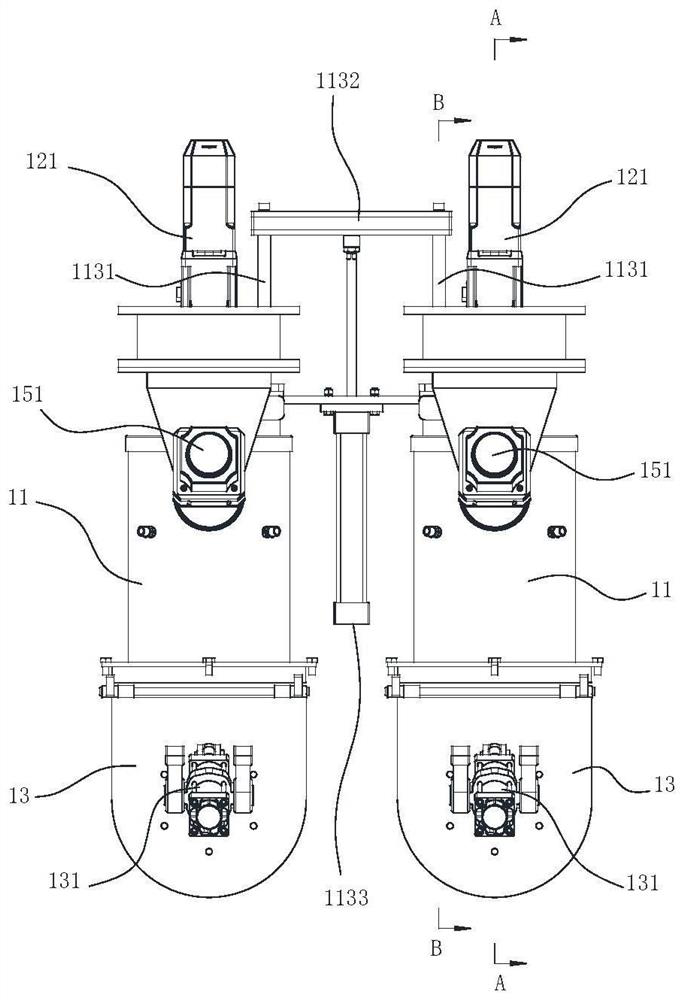
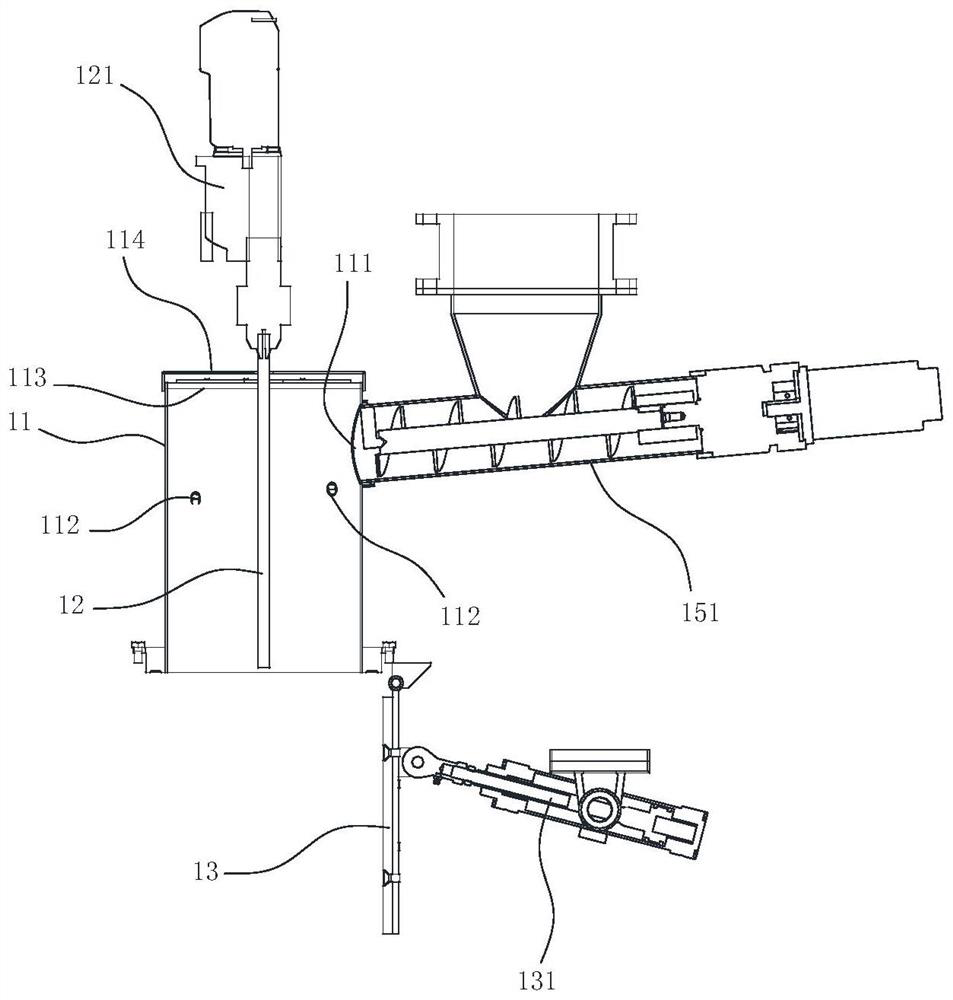
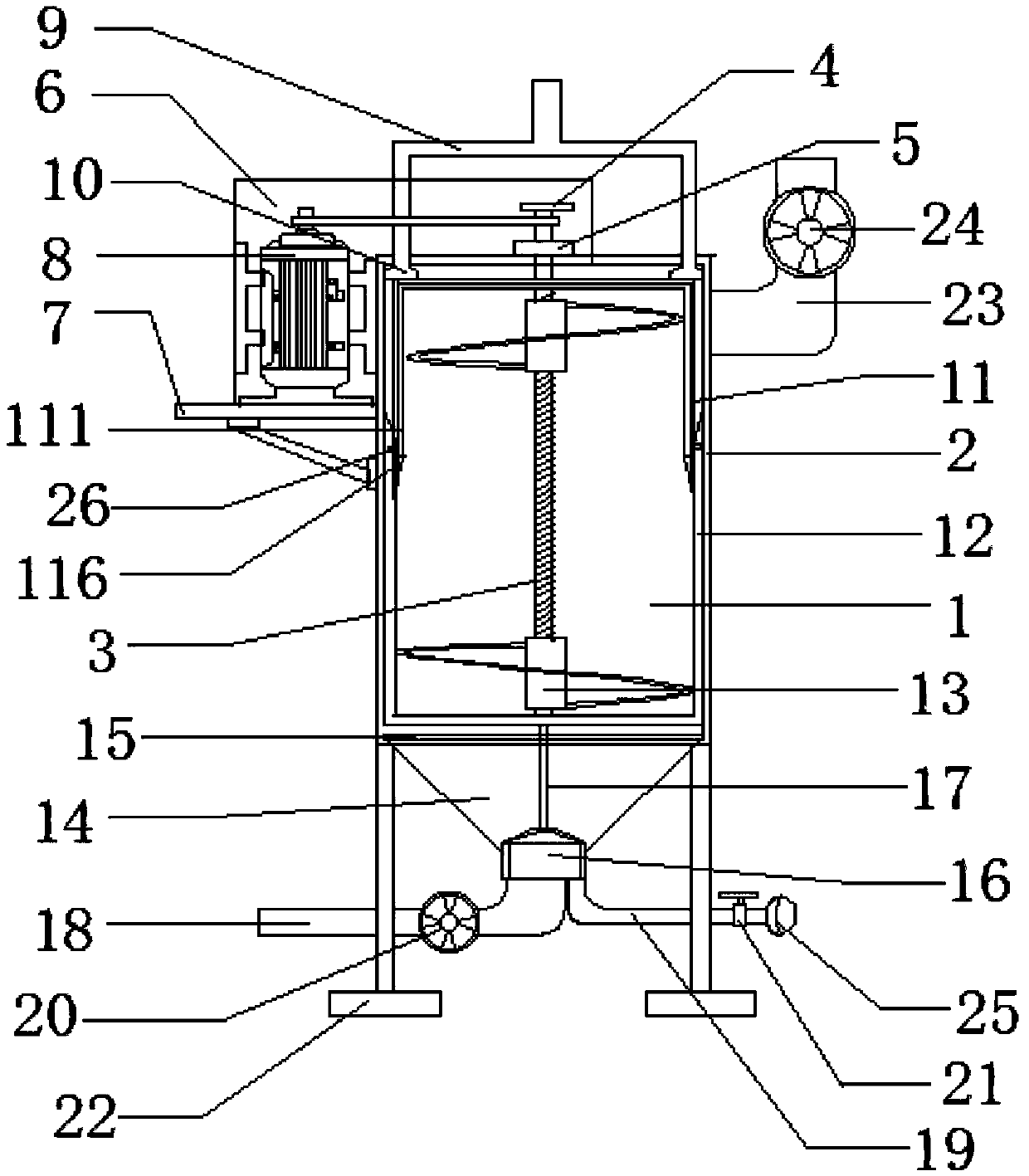
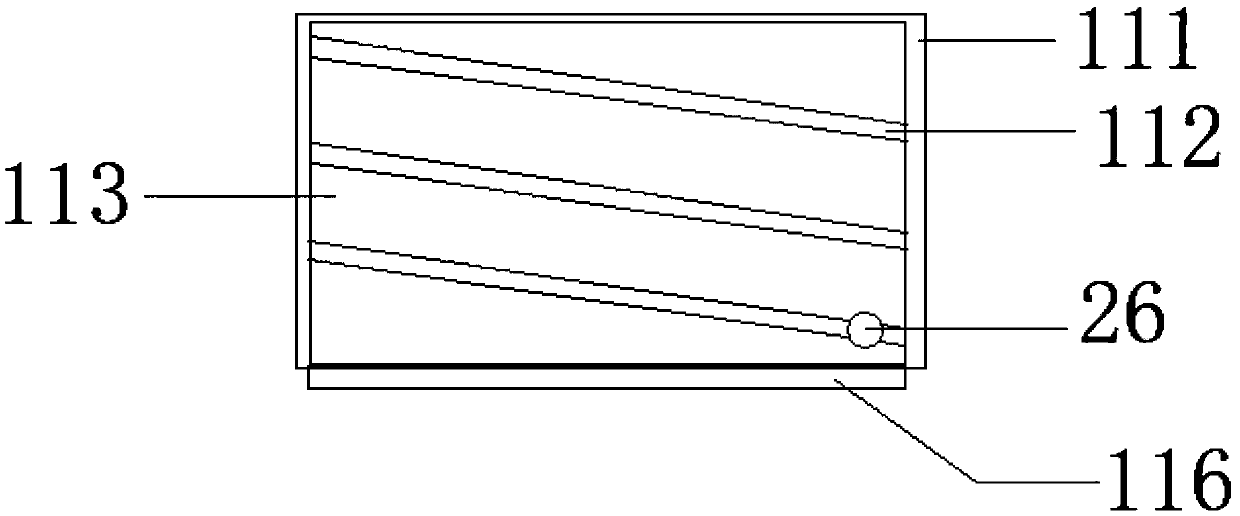
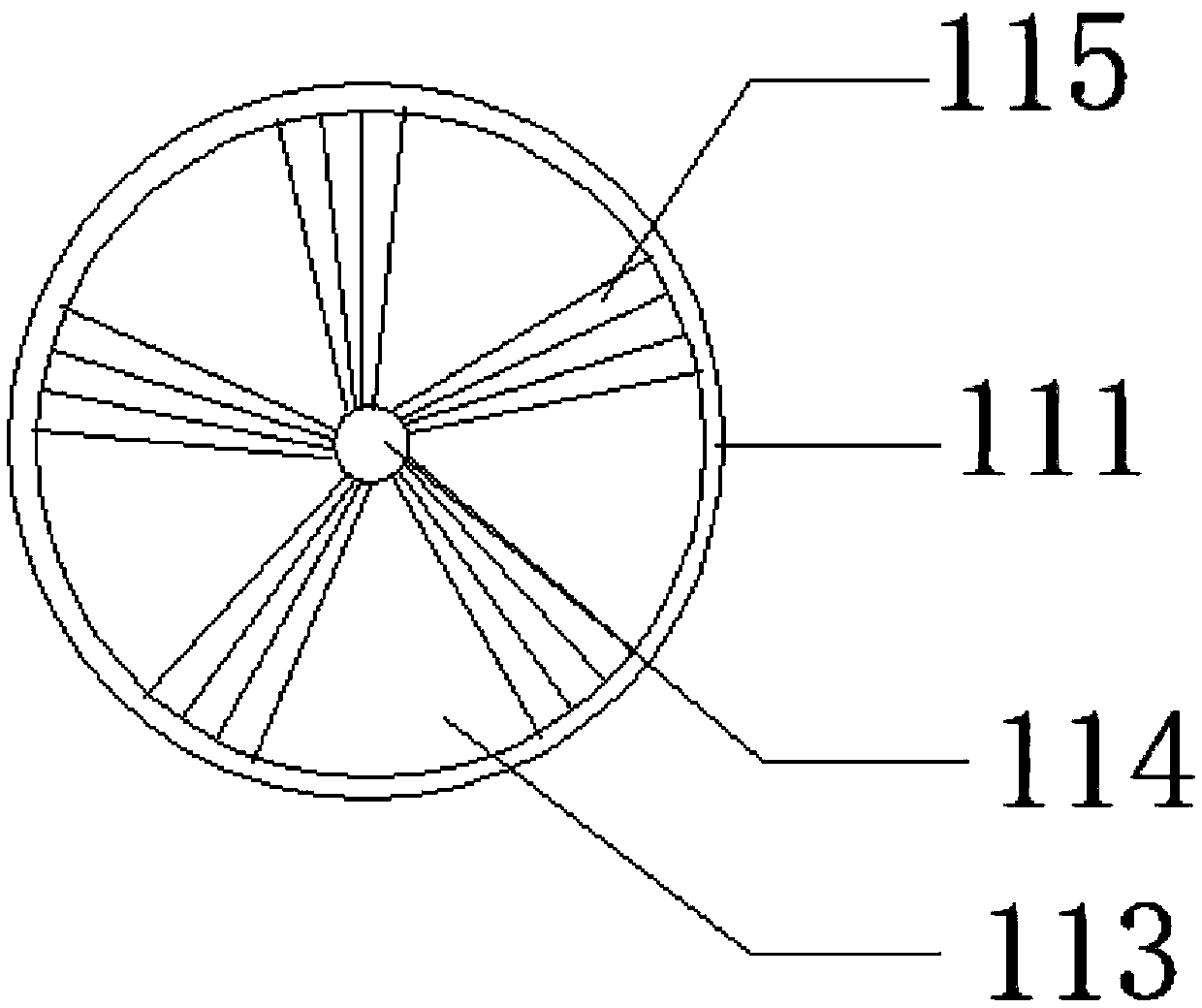
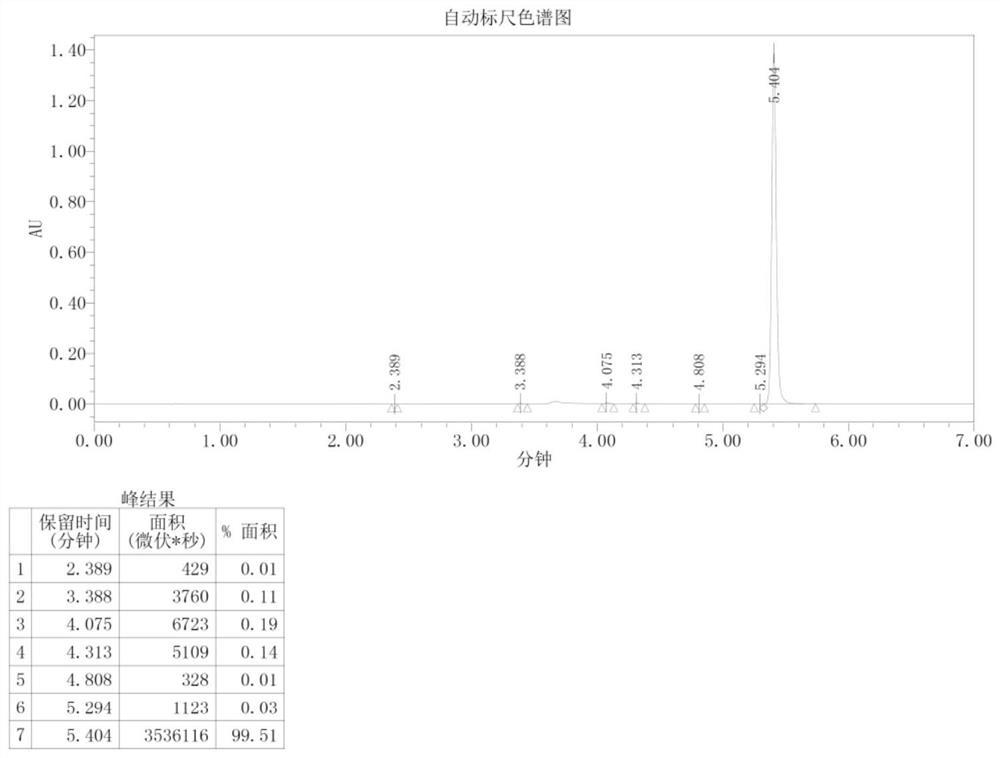
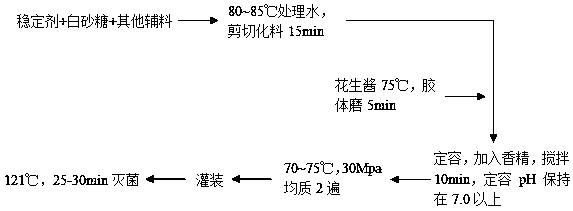
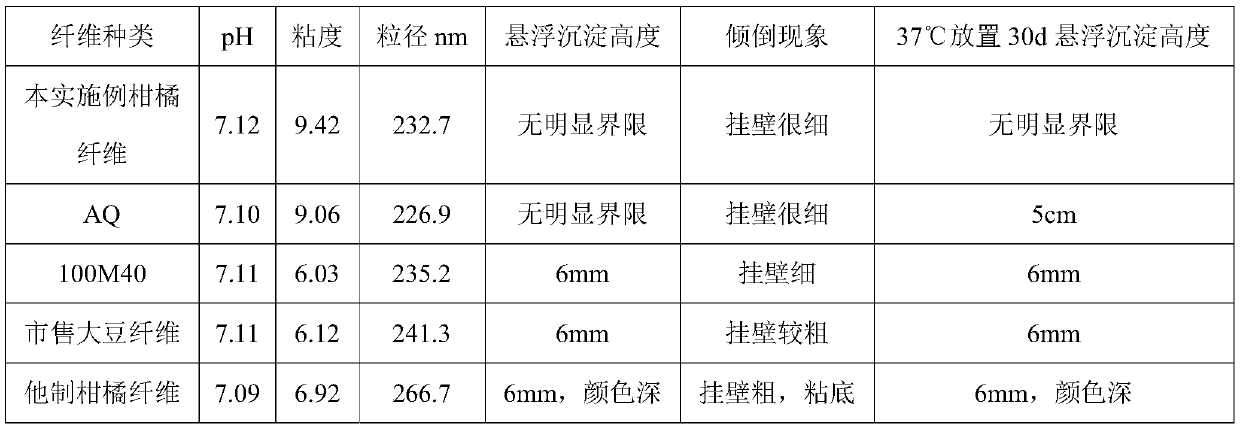
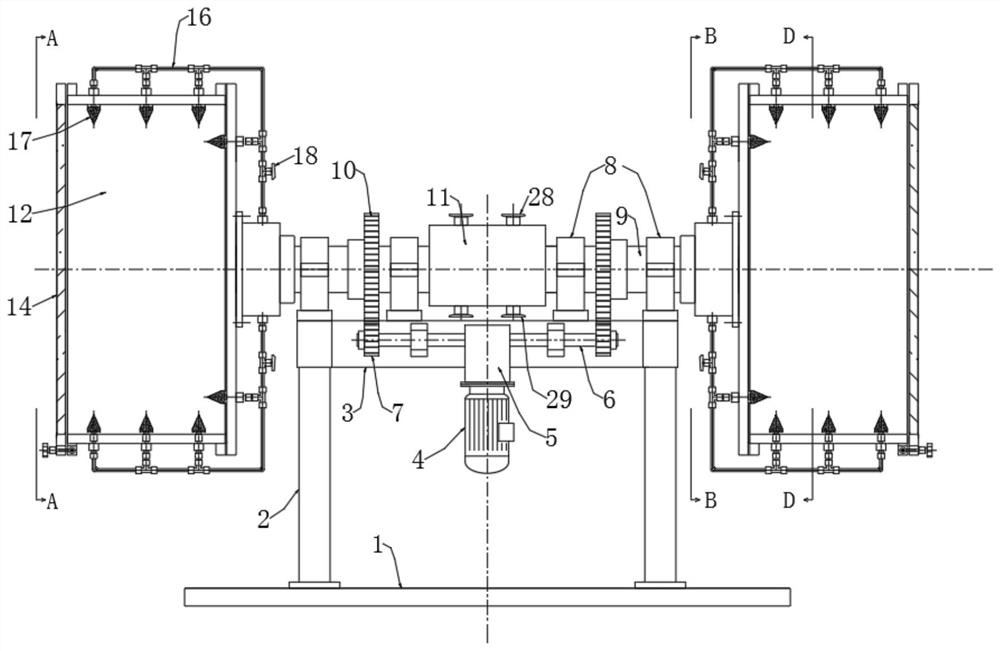
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32results about How to "Reduce wall hanging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
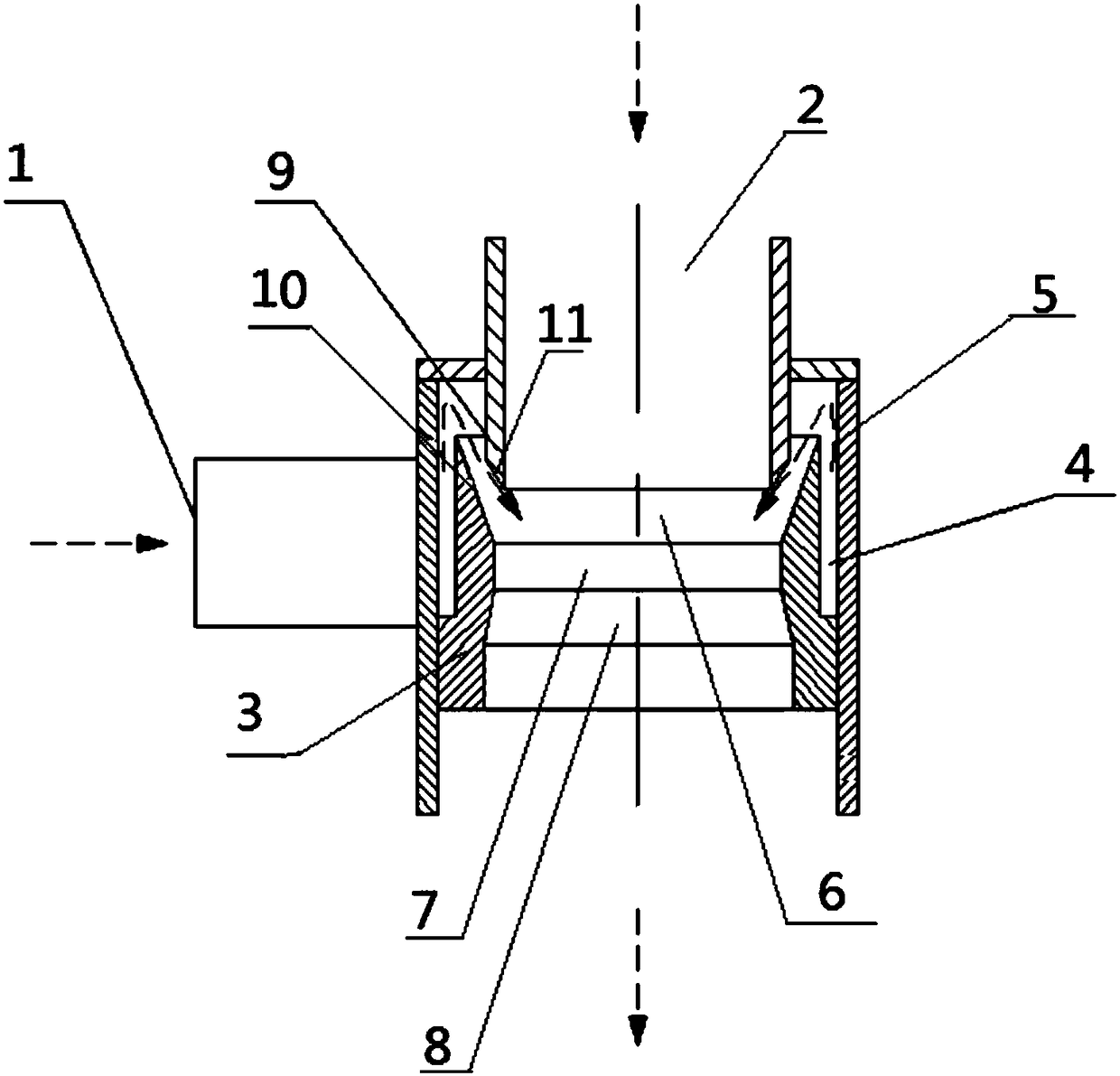
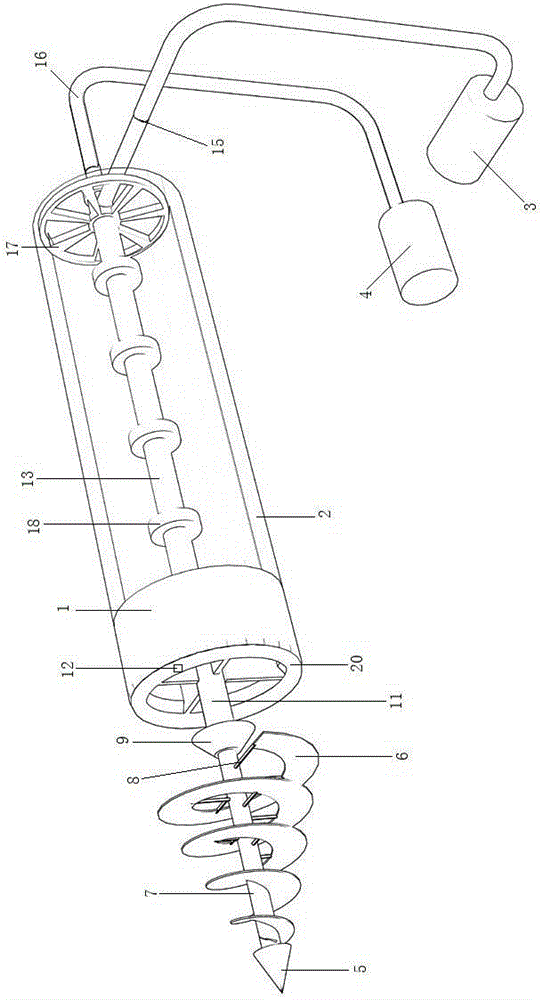
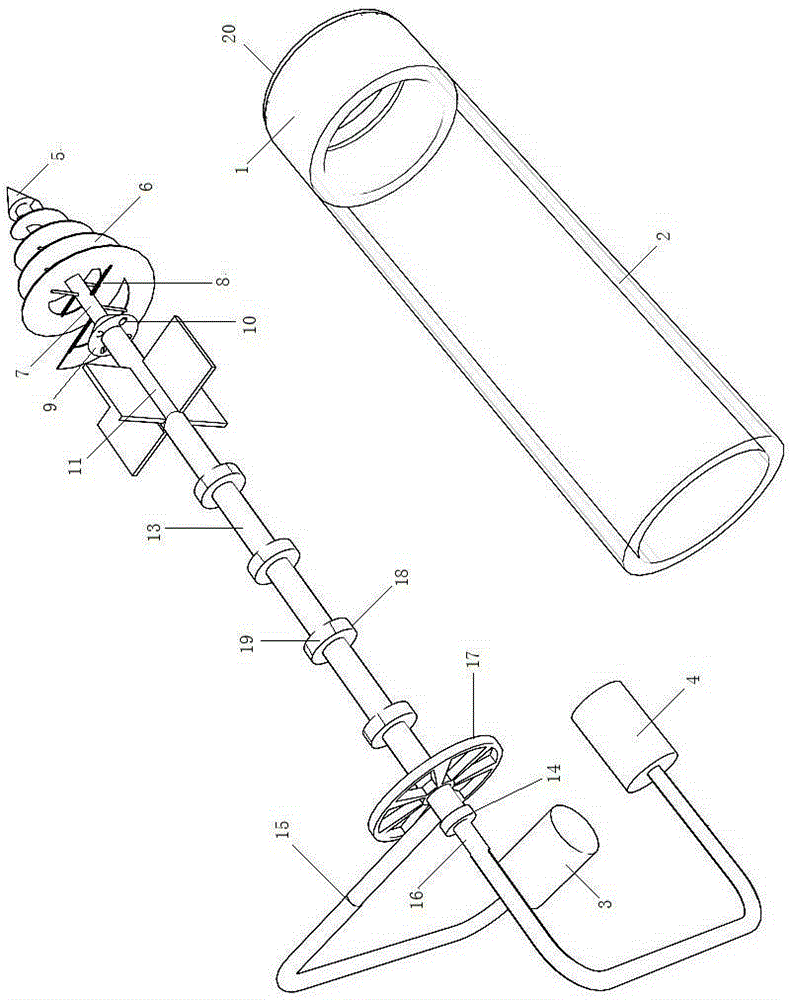
Fracturing base liquid mixer
PendingCN108371894AAchieve energy efficiency ratioCanto Efficiency RatioFlow mixersTransportation and packagingBusiness efficiencyFracture sites
The invention relates to the technical field of water-powder mixing or liquid mixing equipment in the construction operations of oil and gas fields and particularly relates to a fracturing base liquidmixer used in a construction process of an oil field fracturing site. The fracturing base liquid mixer comprises a rotational flow premixing device which comprises a liquid inlet, a feeding hole, a connecting component and an annulus, wherein the feeding hole is vertically formed, the liquid inlet is horizontally formed, the side wall of the feeding hole is connected with a sleeve, the connectingcomponent is arranged in the sleeve, the annulus is formed by the connecting component and the side wall of the feeding hole and is communicated with the liquid inlet, an oblique side is arranged atthe lower end part of the side wall of the feeding hole, an oblique plane is arranged at the upper part of the connecting component, and the oblique plane and the oblique side form certain angles witha vertical plane and are 0-80 degrees; and a reduced section, a throat pipe and a dispersion pipe are sequentially arranged at