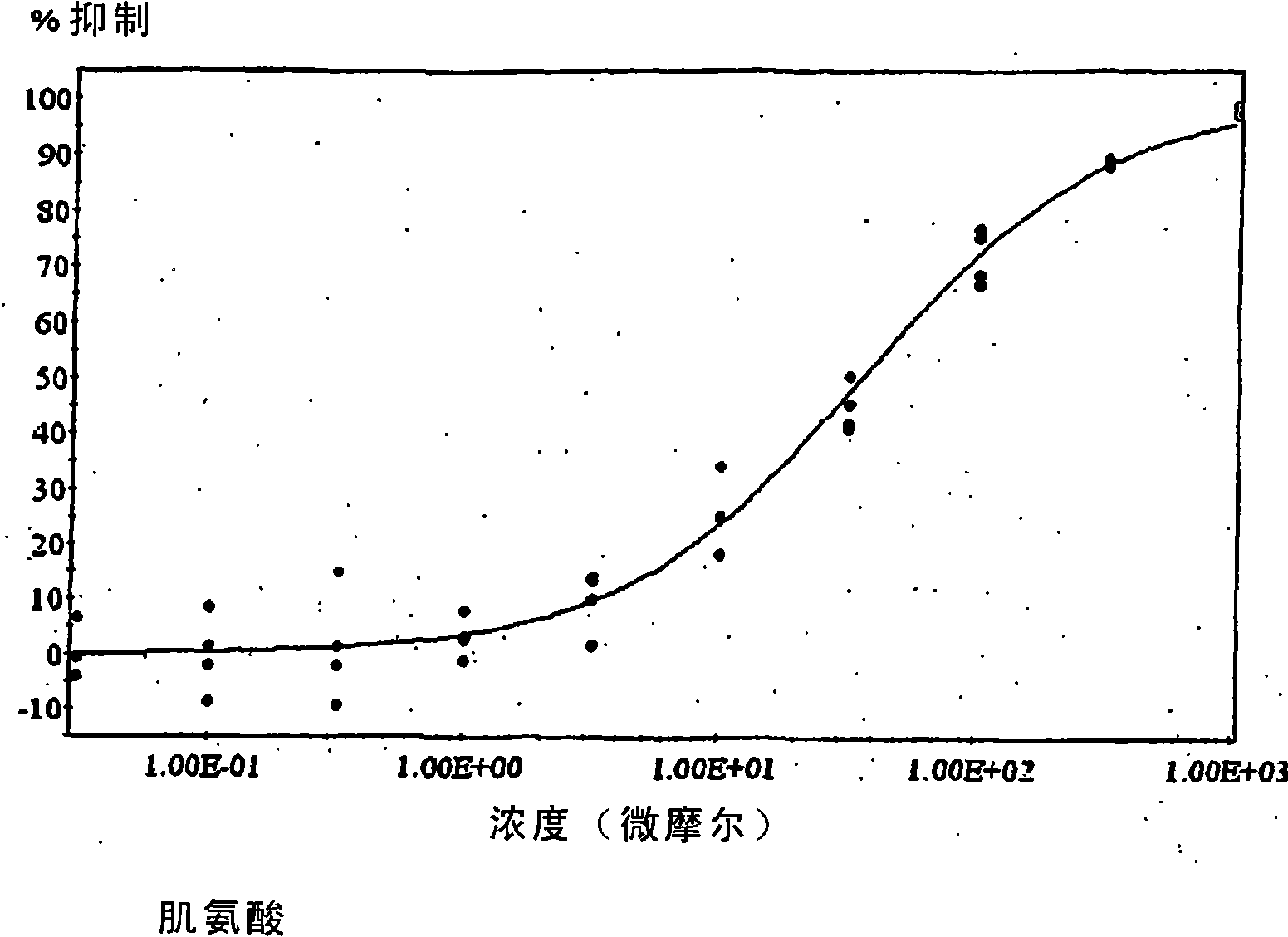
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
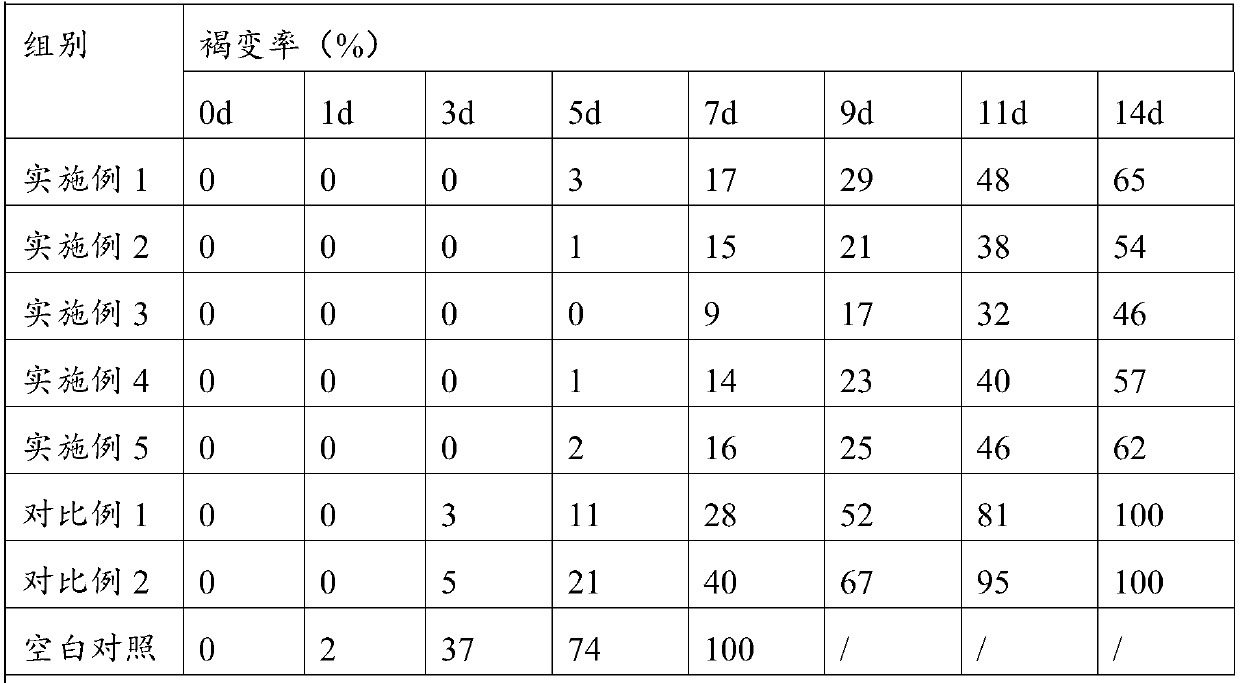
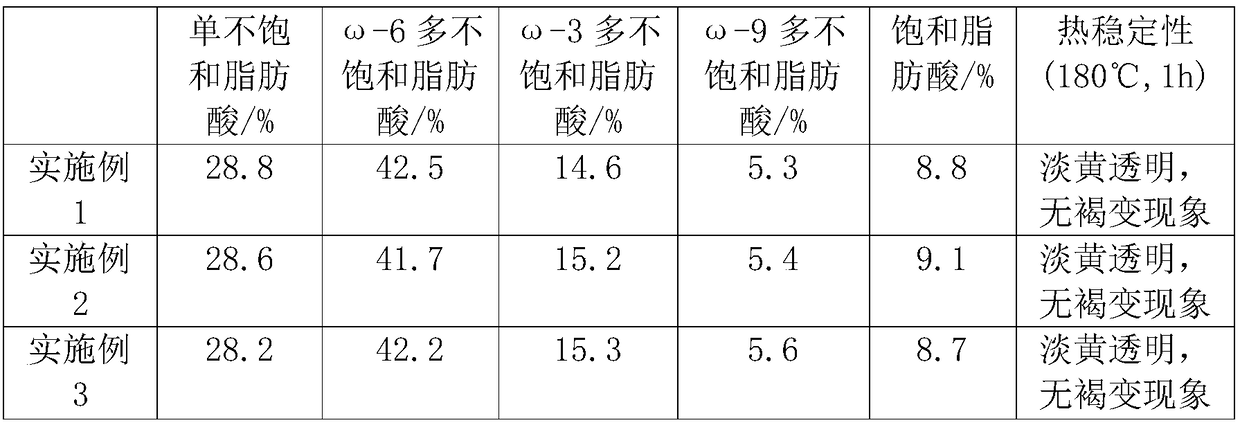
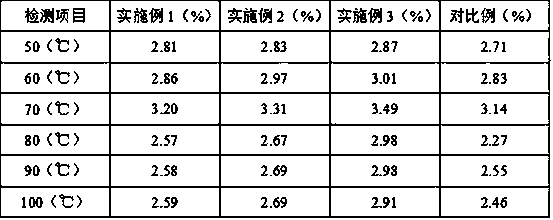
58 results about "Carnosol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
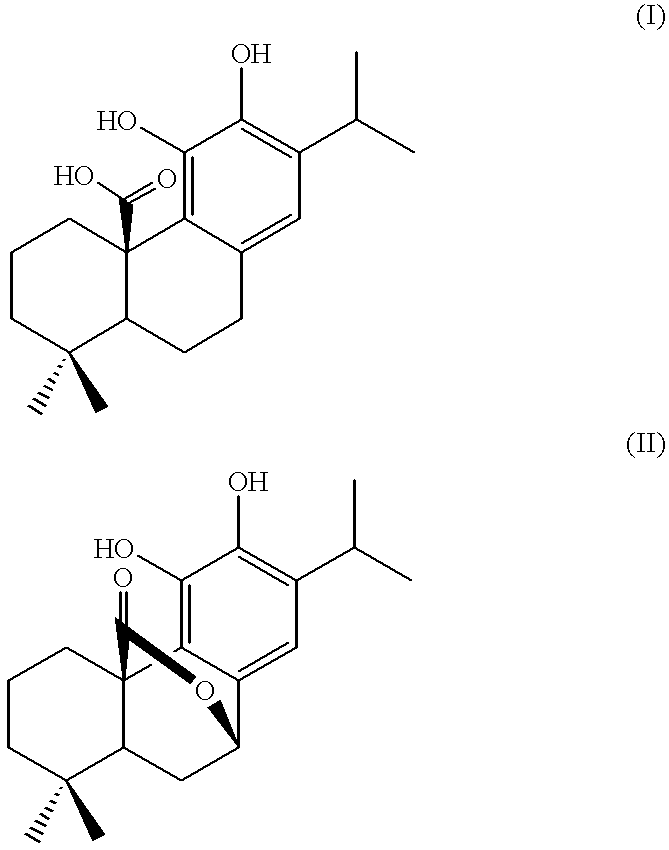
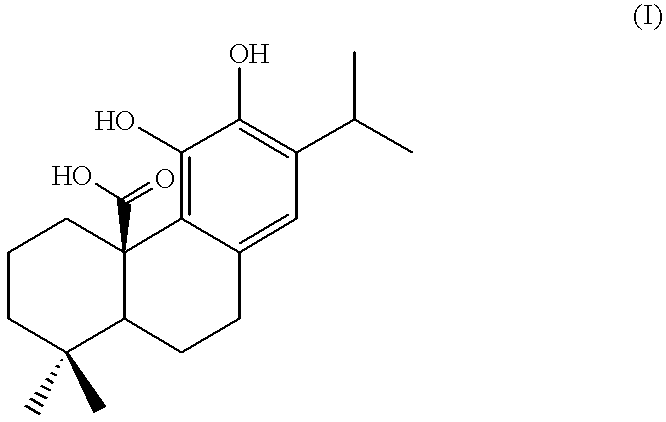
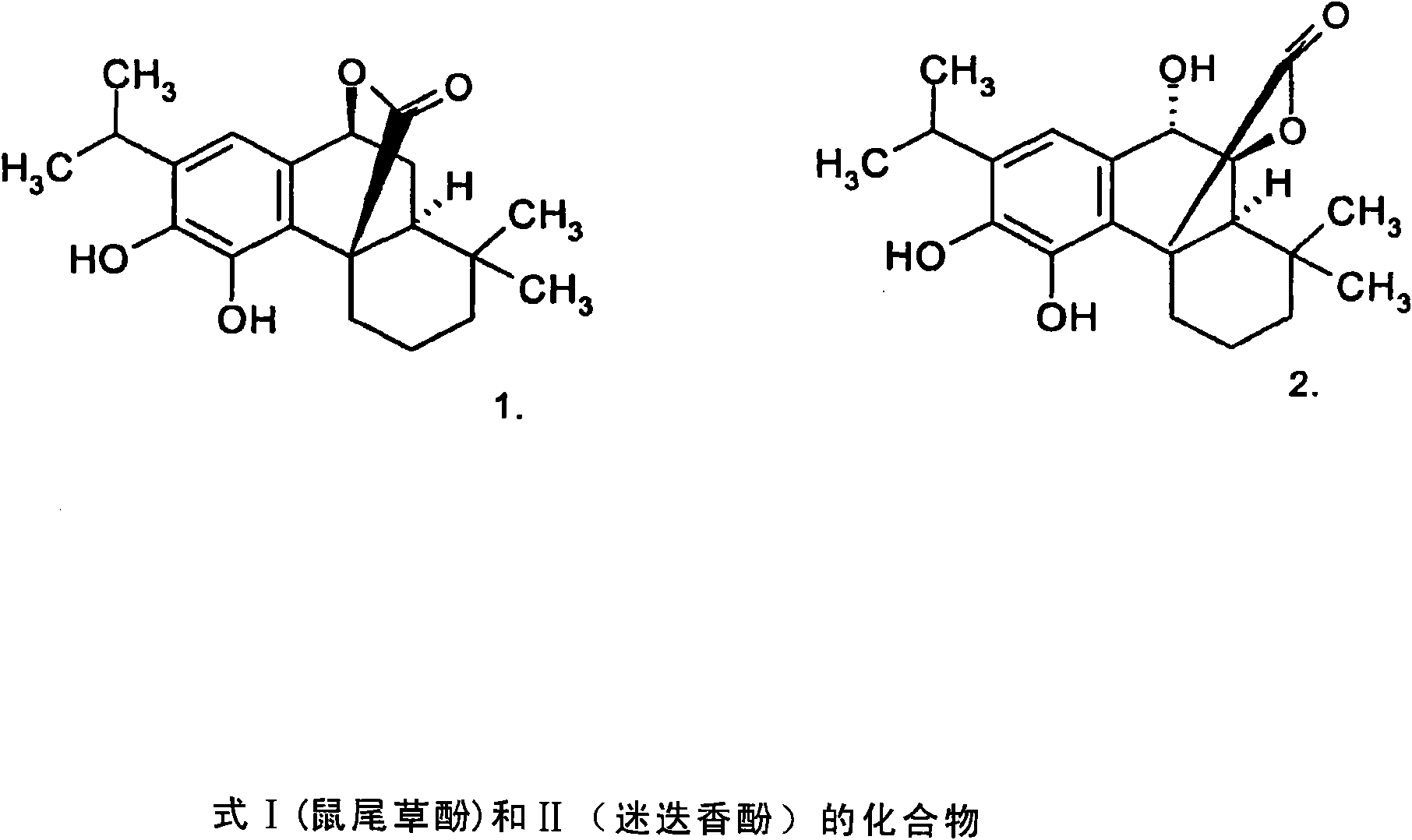
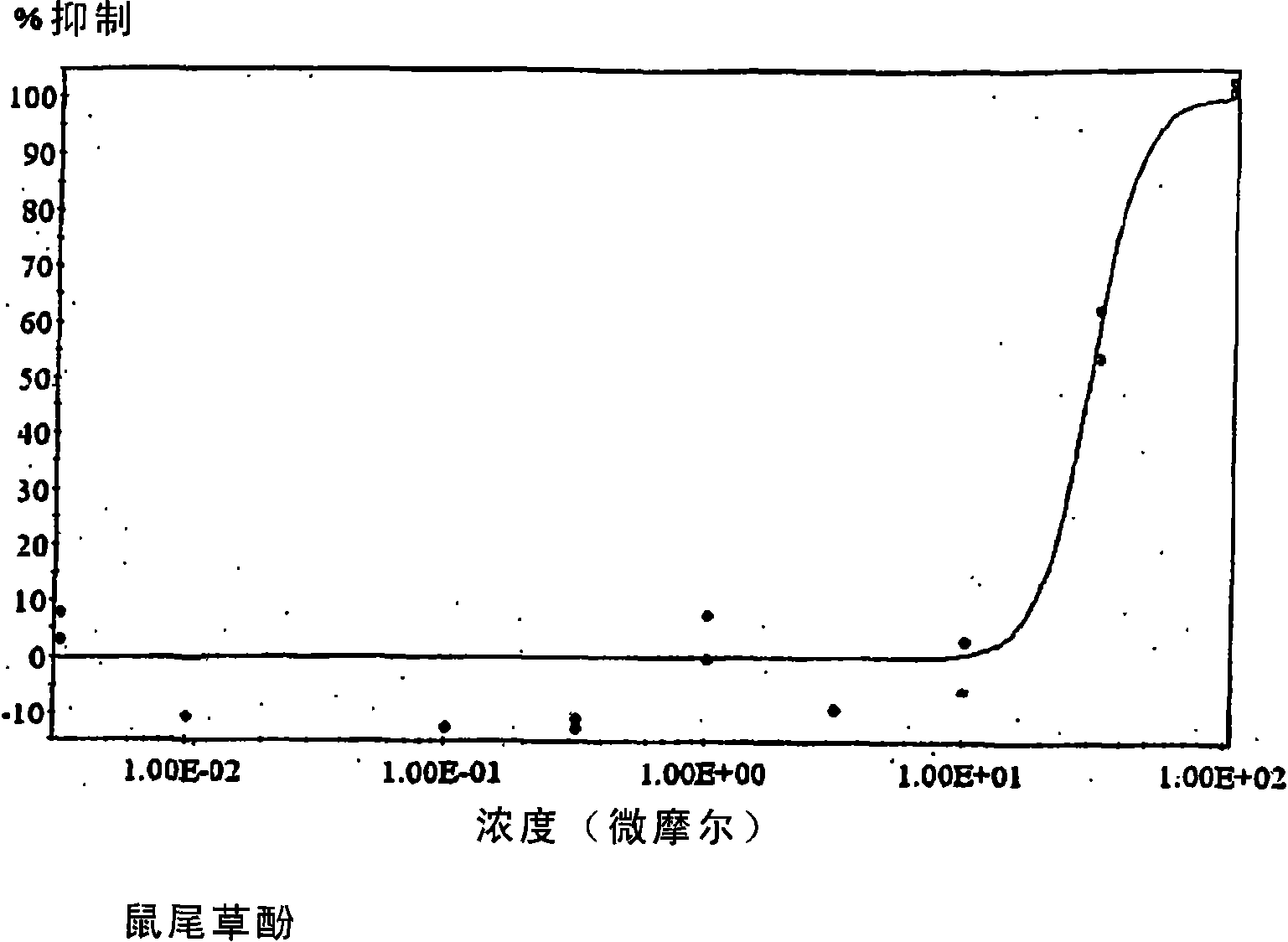
Carnosol is a phenolic diterpene found in the herbs rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) and Mountain desert sage (Salvia pachyphylla). It has been studied in-vitro for anti-cancer effects in various cancer cell types.
Method for preventing off-flavor development and preserving seasoning flavor in irradiated meat and meat products
InactiveUS6099879ASlow onsetReduce developmentMilk preparationDough treatmentAdditive ingredientFood flavor
A method comprising the step of treating meat and meat products, including fish, poultry, fish products, and poultry products, with a stabilizing amount of rosemary extract or rosemary extract in combination singly or collectively with tocopherols, ascorbic acid, citric acid, or sodium tripolyphosphate, prior to exposure of the meat or meat products to ionizing radiation, enhances the flavor and shelf life thereof. In addition, the active antioxidant ingredients of rosemary extract may be used individually or collectively as a replacement for rosemary extract, these being carnosic acid, carnosol, and rosmarinic acid, which have been found equivalent to or superior to rosemary extract itself for purposes of the present invention when used in the concentrations set forth herein.
Owner:KALAMAZOO HLDG INC
Rosmarinus officinalis extract and its preparing process and application
InactiveCN101040901AEffective quality controlEasy to operateAntinoxious agentsBlood disorderDiseaseUrsolic acid
The invention relates to a Rosmarinus officinalis extract, its preparing process and use, wherein the active constituents of the extract include carnosic acid 15-40%, carnosol 5-12% and ursolic acid 14-35%. The preparing process comprises drying the Rosmarinus officinalisl medicinal material in shade, cutting into chunks, charging solvent for extracting, cooling down the merged filtrate and filtrating, decolorizing with activated charcoal, drying and disintegrating. The extract can be used for preparing medicament for treating ischemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:YUNNAN LONGRUN PHARMA
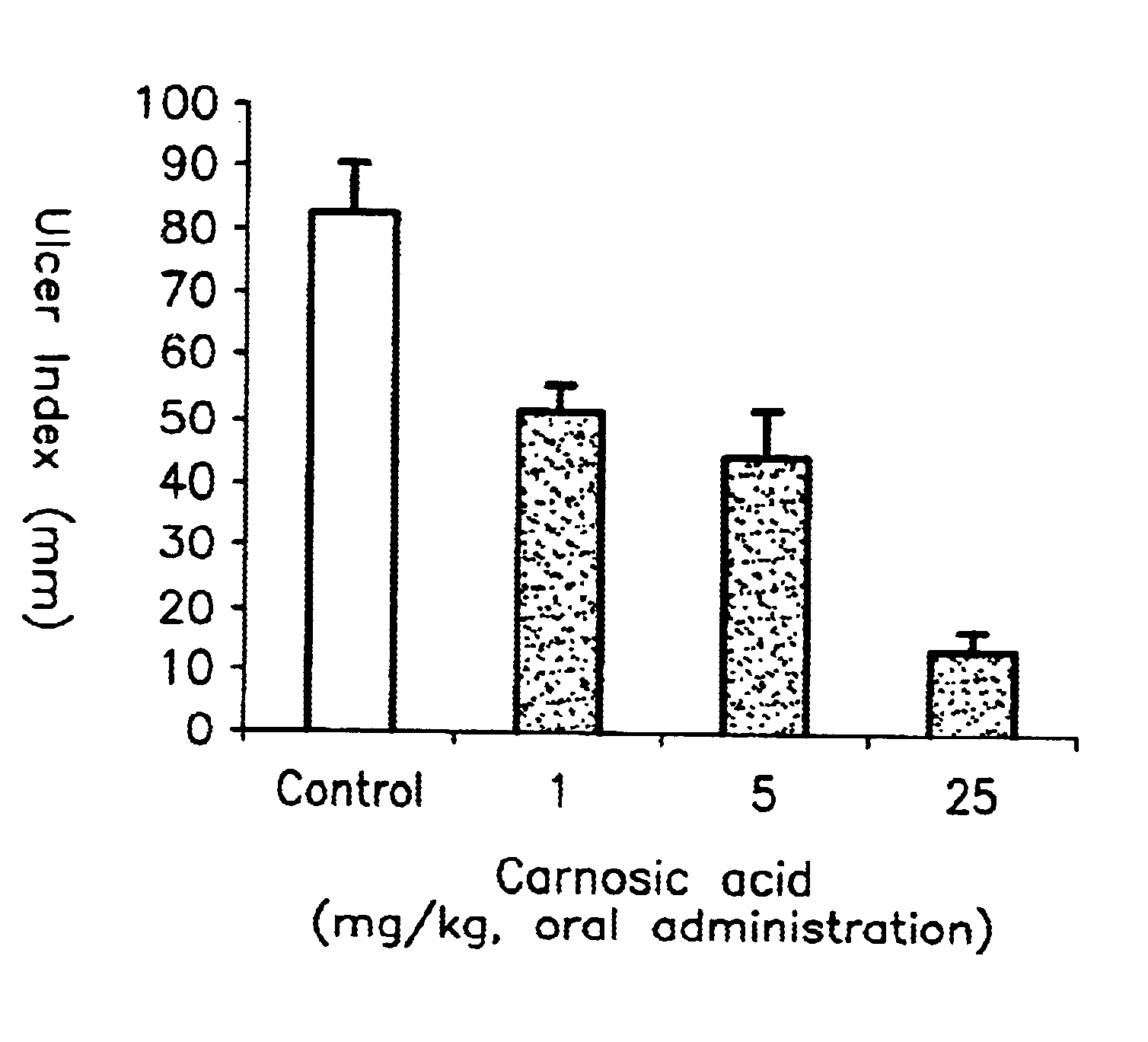
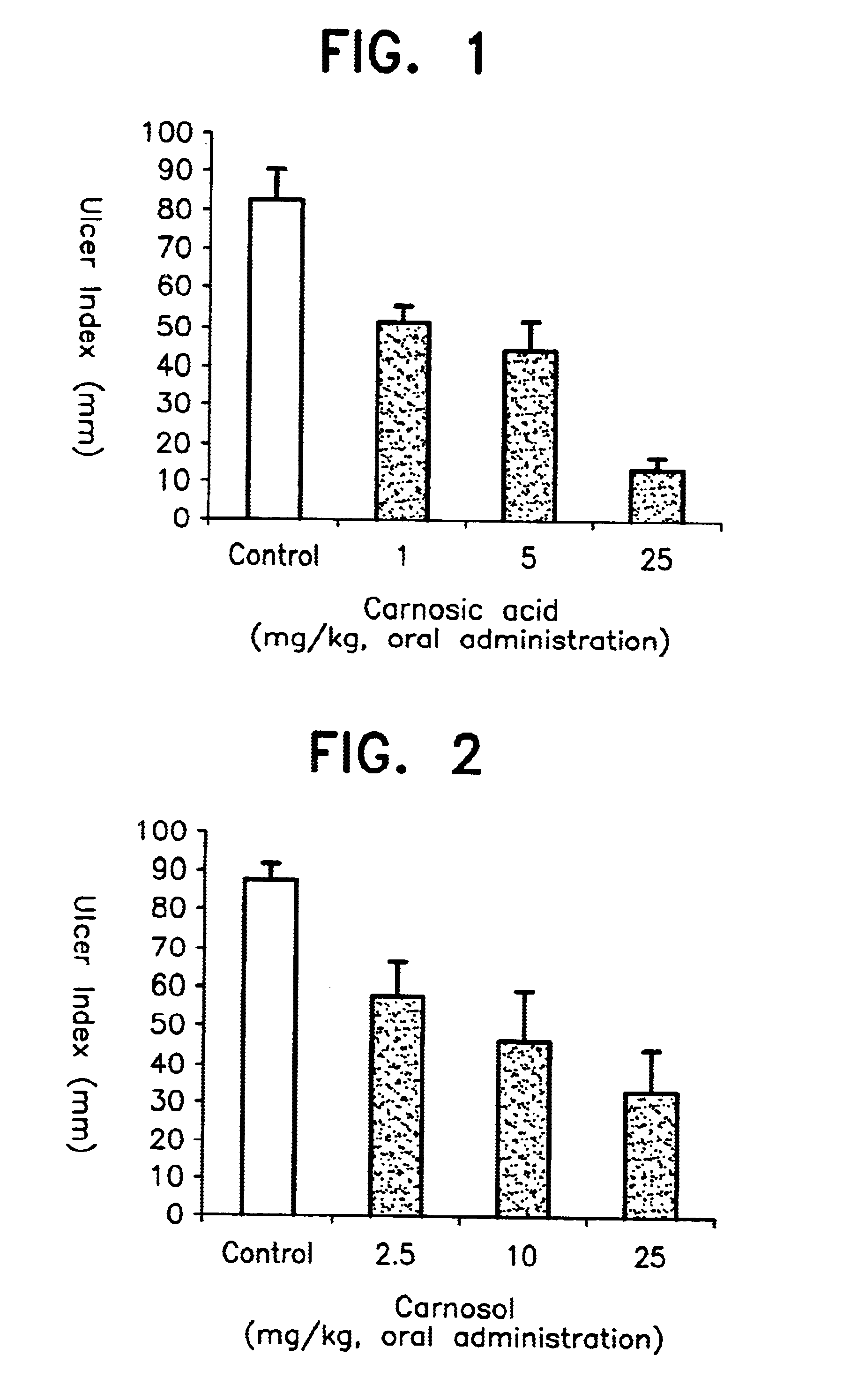
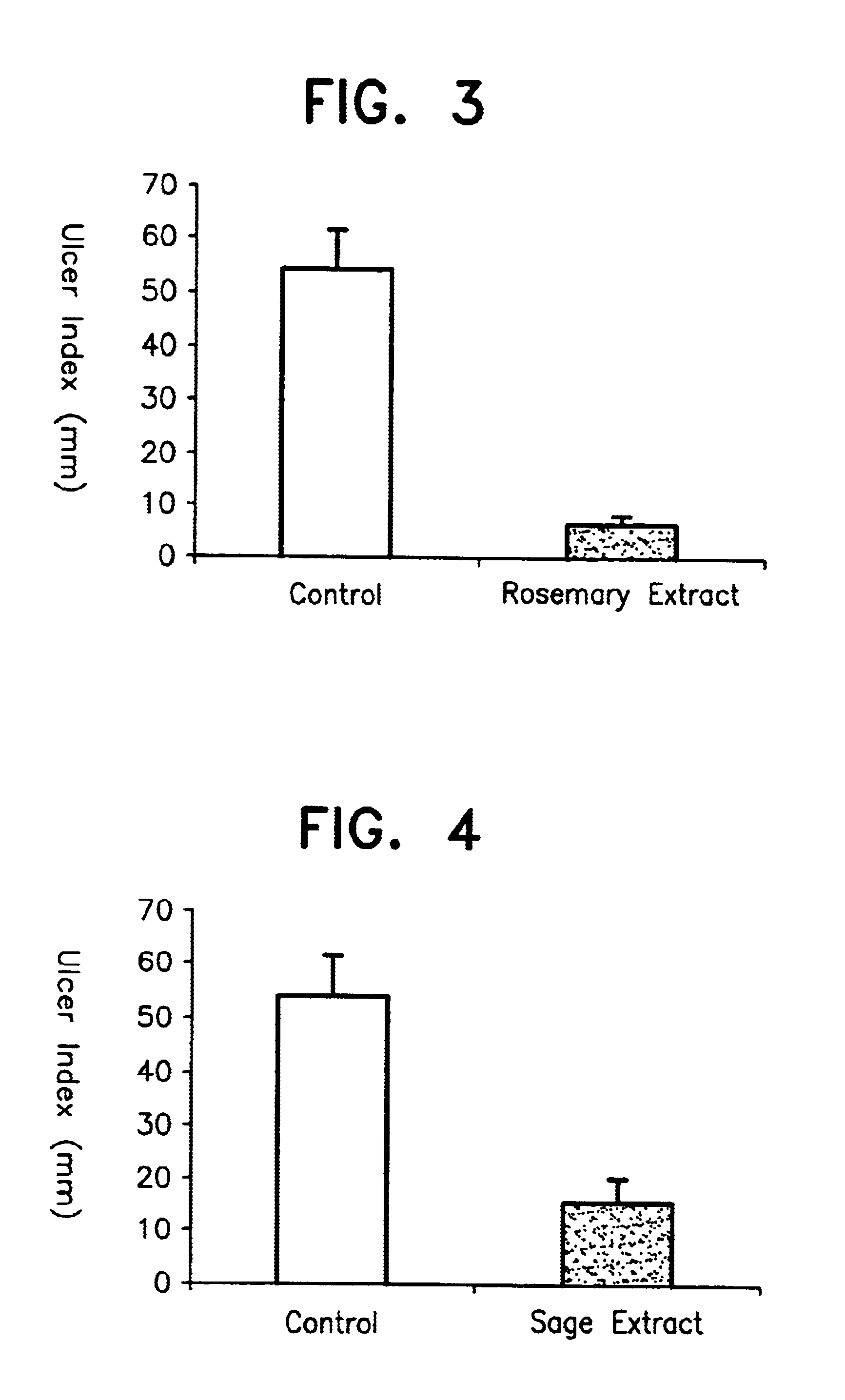
Method of treating ulcers
A method of treating ulcers comprising administering an effective amount of carnosic acid and / or carnosol or a plant extract containing carnosic acid and / or carnosol as an effective ingredient to a subject having such ulcers.
