Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1762 results about "Decarboxylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
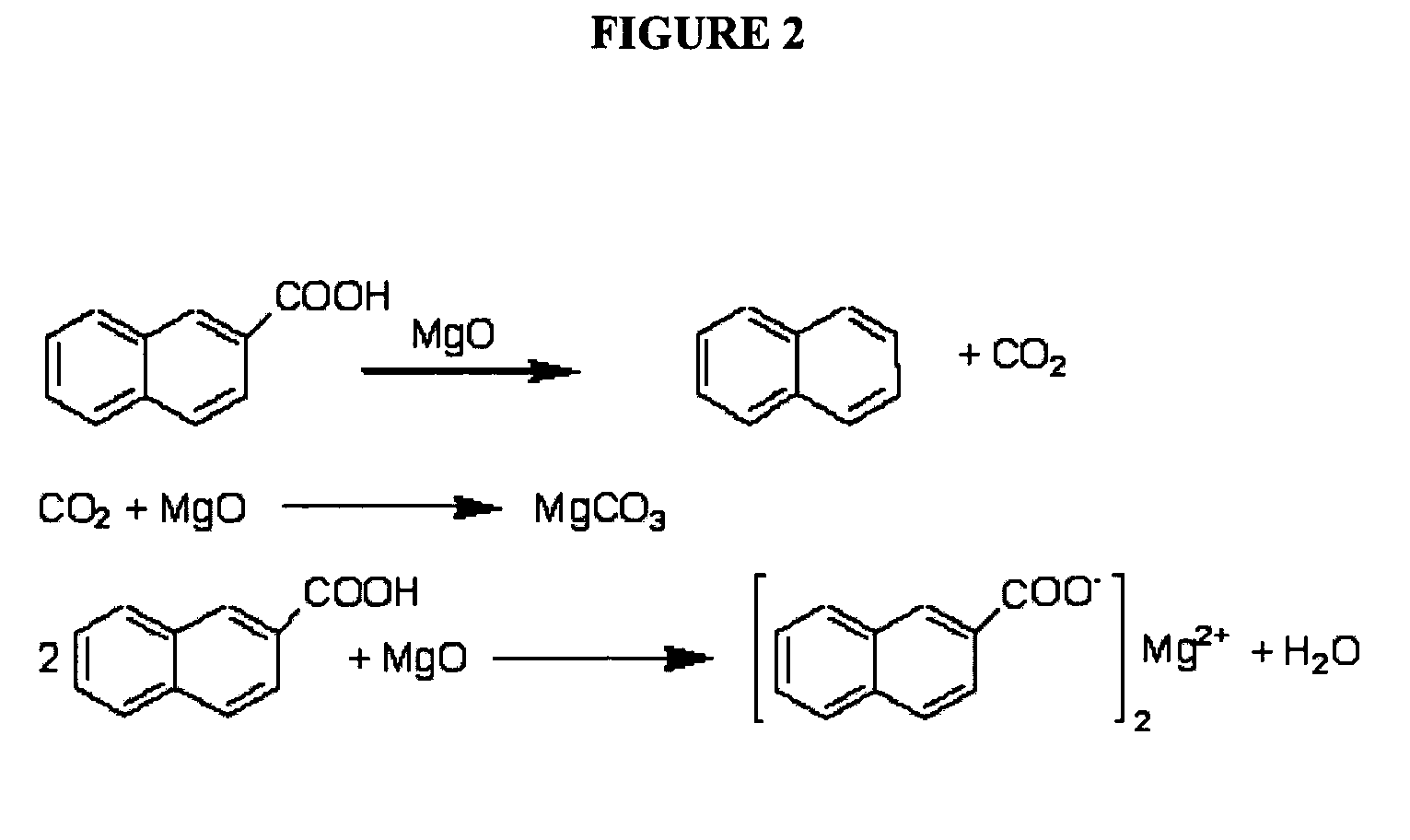
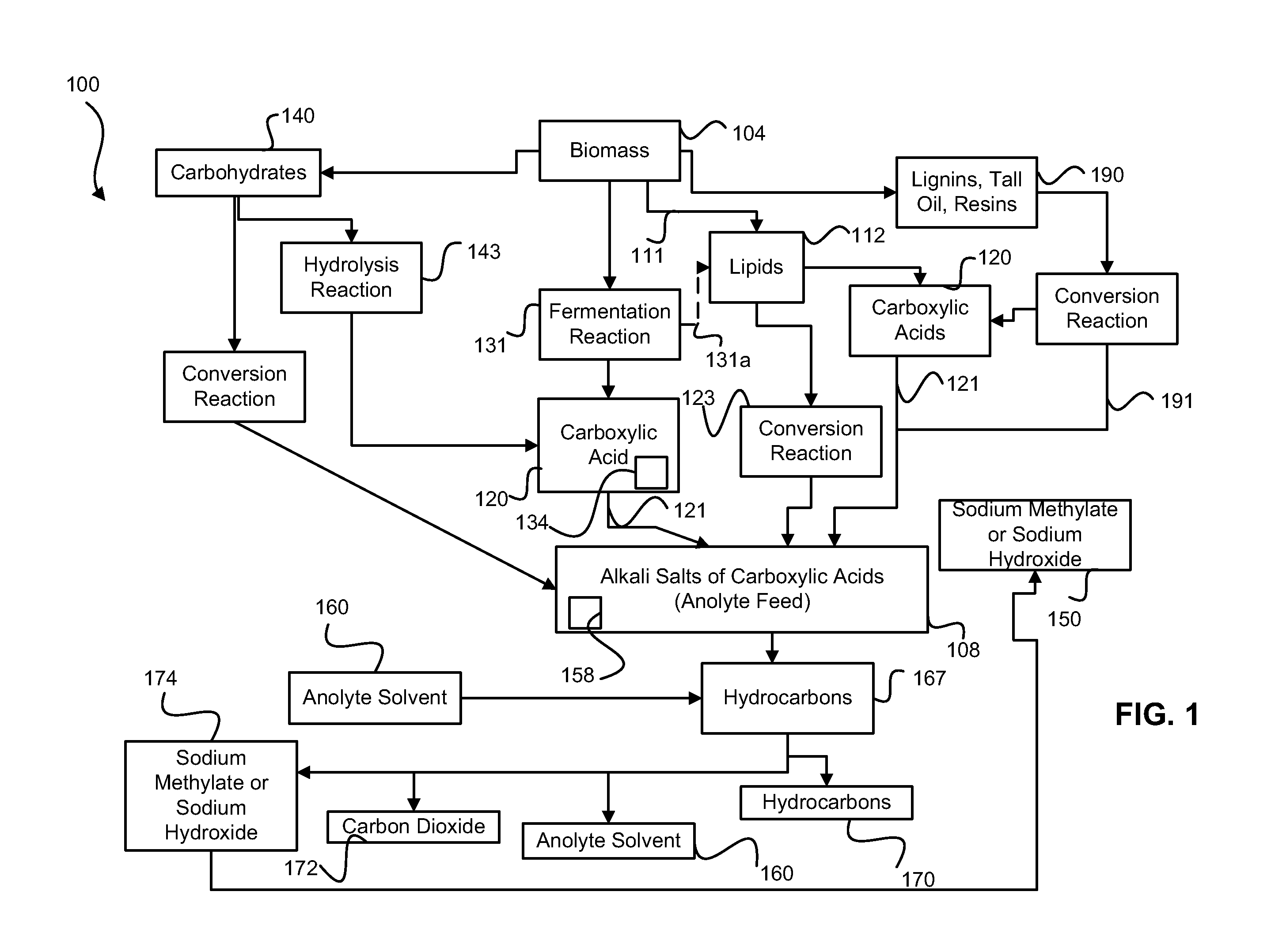
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO₂). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carboxylation, the addition of CO₂ to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylases or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases (EC number 4.1.1).
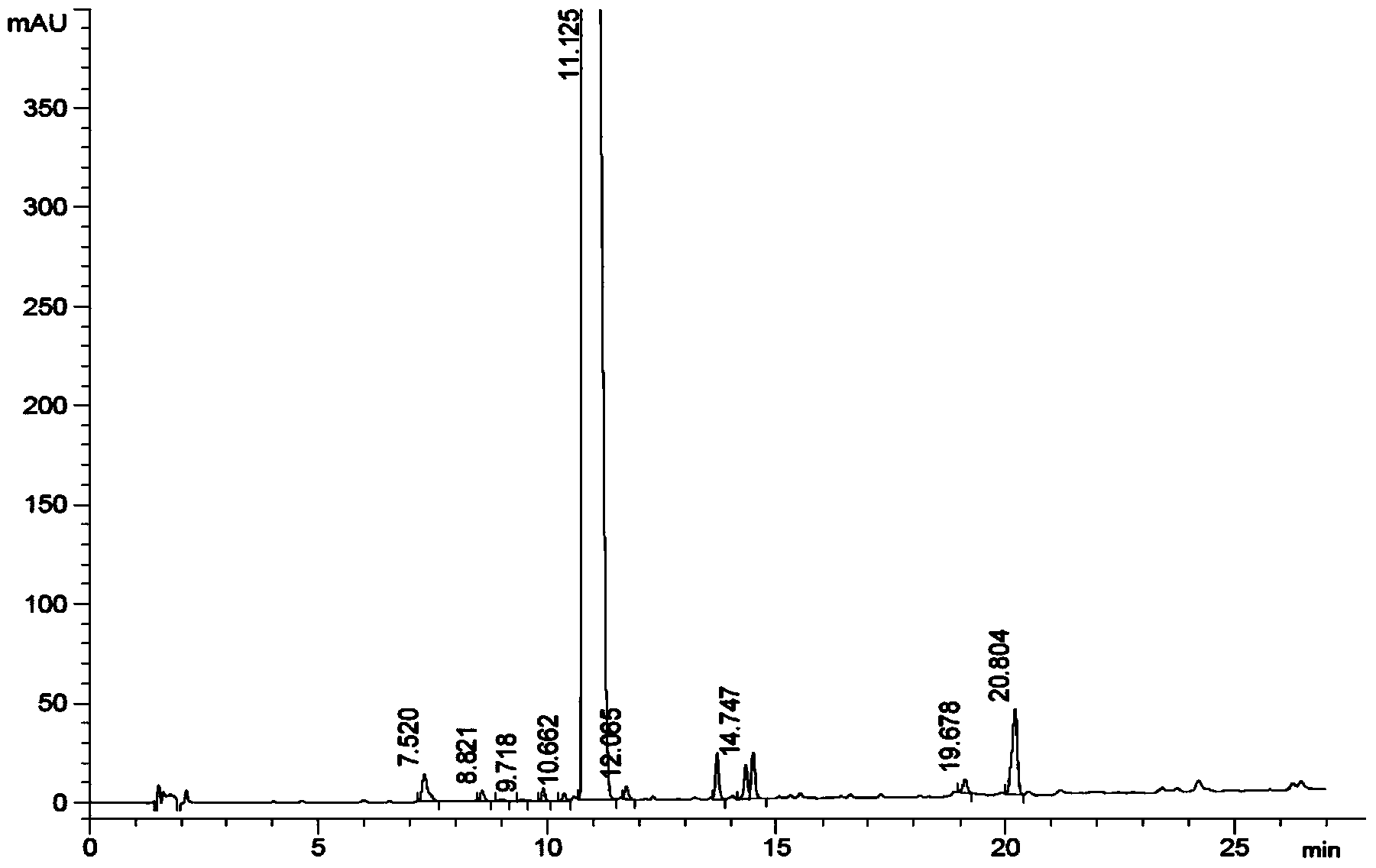
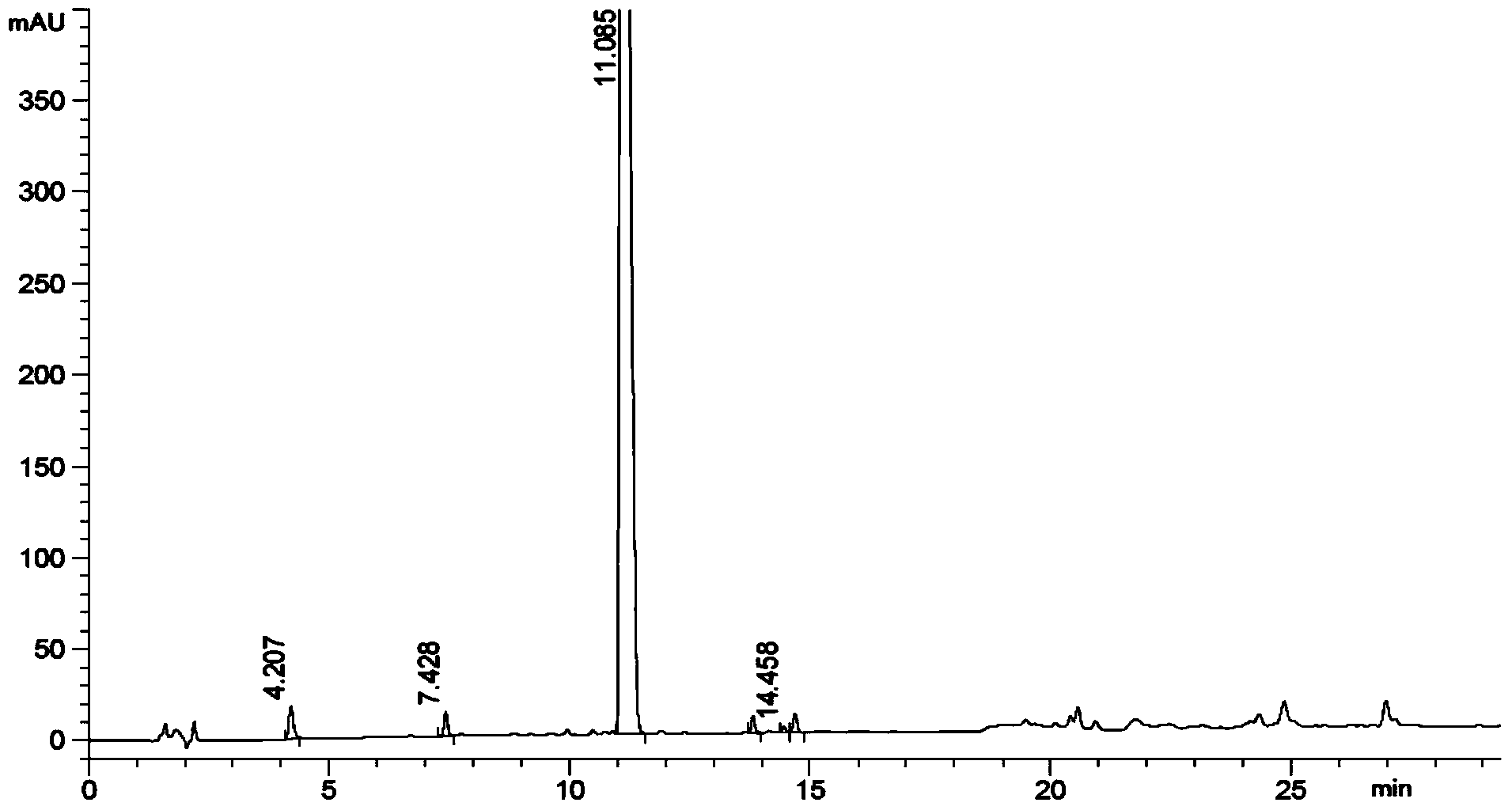
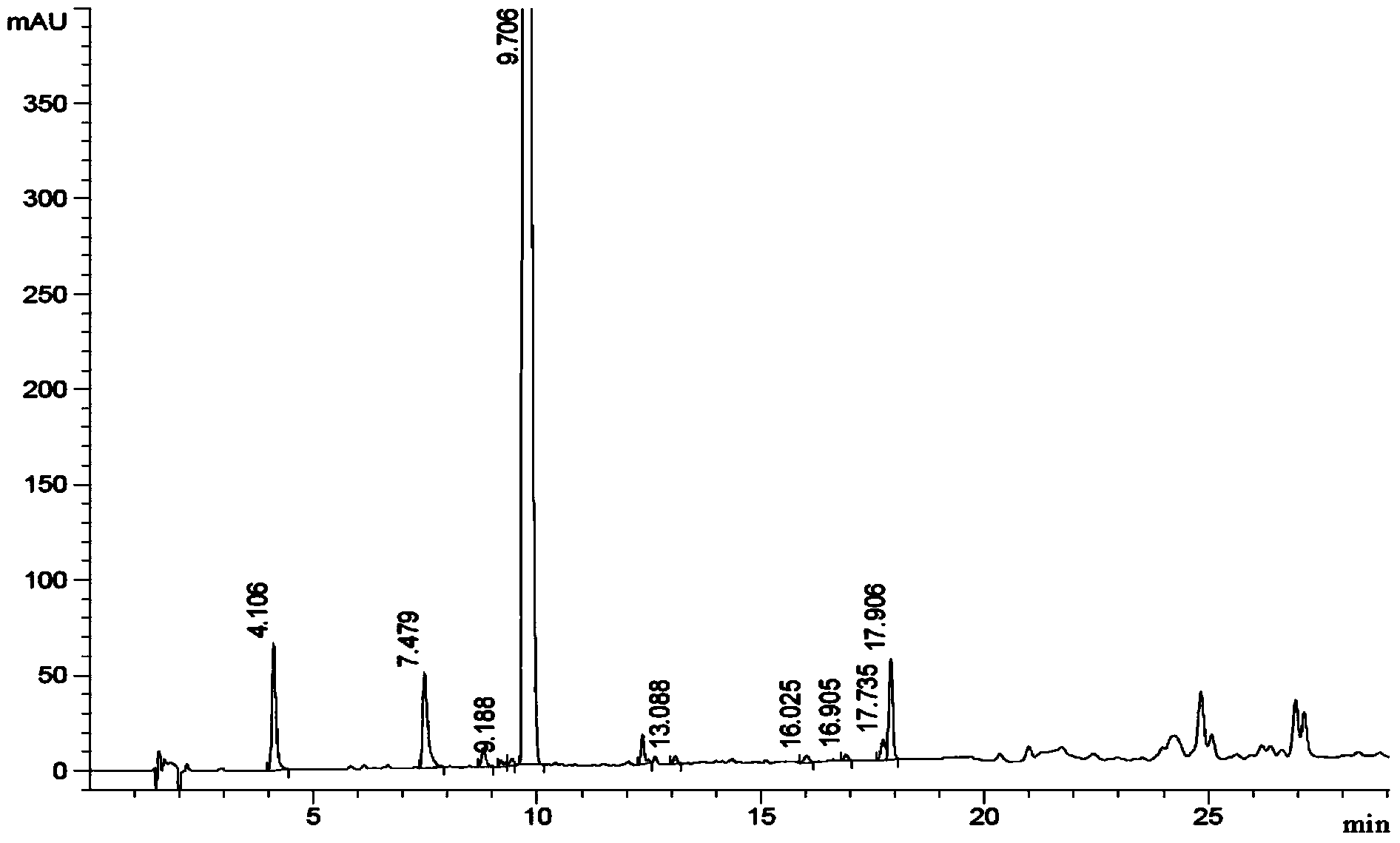
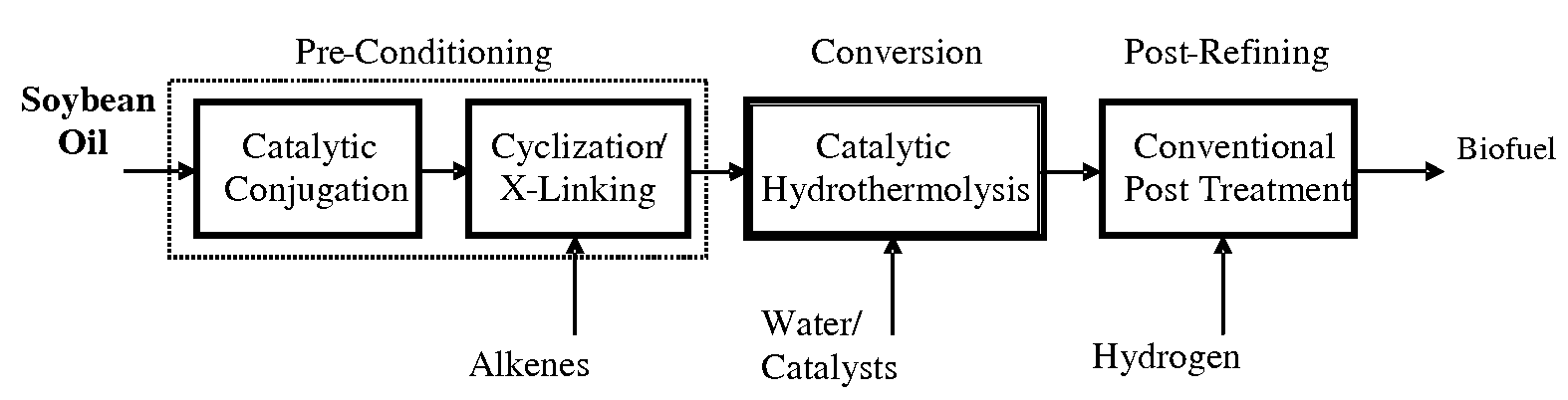
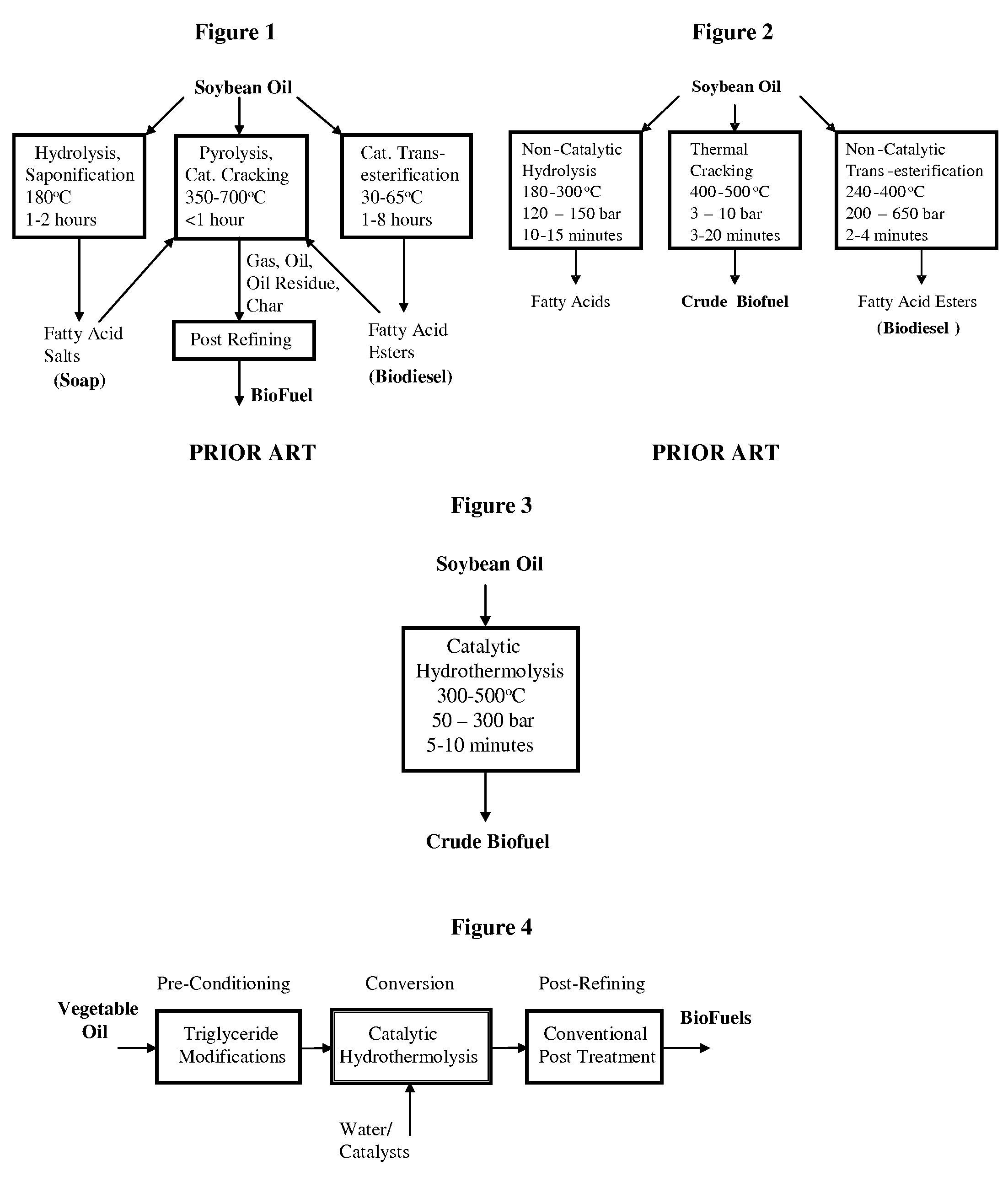
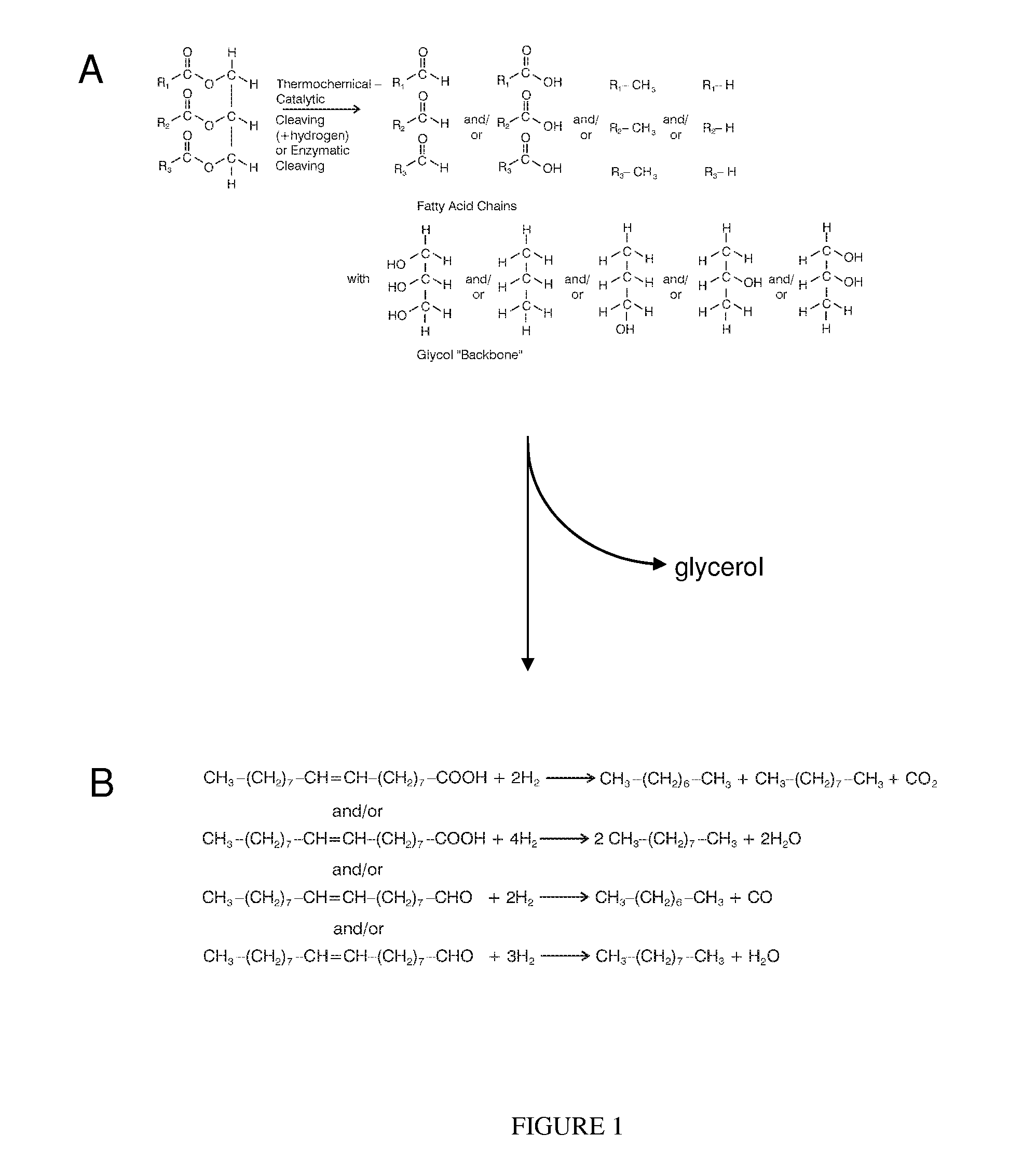
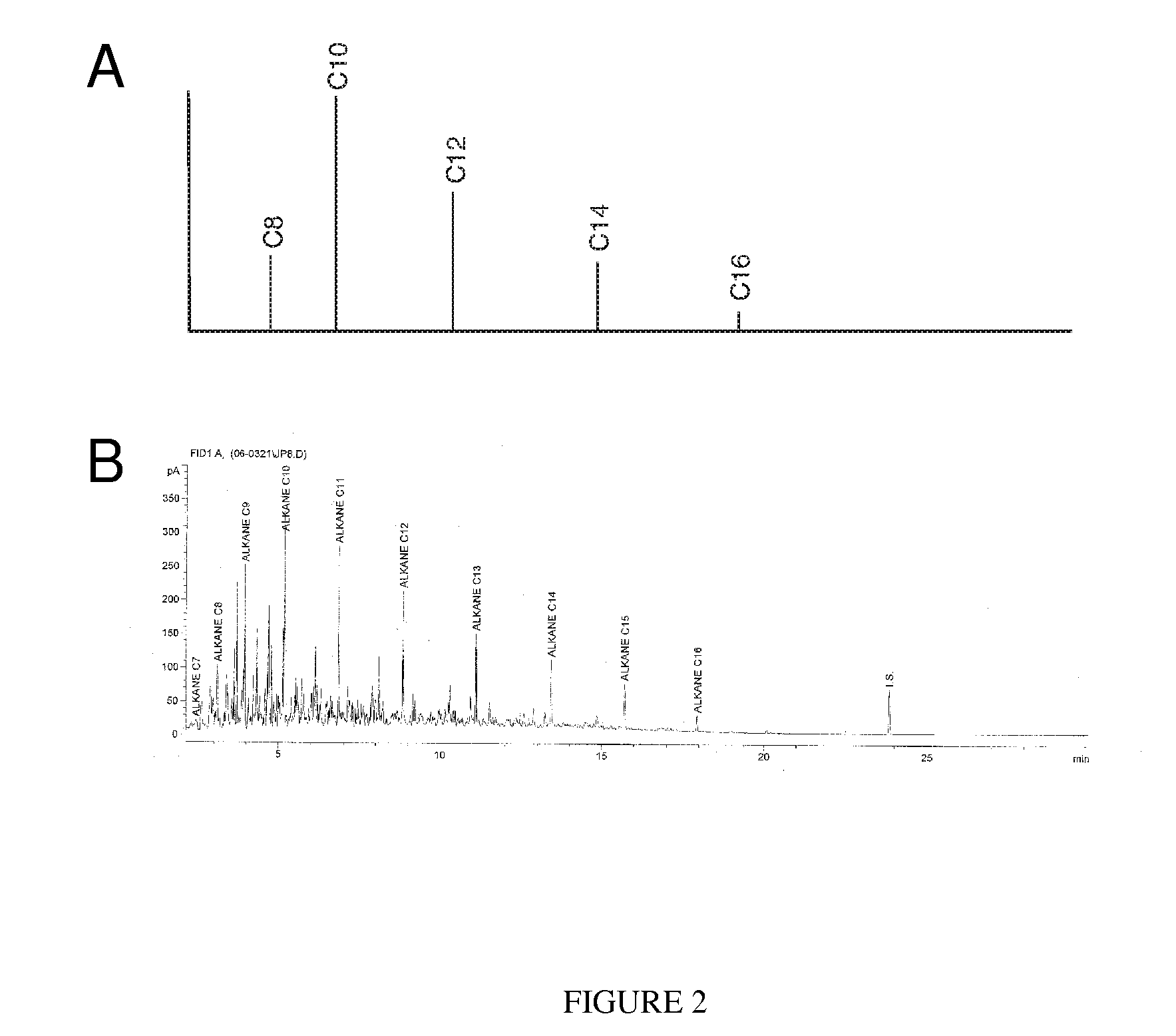
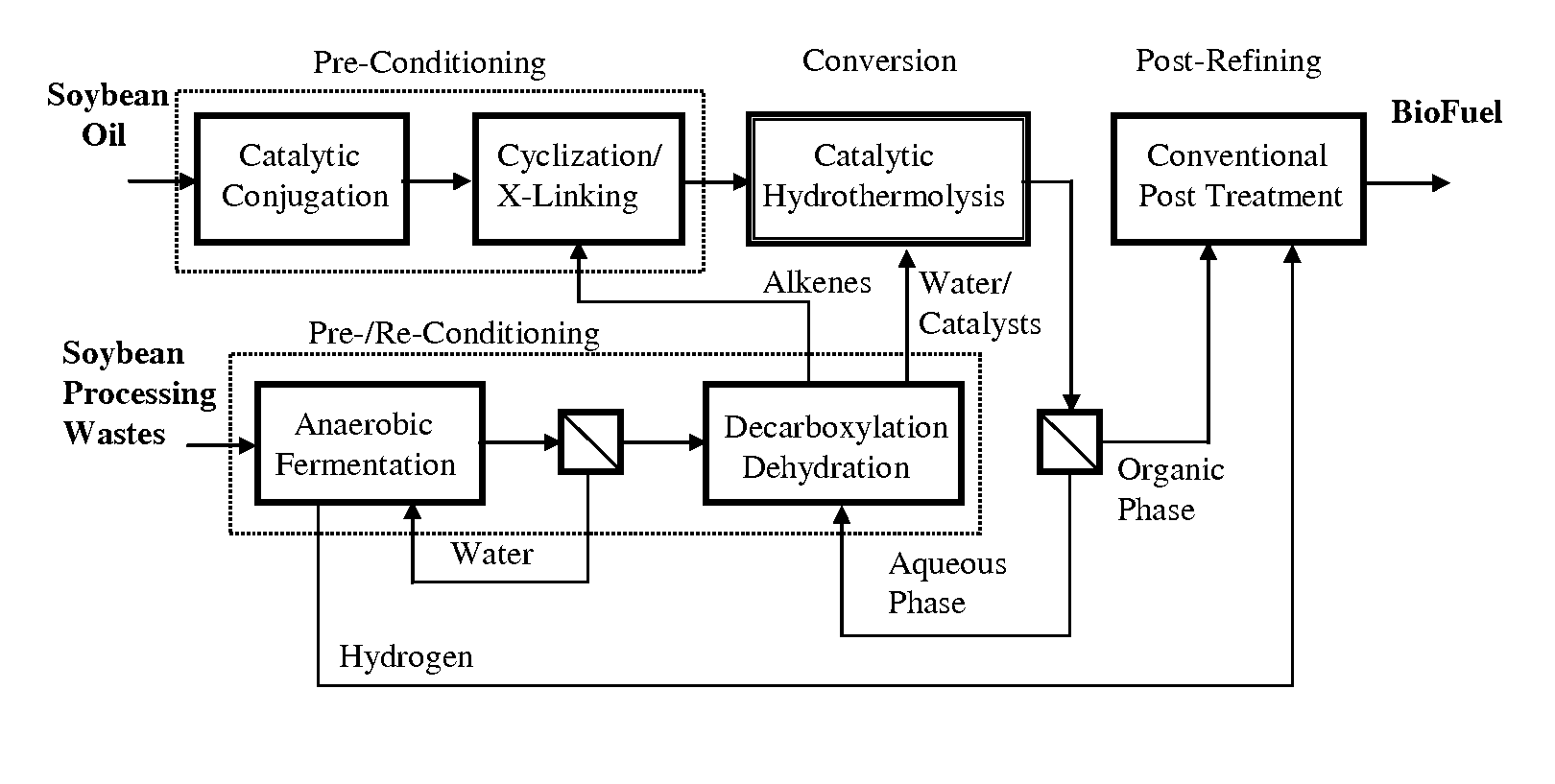
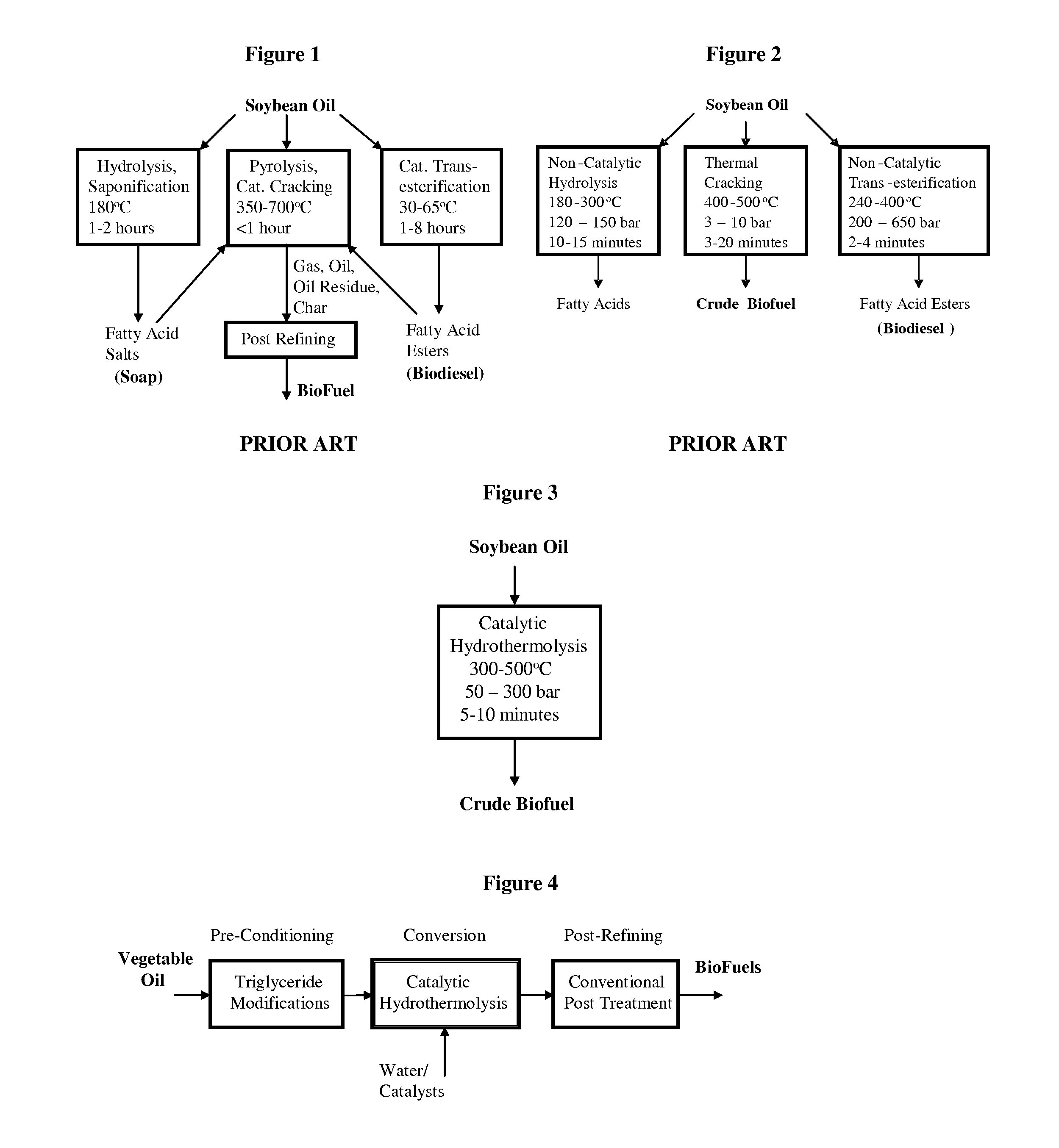
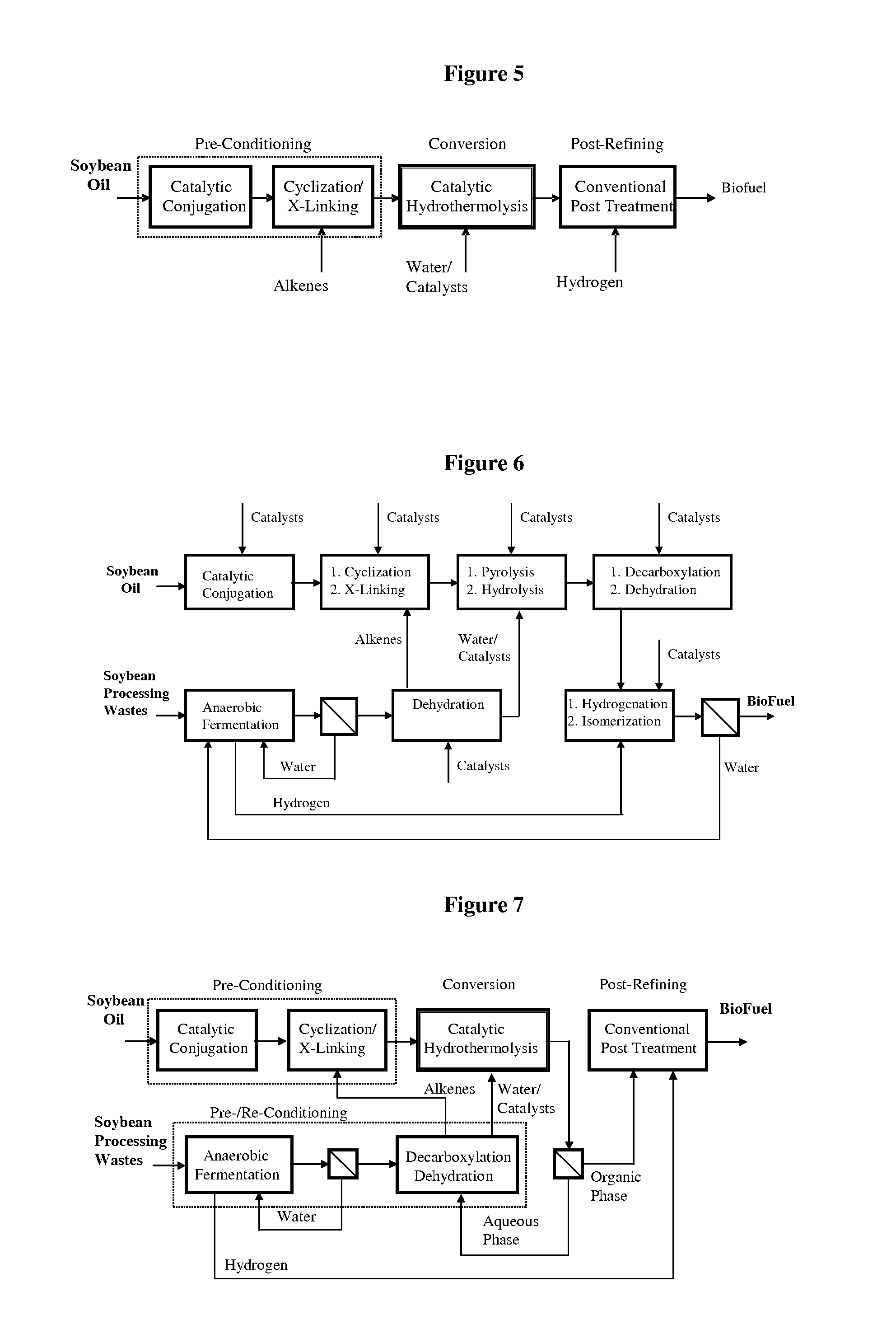
Method of converting triglycerides to biofuels
ActiveUS7691159B2Improve chemical and physical and combustion qualityImprove thermal stabilityFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationCross-linkIsomerization
A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process including the steps of (a) preconditioning unsaturated triglycerides by catalytic conjugation, cyclization, and cross-link steps; (b) contacting the modified triglycerides with hot-compressed water containing a catalyst, wherein cracking, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, aromatization, or isomerization, or any combination thereof, of the modified triglycerides produce a crude hydrocarbon oil and an aqueous phase containing glycerol and lower molecular weight molecules, and (c) refining the crude hydrocarbon oil to produce various grades of biofuels. A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process further including the steps of (a) carrying out anaerobic fermentation and decarboxylation / dehydration, wherein the anaerobic