Examining AMOLED signatures in digital forensic technologies.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Forensics Background
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has emerged as a significant focus in digital forensics due to its widespread adoption in modern mobile devices. This display technology, characterized by its self-illuminating pixels and superior contrast ratios, has become increasingly prevalent in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices over the past decade.
The forensic significance of AMOLED displays lies in their unique operational characteristics, which can leave distinct digital signatures. Unlike traditional LCD screens, AMOLED displays emit light directly from each pixel, resulting in varying levels of power consumption and potential burn-in effects. These properties create opportunities for forensic analysts to extract valuable information from devices equipped with AMOLED screens.
The evolution of AMOLED technology in consumer electronics has been rapid, with manufacturers continuously improving display quality, energy efficiency, and durability. This progression has led to the development of various AMOLED variants, including Super AMOLED, Dynamic AMOLED, and Flexible AMOLED, each presenting unique forensic challenges and opportunities.
In the context of digital forensics, AMOLED signatures can manifest in several ways. Screen burn-in, a phenomenon where static images leave persistent marks on the display, can provide insights into a device's usage patterns and potentially reveal sensitive information. Additionally, the power consumption profiles of AMOLED displays can be analyzed to infer user activity and application usage, even when traditional data recovery methods are ineffective.
The forensic examination of AMOLED signatures requires specialized knowledge and tools. Investigators must understand the underlying technology, its vulnerabilities, and the potential artifacts it can produce. This includes familiarity with AMOLED display architecture, pixel structures, and the impact of various display technologies on data retention and recovery.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, so too must forensic methodologies. The integration of under-display cameras, foldable displays, and other innovations in AMOLED technology presents new challenges and opportunities for digital forensics. Researchers and practitioners in this field must stay abreast of these developments to effectively leverage AMOLED signatures in their investigations.
The intersection of AMOLED technology and digital forensics highlights the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in modern investigative techniques. It underscores the need for continuous research and development in forensic tools and methodologies to keep pace with rapidly advancing display technologies.
The forensic significance of AMOLED displays lies in their unique operational characteristics, which can leave distinct digital signatures. Unlike traditional LCD screens, AMOLED displays emit light directly from each pixel, resulting in varying levels of power consumption and potential burn-in effects. These properties create opportunities for forensic analysts to extract valuable information from devices equipped with AMOLED screens.
The evolution of AMOLED technology in consumer electronics has been rapid, with manufacturers continuously improving display quality, energy efficiency, and durability. This progression has led to the development of various AMOLED variants, including Super AMOLED, Dynamic AMOLED, and Flexible AMOLED, each presenting unique forensic challenges and opportunities.
In the context of digital forensics, AMOLED signatures can manifest in several ways. Screen burn-in, a phenomenon where static images leave persistent marks on the display, can provide insights into a device's usage patterns and potentially reveal sensitive information. Additionally, the power consumption profiles of AMOLED displays can be analyzed to infer user activity and application usage, even when traditional data recovery methods are ineffective.
The forensic examination of AMOLED signatures requires specialized knowledge and tools. Investigators must understand the underlying technology, its vulnerabilities, and the potential artifacts it can produce. This includes familiarity with AMOLED display architecture, pixel structures, and the impact of various display technologies on data retention and recovery.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, so too must forensic methodologies. The integration of under-display cameras, foldable displays, and other innovations in AMOLED technology presents new challenges and opportunities for digital forensics. Researchers and practitioners in this field must stay abreast of these developments to effectively leverage AMOLED signatures in their investigations.
The intersection of AMOLED technology and digital forensics highlights the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in modern investigative techniques. It underscores the need for continuous research and development in forensic tools and methodologies to keep pace with rapidly advancing display technologies.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for AMOLED signature analysis in digital forensics has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing prevalence of AMOLED displays in mobile devices and the rising importance of digital evidence in criminal investigations. As smartphones and tablets with AMOLED screens become more common, law enforcement agencies and forensic experts are seeking advanced tools to extract and analyze data from these devices.
The global digital forensics market, which encompasses AMOLED signature analysis, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the escalating number of cybercrimes, the proliferation of digital devices, and the growing awareness of the importance of digital evidence in legal proceedings. The need for sophisticated forensic techniques to examine AMOLED displays is particularly acute in cases involving mobile device analysis, as these screens are increasingly used in high-end smartphones and tablets.