Owner:NAGASE & COMPANY
Composite edible fresh water gel for fruits with high respiration intensity and equipment thereof
InactiveCN109645111AControl changes in total acidityReduce fruit rot rateFruits/vegetable preservation by coatingVitamin CBetaine
The invention provides a fruit fresh keeping agent. The fruit fresh keeping agent is prepared from fresh keepingcompounds, latic acid, chitosan, carnosol or rosmanol, a colloid film former, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, aloe gel powder, cinnamic acid, citric acid, glycerin and the like, wherein the fresh keeping compounds comprise glycine betaine, resveratrol, vitamin C, bacterium resistant plantflavone and the like. The fruit fresh keeping agent forms an inner-outer double-layer water gel during use, the inner-layer water gel includes antioxidation antibacteria fresh keeping components, andthe outer-layer water gel isolates air from the inner-layer water gel. Combination of the inner-layer water gel and the outer-layer water gel has double effects on fruits and effectively prolongs thestorage period of the fruits.
Owner:山东祥维斯生物科技股份有限公司
Production technology for acquiring two antioxidant agents from Rosmarinus officinalis L.
InactiveCN102199092AReduce conversionPromote dissolutionCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationBulk chemical productionCarnosolCounter current
The invention discloses a production technology employing a ultrasonic countercurrent extraction process and a membrane separation (molecular sieve) process to acquire two antioxidants from Rosmarinus officinalis L. The production technology comprises adding 30 to 85% of edible alcohol into fresh rosemary branches and leaves, carrying out a ultrasonic counter current extraction process for a mixture of the edible alcohol and the fresh rosemary branches and leaves to obtain an extracted liquid with a solid-to-liquid ratio of from 1:10 to 1:30, and carrying out a membrane separation (molecular sieve) process to separate two antioxidant agents consisting of a rosemary fat-soluble antioxidant agent (comprising carnosic acid as a representative) and a rosemary water-soluble antioxidant agent (comprising rosmarinic acid as a representative) from the extracted liquid, wherein a heating time of the extracted liquid can be reduced through the membrane separation (molecular sieve) process thus a conversion ratio of rosmarinic acid to carnosol is reduced. A content of carnosic acid in the rosemary fat-soluble antioxidant agent is increased through a CO2 supercritical extraction process. The rosemary water-soluble antioxidant agent (comprising rosmarinic acid as a representative) is separated from a liquid obtained through a concentration process under reduced pressure and a solid-liquid separation process, and a content of rosmarinic acid in the rosemary water-soluble antioxidant agent is increased through recrystallization from ethanol. The production technology has the advantages of simple processes, low energy consumption, high production efficiency, production safety, and no harmful residual solvent due to single edible alcohol usage during all production processes.