the lower part of the feeding hole. The fracturing base liquid mixer canmeet the requirements on the fracturing base liquid during large-scale operations in a fracturing operation site, the blending and mixing efficiencies are improved, the mixing quality of guanidine gum liquid is improved, and the optimal energy efficiency ratio is realized.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH PETROLEUM EQUIP & TECH
Multifunctional processing machine for diced food materials
InactiveCN108202359AEasy to disassemble and repairExtended service lifeMetal working apparatusFood materialMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a multifunctional processing machine for diced food materials. The multifunctional processing machine comprises a slicing device, a shredding device, a push groove device, a dicing device, a transmission device and conveying belts. The slicing device conveys sliced food materials to the shredding device by virtue of the conveying belts, the shredding device is arranged between the two conveying belts, the sliced food materials are cut into shredded food materials by virtue of the up-down reciprocating movement of a blade, the shredded food materials are transferred to the push groove device through the conveying belts, the push groove device drives the shredded food materials to carry out reciprocating movement to be pushed to the dicing device, the blade of the dicing device is mutually vertical to the shredded food materials, and cuts the shredded food materials into diced food materials; and the transmission device provides power for the slicing device, the shredding device, the push groove device, the dicing device and the conveying belts. The multifunctional diced food material processing machine disclosed by the invention is various in function, capable of carrying out batch treatment on the food materials, fully-automatic, high in efficiency and easy to maintain.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