fermentation produces hydrogen, volatile acids, and alcohols from fermentable feedstocks, and the decarboxylation / dehydration produces alkenes from the volatile acids and alcohols, respectively; (b) feeding the alkenes to the cyclization process; (c) feeding the hydrogen to the post refining process; and (d) recycling the aqueous phase containing glycerol to the decarboxylation / dehydration process. A biofuel composition including straight-chain, branched and cyclo paraffins, and aromatics. The paraffins are derived from conversion of triglycerides. The aromatics are derived from conversion of either triglycerides, petroleum, or coal.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
Process for the manufacture of hydrocarbons
A feedstock originating from renewable sources is converted to branched and saturated hydrocarbons without heteroatoms in the diesel fuel distillation range by skeletal isomerisation and deoxygenation carried out by hydrodeoxygenation or alternatively by combined decarboxylation and decarbonylation reactions, whereby the consumption of hydrogen is decreased.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Optimal energy pathway to renewable domestic and other fuels
A novel, energy efficient process of producing jet fuel is disclosed herein. The process is based on utilizing a medium chain fatty acid source such as cuphea oil, which precludes the need for high-energy fatty acid chain cracking to achieve the shorter molecules needed for jet fuels and other fuels with low-temperature flow requirements. In an embodiment, a process for producing a jet fuel comprises providing a medium chain fatty acid source. The method also comprises cleaving the one or more medium chain fatty acid groups from the glycerides to form glycerol and one or more free fatty acids. The method further comprises decarboxylating the one or more medium chain fatty acids to form one or more hydrocarbons for the production of the jet fuel.