Owner:YUZHOU SENYUAN BENCAO NATURAL PRODS
Total diterpene phenol originated from rosemary, its preparation method and use
ActiveCN1698587ARelieve myocardial ischemiaAlleviate Chest PainOrganic chemistryHydroxy compound active ingredientsAdditive ingredientPhenol
The invention relates to the effective parts of rosemary, its preparation method and use, wherein the effective parts of the Rosmarinus officinalisl are diterpenoids phenols extracted from medicinal material of Rosmarinus officinalisl, the content of the phenols is over 45%, and the sum of the content of the carnosol and carnosic acid as the principal ingredients is over 13%. The preparing process comprises curing the Rosmarinus officinalisl medicinal material and cutting it into chunks, charging raffinate for extraction, cooling down the merged extract and filtrating, decolorizing with activated charcoal, concentrating the filtrate and charging in water, filtering, drying and disintegrating the filtering deposit. The effective parts of the Rosmarinus officinalisl can be used for preparing medicament for preventing and treating cardiovascular diseases, epigastric pain, uterocarcinoma, cervical carcinoma, intestinal cancer and breast cancer.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIYUSN HUTCHISON WHAMPOA CHINESE MEDICINE
Edible lollipop packaging film
InactiveCN105254926AExtended shelf lifeGood for stomach and digestionFlexible coversWrappersBiotechnologyCyclodextrin
The invention discloses an edible lollipop packaging film and relates to the technical field of packaging materials. The edible lollipop packaging film is prepared from raw materials in parts by weight as follows: 90-100 parts of plant starch, 25-30 parts of microcrystalline cellulose, 15-20 parts of cyclodextrin, 15-20 parts of dried skim milk, 13-16 parts of fish bone meal, 10-15 parts of silk fibroin protein, 10-15 parts of Chinese herb extracts, 8-12 parts of fenugreek gum, 8-12 parts of mannitol, 6-10 parts of carnosol, 6-10 parts of potassium sorbate, 5-8 parts of sodium trimetaphosphate, 12-15 parts of palm oil, 35-40 parts of ethanol and 200-300 parts of water. The prepared packaging film is non-toxic and harmless and can be eaten together with a lollipop, the added Chinese herb extracts have the functions of invigorating stomach, helping digestion, resisting oxidation and preventing corrosion, the edible value is improved, and the guarantee period of the lollipop is prolonged.
