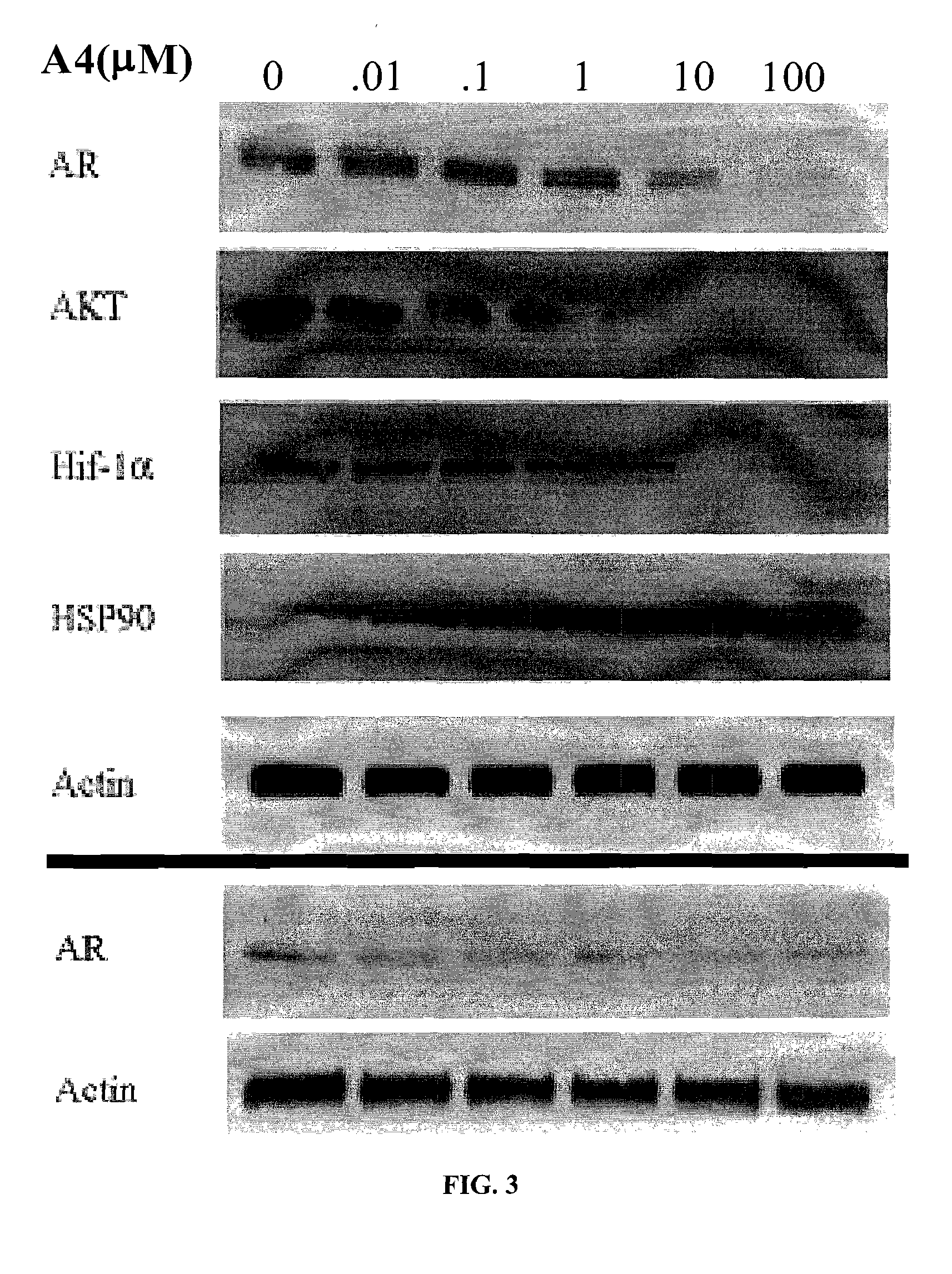
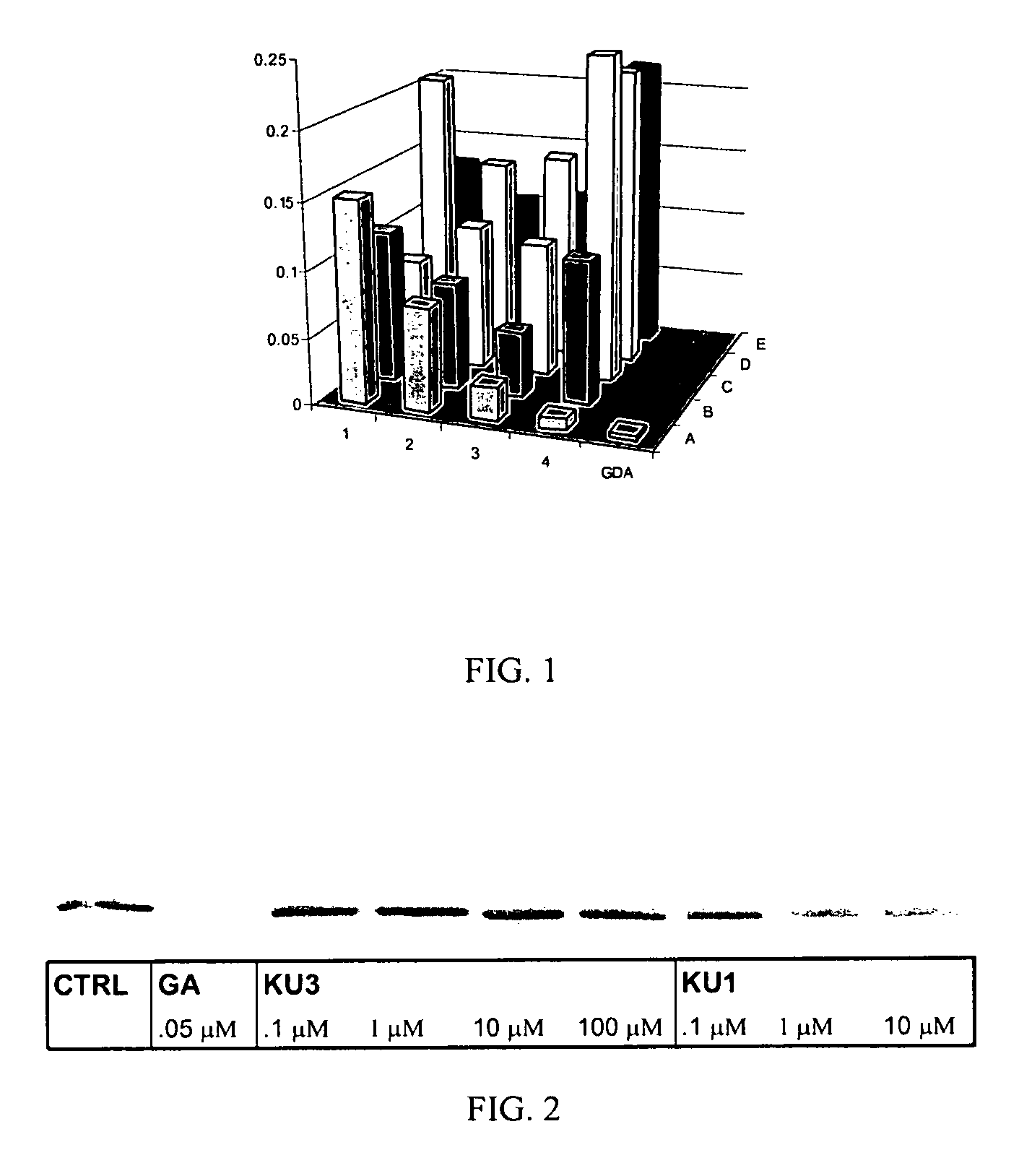
Novobiocin analogues as anticancer agents
Novel analogues and derivatives of novobiocin are provided, including compounds having modifications to the amide side chain, coumarin ring, and sugar moieties. The compounds of the present invention are useful as heat shock protein 90 inhibitors, and may be used as anticancer and neuroprotective agents.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS +1
Pesticidal compositions
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Iscom or iscom-matrix comprising hydrophobic receptor molecules for antigenic substances
PCT No. PCT / SE97 / 00287 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 17, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 17, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 20, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 30726 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 28, 1997Lipid-containing particles such as iscoms, iscom-matrix or vesicles such as micelles or liposomes that comprise one or more hydrophobic receptor molecules for targeting and antigenic substances, which receptor molecules have been integrated in the particle and are chosen from lipid-containing receptors or receptors that are hydrophobic, which receptor molecules bind to the antigenic substances.