Owner:ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL RES CENT FOUNDATIO
Process to upgrade oil using metal oxides
InactiveUS20060016723A1Reduce acidityReduce the numberRefining with metalsLiquid organic insulatorsHydrocotyle bowlesioidesCarboxylic acid
Described herein are compositions and methods for using metal oxides to upgrade oil. Metal oxides may be used as catalysts to reduce the TAN of the oil by converting carboxylic acids such as naphthenic acids into non-corrosive products. In some cases, the conversion occurs by a decarboxylation of the carboxylic acid to produce CO2. A second process promoted by metal oxides is hydrocarbon cracking. Cracking decreases the viscosity and increases the API, and produces lower molecular-weight hydrocarbons that are useful for many fuels and lubricants. Reductions in TAN and the increases in API improve the quality of increase the value of oil.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Process for producing a renewable fuel in the gasoline or jet fuel range
ActiveUS7928273B2Yield maximizationFatty acid isomerisationFatty acid oxidationVegetable oilGasoline
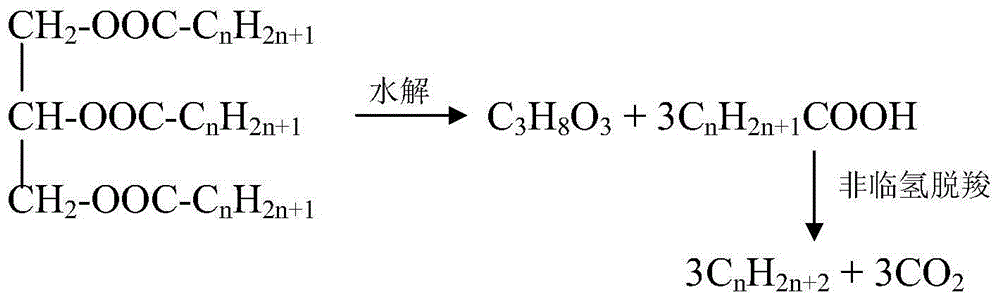
Processes for producing hydrocarbons in the gasoline and jet fuel range. The processes involve the thermal decarboxylation of fatty acids, which can be derived from the hydrolysis of triglycerides, which triglycerides can be vegetable oils, animal fats, or combinations thereof. The resulting hydrocarbons can be hydrocracked, and, optionally, isomerized and / or hydrotreated, to yield hydrocarbons in the jet fuel or gasoline range. Where the resulting hydrocarbons include olefinic double bonds, they can alternatively be combined with low molecular weight olefins, and subjected to olefin metathesis to yield hydrocarbons in the jet fuel or gasoline range.
Owner:BRADIN DAVID
Method of Converting Triglycerides to Biofuels
ActiveUS20080071125A1Improve chemical and physical and combustion qualityImprove thermal stabilityFatty acid chemical modificationBiofuelsIsomerizationPtru catalyst
A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process including the steps of (a) preconditioning unsaturated triglycerides by catalytic conjugation, cyclization, and cross-link steps; (b) contacting the modified triglycerides with hot-compressed water containing a catalyst, wherein cracking, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, aromatization, or isomerization, or any combination thereof, of the modified triglycerides produce a crude hydrocarbon oil and an aqueous phase containing glycerol and lower molecular weight molecules, and (c) refining the crude hydrocarbon oil to produce various grades of biofuels. A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process further including the steps of (a) carrying out anaerobic fermentation and decarboxylation / dehydration, wherein the anaerobic fermentation produces hydrogen, volatile acids, and alcohols from fermentable feedstocks, and the decarboxylation / dehydration produces alkenes from the volatile acids and alcohols, respectively; (b) feeding the alkenes to the cyclization process; (c) feeding the hydrogen to the post refining process; and (d) recycling the aqueous phase containing glycerol to the decarboxylation / dehydration process. A biofuel composition including straight-chain, branched and cyclo paraffins, and aromatics. The paraffins are derived from conversion of triglycerides. The aromatics are derived from conversion of either triglycerides, petroleum, or coal.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
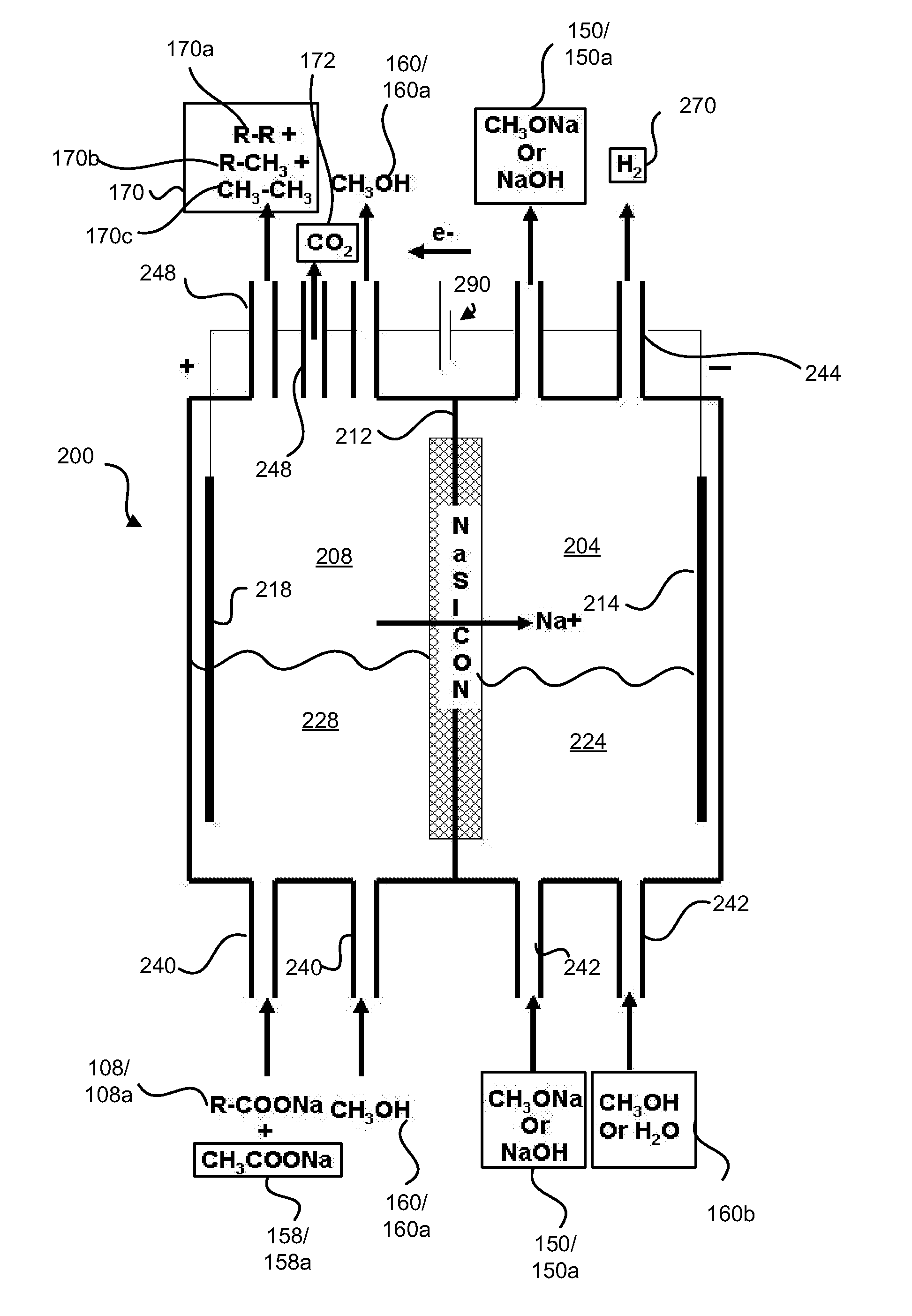
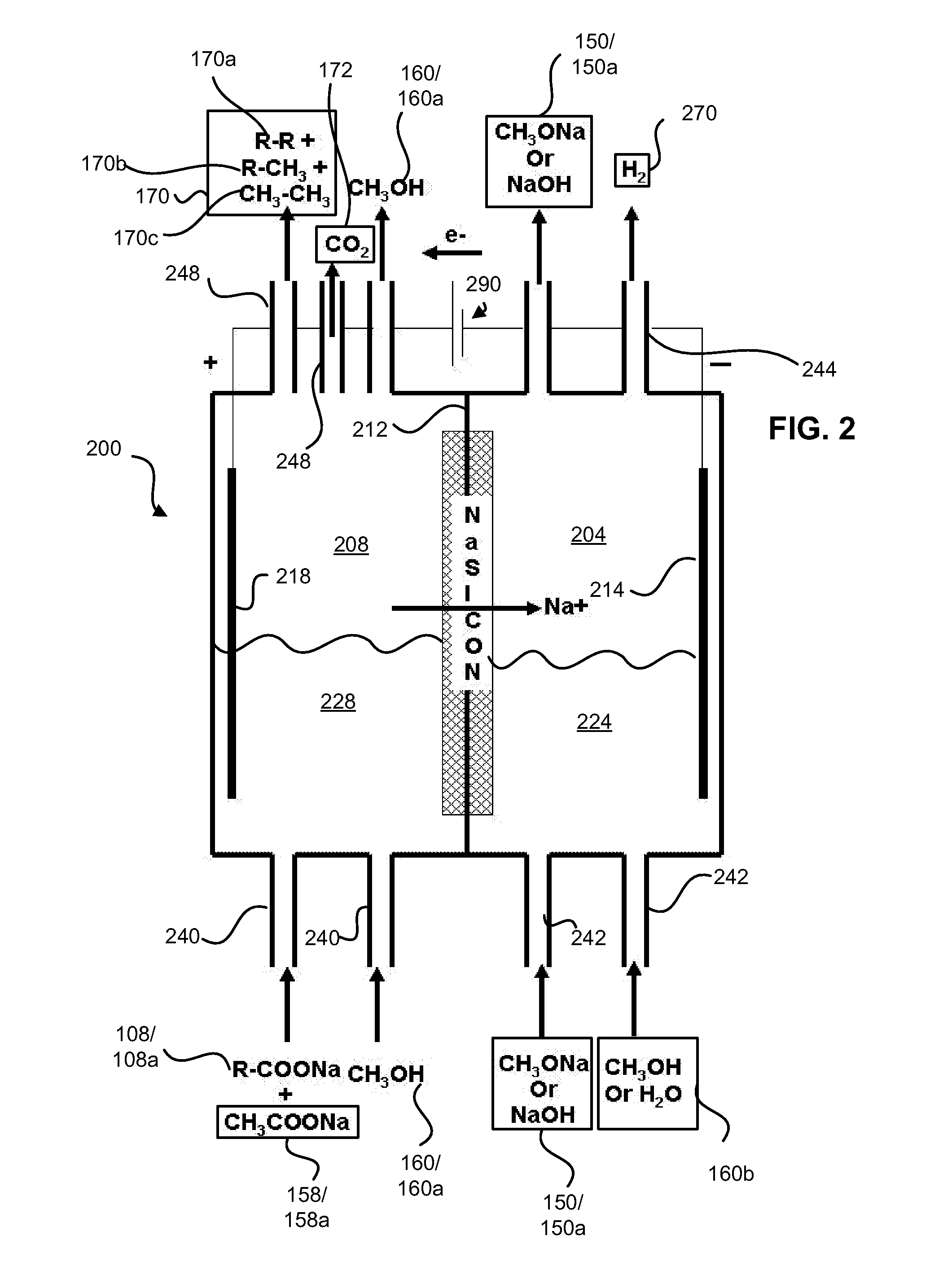
Decarboxylation cell for production of coupled radical products
InactiveUS20110024288A1Avoid mixingLow costCellsElectrolytic organic coupling reactionsAlkali ionsTG - Triglyceride
Owner:CERAMTEC
Method for producing nitrile compound, carboxylic acid compound or carboxylate compound
InactiveUS20060287541A1High yieldBiocideCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationAcetic acidMetal catalyst
The present invention discloses a process for preparing a nitrile compound, a carboxylic acid compound or a carboxylic acid ester compound represented by the formula (2): wherein R represents a cyano group, a carboxyl group or an ester group, R1 and R2 each represent a group which does not participate in the reaction, which may have a substituent, and R1 and R2 may be combined to each other to form a ring, which comprises subjecting an acetic acid compound represented by the formula (1): wherein R, R1 and R2 have the same meanings as defined above, to decarboxylation in the presence of a metal catalyst.
Owner:UBE IND LTD
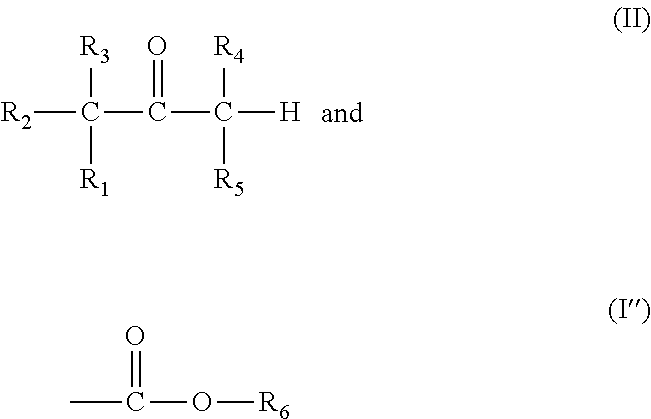
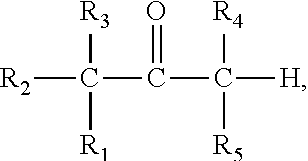
Prodrug comprising beta-keto carboxylic acid, beta-keto carboxylic acid salt or beta-keto carboxylic acid ester for drug delivery
InactiveUS20120065179A1Improve bioavailabilityGood water solubilityBiocideOrganic compound preparationActive agentCarboxylic acid
There is provided a prodrug of a pharmaceutically active agent, such prodrug comprising a beta-keto carboxylic acid, a beta-keto carboxylic acid salt or a beta-keto carboxylic acid ester functional group, a pharmaceutical composition comprising the prodrug, and to the use of the prodrug or composition for treatment of a mammalian subject suffering from a condition which can be cured or alleviated by administration of the pharmaceutically active agent. There is further provided a method of inhibiting decarboxylation of a compound comprising a beta-keto carboxylic acid or a salt thereof with a monovalent cation, characterized in that a dry salt of the beta-keto carboxylic acid with a divalent or polyvalent cation is prepared.
Owner:INFINITON
Conversion of crude tall oil to renewable feedstock for diesel range fuel compositions
ActiveUS20110049012A1Efficient removalEfficient separationFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid hydrogenationVolatilesBoiling point
There is disclosed a method for conversion of crude tall oil into high-quality diesel fuels comprising the steps of: (a) removal of non-oil contaminants present in the crude tall oil and recovering valuable organic compounds present in the crude tall oil, thereby forming a refined tall oil stream; (b) removal of the volatile fraction of the refined tall oil stream from step a), thereby forming a volatiles free oil stream comprising organic components with boiling points, at atmospheric pressure, of 170 degrees C. or higher; (c) separation in a vacuum distillation column of the volatiles free oil stream of step b) into two process streams or phases wherein a first process stream or phase is substantially comprising components with boiling points, at atmospheric pressure, in the range of 170-400 degrees C. and a second process stream or phase is substantially comprising components with boiling points, at atmospheric pressure, over 400 degrees C.; (d) lowering the oxygen content in the stream comprised of components with boiling points in the range 200-400 degrees C. from step c) by decarboxylation and / or decarbonylation.