Owner:界首市佳宝包装材料有限公司
Preparation method of high-purity carnosol
The invention relates to a preparation method of a natural active compound. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: 1, extracting a dry carnosol-containing raw material per kilogram by the use of 3-10 liters of a lipophilic organic solvent for 2-5 times, merging extracts, and condensing to obtain a carnosol-containing extract or solid; 2, dissolving by the use of a 10-90% hydrophilic organic solvent, filtering and precipitating, and carrying out macroreticular resin refining processing on a filtrate to obtain a carnosol-containing precipitate; 3, dissolving the precipitate by the use of a mixed lipophilic organic solvent, standing, precipitating a precipitate; and filtering the precipitate to obtain a carnosol crude product; and 4, crystallizing by the use of a hydrophilic organic solvent so as to obtain high-purity carnosol crystals with the HPLC detection content being more than 95%. The preparation method provided by the invention has advantages of simple operation process and controllable cost, and is suitable for large-scale preparation and production of high-purity carnosol.
Owner:高政 +1
Method of promoting synthesis of nerve growth factor
Owner:NAGASE BEAUTYCARE CO LTD
Preparation method of rosemary extracts
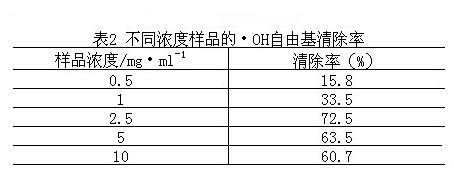
The invention discloses a preparation method of rosemary extracts. According to the method, plant rosemary are used as raw materials, and the rosemary extracts are prepared under certain process conditions. The extracts comprise various antioxidant ingredients including carnosic acid, carnosol, rosmanol, ursolic acid, rosmarinic acid and the like according to certain proportion, the antioxidant activity of the rosemary extracts is measured by an iodine quantity colorimetric method, the.OH free radical clearing activity of the extracts is researched through the electron paramagnetic resonance technology, and the obvious antioxidant effect is discovered. The invention also discloses the rosemary extracts prepared by using the method and an application of the rosemary extracts in the preparation of food additive antioxidants.
Owner:CHANGSHA YAYING BIO TECH
Anti-Degradation Agent
InactiveUS20080044540A1Improve securityImprove heat resistanceBiocideCosmetic preparationsAnti-degradantHeat resistance
There is provided an anti-degradation agent capable of exhibiting an excellent deterioration-inhibiting property for foods, cosmetics, etc., showing a good effect even when added in a small amount, having a high heat resistance, and being free from adverse influence due to light. There are provided (1) an anti-degradation agent comprising a water-insoluble antioxidant, a water-soluble antioxidant and an emulsifying agent; and (2) an anti-degradation agent comprising a water-soluble antioxidant, and carnosol and / or carnosic acid wherein a total content of the carnosol and the carnosic acid is not less than 4% by weight.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Preparation method of antioxidant plant insulating oil
InactiveCN110205182AExtended use timeIncrease profitLiquid organic insulatorsLubricant compositionLipid formationSilica nanoparticles
The invention relates to a preparation method of antioxidant plant insulating oil and belongs to the technical field of insulating oil. The antioxidant plant insulating oil is prepared by adding beta-cyclodextrin embedded sage essential oil microcapsules, sage essential oil contains diterpenoid compounds such as carnosic acid and carnosol which can effectively remove oxygen ions, protect the plantinsulating oil from damage and inhibit the peroxidation effect of lipid at the same time, and an aqueous or alcohol extract of plant sage leaves is an effective antioxidant and an effective free radical scavenger. The antioxidant plant insulating oil is prepared by adding lipophilic silica nanoparticles, and the silica nanoparticles can absorb active oxygen generated during aging of the plant insulating oil, effectively inhibit the oxidation process of plant insulating oil ester molecules, improve the oxidation resistance of the plant insulating oil and the ability to adsorb the active oxygenand effectively adsorb the beta-cyclodextrin embedded sage essential oil microcapsules to avoid the phenomenon of agglomeration of the microcapsules.
Owner:陈霞
Natural food preservative
InactiveCN104770825ABroad antibacterial spectrumEasy to useClimate change adaptationFood preservationNatural foodNisin
The invention relates to a natural food preservative which is composed of, by weight, 5-40 parts of vinegar, 10-15 parts of carnosol, 10-15 parts of rosmanol, 1-1.5 parts of nisin, 1-3 parts of licoflavone, 1-10 parts of sodium citrate, 0.1-0.5 part of tea polyphenol and the balance water. The food preservative aims to be low in production cost and ideal in effect.
Owner:赵志坚
Application of carnosol as inhibitor of inflammasomes
InactiveCN110227075AIncreased mortalityReduced liver fibrosis in miceAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAutoimmune diseaseDrug
Owner:THE FIFTH MEDICAL CENT OF CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL
Edible oil and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses edible oil and a preparation process thereof. The edible oil is prepared from, by weight, 50-60 parts of peanut oil, 30-40 parts of soybean oil, 16-20 parts of camellia-seed oil, 11-15 parts of walnut oil, 10-12 parts of grape seed oil, 8-10 parts of Argan oil, 6-8 parts of cannabis oil, 5-7 parts of rice bran oil, 10-14 parts of mutton fat and 0.1-0.3 part of grease improver; the grease improver is prepared from, by weight, 23-49% of glucose oxidase, 20-30% of phosphatidyl ethanolamine, 9-15% of nano-selenium, 2-3% of vitamin E, 1-2% of tea polyphenol, 5-7% of lycopene, 4-6% of carnosol, 2-4% of chlorogenic acid and 8-10% of phytic acid. The preparation process of the edible oil comprises the steps of preparation of the grease improver, preparation of compound grease and preparation of the edible oil. The edible oil and the preparation process thereof have the advantages that by moderately increasing the proportion of saturated fatty acid in the edible oil, thefatty acid structure is improved, the grease improver is utilized to prevent the occurrence of browning reaction, the content of dissolved oxygen is reduced, and the heat stability and inoxidizability of the edible oil are improved.
Owner:凤台县兴永食用油有限责任公司
Preparation method of salvia extract
InactiveCN107684577AEffective protectionAvoid damagePlant ingredientsSalvia miltiorrhizaSalvia extract
The invention belongs to the field of natural medicines of traditional Chinese medicines, and particularly relates to a preparation method of salvia extract. The preparation method of salvia extract includes steps of damaging the salvia itself through ball-milling during the salvia extracting process; extracting the salvia by means of supercritical carbon dioxide; during the extracting process, adding carnosol and making it fully contact with extract; combining phenolic group of carnosol with danshinolic acid B hydroxyl under the high pressure state, and protecting the danshinolic acid B; thencarrying out the further extraction by enzyme and ultrasound wave so as to obtain sufficient salvia extract; reducing the salvia extract by lithium aluminium hydride to replace danshinolic acid B; removing danshinolic acid B and effectively protecting the danshinolic acid B. The preparation process is gentle in condition, high in extracting efficiency, and small in extractive damage.