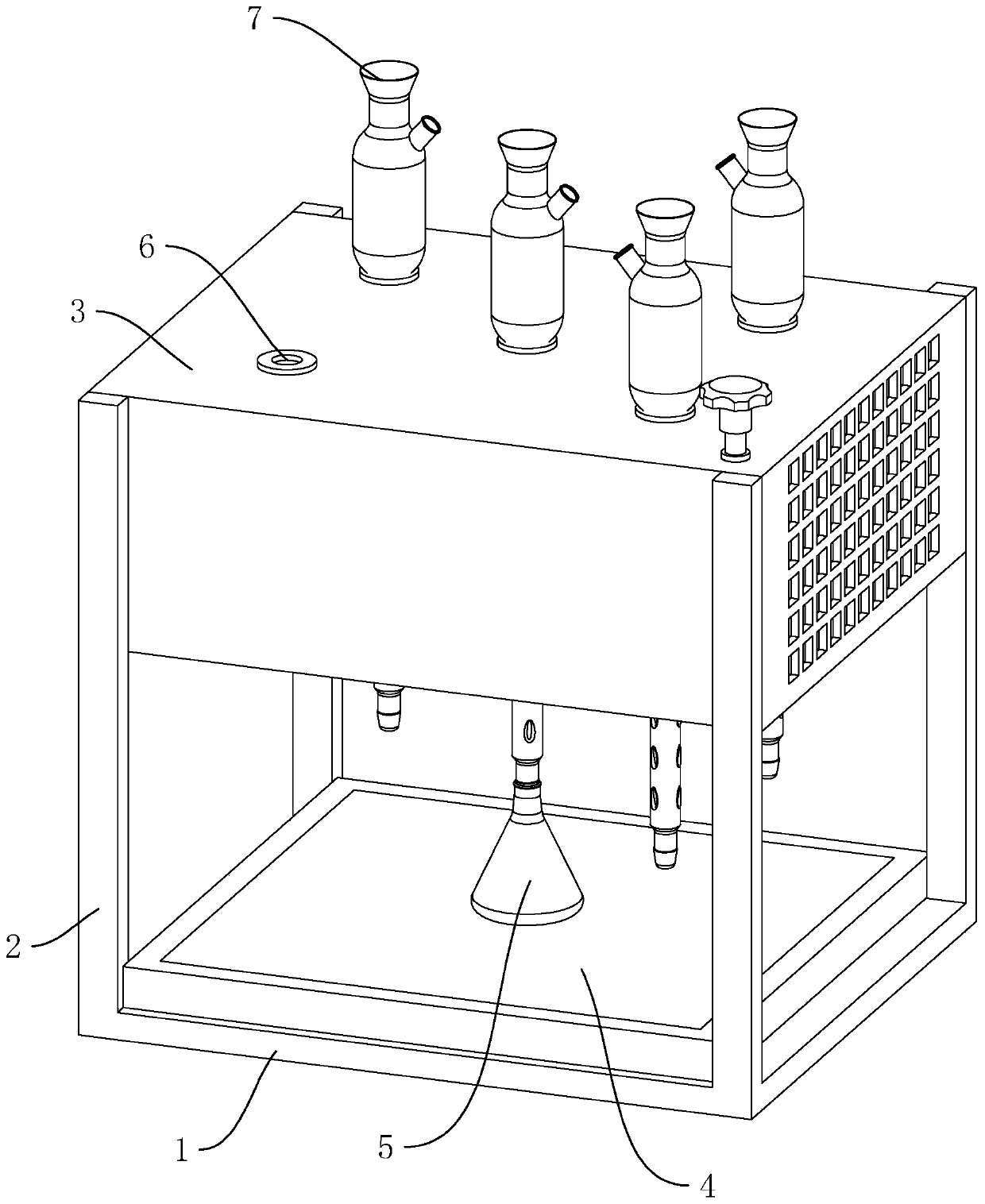
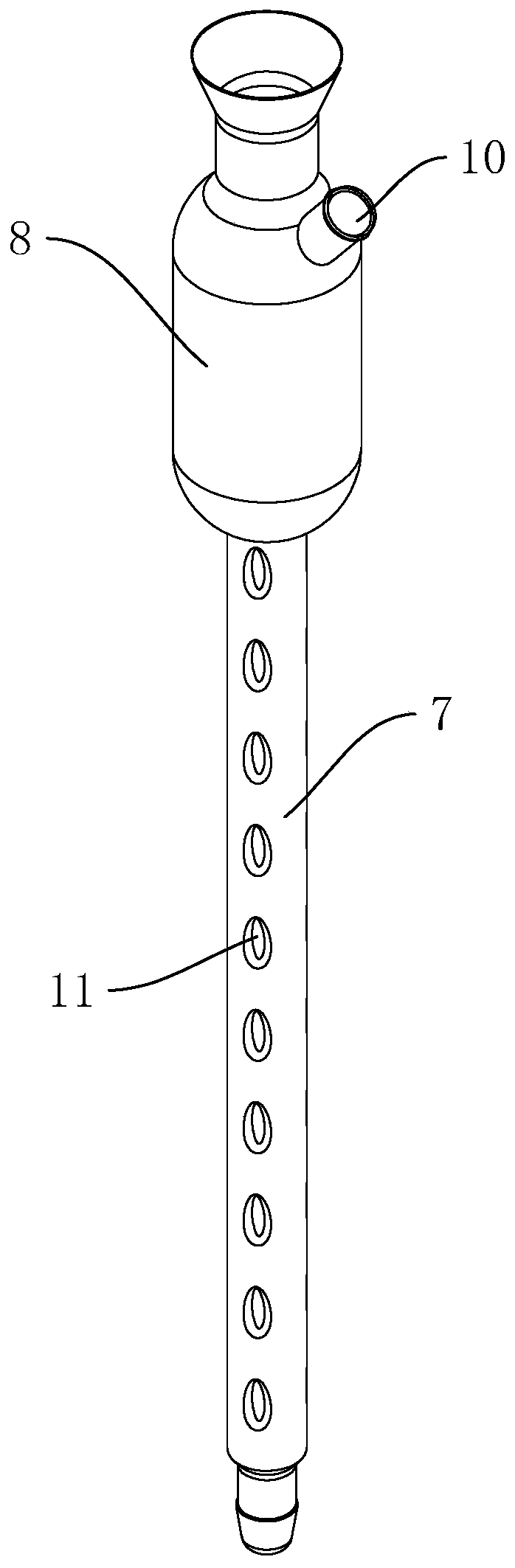
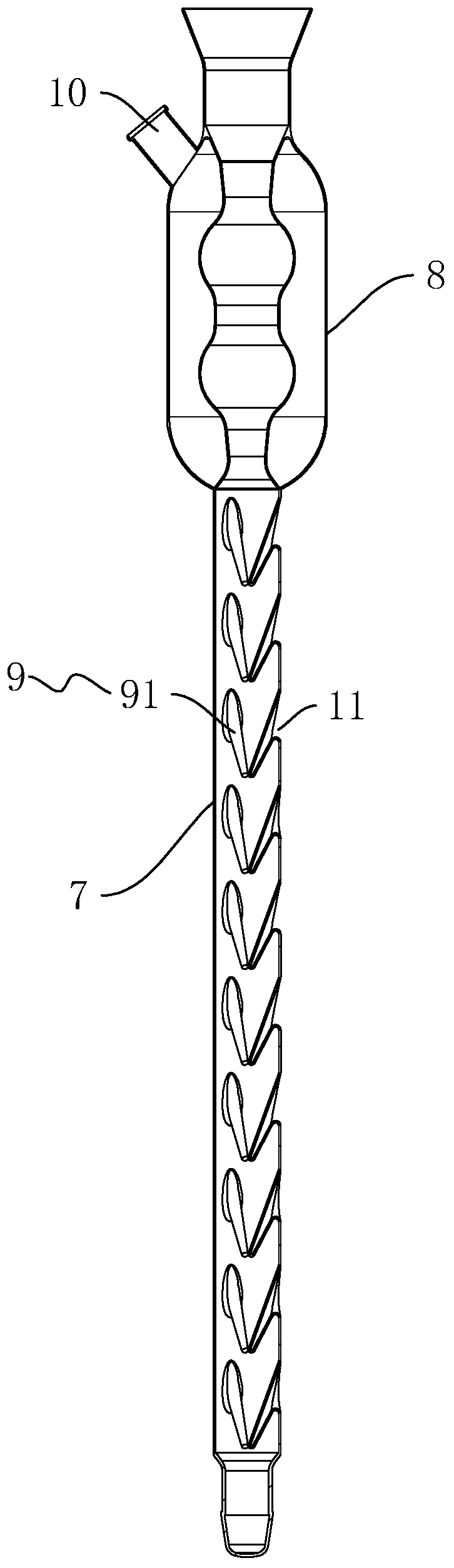
COD digester and application method thereof
ActiveCN110849702ACondensation effect is stableImprove cooling effectPreparing sample for investigationCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsStructural engineeringDigestion
The invention discloses a COD digester, and relates to the field of water sample detection devices. According to the technical scheme, the digester comprises a base, a support arranged on the base anda mounting base arranged at the upper portion of the support; an electric heating furnace plate is arranged on the base; a digestion bottle is placed on the electric heating furnace plate; a plurality of mounting holes are formed in the mounting base in the vertical direction; and reflux condensing pipes are arranged on the mounting holes, the lower ends of the reflux condensing pipes are connected with the digestion bottle, the mounting base is a hollow shell, a cooling fan is arranged in the mounting base and used for blowing air to the reflux condensing pipes for cooling, and vent holes are formed in the two ends, in the air blowing direction of the cooling fan, of the mounting base. Air is blown through the cooling fan to cool the reflux condensing pipes in time, and therefore, the condensation effect of the reflux condensing pipes is more stable.
Owner:台州市绿水青山环境科技有限公司
Production technology of sauce flavor powder
ActiveCN103404824ASmall granularityPromote decompositionFood shapingFood preparationDecompositionFood flavor
The invention discloses a production technology of sauce flavor powder. The technology which allows a raw material sauce to undergo step enzymatic hydrolysis comprises the following steps: 1, adding cellulase for improving the decomposition of celluloses and hemicelluloses; and 2, adding a protease