Owner:MOREIN BROR +2
Novobiocin Analogues
Novobiocin analogues and pharmaceutical composition containing such compounds useful for the treatment and / or prevention of neurodegenerative disorders and autoimmune disorders, as well as cancer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Novobiocin analogues as anticancer agents
Novel analogues and derivatives of novobiocin are provided, including compounds having modifications to the amide side chain, coumarin ring, and sugar moieties. The compounds of the present invention are useful as heat shock protein 90 inhibitors, and may be used as anticancer and neuroprotective agents.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS +1
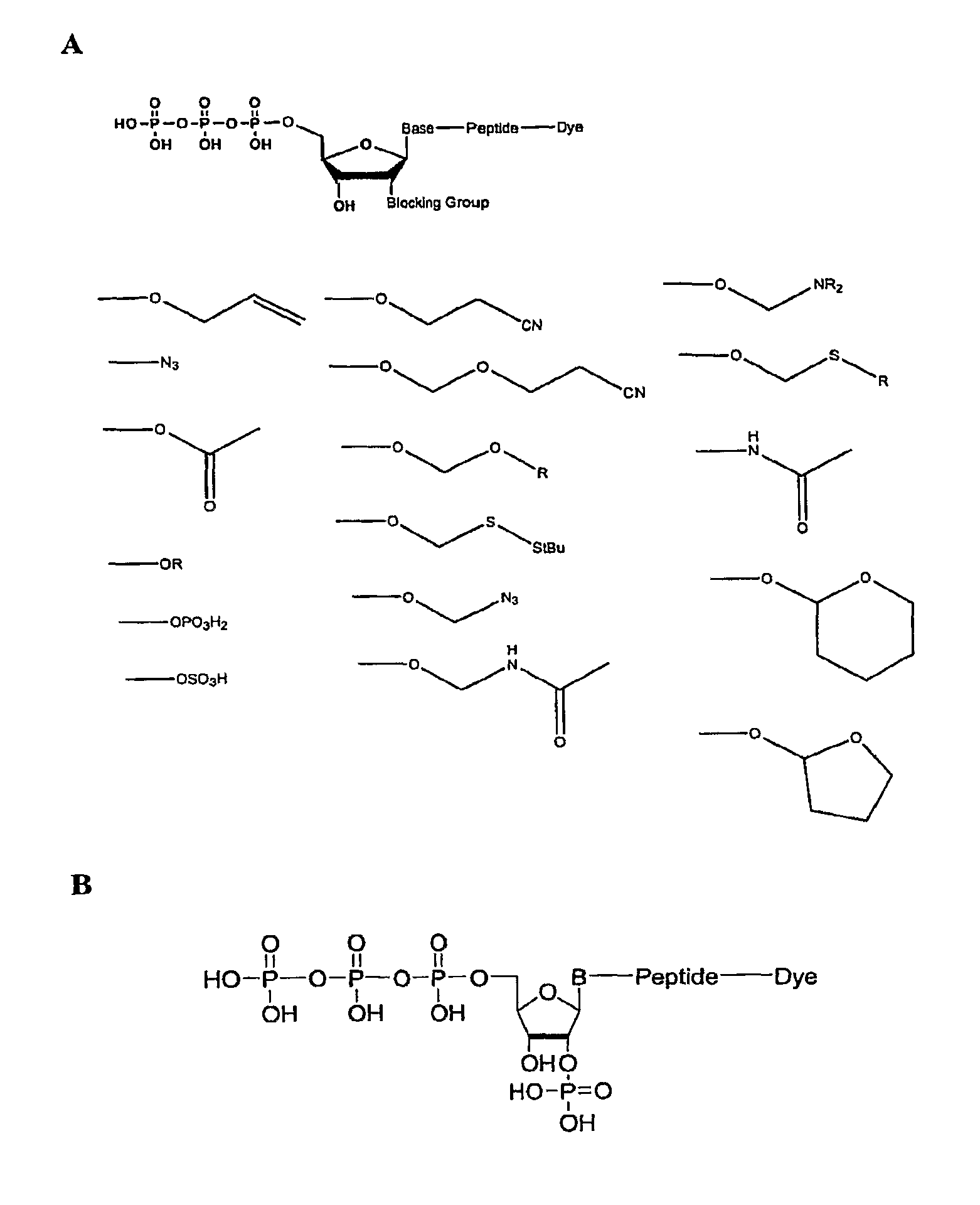
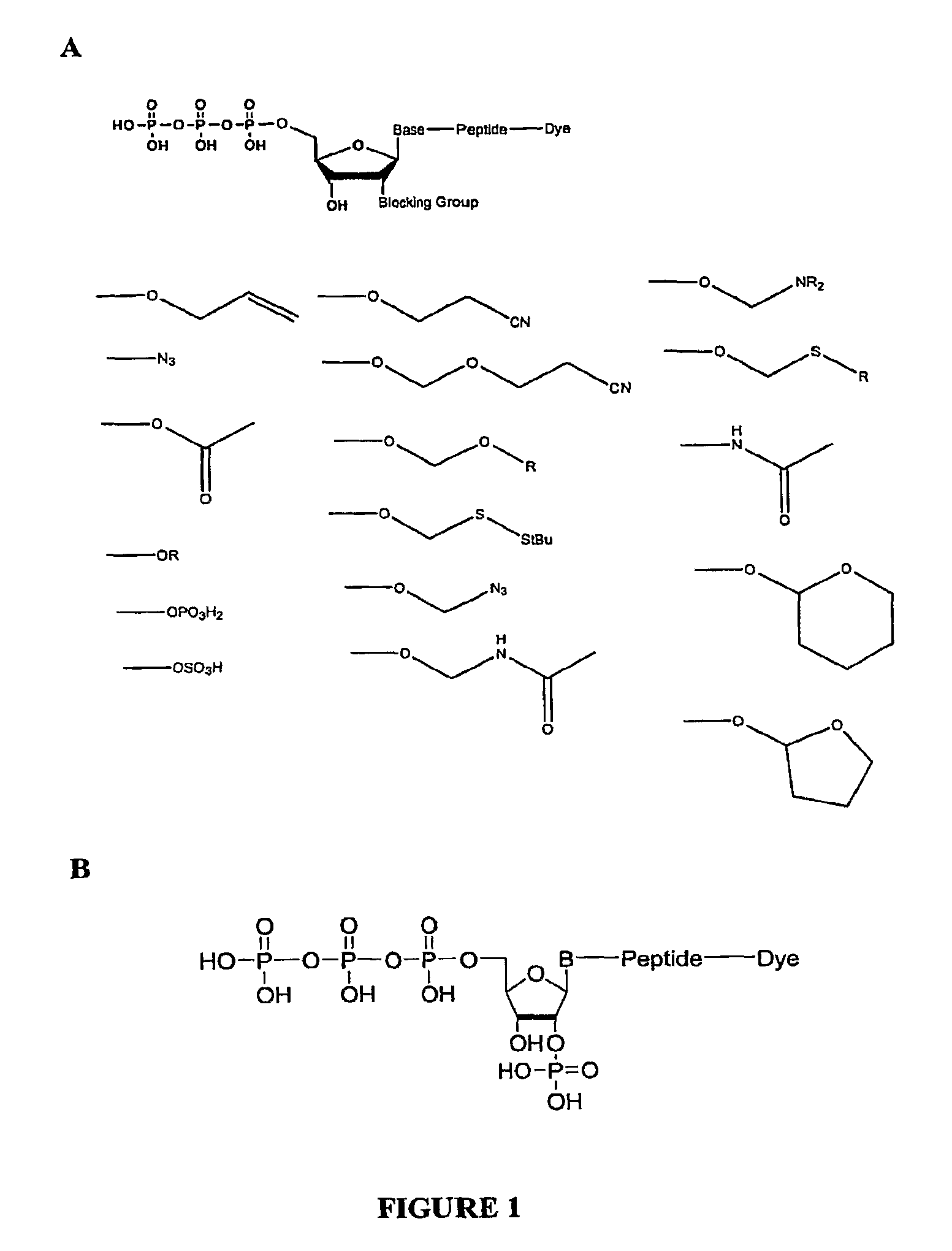
Compositions and methods for nucleotide sequencing
The invention provides nucleoside and nucleotide molecules containing cleavable linkers linking a label such as a dye. The invention also provides nucleosides and nucleotide molecules containing a blocking group, either