Extending AMOLED display functionalities using cloud technologies.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Cloud Integration Background and Objectives
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has revolutionized the display industry with its superior image quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility. As the demand for more advanced and interconnected display solutions grows, the integration of cloud technologies with AMOLED displays presents a promising avenue for extending their functionalities and capabilities.
The evolution of AMOLED technology has been marked by continuous improvements in display performance, including enhanced color accuracy, contrast ratios, and power efficiency. However, the integration of cloud technologies opens up new possibilities for expanding the scope and utility of AMOLED displays beyond their traditional roles.
Cloud integration allows for the seamless connection of AMOLED displays to vast computational resources and data storage capabilities. This synergy enables real-time processing of complex visual data, dynamic content delivery, and advanced user interactions that were previously limited by local hardware constraints.
The primary objective of integrating cloud technologies with AMOLED displays is to create a more versatile and intelligent display ecosystem. This integration aims to enhance user experiences by enabling features such as personalized content delivery, adaptive display settings based on environmental conditions, and collaborative viewing experiences across multiple devices.
Furthermore, cloud integration facilitates the development of innovative applications in various sectors. In healthcare, for instance, cloud-connected AMOLED displays can provide real-time access to patient data and medical imaging, improving diagnostic capabilities and treatment planning. In the automotive industry, these displays can offer enhanced navigation systems and augmented reality features for improved driver assistance and safety.
The convergence of AMOLED and cloud technologies also addresses the growing need for energy-efficient and sustainable display solutions. By offloading computationally intensive tasks to the cloud, local power consumption can be reduced, potentially extending battery life in mobile devices and reducing the overall carbon footprint of display technologies.
As we explore the potential of this technological fusion, it is crucial to consider the challenges and opportunities it presents. Issues such as data security, latency, and connectivity reliability must be addressed to ensure the seamless and safe operation of cloud-integrated AMOLED displays. Additionally, the development of standardized protocols and interfaces will be essential for widespread adoption and interoperability across different platforms and devices.
In conclusion, the integration of cloud technologies with AMOLED displays represents a significant step forward in display technology. By leveraging the strengths of both technologies, we aim to create more intelligent, versatile, and efficient display solutions that can adapt to the evolving needs of users across various industries and applications.
The evolution of AMOLED technology has been marked by continuous improvements in display performance, including enhanced color accuracy, contrast ratios, and power efficiency. However, the integration of cloud technologies opens up new possibilities for expanding the scope and utility of AMOLED displays beyond their traditional roles.
Cloud integration allows for the seamless connection of AMOLED displays to vast computational resources and data storage capabilities. This synergy enables real-time processing of complex visual data, dynamic content delivery, and advanced user interactions that were previously limited by local hardware constraints.
The primary objective of integrating cloud technologies with AMOLED displays is to create a more versatile and intelligent display ecosystem. This integration aims to enhance user experiences by enabling features such as personalized content delivery, adaptive display settings based on environmental conditions, and collaborative viewing experiences across multiple devices.
Furthermore, cloud integration facilitates the development of innovative applications in various sectors. In healthcare, for instance, cloud-connected AMOLED displays can provide real-time access to patient data and medical imaging, improving diagnostic capabilities and treatment planning. In the automotive industry, these displays can offer enhanced navigation systems and augmented reality features for improved driver assistance and safety.
The convergence of AMOLED and cloud technologies also addresses the growing need for energy-efficient and sustainable display solutions. By offloading computationally intensive tasks to the cloud, local power consumption can be reduced, potentially extending battery life in mobile devices and reducing the overall carbon footprint of display technologies.
As we explore the potential of this technological fusion, it is crucial to consider the challenges and opportunities it presents. Issues such as data security, latency, and connectivity reliability must be addressed to ensure the seamless and safe operation of cloud-integrated AMOLED displays. Additionally, the development of standardized protocols and interfaces will be essential for widespread adoption and interoperability across different platforms and devices.
In conclusion, the integration of cloud technologies with AMOLED displays represents a significant step forward in display technology. By leveraging the strengths of both technologies, we aim to create more intelligent, versatile, and efficient display solutions that can adapt to the evolving needs of users across various industries and applications.