Owner:蒋春霞
Efficient litchi fresh keeping agent and preparation and using methods thereof
InactiveCN106578015ANo pollution in the processImprove freshnessFruit and vegetables preservationPropolisNatural food
The invention discloses an efficient litchi fresh keeping agent and preparation and using methods thereof, and belongs to the technical field of food fresh keeping. The litchi fresh keeping agent is prepared from, by weight, 20-40 parts of herb of rosemary, 20-30 parts of fructus forsythiae, 15-35 parts of herb of salvia officinalis, 18-28 parts of licorice roots, 11-21 parts of orange peel, 8-18 parts of propolis and 1-5 parts of chitosan. The litchi fresh keeping agent is simple in preparation method, efficient, safe and low in cost, contains rosmanol, carnosol and flavonoid substances, is an efficient natural food fresh keeping agent, has a very good fresh keeping effect and is worthy of application and popularization.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Dietary and pharmaceutical compositions containing carnosol and/or rosmanol and their uses
The present invention refers to carnosol and rosmanol for use (as medicament) in the treatment of a disorder connected to impaired neurotransmission, as well as to dietary and pharmaceutical composition and their uses.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV +1
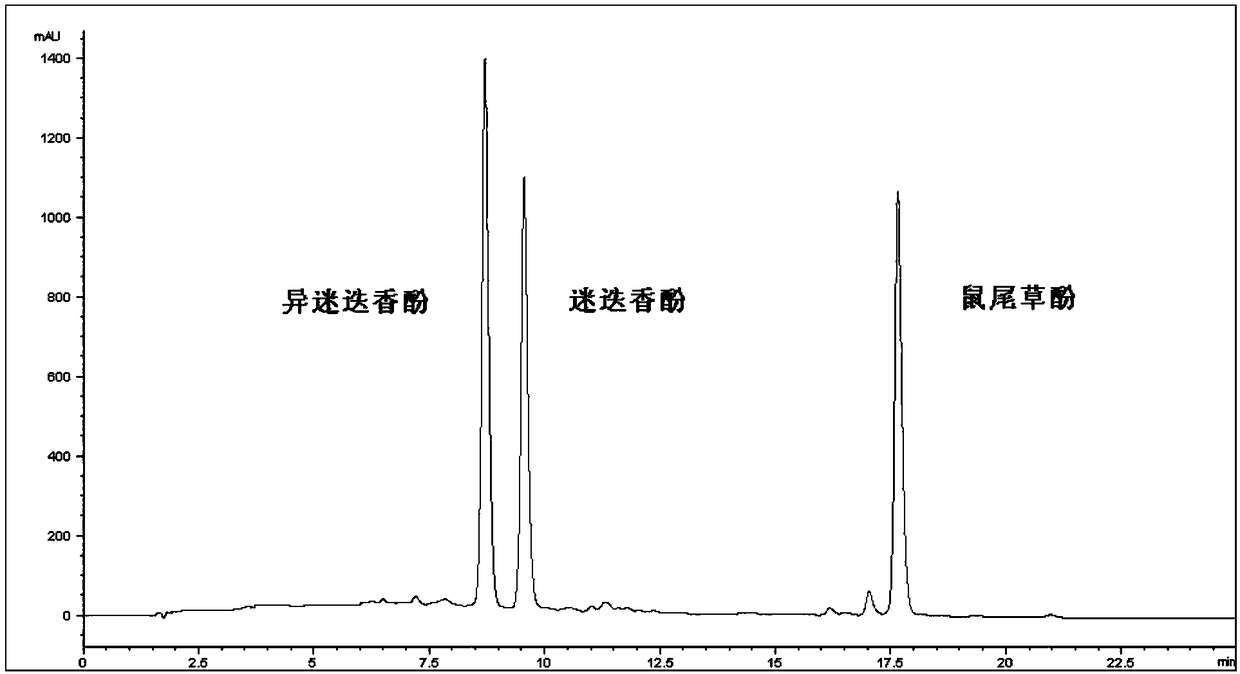
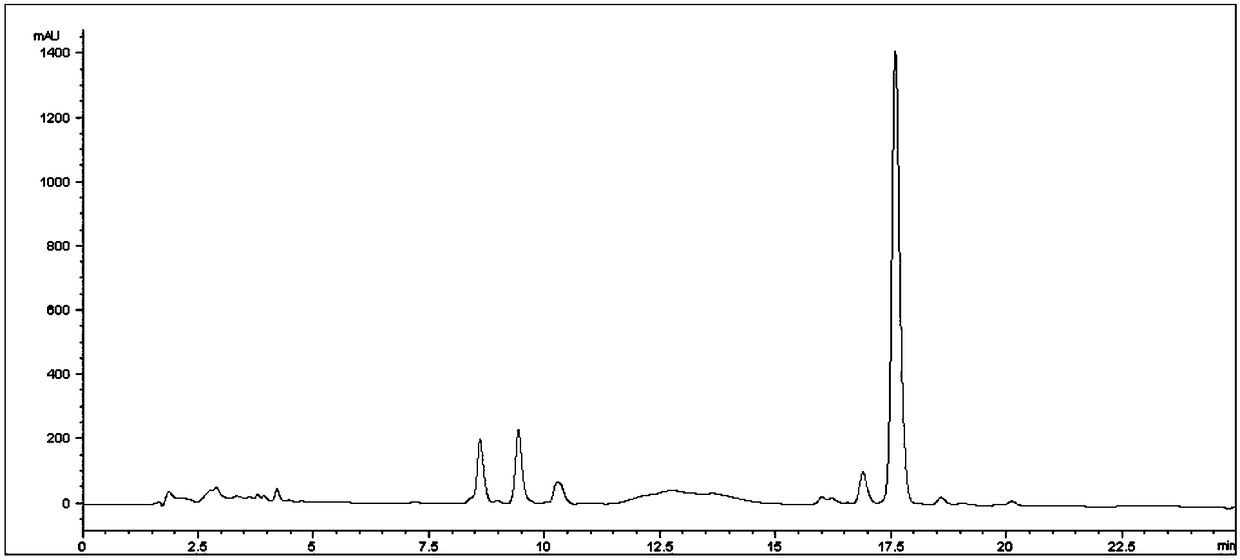
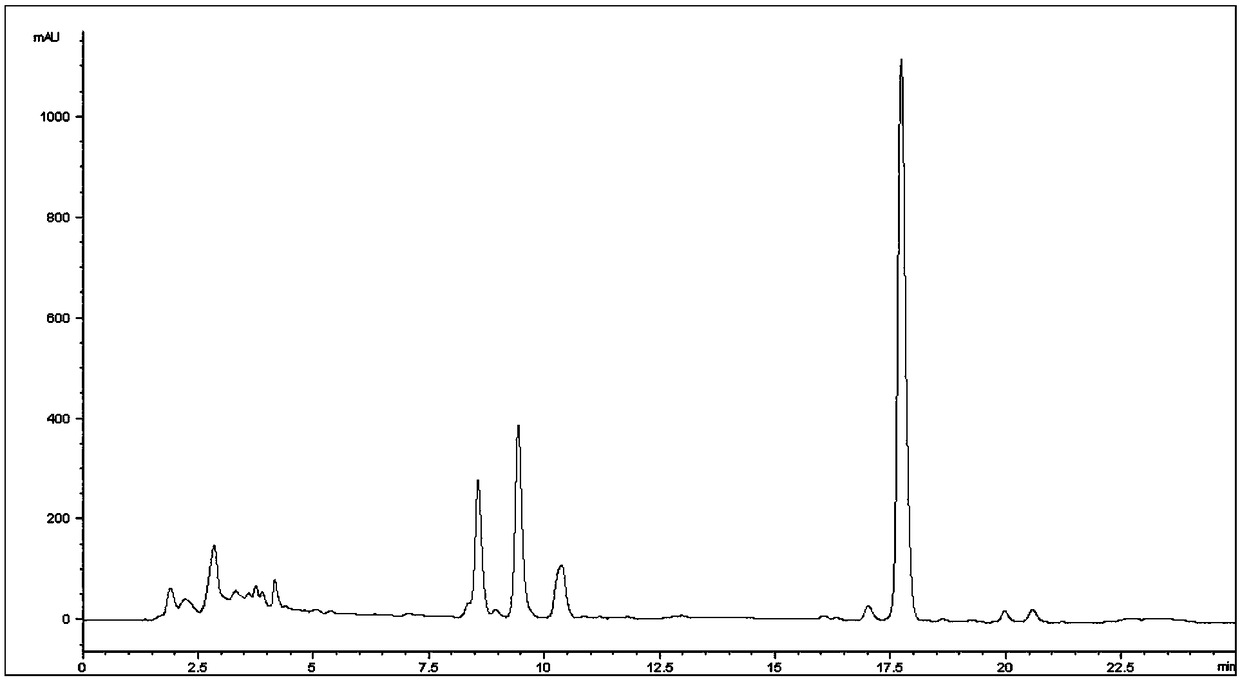
Method for simultaneously preparing high-purity carnosol and carnosic acid from rosemary
ActiveCN108276271AAvoid lostEasy to separateCarboxylic compound separation/purificationDistillationGradient elution
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously preparing high-purity carnosol and carnosic acid from rosemary. The method comprises the steps of extracting the flowers and leaves of the rosemarywith an ethanol aqueous solution to obtain a rosemary extract, and dissolving the extract in water saturated ethyl acetate; separating the obtained solution with positive phase silica gel, carrying out gradient elution according to a ratio of chloroform to methanol to acetic acid being equal to (100-95) to (0-5) to (0-0.001), merging the same components, and carrying out vacuum concentration to obtain crude products of the carnosol and the carnosic acid; then, separately carrying out Sephadex LH-20 gel column chromatography purification on the crude products, eluting a mobile phase with chloroform-methanol or petroleum ether-chloroform-methanol, merging the same components, and drying by distillation under the reduced pressure to obtain the carnosol and the carnosic acid which have the purities of 98% or above. The method can be used for simultaneously preparing the high-purity carnosol and carnosic acid from the rosemary. A gel column can be repeatedly used, and column chromatographyis short in time and high in efficiency. The method is simple, easy to operate and high in yield, thus being suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:BEIJING UNION UNIVERSITY
Natural fiber environment-friendly adsorption material and method for preparing same
ActiveCN105664867AImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsNatural fiberHydroxyethyl cellulose
The invention provides a natural fiber environment-friendly adsorption material and a method for preparing the same.The method includes steps of mixing carboxymethyl celluloses, carboxymethyl hydroxyethyl celluloses, carboxymethyl hydroxypropyl celluloses, sodium cellulose sulfate, sodium alginate and 60-70 parts of water with one another to obtain first mixtures; slowly stirring the mixtures by the aid of glass rods and then stirring the first mixtures by the aid of a magnetic stirrer; adding glyoxylic acid, sodium hydroxide and 20-30 parts of water into the first mixtures, increasing the temperatures and then carrying out reaction; washing filter materials and then freezing and drying the filter materials; adding palm wax, phosphatidylinositol, starch sugar alcohol, carnosol, squalane, chitosan and remaining water into the filter materials to obtain second mixtures; stirring the second mixtures by the aid of the magnetic stirrer; adding ethylene oxide into the second mixtures; stirring the ethylene oxide and the second mixtures by the aid of the magnetic stirrer to obtain third mixtures; reducing the rotational speed of the magnetic stirrer and stirring the third mixtures; filtering the third mixtures and then washing the third mixtures until the third mixtures are neutral; drying the third mixtures and then grinding the third mixtures to obtain powder.The natural fiber environment-friendly adsorption material and the method have the advantages that the natural fiber environment-friendly adsorption material is degradable, and excellent adsorption effects can be realized by the natural fiber environment-friendly adsorption material for heavy metal ions.
Owner:海安腾昱智能科技有限公司
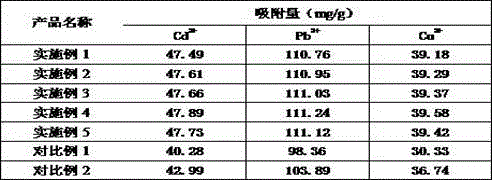
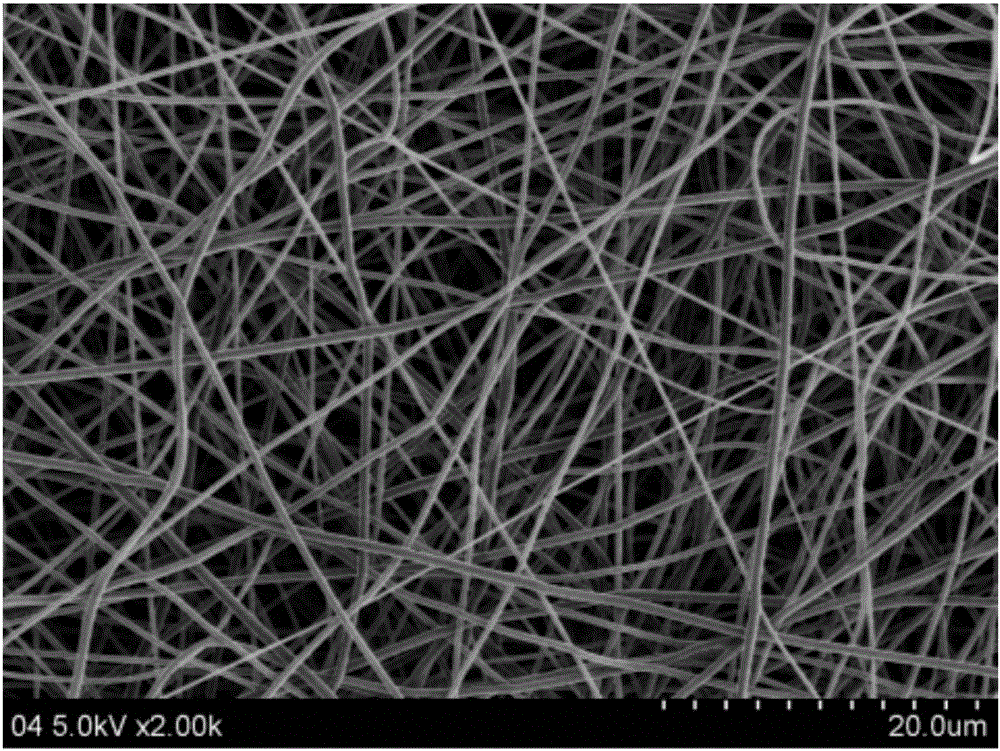
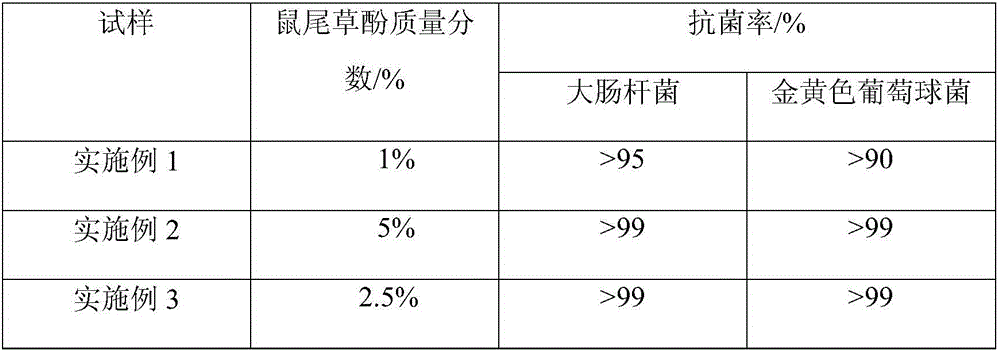
Preparation method of carnosol and chitosan composite nanometer fiber mat
InactiveCN105696195ASimple methodEasy to industrializeSpinning solution filteringOrganic chemistryFiberComposite nanofibers
The invention relates to a preparation method of carnosol and chitosan composite nanofiber felt, comprising: dissolving chitosan in formic acid solution and stirring to obtain chitosan solution; mixing carnosol and chitosan The solution is mixed, stirred, and ultrasonically degassed to obtain a carnosol / chitosan solution, which is then electrostatically spun. The method of the invention is simple and easy to implement, and is easy to be industrialized, and the obtained carnosol composite nanofiber mat can be used in fields such as wound dressings, has excellent antibacterial effect, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
A method for comprehensively extracting carnosol and ursolic acid
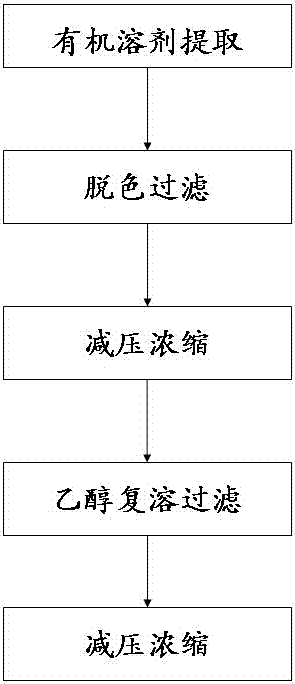
ActiveCN105669432BIncrease contentLight colorSteroidsCarboxylic compound separation/purificationOxalateOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for comprehensive extraction of carnosic acid, carnosol and ursolic acid.According to the method, rosemary flowers or leaves are used as raw materials, an organic solvent is adopted for extraction, the content of obtained rosemary extract is 40-45%, and the ratio of the content of carnosic acid to the content of carnosol in the rosemary extract is 4:1 to 6:1.The method comprises the steps of extraction with the organic solvent, decoloration and filtration, vacuum concentration, ethyl alcohol redissolution and filtration and vacuum concentration.By means of the method, the yield of the rosemary extract can be greatly increased, the ratio of the content of carnosic acid to the content of carnosol in the extract is increased, the content of carnosol in the extract is reduced, and the overall oxidation resistance of the extract is enhanced.