Owner:SUNPINE
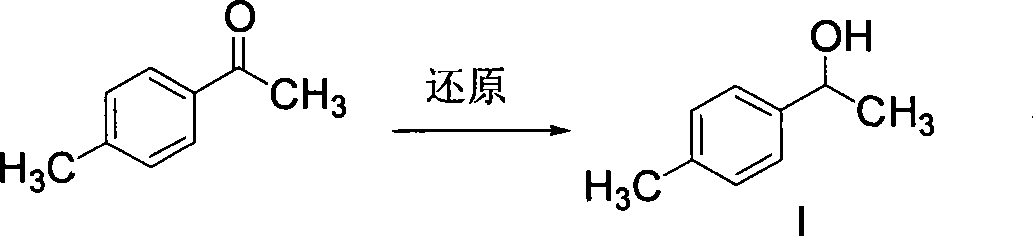
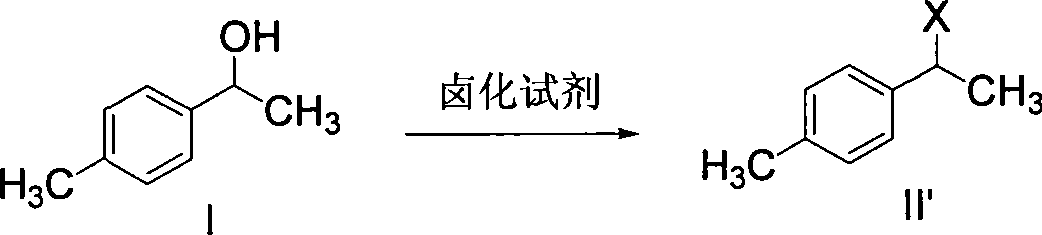
Method for synthesizing loxoprofen sodium
ActiveCN101412670ARaw materials are easy to getUnique craftOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationSolventHydrolysis
The invention discloses a synthetic method for loxoprofen sodium, which is prepared by taking methyl acetophenone as an initial raw material through reduction, acylation or halogen substituent, cyanation, hydrolysis, bromination, condensation, decarboxylation and salifying. The method has the advantages of easily obtained raw material, unique technology, simple and stable operation, and high productive rate in each step of reaction; and all solvents used in the synthesis process can be recycled, so the production cost is reduced greatly. Tests show that the obtained product has reliable quality and stable performance, and can be further used for making preparation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as the loxoprofen sodium.
Owner:ZHEJIANG APELOA JIAYUAN PHARMA +1
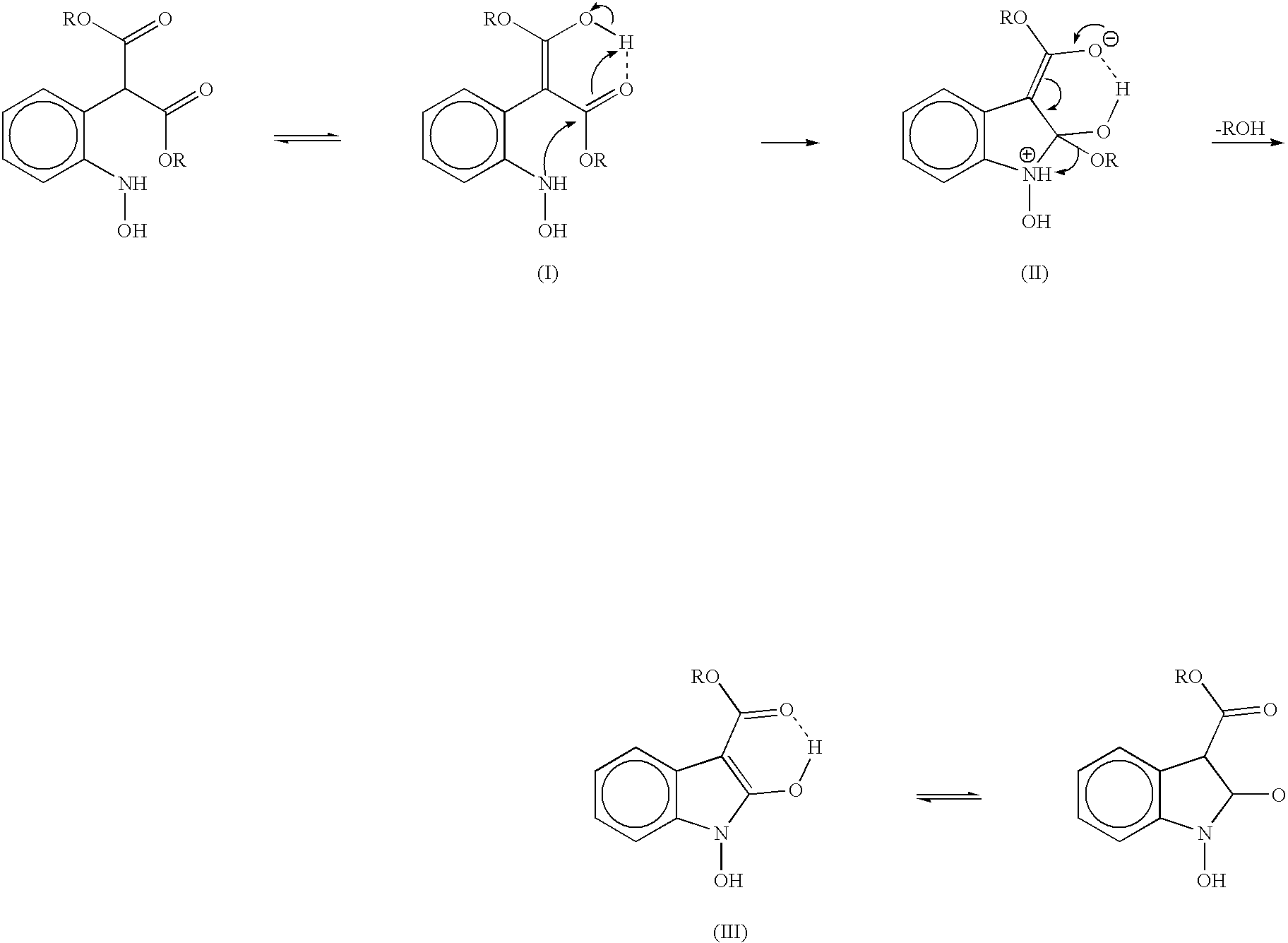
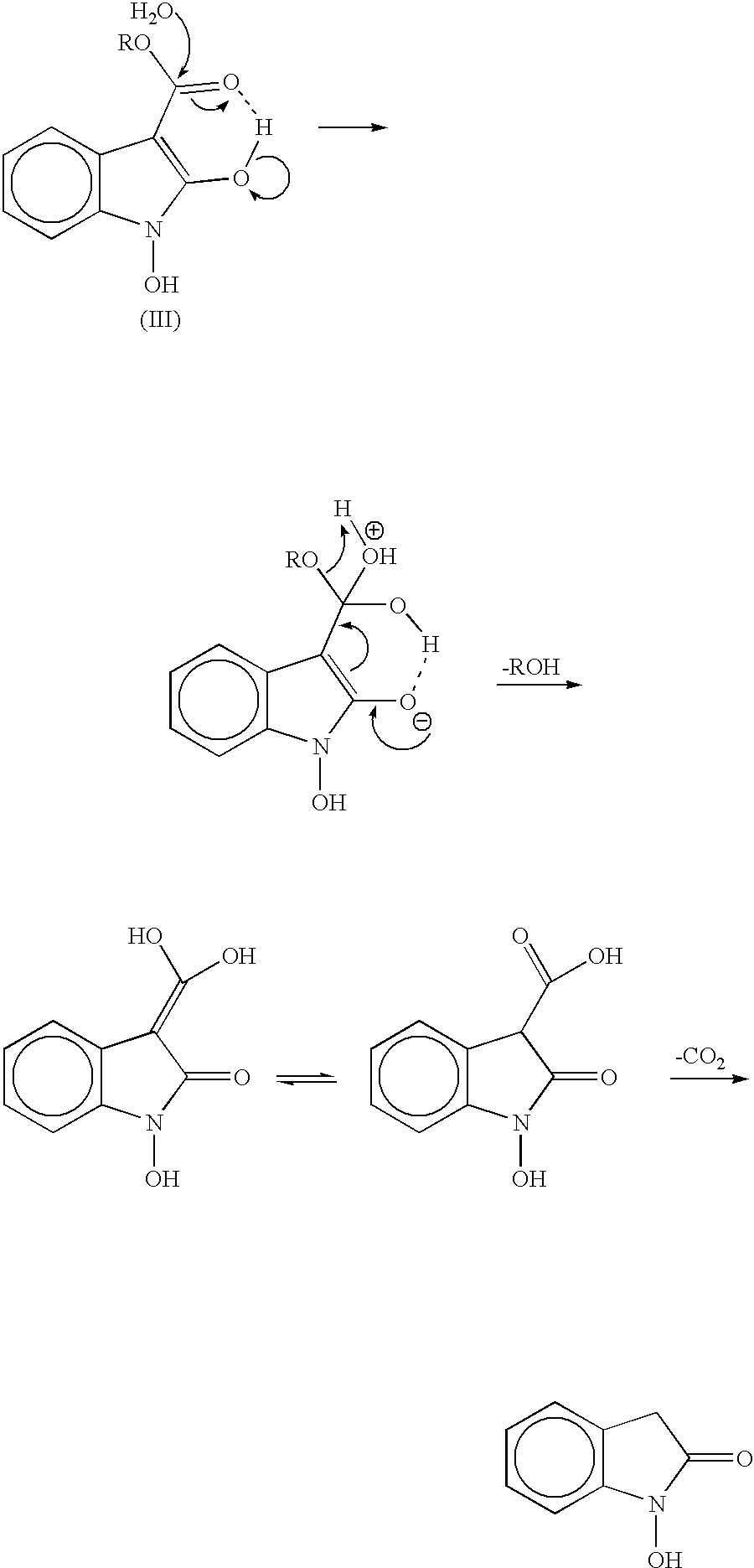
Process for preparing 2-oxindoles and N-hydroxy-2-oxindoles
InactiveUS6469181B1Avoid wastingImprove economyCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationReaction intermediateCarboxylic salt
The present invention provides a processes, having practical utility, for preparing 2-oxindoles, N-hydroxy-2-oxindoles, or mixtures thereof comprising: catalytically hydrogenating a 2-nitroarylmalonate diester to produce a 2-(N-hydroxyamino)arylmalonate diester, a 2-aminoarylmalonate diester, or mixtures thereof as a first reaction intermediate; cyclizing, by intramolecular aminolysis of one ester group, the first reaction intermediate to produce a N-hydroxy-2-oxindole-3-carboxylate ester, 2-oxindole-3-carboxylate ester, or mixtures thereof as a second reaction intermediate; and hydrolyzing and decarboxylating the remaining ester group of the second reaction intermediate to produce the N-hydroxy-2-oxindole, the 2-oxindole, or mixtures thereof, wherein the cyclization reaction and the hydrolysis and decarboxylation reaction are conducted in situ with the catalytic hydrogenation reaction without isolation of said reaction intermediates.
Owner:CATALYTICA PHARMA
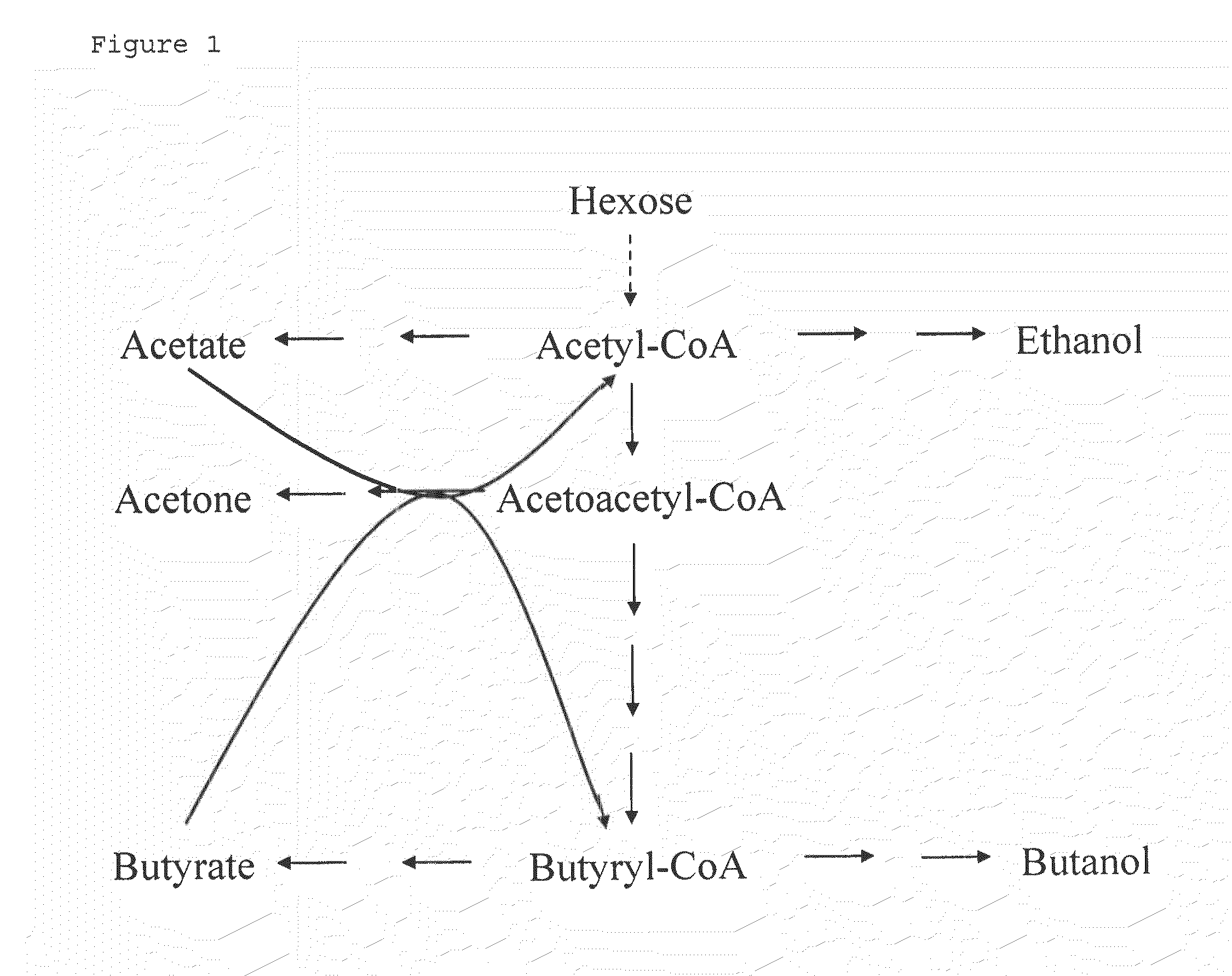
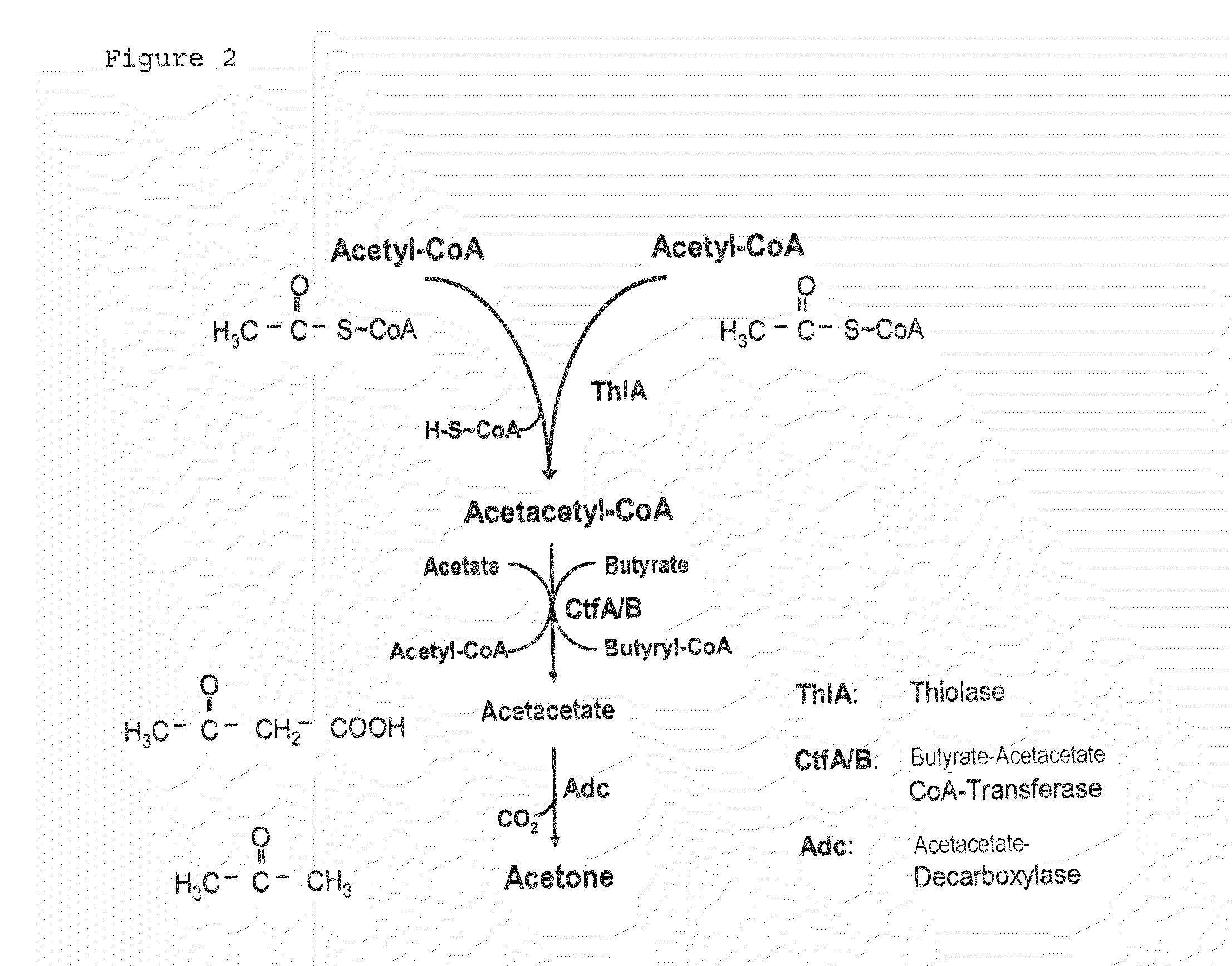
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveUS20100261237A1YieldHigh yieldSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
The invention describes a process for preparing acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone and CO2, which is characterized in that the coenzyme A is not transferred in process step B to an acceptor molecule. In addition, process step B is surprisingly catalysed by enzymes of the classes of acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase.A completely novel metabolic pathway is concerned, because the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never previously been described for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Method for producing cadaverine dicarboxylate
Cadaverine dicarboxylate is produced by performing an enzymatic decarboxylation reaction of a lysine solution while adding a dicarboxylic acid containing 4 to 10 carbons to the lysine solution to maintain pH of the solution at a level sufficient for the enzymatic decarboxylation reaction to occur, for example, 4.0 to 8.0.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
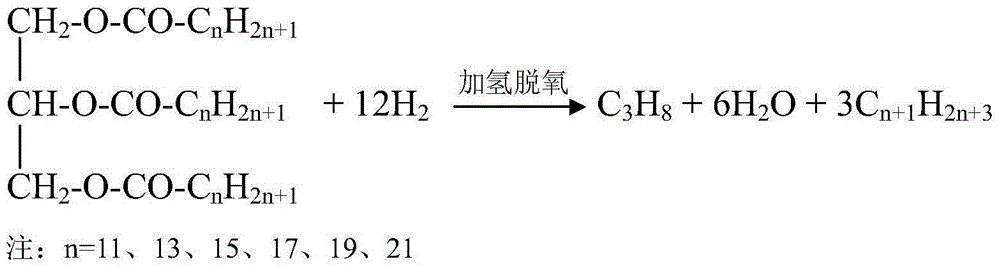
Process for hydrodeoxygenation of feeds derived from renewable sources with limited decarboxylation conversion using a catalyst based on nickel and molybdenum
ActiveUS20100240942A1Yield maximizationOptimization mechanismFatty acid chemical modificationMolecular sieve catalystsHydrogenHydrodeoxygenation
The invention concerns a process for hydrodeoxygenation of feeds derived from renewable sources with conversion by decarboxylation / decarbonylation limited to at most 10%, using a bulk or supported catalyst comprising an active phase constituted by at least one element from group VIB and at least one element from group VIII, said elements being in the sulphide form, and the atomic ratio of the metal (or metals) from group VIII to the metal (or metals) from group VIB being strictly more than 0 and less than 0.095, said process being carried out at a temperature in the range 120° C. to 450° C., at a pressure in the range 1 MPa to 10 MPa, at an hourly space velocity in the range 0.1 h−1 to 10 h−1, and in the presence of a total quantity of hydrogen mixed with the feed such that the hydrogen / feed ratio is in the range 50 to 3000 Nm3 of hydrogen / m3 of feed.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
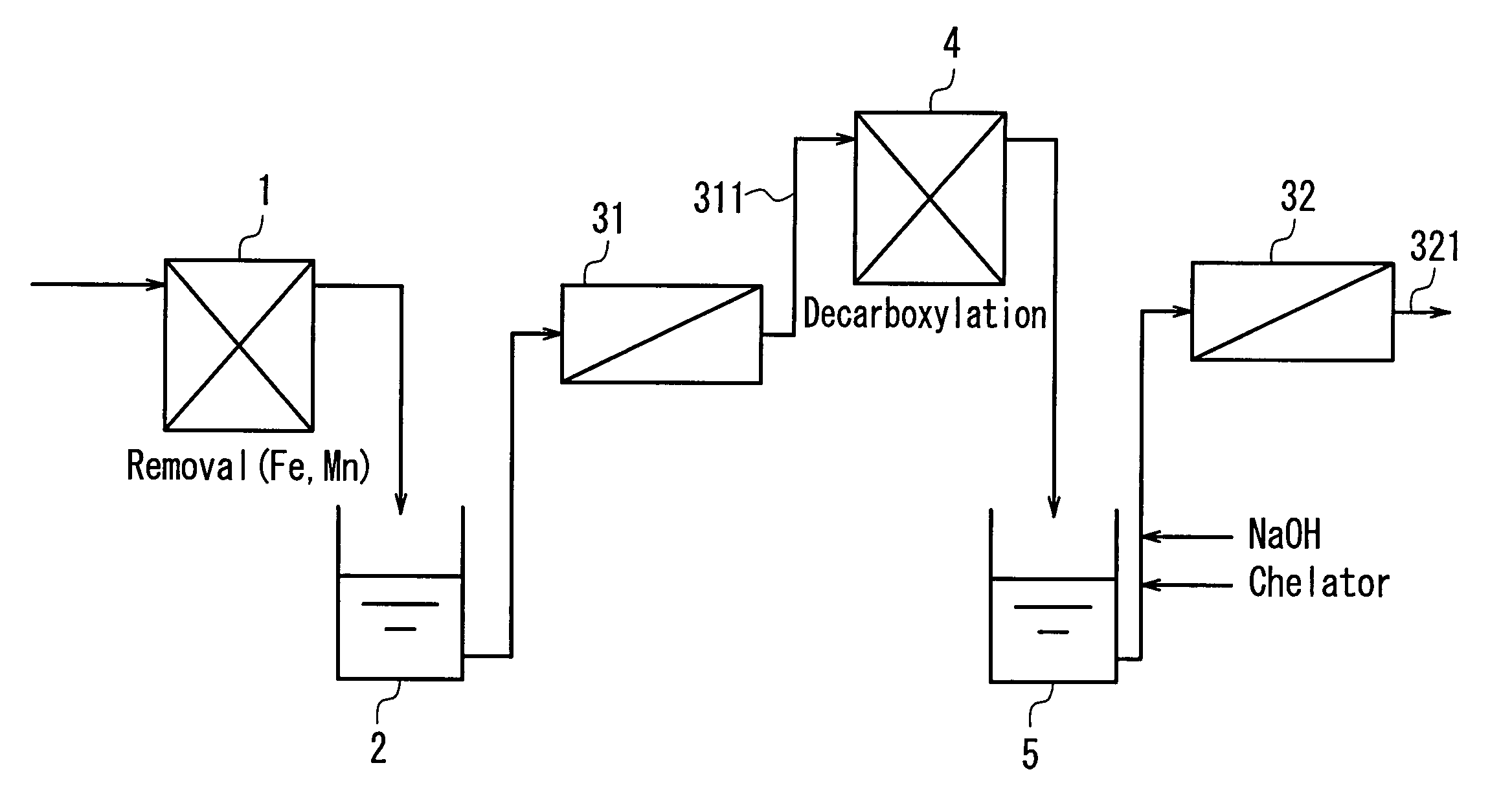
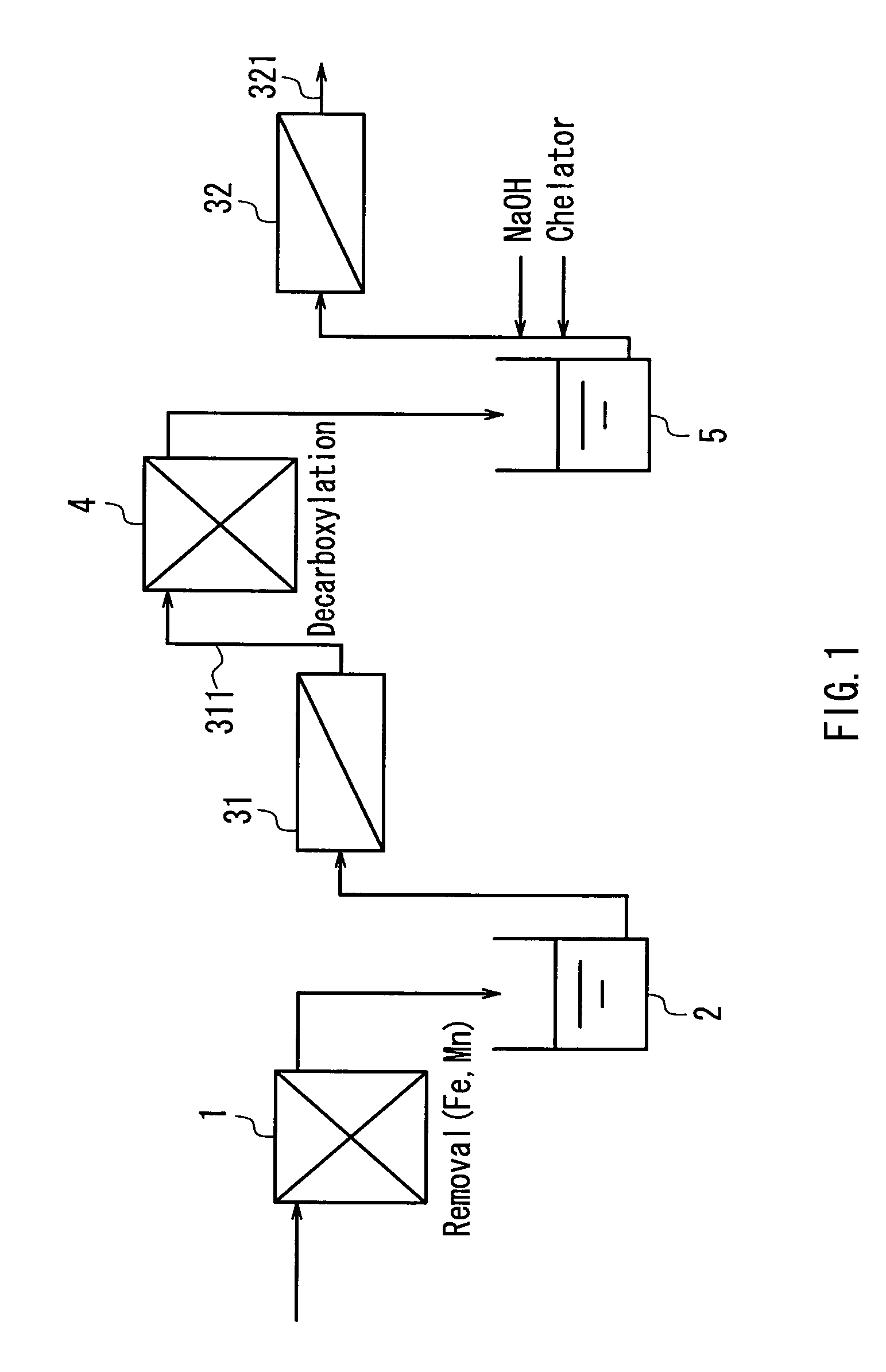
Method of multi-stage reverse osmosis treatment
InactiveUS20040050793A1Easy to separateHigh degreeLiquid degasificationScale removal and water softeningReverse osmosisDecarboxylation