Law enforcement agencies represent a primary market segment for AMOLED signature analysis technologies. These organizations require cutting-edge tools to investigate crimes involving digital devices, such as fraud, theft, and cybercrime. The ability to extract and analyze data from AMOLED displays can provide crucial evidence in criminal cases, making it an essential capability for modern forensic laboratories.
Corporate security departments form another significant market for AMOLED forensic technologies. As businesses increasingly rely on mobile devices for sensitive communications and data storage, the need to investigate potential data breaches or insider threats has grown. AMOLED signature analysis can help corporate investigators recover deleted data or uncover evidence of unauthorized access on company-issued devices.
The legal sector also contributes to the demand for AMOLED forensic technologies. Attorneys and legal consultants often require expert analysis of digital evidence in civil and criminal cases. The ability to extract and interpret data from AMOLED displays can be crucial in litigation involving electronic communications, intellectual property disputes, or employment-related issues.
Academic and research institutions represent an emerging market for AMOLED signature analysis tools. As digital forensics becomes a more established field of study, universities and research centers are investing in advanced technologies to support their educational programs and research initiatives. This sector drives innovation in forensic techniques and contributes to the development of new methodologies for analyzing AMOLED displays.
The market for AMOLED signature analysis in digital forensics is characterized by a need for continuous innovation to keep pace with rapidly evolving display technologies. As manufacturers introduce new AMOLED screen designs and security features, forensic tool developers must adapt their products to maintain effectiveness. This dynamic creates ongoing demand for updated software, hardware, and training services in the digital forensics market.
The global digital forensics market, which encompasses AMOLED signature analysis, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the escalating number of cybercrimes, the proliferation of digital devices, and the growing awareness of the importance of digital evidence in legal proceedings. The need for sophisticated forensic techniques to examine AMOLED displays is particularly acute in cases involving mobile device analysis, as these screens are increasingly used in high-end smartphones and tablets.
Law enforcement agencies represent a primary market segment for AMOLED signature analysis technologies. These organizations require cutting-edge tools to investigate crimes involving digital devices, such as fraud, theft, and cybercrime. The ability to extract and analyze data from AMOLED displays can provide crucial evidence in criminal cases, making it an essential capability for modern forensic laboratories.
Corporate security departments form another significant market for AMOLED forensic technologies. As businesses increasingly rely on mobile devices for sensitive communications and data storage, the need to investigate potential data breaches or insider threats has grown. AMOLED signature analysis can help corporate investigators recover deleted data or uncover evidence of unauthorized access on company-issued devices.
The legal sector also contributes to the demand for AMOLED forensic technologies. Attorneys and legal consultants often require expert analysis of digital evidence in civil and criminal cases. The ability to extract and interpret data from AMOLED displays can be crucial in litigation involving electronic communications, intellectual property disputes, or employment-related issues.
Academic and research institutions represent an emerging market for AMOLED signature analysis tools. As digital forensics becomes a more established field of study, universities and research centers are investing in advanced technologies to support their educational programs and research initiatives. This sector drives innovation in forensic techniques and contributes to the development of new methodologies for analyzing AMOLED displays.
The market for AMOLED signature analysis in digital forensics is characterized by a need for continuous innovation to keep pace with rapidly evolving display technologies. As manufacturers introduce new AMOLED screen designs and security features, forensic tool developers must adapt their products to maintain effectiveness. This dynamic creates ongoing demand for updated software, hardware, and training services in the digital forensics market.
Current Challenges
The examination of AMOLED signatures in digital forensic technologies faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and effectiveness. One of the primary obstacles is the rapid evolution of AMOLED display technology. As manufacturers continually improve their displays, the unique signatures associated with these screens are also changing, making it difficult for forensic experts to maintain up-to-date databases and analysis techniques.
Another challenge lies in the diversity of AMOLED displays across different device manufacturers and models. Each company may implement slightly different technologies or manufacturing processes, resulting in variations in the AMOLED signatures. This heterogeneity complicates the development of standardized forensic methodologies and tools that can be universally applied across all AMOLED devices.