removable or non-removable. The invention additionally provides methods of using the nucleoside and nucleotide molecules containing a cleavable linker and / or a blocking group.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
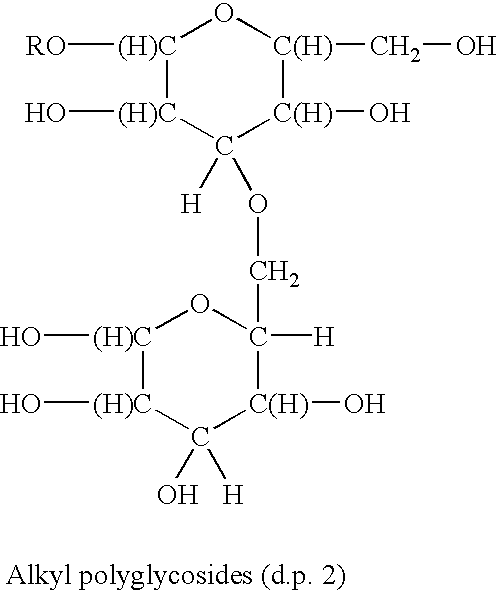
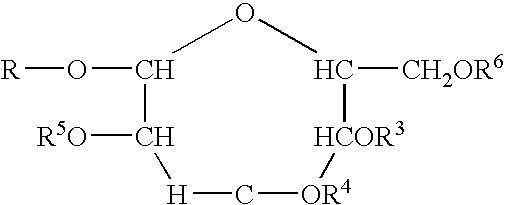
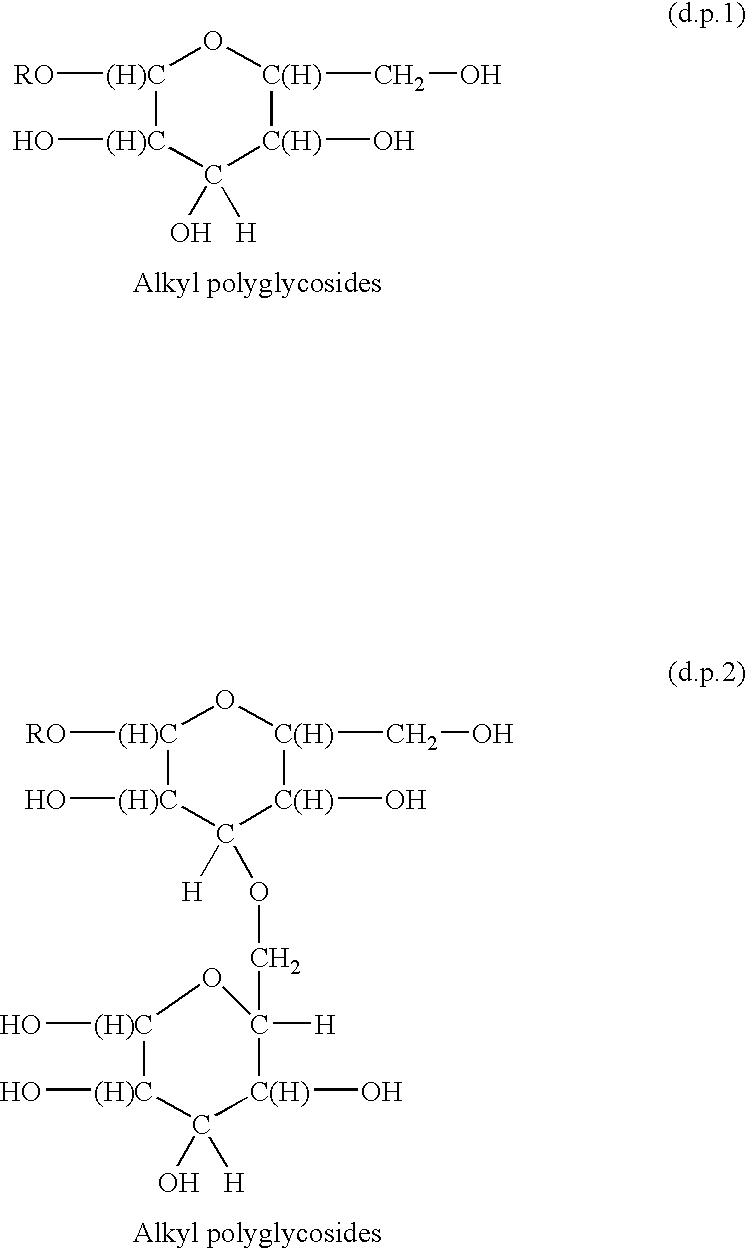
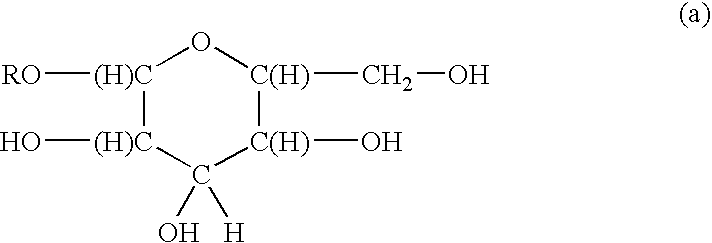
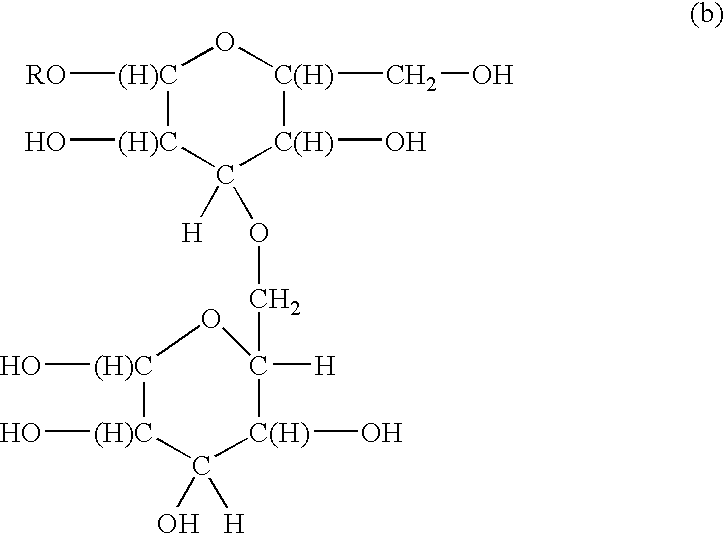
Surfactants based upon alkyl polyglycosides
InactiveUS6627612B1Hydrophobic raw materialRaise the gradeBiocideSugar derivativesGlycosideAlkyl polyglycoside
The invention relates to a series of polyglycoside derivatives that contain water-soluble groups introduced into the molecule by reaction with the hydroxyl groups present in the starting polyglycoside molecule, with the chloro material. The preferred products have more than one water-soluble group per molecule and are made with mild reagents to avoid discoloration and mal odor. The most preferred products have between 2 and 3 functional groups per molecule.