In a multistage osmosis treatment method including: subjecting liquid to reverse osmosis treatment in a first-stage reverse osmosis separation module (31); adding an alkali agent to the obtained permeated water (5) to adjust a pH value of the permeated water (5) in an alkaline region; and further subjecting the permeated water (5) to reverse osmosis treatment in second and subsequent stage reverse osmosis separation modules (32), the supply water (5) to the second-stage reverse osmosis separation module (32) is subjected to at least one treatment selected from deferrization, demanganization, decarboxylation, and addition of a chelator and a scale inhibitor. Because of this, multistage reverse osmosis treatment is provided, in which the separation performance of the second and subsequent stage reverse osmosis membrane modules is enhanced, and liquid can be separated and purified to a high degree, and boron and the like that are not dissociated in a neutral region can be separated at a high blocking ratio.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Synthesis method of tert-butyl-[2-(biphenyl-4-yl)-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl] carbamate
InactiveCN101362708ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getMature technologyCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCarbamateSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a pharmaceutical intermediate of tertiary butyl-(2-(biphenyl-4-yl)-1-(methylol) ethyl) carbamate, which comprises the steps that: diethyl acetamidornalonate and 4-substituent biphenyl are taken as initial raw materials and undergone six steps of reactions including condensation, decarboxylation, hydrolysis, reduction and acylation to obtain the tertiary butyl-(2-(biphenyl-4-yl)-1-(methylol) ethyl) carbamate. The method of the invention has the advantages of available raw materials, convenient operation, high reaction yield rate, recoverable solvents used in the synthesis course, thereby reducing environmental pollution and greatly reducing production cost; according to test results, the products obtained by the method has reliable quality and stable performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method of making fluorinated vinyl ethers
InactiveUS20070004938A1Improve throughputMinimize undesirable reaction byproductOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acid preparationVinyl etherCarbonate ester
The present application provides a process to produce fluorinated vinyl ether by reacting a 2-alkoxypropionyl fluoride with a metal carbonate under anhydrous conditions in a stirred bed reactor at a temperature above the decarboxylation temperature of an intermediate carboxylate to produce a fluorinated vinyl ether. The process is carried out in the absence of solvent. With the process described, fluorinated vinyl ether of a high purity can be obtained in a high throughput manner.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
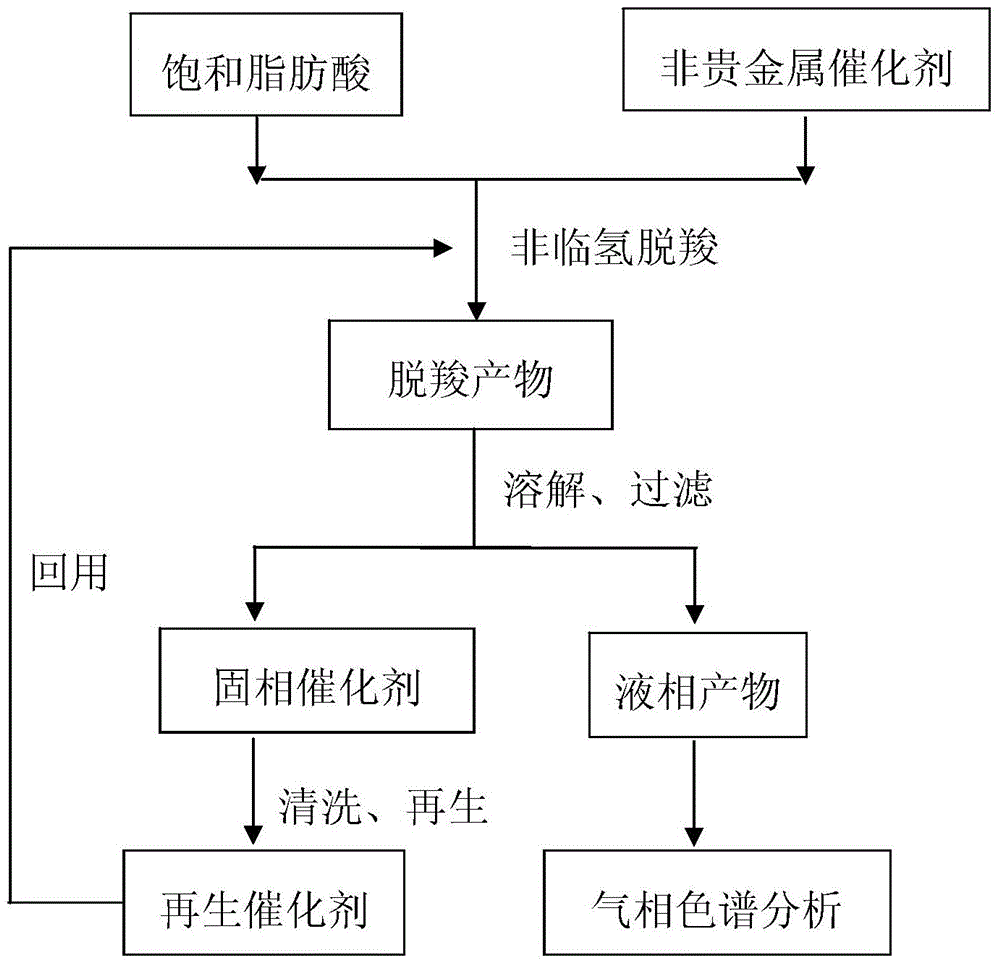
Method for using non-noble metal catalyst to catalyze decarboxylation of saturated fatty acid to prepare long-chain alkane
InactiveCN104403683AEasy to separateIncrease the rate of the decarboxylation reactionFatty acid chemical modificationMolecular sieve catalystsLiquid productAlkane
The invention discloses a method for using non-noble metal catalyst to catalyze decarboxylation of saturated fatty acid to prepare long-chain alkane. The method includes: 1) adding saturated fatty acid and a non-noble metal catalyst into a high-temperature and high-pressure reaction kettle; 2) conducting heating to 300-390DEG C to carry out decarboxylation for 0.5-8h; 3) cooling the decarboxylation product, conducting dissolving by an organic solvent, and performing filtering to obtain a liquid product and a solid catalyst; and 4) cleaning and regenerating the non-noble metal catalyst for reuse. The non-noble metal catalyst is prepared by a co-precipitation method or impregnation method, and the catalyst is regenerated through reductive calcination in hydrogen. The reaction process involved in the invention has the characteristics of no need for a solvent, low energy consumption, and zero emission. The non-noble metal catalyst can effectively catalyze decarboxylation, the catalyst is low in cost and is easy to recover, and the process is simple and green.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Controlled cannabis decarboxylation
The invention is a process for the controlled decarboxylation of cannabis wherein Medicinal Delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and other cannabinoid medicinal substances are decarboxylated through a chemical reaction facilitated by a cofactor. The amount of medicinal cannabis decarboxylated will be directly proportional to the amount of cofactor used. Use a small amount of the cofactor and only some of the medicinal cannabis contained in raw cannabis will be converted from an acidic form into a non-acidic form. Use a large amount of the cofactor and most or all of the medicinal cannabis will be decarboxylated. The reaction is proportional to the molar mass of cofactor.