Market Analysis for Cloud-Enhanced Displays
The market for cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing demand for advanced display technologies in various sectors. This innovative integration of cloud technologies with AMOLED displays opens up new possibilities for enhanced functionality, improved user experiences, and novel applications across multiple industries.
In the consumer electronics sector, smartphones and tablets are expected to be the primary drivers of market growth. The integration of cloud technologies with AMOLED displays allows for real-time content updates, personalized user interfaces, and seamless synchronization across devices. This enhanced functionality is particularly appealing to tech-savvy consumers who value cutting-edge features and seamless connectivity.
The automotive industry presents another significant market opportunity for cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays. As vehicles become increasingly connected and autonomous, there is a growing need for advanced display systems that can provide real-time information, navigation assistance, and entertainment options. Cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays can offer superior visual quality, energy efficiency, and the ability to update content dynamically based on driving conditions or user preferences.
In the healthcare sector, cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays have the potential to revolutionize patient care and medical imaging. These displays can provide high-resolution, color-accurate representations of medical images, with the added benefit of cloud-based storage and retrieval of patient data. This integration enables healthcare professionals to access and analyze medical information more efficiently, potentially improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes.
The retail industry is another sector poised to benefit from cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays. Interactive digital signage and smart mirrors equipped with these displays can offer personalized shopping experiences, real-time inventory information, and targeted advertising. The ability to update content remotely through cloud connectivity ensures that retailers can maintain fresh and relevant messaging across their stores.
Market analysts predict strong growth for cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays in the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include increasing adoption of IoT devices, advancements in 5G technology, and the ongoing digital transformation across industries. The market is expected to see particularly robust growth in regions with high smartphone penetration rates and advanced telecommunications infrastructure, such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific.
However, the market also faces certain challenges. Privacy concerns related to cloud-connected devices and potential security vulnerabilities may impact adoption rates in some sectors. Additionally, the higher cost of cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays compared to traditional display technologies could limit market penetration in price-sensitive segments.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays remains positive. The technology's ability to offer enhanced functionality, improved user experiences, and new application possibilities across multiple industries positions it as a key driver of innovation in the display market for the foreseeable future.
In the consumer electronics sector, smartphones and tablets are expected to be the primary drivers of market growth. The integration of cloud technologies with AMOLED displays allows for real-time content updates, personalized user interfaces, and seamless synchronization across devices. This enhanced functionality is particularly appealing to tech-savvy consumers who value cutting-edge features and seamless connectivity.
The automotive industry presents another significant market opportunity for cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays. As vehicles become increasingly connected and autonomous, there is a growing need for advanced display systems that can provide real-time information, navigation assistance, and entertainment options. Cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays can offer superior visual quality, energy efficiency, and the ability to update content dynamically based on driving conditions or user preferences.
In the healthcare sector, cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays have the potential to revolutionize patient care and medical imaging. These displays can provide high-resolution, color-accurate representations of medical images, with the added benefit of cloud-based storage and retrieval of patient data. This integration enables healthcare professionals to access and analyze medical information more efficiently, potentially improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes.
The retail industry is another sector poised to benefit from cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays. Interactive digital signage and smart mirrors equipped with these displays can offer personalized shopping experiences, real-time inventory information, and targeted advertising. The ability to update content remotely through cloud connectivity ensures that retailers can maintain fresh and relevant messaging across their stores.
Market analysts predict strong growth for cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays in the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include increasing adoption of IoT devices, advancements in 5G technology, and the ongoing digital transformation across industries. The market is expected to see particularly robust growth in regions with high smartphone penetration rates and advanced telecommunications infrastructure, such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific.
However, the market also faces certain challenges. Privacy concerns related to cloud-connected devices and potential security vulnerabilities may impact adoption rates in some sectors. Additionally, the higher cost of cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays compared to traditional display technologies could limit market penetration in price-sensitive segments.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays remains positive. The technology's ability to offer enhanced functionality, improved user experiences, and new application possibilities across multiple industries positions it as a key driver of innovation in the display market for the foreseeable future.
Current AMOLED and Cloud Tech Challenges
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays have revolutionized the visual experience in mobile devices, offering superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency. However, as the technology matures, manufacturers face new challenges in pushing the boundaries of AMOLED capabilities. Simultaneously, cloud technologies have become increasingly integral to modern computing paradigms, offering vast computational resources and data storage capabilities.