for hydrolyzing macromolecular proteins in the sauce to form micro-molecular peptides or amino acids. The obtained zymolytic sauce has the advantages of obviously improved spray drying condition, reduction of the appearance of wall hanging, powder obstruction and scorched particles, and continuous large-batch production.
Owner:保定味群食品科技股份有限公司
Hydraulic pressure-type cable tunnel cleaning device
InactiveCN105275032AWill not cause collapseKeep dryMechanical machines/dredgersDrive shaftButt joint
The invention discloses a hydraulic pressure-type cable tunnel cleaning device, and relates to the technical field of cable casting construction tools. The hydraulic pressure-type cable tunnel cleaning device comprises a conveying device, a water spraying device, a hard flared tube, a soft mud tube, a water pump and a driving motor; the conveying device consists of a conical cover, a conical spiral conveying sheet and a transmission shaft; the conical cover is fixedly arranged on the left end of the transmission shaft; the conical spiral conveying sheet is located behind the conical cover and is fixedly connected with the transmission shaft through support rods; the right part of the transmission shaft penetrates through the water spraying device and is in rotary hermetic match with the water spraying device; the left end of the water spraying device is a truncated cone-shaped water sprinkling cover; a cavity is arranged in the truncated cone-shaped water sprinkling cover; a soft shaft is coaxially arranged in a soft water inlet sleeve pipe; the output end on the left side of the soft shaft is connected with the right end of the transmission shaft; and the right end of the hard flared tube is in butt joint communication with the soft mud tube. The hydraulic pressure-type cable tunnel cleaning device is high in mud cleaning efficiency, small in work resistance and small in water consumption amount and can clean cleanly.