The sensitivity of AMOLED displays to environmental factors and usage patterns also poses a significant challenge. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and screen burn-in can alter the display's characteristics over time, potentially affecting the reliability of forensic analyses based on AMOLED signatures. This variability introduces an element of uncertainty in forensic investigations and may lead to inconclusive or contested results.
Furthermore, the extraction and analysis of AMOLED signatures often require specialized equipment and expertise. Many law enforcement agencies and forensic laboratories may lack the necessary resources or trained personnel to effectively utilize these techniques. This limitation can result in underutilization of AMOLED signature analysis in digital forensic investigations, potentially missing valuable evidence.
Data privacy and legal considerations also present challenges in the field of AMOLED signature analysis. As this technique involves examining detailed characteristics of personal devices, it raises questions about the extent of permissible data collection and analysis in forensic investigations. Balancing the need for thorough forensic examination with individual privacy rights remains a complex issue that requires careful navigation.
The potential for anti-forensic techniques targeting AMOLED signatures is an emerging concern. As awareness of this forensic method grows, criminals may develop ways to manipulate or mask AMOLED signatures, making it more difficult for investigators to rely on this evidence. Staying ahead of such countermeasures requires ongoing research and development in the field of digital forensics.
Lastly, the integration of AMOLED signature analysis with other digital forensic techniques presents both opportunities and challenges. While combining multiple forensic methods can provide more comprehensive and reliable results, it also increases the complexity of investigations and may require new approaches to data correlation and interpretation. Developing effective strategies for integrating AMOLED signature analysis with existing forensic workflows remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
Another challenge lies in the diversity of AMOLED displays across different device manufacturers and models. Each company may implement slightly different technologies or manufacturing processes, resulting in variations in the AMOLED signatures. This heterogeneity complicates the development of standardized forensic methodologies and tools that can be universally applied across all AMOLED devices.
The sensitivity of AMOLED displays to environmental factors and usage patterns also poses a significant challenge. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and screen burn-in can alter the display's characteristics over time, potentially affecting the reliability of forensic analyses based on AMOLED signatures. This variability introduces an element of uncertainty in forensic investigations and may lead to inconclusive or contested results.
Furthermore, the extraction and analysis of AMOLED signatures often require specialized equipment and expertise. Many law enforcement agencies and forensic laboratories may lack the necessary resources or trained personnel to effectively utilize these techniques. This limitation can result in underutilization of AMOLED signature analysis in digital forensic investigations, potentially missing valuable evidence.
Data privacy and legal considerations also present challenges in the field of AMOLED signature analysis. As this technique involves examining detailed characteristics of personal devices, it raises questions about the extent of permissible data collection and analysis in forensic investigations. Balancing the need for thorough forensic examination with individual privacy rights remains a complex issue that requires careful navigation.
The potential for anti-forensic techniques targeting AMOLED signatures is an emerging concern. As awareness of this forensic method grows, criminals may develop ways to manipulate or mask AMOLED signatures, making it more difficult for investigators to rely on this evidence. Staying ahead of such countermeasures requires ongoing research and development in the field of digital forensics.
Lastly, the integration of AMOLED signature analysis with other digital forensic techniques presents both opportunities and challenges. While combining multiple forensic methods can provide more comprehensive and reliable results, it also increases the complexity of investigations and may require new approaches to data correlation and interpretation. Developing effective strategies for integrating AMOLED signature analysis with existing forensic workflows remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
Existing Forensic Methods
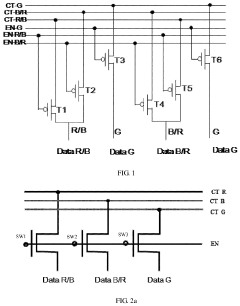
01 AMOLED display driving techniques
Various driving techniques are employed to improve the performance of AMOLED displays. These techniques include methods for compensating for pixel variations, optimizing power consumption, and enhancing image quality. Advanced driving schemes can help reduce image sticking, improve color accuracy, and extend the lifespan of AMOLED displays.- AMOLED display driving techniques: Various techniques for driving AMOLED displays, including methods to improve image quality, reduce power consumption, and enhance overall performance. These techniques may involve specialized driving circuits, pixel structures, or timing control methods to optimize the display's operation.