Owner:HENAN ZHONGDA HENGYUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Bacteriostatic fresh-keeping packaging film and blow molding process thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of packaging films, in particular to an antibacterial fresh-keeping packaging film and a blow molding process thereof, and the packaging film comprises the following components in parts by mass: 30-65 parts of polyethylene resin, 5-16 parts of a composite antibacterial agent, 2-7 parts of a plasticizer, 2-5 parts of an antioxidant and 1-4 parts of a maleic anhydride grafted compatilizer; the composite antibacterial agent is prepared from nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide, nano zinc oxide and carboxymethyl chitosan; the plasticizer comprises ethylene glycol, xylitol and microcrystalline cellulose; the antioxidant comprises caffeic acid and carnosol. Compared with the prior art, the problems that an existing packaging film is not ideal in antibacterial performance, poor in fresh-keeping effect and low in cooling speed during preparation are solved.
Owner:广东中兴塑料纸类印刷有限公司
A kind of preparation method of rosemary extract
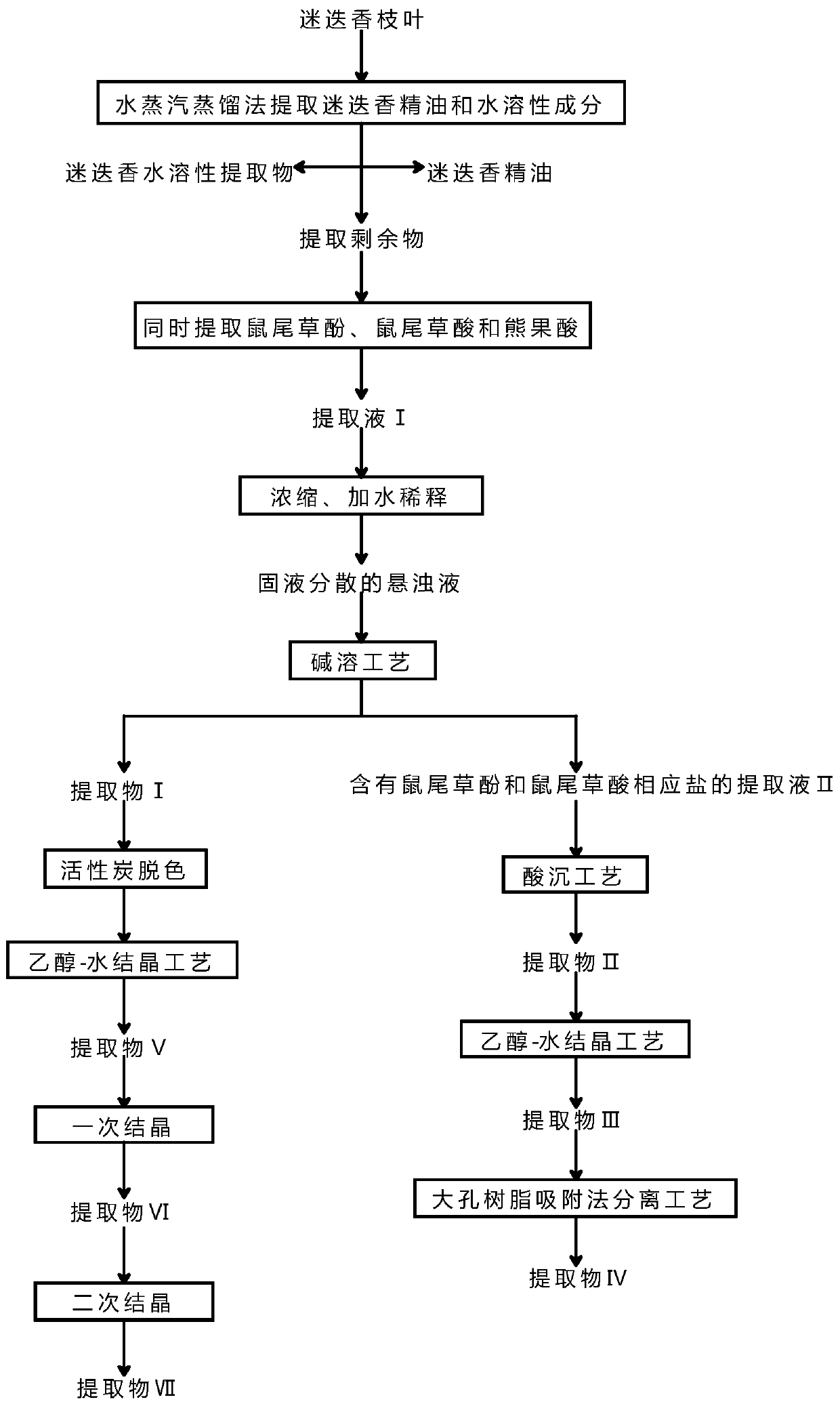
ActiveCN107513095BExtension of timeRegulate acidicOrganic compound preparationSteroidsUrsolic acidTraditional medicine
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rosemary extract. The method comprises the steps of S1, taking rosemary branches and leaves as raw materials and extracting carnosol, carnosic acid and ursolic acid at the same time to obtain an extracting solution I; S2, concentrating the extracting solution I to obtain a concentrated solution; S3, adding water into the concentrated solution for dilution to obtain turbid liquid; S4, treating the turbid liquid by an alkali dissolution process to obtain an extracting solution II and an extract I containing the ursolic acid; S5, treating the extracting solution II by adopting an acid sediment process to obtain an extract II containing the carnosol and the carnosic acid, thus realizing the synchronous extraction and separation of the extract containing the carnosol and the carnosic acid and the extract containing the ursolic acid.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
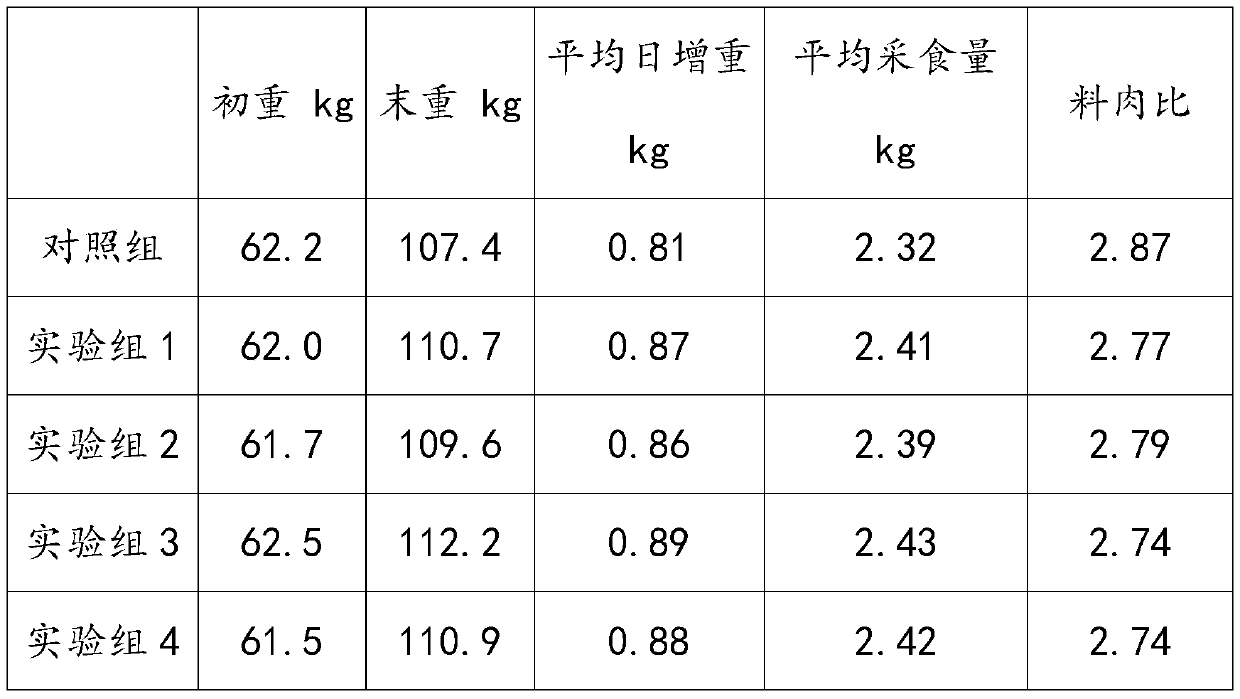
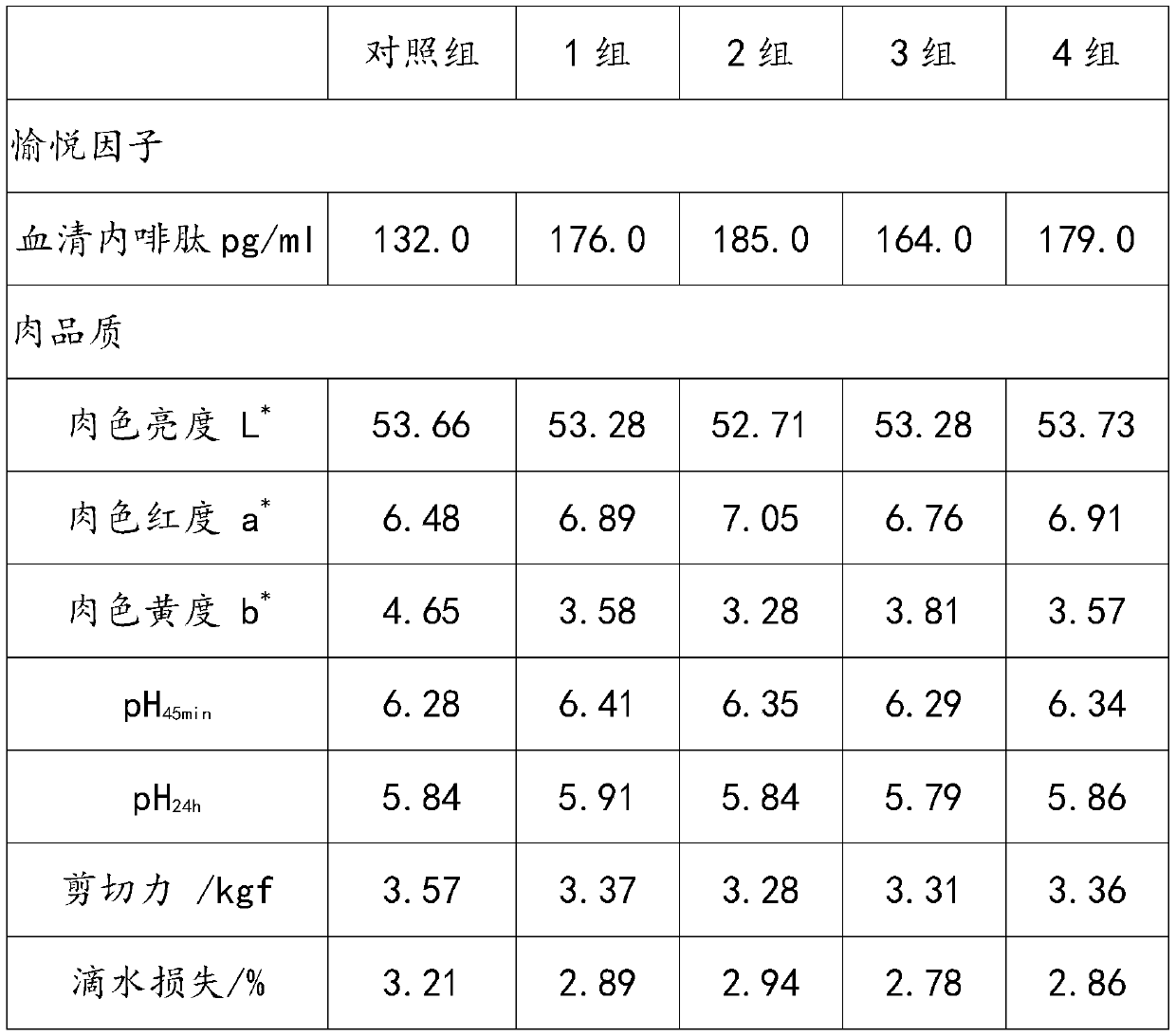
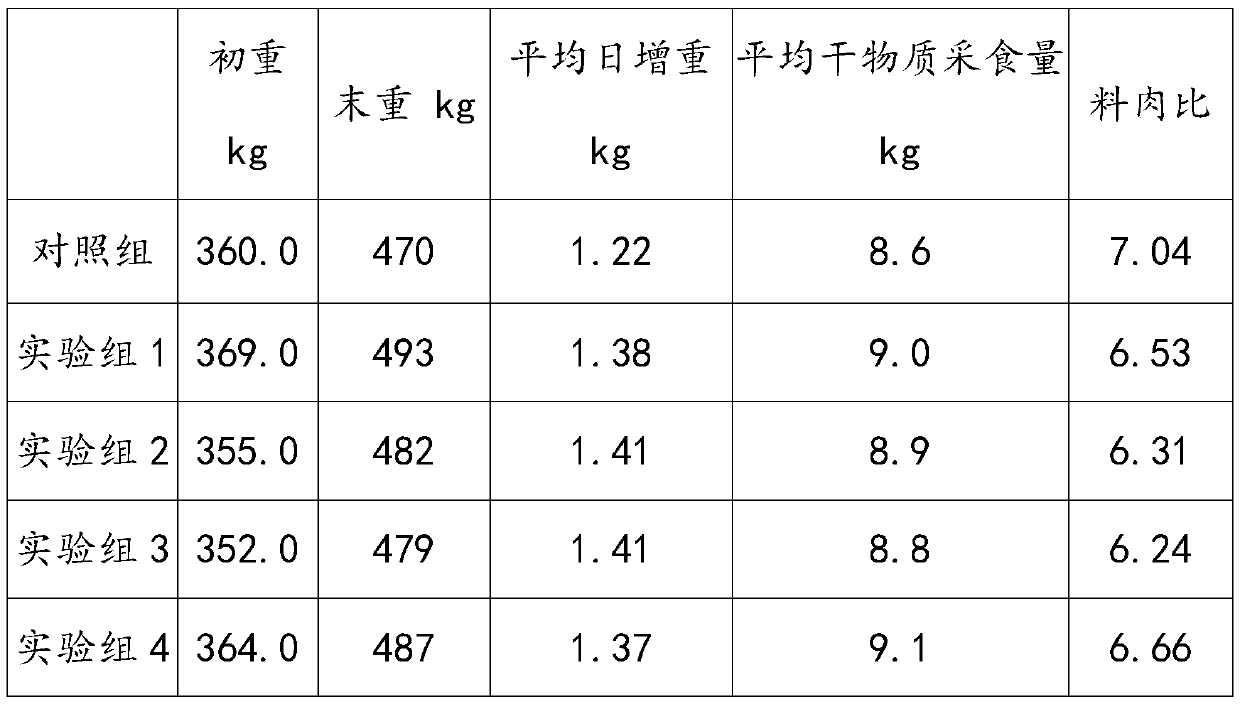
Feed additive capable of promoting quality of animal meat and preparation method and application of feed additive
InactiveCN109845897AImprove qualityIncrease pleasureFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFood additiveBiotechnology
The invention discloses a feed additive capable of promoting quality of animal meat and a preparation method and application of the feed additive. The feed additive comprises the following componentsin parts by weight of 10-20 parts of capsaicine, 20-40 parts of a pummelo pericarp extract, 20-40 parts of a cortex eucommiae extract and 20-30 parts of a rosemary extract, wherein the mass content ofcapsicine in the capsaicine is not less than 10%, the mass content of naringin in the pummelo pericarp extract is not less than 5%, the mass content of chlorogenic acid in the cortex eucommiae extract is not less than 10%, and the mass content of carnosic acid and / or carnosol in the rosemary extract is not less than 5%. The feed additive disclosed by the invention can be used for improving the delighted sense and meat quality of animals, can also improve the production properties of the animals, can reduce the occurrence of epidemic diseases, can be adapted to the developing direction of green healthy aquaculture, and is suitable for production of superior safe meat foods; and besides, during research, the inventor finds that the cortex eucommiae extract as an effective component in the feed additive can also prevent the occurrence of bacterial epidemic diseases, and has favorable effects on preventing piggies from suffering from diarrhea.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LEADER BIO TECH