The integration of AMOLED displays with cloud technologies presents both opportunities and challenges. One of the primary hurdles is the optimization of power consumption. While AMOLED displays are inherently more energy-efficient than their LCD counterparts, the constant connectivity required for cloud integration can significantly drain battery life. Balancing the power needs of high-resolution displays with the energy demands of cloud communication protocols remains a critical challenge.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose significant obstacles. As displays become more interconnected with cloud services, the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information increases. Ensuring end-to-end encryption and secure data transmission between AMOLED devices and cloud servers is crucial, especially in applications involving personal or confidential data.
Latency issues present another major challenge. Cloud-based functionalities often require real-time responsiveness, particularly in interactive applications. The delay between user input on the AMOLED display and the cloud-processed response can impact user experience, necessitating the development of low-latency communication protocols and edge computing solutions.
Compatibility and standardization pose additional hurdles. The diverse ecosystem of AMOLED display technologies and cloud platforms requires the establishment of universal standards to ensure seamless integration. This includes developing common APIs, data formats, and communication protocols that can work across different manufacturers and cloud service providers.
The scalability of cloud infrastructure to support millions of AMOLED devices simultaneously is another significant challenge. As more devices leverage cloud-based functionalities, the demand for computational resources and data storage will increase exponentially. Cloud service providers must develop robust, scalable architectures capable of handling this growing demand without compromising performance or reliability.
Lastly, the challenge of content adaptation and rendering for diverse AMOLED display specifications cannot be overlooked. Cloud-based services must be capable of dynamically adjusting content to suit various screen sizes, resolutions, and color gamuts, ensuring optimal visual quality across a wide range of devices. This requires sophisticated algorithms for real-time content optimization and rendering, taking into account the unique characteristics of AMOLED technology.
The integration of AMOLED displays with cloud technologies presents both opportunities and challenges. One of the primary hurdles is the optimization of power consumption. While AMOLED displays are inherently more energy-efficient than their LCD counterparts, the constant connectivity required for cloud integration can significantly drain battery life. Balancing the power needs of high-resolution displays with the energy demands of cloud communication protocols remains a critical challenge.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose significant obstacles. As displays become more interconnected with cloud services, the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information increases. Ensuring end-to-end encryption and secure data transmission between AMOLED devices and cloud servers is crucial, especially in applications involving personal or confidential data.
Latency issues present another major challenge. Cloud-based functionalities often require real-time responsiveness, particularly in interactive applications. The delay between user input on the AMOLED display and the cloud-processed response can impact user experience, necessitating the development of low-latency communication protocols and edge computing solutions.
Compatibility and standardization pose additional hurdles. The diverse ecosystem of AMOLED display technologies and cloud platforms requires the establishment of universal standards to ensure seamless integration. This includes developing common APIs, data formats, and communication protocols that can work across different manufacturers and cloud service providers.
The scalability of cloud infrastructure to support millions of AMOLED devices simultaneously is another significant challenge. As more devices leverage cloud-based functionalities, the demand for computational resources and data storage will increase exponentially. Cloud service providers must develop robust, scalable architectures capable of handling this growing demand without compromising performance or reliability.
Lastly, the challenge of content adaptation and rendering for diverse AMOLED display specifications cannot be overlooked. Cloud-based services must be capable of dynamically adjusting content to suit various screen sizes, resolutions, and color gamuts, ensuring optimal visual quality across a wide range of devices. This requires sophisticated algorithms for real-time content optimization and rendering, taking into account the unique characteristics of AMOLED technology.
Existing Cloud-AMOLED Integration Solutions
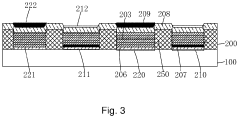
01 Display driving and control
AMOLED displays incorporate advanced driving and control mechanisms to manage pixel illumination, refresh rates, and power efficiency. These functionalities include sophisticated pixel addressing schemes, voltage control circuits, and timing controllers that enable precise control over individual pixels, resulting in high-quality image reproduction and smooth motion handling.- Display driving and control: AMOLED displays utilize advanced driving and control mechanisms to manage pixel illumination, refresh rates, and power efficiency. These functionalities include adaptive refresh rates, dynamic voltage scaling, and sophisticated pixel addressing schemes to enhance image quality and reduce power consumption.