- Fingerprint sensing in AMOLED displays: Integration of fingerprint sensing technology within AMOLED displays, allowing for on-screen fingerprint recognition. This may involve incorporating optical or ultrasonic sensors into the display structure, or using the display pixels themselves for fingerprint detection.
- AMOLED pixel circuit designs: Innovative pixel circuit designs for AMOLED displays, aimed at improving factors such as luminance uniformity, color accuracy, and lifespan of the organic light-emitting diodes. These designs may include compensation circuits, new transistor arrangements, or novel driving schemes.
- Touch sensing in AMOLED displays: Methods for integrating touch sensing functionality into AMOLED displays, potentially using in-cell or on-cell touch technologies. This integration can lead to thinner device profiles and improved touch responsiveness while maintaining display quality.
- AMOLED display manufacturing techniques: Advanced manufacturing processes and techniques specific to AMOLED displays, which may include new deposition methods, patterning technologies, or encapsulation techniques. These innovations aim to improve yield, reduce costs, and enhance the overall quality and durability of AMOLED displays.
02 Fingerprint sensing in AMOLED displays
Integration of fingerprint sensing technology within AMOLED displays allows for secure authentication without the need for a separate sensor. This can be achieved by incorporating optical or ultrasonic sensors beneath the display panel, enabling in-display fingerprint recognition. The technology can be optimized to work with various display structures and pixel arrangements.Expand Specific Solutions03 AMOLED pixel structure and layout
Innovative pixel structures and layouts are developed to enhance the performance of AMOLED displays. These designs can improve factors such as aperture ratio, power efficiency, and color accuracy. Advanced pixel architectures may incorporate additional sub-pixels or utilize novel arrangements to optimize display characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Touch sensing in AMOLED displays
Integration of touch sensing capabilities within AMOLED displays enables interactive functionality without the need for a separate touch panel. Various touch sensing technologies, such as in-cell or on-cell touch, can be incorporated into the display structure. This integration can lead to thinner device profiles and improved touch performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 AMOLED display compensation techniques
Compensation techniques are employed to address issues such as non-uniformity, aging, and temperature-related variations in AMOLED displays. These methods may involve real-time monitoring of pixel characteristics, applying correction factors, or implementing adaptive algorithms to maintain consistent display performance over time.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The AMOLED signature analysis in digital forensics is in a nascent stage, with the market still developing. The technology's maturity varies across companies, with major players like Samsung Electronics, LG Display, and BOE Technology Group leading in AMOLED display production. These firms are likely at the forefront of forensic applications. The market size is growing as AMOLED displays become more prevalent in consumer electronics. However, specialized forensic tools for AMOLED signature analysis are still emerging, indicating a relatively early phase of technological development and market expansion in this niche area.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed a comprehensive AMOLED signature analysis system for digital forensics. Their approach utilizes multi-spectral imaging techniques to capture unique characteristics of AMOLED displays, including sub-pixel arrangements and color gamut variations[2]. BOE's system employs advanced image processing algorithms to extract and analyze minute differences in AMOLED panel structures, allowing for precise device identification[4]. They have also integrated artificial intelligence to improve the accuracy of signature matching and to detect potential tampering or counterfeiting attempts[6]. Furthermore, BOE has implemented a cloud-based database for storing and comparing AMOLED signatures across a wide range of devices.
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, diverse product portfolio, and strong presence in the Chinese market. Weaknesses: Less established in the global forensics market compared to some competitors.
International Business Machines Corp.
Technical Solution: IBM has developed a sophisticated AMOLED signature analysis platform for digital forensics applications. Their approach combines advanced computer vision techniques with quantum computing algorithms to process and analyze AMOLED display characteristics[8]. IBM's system utilizes deep learning models trained on vast datasets of AMOLED signatures to identify minute variations in pixel structures and emission patterns[10]. They have also implemented a novel quantum-resistant encryption method for securing AMOLED signature data, ensuring long-term viability in the face of emerging computational threats[12]. Additionally, IBM has developed a cloud-based platform that allows for real-time collaboration and analysis of AMOLED signatures across multiple forensic teams and jurisdictions.
Strengths: Cutting-edge AI and quantum computing capabilities, global reach, and strong reputation in enterprise solutions. Weaknesses: Less specialized in display technologies compared to dedicated manufacturers.