Owner:SURFATECH
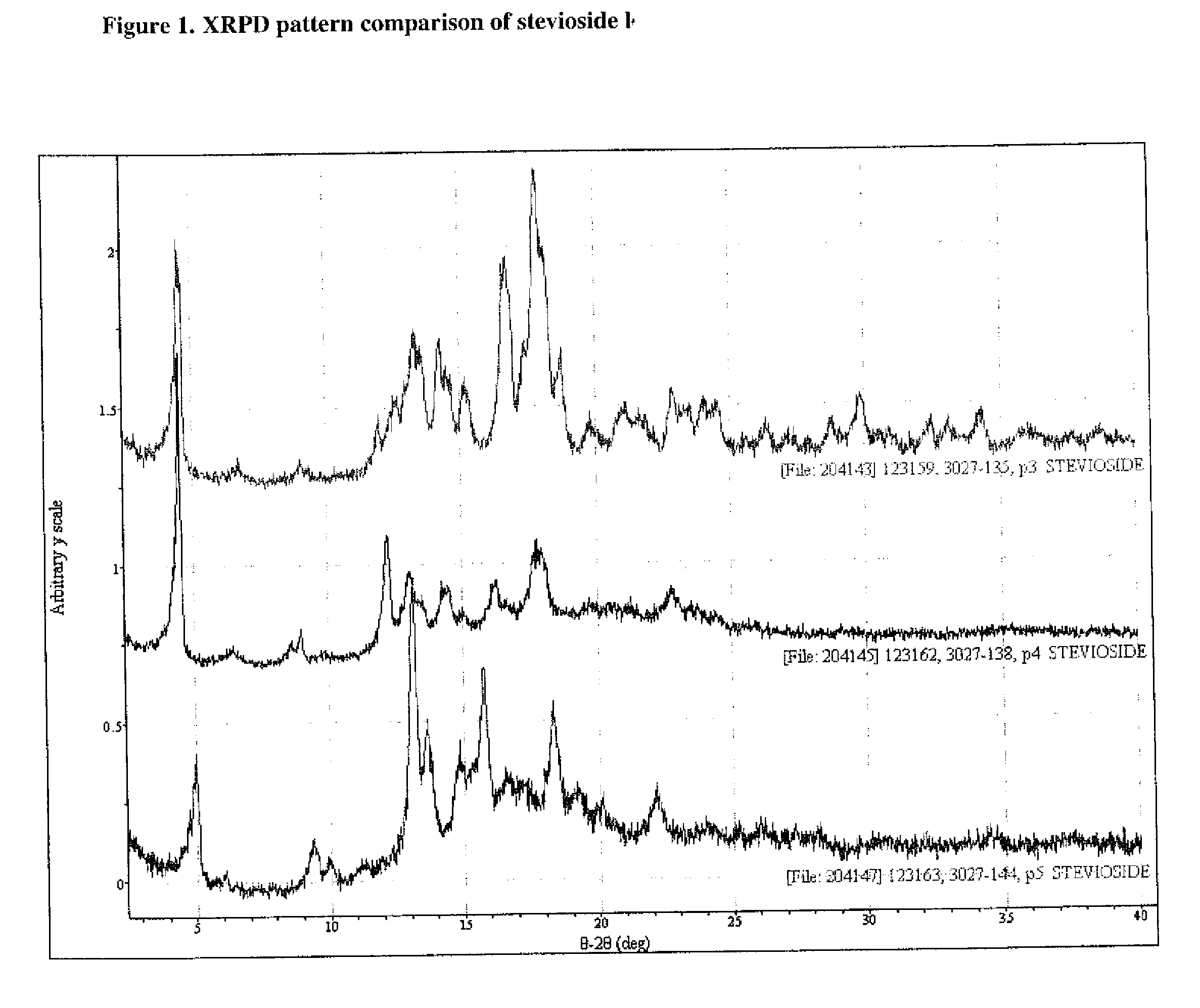
Stevioside Polymorphic and Amorphous Forms, Methods for Their Formulation, and Uses
Exemplary embodiments of this invention encompass a method for purifying a substantially crude stevioside, methods for preparing polymorphic and amorphous forms of stevioside, and the polymorphic and amorphous forms prepared therefrom.
Owner:THE COCA-COLA CO
Preparation and use of sulfated oligosaccharides
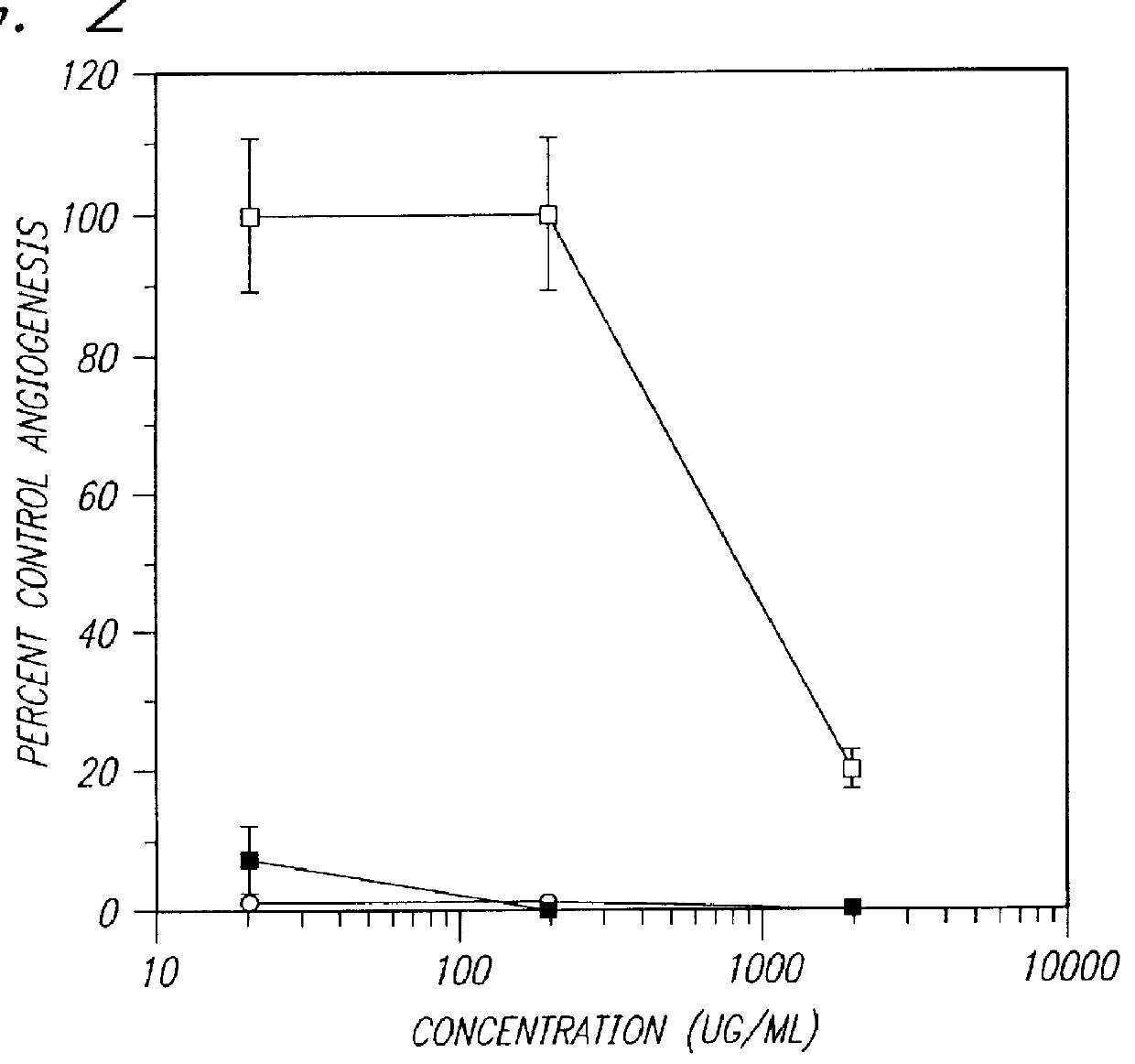
PCT No. PCT / AU96 / 00238 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 28, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 28, 1997 PCT Filed Apr. 24, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 33726 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 31, 1996Sulfated oligosaccharides, wherein the oligosaccharide has the general formula I:R1-(Rx)n-R2(I)wherein R1 and R2 and each Rx represents a monosaccharide unit, all of which may be the same or different, adjacent monosaccharide units being linked by 1->2, 1->3, 1->4 and / or 1->6 glycosidic bonds and n is an integer of from 1 to 6, and use thereof as anti-angiogenic, anti-metastatic and / or anti-inflammatory agents.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Method for Preventing Cancer Metastasis
The present invention relates to the use of a specific family of glycerolipid compounds of formula (I) described in the detailed description or the manufacture of a medicament for the prevention or for the treatment of cancer metastasis.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Polymeric alkylpolyglycoside carboxylates
The products of the invention are polymers of carboxylated alkylpolyglycosides. The products are very mild surfactants that are useful in personal care applications.