Owner:HOSPODOR ANDREW DAVID
Conversion of fatty acids to base oils and transportation fuels
The present invention is directed to methods for processing fatty acids to provide for base oil and transportation fuels, wherein decarboxylation-coupling dimerization of fatty acids provides dimer ketones from which the base oils and transportation fuels may be produced.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Biofuel production by high temperature non-faradaic electrochemical modification of catalysis
InactiveUS20100258447A1High calorific valueEasy to separateElectrolysis componentsEnergy inputMetallurgyBiofuel
A method for producing biofuels from biomass in which a refined biomass material is introduced into a non-Faradaic electrochemical device, preferably at a temperature greater than or equal to about 150° C., and deoxygenated and / or decarboxylated in said device to produce an increased carbon chain fuel.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Method for producing cadaverine dicarboxylate
ActiveUS20050003497A1Produced economicallyAdequate levelBacteriaFermentationCadaverineDicarboxylic acid
Cadaverine dicarboxylate is produced by performing an enzymatic decarboxylation reaction of a lysine solution while adding a dicarboxylic acid containing 4 to 10 carbons to the lysine solution to maintain pH of the solution at a level sufficient for the enzymatic decarboxylation reaction to occur, for example, 4.0 to 8.0.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
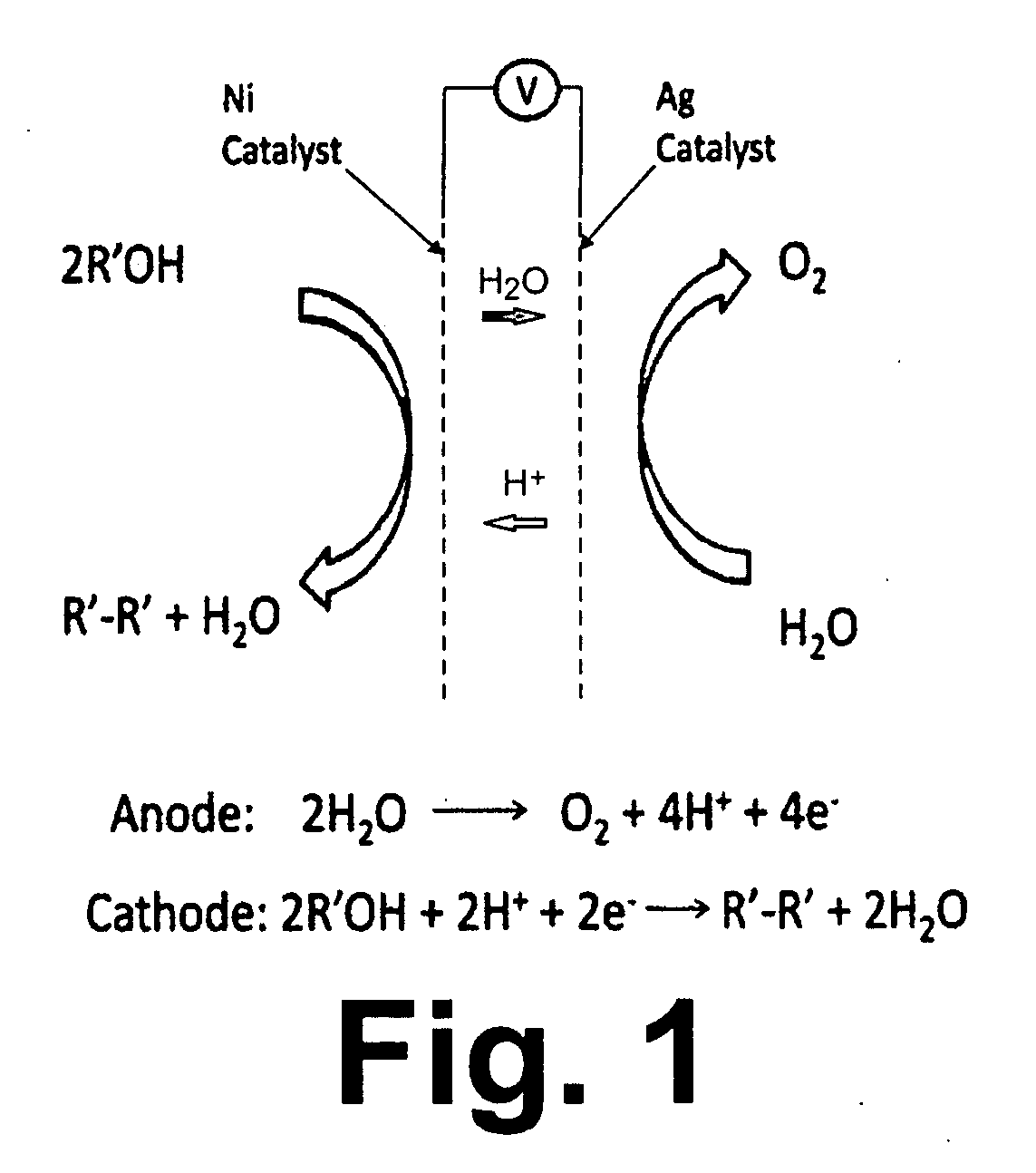
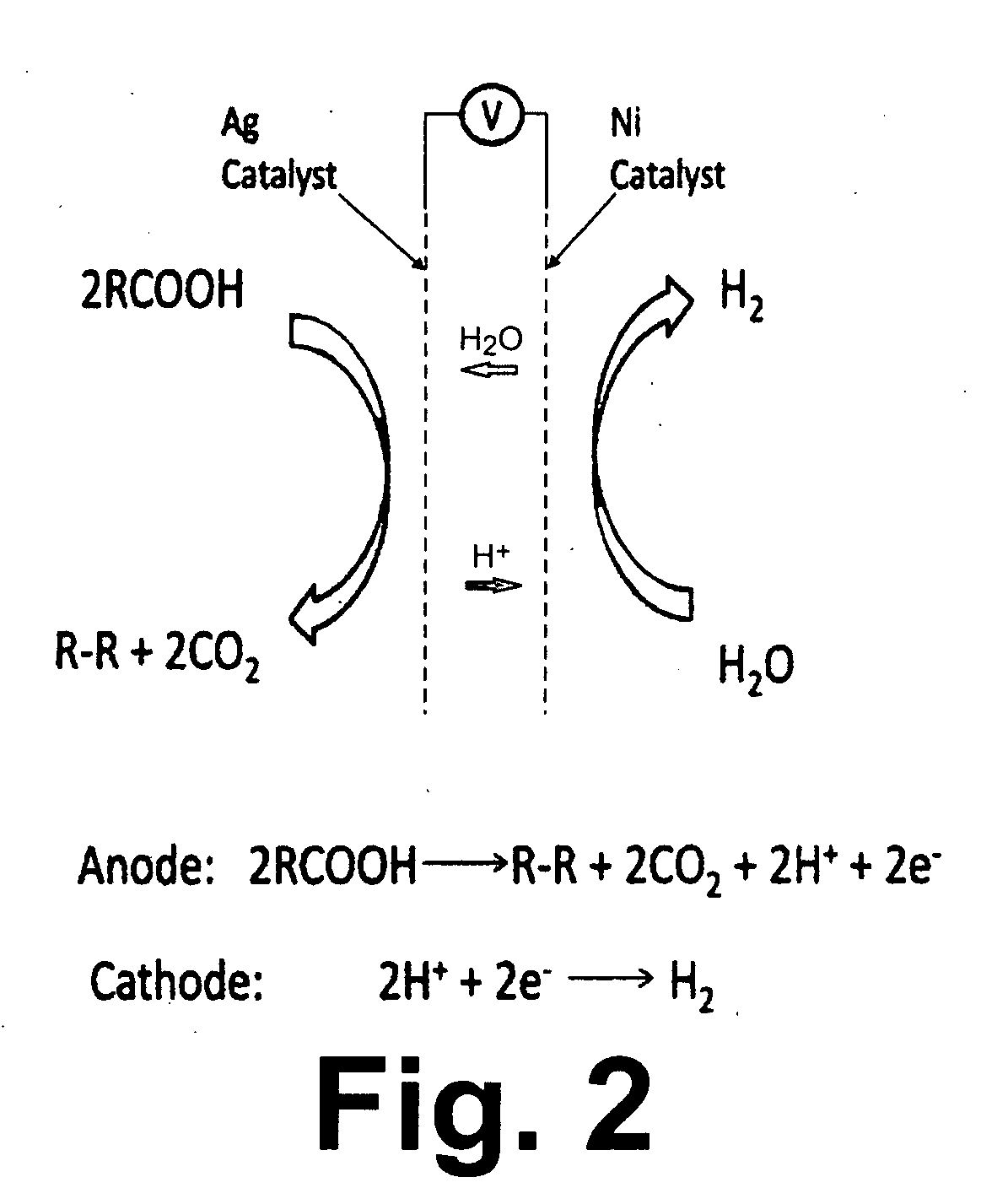
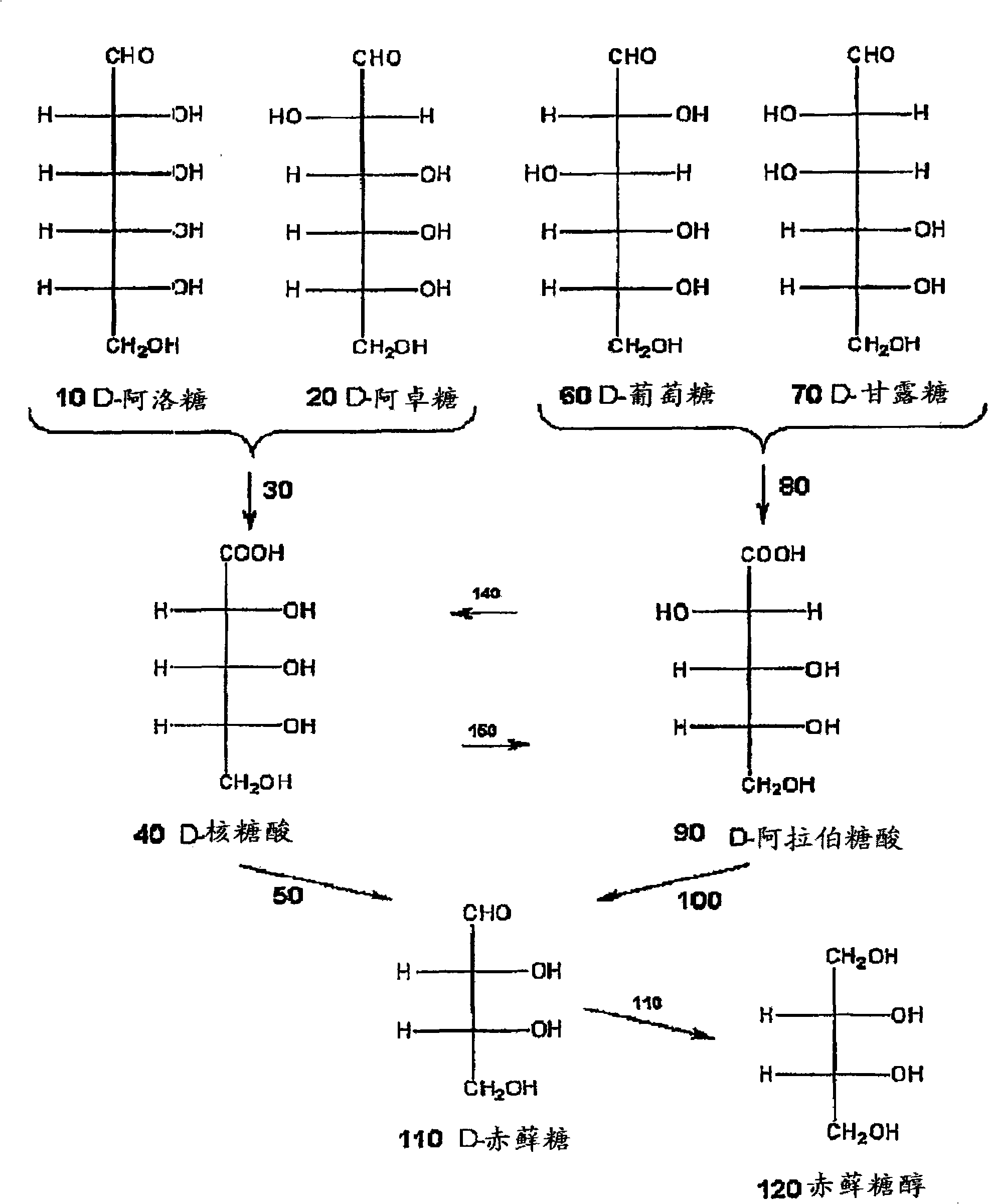
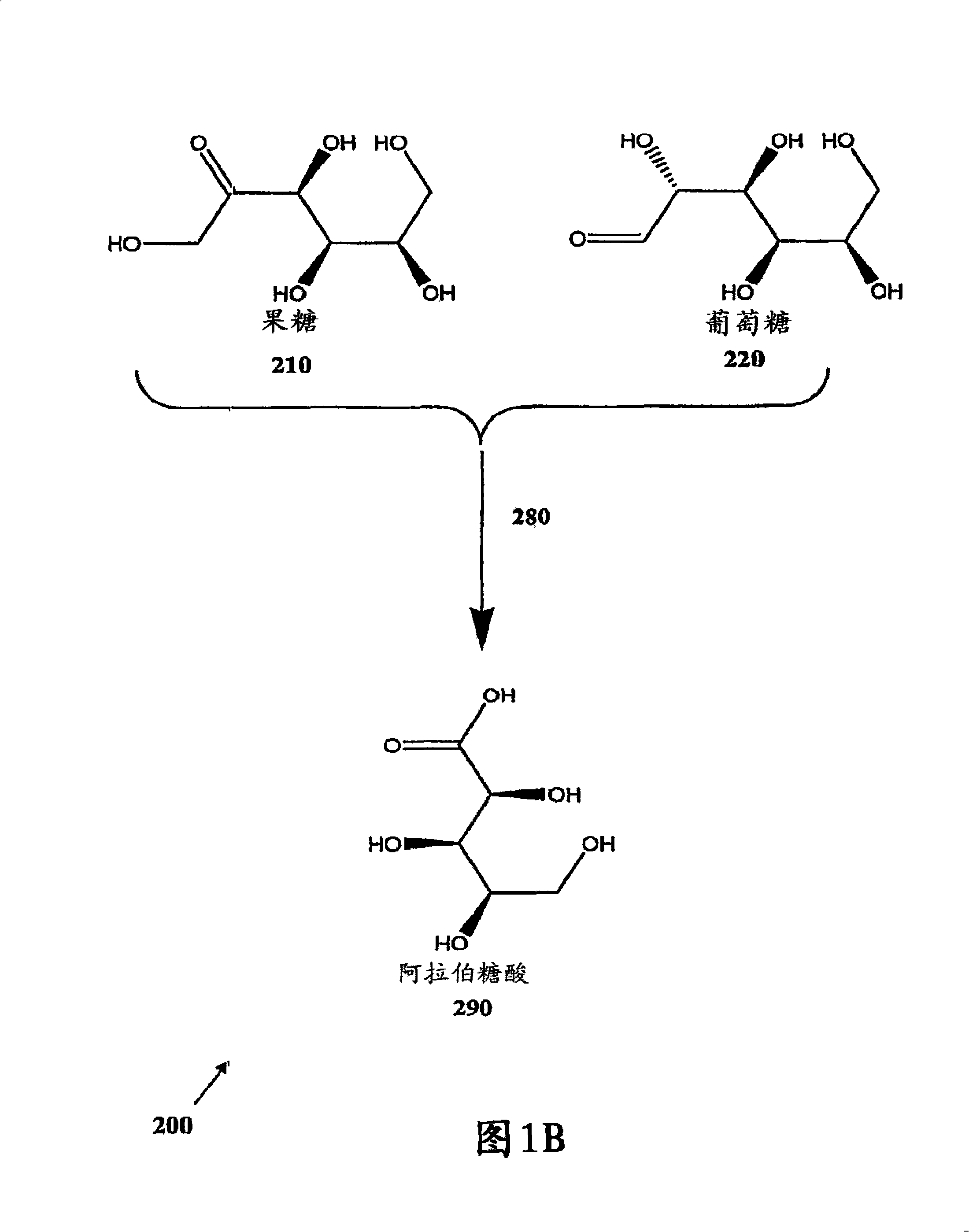
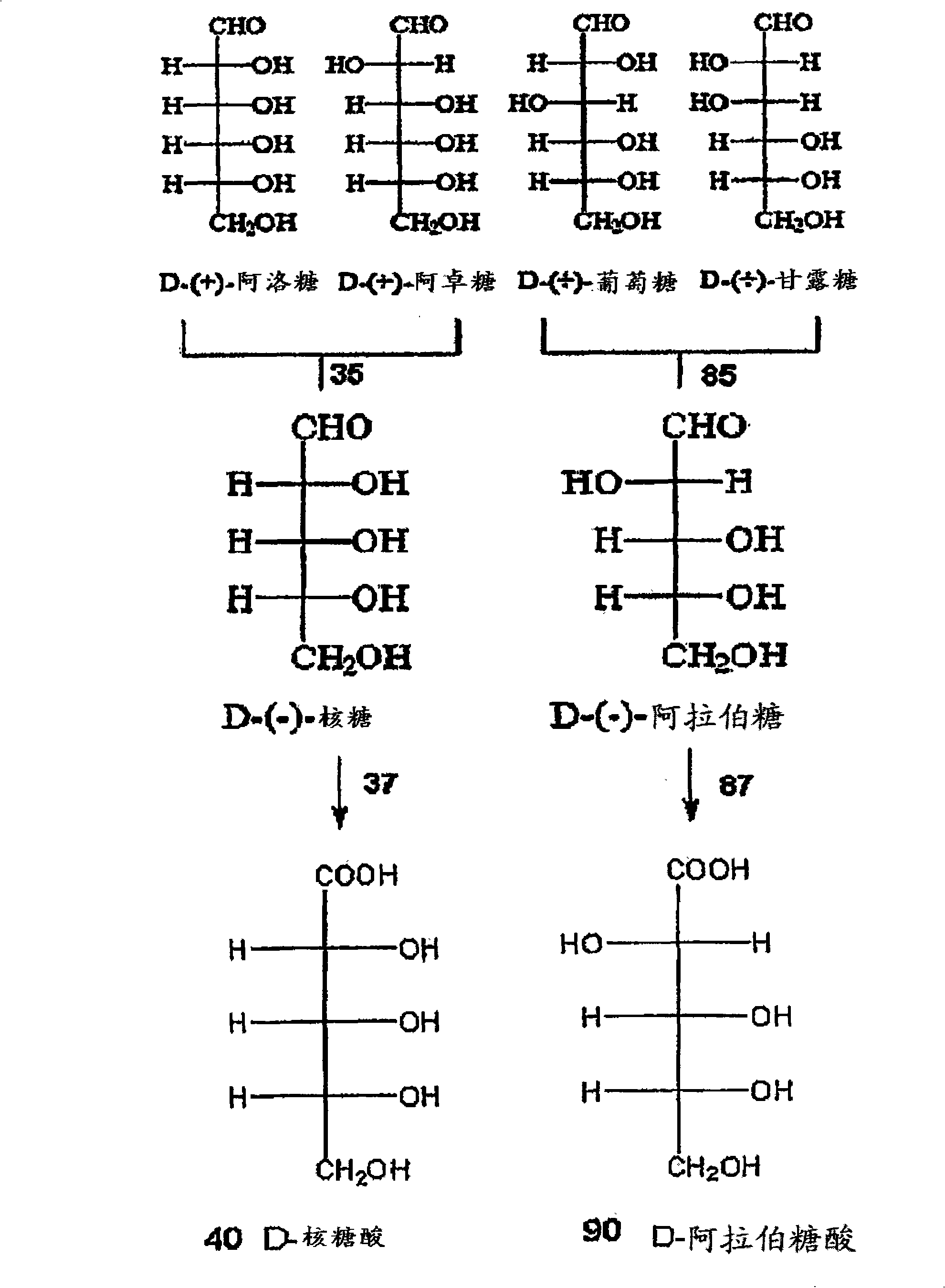
Methods for the electrolytic production of erythrose or erythritol
Owner:DFI USA LLC
Method for the preparation of diols