Owner:DONGYING POWER SUPPLY COMPANY STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +2
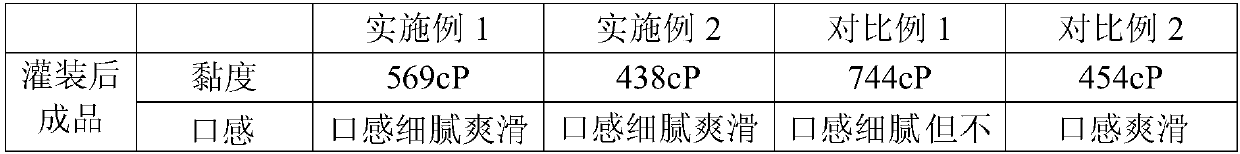
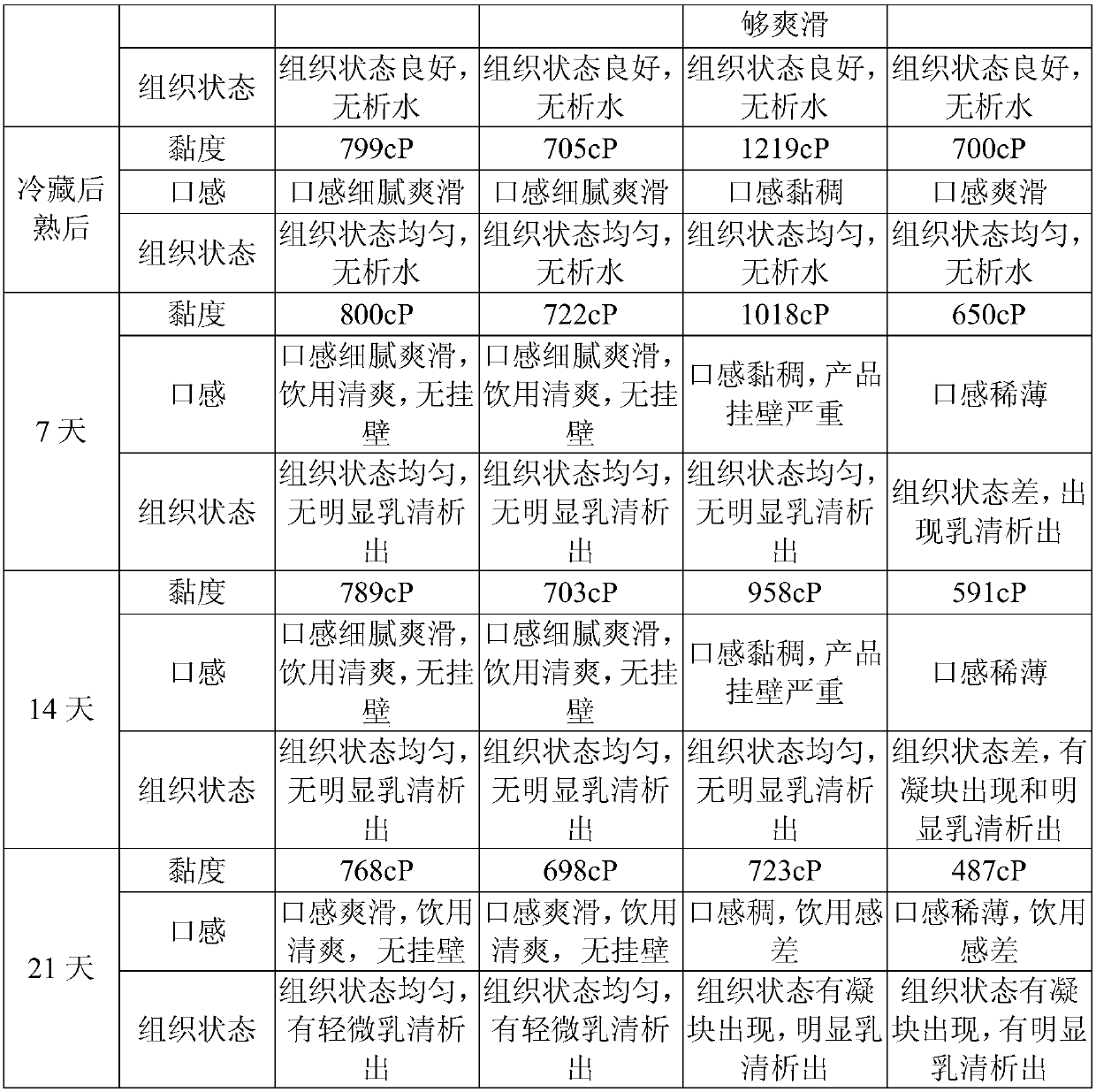
Fermented milk with advantages of drinking experience improving and wall attachment reducing, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107624870AIncrease viscosityReduce wall hangingMilk preparationFood processingChemistryCold preservation
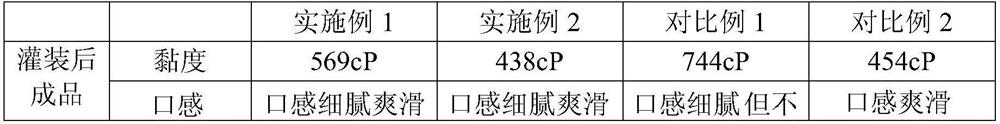
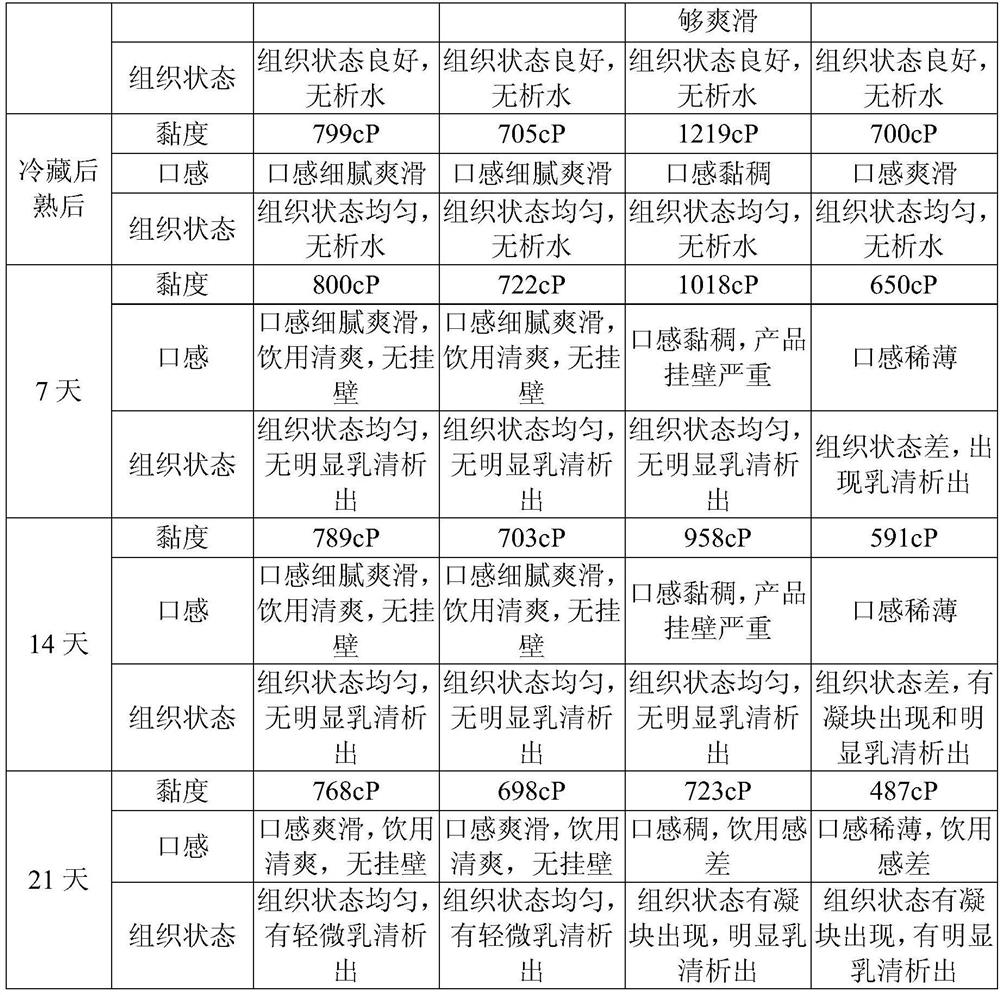
The invention provides a fermented milk with advantages of drinking experience improving and wall attachment reducing, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: dissolving raw materials, degassing, homogenizing, sterilizing, and cooling; adding a fermenting agent, fermenting for 2-3 h at a temperature of 41-43 DEG C, cooling to a temperature of 32-37 DEG C, continuously fermenting, and stopping the fermenting until the acidity achieves 75 DEG T,; carrying out demulsification on the fermented material liquid, and beating the obtained material liquid by using a high-frequency rotor pump through a cold plate until achieving a to-be-filled state; beating into a filling machine through a screw pump, and filling to obtain a finished product; and carrying out cold preservation and after ripening on the finished product, and leaving the factory. According to the present invention, with the application of the preparation method to prepare the fermented milk, the optimal drinking experience can be achieved without the reducing of the product indexes and the increase of the thinning step, and the stability of the shelf life of the product can be ensured by using thesecondary fermentation process during the fermentation.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Cross well cementation method without occupying well mouth
The invention discloses a cross well cementation method without occupying a well mouth. The method comprises the following steps: (S1) the lower end of a 20" surface layer sleeve is connected with a sleeve float shoe, wherein the sleeve float shoe is provided with a side outlet hole on the side wall below a float shoe check valve base; (S2) the 20" surface layer sleeve is directly descended to a base, and is fixed in center through righting blocks in the well mouth; (S3) a drilling table inverts and swings the 20" surface layer sleeve in the position of conveniently connecting with a circulating head of the 20" sleeve below a turntable to shift a derrick to a next well position to perform the cross well cementation operation without occupying the well mouth in the well mouth area; and (S4) the return condition is observed in the well cementation period; and after cement is returned out from the well mouth, the replacement operation is immediately switched to finish the well cementation. The method finishes the well cementation operation by connecting the circulating head in the well mouth area, finishes the 20" surface layer sleeve well cementation operation without occupying well mouth time, finishes the all-well-section sealing by returning cement to the well mouth according to high-temperature and high-pressure shaft completeness requirements, and guarantees the integration of the 20" sleeve and a 30" pile pipe to realize the shaft completeness.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Preparation method for diether diphthalimide
The invention discloses a method for preparing diether diphthalimide. The method comprises the following steps: step (A): in a reaction kettle, enabling a diphenol raw material to react with one or more of strong base and strong alkali and weak acid salt in a non-polar solvent, such as methylbenzene or o-xylene, under an inert atmosphere; and step (B): enabling a reaction product of the step (A) to react with phthalimide in the presence of an ionic liquid catalyst, to obtain the diether diphthalimide. The method is capable of performing a nucleophilic reaction in the non-polar solvent, addingionic liquid as a phase transfer catalyst, and improving a reaction yield. After ending the reaction, impurities are removed through a water extraction method, and wastewater generation is greatly reduced. The diether diphthalimide is obtained by reducing a pressure and evaporating an organic layer, a process is simple, and an obtained product is high in purity.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
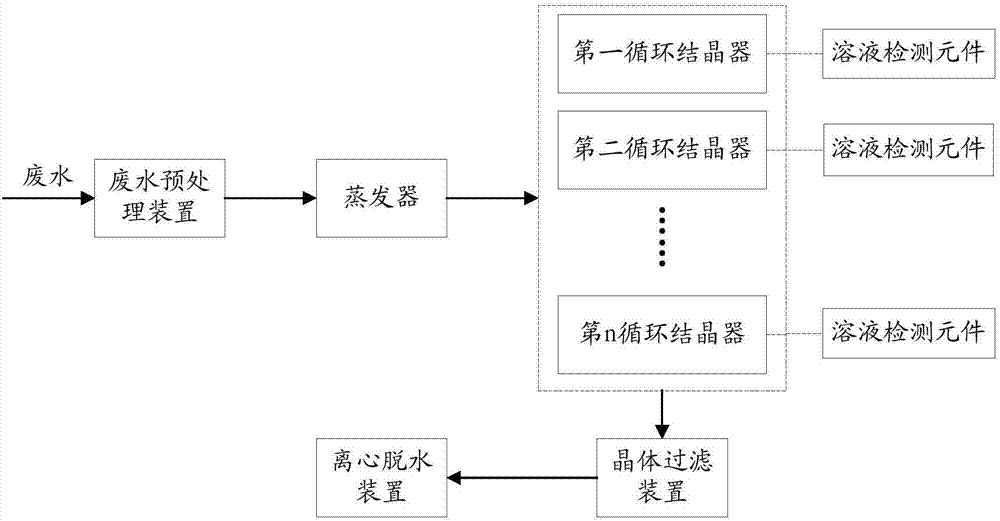
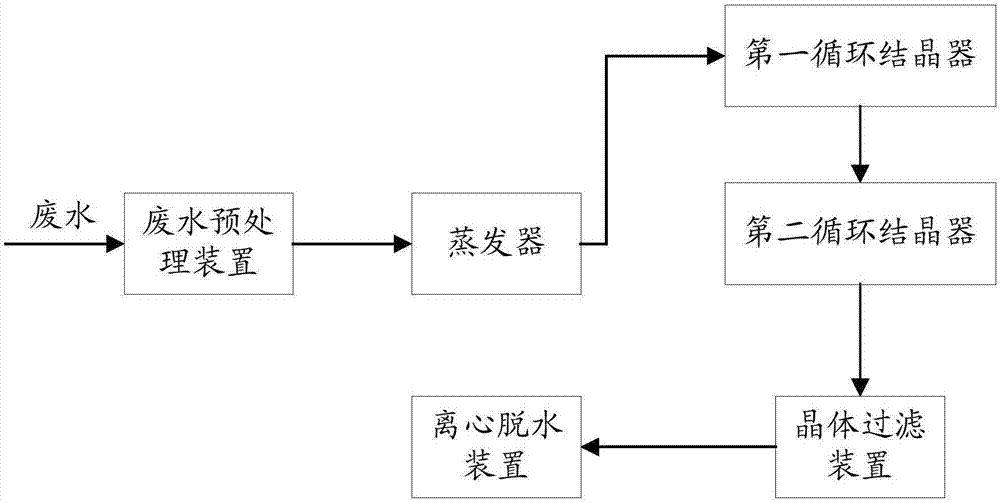
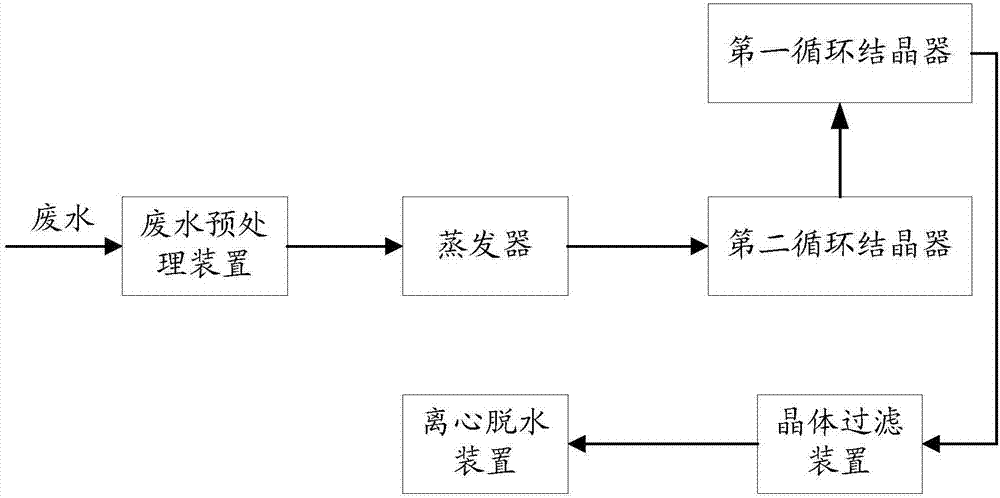
Wastewater treatment system with multiple crystallizer units and wastewater treatment method based thereon
ActiveCN107098532AReduce generationReduce wall hangingWater treatment parameter controlTreatment involving filtrationPre treatmentCrystal filter
The invention discloses a wastewater treatment system with multiple crystallizer units and a wastewater treatment method based thereon and relates to the field of wastewater treatment. The wastewater treatment system comprises a wastewater pretreatment device, a vaporizer, a circulation crystallizer set, a crystal filter, and a dewatering device which are communicated in sequence; the circulation crystallizer set includes a main inlet, a main outlet and multiple circulation crystallizers. The wastewater treatment method comprises: during wastewater treatment, on the basis of results of a solution detection element, when the detection result of any one forced circulation crystallizer of the forced circulation crystallizer group reaches a preset threshold, changing, by a controller, flowing direction of the wastewater within specified time, such that the sequence of the wastewater to flow through the multiple forced circulation crystallizers of the forced circulation crystallizer group is changed. Less lumpy salt is generated in the crystallizers and attach to the walls, tube blockage is relieved, and therefore, operating efficiency of the whole system is thereby improved, with operating cost lowered.
Owner:HORIZON WATER CO LTD
Anti-sticking agent for stainless steel surface coating of polyreactor and preparation method of anti-sticking agent
PendingCN114410155AHigh inhibition efficiencyReduce wall hangingHyaluronic acid coatingsChitin coatingsPolyvinyl alcoholSodium hydrogen sulphite
The invention discloses an anti-sticking agent for a stainless steel surface coating of a polymerization reaction kettle. The anti-sticking agent is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 52%-56% of deionized water, 3%-6% of a sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, 16%-20% of ethanol, 11%-14% of formaldehyde, 5%-7% of mixed phenol, 1%-2% of sodium hydrogen sulfite, 0.1%-1% of chitin and 1%-2% of polyvinyl alcohol. A preparation method of the anti-sticking agent for the stainless steel surface coating of the polymerization reaction kettle comprises the following steps: S1, adding deionized water into a synthesis kettle, starting stirring and heating, and heating the deionized water; aiming at the problems of the traditional anti-sticking agent, the anti-sticking agent is improved, after the improved anti-sticking agent is sprayed on the stainless steel surface layer of the polymerization reaction kettle, the anti-sticking agent shows an excellent anti-sticking effect, the service life is long, the coating effect is good, and the kettle cleaning period is greatly prolonged.
Owner:宁夏顺邦达新材料有限公司
Water jacket for inner heat-storing coal-gas furnace
InactiveCN101892088AEasy to manufactureEasy to installCombustible gas productionDecompositionEngineering