- Pixel structure and light emission: AMOLED displays feature unique pixel structures and light emission technologies. This includes the use of organic light-emitting materials, thin-film transistors for pixel control, and various sub-pixel arrangements to achieve high color accuracy, contrast ratios, and viewing angles.
- Touch integration and sensing: Modern AMOLED displays often incorporate touch functionality directly into the display stack. This integration enables features such as in-display fingerprint sensing, pressure-sensitive touch, and improved touch accuracy while maintaining the thinness of the overall display module.
- Power management and efficiency: AMOLED displays employ various power management techniques to optimize energy consumption. These include selective pixel dimming, dark mode optimization, and adaptive brightness control, which help extend battery life in mobile devices while maintaining display quality.
- Flexible and foldable display technologies: AMOLED technology enables the development of flexible and foldable displays. These displays utilize specialized materials and manufacturing processes to create bendable screens that can be folded or rolled while maintaining functionality, opening up new form factors for mobile devices.
02 Pixel structure and light emission
AMOLED displays utilize unique pixel structures and light-emitting materials to achieve vibrant colors and high contrast ratios. The pixel design often incorporates multiple sub-pixels with different color-emitting organic compounds, allowing for a wide color gamut and improved color accuracy. Advanced light-emitting layers and electrode configurations enhance overall display performance and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Touch integration and sensing
Many AMOLED displays feature integrated touch functionality, combining display and touch-sensing capabilities into a single panel. This integration can include in-cell or on-cell touch sensors, reducing overall device thickness and improving touch responsiveness. Advanced sensing technologies may also enable features such as pressure sensitivity and stylus support.Expand Specific Solutions04 Power management and efficiency
AMOLED displays incorporate various power management techniques to optimize energy consumption and extend battery life in mobile devices. These may include pixel-level power control, selective pixel illumination, and adaptive brightness algorithms. Advanced power management circuits and voltage regulation schemes help maintain display performance while minimizing power usage.Expand Specific Solutions05 Display flexibility and form factor
AMOLED technology enables the development of flexible and foldable displays, allowing for innovative device form factors. These displays incorporate specialized substrate materials, flexible encapsulation layers, and unique pixel architectures to maintain performance while bending or folding. Advanced manufacturing techniques and materials science contribute to the durability and reliability of flexible AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Display-Cloud Ecosystem
The market for extending AMOLED display functionalities using cloud technologies is in its early growth stage, with significant potential for expansion. The global AMOLED display market is projected to reach substantial size in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for high-quality displays in smartphones, TVs, and other devices. Major players like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology are investing heavily in R&D to integrate cloud technologies with AMOLED displays. These companies are at various stages of technological maturity, with Samsung and LG leading in AMOLED production, while Chinese firms like BOE and TCL CSOT are rapidly advancing their capabilities. The integration of cloud technologies is expected to enhance display performance, enable new features, and create opportunities for innovative applications across multiple industries.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed a cloud-based AMOLED display management system that enhances functionality and user experience. This system utilizes cloud technologies to enable remote control, real-time monitoring, and dynamic content delivery to AMOLED displays. BOE's solution incorporates edge computing capabilities to process data locally, reducing latency and improving response times[1]. The system also features AI-driven algorithms for automatic brightness adjustment and color calibration, optimizing display performance based on ambient conditions and user preferences[3]. Additionally, BOE has implemented a cloud-based firmware update mechanism, allowing for seamless feature upgrades and bug fixes without requiring physical access to the devices[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive cloud integration, AI-driven optimization, and remote management capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential security concerns with cloud connectivity and reliance on stable internet connections for full functionality.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has introduced a cloud-enhanced AMOLED display technology called "Huawei Cloud Screen." This solution integrates Huawei's cloud computing capabilities with AMOLED displays to offer advanced functionalities and improved user experiences. The system utilizes AI algorithms running on Huawei Cloud to dynamically optimize display parameters based on content type, ambient lighting, and user preferences[15]. Huawei's platform also includes a cloud-based eye comfort system that adjusts blue light emission and screen flicker in real-time to reduce eye strain during prolonged usage[17]. The company has developed a cloud-driven multi-screen collaboration feature that allows seamless content sharing and interaction between AMOLED displays on different devices[19]. Additionally, Huawei's solution incorporates a cloud-based security system that protects sensitive information displayed on AMOLED screens through advanced encryption and remote wipe capabilities[21].