Callicarpa longissima extract, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108159195AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove cancer resistanceAntipyreticAnalgesicsNatural productPhenol
The invention discloses a Callicarpa longissima extract, a preparation method and the application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of natural product extraction. A mixture of carnosol, rosmanol and epirosmanol is contained in the Callicarpa longissima extract. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the Callicarpa longissima extract and the application thereof. The mixtureof carnosol, rosmanol and epirosmanol is contained in the Callicarpa longissima extract, and the components are diterpene phenol components respectively, so that the components are of various activities such as preferable oxidation resistance, cancer resistance and anti-inflammation. Through pharmacodynamics study for the Callicarpa longissima extract, a wider space is provided for further application.
Owner:GUANGXI INST OF BOTANY THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
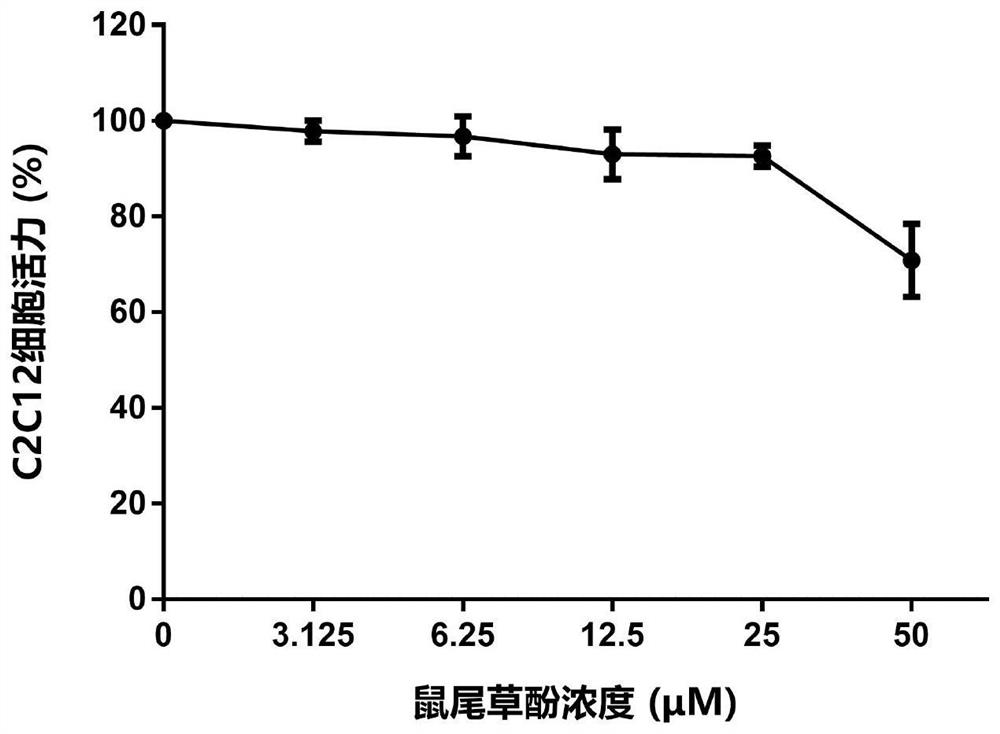
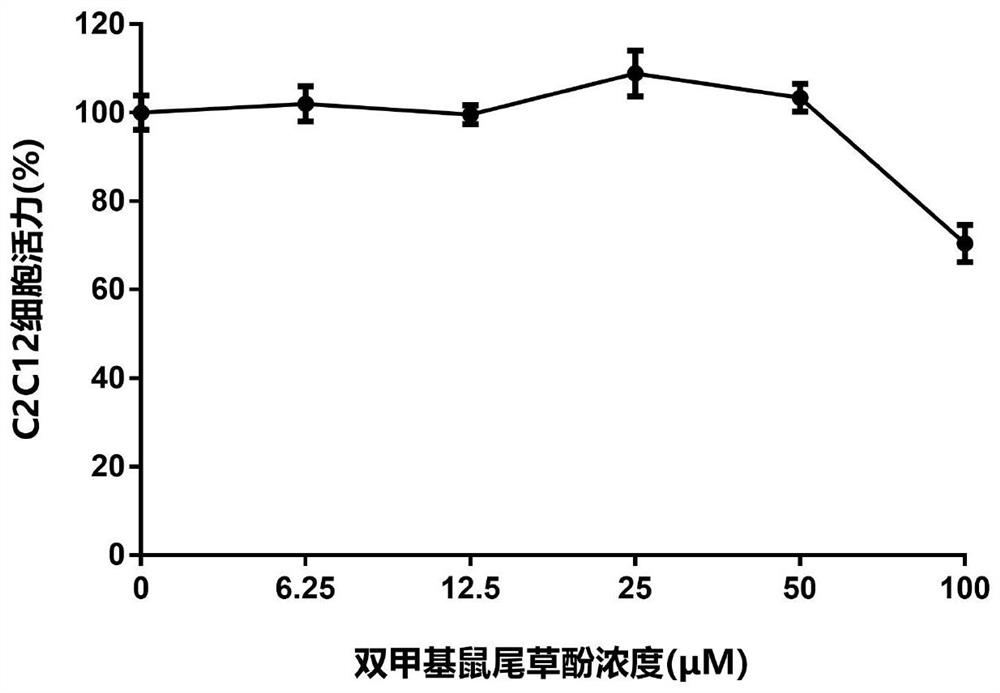
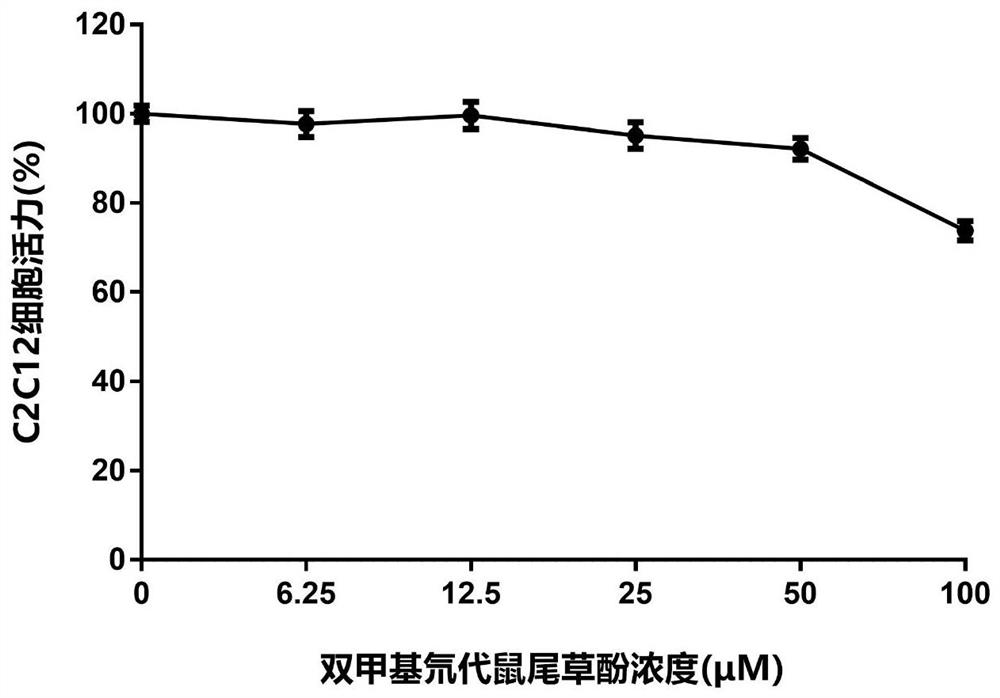
Application of carnosol compounds in preparation of medicines for treating cachexia diseases
ActiveCN113244222AInhibit atrophyRelieve muscle atrophyOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseTumor reduction
The invention innovatively provides application of carnosol compounds in preparation of medicines for treating cachexia for the first time. The carnosol compound comprises a carnosol compound shown as a formula X, dimethyl deuterated carnosol shown as a formula 1, dimethyl carnosol shown as a formula 2 and the like. The invention further provides a novel compound, namely the dimethyl deuterated carnosol shown in the formula 1 and a preparation method thereof. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions for treating cachexia diseases. The invention further provides application of the carnosol compounds in preparation of the medicines for treating tumor cachexia, including amyotrophy caused by tumor tissue, adipopenia caused by the tumor tissue, appetite reduction caused by the tumor tissue, inflammatory response caused by the tumor tissue and tumor cachexia caused by digestive tract related cancers, liver cancer, lung cancer and colon cancer. The invention also provides the application in preparation of medicines or inhibitors for treating or inhibiting amyotrophy, drugs or inhibitors for inhibiting or relieving lipolysis of fat cells, and drugs or inhibitors for inhibiting or relieving weight loss or decrease. The carnosol compounds and medicines have a wide application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of high-purity carnosol
The invention relates to a preparation method of a natural active compound. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: 1, extracting a dry carnosol-containing raw material per kilogram by the use of 3-10 liters of a lipophilic organic solvent for 2-5 times, merging extracts, and condensing to obtain a carnosol-containing extract or solid; 2, dissolving by the use of a 10-90% hydrophilic organic solvent, filtering and precipitating, and carrying out macroreticular resin refining processing on a filtrate to obtain a carnosol-containing precipitate; 3, dissolving the precipitate by the use of a mixed lipophilic organic solvent, standing, precipitating a precipitate; and filtering the precipitate to obtain a carnosol crude product; and 4, crystallizing by the use of a hydrophilic organic solvent so as to obtain high-purity carnosol crystals with the HPLC detection content being more than 95%. The preparation method provided by the invention has advantages of simple operation process and controllable cost, and is suitable for large-scale preparation and production of high-purity carnosol.