The invention relates to a water jacket for an inner heat-storing coal-gas furnace, which is an important composing facility for the coal-gas furnace, wherein a water jacket cavity is arranged between the inner wall and the outer wall of the water jacket. The water jacket is characterized in that a flame-retardant insulating layer is coated on the inner wall of the water jacket corresponding to a hearth region, and is an integral structure which is poured and molded by a flame-retardant insulating pour material, and a reinforcing component is arranged in the flame-retardant insulating layer. The water jacket has simple manufacture, installation and maintenance, stable performance, less thermal loss, high steam decomposition rate and low energy consumption, greatly reduces the scaling phenomenon on the inner wall of the water jacket, and prolongs the service life.
Owner:山东淄博获泽机械有限公司
Production process of brominated butyl rubber
ActiveCN111718436AImprove recycling efficiencyReduce unit consumptionTransportation and packagingMixersThermodynamicsAdhesive glue
The invention provides a production process of brominated butyl rubber. According to the invention, a solvent recovery system in a brominated butyl rubber production process is improved; a steam-watermixer and a glue static mixer are arranged in front of the flash tank; the process includes introducing hot water and steam into a steam-water mixer; introducing the steam-water mixture and the gluesolution into a glue static mixer; heating glue solution, then, and enabling the mixture to enter a flash tank for flash evaporation and subsequent processes, thus increasing the temperature of the materials entering the flash tank; supplying part of gasification heat to colloidal particles and a solvent in advance; forming a dispersion phase of glue liquid drops and water in the conveying pipeline; after entering a flash tank, performing rapid gasification and flash evaporation, forming the pore channels in the surfaces of the colloidal particles, and reducing the sizes of the colloidal particles furtherly under the stirring action in the flash tank, so that the flash solvent removal effect is improved, and the phenomenon that a glue solution adheres to the wall is also reduced, thereby improving the solvent recovery efficiency, reducing the unit consumption of the whole solvent, reducing the risks of pump blockage and shutdown and ensuring the production and operation period of brominated butyl rubber.
Owner:山东京博中聚新材料有限公司
Novel roller dryer
ActiveCN112325585AAvoid cloggingAvoid easy cloggingDrying gas arrangementsDrying solid materialsDrum dryingProcess engineering
The invention discloses a novel roller dryer. The novel roller dryer is composed of a roller, a gas distributor, a rotary joint and a roller driving mechanism. The working principle of the novel roller dryer is as follows: dry gas is introduced into the roller through the rotary joint and the distributor to realize lower semicircular gas inlet and upper semicircular gas outlet in the roller, and agas inlet and a gas outlet in the roller are sequentially changed along with the rotation of the roller to form gas flow from bottom to top in the roller, so that a dried material is in an approximate fluidized state, and drying of the material is further achieved. The novel roller dryer has the advantages of being high in drying efficiency, wide in material application range, capable of meetingthe GMP standard, high in automation degree and the like, and is an ideal substitute product for traditional stirring dryers, rotary dryers, helical ribbon dryers, rake dryers, box dryers and the like.
Owner:上海迪化科技股份有限公司
Stirring device and heat preservation and sound insulation board pouring system
ActiveCN113733350AReduce wall hangingReduce feeding inaccuracyDischarging apparatusMixing operation control apparatusProcess engineeringHeat conservation
The invention belongs to the technical field of heat preservation and sound insulation board production and processing, and particularly relates to a stirring device and a heat preservation and sound insulation board pouring system. The stirring device comprises a stirring barrel, stirring blades and a valve, and a feeding port and a nozzle are formed in the barrel wall; and the feeding port and the nozzle are arranged at the upper half part of the barrel wall. The bottom of the stirring barrel is not provided with a closed-up material collecting structure, and the stirring barrel is of a straight-through structure in the whole vertical direction so that the wall hanging phenomenon of materials can be effectively reduced; the materials are directly released into a mold after being mixed into slurry and do not pass through a redundant conveying device any more, and the phenomenon of inaccurate feeding caused by material solidification is reduced to the maximum extent; and the stirring barrel has a self-cleaning function, turbid liquid generated by cleaning does not need to be discharged and is directly used as a solvent for next stirring, high-frequency cleaning of equipment is realized in the whole processing process, waste liquid is not generated, and the production process is more environment-friendly.
Owner:山东威宝节能科技集团有限公司 +1
A kind of freeze-dried powder and its preparation process
ActiveCN110314131BHas moisturizing effectImprove immunityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyPurslane extract
The invention provides freeze-dried powder for repairing problematic skin and a preparation process thereof, and belongs to the technical field of cosmetics. The freeze-dried powder comprises a phaseA and a phase B, wherein the phase A comprises, by weight, 1-3 parts of oligopeptide-1, 1-3 parts of oligopeptide-3, 8-16 parts of a lactobacillus / eriodictyon californicum fermentation product extract, 6-10 parts of ceramide 3 and 38-66 parts of water; the phase B comprises, by weight, 5-9 parts of oat beta-glucan, 12-18 parts of a purslane extract and 1-3 parts of sodium hyaluronate. The freeze-dried powder has good appearance and no wall hanging phenomenon and can enhance the immunity and body resistance of the skin, thicken the sebum membrane and normalize the metabolism of the skin tissueon the basis of an original moisturizing effect; at the same time, the preparation process of the freeze-dried powder is superior and can reduce the wall hanging rate and the production loss of products and improve the quality.
Owner:广州海梦科化妆品有限公司
Wall-hanging-prevention high-density chemical industry solution storage tower
InactiveCN107651328AReduce wall hangingReduce wasteLarge containersTank wagonsChemical industryHigh density
The invention discloses a wall-hanging-prevention high-density chemical industry solution storage tower comprising a storage tower body. The exterior of the storage tower body is fixedly connected with an outer frame. The axis position of the storage tower body is connected with a fixed supporting shaft in a rotating manner. The two ends of the fixed supporting shaft penetrate the inner walls of the storage tower body and extend to the exterior of the outer frame. The top end of the fixed supporting shaft is fixedly connected with a fixed rotating device. The position, making contact with theouter frame, of the top end of the fixed supporting shaft is fixedly connected with a fixed connection device. The top end of the outer wall of one side of the outer frame is fixedly connected with arotating power box through a supporting frame. A motor is fixedly connected in the rotating power box. The invention relates to the technical field of chemical industry production. By means of the wall-hanging-prevention high-density chemical industry solution storage tower, the wall hanging situation of high-density chemical industry solutions in the storage and processing processes is reduced; meanwhile, the stirring effect of the device is improved, and quality of chemical industry finished products is improved; and meanwhile resource waste is reduced.