Strengths: Strong AI-driven optimizations, innovative eye comfort features, and robust security measures. Weaknesses: Limited global reach due to geopolitical challenges and potential concerns about data sovereignty.
Core Innovations in Display-Cloud Synergy
Amoled double-side display
PatentActiveUS20200219957A1
Innovation
- An AMOLED double-sided display design featuring a substrate with alternating top-emitting and bottom-emitting OLED units, where the anode of top-emitting units is thicker and reflective, and the cathode of bottom-emitting units is thicker and light-transmissive, allowing for single IC control and eliminating mirrored images.
Active-matrix organic light-emitting diode (AMOLED) display module
PatentActiveUS11257882B2
Innovation
- A second conductive layer is uniformly arranged across the AMOLED display panel to ensure consistent common ground voltage distribution to the cathode, maintaining a uniform voltage difference across each OLED element, thereby enhancing luminance uniformity.
Data Security in Cloud-Connected Displays
Cloud-connected displays, particularly AMOLED screens integrated with cloud technologies, present significant data security challenges. As these displays become more sophisticated and interconnected, the volume and sensitivity of data transmitted between devices and cloud servers increase exponentially. This necessitates robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential exploitation of vulnerabilities.
One primary concern is the protection of user data during transmission. Cloud-connected displays often handle sensitive information, including personal user preferences, viewing habits, and potentially biometric data for authentication purposes. Implementing end-to-end encryption protocols, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) or its successor, is crucial to safeguard data in transit. Additionally, secure key management systems must be employed to ensure the integrity of encryption processes.
Another critical aspect is the security of data stored in the cloud. Cloud servers hosting display-related data must adhere to stringent security standards, including regular security audits, access controls, and data isolation techniques. Implementing multi-factor authentication for cloud access and employing advanced intrusion detection systems can significantly enhance the overall security posture.
The potential for man-in-the-middle attacks is a notable concern in cloud-connected display systems. Attackers could potentially intercept and manipulate data flowing between the display and cloud servers, compromising the integrity of the displayed content or extracting sensitive information. To mitigate this risk, implementing certificate pinning and secure device authentication mechanisms is essential.
Privacy considerations also play a crucial role in data security for cloud-connected displays. Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, is paramount. This includes implementing robust data anonymization techniques, providing transparent user consent mechanisms, and establishing clear data retention and deletion policies.
As cloud-connected displays evolve to incorporate more advanced features, such as AI-driven content recommendations or augmented reality overlays, the complexity of data security challenges increases. Developing secure APIs and implementing strict access controls for third-party integrations becomes critical to maintaining the overall integrity of the system.
In conclusion, addressing data security in cloud-connected displays requires a multi-faceted approach, combining encryption, secure storage practices, robust authentication mechanisms, and adherence to privacy regulations. As the technology continues to advance, ongoing research and development in security protocols specific to cloud-connected display systems will be essential to stay ahead of emerging threats and ensure user trust in these innovative technologies.
One primary concern is the protection of user data during transmission. Cloud-connected displays often handle sensitive information, including personal user preferences, viewing habits, and potentially biometric data for authentication purposes. Implementing end-to-end encryption protocols, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) or its successor, is crucial to safeguard data in transit. Additionally, secure key management systems must be employed to ensure the integrity of encryption processes.
Another critical aspect is the security of data stored in the cloud. Cloud servers hosting display-related data must adhere to stringent security standards, including regular security audits, access controls, and data isolation techniques. Implementing multi-factor authentication for cloud access and employing advanced intrusion detection systems can significantly enhance the overall security posture.
The potential for man-in-the-middle attacks is a notable concern in cloud-connected display systems. Attackers could potentially intercept and manipulate data flowing between the display and cloud servers, compromising the integrity of the displayed content or extracting sensitive information. To mitigate this risk, implementing certificate pinning and secure device authentication mechanisms is essential.