Owner:SURFATECH
Functionalized polymeric surfactants based upon alkyl polyglycosides
The invention relates to a series of multifunctional polyglycosides derivatives that are made by the polymerized by the reaction of polyoxyalkylene containing crosslinking reagent and polyglycosides, together with a functionalizing agent that contains a sulfate, sulfonate, quaternary nitrogen, or a phosphate group. The preferred polymers are cross linked having more than one group per molecule. They are made with mild reagents to avoid discoloration and mal odor.
Owner:SURFATECH
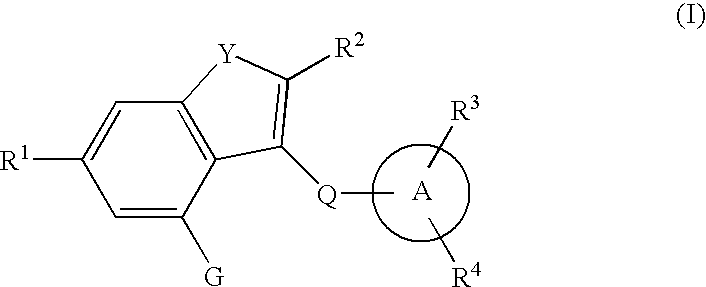
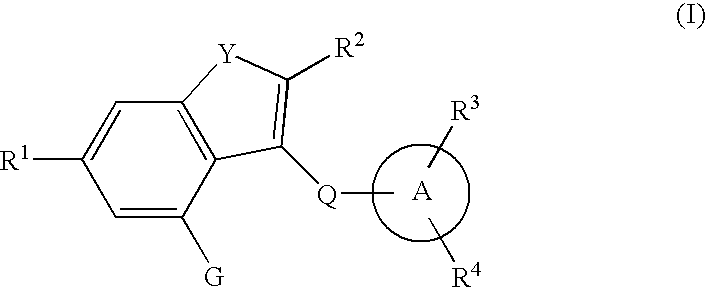
Fused heterocyclic derivative, medicinal composition containing the same, and medicinal use thereof
InactiveUS20060247179A1Good effectReduce doseBiocideAntibiotics chemistryAcute hyperglycaemiaDiabetic complication
The present invention provides fused heterocyclic derivatives represented by the general formula: wherein R1 represents H, halogen, OH, etc.; R2 represents H, halogen or an alkyl group; R3 and R4 represent H, OH, halogen, etc.; Q represents alkylene, etc.; ring A represents aryl or heteroaryl; and G represents , or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, or prodrugs thereof, which exhibit an excellent inhibitory activity in human SGLT and are useful as agents for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with hyperglycemia such as diabetes, postprandial hyperglycemia, impaired glucose tolerance, diabetic complications or obesity, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same, and pharmaceutical uses thereof.
Owner:KISSEI PHARMA
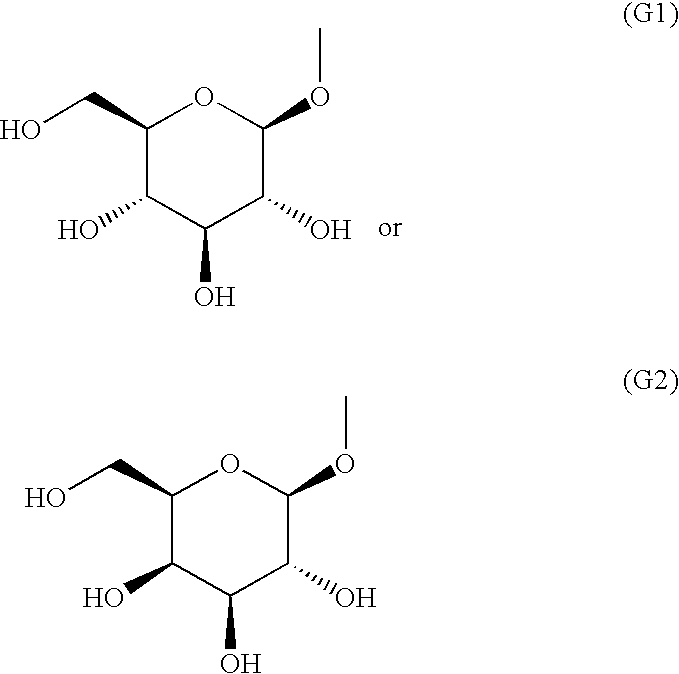
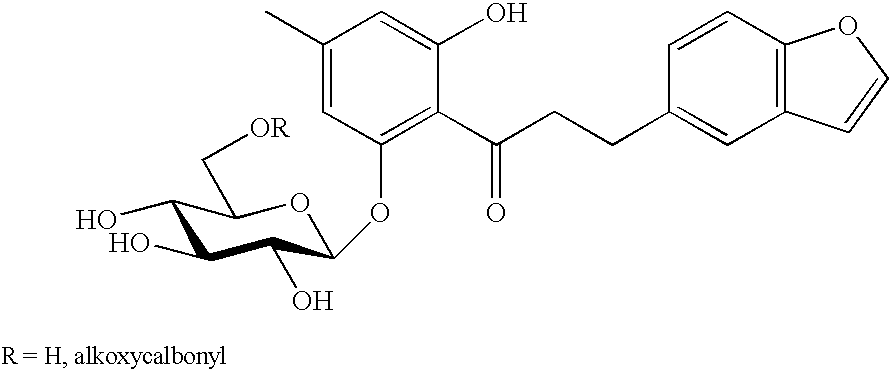
Aryl 5-thio-beta-d-glucopyranoside derivatives and remedies for diabetes containing the same
InactiveUS20050209309A1Accelerate excretion of urinaryIncrease excretionBiocideSenses disorderArylThio-
There is provided a 5-thio-β-D-glucopyranoside compound of the following formula, which has an inhibitory effect on SGLT2 activity, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a hydrate thereof. There is also provided a pharmaceutical preparation, particularly a prophylactic or therapeutic agent for diabetes, diabetes-related diseases or diabetic complications, which comprises such a compound as an active ingredient.