Owner:佛山杰致信息科技有限公司
Production technology of sauce flavor powder
ActiveCN103404824BSmall granularityPromote decompositionFood shapingFood preparationDecompositionFood flavor
The invention discloses a production technology of sauce flavor powder. The technology which allows a raw material sauce to undergo step enzymatic hydrolysis comprises the following steps: 1, adding cellulase for improving the decomposition of celluloses and hemicelluloses; and 2, adding a protease for hydrolyzing macromolecular proteins in the sauce to form micro-molecular peptides or amino acids. The obtained zymolytic sauce has the advantages of obviously improved spray drying condition, reduction of the appearance of wall hanging, powder obstruction and scorched particles, and continuous large-batch production.
Owner:保定味群食品科技股份有限公司
Cross cementing method without occupying the wellhead
The invention discloses a cross well cementation method without occupying a well mouth. The method comprises the following steps: (S1) the lower end of a 20" surface layer sleeve is connected with a sleeve float shoe, wherein the sleeve float shoe is provided with a side outlet hole on the side wall below a float shoe check valve base; (S2) the 20" surface layer sleeve is directly descended to a base, and is fixed in center through righting blocks in the well mouth; (S3) a drilling table inverts and swings the 20" surface layer sleeve in the position of conveniently connecting with a circulating head of the 20" sleeve below a turntable to shift a derrick to a next well position to perform the cross well cementation operation without occupying the well mouth in the well mouth area; and (S4) the return condition is observed in the well cementation period; and after cement is returned out from the well mouth, the replacement operation is immediately switched to finish the well cementation. The method finishes the well cementation operation by connecting the circulating head in the well mouth area, finishes the 20" surface layer sleeve well cementation operation without occupying well mouth time, finishes the all-well-section sealing by returning cement to the well mouth according to high-temperature and high-pressure shaft completeness requirements, and guarantees the integration of the 20" sleeve and a 30" pile pipe to realize the shaft completeness.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
A kind of fermented milk that increases drinking physical examination and reduces hanging wall and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107624870BIncrease viscosityReduce wall hangingMilk preparationFood processingBiotechnologyMicrobiology
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Anti-blocking double-stage material level measurement device
InactiveCN105865579AExtended service lifeImprove performanceMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsTuning forkMeasurement device
The invention discloses an anti-blocking double-stage material level measurement device. The anti-blocking double-stage material level measurement device comprises two relatively parallel tuning fork material level measurement devices and two compressed air anti-blocking devices, wherein two tuning fork material level switches are inserted into the right side wall of a limestone powder bin, the two compressed air anti-blocking devices are inserted into the left side wall of the limestone powder bin, and the two compressed air anti-blocking devices and the two tuning fork material level switches are arranged oppositely respectively. The anti-blocking double-stage material level measurement device has the benefits as follows: the measurement device is long in service life, stable in performance, safe and reliable; wall hanging of limestone powder is effectively reduced through inclined arrangement of a material taking pipeline, and the measurement value is more accurate; by means of the arranged tuning fork material level measurement devices, the high material level and the low material level of the limestone powder can be pre-warned; by means of the arranged compressed air anti-blocking devices, false information and misinformation after material accumulation on a level gauge can be effectively avoided, and data reported by the level gauge are more accurate.
Owner:DATANG ENVIRONMENT IND GRP
Rotary joint for novel roller dryer
PendingCN112179124AAchieve dryingAvoid easy cloggingDrying solid materials with heatDrying chambers/containersEngineeringCaking
The invention discloses a rotary joint for a novel roller dryer. The rotary joint for the novel roller dryer comprises two main bodies, wherein the two main bodies are connected with each other through a spring; a static ring is arranged on the side, away from the spring, of each main body; a movable ring is arranged on the side, away from the spring, of each static ring; and the movable rings areconnected with a main shaft through bearings. According to the rotary joint for the novel roller dryer, movable rings are connected with the main shaft and rotate synchronously with the main shaft, and holes are formed in the movable rings along the circumference and communicate with air guide pipelines respectively; and the static rings are fixed, a partition plate is arranged in the diameter direction of each static ring and axially divides into an upper cavity and a lower cavity, the two cavities are connected with an air inlet pipe and an exhaust pipe of the dryer respectively, and the air guide pipelines are used for guiding dry air into a dryer roller and exhausting wet air out of the dryer roller to achieve the drying of materials, so that the whole device is suitable for treatinglight materials which are easy to fly, easy to cake, easy to hang on the wall, pasty and difficult to treat, and is high in drying efficiency and convenient to use at the same time.
Owner:上海迪化科技股份有限公司
A kind of ethylene oligomerization catalyst and method for continuous production of 1-hexene and 1-octene
ActiveCN113441185BReduce the amount addedReduce generationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsChromium CompoundsPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for continuous production of 1-hexene and 1-octene, comprising: (1) after mixing a solvent and an alkyl aluminum compound in a mixing tank, they are continuously introduced into a reaction kettle, and ethylene is introduced into the reaction kettle. Under the effect of the catalyzer that feeds, ethylene oligomerization reaction occurs, obtains the reaction solution containing 1-hexene and 1-octene; (2) the reaction solution containing 1-hexene and 1-octene enters through overflow line to the overflow tank reactor; (3) the reaction solution obtained by the overflow tank reactor enters the quenching reactor, and uses alcohols as a quenching agent to quench the reaction to obtain 1-hexene and 1-octene. Wherein, the catalyst used is a solution formed by a metal chromium compound, a PNSiNP ligand and an organic boron compound. In the invention, without changing the reaction temperature, the overflow tank adopts a higher temperature, and the polymer from the reaction kettle can be dissolved in the reaction liquid, thereby reducing the possibility of pipeline blockage and improving the continuous operation time of the device.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Mixed oil conveying pipeline facilitating mixed oil cutting
InactiveCN113404897AEasy to adjustImprove the delivery effectCorrosion preventionMultiple way valvesControl valvesMain duct
The invention discloses a mixed oil conveying pipeline facilitating mixed oil cutting, and relates to the field of mixed oil conveying and cutting. The mixed oil conveying pipeline provides the following scheme aiming at the problems that an existing mixed oil conveying pipeline is large in cutting difficulty and high in cost, mixed oil increase is likely to be caused, oil products along the line are affected, and the cutting effect is poor. The mixed oil conveying pipeline comprises a main pipeline body, a control valve ball is arranged on the inner side of the main pipeline body, an oil guide groove is formed in the inner side of the control valve ball, a connecting block is arranged on the side wall of the main pipeline body, the connecting block and the main pipeline body are connected with a limiting sliding block and a fixing bolt, a flow guide valve ball is arranged on the inner side of the connecting block, a flow guide groove is formed in the side wall of the flow guide valve ball, a branch pipeline body is installed on the side wall of the connecting block, and rotating shafts are installed on the side wall of the flow guide valve ball and the side wall of the control valve ball. The mixed oil conveying pipeline is novel in structure, high in mixed oil conveying adjustability, wide in application range, high in stability and use safety and good in conveying effect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Vacuum metering casting device
ActiveCN113944569AReduce wall hangingAvoid cleanupRocket engine plantsEngineeringUltrasonic vibration
The invention discloses a vacuum metering casting device. The vacuum metering casting device comprises a casting tank and a casting mechanism, the casting tank is a cylinder with the periphery sealed and an inner cavity vacuum, an inner cavity of the casting tank is provided with a space for containing an engine, and the upper surface of the casting tank is provided with a casting gate communicated with the inner cavity of the casting tank; the casting mechanism comprises a casting hopper, a casting pipe and a casting valve, the casting hopper is a cylinder with two open ends, the casting pipe is coaxially arranged below the casting hopper, the lower port of the casting hopper coincides with the upper port of the casting pipe, the casting pipe is matched with the casting gate in structure, the casting pipe is in communication with the inner cavity of the casting tank body through the casting gate, and the casting valve is arranged on the casting pipe; the casting mechanism further comprises an ultrasonic vibration unit arranged on the outer side wall of the casting hopper. Through reasonable arrangement of component structures, the ultrasonic vibration unit generates ultrasonic vibration on the casting hopper, wall hanging of slurry on the inner wall of the casting hopper is reduced, the operation safety is improved, meanwhile, the thermal effect generated by ultrasonic vibration can heat the slurry, the casting device is simplified, and the safety is improved.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Machine capable of removing solid residue from bucket
Owner:温州人立环能科技有限公司
A kind of preparation method of diether diphthalimide
The invention discloses a method for preparing diether bisphthalimide, comprising the step (A) making the raw material diphenol and one or more of strong base and strong base weak acid salt in a non-polar Reaction in a solvent such as toluene or o-xylene under an inert atmosphere; (B) reacting the reaction product of step (A) with phthalimide in the presence of an ionic liquid catalyst to obtain diether diphthalimide. In the invention, nucleophilic reaction is carried out in a non-polar solvent, and an ionic liquid is added as a phase transfer catalyst, thereby improving the reaction yield. After the reaction is finished, impurities are washed out by water extraction, which greatly reduces the generation of waste water. Then, the organic layer is evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain the diether diphthalimide, the process is simple, and the obtained product has high purity.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
High-chroma impact-resistant polystyrene and its preparation method and preparation device
The invention provides a high-chroma impact-resistant polystyrene, a preparation method and a preparation device thereof. The preparation device comprises a reaction unit, a devolatilization unit, a purification unit, a cooling unit, a liquid-liquid separation unit and a driving unit which are communicated in sequence. The driving unit is communicated with the reaction unit and a waste liquid collection unit respectively, wherein the liquid-liquid separation unit is communicated with the driving unit through a first pipe, and a cleaning liquid inlet and a cleaning liquid outlet are also arranged on the first pipe, the cleaning liquid inlet is arranged at one end close to the liquid-liquid separating unit, and the cleaning liquid outlet is arranged at one end close to the driving unit. Thefirst pipe needs to be cleaned during the preparation process and the raw material for preparation in the reaction unit comprises linear structural rubber and / or a mixture of linear structural rubberand star rubber. The invention can not only obtain impact polystyrene with high chromaticity, but also effectively control the chromaticity stability of the impact-resistant polystyrene.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
A method for the continuous preparation of pectin and fiber from fruit
A method for continuously preparing pectin and fiber from fruits. The method comprises: first juicing fruits and separating solid components from the fruit juice, and preserving the solid components in high-temperature water and filtering the solution to obtain a first filtrate and a first residue; then adding the first residue to water for heat preservation at high temperature under acidic conditions, and filtering the solution to obtain a second filtrate and a second residue; next, merging the first filtrate and the second filtrate and removing impurities therein, and extracting pectin; subjecting the second residue to a high-temperature alkali treatment followed by bleaching or first subjecting the second residue to bleaching followed by a high-temperature alkali treatment, and then collecting solid matter to obtain a third residue, wherein the high-temperature alkali treatment includes adding the second residue to water for heat preservation under high temperature under basic conditions; and finally, after mixing the third residue, water, and a dispersant, adjusting the pH to 6-8, and homogenizing and drying the solution, to obtain a finished fiber. The finished fiber obtained by the method has excellent dispersibility, water swelling property, and long-term use stability.