ActiveUS20110294178A1Increasing endogenous expressionHigh expressionFungiBacteriaMicroorganismMetabolite
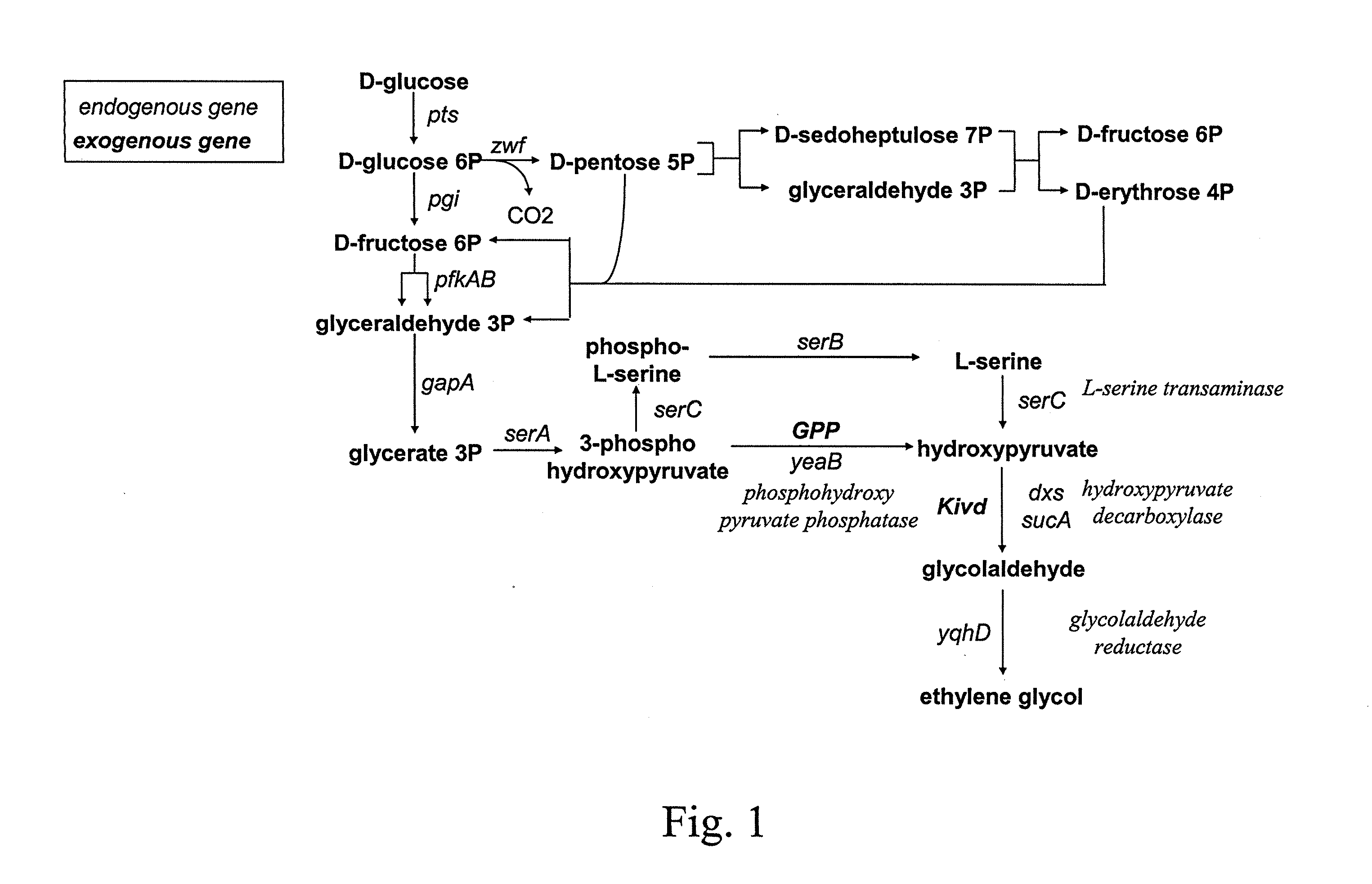
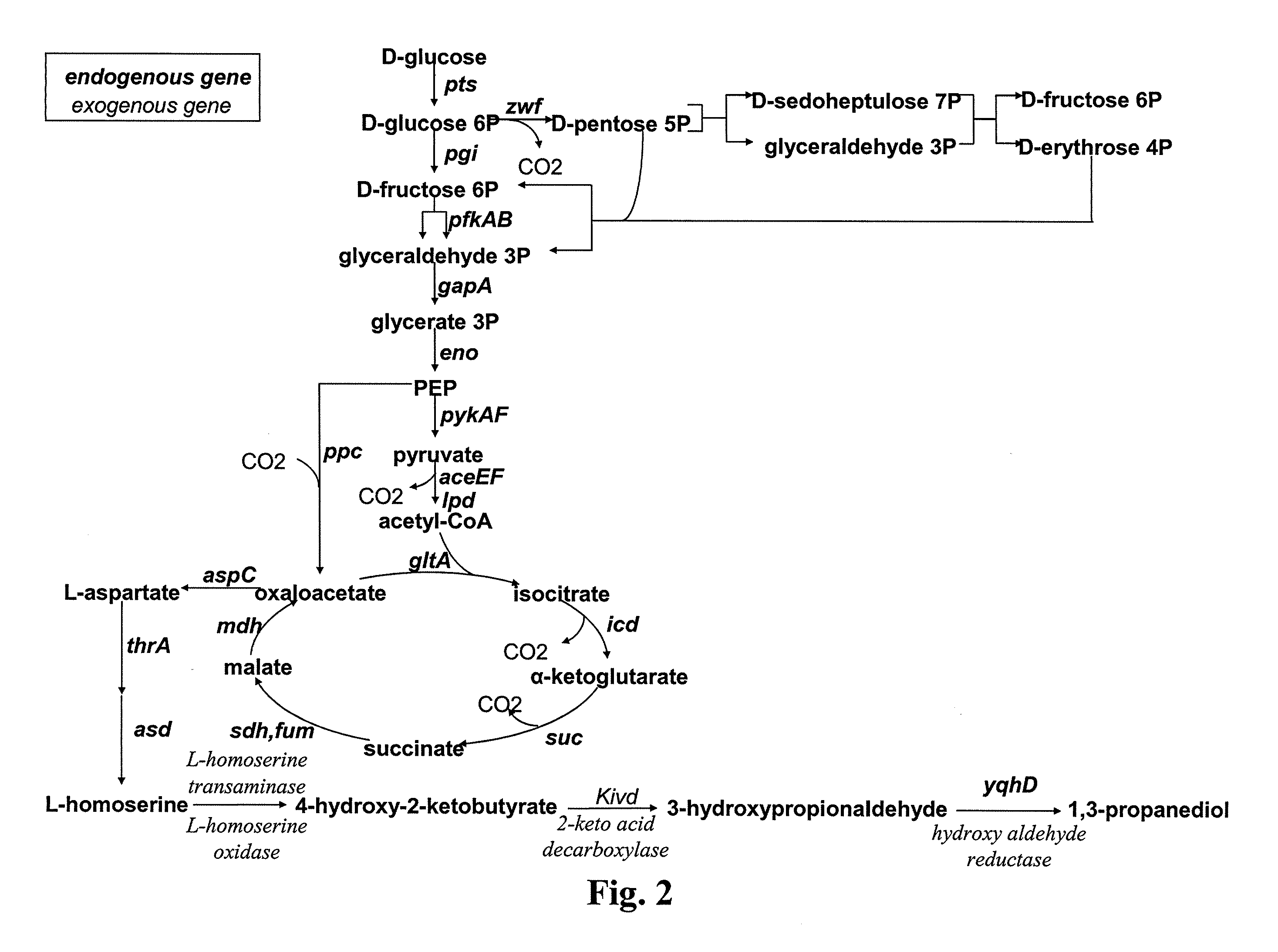
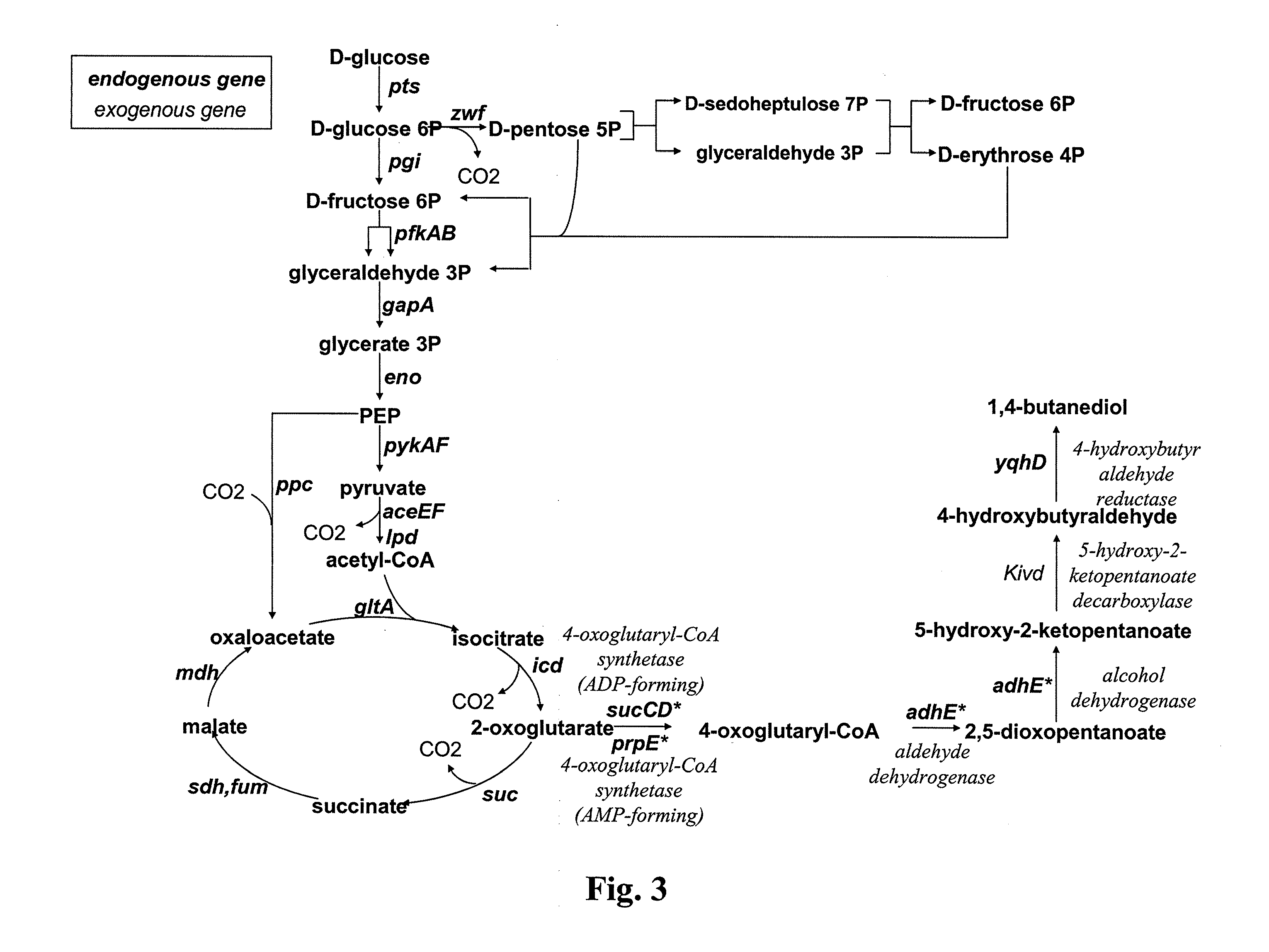
The present invention concerns a new method for the biological preparation of a diol comprising culturing a microorganism genetically modified for the bioproduction of an aliphatic diol, wherein the microorganism comprises a metabolic pathway for the decarboxylation of a hydroxy-2-keto-aliphatic acid metabolite with an enzyme having a 2-keto acid decarboxylase activity, the product obtained from said decarboxylation step being further reduced into the corresponding aliphatic diol, and wherein the microorganism is genetically modified for the improved production of said hydroxy-2-keto-aliphatic acid metabolite.The invention also concerns a modified microorganism for the production of an aliphatic diol.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
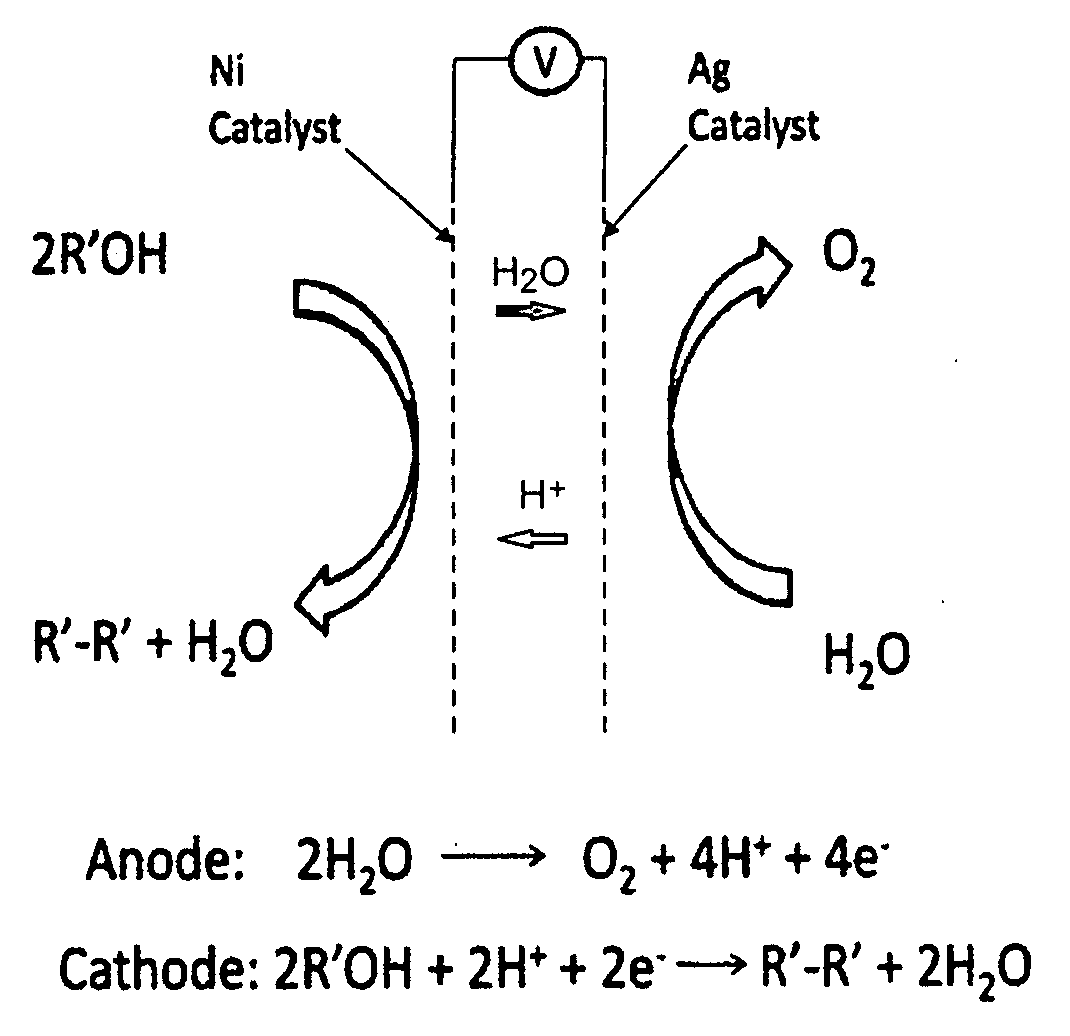
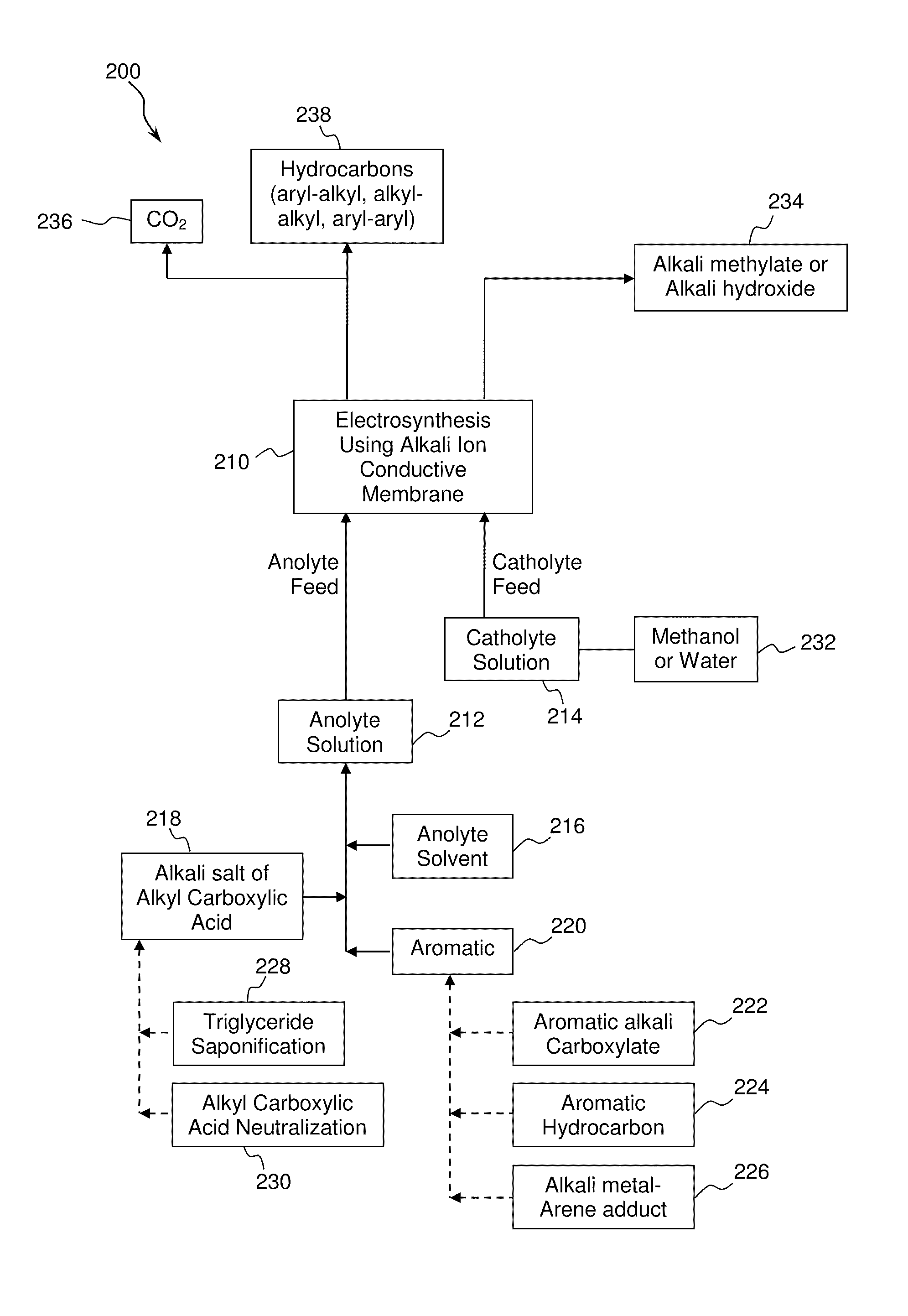
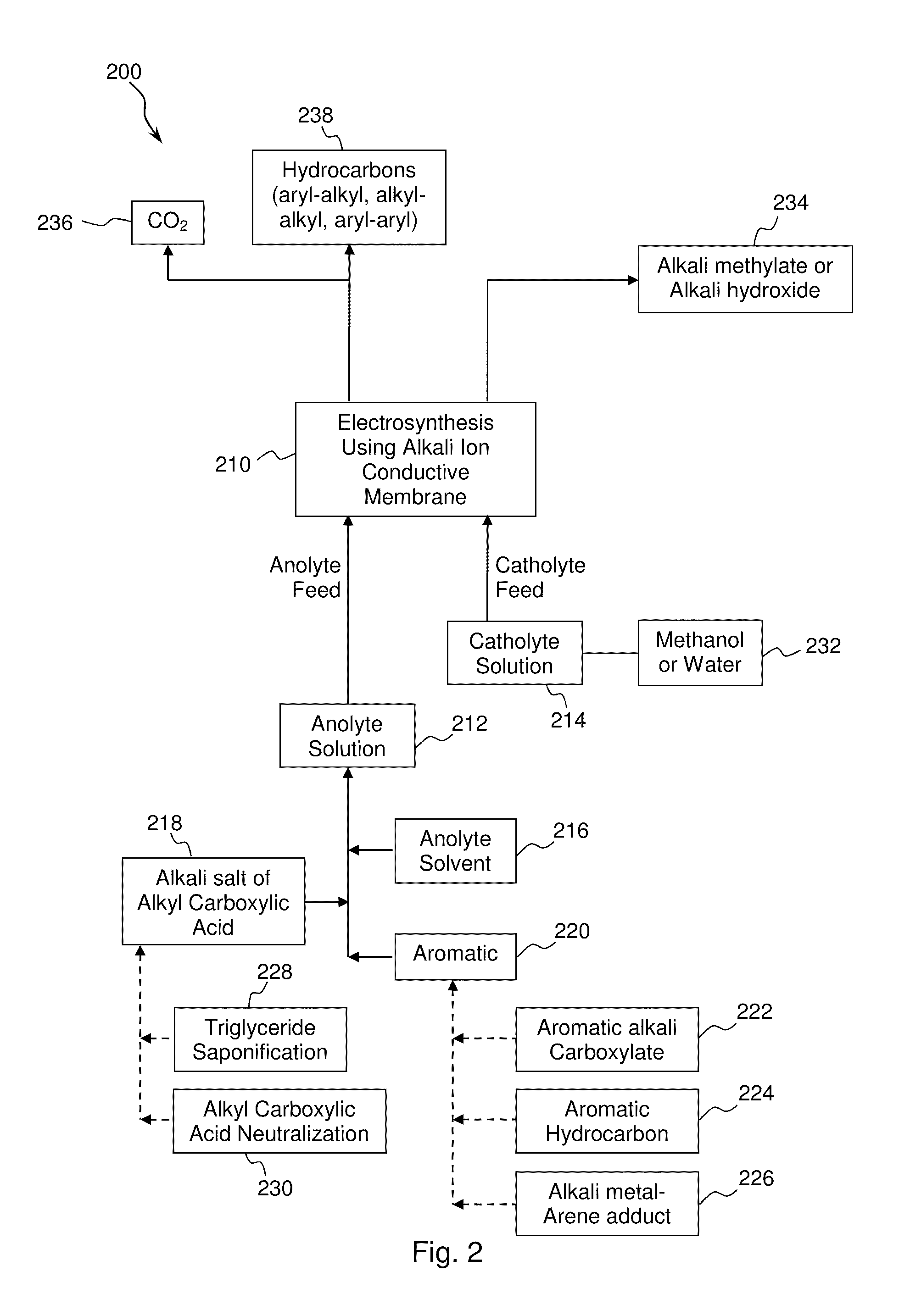
Electrochemical synthesis of aryl-alkyl surfacant precursor
An aryl-alkyl (R—Ar) hydrocarbon is prepared by an electrosynthesis process in an electrolytic cell having an alkali ion conductive membrane positioned between an anolyte compartment configured with an anode and a catholyte compartment configured with a cathode. An anolyte solution containing an alkali metal salt of an alkyl carboxylic acid and an aryl compound is introduced into the anolyte compartment. The aryl compound may include an alkali metal salt of an aryl carboxylic acid, an arene (aromatic) hydrocarbon, or an aryl alkali metal adduct (Ar−M+). The anolyte solution undergoes electrolytic decarboxylation to form an alkyl radical. The alkyl radical reacts with the aryl compound to produce the aryl-alkyl hydrocarbon.