AMOLED Signature Analysis
Detection system and detection method of AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode)
PatentActiveCN108932923A
Innovation
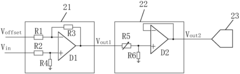
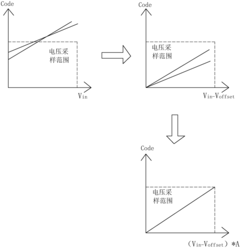
- Set an offset adjuster and a gain adjuster in each detection device, adjust the sampling voltage signal through the offset adjuster so that it is within the voltage sampling range of the analog-to-digital converter, and equalize each signal through the gain adjuster. The sampling gain of the detection device enables each analog-to-digital converter to provide the same sampling encoding value for the same sampling voltage signal.
Active-matrix organic light emitting diode (amoled) panel cell testing circuit and method for repairing data lines via same
PatentActiveUS20200342807A1
Innovation
- An active-matrix organic light emitting diode (AMOLED) panel cell testing circuit with a modified configuration that includes three switches connected to detection control signals, allowing for the connection of parallel lines to repair open circuits in data lines, enabling both screen detection and data line repair.
Legal and Ethical Issues
The examination of AMOLED signatures in digital forensic technologies raises significant legal and ethical concerns that must be carefully addressed. Privacy rights are at the forefront of these issues, as the extraction and analysis of AMOLED display data may infringe upon individual privacy protections. Forensic investigators must navigate the delicate balance between gathering crucial evidence and respecting personal information boundaries.
Legal frameworks governing the use of AMOLED signature analysis in criminal investigations vary across jurisdictions. In some regions, strict regulations may limit the admissibility of such evidence in court, while others may have more permissive standards. This legal landscape necessitates a thorough understanding of local and international laws to ensure compliance and maintain the integrity of forensic processes.
The potential for misuse or unauthorized access to AMOLED signature data presents another ethical challenge. Safeguarding this sensitive information against breaches or exploitation is paramount, requiring robust security measures and stringent access controls. Forensic professionals must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to prevent any mishandling or misinterpretation of the collected data.
Consent and transparency are critical ethical considerations in AMOLED forensic analysis. Individuals whose devices are subject to examination should be informed about the nature and extent of the data extraction process, whenever possible and legally permissible. This transparency fosters trust in the forensic process and upholds the principles of informed consent.
The long-term storage and retention of AMOLED signature data also raise ethical questions. Determining appropriate retention periods and ensuring secure disposal of data after its usefulness has expired are essential aspects of responsible forensic practice. Striking a balance between preserving potentially valuable evidence and protecting individual privacy rights remains an ongoing challenge.
As AMOLED forensic technologies continue to evolve, so too must the legal and ethical frameworks governing their use. Regular review and updating of guidelines, in collaboration with legal experts, ethicists, and technology specialists, are necessary to address emerging challenges and maintain public trust in digital forensic practices.
Legal frameworks governing the use of AMOLED signature analysis in criminal investigations vary across jurisdictions. In some regions, strict regulations may limit the admissibility of such evidence in court, while others may have more permissive standards. This legal landscape necessitates a thorough understanding of local and international laws to ensure compliance and maintain the integrity of forensic processes.
The potential for misuse or unauthorized access to AMOLED signature data presents another ethical challenge. Safeguarding this sensitive information against breaches or exploitation is paramount, requiring robust security measures and stringent access controls. Forensic professionals must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to prevent any mishandling or misinterpretation of the collected data.
Consent and transparency are critical ethical considerations in AMOLED forensic analysis. Individuals whose devices are subject to examination should be informed about the nature and extent of the data extraction process, whenever possible and legally permissible. This transparency fosters trust in the forensic process and upholds the principles of informed consent.
The long-term storage and retention of AMOLED signature data also raise ethical questions. Determining appropriate retention periods and ensuring secure disposal of data after its usefulness has expired are essential aspects of responsible forensic practice. Striking a balance between preserving potentially valuable evidence and protecting individual privacy rights remains an ongoing challenge.
As AMOLED forensic technologies continue to evolve, so too must the legal and ethical frameworks governing their use. Regular review and updating of guidelines, in collaboration with legal experts, ethicists, and technology specialists, are necessary to address emerging challenges and maintain public trust in digital forensic practices.