Owner:HEBEI BROS ILONG FOOD TECH LLC
a drum dryer
ActiveCN112325585BAchieve dryingAvoid cloggingDrying gas arrangementsDrying solid materialsDrum dryingProcess engineering
The invention discloses a novel drum dryer. The drum dryer is composed of a drum, a gas distributor, a rotary joint and a drum driving mechanism. The working principle of the new type drum dryer is: the drying gas is introduced into the drum through the rotary joint and the distributor, so that the air enters the lower semicircle in the drum and the air exits in the upper semicircle. The airflow from bottom to top is formed in the drum, which makes the material to be dried to be in an approximate fluidized state, thereby realizing the drying of the material. The novel drum dryer of the present invention has the advantages of high drying efficiency, wide material adaptability, compliance with GMP standards, and high degree of automation. It is a traditional stirring dryer, rotary dryer, ribbon dryer, rake dryer, box Ideal replacement products such as dryers.
Owner:上海迪化科技股份有限公司
Method for detecting concentration of metal elements in aqueous humor in combination with flow injection and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer
ActiveCN111089893AReduce wall hangingEliminate matrix effects and signal driftPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTrace metalInternal standard
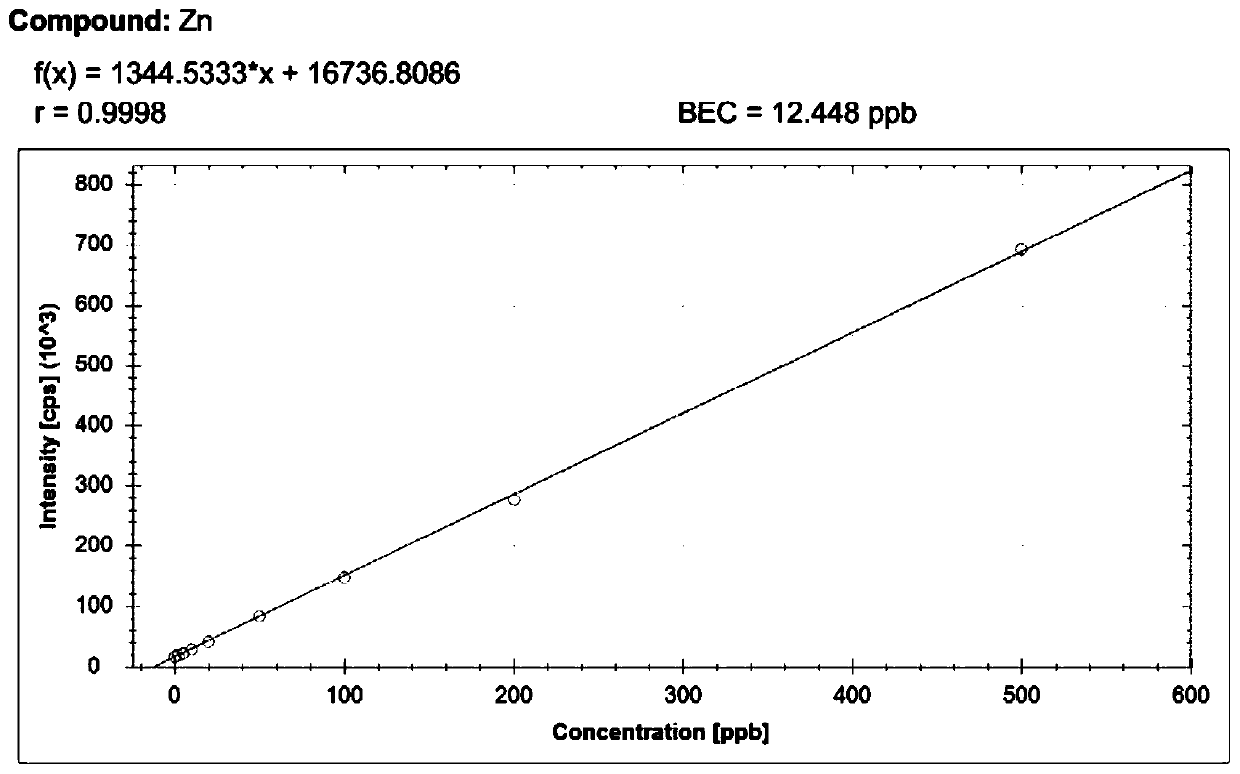
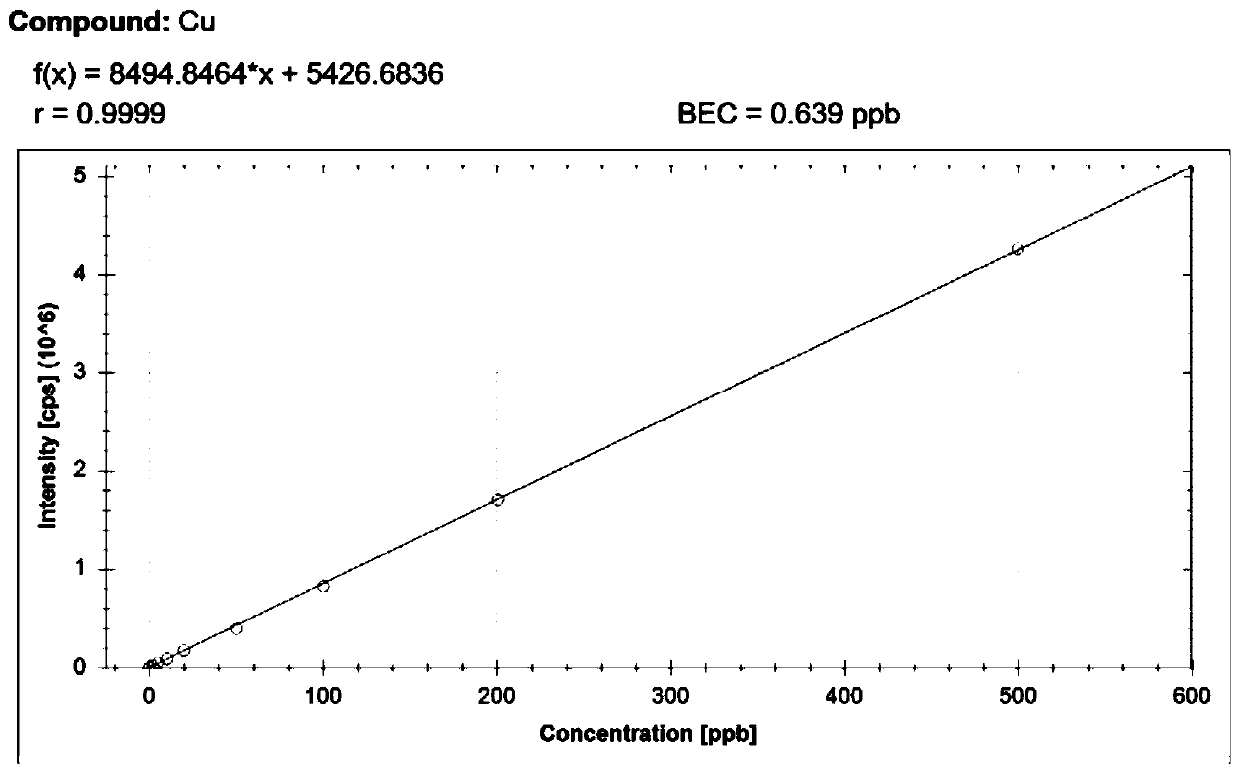
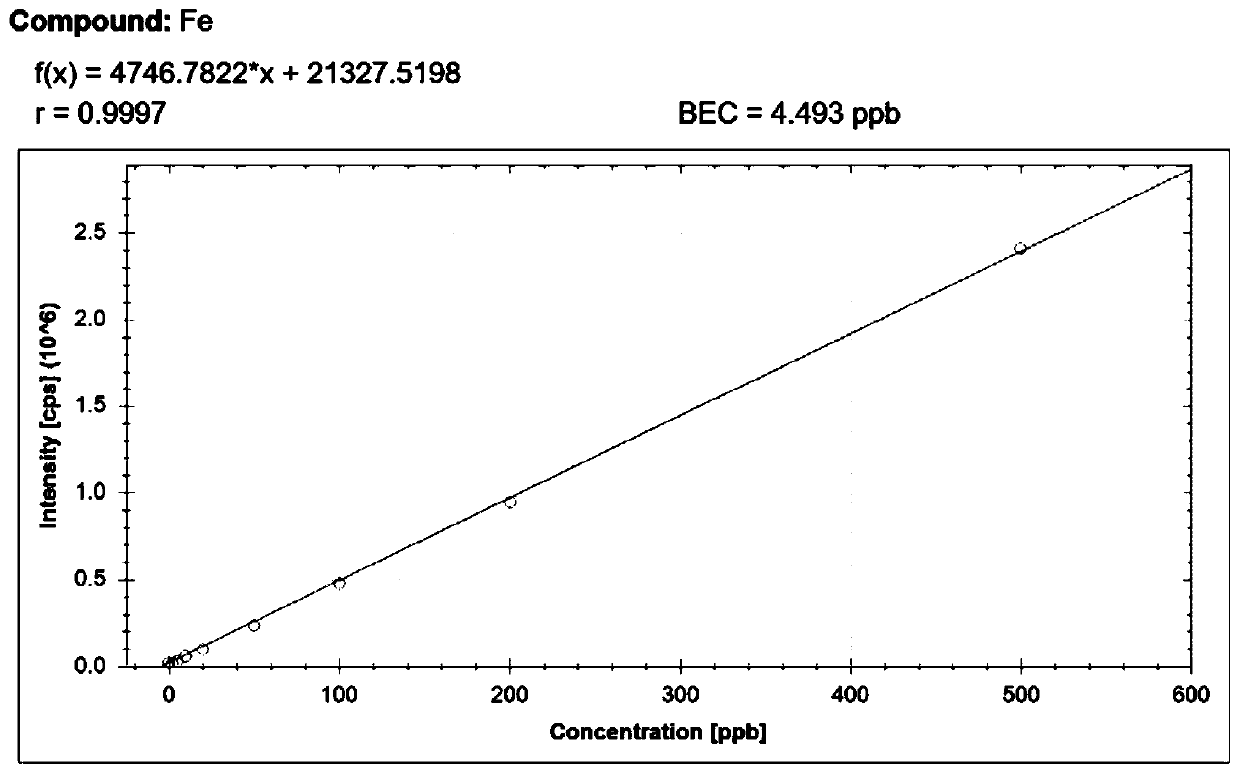
The invention discloses a method for detecting concentration of metal elements in aqueous humor in combination with flow injection and an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer. The method comprises the following steps of first, taking an aqueous humor sample; then, diluting the aqueous humor sample, and adding Triton, methanol, HNO3 and internal standard elements to obtain a diluent; and finally, injecting, by using the flow injection, the sample into the inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer for determining the concentration of the metal elements to be detected. According to themethod, aqueous humor detection pretreatment is adopted for solving the problem that the aqueous humor sample has a wall hanging phenomenon in a sample injecting pipeline, so that the wall hanging ofthe sample in the sample injecting pipeline is greatly reduced. Moreover, by adding the internal standard elements, namely, manually selecting and adding the elements, namely, Sc, In and Ge, that arevery rare in the natural environment, the solution sample volume is standardized, and a matrix effect and signal drift are eliminated. In addition, the values to be set of the relevant parameters ofan instrument are found out, the concentration of trace metal elements in the aqueous humor is successfully detected by applying FI-ICP-MS for the first time, and taking Zn as an example, the detection limit is as low as 2.00 ug / L. The method for detecting the concentration of the metal elements in the aqueous humor in combination with the flow injection and the inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer provides a model for the detection of the trace metal elements in the aqueous humor.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com