Owner:ENLIGHTEN INNOVATIONS INC
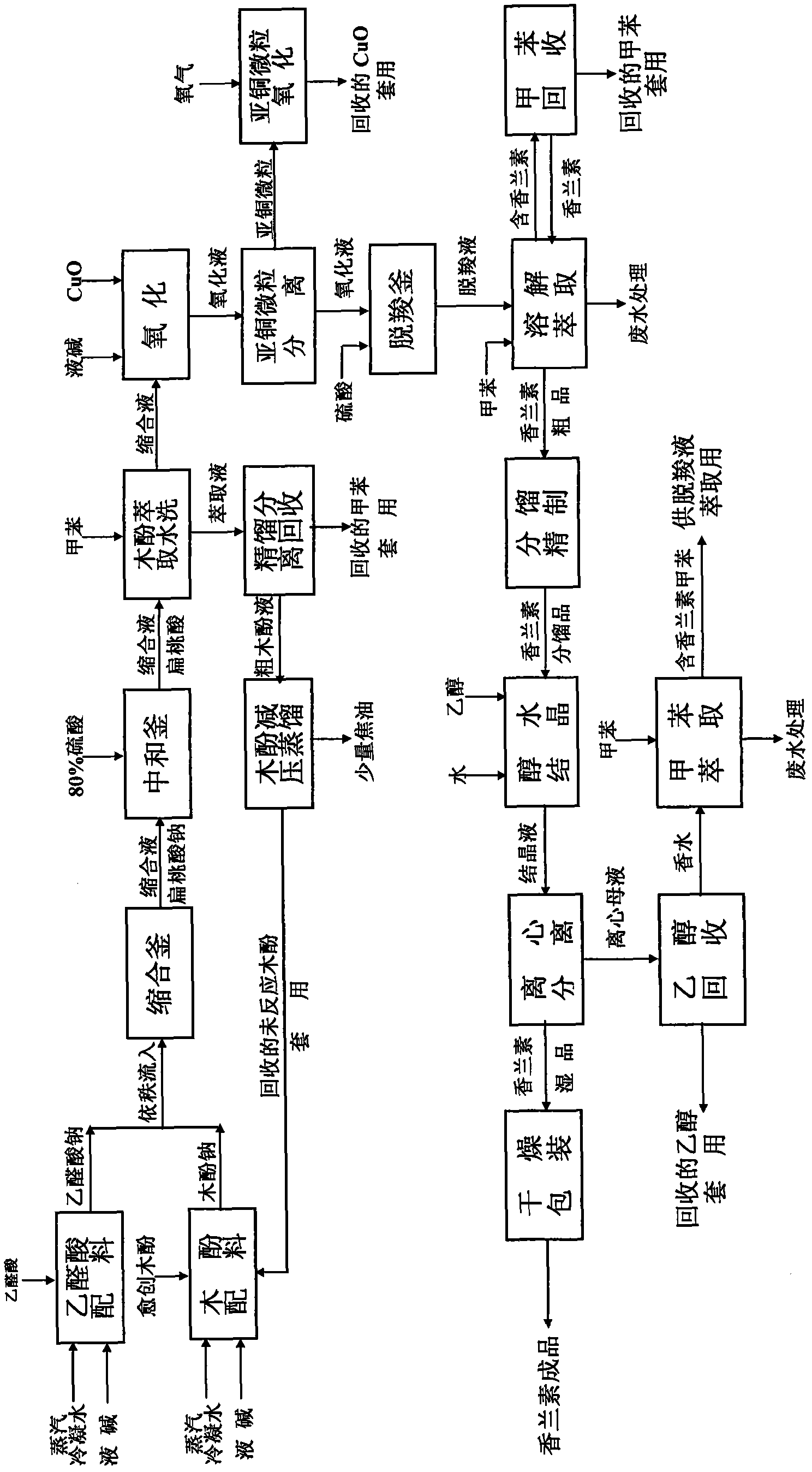
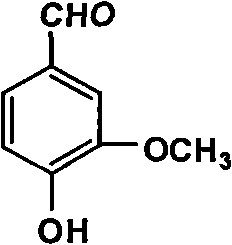
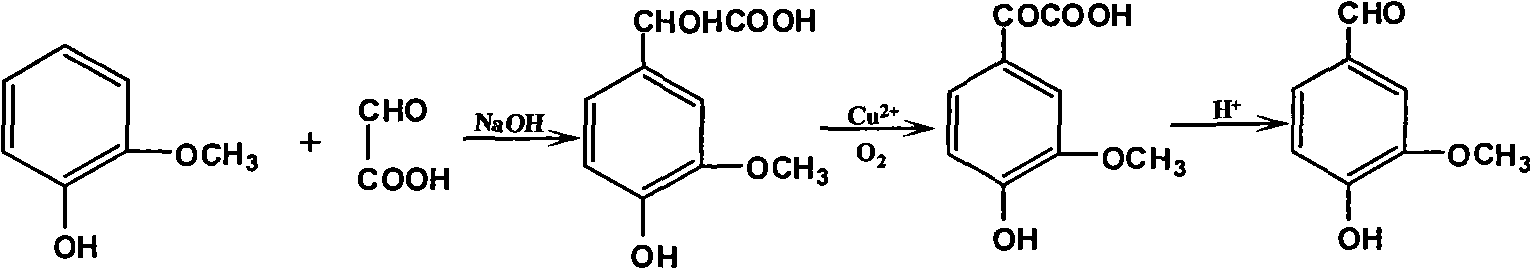
Productive technology of vanlillin by glyoxylic acid method
ActiveCN102010310AReduce organic contentReduce pollution sourcesOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound separation/purificationKetonic acidsFractionation
The invention discloses a productive technology of vanlillin by a glyoxylic acid method. The productive technology comprises a synthesis process, a fractionation process and a purification process, wherein the synthesis process comprises condensation treatment, oxidation treatment and decarboxylation treatment of methyl catechol and glyoxylic acid. The productive technology particularly comprisesthe following steps: respectively converting the methyl catechol and the glyoxylic acid into guaiacol sodium and sodium glyoxylate in a sodium hydroxide system; carrying out condensation treatment onthe guaiacol sodium and the sodium glyoxylate; after recovering the unreacted methyl catechol in a condensation liquid, carrying out oxidation treatment, namely carrying out catalytic oxidation on anethanol group in 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzene sodium glycolate by using copper oxide in the sodium hydroxide system to form a ketone group, thereby generating a corresponding ketonic acid compound; after separating red copper oxide particles from an oxidation liquid, carrying out decarboxylation treatment, namely using sulfuric acid to acidize the oxidation liquid, and simultaneously converting an acid group in the ketonic acid compound into carbon dioxide so as to generate 4-hydroxy-3- methoxybenzaldehyde; and carrying out the fractionation process and the purification process to obtain the vanlillin.
Owner:喜孚狮王龙香料(宁波)有限公司
Processes for preparing of 3,4-alkylenedioxythiophenes and 3,4-dialkoxythiophenes
InactiveUS7202369B2Inhibition formationOrganic chemistryPrinted circuit manufactureCarboxylic acidCopper
The present invention relates to a process for preparing 3,4-dialkoxythiophenes or 3,4-alkylenedioxythiophenes in high yield via the rapid decarboxylation of 3,4-dialkoxythiophenedicarboxylic acid or 3,4-aklylenedioxythiophenedicarboxylic acid in a water-miscible polar solvent in the presence of copper catalyst under an oxygen atmosphere.
Owner:BAIK WOON PHIL
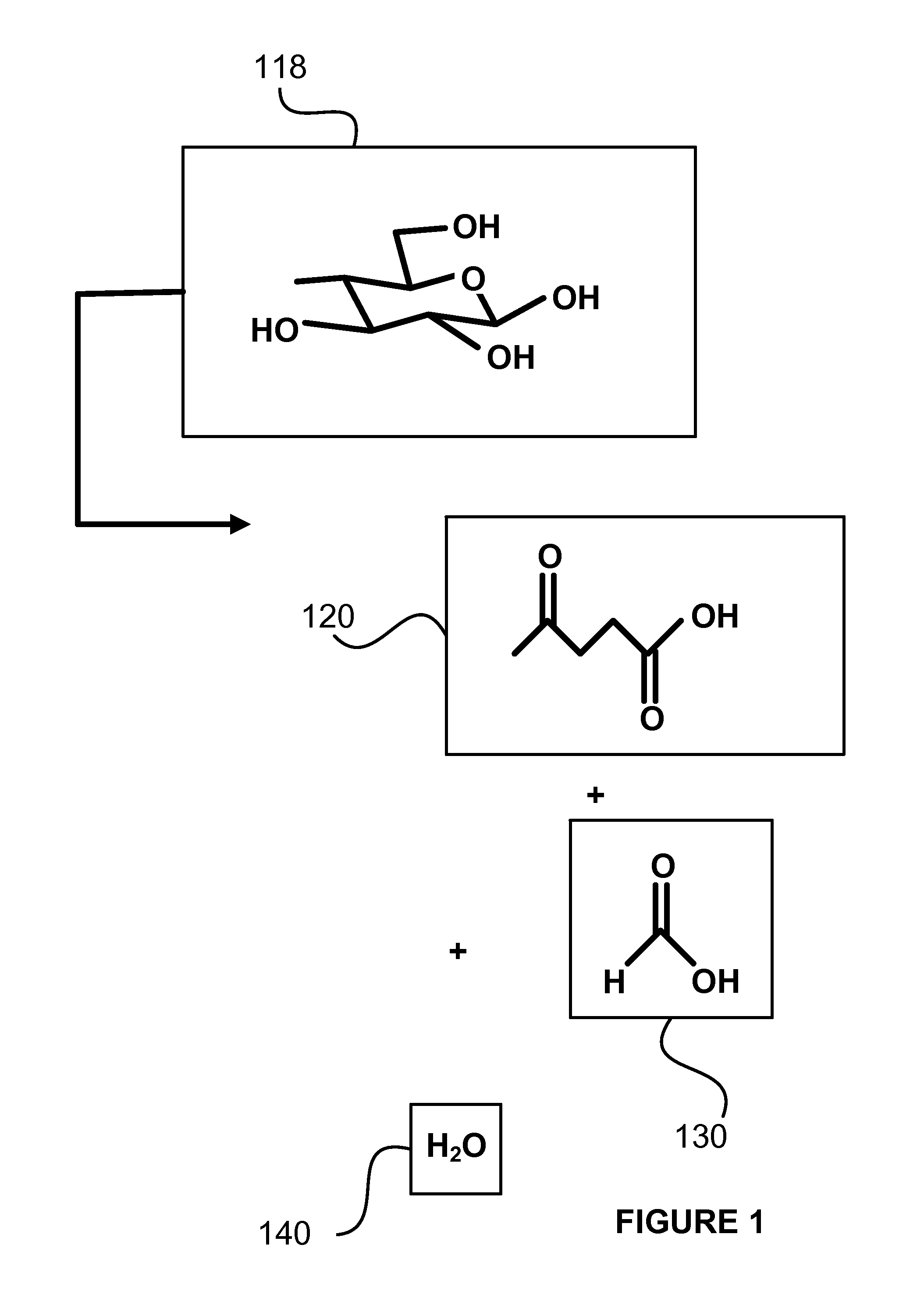
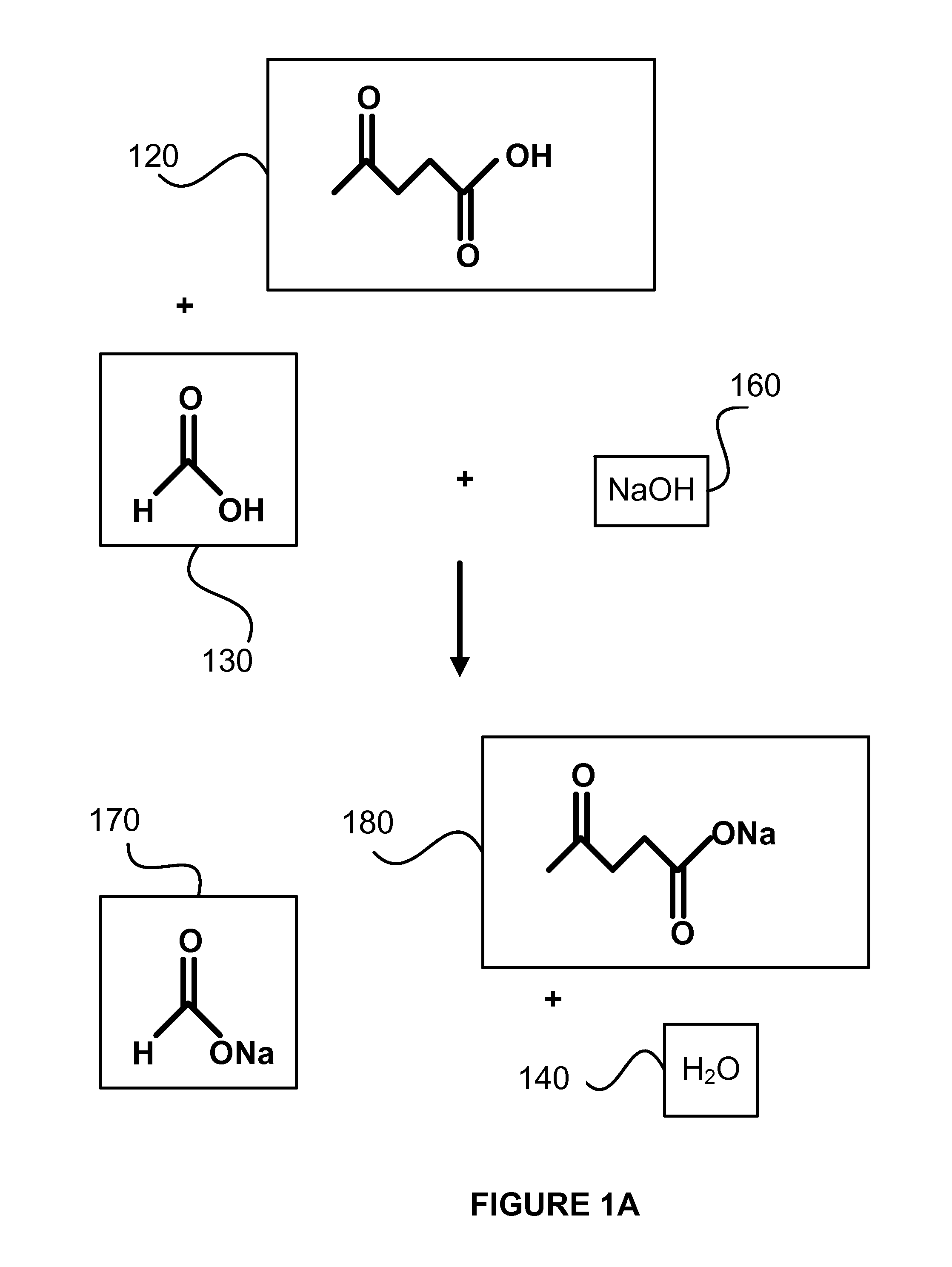
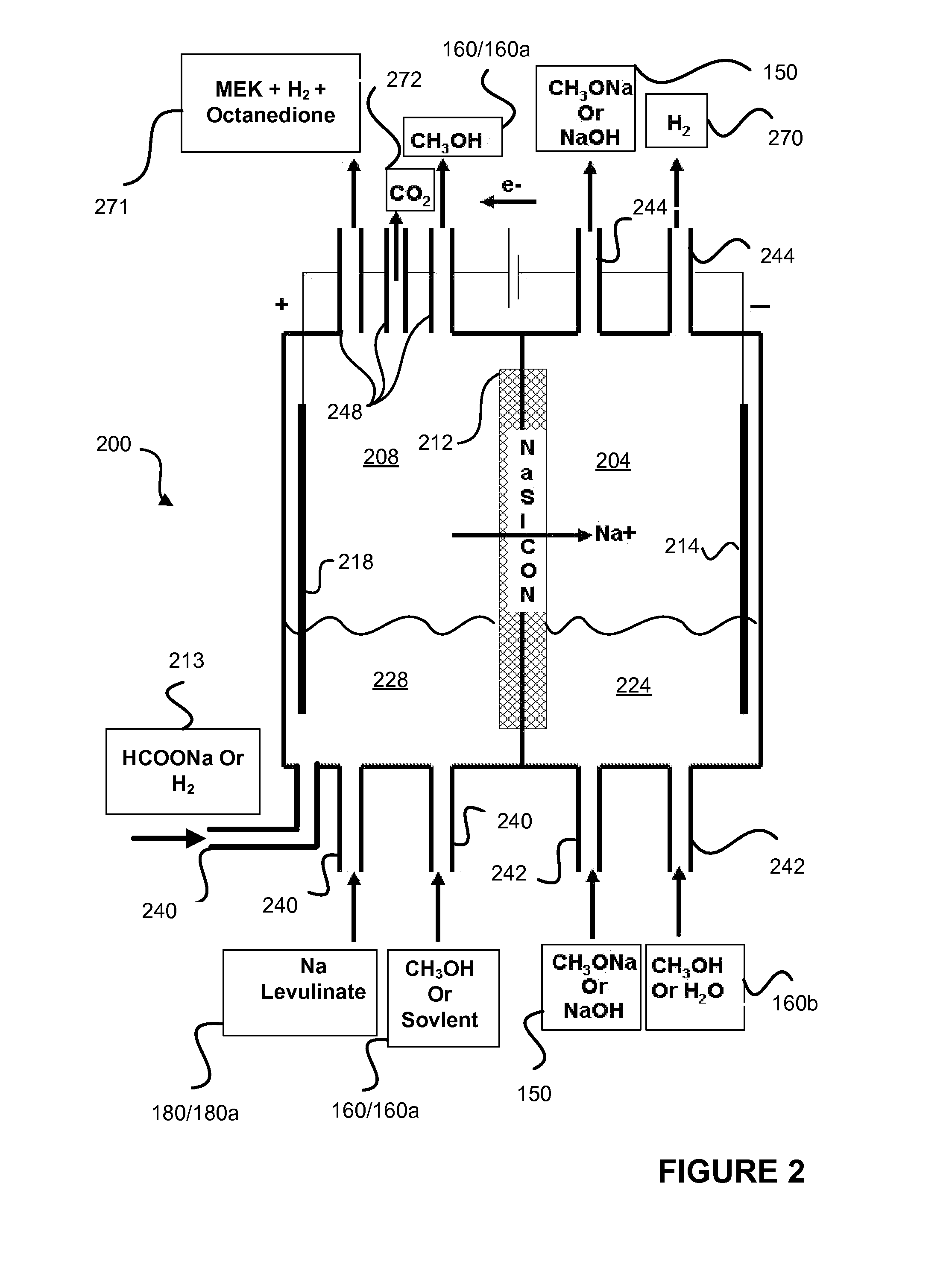
Decarboxylation of levulinic acid to ketone solvents
ActiveUS20140171688A1Low production costCellsOrganic compound preparationPropanoic acidKetone solvents
Ketones, specifically Methyl ethyl ketone (“MEK”) and octanedione, may be formed from six carbon sugars. This process involves obtaining a quantity of a six carbon sugar and then reacting the sugar to form levulinic acid and formic acid. The levulinic acid and formic acid are then converted to an alkali metal levulinate and an alkali metal formate (such as, for example, sodium levulinate and sodium formate.) The alkali metal levulinate is placed in an anolyte along with hydrogen gas that is used in an electrolytic cell. The alkali metal levulinate within the anolyte is decarboxylated to form MEK radicals, wherein the MEK radicals react with hydrogen gas to form MEK, or MEK radicals react with each other to form octanedione. The alkali metal formate may also be decarboxylated in the cell, thereby forming hydrogen radicals that react with the MEK radicals to form MEK.
Owner:ENLIGHTEN INNOVATIONS INC
Synthetic method of kyprolis
ActiveCN103641890AHigh reaction yieldHigh yieldPeptidesBulk chemical productionAcetic acidMorpholine
The invention relates to the technical field of drug synthesis, and particularly relates to a synthetic method of kyprolis. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: carrying out condensation reaction on morpholine-4-base acetic acid, L-homophenylalanine ester and salt, and then carrying out decarboxylation protection to generate a compound V; carrying out the condensation reaction on the decarboxylation, the salt and N-Boc-L-leucine, and then carrying out deamination protection to generate a compound VI; carrying out the condensation reaction on the compound V and the compound VI, and then carrying out decarboxylation protection to generate a compound VII; carrying out the condensation reaction on the compound VII and a compound VIII to obtain the kyprolis. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for enhancing the reaction yield by adopting a converging synthetic method; the used reagent is easy, convenient, easy to obtain and less in pollution. The process disclosed by the invention only relates to the condensation and deprotection between amino acids and is simple and controllable in reaction and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:重庆兴泰濠制药有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com





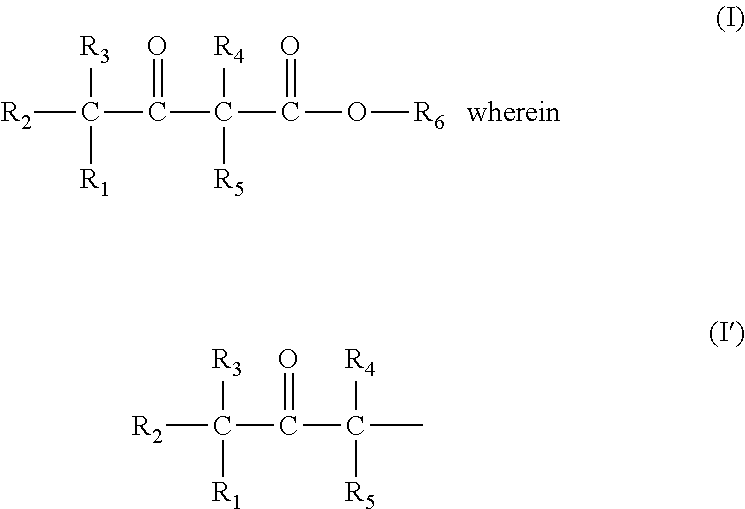



![Synthesis method of tert-butyl-[2-(biphenyl-4-yl)-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl] carbamate Synthesis method of tert-butyl-[2-(biphenyl-4-yl)-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl] carbamate](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.sutd.idm.oclc.org/patent_img/1cb8116e-6b5a-4654-a02f-0ee8a1dcaada/a200810120924c00021.PNG)
![Synthesis method of tert-butyl-[2-(biphenyl-4-yl)-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl] carbamate Synthesis method of tert-butyl-[2-(biphenyl-4-yl)-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl] carbamate](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.sutd.idm.oclc.org/patent_img/1cb8116e-6b5a-4654-a02f-0ee8a1dcaada/a200810120924d00081.PNG)