Owner:TAISHO PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
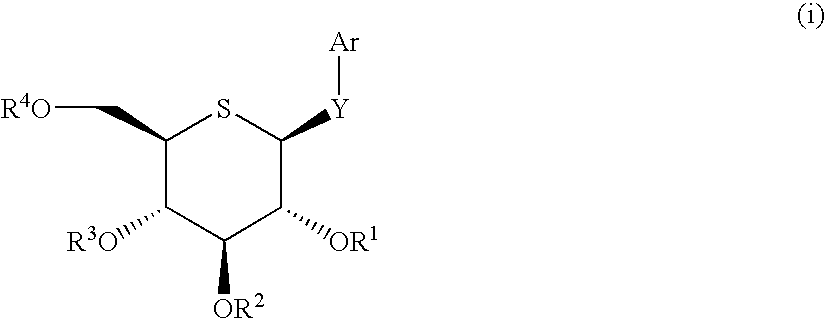
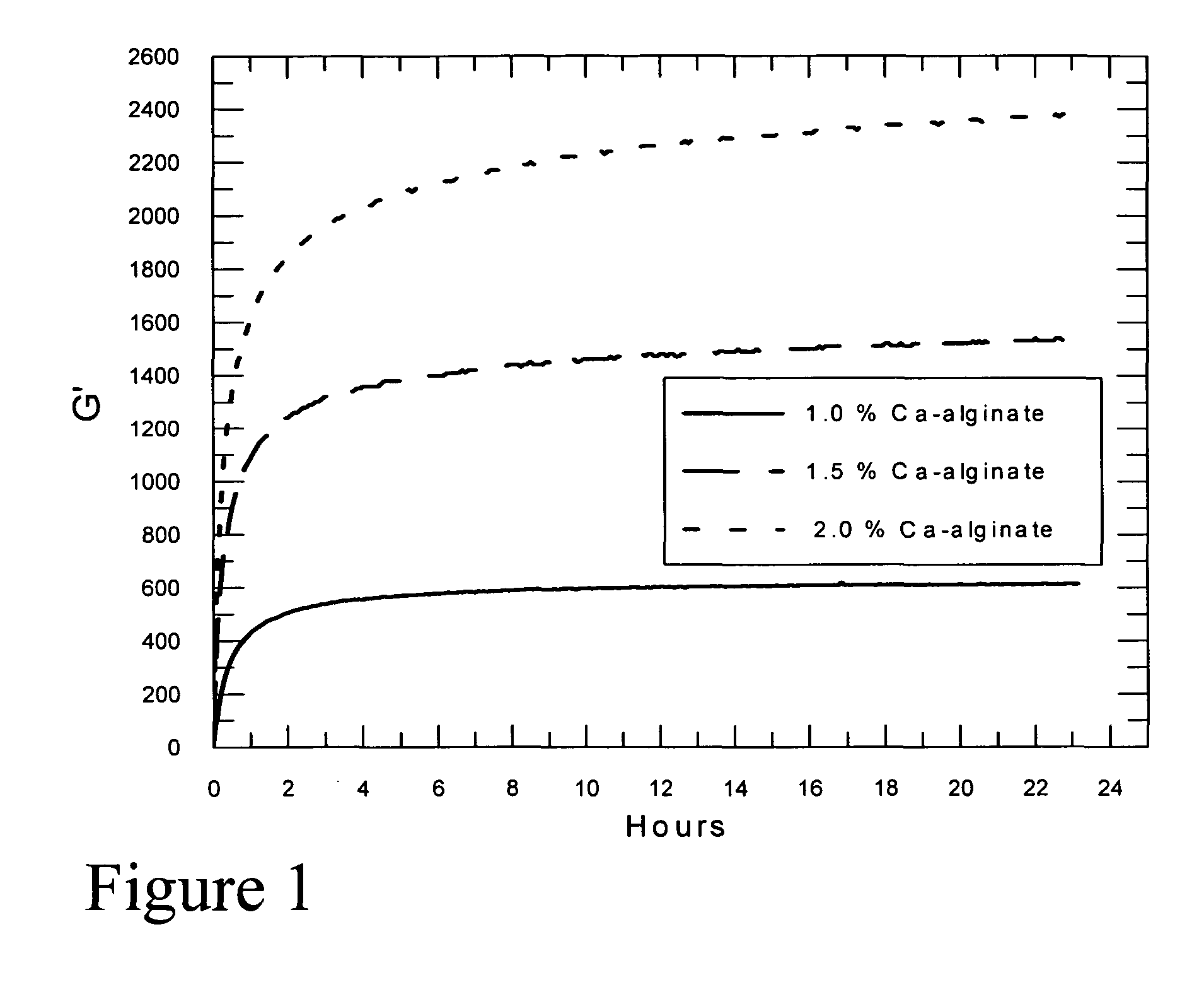
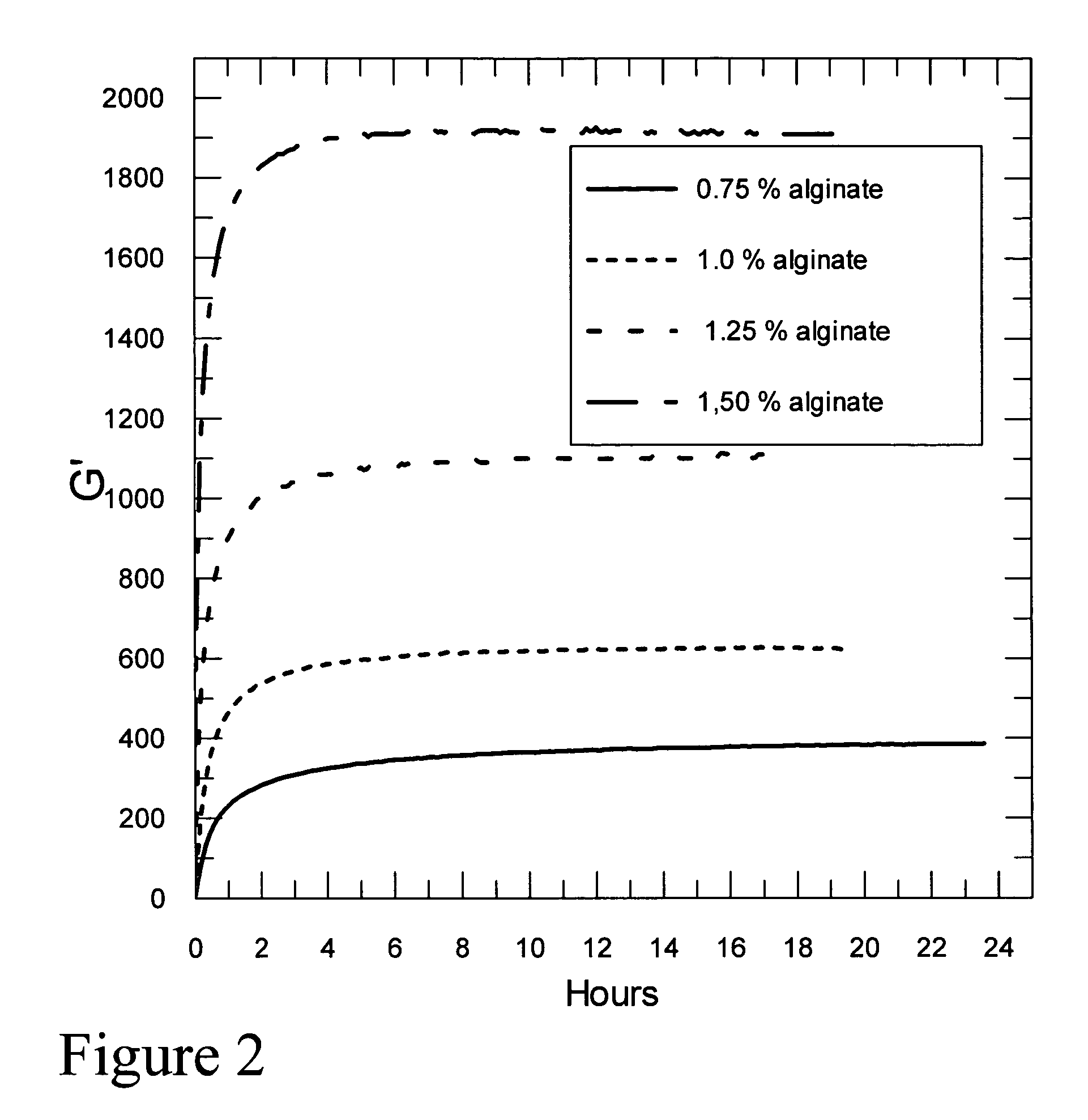
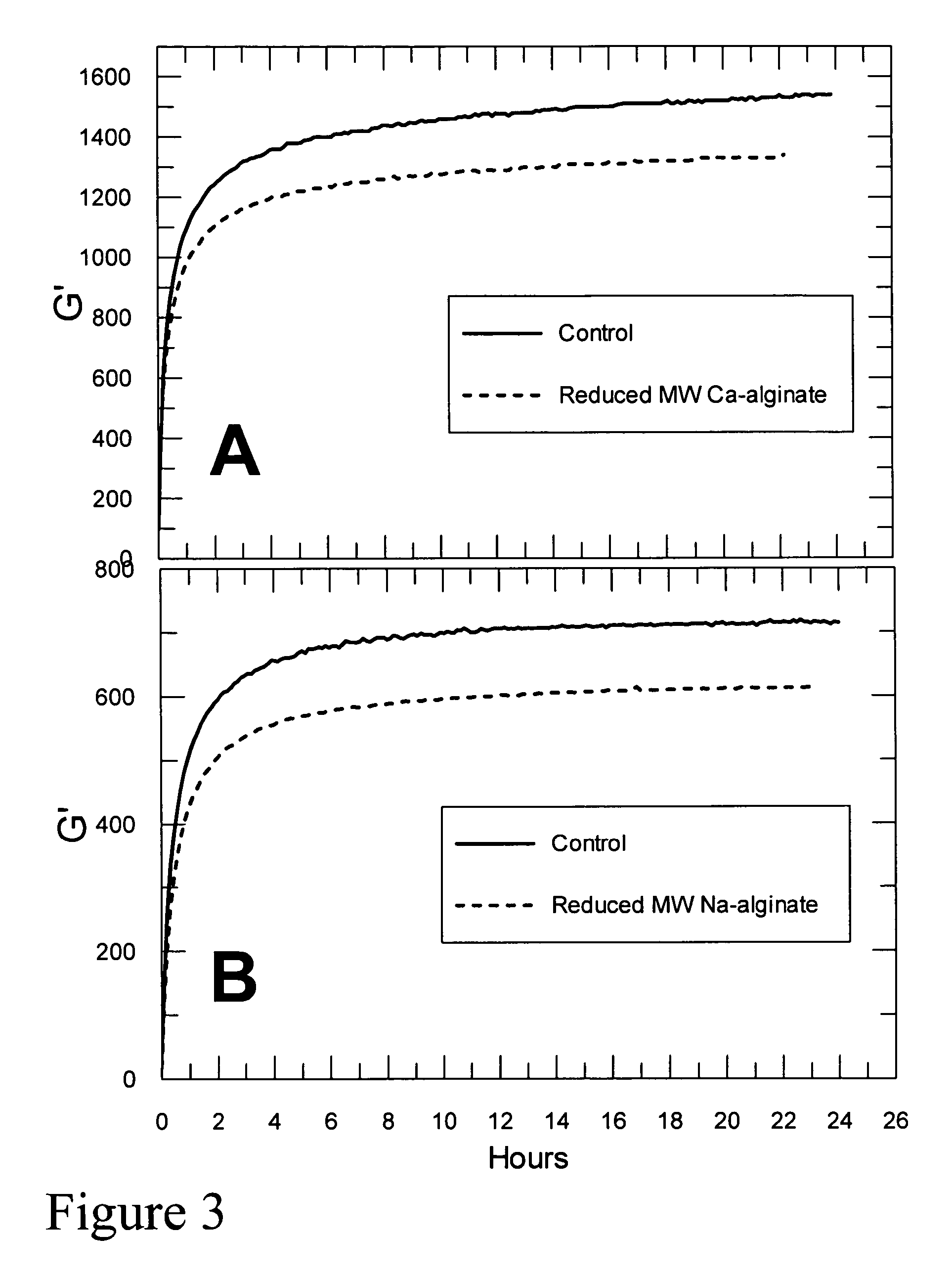
Self-gelling alginate systems and uses thereof
Kits and compositions for producing an alginate gel are disclosed. The kits and compositions comprise soluble alginate and insoluble alginate / gelling ion particles. Methods for dispensing a self-gelling alginate dispersion are disclosed. The methods comprise forming a dispersion of insoluble alginate / gelling ion particles in a solution containing soluble alginate, and dispensing the dispersion whereby the dispersion forms an alginate gel matrix. The methods may include dispensing the dispersion into the body of an individual. An alginate gel having a thickness of greater than 5 mm and a homogenous alginate matrix network and homogenous alginate gels free of one or more of: sulfates citrates, phosphates, lactatates, EDTA or lipids are disclosed. Implantable devices comprising a homogenous alginate gel coating are disclosed. Methods of improving the viability of pancreatic islets, or other cellular aggregates or tissue, following isolation and during storage and transport are disclosed.