Cross-Device Compatibility
Cross-device compatibility is a critical aspect of AMOLED signature analysis in digital forensic technologies. As AMOLED displays become increasingly prevalent across various devices, forensic investigators face the challenge of ensuring consistent and reliable signature detection across different hardware configurations.
One of the primary concerns in cross-device compatibility is the variation in AMOLED panel specifications among manufacturers. Different devices may employ AMOLED displays with varying pixel densities, color gamuts, and refresh rates. These disparities can potentially affect the characteristics of AMOLED signatures, necessitating robust forensic tools capable of adapting to diverse display parameters.
To address this challenge, forensic technologies must incorporate adaptive algorithms that can calibrate their analysis based on device-specific AMOLED characteristics. This approach involves developing a comprehensive database of AMOLED panel specifications for various devices and implementing dynamic adjustment mechanisms within forensic tools.
Another crucial factor in cross-device compatibility is the impact of software-level display optimizations. Many devices implement custom color management systems and display enhancement features, which can alter the visual output of AMOLED screens. Forensic technologies must account for these software-induced variations to ensure accurate signature detection across different device ecosystems.
Standardization efforts play a vital role in improving cross-device compatibility for AMOLED signature analysis. Industry-wide initiatives to establish common protocols for AMOLED display characterization and signature extraction can significantly enhance the interoperability of forensic tools across diverse device landscapes.
Furthermore, the development of device-agnostic signature detection techniques is essential for achieving optimal cross-device compatibility. These methods focus on identifying universal AMOLED characteristics that remain consistent across different hardware implementations, thereby reducing the reliance on device-specific calibration.
As the AMOLED technology landscape continues to evolve, forensic tools must maintain adaptability to accommodate emerging display technologies and form factors. This includes addressing challenges posed by flexible AMOLED displays, under-display cameras, and other innovations that may impact signature characteristics.
In conclusion, achieving robust cross-device compatibility in AMOLED signature analysis requires a multifaceted approach. This involves adaptive algorithms, comprehensive device databases, standardization efforts, and the development of device-agnostic detection techniques. By addressing these challenges, digital forensic technologies can ensure reliable and consistent AMOLED signature analysis across the diverse ecosystem of modern devices.
One of the primary concerns in cross-device compatibility is the variation in AMOLED panel specifications among manufacturers. Different devices may employ AMOLED displays with varying pixel densities, color gamuts, and refresh rates. These disparities can potentially affect the characteristics of AMOLED signatures, necessitating robust forensic tools capable of adapting to diverse display parameters.
To address this challenge, forensic technologies must incorporate adaptive algorithms that can calibrate their analysis based on device-specific AMOLED characteristics. This approach involves developing a comprehensive database of AMOLED panel specifications for various devices and implementing dynamic adjustment mechanisms within forensic tools.
Another crucial factor in cross-device compatibility is the impact of software-level display optimizations. Many devices implement custom color management systems and display enhancement features, which can alter the visual output of AMOLED screens. Forensic technologies must account for these software-induced variations to ensure accurate signature detection across different device ecosystems.
Standardization efforts play a vital role in improving cross-device compatibility for AMOLED signature analysis. Industry-wide initiatives to establish common protocols for AMOLED display characterization and signature extraction can significantly enhance the interoperability of forensic tools across diverse device landscapes.
Furthermore, the development of device-agnostic signature detection techniques is essential for achieving optimal cross-device compatibility. These methods focus on identifying universal AMOLED characteristics that remain consistent across different hardware implementations, thereby reducing the reliance on device-specific calibration.
As the AMOLED technology landscape continues to evolve, forensic tools must maintain adaptability to accommodate emerging display technologies and form factors. This includes addressing challenges posed by flexible AMOLED displays, under-display cameras, and other innovations that may impact signature characteristics.
In conclusion, achieving robust cross-device compatibility in AMOLED signature analysis requires a multifaceted approach. This involves adaptive algorithms, comprehensive device databases, standardization efforts, and the development of device-agnostic detection techniques. By addressing these challenges, digital forensic technologies can ensure reliable and consistent AMOLED signature analysis across the diverse ecosystem of modern devices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!