Privacy considerations also play a crucial role in data security for cloud-connected displays. Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, is paramount. This includes implementing robust data anonymization techniques, providing transparent user consent mechanisms, and establishing clear data retention and deletion policies.
As cloud-connected displays evolve to incorporate more advanced features, such as AI-driven content recommendations or augmented reality overlays, the complexity of data security challenges increases. Developing secure APIs and implementing strict access controls for third-party integrations becomes critical to maintaining the overall integrity of the system.
In conclusion, addressing data security in cloud-connected displays requires a multi-faceted approach, combining encryption, secure storage practices, robust authentication mechanisms, and adherence to privacy regulations. As the technology continues to advance, ongoing research and development in security protocols specific to cloud-connected display systems will be essential to stay ahead of emerging threats and ensure user trust in these innovative technologies.
Energy Efficiency of Cloud-Enhanced AMOLEDs
Cloud-enhanced AMOLED displays represent a significant advancement in energy efficiency for mobile devices. By leveraging cloud technologies, these displays can offload certain computational tasks, reducing the processing burden on local hardware and consequently lowering power consumption. This approach allows for more complex visual rendering and data processing to occur in the cloud, with only the final output being transmitted to the device's display.
The energy efficiency gains of cloud-enhanced AMOLEDs are multifaceted. Firstly, by utilizing cloud computing resources for intensive graphical calculations, the device's GPU and CPU can operate at lower clock speeds or even enter idle states more frequently. This directly translates to reduced power draw from these components, which are typically among the most energy-hungry in a mobile device.
Furthermore, cloud enhancement enables more sophisticated power management strategies. For instance, the cloud can analyze user behavior patterns and predict display content, allowing for preemptive adjustments to AMOLED pixel illumination. This predictive capability can lead to more efficient use of the display's self-emitting pixels, potentially reducing overall energy consumption without compromising visual quality.
Another aspect of energy efficiency lies in the optimization of data transmission. Cloud-enhanced AMOLEDs can employ advanced compression algorithms and selective rendering techniques, ensuring that only essential visual data is sent to the device. This minimizes the energy expended on data transfer and decompression, which can be significant in wireless environments.
Moreover, the cloud infrastructure can dynamically adjust the complexity of rendered content based on the device's current battery level or power state. This adaptive approach ensures that energy consumption is optimized in real-time, extending battery life while maintaining an acceptable level of visual fidelity.
The integration of cloud technologies also opens up possibilities for collaborative energy management across multiple devices. In scenarios where multiple cloud-enhanced AMOLEDs are in use within proximity, the cloud can orchestrate display content and processing tasks to minimize redundant computations and maximize overall energy efficiency across the device ecosystem.
The energy efficiency gains of cloud-enhanced AMOLEDs are multifaceted. Firstly, by utilizing cloud computing resources for intensive graphical calculations, the device's GPU and CPU can operate at lower clock speeds or even enter idle states more frequently. This directly translates to reduced power draw from these components, which are typically among the most energy-hungry in a mobile device.
Furthermore, cloud enhancement enables more sophisticated power management strategies. For instance, the cloud can analyze user behavior patterns and predict display content, allowing for preemptive adjustments to AMOLED pixel illumination. This predictive capability can lead to more efficient use of the display's self-emitting pixels, potentially reducing overall energy consumption without compromising visual quality.
Another aspect of energy efficiency lies in the optimization of data transmission. Cloud-enhanced AMOLEDs can employ advanced compression algorithms and selective rendering techniques, ensuring that only essential visual data is sent to the device. This minimizes the energy expended on data transfer and decompression, which can be significant in wireless environments.
Moreover, the cloud infrastructure can dynamically adjust the complexity of rendered content based on the device's current battery level or power state. This adaptive approach ensures that energy consumption is optimized in real-time, extending battery life while maintaining an acceptable level of visual fidelity.
The integration of cloud technologies also opens up possibilities for collaborative energy management across multiple devices. In scenarios where multiple cloud-enhanced AMOLEDs are in use within proximity, the cloud can orchestrate display content and processing tasks to minimize redundant computations and maximize overall energy efficiency across the device ecosystem.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!