Owner:FMC BIOPOLYMER AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

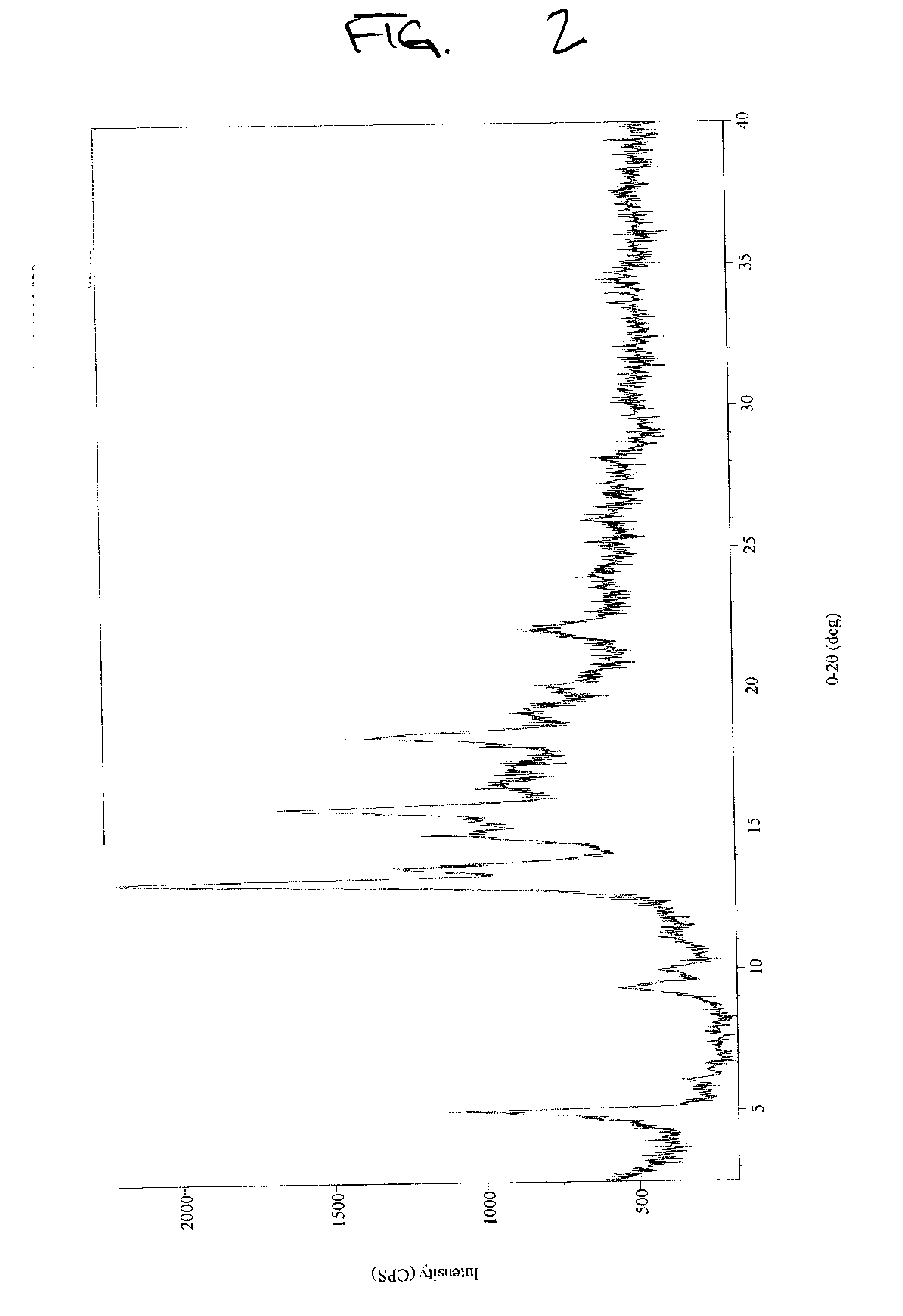
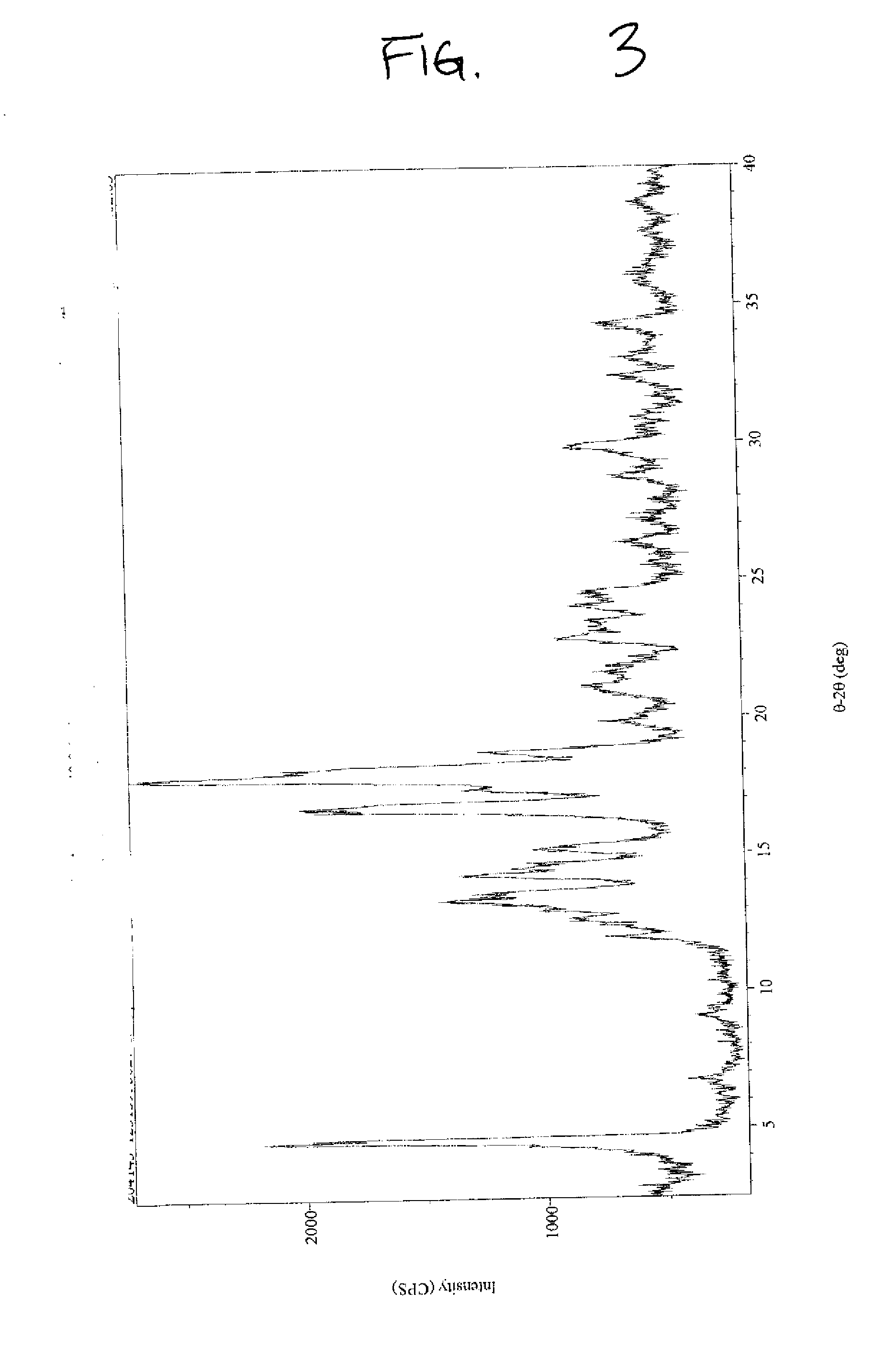
![3-β-D-ribofuranosylthiazolo[4-5-d]pyridimine nucleosides and uses thereof 3-β-D-ribofuranosylthiazolo[4-5-d]pyridimine nucleosides and uses thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.sutd.idm.oclc.org/patent_img/aface2a3-2e71-42ae-936e-cb2a5aaaf846/US06924271-20050802-D00000.png)
![3-β-D-ribofuranosylthiazolo[4-5-d]pyridimine nucleosides and uses thereof 3-β-D-ribofuranosylthiazolo[4-5-d]pyridimine nucleosides and uses thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.sutd.idm.oclc.org/patent_img/aface2a3-2e71-42ae-936e-cb2a5aaaf846/US06924271-20050802-D00001.png)
![3-β-D-ribofuranosylthiazolo[4-5-d]pyridimine nucleosides and uses thereof 3-β-D-ribofuranosylthiazolo[4-5-d]pyridimine nucleosides and uses thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.sutd.idm.oclc.org/patent_img/aface2a3-2e71-42ae-936e-cb2a5aaaf846/US06924271-20050802-C00001.png)



![Crystalline form of 1-chloro-4-(beta-D-glucopyranos-1-yl)-2-[4-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)-benzyl]-benzene, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments Crystalline form of 1-chloro-4-(beta-D-glucopyranos-1-yl)-2-[4-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)-benzyl]-benzene, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.sutd.idm.oclc.org/patent_img/e018e28e-a3d7-43a6-9df9-4da07d78e0e6/US20070249544A1-20071025-D00001.png)
![Crystalline form of 1-chloro-4-(beta-D-glucopyranos-1-yl)-2-[4-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)-benzyl]-benzene, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments Crystalline form of 1-chloro-4-(beta-D-glucopyranos-1-yl)-2-[4-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)-benzyl]-benzene, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.sutd.idm.oclc.org/patent_img/e018e28e-a3d7-43a6-9df9-4da07d78e0e6/US20070249544A1-20071025-C00001.png)
![Crystalline form of 1-chloro-4-(beta-D-glucopyranos-1-yl)-2-[4-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)-benzyl]-benzene, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments Crystalline form of 1-chloro-4-(beta-D-glucopyranos-1-yl)-2-[4-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)-benzyl]-benzene, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.sutd.idm.oclc.org/patent_img/e018e28e-a3d7-43a6-9df9-4da07d78e0e6/US20070249544A1-20071025-C00002.png)