Owner:高政 +1
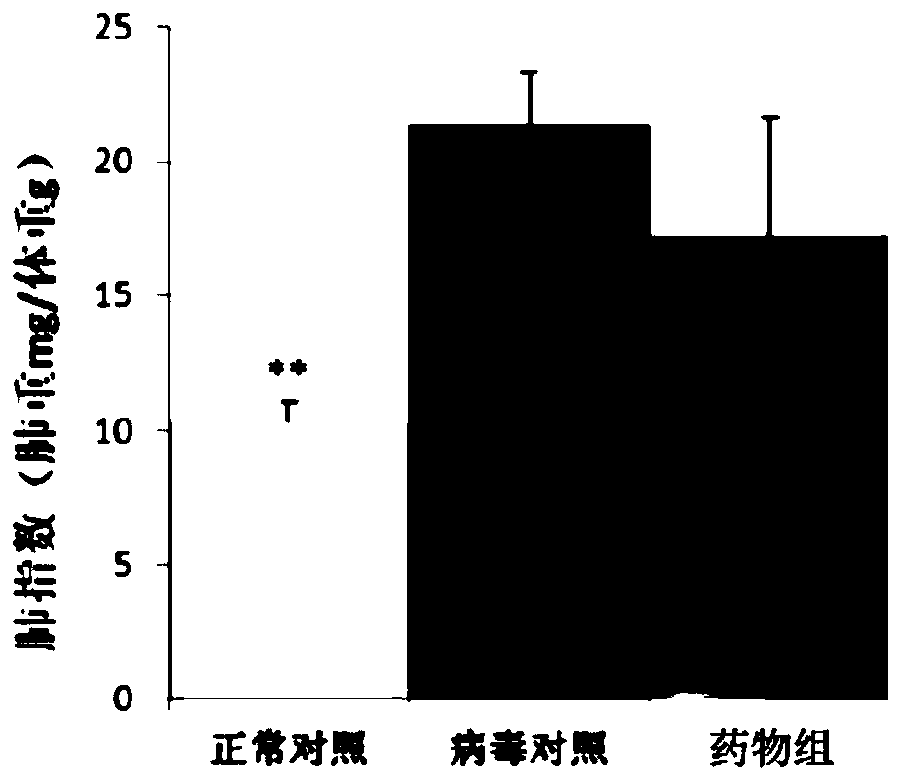
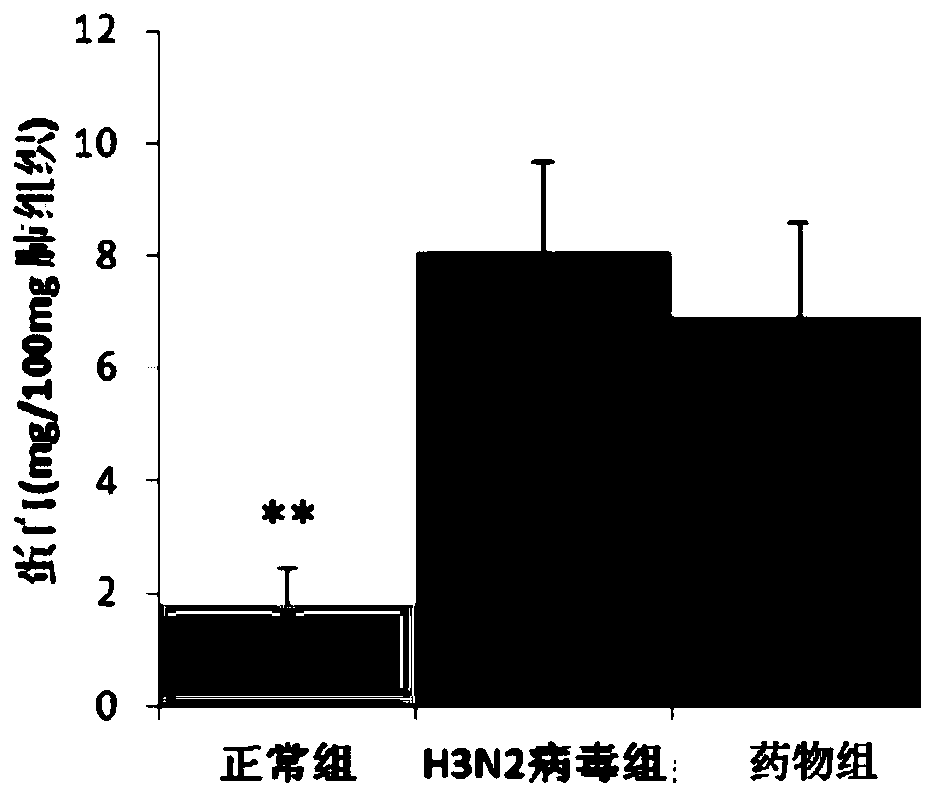
Application of rosemary extract in antiviral pneumonia medicine
InactiveCN111202766ALower total protein contentReduce permeabilityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsALI - Acute lung injuryTotal protein
The invention relates to the technical field of pharmacy, and in particular to an application of rosemary extract in antiviral pneumonia medicines. In the application, the rosemary extract comprises rosmarinic acid, carnosic acid and carnosol. The invention also discloses an antiviral pneumonia medicine and a preparation method thereof. The medicine takes rosmarinic acid, carnosic acid and carnosol as active ingredients and also contains a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier to prepare a pharmaceutically acceptable dosage form. The rosemary extract components have a remarkable treatment effecton acute lung injury induced by influenza virus. The rosemary extract can significantly reduce lung index, reduce total protein content in lung, inhibit release of TNF-alpha, RANTETS and IL-6 in serum and lung, promote secretion of IL-10, significantly inhibit replication of influenza virus in lung, and reduce inflammatory injury caused by viral infection.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Zero trans fatty acid soybean oil and production process thereof
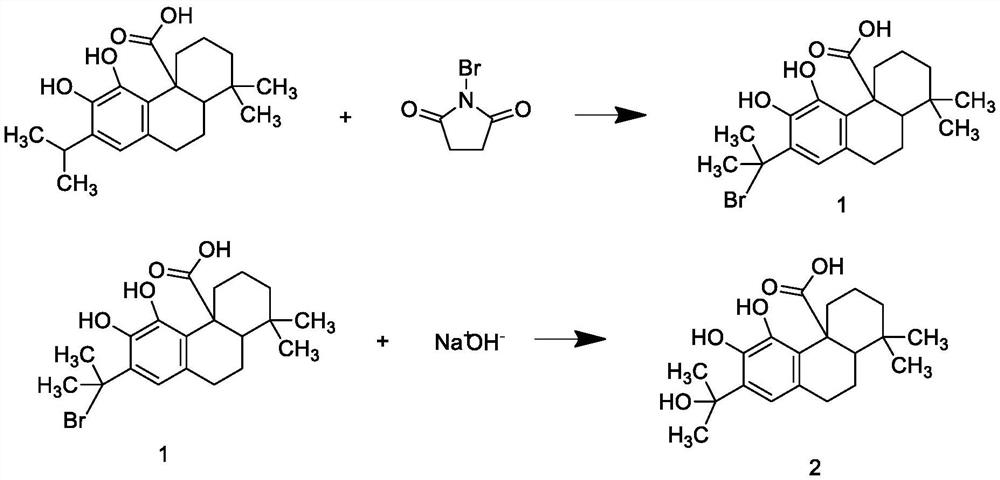
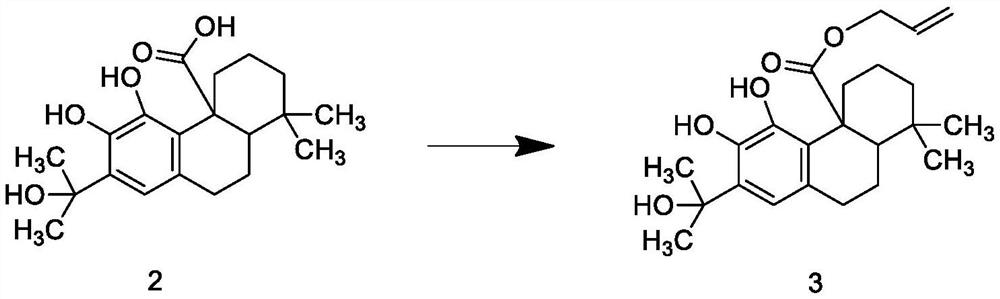
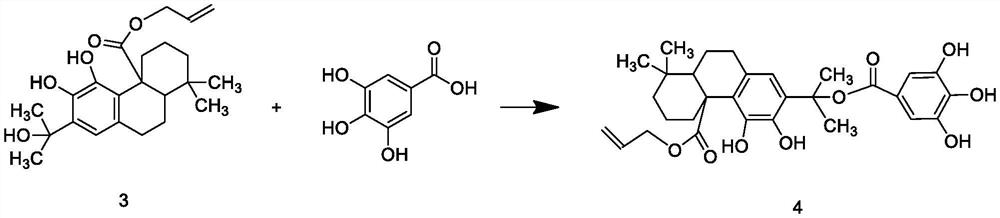
PendingCN113412864AAnti-inflammatoryAntibacterialOrganic compound preparationFatty substance preservation using additivesGallic acid esterCarboxyl radical
The invention discloses zero trans fatty acid soybean oil and a production process thereof, and belongs to the technical field of edible oil, an antioxidant composition comprises an antioxidant A and rosmarinic acid, bromine on N-bromosuccinimide can replace hydrogen on carnosol benzyl, bromine can be replaced by alcoholic hydroxyl through hydrolysis to obtain an intermediate product 2, esterification protection is performed on carboxyl of the intermediate product 2 through reaction to obtain an intermediate product 3; esterification reaction is performed on alcoholic hydroxyl groups on the intermediate product 3 and carboxyl groups on gallic acid to obtain an intermediate product 4, and allyl groups of the protected group part of the intermediate product 4 are removed under the catalysis of a catalyst to become carboxyl groups again and the antioxidant A is obtained; the antioxidant A and the rosmarinic acid both have ester bonds and carboxyl groups, and after the antioxidant composition is compounded, the dispersity of the rosmarinic acid in grease can be improved according to the principle of similar dissolvability, so that the antioxidant composition has a better antioxidant effect.
Owner:安徽乐氏食品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com